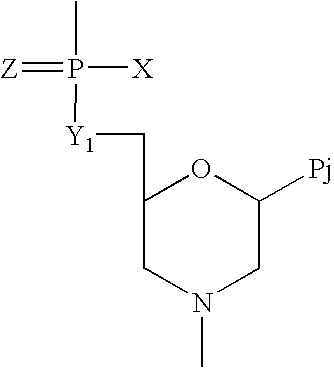
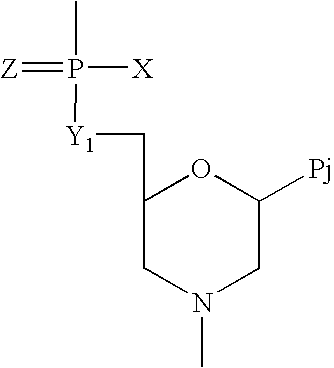
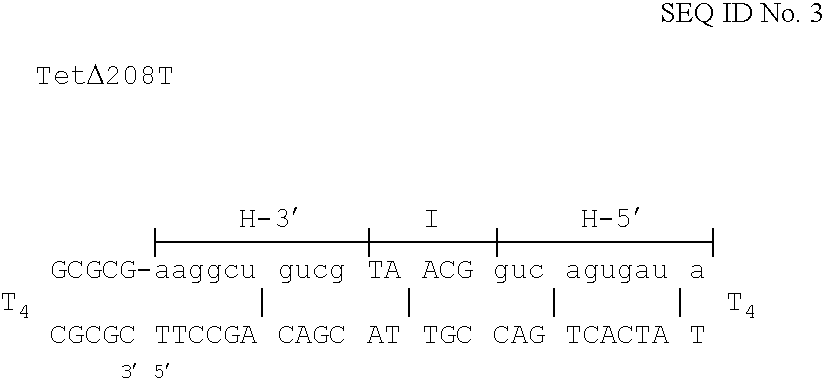Patents
Literature
96 results about "Heteroduplex" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
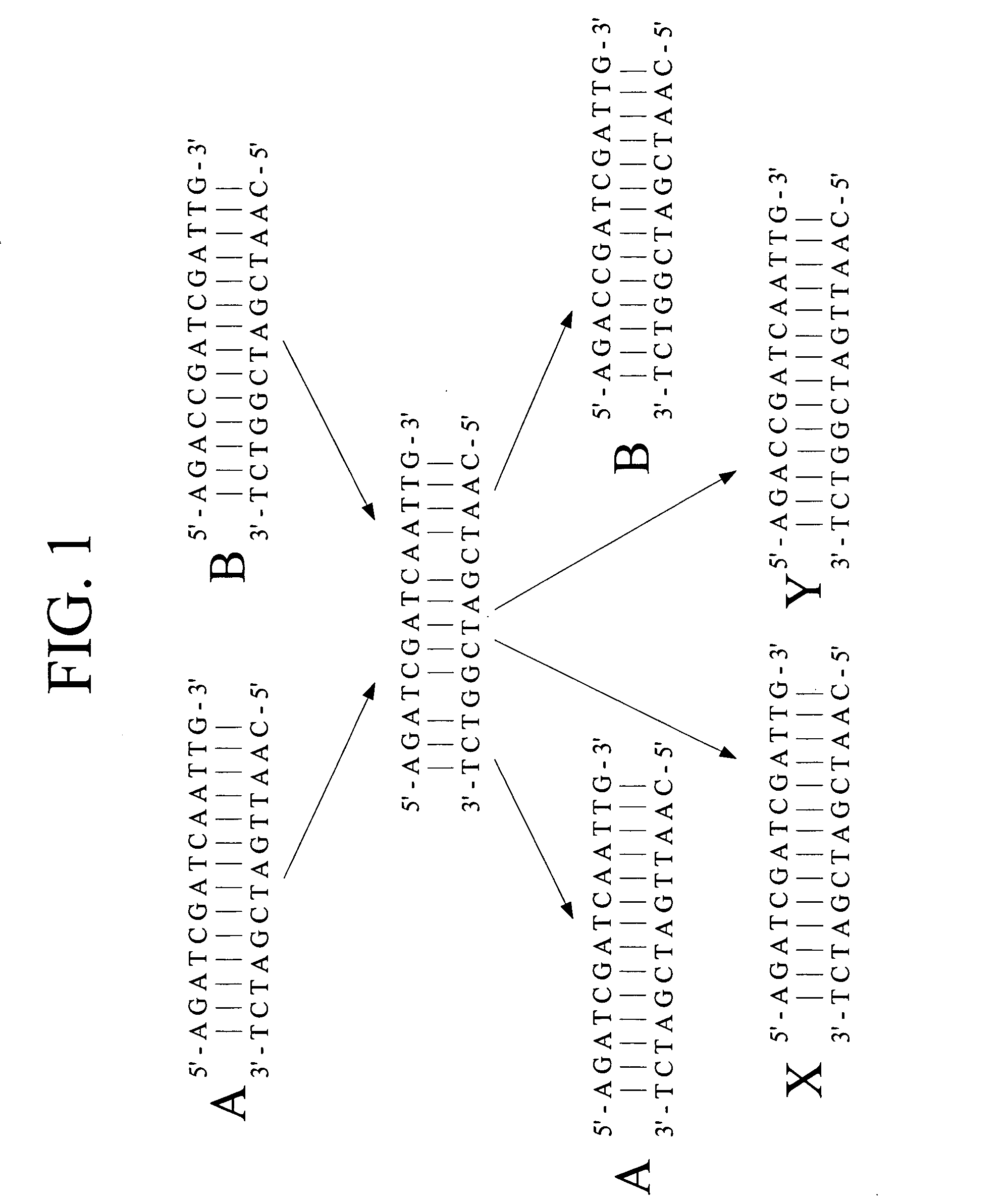
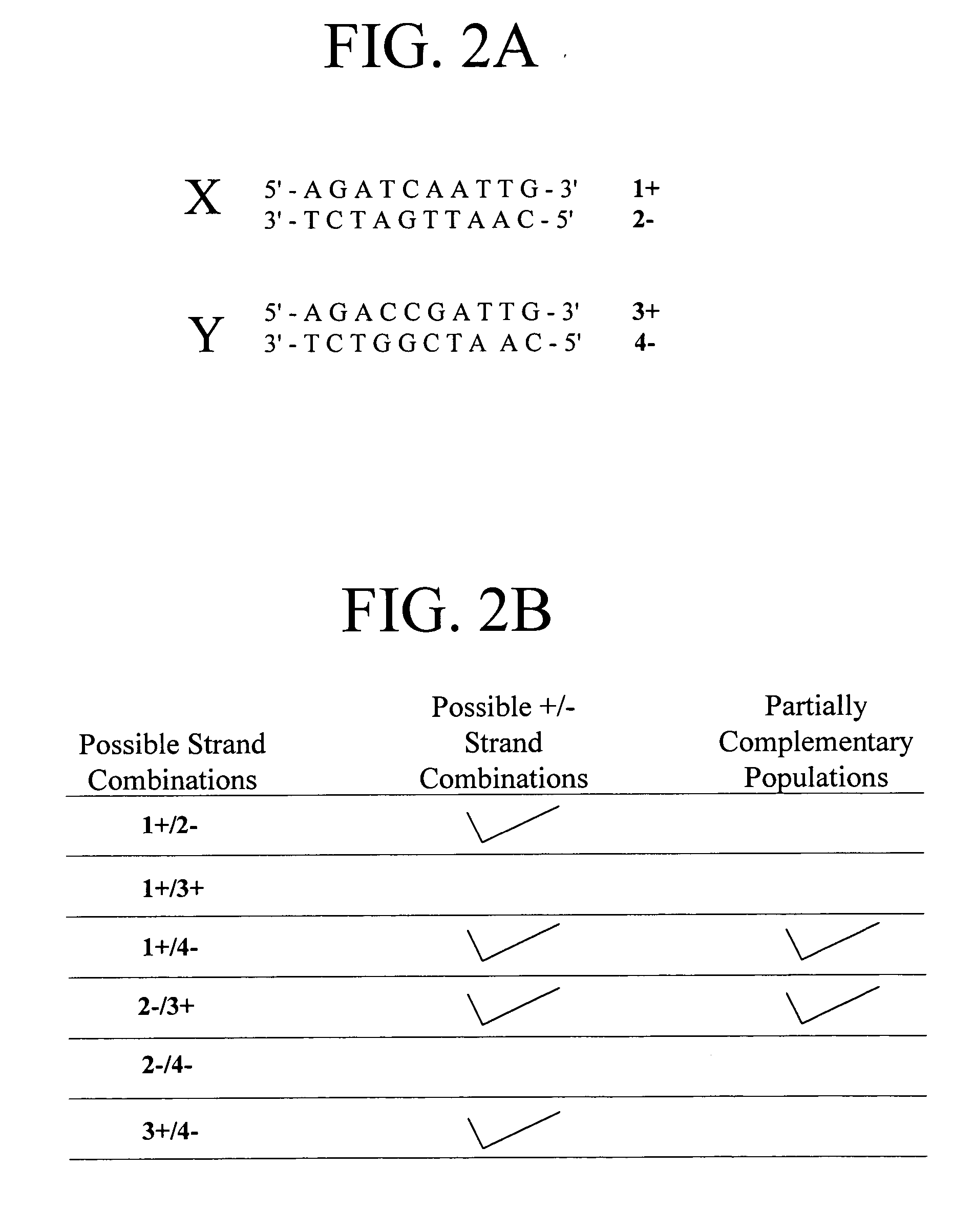
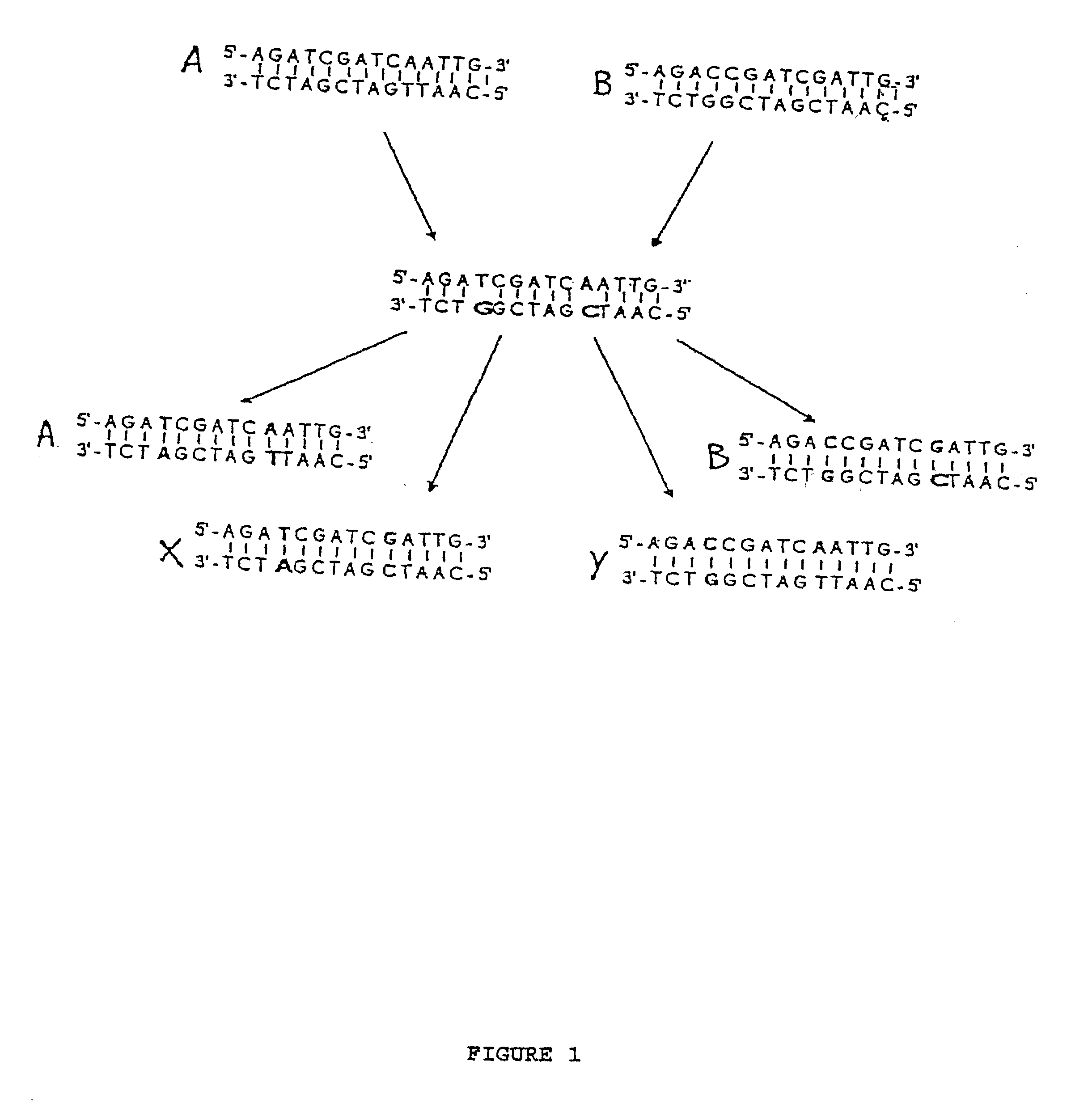
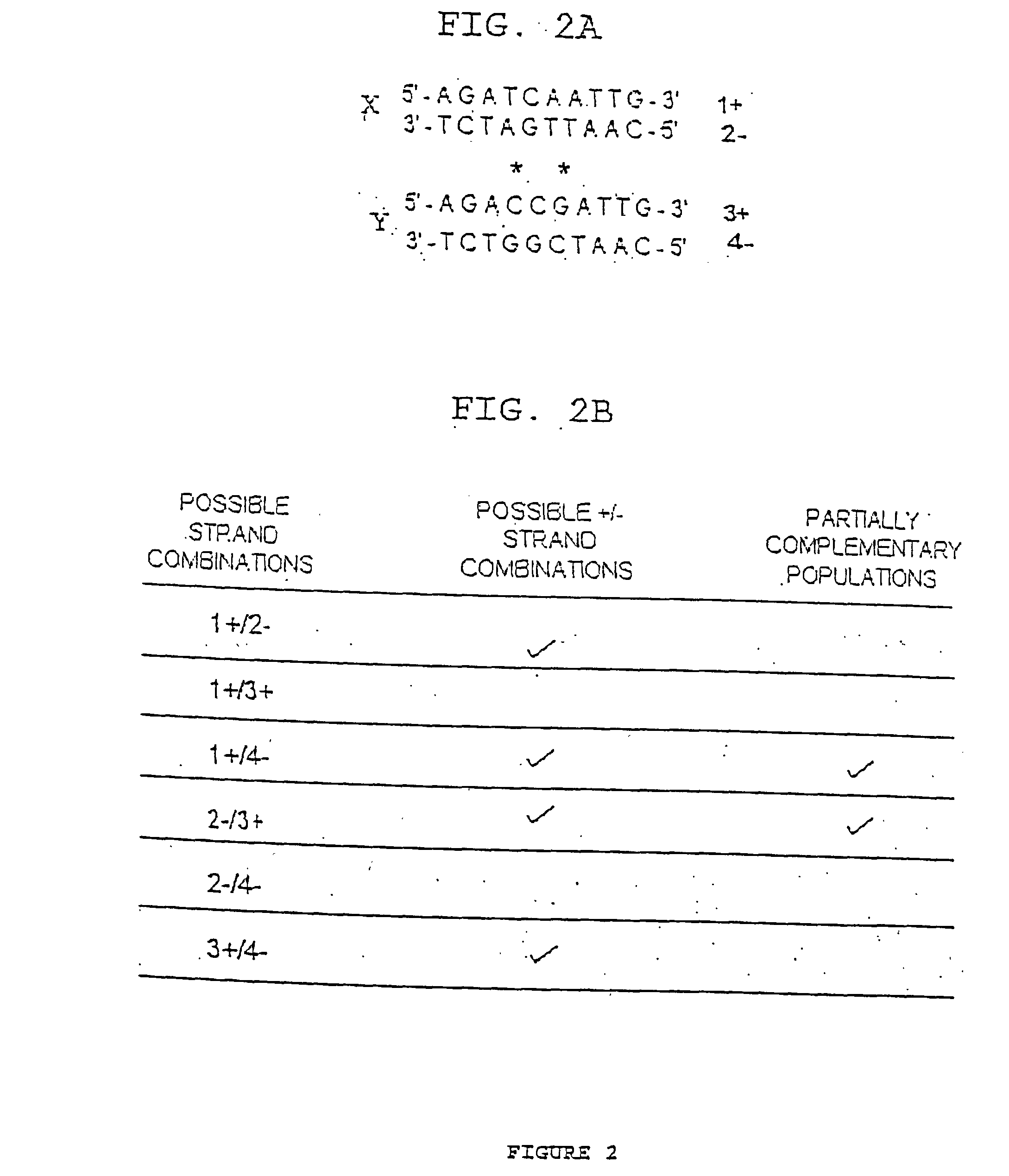
A heteroduplex is a double-stranded (duplex) molecule of nucleic acid originated through the genetic recombination of single complementary strands derived from different sources, such as from different homologous chromosomes or even from different organisms.
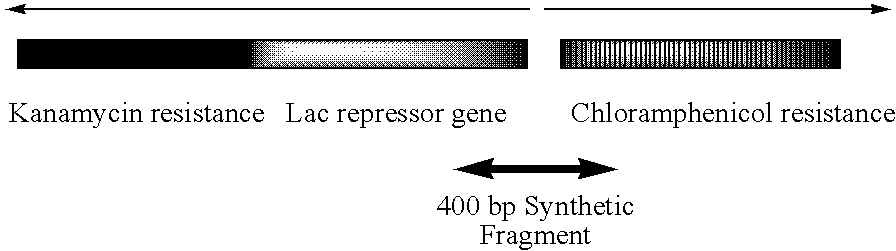
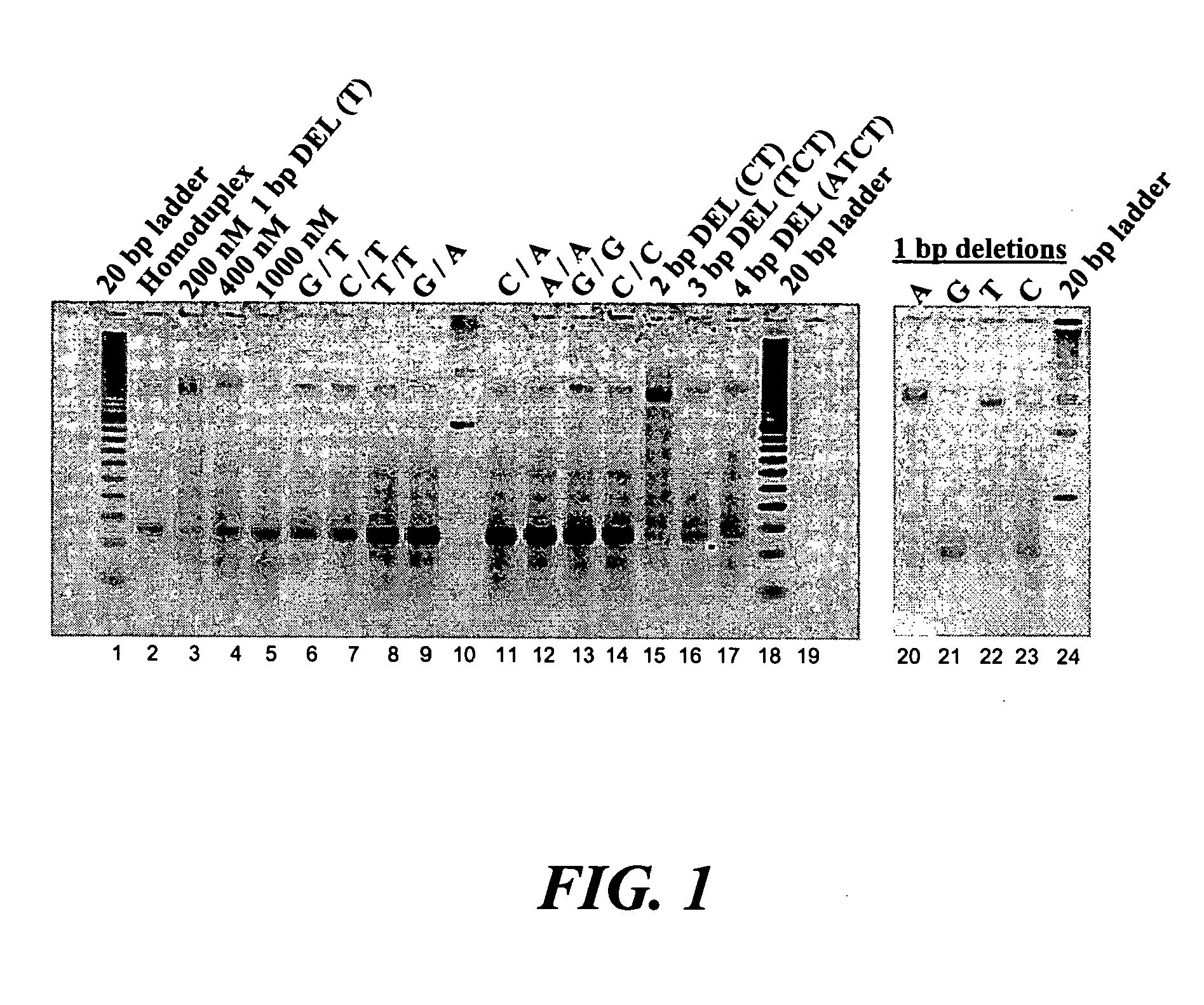
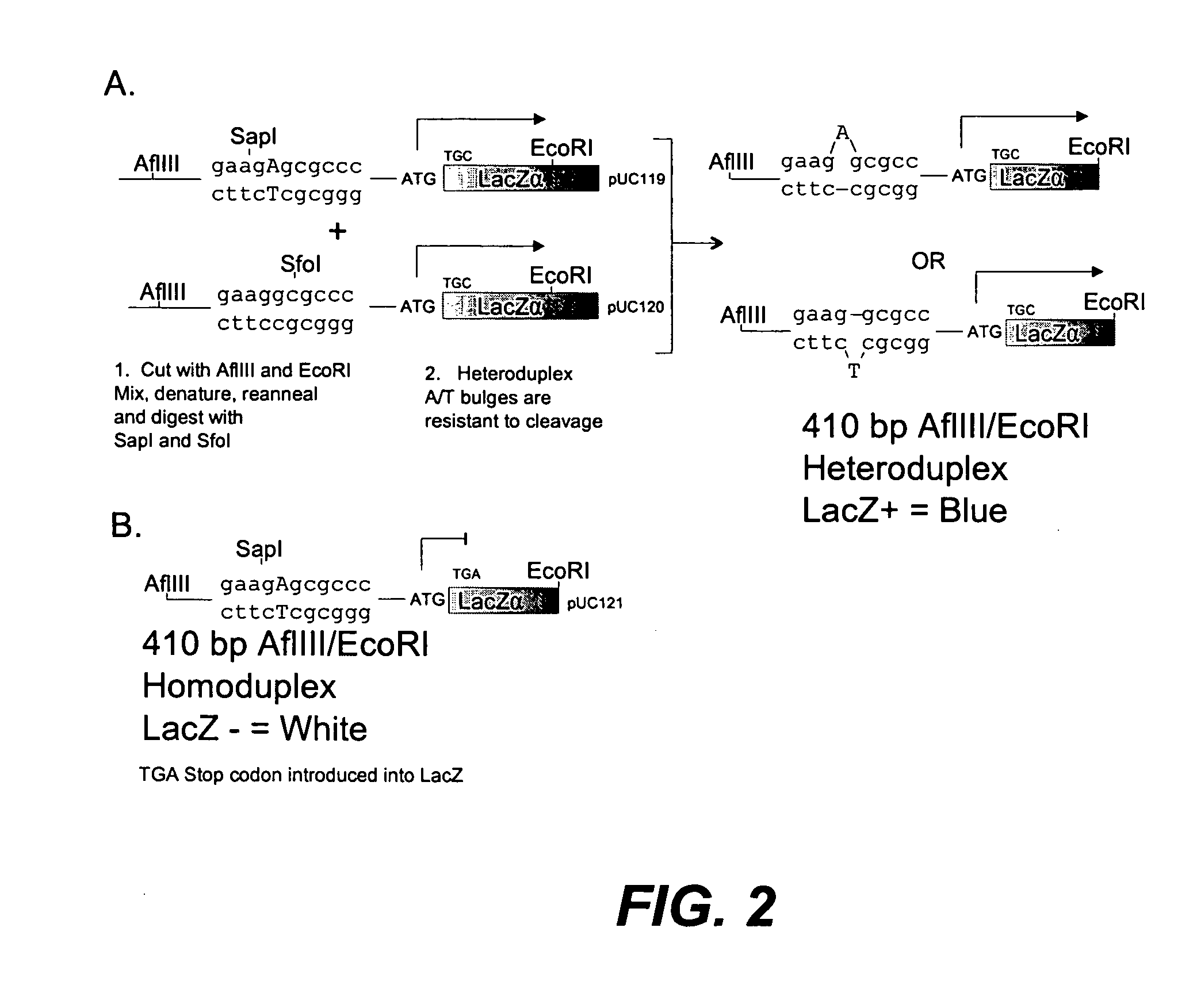
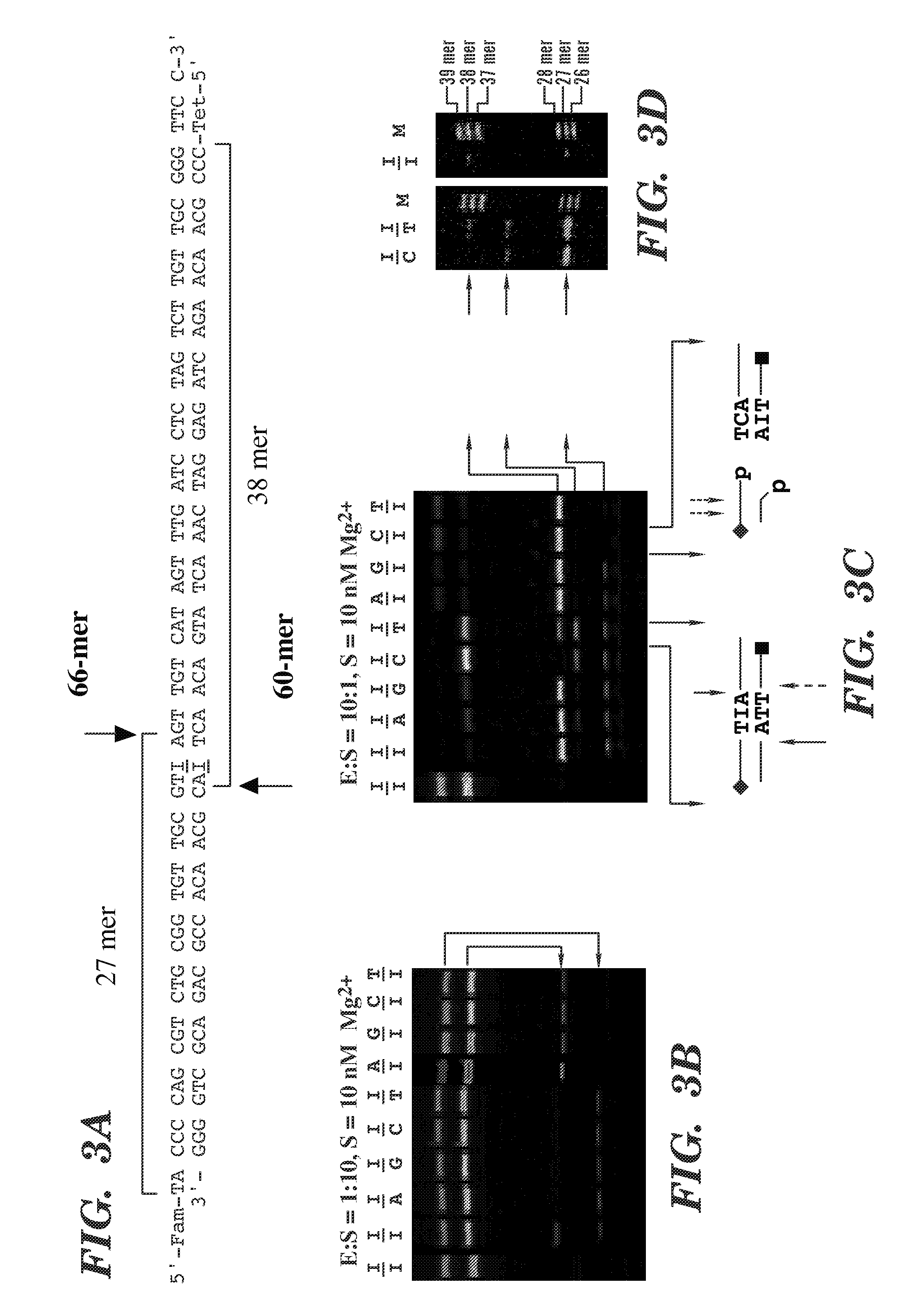
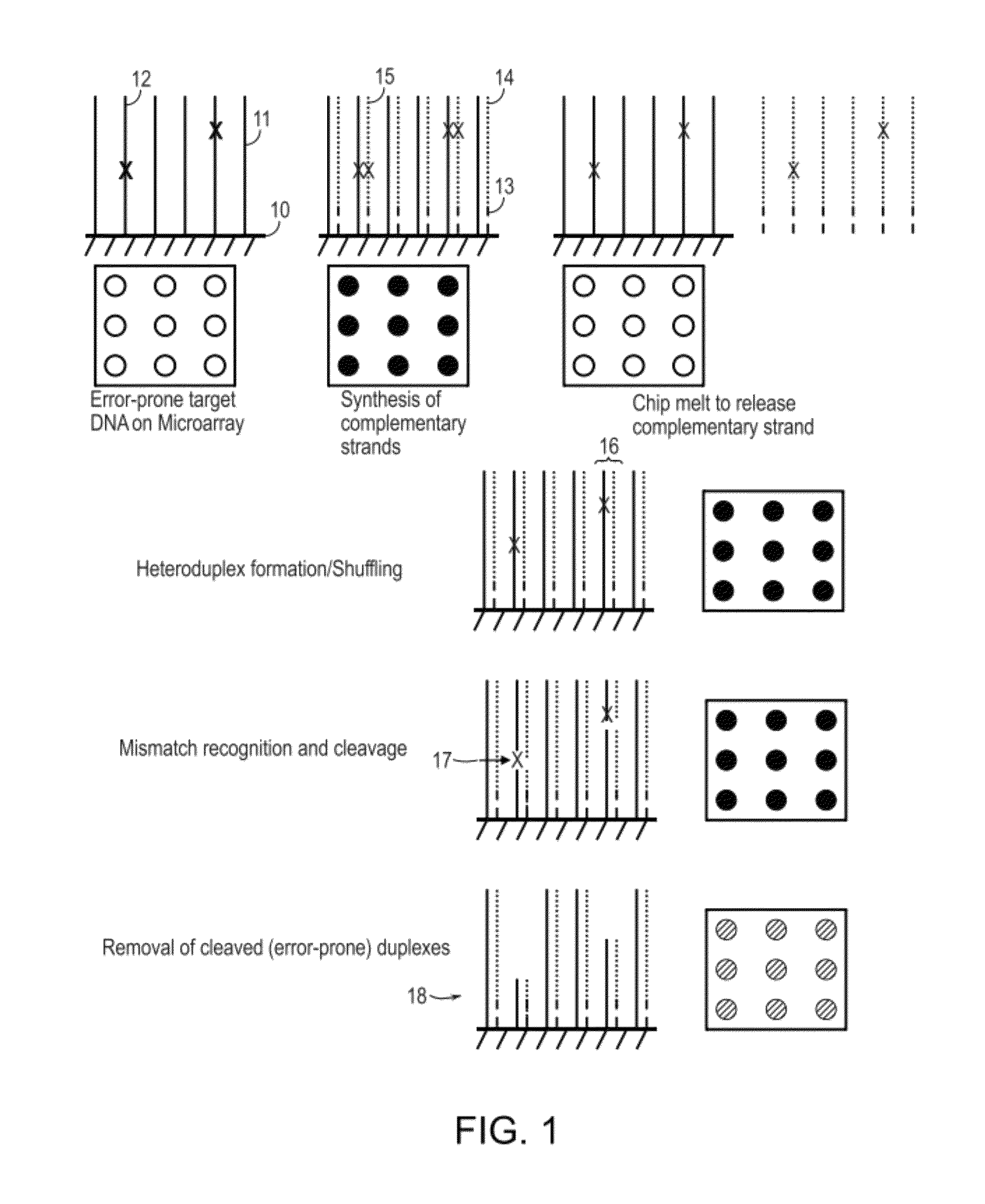
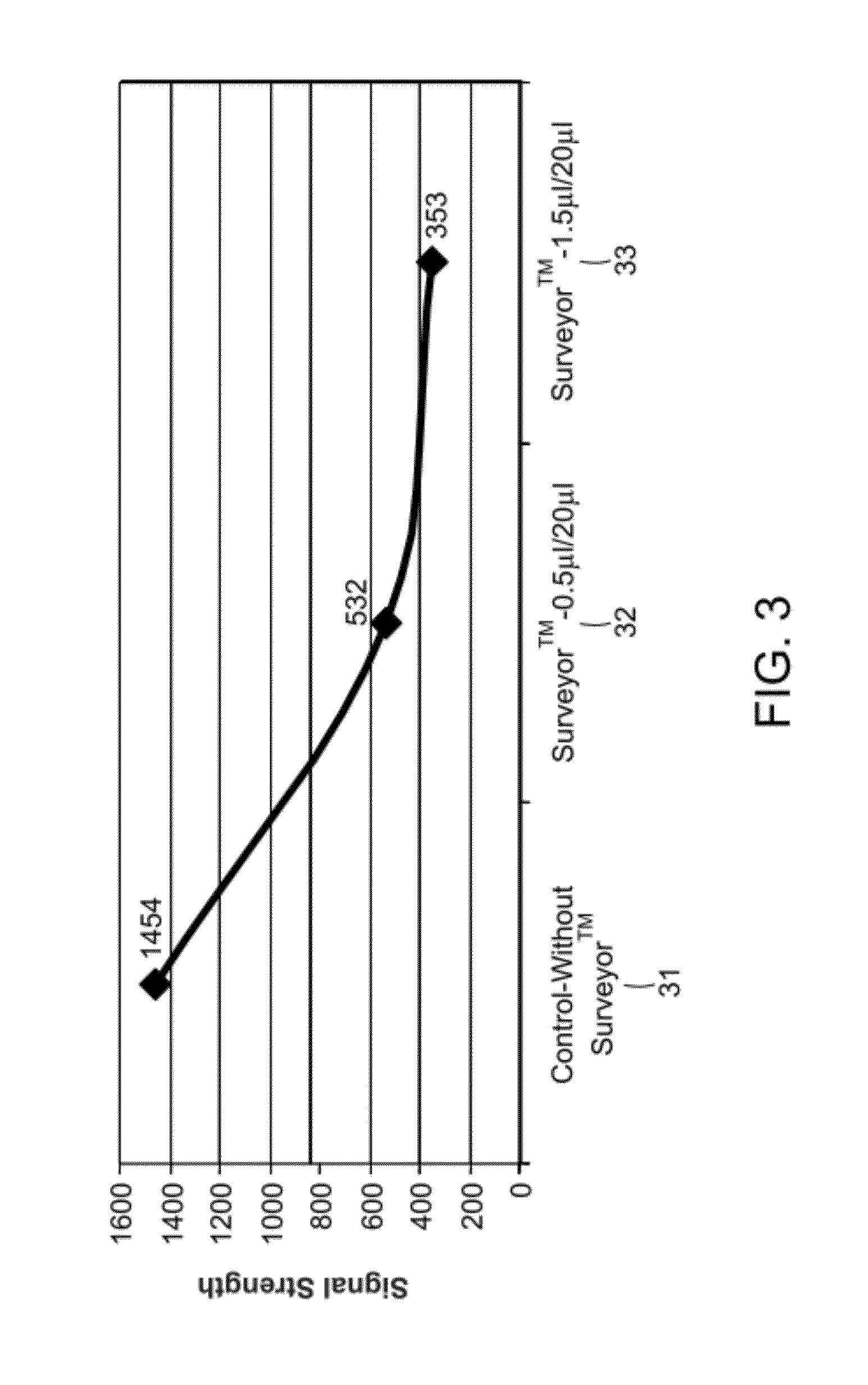
Error reduction in automated gene synthesis
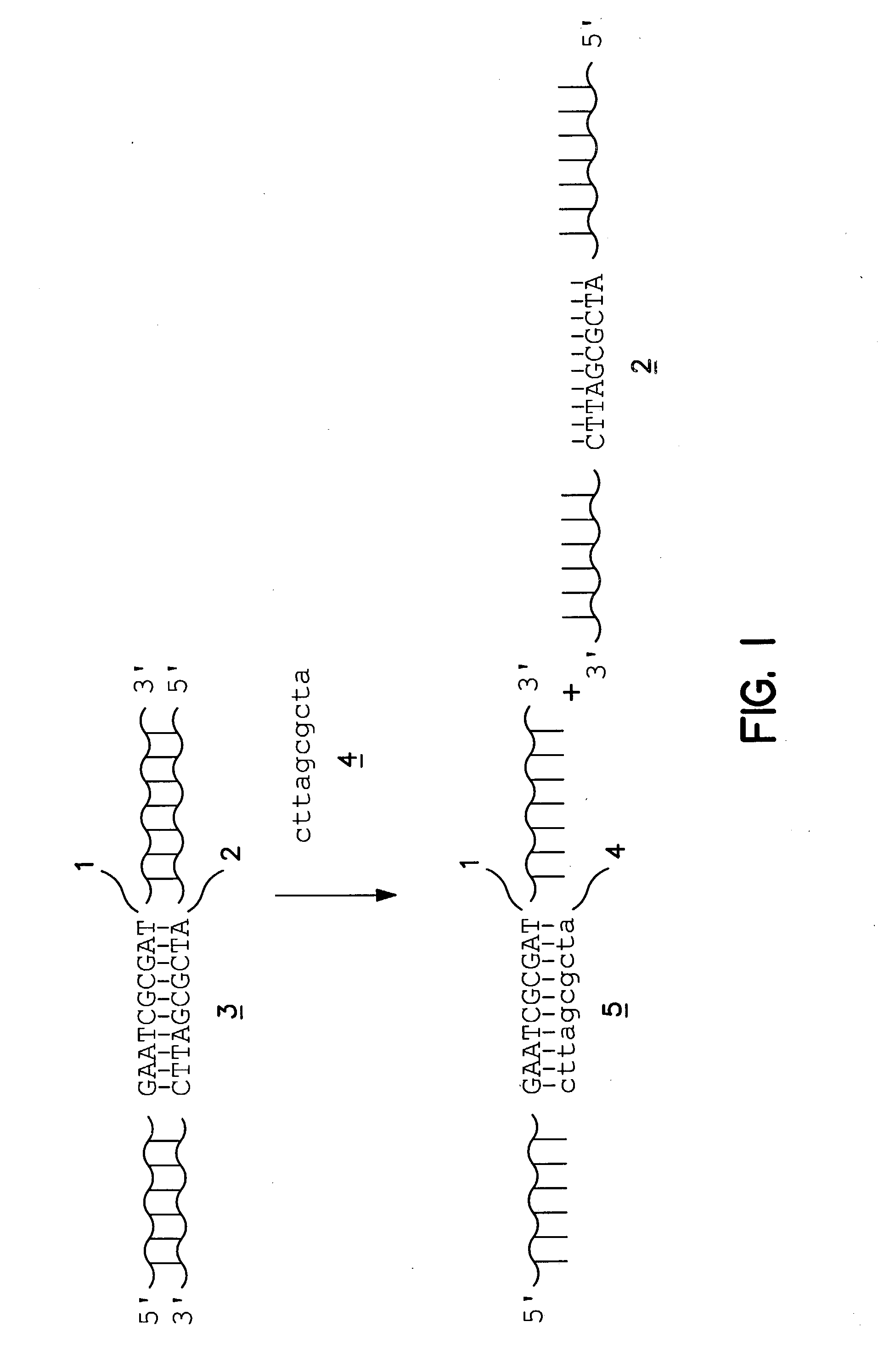
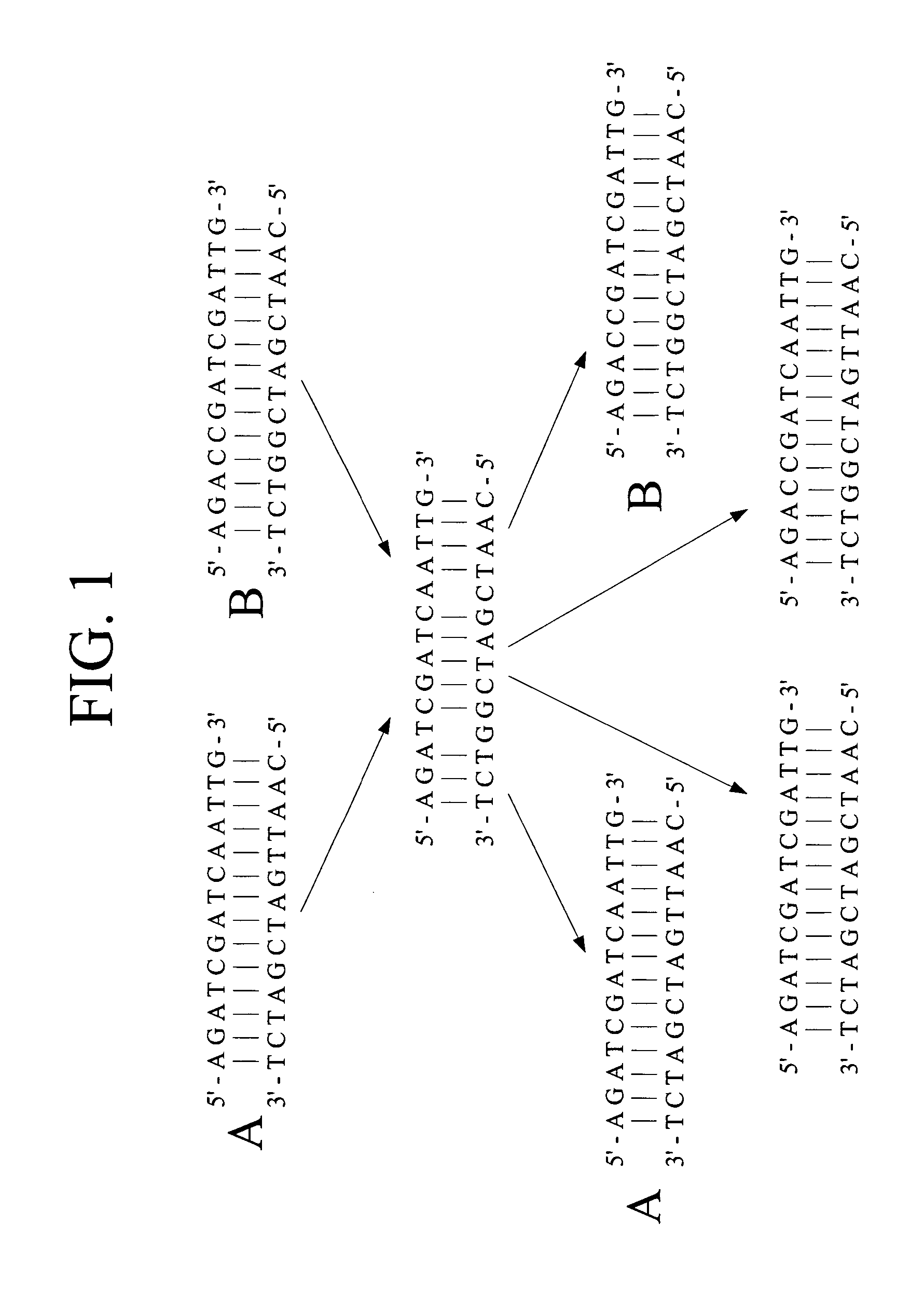
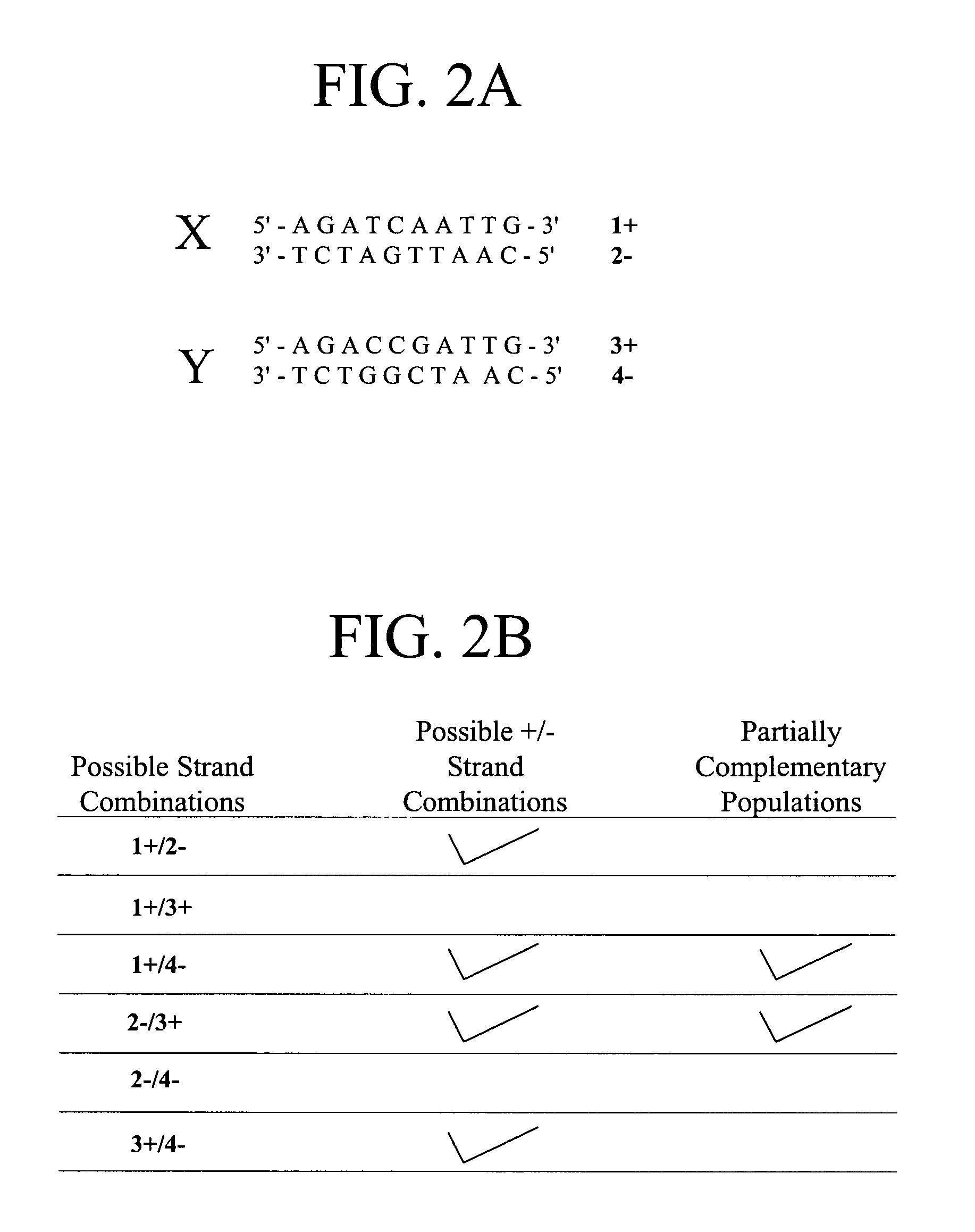
In embodiments of the present invention, methods are provided for removing double-stranded oligonucleotide (e.g., DNA) molecules containing one or more sequence errors, generated during nucleic acid synthesis, from a population of correct oligonucleotide duplexes. In one embodiment, the oligonucleotides are generated enzymatically. Heteroduplex (containing mismatched bases) oligonucleotides may be created by denaturing and reannealing the population of duplexes. The reannealed oligonucleotide duplexes are contacted with a mismatch recognition protein that interacts with (e.g., binds and / or cleaves) the duplexes containing a base pair mismatch. The oligonucleotide heteroduplexes that have interacted with such a protein are separated, simultaneously with contacting or sequentially in a separate step, from homoduplexes. These methods are also used in another embodiment to remove heteroduplex oligonucleotides (e.g., DNA) that are formed directly from chemical nucleic acid synthesis. In other embodiments of the present invention, kits and compositions useful for the methods are provided.
Owner:BLUE HERON BIOTECH
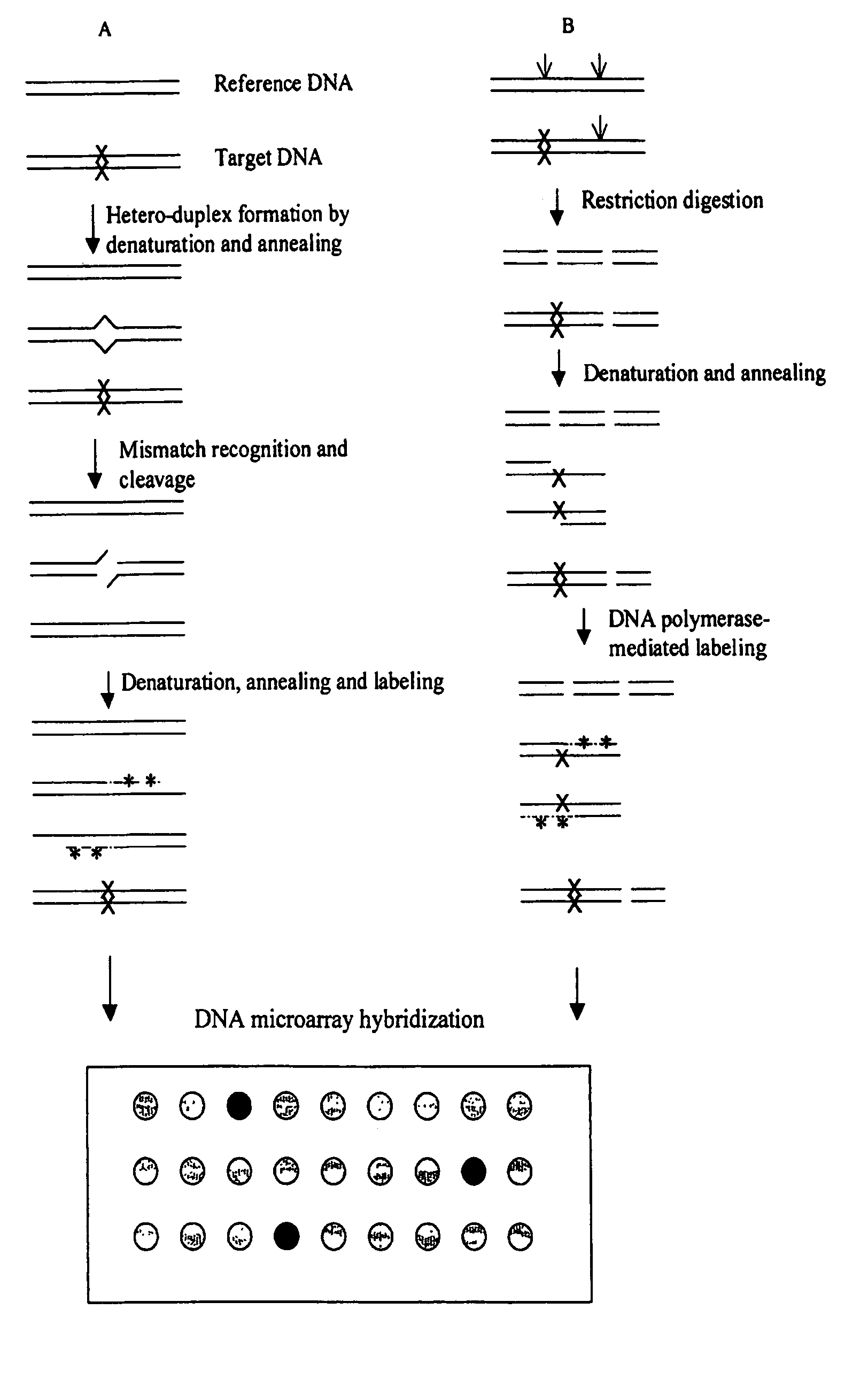
Methods for detecting and localizing DNA mutations by microarray
InactiveUS7378245B2Reduce impactMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNA microarrayHeteroduplex
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OREGON
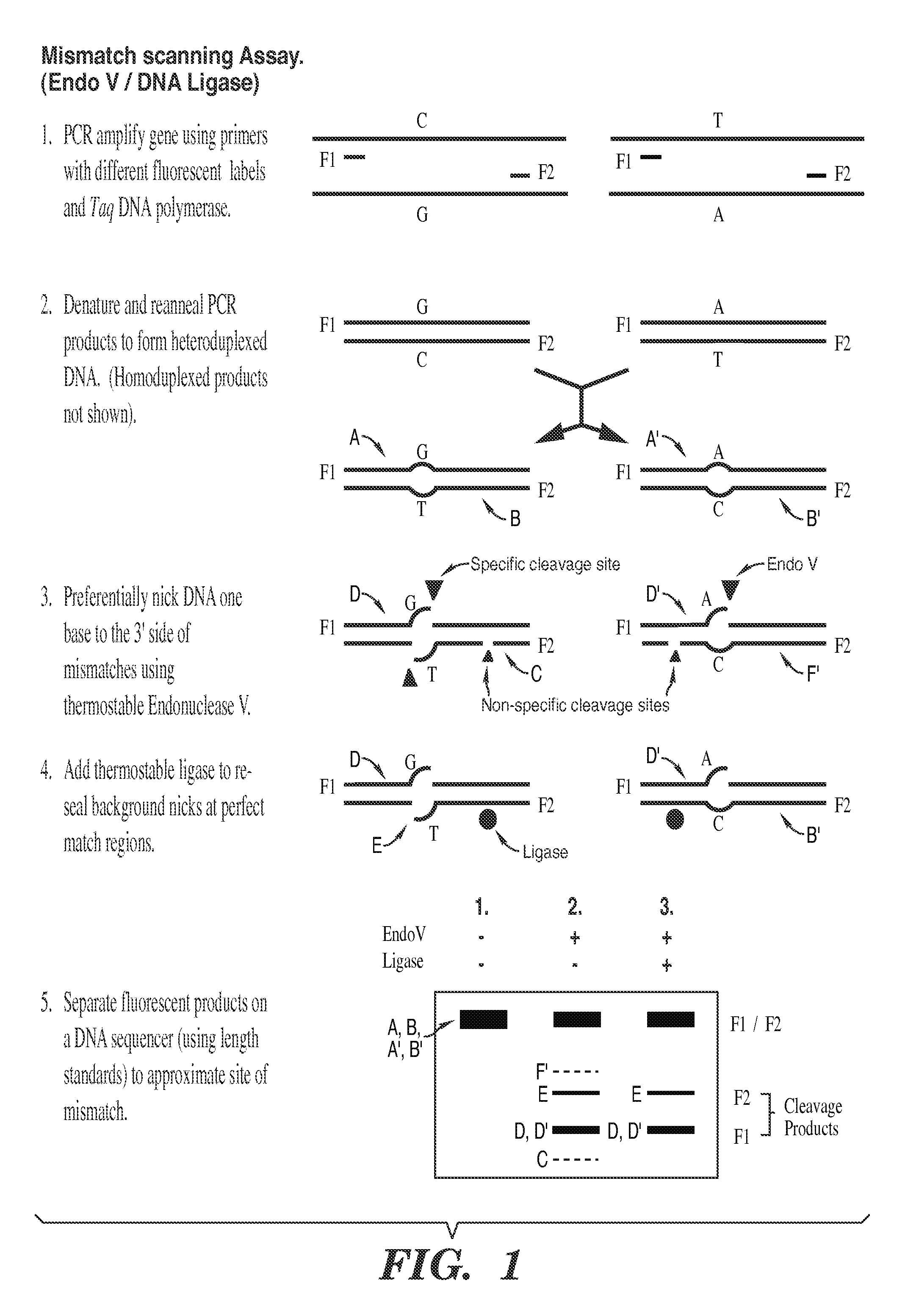
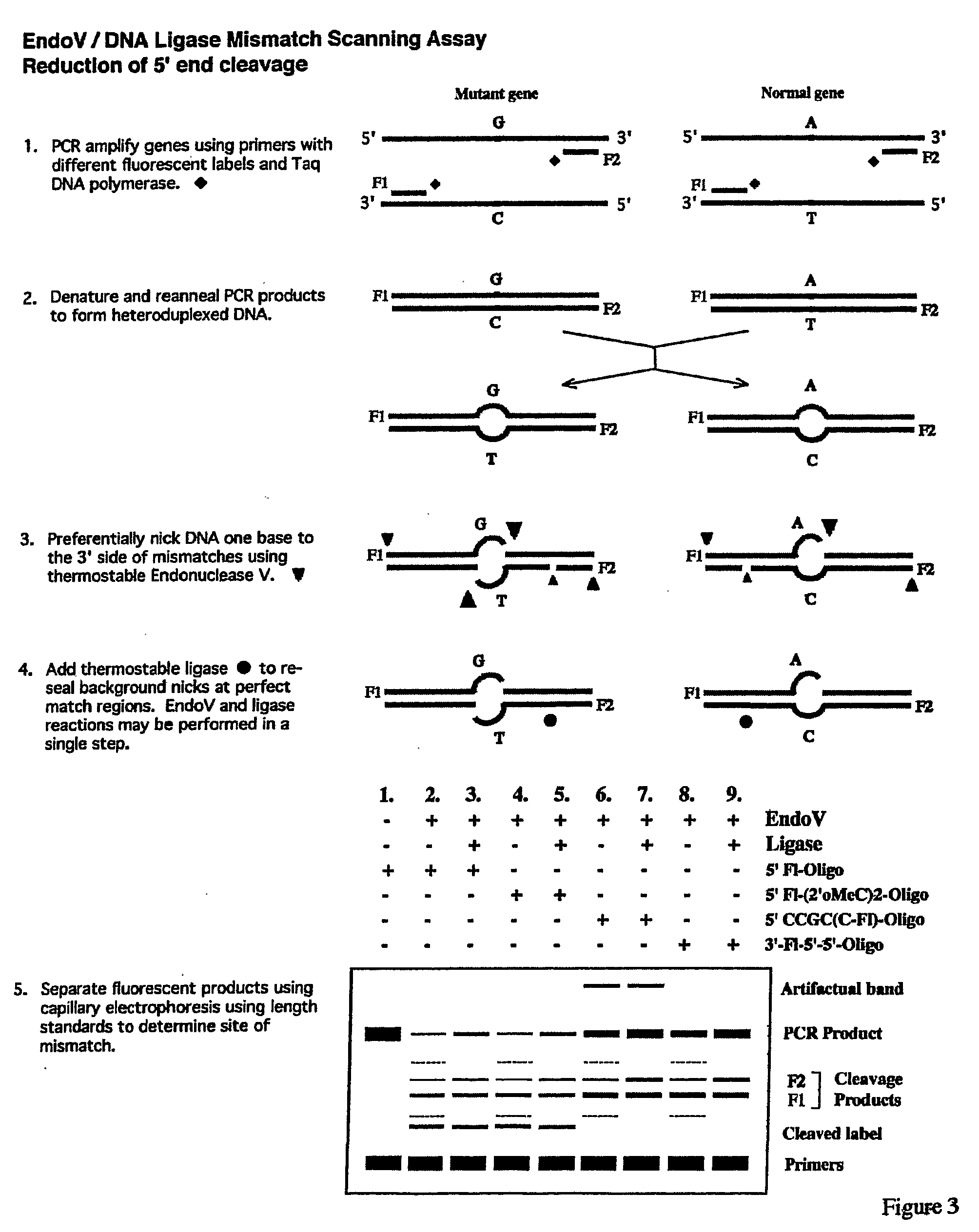
Detection of nucleic acid differences using combined endonuclease cleavage and ligation reactions
InactiveUS7807431B2Wide applicabilityImprove throughputSugar derivativesHydrolasesHeteroduplexSingle nucleotide mutation
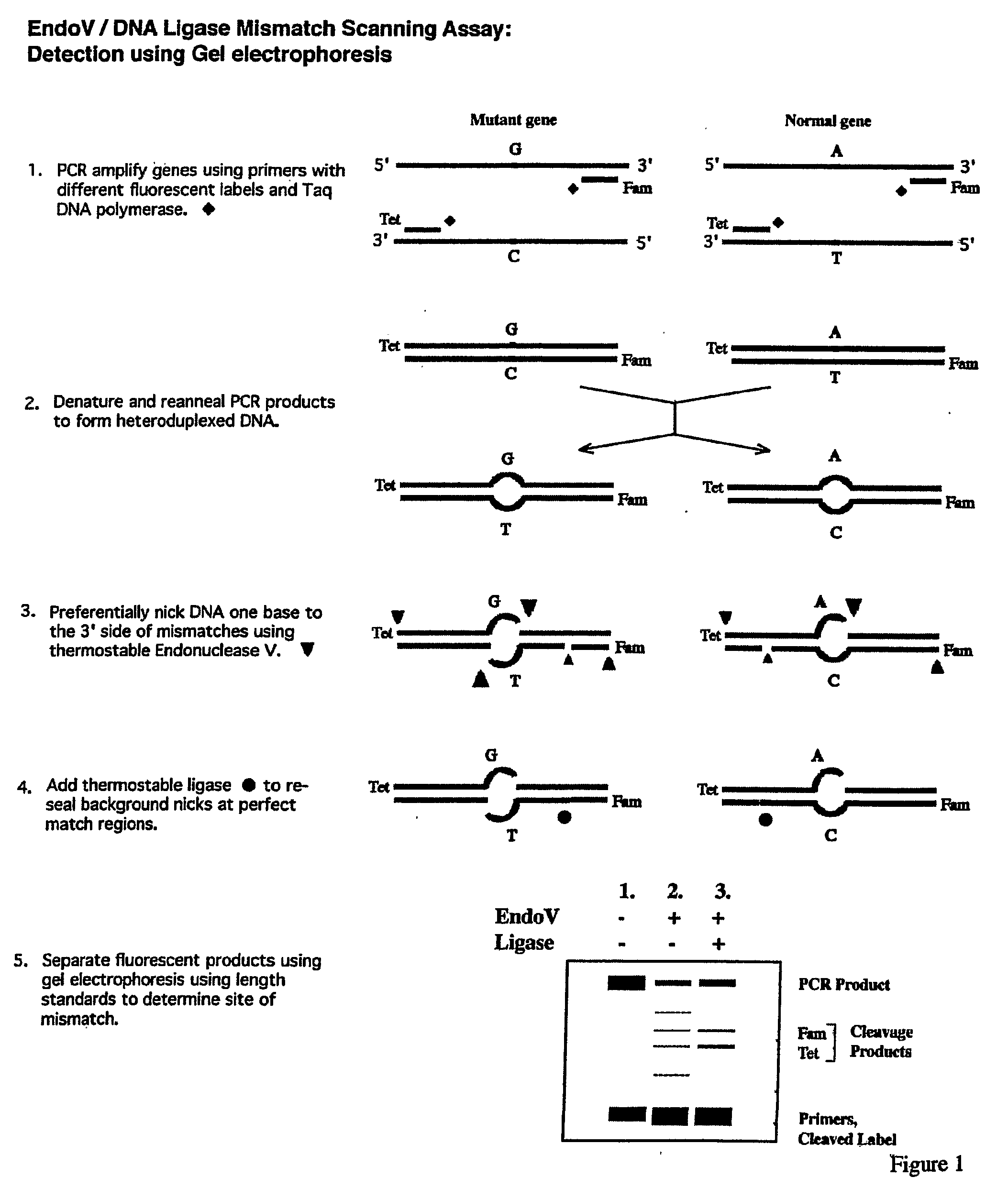
The present invention is a method for detecting DNA sequence differences including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods and apparatuses for chip-based DNA error reduction
ActiveUS9422600B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeterologousHeteroduplex
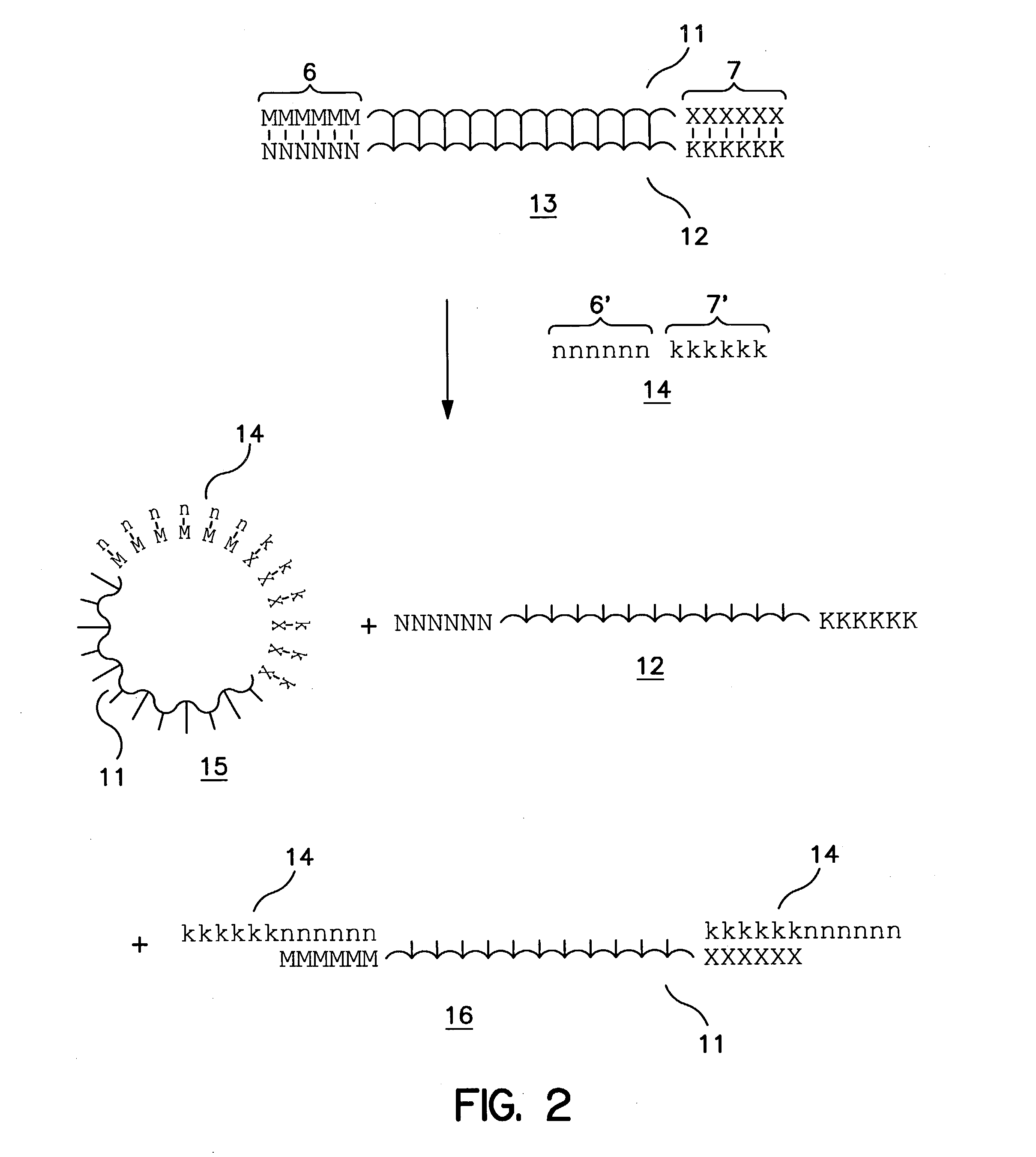
Methods and apparatus relate to reduction of sequence errors generated during synthesis of nucleic acids on a microarray chip. The error reduction can include synthesis of complementary stands (to template strands), using a short universal primer complementary to the template strands and polymerase. Heteroduplex can be formed be melting and re-annealing complementary stands and template strands. The heteroduplexes containing a mismatch can be recognized and cleaved by a mismatch endonuclease. The mismatch-containing cleaved heteroduplexes can be removed from the microarray chip using a global buffer exchange. The error free synthetic nucleic acids generated therefrom can be used for a variety of applications, including synthesis of biofuels and value-added pharmaceutical products.
Owner:GEN9
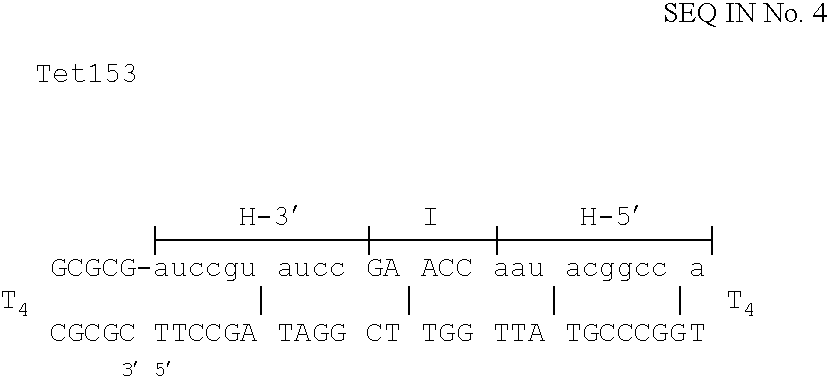
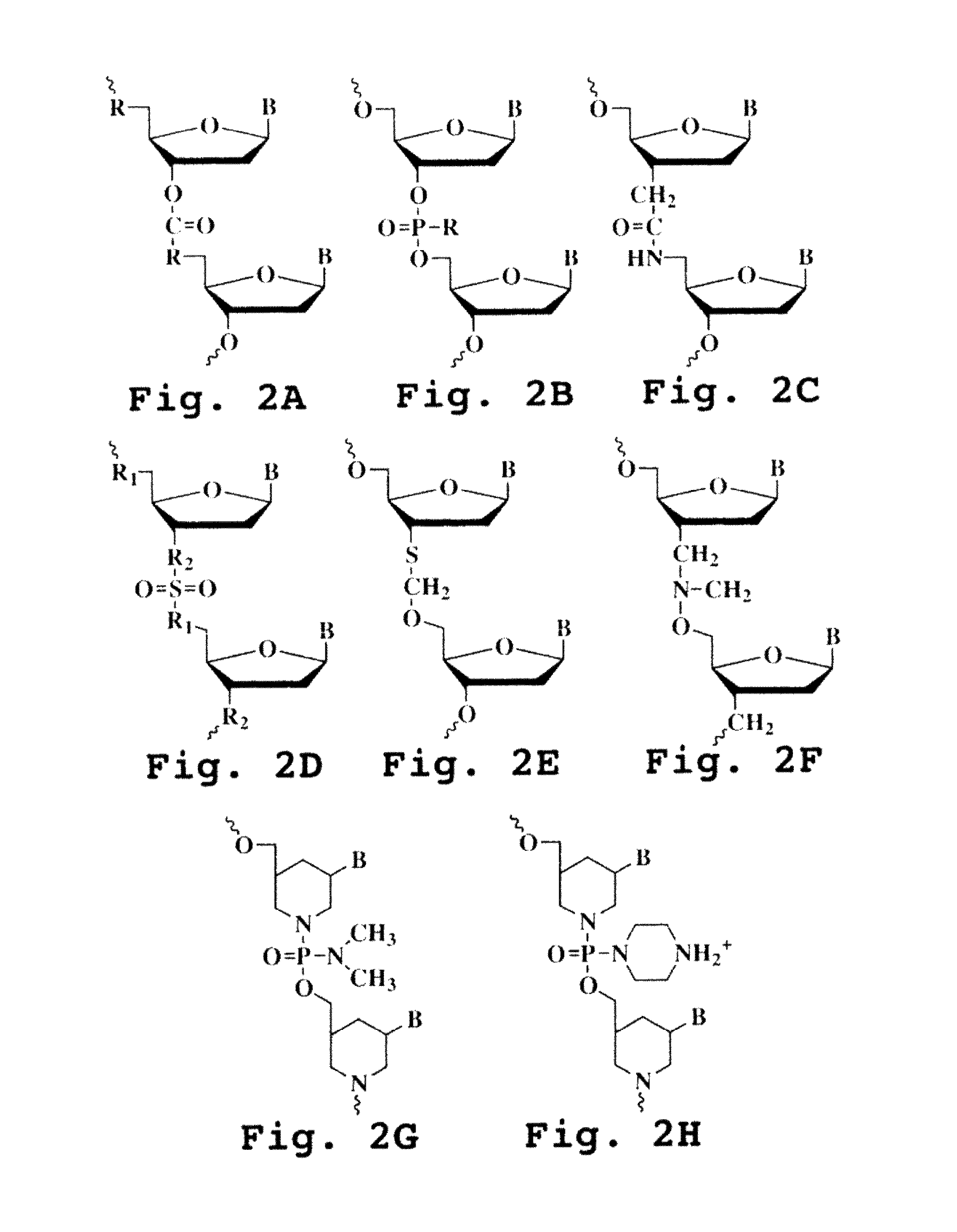
Eukaryotic use of improved chimeric mutational vectors
The invention is based on the reaction of recombinagenic oligonucleotides in a cell-free system containing a cytoplasmic cell extract and a test duplex DNA on a plasmid. The reaction specifically converts a mutant kanr gene to recover the resistant phenotype in transformed MutS, RecA deficient bacteria and allows for the rapid and quantitative comparison of recombinagenic oligonucleobases. Using this system a type of Duplex Mutational Vector termed a Heteroduplex Mutational Vector, was shown to be more active in than the types of mutational vectors heretofore tested. Further improvements in activity were obtained by replacement of a tetrathymidine linker by a nuclease resistant oligonucleotide, such as tetra-2'-O-methyl-uridine, to link the two strands of the Duplex Mutational Vector and removal of the DNA-containing intervening segment. The claims concern Duplex Mutational Vectors that contain the above improvements. In an alternative embodiment the claims concern a reaction mixture containing a recombinagenic oligonucleobase, a cell-free enzyme mixture and a duplex DNA containing a target sequence. In yet an alternative embodiment, the invention concerns the use of such mixture to test improvements in recombinagenic oligonucleobases, as well as to test the effects of compounds on the activity of the cell-free enzyme mixture and also to make specific changes in the target DNA sequence.
Owner:CIBUS
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
ActiveUS20090110689A1Suppress immune responseSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderHeteroduplexAutoimmune condition
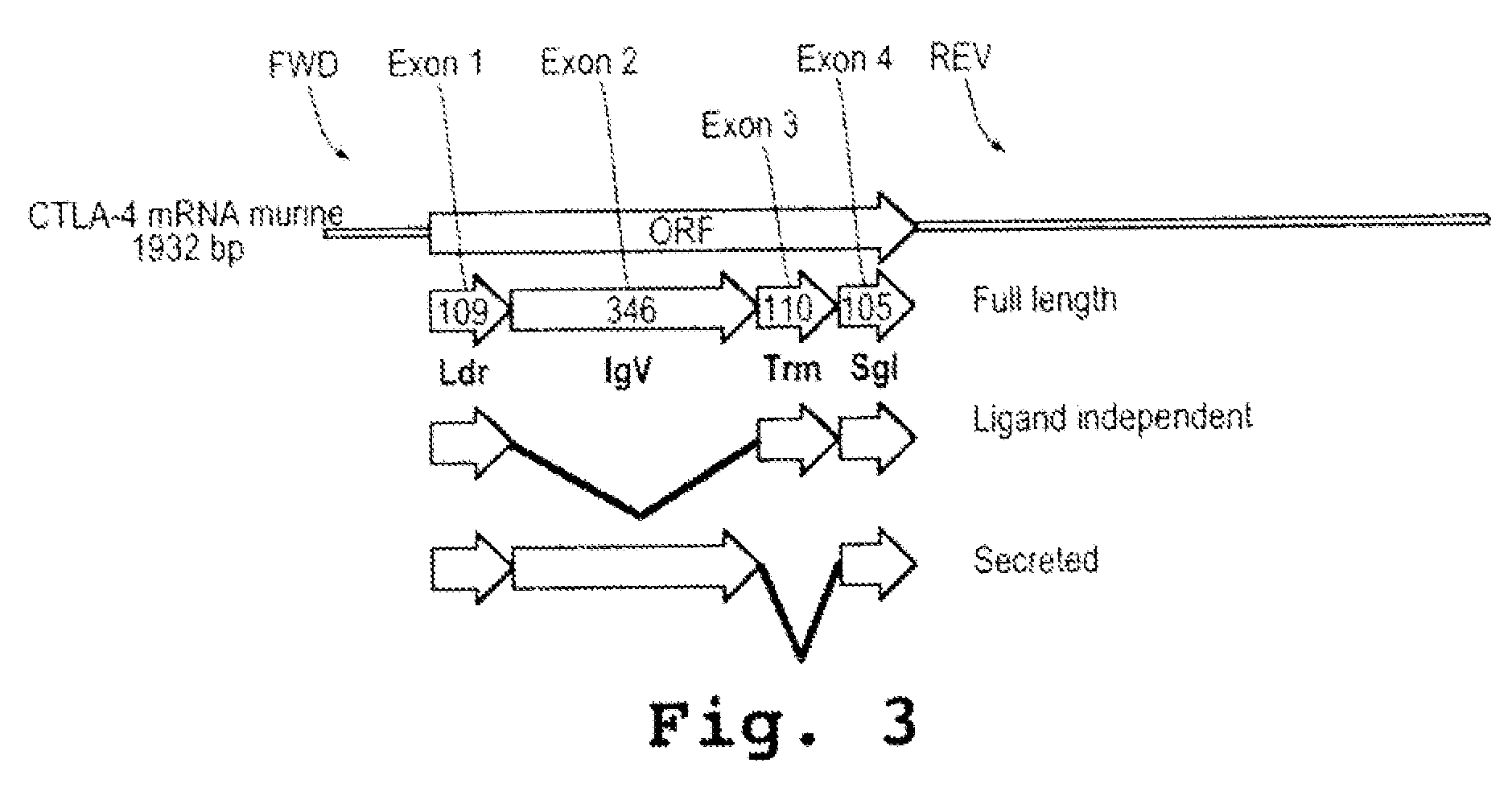
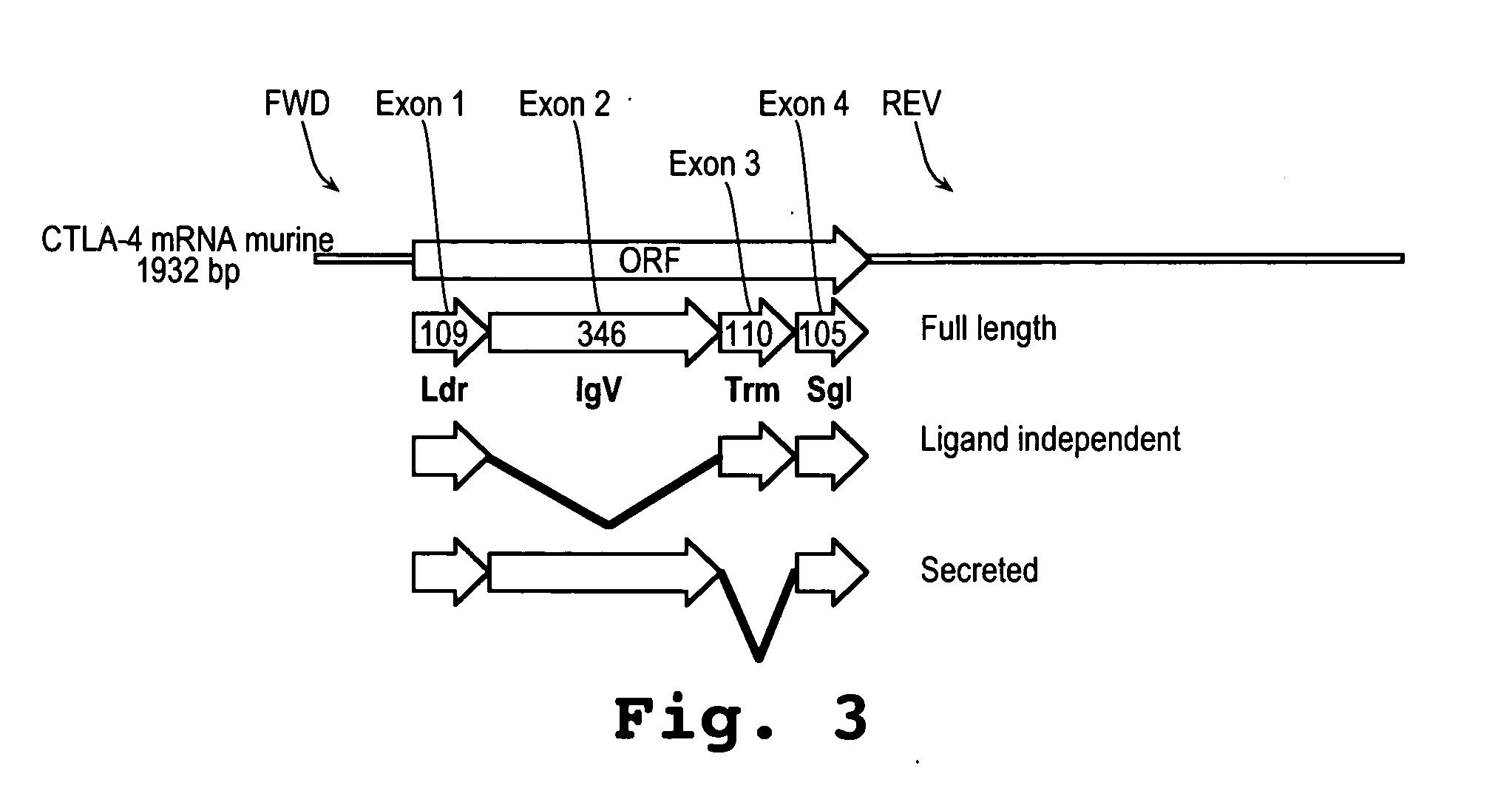
A method and compound for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection are disclosed. The compound is an antisense oligonucleotide analog compound having a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region identified by SEQ ID NO: 22 in SEQ ID NO: 1, spanning the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed mRNA of the subject. The compound is effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
Provided are methods and antisense oligonucleotide analogs for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection. The oligonucleotide analogs provided herein comprise a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region that spans the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA. Also provided are methods of use, in which the oligonucleotides are effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method of synthesizing cdna
ActiveUS20060246453A1High yieldIncrease chanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexReverse transcriptase
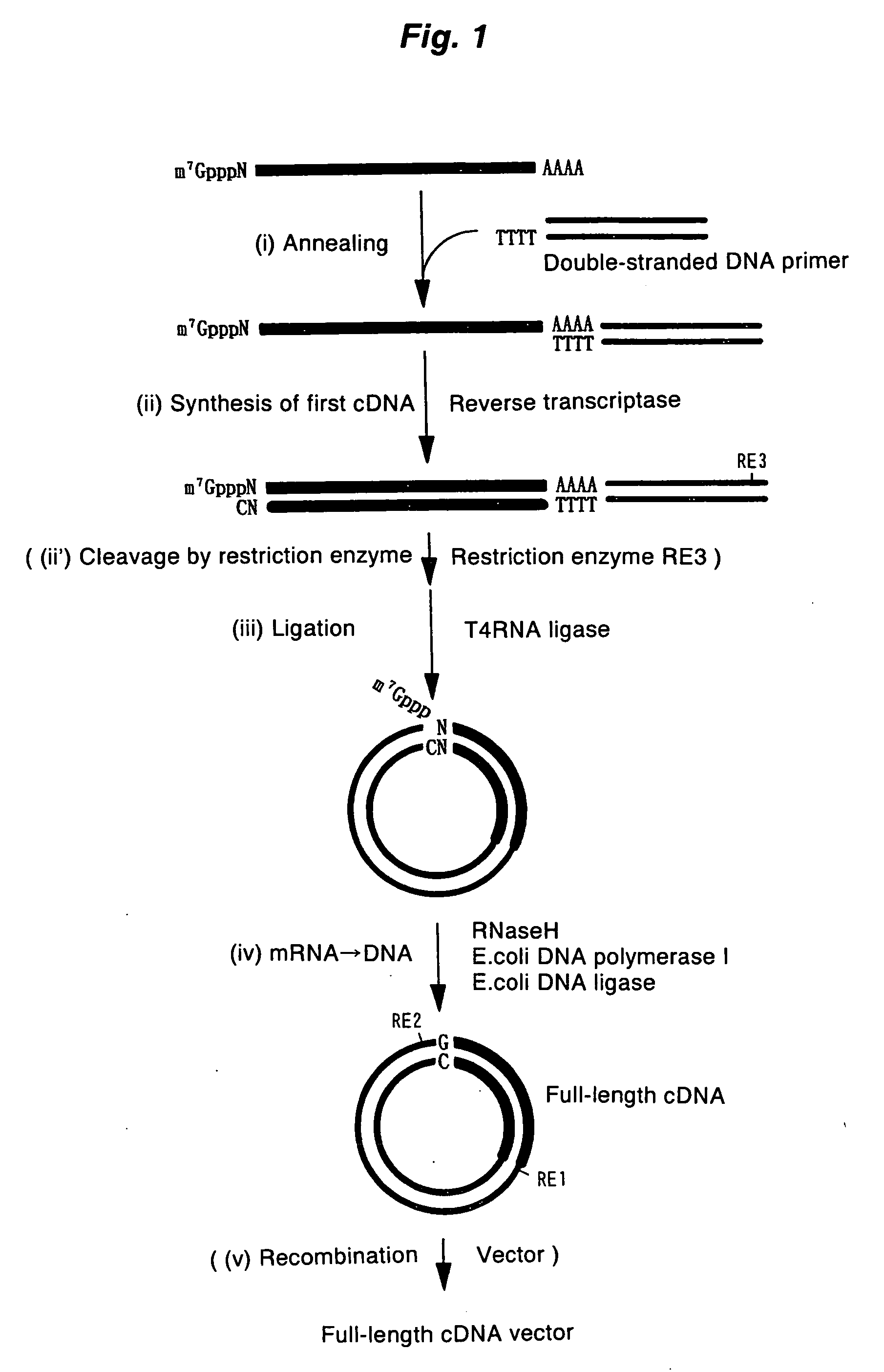
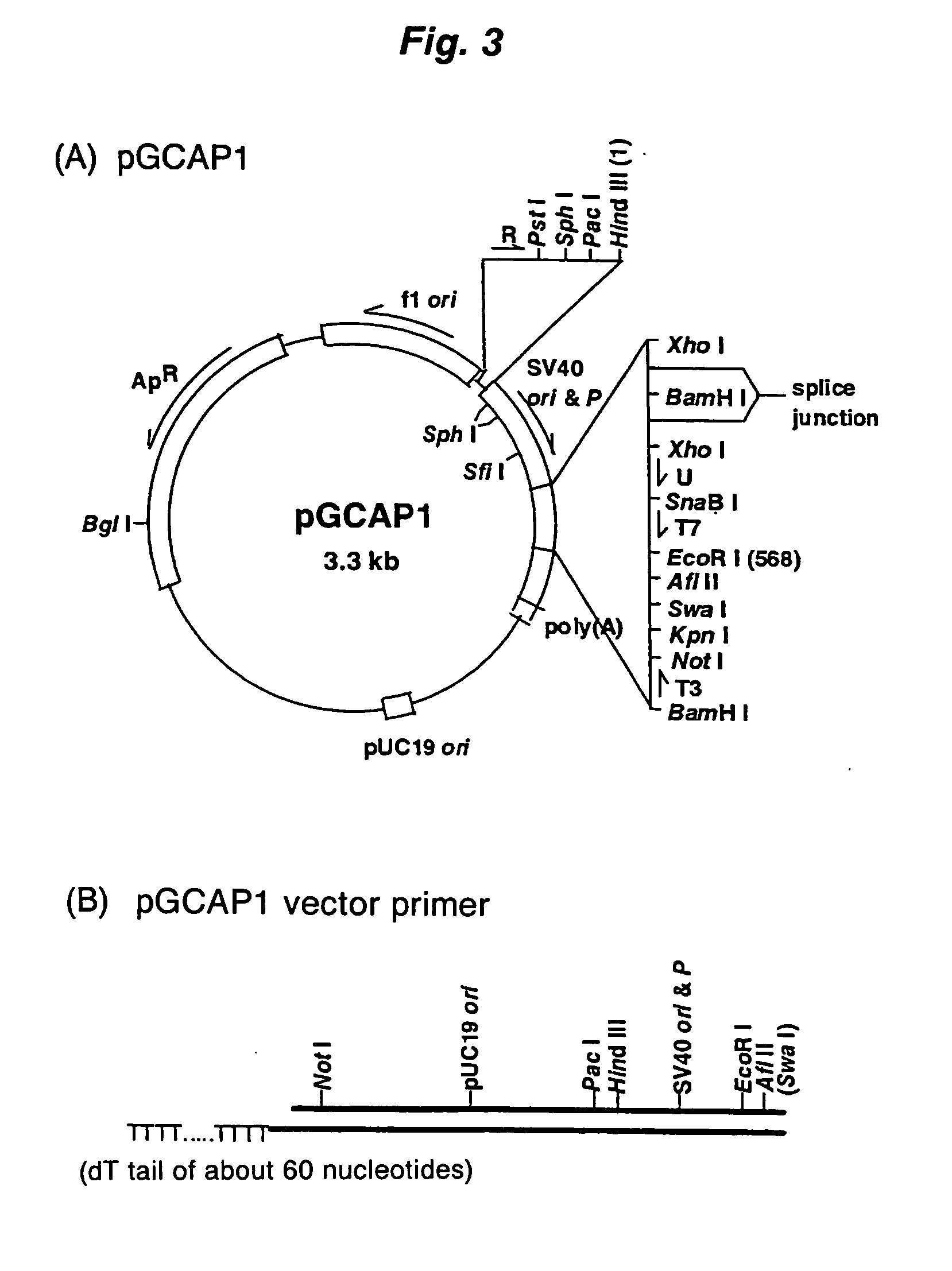
A method for synthesizing cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a nucleotide adjacent to a cap structure of mRNA, which comprises (i) a process for annealing a double-stranded DNA primer and an RNA mixture containing mRNA possessing a cap structure, (ii) a process for preparing a conjugate of an mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and a double-stranded DNA primer by synthesizing the first-strand cDNA primed with the double-stranded DNA primer using reverse transcriptase, and (iii) a process for circularizing the conjugate of the mRNA / cDNA heteroduplex and the double-stranded DNA primer by joining the 3' and 5' ends of the DNA strand containing cDNA using ligase. This method enables us to efficiently synthesize a full-length cDNA possessing a consecutive sequence starting with a transcription-start-site nucleotide from a small amount of RNA by small processes.
Owner:KOKURITSU SHINTAI SHIYOUGAISHI +2
Oligonucleotide analog and method for treating flavivirus infections
InactiveUS20050096291A1Inhibition of replicationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousHeteroduplex
A method of inhibiting replication of a flavivirus in animal cells, and an oligonucleotide compound for use in the method are disclosed. The oligonucleotide analog (i) has a nuclease-resistant backbone, (ii) is capable of uptake by the cells, (iii) contains between 8-40 nucleotide bases, and (iv) has a sequence of at least 8 bases complementary to a region of the virus' positive strand RNA genome that includes at least a portion of SEQ ID NOS:1-4. Exposure of cells infected with a flavivirus to the analog is effective to form within the cells, a heteroduplex structure composed of the virus ssRNA and the oligonucleotide, characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45 ° C., and having disrupted base pairing between the virus' 5′ and 3′ cyclization sequences.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for isolating one strand of a double-stranded nucleic acid
InactiveUS20030148277A1Fast dynamicsIncrease temperatureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousHeteroduplex
The present invention provides methods and kits for isolating one strand of a double-stranded target nucleic acid. The method capitalizes on the differences in the kinetics and thermodynamic stabilities between conventional DNA / DNA, DNA / RNA and RNA / RNA duplexes and heteroduplexes in which one strand of the heteroduplexe is a nucleobase polymer having a net positively charged or net neutral backbone, such as a PNA.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Detection of nucleic acid differences using endonuclease cleavage/ligase resealing reactions and capillary electrophoresis or microarrays
InactiveUS20090123913A1Reduce noiseObstruction is producedMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeteroduplexA-DNA
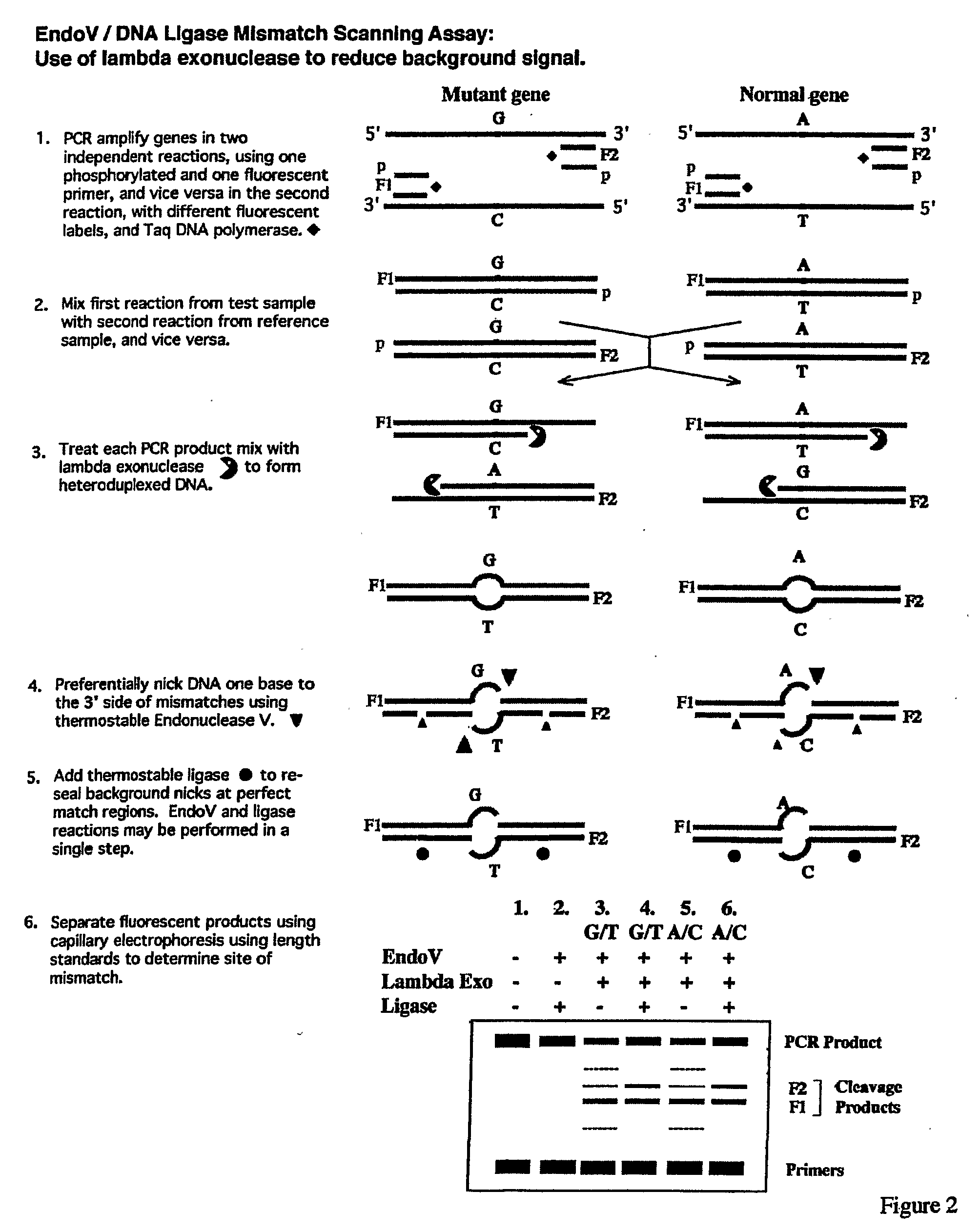
The present invention is directed to various methods for detecting DNA sequence differences, including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and, to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Oligonucleotide analog and method for treating flavivirus infections
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Polynucleotide sequence variants
InactiveUS20040142433A1High occurrenceGenetic material ingredientsFermentationHeterologousHomopolynucleotide
We describe here an in vitro method of redistributing sequence variations between non-identical polynucleotide sequences, by making a heteroduplex polynucleotide from two non-identical polynucleotides; introducing a nick in one strand at or near a base pair mismatch site; removing mismatched base(s) from the mismatch site where the nick occurred; and using the opposite strand as template to replace the removed base(s) with bases that complement base(s) in the first strand. By this method, information is transferred from one strand to the other at sites of mismatch.
Owner:NOVICI BIOTECH
Immunosuppression compound and treatment method
InactiveUS20070111962A1Suppress immune responseRaise the ratioOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHeterologousHeteroduplex
A method and compound for suppressing an immune response in a mammalian subject, for the treatment or prevention of an autoimmune condition or transplantation rejection are disclosed. The compound is an antisense oligonucleotide analog compound having a targeting sequence complementary to a preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA region identified by SEQ ID NO: 1, spanning the splice junction between intron 1 and exon 2 of the preprocessed mRNA of the subject. The compound is effective, when administered to a subject, to form within host cells, a heteroduplex structure (i) composed of the preprocessed CTLA-4 mRNA and the oligonucleotide compound, (ii) characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C., and (iii) resulting in an increased ratio of processed mRNA encoding ligand-independent CTLA-4 to processed mRNA encoding full-length CTLA-4.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
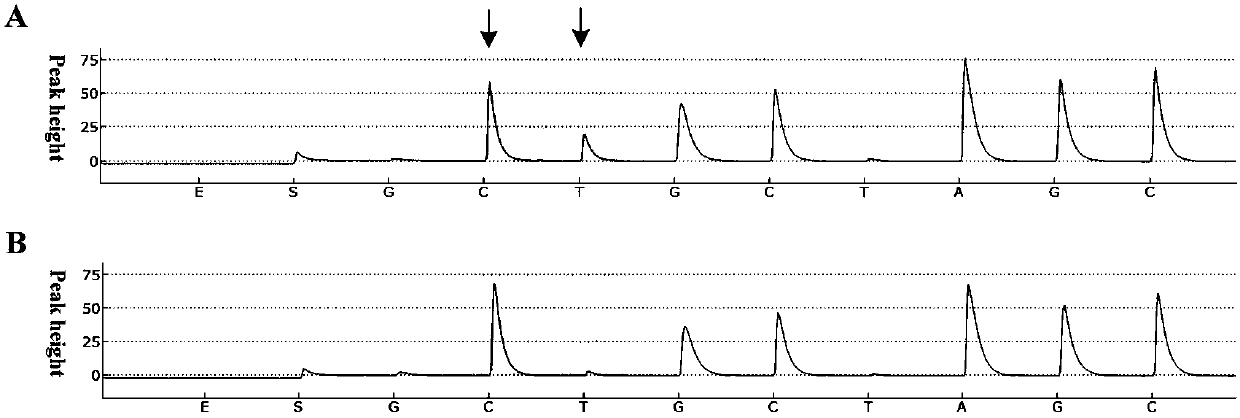
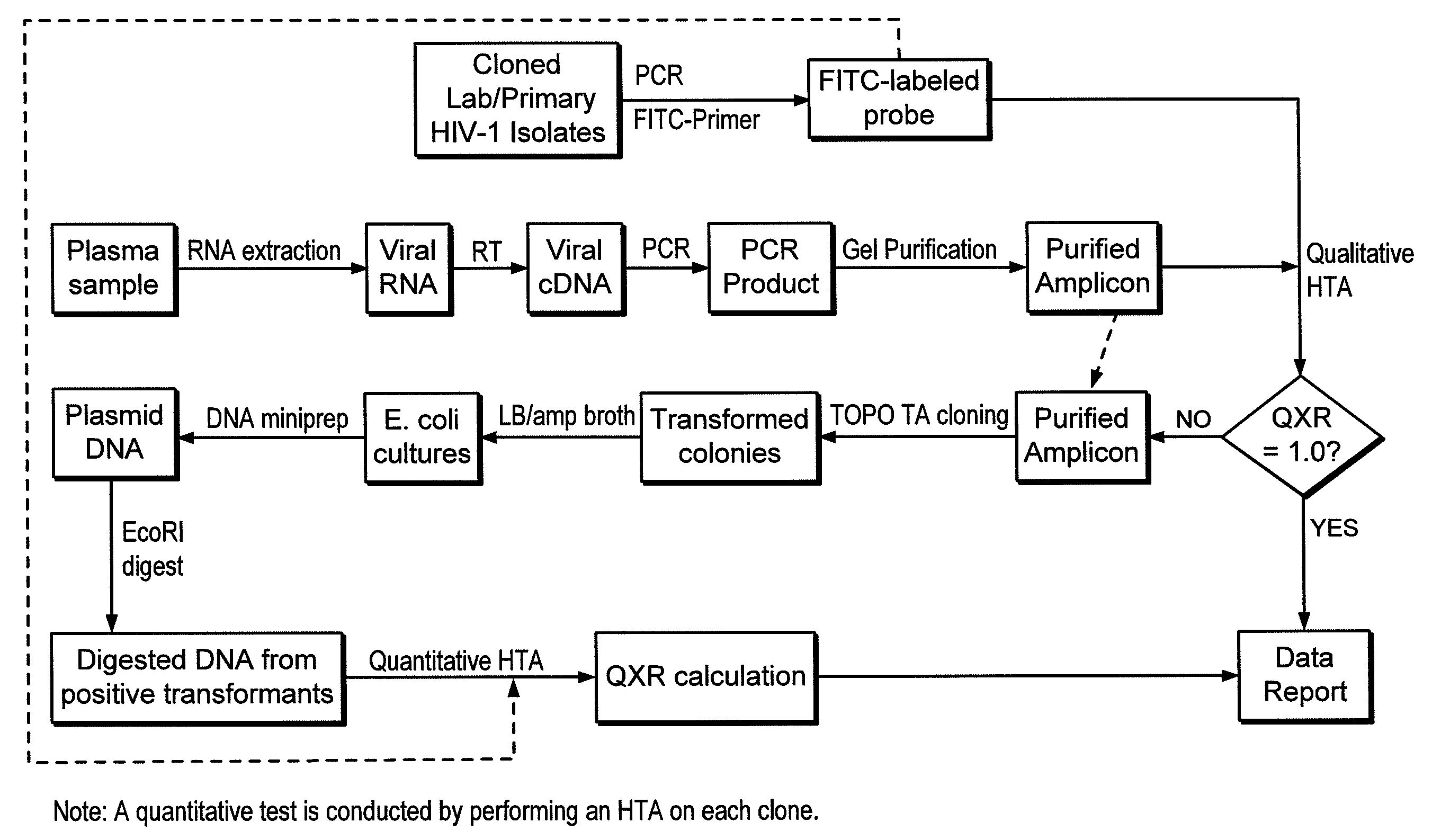
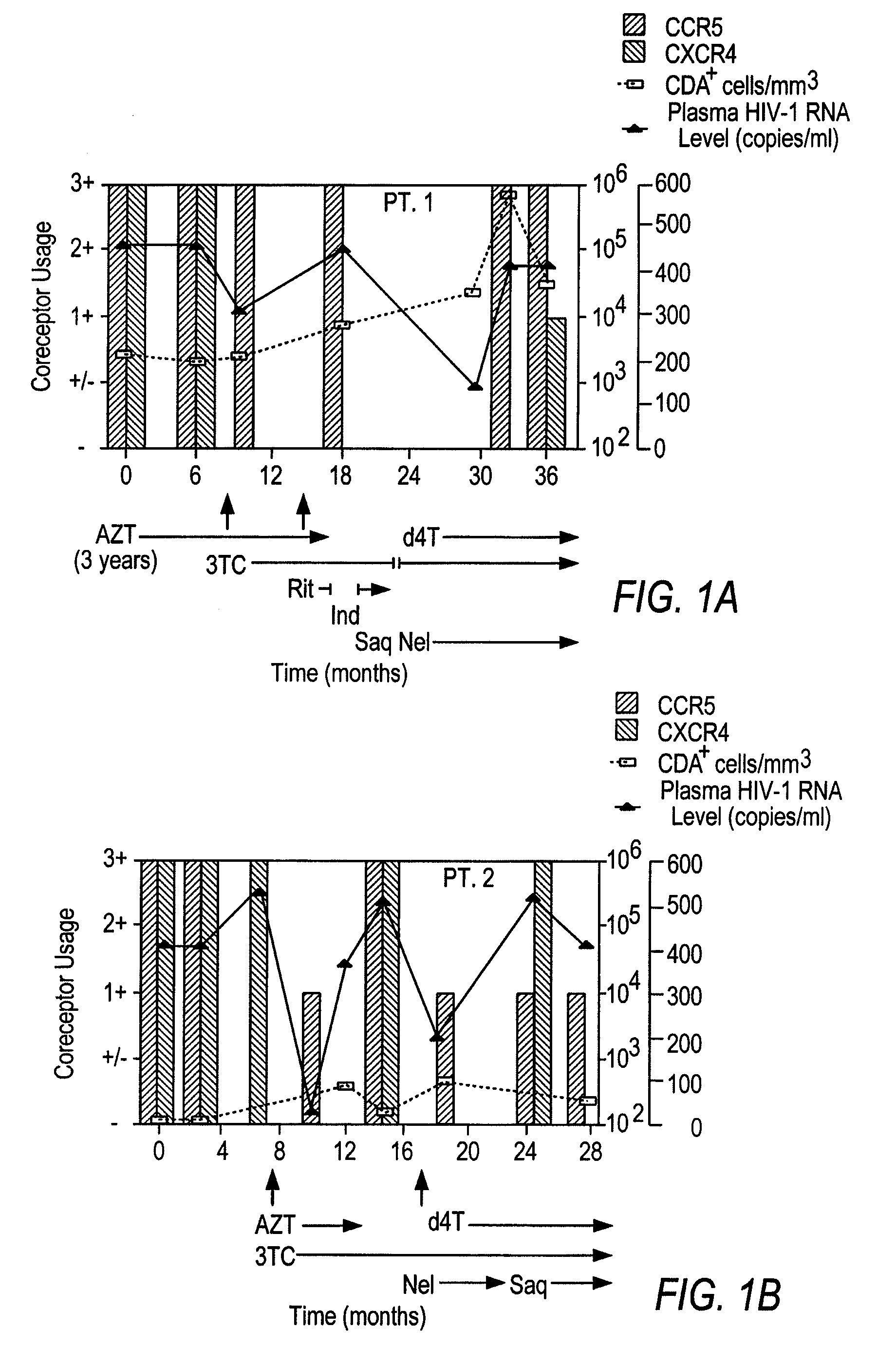
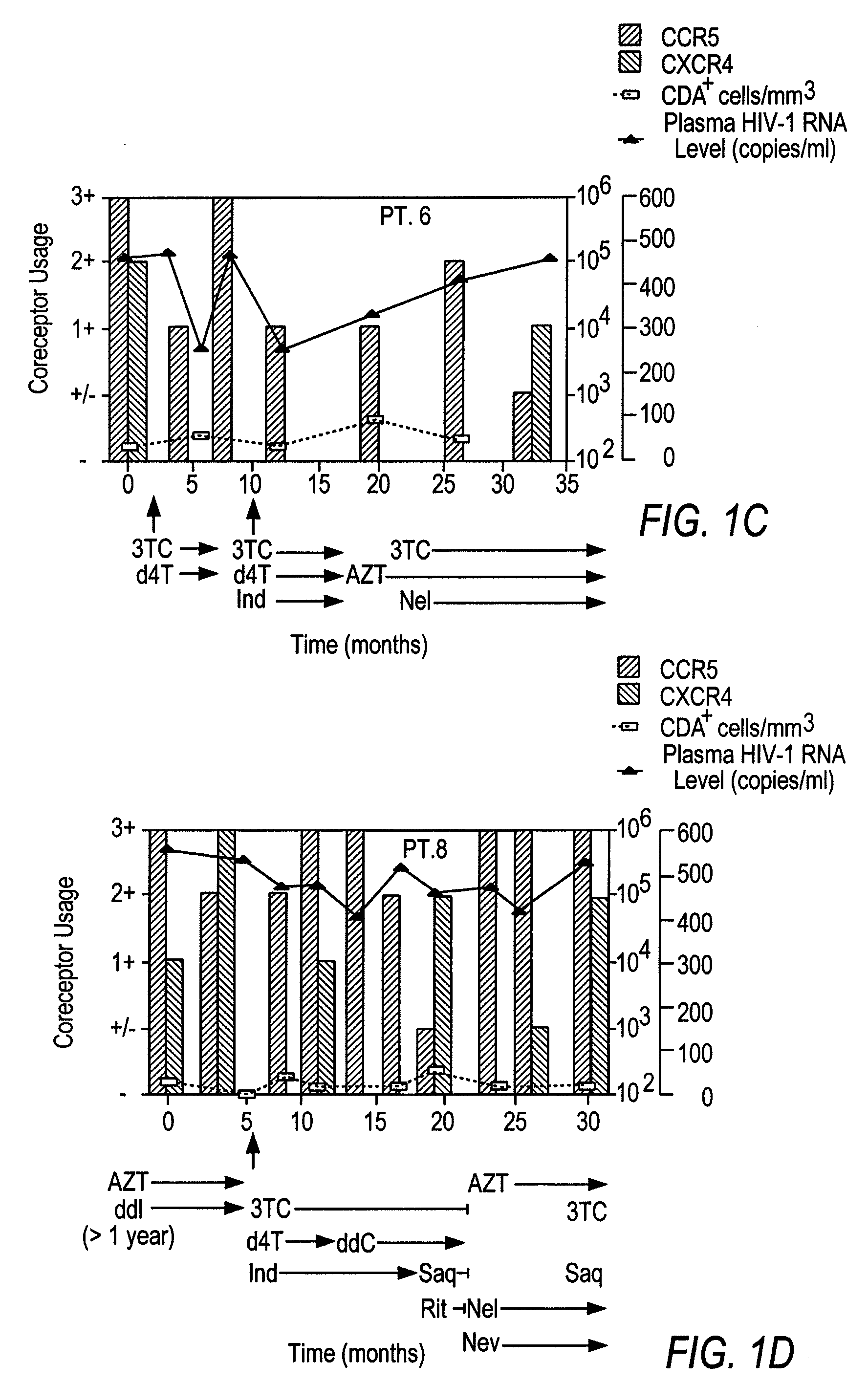
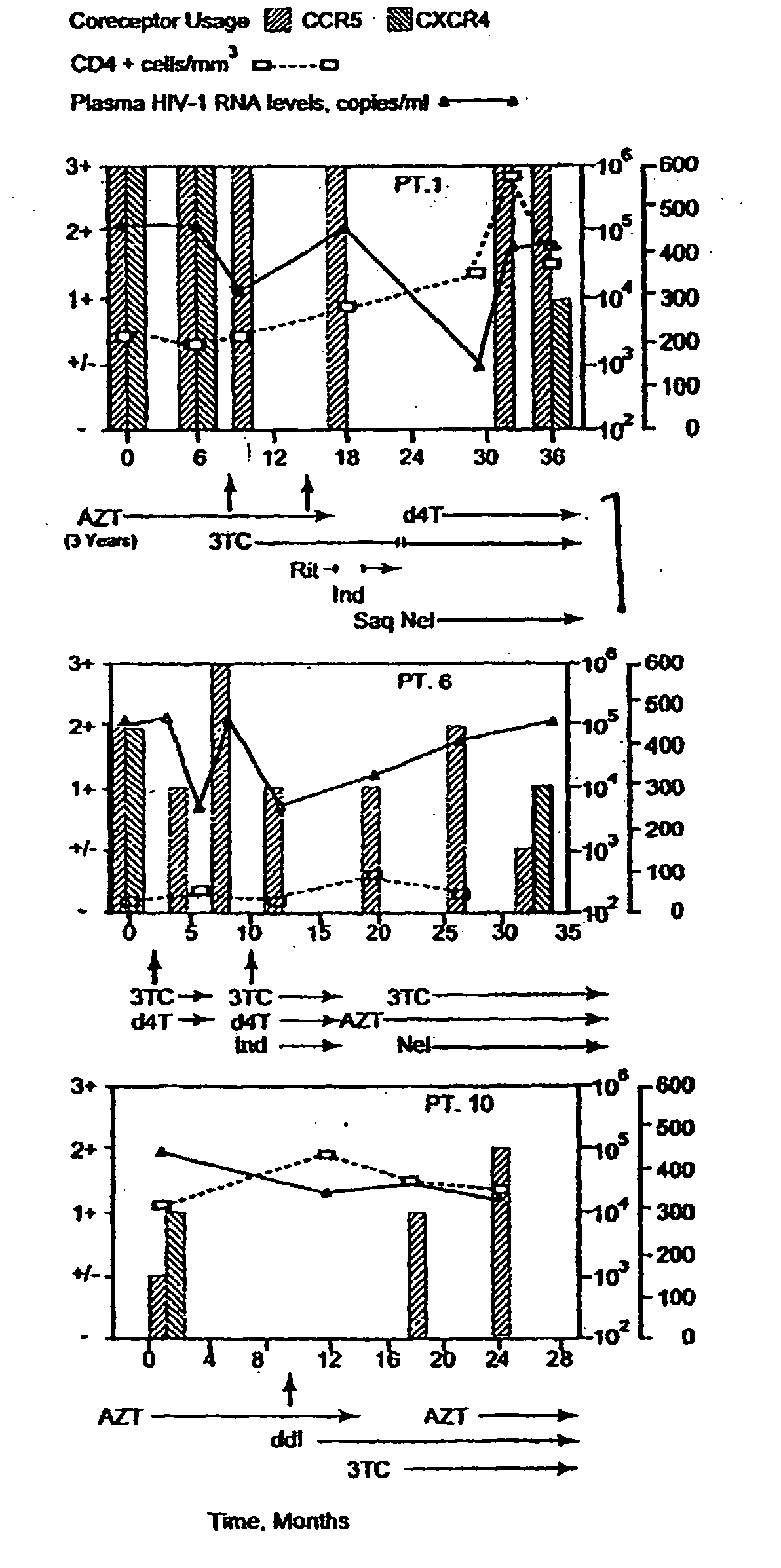
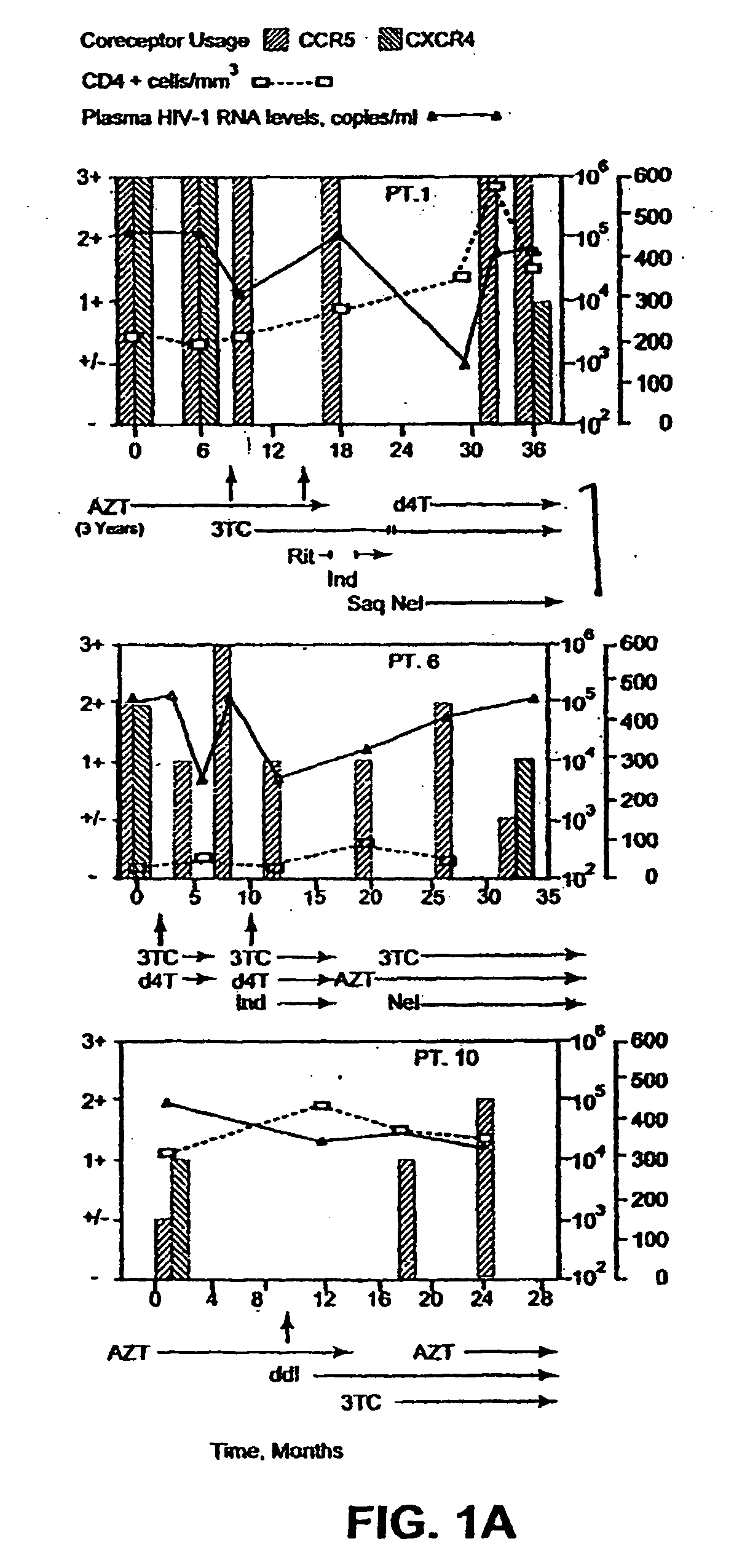
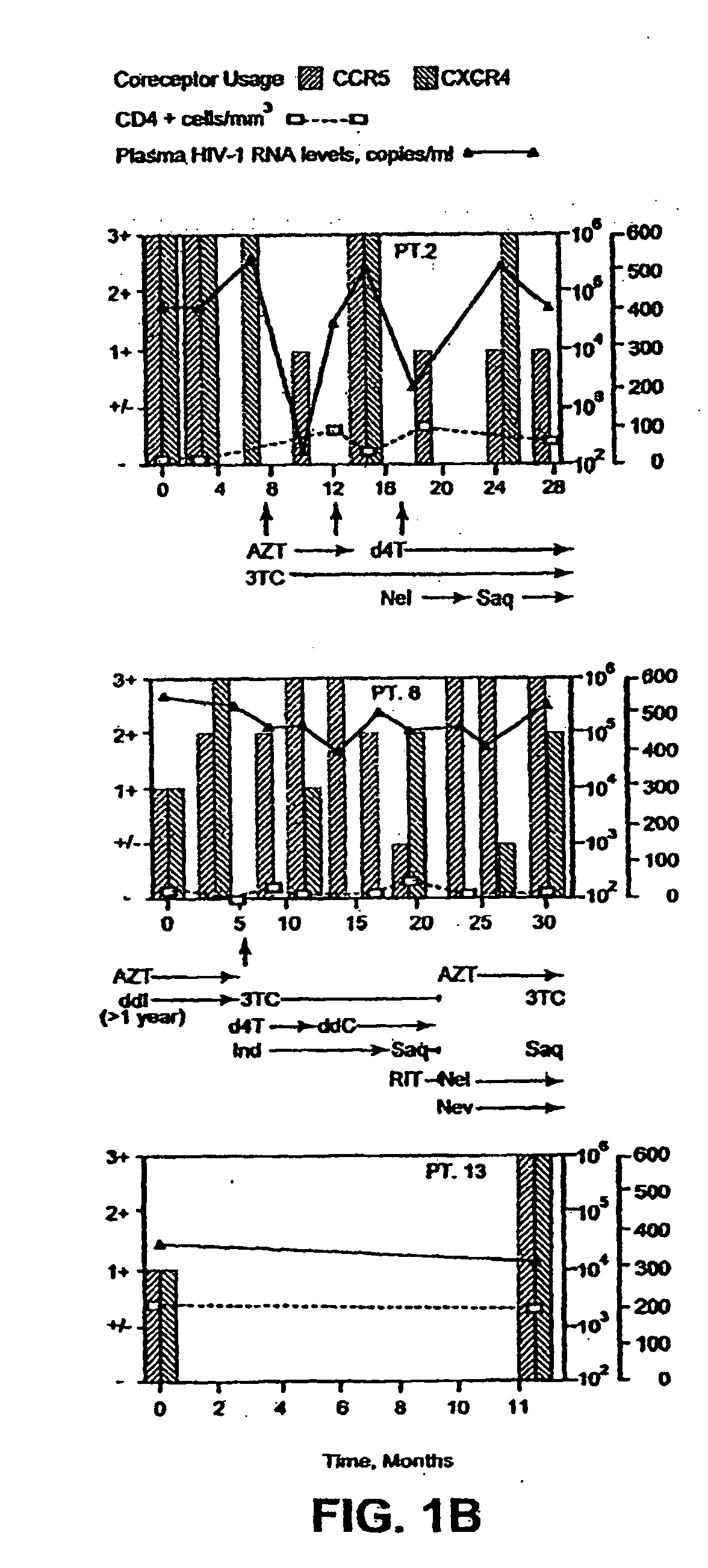
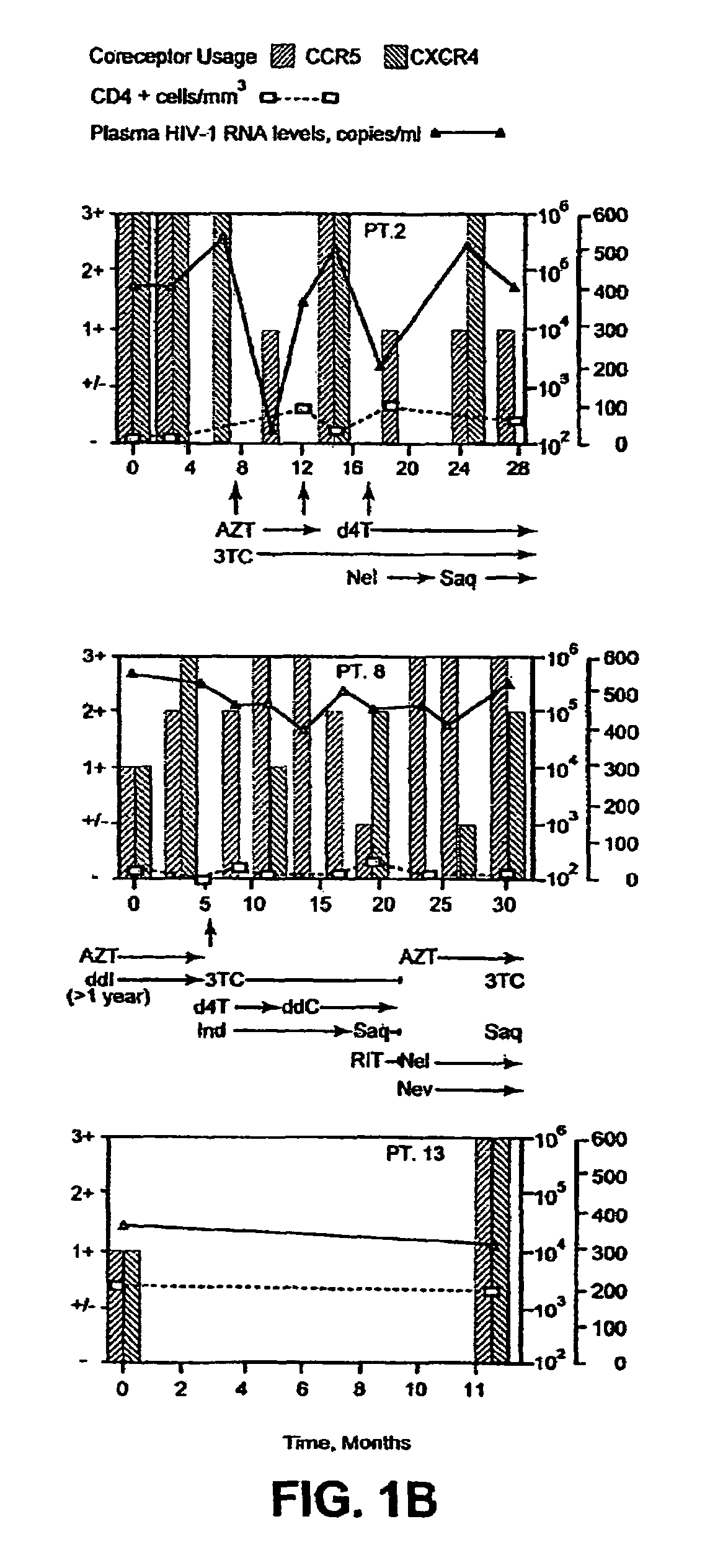
Heteroduplex tracking assay
InactiveUS20060194227A1Accurately predict disease prognosis over timeGood treatment effectMicrobiological testing/measurementVertebrate cellsHeterologousHeteroduplex
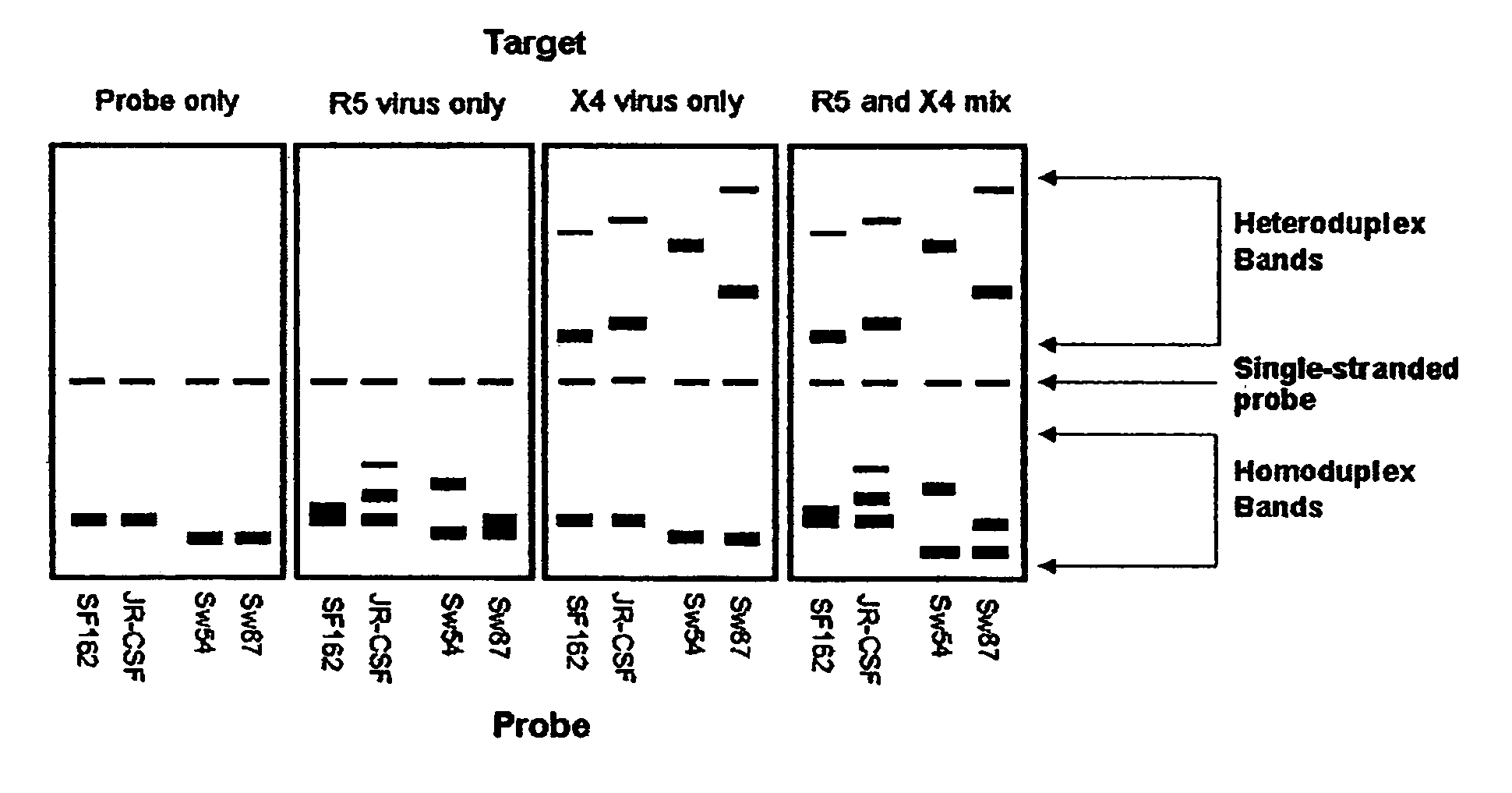
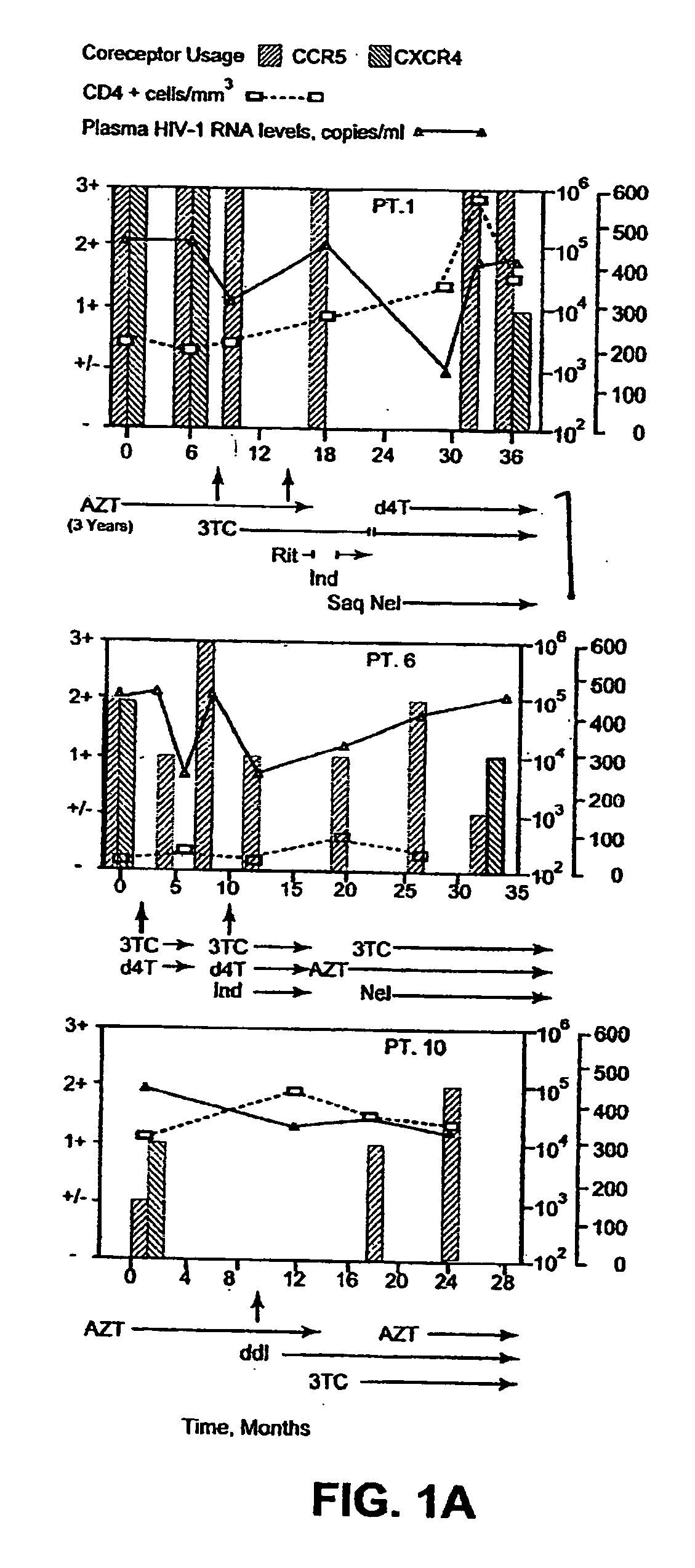
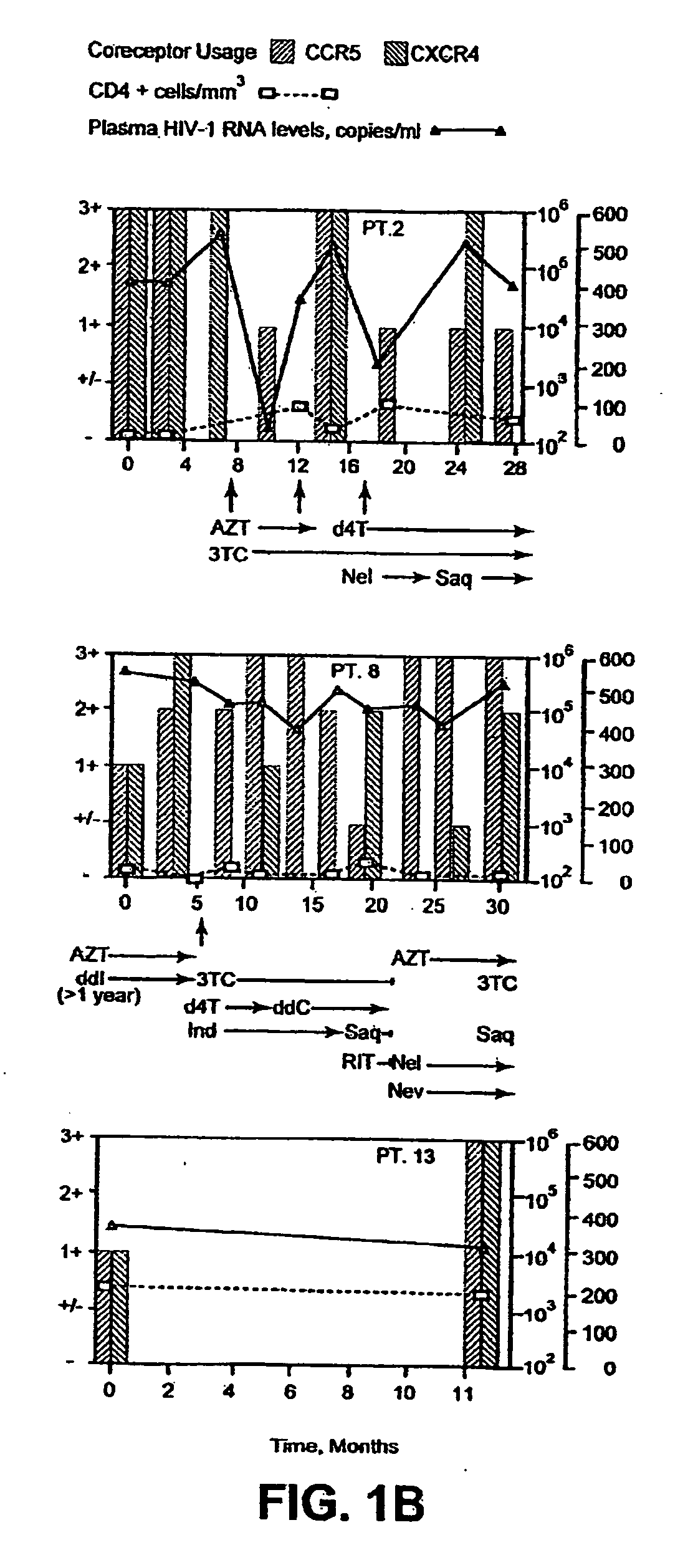
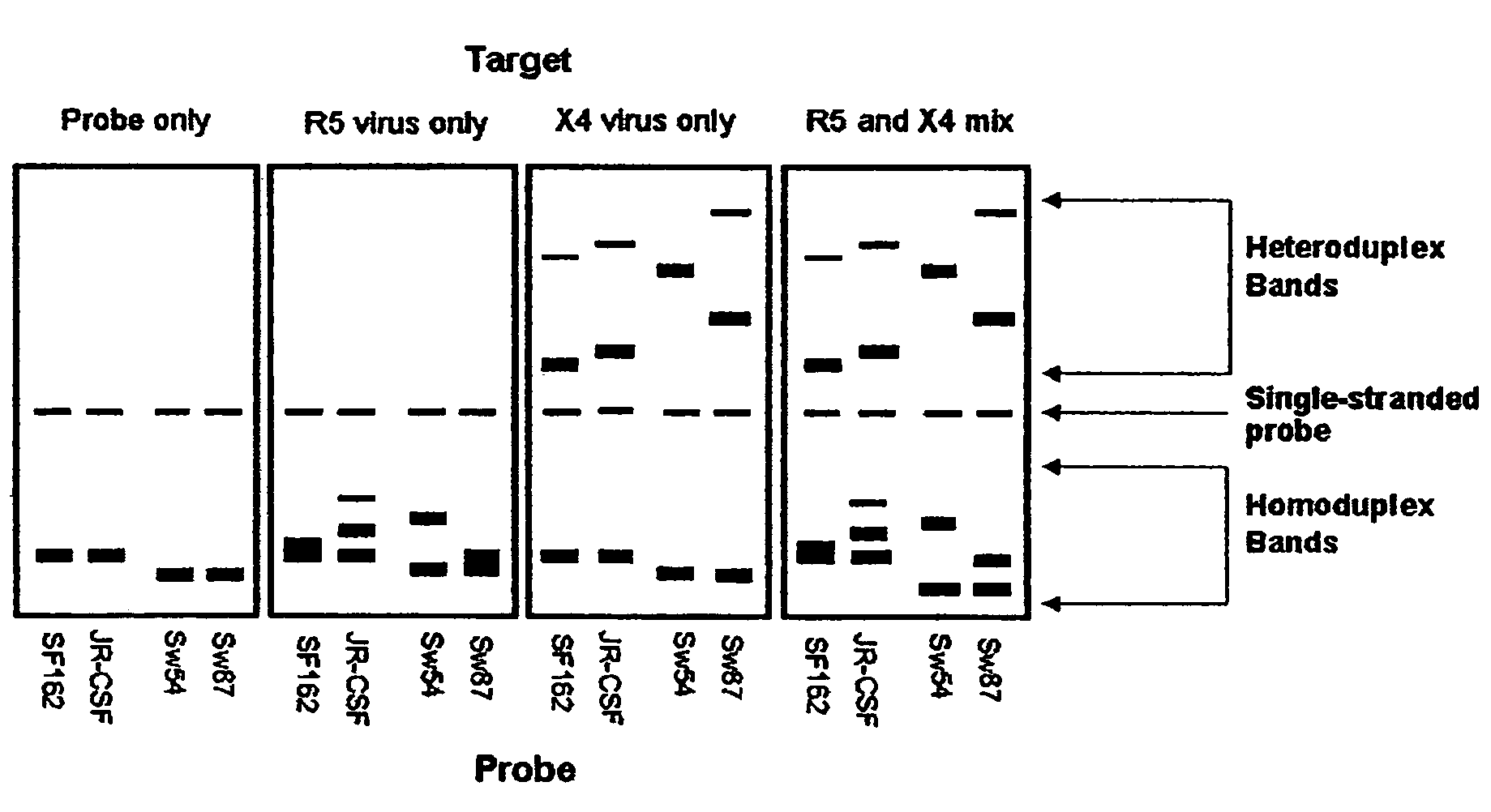
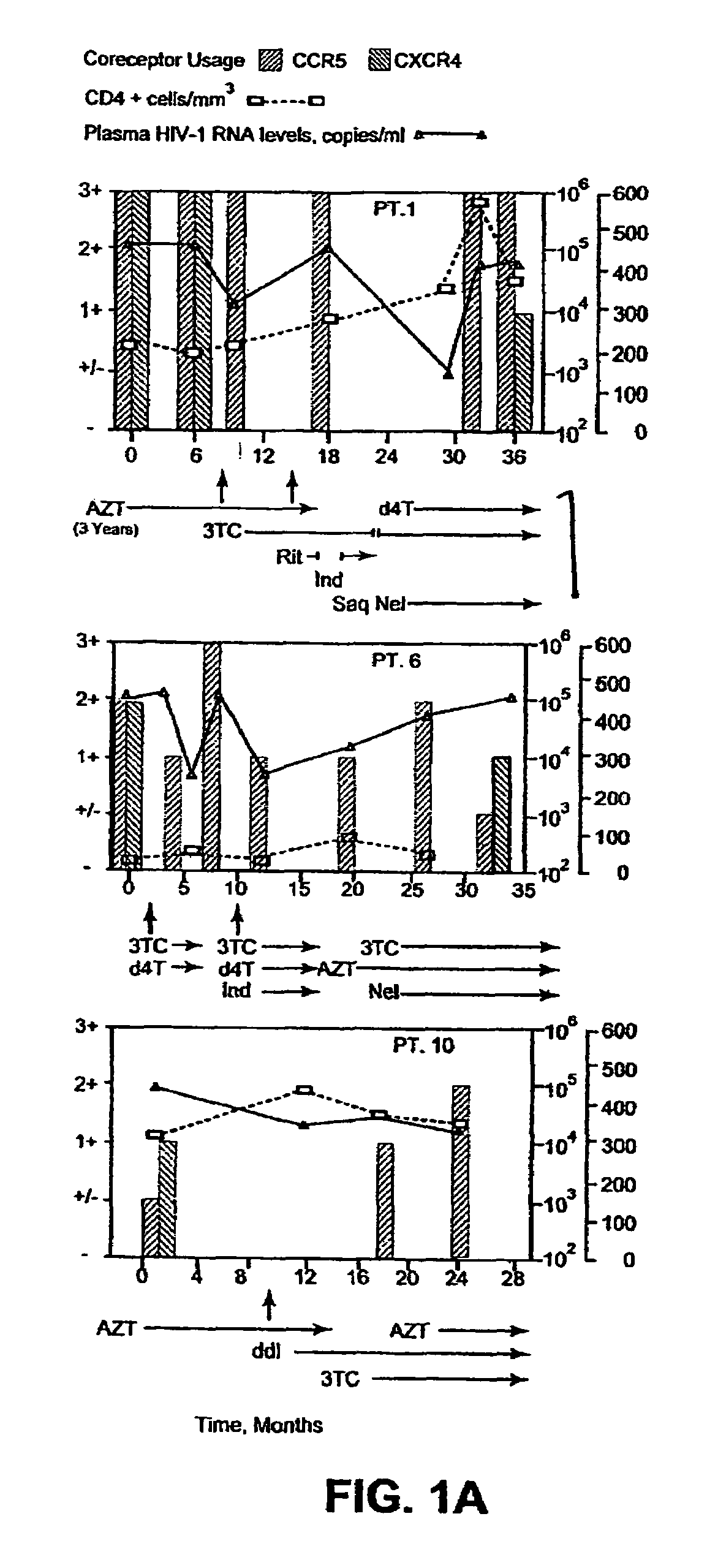
A change in viral tropism occurs in many HIV positive individuals over time and may be indicated by a shift in coreceptor use from CCR5 to CXCR4. The shift in coreceptor use to CXCR4 has been shown to correlate with increased disease progression. In patients undergoing HAART, the predominant populations of virus may be shifted back to CCR5-mediated entry after the CXCR4-specific strains have emerged. The present invention relates to a diagnostic method to monitor coreceptor use in the treatment and clinical management of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The present invention further relates to a diagnostic method applied to HIV-positive individuals undergoing HAART to monitor the suppression of CCR5- or CXCR4-specific strains. The diagnostic methods may be used to assist in selecting antiretroviral therapy and to improve predictions of disease prognosis over time. The methods of the invention include cell-based methods, including cell fusion assays, and molecular-based methods, including heteroduplex tracking assay, to both quantitatively and qualitatively analyze patient-derived HIV for coreceptor usage.
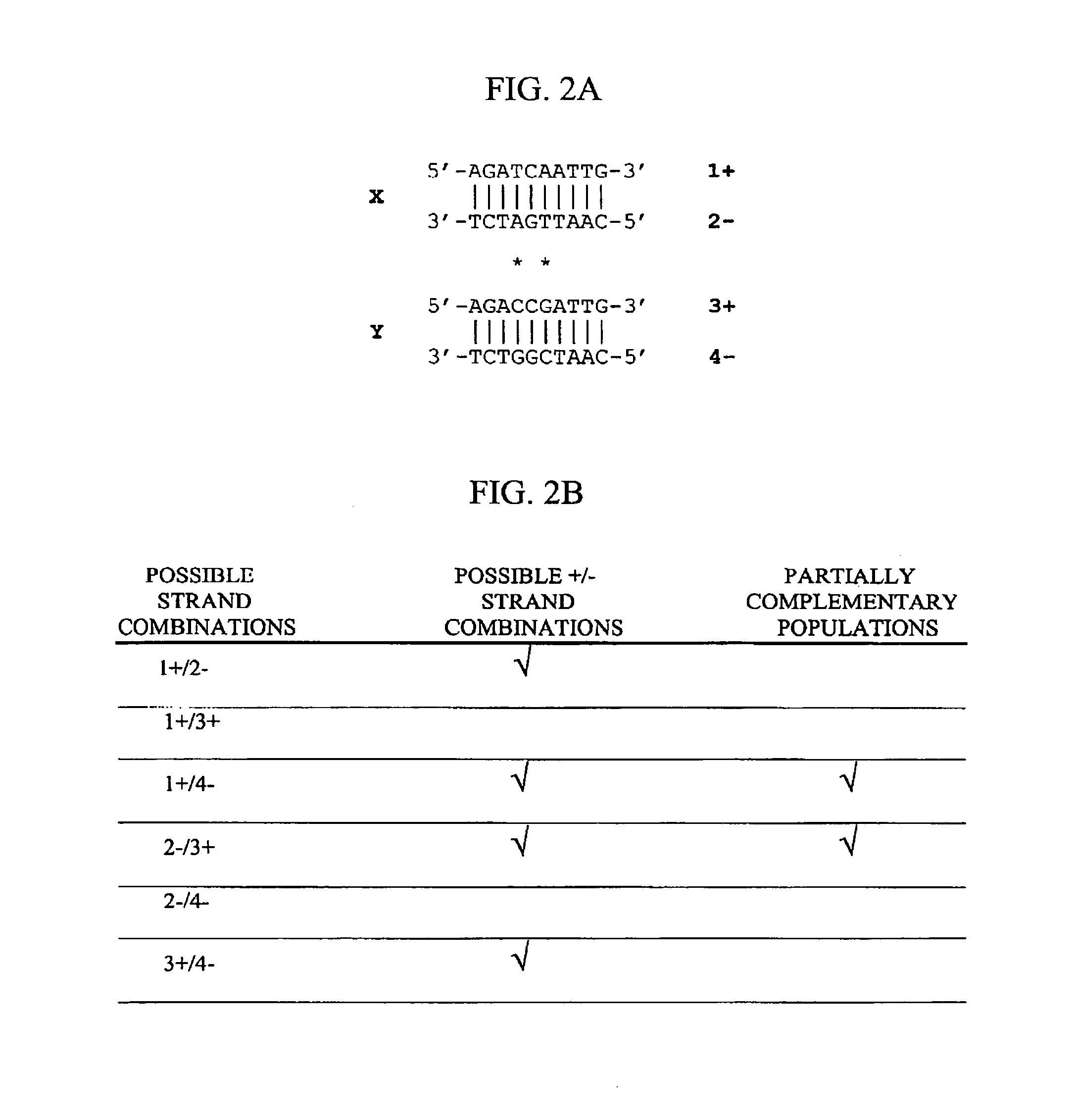
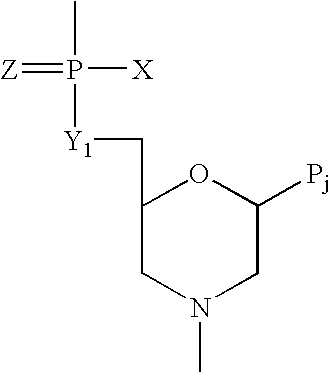
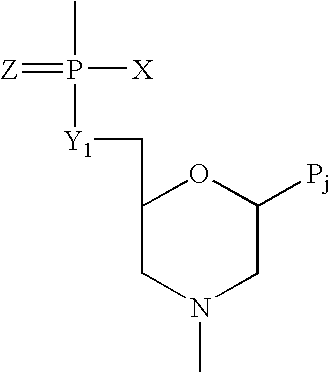
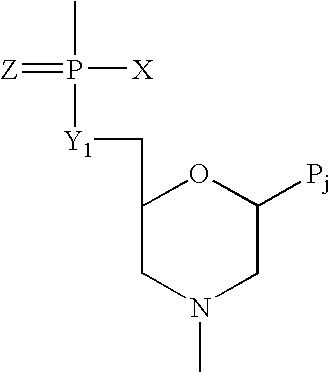
Method of increasing complementarity in a heteroduplex
We describe here an in vitro method of increasing complementarity in a heteroduplex polynucleotide sequence. The method uses annealing of opposite strands to form a polynucleotide duplex with mismatches. The heteroduplex polynucleotide is combined with an effective amount of enzymes having strand cleavage activity, 3' to 5' exonuclease activity, and polymerase activity, and allowing sufficient time for the percentage of complementarity to be increased within the heteroduplex. Not all heteroduplex polynucleotides will necessarily have all mismatches resolved to complementarity. The resulting polynucleotide is optionally ligated. Several variant polynucleotides result. At sites where either of the opposite strands has templated recoding in the other strand, the resulting percent complementarity of the heteroduplex polynucleotide sequence is increased. The parent polynucleotides need not be cleaved into fragments prior to annealing heterologous strands. Therefore, no reassembly is required.
Owner:NOVICI BIOTECH
Nucleic acid molecules encoding endonucleases and methods of use thereof
We describe here an in vitro method of increasing complementarity in a heteroduplex polynucleotide sequence. The method uses annealing of opposite strands to form a polynucleotide duplex with mismatches. The heteroduplex polynucleotide is combined with an effective amount of enzymes having strand cleavage activity, 3' to 5' exonuclease activity, and polymerase activity, and allowing sufficient time for the percentage of complementarity to be increased within the heteroduplex. Not all heteroduplex polynucleotides will necessarily have all mismatches resolved to complementarity. The resulting polynucleotide is optionally ligated. Several variant polynucleotides result. At sites where either of the opposite strands has templated recoding in the other strand, the resulting percent complementarity of the heteroduplex polynucleotide sequence is increased. The parent polynucleotides need not be cleaved into fragments prior to annealing heterologous strands. Therefore, no reassembly is required.
Owner:NOVICI BIOTECH
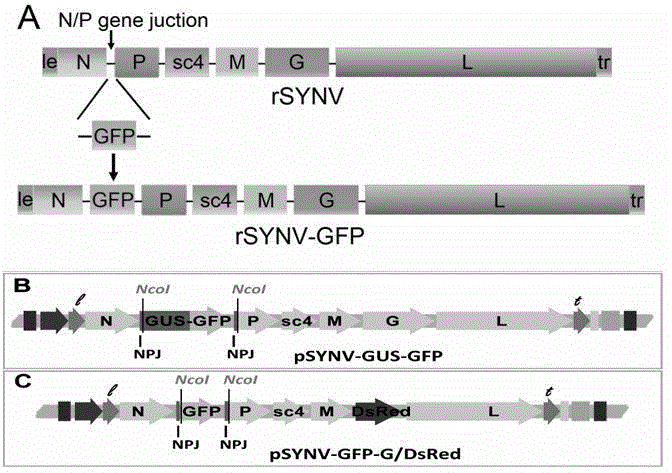
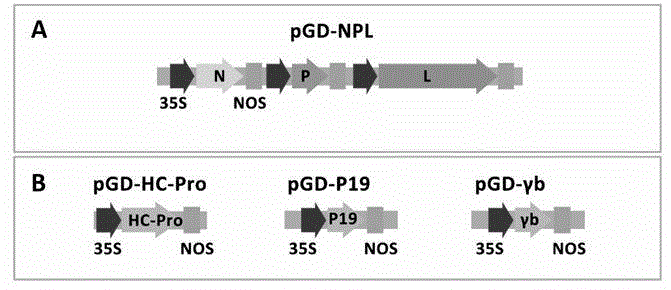
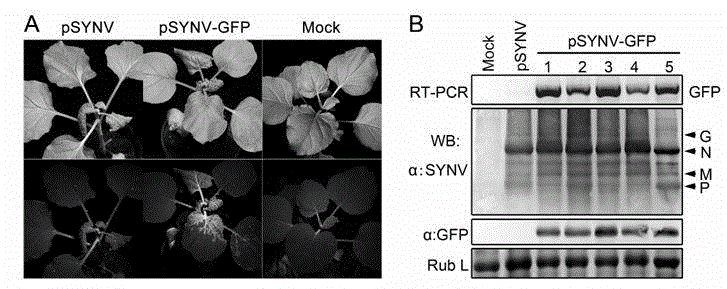
Recombinant plant rhabdovirus vector and construction method thereof
ActiveCN104962580AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousPlant rhabdovirus
The invention discloses a recombinant plant rhabdovirus vector and a construction method thereof. The recombinant plant rhabdovirus vector comprises a modified plant rhabdovirus genome, a transcription unit which is induced newly and a heteroduplex nucleotide sequence, wherein the transcription unit is inserted into the plant rhabdovirus genome to express the heteroduplex nucleotide sequence, the heteroduplex nucleotide sequence is replaced into a glycoprotein transcription unit of a recombinant plant rhabdovirus; the recombinant plant rhabdovirus has copying and infecting capacity, and one antigenic polypeptide or other protein is coded by the heteroduplex nucleotide sequence. The virus expression vector is the first one which can express a negative-sense RNA virus vector of foreign protein on plants, and the recombinant plant rhabdovirus vector has the advantages that the expression quantity is high, the expression stability is good, a relative long foreign gene segment can be inserted, and inserted foreign gene segment is not prone to loosing; the recombinant plant rhabdovirus vector can be used for expressing of multiple kinds of foreign protein and can also be used for preparing animal vaccines, and wide application values and application prospects are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Strand displacement methods employing competitor oligonucleotides for isolating one strand of a double-stranded nucleic acid
InactiveUS6787310B2Promote formationEliminate needSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousHeteroduplex
The present invention provides methods and kits for isolating one strand of a double-stranded target nucleic acid. The method capitalizes on the differences in the kinetics and thermodynamic stabilities between conventional DNA / DNA, DNA / RNA and RNA / RNA duplexes and heteroduplexes in which one strand of the heteroduplexe is a nucleobase polymer having a net positively charged or net neutral backbone, such as a PNA.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Low abundance gene mutation enriching method based on removing wild sequences
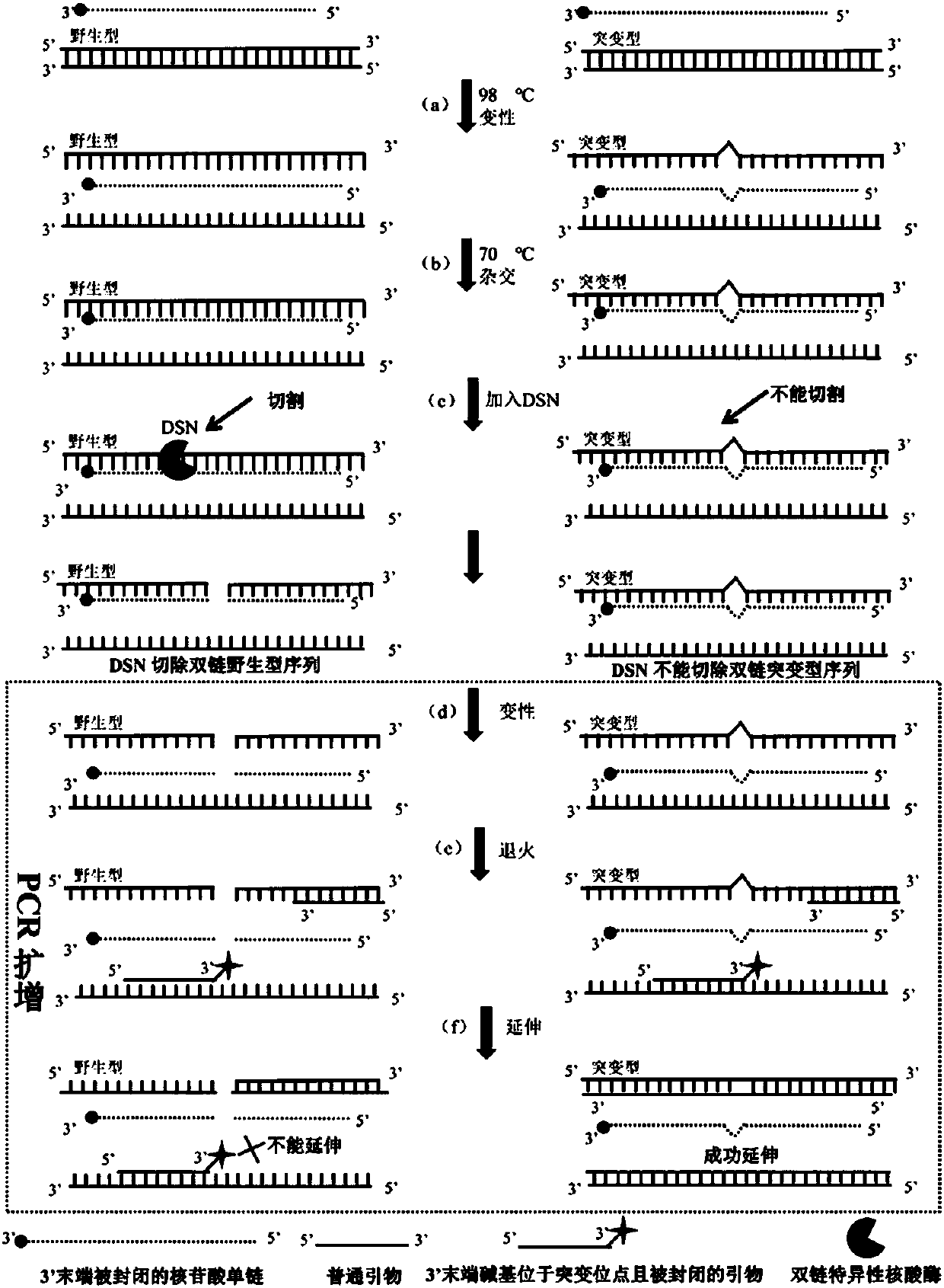
ActiveCN107893109AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexNucleotide
The invention discloses a low abundance gene mutation enriching method based on removing wild sequences. According to the method, before PCR amplification, a sample DNA used as a DNA template is processed, so that nucleotide single chains which contain mutation loci and are sealed at the 3' tail end are used as hybrid chains to be hybridized with wild and mutation type sequences, and duplex-specific nuclease can specifically remove a homoduplex DNA completely formed by the hybrid chains and the mutation type sequences in complete complementary pairing with the wild sequences but cannot removea heteroduplex DNA formed by the hybrid chains and the mutation type sequences in incomplete complementary pairing. Removed products are subjected to the PCR amplification, the 3' tail end of a primerused by the PCR amplification is located on the mutation loci and is sealed, under the effect of a polymerase with a 3'-5' proofreading activity, the wild sequences cannot be amplified, but the mutation type sequences can be amplified in an index mode, therefore the low abundance gene mutation sequences are effectively enriched, and the enriching sensitivity and accuracy are improved; meanwhile,according to the method, multiple mutation type sequences can also be enriched simultaneously, and therefore, the amplification efficiency is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method of increasing complementarity in a heteroduplex
We describe here an in vitro method of increasing complementarity in a heteroduplex polynucleotide sequence. The method uses annealing of opposite strands to form a polynucleotide duplex with mismatches. The heteroduplex polynucleotide is combined with an effective amount of enzymes having strand cleavage activity, 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity, and polymerase activity, and allowing sufficient time for the percentage of complementarity to be increased within the heteroduplex. Not all heteroduplex polynucleotides will necessarily have all mismatches resolved to complementarity. The resulting polynucleotide is optionally ligated. Several variant polynucleotides result. At sites where either of the opposite strands has templated recoding in the other strand, the resulting percent complementarity of the heteroduplex polynucleotide sequence is increased. The parent polynucleotides need not be cleaved into fragments prior to annealing heterologous strands. Therefore, no reassembly is required.
Owner:NOVICI BIOTECH
Heteroduplex tracking assay
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Antisense composition and method for treating cancer
InactiveUS20050261249A1Confirm specificity of bindingLimited to nonOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTransdifferentiationHeteroduplex
A method and composition for of treating cancer, and in particular, for arresting the progression of a solid or primary cancer to a more invasive, metastatic state, are disclosed. The composition includes a substantially uncharged antisense compound (i) having a nuclease-resistant backbone, (ii) capable of uptake by target cancer cells in the subject, (iii) containing between 10-40 nucleotide bases, and (iv) having a base sequence effective to hybridize to a region of processed or preprocessed human SNAIL RNA transcript. The compound, when administered to the subject, is effective to form within target cancer cells in the subject, a base-paired heteroduplex structure composed of human SNAIL RNA transcript and the oligonucleotide compound, where this structure is characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C. The compound is administered in an amount sufficient to inhibit SNAIL expression in target cancer cells, thereby to inhibit the progression of the patient's cancer to a more invasive, metastatic state. Also disclosed are methods for preventing the transdifferentiation of peritoneal mesothelial cells and failure of ultrafiltration in a patient undergoing peritoneal dialysis, by including the compound in the patient dialysis fluid.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Double-labelling fluorescence activation type probe and method for detecting DNA by adopting same
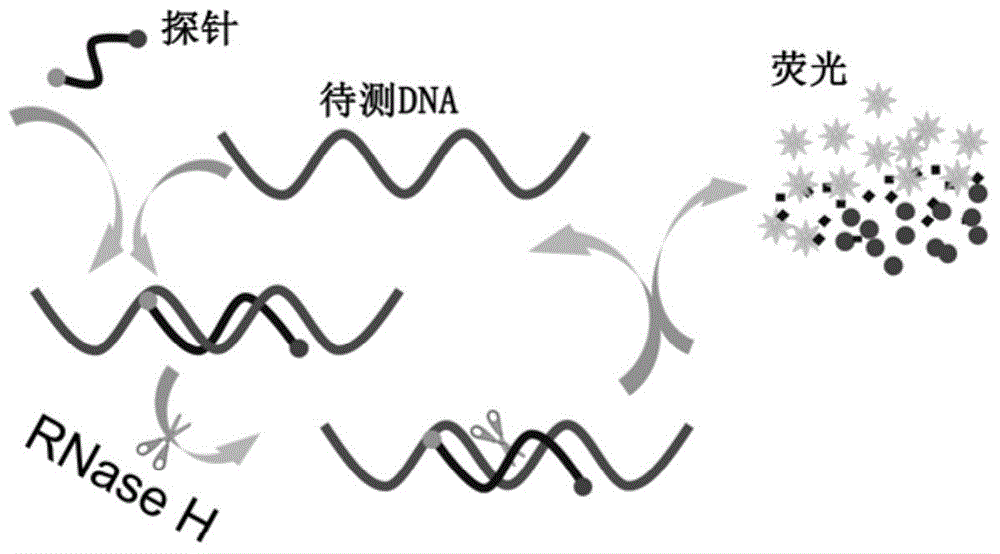
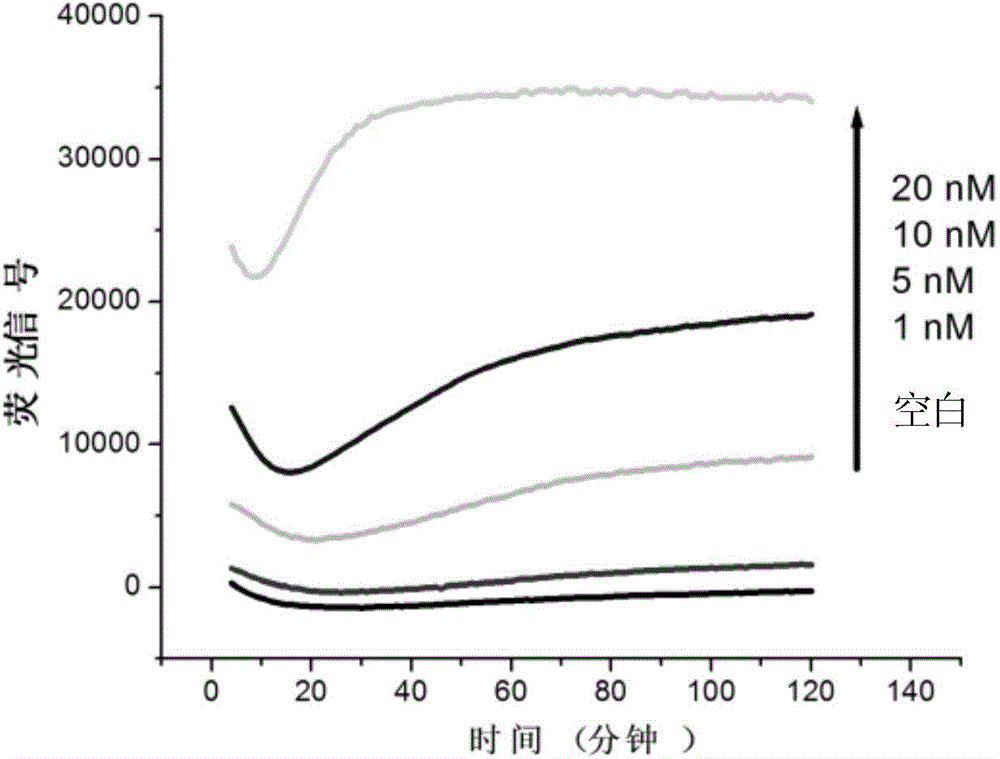
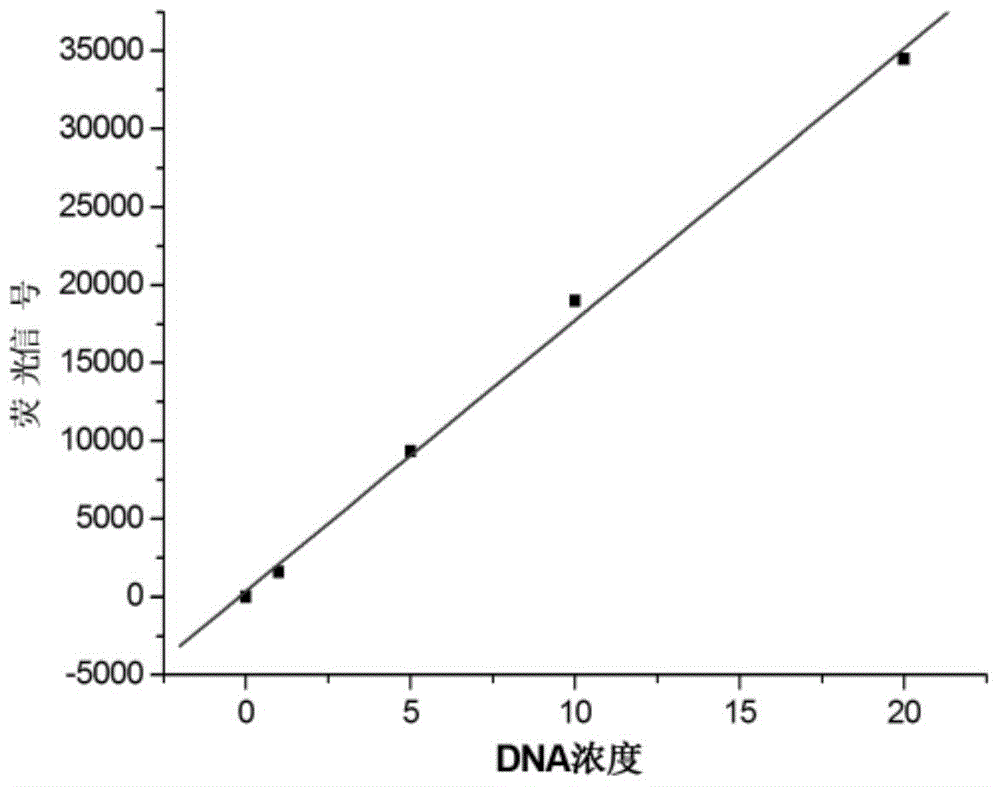
InactiveCN104946634ASimple structureEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle-Stranded RNAHeteroduplex
The invention discloses a double-labelling fluorescence activation type probe and a method for detecting DNA by adopting the same. The probe is a single stranded RNA which is complementary with a basic group of to-be-detected DNA and has the length of 5-40 basic groups or is a single stranded DNA which is complementary with a basic group of to-be-detected DNA and has the length of 5-40 basic groups; 1 / 5-4 / 5 of basic groups in the DNA sequence are RNA basic groups; The two ends of the probe are labeled with a fluorophore and a quenching group. The probe is simple in structure and fluorescence is completely quenched; when the probe hybridizes with the to-be-detected DNA to form DNA / RNA heteroduplex, RNase H hydrolyzes an RNA chain in a DNA / RNA structure in a specificity manner to enable the fluorophore to be away from the quenching group and enable a fluorescence signal to be recovered; simultaneously, the dissociative probe further hybridizes with the to-be-detected DNA, is hydrolyzed by RNase H and generates the fluorescence signal; circulation is performed in such a way, so that the system fluorescence signal is remarkably amplified to realize rapid and high-sensitive detection of the to-be-detected DNA. The probe can be used for quantitative detection of DNA in an amplification product.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
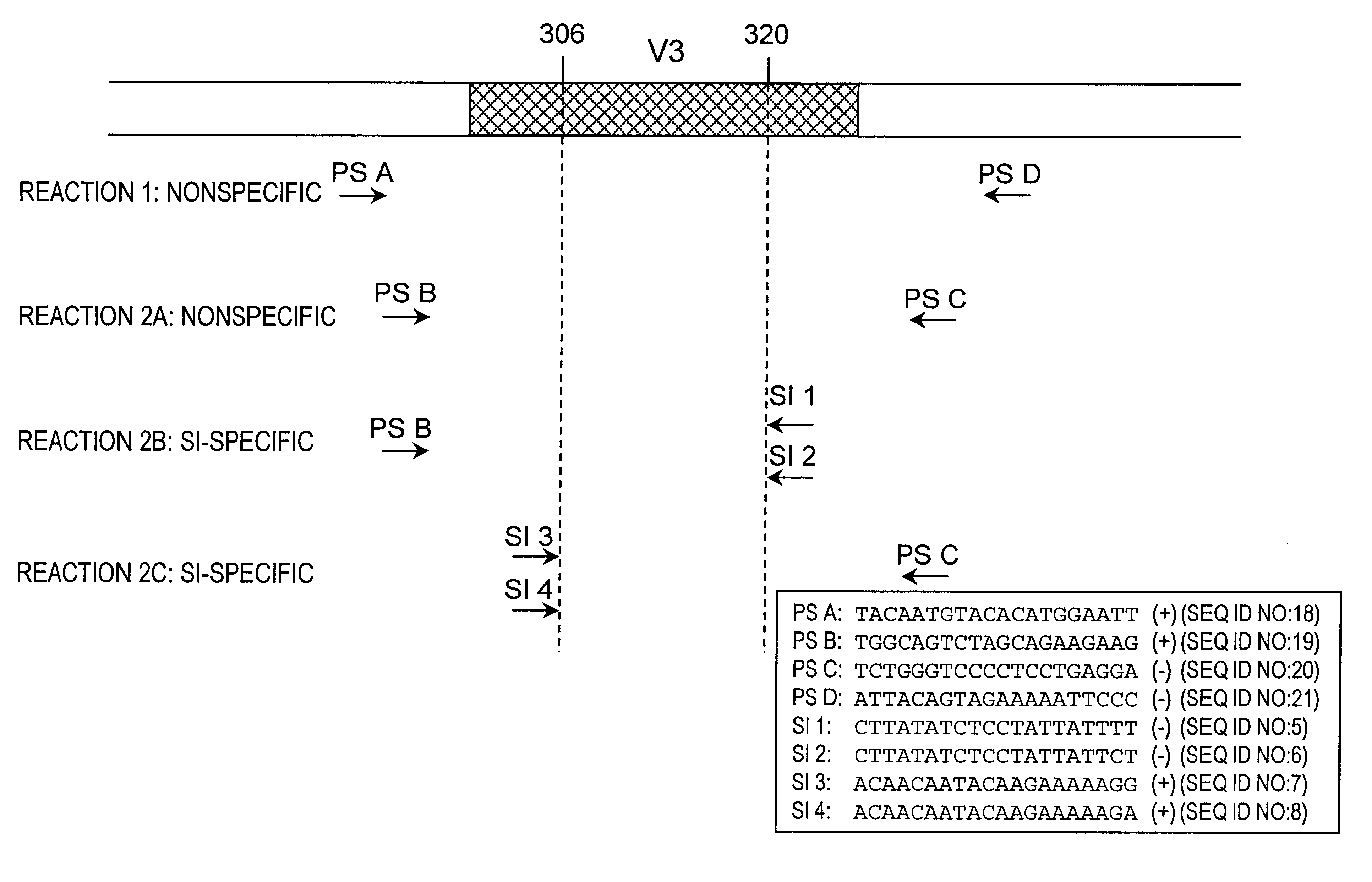
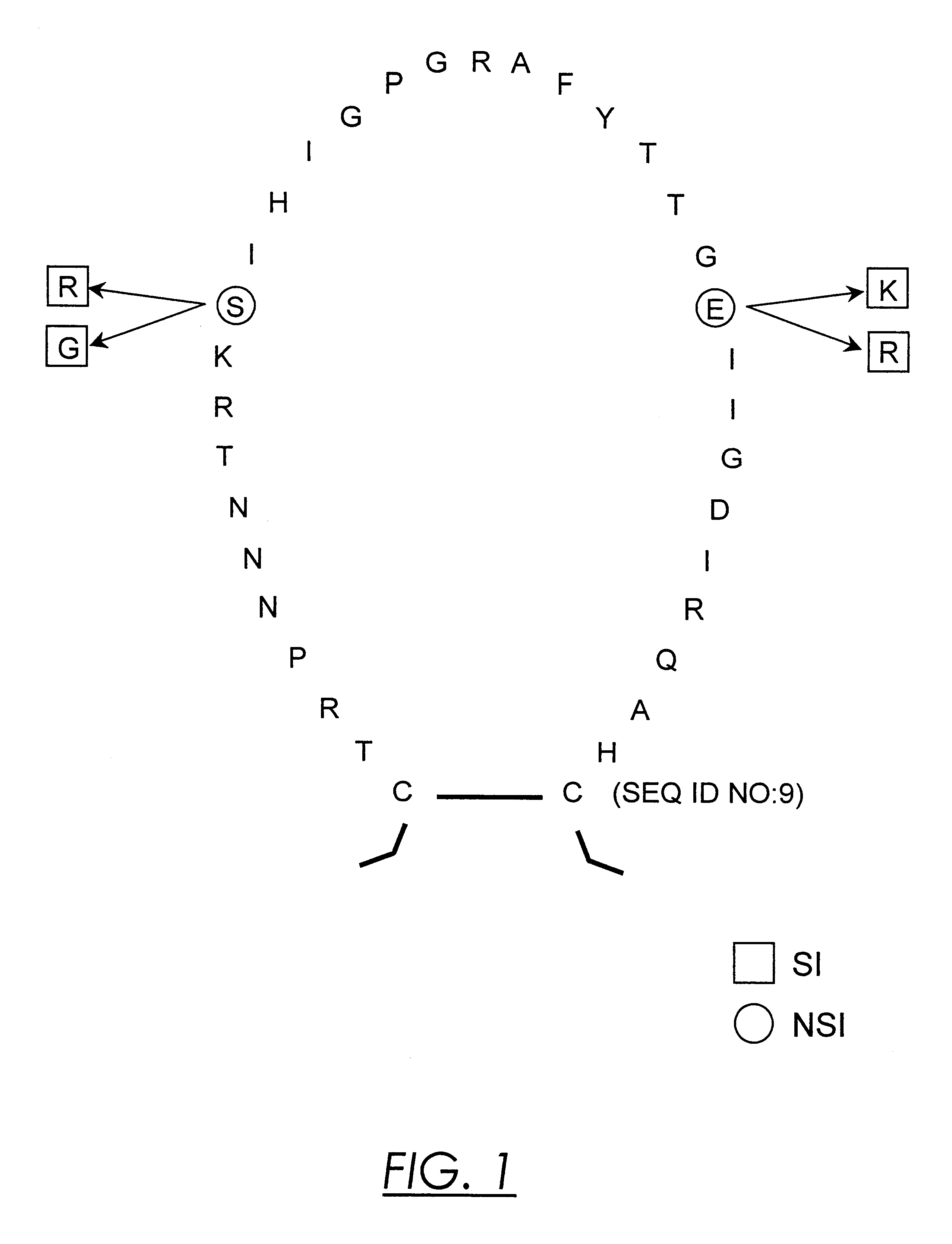
Nucleic acids and methods for the discrimination between syncytium inducing and non syncytium inducing variants of the human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS6379881B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexImmunodeficiency virus
This invention is in the area of molecular biology / virology and presents oligonucleotides with nucleotide-sequences specific for SI HIV-1 strains. These oligonucleotides may be used for in vitro determination of biological phenotype of HIV-1 strain in biological material from HIV-infected individuals by a number of techniques such as Southern and Northern blot analysis, PCR, NASBA, in situ hybridization, branched DNA hybridization, heteroduplex tracing hybridization and liquid hybridizations. HIV-1 phenotyping may i.e. be used as a diagnostic marker for disease progression or for testing efficacy of antiviral therapy.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV +1
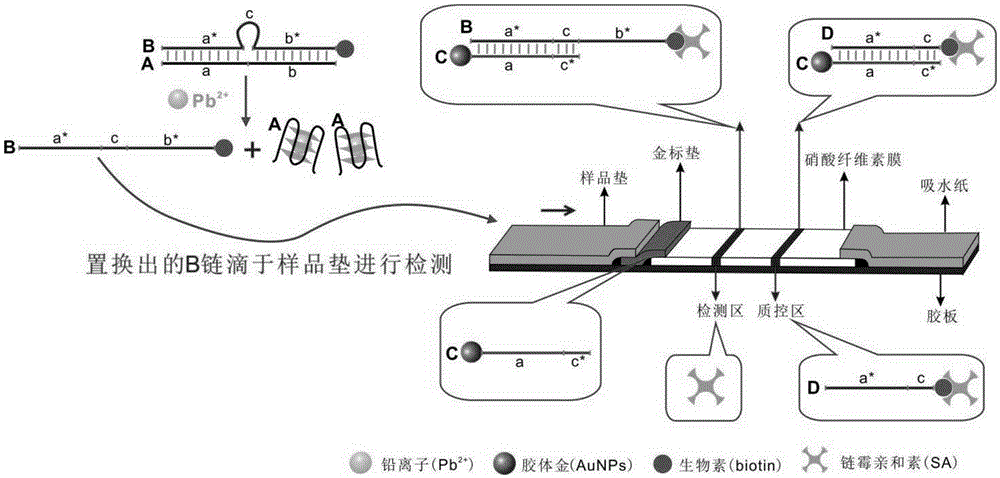
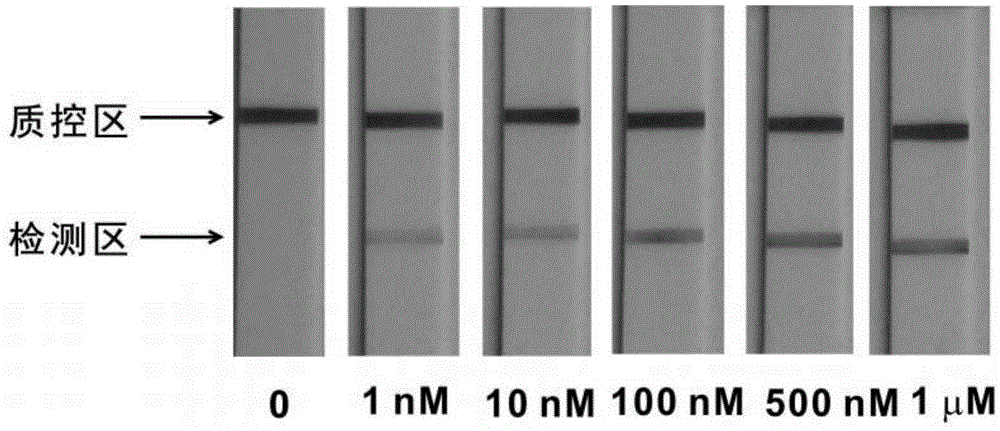
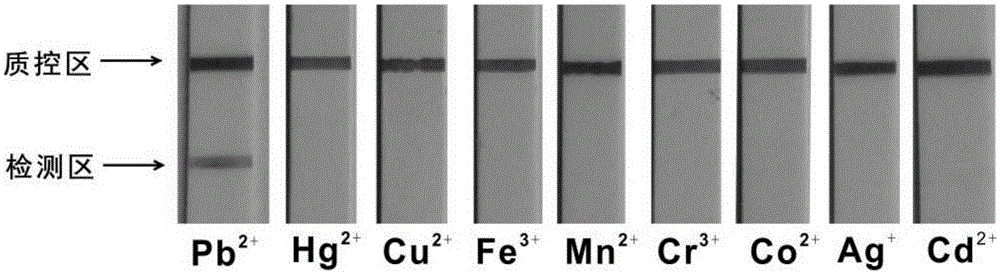
Lead ion visual detection method and detection kit
The invention discloses a lead ion visual detection method and detection kit. The detection kit comprises a test strip detection platform, a buffer system and nucleotide sequences A, B C and D. By means of the characteristics that the A, B, C and D are partially complementary in sequence and the A has a lead ion specific recognition element, A-B heteroduplex and lead ion recognition are utilized, the A and lead ions form a G-tetramer structure, and the A is dissociated out; then the B-chain obtained through replacement is dripped onto a sample pad of the test strip for detection, and the B forms a macroscopic strip in the detection area by continuing to be combined with the C. Neither traditional 8-17DNAzyme nor RNA synthesis nor antibodies are needed, the detection result is directly macroscopic, operation is easy, cost is low, and the lead ion visual detection method and detection kit are suitable for being used and popularized in units. The lead detection limit of the method is 1 nM which is lower than 72 nM, the maximum allowable limit, ruled by the USEPA, of lead ions in drinking water.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Heteroduplex tracking assay
A change in viral tropism occurs in many HIV positive individuals over time and may be indicated by a shift in coreceptor use from CCR5 to CXCR4. The shift in coreceptor use to CXCR4 has been shown to correlate with increased disease progression. In patients undergoing HAART, the predominant populations of virus may be shifted back to CCR5-mediated entry soon after the CXCR4-specific strains have emerged. The present invention relates to a diagnostic method to monitor coreceptor use in the treatment and clinical management of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The present invention further relates to a diagnostic method applied to HIV-positive individuals undergoing HAART to monitor the suppression of CCR5- or CXCR4-specific strains. The diagnostic methods may be used to assist in selecting antiretroviral therapy and to improve predictions of disease prognosis over time. The methods of the invention include cell-based methods, including cell fusion assays, and molecular-based methods, including heteroduplex tracking assay, to both quantitatively and qualitatively analyze patient-derived HIV for coreceptor usage.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
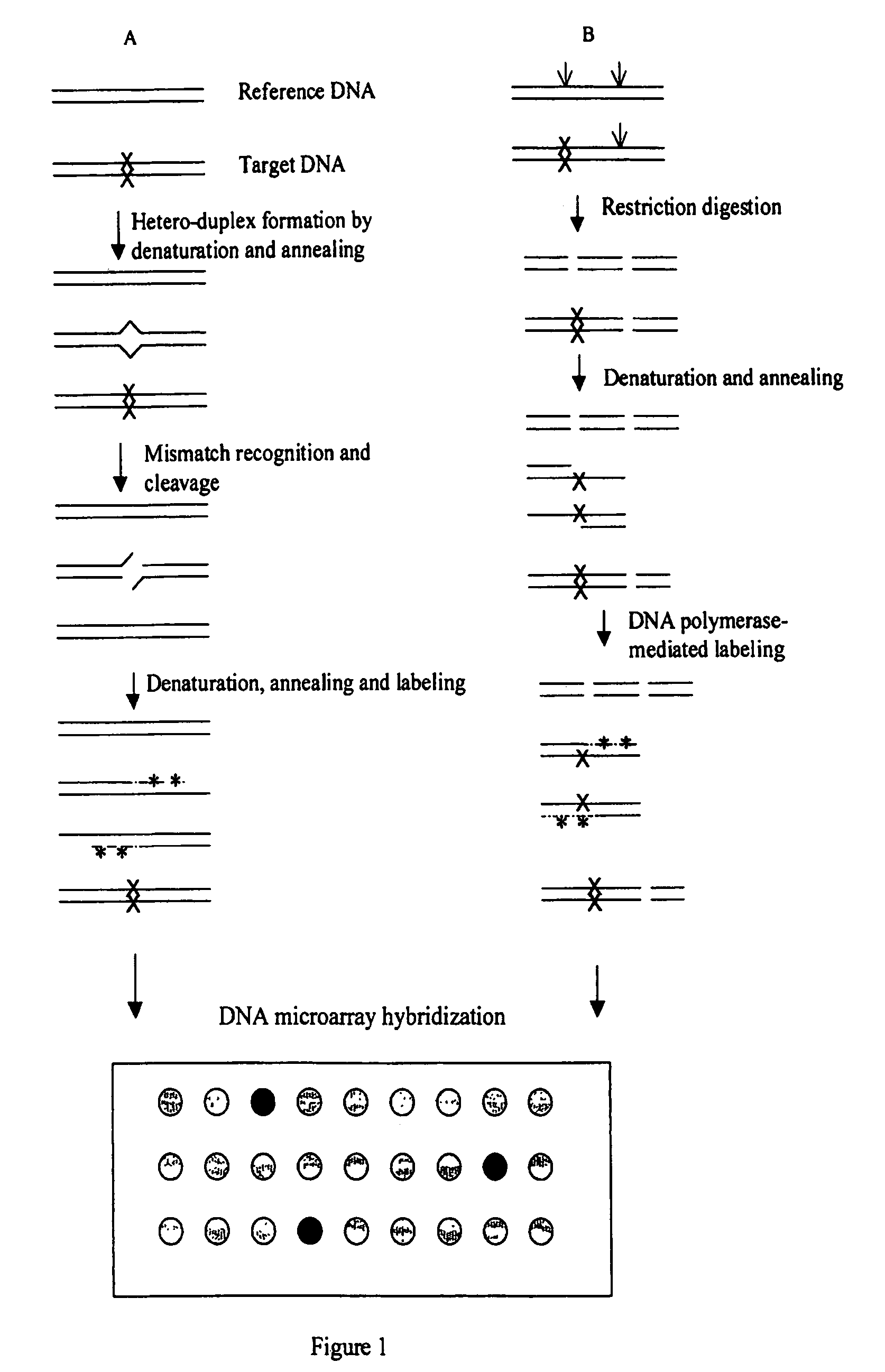
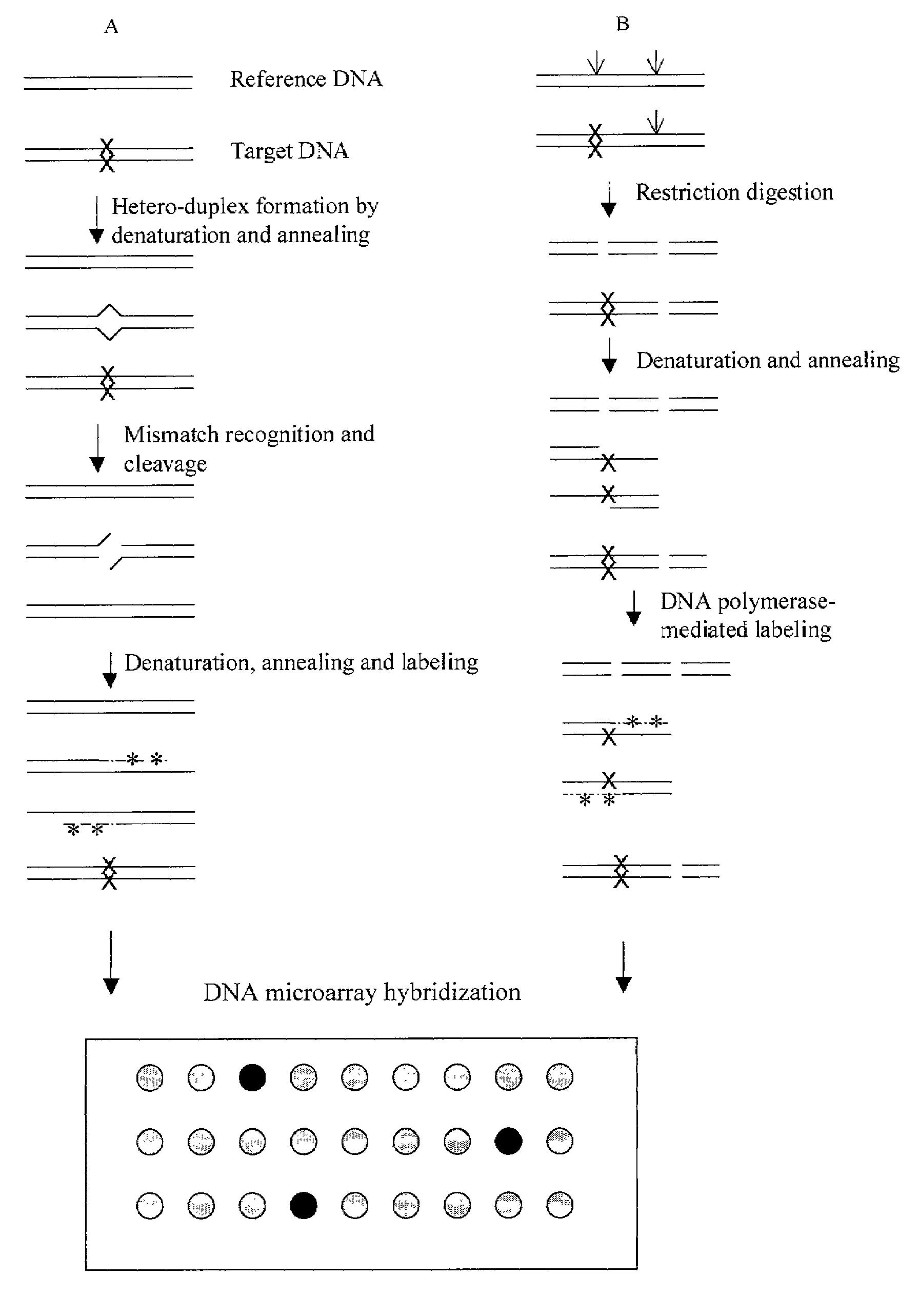
Methods for detecting and localizing DNA mutations by microarray
InactiveUS7141371B2Reduce the impactReduce impactMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHeterologousDNA microarray
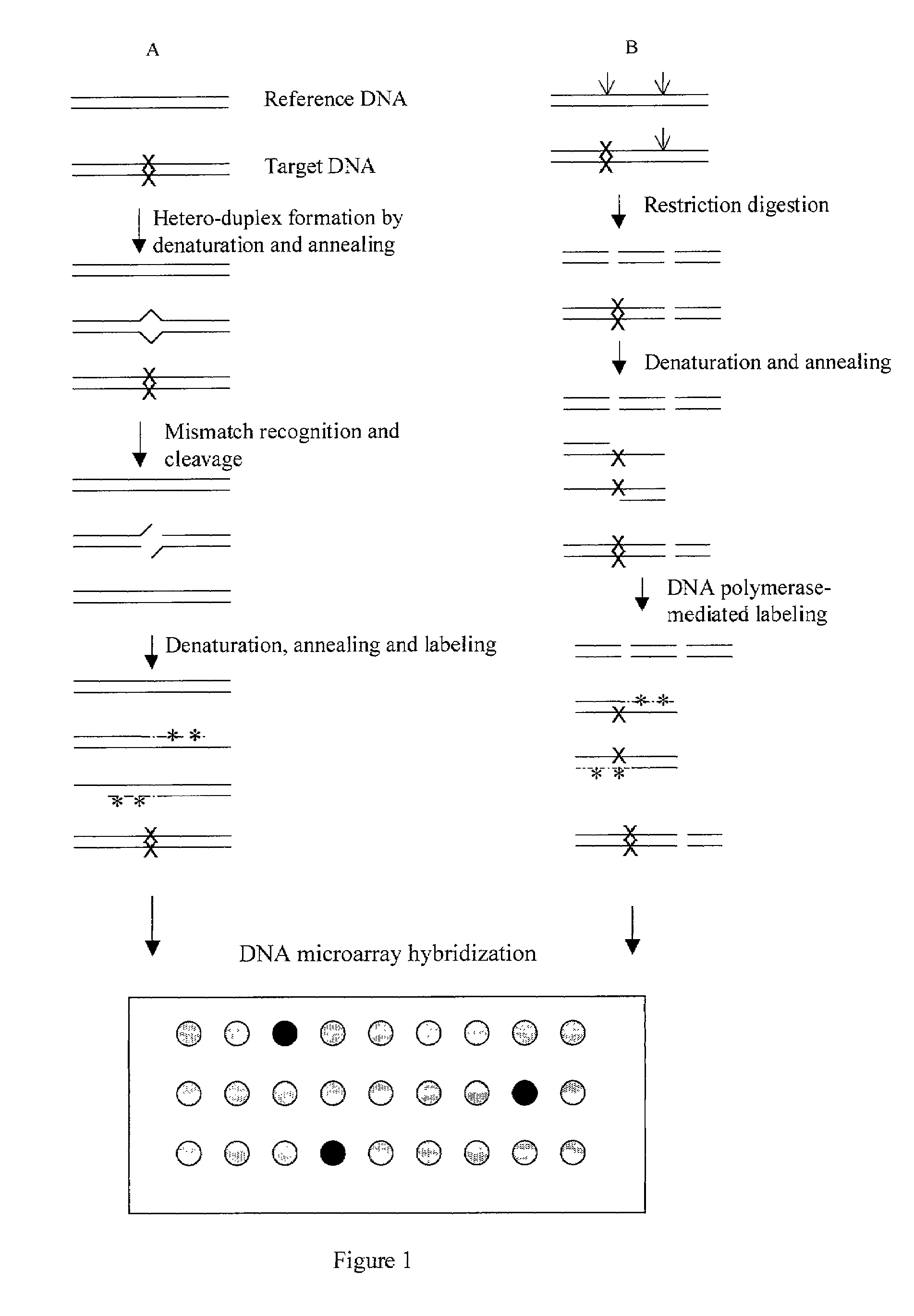
This disclosure provides methods for detecting and localizing DNA mutations by DNA microarray. In various embodiments, the described methods include use of restriction endonuclease(s) and / or mismatch-recognition nuclease(s) to detect and / or localize mutations. In one representative method, reference and target DNA are digested using one or more restriction endonucleases, resultant DNA strands are labeled (e.g., using a DNA polymerase), and the labeled mixture of DNAs is hybridized to a microarry. In another representative method, reference and target DNA are denatured and annealed to form a mixture containing heteroduplex DNA, one or more mismatch-recognition nuclease(s) are used to nick or cleave at least a portion of the heteroduplex DNA, resultant DNA strands are labeled (e.g., using a DNA polymerase) and the labeled mixture of DNAs is hybridized to a microarray.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF OREGON
Heteroduplex tracking assay
InactiveUS7344830B2Accurately predict disease prognosis over timeGood treatment effectMicrobiological testing/measurementVertebrate cellsHeterologousHeteroduplex
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
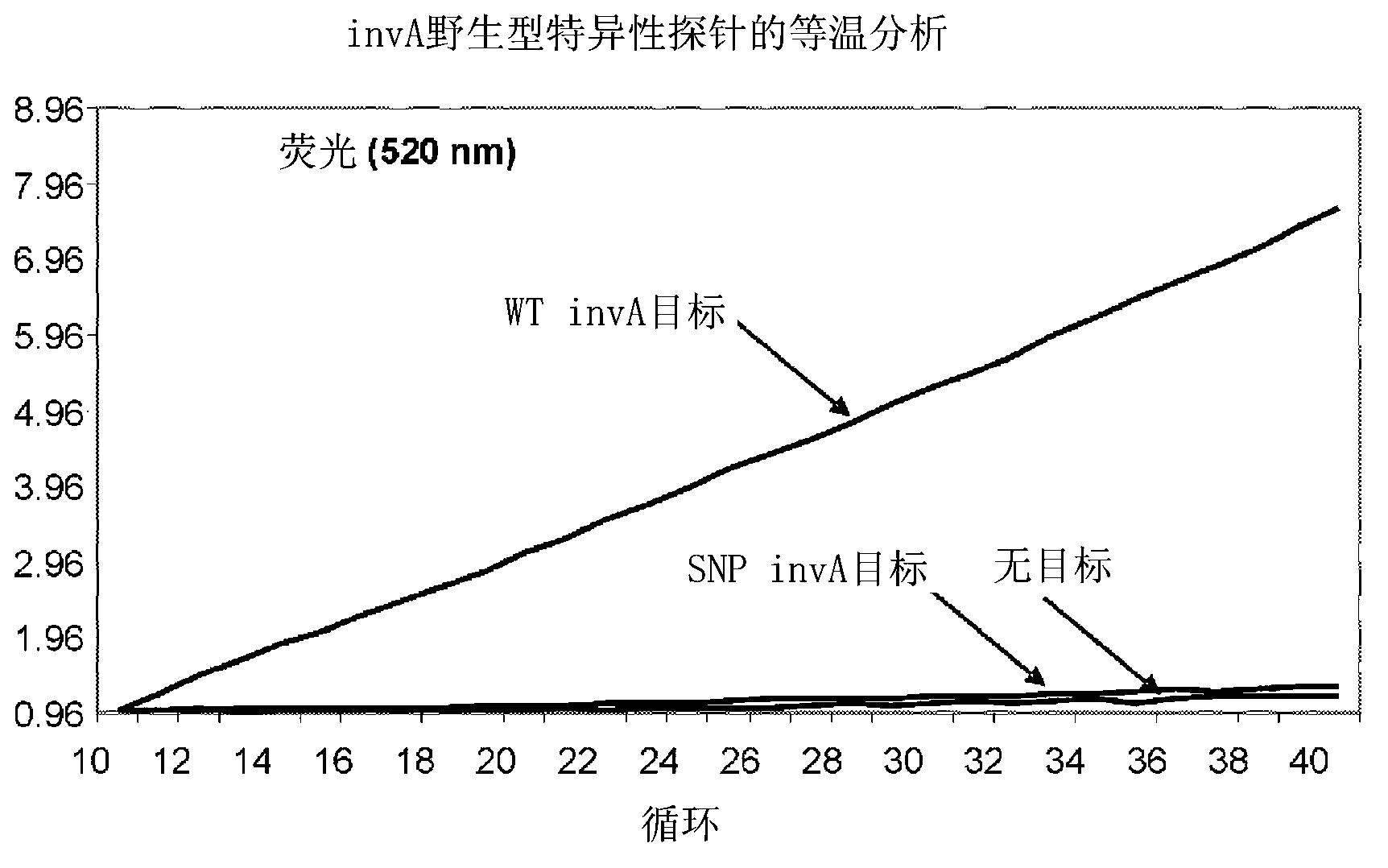
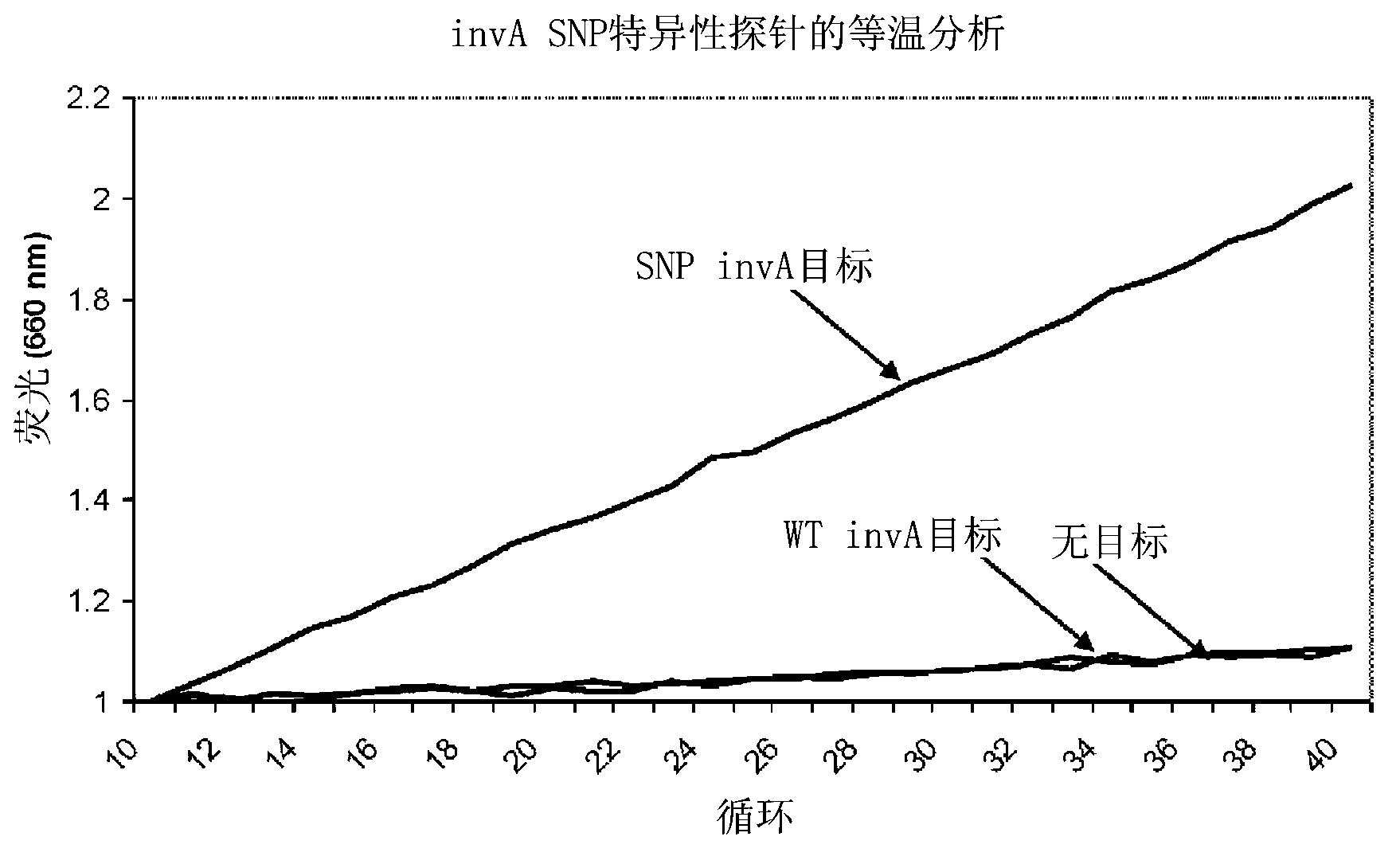
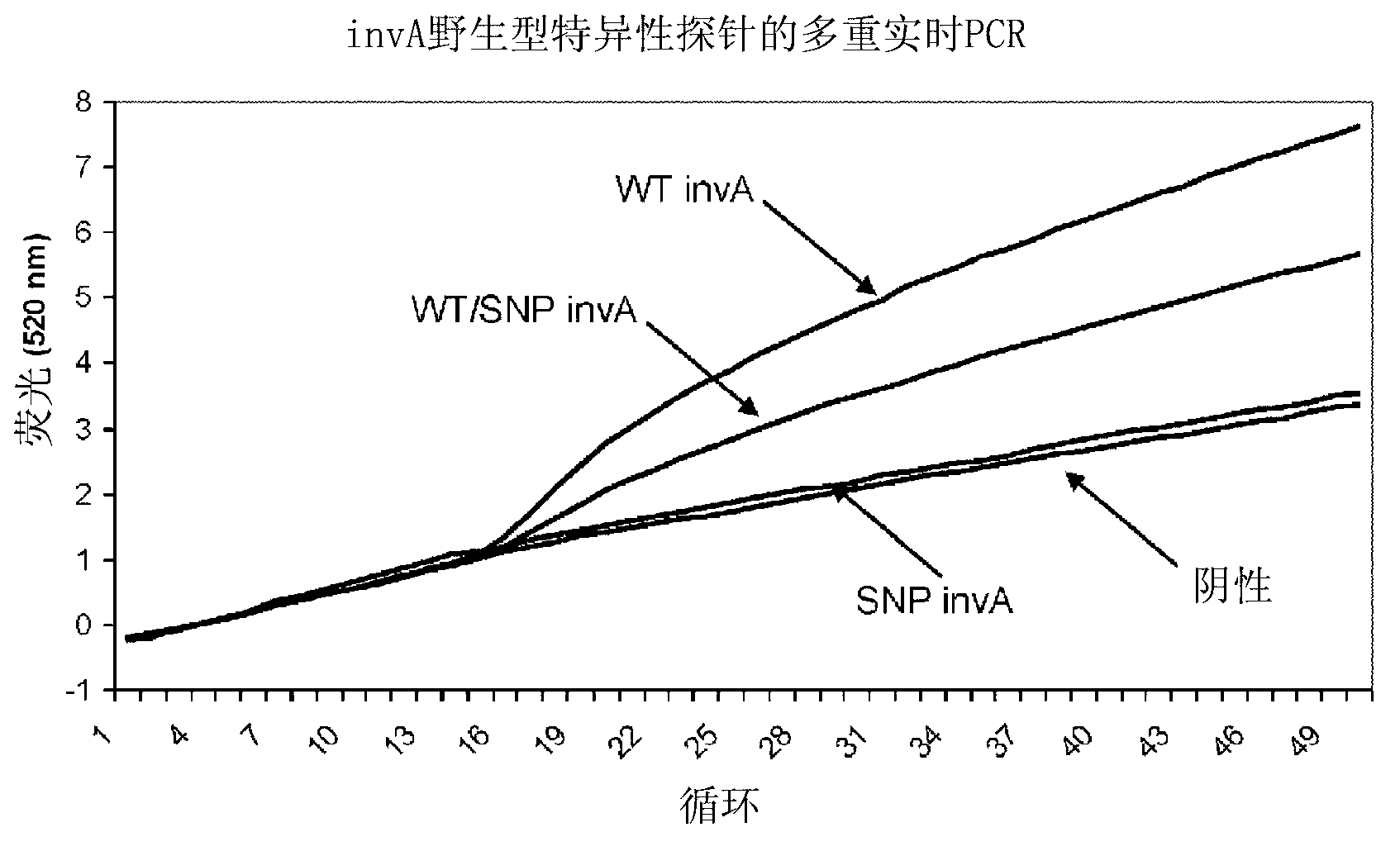
Real time pcr detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms
InactiveCN103154271AEasy diagnosisFriendly and reliable diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHeteroduplexNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed are methods and kits for the detection of a polymorphism during real-time PCR. Real-time PCR amplification of a target nucleic acid sequence is performed using PCR primer primers that anneal to sequences flanking a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of interest. The real-time PCR reaction includes a labeled probe comprising a RNA sequence that is designed to anneal to DNA sequences at the location of the SNP. An RNA:DNA heteroduplex can then form between the SNP in the PCR fragment and the probe's RNA sequences that are complementary to the SNP. RNase H cleavage of the RNA sequence in the RNA:DNA heteroduplex results in increase in intensity of the signal generated from the label that is indicative of the presence of an SNP in the target nucleic acid.
Owner:SAMSUNG TECHWIN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com