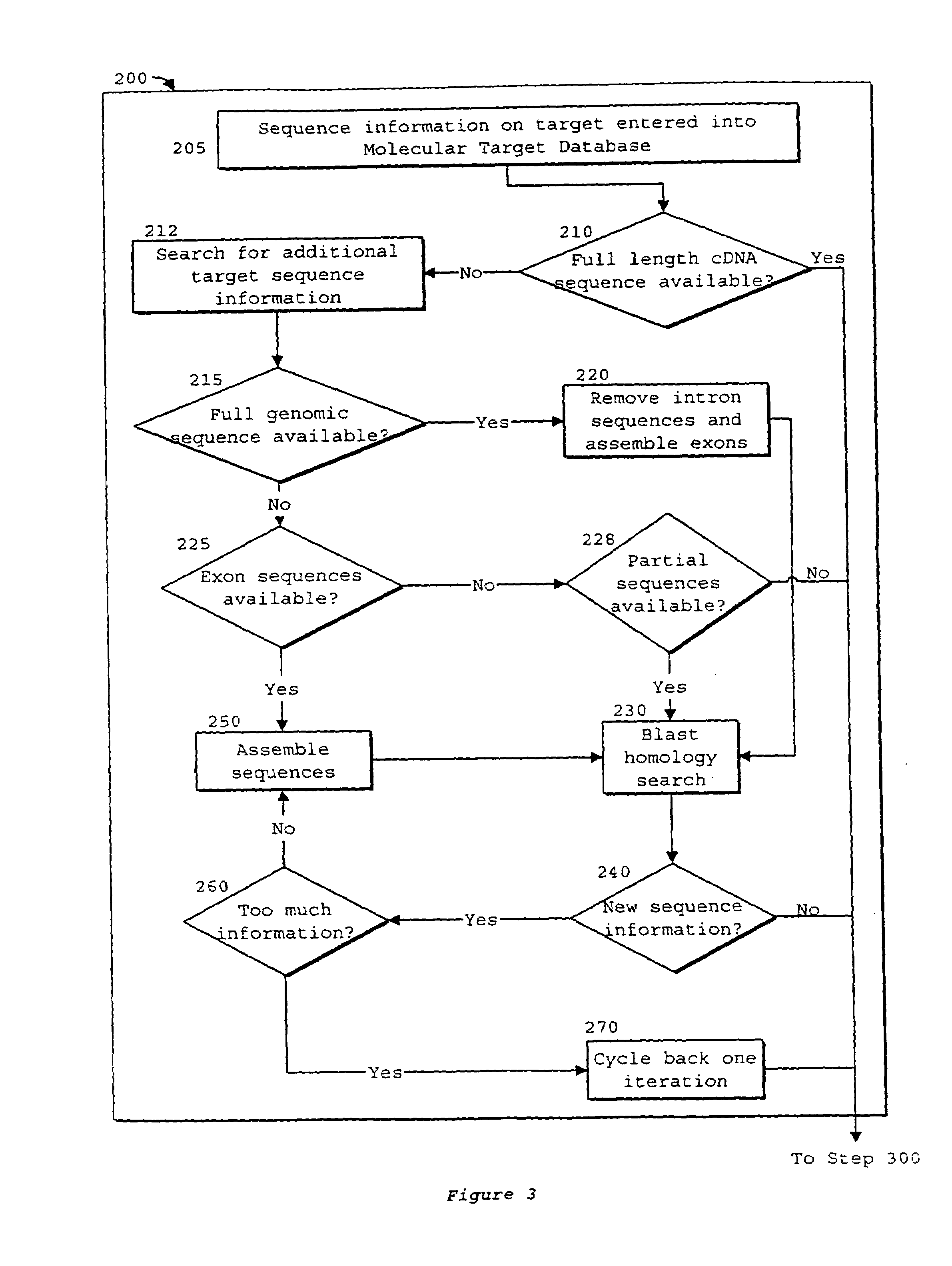
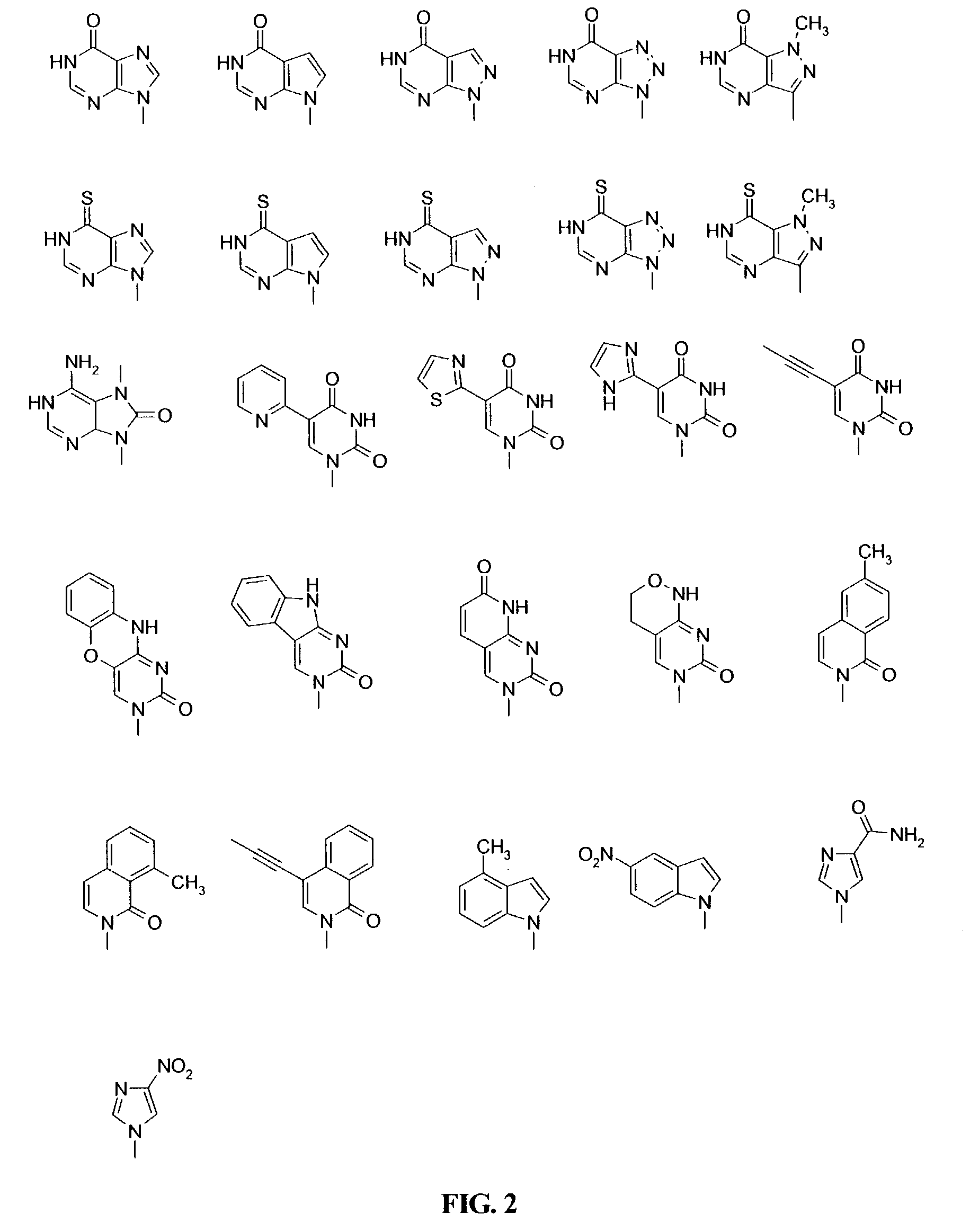
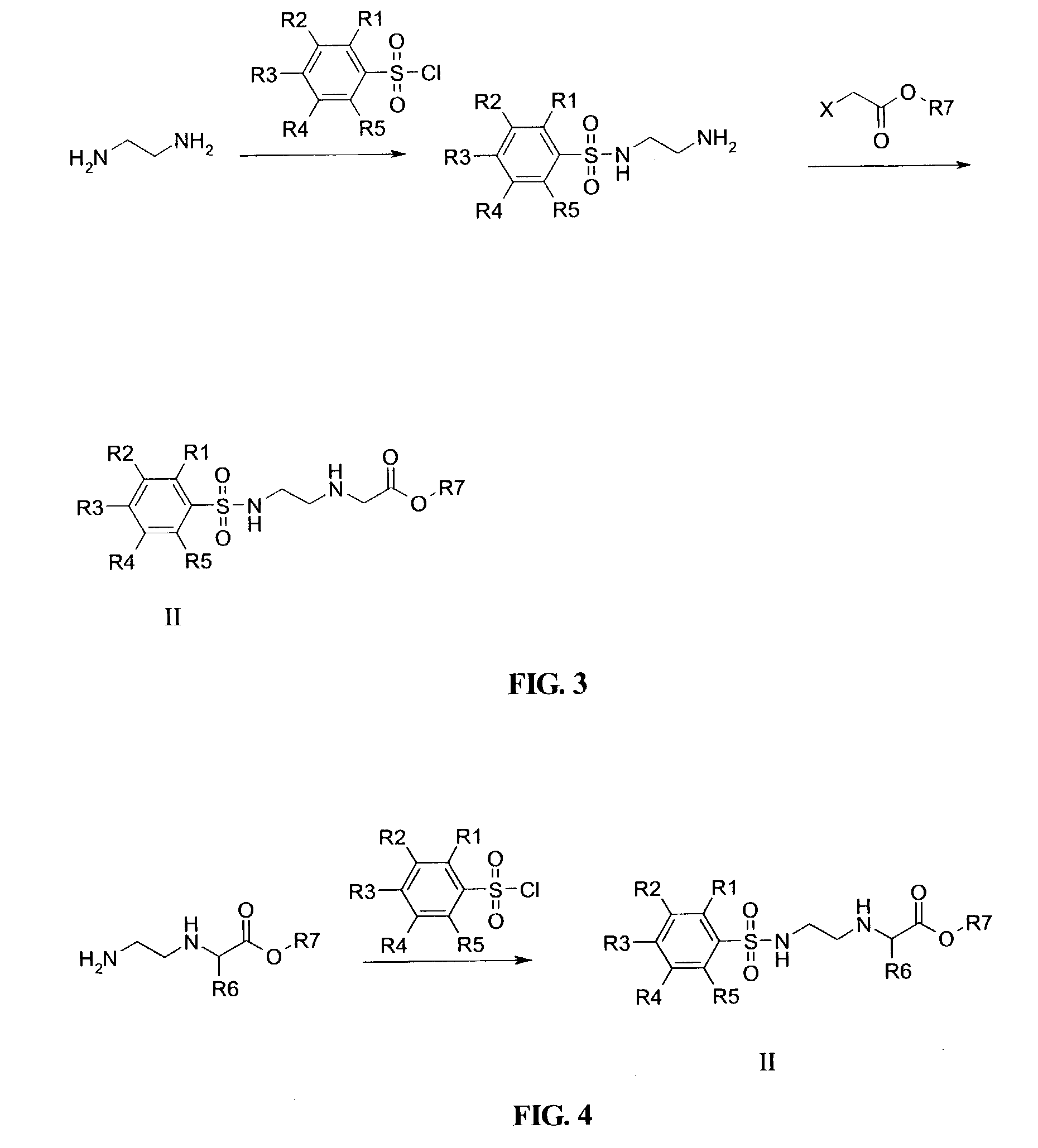
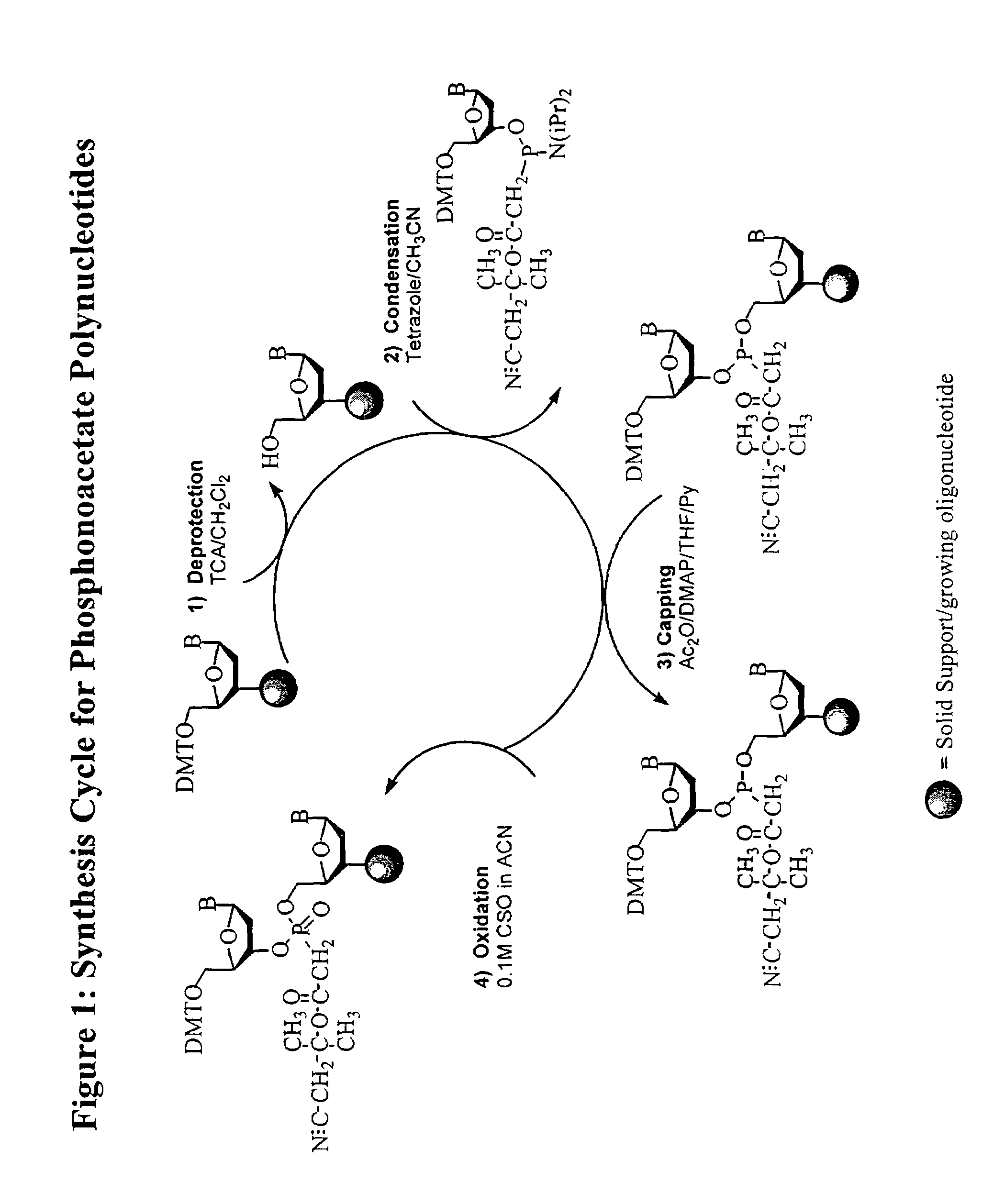
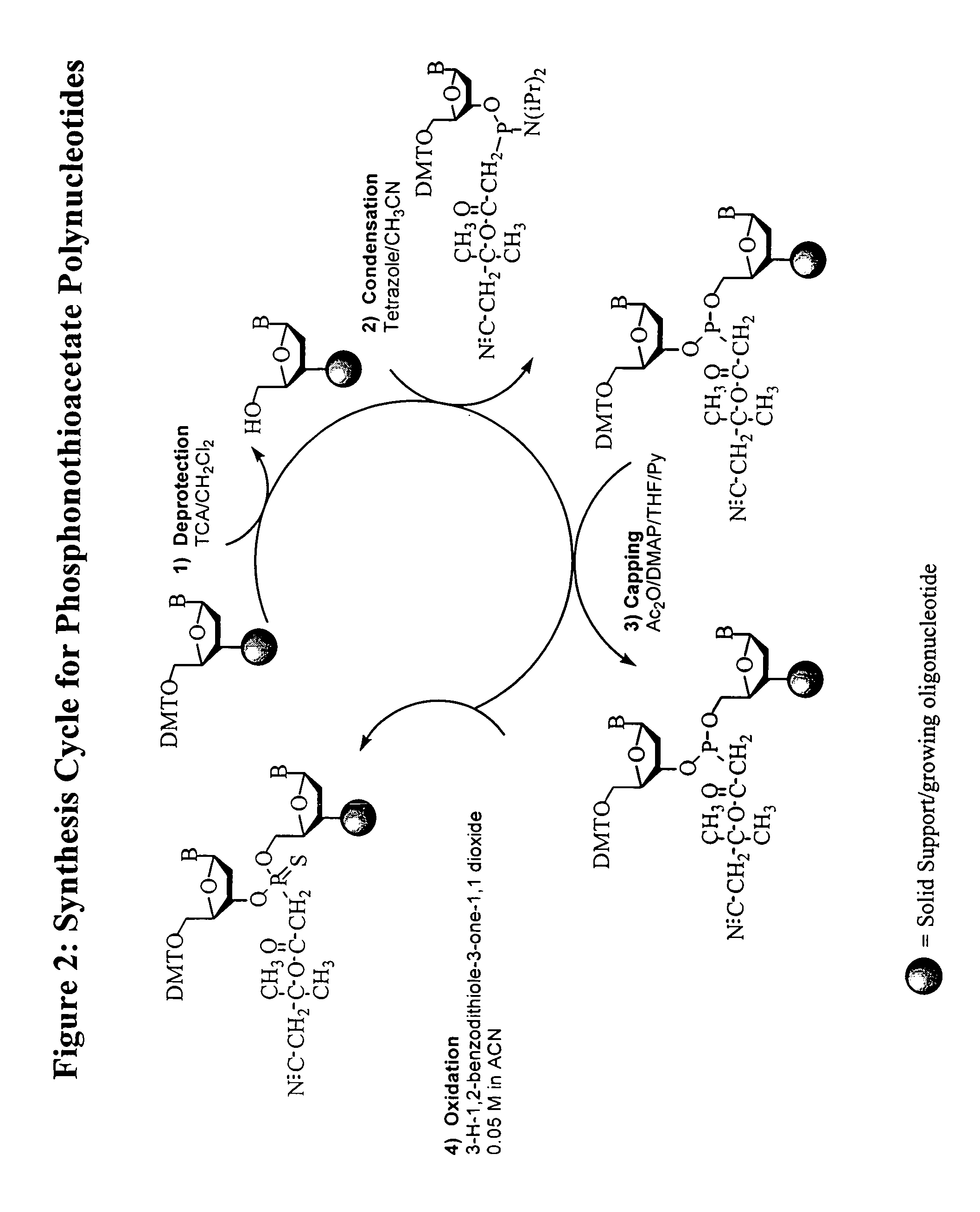
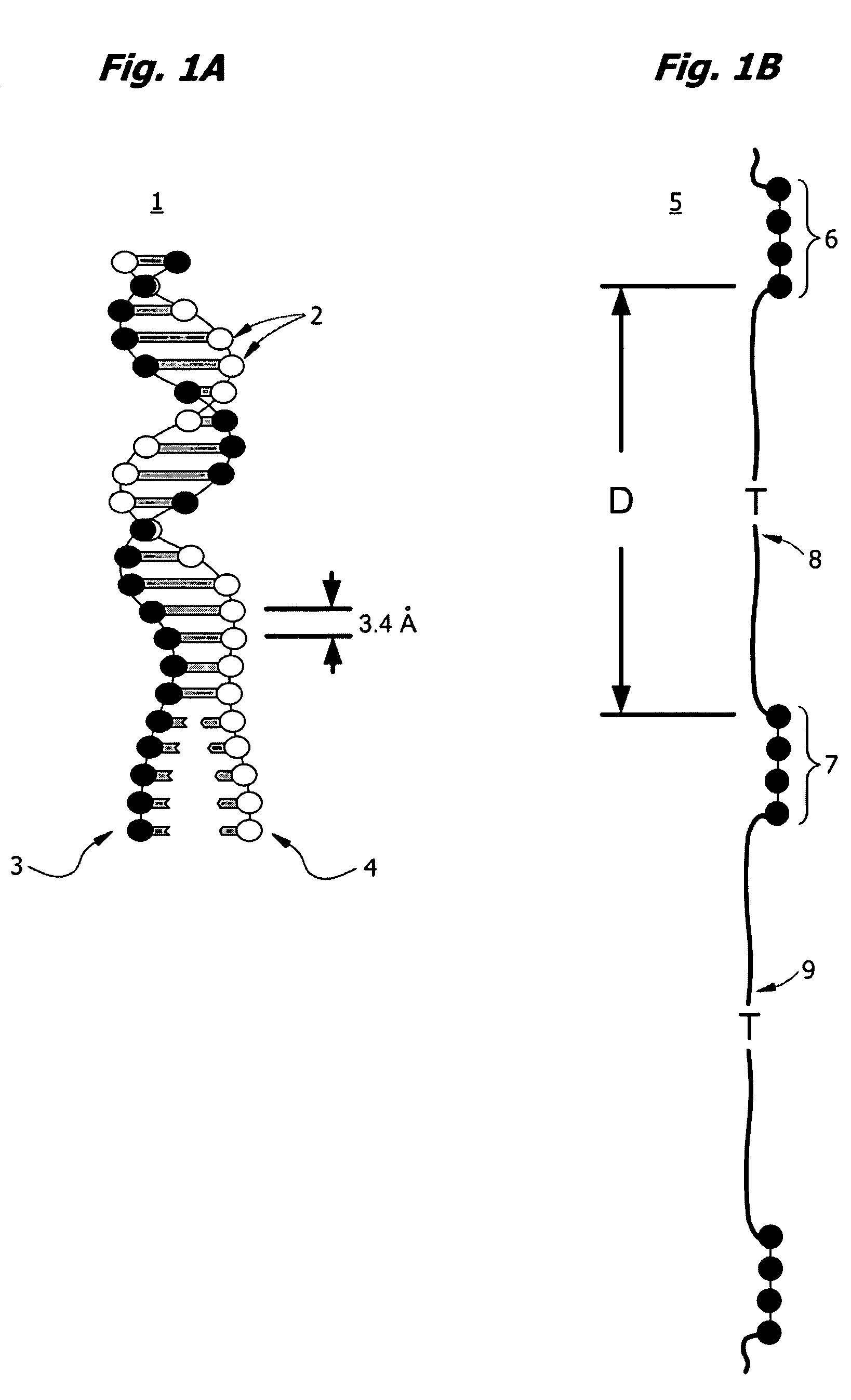
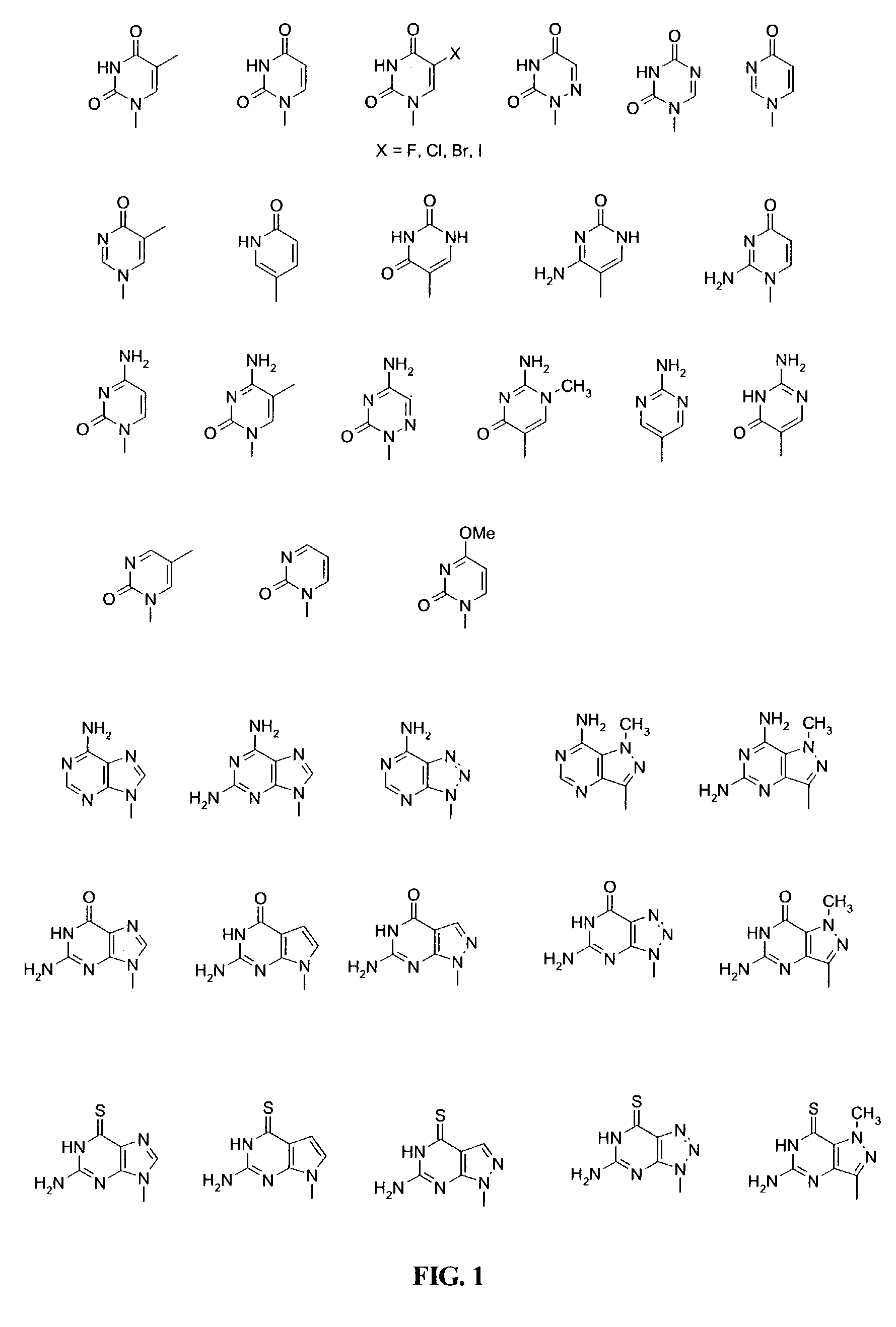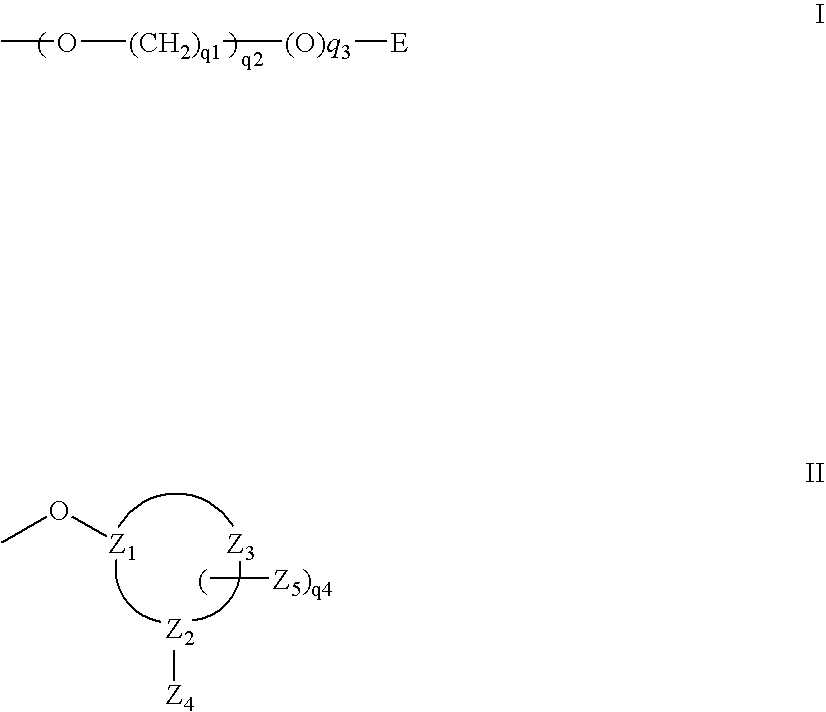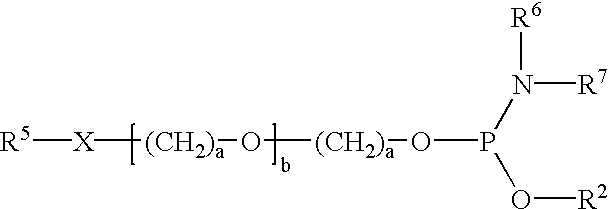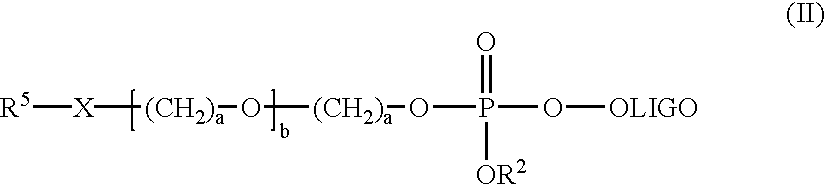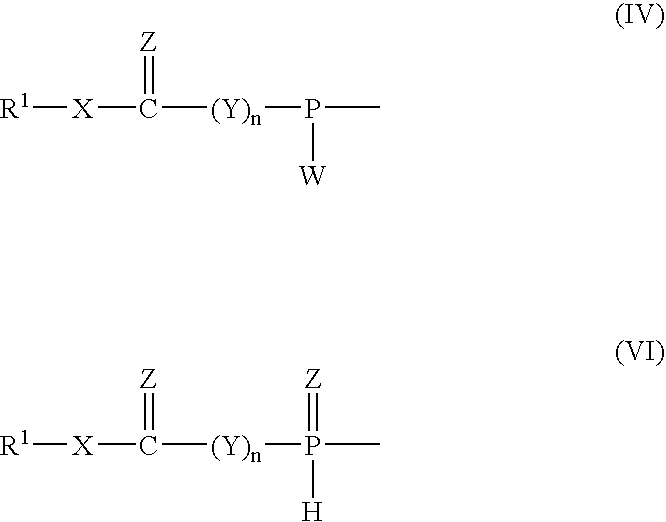Patents
Literature
262 results about "Nucleobase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
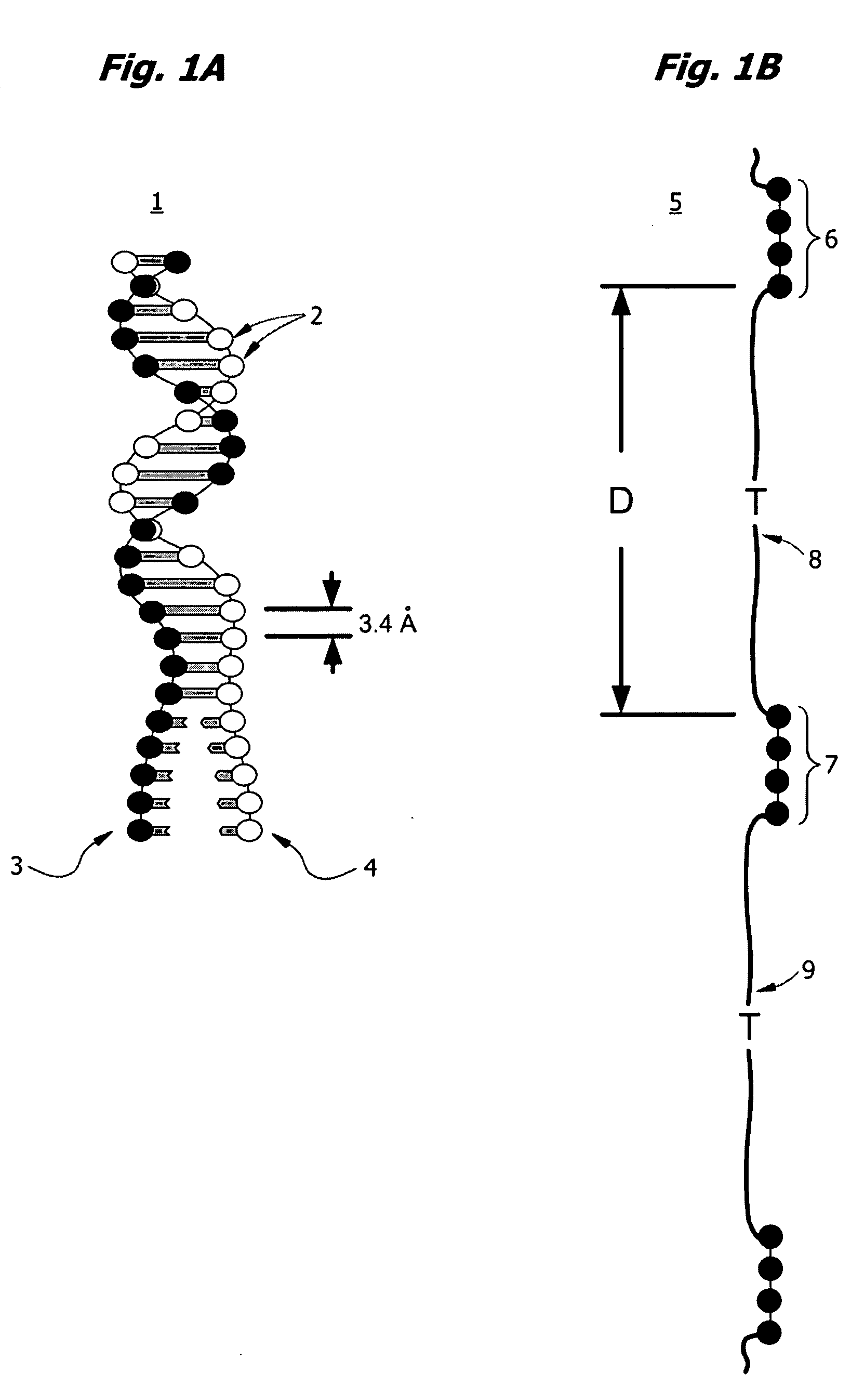
Nucleobases, also known as nitrogenous bases or often simply bases, are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which in turn are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
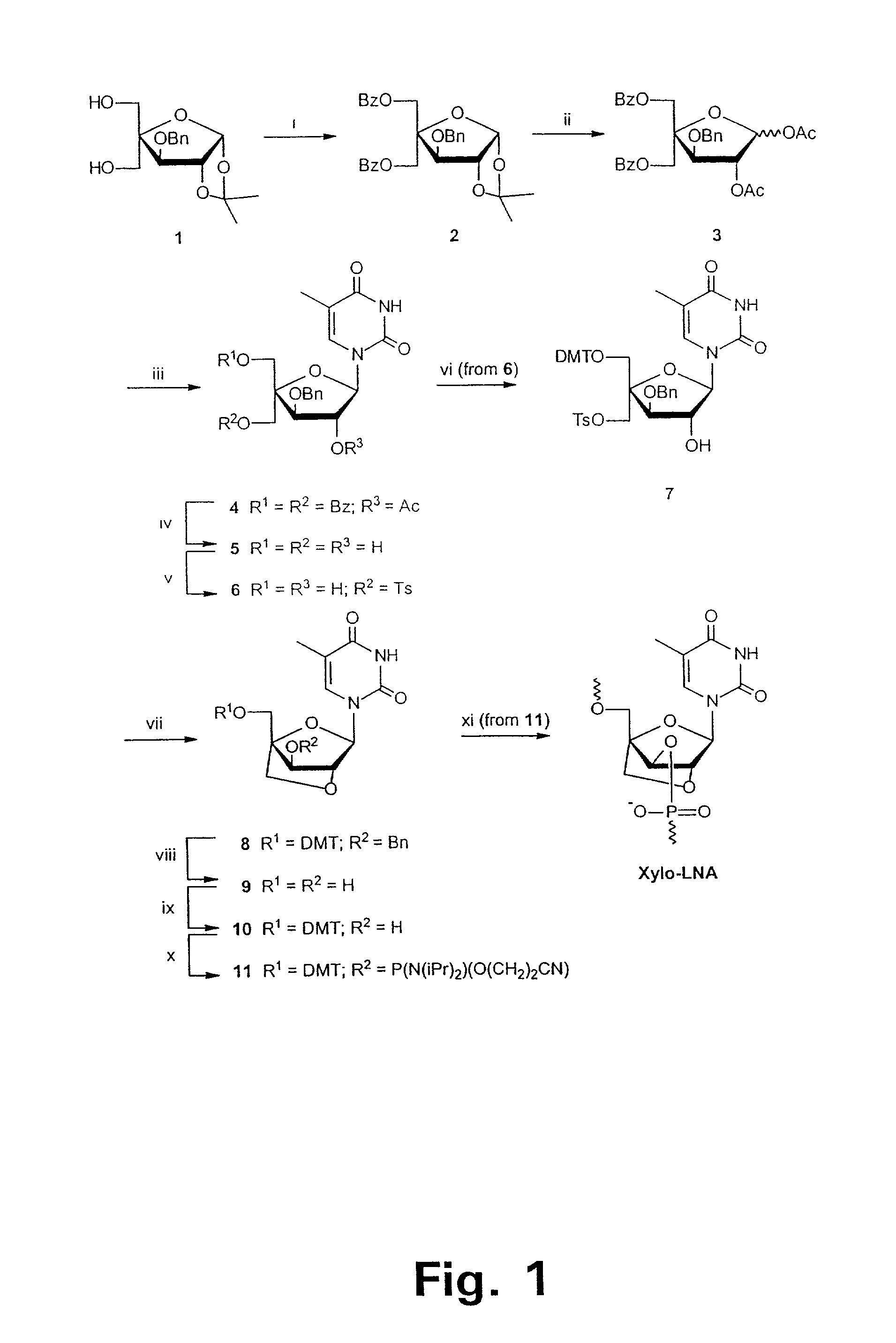
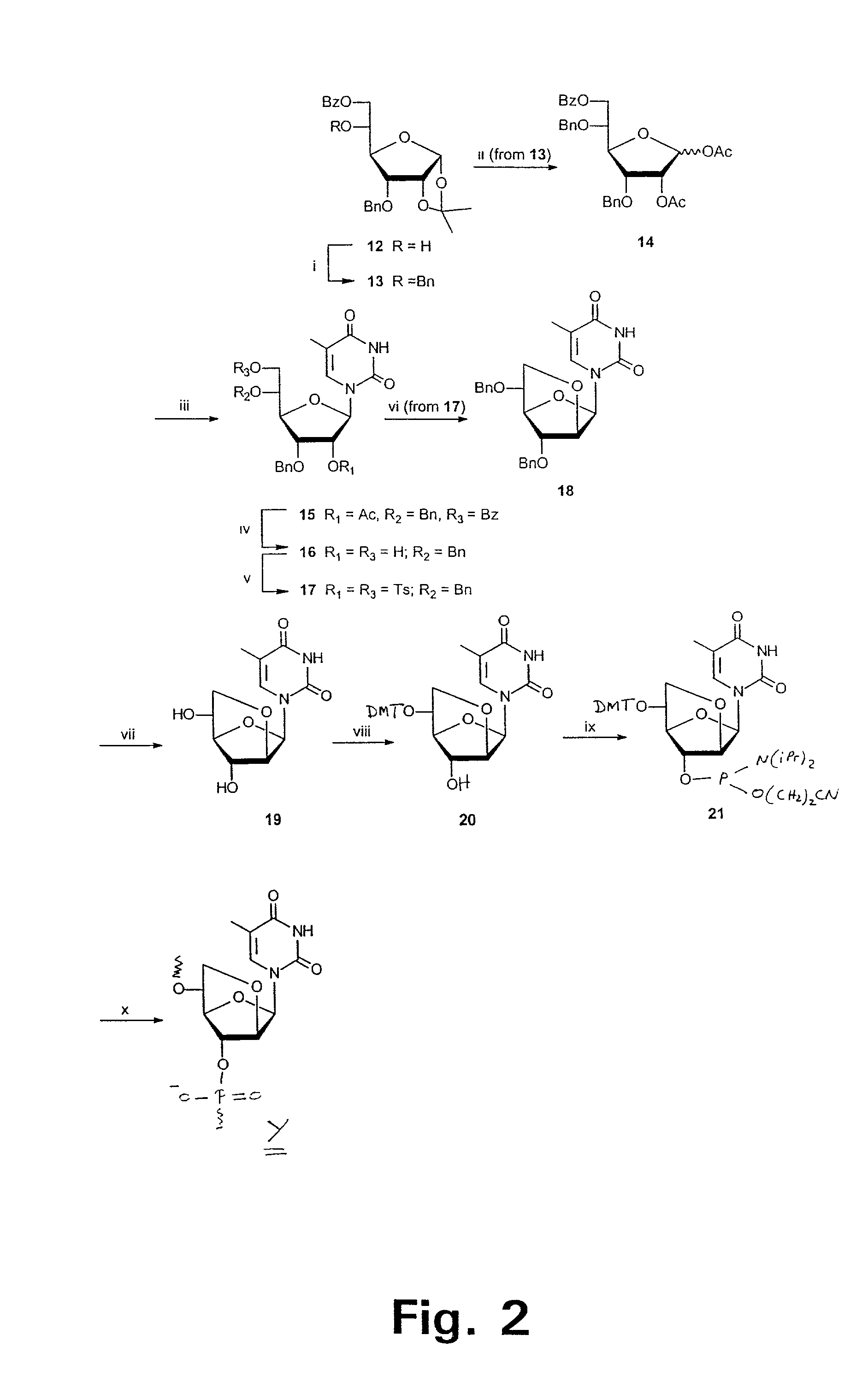
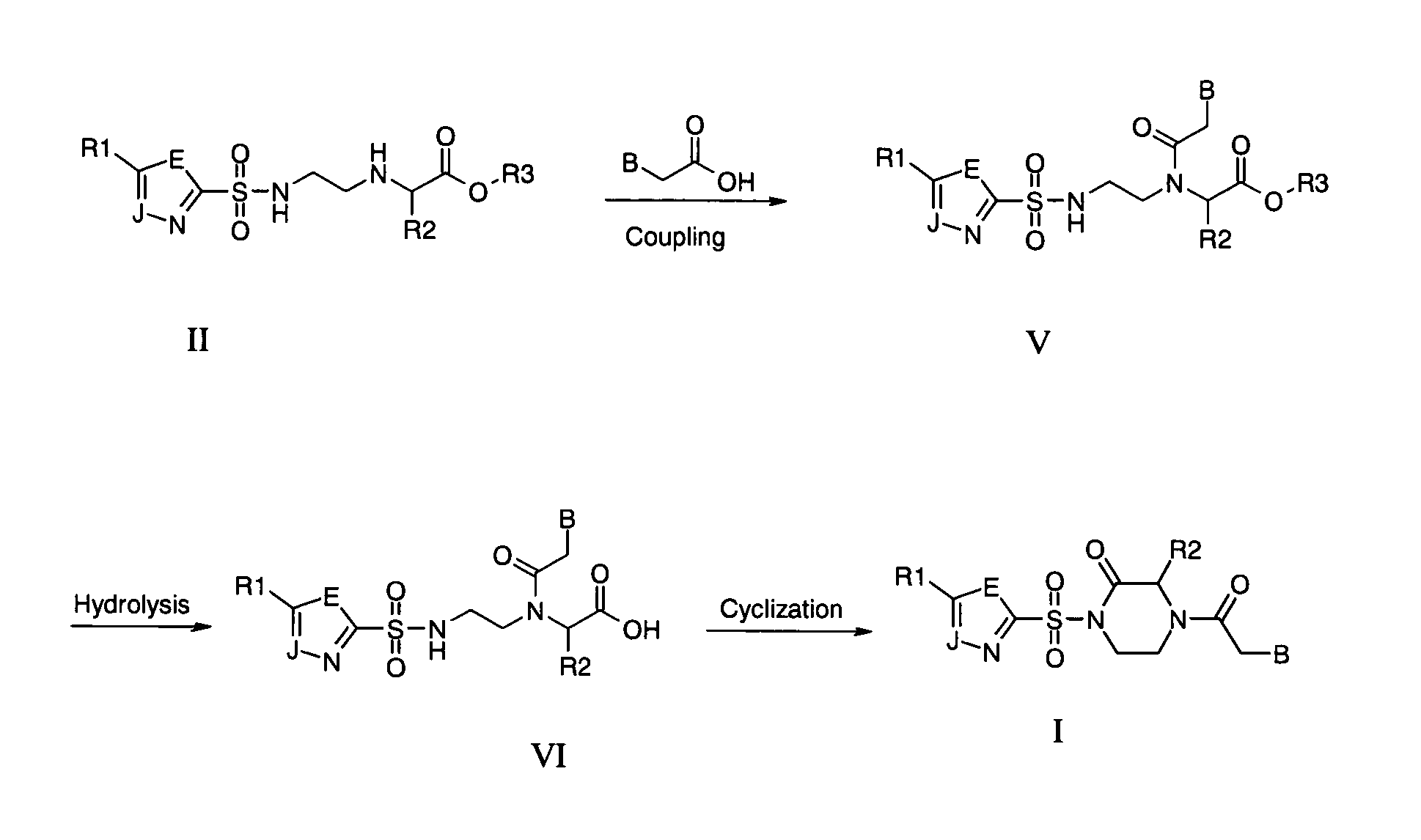
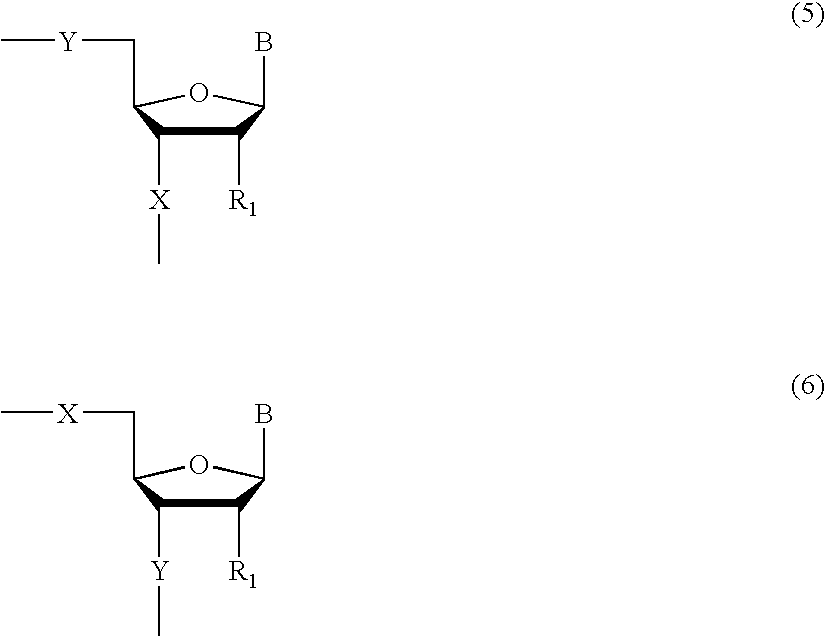
Xylo-LNA analogues
Based on the above and on the remarkable properties of the 2′-O,4′-C-methylene bridged LNA monomers it was decided to synthesise oligonucleotides comprising one or more 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer(s) as the first stereoisomer of LNA modified oligonucleotides. Modelling clearly indicated the xylo-LNA monomers to be locked in an N-type furanose conformation. Whereas the parent 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleosides were shown to adopt mainly an N-type furanose conformation, the furanose ring of the 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl monomers present in xylo-DNA were shown by conformational analysis and computer modelling to prefer an S-type conformation thereby minimising steric repulsion between the nucleobase and the 3′-O-phopshate group (Seela, F.; Wömer, Rosemeyer, H. Helv. Chem. Acta 1994, 77, 883). As no report on the hybridisation properties and binding mode of xylo-configurated oligonucleotides in an RNA context was believed to exist, it was the aim to synthesise 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer and to study the thermal stability of oligonucleotides comprising this monomer. The results showed that fully modified or almost fully modified Xylo-LNA is useful for high-affinity targeting of complementary nucleic acids. When taking into consideration the inverted stereochemistry at C-3′ this is a surprising fact. It is likely that Xylo-LNA monomers, in a sequence context of Xylo-DNA monomers, should have an affinity-increasing effect.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
High throughput nucleic acid sequencing by expansion
ActiveUS20090035777A1Easy to detectIncreasing linear separationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleic acid sequencing
Nucleic acid sequencing methods and related products are disclosed. Methods for sequencing a target nucleic acid comprise providing a daughter strand produced by a template-directed synthesis, the daughter strand comprising a plurality of subunits coupled in a sequence corresponding to a contiguous nucleotide sequence of all or a portion of the target nucleic acid, wherein the individual subunits comprise a tether, at least one probe or nucleobase residue, and at least one selectively cleavable bond. The selectively cleavable bond(s) is / are cleaved to yield an Xpandomer of a length longer than the plurality of the subunits of the daughter strand, the Xpandomer comprising the tethers and reporter elements for parsing genetic information in a sequence corresponding to the contiguous nucleotide sequence of all or a portion of the target nucleic acid. Reporter elements of the Xpandomer are then detected. Corresponding products, including Xpandomers and oligomeric and monomeric substrate constructs are also disclosed.
Owner:STRATOS GENOMICS
System of components for preparing oligonucleotides
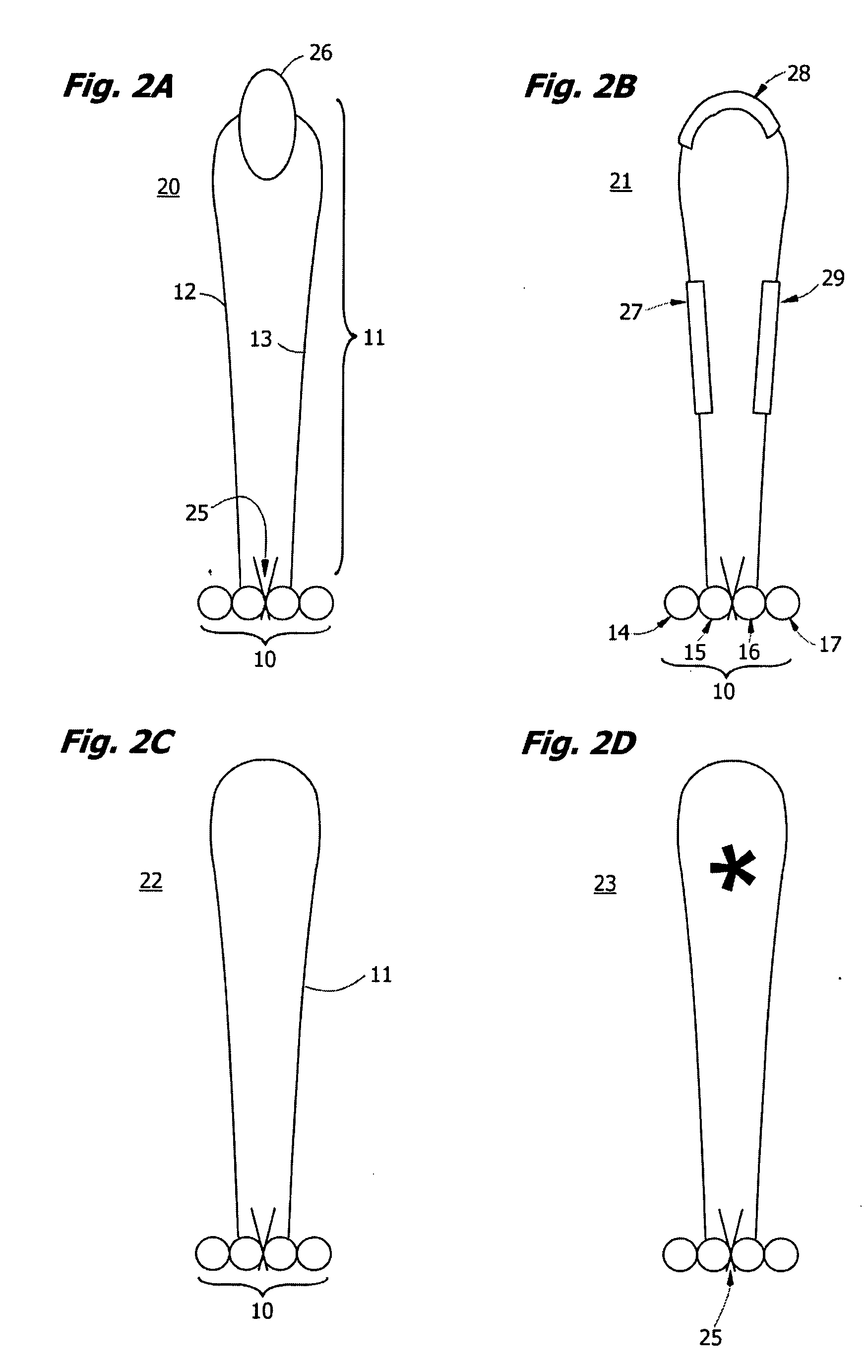
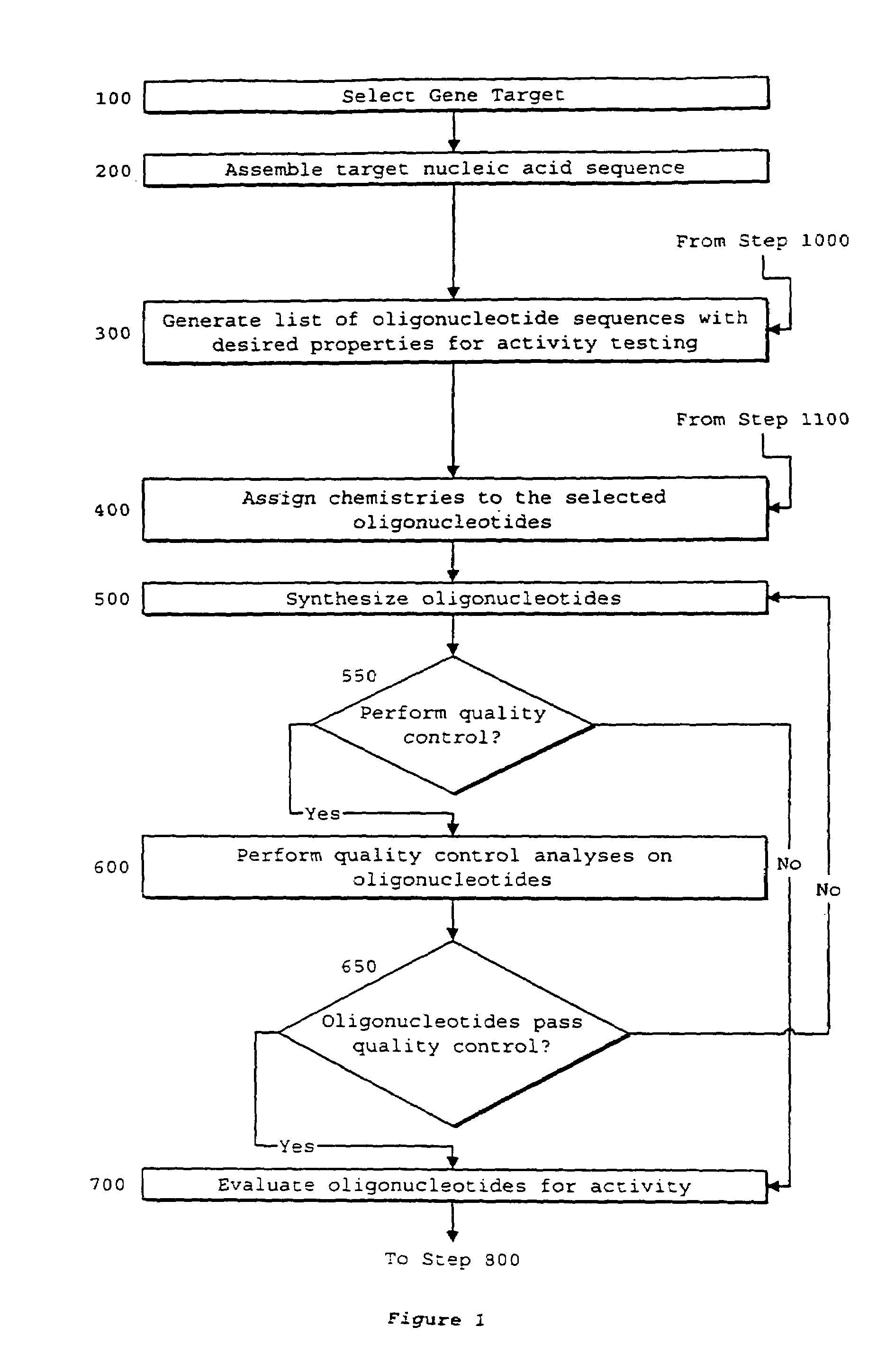
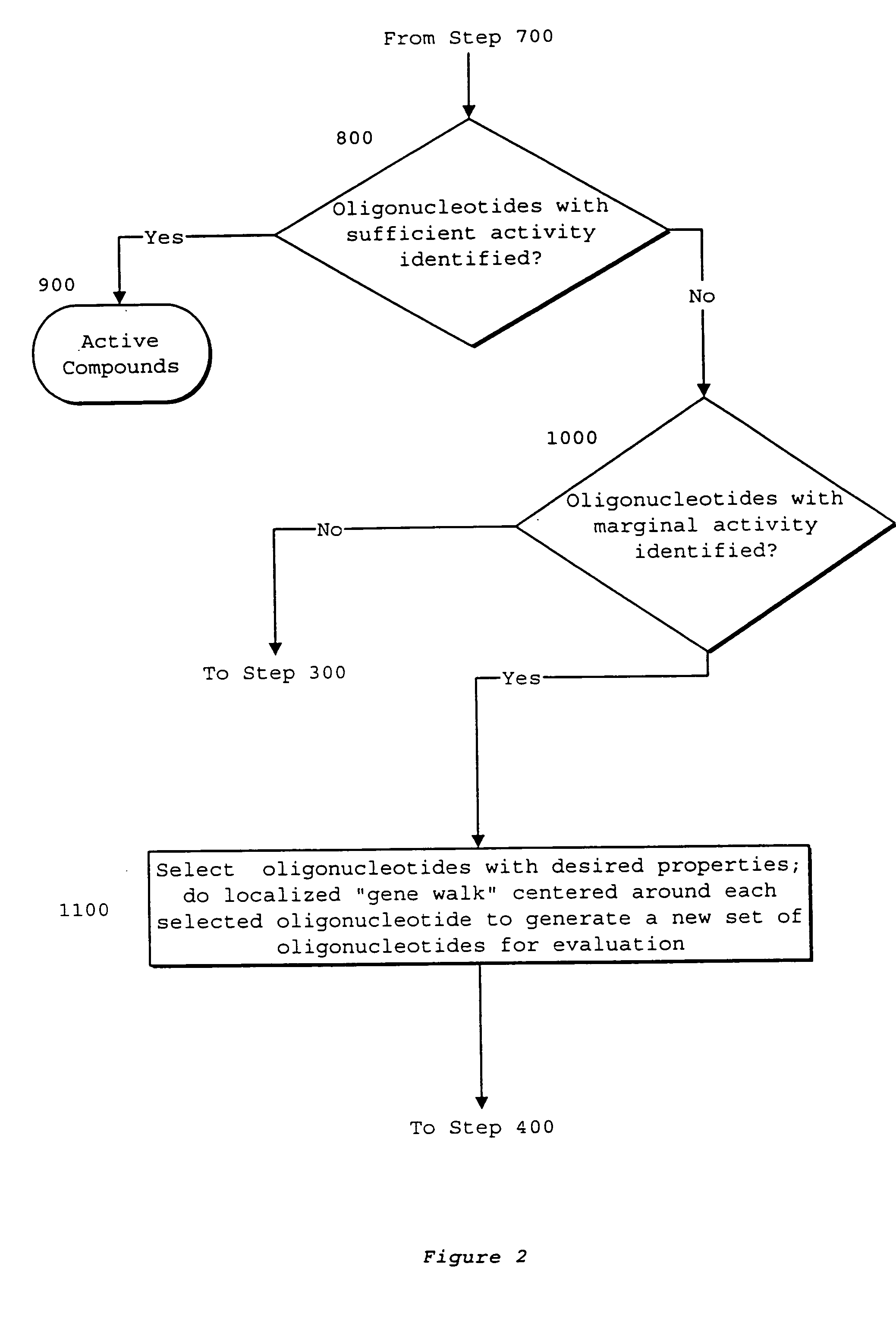
Interative, preferably computer based iterative processes for generating synthetic compounds with desired physical, chemical and / or bioactive properties, i.e., active compounds, are provided. During iterations of the processes, a target nucleic acid sequence is provided or selected, and a library of candidate nucleobase sequences is generated in silico according to defined criteria. A “virtual” oligonucleotide chemistry is chosen and a library of virtual oligonucleotide compounds having the selected nucleobase sequences is generated. These virtual compounds are reviewed and compounds predicted to have particular properties are selected. The selected compounds are robotically synthesized and are preferably robotically assayed for a desired physical, chemical or biological activity. Active compounds are thus generated and, at the same time, preferred sequences and regions of the target nucleic acid that are amenable to oligonucleotide or sequence-based modulation are identified.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
PNA monomer and precursor
InactiveUS7022851B2Improve efficiencyImprove convenienceSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBase JOligomer
This application relates to monomers of the general formula (I) for the preparation of PNA (peptide nucleic acid) oligomers and provides method for the synthesis of both predefined sequence PNA oligomers and random sequence PNA oligomers: whereinR1, R2, R3, R4, R5 is independently H, halogen, C1–C4 alkyl, nitro, nitrile, C1–C4 alkoxy, halogenated C1–C4 alkyl, or halogenated C1–C4 alkoxy, wherein at least one of R1, R3, and R5 is nitro;R6 is H or protected or unprotected side chain of natural or unnatural α-amino acid; andB is a natural or unnatural nucleobase, wherein when said nucleobase has an exocyclic amino function, said function is protected by protecting group which is labile to acids but stable to weak to medium bases.
Owner:PANAGENE INC
PNA monomer and precursor
ActiveUS7211668B2Improve efficiencyImprove convenienceOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSide chainNucleobase
Owner:PANAGENE INC
Pharmaceutical Composition
InactiveUS20100004320A1Reduce depressionEffectively repressedAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideNucleobase
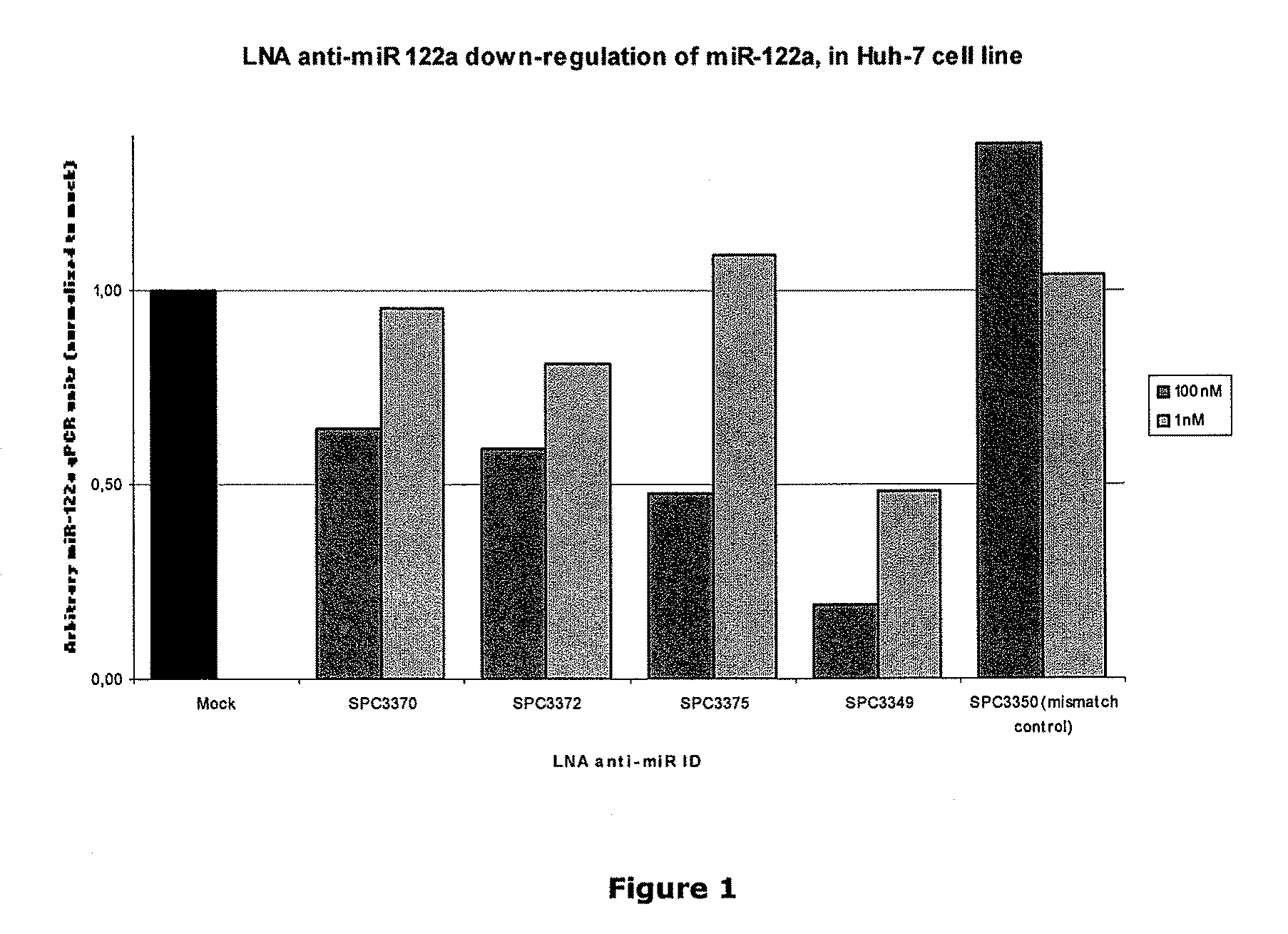
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising short single stranded oligonucleotides, of length of between 8 and 17 nucleobases which are complementary to human microRNAs. The short oligonucleotides are particularly effective at alleviating miRNA repression in vivo. It is found that the incorporation of high affinity nucleotide analogues into the oligonucleotides results in highly effective anti-microRNA molecules which appear to function via the formation of almost irreversible duplexes with the miRNA target, rather than RNA cleavage based mechanisms, such as mechanisms associated with RNaseH or RISC.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Oligonucleotides comprising a modified or non-natural nucleobase
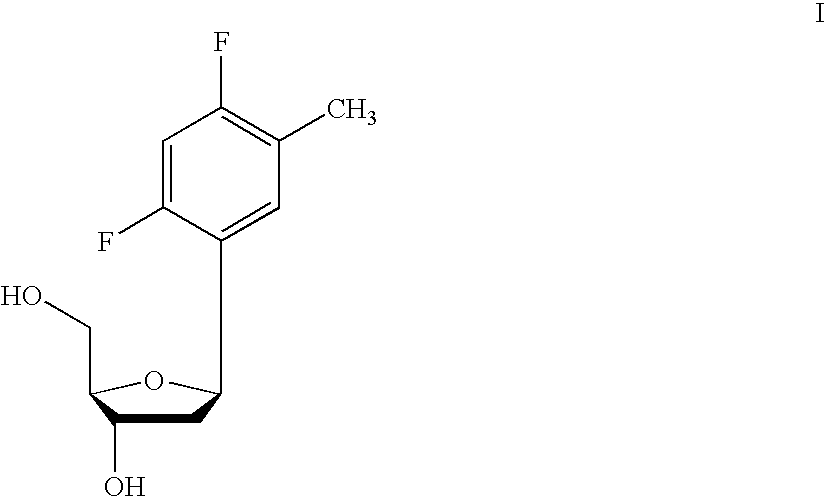
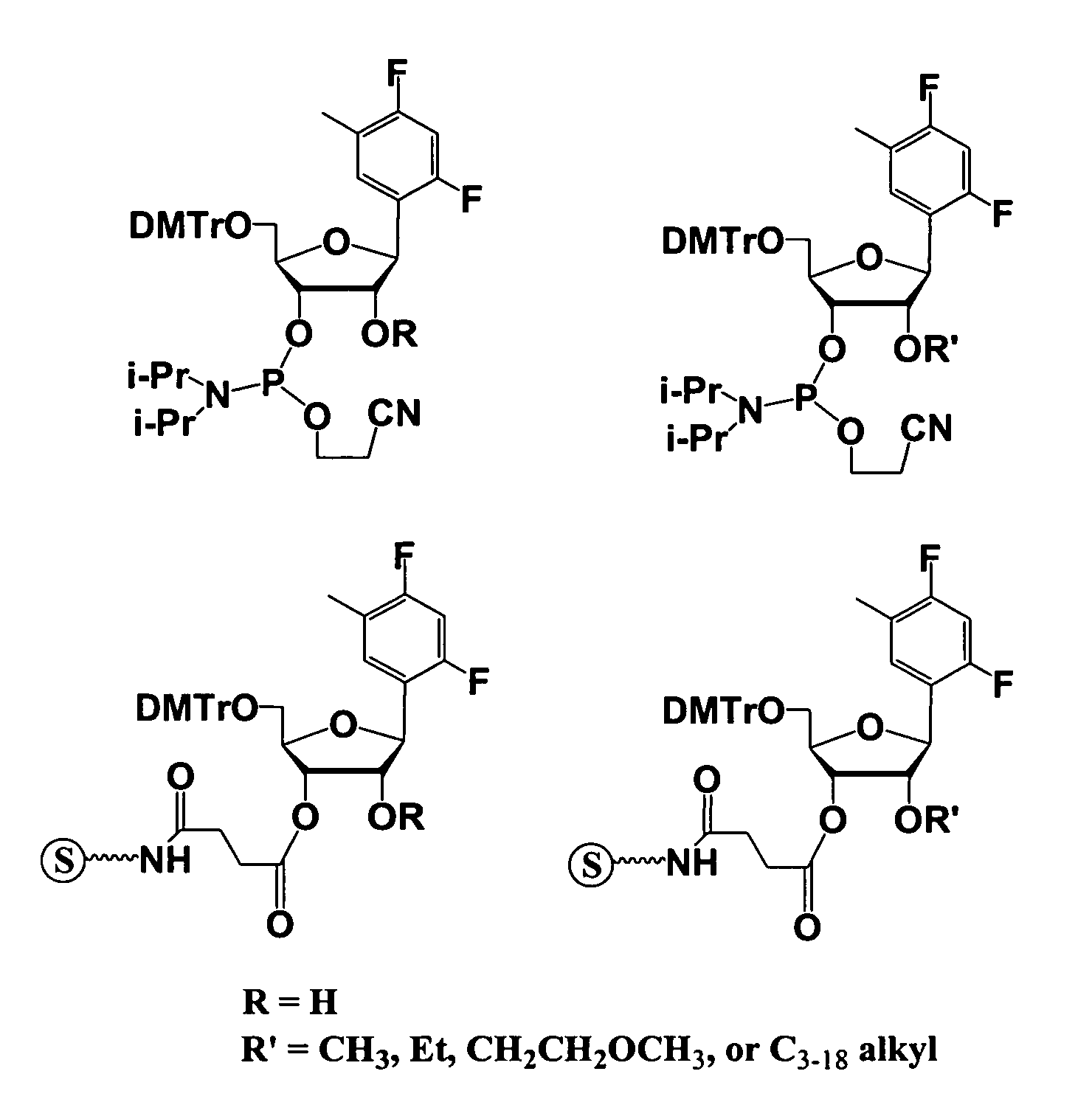
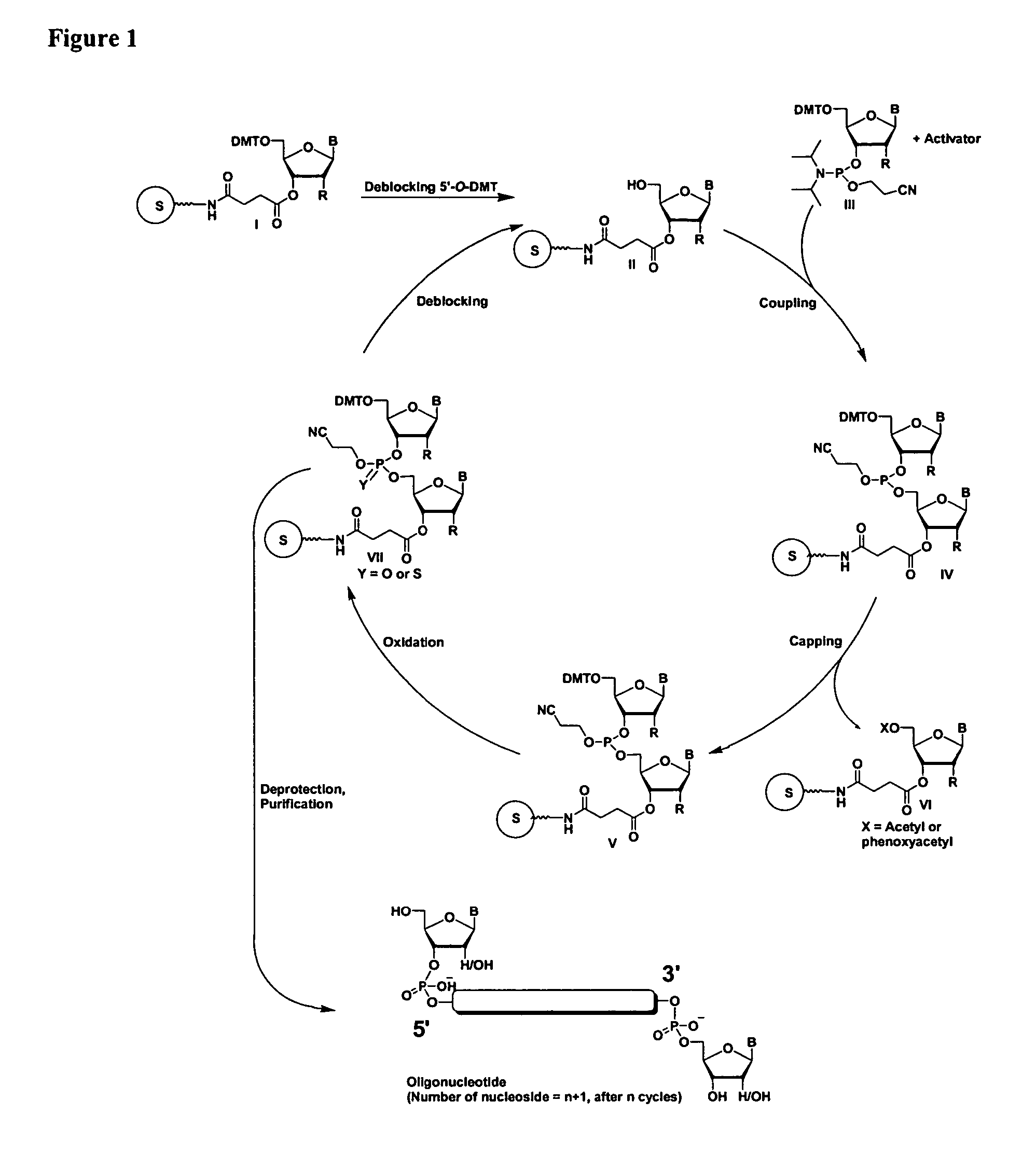
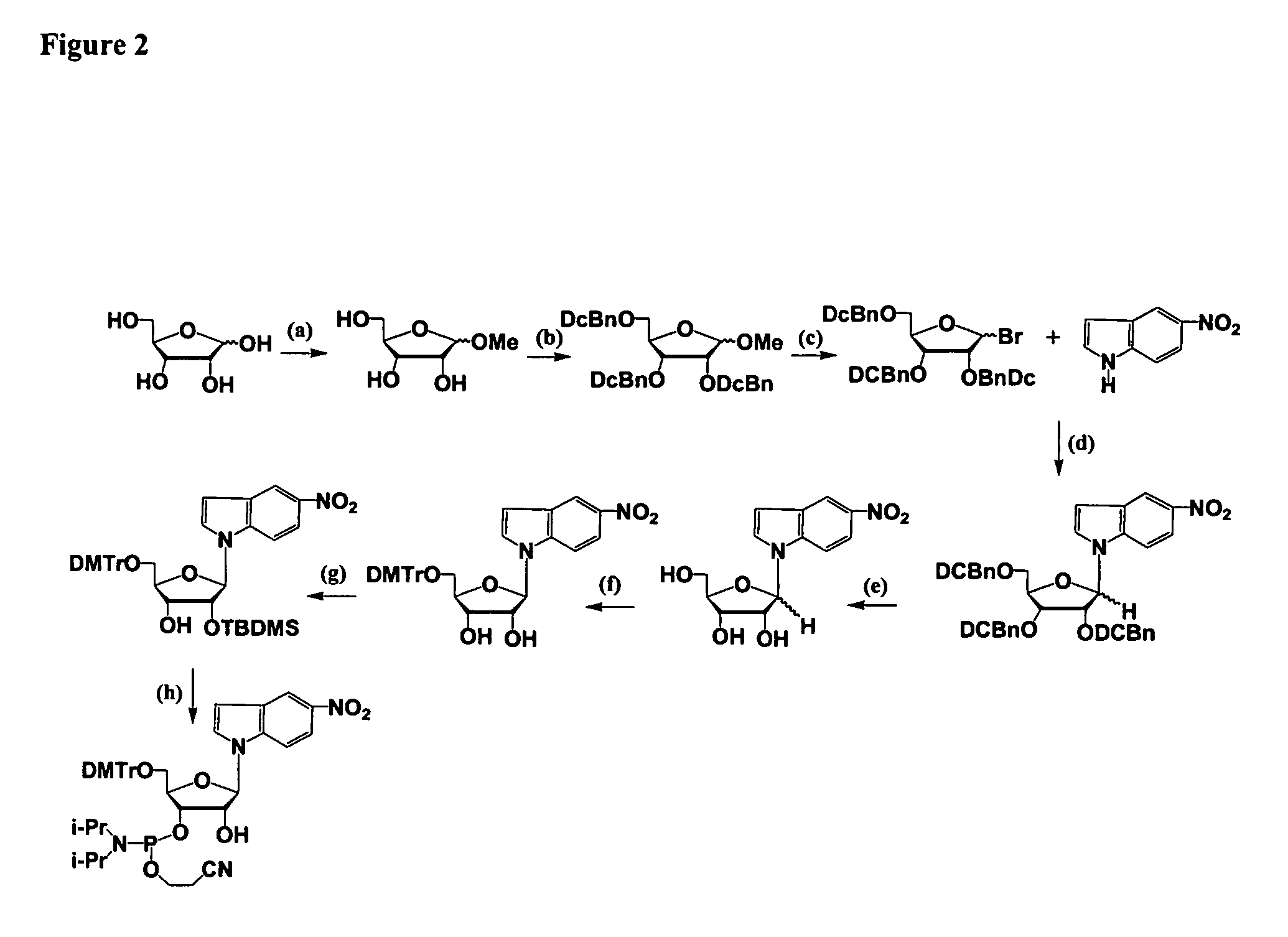
One aspect of the present invention relates to a double-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl, nitroindolyl, nitropyrrolyl, or nitroimidazolyl. In a preferred embodiment, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl. In certain embodiments, only one of the two oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide contains a non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, both of the oligonucleotide strands comprising the double-stranded oligonucleotide independently contain a non-natural nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide strands comprise at least one modified sugar moiety. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a single-stranded oligonucleotide comprising at least one non-natural nucleobase. In a preferred embodiment, the non-natural nucleobase is difluorotolyl. In certain embodiments, the ribose sugar moiety that occurs naturally in nucleosides is replaced with a hexose sugar, polycyclic heteroalkyl ring, or cyclohexenyl group. In certain embodiments, at least one phosphate linkage in the oligonucleotide has been replaced with a phosphorothioate linkage.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Use of Oligonucleotides with Modified Bases as Antiviral Agents
The present invention relates to the use of oligonucleotides having modified nucleobases to inhibit gene expression and / or replication of viruses in a subject. The modified nucleobases may be mercapto-modified bases or hydroxy-modified nucleobases. It is contemplated that the oligonucleotides further comprise a nuclease complex which enhances anti-viral activity of the oligonucleotides.
Owner:BALTIC TECH DEV
Phosphinoamidite carboxylates and analogs thereof in the synthesis of oligonucleotides having reduced internucleotide charge
InactiveUS7067641B2Reduced internucleotide chargeImprove stabilitySugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsHydrogenHalogen
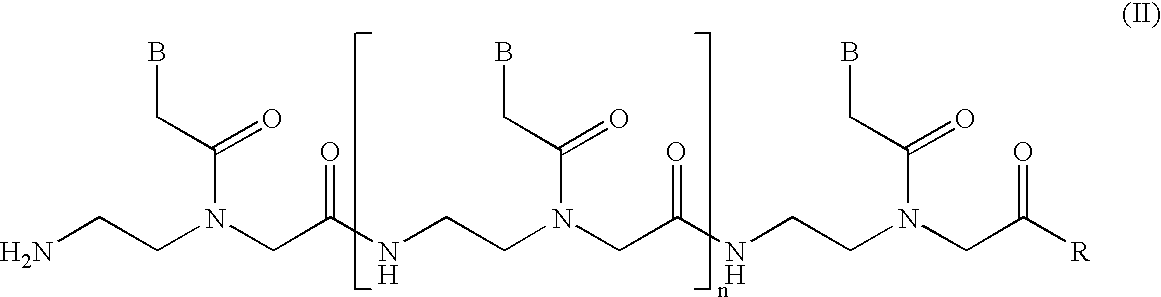
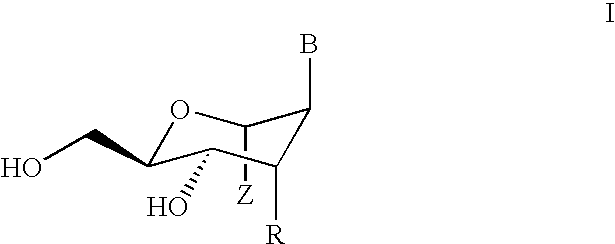
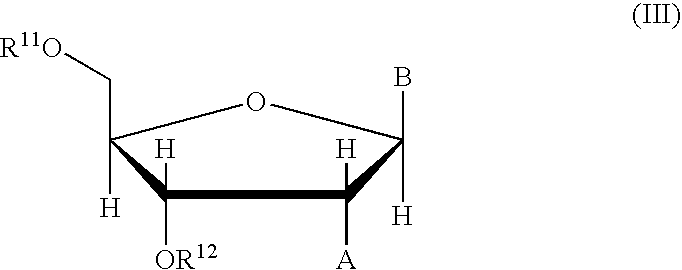
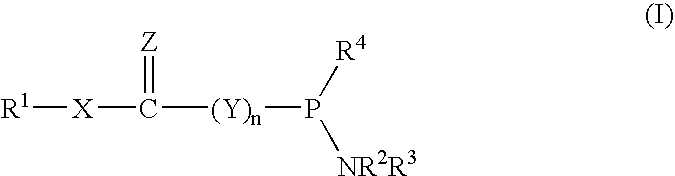
Nucleoside phosphinoamidite carboxylates and analogs are provided that have the structure of formula (III)wherein A is hydrogen, hydroxyl, lower alkoxy, lower alkoxy-substituted lower alkoxy, halogen, SH, NH2, azide or DL wherein D is O, S or NH and L is a heteroatom-protecting group, unsubstituted hydrocarbyl, substituted hydrocarbyl, heteroatom-containing hydrocarbyl, or substituted heteroatom-containing hydrocarbyl; B is a nucleobase; and one of R11 and R12 is a blocking group and the other is (IV) or (VI)in which W, X, Y, Z, R1 and n are as defined herein.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
High throughput nucleic acid sequencing by expansion
ActiveUS7939259B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleotide sequencing
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of Bcl-2
InactiveUS20050203042A1Comparable and enhanced biological effectInteresting biological propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNucleobase
The present invention provides improved oligomeric compound, in particular oligonucleotide compounds, and methods for modulating the expression of the Bcl-2 gene in humans. In particular, this invention relates to oligomeric compounds of 10-30 nucleobases in length which comprise a target binding domain that is specifically hybridizable to a region ranging from base position No. 1459 (5′) to No. 1476 (3′) of the human Bcl-2 mRNA, said target binding domain having the formula: 5′-[(DNA / RNA)0-1-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA / LNA*)4-14-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA)0-1]-3 and said target binding domain comprising at least two LNA nucleotides or LNA analogue nucleotides linked by a phosphorothioate group (—O—P(O,S)—O—). In particular the oligo is predominantly or fully thiolated. The invention also provides the use of such oligomers or conjugates or chimera for the treatment of various diseases associated with the expression of the Bcl-2 gene, such as cancer.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
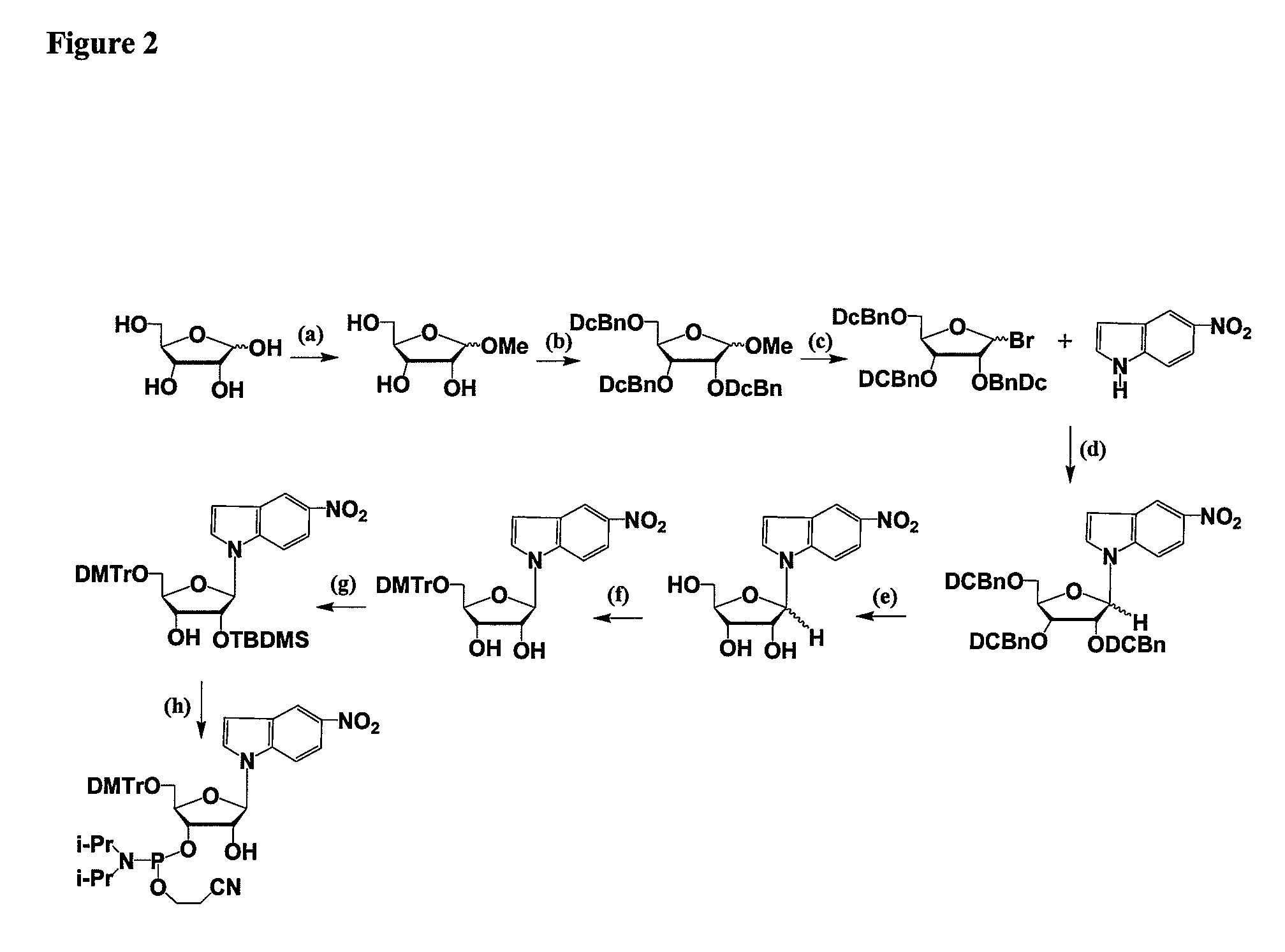
RNAi Agents Comprising Universal Nucleobases
InactiveUS20080213891A1Broad scopeReduce needSugar derivativesPolymorphism usesNitroimidazoleViral Genes
One aspect of the present invention relates to an oligonucleotide agent comprising at least one universal nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the universal nucleobase is difluorotolyl, nitroindolyl, nitropyrrolyl, or nitroimidazolyl. In a preferred embodiment, the universal nucleobase is difluorotolyl. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide is double-stranded. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide is single-stranded. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of altering the expression level of a target in the presence of target sequence polymorphism. In a preferred embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression of different alleles of a gene. In another preferred embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression level of two or more genes. In another embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression level of a viral gene from different strains of the virus. In another embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression level of genes from different species.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
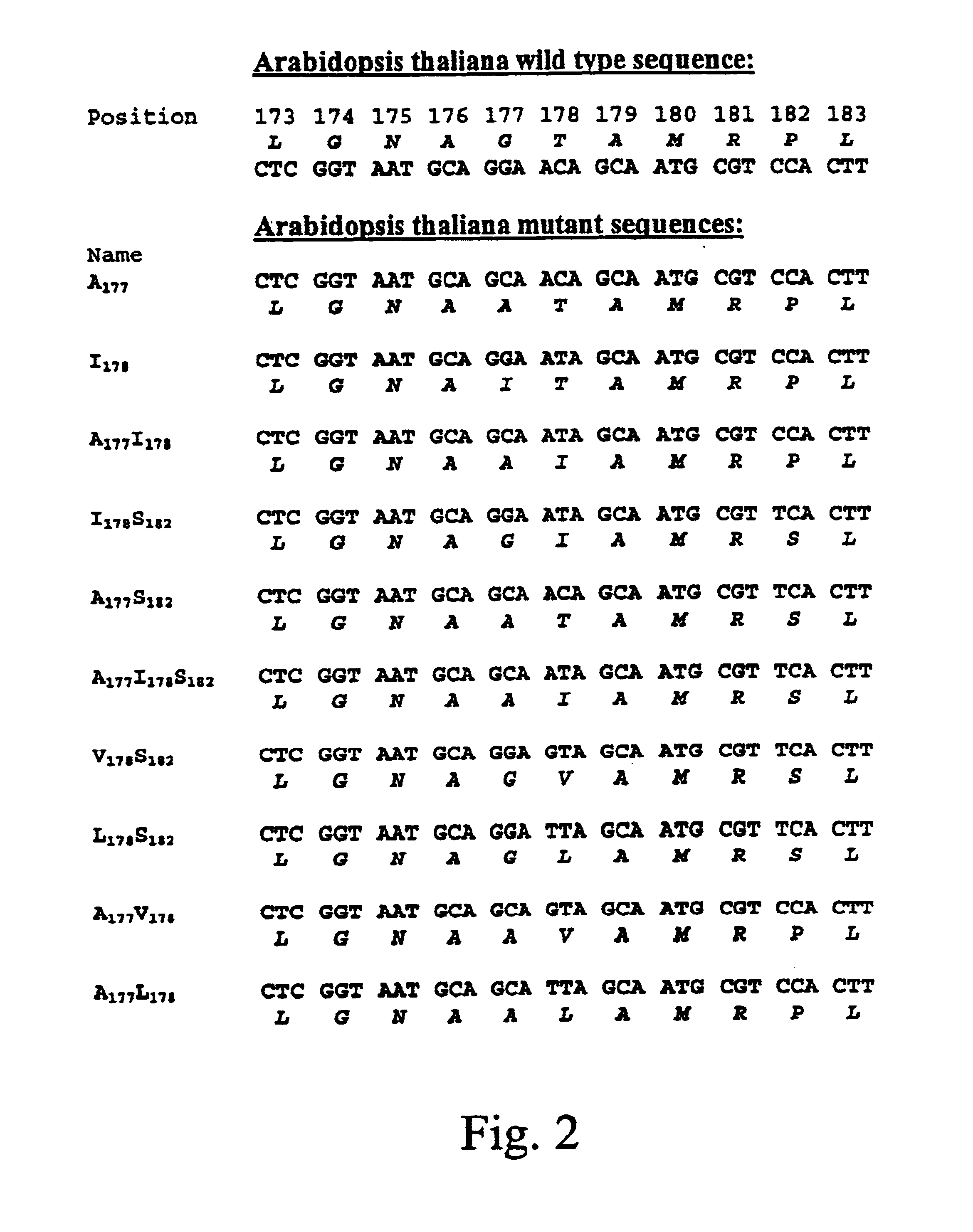
Methods of making non-transgenic herbicide resistant plants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide.
Owner:CIBUS
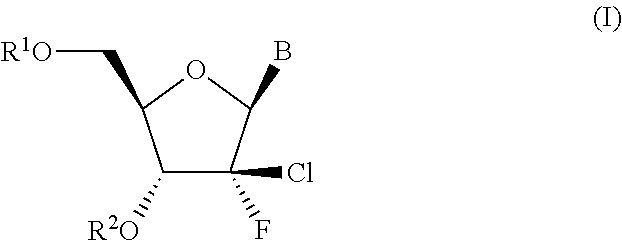
Process for preparing branched ribonucleosides from 1,2-anhydroribofuranose intermediates
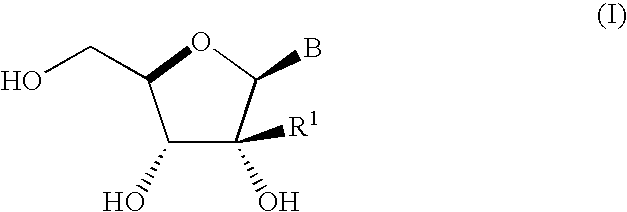
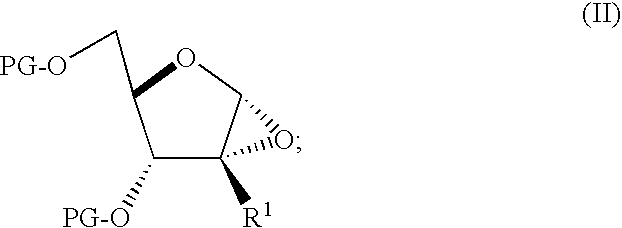
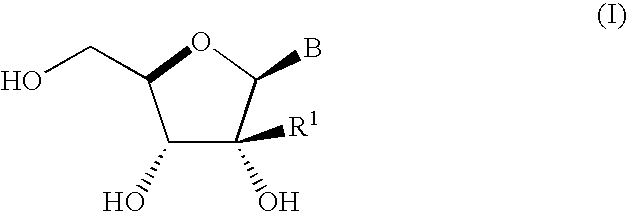
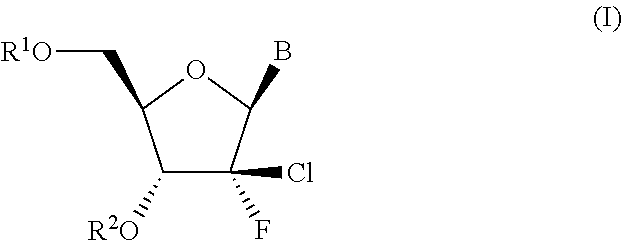
A process is provided for the preparation of branched-chain ribonucleosides of formula (I):from the 1,2-anhydroderivatives of formula (II).wherein PG is a hydroxyl protecting group, B is a purine or pyrimidine nucleobase, and R1 is C1-6 alkyl. The compounds of formula (I) are inhibitors of HCV polymerase useful in the treatment of HCV infection.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
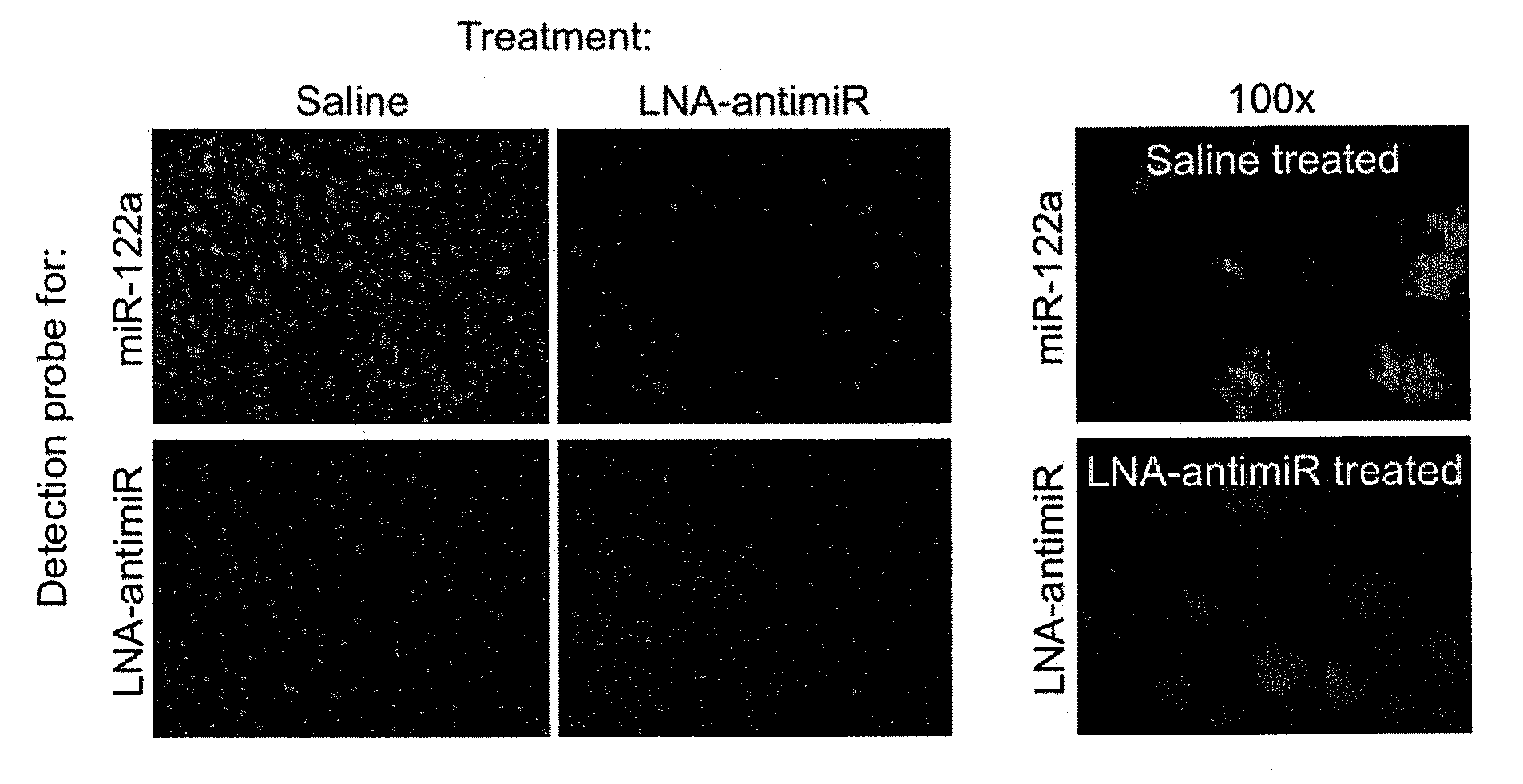
Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Anti-Mirna Antisense Oligonucleotides
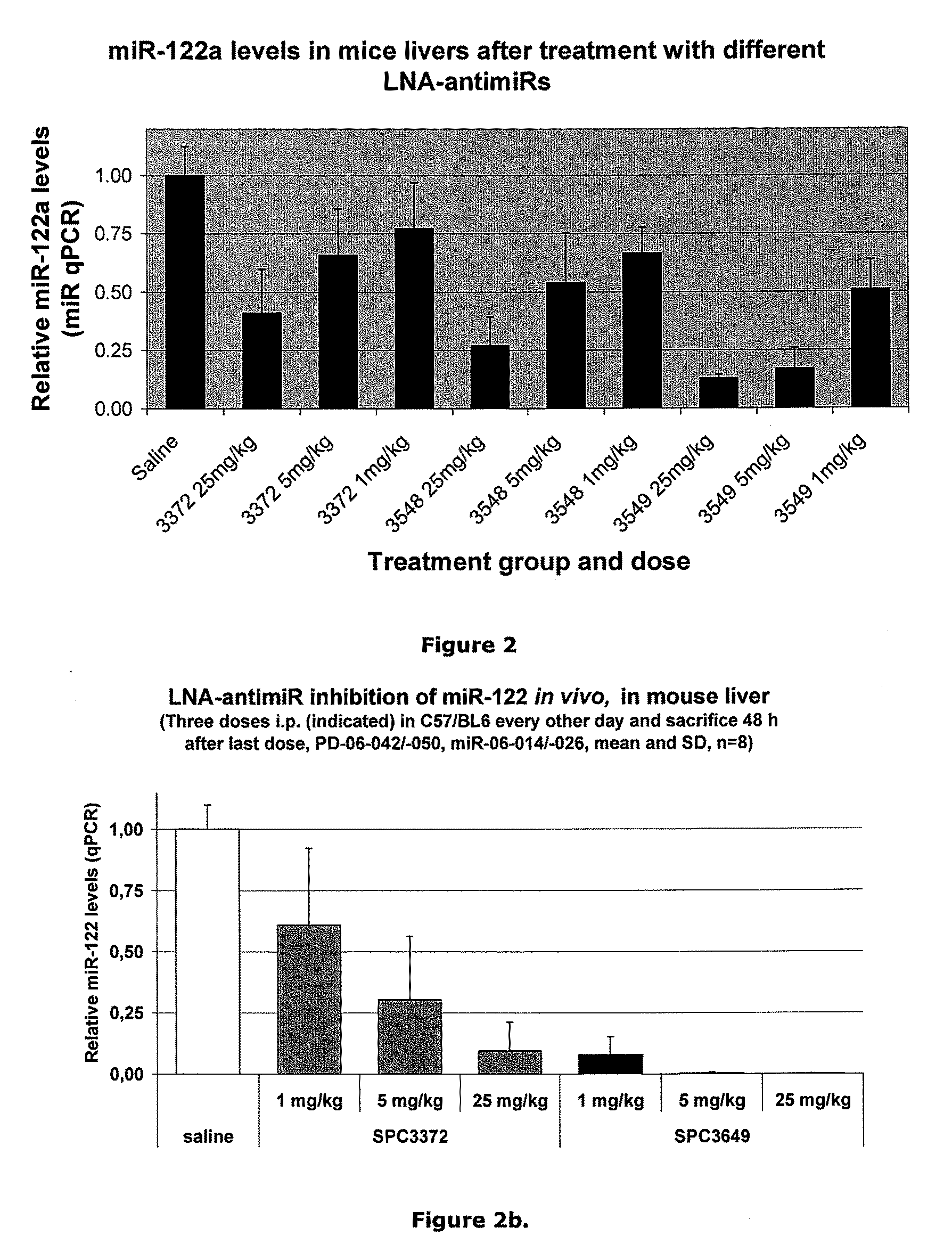
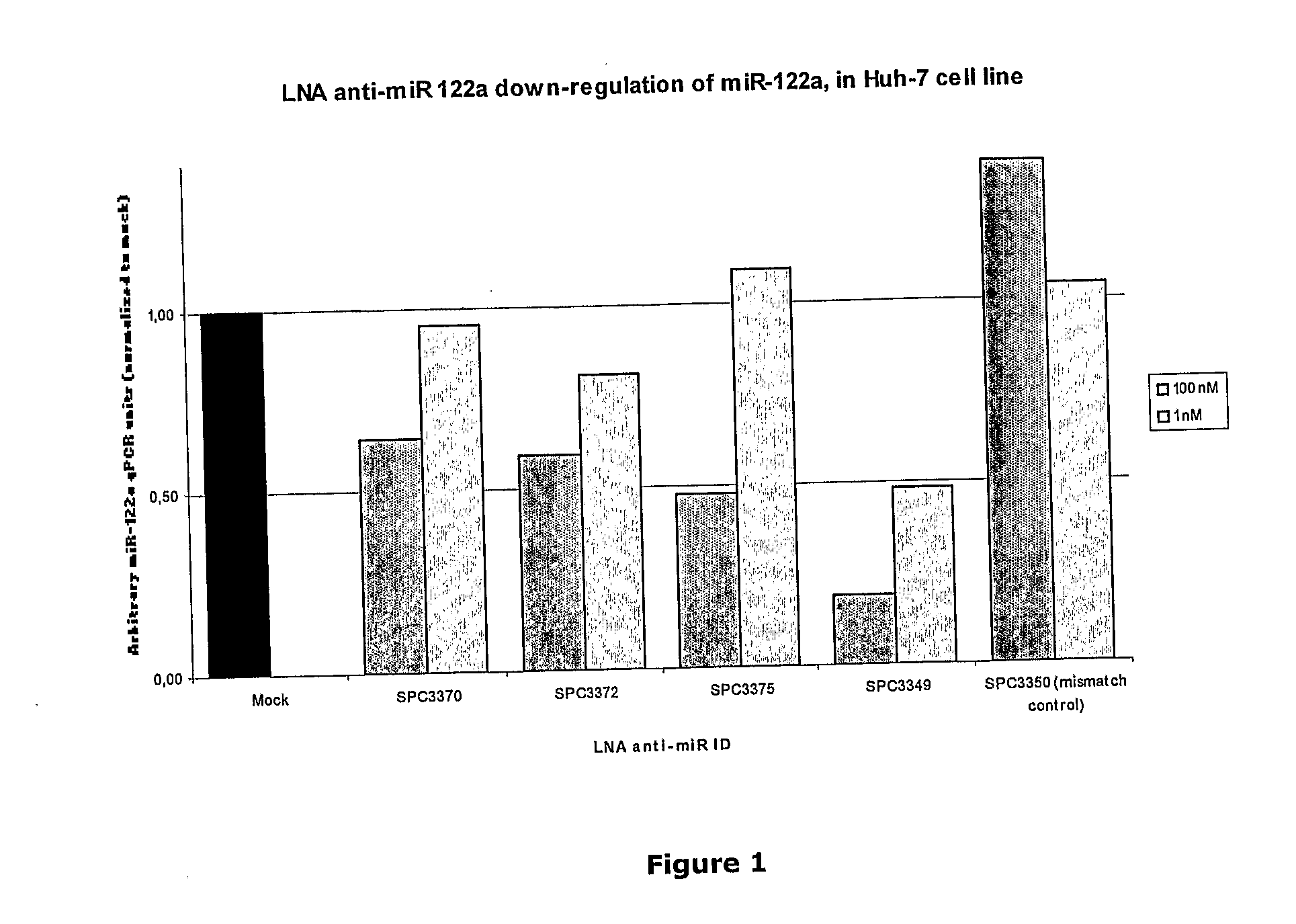
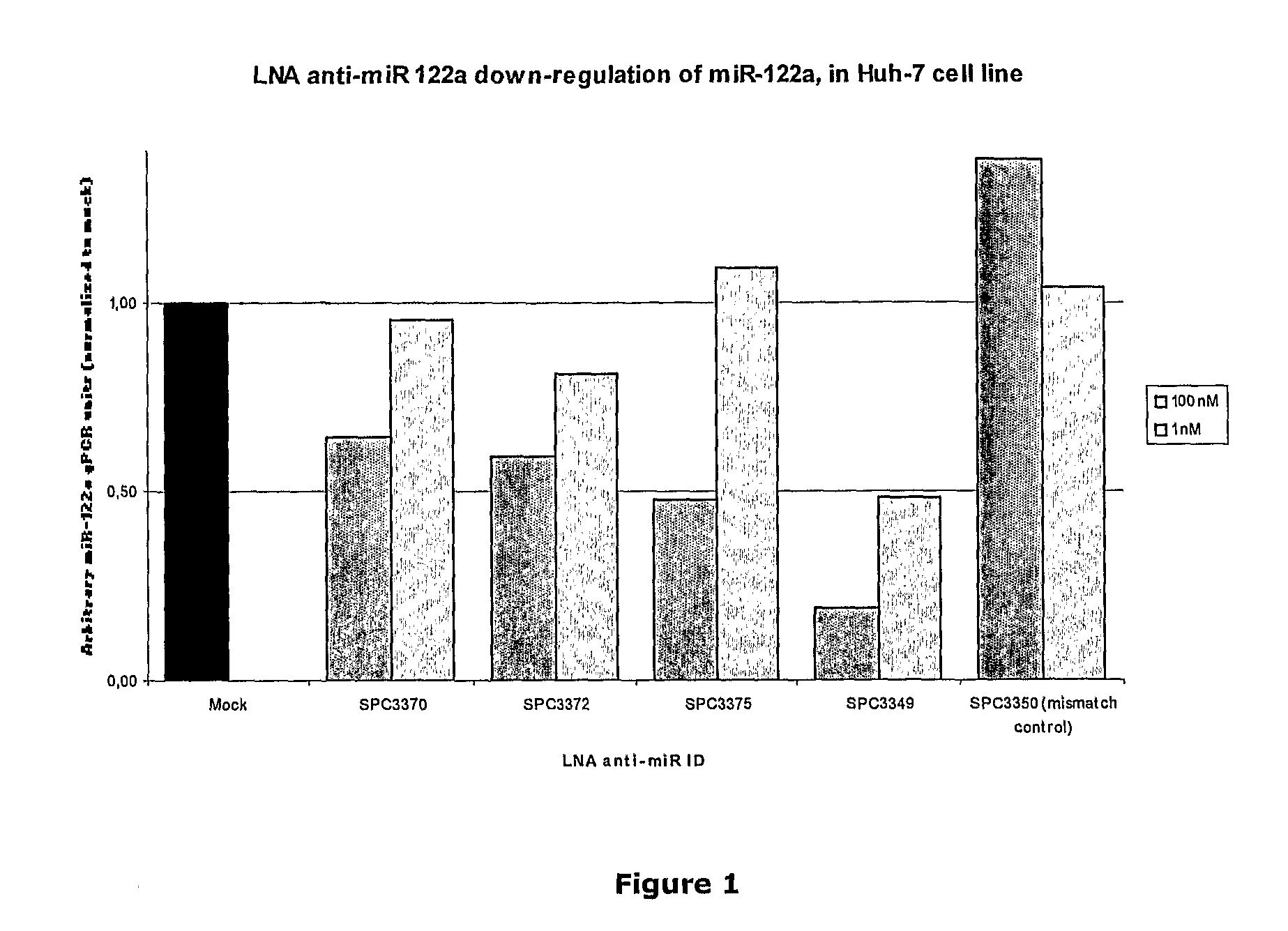
ActiveUS20100286234A1Reduced microRNA levelAvoid off-target effectsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleobaseRNA Cleavage
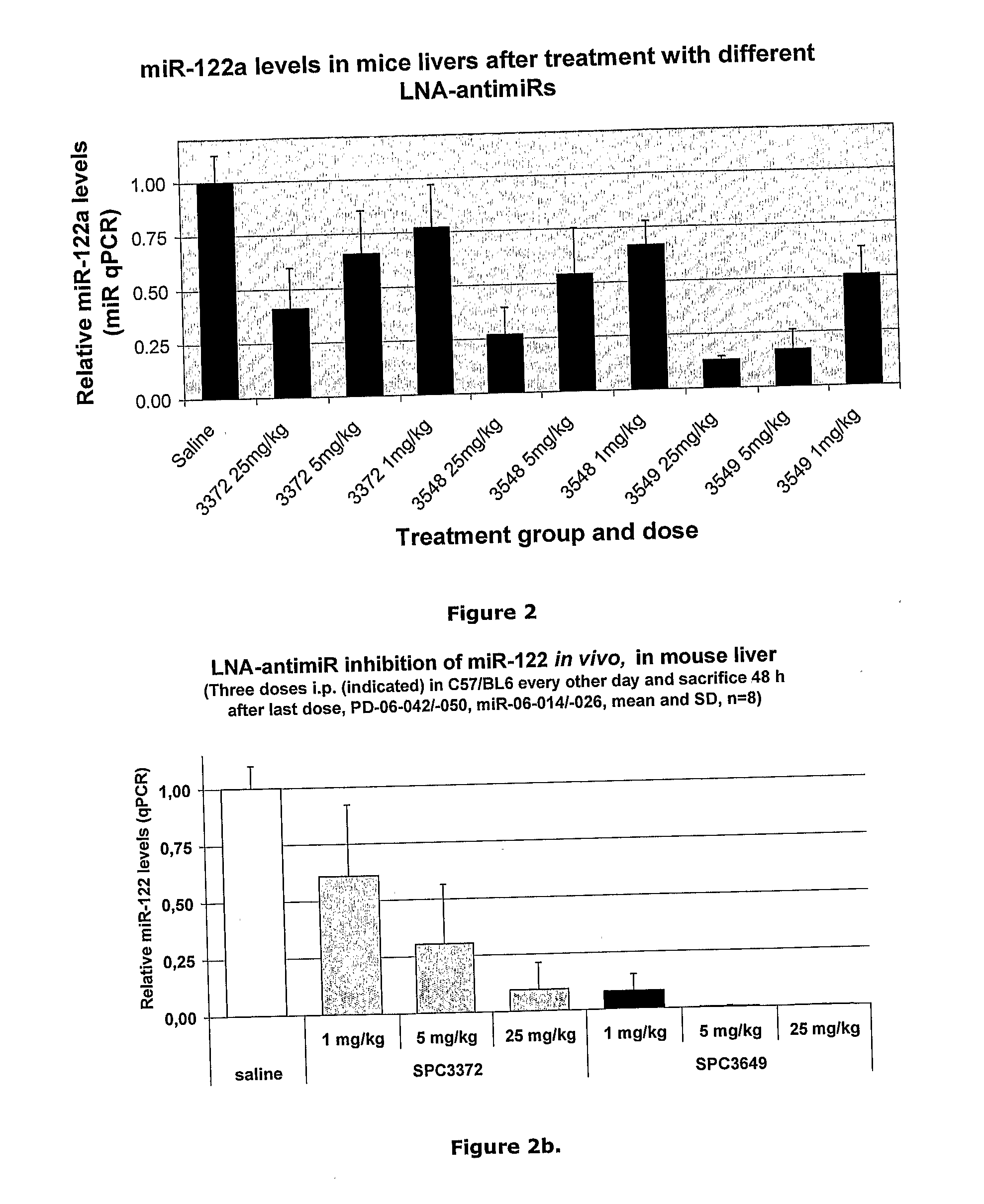
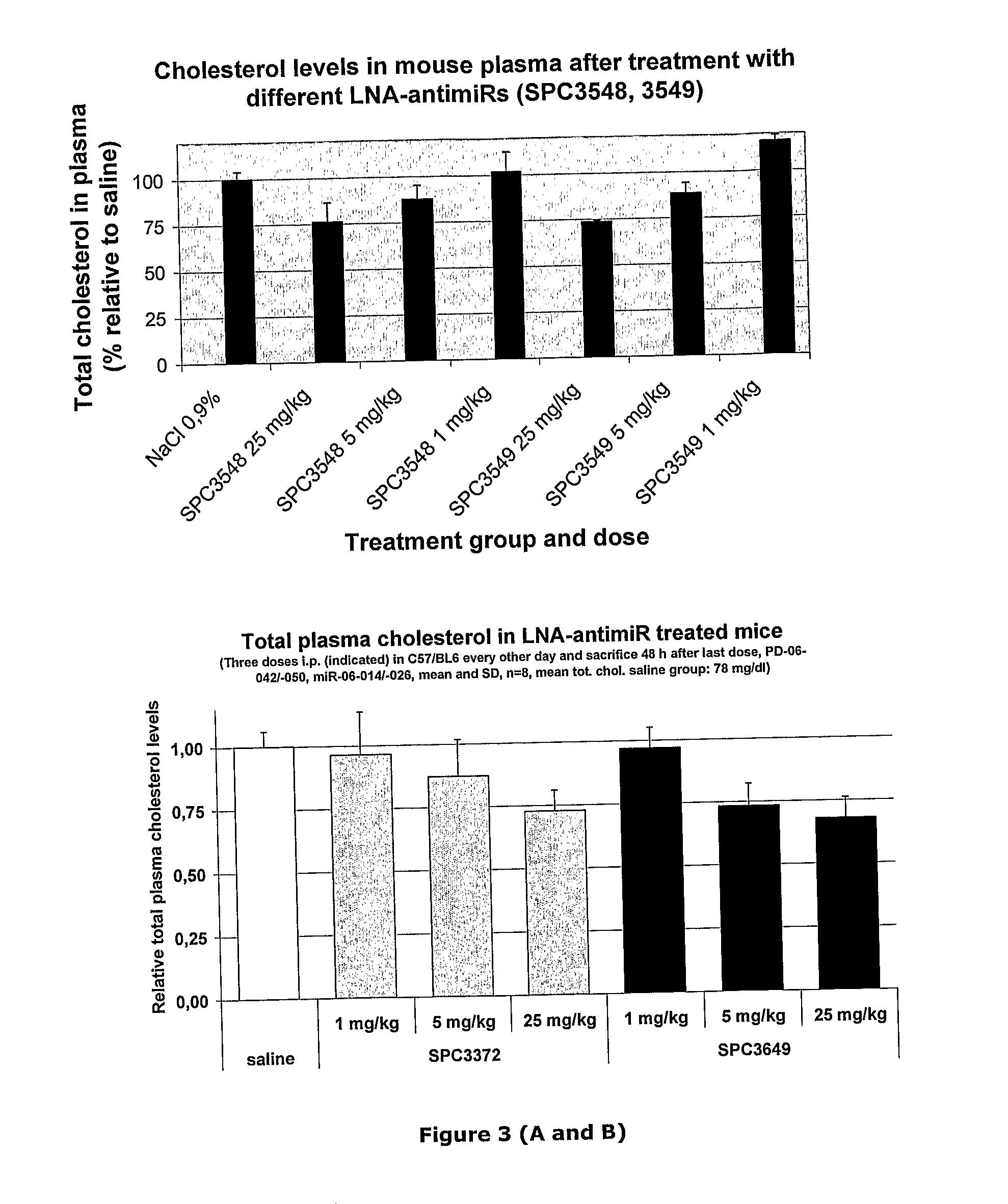
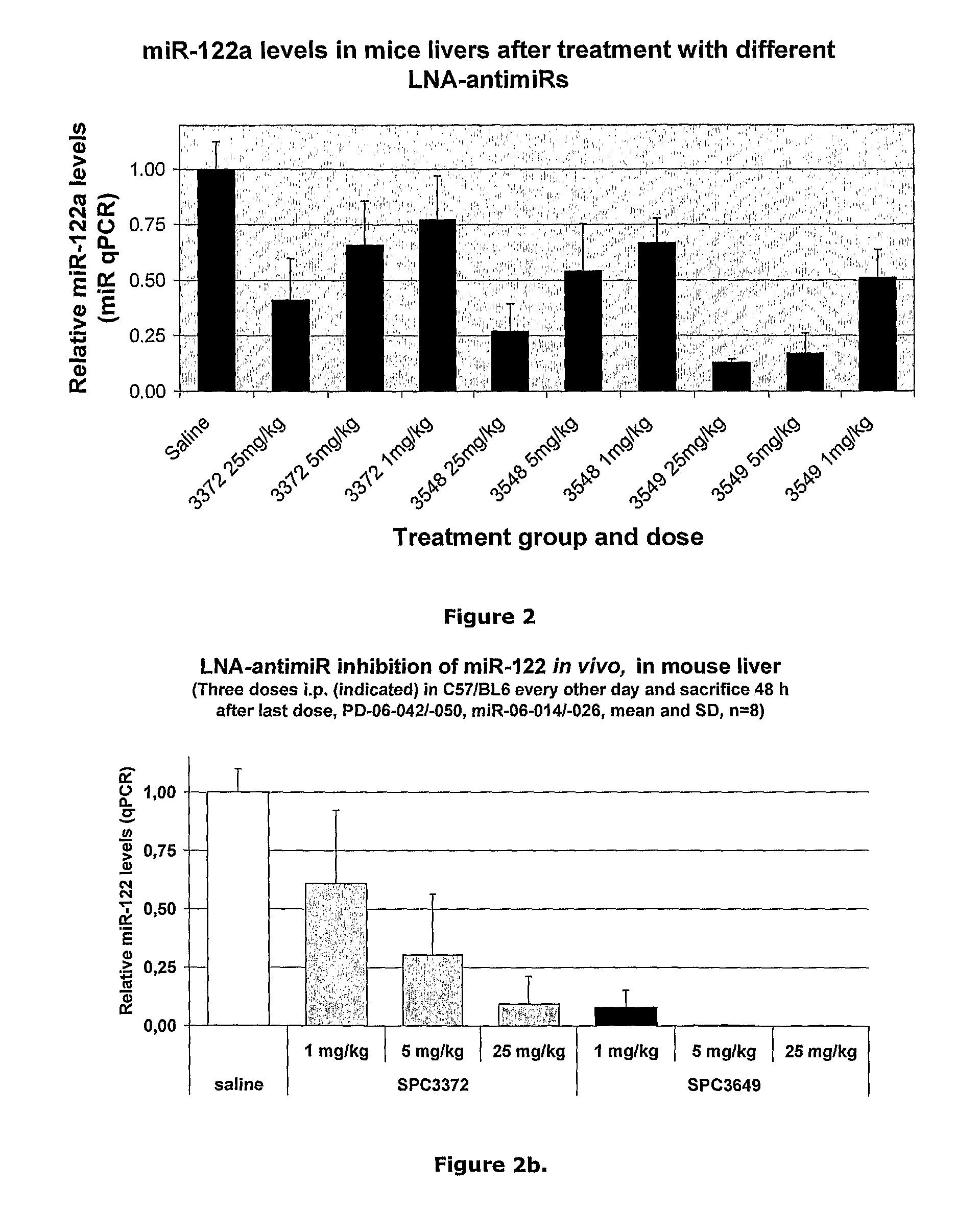
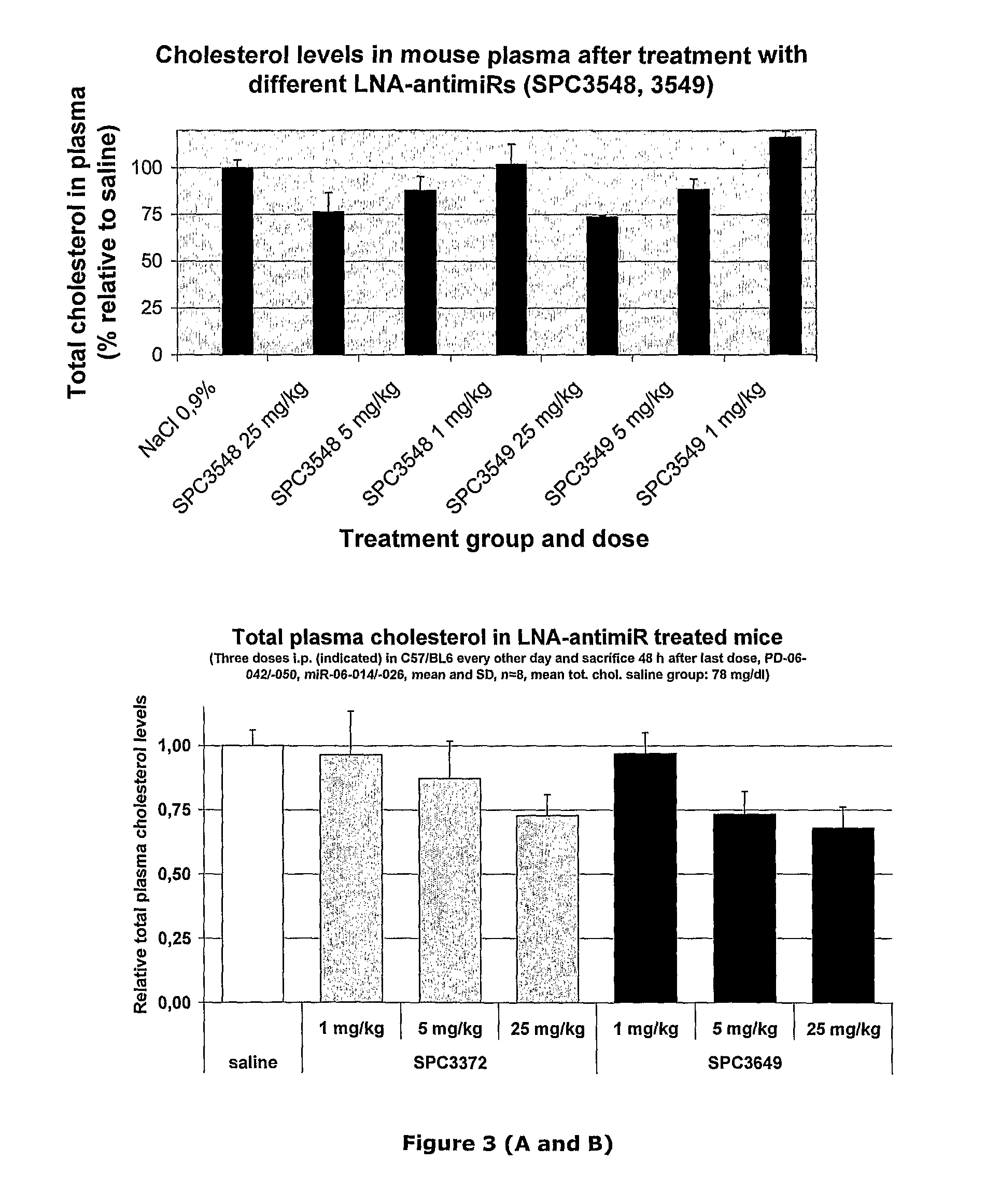
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising short single stranded oligonucleotides, of length of between 8 and 26 nucleobases which are complementary to human microRNAs selected from the group consisting of miR19b, miR21, miR122a, miR155 and miR375. The short oligonucleotides are particularly effective at alleviating miRNA repression in vivo. It is found that the incorporation of high affinity nucleotide analogues into the oligonucleotides results in highly effective anti-microRNA molecules which appear to function via the formation of almost irreversible duplexes with the miRNA target, rather than RNA cleavage based mechanisms, such as mechanisms associated with RNaseH or RISC.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
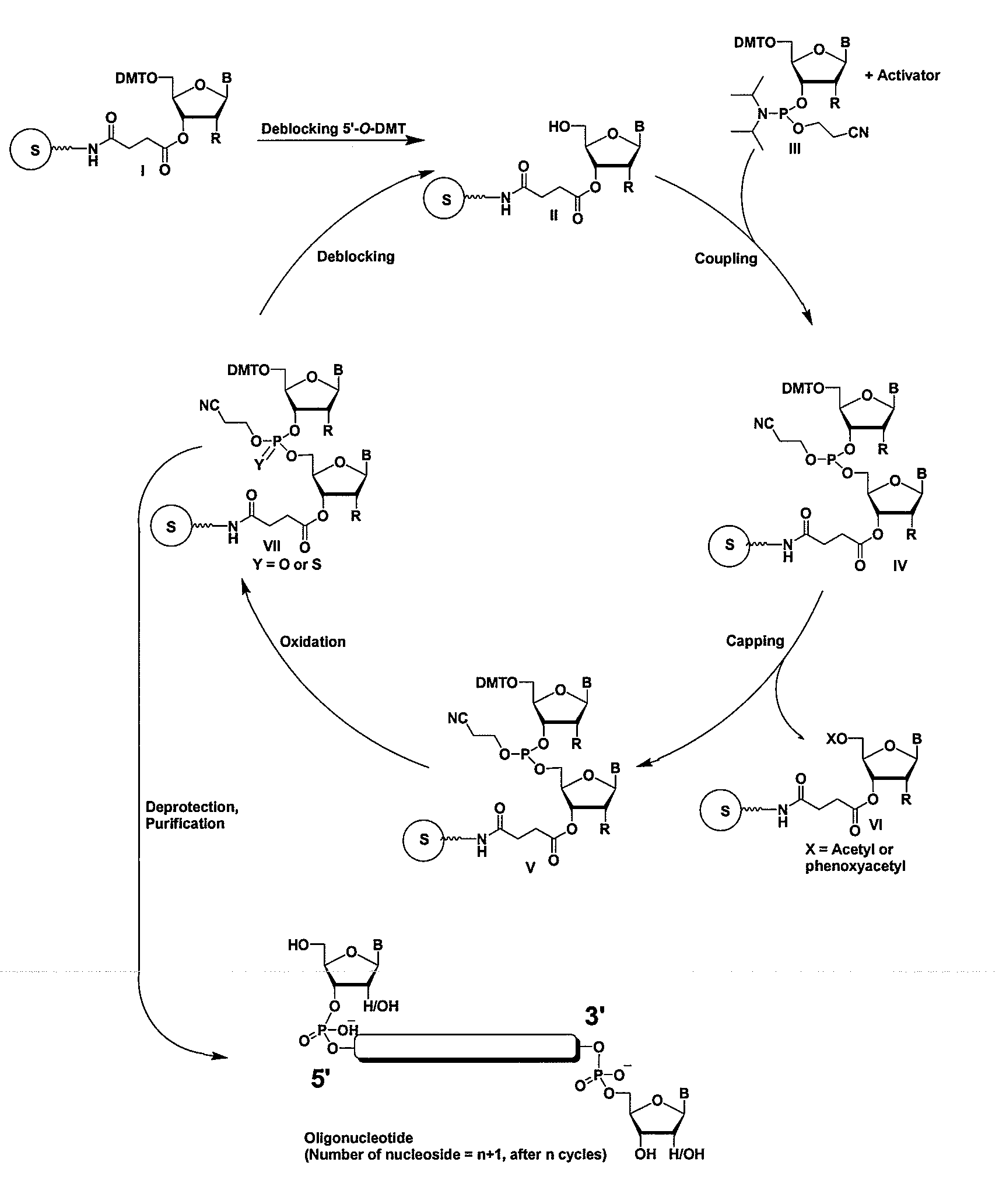
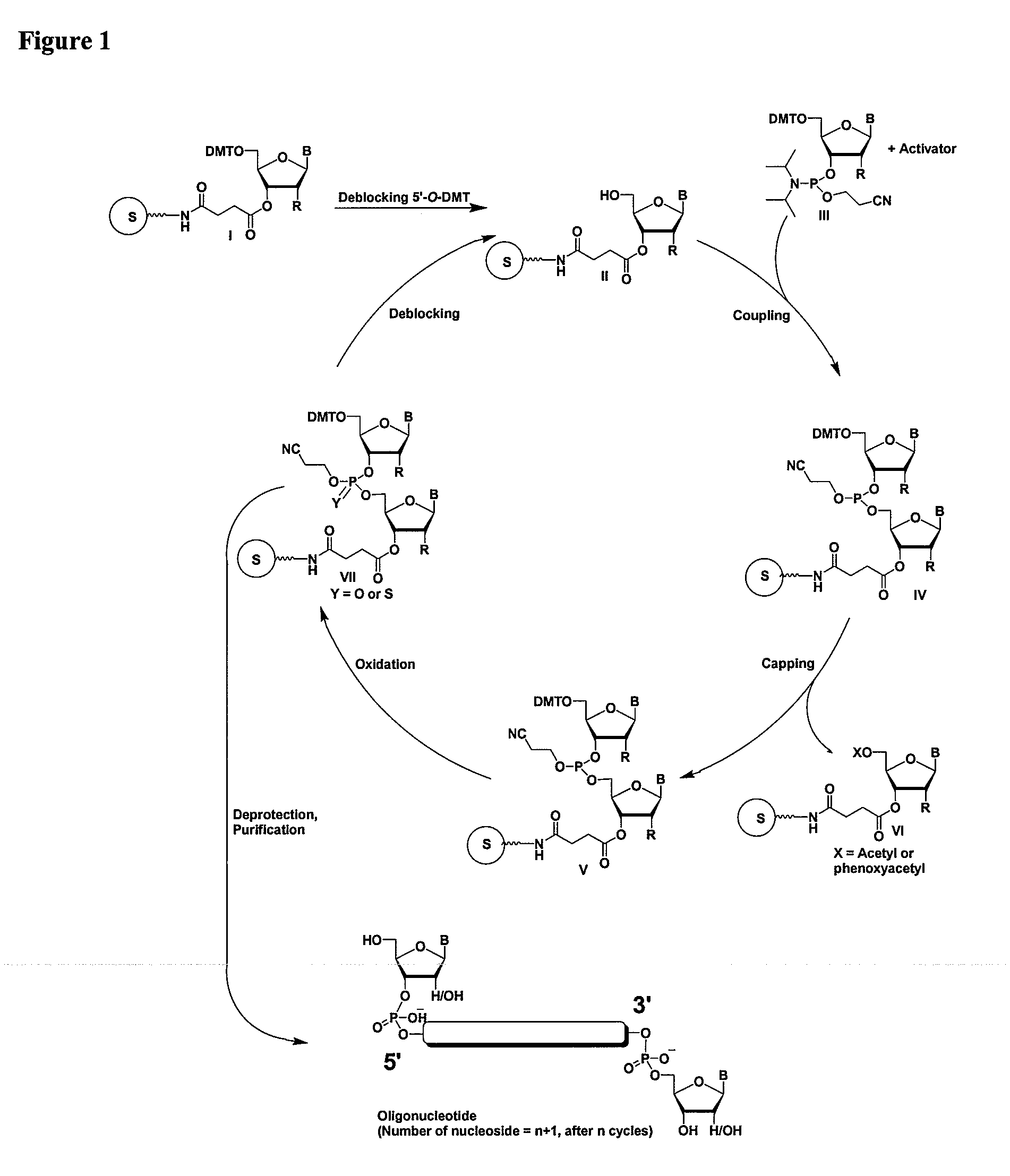
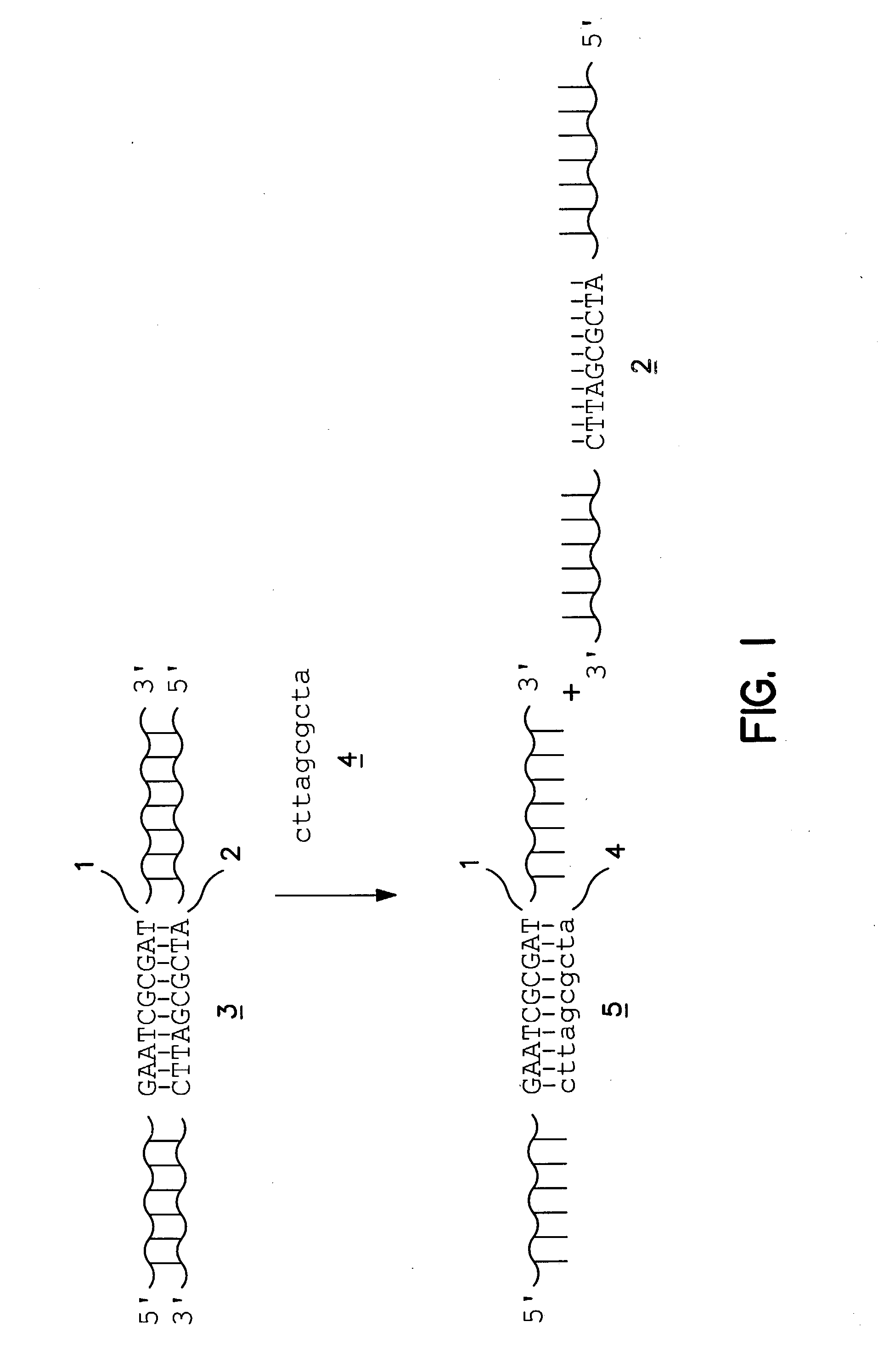
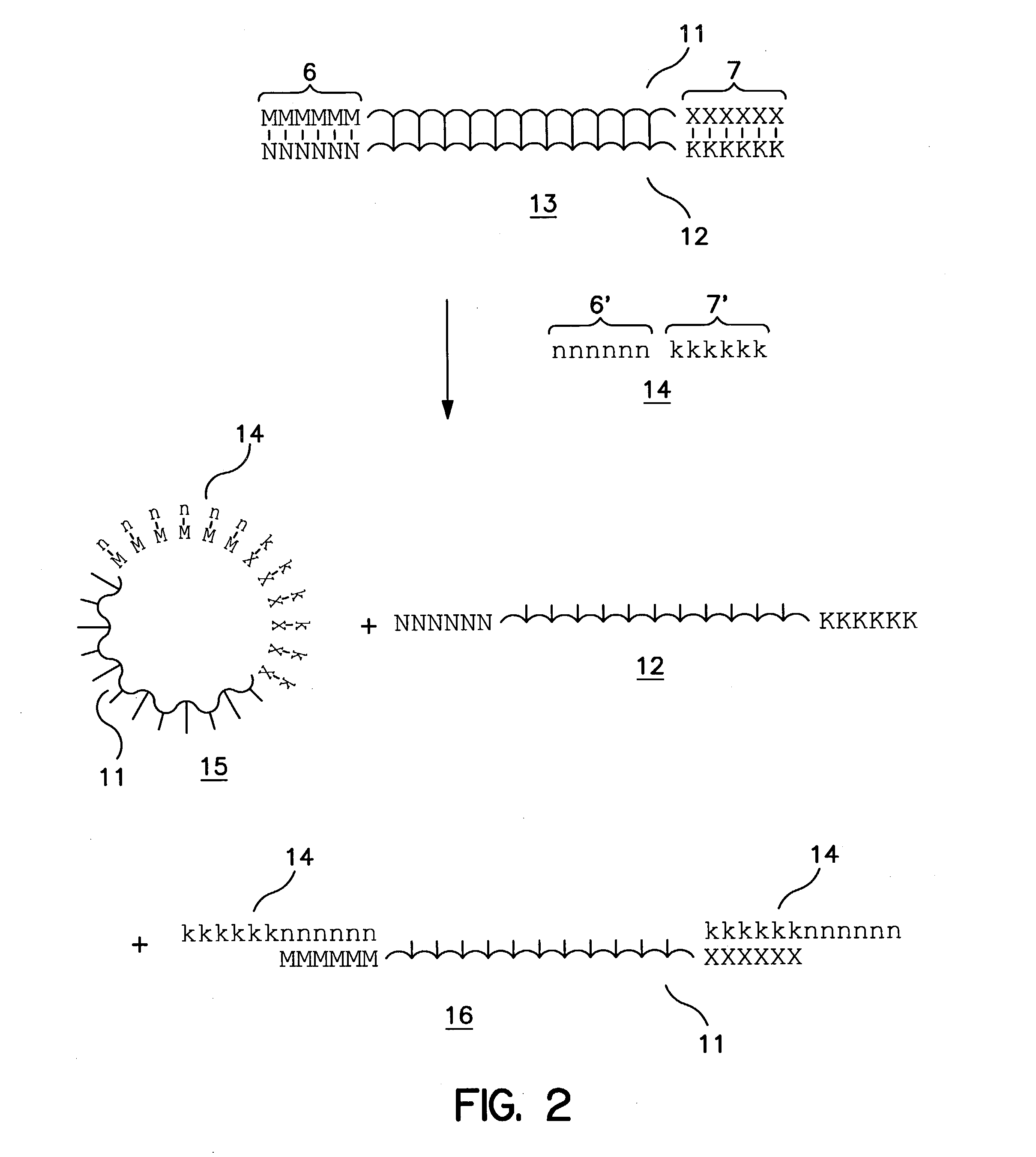
Methods and compositions for the tandem synthesis of two or more oligonucleotides on the same solid support
InactiveUS20060149046A1Simple and smooth and efficientWide range of applicationsEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesOligonucleotide primersCombinatorial chemistry
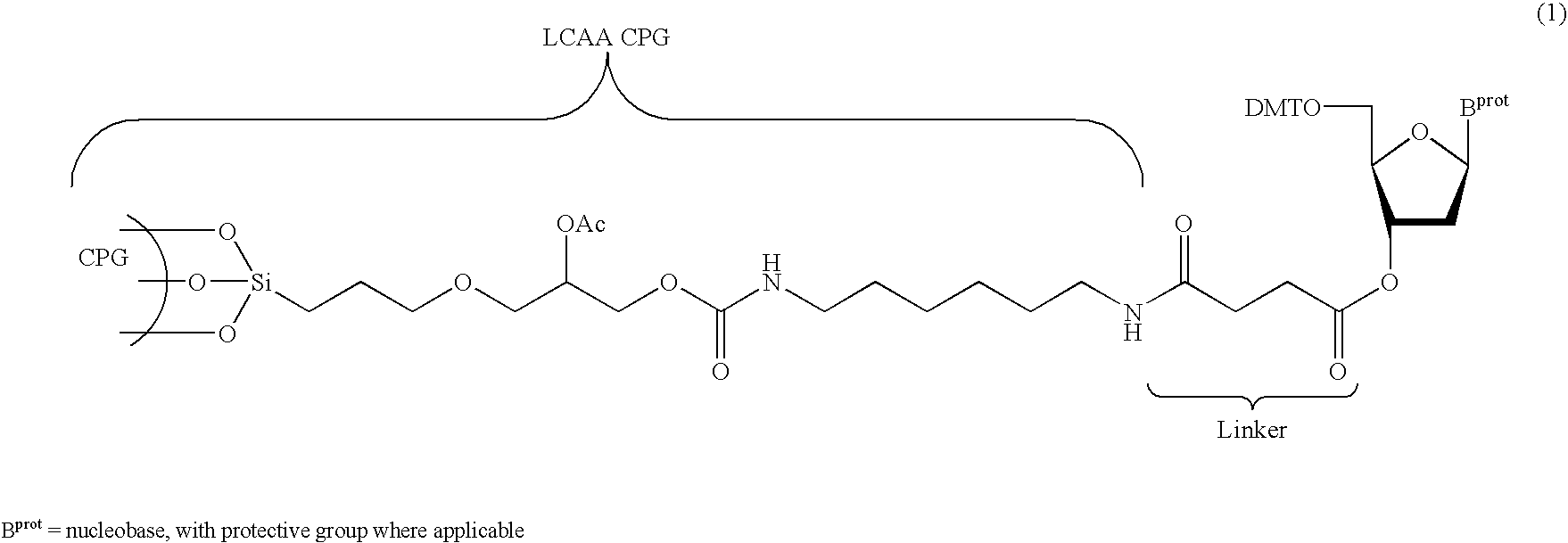
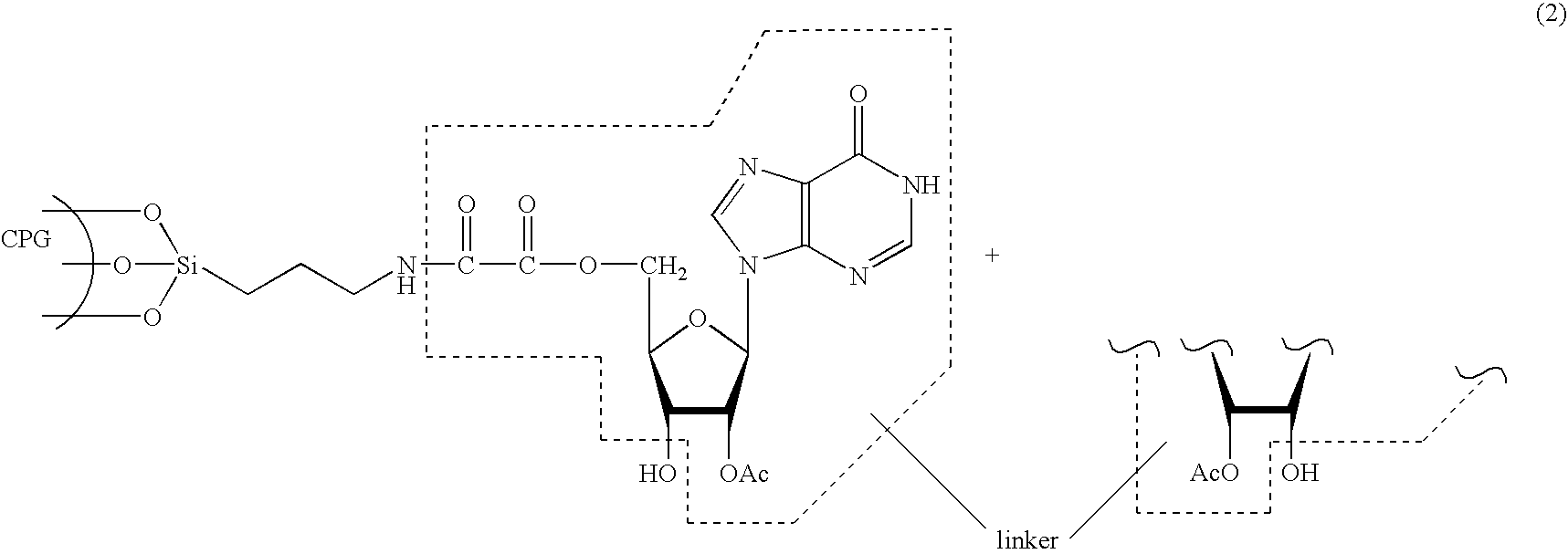
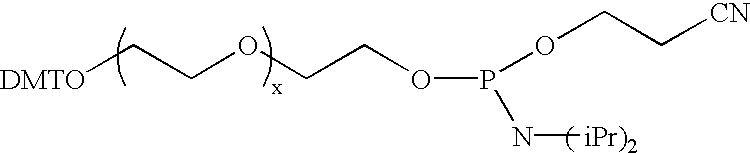
The present invention relates to novel methods and novel solid support materials for the tandem synthesis of two or more different oligonucleotides on the same solid support in one synthetic run. The methods involve novel support preparations comprised of two or more types of orthogonally protected anchor groups. Subsequent to the selective removal of the first of the respective protective groups, the first oligonucleotide is assembled on the deblocked anchor groups according to standard methods, preferably via phosphoramidite chemistry. Following the capping of said first oligonucleotide, the anchor groups blocked by the second type of protective group are selectively liberated and serve is the starting point for the assembly of a second oligonucleotide, and so forth. After completion of all of the syntheses on the solid support, the oligonucleotides are released from the solid support and deprotected at the nucleobases, using standard methods. Preparations obtained using the method of this invention, generally contain two or more different oligonucleotides. Such preparations are particularly useful in applications that require pairs of oligonucleotide primers, several probes at a time, duplexed nucleic acid fragments, or other combinations of oligonucleotides that are useful in applications such as PCR, sequencing, multiplexed genotyping, cloning and RNA interference. The invention includes procedures for the preparation of the novel solid supports of the invention.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Pseudonucleotide comprising an intercalator
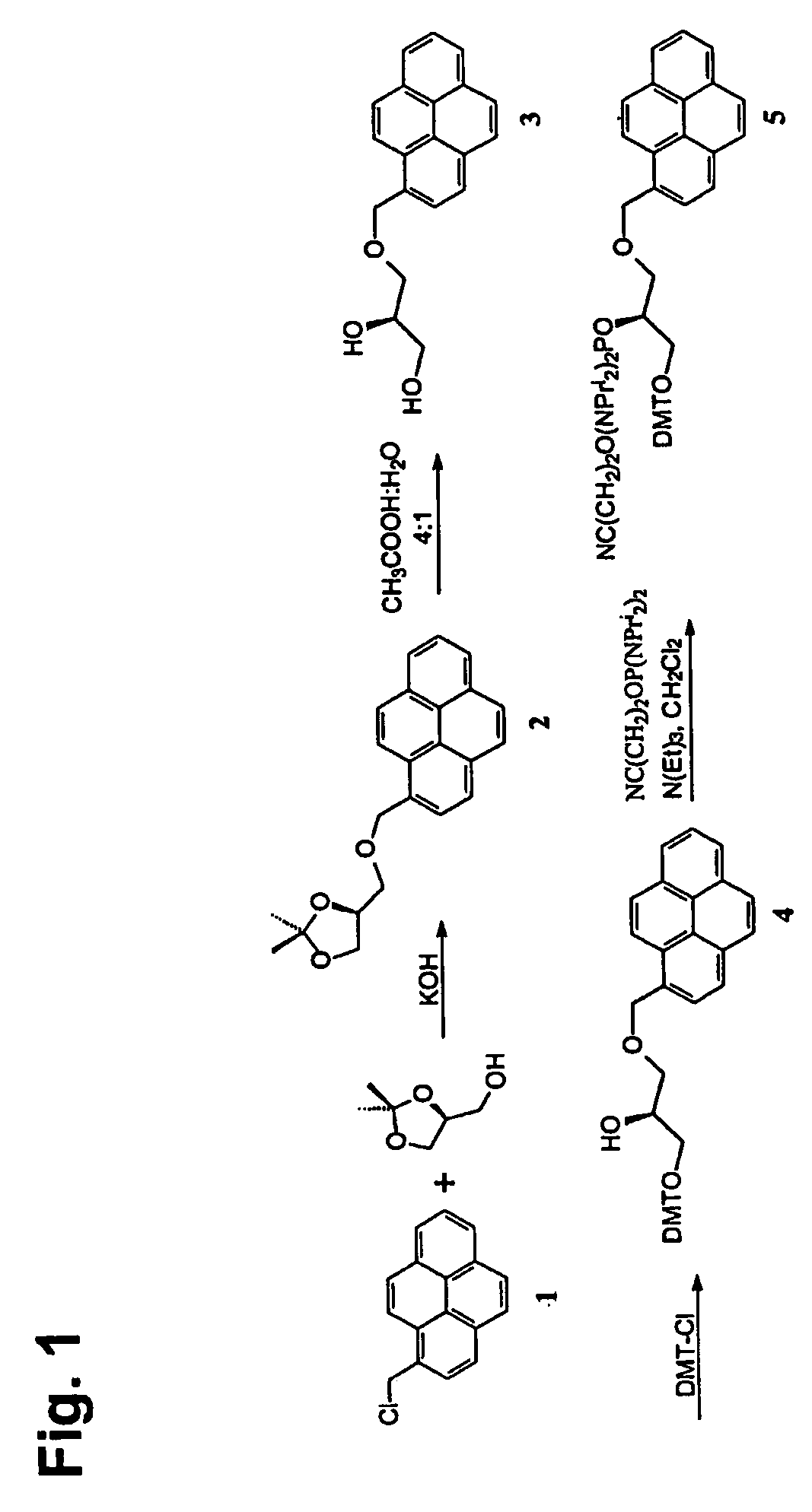
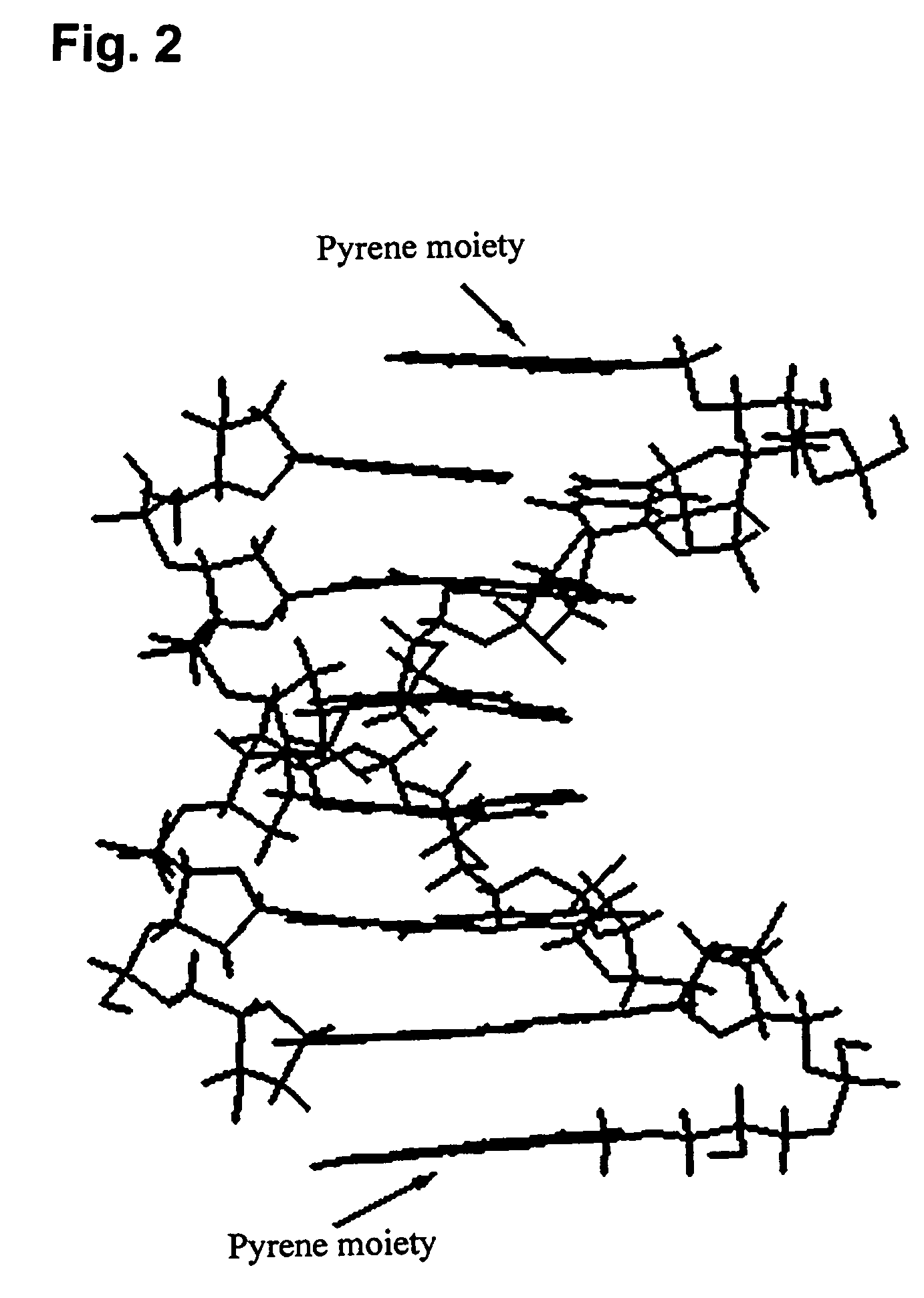
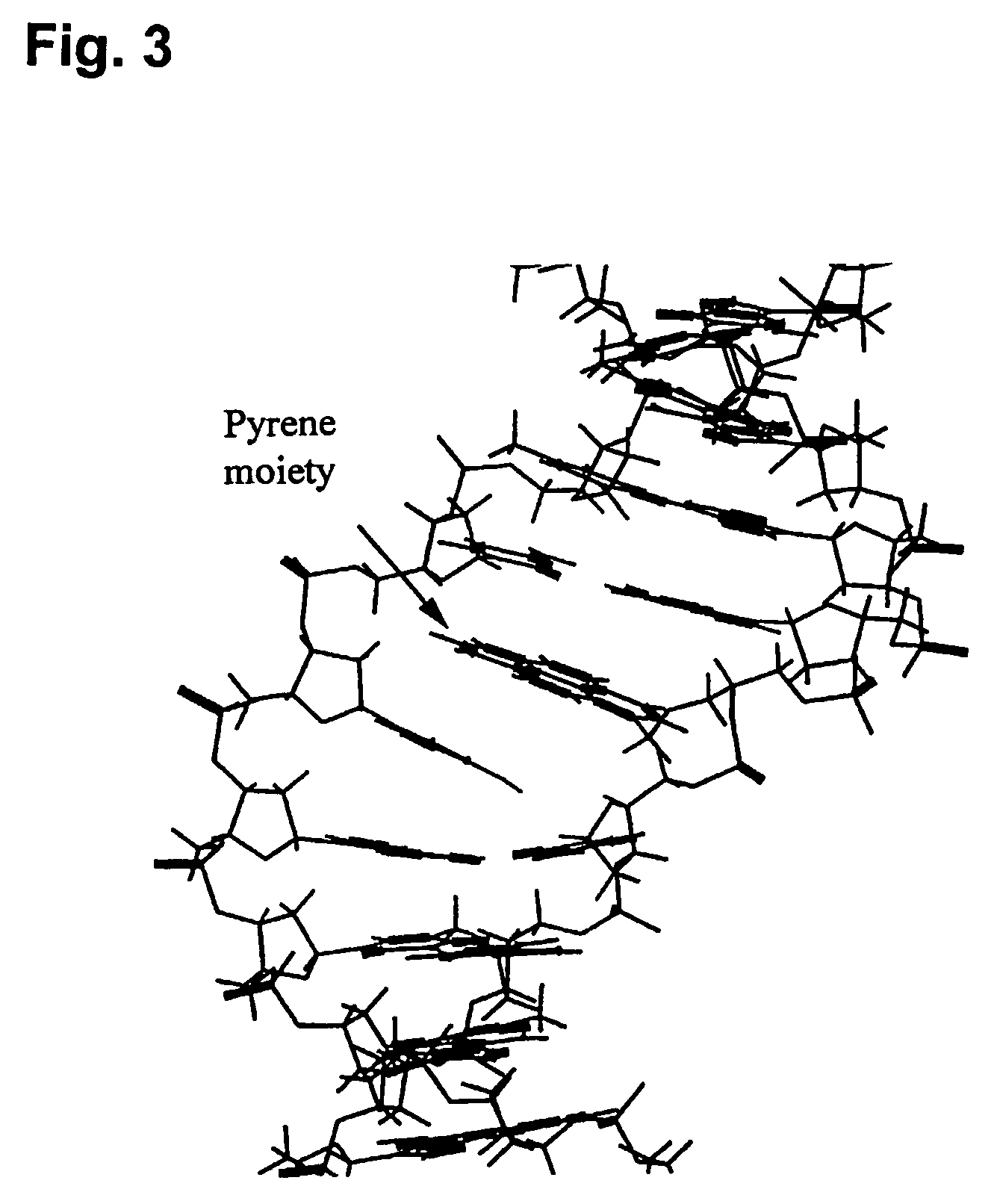
InactiveUS20060014144A1Strong specificityHigh melting temperatureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleobaseNucleic acid analogue
The present invention relates to intercalator pseudonucleotides. Intercalator pseudonucleotides according to the invention are capable of being incorporated into the backbone of a nucleic acid or nucleic acid analogue and they comprise an intercalator comprising a flat conjugated system capable of co-stacking with nucleobases of DNA. The invention also relates to oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues comprising at least one intercalator pseudo nucleotide. The invention furthermore relates to methods of synthesising intercalator pseudo nucleotides and methods of synthesising oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues comprising at least one intercalator pseudonucleotide. In addtition, the invention describes methods of separating sequence specific DNA(s) from a mixture comprising nucleic acids, methods of detecting a sequence specific DNA (target DNA) in a mixture comprising nucleic acids and / or nucleic acid analogues and methods of detecting a sequence specific RNA in a mixture comprising nucleic acids and / or nucleic acid analogues. In particular said methods may involve the use of oligonucleotides comprising intercalator pseudo nucleotides. The invention furthermore relates to pairs of oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues capable of hybridising to one another, wherein said pairs comprise at least one intercalator pseudonucleotide. Methods for inhibiting a DNAse and / or a RNAse and methods of modulating transcription of one or more specific genes are also described.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Oligonucleotide conjugates
InactiveUS7563618B2Inhibit telomerase enzymatic activityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTelomeraseNucleobase
Oligonucleotide conjugates, where an oligonucleotide is covalently attached to an aromatic system, are provided. In particular embodiments the oligonucleotide is complementary to the RNA component of human telomerase and is covalently attached to a nucleobase via an optional linker. The conjugates inhibit telomerase enzyme activity.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Pharmaceutical composition comprising anti-mirna antisense oligonucleotide
ActiveUS8163708B2Effectively repressedHigh affinitySugar derivativesMetabolism disorderNucleobaseRNA Cleavage
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Piperazine-based nucleic acid analogs
InactiveUS6841675B1Quick assemblyEasy to assembleOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesOligomerNucleobase
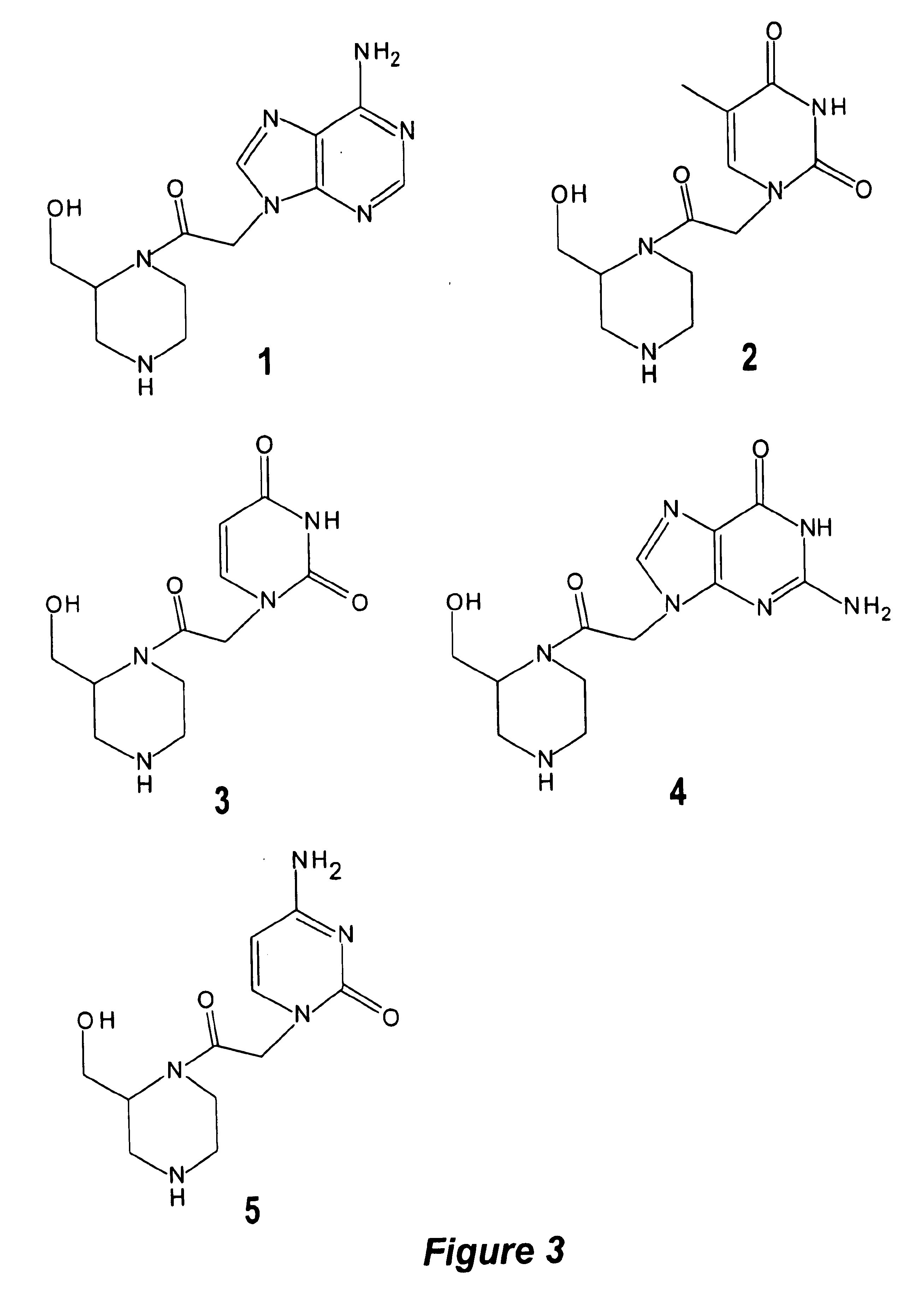
A novel nucleoside analog is disclosed which comprises a piperazine ring in the place of the ring ribose or deoxyribose sugar. Monomers utilizing a broad variety of nucleobases are disclosed, as well as oligomers comprising the monomers disclosed herein linked by a variety of linkages, including amide, phosphonamide, and sulfonamide linkages. A method of synthesizing the nucleoside analogs is also disclosed.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Oligonucleotides comprising a modified or non-natural nucleobase
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
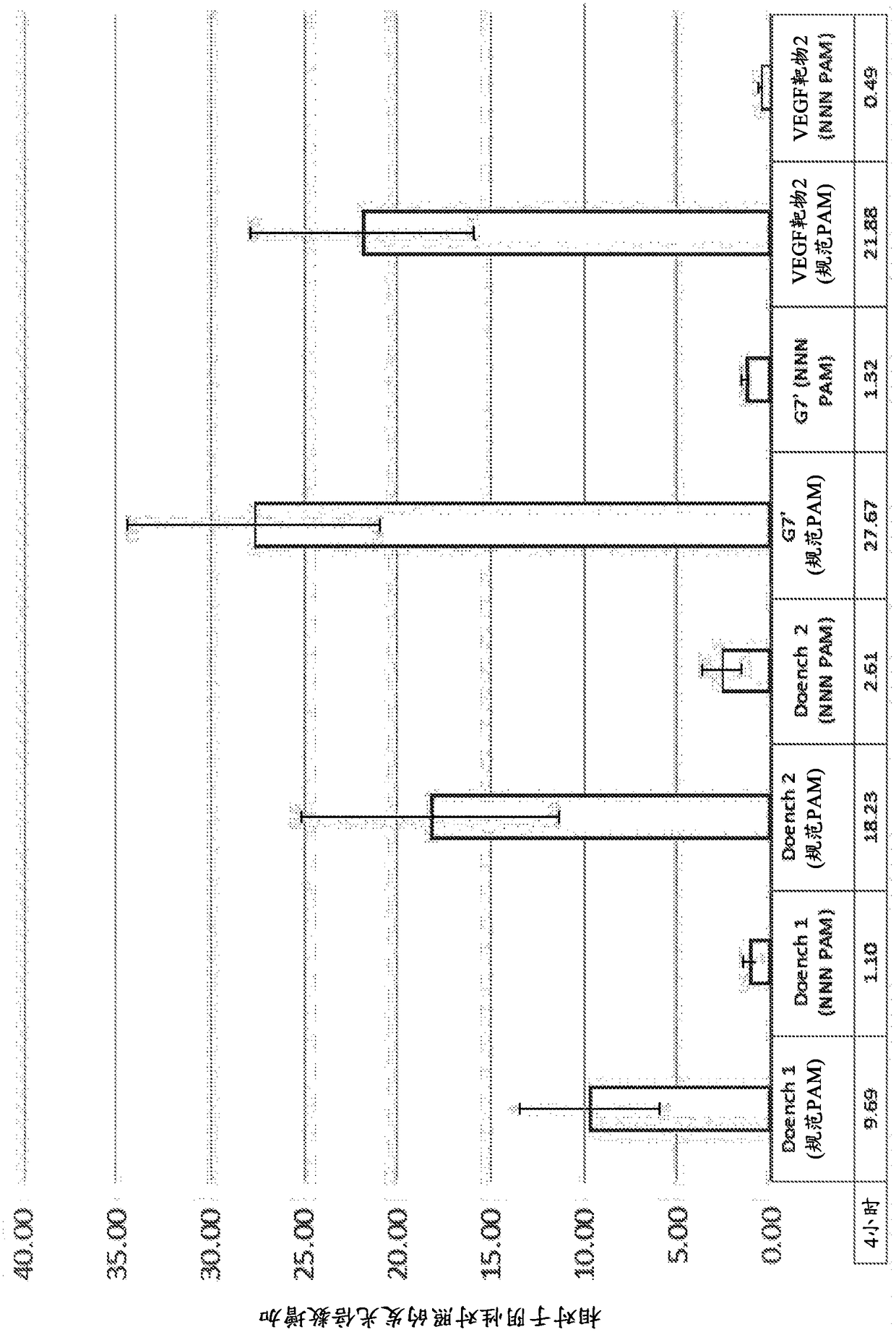
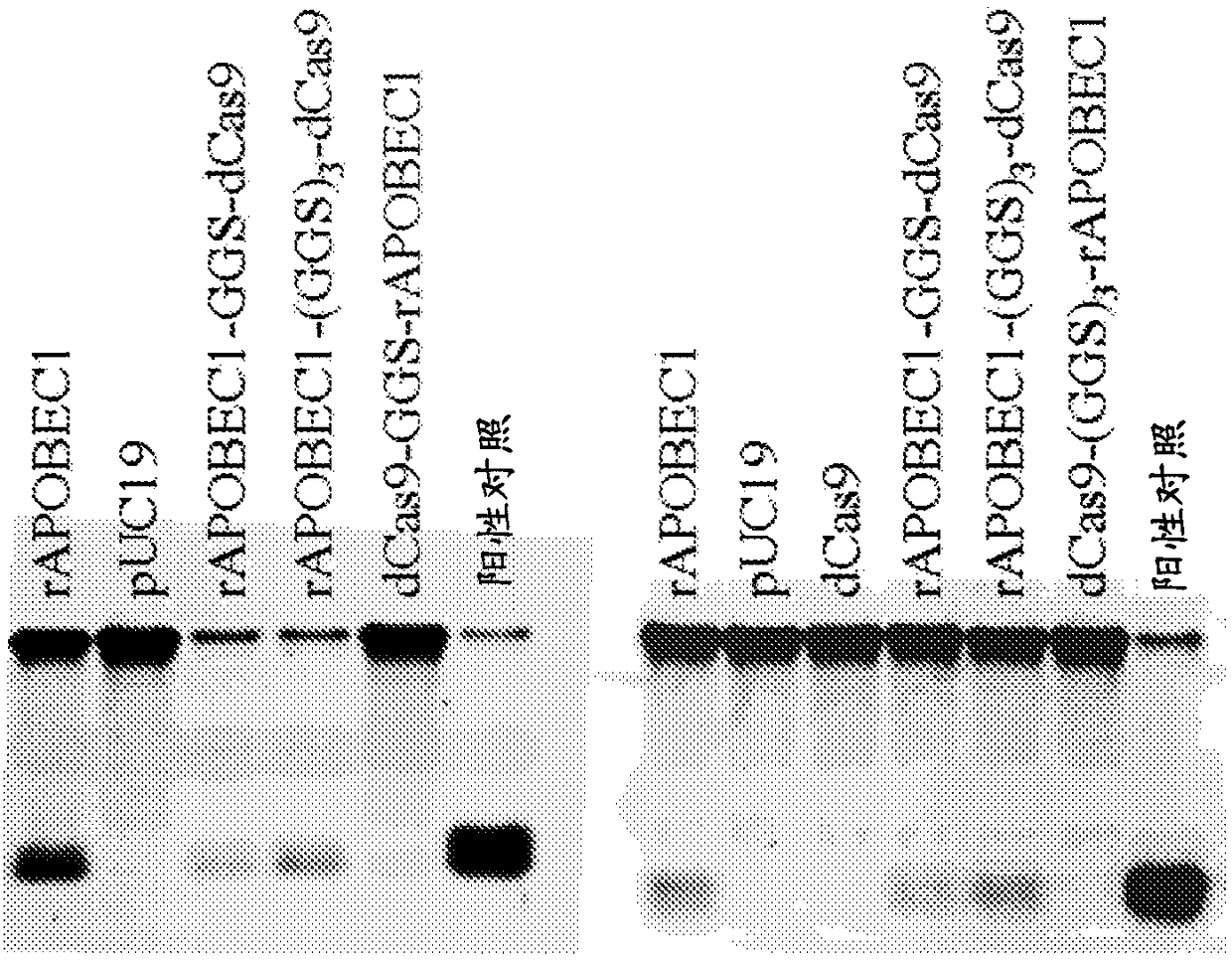
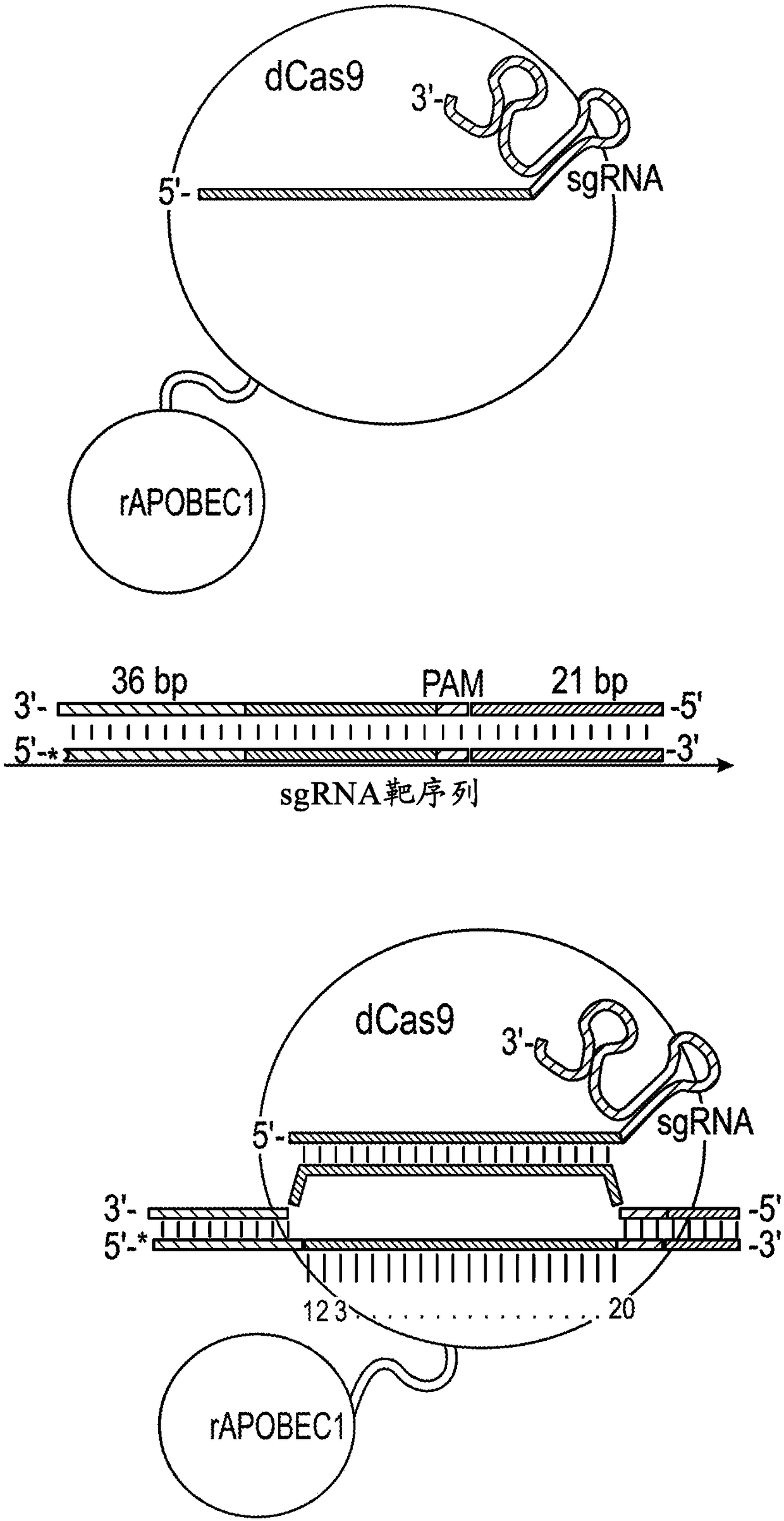
Nucleobase editors and uses thereof
Some aspects of this disclosure provide strategies, systems, reagents, methods, and kits that are useful for the targeted editing of nucleic acids, including editing a single site within the genome ofa cell or subject, e.g., within the human genome. In some embodiments, fusion proteins of Cas9 and nucleic acid editing proteins or protein domains, e.g., deaminase domains, are provided. In some embodiments, methods for targeted nucleic acid editing are provided. In some embodiments, reagents and kits for the generation of targeted nucleic acid editing proteins, e.g., fusion proteins of Cas9 andnucleic acid editing proteins or domains, are provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods for isolating one strand of a double-stranded nucleic acid
InactiveUS20030148277A1Fast dynamicsIncrease temperatureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousHeteroduplex
The present invention provides methods and kits for isolating one strand of a double-stranded target nucleic acid. The method capitalizes on the differences in the kinetics and thermodynamic stabilities between conventional DNA / DNA, DNA / RNA and RNA / RNA duplexes and heteroduplexes in which one strand of the heteroduplexe is a nucleobase polymer having a net positively charged or net neutral backbone, such as a PNA.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
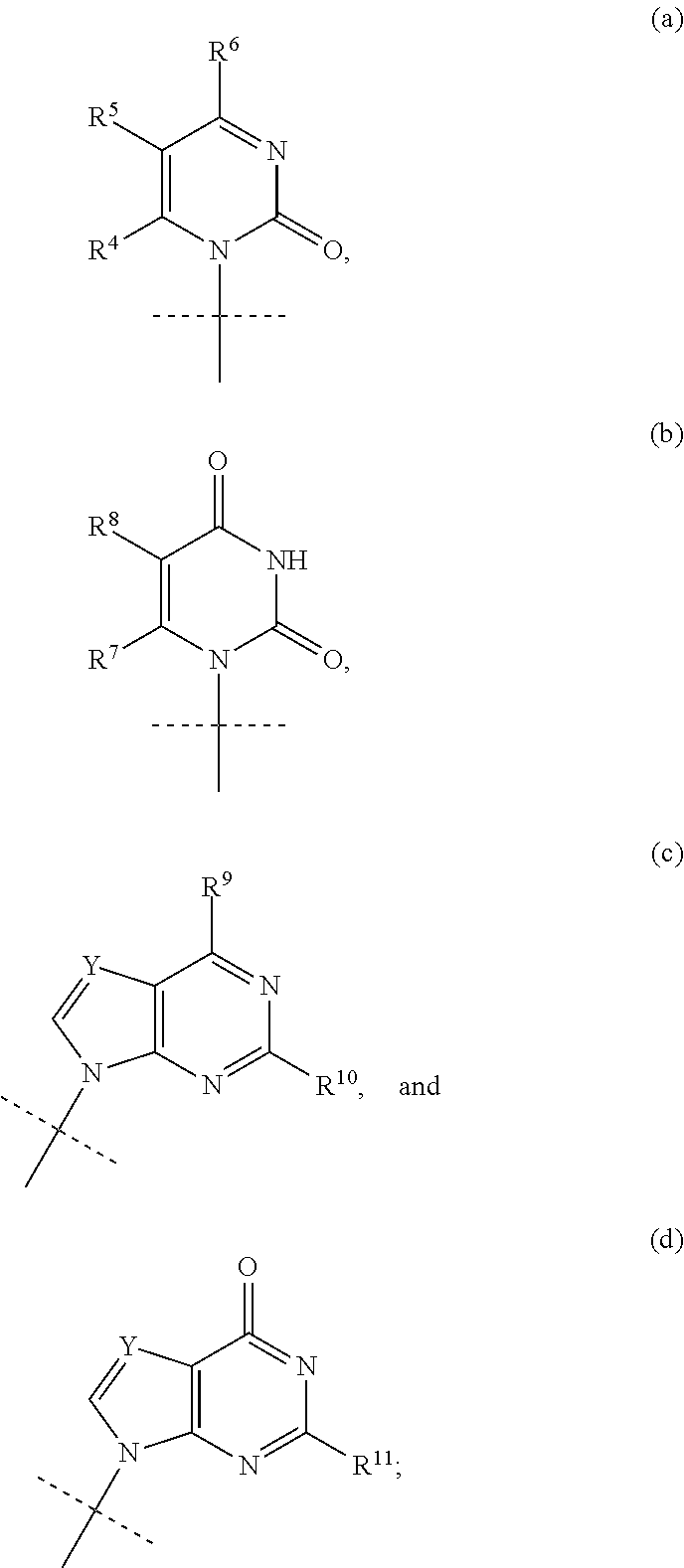
HCV polymerase inhibitors
The invention provides compounds of the formula:wherein B is a nucleobase selected from the groups (a) to (d):and the other variables are as defined in the claims,which are of use in the treatment or prophylaxis of hepatitis C virus infection, and related aspects.
Owner:MEDIVIR AB
Mobility-modified nucleobase polymers and methods of using same
InactiveUS6743905B2Expanded repertoireAdd additional massSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCapillary electrophoresisPhosphate
The present invention relates generally to nucleobase polymer functionalizing reagents, to mobility-modified sequence-specific nucleobase polymers, to compositions comprising a plurality of mobility-modified sequence-specific nucleobase polymers, and to the use of such polymers and compositions in a variety of assays, such as, for example, for the detection of a plurality of selected nucleotide sequences within one or more target nucleic acids. The mobility-modifying polymers of the present invention include phosphoramidite reagents which can be joined to other mobility-modifying monomers and to sequence-specific oligonucleobase polymers via uncharged phosphate triester linkages. Addition of the mobility-modifying phosphoramidite reagents of the present invention to oligonucleobase polymers results in unexpectedly large effects the mobility of those modified oligonucleobase polymers, especially upon capillary electrophoresis in non-sieving media.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Alkylated hexitol nucleoside analogues and oligomers thereof
The present invention is directed to nucleoside analogues with as substitute for the sugar part a 1,5-anhydrohexitol moiety, doexygenated and substituted with a nucleobase at the 2-position, of which the hexitorl ring is further substituted with at least one alkoxy substituent at the 3-position or at the 1-position, and to oligonucleotides wherein at least some of the nucleotides are part of the afore mentioned hexitol nucleoside analogues and exhibit sequence-specific hydridization to complementary sequences of nucleic acids, and maintaining or improving the hybridisation strength. The invention further relates to nucleoside analogues with a 1,5-anhydrohexitol moiety as the sugar part, deoxygenated and substituted with a nucleobase at the 2-position, of which the hexitol ring is substituted with a methoxy substituent at the 1-position, having at the same time either a hydroxy or an alkoxy group at the 3-position, or having a 3-deoxygenated position. The inclusion of one or more of the afore mentioned hexitol nucleoside analogues in oligonucleotides provides, inter alia, either for improved binding or for maintained binding of these oligonucleotides to a complementary strand. This invention further relates to the chemical synthesis of these oligomers which are useful diagnostics, therapeutics and as research agents.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
Phosphinoamidite carboxylates and analogs thereof in the synthesis of oligonucleotides having reduced internucleotide charge
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Oligonucleotide For Detecting Target Dna Or Rna
An oligonucleotide that can be used for detecting the presence of a target DNA or RNA in a sample, a method for detecting a target DNA or RNA by using the oligonucleotide, and a kit comprising the oligonucleotide are provided. The oligonucleotide comprises a nucleoside labeled with a fluorophore and at least one neighboring nucleoside positioned next to the fluorophore-labeled nucleoside, the nucleobase of the neighboring nucleoside being thymine or cytosine.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
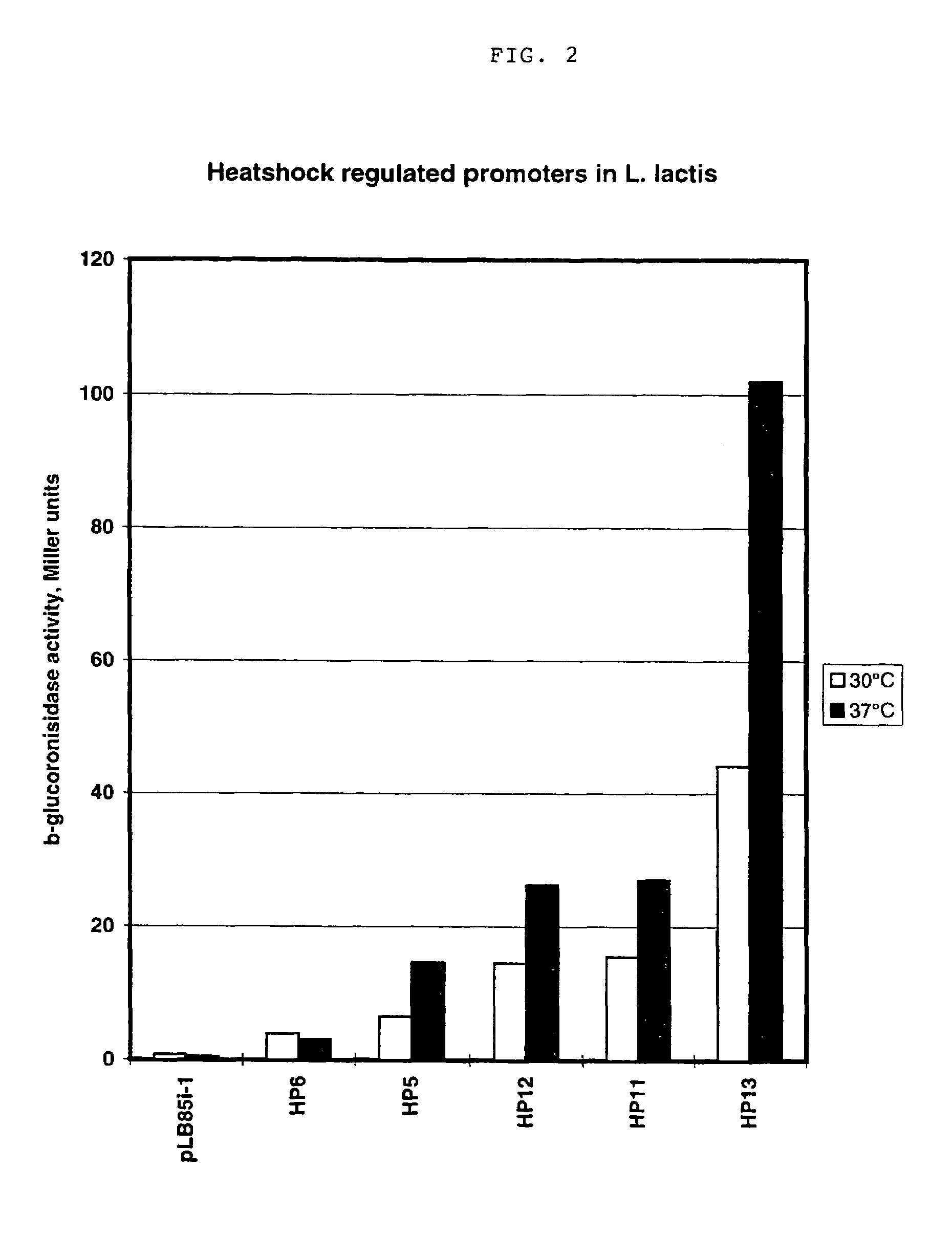
Artificial promoter libraries for selected organisms and promoters derived from such libraries
InactiveUS7199233B1Strong impactNone is suitable for purposeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleobase
An artificial promoter library (or a set of promoter sequences) for a selected organism or group of organisms is constructed as a mixture of double stranded DNA fragments, the sense strands of which comprise at least two consensus sequences of efficient promoters from said organism or group of organisms, or parts thereof comprising at least half of each, and surrounding intermediate nucleotide sequences (spacers) of variable length in which at least 7 nucleotides are selected randomly among the nucleobases A, T, C and G. The sense strands of the double stranded DNA fragments may also include a regulatory DNA sequence imparting a specific regulatory feature, such as activation by a change in the growth conditions, to the promoters of the library. Further, they may have a sequence comprising one or more recognition sites for restriction endonucleases added to one or both of their ends. The selected organism or group of organisms may be selected from prokaryotes and from eukaryotes; and in prokaryotes the consensus sequences to be retained most often will comprise the −35 signal (−35 to −30): TTGACA and the −10 signal (−12 to −7): TATAAT or parts of both comprising at least 3 conserved nucleotides of each, while in eukaryotes said consensus sequences should comprise a TATA box and at least one upstream activation sequence (UAS). Such artificial promoter libraries can be used, e.g., for optimizing the expression of specific genes in various selected organisms.
Owner:JENSEN PETER RUHDAL +1
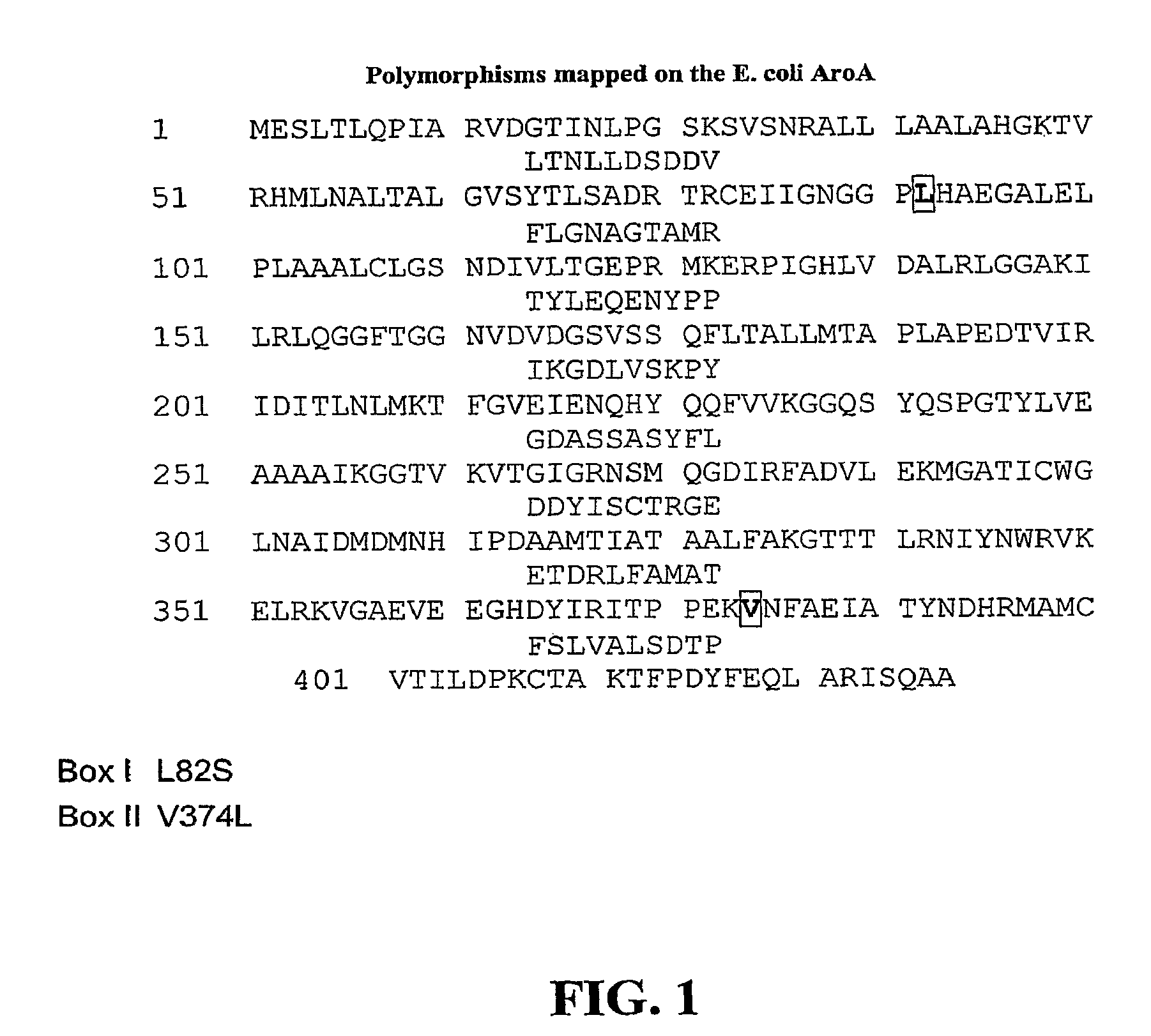
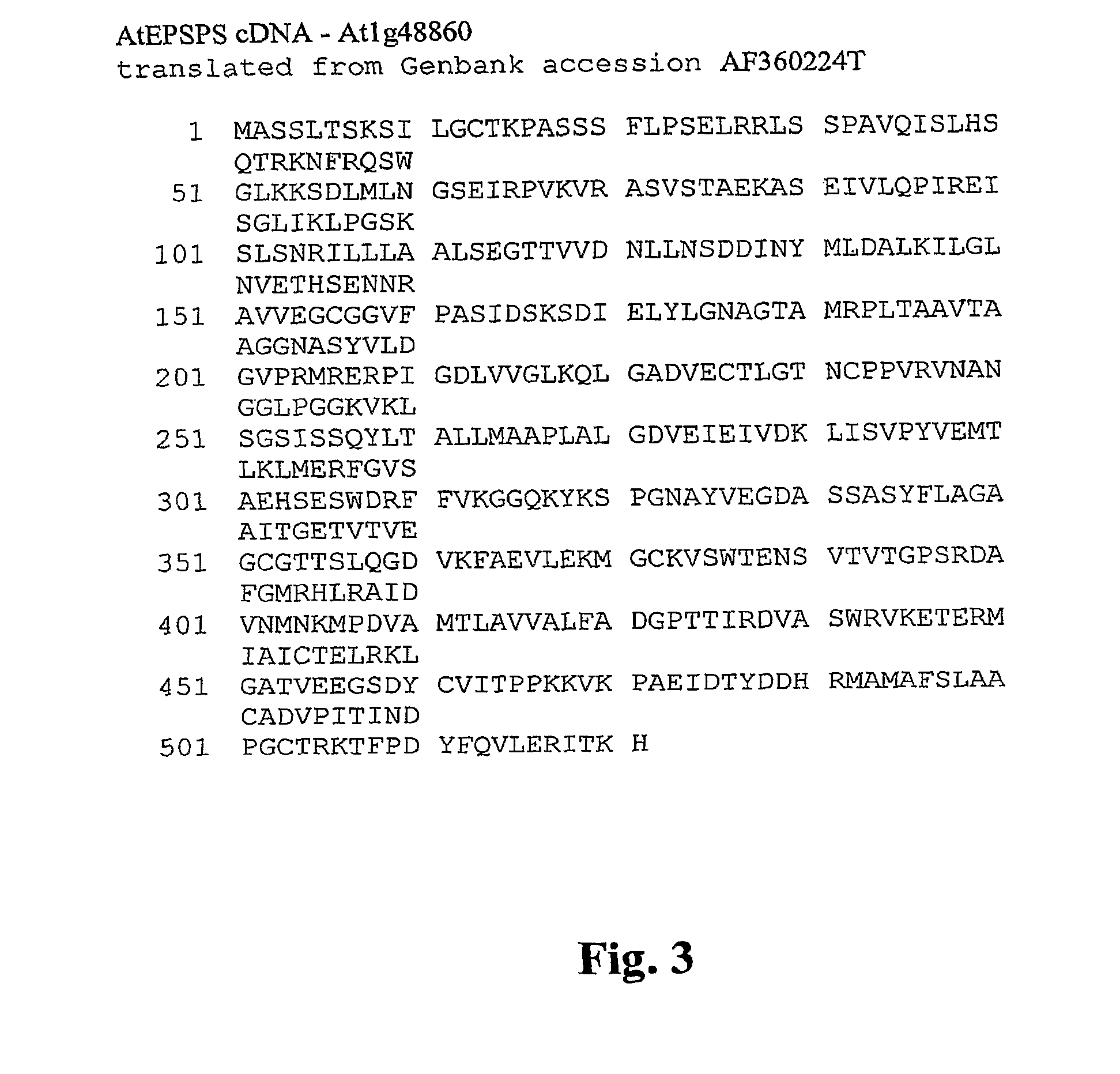
EPSPS mutants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. Additionally the present invention relates to mutant E. coli cells that contain mutated EPSPS genes.
Owner:CIBUS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com