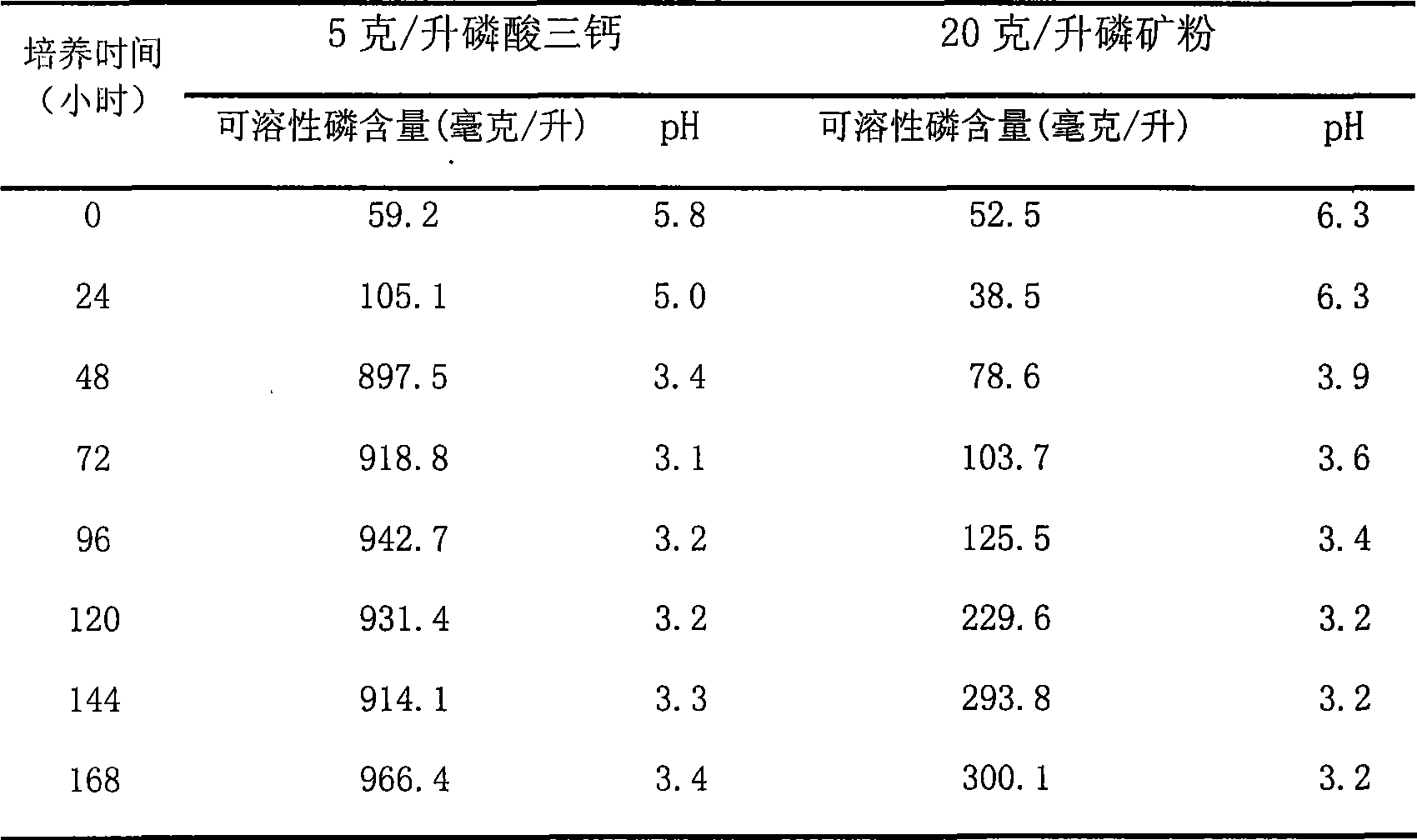
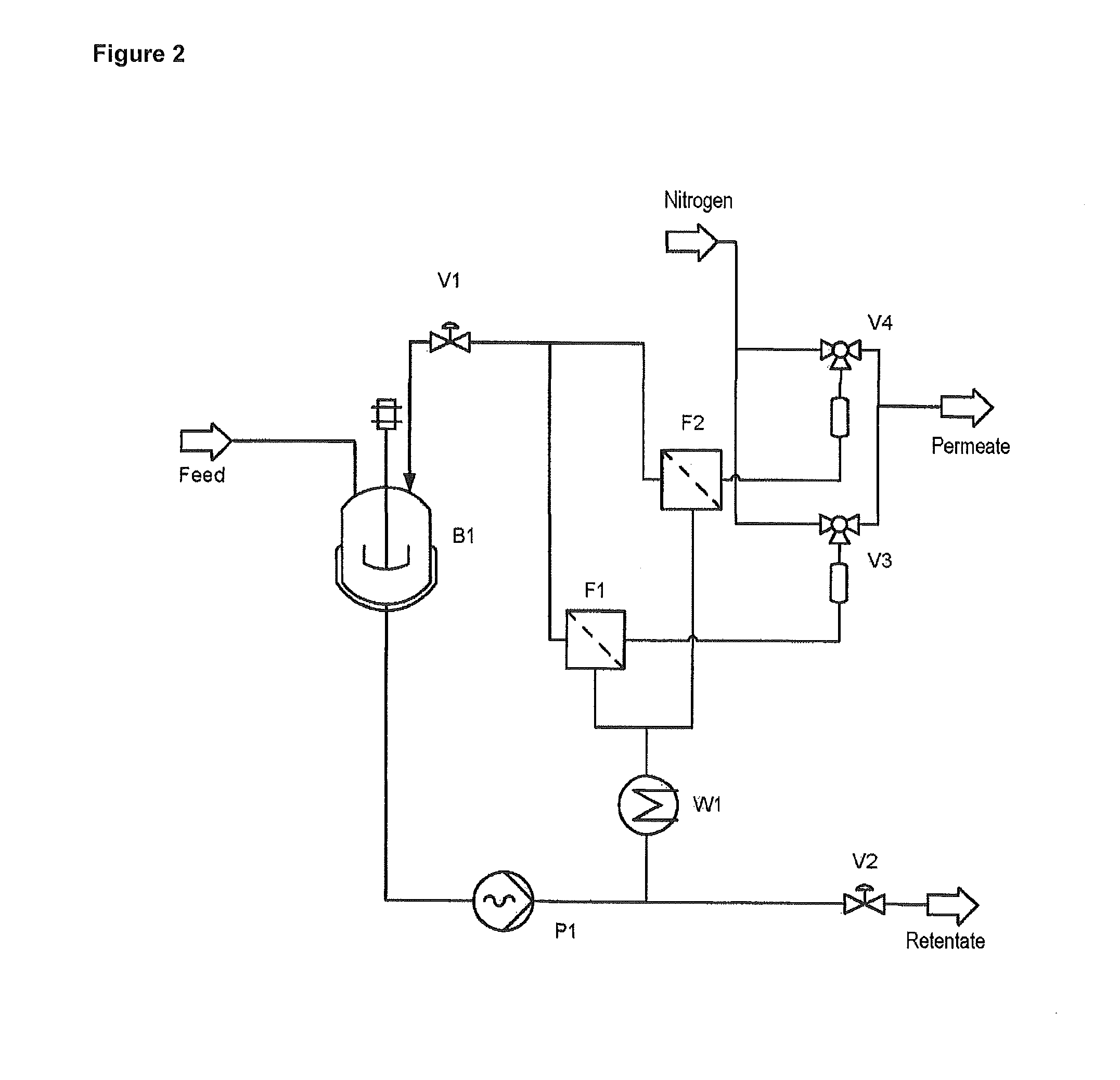
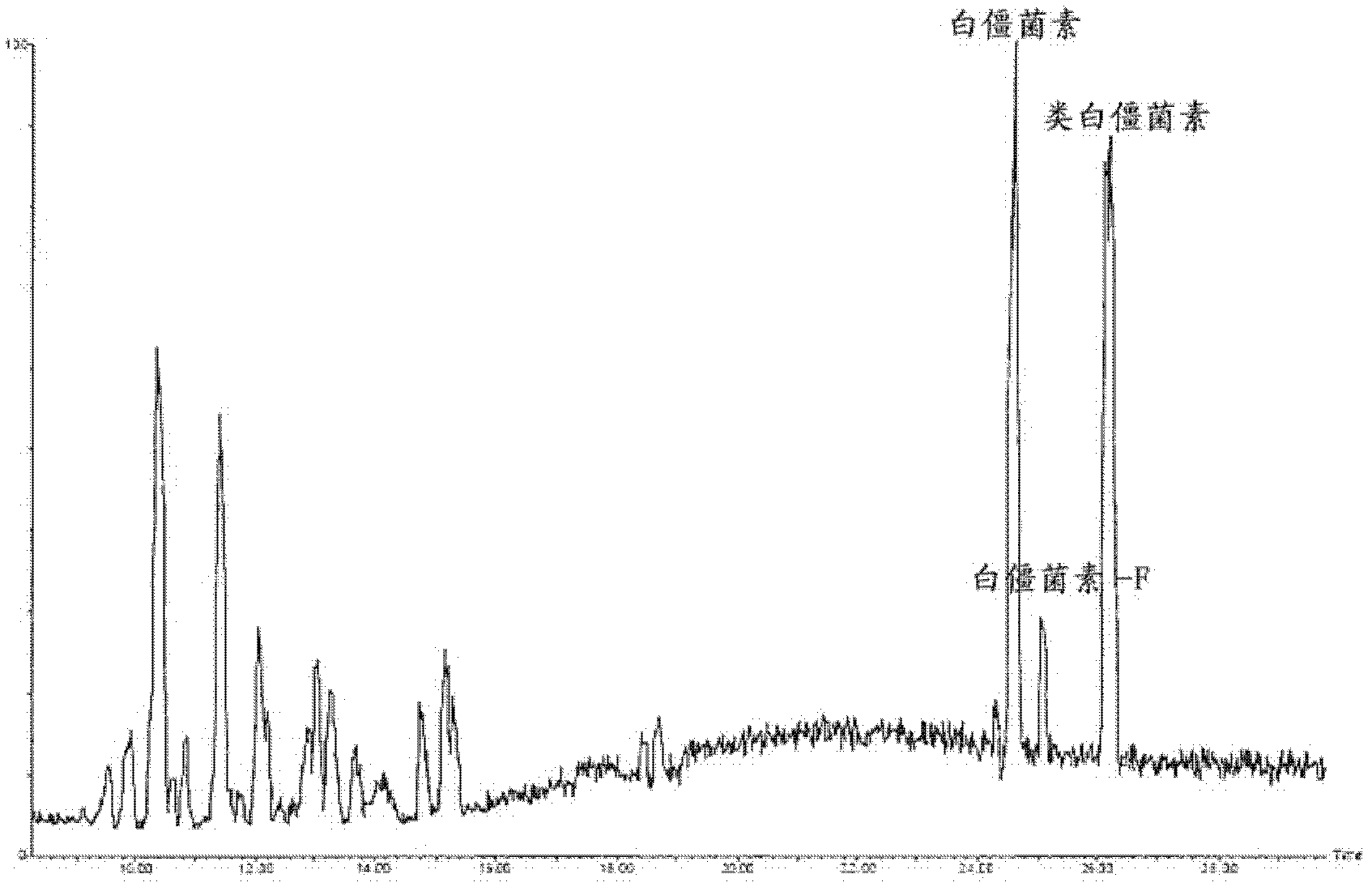
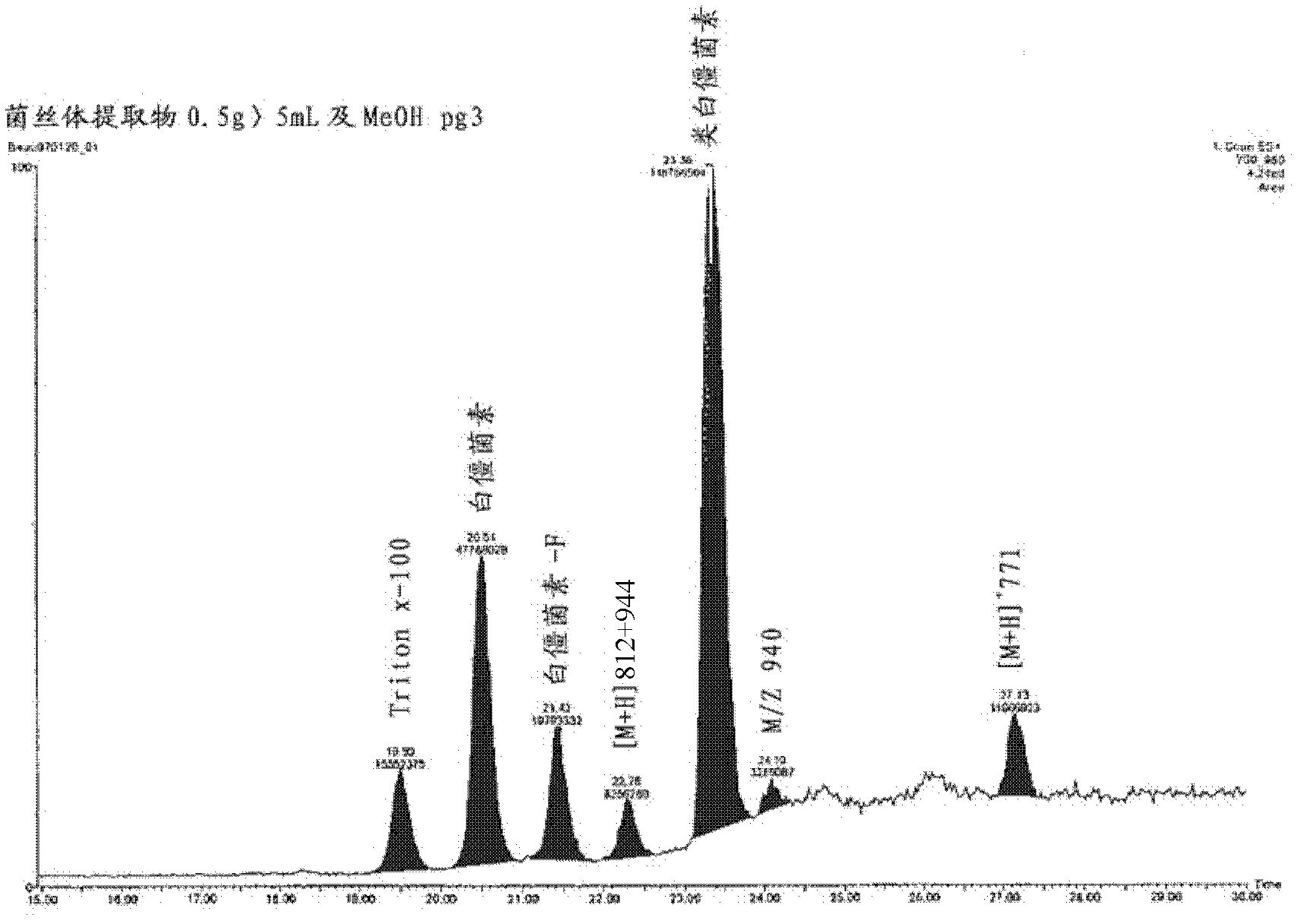
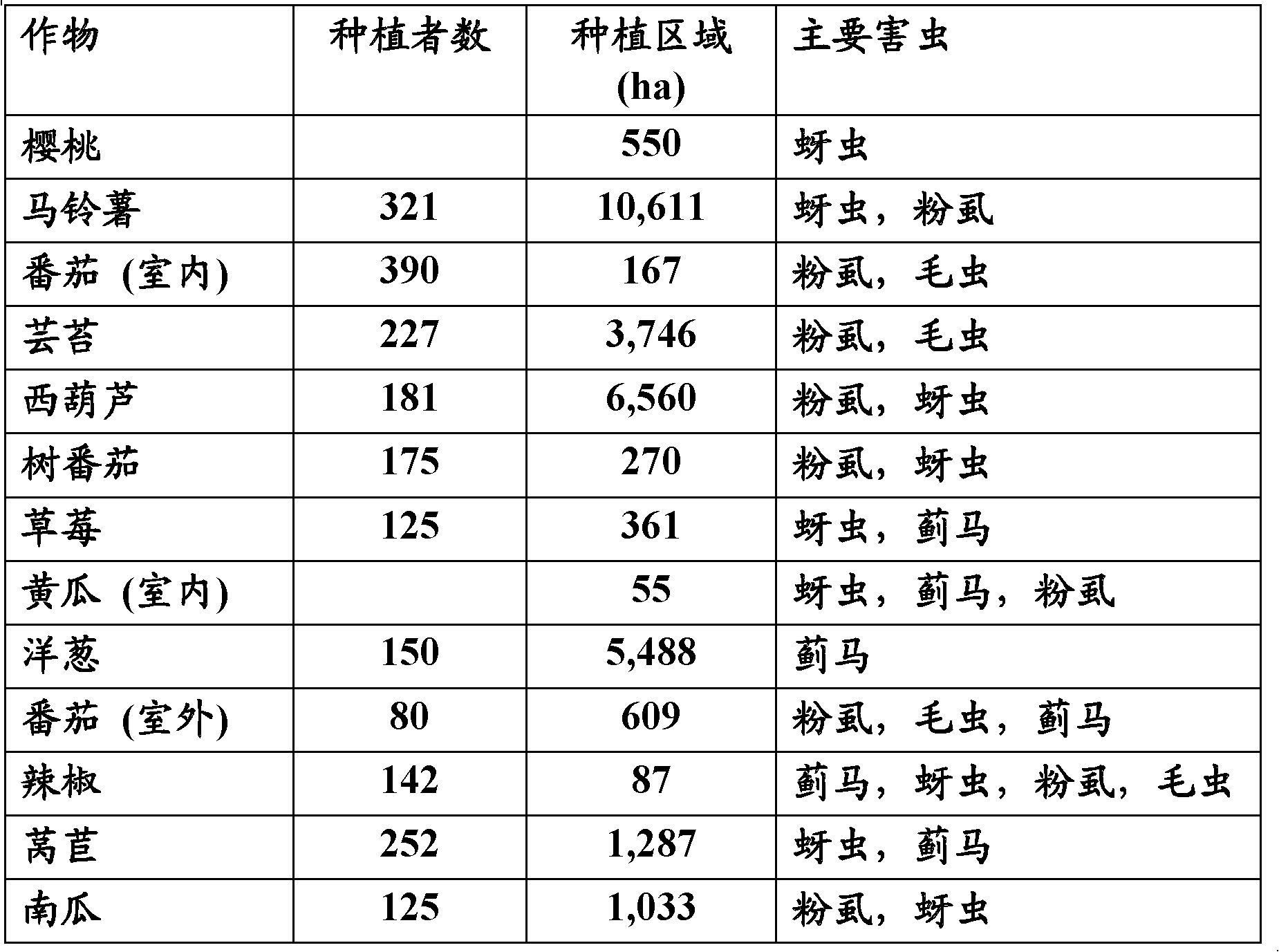
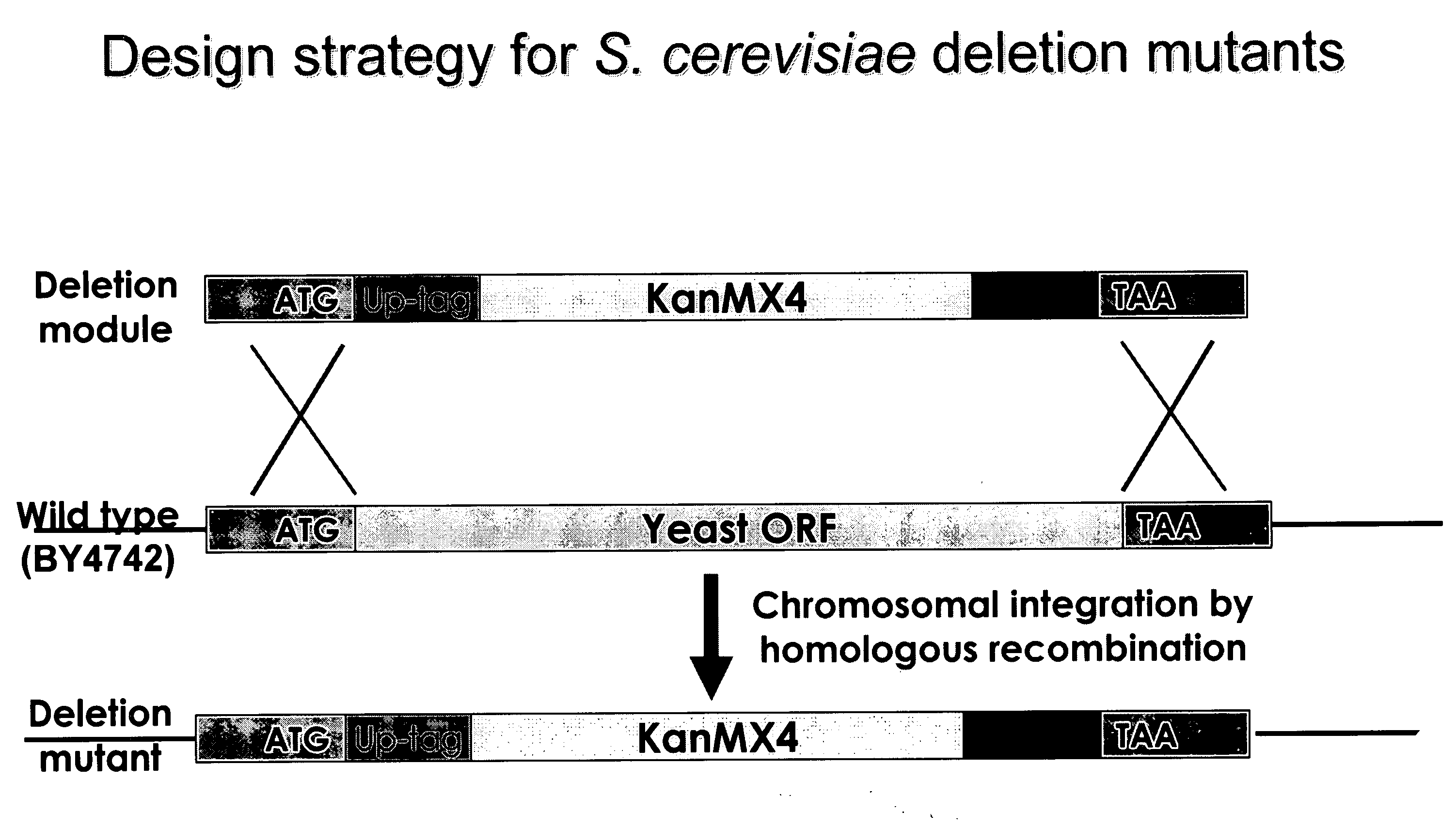
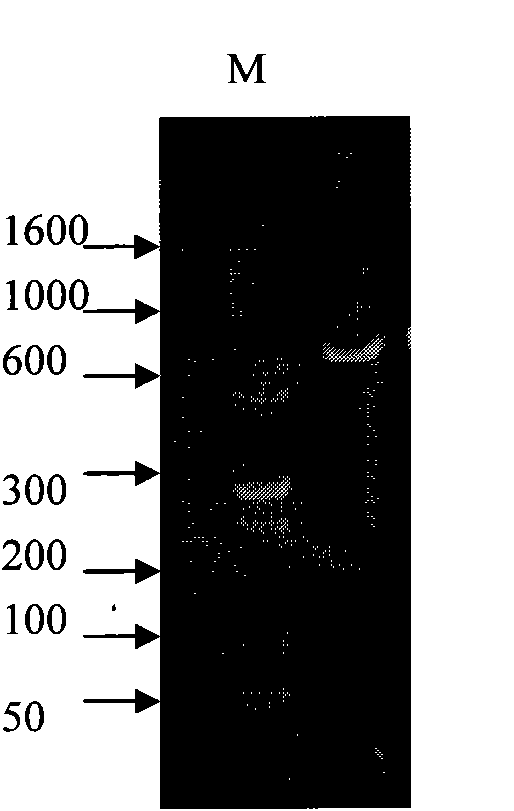
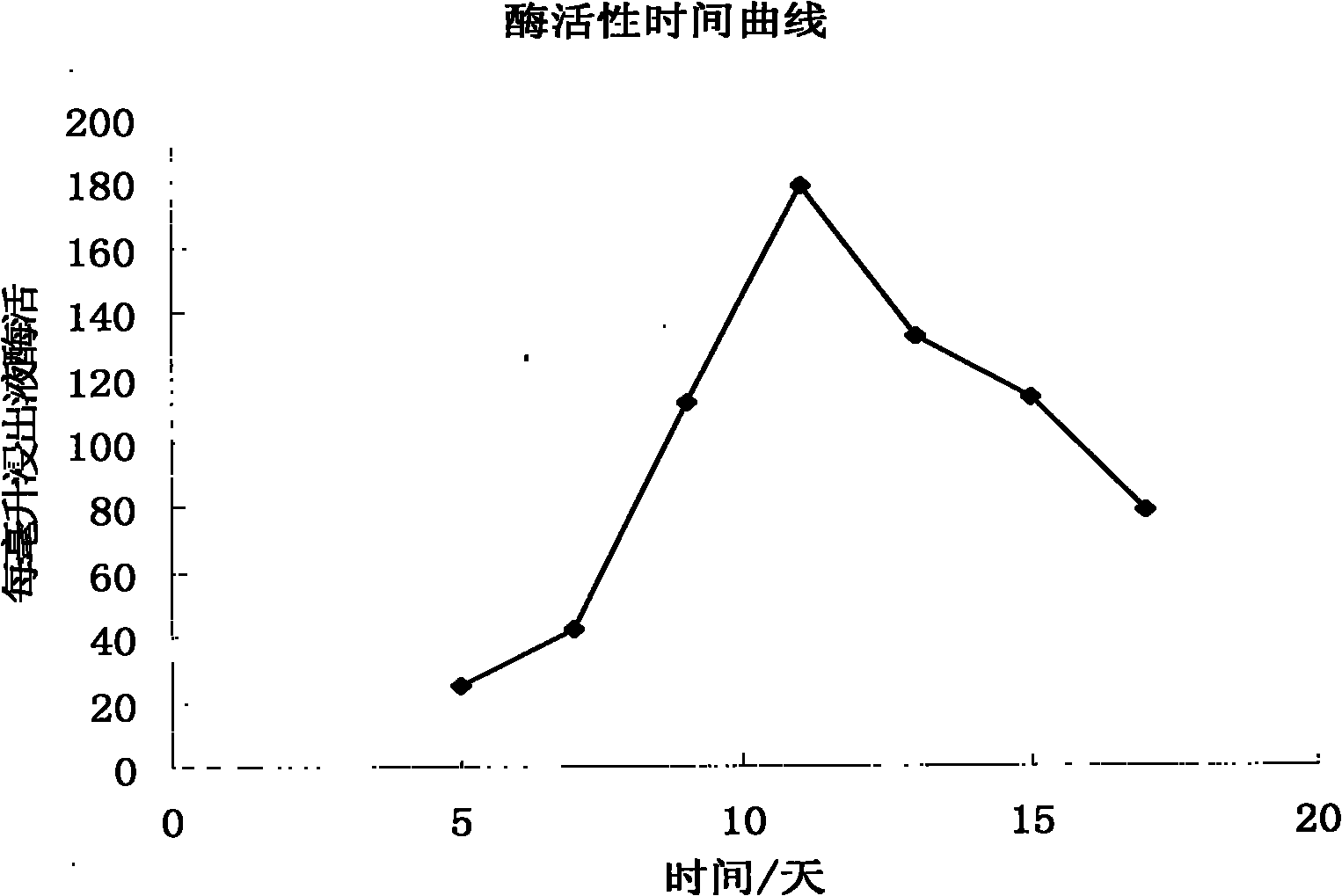
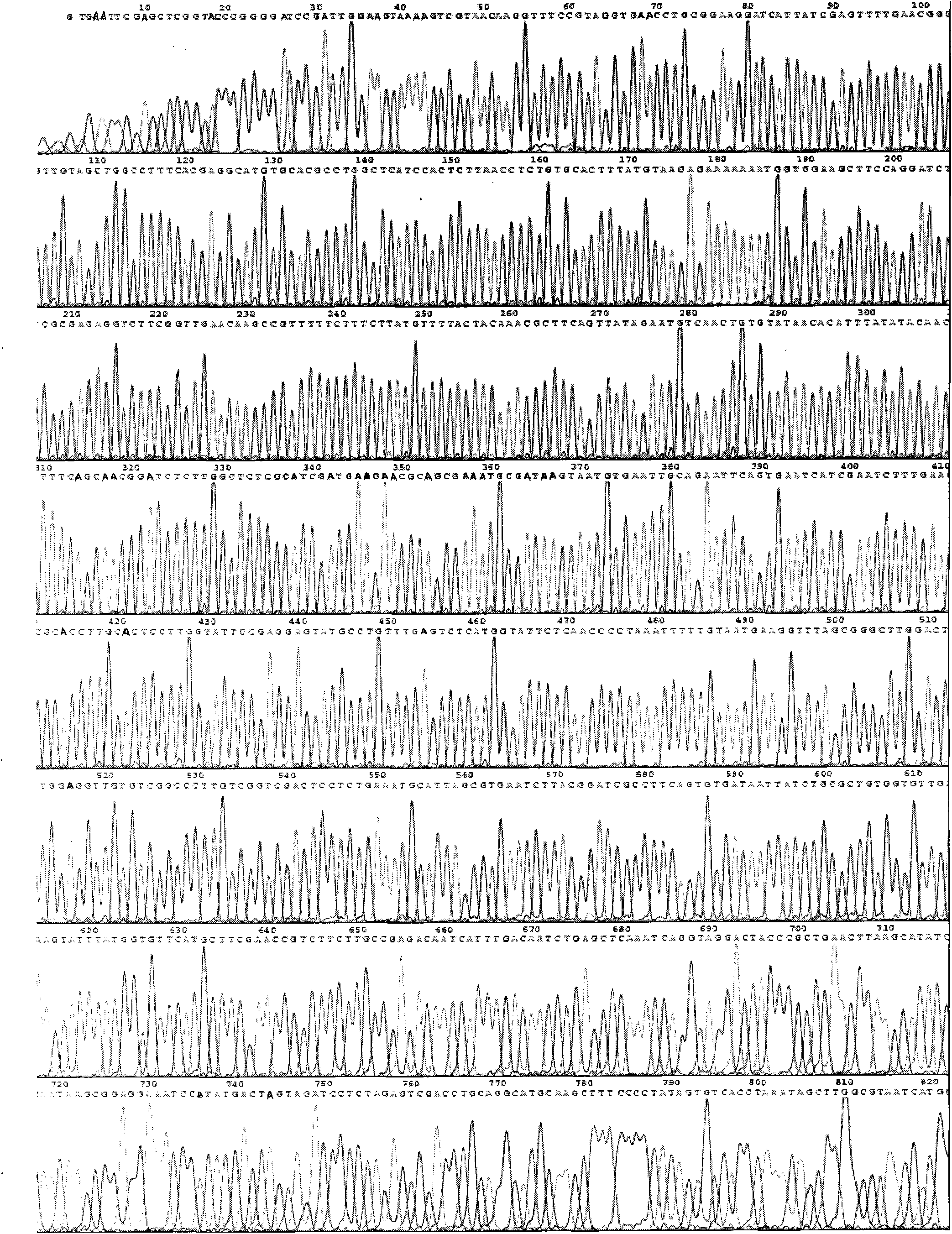
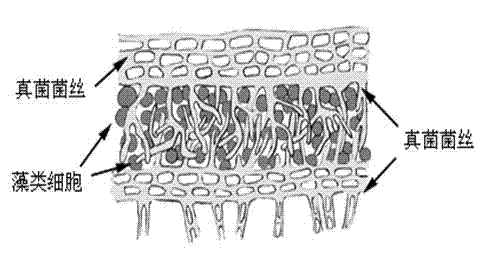
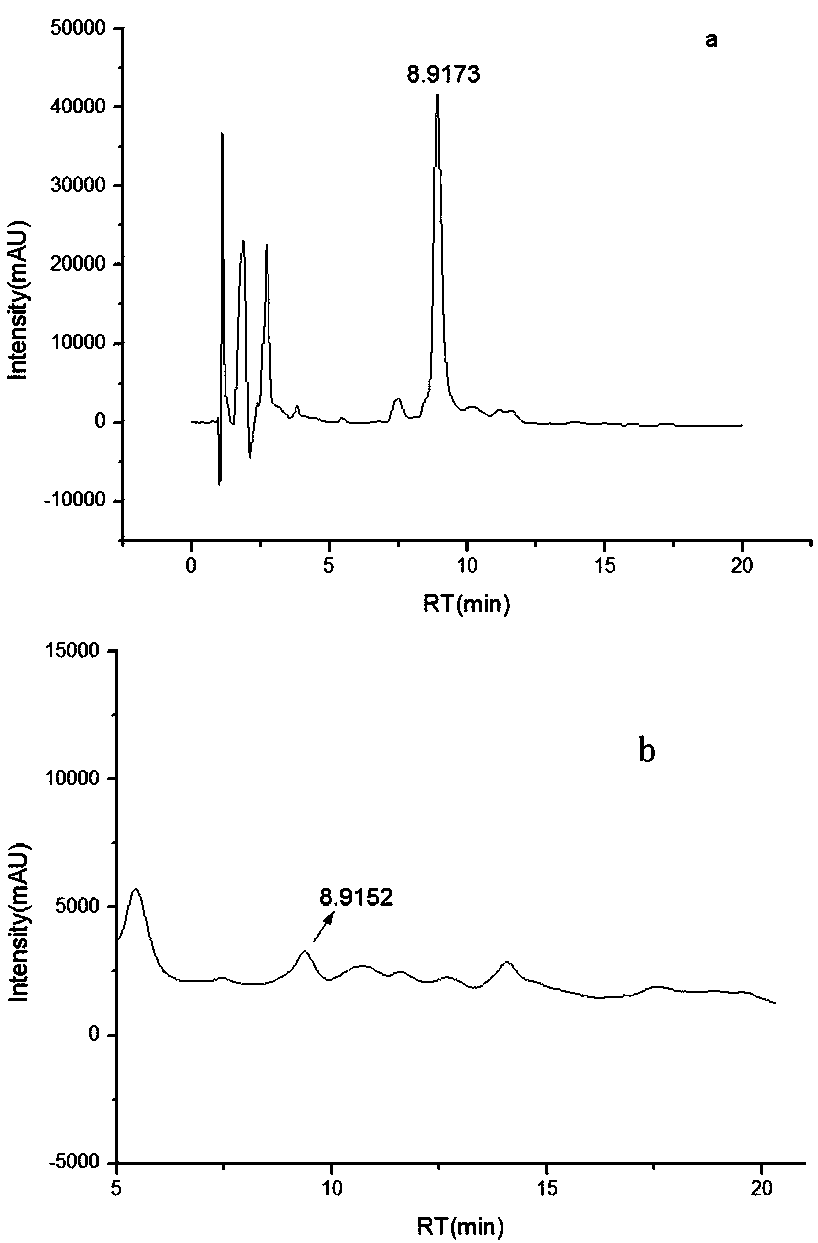
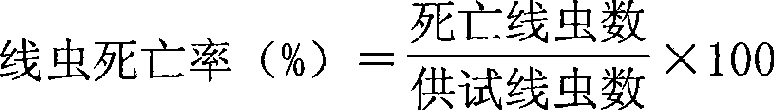Patents
Literature
354 results about "Fungal strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Candida is a strain of fungus that can cause an infection in your skin, among other locations. In normal conditions, your skin may host small amounts of this fungus. Problems arise when it begins to multiply and creates an overgrowth.
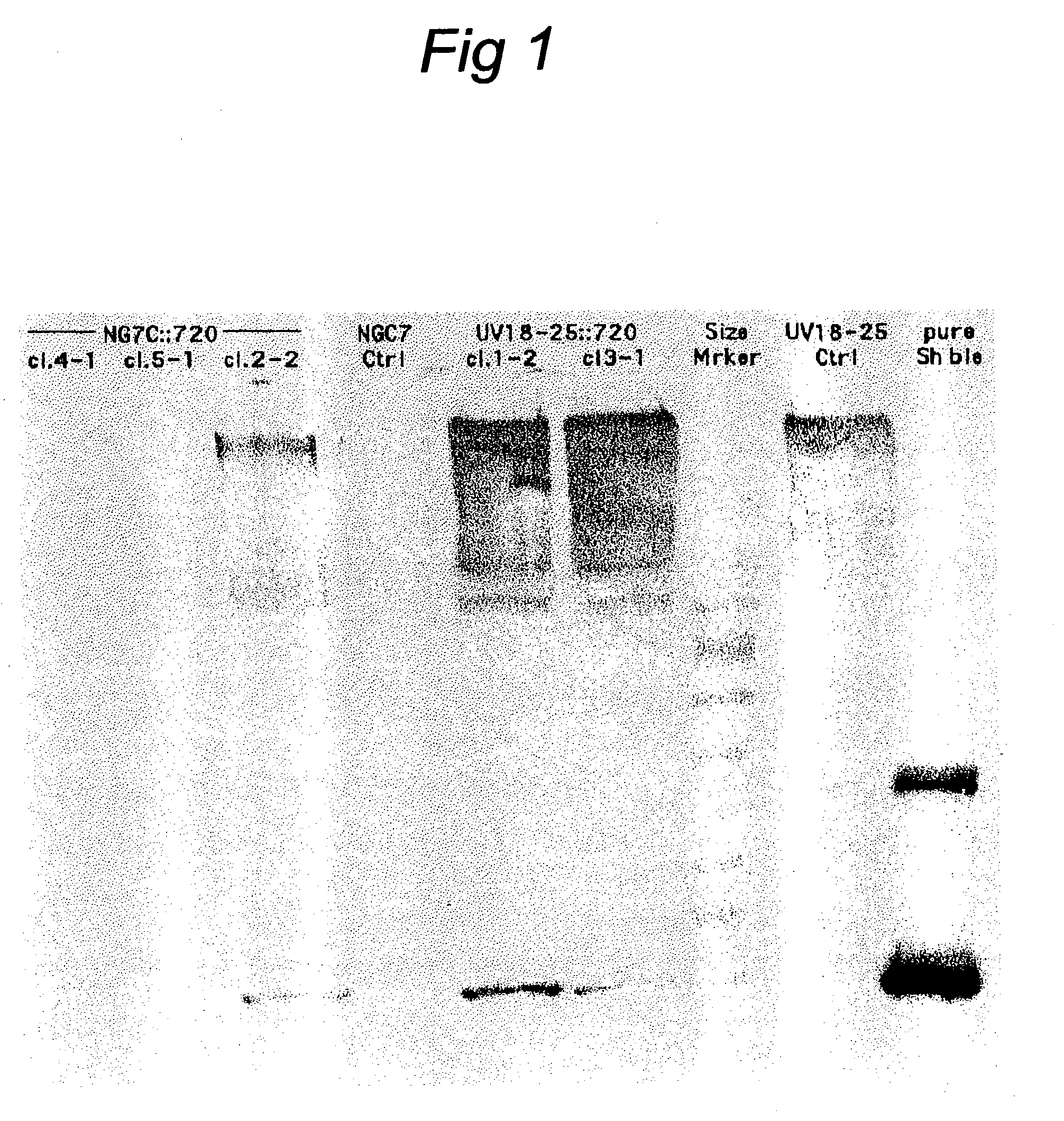
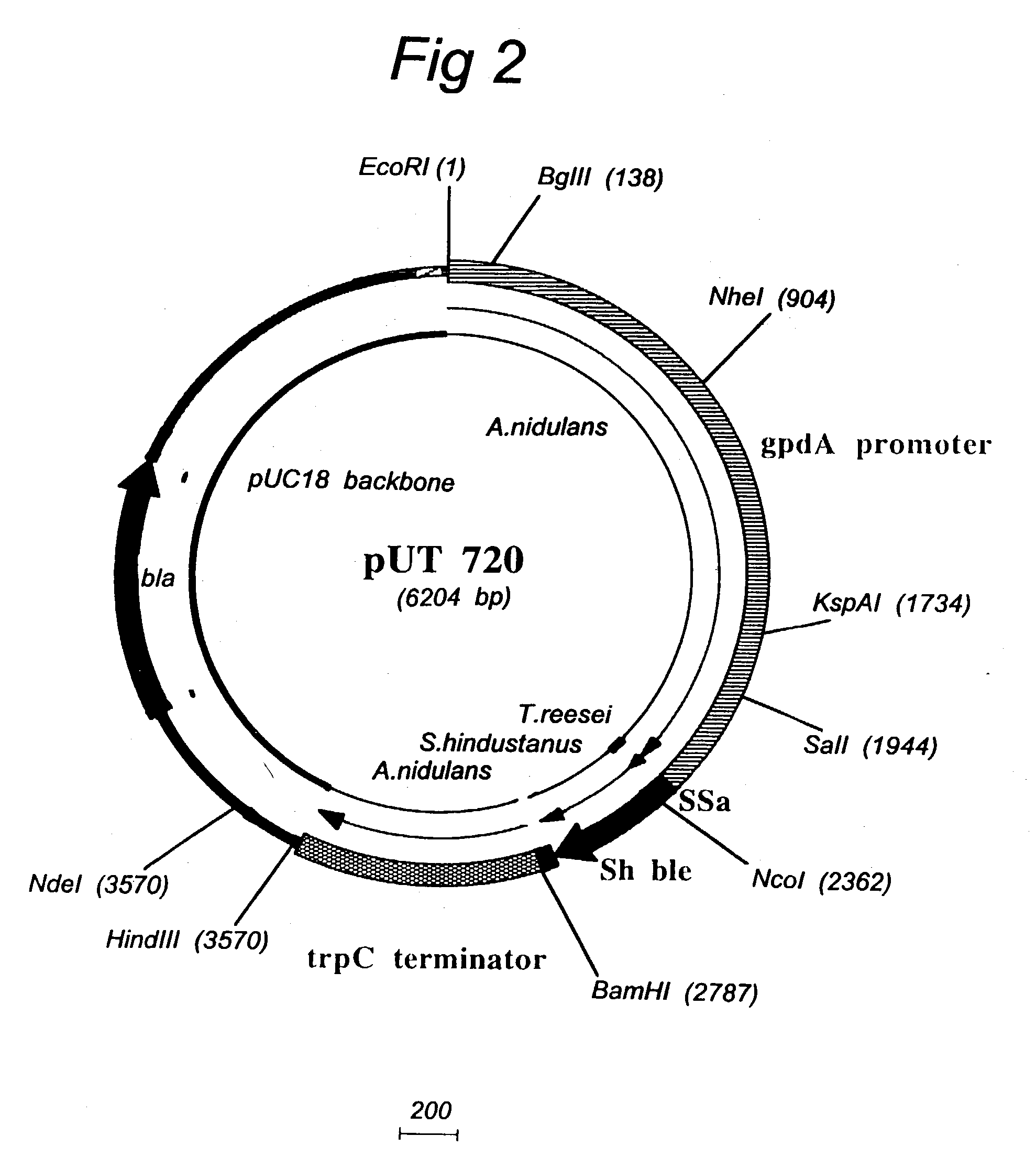
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Polymicrobial Formulations For Enhancing Plant Productivity
ActiveUS20090308121A1Promote plant growthReduce disease incidenceBiocideFungiBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention relates to eco-friendly compositions and methods for providing plant growth enhancing formulations comprising mixtures of microbial isolates. In particular, numerous bacterial and fungal strains were isolated from a variety of soil types, from rhizospheres and from root nodules of leguminous plants, in designed combinations, for providing plant growth and plant productivity enhancing formulations. These specifically designed polymicrobial formulations would further provide protection against plant pathogens lowering the need for nitrogen containing fertilizers, solubilize minerals, protect plants against pathogens, and make available to the plant valuable nutrients, such as phosphate, thus reducing and eliminating the need for using chemical fertilizers and chemical pesticides.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Culturing method for sporocarp of Morchella
ActiveCN105993590ANot easy to bringSimple and fast operationCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologySoil treatment
The invention discloses a culturing method for sporocarp of Morchella. The culturing method comprises the following steps: fungal strain preparation, fungal strain culturing, soil treatment, sowing, covering and temperature preservation, management in the growth period of mycelia, fruiting acceleration treatment, management in a fruiting period, and harvesting. According to the invention, operation steps like drawing of fungal strains from a fungal strain bottle or a fungal strain bag, fungal strain hydration, and placement of a large amount of nutrition material bags on the surface of soil in a traditional technology are removed, so the field-cultivation or indoor-cultivation technique for the Morchella is more simple and convenient; the cost of the nutrition material bags is reduced by three fourth or more; the generation cost of cultivation of the Morchella is greatly reduced; the technical difficulty of the cultivation of the Morchella is greatly decreased; and economic benefits are greatly improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fungal pharmaceutical mycoplasm with blood sugar lowering efficacy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102428832AAvoid secondary damageEnsure safetyAnthropod material medical ingredientsMetabolism disorderPhellinus igniariusInonotus obliquus
The invention belongs to the field of biofermentation engineering. A pharmaceutical medium and a fungal strain which have blood sugar lowering efficacy are used as bidirectional fermentation raw materials, wherein the pharmaceutical medium is mainly composed of the following raw materials: cornel, gynostemma, momordica grosvenori, winged euony twigs, balsam pear and polyrhachis vicina; the fungalstrain is composed of the following strains: inonotus obliquus, cordyceps, phellinus igniarius, polystictus versicolor, and grifola frondosa; and bi-directional multi-fungi fermentation is carried out between multiple edible and pharmaceutical fungi and Chinese herbal medicines by a bidirectional fermentation process, thus organisms in two kingdoms or three kingdoms are organically combined to obtain an entirely new blood-sugar-lowering pharmaceutical mycoplasm product. The obtained product can generate 1+1>2 physiological function efficiency for hypoimmunity, has the actions of obviously lowering blood sugar but not increasing insulin concentration, has significant positive effects on helping treating and controlling diabetic complications, and can be used as an oral medicament for preventing and treating diabetes or a health-care product for adjusting blood sugar.
Owner:DALIAN BAIXIANGJU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Fungus strain and uses thereof
InactiveCN101486970APromote growthLarge biomassBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
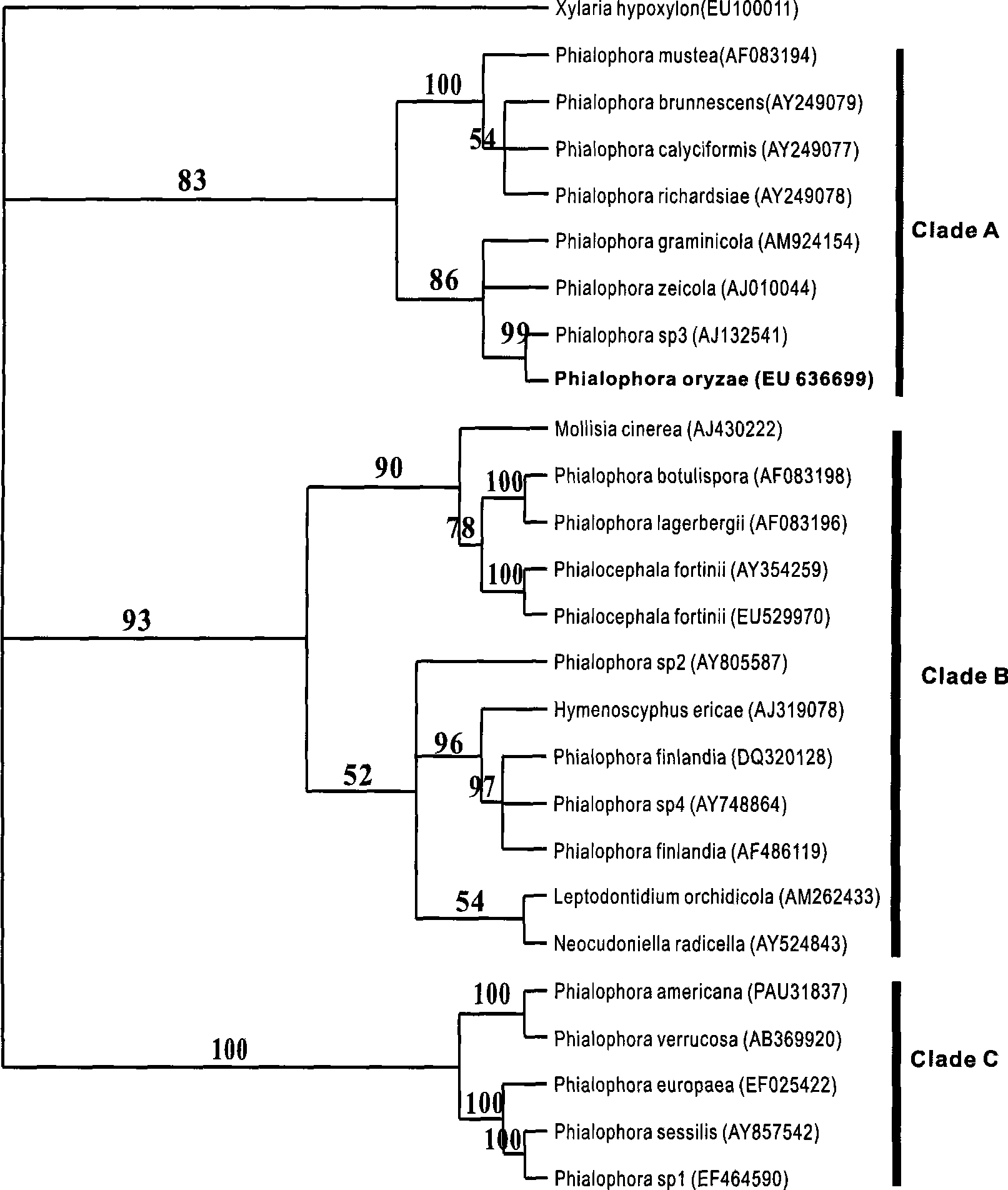
The invention discloses a fungus strain, which is Phialophora oryzae R5-6-1 fungus strain with the preservation organization of China General Microbiological Culture Center of Microbial Culture Collection Management Committee, the preservation date of October 27th, 2008 and the preservation number of CGMCC 2737. The fungus strain can be used for improving the growth of vegetables especially paddy rice and increasing the live weight thereof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
InactiveUS20040002136A1Minimise risk of degradationAvoid necessityFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyMutant
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Penicillium, as well as preparation method and application
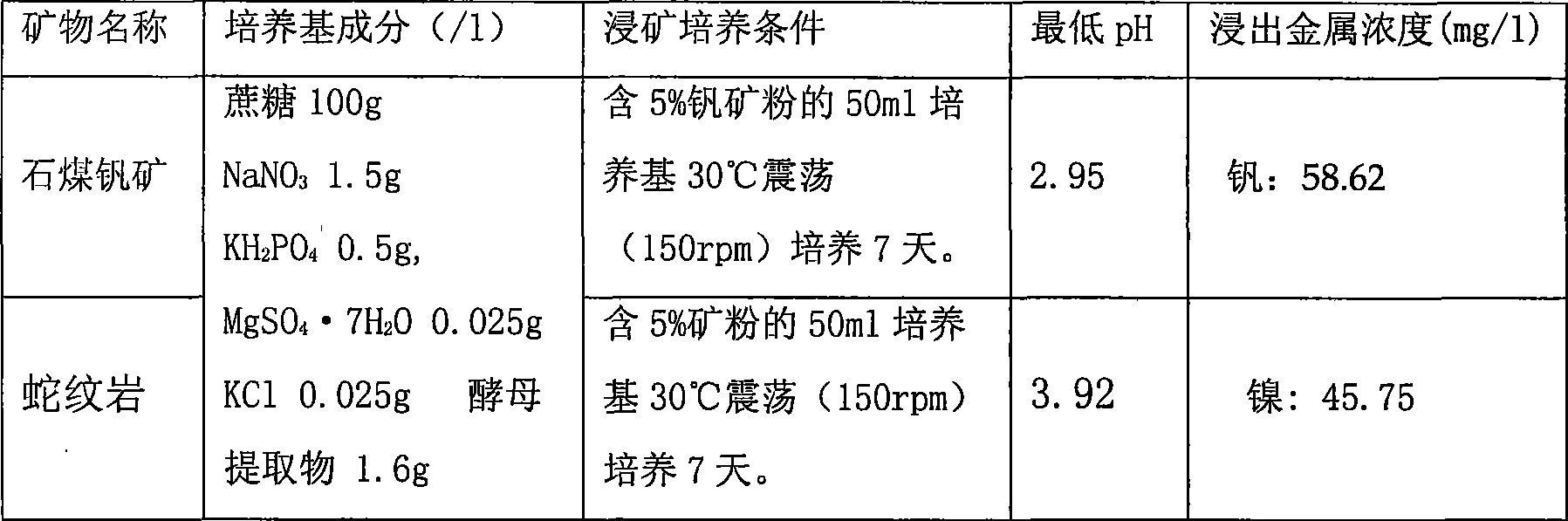
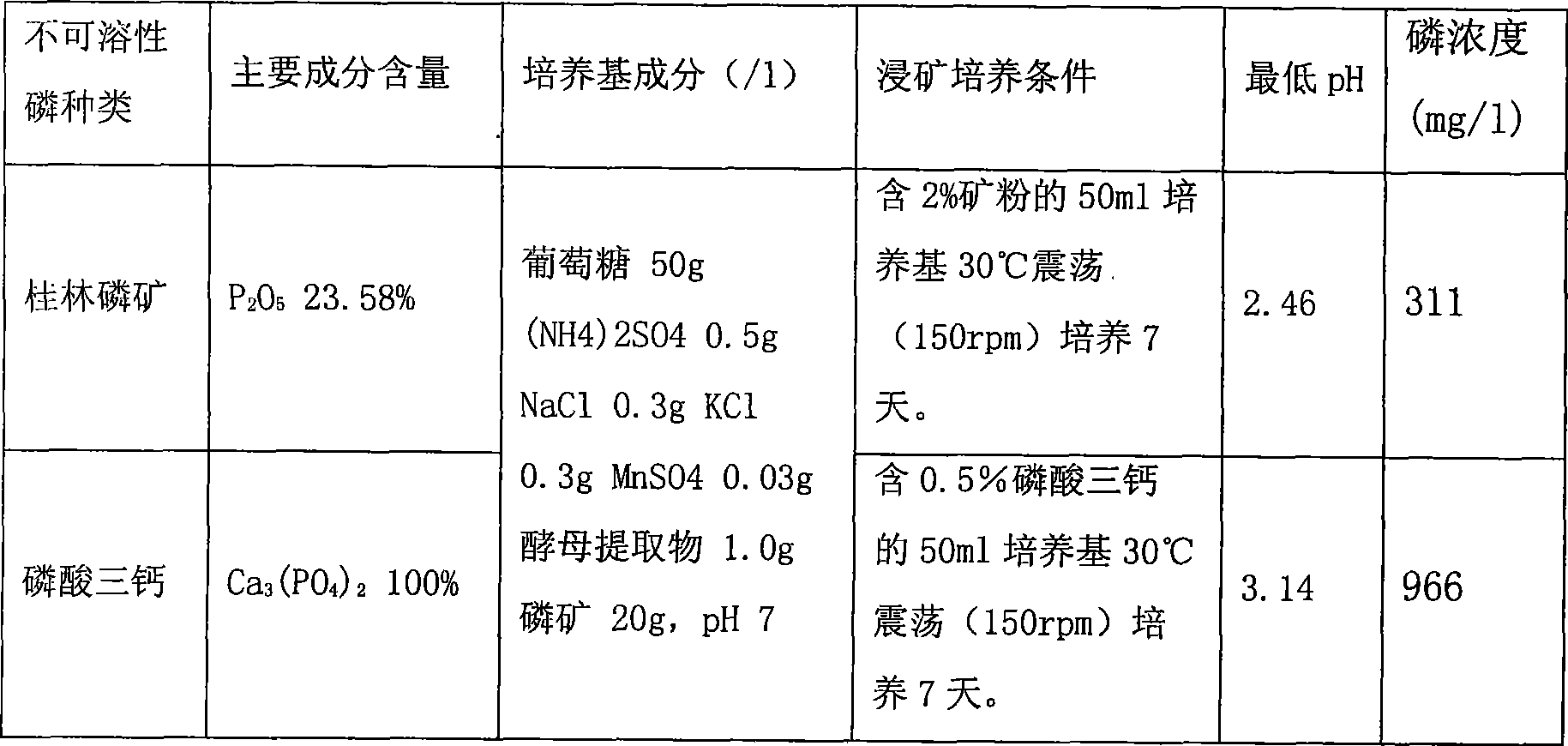
InactiveCN101434909AReach pollutionReduce pollutionFungiMicroorganism based processesEcological environmentPhosphate
The invention discloses a Penicillium, a preparation method and applications thereof, Penicillium fungus PSM11-5 is separated from a vanadium ore sample; insoluble tricalcium phosphate, sodium metavanadate, cobalt hydroxide and basic nickel carbonate are taken as indicating compounds; and a fungal strain is screened by testing the capability of decomposing the tricalcium phosphate, the sodium metavanadate, the cobalt hydroxide and the basic nickel carbonate. The Penicillium PSM11-5 is Penicillium sp.PSM11-5 CCTCCM208207. The strain is utilized for carrying out biological leaching of phosphorus and biological metallurgy, metals of phosphorus, vanadium, nickel, cobalt and the like are leached from lean ores, discarded ores, submarginal ores, difficult-to-mine ores, difficult dressing ores and refractory ores, thereby fully utilizing the mineral resources, reducing the metallurgical costs and protecting the ecological environment. The PSM11-5 is utilized for leaching the phosphorus from low-grade phosphate rock powder, a biological fertilizer is prepared to be applied to the soil, thereby leading the soil to contain higher content of soluble phosphorus which can be utilized by crops; the strain further leaches insoluble phosphorus which is deposited in the soil before, thereby reducing phosphorus fertilizer and reducing gas pollution caused by the phosphorus fertilizer and water pollution caused by the phosphorus fertilizer.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for the preparation of homopolysaccharides
ActiveUS20110151517A1High specific viscosityReduce contentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMembranesHomopolysaccharideGlycoside formation
A process for the preparation of aqueous solutions of glucans having a β-1,3-glycosidically-linked main chain and side groups having a β-1,6-glycosidic bond by fermentation of fungal strains. The fungal strains secrete the glucans into the fermentation broth, in an aqueous culture medium, and the separation of the glucans from the fermentation broth is effected using asymmetrical filter membranes.
Owner:WINTERSHALL HLDG
Aspergillus niger fungus capable of poisoning plant parasitic nematodes, preparation method and application thereof
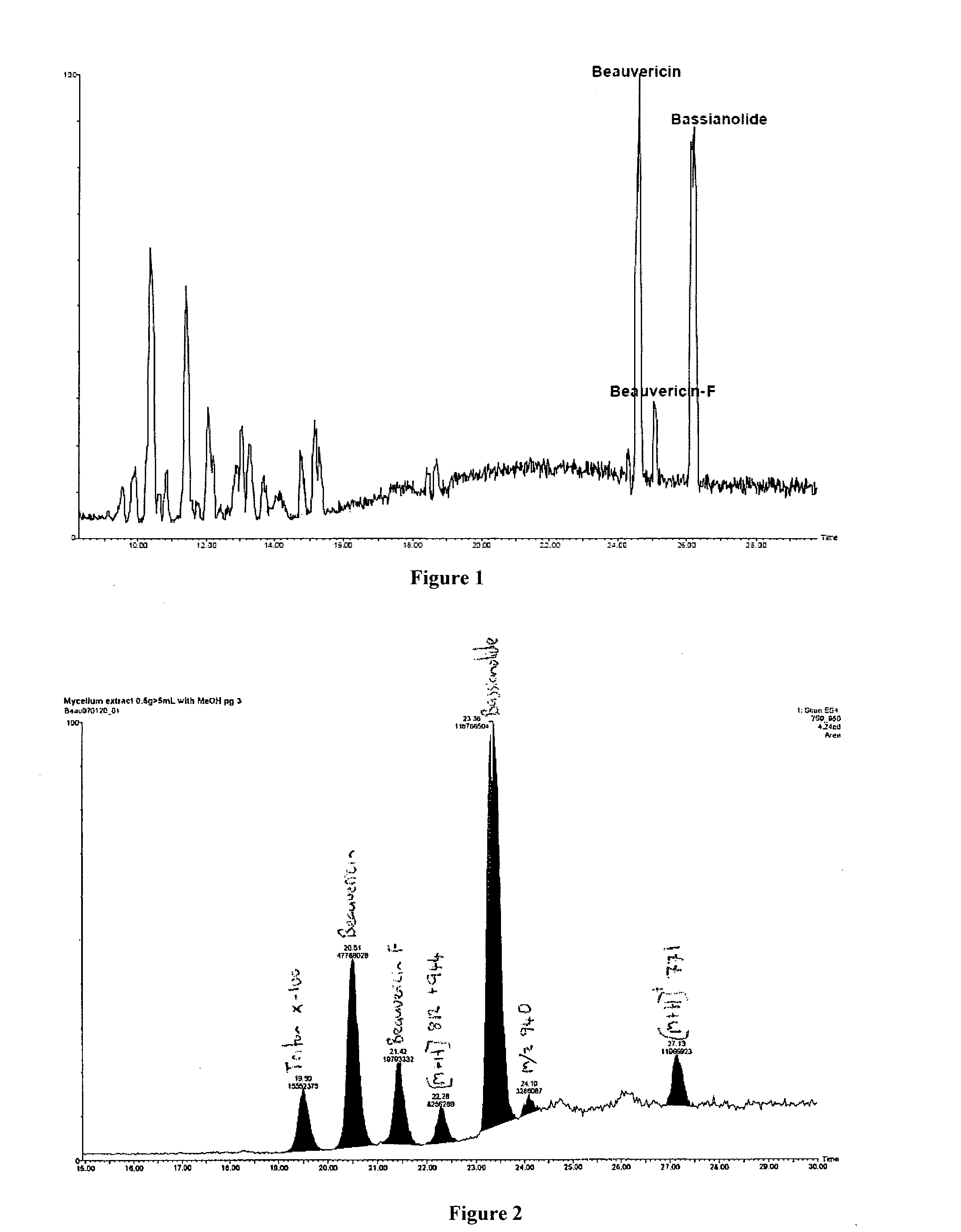
The invention relates to a culture method of a fungus capable of poisoning plant parasitic nematodes, and a preparation method of a metabolite thereof and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial pesticides. A fungus strain (Aspergillus niger Y-61) related in the invention was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 7, 2008, and the collection number is CGMCC No.2631. The taxonomic status of the Y-61 is a mitosporic fungus, hyphomycetes, moniliales, moniliaceae, aspergillus and aspergillus niger. The fungus metabolite is prepared by liquid fermentation and culture, has outstanding characteristics of high toxicity to the plant parasitic nematodes, especially root-knot nematodes, and has obvious nematodes killing effect; and the influence of the strain fermentation broth on Meloidogyne incognita juveniles (J2) and oocyst hatching is determined indoors. Treatment of the fermentation broth with different diluted concentrations is significantly different from the aseptic water treatment, and the preventive effect of the fermentation broth with less than one-fifth concentration is be equivalent to that of 10mug / ml of cadusafos. The fungus has good application and development prospects.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Entomopathogenic Fungi and Uses Thereof
Owner:GREENTIDE
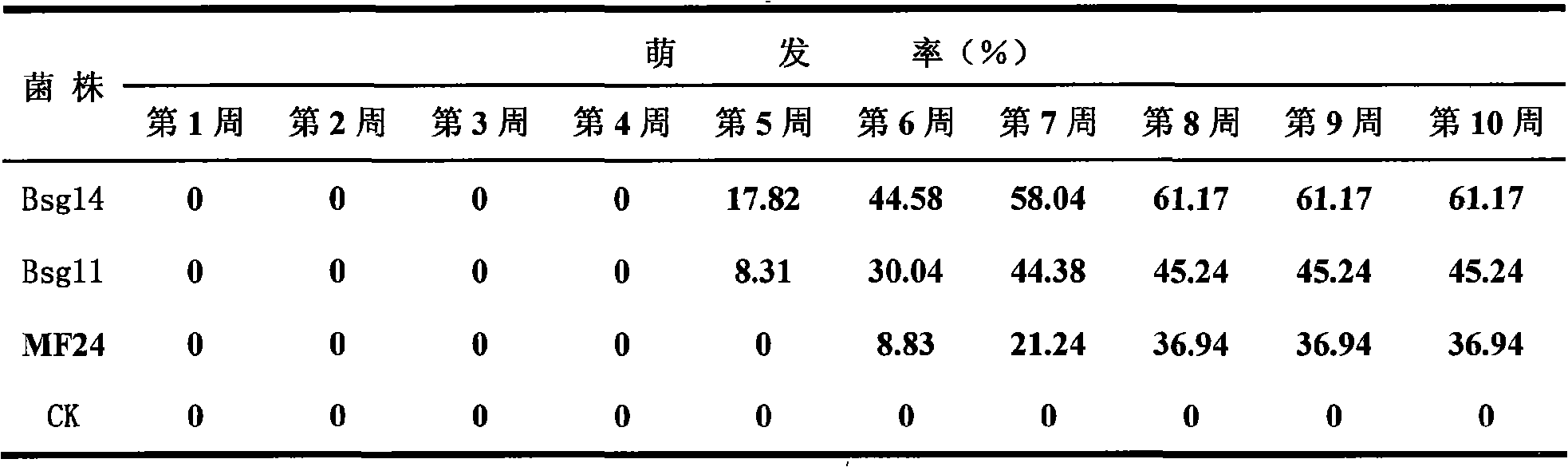
Three fungus strains for promoting germination of arethusa seeds
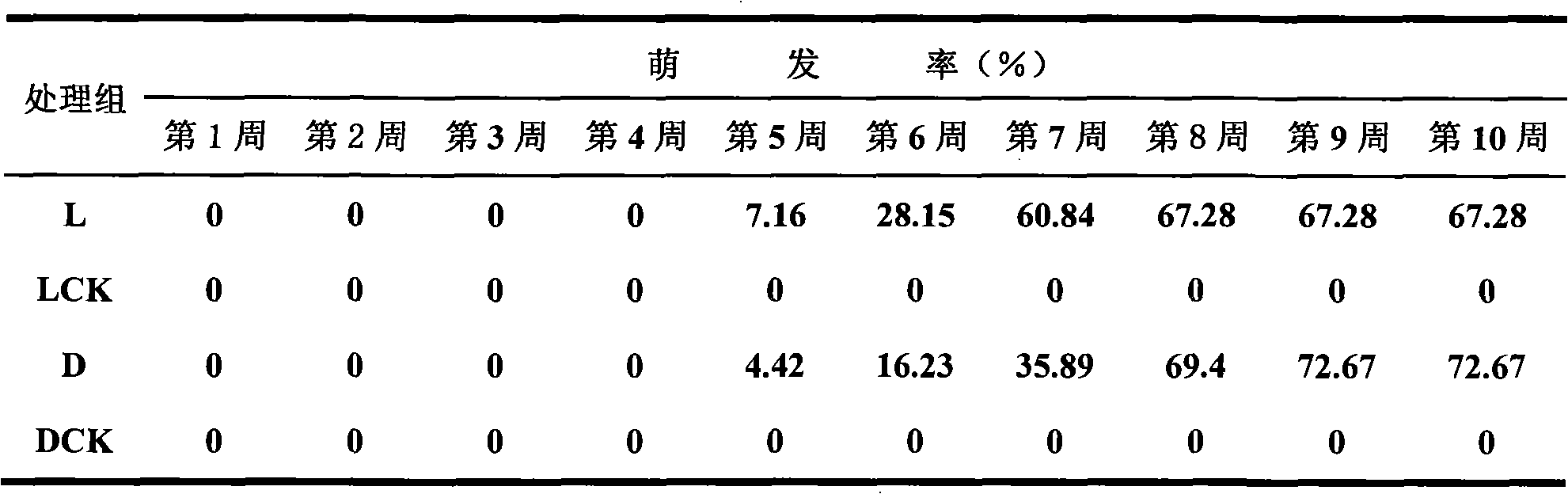
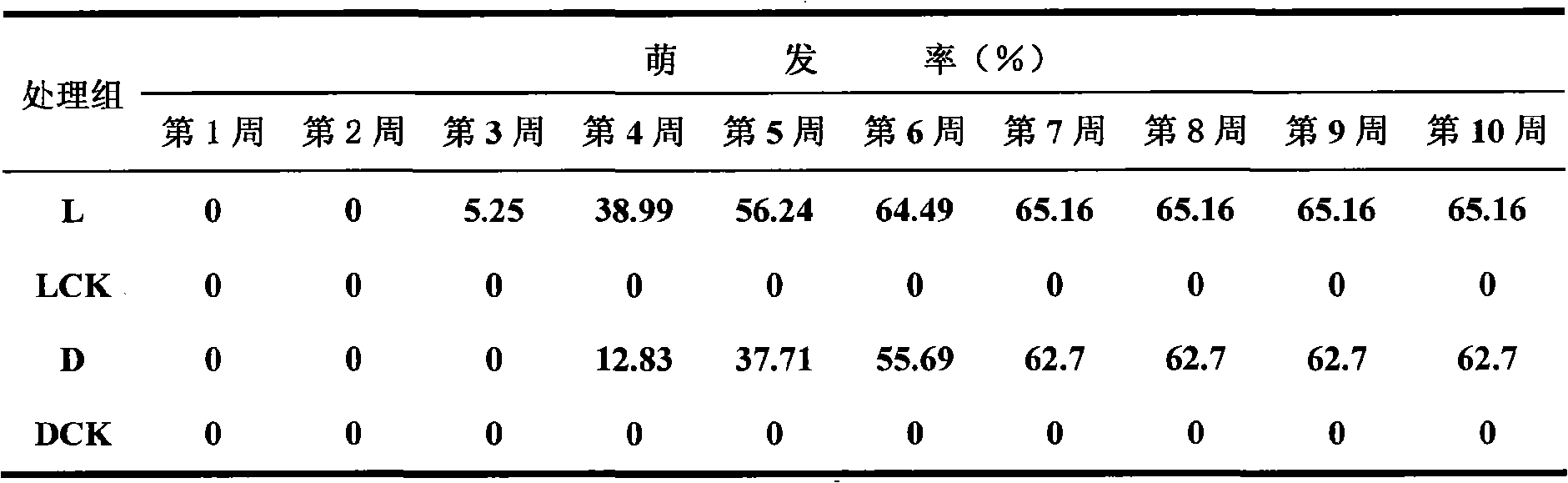
The invention discloses three fungus strains for promoting the germination of arethusa seeds. The classification names of the three fungus strains are respectively Rhizoctonia sp. Bsg11 with the preservation serial number of CGMCC No.2450, Tulasnella sp. Bsg14 with the preservation serial number of CGMCC No.2451 and Mycena sp. MF24 with the preservation serial number of CGMCC No.1350. The three effective fungus strains have an important meaning for solving the germination problem of arethusa seeds; and the three effective fungus strains can be seeded together with the arethusa seeds, are used for the cultivation of the cultured seedlings or the large fields of a seedling culture disk or a flowerpot or a seedbed and have an application value for replacing tissue culture to obtain seedlings.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Liriope spicate endogenous aspergillus fungus and application thereof to preparation of steroid saponin
ActiveCN107739718AAvoid pollutionAvoid disadvantagesFungiMicroorganism based processesSnow moldMicroorganism
The invention provides a liriope spicate endogenous aspergillus fungus and application thereof to preparation of steroid saponin, and relates to the technical field of microorganisms. The fungus mainly solves the problems that due to the factors that the liriope spicate steroid saponin is mostly and directly from liriope spicate extracts, the liriope spicate steroid saponin content is low, the saponin extraction cost is high, and the like, the market delivery quantity of the liriope spicate steroid saponin is limited. The aspergillus fungus is separated from living body tuberous roots of liriope spicata var. prolifera, and belongs to aspergillus sp. through 18S rDNA sequence identification; the aspergillus fungus is preserved in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection); the preservation data is December 7, 2016; the preservation number is CCTCC No.M2016721. The liriope spicate produced by a liriope spicate GAP (Good Agricultural Practices) base (the liriope spicate source areain Oumao town, Xiangyang city in Hubei province ) is used; the liriope spicate steroid saponin is generated through liriope spicate endogenous fungus plant liquid fermentation. The endogenous fungus is an important microorganism for finding a new resource of the liriope spicate steroid saponin.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Novel composite bacterial agent for degrading crop straw
InactiveCN101948753AWide range of useWide variety of sourcesFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a fungal composite bacterial agent. The fungal composite bacterium agent is prepared by the following steps of: separating and purifying soil and a plant sample to obtain different fungal strains; selecting the fungal strains with high cellulose and ligninolytic enzyme generating capacity from the fungal strains; and optimally combining and proportioning to obtain cladosporium sphaerospermum fungus, auricularia polytricha and champgnon which can effectively degrade the lignin or the cellulose of the straw. The composite bacterial agent is applied to composting of the crop straw and can compost the crop straw in 10 to 15 days without the condition of high temperature.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Bottle cultivation method for Hypsizigus marmoreus
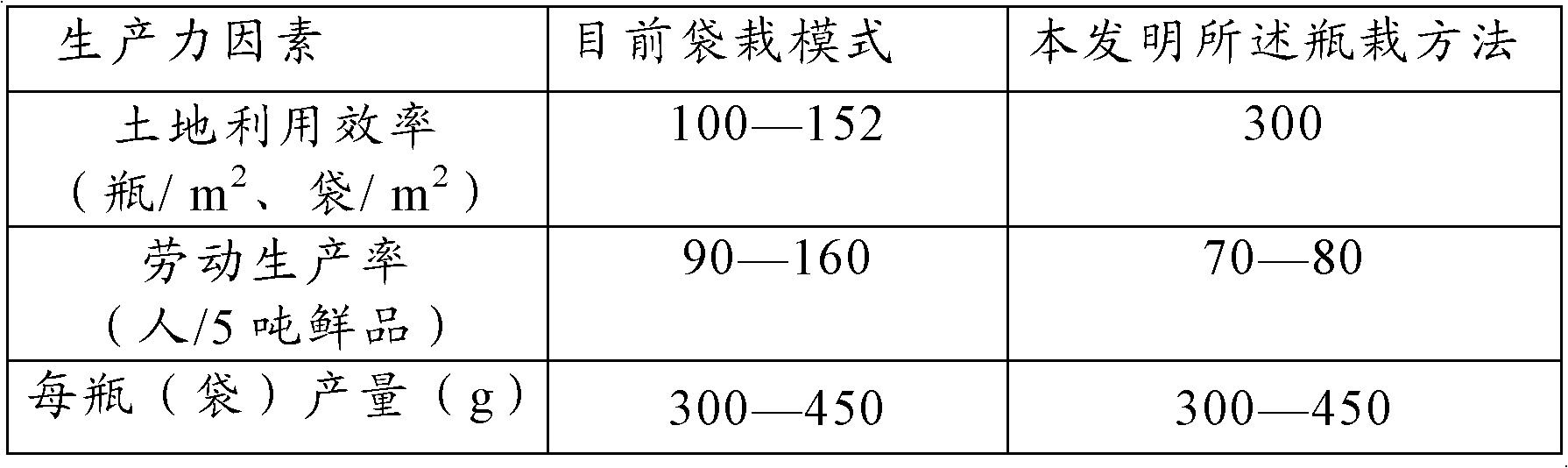
The invention discloses a bottle cultivation method for Hypsizigus marmoreus. The bottle cultivation method for the Hypsizigus marmoreus comprises the following steps of: inoculating the Hypsizigus marmoreus on a bottled culture medium, wherein the inoculation ratio is that each bottle of fungal strains are inoculated on 32 to 40 bottles of culture bottles; performing mycelium culture under the conditions of temperature of between 18 and 25 DEG C, humidity of 60 to 80 percent and CO2 concentration of 1,500 to 5,500 ppm; after the Hypsizigus marmoreus are matured, performing mycelium stimulation and supplementing a small amount of water; performing inducement to primordium; after mushroom buds are generated, performing inhibition period culture for 3 to 5 days; when the mushroom buds grow out of the bottleneck, sleeving a plastic sleeve; performing elongating stage culture; and harvesting after the harvesting standard is reached. In the bottle cultivation method, the period is 105 to 125 days and average yield of a single bottle is 300 to 450g. The bottle cultivation method is a factory-like bottle cultivation method using sawdust, cotton seed hulls and corn cobs as main raw materials. By the bottle cultivation method, the mechanization level and the automation degree of the Hypsizigus marmoreus can be increased greatly; production cost is effectively reduced; stable quality isguaranteed; and a popularization prospect is achieved.
Owner:郑雪平
Method for breeding high-nucleic acid yeast and method for preparing ribonucleic acid by using high-nucleic acid yeast
InactiveCN101928674AHigh purityHigh yieldFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyVirulent characteristics
The invention relates to a method for breeding a high-nucleic acid yeast from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which comprises the following steps: culturing a large amount of preserved Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains in an appropriate yeast growth medium, breeding initial strains, carrying out secondary screening on the initial strains and selecting growth media to obtain high-nucleic acid yeast strains for industrial production. Virulence tests show that thalli and metabolites can not cause intoxicating reactions. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae used in the method is one firstly recommended by Ministry of Health P.R.China for health food among fungi strains. The high-nucleic acid yeast bred from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae is used for the industrial production of nucleic acid, the bred high-nucleic acid yeast proves to be Saccharomyces cerevisiae by another microbiological assay and belongs to the traditional strains for producing beer, and the nucleic acid content of the thalli can be up to 12-14%(W / W) in the optimal culture condition. The method can be widely used for large-scale industrial production, and the prepared nucleic acid can be trustingly used in fields of health food, medicaments, infant food and the like.
Owner:大连珍奥生物技术股份有限公司
Huperzia serrata endogenetic epiphyte and uses thereof
The invention discloses endophytic fungi from huperzia serrata. The invention is obtained through being separated from the living body of pteridophyta huperzia serrata by adopting endophytic fungi separation and purification technology, and is identified through biosystematics to be acremonium endophytium. The preservation number of the strain is CCTCC M 206118. The invention generates Huperzine A analogous compound through the strain liquid fermentation of the endophytic fungi from huperzia serrata, and is significant micro organism for searching the Huperzine A new resource of the active component for curing the presenile dementia.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Entomopathogenic Fungi and Uses Thereof ?
The present invention provides a strain of entomopathogenic Beauveria bassiana, compositions comprising the entomopathogenic fungi strain or metabolites of the strain, and the use of the entomopathogenic fungi strain and compositions as biological control agents. Methods for the biological control of phytopathogenic insects using an entomopathogenic Beauveria bassiana fungi strain or one or more metabolites thereof, optionally together with other entomopathogenic fungi including fungi selected from strains of Lecanicillium spp., Paecilomyces fumosoroseus, and compositions comprising said fungi or metabolites thereof are also provided.
Owner:BIOTELLIGA HLDG
Potentiation of antifungal compounds
The invention provides methods and models for understanding how HDAC inhibitors interact with antifungal azole compounds to potentiate the activity of such compounds, using fungal strains which have selective knockouts of fungal HDAC genes. The invention further provides methods for testing antifungal agents for potential synergy with fungal HDAC inhibitors, and thus provides antifungal compound which are identified according to the methods of the invention, and methods for treatment of fungal infections using such compounds.
Owner:METHYLGENE
Microbial compositions for use in combination with soil insecticides for benefiting plant growth
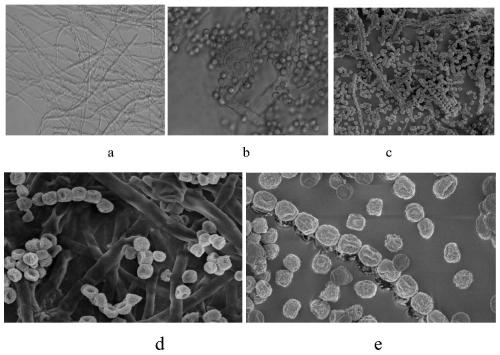
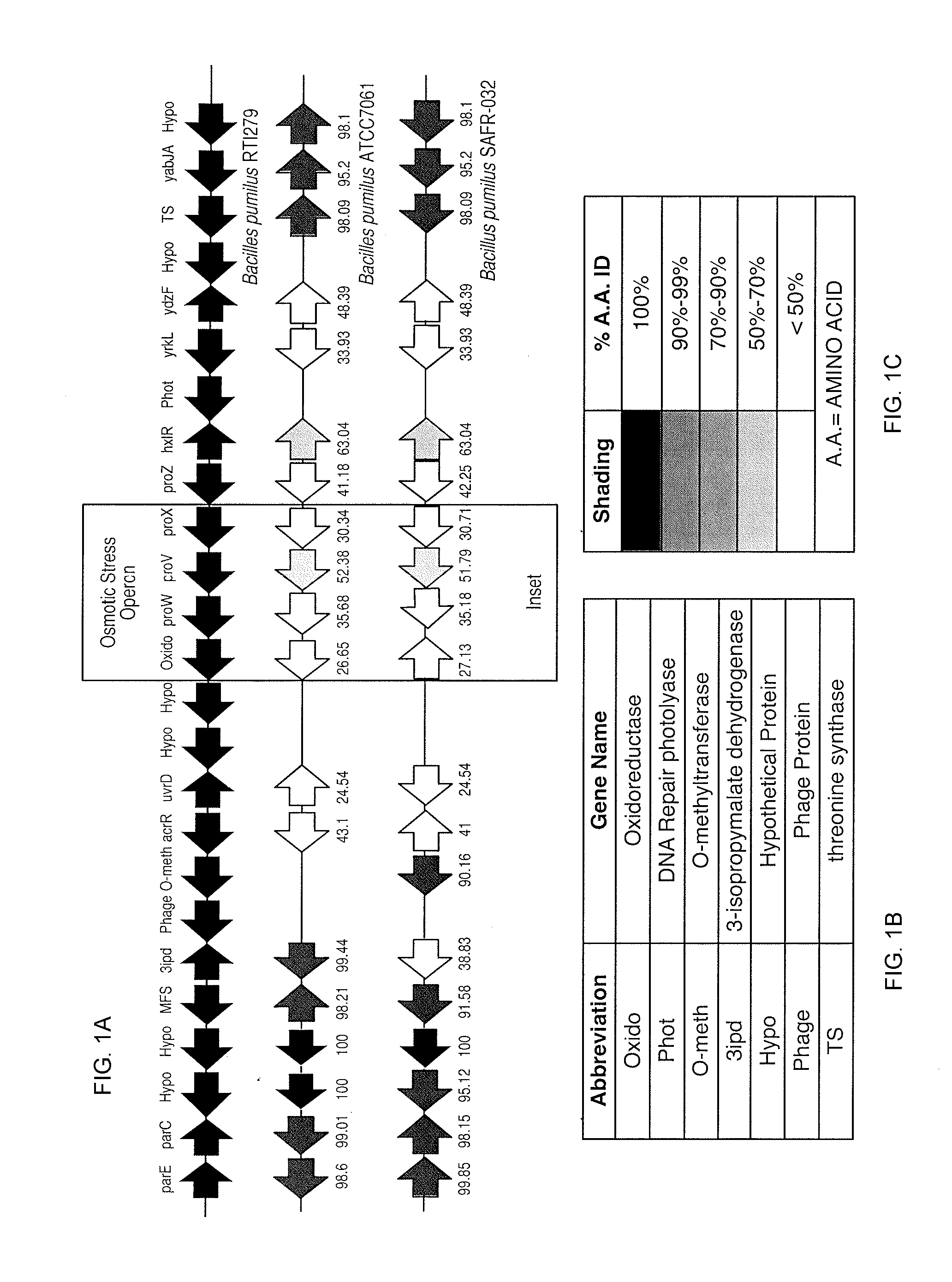
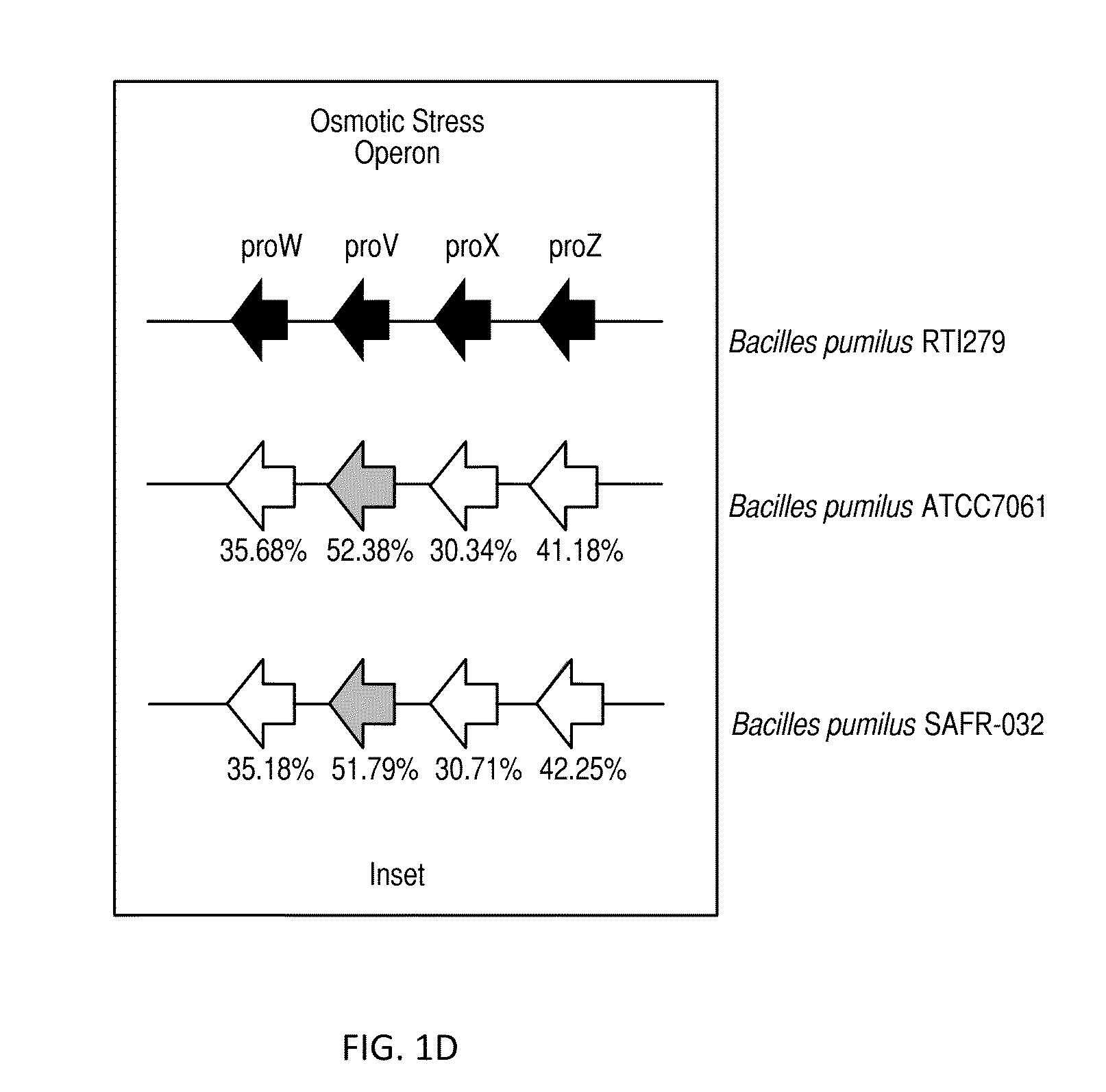
Compositions and methods are provided for benefiting plant growth. The compositions contain isolated bacterial or fungal strains having properties beneficial to plant growth and development that can provide beneficial growth effects when delivered in a liquid fertilizer in combination with a soil insecticide to plants, seeds, or the soil or other growth medium surrounding the plant or seed. The beneficial growth effects include one or a combination of improved seedling vigor, improved root development, improved plant health, increased plant mass, increased yield, improved appearance, improvedresistance to osmotic stress, improved resistance to abiotic stresses, or improved resistance to plant pathogens. The isolated bacterial strains include those of the Bacillus species including speciessuch as Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FMC CORP
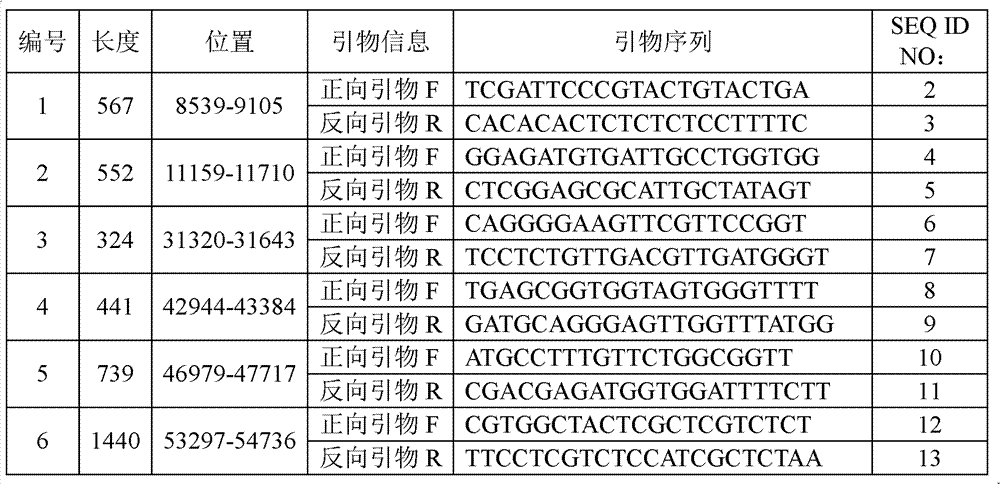
Nucleic acid, method for identifying pathotype of fungus strain and kit
The invention provides a nucleic acid. The nucleic acid has the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1 or has specific sequences in the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also provides a nucleic acid complementary with the above nucleic acid. The invention also provides a method for identifying the pathotype of a fungus strain. The fungus strain is verticillium dahliae. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a sample to be detected of complete genome DNA containing verticillium dahliae; (2) detecting whether a first molecular marker exists in the sample to be detected, wherein the first molecular marker is the above nucleic acid; and (3) judging the pathotype of verticillium dahliae according to the detection result in the step (2). The invention also provides a kit.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
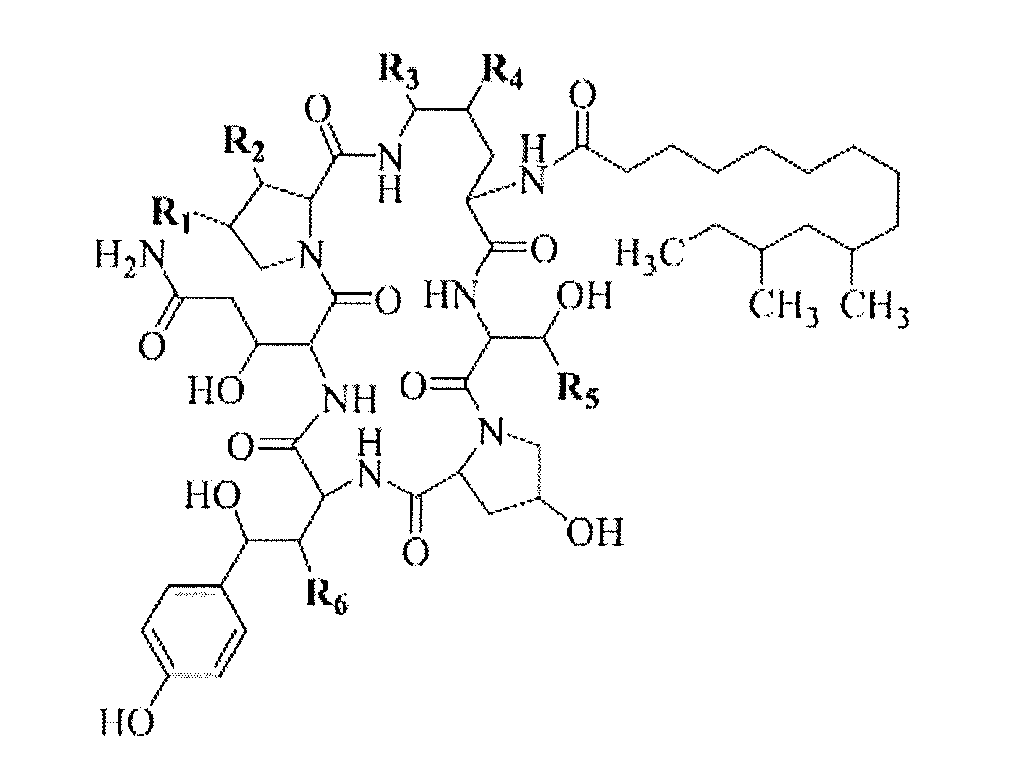
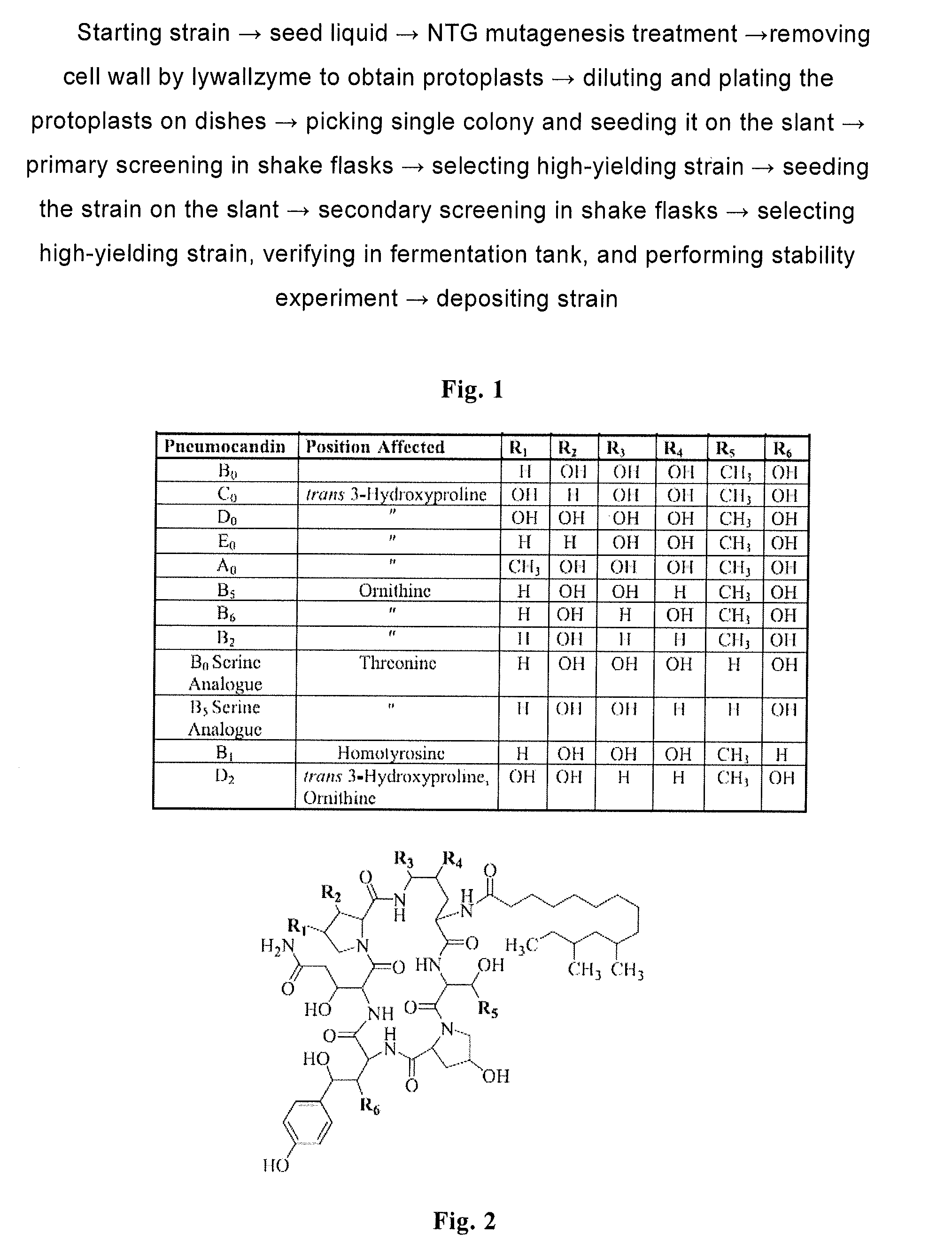
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof
High yield antibiotics producing fungus strain, preparation method and use thereof are provided. The fungus strain is a mutant derived from Glarea lozoyensis, and deposited in CGMCC with the accession number of CGMCC 2933. The preparation method concludes following steps: (a) mixing the culture media of Glarea lozoyensis strain ATCC 20957 with nitrosoguanidine, and obtaining mixture a; (b) mixing lywallzyme with the mixture a, and obtaining protoplasts; (c) regenerating the protoplasts, and obtaining single clones; and (d) culturing the single clones, then obtaining the mutant strain. This fungus strain has stable genetic and producing property, produces little impurities in fermentation, and is suitable to be used in industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECHWELL BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD
Methods For Producing Multiple Recombinant Polypeptides In A Filamentous Fungal Host Cell
ActiveUS20140212977A1Easy to modifyIncrease productionMicroorganismsOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyOrganism
The present invention relates to methods for constructing a filamentous fungal strain for production of multiple recombinant polypeptides having biological activity. The present invention also relates to methods for producing multiple recombinant polypeptides having biological activity in a filamentous fungal strain. The present invention also relates to filamentous fungal strains expressing multiple recombinant polypeptides having biological activity.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Fungus strain irpex iacteus for producing laccase, and culturing method and application thereof
InactiveCN101855973AGrow fastShorten the fermentation cycleOxidoreductasesHorticultureBio engineeringFermentation
The invention relates to a novel fast-growing fungus strain irpex iacteus for producing laccase efficiently, and a culturing method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The irpex iacteus sdu-5 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 28, 2009, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.3548. The strain can produce the laccase economically and efficiently under the condition that an inducer is added into a liquid nutrient medium or no inducer is added into a solid fermentation nutrient medium.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Harvesting method of microalgae mediated by fungus
InactiveCN102391953AControl the cost of collectionEconomic gainUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesHigh densityFiltration
The invention provides a harvesting method of microalgae mediated by fungus. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) transferring microalgae; (2) culturing the microalgae in high density; (3) culturing spores of fungus capable of balling; (4) adding fresh spore suspension into a microalgae culture medium; (5) forming a fungus-mediated large-grained fungus-algae homobium; and (6) harvesting the large-grained bacillus-algae homobium by a filtration method. According to the method, the fungus strain capable of balling is introduced and cultured in a mixing way in the microalgae culture medium to be harvested, so that the aim of symbiosis and balling of fungus and microalgae can be achieved, and the fungus-mediated large-grained fungus-algae homobium can be harvested by virtue of a simple filtration method.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Fungal strains and methods of use
ActiveUS20180037919A1High protein yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesBiotechnologyEnzyme
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Efficient biocontrol trichoderma asperellum for tobacco fusarium root rot and application thereof
ActiveCN112852638AClear growth-promoting effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides efficient biocontrol trichoderma asperellum for tobacco fusarium root rot and application thereof, the preservation name of the trichoderma asperellum is trichoderma asperellum Tr-0111, the trichoderma asperellum is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation date is August 21, 2020, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2020441; according to the research, soil microorganisms are separated and screened to obtain an efficient biocontrol fungus strain with a relatively good inhibiting effect on tobacco fusarium root rot, the variety of the strain is determined by utilizing a method of combining traditional morphology and modern molecular biology, and the growth promoting effect of the strain on tobacco is determined; a foundation is laid for further development of research on the control effect and bacteriostatic active substances of efficient biocontrol bacteria potted plants and productization and industrial production of biocontrol bacteria, and the efficient biocontrol trichoderma asperellum has certain scientific basis and application value for biological control of soil-borne diseases in main tobacco-growing areas in Henan province.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Fungus strain for degrading polyurethane plastic and culture method and application of fungus strain
The invention provides a fungus strain A. flavus G10 for degrading polyurethane plastic. The microorganism preservation number of the fungus strain A. flavus G10 is GDMCC 60537. The invention also provides a method for culturing the fungus strain A. flavus G10. The method includes the steps of isolating the fungus strain from the intestinal tract of a cricket; adopting PU as a unique carbon sourcefor culturing the fungus strain in a liquid culture medium to obtain a culture solution; diluting the culture solution and coating a solidified nutrient agar culture medium containing tetracycline antibiotics and a potato glucose agar culture medium with the culture solution to obtain cultured growing products. The cultured growing products are subcultured on fresh plates at 30 DEG C until a single fungus strain is obtained on each plate. The fungus strain A. flavus G10 can degrade the polyurethane plastic quickly.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microbial compositions for use in combination with soil insecticides for benefiting plant growth
Compositions and methods are provided for benefiting plant growth. The compositions contain isolated bacterial or fungal strains having properties beneficial to plant growth and development that can provide beneficial growth effects when delivered in a liquid fertilizer in combination with a soil insecticide to plants, seeds, or the soil or other growth medium surrounding the plant or seed. The beneficial growth effects include one or a combination of improved seedling vigor, improved root development, improved plant health, increased plant mass, increased yield, improved appearance, improved resistance to osmotic stress, improved resistance to abiotic stresses, or improved resistance to plant pathogens. The isolated bacterial strains include those of the Bacillus species including species such as Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus licheniformis, and Bacillus subtilis.
Owner:FMC CORP
Application of endophytic cladosporium fungus of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA in preparing steroid saponin
ActiveCN107723247AAvoid pollutionAvoid disadvantagesFungiMicroorganism based processesLiriope spicataMicroorganism
The invention provides application of endophytic cladosporium fungus of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA in preparing steroid saponin, and relates to the technical field of microorganisms. The application is mainly used for solving the problems that most existing steroid saponin of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA is from extracts of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA, tubers of liriopespicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA are long in production period, low in steroid saponin content and high in saponin extraction cost, and accordingly the market volume of the steroid saponin of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA is limited. The fungus is separated from living tubers of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA, authenticated as Cladosporium sp.EF111 by means of the 18 S rDNA sequence, andpreserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection. The preservation date is December 7th, 2016, and the preservation number of CCTCC No:M2016725. According to the application, liriope spicatavar.prolifera Y.T.MA produced by a liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA GAP base which is the original production place of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA in Oumiao town, Xiangyang city in Hubeiprovince, endophytic fungus strain liquid of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA is used for fermentation, and the steroid saponin of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA is produced. The endophyticfungus is an important microorganism for finding new resources of steroid saponin of liriope spicata var.prolifera Y.T.MA.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
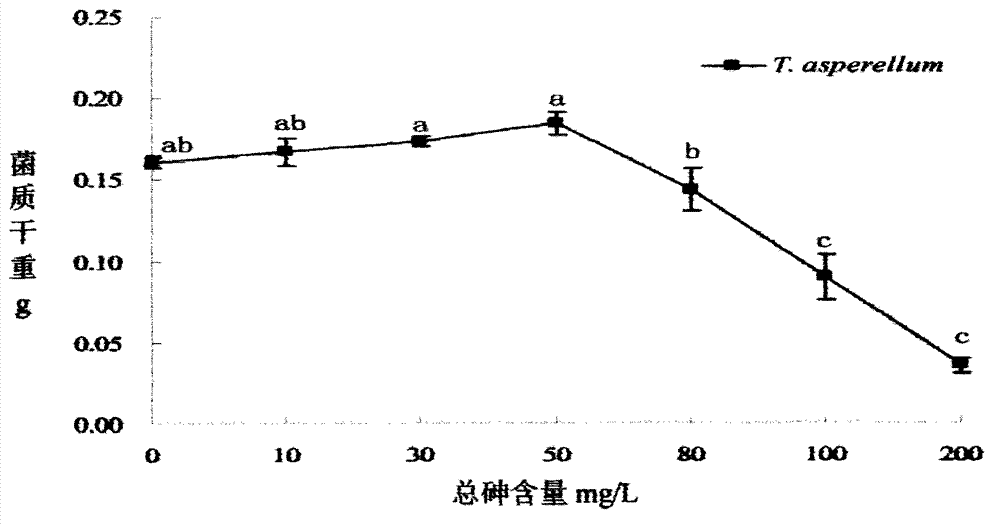
Method for screening trichoderma asperellum and application thereof
InactiveCN102876586AReduce contentGuaranteed normal growthFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementArsenic pollutionScreening method
The invention discloses a method for screening trichoderma asperellum and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting an arsenic pollution soil sample; separating fungi from the soil sample in a laboratory; purifying the fungi, and transferring the purified fungi to a selective culture medium of trichoderma; and culturing the fungi in different arsenic concentrations by taking a fungus strain of which the growth condition is the best on the selective culture medium as an object, and observing the growth condition of a bacterial colony and the tolerance of the bacterial colony on arsenic to screen the trichoderma asperellum.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com