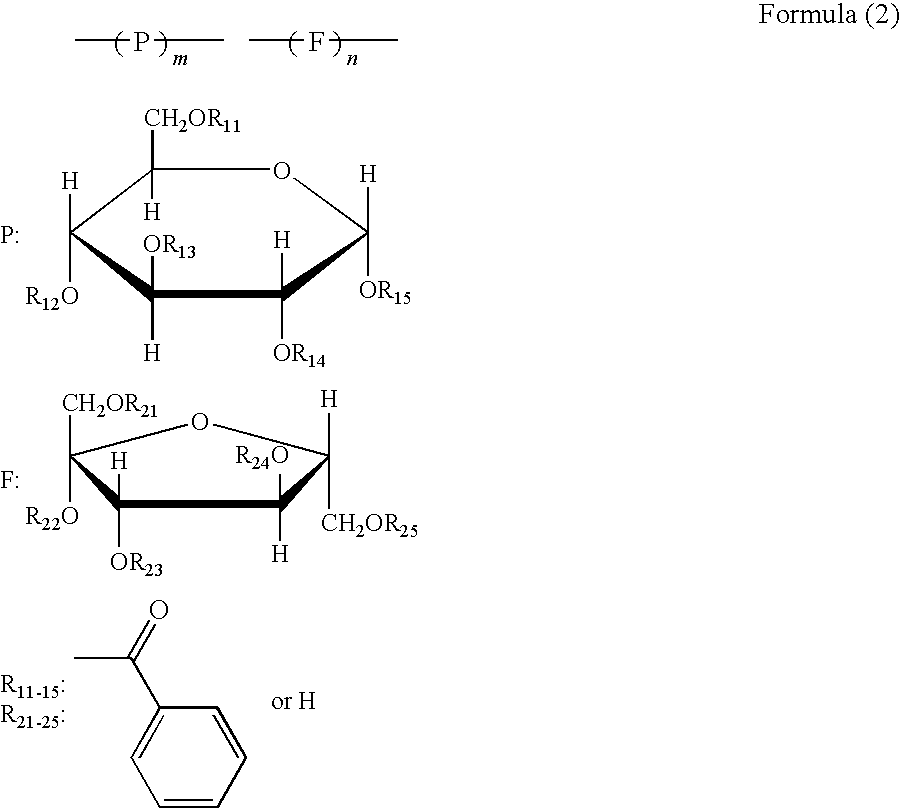
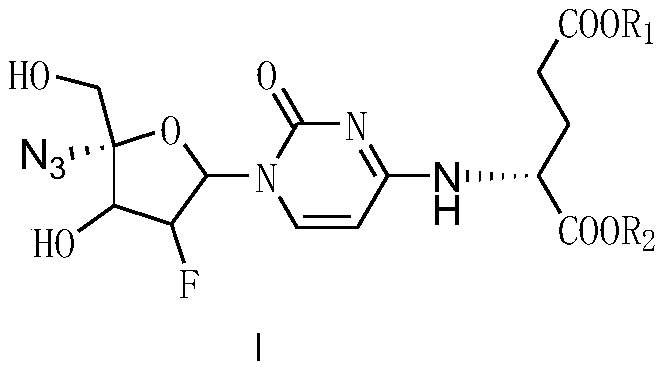
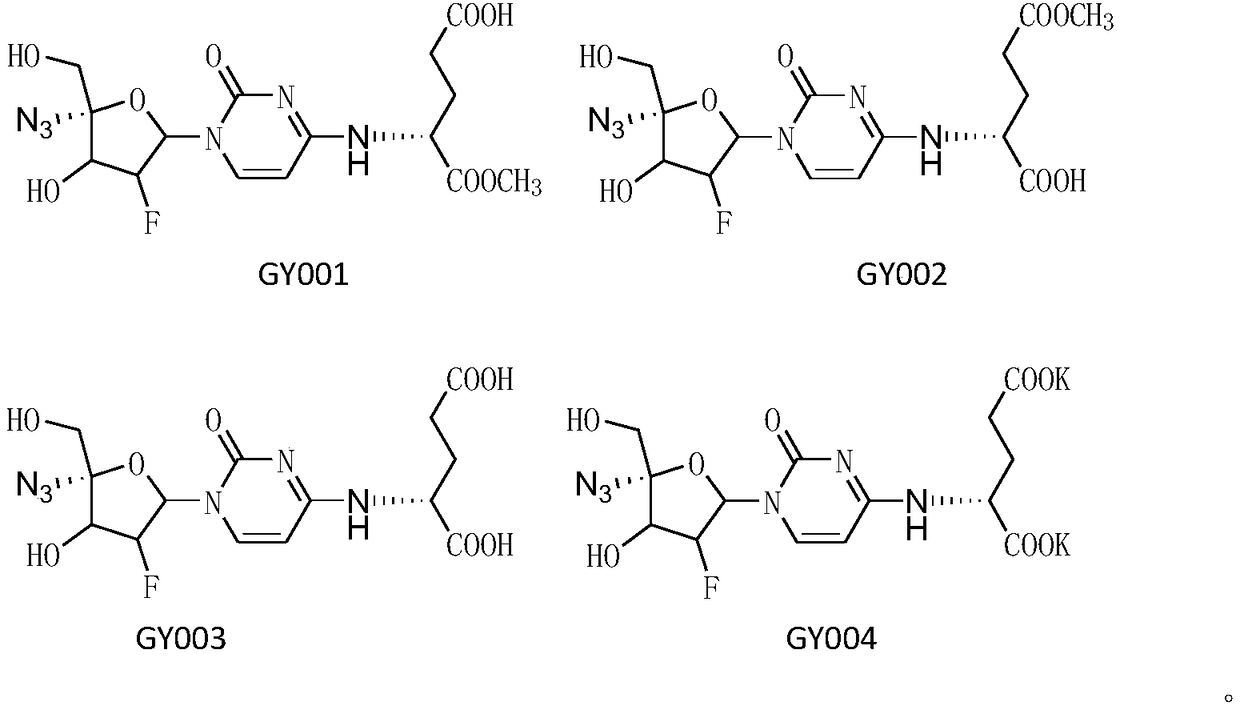
Patents
Literature
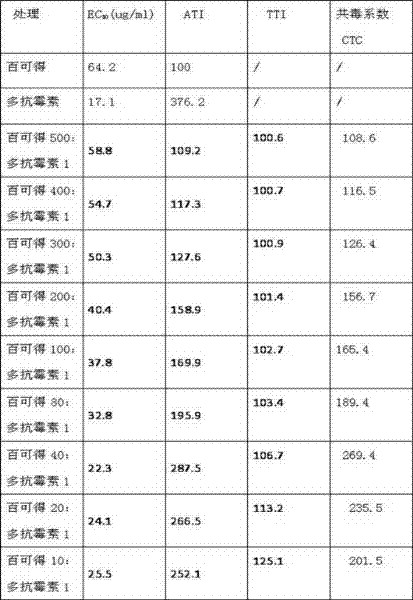
99 results about "Furanose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A furanose is a collective term for carbohydrates that have a chemical structure that includes a five-membered ring system consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The name derives from its similarity to the oxygen heterocycle furan, but the furanose ring does not have double bonds.
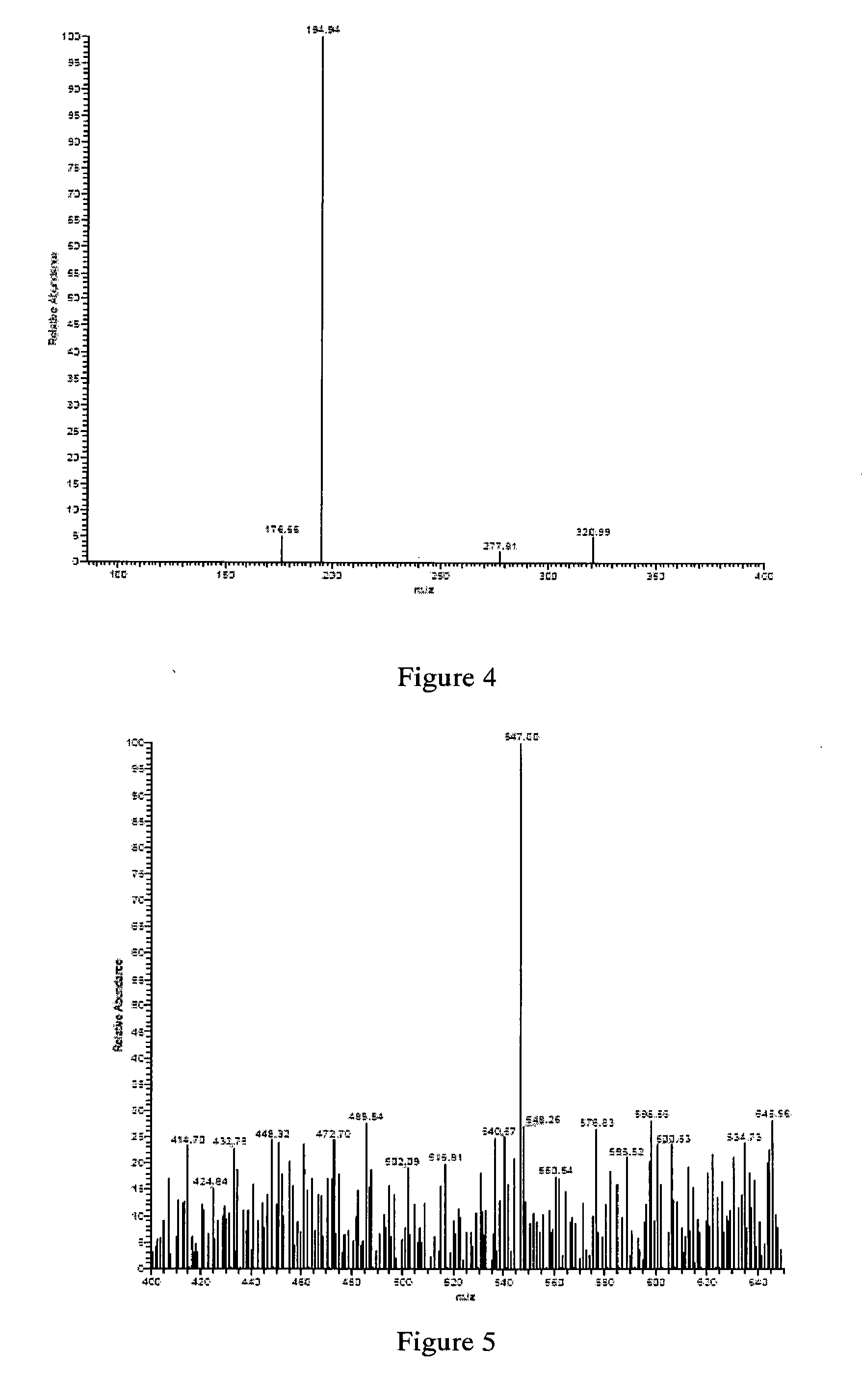
Xylo-LNA analogues
Based on the above and on the remarkable properties of the 2′-O,4′-C-methylene bridged LNA monomers it was decided to synthesise oligonucleotides comprising one or more 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer(s) as the first stereoisomer of LNA modified oligonucleotides. Modelling clearly indicated the xylo-LNA monomers to be locked in an N-type furanose conformation. Whereas the parent 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleosides were shown to adopt mainly an N-type furanose conformation, the furanose ring of the 2′-deoxy-β-D-xylofuranosyl monomers present in xylo-DNA were shown by conformational analysis and computer modelling to prefer an S-type conformation thereby minimising steric repulsion between the nucleobase and the 3′-O-phopshate group (Seela, F.; Wömer, Rosemeyer, H. Helv. Chem. Acta 1994, 77, 883). As no report on the hybridisation properties and binding mode of xylo-configurated oligonucleotides in an RNA context was believed to exist, it was the aim to synthesise 2′-O,4′-C-methylene-β-D-xylofuranosyl nucleotide monomer and to study the thermal stability of oligonucleotides comprising this monomer. The results showed that fully modified or almost fully modified Xylo-LNA is useful for high-affinity targeting of complementary nucleic acids. When taking into consideration the inverted stereochemistry at C-3′ this is a surprising fact. It is likely that Xylo-LNA monomers, in a sequence context of Xylo-DNA monomers, should have an affinity-increasing effect.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Pharmaceutical formulation of cytidine analogs and derivatives
InactiveUS20060128654A1Reduce decompositionImprove solubilityBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsSolubilityCytosine
The present invention provides pharmaceutical formulations of cytidine analogs and derivatives, such as 5-azacytidine, 5-aza-2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine, 5-aza-2′-deoxy-2′-fluorocytidine, 2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine, and cytosine 1-β-D-arabinofuranoside, as well as methods of manufacturing the formulations. In particular, the cytidine analog or derivative is formulated with a cyclodextrin compound to stabilize and / or enhance solubility of the drug. Kits and methods for using the pharmaceutical formulations are also provided, including methods of administering the cytidine analog or derivative to treat conditions or diseases, such as cancer and hematological disorders.
Owner:SUPERGEN
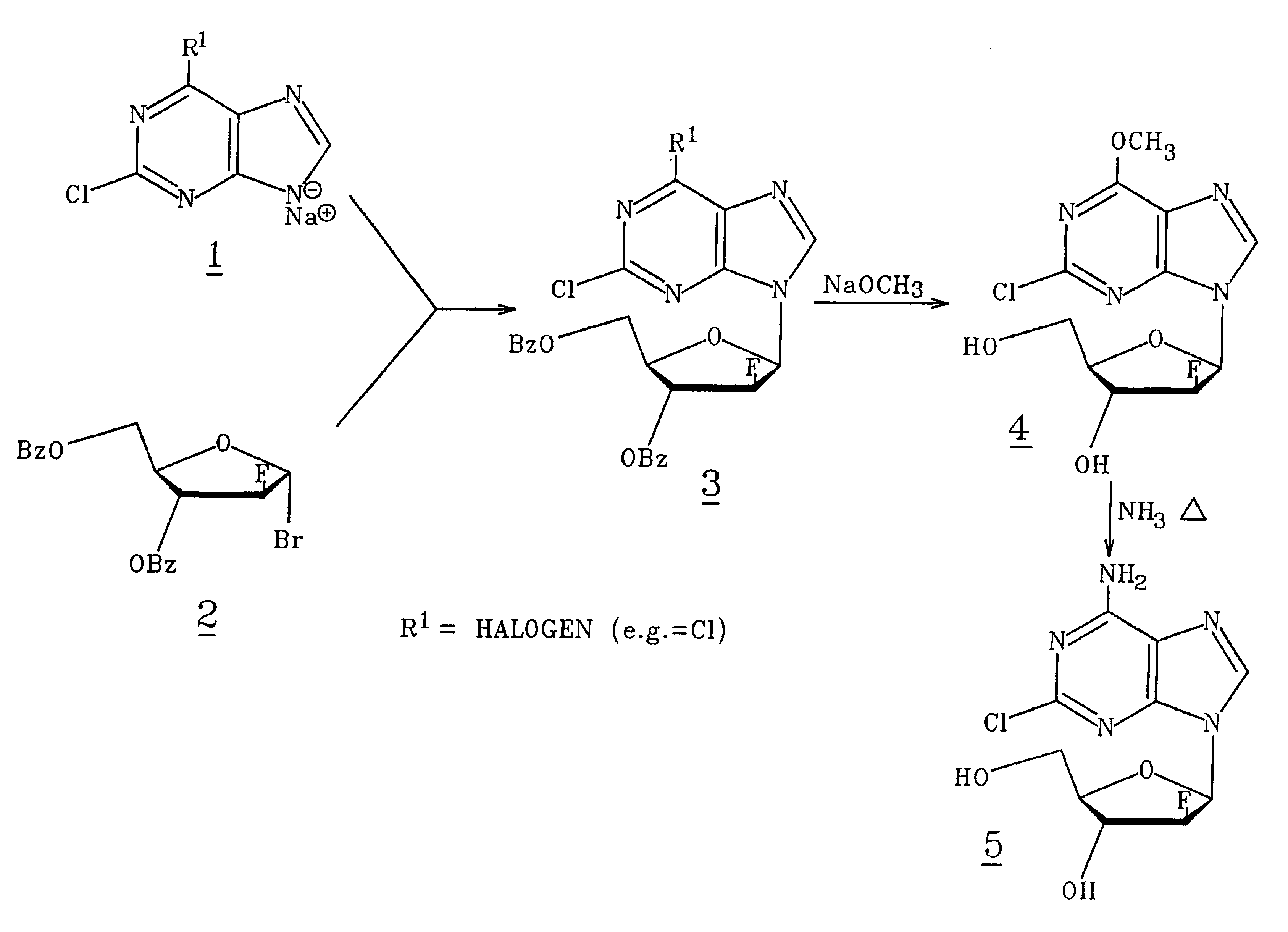
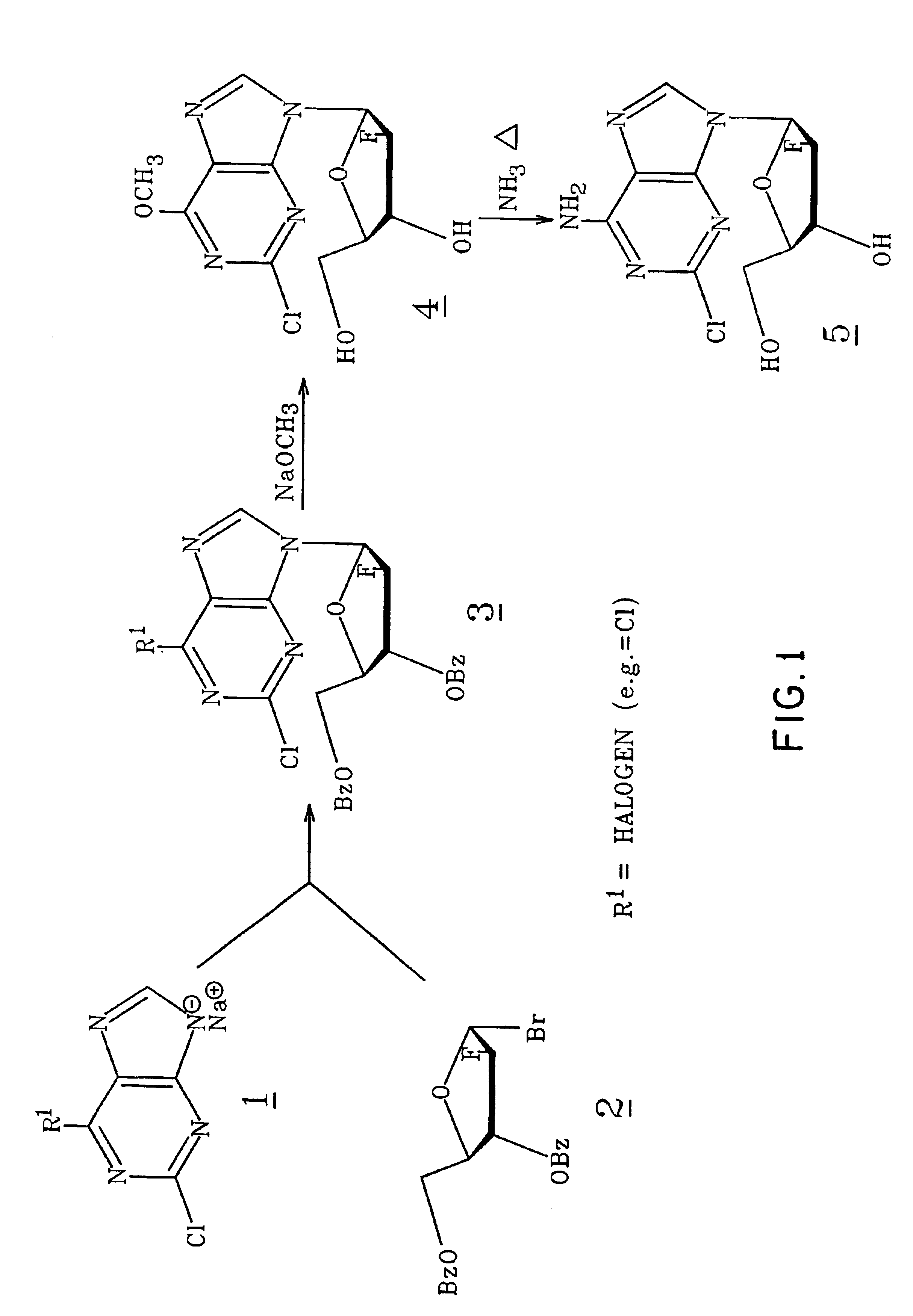
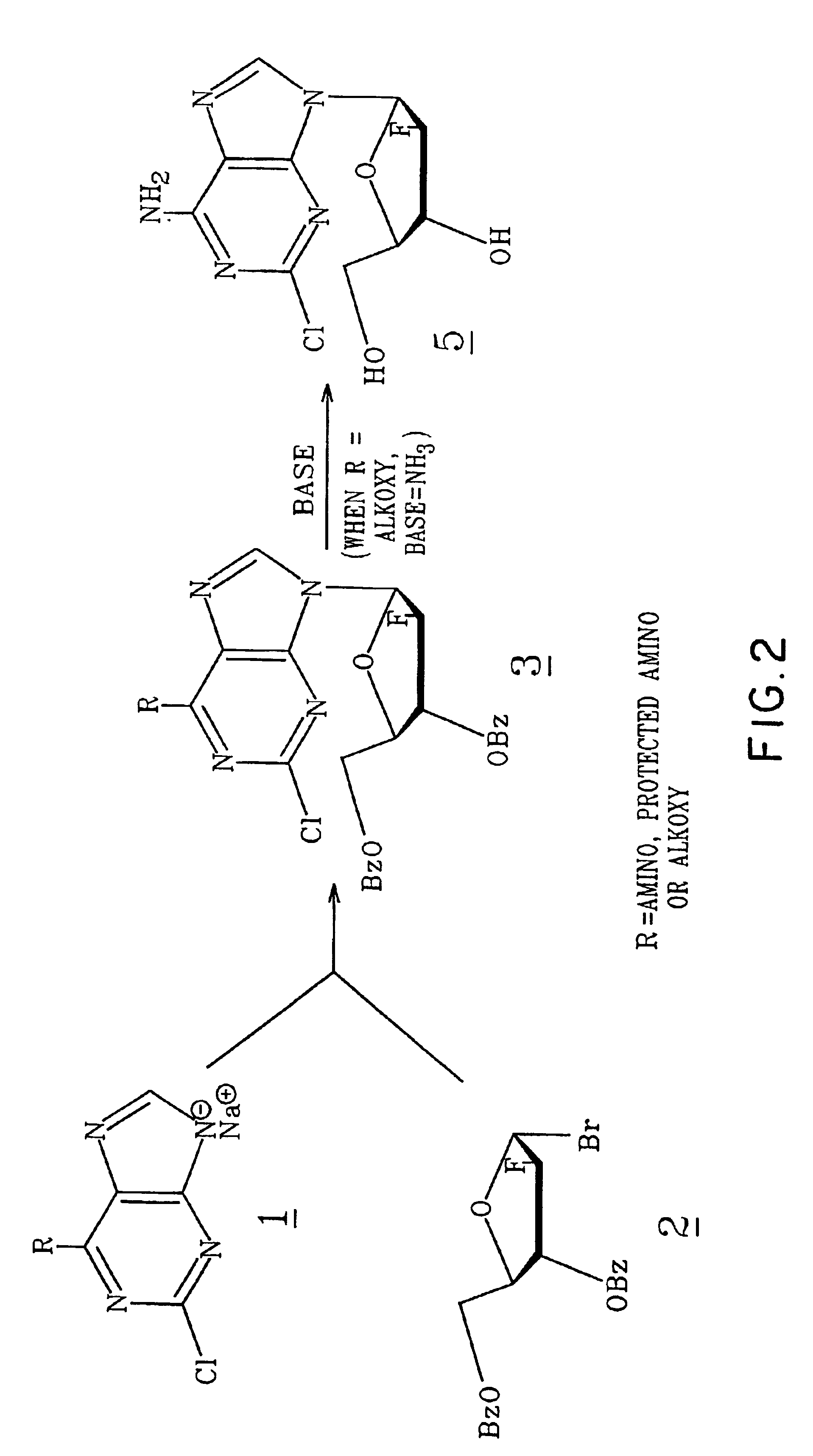
Method for synthesizing 2-chloro-9-(2-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-9H-purin-6-amine
2-Chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-9H-purin-9-amine is synthesized by reacting a 2-chloro-6-substituted purine with a protected and activated 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-arabinofuranose; and reacting with a base such as ammonia to provide 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-arabinofuranosyl)-9H-purin-6-amine. When the purine reactant is substituted in the 6 position with a halogen, a reaction step with an alkoxide is carried out prior to the reaction with ammonia.
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP
Trifluridine intermediate and preparation method of trifluridine
ActiveCN105461772ASolve pollutionSolve productivitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationLewis acid catalysisHomogeneous catalysis
The invention provides a preparation method of a trifluridine intermediate. Under the action of an acidic resin catalyst, 1-chloro-2-deoxy-3,5-di-O-p-chlorobenzoyl-D-ribose and 5-trifluoromethyl-2,4-bis(trimethylsilaneoxy)pyrimidine undergo a condensation reaction so as to obtain the trifluridine intermediate. According to the invention, a heterogeneous catalysis technology is utilized, acidic resin is used as a catalyst, and a traditional Lewis acid catalyst is replaced. Under the precondition of guaranteeing that product quality is controllable, a production technology is greatly improved. Catalytic efficiency is high, and conditions are mild. Purity of the prepared 1-(2'-deoxy-3,5-di-O-p-chlorobenzoyl-beta-D-furanose)-5-trifluoromethyluracil is greatly raised, and the problem that the use of the Lewis acid catalyst leads to severe post-treatment emulsification and environmental pollution and is not beneficial to industrial production is also effectively solved.
Owner:SINOPHARM A THINK PHARMA
Feed additive composition
InactiveUS20150216203A1Improve performanceImprove feed conversionMilk preparationBiocideAlglucerasePentagalacturonic acid
A feed additive composition comprising a direct fed microbial (DFM), in combination with a xylanase (e.g. endo-1,4-β-d-xylanase) and a β-glucanase (and optionally a further fibre degrading enzyme), wherein the DFM is selected from the group consisting of an enzyme producing strain; a C5 sugar-fermenting strain; a short-chain fatty acid-producing strain; a fibrolytic, endogenous microflora-promoting strain; or combinations thereof. The DFM may be selected from the group consisting of: Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS3BP5, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS442, B. subtilis AGTP BS521, B. subtilis AGTP BS918, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS1013, B. subtilis AGTP BS1069, B. subtilis AGTP 944, B. pumilus AGTP BS 1068 or B. pumilus KX11-1, Enterococcus faecium ID7, Propionibacterium acidipropionici P169, Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM-1-3698, Lactobacillus farciminis CNCM-1-3699, a strain having all the characteristics thereof, any derivative or variant thereof, and combinations thereof and the further fibre degrading enzyme may be selected from the group consisting of a cellobiohydrolase (E.C. 3.2.1.176 and E.C. 3.2.1.91), a β-glucosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.21), a β-xylosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.37), a feruloyl esterase (E.C. 3.1.1.73), an α-arabinofuranosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.55), a pectinase (e.g. an endopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.15), an exopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.67) or a pectate lyase (E.C. 4.2.2.2)), or combinations thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Isolated polypeptide having arabinofuranosidase activity
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Antitumor and anticholesterol preparations containing a lipoteichoic acid from streptococcus
InactiveUS6214978B1Improve usabilityImprove liquidityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBackbone chainHyaluronidase
The invention concerns a new lipoteichoic acid which can be isolated from the new Streptococcus sp DSM 8747. The new LTA is called LTA-T. It has a lipid anchor, which is a galacto-furanosyl-beta-1-3-glycerol with different rests of fatty acids esterified in the two adjacent hydroxy groups in the glycerol moiety and a non-glycosylated, linear, unbranched GroP chain with an unusual short hydrophilic GroP chain. The hydrophilic backbone consists of only 10 glycerophosphate units esterified with D-alanine in an extent of 30%. The invention further concerns a pharmaceutical composition with the new LTA-T, optionally together with a monokine and / or hyaluronidase, a method of treating cancer comprising administration of an antitumor effective amount thereof, a method of producing the new compound and the new pharmaceutical composition, two degradation products of the new LTA-T and their use, and the new Streptococcus strain from which the new compound can be isolated.
Owner:LUNAMED
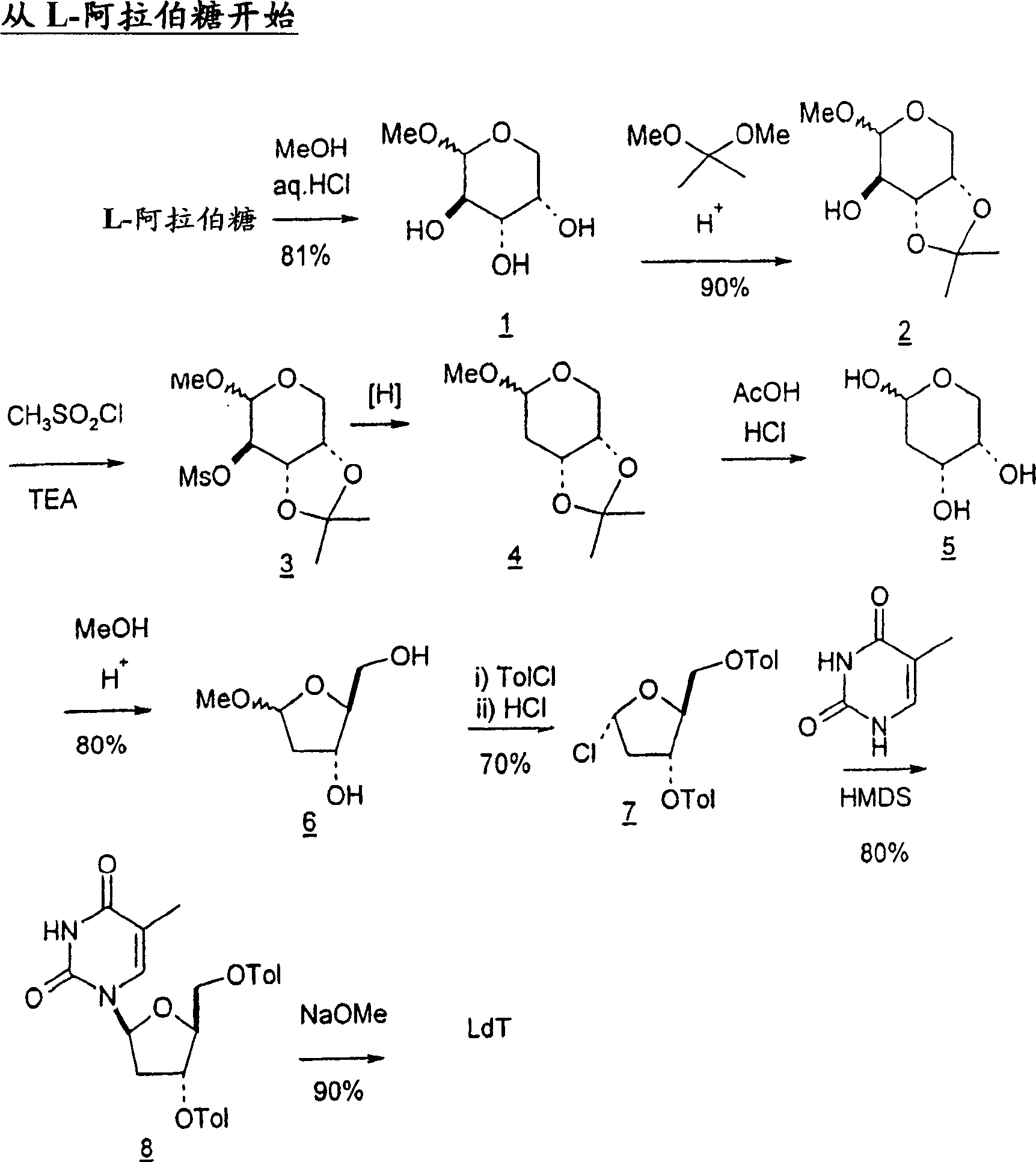
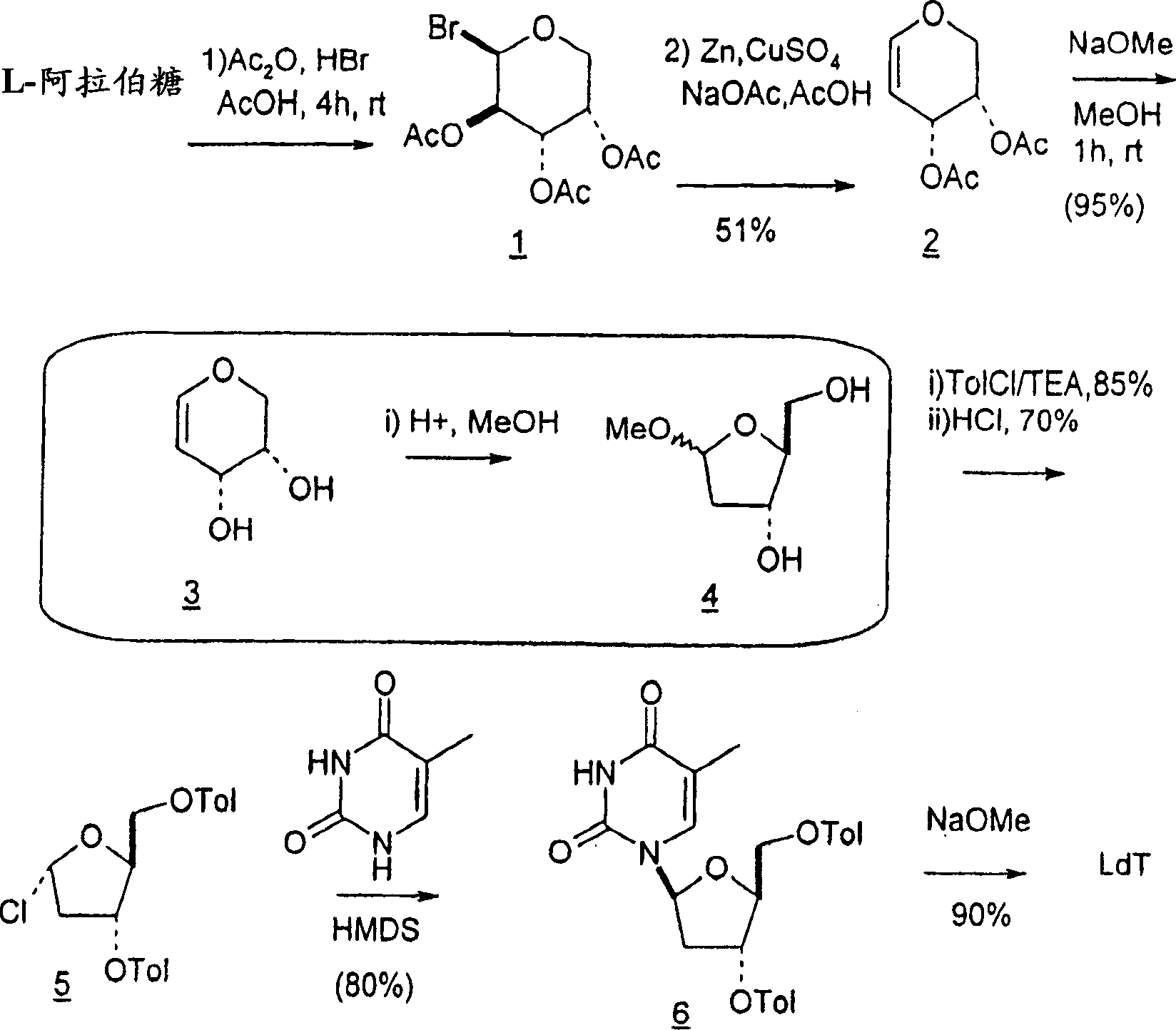
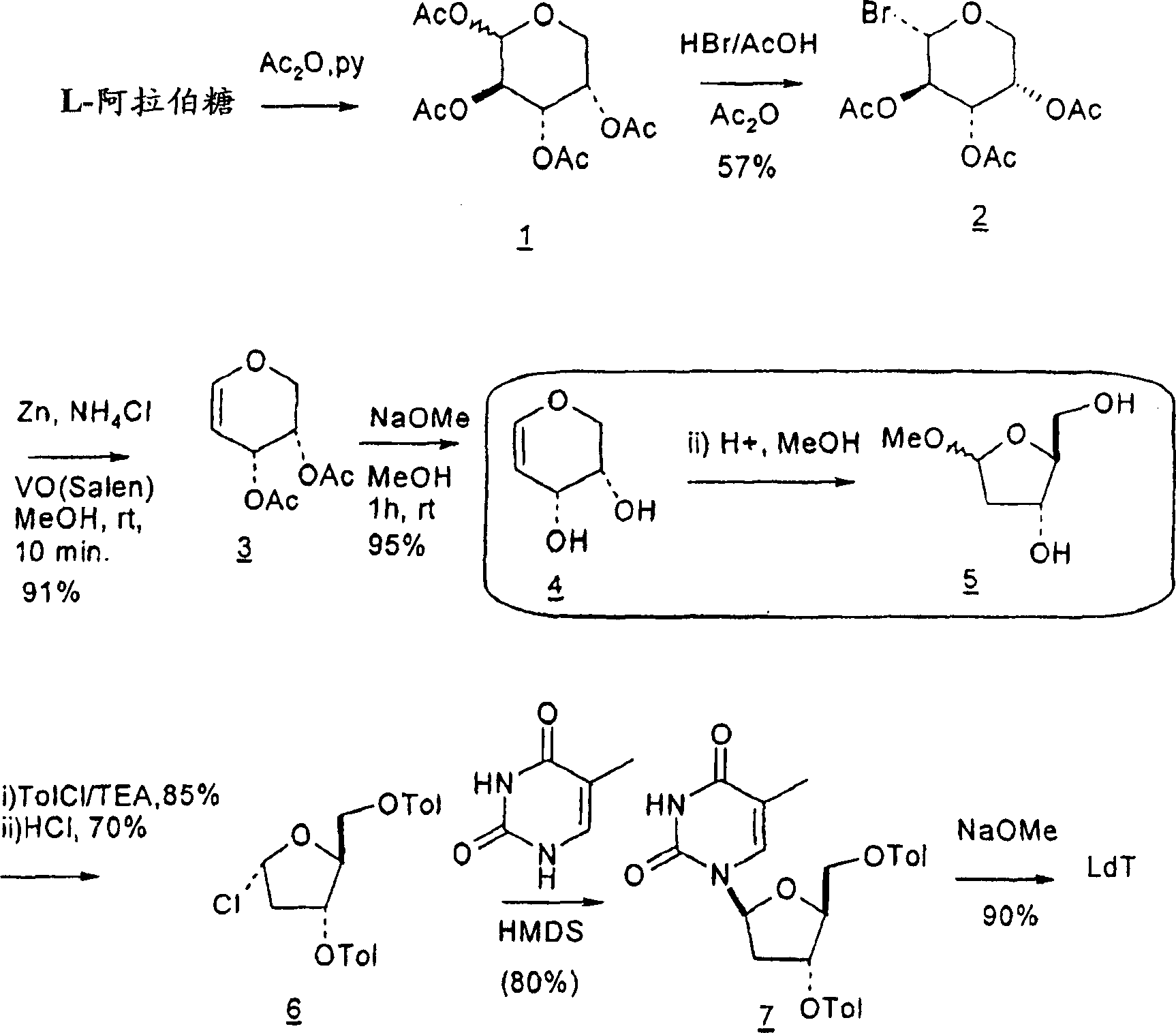
Synthesis of beta-L-2'-deoxy nucleosides
InactiveUS20050059632A1High percent product yieldPercent product yieldEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideDisplacement reactionsAlternative methods
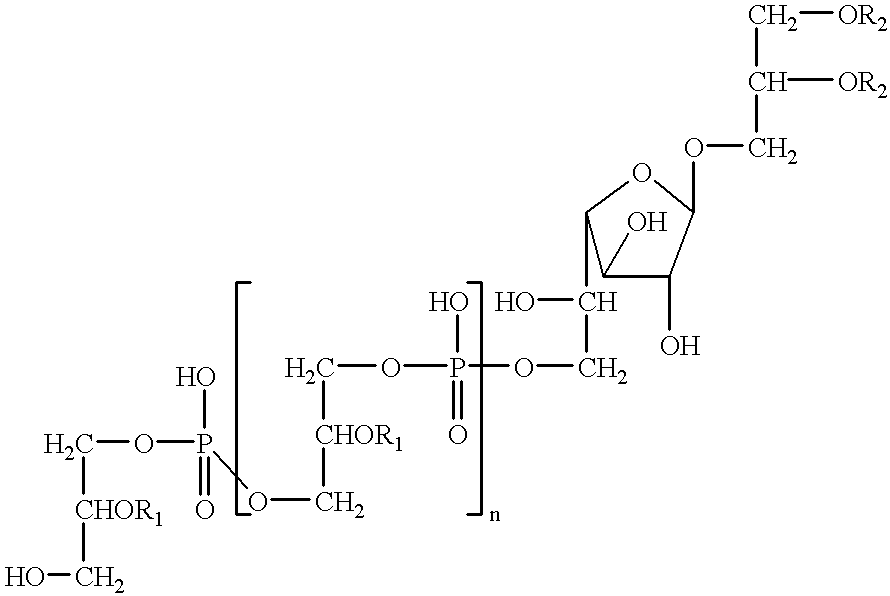
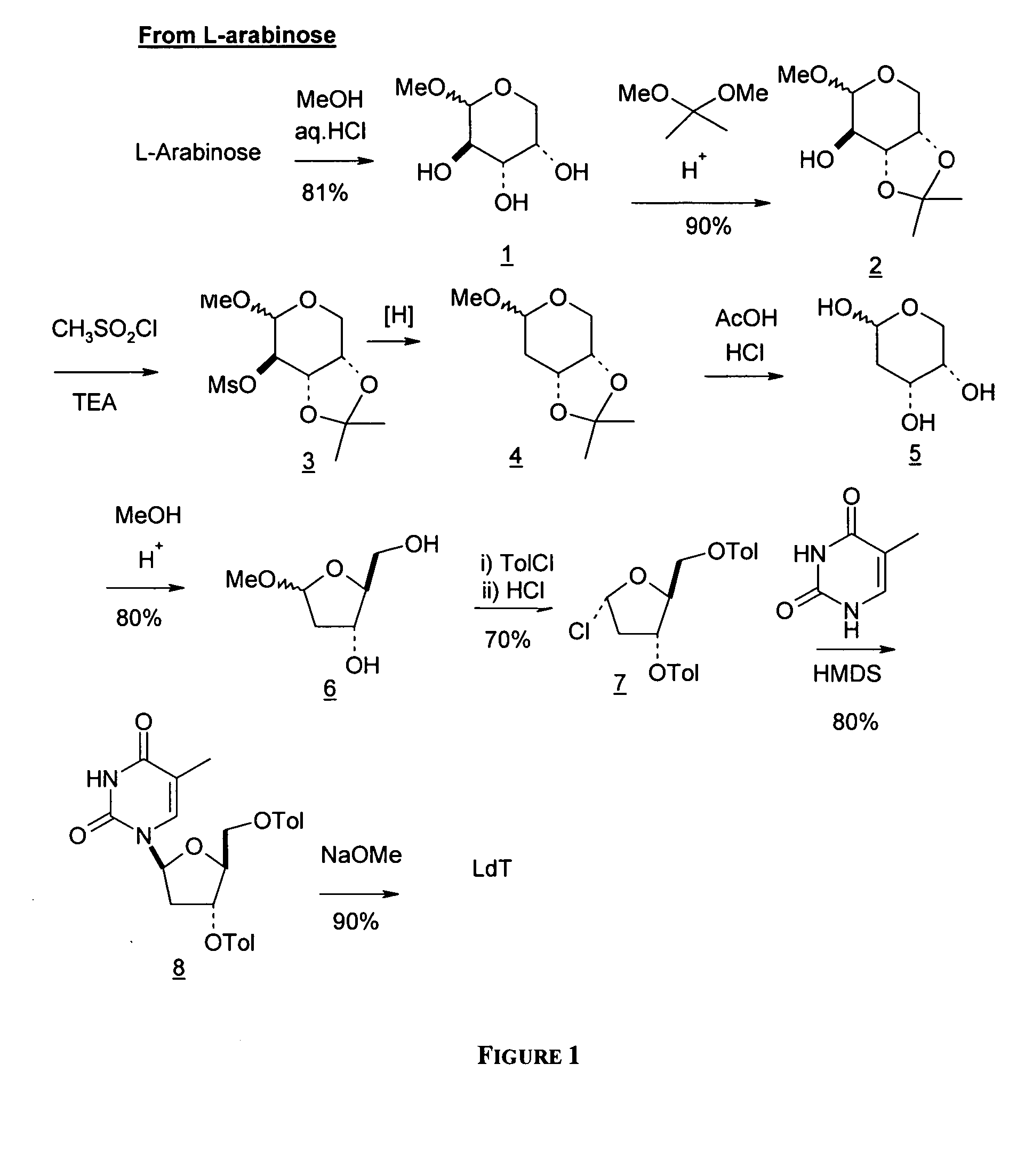
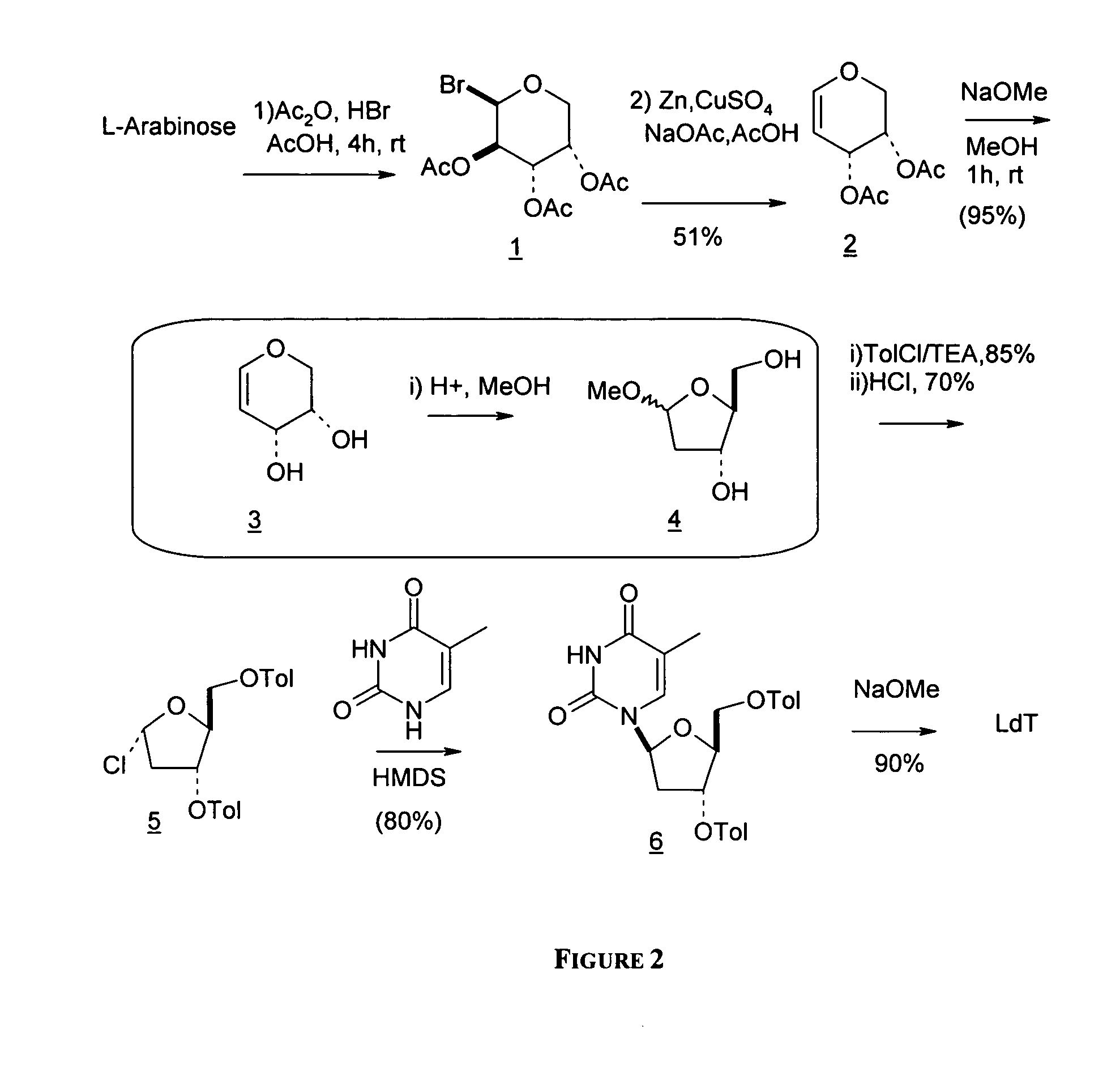
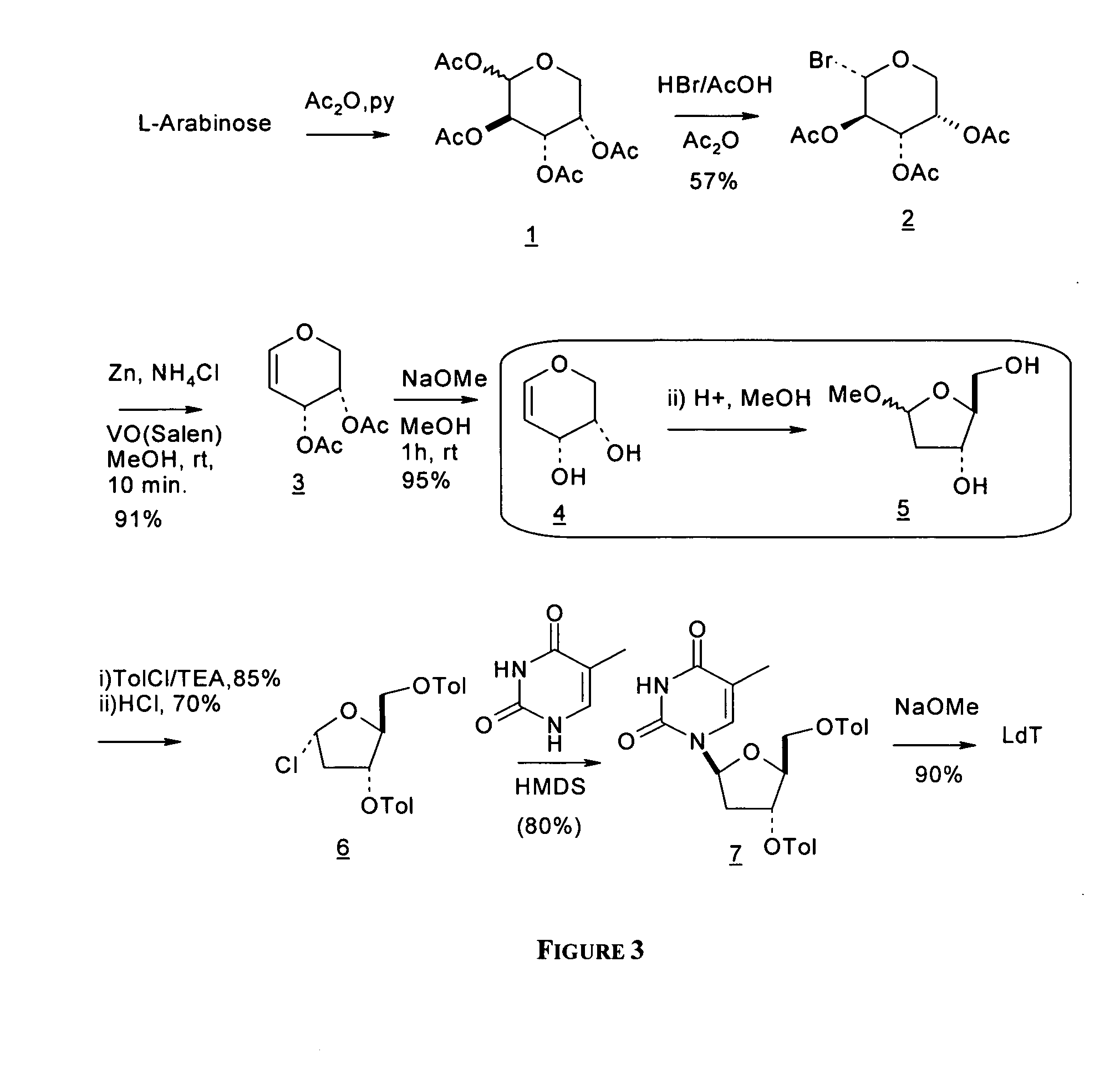
An improved process for the preparation of 2′-modified nucleosides and 2′-deoxy-nucleosides, such as, β-L-2′-deoxy-thymidine (LdT), is provided. In particular, the improved process is directed to the synthesis of a 2′-deoxynucleoside that may utilize different starting materials but that proceeds via a chloro-sugar intermediate or via a 2,2′-anhydro-1-furanosyl-nucleobase intermediate. Where an 2,2′-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate is utilized, a reducing agent, such as Red-Al, and a sequestering agent, such as 15-crown-5 ether, that cause an intramolecular displacement reaction and formation of the desired nucleoside product in good yields are employed. An alternative process of the present invention utilizes a 2,2′-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate without a sequestering agent to afford 2′-deoxynucleosides in good yields. The compounds made according to the present invention may be used as intermediates in the preparation of other nucleoside analogues, or may be used directly as antiviral and / or antineoplastic agents.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
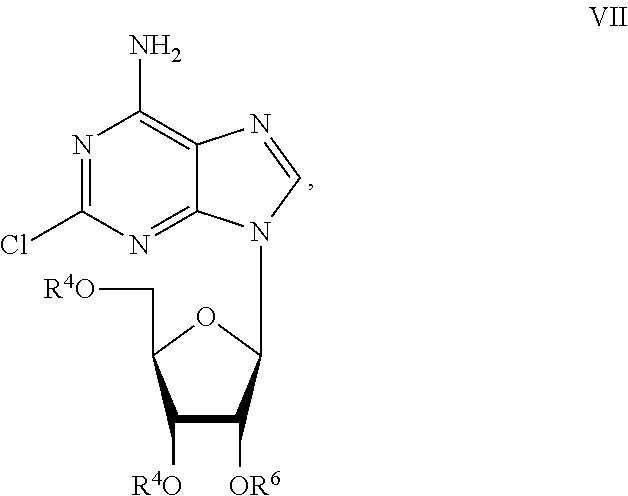
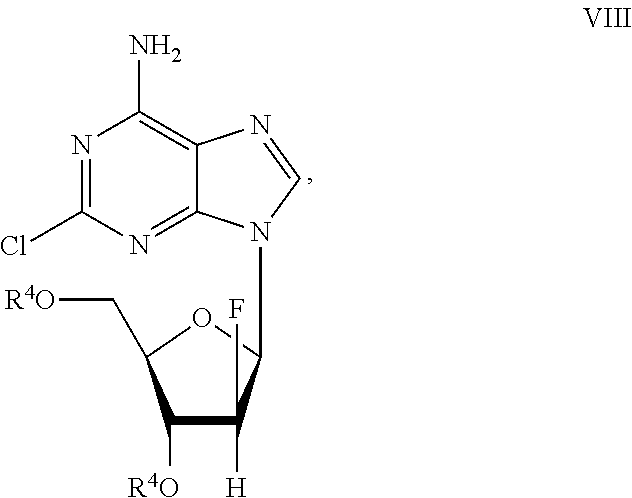
Preparation of 2-chloro-9-(2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-Beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-adenine
A process for making clofarabine comprising: fluorinating a compound of formula VIIwherein each R4 is independently a hydroxy protecting group, OR6 is a leaving group, with a fluorinating agent in the presence of guanidine carbonate to give a compound of formula VIII:wherein R4 is as defined above; and deprotecting the compound of formula VIII to give the clofarabine.
Owner:SCINOPHARM TAIWAN LTD
Novel trichoderma genes
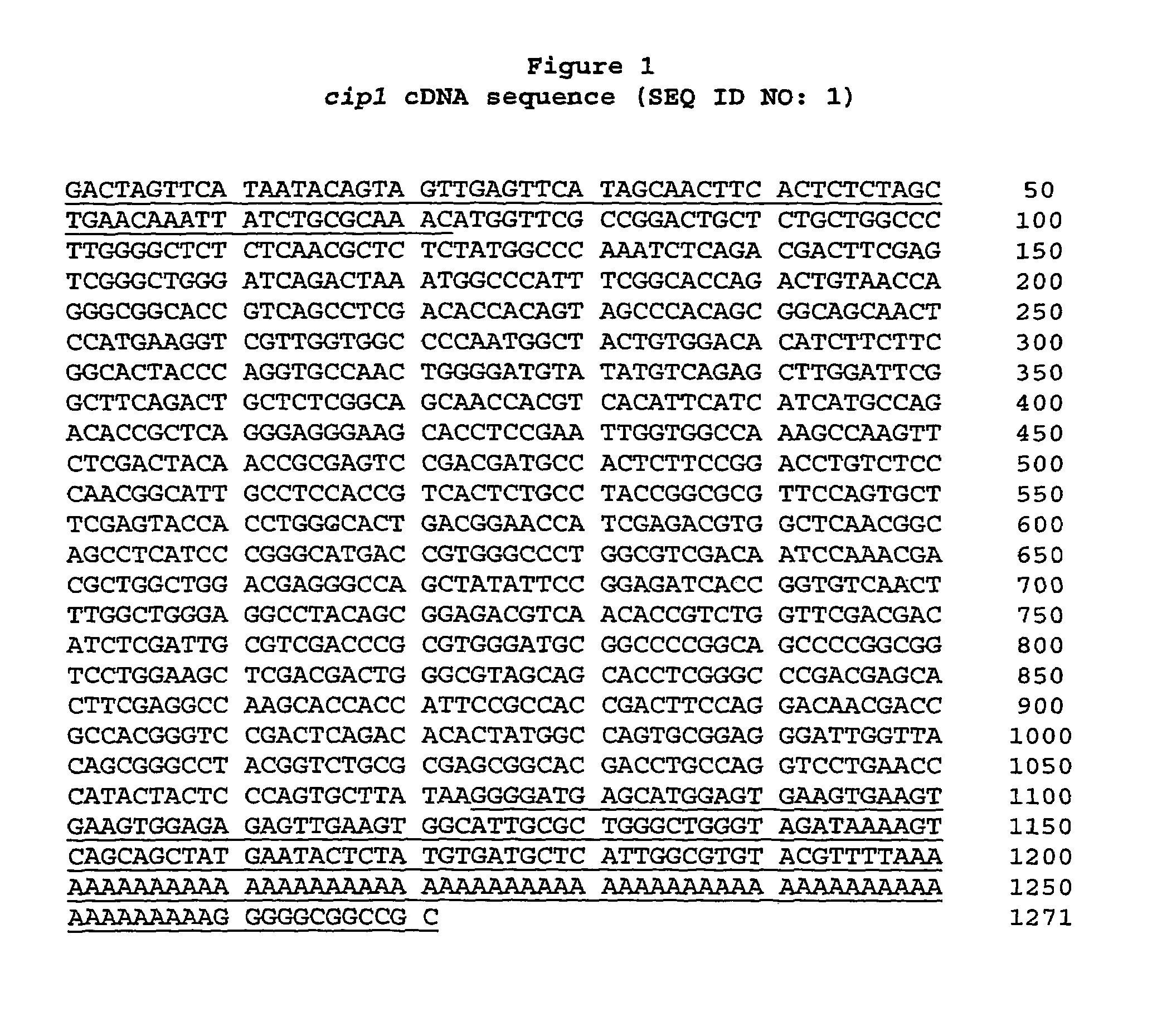
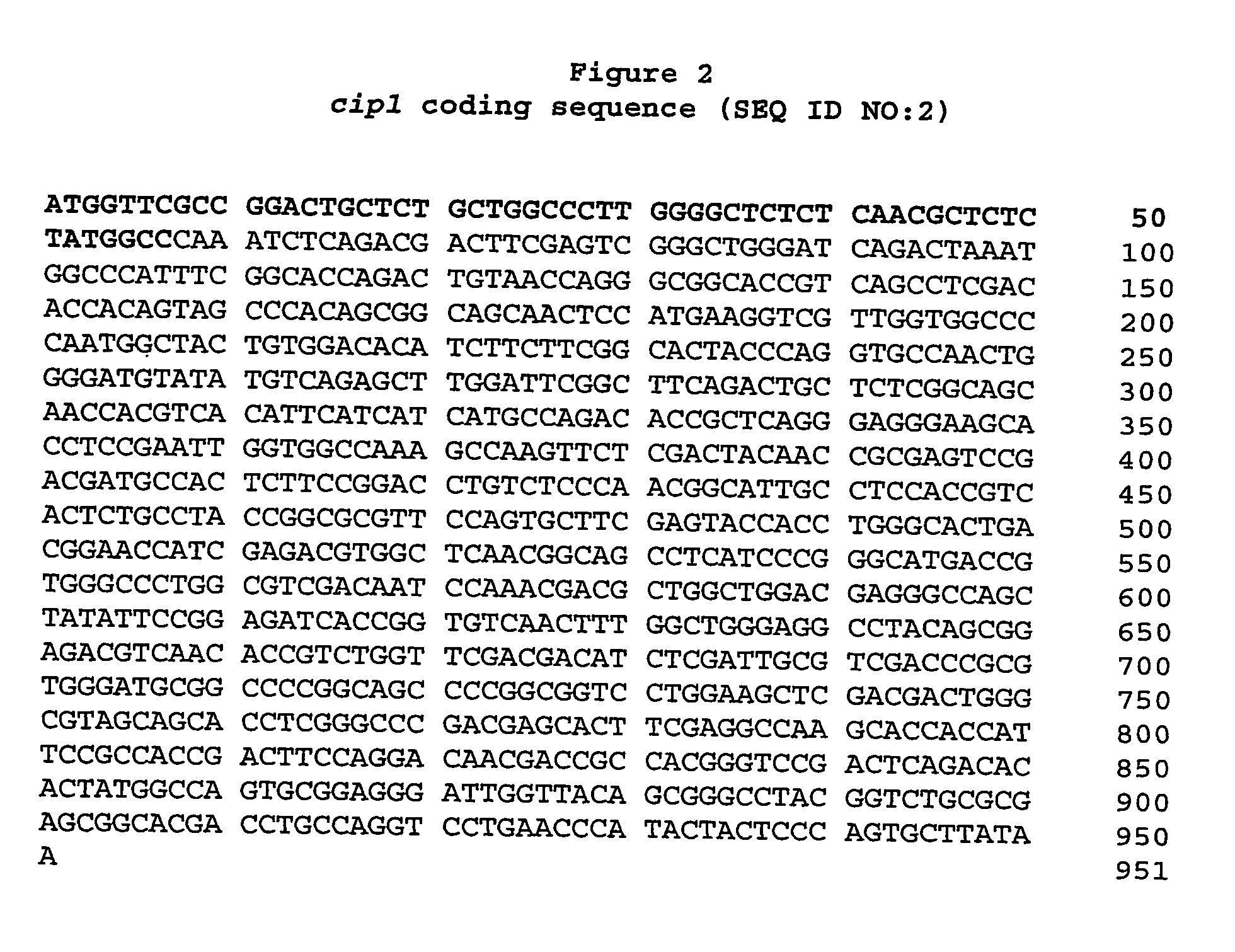
Described herein are novel gene sequences isolated from Trichoderma reesei. Two genes encoding proteins comprising a cellulose binding domain, one encoding an arabionfuranosidase and one encoding an acetylxylanesterase are described. The sequences, CIP1 and CIP2, contain a cellulose binding domain. These proteins are especially useful in the textile and detergent industry and in pulp and paper industry.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Synthesis of beta-l-2'-deoxy nucleosides
An improved process for the preparation of 2'-modified nucleosides and 2'-deoxy-nucleosides, such as, beta-L-2'-deoxy-thymidine (LdT), is provided. In particular, the improved process is directed to the synthesis of a 2'-deoxynucleoside that may utilize different starting materials but that proceeds via a chloro-sugar intermediate or via a 2,2' anhydro-1-furanosyl-nucleobase intermediate. Where an 2,2'-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate is utilized, a reducing agent, such as Red-Al, and a sequestering agent, such as 15-crown-5 ether, that cause an intramolecular displacement reaction and formation of the desired nucleoside product in good yields are employed. An alternative process of the present invention utilizes a 2,2'-anhydro-1-furanosyl base intermediate without a sequestering agent to afford 2'-deoxynucleosides in good yields. The compounds made according to the present invention may be used as intermediates in the preparation of other nucleoside analogues, or may be used directly as antiviral and / or antineoplastic agents.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Fungicide composition
ActiveCN102258047AGood synergyImprove the bactericidal effectBiocideFungicidesUronic acidMethyl palmoxirate
The invention relates to a germicide composition with synergistic effect, in particular to a germicide composition containing iminoctadine tris(albesilate) (bellkute) and polyoxin. The composition contains A) iminoctadine tris(albesilate) (bellkute) and B) polyoxin, wherein the chemical name of A) is 1,1'-iminobis(1,8-octadienyl) iminoctadine tris; the chemical name of B) is 5-{[2-amino-5-O-(aminocarbonyl)-2-deoxy-L-xylosyl]amino}-1,5-dideoxy-1-[3,4-dihydro-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2,4-dioxo-1(2H)-pyrimidyl]-beta-D-sec-D-glucuronic acid; and the mass ratio of the compound A to the compound B is (500:1)-(1:1). The invention provides application of the germicide composition to control of crop diseases. The germicide composition is used for controlling crop powdery mildew and gray mold.
Owner:JIANGSU ROTAM CHEM
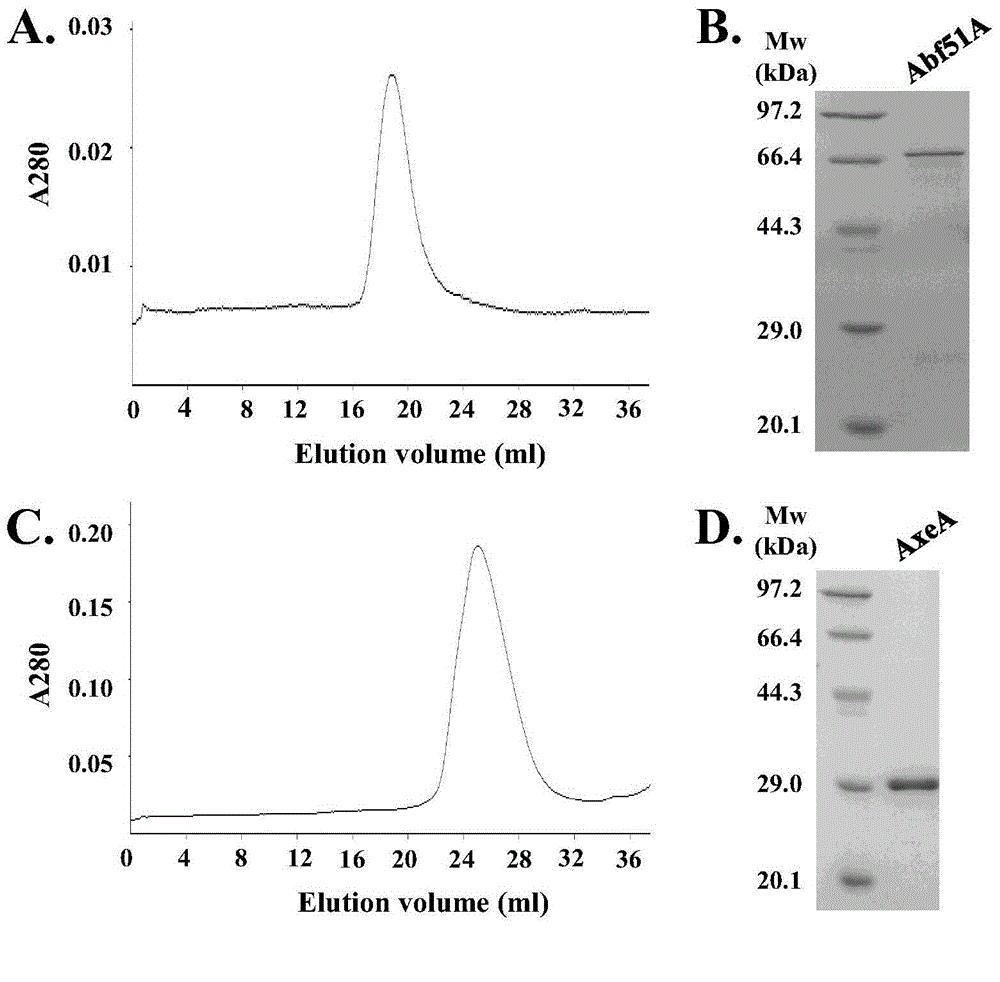
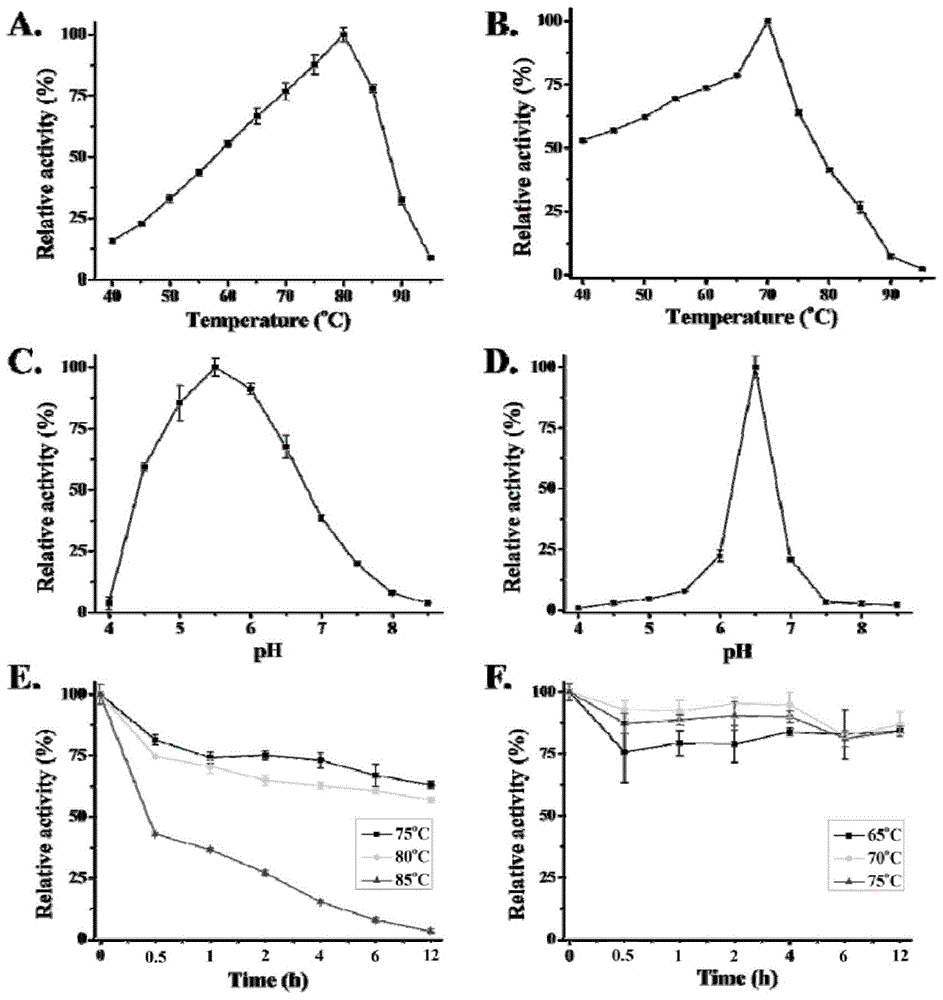
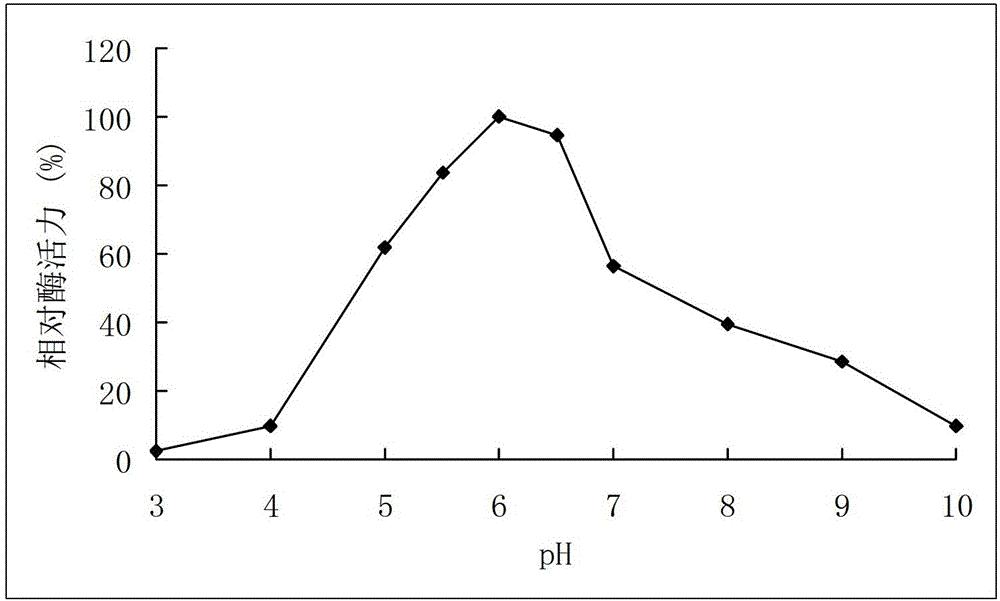
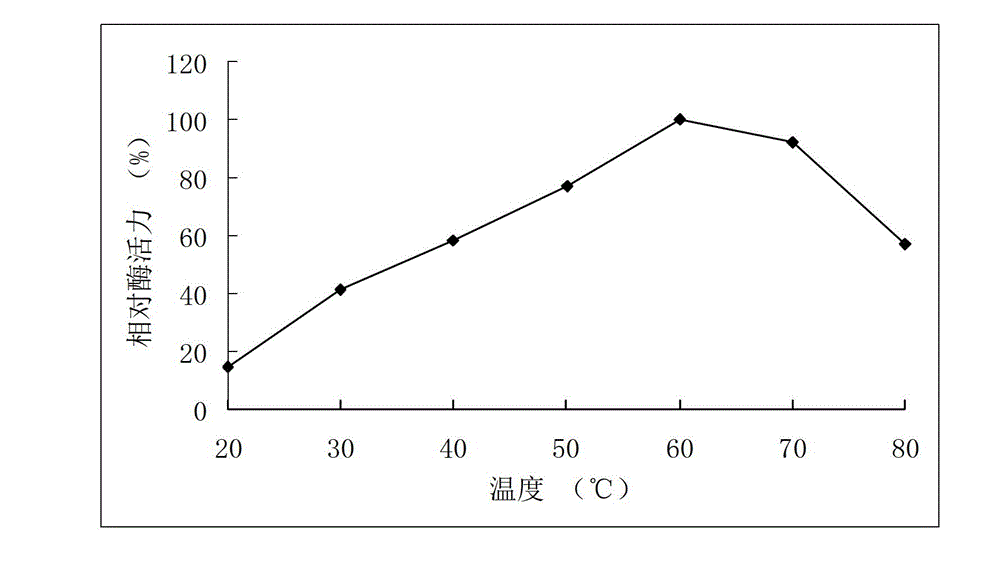
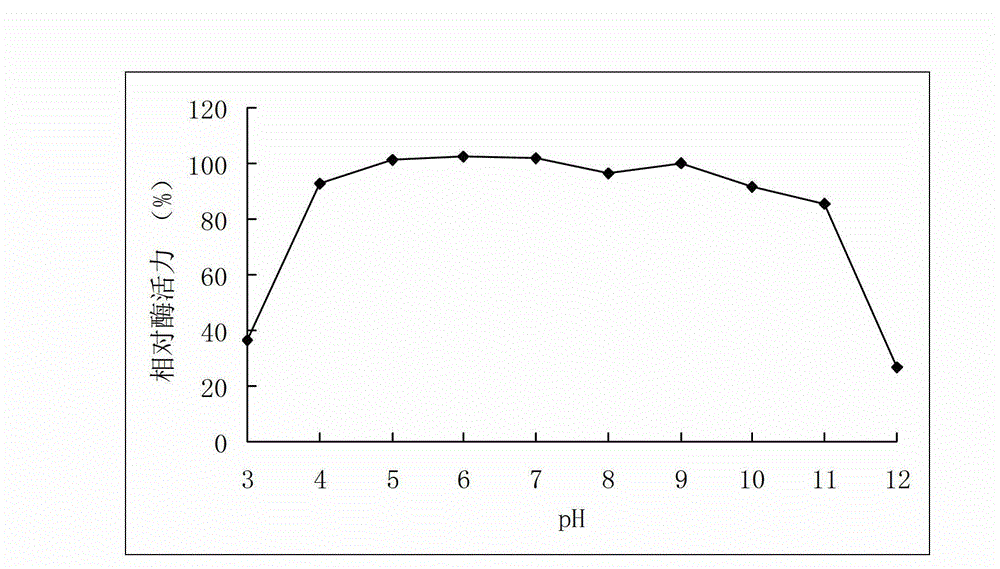
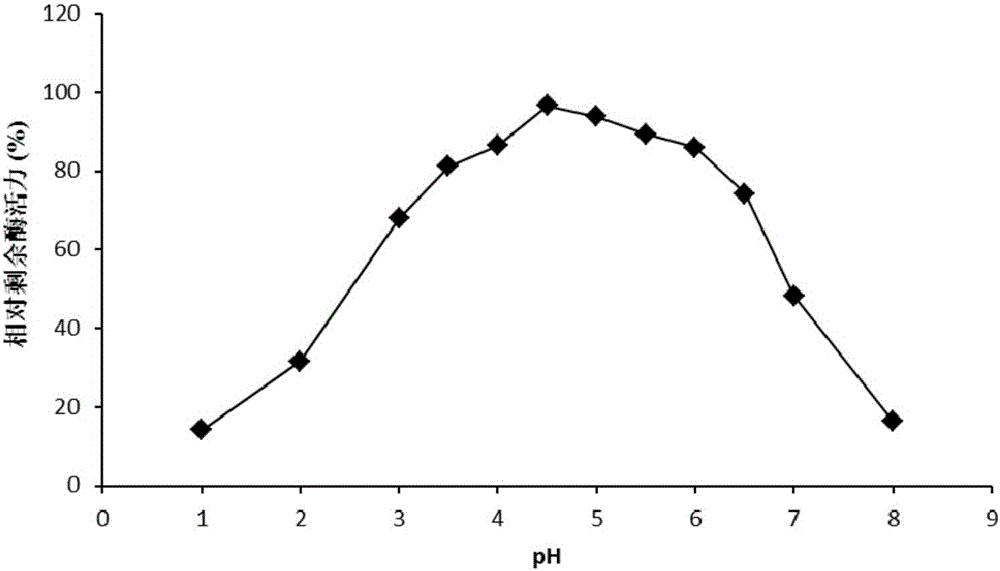
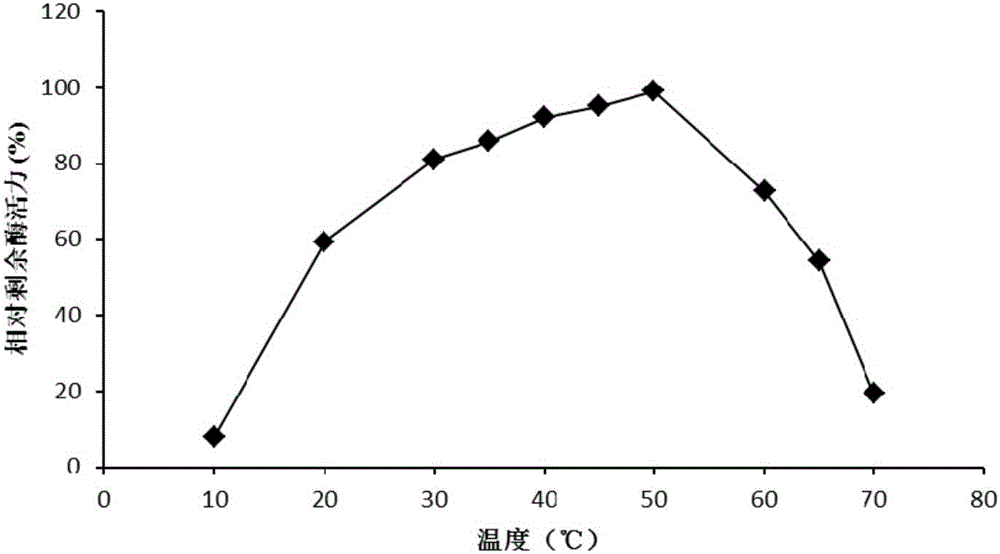
A high-temperature alpha-L-arabinfuranosidease gene, a high-temperature acetylxylan esterase gene, and protein expression and applications of the genes
InactiveCN105734069AImprove thermal stabilityPromote degradationBacteriaHydrolasesCelluloseSide chain
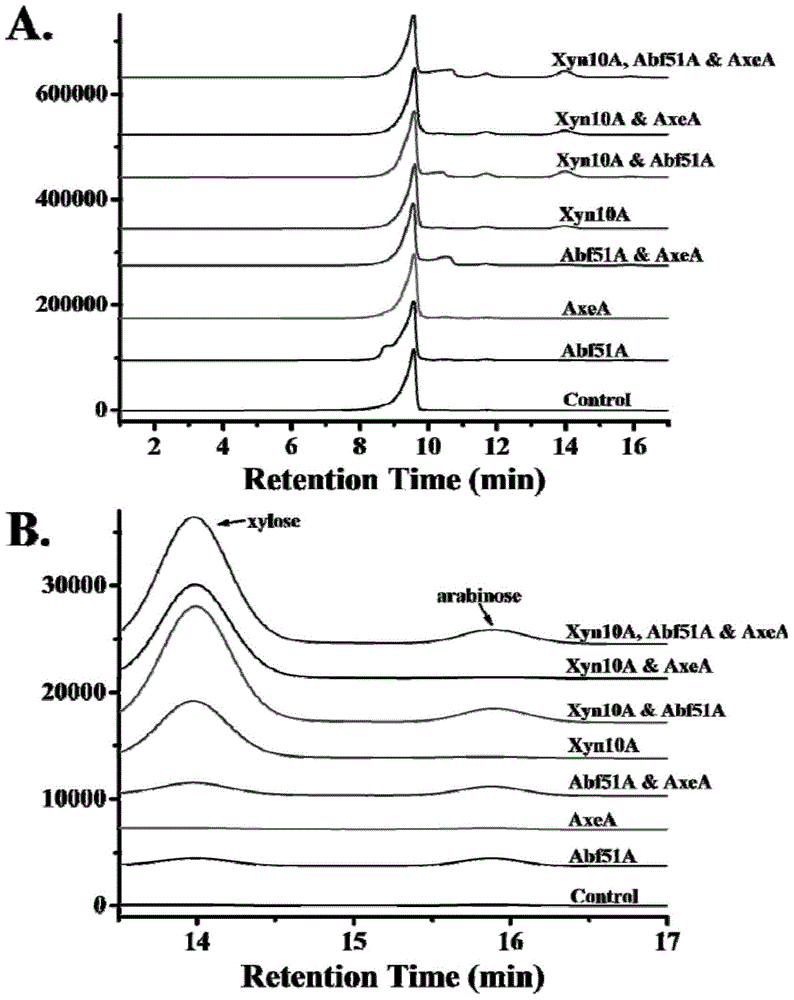
The invention provides a high-temperature alpha-L-arabinfuranosidease gene abf51A and a high-temperature acetylxylan esterase gene axeA which are derived from caldicellulosiruptor lactoaceticus 6A, and protein expression and applications of the genes. High-temperature alpha-L-arabinfuranosidease abf51A and high-temperature acetylxylan esterase axeA are advantaged by high optimum reaction temperatures, good thermal stability, and the like, and can effectively degrade natural xylan side chains at 65-85 DEG C with pH being 4.5-6.5 to produce arabinose, acetic acid and a small amount of xylose. The two enzymes can effectively eliminate steric hindrance of side chains to xylanase, improve biodegradability of the lignocellulose resource, can be widely used as novel enzyme preparations for feed, food, energy, and other fields, and have potential industrial application value.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Eye drop for treating eye dryness
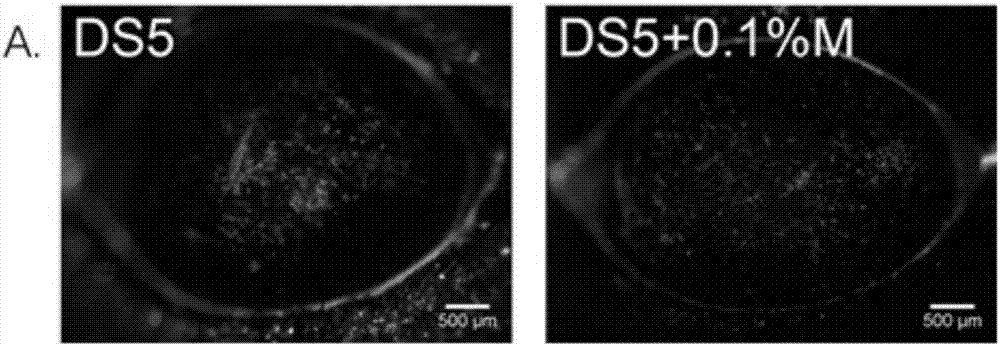
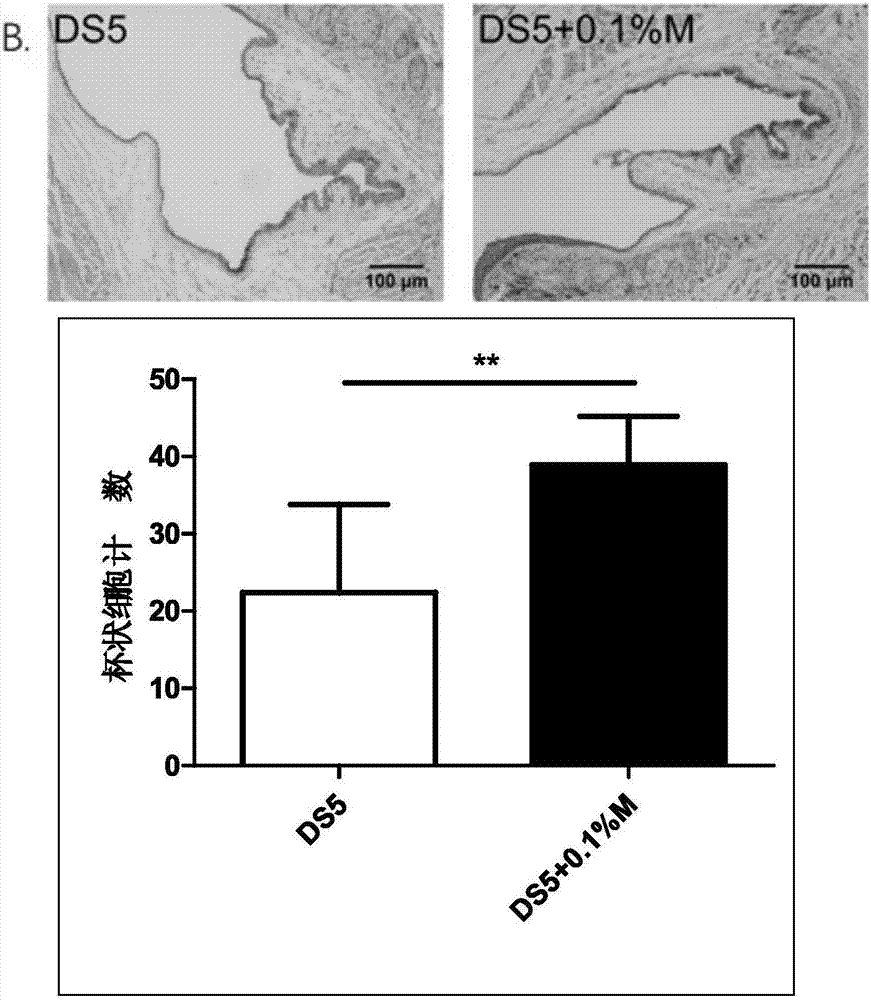
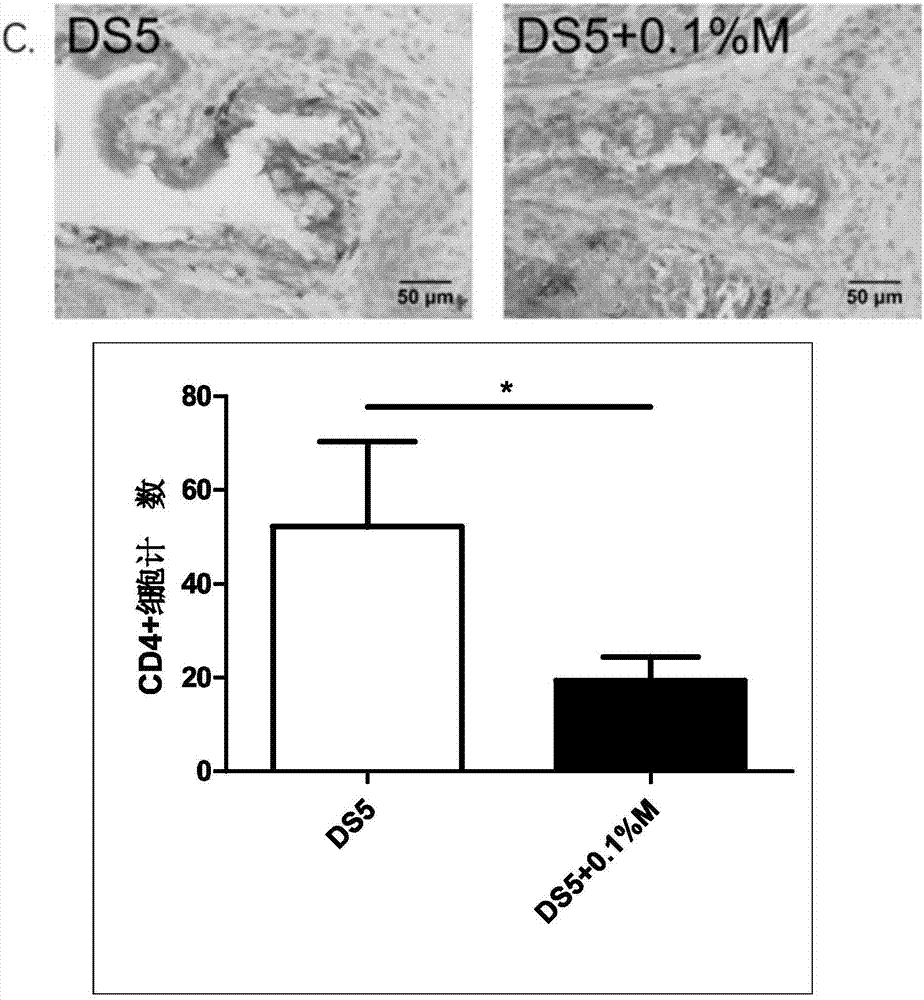
ActiveCN107049938AProtect epithelial barrier functionRecovery quantityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderConjunctivaEye dryness
The invention discloses an eye drop for treating eye dryness. The pH value of the eye drop is 5.0-7.0, the eye drop comprises effective components of 5-hydroxy-1-beta-D-furanose-1H-imidazole-5-carboxamide, and specifically the eye drop consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 0.05-0.1% of 5-hydroxy-1-beta-D-furanose-1H-imidazole-5-carboxamide, a proper amount of a pH value adjusting agent, 0.01-3% of an iso-osmotic agent, 0.003-0.5% of a bacteriostatic agent, 0.001-0.5% of a stabilizer, 0.01-0.5% of a tackifier, 2-5% of a solubilizer and the balance of water. Through partial treatment of the eye drop, epithelial barrier functions of dry eye mouse cornea can be protected, the number of goblet cells of cornea can be recovered, and relatively good anti-inflammatory and immunity inhibition effects can be achieved.
Owner:EYE MEDICAL XIAMEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
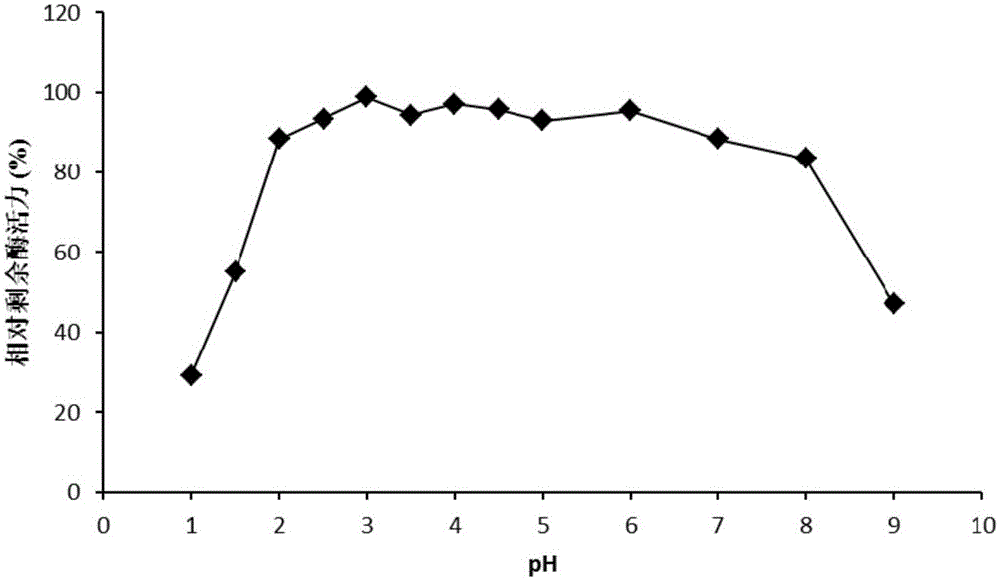
High-temperature resistance arabinfuranosidease Abf51B8, as well as gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102719417AIncrease enzyme activityImprove stabilityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyThermal stability
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, and in particular relates to high-temperature resistance arabinfuranosidease Abf51B8, as well as a gene and an application thereof. The invention provides the arabinfuranosidease Abf51B8 coming from Alicyclobacillussp.B8 with an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a coding gene abf51B8 for coding the arabinfuranosidease. The arabinfuranosidease has the characteristics of optimal pH of 6.0, optimal temperature of 60 DEG C and good thermal stability at 70 DEG C, and can be widely applied to feeds, foods, energy industries and the like serving as a novel enzyme preparation.
Owner:WUHAN SUNHY BIOLOGICAL
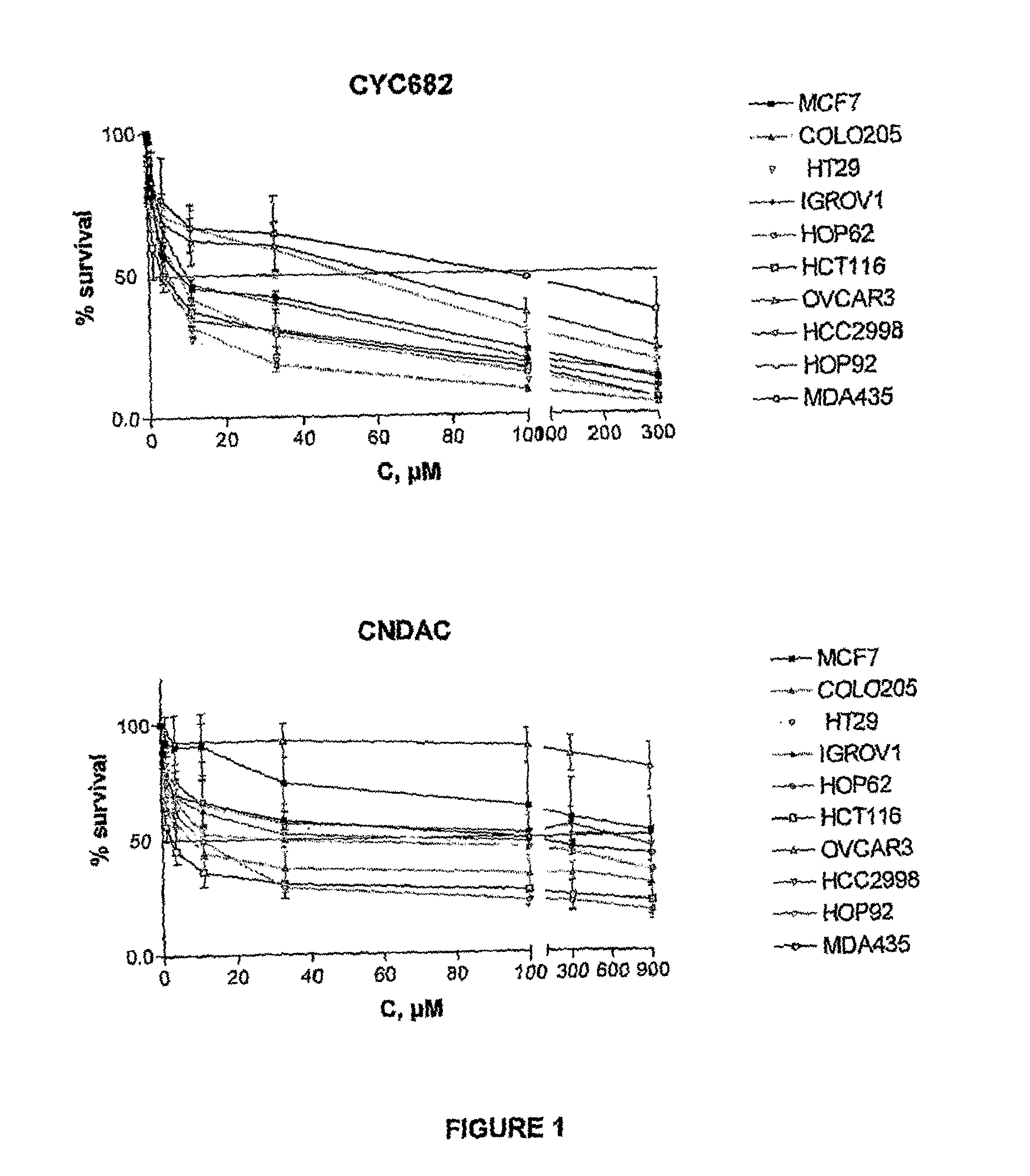
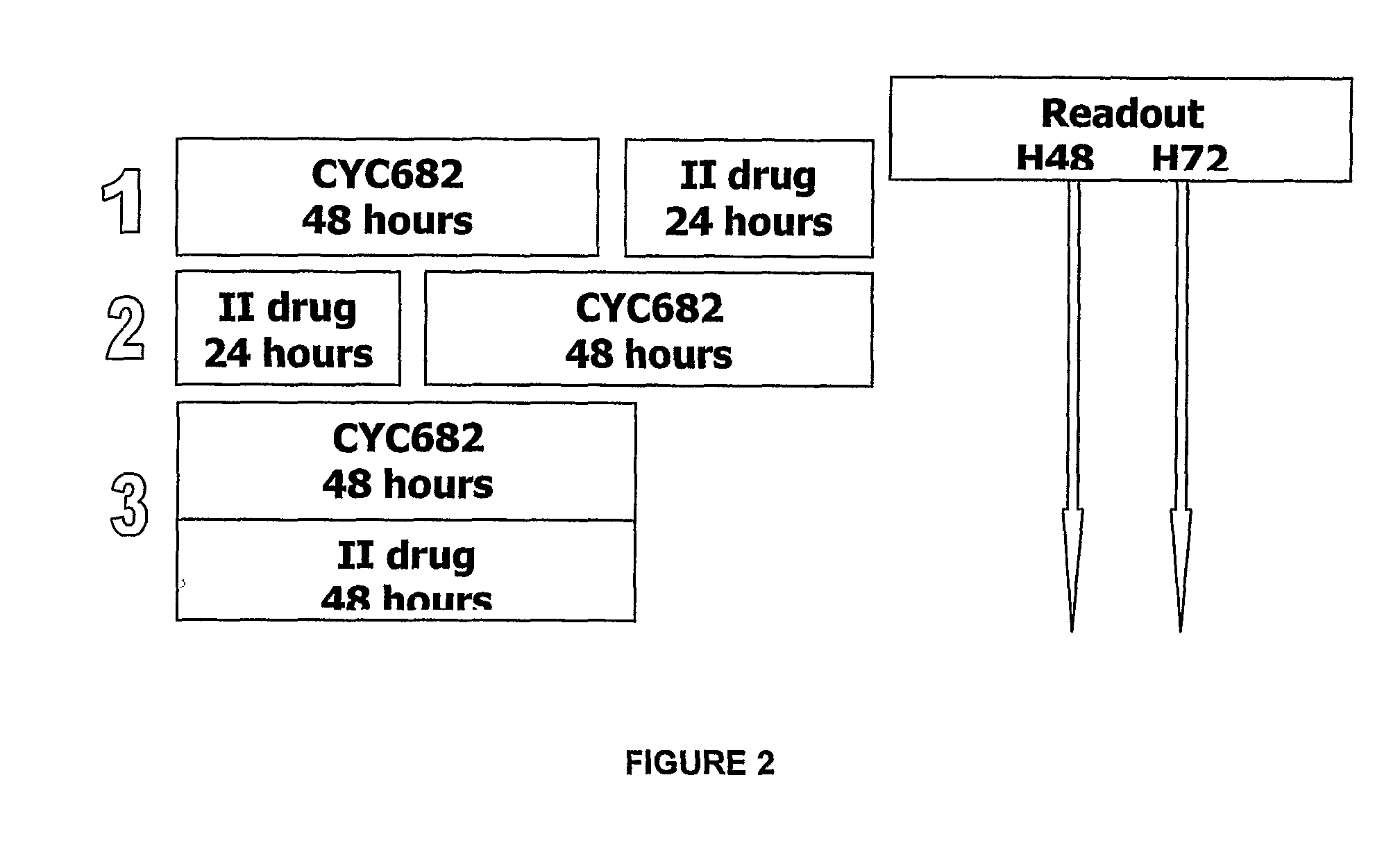
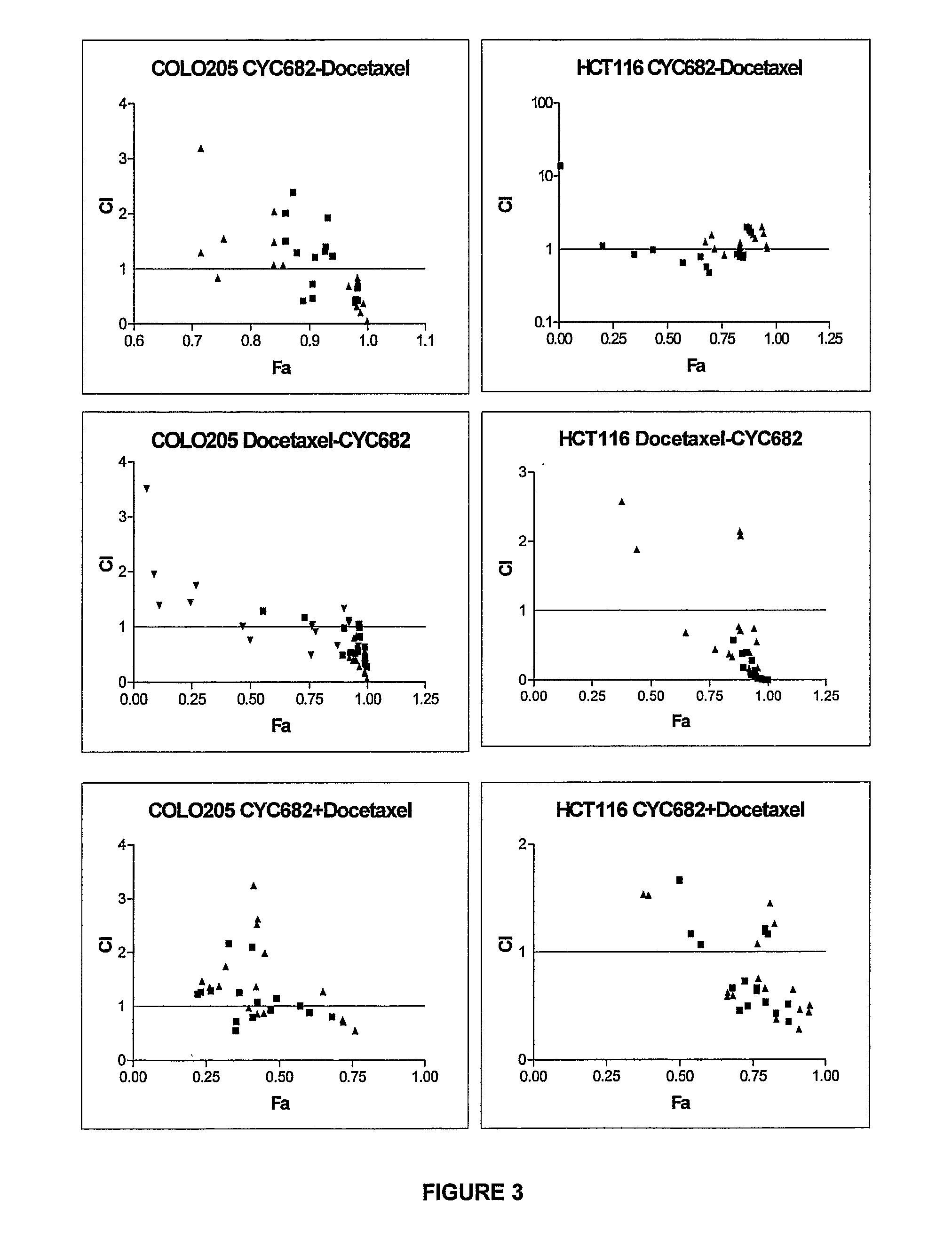
Antiproliferative combination comprising cyc-682 and a cytotoxic agent
A first aspect of the invention relates to a combination comprising 2′-cyano-2′-deoxy-N4-palmitoyl-1-beta-D-arabi-nofuranosyl-cytosine, or a metabolite thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and a cytotoxic agent selected from (a) a vinca alkaloid; (b) a taxane; (c) a cytosine analogue; (d) an anthracycline; and (e) a platinum antineoplastic agent. A second aspect of the invention relates to a pharmaceutical product comprising the above combination as a combined preparation for simultaneous, sequential or separate use in therapy. A third aspect of the invention relates to a method for treating a proliferative disorder, said method comprising simultaneously, sequentially or separately administering the above combination.
Owner:CYCLACEL
High temperature-resistant acid arabinfuranosidease AbfaHLB and gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105779420AIncrease enzyme activityImprove stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesHydrogenBacillus badius
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to a high temperature-resistant acid arabinfuranosidease AbfaHLB and a gene and an application thereof. The arabinfuranosidease AbfaHLB comes from bacillus badius HLB, an amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1, and an encoding gene abfa HLB for encoding the arabinfuranosidease AbfaHLB is provided. The arabinfuranosidease has the advantages that the following properties are realized, the suitable pH (potential of hydrogen) value is 4.5, the suitable temperature is 50 DEG C, and the thermal stability at the temperature of 80 DEG C is good; the arabinfuranosidease is used as a new enzyme preparation, and can be widely applied to feeds, foods, energy source industry and the like.
Owner:北京科为博生物科技有限公司
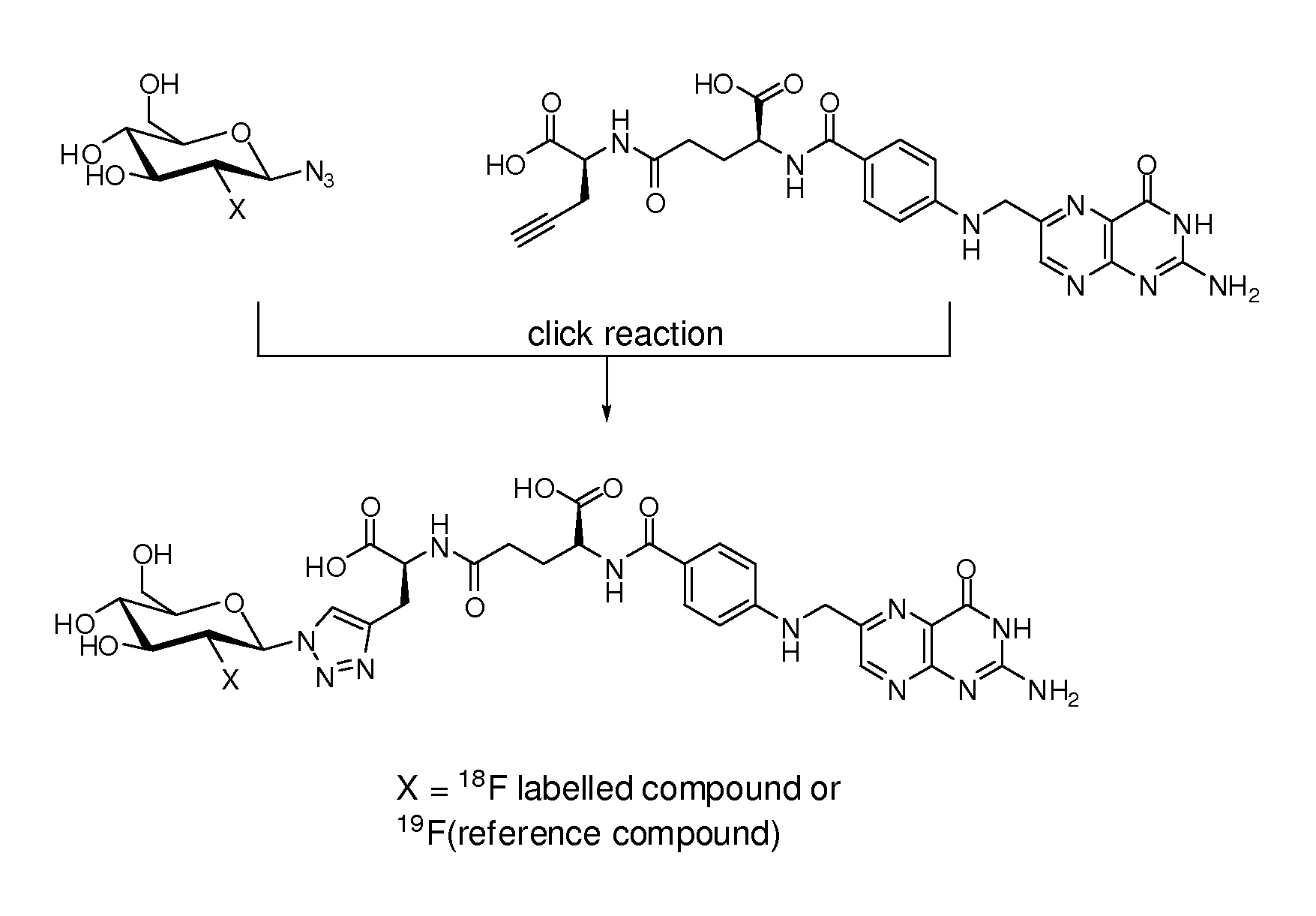
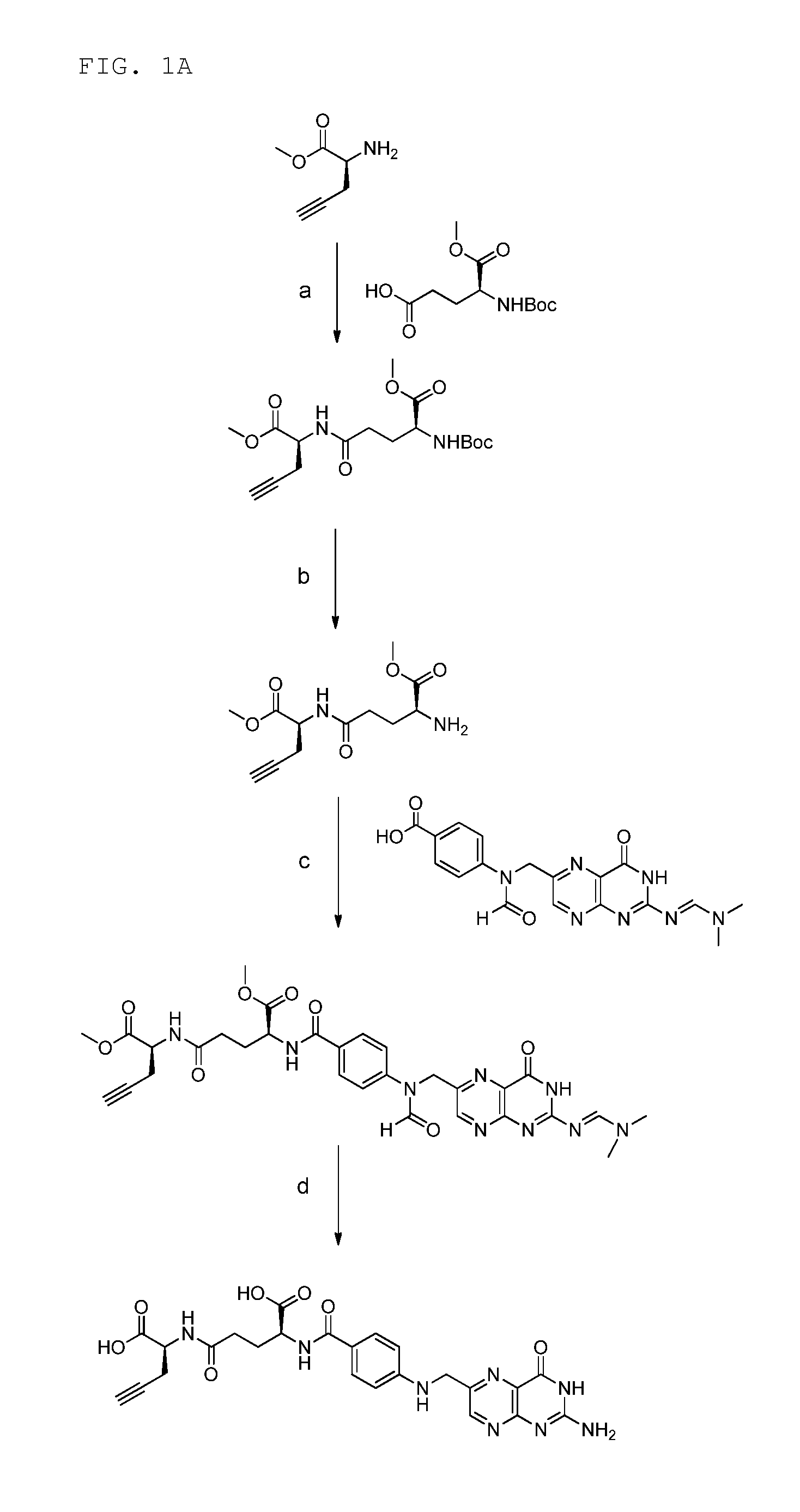
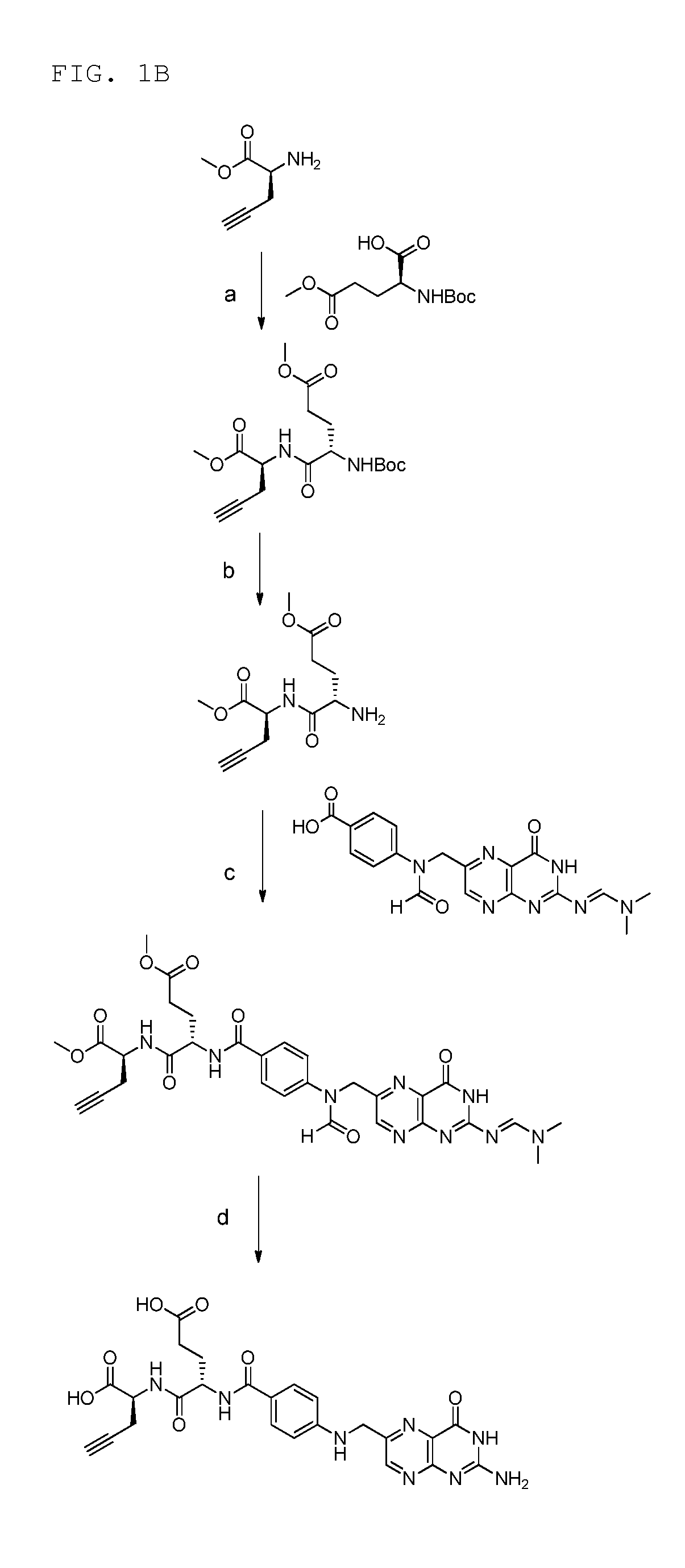
18f-saccharide-folates
ActiveUS20140193337A1Easy to manageIsotope introduction to sugar derivativesSugar derivativesDrugFolic acid
The present invention is directed towards new 18F-folate radiopharmaceuticals, wherein the 18F isotope is linked via a prosthetic group, more specifically via a prosthetic group having a saccharide group, such as a cyclic mono- or oligosaccharide, preferably based on a pyranoside or furanoside, which is covalently linked to the glutamate portion of a folate or derivative thereof, a method of their preparation, as well as their use in diagnosis and monitoring of cancer and inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and therapy thereof.
Owner:MERCK & CIE KG
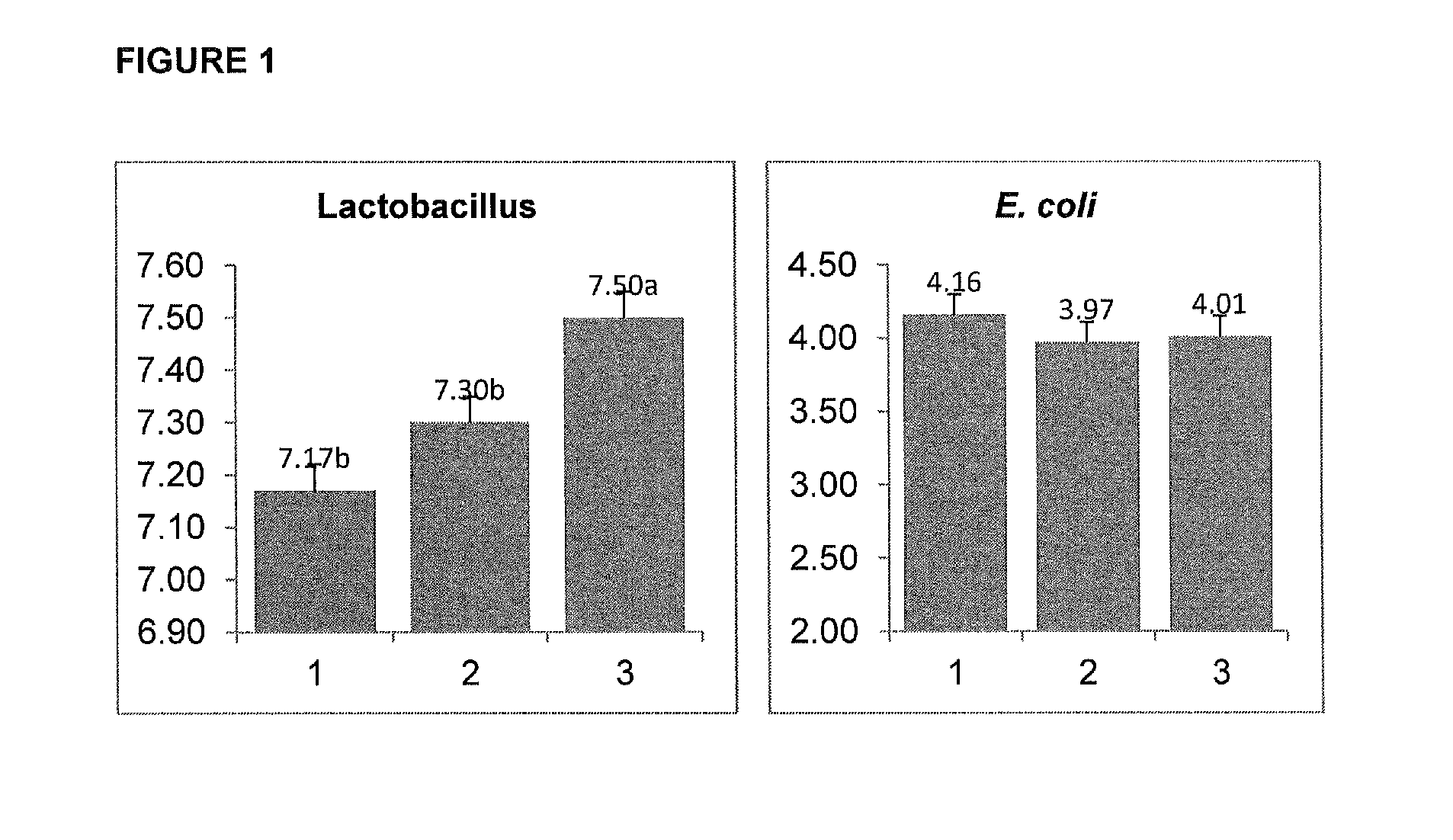
Feed additive composition
InactiveUS20190117706A1Improve feed conversionPromote endogenous populationPeptide/protein ingredientsLactobacillusPectinasePentagalacturonic acid
A feed additive composition comprising a direct fed microbial (DFM), in combination with a xylanase (e.g. endo-1,4-β-d-xylanase) and a β-glucanase (and optionally a further fibre degrading enzyme), wherein the DFM is selected from the group consisting of an enzyme producing strain; a C5 sugar-fermenting strain; a short-chain fatty acid-producing strain; a fibrolytic, endogenous microflora-promoting strain; or combinations thereof. The DFM may be selected from the group consisting of: Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS3BP5, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS442, B. subtilis AGTP BS521, B. subtilis AGTP BS918, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS1013, B. subtilis AGTP BS1069, B. subtilis AGTP 944, B. pumilus AGTP BS 1068 or B. pumilus KX11-1, Enterococcus faecium ID7, Propionibacterium acidipropionici P169, Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM-I-3698, Lactobacillus farciminis CNCM-I-3699, a strain having all the characteristics thereof, any derivative or variant thereof, and combinations thereof and the further fibre degrading enzyme may be selected from the group consisting of a cellobiohydrolase (E.C. 3.2.1.176 and E.C. 3.2.1.91), a β-glucosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.21), a β-xylosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.37), a feruloyl esterase (E.C. 3.1.1.73), an α-arabinofuranosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.55), a pectinase (e.g. an endopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.15), an exopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.67) or a pectate lyase (E.C. 4.2.2.2)), or combinations thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
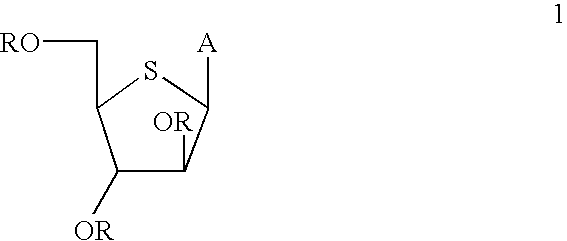
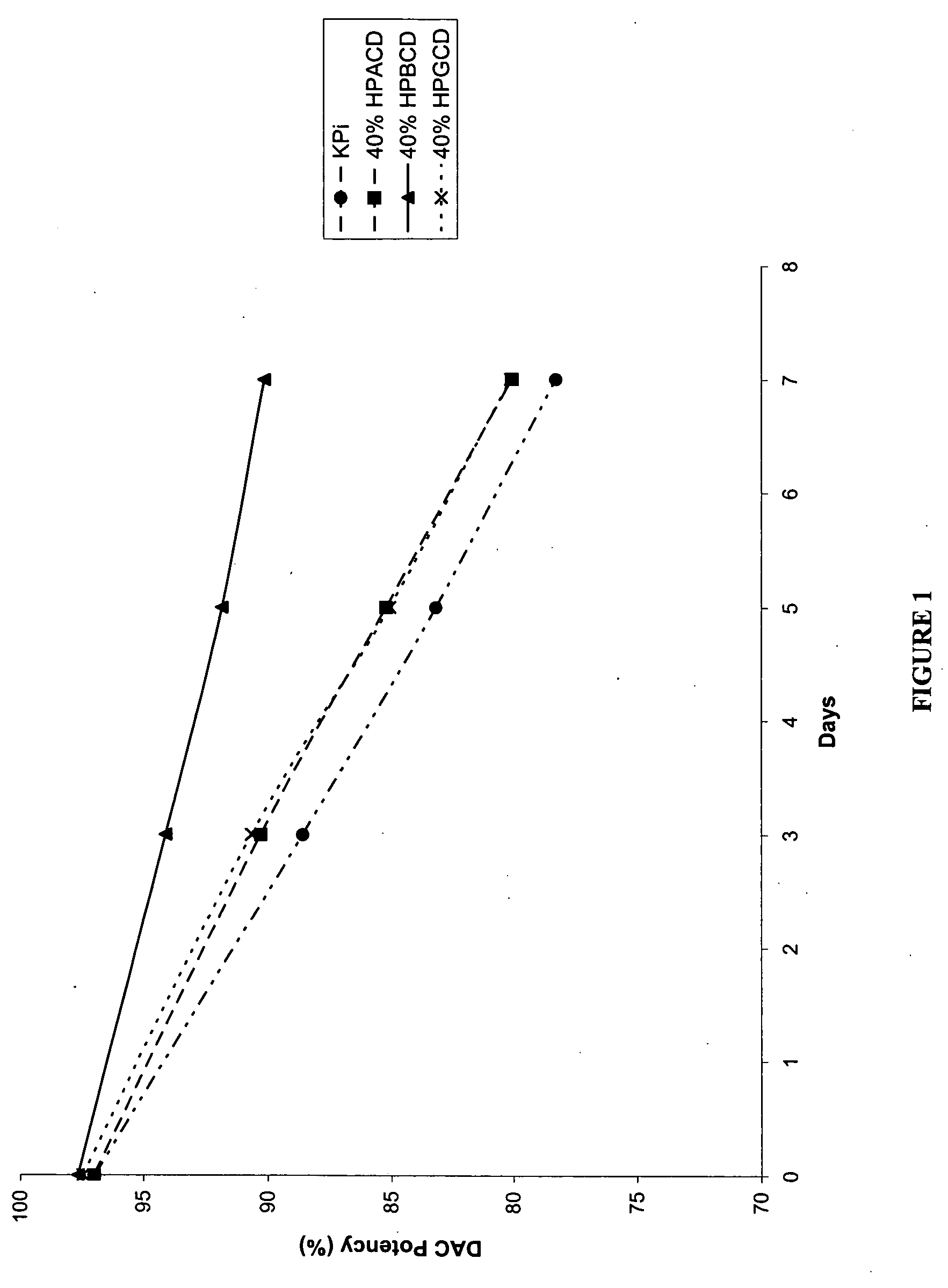
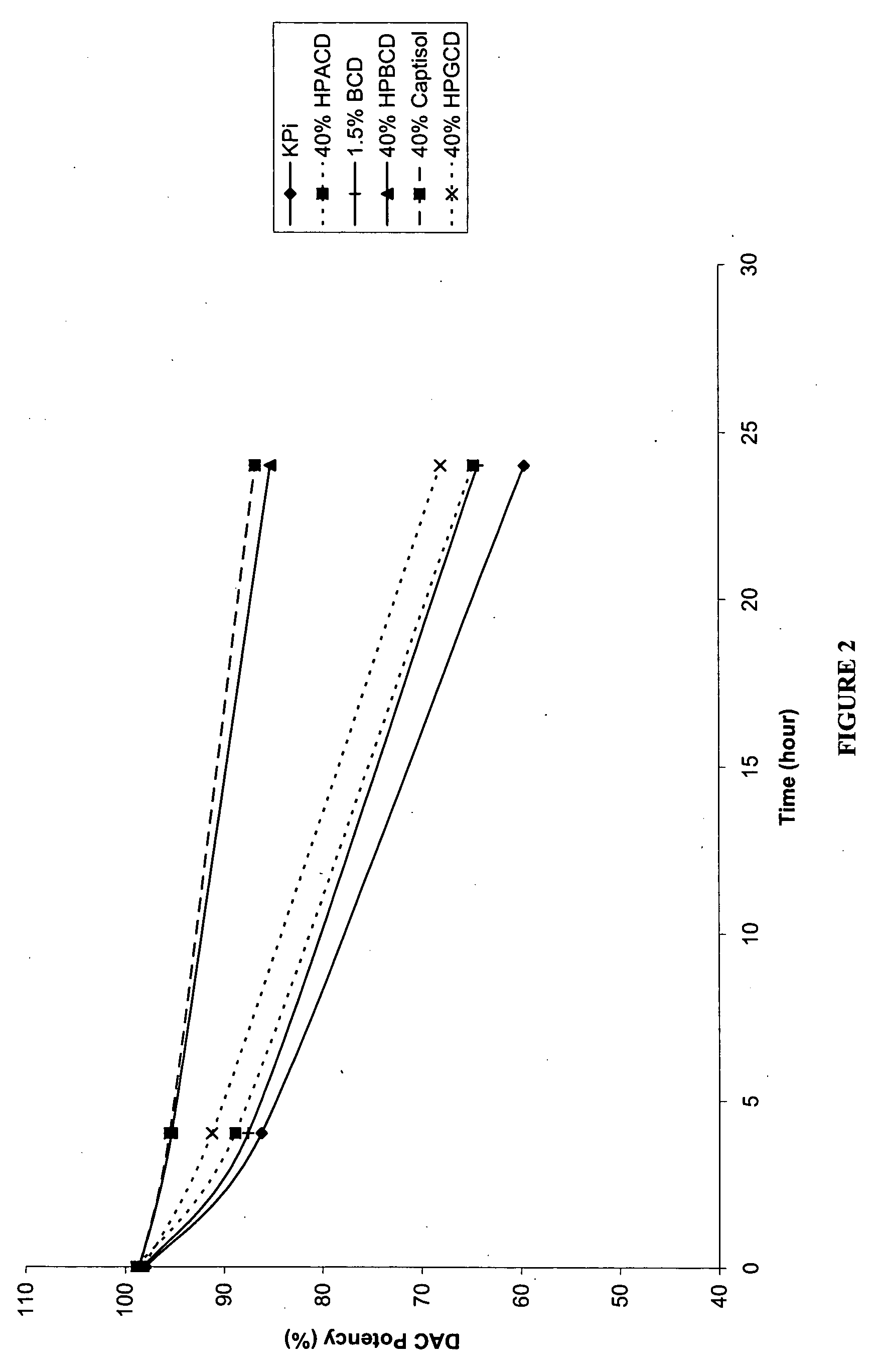
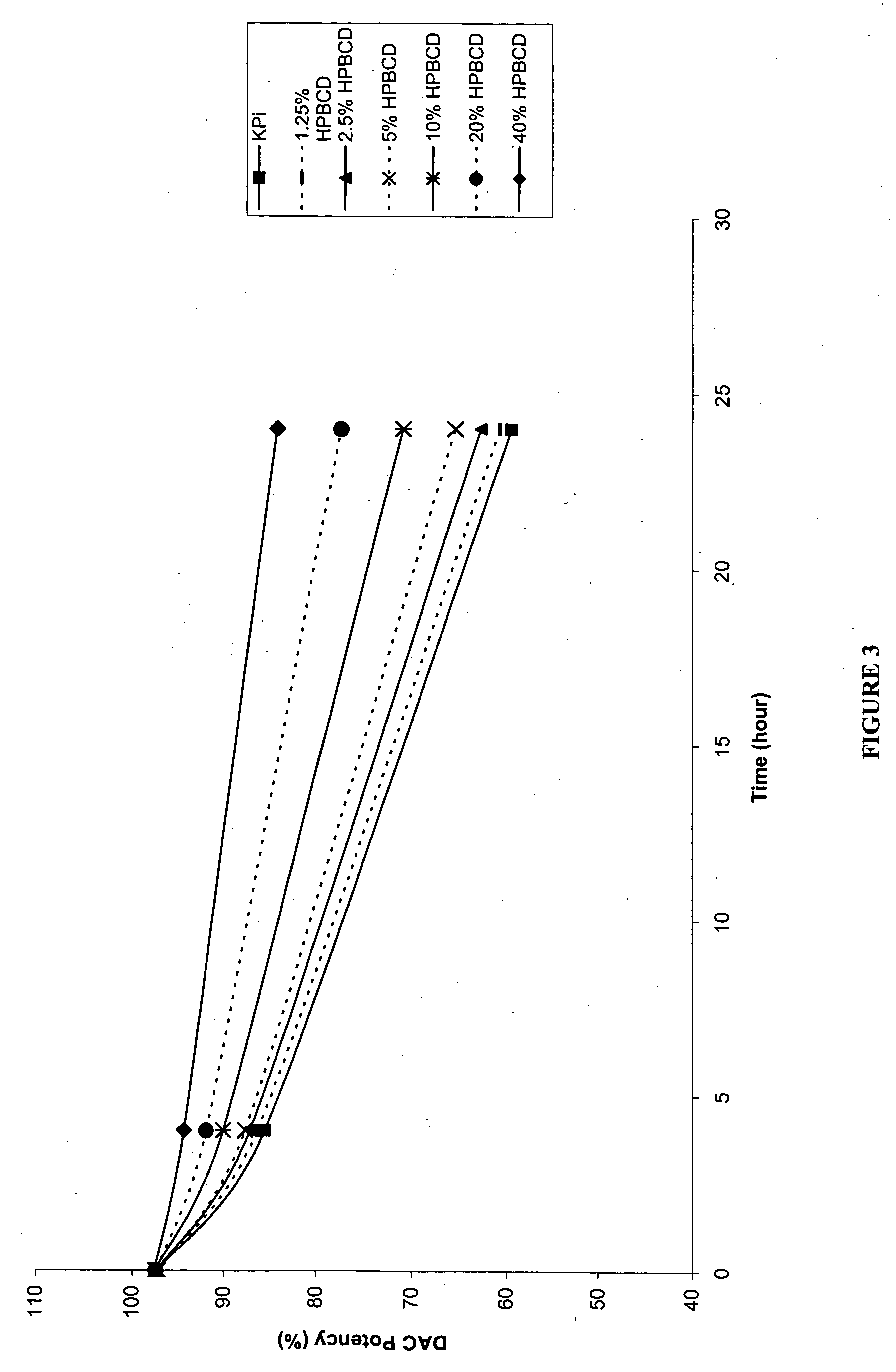
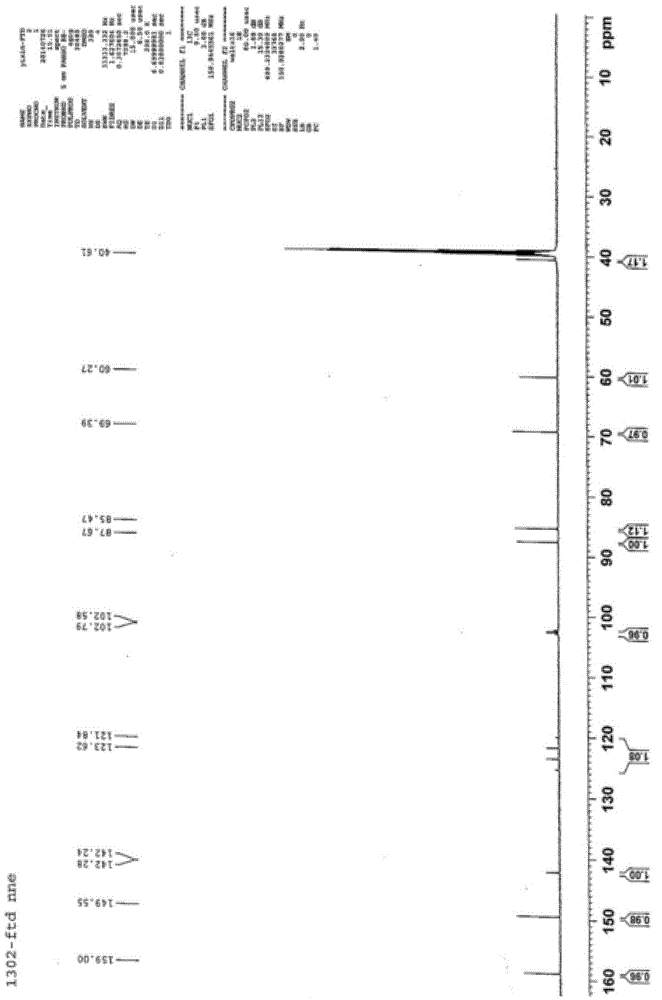
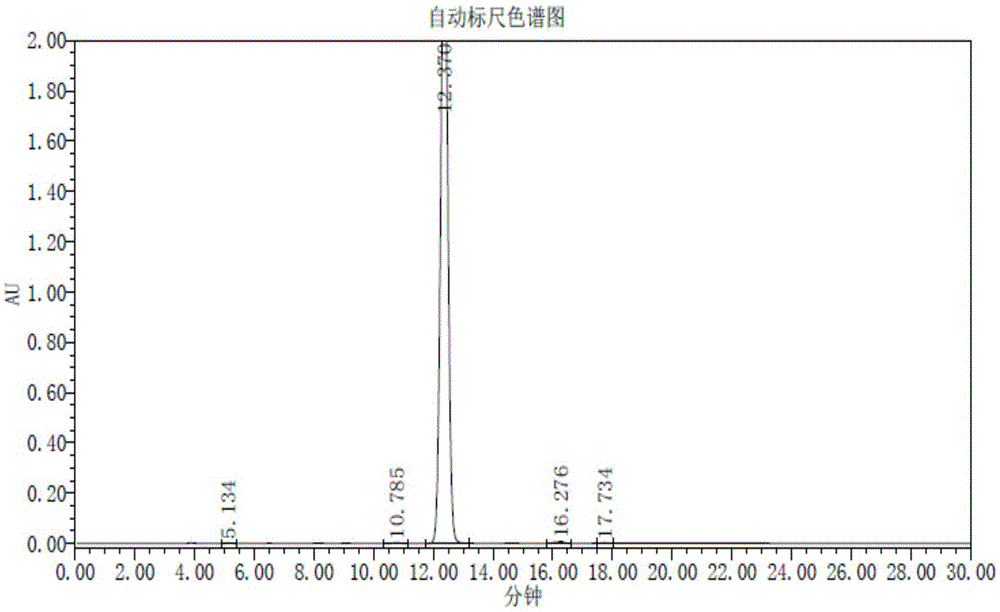
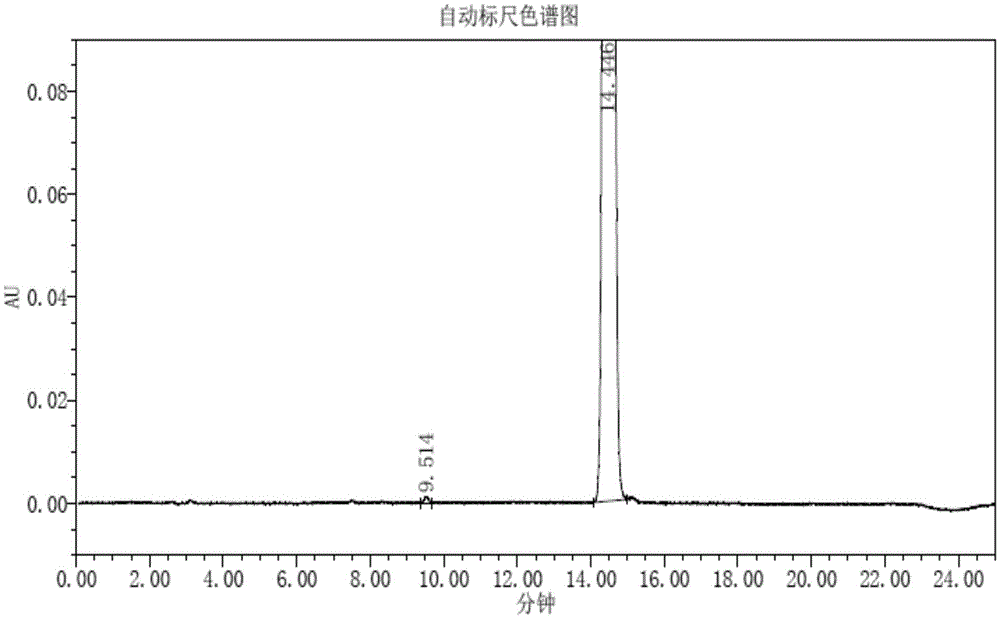
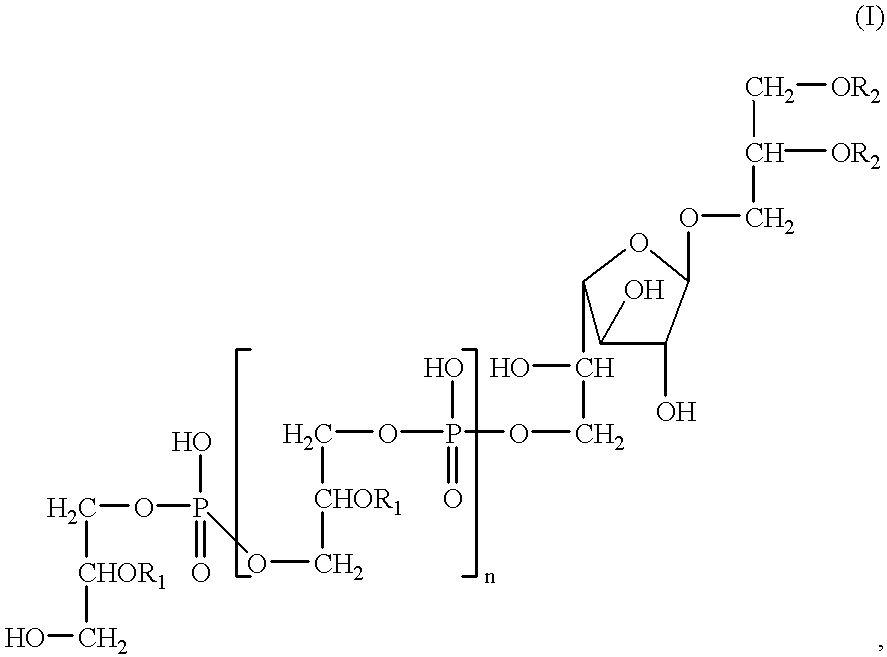
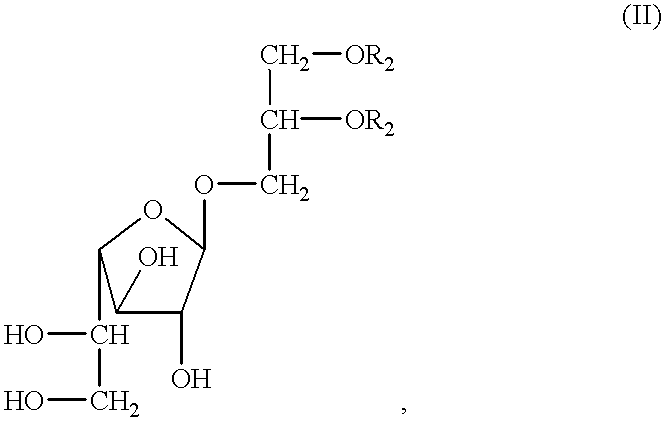
P-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and methods for preparation
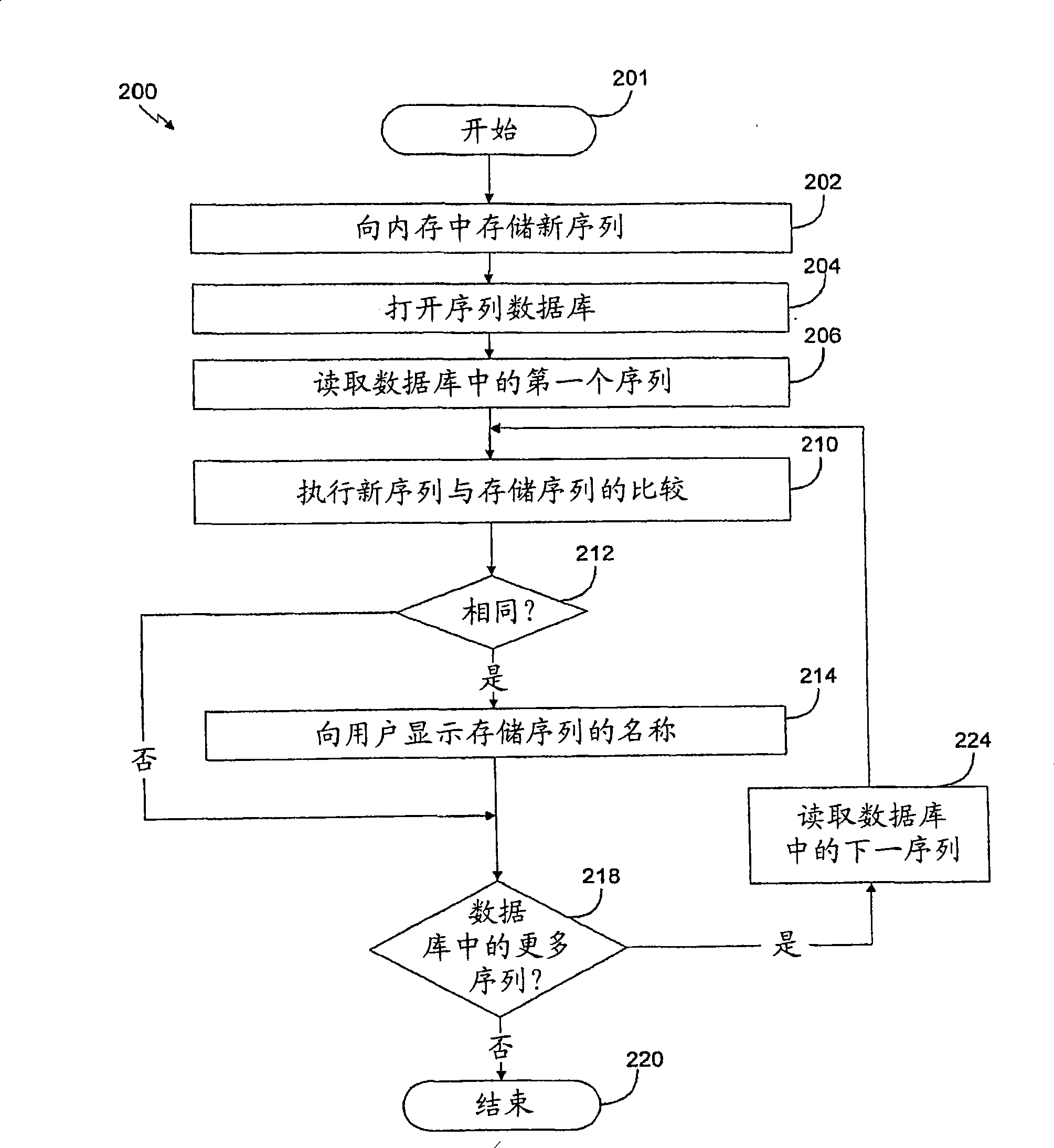
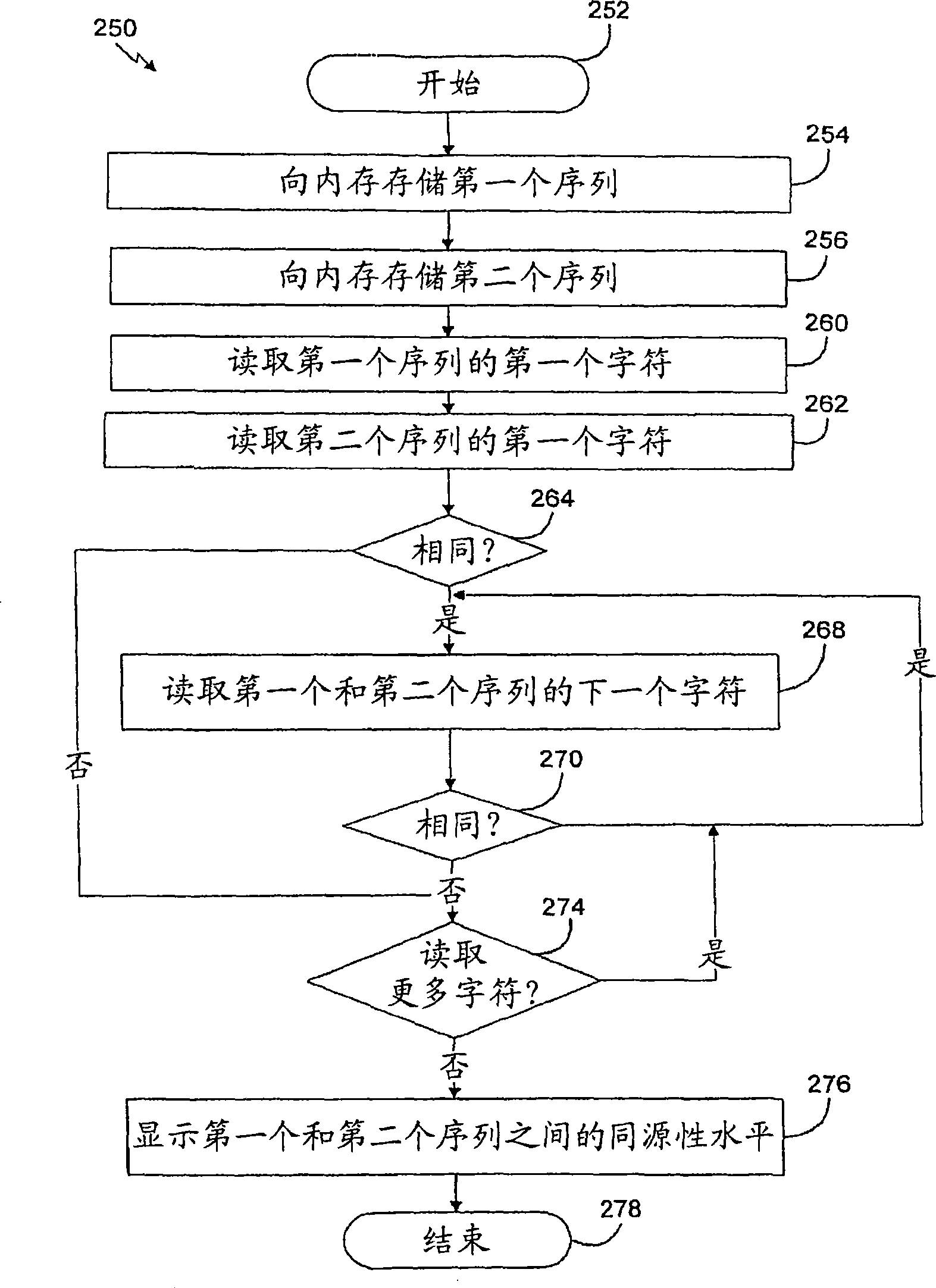
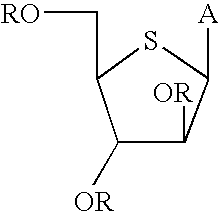
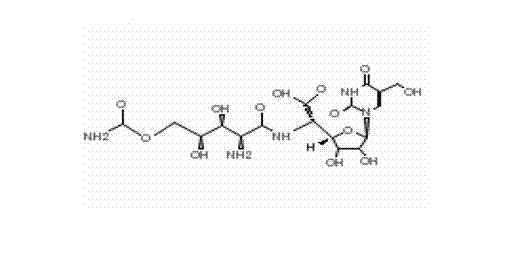
The present disclosure relates to p-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2-one and to its use in treating conditions such as viral infections, tumors, and cancer.Also disclosed is a method of preparing the p-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2-one and methods for producing furanose compounds which are useful intermediates in the preparation of pharmaceutical compounds such as p-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2-one and the like.
Owner:ANDADYS PHARMA INC
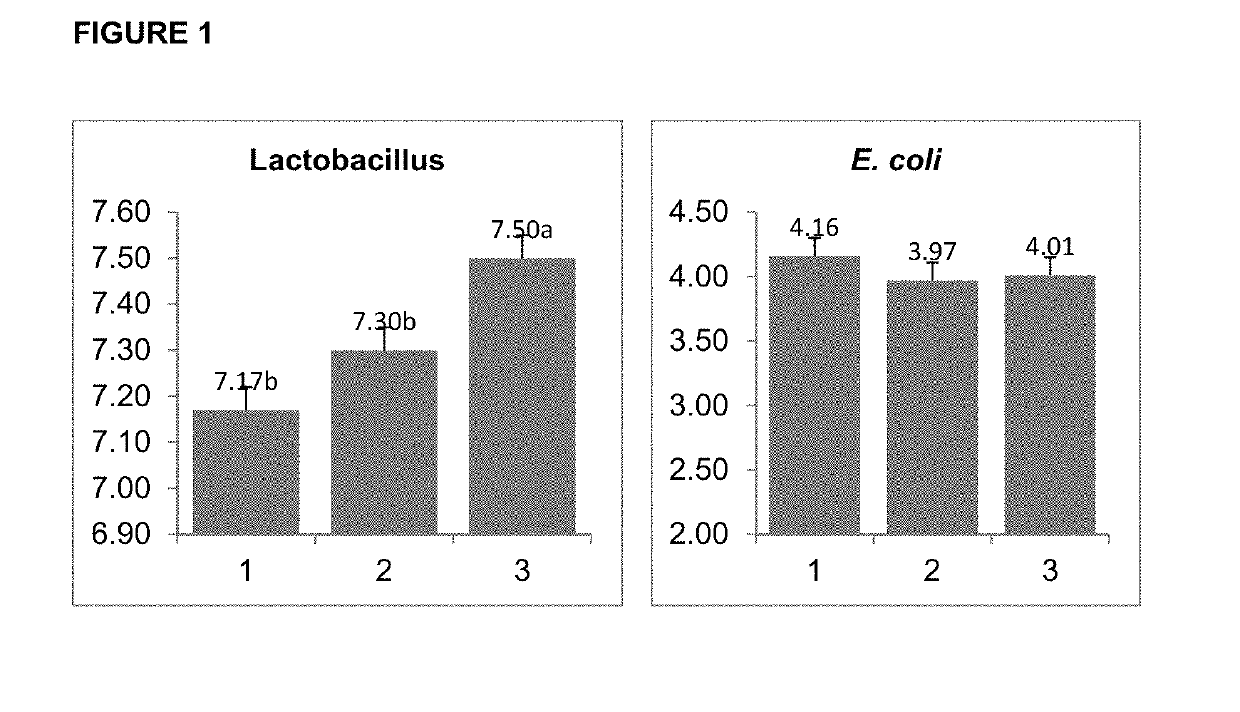
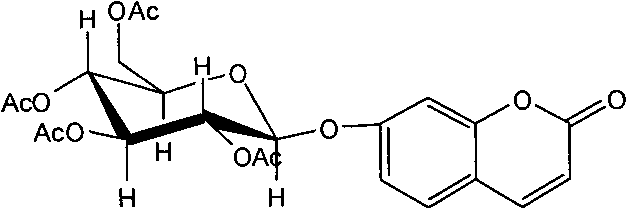
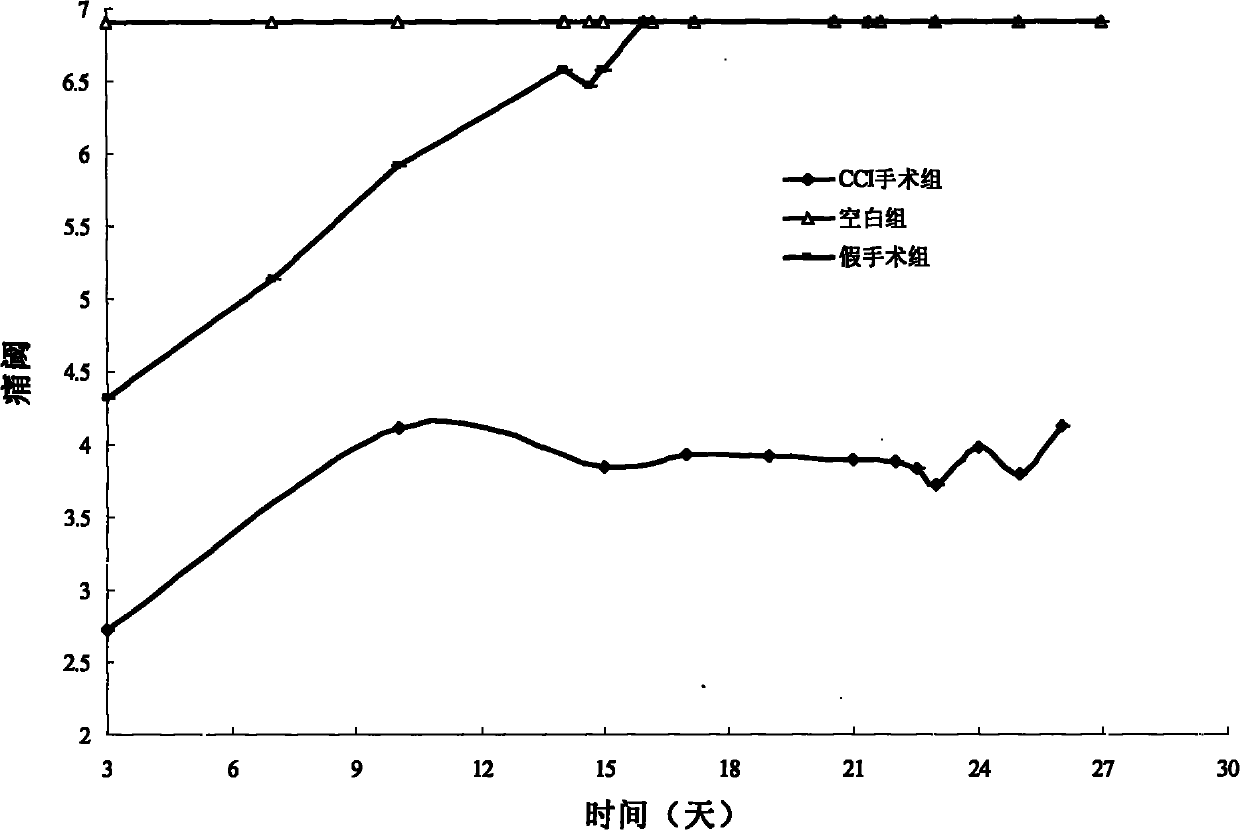
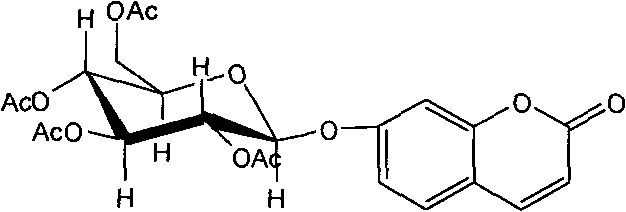
Application of 7-O-beta-D-acetylation sugar-coumarin compounds in treating chronic neuropathic pains
The invention relates to application of 7-O-beta-D-acetylation sugar-coumarin compounds in treating chronic neuropathic pains. The 7-O-beta-D-acetylation sugar-coumarin compounds comprise a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or a solvate thereof, and the application relates to the application of the salt, the ester or the solvate in preparing medicaments for treating the chronic neuropathic pains, wherein a glycosyl part is arbitrary pyranose or furanose, the hydroxy of which is totally acetylated; a representative compound is 7-O-beta-D-acetylation glucose-coumarin; and the structural formula is disclosed in the specification. On a classical sciatic nerve chronic compression injury (CCI) model, through single intragastric administration and continuous intragastric administration for 7 days, the compound shows definite treatment effect of resisting nervous pains. At a dose point appointed by an experiment, the compound can obviously improve the mechanical stimulus pain threshold, the nervous pain resistant efficacy is equivalent to that of Gabapentin which is a contrast medicament, and the duration is superior to that of the Gabapentin. Proved by research results, the compound can be used for treating the chronic neuropathic pains.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt of 5-Amino-3-(2'-O-Acetyl-3'-Deoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)-3H-Thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and Methods for Preparation
The present disclosure relates to p-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2-one and to its use in treating conditions such as viral infections, tumors, and cancer.Also disclosed is a method of preparing the p-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2-one and methods for producing furanose compounds which are useful intermediates in the preparation of pharmaceutical compounds such as p-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidin-2-one and the like.
Owner:ANDADYS PHARMA INC
Optical compensation film, and polarizing plate and liquid crystal display employing the same
InactiveUS20100221457A1Improve visibilityReduce contrastLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic detergent compounding agentsCellulosePyranose
The present invention provides an optical compensation film, which has excellent visibility such as light leakage, uneven color tone and front contrast, and can simultaneously realize retardation and wavelength dispersion. The optical compensation film is characterized by containing a cellulose ester, the following polymer (a), and the following compound (b). (a) A polymer produced by copolymerizing an ethylenically unsaturated monomer having in its molecule a partial structure represented by Formula (1) with at least one ethylenically unsaturated monomer. (b) An esterified compound produced by esterifying all or a part of OH groups in a compound (A) having one furanose structure or one pyranose structure, or an esterified compound produced by esterifying all of or a part of OH groups in a compound (B) containing nor less than 2 and not more than 12 structures of at least one of a furanose structure or a pyranose structure.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
4-amino-acid-substituted pyrimidine nucleoside compound and medicinal application thereof
ActiveCN109265504AThe preparation method is feasibleSugar derivativesAntiviralsFuranViral Myocarditis
The invention discloses a 4-amino-acid-substituted pyrimidine nucleoside compound and a synthesis method and medicinal application thereof and belongs to the field of medicinal chemistry. The compoundhas a structure shown as a formula (I) which is described in the description, wherein in the formula (I), R1 refers to H, CH3, CH2CH3, K and Na, R2 refers to H, CH3, CH2CH3, K and Na, and when R1 andR2 do not represent CH3 at the same time, L-glutamic acid dimethyl ester in 4-(L-glutamic acid dimethyl ester)-1-(2'-deoxidized-2'-beta-fluoro-4'-alpha-nitrine-beta-D-furan glycosyl)cytosine is modified, so that a series of 4-amino-acid-substituted pyrimidine nucleoside derivatives are synthesized, and these compounds have the activity of resisting Coxsackie virus 3. A preparation method is feasible, and the 4-amino-acid-substituted pyrimidine nucleoside compound is applied to drugs for treating viral myocarditis and has a great application prospect.
Owner:HIGH & NEW TECH RES CENT OF HENAN ACAD OF SCI
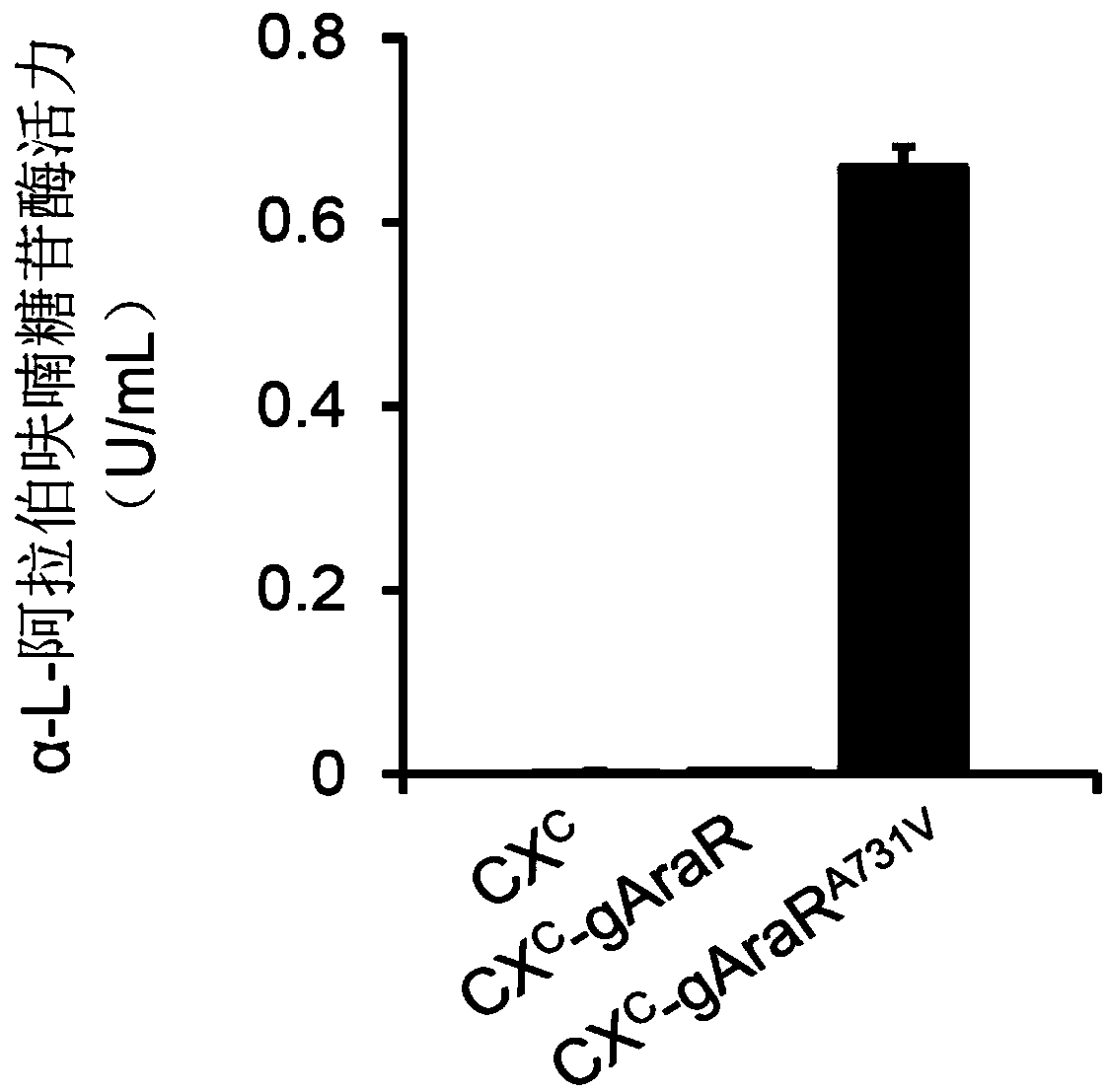
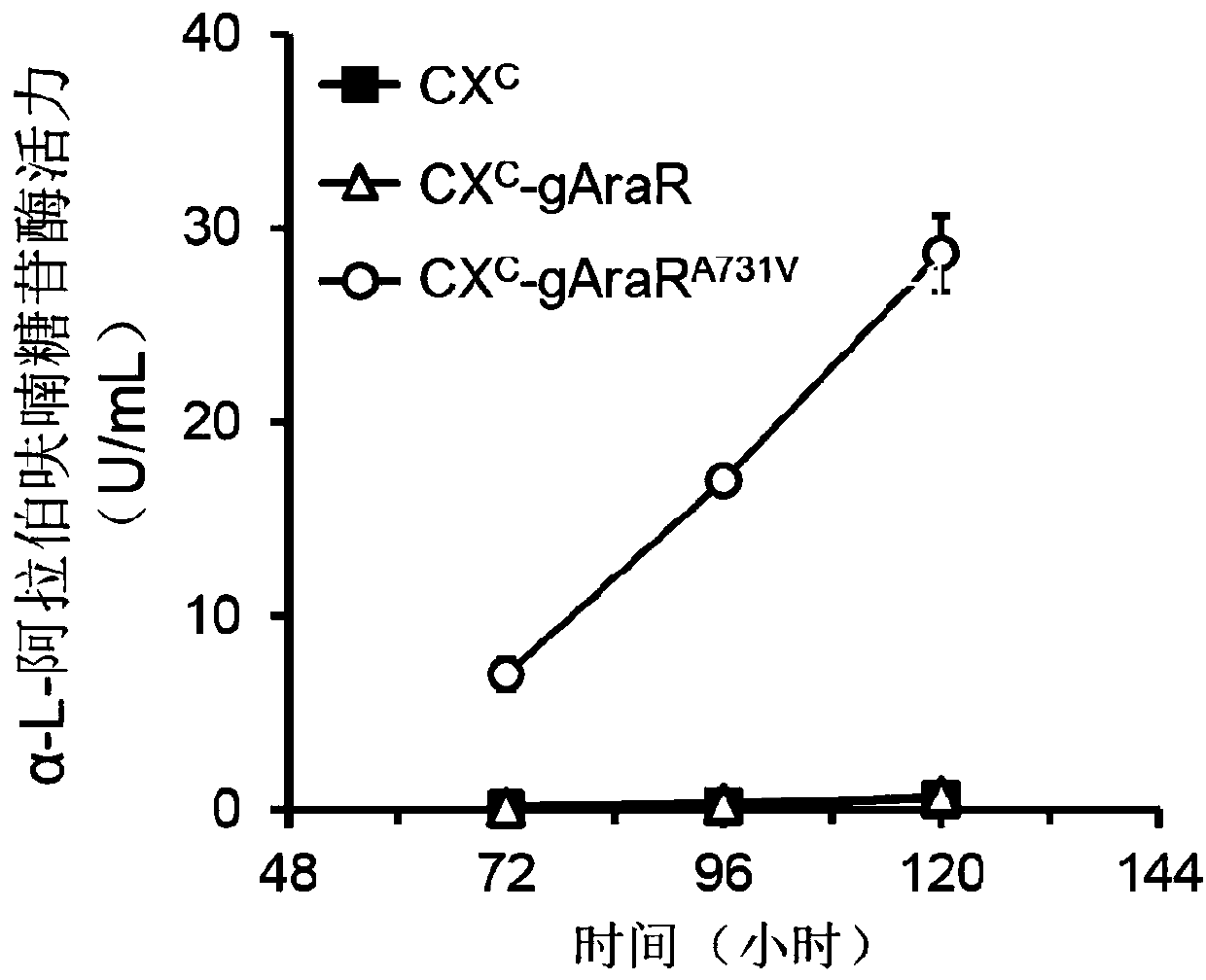
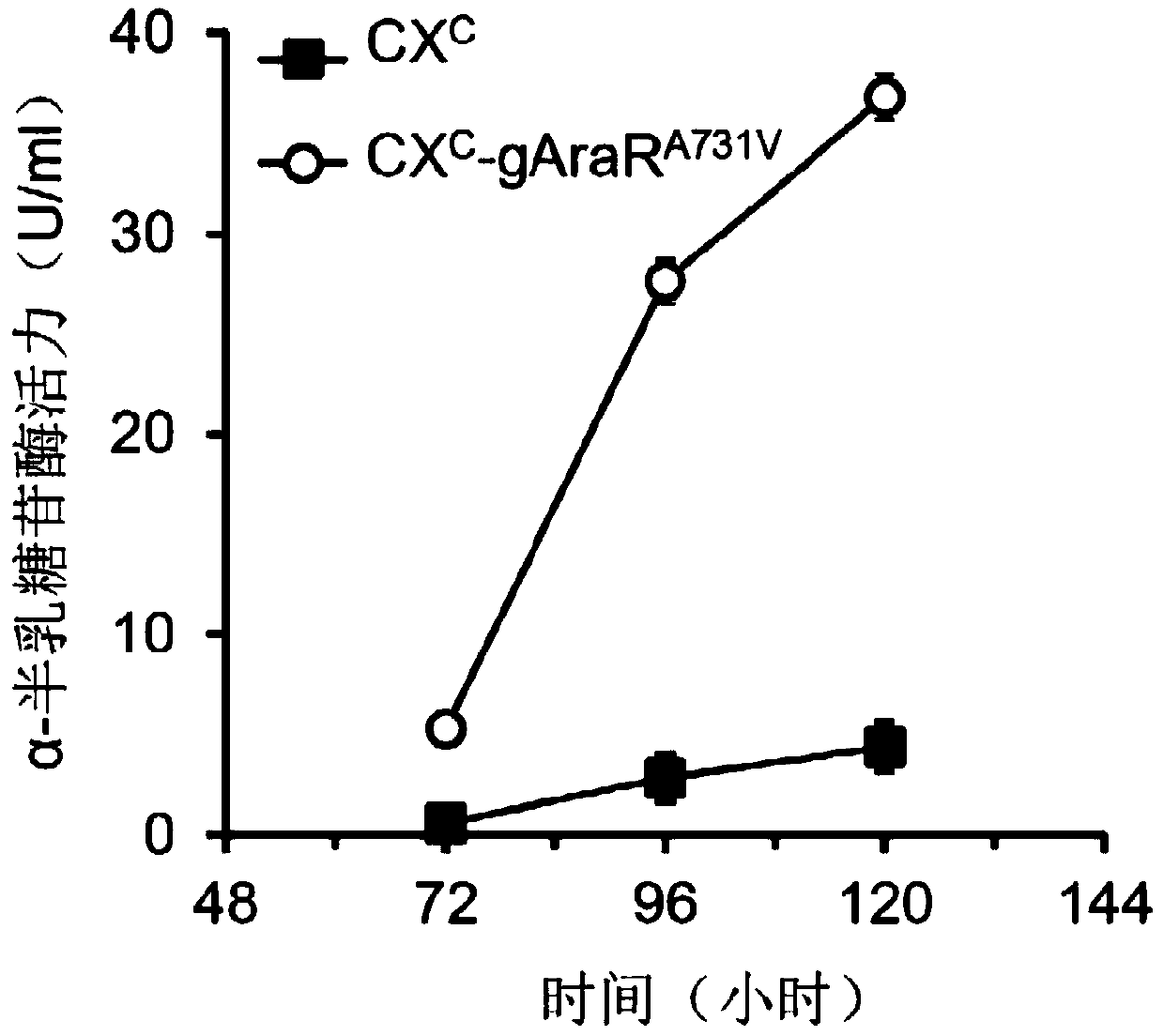
Regulatory protein AraR mutant synthesized by fungus alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and application thereof
The invention discloses a regulatory protein AraR mutant synthesized by fungus alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase. The mutant is obtained by mutating regulatory protein 731st alanine with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 into valine, the amino acid sequence of the mutant is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the nucleotide sequence of the coding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The invention alsodiscloses an application of the regulatory protein mutant in the production of alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and alpha-galactosidase. Experiments confirm that the yield of alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase and alpha-galactosidase can be greatly enhanced by expressing the regulatory protein mutant in a fungal strain.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Cellulolytic enzymes, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, a endoglucanase, a cellobiohydrolase, a beta-glucosidase, a xylanase, a mannanse, a ss-xylosidase, an arabinofiiranosidase, and / or an oligomerase activity, polynucleotides encoding these polypeptides, and methods of making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention is directed to polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, e.g., endoglucanase, cellobiohydrolase, beta-glucosidase, xylanase, mannanse, ss-xylosidase, arabinofuranosidase, and / or oligomerase activity, including thermostable and thermotolerant activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, and making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention provides polypeptides having an oligomerase activity, e.g., enzymes that convert recalcitrant soluble oligomers to fermentable sugars in the saccharification of biomass. The polypeptides of the invention can be used in a variety of pharmaceutical, agricultural, food and feed processing and industrial contexts. The invention also provides compositions or products of manufacture comprising mixtures of enzymes comprising at least one enzyme of this invention.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Preparation of thioarabinofuranosyl compounds and use thereof
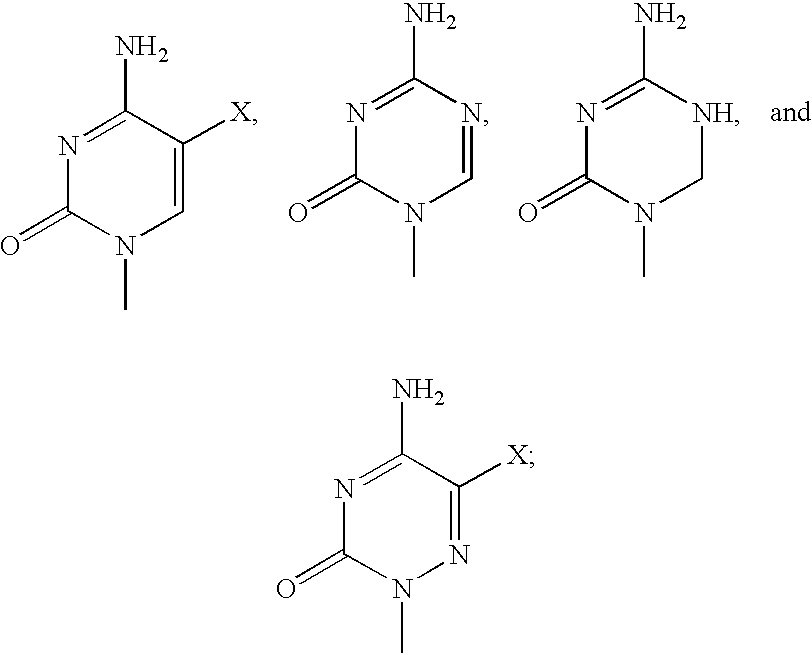
Patients suffering from cancer are treated by being administered a compound represented by the following formula: wherein each R individually is H or an aliphatic or aromatic acyl group; A is selected from the group consisting of wherein X is selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, fluorine, alkoxy, alkyl, haloalkyl, alkenyl, haloalkenyl, alkynyl, amino, monoalkylamino, dialkylamino, cyano and nitro. The above compounds also inhibit DNA replication in mammalian cells.
Owner:SOUTHERN RES INST & IP
Cellulolytic enzymes, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, a endoglucanase, a cellobiohydrolase, a beta-glucosidase, a xylanase, a mannanse, a beta-xylosidase, an arabinofiiranosidase, and / or an oligomerase activity, polynucleotides encoding these polypeptides, and methods of making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention is directed to polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, e.g., endoglucanase, cellobiohydrolase, beta-glucosidase, xylanase, mannanse, beta-xylosidase, arabinofuranosidase, and / or oligomerase activity, including thermostable and thermotolerant activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, and making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention provides polypeptides having an oligomerase activity, e.g., enzymes that convert recalcitrant soluble oligomers to fermentable sugars in the saccharification of biomass. The polypeptides of the invention can be used in a variety of pharmaceutical, agricultural, food and feed processing and industrial contexts. The invention also provides compositions or products of manufacture comprising mixtures of enzymes comprising at least one enzyme of this invention.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Encoding gene of glycoside hydrolase for rapid hydrolysizing xylan to generate single xylose, and application of encoding gene
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to an encoding gene of glycoside hydrolase for rapid hydrolysizing xylan to generate single xylose, and application of the encoding gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The nucleic acid, which is provided by the invention and is shown in the SEQ ID NO. 2, can be expressed in a large amount in yeast, so that a large amount of the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 can be obtained; the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 has the activities of beta-xylosidase, endo-beta-xylanase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidease atthe same time; in addition, the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 can directly degrade birch xylan so as to produce a single product xylose; compared with commercial combination of endo-beta xylanase and beta-xylosidase, the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 is higher in xylose yield and has a higher commercial application value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
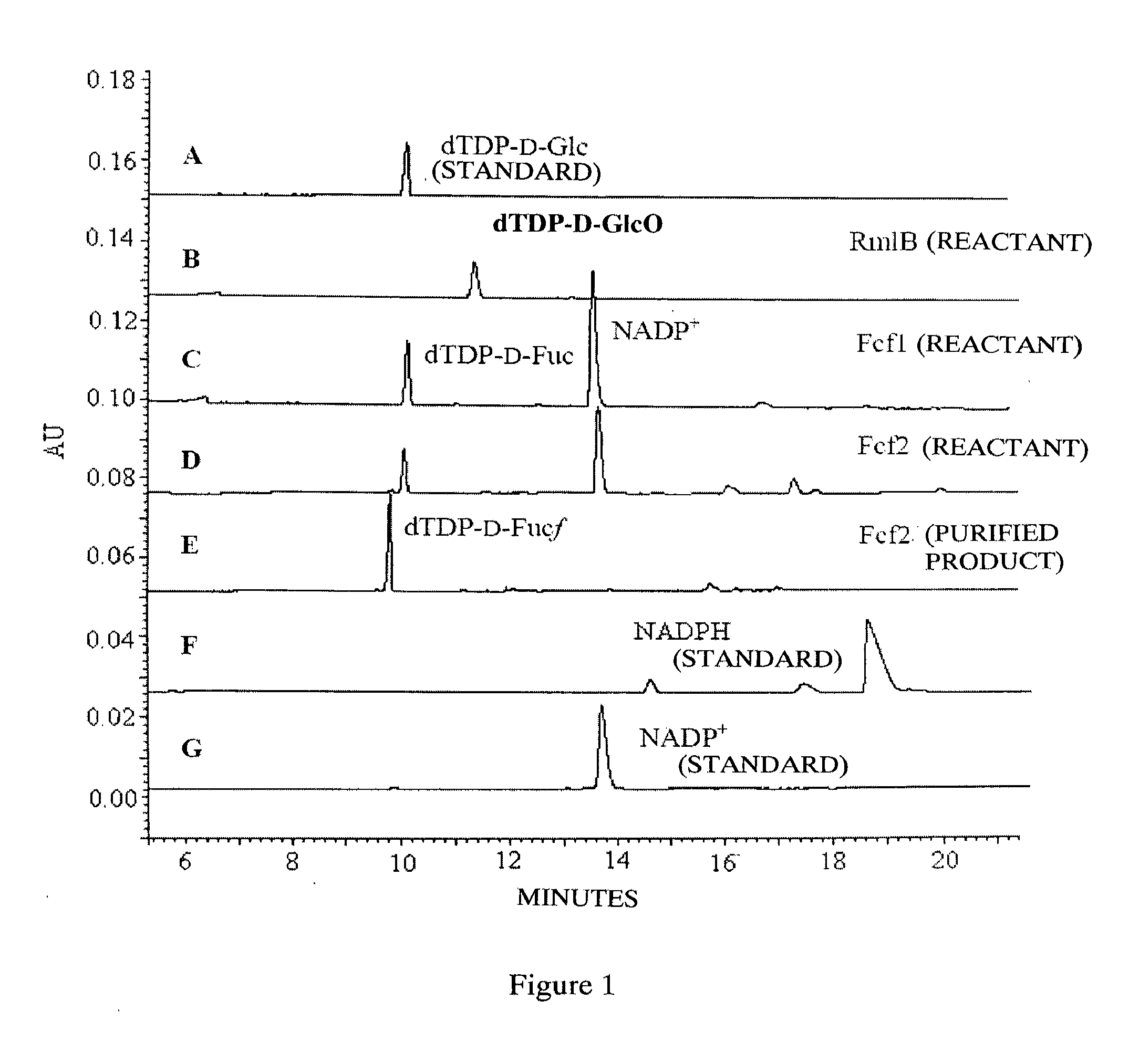
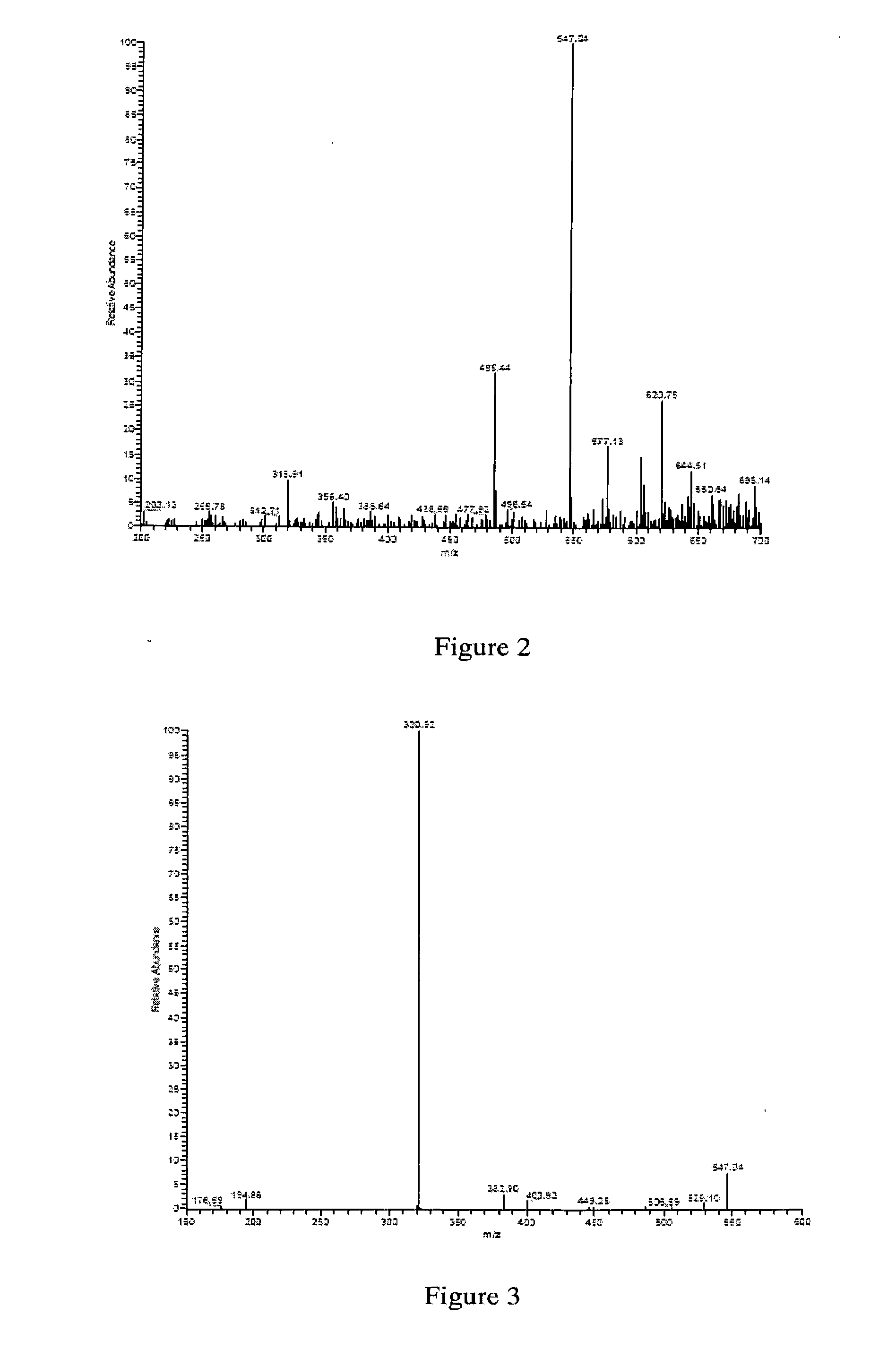
dTDP-BETA-D-FUCOFURANOSE, ITS PREPARATION METHOD AND USE
Provided is a dTDP-β-D-fucofuranose, which is also referred to as dTDP-β-6-deoxy-D-galactofuranose. The dTDP-β-D-fucofuranose is synthesized by using reductase Fcf1 and mutase Fcf2 in the gram-negative bacteria. Also provided are the preparation method of the dTDP-β-D-fucofuranose and use of the dTDP-β-D-fucofuranose for manufacturing a medicament for the treatment of tumors.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![P-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and methods for preparation P-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and methods for preparation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5be63a5a-161b-4dcf-ac51-19497757a9c1/US07928085-20110419-D00001.png)
![P-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and methods for preparation P-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and methods for preparation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5be63a5a-161b-4dcf-ac51-19497757a9c1/US07928085-20110419-D00002.png)
![P-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and methods for preparation P-toluene sulfonic acid salt of 5-amino-3-(2′-O-acetyl-3′-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)-3H-thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and methods for preparation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5be63a5a-161b-4dcf-ac51-19497757a9c1/US07928085-20110419-C00001.png)
![P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt of 5-Amino-3-(2'-O-Acetyl-3'-Deoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)-3H-Thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and Methods for Preparation P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt of 5-Amino-3-(2'-O-Acetyl-3'-Deoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)-3H-Thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and Methods for Preparation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5fab57dc-a9a5-42c9-a792-edf49decf5cb/US20090197826A1-20090806-D00001.png)
![P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt of 5-Amino-3-(2'-O-Acetyl-3'-Deoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)-3H-Thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and Methods for Preparation P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt of 5-Amino-3-(2'-O-Acetyl-3'-Deoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)-3H-Thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and Methods for Preparation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5fab57dc-a9a5-42c9-a792-edf49decf5cb/US20090197826A1-20090806-D00002.png)
![P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt of 5-Amino-3-(2'-O-Acetyl-3'-Deoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)-3H-Thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and Methods for Preparation P-Toluene Sulfonic Acid Salt of 5-Amino-3-(2'-O-Acetyl-3'-Deoxy-Beta-D-Ribofuranosyl)-3H-Thiazole[4,5-d]pyrimidine-2-one and Methods for Preparation](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/5fab57dc-a9a5-42c9-a792-edf49decf5cb/US20090197826A1-20090806-C00001.png)