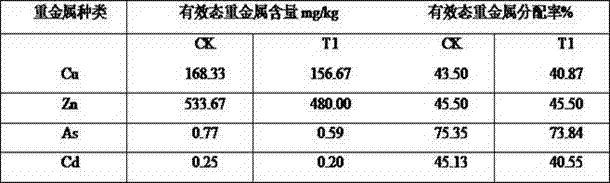
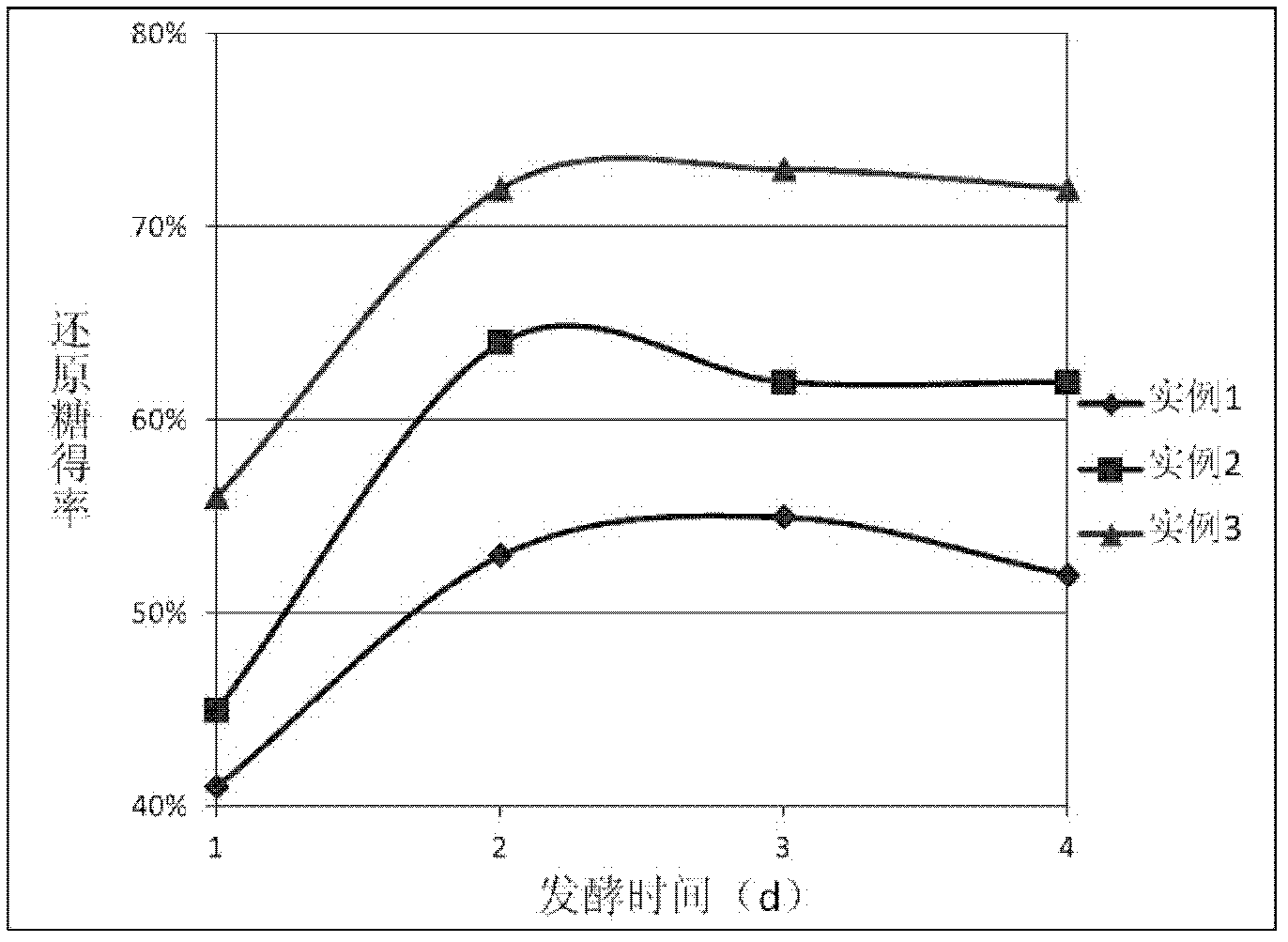
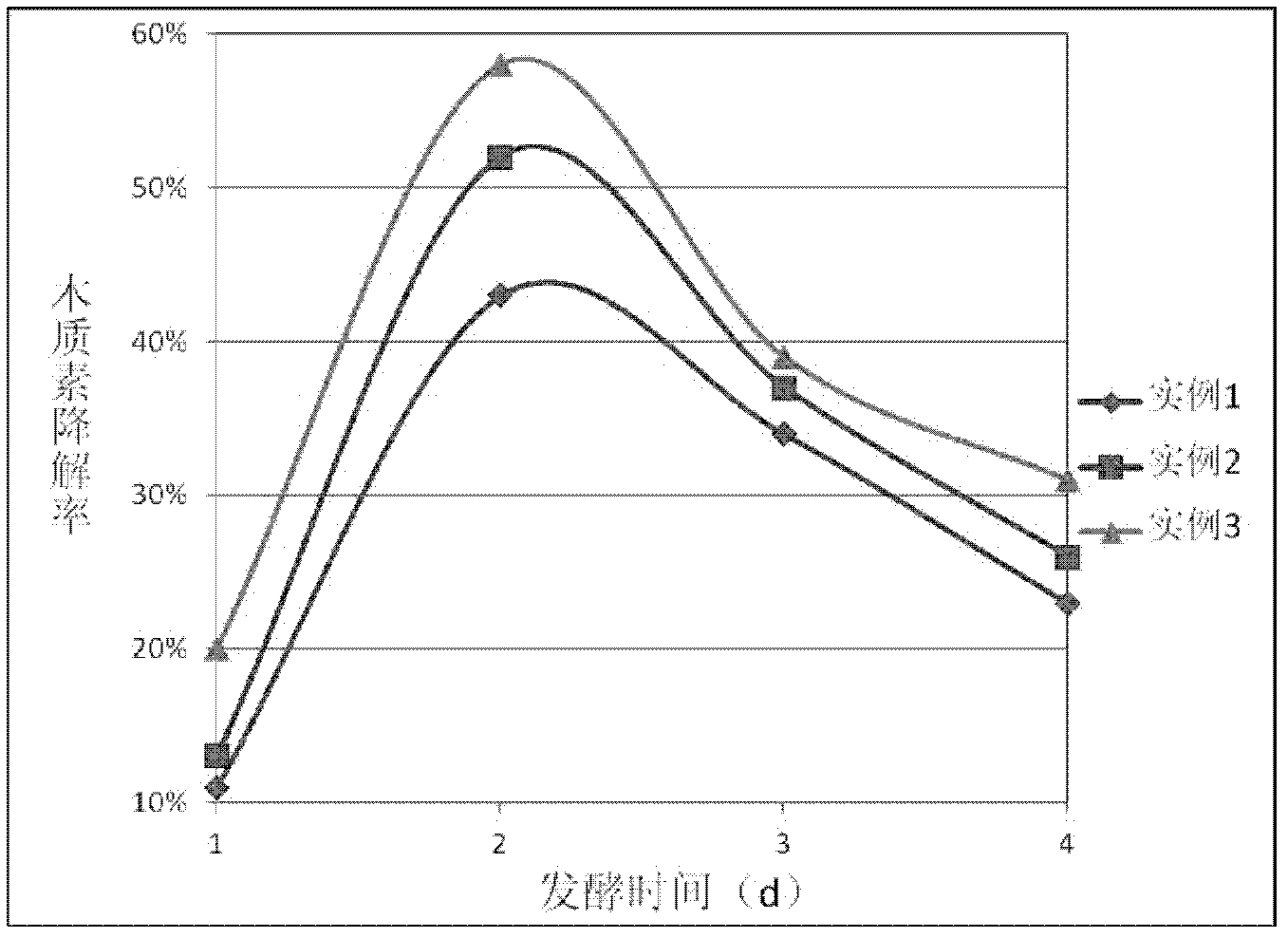
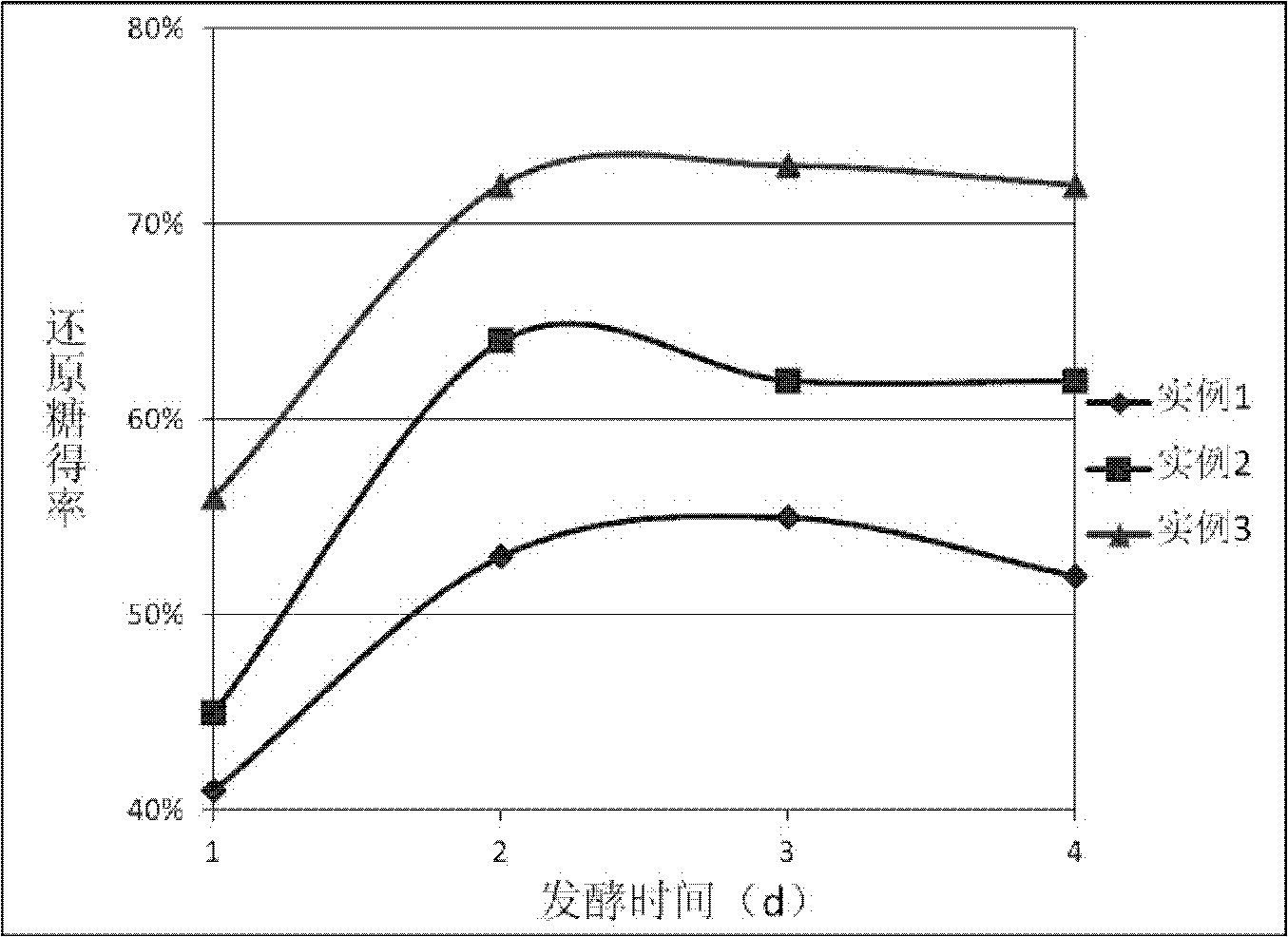
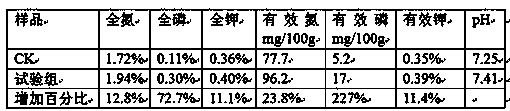
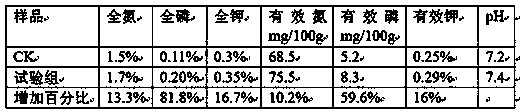
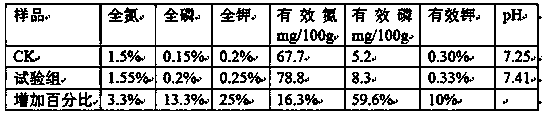
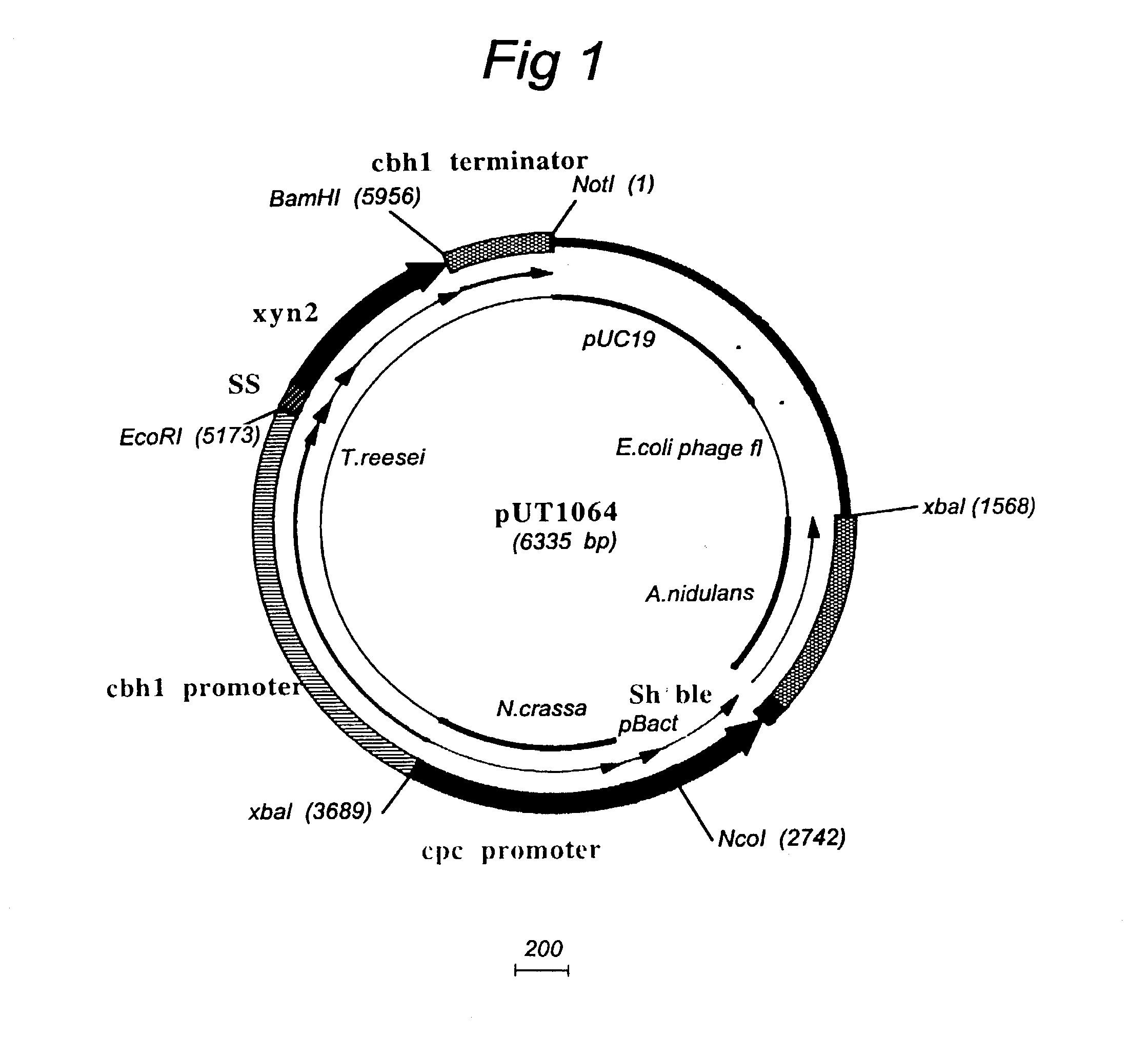
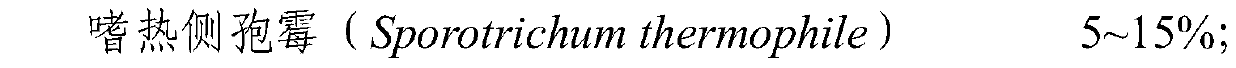Patents
Literature
216 results about "Chrysosporium species" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clinical significance. Species of Chrysosporium are occasionally isolated from skin and nail scrapings, especially from feet, but, because they are common soil saprotrophs, they are usually considered as contaminants.
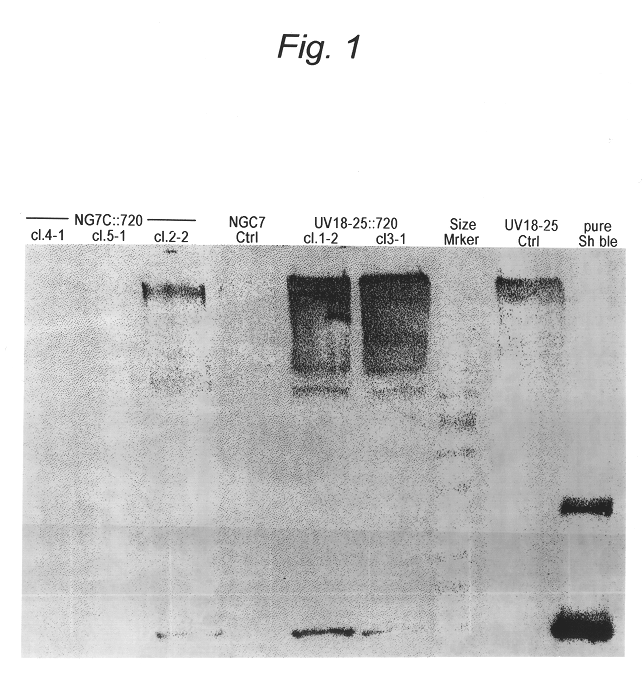
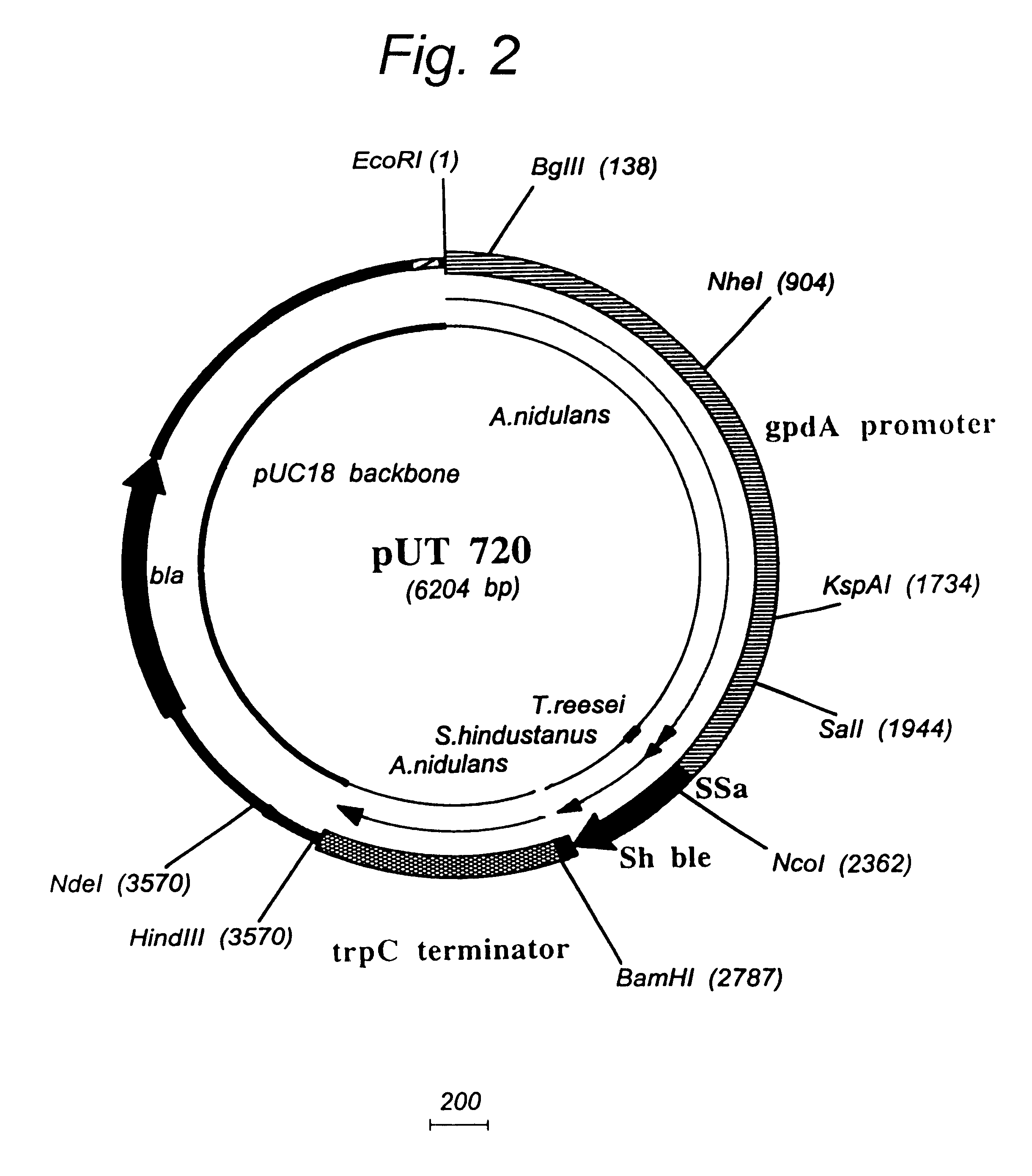
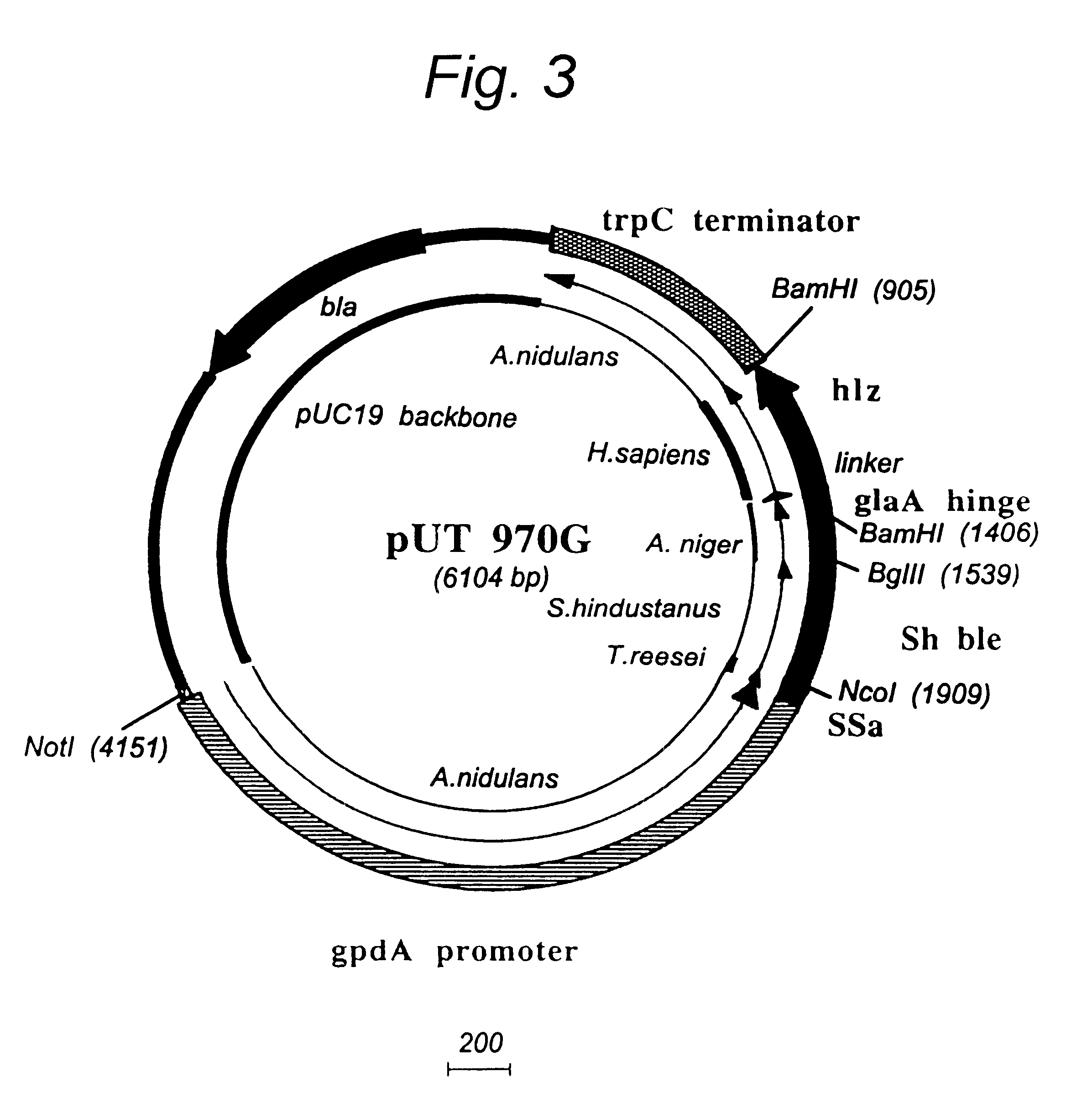
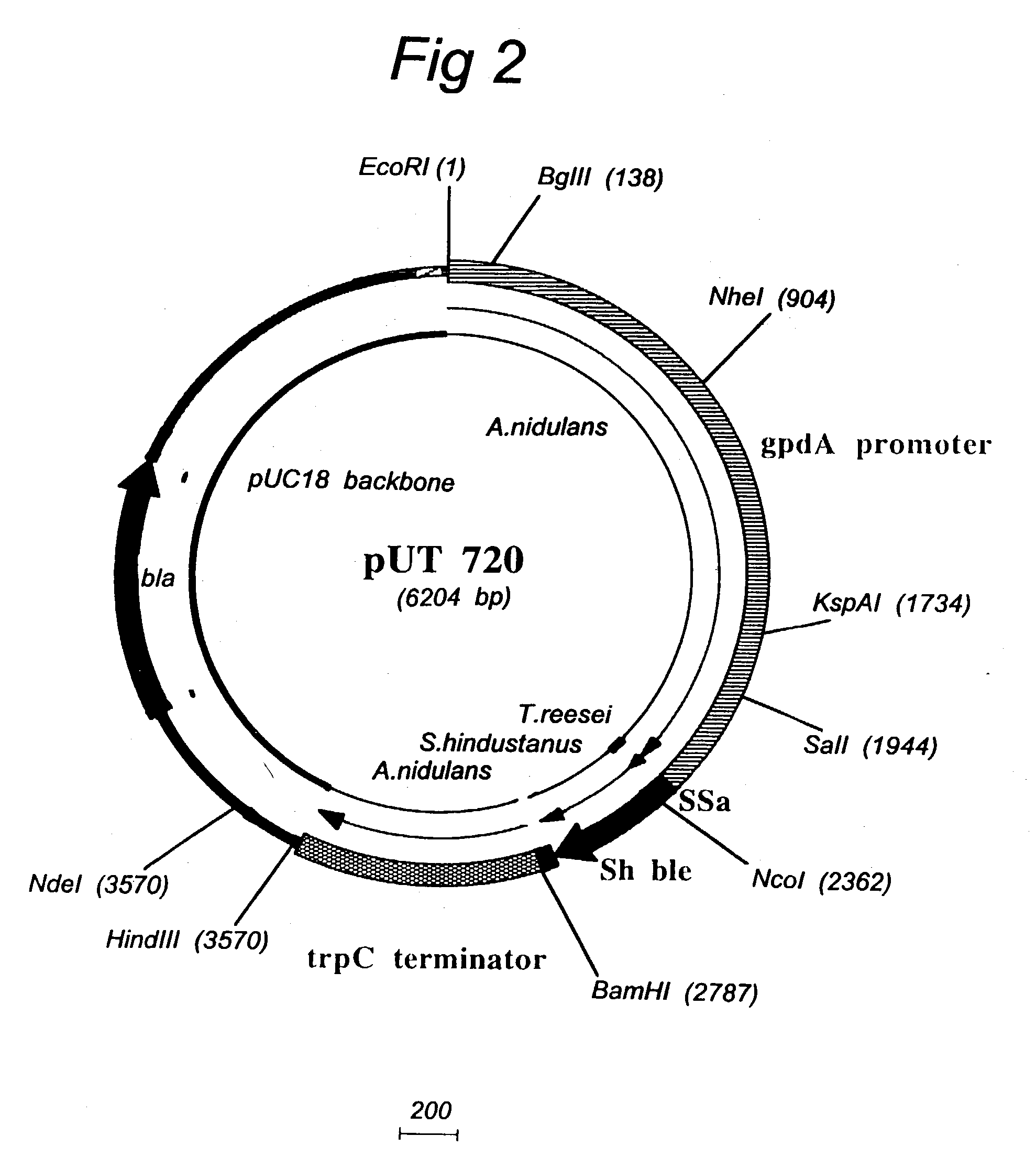
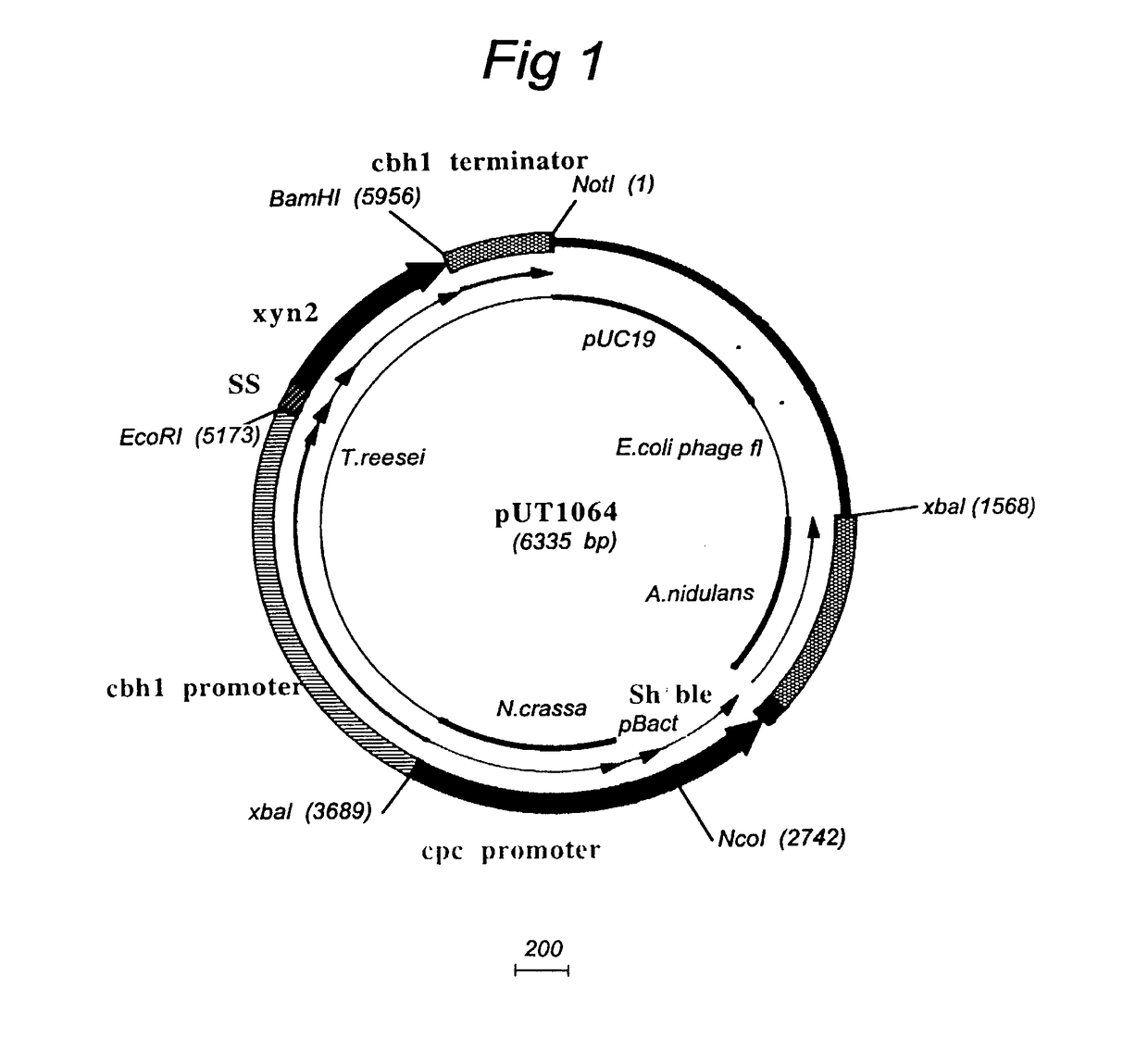
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
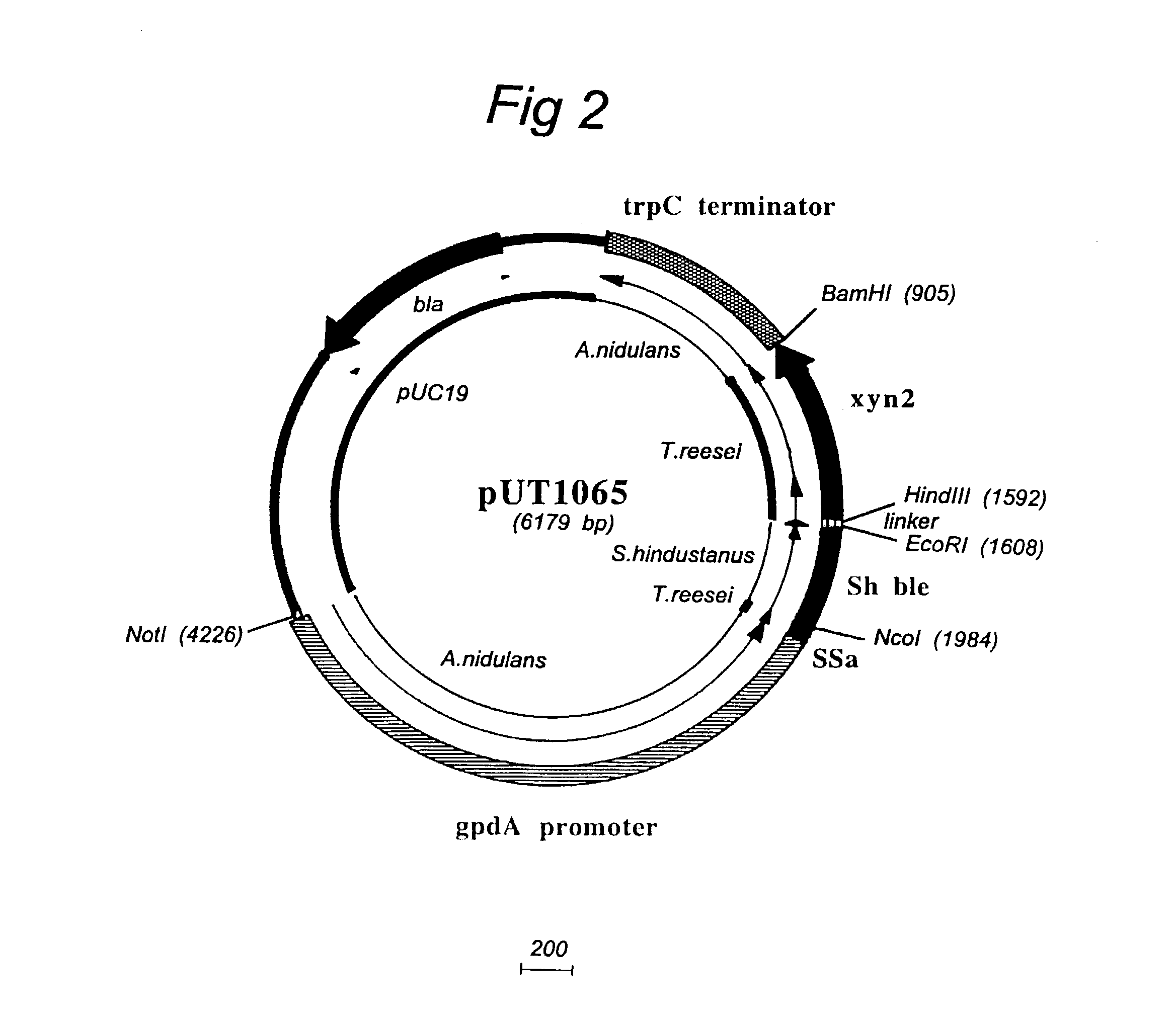
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Compound microbial bacterial preparation for degrading crop straw and preparation method and application of compound microbial bacterial preparation
ActiveCN102690755ASolve shipping problemsSolve storage difficultiesBio-organic fraction processingFungiMetabolitePhosphate
The invention relates to a compound microbial bacterial preparation for degrading crop straw and a preparation method and application of the compound microbial bacterial preparation. The compound microbial bacterial preparation is prepared from bacillus subtilis, bacillus cereus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus flavus, trichoderma reesei, trichoderma longibrachiatum, sporotrichum thermophile and phanerochaete chrysosporium through solid fermentation. The compound microbial bacterial preparation can shorten the decomposition time and improve the decomposition efficiency of the crop straw. Microorganisms generate various effective metabolic products with nitrogen fixation and phosphate solubilizing functions and a high disease and pest resistance effect in the fermentation process, so that the compound microbial bacterial preparation is favorable for improving the soil structure and the yield and the quality of crops.
Owner:DEZHOU YUANHE AGRI TECH DEVCO
Pulping and papermaking process through multiple-composition biological enzyme method
InactiveCN102345244AReduce consumptionImprove product qualityNon-fibrous pulp additionPaper/cardboardBlack liquorWastewater
The invention discloses a pulping and papermaking process through a multiple-composition biological enzyme method. The method is a biopulping method, which adopts a production process for preparing paper pulp through pulping and fermenting by using a multiple-composition biological enzyme method (phanerochaete, phanerochaete chrysosporium, xylanase, glucoamylase, yeast), adopts agricultural straws, rice and wheat straws, cotton stalks, rape stalks, reeds, bamboo, wood and the like as main raw materials, and comprises treatments of glass cutting, impurity removing, puffing, fermenting through multiple-composition biological enzyme, pulp washing, pulp selecting, defibrination and separation to form the pulp. According to the present invention, no black liquid is generated during the pulping process, the water from fermenting and pulping is recycled so as to achieve zero discharge of wastewater.
Owner:王凤忠
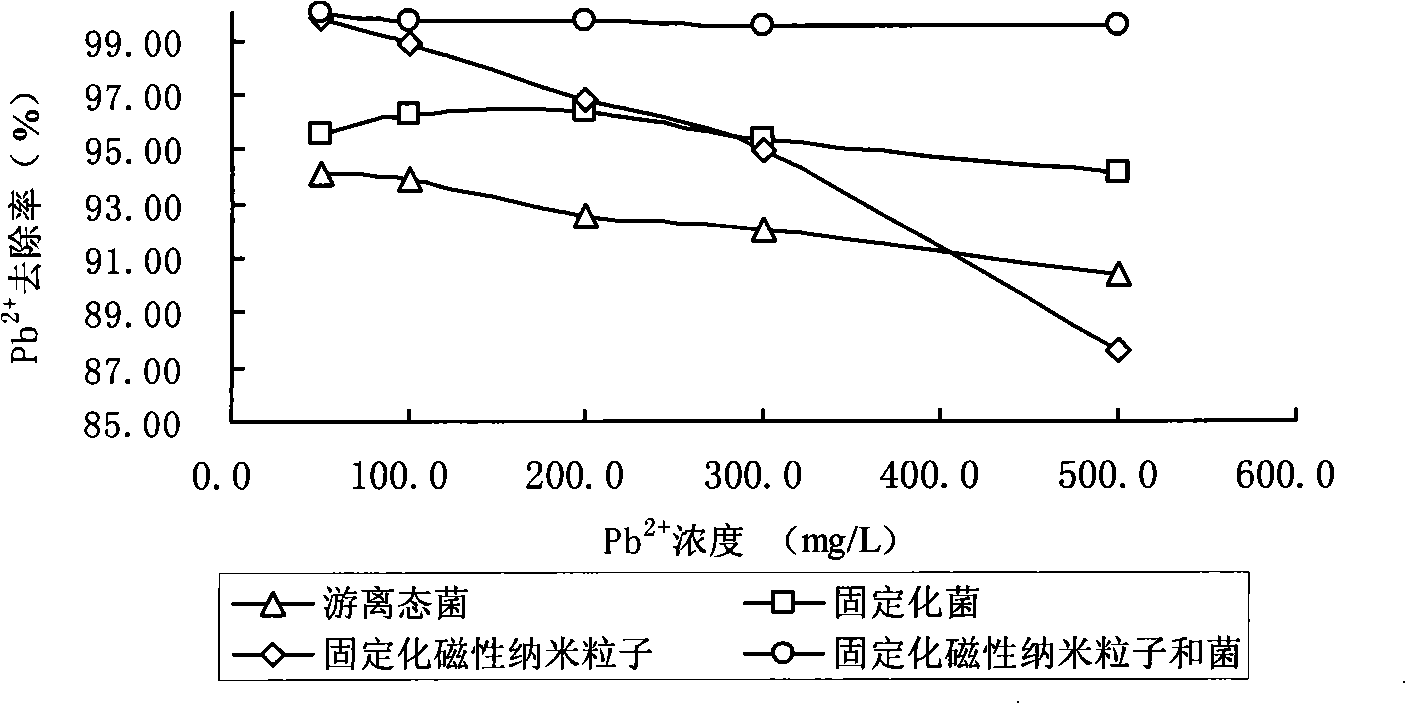
Magnetic biological adsorption agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101314123APlay an auxiliary adsorption effectHigh removal rateOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSorbentWastewater
The invention discloses a magnetic biological sorbent. The sorbent uses calcium alginate as a carrier, and is embedded with phanerochaete chrysosporium powder and magnetic nanometer particles, wherein, the mass ratio of the phanerochaete chrysosporium powder to the magnetic nanometer particles to the calcium alginate is 1 to (0.5-1.25) to (8-10). The invention also discloses a method for preparing the magnetic biological sorbent. The method comprises the following steps of: adding a mixture of the magnetic nanometer particles and the phanerochaete chrysosporium powder into a 1 to 2 mass concentration calcium alginate solution with 1 to 2 mass concentration, the dosage of the mixture in the solution being between 0.125 and 0.225g / mL, stirring evenly, and obtaining the magnetic biological sorbent through an immobilization process. The magnetic biological sorbent has the advantages of high adsorption efficiency, good selectivity, low cost, simple preparation process and treatment process and so on, and can be effectively applied to the treatment of lead metal in industrial wastewater.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts
InactiveUS20040002136A1Minimise risk of degradationAvoid necessityFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyMutant
A novel transformation system in the field of filamentous fungal hosts for expressing and secreting heterologous proteins or polypeptides is described. The invention also covers a process for producing large amounts of polypeptide or protein in an economical manner. The system comprises a transformed or transfected fungal strain of the genus Chrysosporium, more particularly of Chrysosporium lucknowense and mutants or derivatives thereof. It also covers transformants containing Chrysosporium coding sequences, as well expression-regulating sequences of Chrysosporium genes. Also provided are novel fungal enzymes and their encoding sequences and expression-regulating sequences.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Preparation method for sludge aerobic composting composite inoculum
ActiveCN104293694APromote degradationPromote growth and reproductionFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisSludge
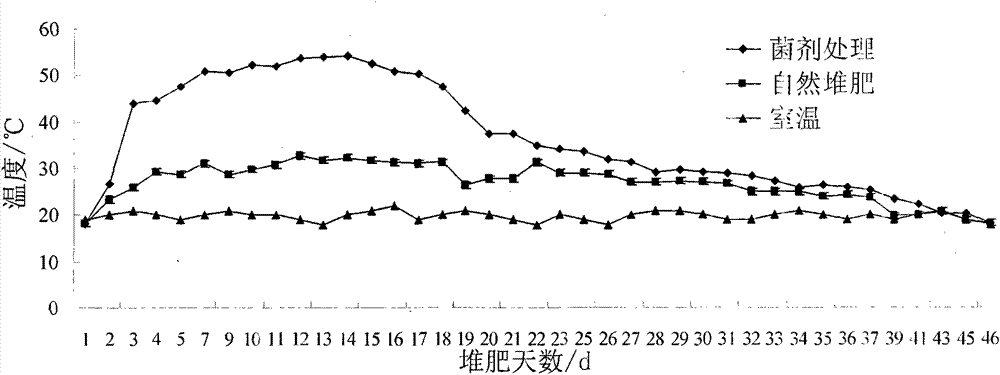
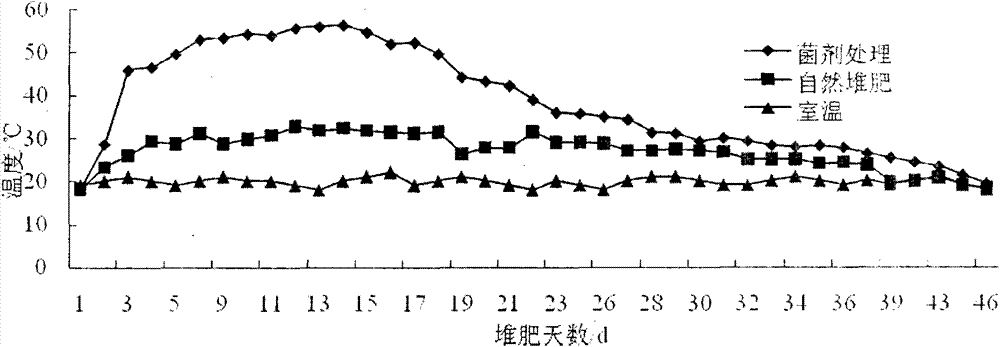
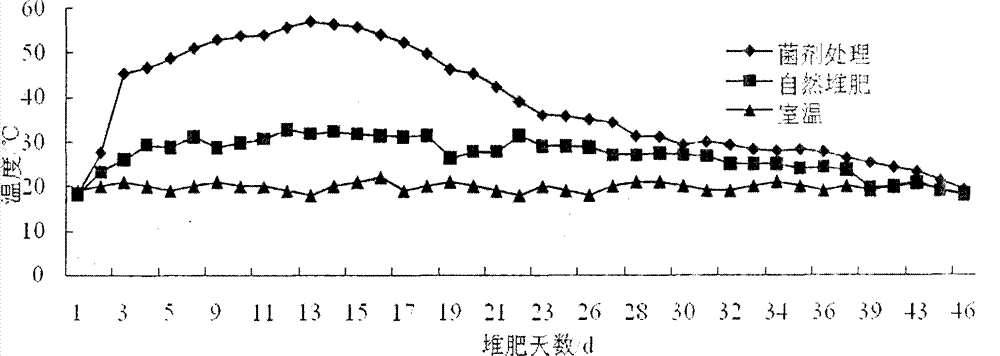
The invention discloses a preparation method for a sludge aerobic composting composite inoculums. According to the method, the Bacillus subtilis (No. 10066), the Bacillus licheniformis (No. 10103), the Lactobacillus acidophilus (No. 6075), the Candida utilis (No. 31272), and the Phanerochaete chrysosporium (No. 40719) that are preserved in China Center of Industrial Culture Collection (CICC) are subjected to individual culture, and are then mixed in proportion and inoculated into a fermentation culture to perform expanded culture, thus obtaining the composite inoculum. At the initial stage of inoculating the composite inoculums to sludge aerobic composting, the time for the compost body to reach a high temperature period is advanced by 4-6 days, the compositing period is shortened by 11-14 days, the stack moisture content is decreased by 18%-25%, and the total nitrogen content of the compost body is increased by 15%-20%, thus improving the composting effect.
Owner:GUANGXI BOSSCO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Complex microbial agent for composting fermentation and application thereof
InactiveCN103497915AQuick breakdownAccelerate the rate of decayBio-organic fraction processingFungiLivestock manureMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a complex microbial agent for composting fermentation and application thereof. The complex microbial agent is a solid inoculant which comprises phanerochaete chrysosporium, streptomyces griseorubens, bacillus subtilis, bacillus methylotrophicus and bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The complex microbial agent is a complex microbial system comprising various microorganisms which have complementary and synergistic functions; the microbial system integrates quick fermentation heat production, biological deodorization and compost material decomposition and degradation and has the effects of a biological fertilizer; the livestock manure compost can be quickly heated to kill off harmful organisms at high temperature; the unpleasant smell is obviously reduced to solve the problem of environment pollution caused by poultry excrement; the microorganisms can be quickly propagated in the poultry excrement fermentation process; the organic matters such as lignocellulose in the excrement can be quickly and effectively decomposed so as to increase the decomposition speed of the compost material and improve the quality of the compost product; the complex microbial agent can be used for producing the biological organic fertilizer so as to reduce the agricultural production cost.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for pre-processing corn stalks through physical-chemical-biological method
InactiveCN105255953AImprove degradation rateImprove availabilityFood processingBiofuelsChrysosporium speciesFermentation
The invention relates to a method for pre-processing corn stalks through a physical-chemical-biological method. The corn stalks are firstly smashed and physically processed, then the corn stalks are chemically processed through dilute alkali, and finally, the corn stalks are biologically processed through phanerochaete chrysosporium and cellulose degradation bacteria. Lignin removal is facilitated due to dilute alkali processing, the corn stalks can be fully degraded easily because of mixed fermentation, the utilizing rate is increased, and microorganisms producing ethyl alcohol are inoculated into the pre-processed stalks to produce ethyl alcohol, or feeding yeast is inoculated to produce protein feed. The method is simple in technology and convenient to implement.
Owner:刘云平
Chrysosporium cellulase and methods of use
A computer-based method and apparatus for the analysis specification and support of work processes. The system is designed to support multiple interdependent decisions, at least some of which require collaboration among multiple participants (116). Work processes are modeled using an application framework (99) used to develop abstract, decision (100) process models. The decision (100) process models are used as a pattern to instantiate concrete process models that incorporate the work defined by the abstract process. The process model is then used to instantiate project models that incorporate the required work from the process. The project models are used to direct and guide the behavior of the participants (116) in the work process.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Microorganism compositions for degrading straw, preparation thereof and method for degradation of straw
InactiveCN1544610ADegradation reachesLower pHMicroorganismsSolid waste disposalBacterial strainChrysosporium species
The invention discloses a microbe combination of degraded stalks and its preparing method as well as a method of degrading the stalks, where the microbe combination includes: liquid bacterial strain, and solid bacterial strain, the liquid bacterial strain is made by culturing plant lactobacillus, Streptococcus faecali, and Candida utilis in the culture medium and the solid bacterial strain is made by culturing Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Pleurotus ostreatus; the method of degrading the stalks by the combination: mixing the liquid bacterial strain with the stalks raw material in weight ratio of 1 to 15000-25000, adding in 0.9% NaCl water solution to make the water ratio reach 65-70%, sealing and fermenting in a sealed container as 25-30deg.C for 7-10 days and take out; adding in the solid bacterial strain and mix uniformly, fermenting at 25-30 deg.C, and when the mycelium grows completely and drying into the finished products. It simulates the ecological mode of biodegrading stalks in the nature, fully uses specific enzyme system of each bacterial strain, and achieves the purpose of biodegrading stalks.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Biological straw decomposition agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103614321ANo antagonistic effectShorten the maturity timeBio-organic fraction processingFungiBacteroidesDecomposition
The invention discloses a biological straw decomposition agent and a preparation method thereof and particularly relates to a biological straw decomposition agent taking funguses and bacteria as raw materials and a production method of the biological straw decomposition agent. According to the biological straw decomposition agent, trichoderma longibrachiatum, aspergillus terreus, phanerochaete chrysosporium, paenibacillus amylolyticus and torulopsis candida are taken as compound stains; a cellulolytic enzyme, a semi-cellulolytic enzyme and a ligninolytic enzyme are mainly produced; the strains have good mutualistic symbiosis and metabiosis effects and have no antagonisms. When the biological straw decomposition agent is used, the decomposition agent is uniformly scattered into fields after crop straws (wheat, corns and rice) are crushed and dispersed on the ground; the dosage of the biological straw decomposition agent is 30kg per 1hm<2> and then the straws and the decomposition agent are ploughed under the ground.
Owner:天津市武清区植保植检站
Composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent used for degradation of garden waste. The composite microbial agent is composed of composite bacterial liquid and a carrier, wherein the composite bacterial liquid comprises Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus siamensis, Bacillus tequilensis and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. The bacterial strains of the composite microbial agent produce synergism, so the composite microbial agent can substantially degrade a variety of macro-molecular components in the garden waste, improve the decomposition degree of the waste, enhance the nutrient structure and microfloras of compost and reduce heavy metal pollution. The invention also relates to a preparation method for the composite microbial agent, a method for degrading and converting the garden waste by using the composite microbial agent and fertilizer prepared from products obtained after degradation and conversion of the garden waste with the composite microbial agent.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Grass suppression straw biomass-base degradable mulching film and application
ActiveCN109135313AImprove toughnessHigh strengthClimate change adaptationPlant protective coveringsFiberAdhesive
The invention discloses a grass suppression straw biomass-base degradable mulching film and application. A method for preparing the grass suppression straw biomass-base degradable mulching film includes S1, biologically pretreating straw, to be more specific, compounding phanerochaete chrysosporium and streptomyces rochei, then inoculating the phanerochaete chrysosporium and the streptomyces rochei on the straw, adjusting carbon-nitrogen ratios and moisture contents of material systems and carrying out aerobic fermentation; S2, softening, disassembling and separating straw fibers, to be ore specific, softening the pretreated straw fibers and disassembling the pretreated straw fibers until the fiber lengths are 0.5-2 cm; S3, forming straw biomass-base mulching films, to be more specific, uniformly mixing the straw fibers, wood pulp, methyl celluloses, sodium alginate, gelatin, polyamide epichlorohydrin resin, alkyl ketene dimmers, polyacrylamide, glycerol, alkenyl succinic anhydride grafted starch adhesive and biochar with one another, and carrying out vacuum dehydration, squeezing, drying and forming to obtain the grass suppression straw biomass-base degradable mulching film. The grass suppression straw biomass-base degradable mulching film can be applied to the field of paddy rice seedling raising.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Corn straw fermentation microorganism agent and preparation method and fermentation method thereof
ActiveCN103642726AReasonable formulaEasy to useBio-organic fraction processingFungiBacillus licheniformisBiotechnology
The invention discloses a corn straw fermentation microorganism agent which consists of phanerochaete chrysosporium, trichoderma koningii, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis and monilia tropicalis. The corn straw fermentation microorganism agent disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the microorganism agent is reasonable in formula and convenient to use; the straw rotting speed is high; the corn straw fermentation microorganism agent has the characteristics of new combination, stable structure, high enzyme activity, high microbial content and the like. The corn straw fermentation microorganism agent can be used for performing high-efficiency and environment-friendly fermentation on corn straw materials, so that a feed can contain a large amount of microorganism live cells, clastic enzymes and other active components, and the utilization rate of the corn straw materials can be effectively increased. The practical significance of solving the problem of environment pollution is achieved; furthermore, the actual application values such as the protein content and the nutritional value in the corn straw materials can be improved; good preconditions are created for recycling application of corn straws.
Owner:TIANJIN OCEAN PAL CAROL BIOTECH
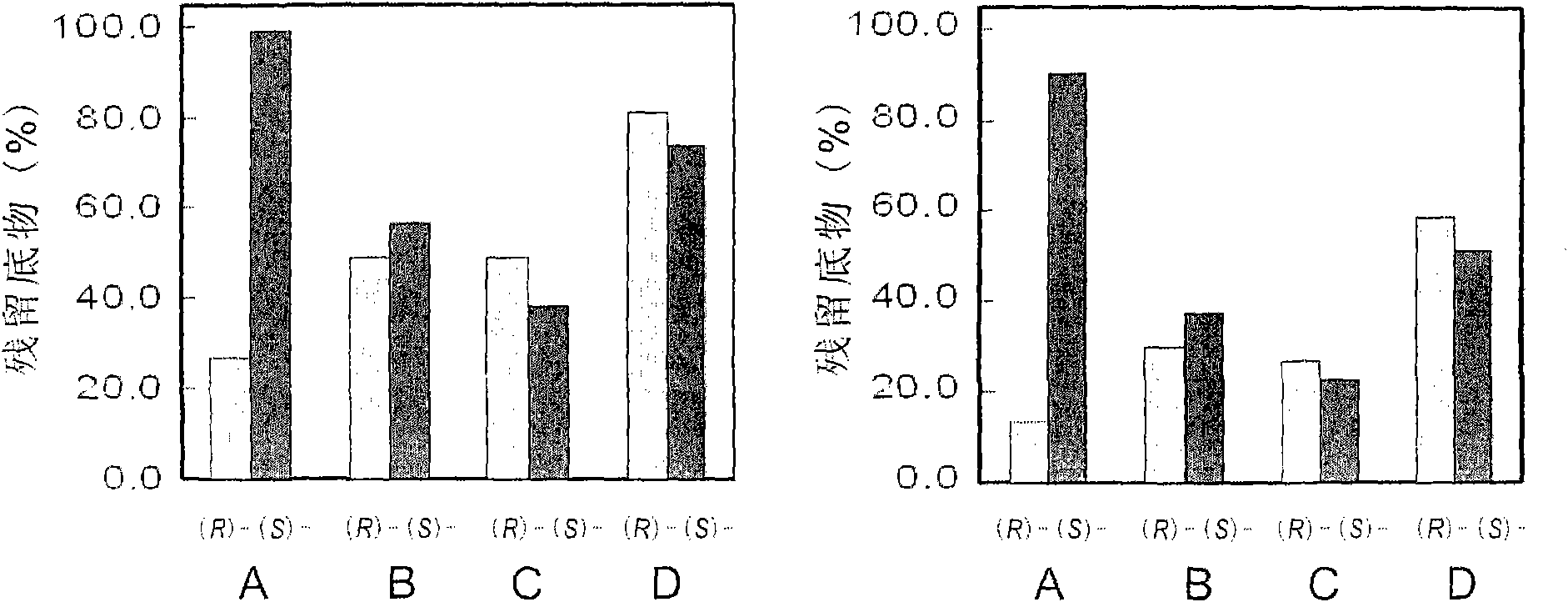
High-enantiomer selectivity epoxide hydrolase and gene coded thereby
The invention belongs to the field biotechnology and discloses use of an RT-PCR method in cloning an epoxide hydrolase gene (PchEHA) from a BKM-F1767 strain (Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F1767) of fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium and a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of a coding region of the PchEHA. Cloned plasmid pTEHA containing the gene, a recombinant expression plasmid pET28EHA containing the gene and a genetic engineering strain Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / PeT28EHA containing the PchEHA gene are provided to prepared the recombinant epoxide hydrolase. The epoxide hydrolase of the invention has catalytic activity for various epoxides and shows enantiomer selectivity of different degrees, particularly high enantiomer selectivity for epoxyethylbenzene. The recombinant epoxide hydrolase of the invention can be used in the fields of the kinetic resolution of a chiral epoxide racemic mixture, the asymmetric catalysis of epoxides, and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Process for preparing fuel ethanol by using straw fiber materials
This invention discloses a method for producing fuel ethanol from a straw fibre raw material, comprising: (1) raw material selection; (2) disintegration; (3) pre-processing; (4) double-enzyme saccharifying; (5) sterilization; (6) enlargement culture and application of Pachysolen tannophilus P-01; (7) fermentation; (8) distillation; characterizing: the pre-processing employs white-rot fungi solid culture to decompose lignin. The procedures comprise: (1) bacterium: Coridus versicolor; (2) crude laccase production: (1) culture media producing condition,(2) fermentation: inoculate 6 parti-color Coriolus versicolor seed stopper per 1000ml, 28-30Deg C, 150rpm shake culture for 7d, remove the hypha by filtration so as to obtain the crude laccase; (3) crude peroxidase production: i. culture media, ii. fermentation: inoculate 6 rings of Phanerochete chrysosporium spores per 100ml, 37-39Deg C, static culture for 9d, remove hypha by filtration so as to obtain crude peroxidase; (4) conditions of enzyme liquid decomposing straw: add 1ml crude peroxidase and crude laccase respectively to the straw powder and mix homogenously, and then decompose the straw at 45Deg C, pH 4.5 for 72h. This invention can improve the ethanol yield and decease cost.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Extraction method of rice-wheat straw fibre for spinning
The invention relates to a spinning straw fiber extraction method. The spinning rice and wheat straw fiber extraction method is characterized in that the method includes the following steps: 1). the steam explosion pretreatment: straws are air-dried and then are cut into segments; 2). the pretreated straws are put in a steam blasting tank; 3). nutrient glucose and urea are recharged; 4). the strain degumming: first, choosing strains: choosing mushroom white rot fungi or planerochaete chrysosporium as the strain; second, to pave the steam explosion straw mixture obtained in the third step to be 10-100mm high; third, poking the strains onto the straw piles; fourth, culturing on the culturing bed; fifth, cleaning; sixth, bleaching; 5). irradiation curing: the bleached straw fiber is irradiated with Gamma rays with the irradiation amount of 2-10kgy to obtain the radiation curing straw fiber; 6). the straw fiber is oiled; 7) the straw fiber is dried; 8) the dried straw fiber is dispersed to obtain the spinning rice and wheat straw fiber. The invention has the characteristics of environmental protection and low cost.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV +1
Compound bacterium agent for treating green wastes of gardens as well as preparation method and application of compound bacterium agent
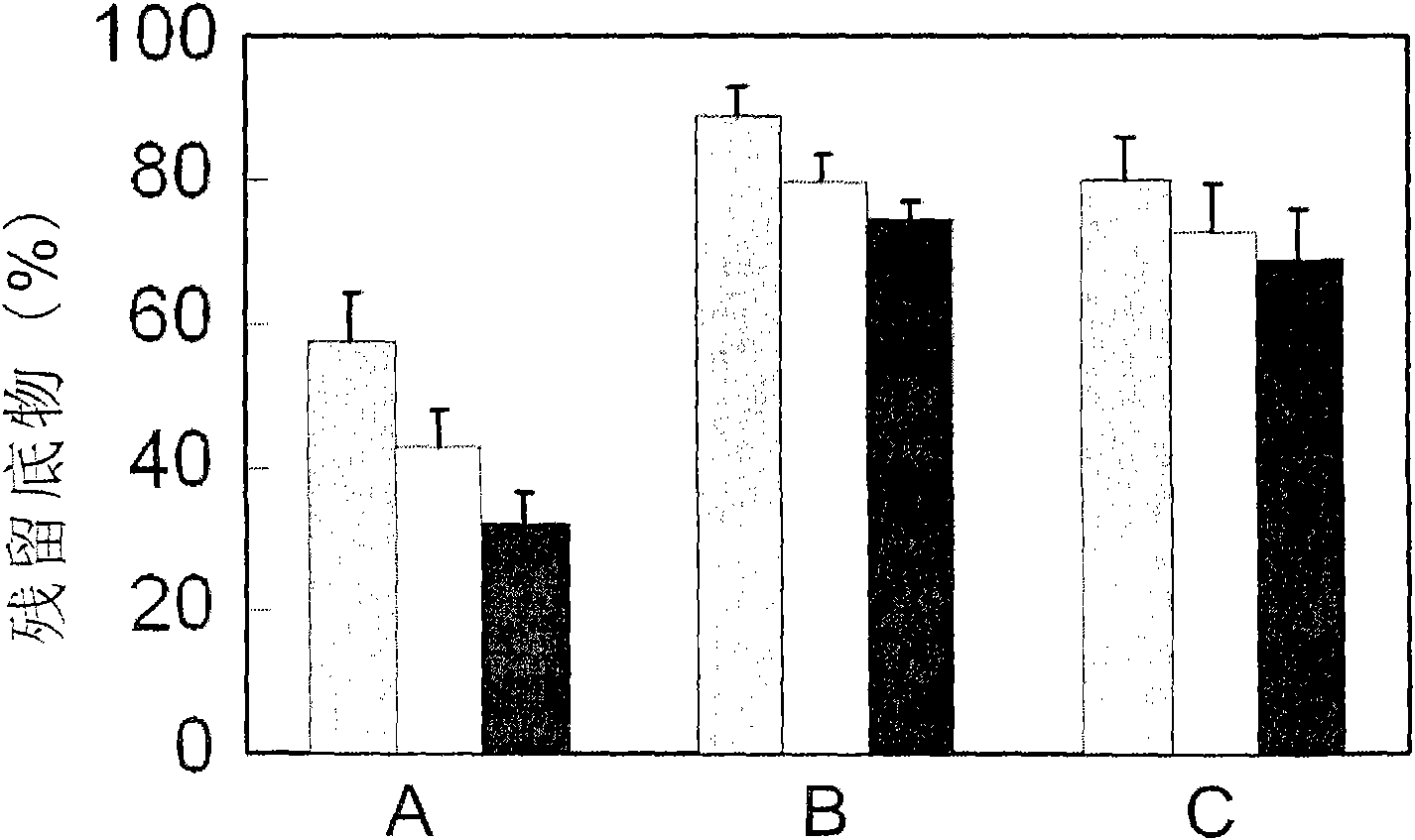
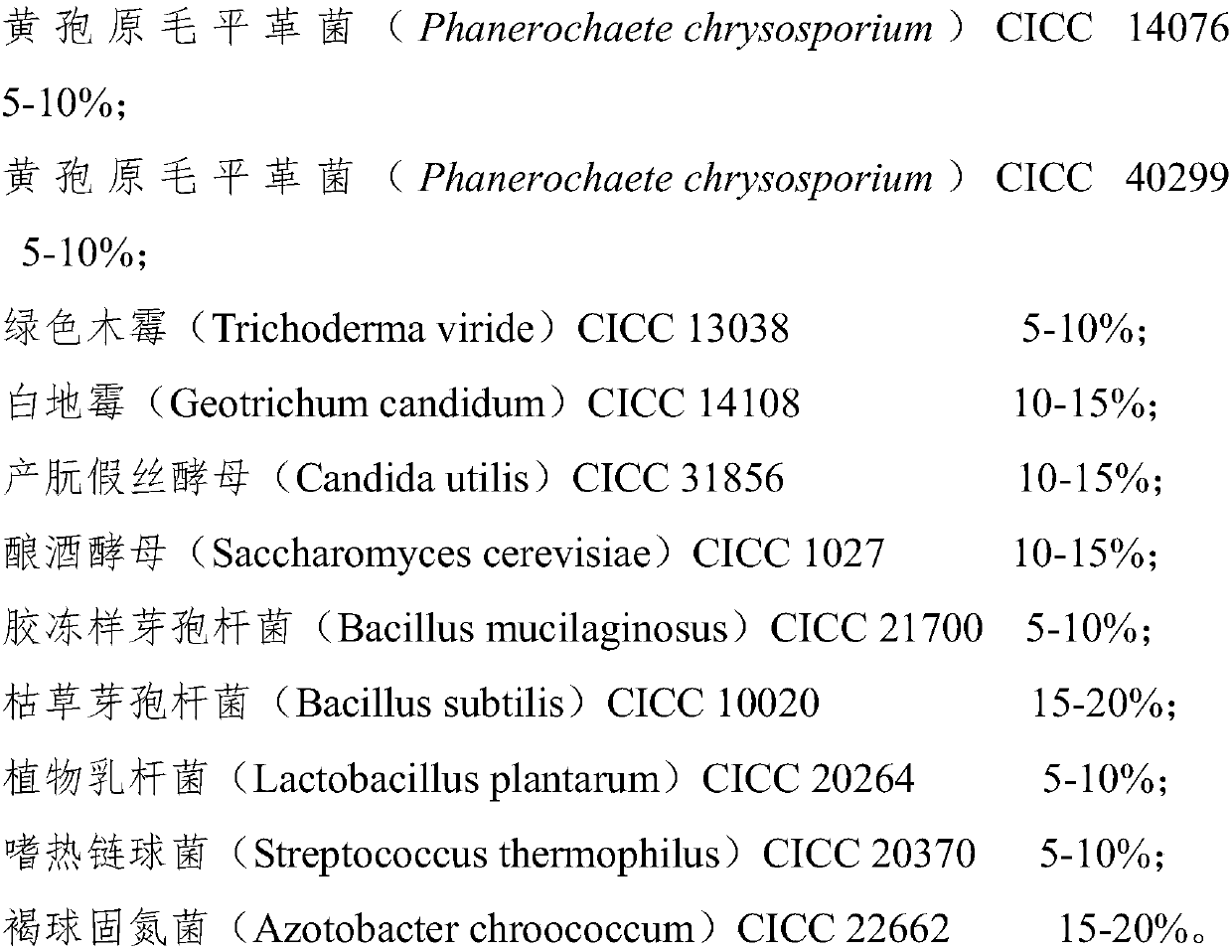
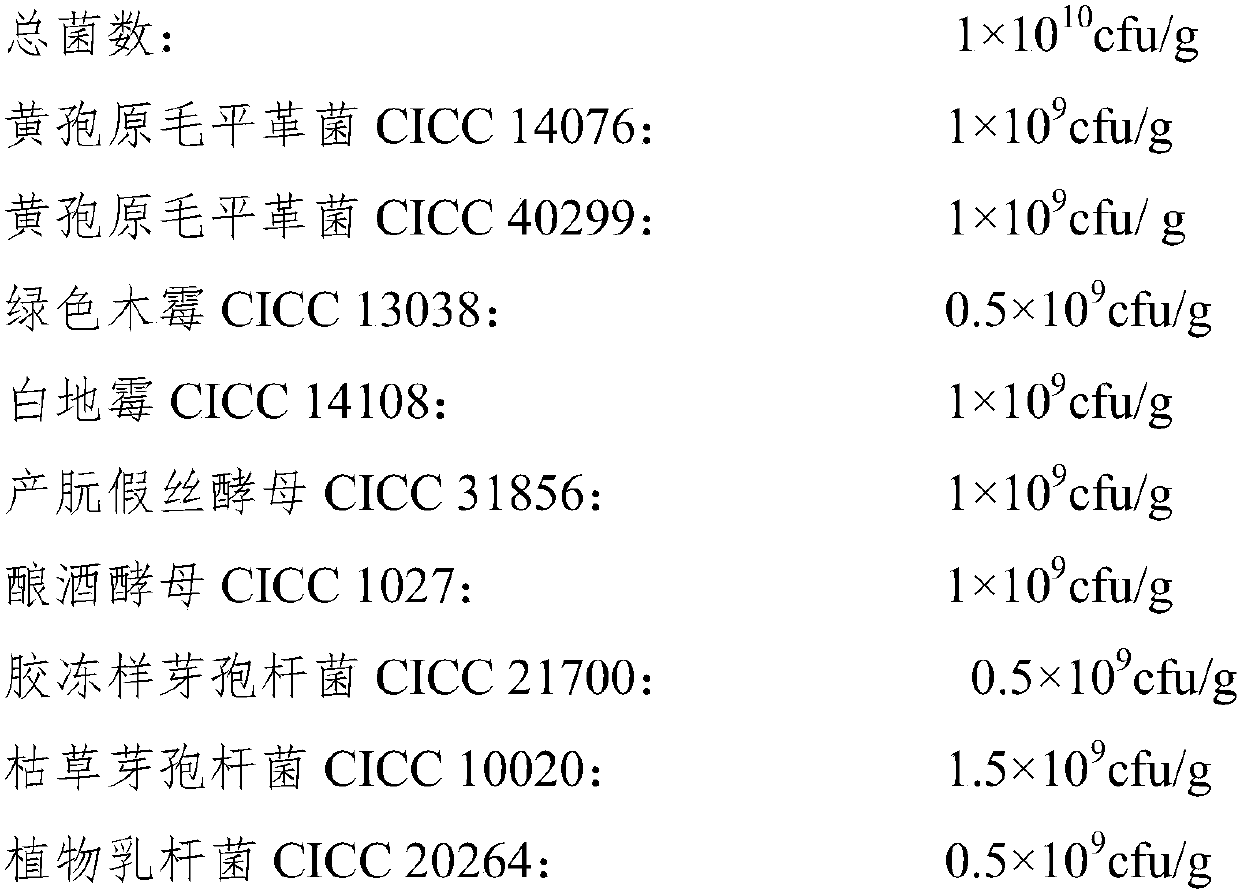
ActiveCN109679860AReduce processing costsIncrease profitFungiBacteriaAzotobacter chroococcumGreen waste
The invention provides a compound bacterium agent for treating green wastes of gardens as well as a preparation method and application of the compound bacterium agent. The compound bacterium agent isprepared from phanerochaete chrysosporium, trichoderma viride, geotrichum candidum, candida utilis, saccharomyces cerevisiae, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus plantarum, streptococcus thermophiles and azotobacter chroococcum. When the compound bacterium agent provided by the invention is used for treating the green wastes of the gardens, a carbon-nitrogen ratio and a carbon-phosphorus ratio are adjusted, without the need of adding any auxiliary material; a whole compost fermentation process can be finished through only independently adding the compound bacterium agent,so that the treatment cost of the green wastes of the gardens is effectively saved and a treatment technology is simplified. Microorganisms in the compound bacterium agent can be rapidly and greatly reproduced in a fermentation process, and rapid temperature raising and ageing of compost are promoted; the treatment time of the green wastes of the gardens is shortened and the compound bacterium agent is suitable for treating the green wastes of the gardens in practice.
Owner:BEIJING GUOHUAN TSINGHUA ENVIRONMENT ENG DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD BEIJING CHINA
Pretreatment fungicide for xylose residue or furfural residue, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102154108AFast startup timeEasy to degradeFungiMicroorganism based processesDry weightBiogas production
The invention relates to a pretreatment fungicide for xylose residue or furfural residue, a preparation method and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of agricultural microbiology. The invention relates to a microbial composite fungicide specially used for promoting the xylose residue or the furfural residue to degrade and improving the production efficiency of methane. The invention firstly adopts liquid fermentation technology to purely breed and ferment all components of the microbial fungicide, and then the components are compounded. The preparation method of the pretreatment fungicide comprises: 0.20-0.40 parts by weight of trichoderma viride liquid, 0.10-0.15 parts by weight of phanerochaete chrysosporium liquid, 0.05-0.10 parts by weight of aspergillus niger liquid, 0.08-0.16 parts by weight of aspergillus oryzae liquid and 0.05-0.10 parts by weight of trametes versicolor liquid, and the dry weight of fermentation hyphae is more than 20g / L. The composite fungicide can be used for improving the composite fungicide speed of the xylose residue or the furfural residue as well as the methane production efficiency; the methane production efficiency is improved by 30-60%; the fermentation time is shortened; the start period is shortened by 3-10 days; and the invention is also good in the effects on the aspects of pretreatment of smashed straws, and methane production.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
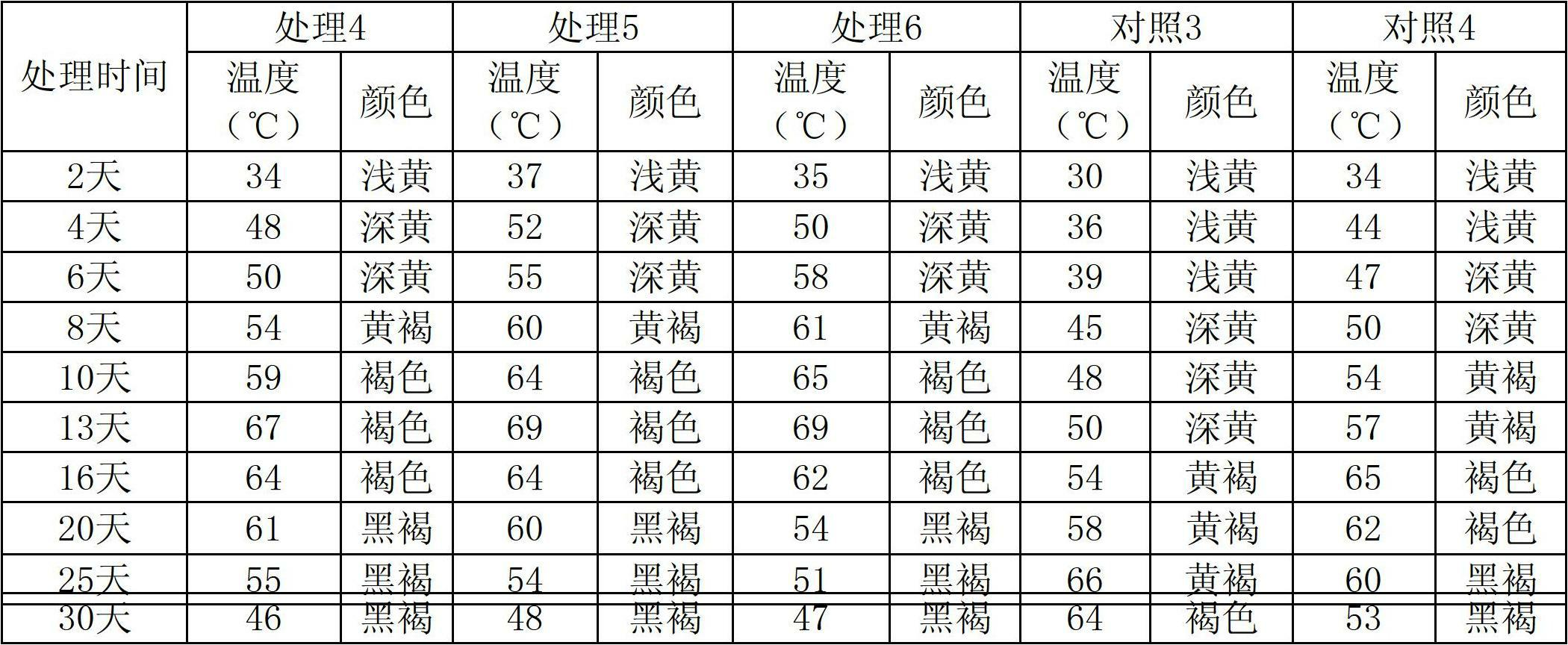
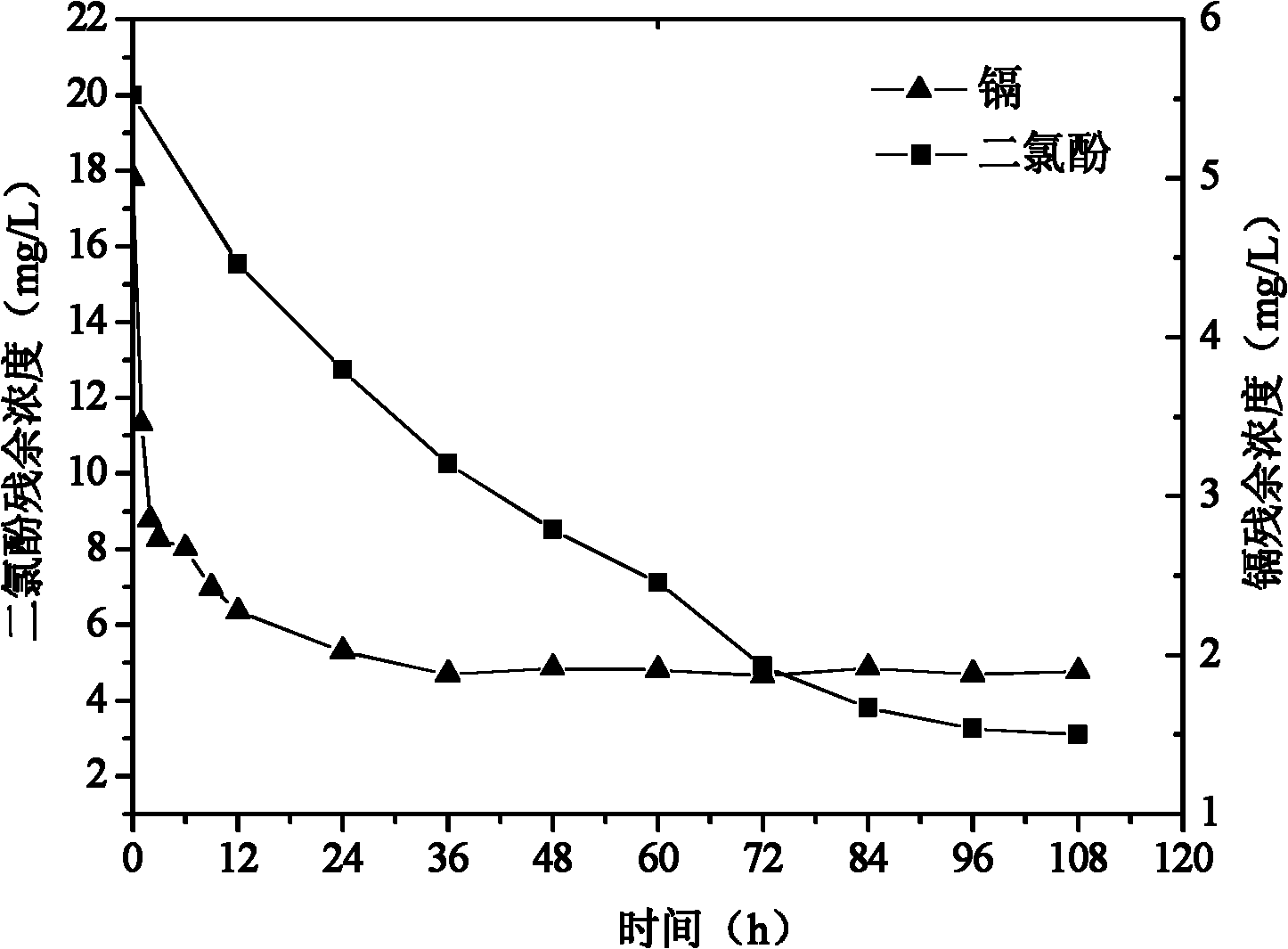
Method for removing cadmium and dichlorophenol in wastewater simultaneously by utilizing P.chrysosporium
InactiveCN102020359ALow process costSimple operating conditionsBiological water/sewage treatmentMicroorganismWastewater
The invention discloses a method for removing cadmium and dichlorophenol in wastewater simultaneously by utilizing P.chrysosporium, comprising the following steps: adding P.chrysosporium pellets into the wastewater containing cadmium and dichlorophenol, wherein the addition amount in each liter of wastewater is 0.3-0.5g in terms of the dry weight of the P.chrysosporium pellets; then, adjusting the pH value of the wastewater to 3.5-8.5, and performing an absorption degradation reaction at the constant temperature of 35-39 DEG C, wherein the revolving speed is controlled at 140-160rpm and the reaction time is not less than 36h during the reaction; and filtering the P.chrysosporium pellets after the reaction, thereby removing the cadmium and dichlorophenol in the wastewater simultaneously. The invention has the advantages of simple operation conditions, wide application range, no need of reformation and pretreatment for the adopted P.chrysosporium pellets, low cost, high microorganism utilization factor and the like, and is easy to implement.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
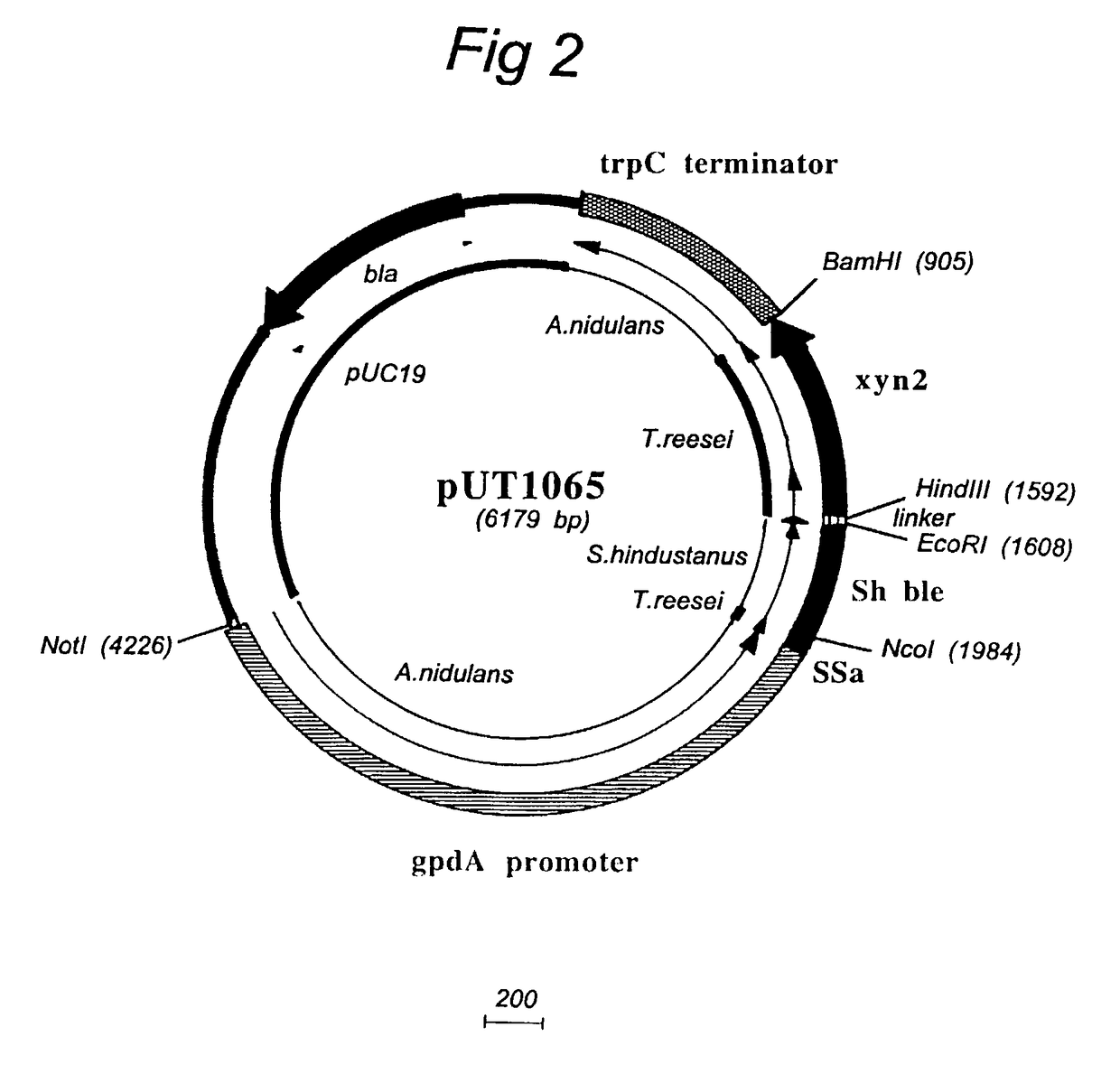
Expression-regulating sequences and expression products in the field of filamentous fungi
InactiveUS7906309B2Promote recoveryPromote growthFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyChrysosporium species
The invention pertains to novel proteins corresponding to Chrysosporium glycosyl hydrolases of families 7 and 10, exhibiting a minimum aminoacid identity of 70 and 75%, respectively, with the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No's 2 and 4, and to a protein corresponding to a Chrysosporium glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase, exhibiting at least 86% amino acid identity with the partial amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 6. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding these proteins, and especially to promoter sequences regulating the expression of the corresponding genes. The preferred host for expressing these genes is a fungus, especially a Chrysosporium strain.
Owner:DYADIC INT USA
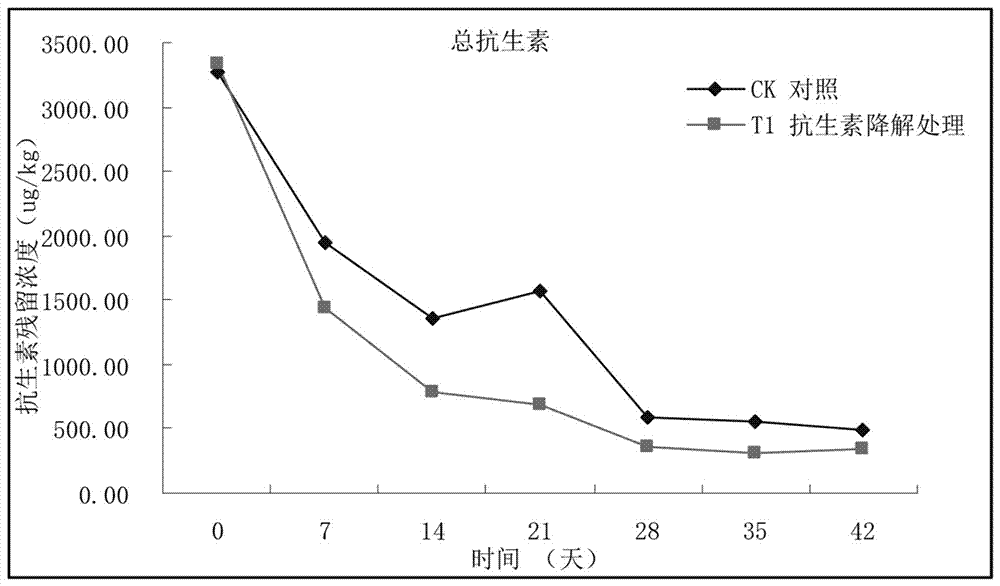
Composting method capable of efficiently degrading antibiotics in livestock excrements
ActiveCN106866234APromote degradationResidue reductionBio-organic fraction processingExcrement fertilisersFecesMacrolide resistance
The invention discloses a composting method capable of efficiently degrading antibiotics in livestock excrements. Degradation of a plurality of antibiotics, such as sulfonamides, tetracyclines, macrolides and fluoroquinolones, in a compost can be obviously promoted by adding an antibiotic degradation promoter with a specific using amount into a composting raw material and using specific composting steps, and meanwhile, available heavy metal content in the compost is reduced. The antibiotic degradation promoter consists of an activated carbon and an attapulgite, and can also be used with a biological activated carbon comprising the activated carbon and phanerochaete chrysosporium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Process for preparing fuel ethanol by using straw fiber materials
This invention discloses a method for producing fuel ethanol from a straw fibre raw material, comprising: (1) raw material selection; (2) disintegration; (3) pre-processing; (4) double-enzyme saccharifying; (5) sterilization; (6) enlargement culture and application of Pachysolen tannophilus P-01; (7) fermentation; (8) distillation; characterizing: the pre-processing employs white-rot fungi solid culture to decompose lignin. The procedures comprise: (1) bacteria selection: Phanerochete chrysosporium, which is donated by Shanghai hydnology institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, is a fugus, and can produce lignin decomposing enzymes under specific culture conditions, comprising lignin peroxidase, manganese dependent peroxidase, laccase, and so on; (2) specific culture media producing conditions: i. add 2g glucose, 0.3g ammonium chloride and 100g water to dry straw per 100g and mix homogenously, sterilize at 121Deg C for 2h, inoculate Phanerochete chrysosporium for culture decomposition; ii. conditions of culture decomposition: inoculation 5%, 37-39Deg C, pH normal, material to volume: 1:5 ( dry material weight: container volume), cycle 30 days. This invention can improve the ethanol yield and decease cost.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of bioorganic fertilizer
InactiveCN104692844ASpeed up the ripening processHigh activityClimate change adaptationExcrement fertilisersDecompositionPotassium
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Straw-degrading composite microbial inoculum and application thereof in pretreatment of ethanol production
The invention relates to a straw-degrading composite microbial inoculum which is prepared by mixing a microbial inoculum No.I and a microbial inoculum No.II, wherein the microbial inoculum No.I comprises phanerochete chrysosporium, cacillus and streptomycete; and the microbial inoculum No.II comprises trichoderma, penicillium, aspergillus and actinomycete. The application method of the high-efficiency straw-degrading composite microbial inoculum in pretreatment of ethanol production comprises the following steps: soaking crushed straws in ammonia water to carry out cleaning treatment; adding a nutrient solution to prepare a fermentation substrate; spraying the high-efficiency straw-degrading composite microbial inoculum, and carrying out fermentation treatment for two days; and filtering,and washing with water to neutral, thus obtaining the pretreatment product for ethanol production. The invention has the following advantages: the treatment of soaking straws in ammonia water is beneficial to removing lignin, increasing the enzyme contact area of celluloses and hemicelluloses and improving the pretreatment efficiency; and by combining the microbial inoculum and the fermentation process to degrade straws, different microbes can secrete complementary enzymes in the degradation process, so that the substrate can be thoroughly degraded, thereby improving the biomass resource utilization rate. Besides, the invention is simple in process and convenient to implement, and can not do harm to the environment.
Owner:AOWEI TIANJIN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Complex microbial agent for stabilizing treatment of stock garbage in cities and towns as well as preparation method and application of complex microbial agent
ActiveCN109852557APromote degradationAltered ion valence diseaseFungiBacteriaMicrobial agentPseudomonas putida
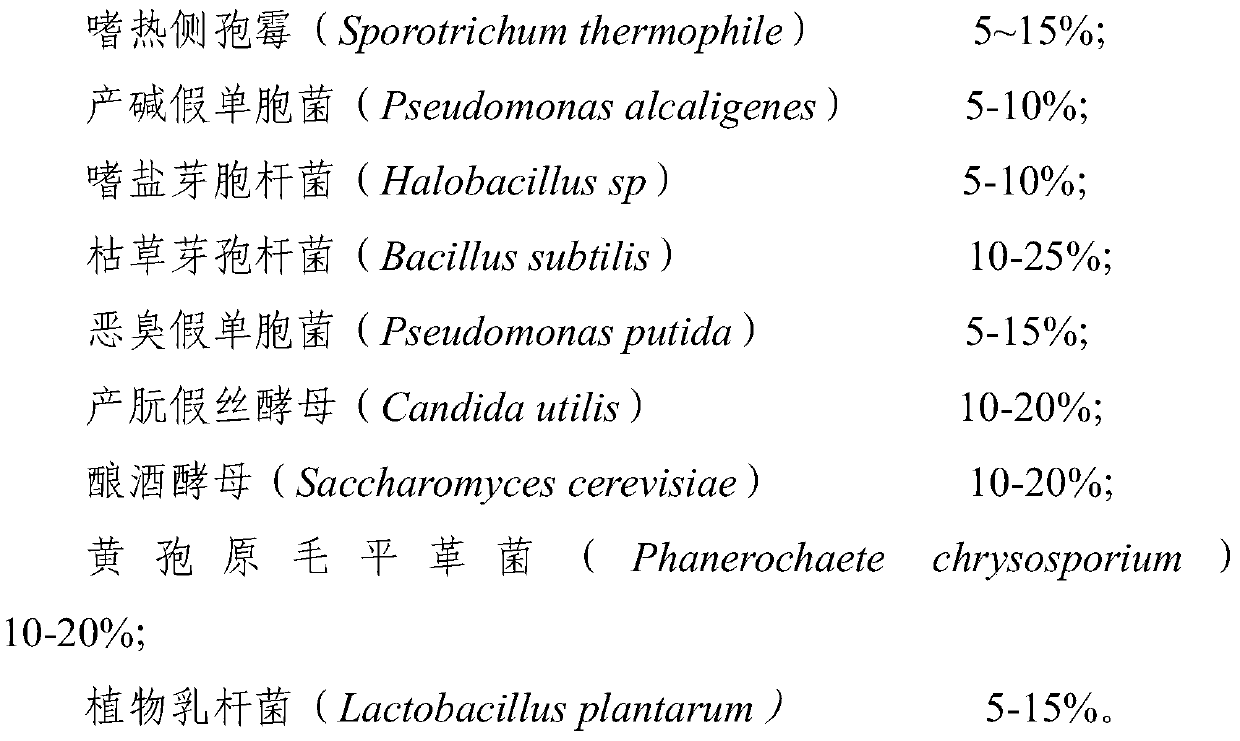
The invention provides a complex microbial agent for stabilizing treatment of stock garbage in cities and towns as well as a preparation method and an application of the complex microbial agent. The complex microbial agent contains sporotrichum thermophile, pseudomonas alcaligenes, halobacillus sp, bacillus subtilis, pseudomonas putida, candida utilis, saccharomyces cerevisiae, phanerochaete chrysosporium and lactobacillus plantarum. Growth metabolism, degradability and activity of all microbial strains in the complex microbial agent can effectively complement and cooperate with one another, the microbial strains can grow and propagate quickly in a landfill system to promote the temperature of a garbage treatment environment to increase quickly, meanwhile, organic matter, BDM and toxic andharmful substances in a landfill can be quickly and efficiently degraded, the stabilizing time of the garbage landfill is greatly shortened, stable harmless treatment of landfill is promoted, and thecomplex microbial agent can be applied to aerobic stabilizing treatment of garbage in cities and towns in practice.
Owner:BEIJING GUOHUAN TSINGHUA ENVIRONMENT ENG DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD BEIJING CHINA
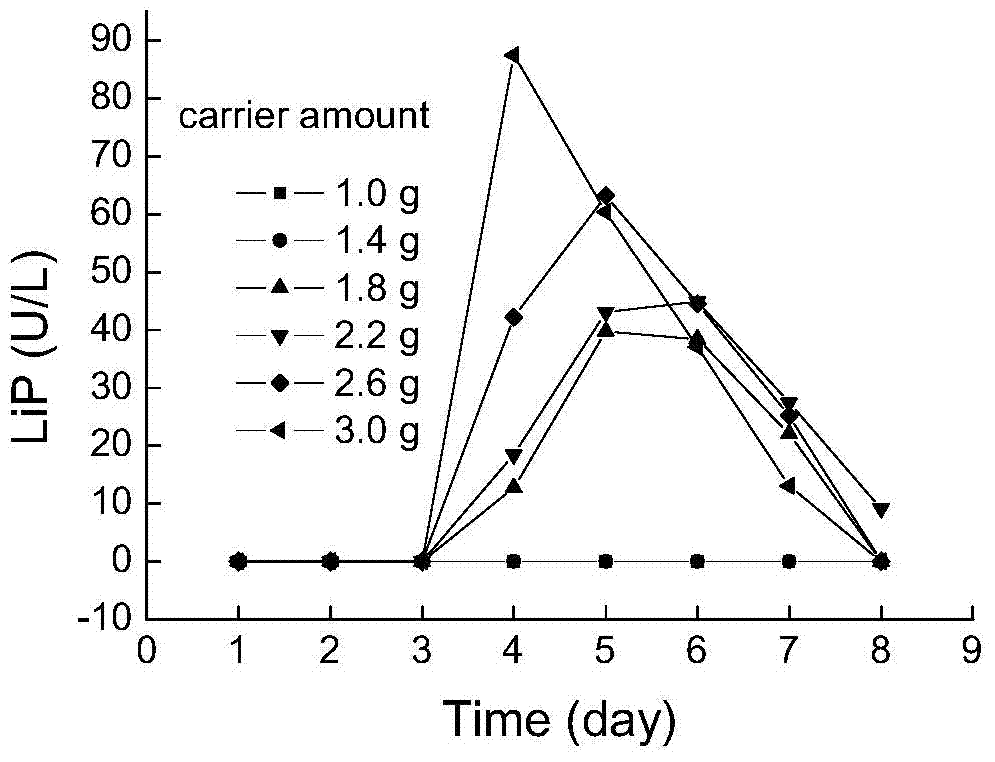
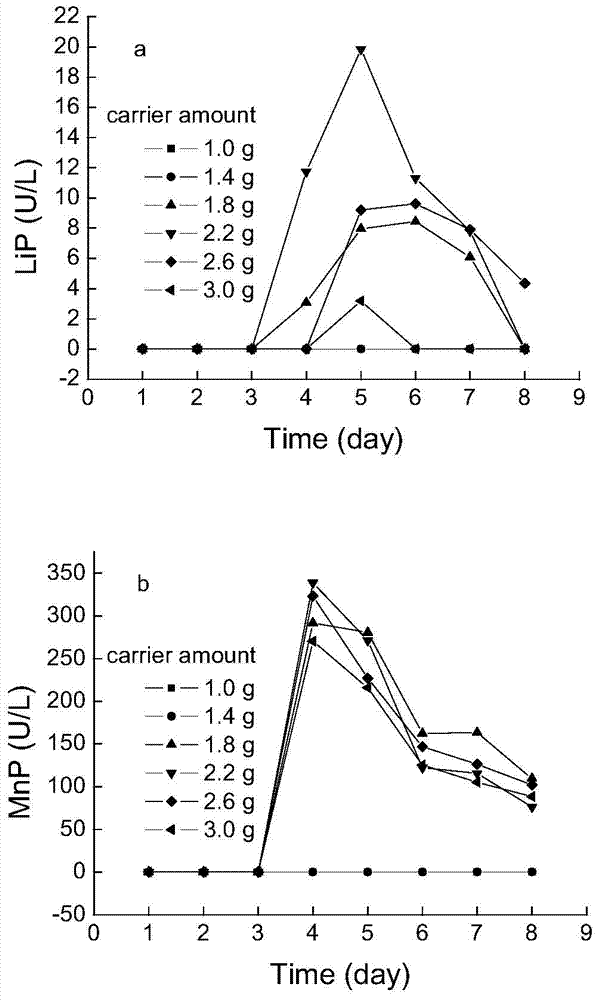
Method for selectively producing lignin-degrading enzymes by using phanerochaete chrysosporium
The invention relates to a method for selectively producing lignin-degrading enzymes by using phanerochaete chrysosporium. The invention provides a method for selectively producing lignin-degrading enzymes by using phanerochaete chrysosporium, which comprises the following steps: fermenting phanerochaete chrysosporium in a culture medium containing an immobilized culture carrier in a non-immersed state, and collecting a fermentation product, namely, a lignin-degrading enzyme. Experiments show that when the method is adopted for carrying out fermentation on a lignin-degrading enzyme, the lignin-degrading enzyme can be selectively obtained under air conditions without feeding pure oxygen or air containing high-concentration oxygen in the process of culturing but just by controlling the concentration of a carbon and nitrogen source in the culture medium and adding a carrier in a non-immersed state. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in condition control, and the obtained lignin-degrading enzyme is strong in selectivity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method for absorbent made from lignin-degrading bacteria modified straw
InactiveCN105080508AImprove adsorption capacitySimple preparation processOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSorbentHemicellulose
The invention discloses a preparation method for an absorbent made from lignin-degrading bacteria modified straw, and belongs to the field of absorbent production. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dewaxing rape straw at first, and then adding a nutrient and a suspension without hyphae for sealed fermentation to obtain lignin-degrading bacteria modified straw; mixing the lignin-degrading bacteria modified straw with epoxy chloropropane for a cross-linking reaction, and then adding a trimethylamine alcoholic solution to obtain the absorbent eventually. The preparation method has the advantages that phanerochaete chrysosporium is utilized for degrading lignin in the rape straw to obtain cellulose and hemicellulose; the adsorption effect and the adsorption capacity of the prepared absorbent are high; moreover, the rape straw is utilized as a raw material for extracting natural cellulose; the preparation process is simple; the production cost is low.
Owner:JIANGSU JINYU ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
Compound bacterium agent for preparing fertilizer
InactiveCN103725638AImprove compost efficiencySolve the reuse problemFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyCandida tropicalis
The invention provides a compound bacterium agent for preparing a fertilizer. The active component of the compound bacterium agent comprises the following bacterium strains: cytophaga fermentans, cellulomonas flavigena, butyrivibrio fibrisolvens, clostridium cellobioparum, (i) Clostridiumpapyrosolvens( / i), (i) Clostridiumtermitidis( / i)(i), ( / i) bacillus megatherium, candida tropicalis, trichoderma reesei and phanerochaete chrysosporium. The compound bacterium agent is mixed with the mushroom dregs of an edible mushroom in a stack retting manner so as to prepare the fertilizer. The compound bacterium agent can be used for obviously improving the fertilizer efficiency of the fertilizer obtained by stacking the mushroom dregs, and is environmental friendly and is used for effectively solving the problem of recycling of the mushroom dregs of the edible mushroom.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Novel expression-regulating sequences and expression products in the field of filamentous fungi
InactiveUS20030187243A1Promote recoveryMinimise risk of degradationFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyChrysosporium species
The invention pertains to novel proteins corresponding to Chrysosporium glycosyl hydrolases of families 7 and 10, exhibiting a minimum aminoacid identity of 70 and 75%, respectively, with the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No's 2 and 4, and to a protein corresponding to a Chrysosporium glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase, exhibiting at least 86% amino acid identity with the partial amino acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 6. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding these proteins, and especially to promoter sequences regulating the expression of the corresponding genes. The preferred host for expressing these genes is a fungus, especially a Chrysosporium strain.
Owner:DYADIC INT USA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com