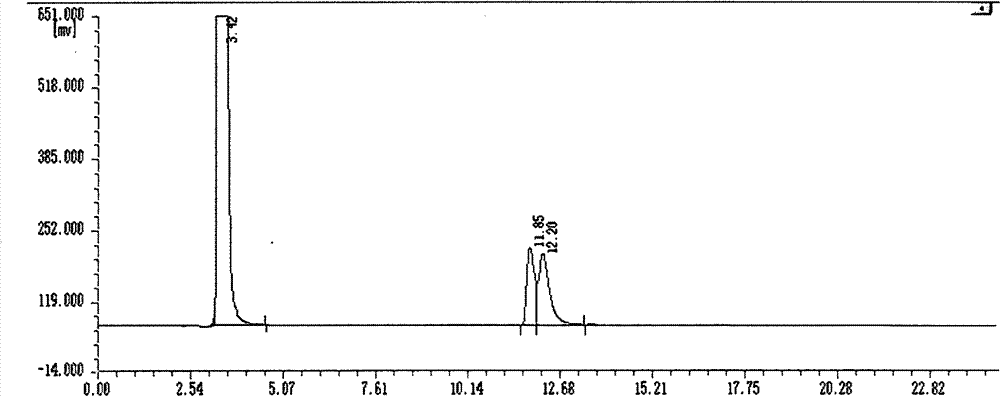
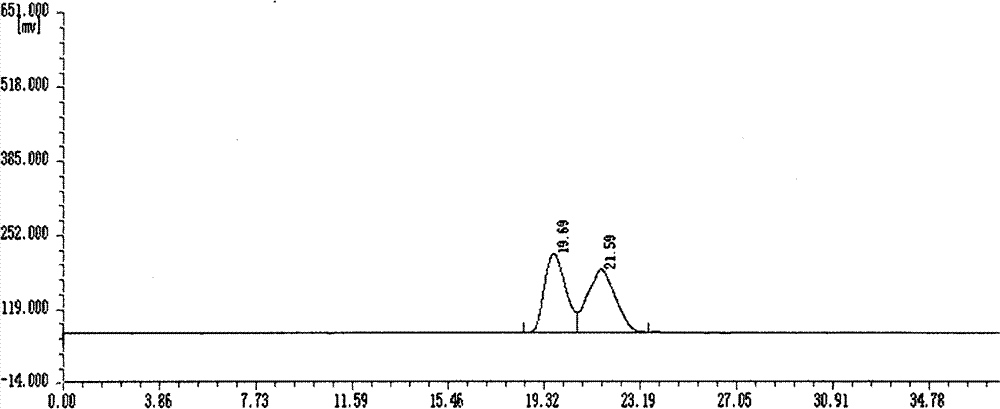
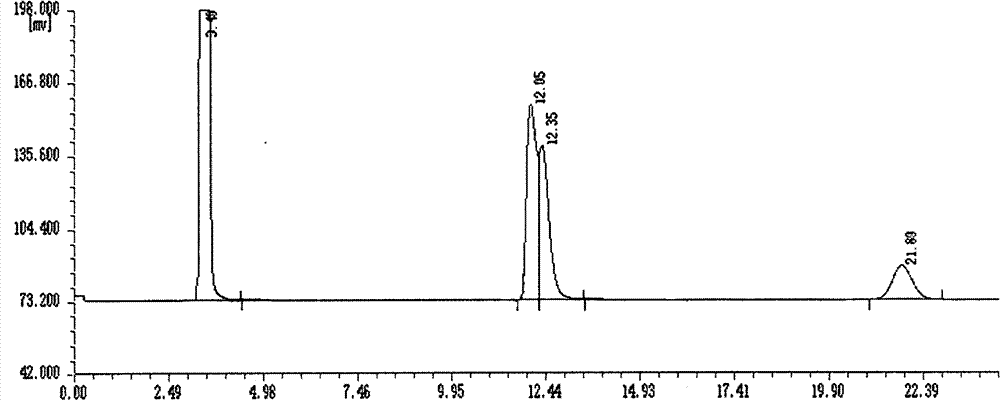
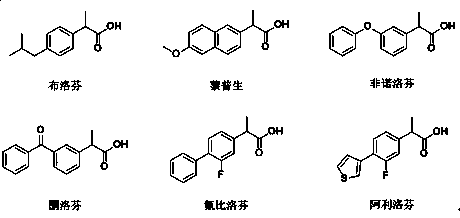
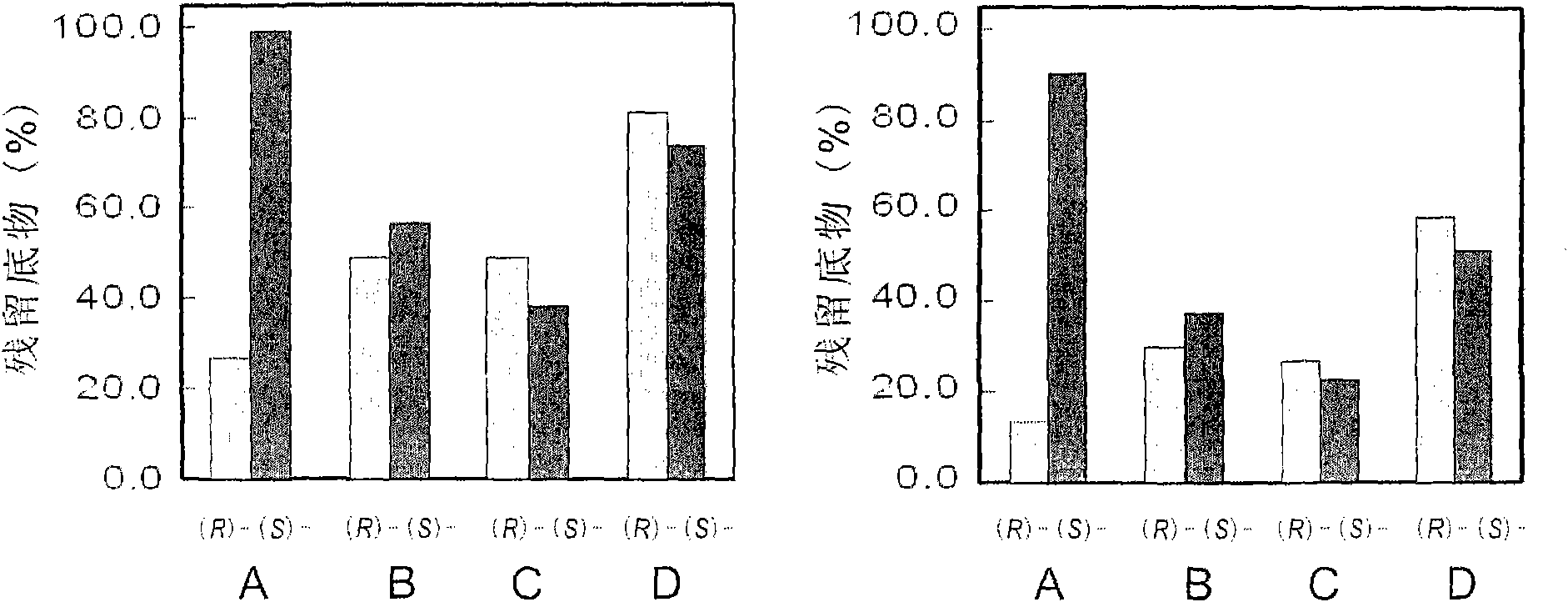
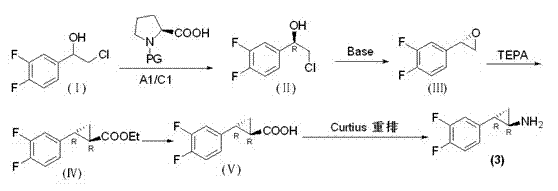
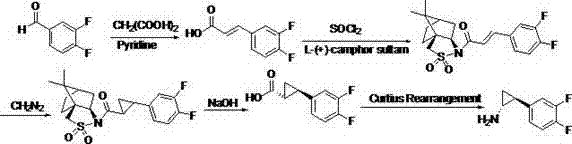
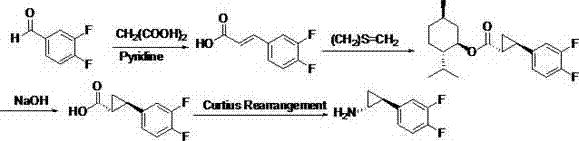
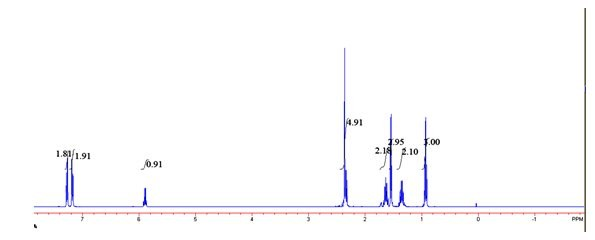
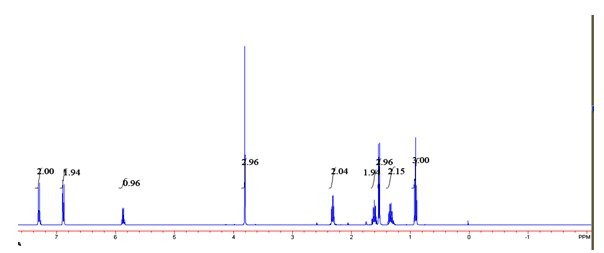
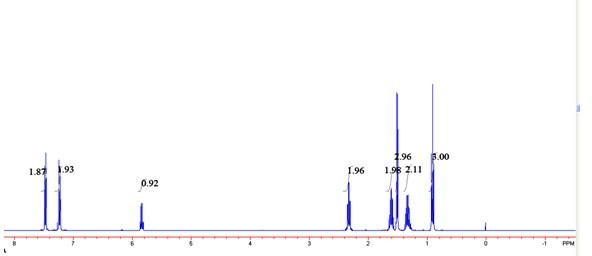
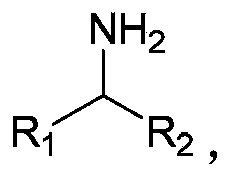
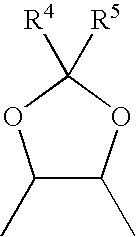
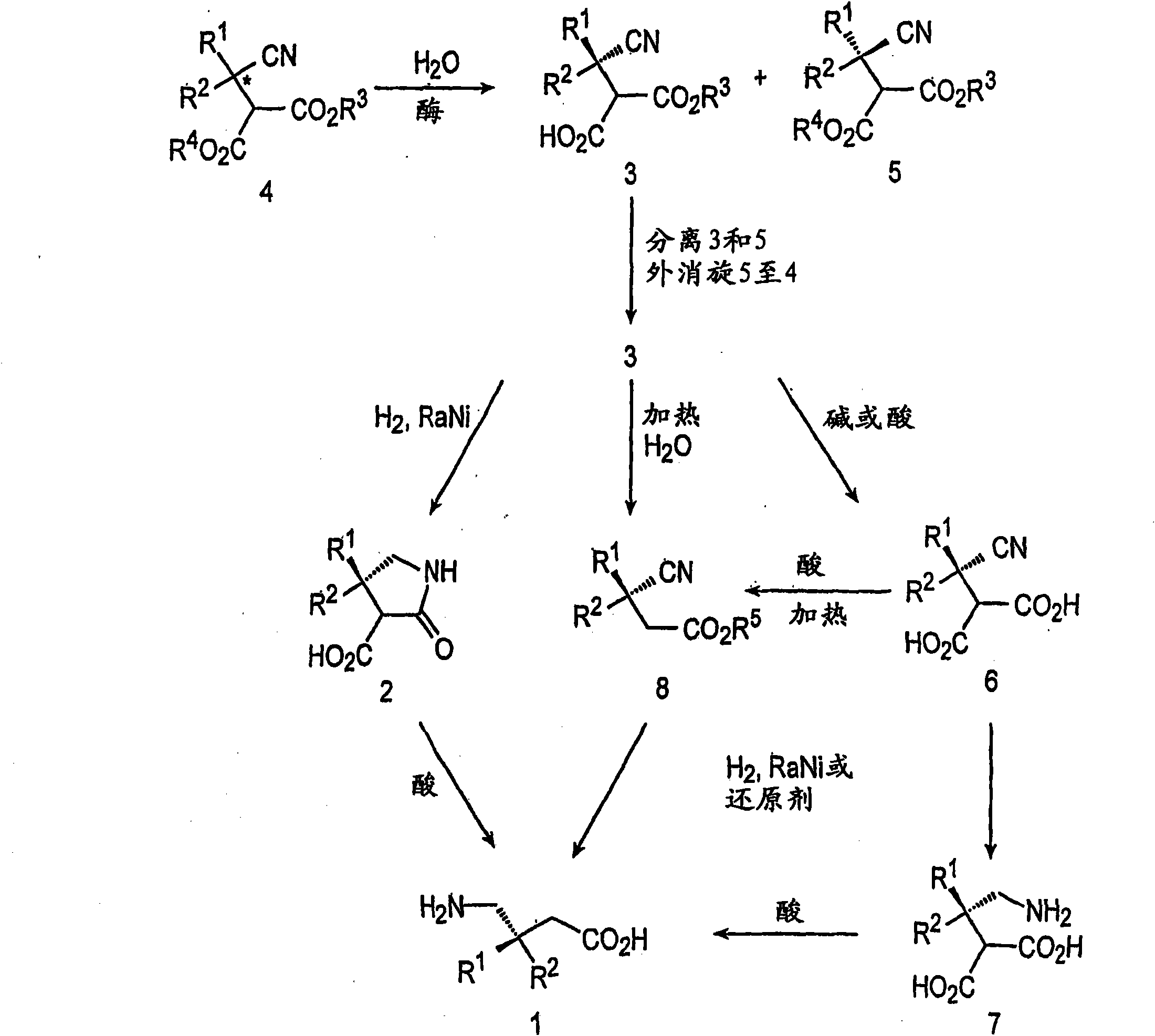
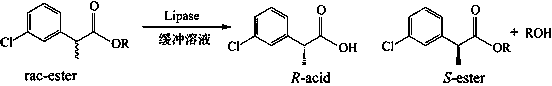
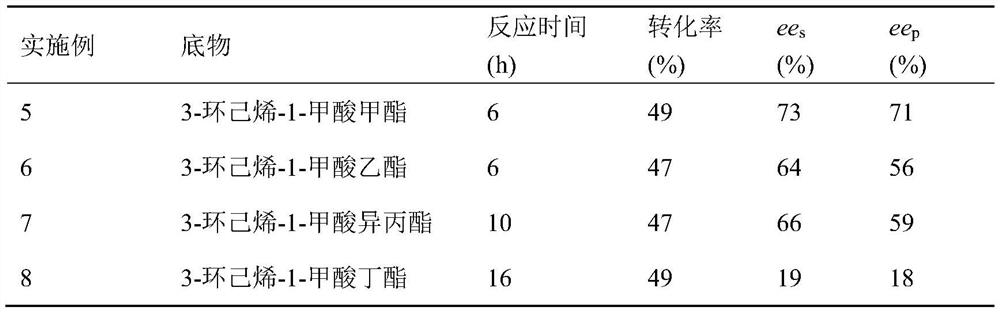
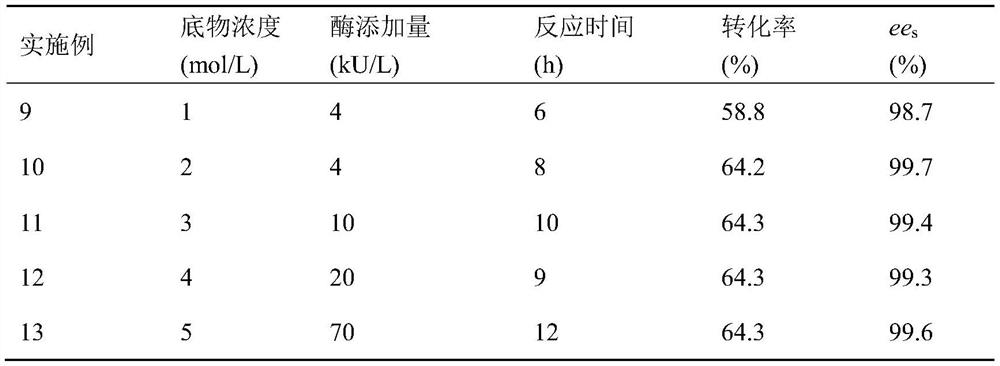
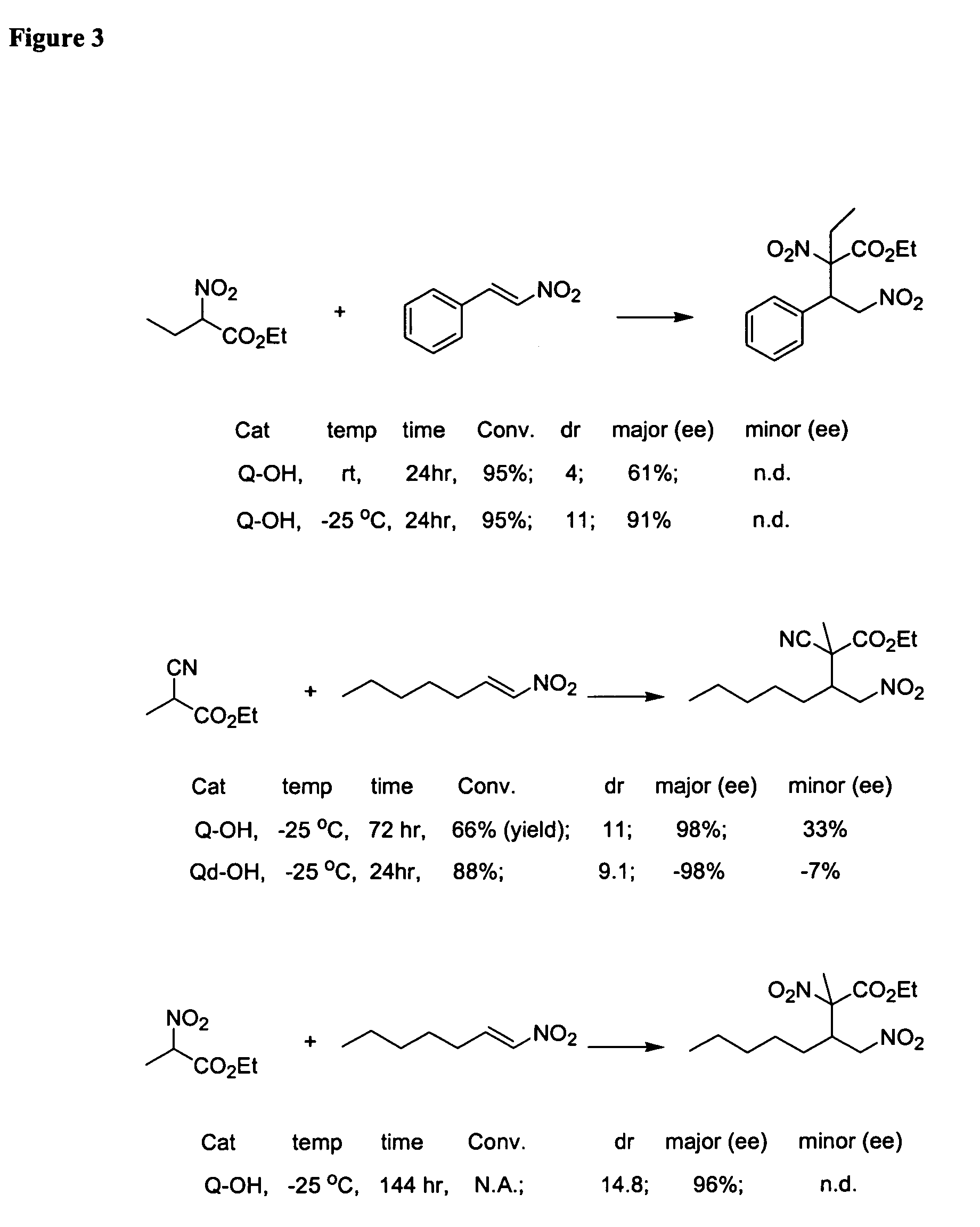
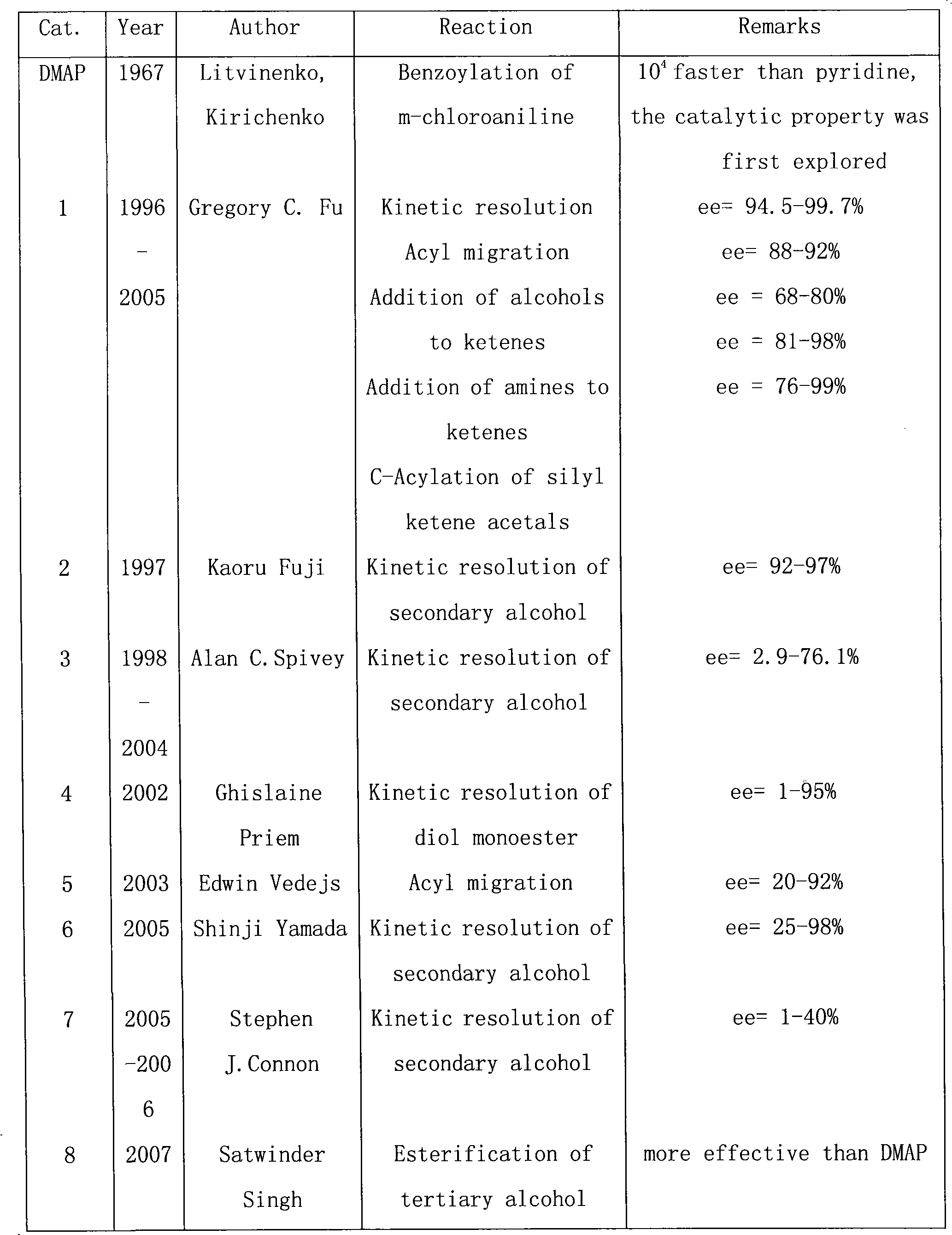
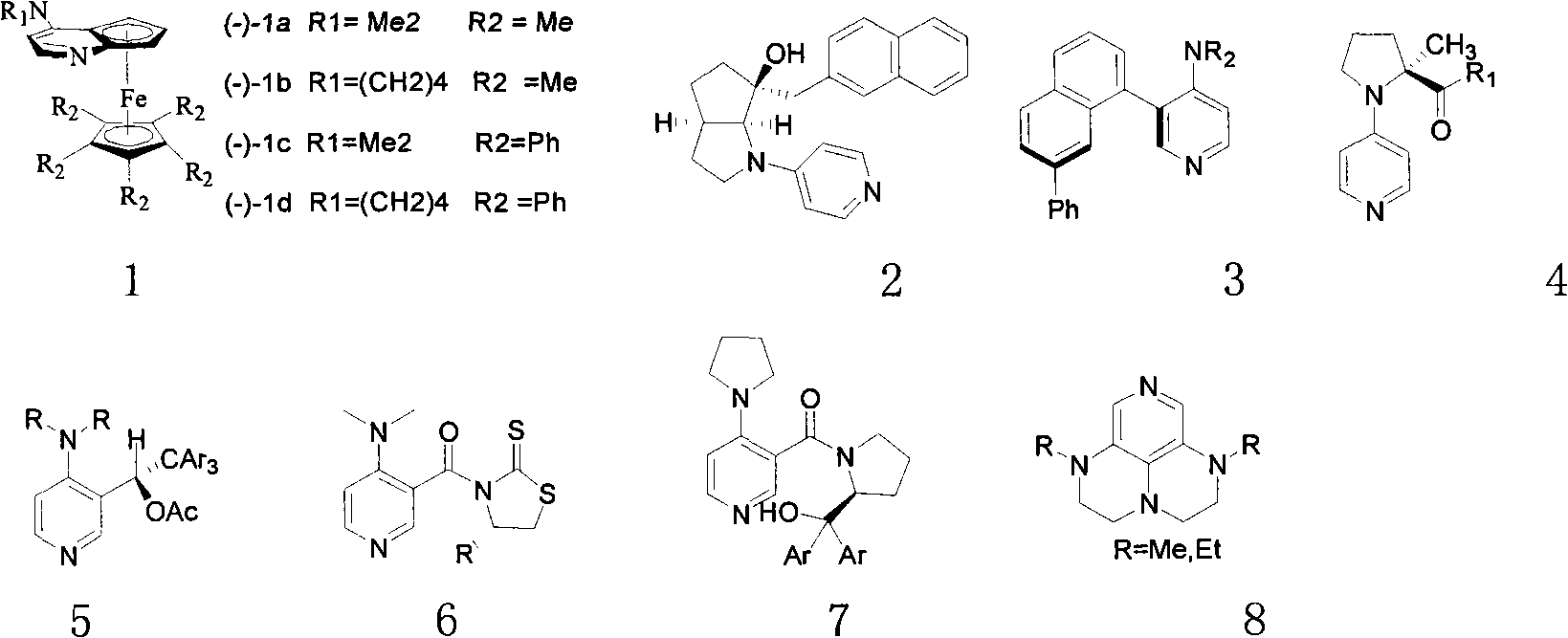
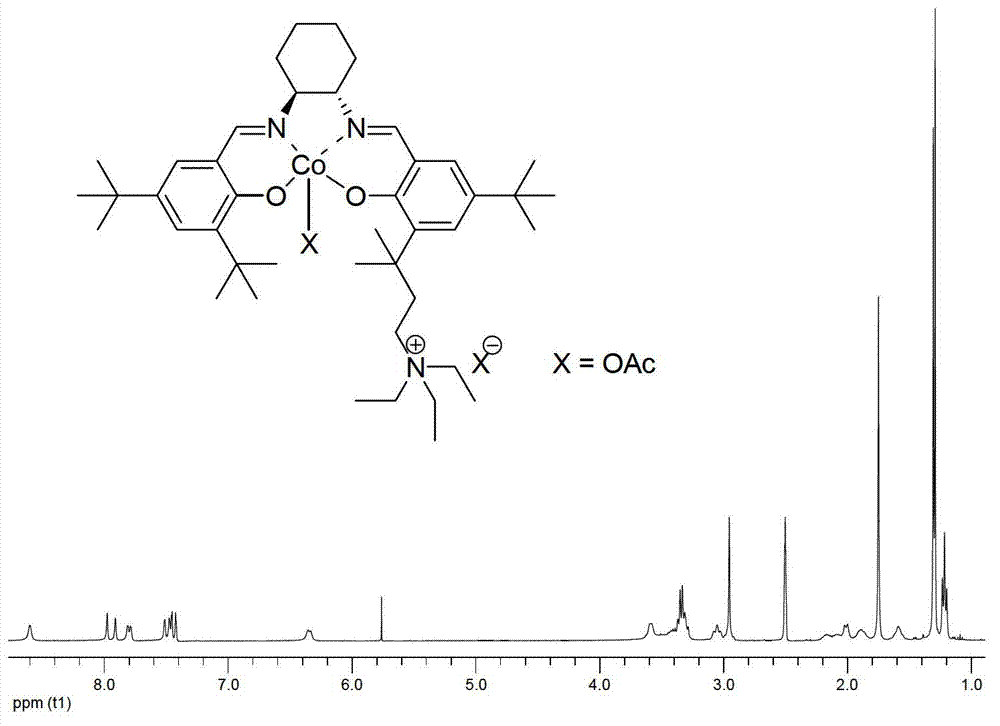
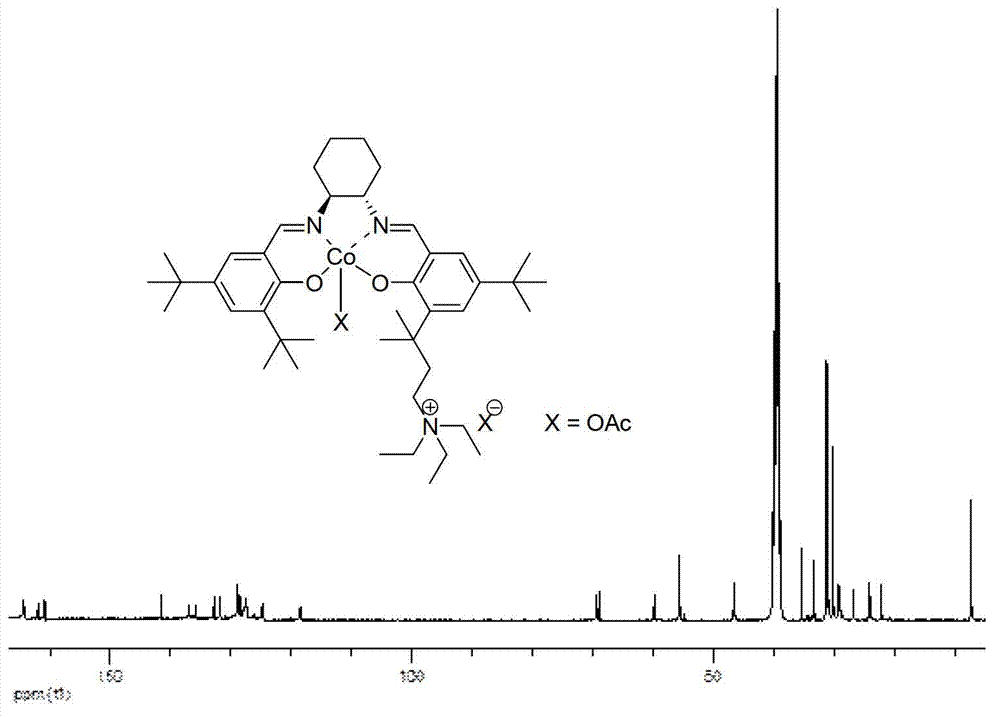
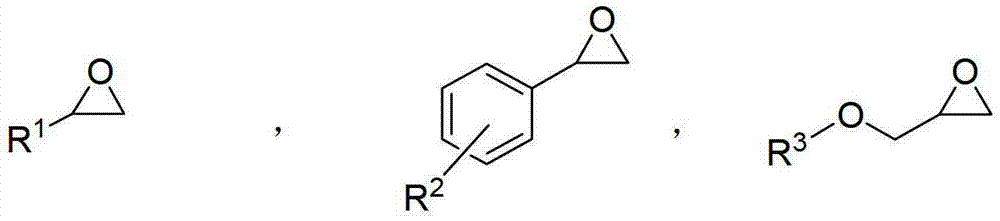
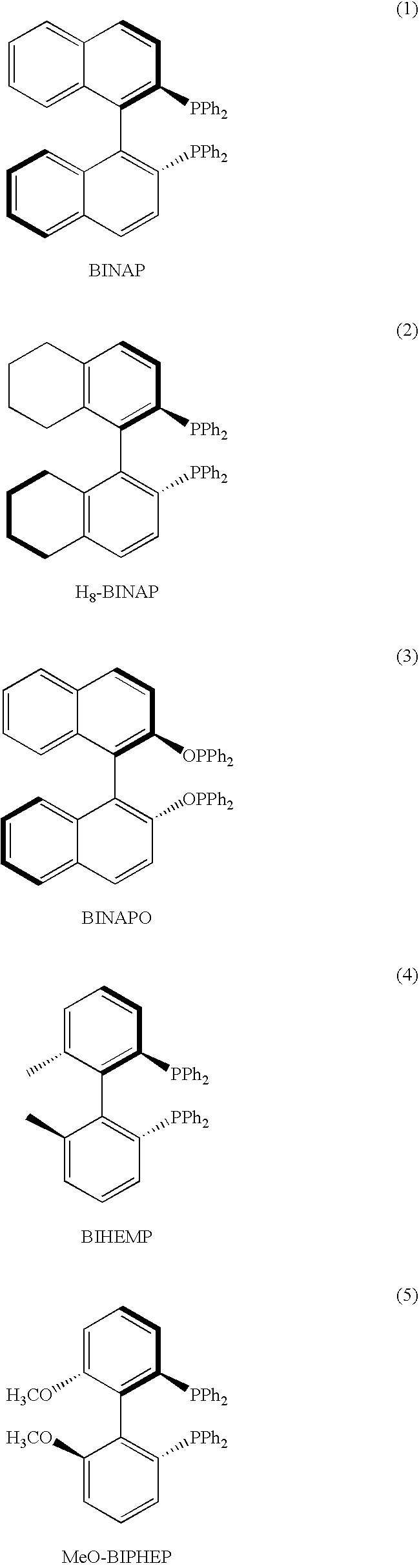
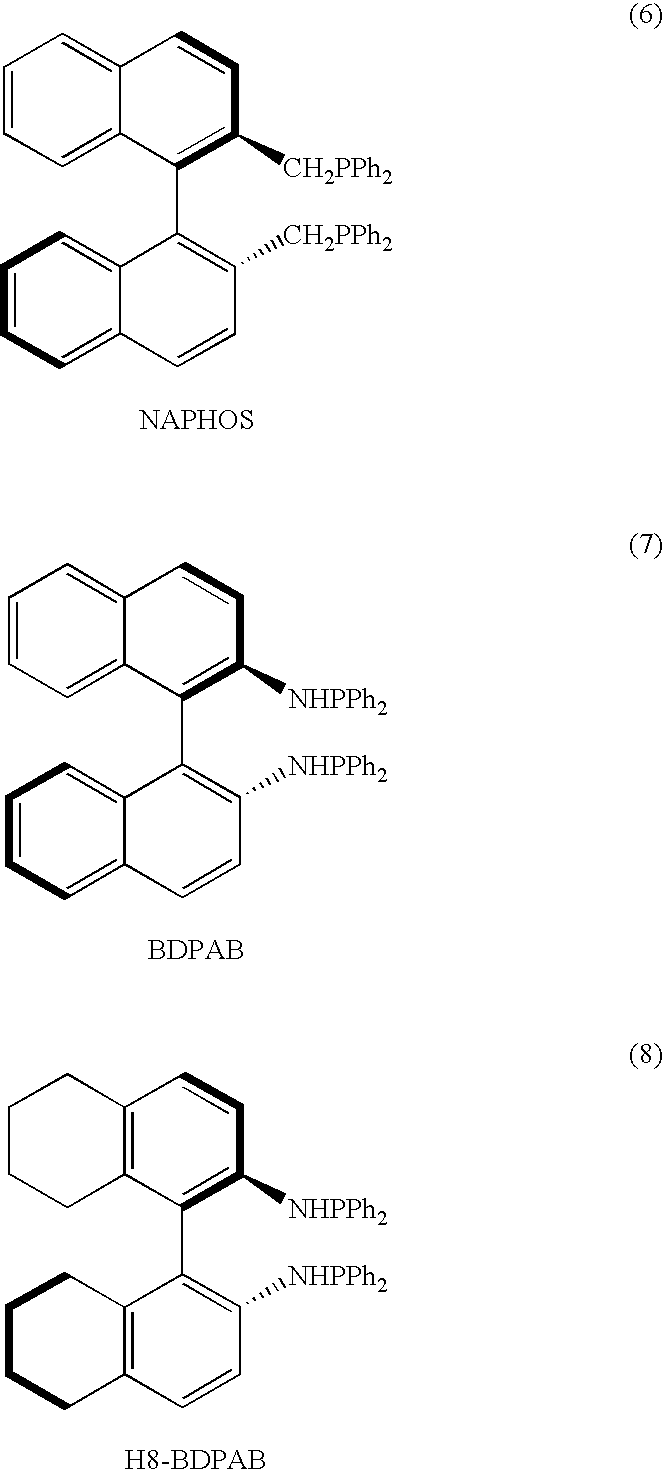
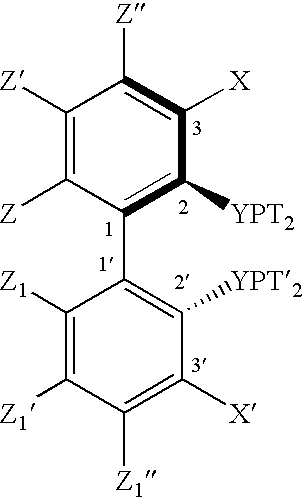
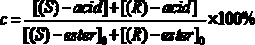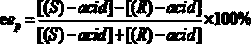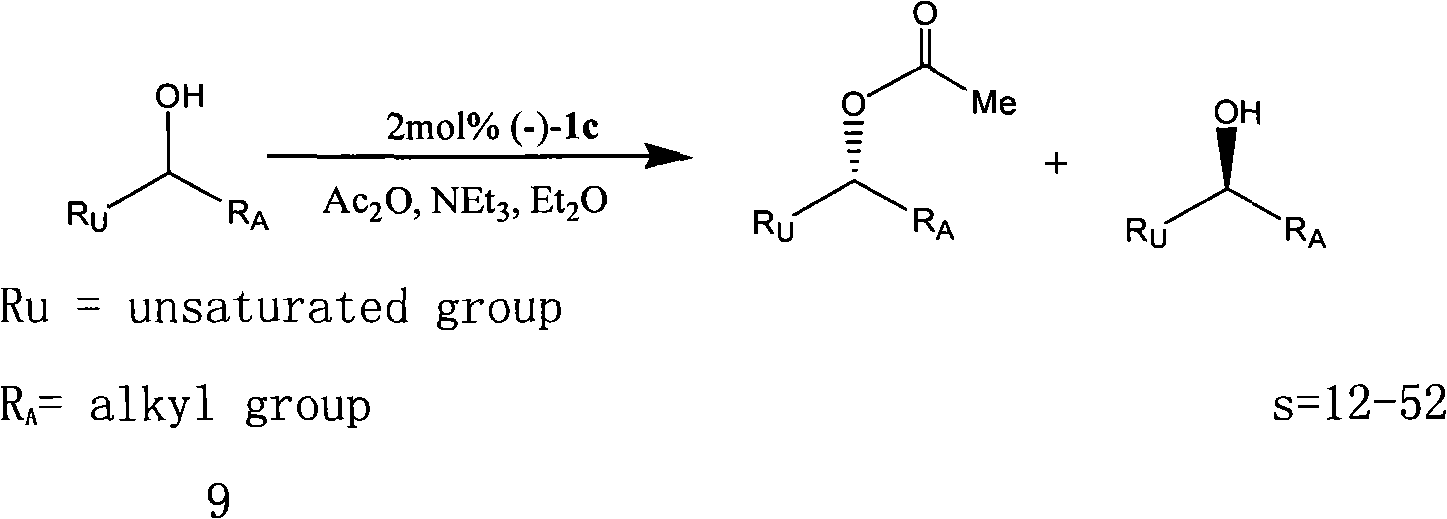Patents
Literature
230 results about "Kinetic resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
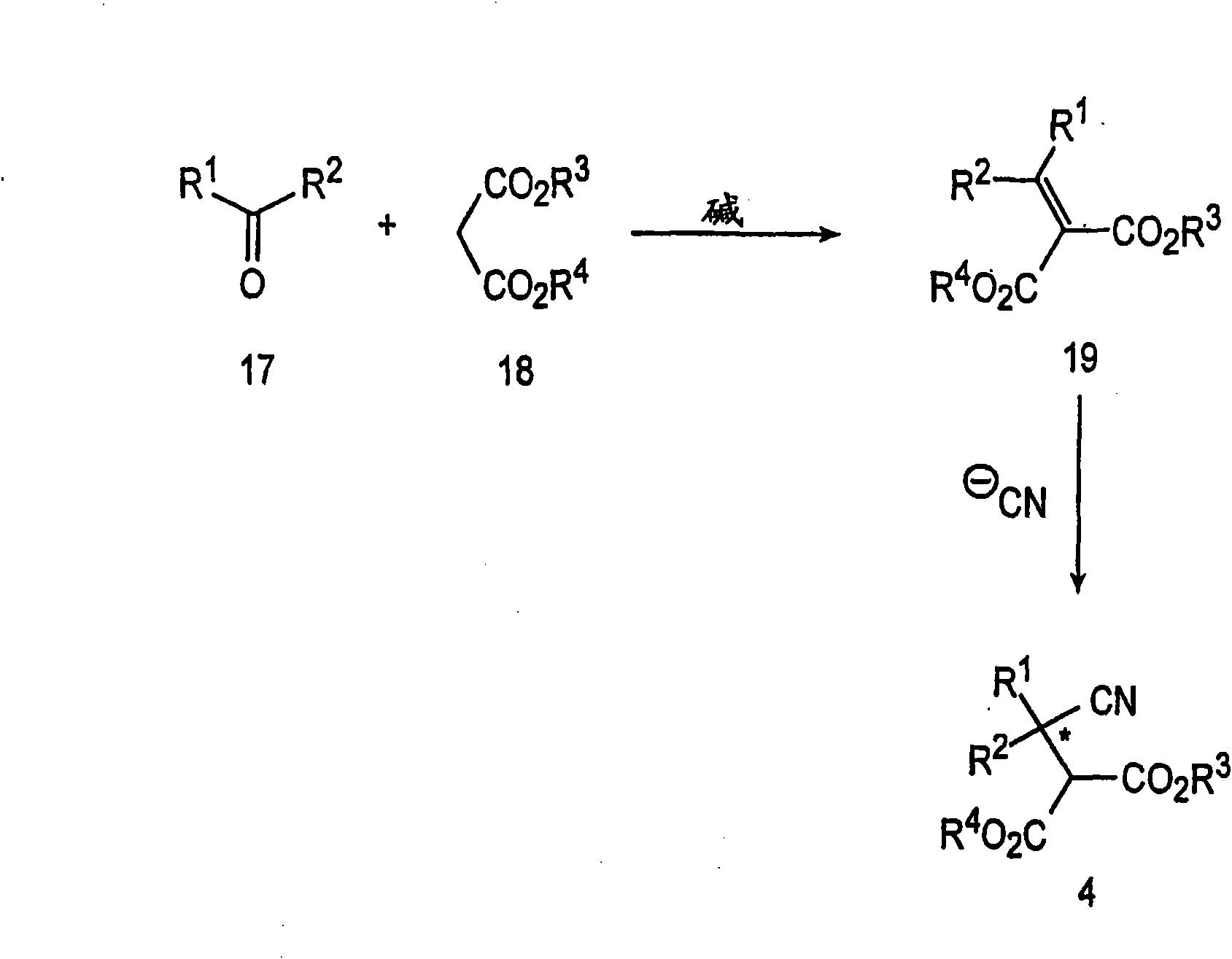
In organic chemistry, kinetic resolution is a means of differentiating two enantiomers in a racemic mixture. In kinetic resolution, two enantiomers react with different reaction rates in a chemical reaction with a chiral catalyst or reagent, resulting in an enantioenriched sample of the less reactive enantiomer. As opposed to chiral resolution, kinetic resolution does not rely on different physical properties of diastereomeric products, but rather on the different chemical properties of the racemic starting materials. This enantiomeric excess (ee) of the unreacted starting material continually rises as more product is formed, reaching 100% just before full completion of the reaction. Kinetic resolution relies upon differences in reactivity between enantiomers or enantiomeric complexes. Kinetic resolution is a concept in organic chemistry and can be used for the preparation of chiral molecules in organic synthesis. Kinetic resolution reactions utilizing purely synthetic reagents and catalysts are much less common than the use of enzymatic kinetic resolution in application towards organic synthesis, although a number of useful synthetic techniques have been developed in the past 30 years.
Preparation method of sofosbuvir intermediate
ActiveCN104151352AEnvironmental protection and green patentsEnvironmental Protection and Green LiteratureGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsKetone solventsKinetic resolution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a sofosbuvir intermediate, which comprises the following step: in an anhydrous non-protonic solvent, carrying out dynamic kinetic resolution on a compound disclosed as Formula (II) under the action of an organic alkali and / or inorganic alkali to prepare a compound disclosed as Formula (I), wherein the non-protonic solvent is one or more of ester solvent, ketone solvent and ether solvent, the organic alkali and / or inorganic alkali account / accounts for 0.1-10 wt% of the compound disclosed as Formula (II), the temperature of the dynamic kinetic resolution is 10-30 DEG C, and the time of the dynamic kinetic resolution is 5-10 hours. The preparation method has the advantages of high conversion rate, high product purity and low cost, and is environment-friendly.
Owner:CHEMVON BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for catalyzing dynamic kinetic resolution of arylamine via racemization catalyst
InactiveCN102533922AGood stability for repeated useMild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistry methodsChemical recyclingChlorobenzenePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for catalyzing dynamic kinetic resolution of arylamine via a racemization catalyst, comprising the following steps of: 1) adding p-chlorophenol, n-pentanoic acid, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 4-dimethylamino-pyridine, and carrying out mixing, filtration, drying, concentration and column chromatography to obtain a pentanoic acid p-chlorophenyl ester acyl donor; 2) carrying out coprecipitation on magnesium chloride solution and aluminum chloride solution and carrying out water-heat treatment to obtain chloridion intercalated hydrotalcite, adding the chloridion intercalated hydrotalcite in lauryl sodium sulfate aqueous solution, and carrying out backflow, cooling, centrifugation, water washing, acetone washing and drying to obtain a carrier; 3) adding palladium salt and the carrier, and carrying out heating, ascorbic acid addition, centrifugation, water washing, acetone washing and freeze-drying to obtain the racemization catalyst; and 4) adding arylamine, the acyl donor, lipase and the racemization catalyst in toluene and placing in a stainless steel reactor to add hydrogen so as to obtain amide. The method provided by the invention is used for catalyzing the dynamic kinetic resolution of arylamine, has rapid reaction rate, low temperature, high conversion rate and high product optical purity, and has great application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Kinetic resolution method of chiral amine
InactiveCN102766672AImprove performanceMeet various requirements of purityFermentationOrganic solventReaction temperature
The invention discloses a kinetic resolution method of chiral amine, comprising the following steps of: adding chiral amine and acyl donor at the mol ratio of 1:0.5-3 into an organic solvent reaction system, adding lipase which accounts for 10-80 wt% of the weight of chiral amine, and reacting at the reaction temperature of 30-70 DEG C for 12-48 hours to obtain amide with the conversion rate of 50% and e.e value being greater than 99%. According to the invention, resolution of chiral amine can be mildly realized under the condition of enzyme catalysis; and simultaneously, the product has good optical purity, high yield and great application values.
Owner:六安佳诺生化科技有限公司
Lipase mutant and uses thereof
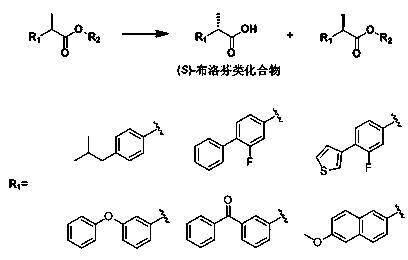
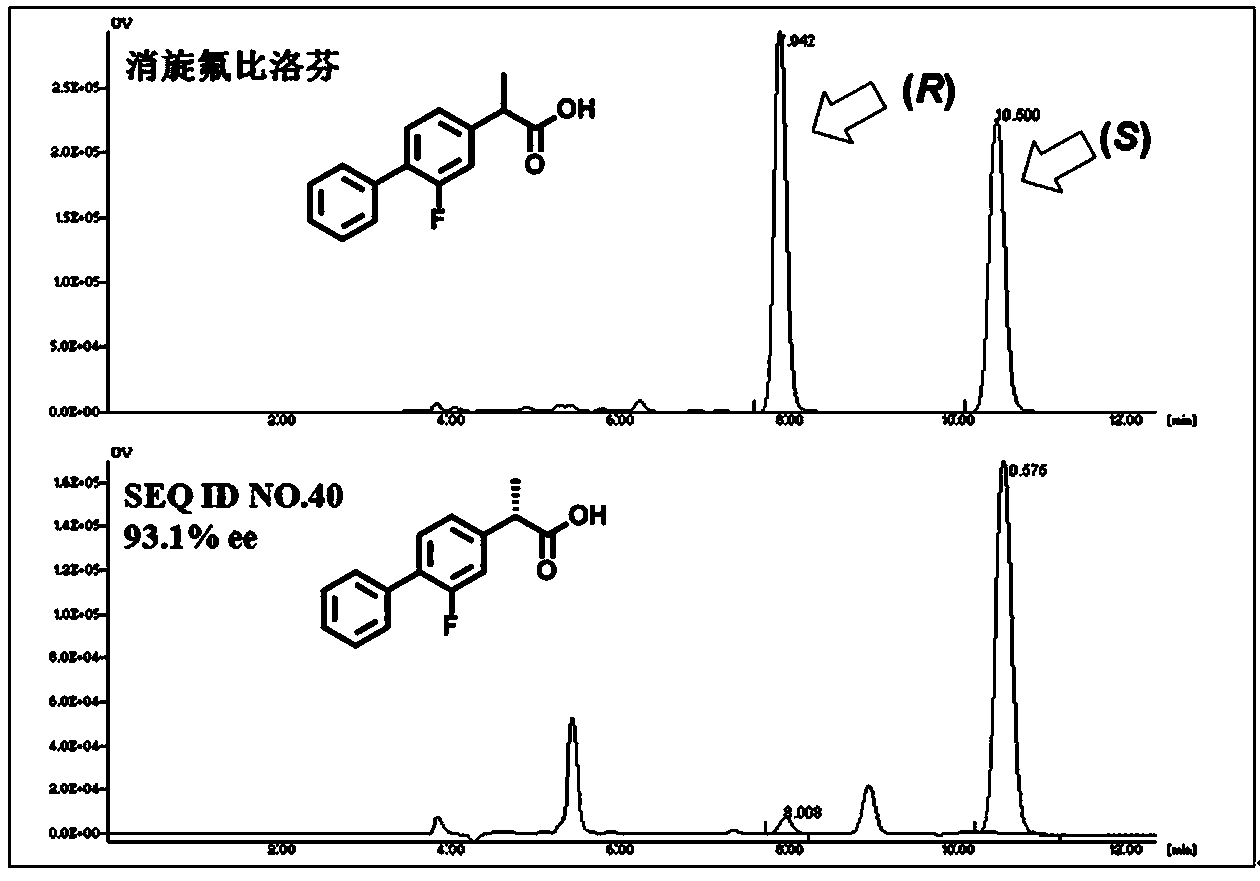
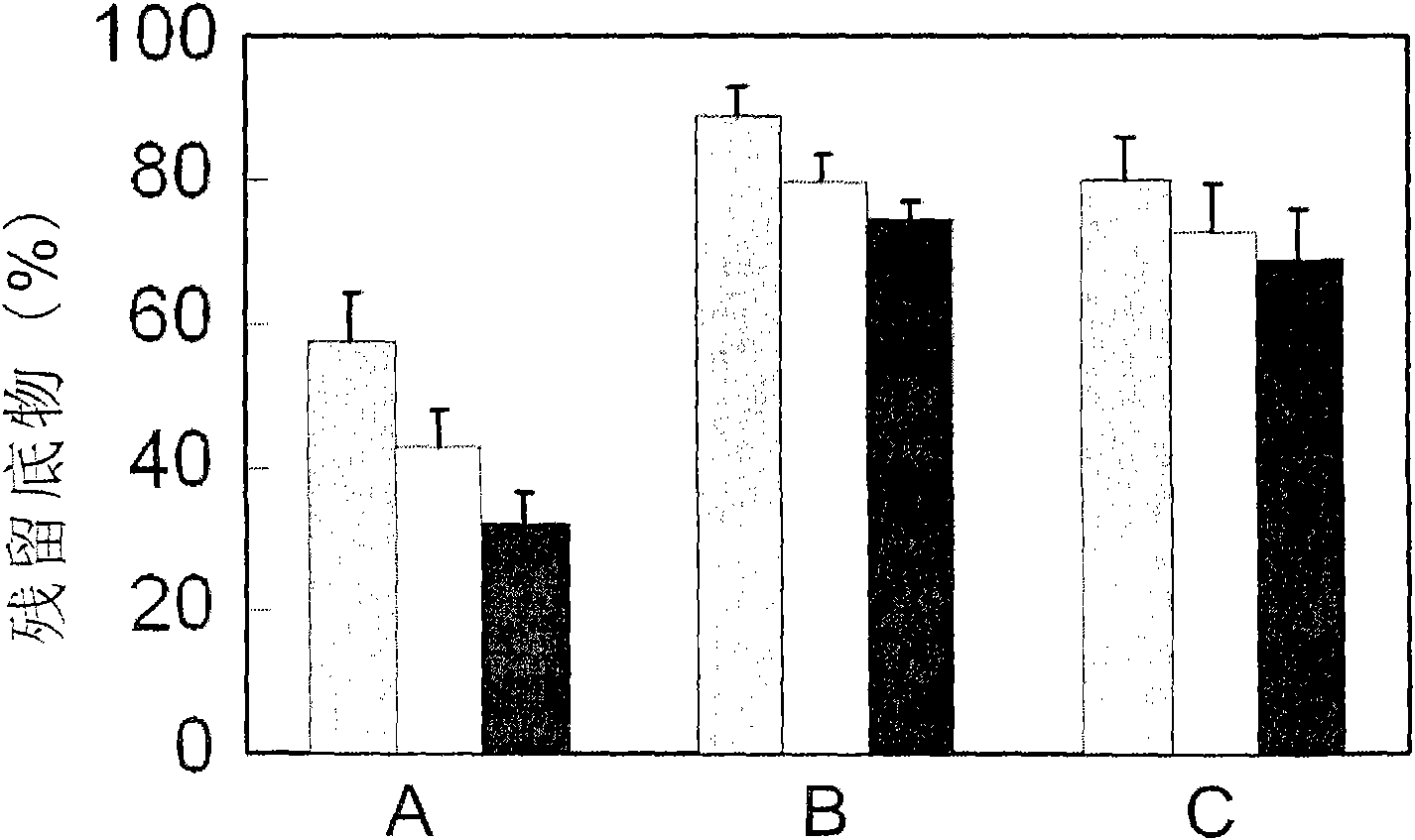
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and relates to a lipase mutant and uses thereof. The mutant is obtained from wild type candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) through mutation. The invention particularly relates to the lipase mutant, a preparing method thereof, and a method of preparing S-configuration ibuprofen type compounds with optical activity through catalysis of hydrolysis of ester derivatives of the ibuprofen type compounds by utilization of the lipase mutant and through kinetic resolution. The wild type candida antarctica lipase B is subjected to mutation to obtain the modified lipase. The lipase is expressed in pichia pastoris engineering bacteria. The lipase comprises an amino acid sequence having at least 85% of identity with the SEQ ID NO.02. The 189 site residue corresponding to the SEQ ID NO.02 of the lipase is an aromatic amino acid residue and the 190 site residue corresponding to the SEQ ID NO.02 of the lipase is a nonpolar amino acid residue. By subjecting the wild type candida antarctica lipase B to mutation, the enantioselectivity of the lipase to the ibuprofen type compounds is improved.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
High-enantiomer selectivity epoxide hydrolase and gene coded thereby
The invention belongs to the field biotechnology and discloses use of an RT-PCR method in cloning an epoxide hydrolase gene (PchEHA) from a BKM-F1767 strain (Phanerochaete chrysosporium BKM-F1767) of fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium and a nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of a coding region of the PchEHA. Cloned plasmid pTEHA containing the gene, a recombinant expression plasmid pET28EHA containing the gene and a genetic engineering strain Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / PeT28EHA containing the PchEHA gene are provided to prepared the recombinant epoxide hydrolase. The epoxide hydrolase of the invention has catalytic activity for various epoxides and shows enantiomer selectivity of different degrees, particularly high enantiomer selectivity for epoxyethylbenzene. The recombinant epoxide hydrolase of the invention can be used in the fields of the kinetic resolution of a chiral epoxide racemic mixture, the asymmetric catalysis of epoxides, and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
A chemical enzymatic resolution preparation method of (r)-1-(1-naphthyl)ethylamine
InactiveCN102277392AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh optical purityFermentationPtru catalystEthyl group
The invention discloses a kinetic resolution method, in particular a method for preparing chemical enzyme of (R)-1-(1-naphthyl) ethylamine by resolution, which using 1-(1-naphthyl) ethylamine as a raw material. In the method, kinetic resolution is performed by using 1-(1-naphthyl) ethylamine which is a racemic mixture as a raw material, phenylethyl acetate as an acyl donor and immobilized lipase from Candida Antarctica as a catalyst under the controlled operation conditions that: the temperature is 30 to 80 DEG C, the volume ratio of the raw material to a solvent is 1:(25-50), the mass ratio of the raw material to the catalyst is 1:(0.02-0.05), and the molar ratio of the raw material to the phenylethyl acetate is 1:(1.2-4.0). The method has the advantages of high catalytic efficiency and environment friendliness.
Owner:倪发根
R-1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanol and synthesis of ester thereof
InactiveCN104262093AOvercoming the problem of low yieldEasy to realize industrial productionOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsP-ChlorophenolKinetic resolution
The invention discloses R-1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanol and a synthetic method of an ester thereof. The preparation method of R-1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanol comprises the following steps: taking 1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanol as a raw material, lipase as a biologic resolution catalyst, acidic resin as a racemization catalyst, and p-chlorophenol ester as an acyl donor, conducting dynamic kinetic resolution to obtain R-1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanol ester, and then conducting LiOH hydrolysis to obtain R-1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanol. The R-1-(3-methylphenyl)ethanol and the synthetic method of the ester thereof disclosed by the invention have the advantages of mild conditions, environment friendliness, good product yield, high selectivity and cheap price and good feasibility of the adopted racemization catalyst, so that the technology has a high application value in industrial production.
Owner:王同俊
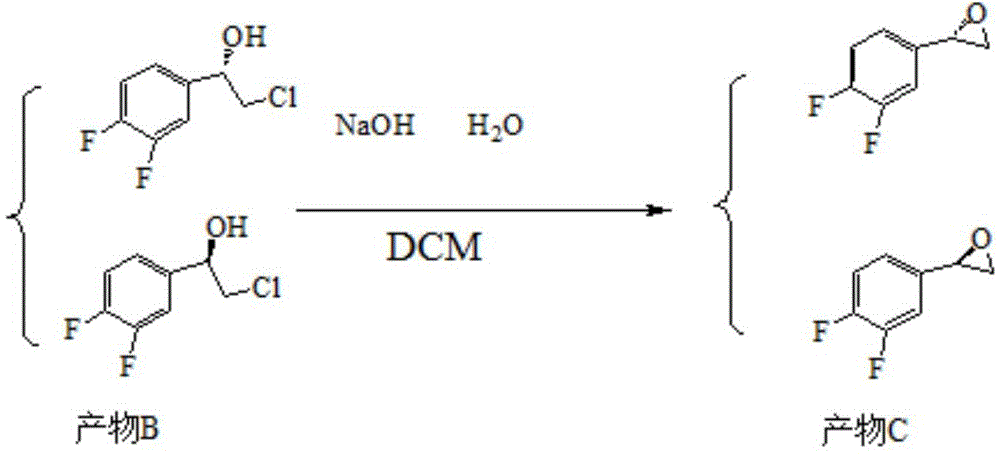
Preparation method of trans-(1R, 2S)-2-(3, 4-difluoro phenyl) cyclopropylamine
InactiveCN102775314AFew stepsEasy to operateHydroxy compound separation/purificationPreparation by rearrangement reactionsEpoxyPtru catalyst
The invention provides a preparation method of trans-(1R, 2S)-2-(3, 4-difluoro phenyl) cyclopropylamine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: enabling racemic chloro phenethyl alcohol (I) and N-protection proline to undergo a reaction under the effects of a condensing agent A1 and a catalyst C1, and obtaining chiral chlorohydrin (II); enabling the chiral chlorohydrin (II) to generate an epoxy compound (III) under the conditions of alkalinity; enabling the epoxy compound (III) and TEPA to react and generate cyclopropyl ethyl formate (IV) under the conditions of alkalinity; removing ester from cyclopropyl ethyl formate (IV) under the conditions of alkalinity, and generating cyclopropanecarboxylic acid (V); and enabling cyclopropanecarboxylic acid (V) and azide to generate a target compound (3) by Curtius rearrangement. The preparation method has the advantages that the steps of a used synthetic process route are few, the operation is simple, and industrial production is achieved easily; a kinetic resolution method is utilized to synthesize chiral chlorohydrin (II) and is simple in reaction conditions and easy to operate; and a TEPA method is utilized synthesize the cyclopropyl ethyl formate, the product yield is high, cis-trans selectivity is good, and the purity is over 99%.
Owner:江苏富泽药业有限公司
Dynamic kinetic resolution method of 1-(1-naphthyl) ethylamine
InactiveCN102392065AIncrease reaction rateReduce the temperatureFermentationPhenethyl alcoholAcetophenone
The invention discloses a dynamic kinetic resolution method for 1-(1-naphthyl) ethylamine, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, adding parachlorophenol, organic acid, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 4-dimethylaminopyridine, carrying out agitating reaction and filtering, drying, concentrating and carrying out column chromatography to obtain an acyl donor; or adding acetophenone and sodium borohydride, carrying out agitating reaction, depressurizing and distilling, washing, extracting, drying and concentrating to obtain phenethyl alcohol, adding the phenethyl alcohol, acetyl chloride and triethylamine, carrying out agitating reaction and washing, drying, concentrating and carrying out column chromatography to obtain an acyl donor; secondly, adding palladium salt and a carrier, heating, adding formaldehyde and sodium hydroxide, heating and centrifuging, washing and vacuum-drying to obtain a racemic catalyst for standby; and thirdly, adding the 1-(1-naphthyl) ethylamine in methyl benzene, the acyl donor, lipase and the racemic catalyst and carrying out hydrogenation reaction to obtain amide. The dynamic kinetic resolution method has high reaction speed, lower temperature, high conversion rate and product optical purity and great application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing (1R, 2R)-2-(3, 4-difluoro phenyl)cyclopropylamine
ActiveCN105712889AReduce usageEasy to operateGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationHydrolysisRaw material
Owner:DAILY FAME TRADING LTD +1
Kinetics resolution method
InactiveCN1649861AReduce consumptionReduce chemical transformationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOxygen-containing compound preparationChemical synthesisChemical transformation
A method for stereoselective chemical synthesis, includes the steps of: (A) reacting a nucleophile and a chiral or prochiral cyclic substrate, said substrate comprising a carbocycle or a heterocycle having a reactive center susceptiable to nucleophilic attack by the nucleophile, in the presence of a chiral non-racemic catalyst to produce a product mixture comprising a stereoisometrically enriched product wherein the product mixture further comprises a catalyst residue, at least a portion of the catalyst residue is in a first oxidation state, and the catalyst residue in the first oxidation state is active in catalyzing degradation of the stereoisomerically enriched product, and (B) chemically or electrochemically changing the oxidation state of the catalyst residue form the first oxidation state to a second oxidation state, wherein catalyst residue in the second oxidation state is less active in catalyzing degradation of the stereoisomerically enriched product than is catalyst residue in the first oxidation state. The method reduces erosion of the chiral purify of the stereoisomerically enriched product and reduces the chemical transformation to side products of the stereoisomerically enriched product and co-product(s).
Owner:SHASUN PHARMA SOLUTIONS LTD
Kinetic resolution method of secondary alcohol
InactiveCN102154431AImprove performanceMeet various requirements of purityFermentationOrganic acidAlcohol
The invention discloses a secondary alcohol kinetic resolution method which comprises the following steps of: (1) adding parachlorophenol, organic acid, dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 4- dimethylamino pyridine, the molar ratio of which is 1:1-2:1-2:0.03-0.05, stirring and reacting for 3 to 7 hours, filtrating, drying filtrate, concentrating and carrying out column chromatography so as to obtain pure ester being used as acyl donor for standby application; (2) adding secondary alcohol, acyl donor and 5 to20mg / mL lipase into 2-6mL of organic solvent, wherein the molar ratio between the secondary alcohol and the acyl donor is 1:0.5 to 3, reacting for 0.5 to 3 hours at the reaction temp[rapture of 30 to 60 DEG C so as to obtain ester with 50% conversion rate and 99% of e.e value. In the method, the conversion rate of the secondary alcohol reaches 50% in a very short time; the e.e value of the obtained ester reaches nearly 100%, properties of products is greatly increased, various requirements on purity can be met and very great application value is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing dexiotropous antifoim dichlor chrysanthemic acid in high optical purity through method of induced crystallization
InactiveCN1480445AHigh optical purityHigh selectivityCarboxylic compound separation/purificationOrganic solventChrysanthemic acid
A process for preparing high-optical-purity R(+)-trans-dichlorochrysanthemic acid by induced crystallizing method includes dissolving chiral dichlorochrysanthemic acid in hot solvent to become supersaturated solution, adding the inducing crystal seeds, slow natural crystallizing, drying and testing its 4 isomers by gas-phase chromatography. Its advantage is high optical purity increased by 5-10%.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of R-3, 5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol
InactiveCN104230667AEasy to operateHigh yieldOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystP-Chlorophenol
The invention discloses a preparation method of R-3, 5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, 3, 5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol is taken as a raw material, chlorophenol acetate is taken as an acyl donor, Novozym435 is taken as a resolution catalyst, acidic resin is taken as a racemic catalyst, and then dynamic kinetic resolution is performed to obtain R-3, 5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol acetate. Then, ester is hydrolyzed to obtain R-3, 5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol, the final product yield can be more than 90%, and the ee value of the product is more than 99%. The method is simple to operate, the used racemic catalyst has the characteristics of low price, easiness in obtainment, reusability, high product yield, good optical purity and the like, and the method further has great guide and application values in production and preparation processes of R-3, 5-bis (trifluoromethyl) phenyl ethanol.
Owner:王际宽
Supported Pd catalyst and application thereof
ActiveCN103962166AHigh selectivityInhibit side effectsAmino compound purification/separationMolecular sieve catalystsKinetic resolution1-phenylethanamine
The invention relates to a supported Pd catalyst and application thereof to racemization and dynamic kinetic resolution of amine compounds. The supported Pd catalyst shows high catalytic activity and product selectivity more than 97% when being applied to racemization reaction of (S)-1-phenylethylamine. When the Pd catalyst is applied to dynamic kinetic resolution of 1-phenylethylamine, the yield of a target amide reaches 95% or more. According to the technical scheme, the application scope of the catalyst for racemization and dynamic kinetic resolution of amine compounds is substantially expanded. The preparation method of the catalyst is simple, environment-friendly and wide in application scope.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
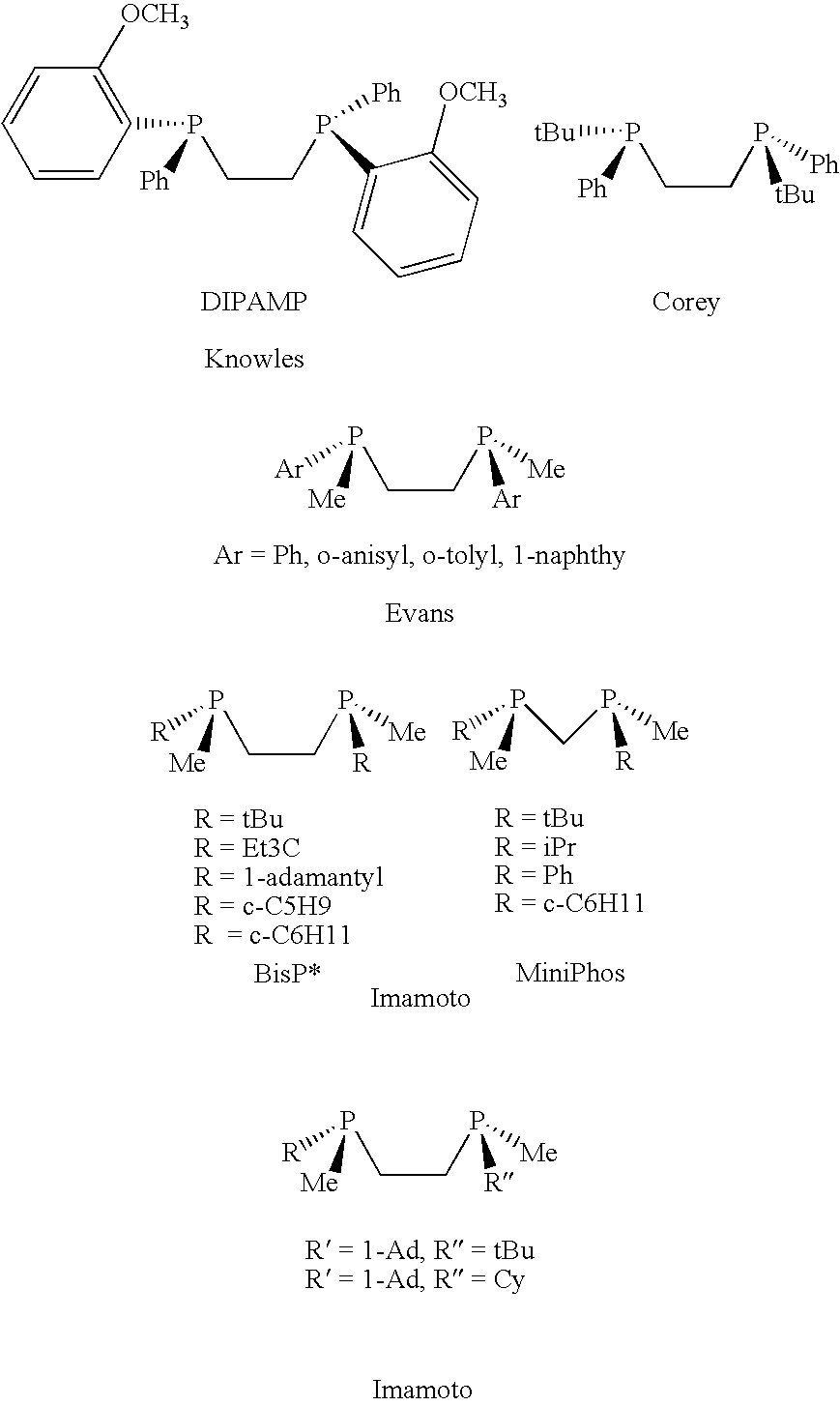
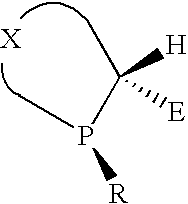
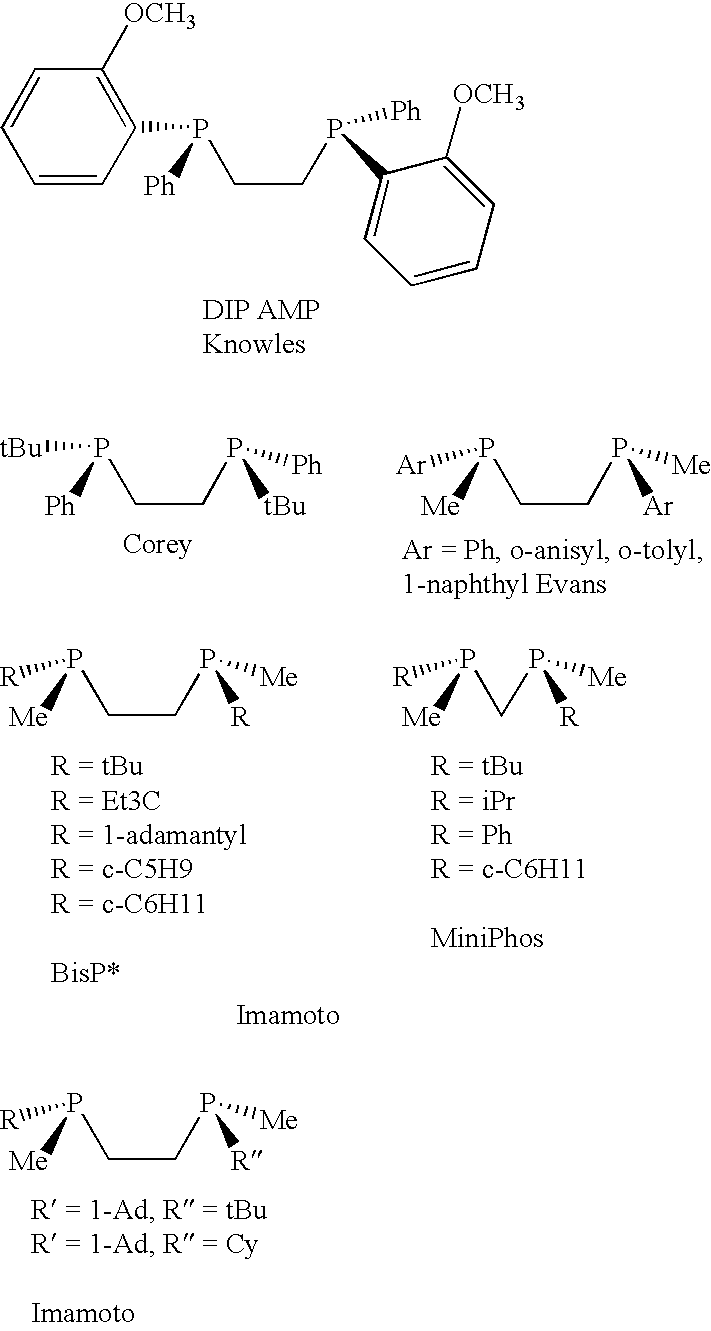
P-chiral phospholanes and phosphocyclic compounds and their use in asymmetric catalytic reactions
InactiveUS7169953B2SelectiveGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesAsymmetric synthesesIsomerizationCycloaddition
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Supported metal palladium catalyst, its preparation and its application
InactiveCN102784660AImprove catalytic performanceEfficient splitMolecular sieve catalystsFermentationMetal catalystPalladium catalyst
The invention discloses a supported metal palladium catalyst, its preparation method and its use. The metal loading amount of the catalyst is 1.0-5.0wt%, the specific surface area of the catalyst is 300-900m<2> / g, the pore volume of the catalyst is 0.3-1.0cm<3> / g, the pore diameter of the catalyst is 3.0-10.0nm, and the metal particle diameter of the catalyst is 1.0-8.0nm. In the invention, the preparation of the high-stability metal catalyst with uniform and controllable dimension is realized through a three-step method. The supported metal palladium catalyst can be used for the dynamic kinetic resolution of a secondary alcohol through combining with a lipase, and the catalytic performance of the supported metal palladium catalyst is further better than that of supported metal palladium catalysts prepared through traditional dipping reduction methods. The supported metal palladium catalyst has the advantages of realization of the efficient resolution of the secondary alcohol in a one-pot reaction system, multiple repeated use, and substantial cost reduction.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
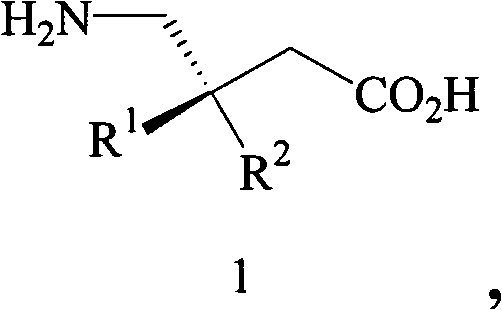
Preparation of pregabalin and related compounds
Materials and methods for preparing (S)-(+)-3-aminomethyl-5-methyl-hexanoic acid and structurally related compounds via enzymatic kinetic resolution are disclosed.
Owner:厄普约翰美国1有限责任公司
Method for stereoselective enzymatic hydrolysis to resolve 2-(3-chlorophenyl)propionic acid enantiomers
The present invention describes a method for lipase kinetic resolution of 2-(3-chlorophenyl)propionic acid enantiomers. By use of efficient selective lipase, racemic 2-(3-chlorophenyl)propionate is catalytically hydrolyzed in an aqueous medium to resolve 2-(3-chlorophenyl)propionic acid. Through addition of surfactant PEG400 to the reaction system, the substrate conversion rate is greatly increased. The optical purity of the product is >=97%, and the conversion rate is >=40%. Compared with other resolution technologies, the method has mild reaction conditions, simple operation and low environmental pollution, and provides a feasible method for the production of (S)-Pirprofen in the pharmaceutical industry.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Carboxyesterase and application thereof to production of cyclohexene formic acid by kinetic resolution of cyclohexene formate
ActiveCN112813131AGood prospects for industrial application developmentHigh optical purityBacteriaHydrolasesPtru catalystFormate
The invention discloses carboxylesterase and an application thereof to production of cyclohexene formic acid by kinetic resolution of cyclohexene formate. In the application of the carboxylesterase as a catalyst to preparation of chiral cyclohexene formic acid by asymmetric resolution of chiral cyclohexene formate, the carboxylesterase is good in substrate tolerance, high in optical purity (the ees value reaches 99% or above), mild in reaction condition, environment-friendly, simple and convenient to operate and easy to industrially amplify. Therefore, the carboxylesterase and a gene thereof have good industrial application and development prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
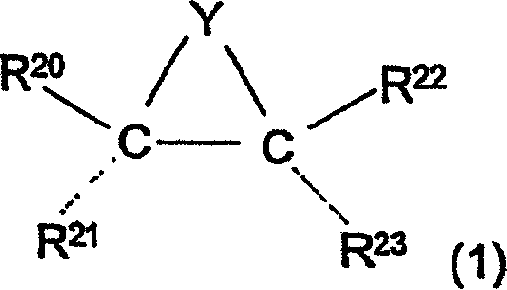
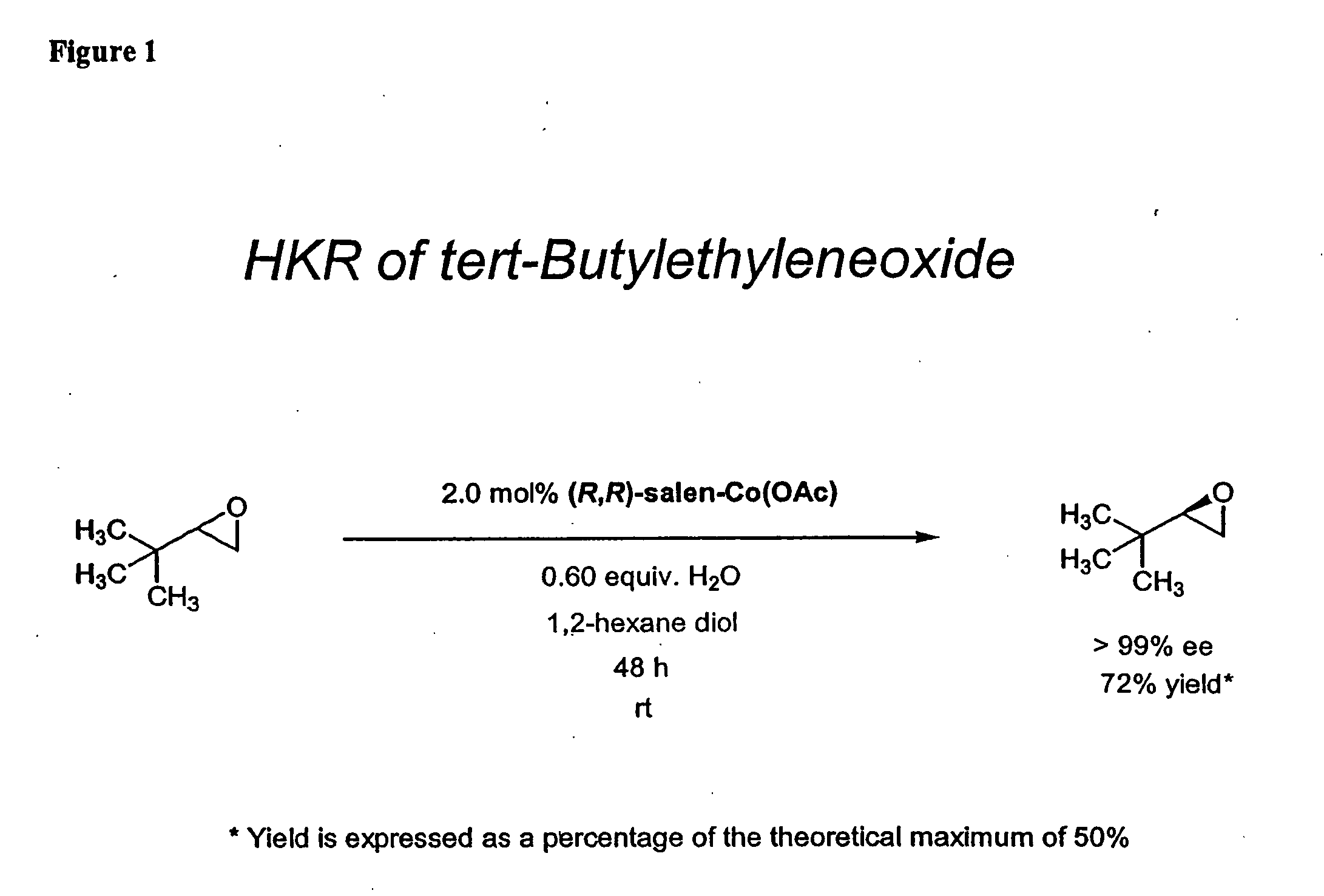
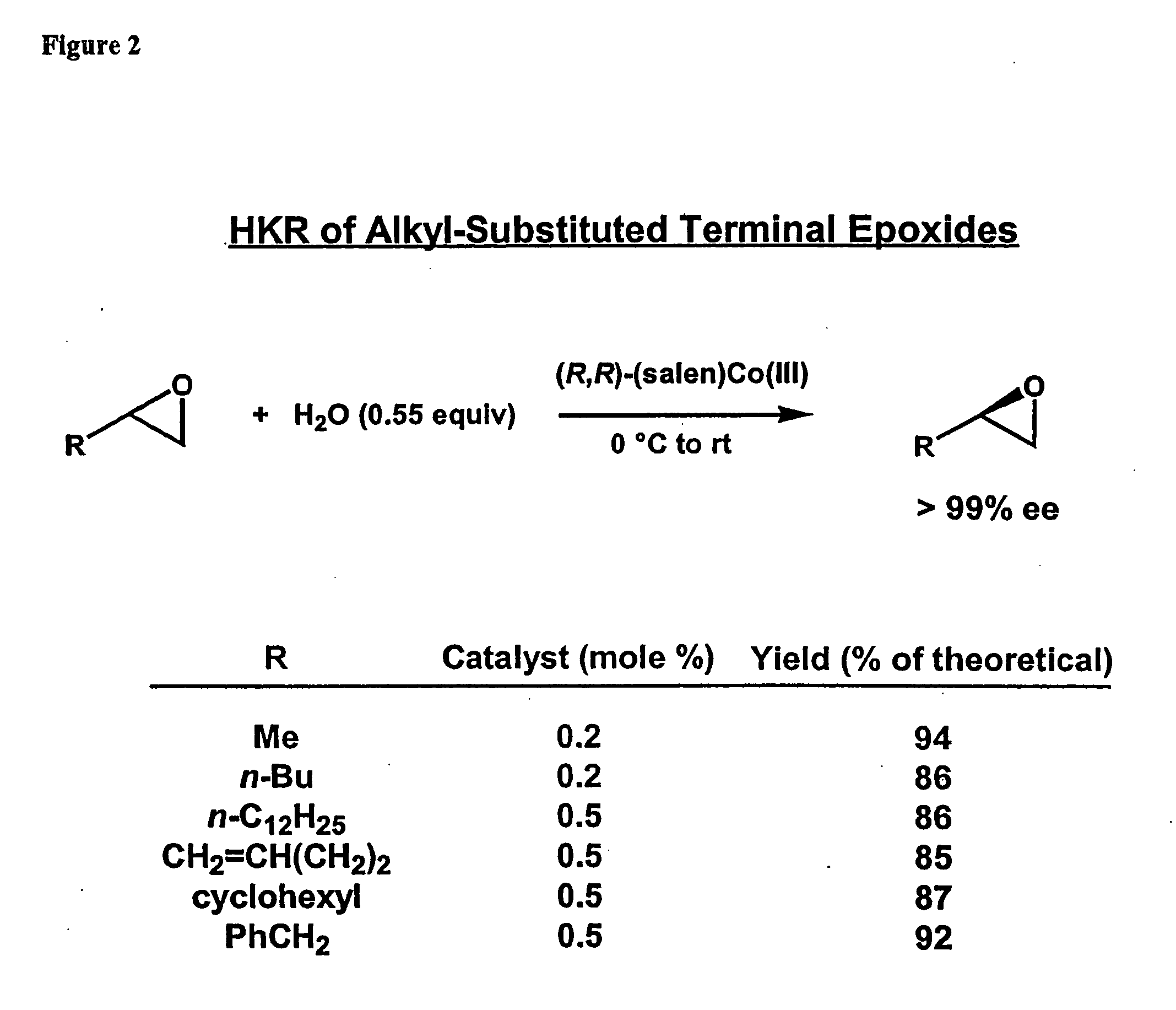
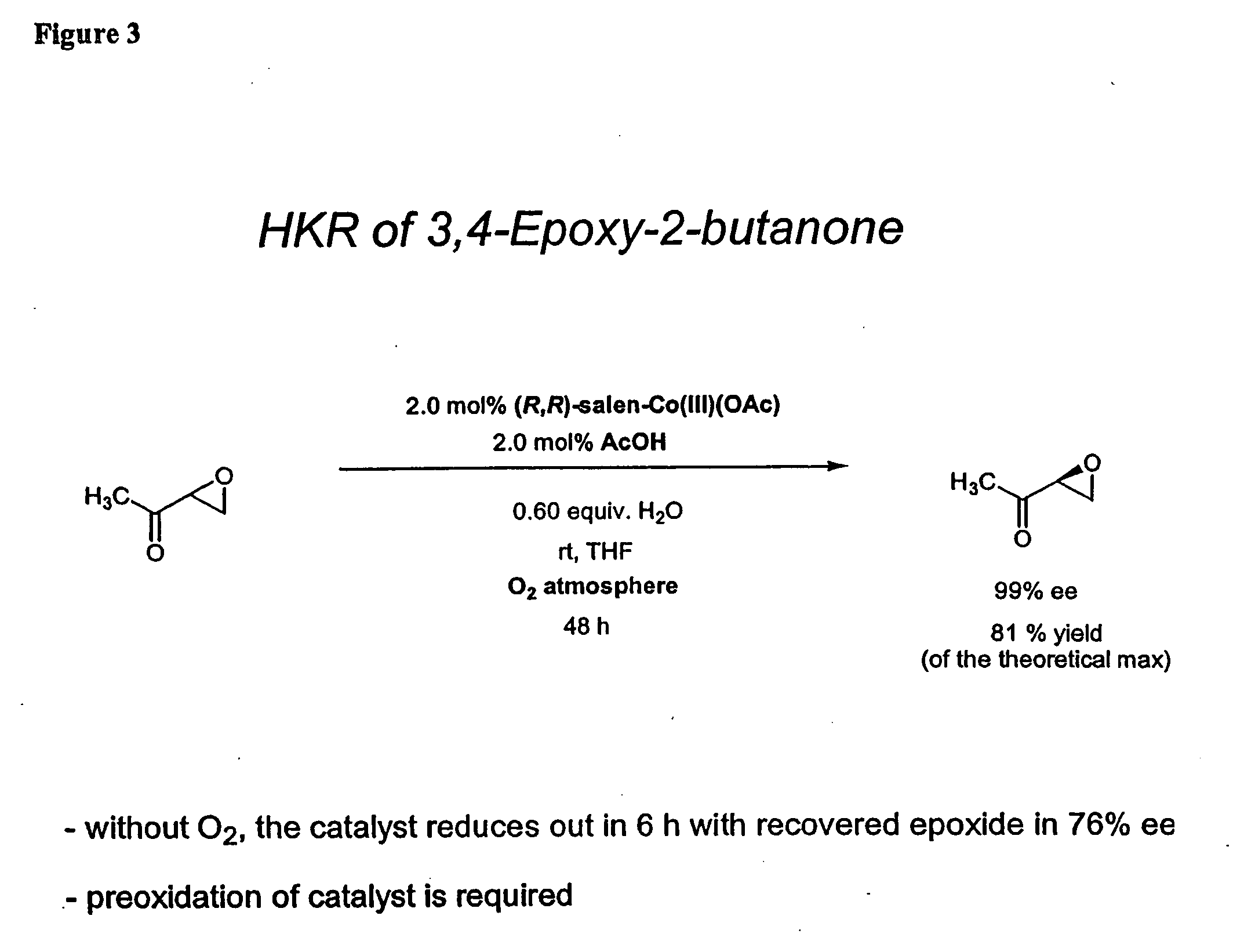
Hydrolytic kinetic resolution of cyclic substrates
InactiveUS20050187392A1Silicon organic compoundsCarbamic acid derivatives preparationChemical synthesisHydrolysis kinetics
The present invention relates to a process for stereoselective or regioselective chemical synthesis which generally comprises reacting a nucleophile and a chiral or prochiral cyclic substrate in the presence of a non-racemic, chiral catalyst to produce a stereoisomerically- and / or regioisomerically-enriched product. The present invention also relates to hydrolytic kinetic resolutions of racemic and diastereomeric mixtures of epoxides.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
P-chiral phospholanes and phosphocyclic compounds and their use in asymmetric catalytic reactions
InactiveUS7105702B2SelectiveGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesAsymmetric synthesesIsomerizationCycloaddition
Chiral ligands and metal complexes based on such chiral ligands useful in asymmetric catalysis are disclosed. The metal complexes according to the present invention are useful as catalysts in asymmetric reactions, such as, hydrogenation, hydride transfer, allylic alkylation, hydrosilylation, hydroboration, hydrovinylation, hydroformylation, olefin metathesis, hydrocarboxylation, isomerization, cyclopropanation, Diels-Alder reaction, Heck reaction, isomerization, Aldol reaction, Michael addition; epoxidation, kinetic resolution and [m+n] cycloaddition. Processes for the preparation of the ligands are also described.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
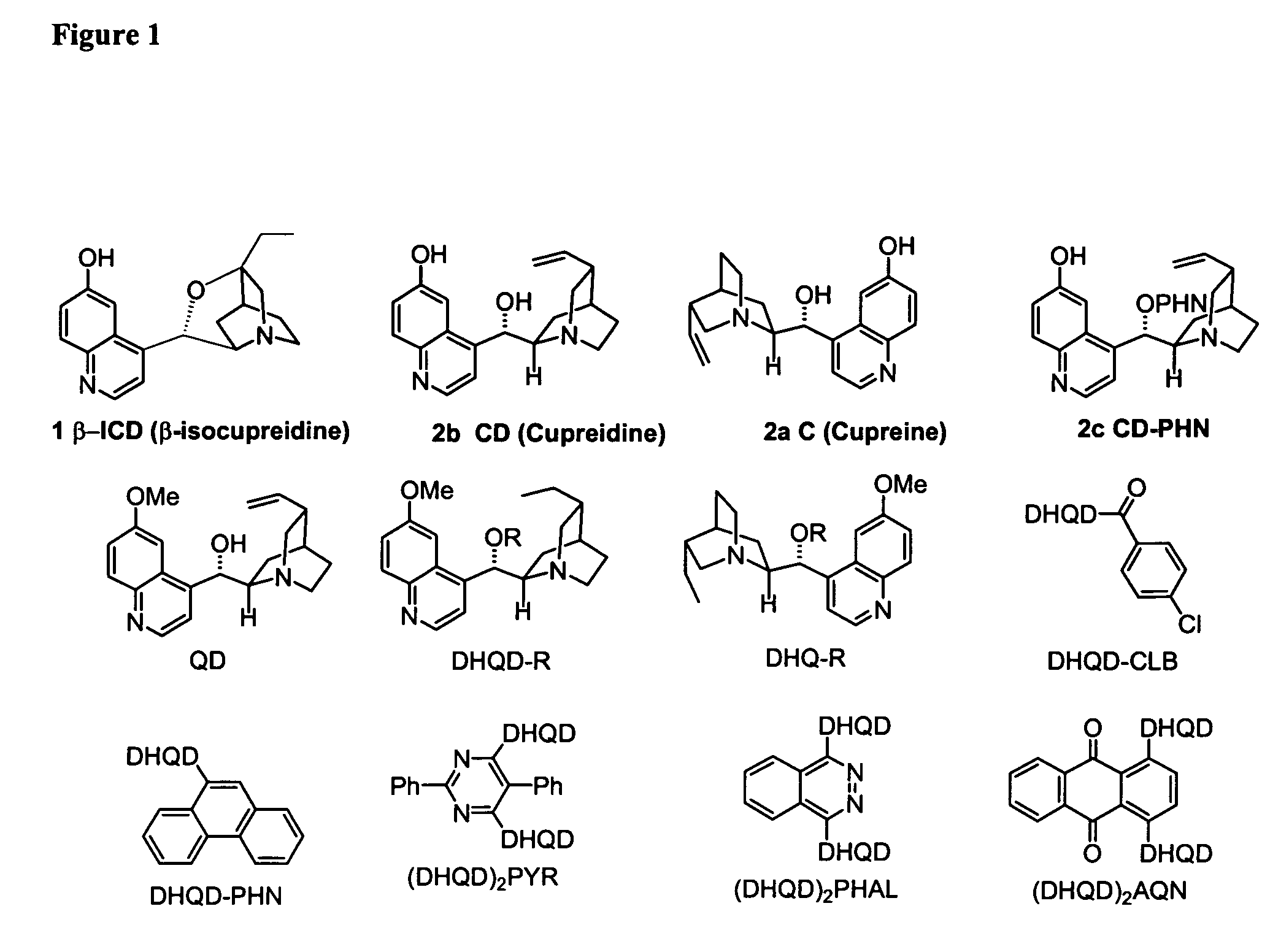
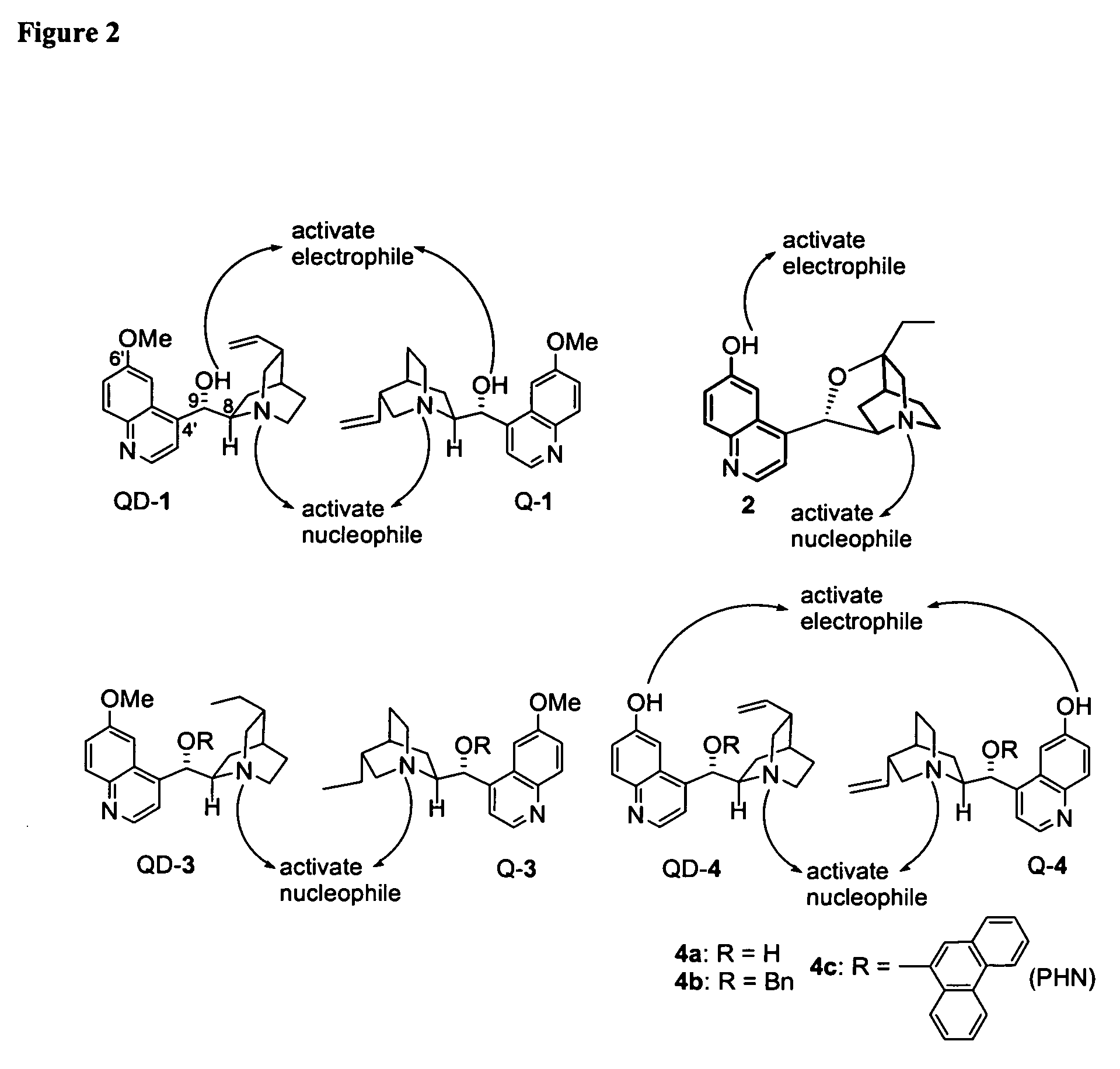
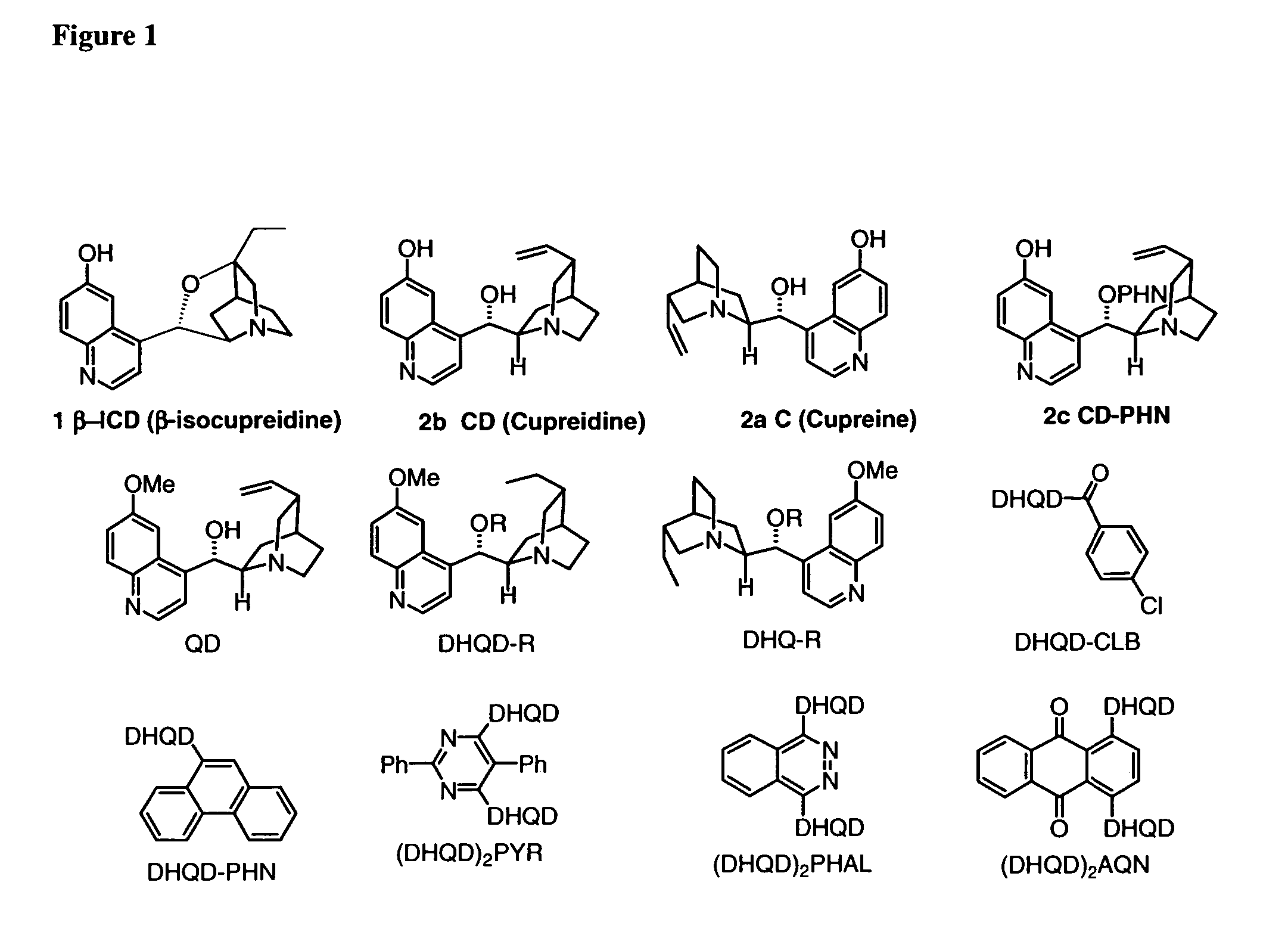
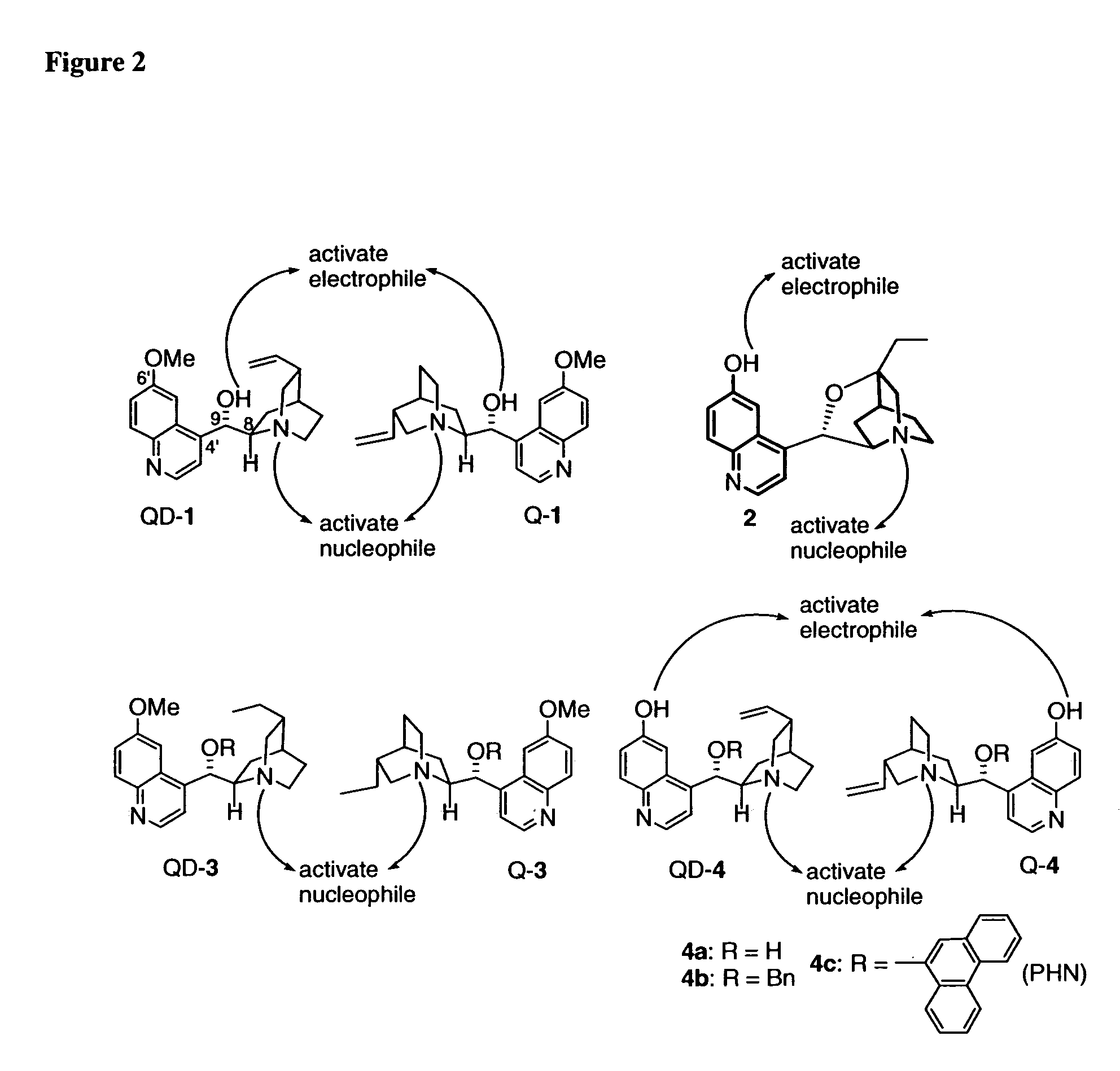
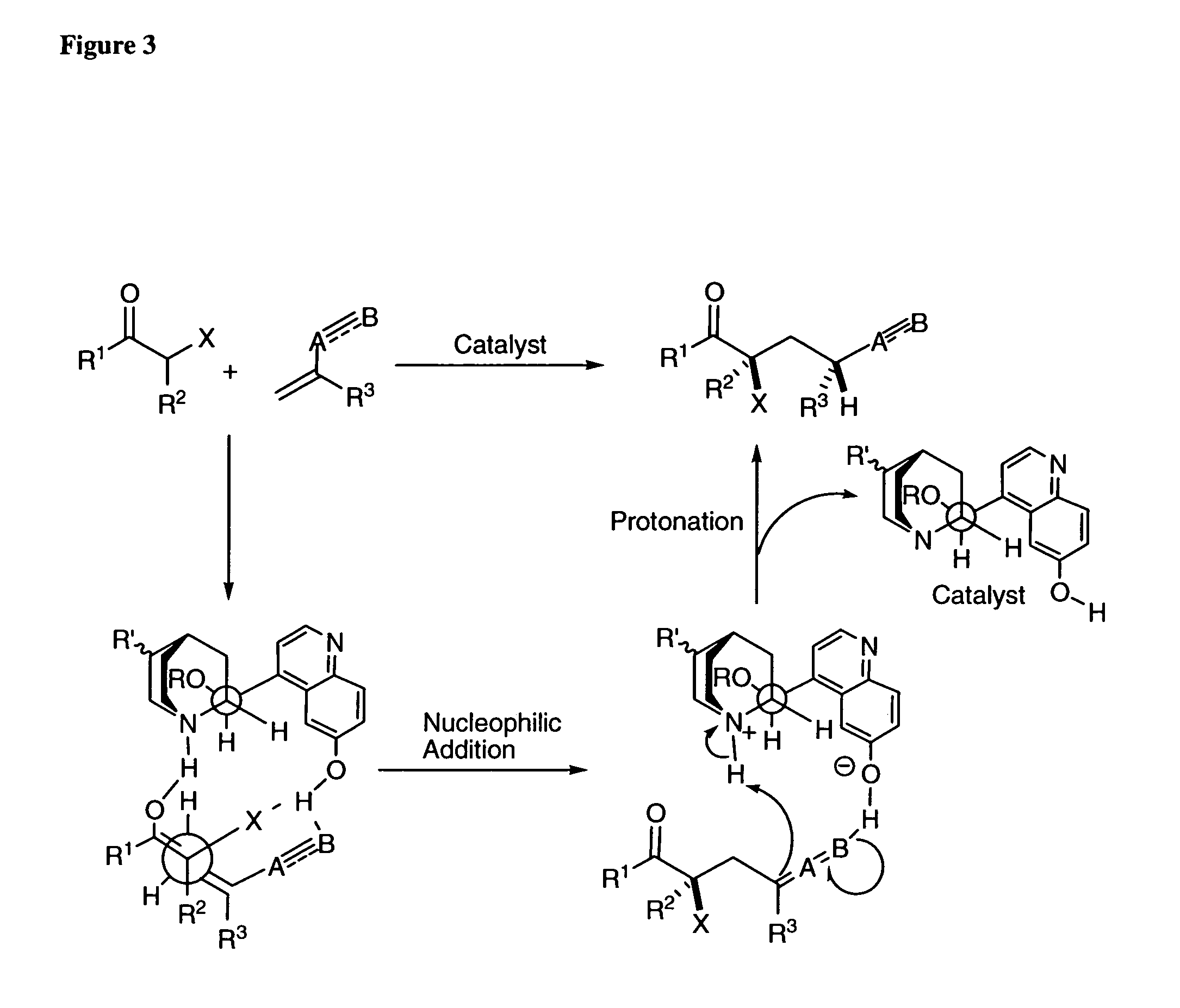
Asymmetric Michael and Aldol additions using bifunctional cinchona-alkaloid-based catalysts
InactiveUS20060014956A1Silicon organic compoundsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationLeaving groupKetone
One aspect of the present invention relates to quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts. Another aspect of the invention relates to a method of preparing a derivatized quinine-based or quinidine-based catalyst comprising 1) reacting quinine or quinidine with base and a compound that has a suitable leaving group, and 2) converting the ring methoxy group to a hydroxy group. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a chiral, non-racemic compound from a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or azo compound or prochiral aldehyde or prochiral ketone, comprising the step of: reacting a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or azo compound or prochiral aldehyde or prochiral ketone with a nucleophile in the presence of a catalyst; thereby producing a chiral, non-racemic compound; wherein said catalyst is a derivatized quinine or quinidine. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of kinetic resolution, comprising the step of: reacting racemic chiral alkene with a nucleophile in the presence of a derivatized quinine or quinidine.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
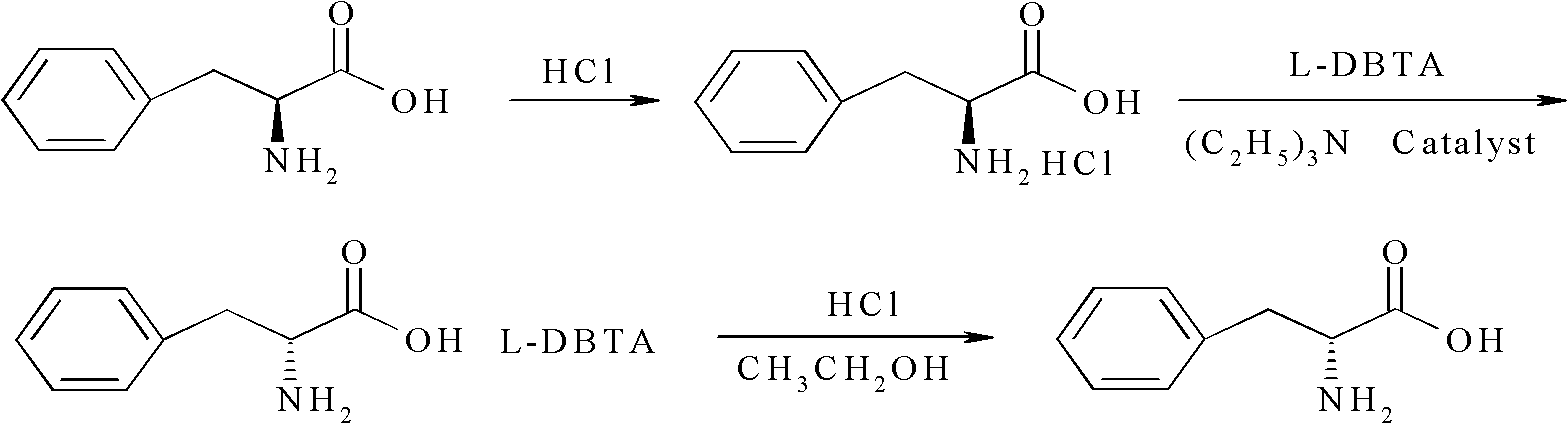
Method for preparing D-phenylalanine through dynamic kinetic resolution
InactiveCN102010345AHigh split yieldReduce operating costsOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationSolventOperating cost
The invention discloses a method for preparing D-phenylalanine through dynamic kinetic resolution. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting L-phenylalanine serving as raw materials with hydrochloric acid to generate L-phenylalanine hydrochloride; racemizing and resolving under the action of a solvent and a racemization catalyst by taking the L-phenylalanine hydrochloride as a substrate and dibenzoyl tartaric acid (L-DBTA) as a resolving agent to obtain D-phenylalanine.L-DBTA disalt; and finally performing triethylamine resolution to prepare the target product D-phenylalanine. Compared with the prior art, the method directly takes the L-phenylalanine as the resolving substrate, mild alcohol as the solvent and an aldehyde pyridine compound as the racemization catalyst, racemizes and resolves the L-phenylalanine into the D-phenylalanine.L-DBTA disalt, has a theoretical conversion rate of about 100 percent, greatly improves the resolution yield, reduces the operating cost, ensures stable product quality and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAYI GRP CO
4-(N,N-dimethyl) aminopyridine derivate and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN101891678ALower synthesis costOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAlcoholSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a 4-(N,N-dimethyl) aminopyridine derivate and a synthesis method thereof. The derivate has a structural formula shown in the specification of the invention, wherein R is -PH and -CN. Under the more common condition or microwave condition, the invention synthesizes 11 4-(N,N-dimethyl) aminopyridine derivates with higher yields. A chiral N,N dimethyl aminopyridine analogue is applied to asymmetric kinetic resolution of secondary alcohol 1-phenylethanol to obtain a medium value of ee percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
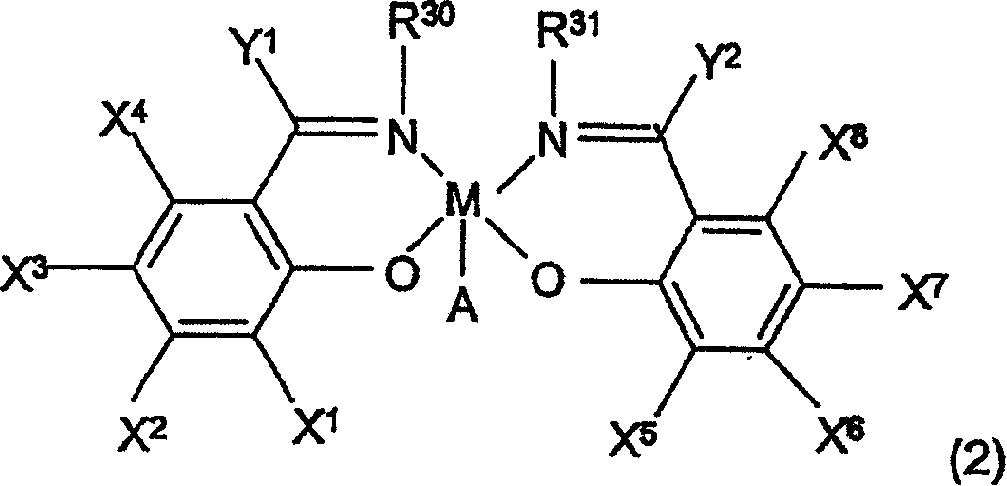
High-activity bifunctional catalyst for preparing chiral epoxy alkane and diol and application thereof
ActiveCN103242375AHigh catalytic activityHigh enantioselectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEpoxyAlkane
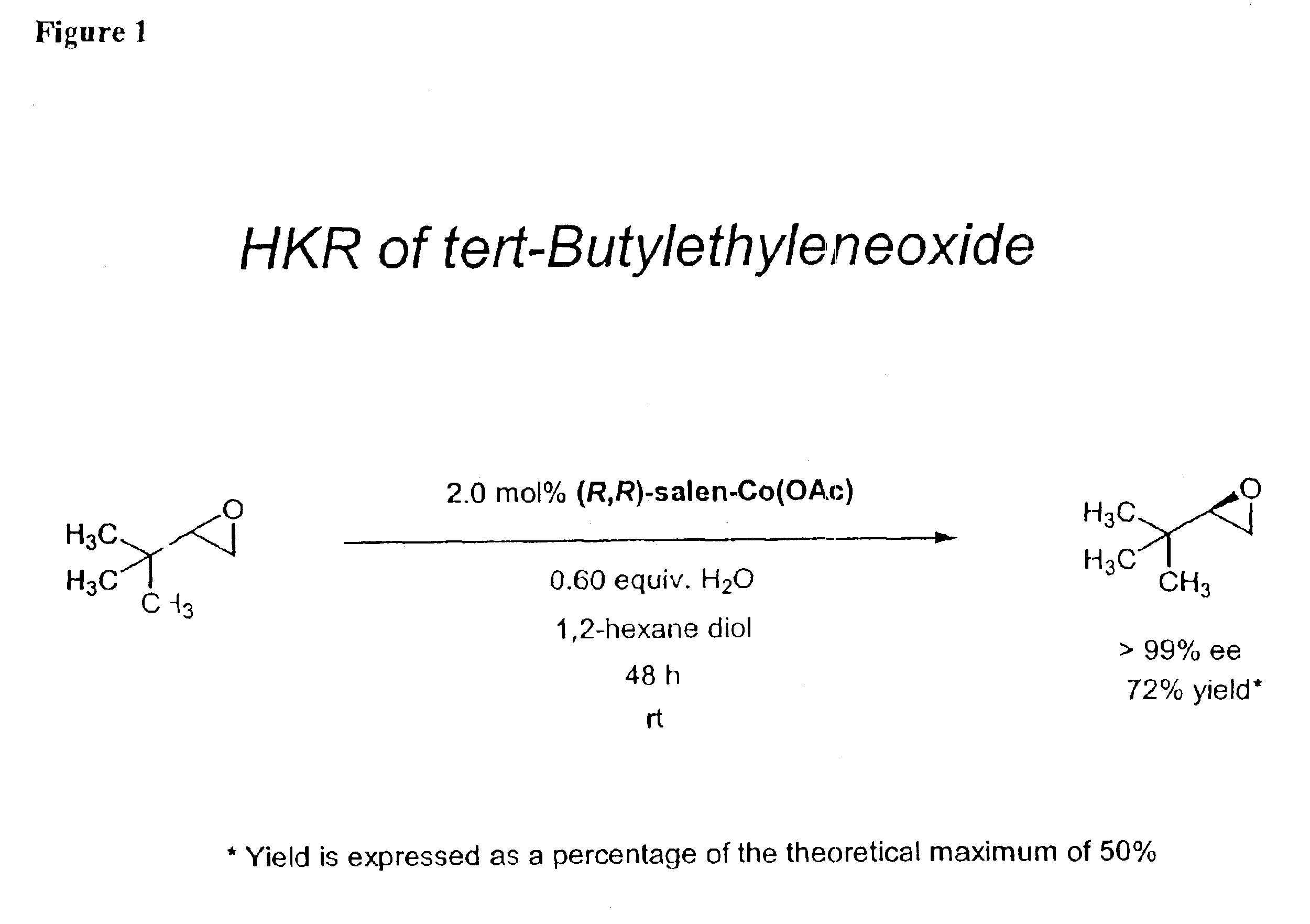
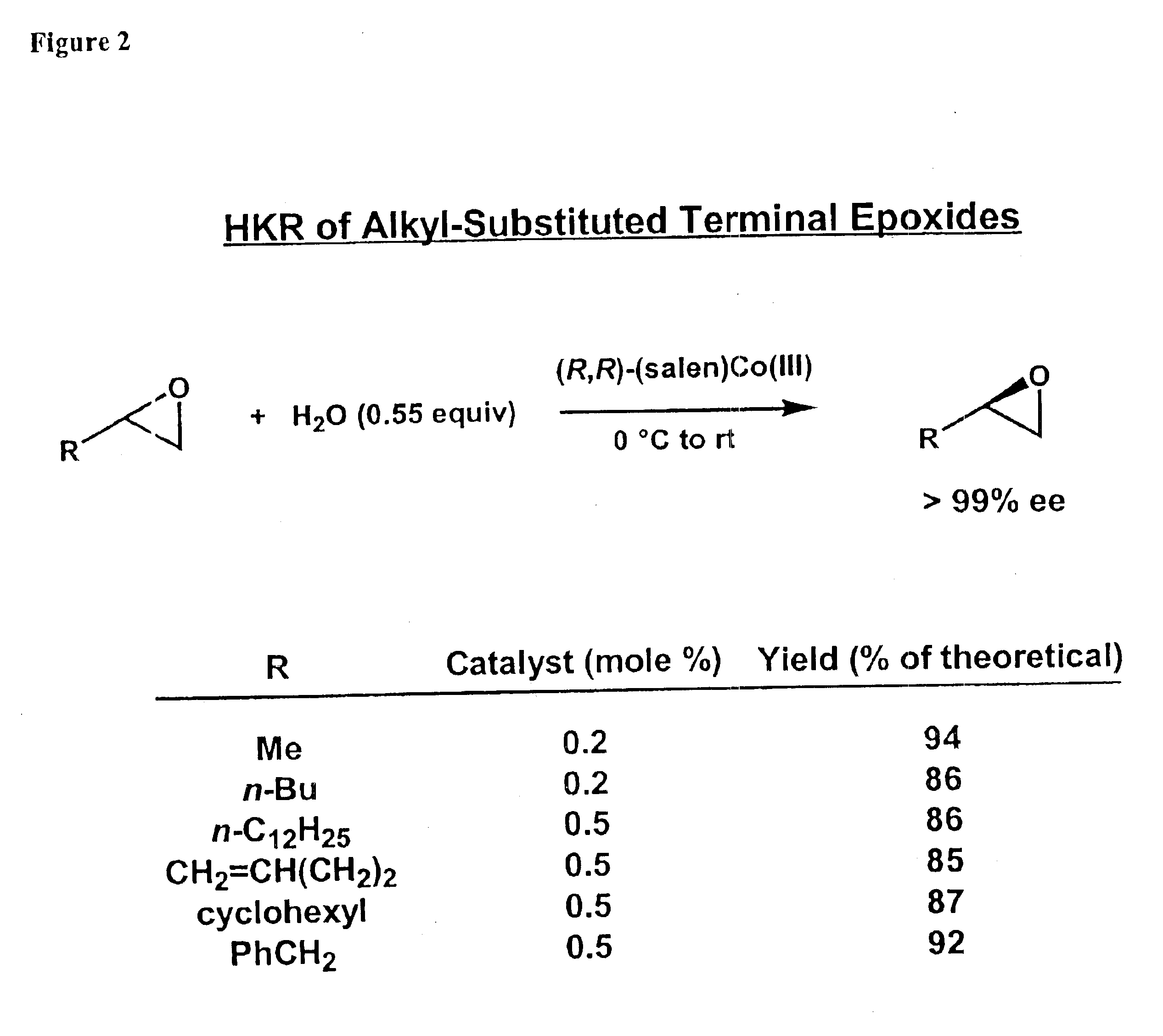
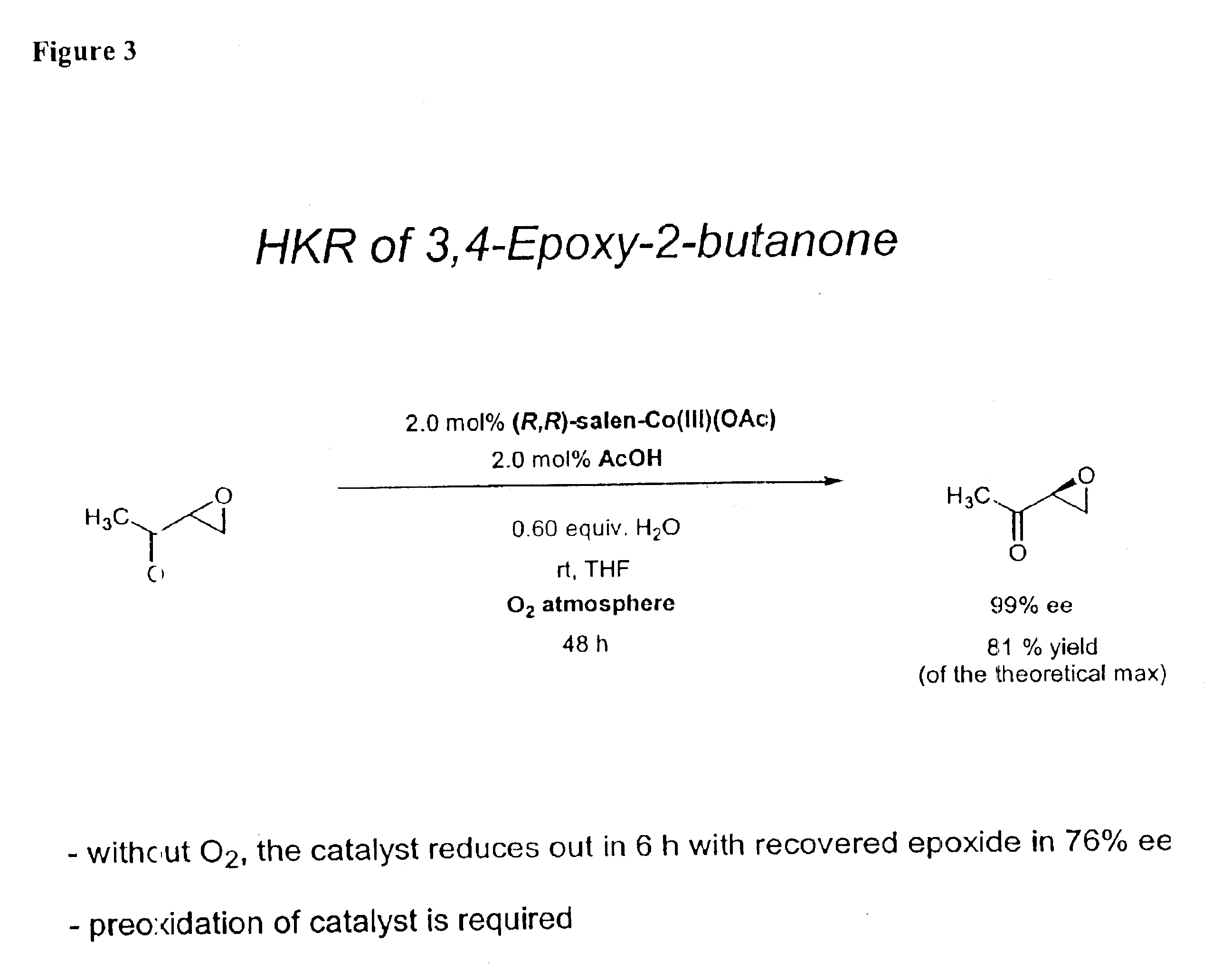
The invention relates to a high-activity bifunctional catalyst for preparing chiral epoxy alkane and diol and application thereof. The catalyst is a tetradentate Schiff-base cobalt complex, and a molecule of the catalyst at least contains one quaternary ammonium or phosphonium salt group. Due to the quaternary ammonium or phosphonium salt group, on one hand, the solubility of the catalyst in a reaction system can be improved; and on the other hand, a role in stabilizing trivalent cobalt ions is played, and the trivalent cobalt ions are effectively inhibited from being transformed into inactive divalent cobalt ions. The catalyst can efficiently catalyze the hydrolytic kinetic resolution reaction of a variety of racemic-end-position epoxy alkanes at a lower concentration so as to prepare high-optical-purity end-position epoxy alkanes and corresponding chiral diol products.
Owner:SHENYANG GOLD JYOUKI TECH
Ortho substituted chiral phosphines and phosphinites and their use in asymmetric catalytic reactions
InactiveUS6855657B2Organic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsIsomerizationCycloaddition
3,3′-Substituted chiral biaryl phosphine and phosphinite ligands and metal complexes based on such chiral ligands useful in asymmetric catalysis are disclosed. The metal complexes are useful as catalysts in asymmetric reactions, such as, hydrogenation, hydride transfer, allylic alkylation, hydrosilylation, hydroboration, hydrovinylation, hydroformylation, olefin metathesis, hydrocarboxylation, isomerization, cyclopropanation, Diels-Alder reaction, Heck reaction, isomerization, Aldol reaction, Michael addition, epoxidation, kinetic resolution and [m+n] cycloaddition. The metal complexes are particularly effective in Ru-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of beta-ketoesters to beta-hydroxyesters and Ru-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of enamides to beta amino acids.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Method for preparing optically pure R-1-naphthylethylamine by splitting
The invention relates to a method for preparing optically-pure R-1-naphthylethylamine by splitting. The method comprises the following steps: introducing hydrogen into a high-pressure kettle filled with 1-naphthylethylamine serving as a raw material, Novozym435 serving as a splitting catalyst and D-(-)-O-acetyl mandelic acid serving as an acyl donor and KT-02 (nickel type catalyst) serving as a racemization catalyst for reacting, and fully transforming the 1-naphthylethylamine to obtain (R)-(1-(1-naphthyl)ethyl)acetamide (ee value is 99 percent); and purifying amide, performing acidolysis to obtain a R-1-naphthylethylamine salt, and performing the operation of alkalization, distillation, drying, concentration and the like on the R-1-naphthylethylamine salt to obtain the R-1-naphthylethylamine, wherein the product yield and the ee value in the whole steps can be over 90 percent. The method has the characteristics of adoption of cheap and readily-available racemization catalyst, complete utilization of the raw material, high product yield and the like. The method has extremely high guidance and application values in the production and preparation of the R-1-naphthylethylamine.
Owner:六安佳诺生化科技有限公司
Nucleophilic kinetic resolution of cyclic substrates using silyl azides
InactiveUS6841667B2Silicon organic compoundsCarbamic acid derivatives preparationChemical synthesisHydrolysis kinetics
The present invention relates to a process for stereoselective or regioselective chemical synthesis which generally comprises reacting a nucleophile and a chiral or prochiral cyclic substrate in the presence of a non-racemic, chiral catalyst to produce a stereoisomerically- and / or regioisomerically-enriched product. The present invention also relates to hydrolytic kinetic resolutions of racemic and diastereomeric mixtures of epoxides.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Asymmetric carbon-carbon-bond-forming reactions catalyzed by bifunctional cinchona alkaloids
InactiveUS7582764B2Carbamic acid derivatives preparationCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationThioureaDiimide
One aspect of the present invention relates to quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain a hydroxy group at the 6′ position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an O-aryl group or an O-aroyl group at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an optionally substituted O-diazene group or an optionally substituted O-benzoyl group at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain a thiourea at the C9 position. In certain embodiments, the quinine-based and quinidine-based catalysts contain an NH(═S)NH-aryl group at the C9 position. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of preparing a chiral, non-racemic compound from a prochiral electron-deficient alkene or prochiral imine, comprising the step of: reacting a prochiral alkene or imine with a nucleophile in the presence of a catalyst; thereby producing a chiral, non-racemic compound; wherein said catalyst is a derivatized quinine or quinidine. In certain embodiments, the nucleophile is a malonate or β-ketoester. In certain embodiments the nucleophile is an alkyl or aryl or aralkyl 2-cyano-2-alkylacetate. In certain embodiments the nucleophile is an alkyl or aryl or aralkyl 2-cyano-2-alkylacetate.Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of kinetic resolution, comprising the step of: reacting a racemic aldehyde or racemic ketone with a nucleophile in the presence of a derivatized quinine or quinidine, thereby producing a non-racemic, chiral compound. In certain embodiments, the kinetic resolution is dynamic.
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com