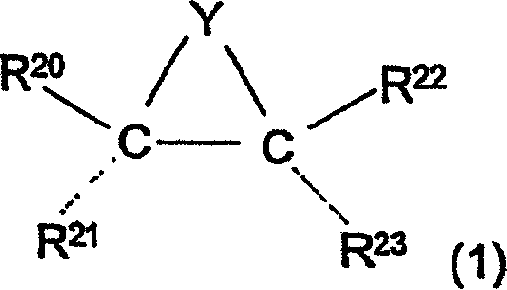
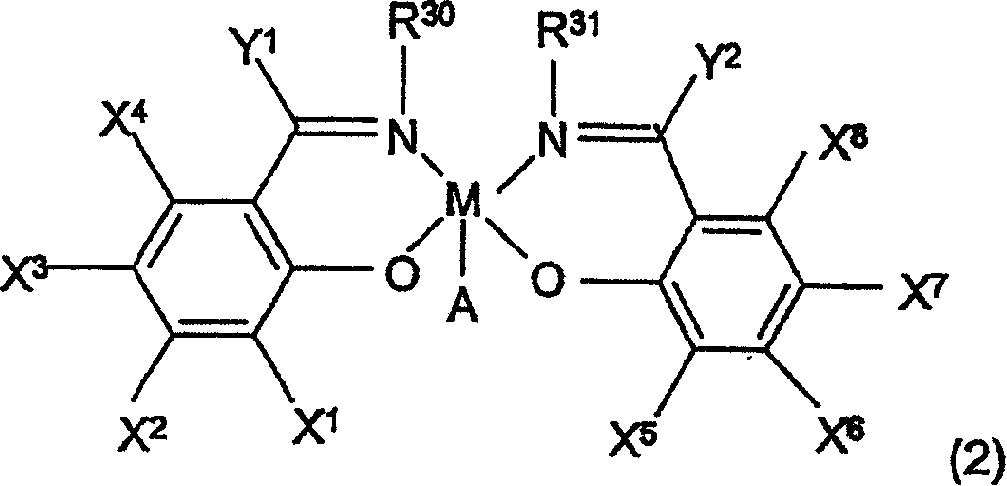
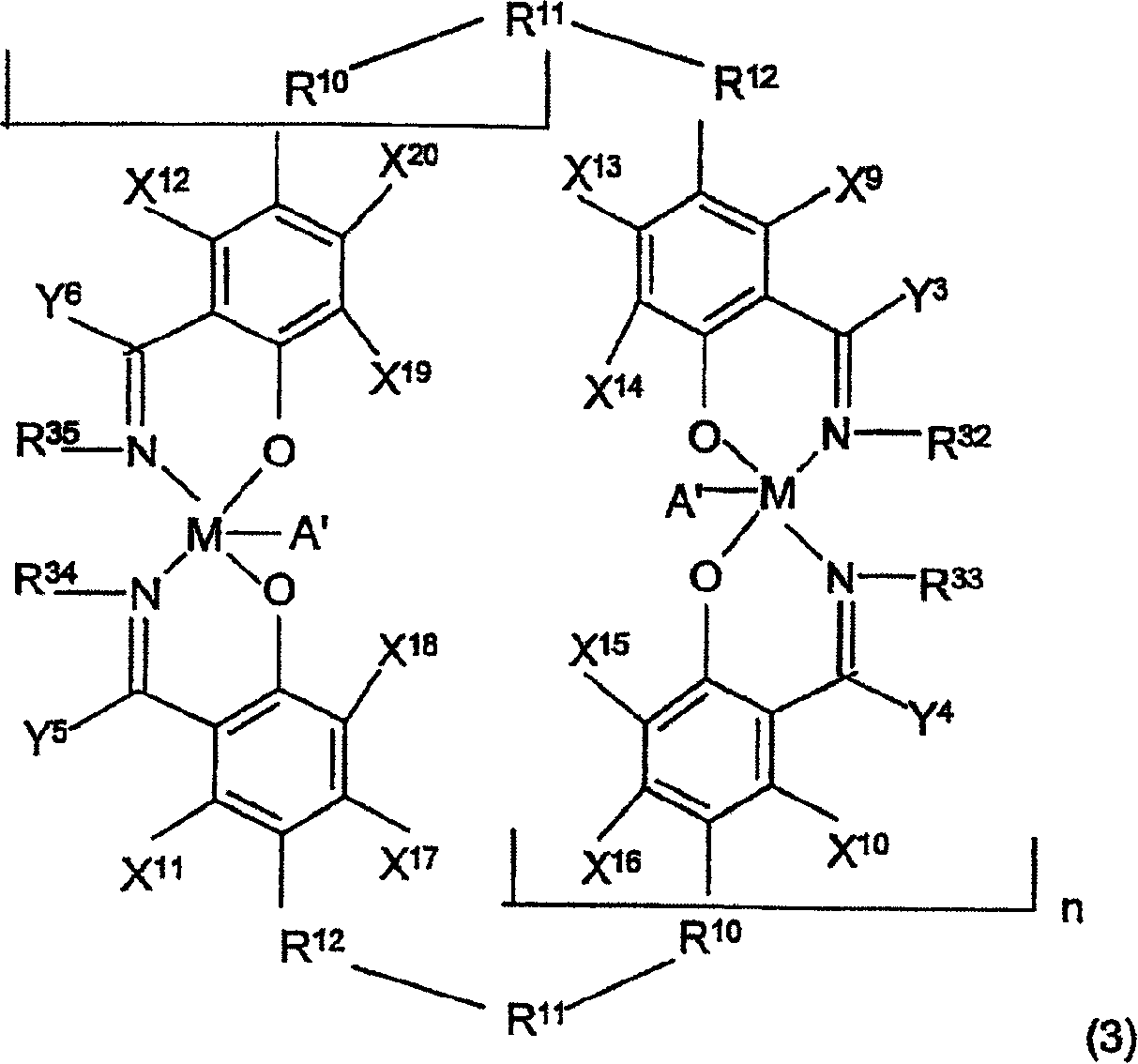
Kinetics resolution method
A chemical synthesis and catalyst technology, applied in organic chemistry methods, chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low efficiency, reduced product yield, chiral purity and chemical purity, etc., to reduce consumption , the effect of cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] Racemic epichlorohydrin is resolved into (R)-epichlorohydrin according to the following reaction scheme:
[0138]
[0139] (S,S)-Co(II)-salen complex (60.06 g) was mixed with o-dichlorobenzene (304 g) and activated by adding acetic acid (11.98 g, 2 equivalents) to the mixture.
[0140] The active catalyst solution (369 g) was charged to a 2.5 liter jacketed reaction kettle, and then racemic epichlorohydrin (1740 g) was added to the kettle. Water (258 g) was added to the reactor at a constant flow rate for 3 hours and hydrolytic kinetic resolution of epichlorohydrin was carried out at 5°C. The mixture was stirred until the product mixture exhibited greater than 99% enantiomeric balance, ie, an additional time of about 1.5 hours. The product mixture contained 35% by weight of (R)-epichlorohydrin (47% theoretical yield), 0.2% by weight of (S)-epichlorohydrin, 3.4% by weight of water, 46% by weight of CPD, 0.8% by weight % of glycidol, 0.9% by weight of dichloropropano...
Embodiment 2
[0159] Resolution of racemic epichlorohydrin to (S)-epichlorohydrin
[0160] (R,R)-Co(II)-salen complex (3 g, 4.97 mmol, 0.5 mol%) was added to a 125 mL 3-neck jacketed round bottom flask with a mechanical stirrer.
[0161] Then add CH to the bottle 2 Cl 2 (12 mL, 4 volumes). Then glacial acetic acid (0.57 mL, 9.96 mmol, 1.0 mol%, 2 equivalents relative to the catalyst) was added to the vessel in one portion. The resulting mixture was stirred under an open atmosphere for 0.5 h, resulting in a black mixture. Visual inspection of the reaction mixture confirmed the absence of a bright red solid and the presence of a dark brown solution. The flask was then equipped with a cold finger (dry ice / IPA). CH removal at ambient temperature and house vacuum 2 Cl 2 to dry, and the CH 2 Cl 2 The distillate is discharged as waste.
[0162] Racemic epichlorohydrin (78 mL, 1.0 mole) was then added to the bottle. The reaction mixture was stirred and the temperature of the reaction mix...
Embodiment 3
[0166] Resolution of racemic epichlorohydrin using the (R,R)-Co(II)-salen complex in a process similar to that described in Example 1 above gave >99% e.e. of (S)-epichlorohydrin, And the product mixture is treated with several possible reducing agents as additives. The reaction mixture was then divided into eight portions (12 g each) in separate scintillation vials, each equipped with a magnetic stir bar. The effect of catalyst deactivation and the stability of resolved (S)-epichlorohydrin were analyzed with respect to time and temperature. Two of the eight scintillation vials were used as controls, to which nothing was added, and the remaining six (6) fractions were individually treated with 5.51 mmol (about 2 equivalents relative to catalyst present) of the different additives.
[0167] The composition of the product mixture was monitored over time by gas chromatographic analysis using o-dichlorobenzene co-solvent as an internal standard. The results are shown in Table III...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com