Hepatocellular carcinoma marker
A technology of hepatocellular carcinoma and markers, applied in biological testing, biomaterial analysis, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as stagnation and failure to provide
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0246] (1) 18 Preparation of O-labeled peptides
[0247] The culture supernatants of two kinds of hepatocellular carcinoma culture strains (HLF strain and HAK1A strain) and protein samples prepared from the cancerous and non-cancerous parts of the pathological tissues of hepatocellular carcinoma patients were injected into the NPA lectin-bound The column captures the NPA-binding glycopeptide group, treats it with trypsin and fragments it into peptides, and passes through the NPA lectin column again to capture the NPA lectin-binding glycopeptide group again. The obtained candidate glycopeptides are treated with peptide-N-glycosidase (glycopeptidase F, PNGase) to remove the N-binding sugar chains and replace them with the introduction of Asn with sugar chains 18 O to label the peptide with a stable isotope. (Thus, whether or not a sugar chain is bound to the peptide was clearly confirmed by experiments, and to which Asn on the peptide sequence the sugar chain was bound was kno...
Embodiment 1
[0321] (Example 1) Tissue lectin array resolution
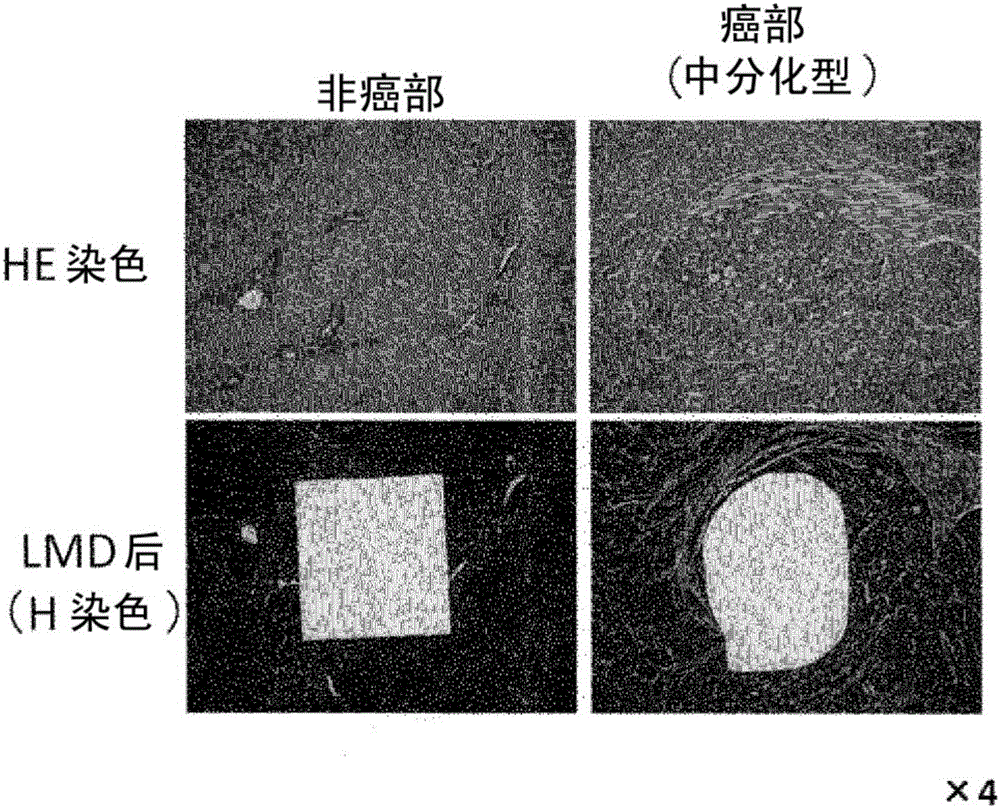
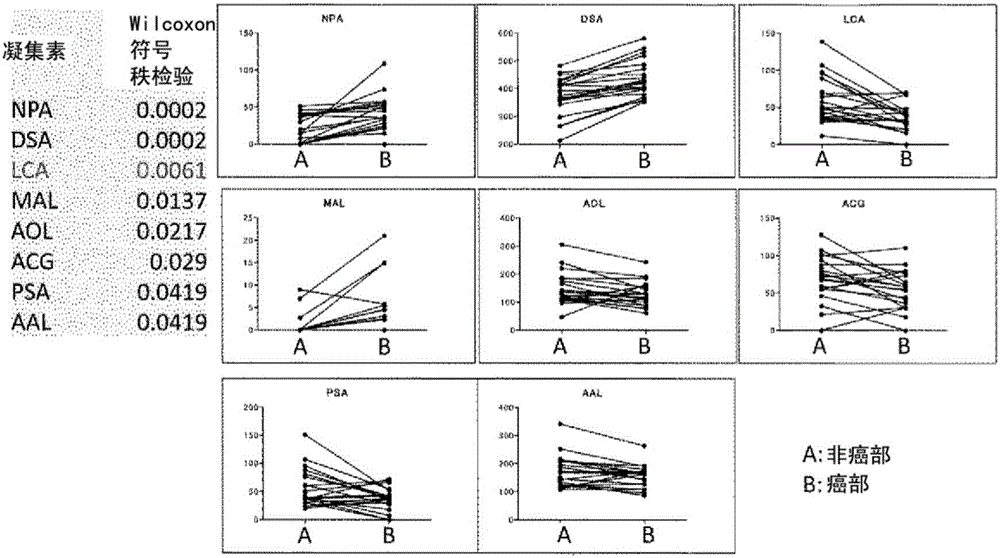
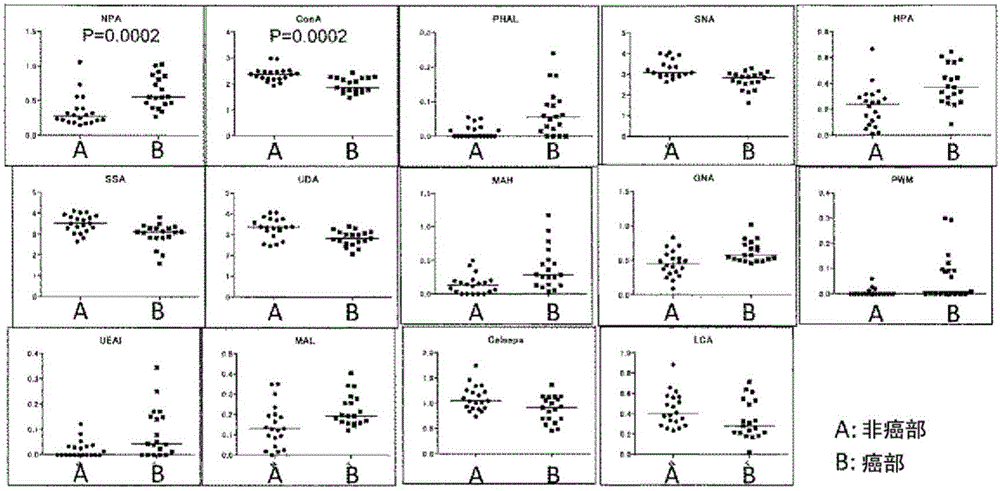
[0322] The lectin microarray used in this study is a system that immobilizes 45 kinds of plant lectins with different specificities on the same substrate, and simultaneously analyzes the interactions (binding properties) with sugar chains on glycoproteins to be analyzed (Kuno et al., Nature Methods 2, 851-856, 2005). Using this system, an attempt was made to screen for a lectin that forms a significant high signal value in a quantitative assay system for hepatocellular carcinoma tissue, or an optimal lectin that can specifically stain cancer in tissue staining. In this experiment, formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded liver tissues from patients with HCC were used. Specific areas of cancerous and non-tumor liver parenchyma (non-cancerous) were made into tissue fragments by laser microdissection (LMD) and collected, followed by protein extraction and lectin array analysis after fluorescent labeling. The basic protocol follo...
Embodiment 2
[0338] (Example 2) NPA lectin reaction of hepatocellular carcinoma cultured cells and liver cancer patient tissues based on sandwich ELISA Responsive research
[0339] Seven cultured hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HuH-7, HepG2, KYN-1, KYN-2, HAK-1A, HAK-1B, HLF) whose reactivity to NPA was previously confirmed by lectin array were studied and Can Liver Cancer Patient Tissues Be Constructed? Figure 5 The sandwich ELISA system shown in b. It should be noted that the basic protocol for extracting protein from cultured cells to fluorescent labeling was carried out according to the method of Tateno et al. or Toyoda et al. (Methods Enzymol 478, 181-195, 2010, Genes Cells 16, 1-11, 2011). It should be noted that the preparation of samples from tissue specimens was carried out according to Example 1.
[0340] (2-1) Protein extraction from cultured cells
[0341] Adjust the cultured liver cancer cell lines to 2×10 in each 1.5mL tube 6 indivual. After the pellets were fo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com