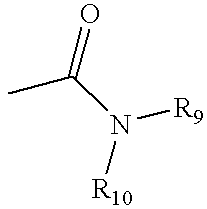
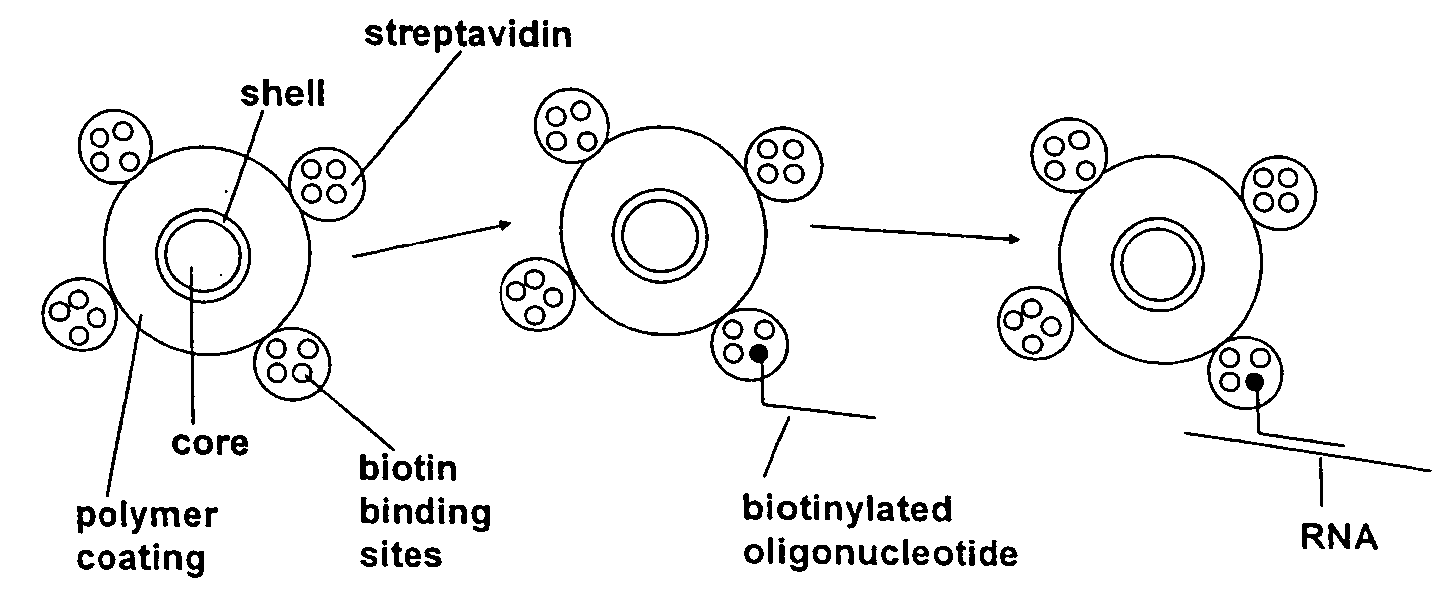
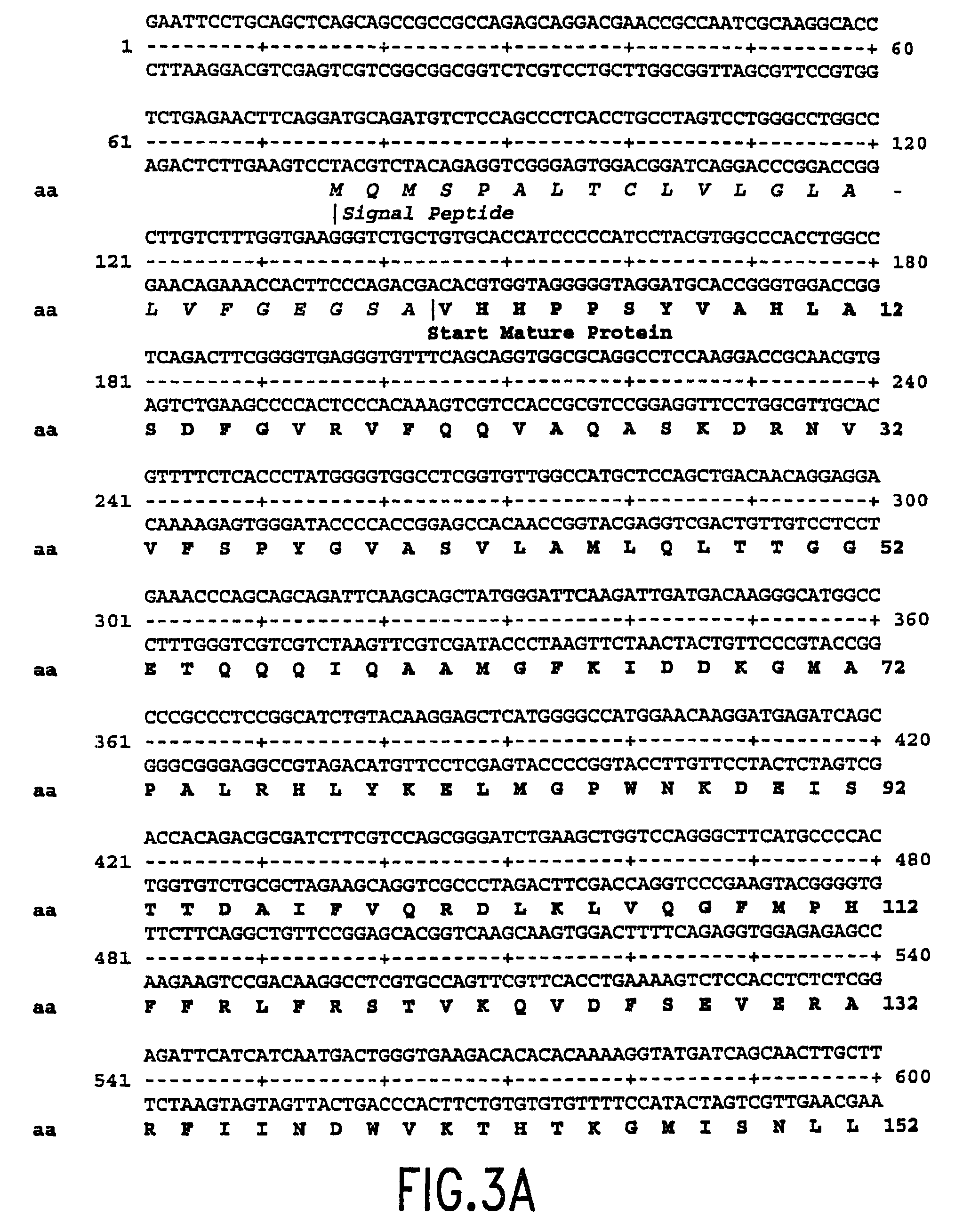
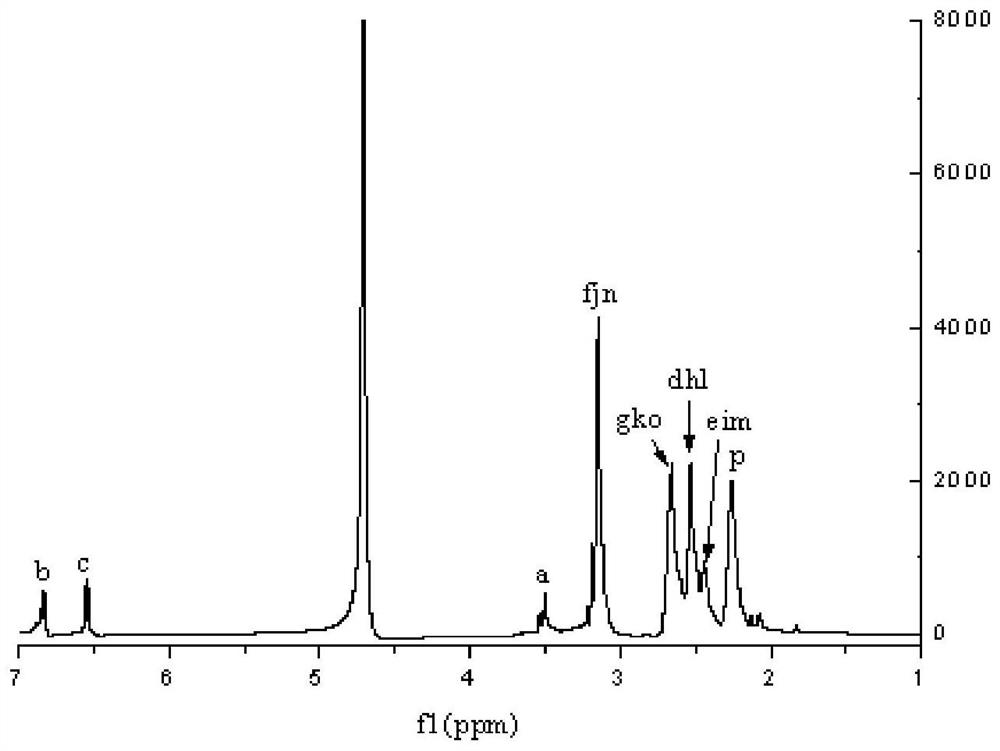
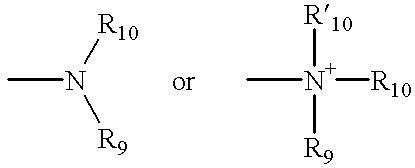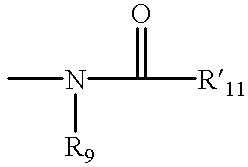Patents
Literature
43 results about "Reactive center" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
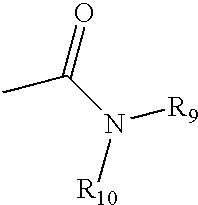
A reactive center, also called a propagating center, in chemistry is a particular location, usually an atom, within a chemical compound that is the likely center of a reaction in which the chemical is involved. In chain-growth polymer chemistry this is also the point of propagation for a growing chain. The reactive center is commonly radical, anionic, or cationic in nature, but can also take other forms.
Matrices for drug delivery and methods for making and using the same
In one aspect, biocompatible matrices such as sol-gels encapsulating a reaction center may be administered to a subject for conversion of prodrugs into biologically active agents. In certain embodiments, the biocompatible matrices of the present invention are sol-gels. In one embodiment, the enzyme <SMALLCAPS>L< / SMALLCAPS>-amino acid decarboxylase is encapsulated and implanted in the brain to convert <SMALLCAPS>L< / SMALLCAPS>-dopa to dopamine for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMA
Methods and compositions relating to single reactive center reagents
InactiveUS20050123974A1Shorten binding timeIncrease temperatureMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsCombinatorial chemistryReactive center
Methods of preparing single reactive center reagents are encompassed by the invention. The invention also includes compositions of single reactive center reagents and methods of use thereof for labeling and analyzing polymers such as nucleic acids.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Matrices for drug delivery and methods for making and using the same
In one aspect, biocompatible matrices such as sol-gels encapsulating a reaction center may be administered to a subject for conversion of prodrugs into biologically active agents. In certain embodiments, the biocompatible matrices of the present invention are sol-gels. In one embodiment, the enzyme L-amino acid decarboxylase is encapsulated and implanted in the brain to convert L-dopa to dopamine for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:BABICH JOHN W +2
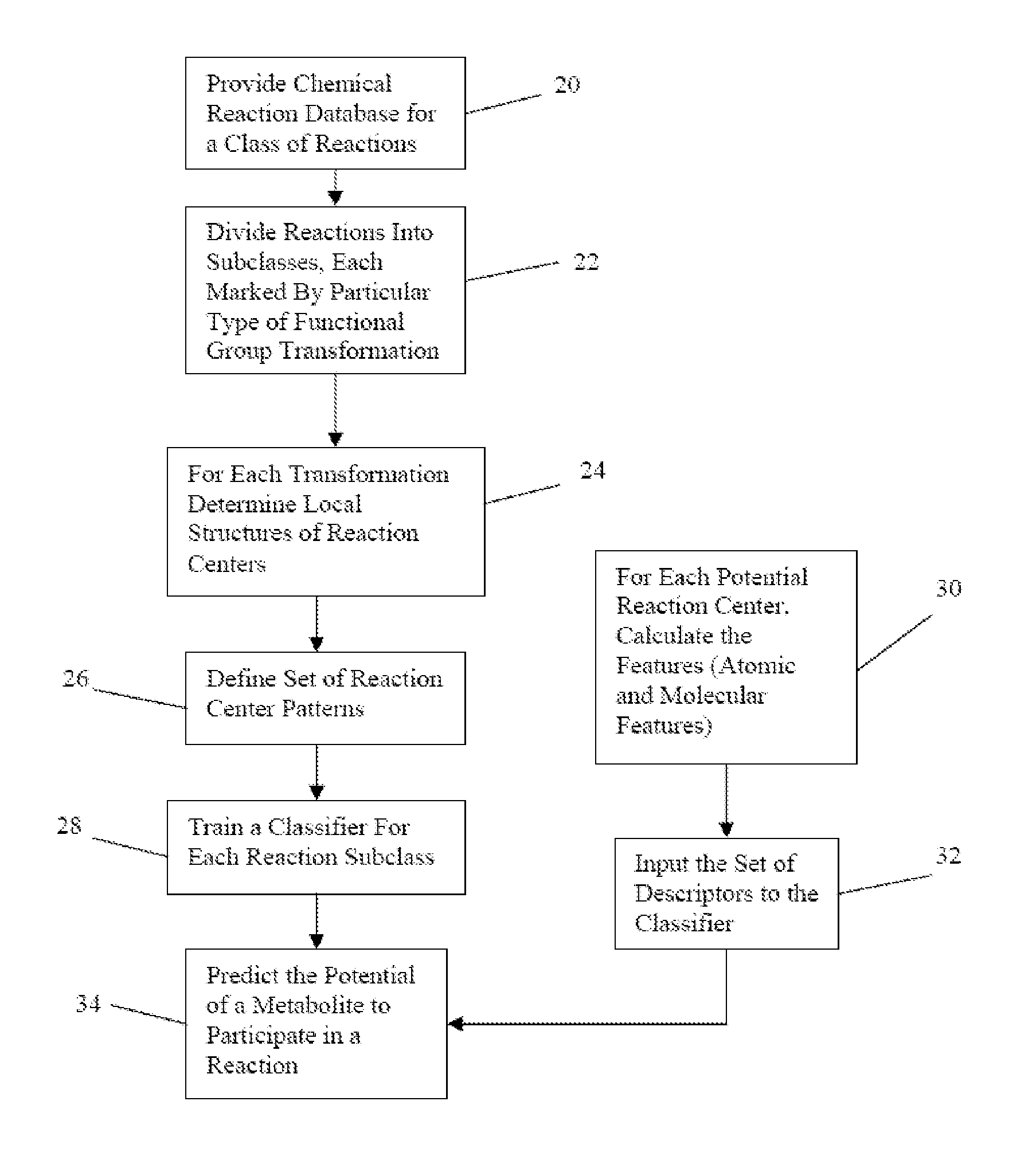
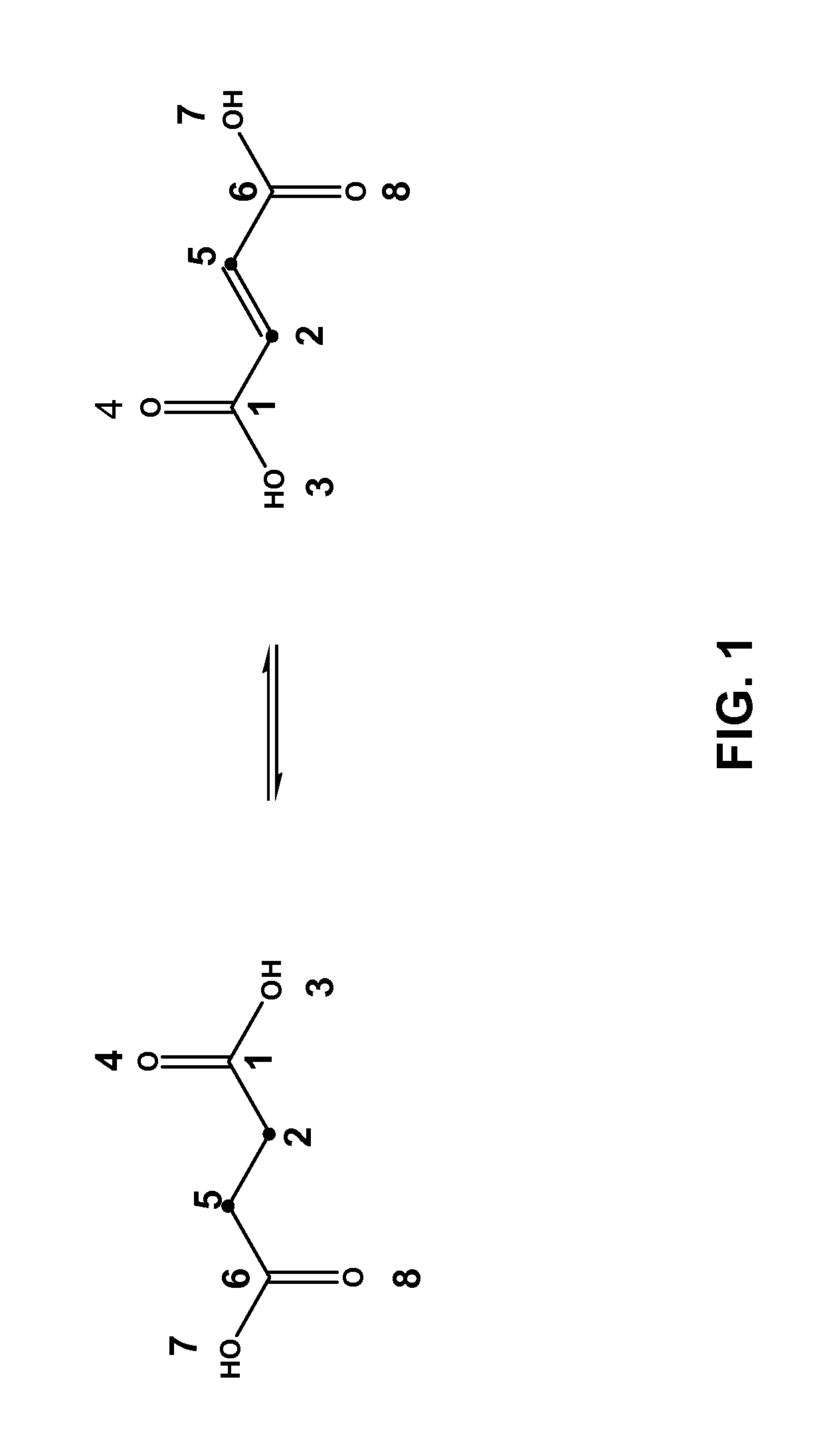
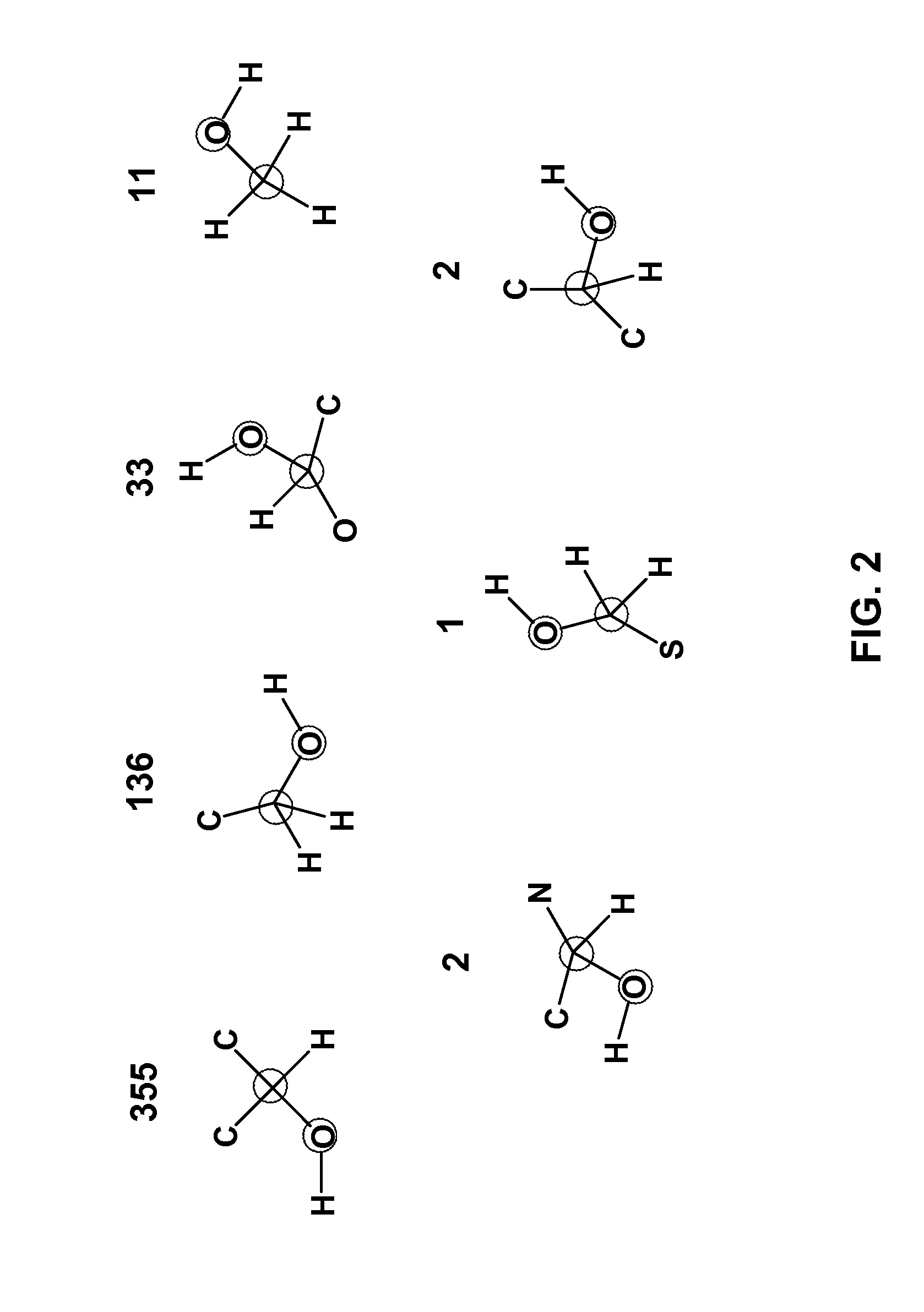
Method for predicting enzyme-catalyzed reactions
InactiveUS20080177478A1Chemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designSupport vector machineMetabolite
The reactivity of given metabolites is assessed using selected empirical atomic properties in the potential reaction center. Metabolic reactions are represented as biotransformation rules. These rules are generalized from the patterns in reactions. These patterns are not unique to reactants but are widely distributed among metabolites. Using a metabolite database, potential substructures are identified in the metabolites for a given biotransformation. These substructures are divided into reactants or non-reactants, depending on whether they participate in the biotransformation or not. Each potential substructure is then modeled using descriptors of the topological and electronic properties of atoms in the potential reaction center; molecular properties can also be used. A Support Vector Machine (SVM) or classifier is trained to classify a potential reactant as a true or false reactant using these properties.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
New method for superfine particle surface modification
InactiveCN1580137AChange surface propertiesGood dispersionPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsSolventRosin
The invention refers to a kind of new method of superfine inorganic solid particle's surface modification method. It includes the following steps: in the condition of certain temperature, mechanical milling, the protection of nitrogen gas and the existence of catalyzer, choose the superfine particle as the reaction core, pass through the polycondensation with the monomer of ABx or AxB and graft the super-ramus polymer onto the surface of superfine particle. The surface character of superfine particle modified by the super-ramus polymer grafting is changed greatly and can disperse well in all kind of matrixes of rosin and solvent. The method can finish the task in one step. The modified inorganic solid particle can be applied to macromolecule composites, electric bloching material, plastics, dope, latex, antibiotic material and other fields and has a promising industrial application.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Kinetics resolution method
InactiveCN1649861AReduce consumptionReduce chemical transformationGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOxygen-containing compound preparationChemical synthesisChemical transformation
A method for stereoselective chemical synthesis, includes the steps of: (A) reacting a nucleophile and a chiral or prochiral cyclic substrate, said substrate comprising a carbocycle or a heterocycle having a reactive center susceptiable to nucleophilic attack by the nucleophile, in the presence of a chiral non-racemic catalyst to produce a product mixture comprising a stereoisometrically enriched product wherein the product mixture further comprises a catalyst residue, at least a portion of the catalyst residue is in a first oxidation state, and the catalyst residue in the first oxidation state is active in catalyzing degradation of the stereoisomerically enriched product, and (B) chemically or electrochemically changing the oxidation state of the catalyst residue form the first oxidation state to a second oxidation state, wherein catalyst residue in the second oxidation state is less active in catalyzing degradation of the stereoisomerically enriched product than is catalyst residue in the first oxidation state. The method reduces erosion of the chiral purify of the stereoisomerically enriched product and reduces the chemical transformation to side products of the stereoisomerically enriched product and co-product(s).
Owner:SHASUN PHARMA SOLUTIONS LTD
Modification method for cathode activated charcoal of ultracapacitor
InactiveCN1482634AHigh specific capacitanceImprove the modification methodElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitor manufactureCapacitanceLead phosphate
A process for the modification of activated charcoal material for the use of super capacitor negative electrode, wherein a nanometer level lead phosphate or lead sulfate modification layer is first formed in the activated charcoal micropore, then the barium sulfate reactive center is redeposited. After modification, the capacity of the active compound is increased by about 67%, the electrochemical window is expanded by 150 mV, thus improving the weight ratio energy capacity of the assortment type super capacitor. íí
Owner:江苏隆源双登电源有限公司
Modification method of alumina carrier as well as preparation method and application of silver catalyst supported by alumina carrier
ActiveCN103357440ALarge specific surface areaMany active centersCatalyst carriersOrganic chemistryEthyleneSilver catalyst
The invention relates to a modification method for forming an alpha-alumina carrier of a silver catalyst used for producing ethylene oxide through ethylene oxidation. The method has the beneficial effect of increasing the pore canal and specific surface area of the carrier by carrying out acid-alkali combined treatment on the formed alpha-alumina carrier. The silver catalyst prepared from and supported by the alpha-alumina carrier prepared by the method is beneficial to increase of reaction centers and diffusion of products. The modified alpha-alumina carrier shows good selectivity when applied to the reaction process of producing ethylene oxide through ethylene oxidation.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing pentanediamine by catalyzing lysine decarboxylation with solid superacid
ActiveCN112125810AReduce usageConducive to large-scale industrial productionAmino preparation from aminesCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystStrong acids
The invention provides a method for preparing pentanediamine by catalyzing lysine decarboxylation with solid superacid, which comprises the following steps: putting lysine or lysine salt, water and solid superacid catalyst into a high-pressure reaction kettle, and reacting to obtain a pentanediamine-containing water solution; the solid superacid catalyst used in the method is a supported catalystand comprises a solid superacid carrier for providing an acidic environment and a reaction center, the solid superacid carrier effectively avoids the use of liquid strong acid and remarkably relievesthe problem of equipment corrosion, and the catalyst is simple in preparation process, easy to separate from a product and very wide in industrial application prospect.
Owner:郑州中科新兴产业技术研究院
Insect inhibiting plant serpin mutants
InactiveUS20100333236A1Specific resistanceControl damageBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityWild type
The present invention relates to a method to limit insect and / or mite damage in plants, by the use of mutant plant proteinase inhibitors. More specifically, it relates to the use of mutant serpins of which the reactive center loop has been replaced by an artificial sequence. Preferably, the mutant serpins use an Arabidopsis thaliana serpin-1 backbone, or a homologue thereof. The mutant serpins have a specificity other than the wild-type serpins, and by modulating the reactive loop center, specific inhibitors against specific insect and / or mite proteases can be developed. Those mutant serpins can be used to inhibit or limit insect and / or mite damage, such as the damage caused by insect feeding.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Methods for modulating angiogenesis via VEGF
InactiveUS7241446B2Peptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAngiogenesis growth factorApoptosis
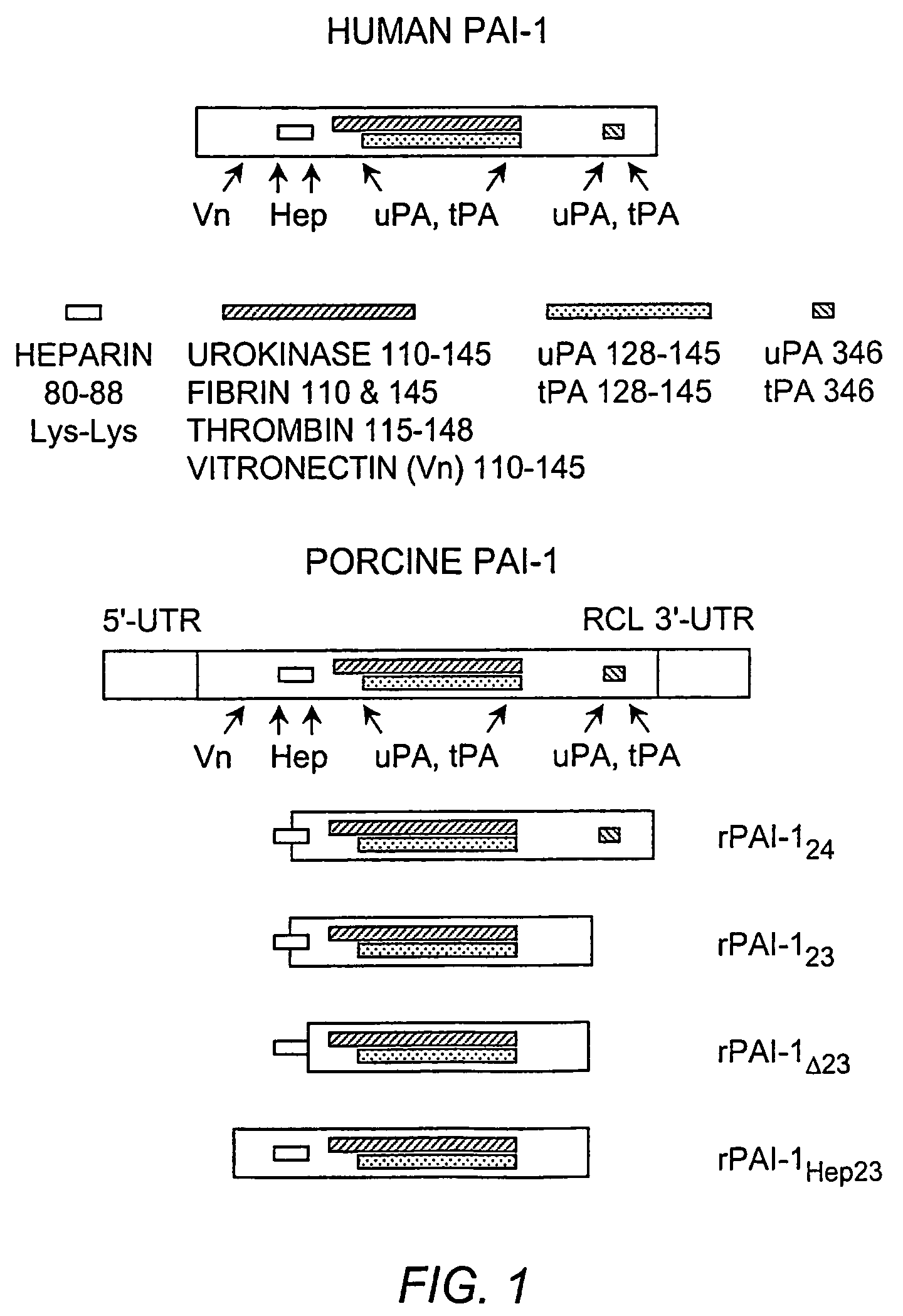
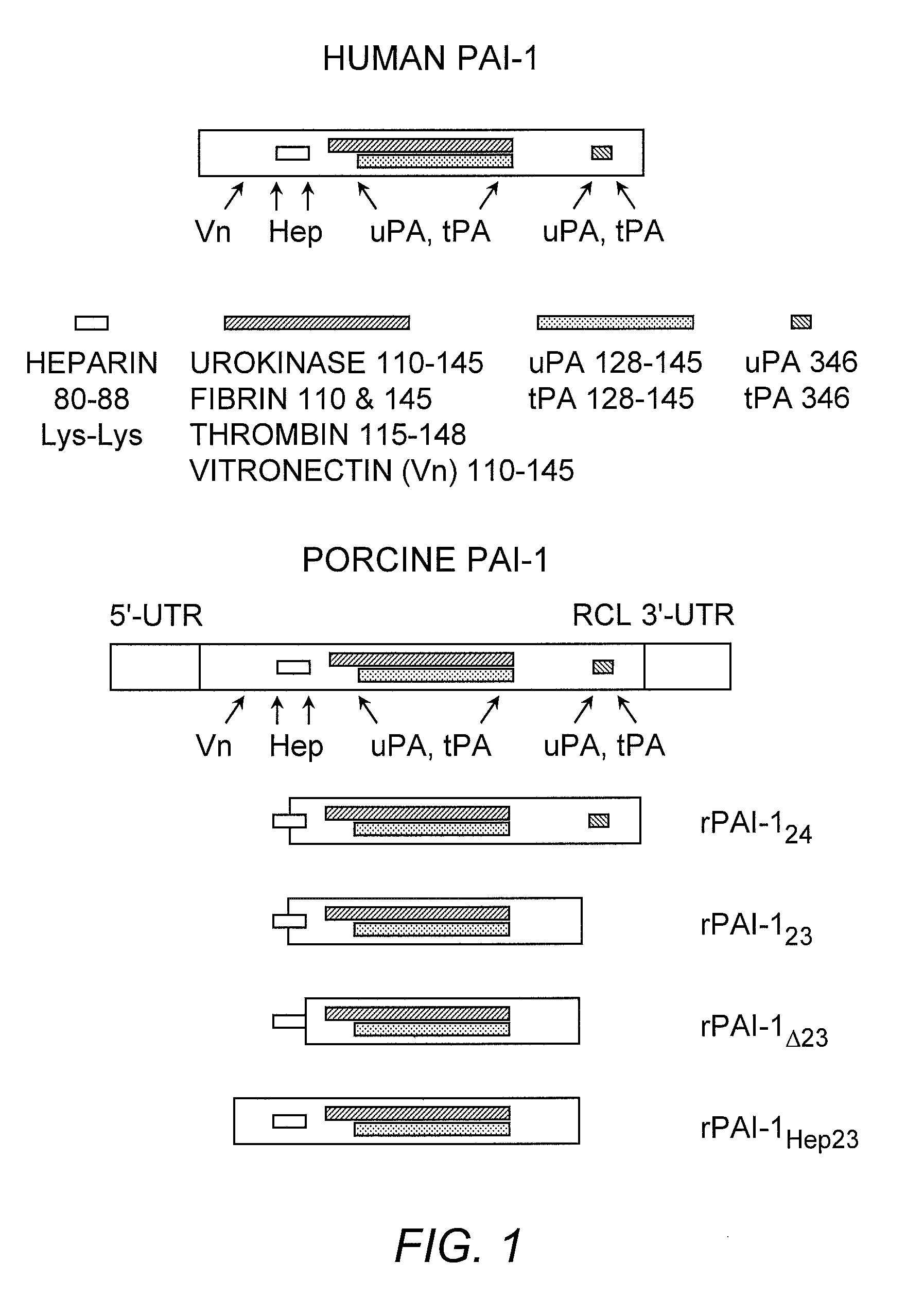
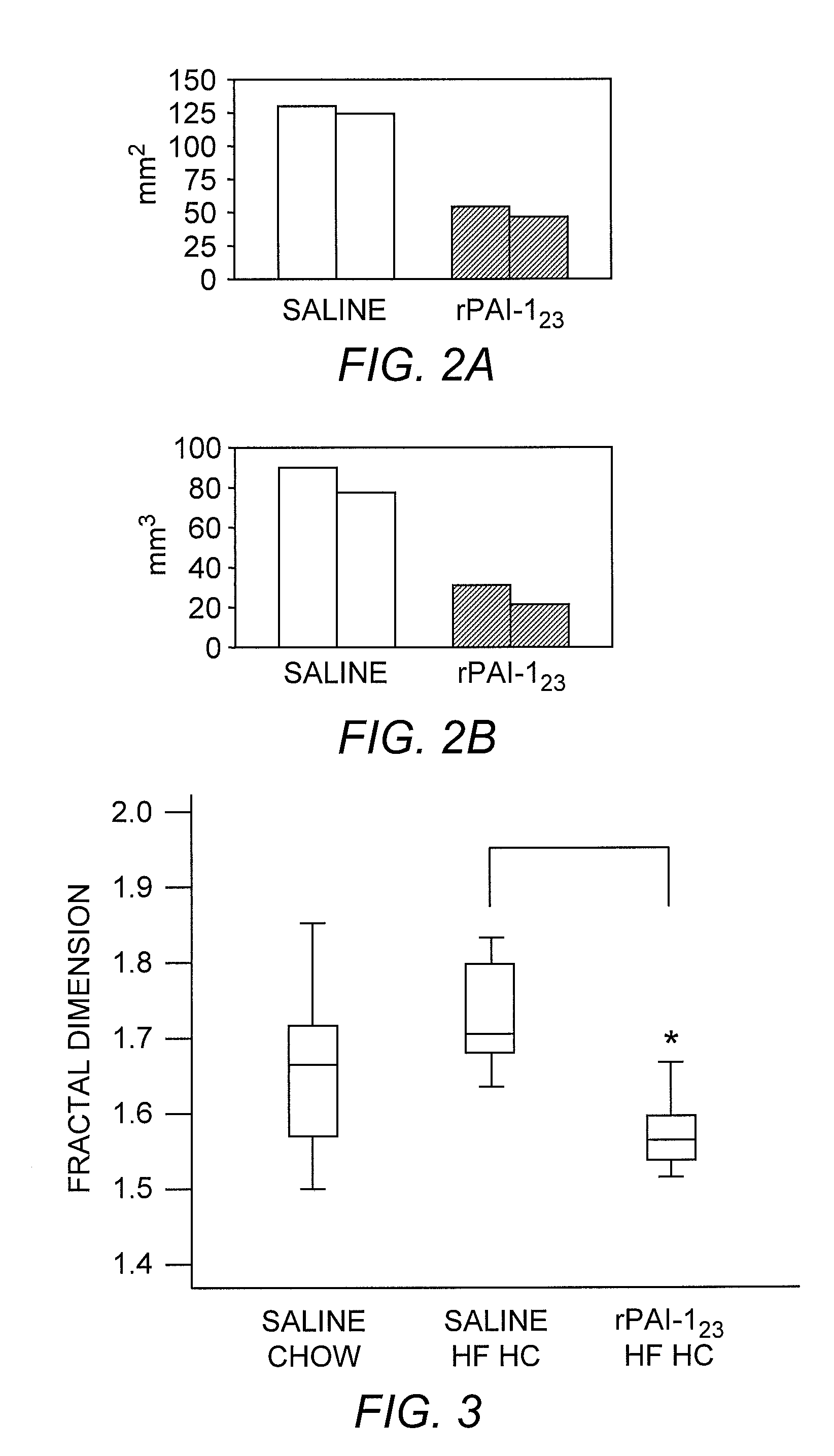
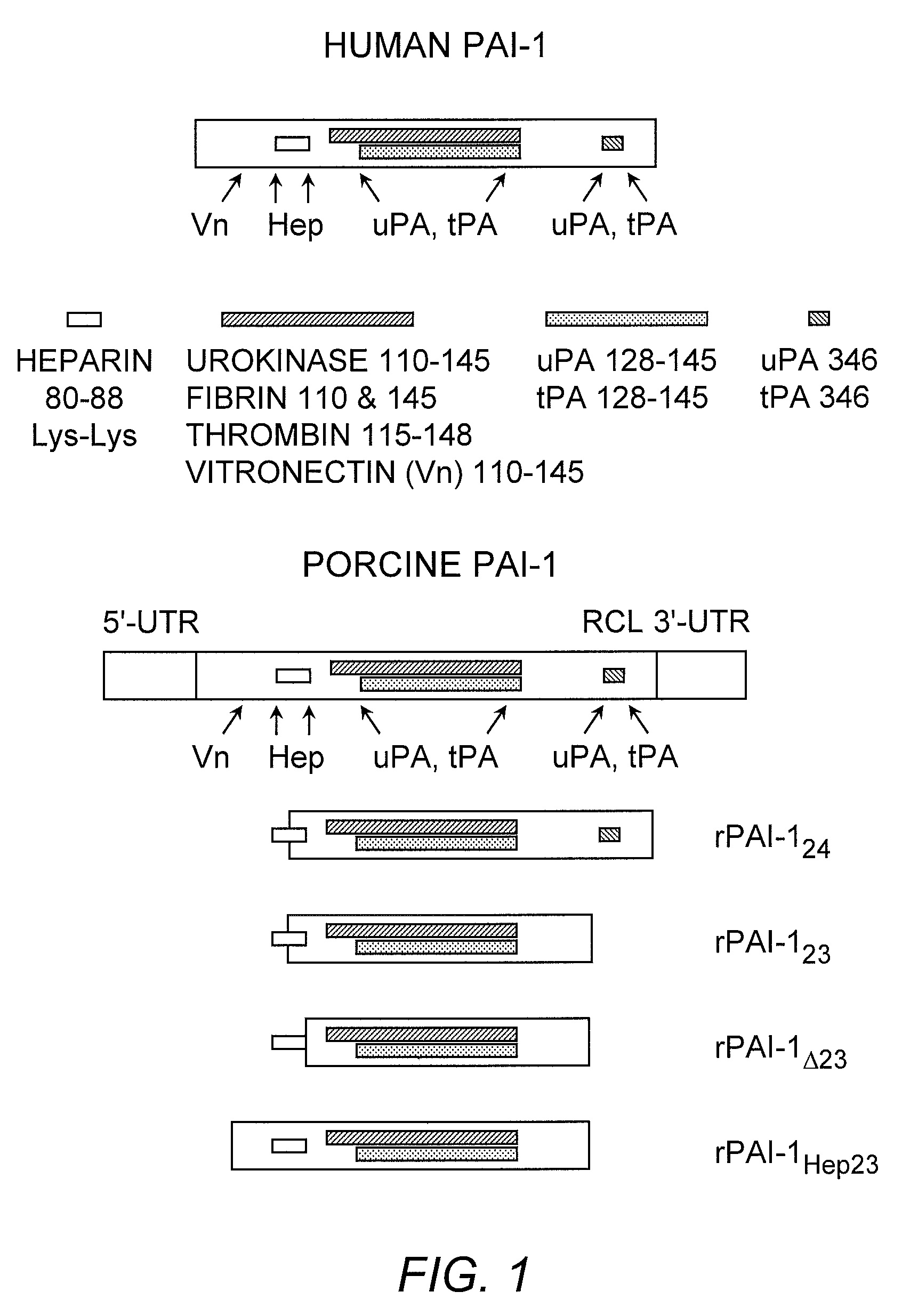
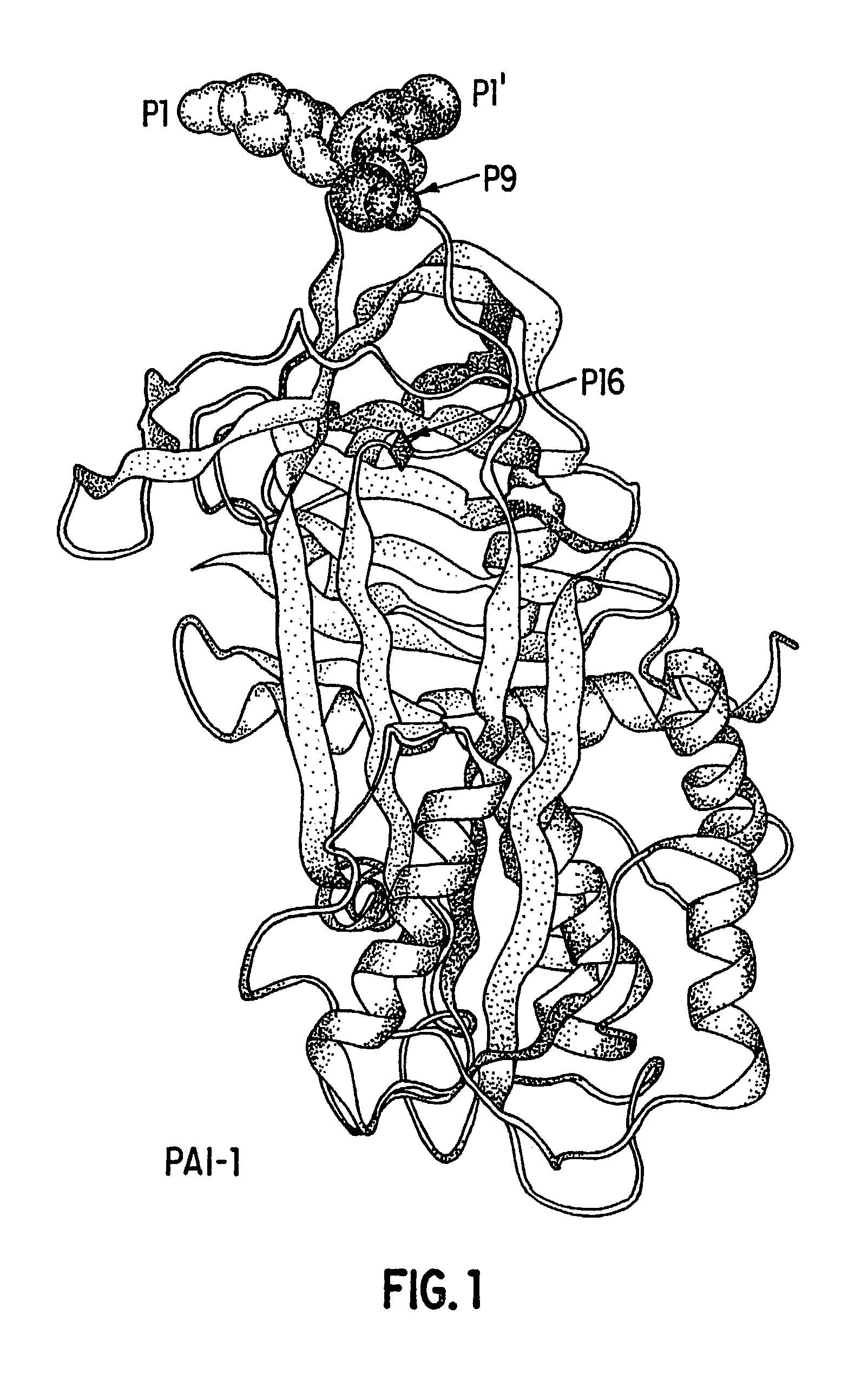
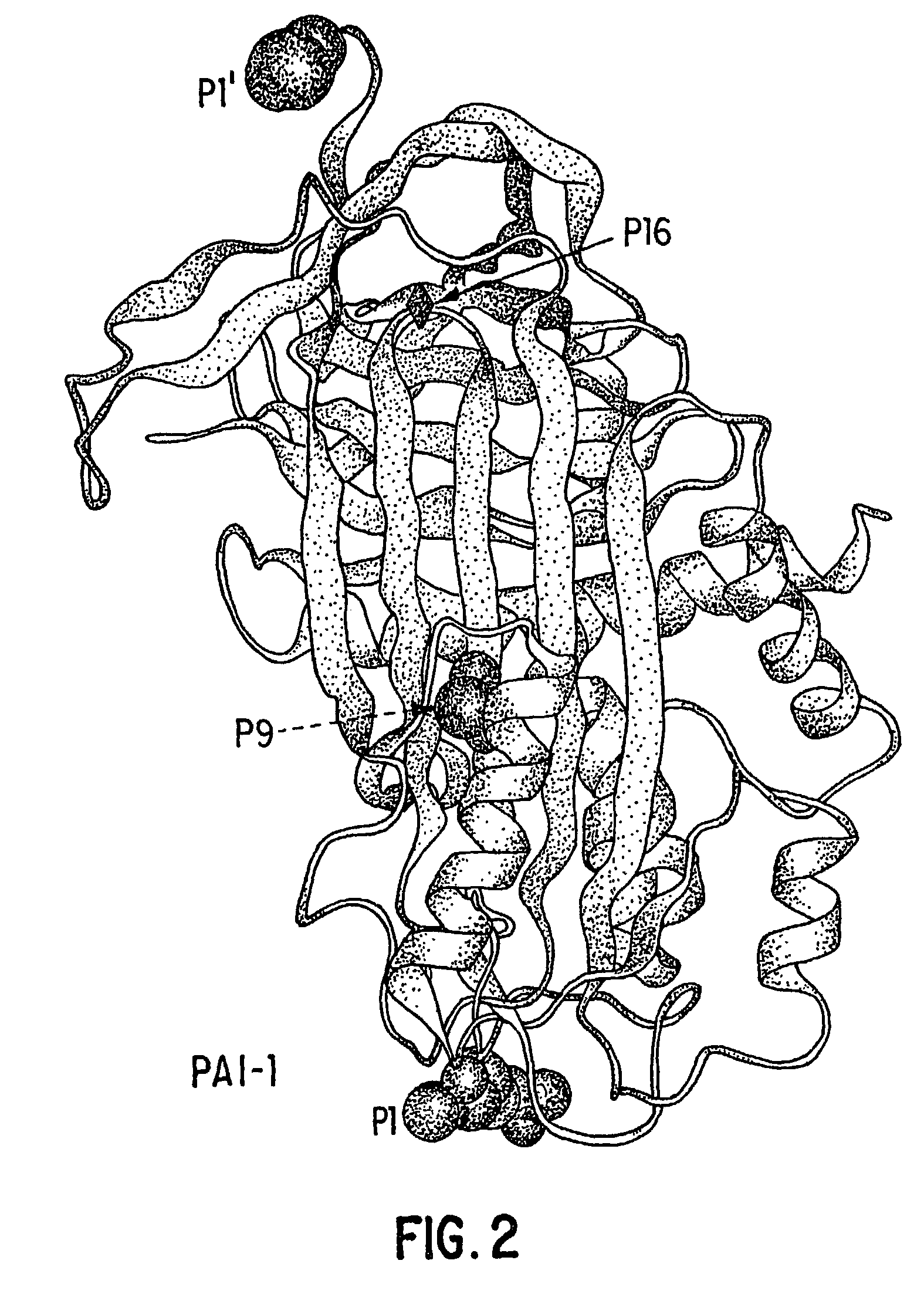
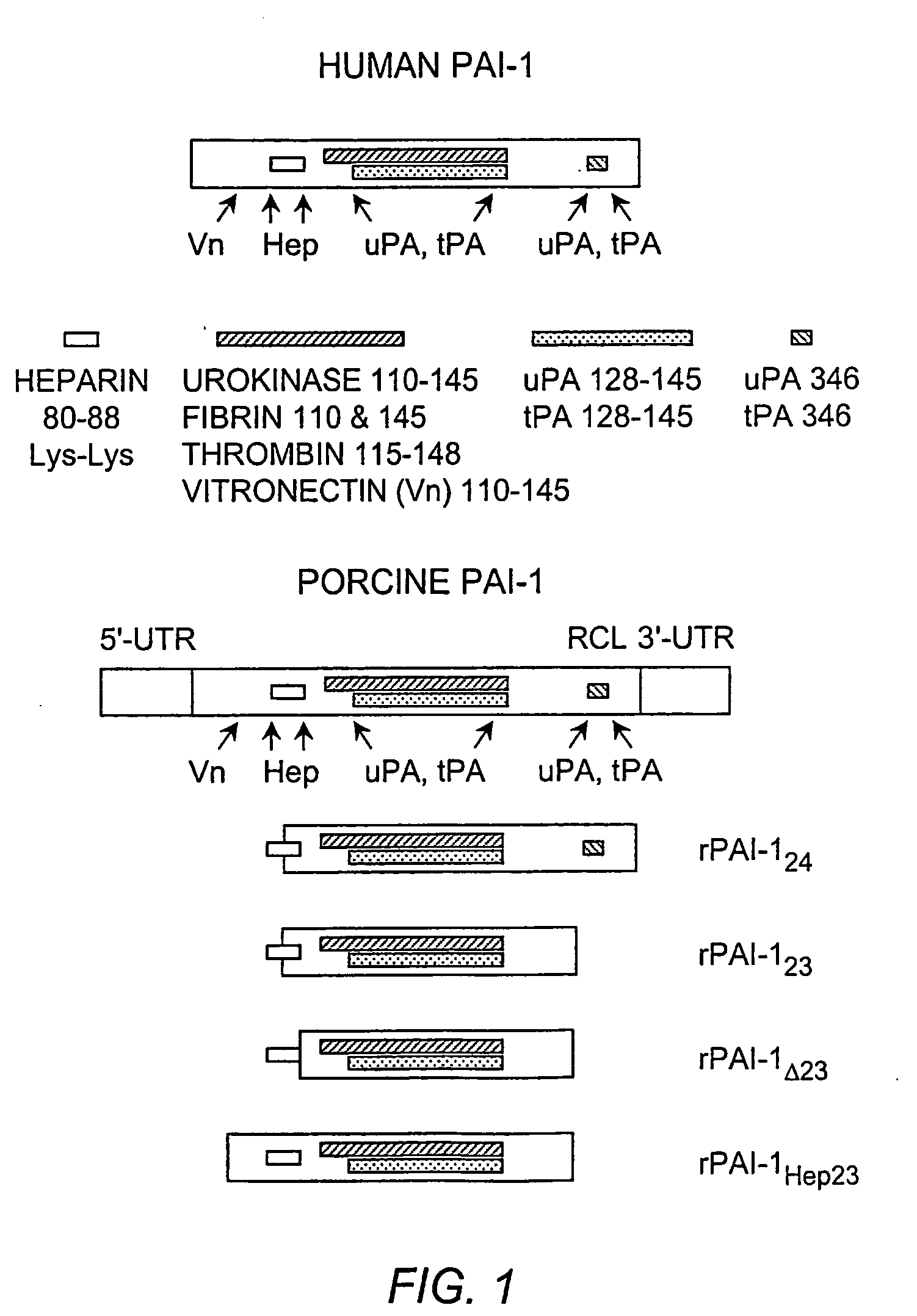
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1–3 and kringles 1–4.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Methods for modulating angiogenesis
InactiveUS20070191277A1Stimulating and inhibiting angiogenesisPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAngiostatinAngiogenesis growth factor
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore, the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1-3 and kringles 1-4. A truncated proteolytic plasmin protein of 34 kDa is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
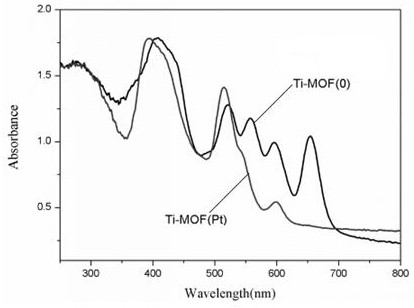
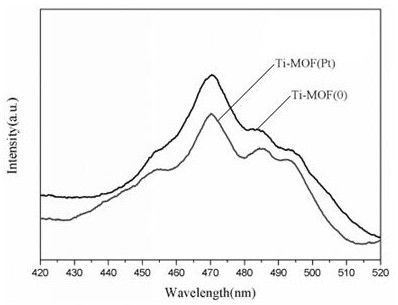
Preparation method and application of porphyrin-metal organic framework material
ActiveCN111804341AWide light absorption rangeTake advantage ofOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionBenzoic acidCharge carrier
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a porphyrin-metal organic framework material. The preparation method of the porphyrin-metal organic framework material comprises the following steps: dissolving a mixture of Ti (OBu) 4, Pt-TCPP and benzoic acid into DEF, and stirring for 20-35 minutes at room temperature; heating the mixture at 100-150 DEG C for 5-7 days, centrifugingthe obtained product, washing with acetone for 3 times, and drying at 35-50 DEG C in vacuum for 5-8 hours; and reducing the dried solid for 2-5 h at the temperature of 200-240 DEG C under hydrogen, and obtaining the porphyrin-metal organic framework material. According to the porphyrin-metal organic framework material prepared by the method, the distance from a photo-generated charge carrier to areaction center can be shortened, the photo-generated electron transfer and separation speed is increased, photocatalytic hydrogen production can be promoted, and the hydrogen production rate is as high as 32332.8 [mu] mol g <-1 > h <-1 >.
Owner:CHONGQING TECH & BUSINESS UNIV +1
Methods for modulating angiogenesis
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore, the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1-3 and kringles 1-4. A truncated proteolytic plasmin protein of 34 kDa is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
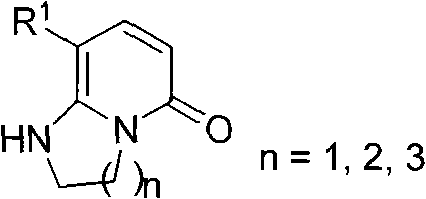
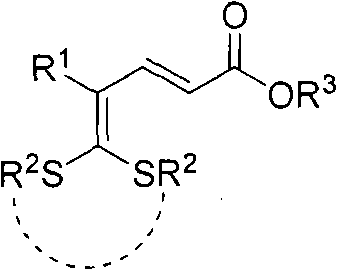
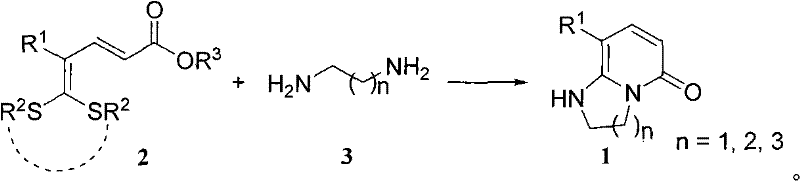
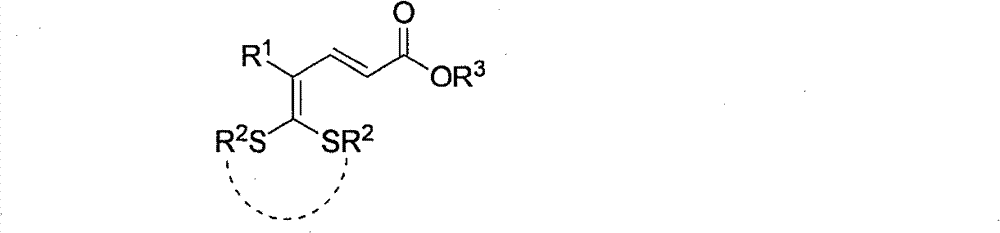
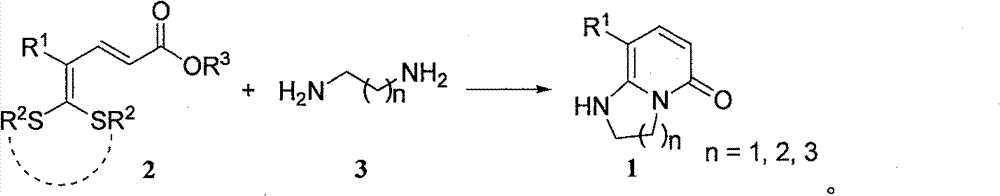
Synthetic method of bicyclic pyridone derivative
InactiveCN102234274AWith structural diversityEasy to manufactureOrganic chemistryReactive centerStructural diversity
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a bicyclic pyridone derivative with potential bioactivity, comprising the following steps that: 5,5-bisalkylthio-2,4-pentadienoic acid ester used as a raw material with the characteristics of being easy to prepare, having structural diversity and multiple reactive centers and a bimolecular nucleophilic reagent organic diprimary amine is subject tosubstitution / condensation in refluxing to synthesize the bicyclic pyridone derivative. Compared with the reported synthetic methods of the bicyclic pyridone derivative, the method disclosed in the invention has the advantages of being convenient for raw materials, simple operation, mild reaction conditions and high efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for modulating angiogenesis
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPAI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore, the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1-3 and kringles 1-4. A truncated proteolytic plasmin protein of 34 kDa is also provided.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Novel PET material and preparation method thereof, pellet and fiber product
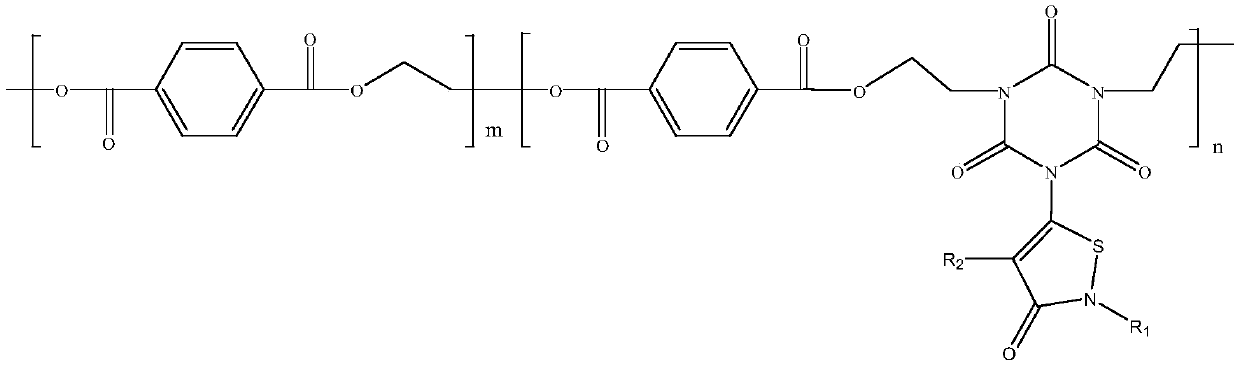
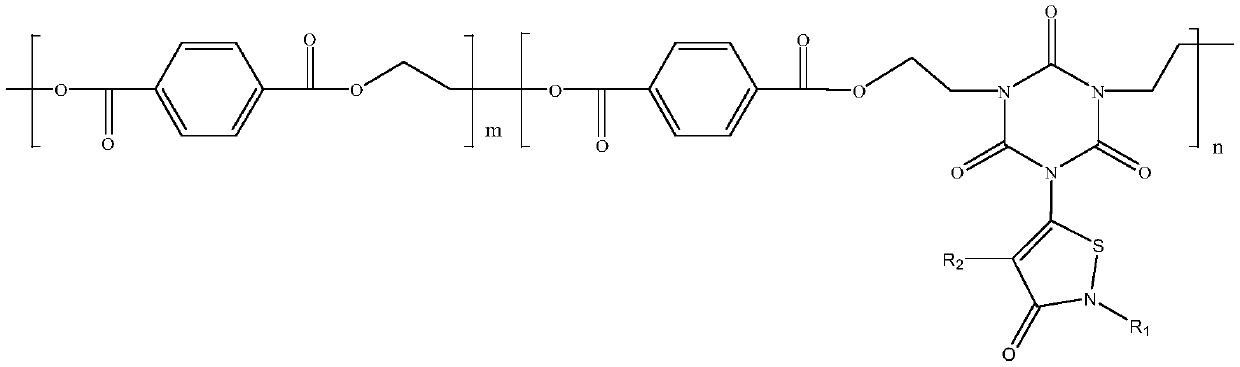
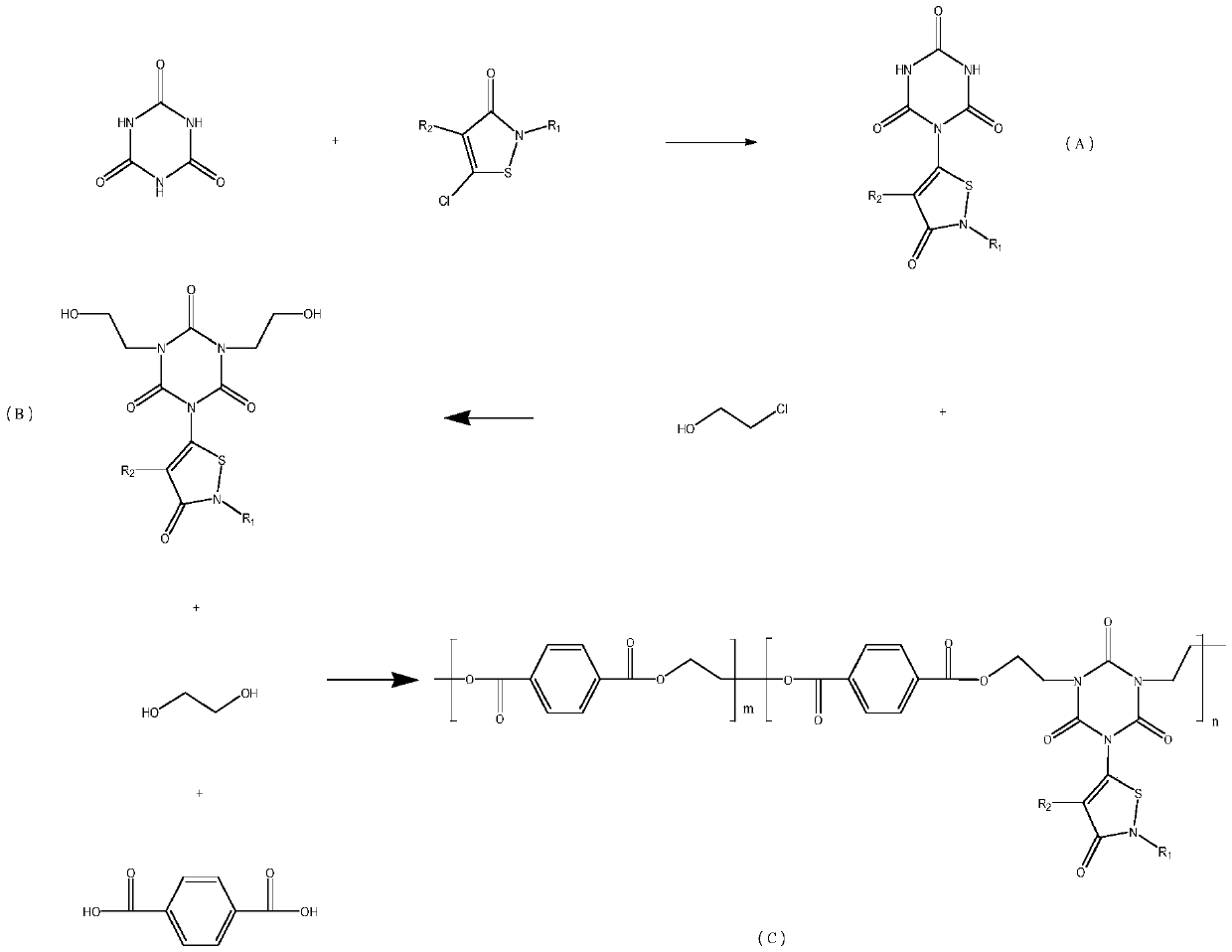
ActiveCN110903470AHigh reactivityEfficient Flame RetardancyMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentArtifical filament manufactureFiberGlycol synthesis
The invention discloses a novel PET material and a preparation method thereof, a pellet and a fiber product. According to the invention, isocyanurate, a 5-chloro-2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one derivative, chloroethanol, terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol are used as raw materials, so the defect that traditional PET fibers have single and insufficient performance is overcome; meanwhile, reactionsteps are simple, operation is easy, and the defect of single performance of the traditional PET fibers are is overcome by adjusting the structure of a polymer; due to the addition of isocyanurate, the reaction activity of -NH2 is high, -NH2 can serve as a reaction center, high nitrogen content is obtained, and outstanding effect on the flame retardance of the material is achieved; as the 5-chloro-2-methyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one derivative is added, broad-spectrum bactericidal and mildew-proof effects are obtained, and the flame-retardant effect of the material can be further improved due to theexistence of N in a five-membered ring; in addition, the existence of different substituent groups endows the molecular structure of the material with flexibility, so the wide popularization and application of the material are facilitated.
Owner:东莞市道尔新材料科技有限公司
Compound for generating nucleic acid cross-linking action by induction and its preparing method and use
InactiveCN101012191AEasy to makeTo achieve a double therapeutic effectOrganic chemistryHydroxy compound active ingredientsSynthesis methodsPhenol
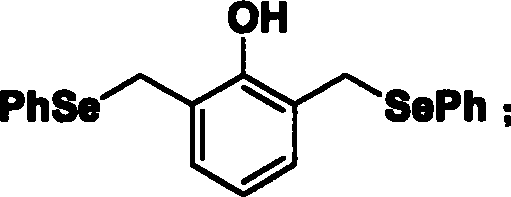
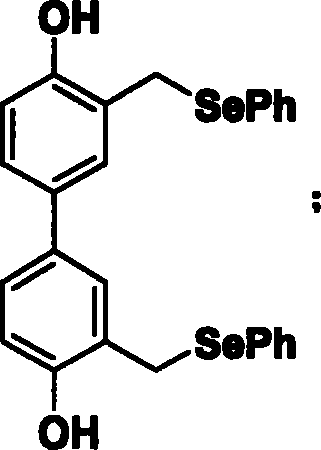
The invention discloses a compound to induce structure to generate crosslinking action of nucleic acid, which comprises the following steps: transmitting phenolic hydroxyl group in the 2, 6-dimethyl phenol, diphenol or hydroquinone into benzyl bromine under alkaline condition; substituting benzyl bromine group into selenium benzene group acted by sodium borohydride and diphenyl sulphone diselenide; stripping protection to obtain compound 1, compound 2 or compound 3.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for superfine particle surface modification
InactiveCN1260309CChange surface propertiesGood dispersionPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
The invention relates to a new method for surface modification of ultrafine inorganic solid particles. It includes under the conditions of certain temperature, mechanical stirring, nitrogen protection and the presence of catalyst, with ultrafine particles as the reaction center core, and AB x or A x One-step polycondensation reaction of monomer B occurs, and a hyperbranched polymer is grafted on the surface of ultrafine particles. The surface properties of the superfine particles modified by the hyperbranched polymer grafting obtained are greatly changed, and can be well dispersed in various resin matrices and solvents. The method is simple and easy to complete in one step, and the modified inorganic solid particles can be widely used in polymer composite materials, electronic packaging materials, plastics, coatings, rubber, antibacterial materials and other fields, and the industrial application prospect is broad.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
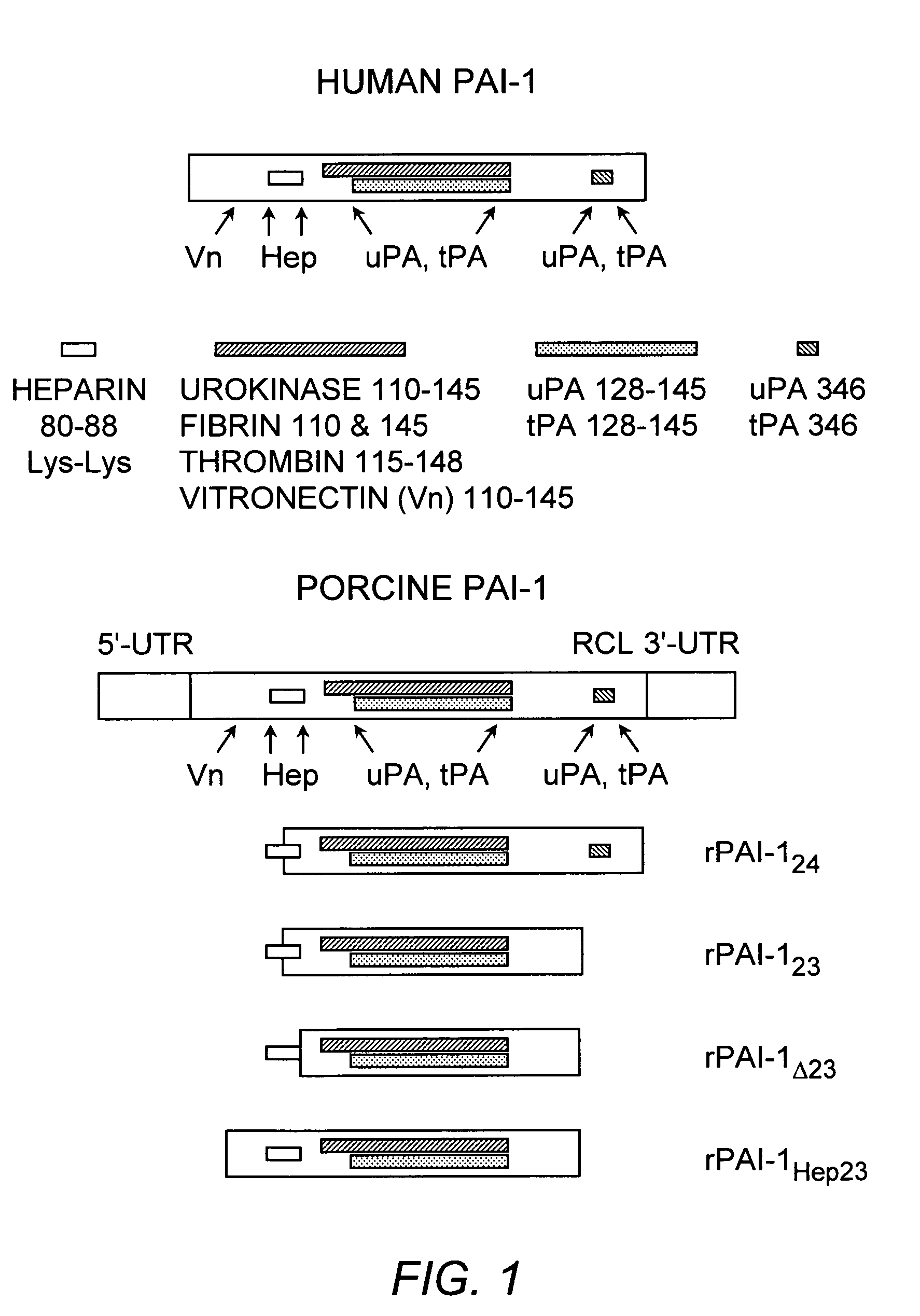
Mutant plasminogen activator-inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) and uses thereof
Mutants of the human PAI-1 protein are described which are inhibitors of neutrophil elastase or are inhibitors of vitronectin (Vn)-dependent cell migration. These mutants preferably comprise one or two amino acid substitutions in the reactive center loop of PAI-1, particularly at positions 331 and 346 of the mature protein. These mutants are notable in being resistant to inactivation by elastase, having high affinity for Vn, or both properties. These mutant proteins as pharmaceutical compositions are used to inhibit elastase in a subject, thereby treating a number of disorders associated with elastase activity, most notatably emphysema, ARDS, inflammatory lung injury and cystic fibrosis. The mutants which interact with Vn are used to inhibit cell migration in a subject, thereby treating diseases or conditions associated with undesired cell migration and proliferation, particularly of smooth muscle cells. Such conditions include atherosclerosis, post angioplasty restenosis, fibrosis associated with chronic inflammation or chemotherapy, tumor invasion and metastasis and conditions in which angiogenesis is pathogenic. Also disclosed are peptides of such mutant proteins, mutant-specific antibodies, nucleic acid molecules, particularly DNA, encoding the mutant protein and host cells transformed by such nucleic acids.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Preparation method and application of sulfur-doped carbon skeleton coated heptairon octasulfide nanoparticle double-reaction-center Fenton-like catalyst
ActiveCN114588917AImprove transmission efficiencyPromotes Fenton-like degradation processWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsPtru catalystTetracycline Hydrochloride
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a Fenton-like catalyst, in particular to a preparation method and application of a sulfur-doped carbon skeleton coated octasulfide heptairon nanoparticle double-reaction-center Fenton-like catalyst. The invention aims to solve the problems of metal ion leaching, poor stability, easy agglomeration and narrow reaction pH range of the existing Fenton-like catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing an MIL-101 (Fe) precursor, and then calcining and vulcanizing to obtain the sulfur-doped carbon skeleton coated octasulfide heptairon nanoparticle double-reaction-center Fenton-like catalyst. The invention discloses a sulfur-doped carbon skeleton coated heptairon octasulfide nanoparticle double-reaction-center Fenton-like catalyst which is used for degrading antibiotics. Under the neutral condition, the degradation rates of tetracycline hydrochloride, norfloxacin and amoxicillin within 40 min can reach 100%, 97.8% and 98.9% respectively, and after 5 times of circulation, the removal rate of amoxicillin can still be kept at 91.1%.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Modified serpins for the treatment of bradykinin-mediated disease
PendingUS20200010533A1Strong specificityReduce sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseKinin
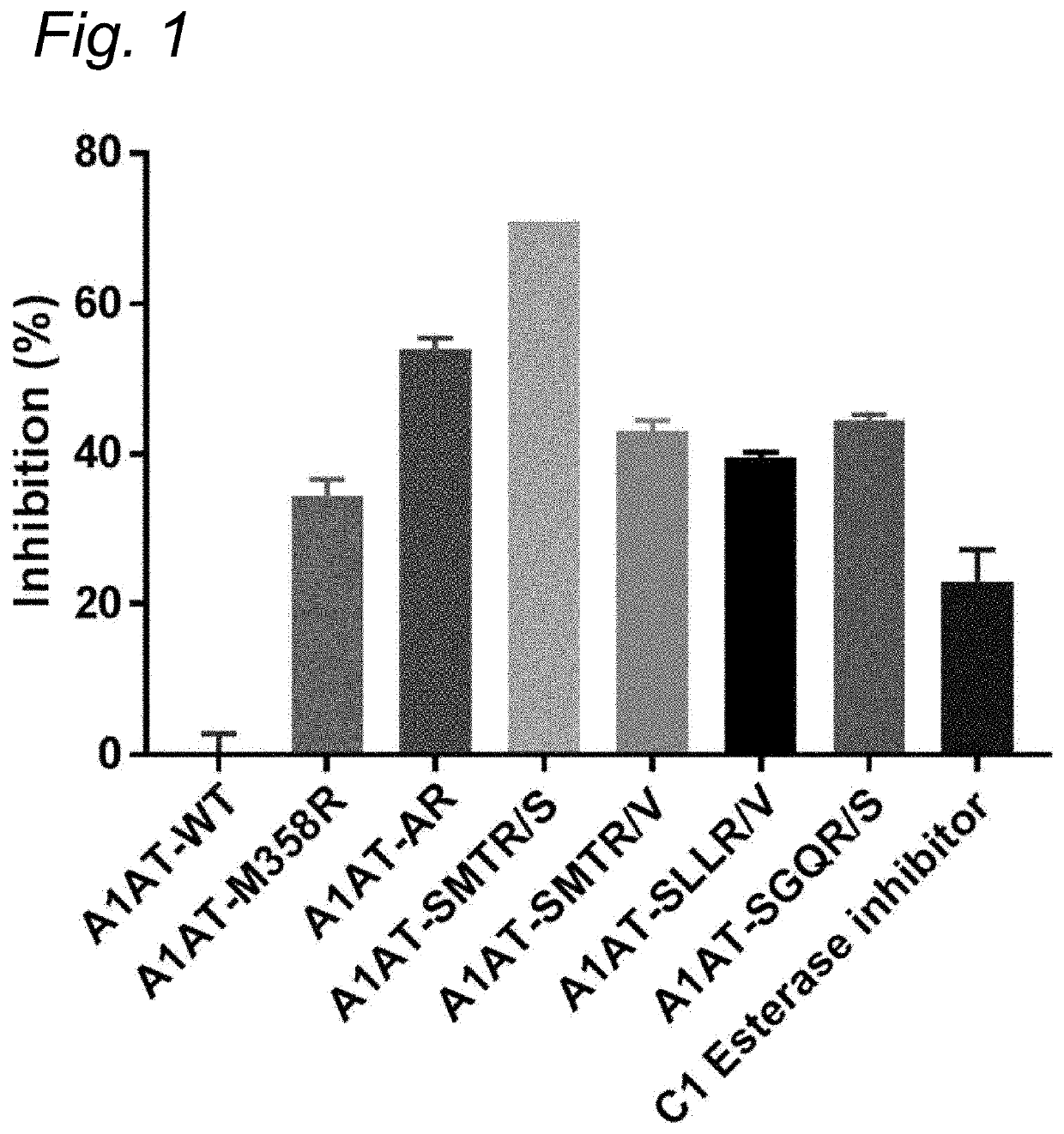
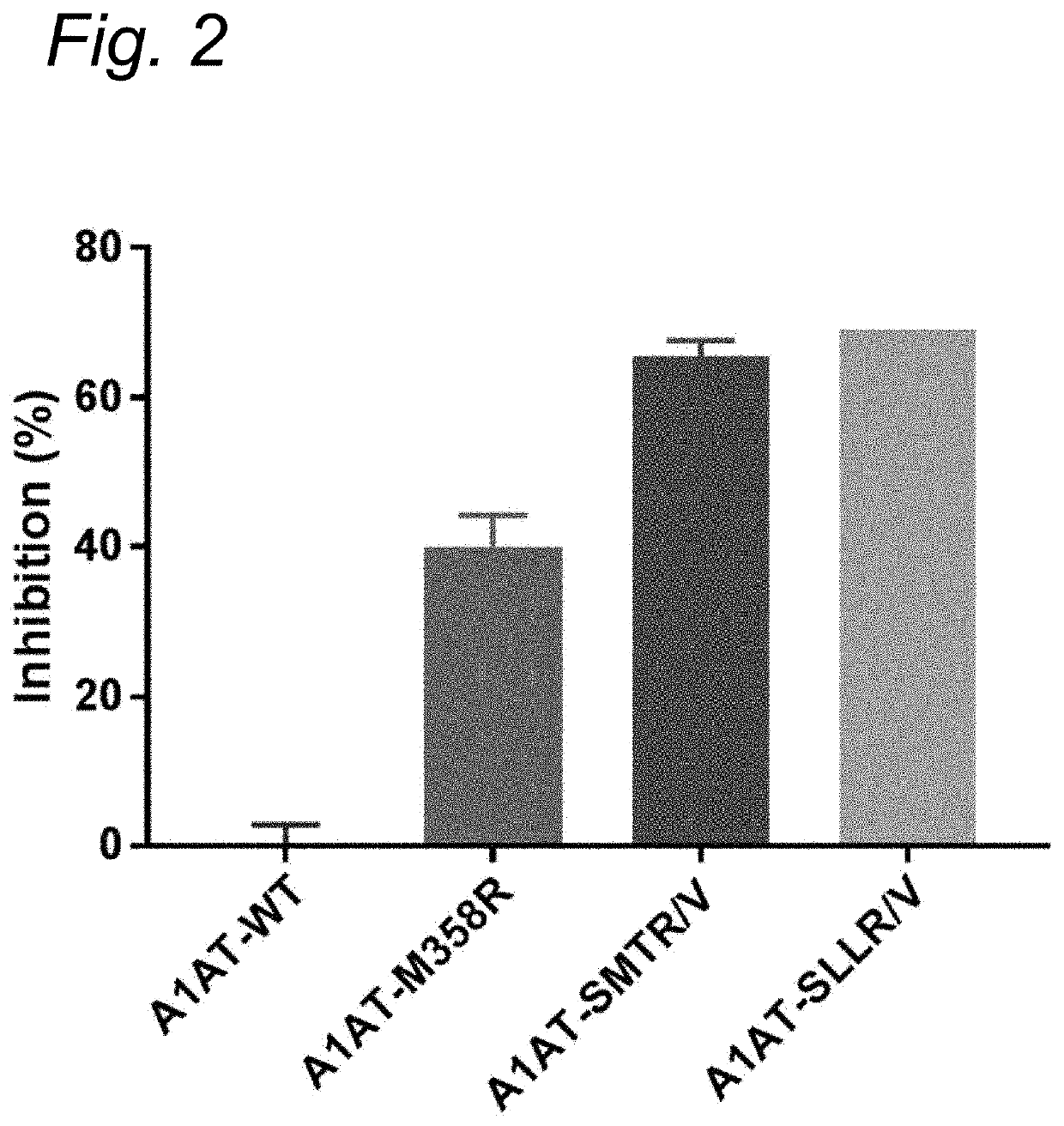
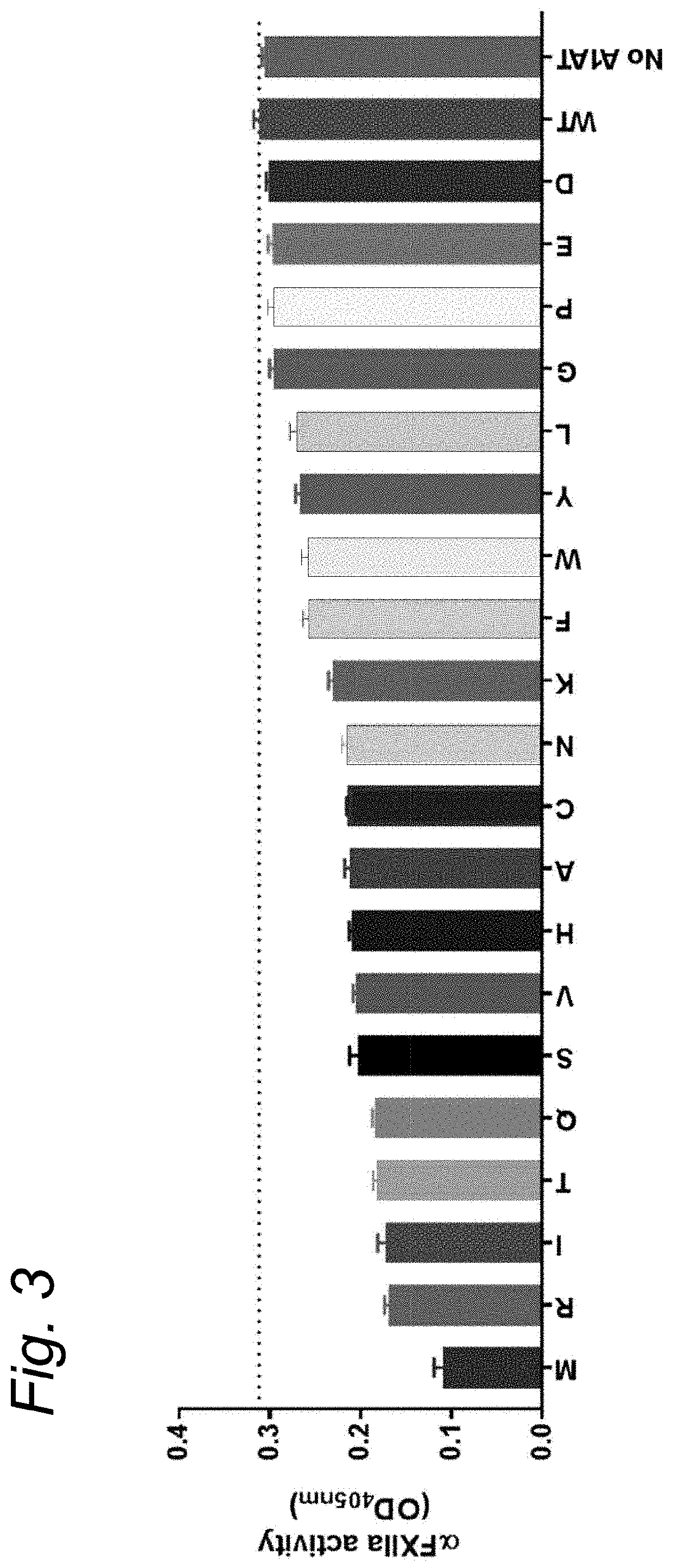
The present invention relates to modified serpins for use in the treatment of bradykinin-mediated diseases. The modified serine protease inhibitors (serpins) have mutations in one or more of the P4, P3, P2, P1 and P1′ residues of their reactive center loop, which mutations increase the serpin's inhibition of plasma kallikrein (PK) as compared to the corresponding unmodified serpin. The mutations in the modified serpins of the invention further ensure that serpins display substantially no inhibition of at least thrombin and activated protein C. A modified serpin of the invention further preferably shows increased inhibition of at least one of an active form of Factor XII (FXII) and plasmin as compared to the corresponding unmodified serpin, and, preferably, the serpin inhibits at least one of an active form of FXII and PK stronger than they are inhibited by C1 esterase inhibitor. Preferably the modified serpin is a modified α1-antitrypsin. The invention further pertains to nucleic acid molecule encoding the modified serpins of the invention, e.g. a gene therapy vector, and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the modified serpins of the invention or such gene therapy vectors.
Owner:PRECLINICS GES FUER PRAEKLINISCHE FORSCHUNG
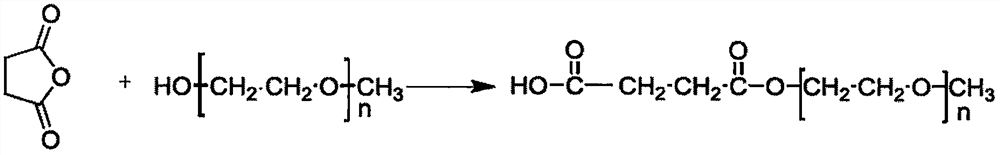
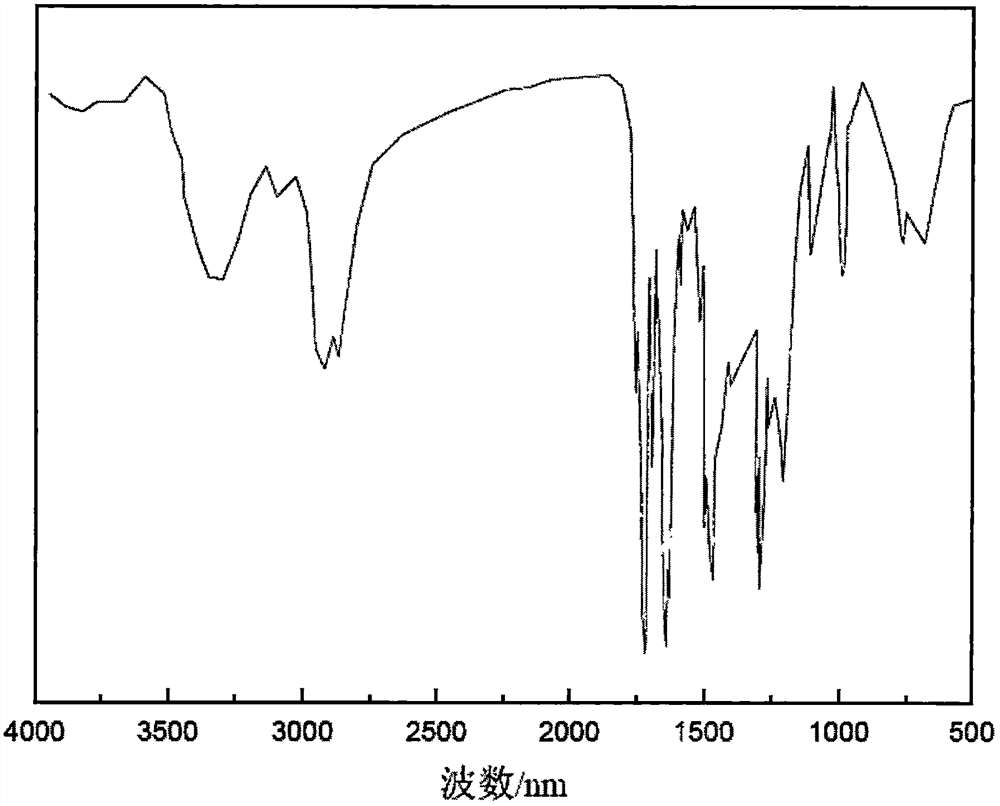
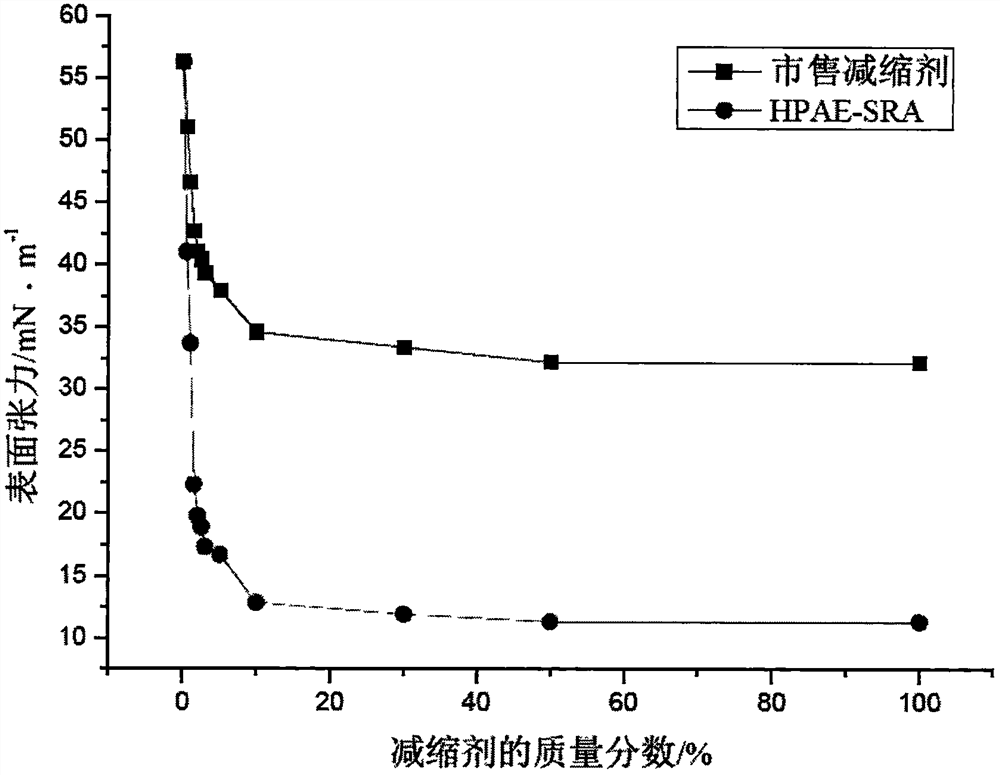
A kind of preparation method of hyperbranched shrinkage reducer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a hyperbranched shrinkage reducing agent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a precursor monomer N,N-dihydroxyethyl-3-aminomethyl acrylate from diethanol amine and methyl acrylate, and then synthesizing hydroxyl-terminated hyperbranched poly(amine-ester)(HPAE) utilizing trimethylolpropane as a reaction central nucleus through an approved one-step method; secondly, synthesizing a micromolecule shrinkage reducing agent SRA from succinic anhydride and polyoxyethylene alkyl ether; and finally, carrying out terminal modification on HPAE by virtue of the micromolecule shrinkage reducing agent SRA, so as to obtain the hyperbranched shrinkage reducing agent HPAE-SRA. According to the preparation method, the micromolecule shrinkage reducing agent SRA is successfully grafted to the surface of an HPAE molecule, the obtained HPAE-SRA is capable of substantially reducing the shrinkage of cement, and the shrinkage reducing rates of mortar in 3d or 28d are respectively 48.8% and 36.6%; and the doping of the shrinkage reducing agent has little influence to compressive strength and is beneficial to the rupture strength.
Owner:SHAANXI RAILWAY INST
Multistage reaction center oxidation catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111229211AEfficient degradationIncrease concentrationWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsActivated carbonSilica particle
The invention provides a multistage reaction center oxidation catalyst. The catalyst comprises an activated carbon matrix, and metal colattice doped silicon dioxide particles which are adsorbed in gaps of the activated carbon matrix. By means of the adsorption function of the activated carbon and the microbattery function of the silicon dioxide particles, the catalyst, when being applied to the field of water treatment, achieves rapid degradation of pollutants, and a contact metal redox reaction is not generated in the system any more, so that the service life and the stability of the catalystare improved. The invention further provides a preparation method of the catalyst, a solvent method is adopted for preparing the metal colattice doped silicon dioxide particles, energy consumption islow, components are uniform, operation is easy, and wide application prospects are achieved.
Owner:天津市海跃水处理高科技有限公司 +1
A kind of production method of chemically modified carbon black
ActiveCN103980743BEasy to adjustReduce manufacturing costInorganic pigment treatmentCombustion chamberModified carbon
The invention relates to a production method of chemically modified carbon black. The production of carbon black with tar as a raw material and air as a combustion enhancer is the main production method in China at present. Four cylinders are installed in the combustion chamber of the carbon black furnace and the throat of the reaction center. The silicon chloride supply pipe is introduced into silicon tetrachloride at a weight ratio of 5-10% of the carbon black output during production, and the temperature of the reaction chamber is 1600-1800°C, which can complete the chemical modification of carbon black. Compared with unmodified carbon black, the anti-corrosion resistance of modified carbon black is 15-30% higher; the yield is 0.8-4% higher than that of unmodified carbon black.
Owner:烁元新材料(东营)股份有限公司
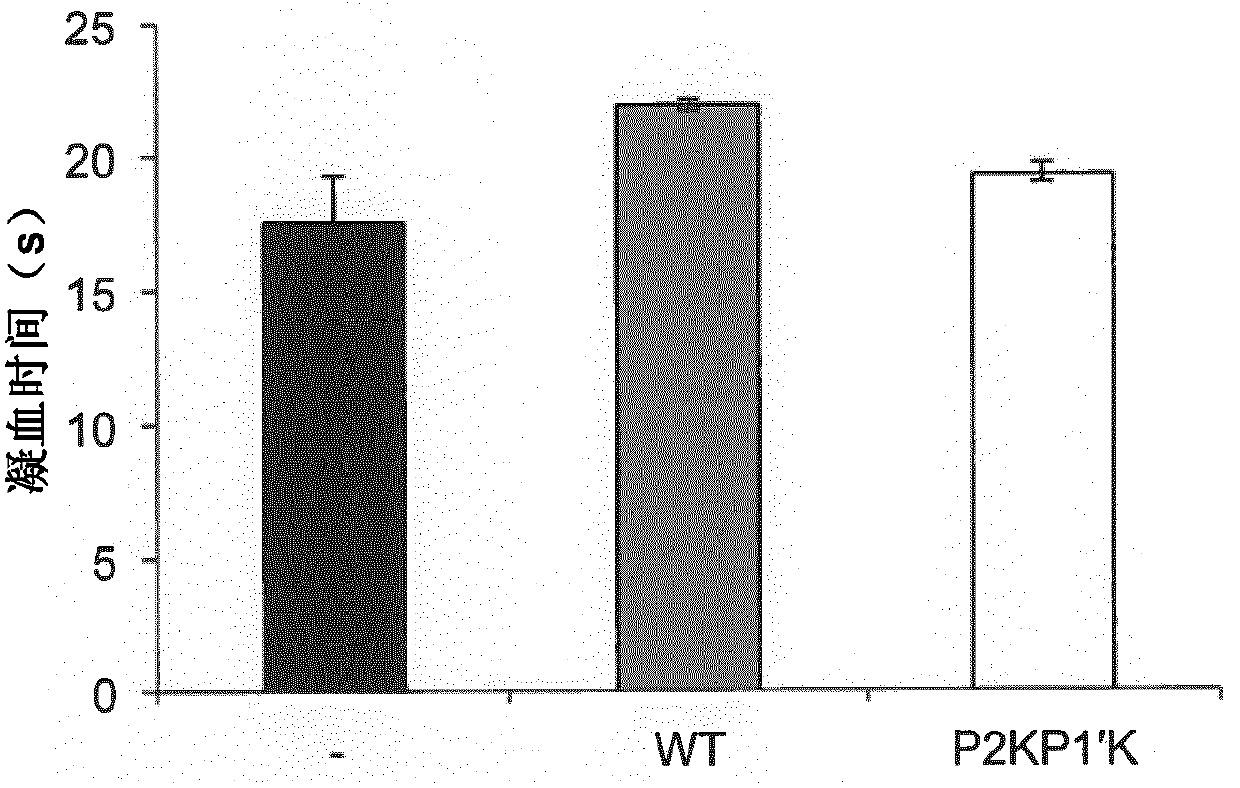
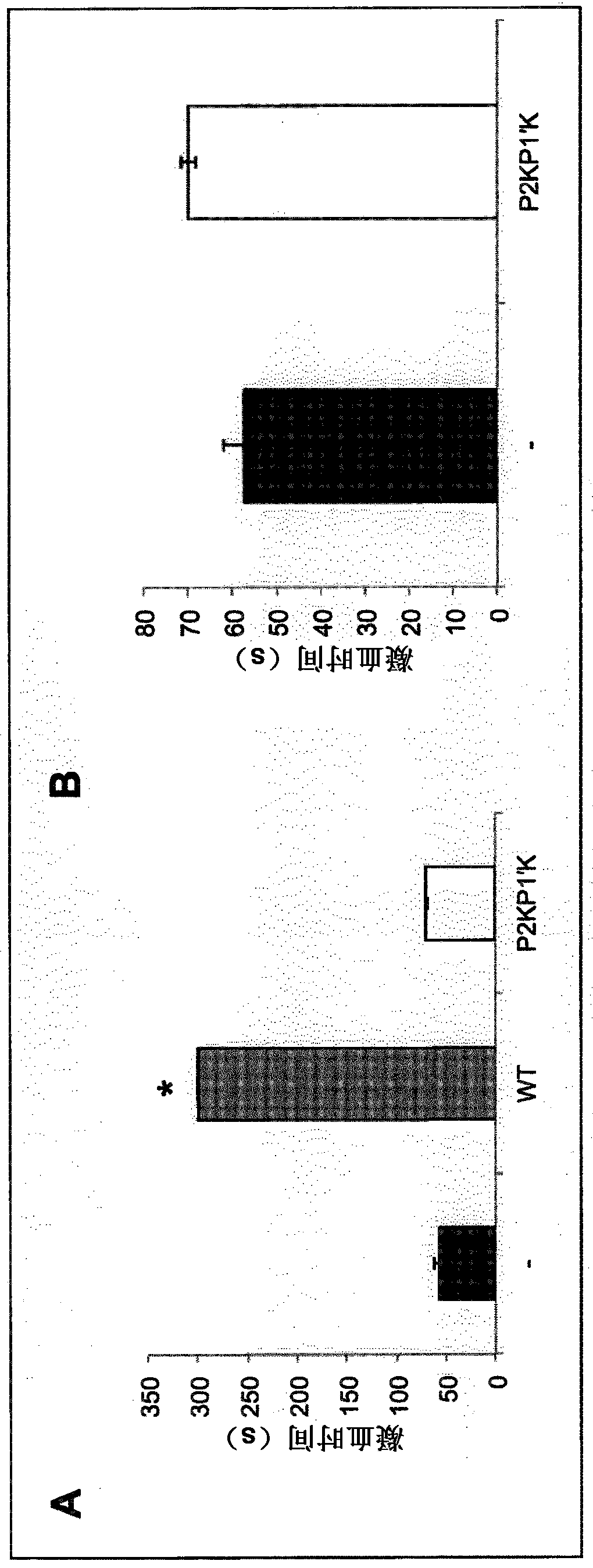
Modified serine protease inhibitors for use in the treatment of bleeding disorders
ActiveCN105992771BSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsSerine Protease InhibitorsReactive center
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Synthetic method of bicyclic pyridone derivative
InactiveCN102234274BWith structural diversityEasy to manufactureOrganic chemistryReactive centerStructural diversity
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vegetation total primary productivity inversion method and system based on chlorophyll fluorescence
PendingCN113990400AMake up timeMake up spaceCheminformatics data warehousingChemical processes analysis/designVegetationSoil science
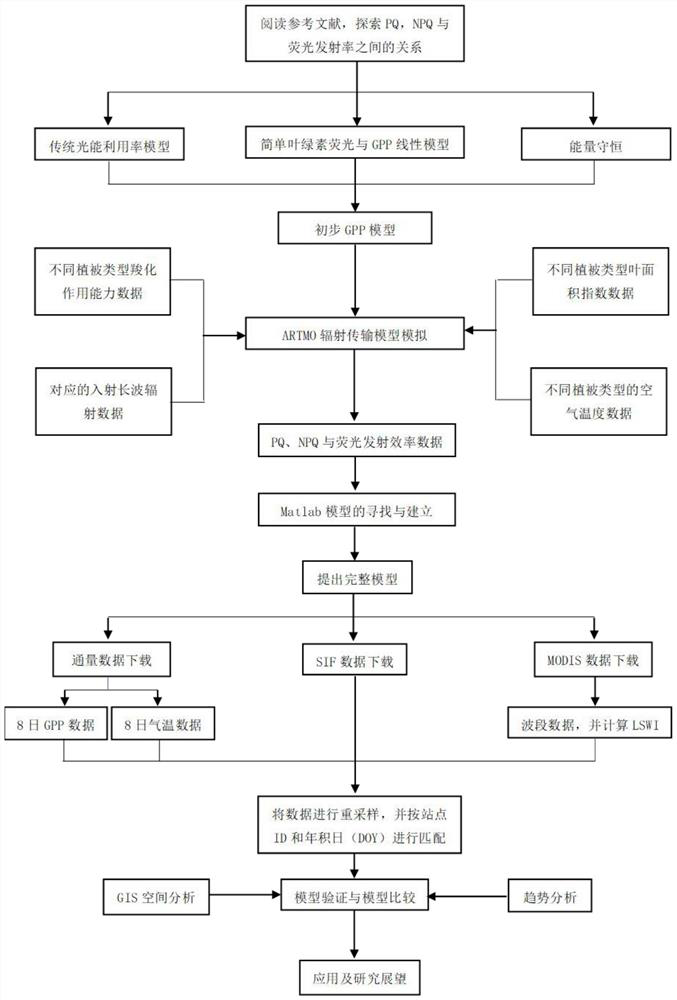
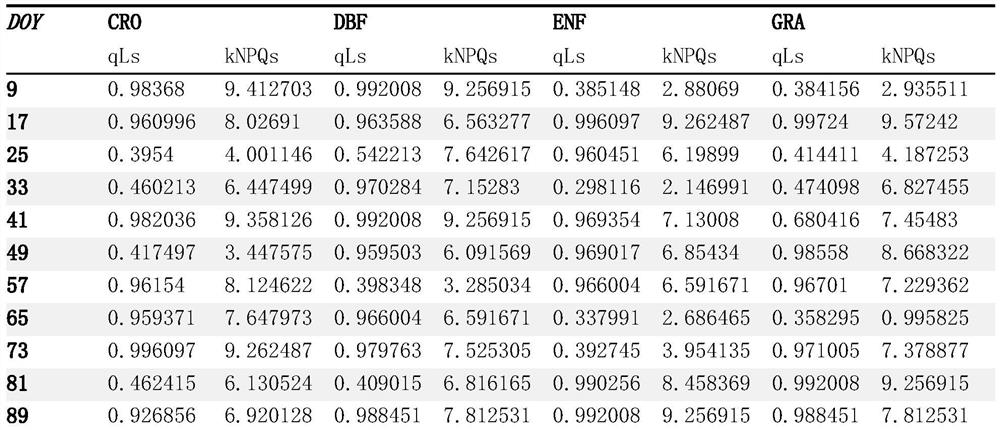
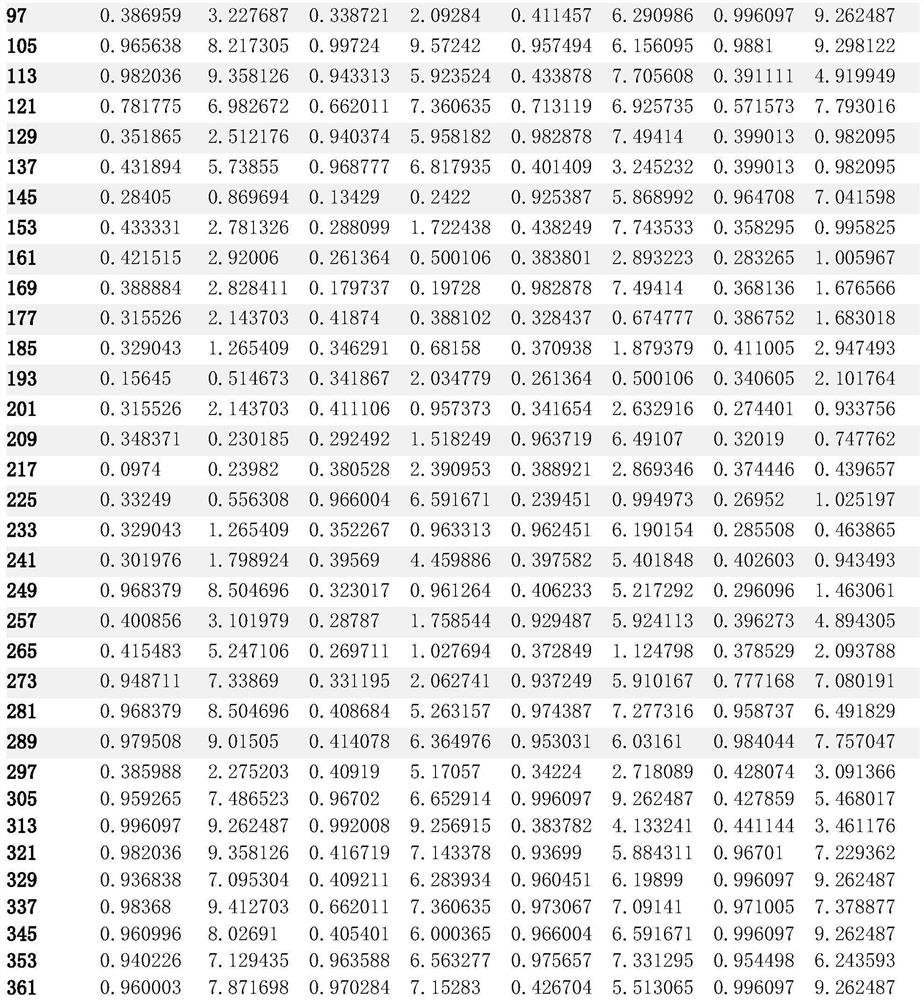
The invention discloses a vegetation total primary productivity inversion method and system based on chlorophyll fluorescence. The method comprises the following steps: A, performing inversion through an SCOPE model to obtain a relationship among fluorescence emission efficiency, a chlorophyll function reaction center opening ratio and a continuous heat dissipation rate; B, analyzing SCOPE model parameters by adopting global sensitivity analysis (GSA), and selecting decisive parameters as classification parameters of plant functional PFTs; C, acquiring ground monitoring data, chlorophyll fluorescence data, surface reflectance data and temperature data of the research area, and respectively calculating a temperature stress factor and a water stress factor; and D, constructing a chlorophyll fluorescence inversion GPP model and calculating the vegetation total primary productivity GPP. According to the method, the fluorescence emission efficiency LUEf is obtained through inversion of the SCOPE model, then the temperature stress factor and the water stress factor are obtained in combination with various data, then the chlorophyll fluorescence inversion GPP model is obtained through training, and the vegetation total primary productivity GPP is obtained through inversion.
Owner:浙江时空智子大数据有限公司
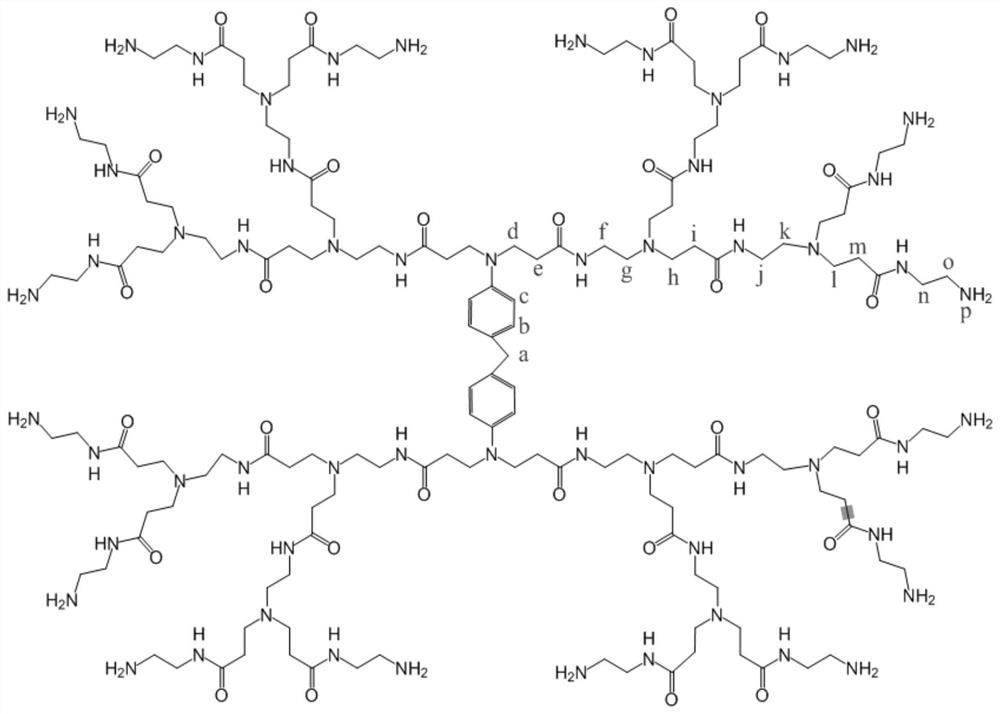
A kind of polyamide-amine hyperbranched polymer and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110452376BReduce usageEasy to prepareHydrocarbon oil dewatering/demulsificationPolymer scienceEnd-group
The invention discloses a polyamide-amine hyperbranched polymer, a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of petroleum additives. The polyamide-amine hyperbranched polymer of the present invention is a polyamide-amine hyperbranched polymer with 4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane as the reaction center and an amine terminal group. The preparation method of the present invention is simple, comprising the following steps: reacting 4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane and methyl acrylate at room temperature for 24 hours to prepare 0.5G ester with 4,4'-diaminodiphenylmethane as the core; Then add stoichiometric ratio of ethylenediamine and methyl acrylate, and prepare the polyamide-amine demulsifier with hyperbranched structure through normal temperature reaction, staged temperature rise reaction and other steps. The polyamide-amine hyperbranched polymer of the present invention is used as a demulsifier, which can quickly demulsify the oil-in-water emulsion under the condition of 50-70°C, and realize the effective separation of oil-water. The emulsion efficiency can reach 99.5%, and it has the characteristics of fast demulsification rate, less dosage and high demulsification efficiency.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Methods for modulating angiogenesis via vegf
InactiveUS20050215466A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsAngiostatinAngiogenesis growth factor
Recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) isoforms which lack the reactive center loop and contain the complete heparin-binding domain or lack at least a portion of the heparin-binding domain are described. The rPΛI-1 isoforms disclosed herein may be used to modulate angiogenesis through blocking release of VEGF from a VEGF-heparin complex. Furthermore the rPAI-1 proteins may be used to inhibit cell proliferation and migration, induce apoptosis, and produce proteolytic fragments corresponding to angiostatin kringles 1-3 and kringles 1-4.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com