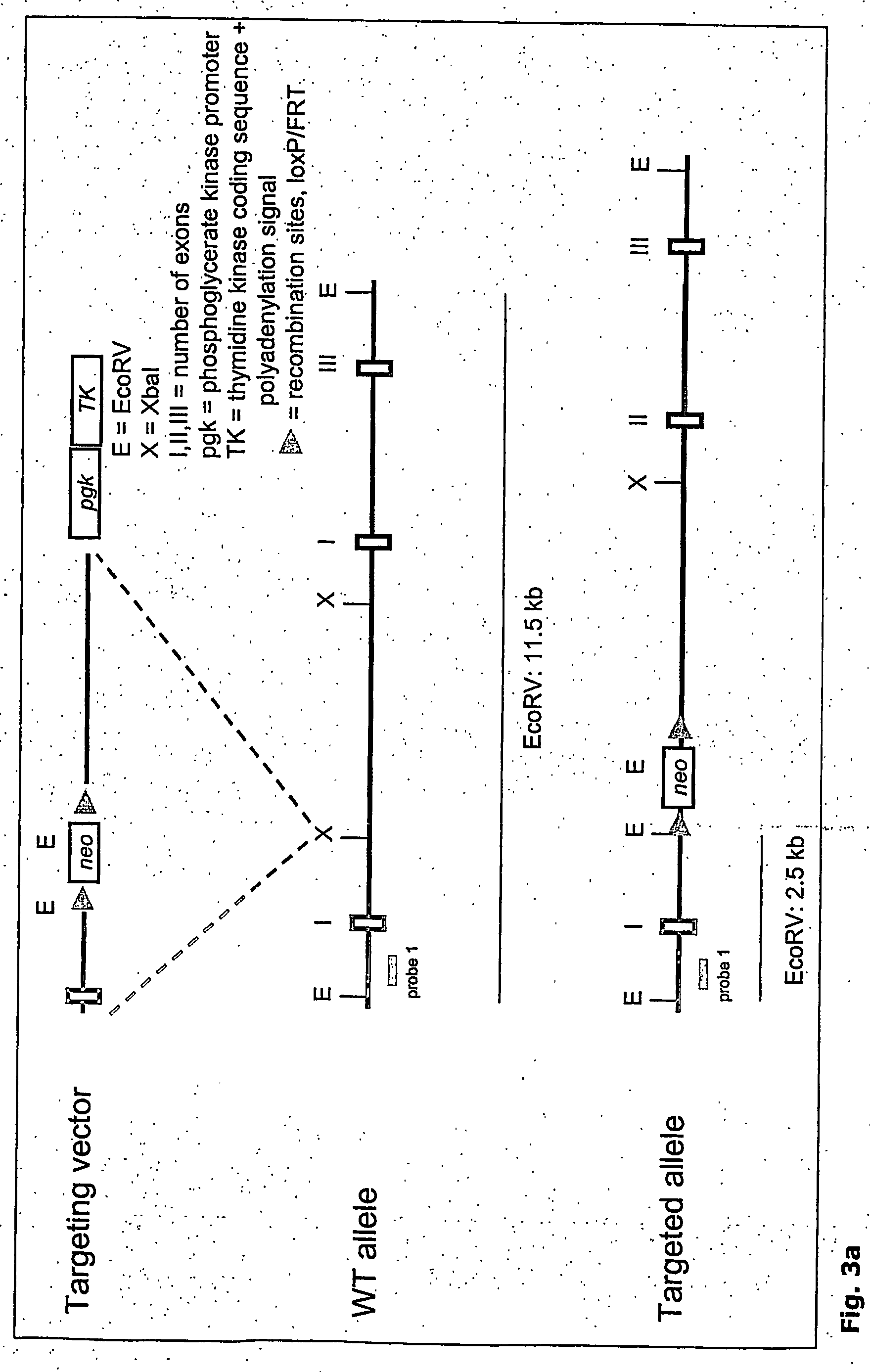
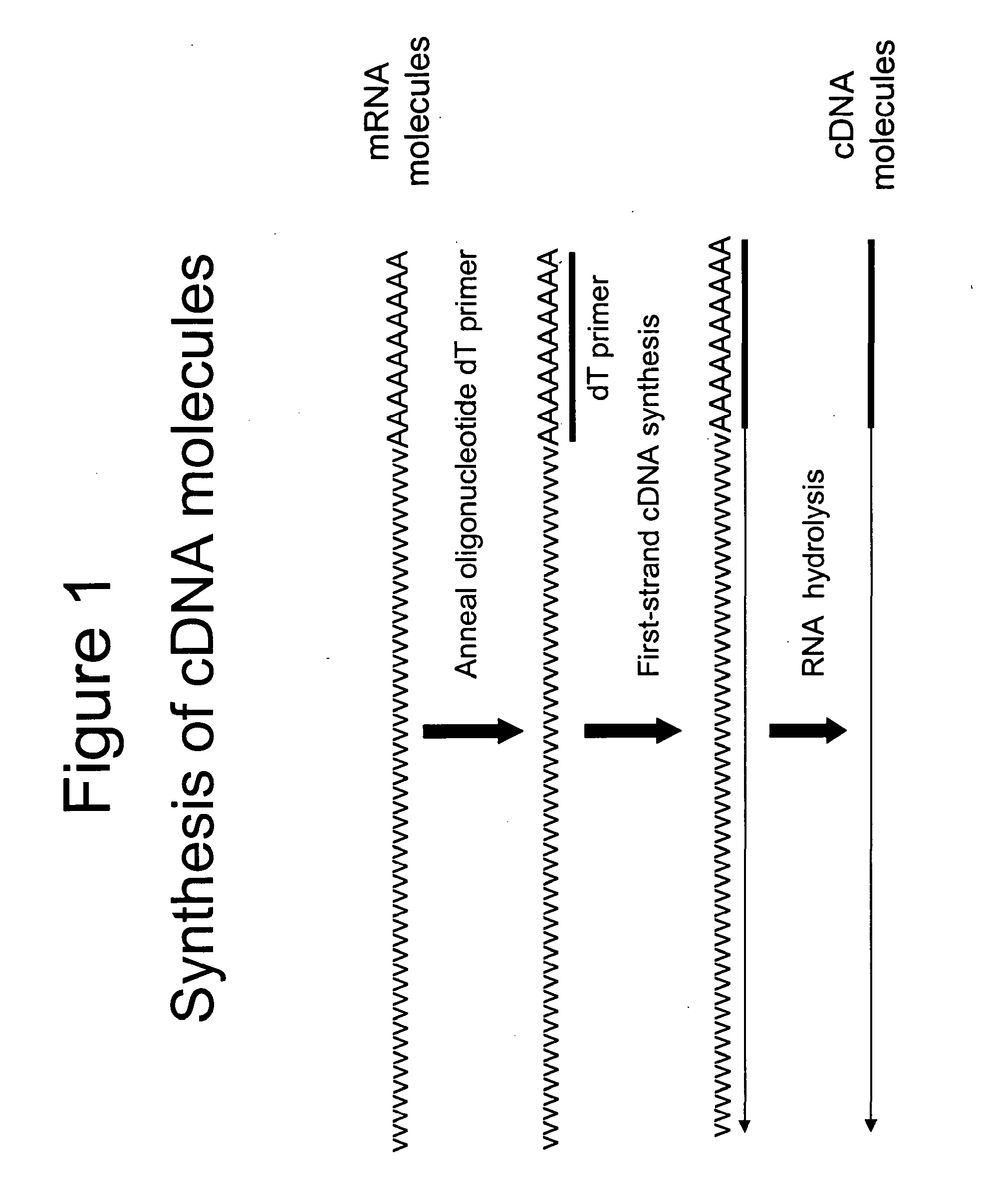
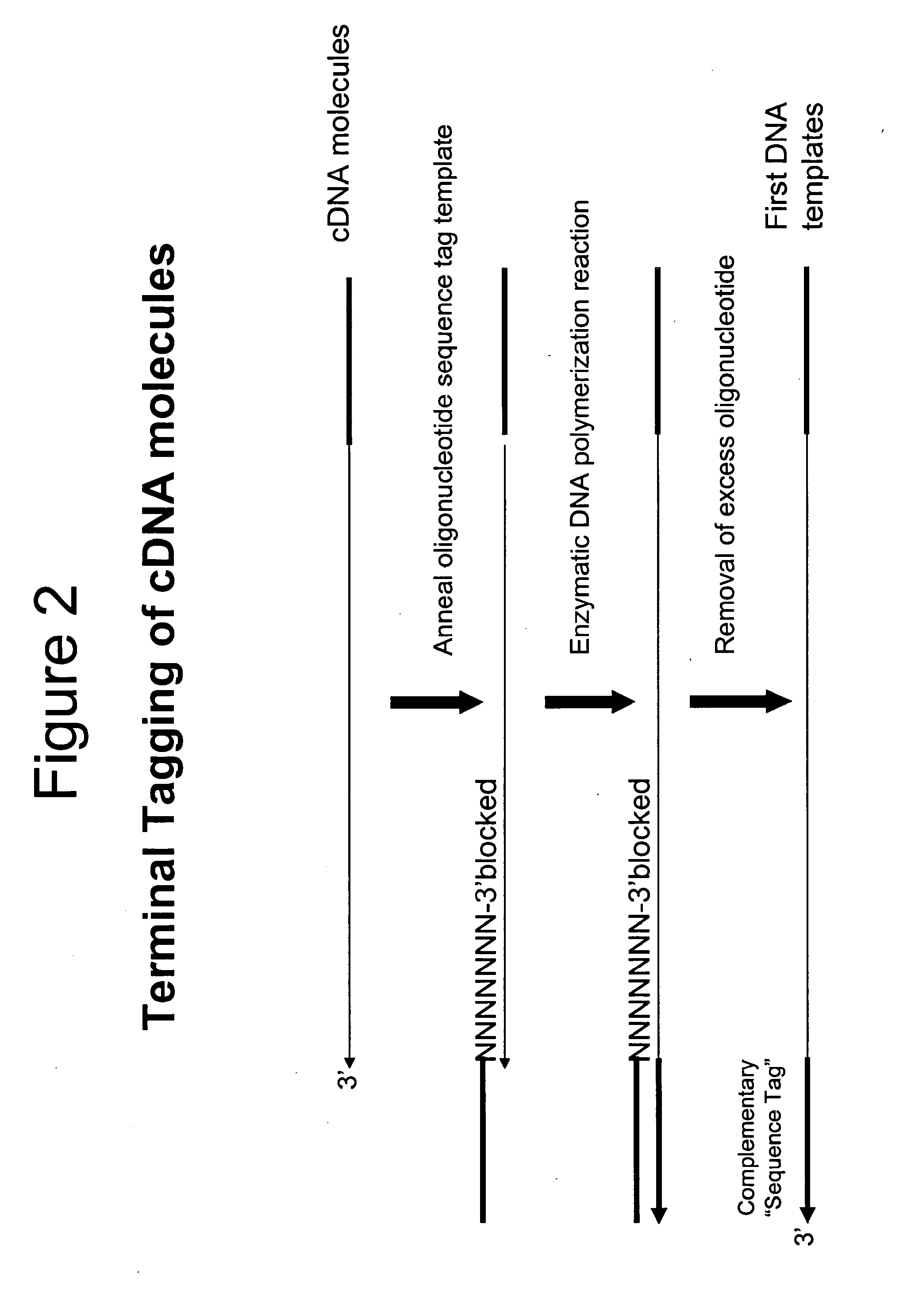
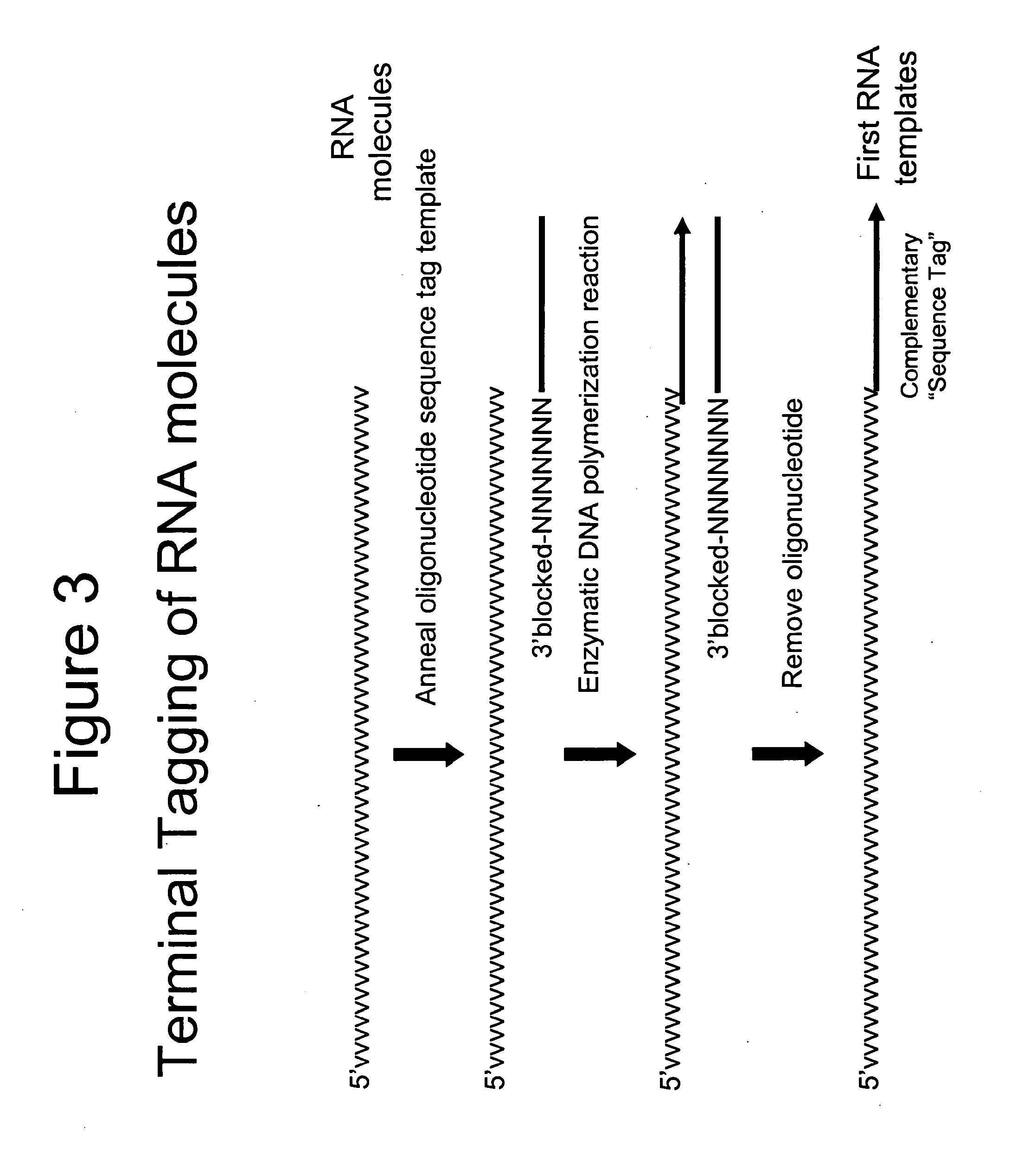
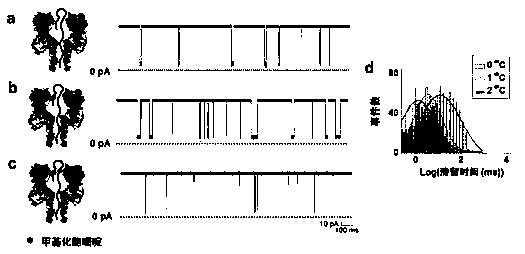
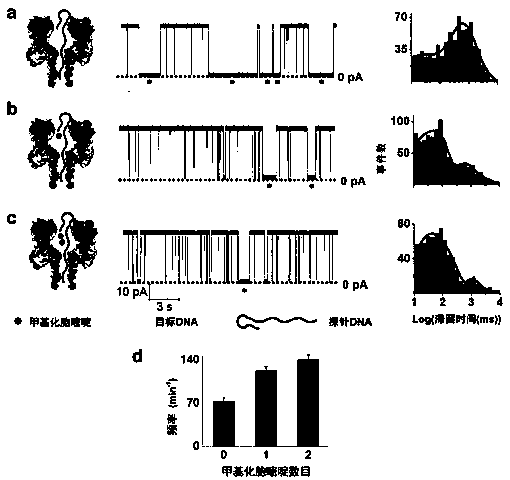
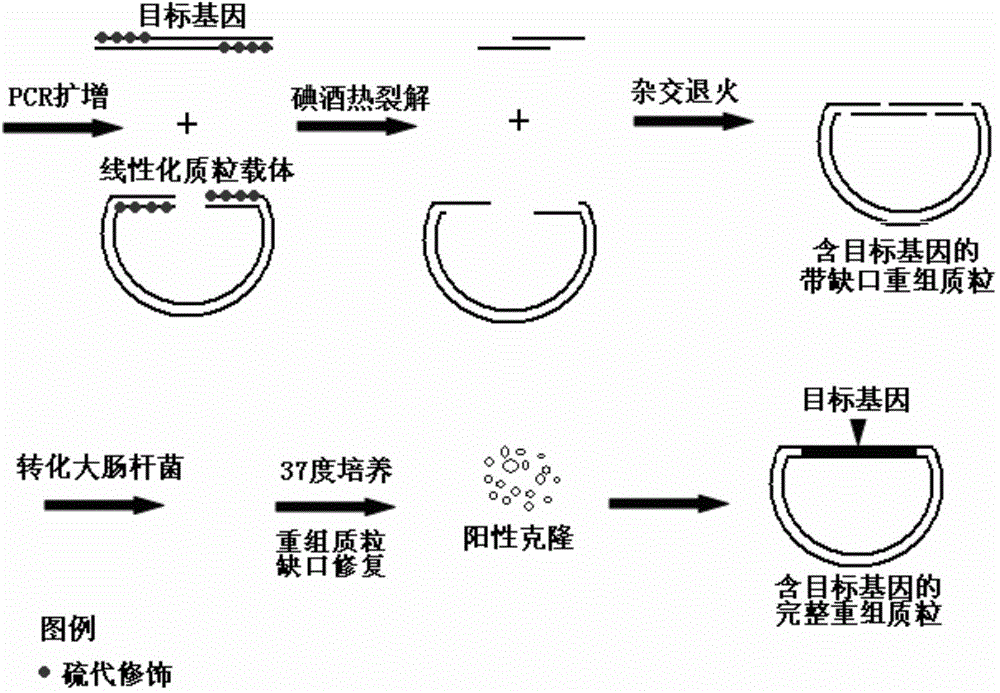
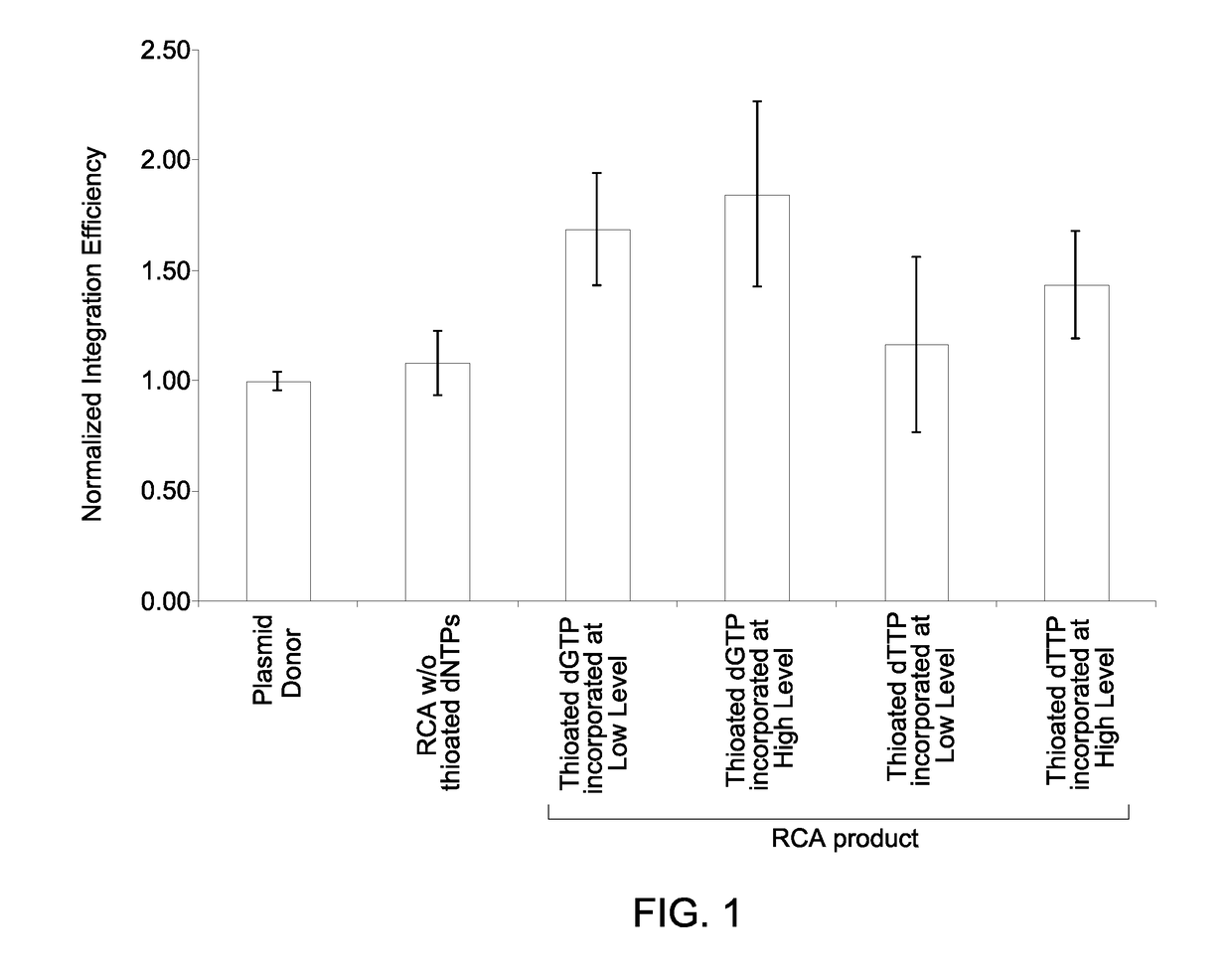
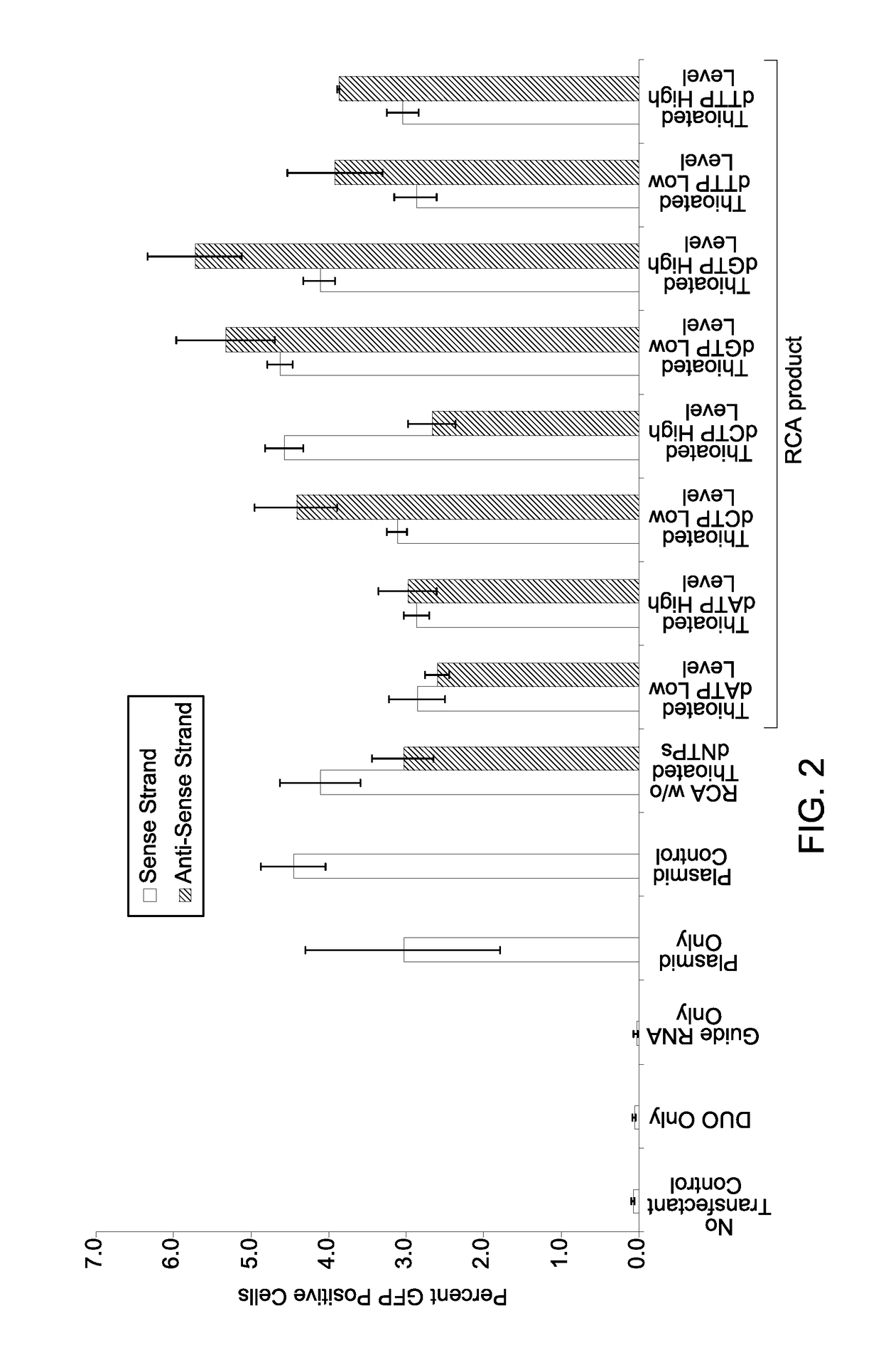
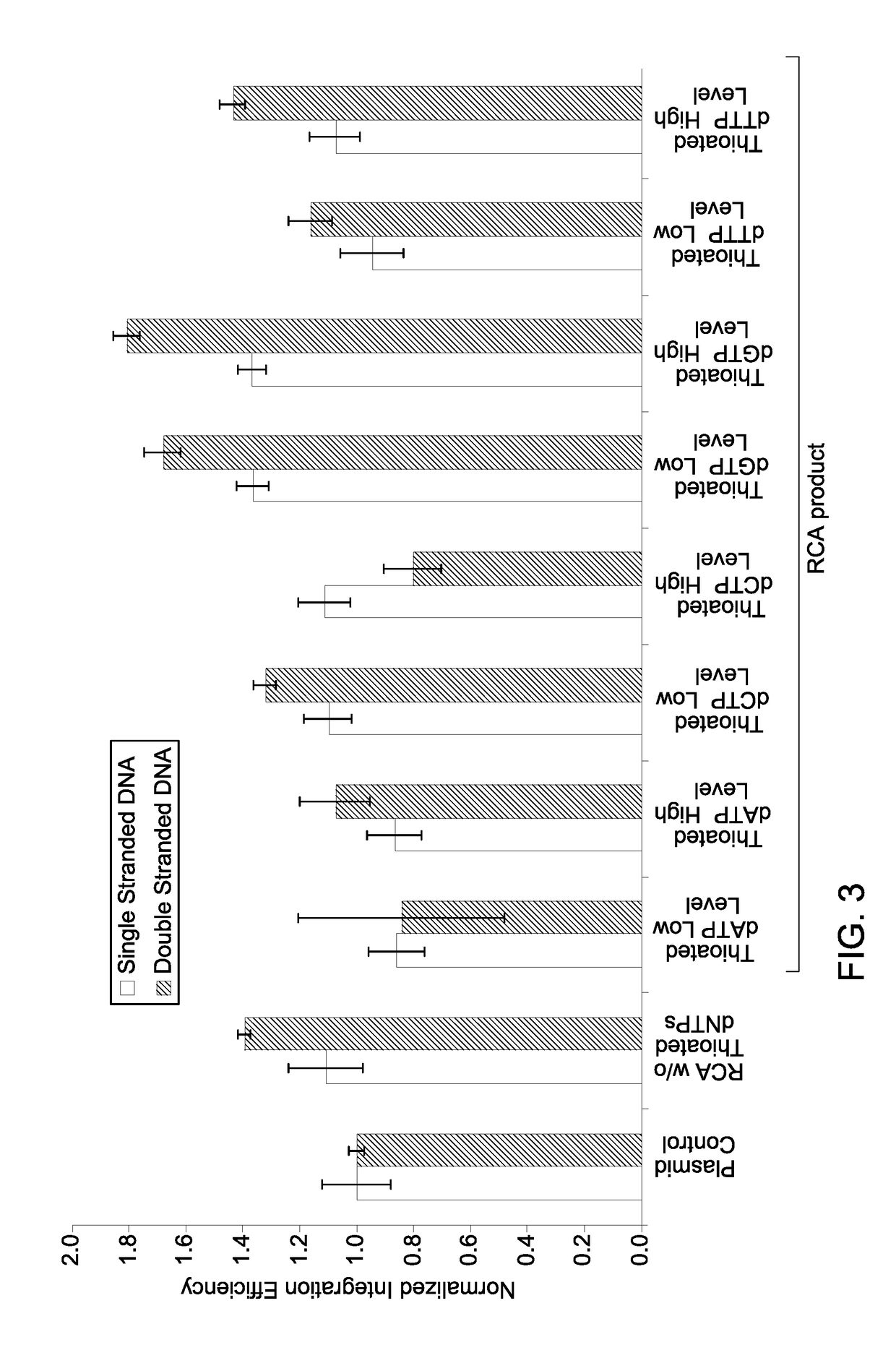
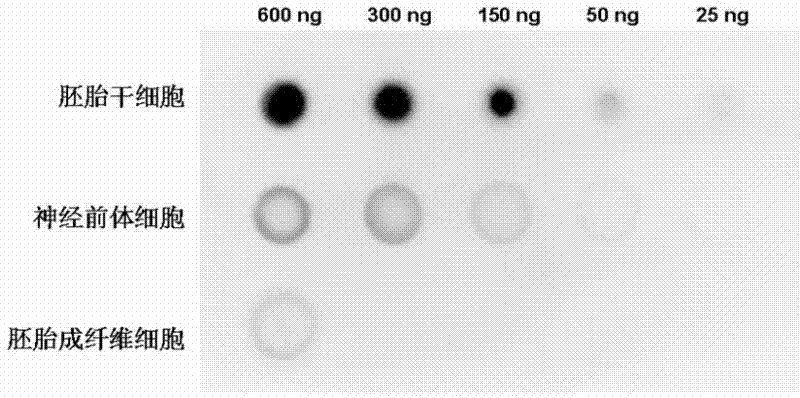
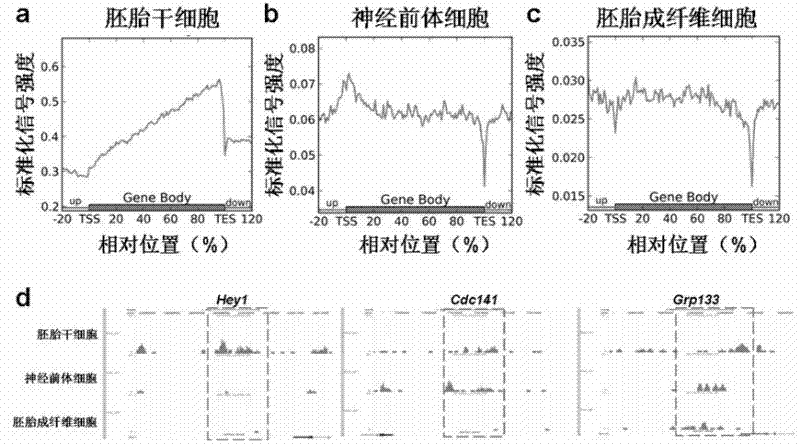
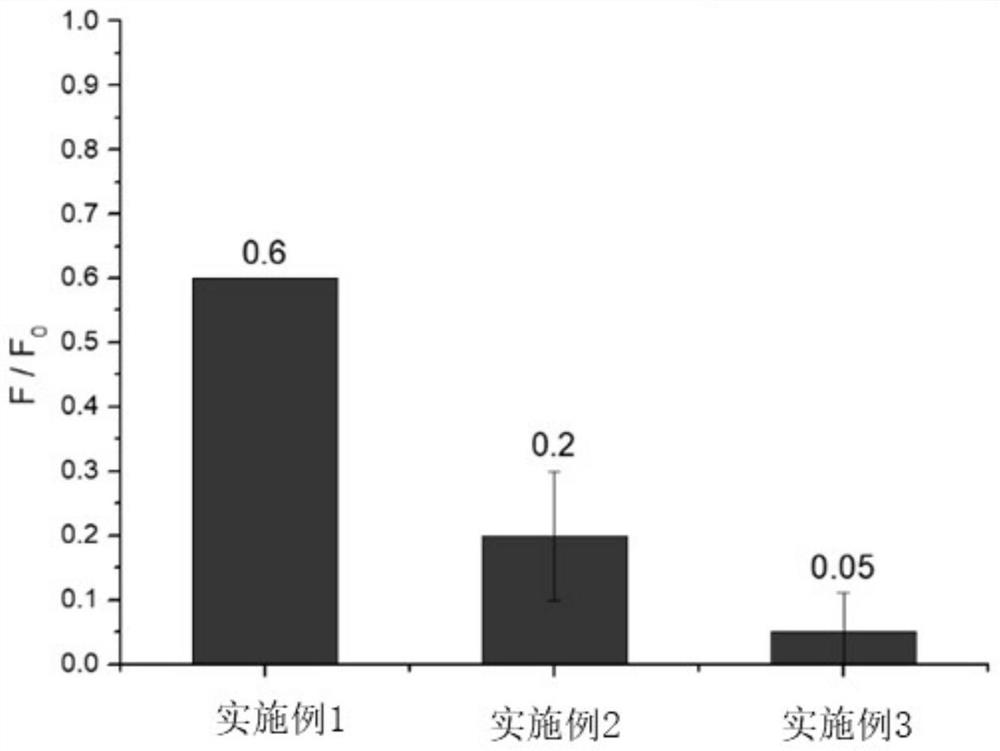
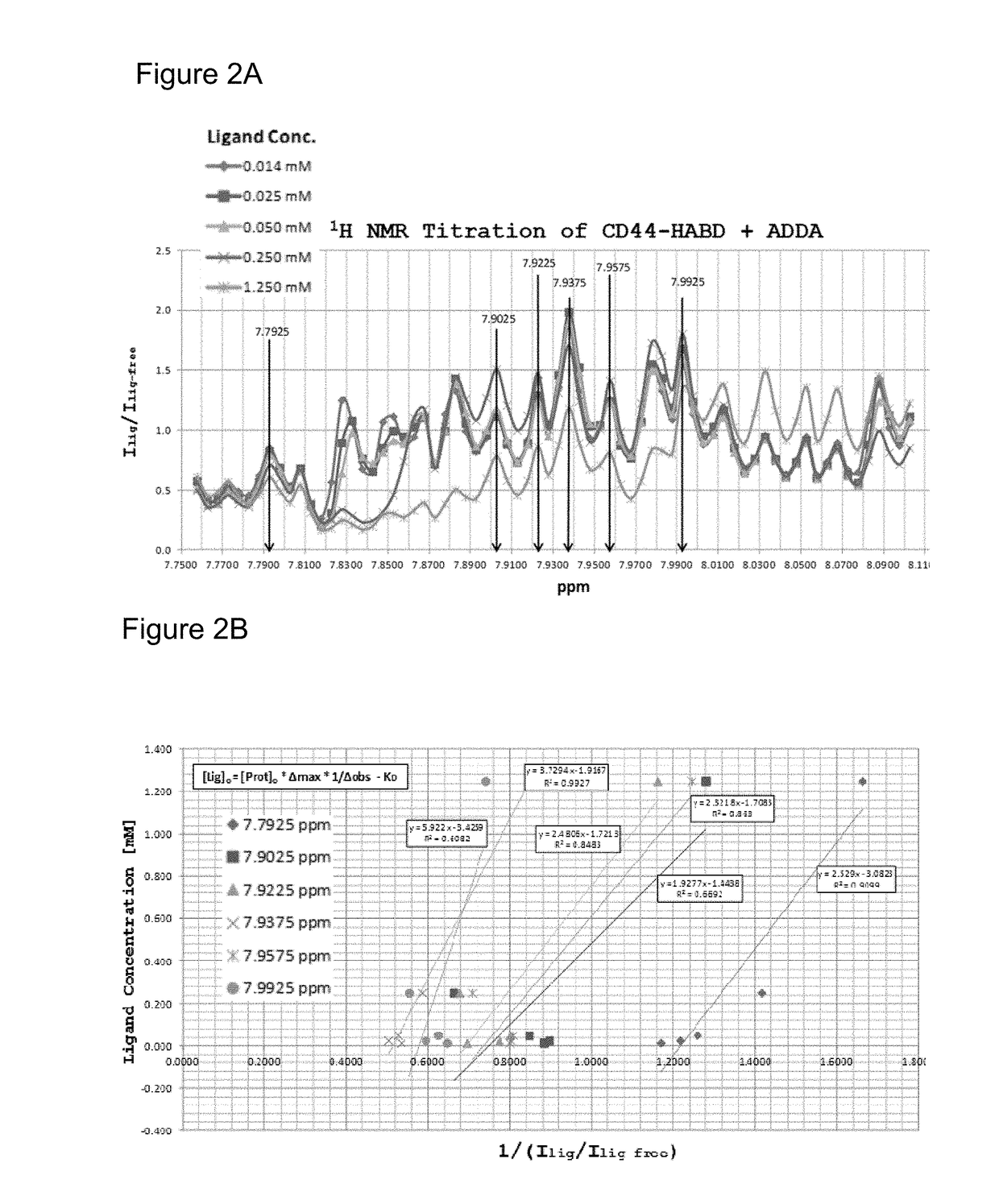
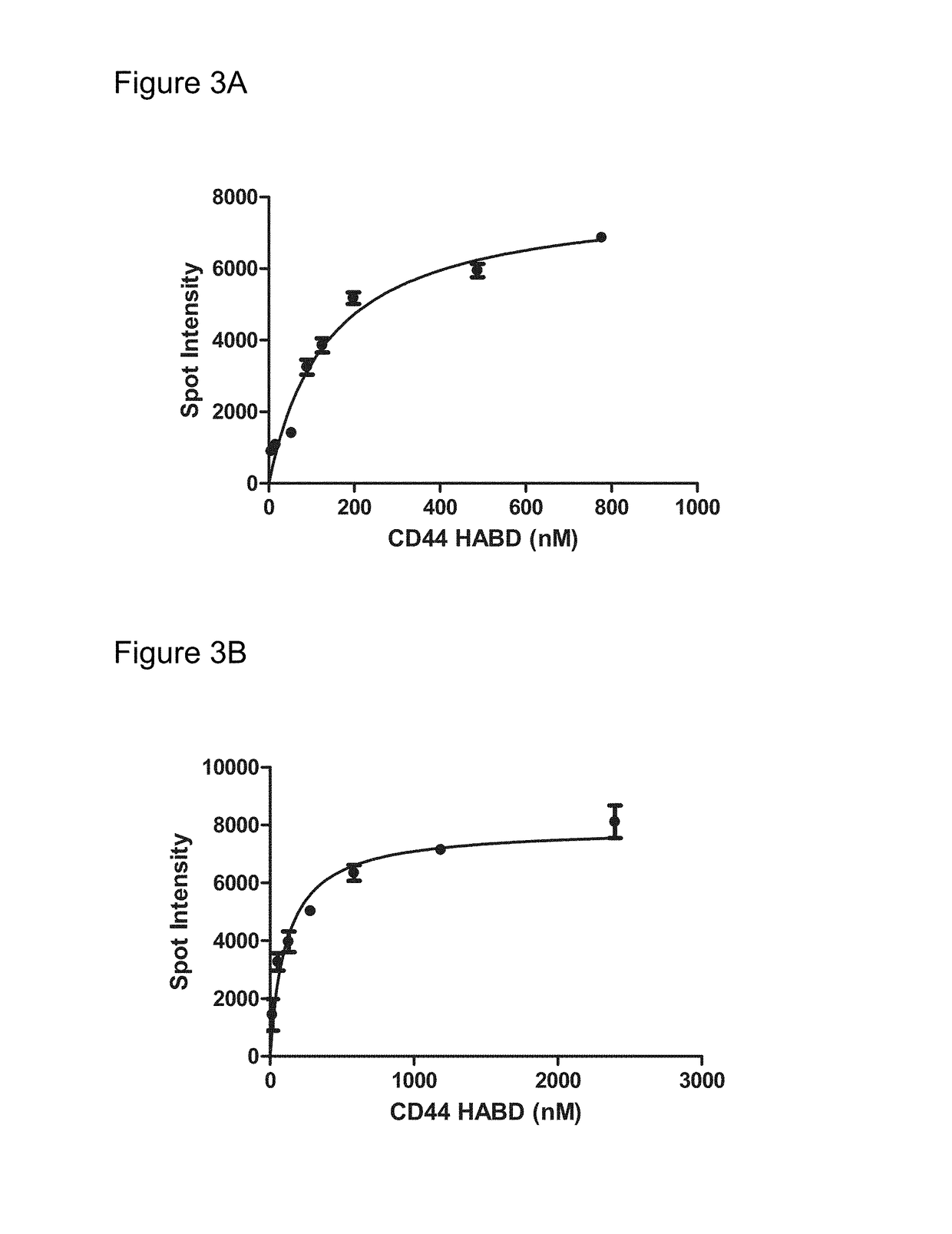
Patents
Literature
56 results about "DNA Modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA Modifications. DNA modifications are covalent modifications of the DNA bases, with the most commonly studied eukaryotic DNA modification being methylation at the five position of cytosine, leading to the formation of 5-methyl-cytosine (5mC; for a recent review of the functions of 5mC in mammals see Ref. [23]).
Nucleic acid nano structure carrier-precious metal photosensitive contrast agent composite for living organism photo-acoustic imaging, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104324375ARealize the combinationHigh Photoacoustic Imaging CapabilityEnergy modified materialsInorganic non-active ingredientsNano structuringWhole body
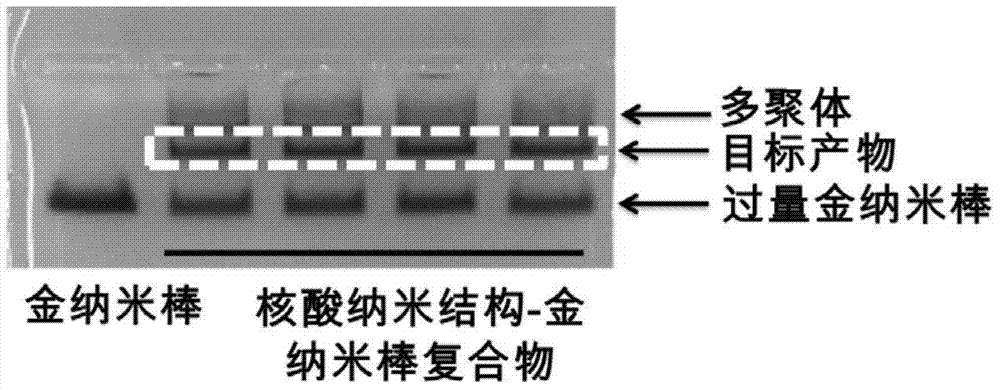
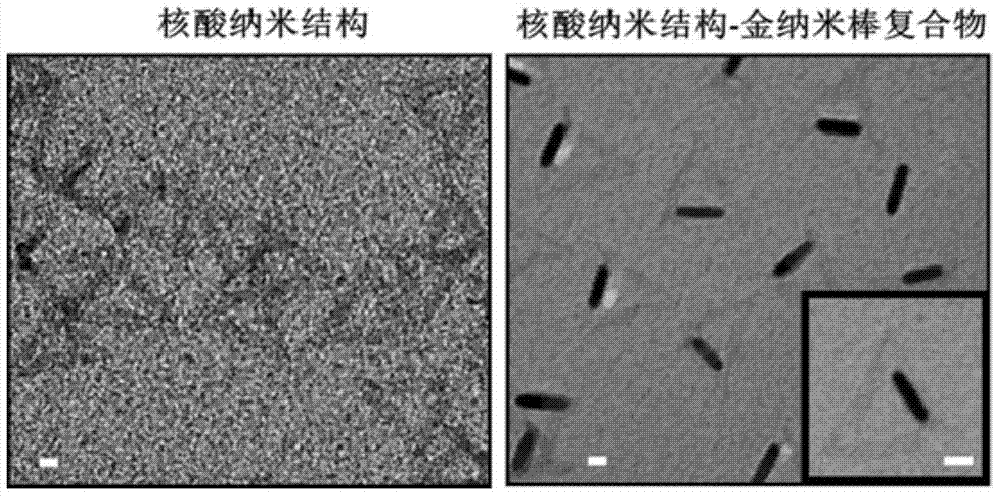
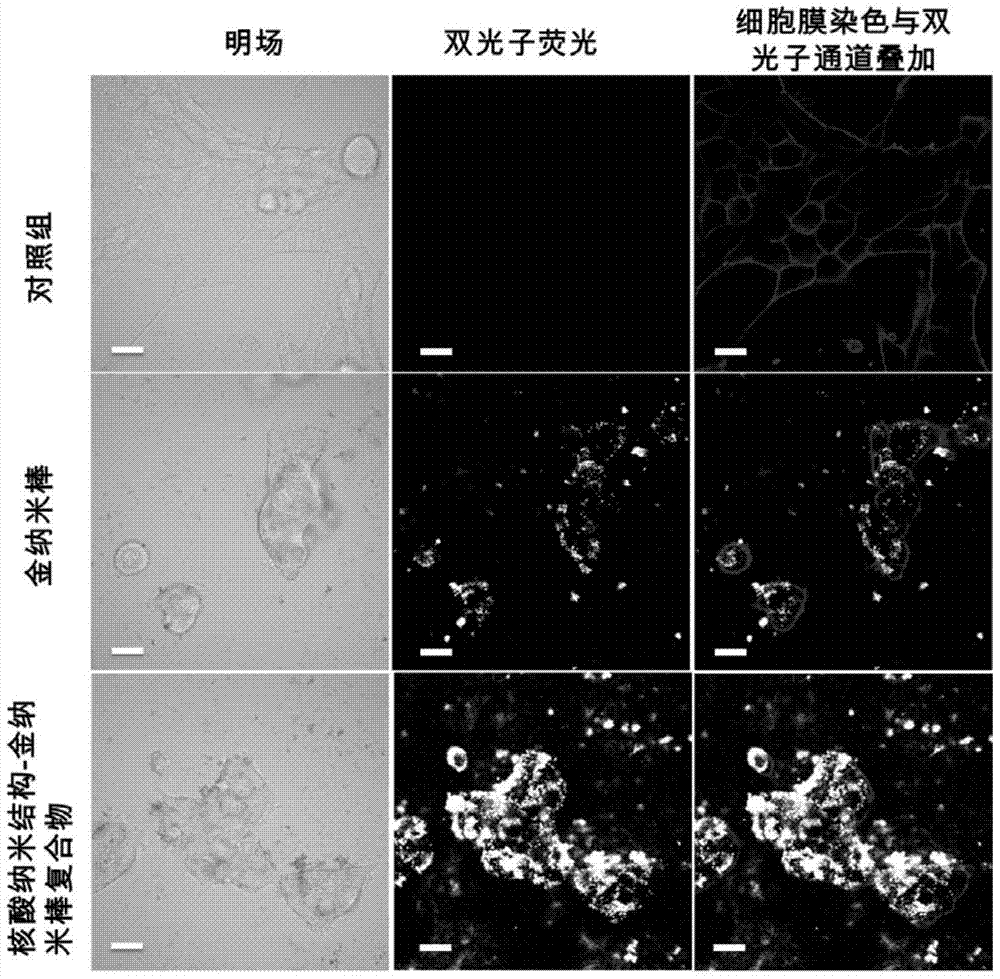
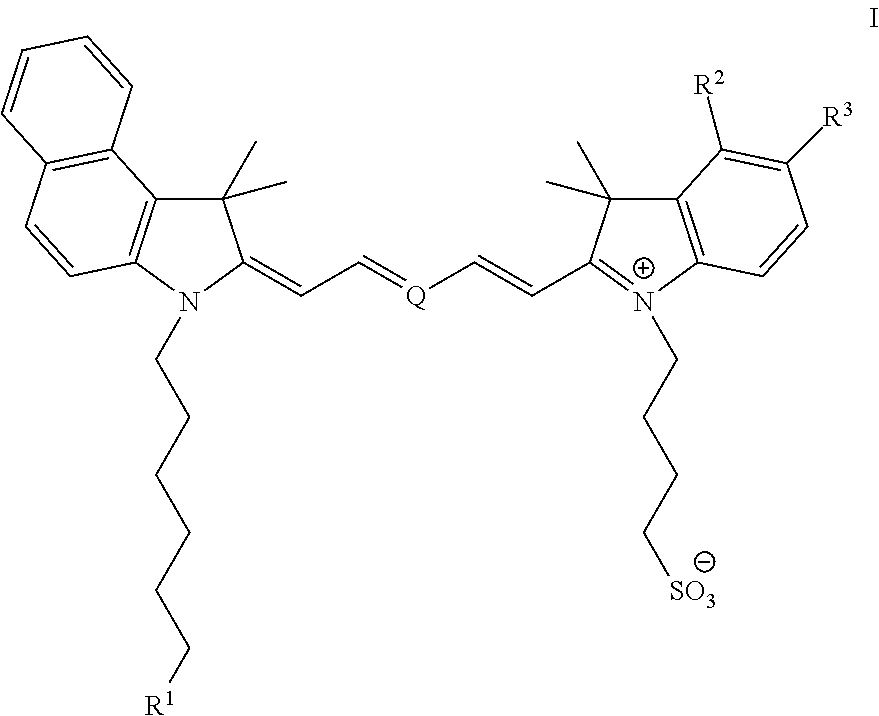
The invention discloses a nucleic acid nano structure carrier, a nucleic acid nano structure carrier-precious metal photosensitive contrast agent composite comprising the same, and preparation methods and applications of the carrier and the composite. The nucleic acid nano structure is a random two-dimensional and / or three-dimensional nano structure constructed by a DNA paper-folding technology. The precious metal components are used to carry out DNA modification on the surface of the carrier and selected from one or more of gold nano rods, gold nano shells, silver-coated gold nano rods, and gold nano cages. The provided composite is used as a photo-acoustic imaging probe, is capable of guaranteeing the absorption contrast enhancing effect of the photo-acoustic contrast agent which is coupled to the composite, and moreover can prominently improve the targeting performance of the contrast agent on tumors. Furthermore, the precious metal photosensitive components which are coupled to the carrier are enriched in the inner of tumor tissues, and thus the solved is the problems that conventional contrast agent is distributed over the whole human body or the contrast agent can only stay on the tumor surfaces. The preparation method has the advantages of simple technology, low cost, convenience, and easy application.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA +1
Nucleotide derivatives
The present invention provides compounds and methods for attaching fluorescent labels to biological molecules such as nucleotides. The compounds and methods are useful for biological assays including DNA modification reactions.
Owner:LI COR
Method and test kit for analyzing DNA repair
InactiveUS20020022228A1Solution presentedQuick fixSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JPurine
A method for analyzing the repair of DNA modifications and base mispairings as well as apurinic and apyrimidinic sites by DNA repair enzymes, comprising the following steps: contacting (a) single- or double-stranded DNA molecules which were covalently coupled to a solid-phase matrix carrying primary or secondary amino groups by reaction with a reactive squaric acid derivative, and which have modifications and / or base mispairings and / or apurinic or apyrimidinic sites, with (b) a composition containing DNA repair enzymes; and determining the elimination of the DNA modifications and / or base mispairings and / or apurinic or apyrimidinic sites. The DNA molecules are covalently coupled to the solid state matrix via a primary or secondary amino group incorporated in the DNA molecule at the 5'-end or at the 3'-end of the DNA or in the 2'-position of at least one deoxyribosyl residue.
Owner:RUBYCON CORPORATION
Methods of x-aptamer generation and compositions thereof
Provided herein are methods for a novel bead-based next-generation “X-aptamer” selection scheme that extends aptamer technology to include X-modified bases, thus resulting in X-aptamers, at any position along the sequence because the aptamers are chemically synthesized via a split-pool scheme on individual beads. Also provides are application to a wide range of commonly used DNA modifications, including, but not limited to, monothioate and dithioate backbone substitutions. This new class of aptamer allows chemical modifications introduced to any of the bases in the aptamer sequence as well as the phosphate backbones and can be extended to other carbohydrate-based systems.
Owner:AM BIOTECH +1
Automated gene-targeting using non-toxic detectable markers
InactiveUS20060179502A1Rapid and reliable distinctionReduces variability of recoveryAnimal cellsStable introduction of DNAGene targetsFluorescence
The invention relates to a method that enables automated identification and isolation of cells harbouring a predetermined genetic modification (homologous recombination) using detectable / sortable markers, e.g. fluorescence markers, to identify homologous DNA modifications. Suitable vectors are also provided.
Owner:ARTEMIS PHARMA
Terminus-Specific DNA Modification Using Random-Sequence Template Oligonucleotides
A method is provided for analyzing DNA molecules having unknown 3′ terminal sequences. The method involves contacting a DNA molecule with a plurality of template oligonucleotides blocked at their 3′ termini such that the template oligonucleotides are not extendable by DNA polymerase. The 3′ proximal portions of each of the template oligonucleotides comprise a region of random sequence and the 5′ proximal portions of each of the template oligonucleotides comprise the complement of a tag sequence. The DNA molecule and the template oligonucleotides are combined under conditions wherein the 3′ terminus of the DNA molecule hybridizes to the 3′ proximal portion of a template oligonucleotide and is extended by a DNA polymerase to produce a DNA molecule comprising a 3′ terminal tag sequence, and wherein the template oligonucleotide is not extended.
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
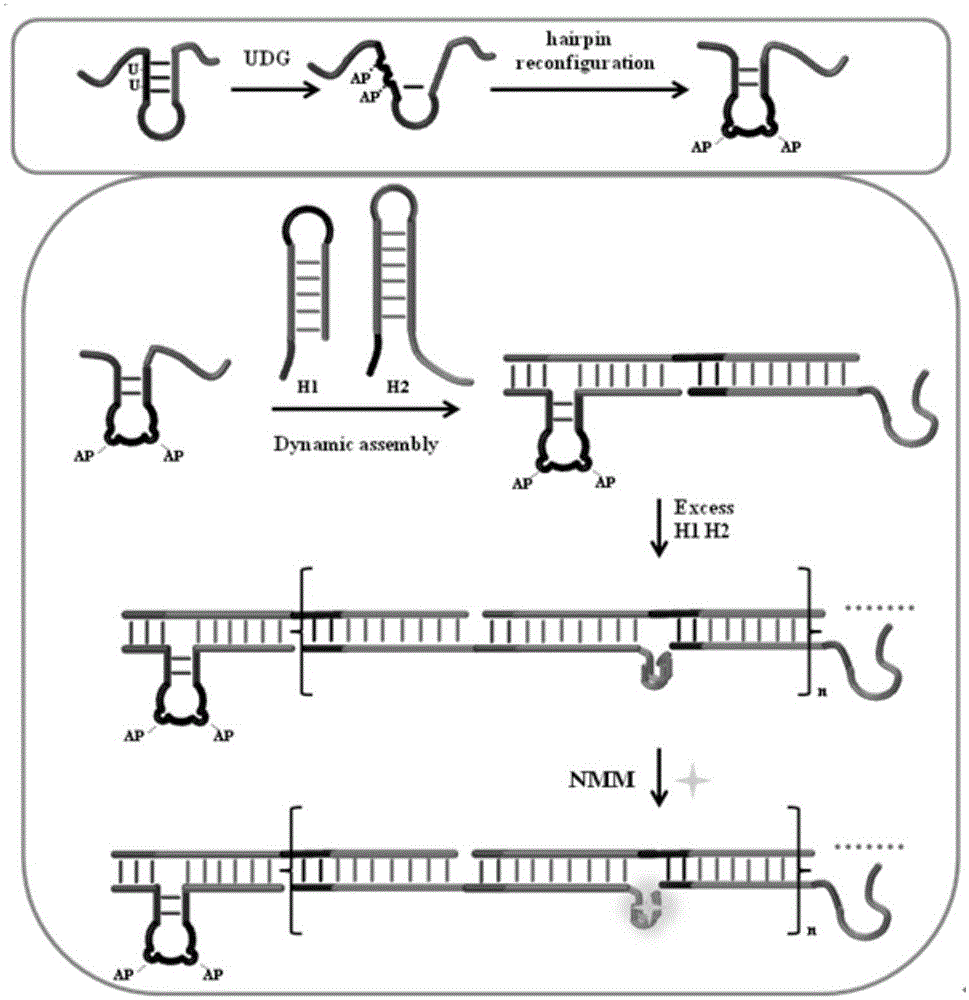
High-sensitivity uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) detection using DNA three-direction section activated hybridization chain reaction
ActiveCN105132522AImplement the buildLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementNano-deviceDNA Modification
The invention relates to high-sensitivity uracil DNA glycosylase (UDG) detection using DNA three-direction section activated hybridization chain reaction. UDG is used as a model to develop an identification mechanism of hairpin reconstruction, and action of DNA modification enzyme on substrate is converted into the triggering process of the hybridization chain reaction so as to cause the self-assembling process of DNA and build a universal DNA nano device. The device can be used for the high-sensitivity detection and inhibitor screening of the DNA modification enzyme (especially the UDG), and has potential application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
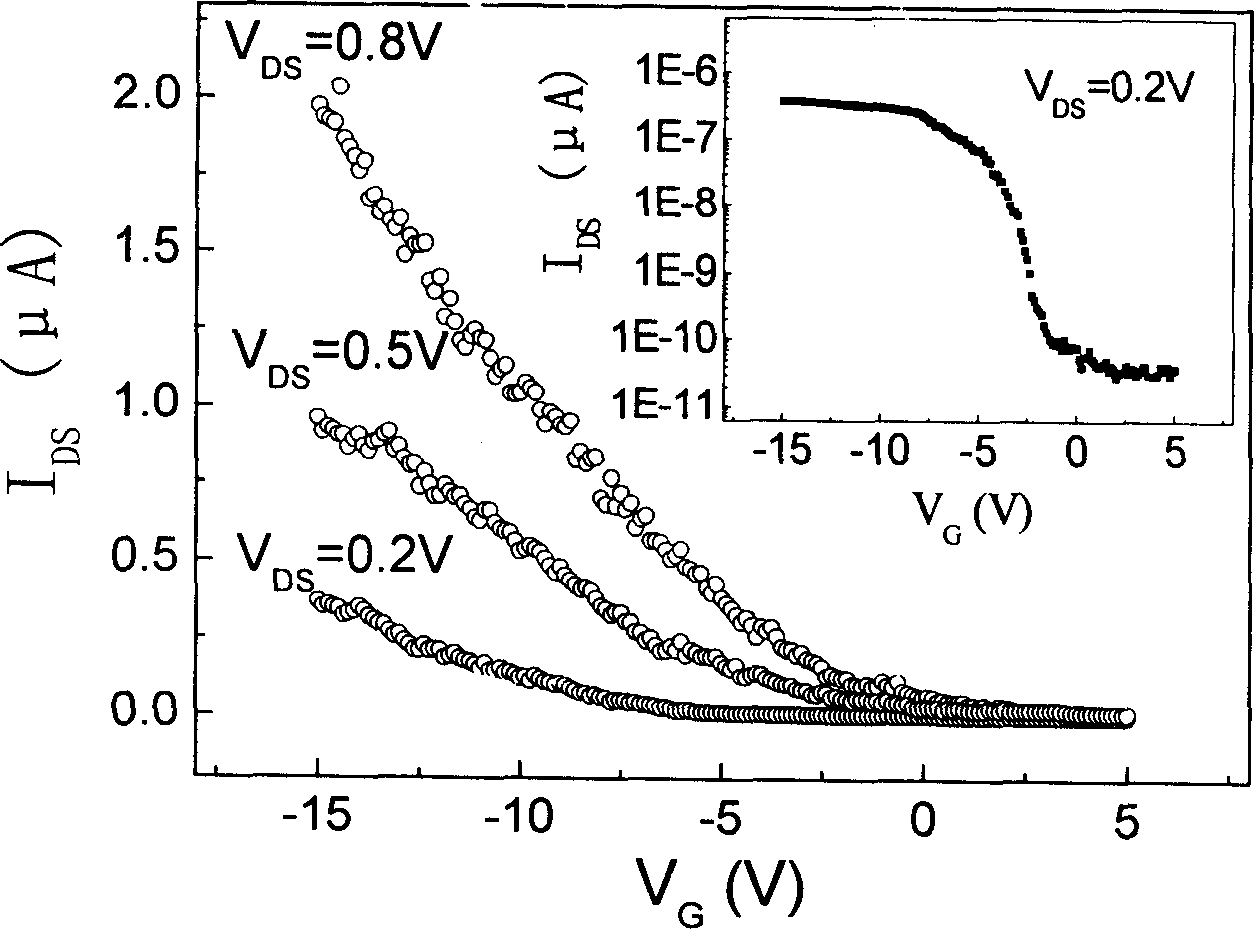
Method for structuring field effect transistor in multiple channels from Nano carbon tubes
InactiveCN1697146AHigh transconductanceImprove switching performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid layerEtching
The method includes following steps: (1) carrying out surface activation treatment for Nano carbon tube; (2) carrying out chemical modification or DNA modification of surface functional molecule for Nano carbon tube in order to prepare stable and dispersive suspension liquid of Nano carbon tube; (3) fabricating pattern of electrode couple on surface of silicon piece of containing insulating layer through photo etching; (4) dripping suspension liquid of Nano carbon tube onto surface of electrode couple prepared in step (3) to form even distributed liquid layer; (5) applying DC or AC electric field to implement multiple strips of Nano carbon tube to let them connect to between two kinds of electrodes dividually and in parallel; (6) carrying out irradiation treatment for device of field effect transistor (FET) prepared at step (5) through ultraviolet radiation. The invention can control multiple strips of Nano carbon tube to construct channels for FET or to be as leads for electrodes.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
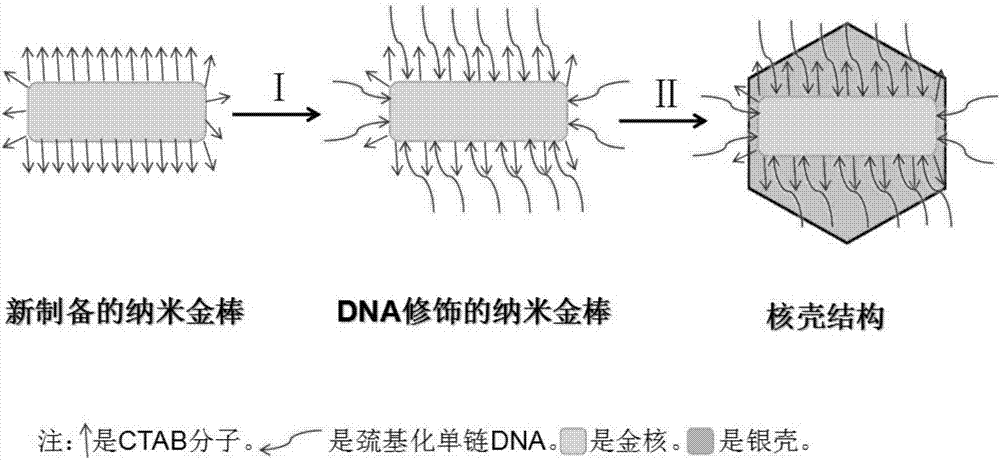
Novel nanoparticles with core-shell structures and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107243629AStructural properties are stableStrong Raman enhancement effectTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusGold nanorodSurface plasmon
The invention discloses novel nanoparticles with core-shell structures. A preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding CTAB solution into a container, adding HAuCl4 solution, and then adding NaBH4 solution to obtain seed crystal; adding the CTAB solution into another container, sequentially adding the HAuCl4 solution, silver nitrate solution, L-AA solution and the seed crystal to prepare gold nanorods; (2) carrying out DNA modification on the gold nanorods to obtain gold nanorods stably protected by thiolated DNA; and (3) centrifuging the gold nanorods, dissolving the gold nanorods in the CTAB solution, sequentially adding SDS solution, the silver nitrate solution and the L-AA solution, and standing to obtain the novel nanoparticles with the core-shell structures. The nanoparticles disclosed by the invention are high in stability, thin silver covers the two ends of each core-shell structure, most of each connected DNA single strand is exposed outside, and each tip part has a higher surface plasma effect; and the nanoparticles have a high application value in the fields of bio-optoelectronics, biological nanometer detection and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG BOAOKE BIOTECH
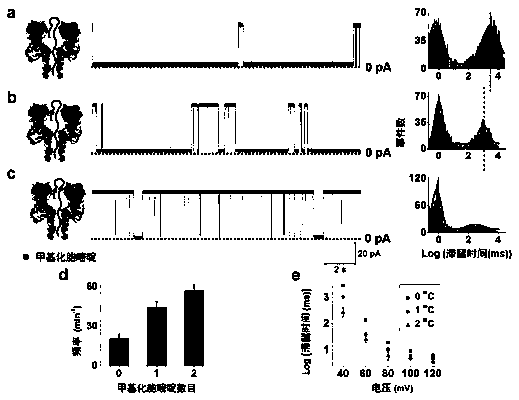
Single-molecule analysis method for detecting methylated DNA
ActiveCN105372303ASmall amount of sampleHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesSingle strandDNA Modification
The invention relates to a single-molecule analysis method for detecting methylated DNA. According to the method, in an electrolytic tank containing a tetramethyl ammonium salt electrolyte or a tetraethyl ammonium salt electrolyte or a tetrapropyl ammonium salt electrolyte or a tetrabutyl ammonium salt electrolyte, a nanopore sensor distinguishes and detects DNA of different methylation levels through current electrochemical signals, wherein DNA of different methylation levels includes un-methylated DNA, mono-methylated DNA and multi-methylated DNA, and the structural forms of DNA include a single-stranded structural form, a double-stranded structural form and a hairpin structural form. According to the single-molecule analysis method for detecting methylated DNA, the quantity of needed samples is small, sensitivity is high, and single-base resolution is achieved; nanopore and DNA modification, DNA amplification and marking are not needed, operation is easy, and high applicability is achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Iodine dissociation type gene cloning method based on sulfo-modifiers
The invention discloses an iodine dissociation type gene cloning method based on sulfo-modifiers. According to the method, phosphodiester bonds between the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of primers of a target gene and a plasmid vector are amplified into the sulfo-modifiers; a base sequence at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of forward primers of the target gene and the plasmid vector and a base sequence at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends of reverse primers of the target gene and the plasmid vector are matched in a supplementary mode; after the target gene and the plasmid vector are subjected to PCR amplification, a PCR product is purified; iodine selectively breaks the phosphodiester bonds of the sulfo-modifiers, and under the combined action of existence of the sulfo-modifiers at the positions of 1-15, 16, 17, 18, 19 or 20 of the 5' ends and iodine heat treatment, DNA will generate a 3' single-link protruding end where 20 nucleotides grow. Through the method, cloning of the target gene does not rely on restriction endonuclease, DNA ligase or any other DNA modification enzyme, operation flux is large, and the method can be applied to large-scale gene cloning.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGSHI JUNCHI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Site-specific DNA modification using a donor DNA repair template having tandem repeat sequences
A method of site-specific modification of an endogenous target DNA of a eukaryotic cell is provided. The method includes contacting the endogenous target DNA having an intended modification site with (i) a gene editing system configured to introduce a double strand break in the endogenous target DNA at or near the intended modification site, and (ii) a donor DNA repair template comprising a plurality of tandem repeat sequences. In the method, each of the plurality of tandem repeat sequences comprises an exogenous donor DNA sequence flanked by a donor 5′ flanking sequence and a donor 3′ flanking sequence. The donor 5′ flanking sequence and the donor 3′ flanking sequence are homologous to a continuous DNA sequence on either side of the intended modification site in the endogenous target DNA.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
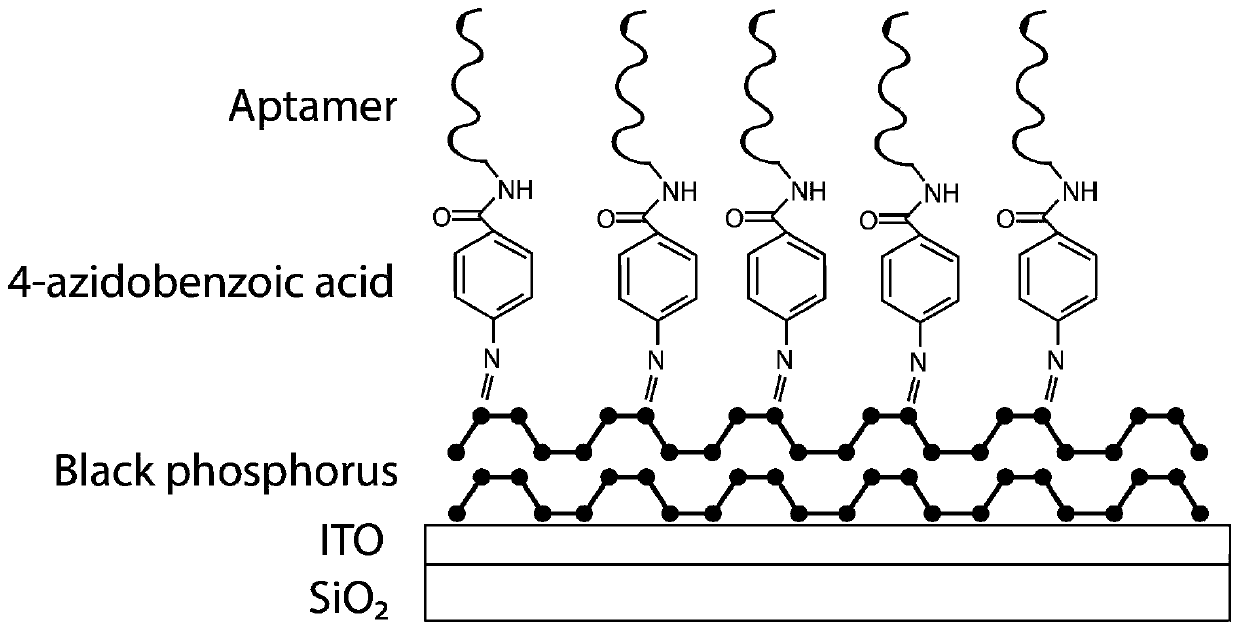
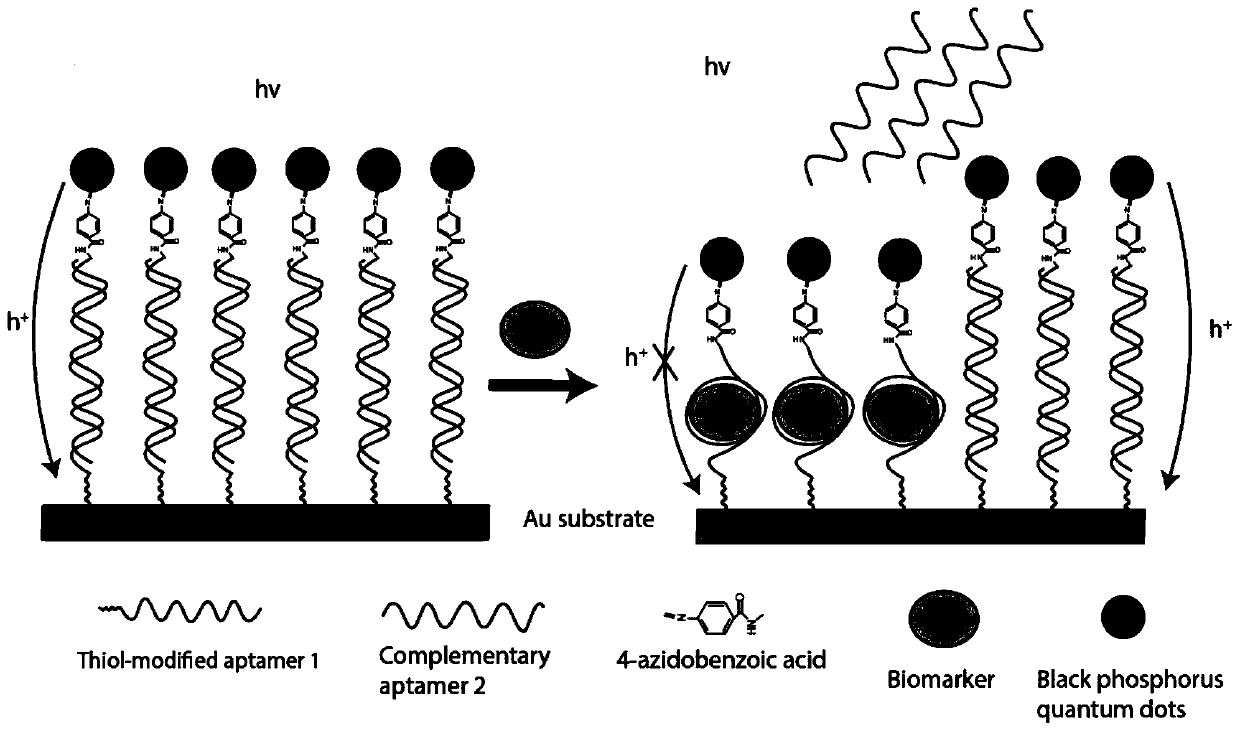
Two-dimensional black phosphorus photoelectrochemical electrode based on DNA modification, preparation method and application
ActiveCN111579611AEasy to oxidizeImprove overall lifespanBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesBenzoic acidBlack phosphorus
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectrochemical biosensors, and discloses a two-dimensional black phosphorus photoelectrochemical electrode based on DNA modification, a preparation method and an application. 4-azidobenzoic acid is modified on a surface of black phosphorus in a covalent bond functionalization mode, and a 4-AB-BP thin film is deposited on a surface of the ITO electrode through a dropwise coating method; and sulfo-NHS / EDC condensation on an amino group connected with a 5'end of ligand and a carboxyl group of benzoic acid is carried out to prepare aptamer covalent functionalized modified black phosphorus ITO, and a molar ratio of black phosphorus to 4-azidobenzoic acid is 1: 6. The method is advantaged in that the covalent functionalized black phosphorus is applied to a photoelectrochemical biosensor for the first time, compared with an existing black phosphorus biosensor, the 4-azidobenzoic acid is used for modification, the service life of the blackphosphorus can be prolonged, the aptamer is bonded to the black phosphorus through the covalent bond, the service life of the black phosphorus modified ITO electrode is prolonged, and sensitivity of the black phosphorus modified ITO electrode is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV
Epigenetic DAP-seq sequencing library building method
ActiveCN111155175ARetain modificationEnrichment method is simpleVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationEpigenetic ProfileDNA Modification
The invention belongs to the field of high-throughput sequencing library building, and particularly relates to an epigenetic DAP-seq sequencing library building method. The sequencing library buildingmethod provided by the invention mainly comprises the processes of vector building, TF in-vitro expression pre-experiment, DAP-seq library building and the like. According to the sequencing library building method provided by the invention, the genome DNA extracted from cells can be directly combined with target TF, so that genome DNA modification can be reserved, and compared with the prior art,the sequencing library building method is closer to an in-vivo test.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENE DENOVO BIOTECH
Application of DNA three-way regulation activation based hybridization chain reaction to high sensitivity detection of DNA methyltransferase
ActiveCN105087755AImplement the buildExempt from markingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationDNA Modification
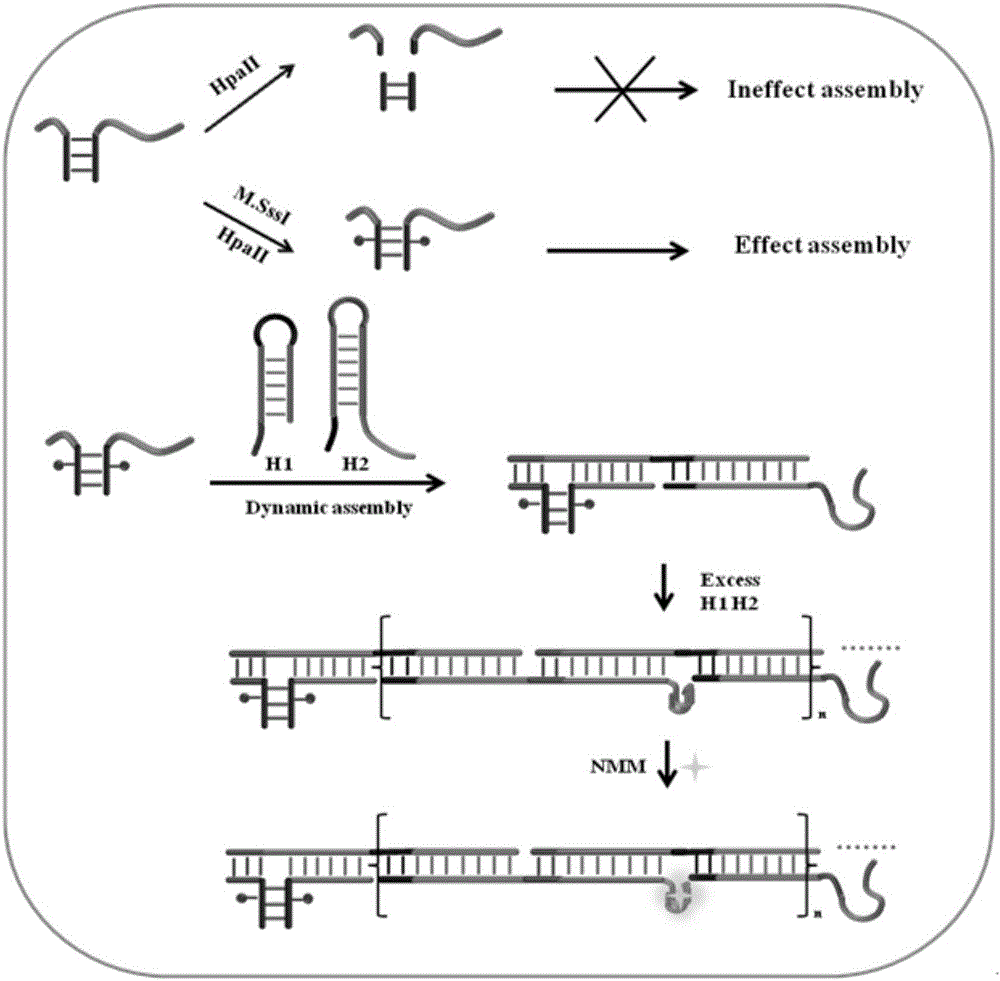
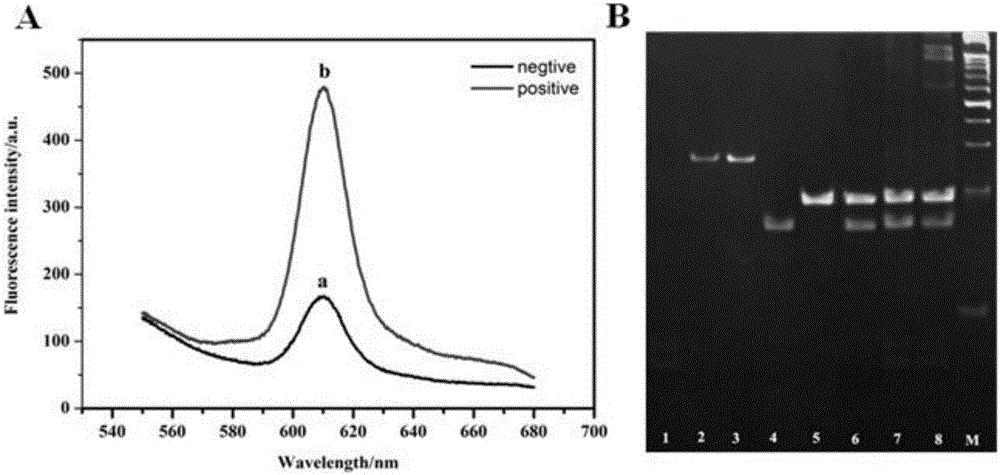
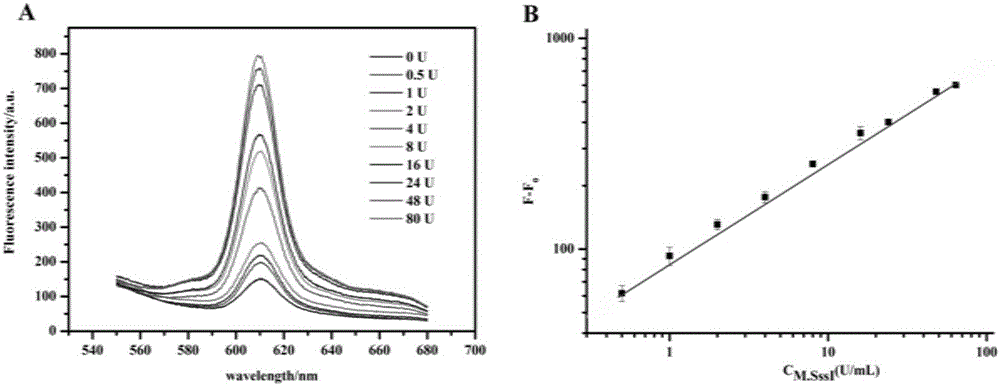
The present invention relates to application of DNA three-way regulation activation based hybridization chain reaction to high sensitivity detection of DNA methyltransferase. The present invention uses DNA methyltransferase M.SssI as a model to develop an enzyme protection cleavage recognition mechanism, which converts the effect of enzyme on a substrate into a trigger process of a hybridization chain reaction, thereby causing a DNA self-assembly process and achieving construction of a universal DNA nanodevice. The device can be applied to high sensitivity detection of DNA modification enzyme (especially DNA methyltransferase) and inhibitor screening, and has potential application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Quantitative sequencing method for genome DNA modifications in full genome range
InactiveCN102329873AReduce the impactLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineDNA Modification
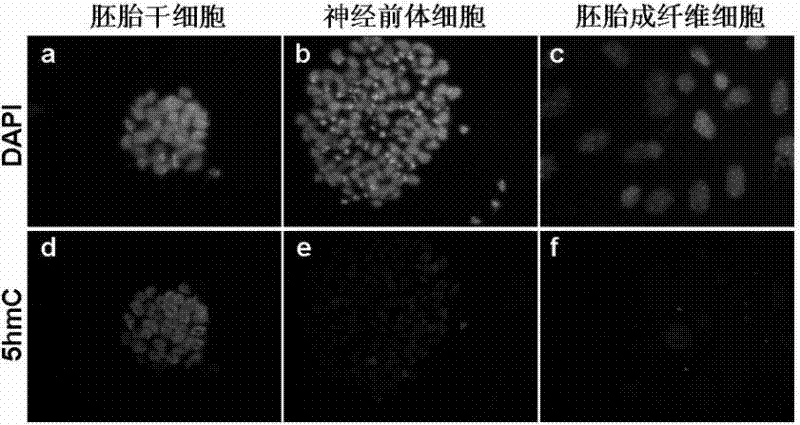
The invention belongs to the technical field of second generation gene sequencing, in particular to a quantitative sequencing method for genome DNA modifications (such as 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (namely 5hmC), 5-methylation cytosine (namely 5mC), 5-carboxyl cytosine (namely 5caC), 5-formoxyl cytosine (namely 5fC) and the like) in a full genome range. Specific sequence tags (namely Barcode) are respectively added to multiple to-be-detected samples by adopting a tag method, and the samples are mixed together for DNA fragment immuno-precipitation) of corresponding modifications, so that quantitative sequencing of the genome DNA modifications in the full genome range is realized. The method comprises the following steps of: extraction of genome DNA, preparation of Barcode samples, DNA fragment immuno-precipitation experiments of the corresponding modifications, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of specific products, and sequencing on an illumina GA ll platform. The method can be used for quantitatively comparing the DNA of the corresponding modifications in multiple samples at the same time in the full genome range and accurately positioning the content difference of the DNA of different areas and different modifications.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
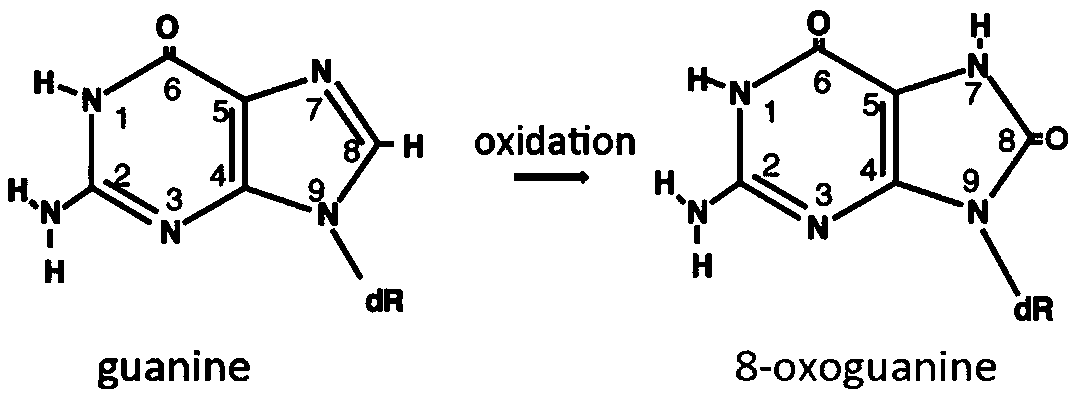
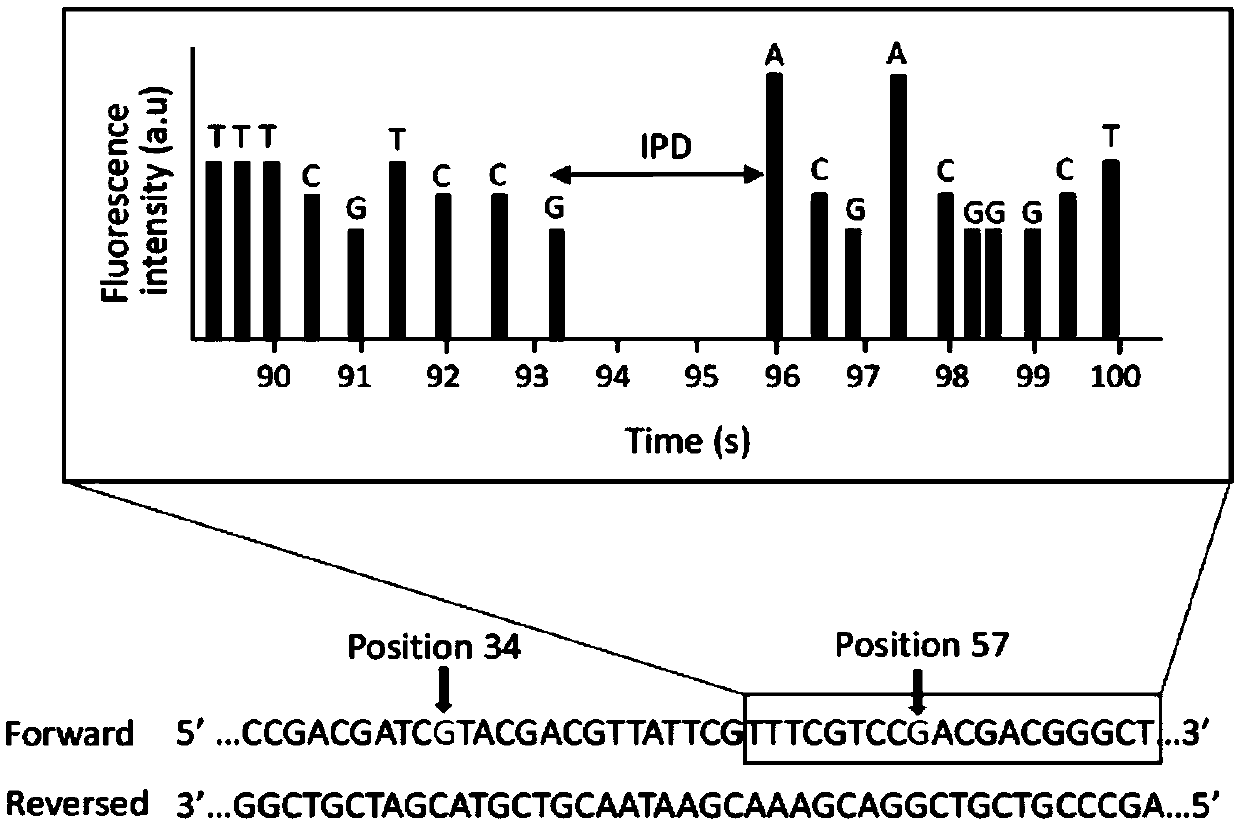
Detection method of oxidation modified nitrogenous bases
InactiveCN109097460AAutomate operationEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrogenDNA Modification
The invention relates to the field of DNA modification detection, in particular to a detection method of oxidation modified nitrogenous bases. IPD (interpulse duration) values of different nitrogenousbases are measured with the detection method of oxidation modified nitrogenous bases, and the oxidation modified nitrogenous bases are obtained according to different IPD values. The IPD values of the oxidation modified nitrogenous bases are found to be different from those of unmodified nitrogenous bases, and accordingly, whether the nitrogenous bases are modified can be distinguished.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
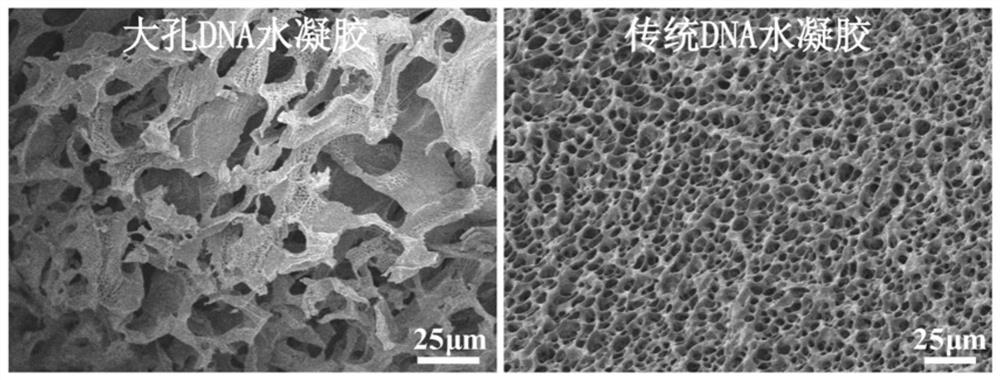
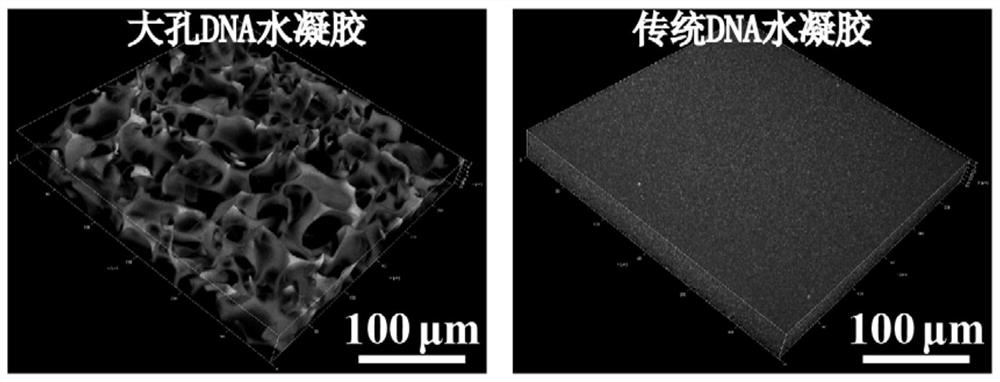
Preparation method of high-strength DNA hydrogel with macroporous structure
ActiveCN111793239AImprove mechanical propertiesFast response to the outside worldPolymer scienceFoaming agent
The invention provides a preparation method of high-strength responsive DNA hydrogel with a macroporous structure. According to the preparation method, a polymer monomer and a DNA chain with a modification group at a 5' end are concentrated into a micro-liquid phase around an ice crystal under a freezing condition, and polymerization is conducted under the action of an initiator; i.e., DNA is grafted to a polymer chain through a polymerization reaction between DNA modification groups and a polymer monomer; due to interaction between DNA chains, two or more DNA chains can be connected together,so the DNA serves as a cross-linking unit to connect polymer chains into a polymer network, and the DNA hydrogel is formed; the ice crystal functions as a pore-foaming agent, and after the reaction is finished, temperature is raised, so the ice crystals are melted, and the interconnected macroporous structure is left; and in the process, a freezing polymerization method is introduced into preparation of the DNA hydrogel, the obtained DNA hydrogel is good in mechanical property and high in response speed, and the application field of the DNA hydrogel is widened.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for detecting thrombin by virtue of SERS enhanced controllable chain-shaped assembly
The invention relates to a method for detecting thrombin by virtue of an SERS enhanced controllable chain-shaped assembly, belonging to the field of nano-sensing detection. According to the method, DNA molecules of two aptamers of the thrombin are respectively modified to the surfaces of an Au@ nano-particle and an Ag nano-particle, an alternate-arrayed chain-shaped structure is formed between thetwo nano-particles by controlling the DNA modification amounts of the surfaces of the nano-particles through the combination between assembly molecules and the thrombin when the thrombin exists, anda relatively strong Raman signal enhancement effect is achieved; and when the content of the thrombin is higher, the chain structure is longer, and the Raman signal strength is stronger, and the quantitative determination of the thrombin can be realized according to the corresponding relation between the content of the thrombin and the Raman signal strength. The method is simple in operation and high in sensitivity, and the thrombin in a serum sample can be detected; and by utilizing the nano-structure assembly, an important theoretical foundation is provided for detection of other target objects taking the aptamers as recognition molecules.
Owner:嘉兴劲境电子商务有限公司
Method for improving cleavage of DNA by endonuclease sensitive to methylation
The present invention concerns novel methods for improving cleavage of DNA by rare-cutting endonucleases, overcoming DNA modification constraints, particularly DNA methylation, thereby giving new tools for genome engineering, particularly to increase the integration efficiency of a transgene into a genome at a predetermined location, including therapeutic applications and cell line engineering.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Multi-copy monomolecular nucleic acid array chip
InactiveCN1876840AHigh detection sensitivityThe level of optical inspection technology has improvedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationDisease
The invention relates to a new monomolecular nucleotide microarray chip with high density and distinguishability. A plurality of polymer high molecule containing nucleotide fragment of this chip can randomly fix on a solid base-plate and can form a monomolecular nucleotide microarray with high density, and can make every array point contain one polymer high molecule, in which the said polymer high molecule contains some similar copies of nucleotide fragment. This chip can be assembled to many kinds of chips used for functional genom study, testing order of complete gene of special types, gene transferring and expression efficiency testing, and testing of kinds of genom DNA modification chart(such as DNA methylation chart). This chip will have great value in the fields of molecular mechanism study in human being life process, genom DNA information decoding, individualized medicine, disease predicting and precaution, medicine developing and individuation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Process for detection of DNA modifications and protein binding by single molecule manipulation
ActiveCN108588208APrecise positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA ModificationProtein L
The present invention relates to a method for determining whether a protein binds to a specific DNA sequence. This method is useful in particular for identifying modifications to the DNA sequence (e.g. methylations) via the binding of proteins that specifically recognize those modifications (e.g. antibodies), but also to identify the binding sequence on DNA of a variety of proteins.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECH SCI (C N R S) +2
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) phosphorothioation modifier gene cluster
ActiveCN105087554AImprove dynamicsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) phosphorothioation modifier gene cluster. DNA phosphorothioation modifiers controlled by the gene cluster are single-chain modifiers, selective sequence sites are CpsC, the integral phosphorothioation modifier gene cluster comprises four genes including an encoding cysteine desulfurase gene and a 3' phosphoadenosine-5' phosphosulfate (PAPS) reductase gene, and encoding proteins of the two other genes are members of ABC transport protein families and DUF4007 super-families respectively. The DNA phosphorothioation modifier gene cluster has the advantages that the genes and the proteins of the genes can be used in the bio-pharmaceutical science fields of heterogeneous-source host DNA modification, epigenetics, cell-free phosphorothioation modification system construction, oligonucleotide medicine modification and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
A method for measuring DNA hybridization using graphene-modified high electron mobility transistors
ActiveCN104101626BEnable hybridization detectionAchieving DNA Hybridization DetectionMaterial electrochemical variablesDna recognitionA-DNA
The invention relates to a hybridization method for measuring DNA by modifying a high electron mobility transistor with graphene, using graphene to modify a high electron mobility transistor and immobilizing probe DNA to measure DNA hybridization, so as to realize a fast, sensitive and novel current response mode A method for measuring DNA hybridization using graphene-modified high-electron-mobility transistors for DNA hybridization detection. The method first uses molecular beam epitaxy to construct high-electron-mobility transistors; then graphene is used to immobilize probe DNA to HEMT gates Surface; finally drop the target DNA for hybridization measurement to obtain the response current. Using this method, the DNA hybridization detection of actual samples can be realized. The method simplifies the process of immobilizing the probe DNA on the surface of the device, and discards the complicated chemical process. Novel DNA hybridization recognition patterns were obtained in this method.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
DNA-linked enzyme-coupled assays
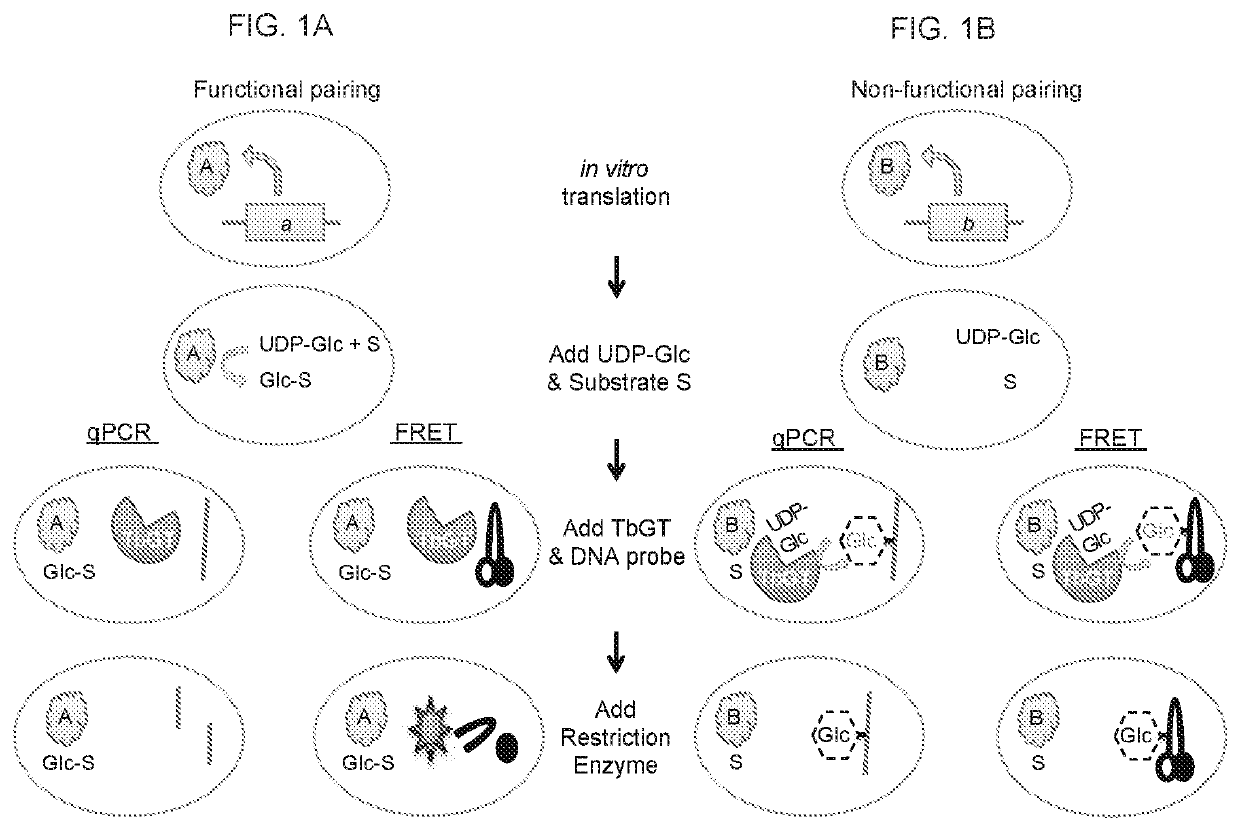
ActiveUS10829798B2Improve throughputReduced activityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopyDNA Modification
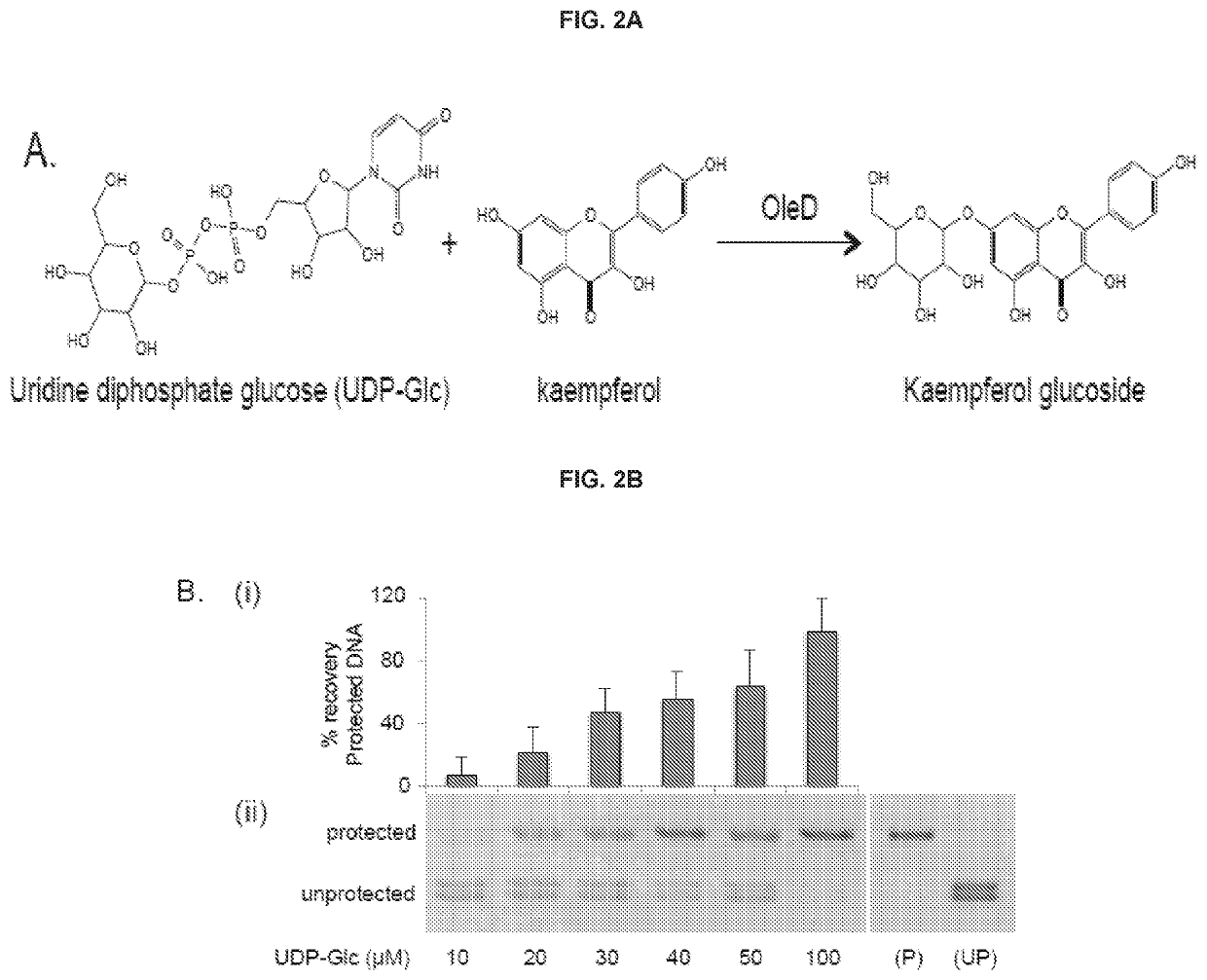
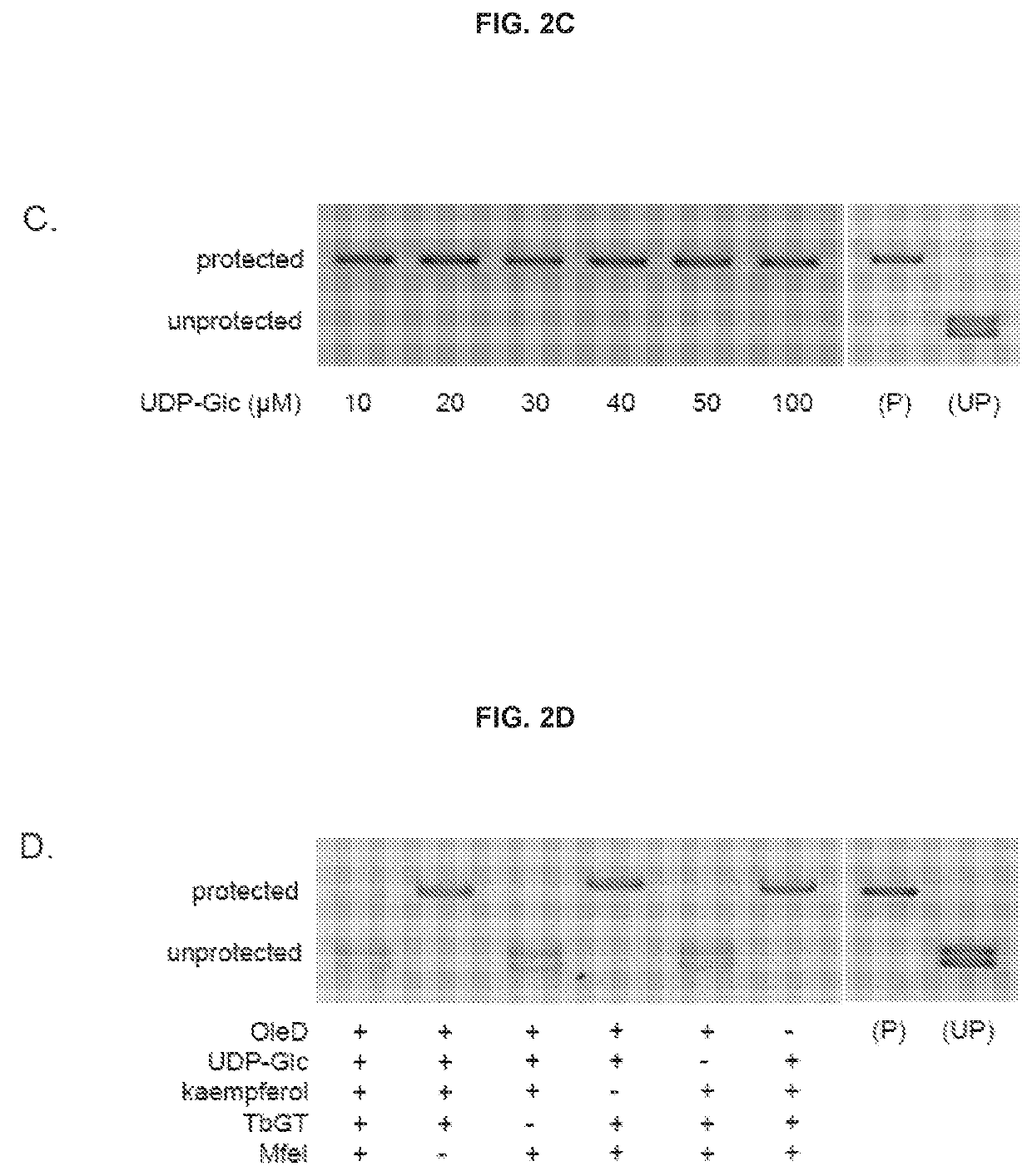
Traditional enzyme characterization methods are low-throughput, and therefore limit engineering efforts in synthetic biology and biotechnology. Here we propose a DNA-linked enzyme-coupled assay (DLEnCA) to monitor enzyme reactions in a high-throughput manner. Throughput is improved by removing the need for protein purification and by limiting the need for liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS) product detection by linking enzymatic function to DNA modification. DLEnCA is generalizable for many enzymatic reactions, and here we adapt it for glucosyltransferases, methyltransferases, and oxidoreductases. The assay utilizes cell free transcription / translation systems to produce enzymes of interest, while UDP-Glucose and T4-β-glucosyltransferase are used to modify DNA, which is detected post-reaction using qPCR or similar means of DNA analysis. For monitoring methyltransferases, consumption of SAM is observed by coupling to EcoRI methyltransferase. For monitoring oxidoreductases, consumption of NADH is observed by coupling to Taq or E. coli DNA ligase. OleD and two glucosyltransferases from Arabidopsis were used to verify the assay's generality toward glucosyltransferases. Two methyltransferases from human and Arabidopsis were used to verify the assay's generality towards methyltransferases. We show DLEnCA's utility by mapping out the substrate specificity for these enzymes and observing the multiple steps of a biosynthetic pathway.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multiplexed profiling of RNA and DNA modifications
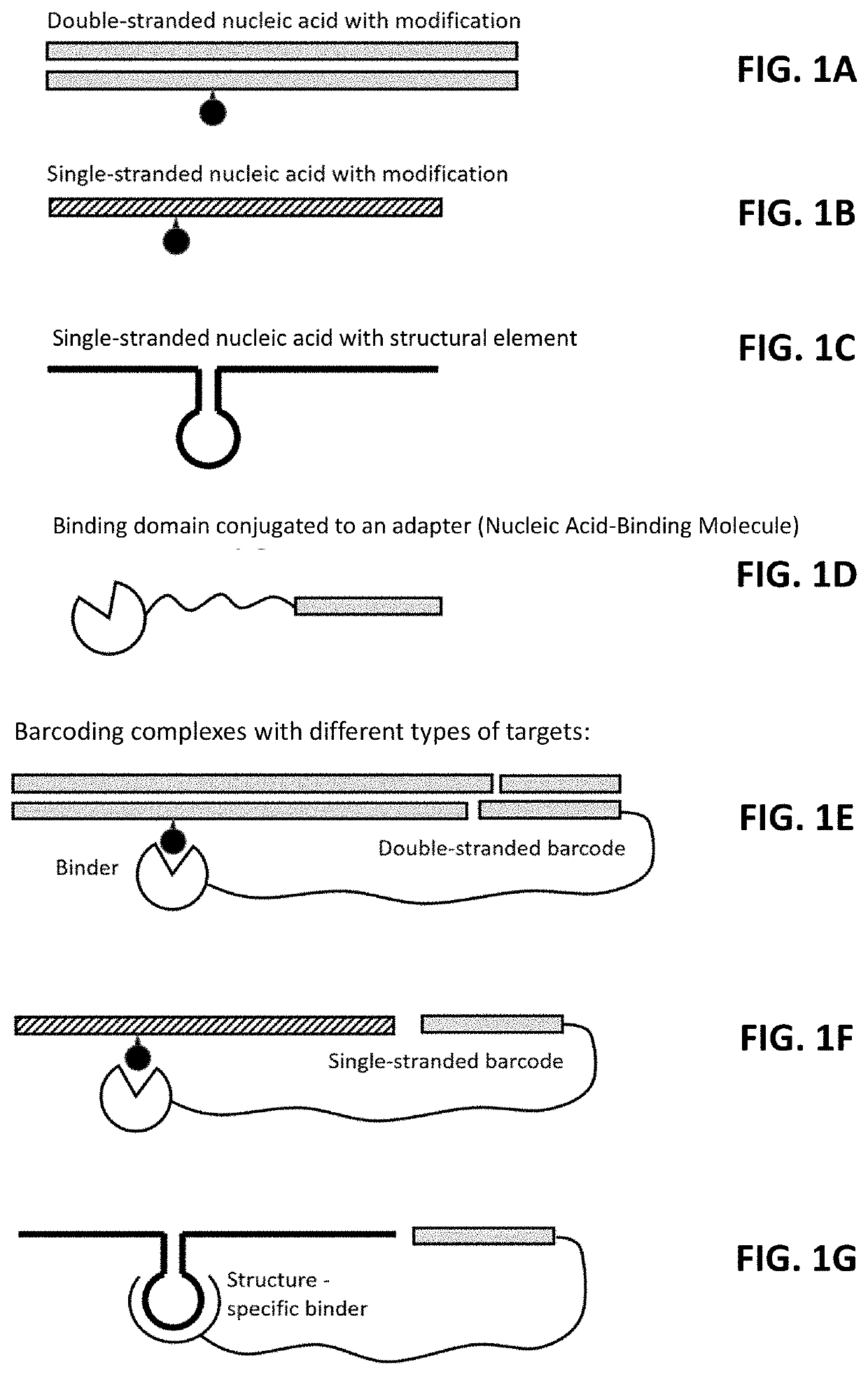
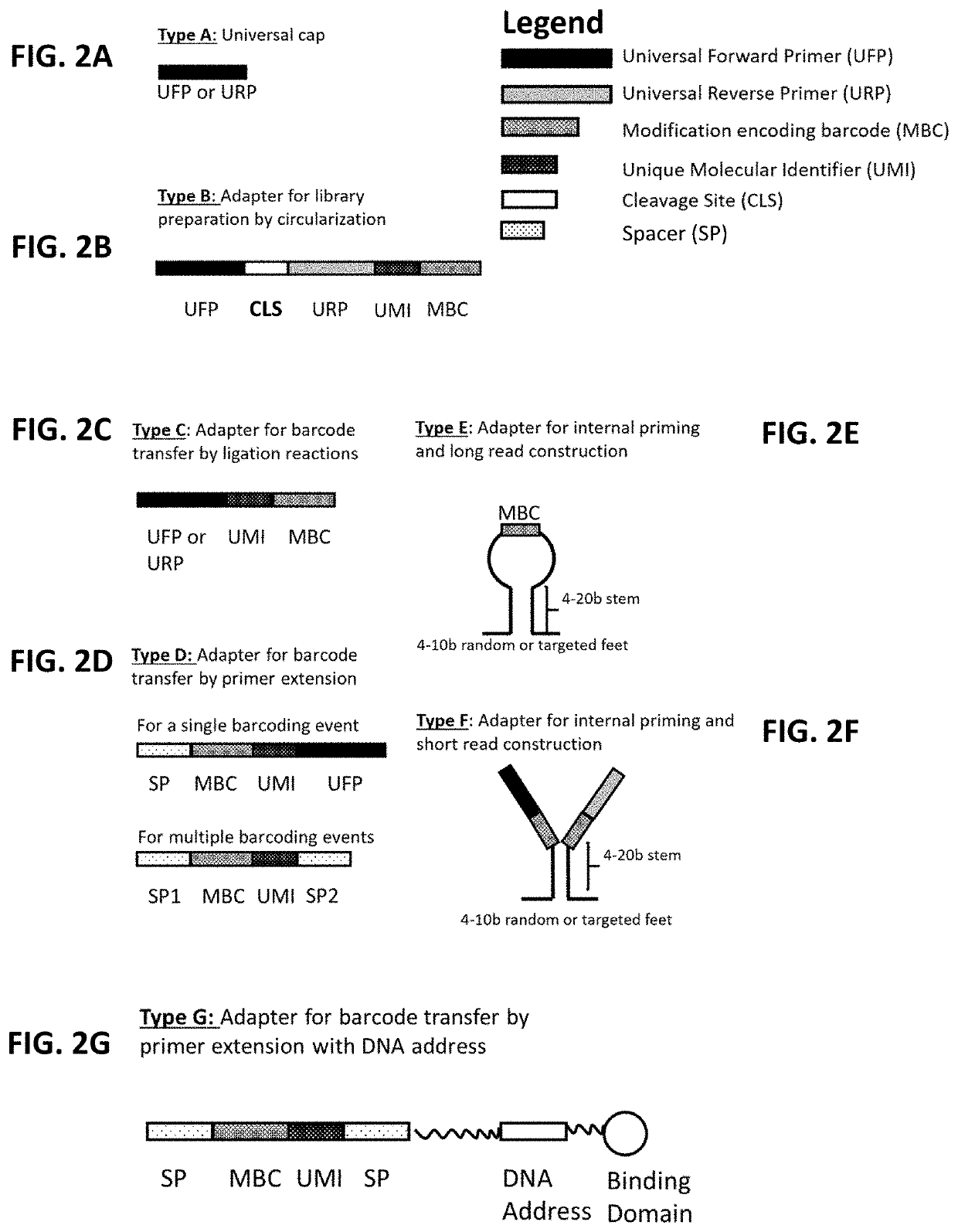
Provided herein are compositions and methods for the multiplexed profiling of RNA and DNA modifications across transcriptomes and genomes, respectively. The methods combine molecular recognition of non-canonical features (e.g., base modifications, backbone modifications, lesions, and / or structural elements) of a target nucleic acid with a step of writing the information from this recognition event into the neighboring genetic sequence of the target nucleic acid using a barcode. The resultant barcoded nucleic acids are then converted into sequencing libraries and read by DNA / RNA sequencing methods. This step reveals the sequence of the barcode, which is correlated with the non-canonical feature in the target nucleic acid(s). The high throughput profiling methods described herein allow for localization of one or more modifications in a target nucleic acid. The methods also allow for identification of the nature and location of several or all DNA / RNA modifications in parallel.
Owner:ALIDA BIOSCIENCES INC
Process for detection of dna modifications and protein binding by single molecule manipulation
InactiveCN105122063APrecise positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDNA ModificationProtein L
The present invention relates to a method for determining whether a protein binds to a specific DNA sequence. This method is useful in particular for identifying modifications to the DNA sequence (e.g. methylations) via the binding of proteins that specifically recognize those modifications (e.g. antibodies), but also to identify the binding sequence on DNA of a variety of proteins.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +2
Biosensor for ctDNA detection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113186254AAchieving Regulatory Dynamic RangeMicrobiological testing/measurementGold particlesNanoparticle
The invention provides a preparation method of a biosensor for ctDNA detection, which comprises the following steps: preparing gold nanoparticles: mixing and heating chloroauric acid and ultrapure water, then adding a sodium citrate solution, continuously conducting heating and reacting, conducting cooling to room temperature after the reaction is finished, conducting filtering to obtain the gold nanoparticles, and conducting preserving at low temperature for later use; and conducting DNA modification: carrying out annealing treatment on DNA, then uniformly mixing the DNA subjected to annealing treatment with the prepared gold nanoparticles, carrying out standing treatment, then adding a sodium citrate solution, then adding a phosphate buffer solution, carrying out standing, finally adding water, and carrying out centrifugal washing, thus obtaining the biosensor for ctDNA detection.
Owner:山东雷泽生物科技有限责任公司
Methods of X-aptamer generation and compositions thereof
Provided herein are methods for a novel bead-based next-generation “X-aptamer” selection scheme that extends aptamer technology to include X-modified bases, thus resulting in X-aptamers, at any position along the sequence because the aptamers are chemically synthesized via a split-pool scheme on individual beads. Also provides are application to a wide range of commonly used DNA modifications, including, but not limited to, monothioate and dithioate backbone substitutions. This new class of aptamer allows chemical modifications introduced to any of the bases in the aptamer sequence as well as the phosphate backbones and can be extended to other carbohydrate-based systems.
Owner:AM BIOTECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com