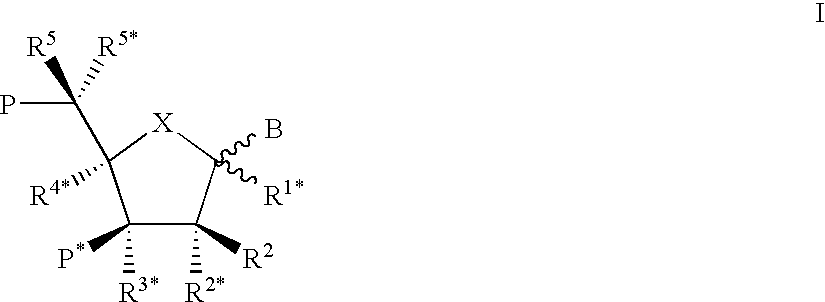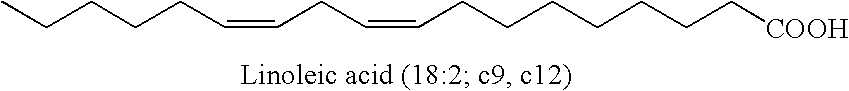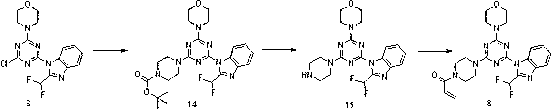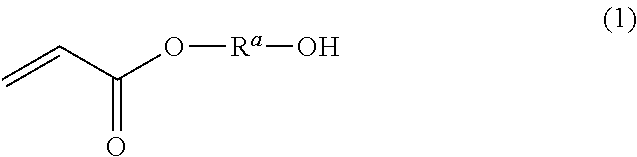Patents
Literature
54 results about "Methylene bridge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In organic chemistry, a methylene bridge, methylene spacer, or methanediyl group is any part of a molecule with formula -CH₂-; namely, a carbon atom bound to two hydrogen atoms and connected by single bonds to two other distinct atoms in the rest of the molecule. It is the repeating unit in the skeleton of the unbranched alkanes.
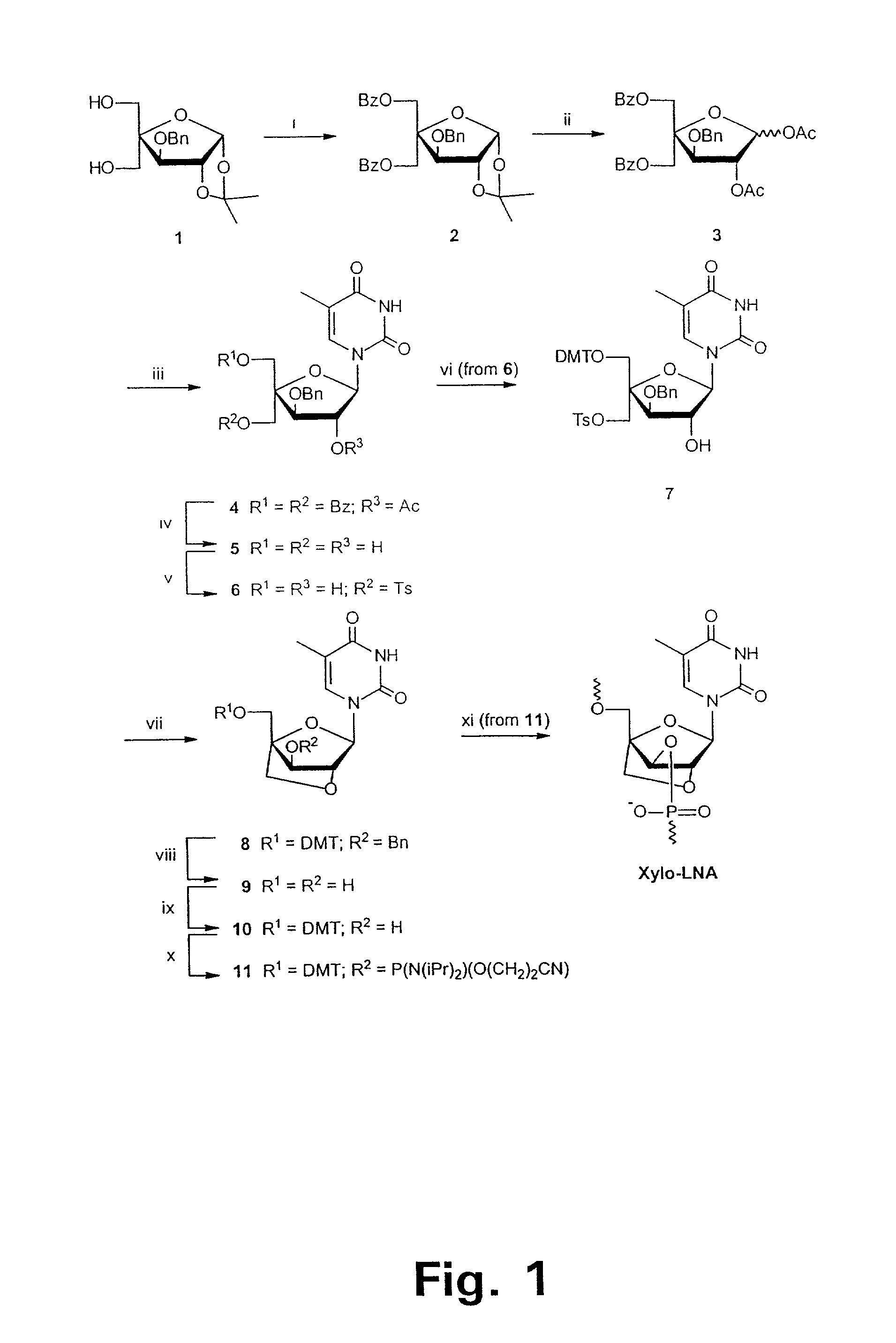
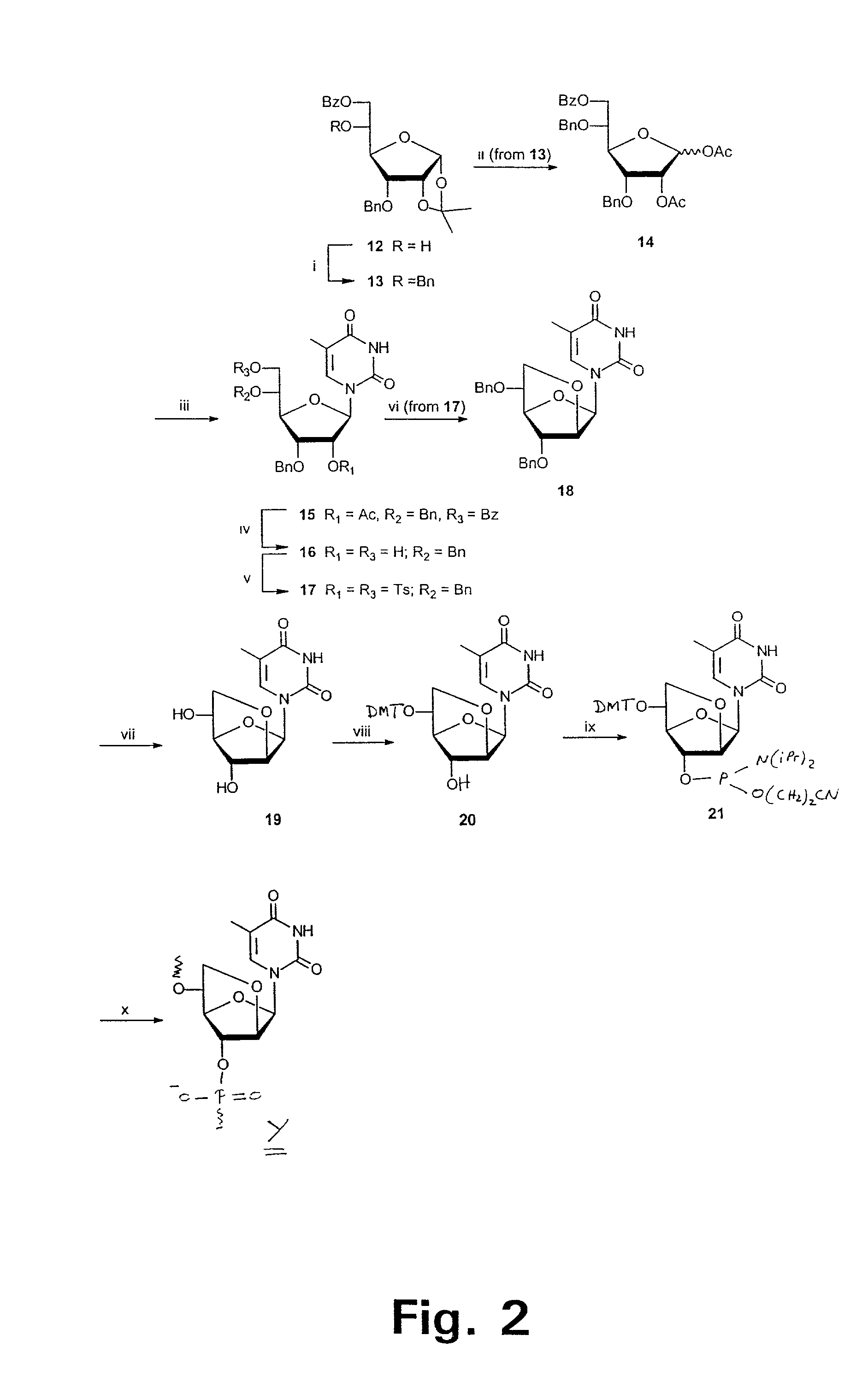
Xylo-LNA analogues
Based on the above and on the remarkable properties of the 2′-O,4′-C-methylene bridged LNA monomers it was decided to synthesise oligonucleotides comprising one or more 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer(s) as the first stereoisomer of LNA modified oligonucleotides. Modelling clearly indicated the xylo-LNA monomers to be locked in an N-type furanose conformation. Whereas the parent 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleosides were shown to adopt mainly an N-type furanose conformation, the furanose ring of the 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl monomers present in xylo-DNA were shown by conformational analysis and computer modelling to prefer an S-type conformation thereby minimising steric repulsion between the nucleobase and the 3′-O-phopshate group (Seela, F.; Wömer, Rosemeyer, H. Helv. Chem. Acta 1994, 77, 883). As no report on the hybridisation properties and binding mode of xylo-configurated oligonucleotides in an RNA context was believed to exist, it was the aim to synthesise 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer and to study the thermal stability of oligonucleotides comprising this monomer. The results showed that fully modified or almost fully modified Xylo-LNA is useful for high-affinity targeting of complementary nucleic acids. When taking into consideration the inverted stereochemistry at C-3′ this is a surprising fact. It is likely that Xylo-LNA monomers, in a sequence context of Xylo-DNA monomers, should have an affinity-increasing effect.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
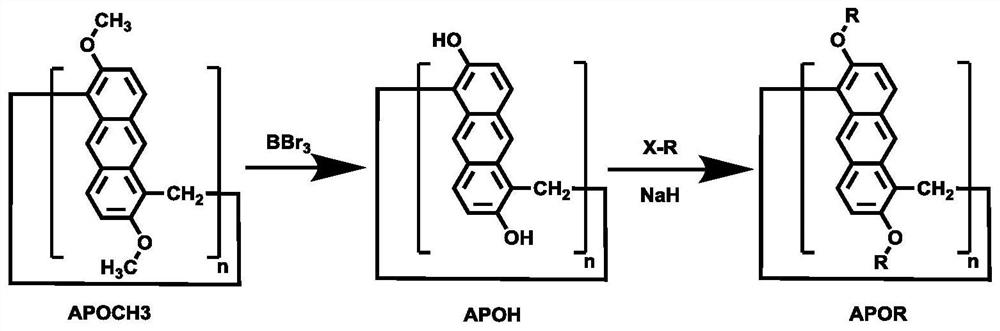
Activated arylamine-based polybenzoxazines
InactiveUS6160079AFacilitate ring openingLow polymerization temperatureSilicon organic compoundsGlass transitionElectron
Arylamines with electron donating groups such as alkyl and alkoxy groups in the meta position on the aromatic ring change the polymerization temperature of the benzoxazine prepared therefrom and offer an opportunity for an additional crosslinking site (the para position on the aromatic amine can couple to a Mannich base generated by the opening of the oxazine ring of the benzoxazine or a methylene bridge generated by a degradation reaction). Naphthenic amines with an alkyl or alkoxy substituent on the 5th through the 8th carbon atom on the naphthalene ring can function similarly. The polymers for benzoxazines prepared from at least 10% substituted aromatic or naphthenic amines are useful due to low polymerization temperatures and higher Tg (glass transition temperature).
Owner:EDISON POLYMER INNOVATION EPIC
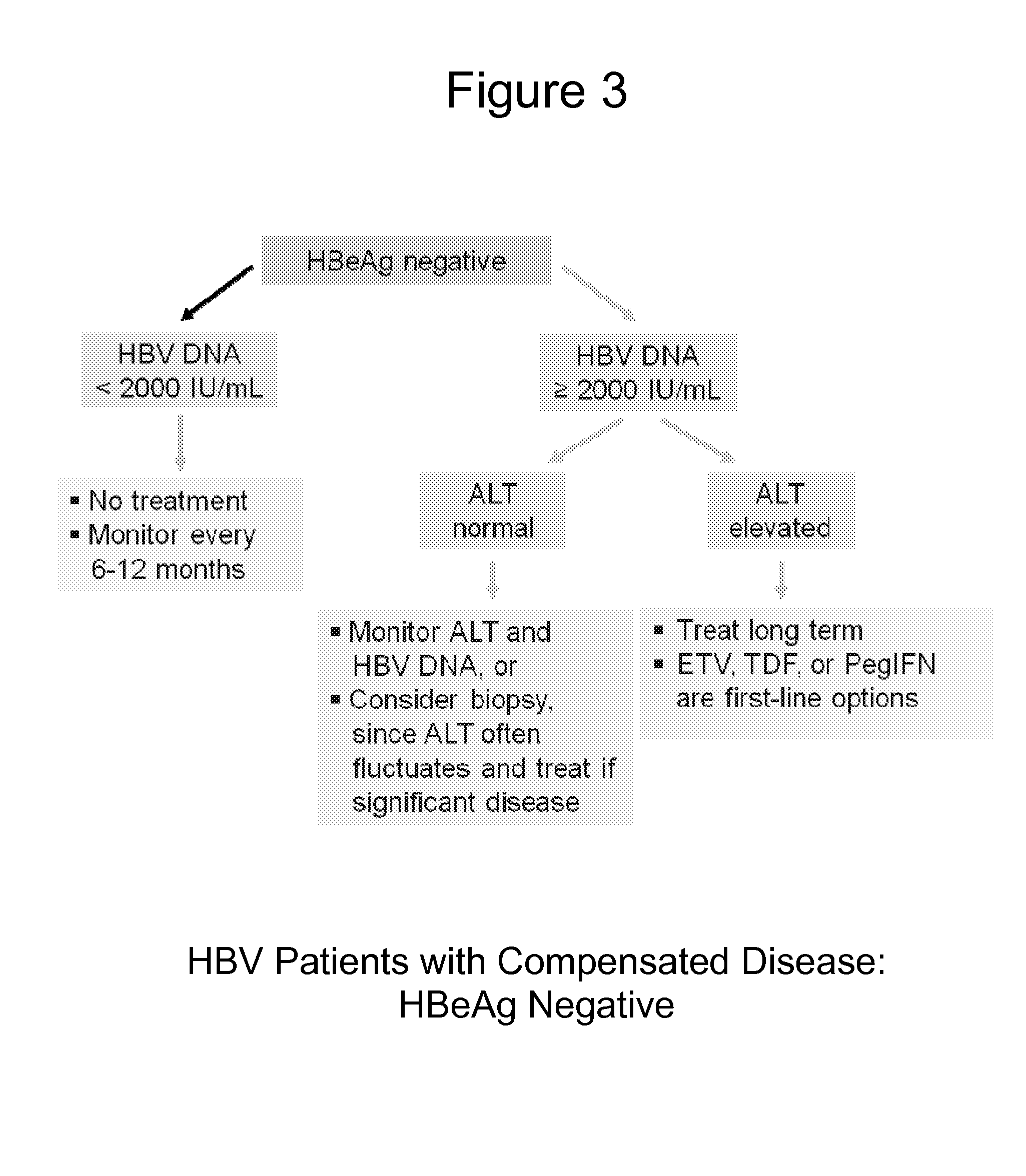
HBV antisense inhibitors
ActiveUS8598334B2Promoting seroconversionReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesOligomerMethylene bridge
Antisense oligomers useful for modulating hepatitis B virus infections, and for the treatment of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis B virus-related conditions in animals including humans. More particularly, antisense oligomers with modified nucleotides for treatment of HBV in animals, more particularly antisense oligomers comprising 2′O-4′C-methylene-bridged sugars, or nucleotides with other 2′O-4′C bridged sugars, also known as locked nucleic acids (LNA), for treatment of HBV in animals, and more particularly for treatment of HBV in humans.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LTD
Preparation method for 5-fluorocytosine
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicinal chemical synthesis, and particularly relates to a preparation method for 5-fluorocytosine. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dropwise adding ethyl formate in xylene, carrying out a condensation reaction with methyl fluoroacetate under the action of a metal catalyst, and heating, stirring and carrying out heating heat preservation to obtain an intermediate; carrying out chlorination substitution on the intermediate with a chlorinating agent in the presence of an organic amine catalyst to obtain a chlorination product; carrying out ammoniation substitution on the chlorination product in an ammonia gas pressure environment and under the action of phase transfer catalysts (N-alkyl phosphoramide, methylene bridged phosphate and tetrabutylammonium bromide to obtain an ammoniation product; carrying out acidic hydrolysis on the ammoniation product to obtain 5-fluorocytosine. The 5-fluorocytosine prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is high in yield and high in purity; use of highly-toxic fluorine is avoided during the preparation process, thus reducing damage and injury to equipment and operating personnel during a production process.
Owner:SHANDONG JINCHENG PHARMA & CHEM
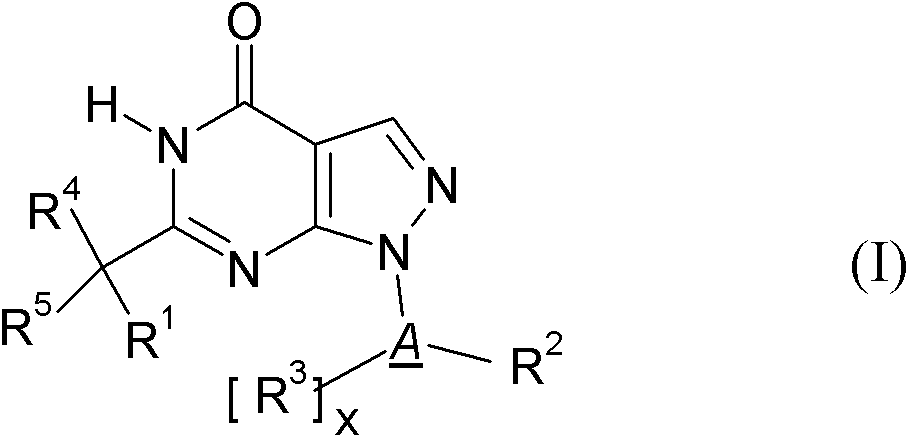
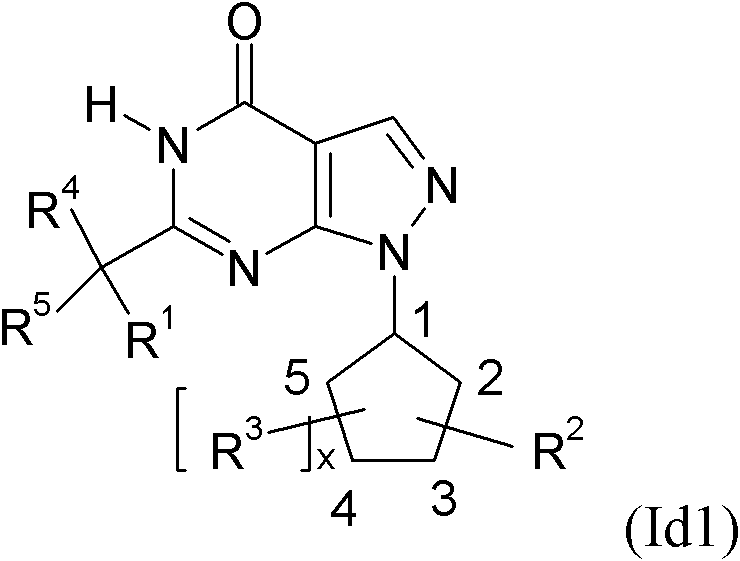
Pyrazolopyrimidines and their use for the treatment of CNS disorders
The invention relates to novel cycloalkyl- or cycloalkenyl-substituted pyrazolopyrimidinones of formula (I), wherein A is selected from the group A1 consisting of a C3-C8-cycloalkyl group or a C4-C8-cycloalkenyl group, whereby the members of C3-C8-cycloalkyl group being selected from the group of cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, cycloheptanyl and cyclooctanyl; and the members of the C4-C8-cycloalkenyl group, being selected from cyclobutenyl, cyclopentenyl, cyclohexenyl, cycloheptenyl, cyclooctenyl, cyclopentadienyl, cyclohexadienyl, cycloheptadienyl, cyclooctadienyl, cycloheptatrienyl, cyclooctathenyl, cyclooctatetraenyl. The new compounds shall be used for the manufacture of medicaments, in particular medicaments for improving perception, concentration, learning and / or memory in patients in need thereof. Chemically, the compounds are characterised as pyrazolopyrimidinones with a cycloalkyl-moiety directly bound to the 1 position of the pyrazolopyrimidinone and a second substituent in the 6 position which is bound via an optionally substituted methylene-bridge. Further aspects of the present invention refer to a process for the manufacture of the compounds and their use for producing medicaments.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
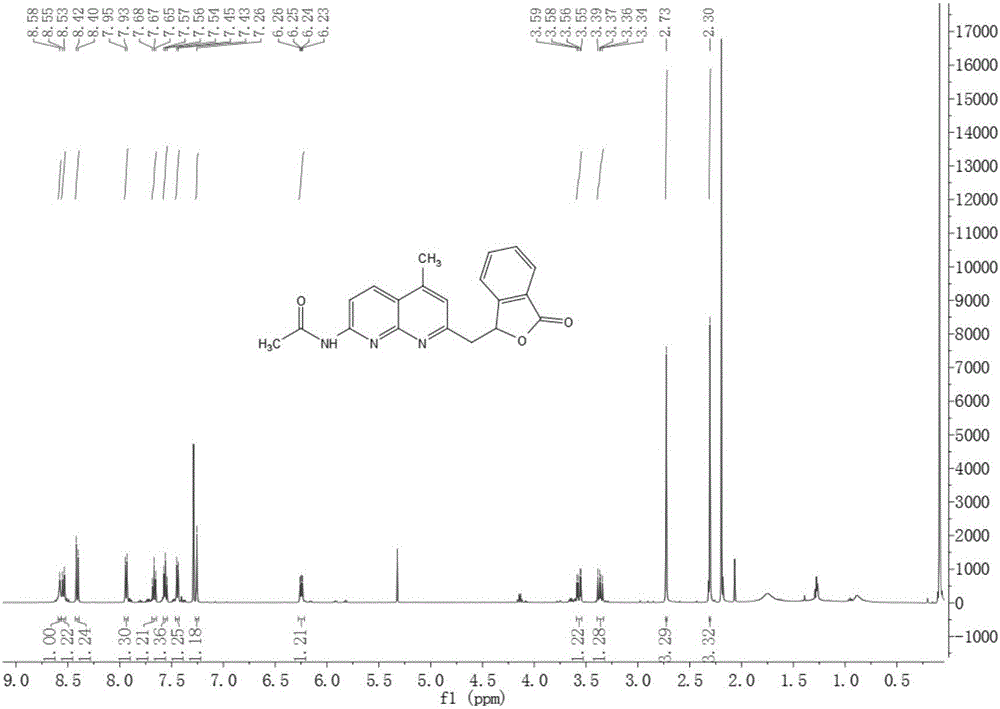
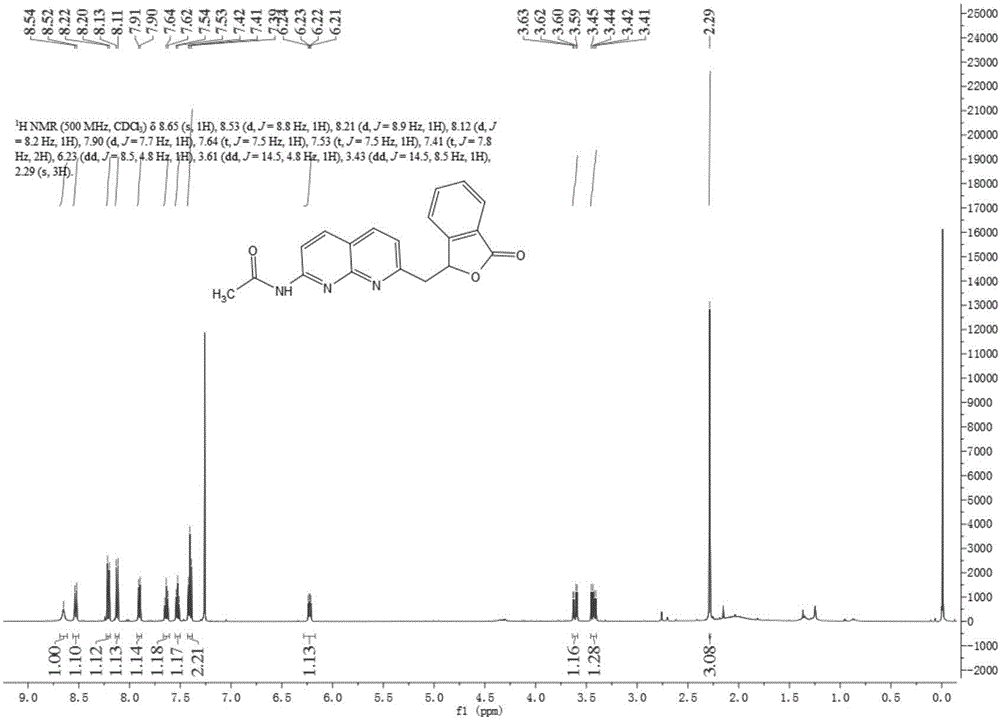
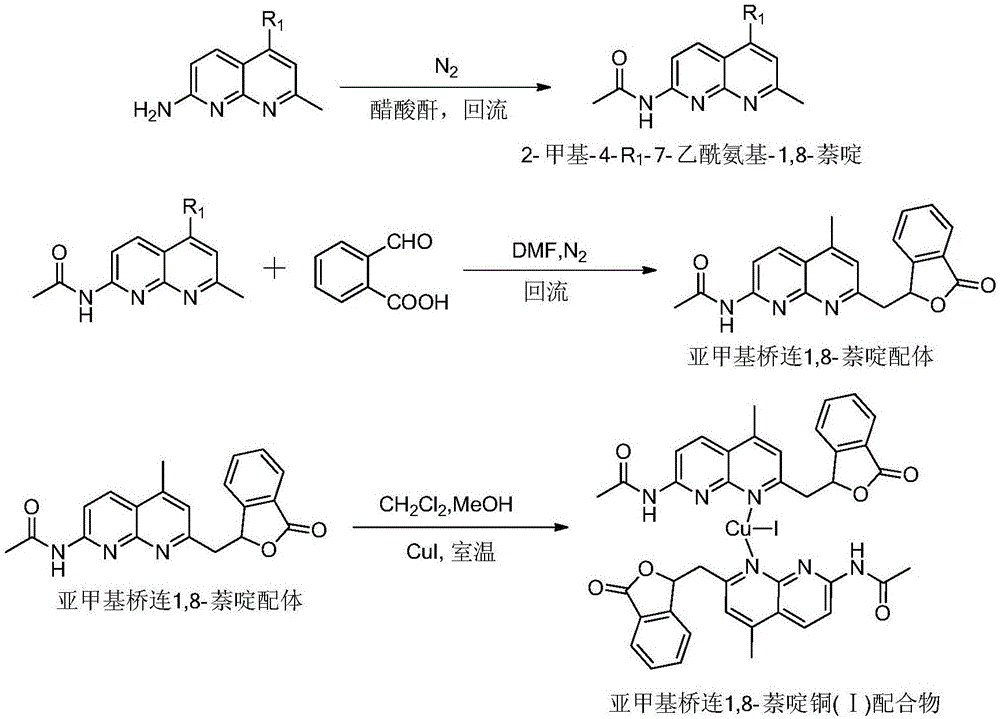
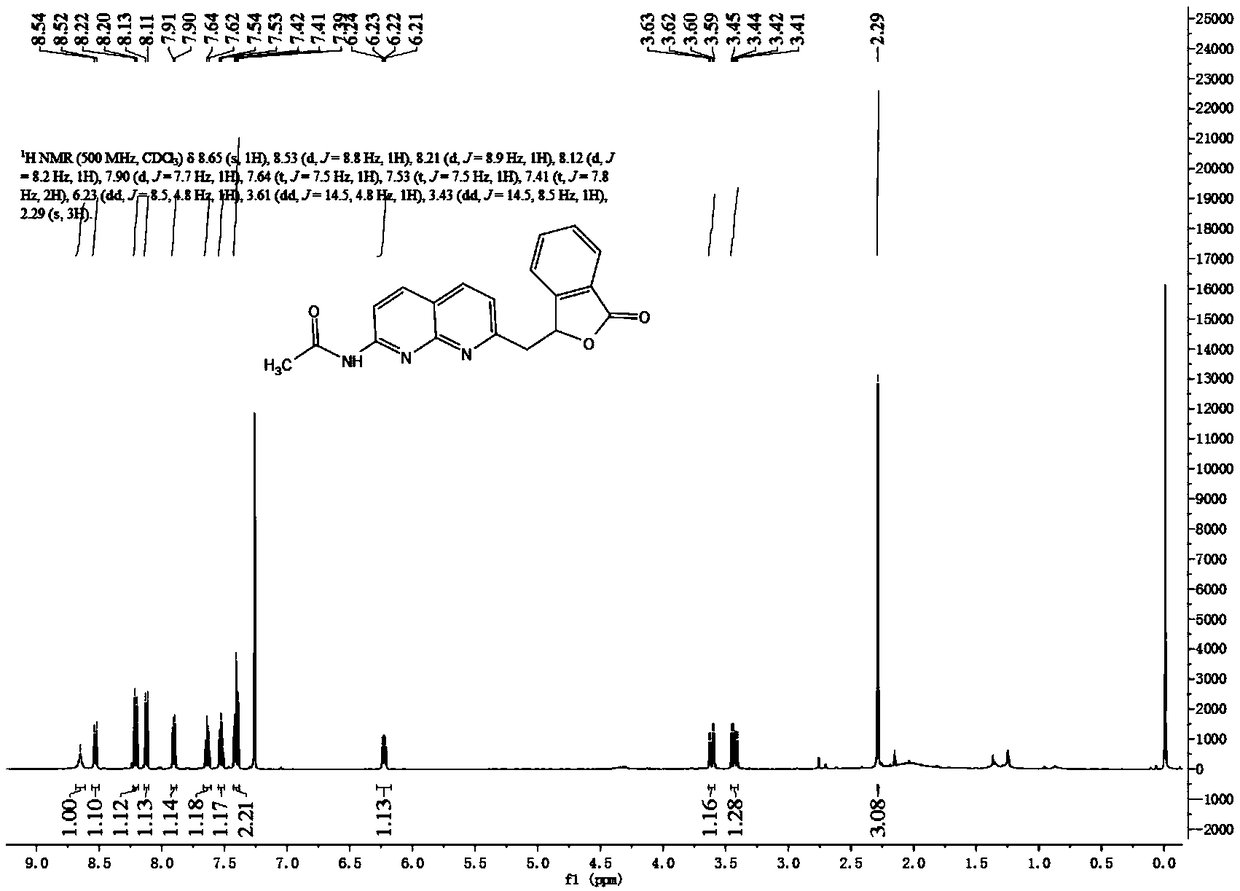
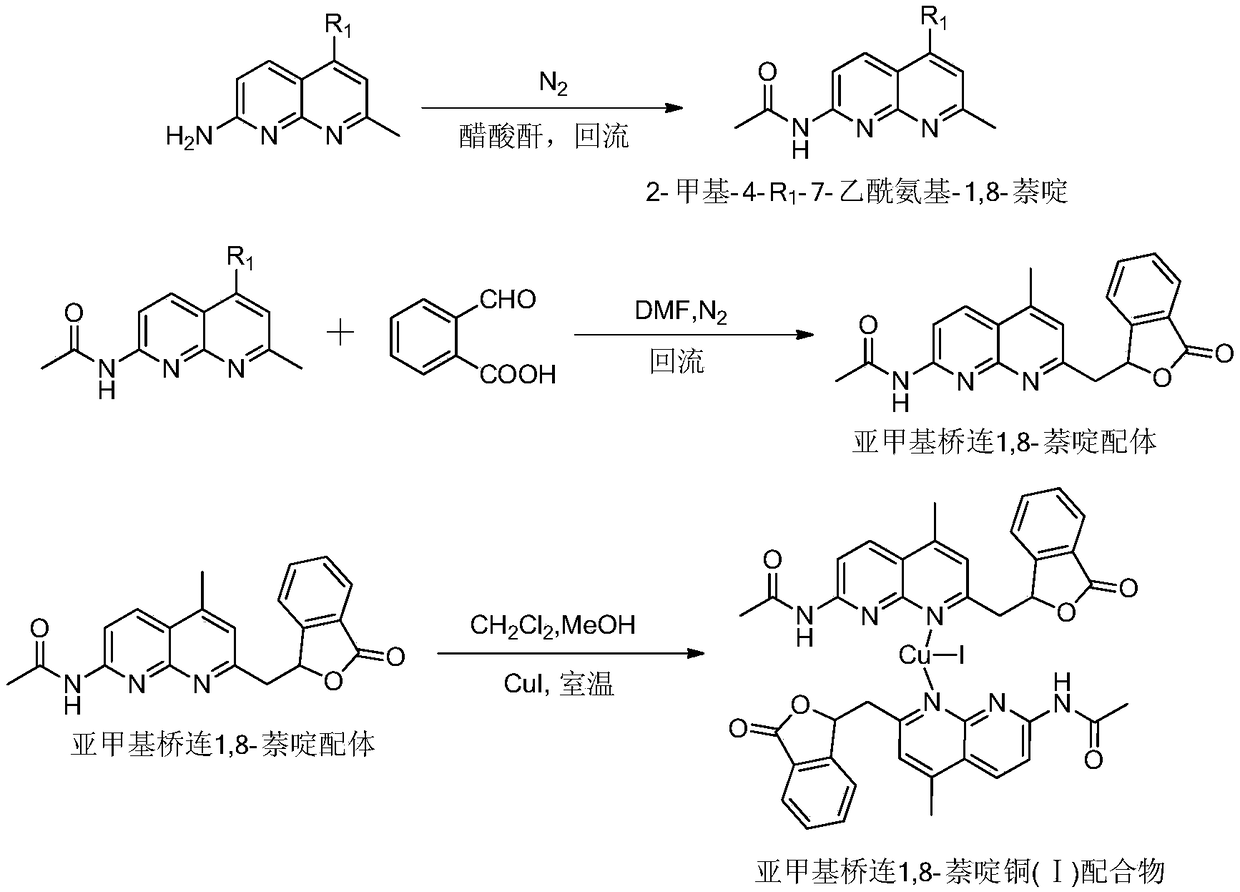
Methylene bridging 1,8-naphthyridine ligand and copper (I) complex, preparing method and application
InactiveCN106243105ASimple ingredientsShort reaction processGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMethylene bridgeHydrogen
The invention discloses a methylene bridging 1,8-naphthyridine ligand and copper (I) complex, a preparing method and an application. The molecular formula of the methylene bridging 1,8-naphthyridine ligand and copper (I) complex is shown in the specification, wherein R1 is hydrogen or methyl. The methylene bridging 1,8-naphthyridine ligand and copper (I) complex is the first complex obtained in the mode that an activation reaction is carried out through a SP3C-H key under the condition that a catalyst is free so far, and it is firstly achieved that a C-C key is activated and constructed through the catalyst-free SP3C-H key. The copper (I) complex can be used as a catalyst of a coupling reaction between aryl halide and imidazole compound C-N, and the yield is high.
Owner:HONGHE COLLEGE
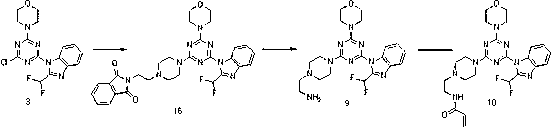
Piperazinotriazines as PI3K inhibitors for use in the treatment antiproliferative disorders
InactiveCN103002899AProlonged diffusion timeShorten Diffusion TimeNervous disorderOrganic chemistryDiseaseAcyl group
The invention relates to compounds of formula (I) R<1> is methyl, n-hexyl, aminoethyl, methylaminoethyl, ethylaminoethyl, dimethylaminoethyl, acryloylaminoethyl, methacryloylaminoethyl, methoxyethyl, ethoxyethyl, C1-C4-alkyl- sulfonyl, acryloyl, or methacryloyl; or R<1> is aminoethyl, acryloyl or acryloylaminoethyl carrying a linker and a tag, and R<2> and R<3>, independently of each other, are hydrogen or C1-C4-alkyl, or R<2> and R<3> together form a methylene or an ethylene bridge; and tautomers, solvates and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. These compounds are effective in preventing or treating a disease or disorder modulated by PI3 kinases and / or mTOR, in particular treating a hyperproliferative disorder.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
Methylene bridged metallocenes as olefin-polymerization-catalyst components
A new class of methylene-bridged metallocenes of formula (I), wherein M is a transition metal of group 3, 4, 5, 6, lanthanide or actinide; X is a monoanionic sigma ligand; R<1 >can be alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, alkylaryl or arylalkyl radicals; R<2 >can be halogen, alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, alkylaryl or arylalkyl radical; p is 0-3; m is 0-2; and n is 0-4. Furthermore, the corresponding ligands, a new process for their preparation and catalysts systems containing said methylene-bridged metallocenes are described.
Owner:BASELL POLYOLEFINE GMBH
Process for preparing cyclopentadienyl compounds
InactiveUS6162937AImprove economyLow yieldSilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationAlpha-olefinSolvent
A process for preparing bis-cyclopentadienyl compounds bridged by a methylene group is reported, said process comprising reacting formaldehyde with a cyclopentadienyl compound in the presence of a base and of a solvent having a dielectric constant ( epsilon ), measured at 25 DEG C., higher than 7. The bridged compounds, obtainable in high yields with this simple single-step process, can be used to prepare ansa-metallocenes, active as catalyst components in the polymerization of olefins.
Owner:MONTELL TECH CO BV
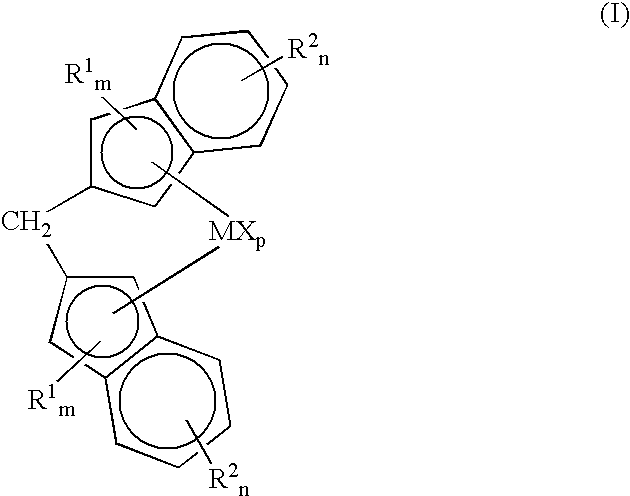
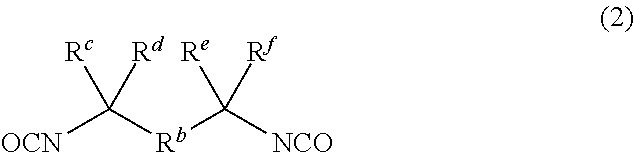
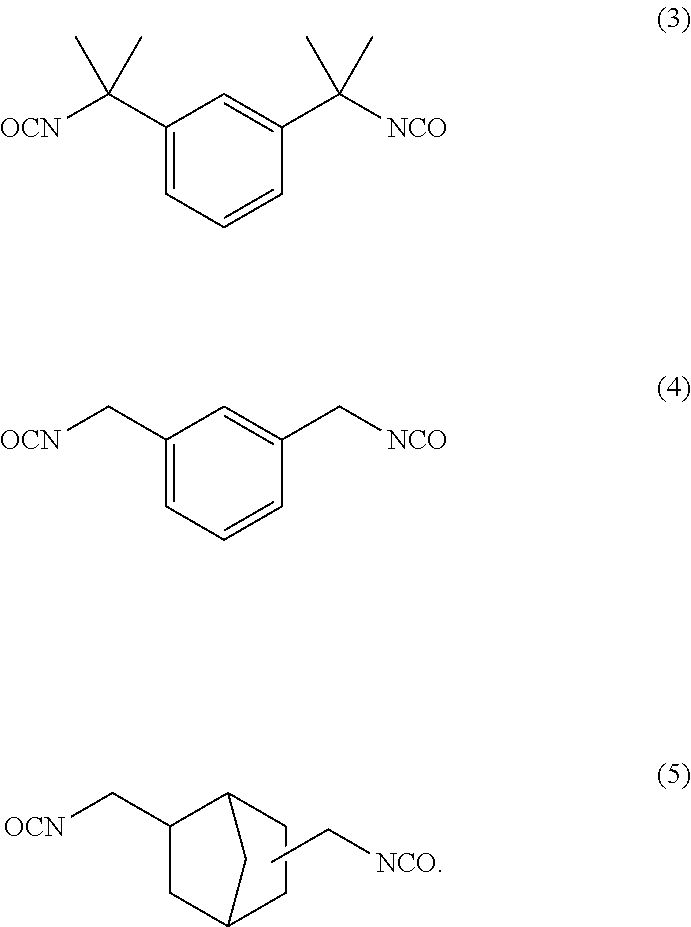
Dental polymerizable monomer compositions
ActiveUS20170181932A1Appropriate viscosityGood compatibilityImpression capsOrganic chemistryMonomer compositionMeth-
Provided are dental polymerizable monomer compositions that can give cured products having high toughness and high rigidity, and dental compositions containing such dental polymerizable monomer compositions and cured products thereof having high mechanical properties. The dental polymerizable monomer composition includes a urethane acrylate compound (A) and a polymerizable compound (B) having at least one polymerizable group selected from methacryloyl groups and acryloyl groups, the urethane acrylate compound (A) being obtained by reacting a specific hydroxyacrylate (a1) with a diisocyanate (a2) having two isocyanate groups bonded to a divalent C6-9 aromatic hydrocarbon group or a divalent C6-9 bridged cyclic hydrocarbon group via a methylene group optionally substituted with a hydrocarbon group in place of a hydrogen atom, the proportion of the number of acryloyl groups present in the urethane acrylate compound (A) being 10% to less than 90% relative to the total number of (meth)acryloyl groups in the monomer composition.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC +2
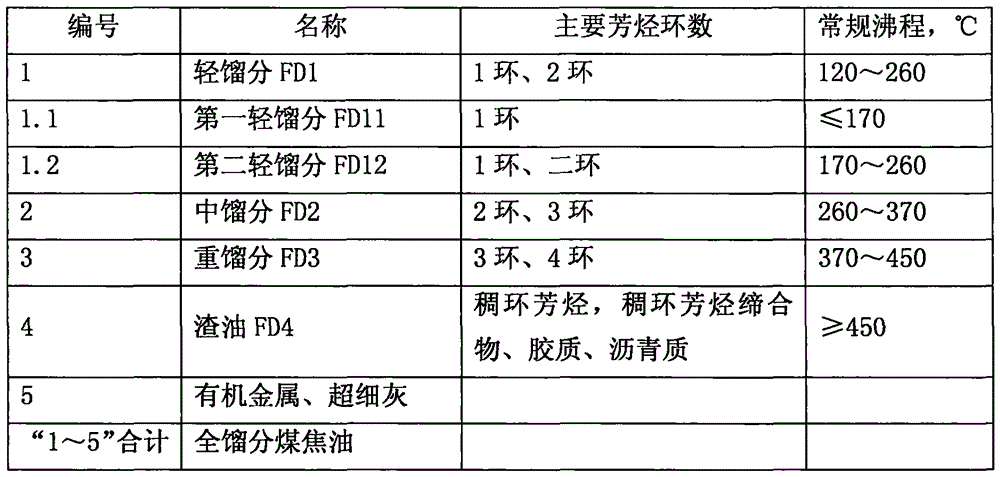
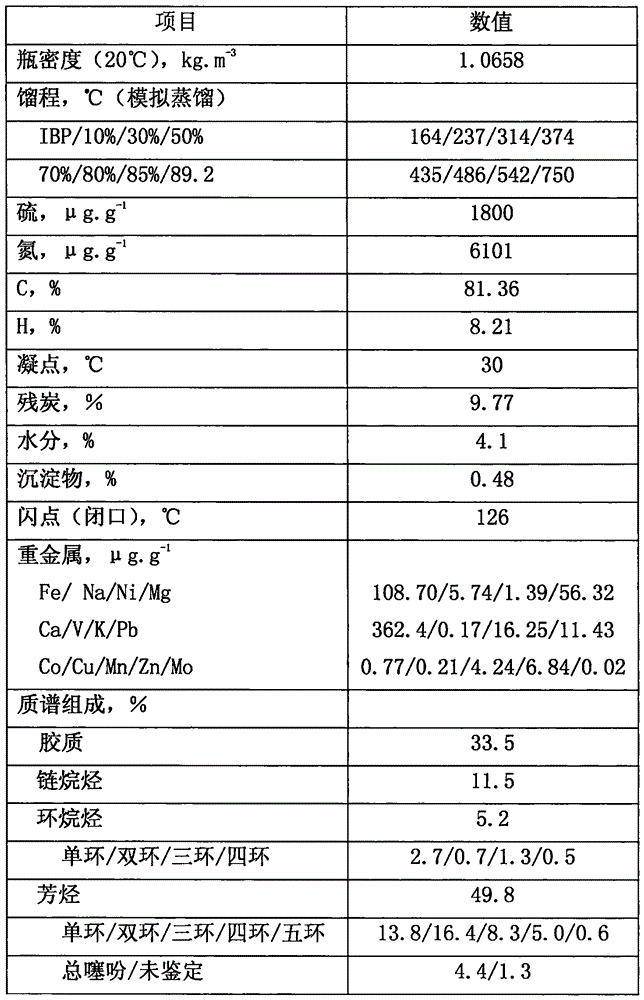
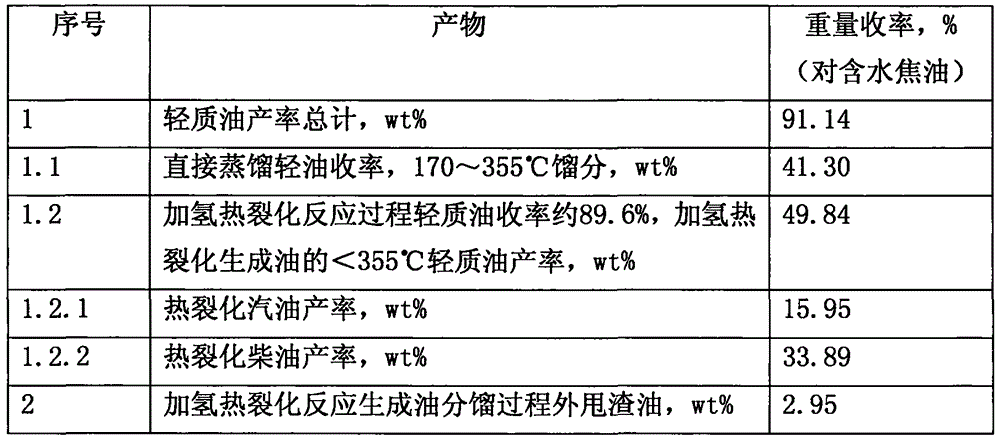
Inferior hydrocarbon hydrogenated thermal cracking method for setting hydrogenated aromatic hydrocarbon light-saturation reaction process
ActiveCN106190283ALightweight conversion rate increasedObvious hydrodecharging reactionTreatment with hydrotreatment processesPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMethylene bridge
The invention relates to an inferior hydrocarbon hydrogenated thermal cracking method for setting a hydrogenated aromatic hydrocarbon light-saturation reaction process. In the hydrogenated aromatic hydrocarbon light-saturation reaction process R10 of inferior hydrocarbons HDS such as metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, colloidal matters and coal-tar heavy oil with high asphaltene content, based on the rule that the super-delocalized energy of pi bonds of middle aromatic rings of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is higher than that of pi bonds of outer-side aromatic rings, a hydrogenated aromatic hydrocarbon light-saturation reaction for the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is carried out under the condition of giving priority to liquid-phase reactions so as to saturate the middle aromatic rings, and methylene bridge bonds with low dissociation energy, which are located at middle positions of polycyclic-structured aromatic hydrocarbons, are produced while the HDS are subjected to a carbon residue removing reaction, so that a thermal cracking material rich in bonds which are appropriate to cracking is provided for a hydrogenated thermal cracking reaction process R20, and the increase of yield of six-membered cyclic hydrocarbons is facilitated; and the efficiency of a liquid-phase reaction of a reaction space can be increased due to low hydrogen-to-oil ratio operation of the R10, a heater can be arranged between the R10 and the R20, the R10 employs hydrogen-supplying hydrocarbon flow for joint processing, and thus the effect is better.
Owner:洛阳瑞华新能源技术发展有限公司
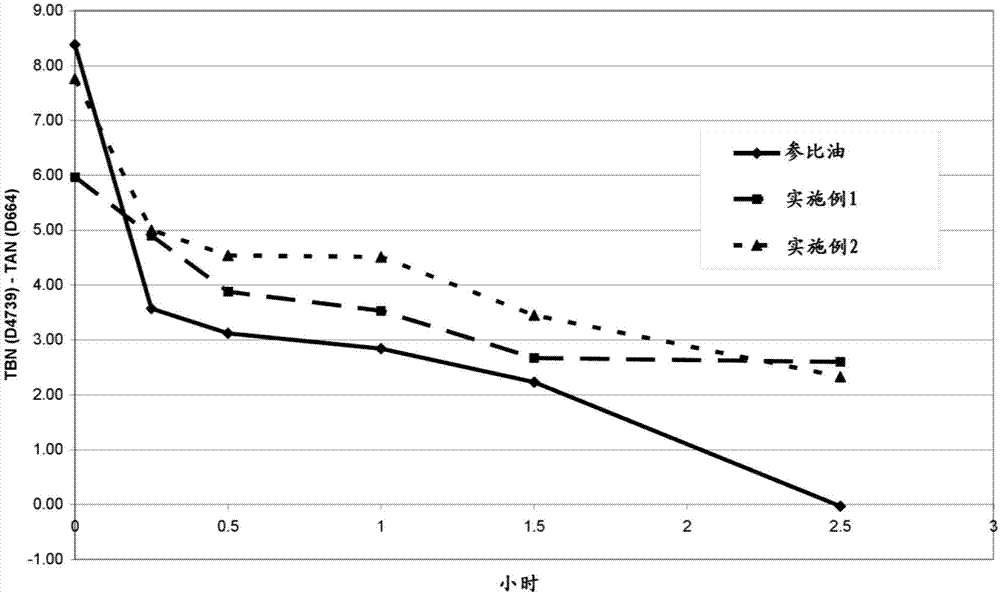
Method of reducing the rate of depletion of basicity of lubricating oil composition in use in engine
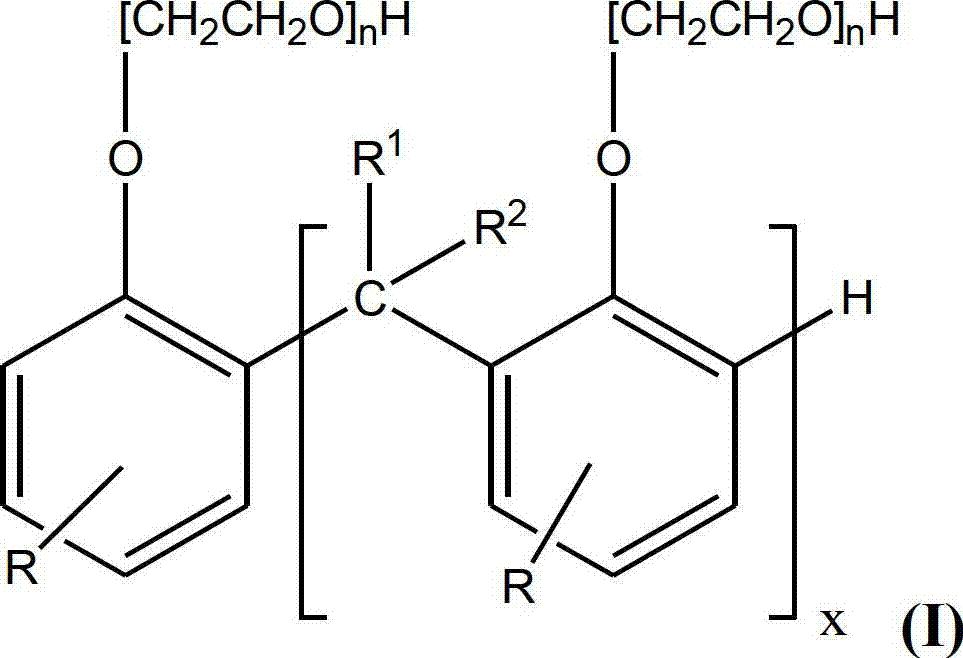
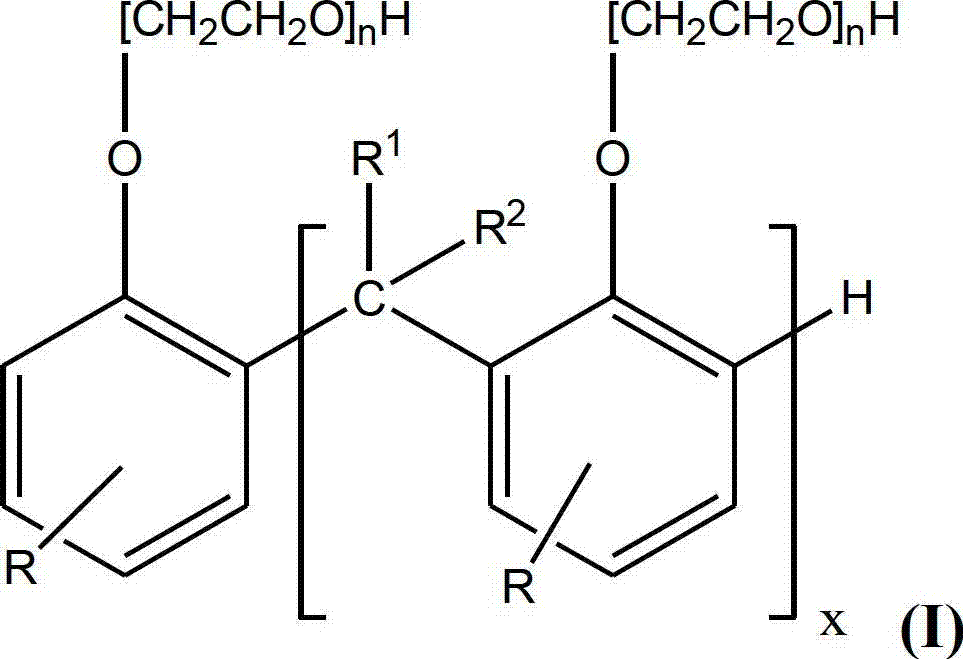
Disclosed is a method of reducing the rate of depletion of basicity (as determined by ASTM D2896) of a lubricating oil composition in use in an engine. The lubricating oil composition includes at least one overbased alkali or alkaline earth metal detergent. The method comprises adding to the lubricating oil composition one or more compounds of Formula (I): (see formula I) wherein: x is 1 to 50, preferably 1 to 40, more preferably 1 to 30; R1 and R2 are H, hydrocarbyl groups having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, or hydrocarbyl groups having 1 to 12 carbon atoms and at least one heteroatom; R is a hydrocarbyl group having 9 to 100, preferably 9 to 70, most preferably, 9 to 50, carbon atoms; and n is 0 to 10, or alkaline earth metal salts thereof. The compounds of formula (I) are preferably methylene-bridged alkyl phenols or ethoxylated methylene-bridged alkyl phenols.
Owner:INFINEUM INT LTD
Preparation method of methylene bridged cucurbituril
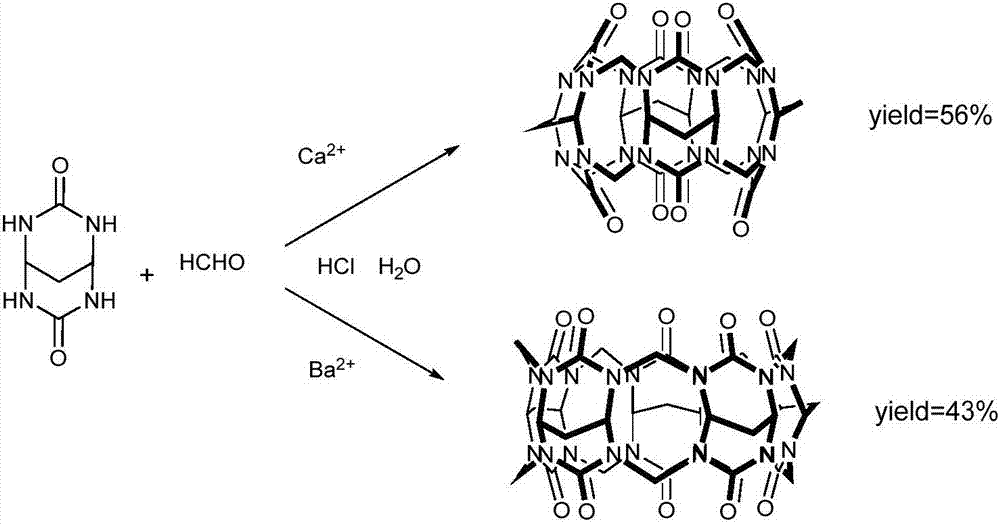
The invention relates to a preparation method of methylene bridged cucurbituril. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing 1,1,3,3-malonaldehyde tetramethyl acetal and urea into methylene bridged glycoluril at first; then feeding the methylene bridged glycoluril, paraformaldehyde and calcium salt or barium salt into a mixed solution of water and hydrochloric acid, reacting and refluxing, wherein the mass ratio of the methylene bridged glycoluril to formaldehyde is 1: (0.4-1), the volume ratio of the water to the hydrochloric acid is 1: (1-3), the ratio of the mass of the methylene bridged glycoluril to the volume of the hydrochloric acid is 1: 1-3, the mass ratio of the methylene bridged glycoluril to the calcium salt is 1: 0.05-0.4, and the mass ratio of the methylene bridged glycoluril to the barium salt is 1: 0.1-0.3; and carrying out cooling, suction filtration and washing to obtain the methylene bridged cucurbituril [4] or the methylene bridged cucurbituril [5]. The methylene bridged cucurbituril [4] and the methylene bridged cucurbituril [5] are synthesized in an oriented manner by using metal salt as a template, the method is simple and convenient, a purification process is simple, and the yield is obviously increased.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
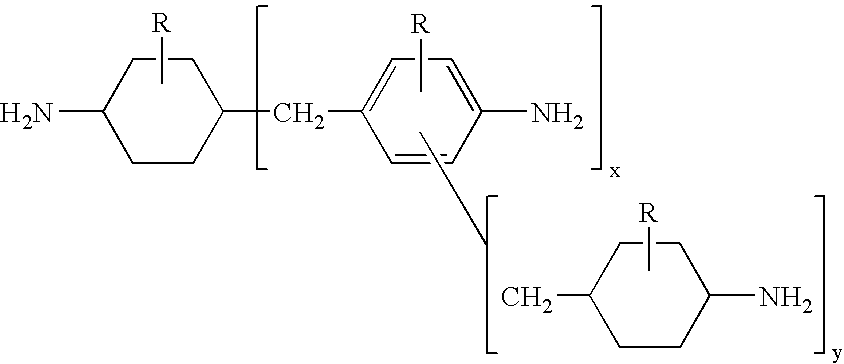
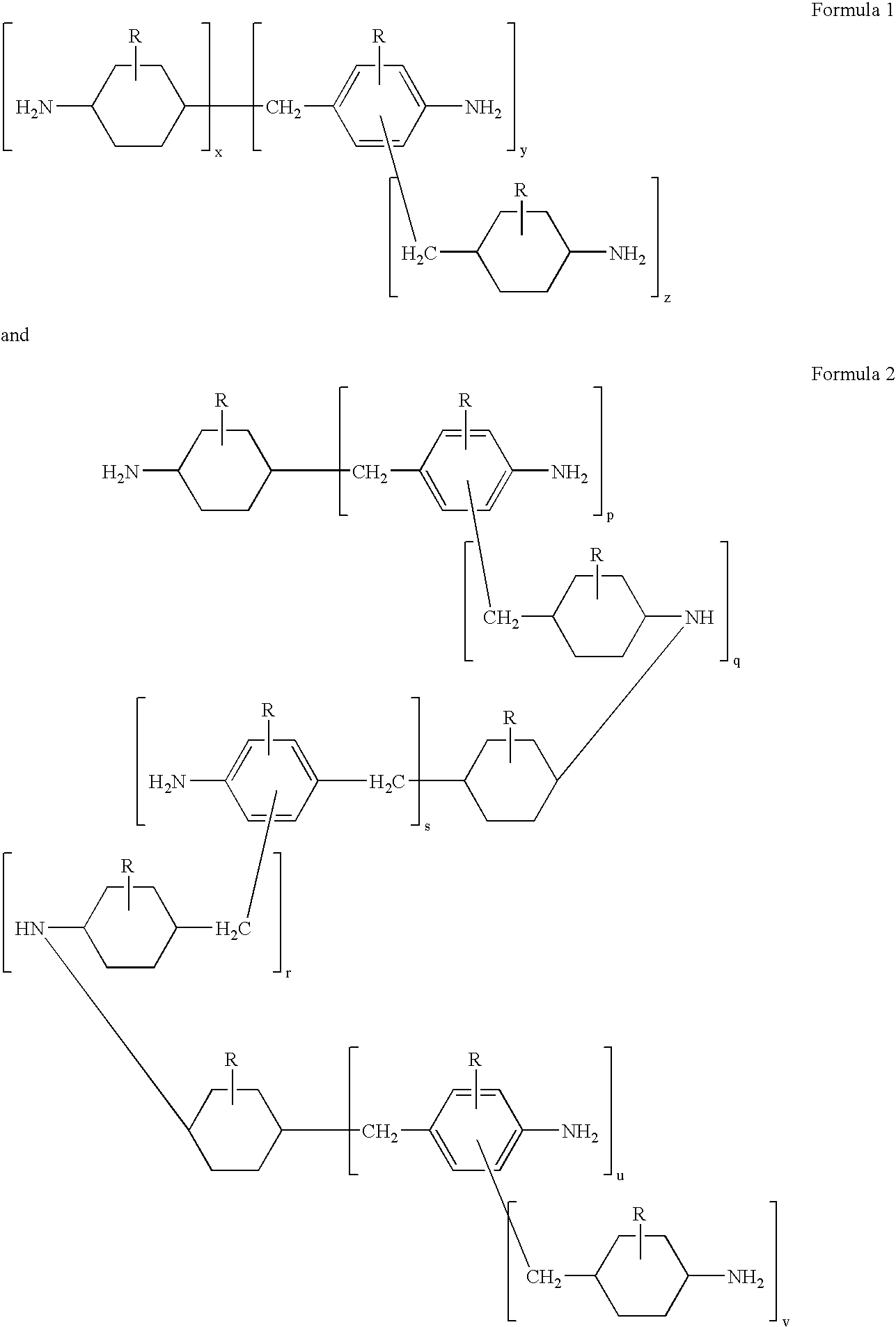
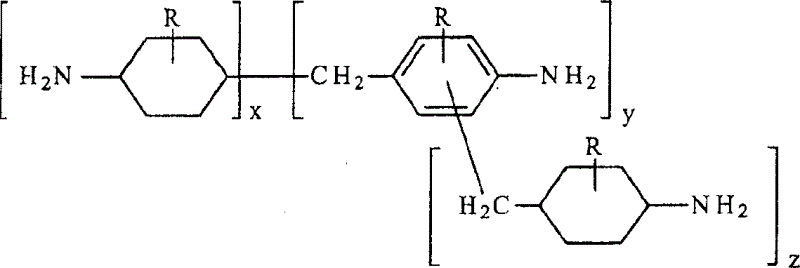
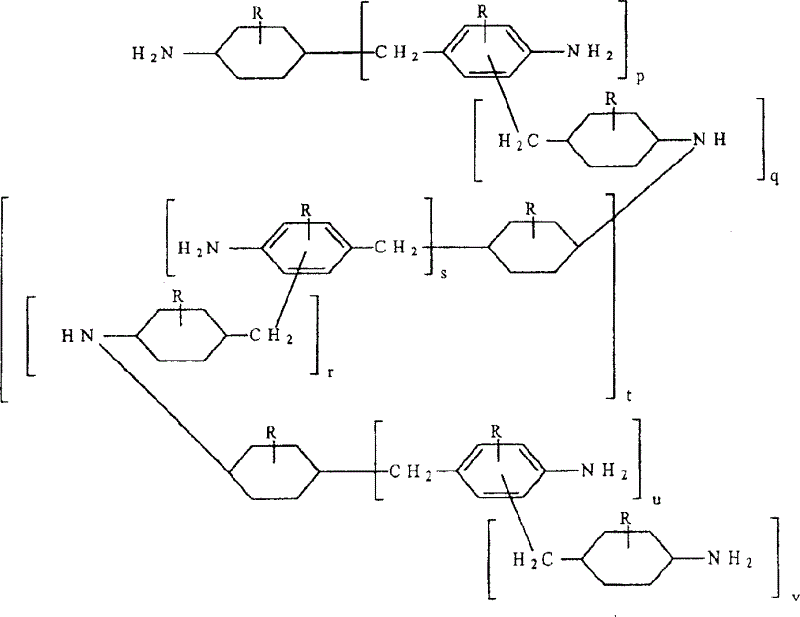
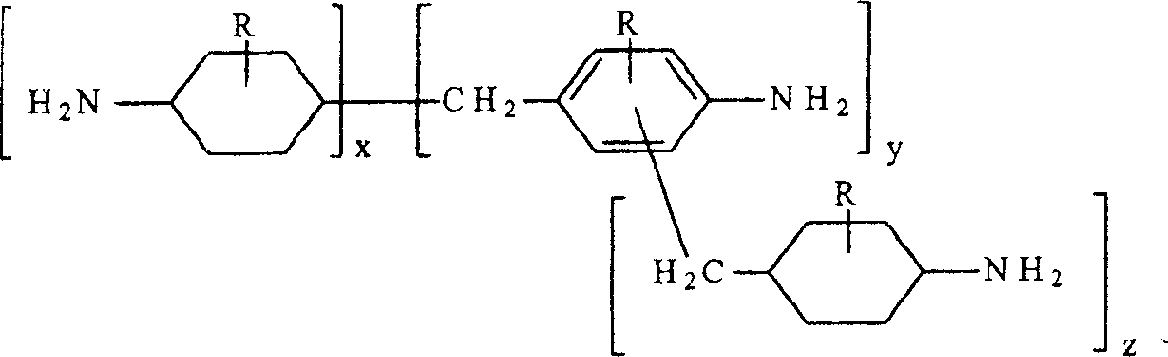
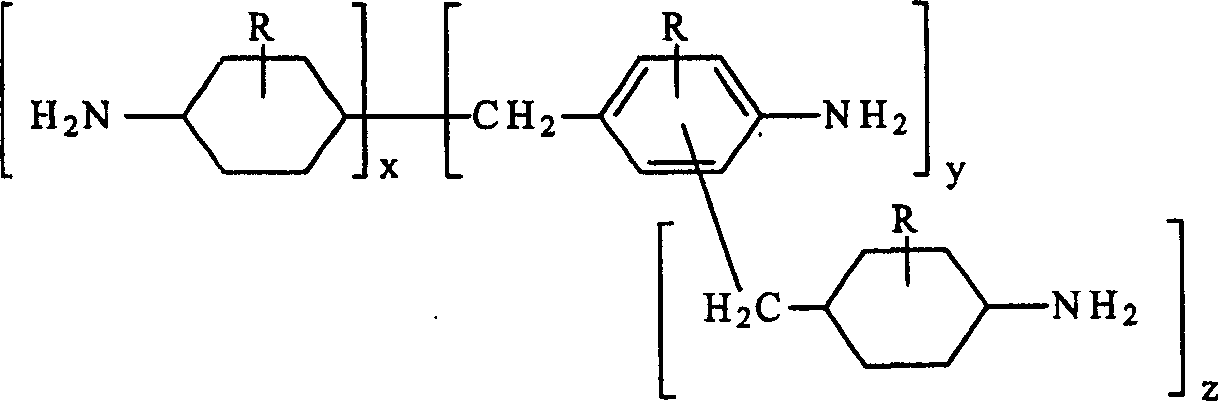
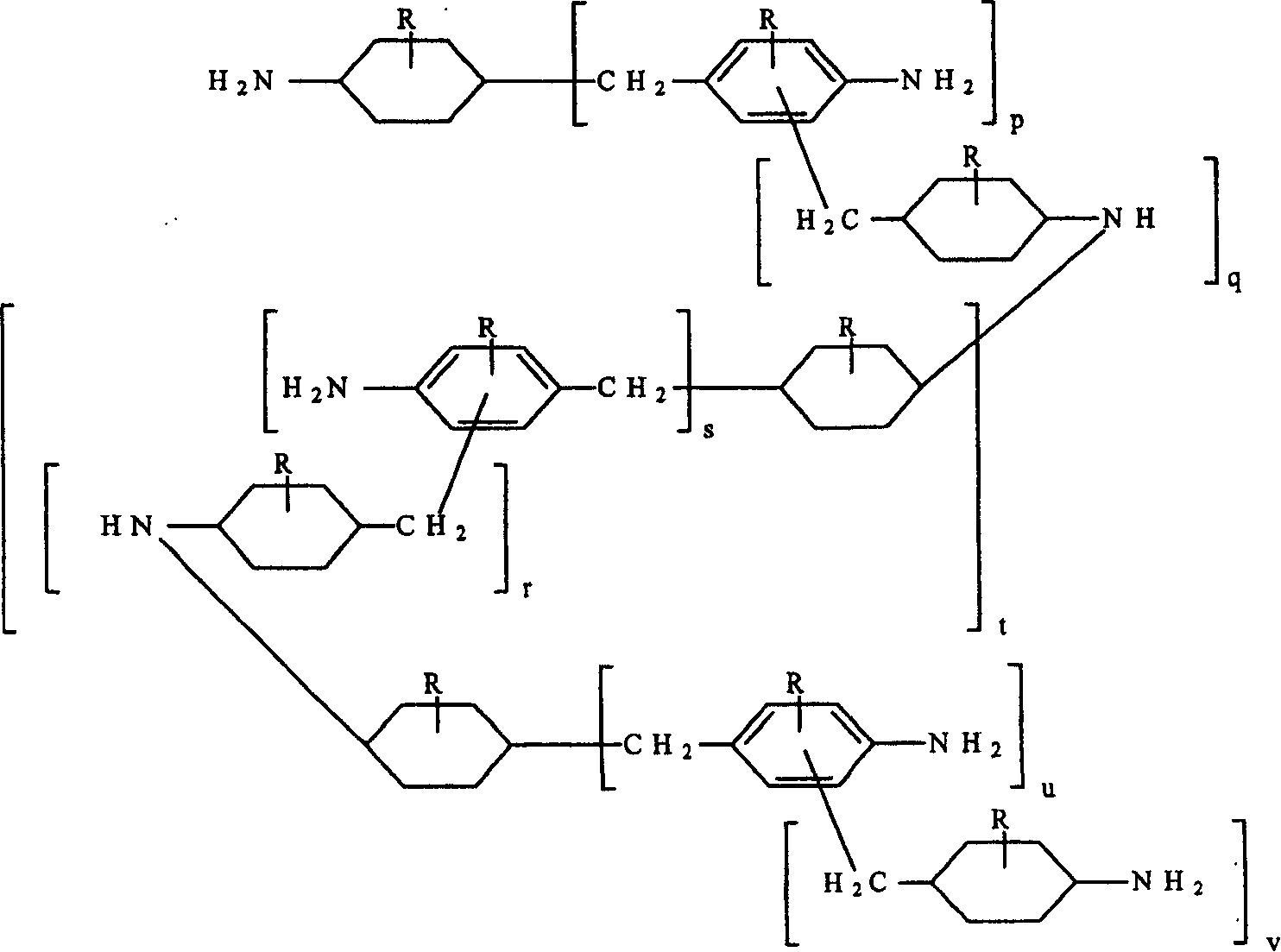
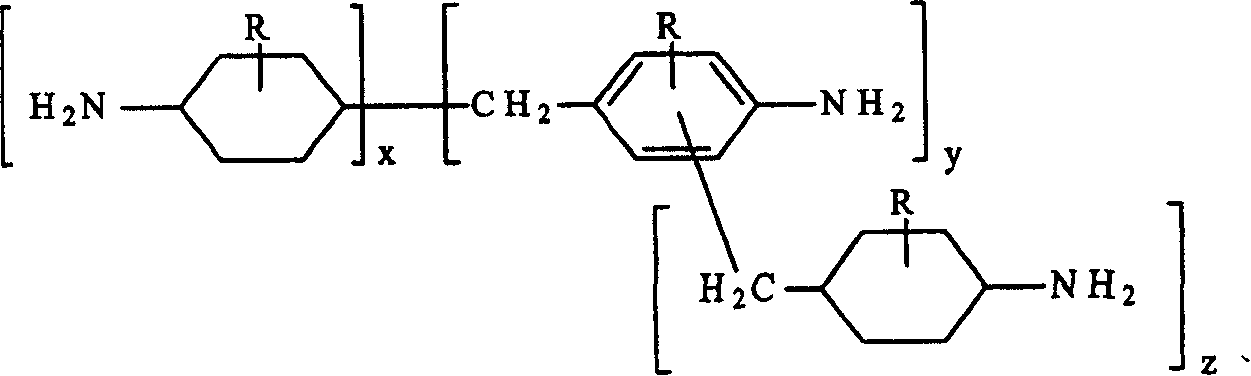
Hydrogenation of methylenedianiline homologs and epoxy resins cured with same
ActiveUS6962964B2Good chemical resistanceHigh elongationOrganic compound preparationDiaryl/thriaryl methane dyesEpoxyMethylene bridge
This invention relates to improved polyepoxide resins cured with a mixture of methylene bridged poly(cycloaliphatic-aromatic)amines and a process for preparing such polyepoxide resins as well as to the methylene bridged poly(cycloaliphatic-aromatic)amine compositions and a method of making them. The improvement resides in using a curative (herein referred to as “Heavy MPCA”) comprised of the partially hydrogenated condensation product of formaldehyde and aniline or methyl substituted aniline containing a substantial amount (from 35 to 85% by weight, preferably 40 to 60% by weight) of oligomers in the form of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 aniline or methyl substituted aniline derivatives.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Hydrogenation of methane diphenylamine homolog and epoxy resin cured therefrom
ActiveCN1519265AImprove thermal performanceGood chemical resistanceOrganic chemistryRodsEpoxyMethylene bridge
This invention relates to improved polyepoxide resins cured with a mixture of methylene bridged poly(cycloaliphatic-aromatic)amines and a process for preparing such polyepoxide resins as well as to the methylene bridged poly(cycloaliphatic-aromatic)amine compositions and a method of making them. The improvement resides in using a curative (herein referred to as 'Heavy MPCA') comprised of the partially hydrogenated condensation product of formaldehyde and aniline or methyl substituted aniline containing a substantial amount (from 35 to 85% by weight, preferably 40 to 60% by weight) of oligomers in the form of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 aniline or methyl substituted aniline derivatives.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Stainblocker polymers
InactiveUS20060248655A1Surface-active detergent compositionsLight resistant fibresMethylene bridgeNuclear chemistry
Disclosed herein is a composition of matter comprising salts of methylene bridged mixed sulfonated diphenyl oxides and methods of making and using the same.
Owner:LENKSESS CORP
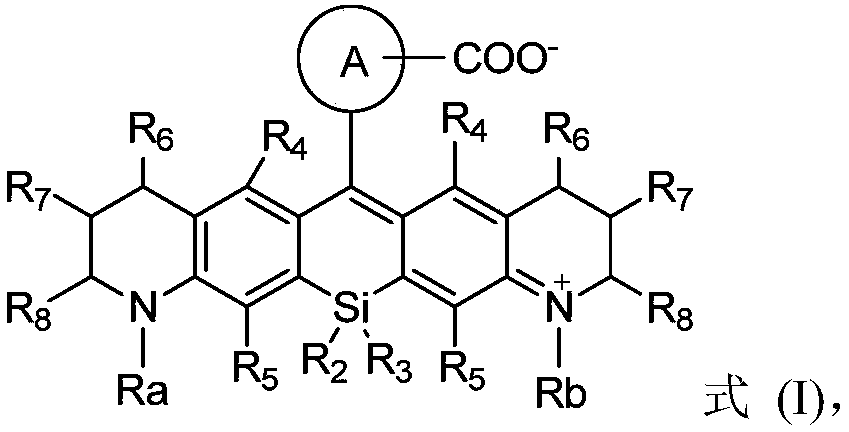
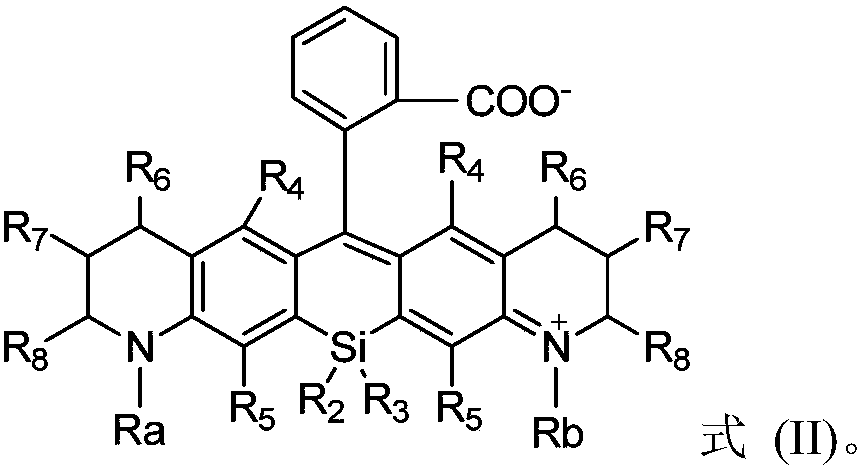
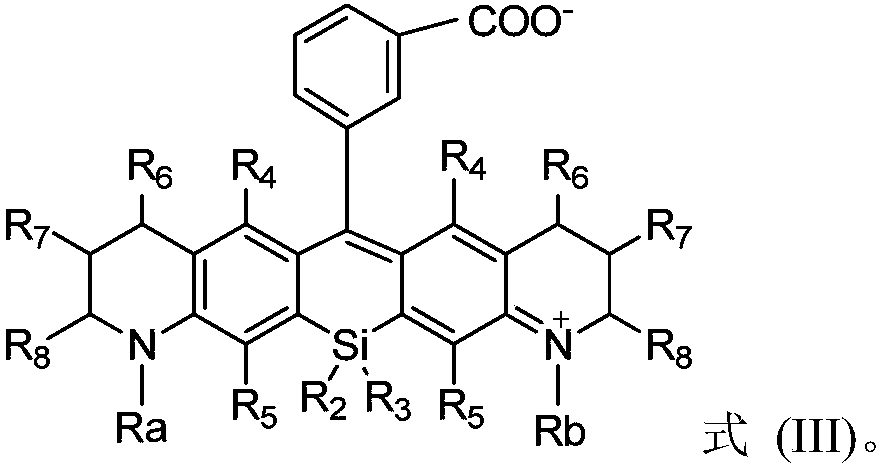
Silicon-based rhodamine derivative and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110922783AFulfilling Analytical Imaging RequirementsPromote absorptionAzo dyesLuminescent compositionsSilylationHydrolysis
The invention provides a silicon-based rhodamine derivative and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out a reductive amination / methylene bridging reaction on a compound represented by a formula (I') to obtain a compound represented by a formula (II'); (2) carrying out a silylation / oxidation reaction on the compound represented by the formula (II') toobtain a compound represented by a formula (III'); and (3) carrying out a metal reagent addition / hydrolysis protection group removing reaction on the compound represented by the formula (III') so asto obtain a silicon-based rhodamine derivative. The method according to the embodiments of the invention is high in synthesis efficiency, simple in reaction condition and convenient to operate, can achieve the large-scale preparation of silicon-based rhodamine derivatives, substantially enriches the substrate selection range, can synthesize silicon-based rhodamine derivatives difficultly synthesized by adopting the previous methods, and easily achieves the further modification and application of silicon-based rhodamine derivatives.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST
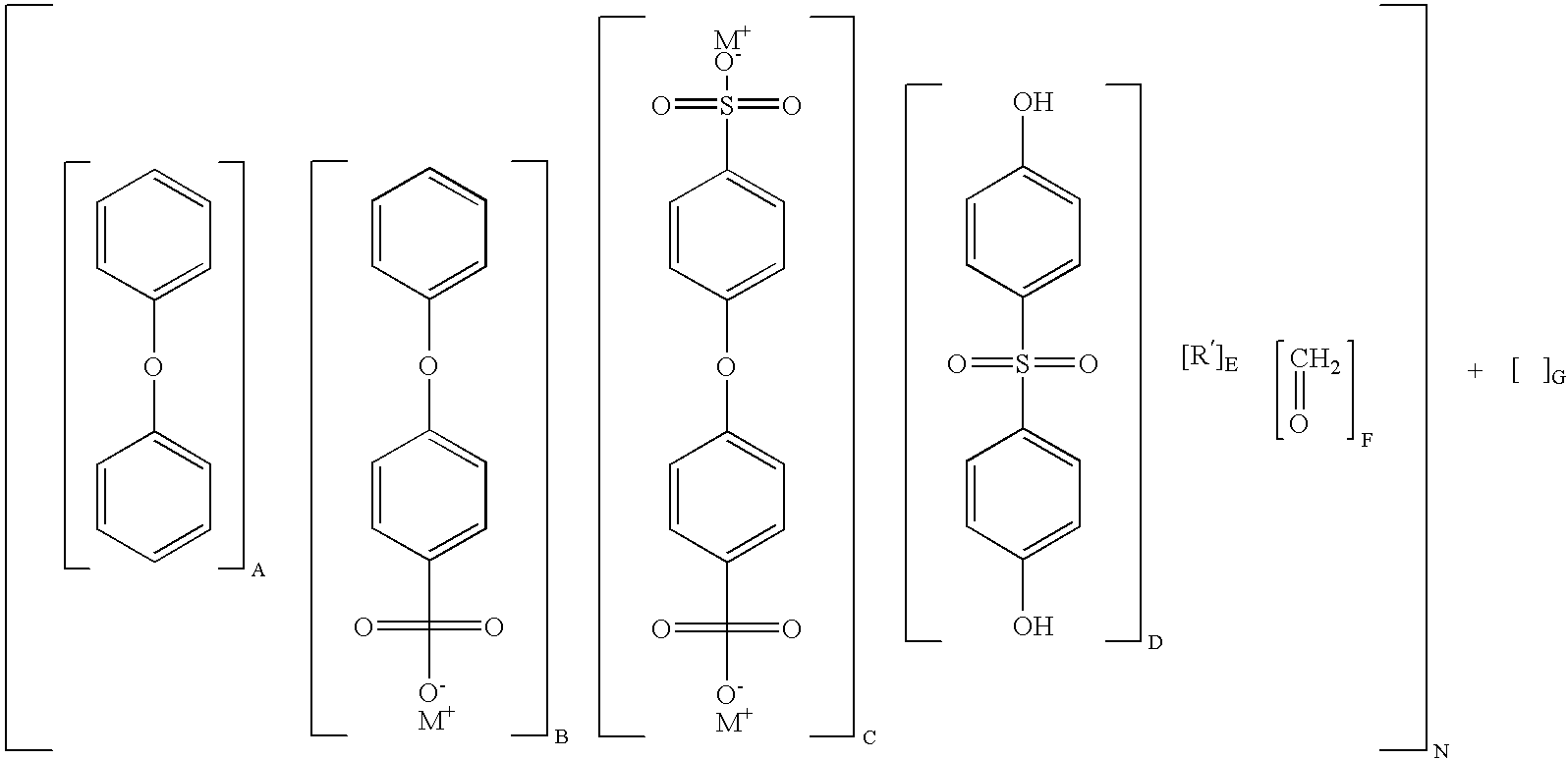
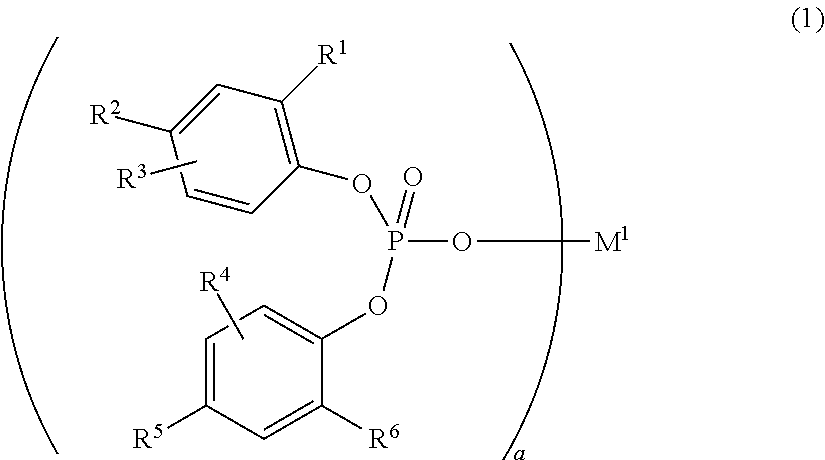
Novel compound, composition including same, olefin-based resin composition, molded article thereof, and method for improving impact resistance of molded article
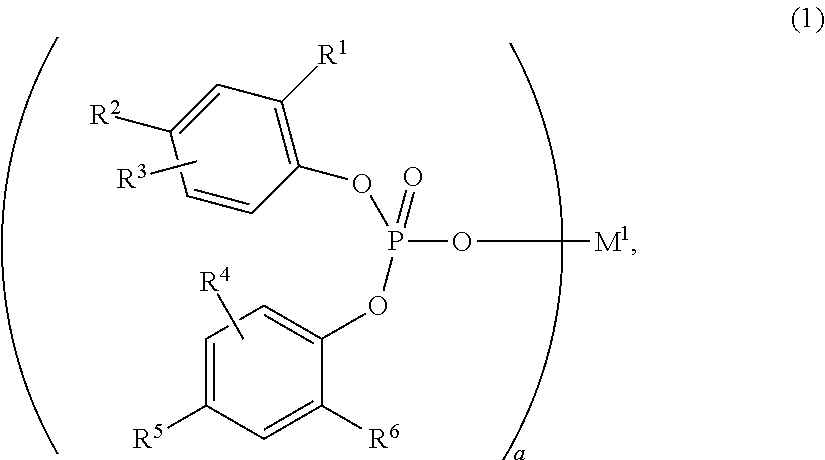
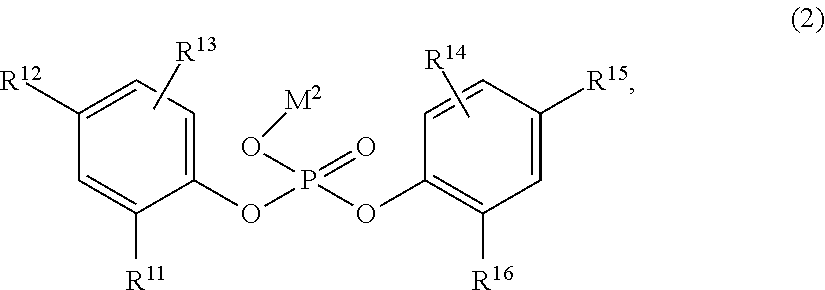
InactiveUS20190284217A1Improve impact resistanceLow shrinkage anisotropyPhosphorus organic compoundsAlkaline earth metalLanthanide
Provided are: a novel compound capable of yielding a molded article of a resin composition, which molded article exhibits excellent impact resistance and has low shrinkage anisotropy; a composition containing the same; an olefin-based resin composition; a molded article thereof; and a method of improving the impact resistance of a molded article. The novel compound is a compound (A) represented by the following Formula (1), where R1 to R6 each independently represent a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, or the like; R1 and R6 are optionally linked together to form a methylene bridge; R2 and R3, and / or R4 and R5 are optionally linked together to form a fused ring with a benzene ring; at least one of R1 to R6 represents a halogen atom or a cycloalkyl group, or forms a fused ring; a represents 1 to 3; and M1 represents a hydrogen atom, sodium, lithium, an alkaline earth metal atom, a transition metal atom, a base metal atom, a polyvalent metal inorganic group, an ammonium group, a sulfonium group, or a lanthanoid:
Owner:ADEKA CORP
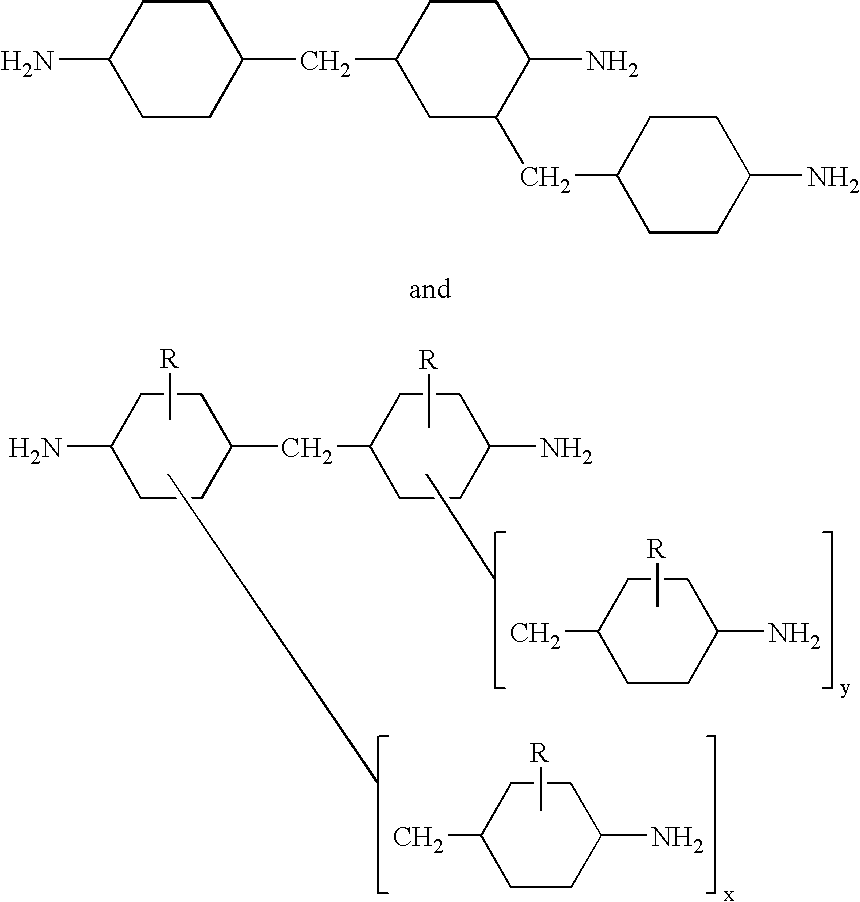
Mixed polycycloaliphatic amines (MPCA) and MPCA alkylates
Mixed polycycloaliphatic amines (MPCA) and alkylates thereof (MPCA alkylates), methods for making mixed polycycloaliphatic MPCA amines and MPCA alkylates thereof, as well as polymeric compositions, such as spray-applied polyurea coating compositions, comprising said mixed amines MPCA and MPCA alkylates thereof are described herein. In one embodiment, the polymeric composition comprises an isocyanate component, and a resin component comprising an organic compound having the following Formula I:where R1, R2 and R3 are each independently selected from a hydrogen atom, an alkyl group comprising from 1 to 20 carbon atoms, an aryl group comprising from 3 to 12 carbon atoms, an aralkyl group comprising from 3 to 12 carbon atoms and combinations thereof, provided that there is at least one alkyl group within Formula I, and X is a methylene bridged polycycloaliphatic amine (MPCA).
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
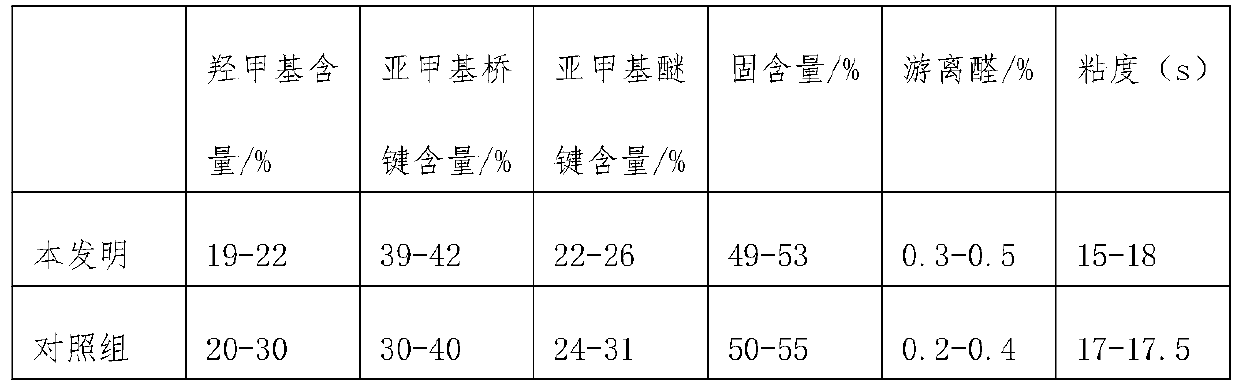
Bisphenol A formaldehyde phenolic resin and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN108948299AImprove adhesionLow polarity of bonding surfaceAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesBenzeneChemical reaction
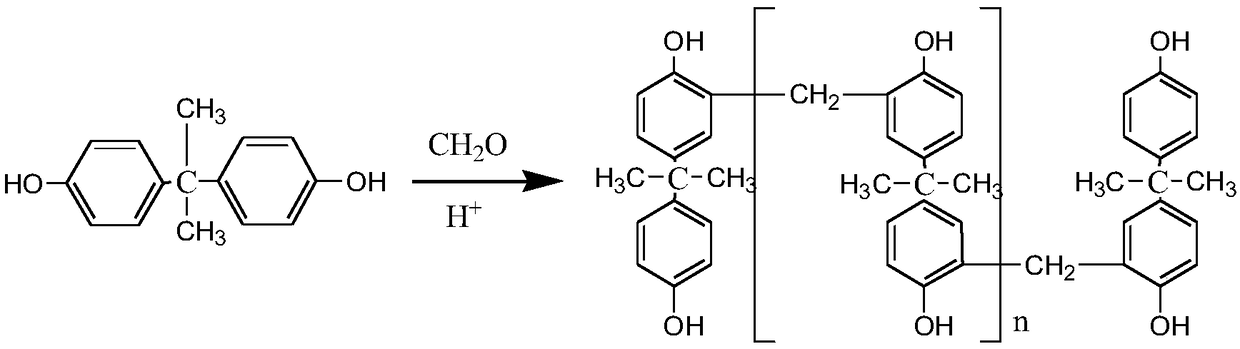
The invention discloses bisphenol A formaldehyde phenolic resin and a synthetic method thereof. The molecular weight of the bisphenol A formaldehyde phenolic resin is 2000-3000, and the molecular weight is higher than that of existing bisphenol A formaldehyde phenolic resin. The bisphenol A formaldehyde phenolic resin is prepared from bisphenol A and formaldehyde free radicals which are polymerized by means of the method. The bisphenol A formaldehyde phenolic resin has excellent glueyness. On the one hand, original hydroxyl and benzene rings and active sites of bisphenol A are retained and themolecular weight of bisphenol A is also improved; on the other hand, as the polymer structure contains a great many of active sites, in the gluing process, chemical reactions happen or a curing agentis added to generate an undissolved polymer of a three-dimensional netty structure. Meanwhile, a condensation reaction is carried out on bisphenol A and formaldehyde to form methylene bridged bisphenol A. Therefore, the related molecular weight of the polymer is increased greatly, the polymer is then reacted with a bonding substrate, and can react through active groups, so that the bisphenol A formaldehyde phenolic resin is adhered quickly to achieve the adhering purpose.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polymethylene-bridged ferrocenyl bipyrazole and synthetic method thereof
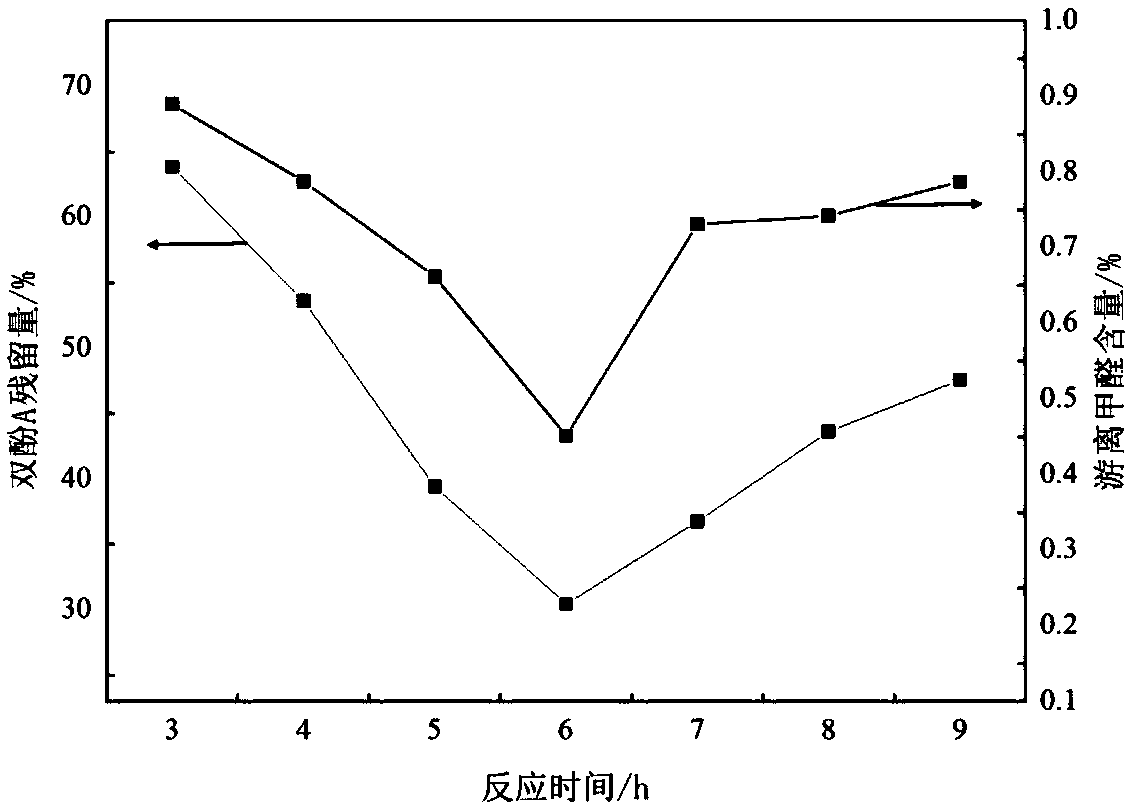
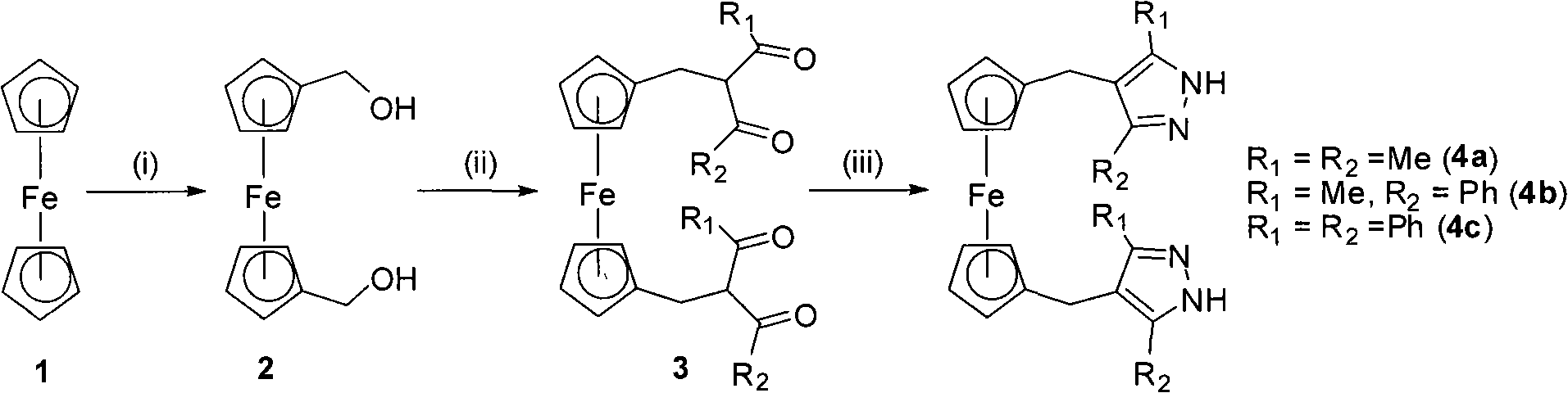
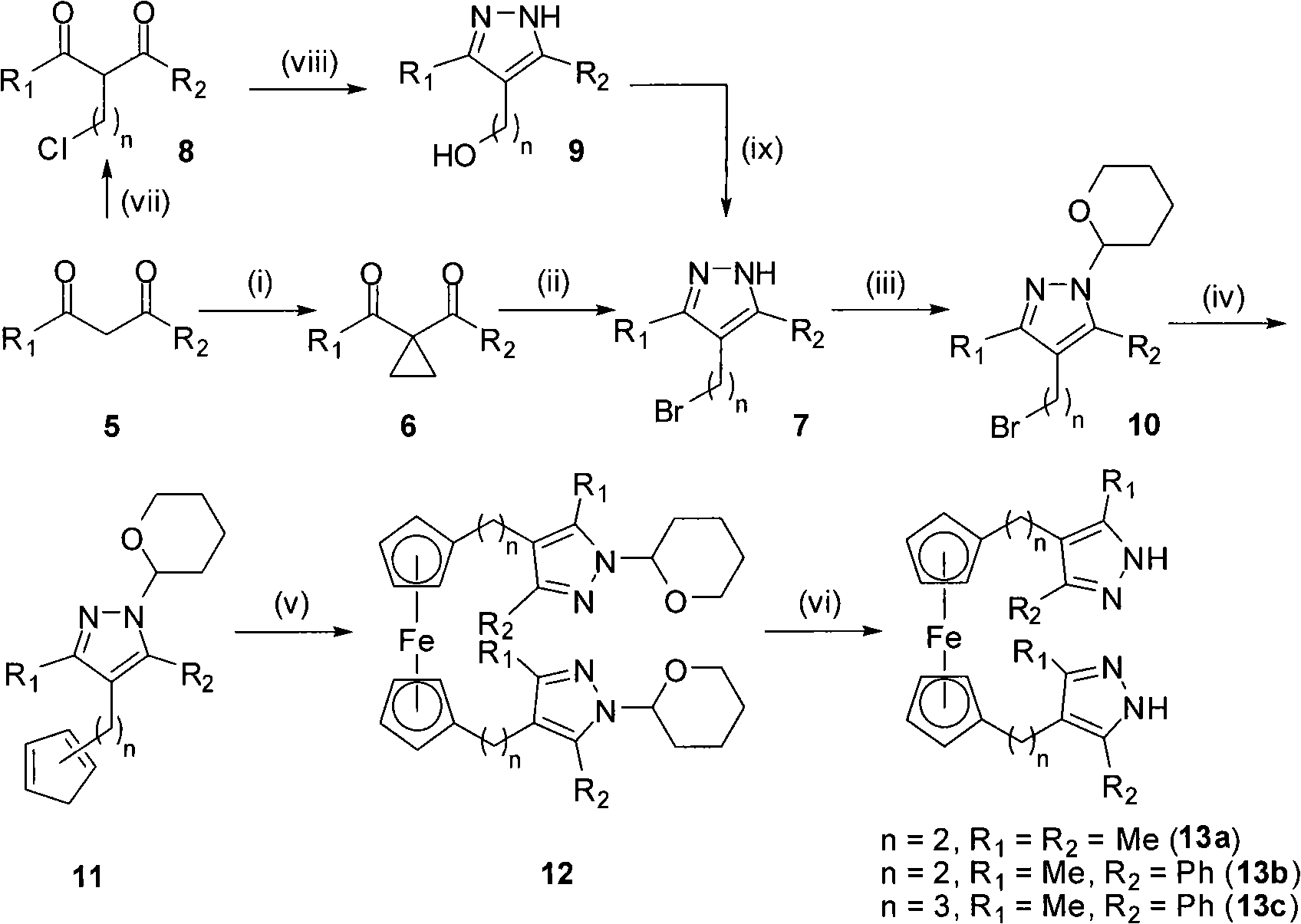
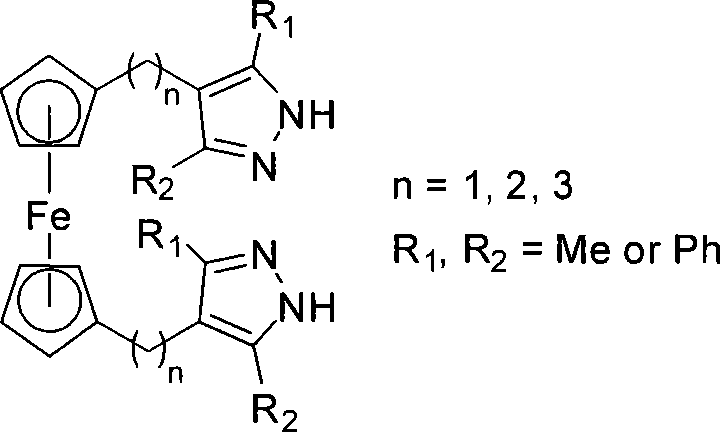
The invention discloses polymethylene-bridged ferrocenyl bipyrazole (a general formula is Fc-[(CH2)n-R1R2PzH]2, wherein Fc is 1,1'-ferrocenyl; n is between 1 and 3; R1R2 is 3,5-disubstituent; and Pz is 4-pyrazolyl) and a synthetic method thereof. Bipyrazole Fc-[(CH2)n-R1R2PzH]2 that n is equal 1 and R1 and R2 are different substituents is obtained by taking ferrocene as an initial raw material through a methylation, alkylation and condensation three-step reaction; and the synthesis of ferrocenyl-bis(4-methylene-3,5-dimethylpyrazole) that n is equal 1 and R1 is equal to R2 and is equal to methyl by utilizing a literature report method needs a five-step reaction. The method is utilized to take 1,3-diketone as a raw material to synthesize bipyrazole Fc-[(CH2)n-R1R2PzH]2 that n is equal to 2 and 3, and R1 and R2 are different substituents through a six-step or seven-step reaction respectively. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, cheap and easily-obtained raw materials and high yield of target products. Compared with the prior synthetic method, the method can synthesize methylene-bridged ferrocenyl bipyrazole that n is equal to 1 more easily, and can effectively synthesize the polymethylene-bridged ferrocenyl bipyrazole that n is more than or equal to 2, R1 and R2 are different substituents and the general formula is the Fc-[(CH2)n-R1R2PzH]2.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for selectively preparing different cyclic fullerene derivatives in iodine-alkali system
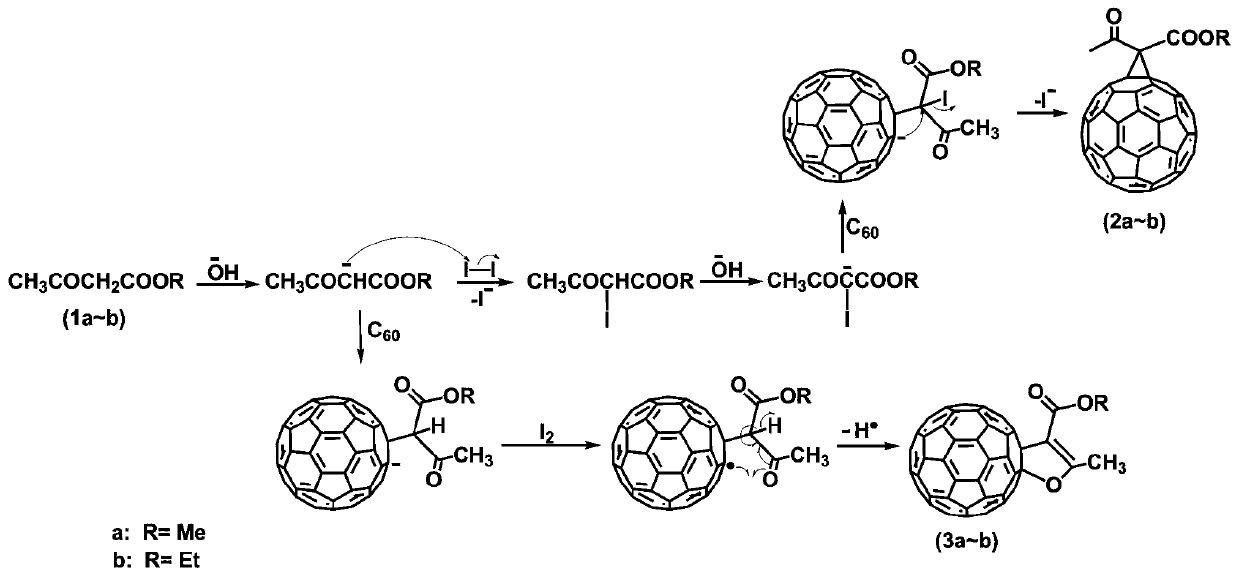
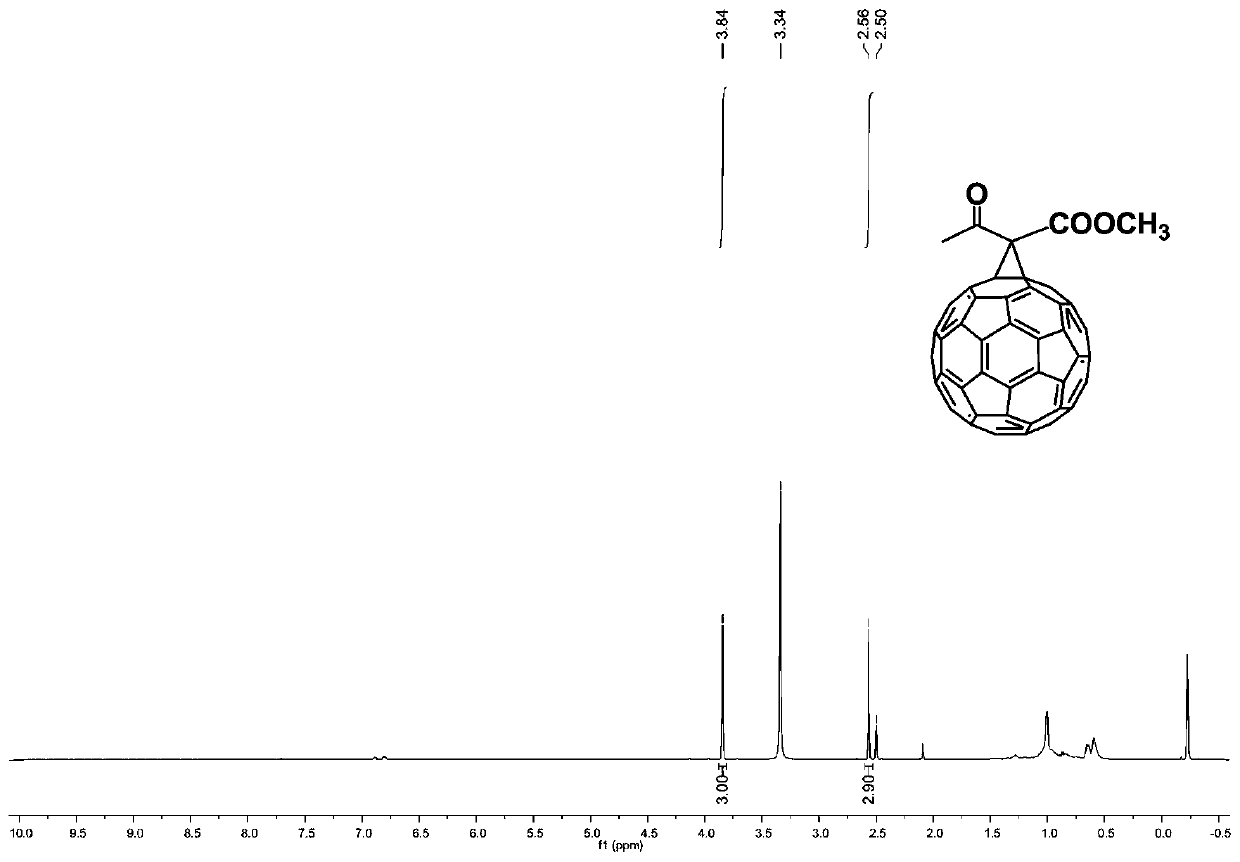
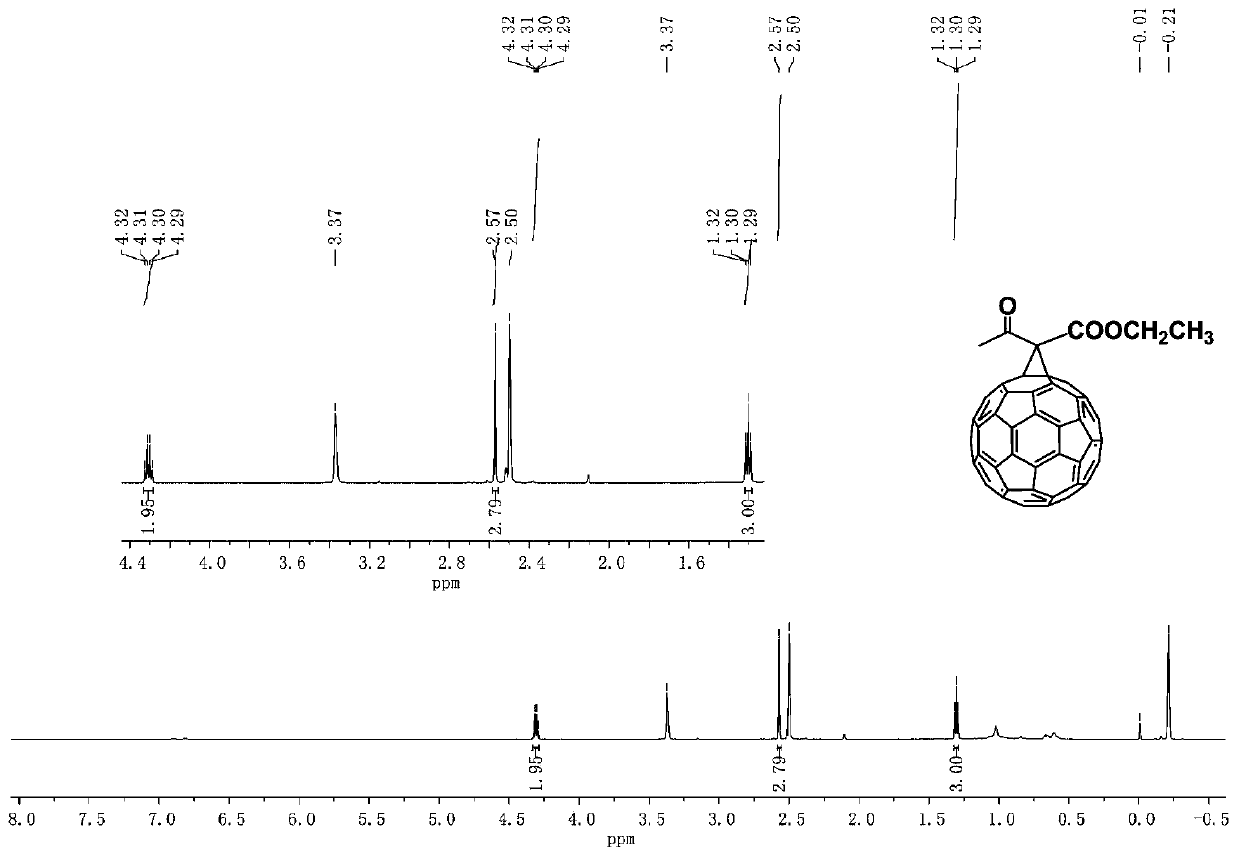
ActiveCN109879273AEasy to prepareShort reaction timeFullerenesPhotovoltaic energy generationMethylene bridgeHydrogen
The invention discloses a method for selectively preparing different cyclic fullerene derivatives in an iodine-alkali system. According to the method, selective preparation for methylene bridged fullerene derivative and dihydrofuran cycle-bound fullerene derivative can be realized by regulating and controlling the time of iodine adding; at the beginning of reaction of the two derivatives, an active methylene carbon anion is formed by depriving hydrogen from active methylene in acyloxy carboxylic ester by alkali; selectivity is achieved due to different time of iodine adding during the reactionprocess of the two derivatives; a first process is the active methylene iodination reaction under the existence of abundant iodine in the system; a second process is the preparation of C60 anion containing substituent group by only attacking C60 by the formed active methylene carbon anion due to no iodine existing in the system at first. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages ofhigh conversion rate of target products, almost no by-products, no heavy metal catalyst, mild reaction conditions, easiness in operation and simple separation and purification steps.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Phenalkamine epoxy curing agents from methylene bridged poly(cyclohexyl-aromatic) amines and epoxy resin compositions containing the same
PendingUS20210139642A1Good coating effectLow appearance requirementsOrganic chemistryEpoxy resin adhesivesPolymer scienceMethylene bridge
The present invention relates to a new structural class of phenalkamine, phenalkamine curing agent compositions, methods of making such phenalkamine, and methods of making such compositions. The phenalkamine curing agent compositions of the present invention can be prepared by reacting cardanol with an aldehyde compound and a mixture of methylene bridged poly(cycloaliphatic-aromatic)amines. These curing-agent compositions may be used to cure, harden, and / or crosslink an epoxy resin.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Method for optimized isolation of RNA from fixed tissue
ActiveUS20110111967A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBasic amino acidsMethylene bridge
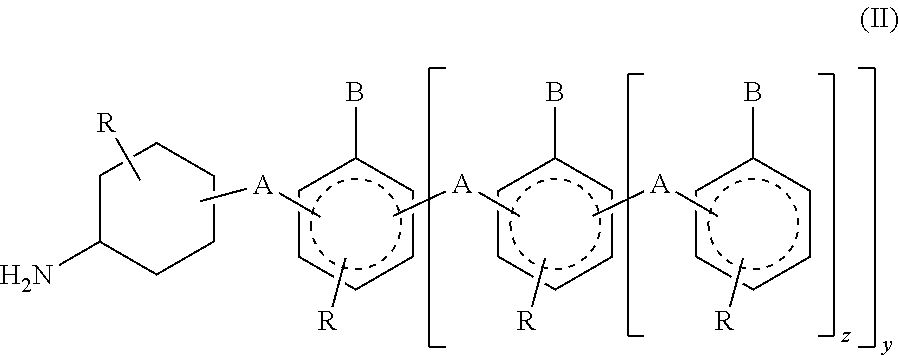
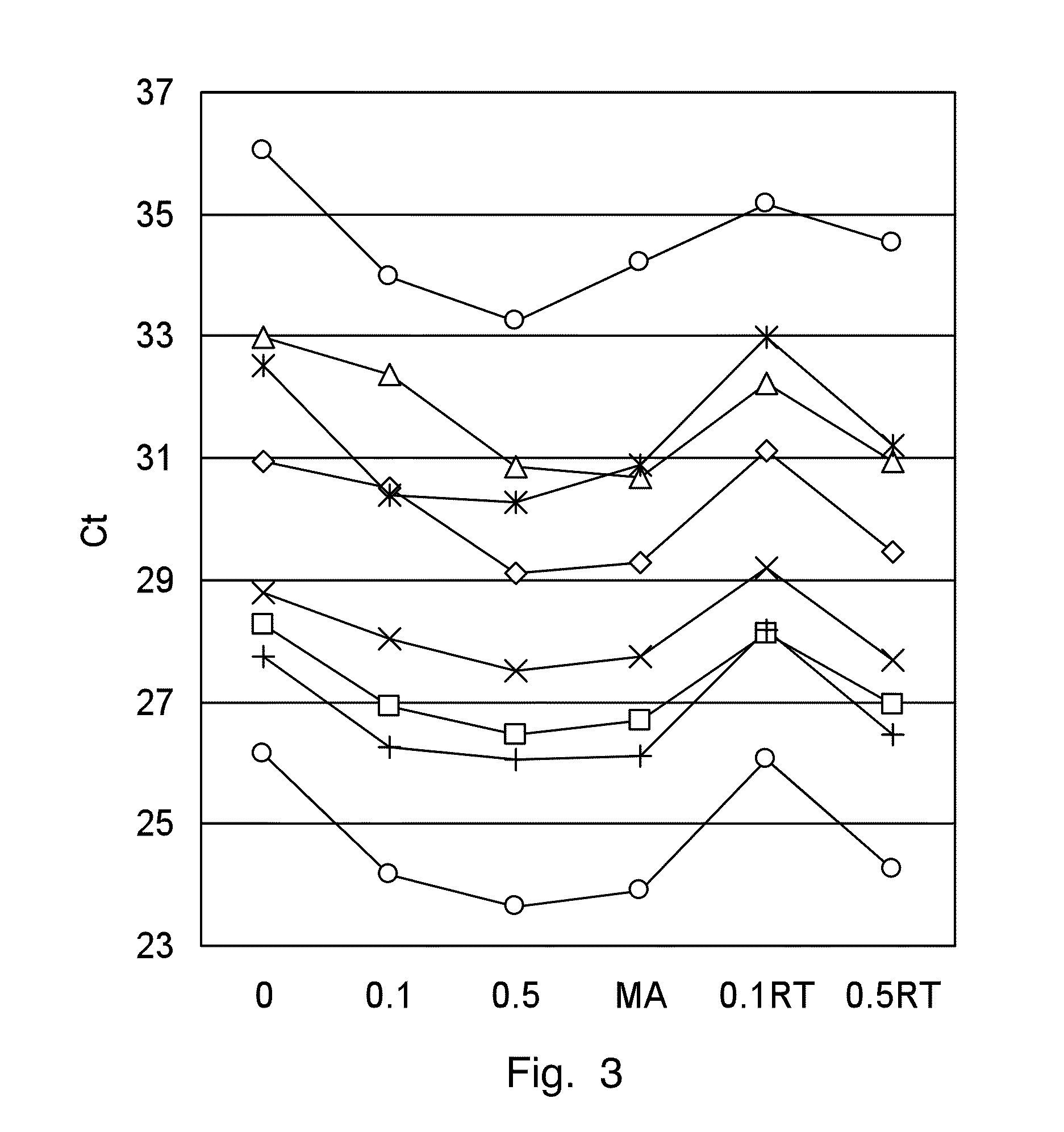
In invention relates to a method for the isolation of RNA from tissue pretreated with formaldehyde comprising homogenizing the sample in the presence of a guanidinium salt in aqueous solution, and incubating the sample in the presence of 0.1 M to 5 M ammonium salt at a temperature between 50° C. and 100° C. The heat treatment in the presence of an ammonium salts demodifies RNA by reverting methylol groups which are formed in the presence of formaldehyde between amino groups in nucleobases of RNA and in basic amino acids, and by cleavage of methylene bridges between amino groups in nucleobases of RNA and basic amino acids, to provide high RNA recoveries and consistently high quality of RNA for further reaction, e.g. for reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction or microarray analysis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BERN
Method for whole-process alkaline synthesis of urea resin wood adhesive
ActiveCN110452344AReduce the content of ether linkagesSolve rearrangement to methylene bridgesAldehyde/ketone condensation polymer adhesivesMethylene bridgeAdhesive
The invention belongs to the technical field of artificial board production and in particular discloses a method for whole-process alkaline synthesis of a urea resin wood adhesive. In the synthesis process, a composite alkali catalyst is used, the whole synthesis process is implemented under an alkaline condition, and formaldehyde and urea are added for multiple times, specifically, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, adding a formaldehyde solution into a reaction kettle to react with primary urea in different batches, and secondly, adding secondary urea into the reaction kettleto implement reactions in different batches. The urea resin wood adhesive synthesized by using the method has structure performance similar to that of a urea resin synthesized by using an alkali-acid-alkali process, the problem that a primary polymer generated at an alkali reaction stage in the alkali-acid-alkali process can be partially rearranged as a methylene bridge bond at the alkali reaction stage can be solved, and the content of an ether bond in the urea resin can be reduced. By adopting the method, the industry knowledge that a urea resin cannot be synthesized by using an alkali onlyis contradicted, and the blank of synthesizing the urea resin by using the alkali only is made up.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
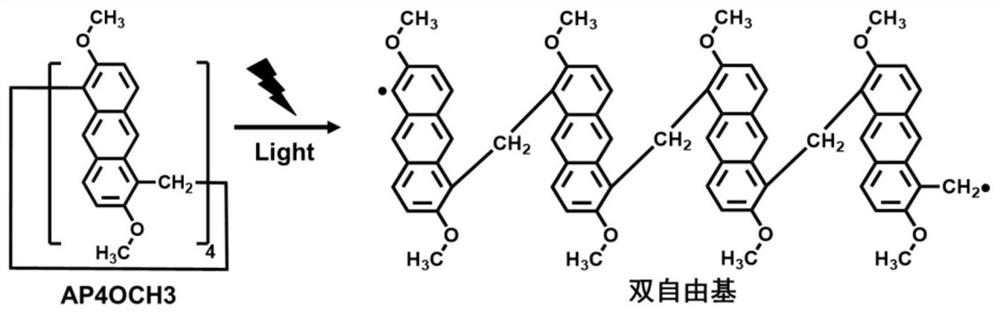
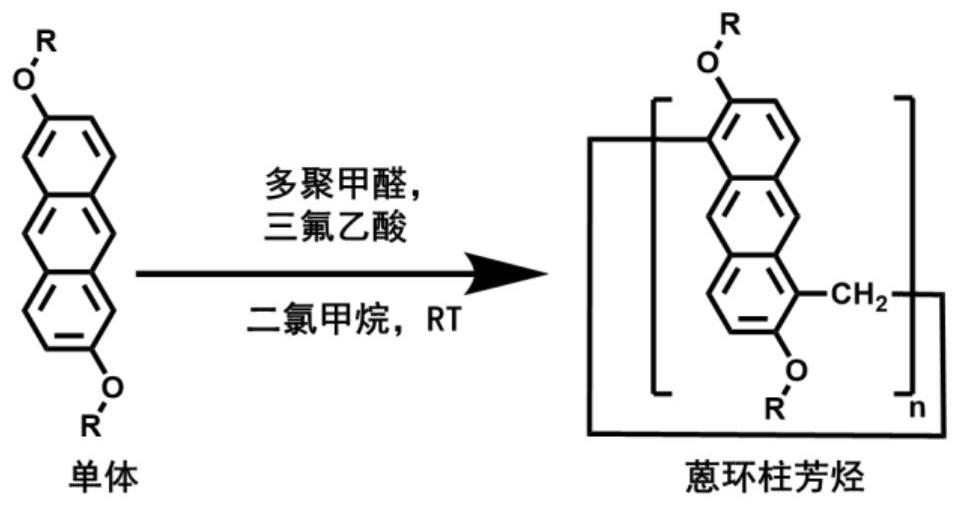
Anthracene ring pillar aromatic hydrocarbon initiator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112409510ALong absorption wavelengthGood water solubilityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationMethyl groupPolymerization
The invention relates to the technical field of photo initiators, and provides an application of anthracene ring pillar aromatic hydrocarbon as a photo-polymerization initiator and a preparation method thereof. Anthracene ring pillar aromatic hydrocarbon has a large ring structure formed by methylene bridged anthracene units. The initiator is a novel photo initiator. Under light irradiation, anthracene ring pillar aromatic hydrocarbon large ring molecules are broken to form double-free-radical straight-chain oligomers, and the photo-polymerization reaction of monomers can be efficiently initiated. Compared with developed pillar aromatic hydrocarbons and anthracene ring pillar aromatic hydrocarbon initiators, the absorption wavelength of the anthracene ring pillar aromatic hydrocarbons is long, strong light absorption is achieved between 200 nm and 450 nm, and photo-induced polymerization of near ultraviolet visible light can be achieved. Compared with a traditional commercial photo initiator, the photo initiator provided by the invention is safe and non-toxic, small molecular fragments are not generated after light irradiation, and the migration of the photo initiator can be greatly reduced, so that the problems of toxicity, odor and the like of a photo-polymerization curing product are avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED MATERIAL BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
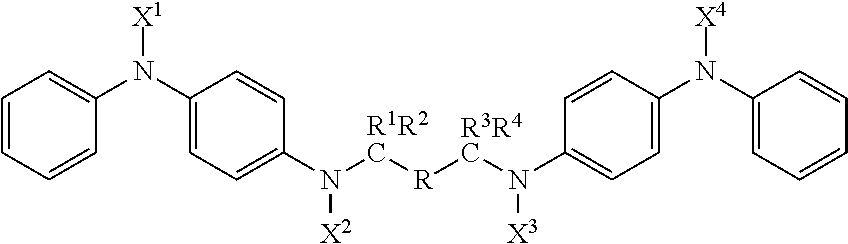
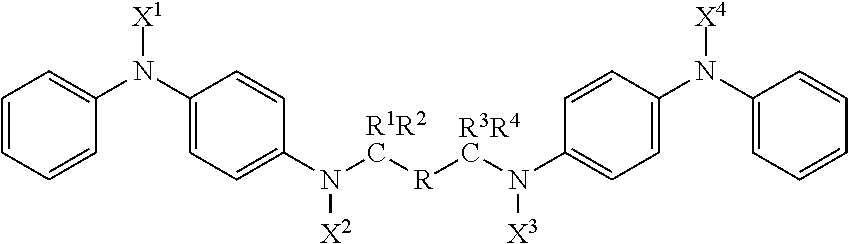
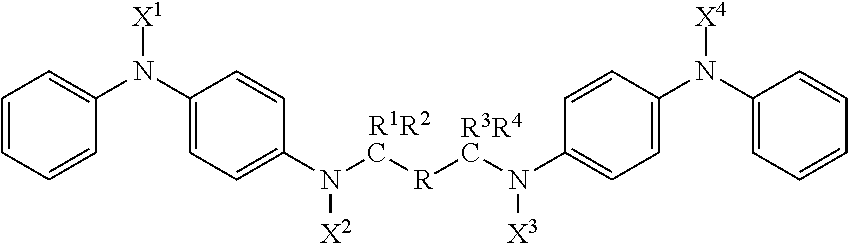
Compounds with antidegradant and antifatigue efficacy and compositions including said compounds
ActiveUS20170174615A1Demonstrated efficacyImparting resistanceOrganic compound preparationSpecial tyresArylCompound a
A compound represented by the formula:wherein R is selected from the group consisting of (i) substituted or unsubstituted alkyl with C=0 to 12 inclusive; (ii) substituted or unsubstituted aryl; and (iii) substituted and unsubstituted alkylaryl;wherein X1, X2, X3 and X4 are each selected from the group consisting of alkyl, aryl, alkylaryl groups and hydrogen; wherein R1, R2, R3, and R4 are each selected from the group consisting of alkyl, aryl, alkylaryl groups and hydrogen and R2 and R3 may optionally be bridged by a polymethylene group; wherein when C=0 in R, the combined group R1 R2 is the same as the combined group R3 R4; and wherein when C=1 in R, each of R1, R2, R3, and R4 are hydrogen.
Owner:FLEXSYS HLDG INC
Hydrogenation of methane diphenylamine homolog and epoxy resin cured therefrom
InactiveCN1297584CImprove thermal performanceGood chemical resistanceOrganic chemistryRodsEpoxyMethylene bridge
This invention relates to improved polyepoxide resins cured with a mixture of methylene bridged poly(cycloaliphatic-aromatic)amines and a process for preparing such polyepoxide resins as well as to the methylene bridged poly(cycloaliphatic-aromatic)amine compositions and a method of making them. The improvement resides in using a curative (herein referred to as 'Heavy MPCA') comprised of the partially hydrogenated condensation product of formaldehyde and aniline or methyl substituted aniline containing a substantial amount (from 35 to 85% by weight, preferably 40 to 60% by weight) of oligomers in the form of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 aniline or methyl substituted aniline derivatives.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Methylene bridged 1,8-naphthyridine ligand and copper (i) complex, preparation method and application
InactiveCN106243105BSimple ingredientsShort reaction processGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMethylene bridgePtru catalyst
Owner:HONGHE COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com