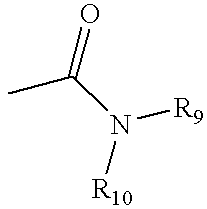
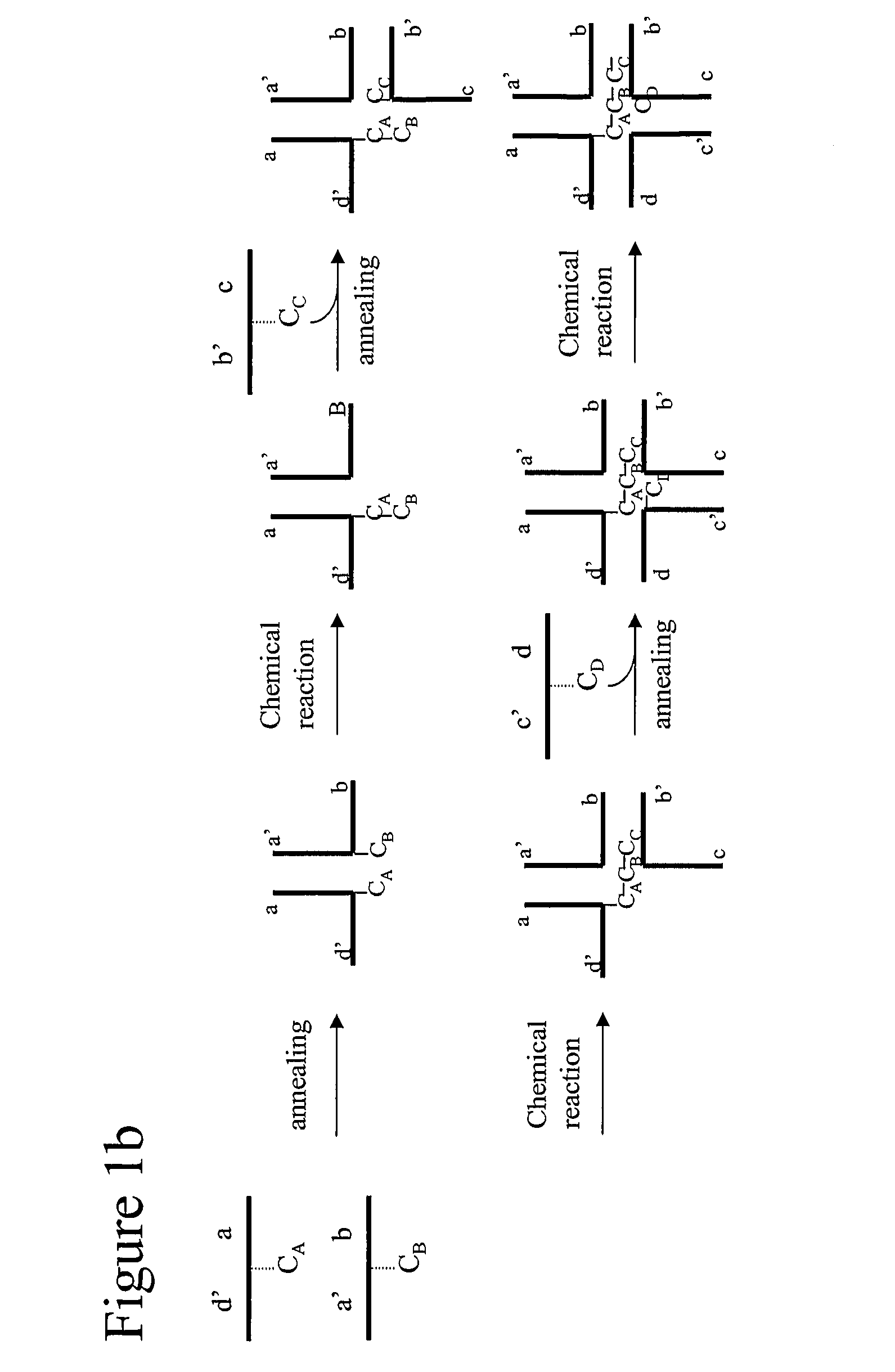
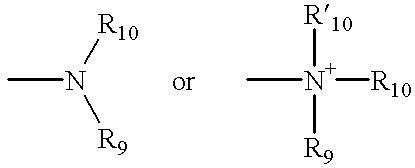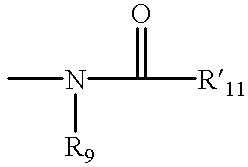Patents
Literature
67 results about "Reaction centre" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
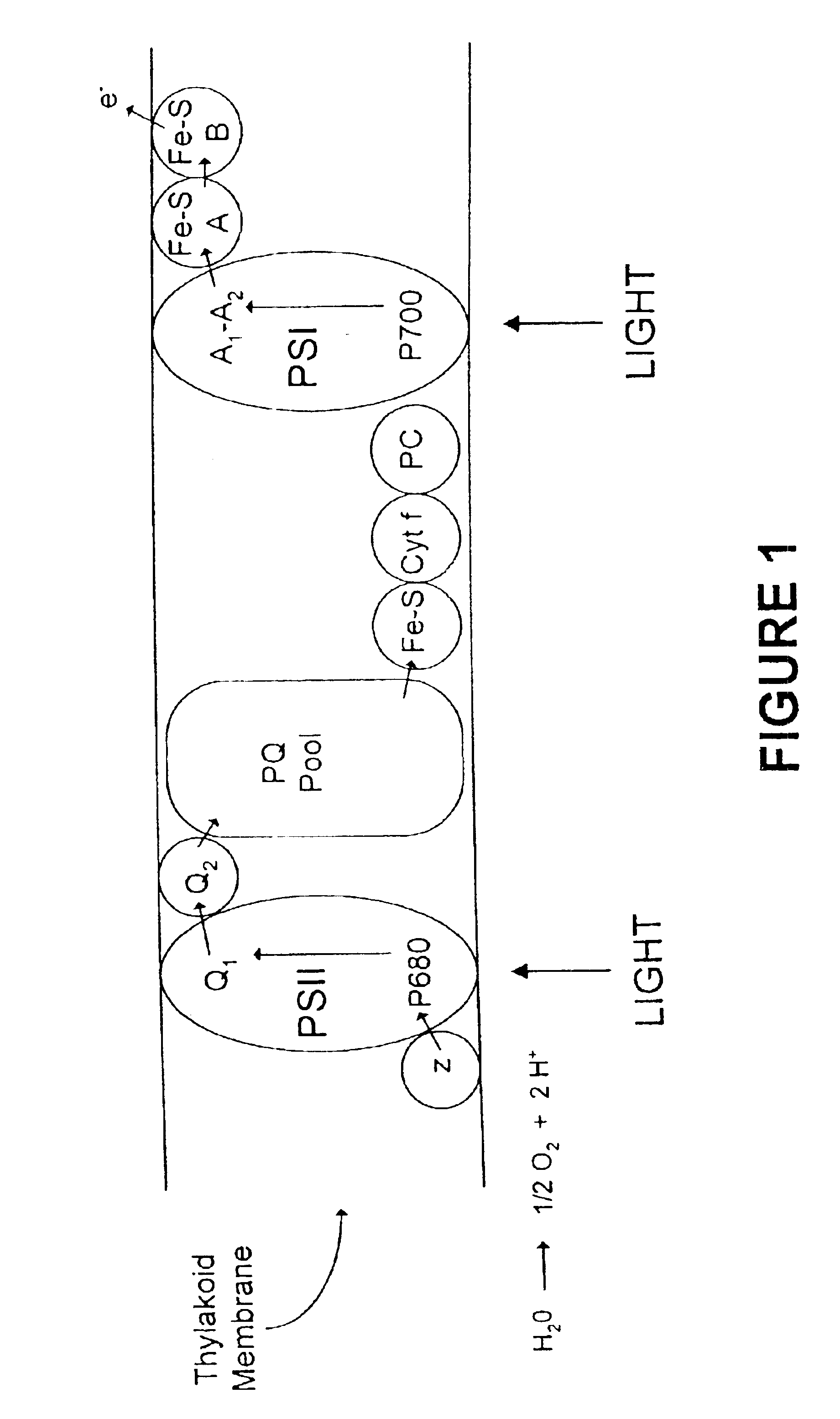
A photosynthetic reaction centre is a complex of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis.
Matrices for drug delivery and methods for making and using the same
In one aspect, biocompatible matrices such as sol-gels encapsulating a reaction center may be administered to a subject for conversion of prodrugs into biologically active agents. In certain embodiments, the biocompatible matrices of the present invention are sol-gels. In one embodiment, the enzyme <SMALLCAPS>L< / SMALLCAPS>-amino acid decarboxylase is encapsulated and implanted in the brain to convert <SMALLCAPS>L< / SMALLCAPS>-dopa to dopamine for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMA
Methods and systems for monitoring reactions
ActiveUS20120052490A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal sourceSignal processing
Methods and systems for monitoring reactions by observing signals deriving from those reactions, using signal processing that allows differentiation between signals that are otherwise optically overlapping by conventional detection methods. Centroid determination is used to identify signal sources that are presenting confounding overlapping signals due to their physical proximity, and / or to identify discrete signals from different reaction centers.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Matrices for drug delivery and methods for making and using the same
In one aspect, biocompatible matrices such as sol-gels encapsulating a reaction center may be administered to a subject for conversion of prodrugs into biologically active agents. In certain embodiments, the biocompatible matrices of the present invention are sol-gels. In one embodiment, the enzyme L-amino acid decarboxylase is encapsulated and implanted in the brain to convert L-dopa to dopamine for treatment of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:BABICH JOHN W +2
System and method to identify the metabolites of a drug
InactiveUS20080120041A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyMolecular entity identificationChemical processes analysis/designReaction ruleMetabolite
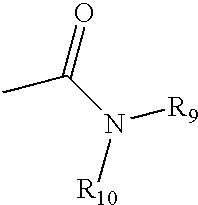
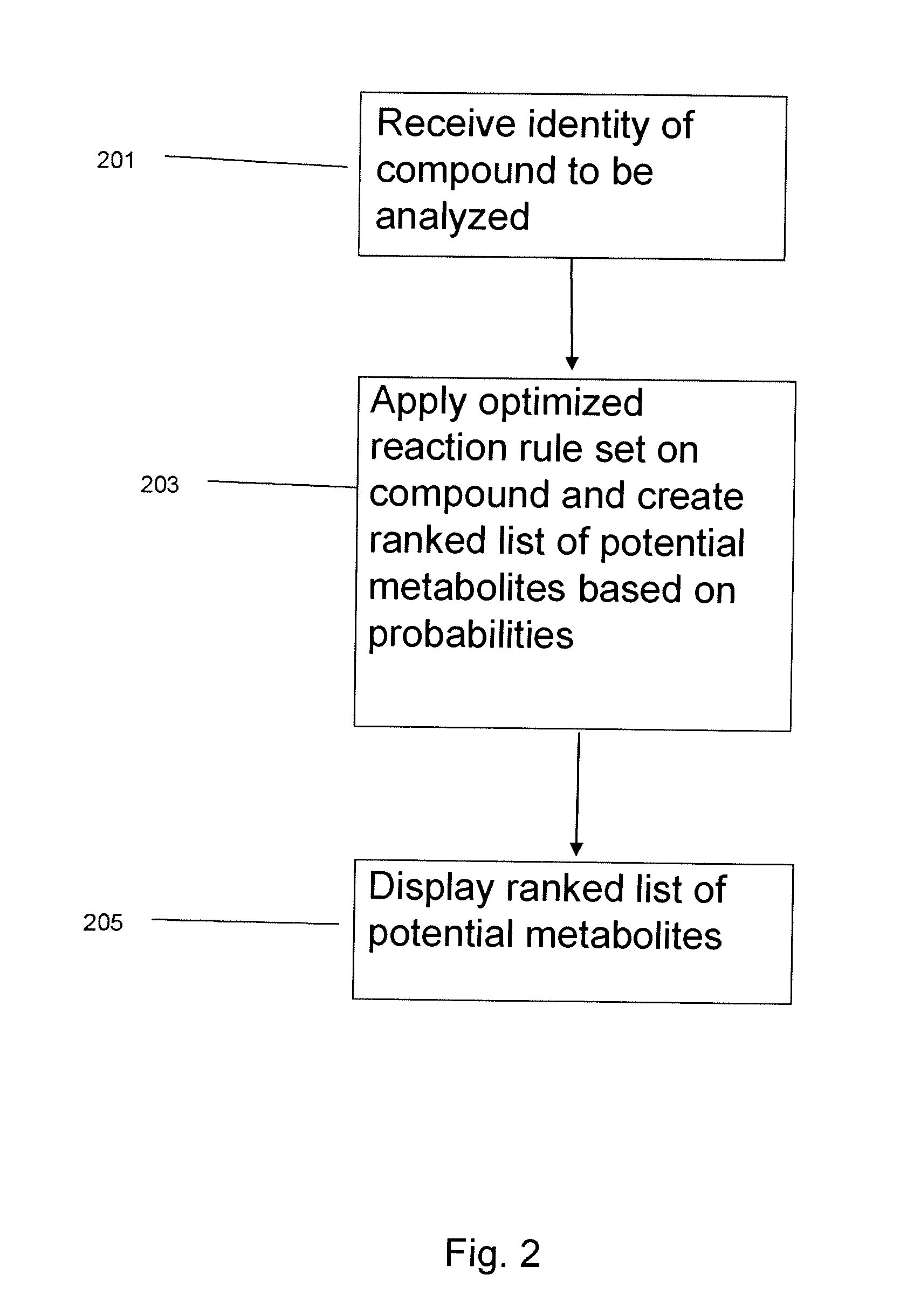
The invention provides for a method for predicting potential metabolites for a compound, comprising the steps of receiving a target compound from a user applying a set of optimized reaction rules to said target compound to generate a list of potential metabolites and calculating a probability score for each product compound on said list of potential metabolites. The reaction set is optimized by starting from a starting set of reaction rules and replacing at least one reaction rule for a reaction center in said starting set of reaction rules by one, or preferably two or more new rules, which are defined to apply to a reaction of said reaction center, but now specifying or differentiating based on the structural environments of said reaction center, if at least one of said new rules has a higher probability score than the replaced reaction rule when the starting set of reaction rules and the optimized set of reaction rules are both tested with a database of known metabolites of compounds.
Owner:NV ORGANON
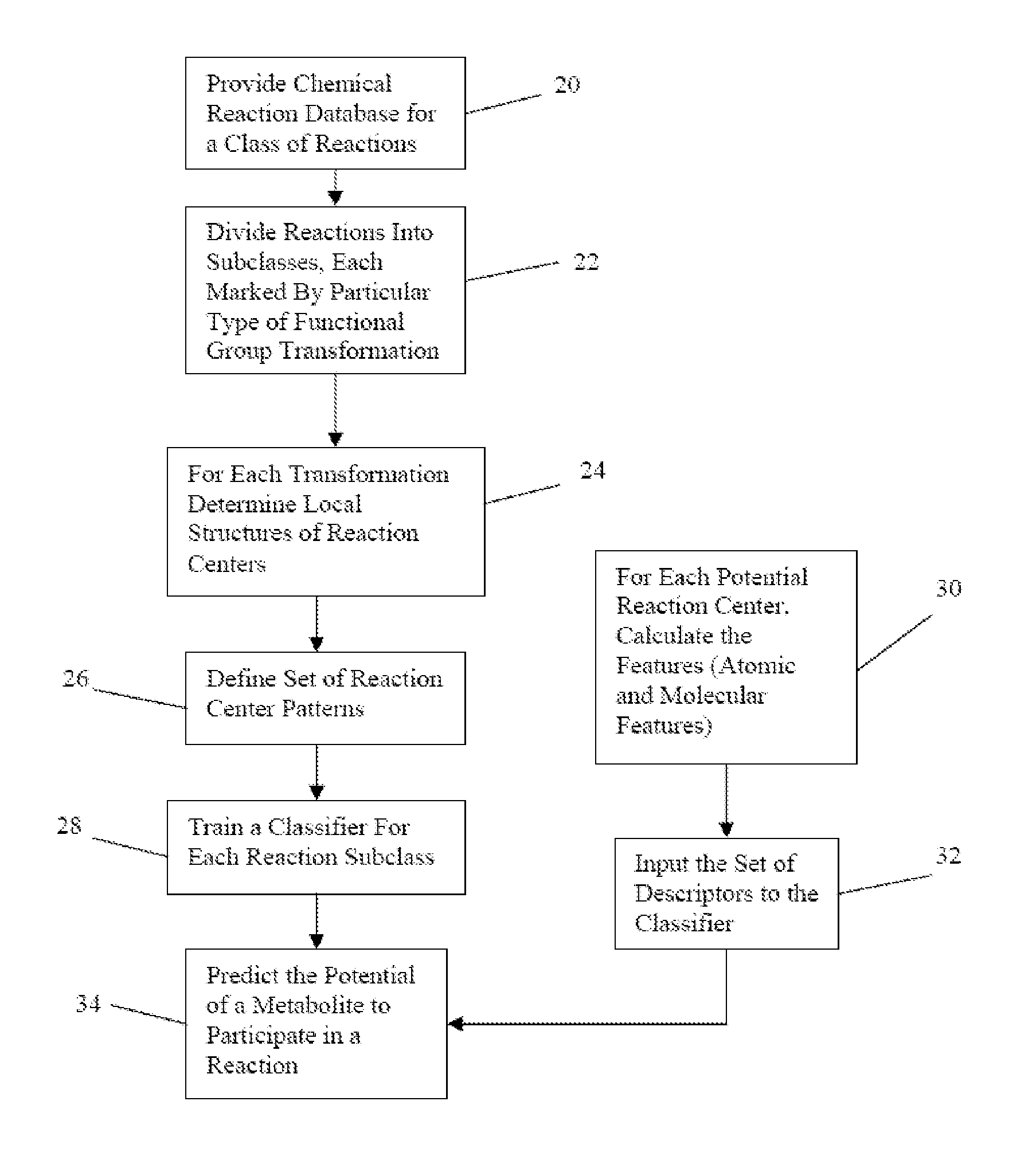
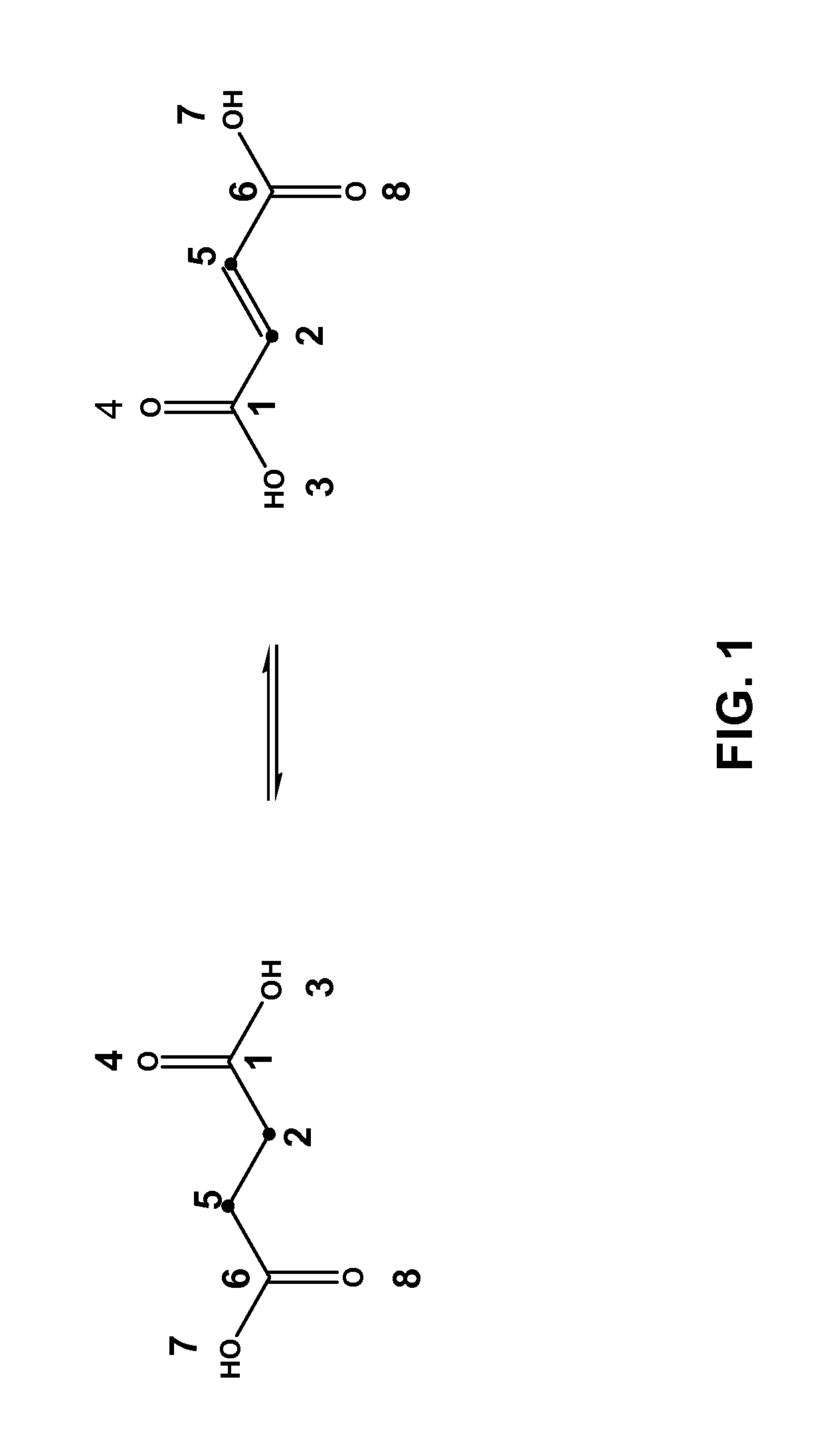
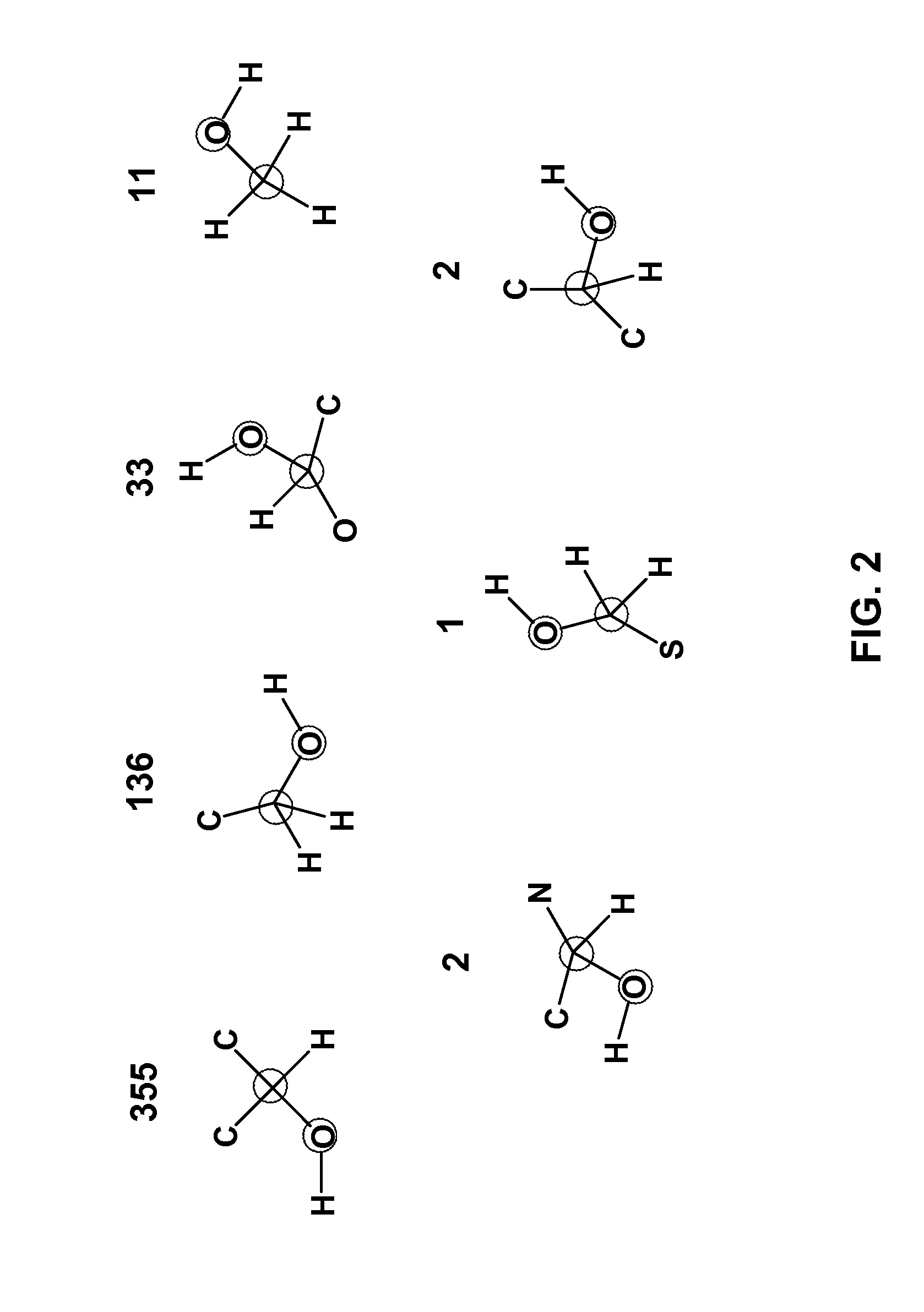
Method for predicting enzyme-catalyzed reactions
InactiveUS20080177478A1Chemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designSupport vector machineMetabolite
The reactivity of given metabolites is assessed using selected empirical atomic properties in the potential reaction center. Metabolic reactions are represented as biotransformation rules. These rules are generalized from the patterns in reactions. These patterns are not unique to reactants but are widely distributed among metabolites. Using a metabolite database, potential substructures are identified in the metabolites for a given biotransformation. These substructures are divided into reactants or non-reactants, depending on whether they participate in the biotransformation or not. Each potential substructure is then modeled using descriptors of the topological and electronic properties of atoms in the potential reaction center; molecular properties can also be used. A Support Vector Machine (SVM) or classifier is trained to classify a potential reactant as a true or false reactant using these properties.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
In-situ-doped cobalt fenton catalyst as well as synthetic method and application thereof
InactiveCN108940342ASmall response rangeBroaden the response rangePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater treatment compoundsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTElectron
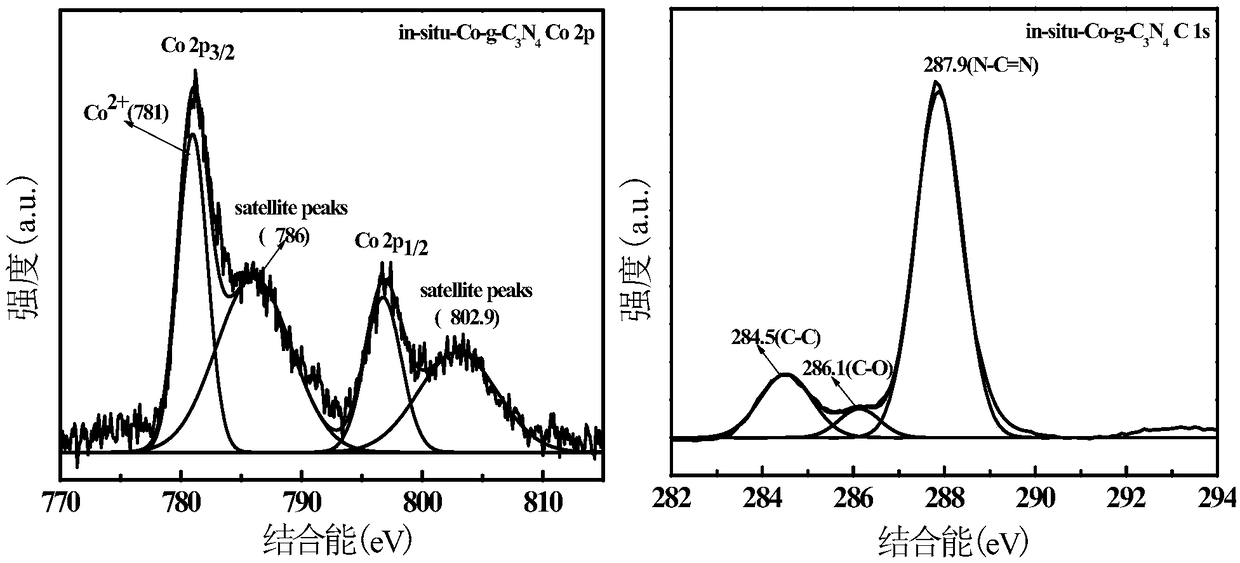
The invention discloses an in-situ-doped cobalt fenton catalyst as well as a synthetic method and application thereof. The synthetic method of the in-situ-doped cobalt fenton catalyst comprises the following steps: adding a cobalt source into a precursor; and then synthesizing the in-situ-doped cobalt fenton catalyst through an in-situ doping roasting process, wherein the precursor is tripolycyanamide, cyanamide, dicyandiamide or urea. The in-situ-doped cobalt fenton catalyst (in-situ-Co-g-C3N4) disclosed by the invention shows a classic carbon nitride sheet laminated structure, due to formation of a C-O-Co bond in the structure, formation of a double-reaction center is promoted, H2O2 and pollutants are separately reduced and decomposed in an electron-rich center and an electron-deficientcenter, so that the problem of loss of active ingredients caused by self-oxidative reduction of metal ions is avoided. The in-situ-Co-g-C3N4 has a good removal effect on novel organic pollutants whichare difficultly degraded under a neutral condition, and in a process of degrading the pollutants, the in-situ-Co-g-C3N4 has strong ability of activating H2O2 and also has good stability, and moreover, a dissolution ratio of cobalt ions is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Covalent organic framework material of bionic photosystem I and preparation and application of covalent organic framework material
ActiveCN111454459ARealize the decomposition of hydrogenOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHydrogen productionPhotosystem IMaterials science
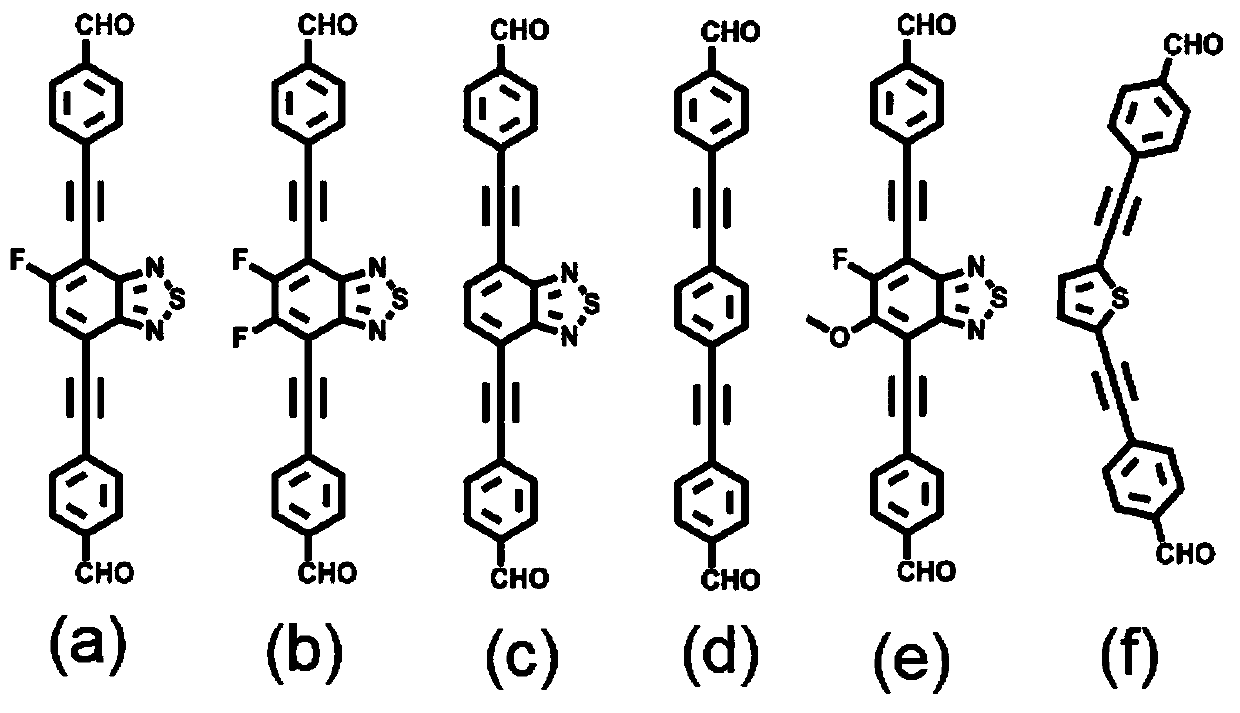
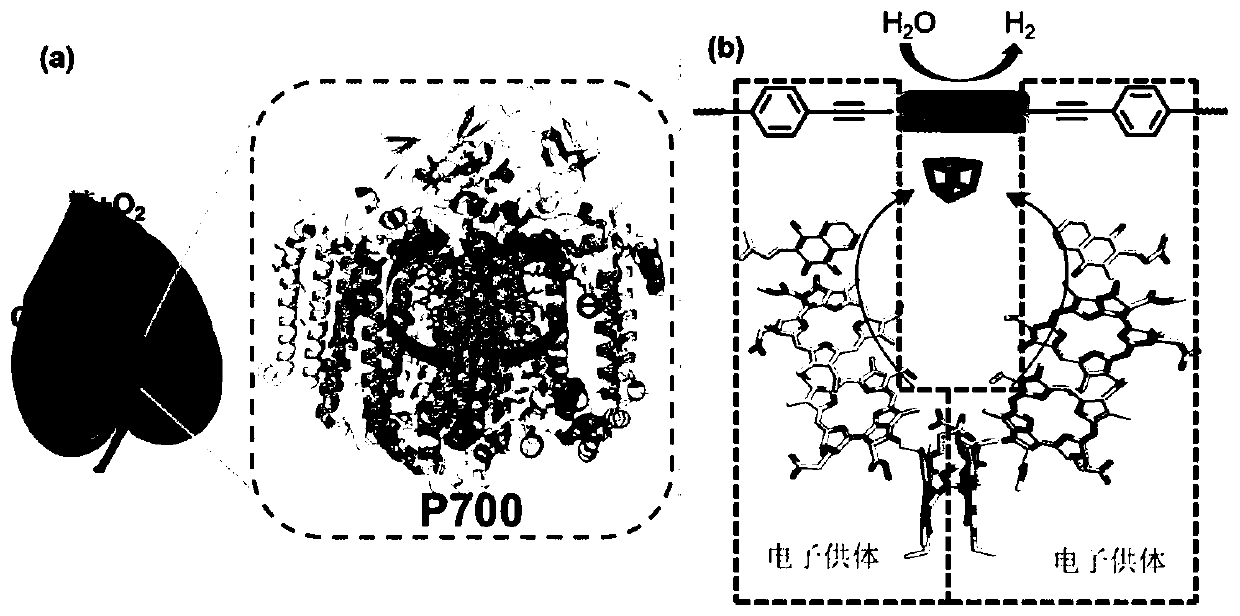
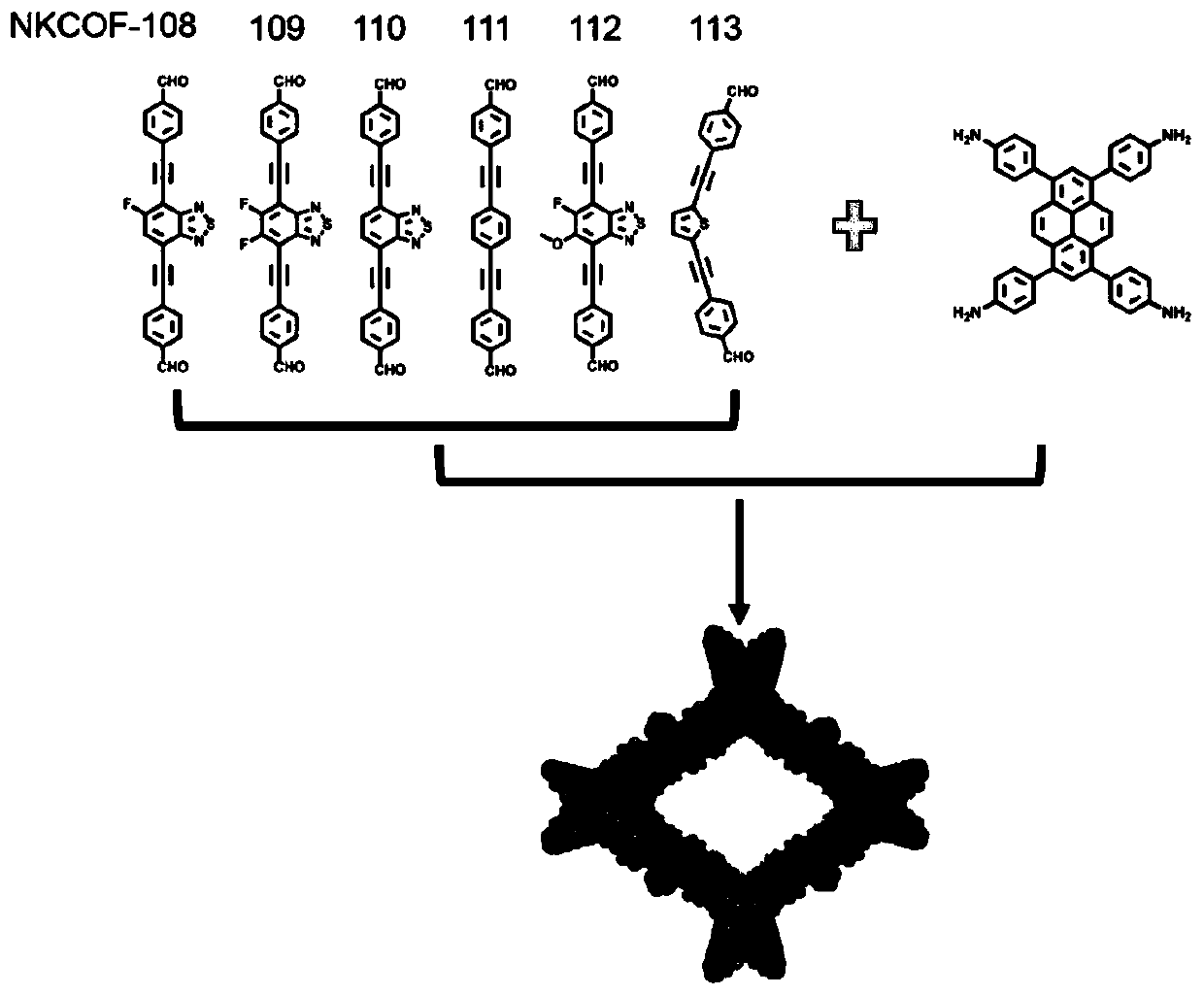
The invention relates to synthesis of a functionalized covalent organic framework and an application technology of the functionalized covalent organic framework in hydrogen production by photolysis ofwater, and the structure and reaction mechanism of the photosynthesis reaction center in nature are creatively simulated and the covalent organic framework material is designed and developed as a newlight-harvesting material. The present invention is a crystalline material formed by covalently linking imine bonds formed by a Schiff base condensation reaction of organic monomers. The covalent organic framework material obtained by the method has a large specific surface area and a regular pore channel structure with an adjustable pore diameter, and is beneficial to mass transfer of reactantsand products in the catalytic process. The covalent organic framework material has high stability and durability for hydrogen production through catalytic water decomposition under visible light, andthe hydrogen production rate can reach up to 11.6 mmol / g / h.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
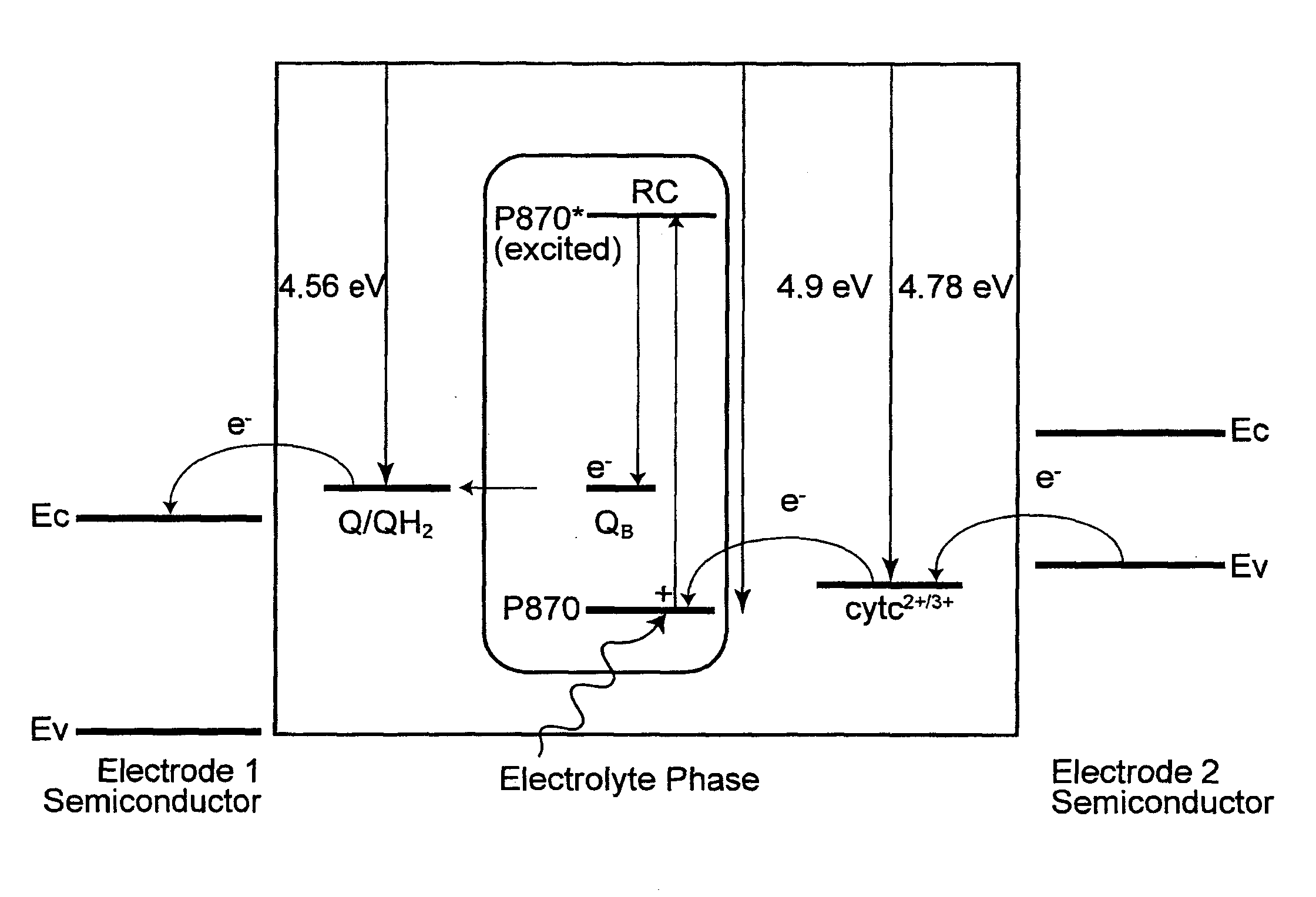
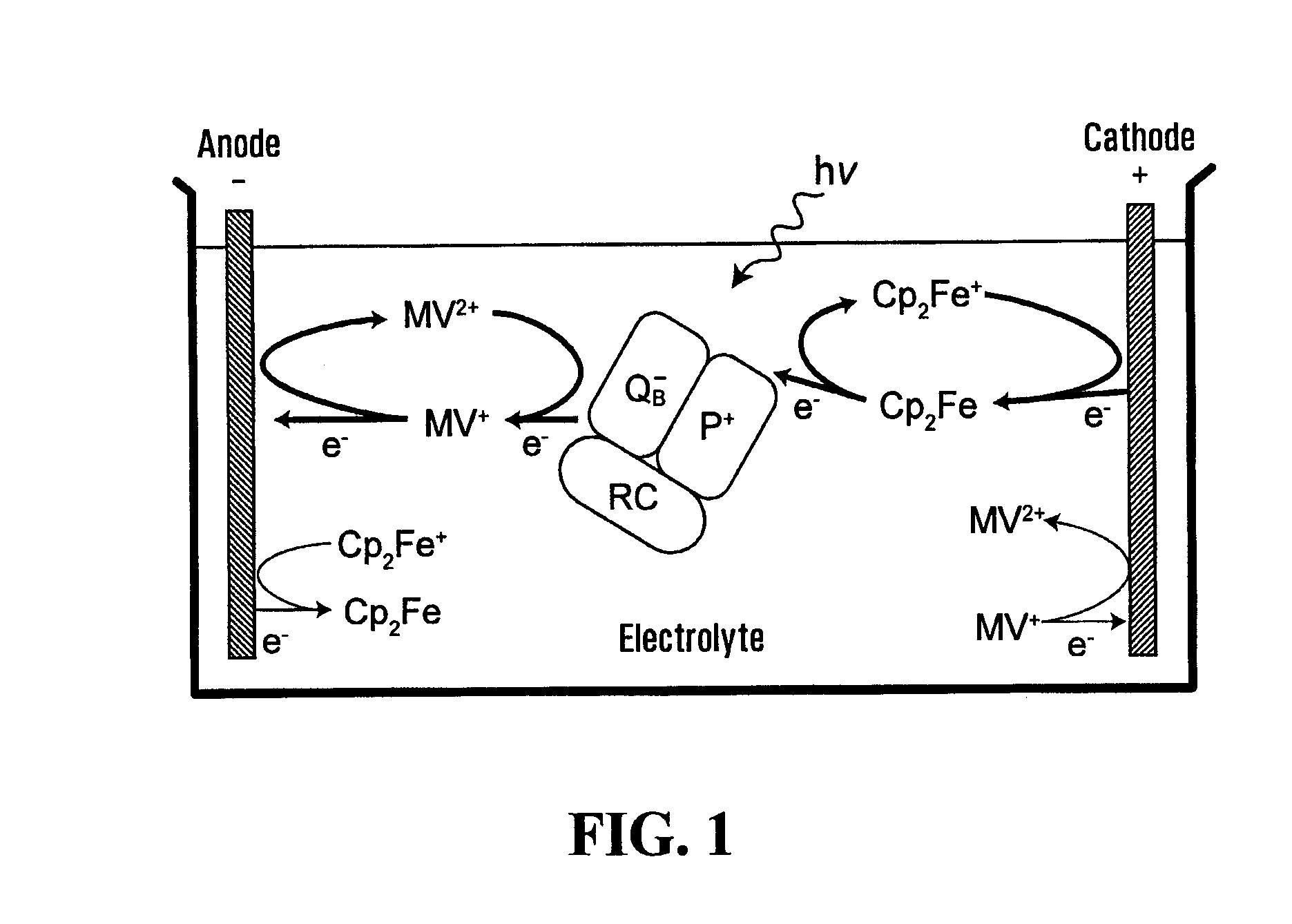
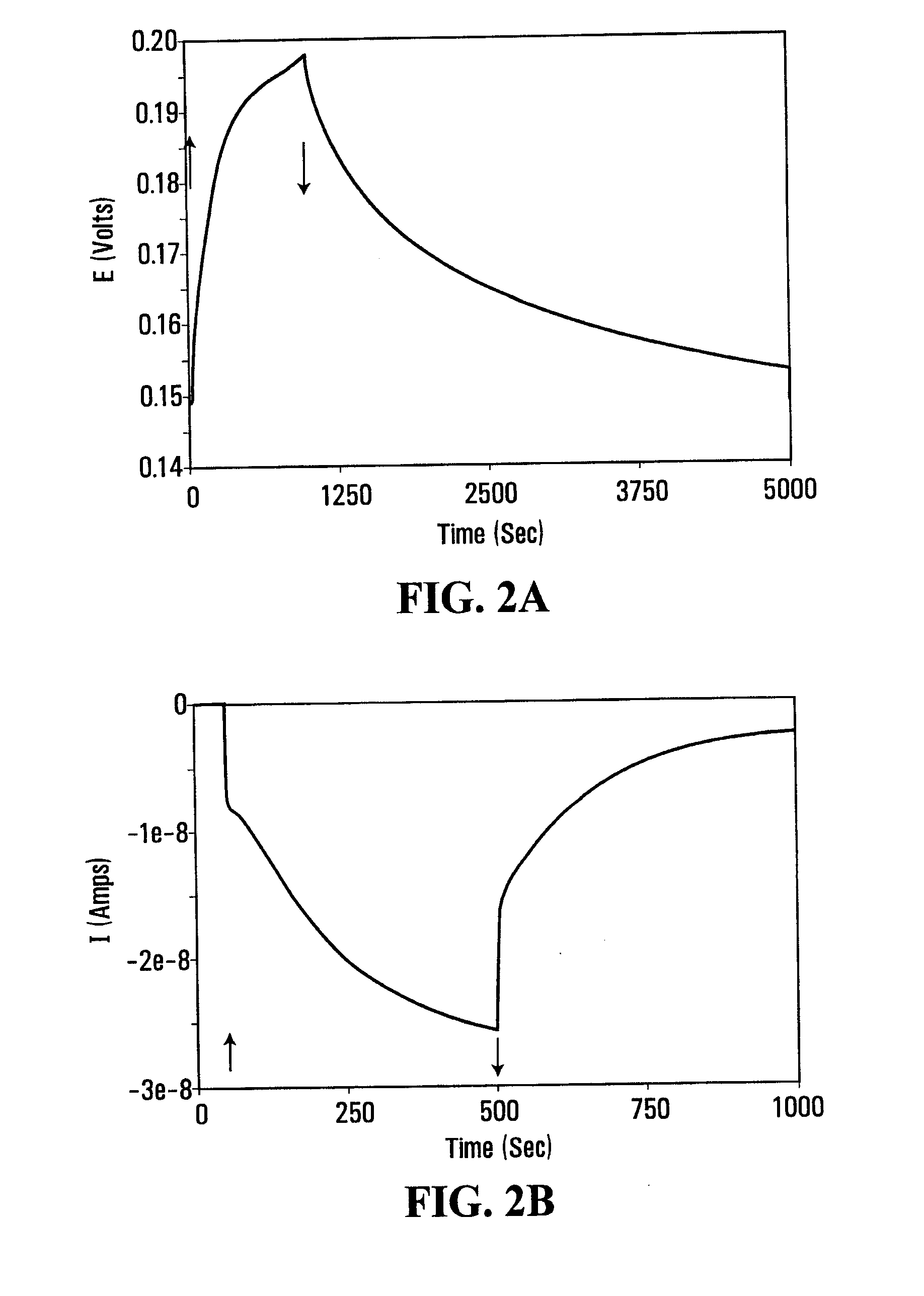
Electrochemical photovoltaic cells
The invention provides a bio-photovoltaic device, in which a photoelectric center, exemplified by a biological photosynthetic reaction center (RC), is dispersed and mobile in a medium, such as an aqueous solution. The charges generated by the illuminated RC are transferred to electrodes via one or more mediators. In selected embodiments, the difference between the reaction rates of two types of mediator at the electrode surfaces, in conjunction with other charge transfer reaction equilibria, determines the direction of the photocurrent in the device. In an exemplified embodiment, the magnitude of the photocurrent is proportional to the incident light intensity, and the current increases nonlinearly with an increase in the RC concentration in the medium.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
THAQ/graphene composite material and preparation method thereof as well as battery positive electrode and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN103515609AEfficient conductionFast conductionSecondary cellsNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesExertionElectrochemistry
The invention discloses a THAQ / graphene composite material and a preparation method thereof as well as a battery positive electrode and a lithium ion battery, and belongs to the field of electrochemistry materials, wherein the THAQ / graphene composite material comprises 50-95wt% of THAQ and 5-50wt% of graphene. The THAQ / graphene composite material provided by the invention comprises grapheme with high conductivity, and thus electrons can be effectively and fast conducted to the THAQ molecular activity reaction center of the surface of the graphene, thereby being beneficial to the improvement on the exertion of the THAQ numerator capacity.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
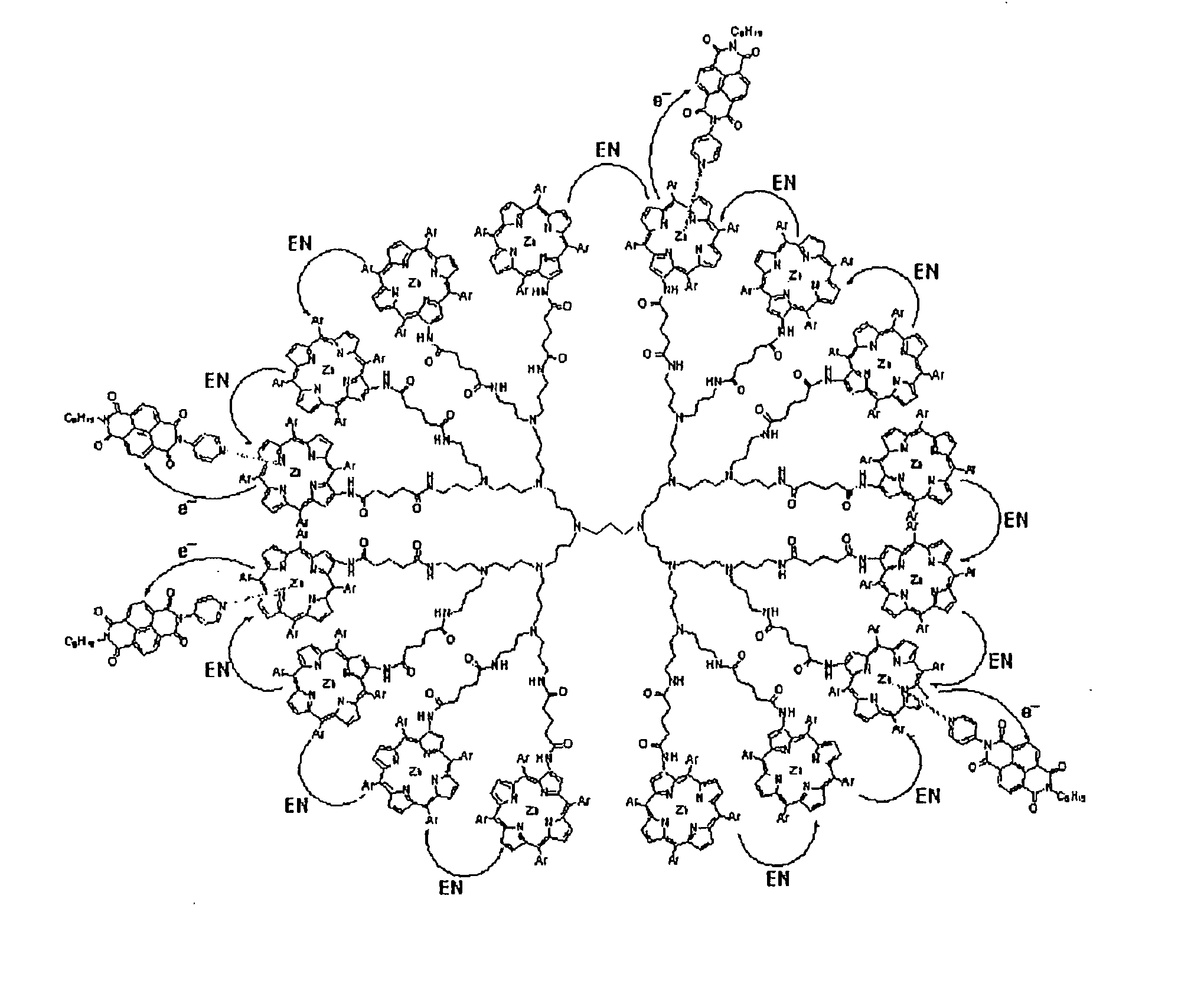
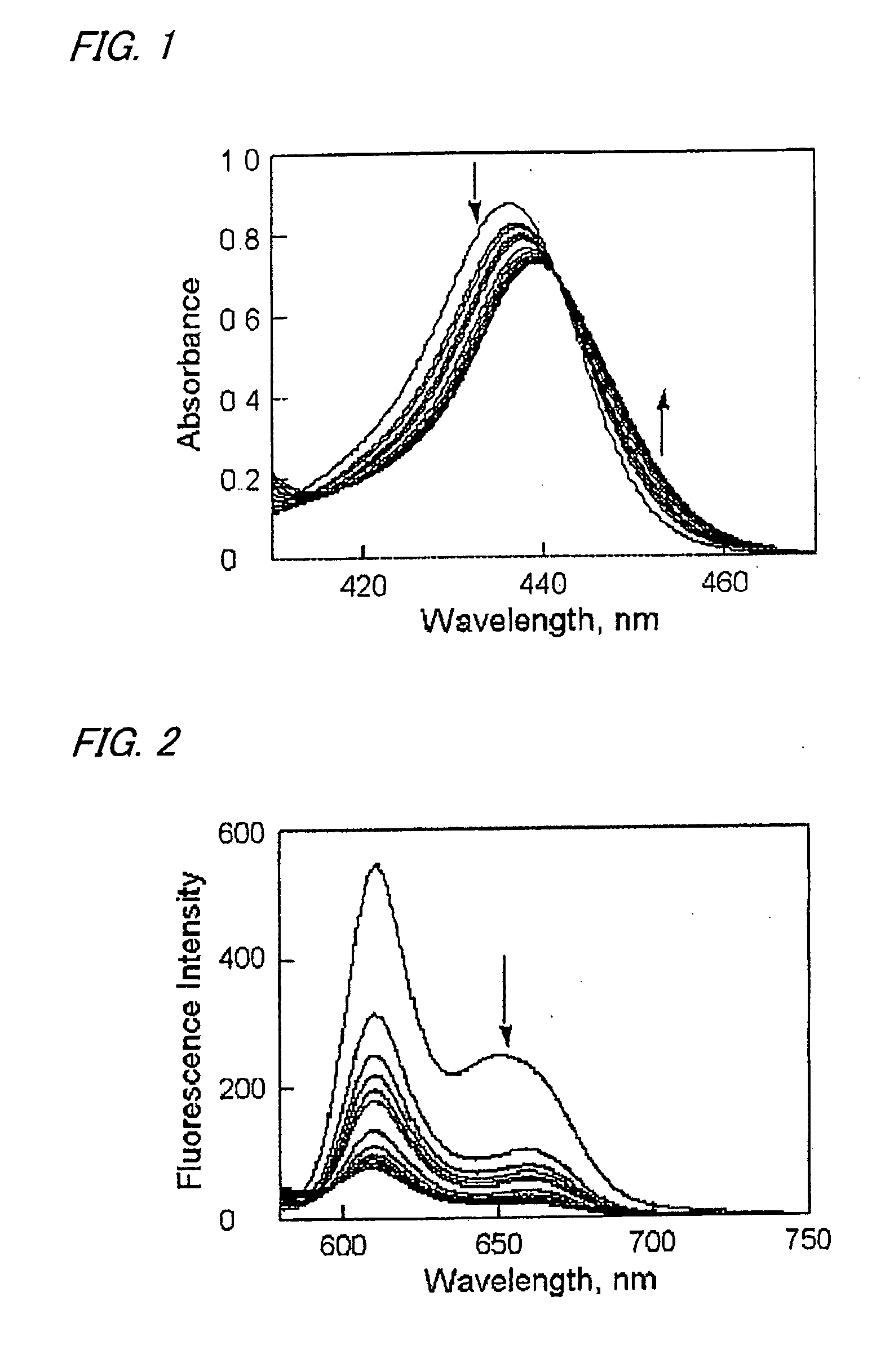
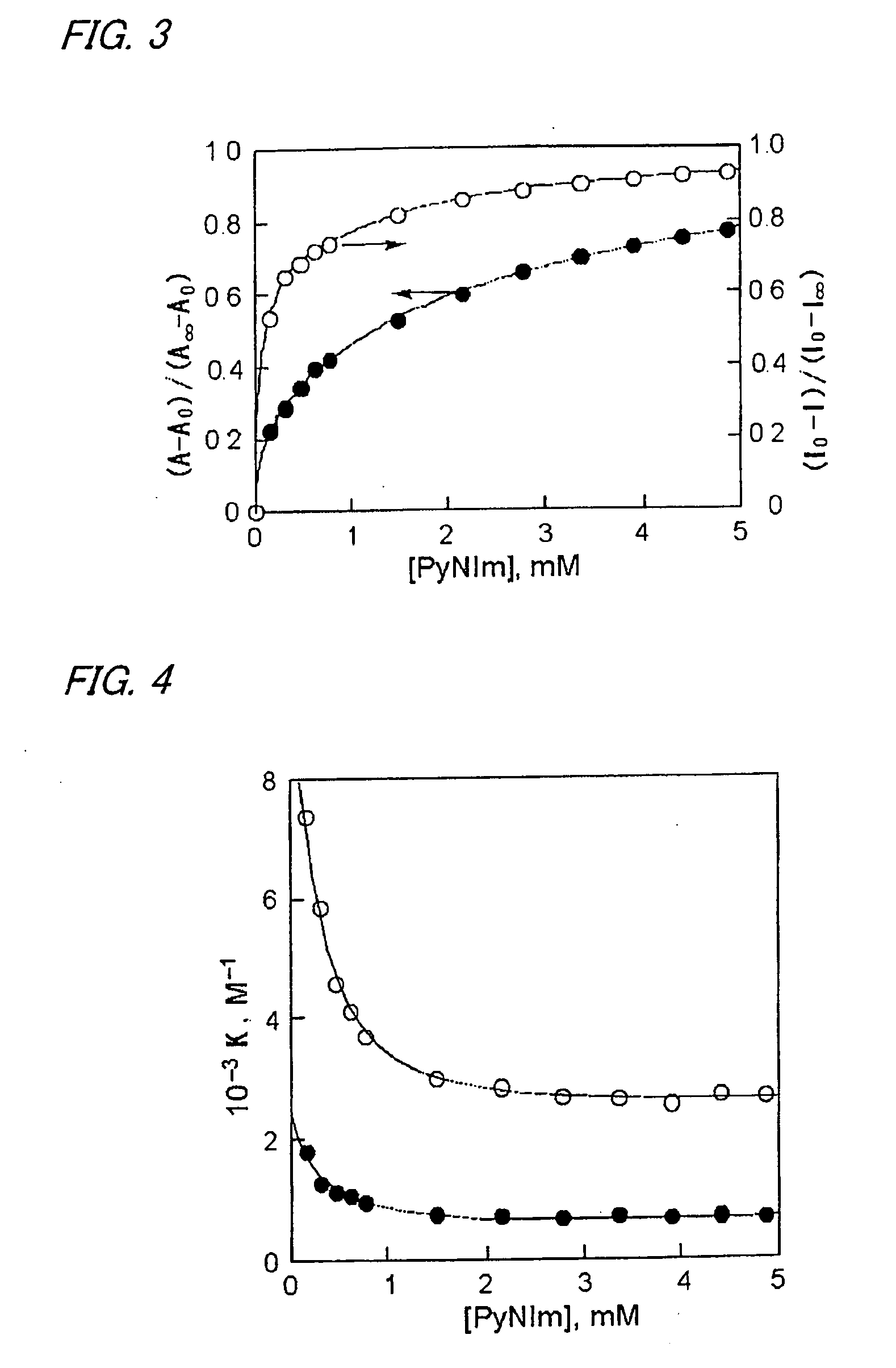
Supramolecular Complex of Pyridylnaphthalenediimide with Zinc Porphyrin Dendrimer Having Multiplicity of Artificial Photosynthetic Reaction Center
InactiveUS20070227590A1Improve light-harvesting capabilityImprove lighting effectsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSeparated stateDendrimer
A light energy conversion system having a multiplicity of artificial photosynthetic reaction centers and exhibiting a high light-harvesting capability and charge separation capability, constructed by the use of a zinc porphyrin dendrimer supramolecular complex formed by the use of a coordinate bond. Using a zinc porphyrin dendrimer as a spherical zinc porphyrin oligomer, a supramolecule with pyridylnaphthalenediimide was constructed. With respect to the zinc porphyrin dendrimer / pyridylnaphthalenediimide supramolecule, when photoexcitation of the zinc porphyrin was realized, a charge-separated state was generated by photoinduced electron transfer and the lifetime thereof was strikingly long, up to 830 microseconds.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Methods and systems for monitoring reactions
ActiveUS8465922B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSignal sourceSignal processing
Methods and systems for monitoring reactions by observing signals deriving from those reactions, using signal processing that allows differentiation between signals that are otherwise optically overlapping by conventional detection methods. Centroid determination is used to identify signal sources that are presenting confounding overlapping signals due to their physical proximity, and / or to identify discrete signals from different reaction centers.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Preparation process for nano composite of polyester / clay
The invention discloses a polyester / clay nano-composite preparing method, inserting polyethylene glycol terephthalate polycondensation catalyst and organic intercalation agent at the same time, to enlarge their space, beneficial to macromolecular chains of polyethylene glycol terephthalate entering into the montmorillonite layers, simultaneously the catalytic reaction centre in the layer, using large amount of polymerization heat to further open them, even dissociating them, for improving montmorillonite dispersive uniformity, and high thermal stability.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mass continuous safe production diazomethane reactor and working method thereof
ActiveCN101844063AReduce the risk of explosionSimple structureTransportation and packagingMixersLiquid wasteDiazald
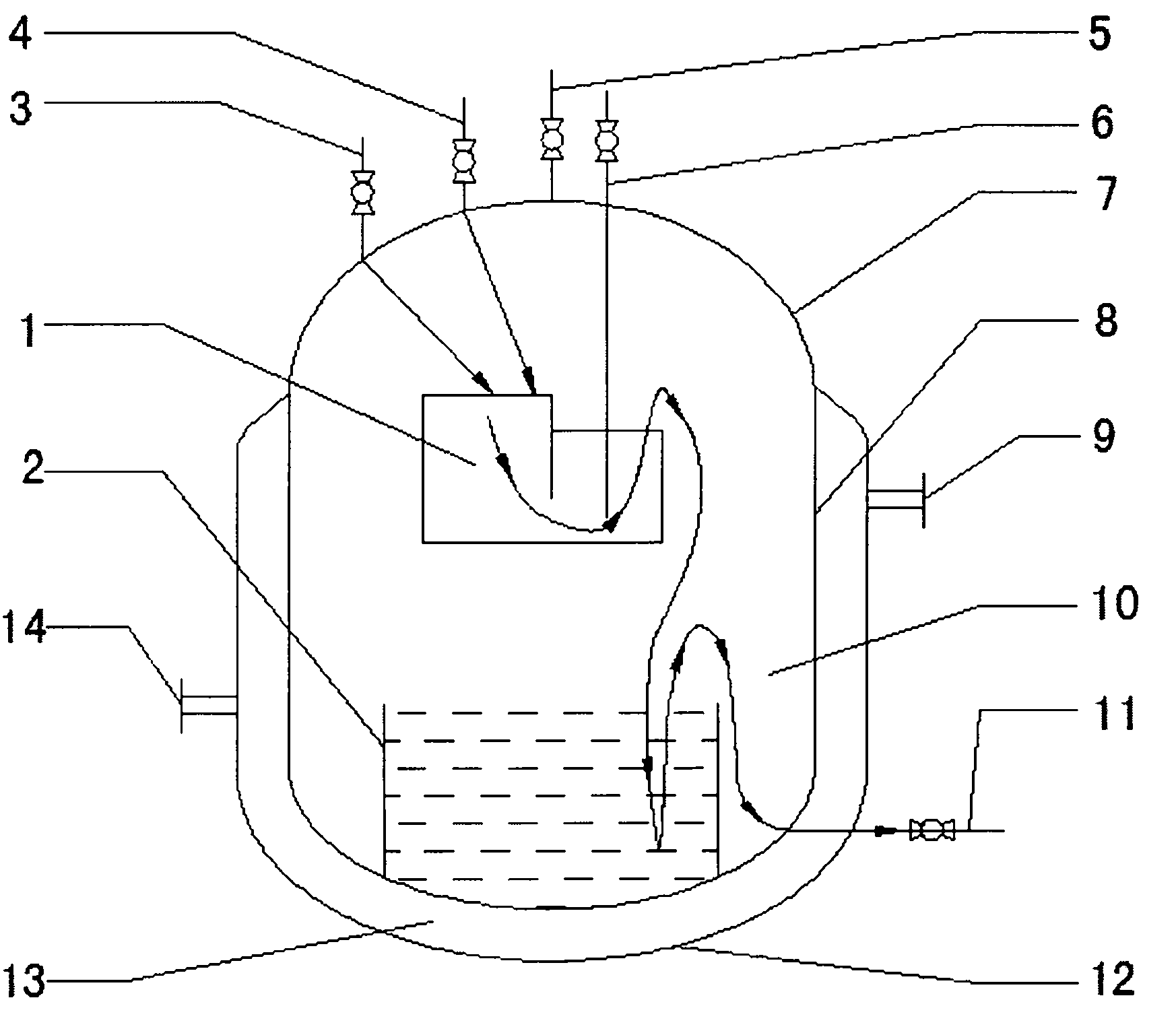
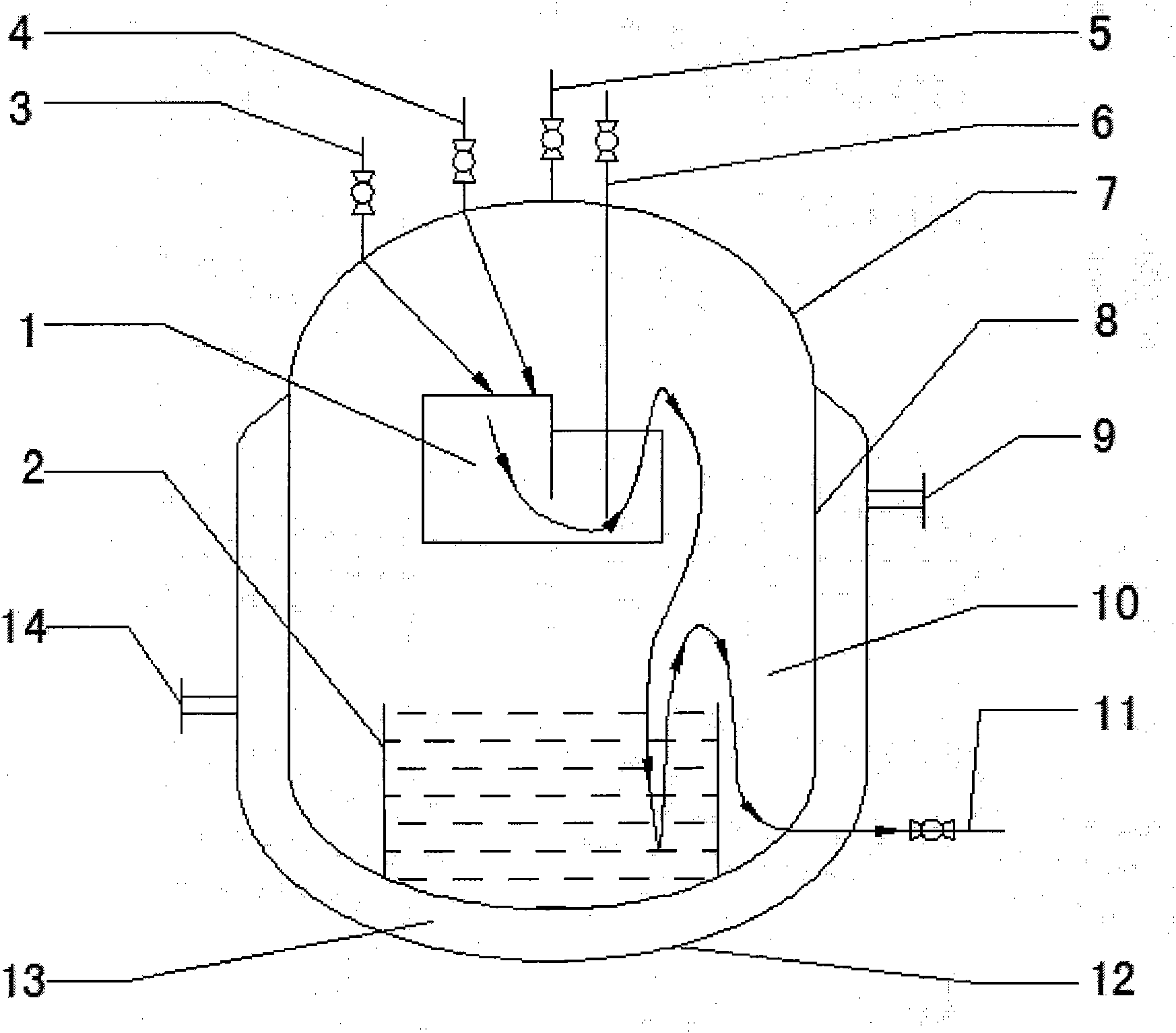
The invention relates to a mass continuous safe production diazomethane reactor, which consists of a cavity body, a reaction center I, a reaction center II, a raw material A dripping port, a raw material B dripping port, a N2 air suction bubbling tube, a diazomethane discharging tube, a cooling jacket, a cooling medium inlet, a cooling medium outlet and a waste liquid discharging tube, wherein the cavity body consists of an upper seal end a reactor wall and a lower seal end. Working method comprises the following steps that: (1) diazald and NaOH enter the reaction center I inside the cavity body of the reactor respectively through the raw material A dripping port and the raw material B dripping port to be contacted and reacted with each other to generate diazomethane; (2) reaction liquid inside the reaction center I slowly flows into the reaction center II from an overflow port above the reaction center I, the raw materials which are not completely reacted are continuously reacted with each other to generate the diazomethane gas during the process. The reactor has the advantages that: under the condition that the explosion danger is reduced, the device has simple structure, mass and continuous production of the diazomethane can be realized, and the diazomethane is free from being stored and can be directly used.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN
Microwave-assisted continuous flow large-scale polypeptide synthesis method and device
InactiveCN101538310ATo achieve the purpose of automatic controlLower activation energyPeptide preparation methodsSynthesis methodsContinuous flow
The invention provides a microwave-assisted continuous flow large-scale polypeptide synthesis method and a device thereof. The device mainly comprises a reaction kettle, a microwave reaction center and a connecting pipeline, and an on-line detection device and a power device are arranged on the connecting pipeline between the reaction kettle and the microwave reaction center. The invention leads reaction substances to flow cyclically between the reaction kettle and the microwave reaction center, thereby achieving the purposes of locally adding microwave radiation in a reaction system, shortening the reaction time, realizing the large-scale rapid synthesis of target products and increasing the yield of polypeptides to kilograms or tens of kilograms.
Owner:CHINESE PEPTIDE CO
Preparation of copper-bismuth-silicon dioxide catalyst
InactiveCN106111148AImprove stabilityEnhanced interactionOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPhysical chemistryAlkyne
The invention relates to the preparation of a copper bismuth / silicon dioxide catalyst. It is characterized in that a copper-bismuth / silicon dioxide catalyst is prepared by a "one-pot method", the content of copper oxide is 10-40%, the content of bismuth is 1-10%, and the rest is silicon dioxide. Copper-bismuth species are highly dispersed on the inner and outer surfaces of silica, which improves the reaction center of the catalyst, enhances the wear resistance of the catalyst, and reduces the desolvation of copper ions. In the application of alkynylation reaction to synthesize 1,4-butynediol, the copper-bismuth catalyst has good activity, high selectivity, and low amount of copper species desolvation.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
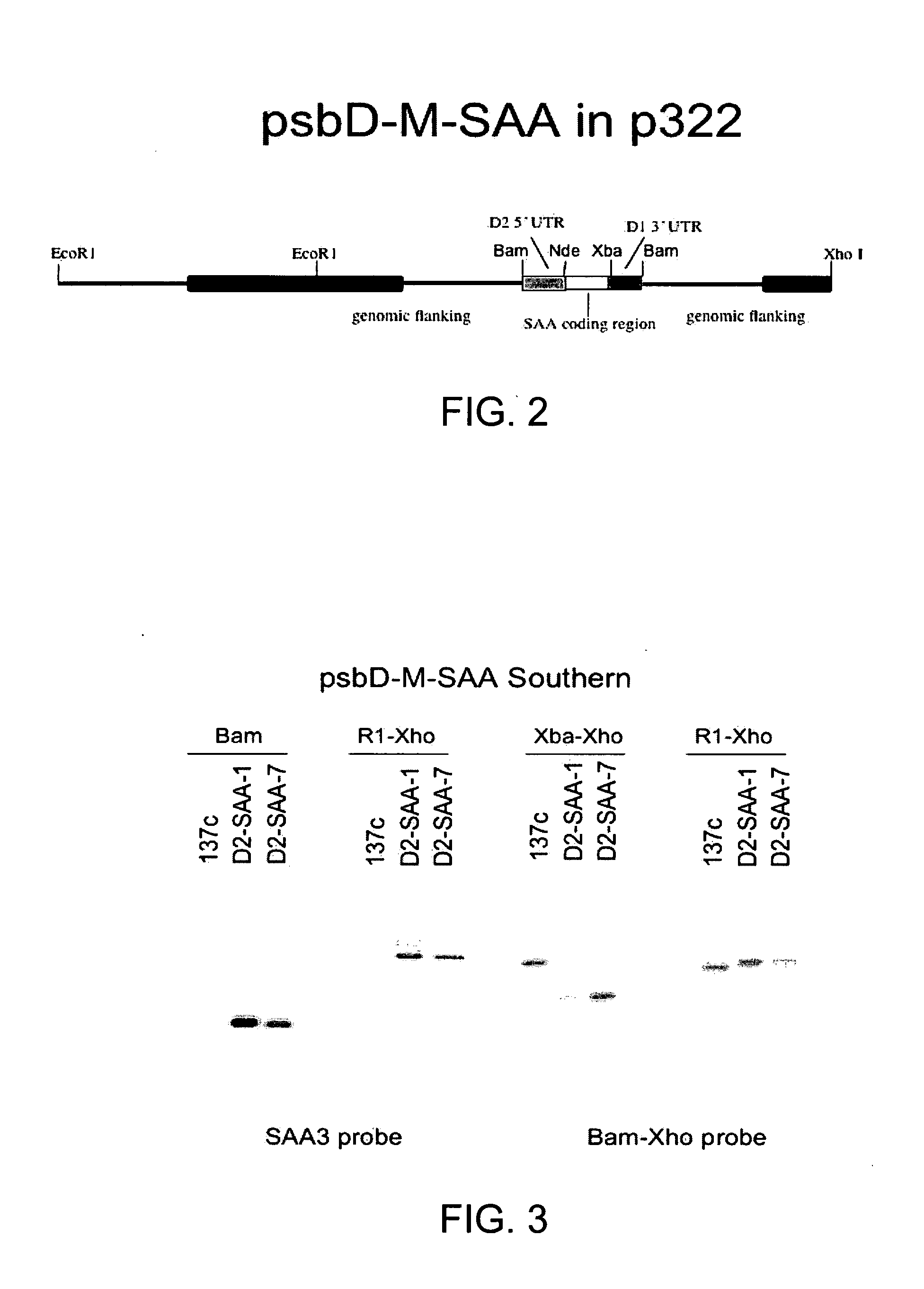
Robust expression of a bioactive mammalian protein in chlamydomonas chloroplast
InactiveUS20070298050A1Robust expressionEliminate competitionBiocideUnicellular algaeHeterologousMammal
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer chloroplast comprising heterologous mammalian genes via a direct replacement of chloroplast Photosystem II (PSII) reaction center protein coding regions to achieve expression of combinant protein above 5% of total protein. When algae is used, algal expressed protein is produced predominantly as a soluble protein where the functional acitivity of the peptide is intact. As the host algae is edible, production of biologics in this organism for oral delivery or proteins / peptides, especially gut active proteins, without purification is disclosed.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for predicting enzyme-catalyzed reactions
InactiveUS8401797B2Chemical property predictionChemical processes analysis/designSupport vector machineMetabolite
The reactivity of given metabolites is assessed using selected empirical atomic properties in the potential reaction center. Metabolic reactions are represented as biotransformation rules. These rules are generalized from the patterns in reactions. These patterns are not unique to reactants but are widely distributed among metabolites. Using a metabolite database, potential substructures are identified in the metabolites for a given biotransformation. These substructures are divided into reactants or non-reactants, depending on whether they participate in the biotransformation or not. Each potential substructure is then modeled using descriptors of the topological and electronic properties of atoms in the potential reaction center; molecular properties can also be used. A Support Vector Machine (SVM) or classifier is trained to classify a potential reactant as a true or false reactant using these properties.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Robust expression of a bioactive mammalian protein in chlamydomonas chloroplast
InactiveUS7678561B2Robust expressionEliminate competitionBiocideUnicellular algaeHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
Methods and compositions are disclosed to engineer chloroplast comprising heterologous mammalian genes via a direct replacement of chloroplast Photosystem II (PSII) reaction center protein coding regions to achieve expression of recombinant protein above 5% of total protein. When algae is used, algal expressed protein is produced predominantly as a soluble protein where the functional activity of the peptide is intact. As the host algae is edible, production of biologics in this organism for oral delivery or proteins / peptides, especially gut active proteins, without purification is disclosed.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Preparation for removing epiphytic algae from alga body and application thereof
InactiveCN102246817AAvoid Metabolic DisordersNo toxic effectBiocideAnimal repellantsMarine algaesShikimic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of marine organisms, and relates to a preparation for removing epiphytic algae from an alga body and an application thereof. The preparation for removing adherent unwanted algae from an alga body is a plant herbicide. The preparation for removing adherent unwanted algae from an alga body is mixed with seawater, and then the alga body is immersed in seawater to remove adherent unwanted algae, wherein 1-5 g of preparations are added into 1 liter of seawater, and the immersion time is 5-10 minutes. The preparation for inhibiting epiphytic algae of theinvention is a plant herbicide; the action mechanism is that primary reactions of photosynthesis of epiphytic unwanted algae is inhibited, and PSII and the shikimic acid cycle at the photosynthetic reaction center, which prevent metabolic disorder due to drug absorption of glue-producing algae, are mainly inhibited; the preparation of the invention has strong specificity, is economical and effective, has simple operation; epiphytic unwanted algae on the alga body are observed to be withered, shrunk, dry and dead within several days; the purposes of inhibiting epiphytic unwanted algae and keeping glue-producing algae alive are reached; and the contaminated glue-producing algae are recovered to have smooth surfaces and can grow healthily again.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-biofilm material grafted with high-density acid groups for catalyzing bacterium cracking, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an anti-biofilm material grafted with high-density acid groups for catalyzing bacterium cracking, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: activating a material by using plasma to make the material generate surface free radicals; and exposing the material to air to generate active oxygen reaction centers, adding the material into an excessive amount of an acid group-containing unsaturated monomer, starting a surface polymerization reaction, and cleaning and drying the obtained material after the reactionis finished in order to obtain the anti-biofilm material with the surface being grafted with the high-density acid groups for catalyzing bacterium cracking. The high-density acid groups grafted on thesurface of the obtained material can generate superhydrophilic surface energy to catalyze the bacterium cracking in order to make the material have an antibacterial function, especially an anti-biofilm function, and the material adopts a bacterial lipid film as the target spot. Quaternary ammonium salts, metal ions and other antibacterial agents having large biotoxicity and being unfriendly to the environment are not used in the invention, so the material can be widely applied. Antibiotic embedding is avoided, and the risks of drug resistance, generation of super bacteria and emergency and out-of-control of epidemic diseases are reduced.
Owner:杭州中科理化生物医药技术有限公司
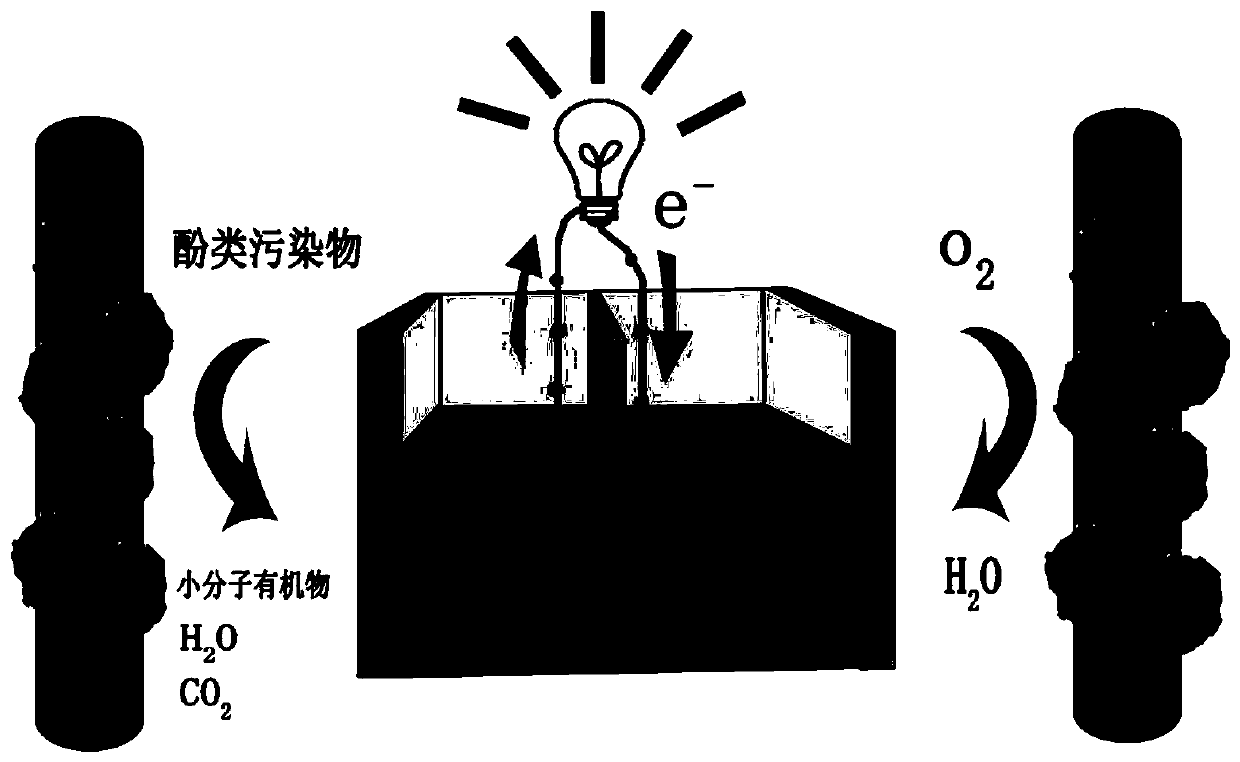
Phenolic sewage power generation device based on single-enzyme inorganic composite nanoflowers and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110085877AHigh catalytic activityLarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesOxygenProcess design
The invention discloses a phenolic sewage power generation device based on single-enzyme inorganic composite nanoflowers and a preparation method and an application thereof. The device includes a cathode electrode, an anode electrode and a cathode and cathode bipolar chamber, wherein the cathode electrode and the anode electrode are graphite felt electrodes modified by the laccase inorganic composite nanoflowers (AuNPs / Chit-RGO / Lac nanoflower) loaded by gold nanoparticles / chitosan-reduced graphene oxide, substrates are oxygen and phenolic contaminants, and the substrates in the bipolar chamberare catalyzed by copper ions of different valences in the laccase catalytic reaction center. The device is advantaged in that an electrode material has good holding capacity, fuel cells with the samepositive and negative electrodes are designed through utilizing different valence states of the laccase reaction center, and problems of poor fuel cell enzyme immobilization effect, low output current and complicated process design in the prior art are solved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
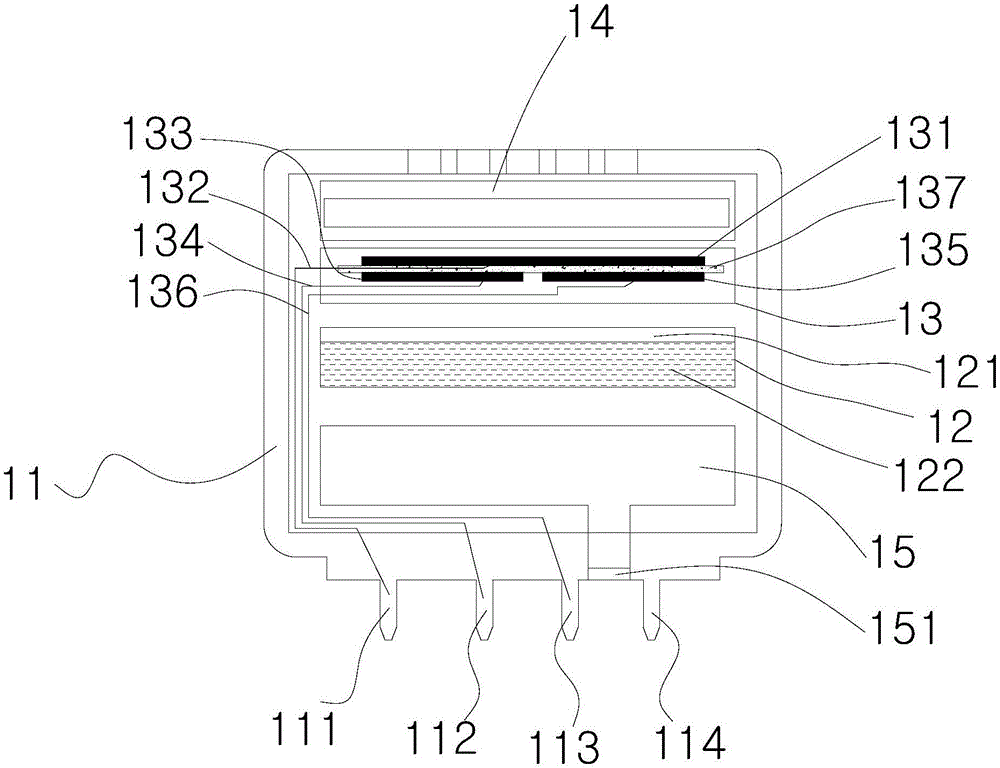
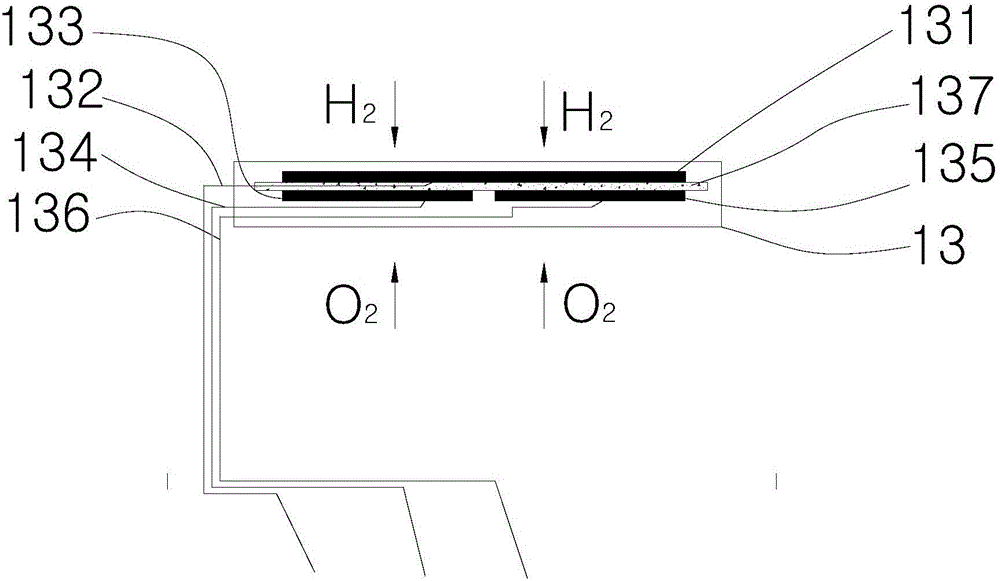
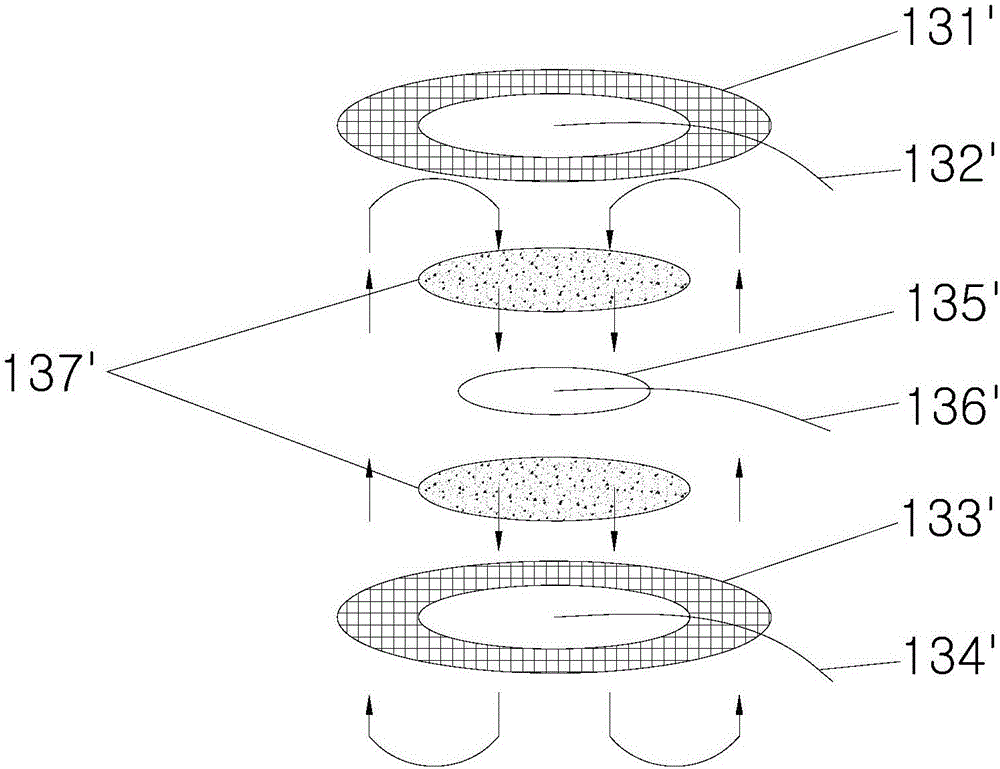
Hydrogen sensor
InactiveCN106596684APrevent leakageAvoid electrolyte drying upMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansProtonHydrogen sensor
The invention relates to a hydrogen sensor comprising a sensor shell and a gas reaction center in the sensor shell. The gas reaction center comprises a work electrode, a counter electrode, a reference electrode and solid electrolyte. The work electrode, the counter electrode and the reference electrode are fixed to the electrolyte. The solid electrolyte is used in the hydrogen sensor, because the electrolyte is solid and the work electrode, the counter electrode and the reference electrodes are fixed to the electrolyte and can make full contact with the electrolyte, the contact area of the electrodes and the electrolyte is increased, the whole electrodes can conduct proton transfer, the poor contact phenomenon between the electrolyte and the electrodes and the sensor liquid leakage or electrolyte dryout phenomenon can be avoided, and response speed of the hydrogen sensor is greatly increased.
Owner:ASENSOR TECH
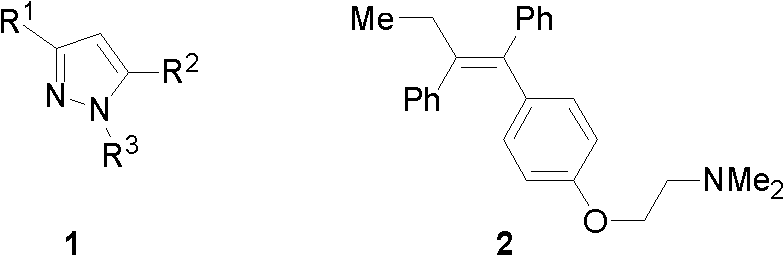
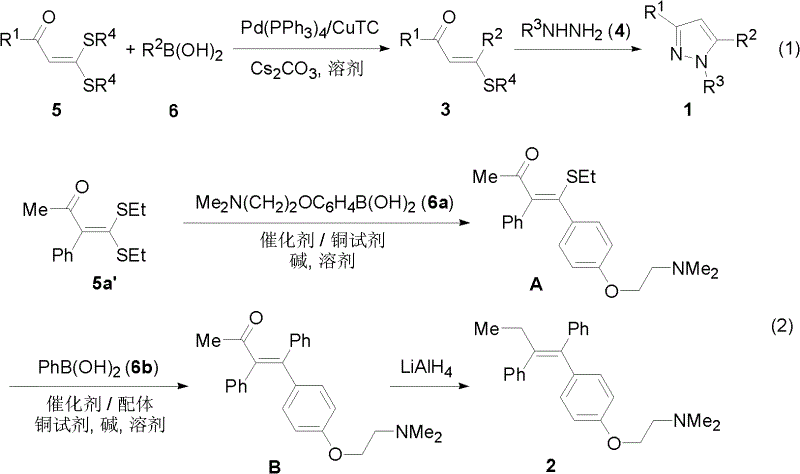
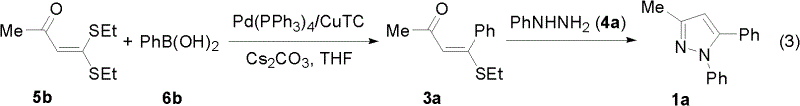
Preparation method of tetra-substituted olefin and its pyrazole derivative
InactiveCN102617472AWith structural diversityEasy to manufactureOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationStructural diversityReaction centre
The invention discloses a method for preparing a pyrazole derivative and a tetra-substituted olefin (Z)-Tamoxifen which is a clinical drug for treating the breast cancer from a polysubstituted sulfo-olefin. The pyrazole derivative is prepared by carrying out a condensation cyclization reaction on a raw material alpha-oxoketone monothioacetal which is easy to prepare and has a structure diversity and various reaction centers and a nucleophilic reagent hydrazine at a reflux temperature; and the tetra-substituted olefin (Z)-Tamoxifen is prepared by carrying out a coupling reaction on the raw material alpha-oxoketone monothioacetal and arylboric acid at 50DEG under the catalysis of Pd. Compared with reported preparation methods of the pyrazole derivative and (Z)-Tamoxifen, the preparation method makes products have the advantages of good regioselectivity and stereoselectivity, easily available raw material, simple operation, mild preparation reaction conditions, and high efficiency.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
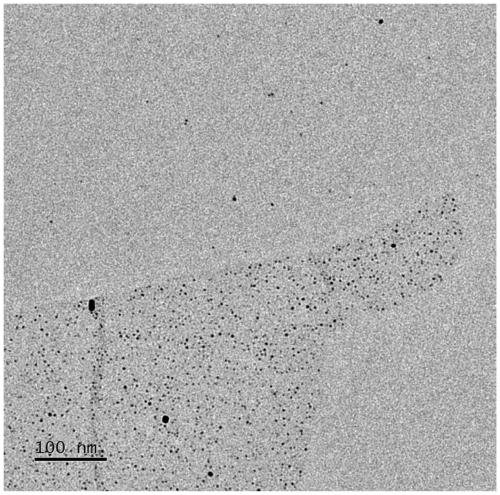
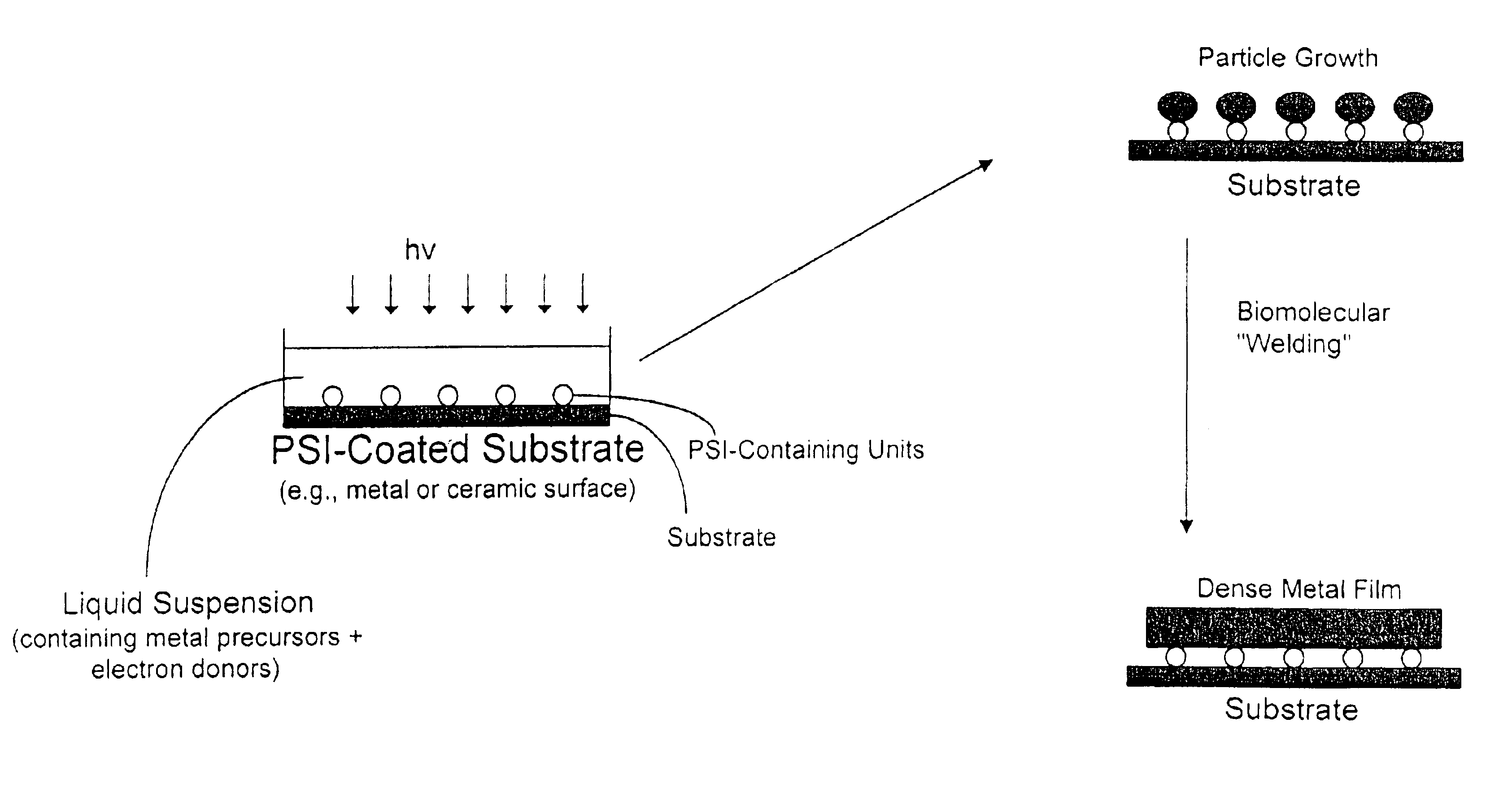
Photobiomolecular deposition of metallic particles and films
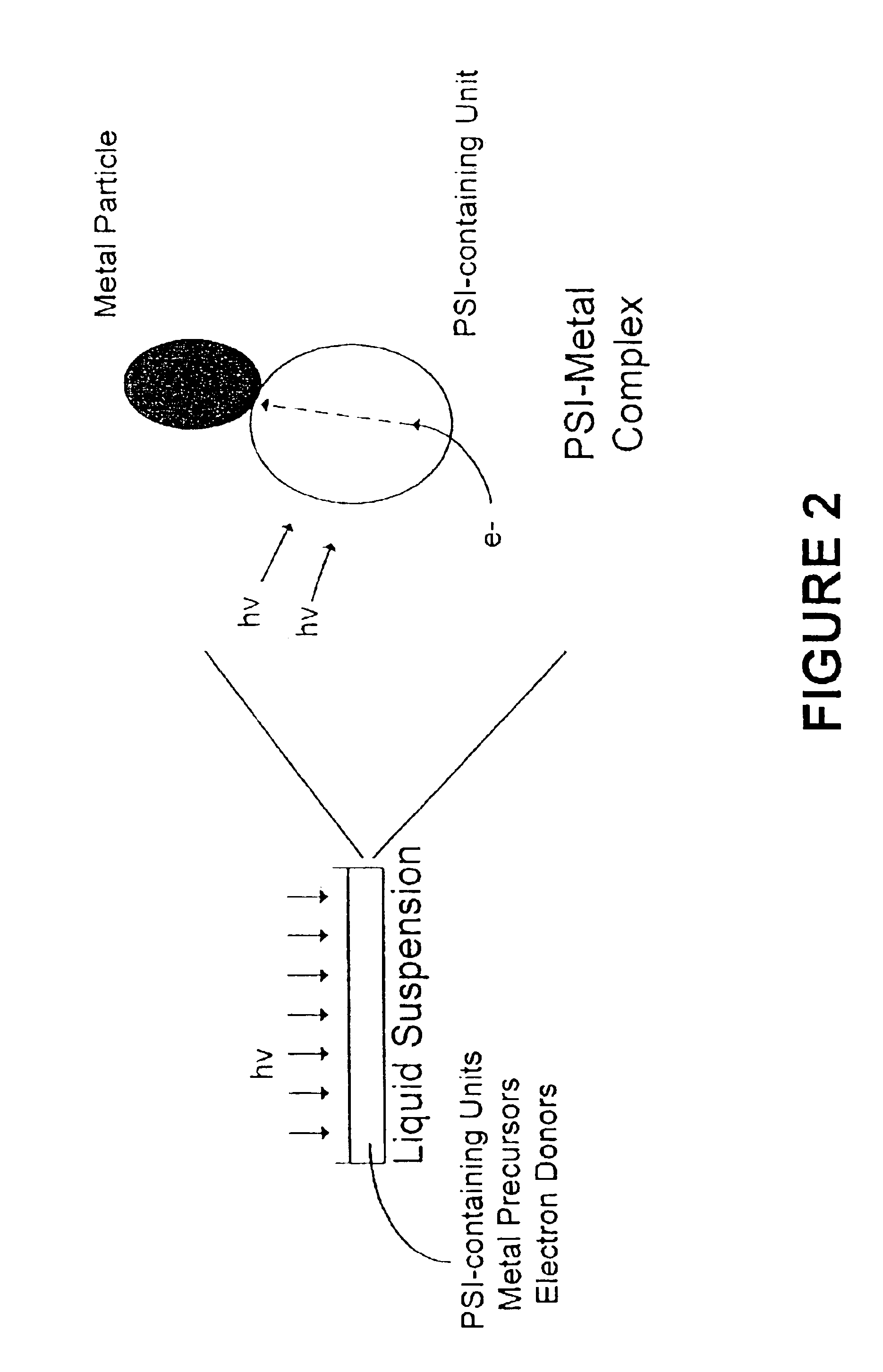
The method of the invention is based on the unique electron-carrying function of a photocatalytic unit such as the photosynthesis system I (PSI) reaction center of the protein-chlorophyll complex isolated from chloroplasts. The method employs a photo-biomolecular metal deposition technique for precisely controlled nucleation and growth of metallic clusters / particles, e.g., platinum, palladium, and their alloys, etc., as well as for thin-film formation above the surface of a solid substrate. The photochemically mediated technique offers numerous advantages over traditional deposition methods including quantitative atom deposition control, high energy efficiency, and mild operating condition requirements.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Mass continuous safe production diazomethane reactor and working method thereof
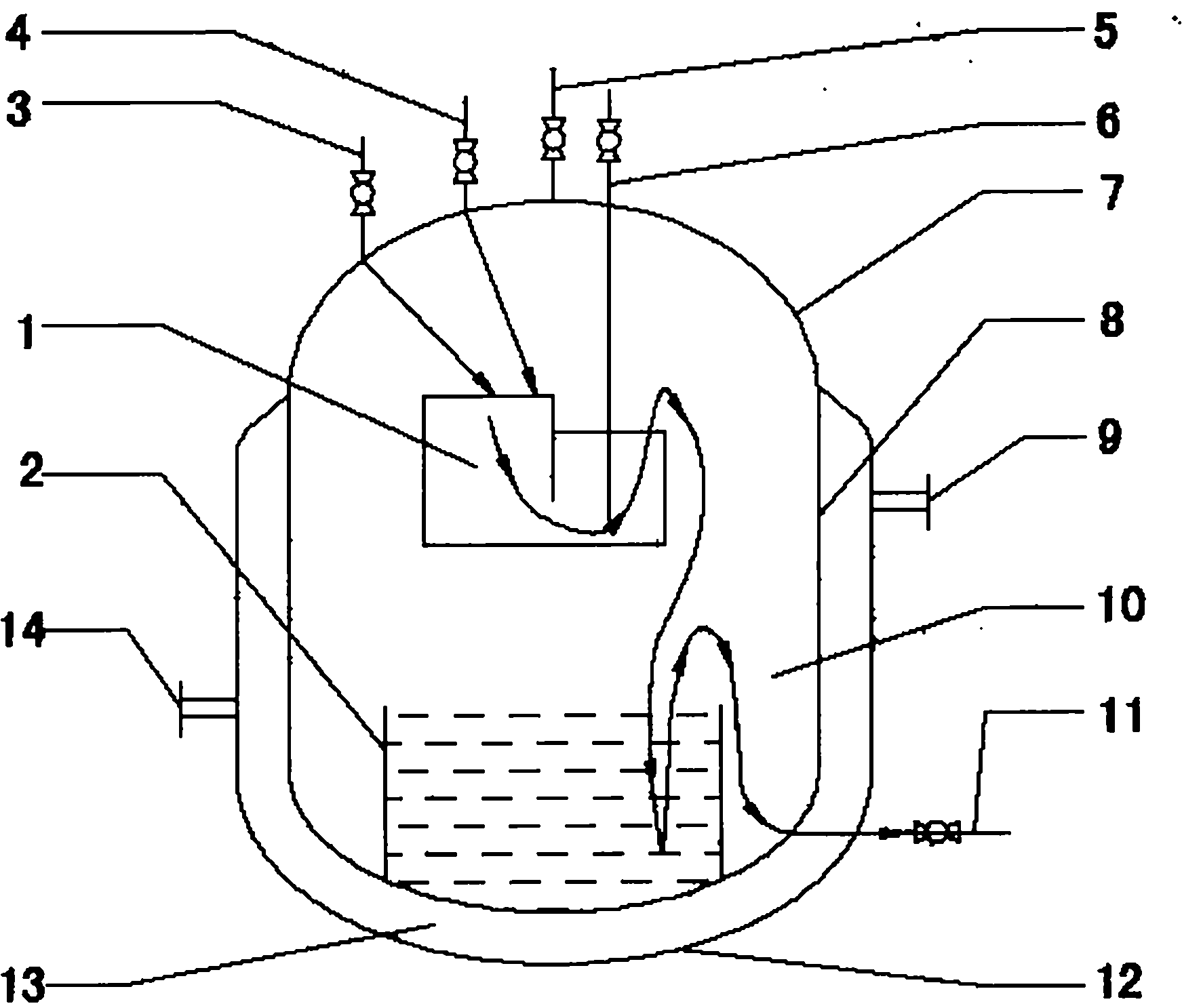
ActiveCN101844063BReduce the risk of explosionSimple structureTransportation and packagingMixersEngineeringReaction centre
The invention relates to a mass continuous safe production diazomethane reactor, which consists of a cavity body, a reaction center I, a reaction center II, a raw material A dripping port, a raw material B dripping port, a N2 air suction bubbling tube, a diazomethane discharging tube, a cooling jacket, a cooling medium inlet, a cooling medium outlet and a waste liquid discharging tube, wherein the cavity body consists of an upper seal end a reactor wall and a lower seal end. Working method comprises the following steps that: (1) diazald and NaOH enter the reaction center I inside the cavity body of the reactor respectively through the raw material A dripping port and the raw material B dripping port to be contacted and reacted with each other to generate diazomethane; (2) reaction liquid inside the reaction center I slowly flows into the reaction center II from an overflow port above the reaction center I, the raw materials which are not completely reacted are continuously reacted with each other to generate the diazomethane gas during the process. The reactor has the advantages that: under the condition that the explosion danger is reduced, the device has simple structure, mass and continuous production of the diazomethane can be realized, and the diazomethane is free from being stored and can be directly used.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN
Structural nucleic acid guided chemical synthesis
ActiveUS20110045990A1Increase opportunitiesImprove responseSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesChemical synthesisChemical compound
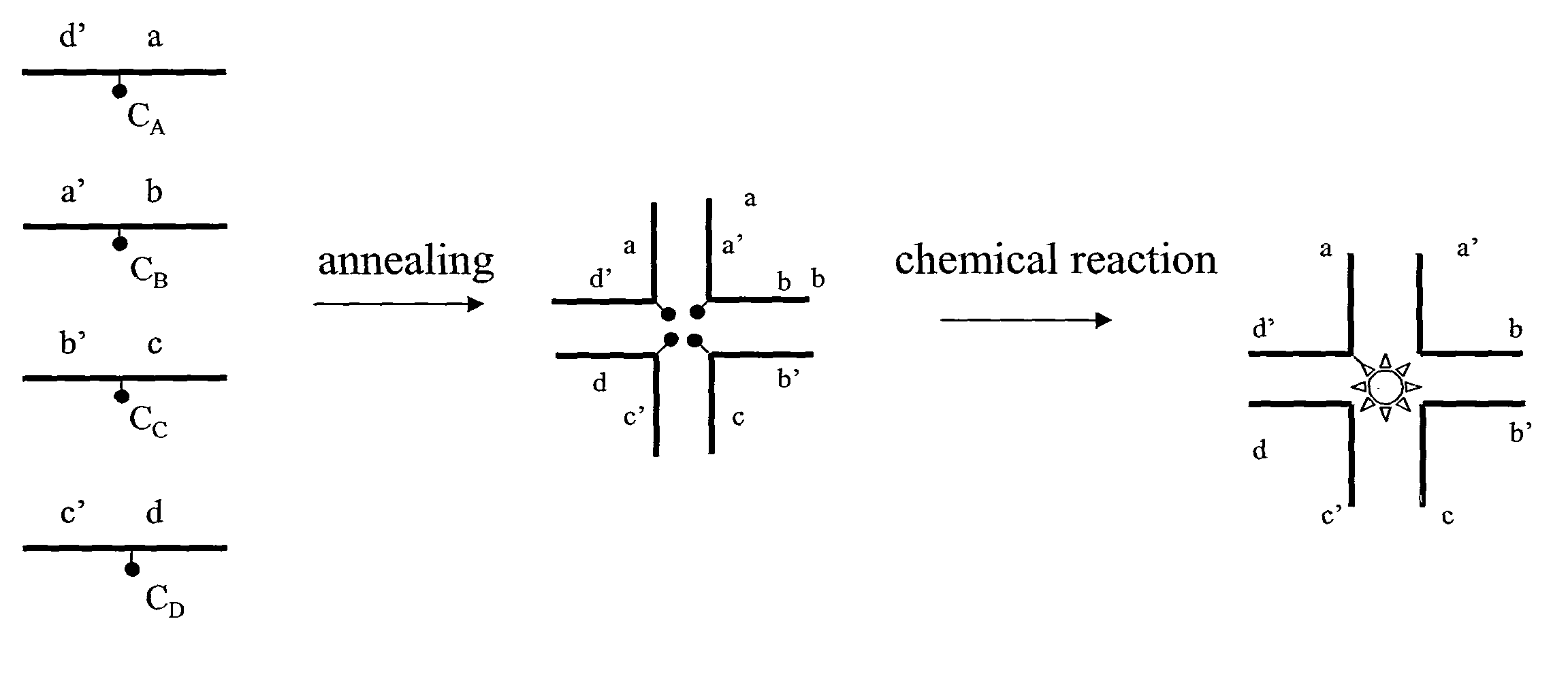
Disclosed is a composition comprising a nucleic acid and a chemical compound, said composition forming a star structure defining 3 or more stems extending from a reaction center. The stems are formed by a nucleic acid duplex and the chemical compound has been formed in the reaction center as the reaction product of 3 or more chemical groups.The advantage of the composition is that a close proximity is provided between the chemical groups in the reaction center, thereby promoting a reaction. The invention also relates to a method for preparation of the composition. The advantage of the method is that it does not require the pre-synthesis of a large number of templates and that it is not dependent upon codon / anti-codon recognition for an encoded molecule to be formed.
Owner:VIPERGEN
Structural nucleic acid guided chemical synthesis
ActiveUS8202823B2Increase opportunitiesImprove responseSugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsChemical synthesisChemical compound
Owner:VIPERGEN
Preparation method of adhesive
InactiveCN102382619AEasily brokenImprove water resistanceProtein adhesivesGlue/gelatin preparationAcetic acidAdhesive
The invention discloses a preparation method of an adhesive. The preparation method comprises adding isolated soy protein into water, enabling the adding ratio to be 10% to 30% by weight, obtaining isolated soy protein solution by even mixing, placing the isolated soy protein solution in an ultrasonic cleaning device and performing ultrasonic processing for 40 minutes to 50 minutes at the temperature of 50 DEG C to 60 DEG C, adding sodium dodecyl sulfate into the isolated soy protein solution, enabling the adding ratio to be 1% to 8% by weight, mixing for 1 hour to 2 hours, then adding in urea and bamboo acetic acid, mixing for 1 hour to 2 hours, enabling the added urea to be 5% to 12% by weight and the added bamboo acetic acid to be 1% to 5% by weight, and obtaining the adhesive by even mixing. The preparation method of the adhesive is a modified process of an isolated soy protein adhesive, ultrasonic waves enable the reaction center of soy protein to be exposed, and chemical modification of sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea are combined to achieve enhancement of bonding strength and hydrophobicity and improvement of water resistance of the adhesive, and the biological antiseptic bamboo acetic acid is combined, thereby improving antibiotic performance.
Owner:DALIAN JIARUILONG TECH
Preparing method of nanometer alumina reinforced A356 aluminum alloy
The invention relates to a preparing method of nanometer alumina reinforced A356 aluminum alloy. The preparing method comprises the following steps of: adsorbing Sn2+ ions on the surface of nanometerAl2O3np by using sensitizing liquid in an acidic environment, obtaining shell-type particles with nanometer Al2O3np as a core and Pd-Sn adsorbed on the surface as a chemical plating reaction center ina later activation process, and finally obtaining Cu-coated Al2O3np particles through chemical plating. Obtained powder and pure aluminum powder are mixed according to a certain proportion and are cold pressed to obtain prefabricated blocks. The prefabricated blocks are added into A356 aluminum alloy melt as required, Cu-coated Al2O3np is dispersed under the action of a high-energy ultrasonic instrument, grains are refined by high-energy ultrasonic vibration in the casting solidification process, and the whole process is carried out in a gas atmosphere. The product prepared by the method hasexcellent mechanical properties, and meanwhile the preparing method has the advantages of being simple, safe, low in cost, easy to apply and controllable.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Fusion nuclear energy collection system
The invention discloses a fusion nuclear energy collection system, which consists of an energy storage body, automatic doors, a fusion reaction center, a liquid container and liquid, wherein the liquid is contained in the liquid container; the energy storage body is arranged in the liquid container; a plurality of automatic doors are arranged on the energy storage body; and the fusion reaction center is arranged in the energy storage body. By the scheme, huge uncontrollable energy generated by nuclear fusion can drive the high-pressure liquid in the energy storage body to flow out of the energy storage body to form intense pressure for human beings to use.
Owner:任永斌
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com