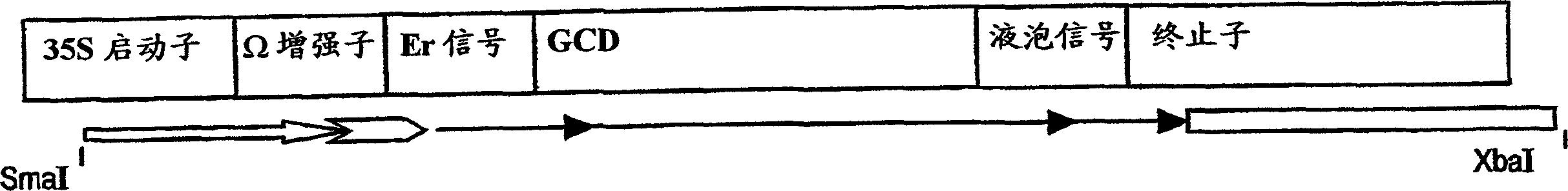Production of high mannose proteins in plant culture
A high mannose and protein technology, applied in the field of plant culture and production of these proteins, can solve the problems of complex purification scheme, low biological activity, high cost of recombinant enzymes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0216] Construction of expression plasmids
[0217] This example describes the construction of exemplary expression plasmids and is used in conjunction with the related examples below, as detailed below.
[0218] Use forward primer: 5′CA GAATTC GCCCGCCCCTGCA 3' (also represented by SEQ ID NO: 1) and reverse primer: 5' CTC AGATCT TGGCGATGCCACA 3' (also represented by SEQ ID NO: 2) amplifies the cDNA encoding hGCD (ATTC clone number 65696).
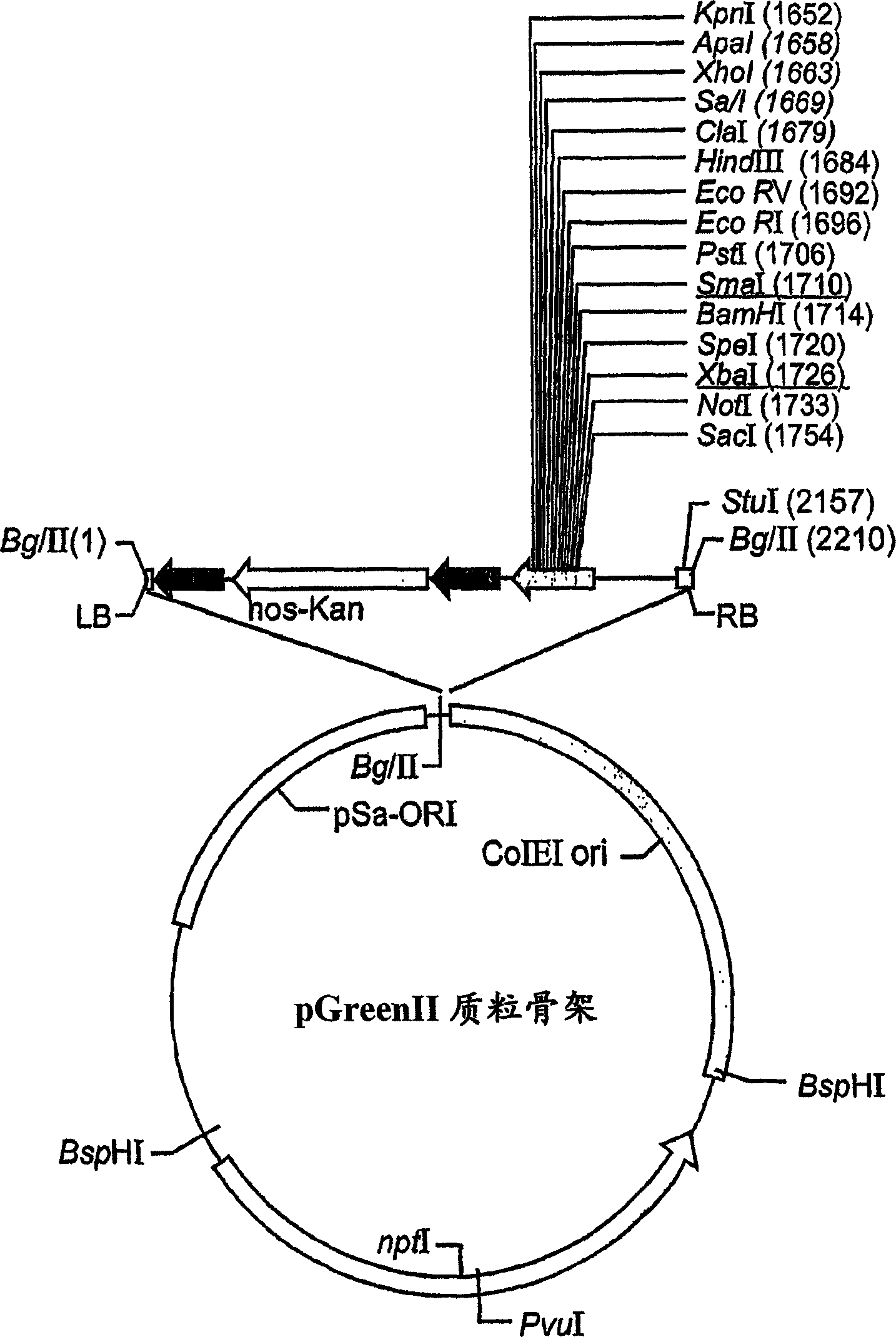
[0219] Purified PCR DNA products were digested with endonucleases EcoRI and BglII (see underlined recognition sequences in primers) and ligated into an intermediate vector with expression cassette CE-T digested with the same enzymes. CE-T includes the targeting signal MKTNLFLFLIFSLLLSLSSAEA (also represented by SEQ ID NO: 3) from the alkaline endochitinase gene [Arabidopsis], and the vacuolar targeting signal from tobacco chitinase A: DLLVDTM * (also represented by SEQ ID NO: 4).
[0220] The expression cassette was ...
Embodiment 2
[0224] Transformation of Carrot Cells and Selection of Transformed Cells Expressing rhGCD
[0225] This example describes an exemplary method of the invention for transforming carrot cells, as used in the following examples.
[0226] Carrot cells were transformed using the Agrobacterium transformation method described previously [Wurtele and Bulka (1989), supra]. The genetically modified carrot cells were plated on Murashige and Skoog (MS) agar medium containing antibiotics for selection of transformants. As shown in Figure 2, extracts prepared from calli were tested for expression of GCD by Western blot analysis using an anti-hGCD antibody and compared with recombinant glucocerebrosidase injection standard (positive control) and untransformed cells extract (negative control) for comparison. One callus (No. 22) was selected from various calli tested for expanded culture and protein purification.
[0227] Western blotting was performed as follows.
[0228] For this te...
Embodiment 3
[0238] Purification of recombinant active HGCD protein from transformed carrot cells
[0239] The recombinant hGCD expressed by transformed carrot cells was bound to the cell inner membrane but not secreted into the medium. Mechanical disruption of the cells left rGCD associated with insoluble membrane fragments (data not shown). The rGCD is then dissolved with mild detergent to separate it from cell debris and other insoluble components. The soluble enzyme was further purified using chromatographic techniques including cation exchange chromatography and hydrophobic interaction chromatography columns as described in the experimental procedures.
[0240]To separate medium from insoluble GCD, frozen cell pellets containing approximately 100 g wet weight cells were thawed and centrifuged at 17000 xg for 20 min at 4°C. Insoluble material and intact cells were washed by resuspending in 100 ml of wash buffer (20 mM sodium phosphate pH 7.2, 20 mM EDTA) and pelleted by cen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com