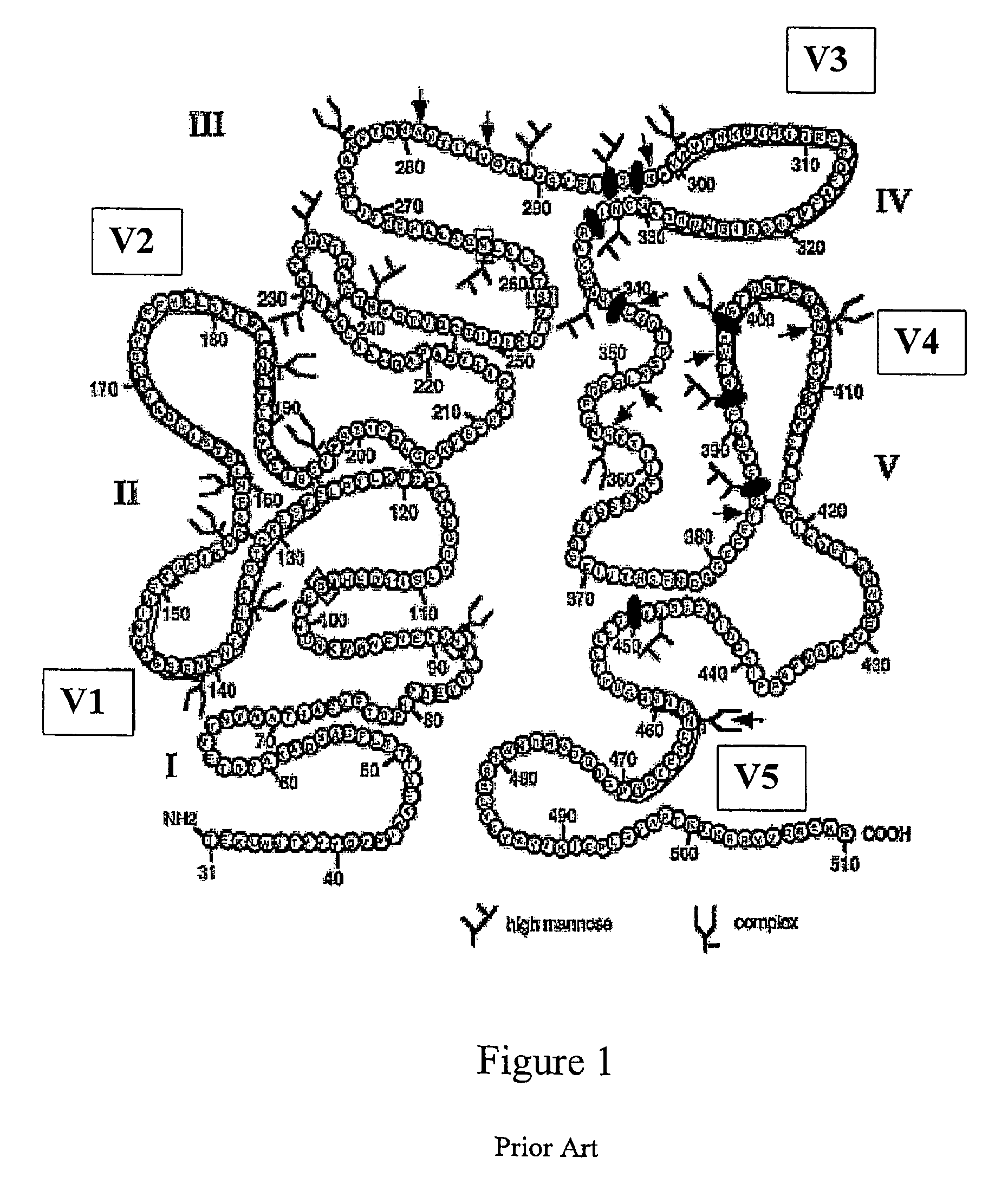
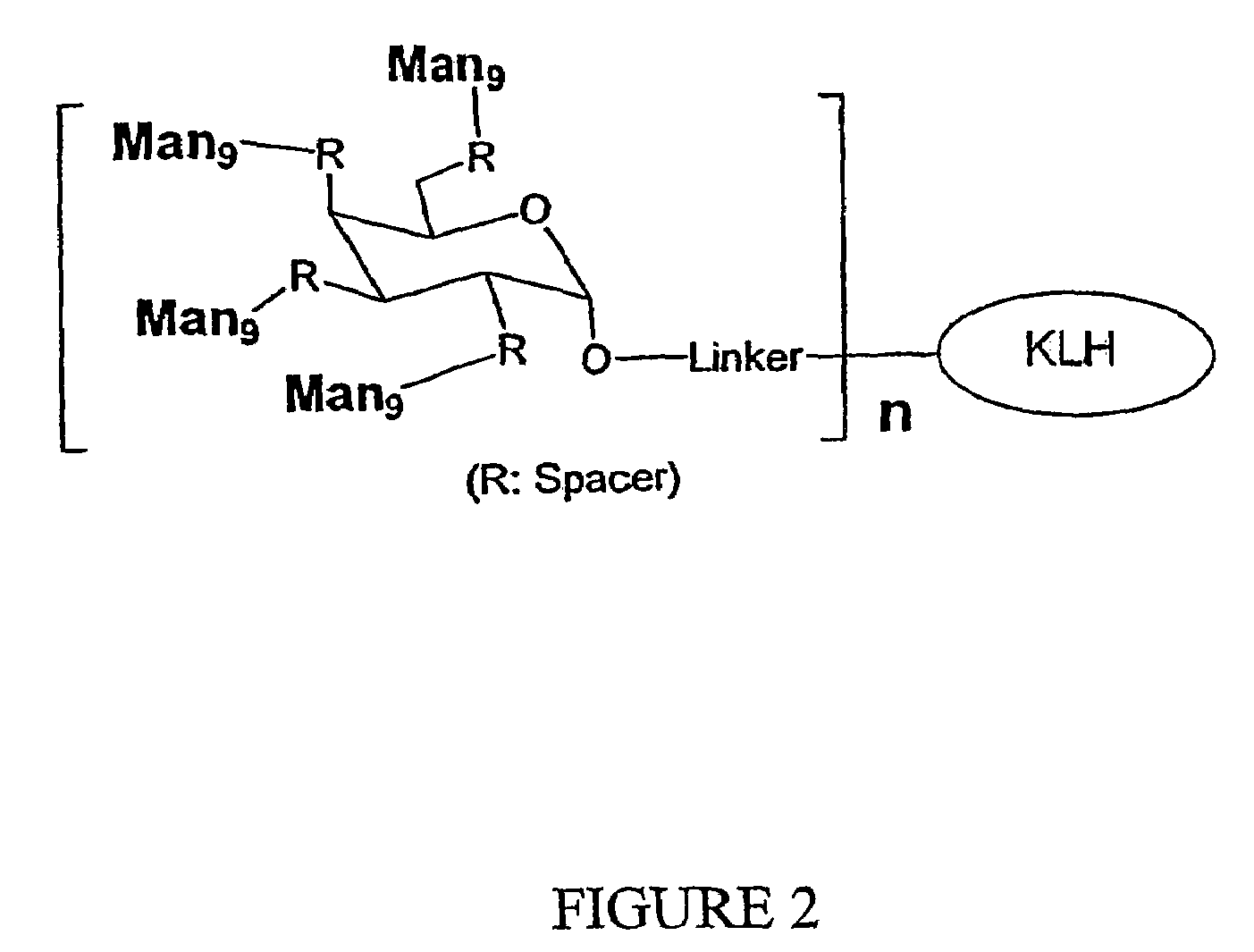
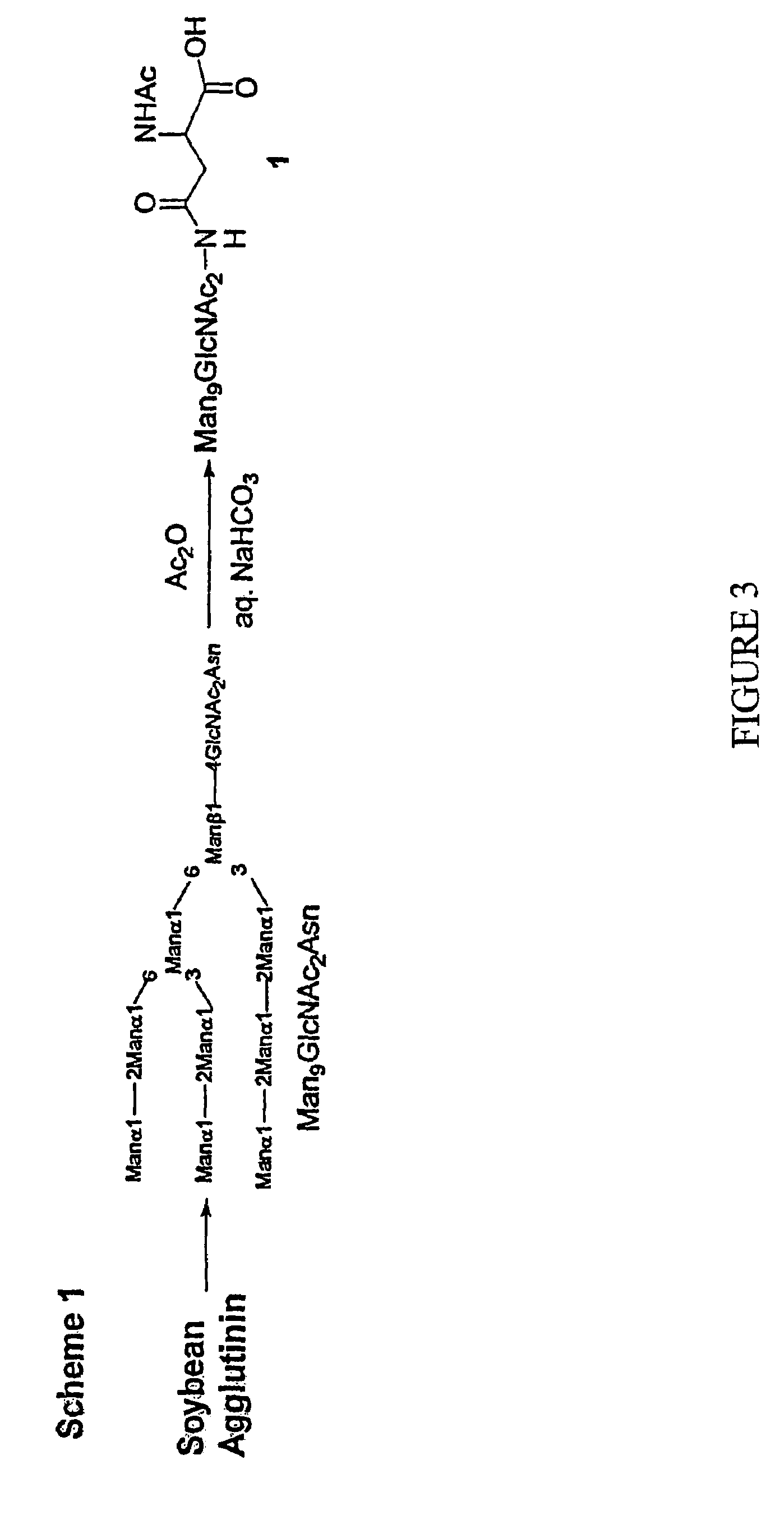
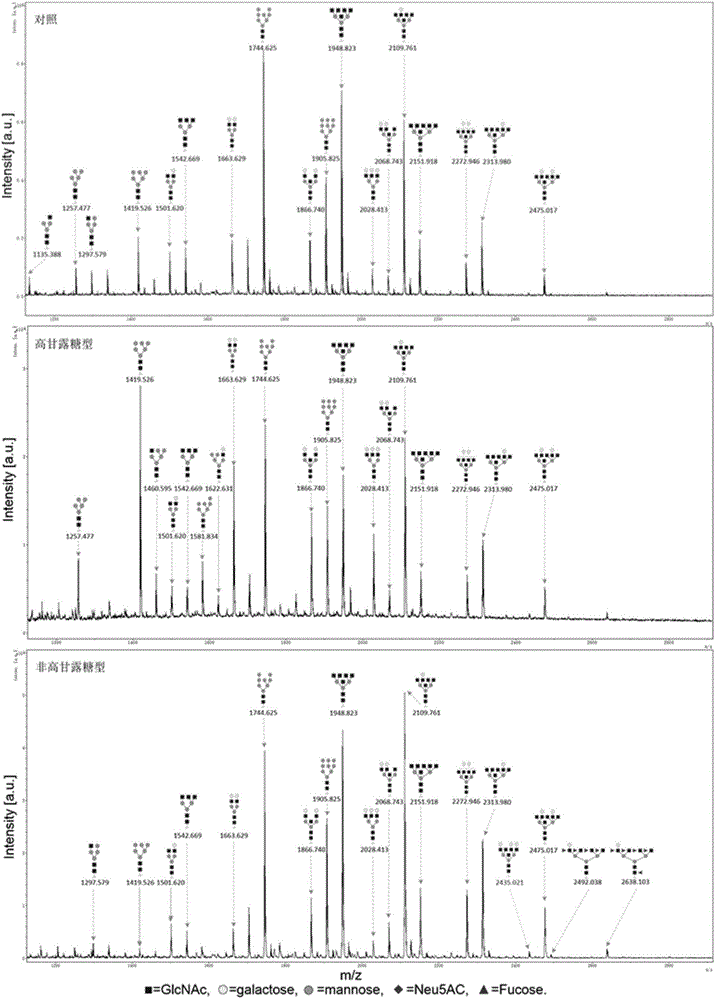
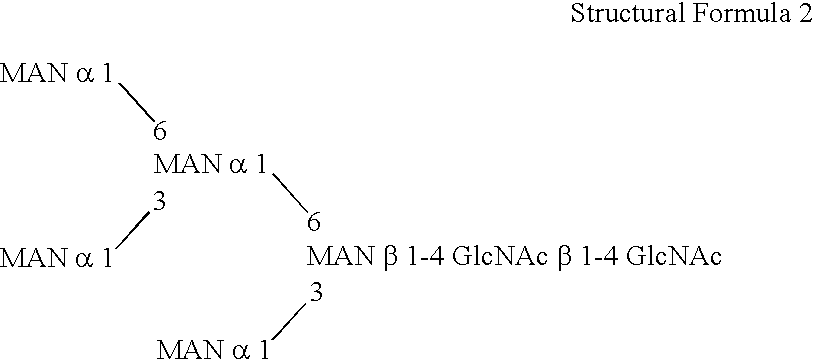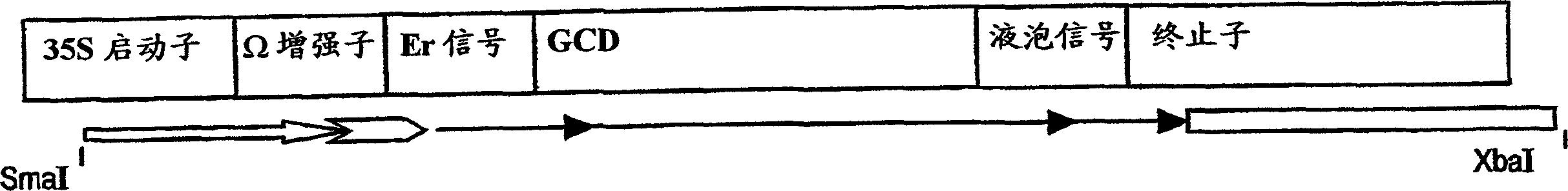Patents
Literature
75 results about "High mannose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
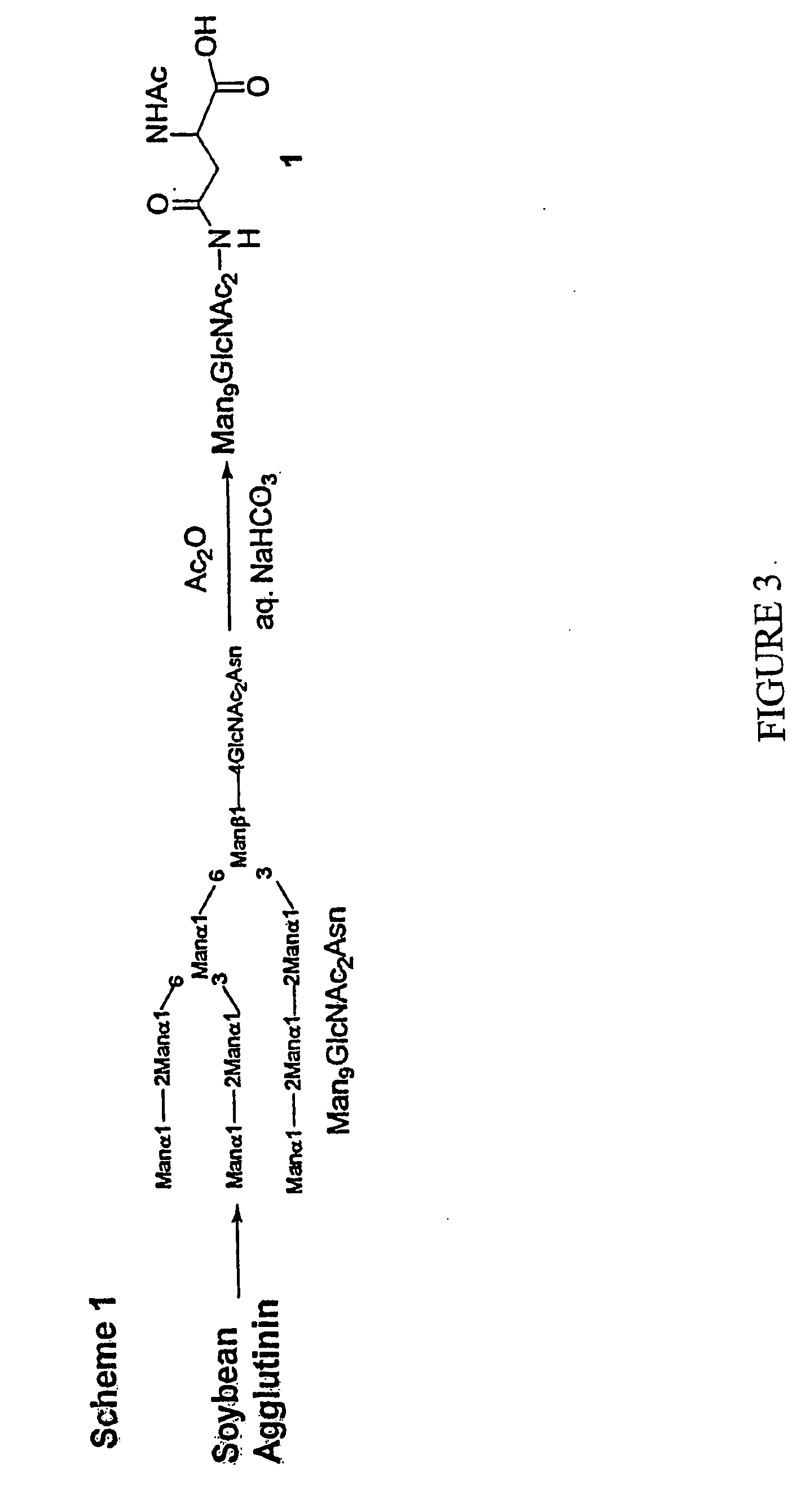
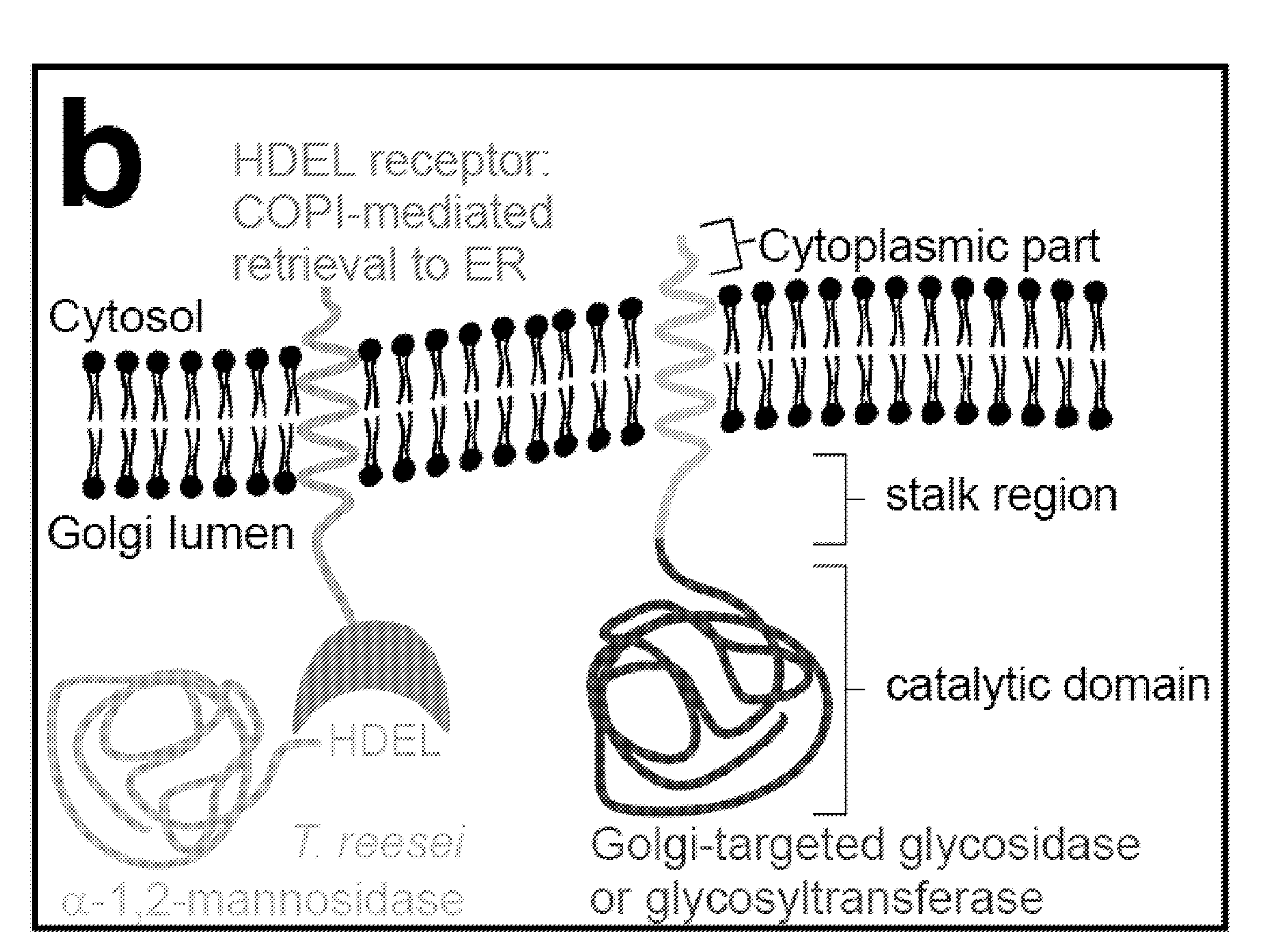
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
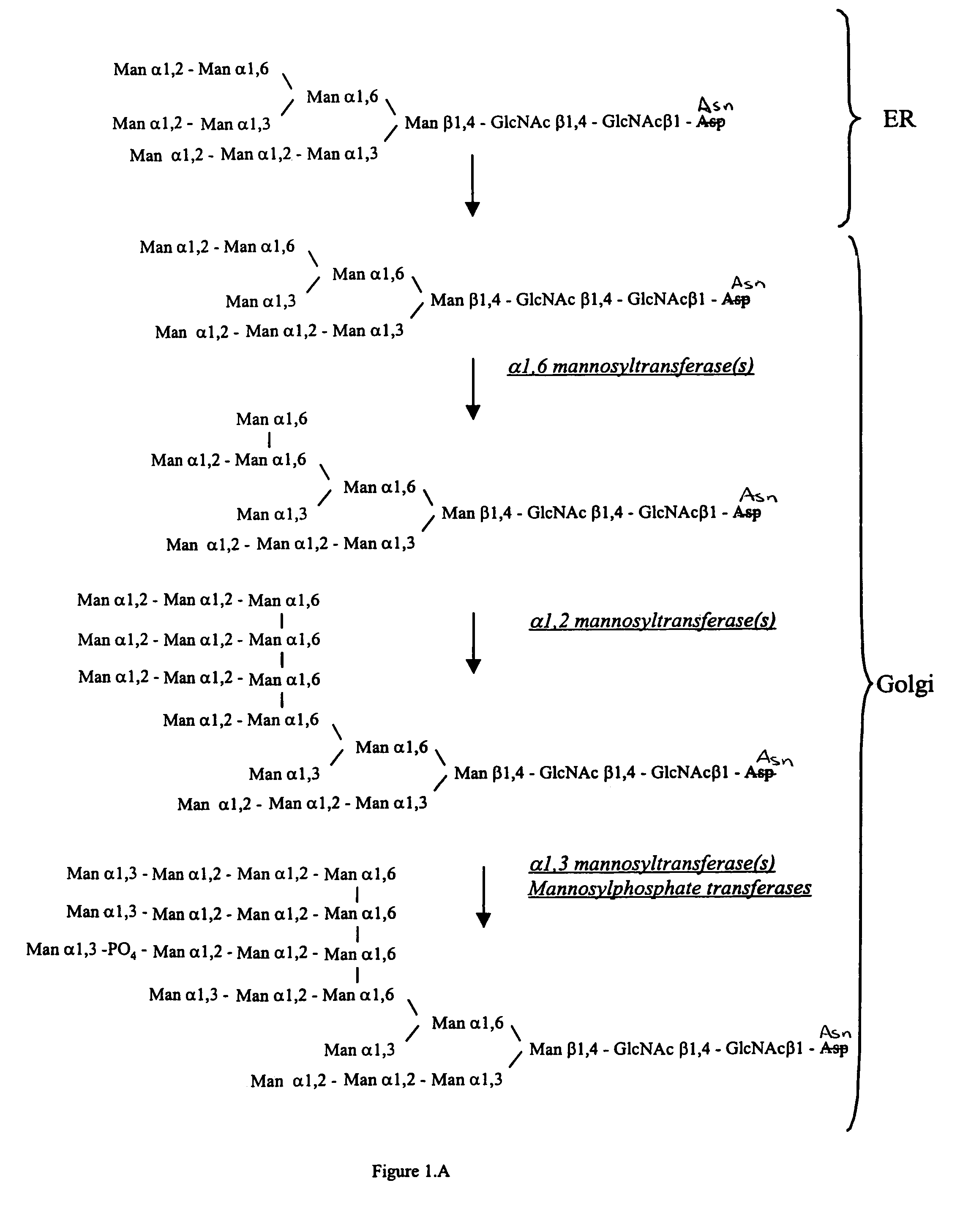
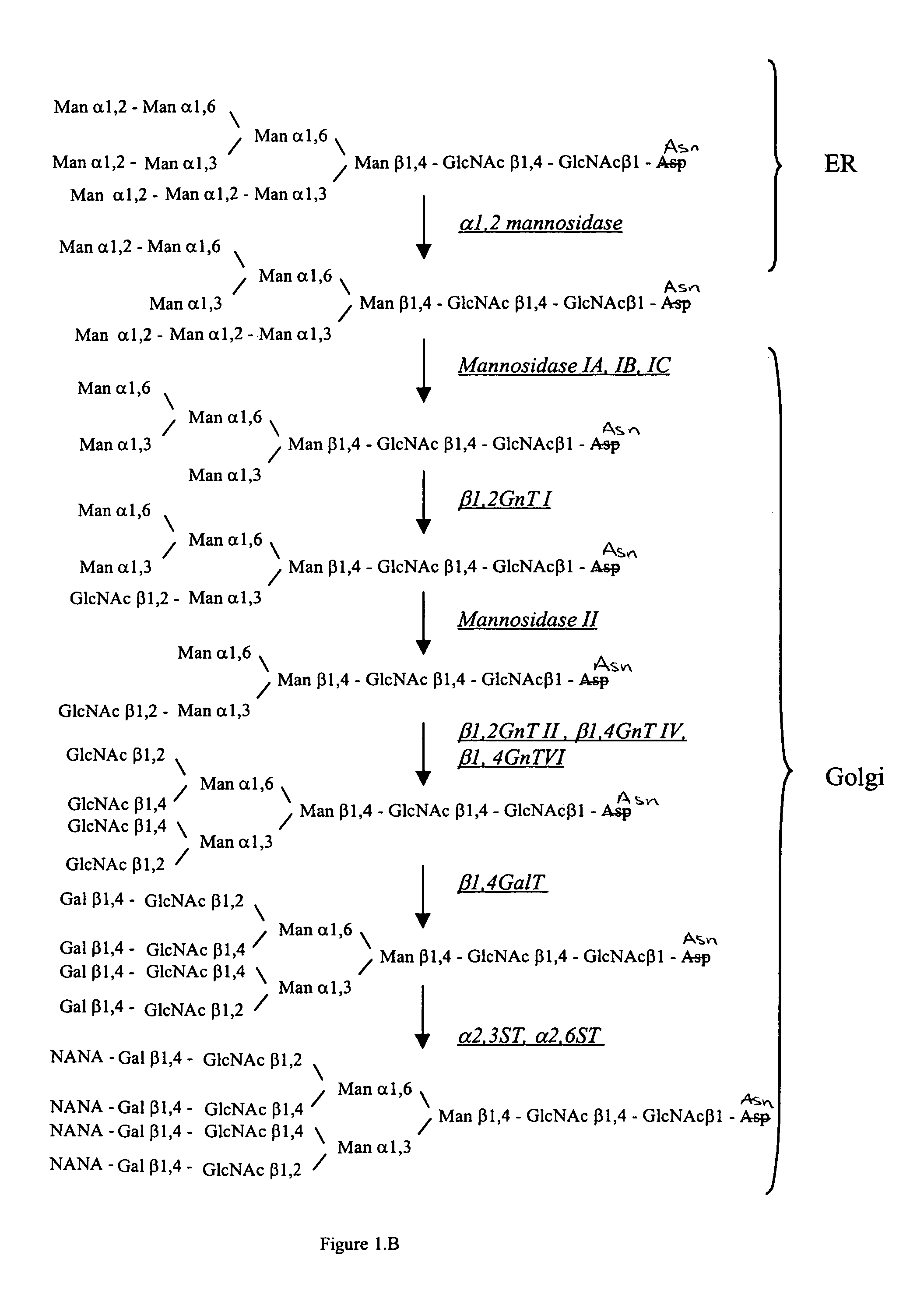
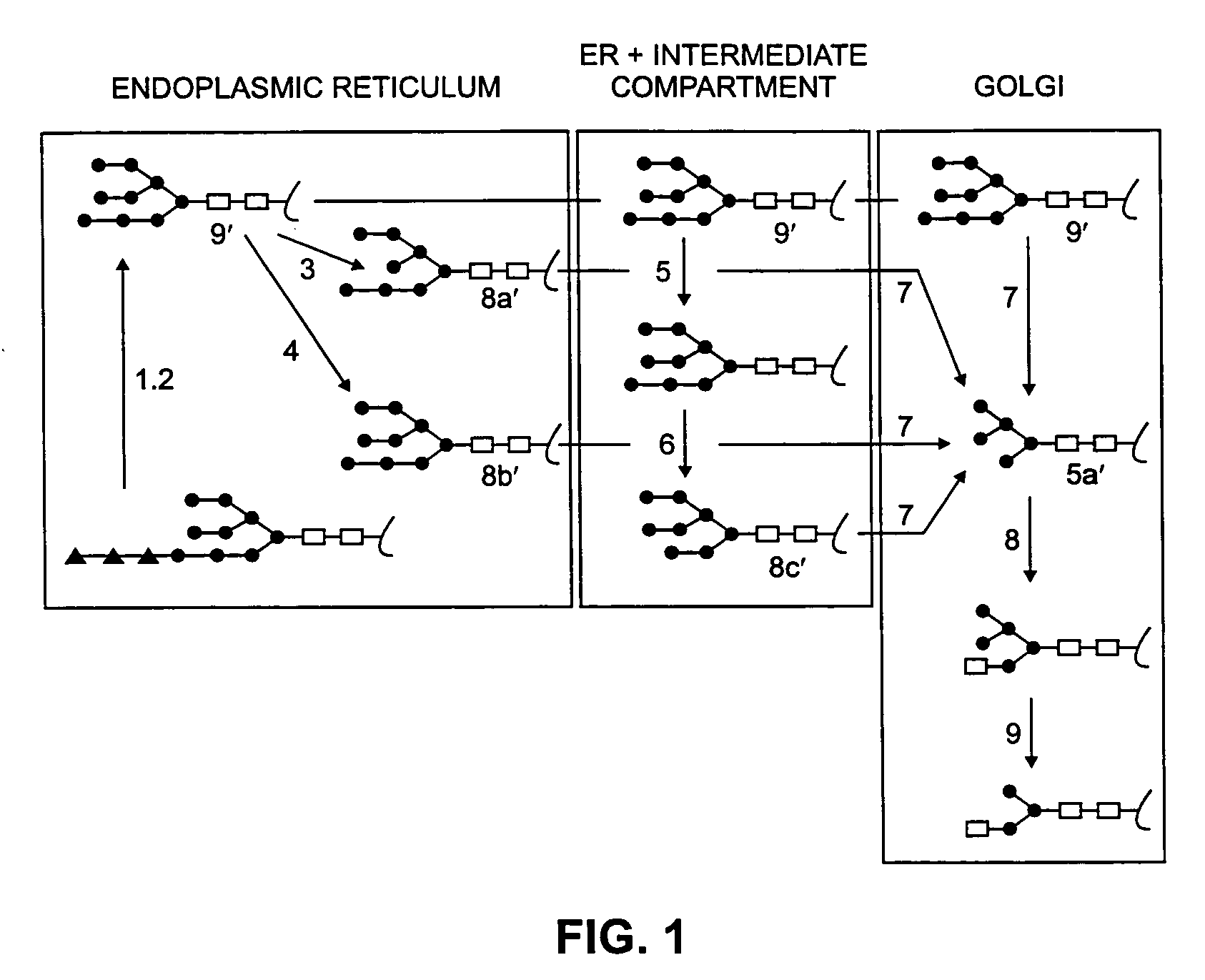
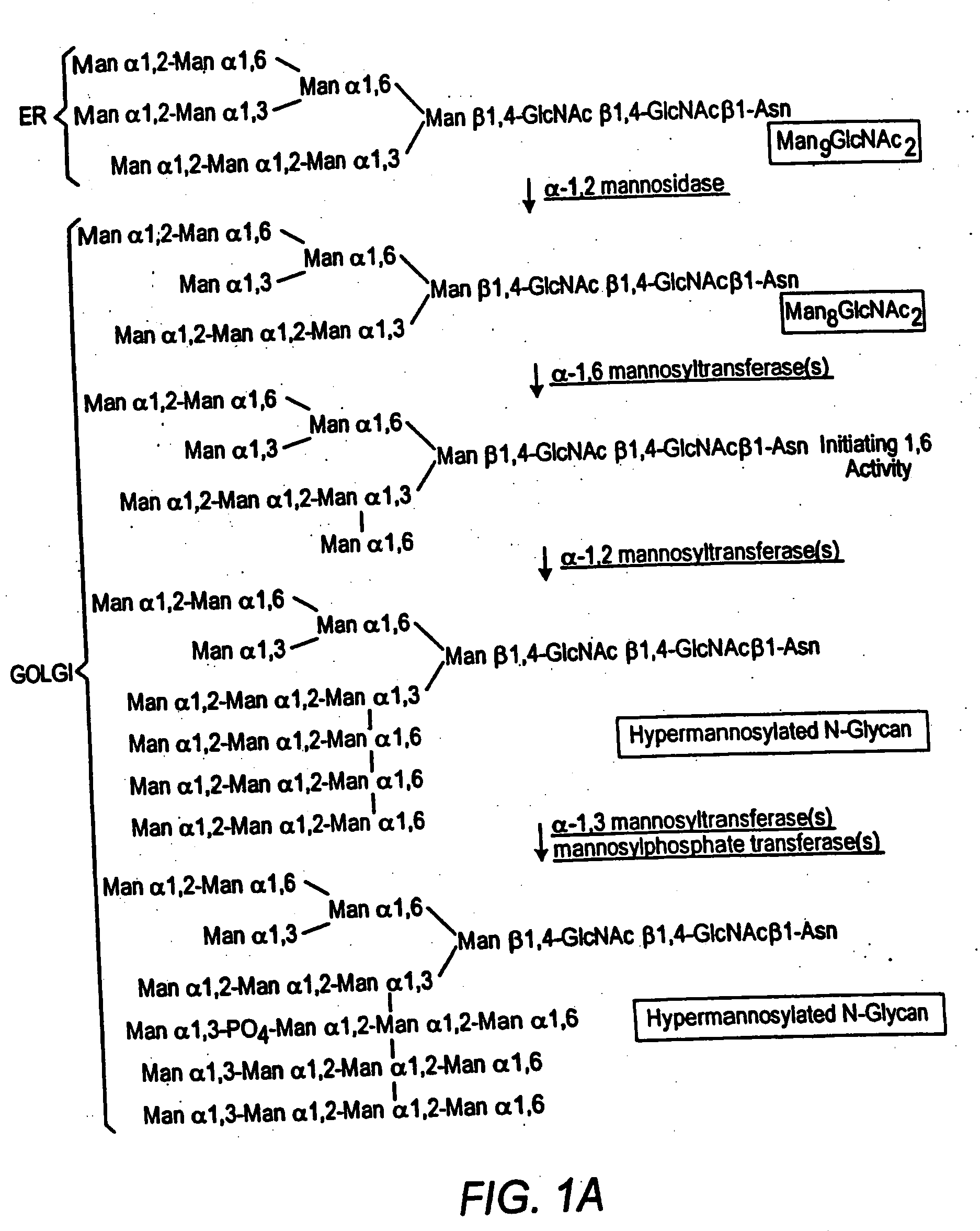
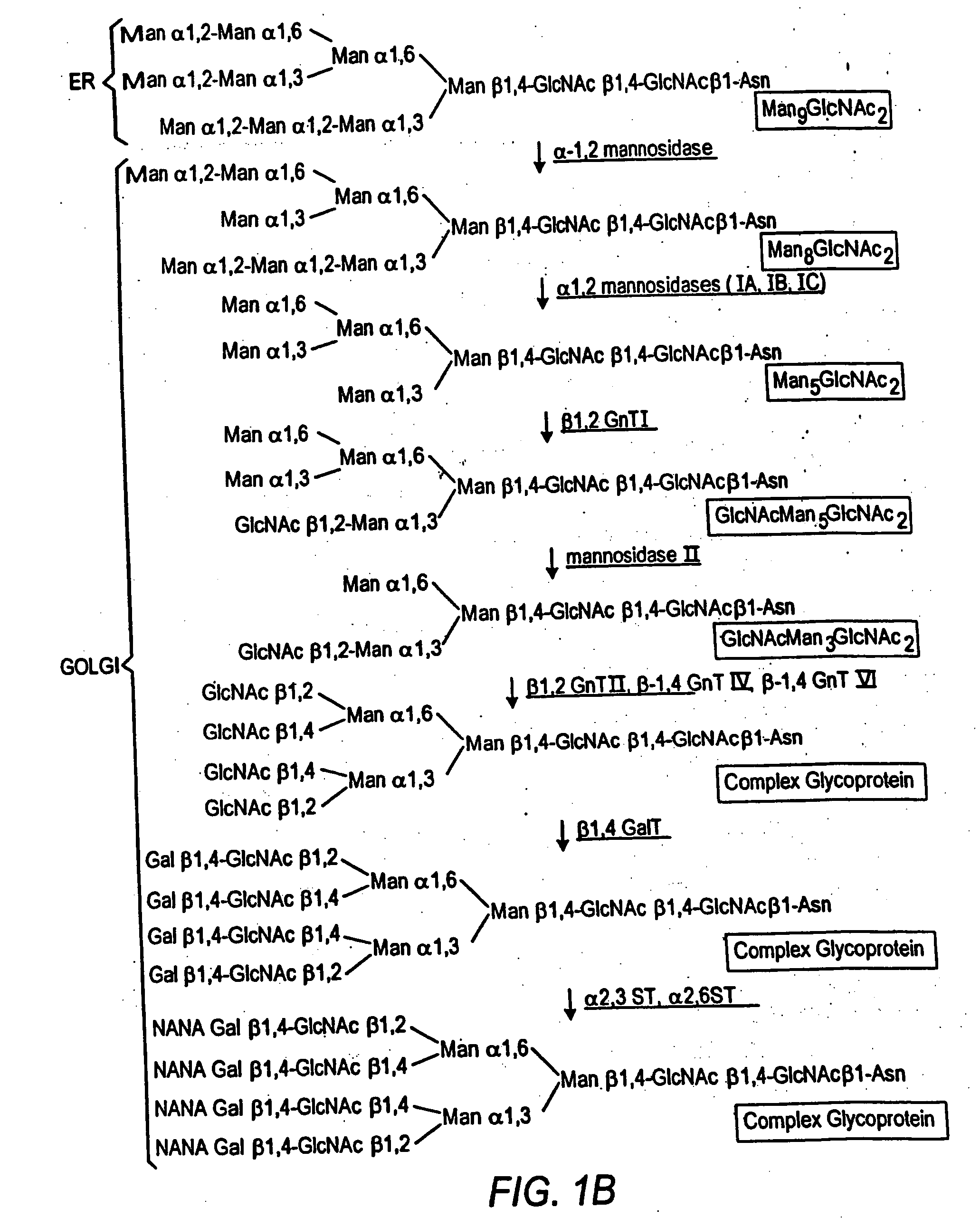
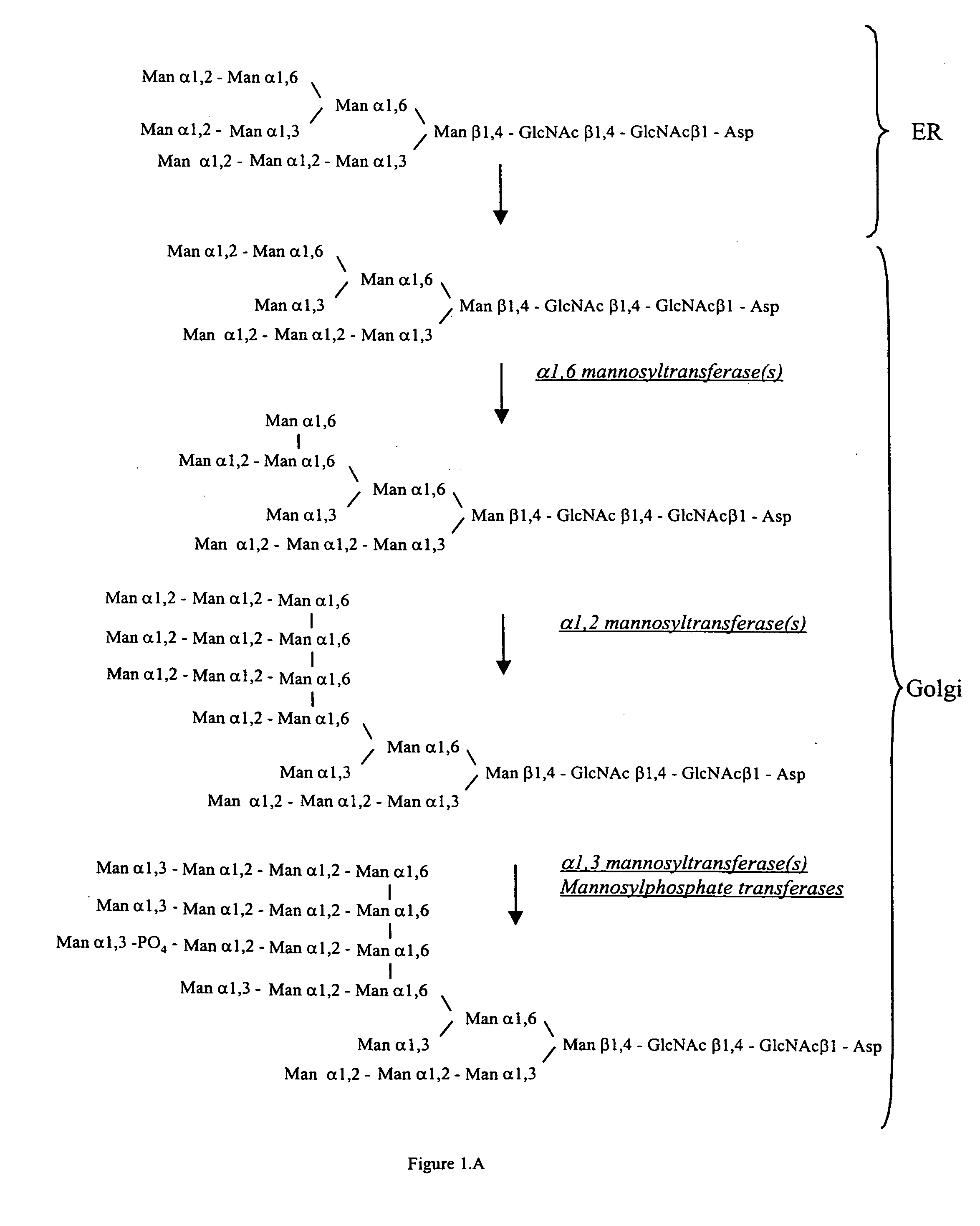
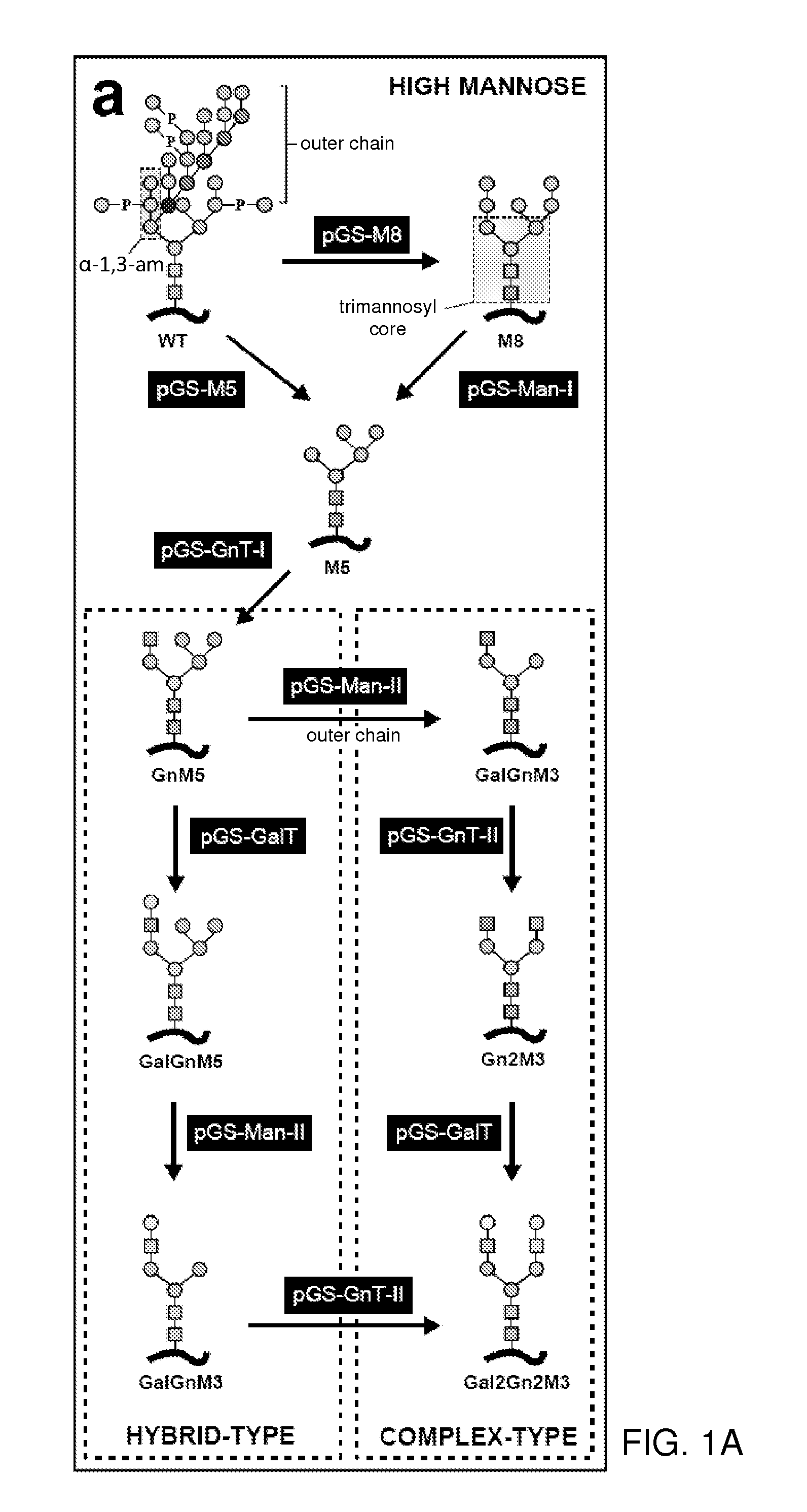
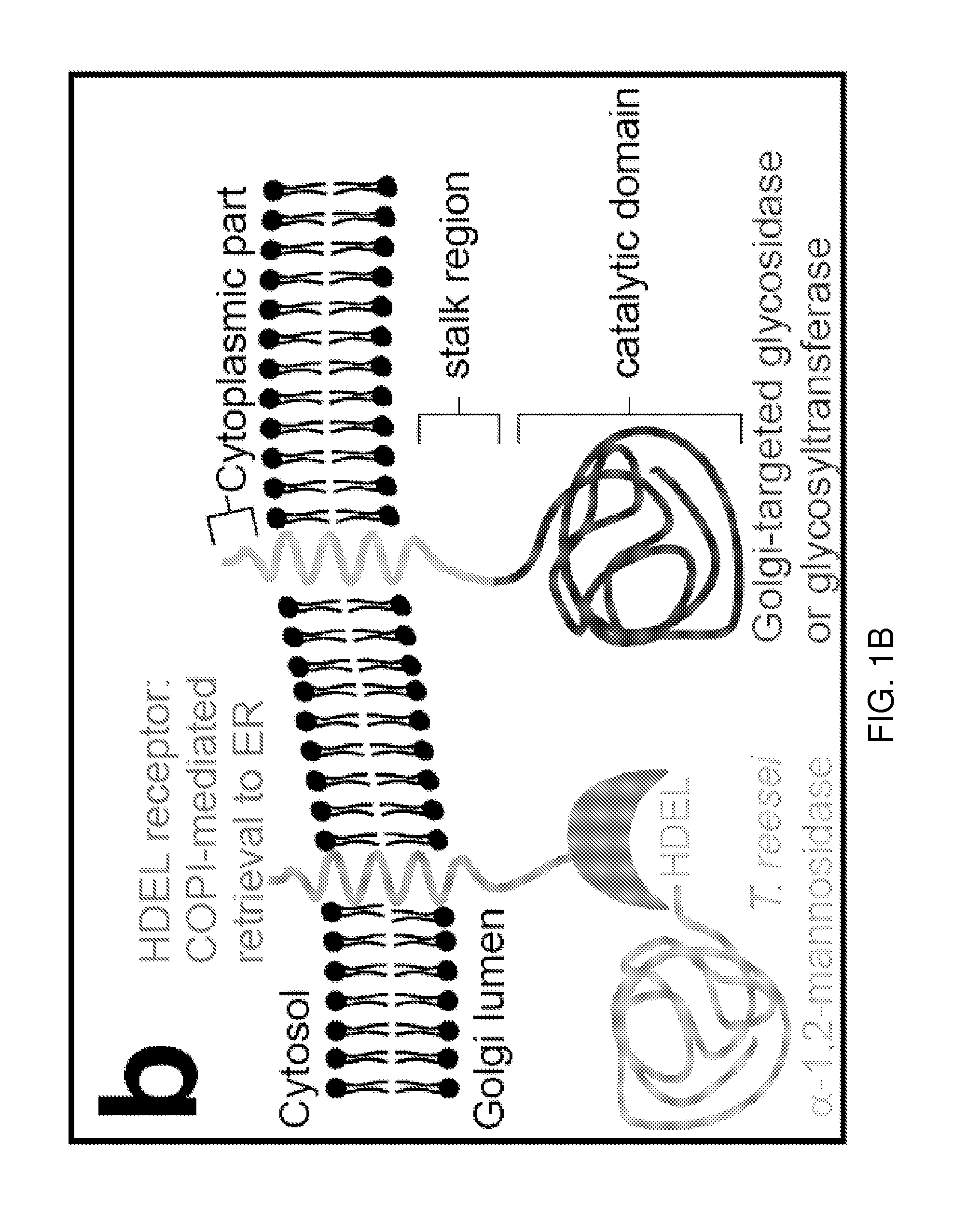
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. Thelower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
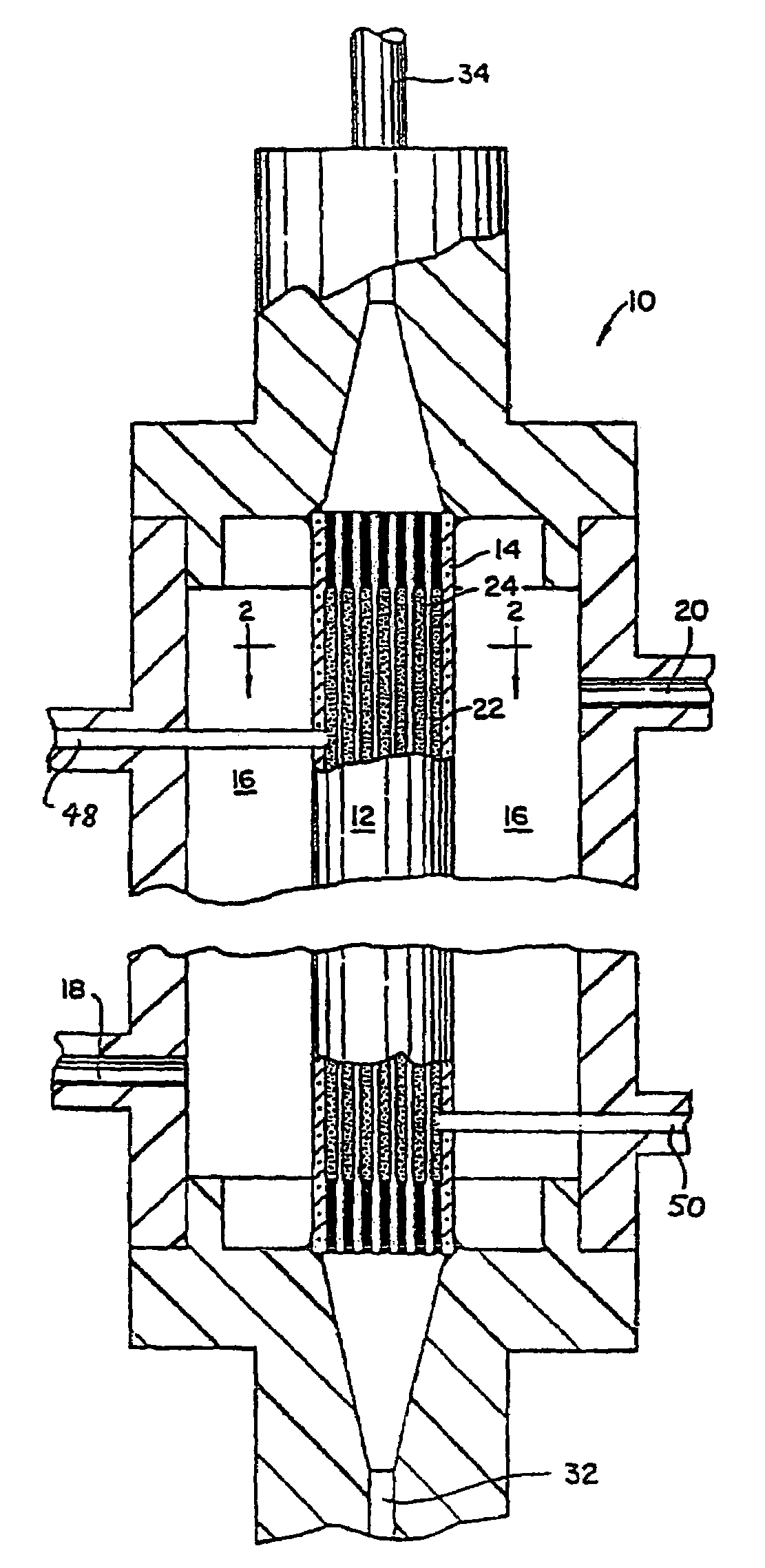
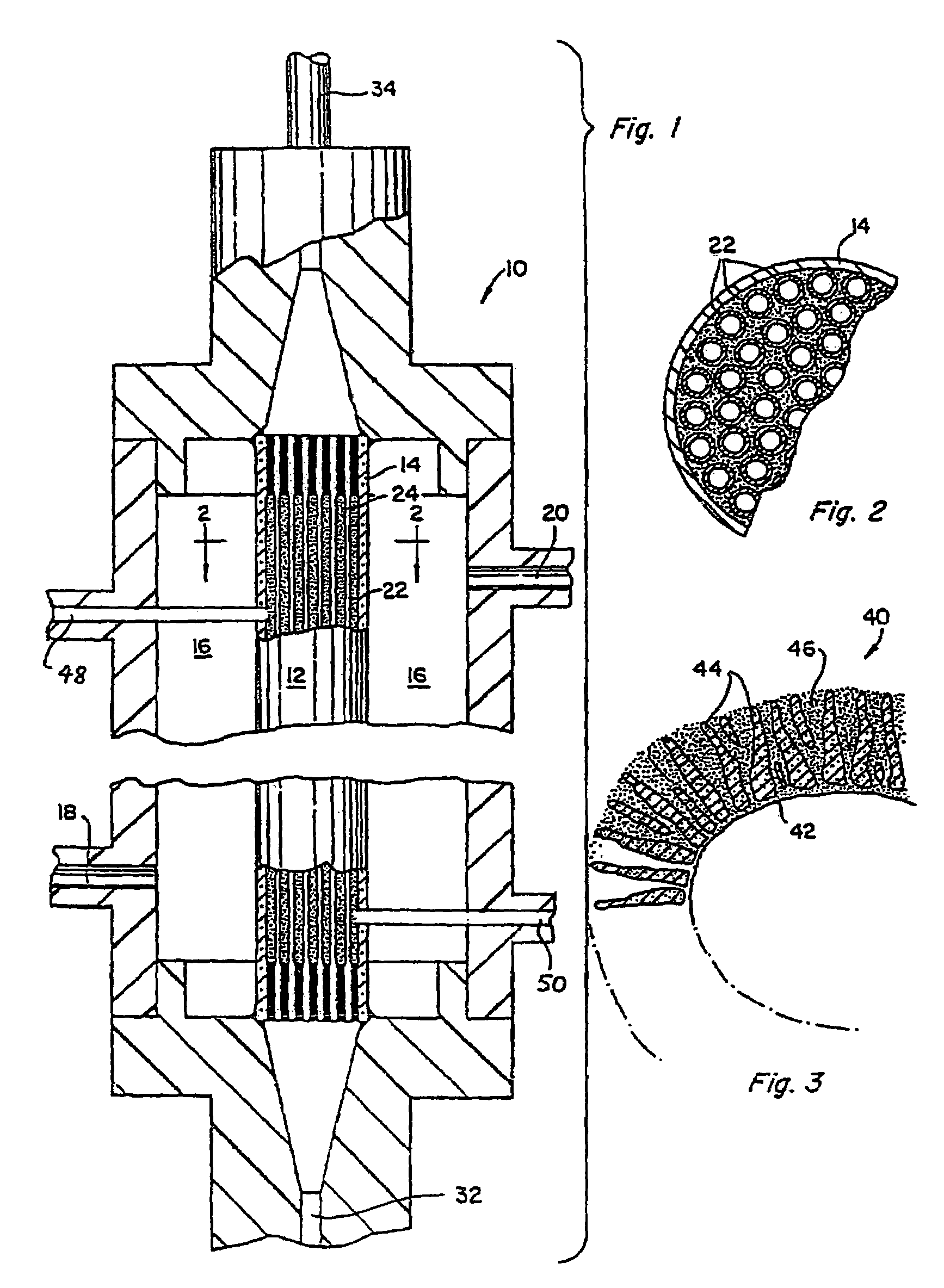
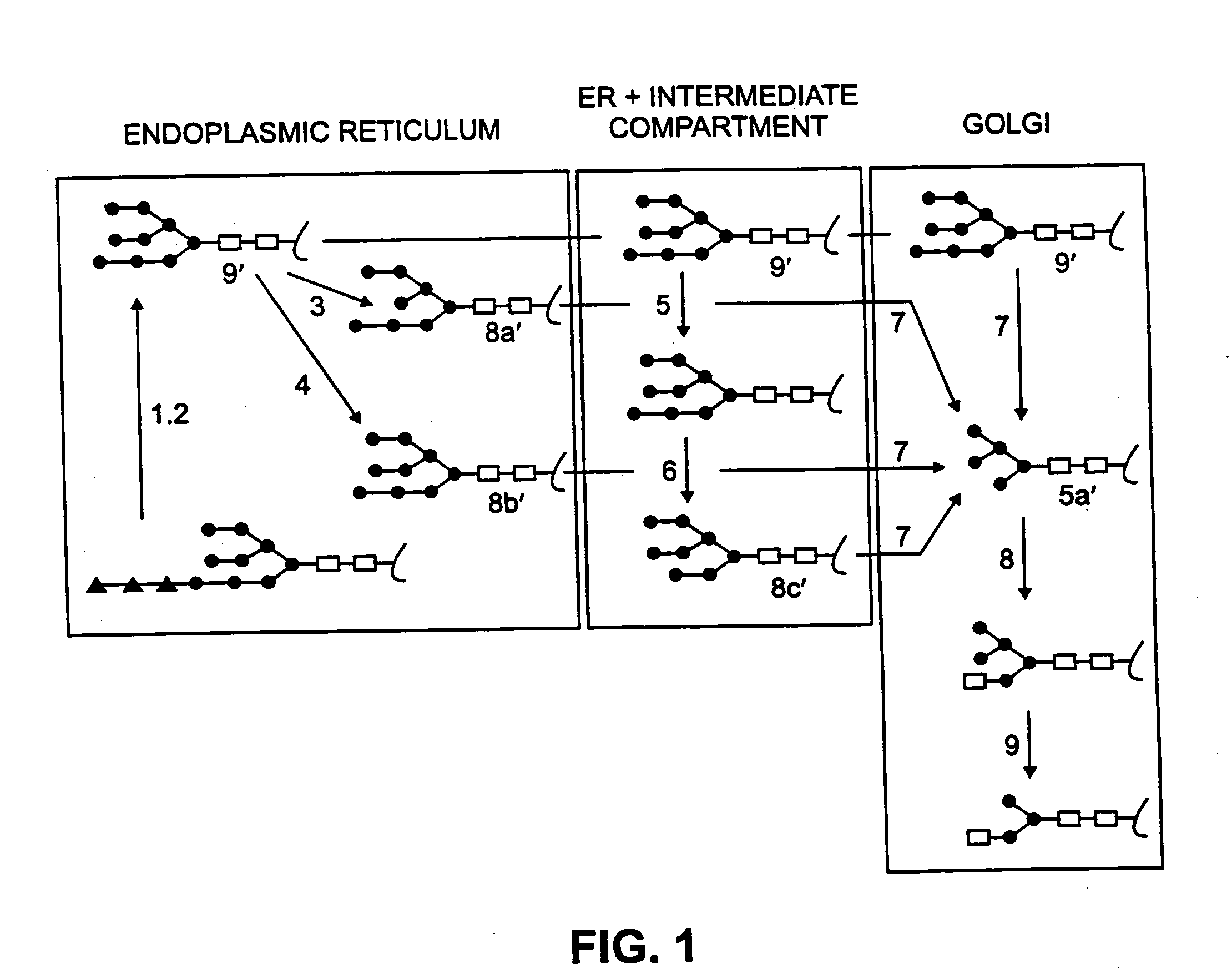
Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
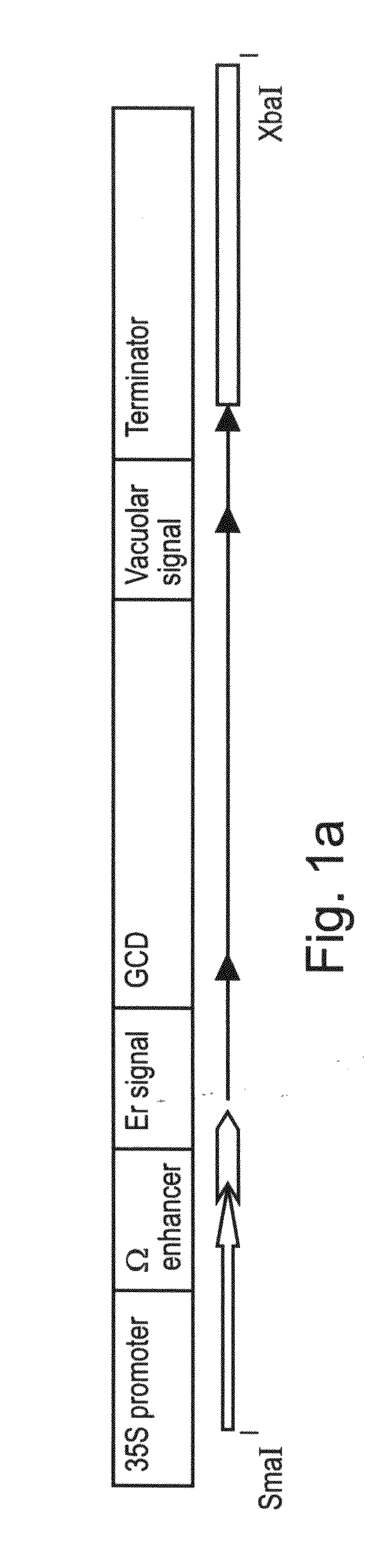
ActiveUS20090208477A1High glycosylationEfficient targetingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh mannosePlant roots
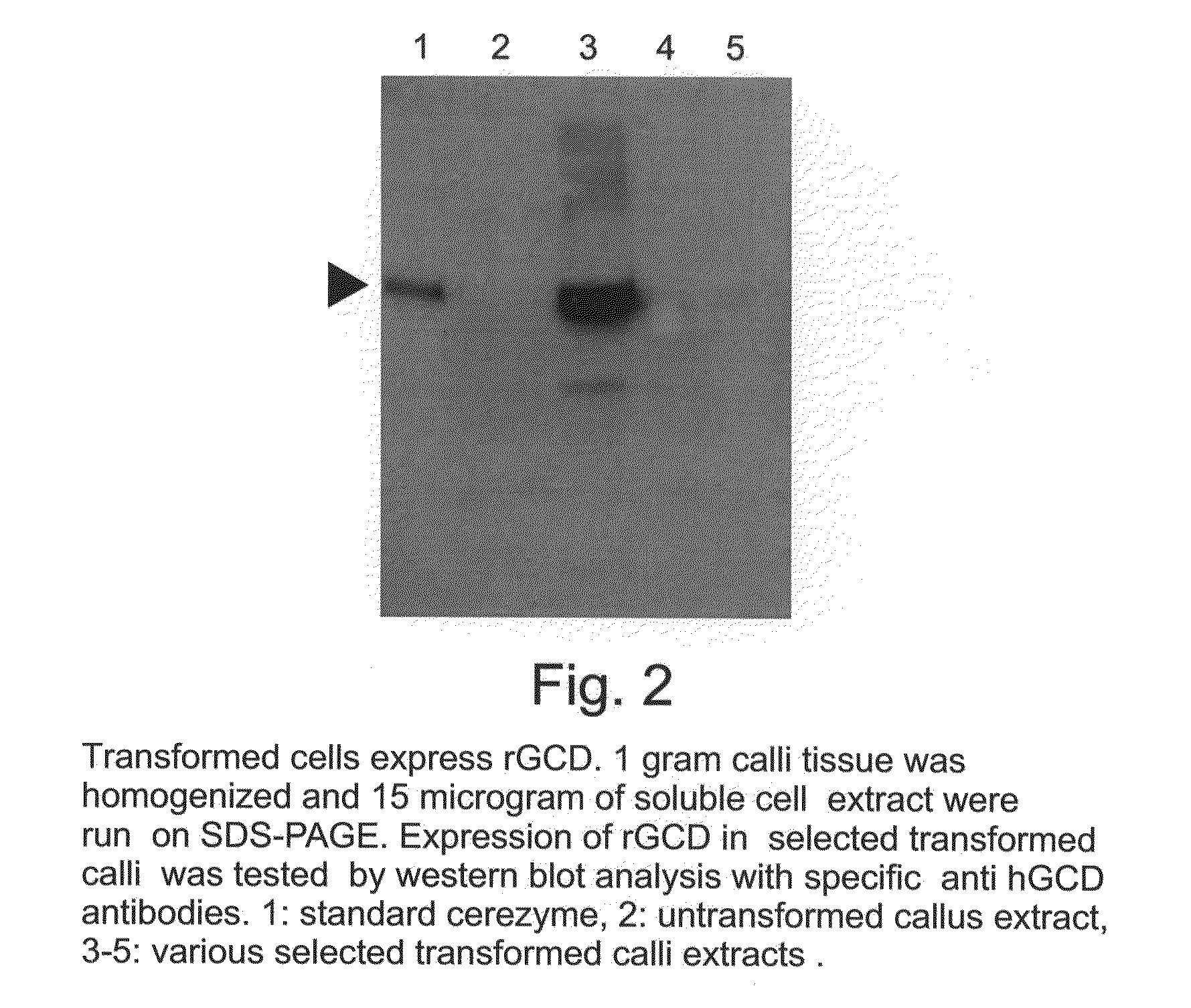
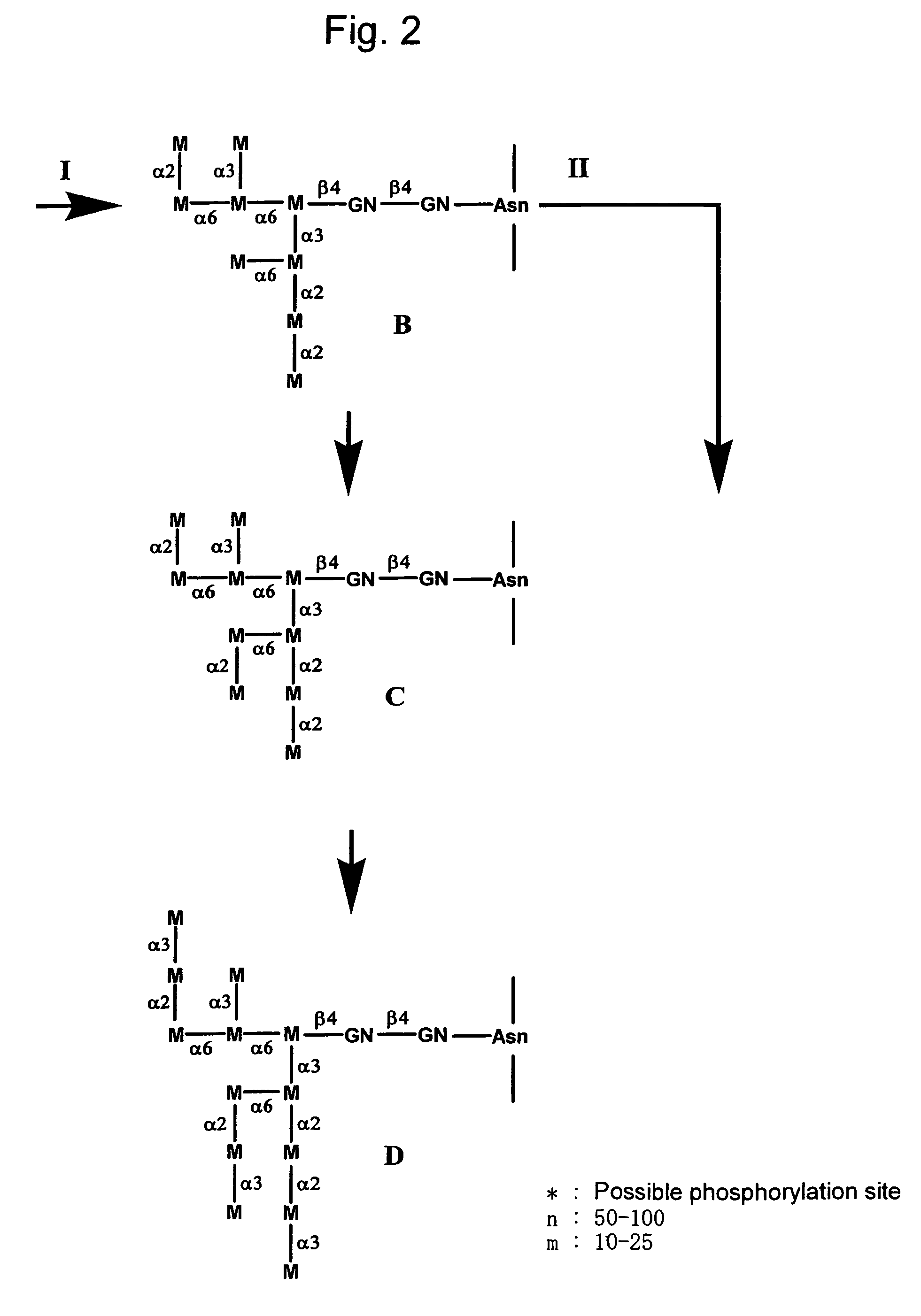
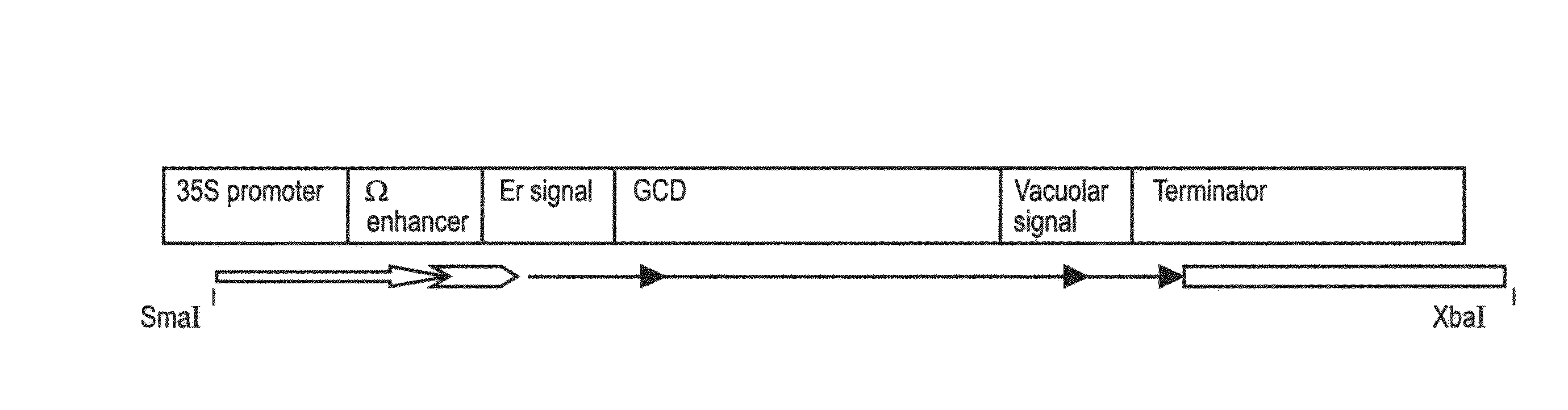
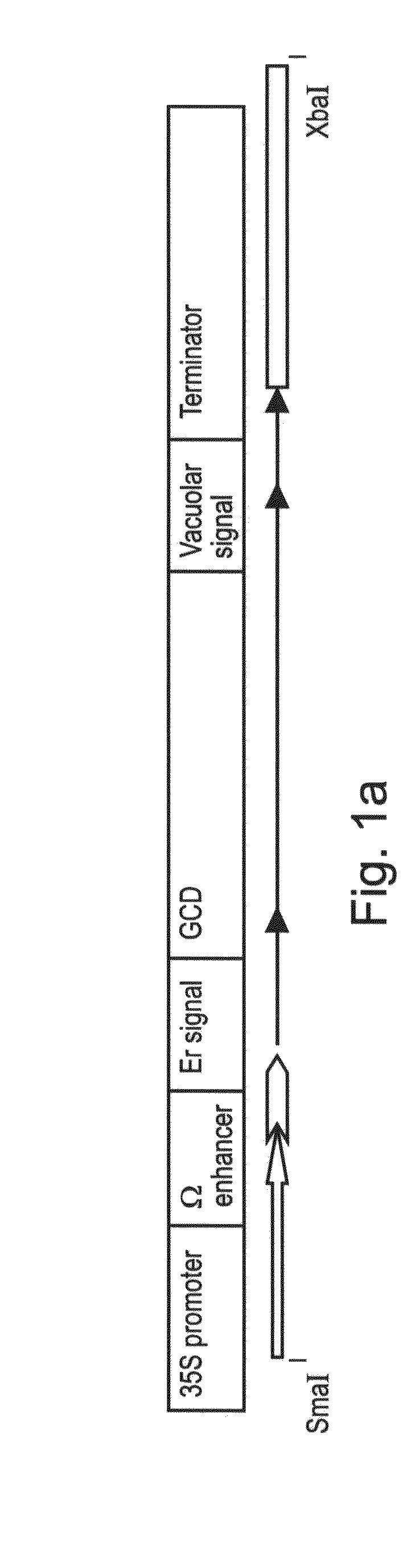
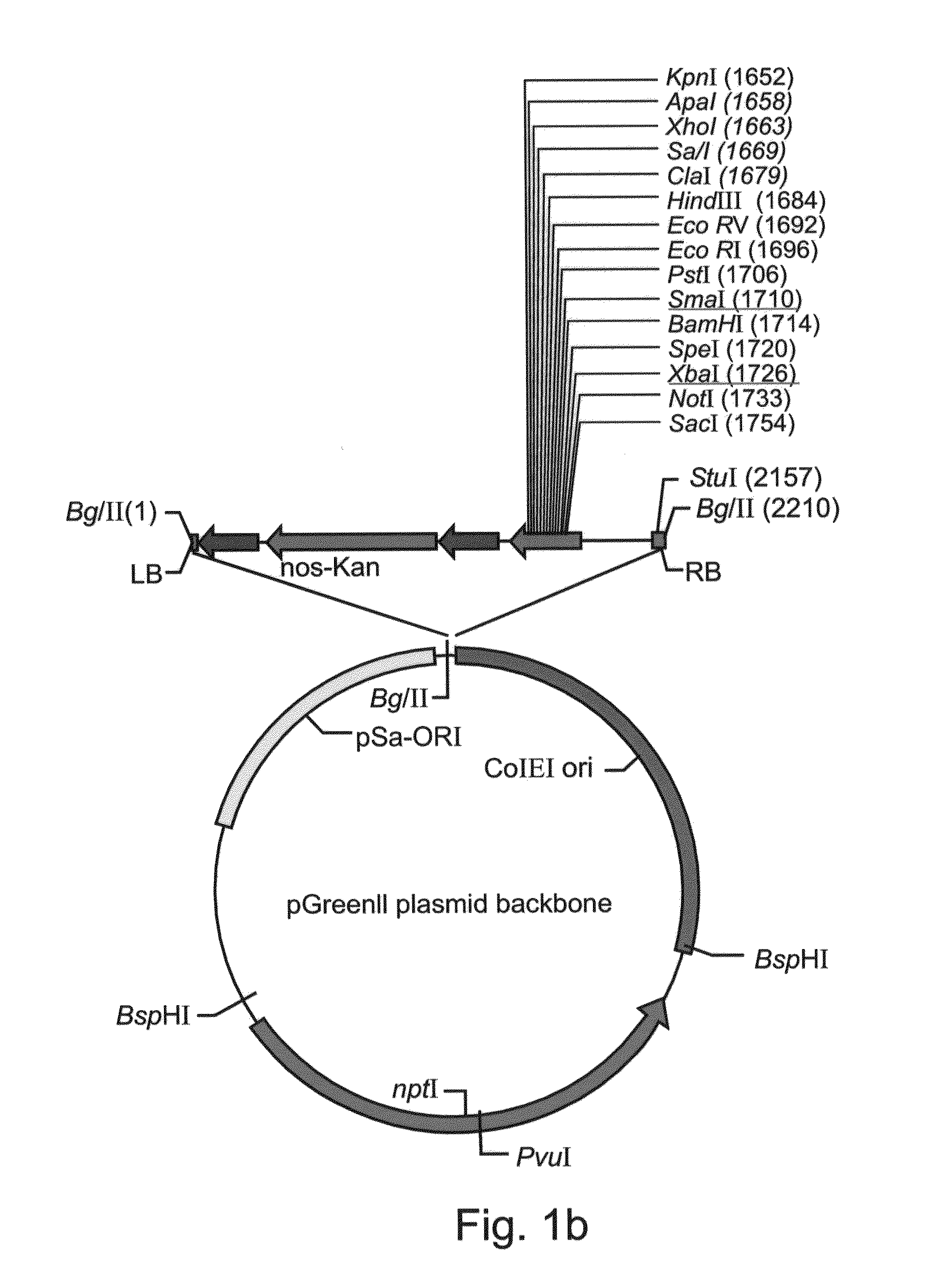
A device, system and method for producing glycosylated proteins in plant culture, particularly proteins having a high mannose glycosylation, while targeting such proteins with an ER signal and / or by-passing the Golgi. The invention further relates to vectors and methods for expression and production of enzymatically active high mannose lysosomal enzymes using transgenic plant root, particularly carrot cells. More particularly, the invention relates to host cells, particularly transgenic suspended carrot cells, vectors and methods for high yield expression and production of biologically active high mannose Glucocerebrosidase (GCD). The invention further provides for compositions and methods for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:PROTALIX
High mannose proteins and methods of making high mannose proteins
InactiveUS7138262B1Prevent removalInhibitory activitySenses disorderNervous disorderHigh mannoseOligosaccharide
The invention features a method of producing a high mannose glucocerebrosidase (hmGCB) which includes: providing a cell which is capable of expressing glucocerebrosidase (GCB), and allowing production of GCB having a precursor oligosaccharide under conditions which prevent the removal of at least one mannose residue distal to the pentasaccharide core of the precursor oligosaccharide of GCB, to thereby produce an hmGCB preparation. Preferably, the condition which prevents the removal of at least one mannose residue distal to the pentasaccharide core is inhibition of a class 1 processing mannosidase and / or a class 2 processing mannosidase. The invention also features an hmGCB preparation and methods of using an hmGCB preparation.
Owner:SHIRE HUMAN GENETIC THERAPIES INC
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. The lower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Method for removal of viruses from blood by lectin affinity hemodialysis
ActiveUS7226429B2Reduce loadReduce in quantityOther blood circulation devicesViral antigen ingredientsHemodialysisHigh mannose
The present invention relates to a method for using lectins that bind to pathogens having high mannose surface glycoproteins or fragments thereof which contain high mannose glycoproteins, to remove them from infected blood or plasma in an extracorporeal setting. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method for reducing viral load in an individual comprising the steps of obtaining blood or plasma from the individual, passing the blood or plasma through a porous hollow fiber membrane wherein lectin molecules are immobilized within the porous exterior portion of the membrane, collecting pass-through blood or plasma and reinfusing the pass-through blood or plasma into the individual.
Owner:AETHLON MEDICAL INC
Methylotroph producing mammalian type sugar chain
ActiveUS20060148039A1FungiImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
InactiveUS20060078963A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyHigh mannose
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. The lower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Encapsulation system
InactiveUS20090214660A1Improve protectionReduce the degradation rateBiocideNervous disorderMedicineFunctional integrity
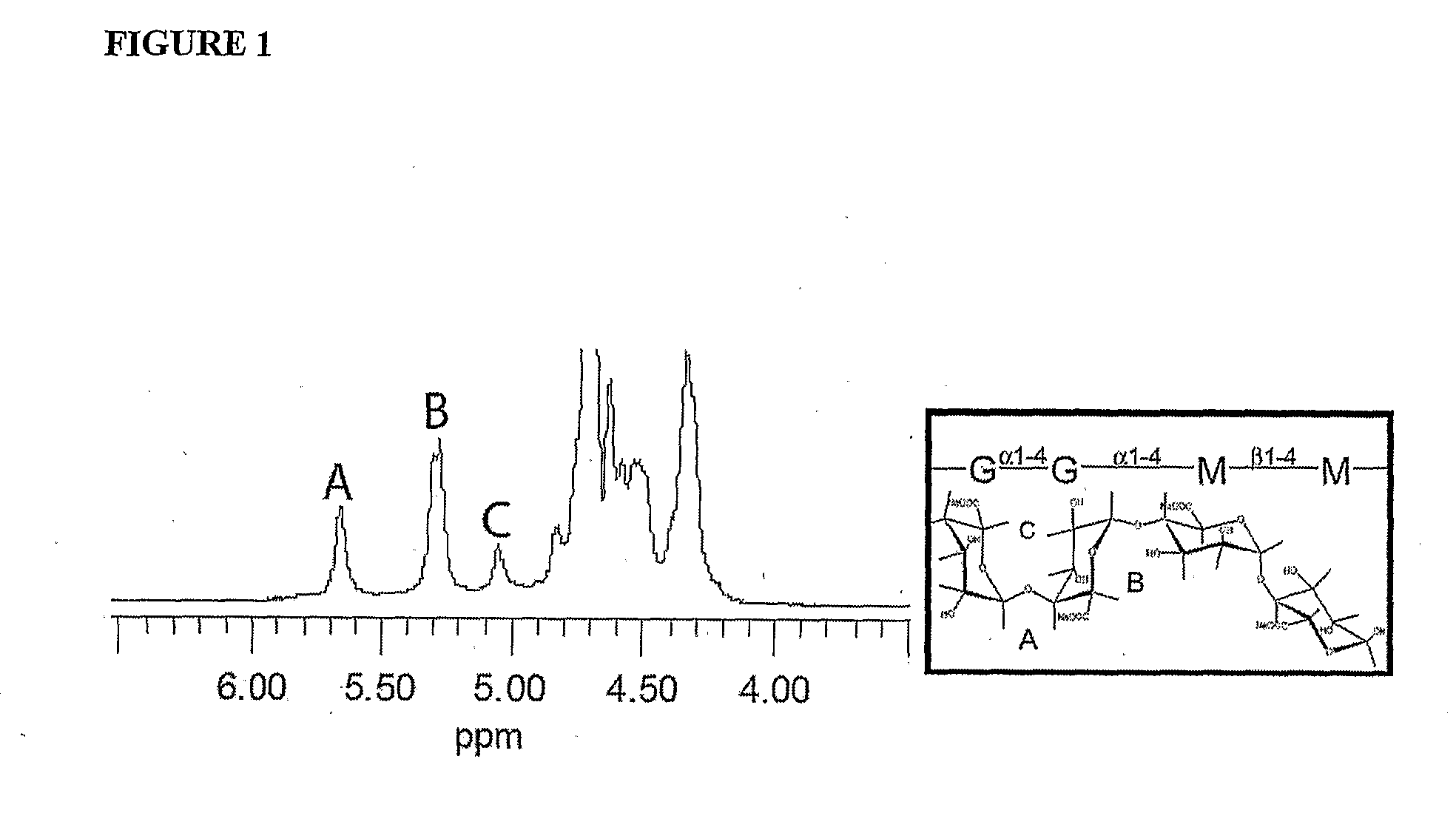
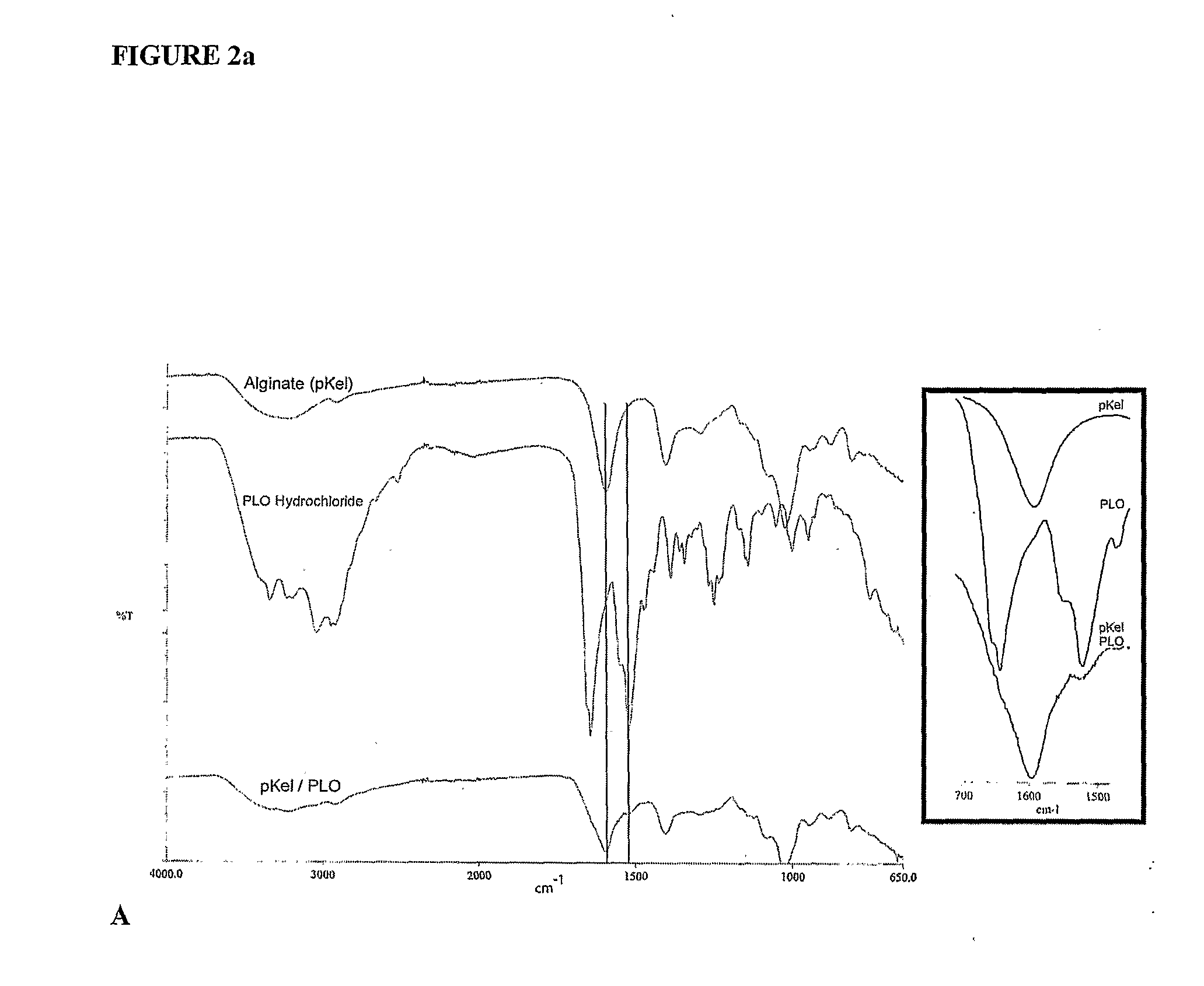
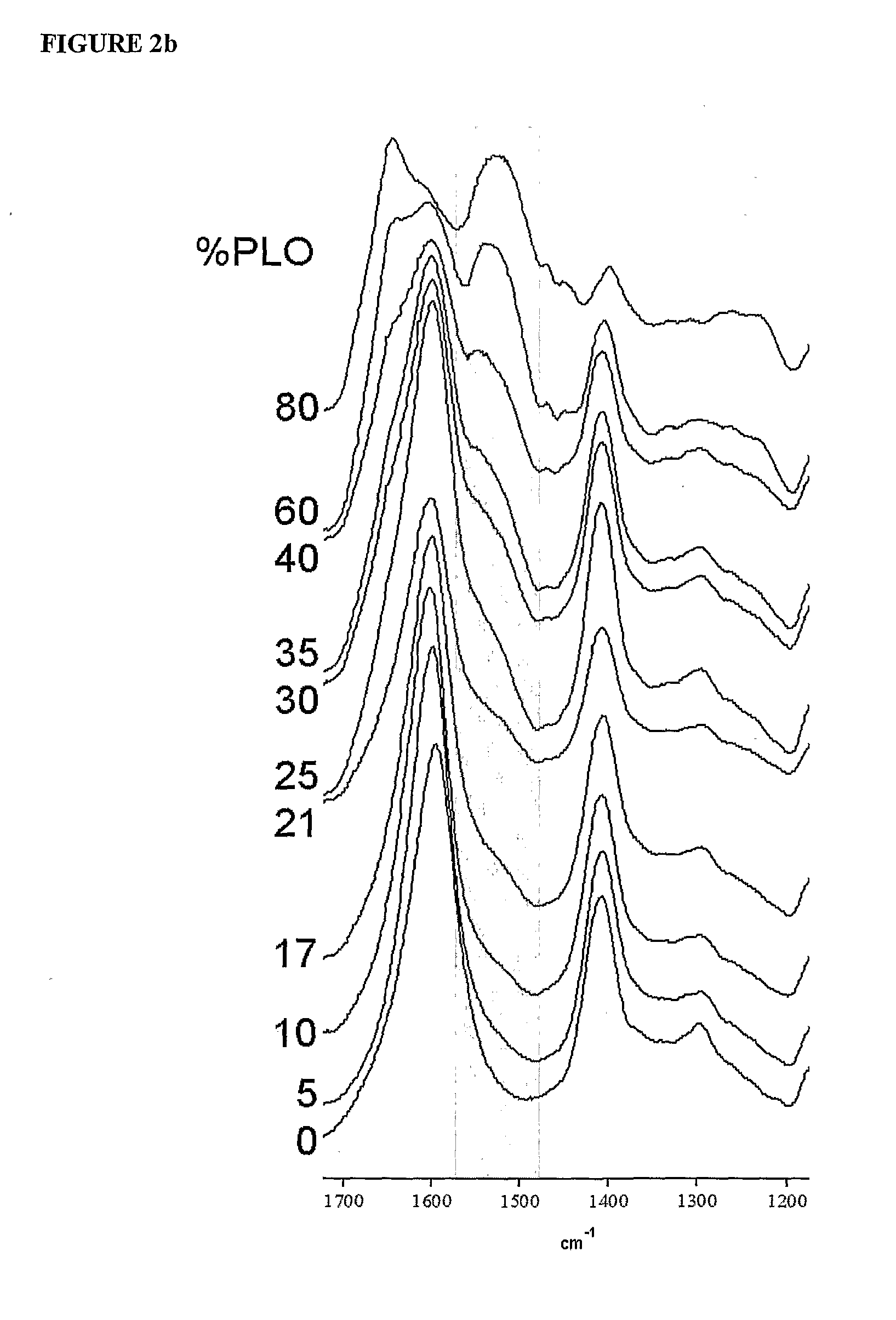
The present invention is directed to a composition comprising high mannuronic acid-containing alginate and a polycation having a polydispersity index of less than 1.5. The composition is particularly useful for making biocompatible microcapsules containing living cells for allo- or xeno-transplantation. Such microcapsules have enhanced durability and can maintain their structural and functional integrity over long periods of time compared to prior art alginate microcapsules.
Owner:LIVING CELL PRODS
Production of proteins carrying oligomannose or human-like glycans in yeast and methods of use thereof
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. The lower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce O-glycans or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:RECOPHARMA AB
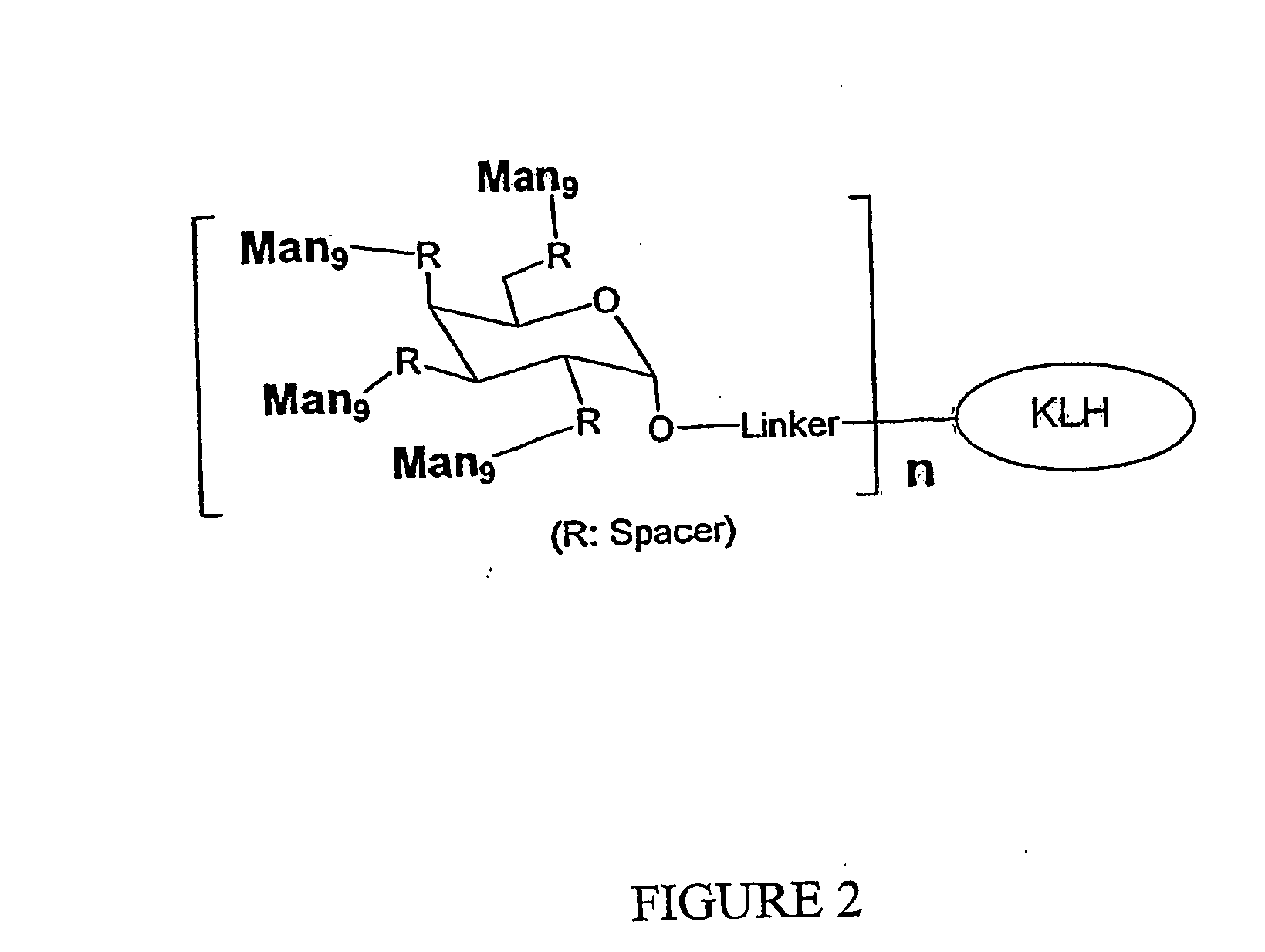
Carbohydrate-based synthetic vaccines for hiv
InactiveUS20050244424A1Increase productionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHigh mannoseReactive site
The present invention relates to a constructed to oligosaccharide cluster, optionally bonded to an immunogenic protein, that can be administered to a subject to induce an immune response for increasing production of 2G12 and / or used in assays as reactive sites for determining compounds that inactivate and / or bind the high-mannose oligosaccharide cluster. Compositions comprising these clusters, methods of using these clusters and compositions are disclosed.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
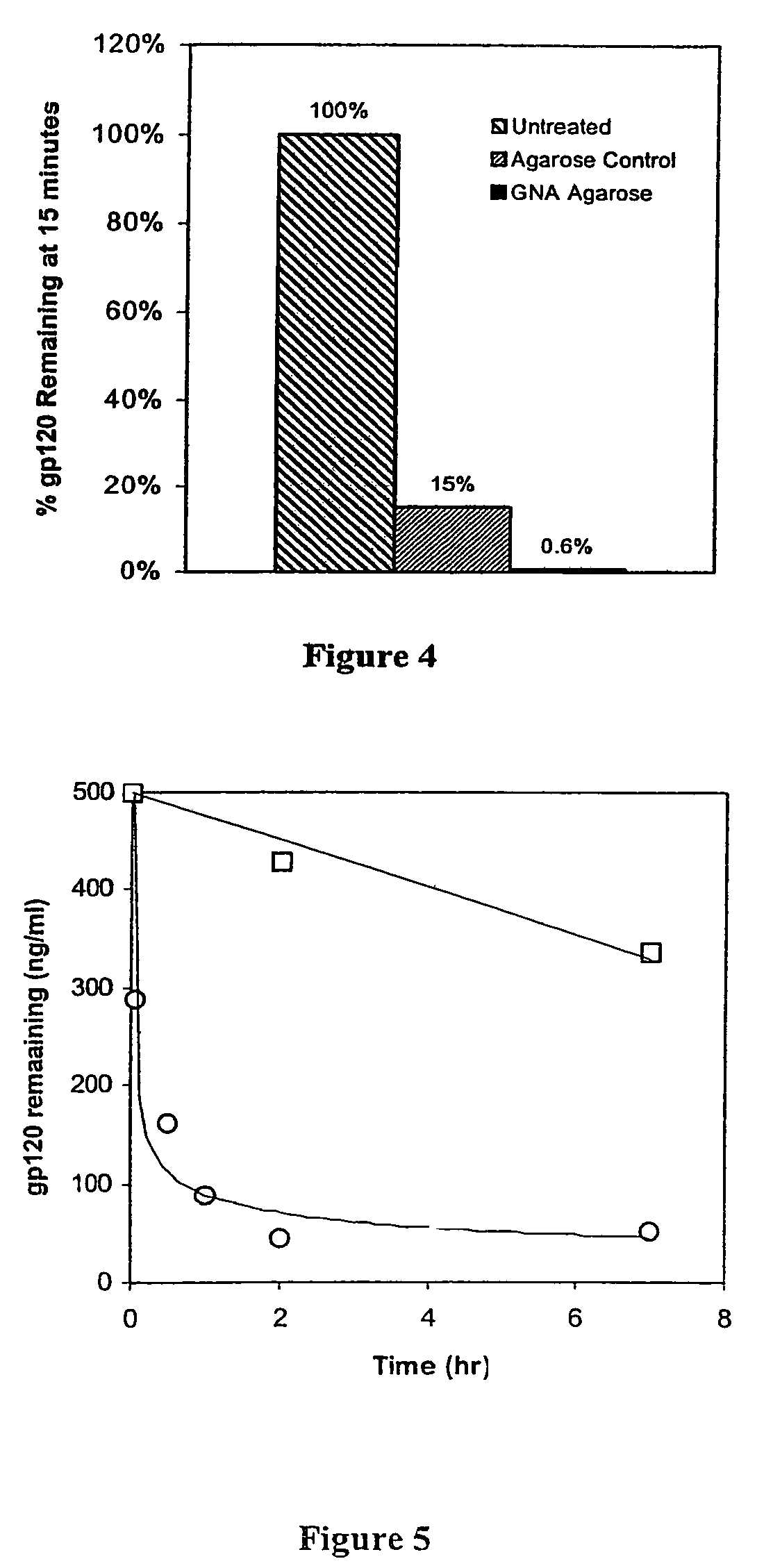
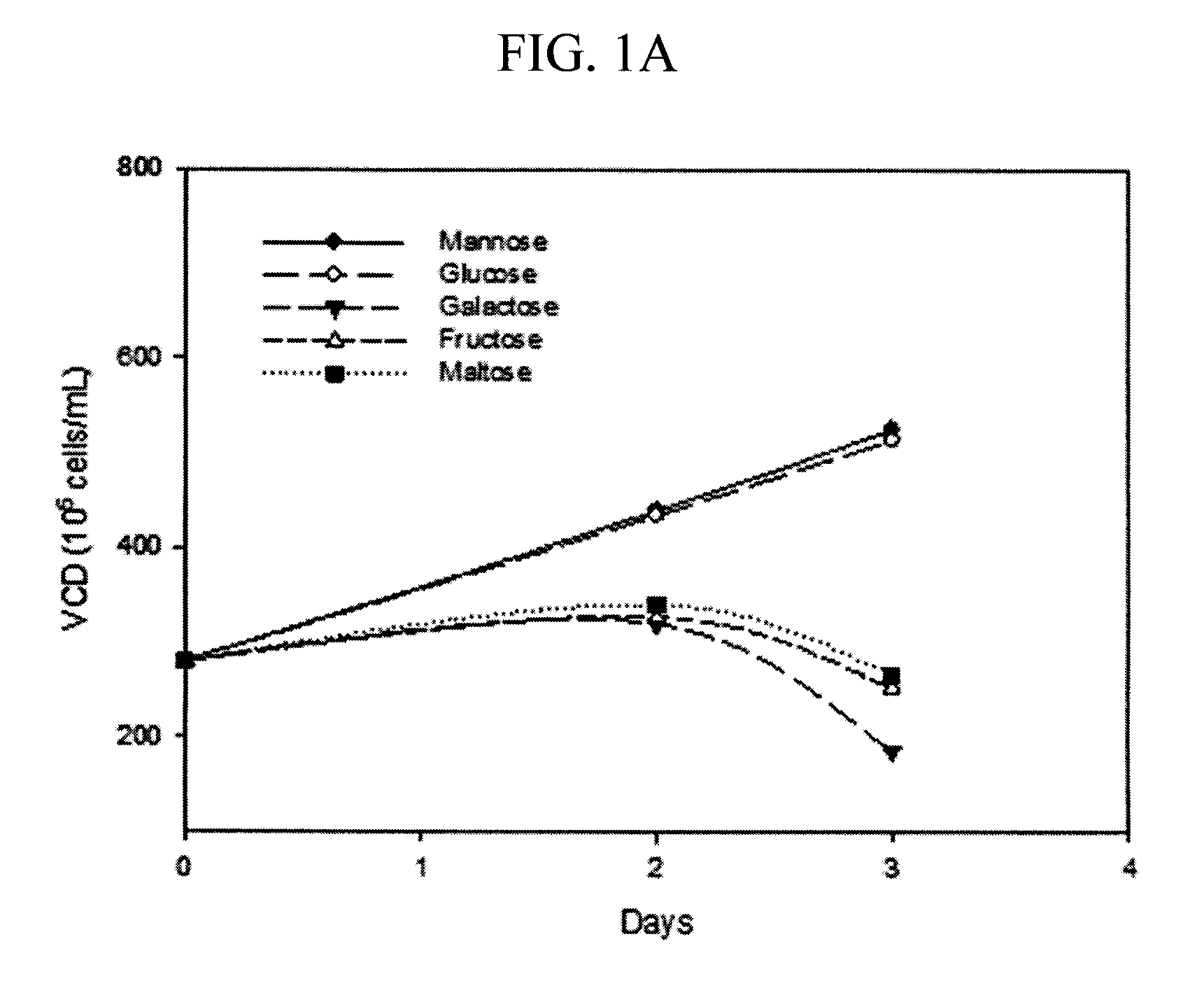
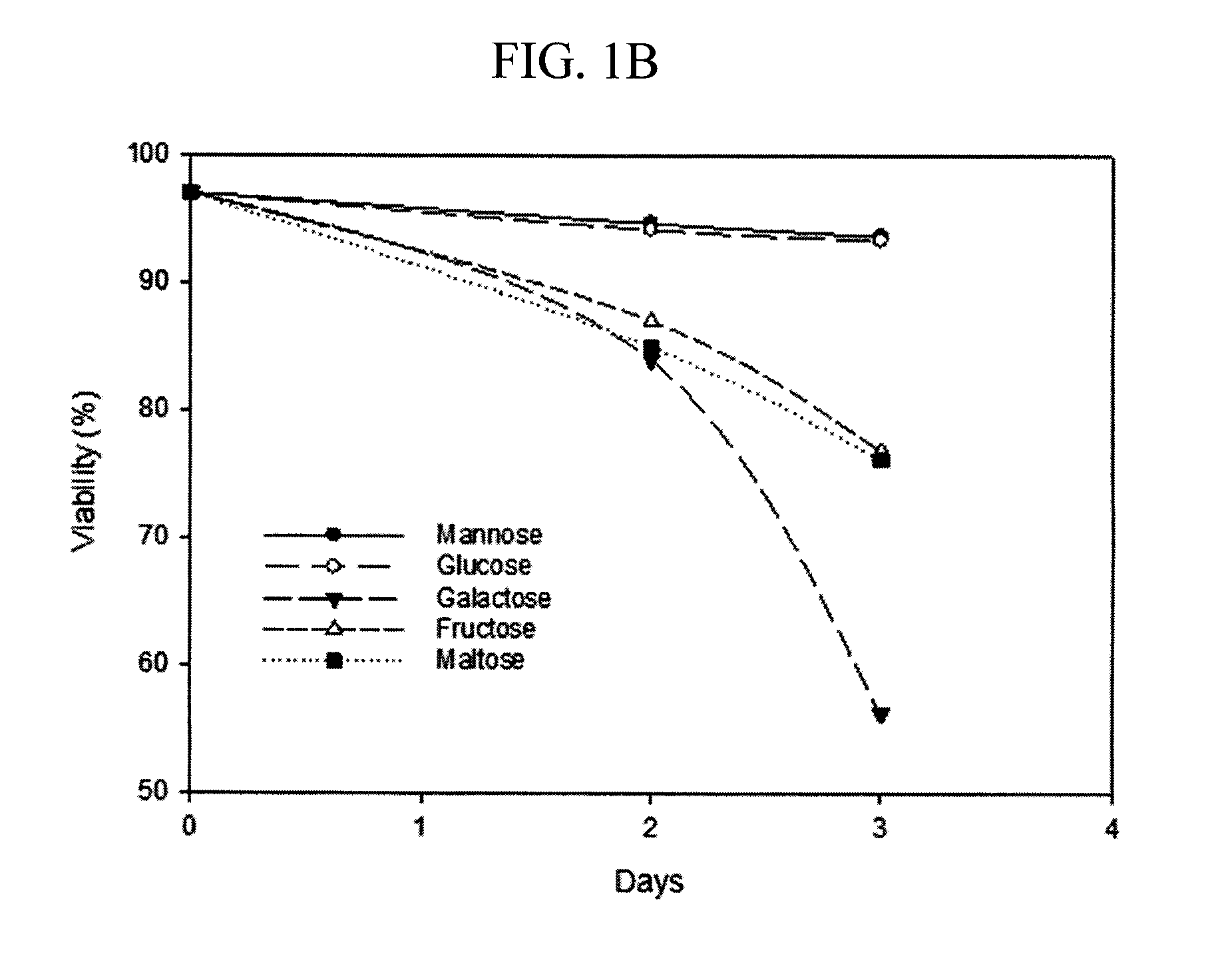
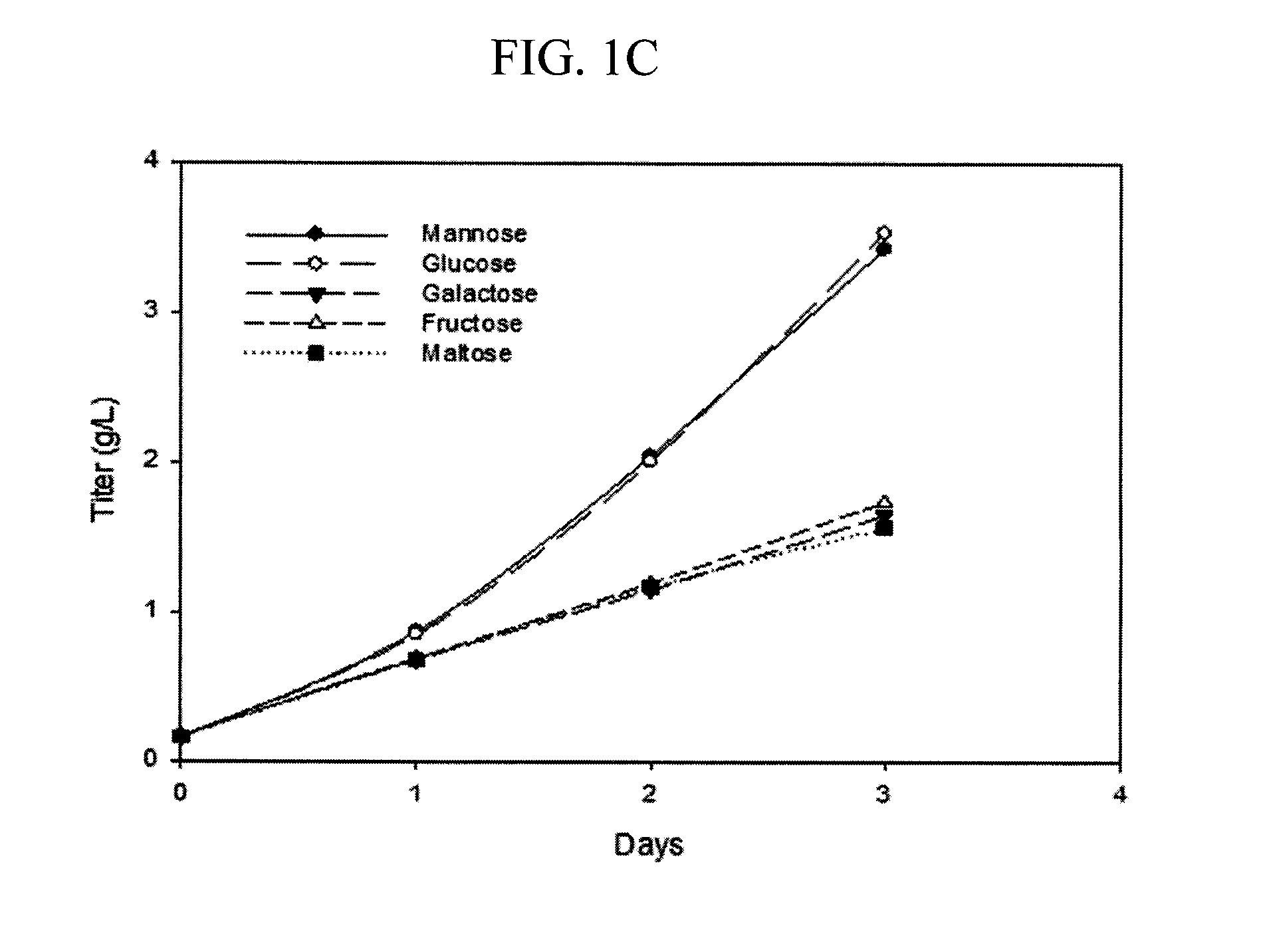
Methods for increasing mannose content of recombinant proteins
The present invention relates to methods of upregulating the high mannose glycoform content of a recombinant protein during a mammalian cell culture by manipulating the mannose to total hexose ratio in the cell culture media formulation.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Carbohydrate-based synthetic vaccines for HIV
The present invention relates to a constructed oligosaccharide cluster, optionally bonded to an immunogenic protein, that can be administered to a subject to induce an immune response for increasing production of 2G12 and / or used in assays as reactive sites for determining compounds that inactivate and / or bind the high-mannose oligosaccharide cluster. Compositions comprising these clusters, methods of using these clusters and compositions are disclosed.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Method for separating and identifying glycoprotein N-sugar chain structure
InactiveCN104133027AHigh sensitivityRich sugar chain informationComponent separationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)High mannose
The invention discloses a method for separating and identifying glycoprotein N-sugar chain structure, and belongs to the technical field of sugar chain detection. According to the method, concanavalin (ConA) is used to separate and enrich high-mannose type and non-high-mannose type N-sugar chains; matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) is used to detect; a signal-to-noise ratio of 6 is used as a threshold value to carry out data screening; and a Glycoworkbench software is used to analyze. Structure shows that 23 N-sugar chains are identified from a reference group; 29 N-sugar chains are identified from two parts of the high-mannose type and non-high-mannose type; and the identified N-sugar chains are six more than that before ConA enrichment. The method has higher sensitivity and more abundant sugar chain information and has obvious advantage for identification of low kurtosis sugar chains.
Owner:苏州中科纳泰生物科技有限公司
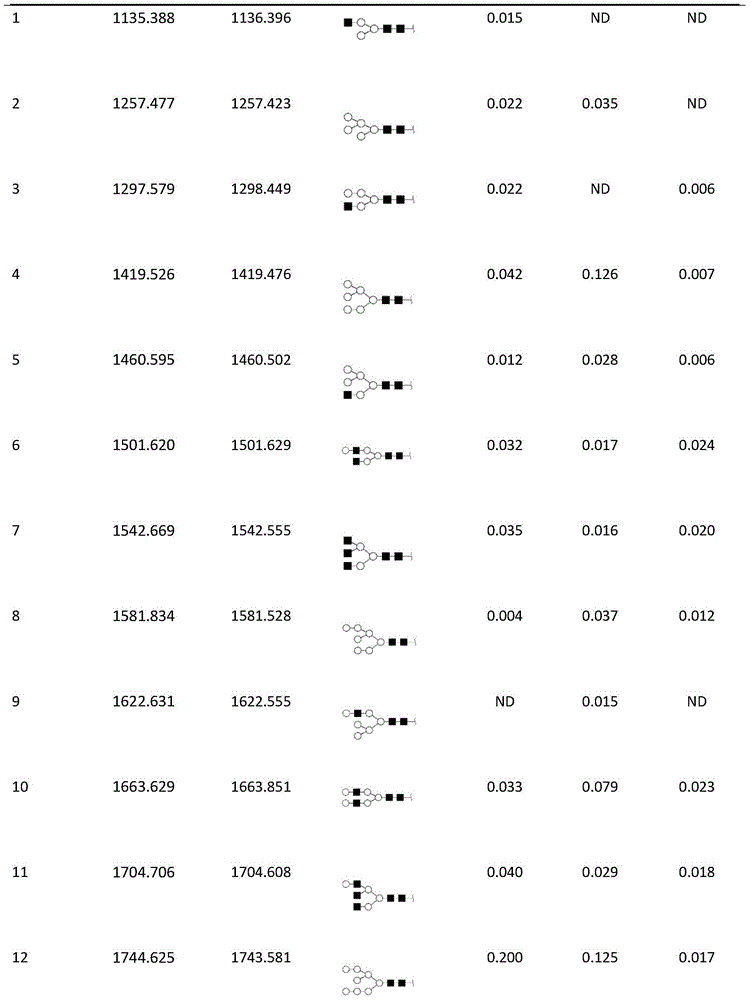
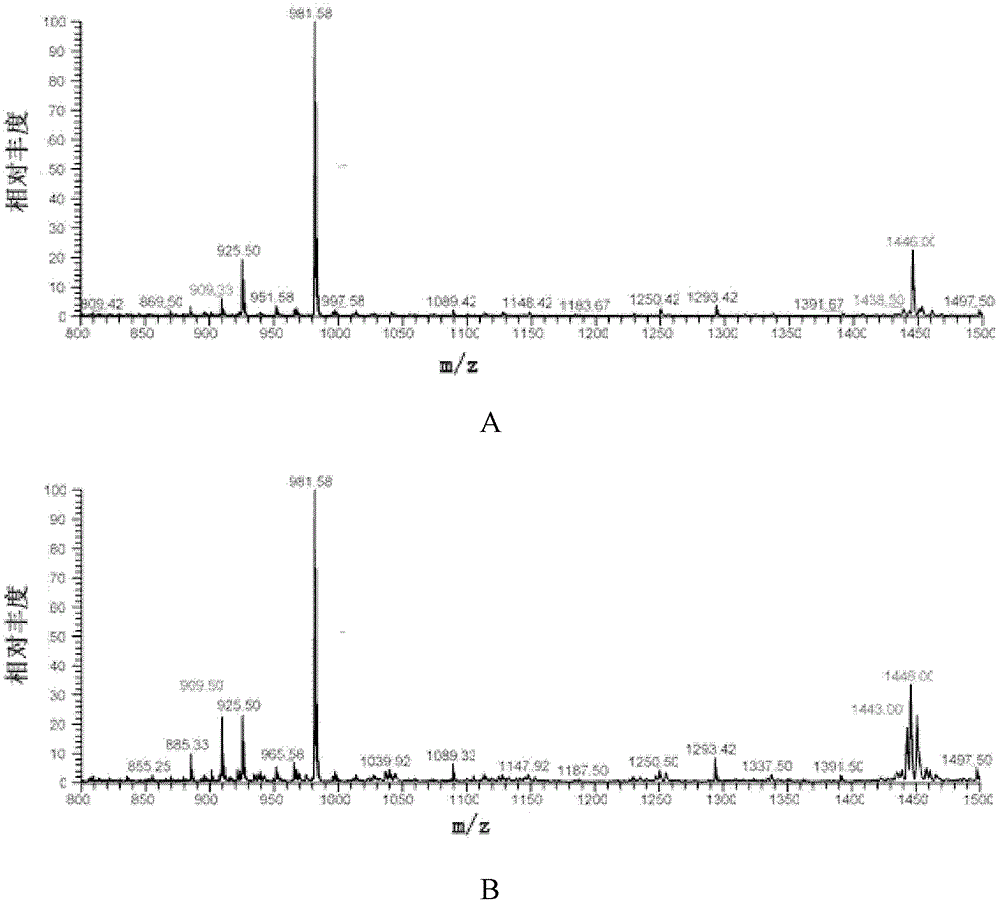
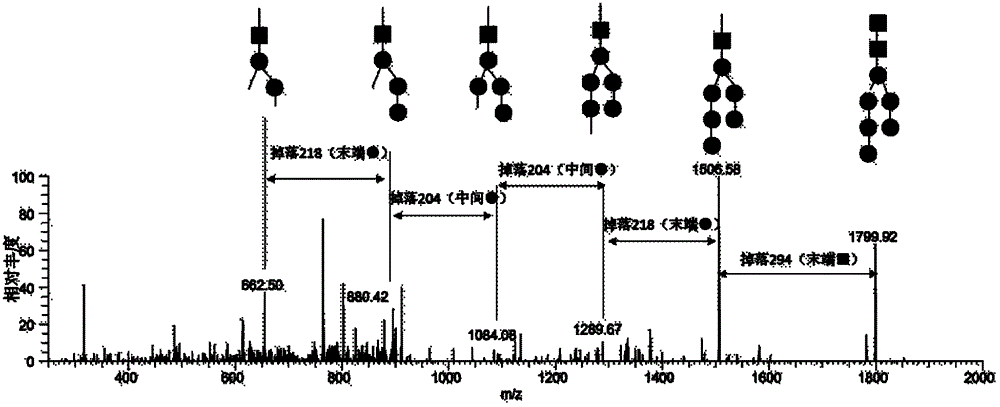
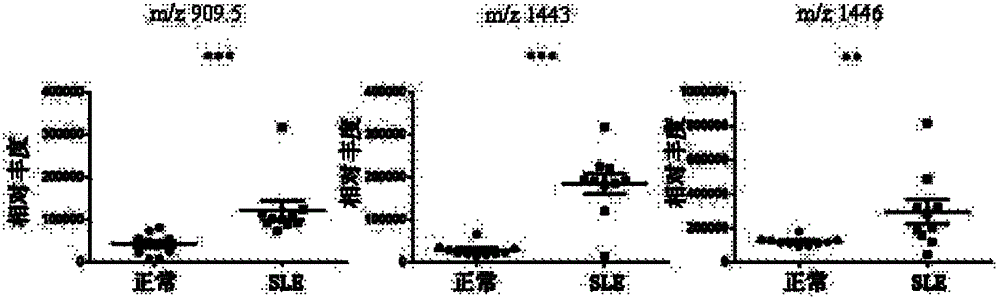
Diagnostic marker for systemic lupus erythematosus
The invention relates to a diagnostic marker for systemic lupus erythematosus, and in particular discloses application of a reagent for specific detection of high mannose type N-linked carbohydrate chain level in a serum antibody to preparation of a diagnostic tool for diagnosis and / or prognosis assessment of systemic lupus erythematosus. The increase of the high mannose type N-linked carbohydrate chain level in the serum antibody is closely related to the occurrence of systemic lupus erythematosus. Therefore, the diagnostic marker can be used for early diagnosis and / or prognostic assessment of systemic lupus erythematosus, and further can be used for guiding treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.
Owner:杭州中赢生物医疗科技有限公司
High mannose proteins and methods of making high mannose proteins
InactiveUS20070031945A1Efficiently target mannose receptorPrecise deliveryBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHigh mannoseOligosaccharide
The invention features a method of producing a high mannose glucocerebrosidase (hmGCB) which includes: providing a cell which is capable of expressing glucocerebrosidase (GCB), and allowing production of GCB having a precursor oligosaccharide under conditions which prevent the removal of at least one mannose residue distal to the pentasaccharide core of the precursor oligosaccharide of GCB, to thereby produce an hmGCB preparation. Preferably, the condition which prevents the removal of at least one mannose residue distal to the.pentasaccharide core is inhibition of a class 1 processing mannosidase and / or a class 2 processing mannosidase. The invention also features an hmGCB preparation and methods of using an hmGCB preparation.
Owner:SHIRE HUMAN GENETIC THERAPIES INC
Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
Owner:普罗塔里克斯有限公司
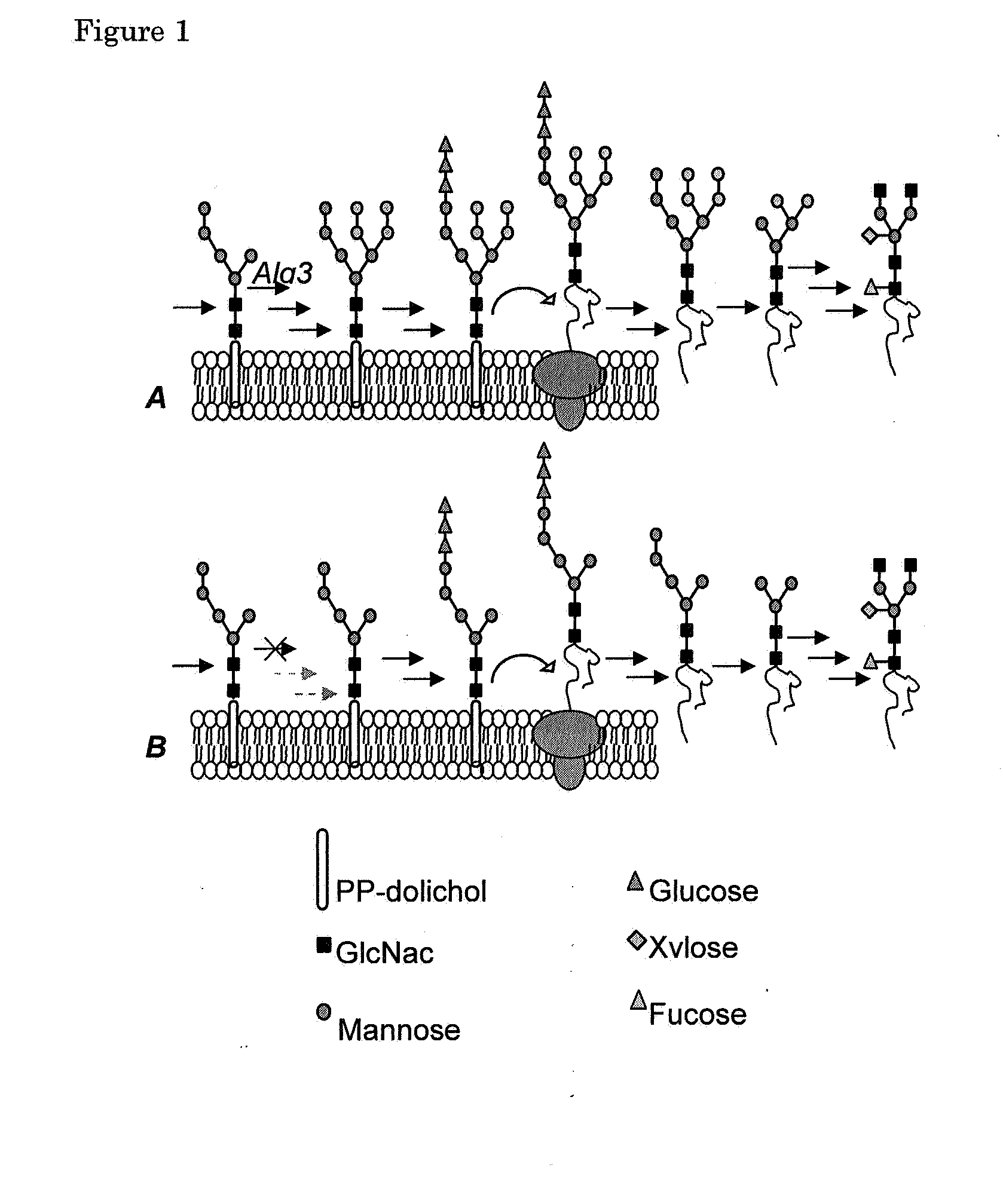
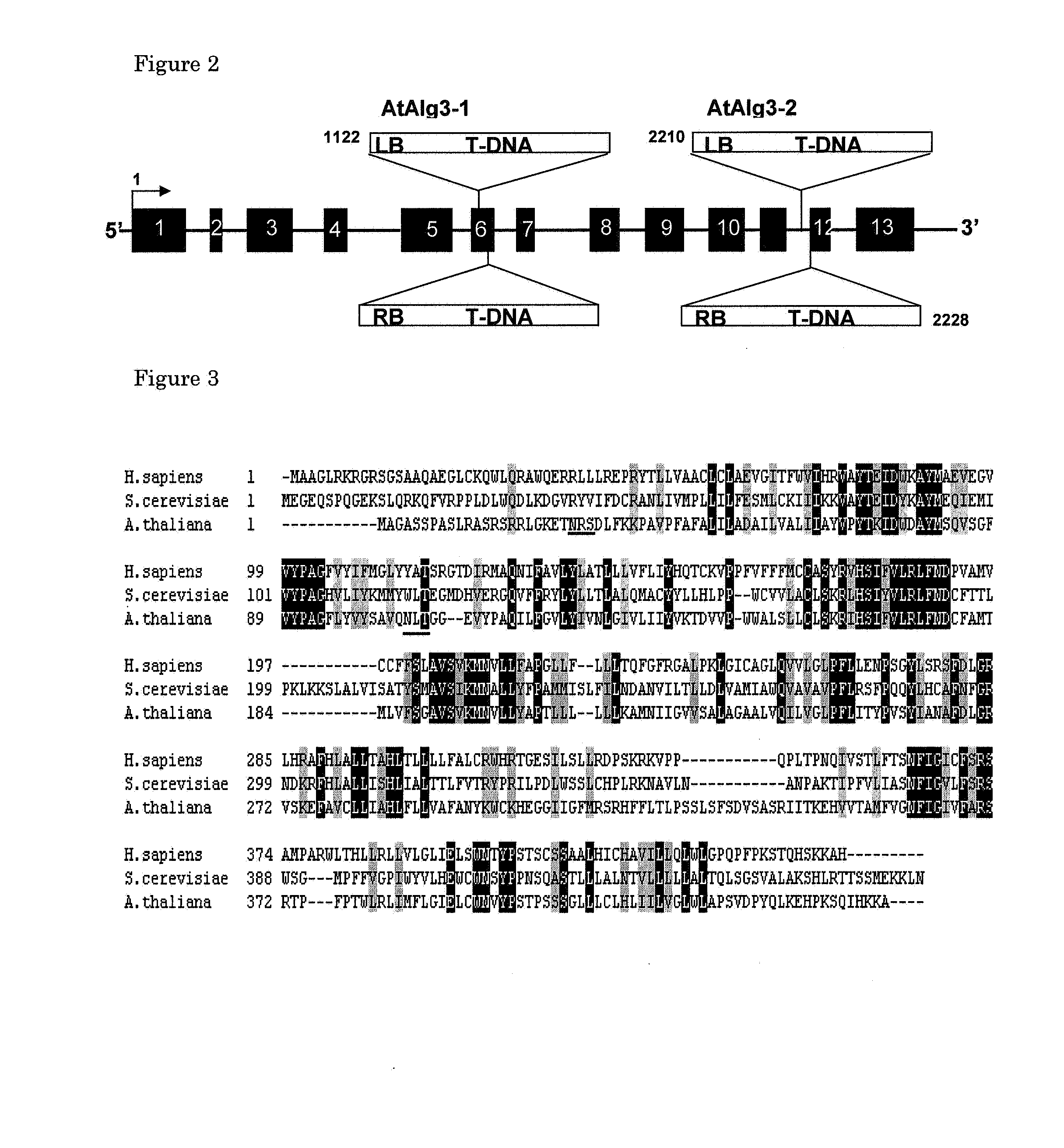
Alg3 mutant
The present invention relates to a method to produce proteins reduced in high mannose type glycans in a plant or plant cell by partially inhibiting the expression of the Alg3 gene in said plant or plant cell. Said partial inhibition can be provided for by inserting the Alg3 mutant gene from Arabidopsis as derived from the plant line Salk_040296c or by partially inhibiting the endogenous Alg3 gene by providing the plant or plant cell either with an antisense expression, a sense co-suppressing or with an RNA inhibition genetic construct. Optionally also tissue-specific expression of said inhibiting constructs can yield partial inhibition in a plant.
Owner:STICHTING DIENST LANBOUWKUNDIG ONDERZOEK
Highly Potent Acid Alpha-Glucosidase With Enhanced Carbohydrates
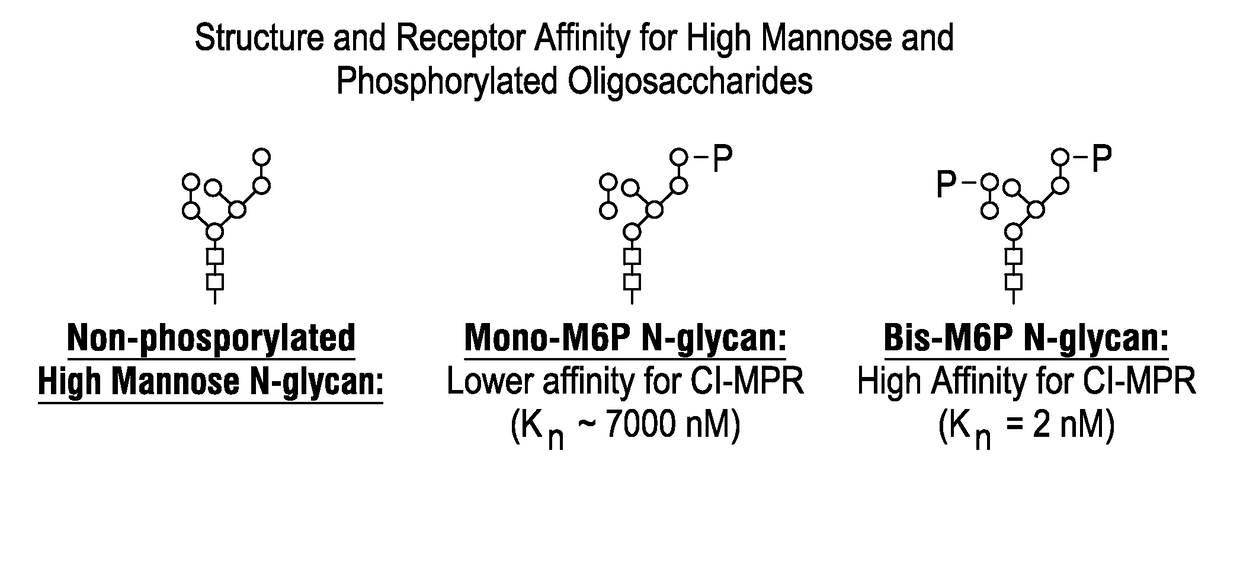
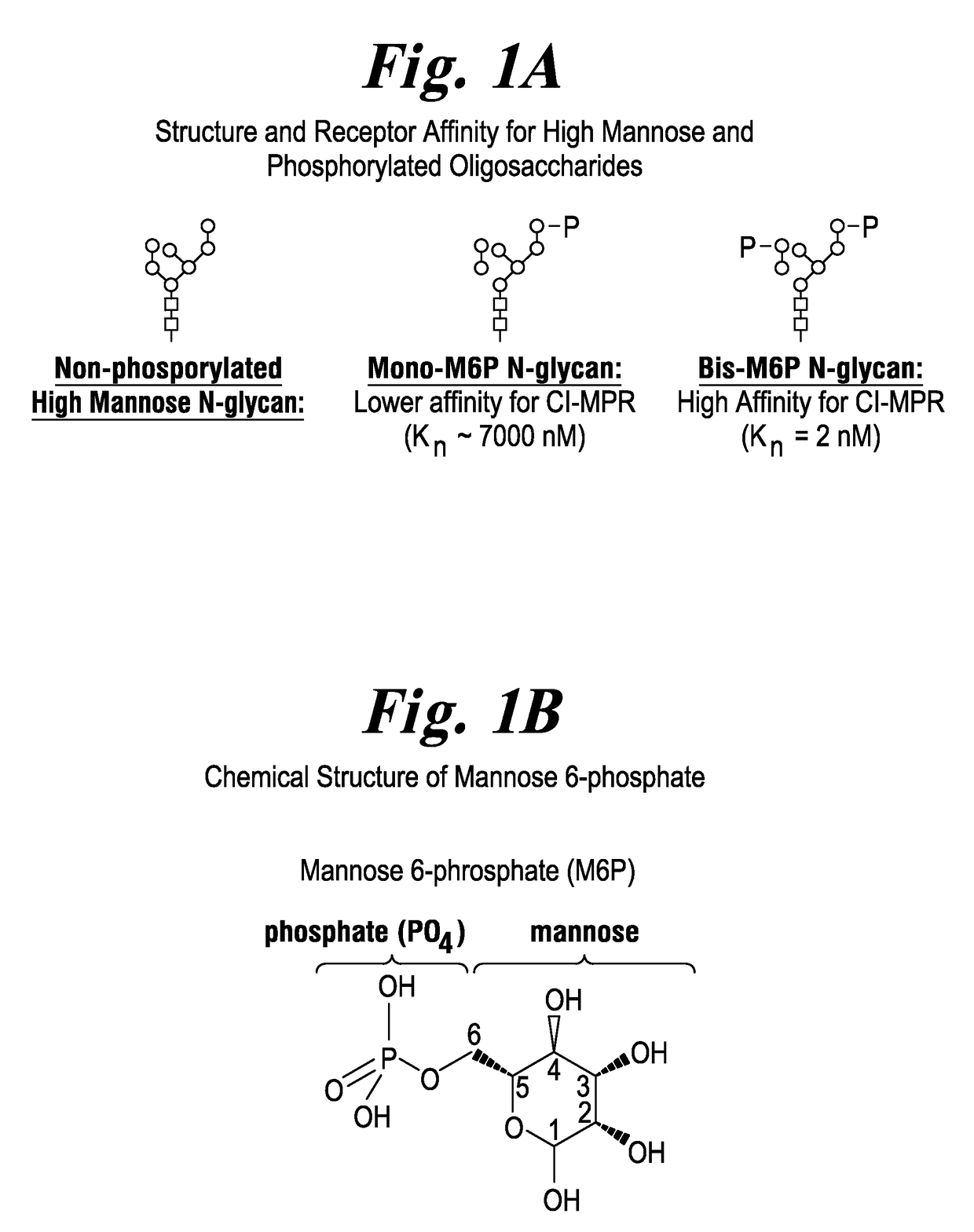
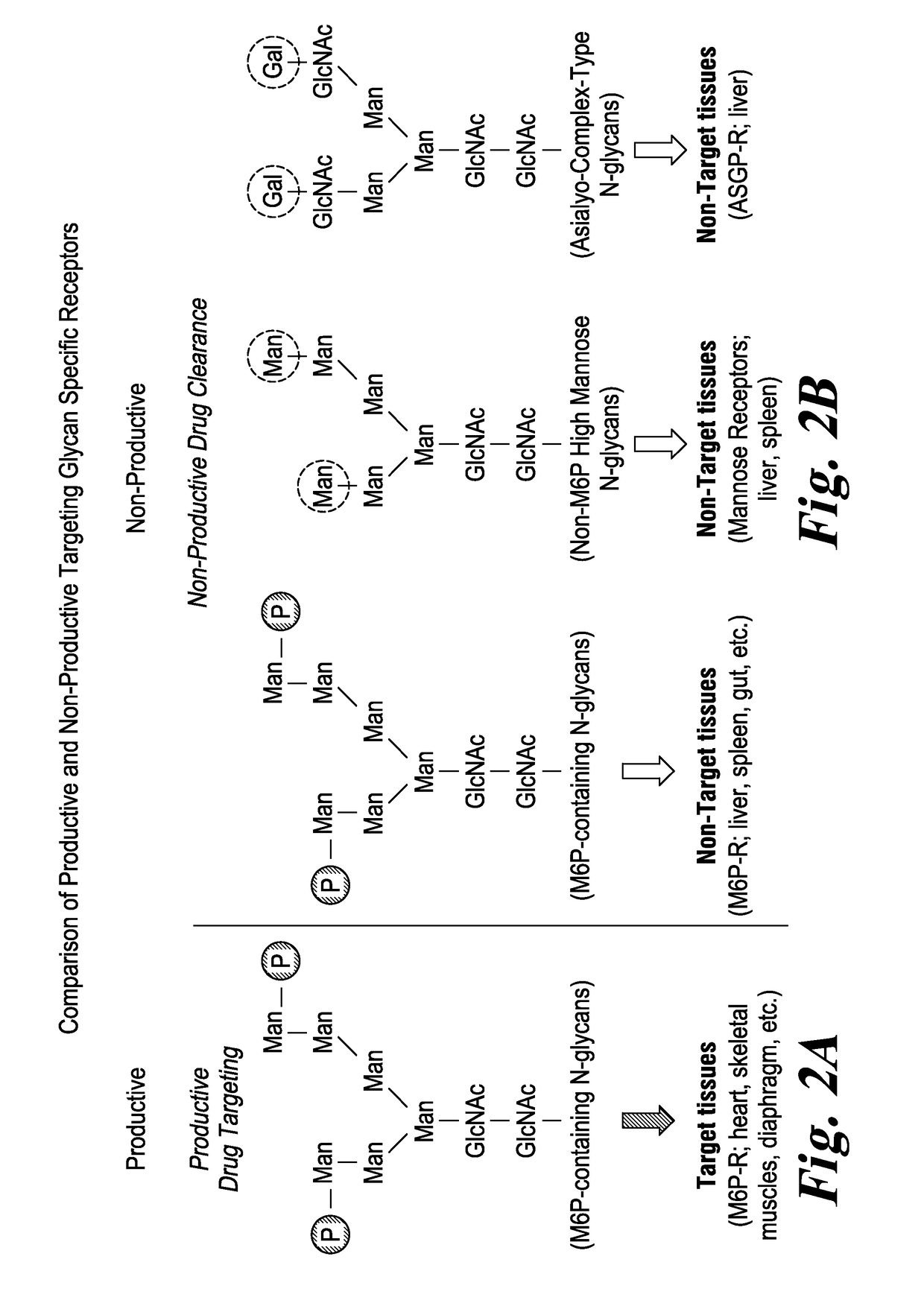
ActiveUS20170298335A1Efficient targetingMinimize non-productive clearancePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderAcid alpha-glucosidaseAlglucerase
Recombinant human alpha glucosidase (rhGAA) composition derived from CHO cells that contains a more optimized glycan composition consisting of a higher amount of rhGAA containing N-glycans carrying mannose-6-phosphate (M6P) or bis-M6P than conventional rhGAAs, along with low amount of non-phosphorylated high mannose glycans, and low amount of terminal galactose on complex oligosaccharides. Compositions containing the rhGAA, and methods of use are described.
Owner:AMICUS THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for removal of viruses from blood by lectin affinity hemodialysis
InactiveUS20070218458A1Reduce loadReduce in quantityOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationHemodialysisHollow fibre membrane
The present invention relates to a method for using lectins that bind to pathogens having high mannose surface glycoproteins or fragments thereof which contain high mannose glycoproteins, to remove them from infected blood or plasma in an extracorporeal setting. Accordingly, the present invention provides a method for reducing viral load in an individual comprising the steps of obtaining blood or plasma from the individual, passing the blood or plasma through a porous hollow fiber membrane wherein lectin molecules are immobilized within the porous exterior portion of the membrane, collecting pass-through blood or plasma and reinfusing the pass-through blood or plasma into the individual.
Owner:AETHLON MEDICAL INC
Chimeric antigens for eliciting an immune response
ActiveUS8029803B2Effective presentationImprove efficiencyBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseMHC class IHepatitis B immunization
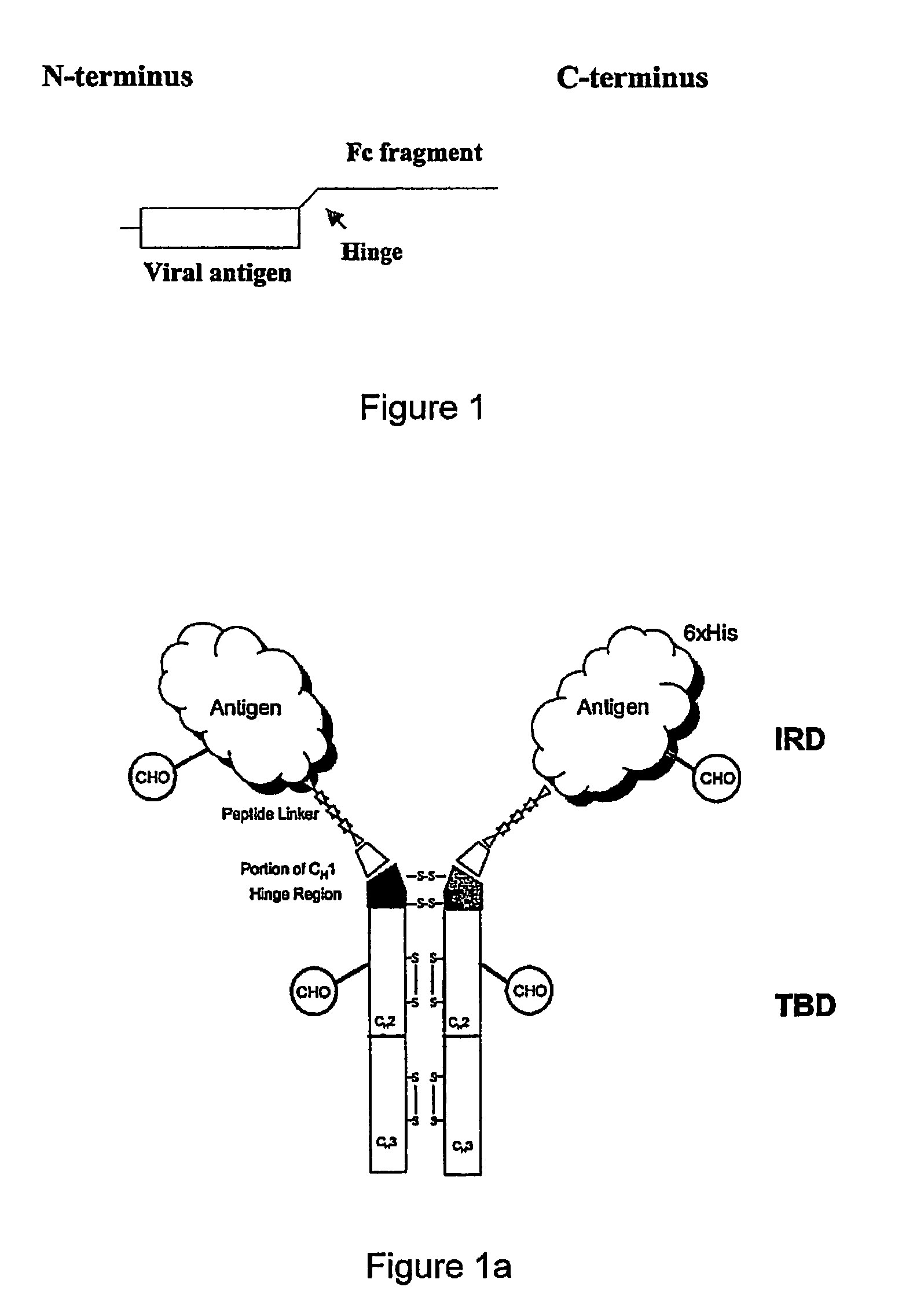
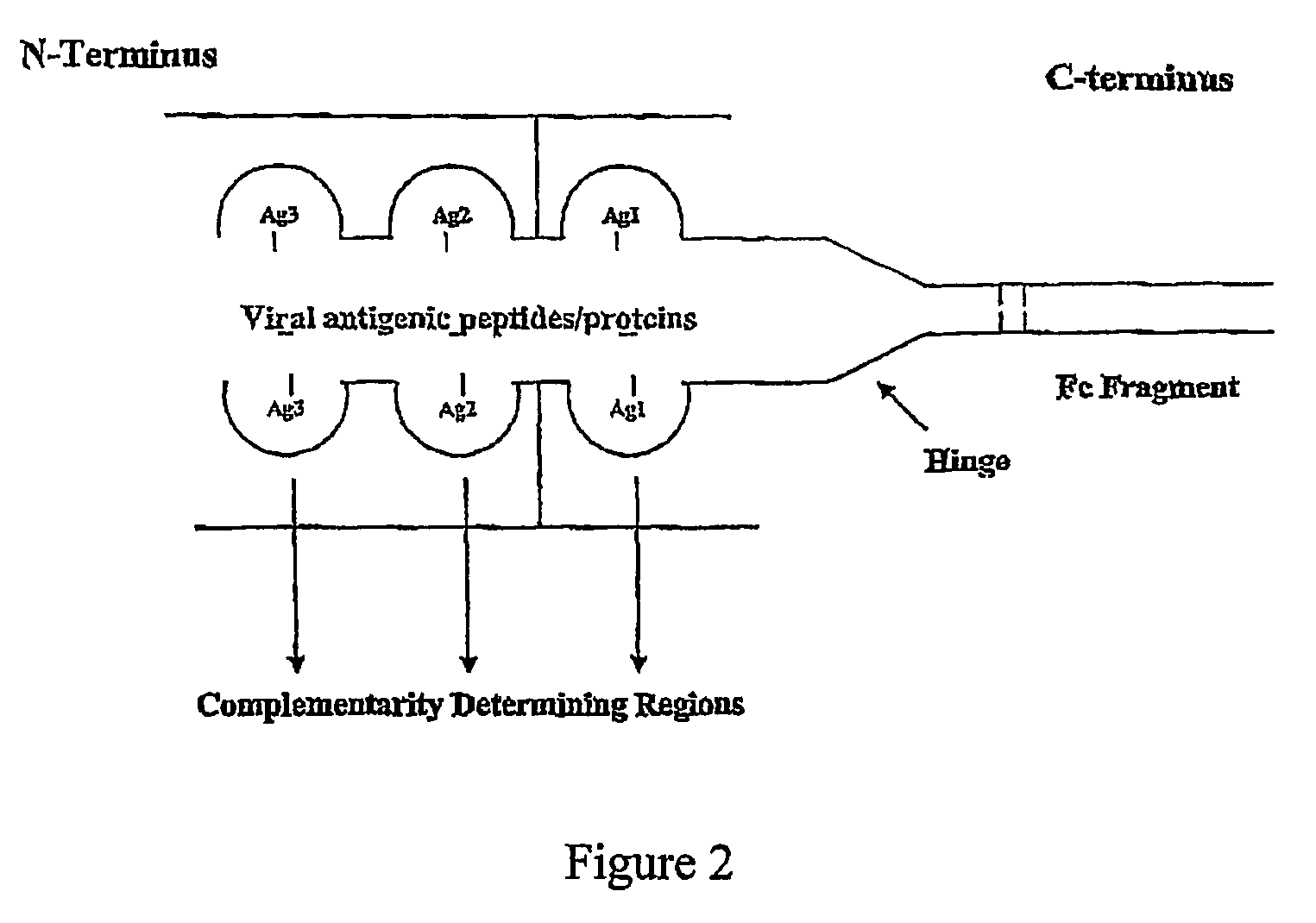
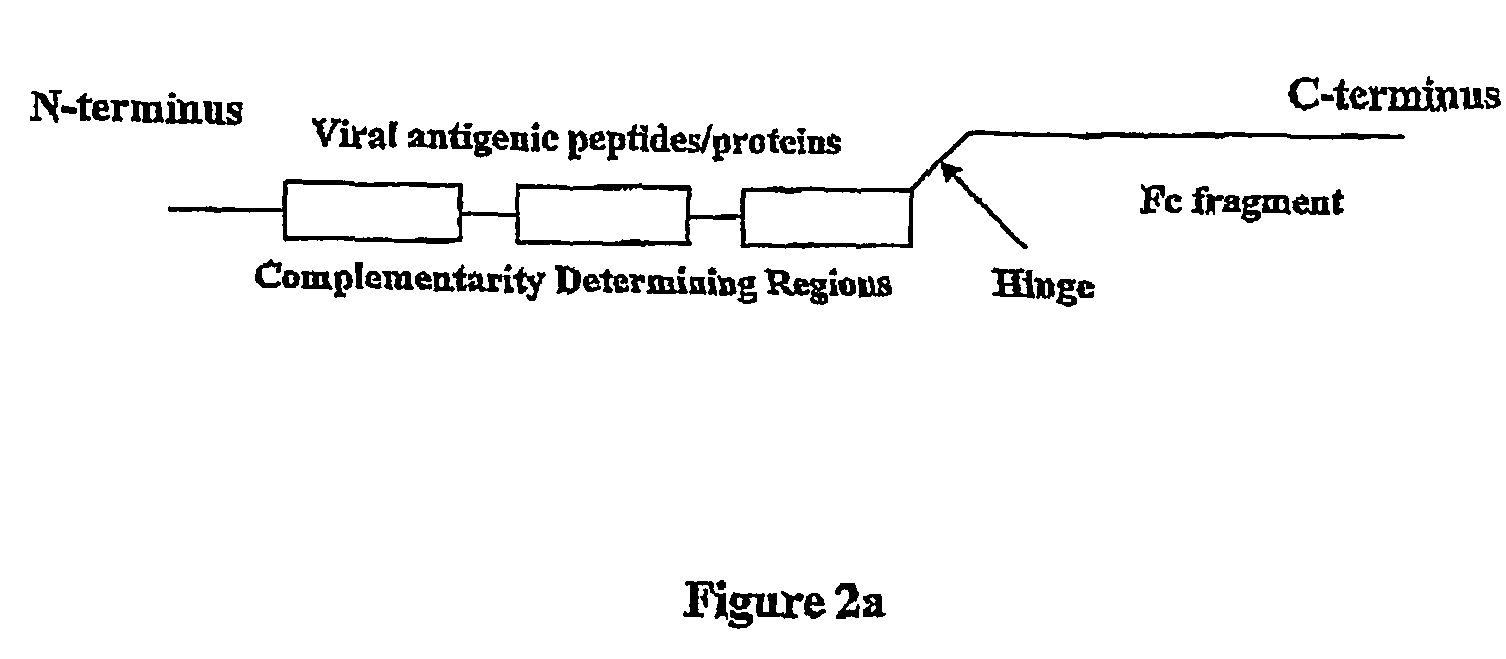
Disclosed herein are the nucleotide sequences, deduced amino acid sequences as well as methods and compositions necessary to elicit immune responses against chronic Hepatitis B infections in animals and humans. Immune response is enhanced by fusing relevant viral antigens with xenotypic immunoglobulin heavy chain region through a peptide linker and producing the fusion proteins in Baculovirus expression system to incorporate high mannose glycosylation. By virtue of the antibody component, the fusion proteins bind to Fc receptors on the surface of antigen presenting cells, are taken up, processed and derived peptides are presented on MHC Class I, which elicit a CTL (Th1) response. In a similar fashion, due to cross priming and presentation on MHC Class II, will elicit a humoral (Th2) response. In addition, disclosed are the methods of cloning, expression and production of the fusion proteins.
Owner:KAIMI BIOMEDICINE (CHENGDU) CO LTD
Isolated polypeptide binding to a sugar chain, polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide and use of the polypeptide and polynucleotide
InactiveUS7867732B2Efficient purificationEasy quantityEgg immunoglobulinsBacteriaHigh mannosePurification methods
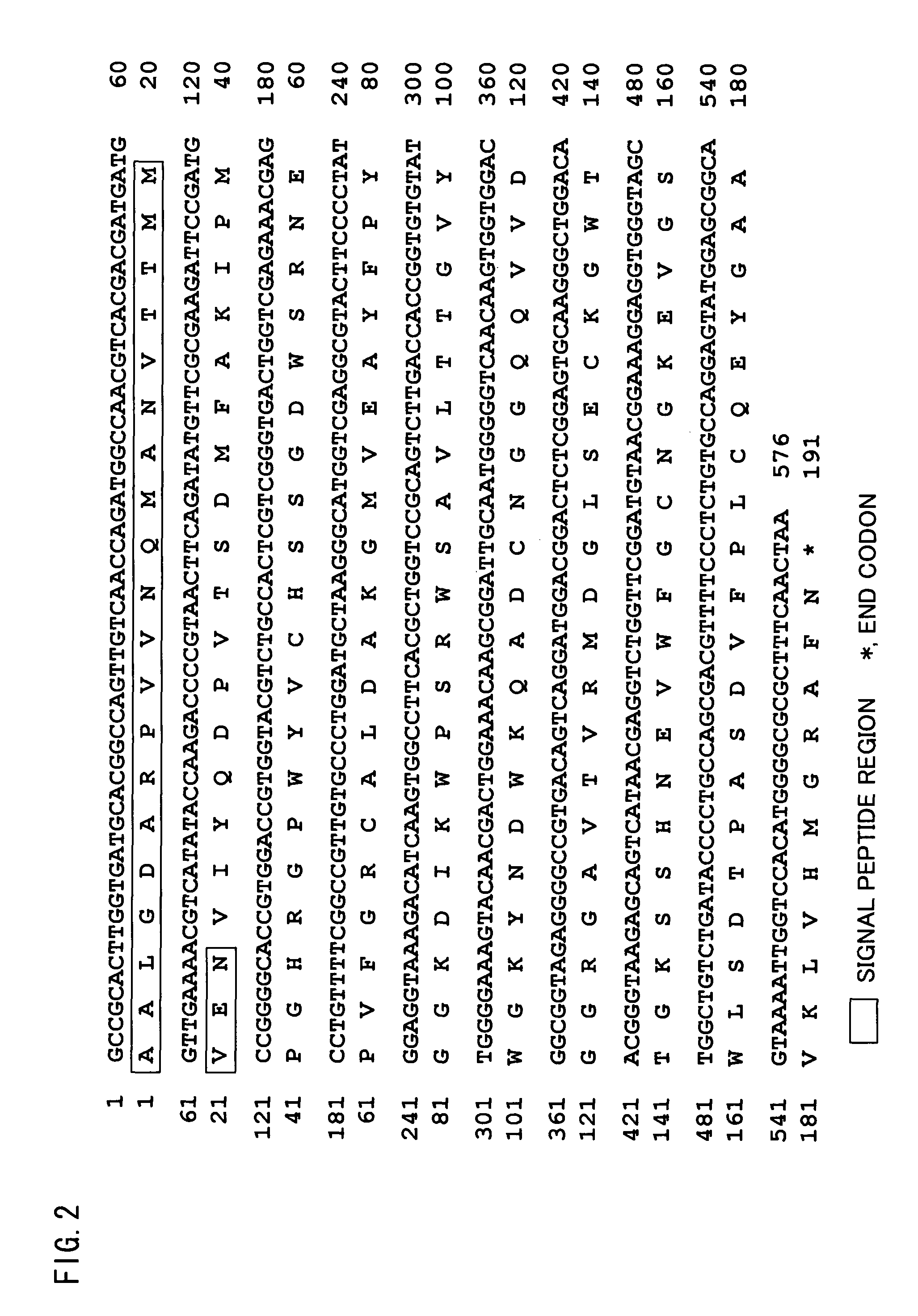
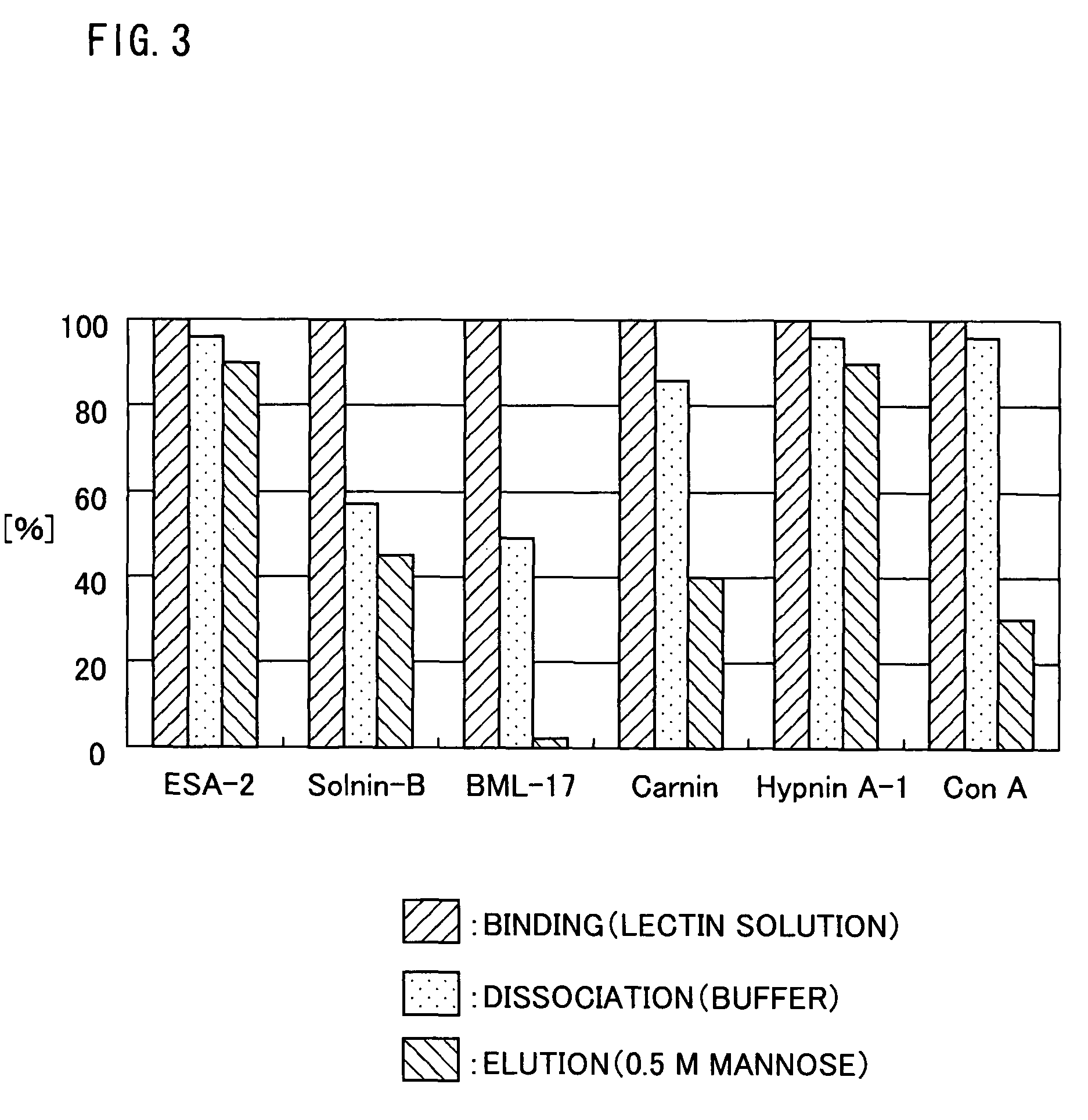
In one embodiment of the present application, a polypeptide capable of binding to a sugar chain is disclosed, particularly a high-mannose-type sugar chain bound to an antibody, more preferably a sugar chain bound to a chicken antibody. Also disclosed is a method for the purification of an antibody (specifically a chicken antibody) as a representative application of the polypeptide. Further disclosed is means for the purification. The polypeptide, BML-17, is a novel lectin made of 168 amino acid residues isolated from Bryopsis maxima. By using BML-17, it becomes possible to purify an antibody (e.g., a chicken antibody) readily and with high efficiency.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY
Methylotrophic yeast producing mammalian type sugar chain
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
InactiveUS20100196345A1Efficient productionSufficient quantityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPlant rootsHigh mannose
A device, system and method for producing glycosylated proteins in plant culture, particularly proteins having a high mannose glycosylation, while targeting such proteins with an ER signal and / or by-passing the Golgi. The invention further relates to vectors and methods for expression and production of enzymatically active high mannose lysosomal enzymes using transgenic plant root, particularly carrot cells. More particularly, the invention relates to host cells, particularly transgenic suspended carrot cells, vectors and methods for high yield expression and production of biologically active high mannose Glucocerebrosidase (GCD). The invention further provides for compositions and methods for the treatment of lysosomal storage diseases.
Owner:PROTALIX
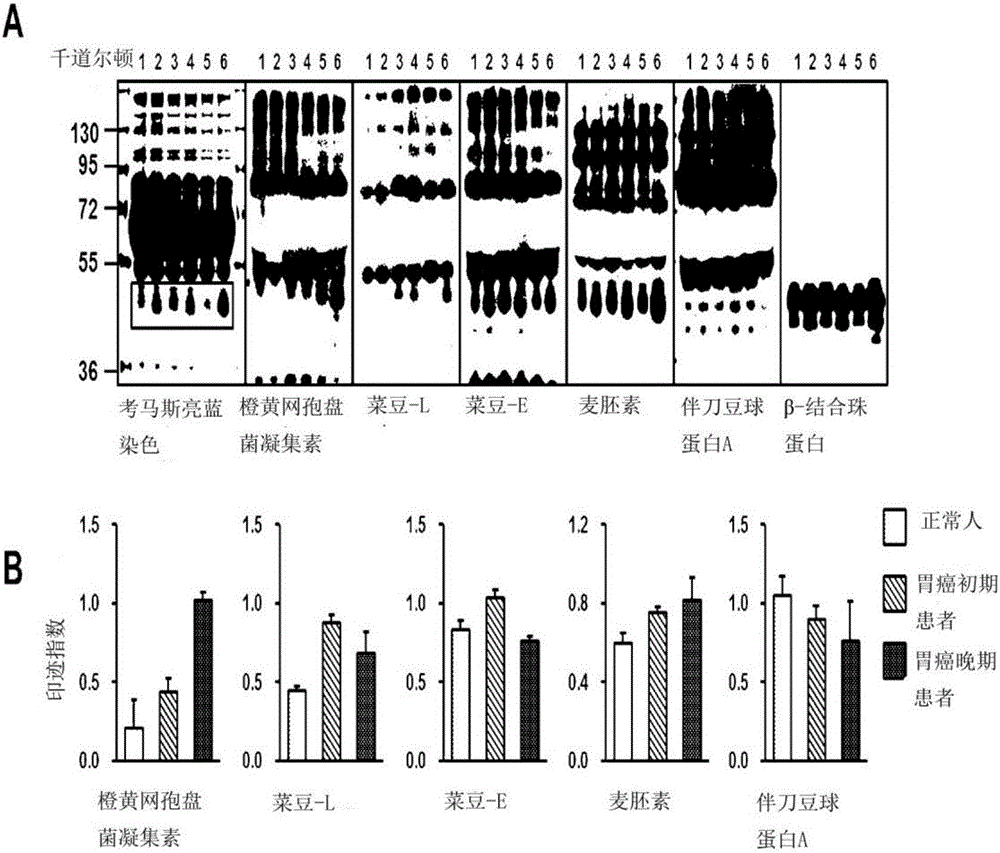
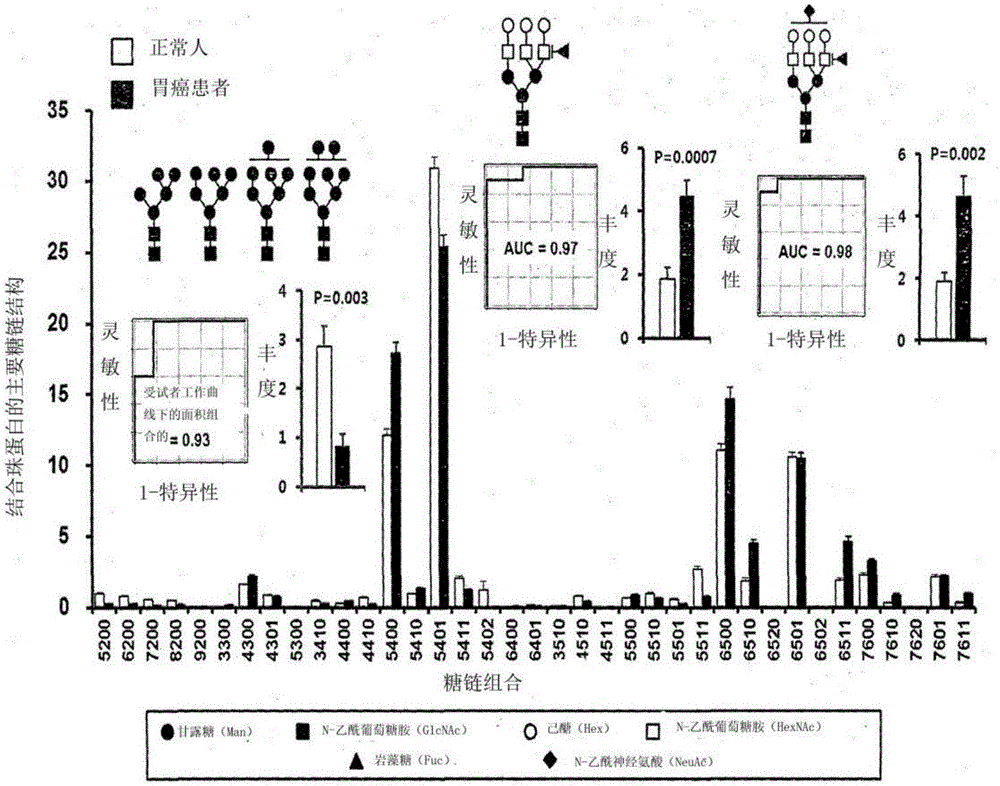
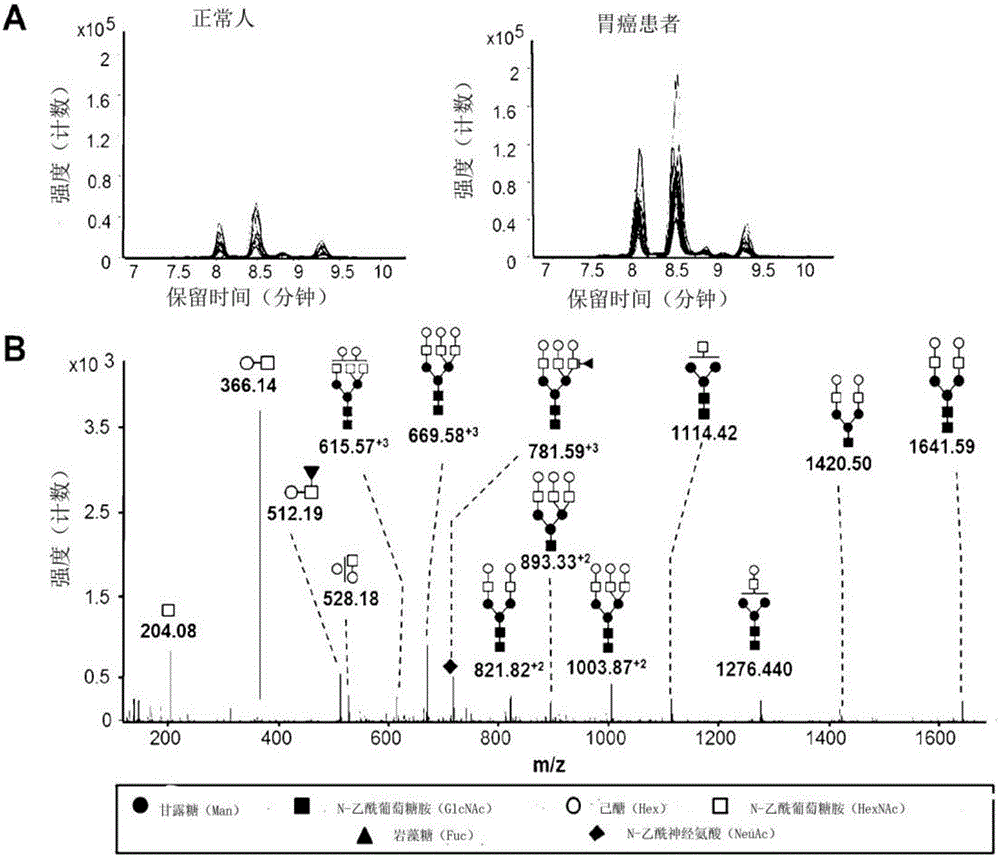
Novel method for gastric cancer diagnosis
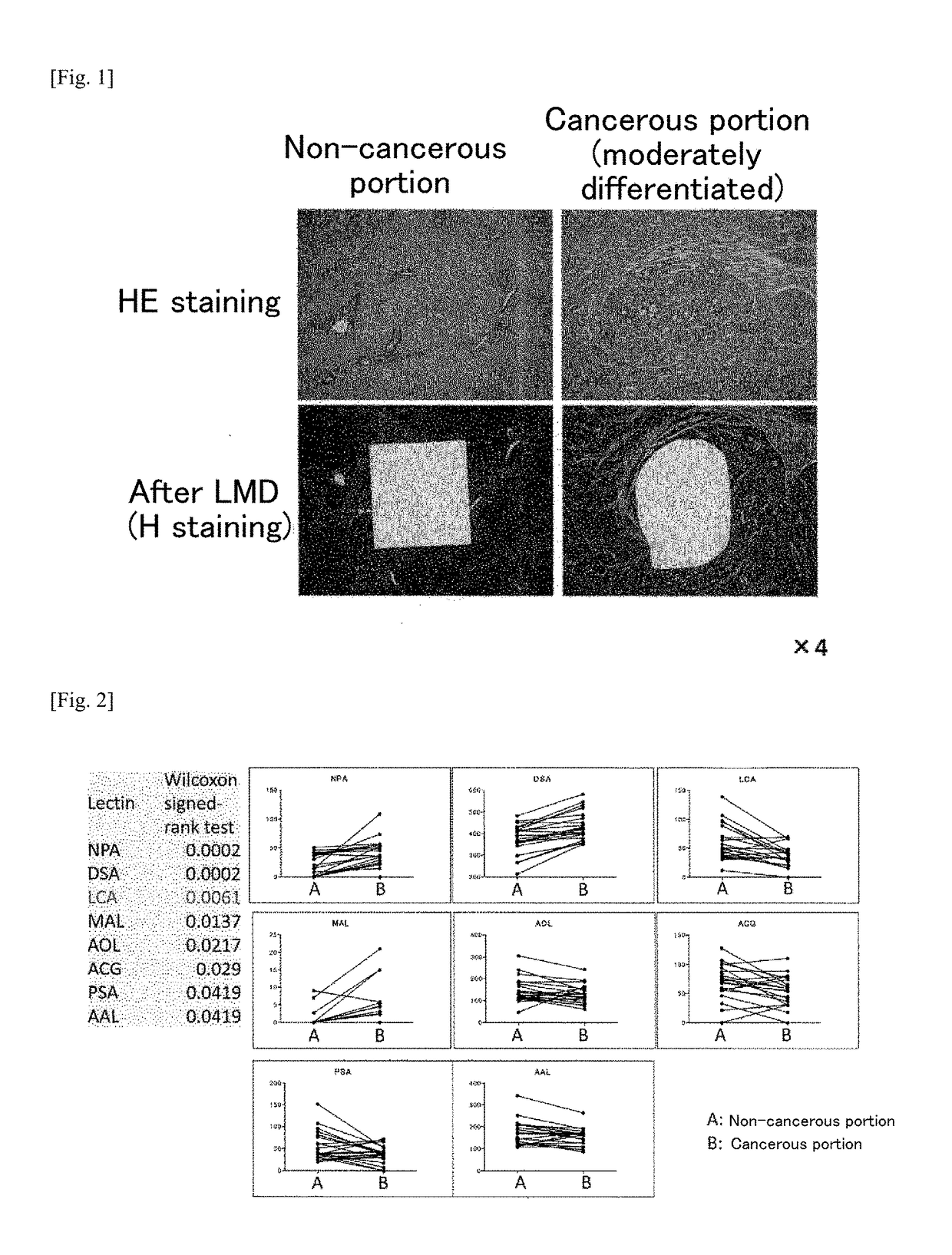
InactiveCN106029906AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFucosylationHigh mannose
The present invention relates to a method for gastric cancer diagnosis through the detection of glycan changes, and to a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis. More specifically, based on, among the changes in N-linked glycosylation of the gastric cancer patient-derived haptoglobin, which are detected through lectin and mass spectrometry, the increase in fucosylation, the increases or significant changes in particular glycan structures according to the classification of antennary, or the reduction in high-mannose structure of the N-linked glycan compared with normal persons, the discovered N-glycosylation structures can be favorably used for a method for gastric cancer diagnosis using lectin, as a diagnostic marker, or mass spectrometry, and a kit for diagnosing gastric cancer.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
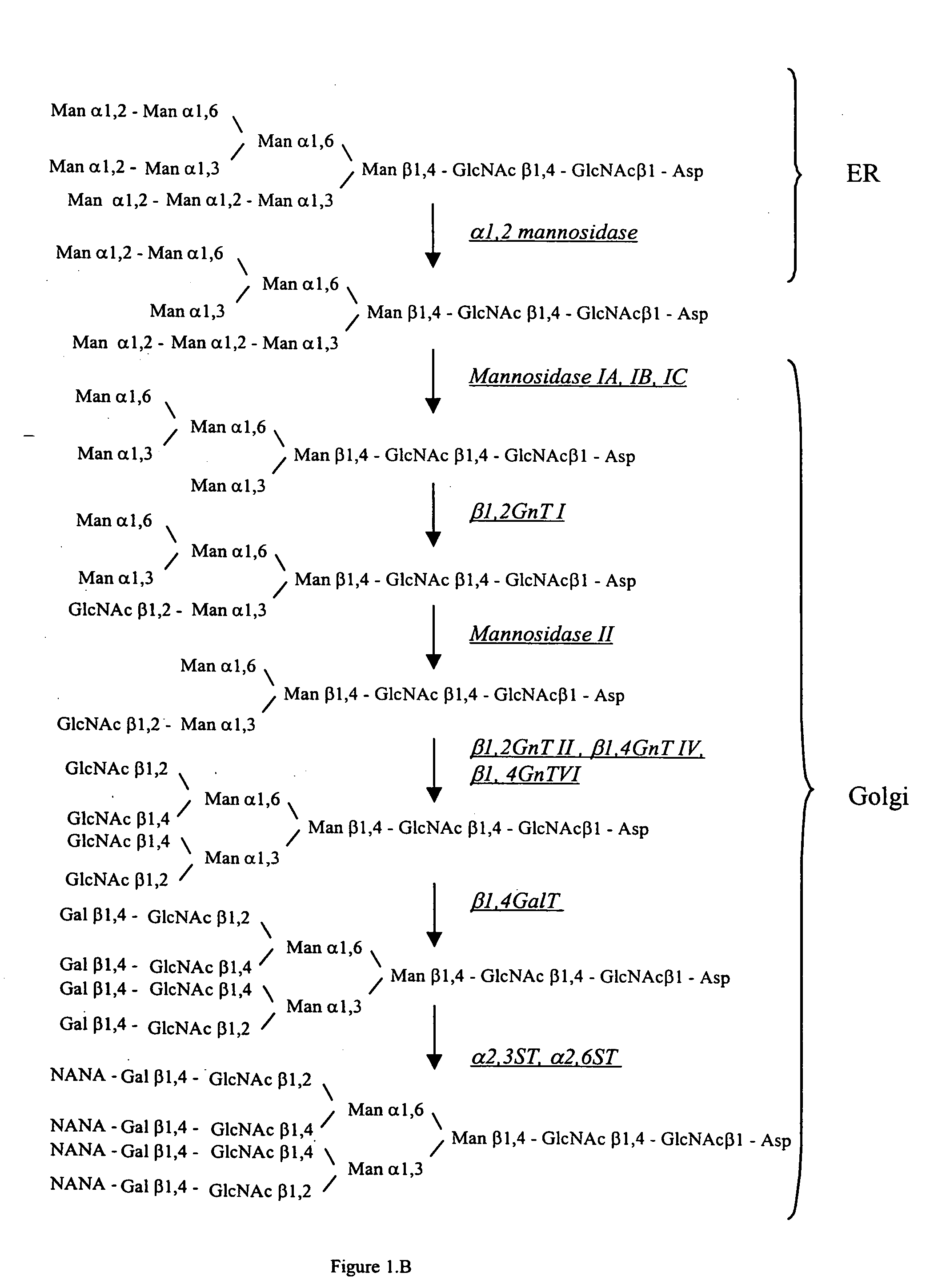
Methods for producing substantially homogeneous hybrid or complex n-glycans in methylotrophic yeasts
InactiveUS20120029174A1Highly efficient and effective engineeringDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsYeastBiotechnology
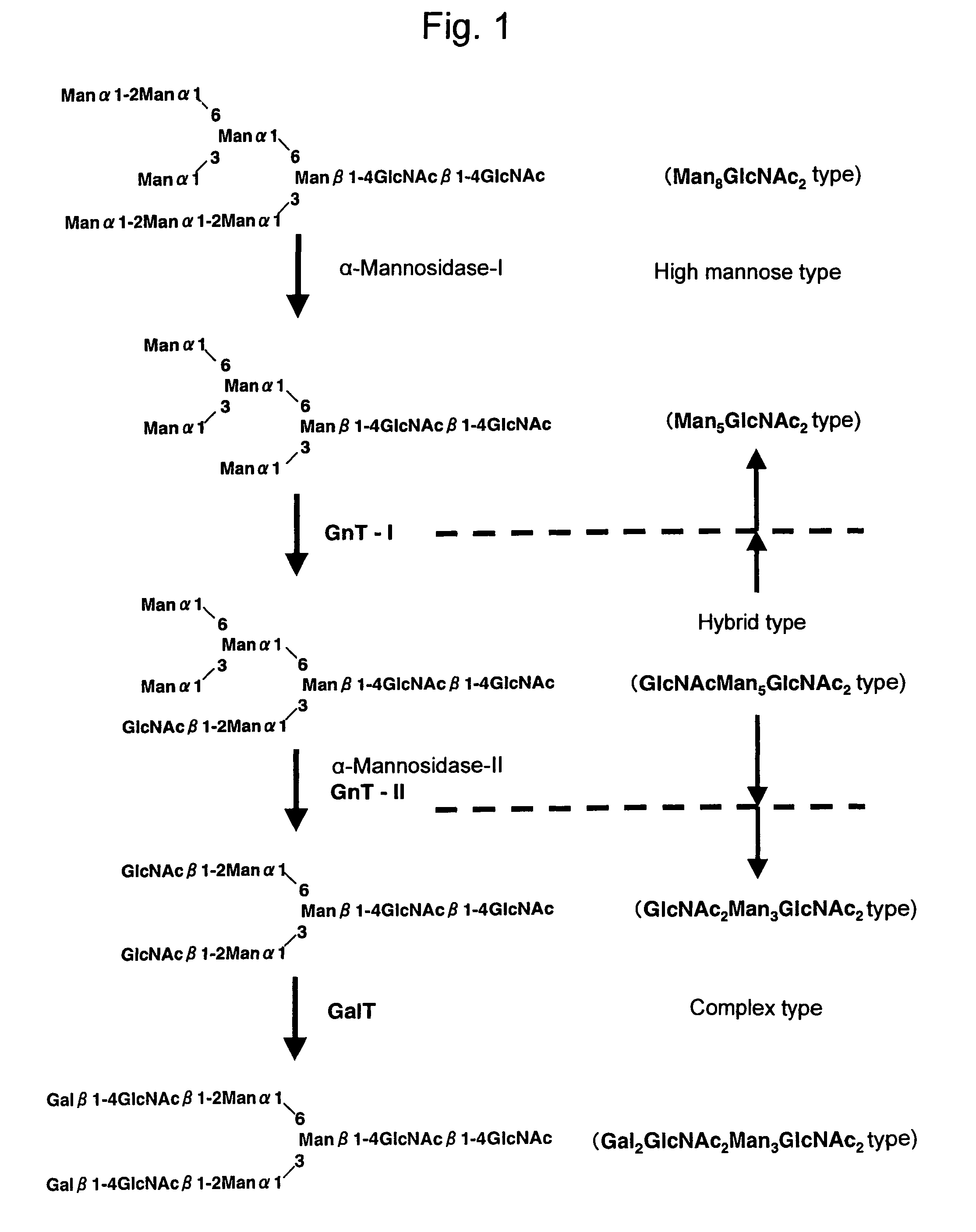
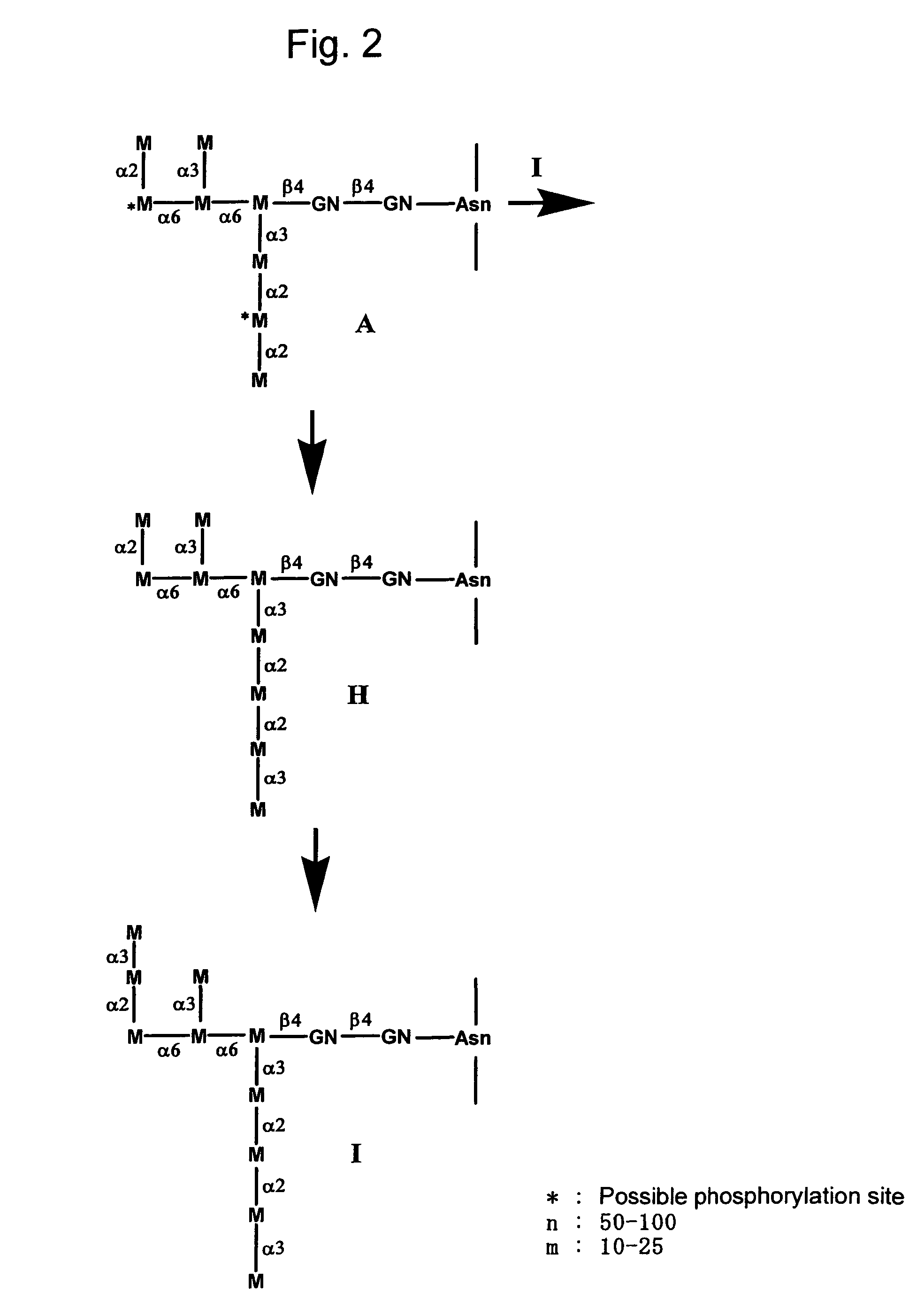
The present invention provides methods for effectively and efficiently converting methylotrophic yeast's heterogeneous high mannose-type N-glycosylation to mammalian-type N-glycosylation by disruption of an endogenous glycosyltransferase gene (OCH1) and step-wise introduction of heterologous glycosidase and glycosyltransferase activities. Each engineering step includes a number of stages: transformation with an appropriate vector, cultivation of a number of transformants, performance of sugar analysis and heterologous protein expression analysis, and selection of a desirable clone. The selected clone is then subjected to the next engineering step.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +2
Hepatocellular carcinoma marker
InactiveUS20170219590A1Library screeningPreparing sample for investigationHigh mannoseHepatocellular carcinoma
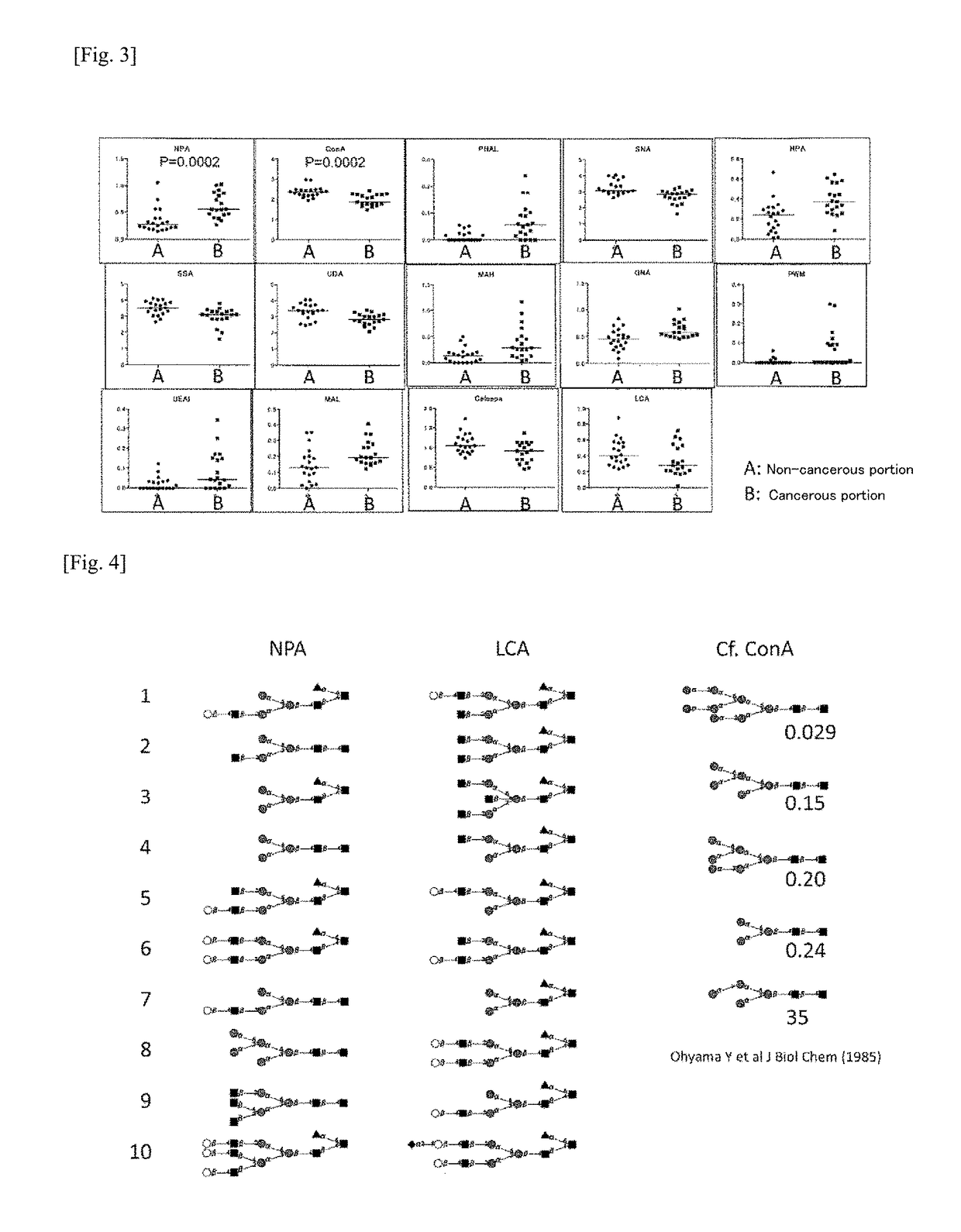
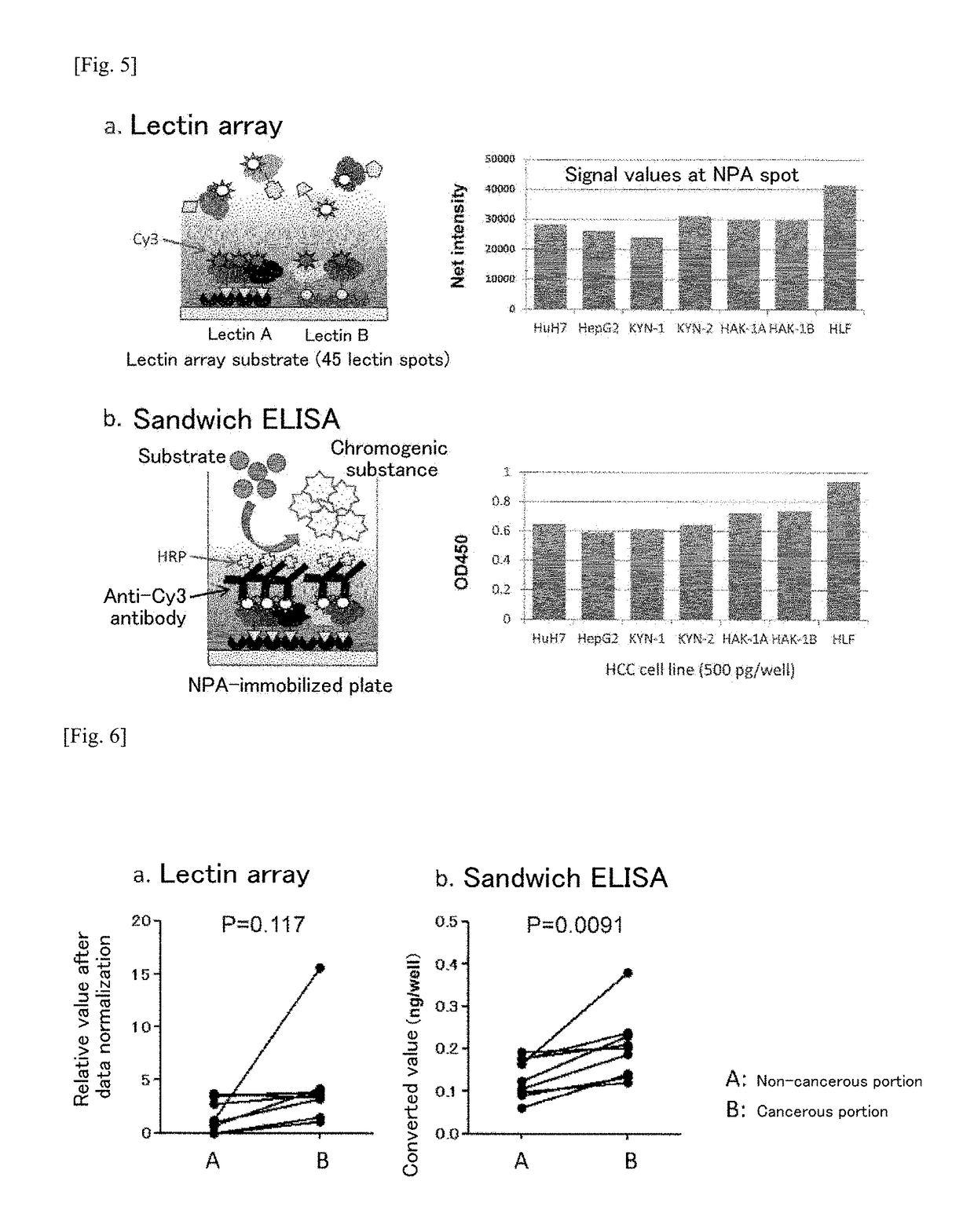
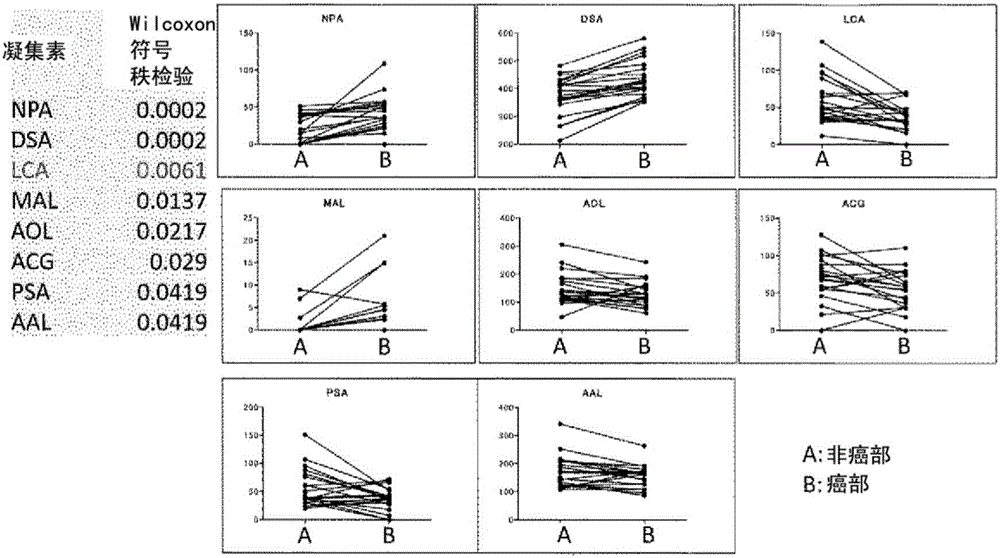
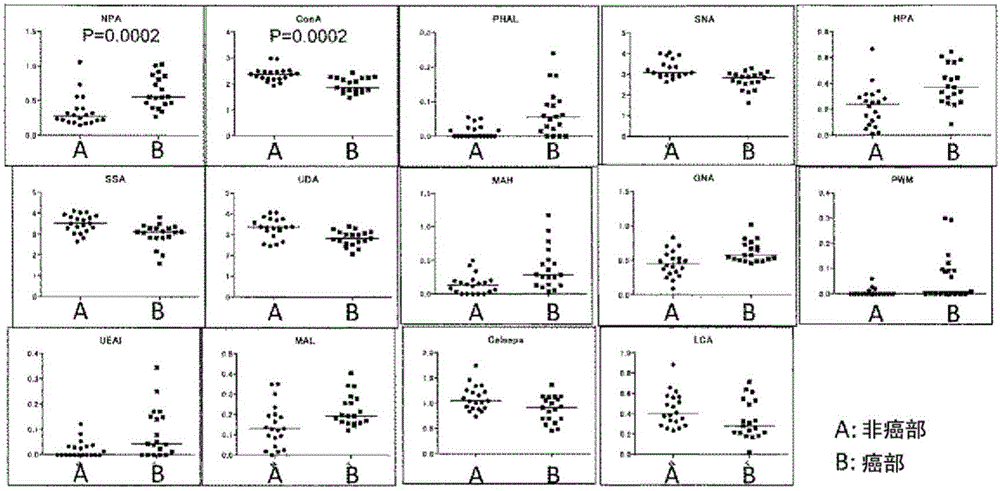
The problem addressed by the present invention is to provide a marker for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma, wherein the hepatocellular carcinoma marker comprises a glycoprotein that first becomes present in the liver with the occurrence of cancer, without depending on changes in the state of the liver. The present invention provides a hepatocellular carcinoma marker comprising an NPA lectin-binding glycoprotein having an NPA lectin-binding glycan epitope that has at least one of the following properties (1) to (5): (1) the glycan epitope does not include core fucose (fucose α1→6 glycan); (2) the glycan epitope comprises a complex-type glycan having three (four or fewer) mannoses; (3) the glycan epitope does not include a high-mannose-type glycan having five or more mannoses; (4) the glycan epitope comprises a complex-type glycan that does not depend on the property of binding to LCA lectin; and (5) the glycan epitope comprises a complex-type glycan that does not depend on the property of binding to ConA lectin. By detecting the hepatocellular carcinoma marker of the present invention in a test sample, it is possible to determine the presence of hepatocellular carcinoma or the level of progression or malignancy of carcinoma.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Hepatocellular carcinoma marker
ActiveCN106662588AReduce functionPreparing sample for investigationBiological material analysisEpitopeHigh mannose
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a hepatocellular carcinoma marker which can be used for detecting the presence of hepatocellular carcinoma and comprises a glycoprotein that can occur in the liver only when the carcinoma is developed regardless of the change in the condition of the liver. The present invention provides a hepatocellular carcinoma marker which comprises an NPA lectin-binding glycoprotein containing an NPA lectin-binding sugar chain epitope having at least one property selected from the following properties (1) to (5) (1) the sugar chain epitope does not contain core fucose (a fucose alpha 1(arrow) 6 sugar chain); (2) the sugar chain epitope contains a composite sugar chain that contains three (less than four) mannose molecules; (3) the sugar chain epitope does not contain a high-mannose-type sugar chain containing five or more mannose molecules; (4) the sugar chain epitope comprises a composite sugar chain that does not rely on the bindability to LCA lectin; and (5) the sugar chain epitope comprises a composite sugar chain that does not rely on the bindability to ConA lectin. The presence of the development of hepatocellular carcinoma or the degree of the progression or malignancy of the carcinoma can be determined by detecting the hepatocellular carcinoma marker of the present invention in a sample of interest.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Process To Improve Activity Of Mannoprotein As Wine Stabiliser
InactiveUS20080107784A1High activityReduce turbidityMilk preparationAlcoholic beverage preparationTartratePrecipitation
The present invention describes a process to improve the activity as wine stabiliser of a mannoprotein, comprising treating a mannoprotein with a basic solution at a pH of at least 9. The mannoprotein obtainable by this process is more effective in stabilising wine against tartrate precipitation or protein haze formation when compared with the mannoprotein prior to the treatment with basic solution.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 as well as expression and purification methods and application thereof
ActiveCN102351952AImprove uniformityBiologically activeFungiPeptide/protein ingredientsPichia pastorisPurification methods
The invention discloses low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 as well as expression and purification methods thereof. The low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 is protein obtained after replacing Asn in the N46 bit in the IFN-lambda1 mature peptide sequence into Gln. The blockage on the high-mannose modification process of the N-glycosylation site of the IFN-lambda1 by the Pichia pastoris is realized so that the IFN-lambda1-Nm genes are correctly expressed in the Pichia pastoris in a high-efficiency secretory way, the uniformity of the expressed recombination IFN-lambda1-Nm protein is obviously improved, the expression level is higher than 65mg / L, the purity of the expressed recombination protein after two-step column chromatography is higher than 98 percent, and the low-saccharification modified recombination IFN-lambda1-Nm protein has the same biological activity as the original Pichia pastoris expressed wild IFN-lambda1 and simultaneously has better safety. The invention provides an effective method for efficient low-cost mass production of low-saccharification mutant interferon lambda1 with biological activity and good uniformity, higher practical application values are realized, and the application prospects are wide.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
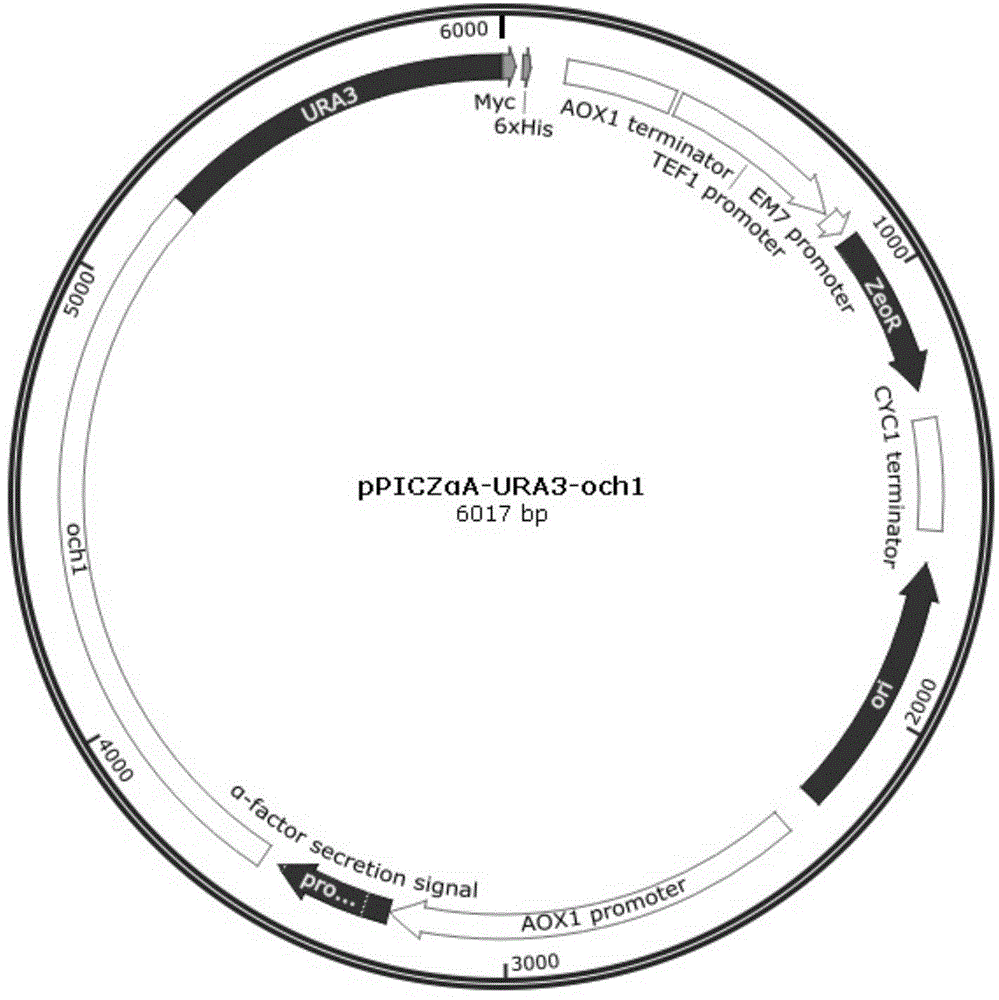
Construction method of Pichia pastoris expressed by OCH1 defect anti-CD20 tetravalent antibody
InactiveCN105779490AInhibition formationNarrowing Glycosylation DifferencesFungiHybrid immunoglobulinsPichia pastorisHigh mannose
The invention discloses a construction method of Pichia pastoris expressed by an OCH1 defect anti-CD20 tetravalent antibody. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out the alpha-1,6-mannosyl transferase OCH1 of a strain JC308, connecting reconstructed och1 having no expression ability and a screening label to pPICZalphaA, introducing the obtained pPICZalphaA to wild Pichia pastoris JC308, carrying out homologous recombination, screening to obtain an OCH1 defect strain denoted as detaoch1, connecting the sequence of a synthesized anti-CD20 tetravalent antibody with a Pichia pastoris expression plasmid pPIC9, and introducing the obtained product to the OCH1 defect strain detaoch1 to obtain the Pichia pastoris. The Pichia pastoris alpha-1,6-mannosyl transferase (OCH1) gene is knocked out to prevent formation of high-mannose carbohydrate chains, so glycosylation difference between yeast expression proteins and human natural proteins is shortened, and the safety of medicinal proteins is guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING JIZHI XINCHUANG TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com