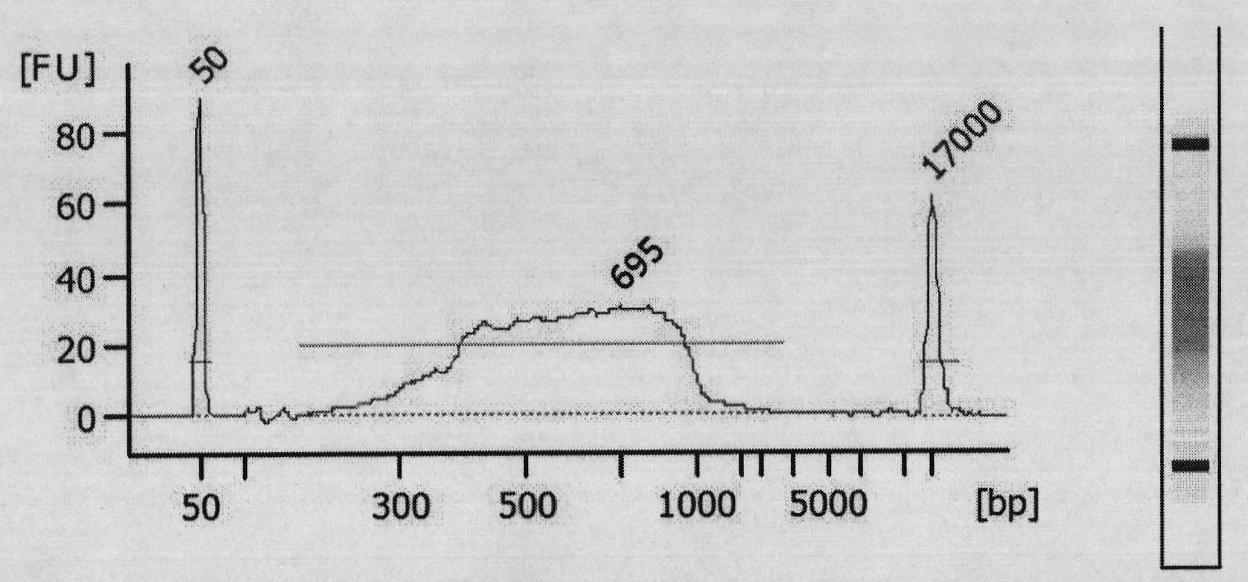
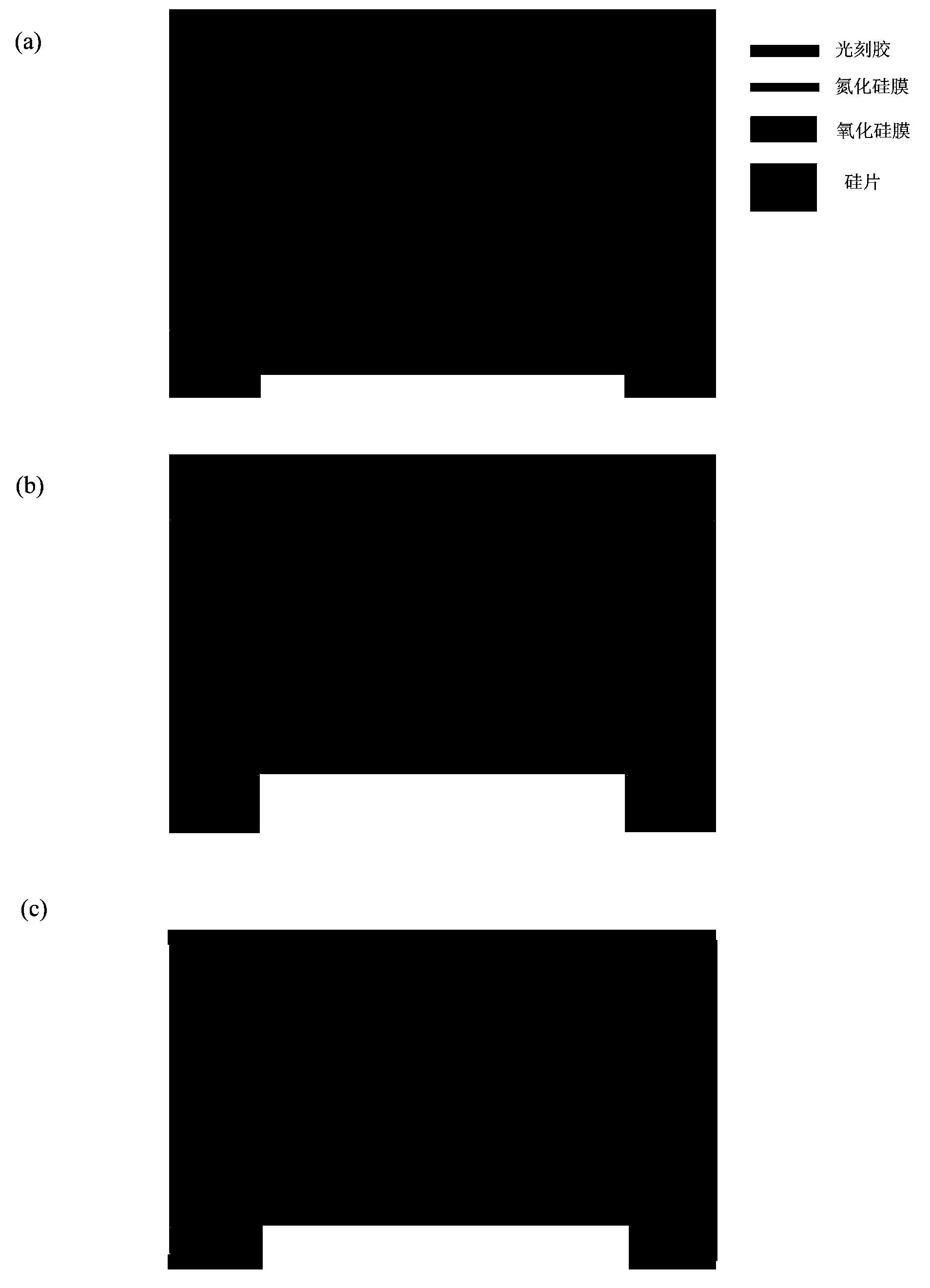
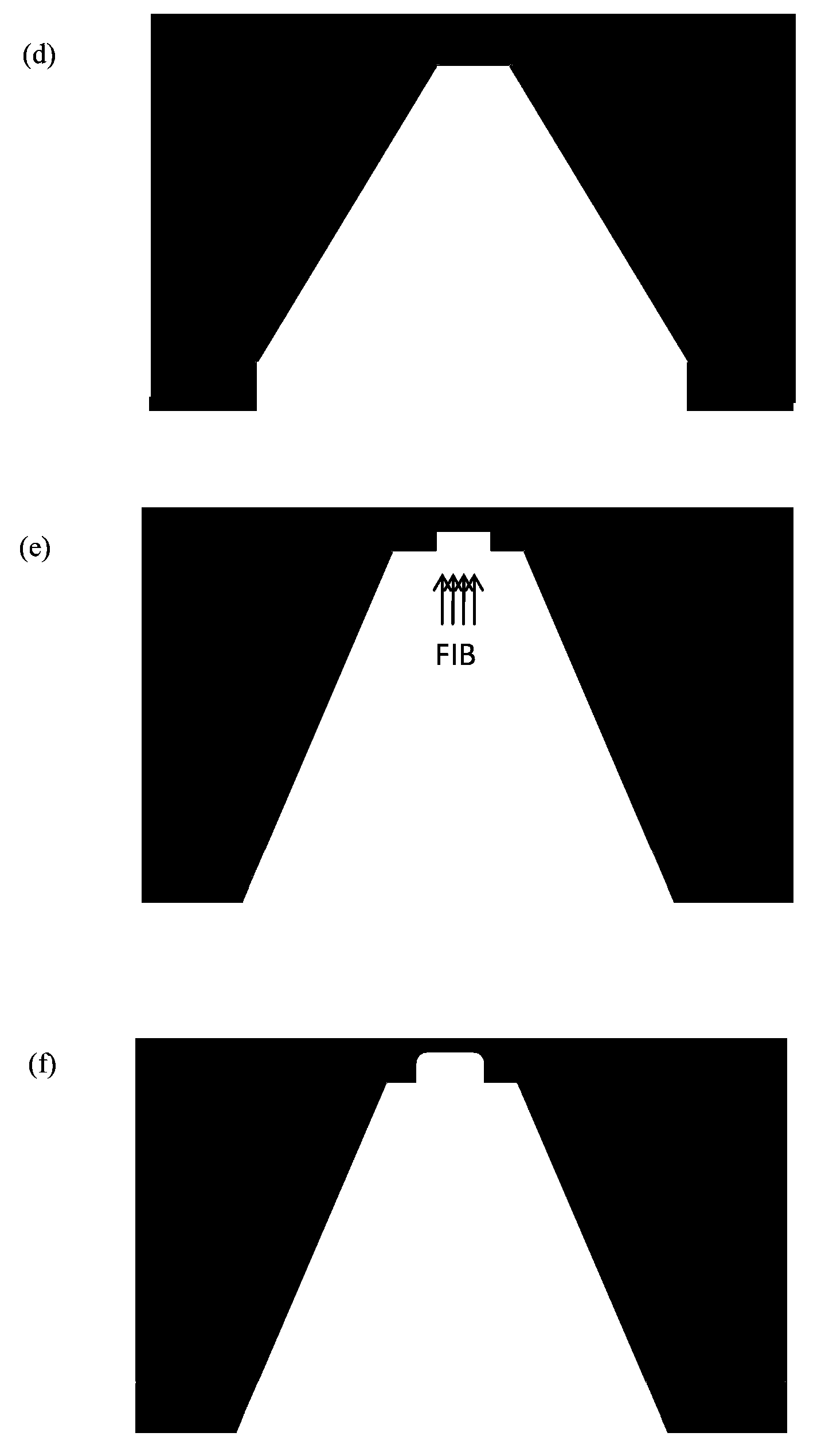
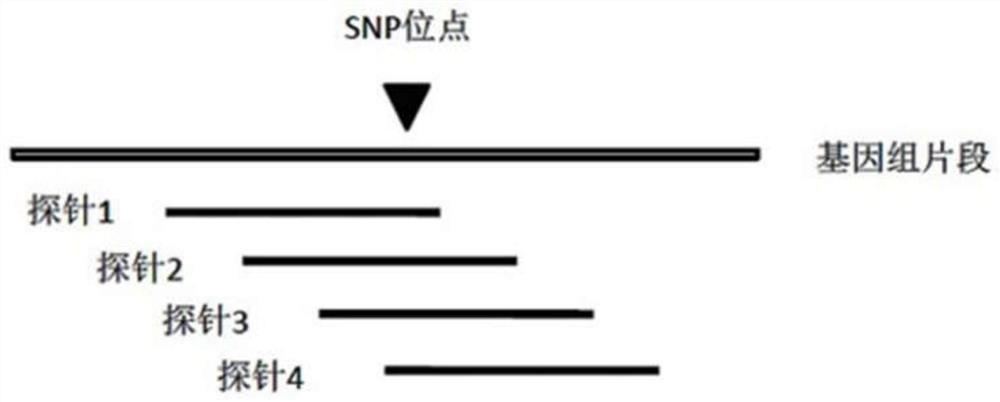
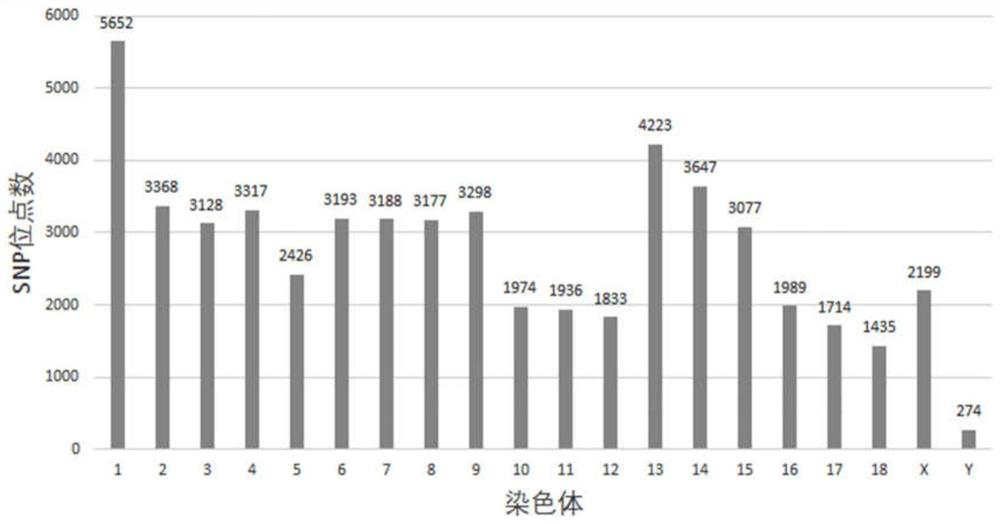
Patents
Literature
245results about How to "Lower Sequencing Costs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
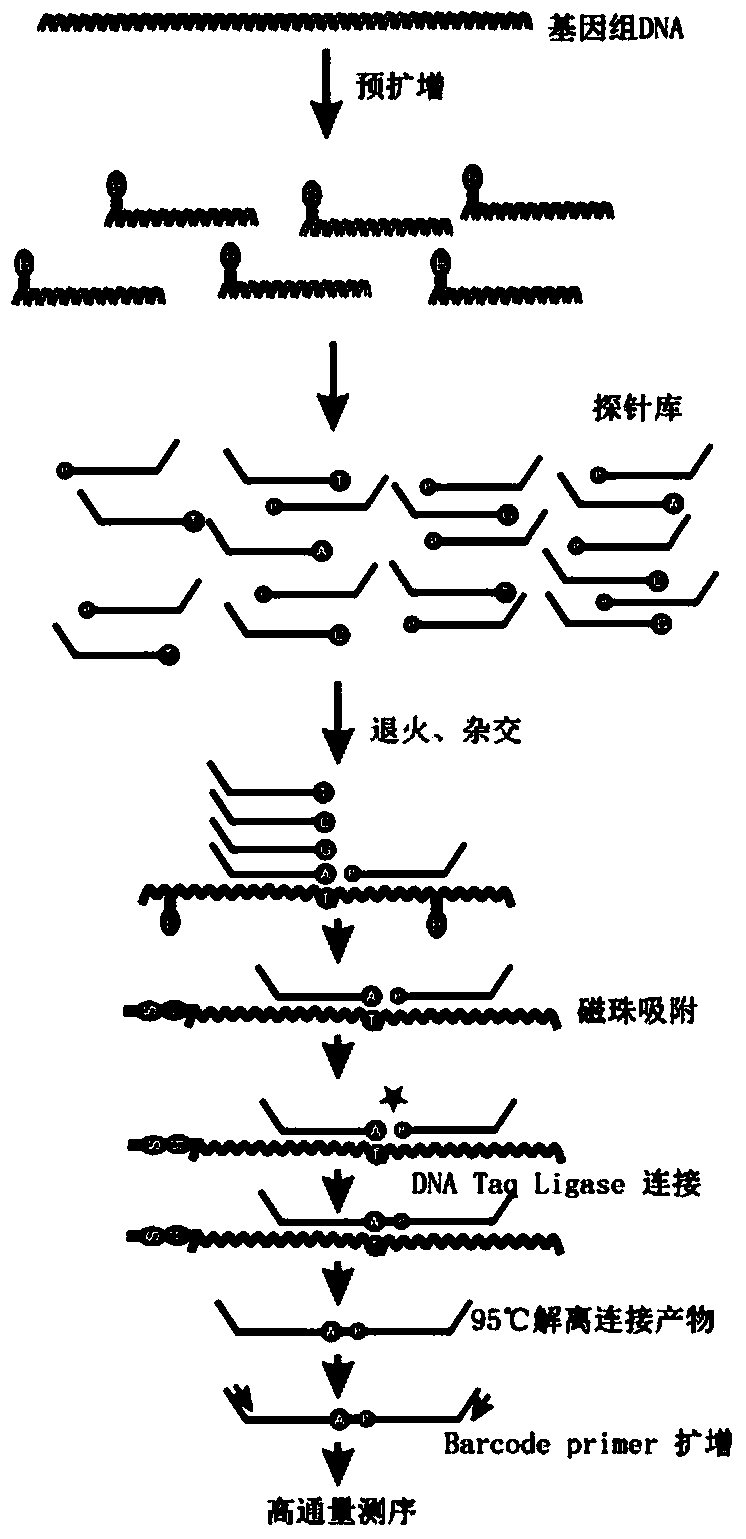
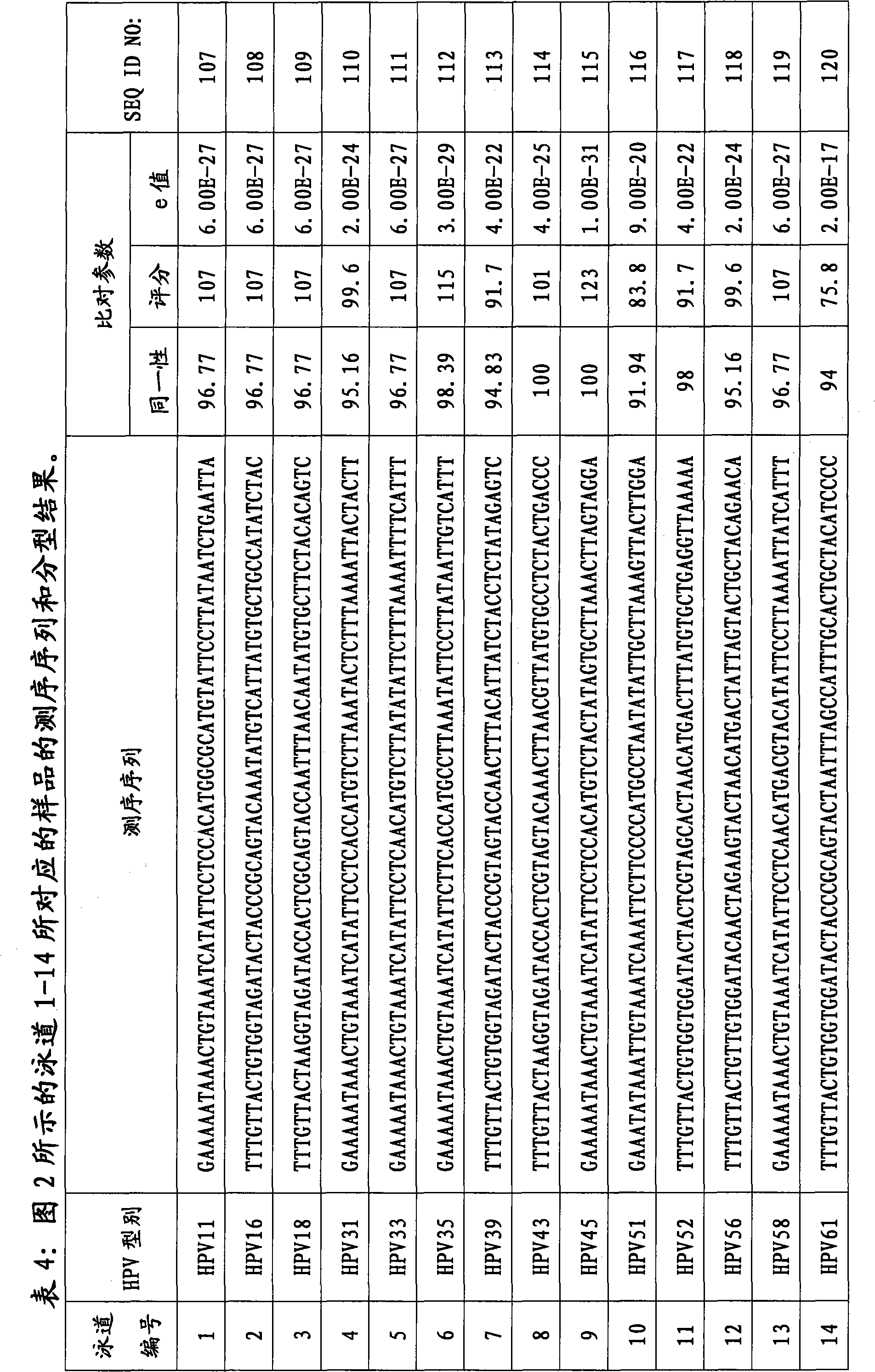
Double-label joint sequence for detection of tumor mutation and detection method
ActiveCN106086162AEasy to distinguishIncrease sample sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMutation detectionBioinformatics
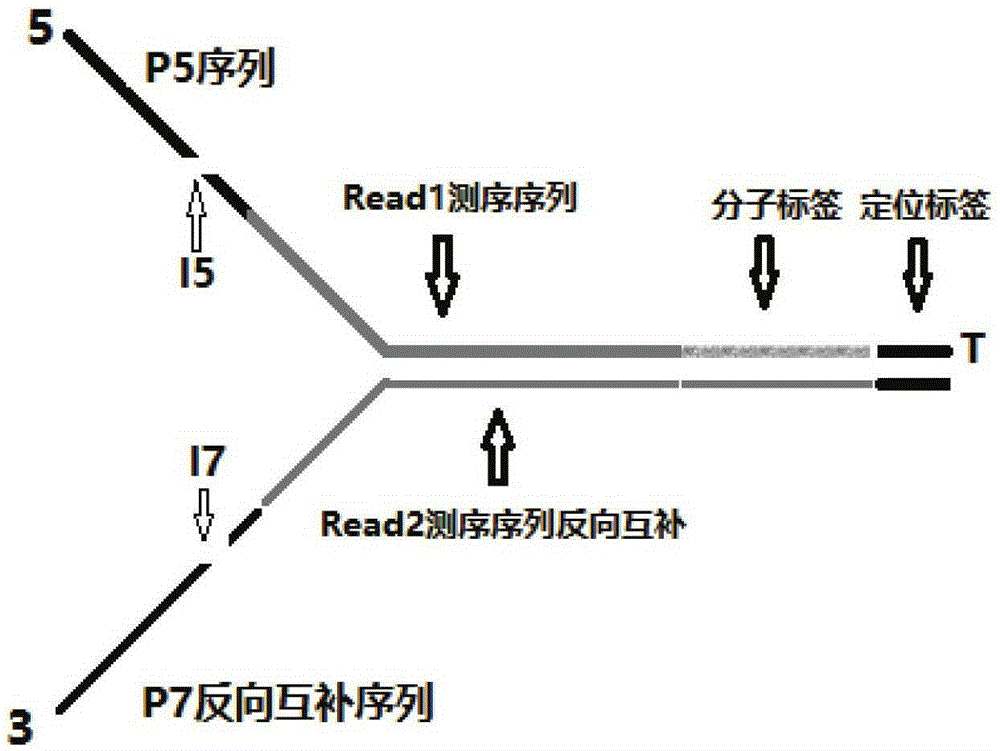
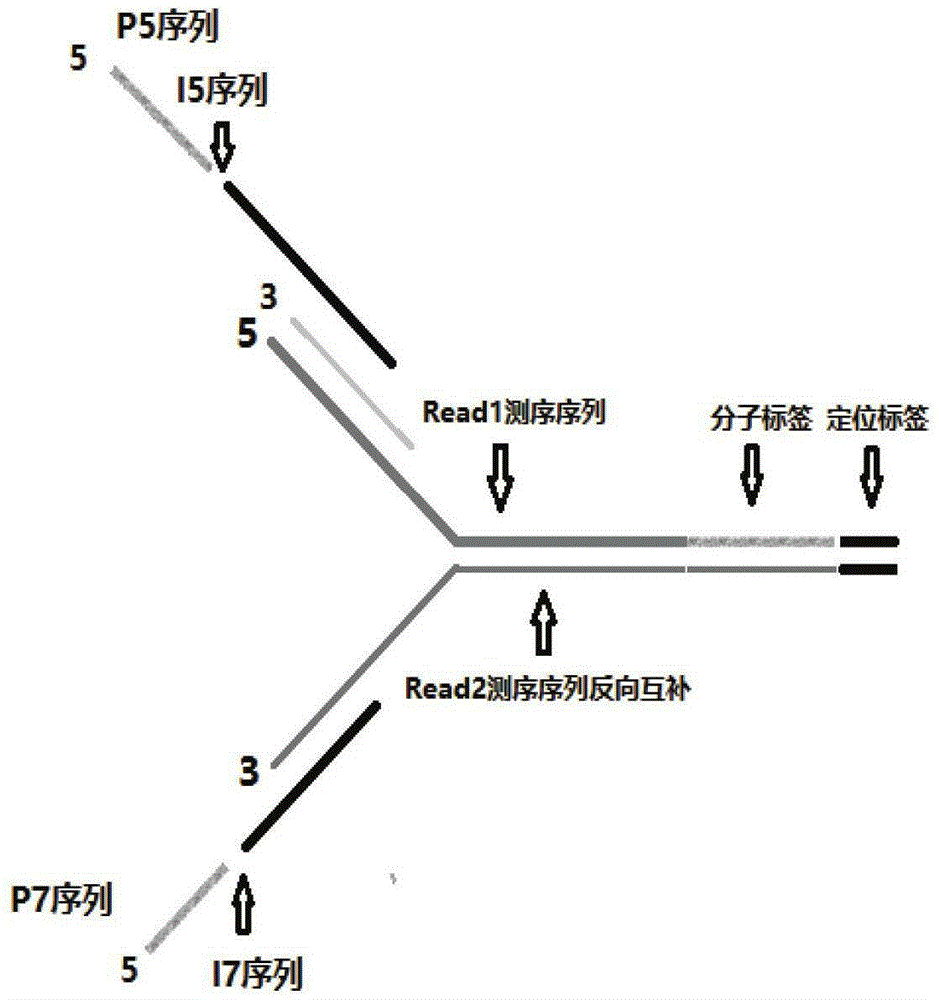
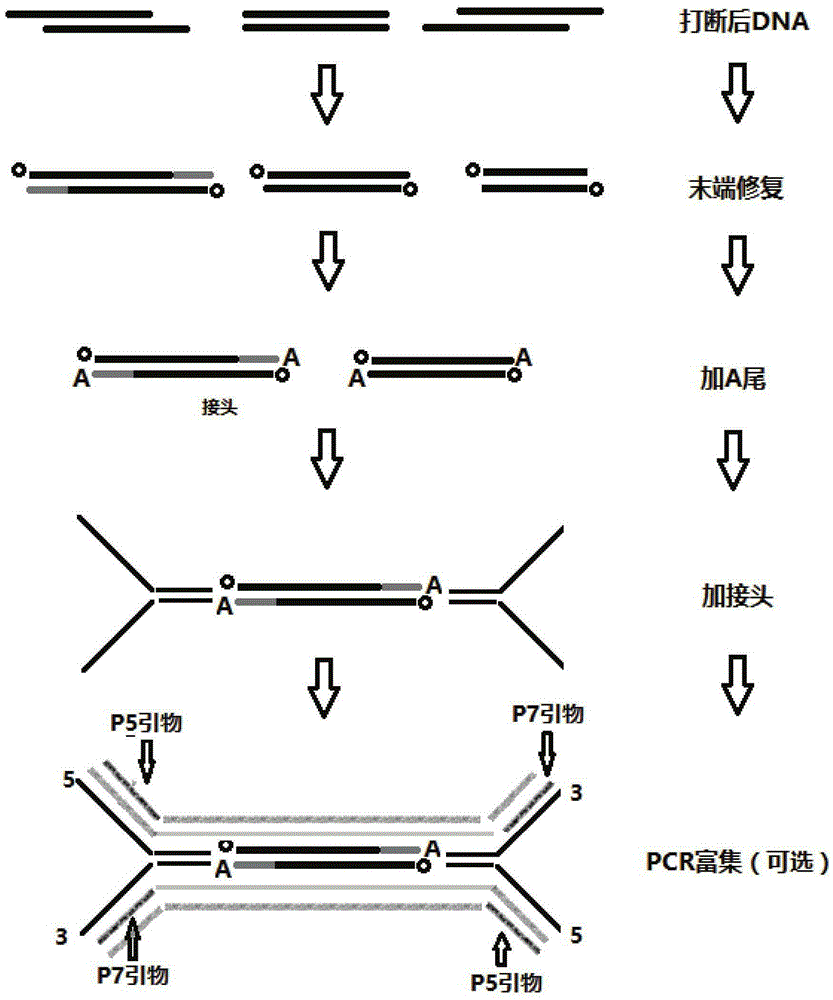
The invention discloses a double-label joint sequence for detection of tumor mutation, and is characterized in that the joint sequence is synthesized by a joint primer P5 and a joint primer P7, wherein the joint primer P5 has the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the joint primer P7 has the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also provides a database building method and a sequencing method. With use of a double-label joint, the tumor mutation rate of 1*10<-5> can be accurately detected, the tumor mutation detection sensitivity is effectively improved, and with combination of the flux of high-flux sequencing, one-time sequencing can detect multiple mutation loci of multiple genes.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
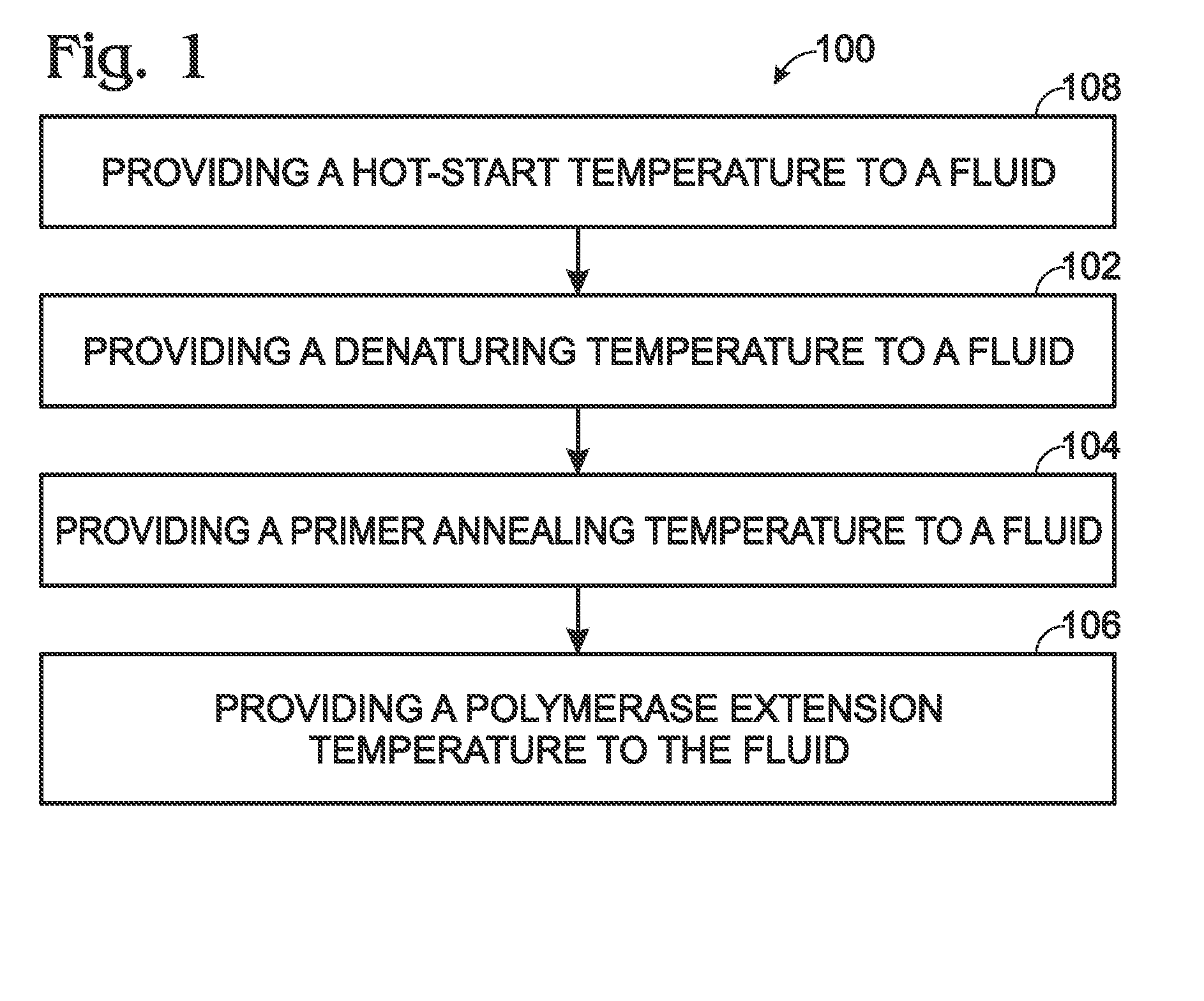
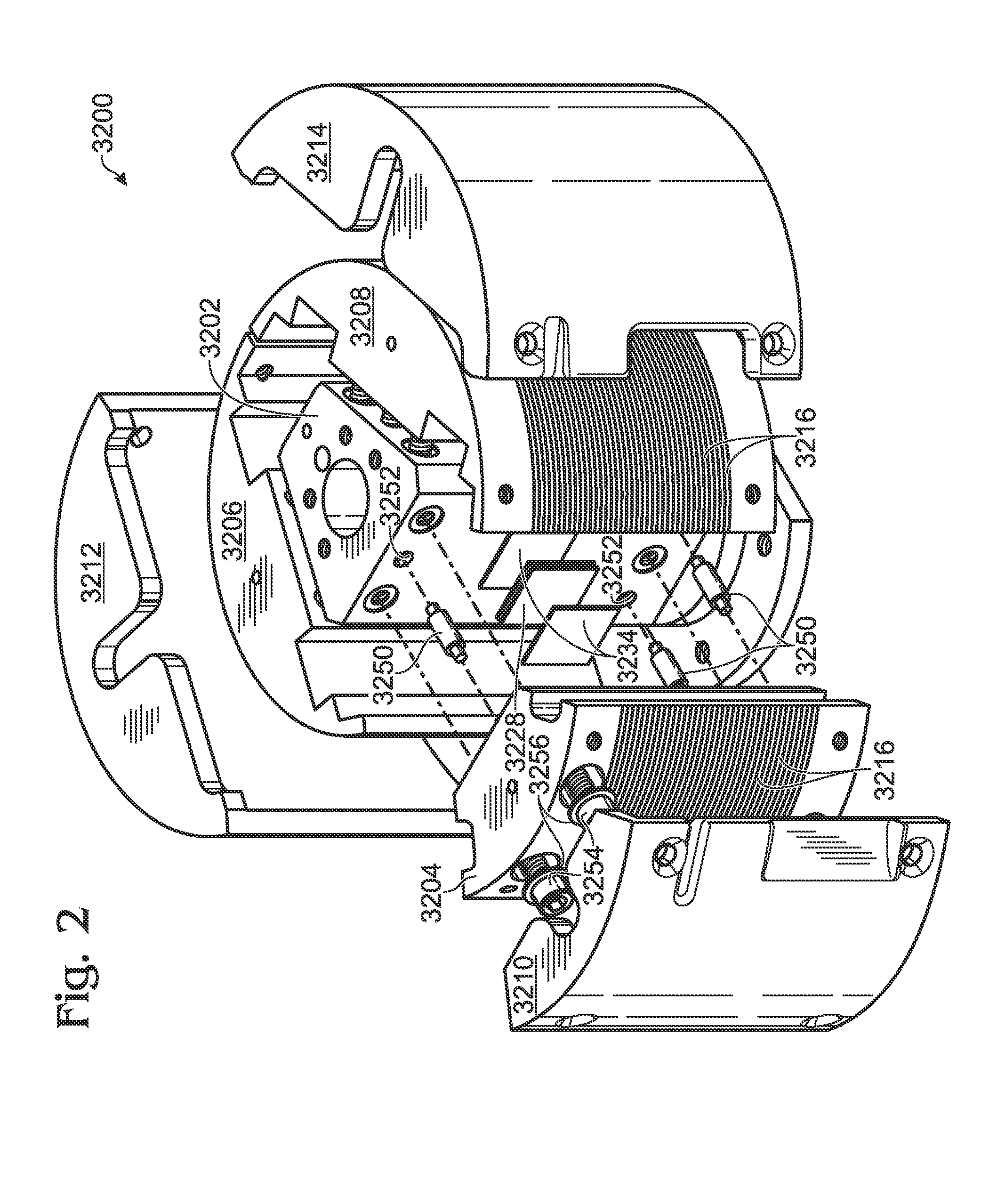
Flow-based thermocycling system with thermoelectric cooler
ActiveUS20110212516A1Lower Sequencing CostsPromote PCRBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChillerEngineering
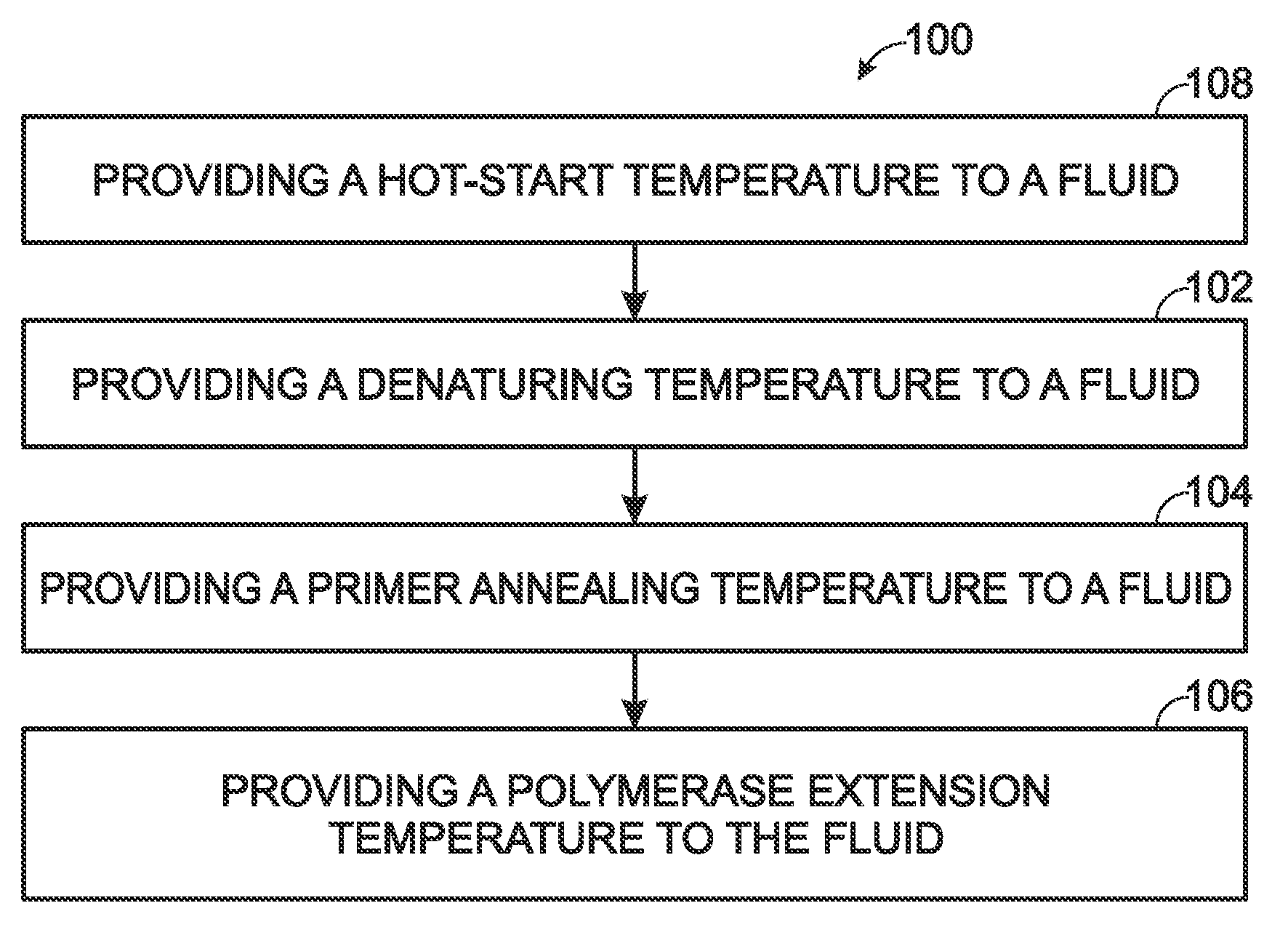
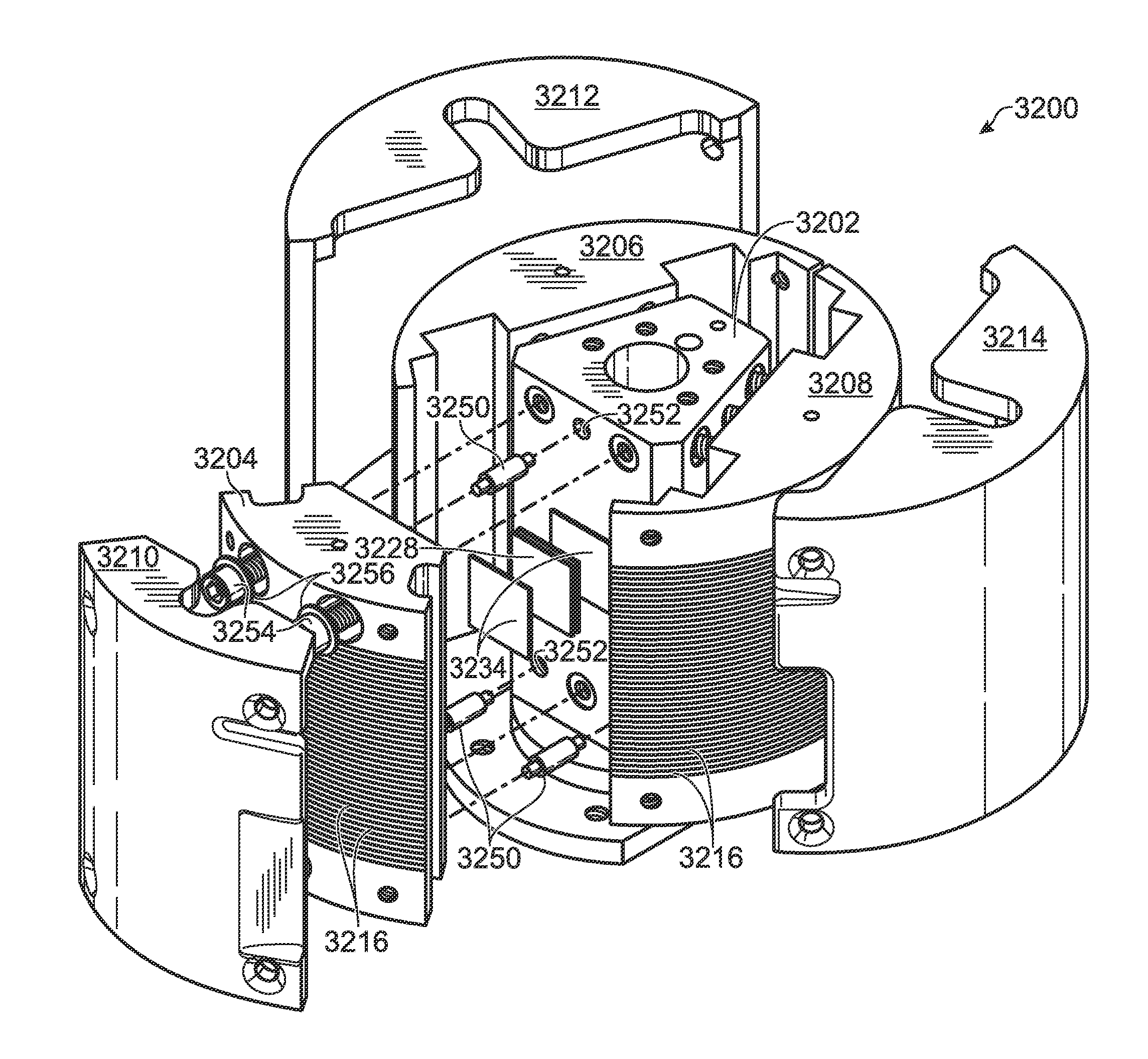
Thermocycling system, including methods and apparatus, for performing a flow-based reaction on a sample in fluid. The system may include a plurality of segments defining at least two temperature regions, and also may include a plurality of heating elements configured to maintain each temperature region at a different desired temperature. At least one of the heating elements may be a thermoelectric cooler operatively disposed to transfer heat to and / or from a temperature region The system further may include a fluid channel extending along a helical path that passes through the temperature regions multiple times such that fluid flowing in the channel is heated and cooled cyclically.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Kit for testing and identifying genetic cardiac hypertrophy related gene mutation
The invention relates to a kit for detecting genetic cardiac hypertrophy related gene mutation samples, particularly to a product for detecting genetic cardiac hypertrophy related genes by a massively parallel sequencing platform technology. The method involved in the kit comprises: a) uniquely designing and preparing a capture probe, which is directed at all exon fragments of genes ACTC1, ACTN2, BRAF, CALR3, CASQ2, CSRP3, GLA, HRAS, JPH2, KRAS, LAMP2, LDB3, MAP2K1, MYBPC3, MYH6, MYH7, MYL2, MYL3, MYLK2, MYOZ2, PRKAG2, RAF1, SOS1, TCAP, TNNC1, TNNI3, TNNT2, TPM1, TTN, TTR, and VCL; b) designing unique joints with tag sequences; c) using universal primers to conduct PCR amplification on probe sequences; and d) designing unique operations for capture of mixed target fragments. The massively parallel sequencing platform prepared by the method and the kit has the advantages of high sample throughput, high efficiency, and easy operation, thus greatly reducing the sequencing testing cost.
Owner:康旭基因技术(北京)有限公司
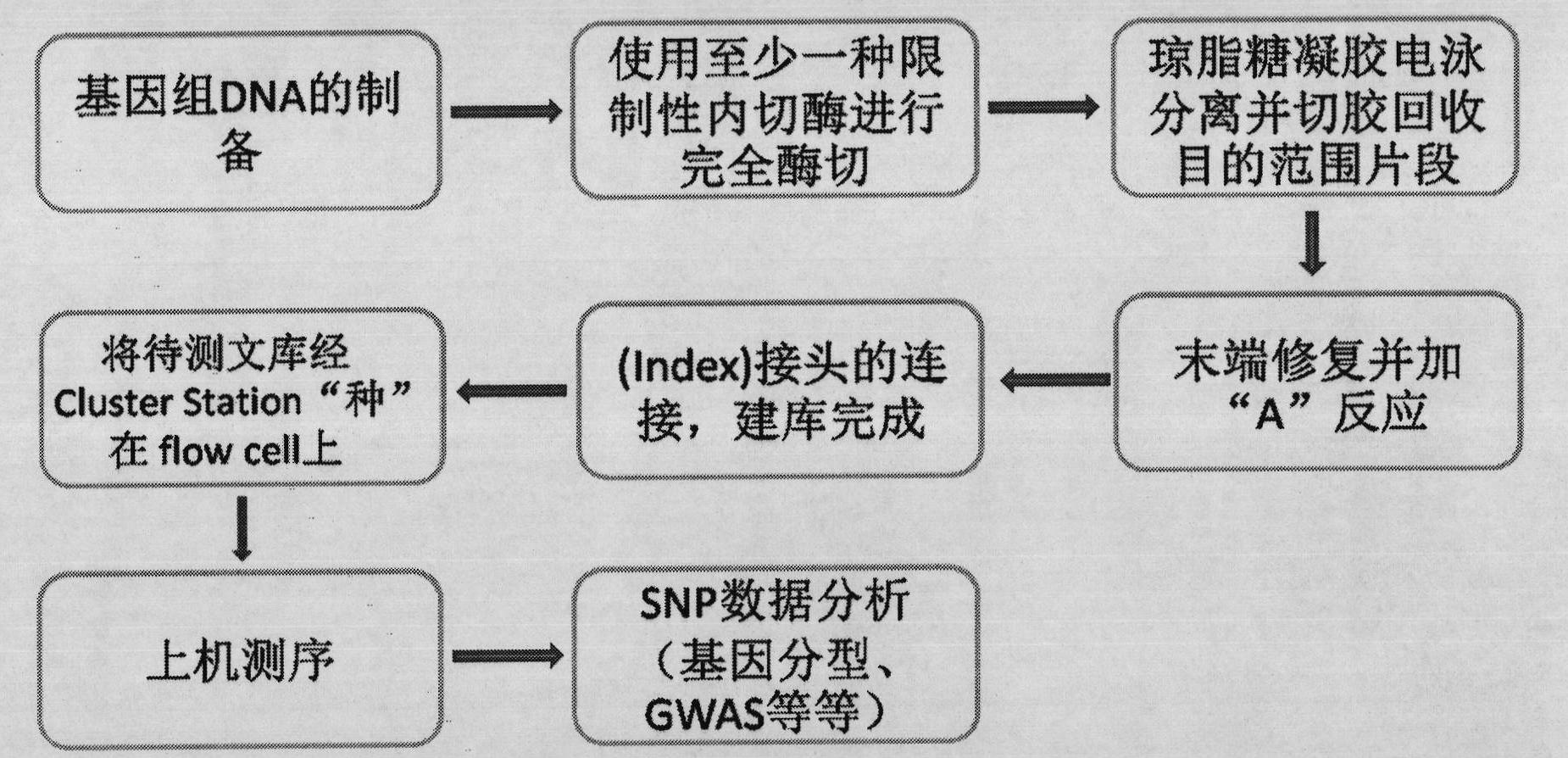
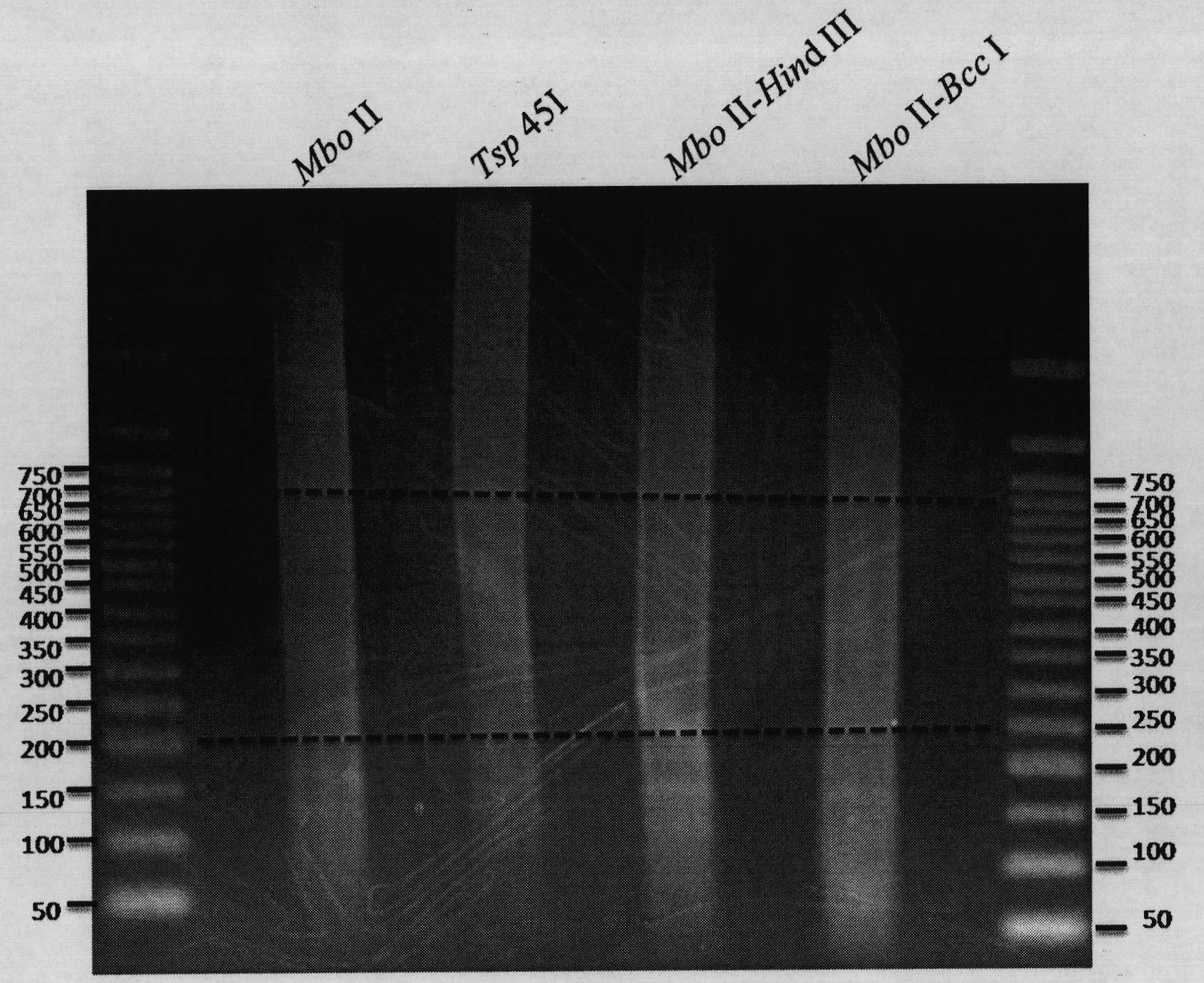
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library and preparation method thereof as well as method and device for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
ActiveCN102061526ASimple processEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationEnzyme digestionGenomic DNA
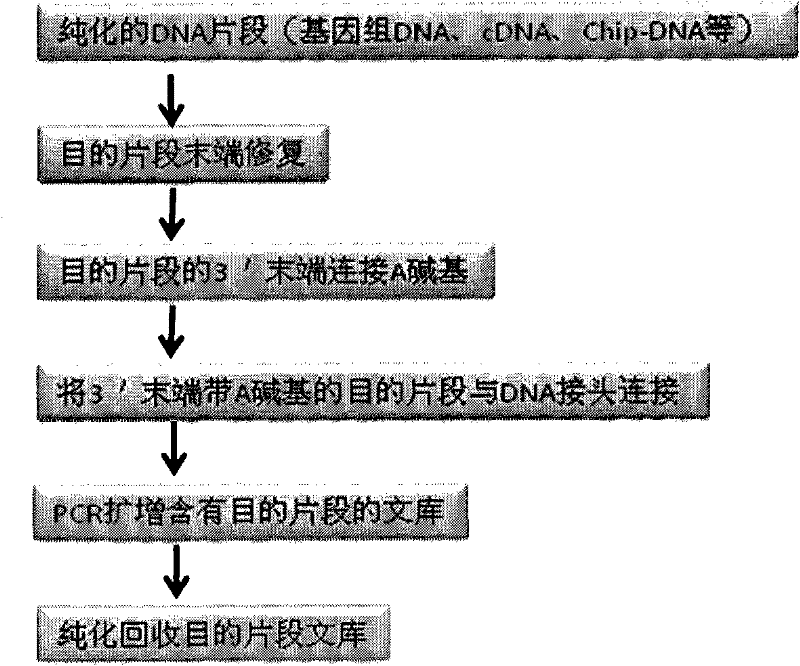
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) library and a preparation method thereof as well as a method and device for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Particularly, the preparation method of the DNA library comprises the following steps: 1) using at least one type of restriction endonuclease to perform enzyme digestion on a sample genomic DNA, thus obtaining enzyme digestion products; 2) separating the enzyme digestion products to obtain 100-1000bp DNA fragments; and 3) repairing the tail ends of the DNA fragments obtained in the step 2). Preferably, the preparation method also comprises the following steps: 4) adding basic groups A to the tail ends of the DNA fragments obtained in the step 3); and 5) connecting the DNA fragments obtained in the step 4) with sequencing joints. The method for detecting the SNPs provided by the invention is easy to operate. The invention also relates to a DNA sequencing method and a genotyping method.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
Sequencing reaction small chamber, gene sequencing reaction bench and gene sequencing system
ActiveCN101368206AReduce concentrationLower requirementHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationDiffusion barrier
The invention provides a sequencing reaction cabinet, used for carrying out the sequencing reaction between DNA fragments and a reagent; the sequencing reaction cabinet comprises a reaction cavity, on the inner wall at one side of which is fixedly provided with a plurality of DNA fragments; a reagent inlet and a reagent outlet which are respectively arranged at the two ends of the inner wall at the other side of the reaction cavity and are respectively used for the reagent to flow into and out of the reaction cavity. In the sequencing reaction cabinet, a plurality of DNA fragments are fixed in the reaction cavity with a small capacity as a short label array for sequencing to lead the sequencing reaction to be carried out in the reagent without a diffusion barrier, thus greatly improving the accessibility between the reagent and the DNA fragments and further shortening the reaction time; the requirements to the concentration and the dosage of the reagent is lower, thus consuming less reagent and reducing the sequencing cost. While a plurality of DNA fragments are simultaneously fixed in the reaction cabinet to provide a platform for realizing the parallel reaction of a plurality of fragments. The sequencing reaction cabinet used for carrying out sequencing reaction between DNA fragments and a reagent realizes the automatization of high pass sequencing and can realizes fast sequencing reaction.
Owner:SHENGZHEN CHINA GENE TECH COMPANY
Method for constructing high-throughput sequencing library and kit
ActiveCN106555226AReduce the difference in amplification efficiencyImprove effectivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationDigestionGene
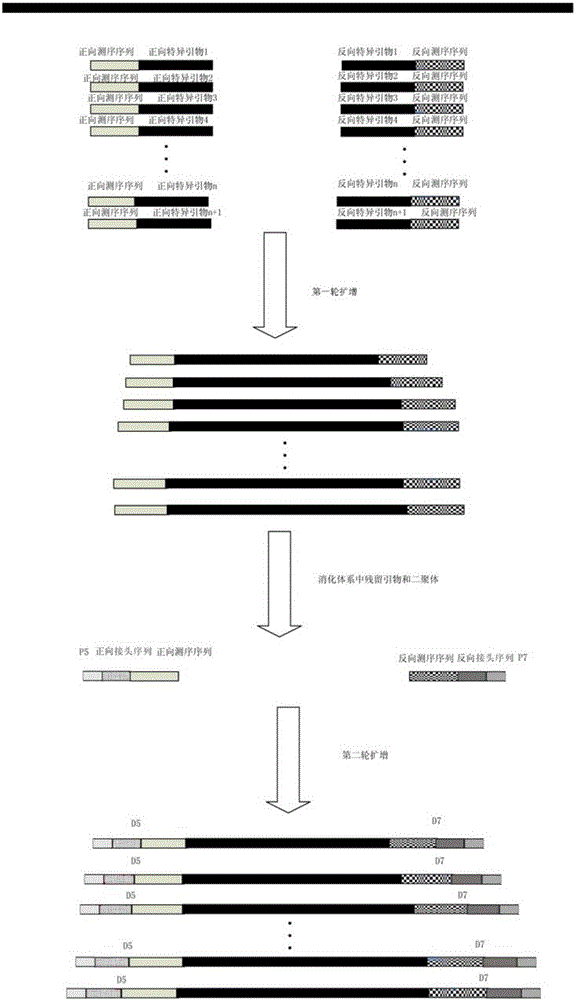
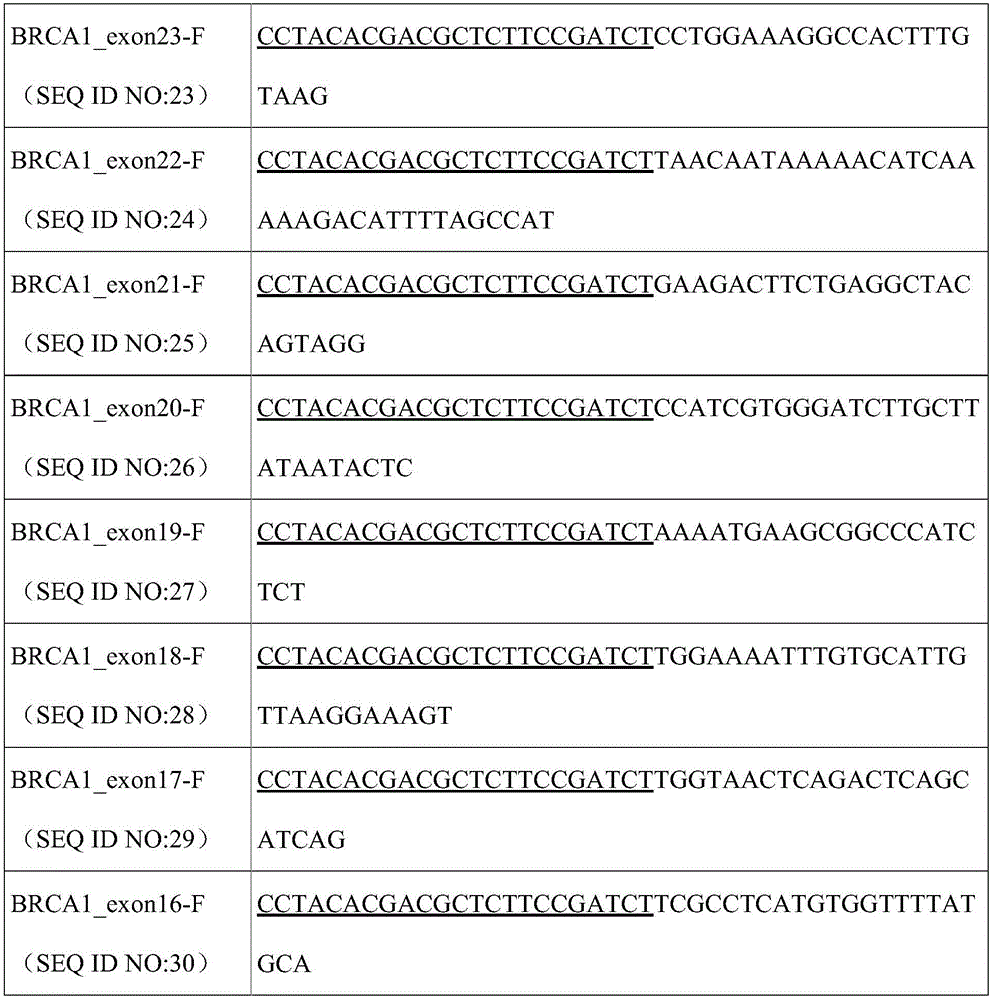
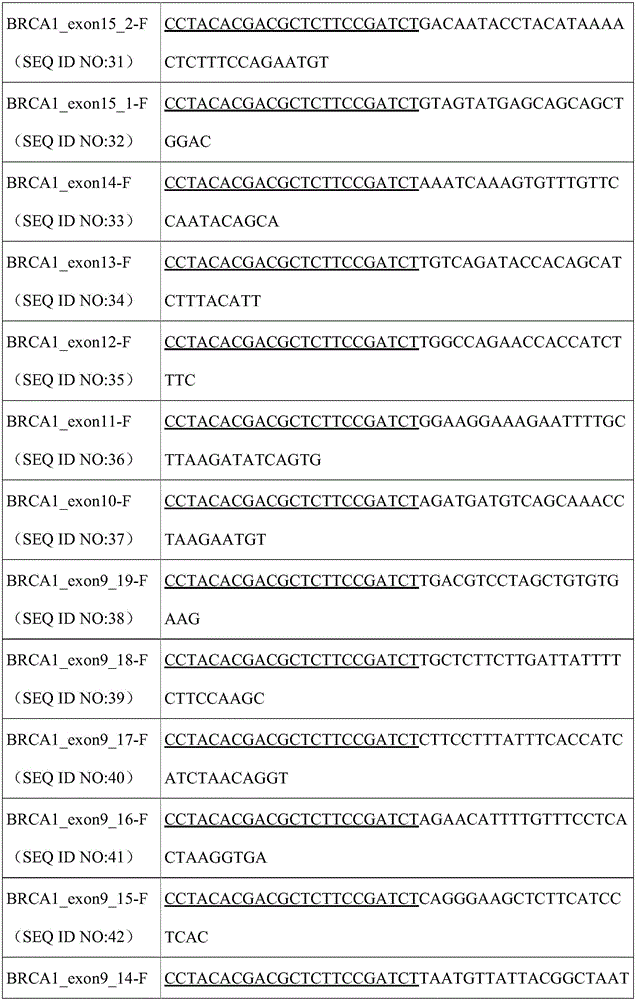
The invention relates to a method for constructing a high-throughput sequencing library capable of capturing a plurality of amplified fragments at the same time and a kit. The method comprises the following steps: first round amplification; primer digestion; second round amplification; purification and recovery; sequencing; and analysis. By virtue of reasonable primer design and PCR policy, a D5 adapter primer sequence and a D7 adapter primer sequence are directly added to the 5' tail end of a PCR product. By introducing a differentiable label sequence for each of samples, the sequencing result of each of the samples during detection by a second generation high-throughput sequencing technology can be found through a unique label sequence thereof. The method can be applied to detecting a plurality of different genetic loci of a large number of samples at the same time, so that the sequencing cost is greatly lowered.
Owner:DALIAN GENTALKER BIO-TECH CO LTD
Decoding and sequencing method by real-time synthesis of two nucleotides into deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
InactiveCN102634586AIncrease the lengthLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic nucleotideDeoxycytidine triphosphate
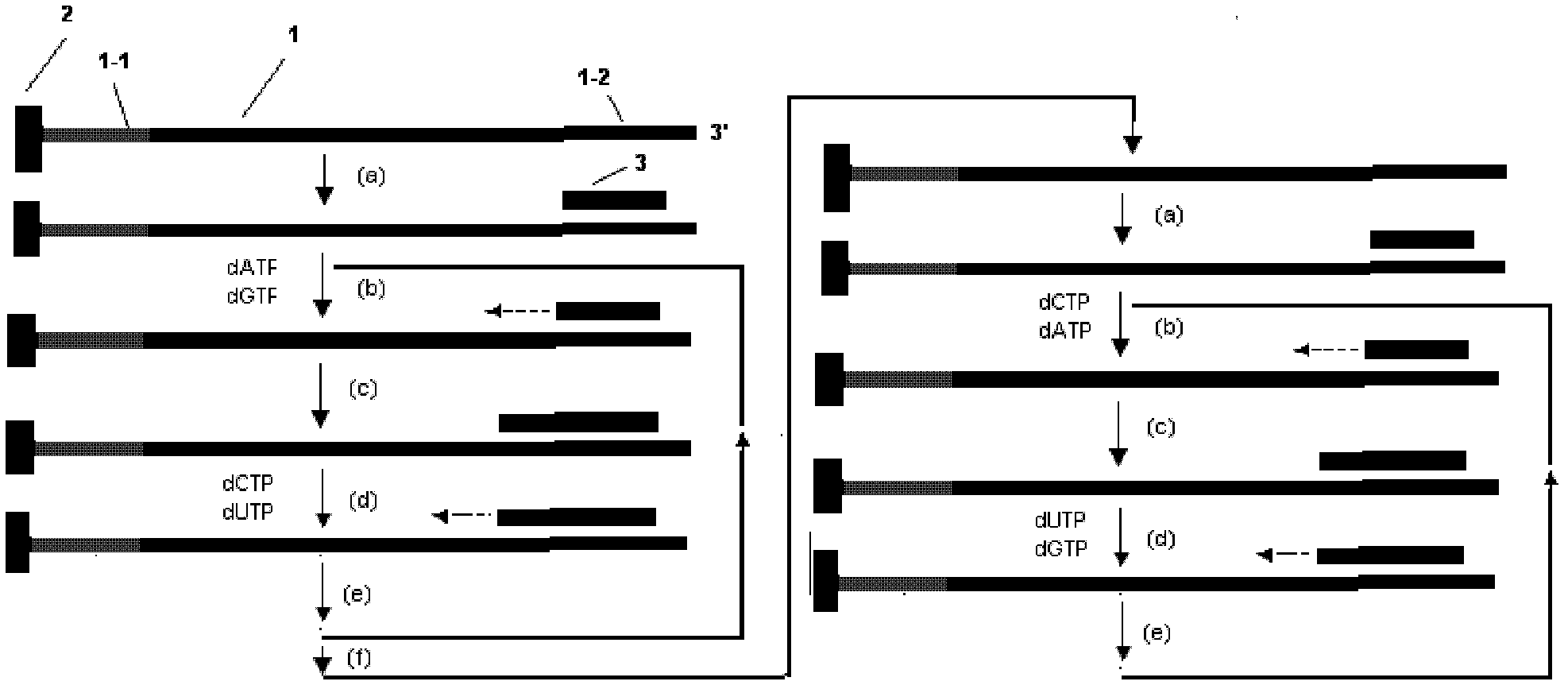
The invention discloses a decoding and sequencing method by real-time synthesis of two nucleotides into deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Single-sequencing reactions are performed on two different nucleotides of X and Y simultaneously and a base sequence fragment code of XYn is obtained according to the quantitative relation between the number of synthesizing nucleotides and the number of the detected molecules which are generated in real time. The sequencing comprises two sets of sequencing reactions on the same template; and in either set of sequencing, a cycle that two different nucleotides synthesize the sequencing reaction simultaneously is performed on deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP), deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) and deoxy-thymidine triphosphate (dTTP) containing four nucleotides in the mode that each nucleotide is used once in a cycle. After a plurality of sequencing reactions, information of a plurality of XYn ranked according to a sequencing order by the first set is obtained. When the set of sequencing reactions is completed, denaturation is performed to eliminate the extended strand of a sequencing primer and the sequencing primer is re-crossed to perform the second set of sequencing reactions; information of a plurality of XYn ranked by the second sequencing reaction is obtained; the specific base sequence of nucleic acid fragment to be detected is assembled by decoding the information of a plurality of XYn ranked according to a sequence order by the two sets.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
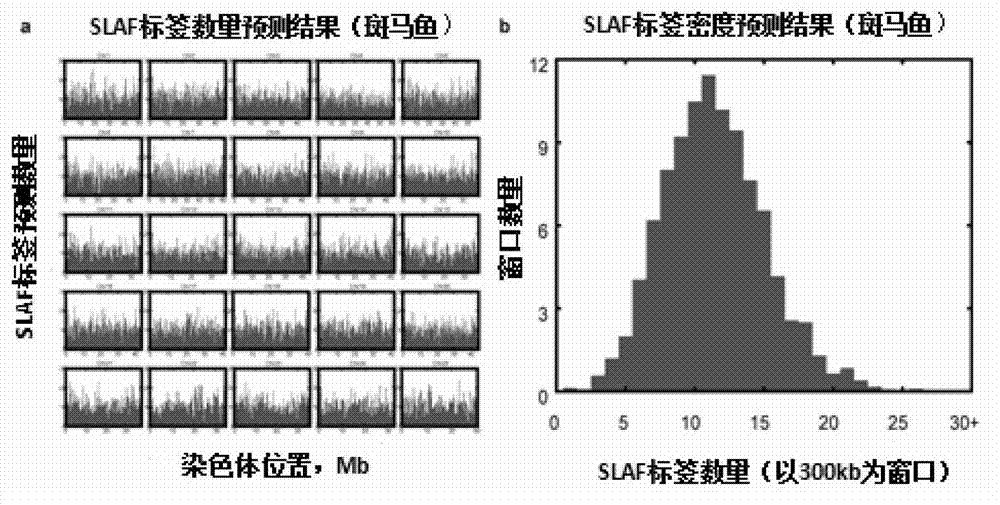
Large-scale genetic typing method based on SLAF-seq (Specific-Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing) technology
ActiveCN103088120AGuarantee label qualityQuality assuranceMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotyping by sequencingGenome
The invention provides a method for carrying out large-scale gene typing based on an n SLAF-seq (Specific-Locus Amplified Fragment Sequencing) technology. Complexity of the genome is reduced by utilizing the SLAF-seq technology, and genetic typing is carried out on large-scale products. High-throughput sequencing is carried out on the genome, marker-developing, genetic map drawing and whole genome association analyzing are carried out on the samples by utilizing the technology. Compared with the conventional method, the large-scale genetic typing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the throughput is greatly improved, and the cost is greatly reduced. The method is mainly applied to marker-developing, genetic map drawing and whole genome association analyzing.
Owner:BIOMARKER TECH
Flow-based thermocycling system with thermoelectric cooler
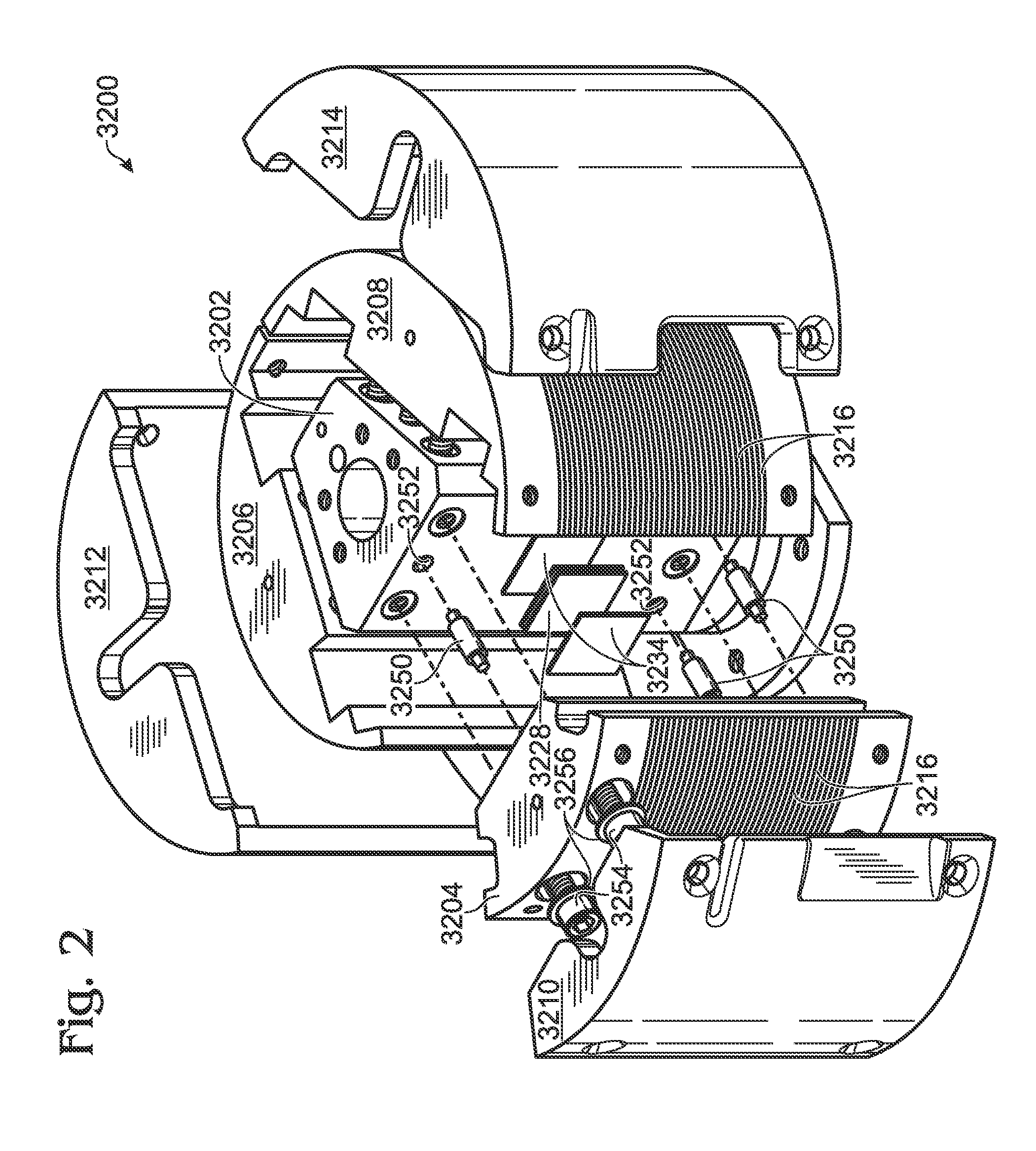
ActiveUS8633015B2Lower Sequencing CostsPromote PCRBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusThermoelectric coolingTwo temperature
Thermocycling system, including methods and apparatus, for performing a flow-based reaction on a sample in fluid. The system may include a plurality of segments defining at least two temperature regions, and also may include a plurality of heating elements configured to maintain each temperature region at a different desired temperature. At least one of the heating elements may be a thermoelectric cooler operatively disposed to transfer heat to and / or from a temperature region The system further may include a fluid channel extending along a helical path that passes through the temperature regions multiple times such that fluid flowing in the channel is heated and cooled cyclically.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
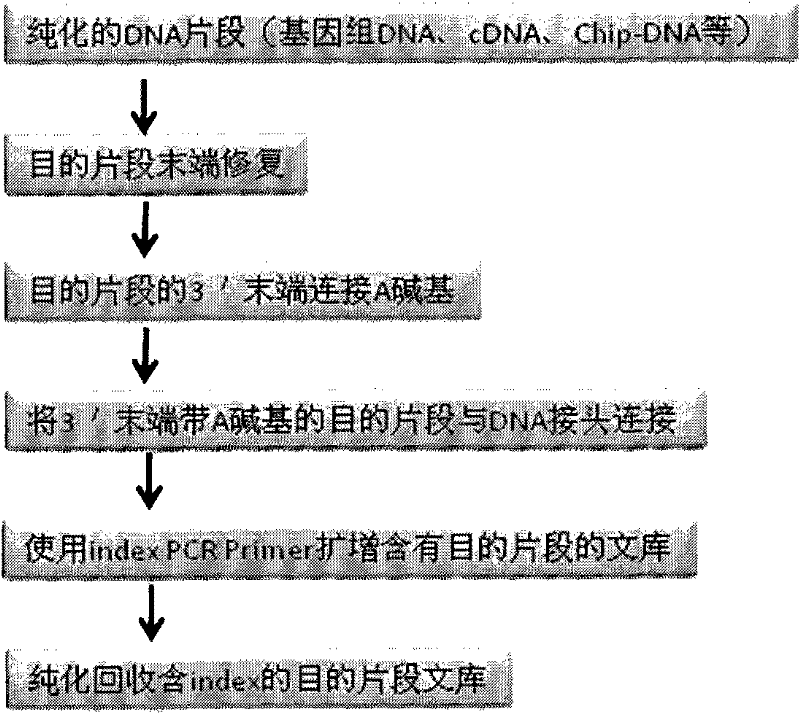
DNA(deoxyribonucleic acid) index library building method based on PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
ActiveCN102409049AImprove production efficiencyHigh sequencing throughputNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyInverse polymerase chain reaction
The invention designs 161 unique index sequences with a length of 8bp, and the indexes are embedded into DNA PCR (deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase chain reaction) primers to form DNA PCR index primers, thus being capable of importing the index sequences through PCR. The invention successfully establishes a method for building a DNA index library, and the method is applied to solexa DNA sequencing.
Owner:BGI TECH SOLUTIONS
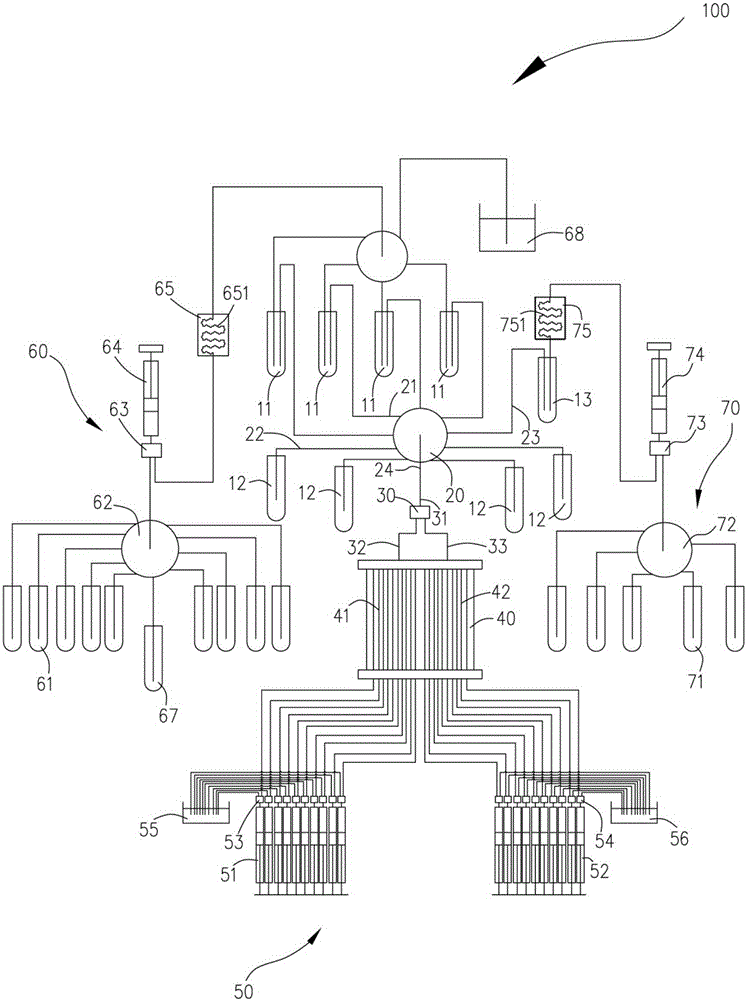
Fluid control device of gene sequencing
ActiveCN105199949AReduce sequencing timeImprove sequencing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid controlFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluid control device of gene sequencing. The fluid control device of gene sequencing comprises a reagent assembly, a first multiported valve, a first three-port valve, a gene sequencing chip and a drive assembly; the reagent assembly is connected with the gene sequencing chip through the first multiported valve and the three-port valve; due to the fact that a first gene sequencing passage and a second gene sequencing passage are arranged in the gene sequencing chip, reagents in the reagent assembly can automatically flow into the first gene sequencing passage and the second gene sequencing passage to conduct reaction and fluorescence image acquisition, when fluorescent sequencing reaction is conducted in the first gene sequencing passage, fluorescence image acquisition can be conducted in the second gene sequencing passage, and the gene sequencing time can be effectively reduced, that is to say, the gene sequencing efficiency is effectively increased. For the fluid control device of gene sequencing, the gene sequencing cost is reduced, and the gene sequencing efficiency is increased.
Owner:GENEMIND BIOSCIENCES CO LTD
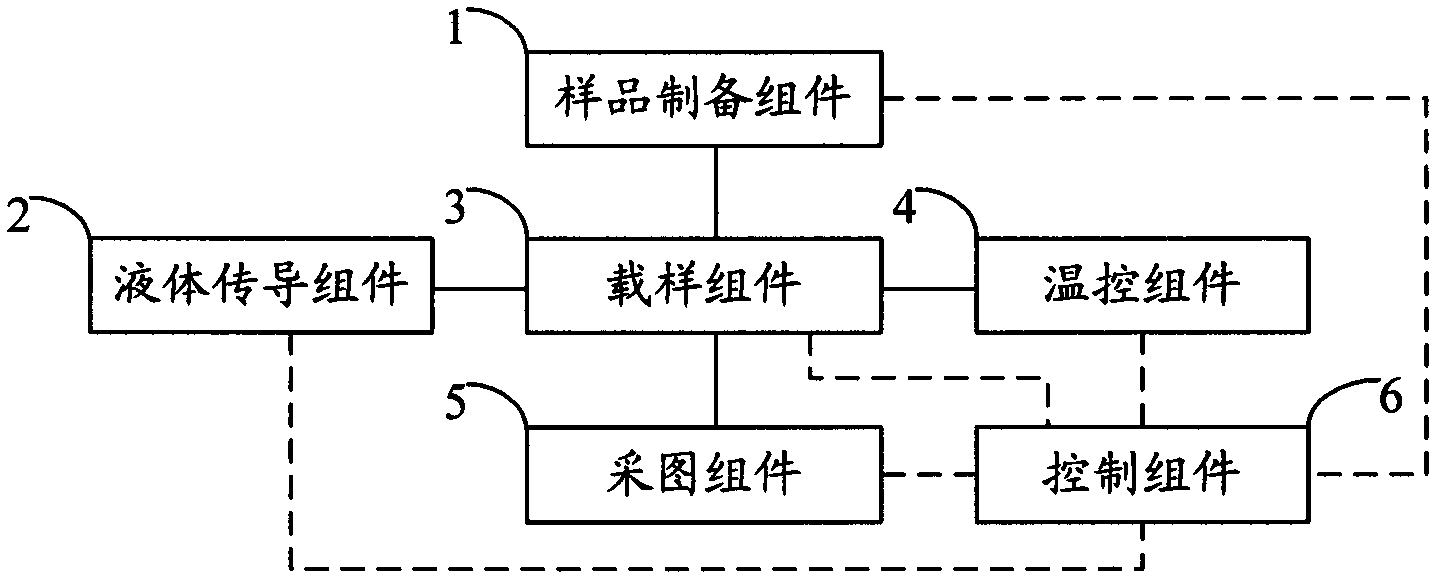
Gene sequencing device and system
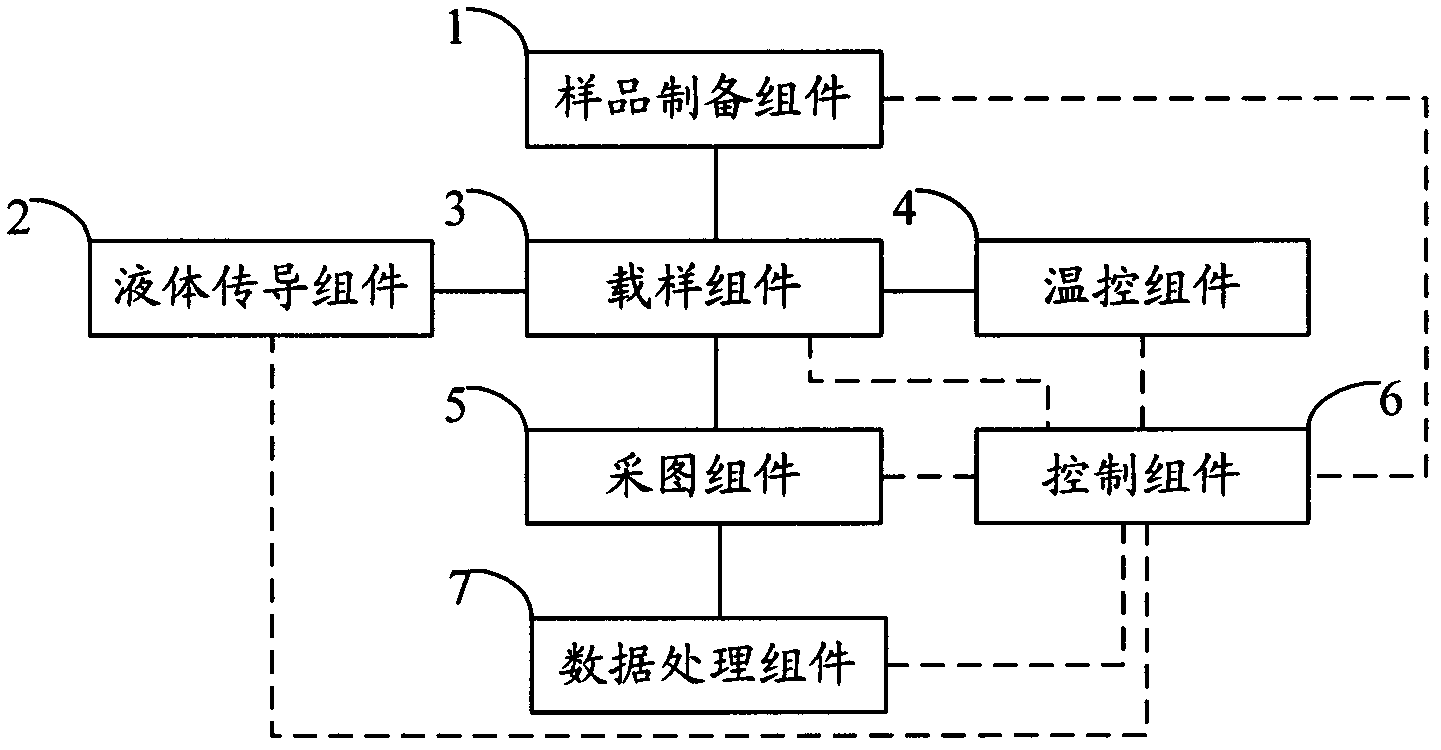
ActiveCN102517206AFully automatedImprove sequencing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlComputer module
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a gene sequencing device and a gene sequencing system. The gene sequencing device comprises a sample preparation component, a liquid conduction component, a sample loading component, a temperature control component, an image acquisition component and a control component. The gene sequencing system comprises a sample preparation control module, a liquid conduction control module, a reaction control module, a temperature control module, an image acquisition control module and a control module. By adopting the gene sequencing device and the gene sequencing system, the integration from sample preparation to data processing can be realized, and full automation of gene sequencing can also be realized. Meanwhile, the high-pass and low-cost gene sequencing can be realized.
Owner:盛司潼
Combined primer for screening human deafness gene mutation and application of combined primer
ActiveCN104561272AImprove throughputLow priceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerGenes mutation
The invention discloses a combined primer for screening human deafness gene mutation. The combined primer comprises a combined forward primer and a combined reverse primer, wherein the combined forward primer consists of two parts namely a joint part P1 sequence and a forward primer sequence, and the combined reverse primer sequentially consists of a joint part P2 sequence, a label sequence and a reverse primer sequence. The invention also discloses a kit for screening the human deafness gene mutation. The invention also discloses applications of the combined primer and the kit in preparation of a reagent for screening the human deafness multi-gene mutation. A primer containing the label (Barcode) sequence is used for differentiating different samples, and at least 32 samples can be detected by performing a method provided by the invention once, so that combined primer can be widely applied to general investigation of deafness susceptible genes. The price of the combined primer disclosed by the invention is far lower than that of imported instruments or reagents, so that the sequencing cost is greatly reduced and then the detection cost is also greatly reduced.
Owner:南京普东兴生物科技有限公司
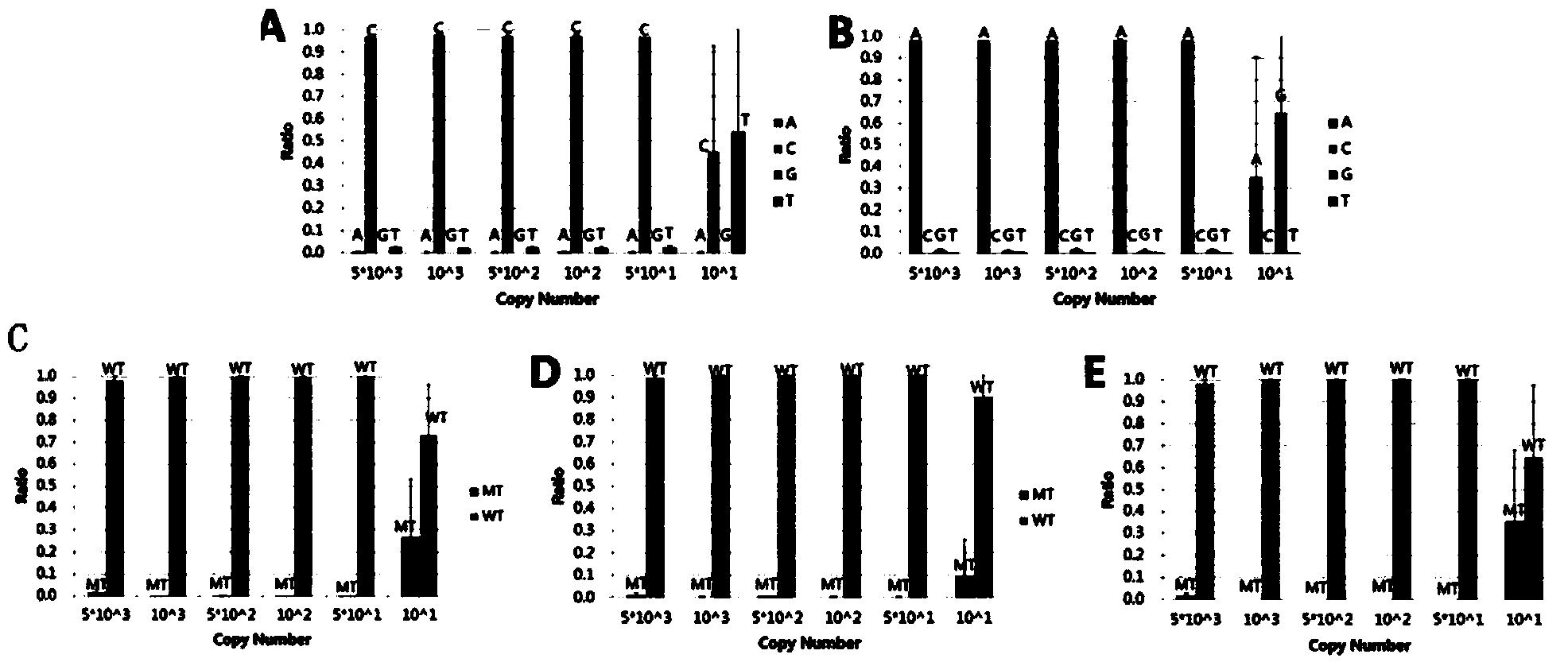
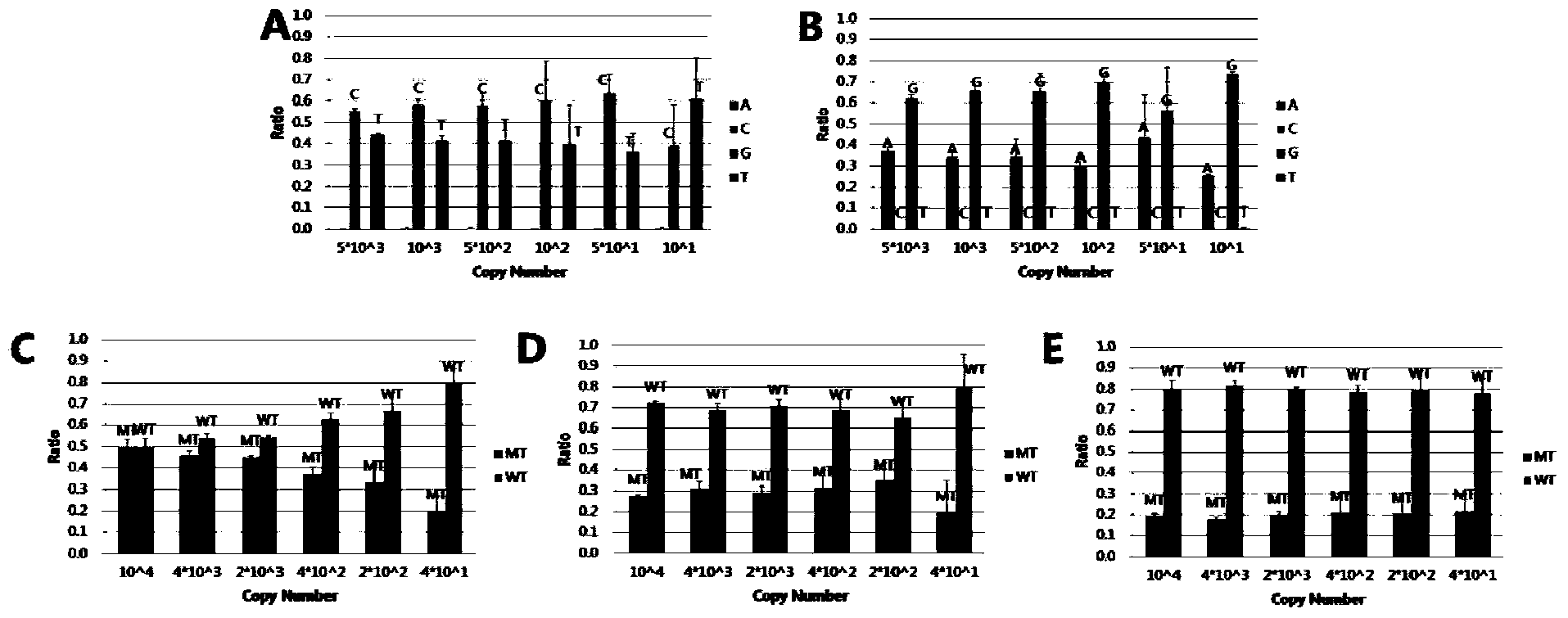
SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) detection method based on high-flux sequencing
ActiveCN104372093AHigh sensitivityFacilitate data analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementRandom mutationHigh flux
The invention discloses an SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) detection method based on high-flux sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: designing probes, carrying out pre-amplification and biotin labeling, hybridizing, connecting, carrying out Barcode specific primer amplification, sequencing, and analyzing SNP site information of the sample according to the sequencing result. The experiment proves that the method enhances the sensitivity of the system, is simple in sample labeling, eliminates the influence of the non-specific amplification product in the pre-amplification so as to be beneficial to data analysis, is simple in the library establishment method, lowers the probability of template random mutation, greatly lowers the sequencing cost, is easy for data analysis, is flexible for site selection and is very suitable for large-scale sample screening on a medium quantity of mutant sites.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Kit, device and method for detecting copy number of embryo chromosomes
ActiveCN102108406ALess bloodReduced number of sequencesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationEmbryo
The invention relates to a kit, device and method for detecting the copy number of embryo chromosomes. By using the kit, device and method provided by the invention, the copy number of embryo chromosomes can be detected non-invasively and economically. The inventor finds that most embryo DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) in maternal plasma are 100bp-250bp segments and the ratio of each chromosome to the whole DNA is equal to the ratio of each chromosome to the DNA at any point or in any interval within the range of 100bp to 250bp in the maternal plasma. According to the method provided by the invention, the copy number of chromosomes to be detected can be determined by simply confirming which chromosome each DNA segment of the DNA at any point or in any interval within the range of 100bp to 250bp comes from, calculating the ratio of the number of DNA segments from the chromosomes to be detected to the number of DNA segments from reference chromosomes in all the DNAs at any point or in any interval within the range of 100bp to 250bp in the same sample, calculating the differences among the samples and determining according to the difference values.
Owner:HANGZHOU BERRYGENOMICS GENE DIAGNOSIS TECH
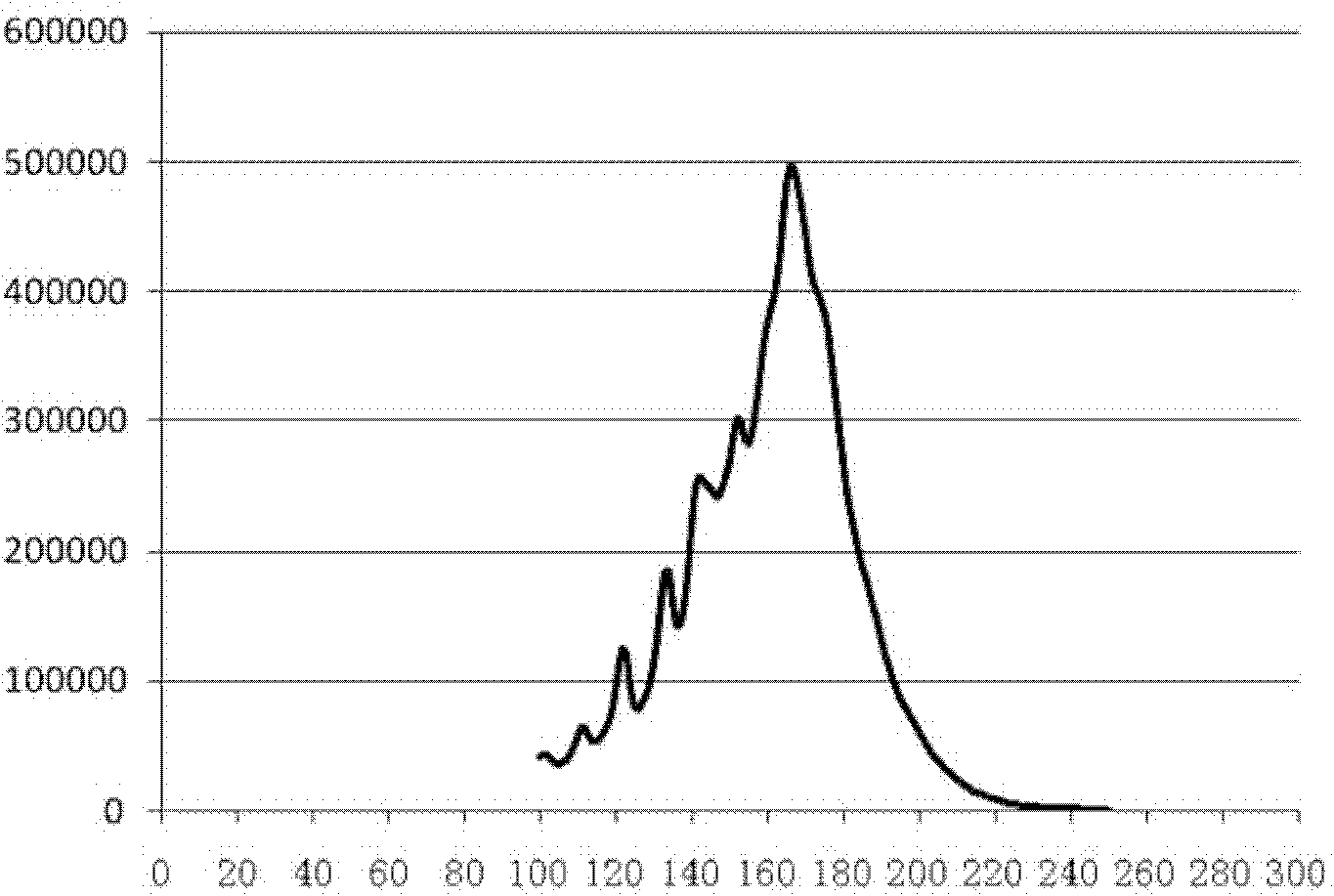
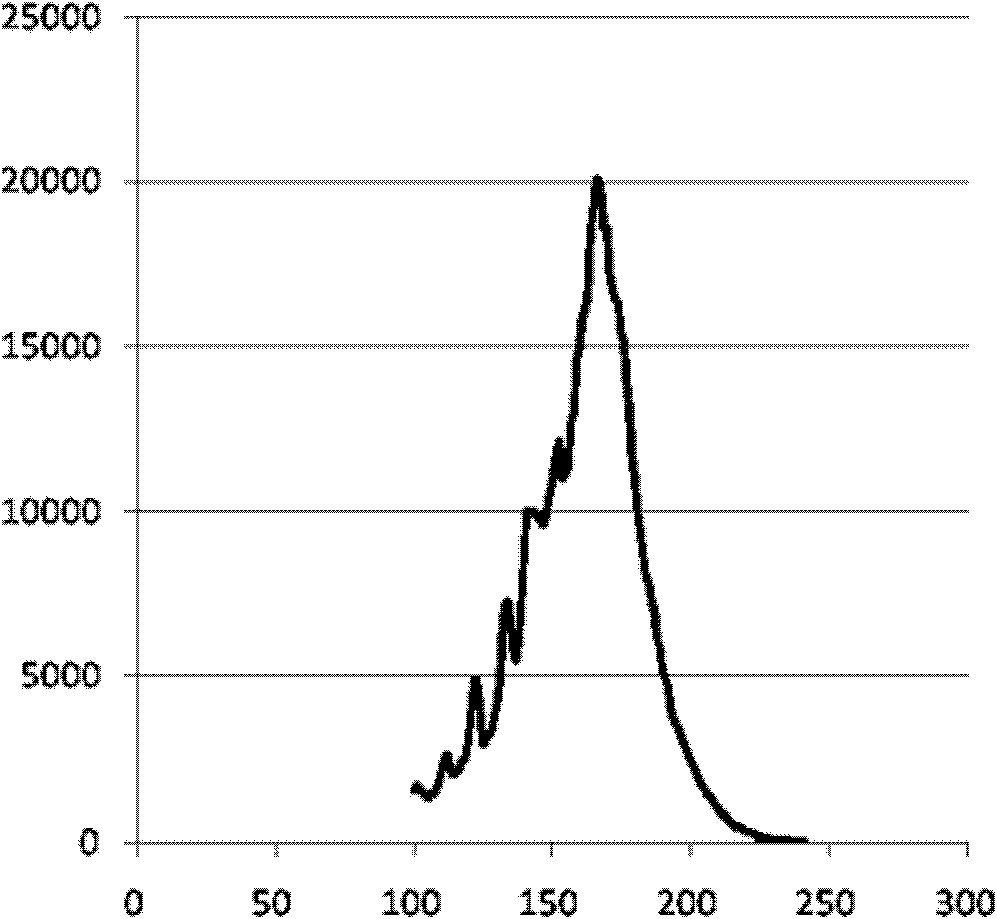
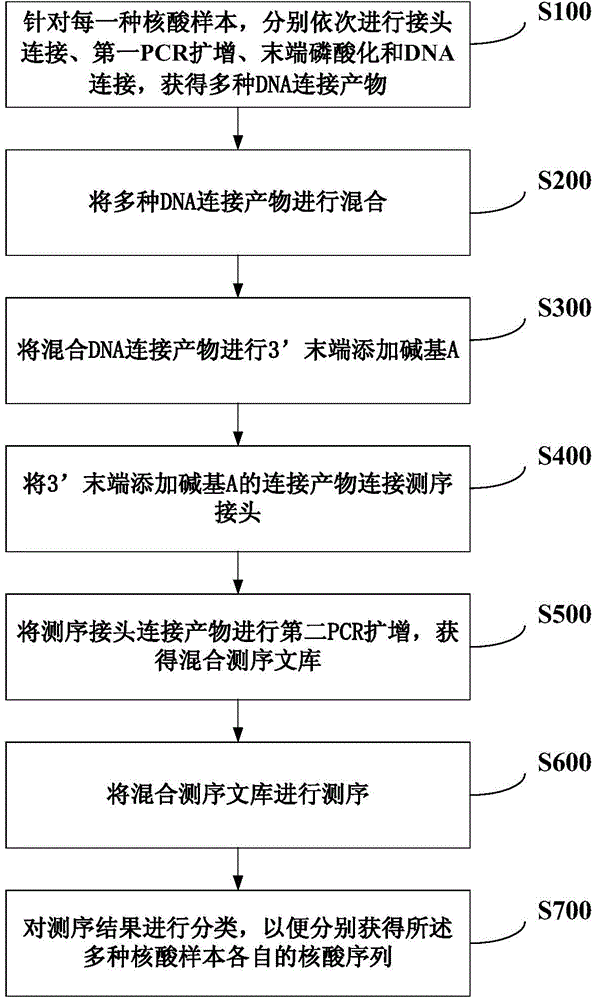
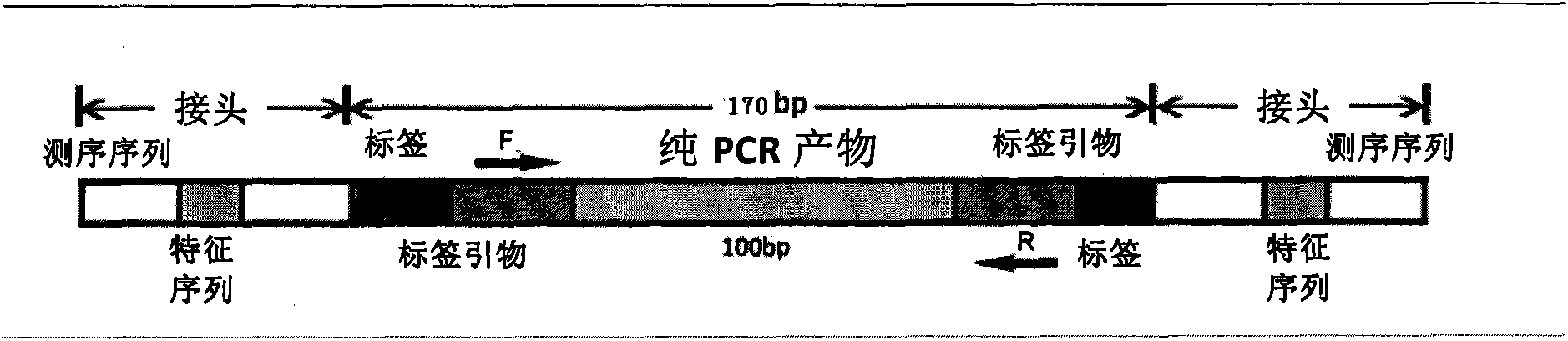
Method for simultaneously sequencing a plurality of nucleic acid samples
InactiveCN103602726AThe sequencing results are accurateGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorylationNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously sequencing a plurality of nucleic acid samples, which comprises: respectively performing adaptor ligation, first PCR amplification, terminal phosphorylation, and DNA ligation in order of the plurality of nucleic acid samples; mixing the plurality of DNA ligation products; adding a base A at the 3'-terminal of the mixed DNA ligation products; connecting the ligation products with the 3'-terminal added with the base A to a sequencing interface; performing second PCR amplification of the sequencing interface-connected products to obtain a mixed sequencing library of the plurality of nucleic acid samples; sequencing the mixed sequencing library; and classifying the sequencing results to respectively obtain respective nucleic acid sequences of the plurality of nucleic acid samples. The method of the invention can simultaneously perform sequencing of a plurality of nucleic acid samples, is accurate in sequencing results, good in repeatability, low in cost, and high in efficiency, makes full use of sequencing flux, and is especially suitable for blood free DNA samples.
Owner:田埂
DNA molecular label for high-throughput detection of human papilloma virus
ActiveCN101921748AImprove throughputLow cost detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHpv detectionDNA
The invention relates to a detection method of human papilloma virus (HPV), in particular to the HPV detection method based on the Solexa sequencing method.
Owner:上海华大基因科技有限公司
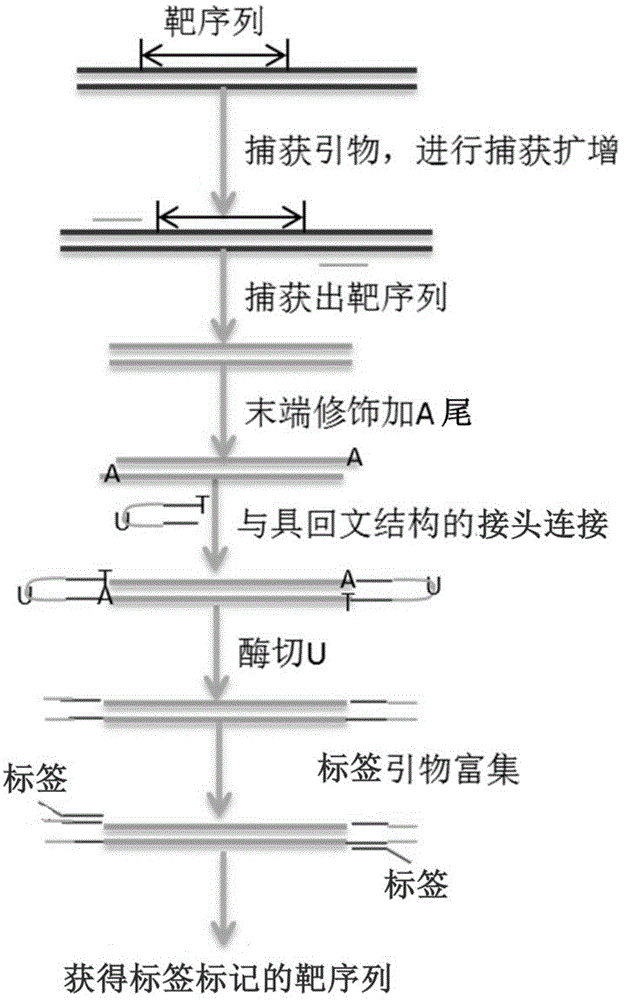
Method and kit for detecting one or more target sequence of multiple samples based on high-throughput sequencing
The invention provides a method or a kit for capturing and labeling one or more target sequences of multiple samples based on high-throughput sequencing. A novel labeling technical scheme is provided by integrating a multiplex amplification technology, a ligation technology and a PCR-index (polymerase chain reaction-index) technology; the target sequences are amplified by virtue of specific capturing primers; by virtue of a ligation reaction, an adaptor, which is provided with a U base and has a known sequence, is introduced to each of two ends of a PCR product; the U bases are cut open by virtue of a USER enzyme; PCR primers are designed in accordance with the known sequences of the adaptors; tag primers are separately introduced to two ends of the PCR product by virtue of a PCR reaction; sample information of the PCR product can be specifically obtained by virtue of the sequences of the tag primers which are introduced to two ends of the PCR product; and then, in accordance with the sequence of the capturing primer of each of the target sequences, a corresponding sequencing result is correspondingly applied to each of the target sequences of the samples.
Owner:大连晶泰医学检验实验室有限公司
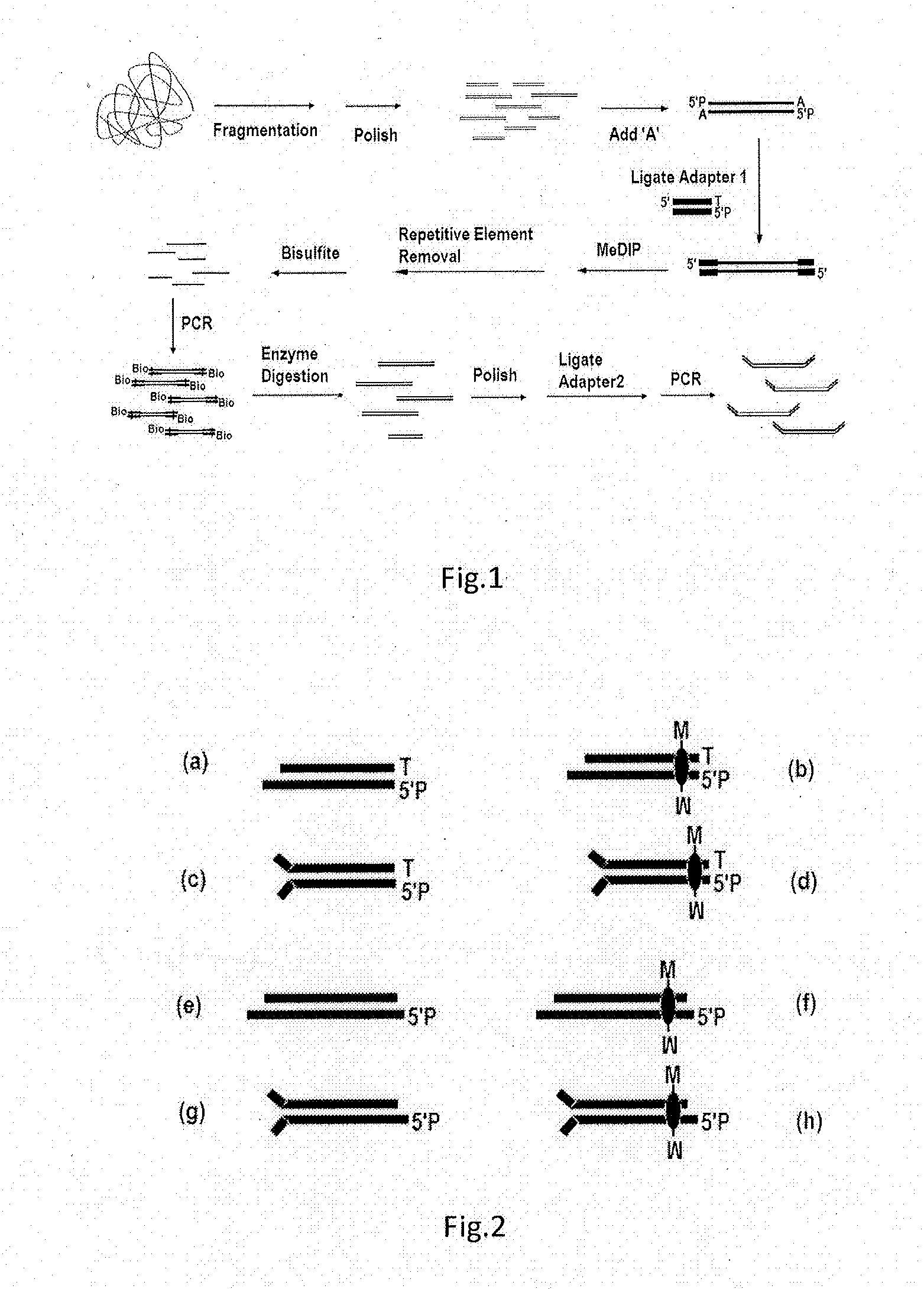
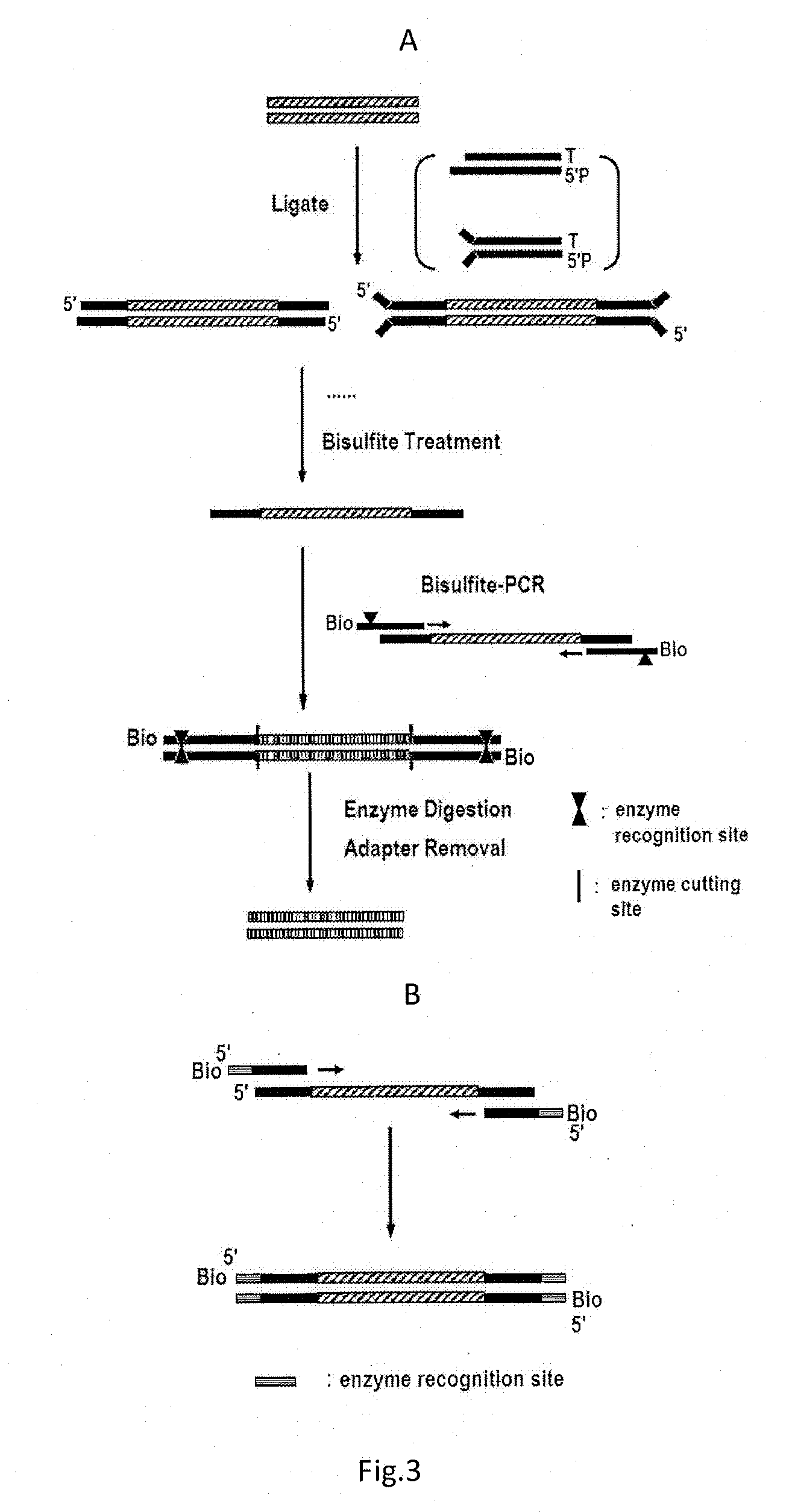
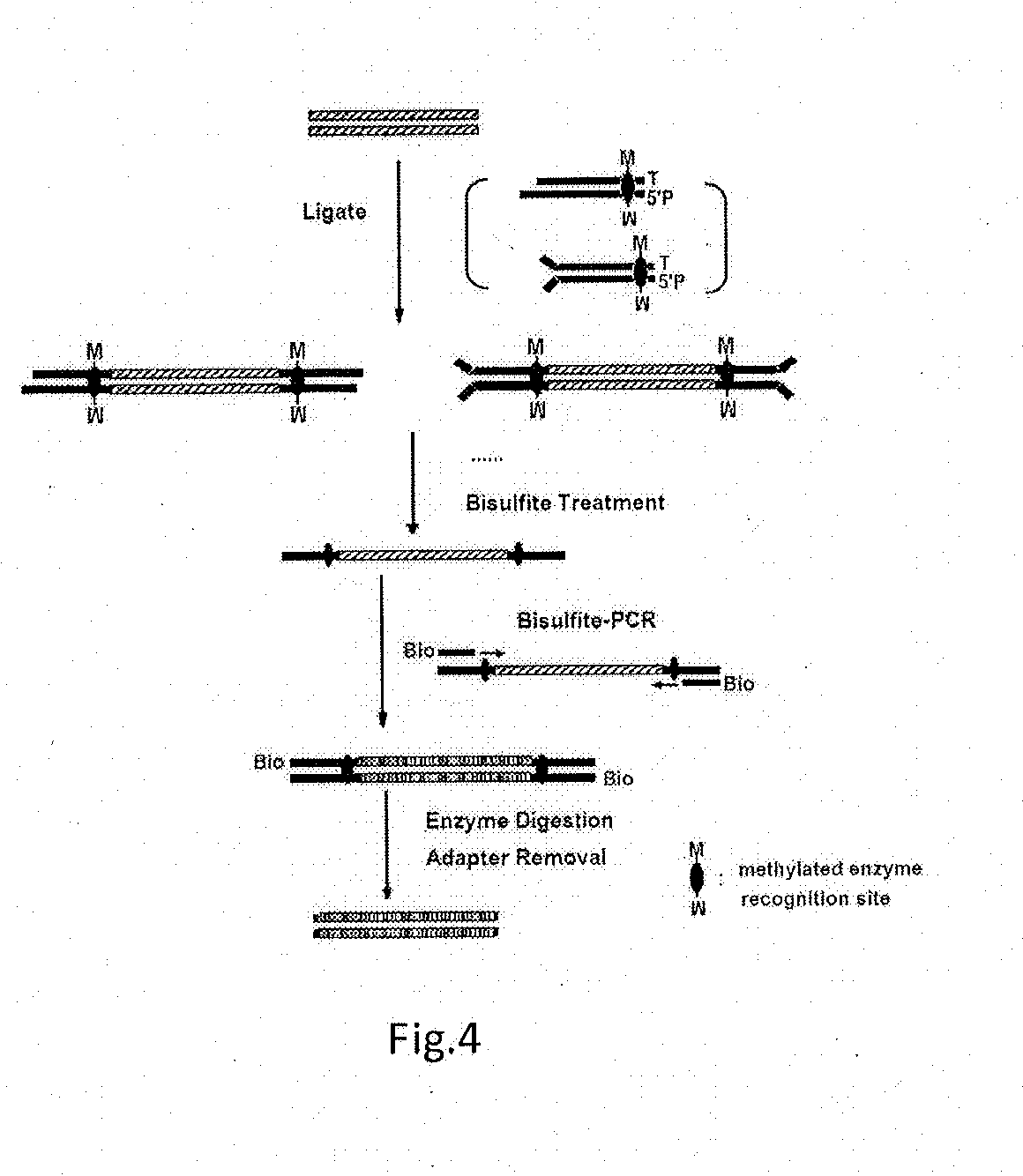
High-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA and use thereof
ActiveUS20130244885A1Improve digestion efficiencyDigestion efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRepetitive SequencesMethylated DNA immunoprecipitation
The present invention provides a high-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA, and use thereof. Particularly, the present invention provides a high-throughput sequencing method for methylated DNA, which combines methylated DNA immunoprecipitation, removal of repetitive sequences, and bisulfite treatment. The site of sequencing library will be decreased, and the cost will be reduced by using the method disclosed in the present invention.
Owner:INST OF PSYCHOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
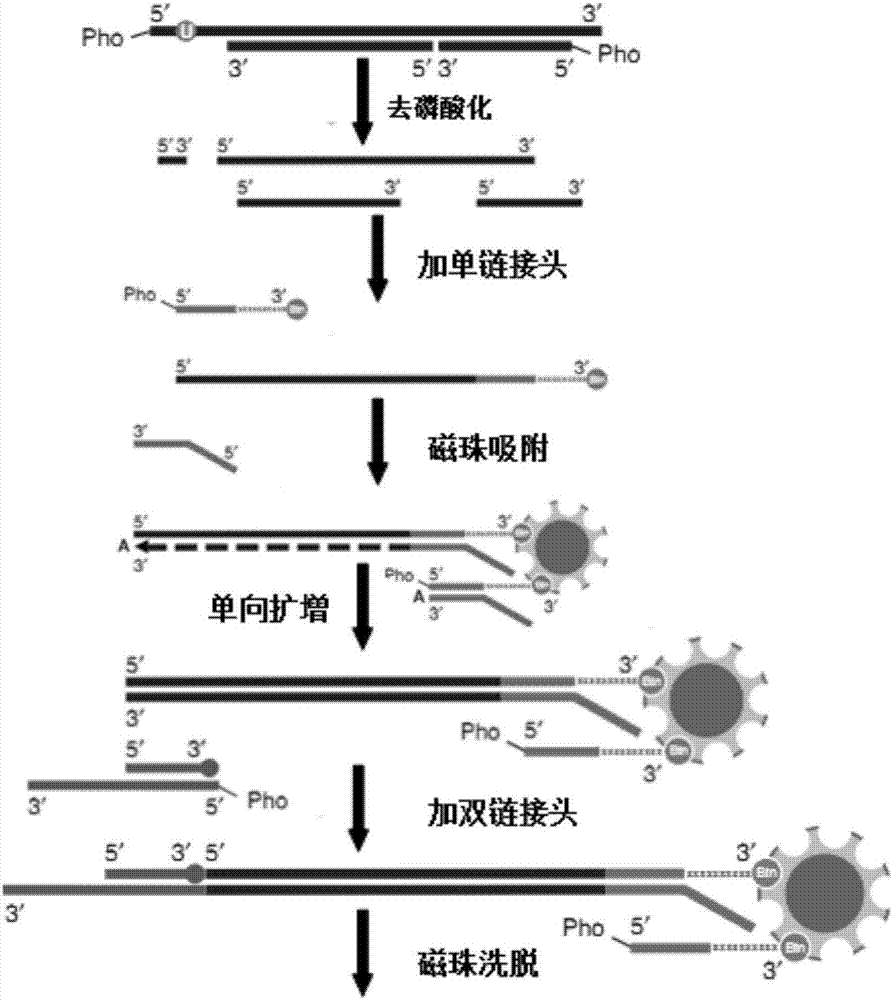
Linker, primer group and kit for cfDNA library construction and library construction method
InactiveCN106867995AAvoid lossEasy to operateNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorylationMolecular genetics
The invention belongs to field of molecular genetics, and particularly relates to a linker, a primer group and a kit for cfDNA library construction and a library construction method. The linker comprises a single-chain linker A and a double-chain linker B; the primer group comprises a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.4-6; the kit comprises the linker and the primer group; the library construction method comprises the following steps: (1) dephosphorylating and denaturating cfDNA, to obtain the single-chain cfDNA; (2) connecting the single-chain cfDNA with a single-chain linker A with a modified 3'terminal, to obtain a single-chain connecting product with a modified 3'terminal; (3) unidirectionally amplifying a first-time connecting product, to obtain a double-chain cfDNA; (4) connecting the double-chain cfDNA with a double-chain linker B, to obtain a double-chain connecting product; (5) removing one chain with modified 3'terminal in the double-chain connecting product; and (6) performing library quality inspection. According to the linker, the primer group and the kit for cfDNA library construction and library construction method, the cfDNA is firstly denaturated so that the double chain is changed to single chain, then the single chain is connected with the linker through a single-chain connecting enzyme so as to cause almost all cfDNA to be captured, the loss of cfDNA can be avoided, and further the detection sensitivity can be improved.
Owner:ANHUI ANKE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GRP) CO LTD
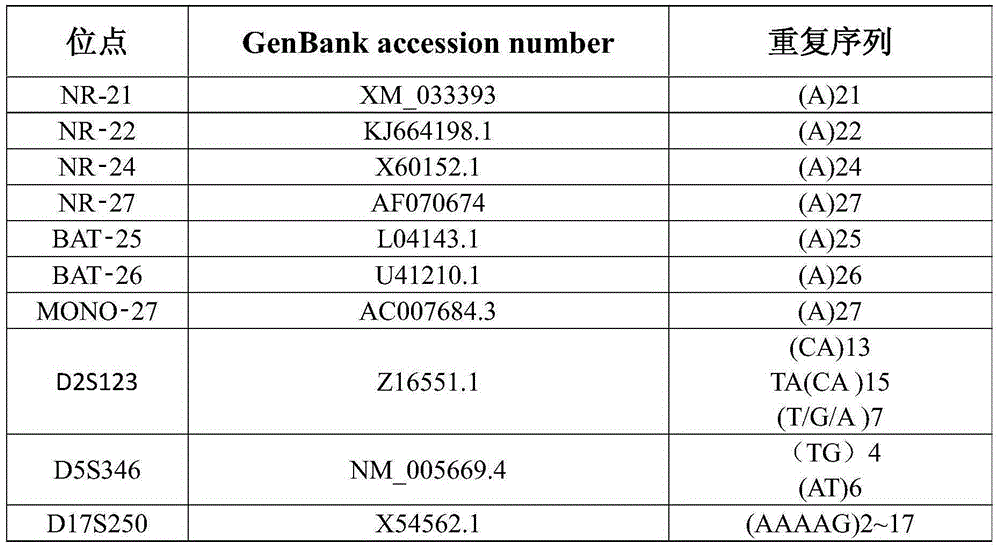
Colon cancer microsatellite instability detection kit based on next generation sequencing platform
InactiveCN105256057AImprove throughputHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosatellite StableEnzyme
The invention discloses a colon cancer microsatellite instability detection kit based on a next generation sequencing platform. The colon cancer microsatellite instability detection kit comprises 4.5-6.5mu l of a primer panel solution, wherein the concentration of solute in the primer panel solution is 45-55 mmole / L; the primer panel solution comprises primers of 10 microsatellite loci; the kit further comprises 8-10mu l of Master Mix and 1.3-1.7ml of non-enzyme water; Master Mix comprises 3-7mu l of 10*LA Taq Buffer and 3-5mu l of 2-4mmol / L dNTPs, and 0.5-1mu l of LA Taq enzyme. By adopting the kit disclosed by the invention, all MSI loci of multiple samples can be simultaneously detected by sequencing once, influence caused by artificial operation can be reduced, and the detection result reliability can be improved.
Owner:湖南宏雅基因技术有限公司
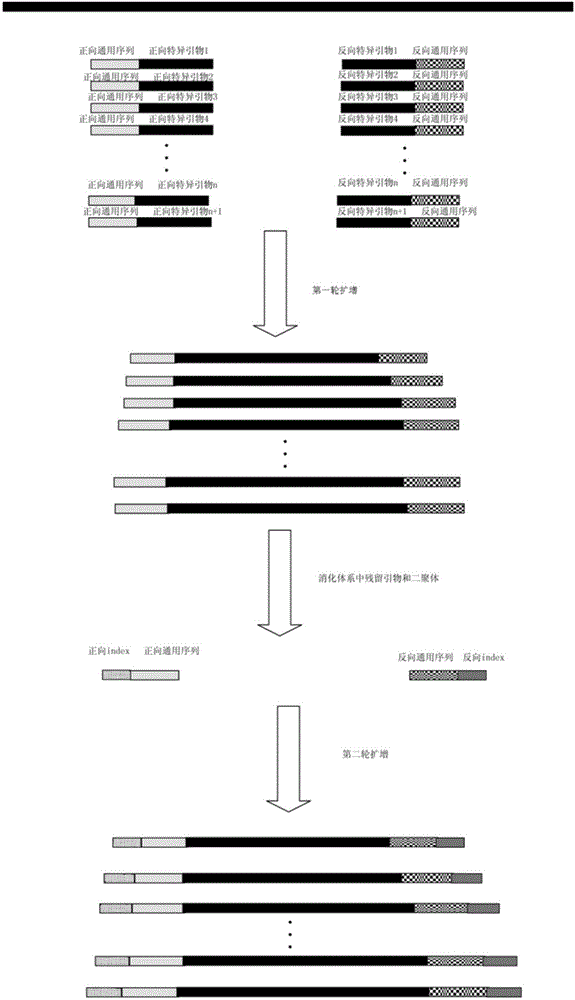
Marker based on high-throughput sequencing and method and kit for capturing one or multiple specific genes of multiple samples
ActiveCN105524983AReduce the difference in amplification efficiencyImprove effectivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementDigestionGene
The invention relates to a marker based on high-throughput sequencing and a method and a kit for capturing one or multiple specific genes of multiple samples. The method includes steps of primary amplification, primer digestion, secondary amplification, mixing, recycling, sequencing and analyzing. In the method, a mixture of a universal sequence and specific primers of all genes is adopted for primary amplification, specific sequences of all genes act in multiple amplification at this moment, and the universal sequence is added in front of each gene; a tag sequence and the universal sequence are adopted for secondary amplification, the universal sequence acts in amplification at this moment, and the tag sequence which is recognizable is added in front of a final product. By introducing a unique primer tag sequence into each sample, when the samples are detected through second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology, a sequencing result of each sample can be retrieved through the corresponding unique primer tag sequence, and the method can be applied to detecting multiple different genetic loci of a lot of samples at the same time, so that sequencing cost is lowered greatly.
Owner:DALIAN GENTALKER BIO-TECH CO LTD
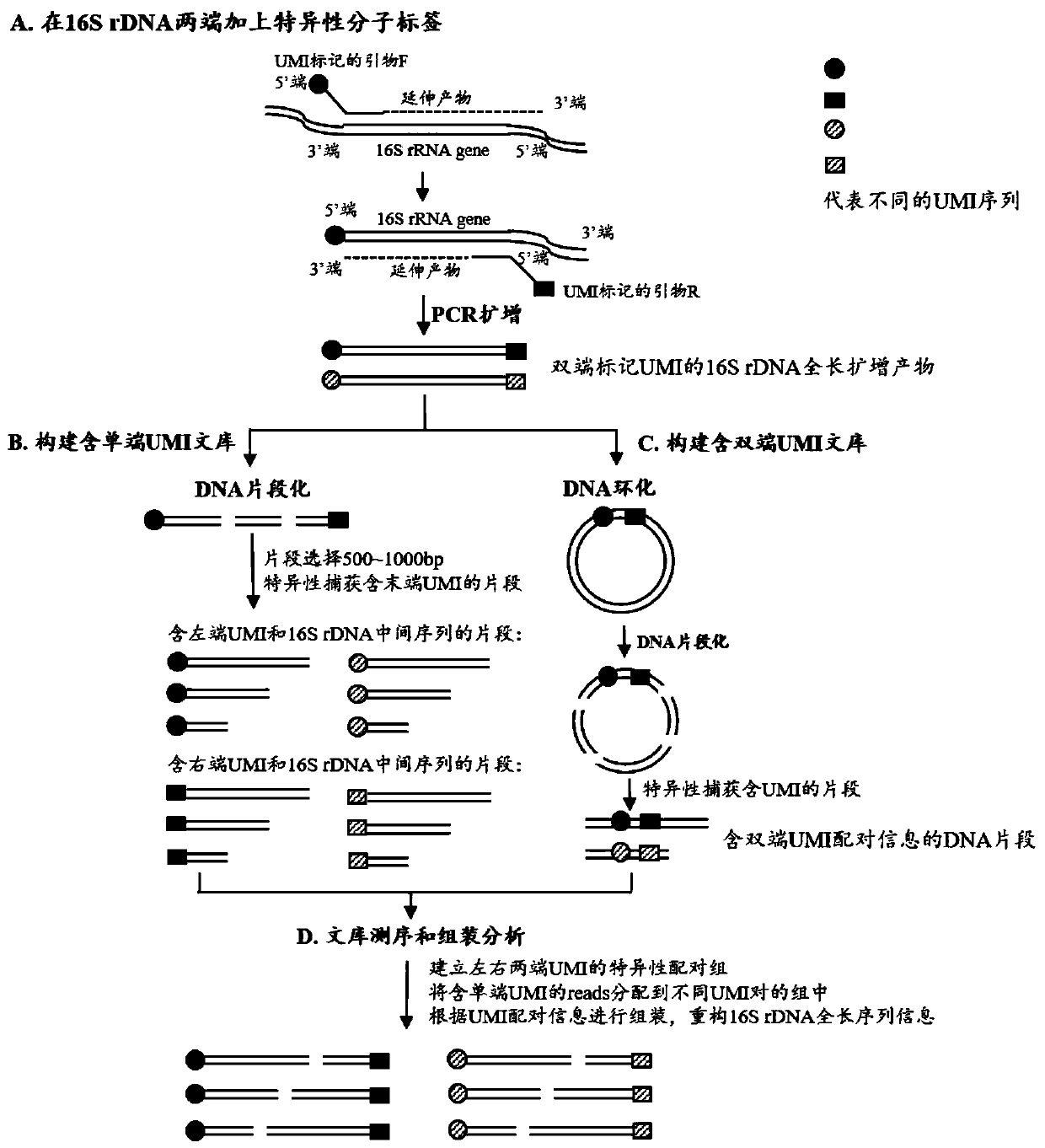
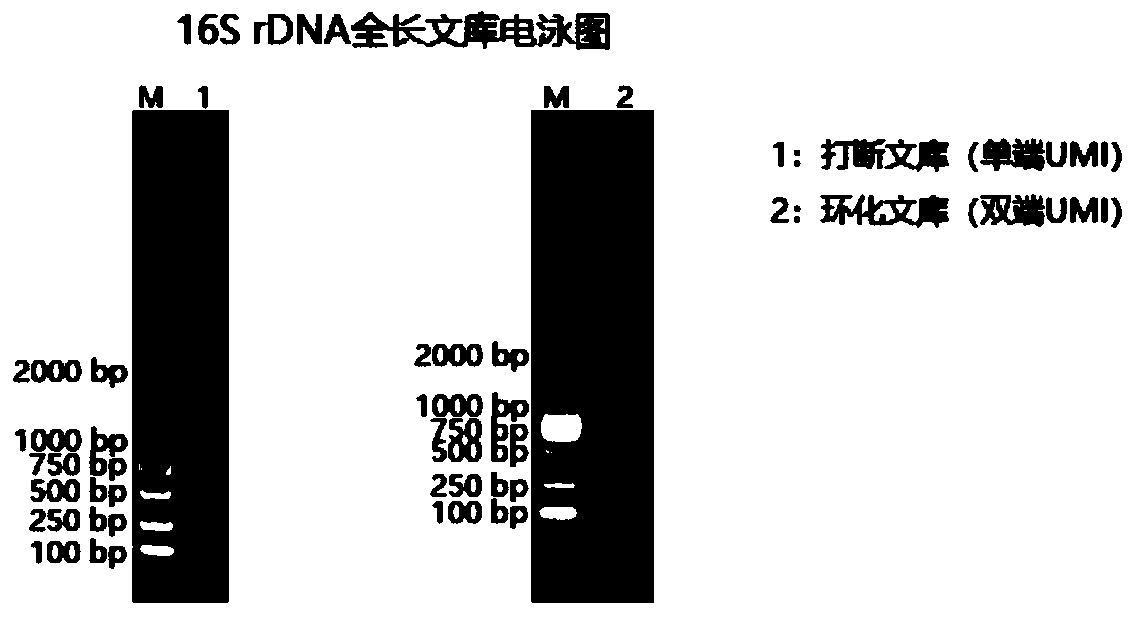
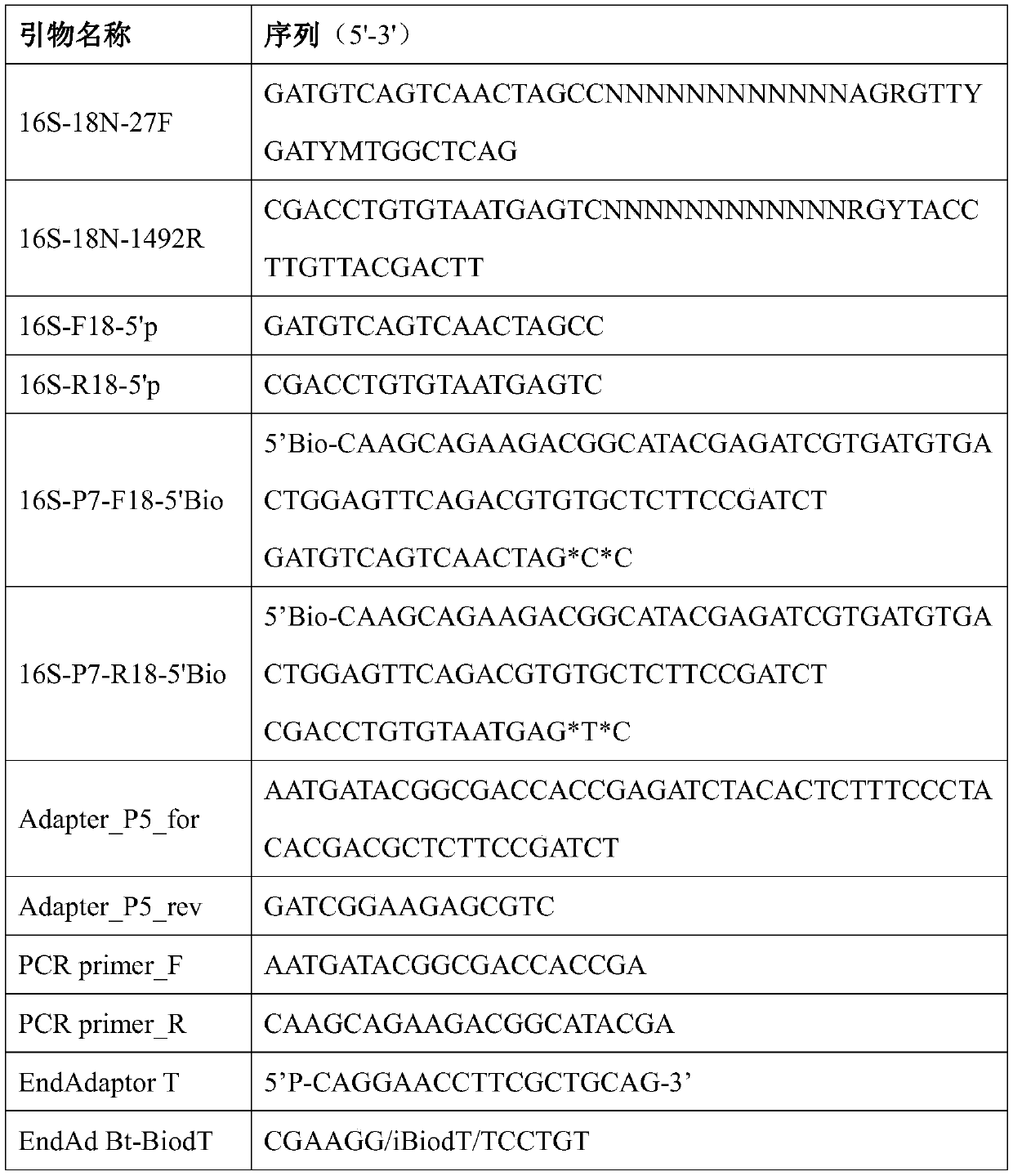
Method for constructing bacterium 16S rDNA overall-length high-throughput sequencing library
PendingCN110004210AHigh sequencing throughputLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMicroorganismBacterial 16S
The invention relates to a method for constructing a bacterium 16S rDNA overall-length high-throughput sequencing library, and relates to the field of microorganism high-throughput sequencing. The method comprises the steps of firstly, adding unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) which are composed of random base groups to the two ends of each 16S rDNA template molecule, conducting PCR amplificationto obtain multiple copied 16S rDNA overall-length amplicons with two ends containing specific UMIs, randomly breaking and connecting joints of the sequencing library, and conducting paired-end sequencing to obtain the UMI sequences and corresponding 16S rDNA fragment sequences; besides, through cyclizing of the 16S rDNA overall-length amplicons and sequencing, obtaining UMI pairing information oftwo ends of the same molecule; conducting reads assembly according to the same UMI and pairing UMI information to increase the splicing length accordingly, and finally conducting assembly to obtain 16S rDNA overall-length sequence information. The method is low in cost, high in accuracy and suitable for high-throughput sequencing platforms; meanwhile, the method can effectively eliminate the influence of PCR amplification preferences, amplification errors and sequencing errors through the UMIs, and thus the bacterium population abundance in a sample is more precisely quantified.
Owner:杭州进一生物科技有限公司
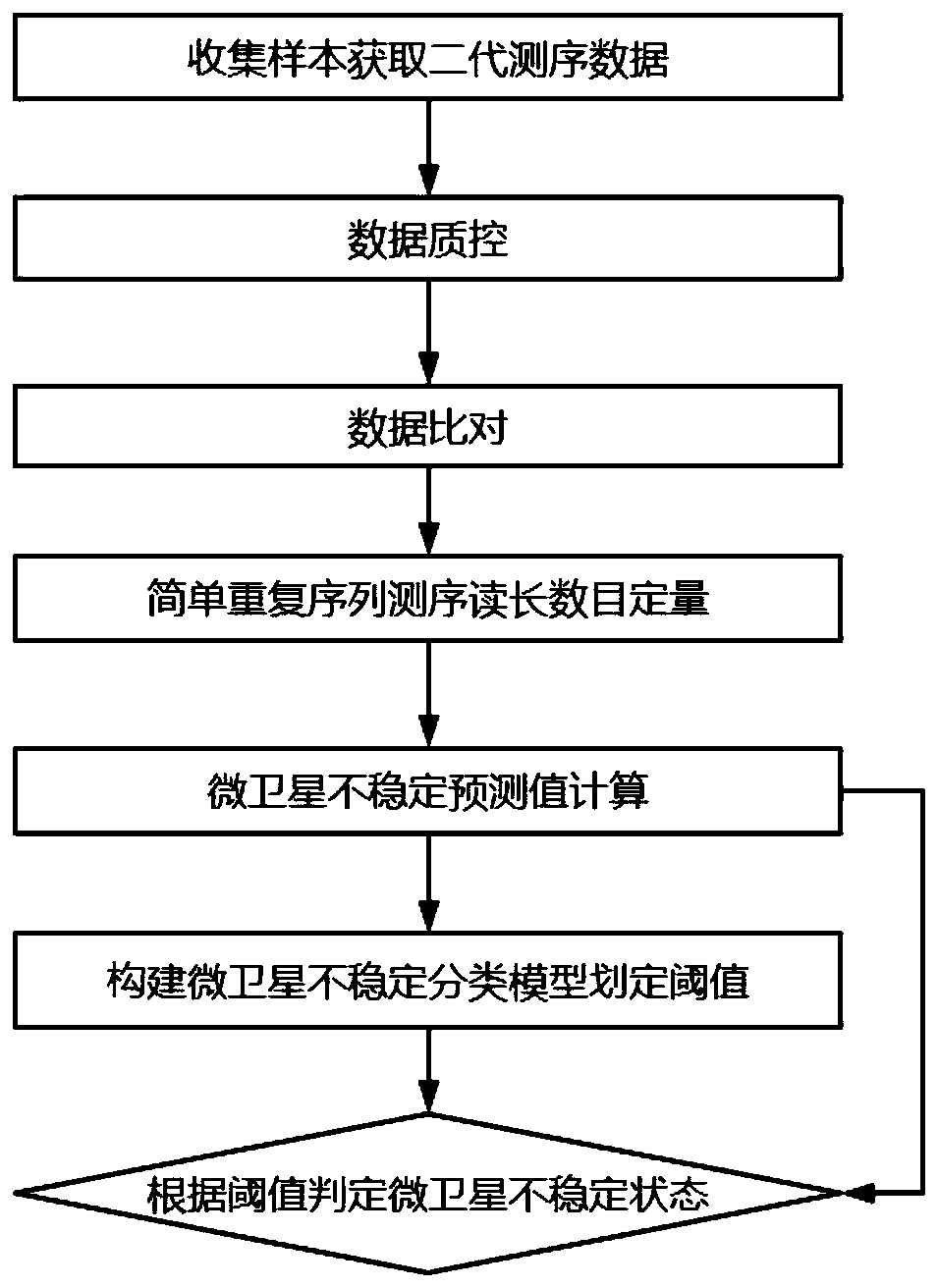
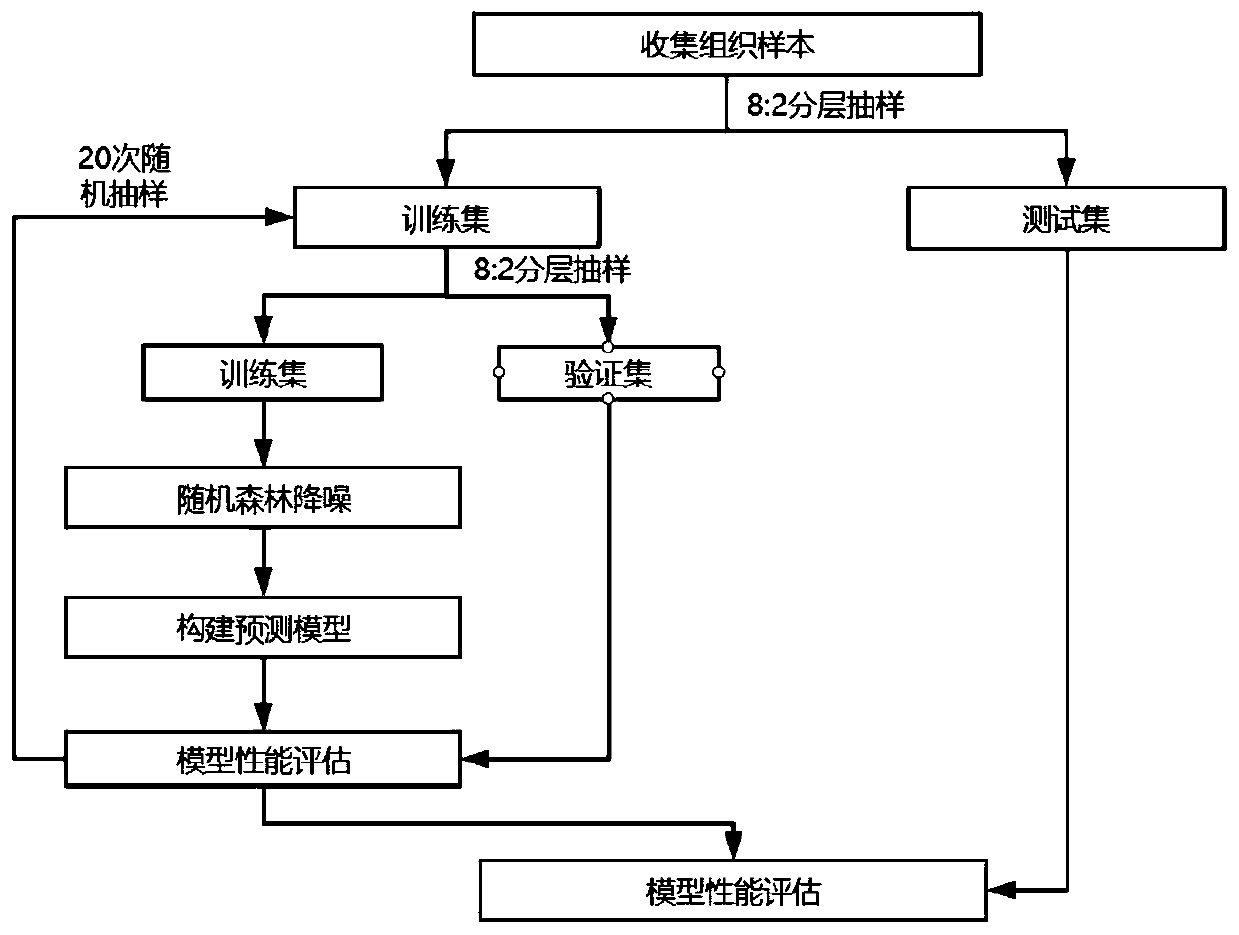
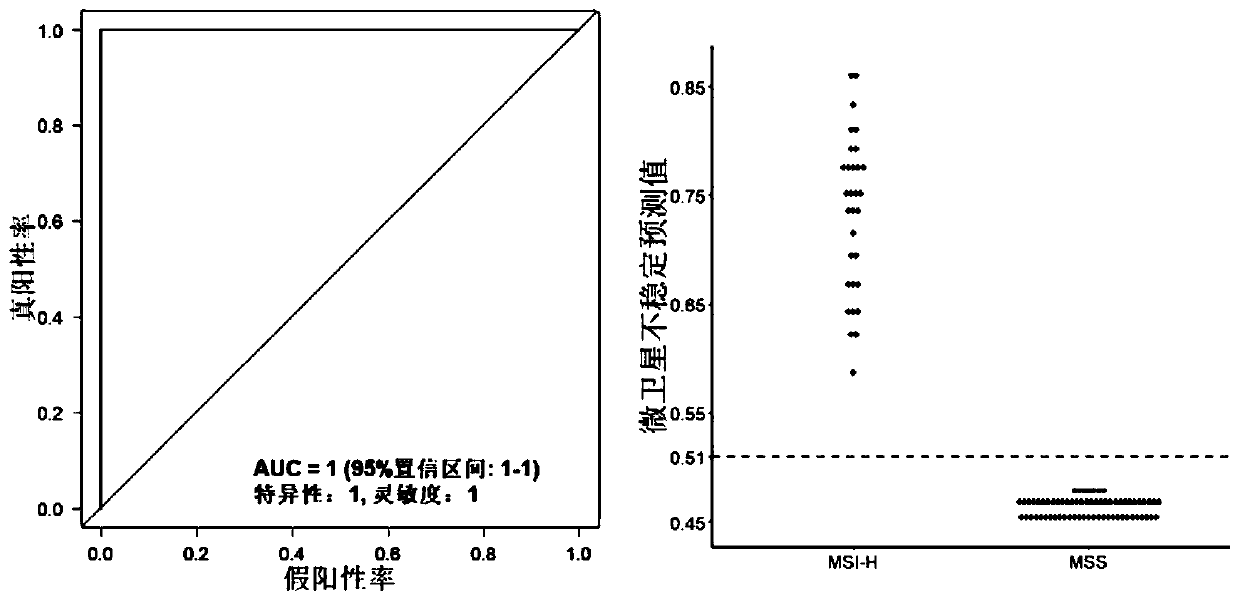
Microsatellite instability prediction method and application thereof
ActiveCN111304303AImprove performanceImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGeneticsScreening method
The invention discloses a microsatellite instability detection and prediction method, a related site screening method, a model construction method and an application. The site screening method comprises the following steps: i) determining a microsatellite instability predicted value of a candidate microsatellite site in a sample; and / or ii) screening sites or site combinations for microsatellite instability detection by using one or more indicators including the microsatellite instability predicted value of the candidate microsatellite site; wherein the microsatellite instability predicted value is a quantified value of an abundance difference between a major allele type and a minor allele type in the candidate microsatellite site. The method provided by the invention is high in accuracy,and can accurately and stably detect the MSI state only on the basis of a single tumor sample.
Owner:BERRY ONCOLOGY CO LTD
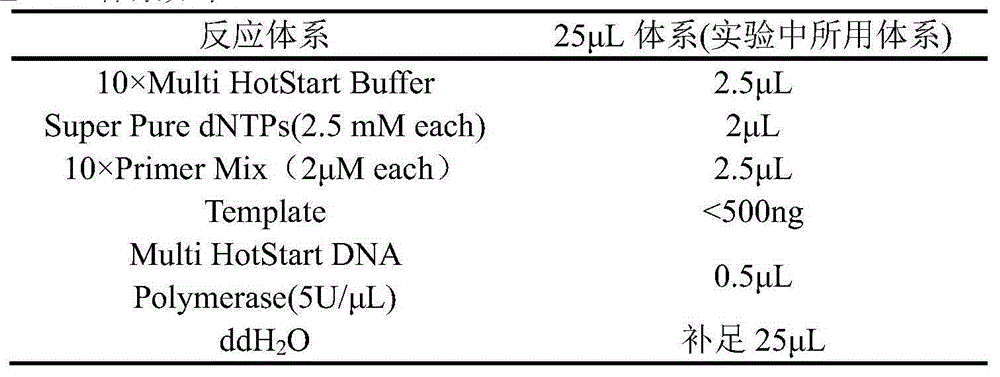
Method of direct DNA sequencing for screening hepatolenticular degeneration disease gene mutation site through PCR amplification
InactiveCN104830966AThe method is simple and fastIdentify mutation sitesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenatal diagnosisAtp7b gene
A method of direct DNA sequencing for screening a hepatolenticular degeneration disease gene mutation site through PCR amplification. The invention relates to a method of direct DNA sequencing after the PCR amplification for screening a disease mutation site of ATP7B gene, thereby providing the basis for accurately diagnosis and prenatal diagnosis of the hepatolenticular degeneration disease. The method includes the processes of primer design, genome DNA extraction, PCR amplification, PCR product purification, PCR product sequencing and sequence comparative analysis and the like, wherein the key to decide effectiveness of the method is specificity and sensitivity of the primer. The primer in the invention is strong in specificity and high in sensitivity and is wide in coverage. The method can detect the all 21 exon regions, promoter regions and partial intron regions of the ATP7B gene, and can provide firm foundation of clinical diagnosis application of the hepatolenticular degeneration through genetic detection.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU
Detection method for biomolecular probe-calibrated specific sites of DNA based on nanopore device
ActiveCN103509852AReduce difficultyShorten speedMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrolytic agentBiology
The invention discloses a detection method for biomolecular probe-calibrated specific sites of DNA based on a nanopore device and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1) calibrating the specific sites of DNA by using a biomolecular probe so as to obtain calibrated DNA; and 2) detecting the specific sites of the calibrated DNA by using a nanopore sequencing device, wherein the calibrated DNA is added into a positive electrode chamber filled with an electrolyte, an external pressure field is introduced to the positive electrode chamber during detection and is used as an external driving field for DNA perforation, voltage is applied between a positive electrode and a negative electrode and used as an external electric field with a direction opposite to the direction of the external pressure field, and an active force of the external pressure field on the DNA in a nanopore during detection is greater than an electric field force. With the method provided by the invention, secondary current signals totally different from those of common unmodified DNA are obtained, the spatial positions and sequence of modified specific sites of the DNA can be characterized through analysis and statistics of the secondary current signals, so a physical map of the long chain DNA is obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Pig 50K liquid phase chip based on targeted capture sequencing, and application thereof
ActiveCN112921076AAvoid uniformityGuaranteed specific capture rateNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPig farmsNucleotide
The invention relates to a pig 50K liquid phase chip based on targeted capture sequencing, and application thereof. The pig 50K liquid phase chip is composed of pig 50K probe mixed liquor and a hybridization capture reagent which are independently packaged; pig 50K probes are DNA double-stranded probes and are nucleotide sequences designed and synthesized according to screened SNP sites; and the SNP sites are screened by comparing the sequencing results of the whole genome of the pig to a pig reference genome. The pig 50K liquid phase chip prepared by the invention is mixed with a pig DNA high-throughput sequencing library; DNA fragments containing target sites in the pig DNA high-throughput sequencing library are captured for amplification and purification; and, after a product is subjected to high-throughput sequencing, a sequencing result is replied to a pig reference genome for comparison, so that the genotyping of the genome of a to-be-detected pig is obtained. When the 50K liquid phase chip prepared by the invention is used for genotyping pigs; and the problems of high cost, inflexibility and incapability of large-scale use in pig farms in China in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Magnetic microsphere with molecular tag sequence, and preparation method for magnetic microsphere
PendingCN112251504AImprove stabilityHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroballoon preparationMagnetic beadMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the field of the molecular biology, and particularly relates to a magnetic microsphere with a molecular tag sequence, and a preparation method for the magnetic microsphere. Amagnetic bead is taken as a molecular tag base, and a chemical bond and enzyme linking method is used for linking three-segment oligo to the magnetic bed in sequence so as to synthesize the magnetic microsphere with a unique oligo sequence. The magnetic microsphere prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention has high stability and accuracy. Meanwhile, the preparation technology of the magnetic microsphere is simple, time consumption is small, raw material sources are convenient, the cost is low, and the unicellular sequencing cost is greatly lowered. The oligo adopted by themagnetic microsphere is a known sequence, the three-segment oligo can be combined to form millions of molecular tags, batch differences are small, the stability and the accuracy of a unicellular sequencing result are obviously improved, and the magnetic microsphere can be widely applied to medical research, bioresearch and the like.
Owner:SINGLERON NANJING BIOTECHNOLOGIES LTD
Recombinant fusion protein in antibody targeting and application thereof in epigenetics
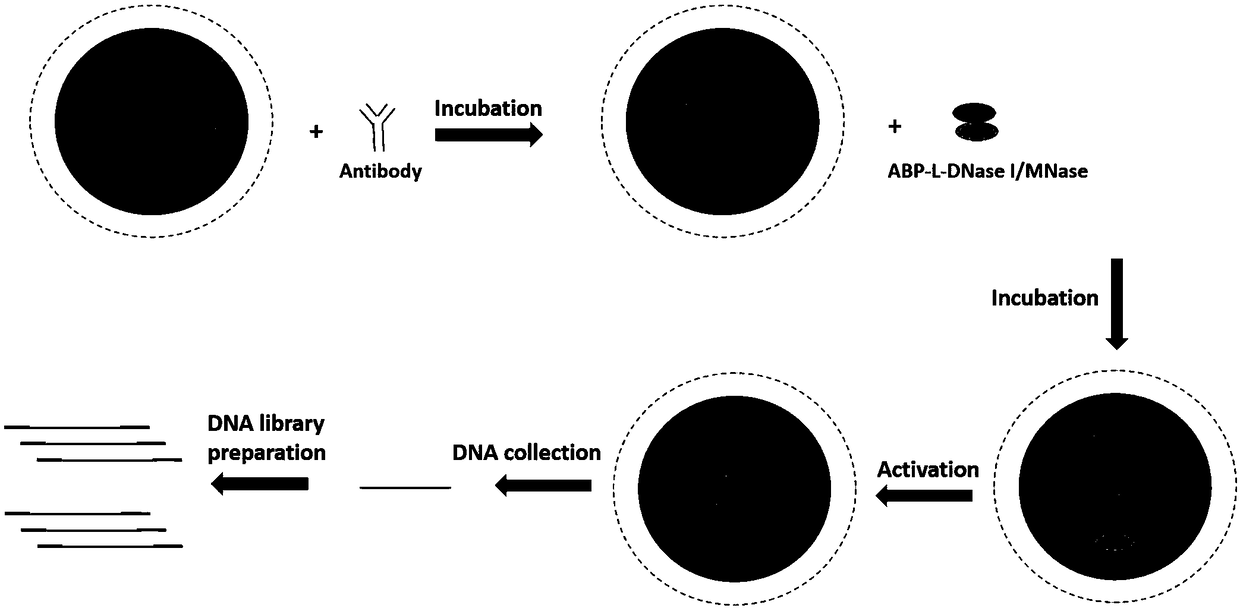
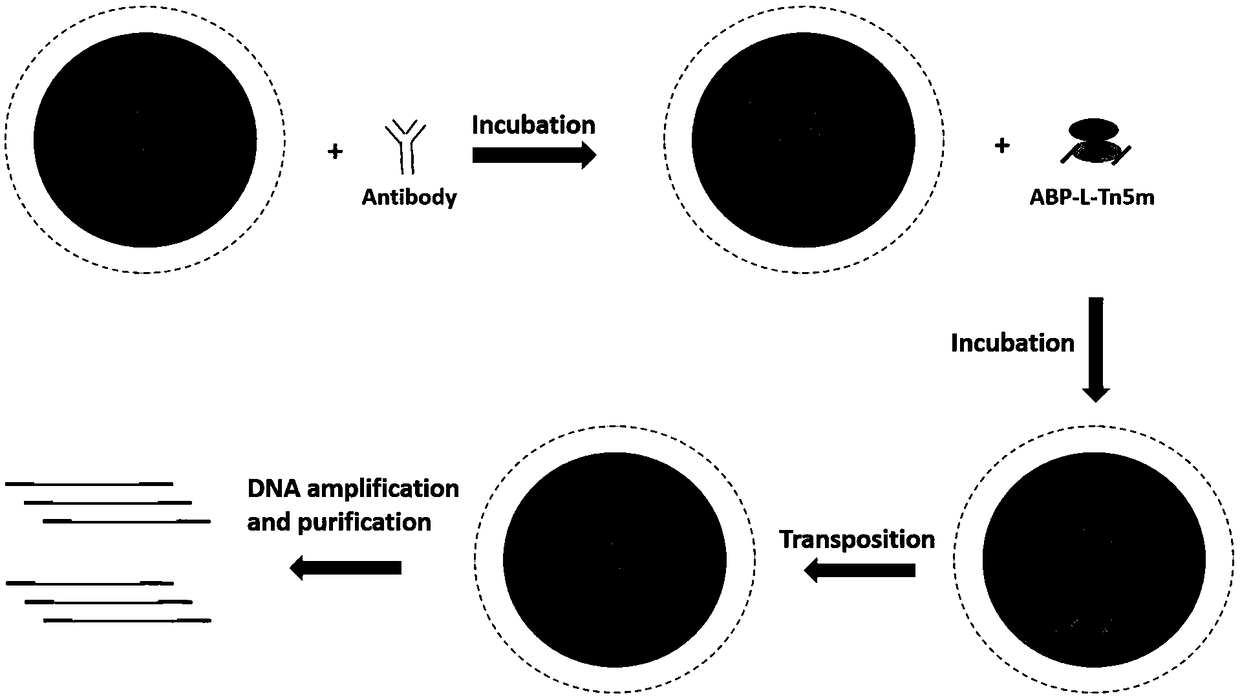
ActiveCN109400714AReduce sequencing depthReduced affinity requirementsHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEpigeneticsDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses recombinant fusion protein in antibody targeting and application thereof in epigenetics. The recombinant fusion protein comprises an ABP-L-DFE structure, wherein ABP is locatedin the N terminal of the recombinant fusion protein and represents a structure domain with a binding antibody function, L represents a connecting peptide, and DFE represents a structure domain with aDNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragmentation function. The recombinant fusion protein disclosed by the invention is capable of improving a ChIP-seq (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation-sequencing) technology,simplifying operation, increasing data quality, reducing operation difficulty and expanding the application range, particularly the application in a small amount of precious cells.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Method and kit for detecting alpha and beta thalassemia point mutation based on next generation sequencing technology
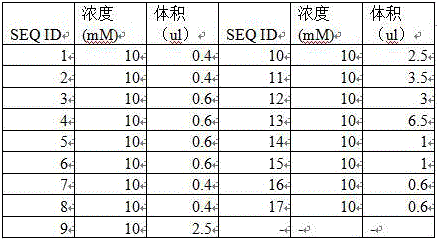
ActiveCN106755329AWide detection rangeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBeta globinBeta thalassemia
The invention relates to a method and kit for detecting alpha and beta thalassemia point mutation based on a next generation sequencing technology .In the detection method, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification primer sequences SEQ ID NO1-17 in exon, regulation and transcription regions of HBA1, HBA2 and HBB genes, PCR marker primer sequences SEQ ID NO18-115 at the 5'-terminal and PCR marker primer sequences SEQ ID NO116-213 at the 3'-terminal involved with alpha and beta thalassemia are included. The detection method comprises the following detection steps: (1) constructing a next generation sequencing library; (2) purifying the next generation sequencing library; (3) sequencing through a next generation sequencer; and (4) performing bioinformatic analysis to obtain a result. The kit for detection comprises the above-mentioned primer sequences and the next generation sequencer solexa. The detection method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation steps, high detection specificity, wide detection range, low cost and the like.
Owner:MATERNAL & CHILD HEALTH HOSPITAL OF GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com