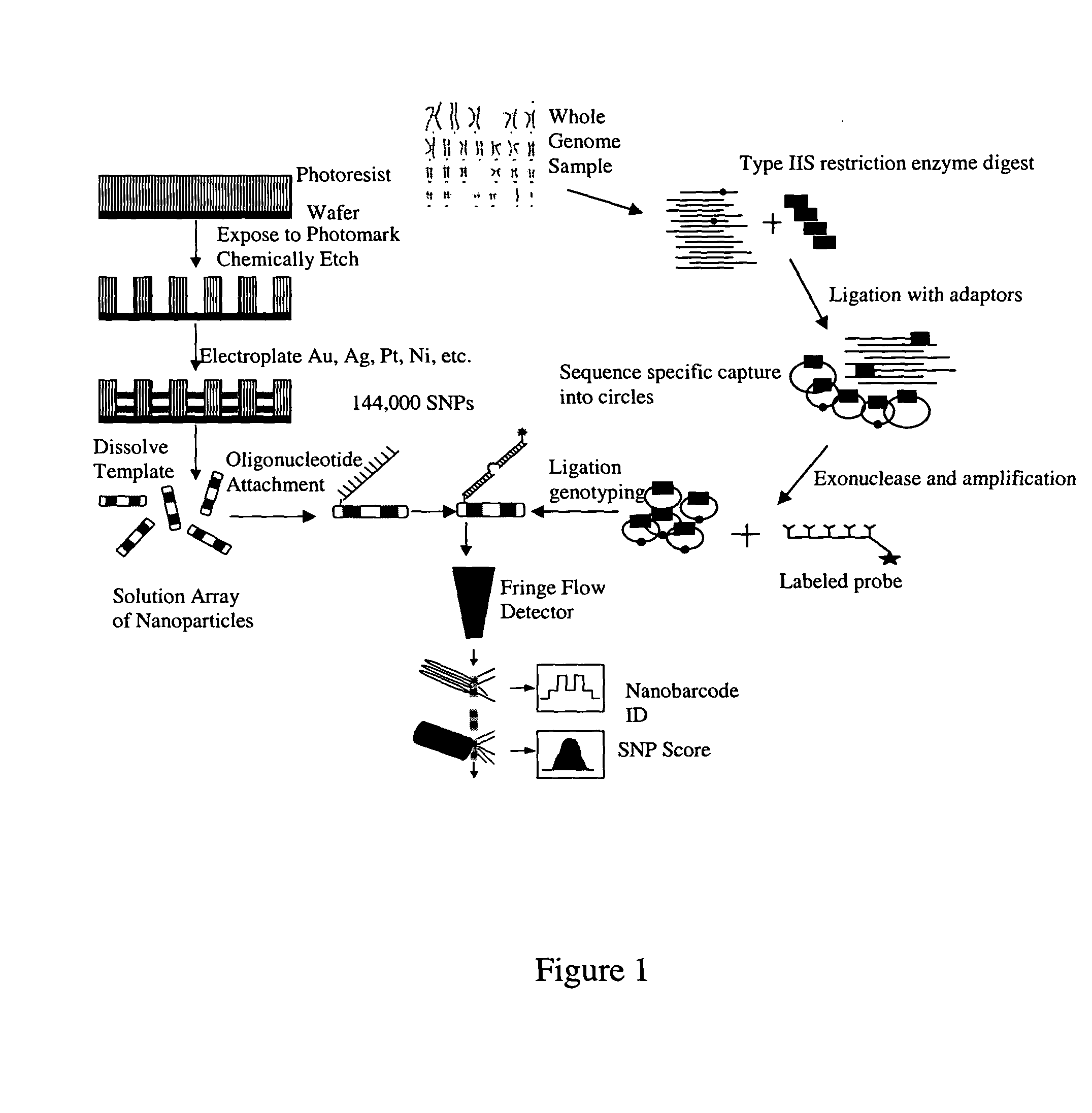
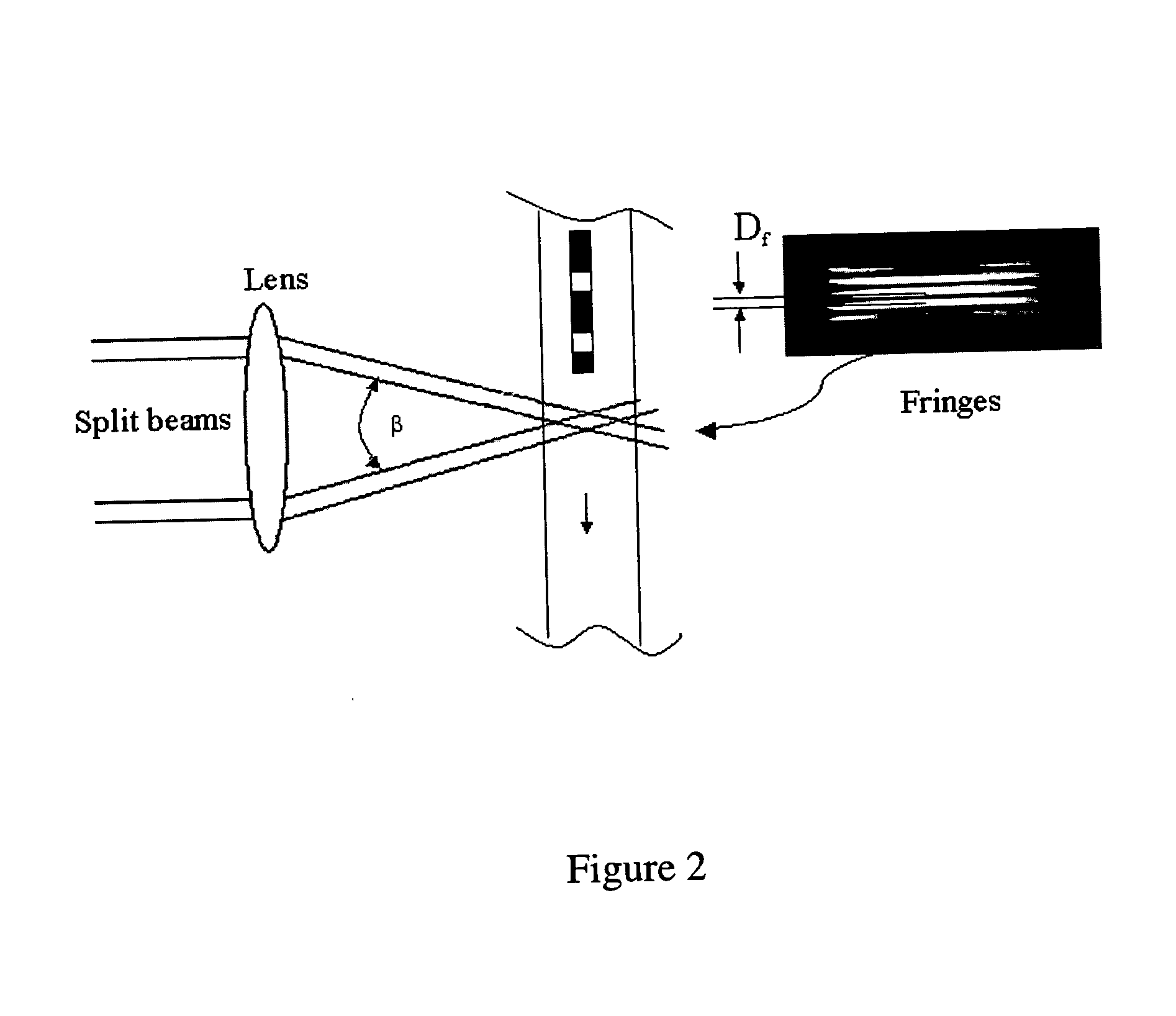
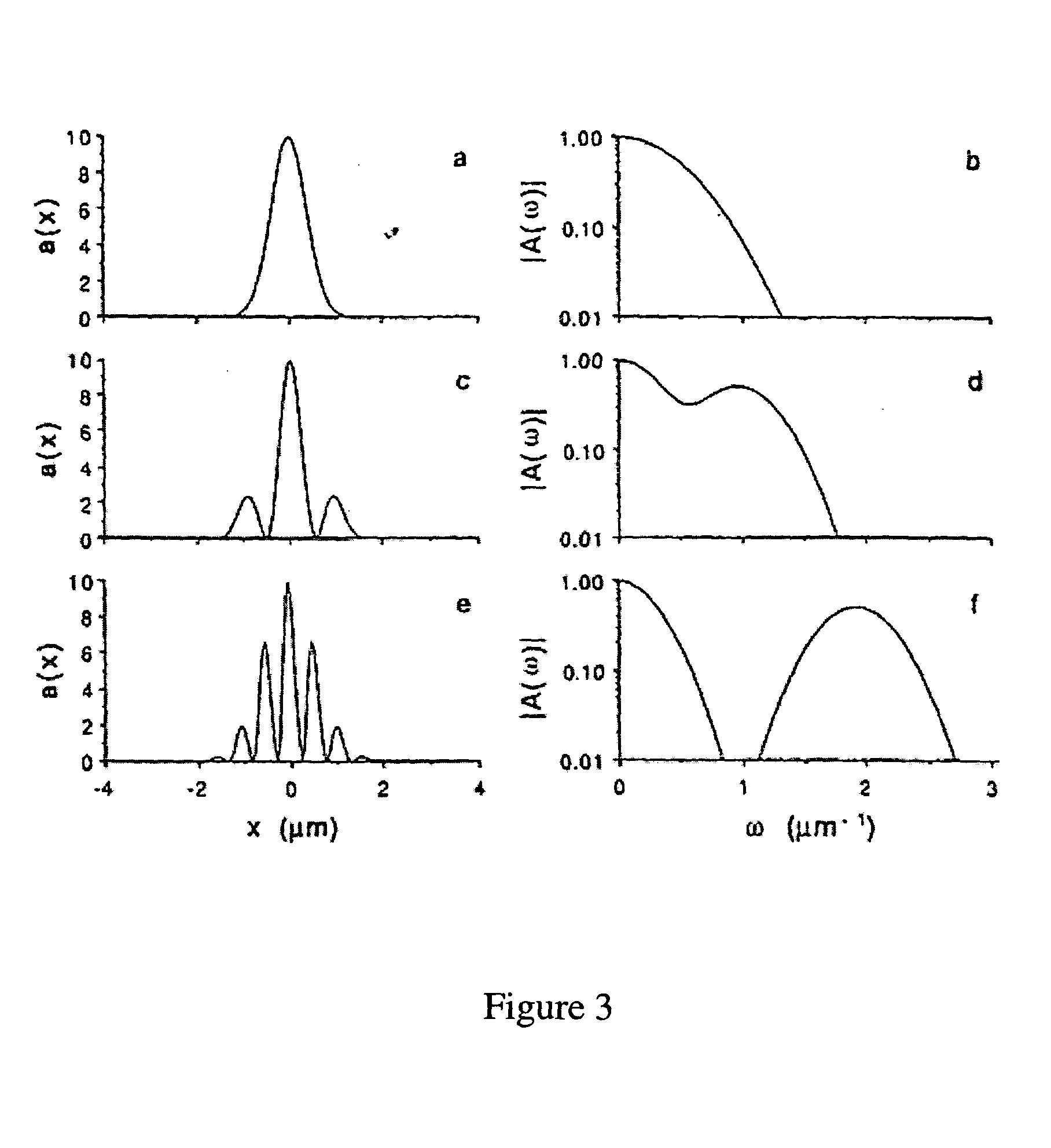
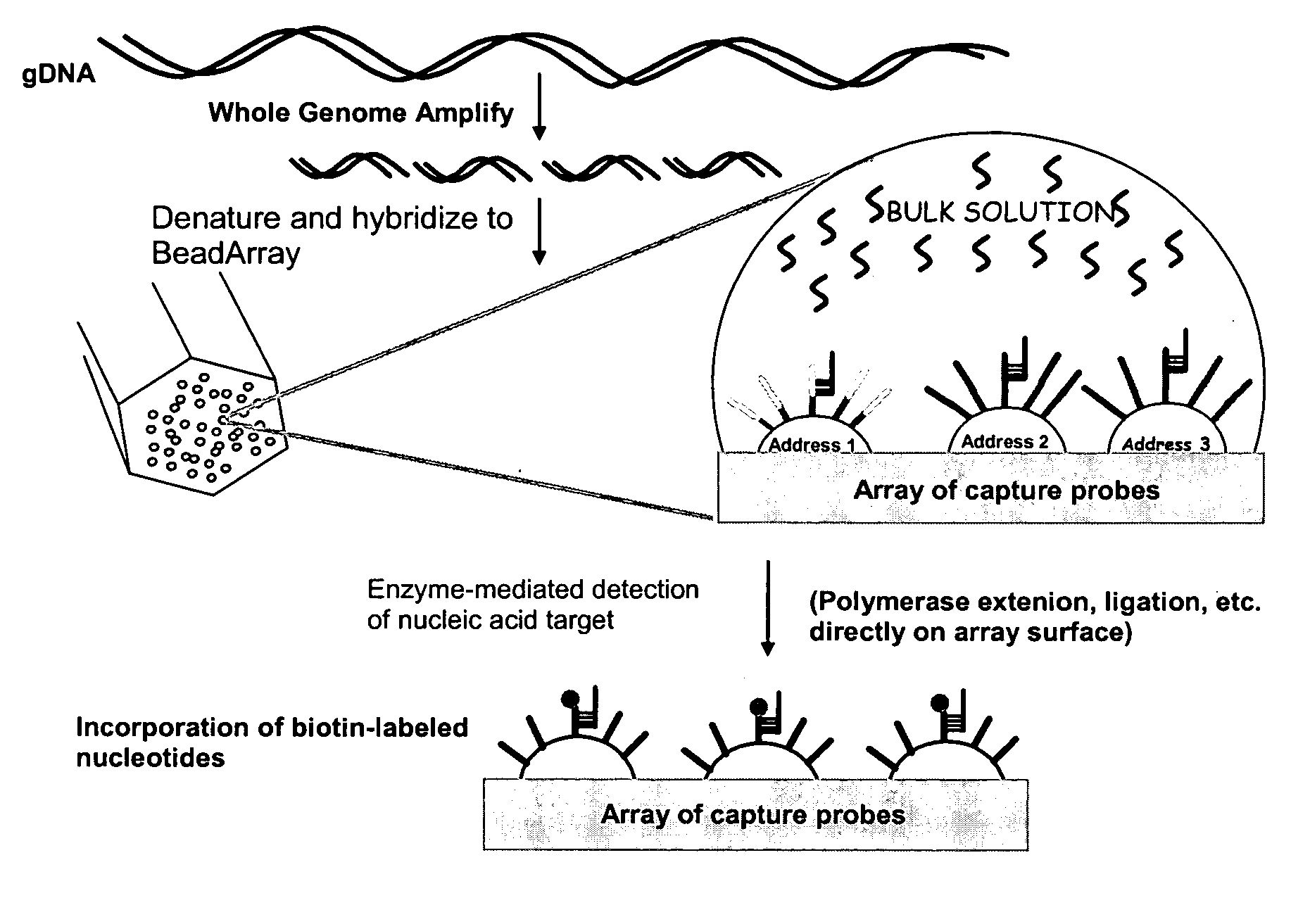
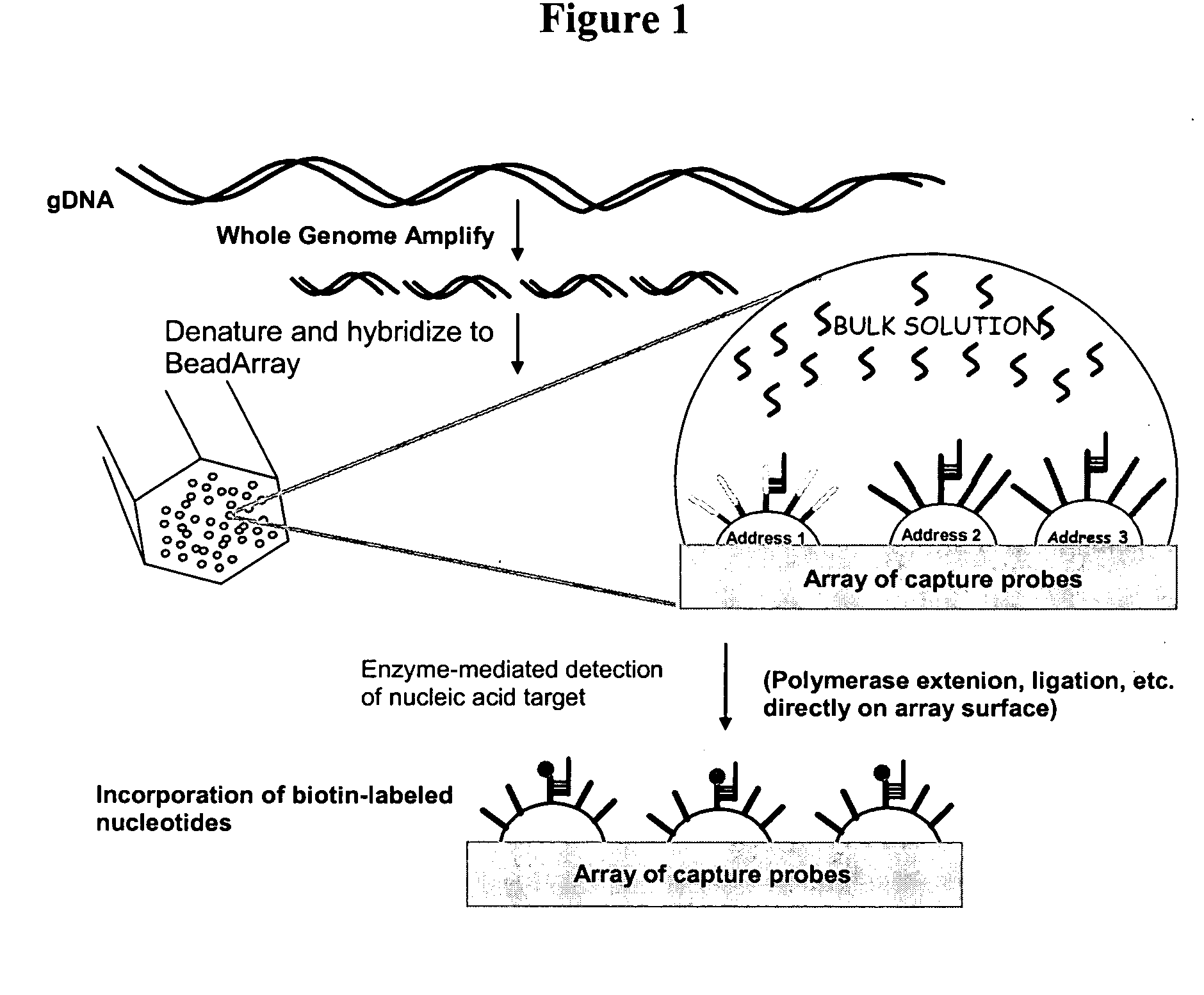
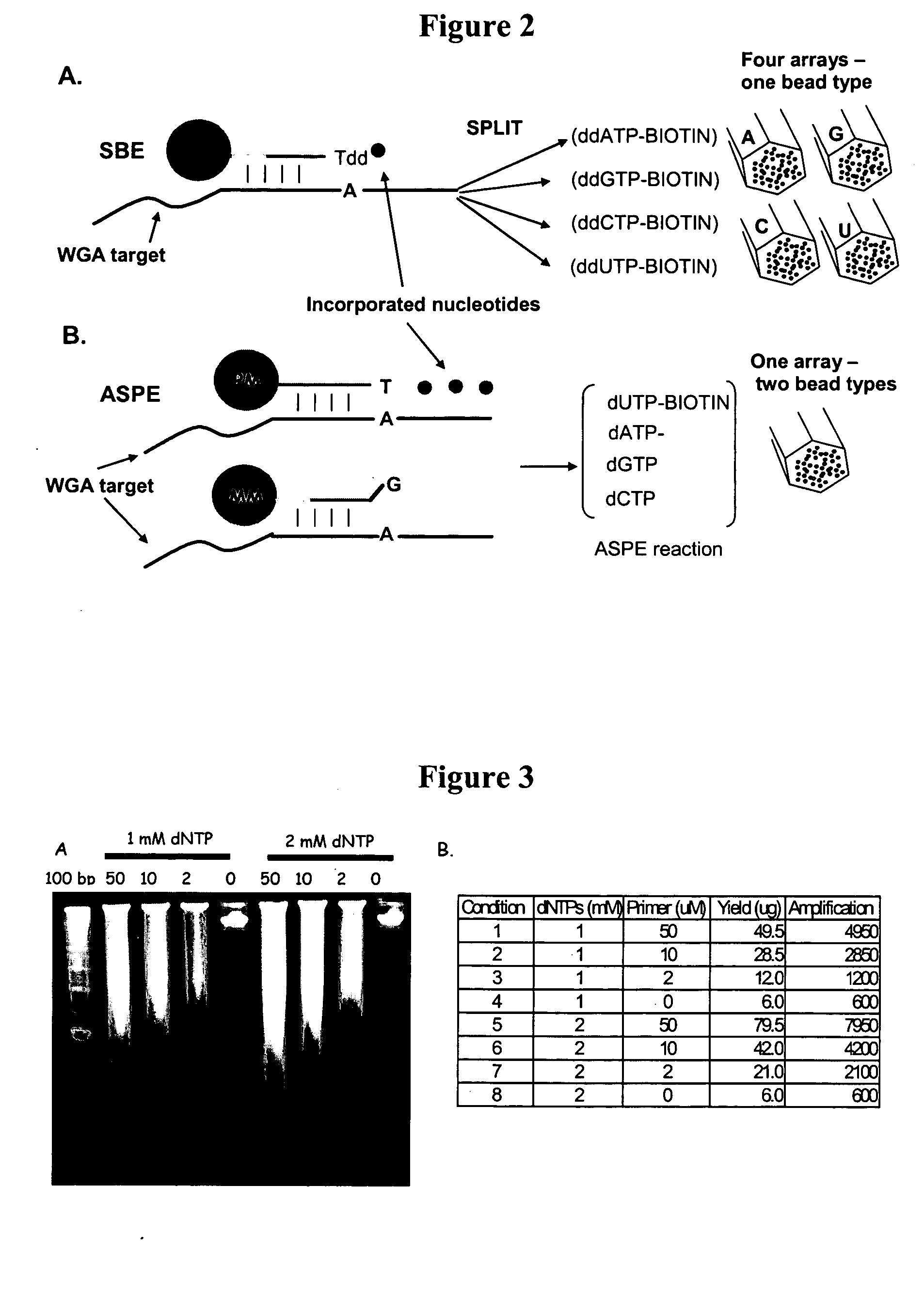
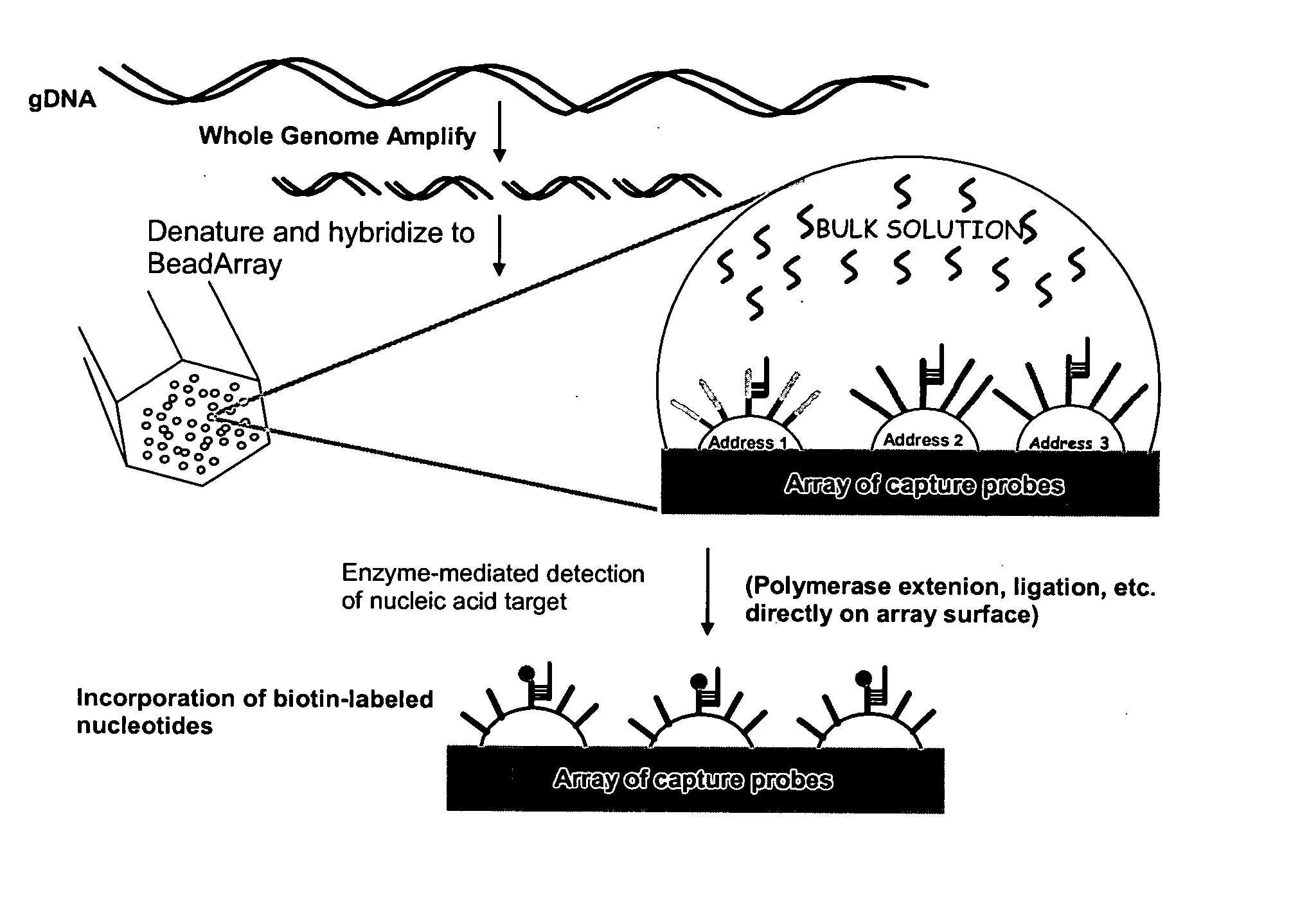
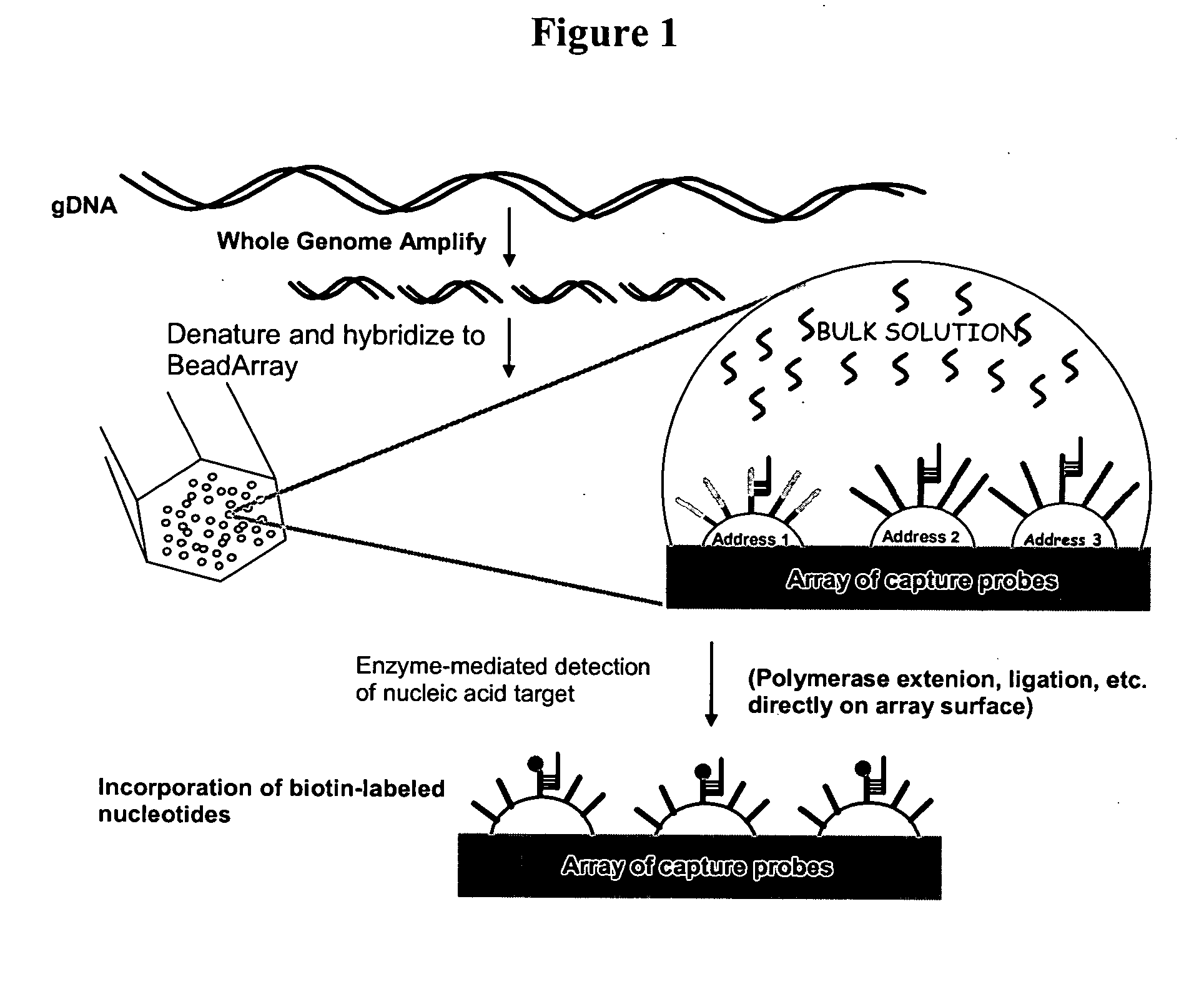
Patents
Literature
317 results about "Genotyping by sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
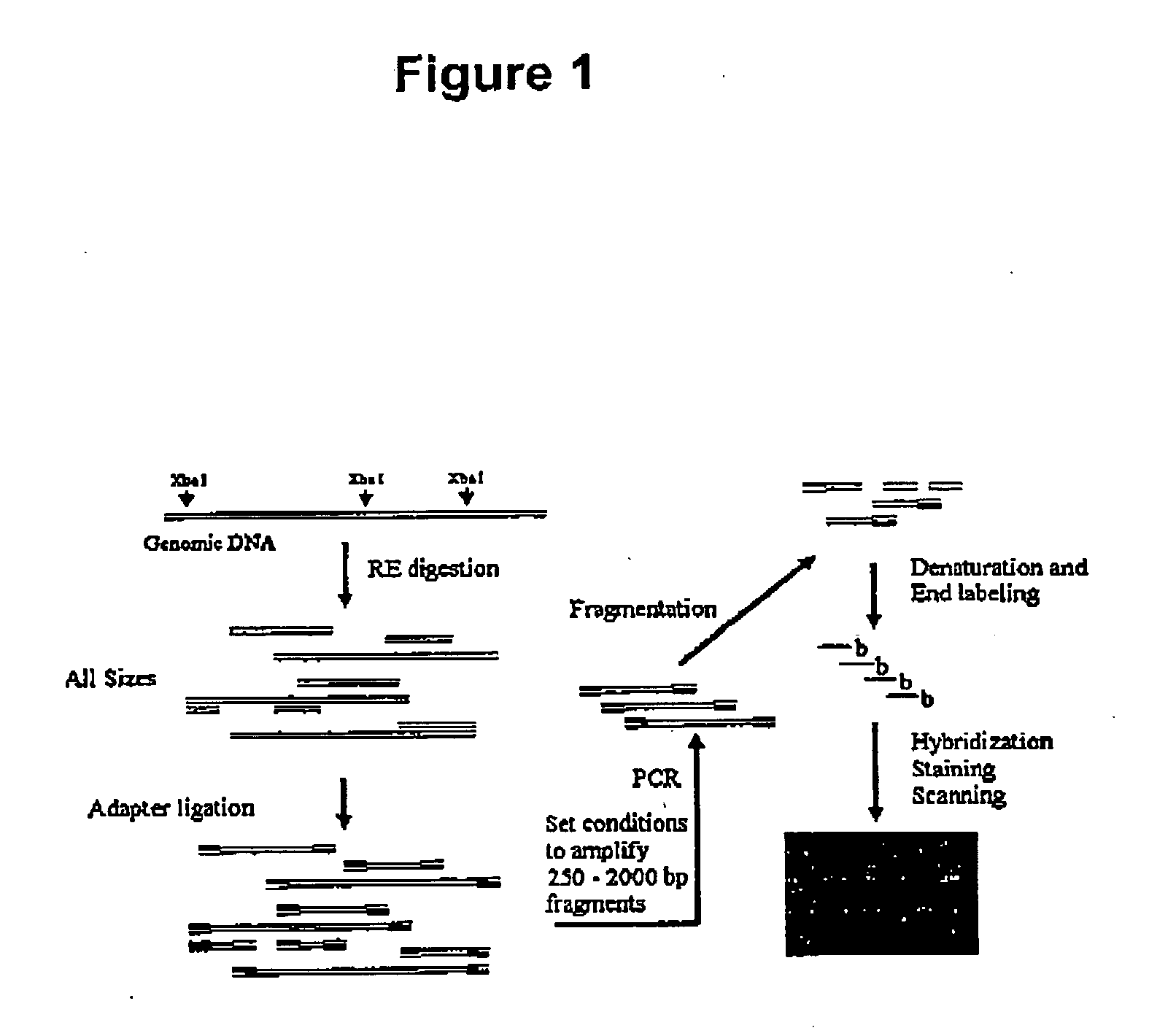
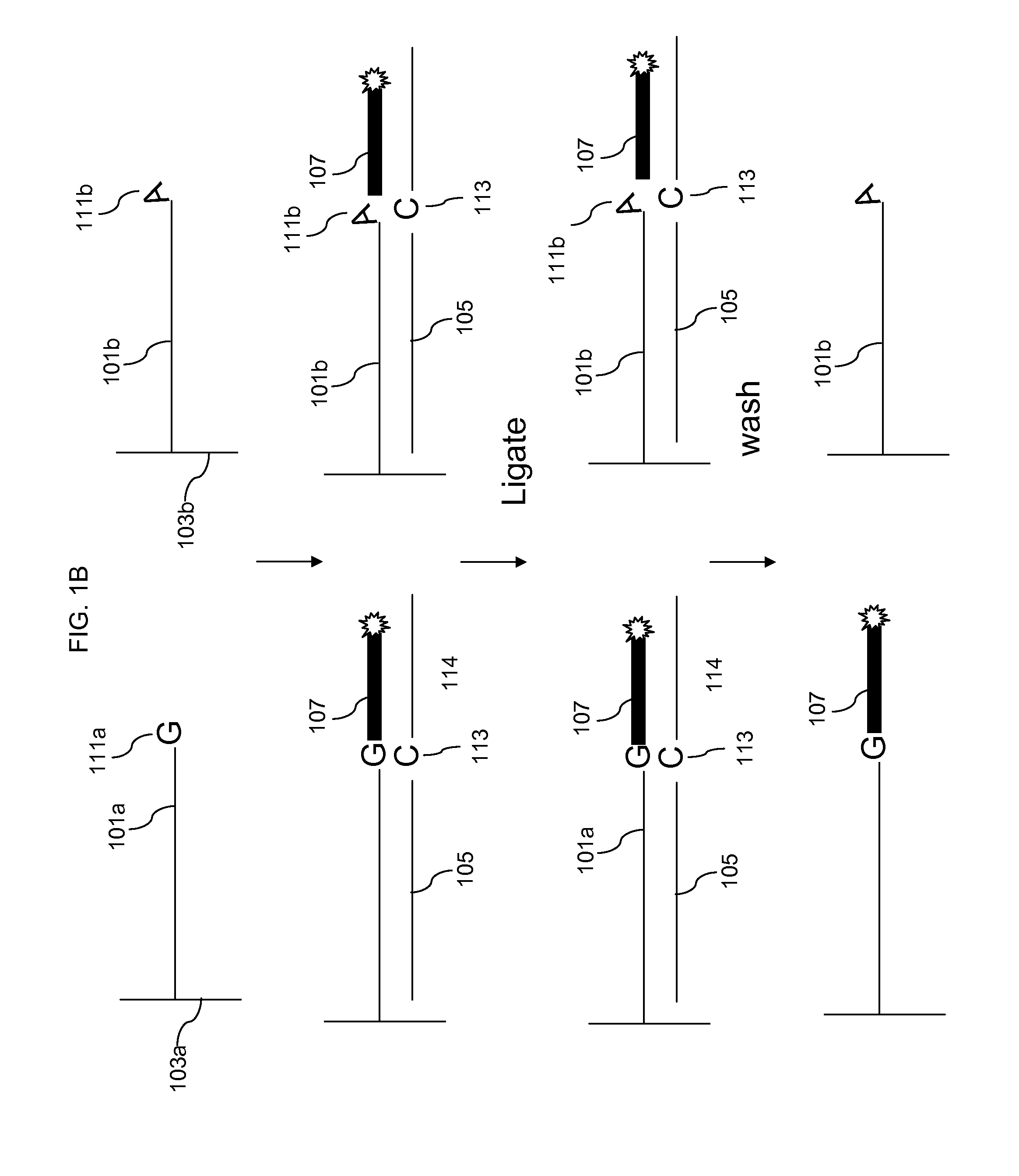
In the field of genetic sequencing, genotyping by sequencing, also called GBS, is a method to discover single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in order to perform genotyping studies, such as genome-wide association studies (GWAS). GBS uses restriction enzymes to reduce genome complexity and genotype multiple DNA samples. After digestion, PCR is performed to increase fragments pool and then GBS libraries are sequenced using next generation sequencing technologies, usually resulting in about 100bp single-end reads. It is relatively inexpensive and has been used in plant breeding. Although GBS presents an approach similar to restriction-site-associated DNA sequencing (RAD-seq) method, they differ in some substantial ways.
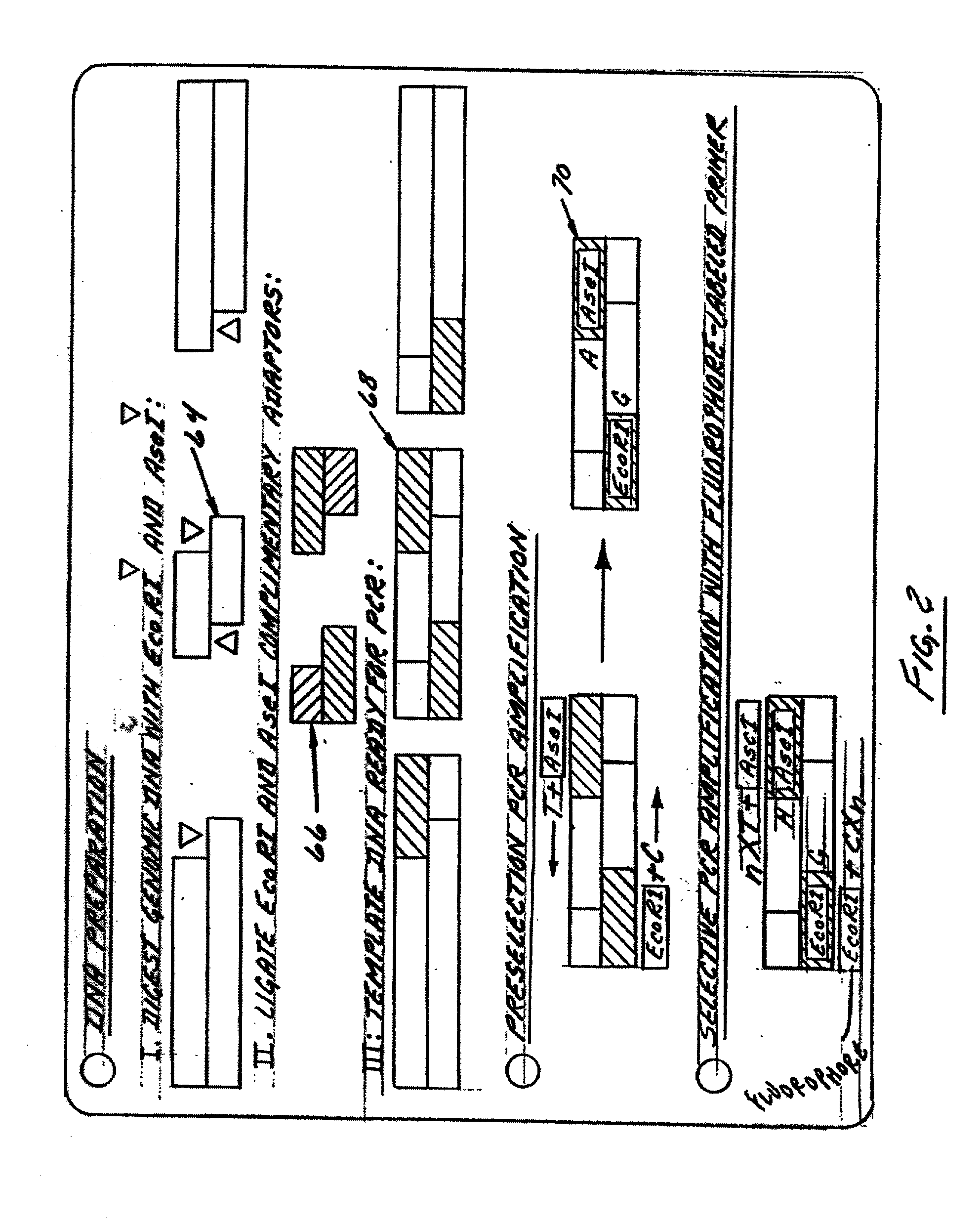
Universal selective genome amplification and universal genotyping system
InactiveUS20050019776A1Enriches SNPsImprove reuseMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSmall fragmentGenomic DNA
The invention relates to methods for isolating and amplifying small fragments of genomic DNA for genotyping polymorphisms in human populations.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
InactiveUS20050181394A1Material nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic SegmentGenotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods and compositions for whole genome amplification and genotyping
This invention provides methods of amplifying genomic DNA to obtain an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Methods are further provided for obtaining amplified genomic DNA representations of a desired complexity. The invention further provides methods for simultaneously detecting large numbers of typable loci for an amplified representative population of genome fragments. Accordingly the methods can be used to genotype individuals on a genome-wide scale.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods for genotyping selected polymorphism
InactiveUS7459273B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsDegenerate oligonucleotide
Methods for genotyping polymorphisms using a locus specific primer that is complementary to a region near a selected polymorphism are described. Methods for synthesizing pools of locus specific primers that incorporate some degenerate positions are also disclosed. A plurality of different sequence capture probes are synthesized simultaneously using degenerate oligonucleotide synthesis. The sequence of the locus specific regions of the capture probes are related in that they have some bases that are identical in each sequence in the plurality of sequences and positions that vary from one locus specific region to another. The sequences are selected based on proximity to a polymorphism of interest and because they conform to a similar sequence pattern.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods and systems for performing multiple reactions by interfacial mixing
Methods and systems of performing multiple reactions in a high throughput format by utilizing interfacial mixing of adjacently positioned reagent slugs in a fluid conduit. Preferred applications of the methods and systems are in performing biochemical analyses, including genotyping experiments for multiple different loci on multiple different patient samples. Microfluidic systems are provided that increase throughput, automation and integration of the overall reactions to be carried out.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Method for identifying polymorphic markers in a population
InactiveUS6799122B2Microbiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionGenomic DNAGenotype
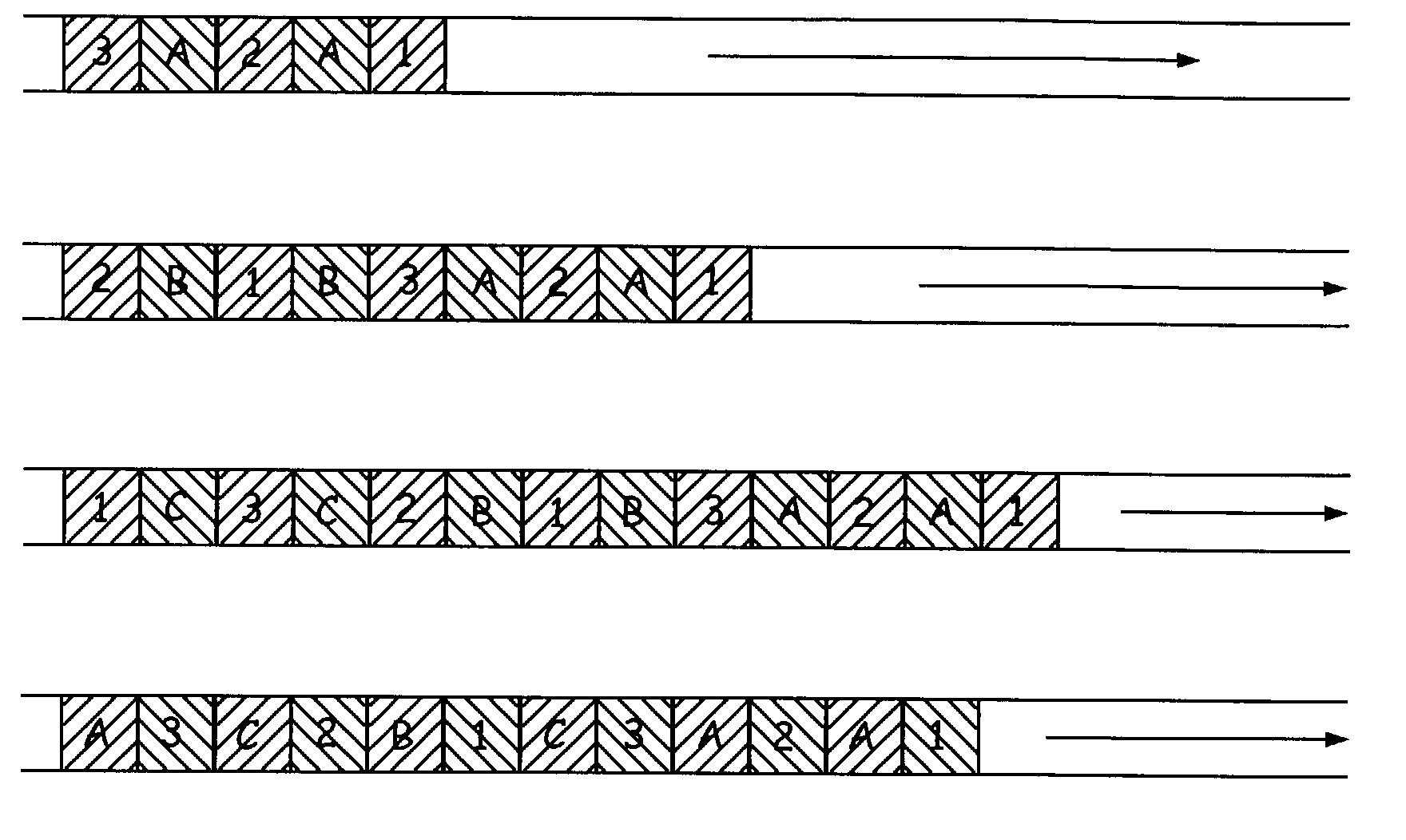
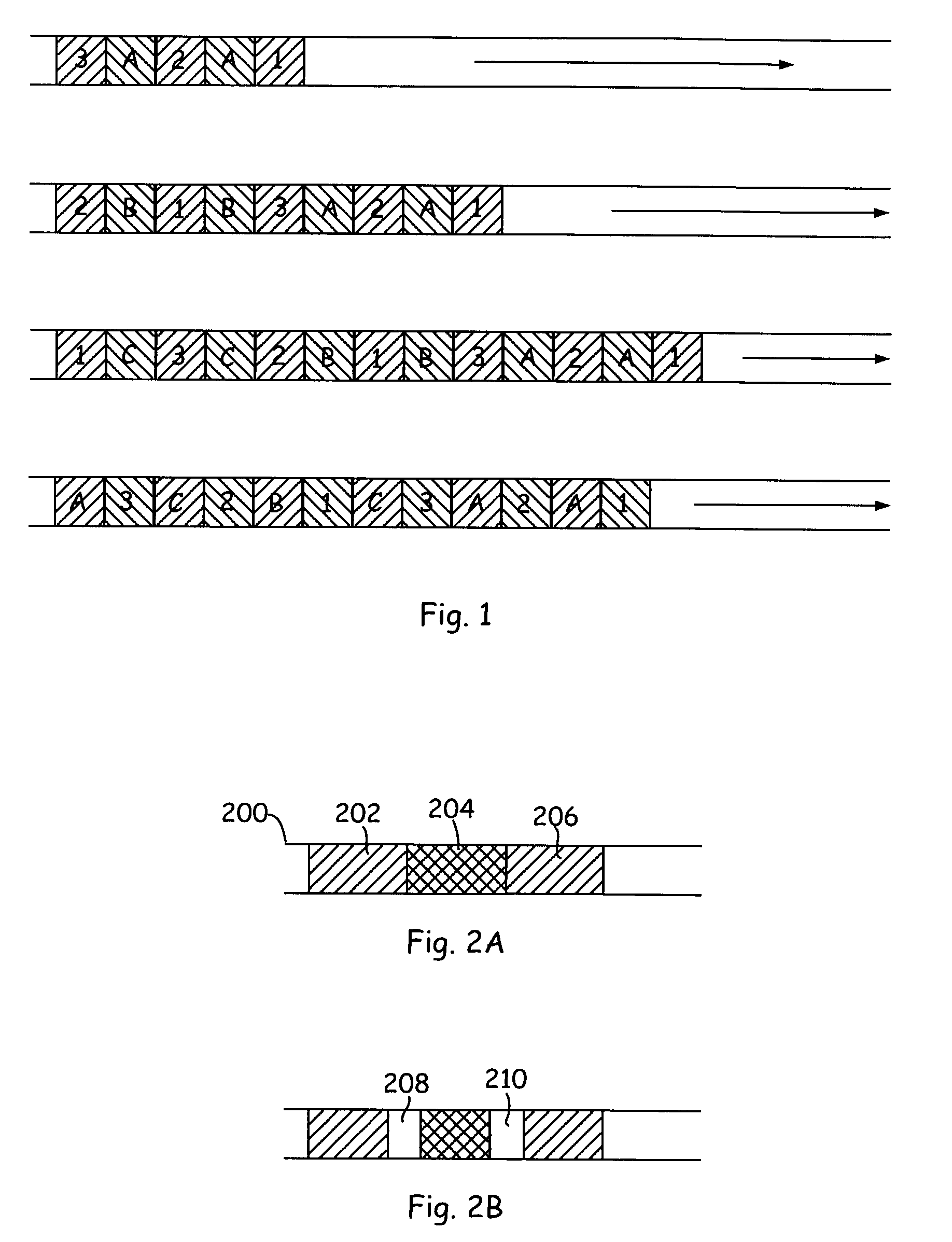
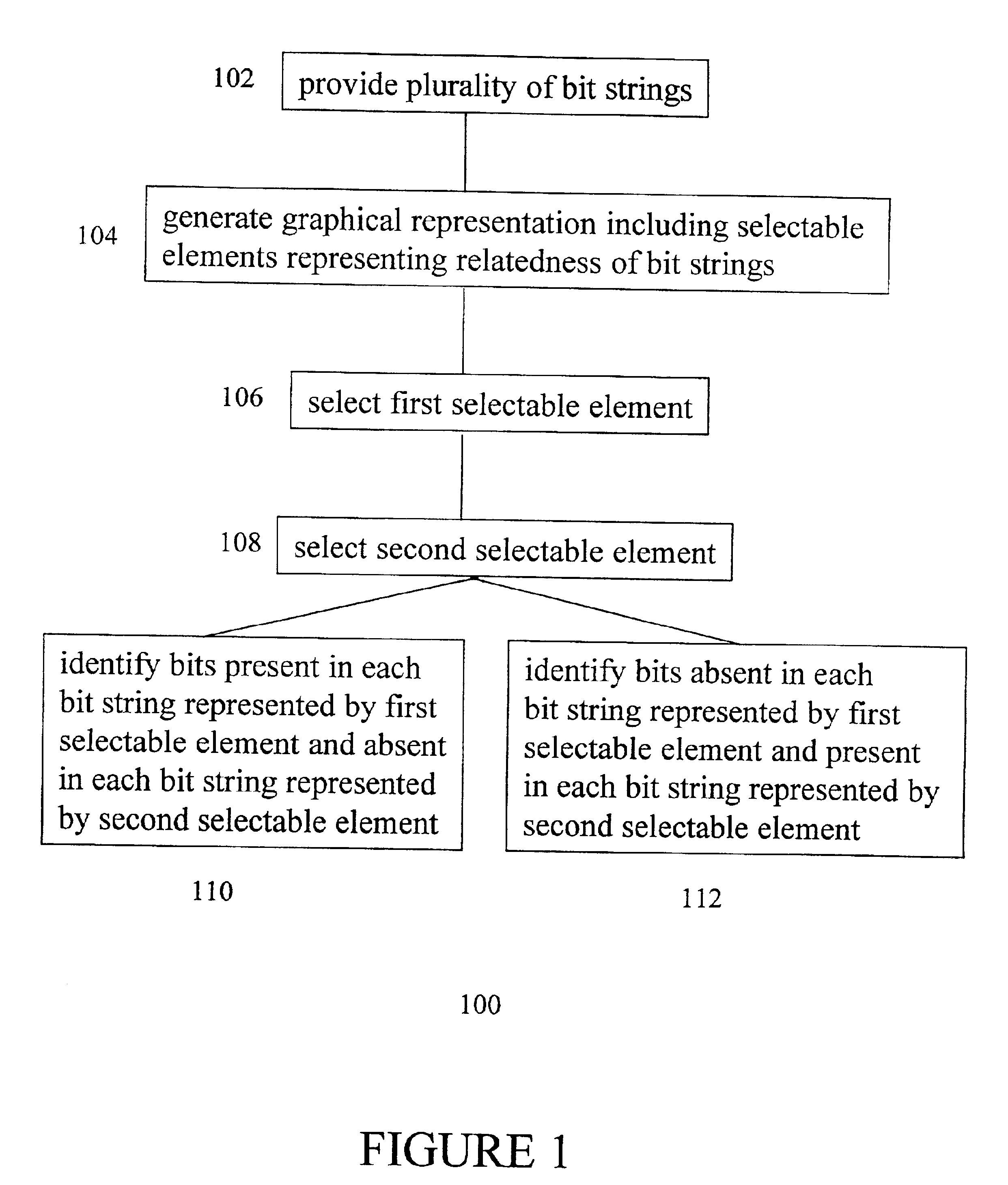
A method is provided for the identification of polymorphic markers in a population. The method includes genotypically characterizing a first sample of a population, selecting one or more individuals of the first sample based upon the genotypic characterization, fabricating a microarray with genomic DNA from each individual selected, and genotyping a second sample of the population using each fabricated microarray as a reference, thereby identifying the polymorphic markers in the population. Also provided is a method for the identification of polymorphic markers in a bacterial population. The method includes phenotypically characterizing a first sample of a population, selecting one or more individuals of the first sample based upon the phenotypic characterization, fabricating a microarray with genomic DNA from each individual selected, and genotyping a second sample of the population using each fabricated microarray as a reference, thereby identifying the polymorphic markers in the population. Also provided is a method for identifying unique bits among a plurality of bit strings including providing a plurality of bit strings, wherein each string has the same number and position of bits, and each bit has a value of 0 or 1, generating a graphical representation-including selectable elements-representing the relatedness of the bit strings, making a selection of a first selectable element, making a selection of a second selectable element, and identifying bits that are present in each bit string represented by the first selectable element and absent in each bit string represented by the second selectable element, or vice-versa.
Owner:BEACON VENTURE MANAGEMENT +1
Methods of genotyping using differences in melting temperature
InactiveUS20060172324A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide primersGenotyping
The present invention relates to the identification of a particular nucleotide polymorphism in a nucleic acid sample in a single reaction utilizing oligonucleotide primers with different melting temperature characteristics.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method for genotyping polymorphisms in humans
ActiveUS7300788B2Easy to analyze and useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMedicineNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides nucleic acid sequences that are complementary, in one embodiment, to a wide variety of human polymorphisms. The invention provides the sequences in such a way as to make them available for a variety of analyses including genotyping a large number of SNPs in parallel. The invention also provides a collection of human SNPs that is useful for genetic analysis within and across populations. As such, the invention relatesd to diverse fields impacted by the nature of genetics, including biology, medicine, and medical diagnostics.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
System and method for genotyping using informed error profiles
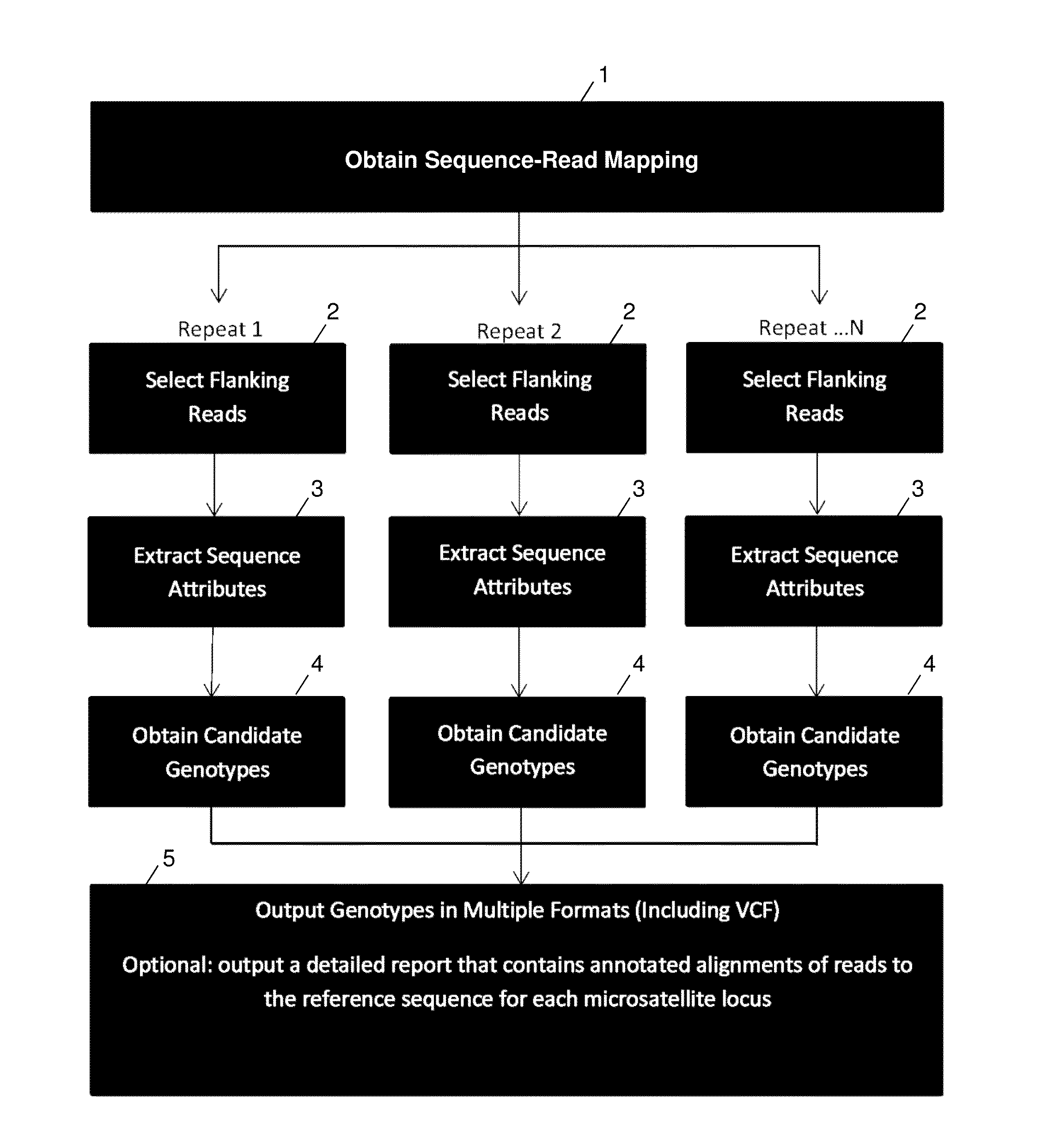
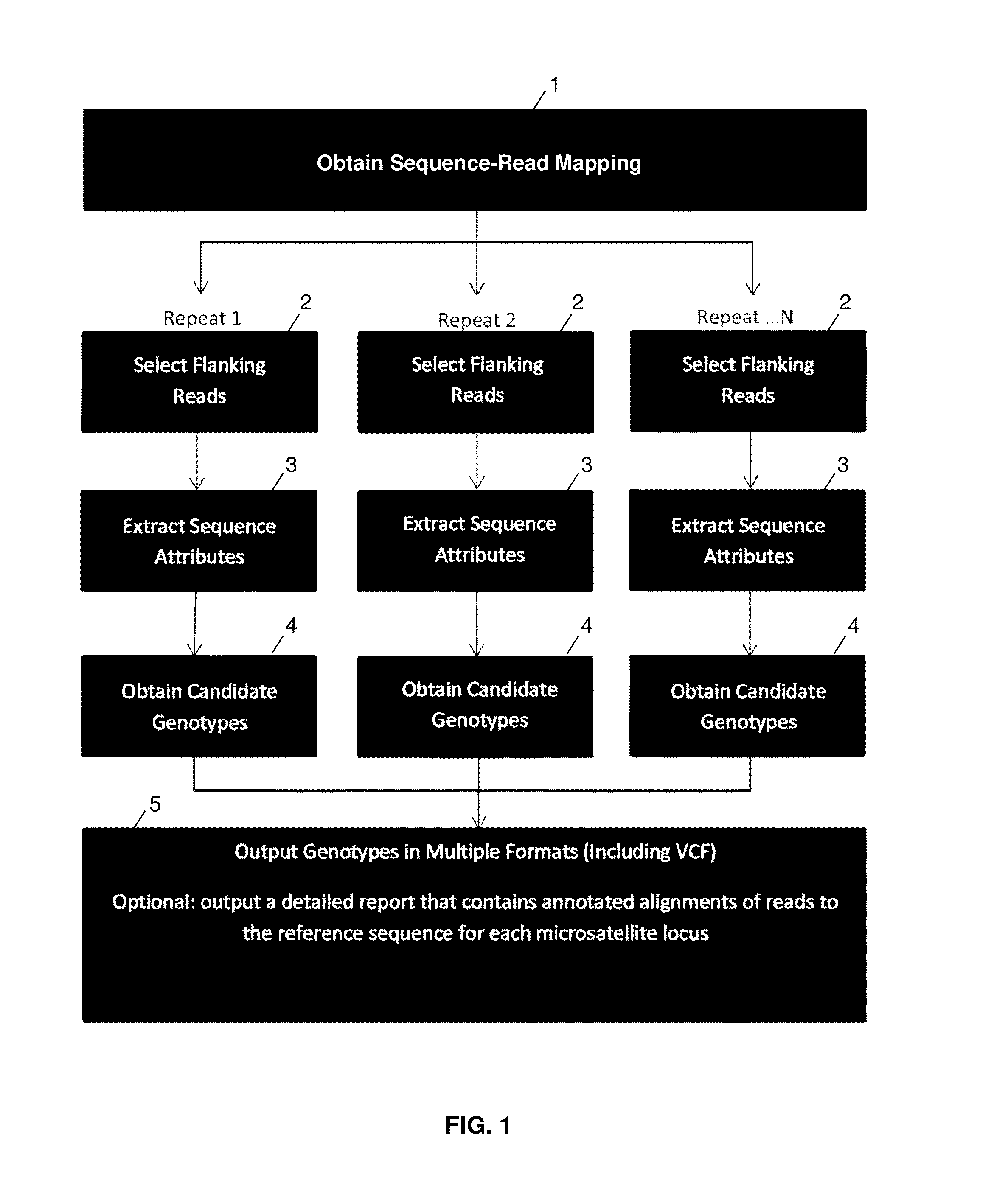
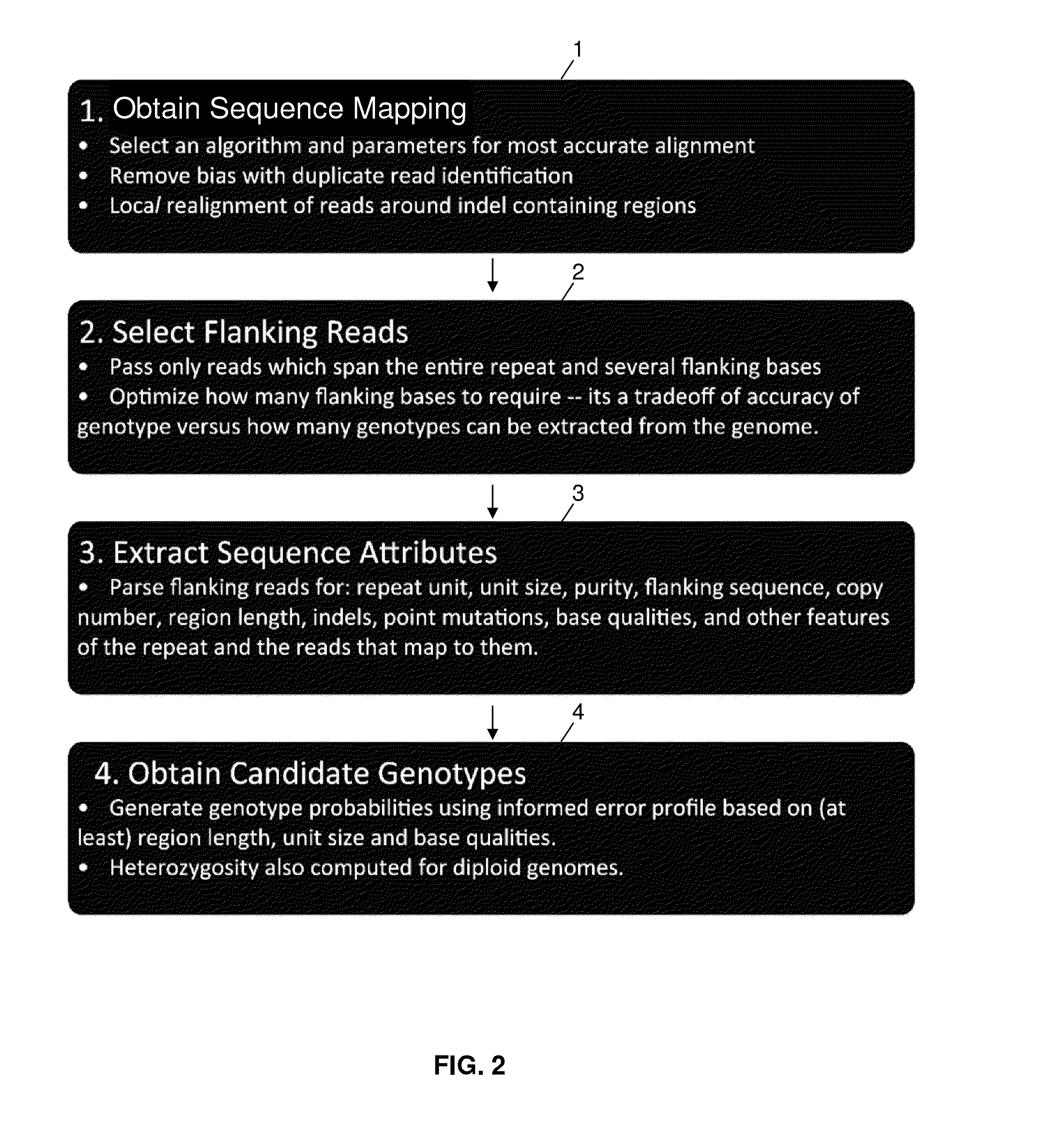
ActiveUS20140114582A1Minimal coverage dataAccurate genotypingProteomicsGenomicsModel selectionAlgorithm
A system and method for genotyping tandem repeats in sequencing data. The invention uses Bayesian model selection guided by an empirically-derived error model that incorporates properties of sequence reads and reference sequences to which they map.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Method of genotyping by determination of allele copy number
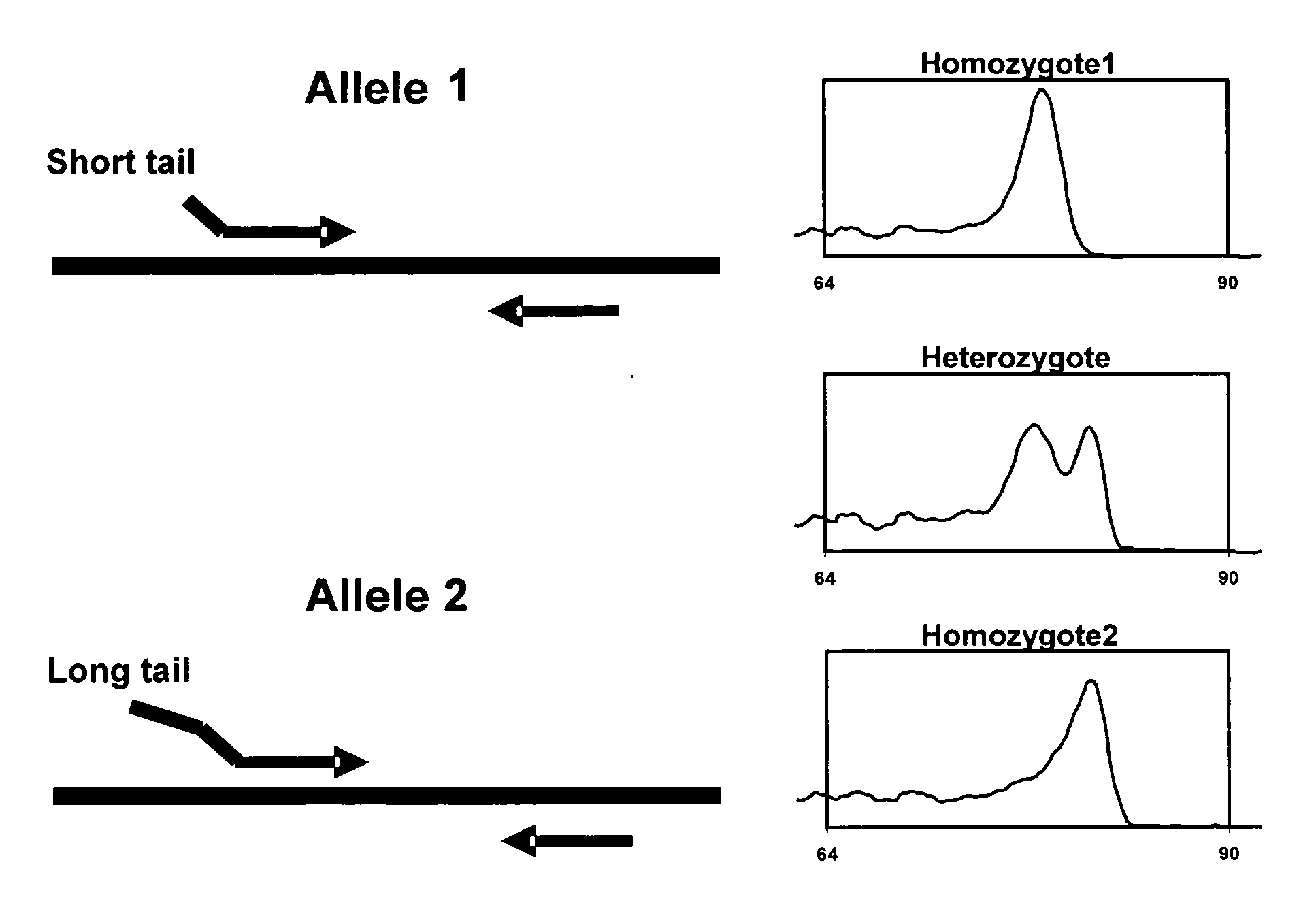
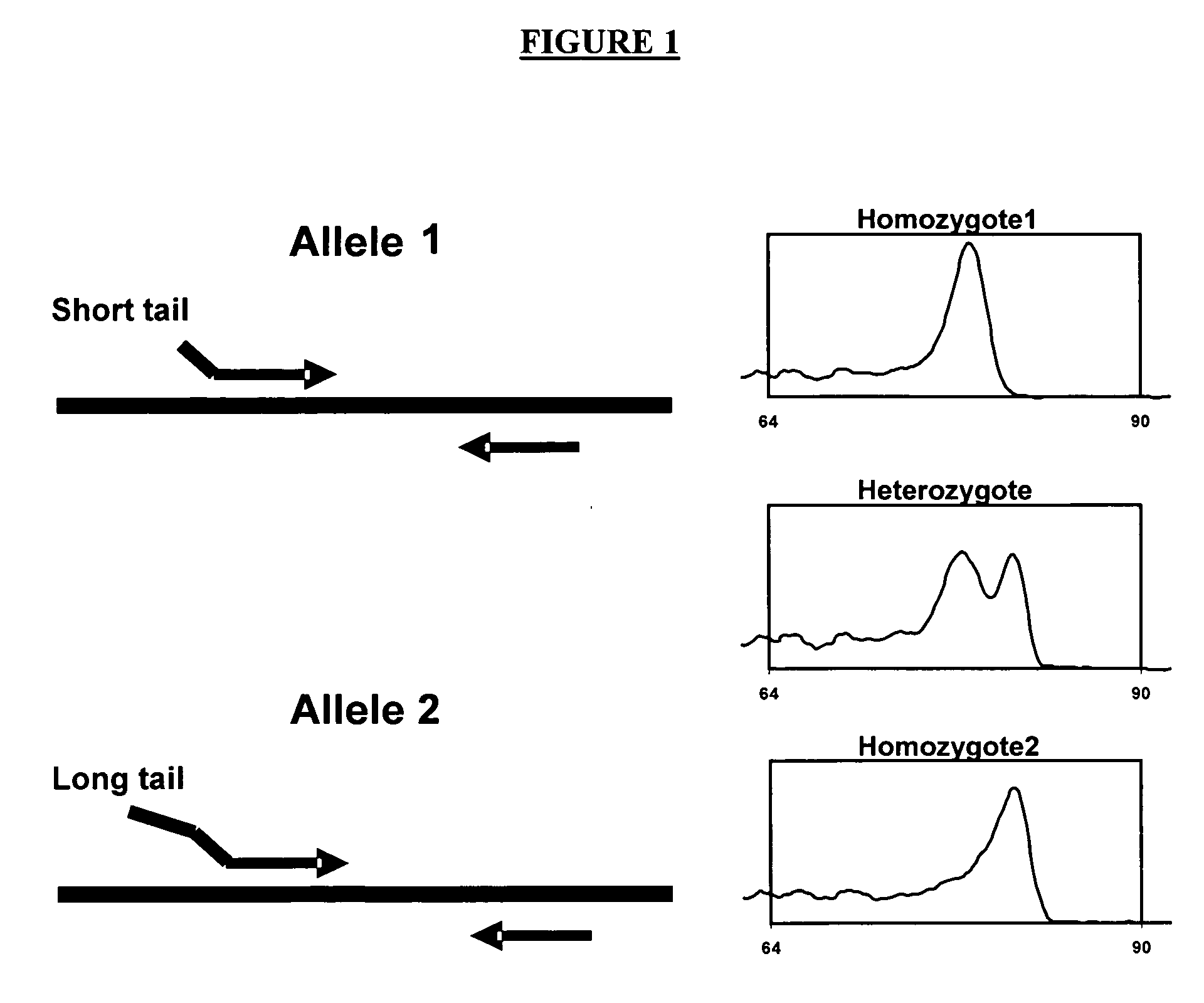
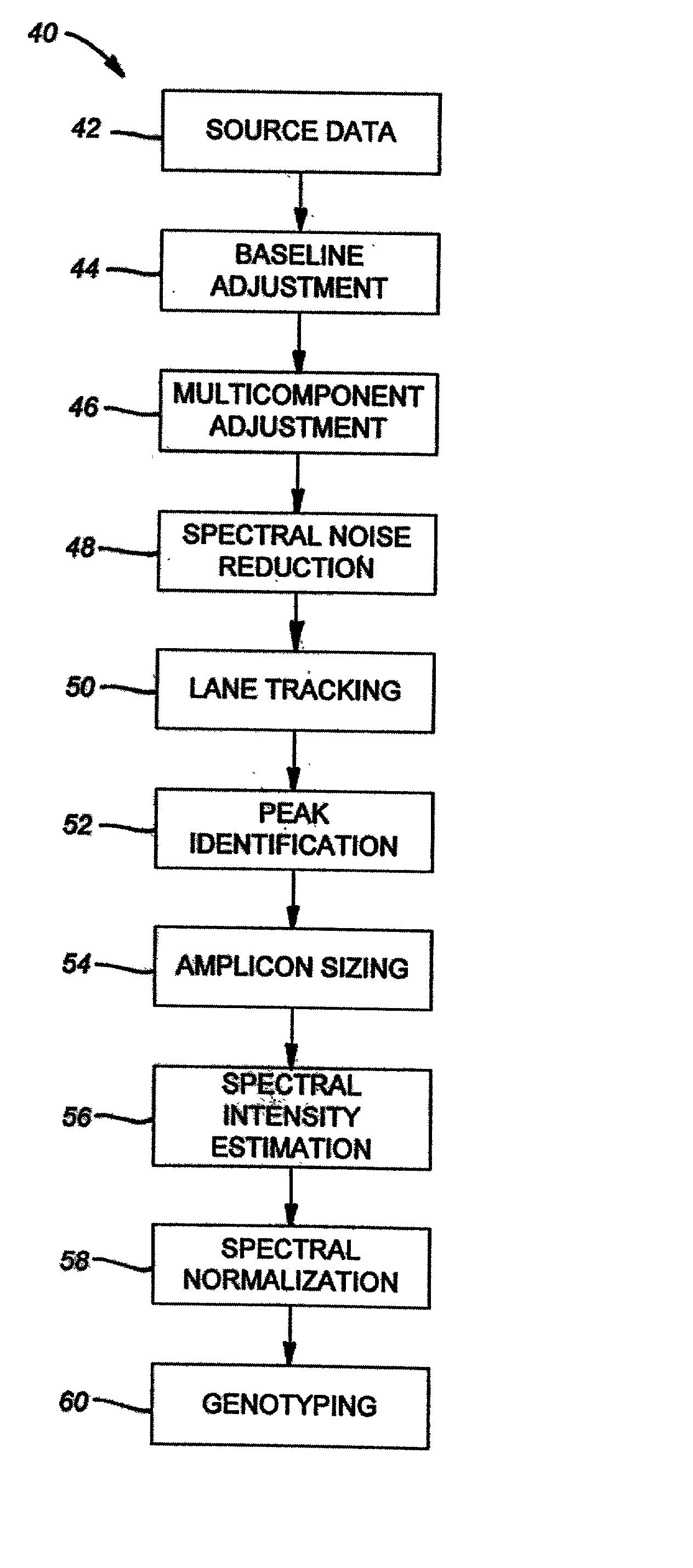
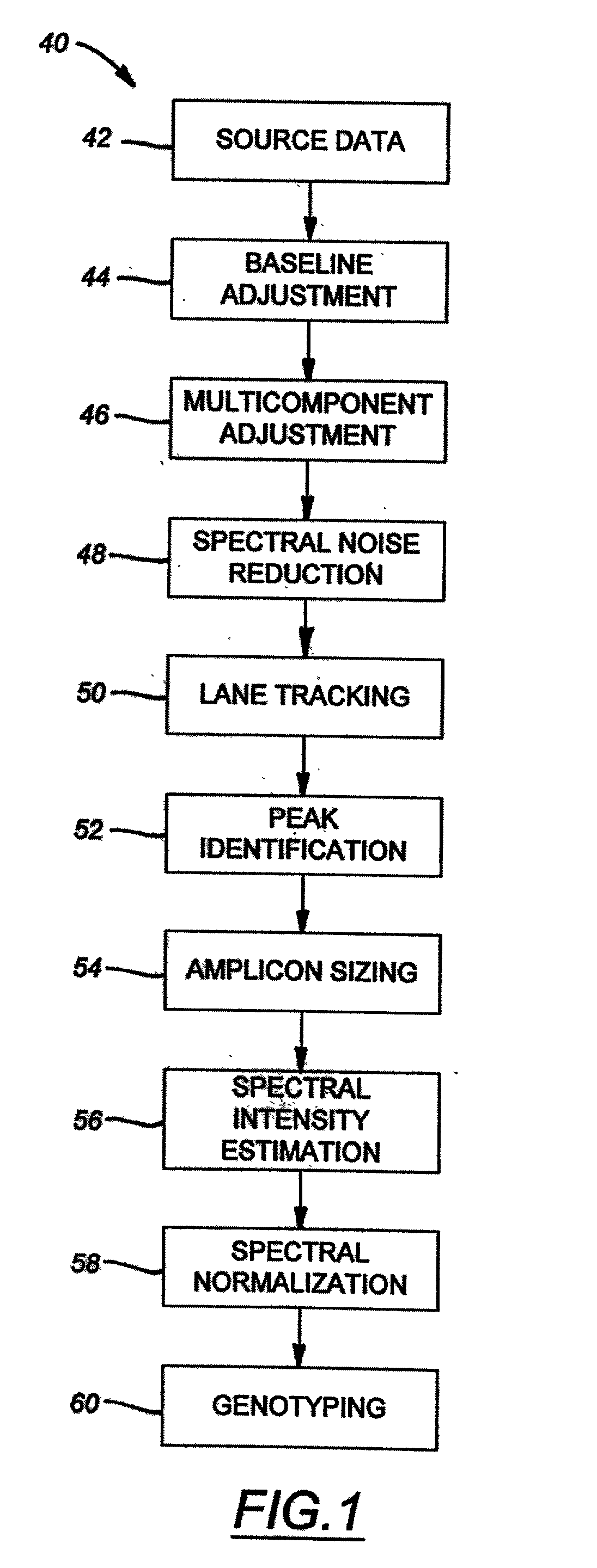
The majority of PCR-based fingerprinting technologies generate dominant genetic markers; homozygote present and heterozygote genotypes cannot be distinguished using conventional detection methods. In contrast, codominant genetic markers provide an unambiguous distinction among each genotype. A genotyping method is described that includes procedures implemented in software. This method quantifies allele copy number and enables recovery of codominant genotypes from markers expressing ostensibly dominant phenotypes. These procedures are designed and implemented to (1) greatly reduce variability attributable to sample assay and detector noise, (2) accurately estimate allele size and copy number, (3) provide normalization criteria for intra- and inter-marker comparisons, and (4) scale the resulting data to determine the genotype of individual markers.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
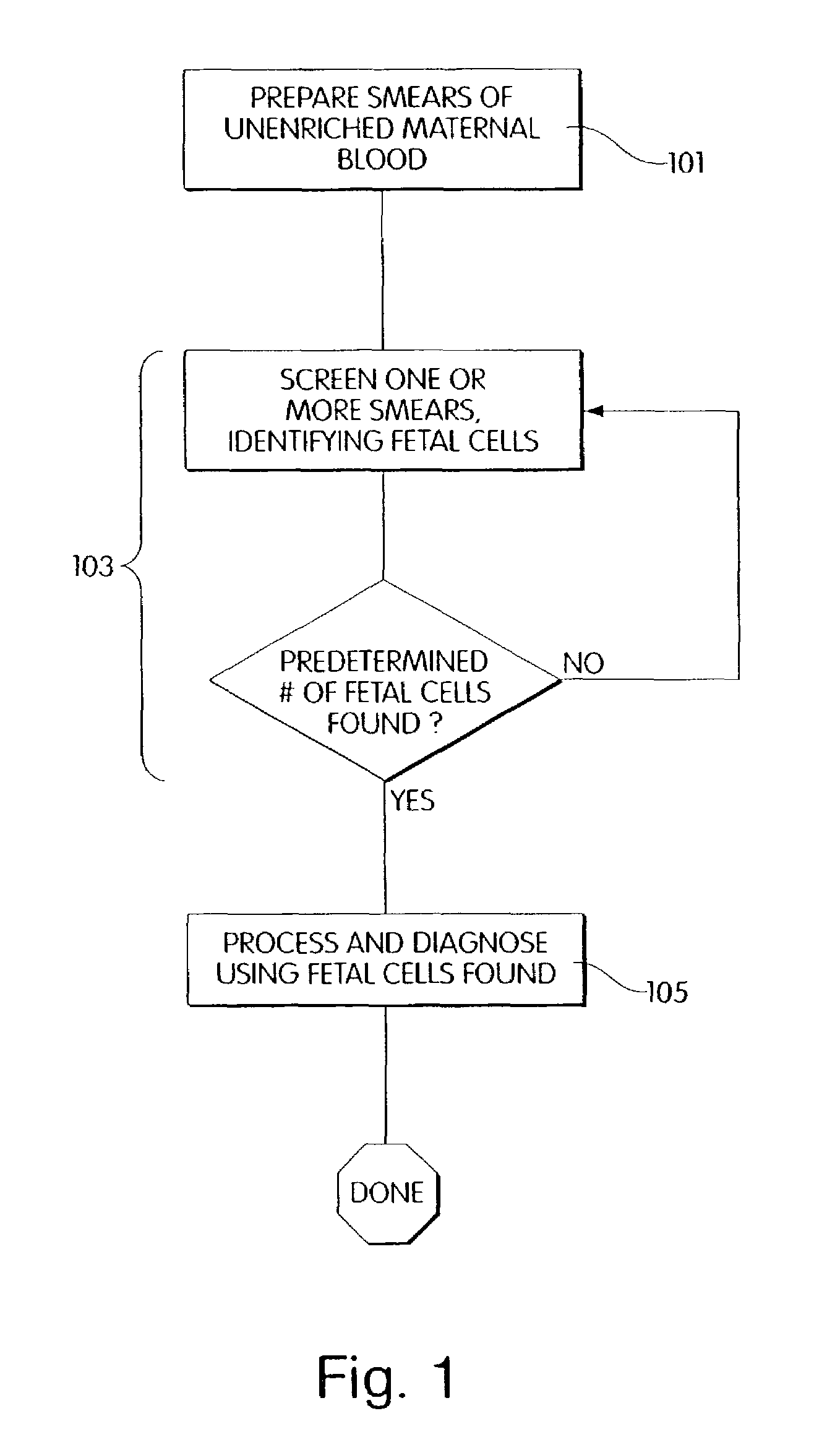
Method and apparatus for computer controlled cell based diagnosis
InactiveUS20060072805A1Minimize timePossible amount of timePreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCancer cellRare cell
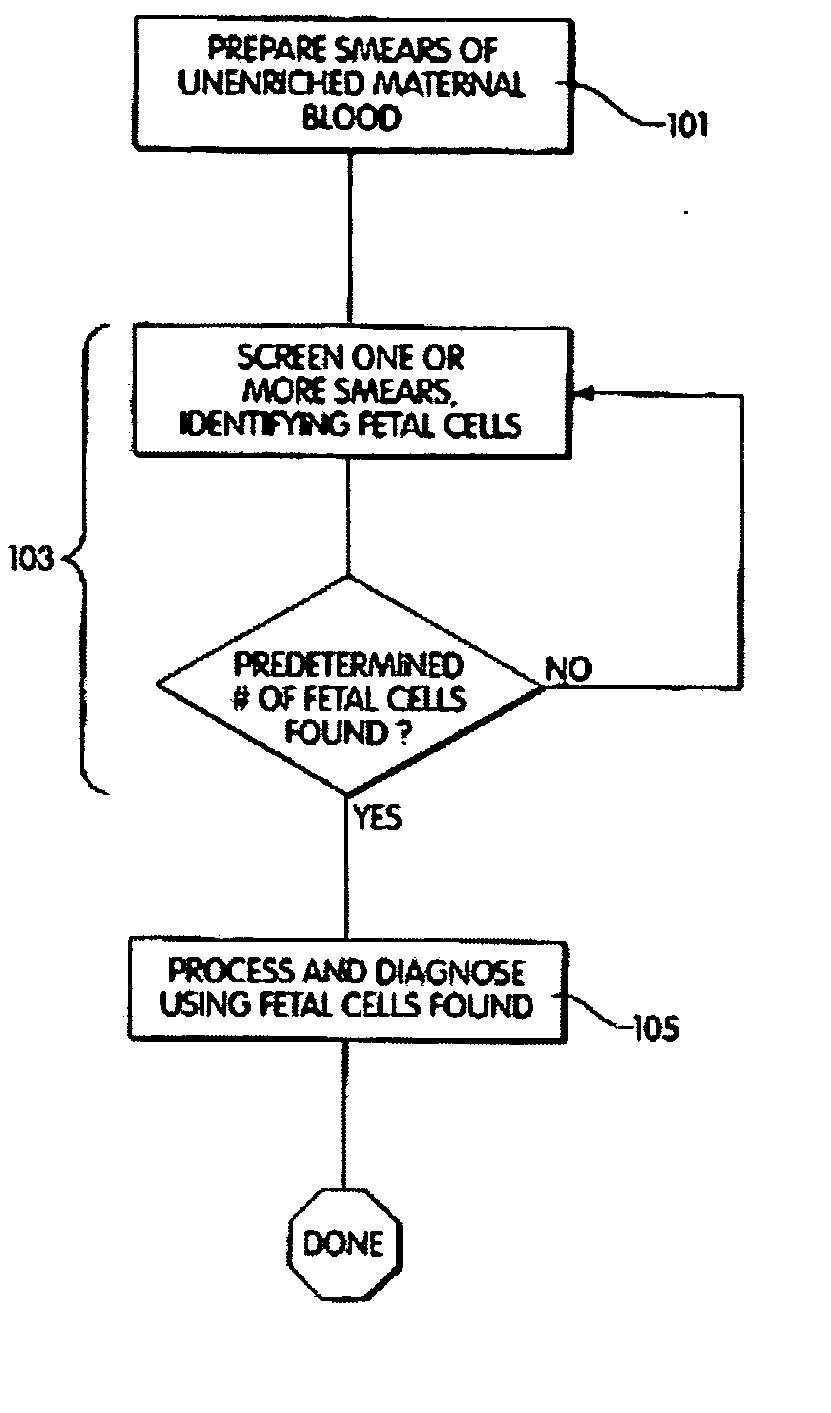
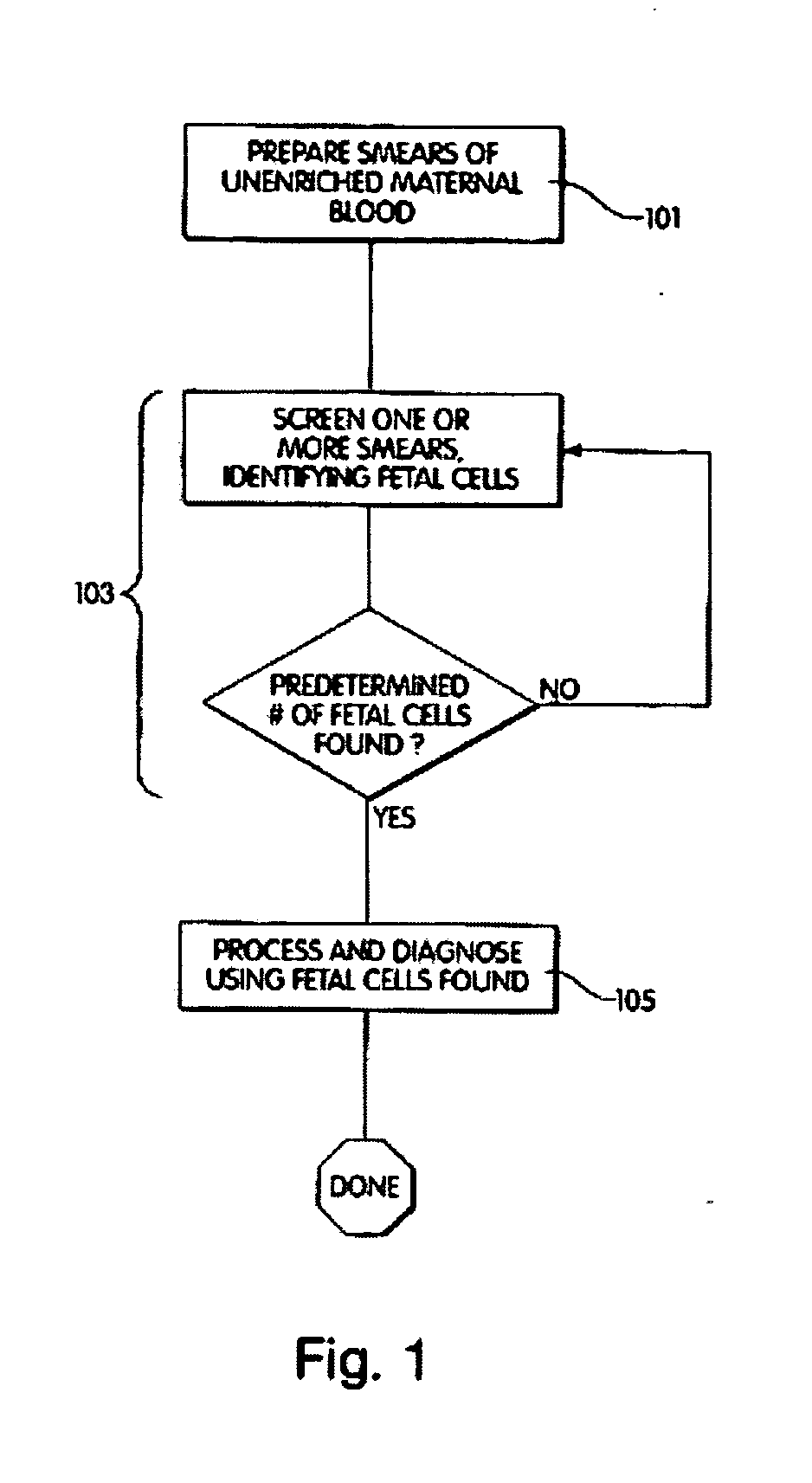
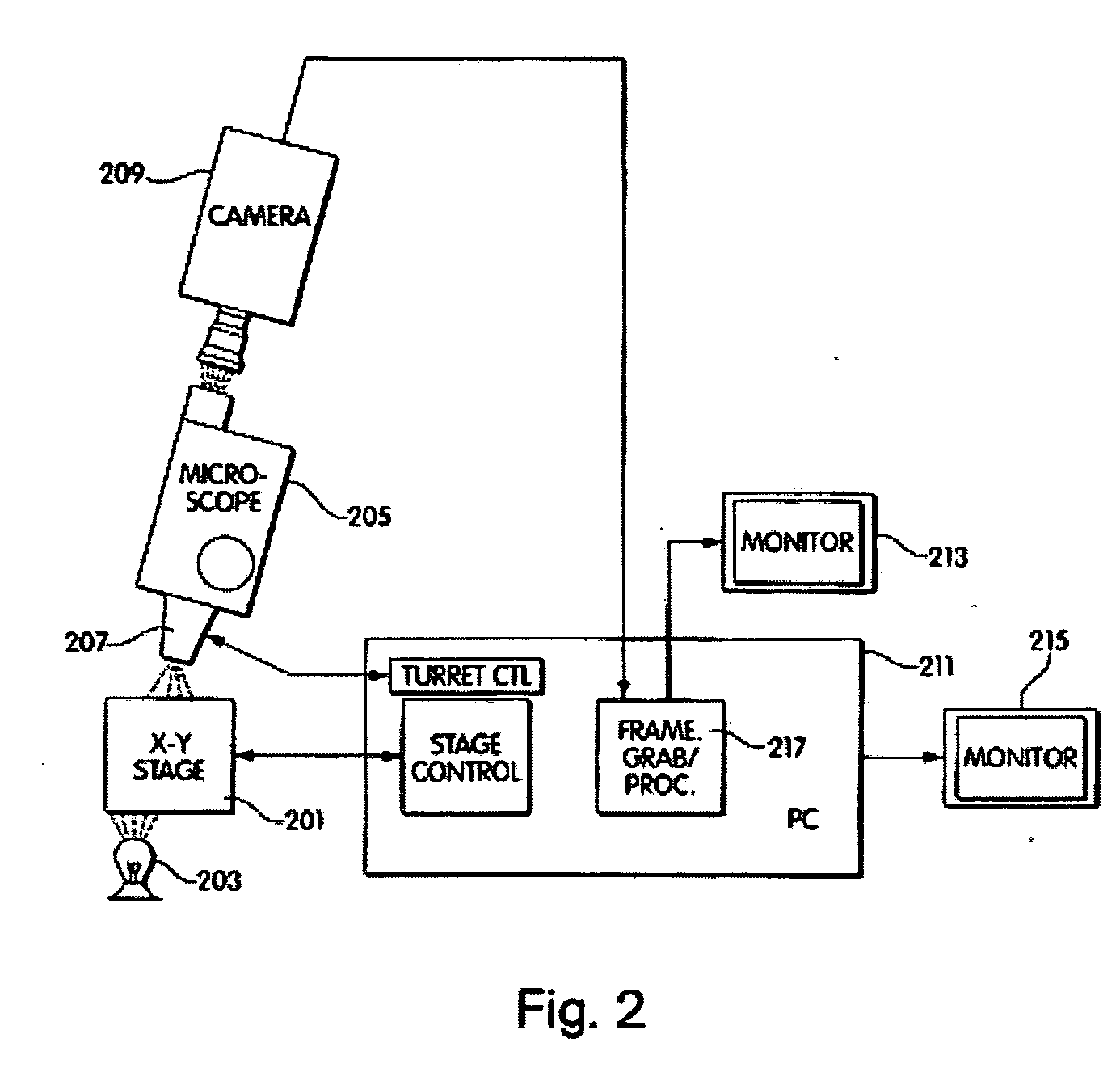
A computer controlled method for detecting and diagnosing a rare cell type in a tissue sample is provided, said method comprising treating the tissue sample such that it generates a first signal indicative of the presence at a location of a rare cell, detecting the first signal, treating the location at which the first signal is detected to generate a second signal indicative of a diagnostically useful cellular characteristic and detecting the second signal. The first signal can be morphological or a color present in a sought cell either before or after staining. The second signal can be generated by in situ PCR or PCR in situ hybridization. In one preferred embodiment, the rare cell type is a fetal cell in a maternal blood tissue sample, said sample consisting of a smear of unenriched maternal blood. In another embodiment, the method is used to diagnose or genotype cancer cells in a blood or tissue biopsy sample.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Genotyping by in situ PCR amplification of a polynucleotide in a tissue biopsy
InactiveUS20040038213A1Facilitated releaseFunction increaseMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionTissue biopsyProteinase activity
Reagents and method for genotyping mice and other animals by in situ Polymerase Chain Reaction amplification of a target polynucleotide in the tissue biopsy. The reagent is comprised of non-ionic detergents, a protease, a buffering agent, a metal ion cofactor, a chelating agent and a salt. The method is comprised of taking a tissue biopsy; admixing it with the reagent; a Lysing Cycle, an inactivation cycle, an amplification step and a detection step.
Owner:KWON JAI W
Screening assays for identifying modulators of the inflammatory or immune response
InactiveUS20030124524A1Modulate inflammatory responseMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeBiological activation
The present invention relates to methods for identifying substances that modulate the immune response in a genotype specific manner. In general, methods of the invention involve genotyping subjects to identify those having a genotype associated with one or more inflammatory disorder. These subjects, or cells derived therefrom, are monitored for a biomarker for activation of the inflammatory system. The subjects or cells are then contacted with a test substance and the biomarker is re-measured. If the biomarker changes to indicate a decreased activation of the inflammatory system, the test substance may have an anti-inflammatory effect on subjects with that genotype.
Owner:ORIG3N INC
Genotyping methods
InactiveUS20050042654A1Minimizing chanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNAGenotyping
Methods for amplifying genomic DNA and genotyping amplified genomic DNA samples are provided. The genotyping methods use genotyping arrays of probes that are allele specific probes for single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The methods also relate to methods for amplifying a plurality of genomic DNA samples from a plurality of individuals in a manner that minimizes the potential for contamination of samples that have not been amplified by amplicons from samples that have already been amplified.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method and apparatus for computer controlled cell based diagnosis
InactiveUS7346200B1Suitable for control and processingMinimize timePreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCancer cellRare cell
A computer controlled method for detecting and diagnosing a rare cell type in a tissue sample is provided, said method comprising treating the tissue sample such that it generates a first signal indicative of the presence at a location of a rare cell, detecting the first signal, treating the location at which the first signal is detected to generate a second signal indicative of a diagnostically useful cellular characteristic and detecting the second signal. The first signal can be morphological or a color present in a sought cell either before or after staining. The second signal can be generated by in situ PCR or PCR in situ hybridization. In one preferred embodiment, the rare cell type is fetal cell in a maternal blood tissue sample, said sample consisting of a smear of unenriched maternal blood. In another embodiment, the method is used to diagnose or genotype cancer cells in a blood or tissue biopsy sample.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Blood Group and Platelet Antigen Genotypes
InactiveUS20080261205A1Reduce in quantityMeet demandSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood collectionRed blood cell
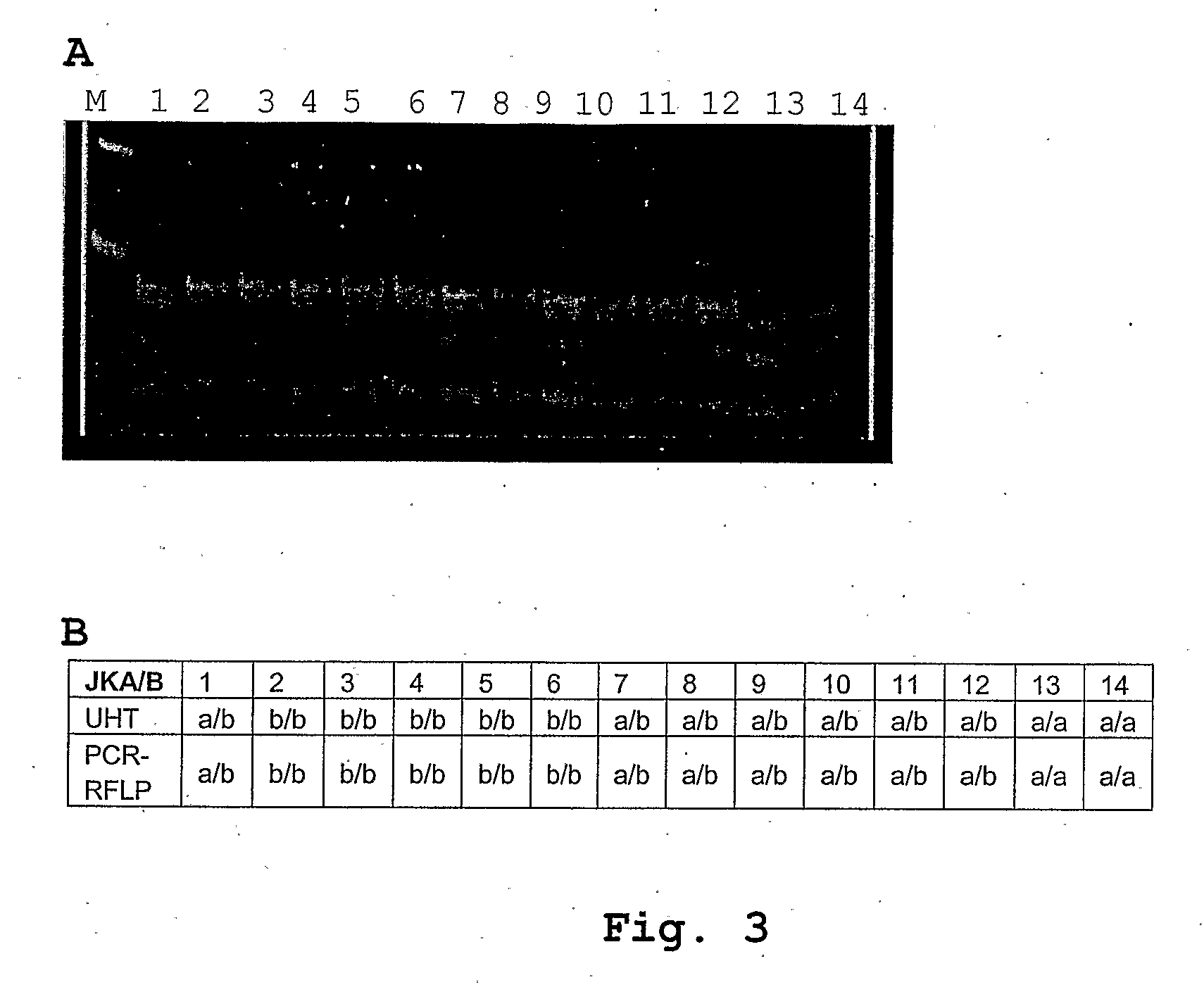
RBC and platelet (Plt) alloimmunization requires antigen-matched blood to avoid adverse transfusion reactions. Some blood collection facilities use unregulated Abs to reduce the cost of mass screening, and later confirm the phenotype with government approved reagents. Alternatively, RBC and Plt antigens can be screened by virtue of their associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). We developed a multiplex PCR-oligonucleotide extension assay using the GenomeLab SNPStream platform to genotype blood for a plurality of blood group antigen-associated SNPs, including but not limited to: RhD (2), RhC / c, RhE / e, S / s, K / k, Kpa / b, Fya / b, FYO, Jka / b, Dia / b, and HPA-1a / b.
Owner:CANADIAN BLOOD SERVICES
Highly orthogonal universal sequences for use in nucleic acid assays
ActiveUS20060172284A1Easy to analyzeDeletion increaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementThird generationOrthogonal sequence
The invention provides a set of highly orthogonal six-code universal sequences for use in bDNA singleplex and multiplex nucleic acid hybridization assays. The six-code orthogonal sequences do not cross-hybridize and thus, minimize or eliminate the 3-mer cross-hybridization inherent in the second and third generation bDNA assays. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may be used in singleplex or multiplex bDNA assays quantitatively and qualitatively to determine mRNA levels in a sample; to screen for and genotype targets, such as viruses, that are present in low volumes in a sample; to screen for and genotype SNPs; and to measure changes in the amount of a gene in a sample such as when gene amplifications or deletions occur. The highly orthogonal universal sequences may also be used as universal capture probes to selectively bind assay components in a way that facilitates their further analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
Oligonucleotide for detecting cytochrome P450 enzyme series mutation site and gene chip
InactiveCN101054601AGood practical valueMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeCytochrome p450 enzyme
The present invention provides a set of oligonucleotide probe for detecting CYP450 enzyme gene hot mutant site and its uses, belonging to clinical molecular diagnosis field. The probe is designed at whole gene sequence of each subtype enzyme of CYP450 and has relative high sensitivity and specifity. The present invention also provides a gene chip for detecting cytochrome P450 enzyme series mutant sites and can detect gene typing of DNA specimen. The inventive probe can be used in P450 genetype diagnosi, clinical medicament and preventing drug adverse reaction.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Composite STR detection method with improved resolving ability in Chinese crowd and kit
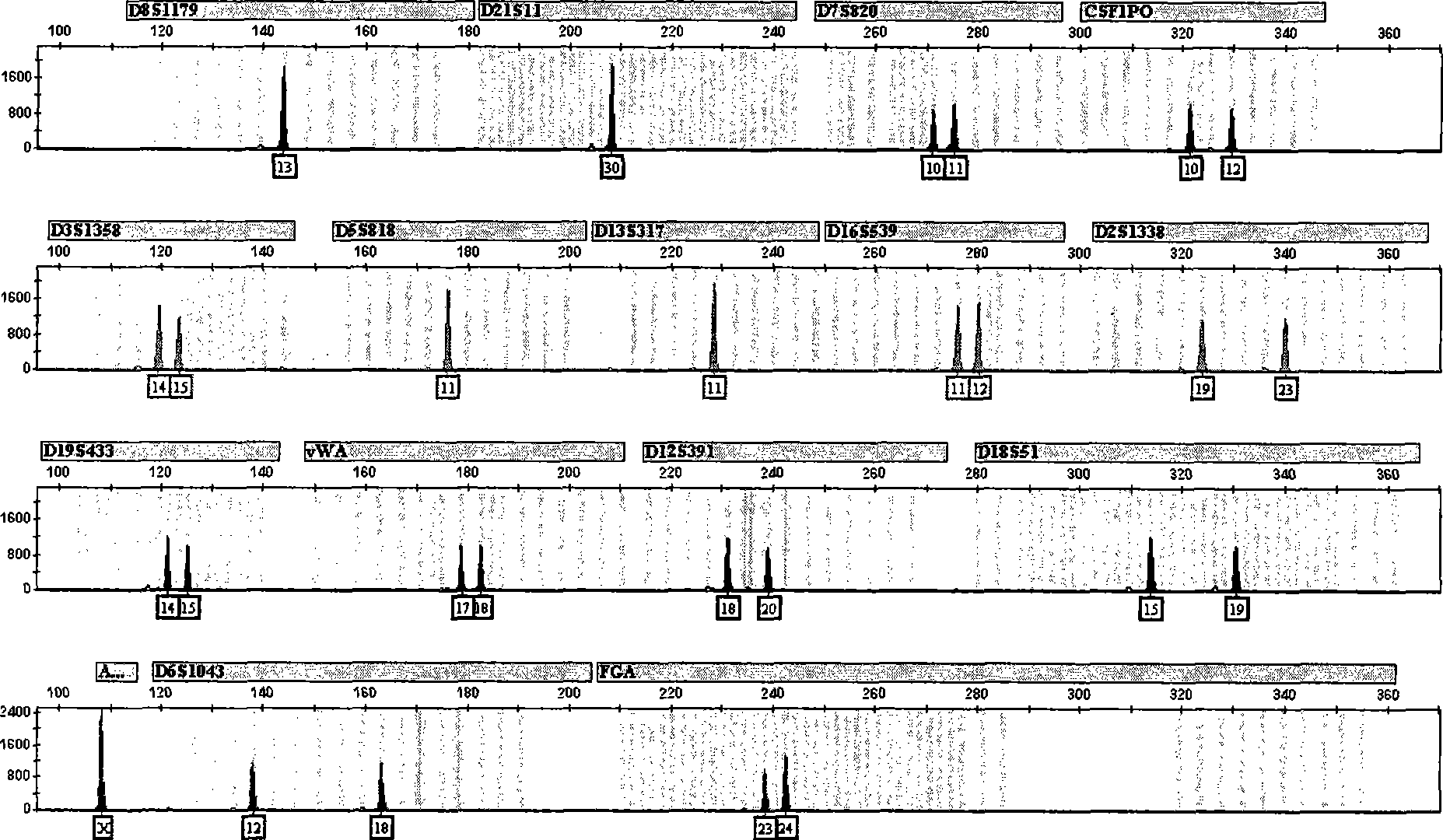
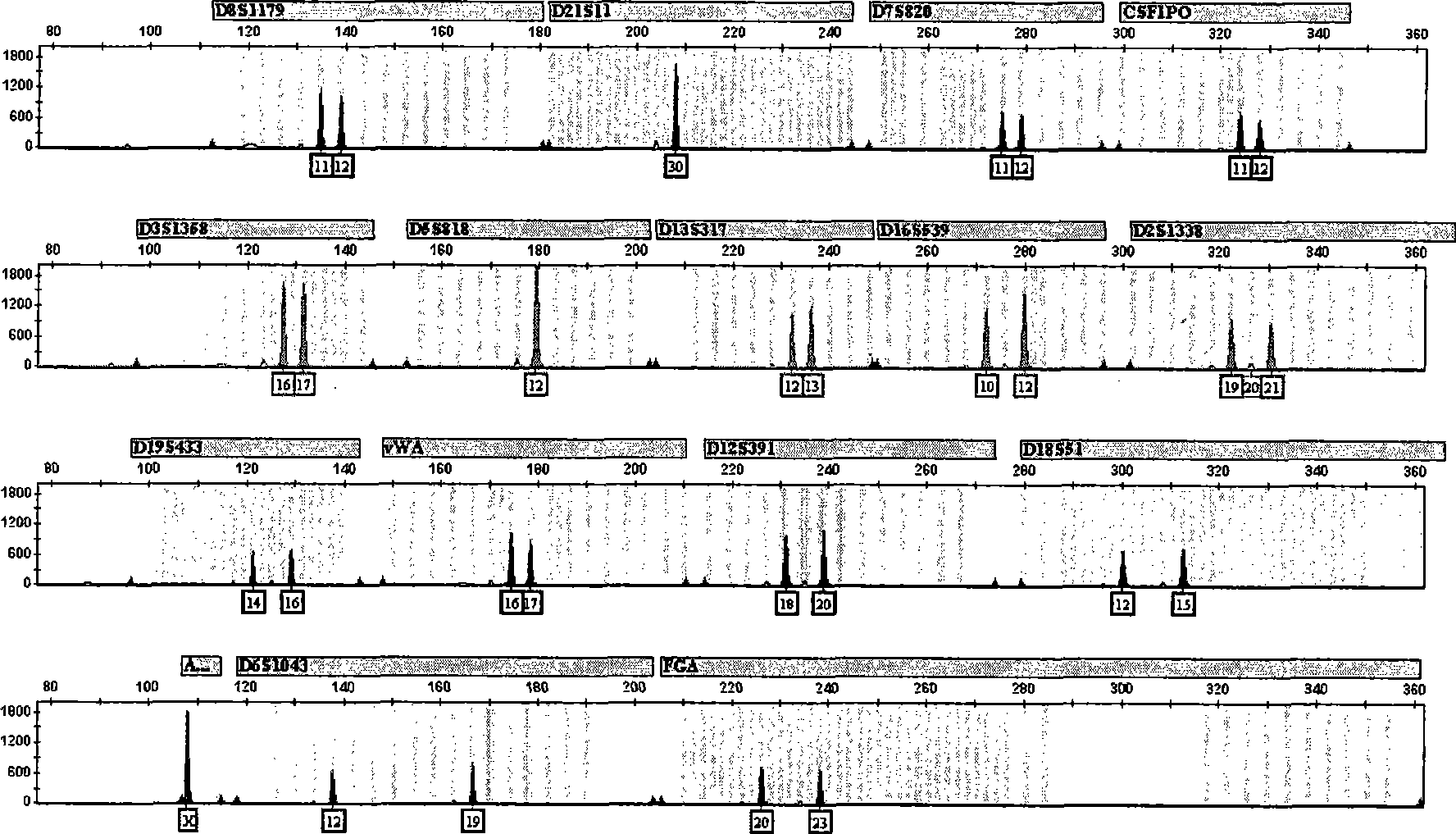
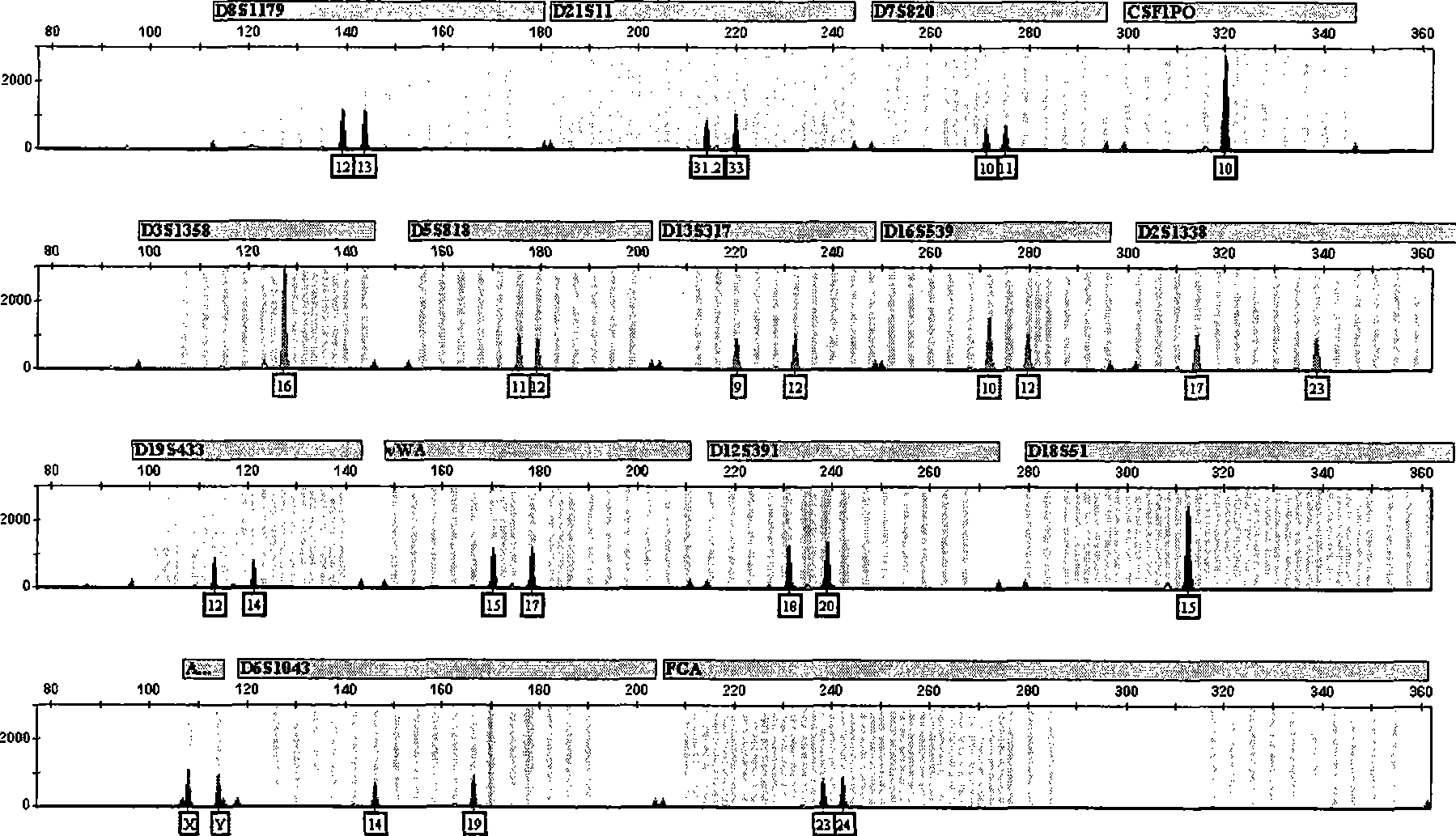
The invention discloses a composite STR determination method with improved resolution capability in Chinese people, in particular a method for carrying out genotyping to the Chinese people. The method comprises synchronous amplification and the analysis of the locus group consisting of the following loca: D8S1179, D21S11, D7S820, CSF1PO, D3S1358, D13S317, D16S539, D2S1338, D19S433, vWA, D18S51, AMEL, FGA, D5S818, and at least one of D6S1043 and D12S391. The invention also discloses a kit and a primer applied to the method.
Owner:APPLERA
Diagnostics and therapeutics for early-onset menopause
InactiveUS20050064453A1Effectively prescribeAvoid developmentSugar derivativesAntipyreticGeneBioinformatics
A method of predicting whether a subject is predisposed to developing early-onset menopause is provided. The method involves genotyping a patient at the IL-1 gene loci.
Owner:DUFF GORDON +2
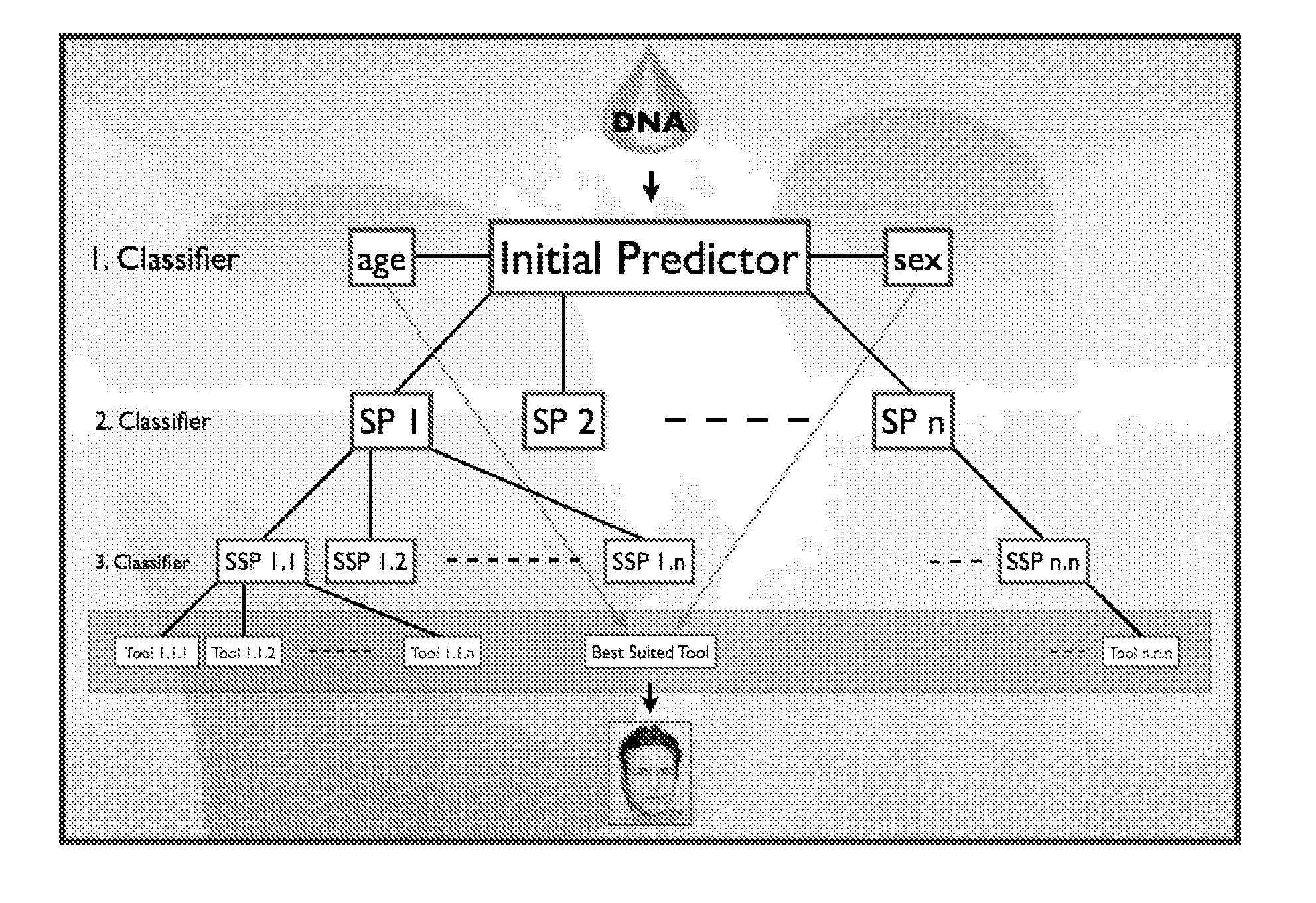
Genome-Wide Association Study Identifying Determinants Of Facial Characteristics For Facial Image Generation
InactiveUS20130039548A1Promote generationBiometric pattern for forensic purposeImage enhancementA-DNAOrganism
The present invention relates to a method for the generation of a facial composite from the genetic profile of a DNA-donor. The method comprises the steps of a) subjecting a biological sample to genotyping thereby generating a profile of genetic markers associated to numerical facial descriptors (NFD) for said sample, b) reverse engineer a NFD from the profile of the associated genetic variants and constructing a facial composite from the reverse engineered numerical facial descriptors (NFDs). The present invention also relates to a method for identifying genetic markers and / or combinations of genetic markers that are predictive of the facial characteristics, (predictive facial markers) of a person, said method comprising the steps of: a) capturing images of a group of individual faces; b) performing image analysis on facial images of said group of individual faces thereby extracting phenotypical descriptors of the faces; c) obtaining data on genetic variation from said group of individual and d) performing a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to identify said predictive facial markers.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Methods of diagnosing early-onset menopause
InactiveUS6730476B1Effectively prescribeAvoid developmentAntipyreticGenetic material ingredientsEarly onsetMedicine
A method of predicting whether a subject is predisposed to developing early-onset menopause is provided. The method involves genotyping a patient at the IL-1 gene loci.
Owner:INTERLEUKIN GENETICS
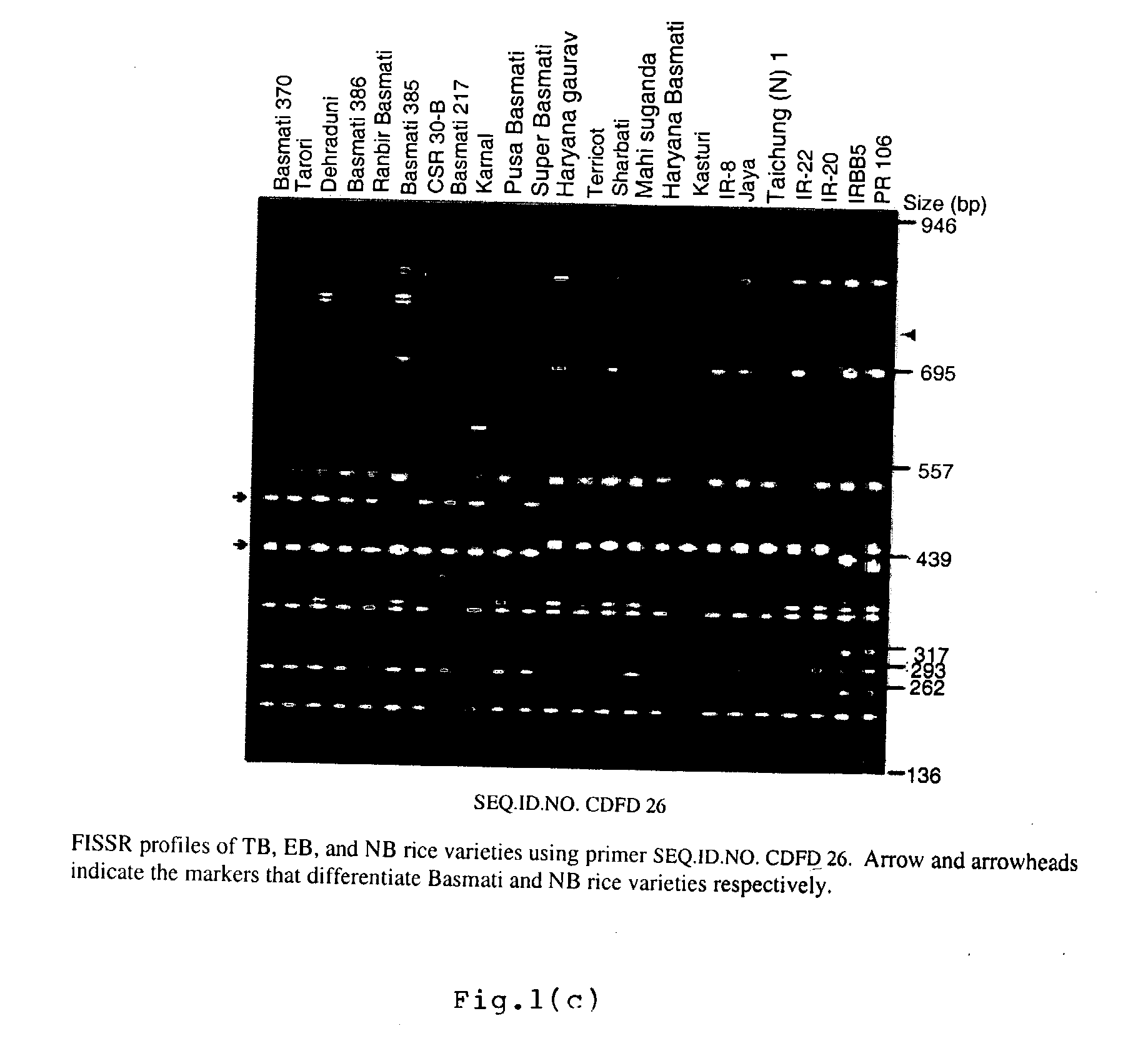
Novel FISSR-PCR primers and methods of identifying genotyping diverse genomes of plant and animal systems including rice varieties, a kit thereof
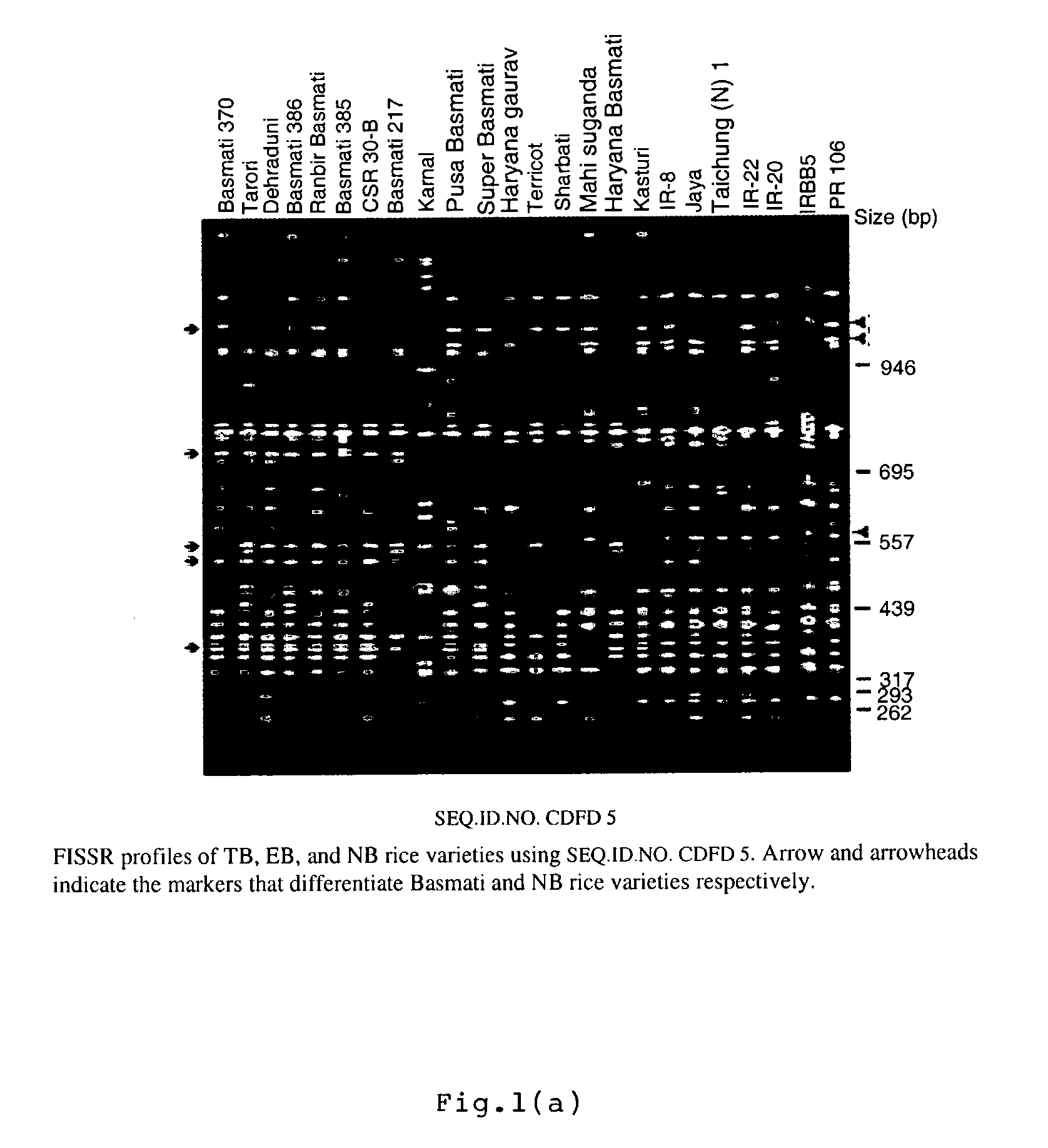
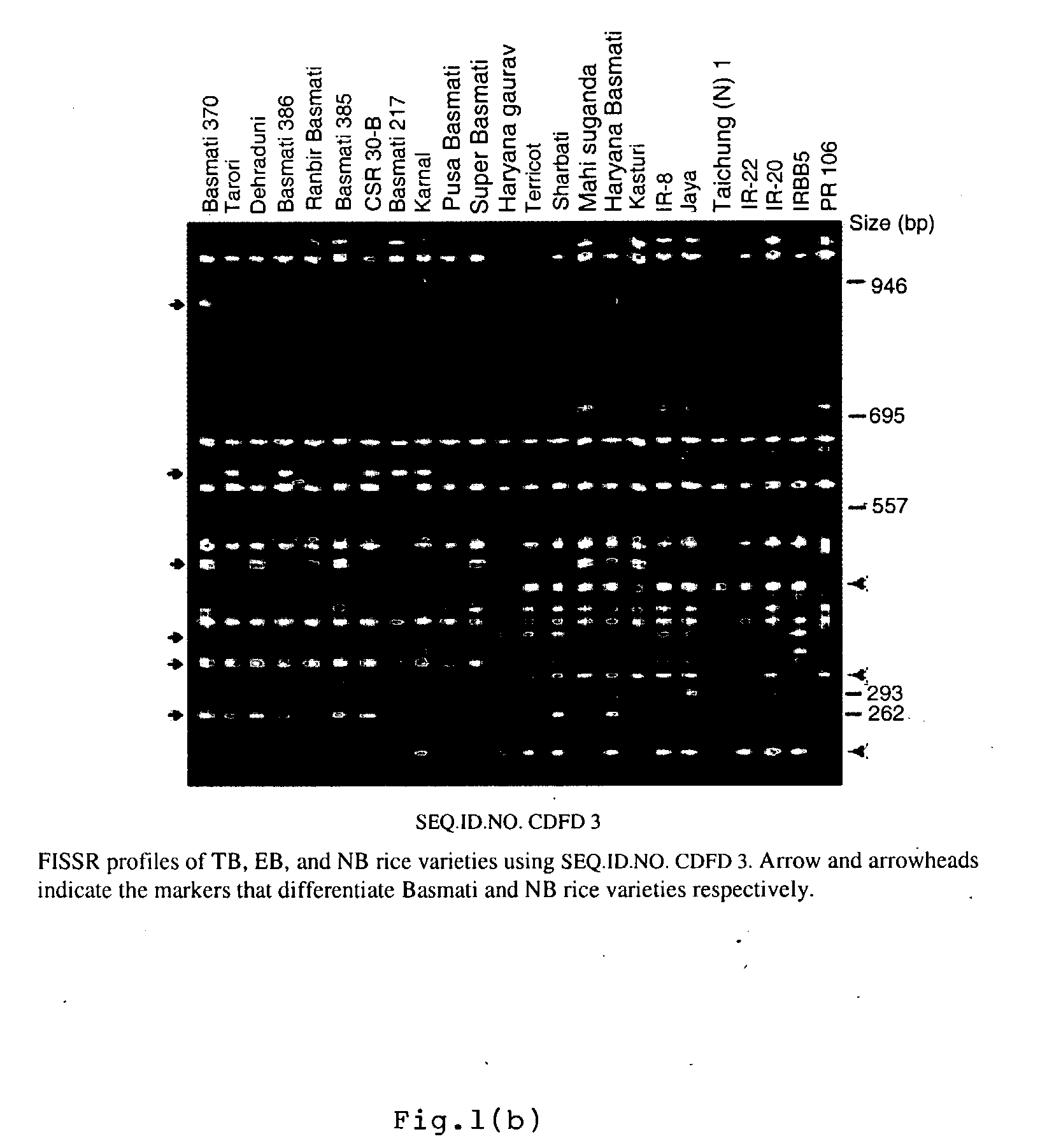
The present invention relates to set of inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR)-PCR primers of SEQ ID Nos. 1 to 37 for genotyping eukaryotes and a method of genotyping diverse genomes of plant and animal systems using FISSR-PCR primers and SSR markers; more particularly, a FISSR and SSR method of distinguishing Basmati rice varieties from Non-Basmati (NB) rice varieties, and Traditional Basmati (TB) rice varieties from Evolved Basmati (NB) rice varieties, and also, a method for determining adulteration of Basmati rice with other rice varieties and a kit thereof.
Owner:CENTRE FOR DNA FINGERPRINTING AND DIAGNOSTICS
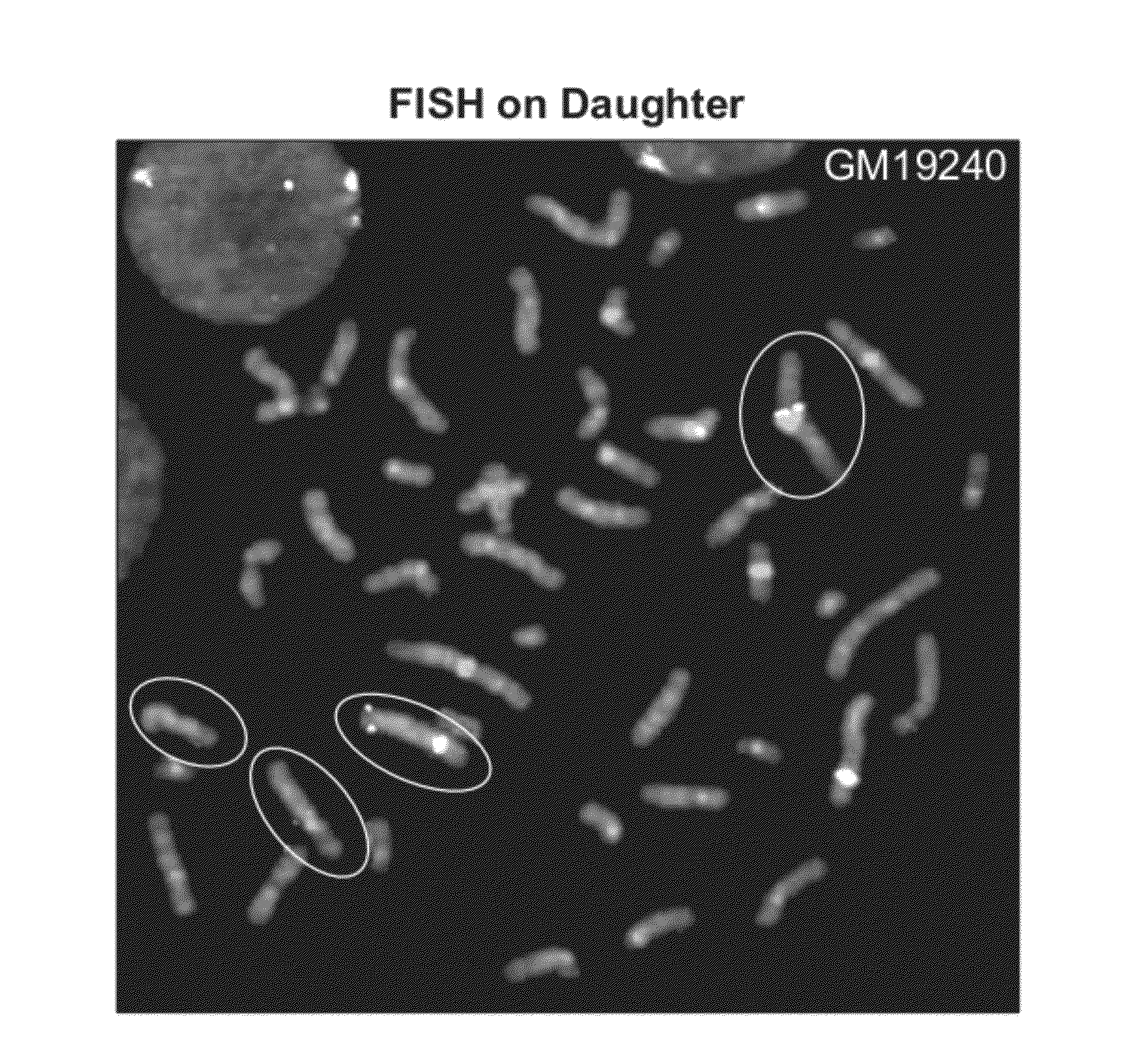
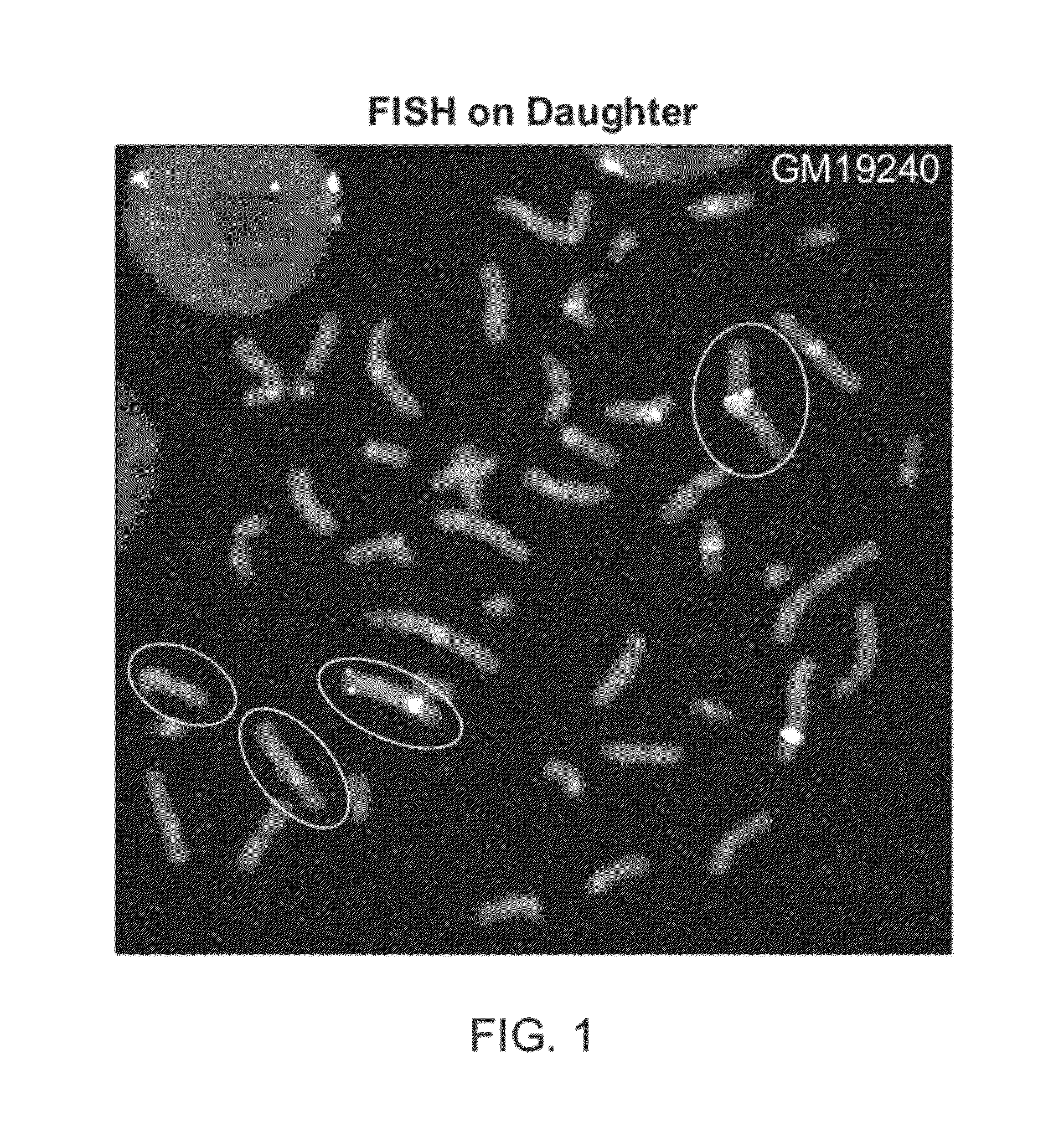
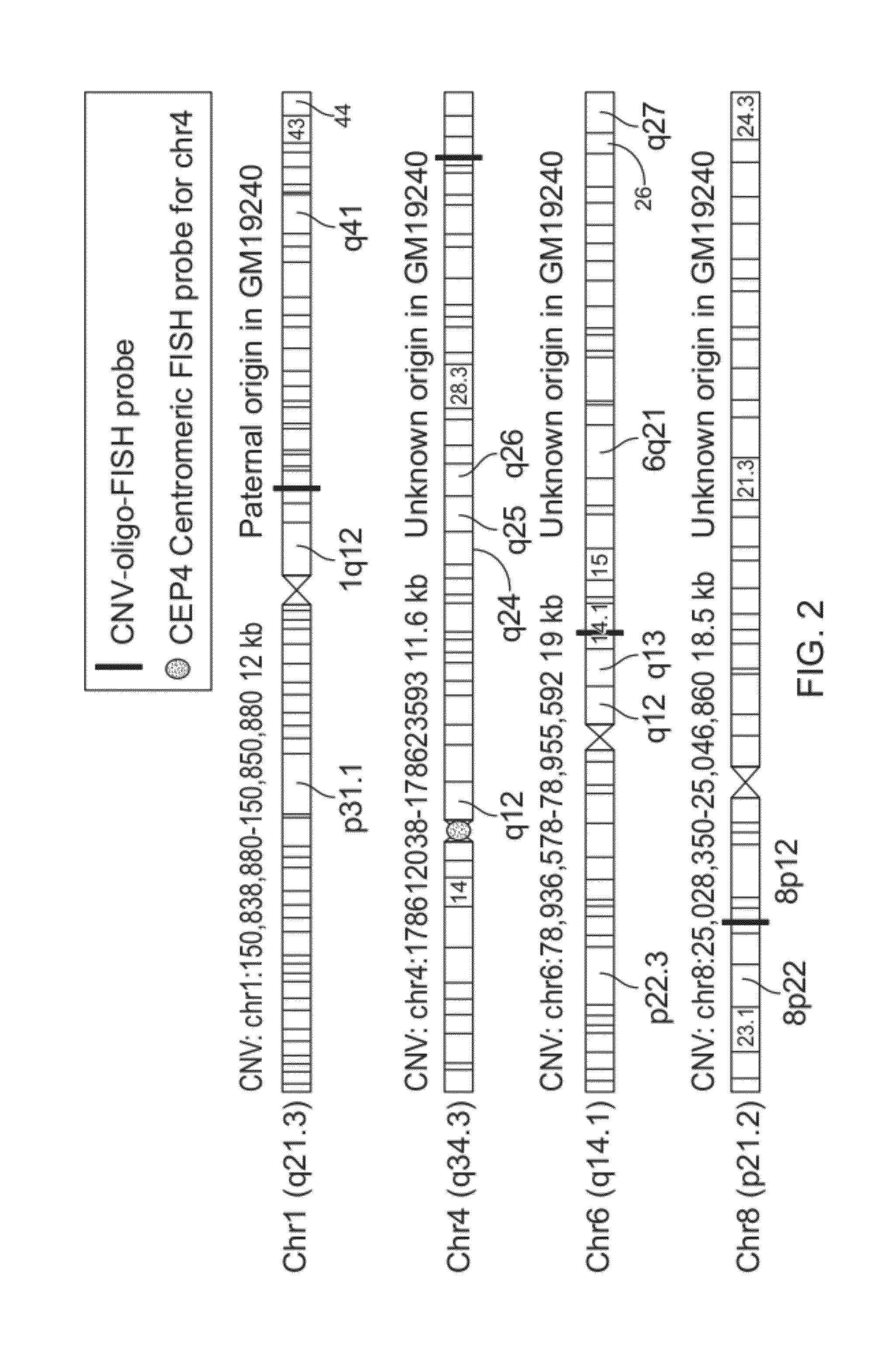
Method for phased genotyping of a diploid genome
InactiveUS20120283108A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiploid genomeGenotyping
A method of sample analysis is provided. In certain embodiments the method comprises: a) obtaining from a diploid individual a chromosomal sample that comprises maternally-derived chromosomes and homologous paternally-derived chromosomes; b) determining the parent of origin of a first chromosome of the sample by detecting a parent-specific copy number variation relative to a second chromosome that is homologous to the first chromosome; c) isolating the first chromosome; and d) genotyping the first chromosome.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
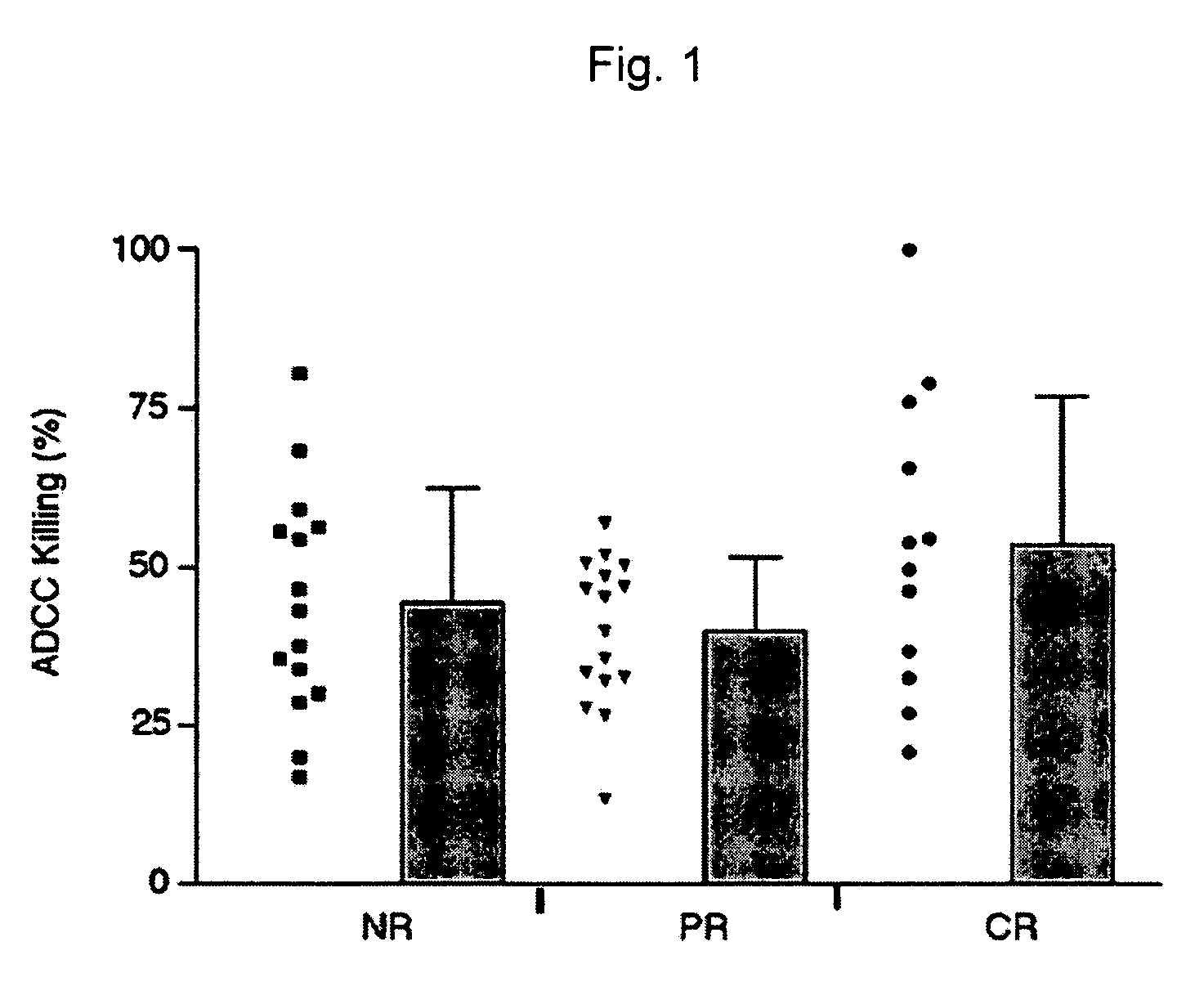
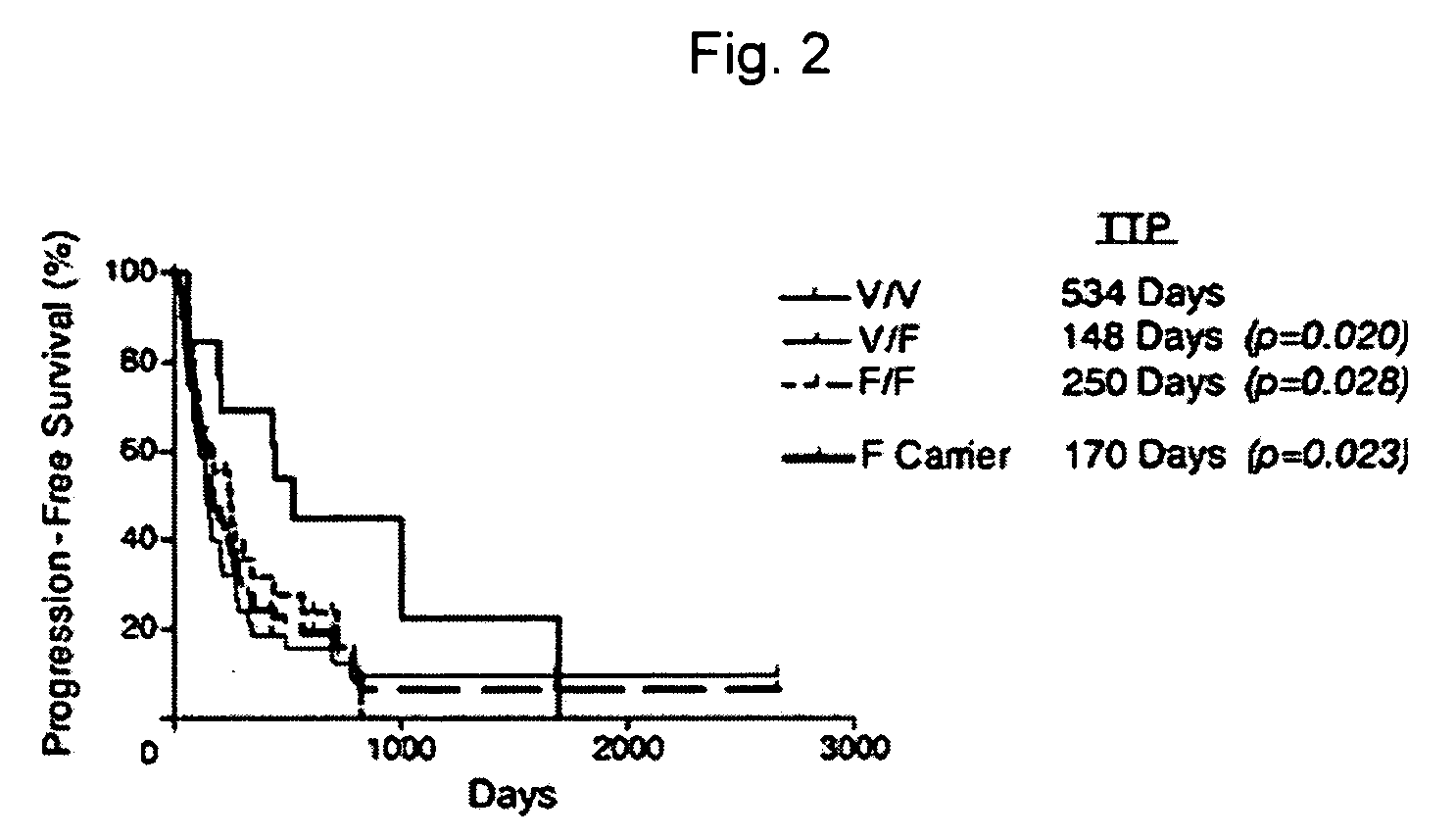
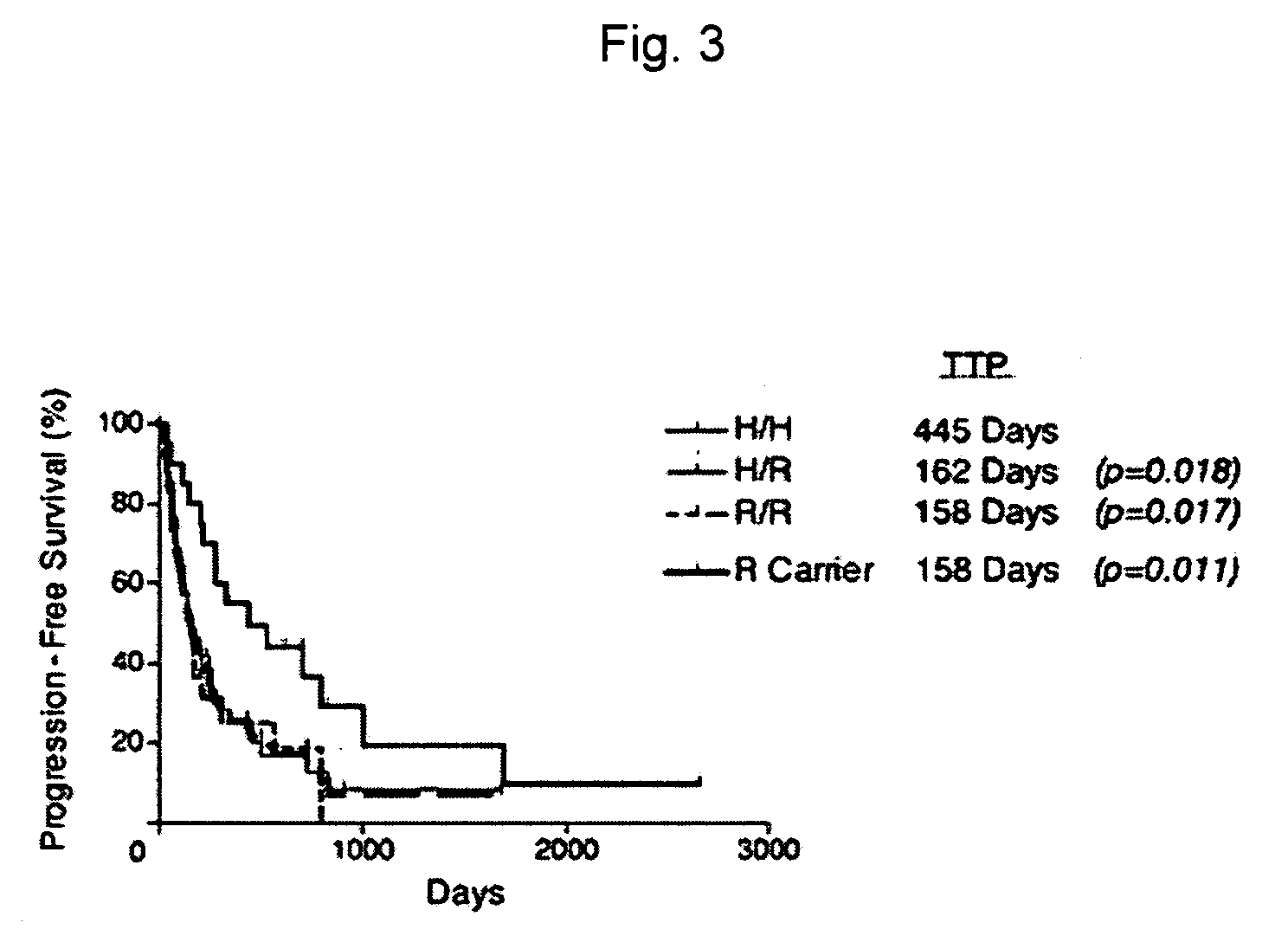
Methods and compositions for determining responsiveness to antibody therapy
ActiveUS20060008825A1Microbiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisMedicineGenotyping
Methods and compositions are provided for determining whether a subject suffering from a neoplastic condition is responsive to an antineoplastic therapy, such as antibody therapy, e.g., Rituximab. In practicing the subject methods, the subject is genotyped to determine whether the subject has a least one favorable FcγR polymorphism, e.g., the 131 H / H genotype or the 158 V / V genotype. In addition, reagents, devices and kits thereof, that find use in practicing the subject methods are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) polymorphic alleles and use of the same to identify DNA markers for reproductive longevity
Disclosed herein are embodiments for genotyping an animal for the presence of polymorphic alleles in the IGF-1R gene that are associated with reproductive longevity and / or ability to better sustain stress, and preferably selecting those animals for future breeding purposes.
Owner:PERFORMANCE GENOMICS
Comprehensive genetic analysis method of susceptibility of complex diseases
InactiveCN101845501AImprove graspReduce genetic analysis timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsCalculation errorGenetic Databases
The invention relates to a comprehensive genetic analysis method of susceptibility of complex diseases, which comprises the following steps: 1) establishing related genetic databases of complex diseases and determining related detection sites; 2) carrying out genotyping for SNPs sites within individual whole genome by using the Affymetrix6.0 chip technology to obtain the corresponding genotype of each SNP site; 3) exporting determined disease-related SNP site typing results from 900,000 SNP site detection results of a 6.0 chip, and calculating a CGR value according to the genotyping results; and 4) carrying out particular and deep genetic analysis for increased-risk diseases and high-risk diseases according to the calculated disease-related CGR value. The invention can improve the certainty of the susceptibility predication of complex diseases of Chinese Han population, shortens genetic analysis time and prevents calculation errors caused by manual calculation.
Owner:孟涛 +1
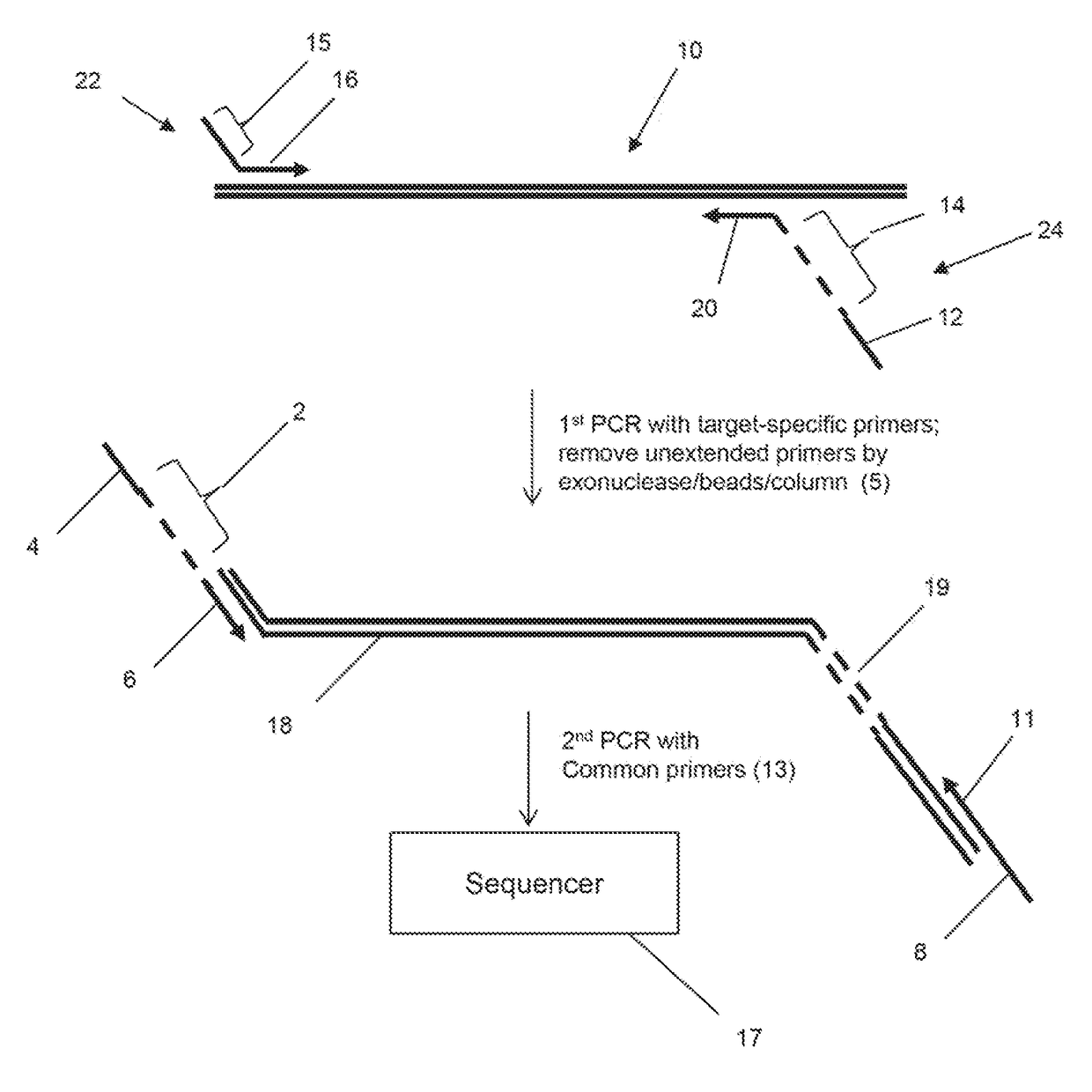
Method for genotyping clonotype profiles using sequence tags
ActiveUS20170335390A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh throughput sequenceContamination
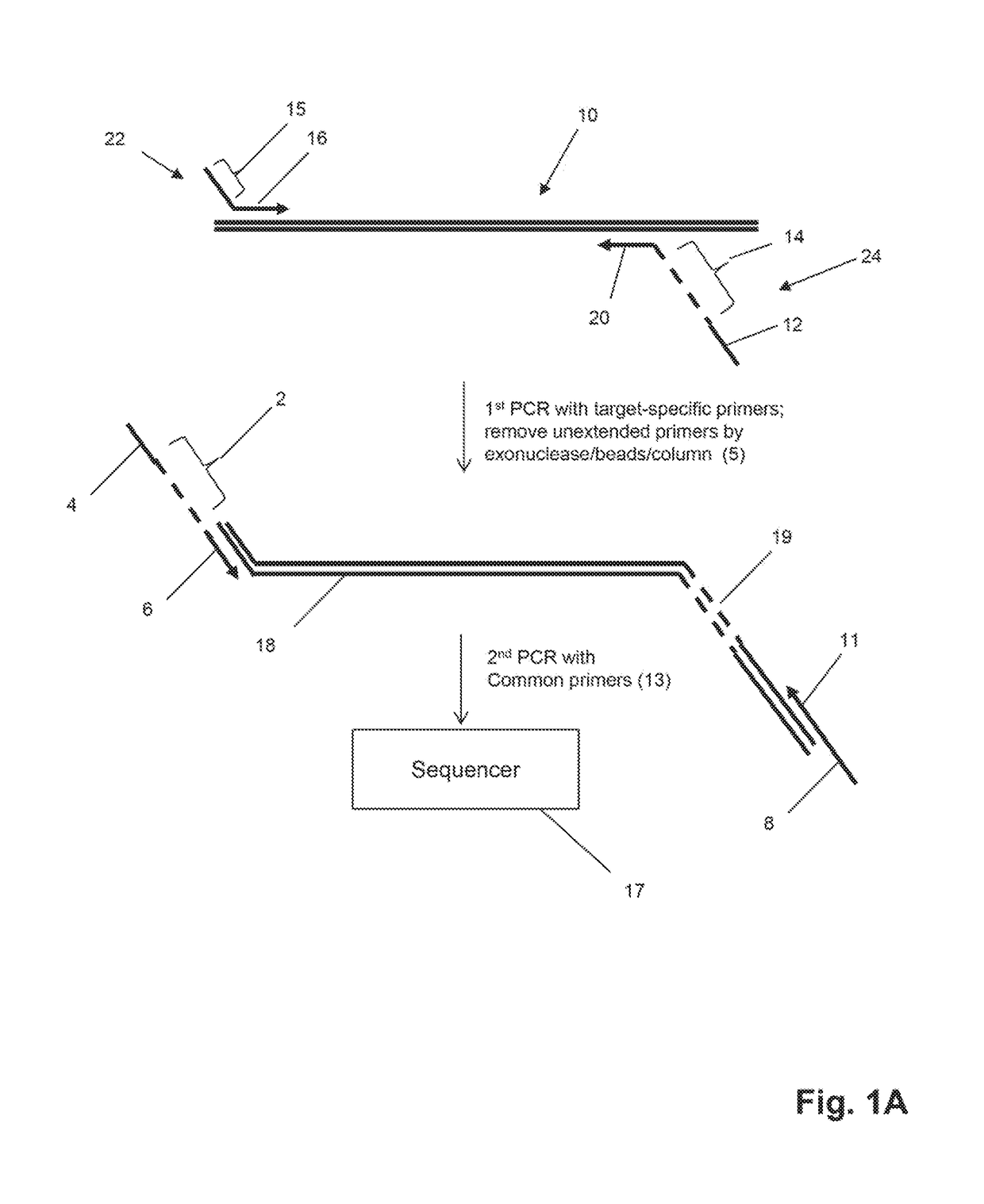
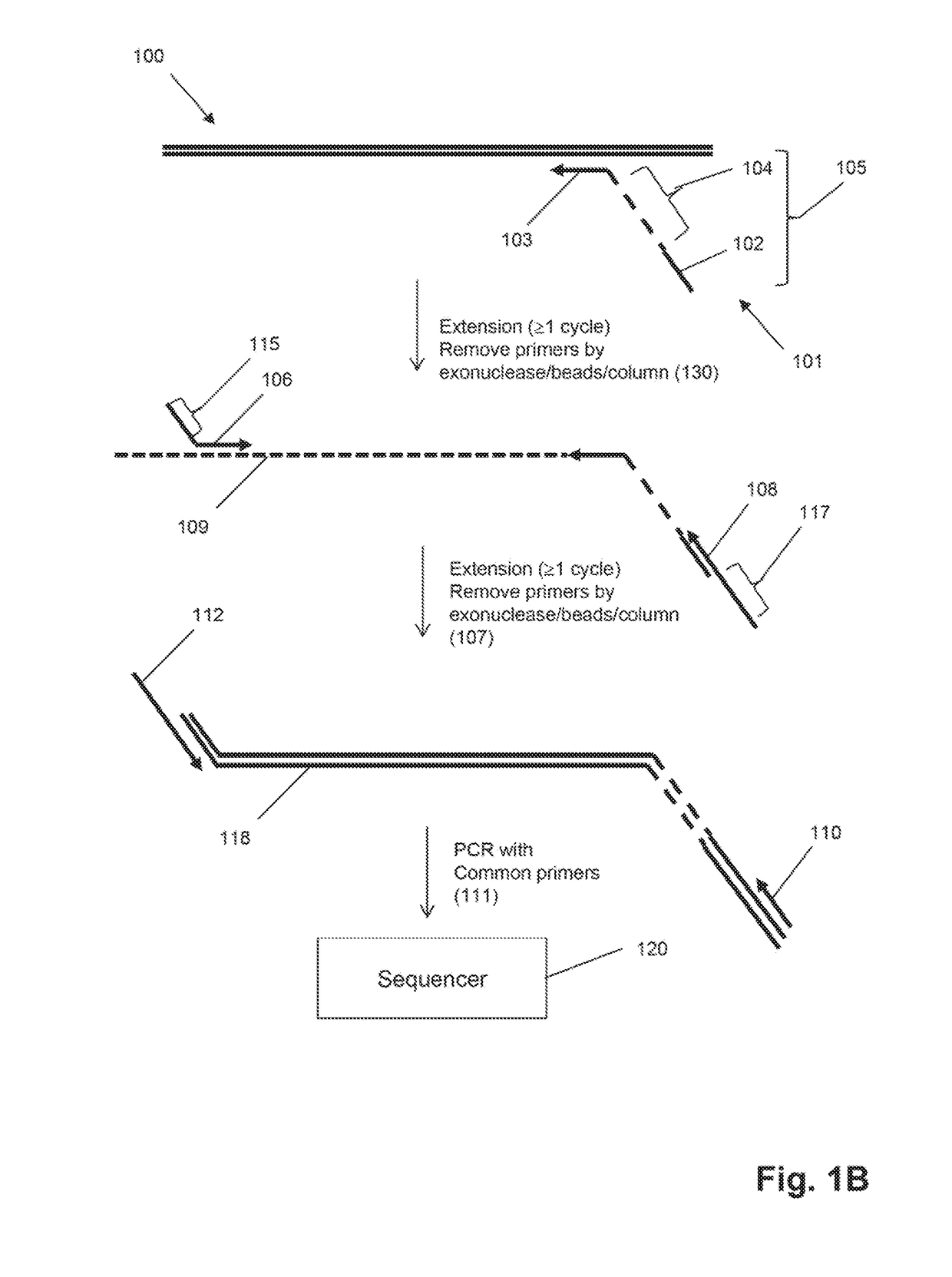
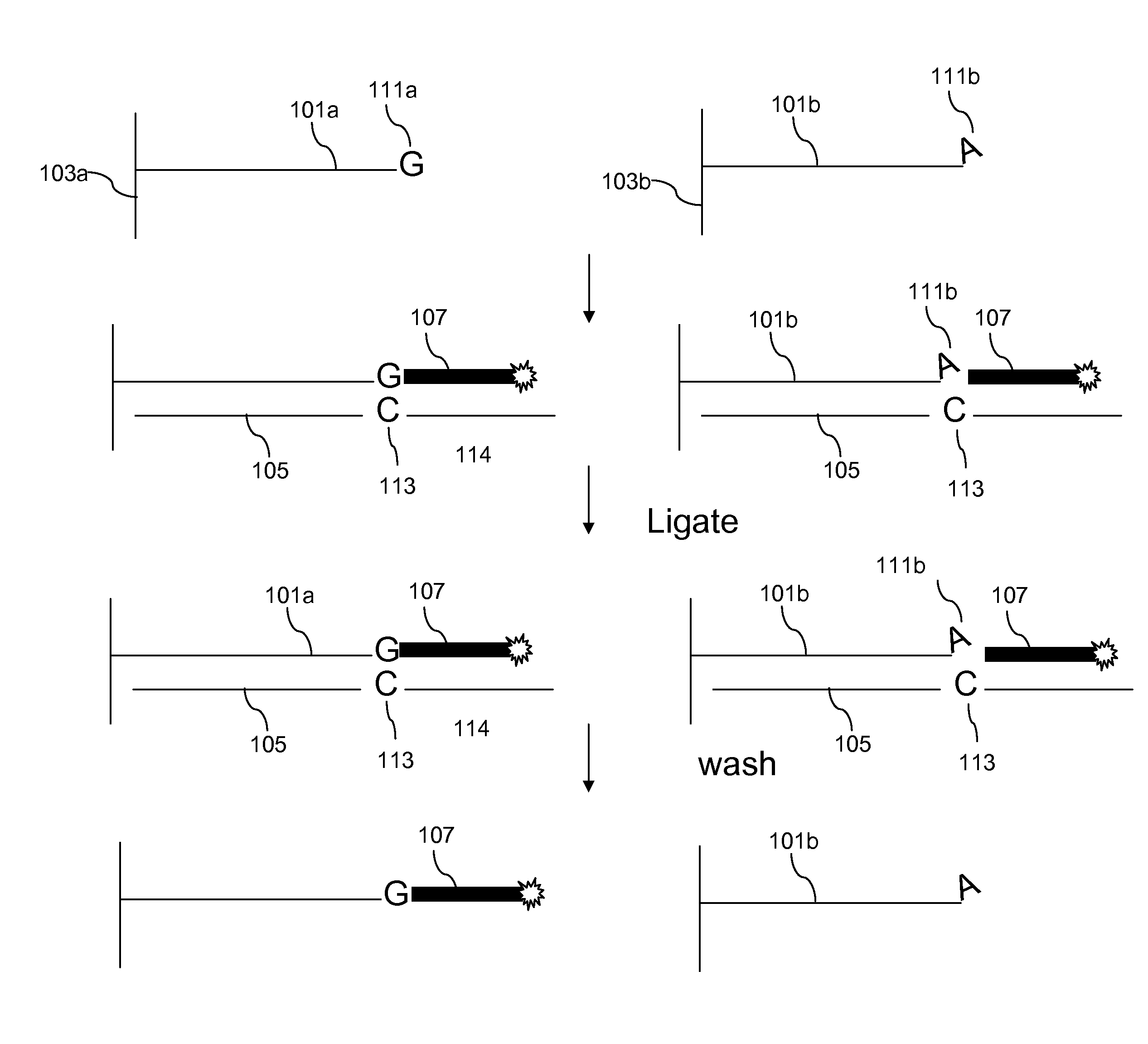
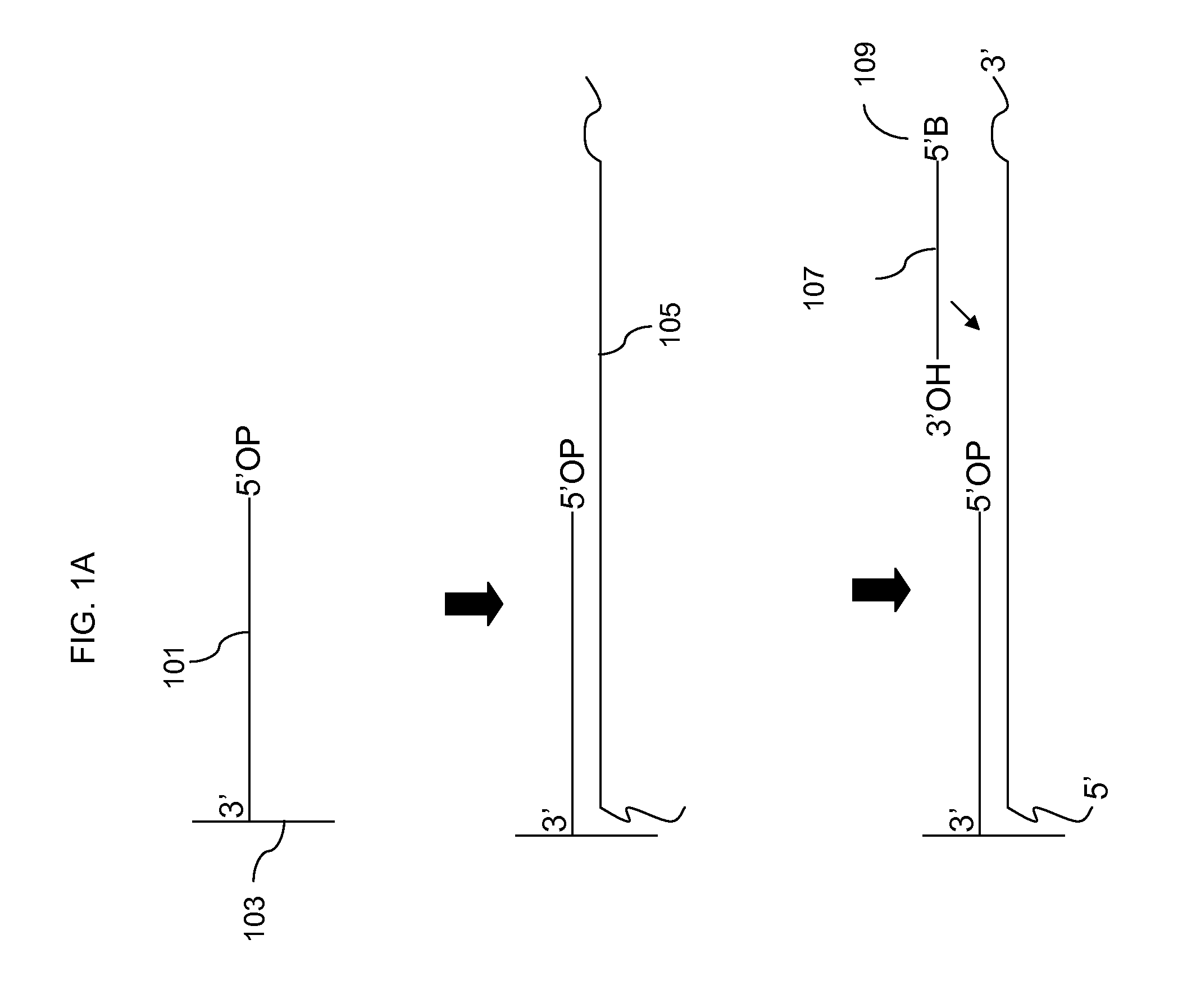
The invention is directed to sequence-based profiling of populations of nucleic acids by multiplex amplification and attachment of one or more sequence tags to target nucleic acids and / or copies thereof followed by high-throughput sequencing of the amplification product. In some embodiments, the invention includes successive steps of primer extension, removal of unextended primers and addition of new primers either for amplification (for example by PCR) or for additional primer extensions. Some embodiments of the invention are directed to minimal residual disease (MRD) analysis of patients being treated for cancer. Sequence tags incorporated into sequence reads provide an efficient means for determining clonotypes and at the same time provide a convenient means for detecting carry-over contamination from other samples of the same patient or from samples of a different patient which were tested in the same laboratory.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Enzymatic methods for genotyping on arrays
The invention relates to methods for enzymatic, genotyping of polymorphisms on solid supports. In some aspects the methods include ligation of allele or base specific interrogation probes to an array probe. The array probe is labeled by ligation of the interrogation probe. Ligation is dependent on the identity of the base immediately adjacent to the end of the array probe. In other aspects array bound probes are labeled by template dependent extension.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Kit for genotyping folate metabolism gene
ActiveCN104131087AIncreased sensitivityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingNucleotide
The invention provides a kit for genotyping folate metabolism gene. The kit includes a PCR reaction liquid and a DNA hybrid membrane strip, the DNA hybrid film strip comprises a matrix vector and probes, four probes for MTHFR genes, two probes for MTRR genes and two probes designed for human genome are sequentially fixed on the matrix vector, each of the probes is an oligonucleotide sequence hybridized with the SNP locus of each of the corresponding gene, and the nucleotide sequences of the probes are represented by SEQ ID NO:1-8. The kit provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, rapid detection, good stability, realization of high or low flux detection, high flexibility, strong maneuverability for small clinical samples in some hospitals, less equipment investment and low cost.
Owner:WUHAN CMLABS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com