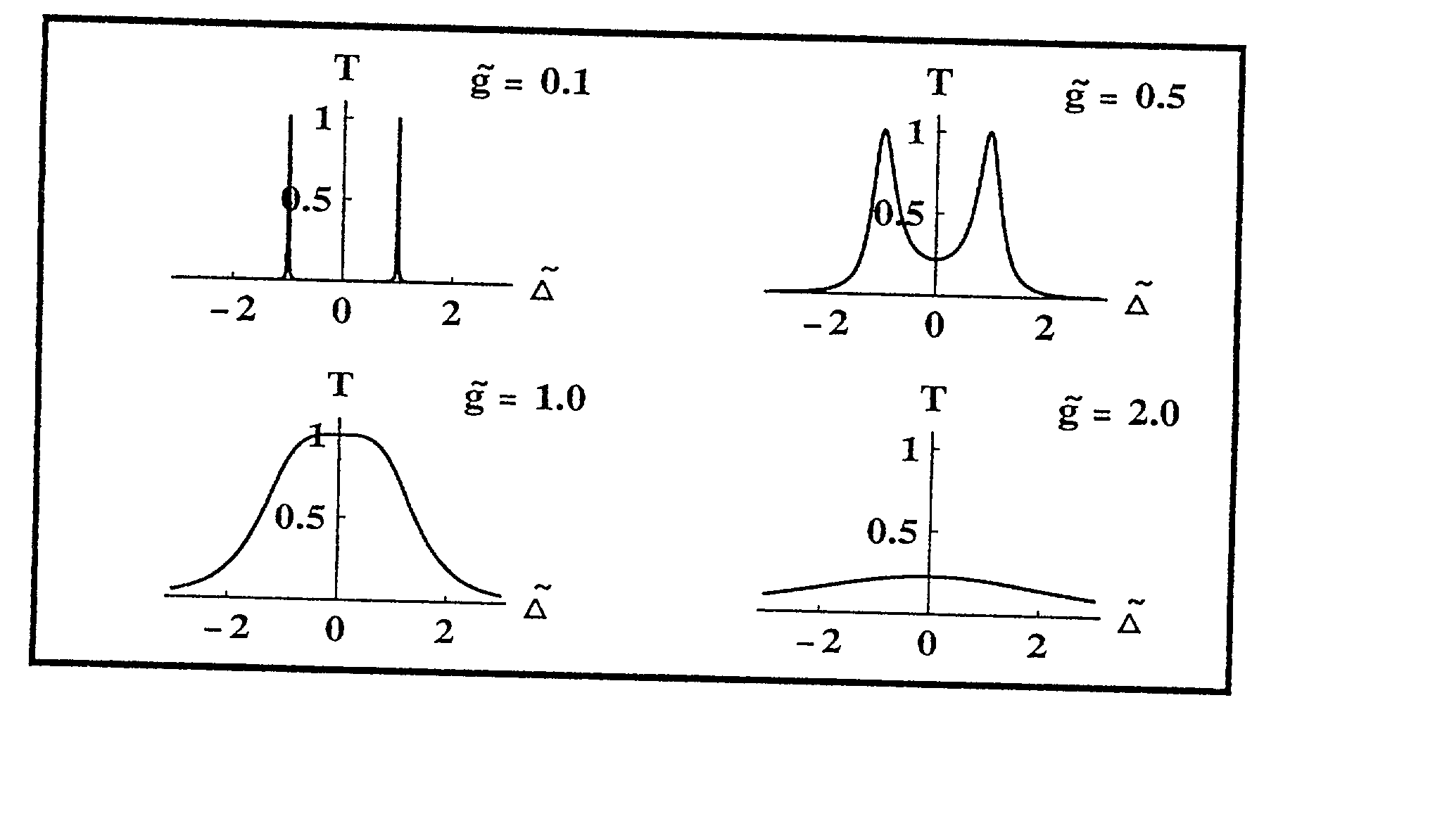
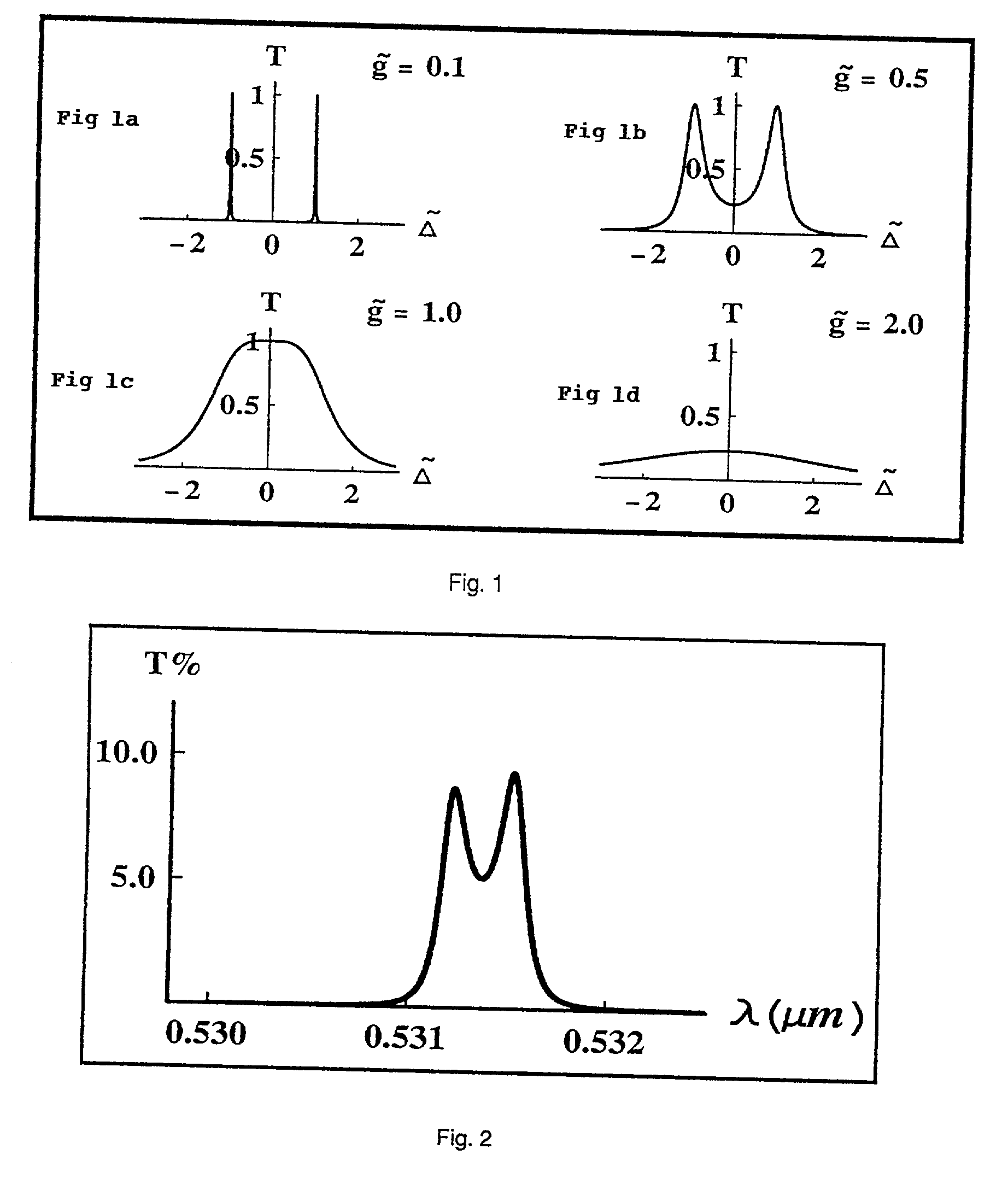
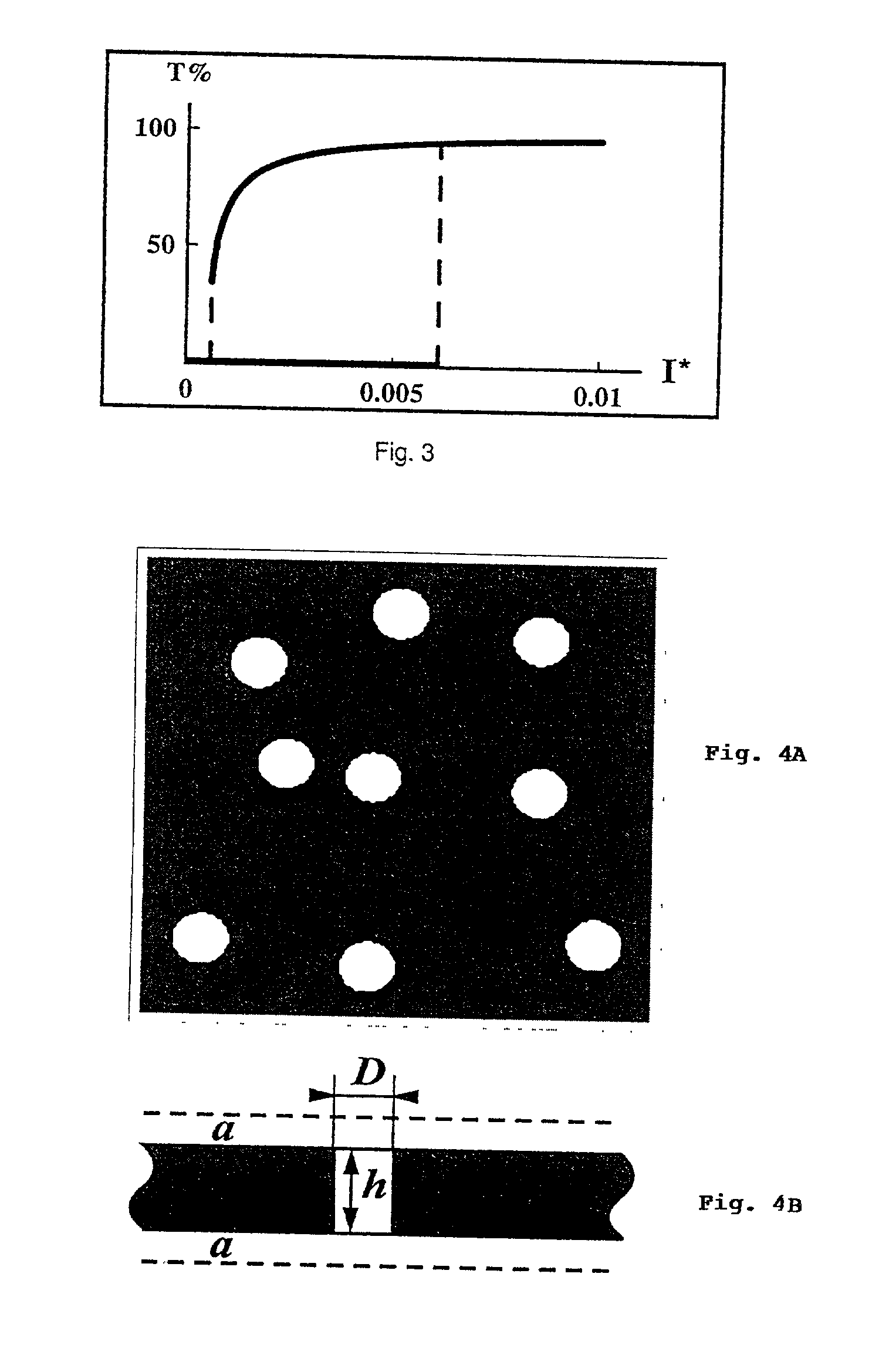
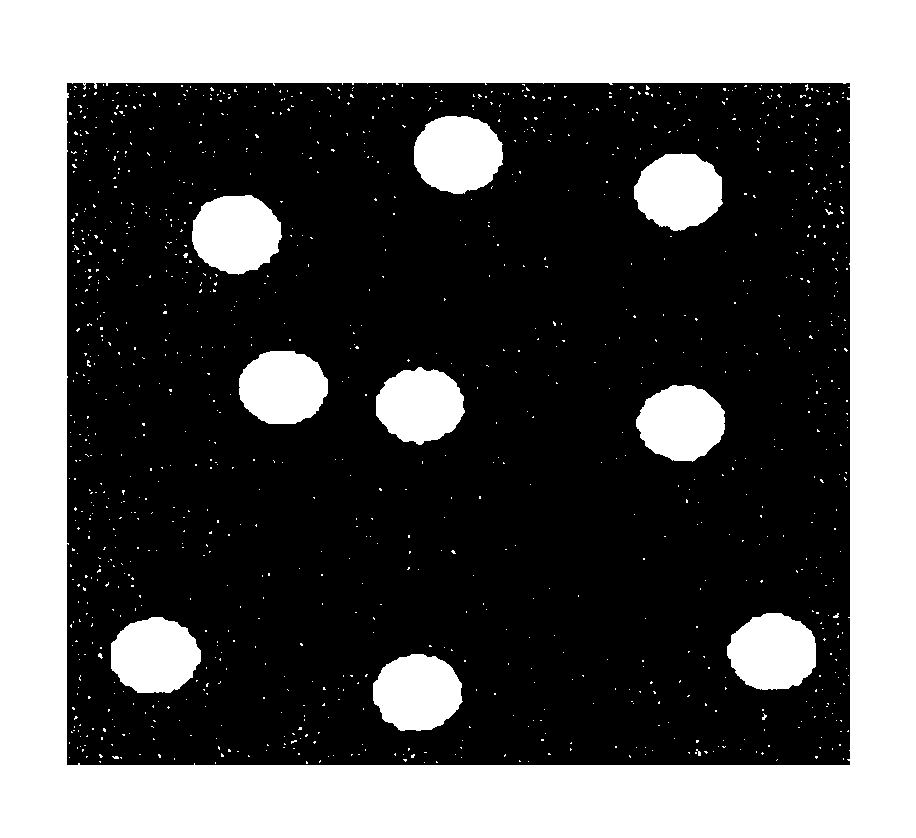
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Nanophotonics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
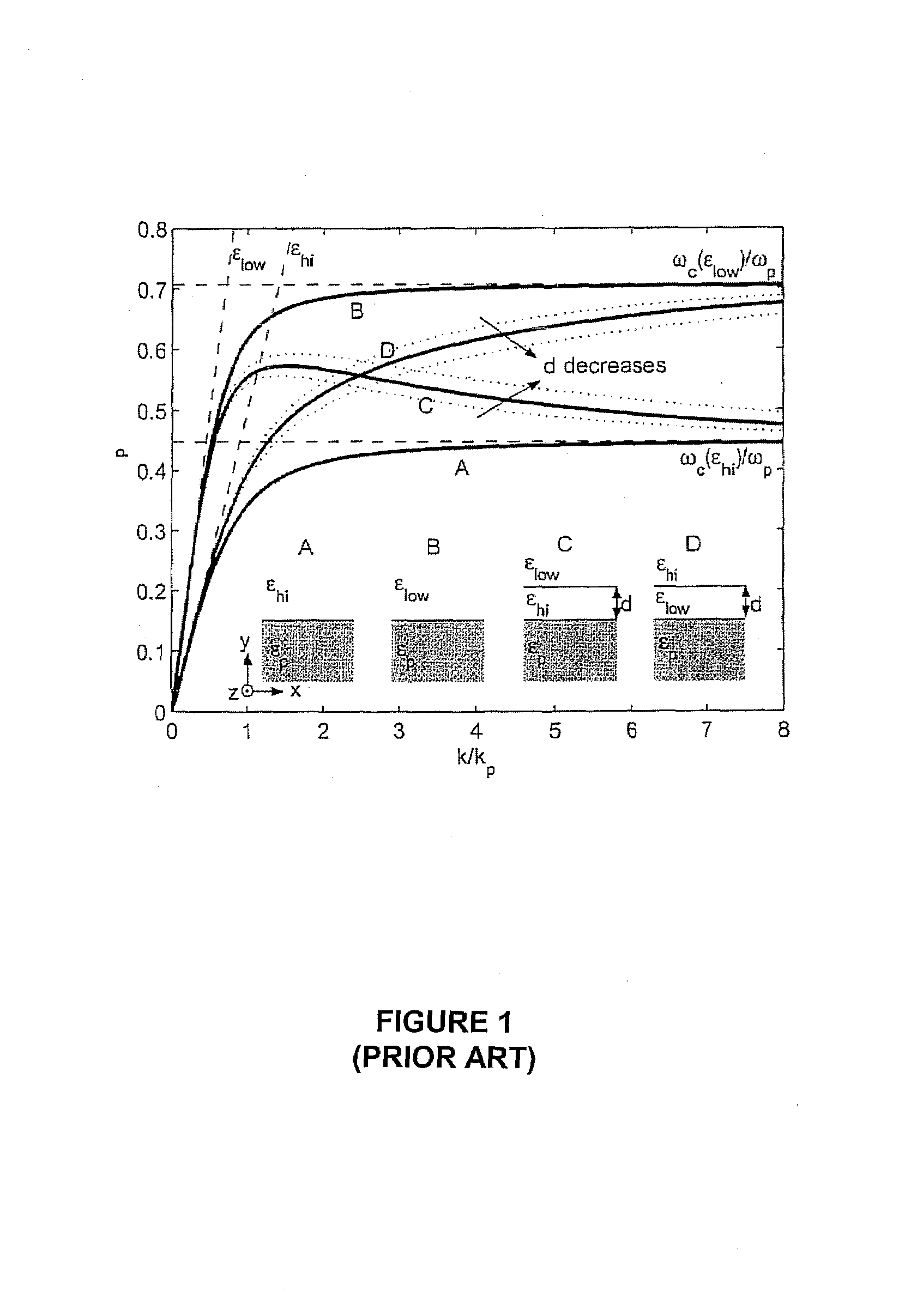
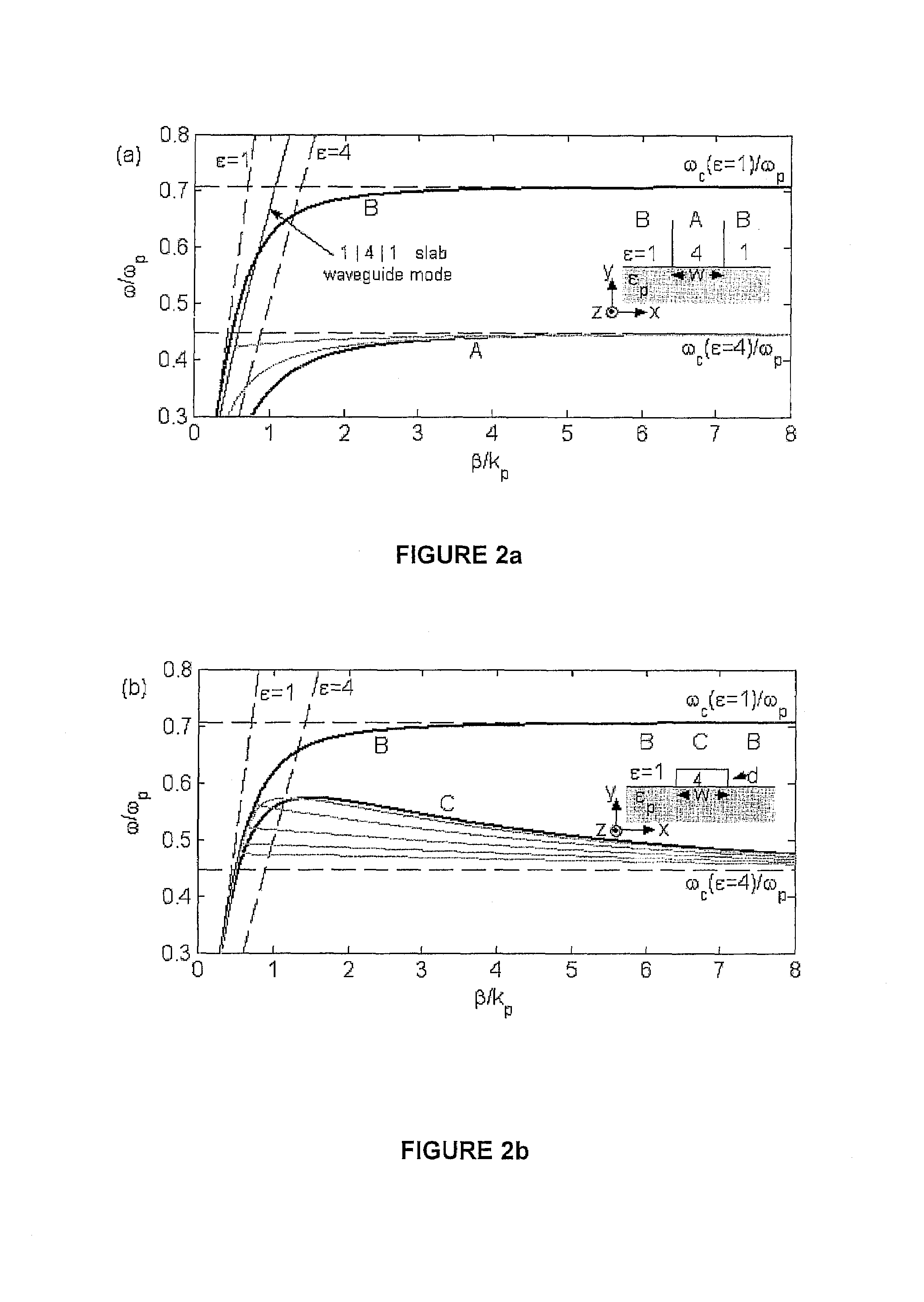
Nanophotonics or nano-optics is the study of the behavior of light on the nanometer scale, and of the interaction of nanometer-scale objects with light. It is a branch of optics, optical engineering, electrical engineering, and nanotechnology. It often (but not exclusively) involves metallic components, which can transport and focus light via surface plasmon polaritons.
Plasmonic nanophotonics methods, materials, and apparatuses
Controlling, guiding, manipulating, and circuiting light and performing surface-enhanced spectroscopy in a medium comprising plasmonic nanomaterials via the excitation of plasmon modes in the materials. The plasmonic nanomaterials are based on metal films with or without arrays of nanoholes and / or on metal nanowires and / or spheroids. Also devices and methods employing such plasmonic nanomaterials.
Owner:NEW MEXICO STATE UNIV TECH TRANSFER
Plasmonic nanophotonics methods, materials, and apparatuses
Controlling, guiding, manipulating, and circuiting light and performing surface-enhanced spectroscopy in a medium comprising plasmonic nanomaterials via the excitation of plasmon modes in the materials. The plasmonic nanomaterials are based on metal films with or without arrays of nanoholes and / or on metal nanowires and / or spheroids. Also devices and methods employing such plasmonic nanomaterials.
Owner:NEW MEXICO STATE UNIV TECH TRANSFER
Molecular imaging and nanophotonics imaging and detection principles and systems, and contrast agents, media makers and biomarkers, and mechanisms for such contrast agents
InactiveUS20090119808A1Enhanced sub-surfaceEnhanced in-depth imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesSurface/boundary effectDepth imagingImage resolution
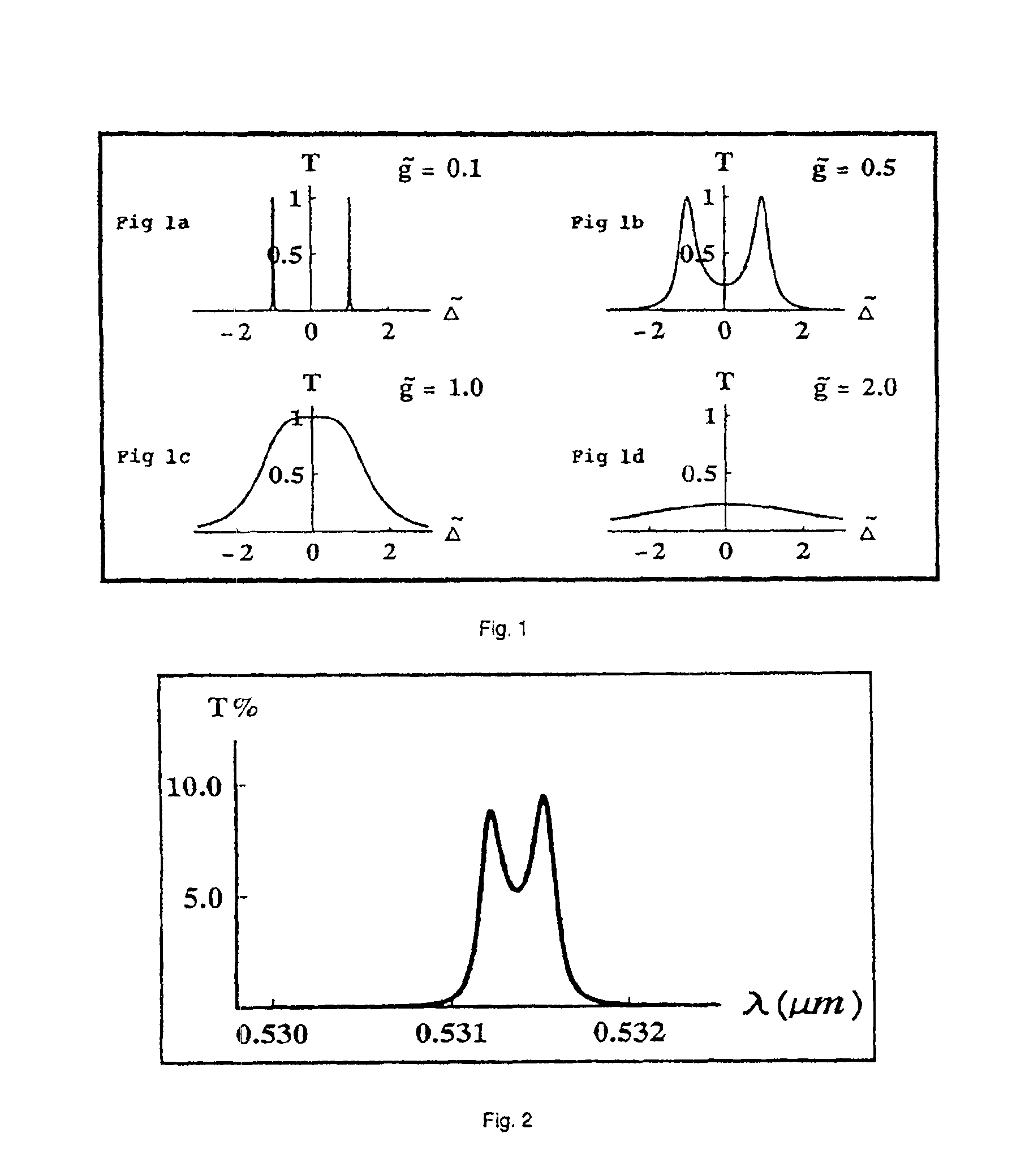
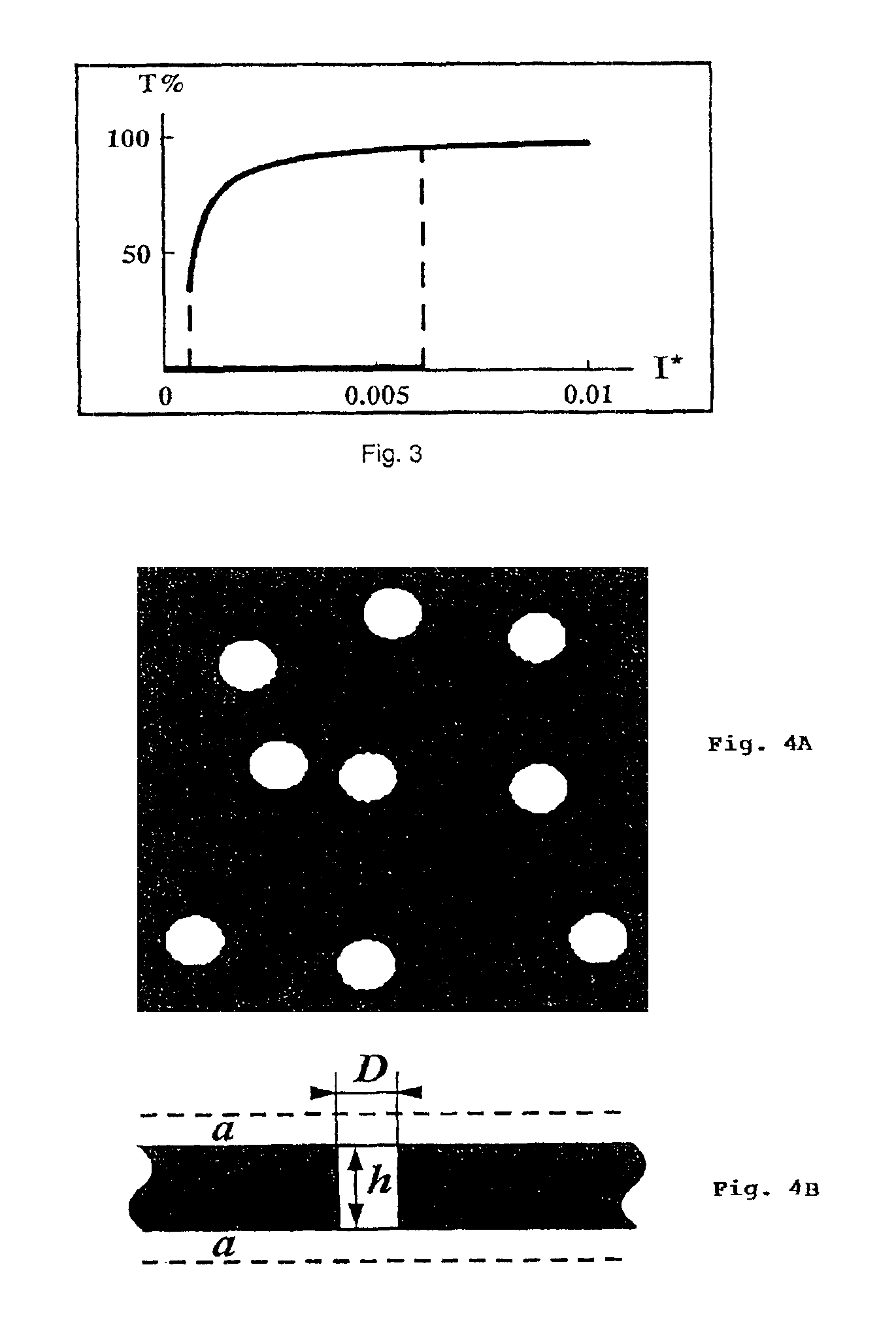
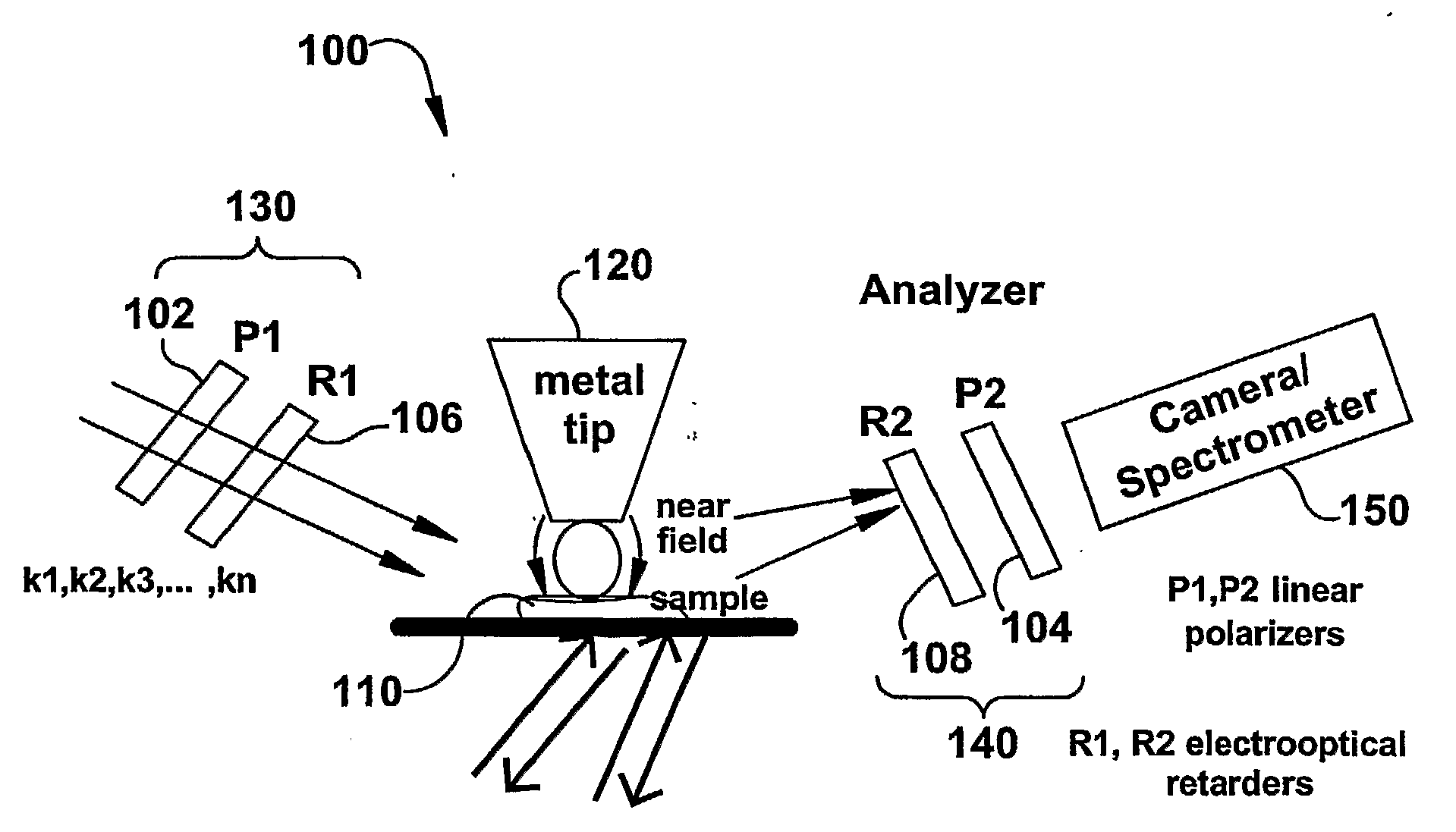
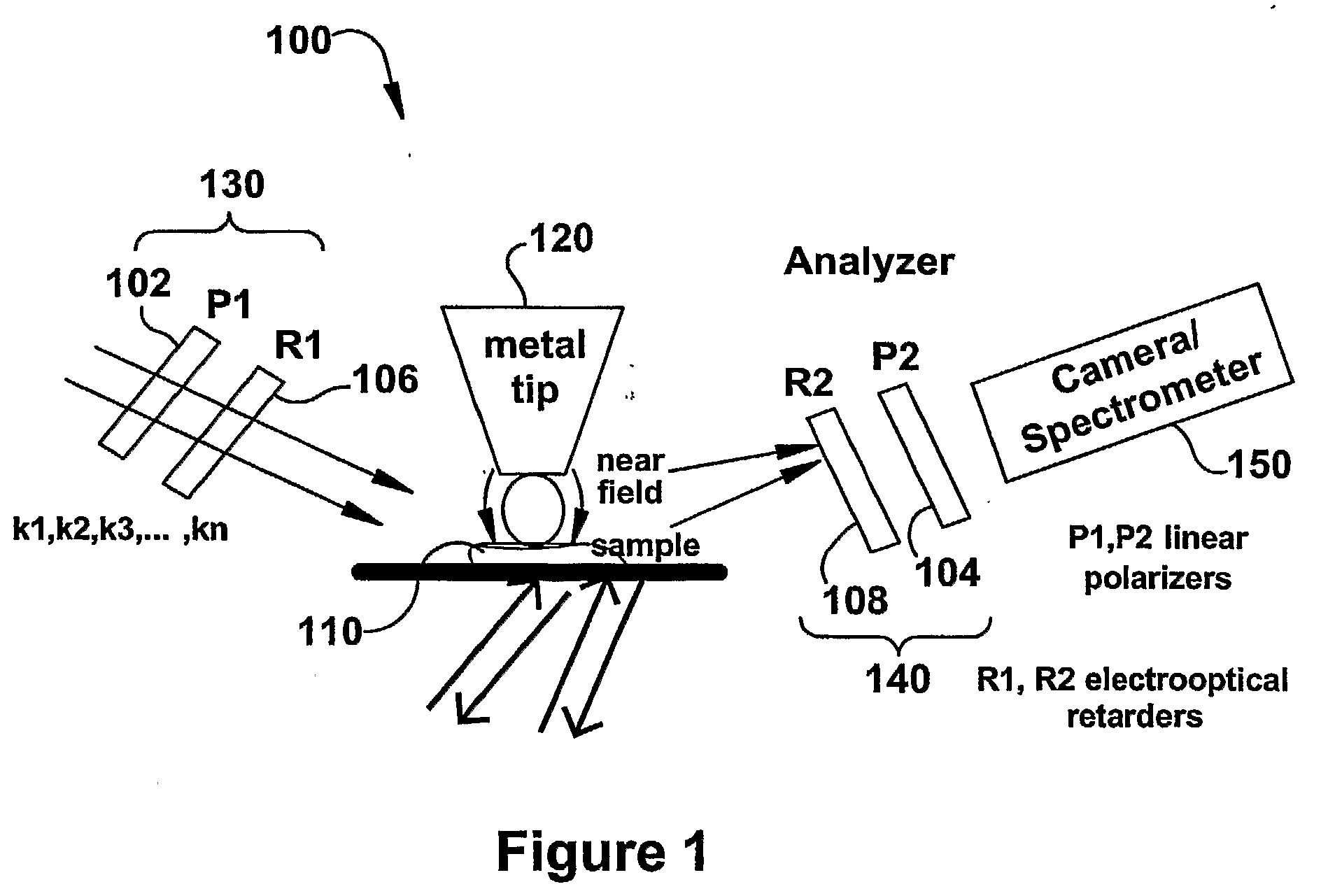
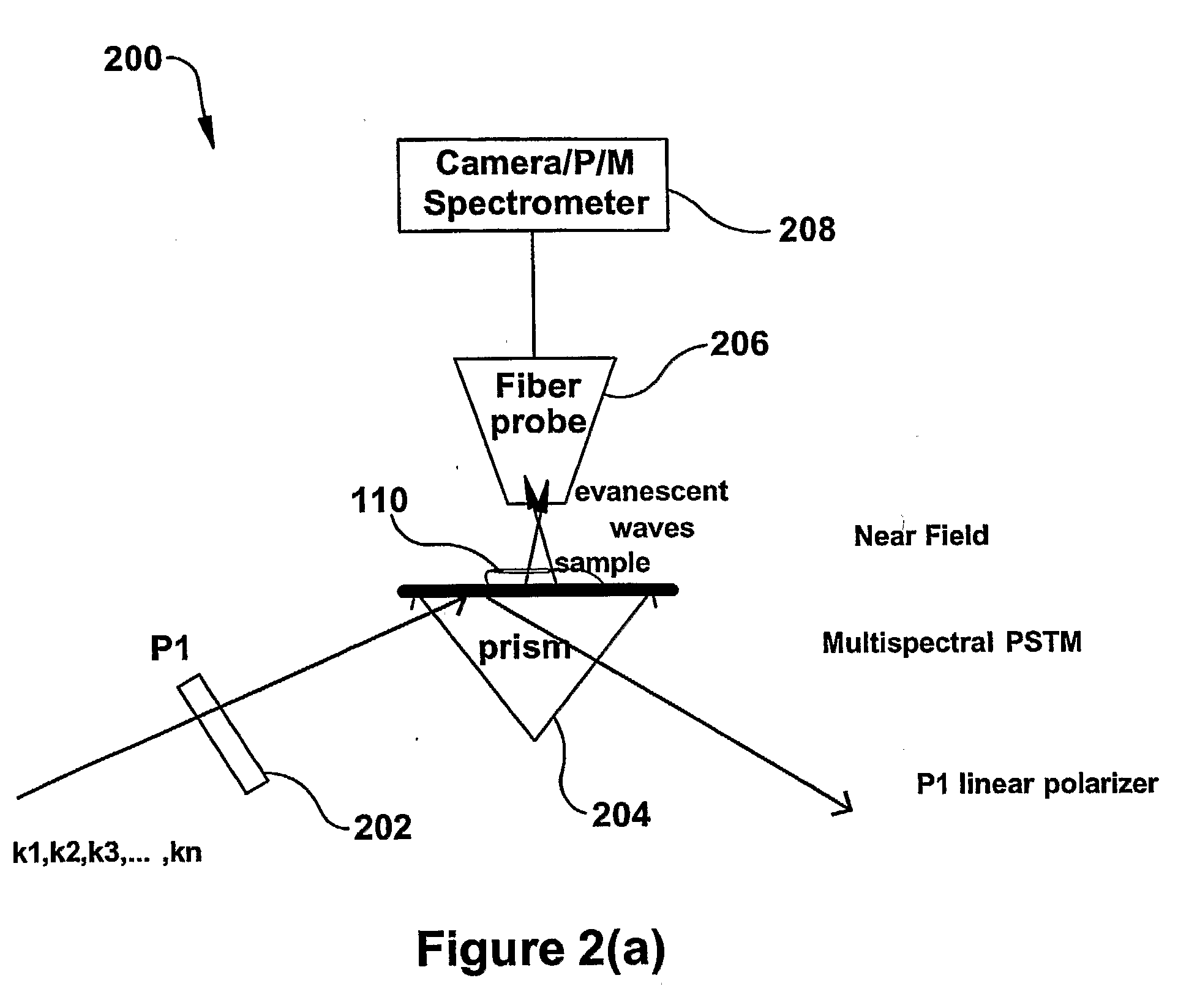
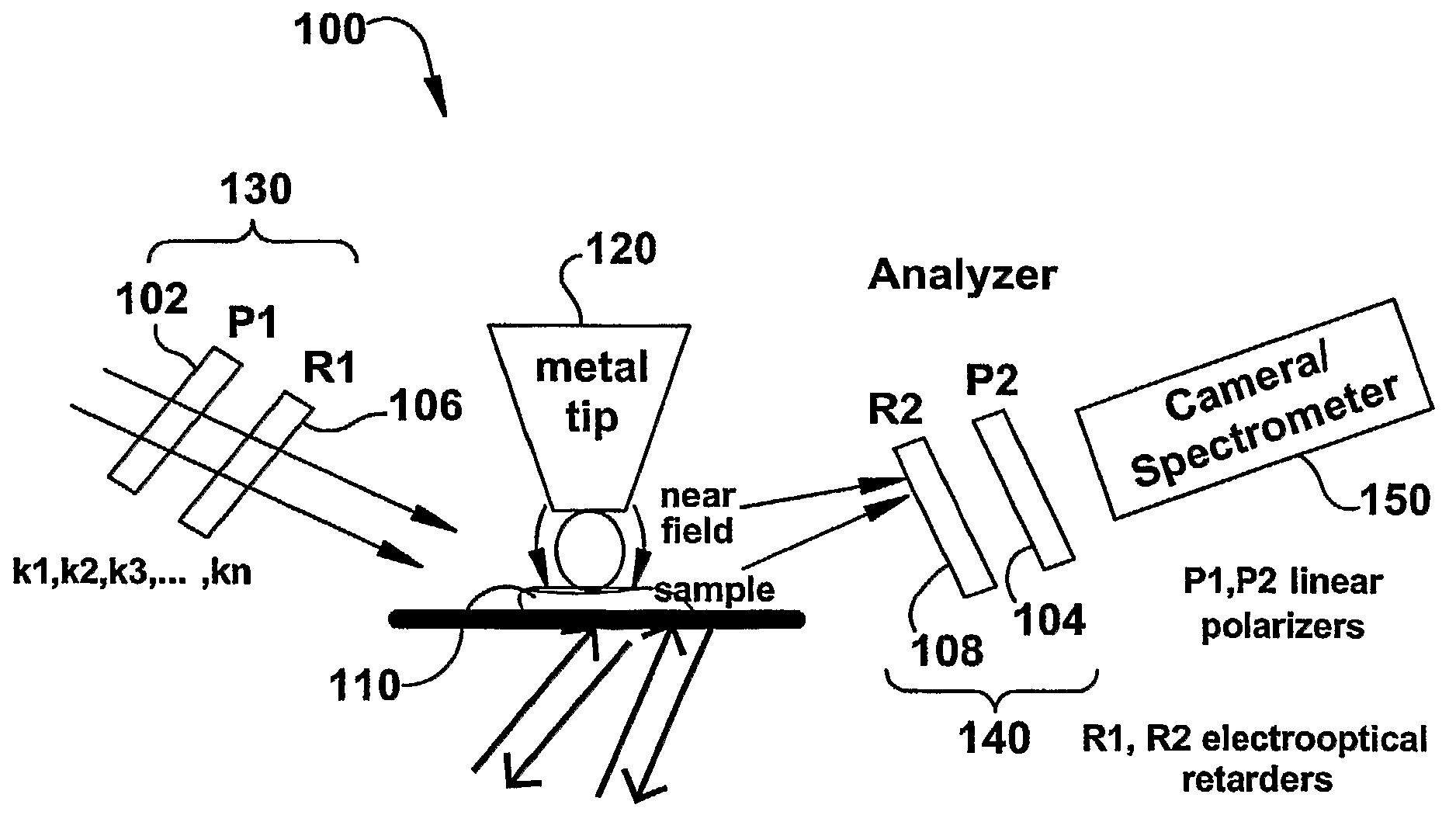
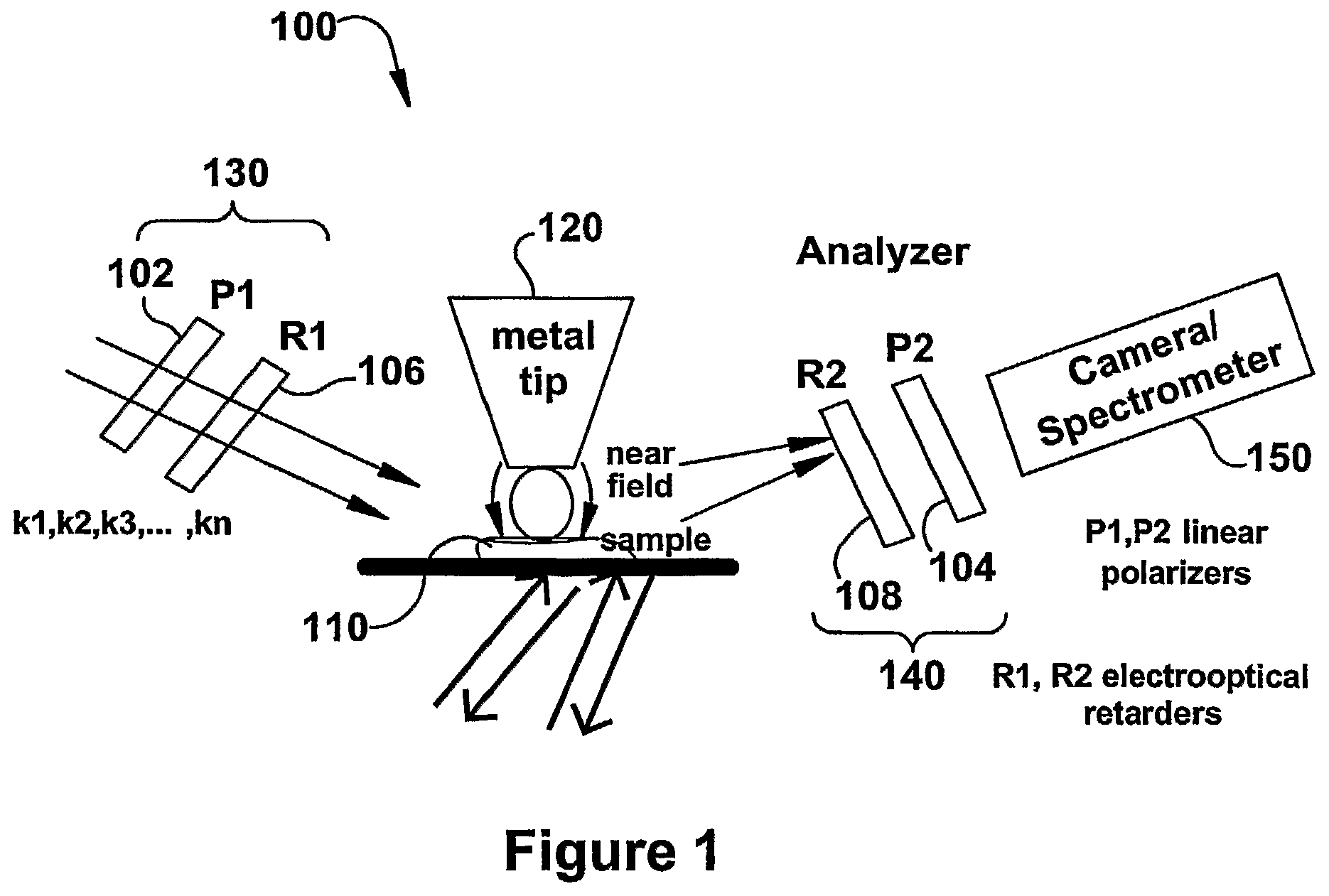
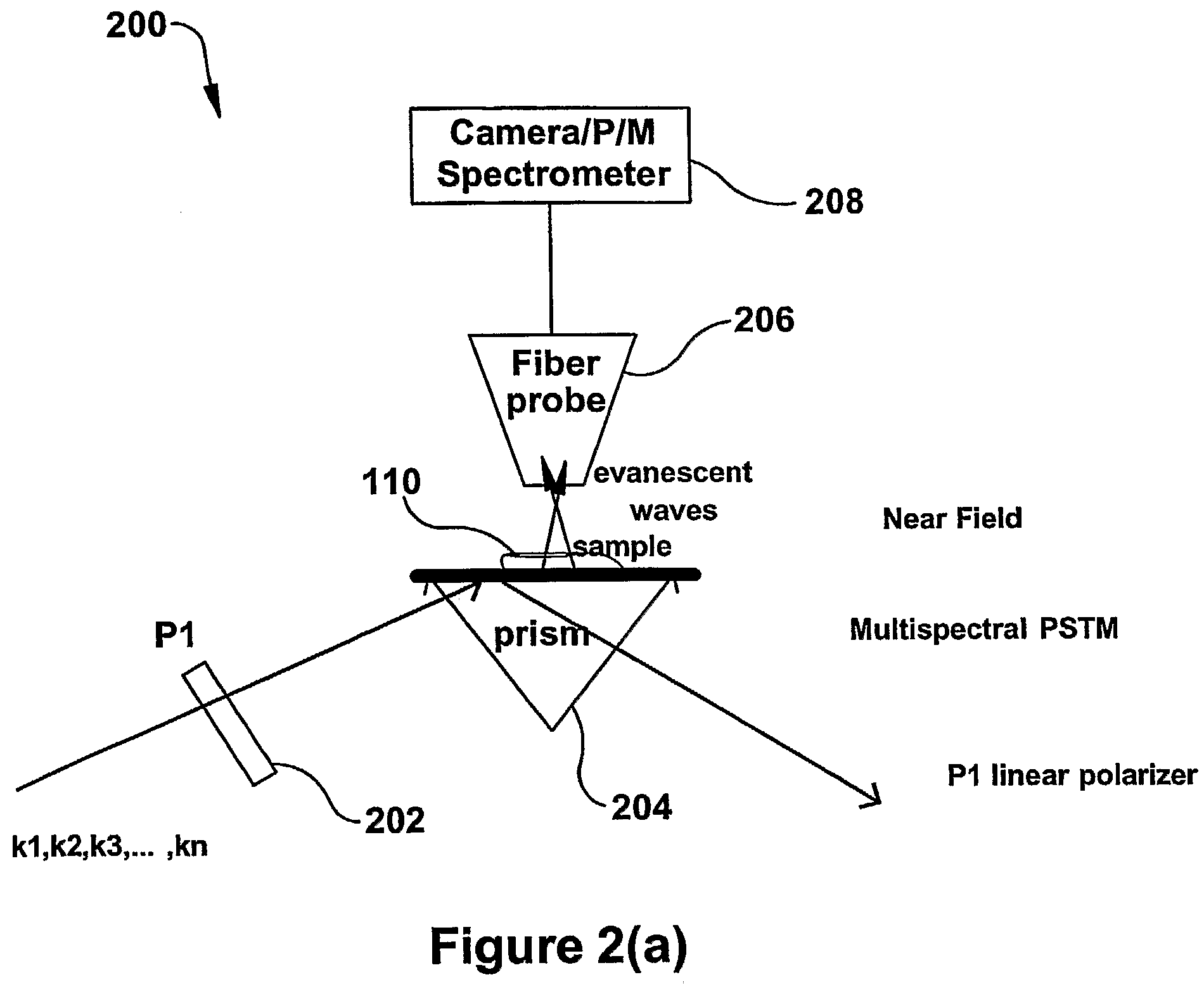
The present invention relates to near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) and near-field / far-field scanning microscopy methods, systems and devices that permit the imaging of biological samples, including biological samples or structures that are smaller than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the present invention permits the production of multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field microscopy systems that can achieve a spatial resolution of less than 100 nanometers. In another embodiment, the present invention permits the production of a multifunctional, multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field / far-field microscopy that can achieve enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imaging of biological samples. In still another embodiment, the present invention relates to the use of polar molecules as new optical contrast agents for imaging applications (e.g., cancer detection).
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
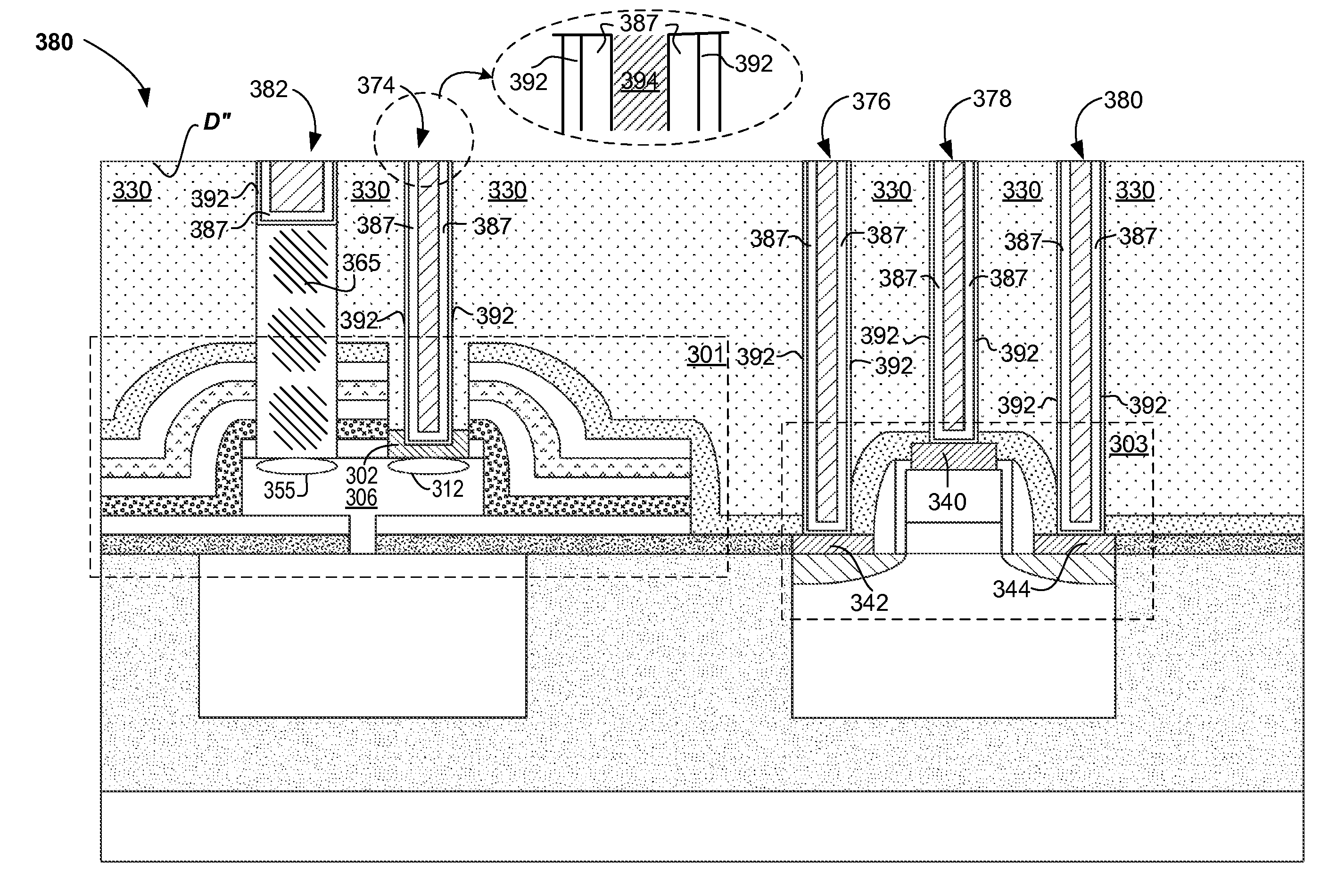
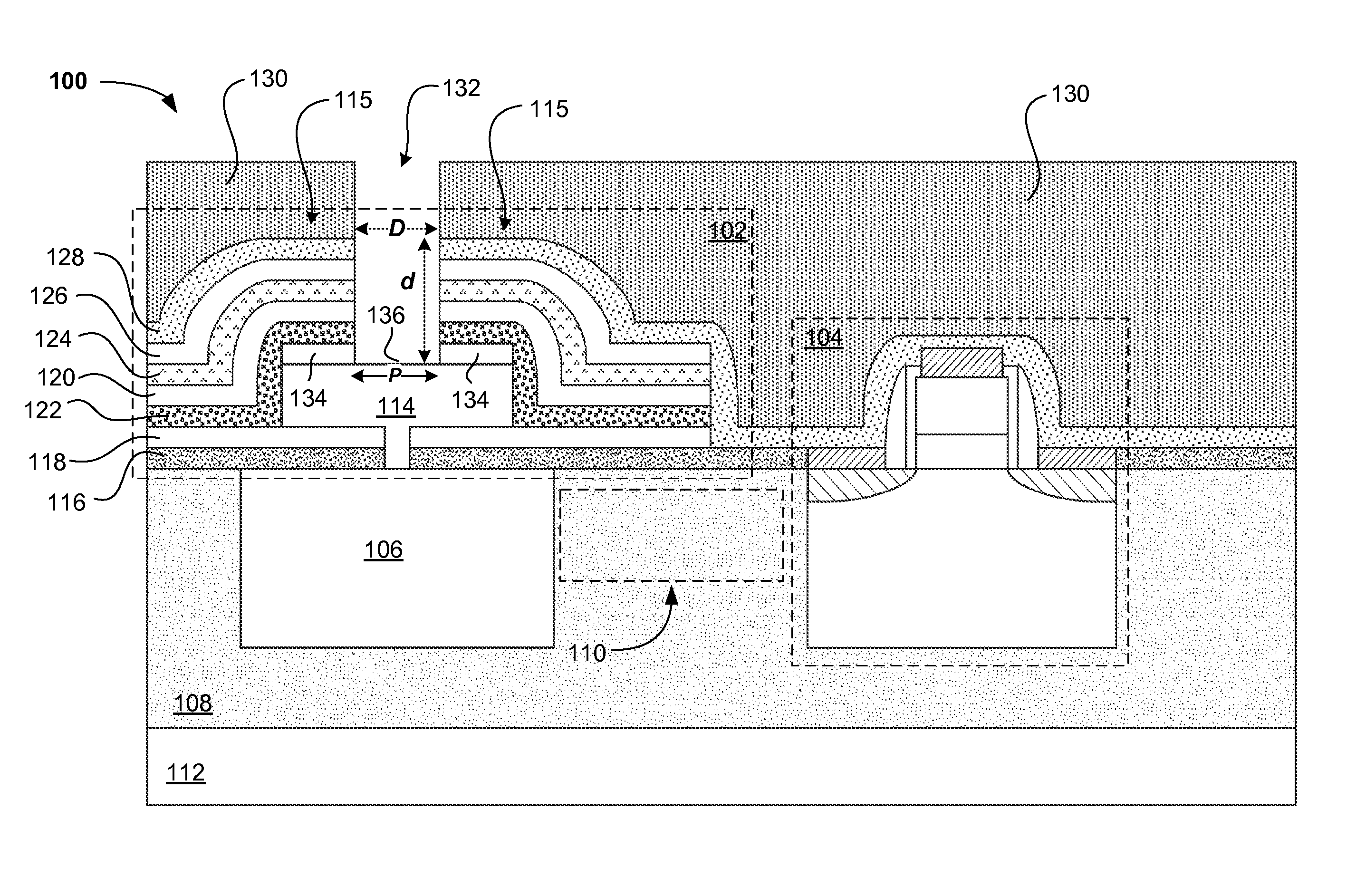
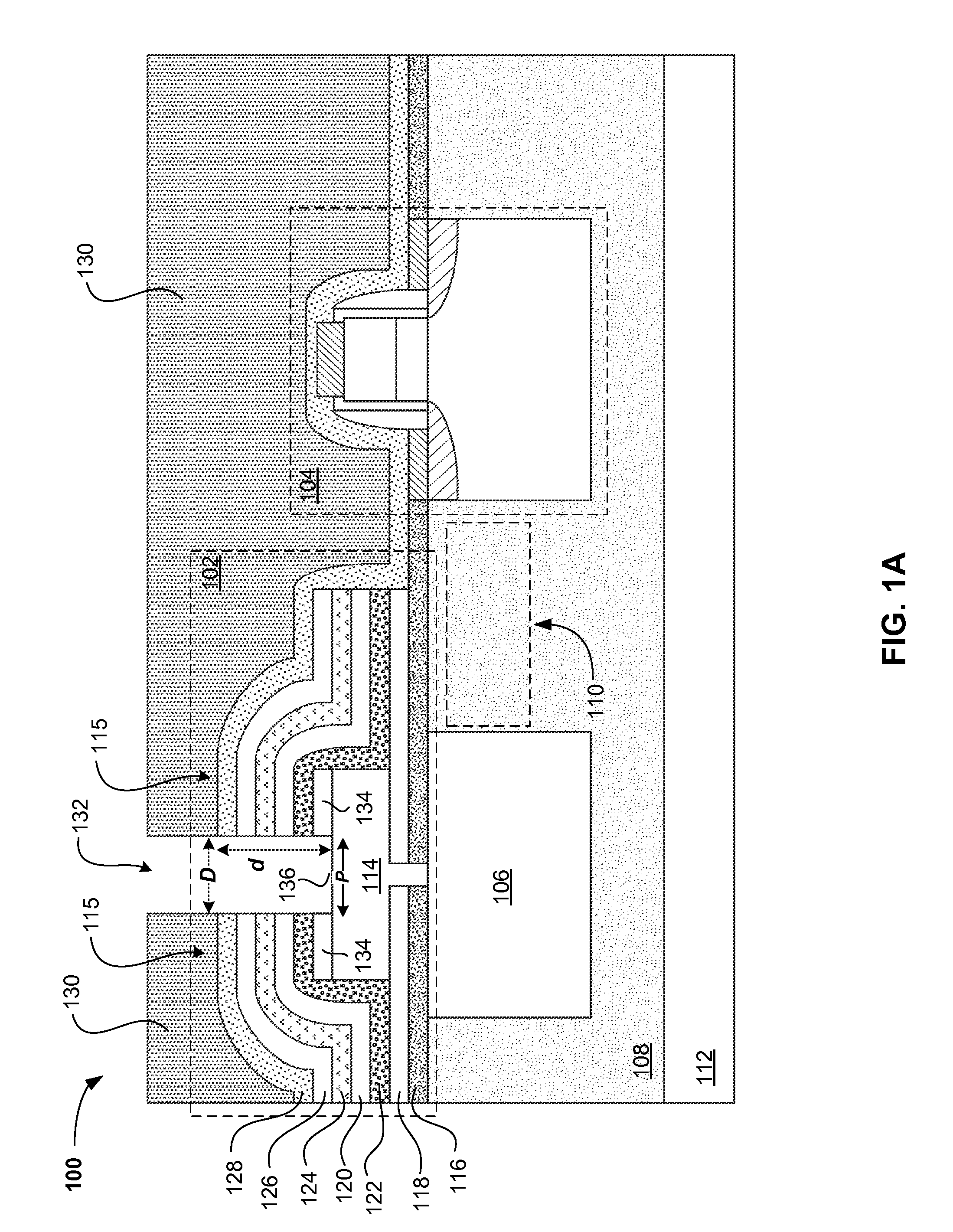
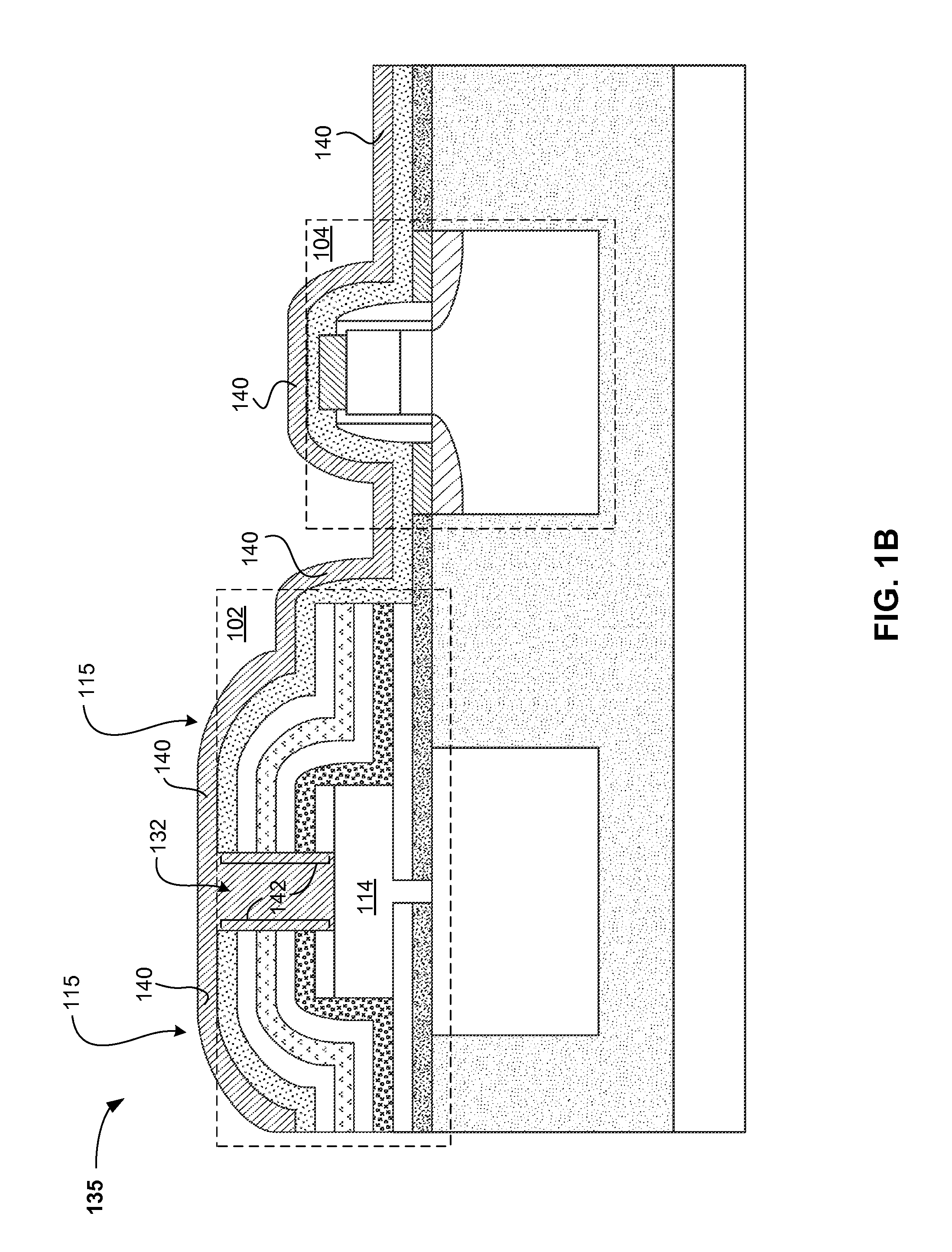
STRESS ENGINEERED MULTI-LAYERS FOR INTEGRATION OF CMOS AND Si NANOPHOTONICS
ActiveUS20140091374A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor structure
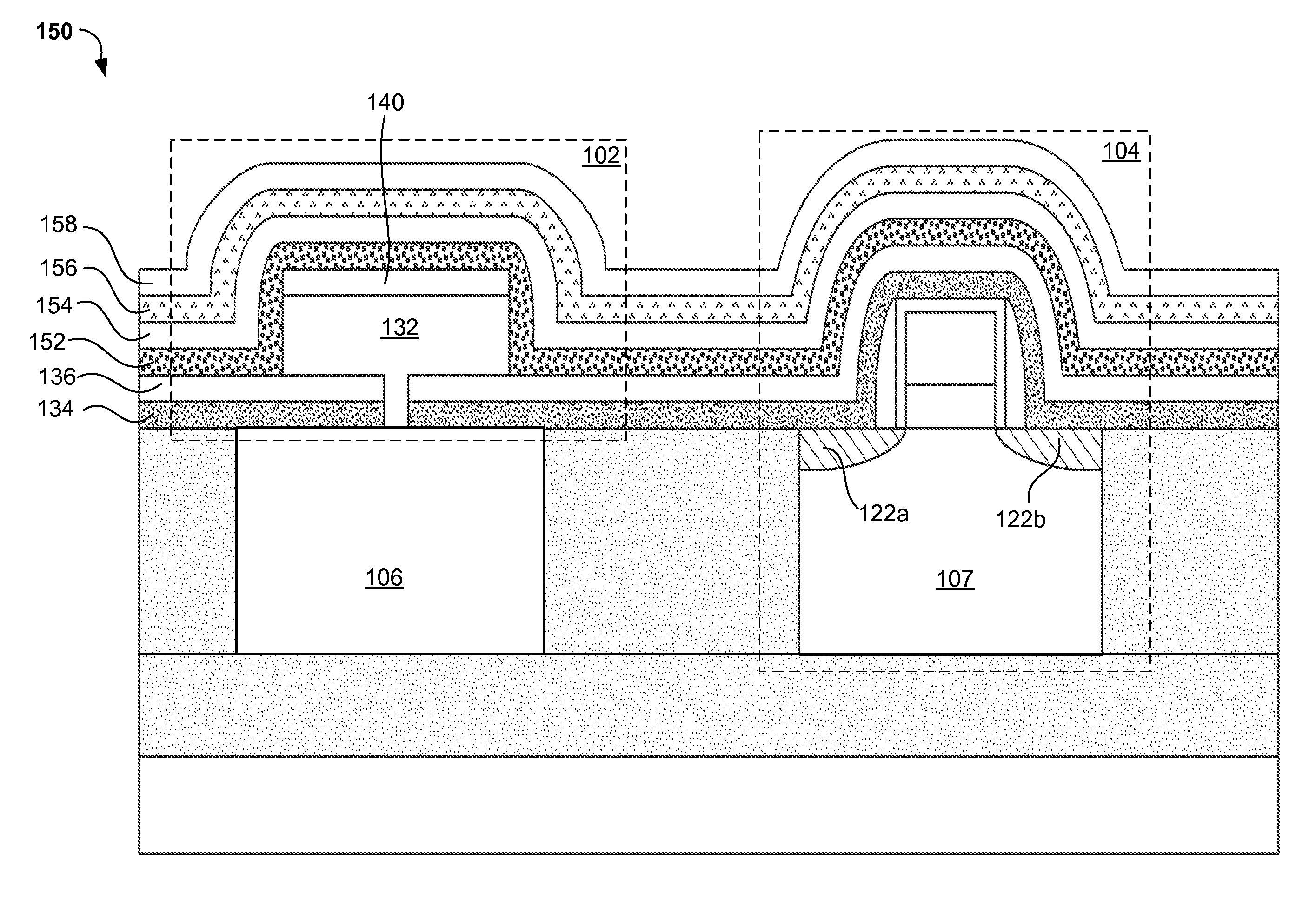
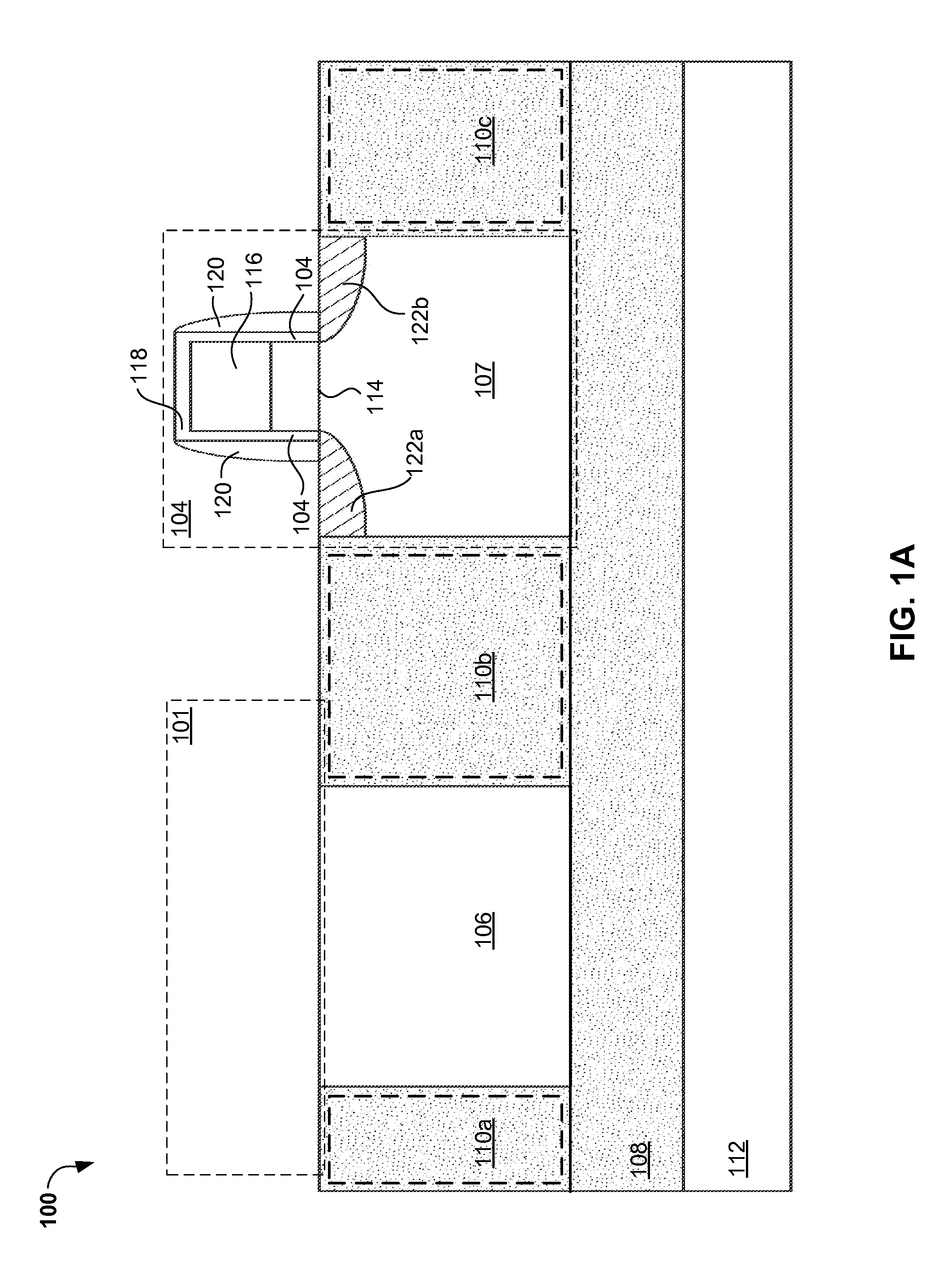
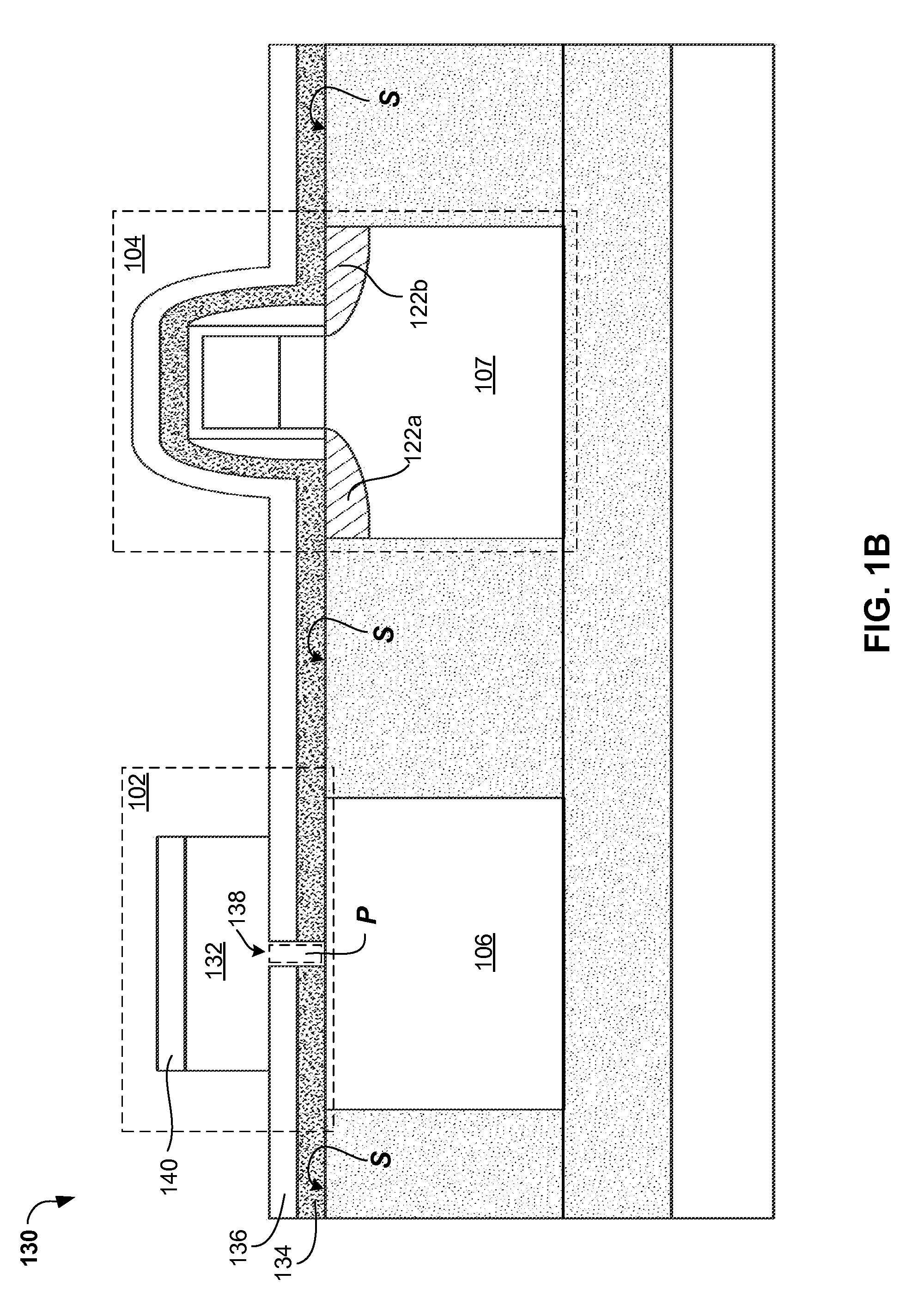
A method of forming an integrated photonic semiconductor structure having a photonic device and a CMOS device may include depositing a first silicon nitride layer having a first stress property over the photonic device, depositing an oxide layer having a stress property over the deposited first silicon nitride layer, and depositing a second silicon nitride layer having a second stress property over the oxide layer. The deposited first silicon nitride layer, the oxide layer, and the second silicon nitride layer encapsulate the photonic device.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
GERMANIUM PHOTODETECTOR SCHOTTKY CONTACT FOR INTEGRATION WITH CMOS AND Si NANOPHOTONICS
ActiveUS20140027826A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
A method of forming an integrated photonic semiconductor structure having a photodetector device and a CMOS device may include depositing a dielectric stack over the photodetector device such that the dielectric stack encapsulates the photodetector. An opening is etched into the dielectric stack down to an upper surface of a region of an active area of the photodetector. A first metal layer is deposited directly onto the upper surface of the region of the active area via the opening such that the first metal layer may cover the region of the active area. Within the same mask level, a plurality of contacts including a second metal layer are located on the first metal layer and on the CMOS device. The first metal layer isolates the active area from the occurrence of metal intermixing between the second metal layer and the active area of the photodetector.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
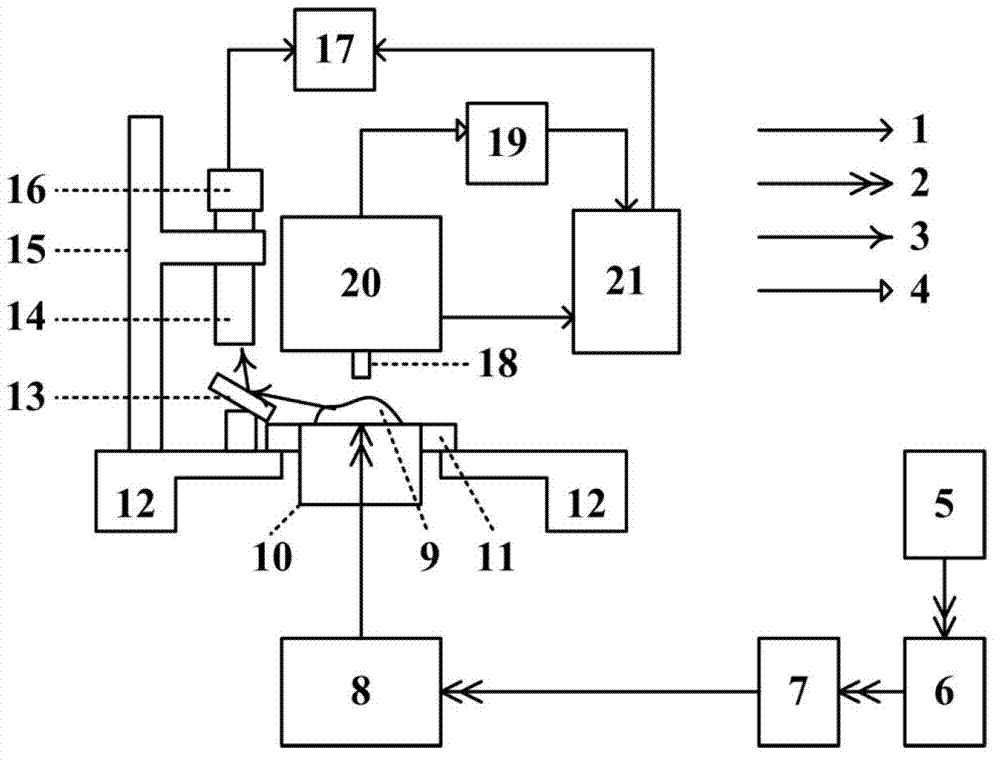
Nano-optics multi-parameter measurement platform
ActiveCN102829961AEasy to study optical propertiesCompact structureColor/spectral properties measurementsUsing optical meansPhotonicsNear field optical microscope
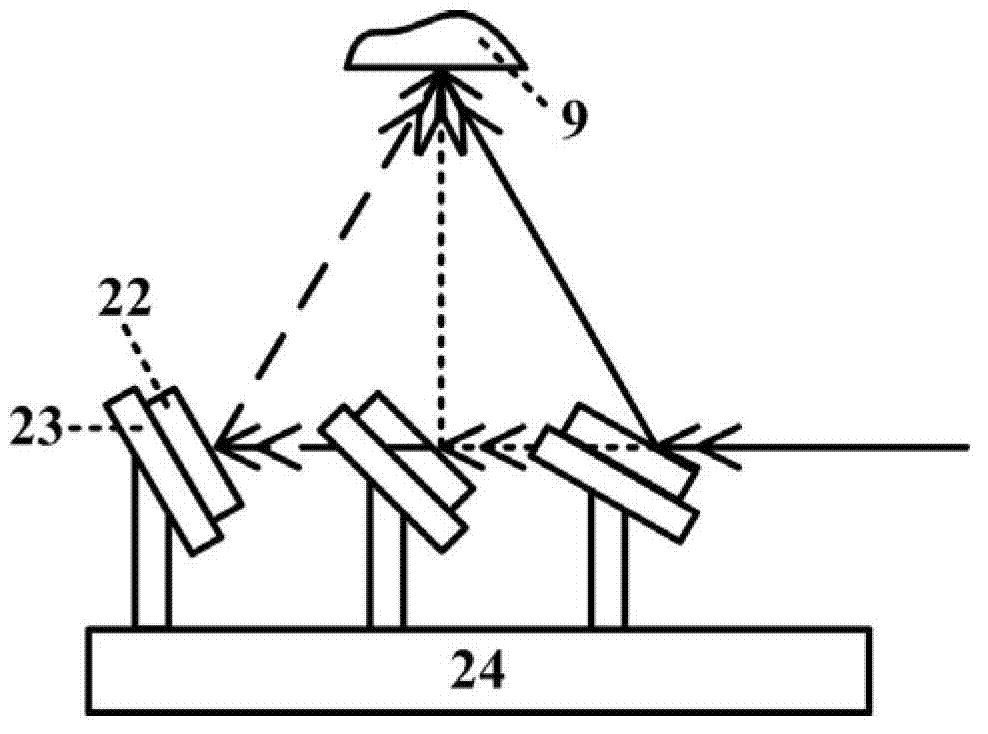
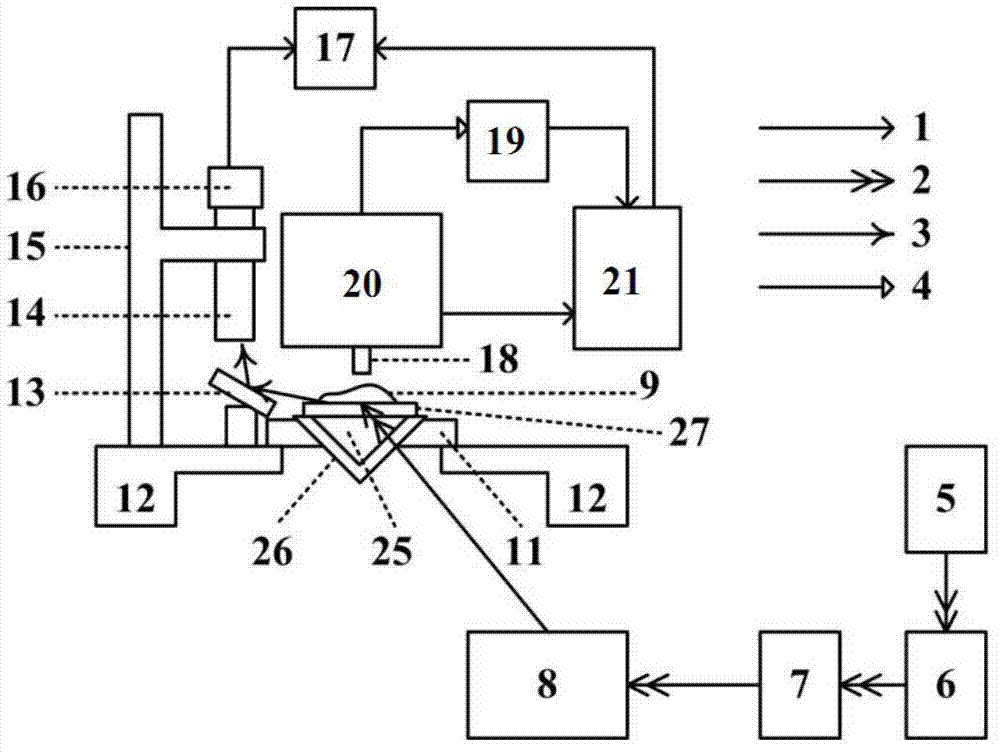
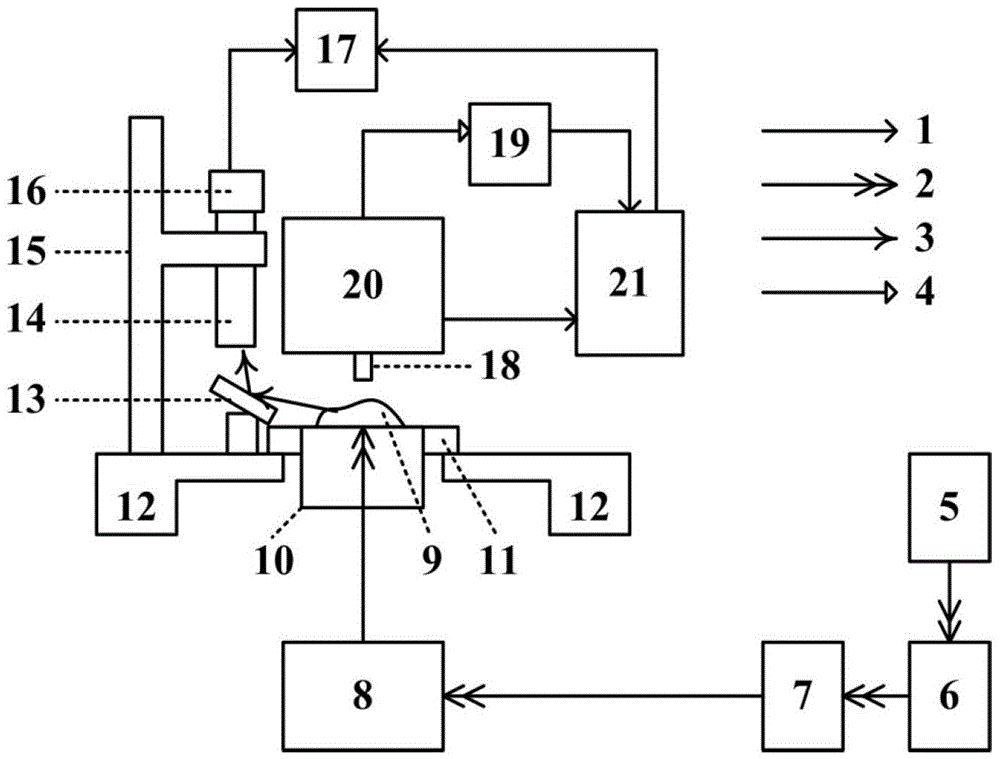
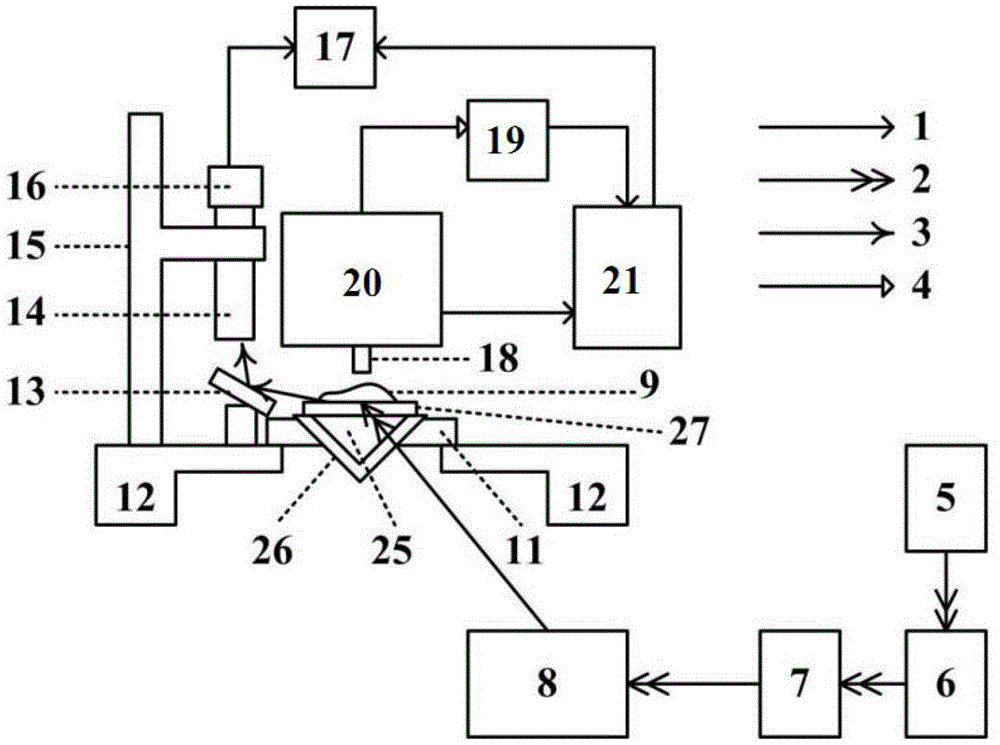
The invention relates to the technical field of reactor engineering and discloses a nanophotonics multi-parameter measurement platform. The nanophotonics multi-parameter measurement platform comprises a multi-parameter variable excitation system, a sample position direction fine-adjusting unit, a microscope observation alignment system, a scanning near-field optical microscope detection system and a computer; the sample position direction fine-adjusting unit is used for mounting a sample to be measured; the multi-parameter variable excitation system provides a lighting excitation light source signal to the sample to be measured; the microscope observation alignment system adjusts an imaging area of the sample to be measured, collects the image information of the sample to be measured, and transmits the image information to the computer to be displayed; the scanning near-field optical microscope detection system collects the optical near-field information of the sample to be measured and transmits the optical near-field information to the computer; and the computer processes the optical near-field information and then displays the processed optical near-field information. The nano-optics multi-parameter measurement platform is compact in structure, can achieve adjustment with multiple degrees of freedom, and can achieve optical excitation of variable excitation wavelength, continuous adjustment of the incident angle and controllable polarization state on a given excitation area of a nano photonics device.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Molecular imaging and nanophotonics imaging and detection principles and systems, and contrast agents, media makers and biomarkers, and mechanisms for such contrast agents
InactiveUS7823215B2Enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesNanoopticsDepth imagingBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM) and near-field / far-field scanning microscopy methods, systems and devices that permit the imaging of biological samples, including biological samples or structures that are smaller than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the present invention permits the production of multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field microscopy systems that can achieve a spatial resolution of less than 100 nanometers. In another embodiment, the present invention permits the production of a multifunctional, multi-spectral, polarimetric, near-field / far-field microscopy that can achieve enhanced sub-surface and in-depth imaging of biological samples. In still another embodiment, the present invention relates to the use of polar molecules as new optical contrast agents for imaging applications (e.g., cancer detection).
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Stress engineered multi-layers for integration of CMOS and Si nanophotonics
ActiveUS8765536B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSSemiconductor structure
A method of forming an integrated photonic semiconductor structure having a photonic device and a CMOS device may include depositing a first silicon nitride layer having a first stress property over the photonic device, depositing an oxide layer having a stress property over the deposited first silicon nitride layer, and depositing a second silicon nitride layer having a second stress property over the oxide layer. The deposited first silicon nitride layer, the oxide layer, and the second silicon nitride layer encapsulate the photonic device.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
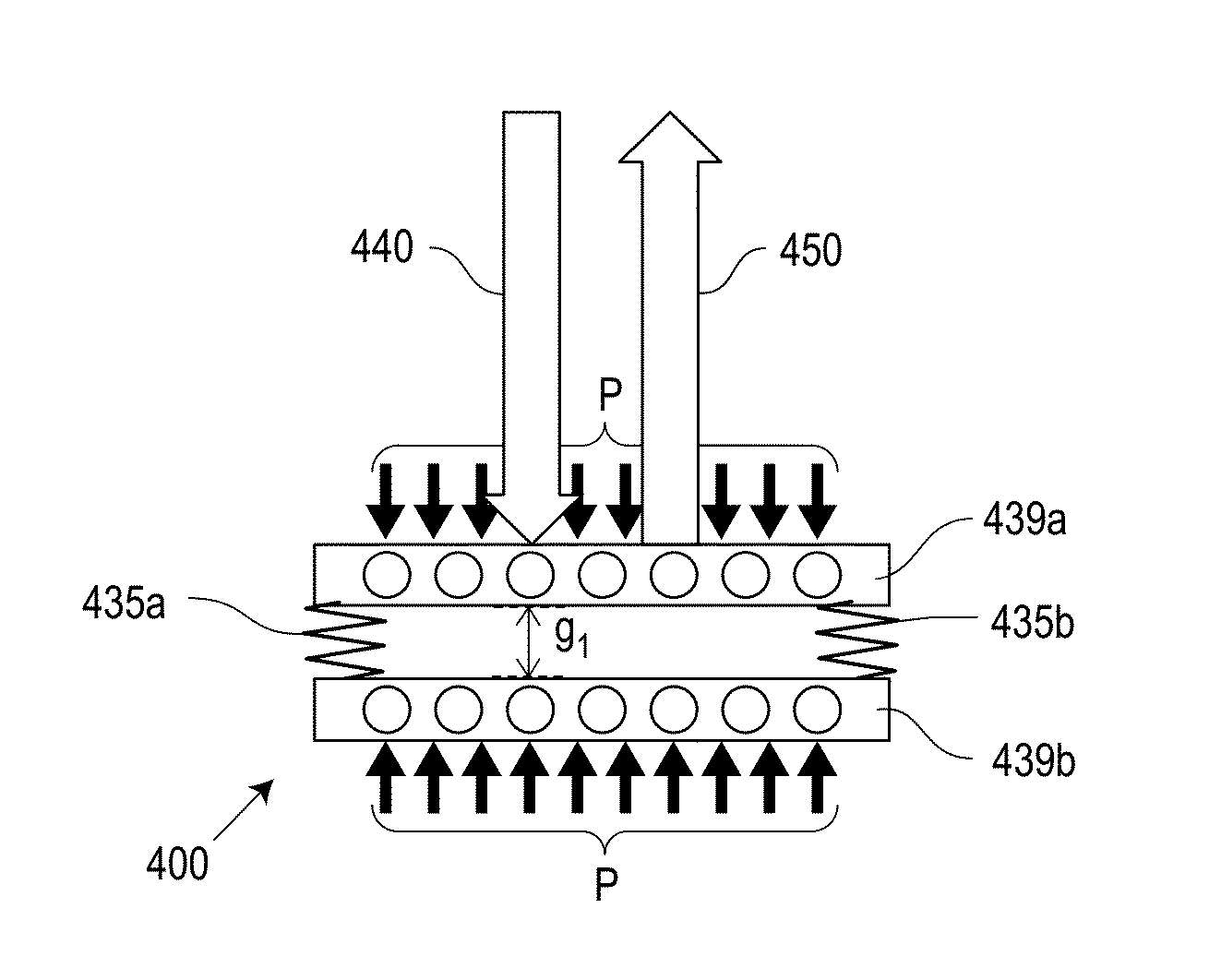
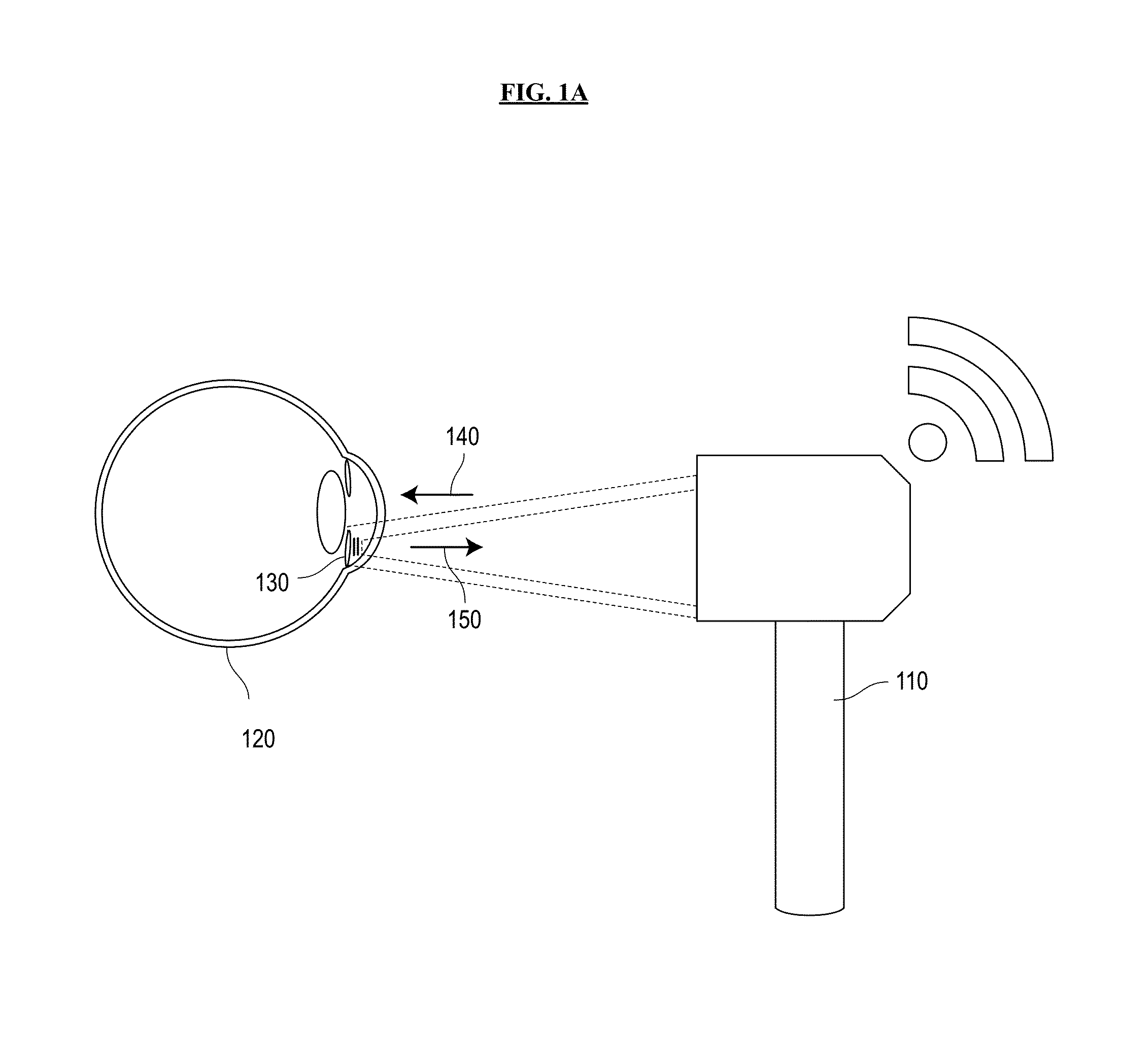
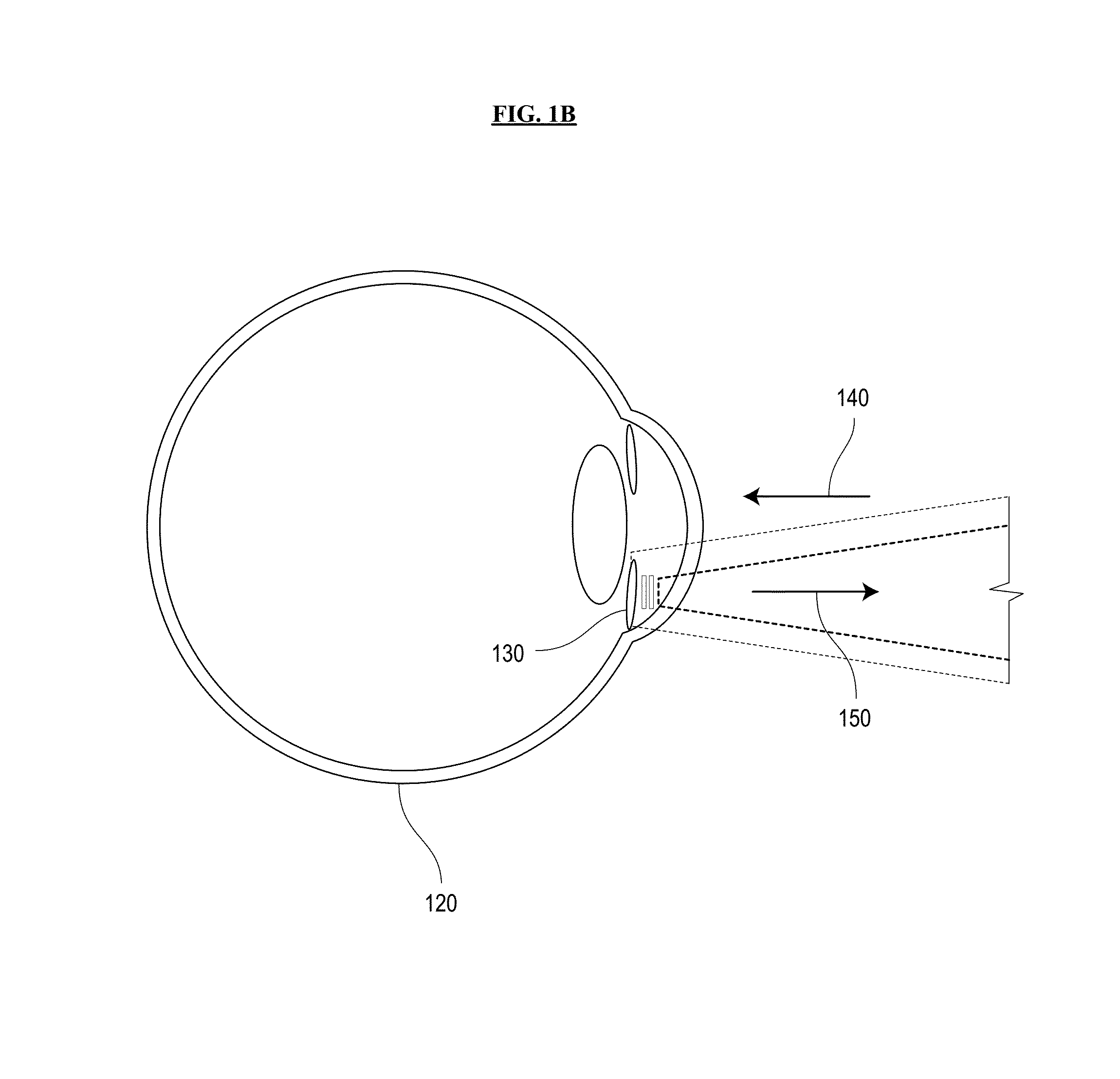
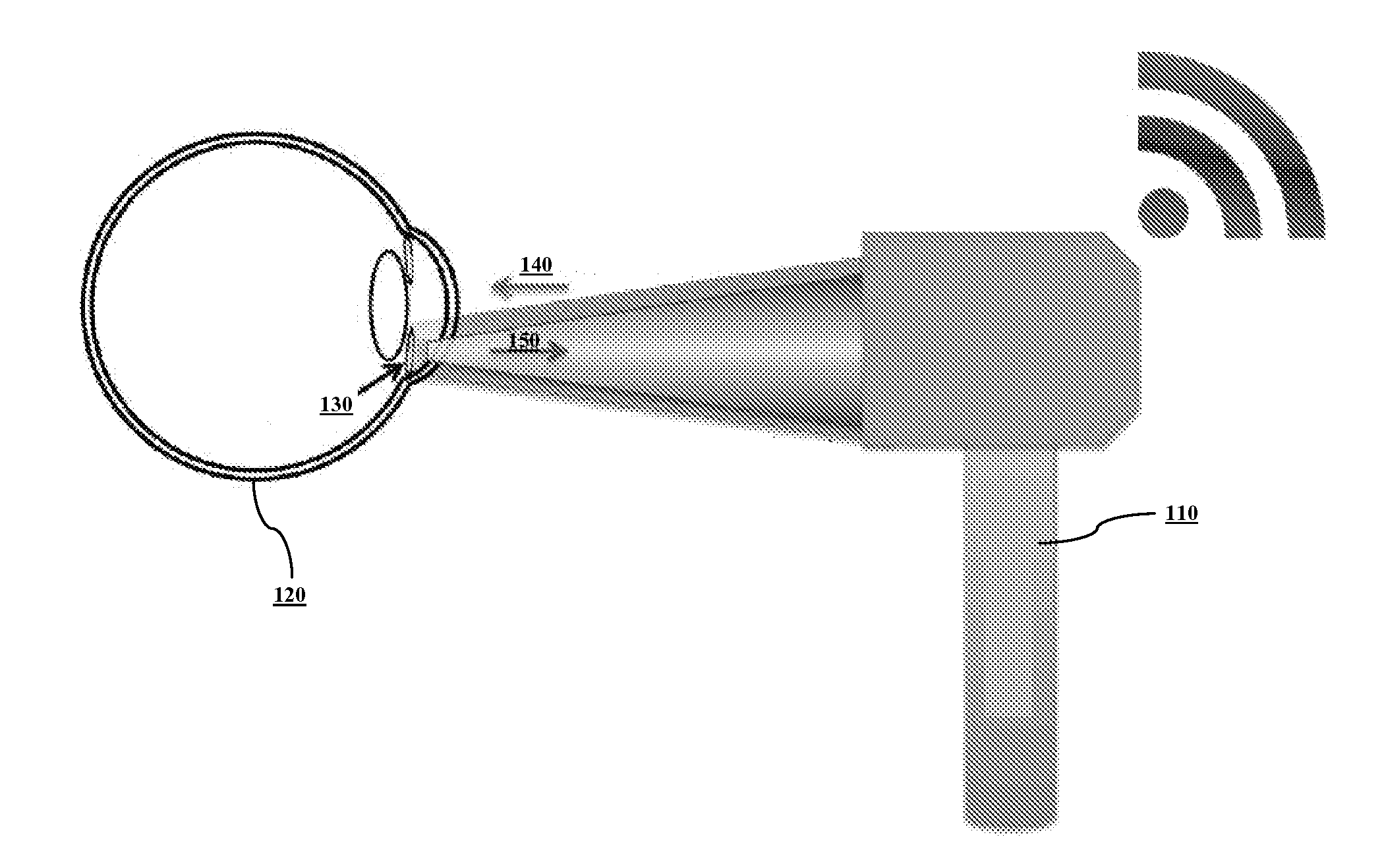
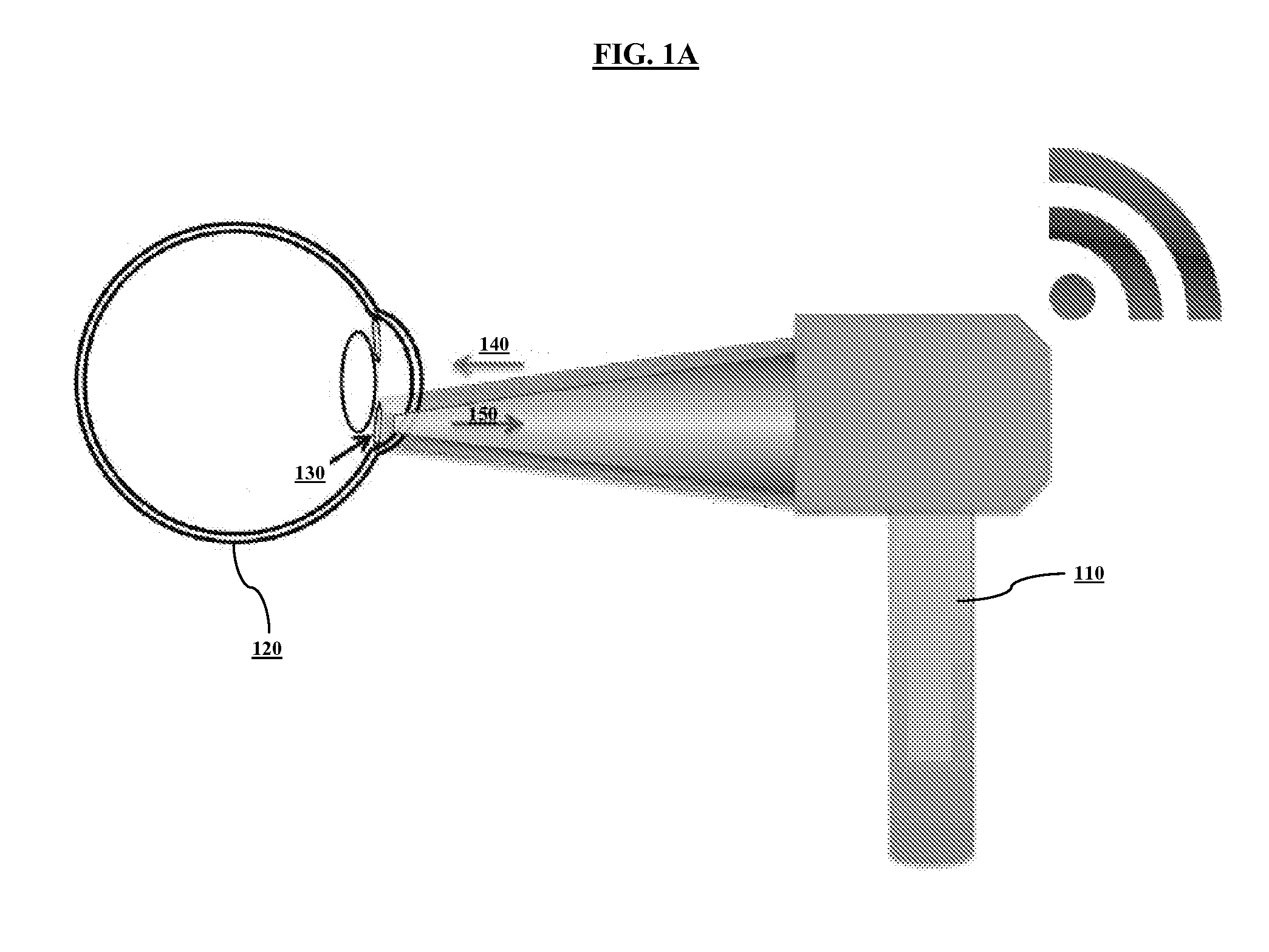
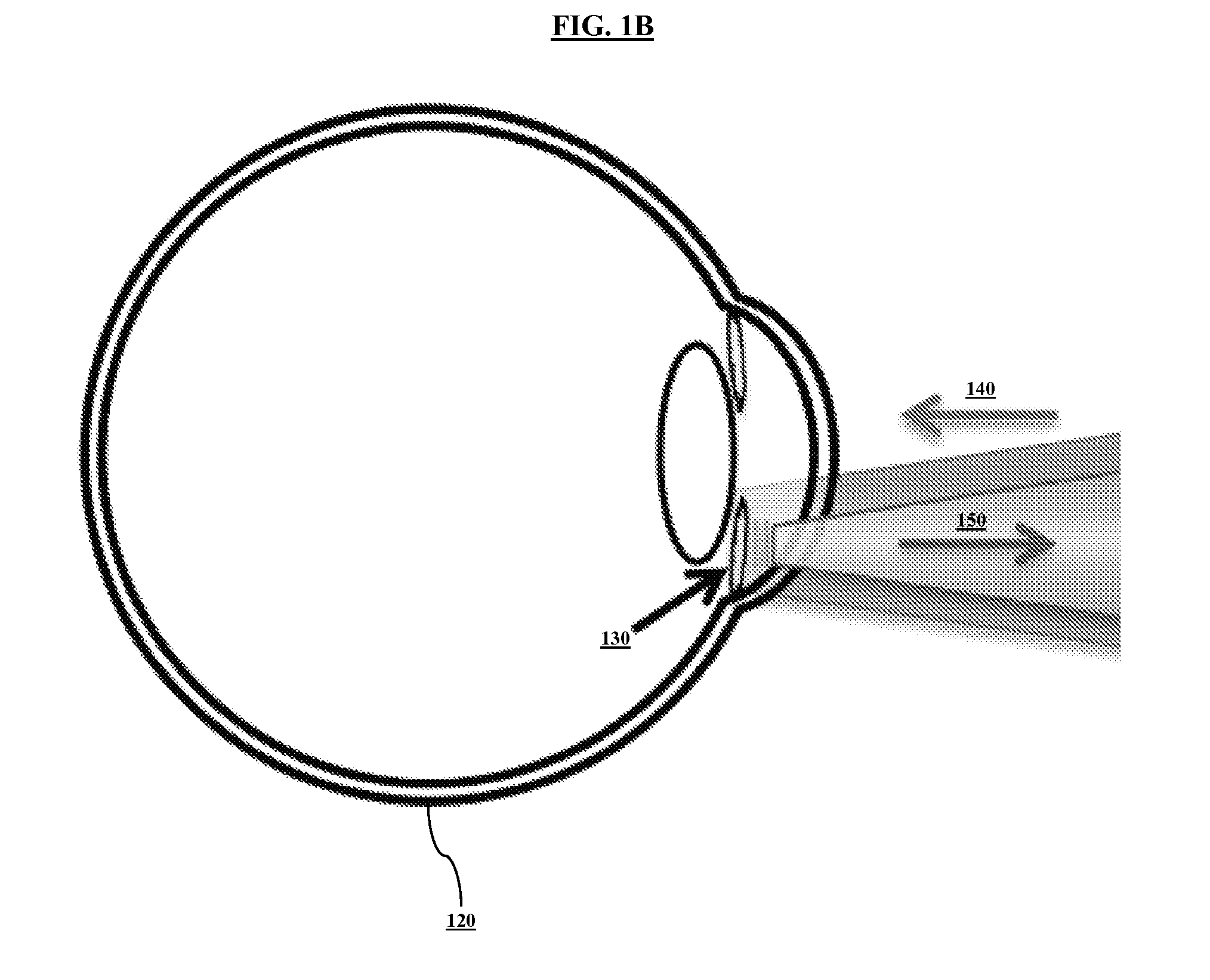
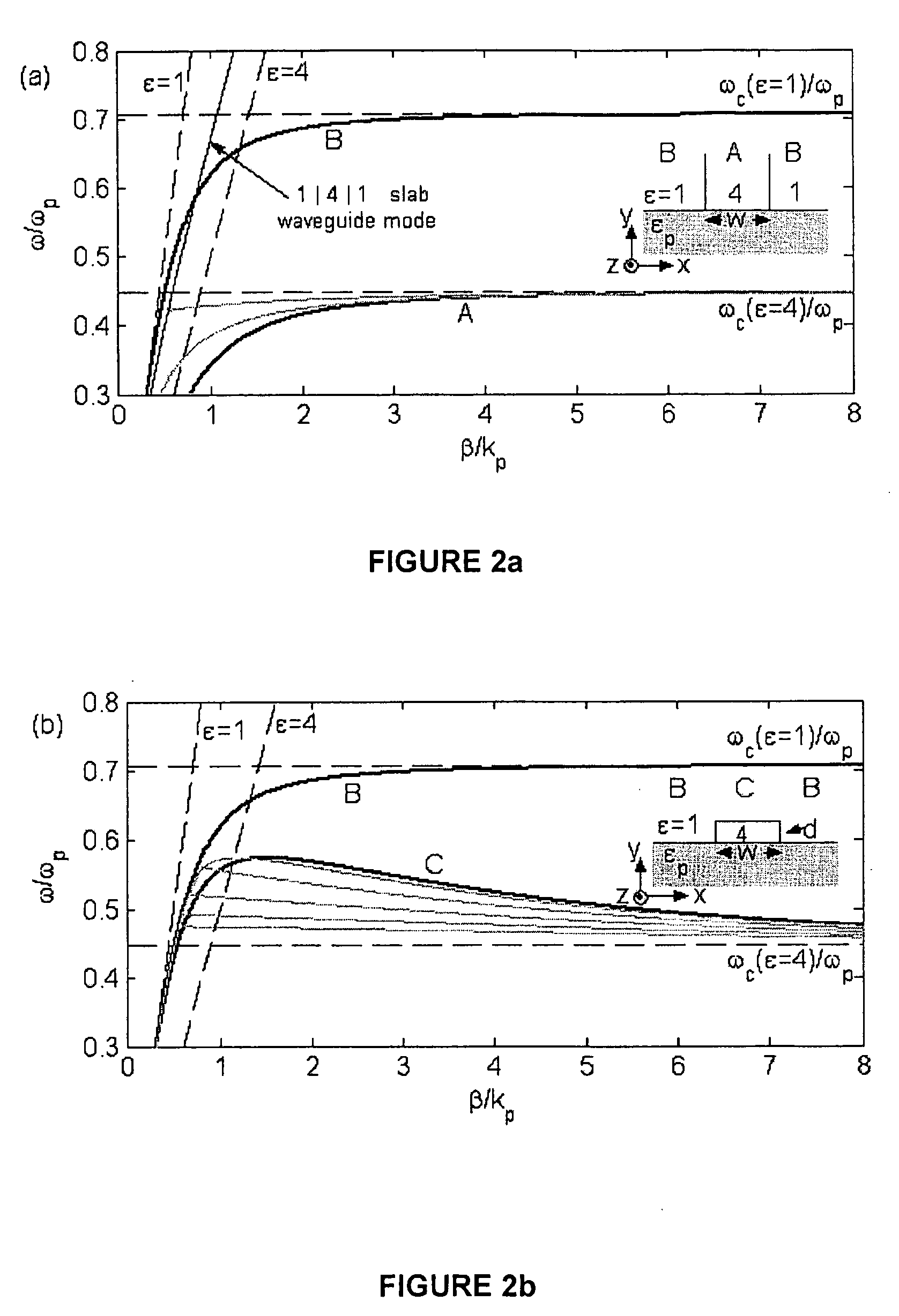
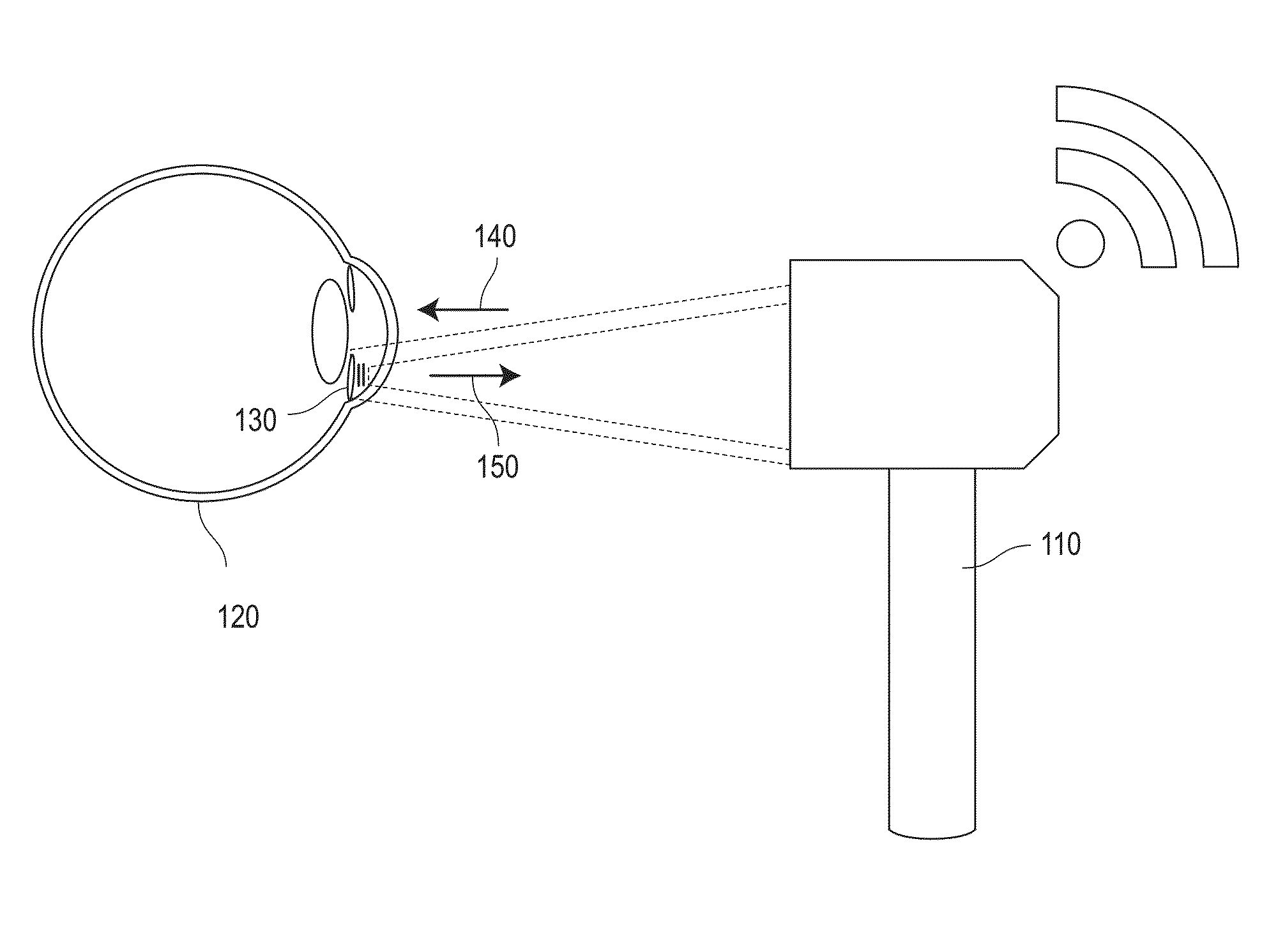
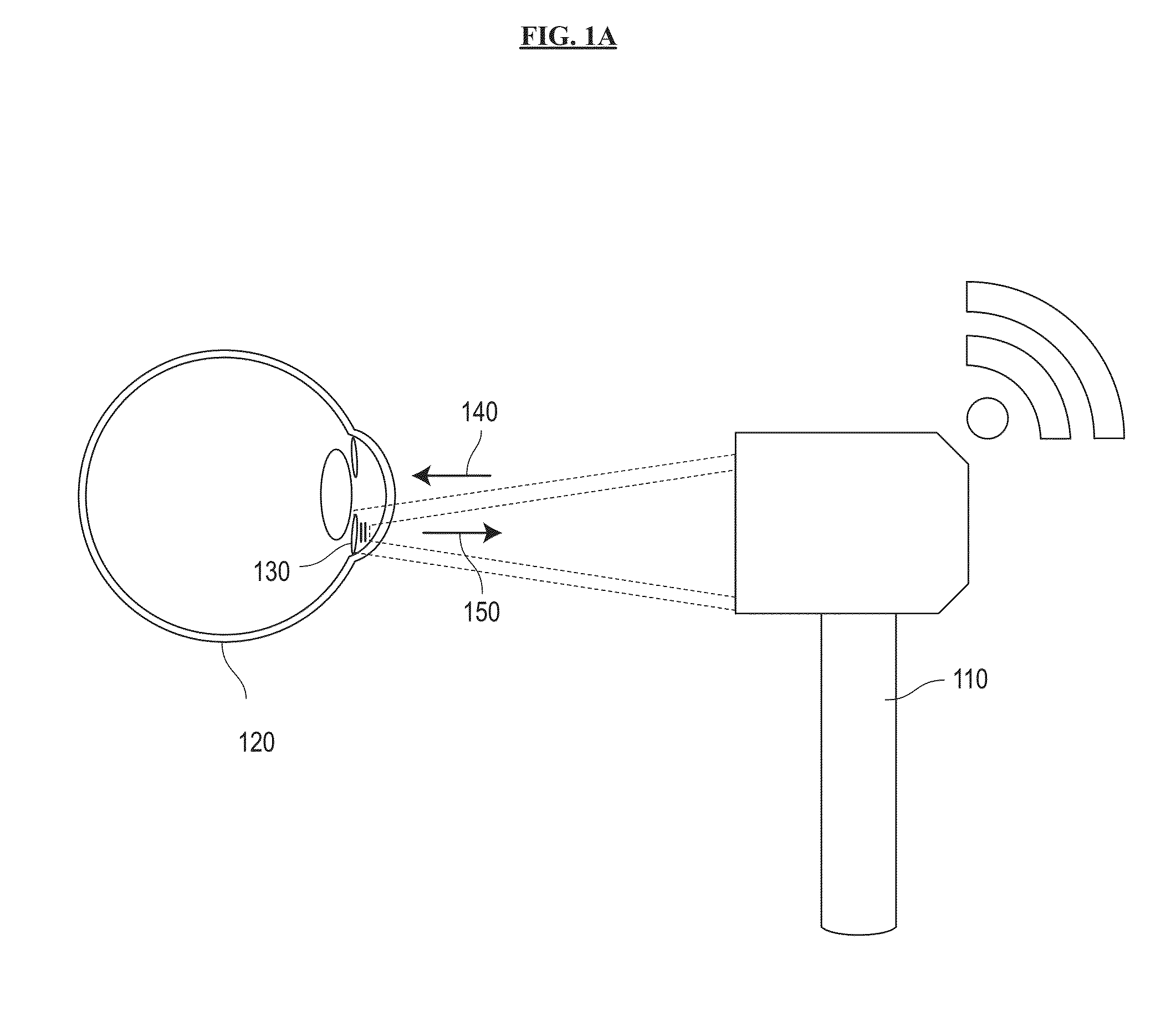
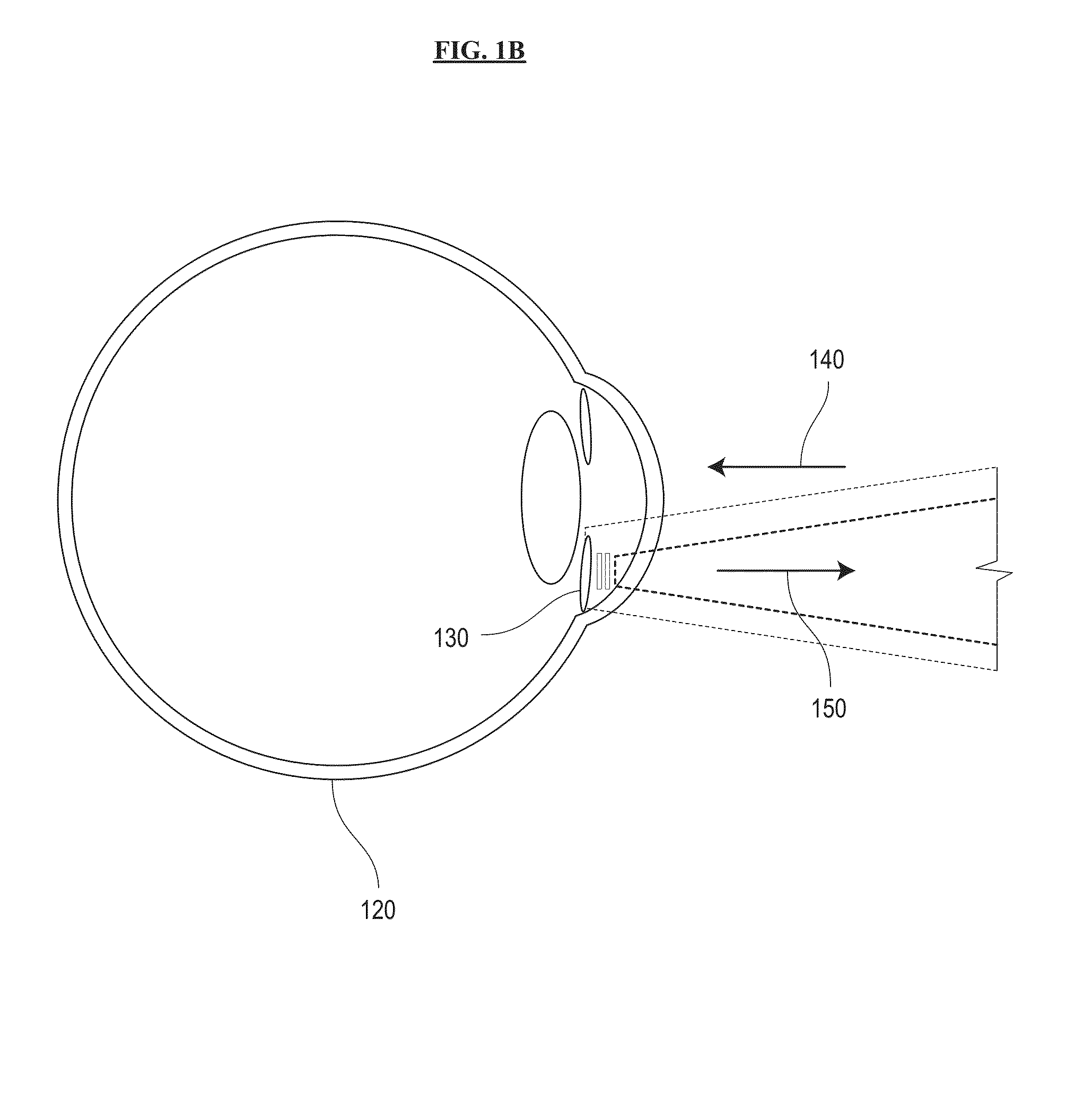
System and method for sensing intraocular pressure
ActiveUS9173564B2Small sizeHigh sensitivityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationImage resolutionIntraocular pressure
Systems and methods of sensing intraocular pressure are described. An example miniaturized intraocular pressure (IOP) monitoring system is provided using a nanophotonics-based implantable IOP sensor with remote optical readout that can be adapted for both patient and research use. A handheld detector optically excites the pressure-sensitive nanophotonic structure of the IOP-sensing implant placed in the anterior chamber and detects the reflected light, whose optical signature changes as a function of IOP. Optical detection eliminates the need for large, complex LC structures and simplifies sensor design. The use of nanophotonic components improves the sensor's resolution and sensitivity, increases optical readout distance, and reduces its size by a factor of 10-30 over previous implants. Its small size and convenient optical readout allows frequent and accurate self-tracking of IOP by patients in home settings.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
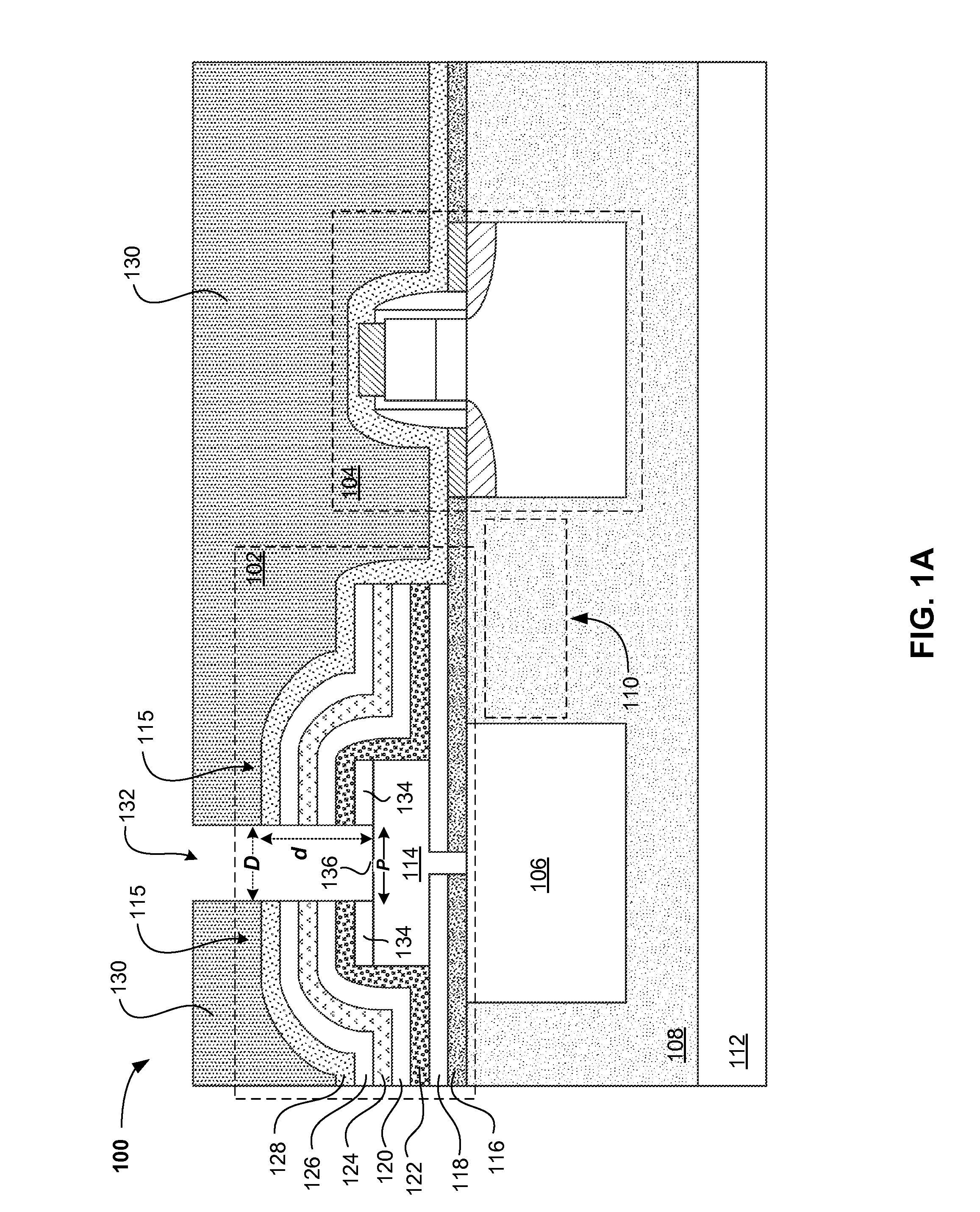
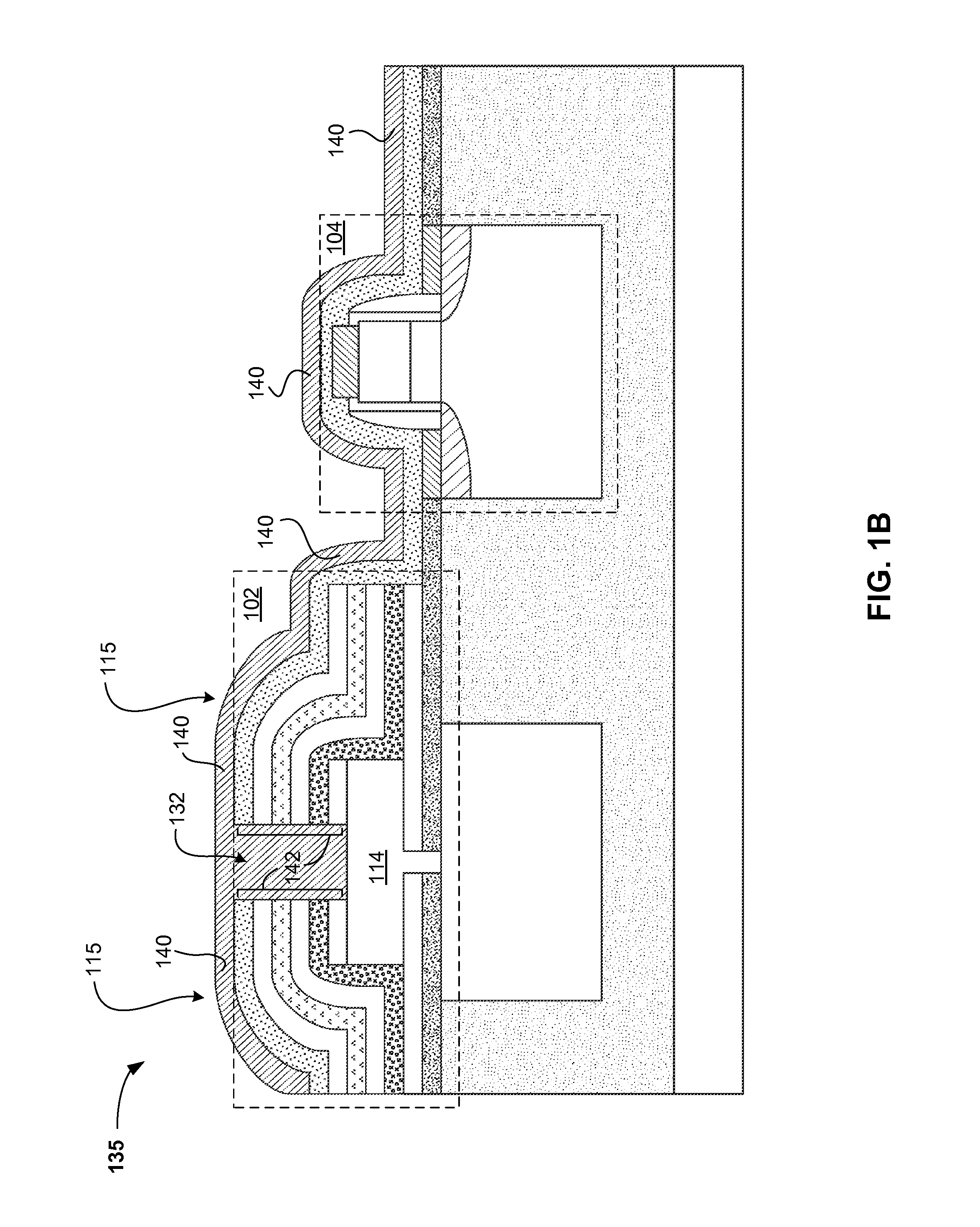
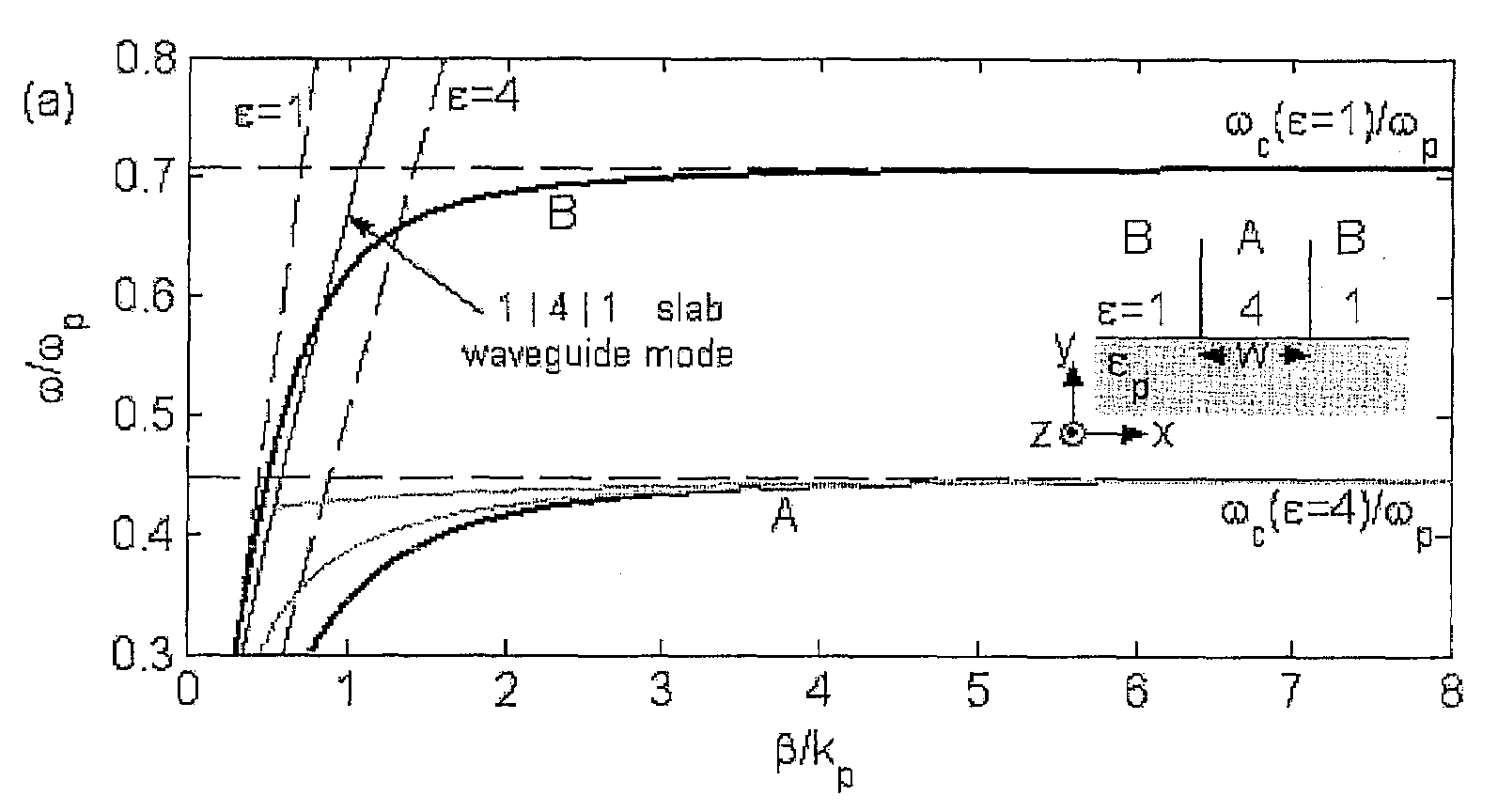
Surface-plasmon index guided (SPIG) waveguides and surface-plasmon effective index guided (SPEIG) waveguides
ActiveUS7184641B2Enhanced couplingNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guidePlasmonic waveguideCoupling
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
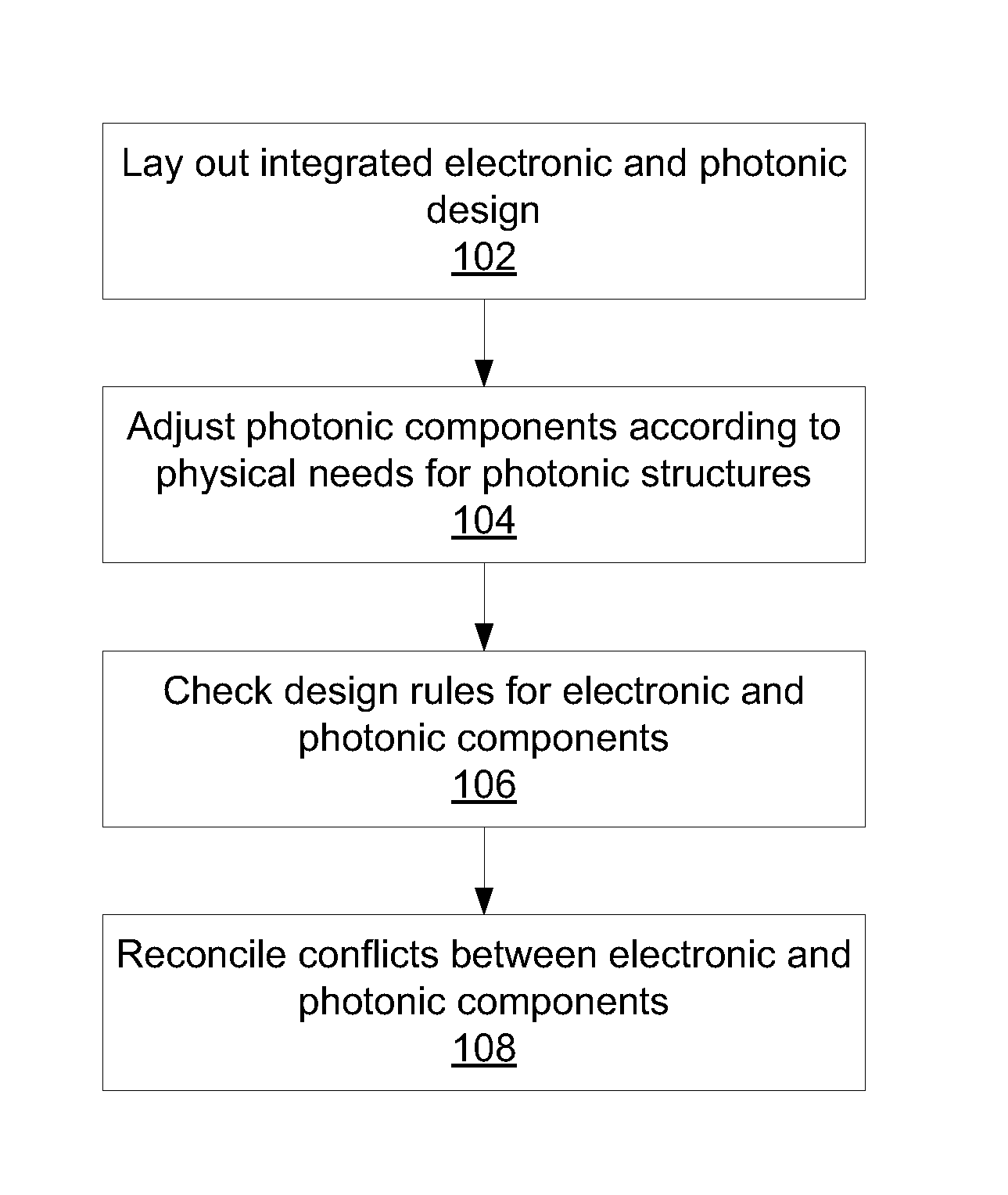
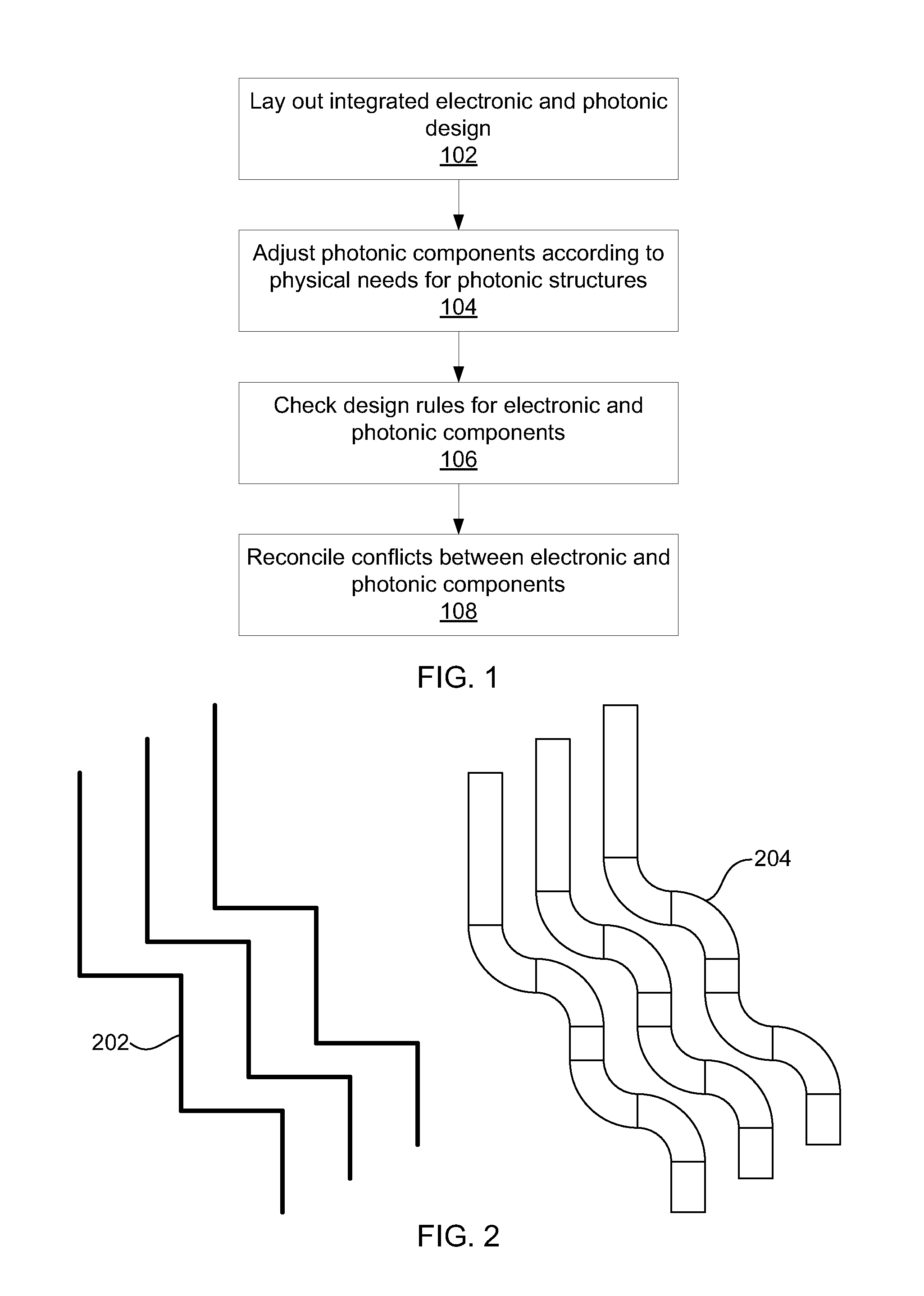
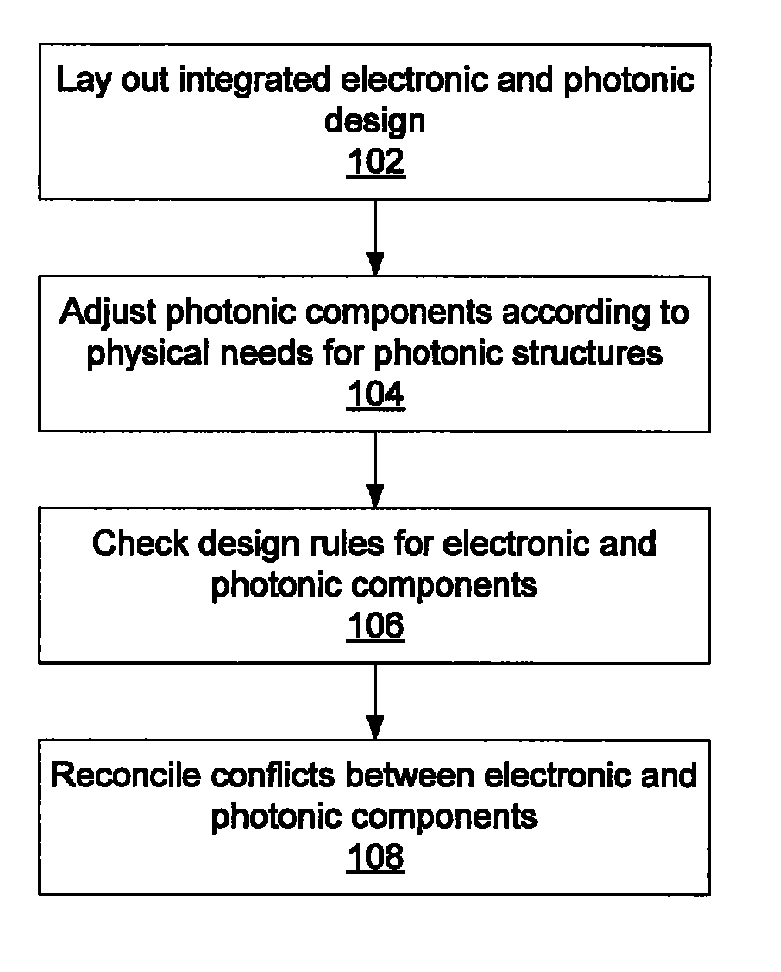
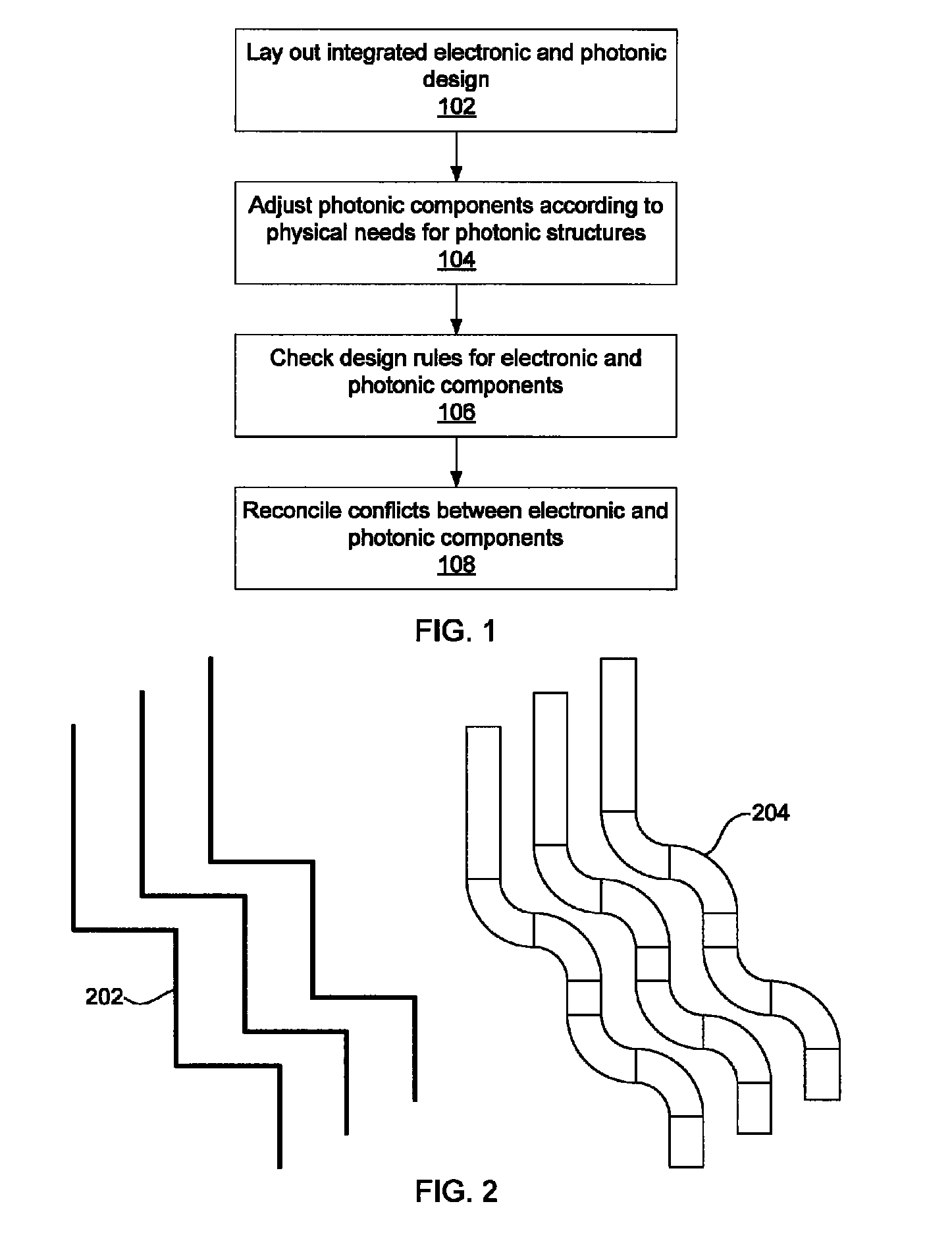
Integrated design environment for nanophotonics
ActiveUS20140007032A1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationGraphicsGraphical user interface
Systems for integrated electronic and photonic design include a graphical user interface (GUI) configured to lay out electronic and photonic design components in a design environment; a design rule checking (DRC) module configured to check design rules for electronic and photonic components according to manufacturing requirements; and a processor configured to adjust photonic components according to photonic design requirements and to reconcile conflicts between electronic and photonic components.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Manufacturing method for nanowire with CuO/ZnO core/shell structure
InactiveCN102104077AUniform diameterUniform lengthFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesCopper foilNanowire array
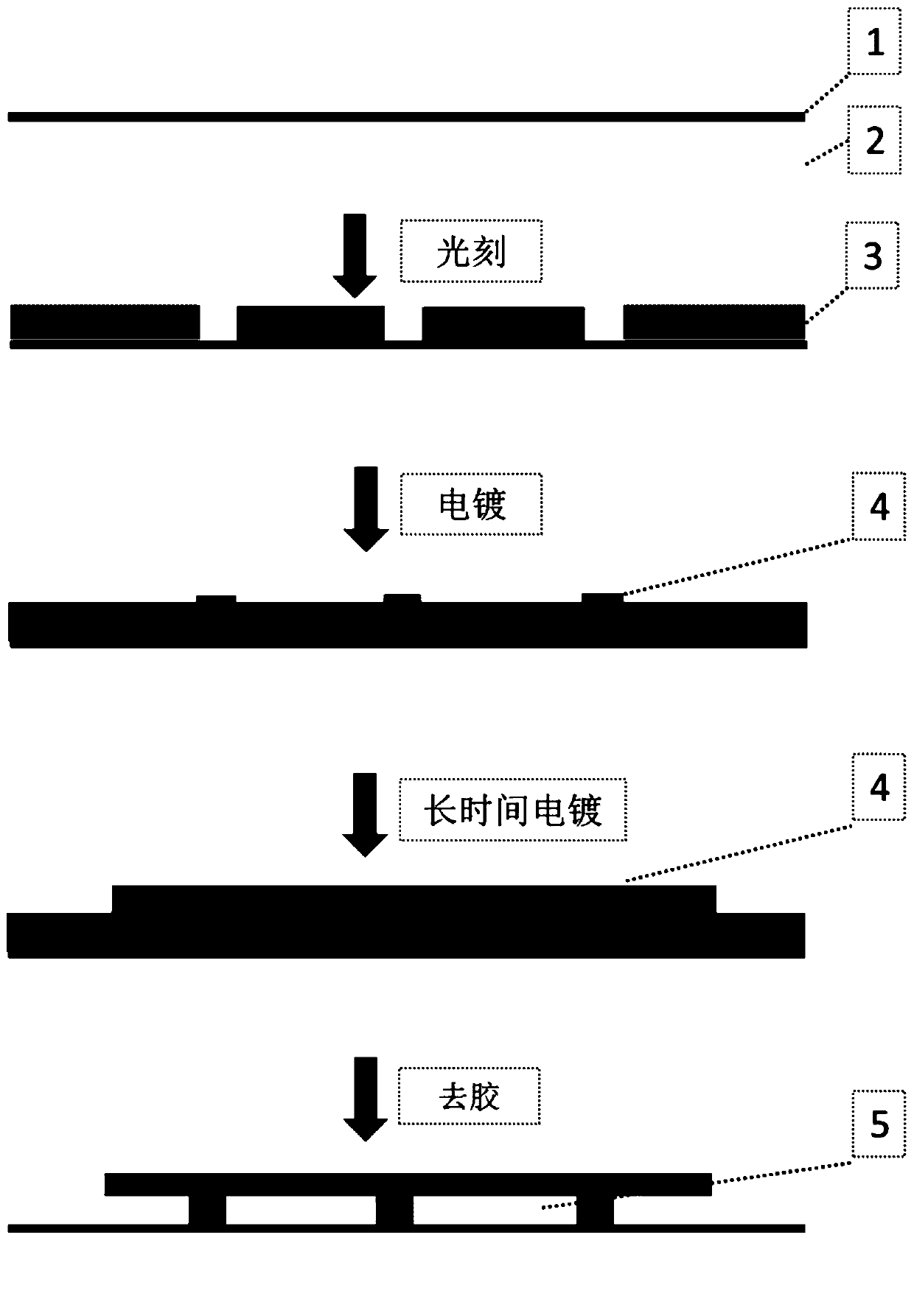
The invention belongs to the field of nanophotonics, and relates to a manufacturing method for a nanowire with a CuO / ZnO core / shell structure. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, heating a copper foil with a cleaned surface in the air by using a thermal oxidation method to grow a CuO nanowire array arranged directionally; 2, dripping saturated zinc acetate ethanol solution onto the CuO nanowire array prepared in the step 1 and naturally airing the solution in the air; and 3, heating the CuO nanowire array covered with zinc acetate on an electric stove of 350 DEG C for 15 to 30 minutes to obtain the CuO / ZnO core / shell structure. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, quickness, low cost, capacity of being produced on a large scale, and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Integrated design environment for nanophotonics
ActiveUS8627240B1Computer programmed simultaneously with data introductionCoupling light guidesPhotonicsIntegrated design
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
System and method for sensing intraocular pressure
ActiveUS20130165762A1Small sizeHigh sensitivityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurementGlaucomaImage resolution
Systems and methods of sensing intraocular pressure are described. In one embodiment, a miniaturized IOP monitoring system is provided using a nanophotonics-based implantable IOP sensor with remote optical readout that can be adapted for both patient and research use. A handheld detector optically excites the pressure-sensitive nanophotonic structure of the IOP-sensing implant placed in the anterior chamber and detects the reflected light, whose optical signature changes as a function of IOP. Optical detection eliminates the need for large, complex LC structures and simplifies sensor design. The use of nanophotonic components improves the sensor's resolution and sensitivity, increases optical readout distance, and reduces its size by a factor of 10-30 over previously reported implants. Its small size and convenient optical readout allows frequent and accurate self-tracking of IOP by patients in home settings. Embodiments can also be used to monitor colonies of animals to support glaucoma research and drug discovery.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Organic/metal nanowire heterojunction, as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an organic / metal nanowire heterojunction, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Due to the self assembly process of organic molecules in liquid phase, metal nanowires dispersed in the liquid phase are embedded therein, so the organic / metal nanowire heterojunctions of different structures are obtained. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process, convenient to operate, low in cost and wide in application, can be used for massive preparation and is environment-friendly. The organic / metal nanowire heterojunction obtained by the method has a smooth surface, a medium waveguide and a metal silver nanowire can be very tightly combined together, very high coupling efficiency of photons and surface plasmon polaritons is achieved, the problems that the surface of the composite material, prepared by the previous method, is unsmooth, the contact area between metal and a medium is small, the integral mechanical structure is unstable and the like are solved, and the method can be used for preparing nanophotonics elements such as a photonics multiplexer or a nano optical sensor.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Germanium photodetector schottky contact for integration with CMOS and Si nanophotonics
ActiveUS8765502B2Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentSolid-state devicesCMOSPhotovoltaic detectors
A method of forming an integrated photonic semiconductor structure having a photodetector device and a CMOS device may include depositing a dielectric stack over the photodetector device such that the dielectric stack encapsulates the photodetector. An opening is etched into the dielectric stack down to an upper surface of a region of an active area of the photodetector. A first metal layer is deposited directly onto the upper surface of the region of the active area via the opening such that the first metal layer may cover the region of the active area. Within the same mask level, a plurality of contacts including a second metal layer are located on the first metal layer and on the CMOS device. The first metal layer isolates the active area from the occurrence of metal intermixing between the second metal layer and the active area of the photodetector.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
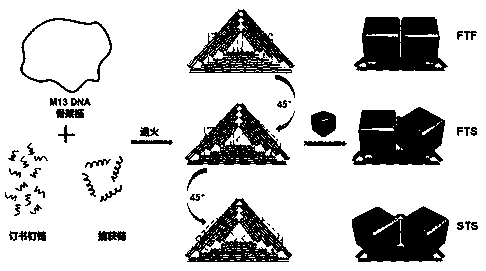
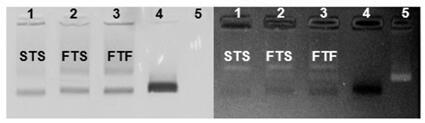
Method for forming dimer structure by assembling DNA origami template and nanometer gold cube based on surface enhanced Raman effect
ActiveCN110057806AEfficient and accurate assemblyEfficient assemblyRaman scatteringFermentationScanning electron microscopeA-DNA
The invention discloses a method for forming a dimer structure by assembling a DNA origami template and a nanometer gold cube based on a surface enhanced Raman effect. The method specifically comprises the five steps of preparation of triangular DNA origami with specific sites; preparation of a sulfydryl DNA modified nanometer gold cube; preparation of three dimer configurations; and high efficiency precise assembly by using agarose gel electrophoresis and a transmission electron microscope representational structure, and surface enhanced Raman scattering by using a scanning electron microscope and dark-field microscope co-location detection assembly structure. The method solves the problems of low assembly repeatability and poor structural stability, a new idea is also provided for construction of nanometer optical materials due to establishment of the method, and the method is of great significance to research of nanophotonics.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Liquid crystal and metal interface charge-based non-linear surface plasmon polaritons device
InactiveCN102135695AAchieving non-linear effectsReduce input powerNon-linear opticsFeedback effectPrism
The invention provides a liquid crystal and metal interface charge-based non-linear surface plasmon polaritons device, belongs to the technical field of micro-nanophotonics, realizs non-linear surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) under milliwatt-order input power, and provides a technical scheme for non-linear SPPs integration of a doped charge generator-based liquid crystal non-linear material. The device can utilize spatial light to excite the SPPs through a prism on a gold film and a nematic liquid crystal interface, wherein the non-linear characteristics of the SPPs realized through an interface charge and nematic liquid crystal feedback effect can be acquired by measuring an optical signal output by prism coupling. The interface charge and nematic liquid crystal-based non-linear SPPs mechanism and the implementation scheme have practical application values in integrated opto chips in the future.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Chip-integrated device and methods for generating random numbers that is reconfigurable and provides genuineness verification
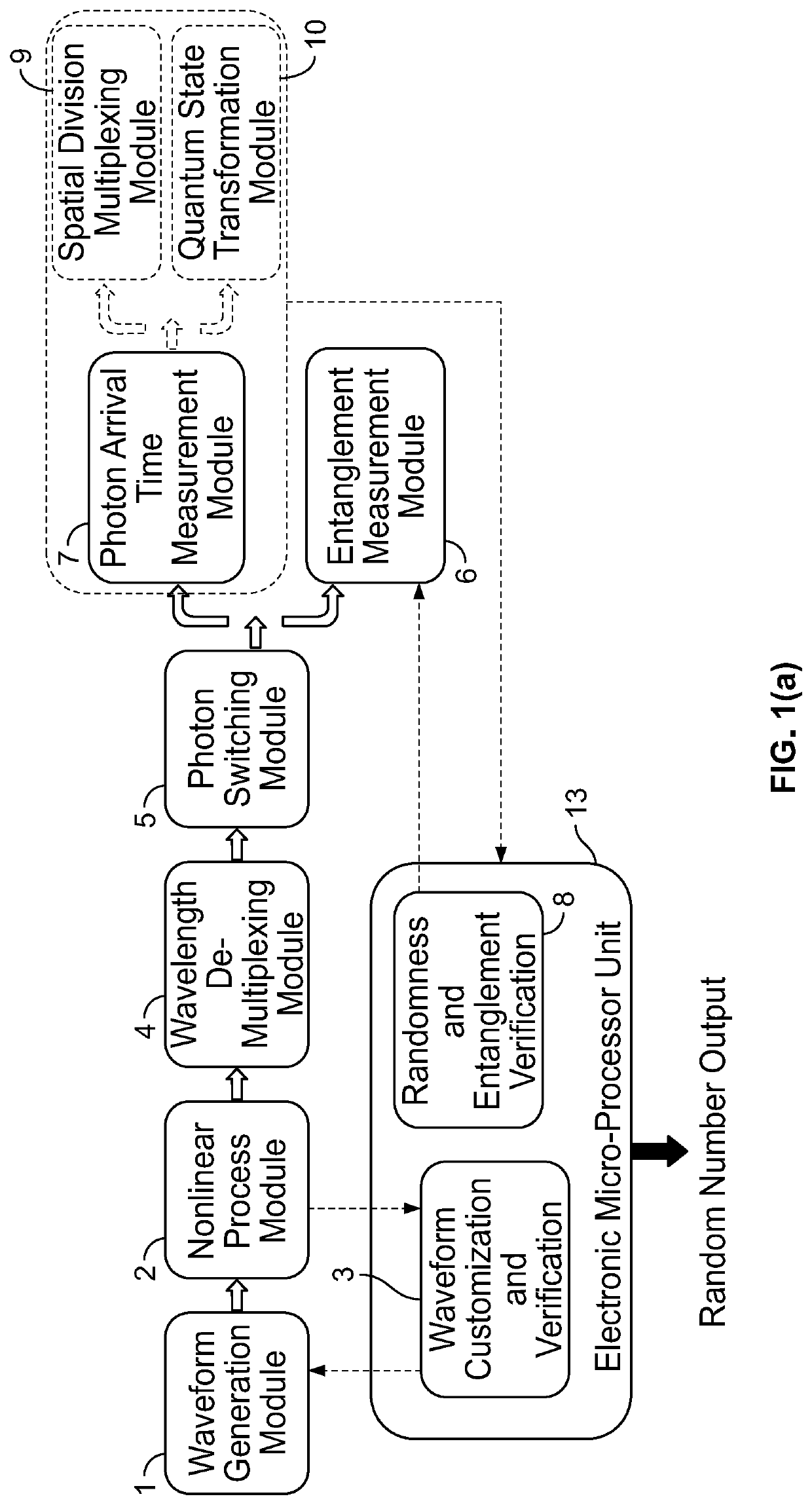
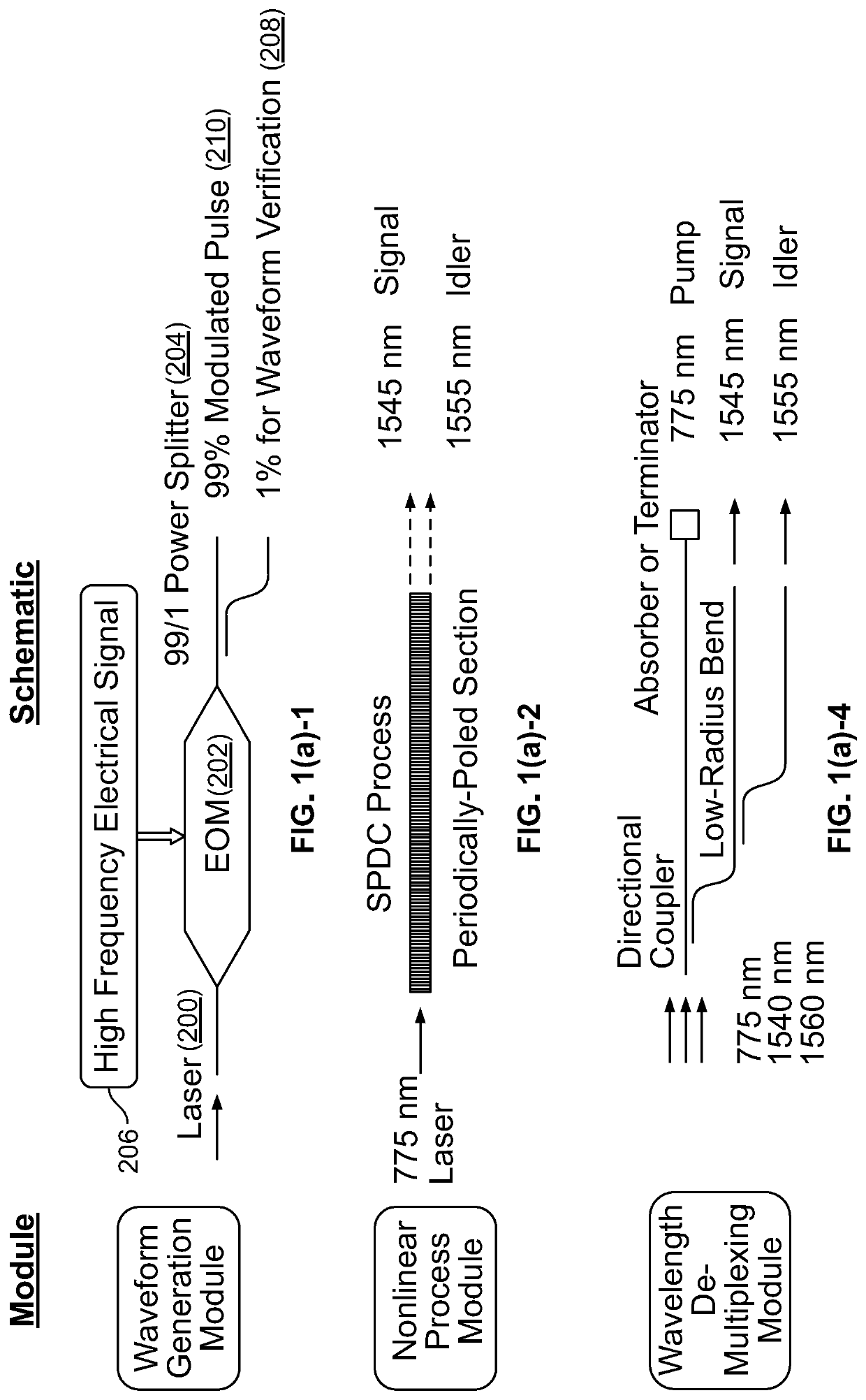
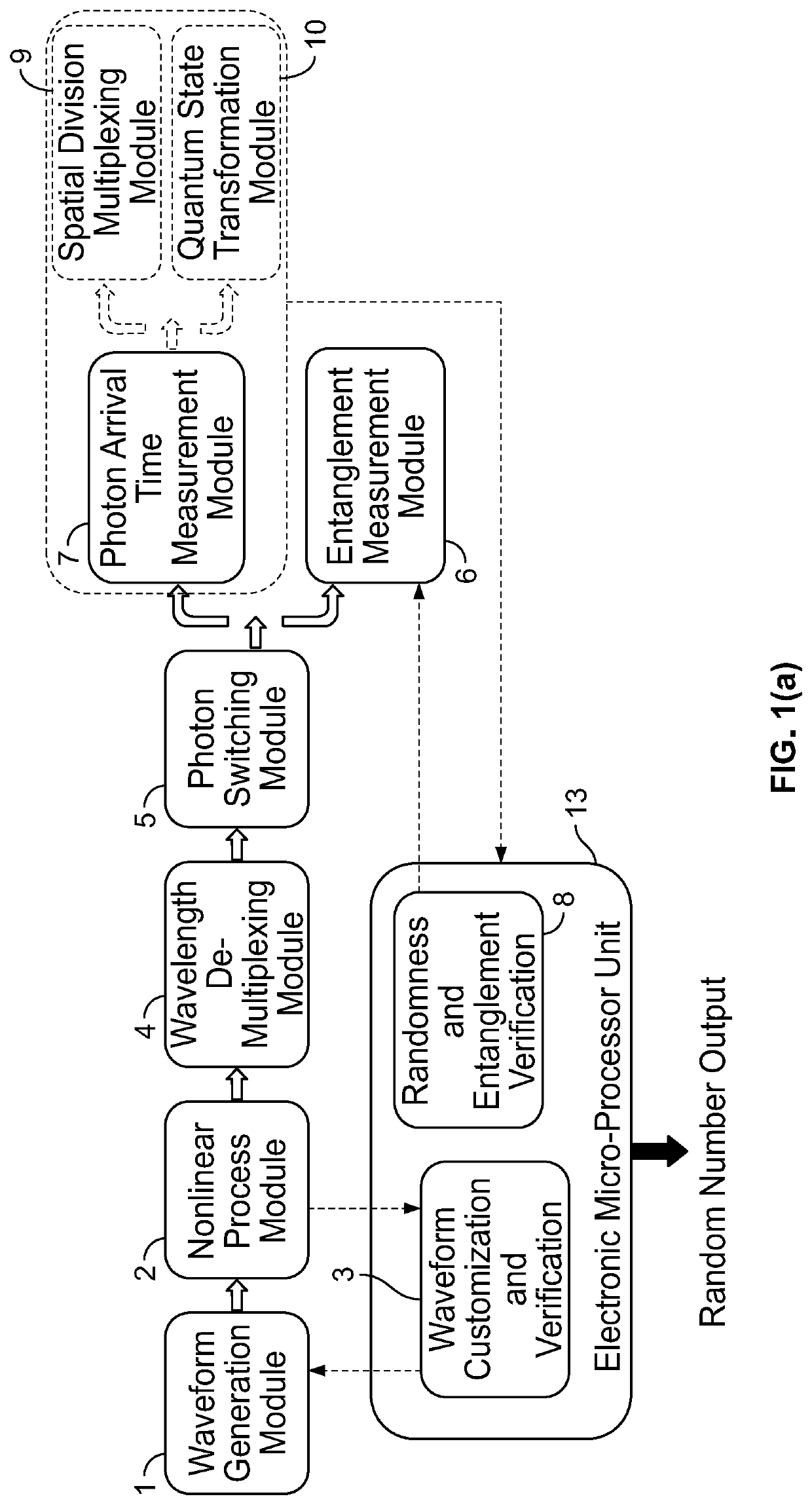
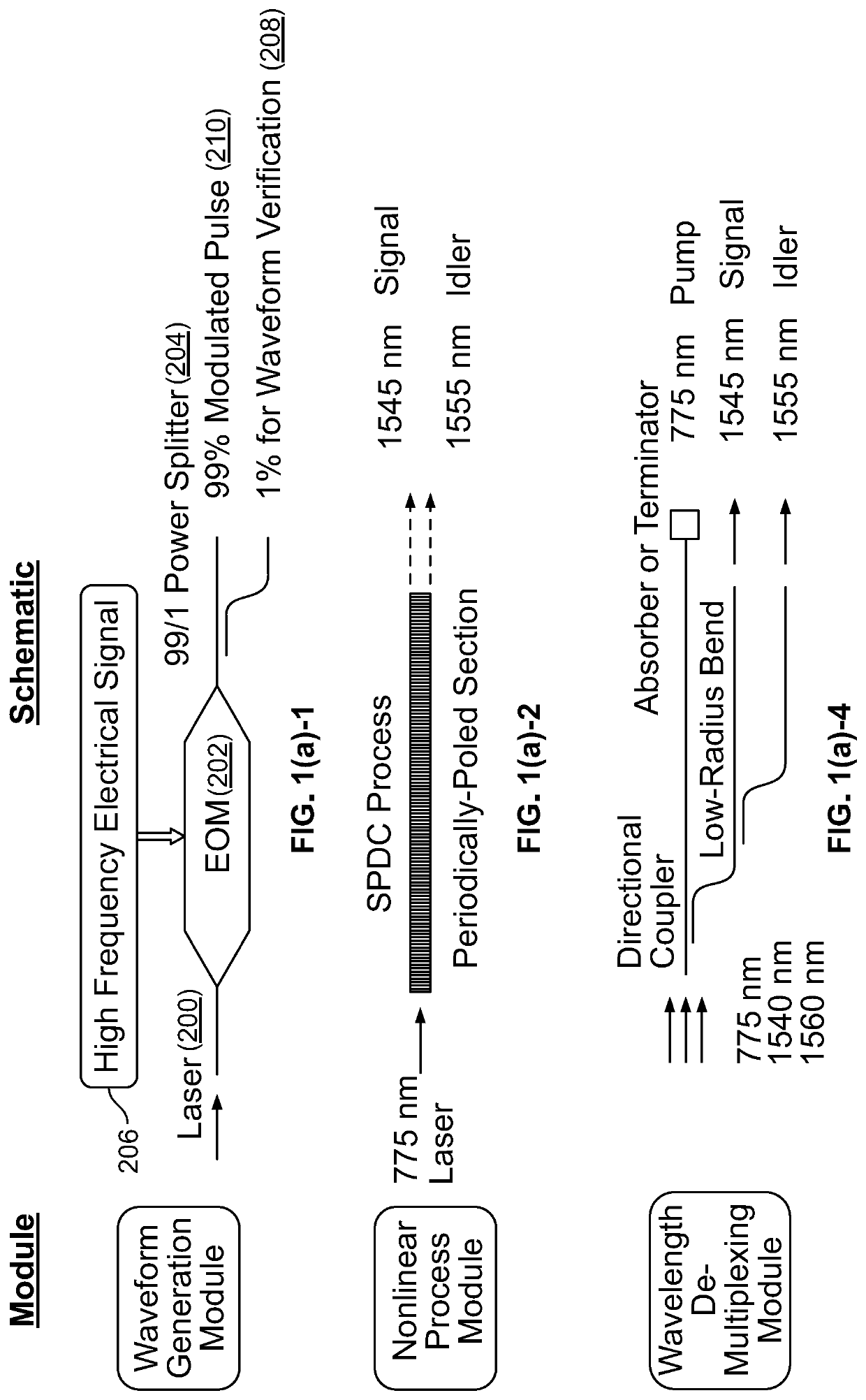
ActiveUS20210141609A1Increase speedHigh speed machiningKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsQuantum entanglementCorrelation function
A device for generation of genuine random numbers, uses quantum stochastic processes in optical parametric nonlinear media. The dimensionality of the random numbers is varied from 2 to over 100,000. Their statistical properties, including the correlation function amongst random numbers, are tailored using linear and nonlinear optical circuits following the parametric nonlinear media. Both the generation and manipulation of random numbers can be integrated on a single nanophotonics chip. By incorporating optoelectric effects, fast streams of random numbers can be created in custom statistical properties, which can be updated or reconfigured in real time, such as at 10 GHz speed. The unpredictability of the random numbers is quantifying by evaluating their min-entropy. The genuineness of quantum random numbers is tested using both statistical tools and independently verified by measuring the quantum entanglement between the photons in real time reducing vulnerability to hostile attack.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Surface-plasmon index guided (SPIG) waveguides and surface-plasmon effective index guided(SPEIG) waveguides
ActiveUS20050259936A1Easy to integrateBroadband couplingNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guidePlasmonic waveguideCoupling
A new class of surface plasmon waveguides is presented. The basis of these structures is the presence of surface plasmon modes, supported on the interfaces between the dielectric regions and the flat unpatterned surface of a bulk metallic substrate. The waveguides discussed here are promising to have significant applications in the field of nanophotonics by being able to simultaneously shrink length, time and energy scales, allowing for easy coupling over their entire bandwidth of operation, and exhibiting minimal absorption losses limited only by the intrinsic loss of the metallic substrate. These principles can be used for many frequency regimes (from GHz and lower, all the way to optical).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for sensing intraocular pressure
ActiveUS20160015266A1Small sizeHigh sensitivityFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsForce measurementImage resolutionMedicine
Systems and methods of sensing intraocular pressure are described. An example miniaturized intraocular pressure (IOP) monitoring system is provided using a nanophotonics-based implantable IOP sensor with remote optical readout that can be adapted for both patient and research use. A handheld detector optically excites the pressure-sensitive nanophotonic structure of the IOP-sensing implant placed in the anterior chamber and detects the reflected light, whose optical signature changes as a function of IOP. Optical detection eliminates the need for large, complex LC structures and simplifies sensor design. The use of nanophotonic components improves the sensor's resolution and sensitivity, increases optical readout distance, and reduces its size by a factor of 10-30 over previous implants. Its small size and convenient optical readout allows frequent and accurate self-tracking of IOP by patients in home settings.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Silicon-based ultra-wide spectrum photon absorber and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of nanophotonics, and provides a silicon-based ultra-wide spectrum photon absorber and a preparation method thereof, and aims to solve the technical problem that inthe prior art, silicon-based optical and photoelectric devices cannot achieve efficient absorption in ultraviolet, visible and near-infrared bands. The absorber comprises a first metal film layer, a first disordered nano bowl array layer, a silicon substrate, a second disordered silicon nano bowl array layer and a second metal film layer, a double-sided disordered metal / silicon nano bowl array composite structure can efficiently absorb more than 80% of incident photons within the waveband range of 200-2500nm, is insensitive to the polarization and angle of incident light, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of photoelectric detection and reverse detection, solar cells, photoelectric sensing and the like.
Owner:苏州斯特科光电科技有限公司
Method for simply preparing Au-Ag dual-metal nanoparticle film of meshed structure
InactiveCN106180754AImprove stabilitySimple methodTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusElectricityOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a method for simply preparing an Au-Ag dual-metal nanoparticle film of a meshed structure. According to the method, a small quantity of AgNO3 is added in the synthetic process of Au seeds, Ag+ is stably adsorbed to the surfaces of Au nanoparticles, and thus the Au nanoparticles have anisotropy in the growing process; and then the Au nanoparticles containing Ag are used as seeds, no inductive agent needs to be added, and the Au-Ag dual-metal nanoparticle film which is of the meshed structure and has a clean surface can be obtained through self-assembling on a gas-liquid interface under the normal temperature condition. The method is simple and rapid, reaction conditions are mild, no inductive agent or organic solvent needs to be added, and the prepared nanoparticle film has extremely good stability and has potential application value in the aspects of surface-enhanced raman, plasma nanometer circuits, nanophotonics, electro-catalysis and new energy application. The method can also be used for preparing other dual-metal nanoparticle film materials.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Directional emission organic semiconductor light emitting diode array based on metal nano electrodes and preparation thereof
PendingCN110085770ARealize the designAchieve preparationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole transport layerNanoscopic scale
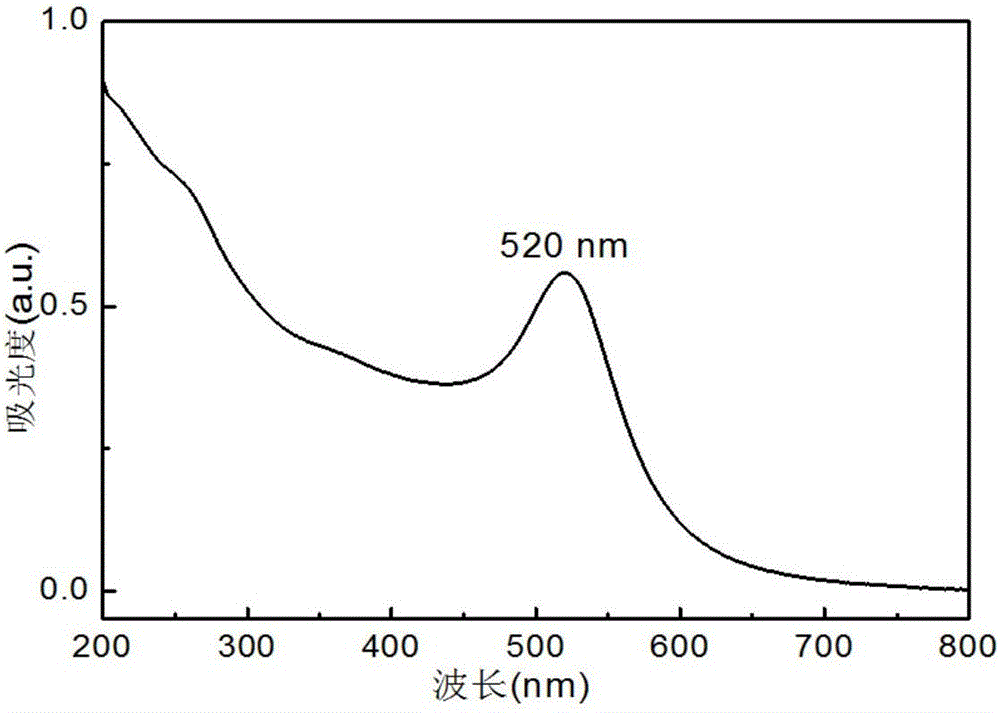
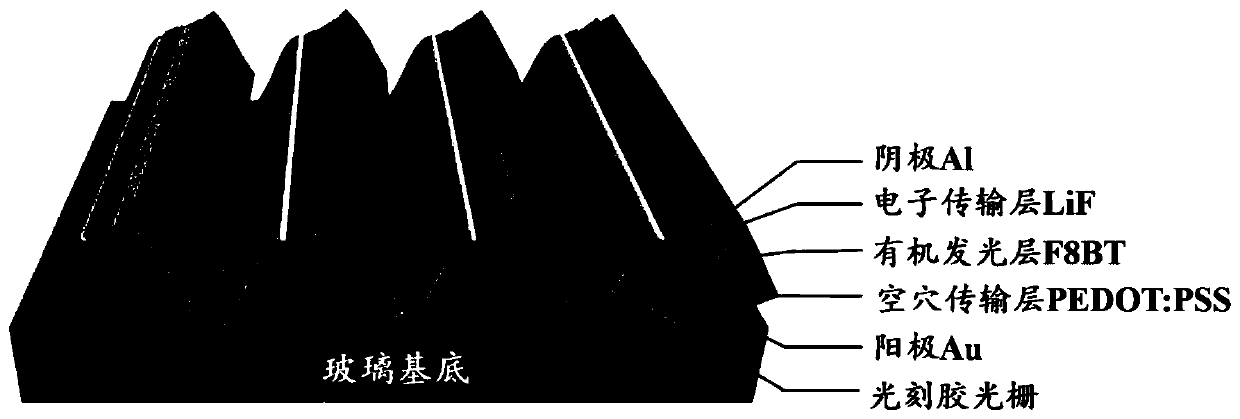
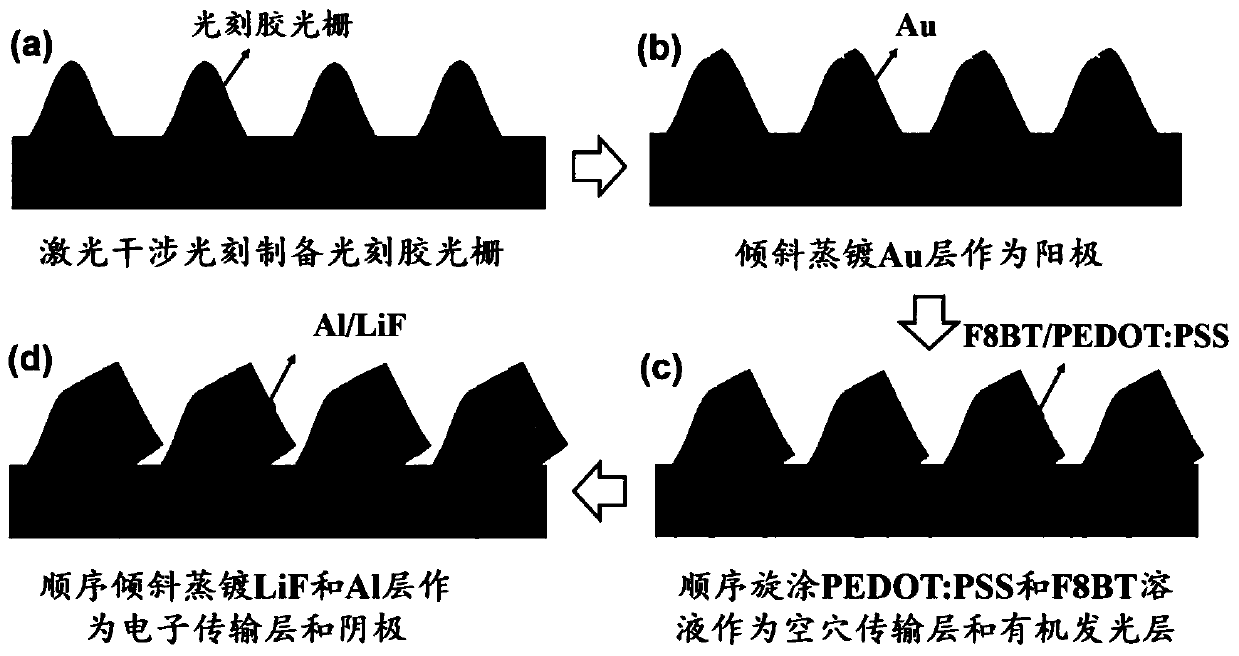
The invention relates to a directional emission organic semiconductor light emitting diode array based on metal nano electrodes and preparation thereof, and belongs to the technical field organic optoelectronics and nanophotonics. On a glass substrate, a photoresist nano grating is utilized to serve as a template, nano-scale organic light emitting diodes parallel to the located inclined planes areprepared on the inclined planes at the same side of each convex grid line of the nano grating, and the nano-scale organic light emitting diode includes an anode layer Au, a hole transport layer PEDOT: PSS, an organic light emitting layer F8BT film, an electron transport layer LiF and a cathode Al which are sequentially laminated outward from the side surface of the convex grid line. The inclinedorganic light emitting diodes are formed on the nano grating structure, and all of the organic light emitting diodes form an array structure. The device achieves the working mode of end emission and obtains the directional emission nano OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) array.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Chip-integrated device and methods for generating random numbers that is reconfigurable and provides genuineness verification
ActiveUS11442697B2Increase speedKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsCorrelation functionHemt circuits
A device for generation of genuine random numbers, uses quantum stochastic processes in optical parametric nonlinear media. The dimensionality of the random numbers is varied from 2 to over 100,000. Their statistical properties, including the correlation function amongst random numbers, are tailored using linear and nonlinear optical circuits following the parametric nonlinear media. Both the generation and manipulation of random numbers are integrated on a single nanophotonics chip. By incorporating optoelectric effects, fast streams of random numbers are created in custom statistical properties, which are updated or reconfigured in real time, such as at 10 GHz speed. The unpredictability of the random numbers is quantifying by evaluating their min-entropy. The genuineness of quantum random numbers is tested using both statistical tools and independently verified by measuring the quantum entanglement between the photons in real time.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
A nanophotonics multi-parameter measurement platform
ActiveCN102829961BEasy to study optical propertiesThe incident angle is continuously adjustableColor/spectral properties measurementsUsing optical meansEffect lightPhotonics
The invention relates to the technical field of reactor engineering and discloses a nanophotonics multi-parameter measurement platform. The nanophotonics multi-parameter measurement platform comprises a multi-parameter variable excitation system, a sample position direction fine-adjusting unit, a microscope observation alignment system, a scanning near-field optical microscope detection system and a computer; the sample position direction fine-adjusting unit is used for mounting a sample to be measured; the multi-parameter variable excitation system provides a lighting excitation light source signal to the sample to be measured; the microscope observation alignment system adjusts an imaging area of the sample to be measured, collects the image information of the sample to be measured, and transmits the image information to the computer to be displayed; the scanning near-field optical microscope detection system collects the optical near-field information of the sample to be measured and transmits the optical near-field information to the computer; and the computer processes the optical near-field information and then displays the processed optical near-field information. The nano-optics multi-parameter measurement platform is compact in structure, can achieve adjustment with multiple degrees of freedom, and can achieve optical excitation of variable excitation wavelength, continuous adjustment of the incident angle and controllable polarization state on a given excitation area of a nano photonics device.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of surface plasmon metamaterial
ActiveCN110629262ASimple processing methodThe process method is stable and cheapVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingOptical cavitySpins
The invention provides a preparation method of a surface plasmon metamaterial, and belongs to the technical field of nanophotonics and nanofabrication. According to the preparation method, the thickness of a spin-coated photoresist is controlled through an electroplating process to realize control over the thickness of an intermediate layer in metal-medium-metal, and different medium thicknesses can serve as an optical cavity and can be coupled with surface plasmons to realize different optical responses; and meanwhile, optical absorption is enhanced by means of the ohmic loss of metal, almost-perfect optical absorption (the absorption rate is close to 100%) and high-quality factor optical cavities are realized by means of the electromagnetic energy localization effect of the surface plasmons. The technical method is simple, stable and cheap and can realize large-area processing.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for realizing micronano all-optical color
InactiveCN102081194AEasy to assembleElectric driveDecorative surface effectsNanoopticsElectricityNanowire
The invention belongs to the field of nanophotonics, and discloses a method for realizing a micronano all-optical color. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging two or three nanowires on a glass substrate in turn to form a cross knot; coupling red light, green light or blue light into the nanowires through optical fibers connected with the nanowires respectively; and synthesizing colored light spots in various colors at the cross knot. In the method, an electric driver or a color filter is not needed; and the method has the advantages of easiness in fabrication and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
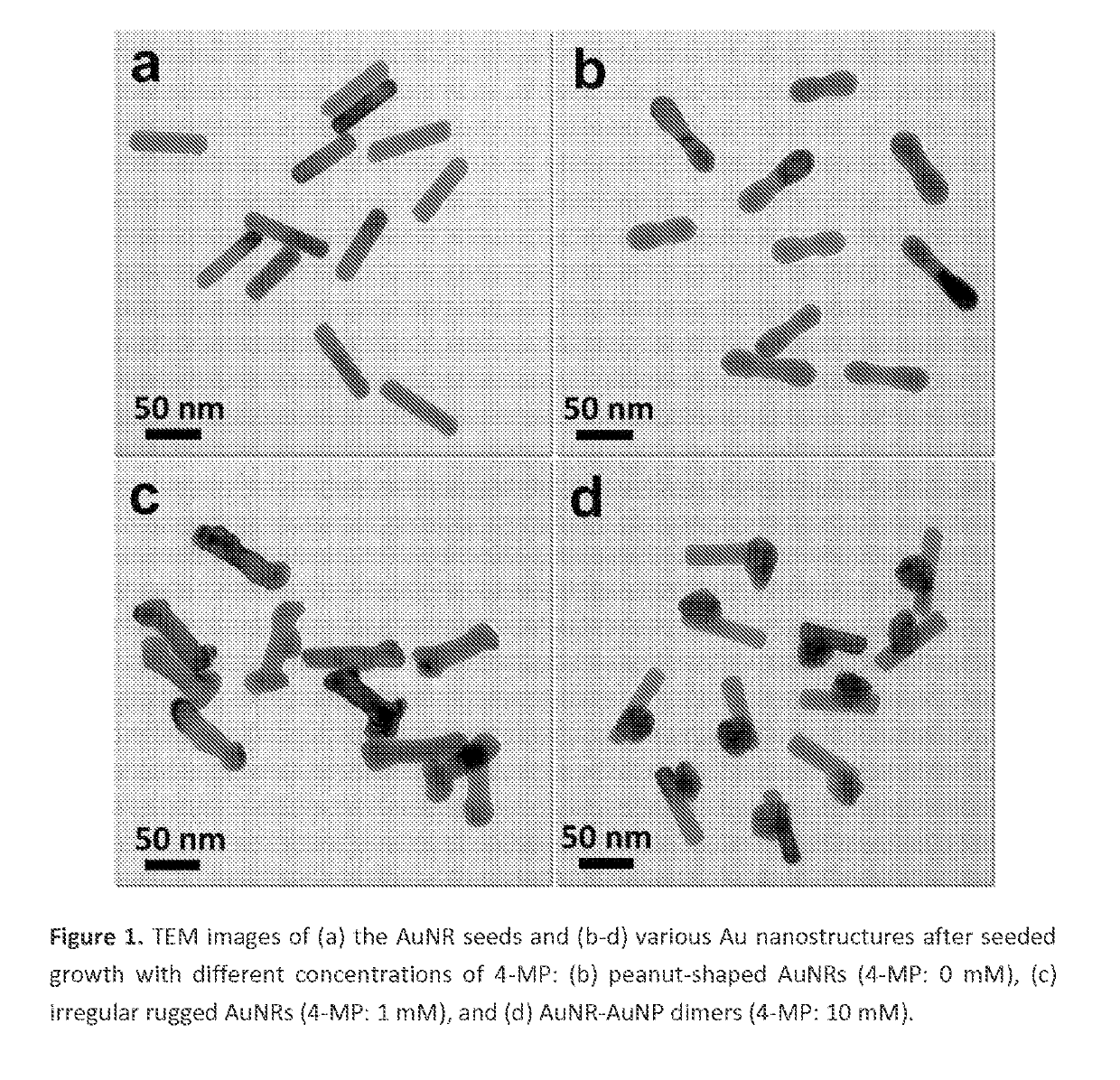
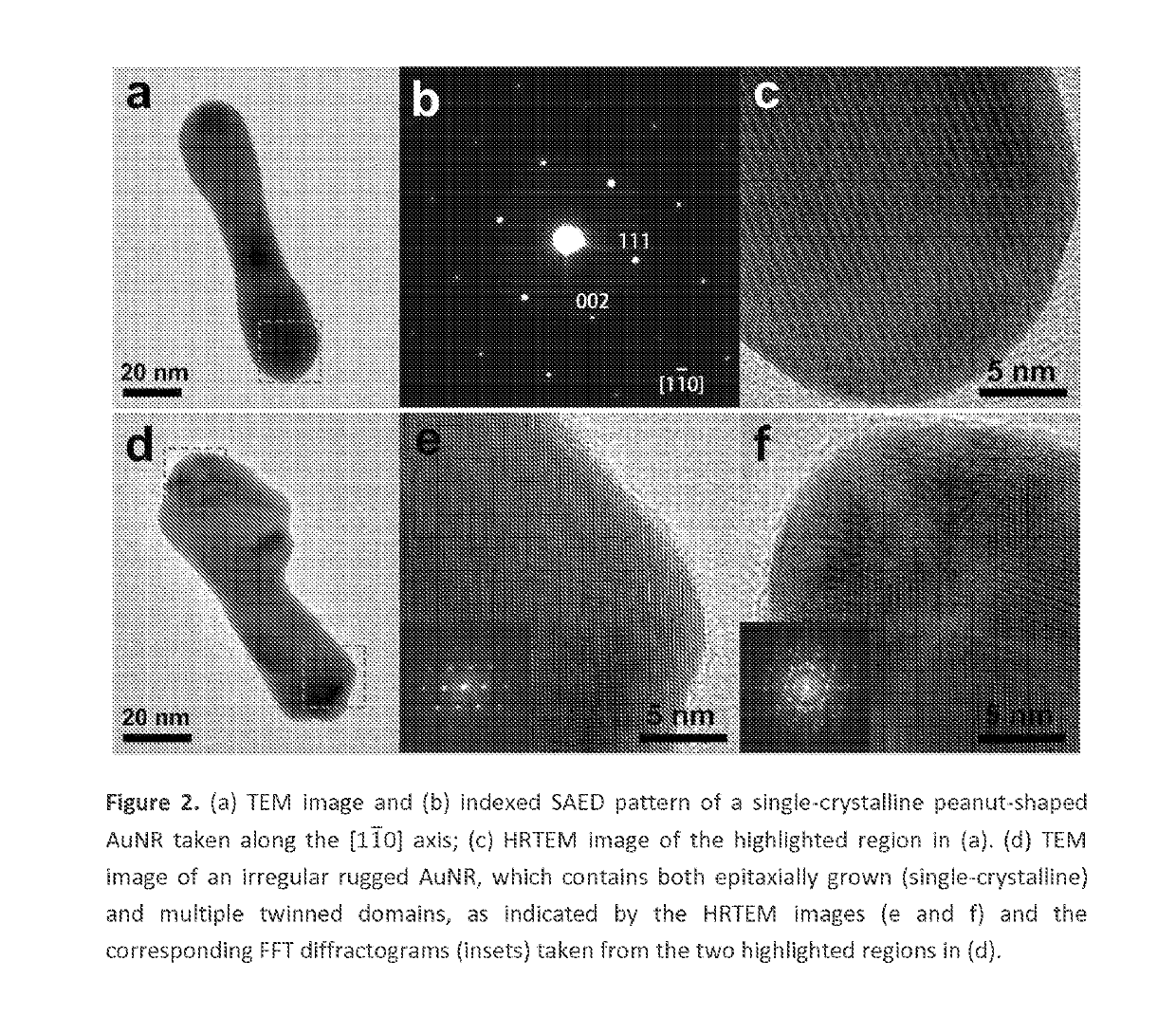
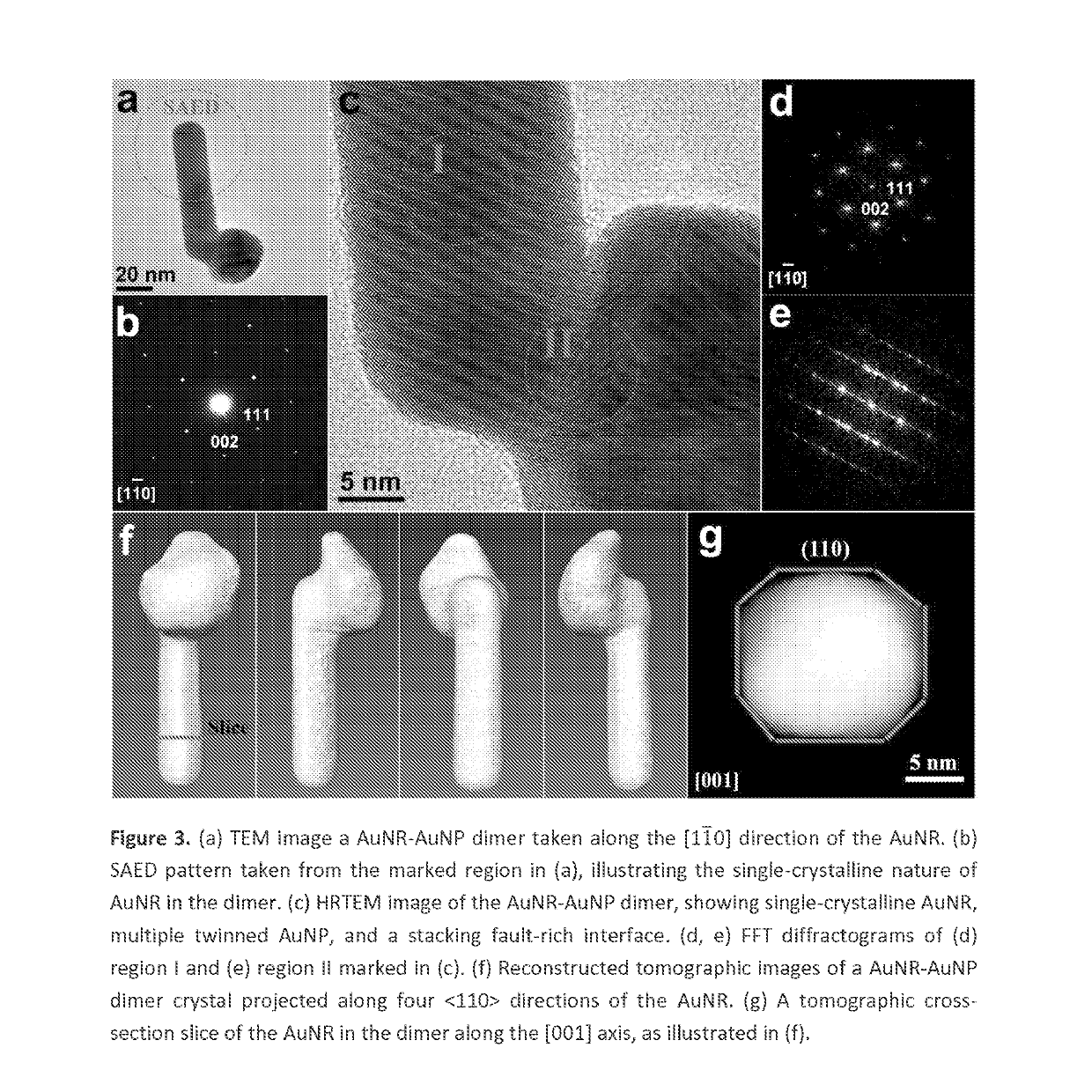
Asymmetric monometallic nanorod nanoparticle dimer and related compositions and methods
ActiveUS10458039B2Promote absorptionImprove photovoltaic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthSolar lightEnergy conversion efficiency
The fabrication of asymmetric monometallic nanocrystals with novel properties for plasmonics, nanophotonics and nanoelectronics. Asymmetric monometallic plasmonic nanocrystals are of both fundamental synthetic challenge and practical significance. In an example, a thiol-ligand mediated growth strategy that enables the synthesis of unprecedented Au Nanorod-Au Nanoparticle (AuNR-AuNP) dimers from pre-synthesized AuNR seeds. Using high-resolution electron microscopy and tomography, crystal structure and three-dimensional morphology of the dimer, as well as the growth pathway of the AuNP on the AuNR seed, was investigated for this example. The dimer exhibits an extraordinary broadband optical extinction spectrum spanning the UV, visible, and near infrared regions (300-1300 nm). This unexpected property makes the AuNR-AuNP dimer example useful for many nanophotonic applications. In two experiments, the dimer example was tested as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate and a solar light harvester for photothermal conversion, in comparison with the mixture of AuNR and AuNP. In the SERS experiment, the dimer example showed an enhancement factor about 10 times higher than that of the mixture, when the excitation wavelength (660 nm) was off the two surface plasmon resonance (SPR) bands of the mixture. In the photothermal conversion experiment under simulated sunlight illumination, the dimer example exhibited an energy conversion efficiency about 1.4 times as high as that of the mixture.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method and application of orthorhombic cesium lead iodide single crystal nanowire
ActiveCN106006722BEasy to prepareExcellent X-ray Fluorescence PropertiesSpecific nanostructure formationMaterial nanotechnologyBrickHigh energy
The invention discloses a preparing method and application of an orthorhombic phase cesium-lead iodide monocrystal nanowire. The preparing method comprises the steps of adding lead iodide to gamma-butyrolactone which is in a protective atmosphere and under stirring at the temperature of 68.5-72.5 DEG C, so that brick red turbid solution is obtained; then adding cesium iodide to the brick red turbid solution to obtain mixed solution; placing the mixed solution in a protective atmosphere at the temperature of 68.5-72.5 DEG C to be stirred constantly for at least 80 min to obtain luminous yellow mixed solution; cooling the luminous yellow mixed solution, and placing the luminous yellow mixed solution in an environment with relative humidity smaller than or equal to 20% and temperature of 68.5-72.5 DEG C to be evaporated to dryness, so that the orthorhombic phase cesium-lead iodide monocrystal nanowire is obtained, wherein the single crystal growth direction of the nanowire is <100>, wire diameter is 0.1-0.15 micron, and wire length is larger than or equal to 100 microns. The nanowire can serve as a basic unit to build a nanowire device or nanowire array device, and can generate X-ray fluorescence of 464+ / -10 and 564+ / -10 nm under the excitation of X rays. The nanomwire is expected to be widely applied to making of nanophotonics basis units, photoelectric detectors, high-energy ray detection and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com