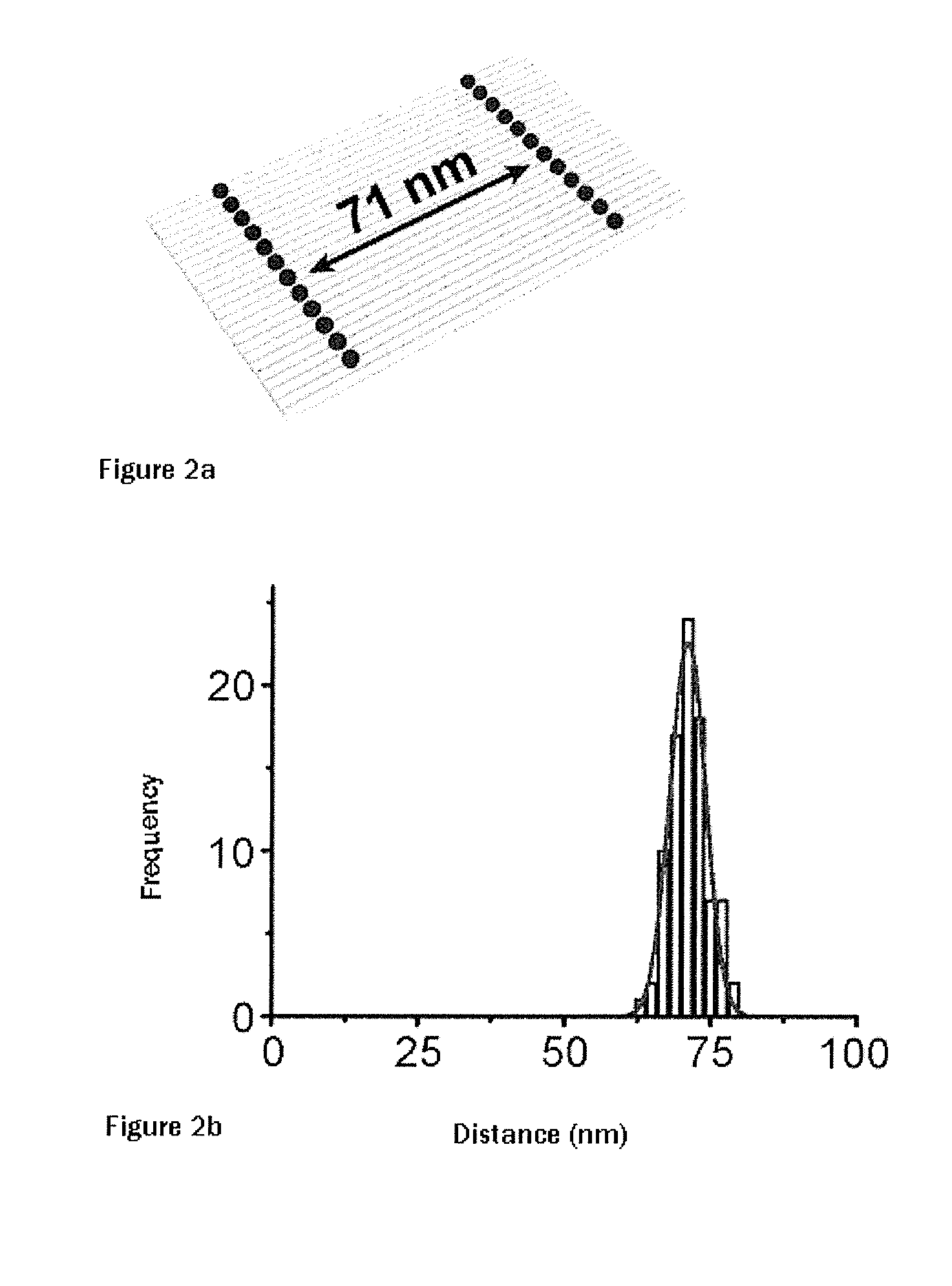
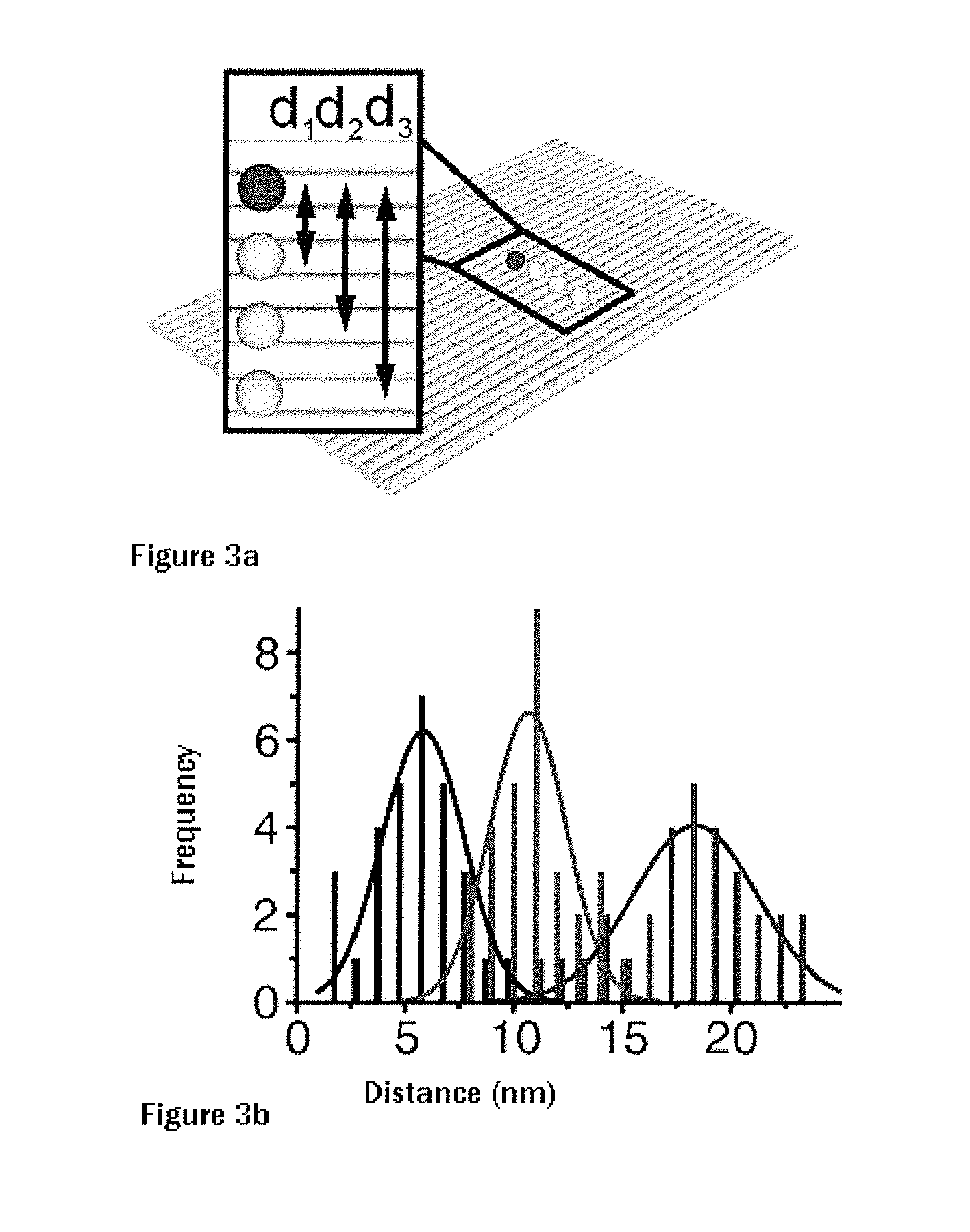
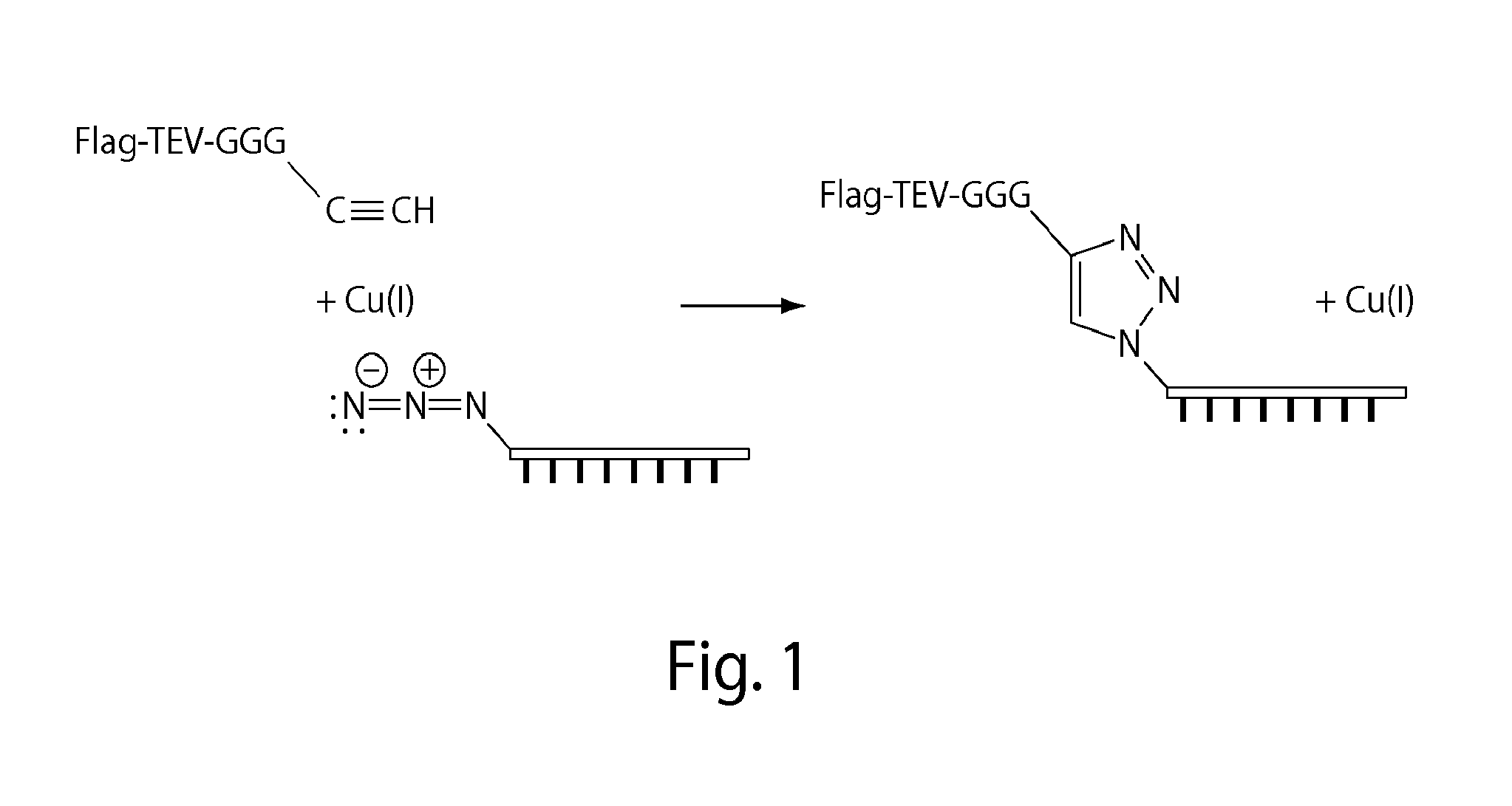
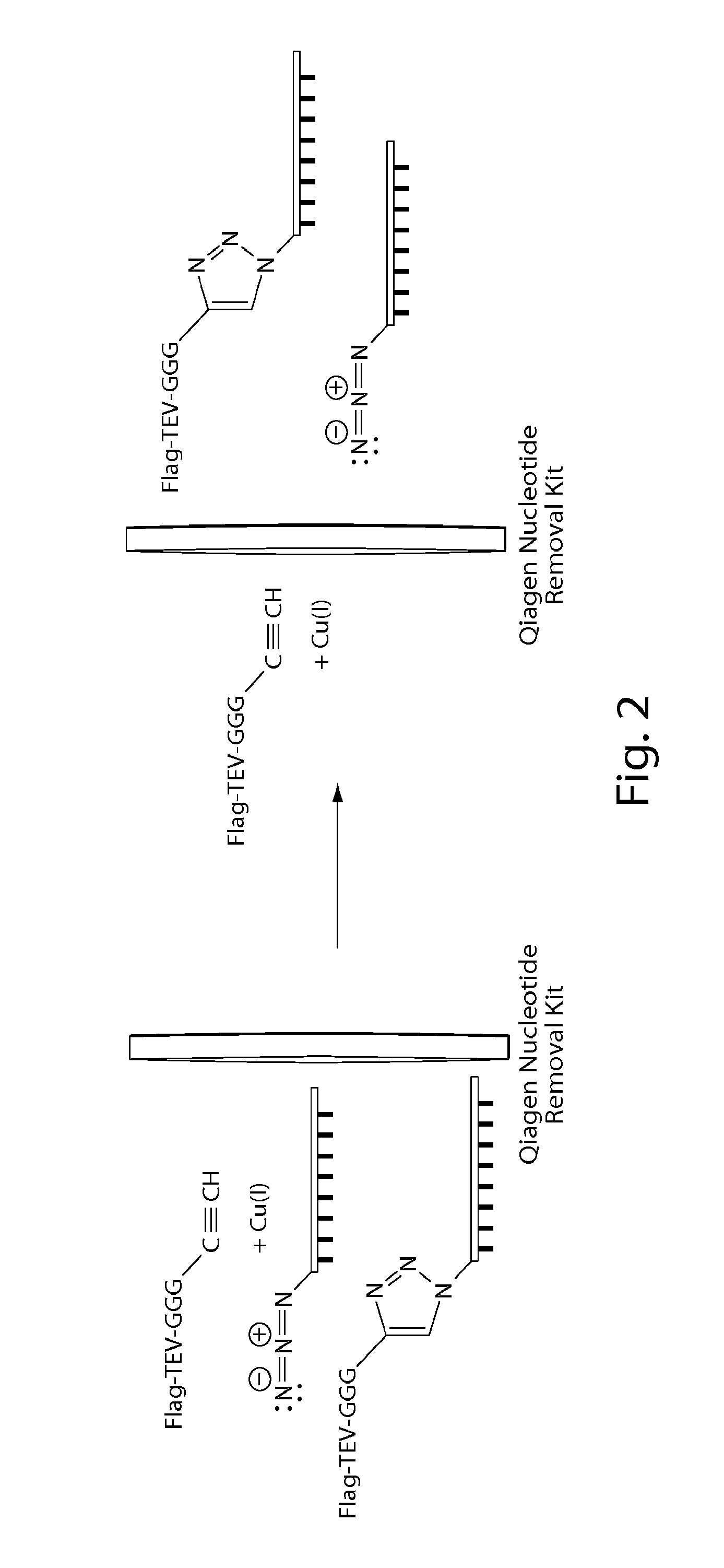
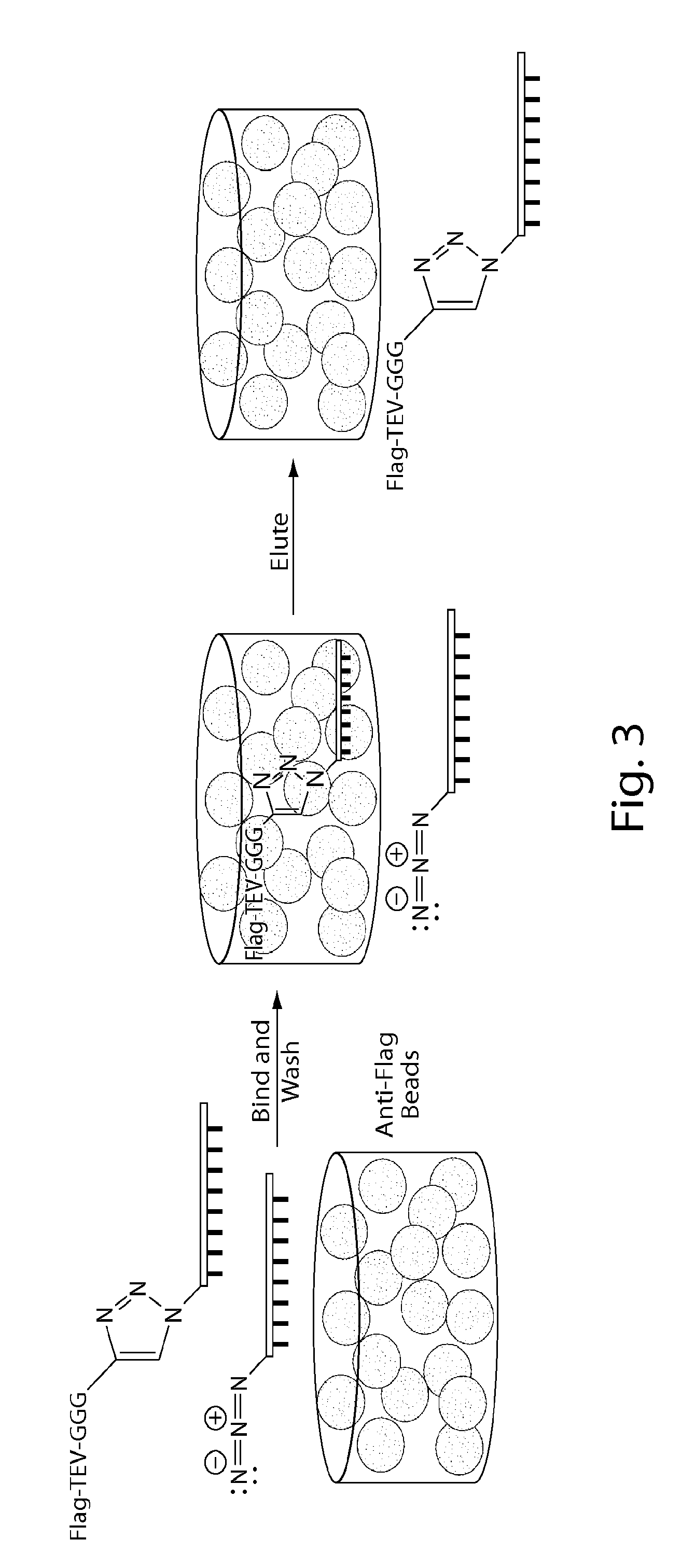
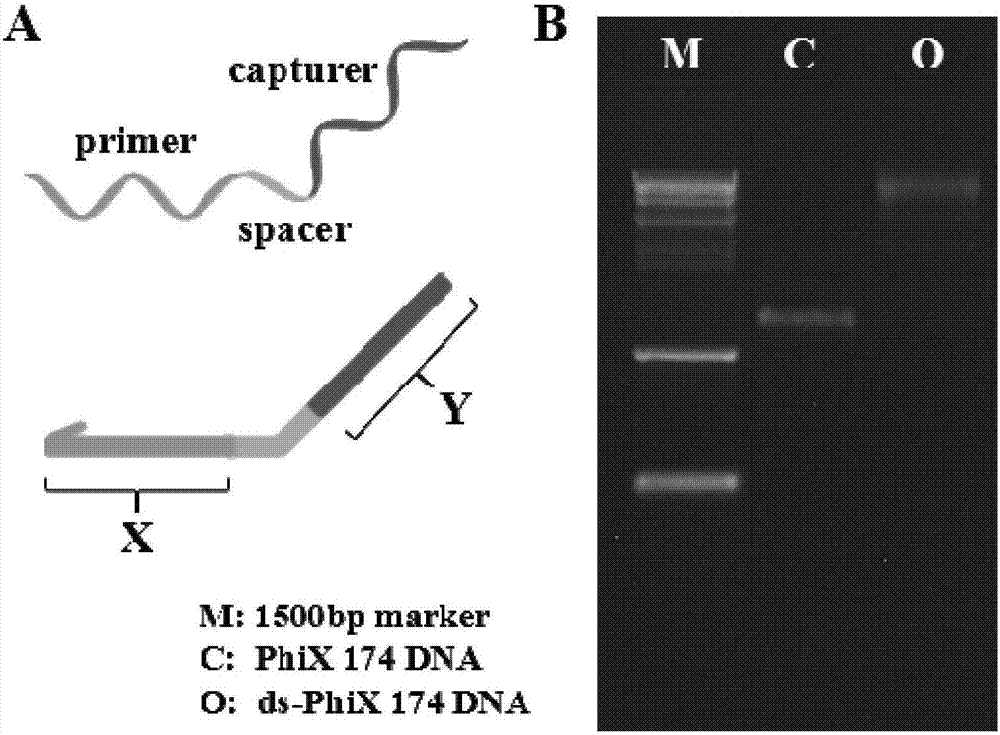
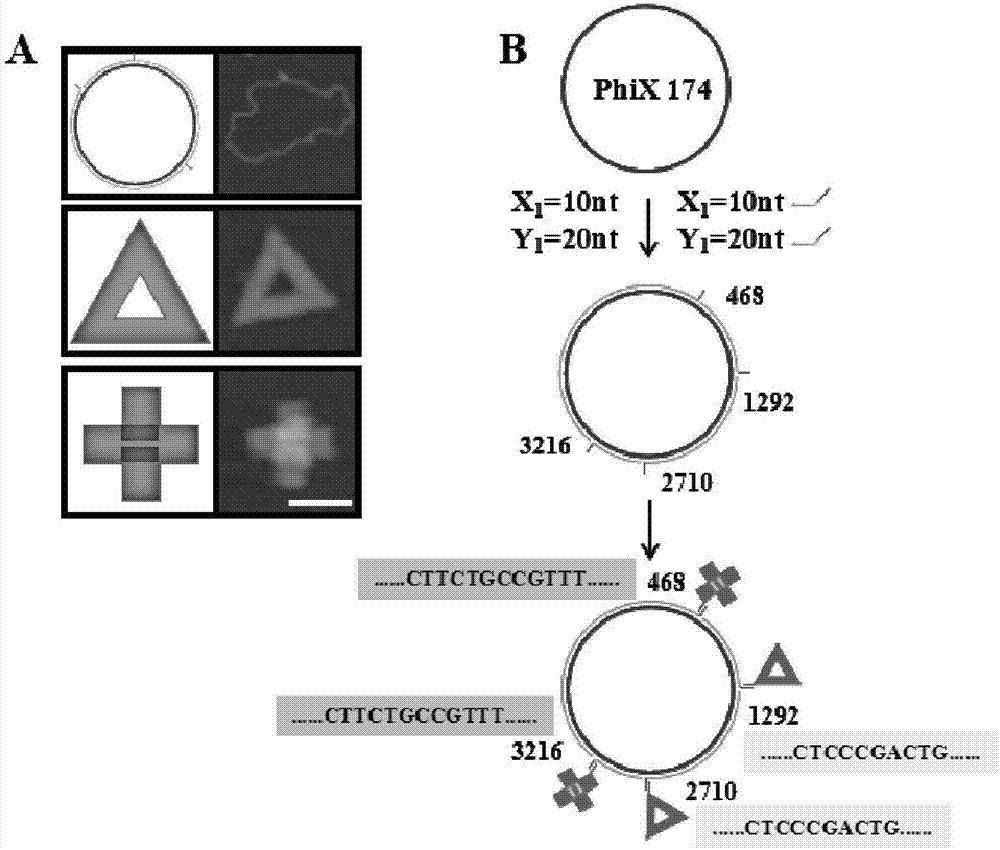
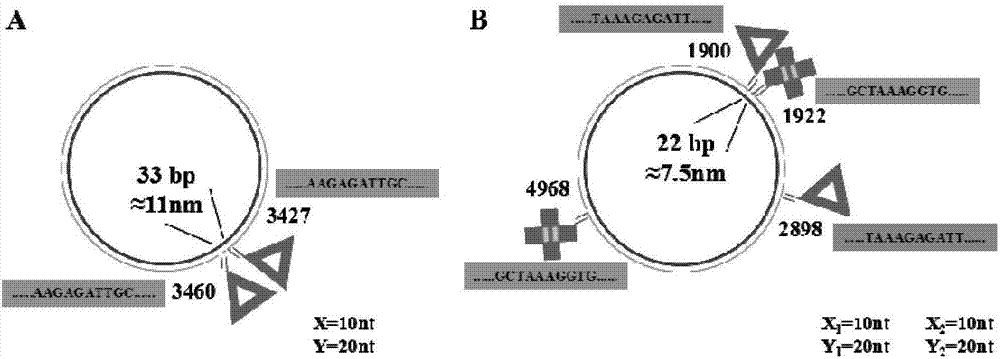
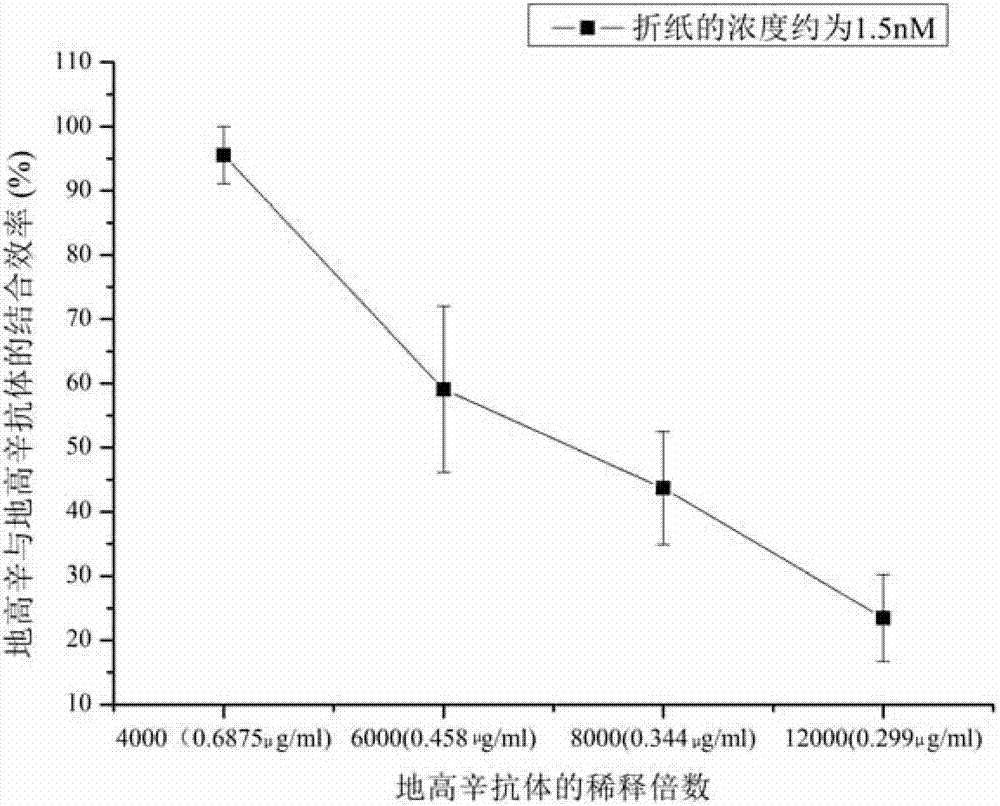
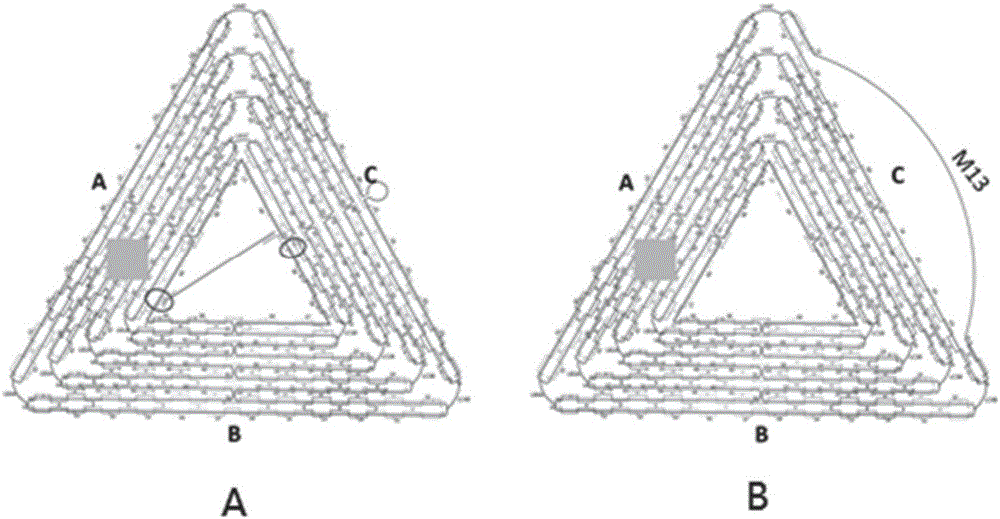
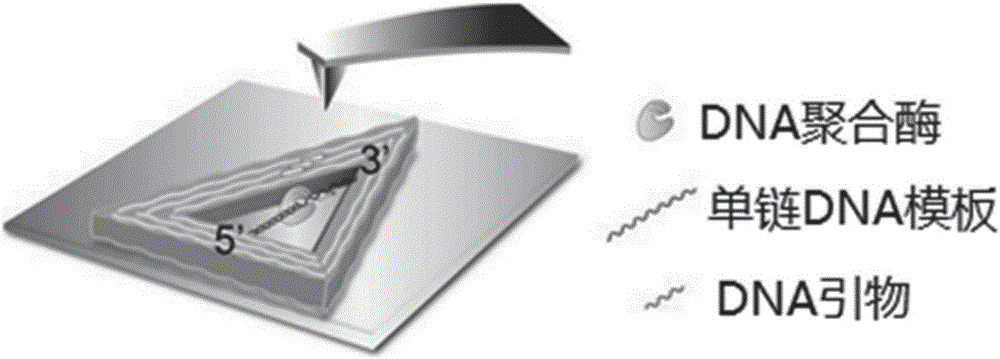
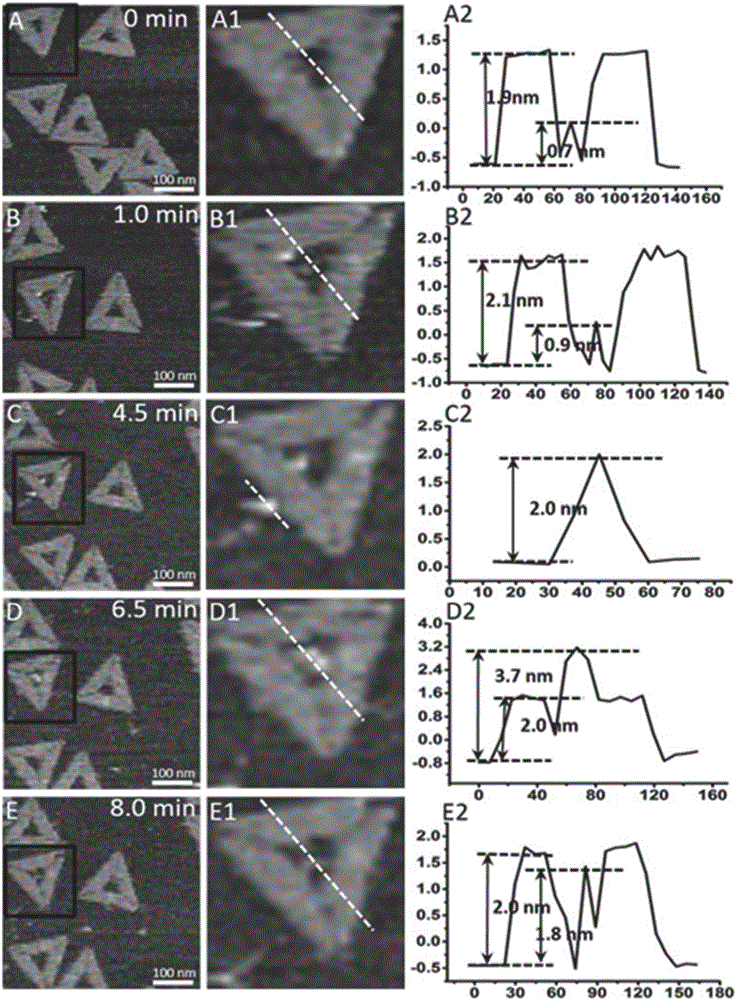
Patents
Literature
103 results about "DNA origami" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
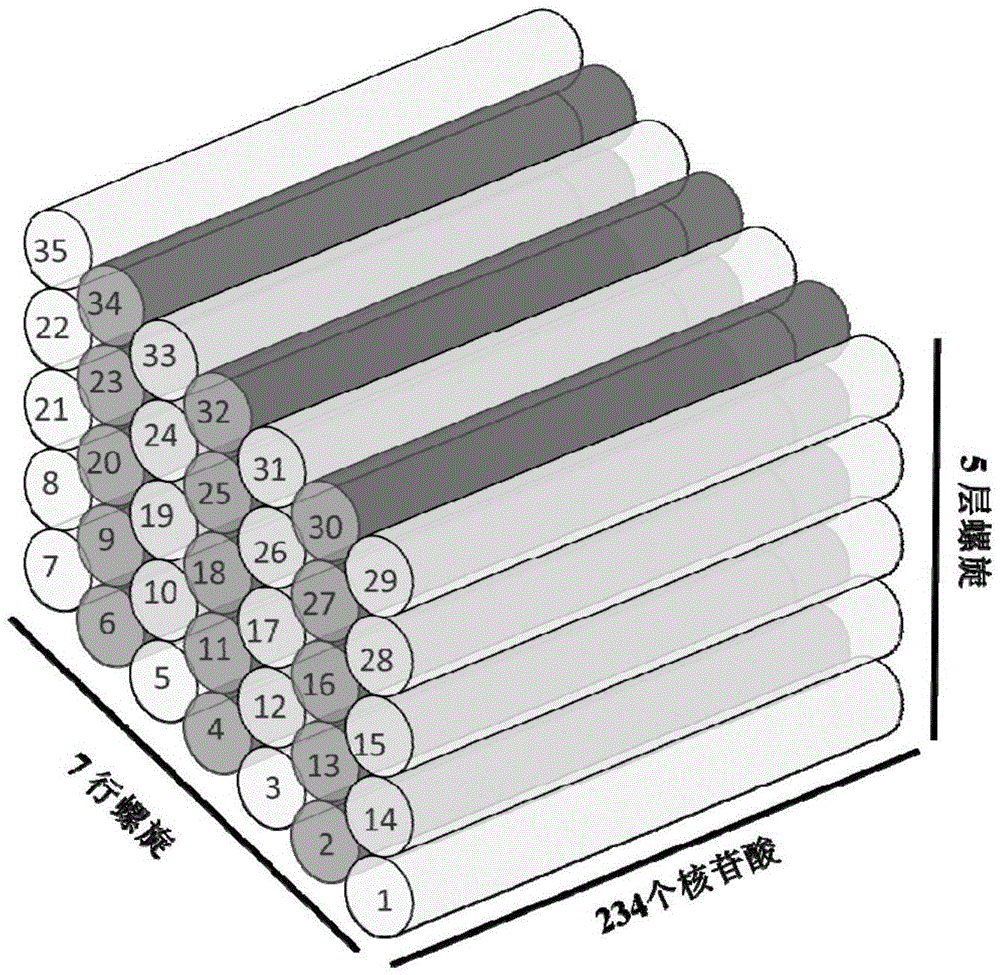
DNA origami is the nanoscale folding of DNA to create non-arbitrary two- and three-dimensional shapes at the nanoscale. The specificity of the interactions between complementary base pairs make DNA a useful construction material, through design of its base sequences. DNA is a well-understood material that is suitable for creating scaffolds that hold other molecules in place or to create structures all on its own.
Nucleic acid nano structure carrier-precious metal photosensitive contrast agent composite for living organism photo-acoustic imaging, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104324375ARealize the combinationHigh Photoacoustic Imaging CapabilityEnergy modified materialsInorganic non-active ingredientsNano structuringWhole body
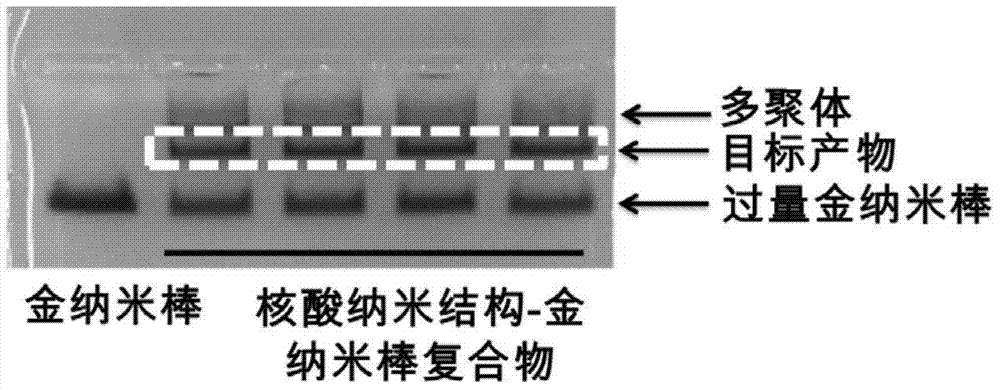
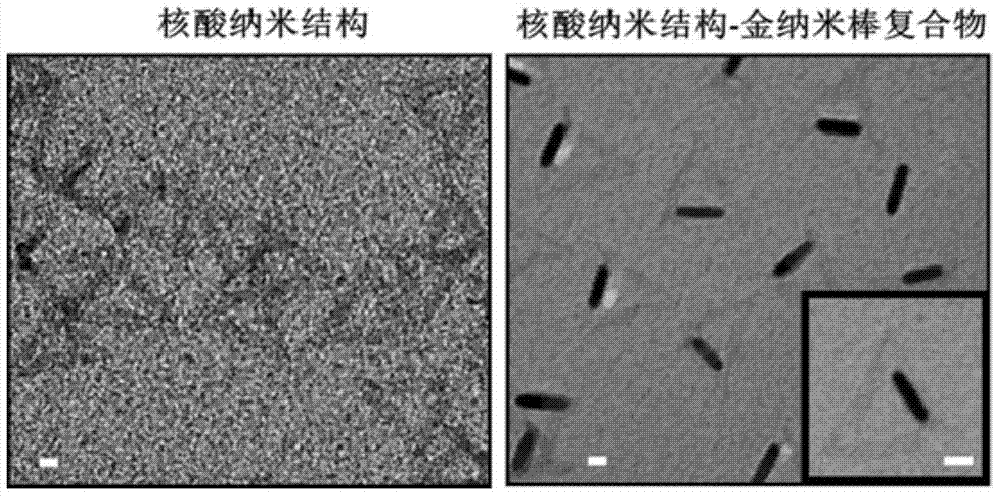
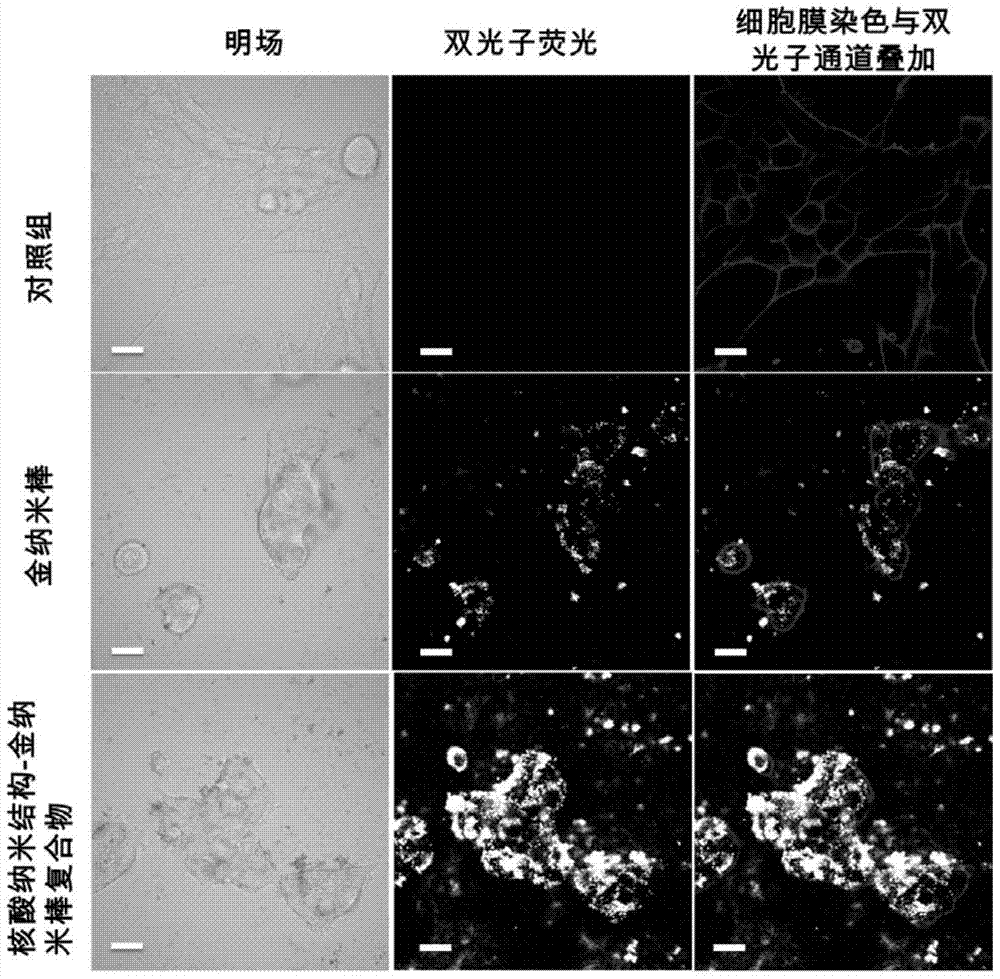
The invention discloses a nucleic acid nano structure carrier, a nucleic acid nano structure carrier-precious metal photosensitive contrast agent composite comprising the same, and preparation methods and applications of the carrier and the composite. The nucleic acid nano structure is a random two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional nano structure constructed by a DNA paper-folding technology. The precious metal components are used to carry out DNA modification on the surface of the carrier and selected from one or more of gold nano rods, gold nano shells, silver-coated gold nano rods, and gold nano cages. The provided composite is used as a photo-acoustic imaging probe, is capable of guaranteeing the absorption contrast enhancing effect of the photo-acoustic contrast agent which is coupled to the composite, and moreover can prominently improve the targeting performance of the contrast agent on tumors. Furthermore, the precious metal photosensitive components which are coupled to the carrier are enriched in the inner of tumor tissues, and thus the solved is the problems that conventional contrast agent is distributed over the whole human body or the contrast agent can only stay on the tumor surfaces. The preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, convenience, and easy application.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA +1
Nucleic acid nano structure for carrying antitumor drugs, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104368004AGuaranteed antitumor activityImprove targetingNanomedicinePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsNano structuringWhole body
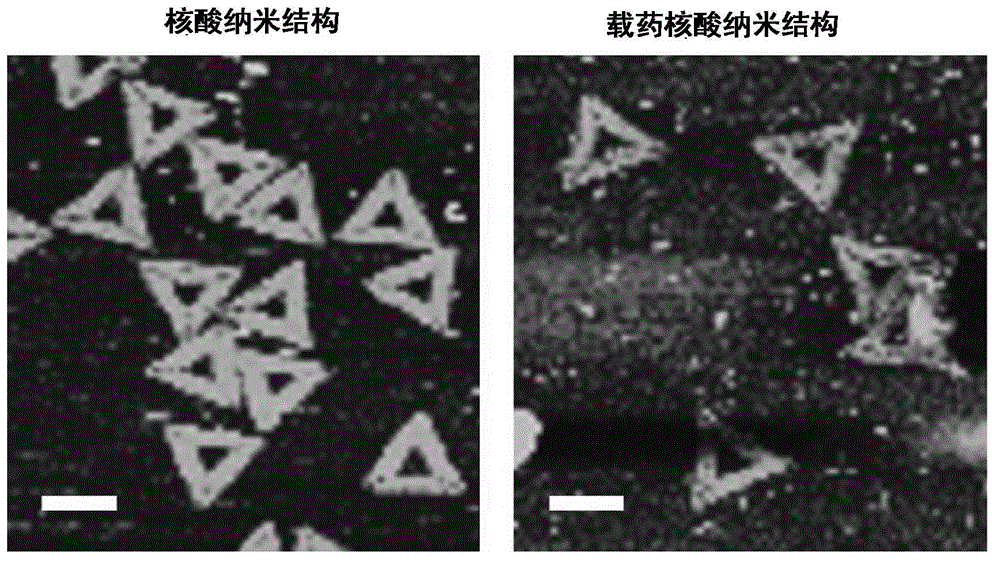
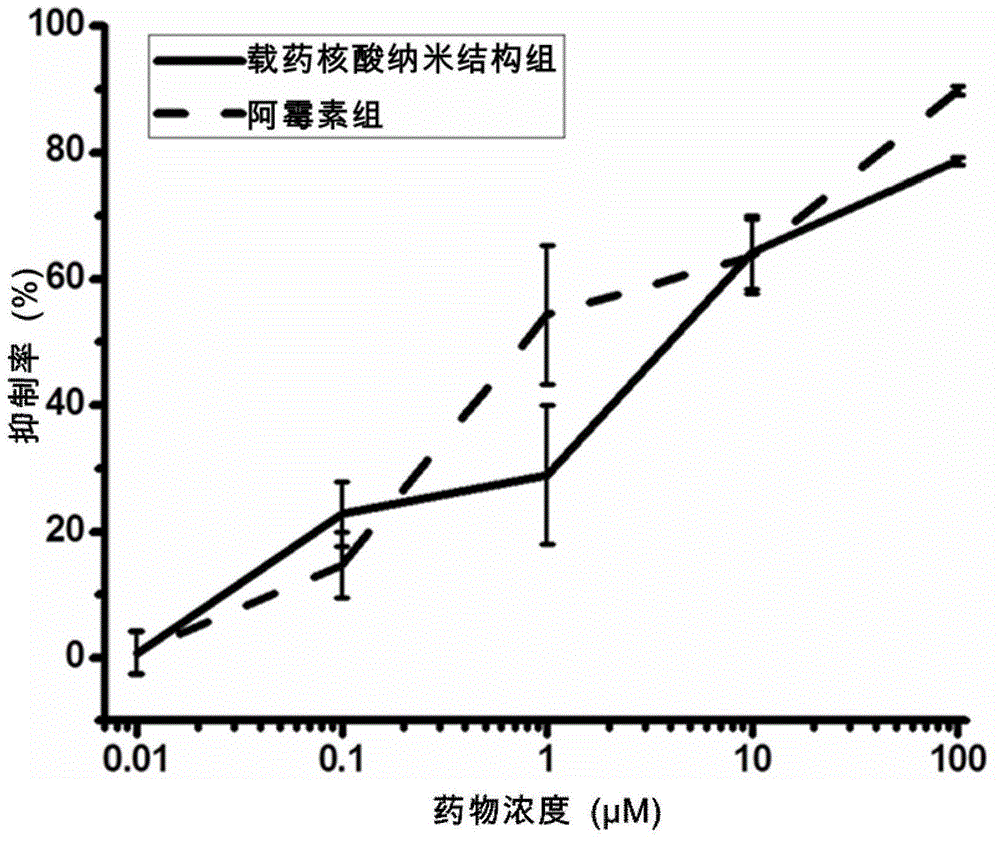
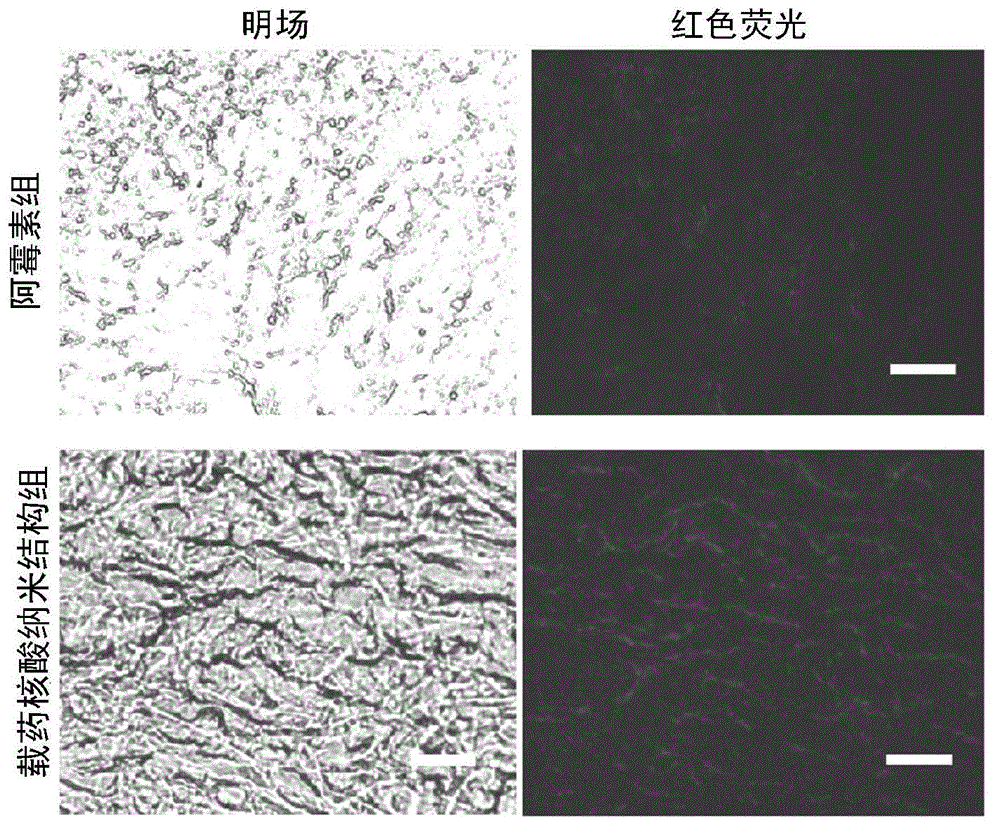
The invention discloses a nucleic acid nano structure for carrying antitumor drugs, a preparation method and applications thereof. The nucleic acid nano structure is a random two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional nano structure constructed through a DNA origami technology. The nucleic acid nano structure is obtained through self-assembly between a scaffold chain and a staple chain for auxiliary folding, wherein the scaffold chain and the stable chain are hybridized according to the base paring principle. The provided nucleic acid nano structure taken as the carrier of antitumor drugs can guarantee the antitumor activity of the carried antitumor drugs, and further improves the targeting property of the antitumor drugs. Thus the antitumor drugs can be enriched in the tumor tissues, and the overall toxicity due to the non-specificity of the antitumor drugs is greatly reduced. Furthermore, the preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, convenience, and easy application.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA +1
Microbial production of pure single stranded nucleic acids
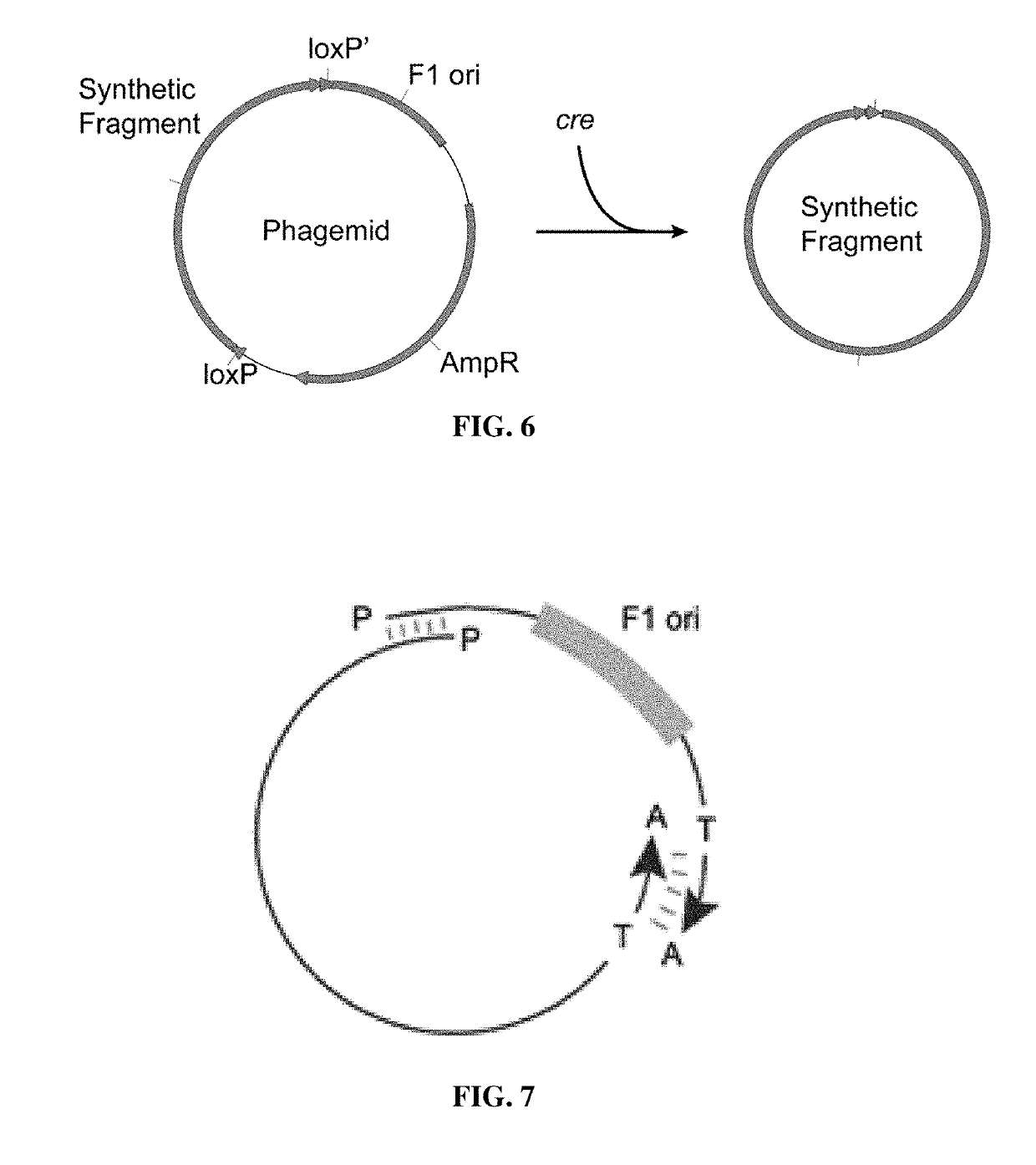
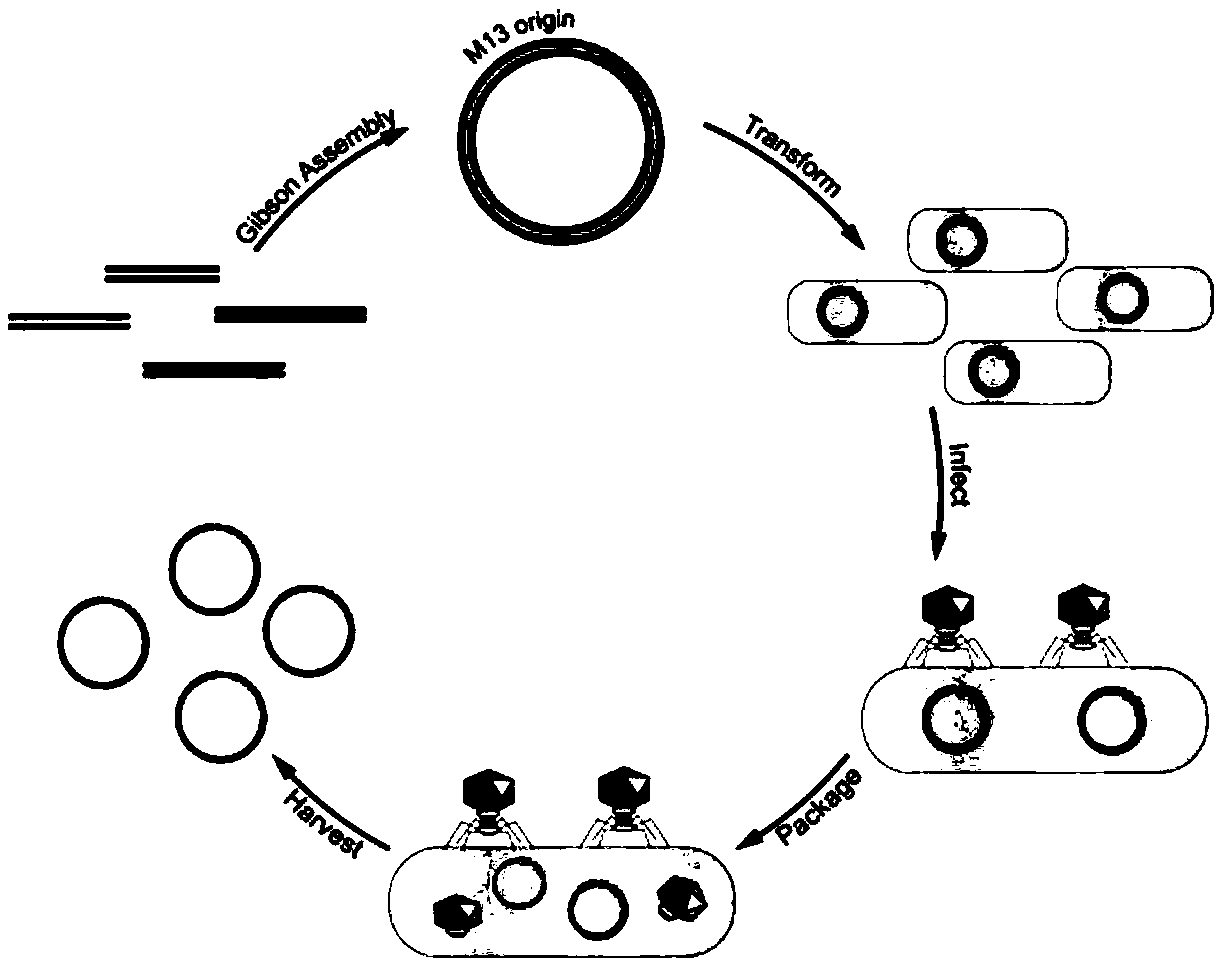
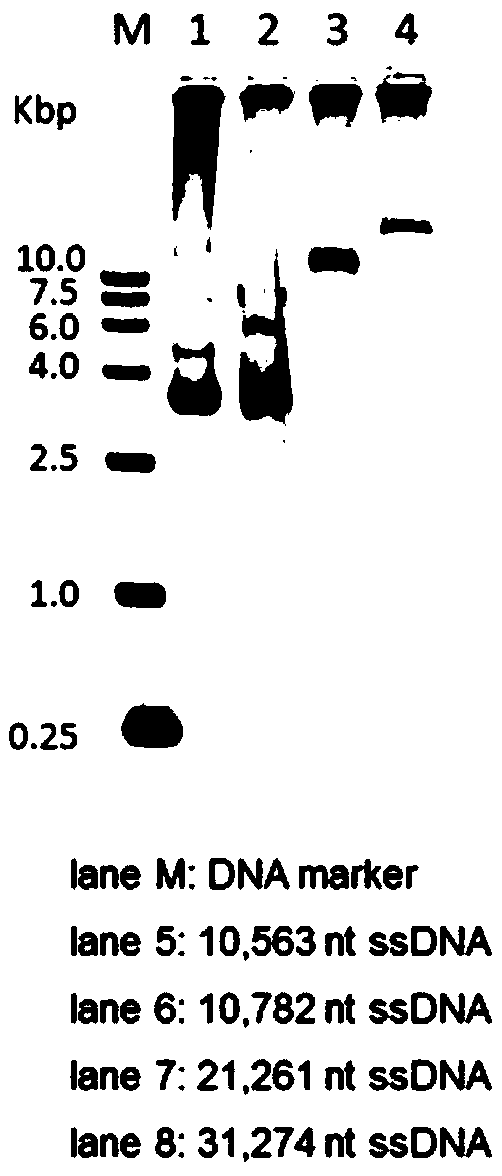
Methods and compositions for bacterial production of pure single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) composed of custom sequence and size have been developed. The methods enable scalability and bio-orthogonality in applications of scaffolded DNA origami, offering one-step purification of large quantities of pure ssDNA amendable for immediate folding of DNA nanoparticles. The methods produce pure ssDNA directly from bacteria. In some embodiments the E. coli helper strain M13cp combined with a phagemid carrying only an f1 -origin allows for, without the need for additional purification from contaminating dsDNA. This system is useful for generalized circular ssDNA synthesis, and here is applied to the assembly of DNA nanoparticles folded both in vitro and direct from phage.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor based on adapter modification and preparing method and application of DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor
ActiveCN104962615AExact Space AddressabilityOvercoming the disadvantages of poor autoimmunityMicrobiological testing/measurementNano structuringAutoimmunity
The invention discloses a DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor based on adapter modification and a preparing method and application of the DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor. The biosensor comprises DNA flexagon and nanogold, the DNA flexagon comprises an adapter nucleotide sequence of a detected object, and the nanogold is nanogold modified by a DNA fragment complementary with the adapter nucleotide sequence. The method includes the following beneficial effects that the DNA flexagon has the accurate space addressability, and the complicated marking step is avoided after the nanogold is added; an adapter can be synthesized in batch with a chemical method, so that the cost is greatly reduced; the shortcoming that the autoimmunity of micromolecule matter is poor is overcome; the DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor has the lower detection limit, and LOD reaches the nanogram stage; an atomic force microscope and electrophoresis are adopted for conducting representation, qualitative and quantitative analysis is carried out by using the characteristic that the nanogold is high in light in an atomic force microscope height map; and compared with a traditional survey method, the advantages of being easy and convenient, reliable, lower in requirement for experiment conditions and the like are achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
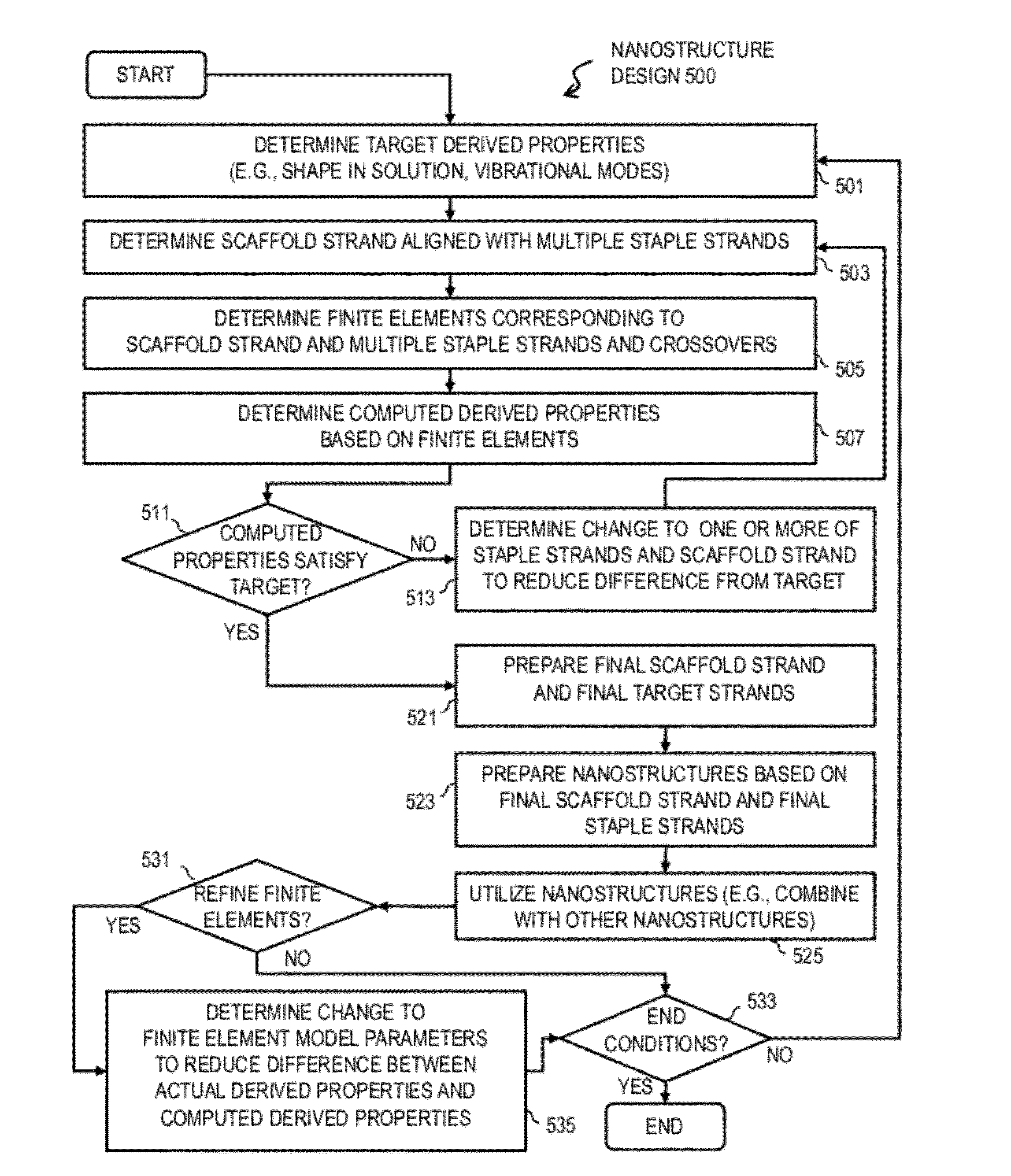
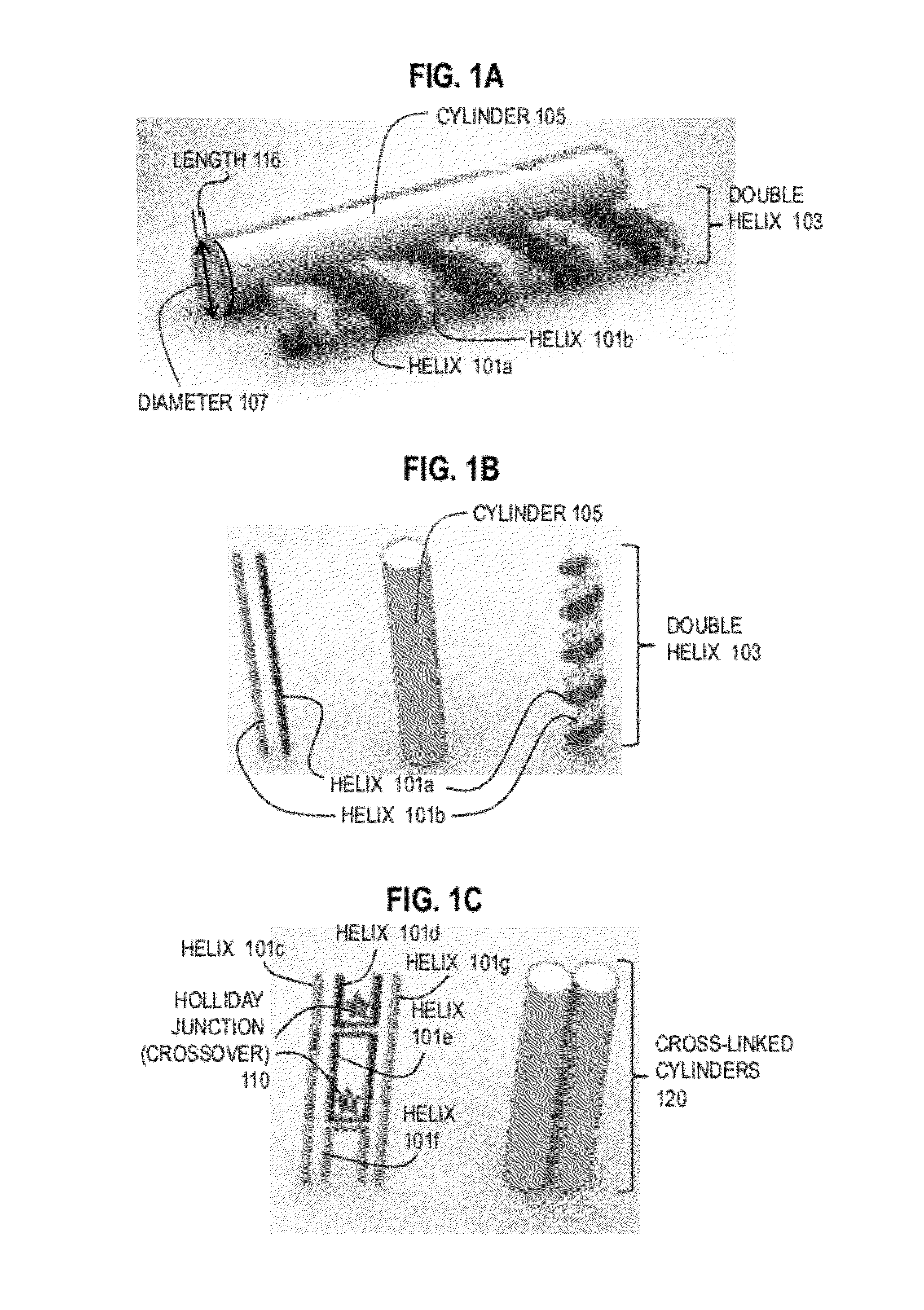
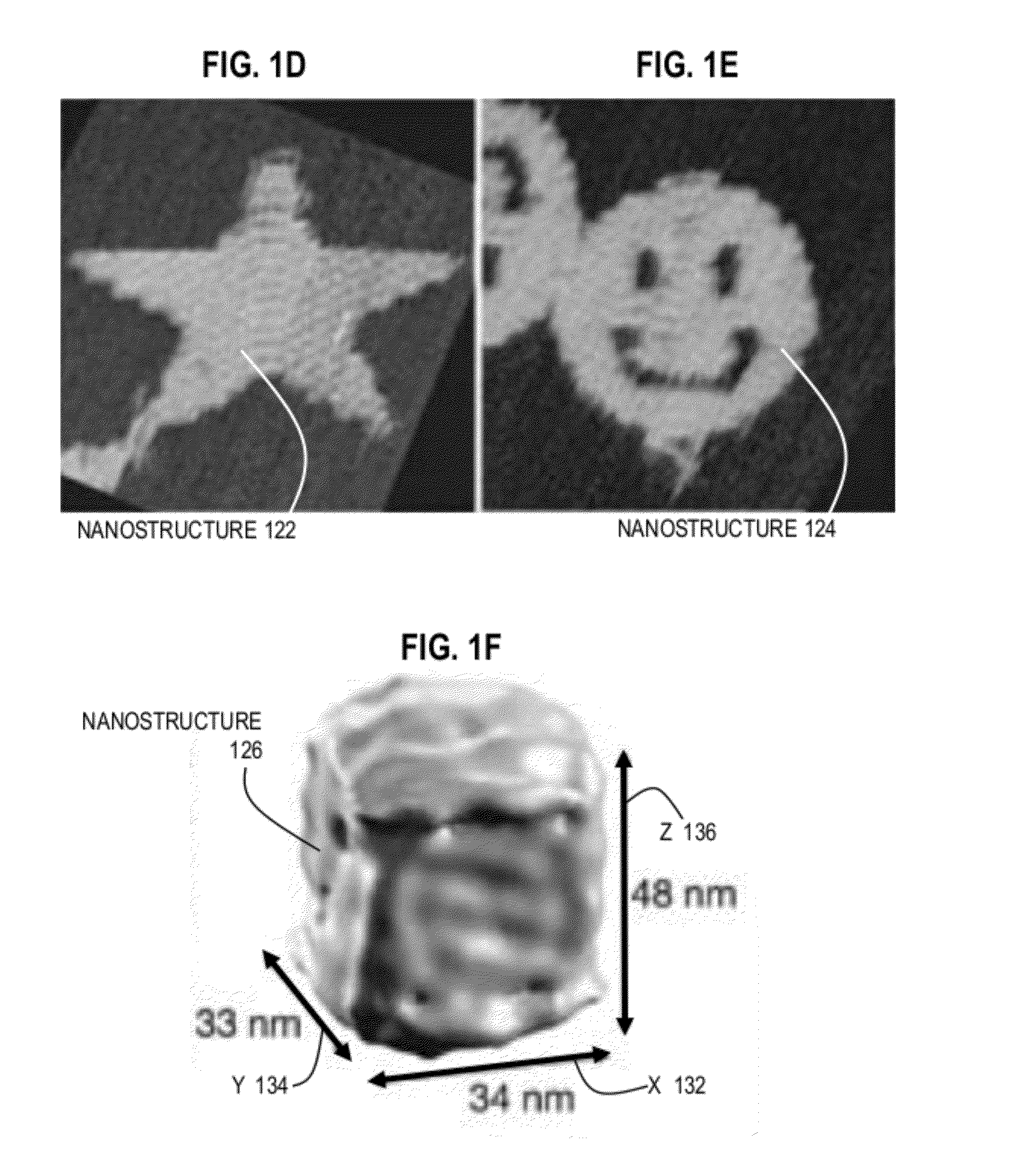
Method and apparatus for controlling properties of nucleic acid nanostructures
ActiveUS20120166152A1Increase flexibilityImprove propertiesComputation using non-denominational number representationSequence analysisChemical physicsDNA origami
Techniques for controlling properties of nucleic acid nanostructures include receiving data that indicates a sequence of nucleotides on at least a first strand of a nucleic acid. Values are determined for at least one physical property for each portion of the at least first strand. Based at least in part on a numerical model and the physical properties for each portion, a value is determined of at least one derived property of a nanostructure that comprises the at least first strand of nucleic acid. In some embodiments, information gained from the numerical model is used iteratively in order to optimize or improve one or more of the properties of the target DNA origami structure.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
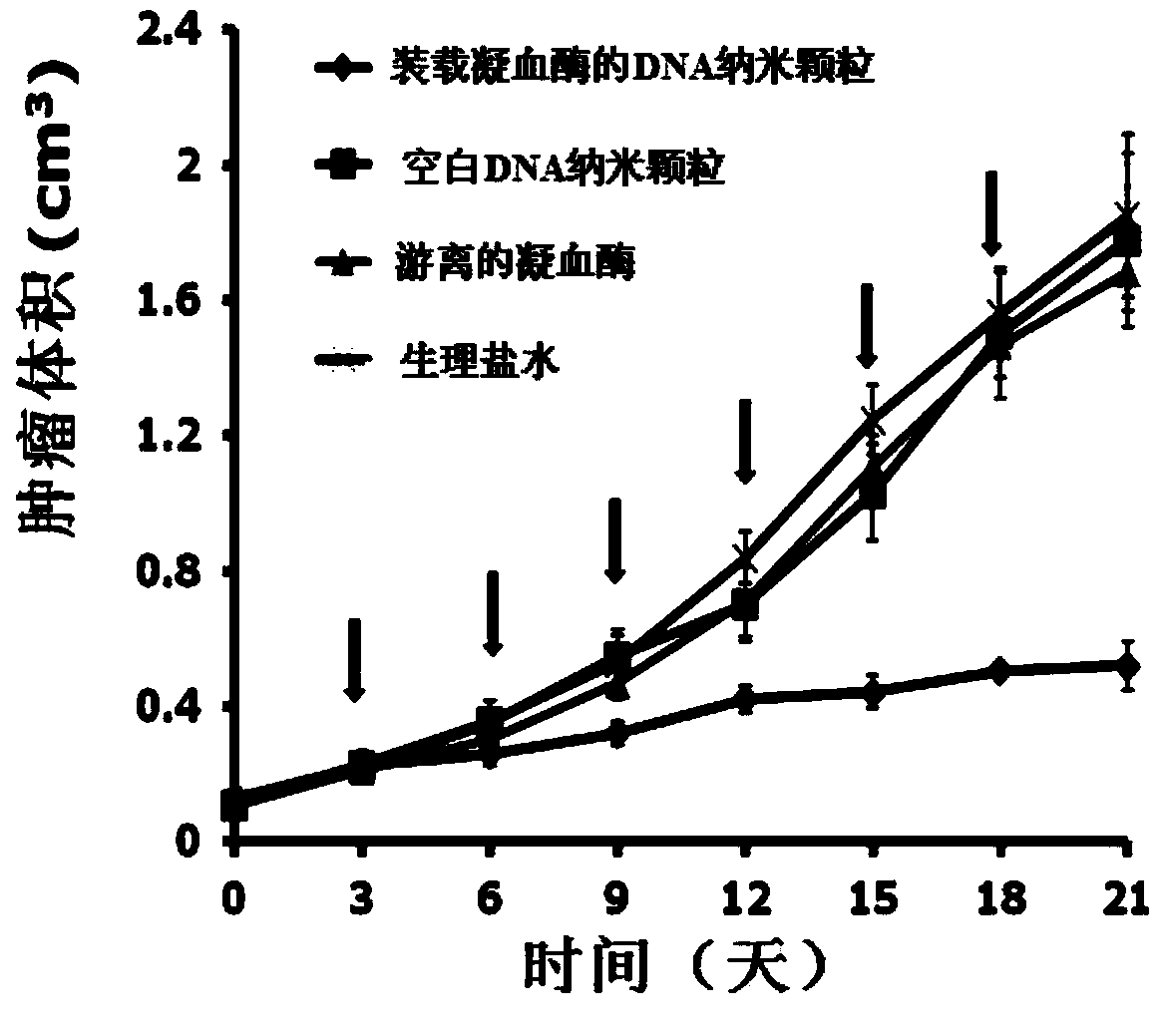
Thrombin-loaded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) self-assembly nano-structure, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103948938AAvoid non-specific coagulation effectsAchieve targeted deliveryPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsNano structuringDNA origami
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thrombin-loaded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) self-assembly nano-structure. The method comprises the following steps: self-assembling a single-stranded DNA molecule into a rectangular nano-structure by utilizing a DNA paper folding technology; immobilizing thrombin on the surface of the rectangular nano-structure, and immobilizing a 'lock' structure capable of answering vascular endothelial specific receptor of a tumor at two long edges of the rectangular nano-structure so as to close the thrombin inside the structure and generate response when thrombin is carried to a tumor blood vessel tissue. Therefore, target delivery and controllable release of the tumor blood vessel tissue by the thrombin can be realized; and the prepared thrombin-loaded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) self-assembly nano-structure can be used for intravenous injection, realizes targeted treatment of tumors, and has a wide clinical application prospect.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Monomolecular gene typing method based on DNA paper folding probe specificity marking and application thereof
InactiveCN106893781AImprove accuracyOvercoming limited quantitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementOptical diffractionFluorescence
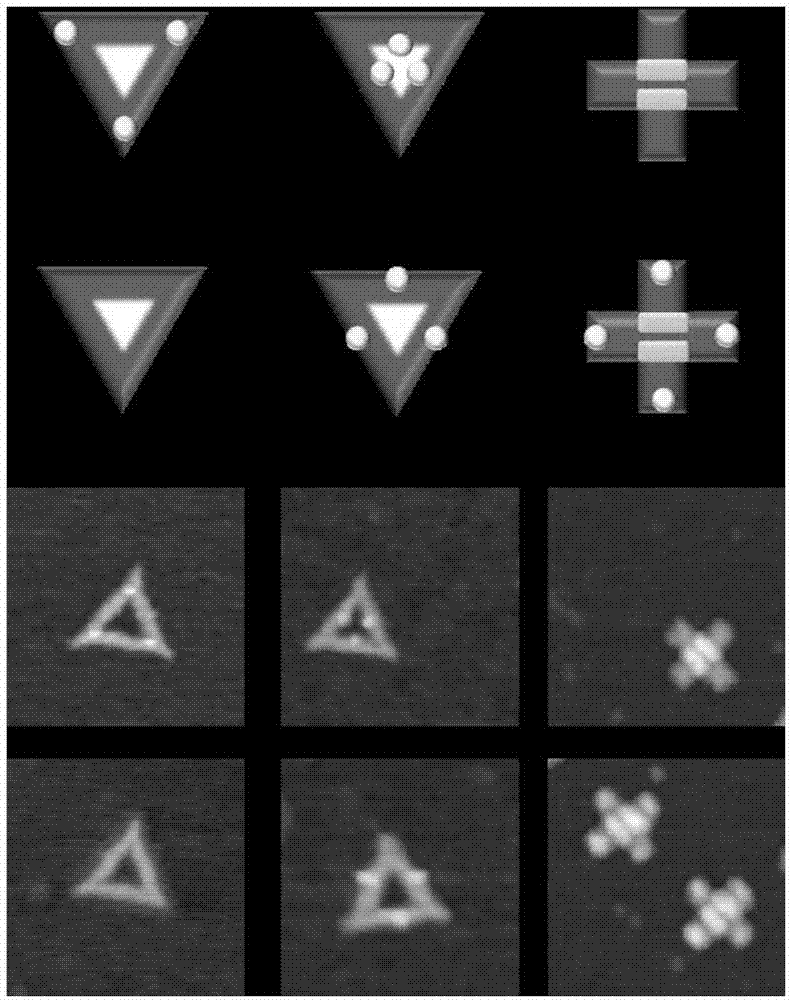
The invention provides a monomolecular gene typing method based on DNA paper folding probe specificity marking and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a DNA paper folding probe; 2) carrying out specificity marking on a target DNA through the DNA paper folding probe; 3) carrying out imaging observation on the marked target DNA under an atomic force microscope. Moreover, the monomolecular gene typing method can also be applied to haplotype typing of patient samples and haplotype typing of practical samples with unknown haplotype information. All in all, according to the method provided by the invention, single nucleotide polymorphism can be effectively detected, and the position of a single basic group is observed at high resolution under the atomic force microscope, so that the problem that fluorescent molecular marking is limited to optical diffraction limit under an electron microscope is successfully avoided, and the method can be widely applied to the research fields such as in situ test of chromogene variation and clinic gene diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nucleic acid nano structure as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107488661AImprove stabilityAnchor size largeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransportation and packagingNano structuringDNA origami
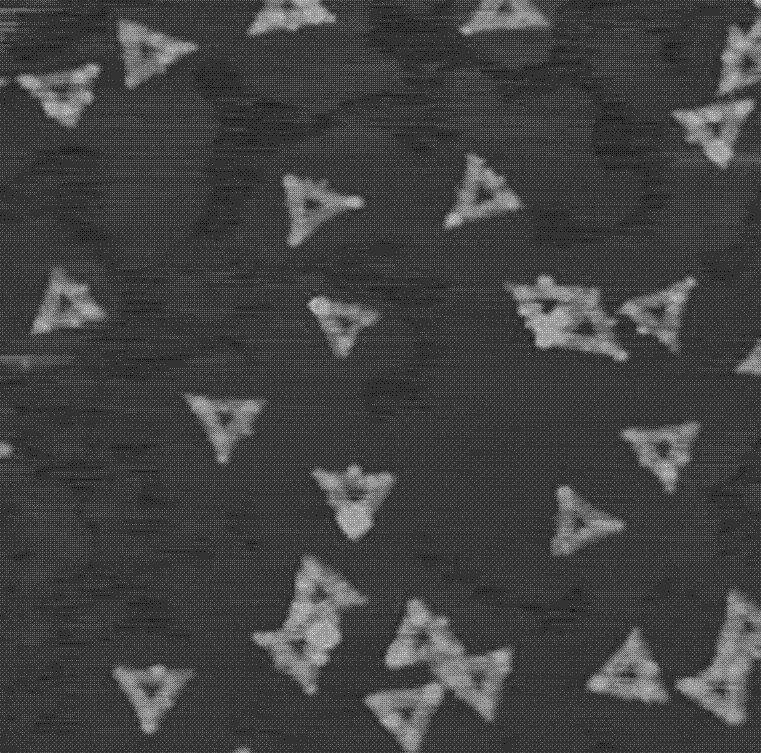
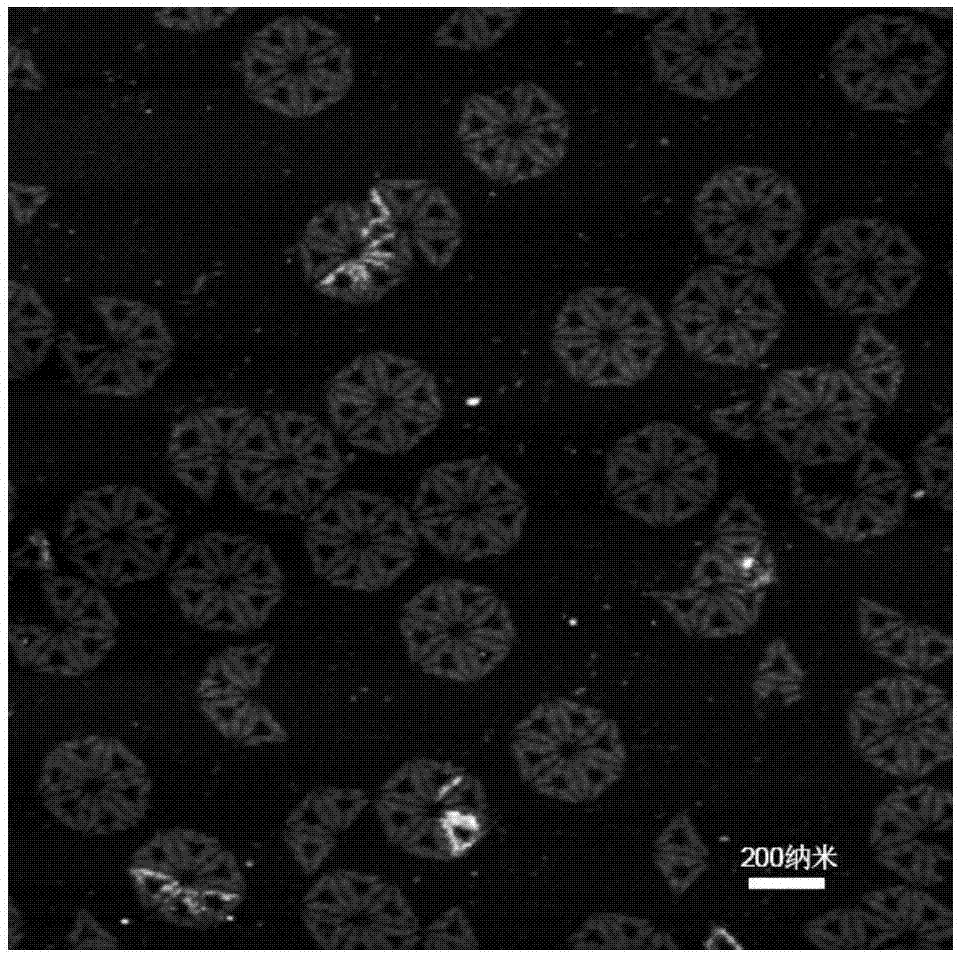
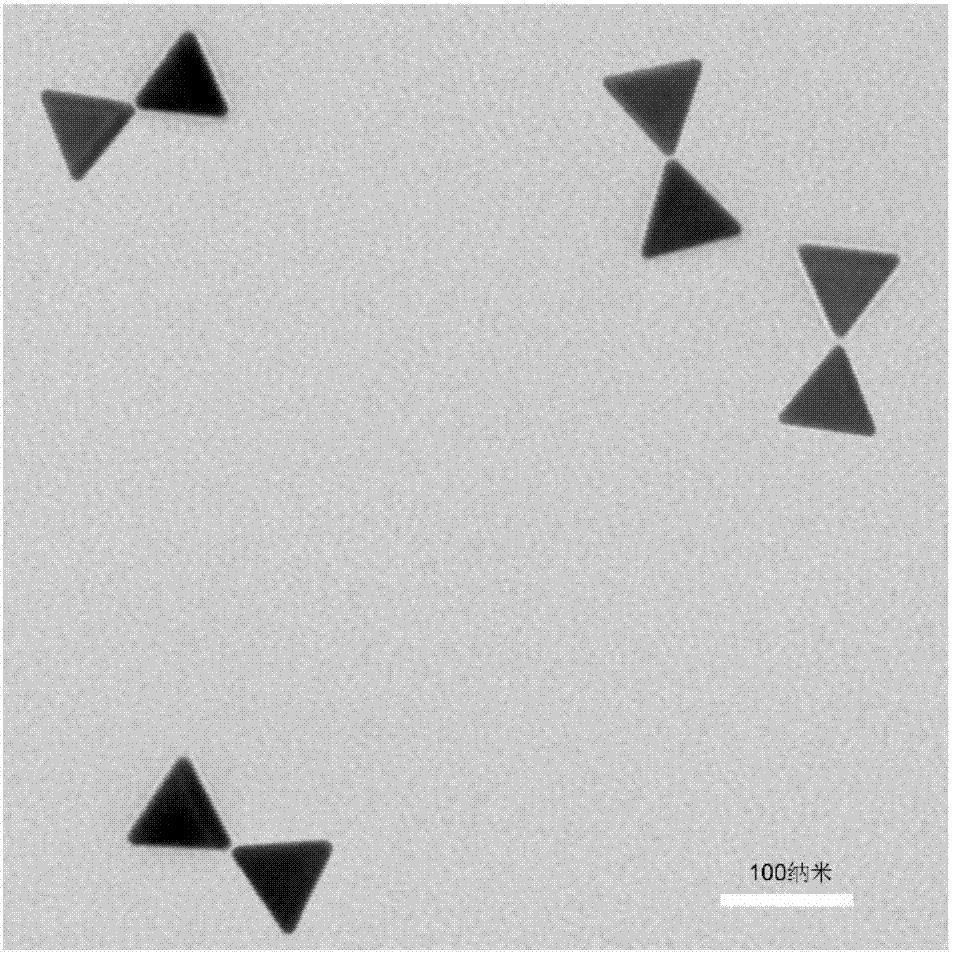
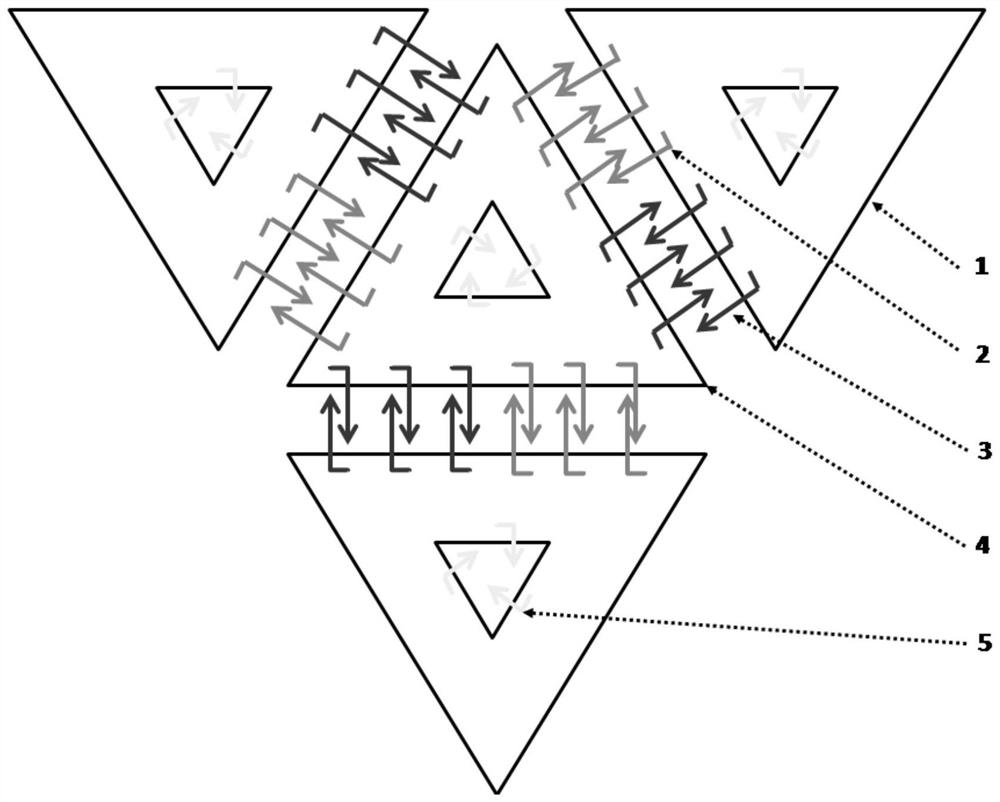
The invention provides a nucleic acid nano structure as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The nucleic acid nano structure is a hexagonal DNA nano structure formed by assembling six triangular DNA paper folding structures constructed by a DNA paper folding technology, and particularly a hexagonal DNA nano structure formed by self-assembling in a mode of carrying out hybridization on scaffold chains and staple chains as well as capturing chains and then respectively carrying out hybridization on connection chains and scaffold chains of six triangular DNA paper folding structures. The nucleic acid nano structure is high in stability, two 80nm gold triangular prisms can be anchored, a prepared golden bow structure can generate a strong electromagnetic field, and single molecule Raman detection is implemented.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
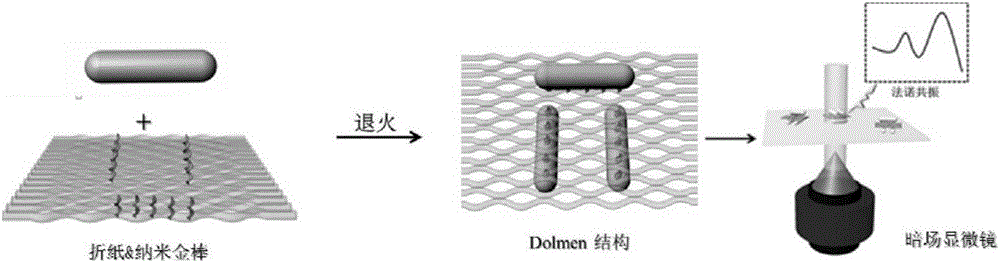
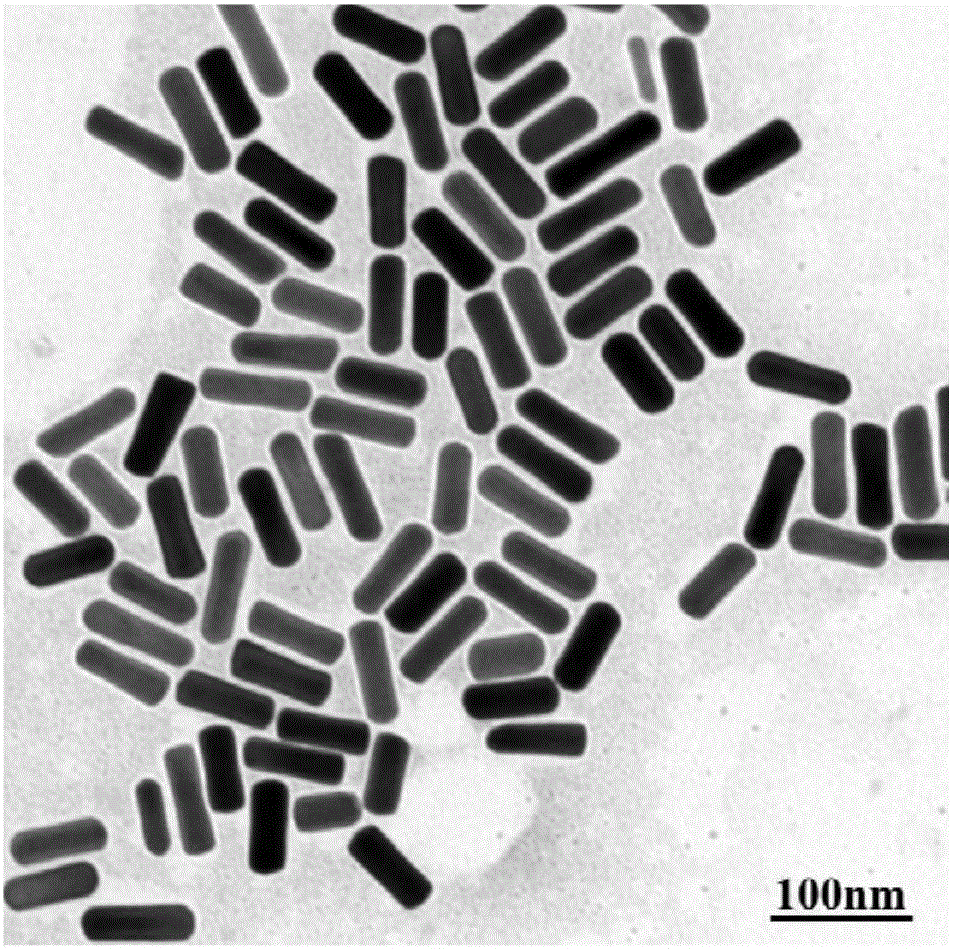
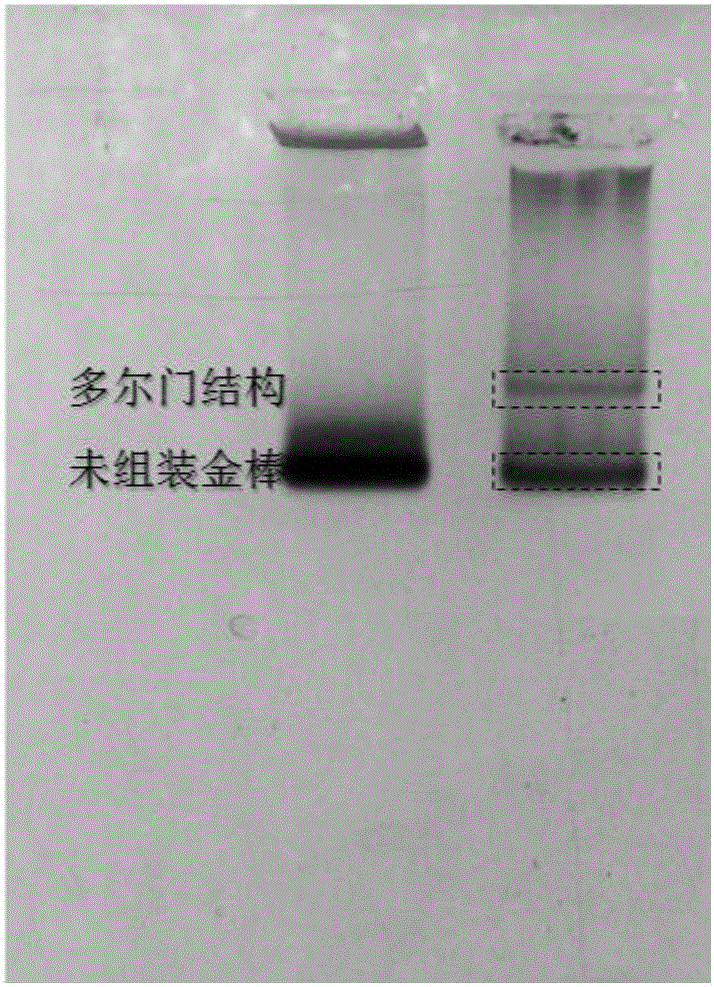
Method for constructing Dolmen structure based on DNA origami template and gold nanorods
ActiveCN106770049AEasy ColocalizationLow costMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingGold nanorodDNA origami
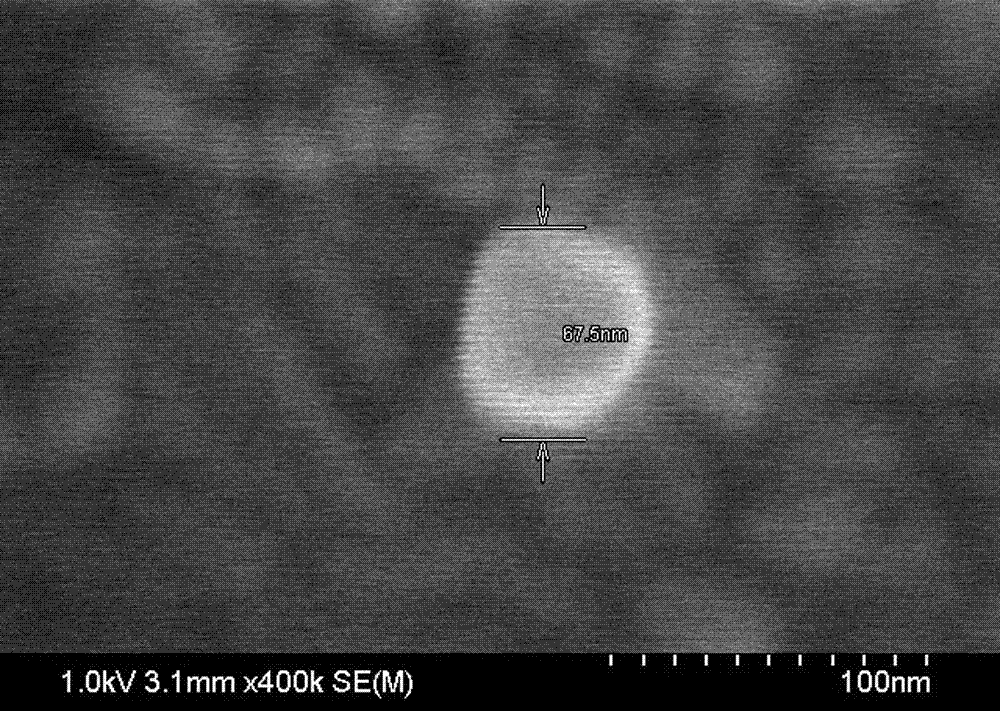
The invention discloses a method for constructing a Dolmen structure based on a DNA origami template and gold nanorods. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing gold nanorods with a specific size by virtue of a seed crystal growth method; secondly, preparing specifically designed rectangular DNA origami; and finally, adding the gold nanorods according to a mole ratio of the gold nanorods to the DNA origami of 5:1, and performing cyclic gradient annealing at 45-20 DEG C to enable the gold nanorods with the specific size to be hybridized with the specifically designed rectangular DNA origami and the Dolmen structure to be constructed with the gold nanorods. The invention also provides a preparation process for preparing the gold nanorods with the specific size by virtue of the seed crystal growth method and preparing the gold nanorods modified by a nucleotide sequence shown by ssDNA1. According to the method provided by the invention, characterization is performed with the help of agarose electrophoresis and a transmission electron microscope, a gold nanorod assembly can be positioned with a scanning electron microscope together easily by use of a characteristic that the gold nanorod assembly has a special color in a dark field image of a dark field microscope, and compared with an etching means, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple, convenient and reliable, having a low cost and relatively low experiment condition requirements, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for controlling properties of nucleic acid nanostructures
ActiveUS8554489B2Increase flexibilityImprove propertiesBiological testingSequence analysisChemical physicsDNA origami
Techniques for controlling properties of nucleic acid nanostructures include receiving data that indicates a sequence of nucleotides on at least a first strand of a nucleic acid. Values are determined for at least one physical property for each portion of the at least first strand. Based at least in part on a numerical model and the physical properties for each portion, a value is determined of at least one derived property of a nanostructure that comprises the at least first strand of nucleic acid. In some embodiments, information gained from the numerical model is used iteratively in order to optimize or improve one or more of the properties of the target DNA origami structure.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
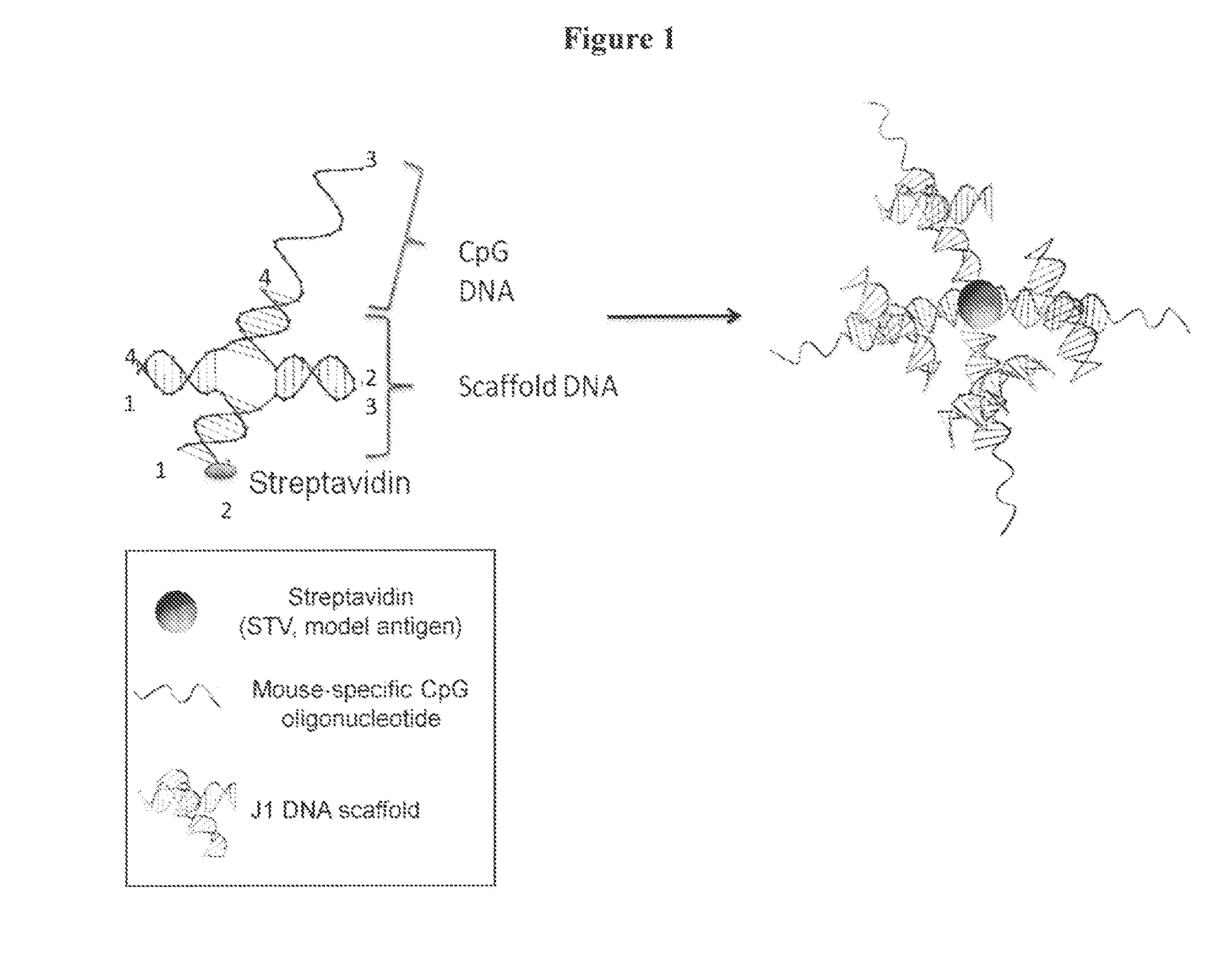
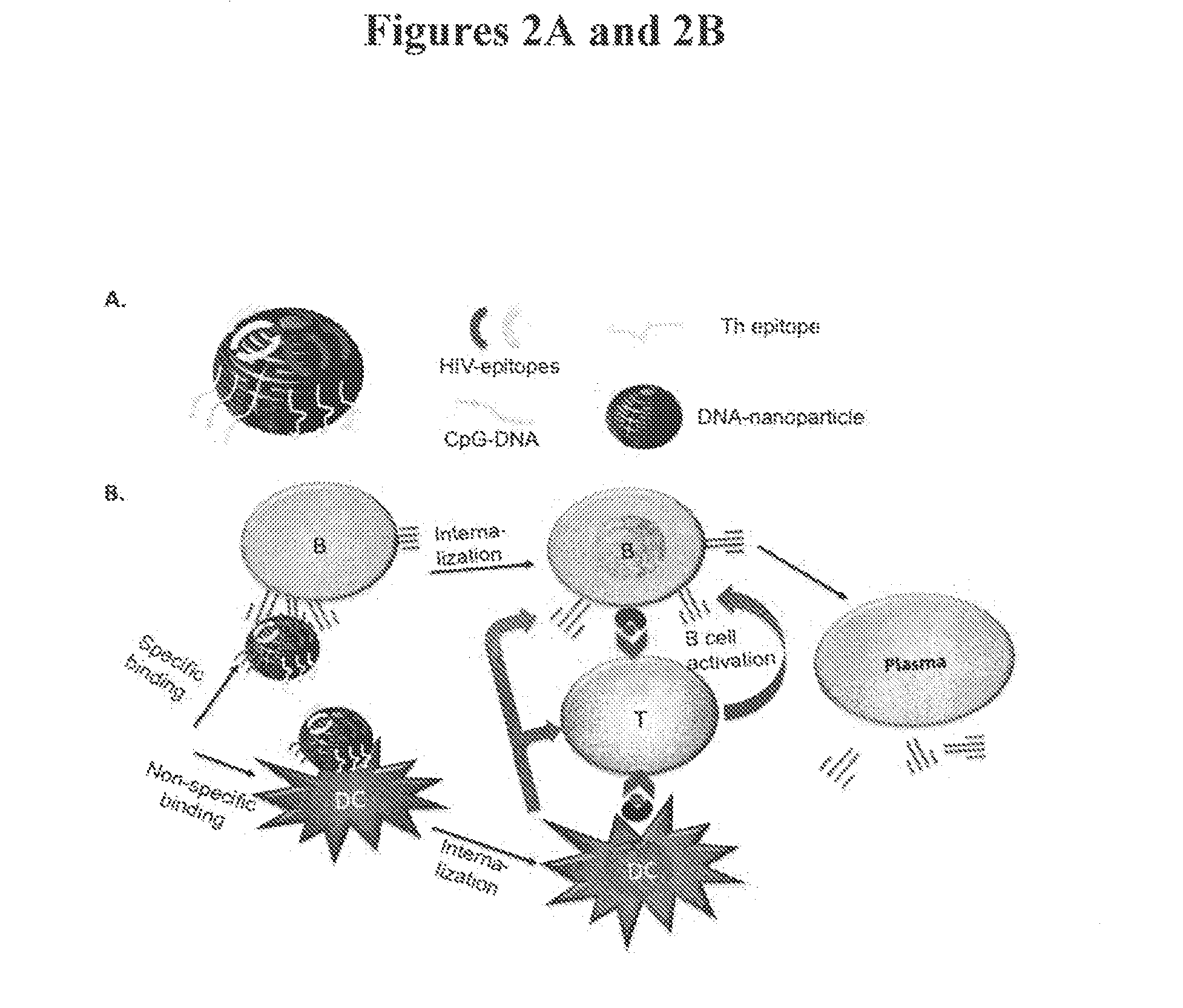
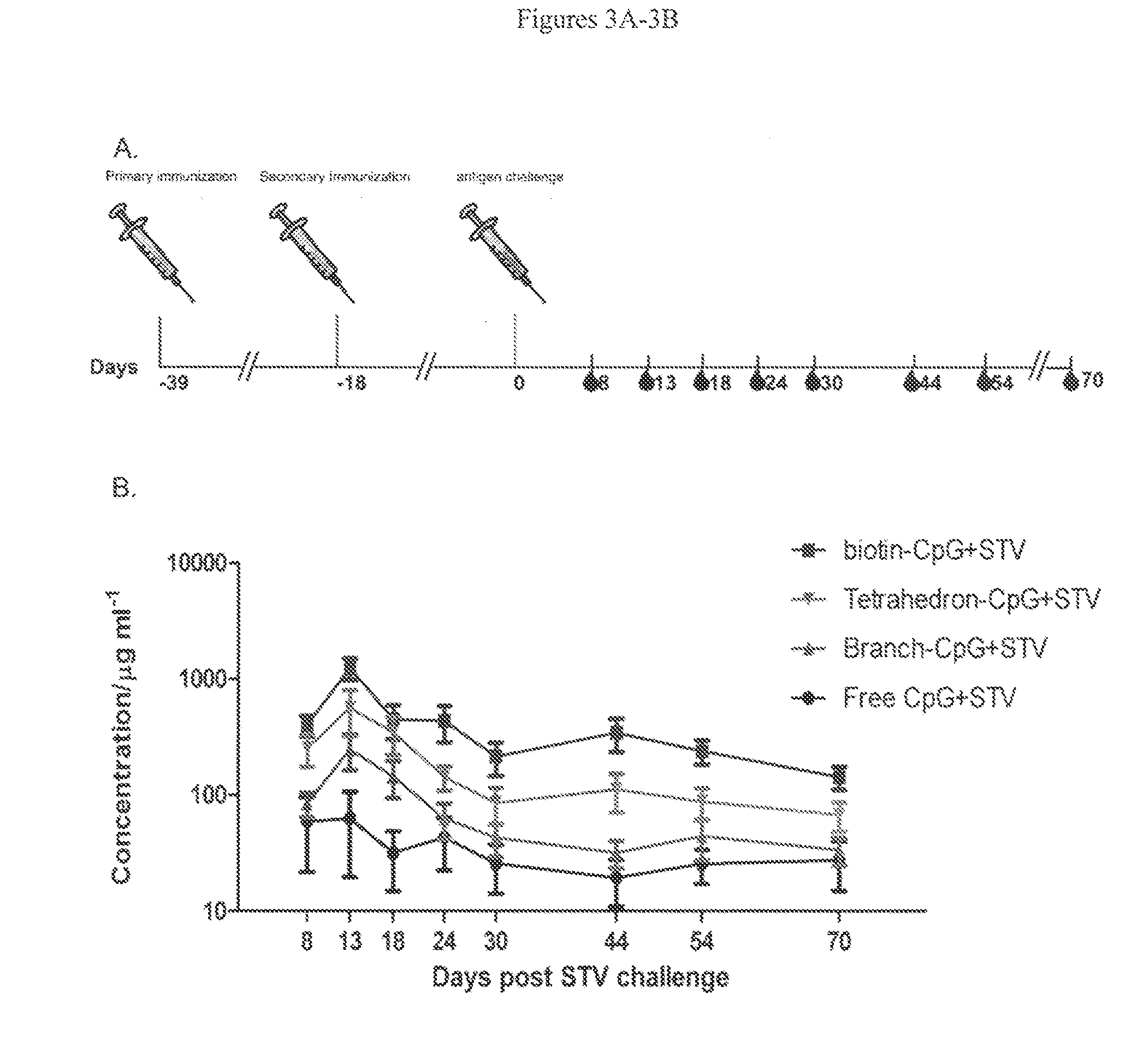
Novel dna-origami nanovaccines
The present invention provides compositions comprising a DNA-nanostructure and at least one targeting moiety, wherein the at least one targeting moiety is linked to the DNA-nanostructure; and wherein the at least one targeting moiety is selected from the group consisting of antigens, aptamers, shRNAs and combinations thereof, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Dna-origami-based standard
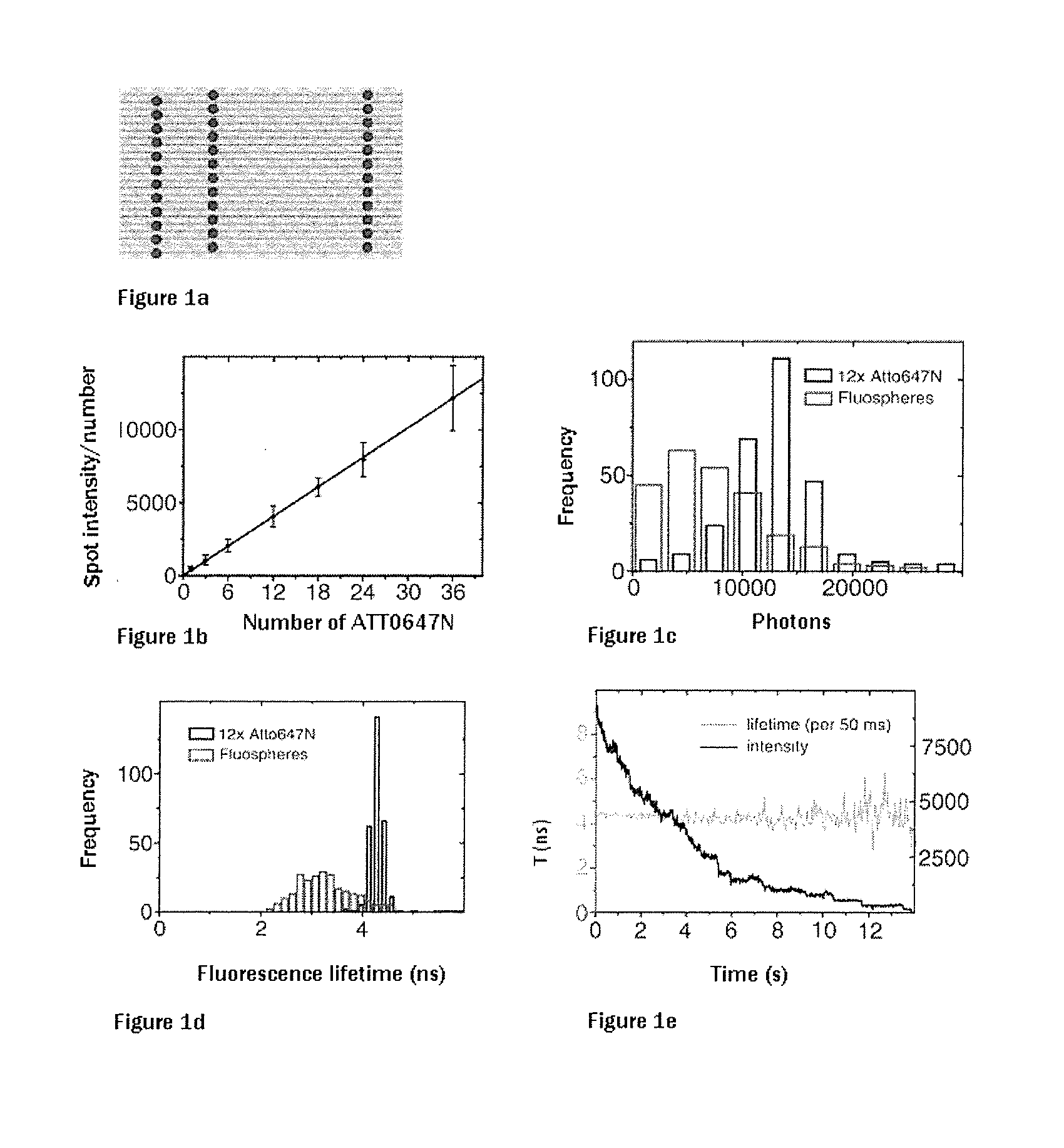
Arrays which utilize labeling molecules for calibrating a measuring device, such as microscopes, have a first structure based on a DNA origami as a calibration sample, wherein the DNA origami is formed into a predetermined structure by short DNA segments. The DNA origami is optionally present in an arranged manner on a support, wherein a number of short DNA segments which form the predetermined structure include a labeling molecule. Optionally, the array can have at least a second structure based on a DNA origami, different from the first structure, as a calibration sample. The array allows quantification of the labeling molecules on the basis of the number of photons per unit time.
Owner:TECH UNIV BRAUNSCHWEIG
Compositions and methods relating to nucleic acid-protein complexes
ActiveUS20160279257A1Spare proteinPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsDNA origamiProtein-protein complex
Provided are methods and compositions relating to conjugation of nucleic acids and proteins of interest under conditions that maintain protein activity. The nucleic acid-protein conjugates may be used in nucleic acid nanostructures such as those generated using DNA origami methods.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Nanoprobe used for specific recognition of DNA sequences, and application method thereof
InactiveCN107245524AAchieve precise positioningHigh resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceA-DNA
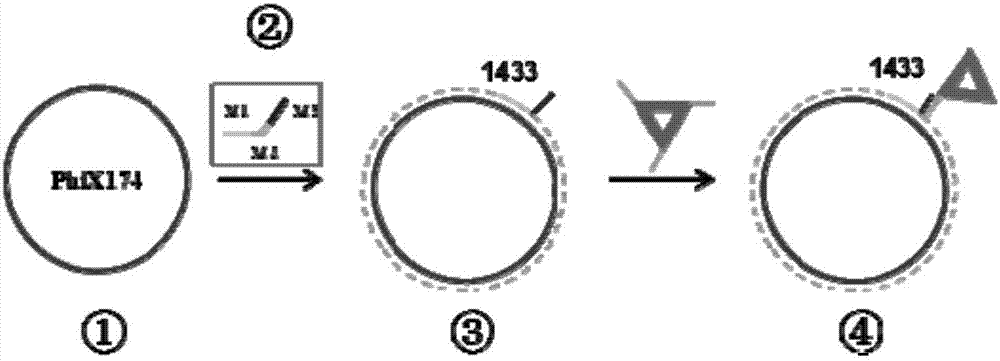
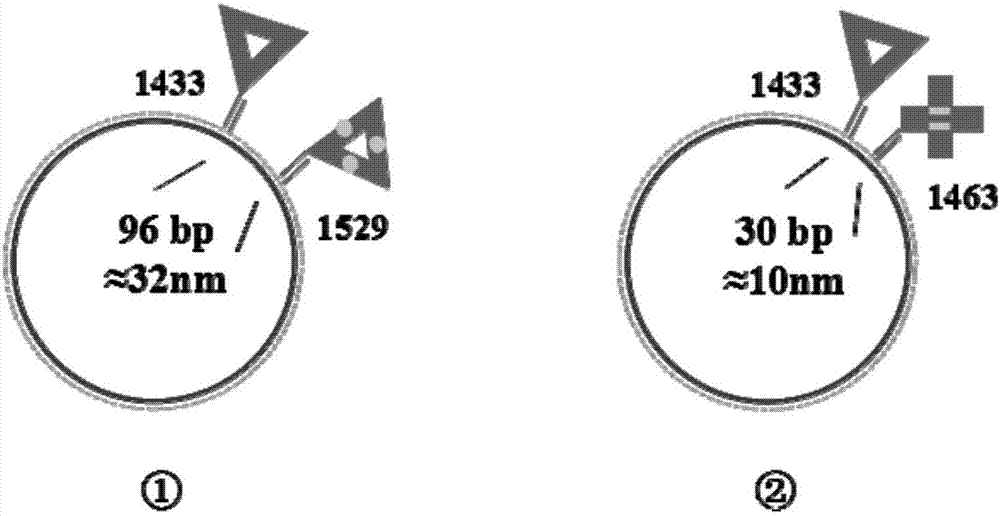
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection analysis and molecular biology, and discloses a nanoprobe used for specific recognition of DNA sequences, and an application method thereof. The application method comprises following steps: 1, a DNA origami probe is prepared, wherein the DNA origami probe is prepared based on Rothemund and Seeman method; 2, a PhiX 174 model based on closed circular single-chain DNA or a Lambda model of linear double chain DNA is constructed, wherein in model construction, a double segmented DNA primer composed of three parts is adopted; 3, specific marking of the DNA origami probe is carried out, wherein an excess amount of the DNA origami probe and a target DNA molecular are subjected to mixed reaction for 12h or longer; and 4, imaging observation is carried out using an atomic force microscope. The application method is capable of realizing accurate positioning of same gene segments on a single-molecular DNA, observation of corresponding sites at high resolution using an atomic force microscope can be realized, a problem that fluorescent molecular marking is limited by optical diffraction limit under electron microscopes is avoided; and the application method can be adopted in the fields such as in situ testing of chromosome genovariation and clinical genetic diagnosis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for detecting polymorphism of single nucleotide with gold nanoparticles
The invention relates to a method for detecting the polymorphism of single nucleotide with gold nanoparticles in the nanotechnology field. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing an unsymmetrical two-dimensional pattern by utilizing a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) origami technology to prepare a DNA origami chip; preparing a colloidal gold probe; hybridizing a DNA short chain and the colloidal gold probe; connecting the particle-size colloidal gold probe and the DNA origami chip in the unsymmetrical two-dimensional pattern; and detecting the polymorphism of the single nucleotide. The invention has the advantages of simpleness, low cost, and the like without strict experimental conditions and complicated enzyme reactions and can realize a DNA hybridization process in a nano-scale liquid-phase reaction and achieve high-sensitivity biomedical detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Nucleic acid nanotube liquid crystals and use for nmr structure determination of membrane proteins
Compositions and methods for preparing nucleic acid nanotubes using DNA origami techniques are described, which provide for nanotubes of predictable and uniform length. The nucleic acid nanotubes thus formed are suitable as liquid crystal preparations enabling liquid-crystal NMR spectroscopy of proteins solubilized in detergent.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
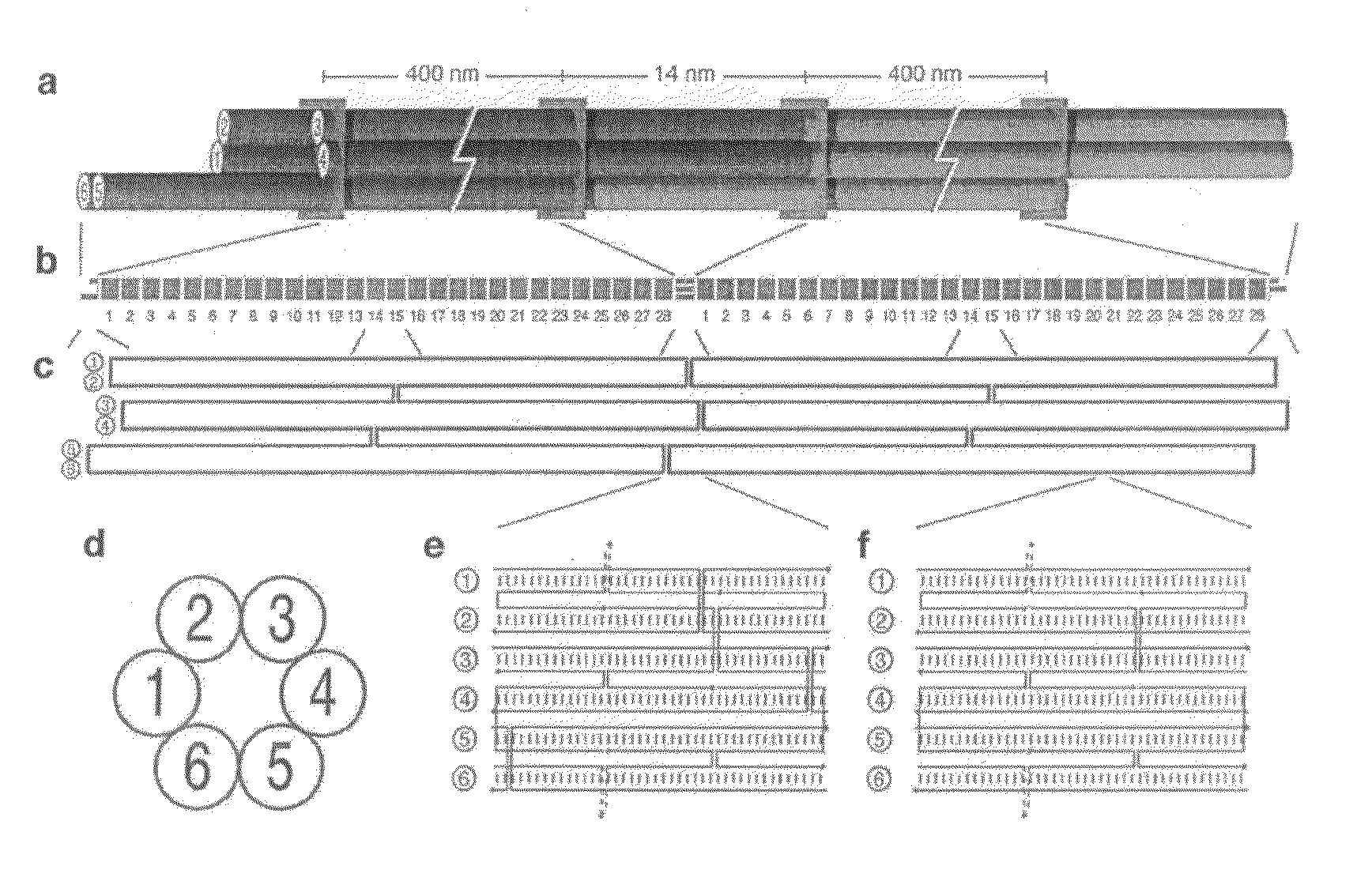
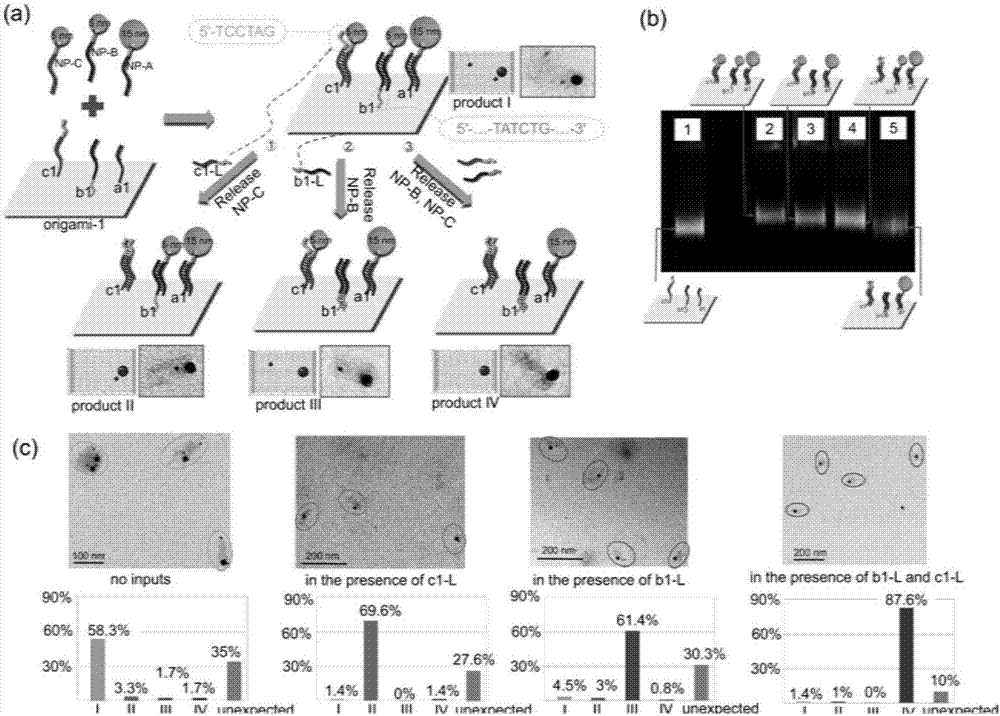
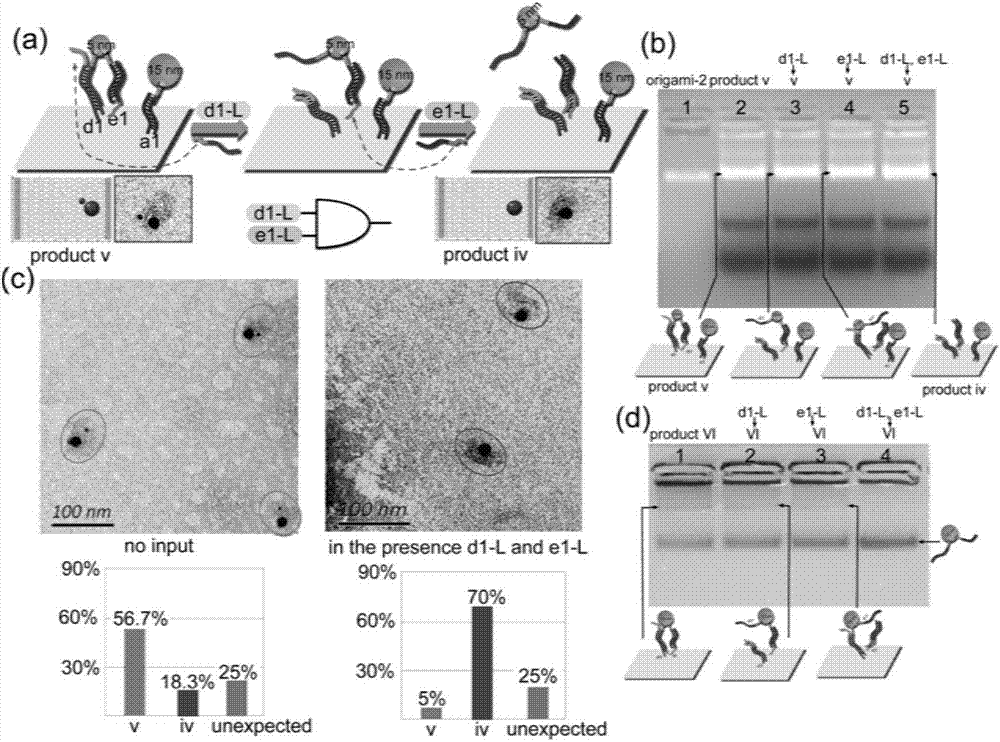
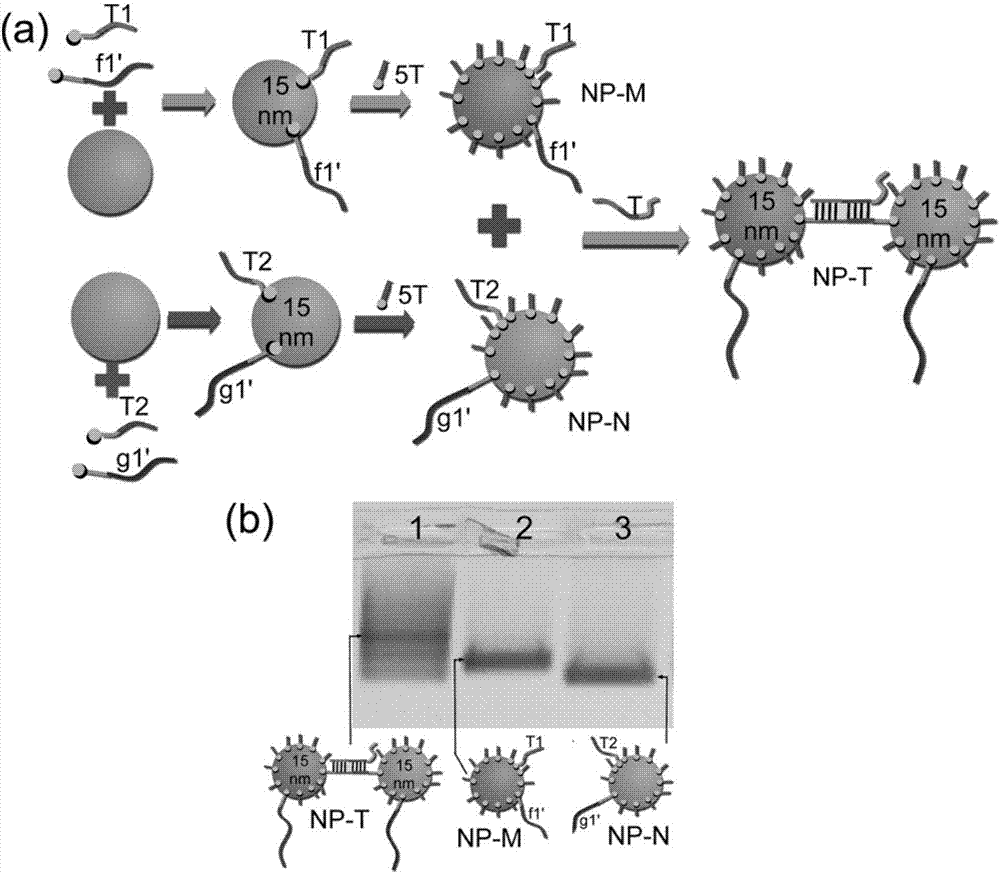
DNA molecular logic gate based on DNA Origami and construction method thereof
ActiveCN107124178AGuaranteed normal operationLogic circuits characterised by logic functionHybridisationNano-deviceGold particles
The invention belongs to the field of molecular computation, and particularly relates to a DNA molecular logic gate based on DNA Origami and a construction method thereof. The logic gate comprises an input signal, a signal converter and an output signal; the signal converter includes a DNA Origami template, a helper chain positioned on the DNA Origami template, and a DNA / AuNP conjugate that can be identified and connected with the helper chain; and the output signal is provided for releasing the DNA / AuNP conjugate from the DNA Origami template. According to the DNA molecular logic gate based on the DNA Origami and the construction method thereof disclosed by the invention, the selective and dynamic release to gold particles is implemented by a special DNA signal on the DNA Origami, and thus, the operation of the logic gate is implemented; moreover, by employing a gold particle dimer connected by the DNA chain, the operation of simultaneously imputing three input chains for the logic gate is implemented. The DNA molecular logic gate and the construction method thereof provide a concept to construct complex molecular circuit and nano device; and through combining with various nano engineering strategies, the DNA molecular logic gate and the construction method thereof can be used for assembling a large programmable structure, and also pave a road for sensitivity detection of various molecular conformations.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Real time in situ characterization method for single biomolecular reaction
The invention discloses a real time in situ characterization method for a single biomolecular reaction. The method comprises the following steps: immobilizing a reactant I on a DNA origami design site; then carrying out atomic force microscope imaging for the reactant I-modified DNA origami; adding a reactant II, wherein the reactant II is correspondingly combined with the reactant I, meanwhile continuously scanning imaging and collecting data. With the method provided by the present invention, the real time in situ detection can be performed, the single biomolecular reaction process can be recorded exactly. In addition, the method is benefit for studying the dynamic process of the single biomolecular reaction on the interface.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
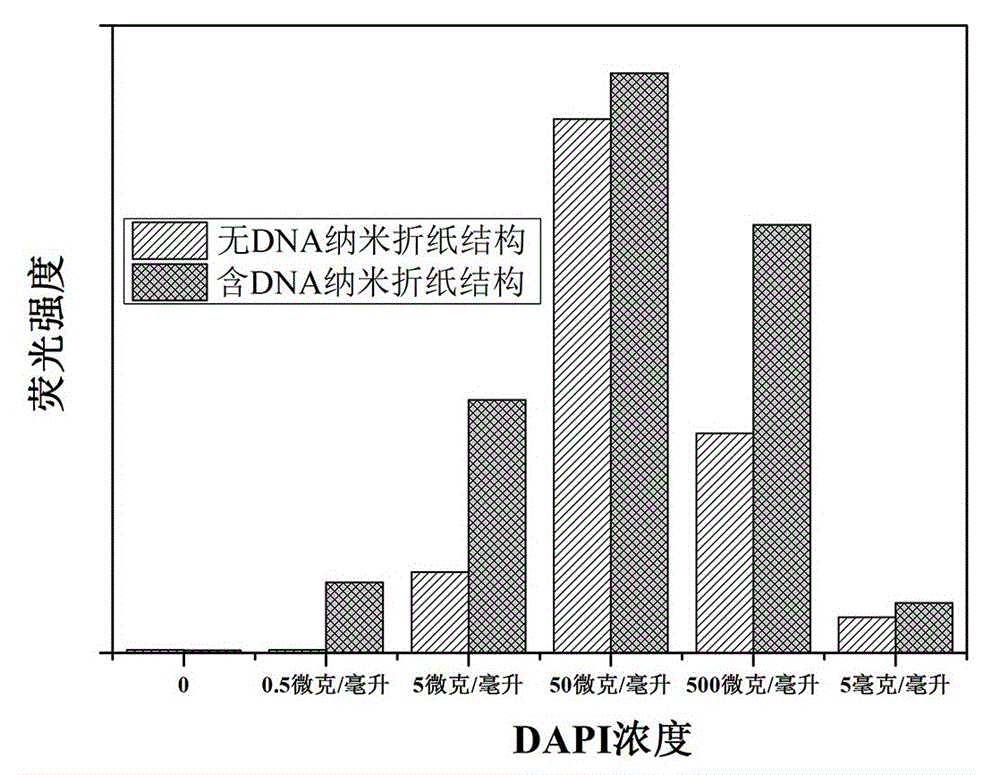
Method for simulation of DNA nano origami structure as drug carrier by DAPI embedding and release
ActiveCN105004703AHigh fluorescence intensityDecreased fluorescence intensityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFluorescence/phosphorescenceBio moleculesA-DNA
The invention relates to a DNA nano-origami structure constructed by rolling circle amplification technology and DNA origami, at the same time utilizes fluorescent dye DAPI with DNA double-strand binding properties and cell membrane penetration properties to label and track the DNA nano-origami structure, thus realizing real-time monitoring and simulation of the drug loading and sustained release process of the DNA nano-origami structure as a drug carrier. And the method also can be applied as a new fluorescent quantitative analysis method to biomolecular detection, like tumor early detection, postoperative monitoring and evaluation, cell imaging and other fields.
Owner:智玺那诺(上海)生物科技有限责任公司
Mechanochemical platform and sensing methods using DNA origami nanostructures
ActiveUS20170108517A1Easy to limitSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein targetDNA origami
A biosensing platform capable of high throughput mechanochemical biosensing comprising a DNA origami nanostructure having a plurality of slots into which recognition elements are strategically placed and apparatus that senses a change in the origami nanostructure in response to the introduction of a target where the apparatus includes a signal transduction unit and signal sensor which exploits mechanical signals in a recognition element which signal includes one or more mechanical tension or mechanochemical rearrangement event. The nanostructure is preferably a 2-dimensional or 3-dimensional arrangement of tiles linked by locking elements, such as aptamers that will open in response to an event such as exposure to a drug molecule, DNA, RNA or protein target.
Owner:KENT STATE UNIV
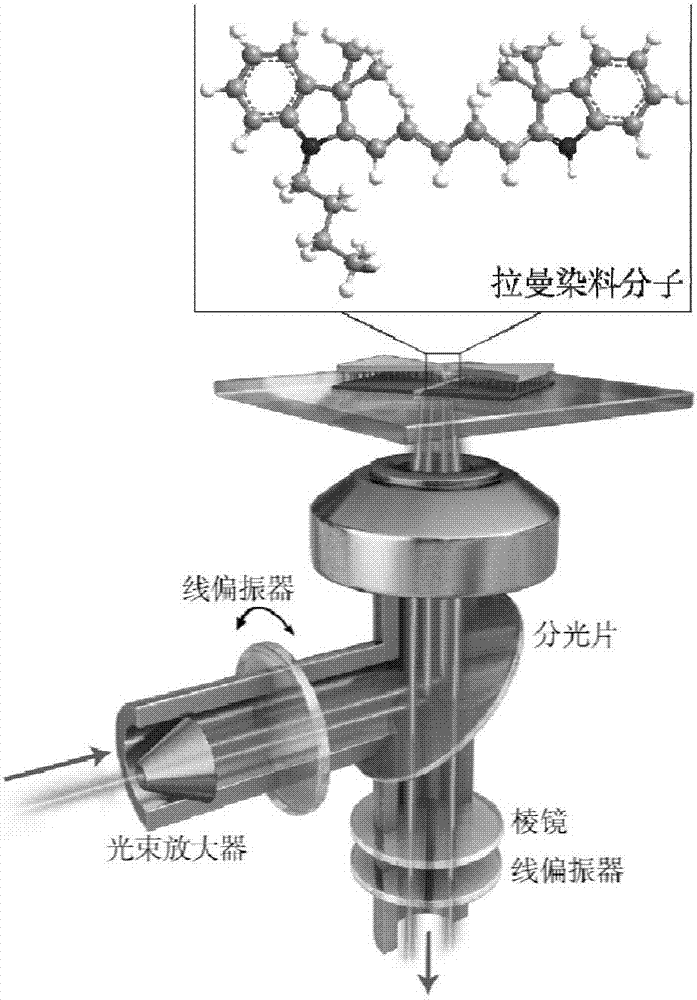
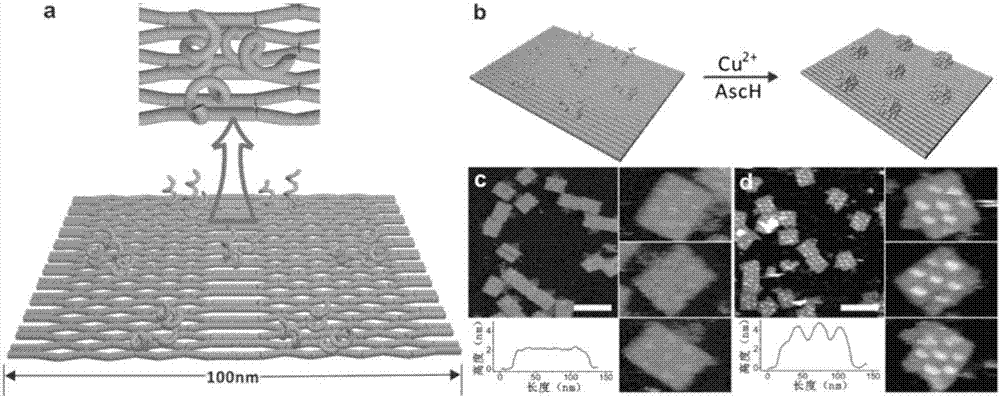
Method for forming dimer structure by assembling DNA origami template and nanometer gold cube based on surface enhanced Raman effect
ActiveCN110057806AEfficient and accurate assemblyEfficient assemblyRaman scatteringFermentationScanning electron microscopeA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for forming a dimer structure by assembling a DNA origami template and a nanometer gold cube based on a surface enhanced Raman effect. The method specifically comprises the five steps of preparation of triangular DNA origami with specific sites; preparation of a sulfydryl DNA modified nanometer gold cube; preparation of three dimer configurations; and high efficiency precise assembly by using agarose gel electrophoresis and a transmission electron microscope representational structure, and surface enhanced Raman scattering by using a scanning electron microscope and dark-field microscope co-location detection assembly structure. The method solves the problems of low assembly repeatability and poor structural stability, a new idea is also provided for construction of nanometer optical materials due to establishment of the method, and the method is of great significance to research of nanophotonics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Nucleic acid structure of which interchain exchange is achieved by support DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and synthesis method thereof
PendingCN105602949AHigh yieldSimple designDNA preparationDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA origamiNucleic acid structure
The invention discloses a nucleic acid structure of which the interchain exchange is achieved by a support DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The nucleic acid structure is a two-dimensional or three-dimensional nucleic acid structure with controllable size and shape, which is formed by achieving interchain exchange by the support DNA. The nucleic acid structure comprises a set of parallel double helices connected by interchain exchange and a single-chain DNA segment, wherein the double helices are formed by carrying out folding and interchain exchange by the support DNA, carrying out specific matching with a plurality of short-chain DNAs and carrying out annealing reaction; and the single-chain DNA is the part of the support DNA which does not form the double helices. The invention provides the multiple nucleic acid structures and synthesis methods thereof. The nucleic acid structure is a variant technique based on DNA paper folding. The invention aims to form the nucleic acid structure with controllable size, shape, complexity and modification by achieving interchain exchange by using the support DNA. The nucleic acid structure is completed by the support DNA / short-chain DNA self-assembly process, and has the advantages of higher yield and simple design; and the predicated two-dimensional and three-dimensional structures can be simultaneously synthesized.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
DNA origami structure, closing and releasing method of DNA origami structure and application of DNA origami structure as drug delivery system
InactiveCN112143727ASolve limitedSolve efficiency problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementInorganic non-active ingredientsGold particlesMedicine
The invention relates to a DNA origami structure, a closing and releasing method of the DNA origami structure and an application of the DNA origami structure as a drug delivery system, and belongs tothe technical field of DNA nano drug delivery. The DNA origami structure is a DNA tetrahedron and comprises three side triangular origamis and a central triangular origami, and three sides of the central triangular origami are connected with the three side triangular origamis respectively; skeleton chains of the central triangular origami and the side triangular origamis are annular single-helix DNA chains of M13 bacteriophage; the central triangular origami and the side triangular origamis are occluded through base complementary pairing of respective internal staple chains and respective skeleton chains; the central triangular origami is complementarily paired with connecting staple chains of the side triangular origamis through a connecting staple chain; and the central triangular origami and the side triangular origamis capture nano-gold particles through capture chains, and the side triangular origamis and the central triangular origami form a three-dimensional tetrahedral origamistructure through traction of the nano-gold particles. According to the invention, the drug loading efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Manufacture method of metal nano circuit patterns based on DNA nano structures
ActiveCN107055465AWith nanoscale resolutionHigh position specificitySpecific nanostructure formationNano structuringDNA origami
The invention provides a manufacture method of metal nano circuit patterns based on DNA nano structures. The method includes taking DNA paper folding structures fixed to surfaces as templates, introducing artificial defects onto the templates, and performing selective metallization on the templates with the artificial defects so as to create the metal nano circuit patterns based on the DNA nano structures. The manufacture method is simple, rapid and effective, and a series of metal nano patterns with only few nanometers of zero-dimensional, one-dimensional and two-dimensional line width can be acquired through accurate positioning of DNA paper folding. DNA paper folding mainly applied to the manufacture method has high biocompatibility, and other needed chemical and biological materials do not have toxicity on human bodies; a novel thought and a novel technical support are provided for creating a nano circuit by 'bottom-to-up' self-assembly and breaking through the limit of conventional photolithography.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting polymorphism of mononucleotide by using biotin-avidin system
InactiveCN101974625ALow costMicrobiological testing/measurementTwo-dimensional graphBiotin-streptavidin complex
The invention provides a method for detecting polymorphism of mononucleotide by using a biotin-avidin system in the technical field of nanometer. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an asymmetric two-dimensional graph by utilizing a DNA paper folding art to prepare a DNA paper folding chip; hybridizing a report probe of a tail end modified biotin with the DNA paper folding chip; connecting streptavidin with the biotin; detecting the polymorphism of the mononucleotide; and imaging by an atomic force microscope. The method has the advantages of no need of restrict experiment conditions or complicated enzyme reaction, simpleness, low cost and the like. By using the method, the DNA hybridizing process can be realized in nanometer scale and liquid phase reaction, and high sensitivity biomedical detection can be reached.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
Biomolecule affinity constant determination method based on DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) origami
InactiveCN102955047AAccurate measurementReduce dosageScanning probe microscopyCrystallographyDNA origami
The invention discloses a biomolecule affinity constant determination method based on DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) origami. The biomolecule comprises a reactant I and a reactant II which are integrated together and dissociated. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) connecting the reactant I to the tail of a staple chain of the DNA origami, and then, executing self-assembly together with a scaffold chain to form the DNA origami; (2) adding the reactant II, after reaching equilibrium in reaction, collecting data by executing scanning imaging with an atomic force microscope, calculating the concentration [AbAg] of a compound of the reactant I and the reactant II, the concentration[Ag] of the free reactant I and the concentration [Ab] of the free reactant II; and (3) substituting the formula K=[AbAg] / [Ag][Ab] with the obtained data to calculate the affinity constant of the reactant I and the reactant II. The method can be used for accurately calculating the affinity constant of the biomolecule at the molecular level, thereby having the advantages of high efficiency, excellent repeatability and less usage of samples.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image visualization method for detecting single molecule DNA duplication
InactiveCN105760715AAids in understanding the mechanism of actionData visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsPolymerase LMolecular level
The invention discloses an image visualization method for detecting single molecule DNA duplication. The method comprises the steps that single-chain DNA and a buffering system of a DNA polymerase Klenow fragment combined with the single-chain DNA are scanned with an atomic force microscope, and DNA duplication is subjected to imaging observation through the atomic force microscope, wherein the single-chain DNA contains dNTP, and the two ends of the single-chain DNA are fixed to two different positions on hollow DNA folded paper respectively. According to the method, the DNA duplication process is tracked on the single molecule level, the whole process of combination of the single-chain DNA and single DNA polymerase, moving between the DNA chain and the DNA polymerase and conversion from the single-chain DNA chain to a double-chain DNA chain is recorded, various forms of state distribution of the DNA chain on the surface of a substrate and the changing situation in the interaction process of DNA and the DNA polymerase can be captured, the biomolecule behavior action mechanism can be understood more easily, and data on the time scale and the space scale in the molecule event obtaining process can be obtained more easily.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and application of sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA to DNA origami
The invention discloses a preparation method of sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and application of the sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) to DNA origami. The preparation method of the sequence and length customized circular single-stranded DNA, disclosed by the invention, comprises the following steps: (1) designing and synthesizing circular double-stranded recombinant phagemid; (2) transforming escherichia coli through the recombinant phagemid and infecting through helper phage to prepare the circular single-stranded DNA with a corresponding form; (3) assembling different origami structures by taking prepared the ssDNA as a framework chain respectively, and carrying out characterization through atomic force microscope imaging. According to the method disclosed by the invention, aiming at the certain specific DNA, various types of single-stranded DNAs with different base sequences and lengths can be designed according to application requirements, so that customization is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method of regulating and controlling in-site catalytic polymerization reaction with bioenzyme on nano material on the basis of DNA
The invention relates to a method of regulating and controlling an in-site catalytic polymerization reaction with a bioenzyme on a nano material on the basis of DNA. According to different adsorption capabilities of a polymerization substrate to single- and double-chain DNAs, single- and double-chain DNAs are stretched out at special sites of a nano structure; the bioenzyme is then conjugated to the nano material to perform the catalytic polymerization reaction; a reagent, which is required in the bioenzyme catalytic polymerization reaction, is added to the nano material after the bioenzyme is conjugated thereto, and according to different demands, reaction conditions are controlled so as to in-site catalyze generation of a high-molecular polymer on the single- and double-chain DNAs on the original nano structure. In the method, by controlling the reaction conditions, nano structures, such as gold nano particle, DNA origami and the like, are modified with the bioenzyme, thereby catalytically generating the polymer on the material modified with the single- and double-chain DNAs by means of the bioenzyme. The method can quickly, on special sites, catalyze an ordered polymerization reaction and can be used for producing a composite high-molecular polymer on various materials, such as noble metal particles, thereby regulating and controlling photo- and electro-activity of the materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Probe machine achievement method and device based on DNA computing
ActiveCN107437003AImprove computing efficiencyEasy to detectSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsDNA origamiThree-dimensional space
The embodiment of the invention provides a probe machine achievement method and device based on DNA computing. The method comprises the steps that preset conditions are obtained according to a mathematical problem to be solved, and DNA sequence coding is conducted on DNA origami structures and DNA single-strands according to the preset conditions respectively; a database containing the DNA origami structures is built; a probe library containing the DNA single-strands is built; the DNA origami structures and the DNA single-strands are subjected to hybrid reaction on a computing platform to obtain a reaction product; the reaction product is detected through a detector to obtain a computing result. According to the method, the DNA origami structures and the DNA single-strands in DNA computing are used, so that a probe machine is built to improve the processing ability of a computer, and the computing result is easy to detect; the problem is effectively solved that the mispairing rate of self-assembling of traditional algorithms is high, and the reliability of the computing result is improved, and free communication between data in a three-dimensional space and specificity assembling are achieved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com