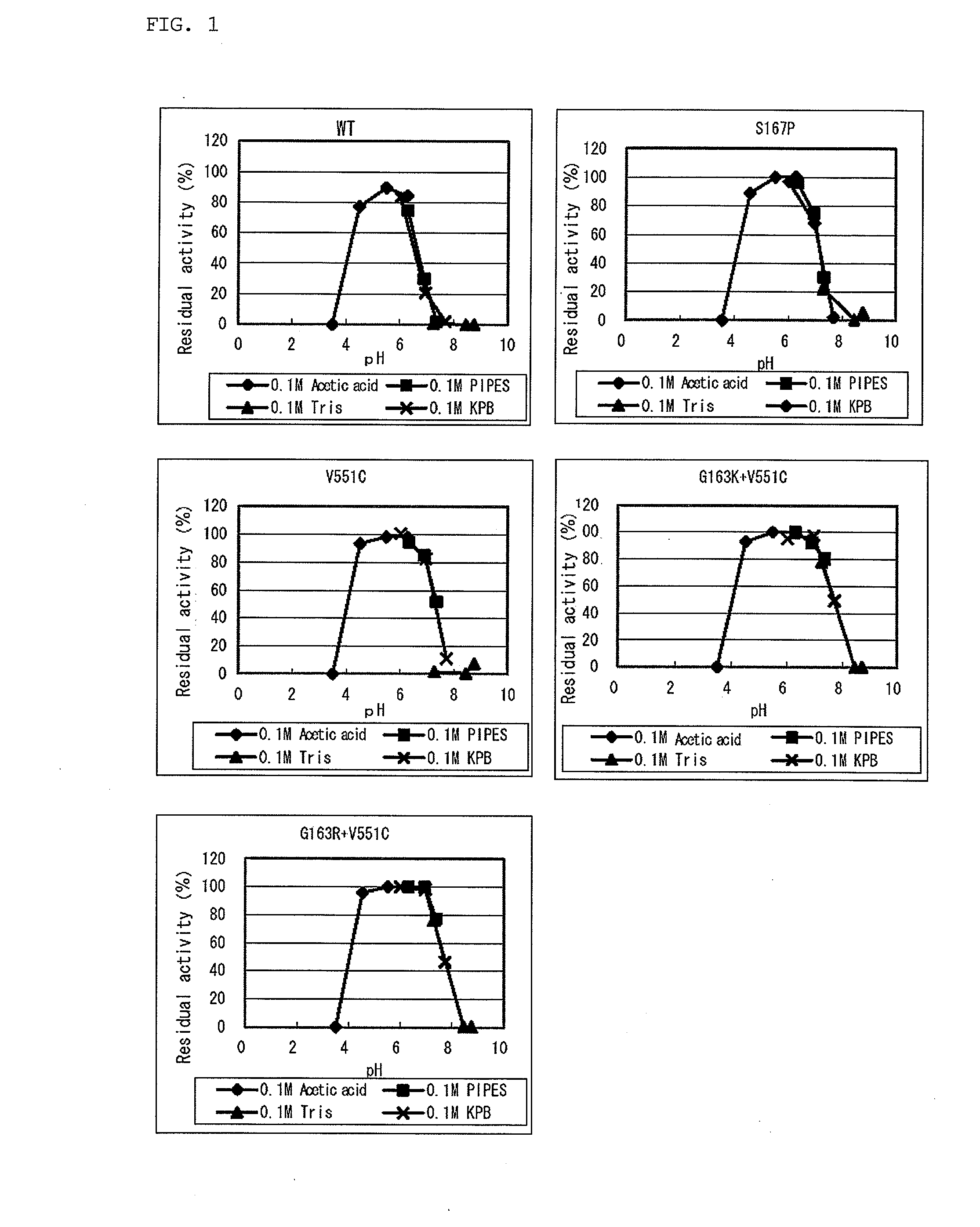
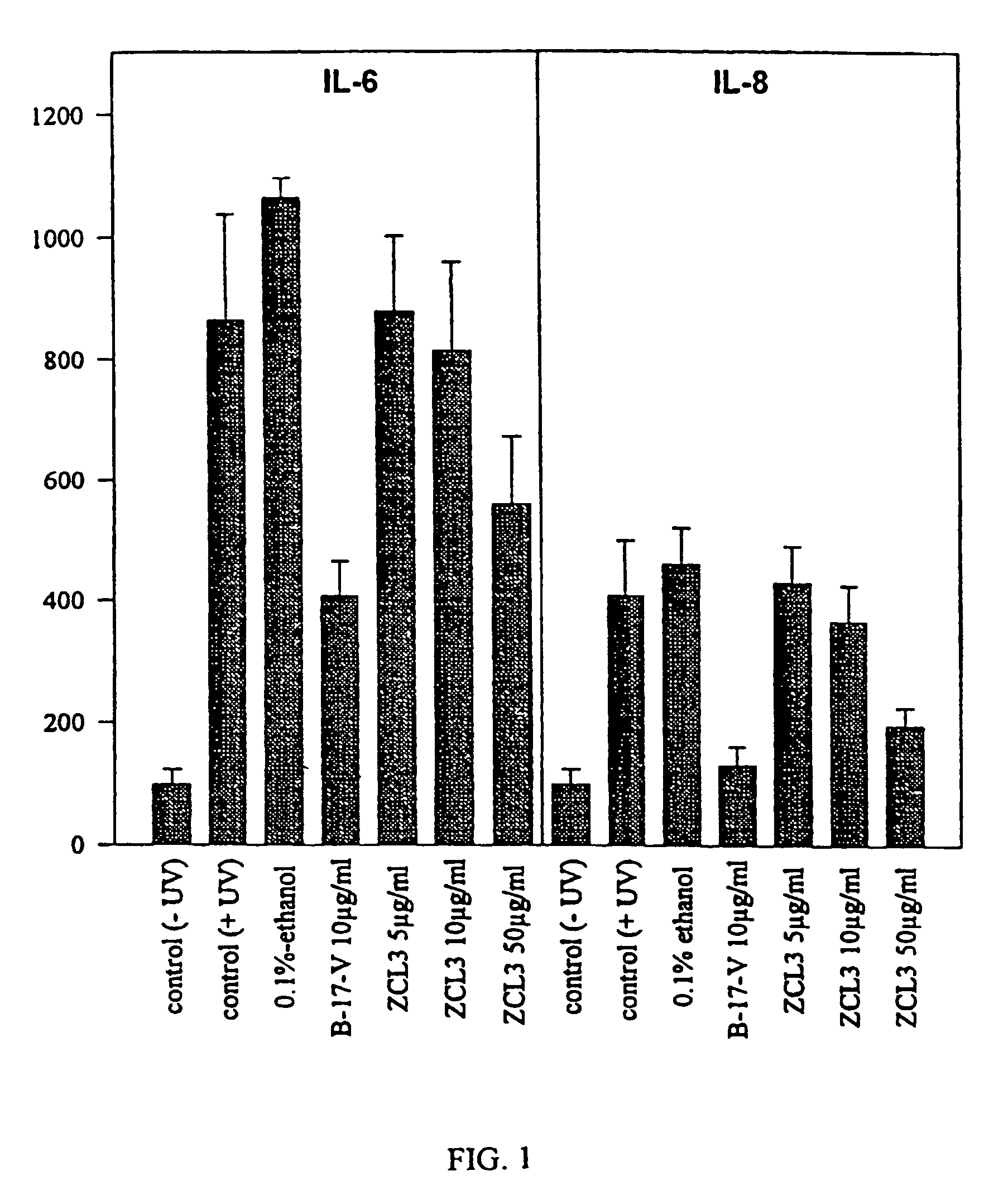
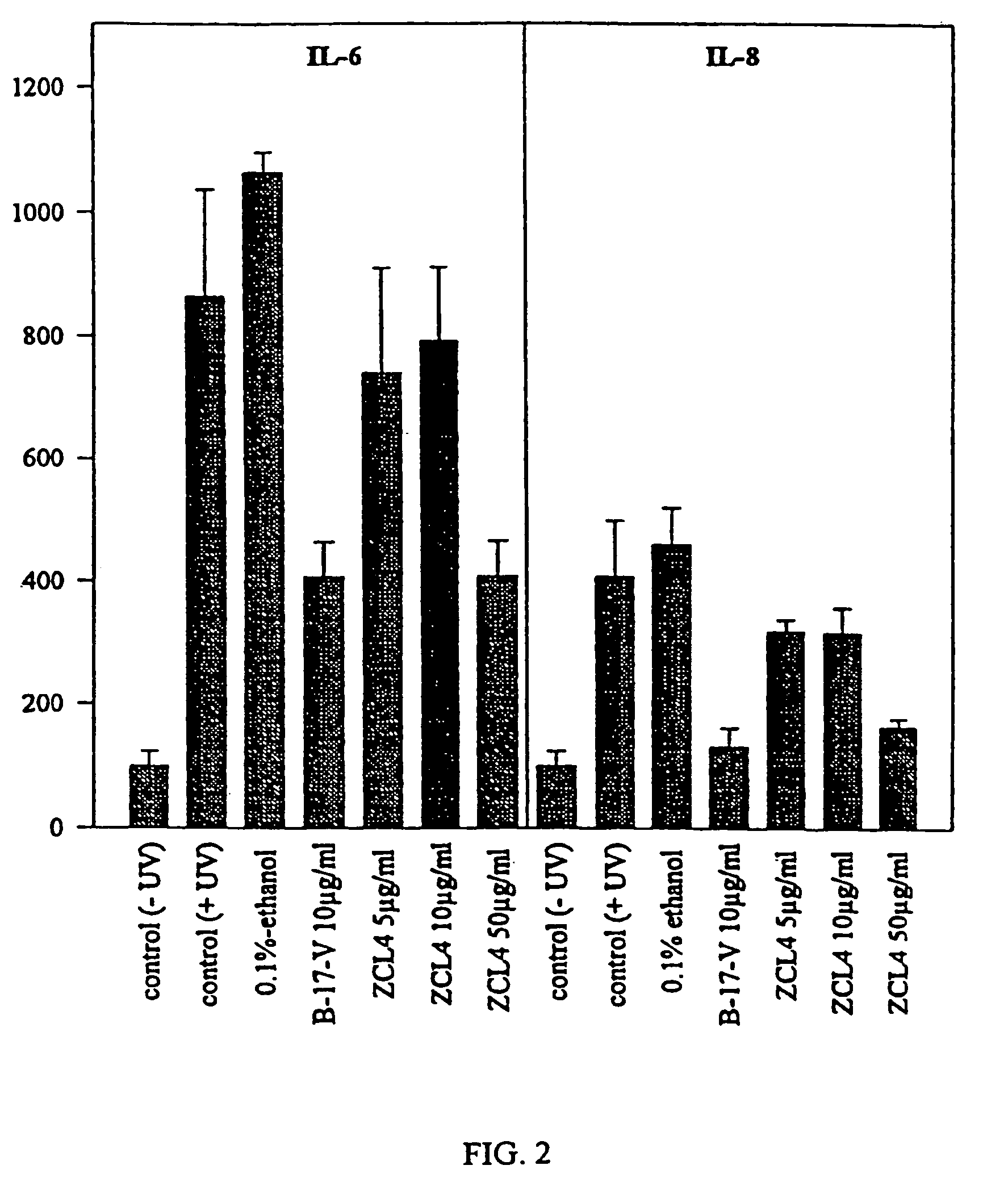
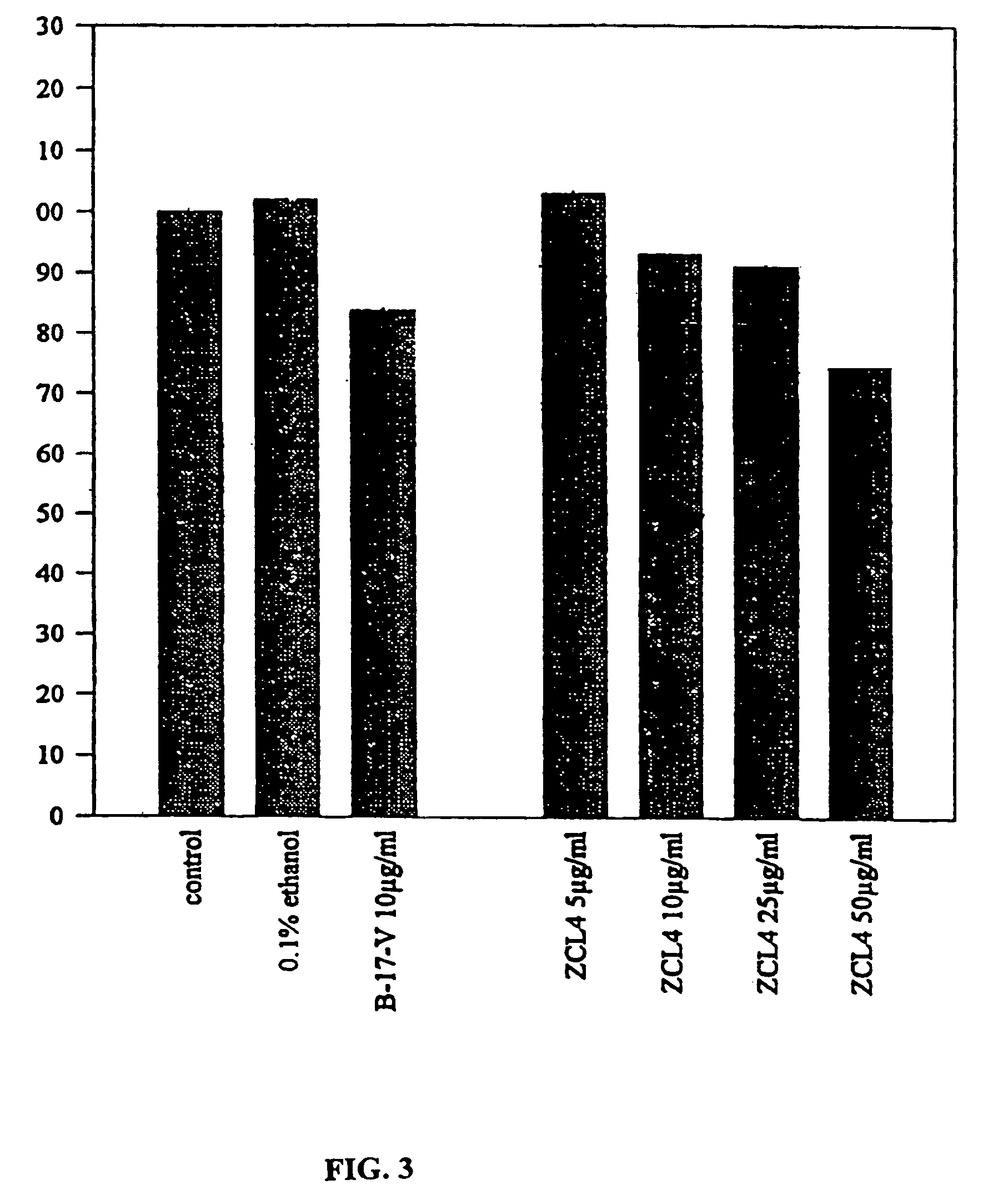
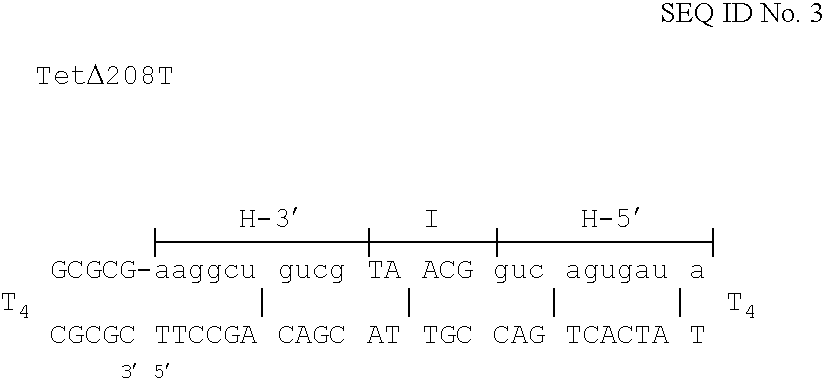Patents
Literature
333 results about "Eukaryote" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Eukaryotes (/juːˈkærioʊt, -ət/) are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, unlike prokaryotes (Bacteria and Archaea), which have no membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes belong to the domain Eukaryota or Eukarya. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (eu, "well" or "true") and κάρυον (karyon, "nut" or "kernel"). Eukaryotic cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and the Golgi apparatus, and in addition, some cells of plants and algae contain chloroplasts. Unlike unicellular archaea and bacteria, eukaryotes may also be multicellular and include organisms consisting of many cell types forming different kinds of tissue. Animals and plants are the most familiar eukaryotes.
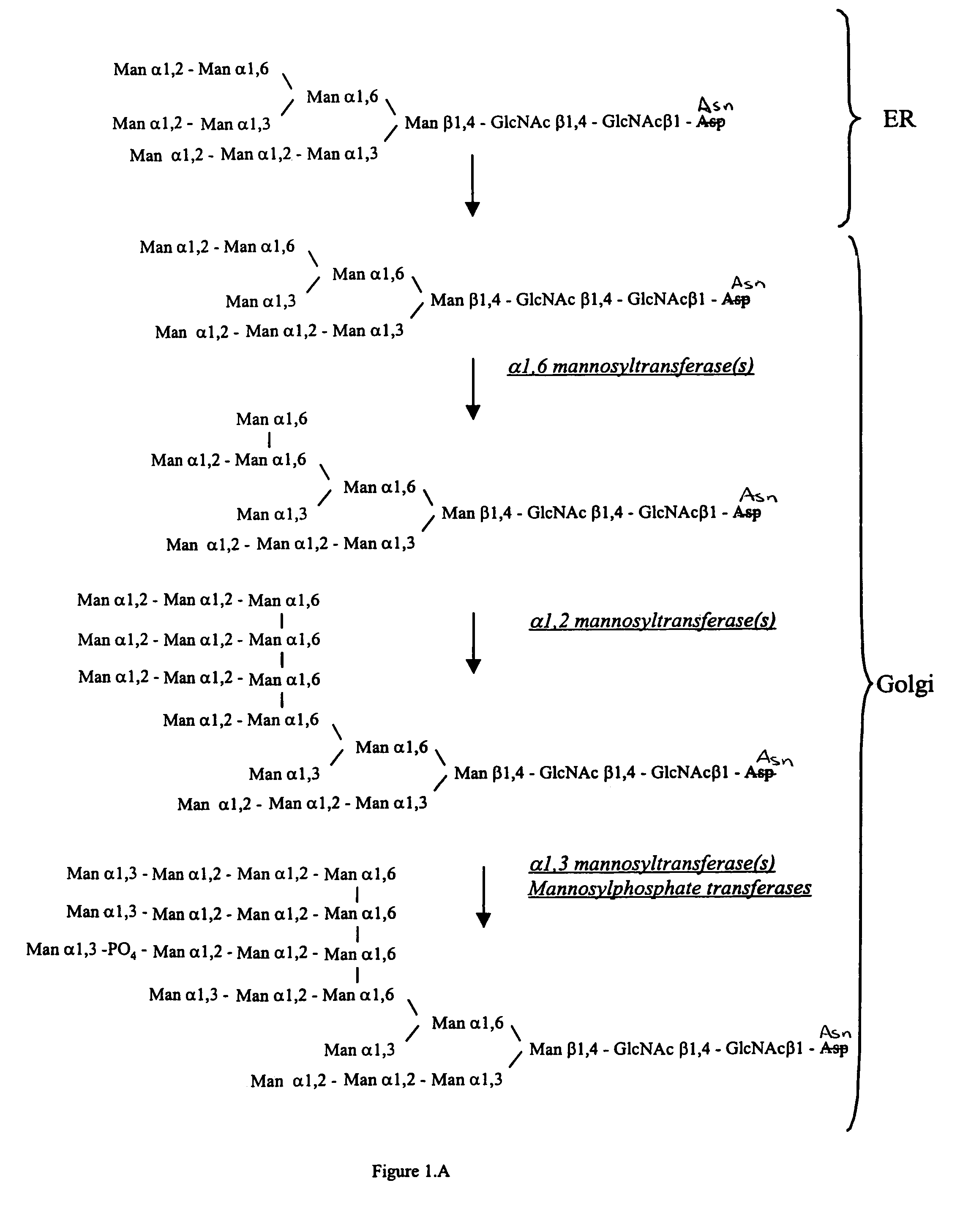
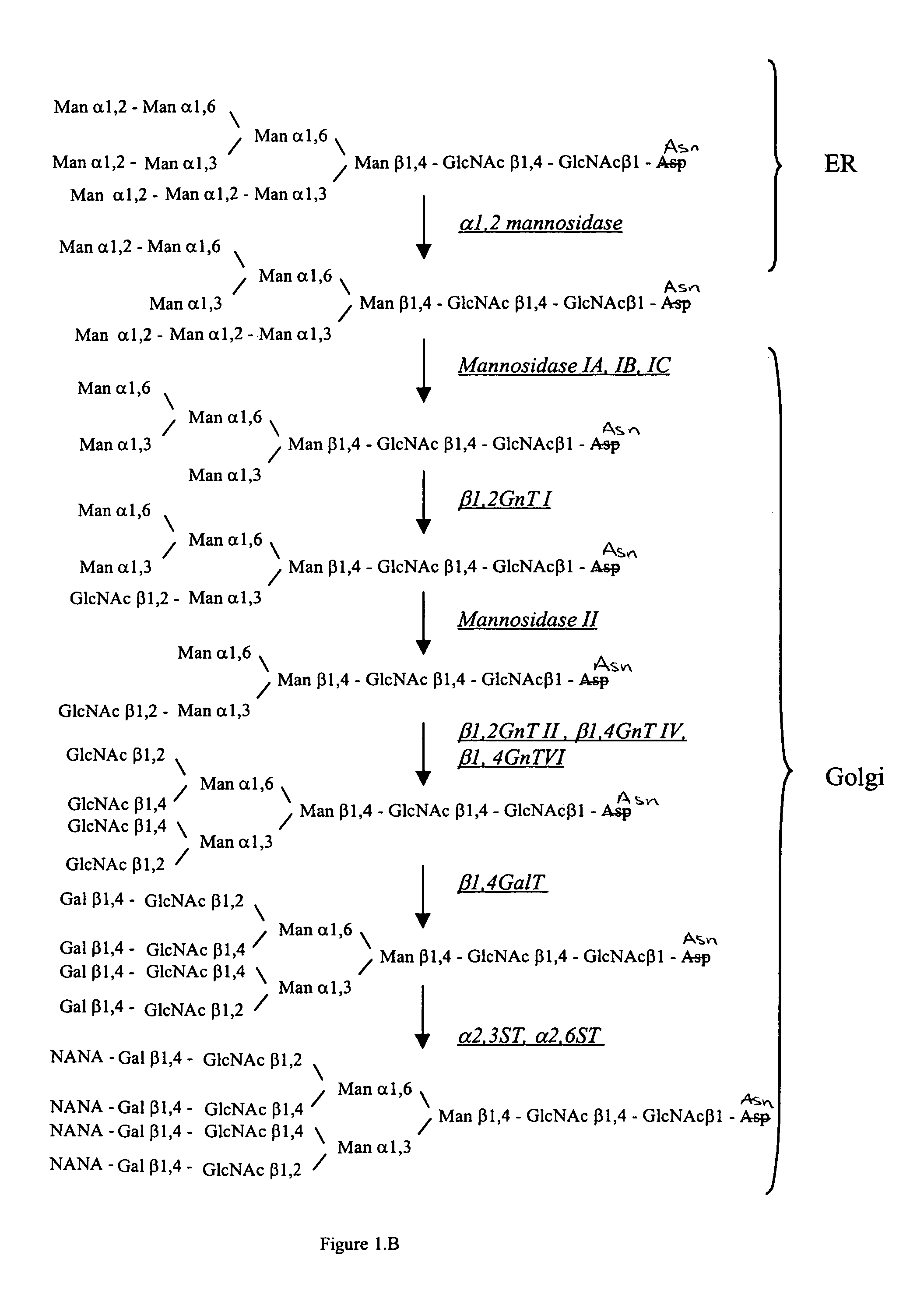
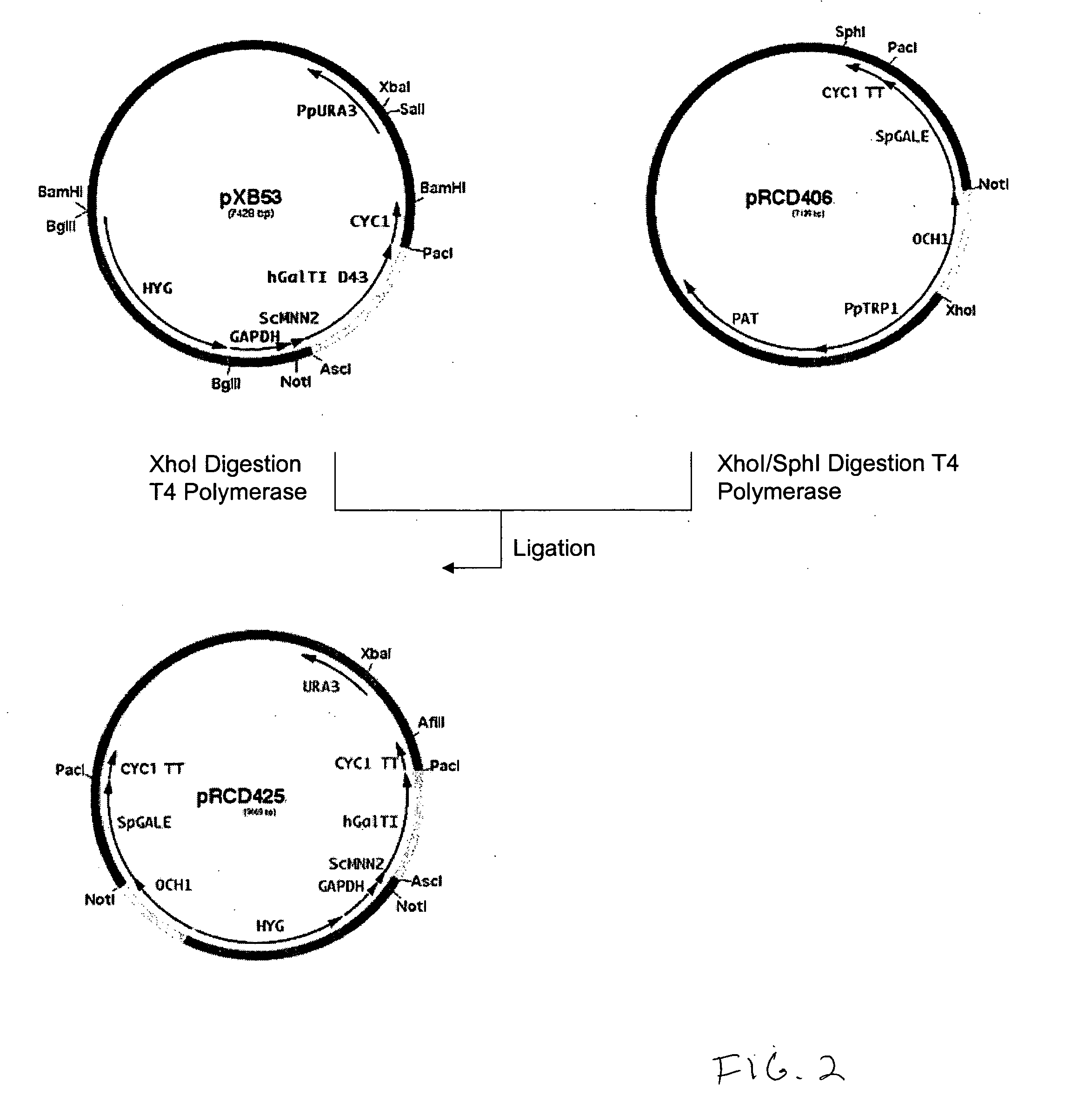
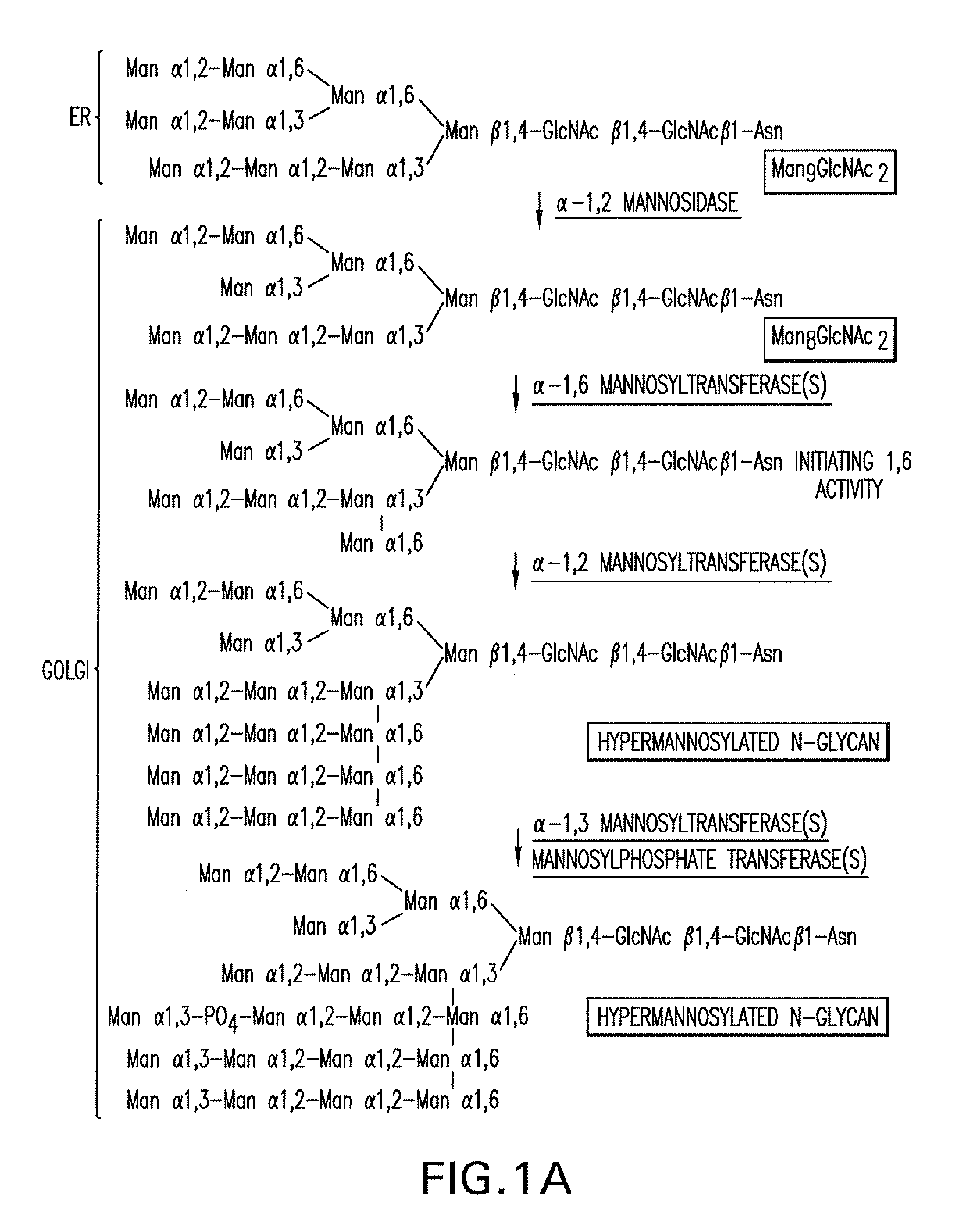
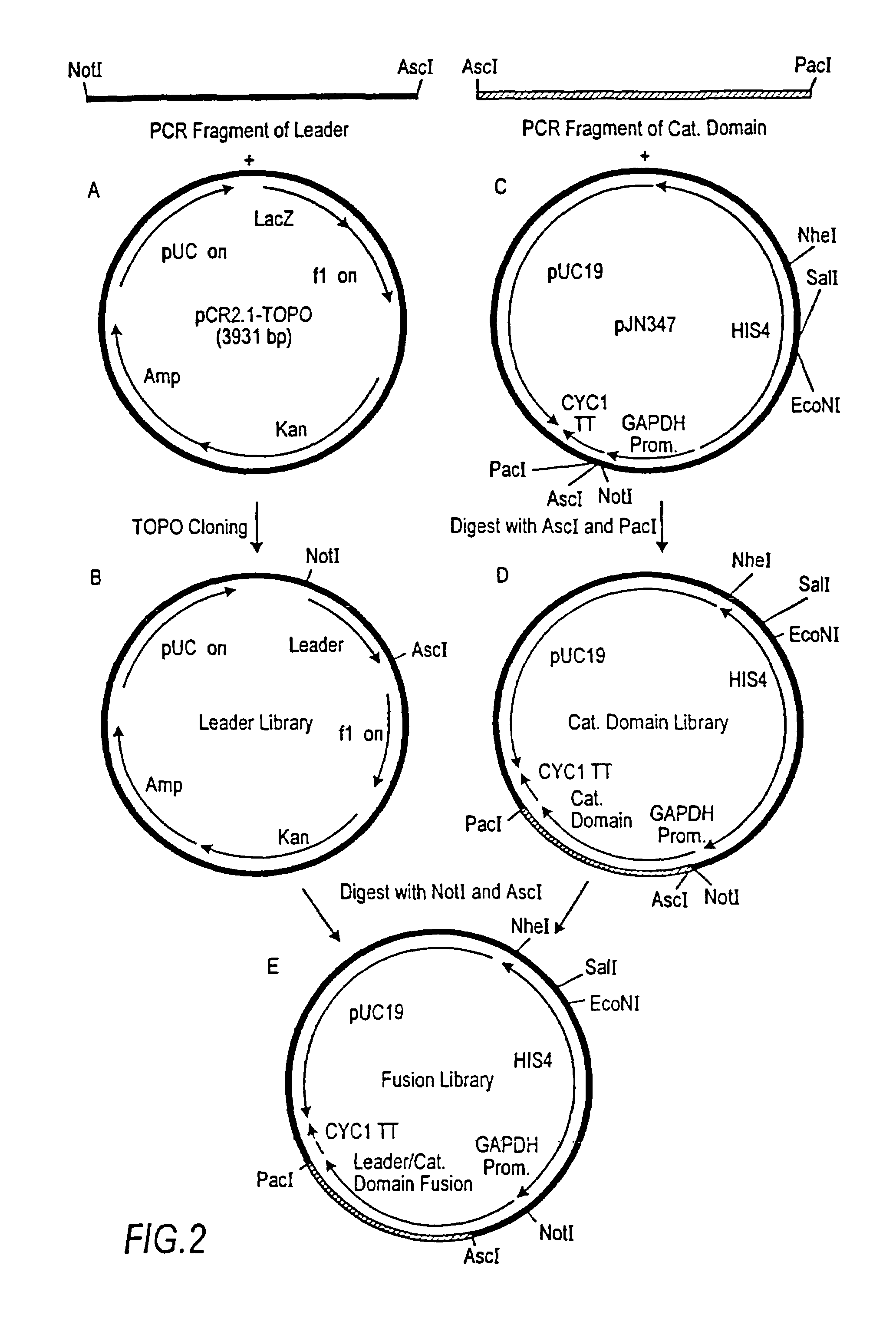
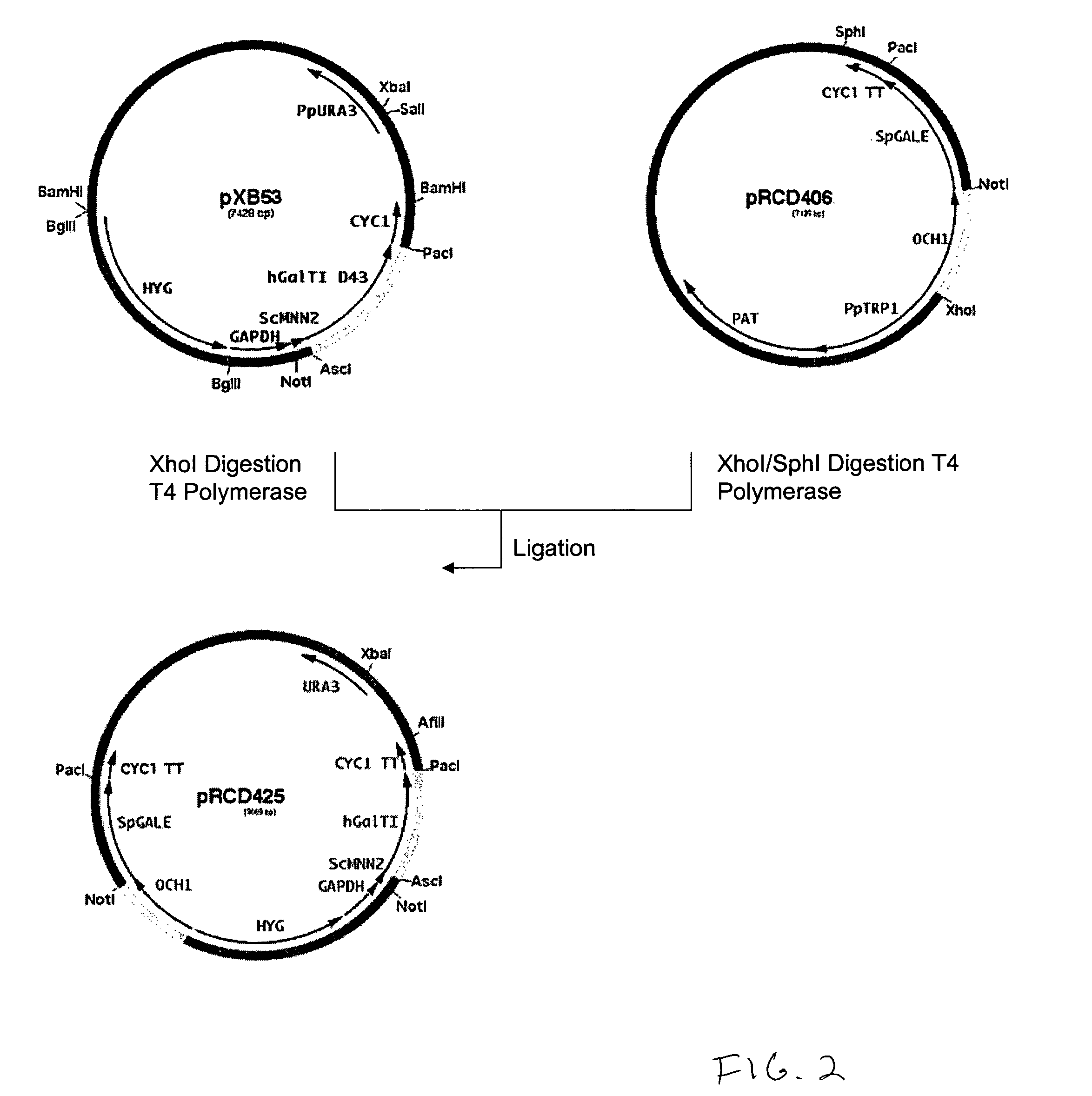
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
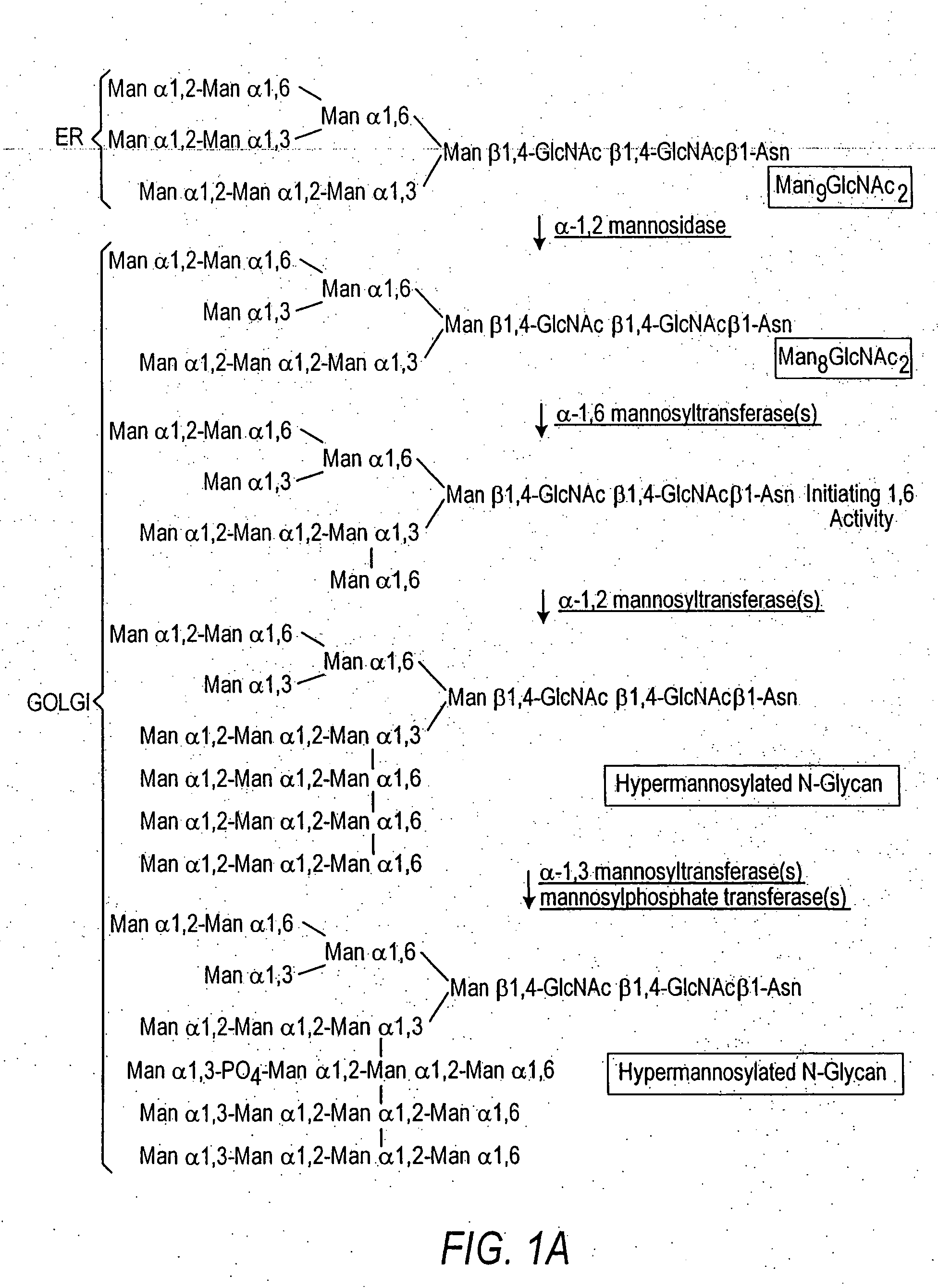
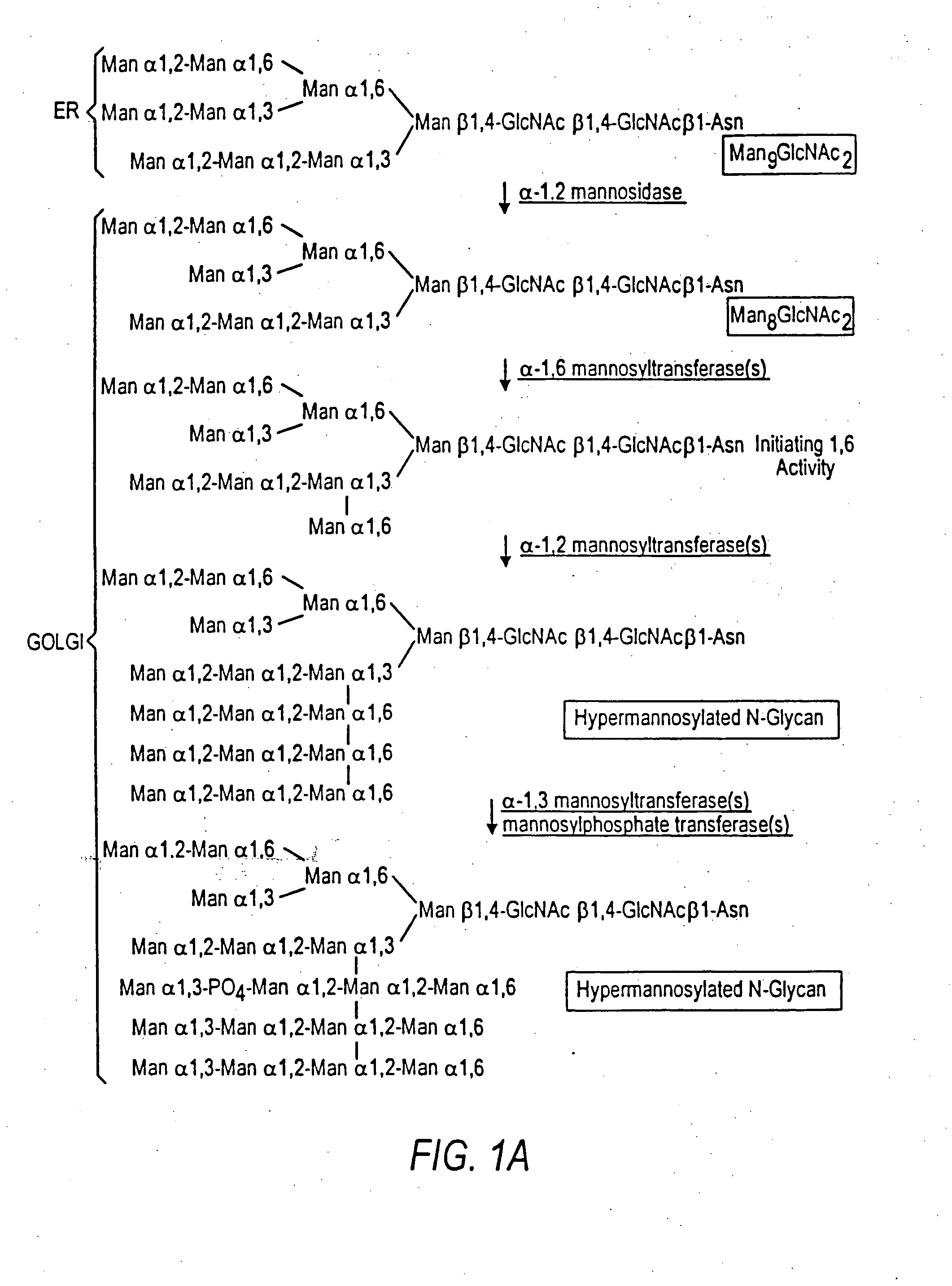
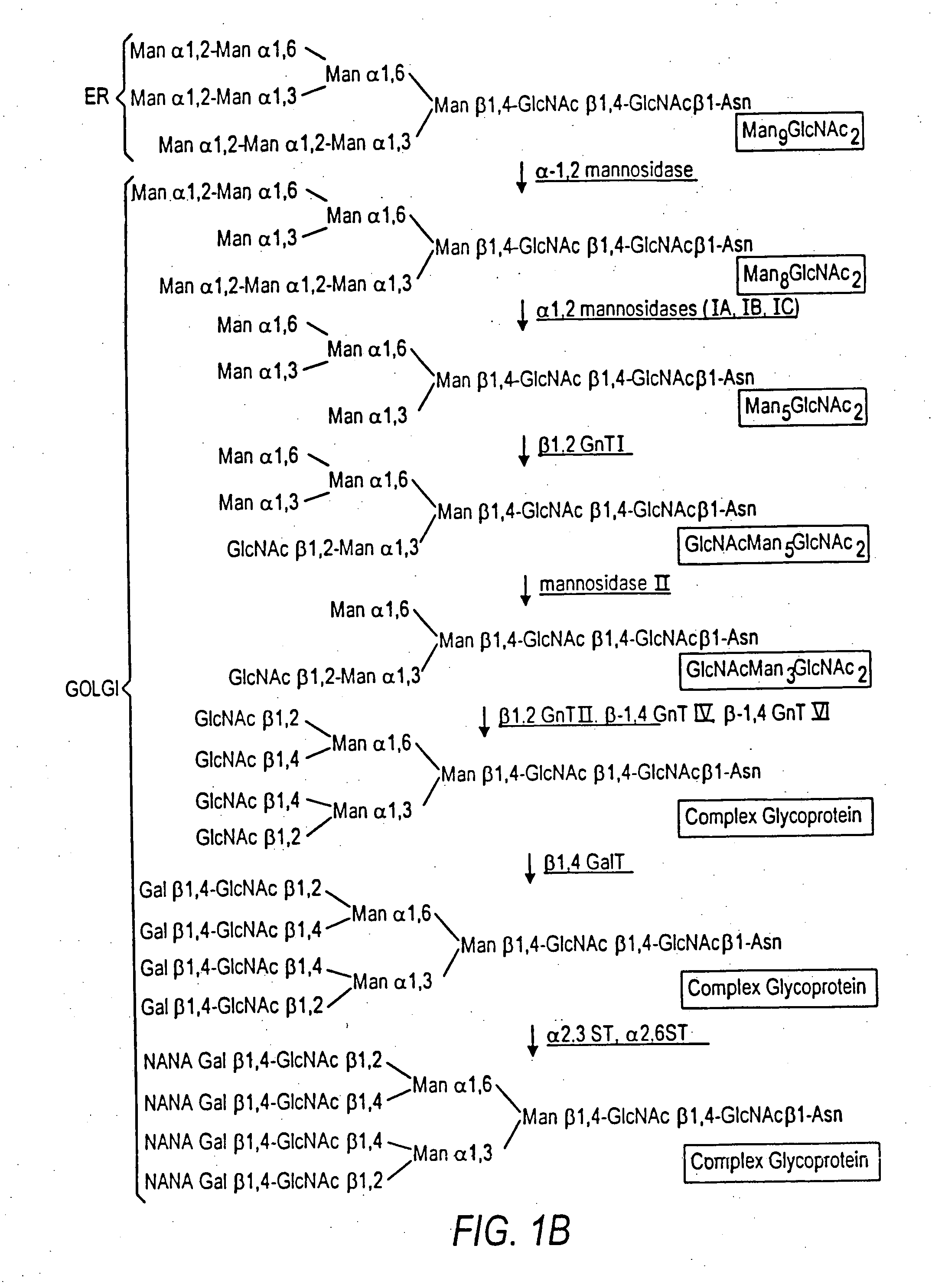
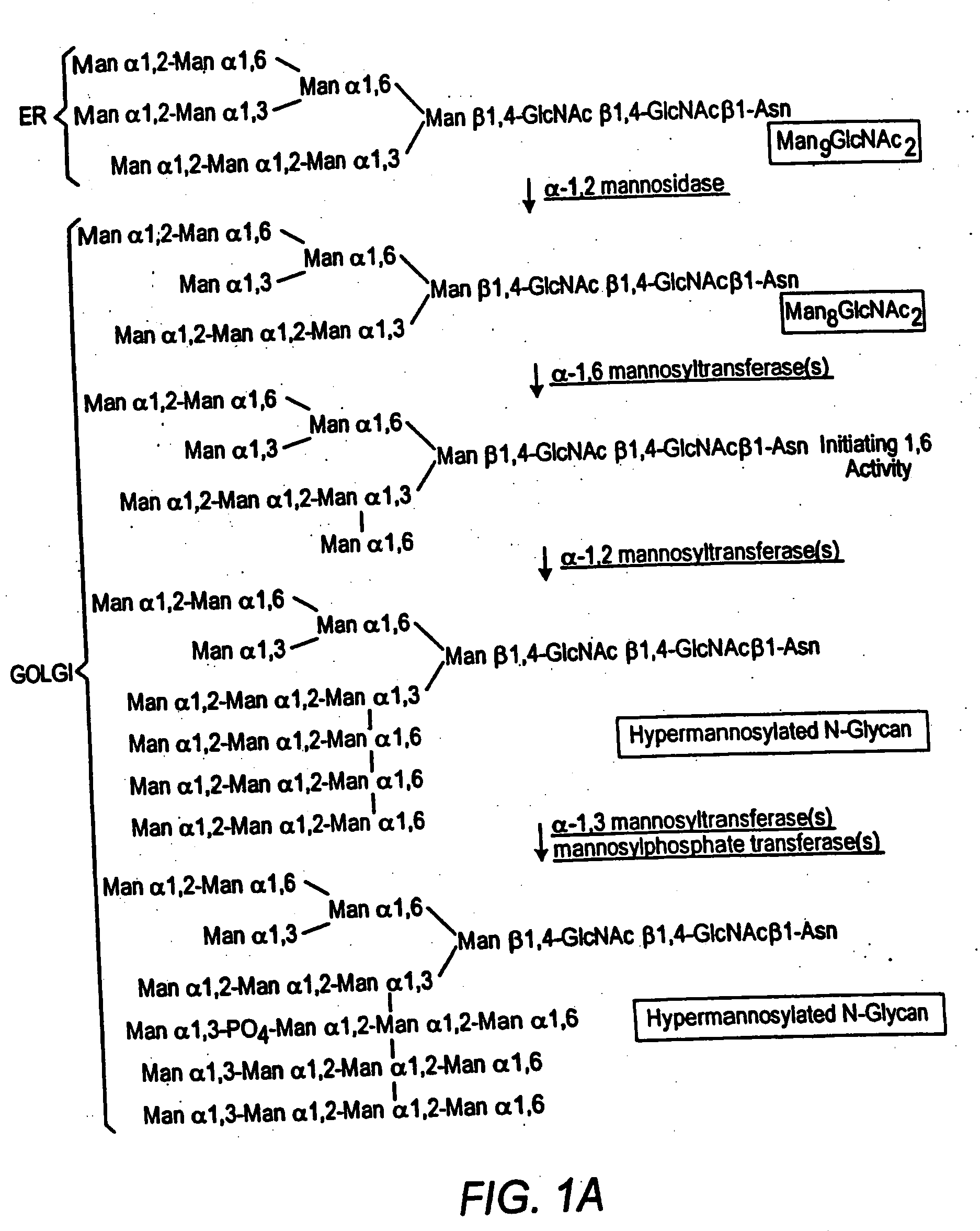
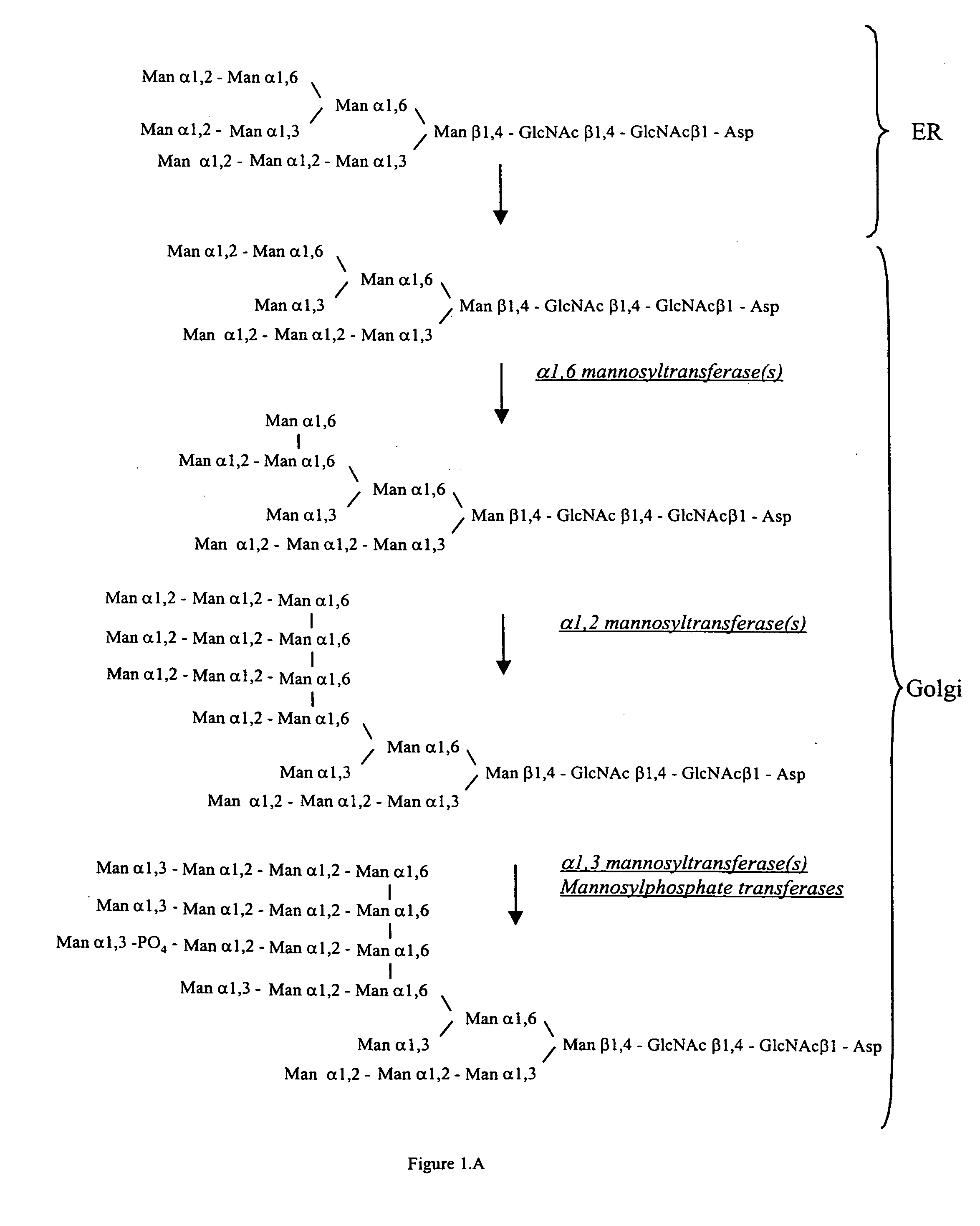
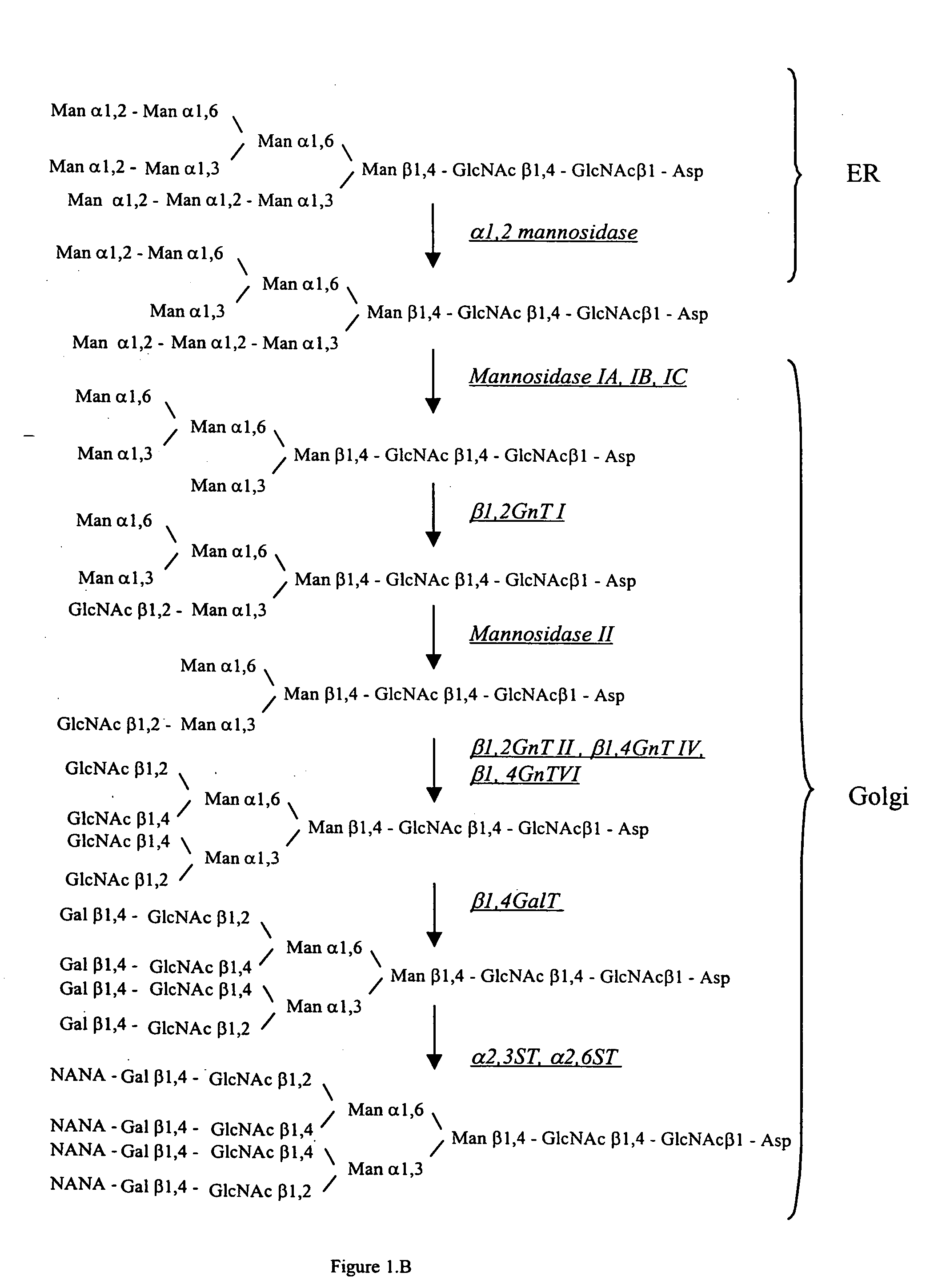
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. Thelower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Production of galactosylated glycoproteins in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20060040353A1Reducing and eliminating activityEfficient workFungiSugar derivativesUDP galactoseSialic acid
The present invention provides a novel lower eukaryotic host cell producing human-like glycoproteins characterized as having a terminal β-galactose residue and essentially lacking fucose and sialic acid residues. The present invention also provides a method for catalyzing the transfer of a galactose residue from UDP-galactose onto an acceptor substrate in a recombinant lower eukaryotic host cell, which can be used as a therapeutic glycoprotein.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Combinatorial DNA library for producing modified N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS7449308B2The overall structure is closedHigh yieldSugar derivativesMicroorganismsHeterologousTherapeutic protein
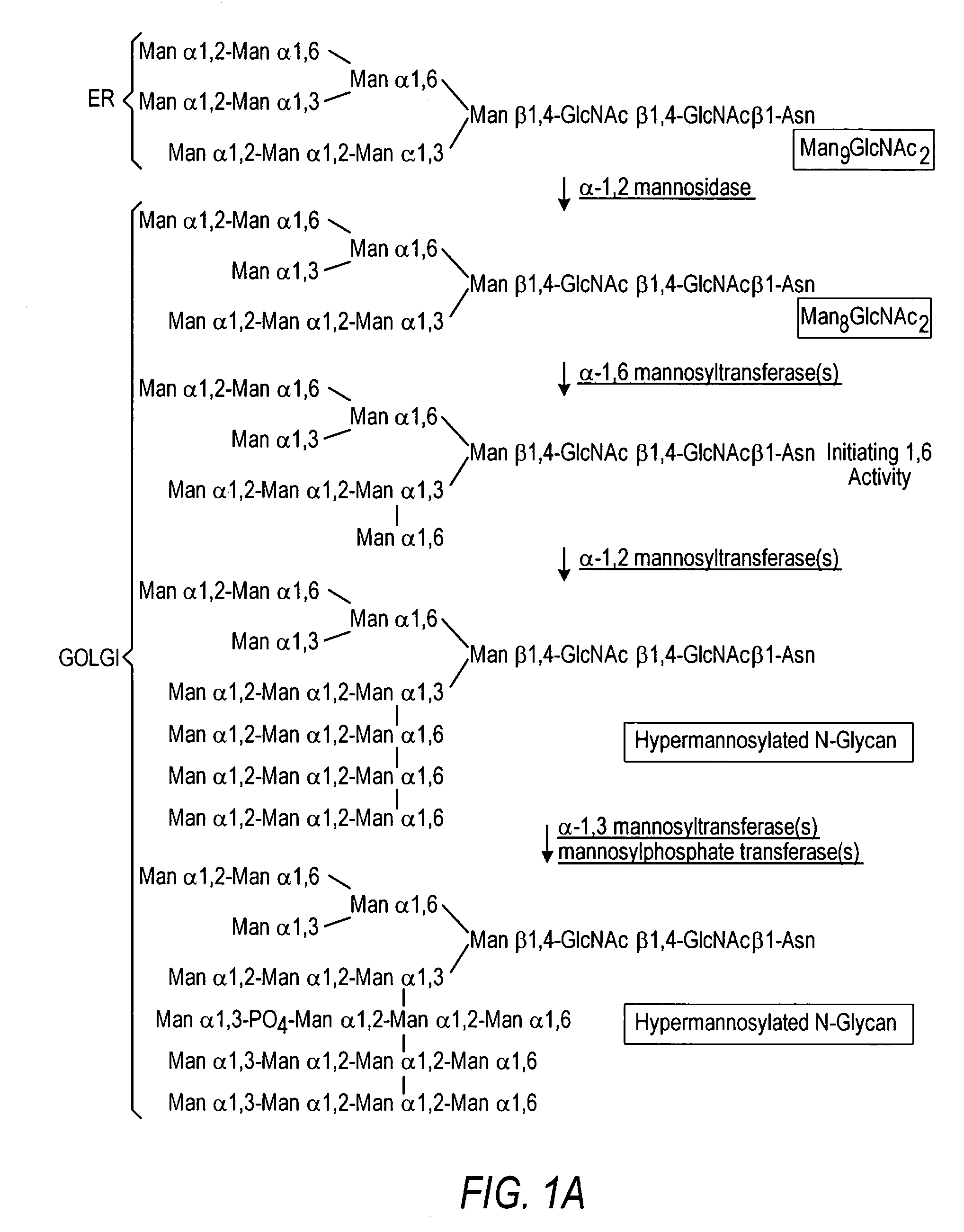
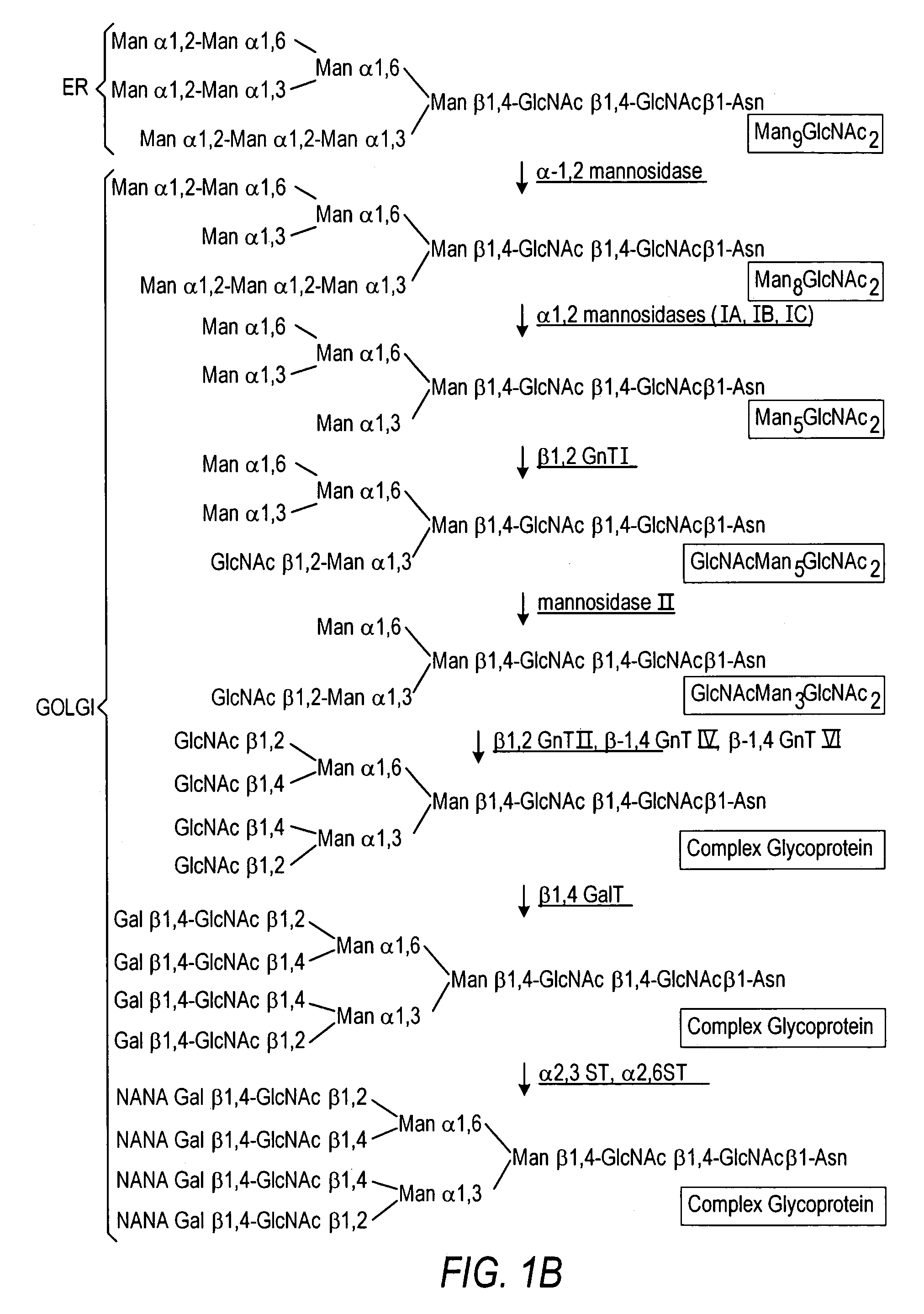
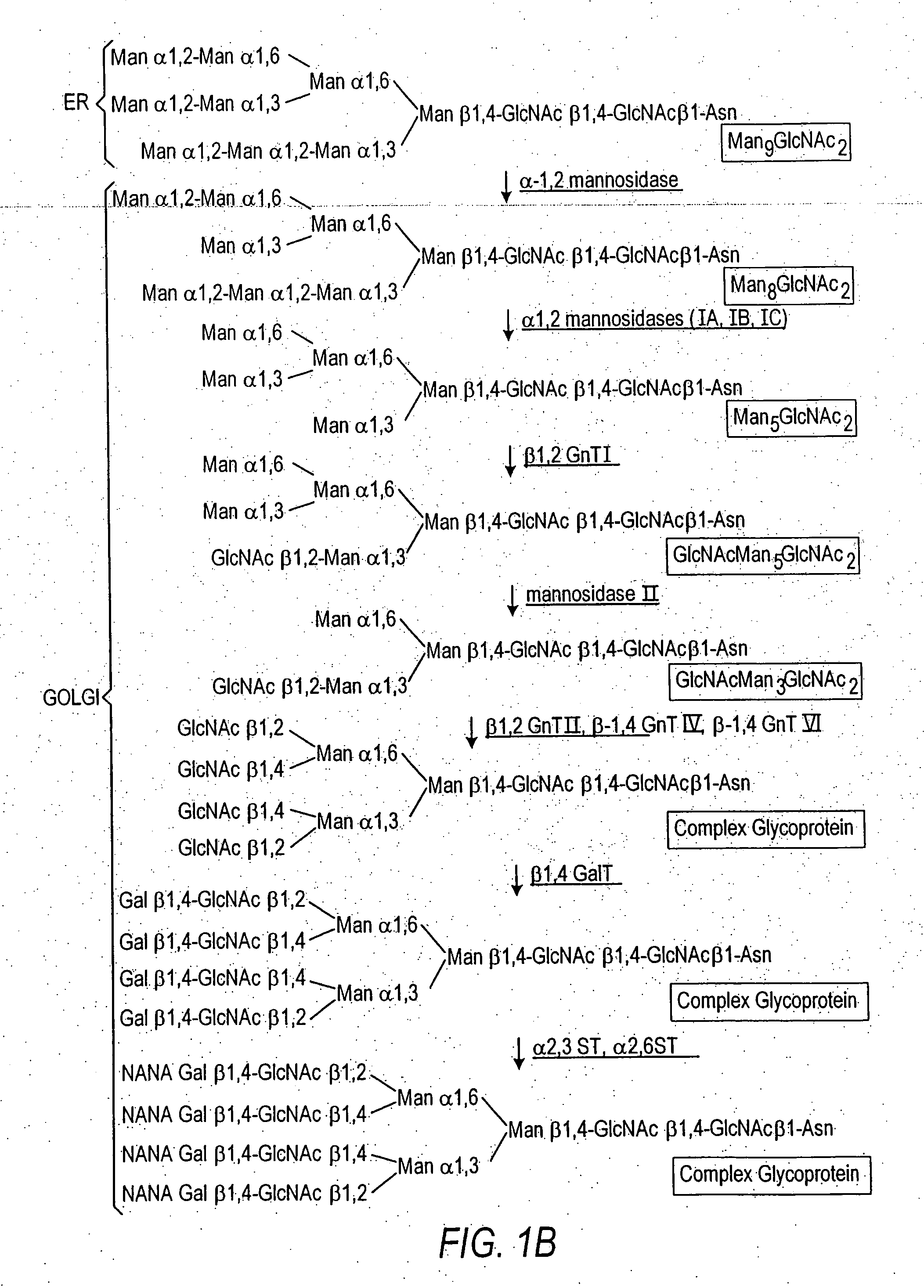
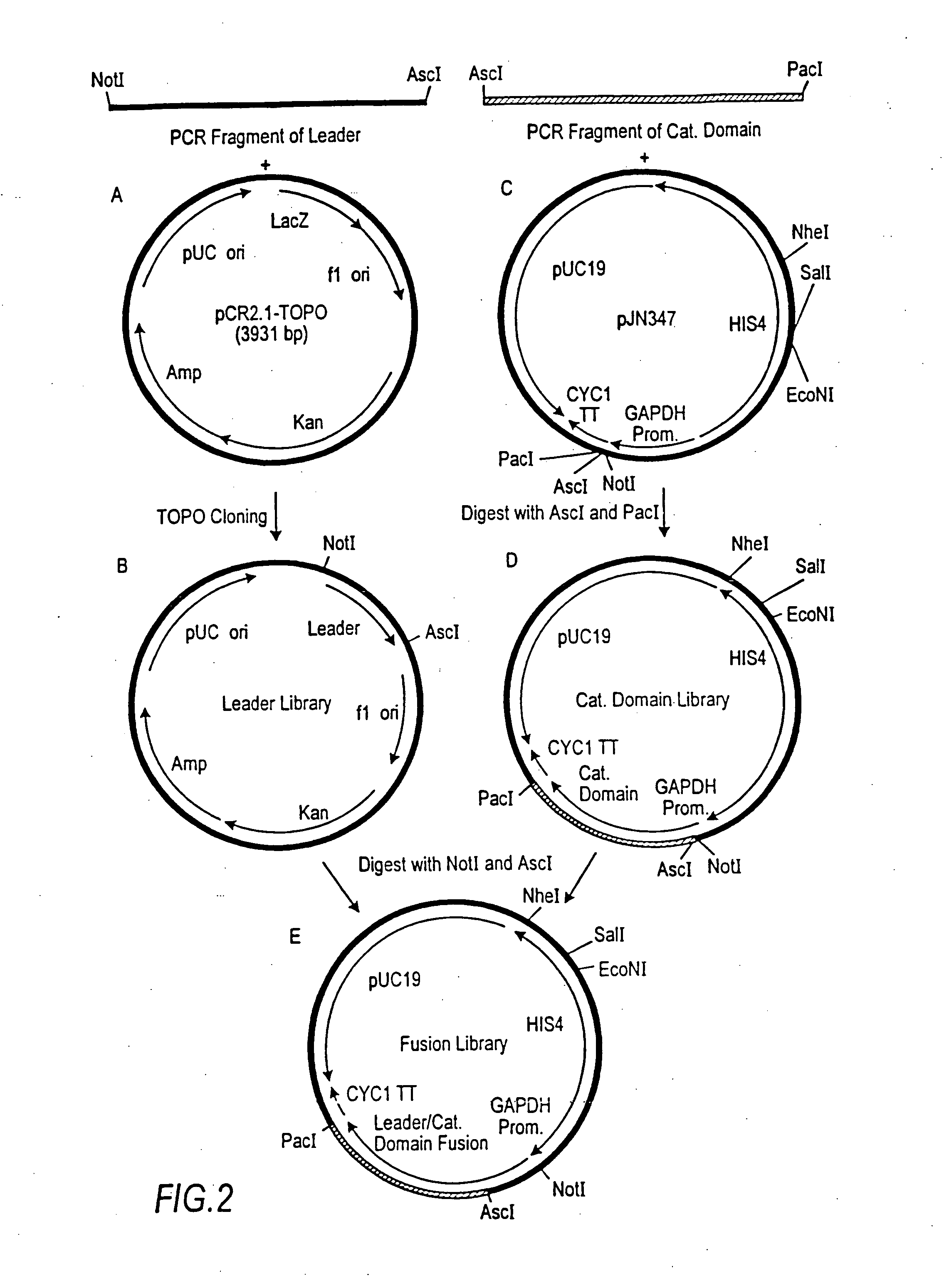
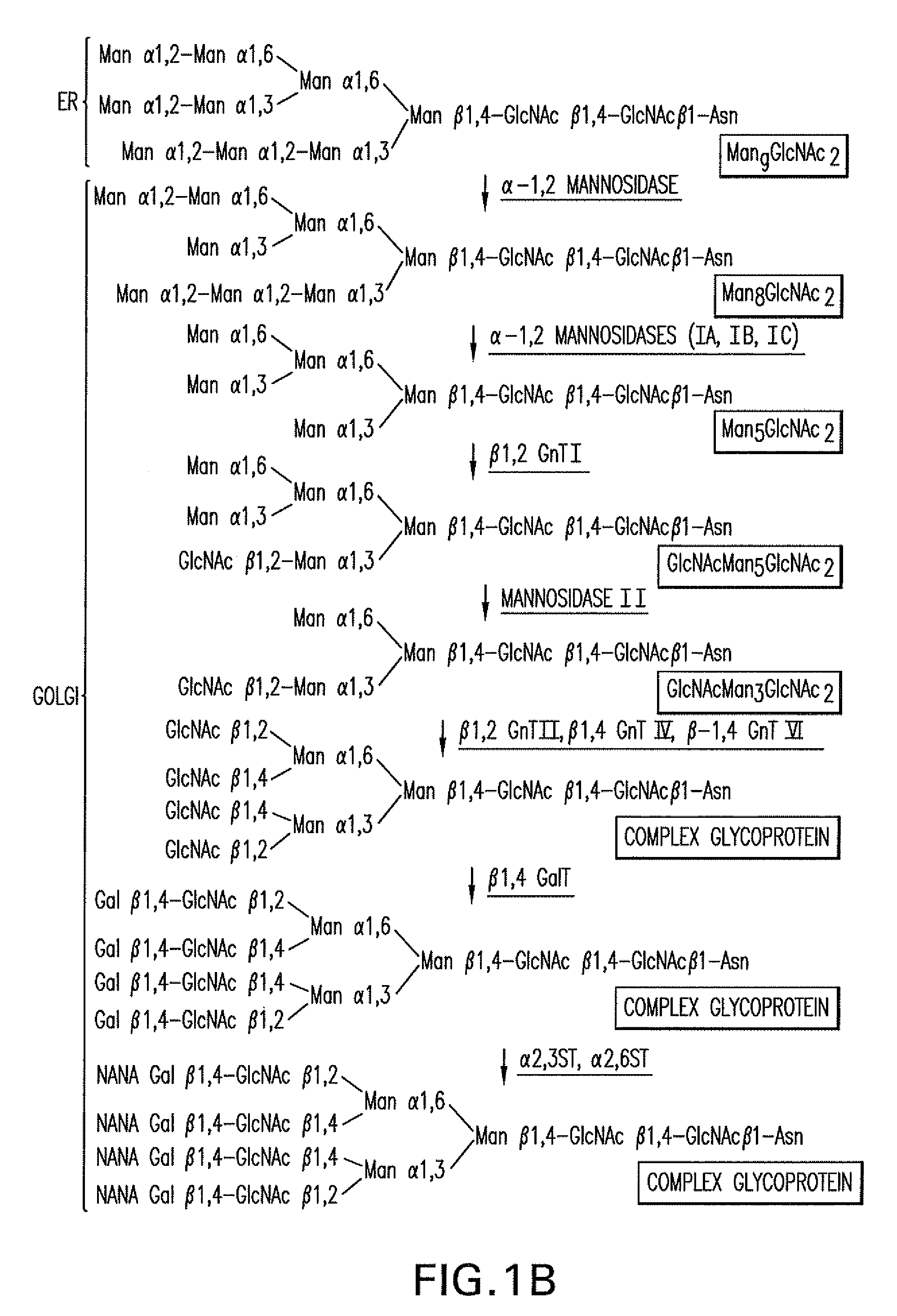
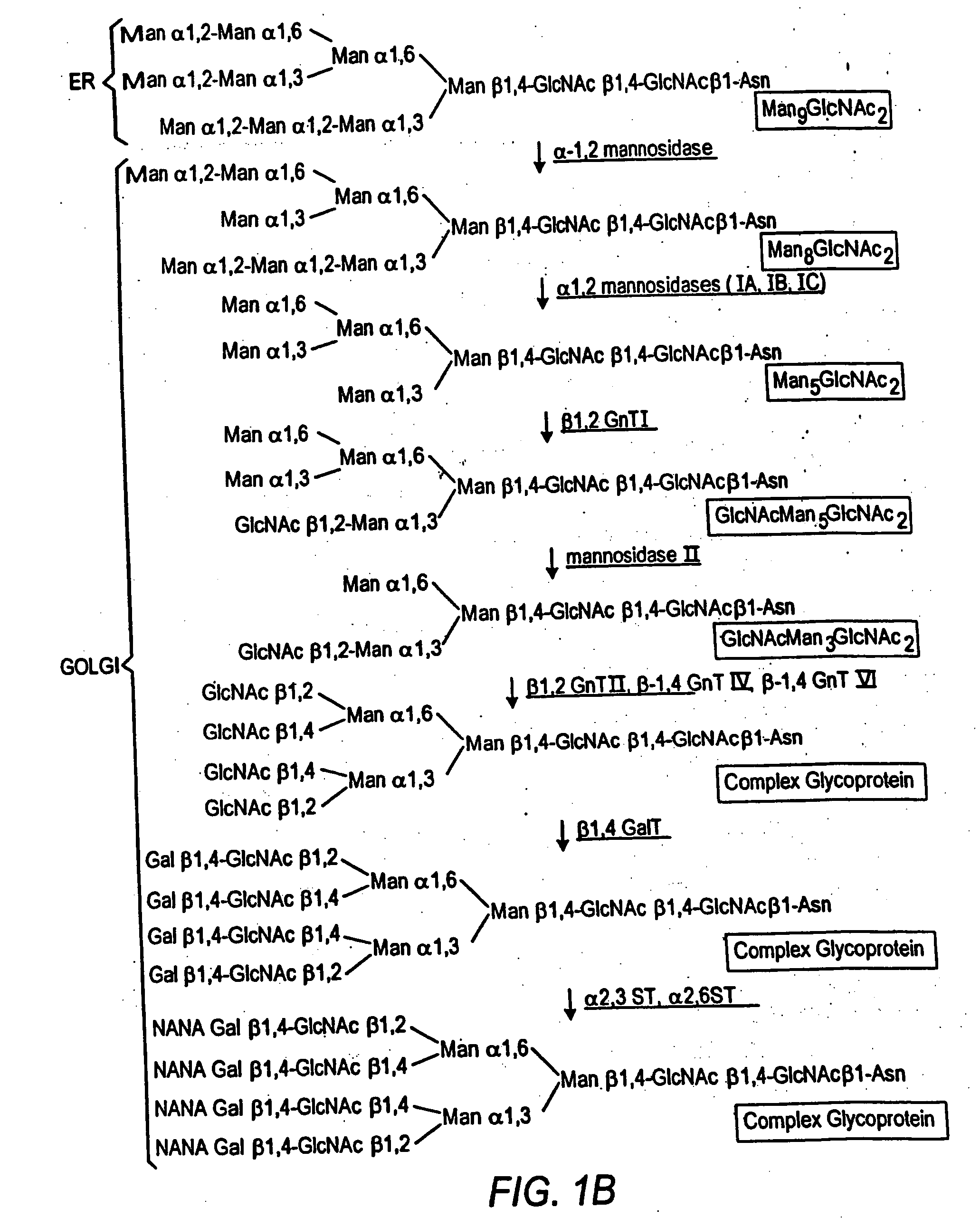
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities such as those involved in glycosylation to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells have a Man5GlcNAc2 core structure which may then be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Production of sialylated N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20060286637A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesHeterologousSialic acid aldolase
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells which have been modified to produce sialylated glycoproteins by the heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferase and / or trans-sialidase, to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. Novel eukaryotic host cells expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities (such as those involved in sialylation) to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Eukaryotic use of non-chimeric mutational vectors
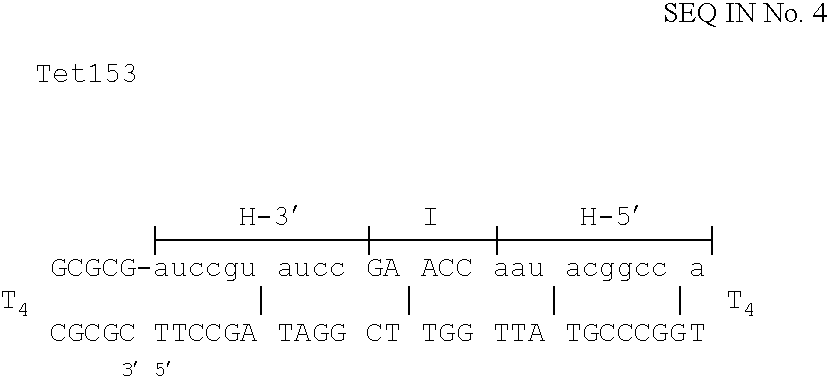
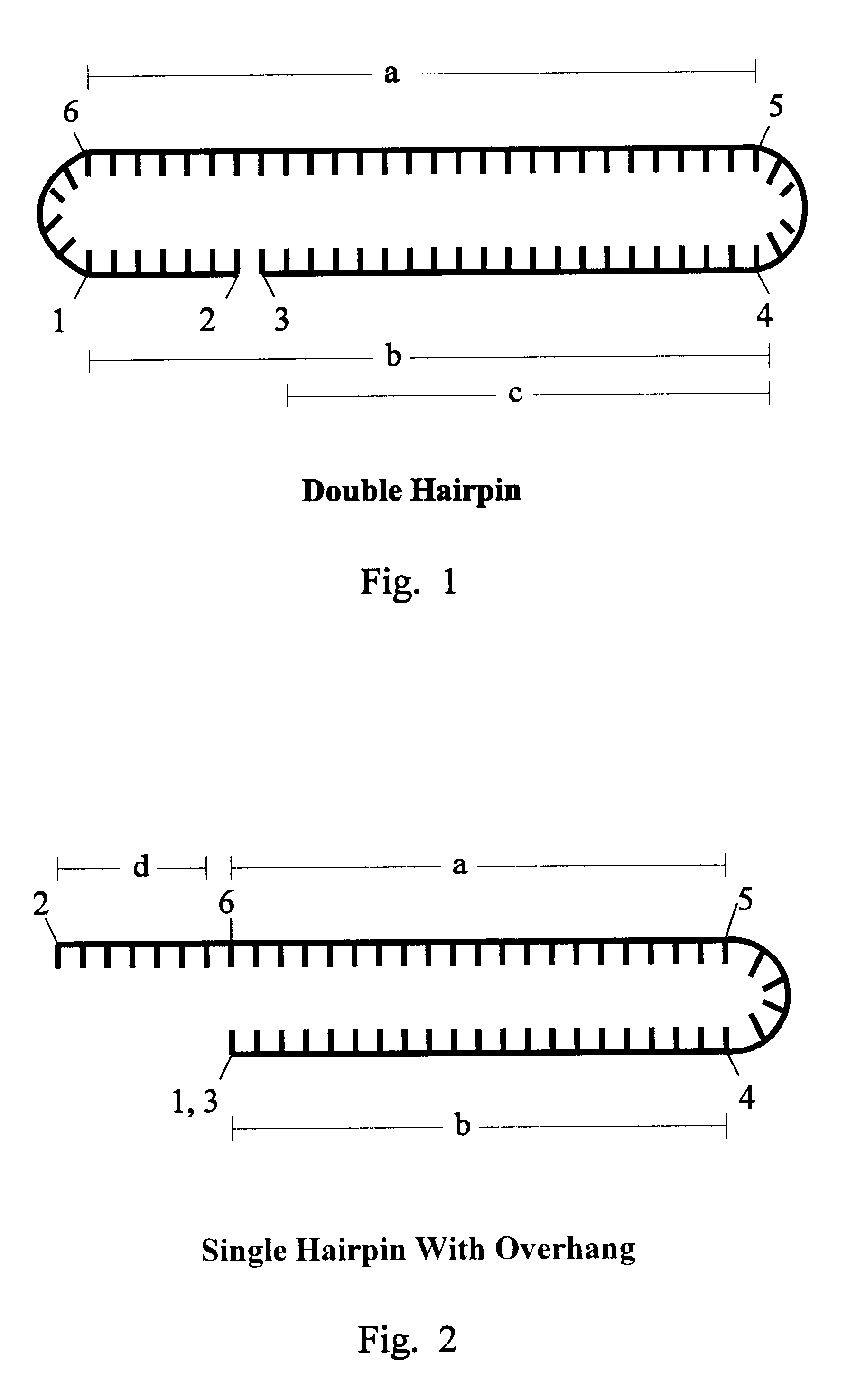
The invention is based on the reaction of Duplex Mutational Vector in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Non-Chimeric Mutational Vector, having no RNA:DNA hybrid-duplex is shown to be an effective substrate for eukaryotic enzymes. The invention concerns the use of Non-Chimeric Mutational Vectors protected from 3' exonuclease attack in eukaryotic cells. Such protection can be conferred by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the recombinagenic oligonucleobase.
Owner:VALIGEN US +1
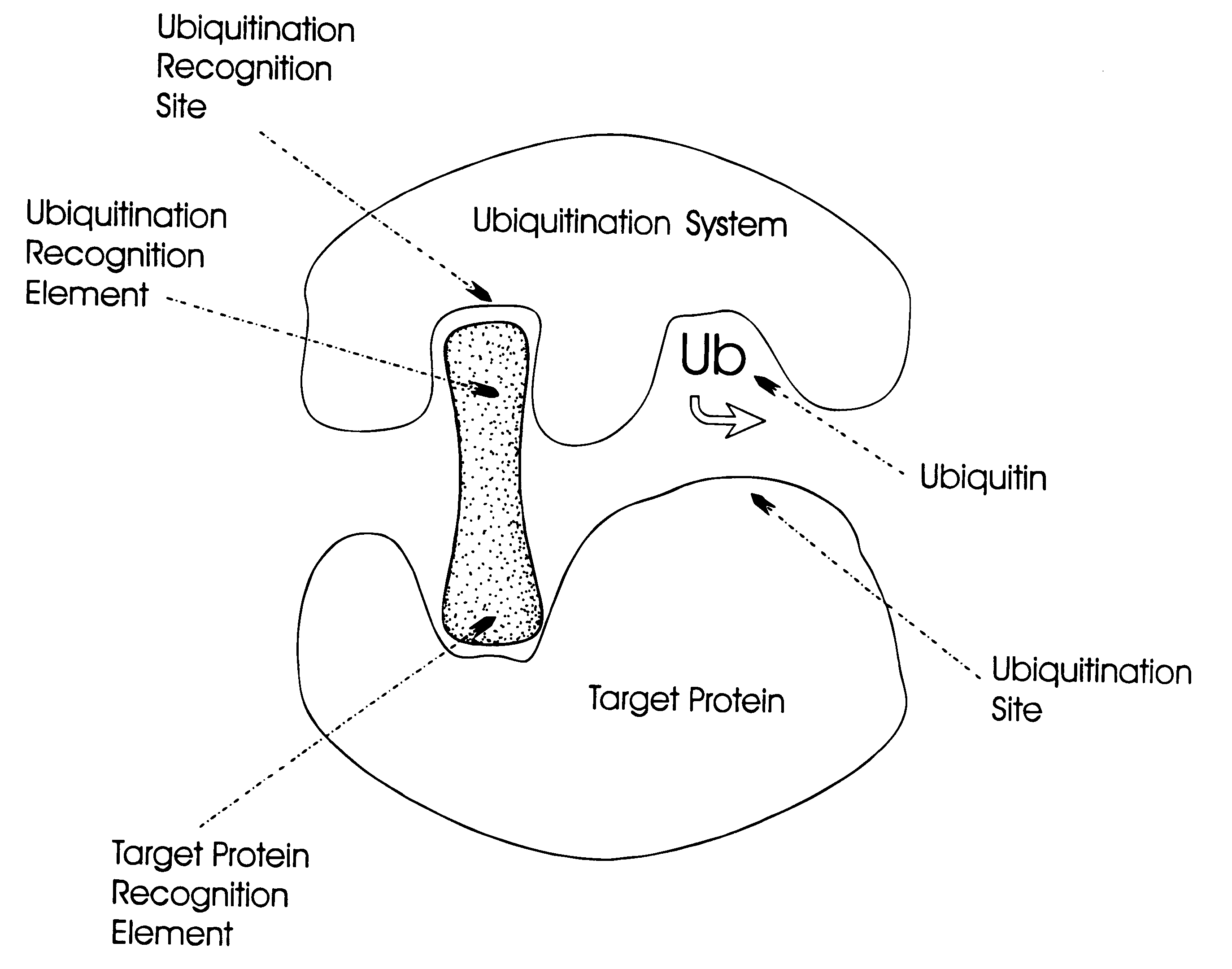
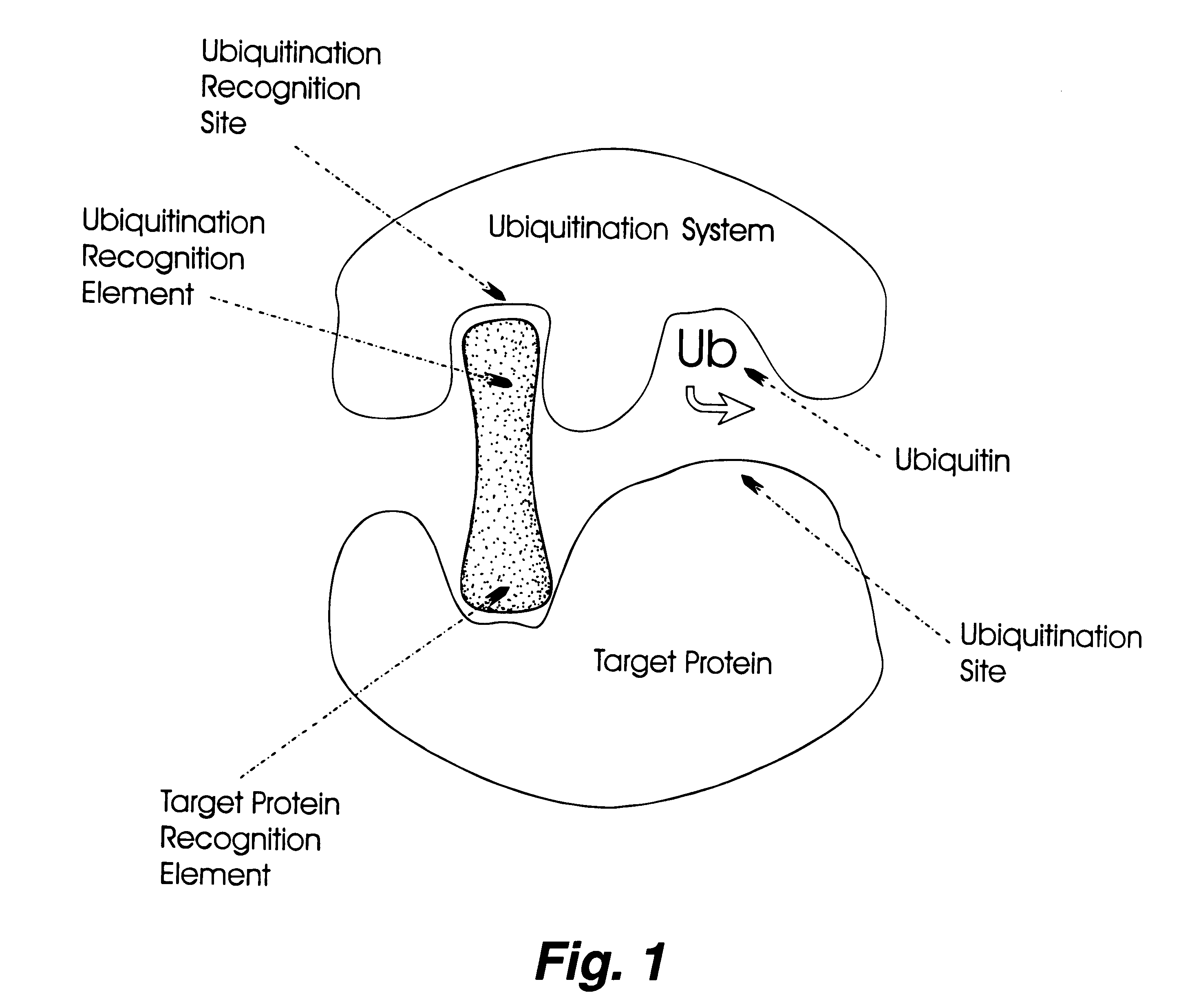
Controlling protein levels in eucaryotic organisms
InactiveUS6306663B1High activityCost-effectiveVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein target
The invention relates to novel compounds comprising a ubiquitination recognition element and a protein binding element. The invention also relates to the use of said compounds for modulating the level and / or activity of a target protein. The compounds are useful for the treatment of disease such as infections, inflammatory conditions, cancer and genetic diseases. The compounds are also useful as insecticides and herbicides.
Owner:WELLSTAT BIOCATALYSIS +1
N-acetylglucosamintransferase III expression in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20050208617A1The overall structure is closedFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationHeterologous
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified lipid-linked oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells exhibit GnTIII activity, which produce bisected N-glycan structures and may be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
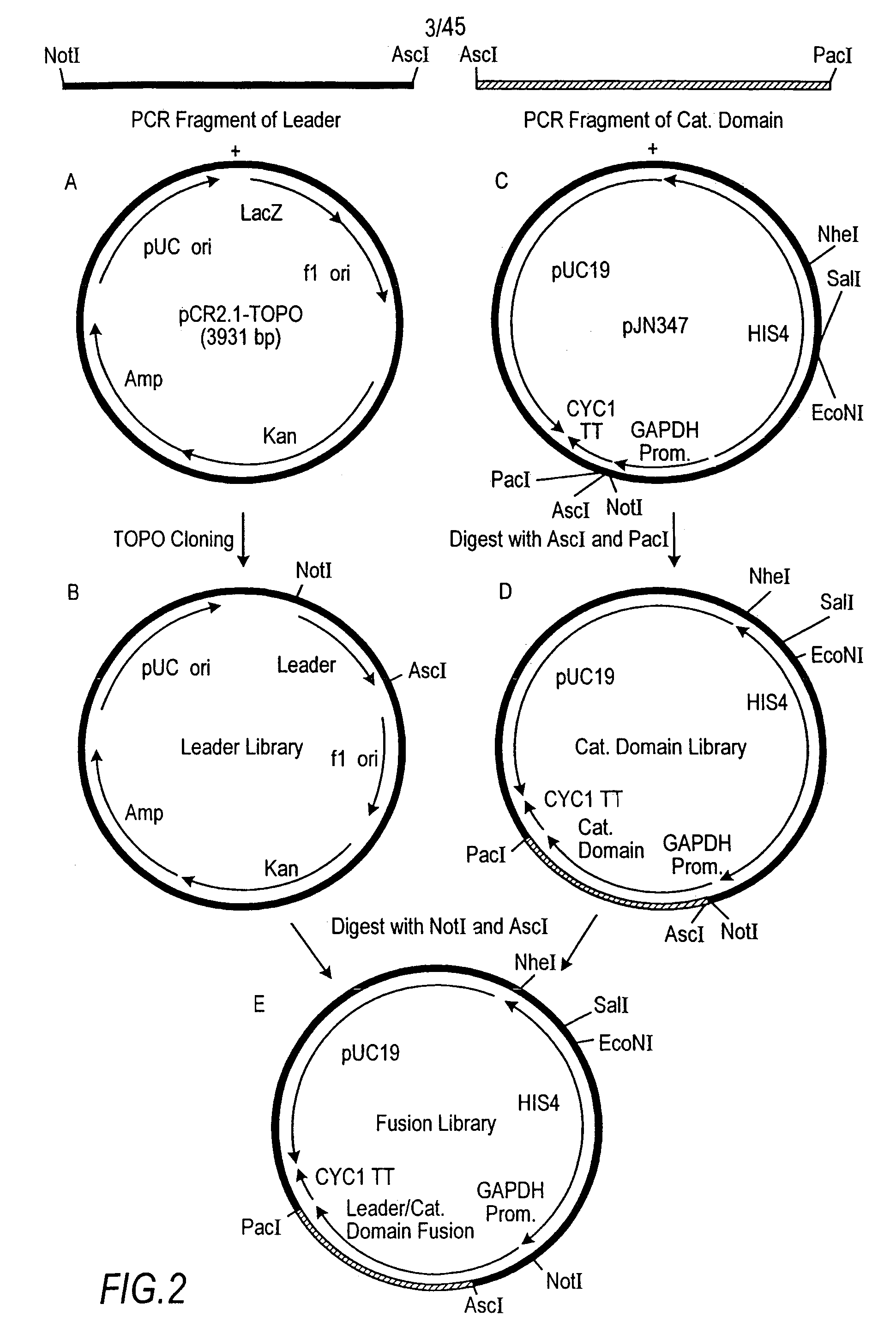
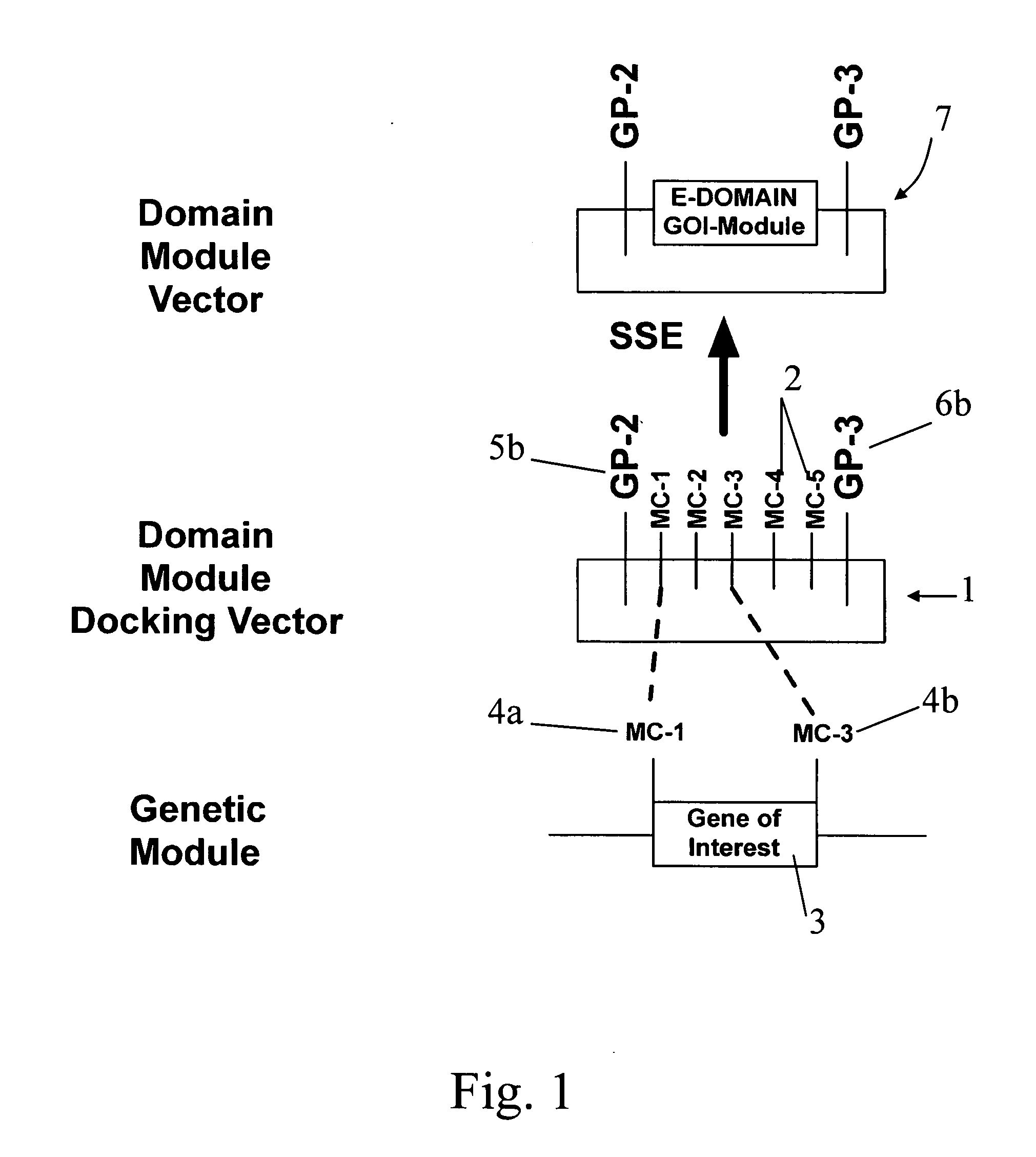
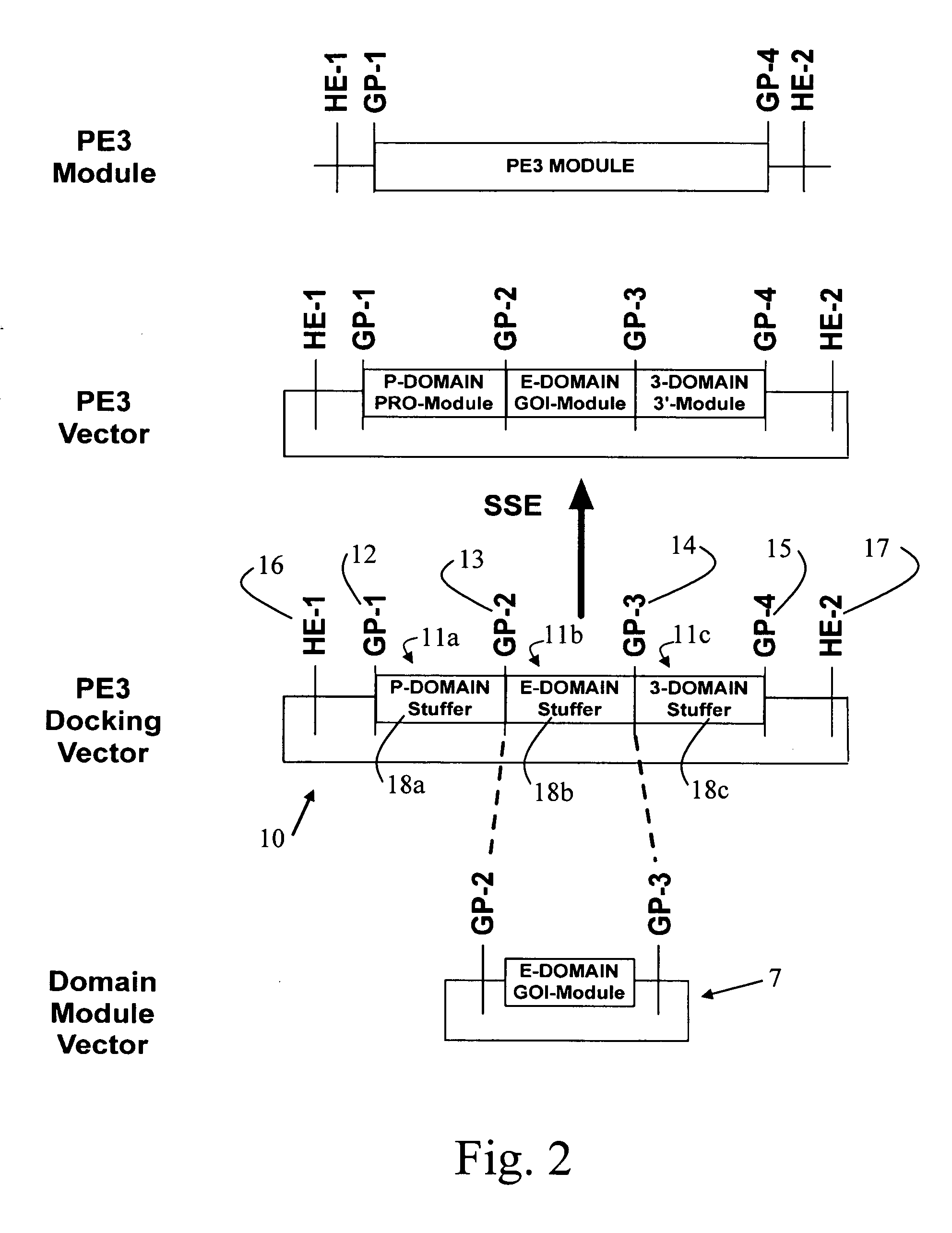
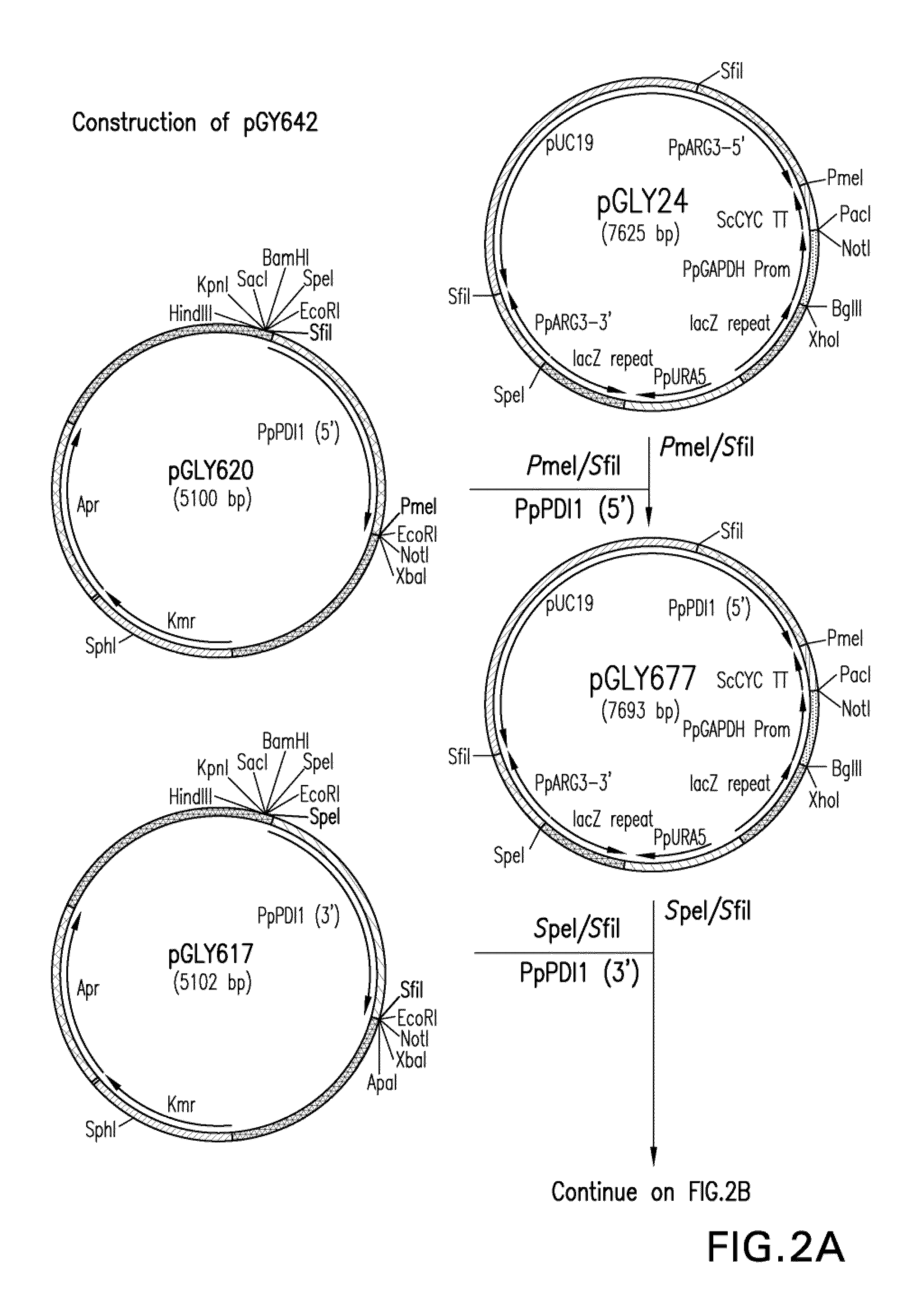
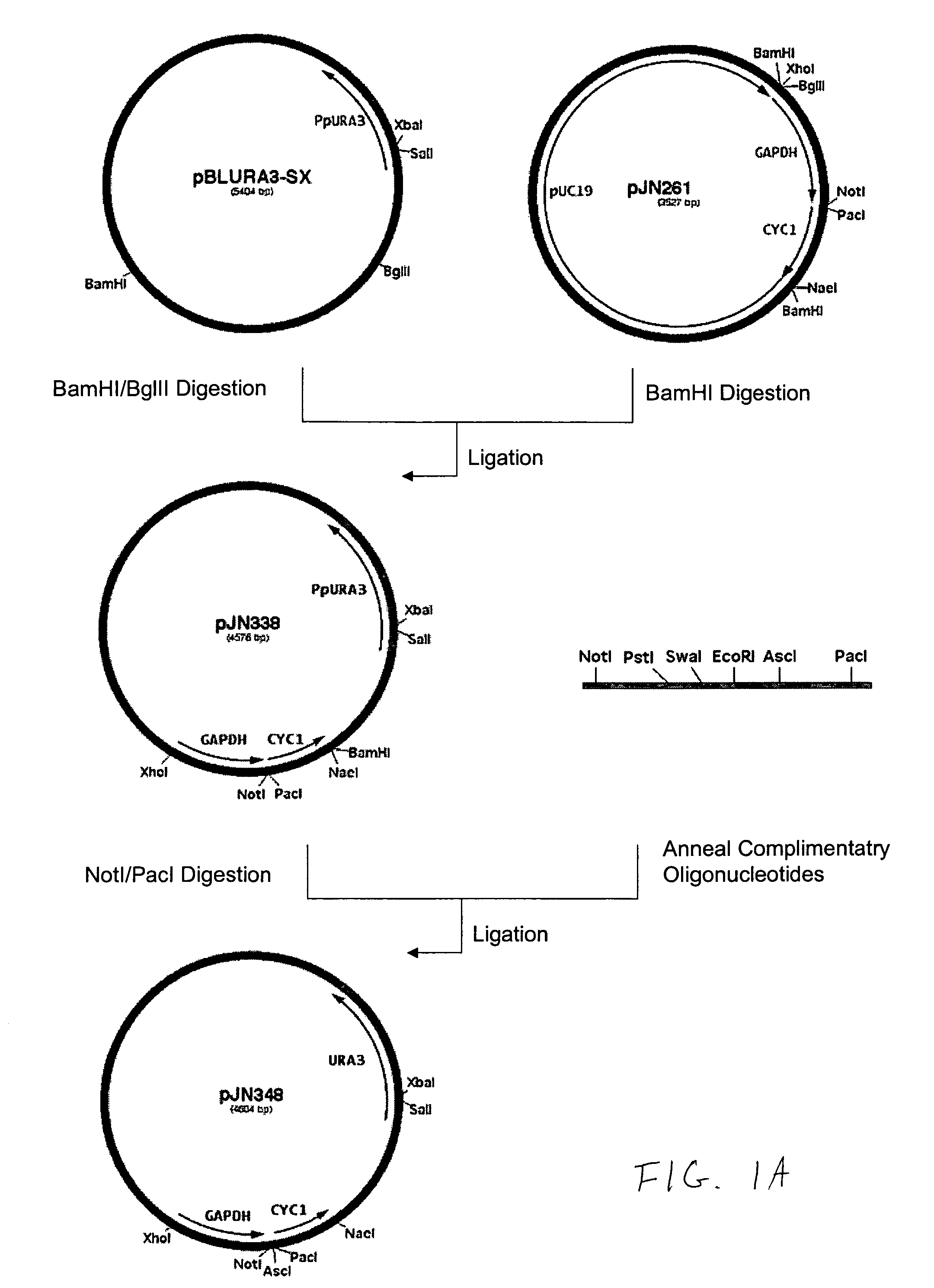
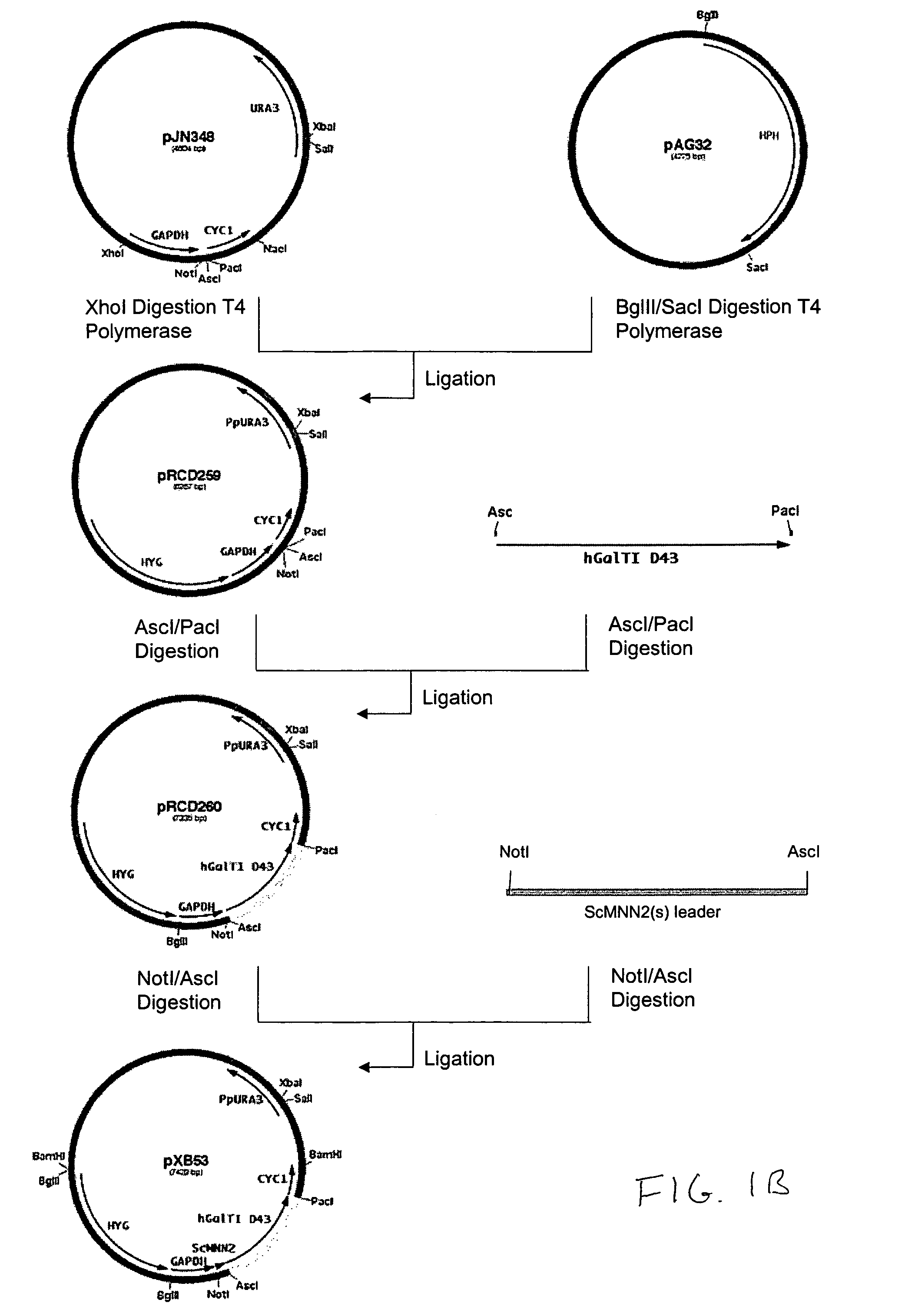
DNA modular cloning vector plasmids and methods for their use
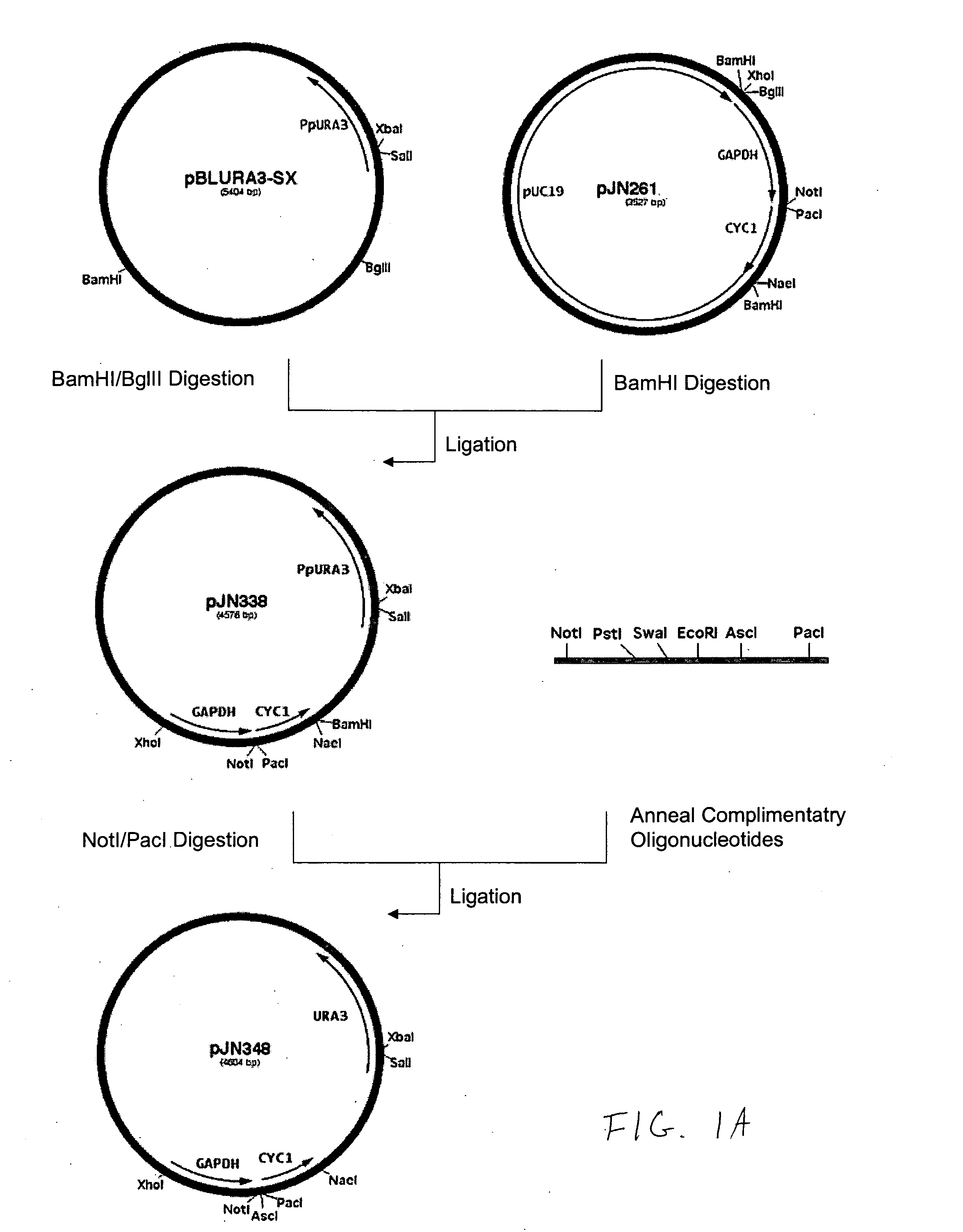
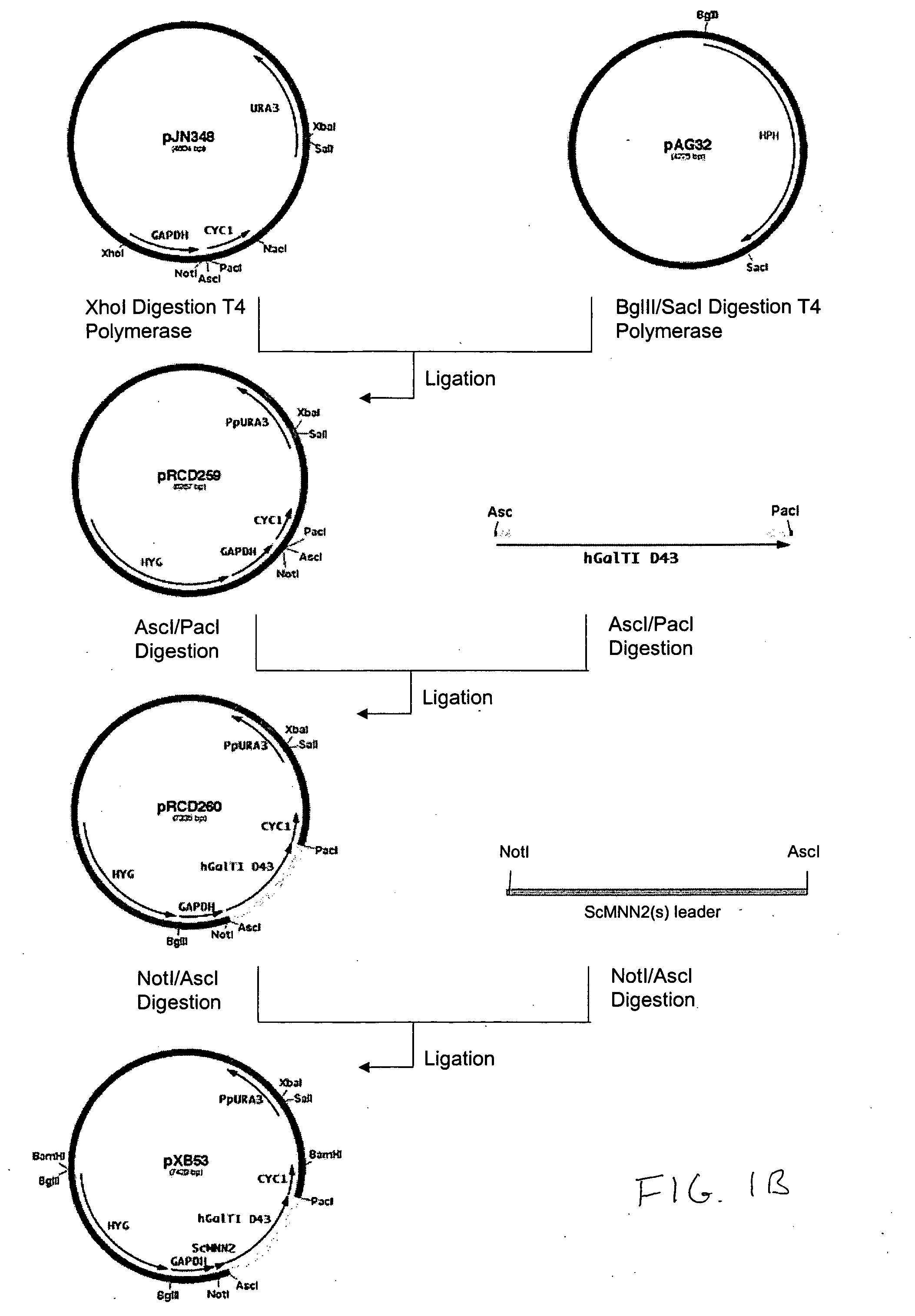
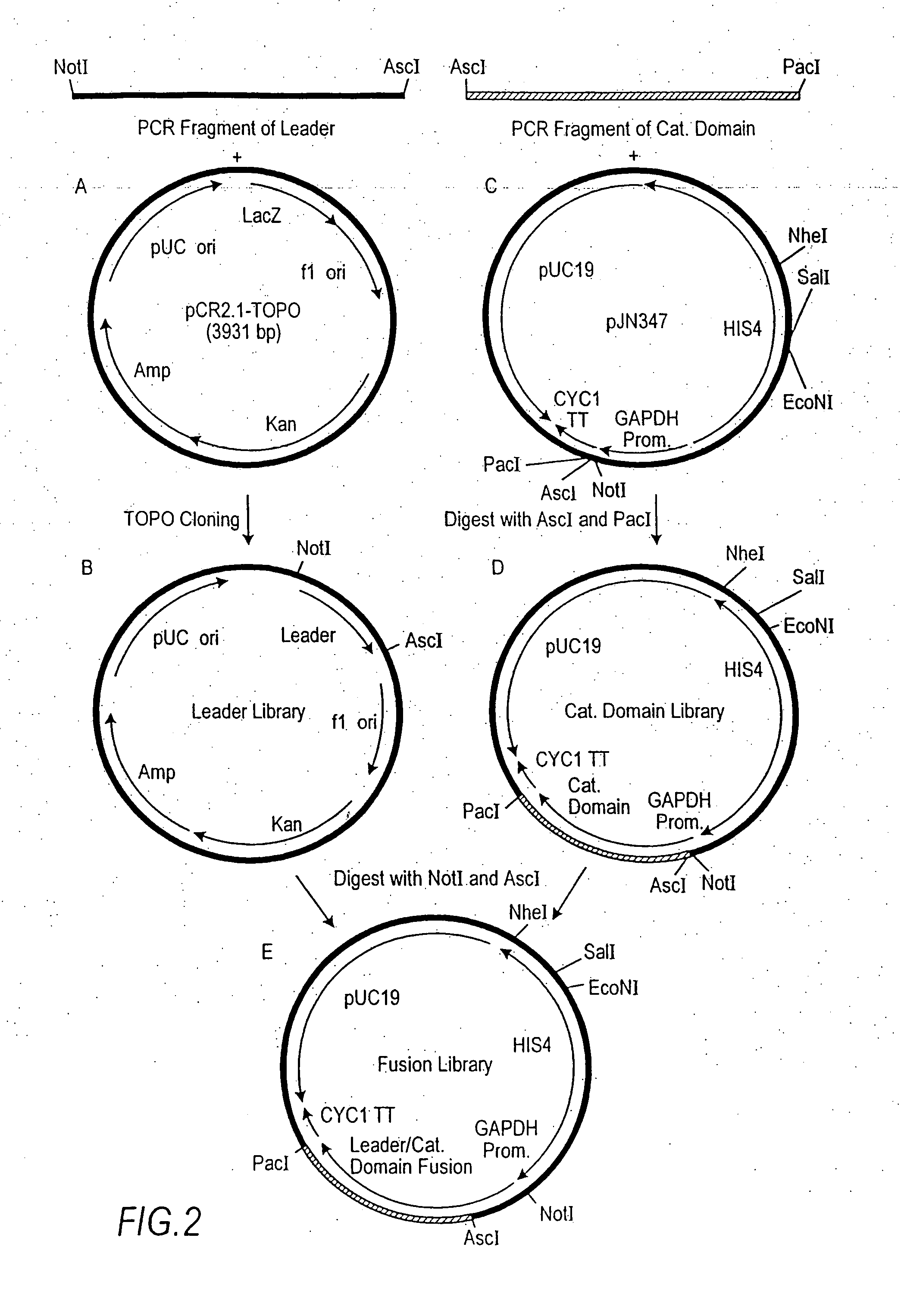
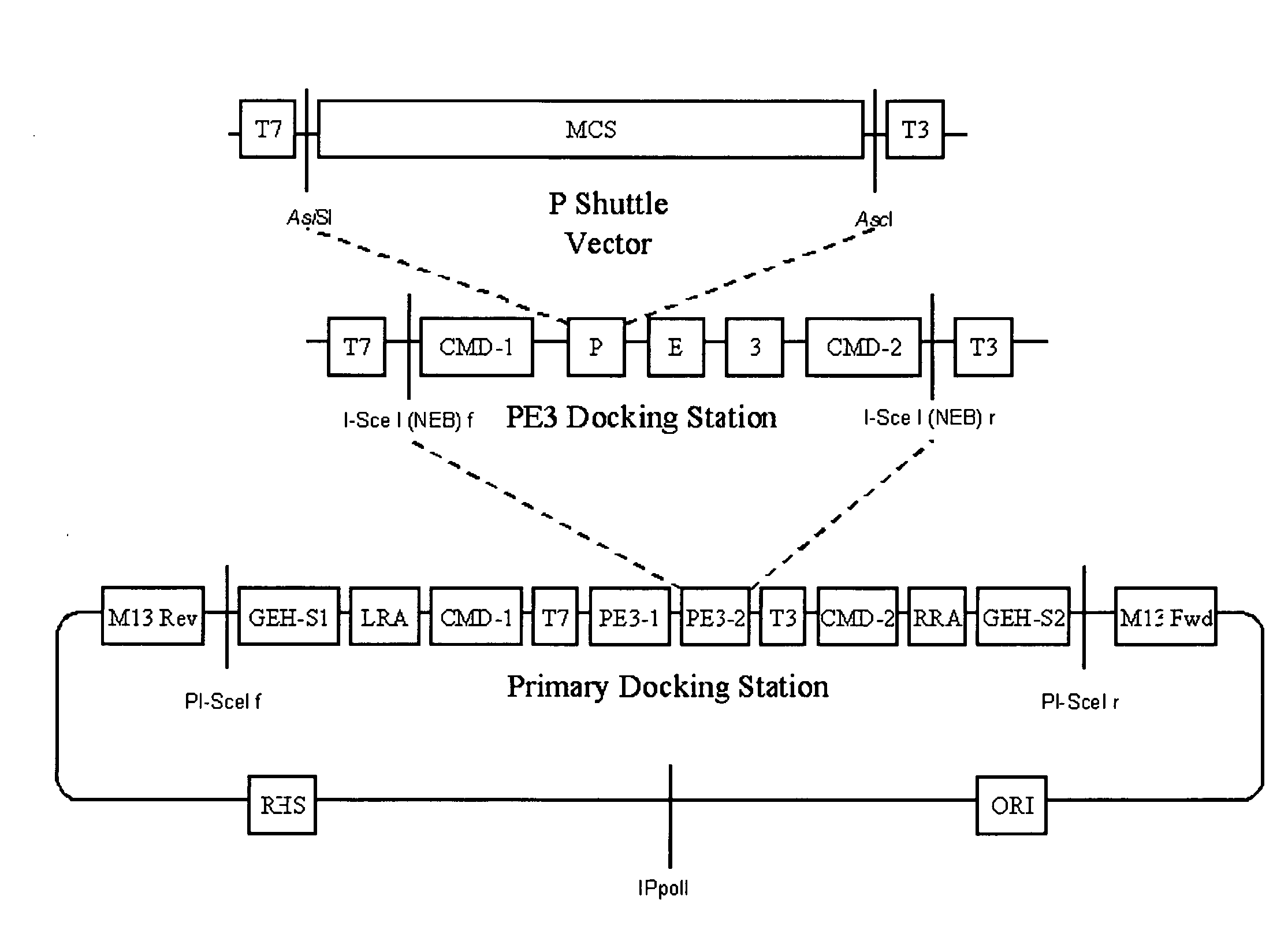
A group of modular cloning vector plasmids for the synthesis of a transgene or other complicated DNA construct, by providing a backbone having docking points therein, for the purpose of gene expression or analysis of gene expression. The invention is useful for assembling a variety of DNA fragments into a de novo DNA construct or transgene by using cloning vectors optimized to reduce the amount of manipulation frequently needed. The module vector contains at least one multiple cloning site (MCS) and multiple sets of rare restriction and / or unique homing endonuclease (“HE”) sites, arranged in a linear pattern. This arrangement defines a modular architecture that allows the user to place domain modules or inserts into a PE3 transgene vector construct without disturbing the integrity of DNA elements already incorporated into the PE3 vector in previous cloning steps. The PE3 transgenes produced using the invention may be used in a single organism, or in a variety of organisms including bacteria, yeast, mice, and other eukaryotes with little or no further modification.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
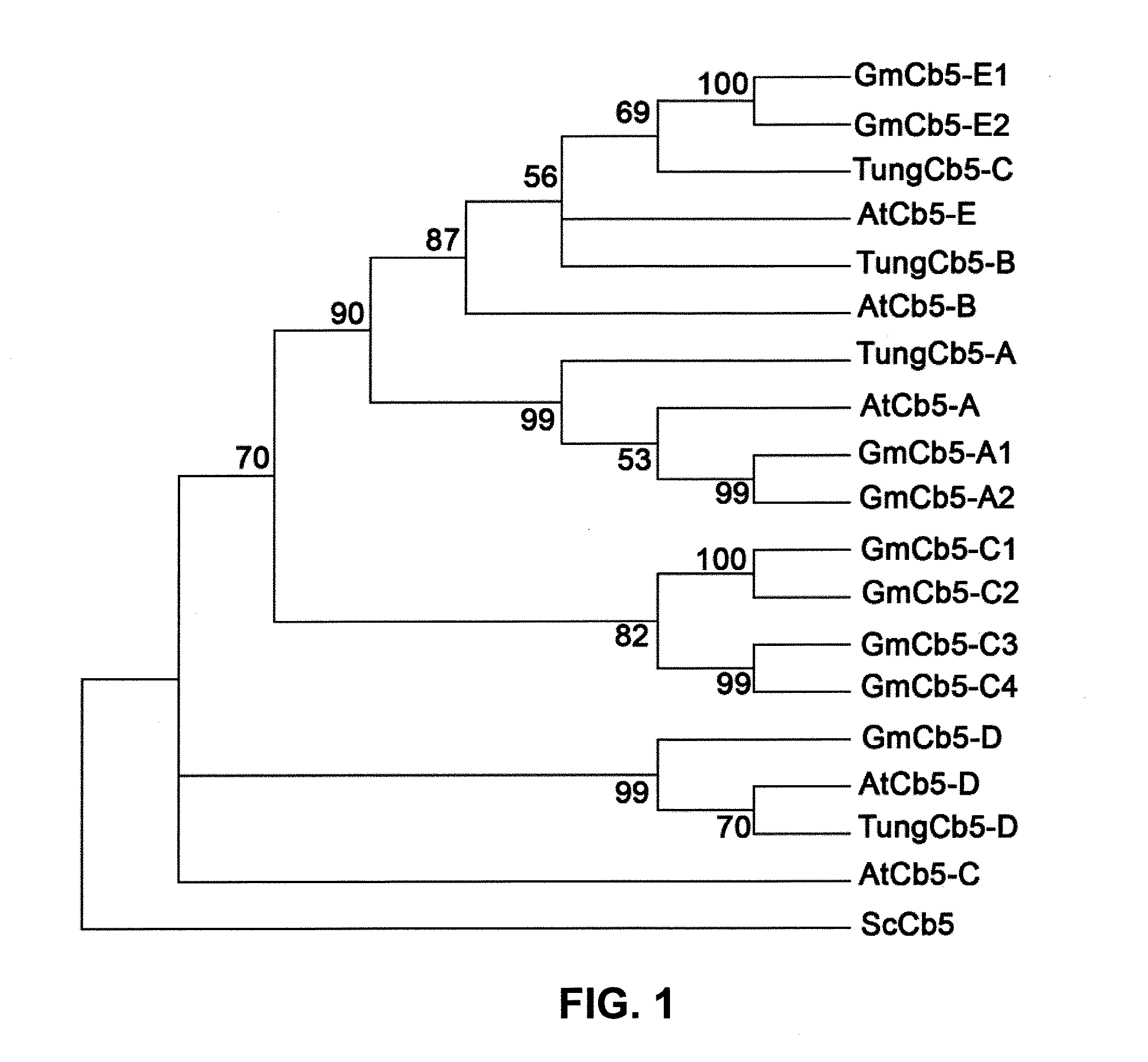
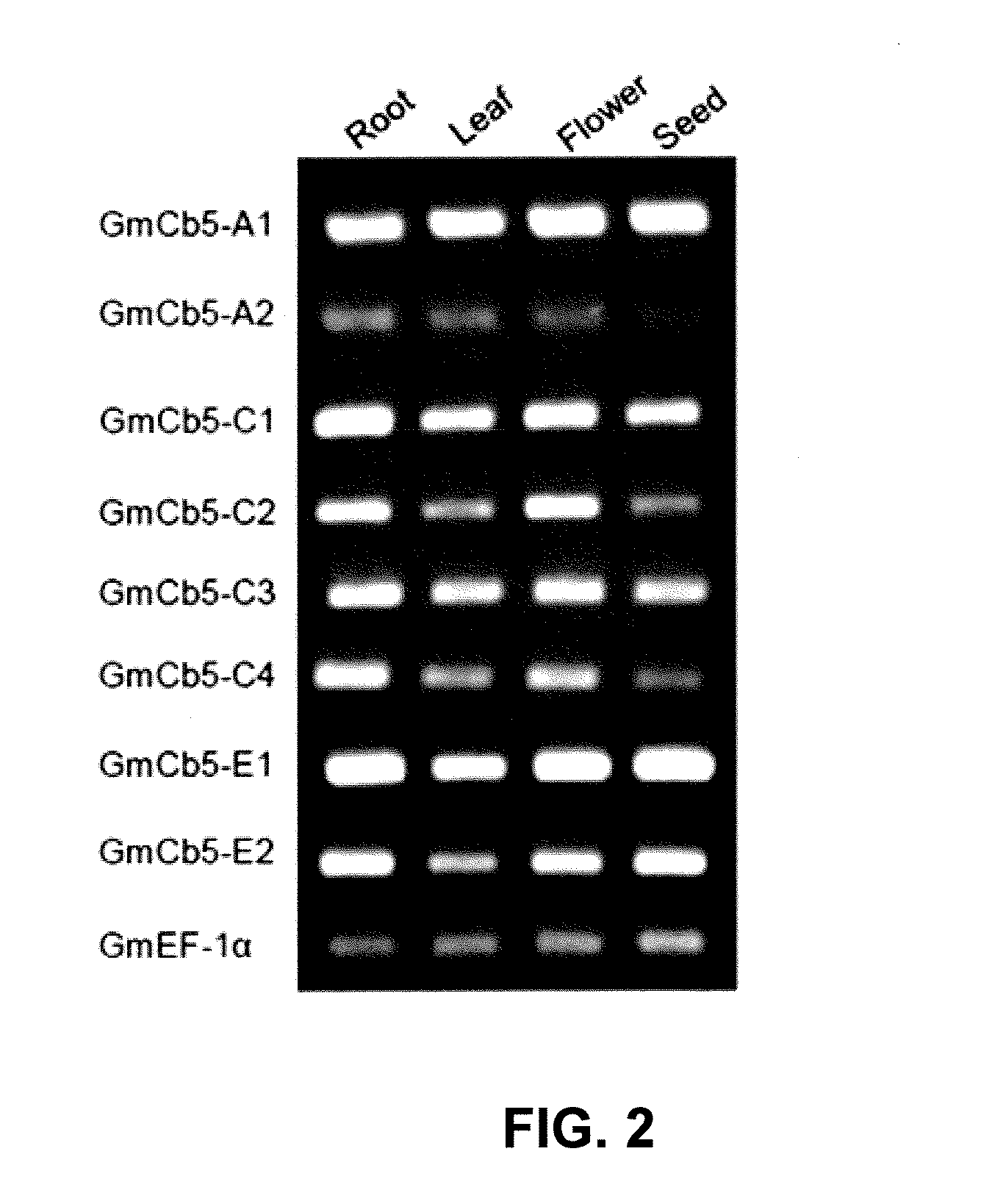
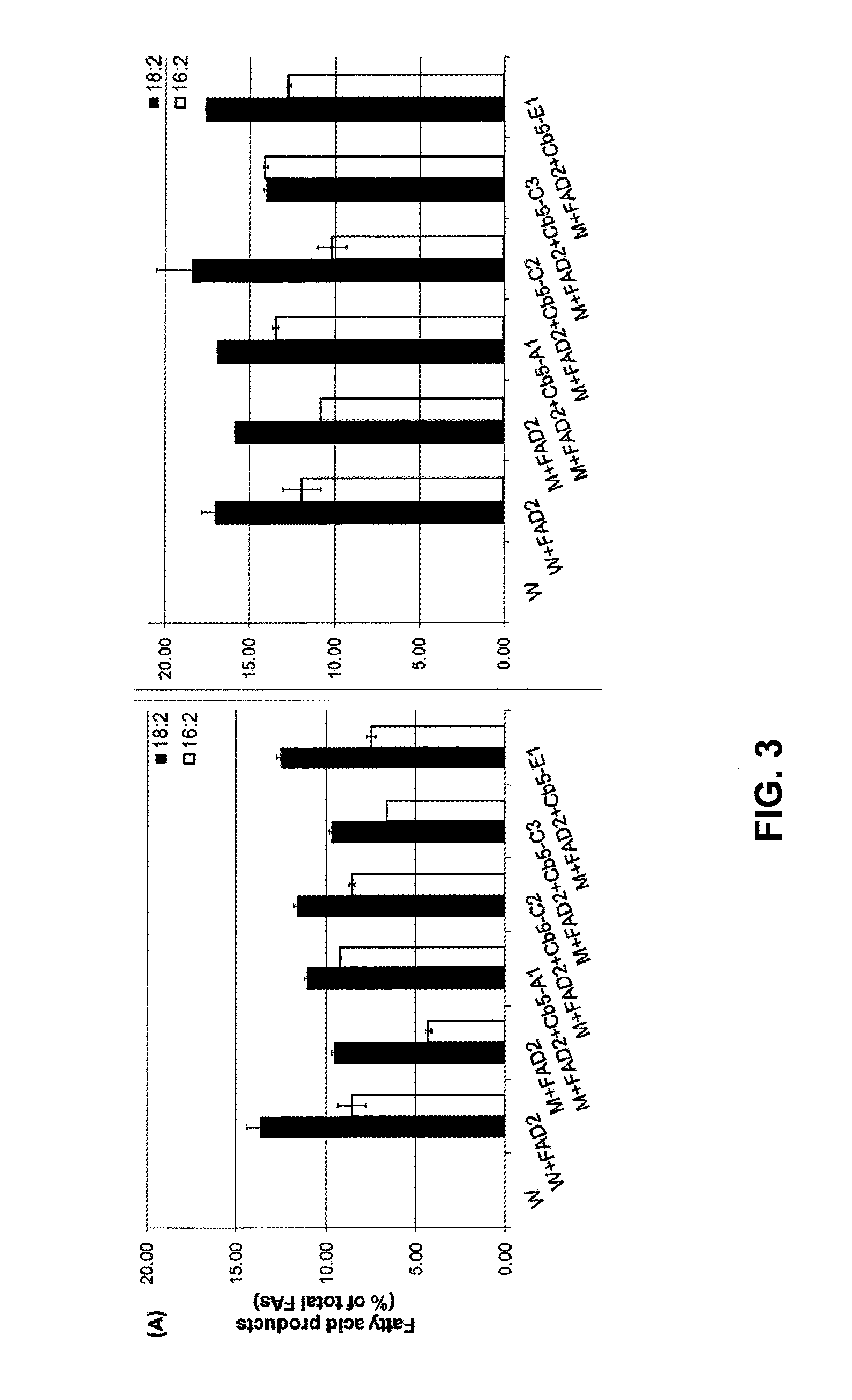
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
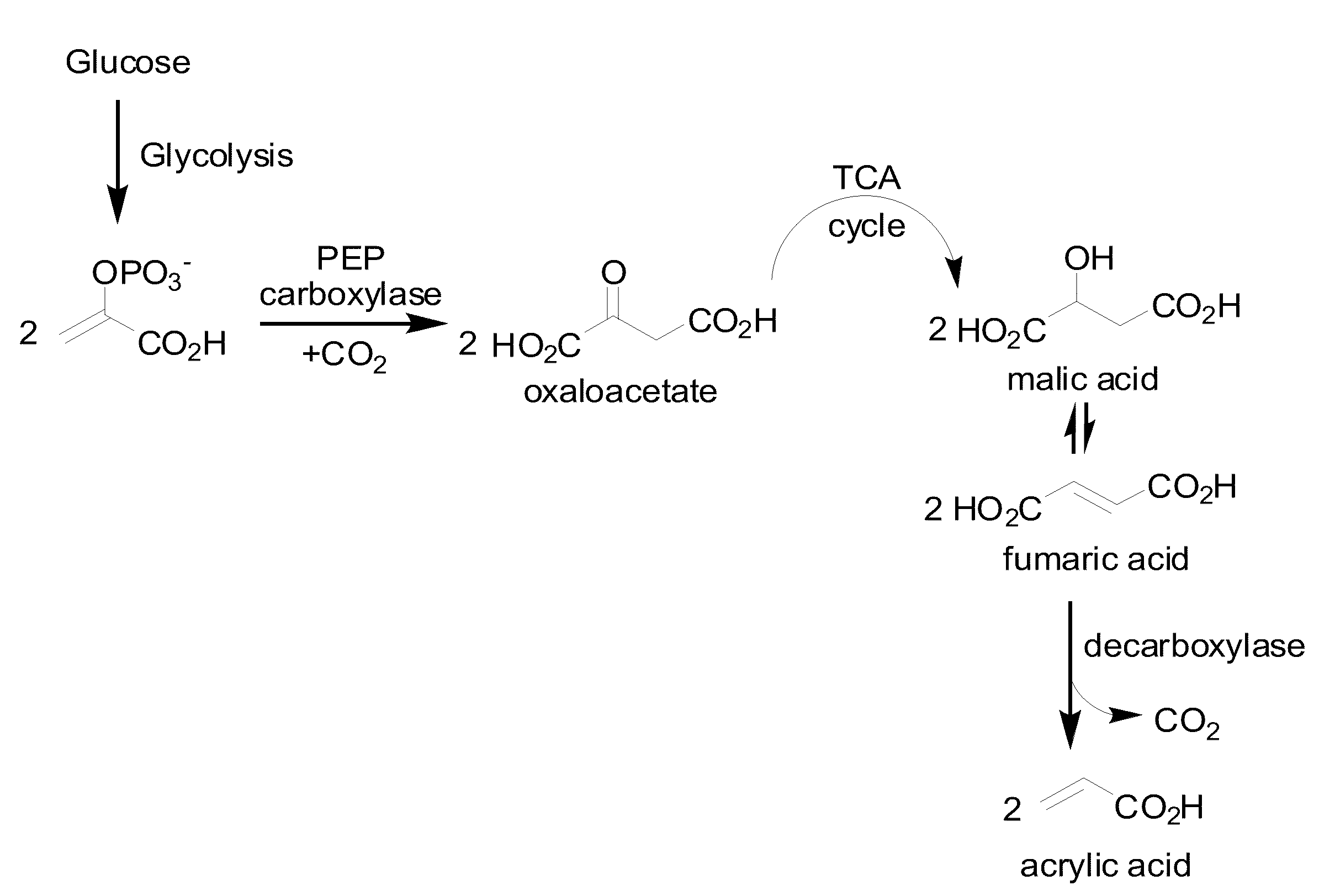
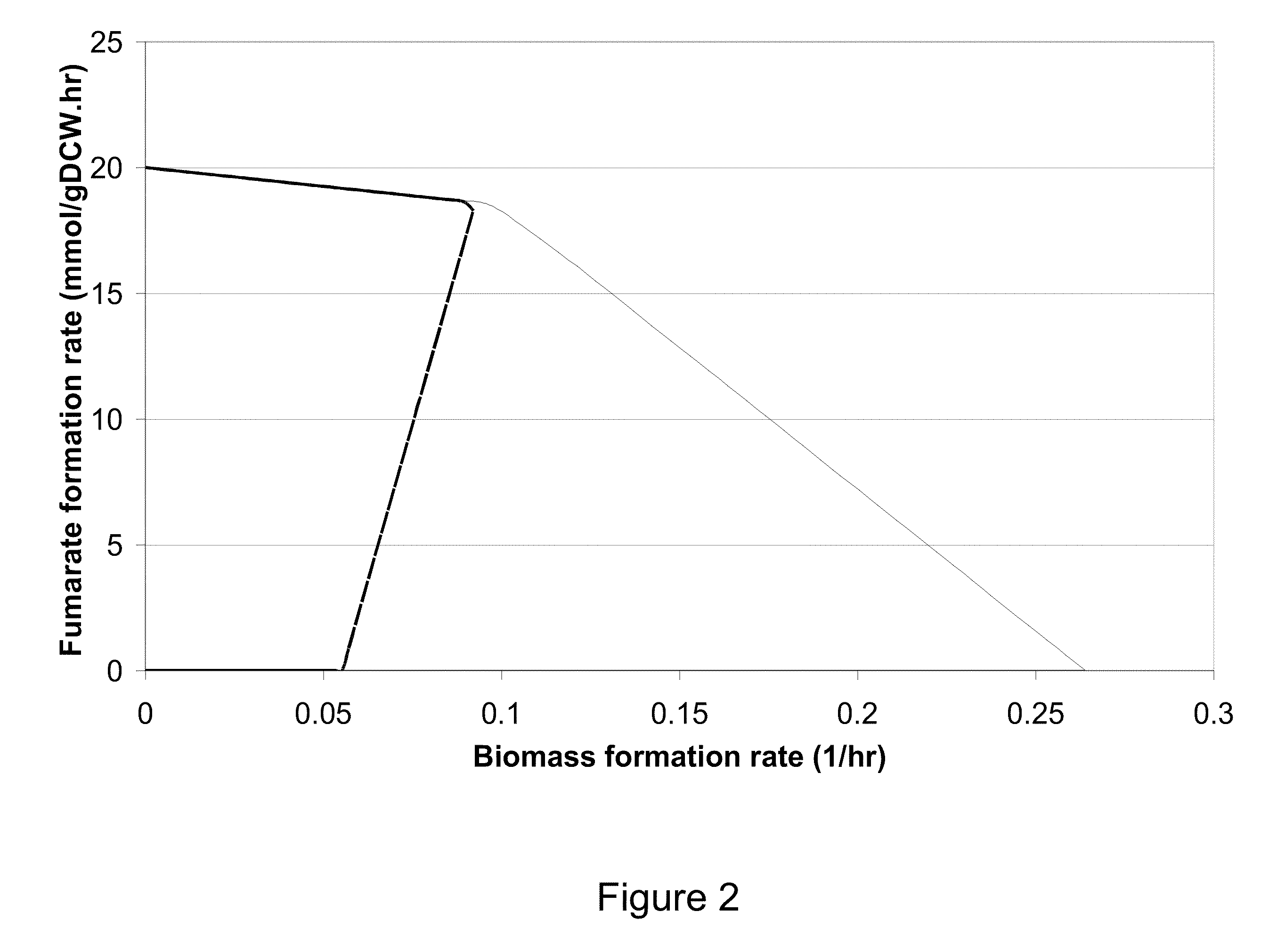
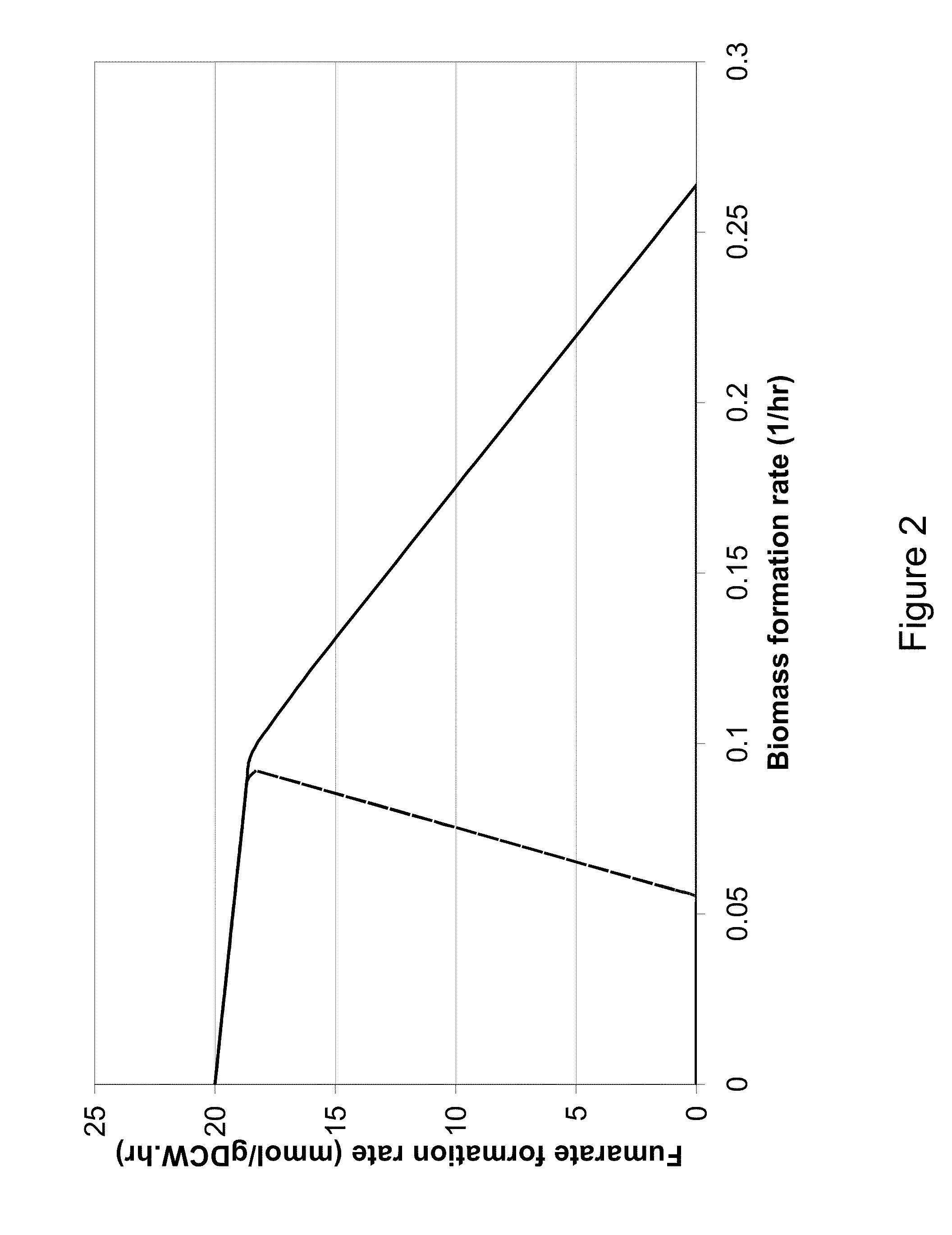
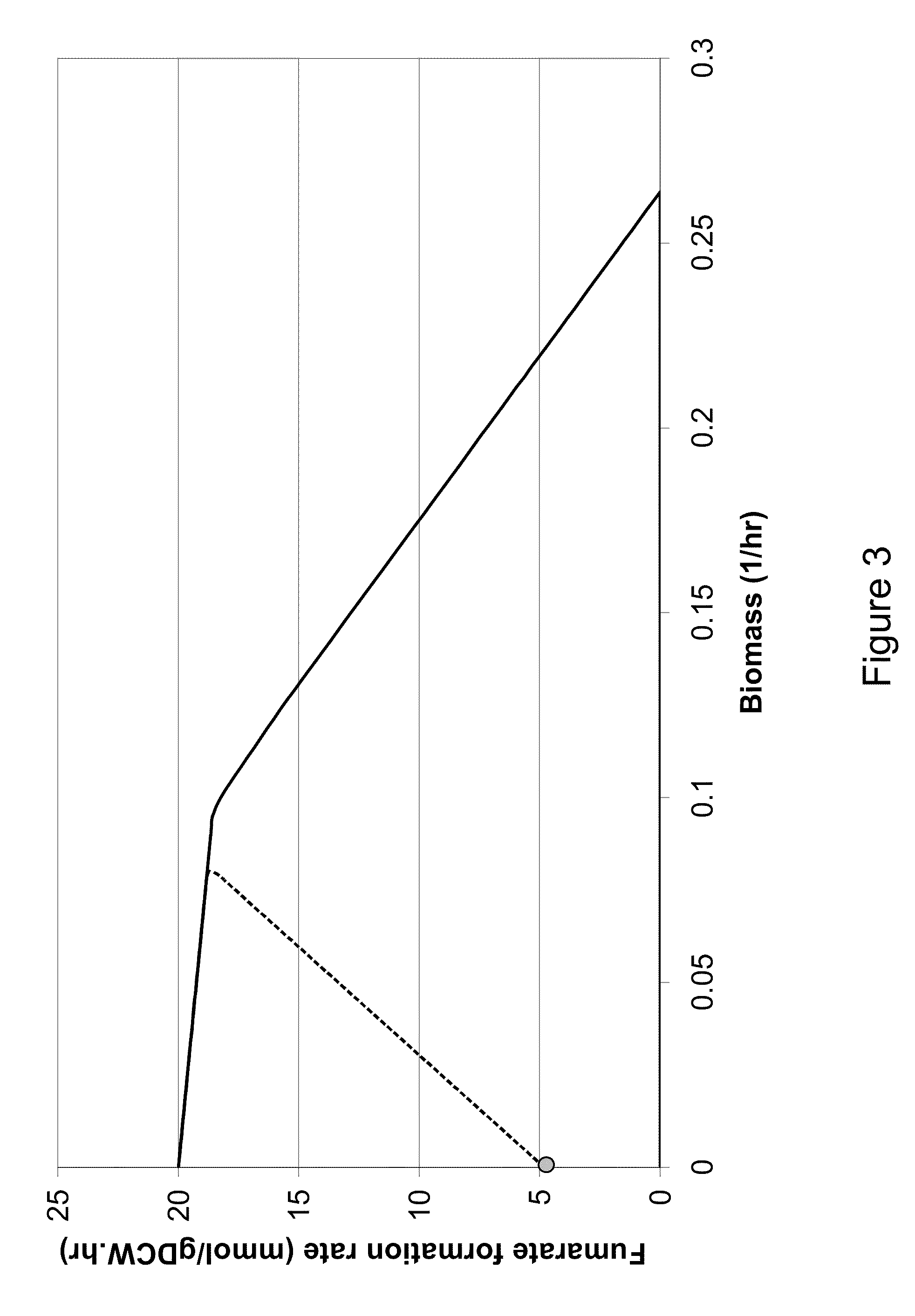
Microorganisms and methods for the biosynthesis of fumarate, malate, and acrylate
A non-naturally occurring eukaryotic or prokaryotic organism includes one or more gene disruptions occurring in genes encoding enzymes imparting increased fumarate, malate or acrylate production in the organism when the gene disruption reduces an activity of the enzyme. The one or more gene disruptions confers increased production of acrylate onto the organism. Organisms that produce acrylate have an acrylate pathway that at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acrylate pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce acrylate, the acrylate pathway comprising a decarboxylase. Methods of producing fumarate, malate or acrylate include culturing these organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Hepatitis C virus asialoglycoproteins
InactiveUS6074852AFacilitate secretionFacilitated releaseNanotechFungiSialic acid aldolaseVirus-like particle
Two Hepatitis C Virus envelope proteins (E1 and E2) are expressed without sialylation. Recombinant expression of these proteins in lower eukaryotes, or in mammalian cells in which terminal glycosylation is blocked, results in recombinant proteins which are more similar to native HCV glycoproteins. When isolated by GNA lectin affinity, the E1 and E2 proteins aggregate into virus-like particles.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
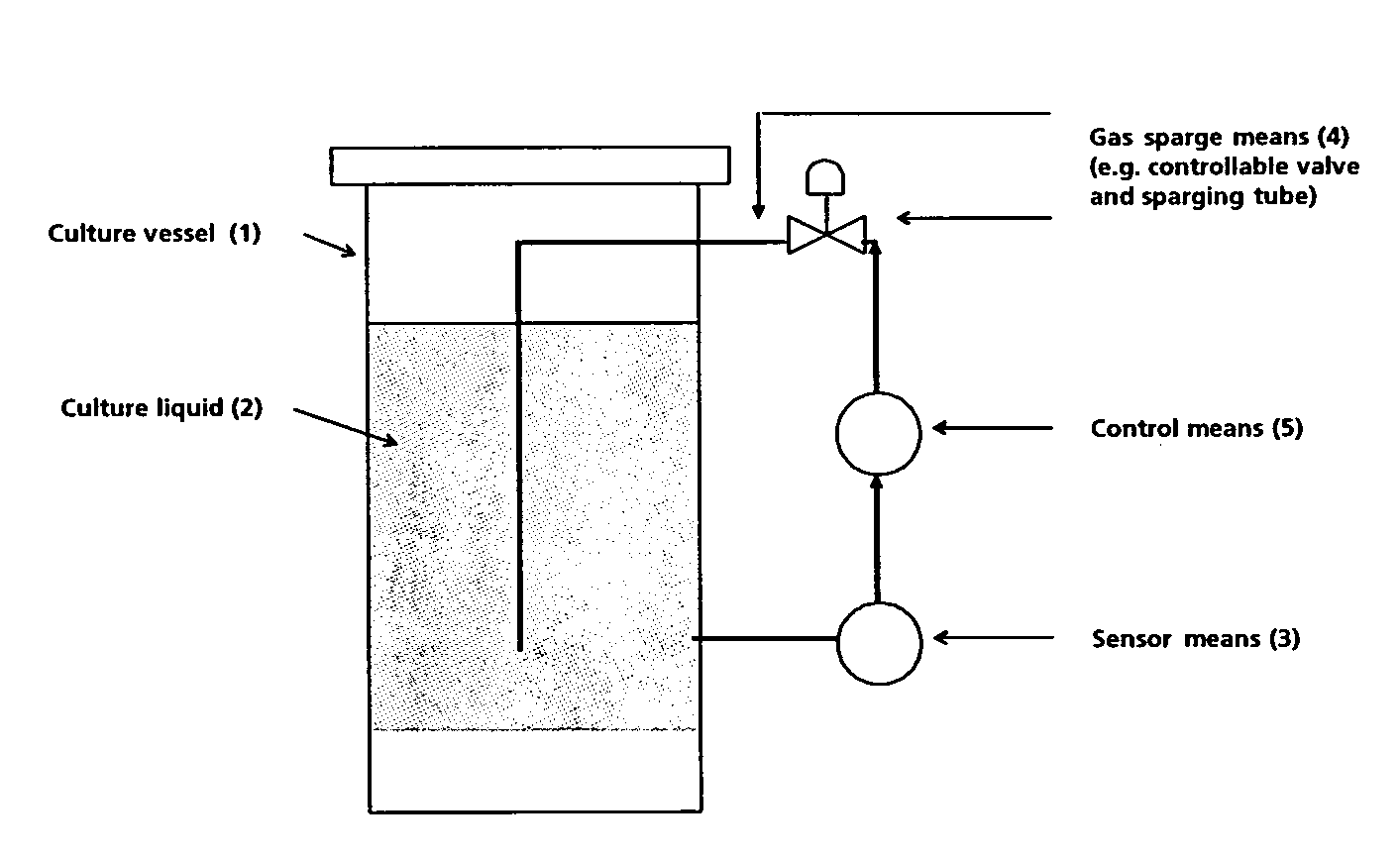
Method for large-scale production of polypeptide in eukaryote cells and a culture vessel suitable therefor
InactiveUS7521210B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFactor VIIaPh control
The invention provides a method for large-scale production of a polypeptide, such as a Factor VII or Factor VIIa polypeptide, in eukaryote cells, such as mammalian cells, contained in a culture liquid, said method comprising: monitoring the concentration of dissolved CO2 in the culture liquid, and constantly or intermittently sparging atmospheric air through the culture liquid, wherein the sparging rate of the air is controlled in relation to the monitored concentration of dissolved CO2 in the culture liquid. The method reduces or eliminates the use of bases while providing an excellent pH control. The invention also provides a culture vessel suitable for the methods.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK HEALTH CARE AG
Method for Increasing the Ratio of Homologous to Non-Homologous Recombination
InactiveUS20080194029A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideSingle-Stranded DNA Binding Proteins
Gene targeting allows the deletion (knock out), the repair (rescuing) and the modification (gene mutation) of a selected gene and the functional analysis of any gene of interest. Targeting of nuclear genes has been a very inefficient process in most eukaryotes including plants and animals due to the dominance of illegitimate integration of the applied DNA into non-homologous regions of the genome. The present invention provides a method for increasing the ratio of homologous to non-homologous recombination of a polynucleotide into a host cell's DNA by suppressing non-homologous recombination. Surprisingly, the number of non-homologous recombination events can be reduced if the polynucleotide is applied as a purified single-stranded DNA, preferably coated with a single strand binding protein.
Owner:HEGEMANN PETER +1
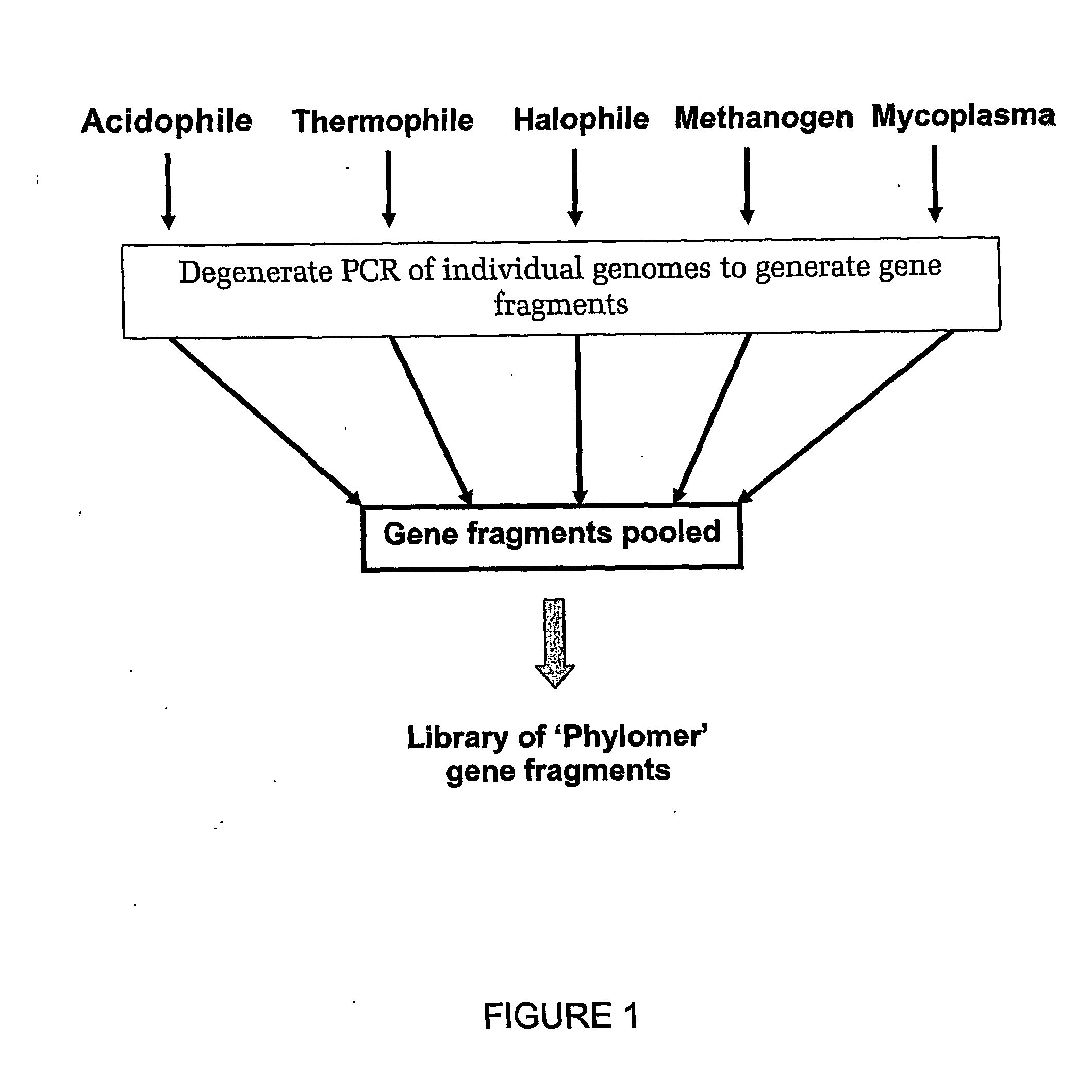
Methods of constructing biodiverse gene fragment libraries and biological modulators isolated therefrom
InactiveUS20070031832A1Enhance nucleotide sequence diversityRaise the possibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningProtein targetOrganism
Methods for producing nucleic acid fragment libraries that express highly diverse peptide domains, wherein the nucleic acid fragments are derived form microorganisms or eukaryotes with compact genomes. Also peptides derived form the libraries wherein the peptides are selected on the basis of their abilities to bind selected target proteins, including c-jun and antibodies raised against dust mite allergens.
Owner:PHYLOGICA
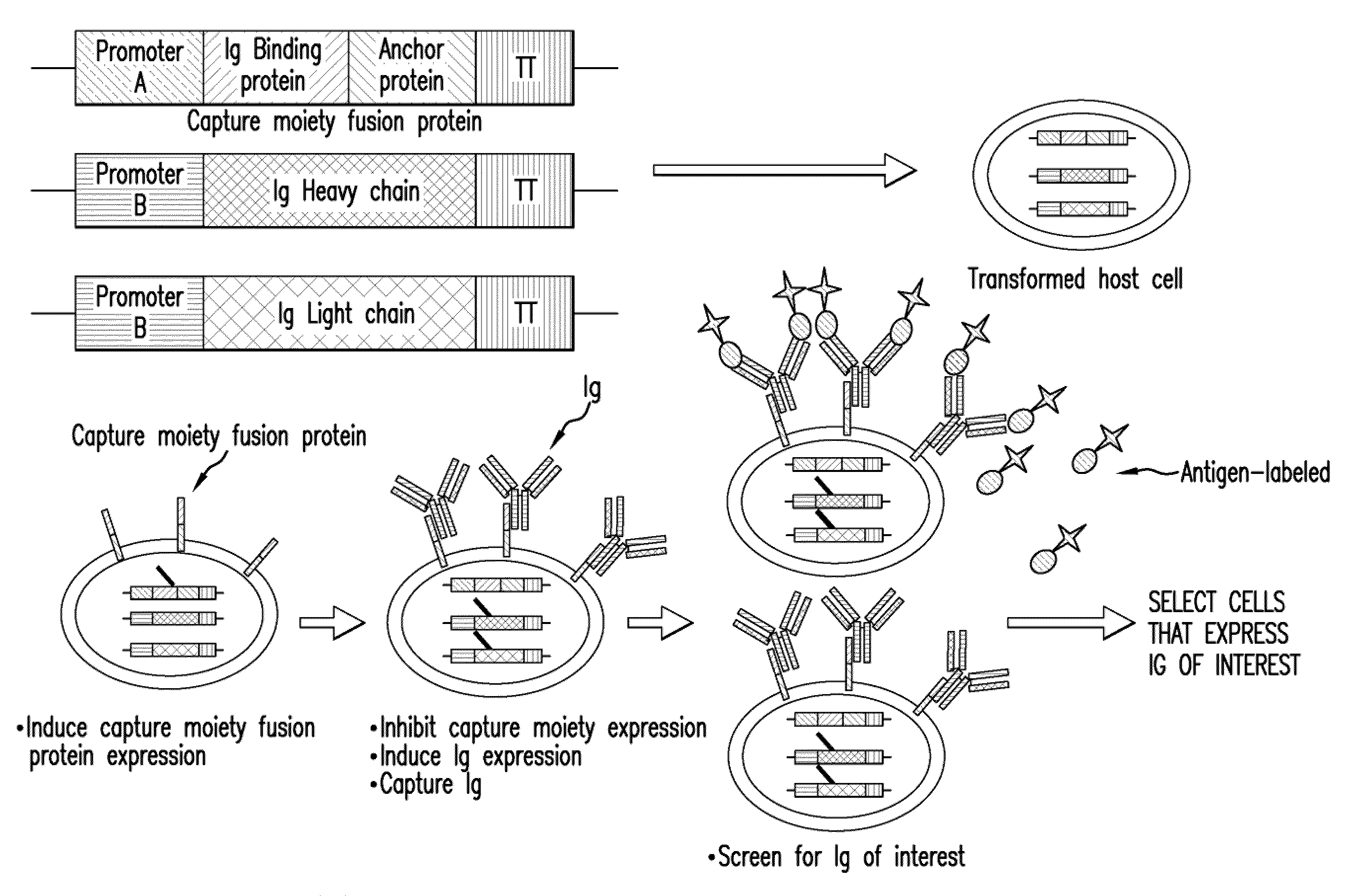
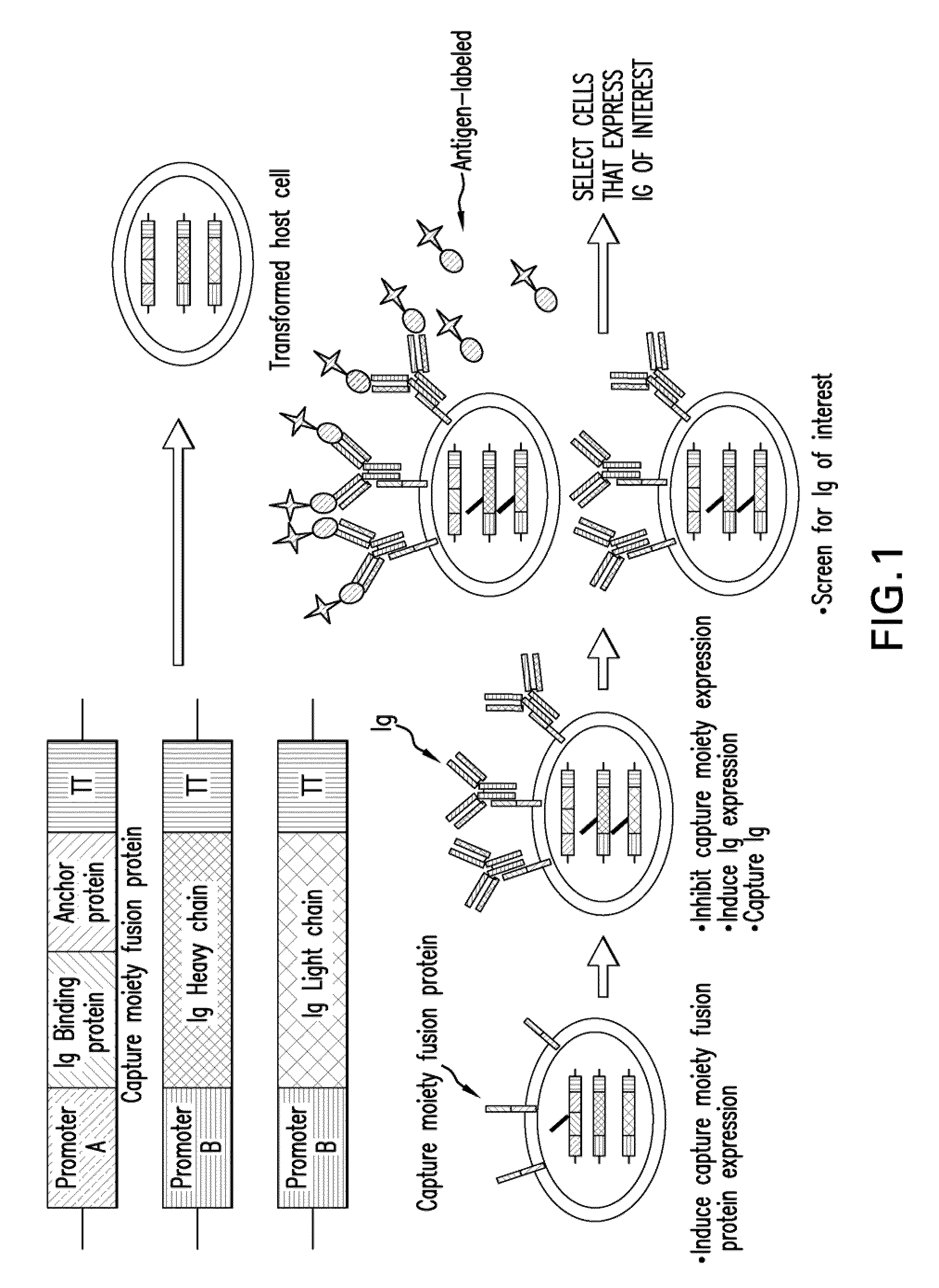
Surface Display of Whole Antibodies in Eukaryotes
ActiveUS20100009866A1Stabilize cytoplasmic mRNAImprove translation efficiencyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLibrary screeningYeastAntigen
Methods for display of recombinant whole immunoglobulins or immunoglobulin libraries on the surface of eukaryote host cells, including yeast and filamentous fungi, are described. The methods are useful for screening libraries of recombinant immunoglobulins in eukaryote host cells to identify immunoglobulins that are specific for an antigen of interest.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase III expression in lower eukaryotes
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells having modified oligosaccharides which may be modified further by heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation. Host cells with modified lipid-linked oligosaccharides are created or selected. N-glycans made in the engineered host cells exhibit GnTIII activity, which produce bisected N-glycan structures and may be modified further by heterologous expression of one or more enzymes, e.g., glycosyltransferases, sugar transporters and mannosidases, to yield human-like glycoproteins. For the production of therapeutic proteins, this method may be adapted to engineer cell lines in which any desired glycosylation structure may be obtained.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. The lower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
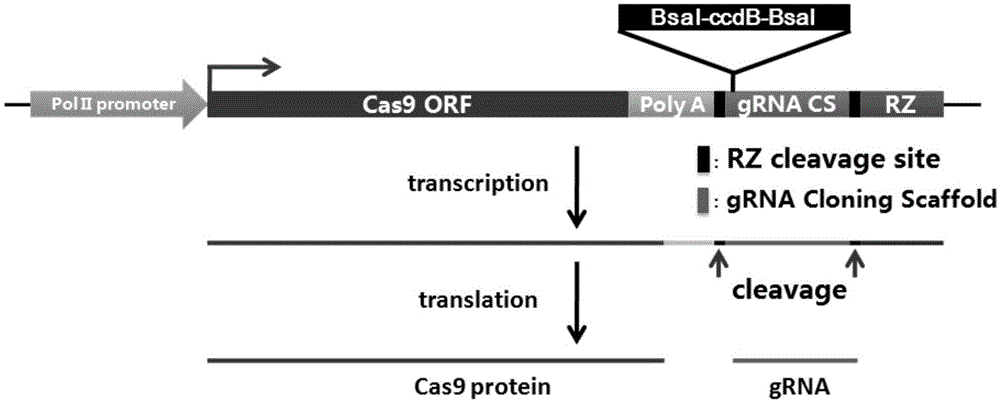
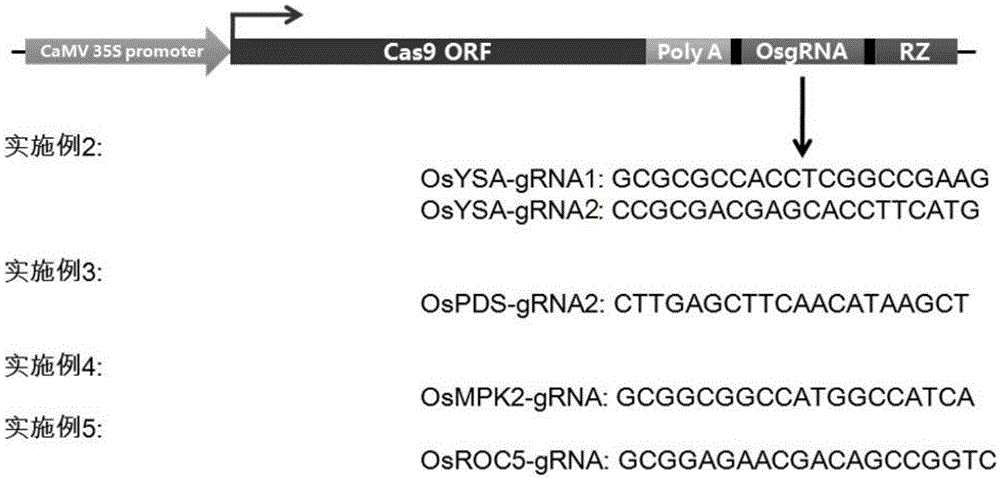
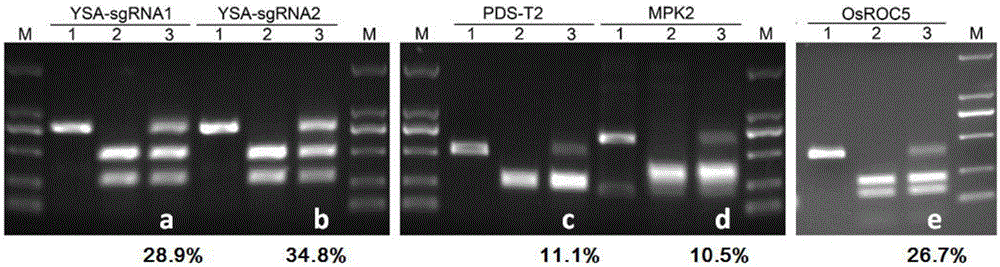
CRISPR/Cas9 single transcription unit directionally modified backbone vector and application thereof
ActiveCN105132451AComplete efficientlyCo-transcriptionVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingGene engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and concretely relates to a CRISPR / Cas9 single transcription unit directionally modified backbone vector and an application thereof. Technical problems to be solved in the invention comprise low species versatility and difficult realization of Cas9 protein expression and gRNA transcription cooperation of present CRISPR / Cas9 genome editing systems. A technical scheme in the invention is characterized in that a CRISPR / Cas9 single transcription unit backbone vector is constructed, and transcription of Cas9 and a guide RNA core unit are regulated by a promoter. The invention also provides a method for constructing a target site specifically modified Cas9-gRNA recombinant vector by adopting the CRISPR / Cas9 single transcription unit backbone vector. The efficient CRISPR / Cas9 single transcription unit backbone vector can effectively realize Pol II promoter driving-based Cas9 and gRNA unit cooperative transcription, and also can realize simple, fast and efficient genome directional heredity modification of various eukaryotes.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
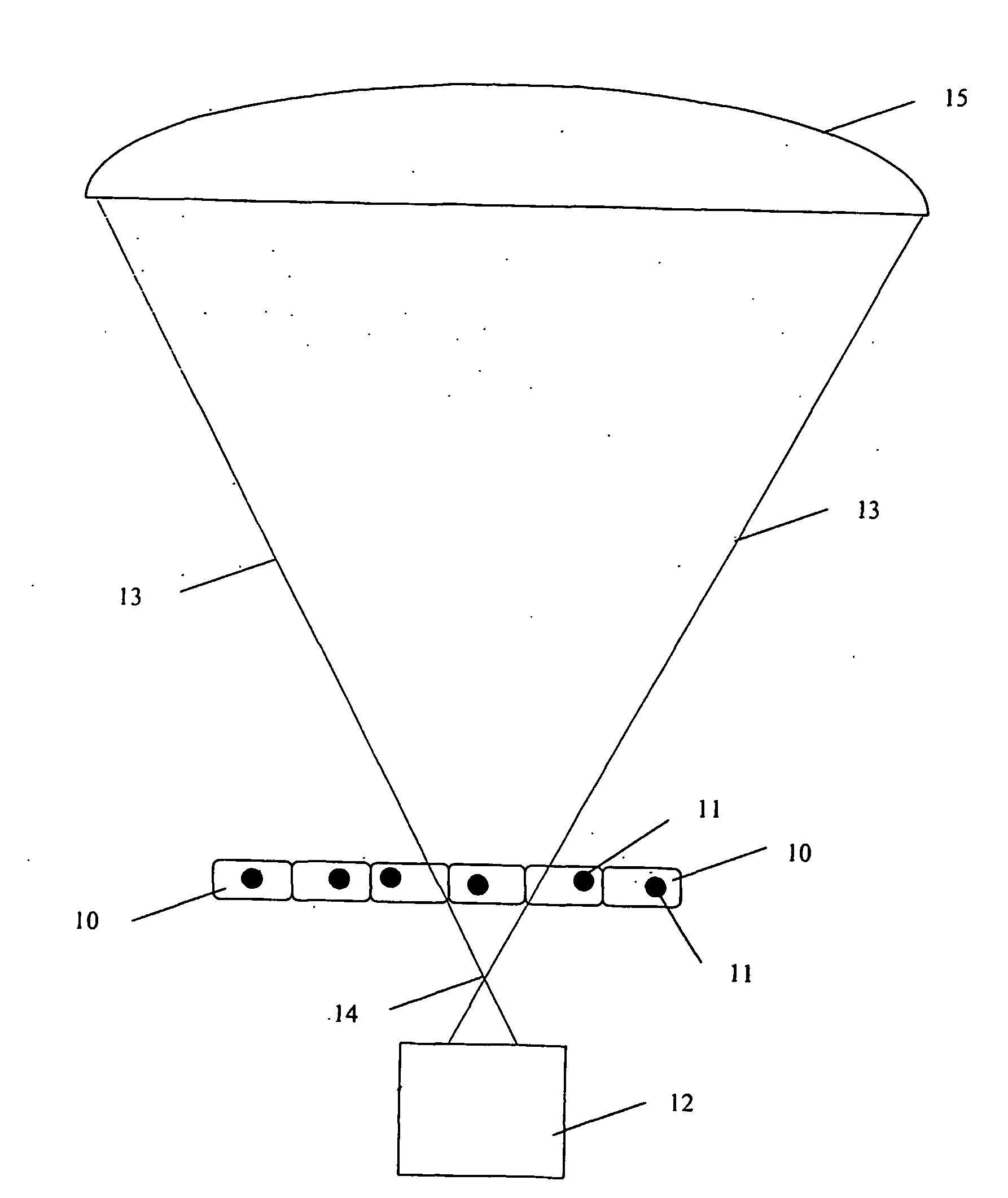
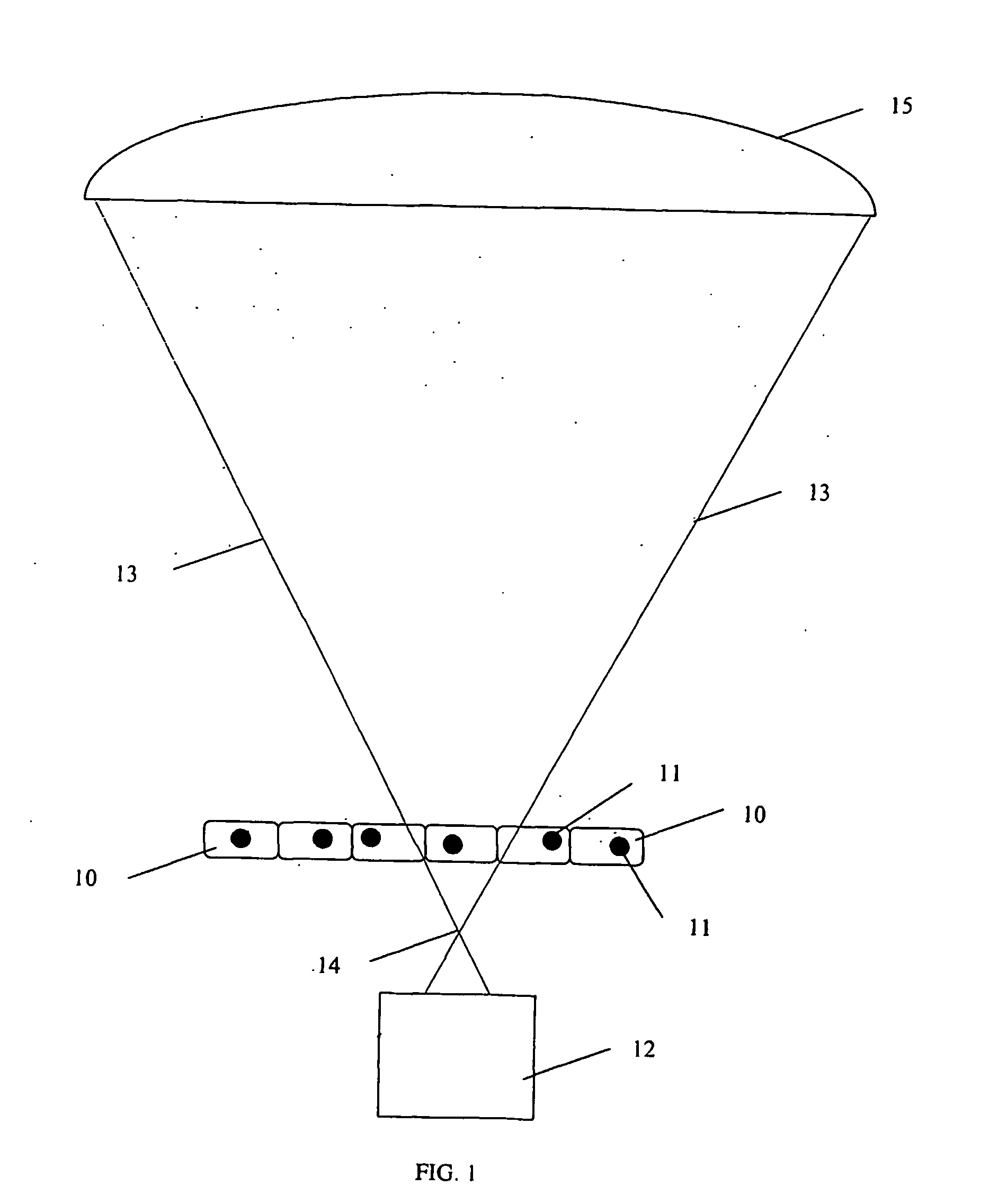
System for molecular imaging
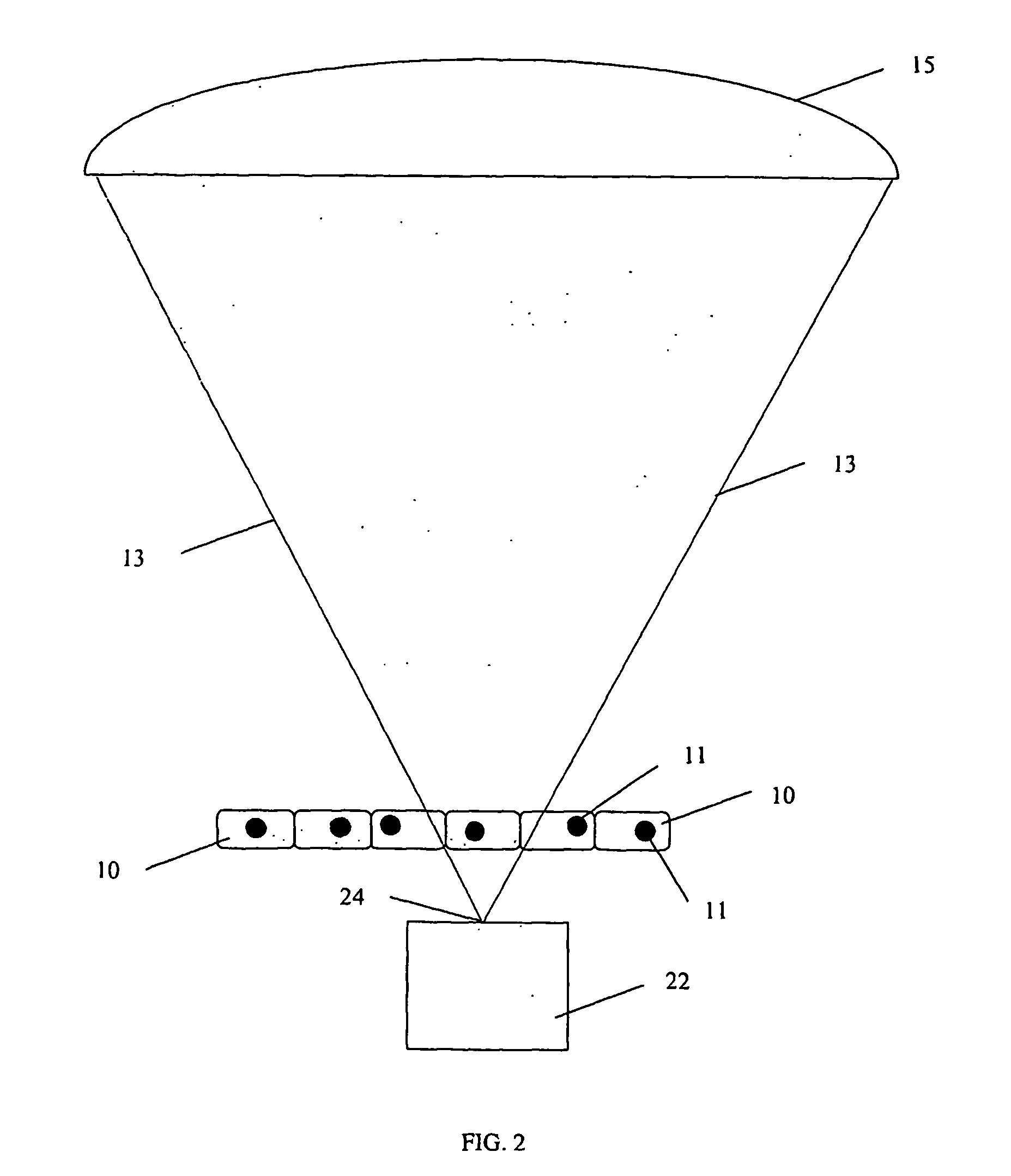
InactiveUS20070025504A1Promote recoveryMass extinctionDiagnostics using lightMicrobiological testing/measurementSensor arrayPhotonics
Charged and neutral particles, photons (13), photonic optics, detectors (15) and sensor arrays are used for application to molecular imaging, communication with biological organisms and monitoring and learning biological activity inside living organisms. The living organisms include among others living tissue, biological organs, cells (10), eukaryotes, prokaryotes, viruses and phages. Molecular imaging can be an effective new tool to understand the mechanisms of life and communicate, modify and control it. Techniques, methods and devices are described to achieve these aims. The probes used in molecular imaging described above will include the full spectrum of photons; charged and uncharged particles (13); chemicals; and biological probes.
Owner:TUMER TUMAY O
Eukaryotic use of improved chimeric mutational vectors
The invention is based on the reaction of recombinagenic oligonucleotides in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test duplex DNA on a plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria and allows for the rapid and quantitative comparison of recombinagenic oligonucleobases. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Heteroduplex Mutational Vector, was shown to be more active in than the types of mutational vectors heretofore tested. Further improvements in activity were obtained by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the Duplex Mutational Vector and removal of the DNA-containing intervening segment. The claims concern Duplex Mutational Vectors that contain the above improvements. In an alternative embodiment the claims concern a reaction mixture containing a recombinagenic oligonucleobase, a cell-free enzyme mixture and a duplex DNA containing a target sequence. In yet an alternative embodiment, the invention concerns the use of such mixture to test improvements in recombinagenic oligonucleobases, as well as to test the effects of compounds on the activity of the cell-free enzyme mixture and also to make specific changes in the target DNA sequence.
Owner:CIBUS
Mutant loxP site and applications thereof
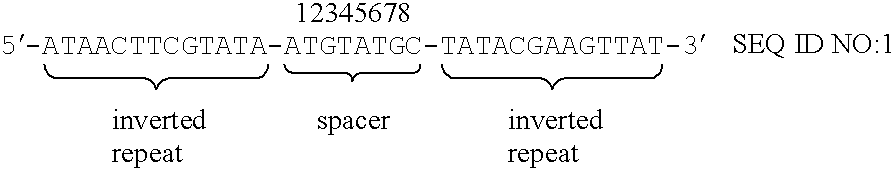
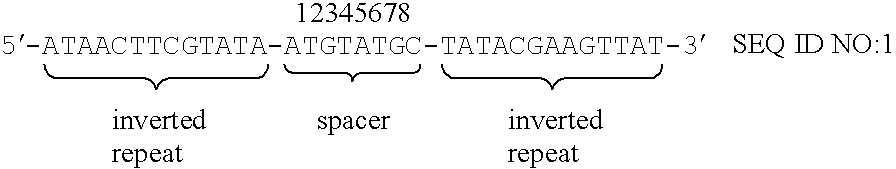
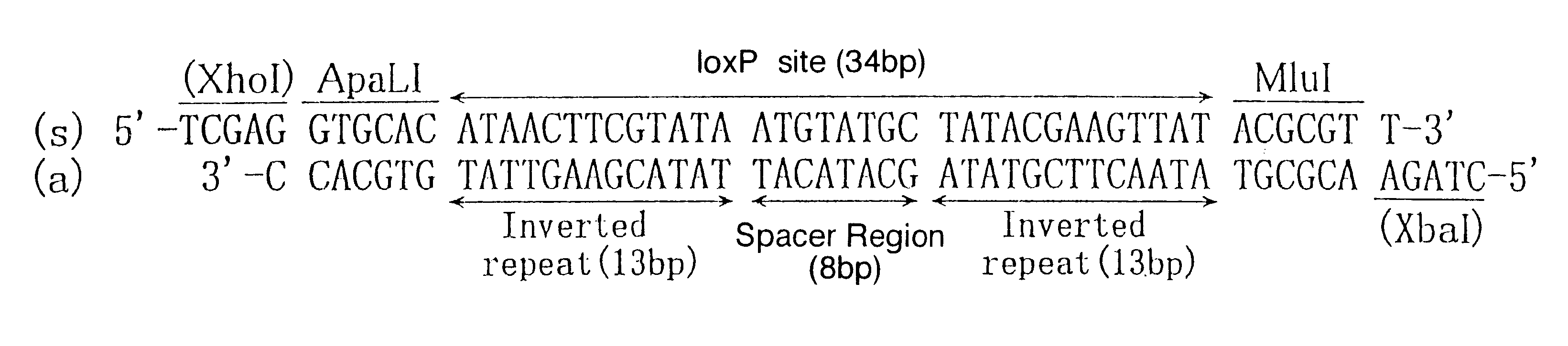
InactiveUS6465254B1Improve efficiencyEfficient replacementBiocideGenetic material ingredientsEscherichia coliNucleotide
Highly efficient gene integration or gene replacement in the higher eucaryote including animal cells can be performed by using mutant loxP site having the following properties (a)-(c) in the present invention.(a) a nucleotide sequence wherein, in a wild-type loxP site of the following formula (SEQ ID NO: 1) derived from E. coli P1 phage, at least one of the bases consisting of second (T), third (G), fourth (T) and fifth (A) bases, and at least one of the bases consisting of sixth (T) and seventh (G) bases within the 8 bases in the central part of the sequence (spacer region) are substituted by different base, and regions except for the spacer region are optionally substituted by any base:(b) a specific recombination between said mutant loxP and the wild-type loxP site can not occur even in the presence of recombinase Cre; and(c) a specific recombination between the mutant loxP sites having identical nucleotide sequences can occur in the presence of recombinase Cre.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Microorganisms and methods for the biosynthesis of fumarate, malate, and acrylate
A non-naturally occurring eukaryotic or prokaryotic organism includes one or more gene disruptions occurring in genes encoding enzymes imparting increased fumarate, malate or acrylate production in the organism when the gene disruption reduces an activity of the enzyme. The one or more gene disruptions confers increased production of acrylate onto the organism. Organisms that produce acrylate have an acrylate pathway that at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acrylate pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce acrylate, the acrylate pathway comprising a decarboxylase. Methods of producing fumarate, malate or acrylate include culturing these organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Production of galactosylated glycoproteins in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS7795002B2Reducing and eliminating activityEfficient workSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsUDP galactoseSialic acid
The present invention provides a novel lower eukaryotic host cell producing human-like glycoproteins characterized as having a terminal β-galactose residue and essentially lacking fucose and sialic acid residues. The present invention also provides a method for catalyzing the transfer of a galactose residue from UDP-galactose onto an acceptor substrate in a recombinant lower eukaryotic host cell, which can be used as a therapeutic glycoprotein.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Site-specific recombination in eukaryotes and constructs useful therefor
InactiveUS7135608B1Effective recombinationEfficient productionEnzymesFermentationMammalSite-specific recombination
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
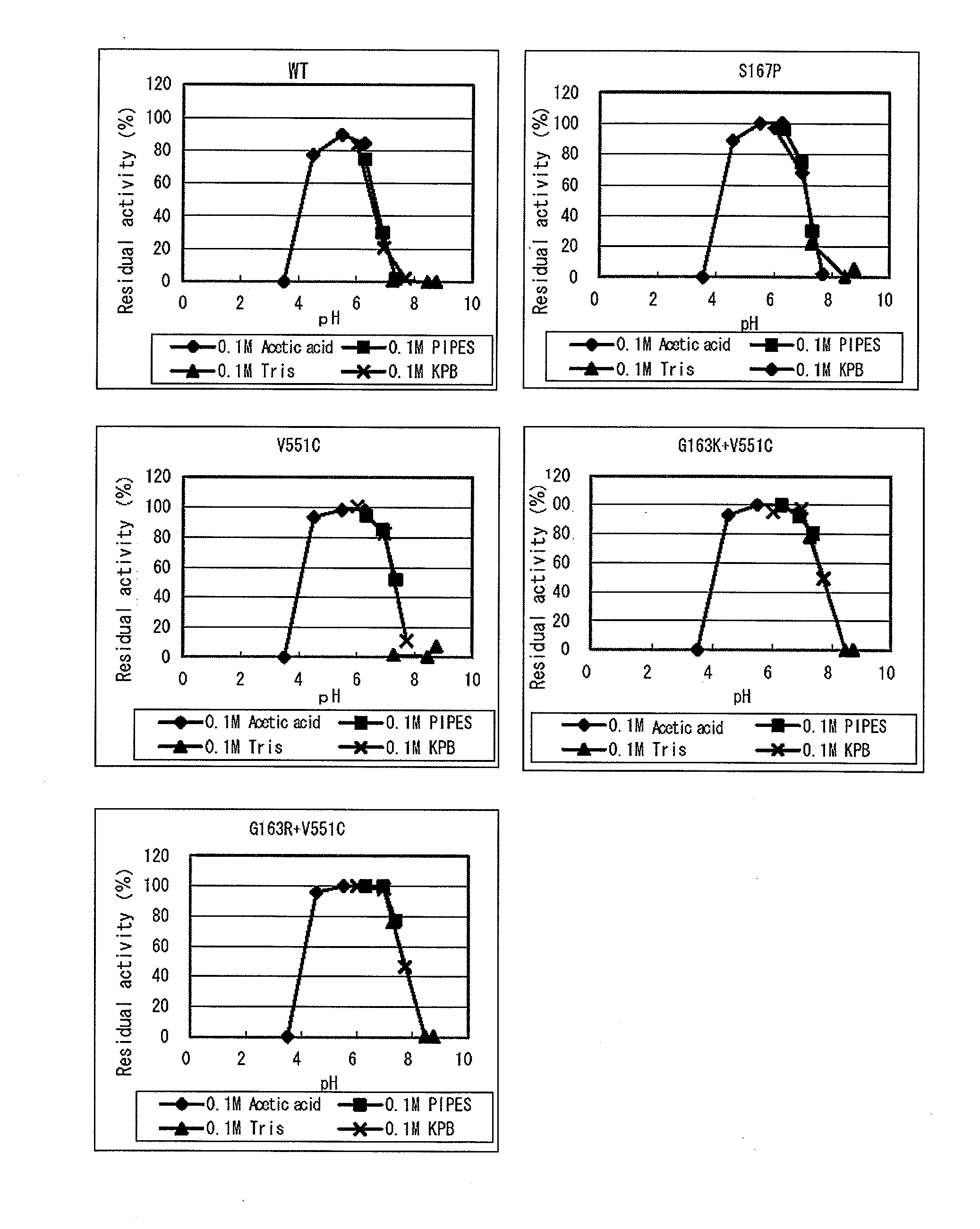
Modified flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveUS20080220460A1Reduce heat-inactivationDecreasing amount of usedFungiBacteriaFlavin adenine dinucleotideGlucose sensors
Object: An object of the present invention is to provide a more practically advantageous enzyme usable as a reagent for measuring blood glucose than the known enzymes used as blood glucose sensors.Method for Achieving the Object: A modified flavin adenine dinucleotide dependent glucose dehydrogenase (FADGDH) with more improved heat stability than FADGDH derived from wild-type FADGDH, the modified FADGDH being derived from preferably a eukaryote, more preferably a filamentous fungus, and furthermore preferably an Aspergillus fungus, and, for example, those having a primary structure with at least one amino acid substituted, deleted, inserted or added to FADGDH having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID Nos. 2 or 46 in the sequence table.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Pharmacological activities of Curcuma longa extracts
InactiveUS7220438B2Increase proliferative activityHigh activityBiocideDrug compositionsCurcuma longa extractWater soluble
This invention concerns to a topical pharmaceutical composition comprising an water soluble Curcuma extract, and suitable excipients for said topical administration; the process for obtaining said pharmaceutical compositions; the use of different Curcuma extracts as photosensitizing agents for the treatment of proliferative diseases; and the use of Curcuma extract or curcuminoids in combination with a radiation for the treatment of proliferative diseases on eukaryote cells.
Owner:ASAC COMPANIA DE BIOTECHA E INVESTIGACION
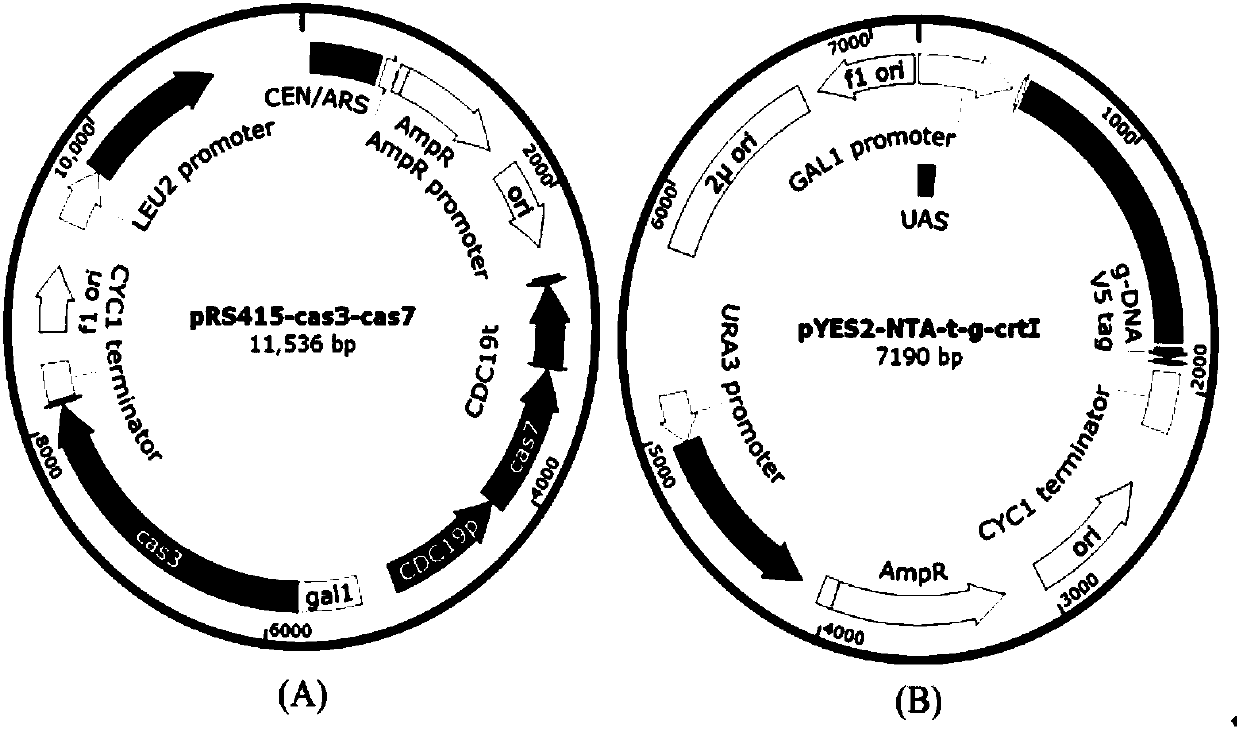
Eukaryotic gene editing method based on gene cas7-3 in I type CRISPR-Cas system
PendingCN107557378AEasy gene editingGene editing fastStable introduction of DNAVector-based foreign material introductionEukaryotic geneEucoenogenes
The invention discloses gene knockout and gene insertion on eukaryotic genomes carried out by two Cas proteins (Cas7 and Cas3) in a 1 class I type CRISPR-Cas system for the first time. The developmentof the method breaks the limitation of dependence on single-gene cas9 and cpf1, and provides a new perspective for performing gene editing on the eukaryotes by multi-gene. By applying the system, thegene editing can be conveniently, rapidly and effectively carried out on eukaryote brewer's yeast genomes. The optimized tool is expected to be widely used in the gene editing of other eukaryotes.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
InactiveUS20060078963A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyHigh mannose
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. The lower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
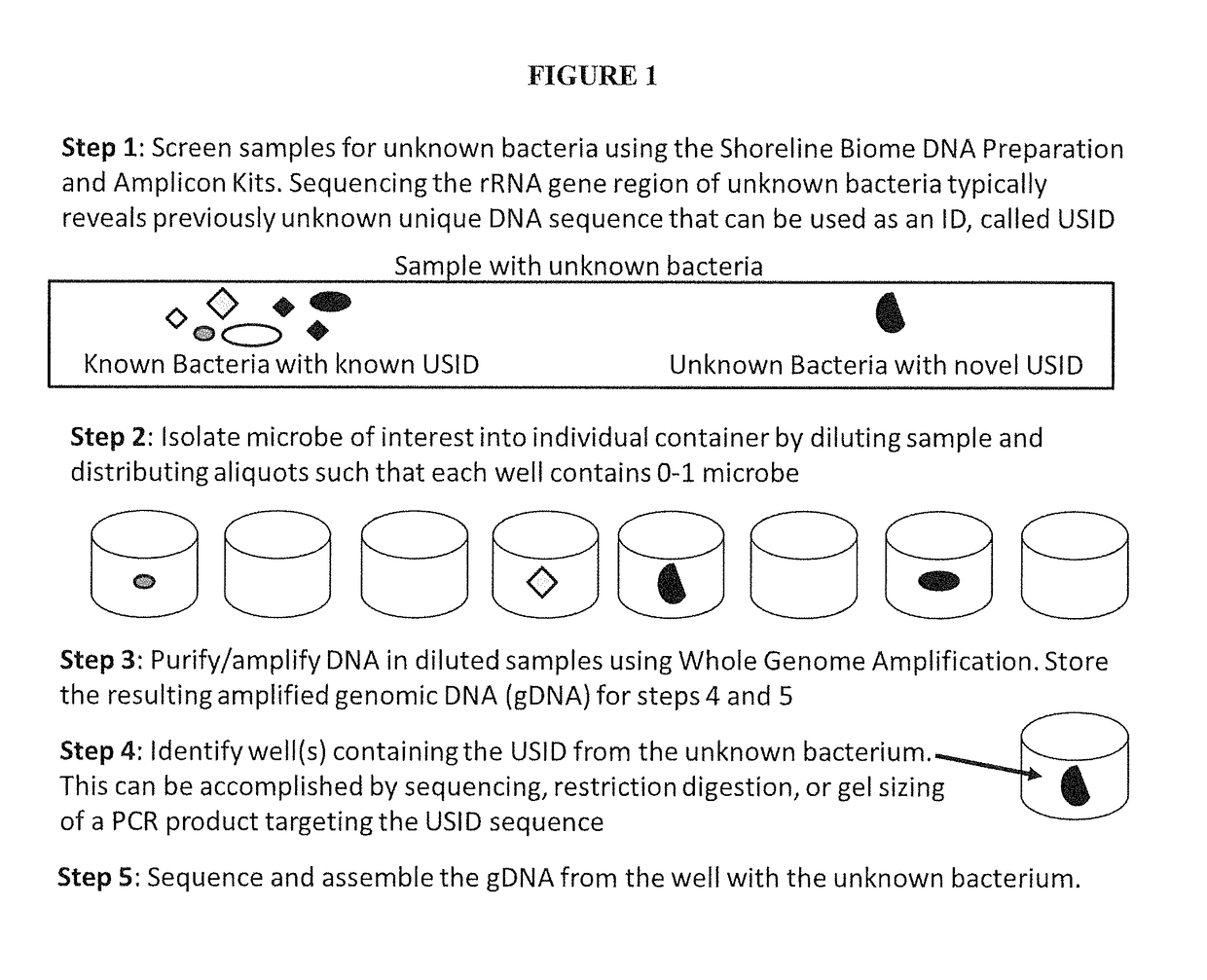
High Throughput Method for Identification and Sequencing of Unknown Microbial and Eukaryotic Genomes from Complex Mixtures
Disclosed are methods for screening biological samples for the presence unknown microbes, such as bacteria and archaea or unknown eukaryotes using rRNA gene sequences or other highly conserved genetic regions, across multiple biological samples using a unique sequence tag (barcode) corresponding to the sample. The screening process tracks the unknown microbe or eukaryote in a diluted sample where the DNA has been prepared using whole genome amplification. The whole genome of the unknown microbe or eukaryote is then sequenced and assembled.
Owner:SHORELINE BIOME LLC
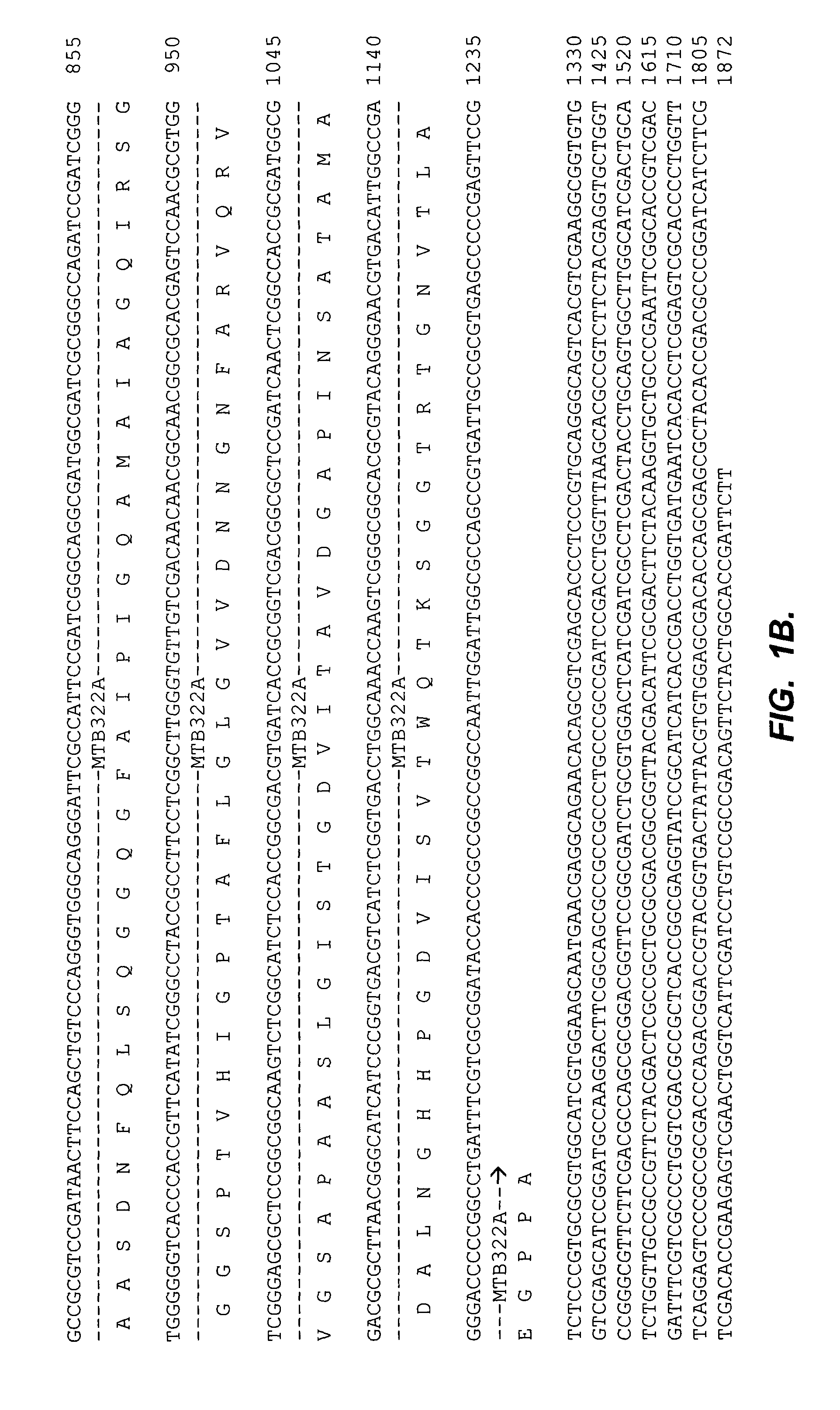
Methods of using a Mycobacterium tuberculosis coding sequence to facilitate stable and high yield expression of the heterologous proteins
InactiveUS7009042B1Stable and high yield expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousAmino acid
The present invention relates generally to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of a fusion polypeptide comprising a Mycobacterium tuberculosis polypeptide, and a heterologous polypeptide of interest, expression vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acids, and methods for producing such fusion polypeptides. In particular, the invention relates to materials and methods of using such M. tuberculosis sequence as a fusion partner to facilitate the stable and high yield expression of recombinant heterologous polypeptides of both eukaryotic and prokaryotic origin.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com