Patents
Literature
81results about How to "Wide support" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
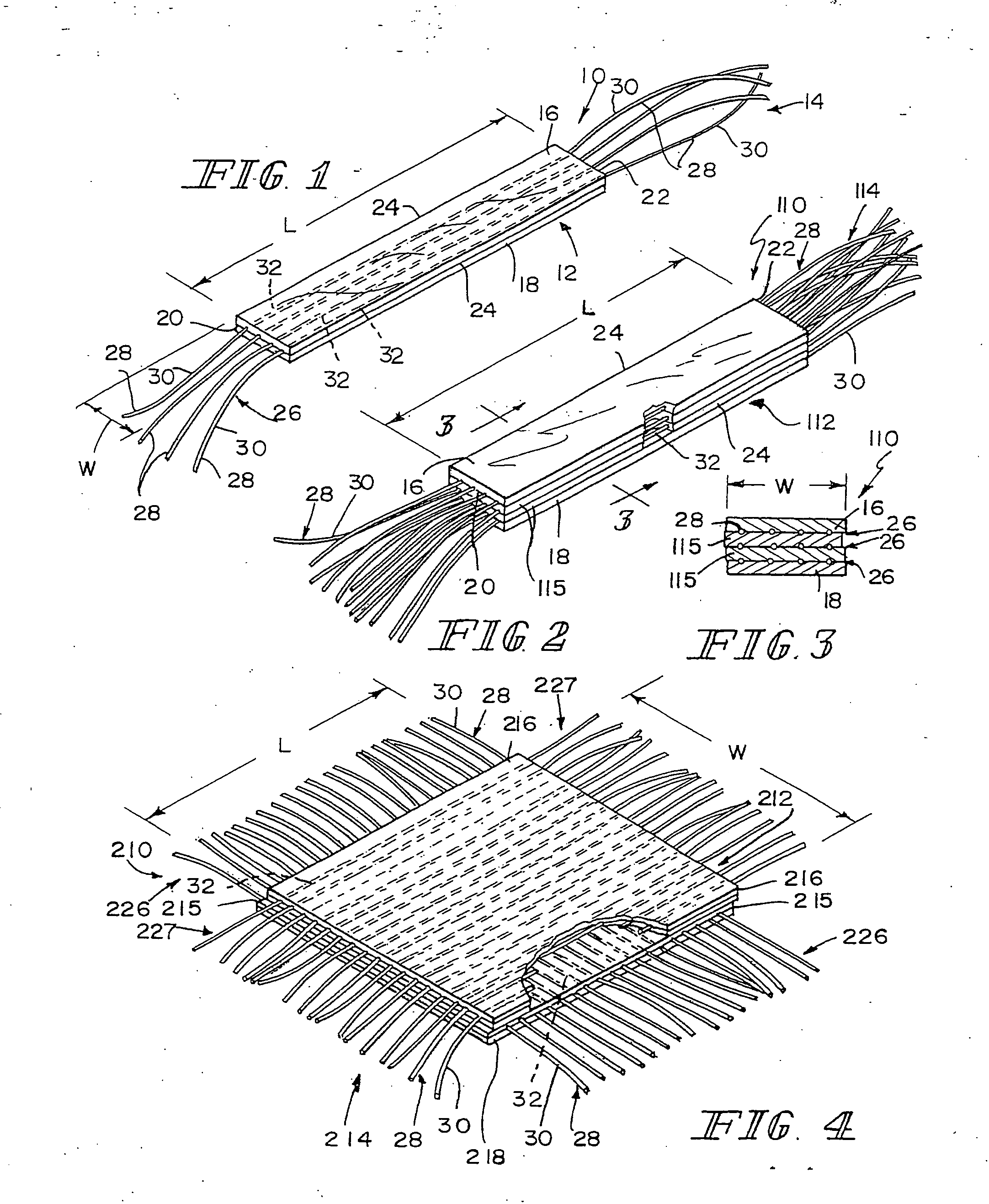
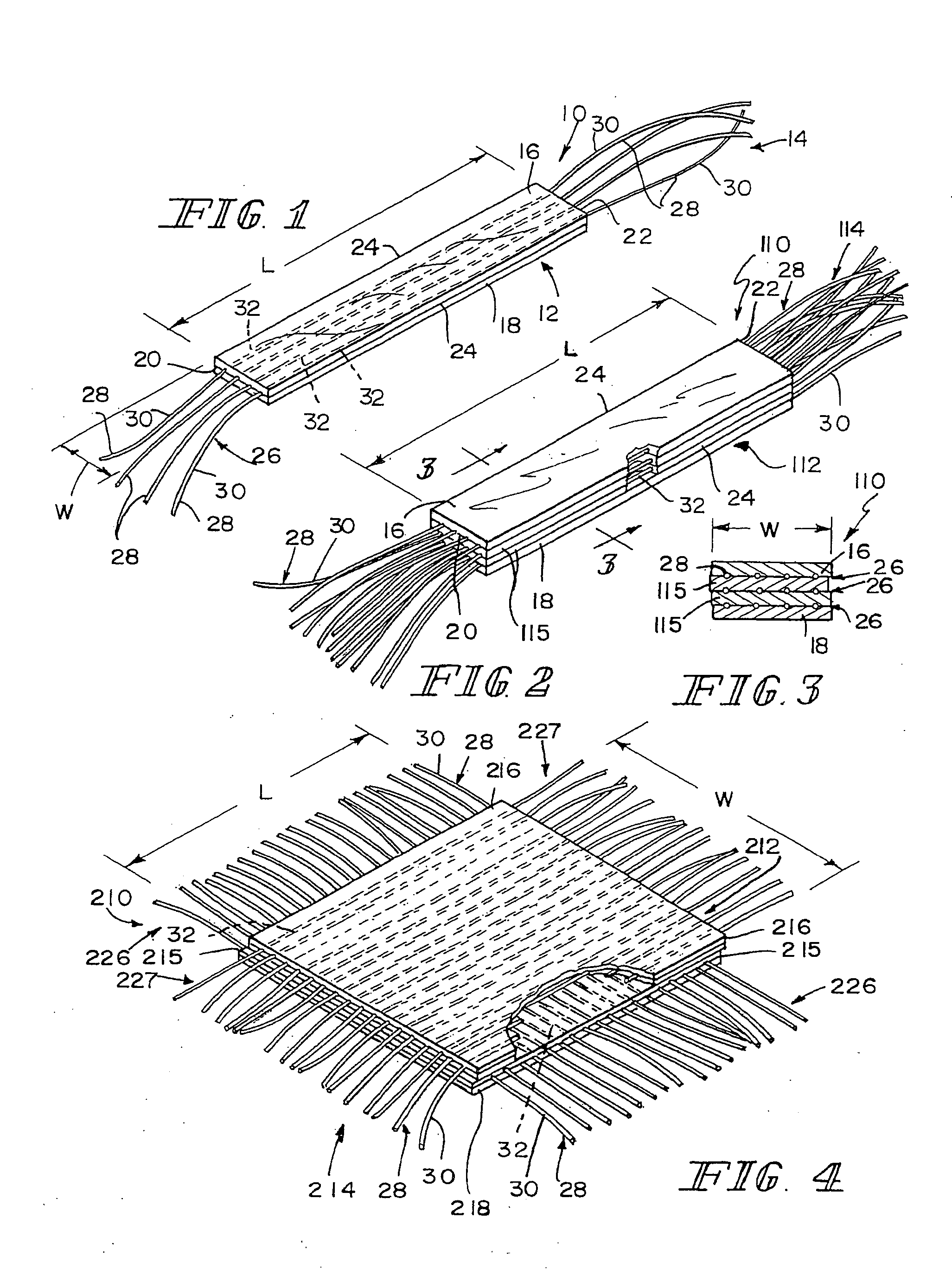
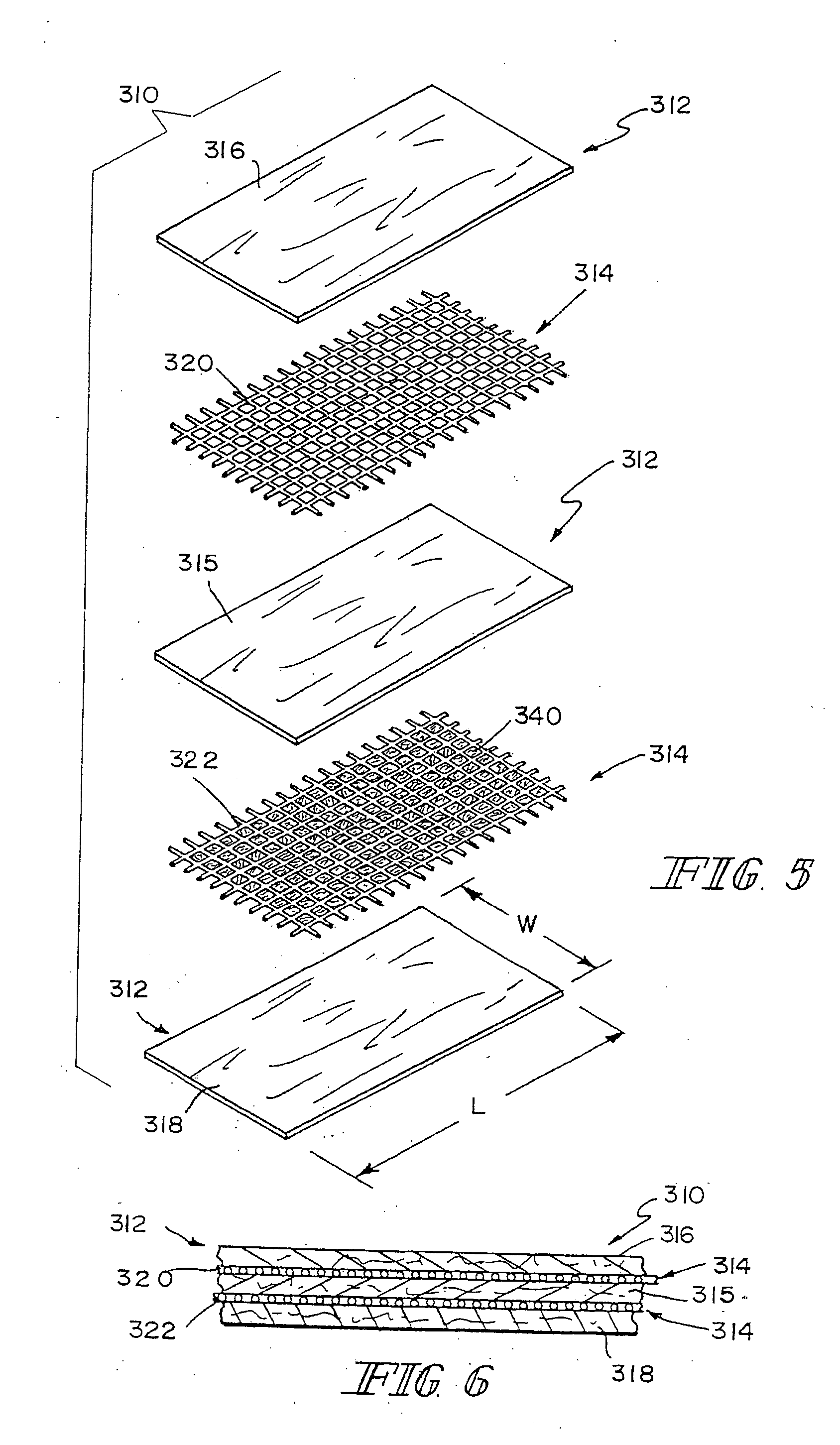
Hybrid biologic-synthetic bioabsorbable scaffolds
ActiveUS8366787B2Increase surface areaGood mechanical integritySuture equipmentsBone implantBioabsorbable scaffoldCell-Extracellular Matrix
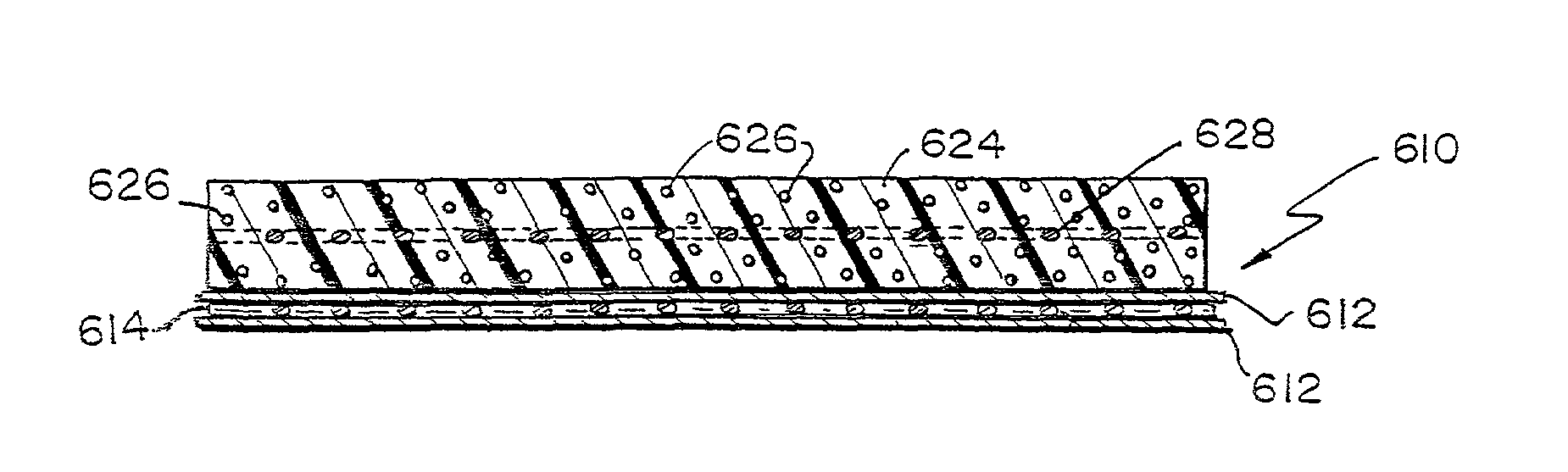
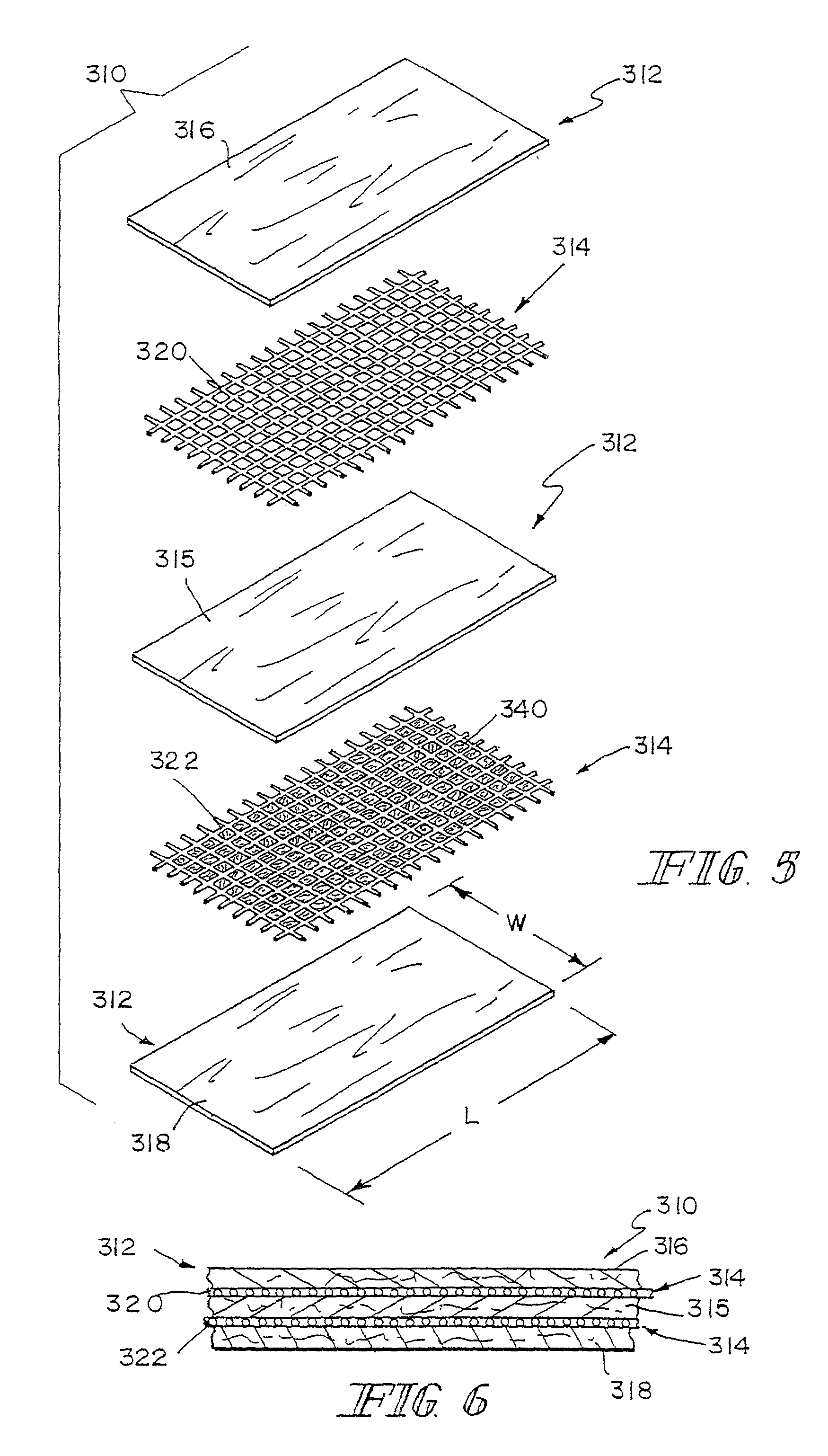
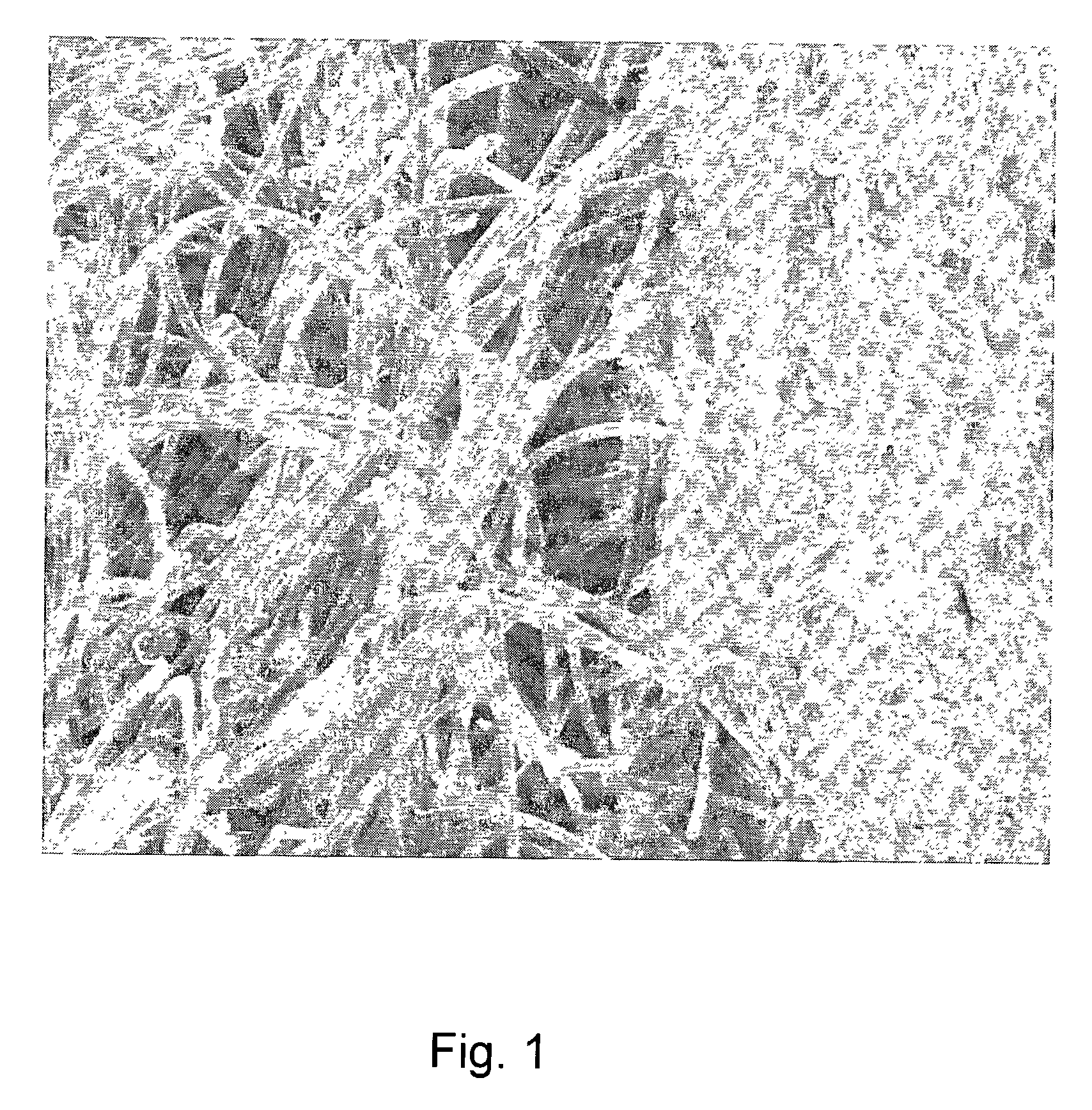
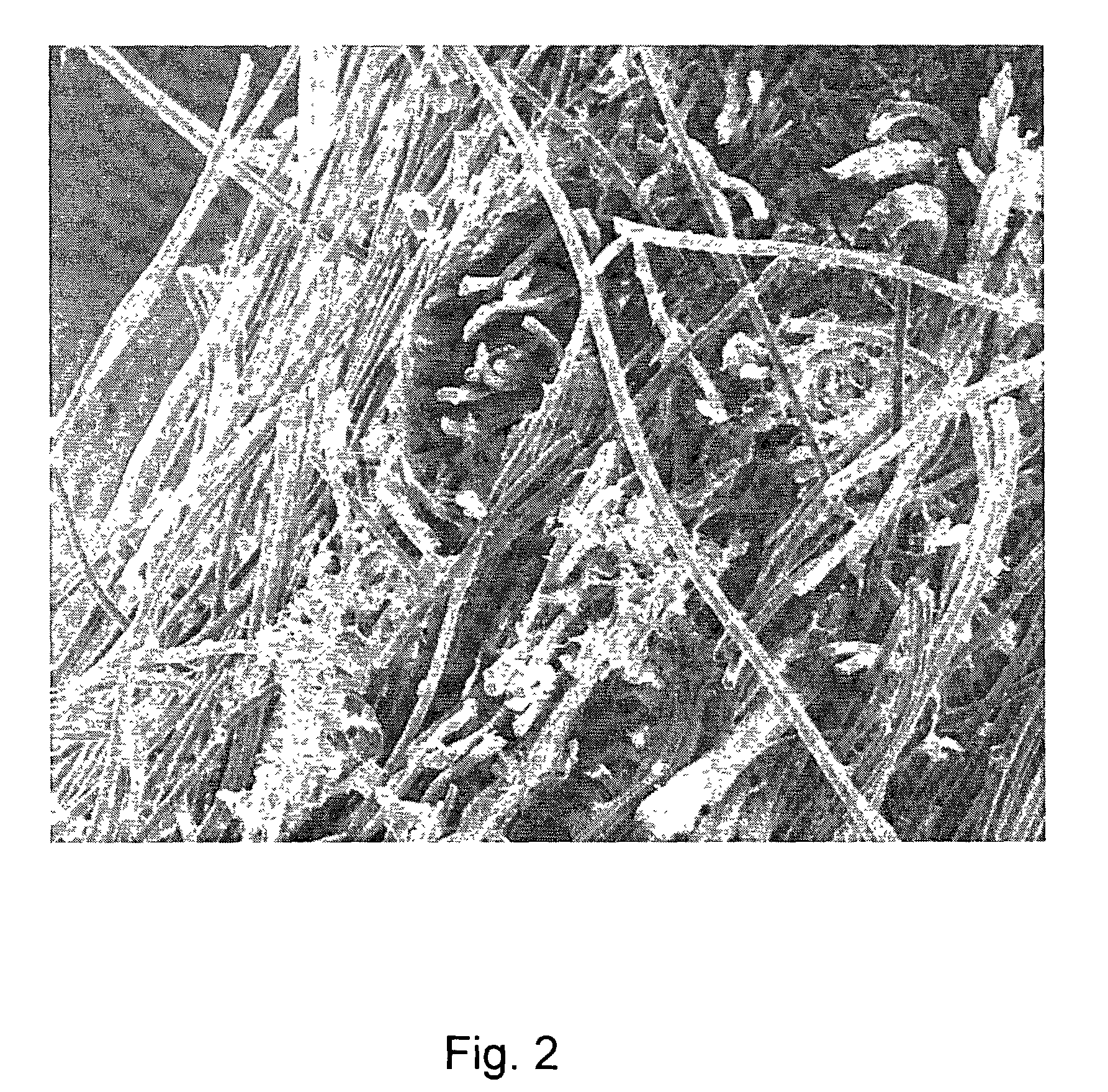
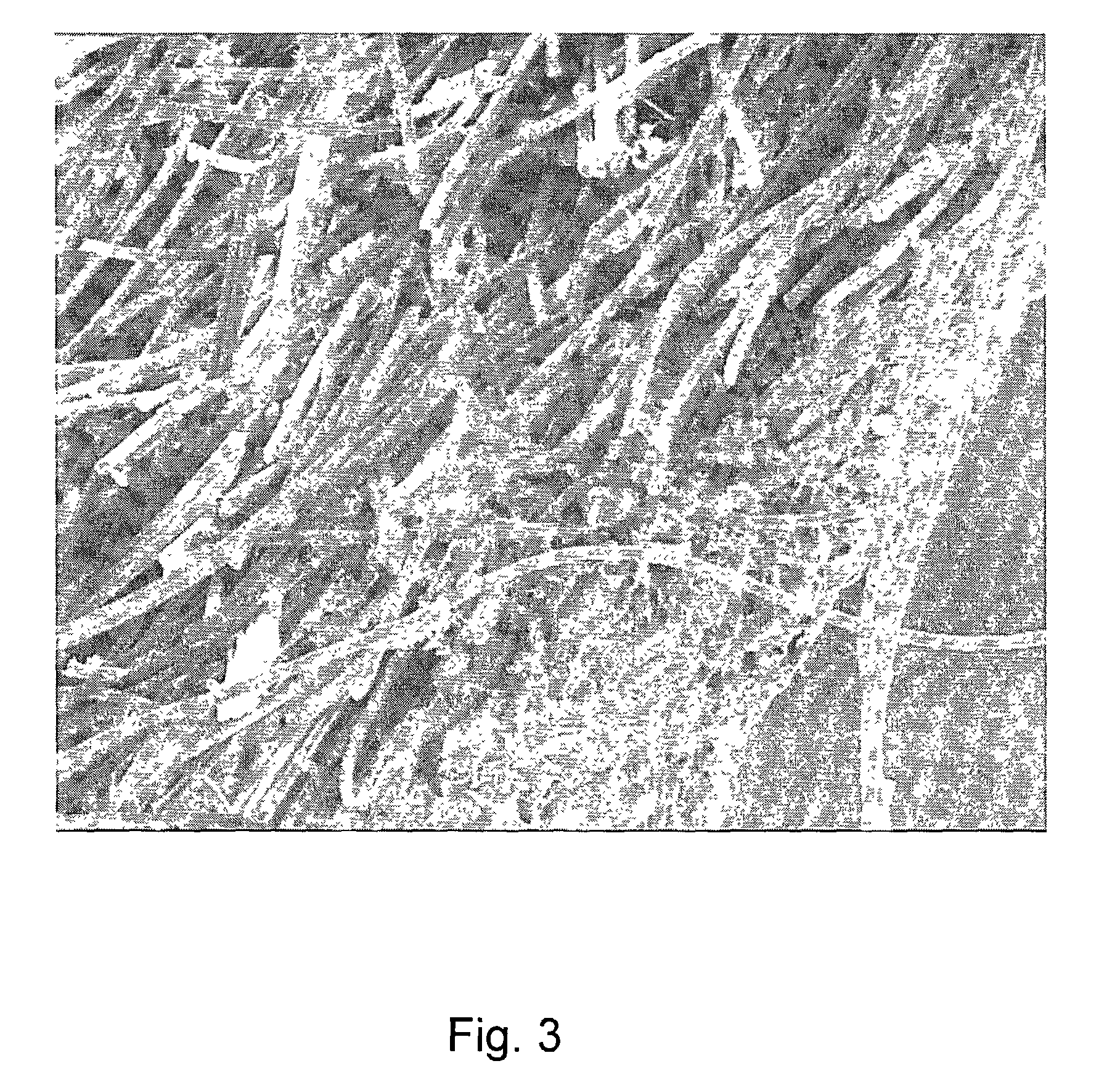
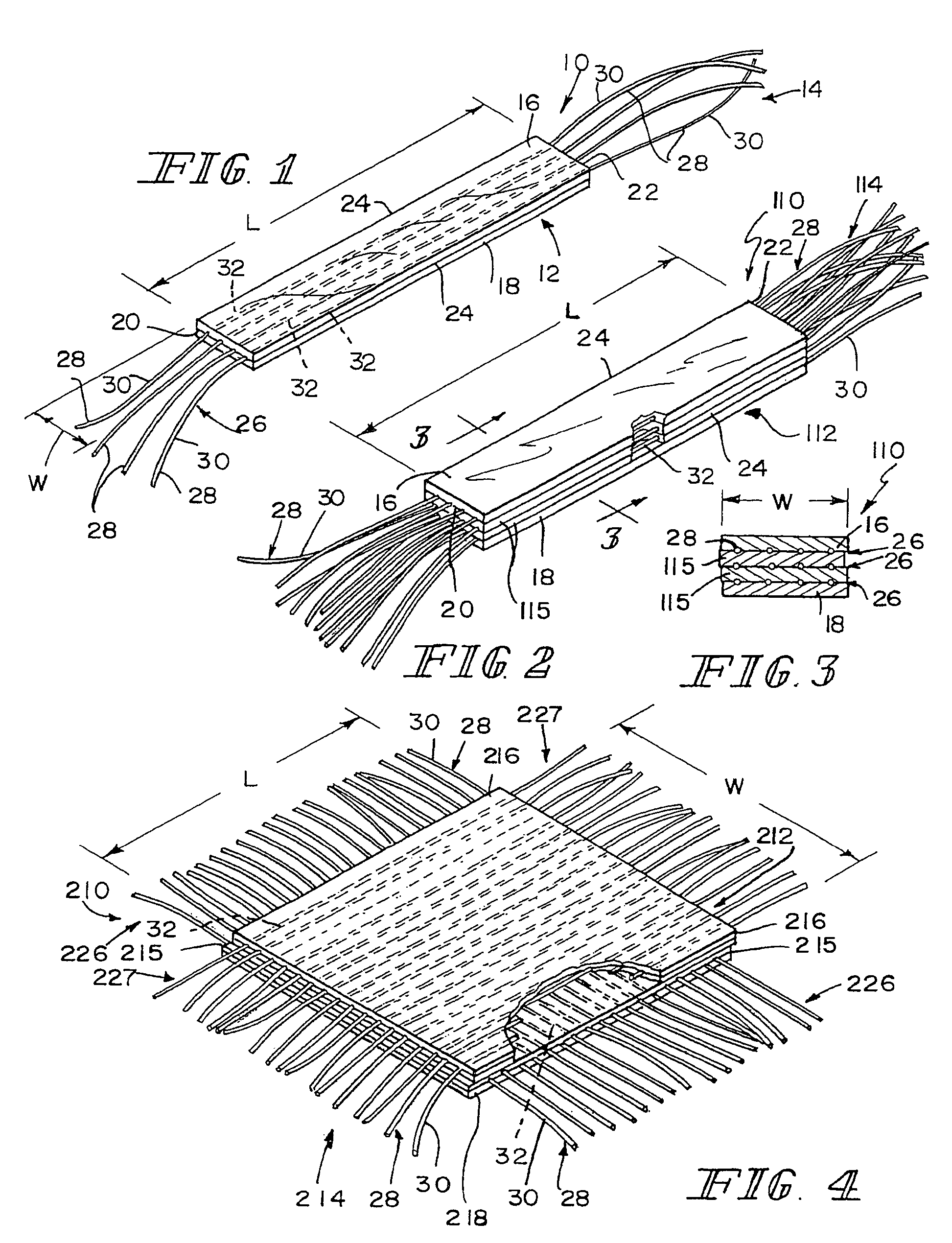
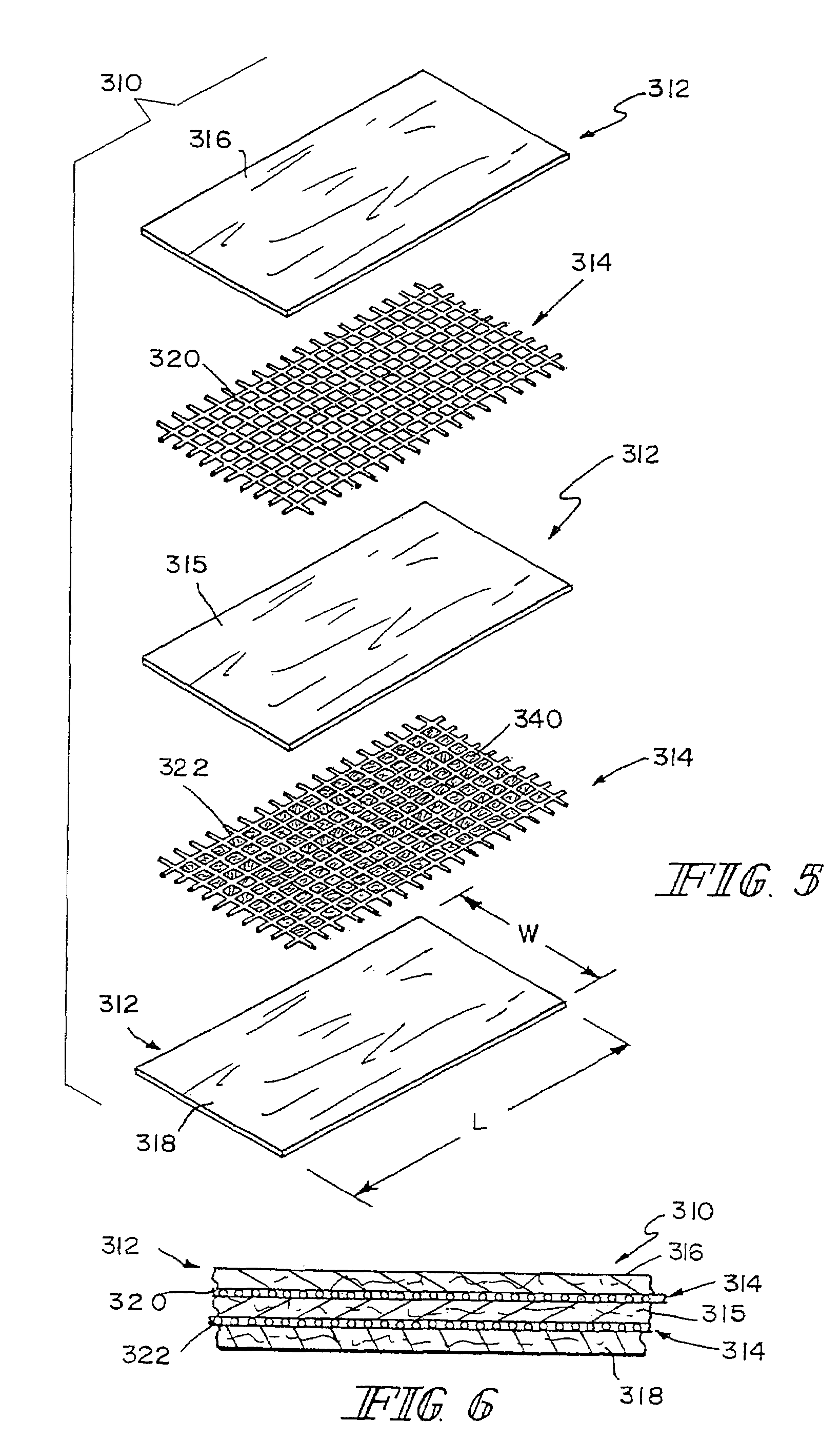
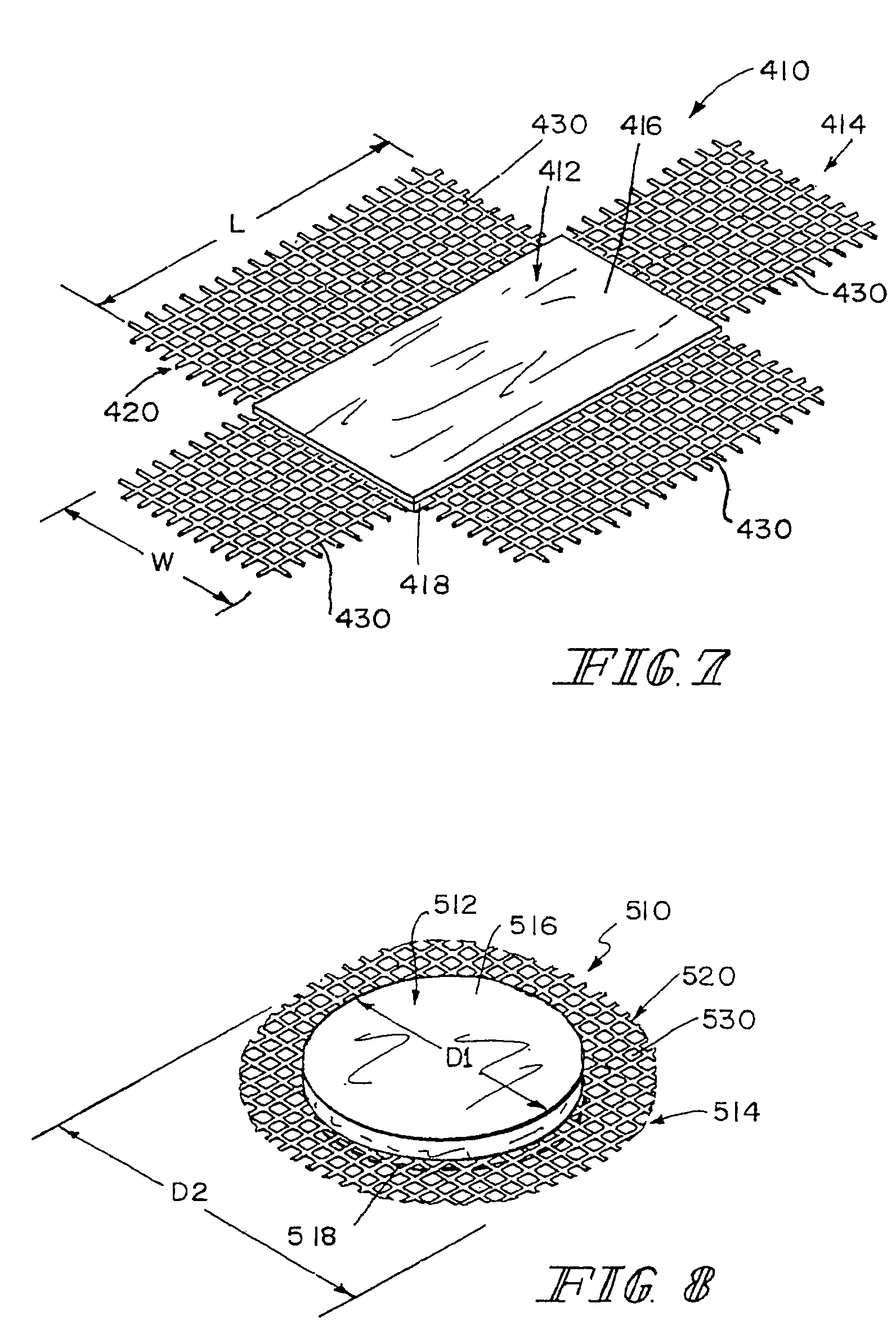
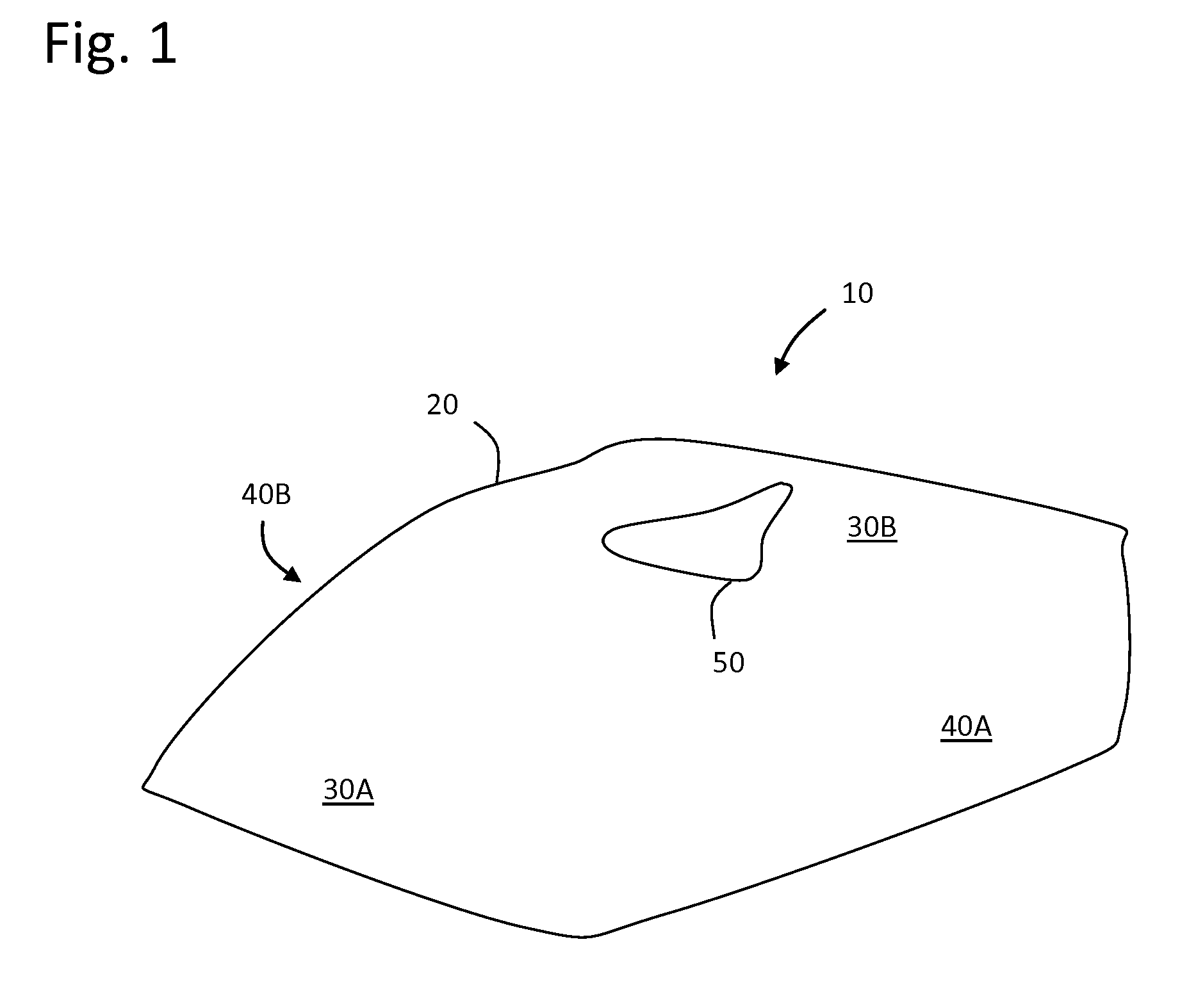
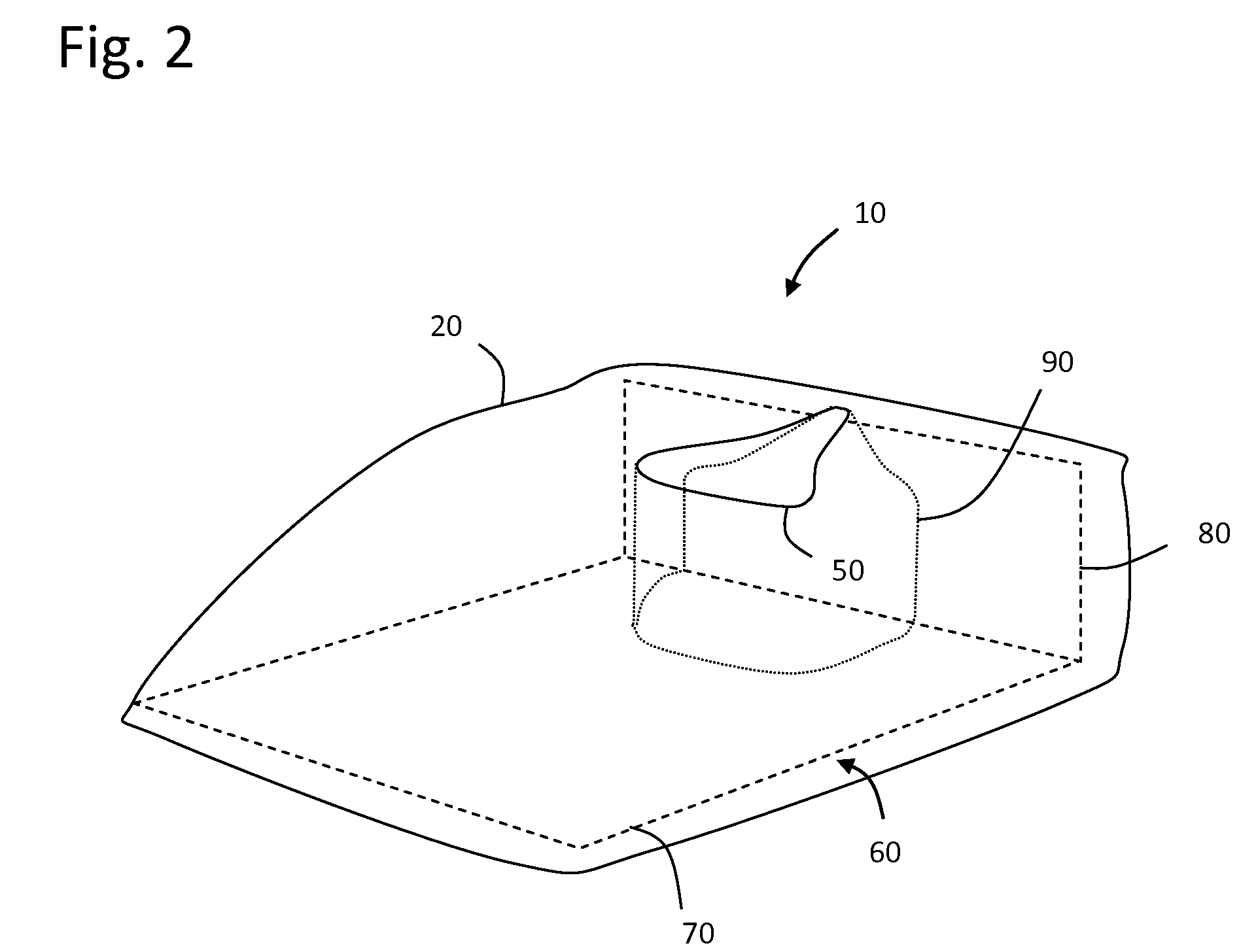
A bioprosthetic device is provided for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, and or reconstruction. The device comprises a naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion and a three-dimensional synthetic portion. In illustrated embodiments, the naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion comprises layers of small intestine submucosa, and the three-dimensional synthetic portion comprises a foam or a three-dimensional mesh, textile, or felt.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Hybrid biologic/synthetic porous extracellular matrix scaffolds
ActiveUS20030021827A1Wide of injuriesWide supportSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
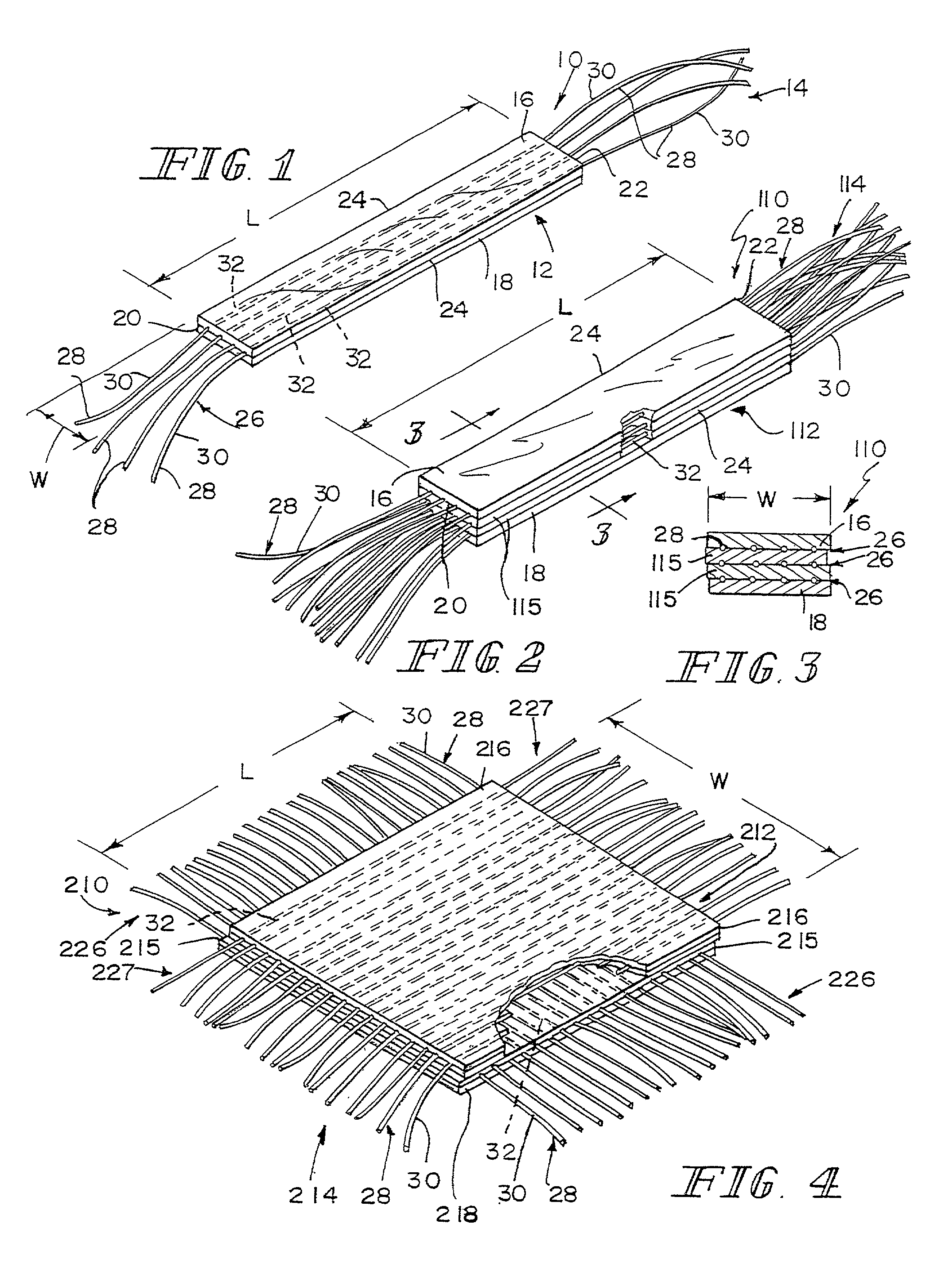
Methods of making a hybrid biologic / synthetic scaffold for repairing damaged or diseased tissue are provided. The methods include the step of suspending pieces of an extracellular matrix material in a liquid to form a slurry, and coating a synthetic mat with the slurry, or mixing or layering the slurry with a synthetic polymer solution. The liquid is subsequently driven off so as to form a foam. Porous implantable scaffolds fabricated by such a method are also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Position adjustable load support mechanism
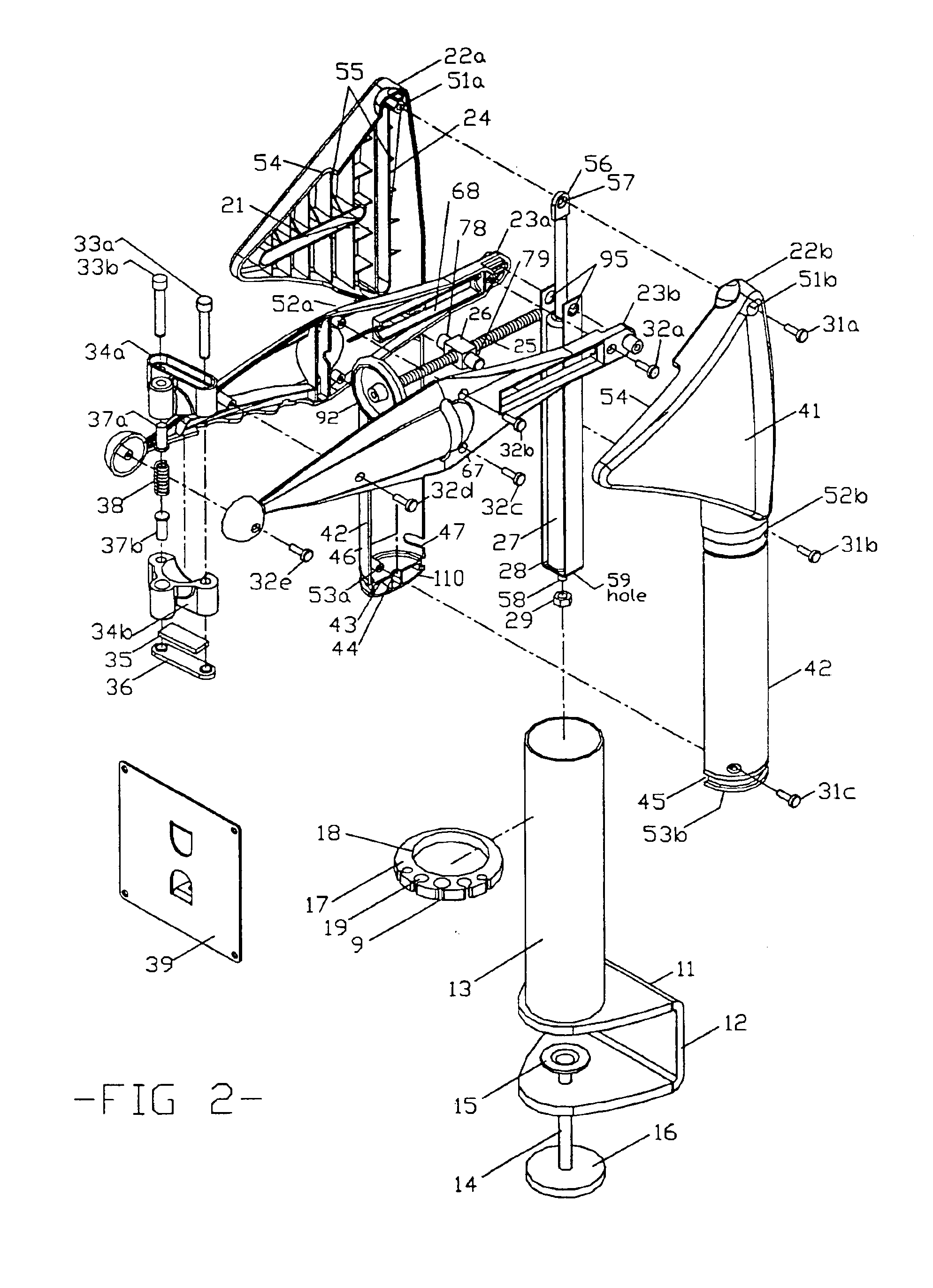
InactiveUS6857610B1Precise positioningLarge range of motionStands/trestlesKitchen equipmentRange of motionGas spring
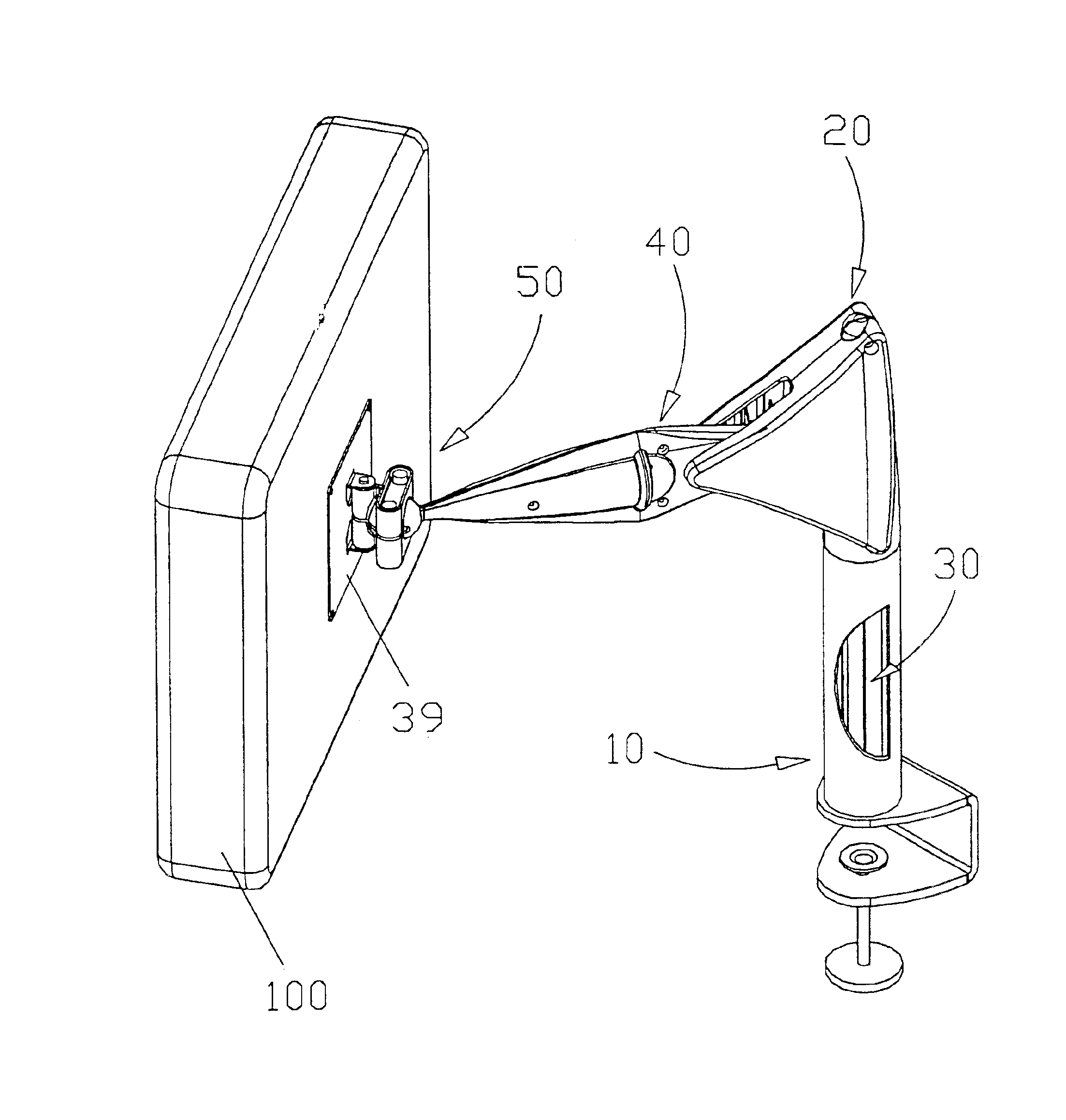
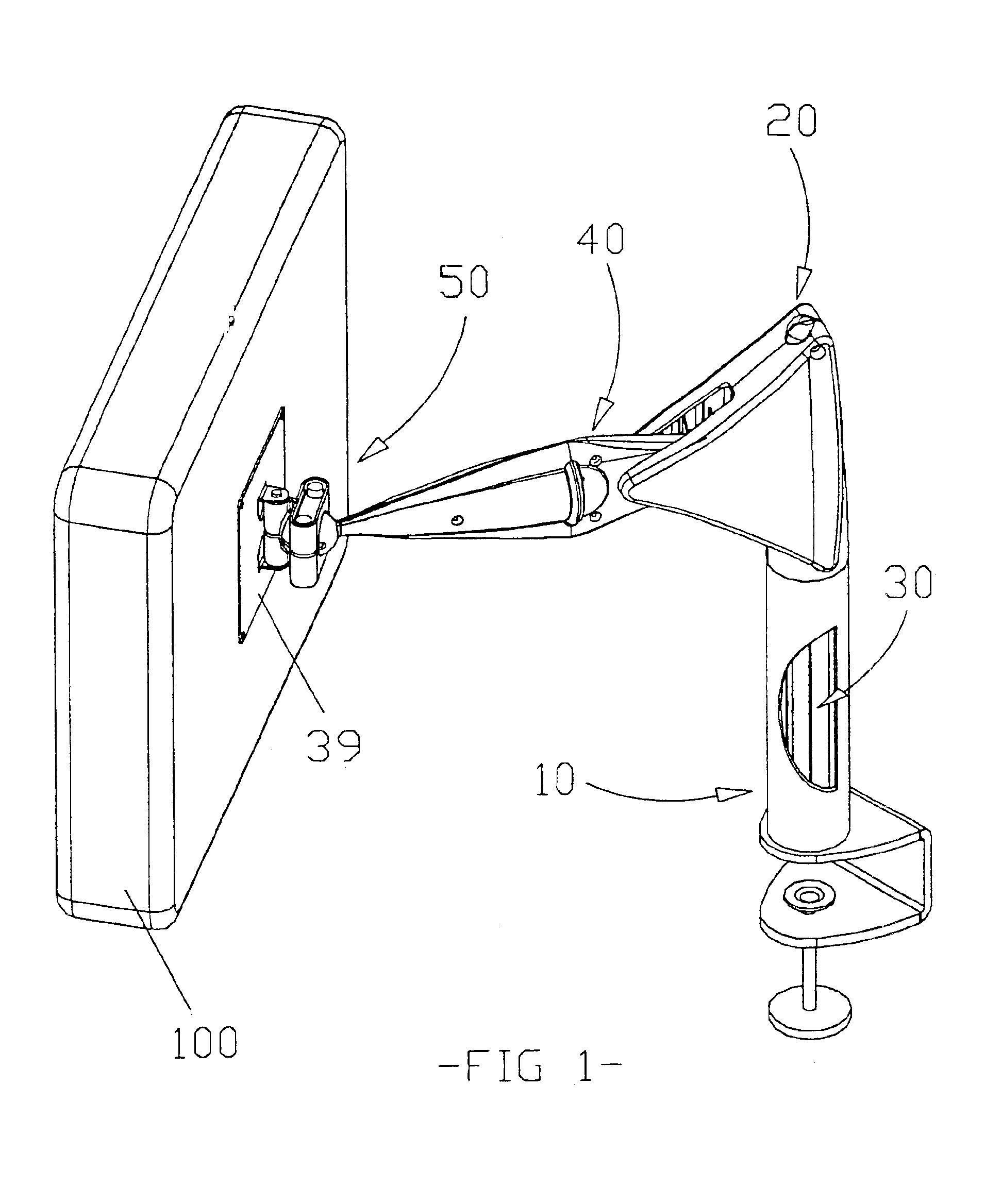
An improved mechanism for positioning loads of varying magnitudes, such as LCD displays, etc. The position of the load can be varied in height and angle according to the requirements of the user. The mechanism incorporates an adjustable sliding fulcrum, a support arm, a housing with four generally perpendicular channels, and a gas spring. The mechanism is initially manually adjusted for a particular load and then it automatically adjusts proportionally for the varying moments generated as the position of the load changes. The load is therefore evenly counterbalanced throughout its range of motion, and its position is maintained.
Owner:CONNER JOHN P +1
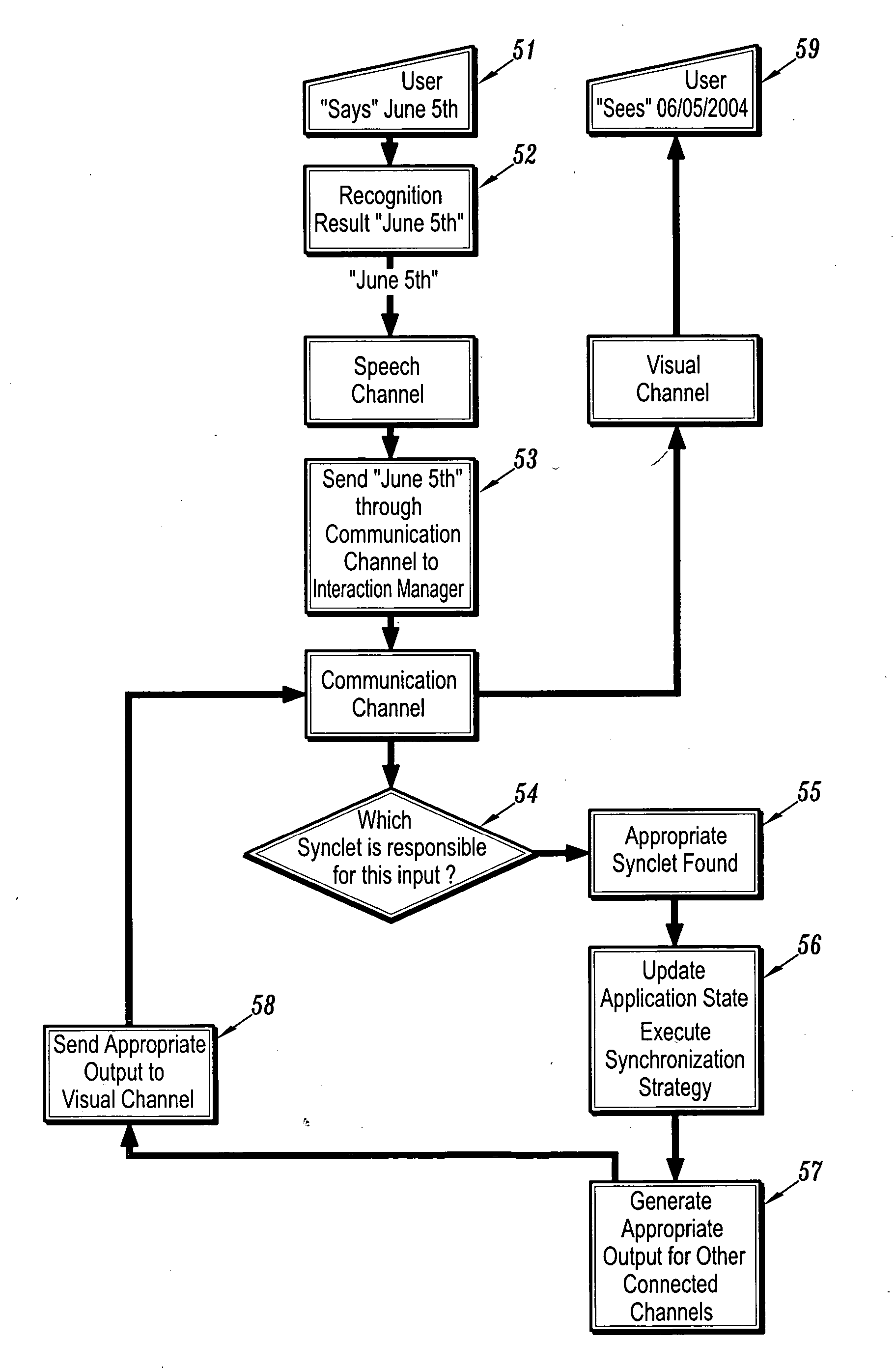
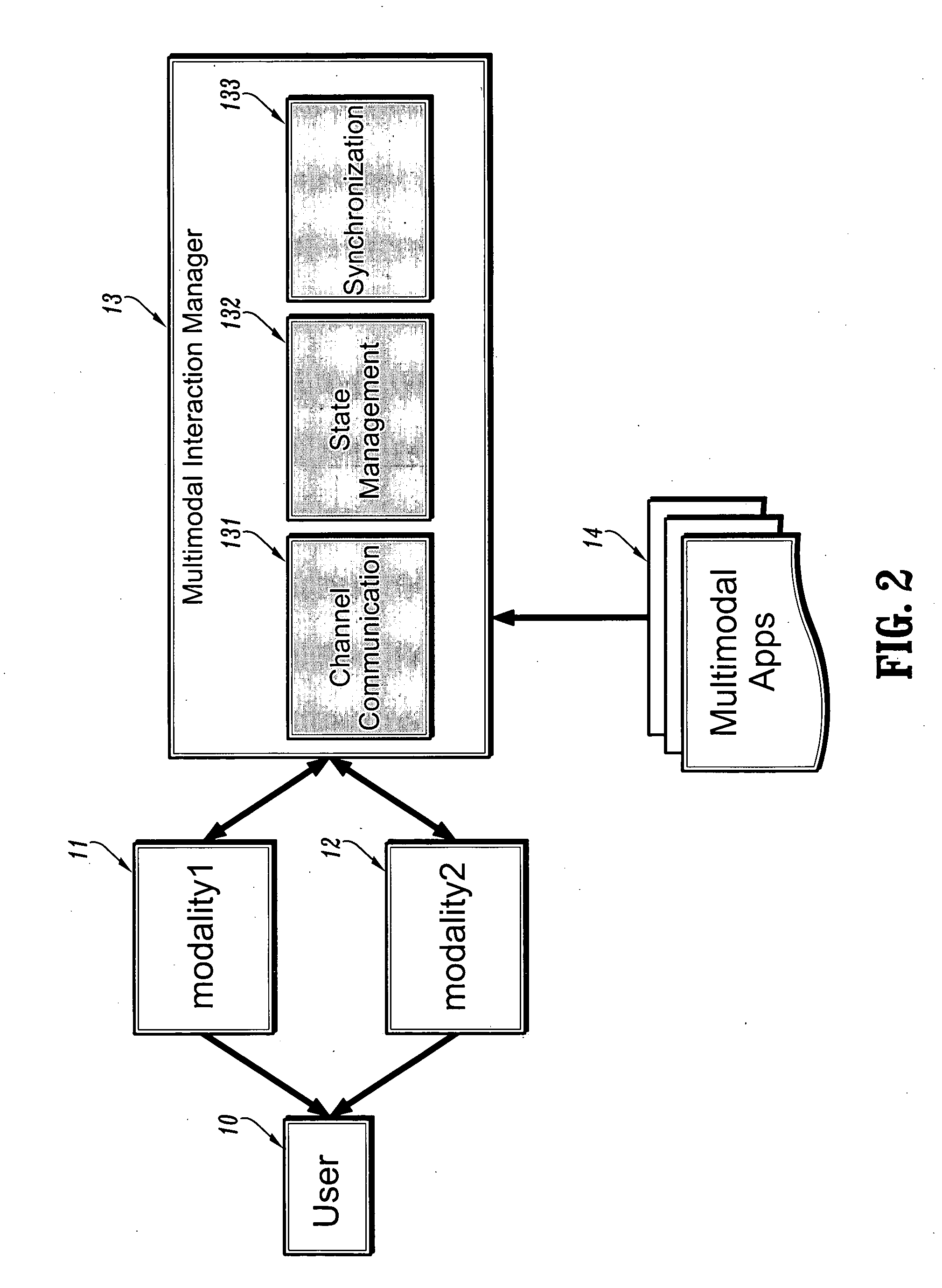
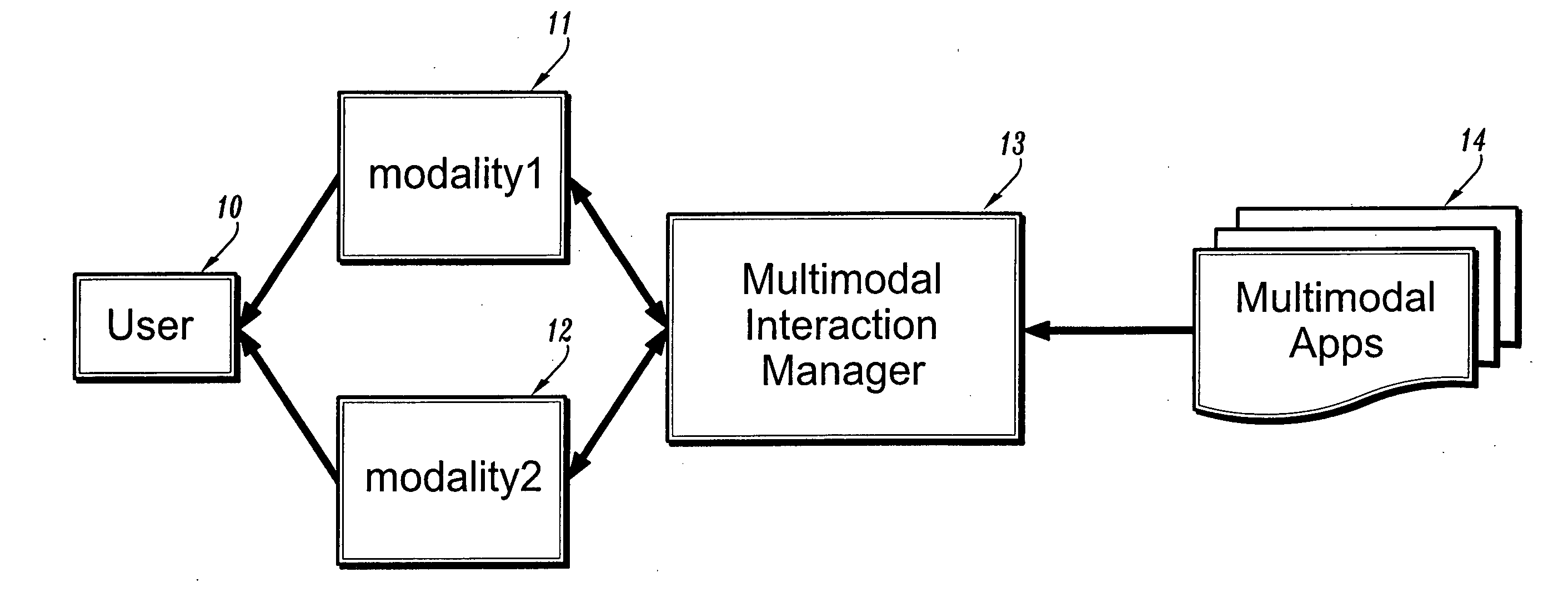
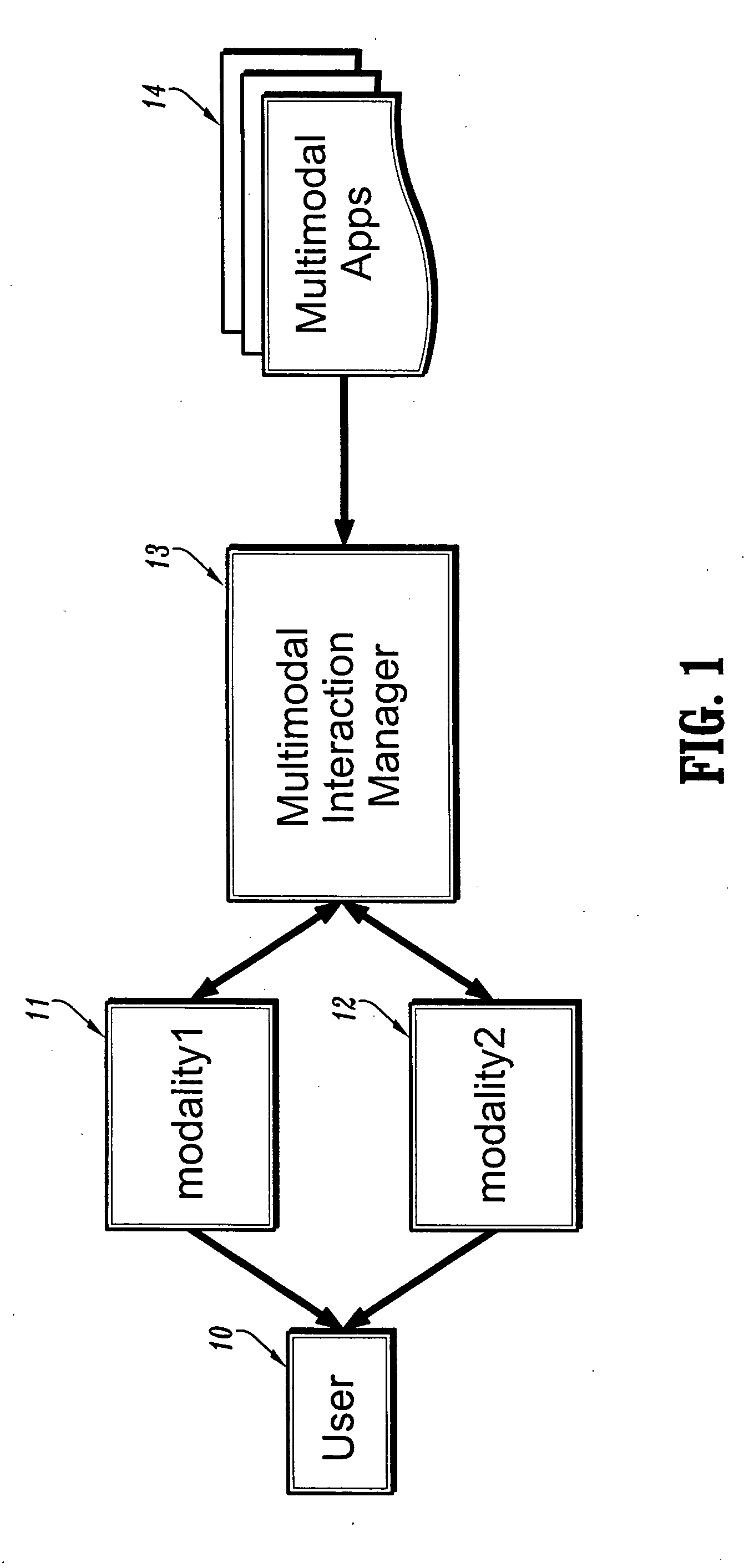
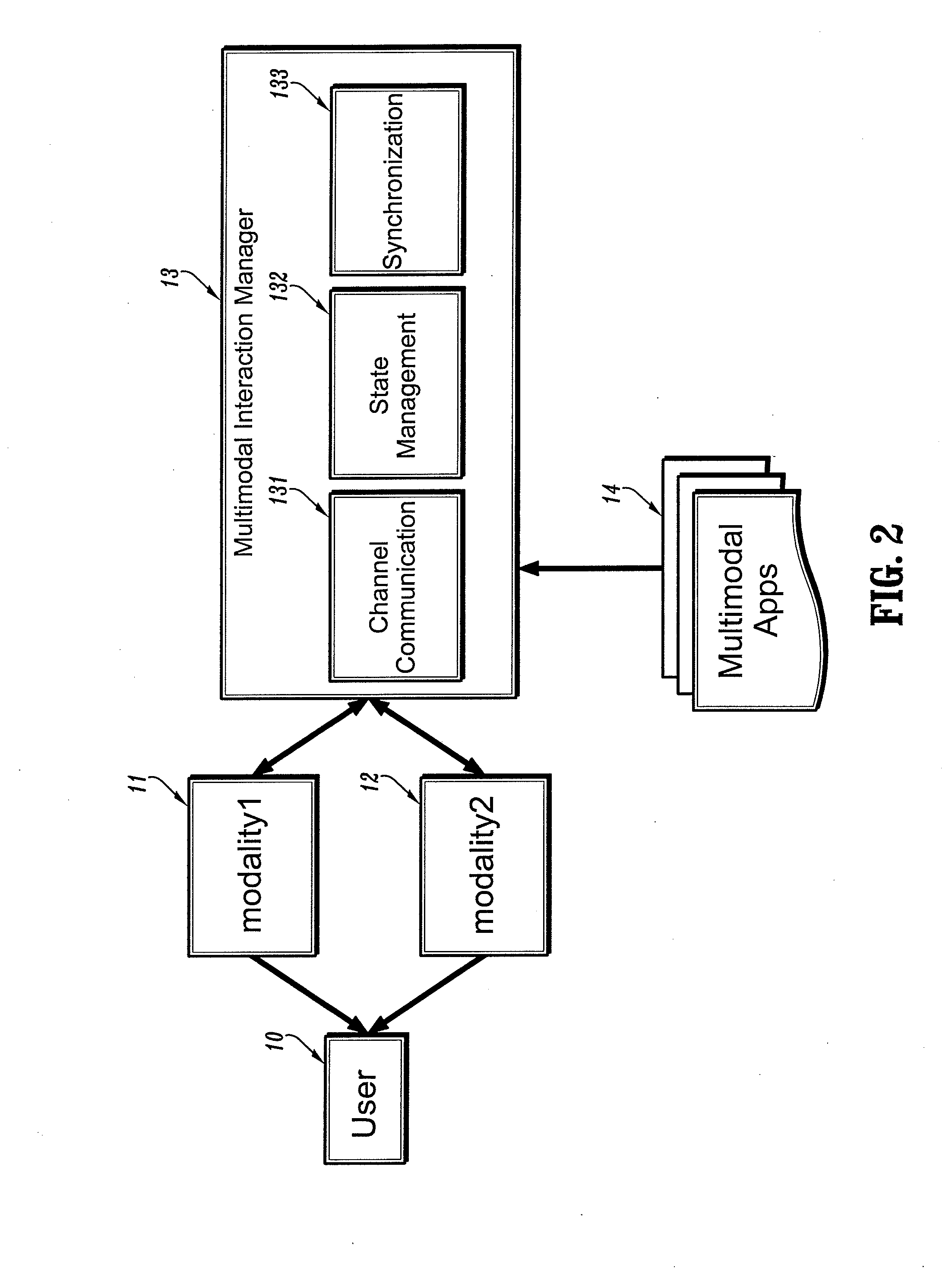
System for factoring synchronization strategies from multimodal programming model runtimes
InactiveUS20060036770A1Wide supportMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication serverInteraction management
A factored multimodal interaction architecture for a distributed computing system is disclosed. The distributed computing system includes a plurality of clients and at least one application server that can interact with the clients via a plurality of interaction modalities. The factored architecture includes an interaction manager with a multimodal interface, wherein the interaction manager can receive a client request for a multimodal application in one interaction modality and transmit the client request in another modality, a browser adapter for each client browser, where each browser adapter includes the multimodal interface, and one or more pluggable synchronization modules. Each synchronization module implements one of the plurality of interaction modalities between one of the plurality of clients and the server such that the synchronization module for an interaction modality mediates communication between the multimodal interface of the client browser adapter and the multimodal interface of the interaction manager.
Owner:IBM CORP
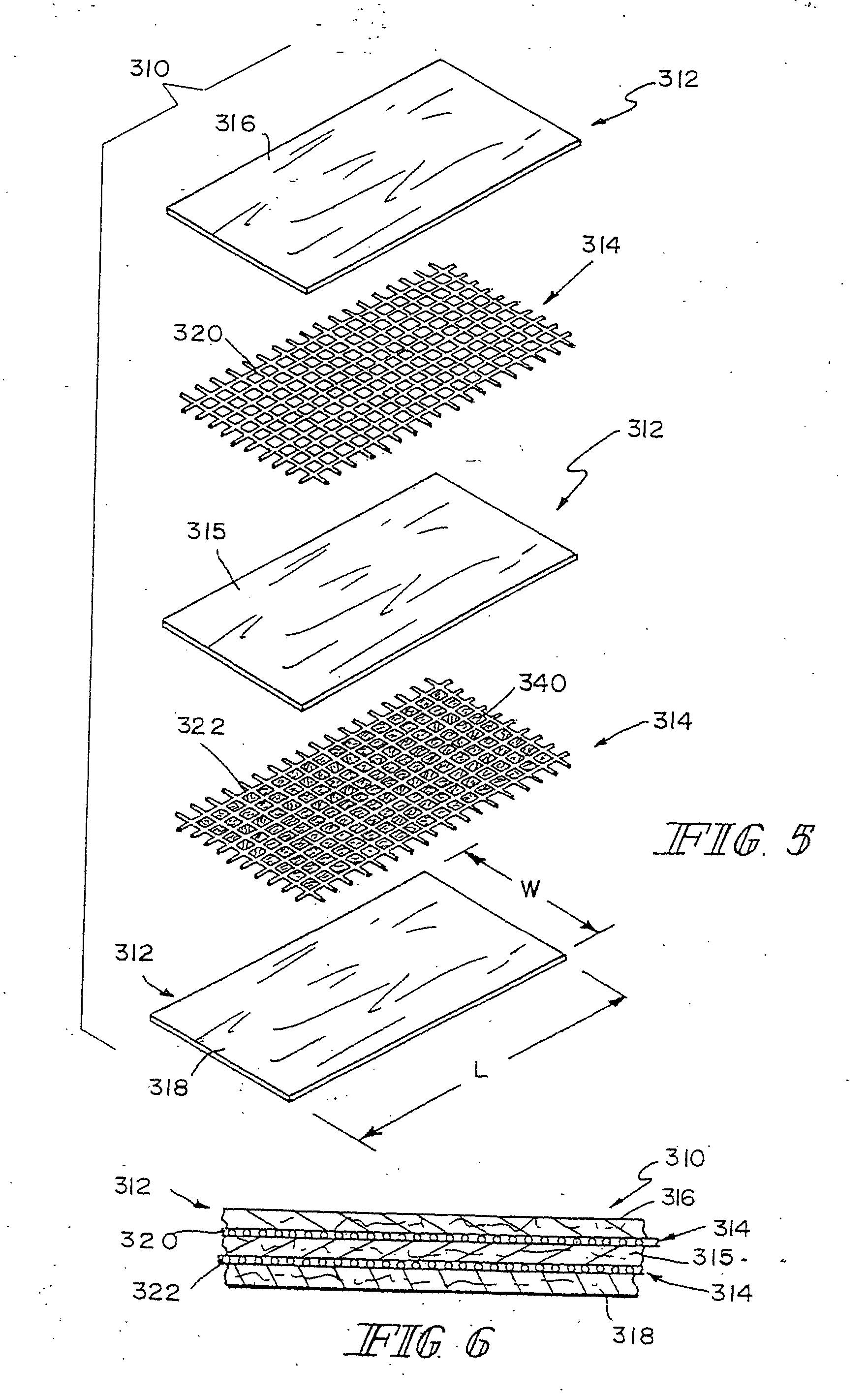
Hybrid biologic-synthetic bioabsorbable scaffolds
InactiveUS20050249772A1Good mechanical integrityProvide mechanical strengthWood working apparatusFlat articlesBioabsorbable scaffoldCell-Extracellular Matrix
A bioprosthetic device is provided for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, and or reconstruction. The device comprises a naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion and a synthetic portion.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Hybrid biologic-synthetic bioabsorbable scaffolds
ActiveUS20050249771A1Enhanced mechanical integrityIncrease surface areaTransferasesWood working apparatusProsthesisBiomedical engineering
A bioprosthetic device is provided for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, and or reconstruction. The device comprises a naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion and a synthetic portion.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
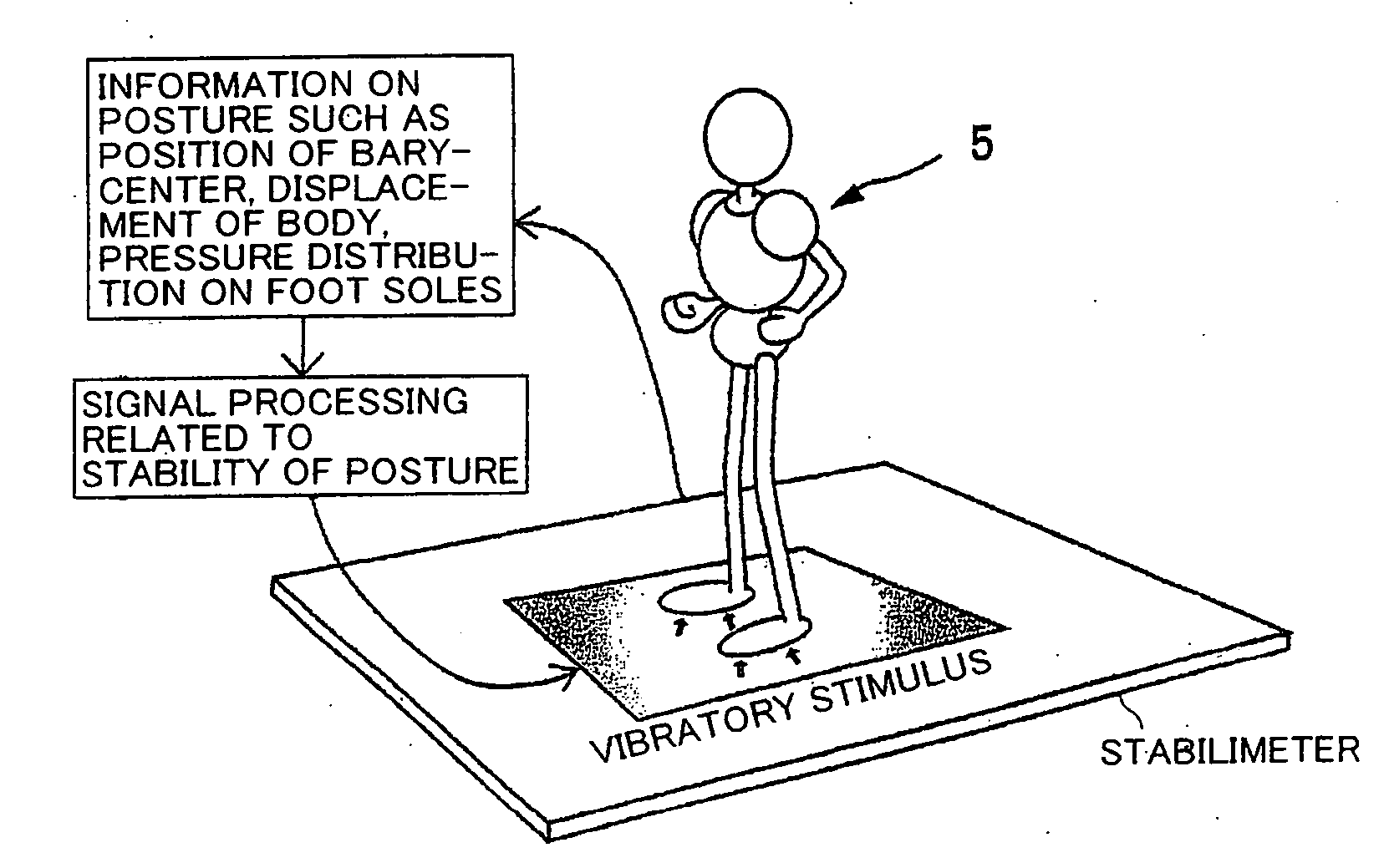
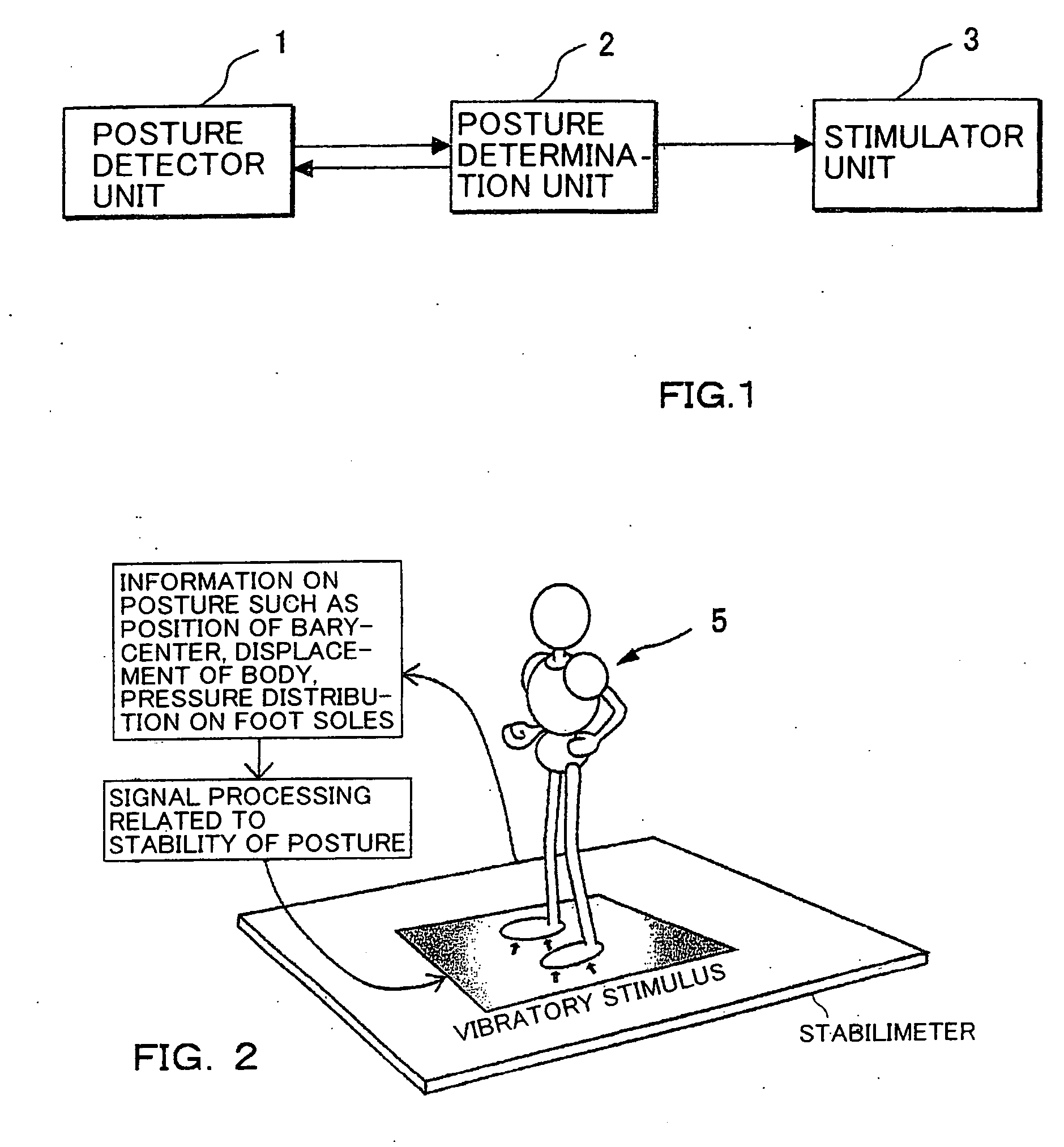
Device and method of applying skin sensory stimulation
InactiveUS20070073196A1Improve stabilityIncrease the areaChiropractic devicesPerson identificationVibrotactile stimulationEngineering
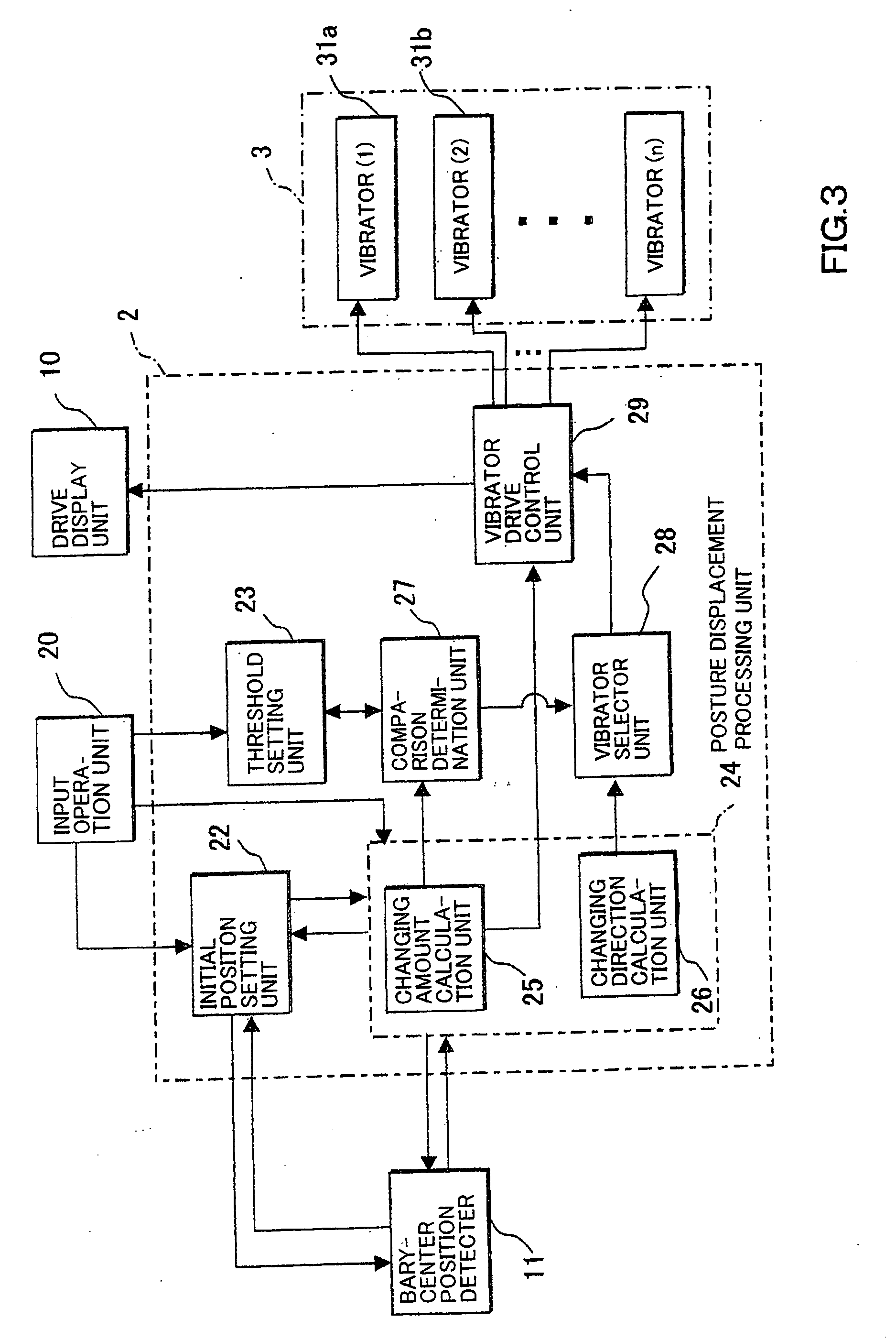
An apparatus generates a cutaneous sense stimulus to call a subject attention to a change in posture based on posture change information (the amount of change in the barycenter, a changing direction of the same, and the like) from a device for detecting a change in posture of the subject. The apparatus has stimulus generating means (a plurality of vibrators) for generating a cutaneous sense stimulus, and stimulus control means for driving the stimulus generating means based on the posture change information. The control means comprises means for selecting a plurality of vibrators arranged substantially parallel with the changing direction based on the changing direction of the barycenter, and sequentially driving the selected vibrators, for example, in a direction substantially opposite to the direction in which the barycenter changes. The control means also drives the vibrators to generate the tactile sense stimulus of a magnitude corresponding to a changing amount of the barycenter. The vibrators are mounted on plantar soles, waist, chest, or the like. The apparatus can accurately notify the subject of a change in posture, and prompt the subject to take actions to maintain the posture.
Owner:TOKAI UNIV +3
Aircraft with a double-T tail assembly
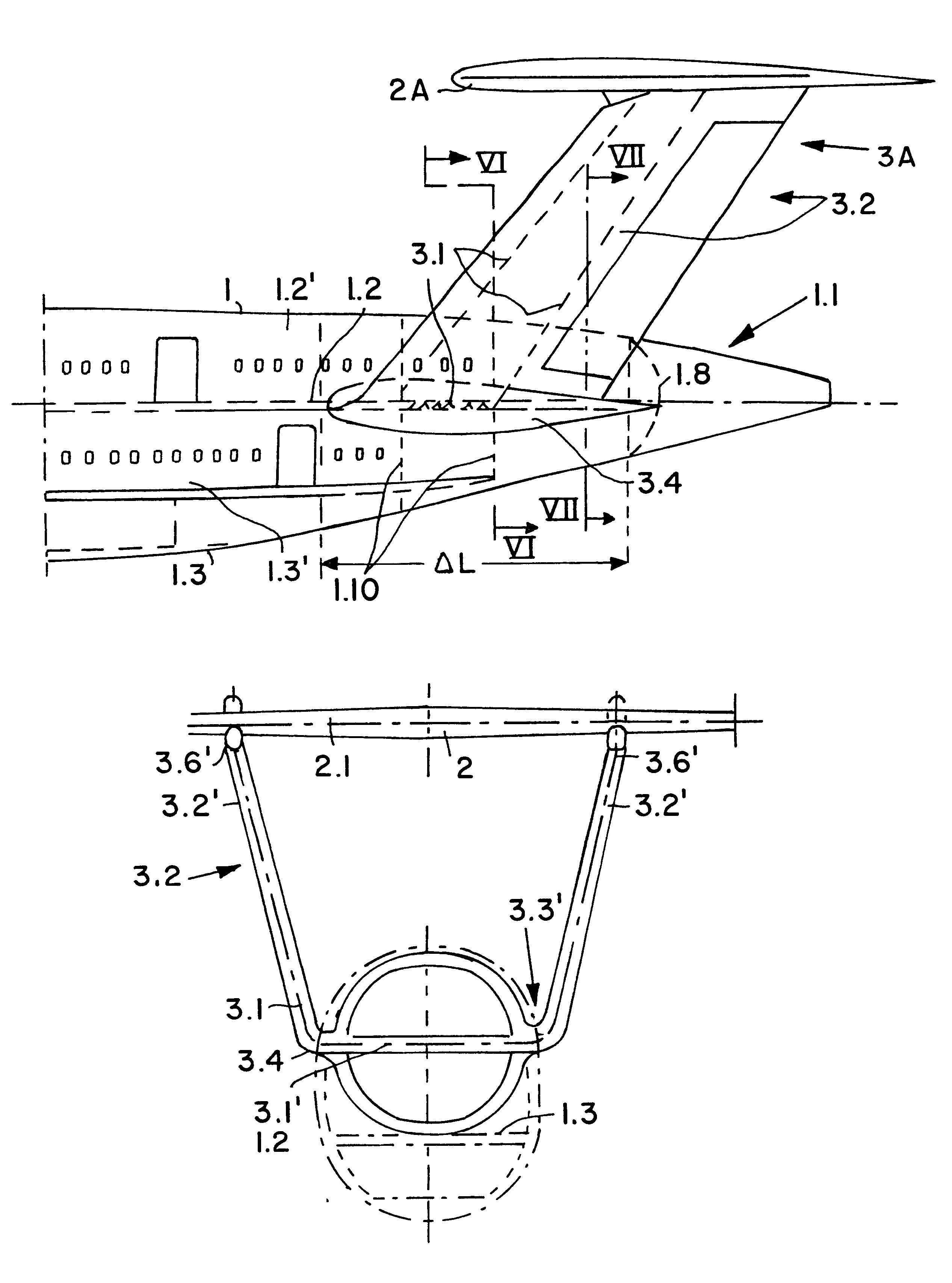
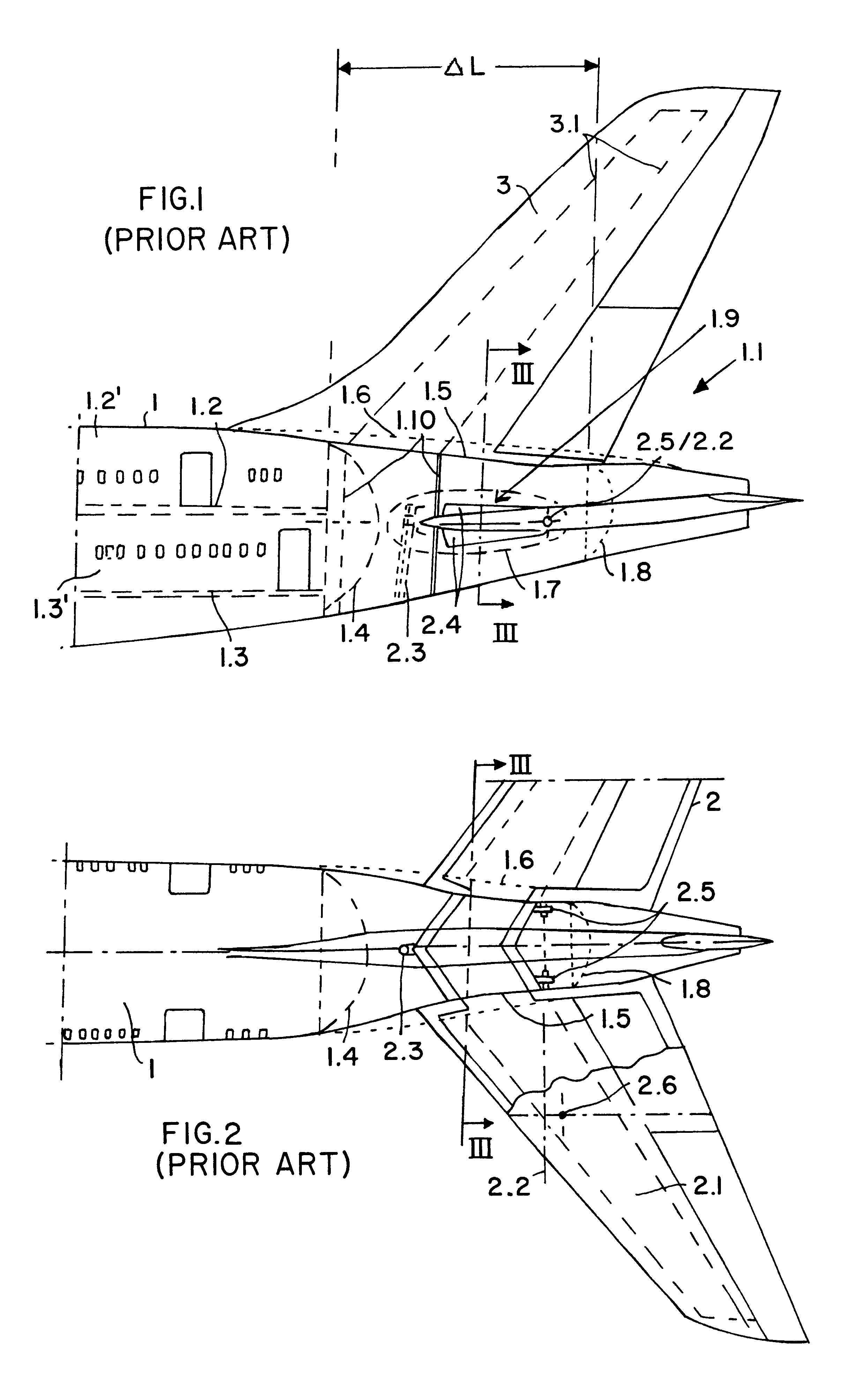
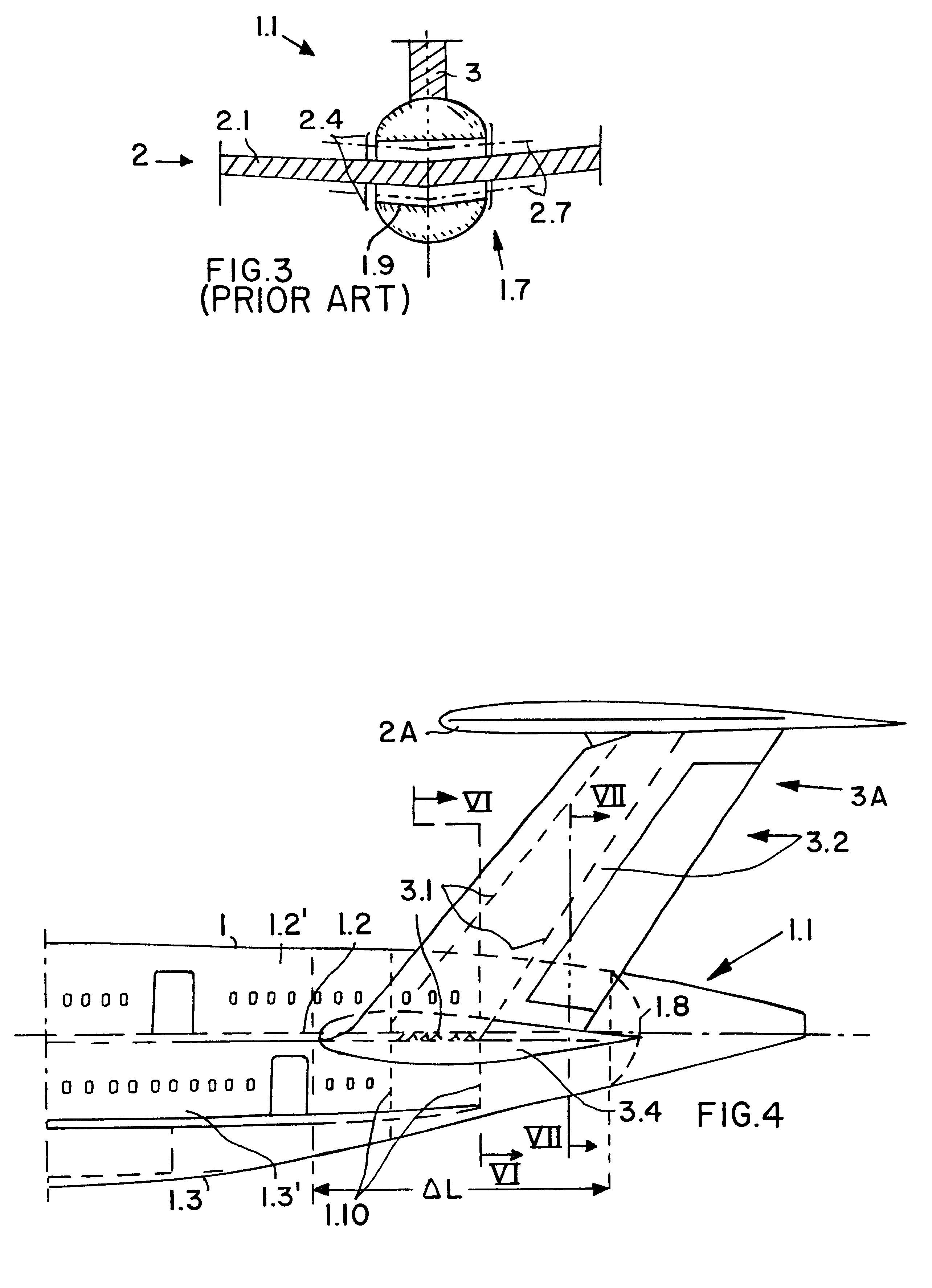
InactiveUS6273363B1Great available interior spaceEasy to manufactureAircraft stabilisationActuated automaticallyRudderAirplane
An aircraft, preferably a large capacity passenger aircraft with two passenger decks, has a double-T tail assembly arranged on its tail section. The double-T tail assembly includes a double fin and rudder assembly and a tailplane and elevator assembly, and provides a significant increase in the usable passenger cabin space in the tail section of the aircraft. The double fin and rudder assembly has a U-shaped structure and comprises two upright stabilizer fins connected to each other by a horizontal torsion box that fixedly extends crosswise through the fuselage tail section within the floor of a cabin deck. The tailplane and elevator assembly is pivotably mounted on the upper tips of the two upright stabilizer fins in a double-T arrangement.
Owner:DAIMLER CHRYSLER AEROSPACE AIRBUS
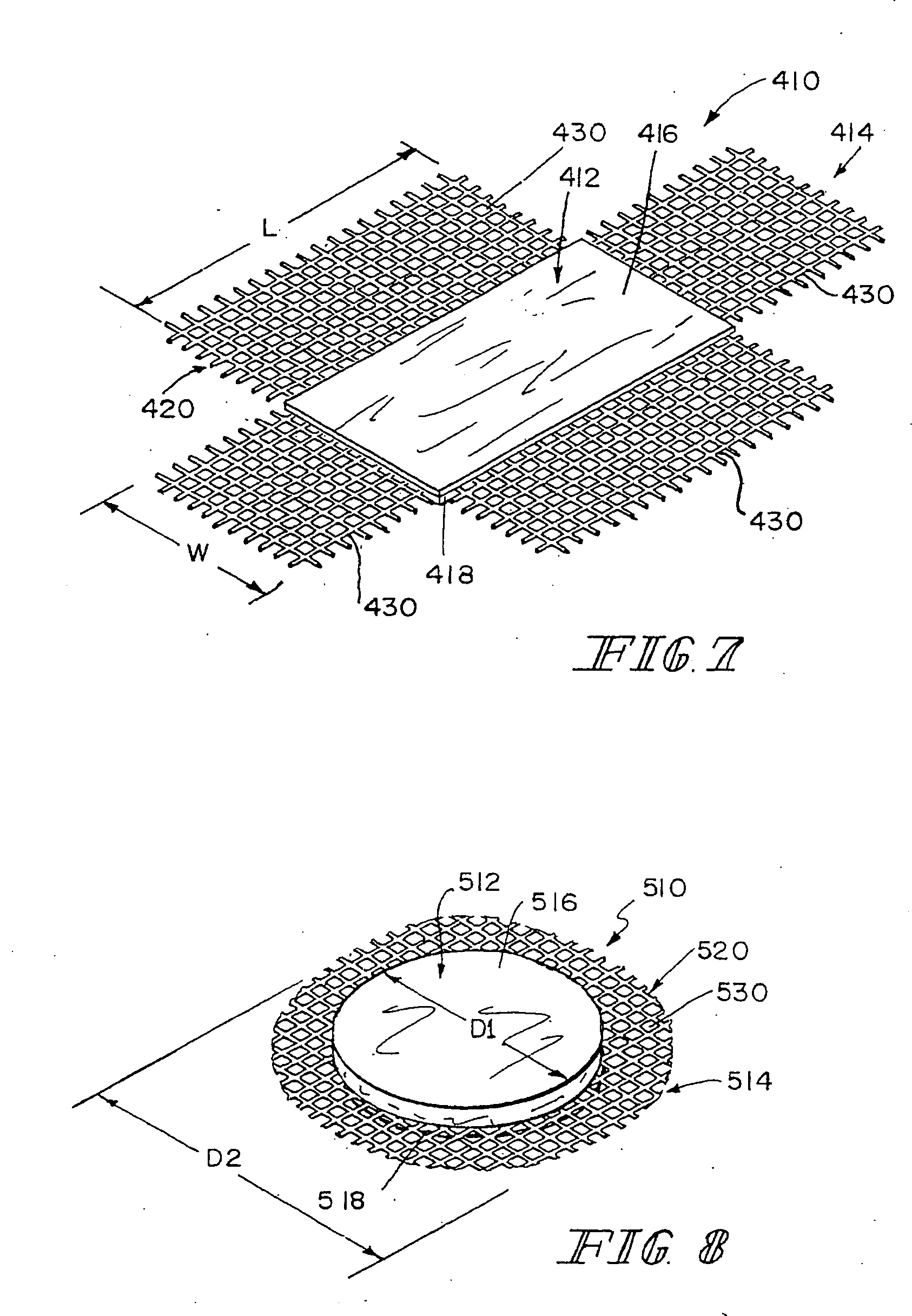
Hybrid biologic/synthetic porous extracellular matrix scaffolds
ActiveUS7914808B2Wide of injuriesWide supportSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Methods of making a hybrid biologic / synthetic scaffold for repairing damaged or diseased tissue are provided. The methods include the step of suspending pieces of an extracellular matrix material in a liquid to form a slurry, and coating a synthetic mat with the slurry, or mixing or layering the slurry with a synthetic polymer solution. The liquid is subsequently driven off so as to form a foam. Porous implantable scaffolds fabricated by such a method are also disclosed.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
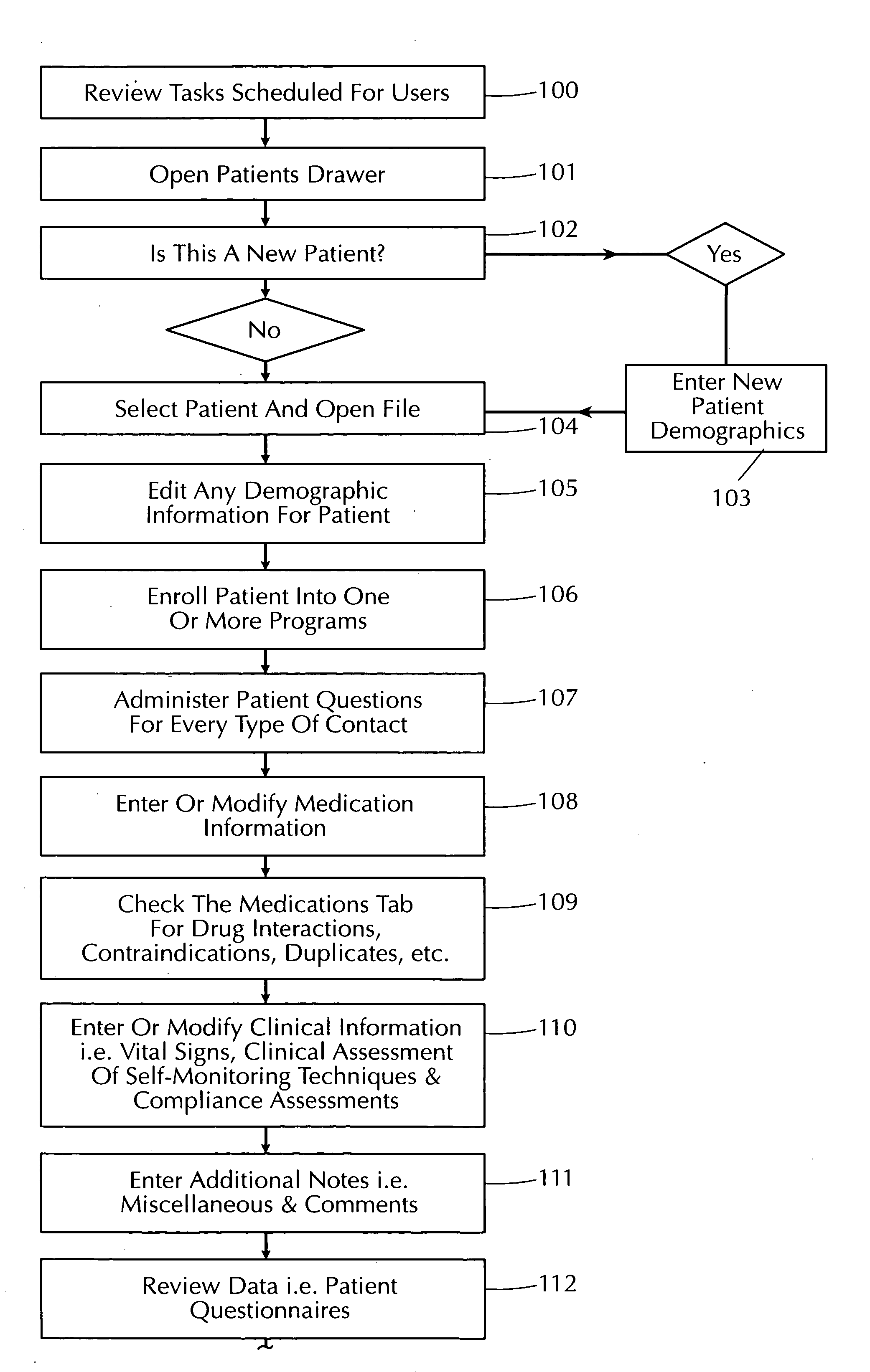
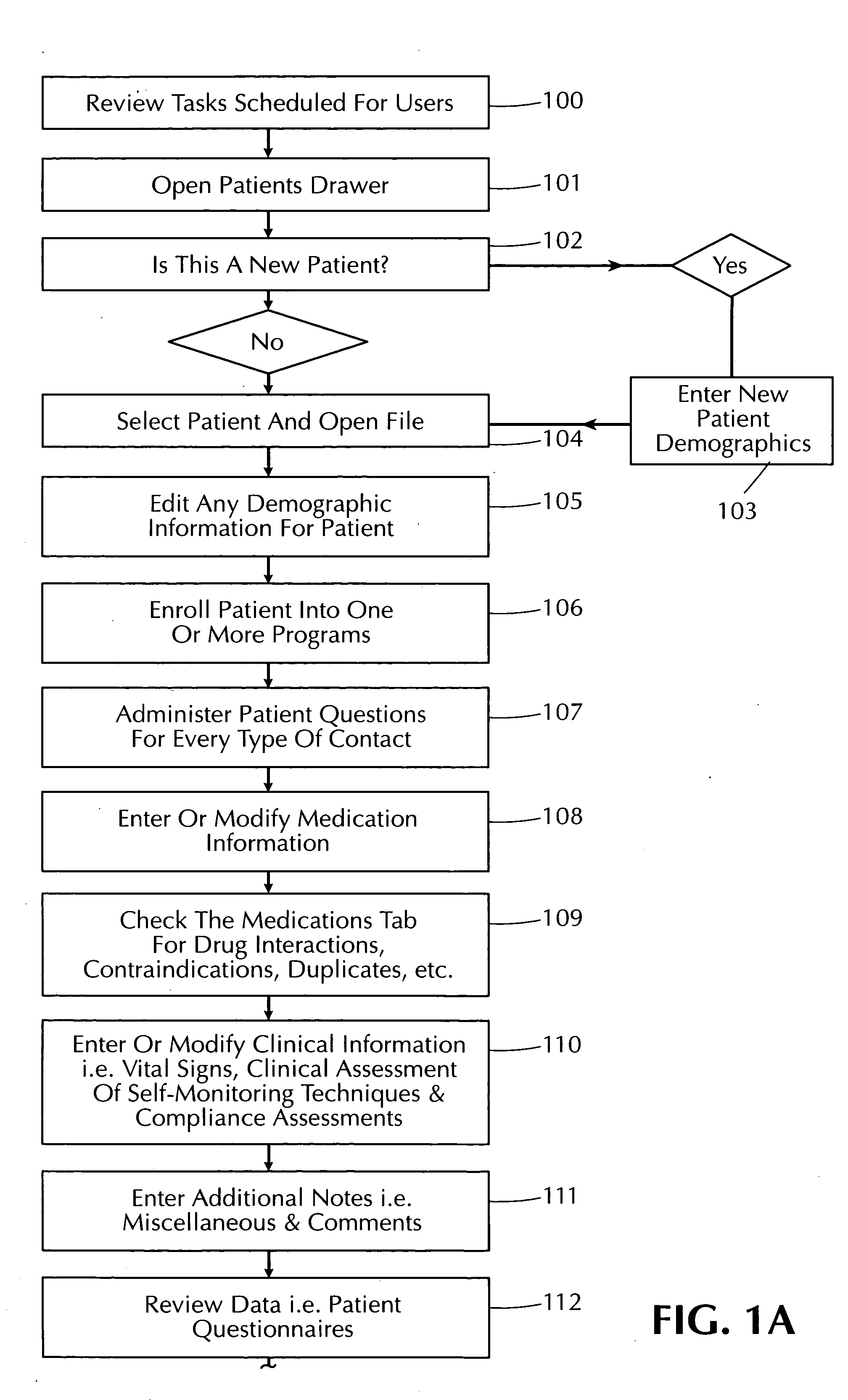
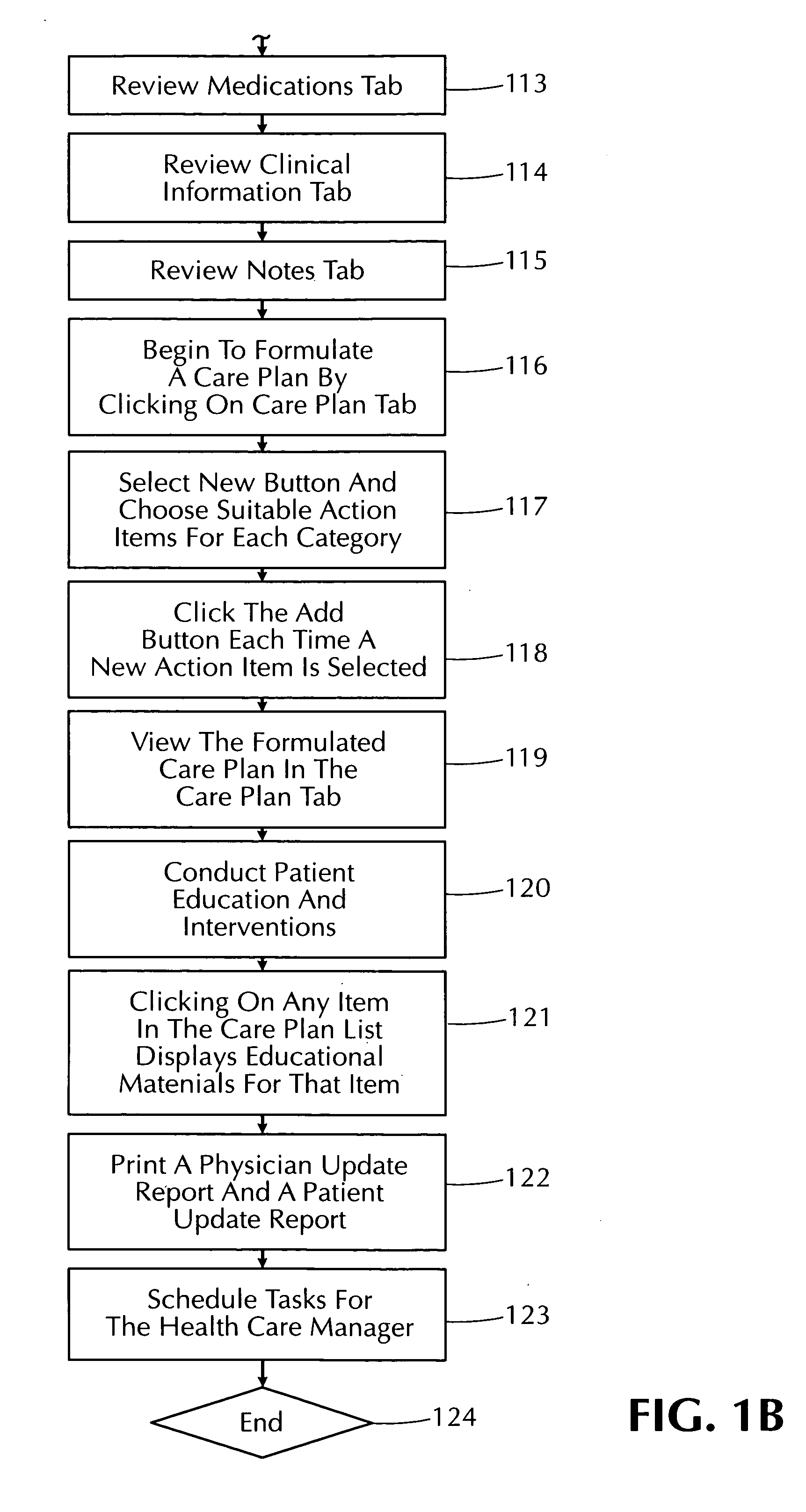
System and method for developing and managing the healthcare plans of patients with one or more health conditions
InactiveUS20060004609A1Efficient captureWide supportData processing applicationsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionDiseaseSystems design
The present invention is an automated disease management system designed to assist healthcare providers in the care management of patients with one or more health conditions. More particularly, this invention relates to a system and method for assisting healthcare providers in developing and monitoring the implementation of patient care plans.
Owner:PFIZER INC
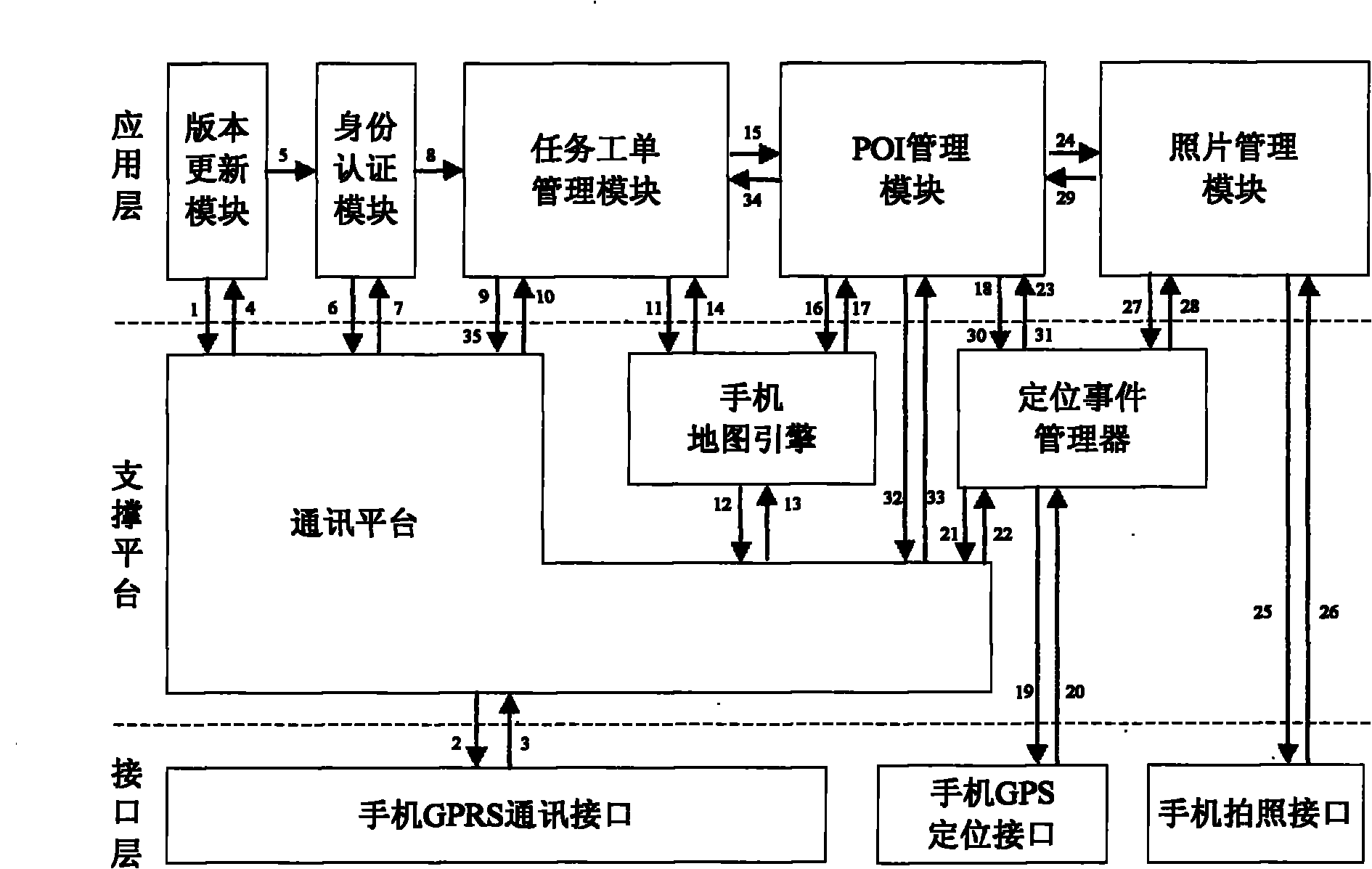
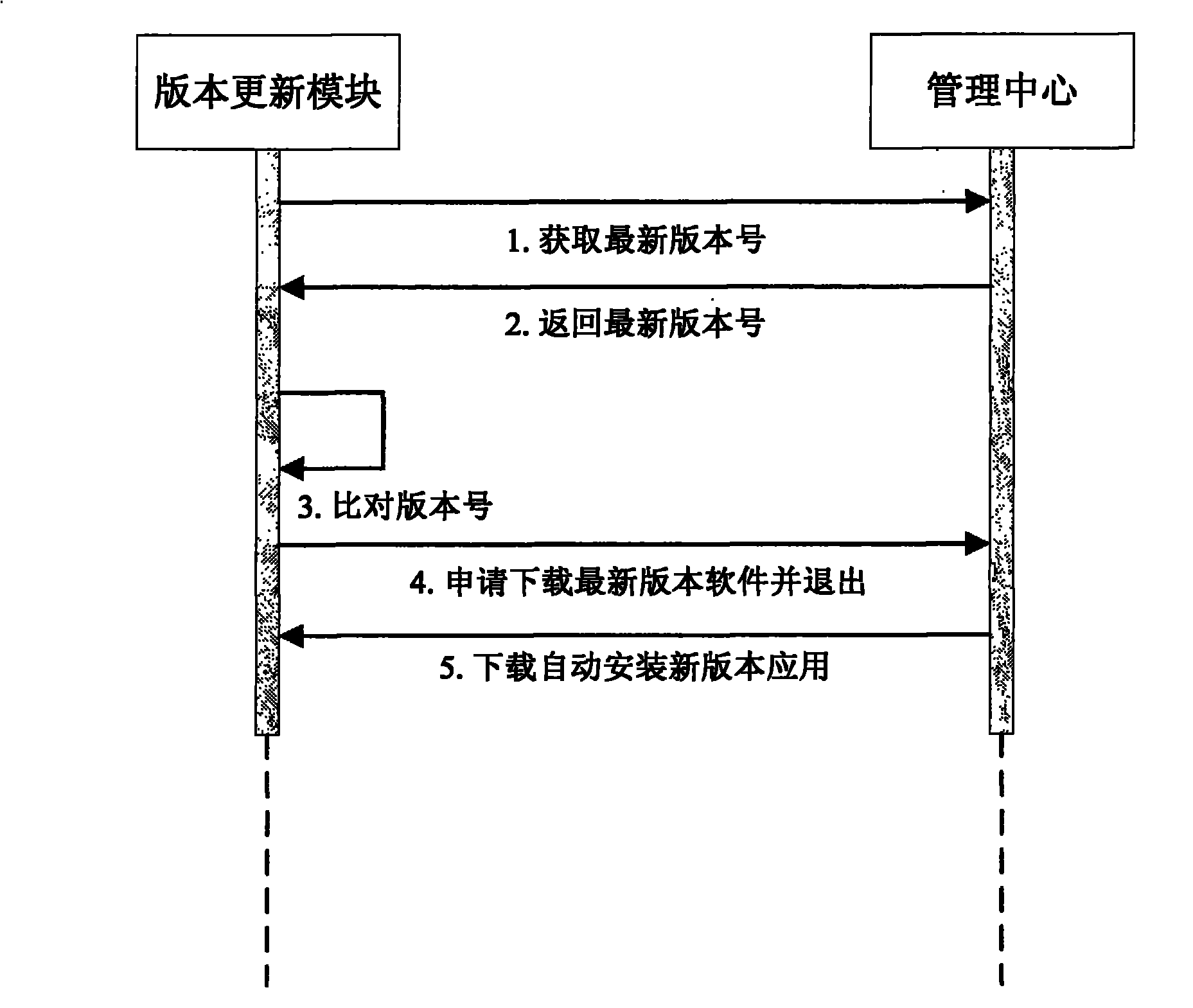
POI data acquisition system and method based on smart phone
ActiveCN101969451AEasy to manageWide supportSubstation equipmentSatellite radio beaconingCommunication interfaceCore function
The invention discloses a POI data acquisition system and method based on a smart phone. The smart phone comprises a GPS positioning interface and a camera photo taking interface. The system comprises an application layer, a support platform, an interface layer and a management center, wherein the application layer calls a support platform to realize the relevant operation in a business function;the support platform realizes the general core function relating to bottom equipment in the business funciton; the interface layer integrates a GPRS communication interface, the GPS positioning interface and the camera photo taking interface and is realized by relevant Java interfaces; and the management center is in charge of distributing tasks to the smart phone and records and feeds back the result information of an acquisition task. The invention also provides a method based on the system. The invention has real-time task work order and step feedback, has the characteristics of wide platform support, visual and convenient use and multi-industry support and realizes the reliable acquisition of POI data.
Owner:福州开睿动力通信科技有限公司
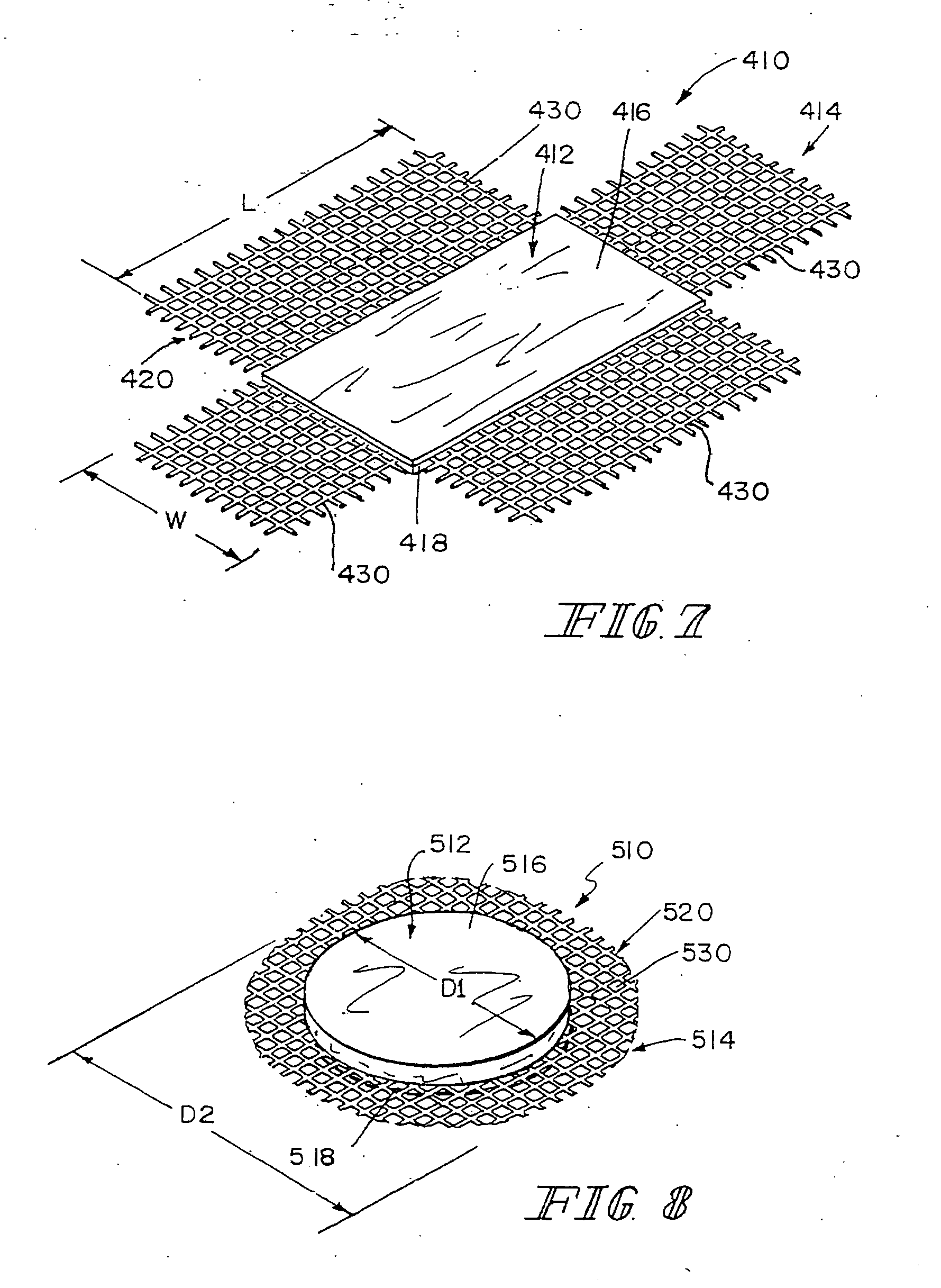
Hybrid biologic-synthetic bioabsorbable scaffolds
ActiveUS7569233B2Wide of injuriesWide supportTransferasesWood working apparatusBioabsorbable scaffoldCell-Extracellular Matrix
A bioprosthetic device is provided for soft tissue attachment, reinforcement, and or reconstruction. The device comprises a naturally occurring extracellular matrix portion and a synthetic portion.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
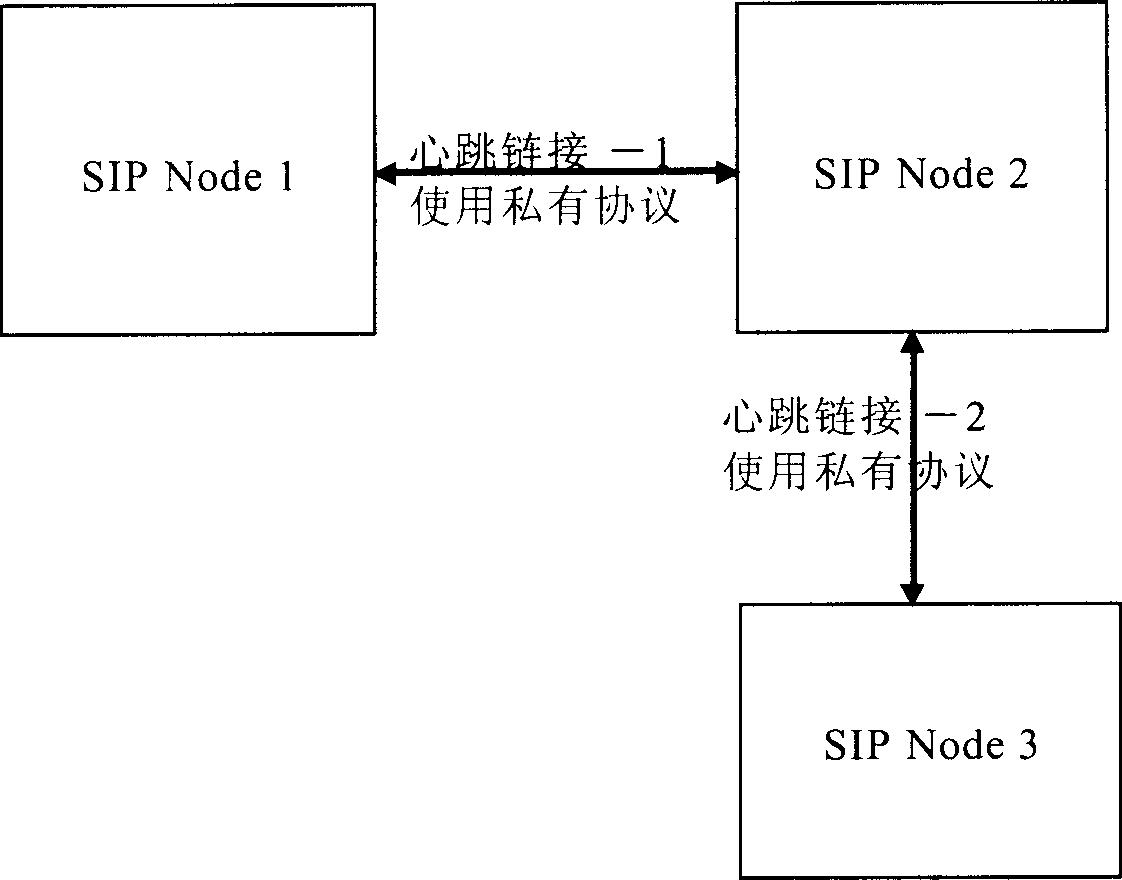
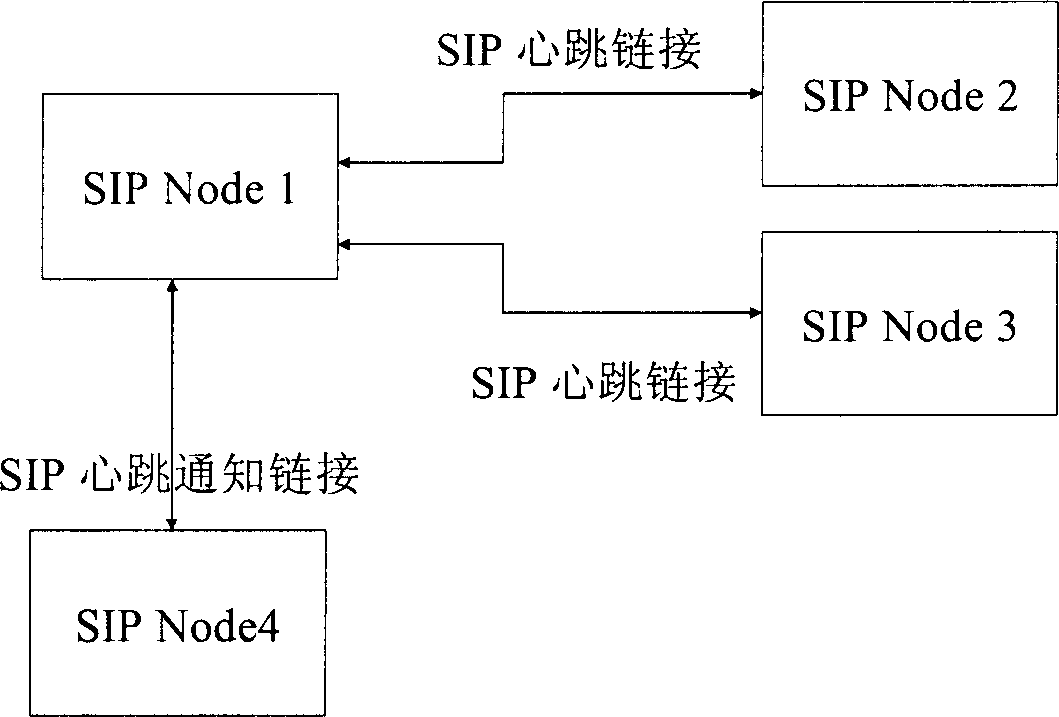
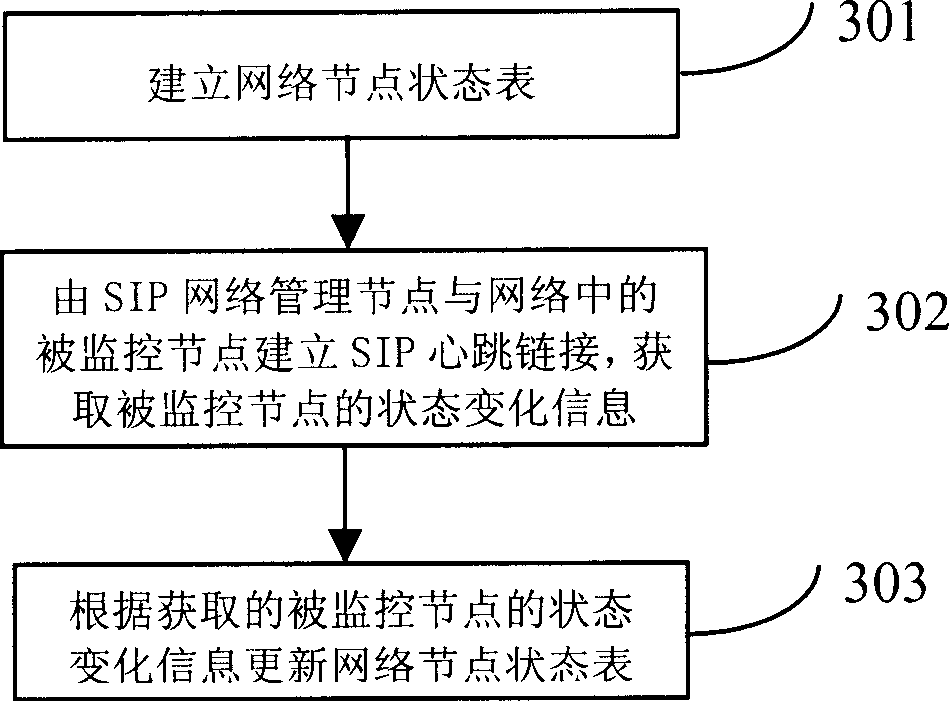
Method and system for acquiring initial protocol network node status of a session
InactiveCN1700694AWide supportReduce loadData switching by path configurationNetwork linkDependability
This invention discloses one method and system to get the initial dialogue network joint, wherein the method comprises the following steps: setting dialogue initial agreement SIP management points; monitoring the SIP network other points through the standard SIP messages; getting other joints status information through management joint order information. The system contains the following parts: at least one reliable servo to provide network linkage; status management servo to monitor network linkage status; at least one reliable order servo to order the forms of the servo joint changes to the status management servo.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
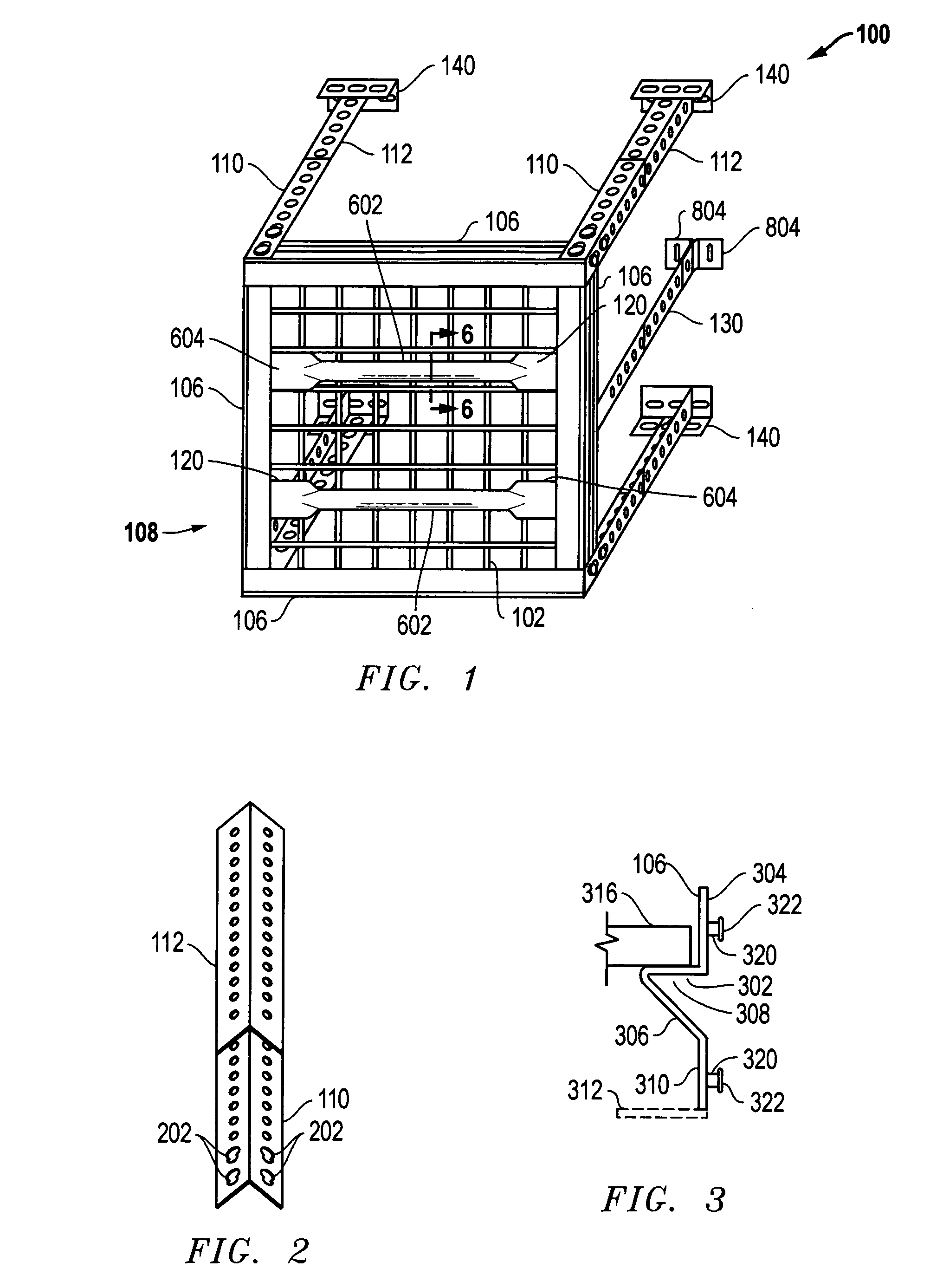
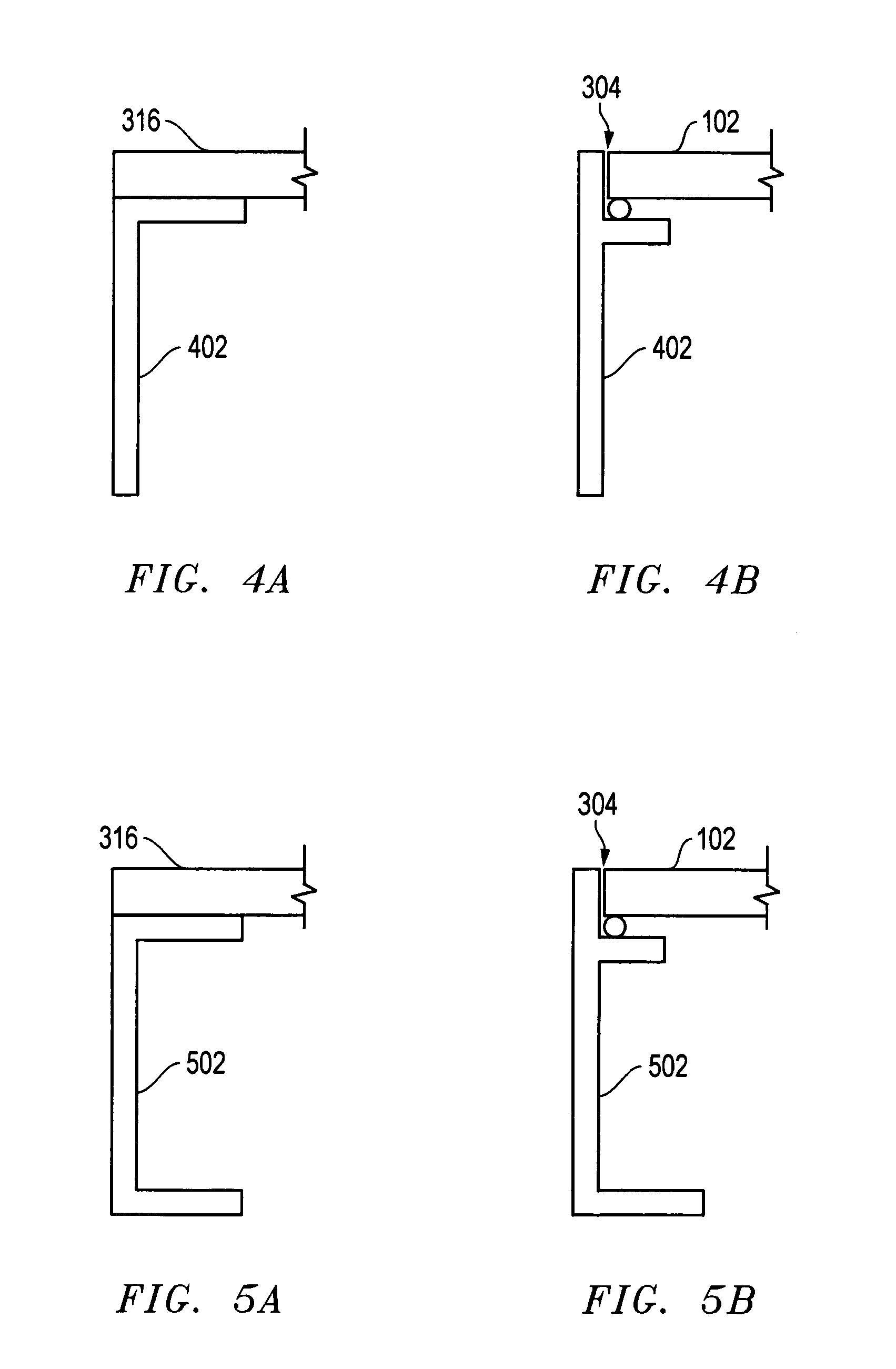
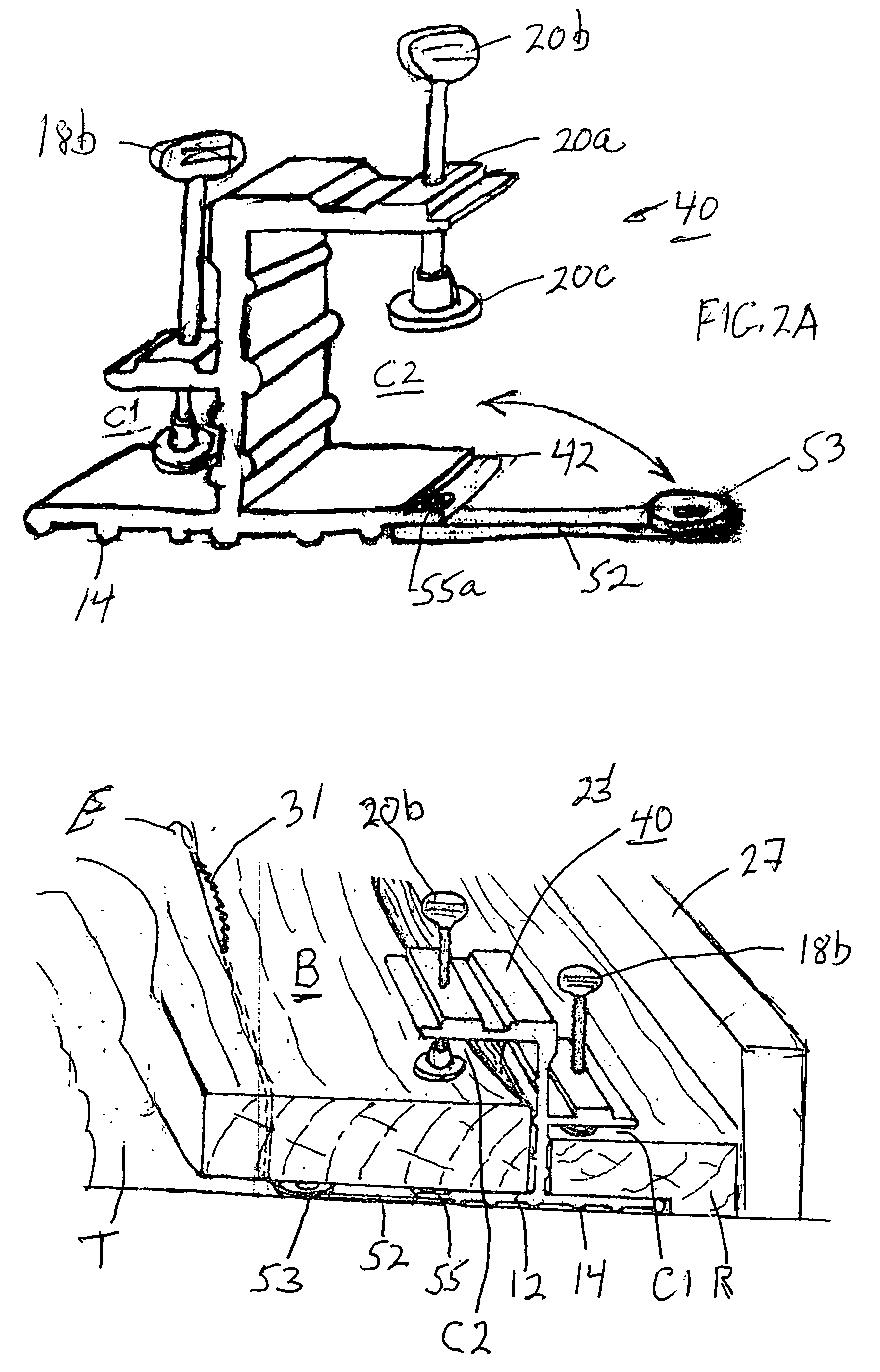
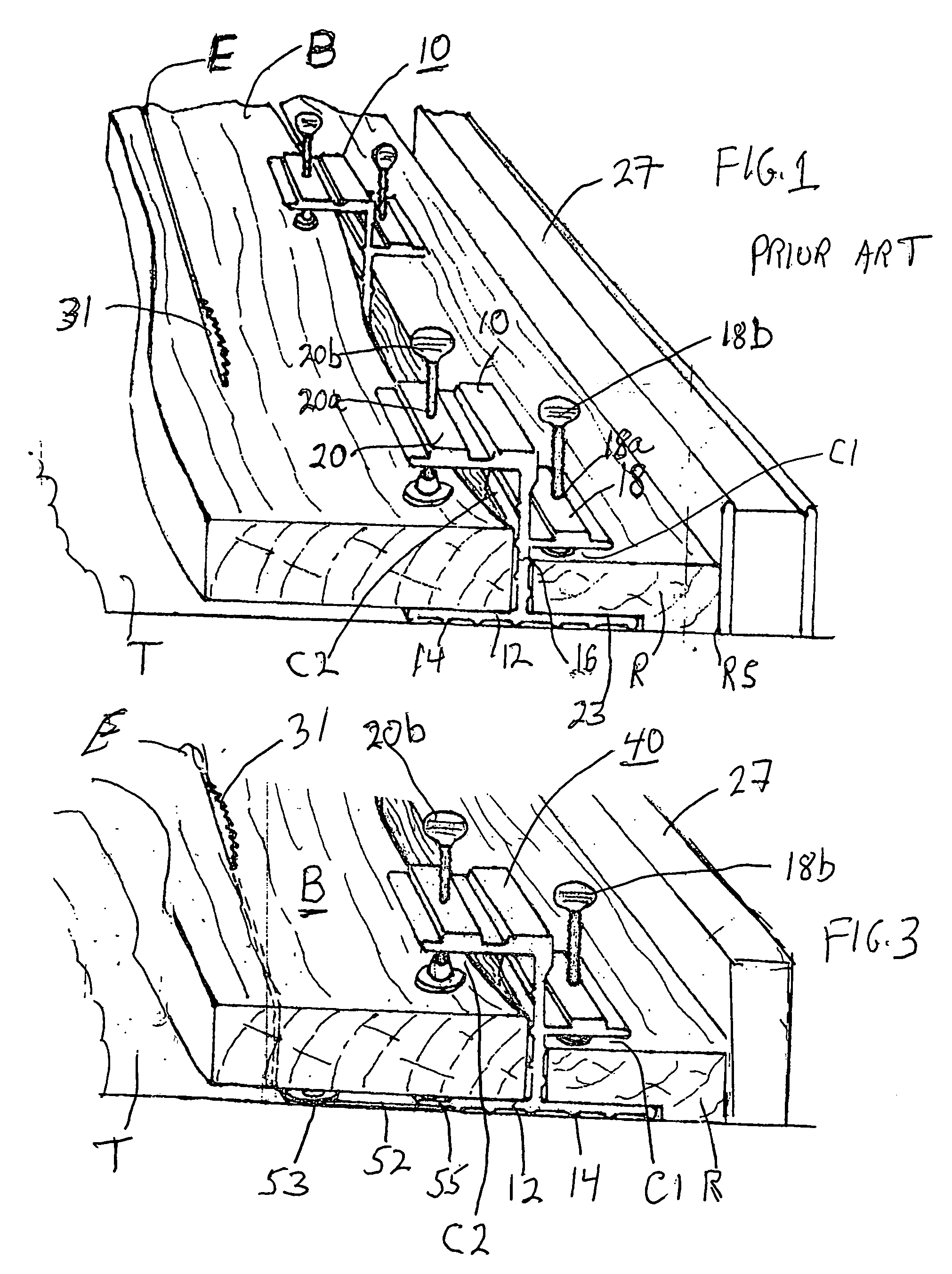
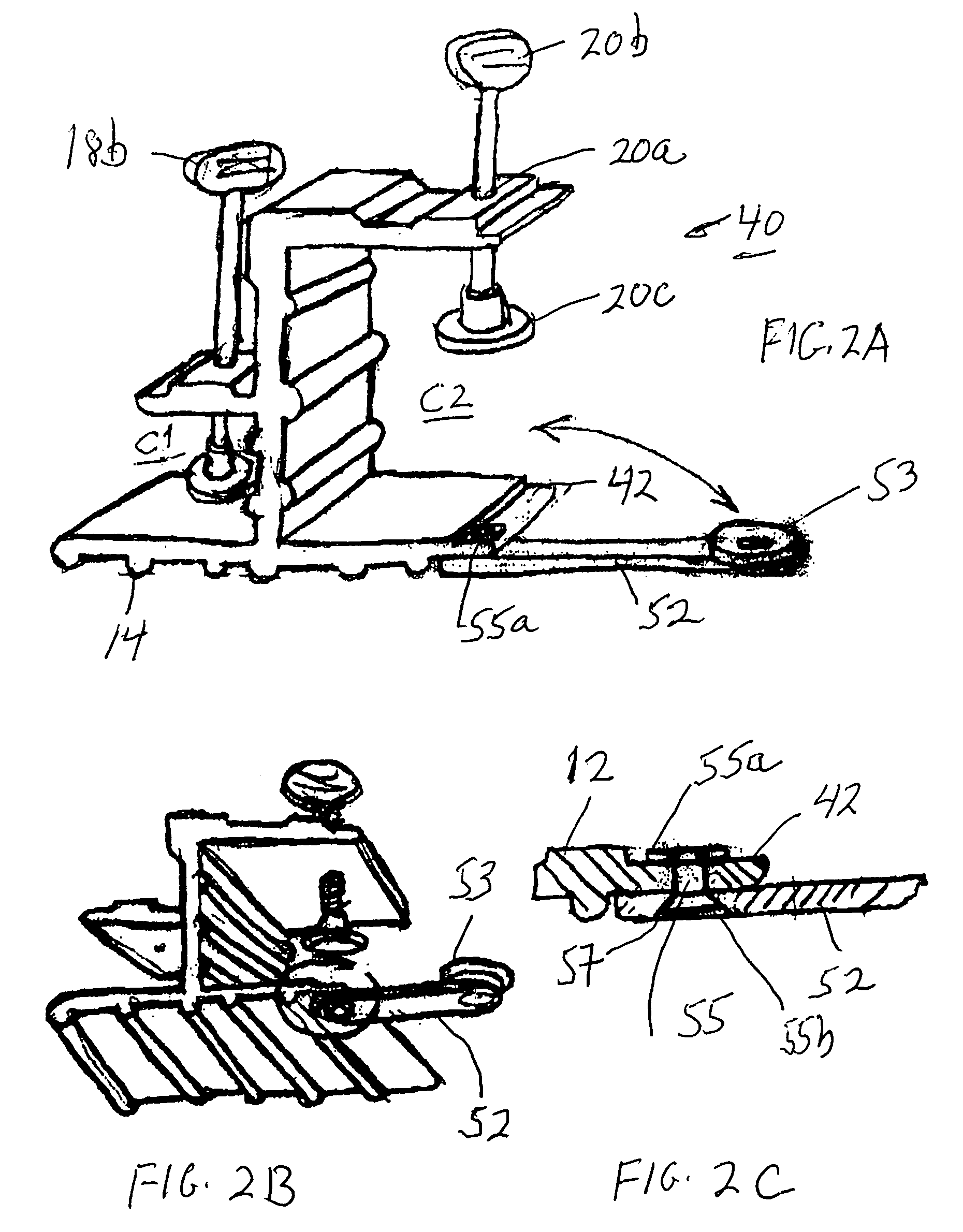
Overhead storage system
InactiveUS7543538B2A large amountEasy to assembleBed-tablesFurniture partsUltimate tensile strengthThreaded fastener
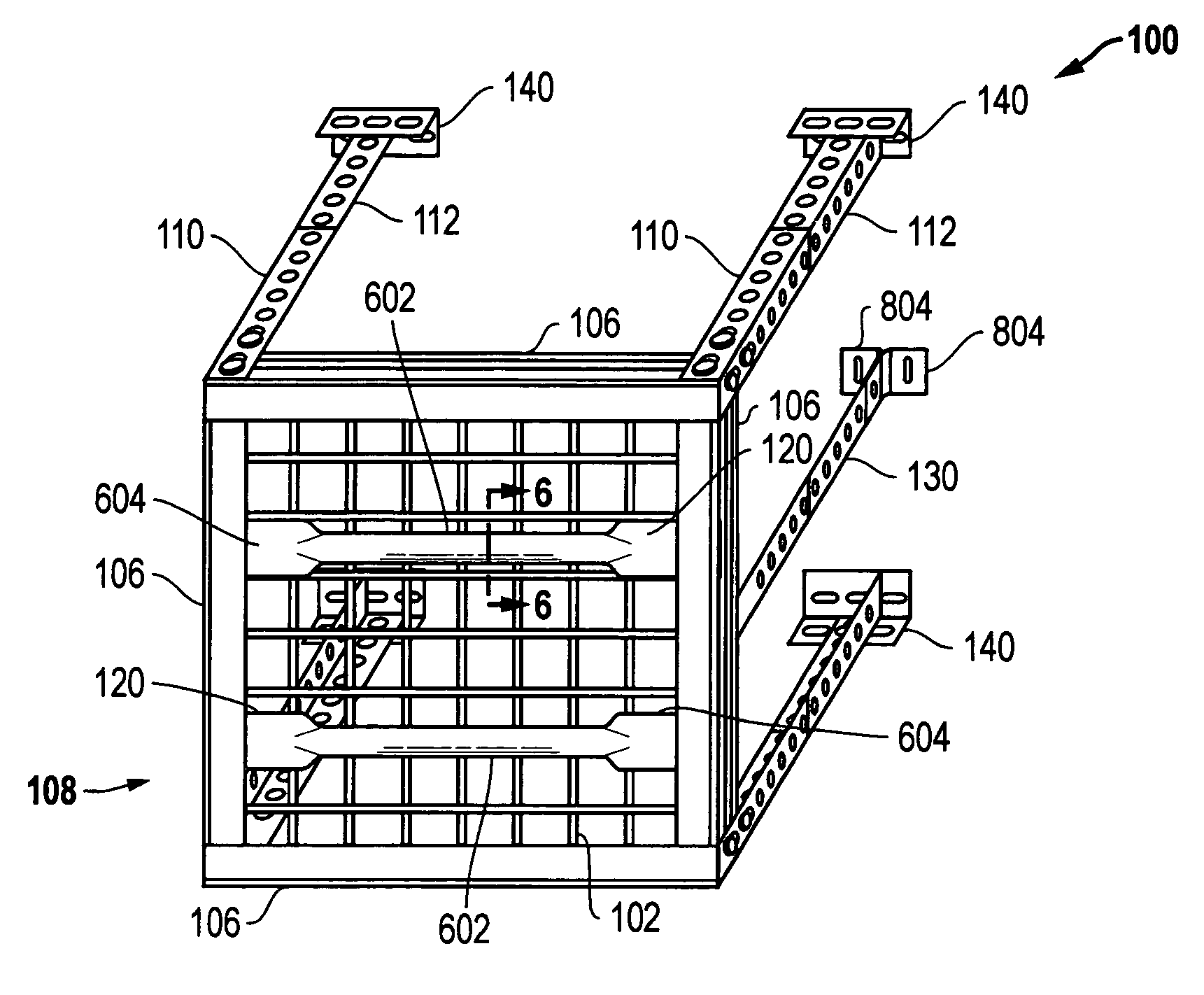
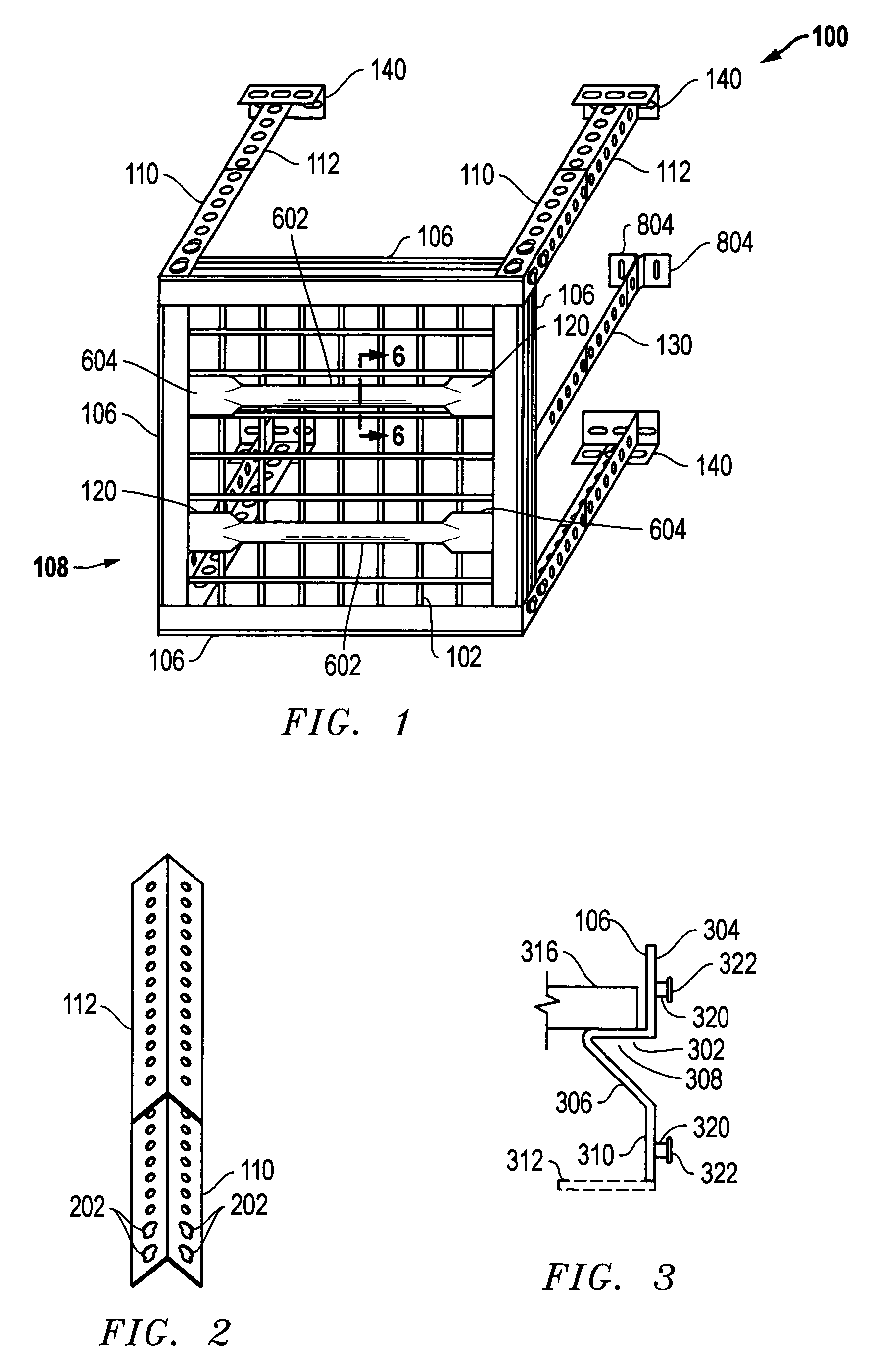
An overhead storage system includes support beams forming a frame to a deck around its perimeter and four corner vertical mounts for suspending the deck from a ceiling. The frame is preferably made of Z-shaped beams supported by vertical L-shaped corner supports to provide strong support for a deck. The Z-shaped beams provide strength and a horizontal surface on which a deck can be rested. A welded wire deck can be strengthened by bonding it to ribs. In some embodiments, center supports can preferably be positioned anywhere along the length of the support beams, and do not require holes in the beams for mounting. The beams are preferably connected to the vertical corner brackets without using threaded fasteners, thereby making the assembly easier for assembly by a homeowner.
Owner:BAEZ MICHAEL
Device support
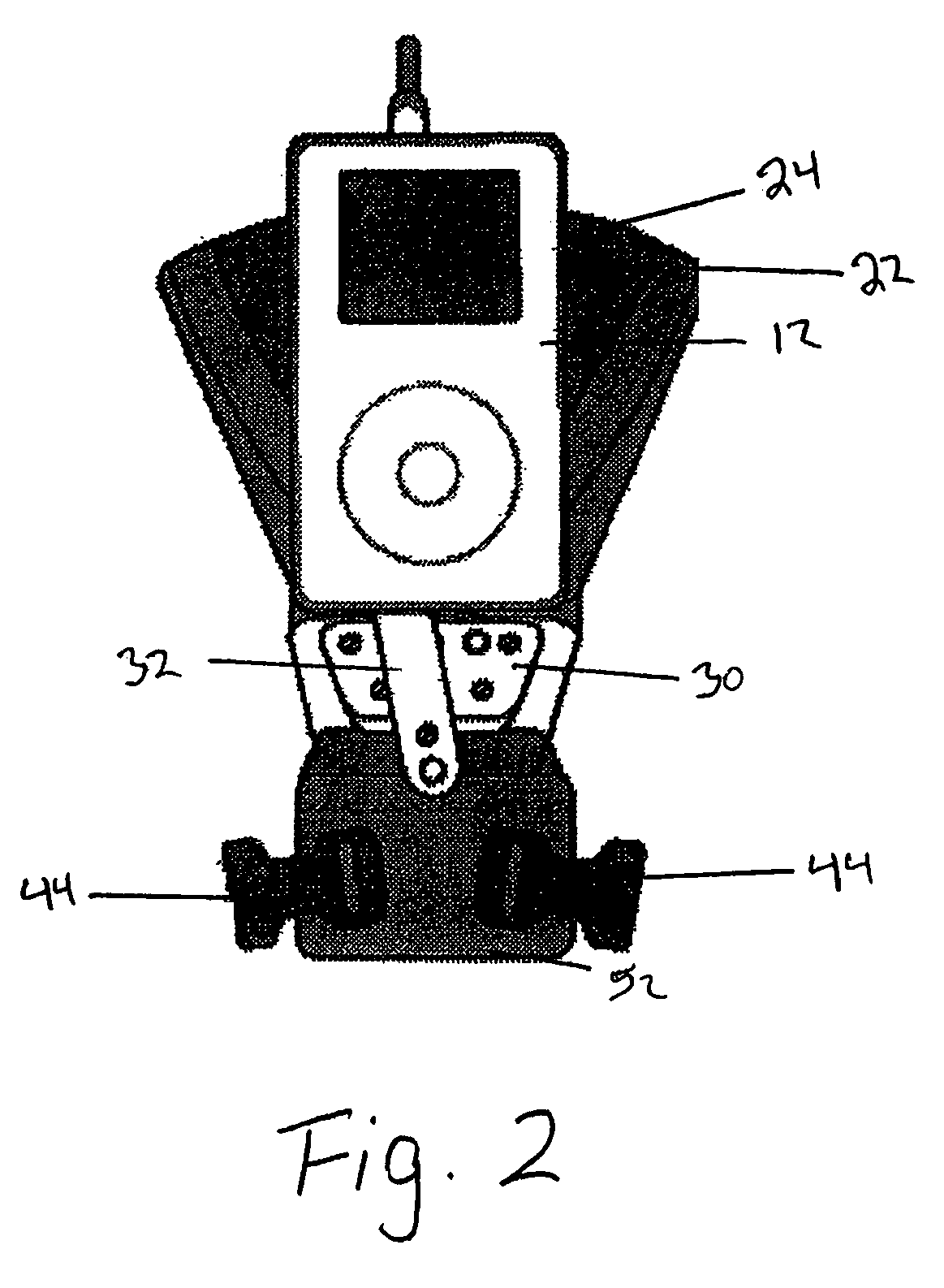
InactiveUS7665641B2Wide supportSolution to short lifeTravelling sacksTravelling carriersSupporting systemEngineering
A support system for devices having a back plate, and a support arm connected to the back plate, the support arm having a plate section with a device connection, the support arm configured to be jointed from the back plate, the back plate and the support arm in conjunction configured to hold a device in any one of a plurality of positions, wherein the support system is configured to be worn by an individual.
Owner:KAUFMAN JASON
Jointer clamp
Owner:GEN TOOLS & INSTR
System for Factoring Synchronization Strategies From Multimodal Programming Model Runtimes
InactiveUS20090013035A1Wide supportMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionApplication serverInteraction management
Owner:HOSN RAFAH A +3
Respiration pillow
A device for face-down, prone respiration comprising a head support made of resilient material having a facial cavity conformable to the contours of a person's face, a plenum cavity in fluid communication with the person's face, a substantially L-shaped support base removably engaged to the head support, a horizontal member of the base engaged underneath the head support and a vertical member of the base engaged to an end of the head support proximate to the facial cavity and in fluid communication with the plenum cavity, the vertical member having at least one air pump intake pathway and at least one exhalation discharge pathway integral to the base whereby air pumped through at least one air pump intake pathway creates a plenum in plenum cavity which is inhaled by person and air exhaled by person is discharged back into plenum cavity and out the at least one exhalation discharge pathway.
Owner:GOFF COMM
Overhead storage system
InactiveUS7421957B2A large amountEasy to assembleBed-tablesFurniture partsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
An overhead storage system includes support beams forming a frame to a deck around its perimeter and four corner vertical mounts for suspending the deck from a ceiling. The frame is preferably made of Z-shaped beams supported by vertical L-shaped corner supports to provide strong support for a deck. The Z-shaped beams provide strength and a horizontal surface on which a deck can be rested. A welded wire deck can be strengthened by bonding it to ribs. In some embodiments, center supports can preferably be positioned anywhere along the length of the support beams, and do not require holes in the beams for mounting. The beams are preferably connected to the vertical corner brackets without using threaded fasteners, thereby making the assembly easier for assembly by a homeowner.
Owner:BAEZ MICHAEL
Data constraints for polyglot data tiers
InactiveUS20160321277A1Guaranteed extensibilityWide supportDatabase distribution/replicationFile access structuresRecord extractData source
A Data Constraint Engine (100) for enforcing data constraints in a polyglot data tier (20) having a plurality of database-specific data stores (21, 22, 23) of various types such as an RDBMS (21), a Triplestore (22), and a MongoDB (23). The Data Constraint Engine uses the concept of a unified data model based on “records” in order to allow data constraints to be defined (using so-called “record shapes”) in a store-agnostic way. The Data Constraint Engine includes APIs (130) for processing incoming requests from remote clients (30) relating to data in the polyglot data tier, for example a request to create or update data in a data store. The APIs extract, from such a request, a record corresponding to the data specified in the request and a data source identifier identifying the data store holding the specified data. Then, on the basis of the record extracted by the interface, an appropriate record shape is extracted from a shapes catalogue (110), the record shape determining the structure of the record. Validators (120) each validate the record against the record shape according to various criteria such as format, data type, cardinality and slot count. If the record is validated, a record dispatcher (140) directs the specified data to the appropriate data store using the data source identifier. Data read from a data store can be validated in the same way.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Word document format checking method
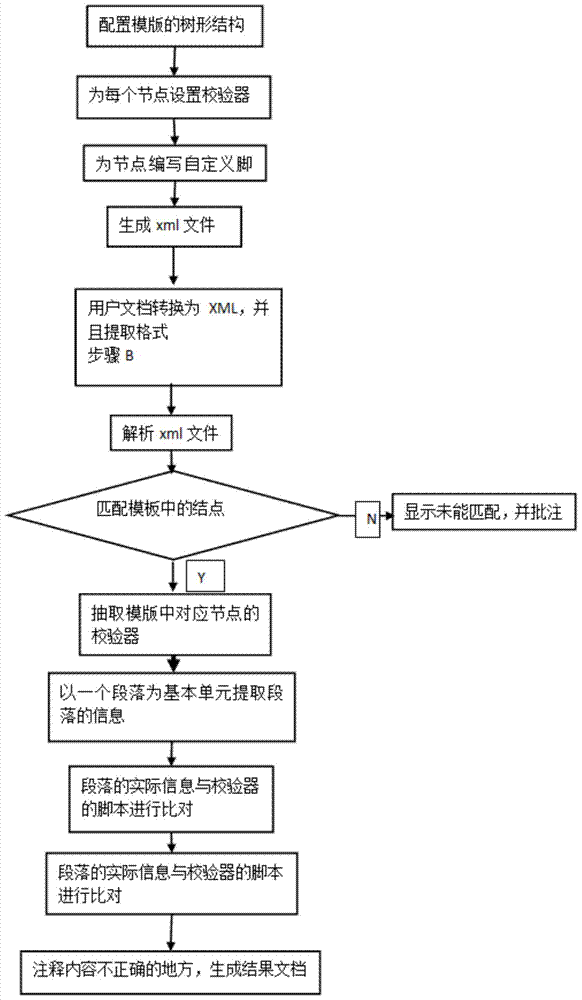
ActiveCN103886098AReduce manpower consumptionWide supportSemi-structured data retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDocument formatDocument preparation
The invention discloses a Word document format checking method. The Word document format checking method comprises the following steps that (A) corresponding template rules for certain kinds of documents are configured, and the template rules comprise modules which form documents, a calibrator needing to be met by each paragraph and the like; (B) through the utilization of the Word-to-xml technology, the documents uploaded by the user are converted into xml files, and specific formats of the documents are extracted in the xml files; (C) according to configured templates, matching checking is carried out on the formats extracted through the documents of the user, specific information of incorrect places is fed back, and result documents are generated. The Word document format checking method has the advantages that the Word document format checking method based on a J2EE helps the user to check the incorrect parts of the formats of the documents, comments are given to facilitate corrosion of the user, and thus consumption of manpower in format checking is reduced. The Word document format checking method is based on the template rules, the templates can be built freely under a framework supported by a system, and support for the documents is quite wide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV CITY COLLEGE
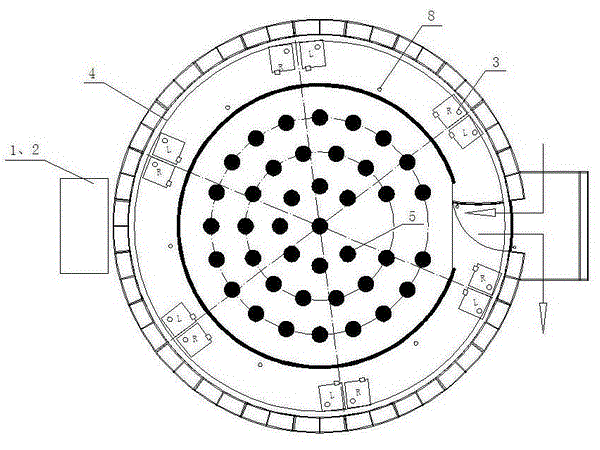
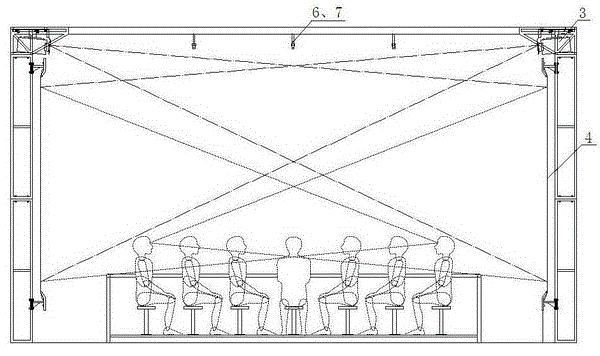
Five-dimensional (5D) 360-degree ring screen digital stereoscopic cinema system
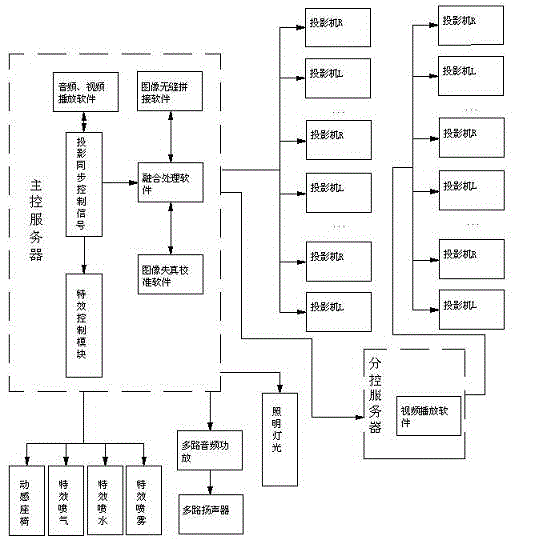
ActiveCN103064245AShocking viewing experienceGood development and application prospectsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Image processing software
A five-dimensional (5D) 360-degree ring screen digital stereoscopic cinema system and a showing device thereof are characterized in that the 5D 360-degree ring screen digital stereoscopic cinema system comprises a main control server, a branch control server, projection equipment, watching equipment and a special effect generating device. The main control server comprises a control module, audio-video playing software and image processing software. According to the 5D 360-degree ring screen digital stereoscopic cinema system, a 5D movie and a 360-degree ring screen movie are combined into a whole, a video signal is output through the main control server, processed through the image processing software and displayed through the projection equipment, a shown stereoscopic image can surround audiences, the stereoscopic image rushes out of a ring screen and reaches to a position in front of eyes of the audiences, and passes through the audiences to a position behind the audiences, scenes provided by a movie and stereoscopic dynamic images surround and penetrate through the positions all around the audiences, the audiences can be personally on the scenes in a high-emulation mode, and the movie images are integral, continuous and lifelike.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINGYING DIGITAL TECH +1
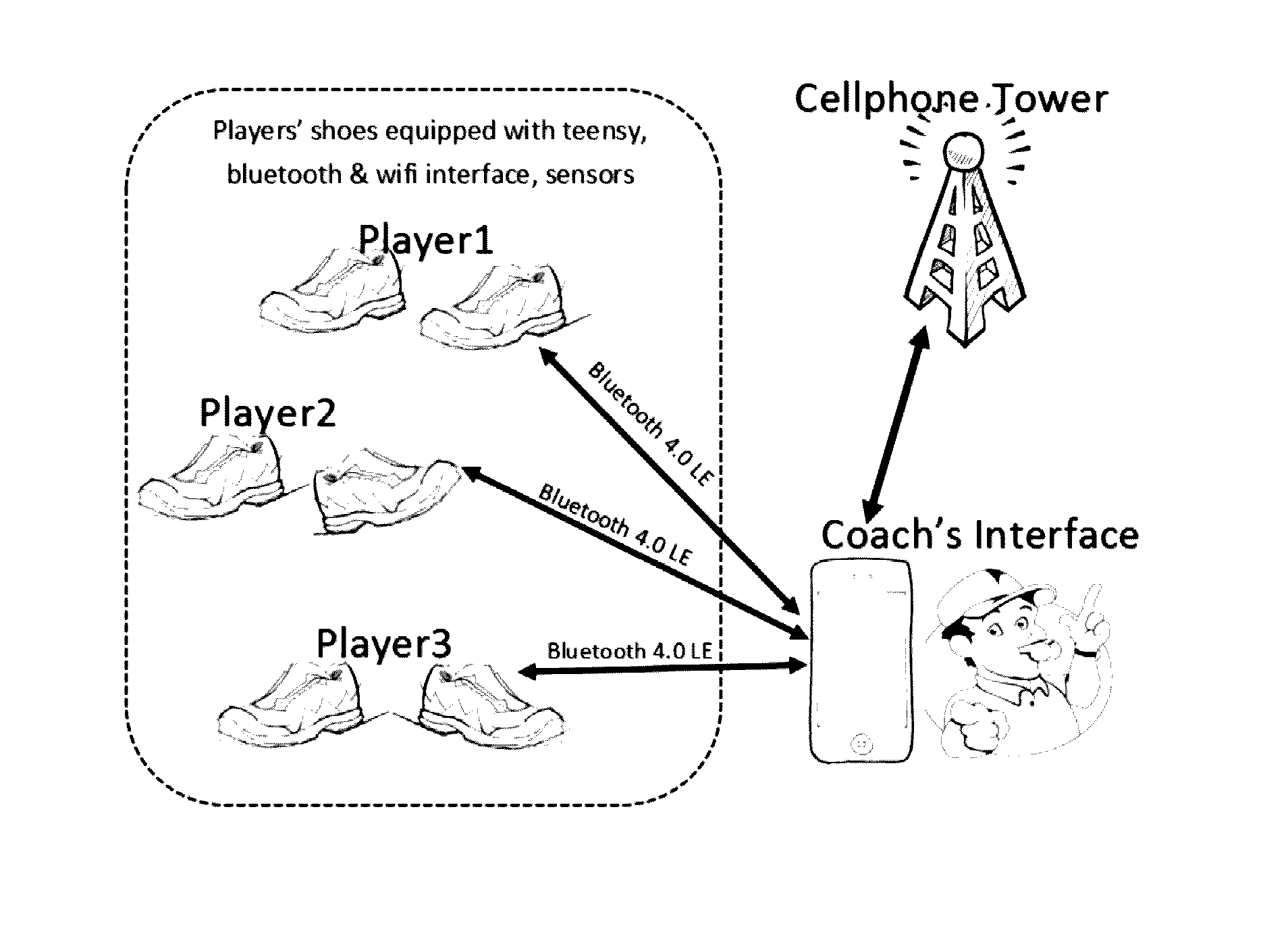
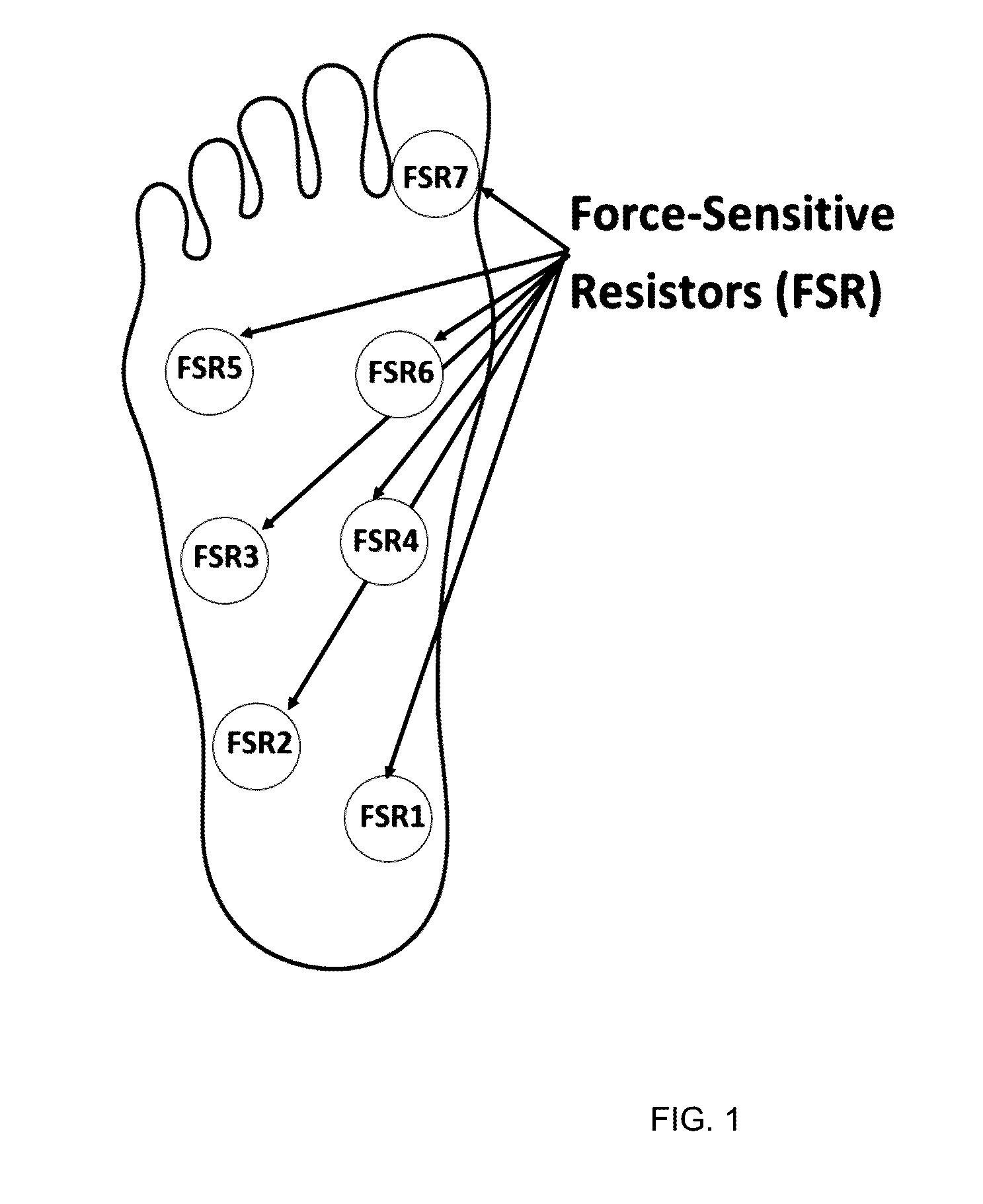
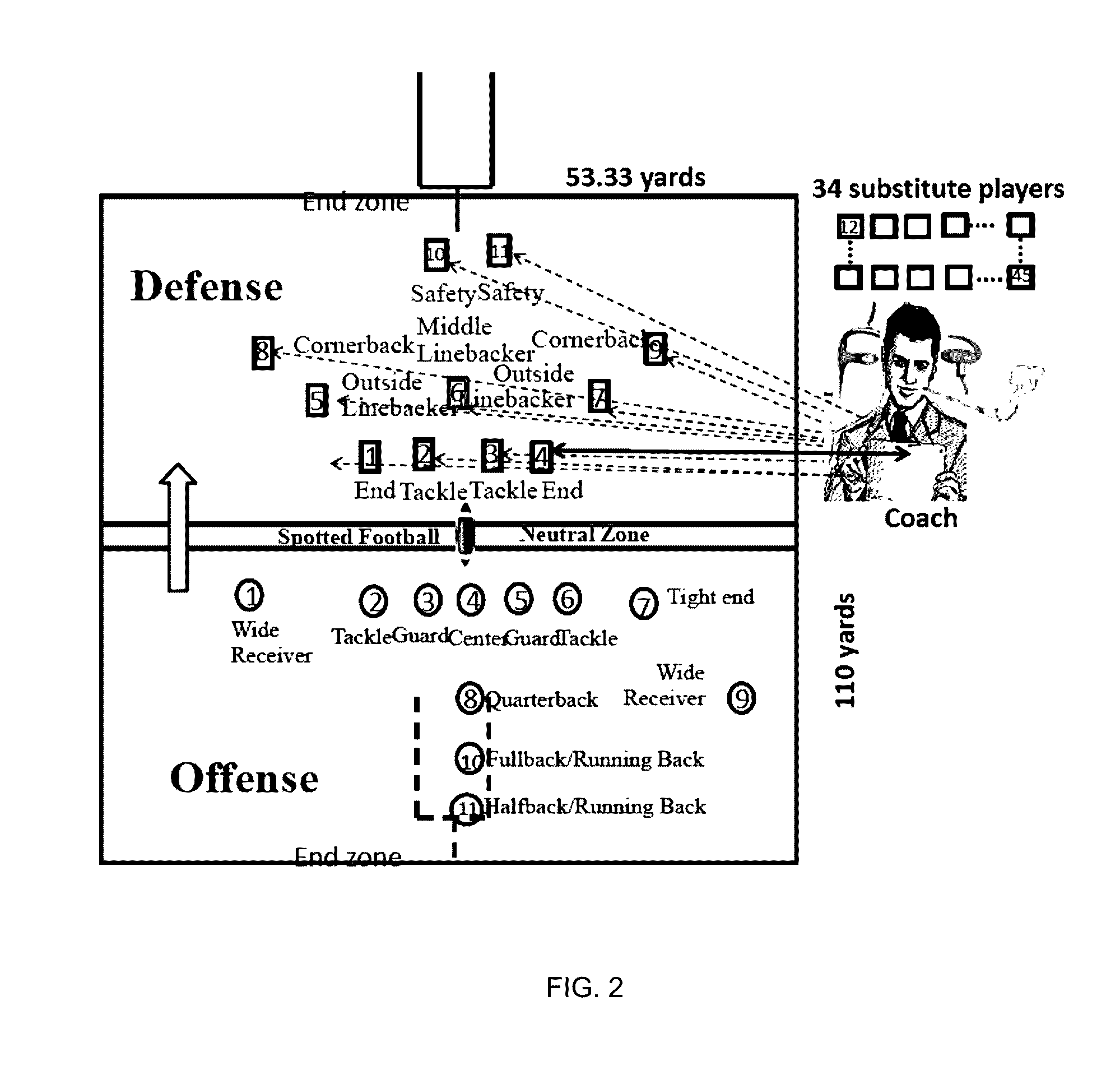
System and method for real-time personnel fatigue level monitoring
ActiveUS20160345865A1Enhancing athlete performanceWide supportPhysical therapies and activitiesGymnastic exercisingAccelerometer dataBody contact
The present invention relates to analyzing fatigue level of users by transmitting pressure data from user's shoes wirelessly for real-time monitoring. Athletes for in body-contact games such as football, are often suddenly forced out of games due to injuries as it is often difficult to ascertain the nature of the injury on the field. The present invention enables a coach to have an ability to monitor performance of the athletes as they play, thus help in determining current level of athlete's injury, and help in preventing career threatening and / or fatal injuries. Further, pressure sensors can be used to determine fatigue detection and can be verified by readings from knock sensor, accelerometer data, etc. Variations in all such sensors for a time slice t-seconds can be used as an indicator for fatigue.
Owner:AGRAWAL DHARMA P
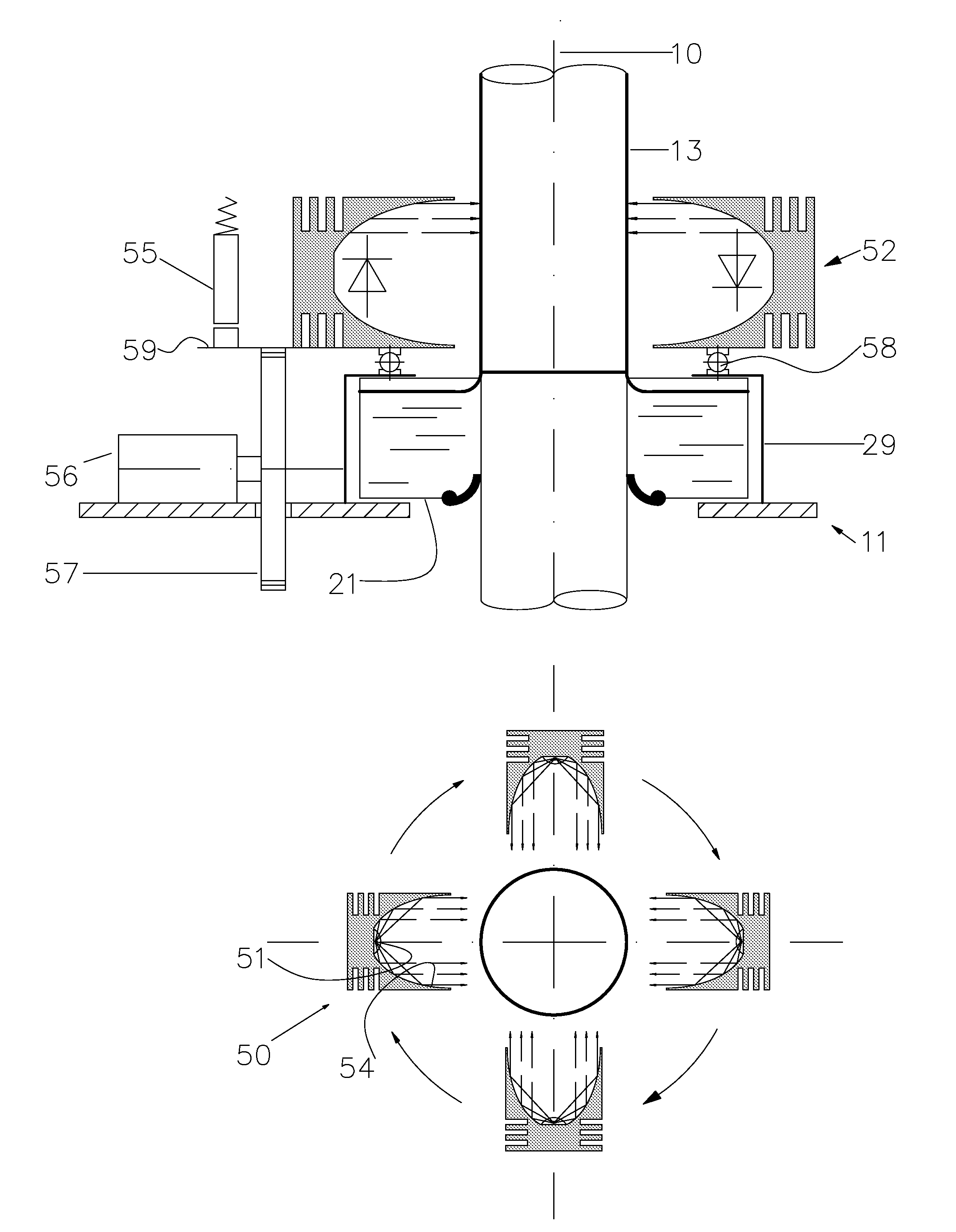
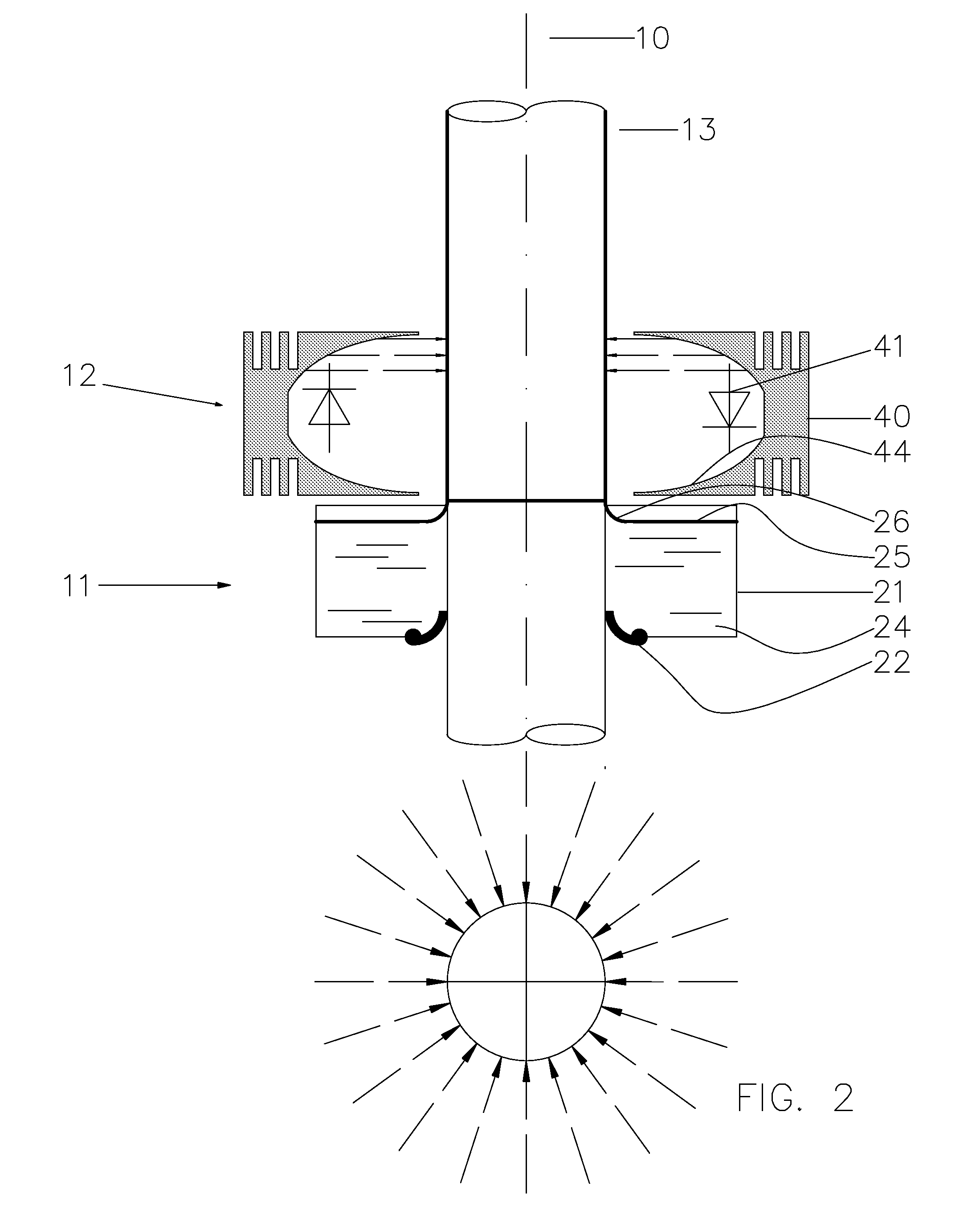
Device for coating a peripheral surface of a sleeve body
InactiveUS20090241788A1Limited floor space requirementWide supportSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPretreated surfacesEngineeringRadiation
A coating device for coating a peripheral surface of a sleeve body with a coating formulation includes a vertical support column for supporting a sleeve body in a vertical position coaxial with a coating axis, a carriage slideable along the vertical support column, and an annular coating stage attached to the carriage and moveable therewith for containing the coating formulation and for coating a layer of the coating formulation onto the peripheral surface of the sleeve body during a sliding movement of the carriage along the vertical support column. The coating device includes an irradiation stage that is arranged to be moveable with the annular coating stage and to provide radiation to at least partially cure the layer of coating formulation onto the peripheral surface so as to prevent flow off of the coating formulation.
Owner:AGFA NV
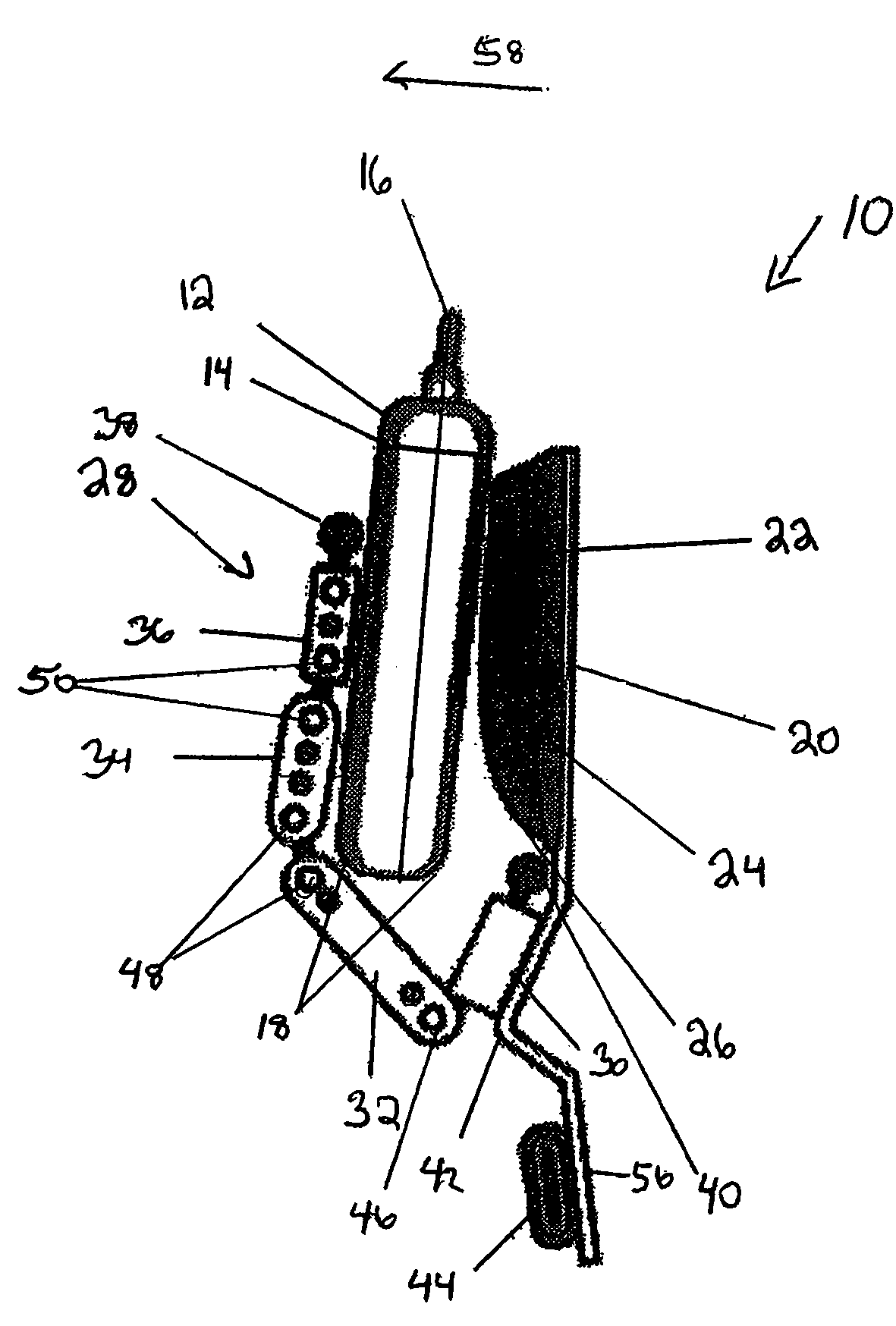
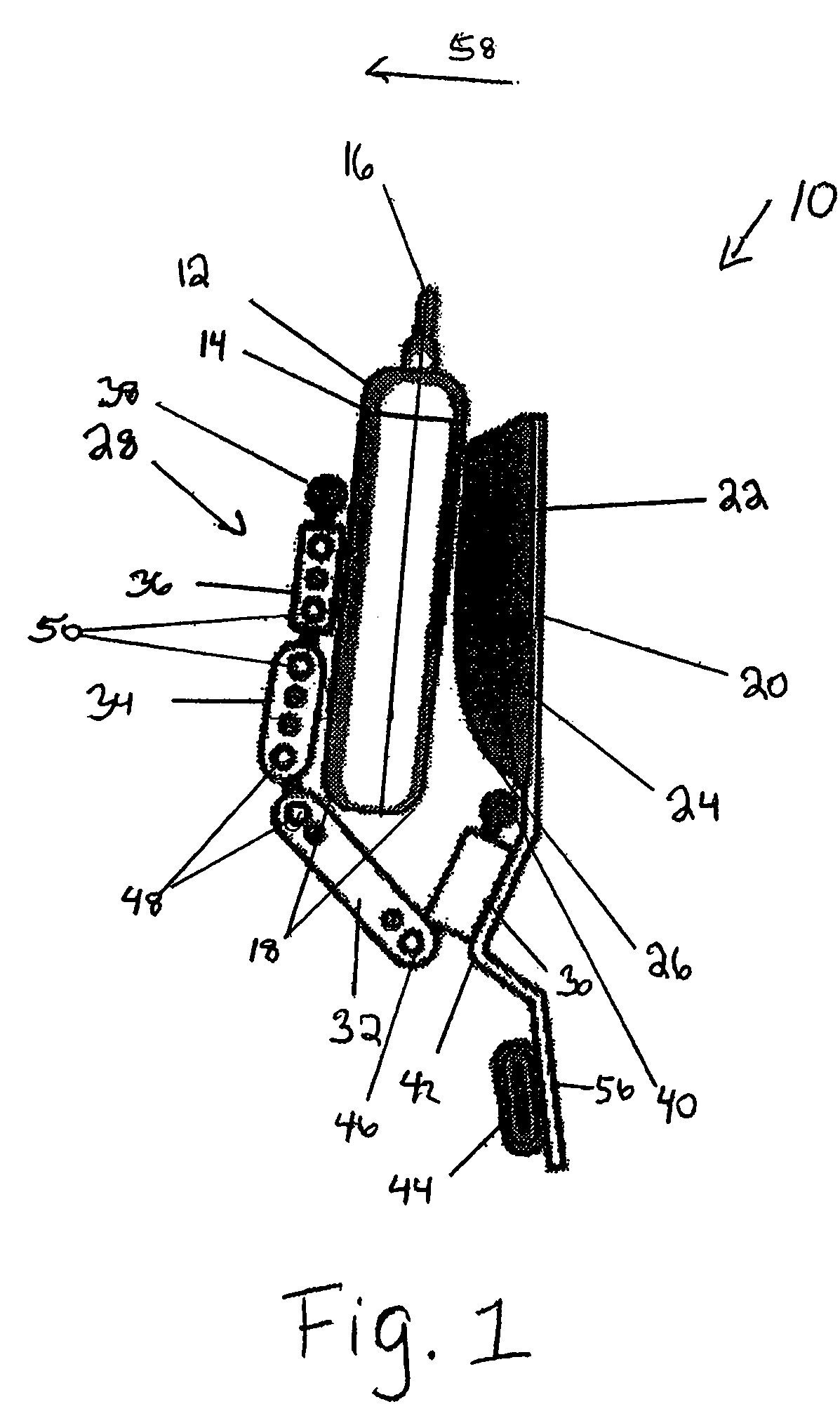
Discretionarily adjustable friction block and tackle balance system and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050283944A1Improved discretionarily adjustable friction blockThe process is simple and effectiveBuilding braking devicesWing openersSash windowBlock and tackle
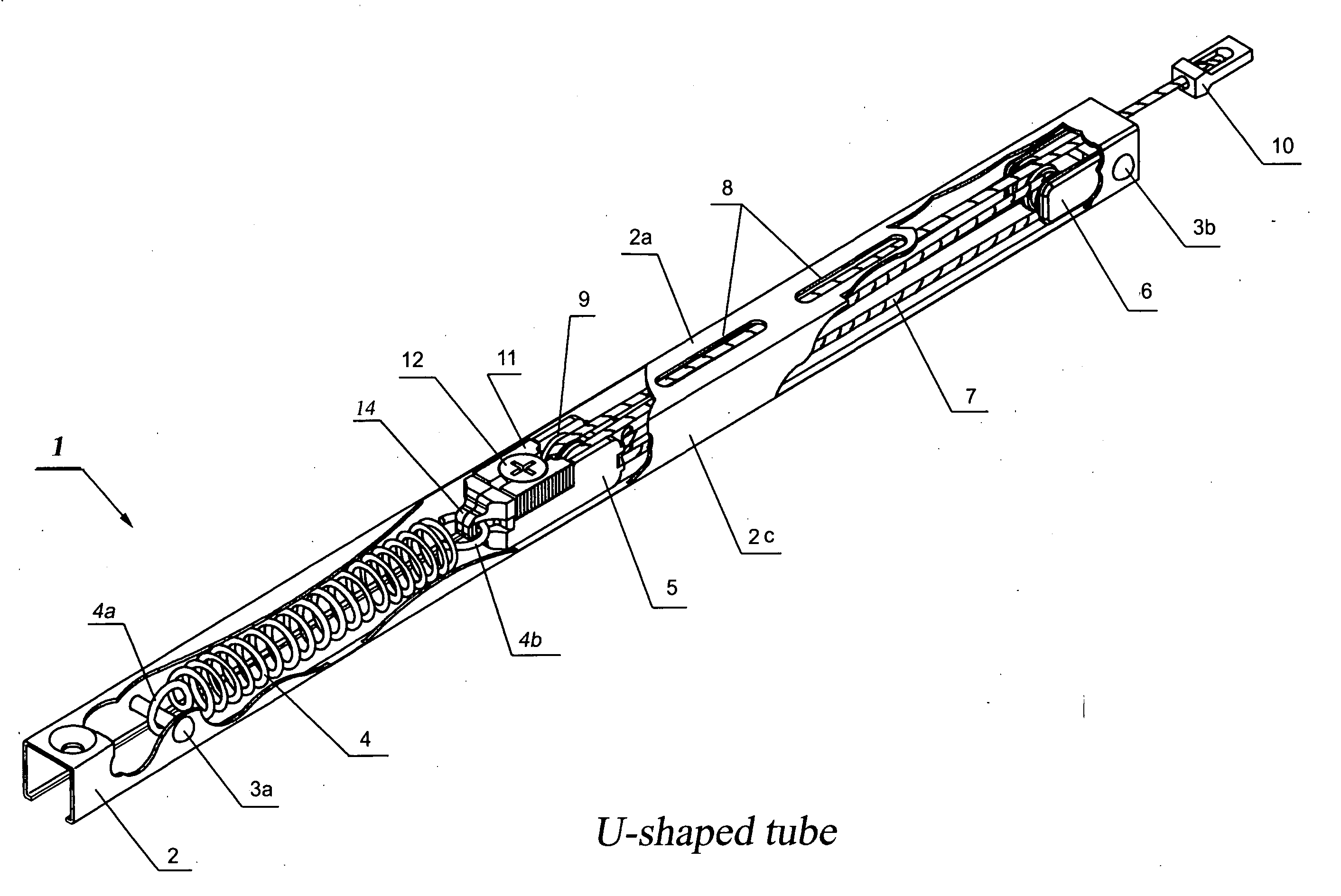
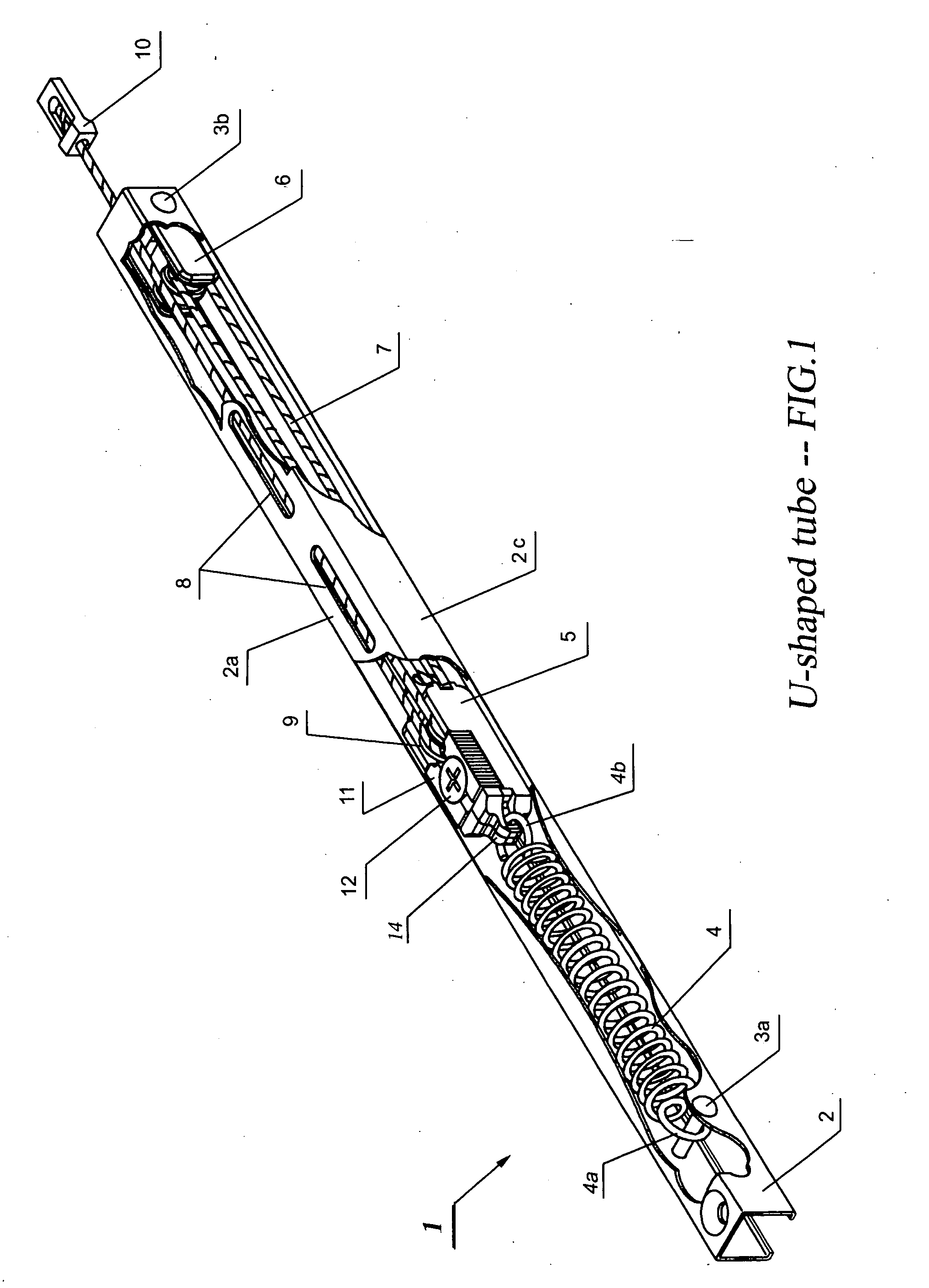
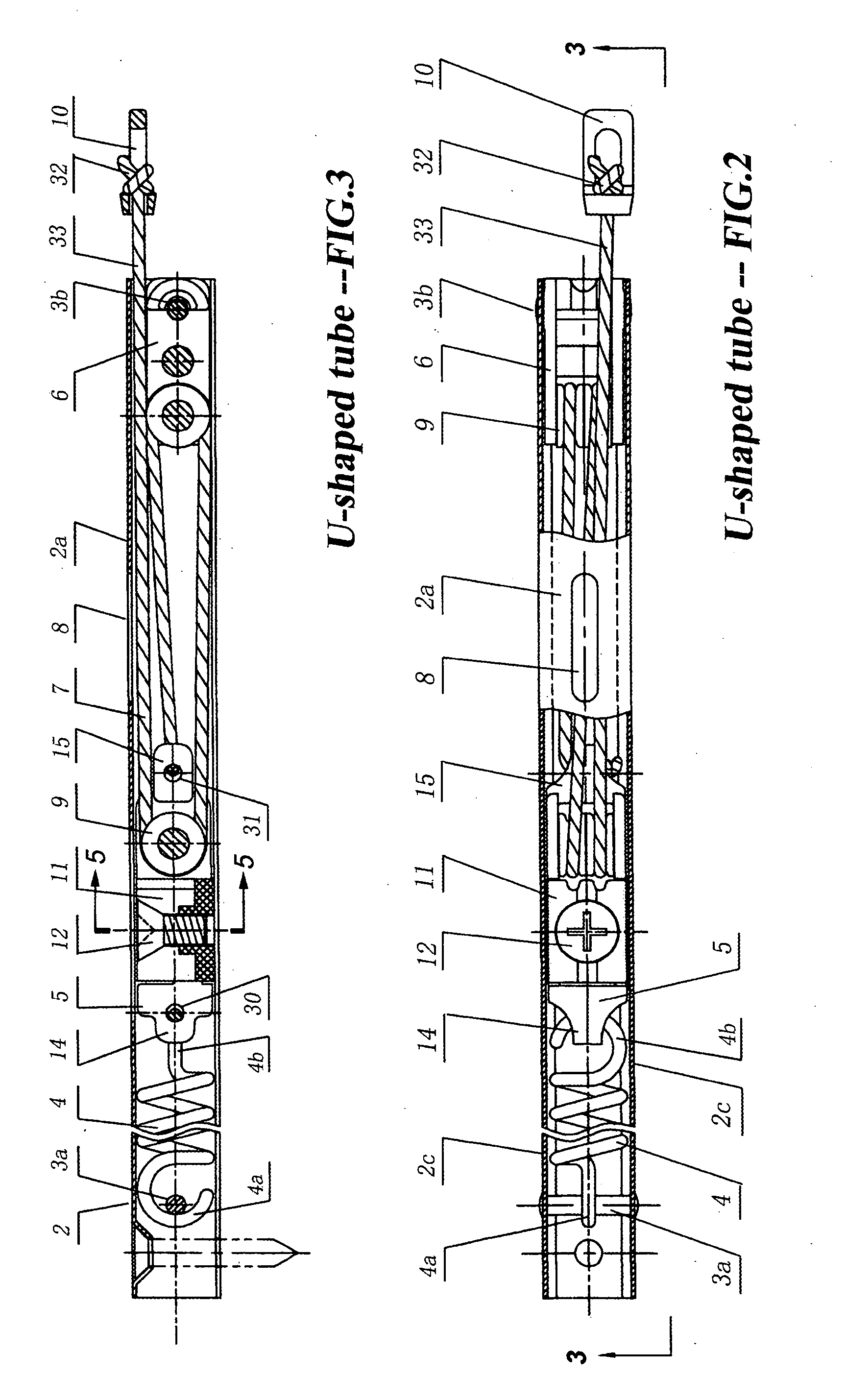
Disclosed is a discretionarily adjustable friction force block and tackle balance system comprising a housing and an adjustable break, wherein means are provided for adjusting the friction force between an inner surface of the housing and the adjustable break. An adjustable balance system comprising a housing, a floating anchor assembly, a fixed anchor assembly, a cord, and an elastic suspension is also disclosed. In an embodiment, the housing is a 3-side or 4-side tube or channel. There is at least one elongated hole or slit on at least one surface of said housing. An adjustable break is mounted inside the floating anchor subassembly. Moving the window sash also causes the floating anchor subassembly to move. When the floating anchor subassembly is moved to a position just under elongated hole on the said housing, the adjust screw installed in the adjustable break is exposed. The desired friction force can be easily created and adjusted by turning the adjust screw in the appropriate direction to splay or retract the adjustable break for balancing window sashes having widely varying sizes and weights.
Owner:WU MINGZE
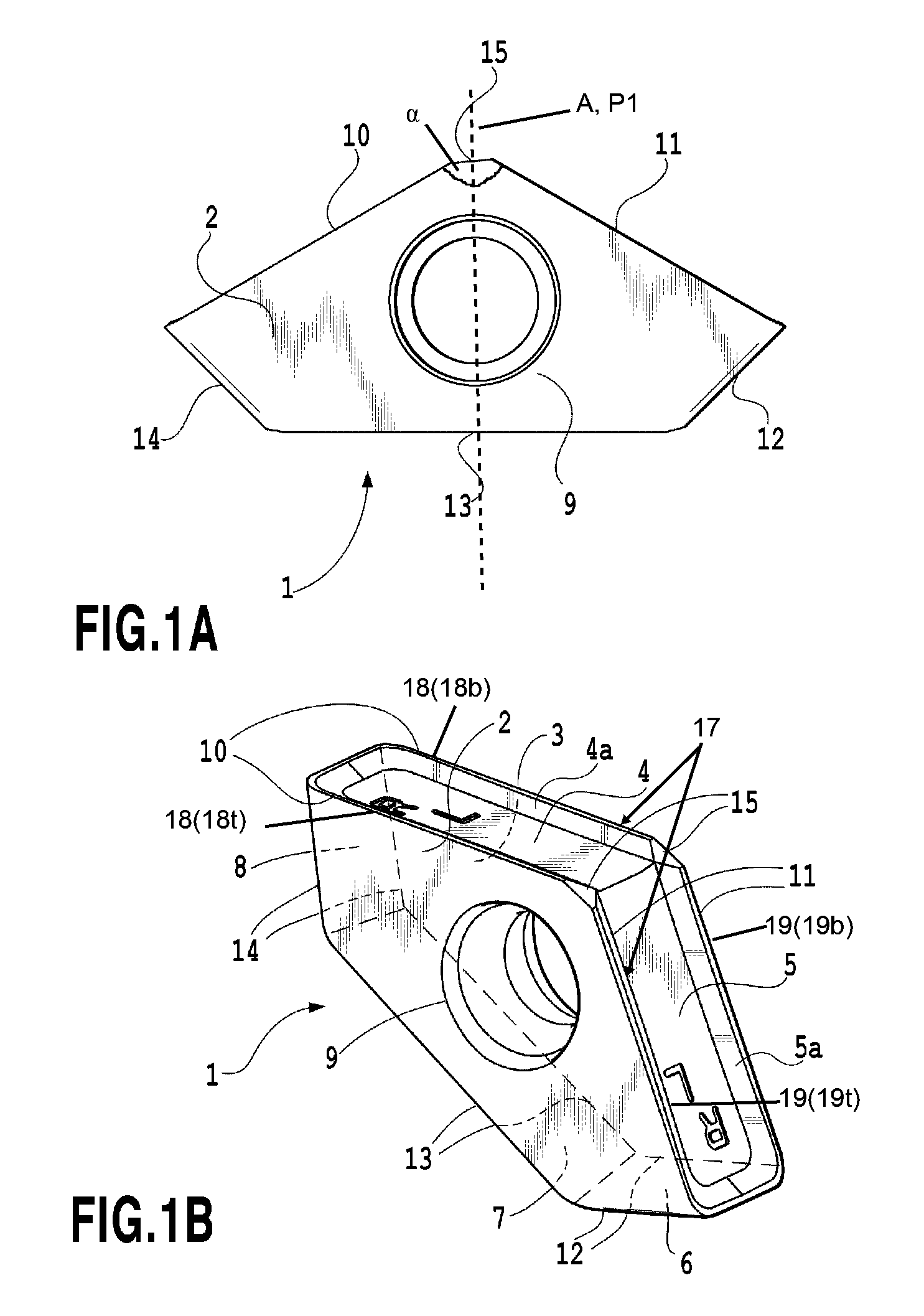
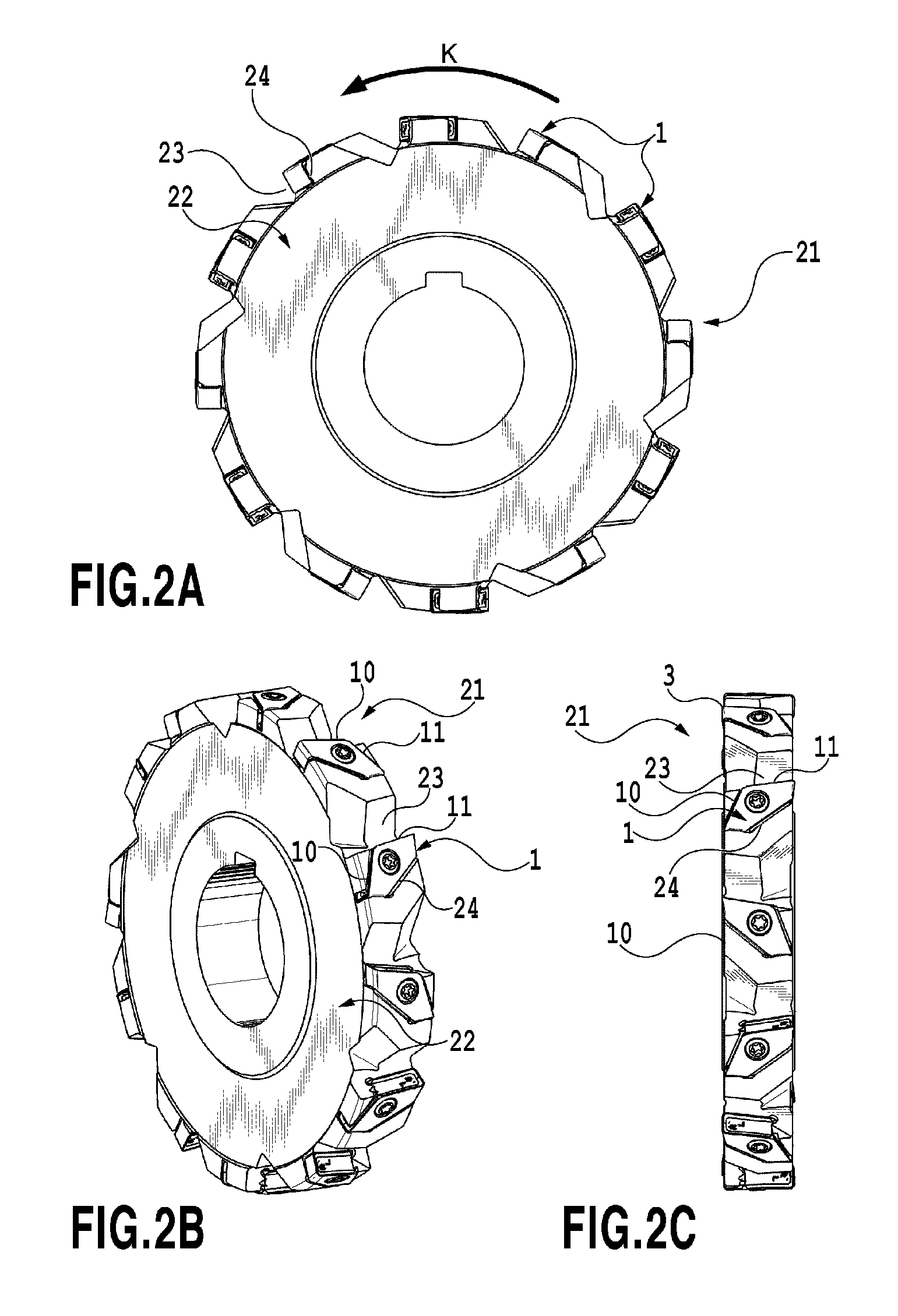
Cutting Insert and Indexable Rotary Cutting Tool
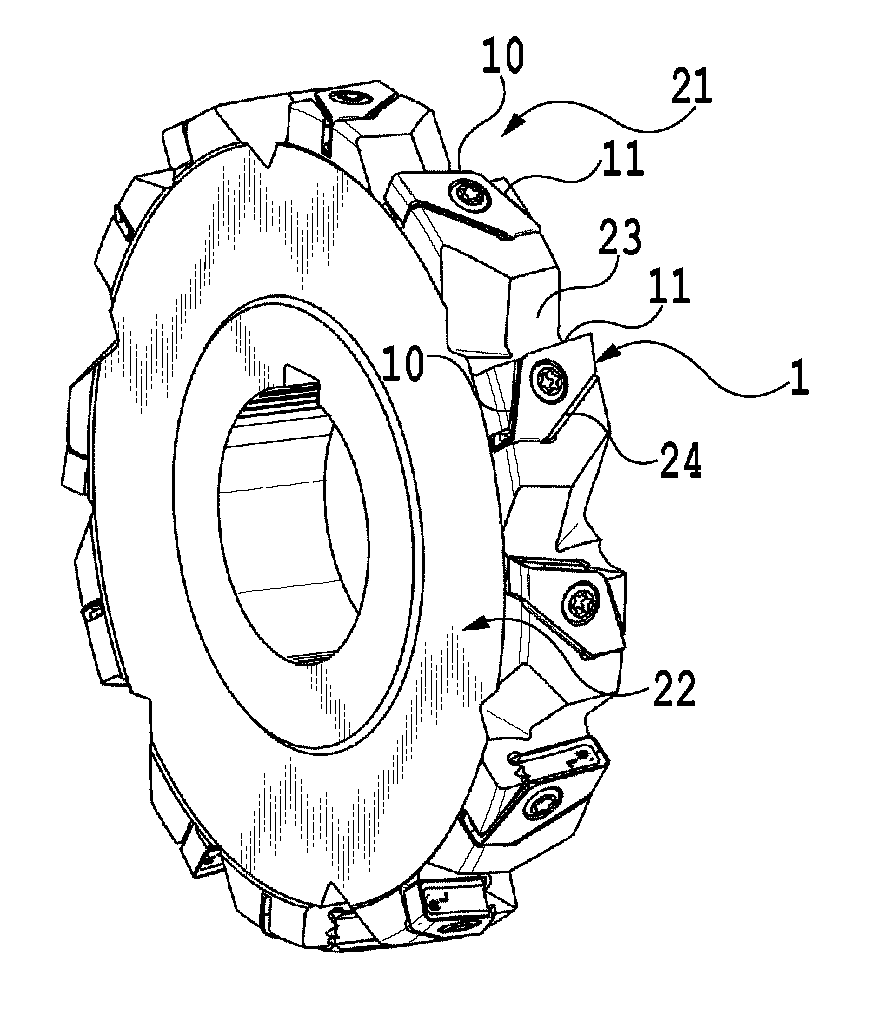
InactiveUS20130129434A1Reduce areaIncrease the areaTransportation and packagingMilling cuttersEngineeringLower face
A cutting insert is arranged in a tangential direction on an outer peripheral portion of a tool body, the cutting insert having a reduced area in a top view thereof. The cutting insert has an upper face, a lower face and at least five side faces extending between the upper and lower faces. The upper face of the cutting insert has at least five intersection portions intersecting with the at least five side faces. The at least five intersection portions include first and second intersection portions and third and fourth intersection portions shorter than the first and second intersection portions, respectively. A cutting edge is formed at each of the first and second intersection portions. A rake face is formed on cutting side faces corresponding to the first and second intersection portions, respectively, while a cutting edge flank is formed on the upper face.
Owner:TUNGALOY CORP
Respiration pillow
A device for face-down, prone respiration comprising a head support made of resilient material having a facial cavity conformable to the contours of a person's face, a plenum cavity in fluid communication with the person's face, a substantially L-shaped support base removably engaged to the head support, a horizontal member of the base engaged underneath the head support and a vertical member of the base engaged to an end of the head support proximate to the facial cavity and in fluid communication with the plenum cavity, the vertical member having at least one air pump intake pathway and at least one exhalation discharge pathway integral to the base whereby air pumped through at least one air pump intake pathway creates a plenum in plenum cavity which is inhaled by person and air exhaled by person is discharged back into plenum cavity and out the at least one exhalation discharge pathway.
Owner:GOFF COMM
A negotiation method for 3G video gateway multi-media decoding and encoding capability
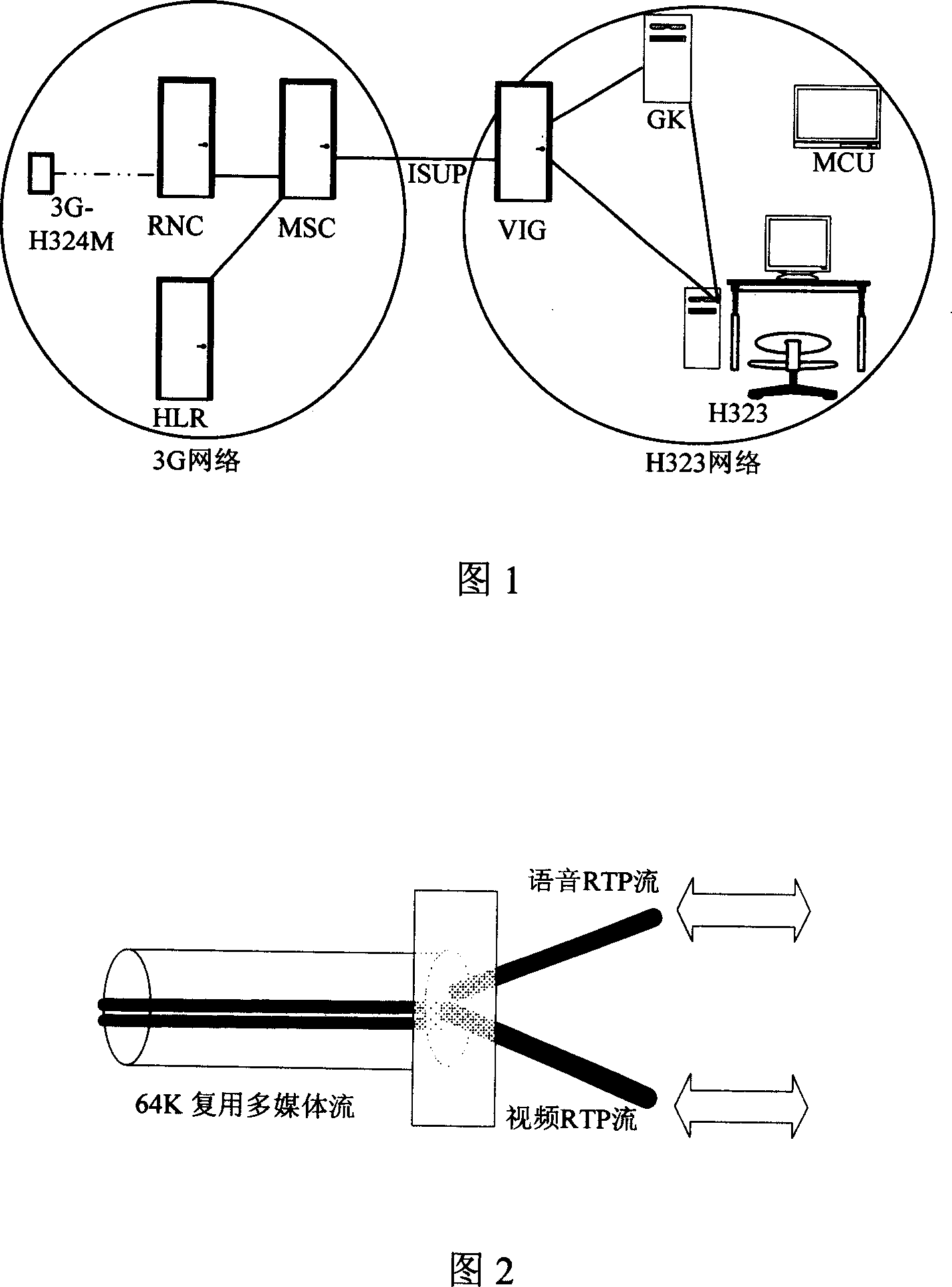
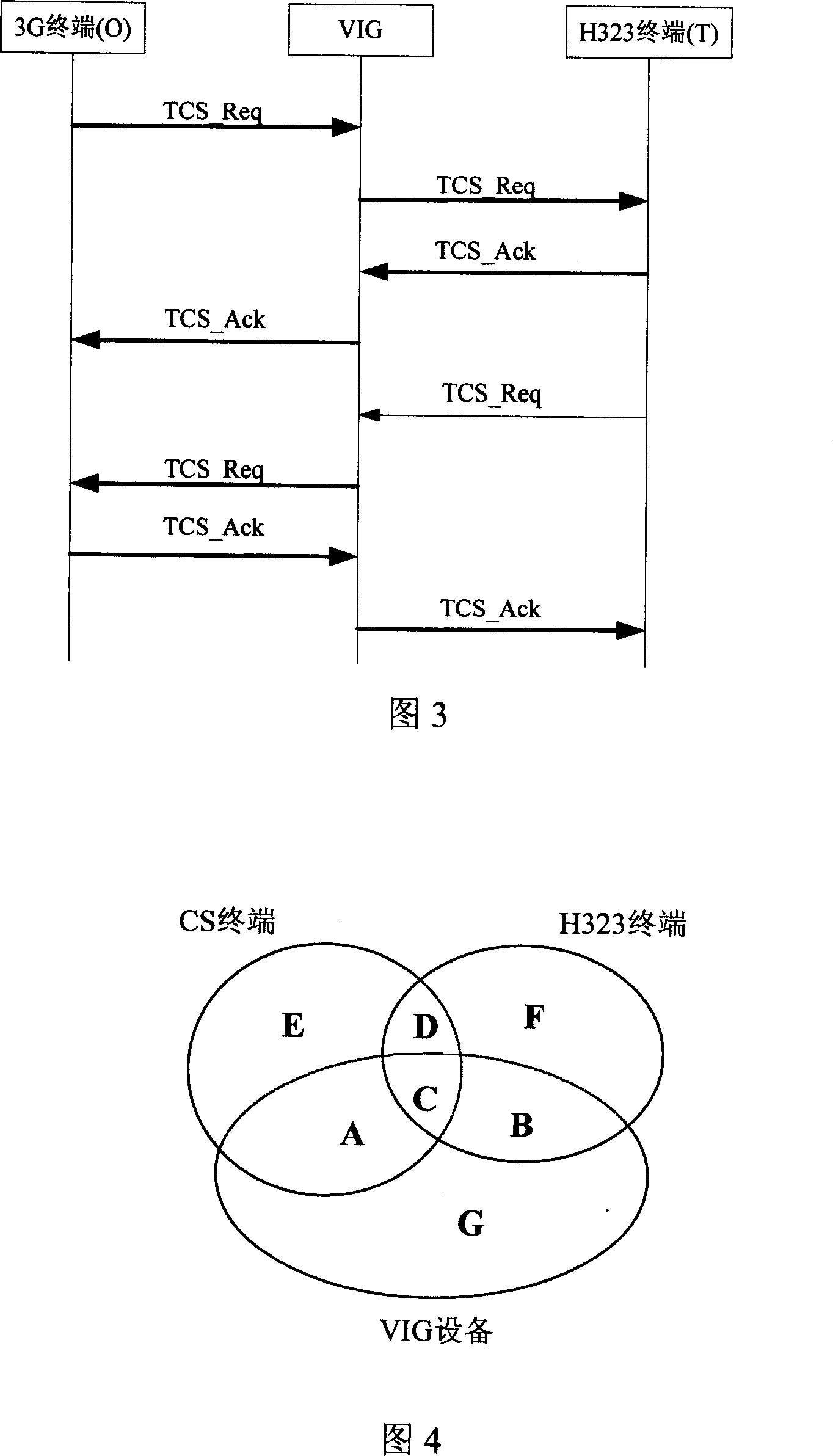
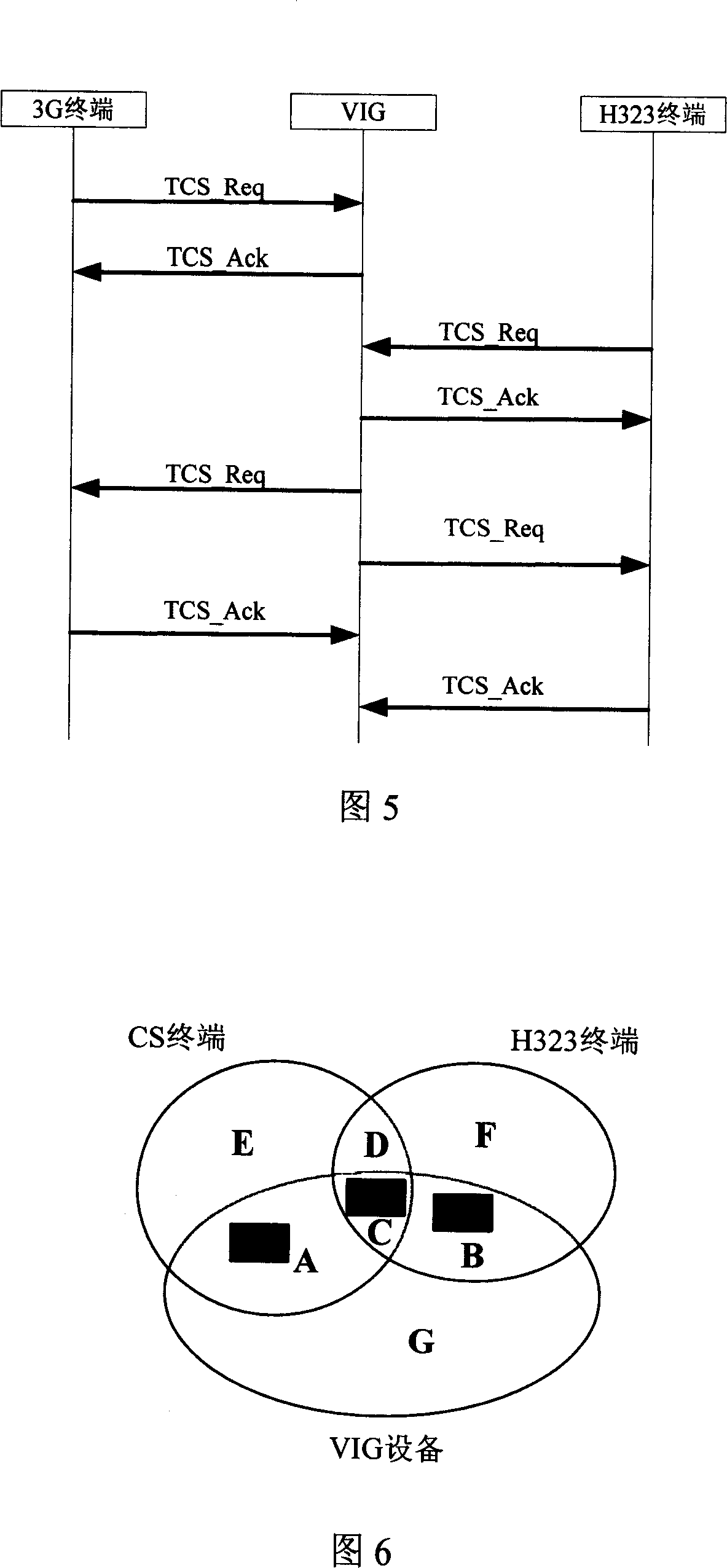
InactiveCN1996970AWide supportGood multimedia effectClosed circuit television systemsStore-and-forward switching systemsThird generationComputer science
This invention relates to one 3G visual network gate multi-media decoding ability negotiation method, which comprises the following steps: a, VIG receives 3G-H324M terminal and H323 terminal send ability require of TCS message and recording decodes by computation with self supportive decode cross set to get first and second decode list; b, judging whether the first and second decode sequence is zero, if yes, releasing calls, if not execution next steps; c, VIG computes the first and second decodes list to get third decode line to judge whether the decode sequence is zero.
Owner:ZTE CORP
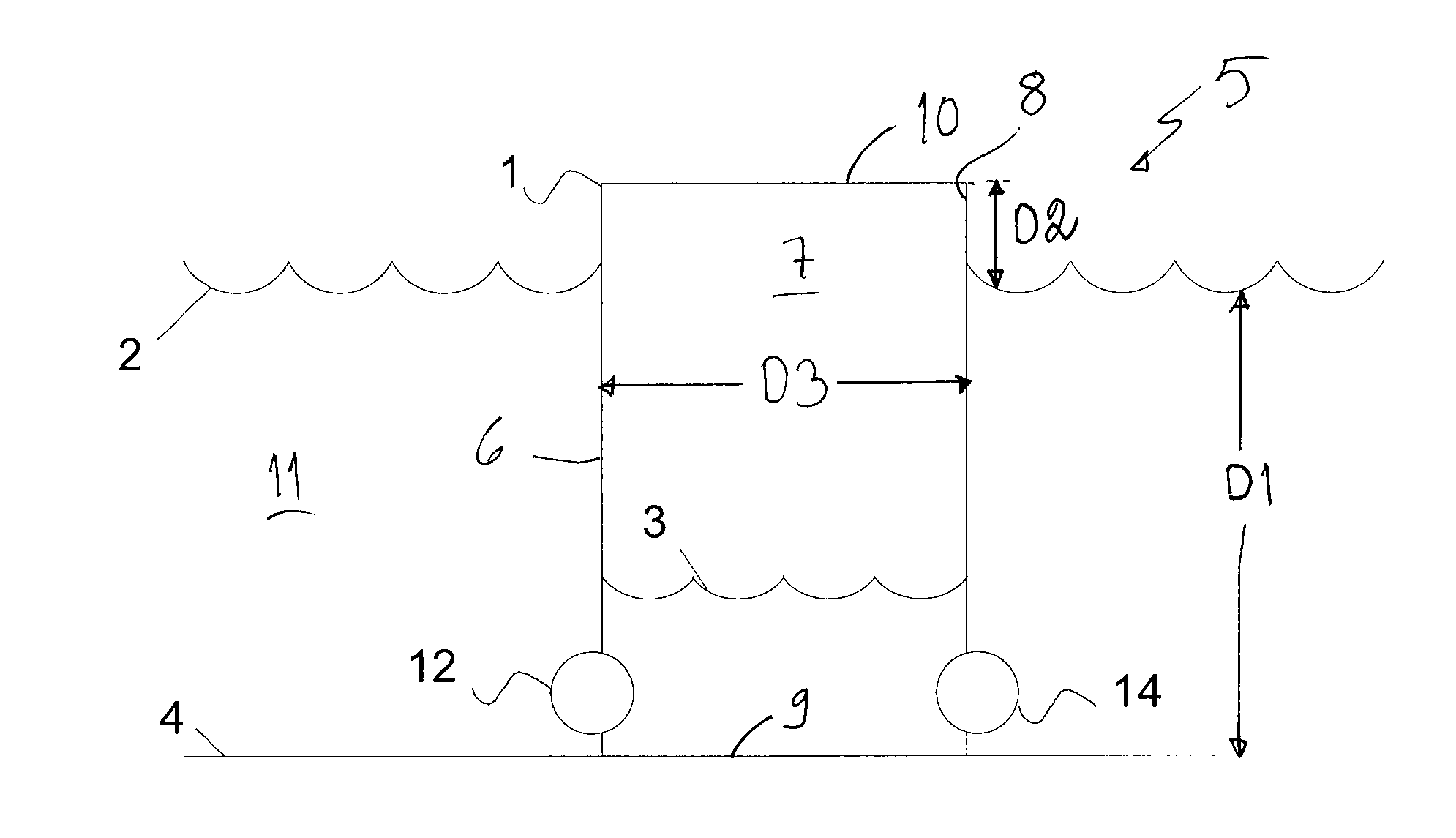
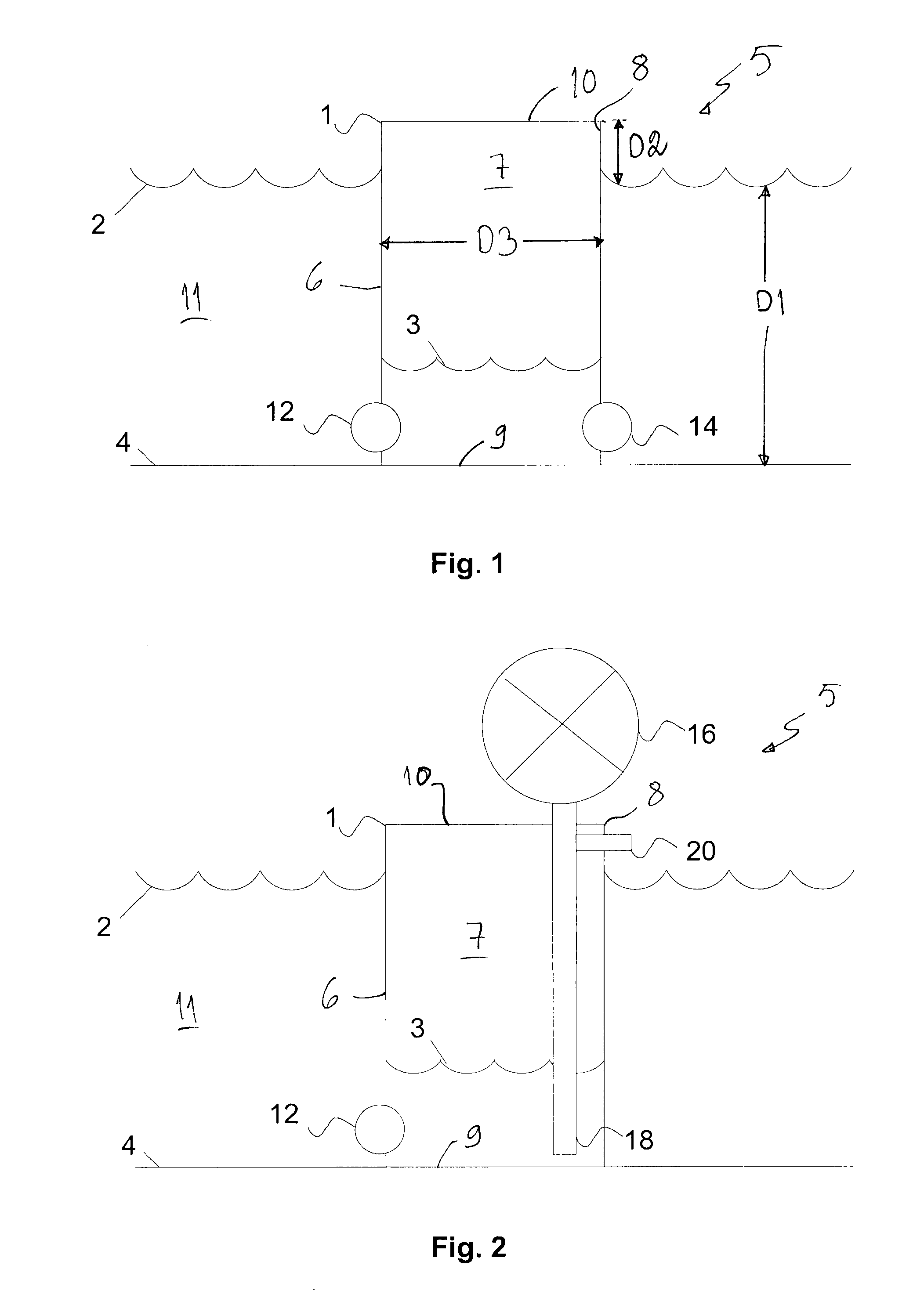
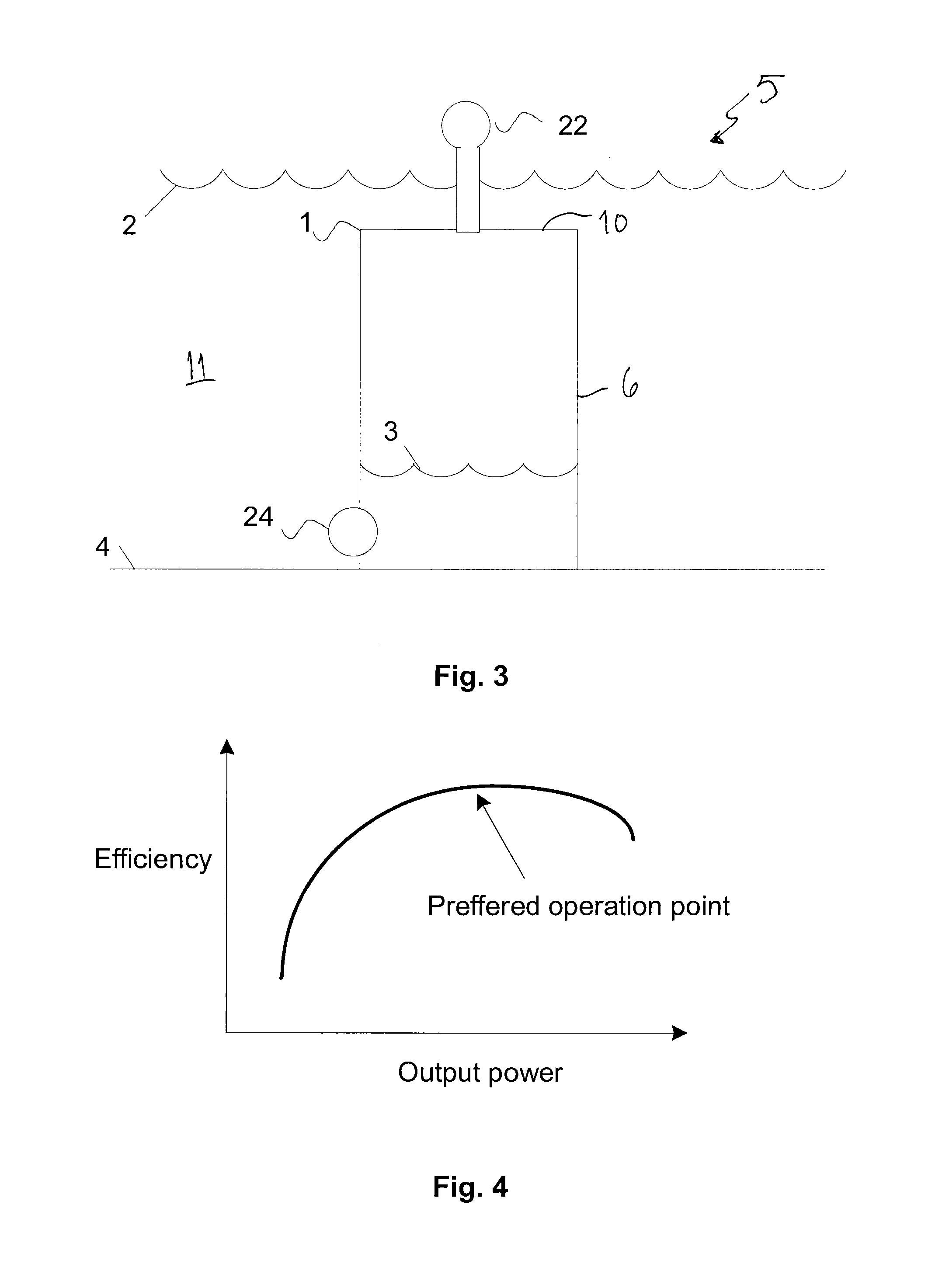
Generating hydroenergy
InactiveUS20120056430A1Improve efficiencyHigh energyGas turbine plantsEmission reduction for energy storagePower stationEngineering
A method of recovering energy from the potential energy of water in a body of water includes providing a reservoir at least partly below a surface of a body of water, leading water from the body of water in the reservoir, and storing potential energy by removing water from the reservoir. A hydroenergy plant recovers energy from the water while leading the water into the reservoir using a turbine and an electric generator coupled to the turbine.
Owner:AALTONEN JANNE +1
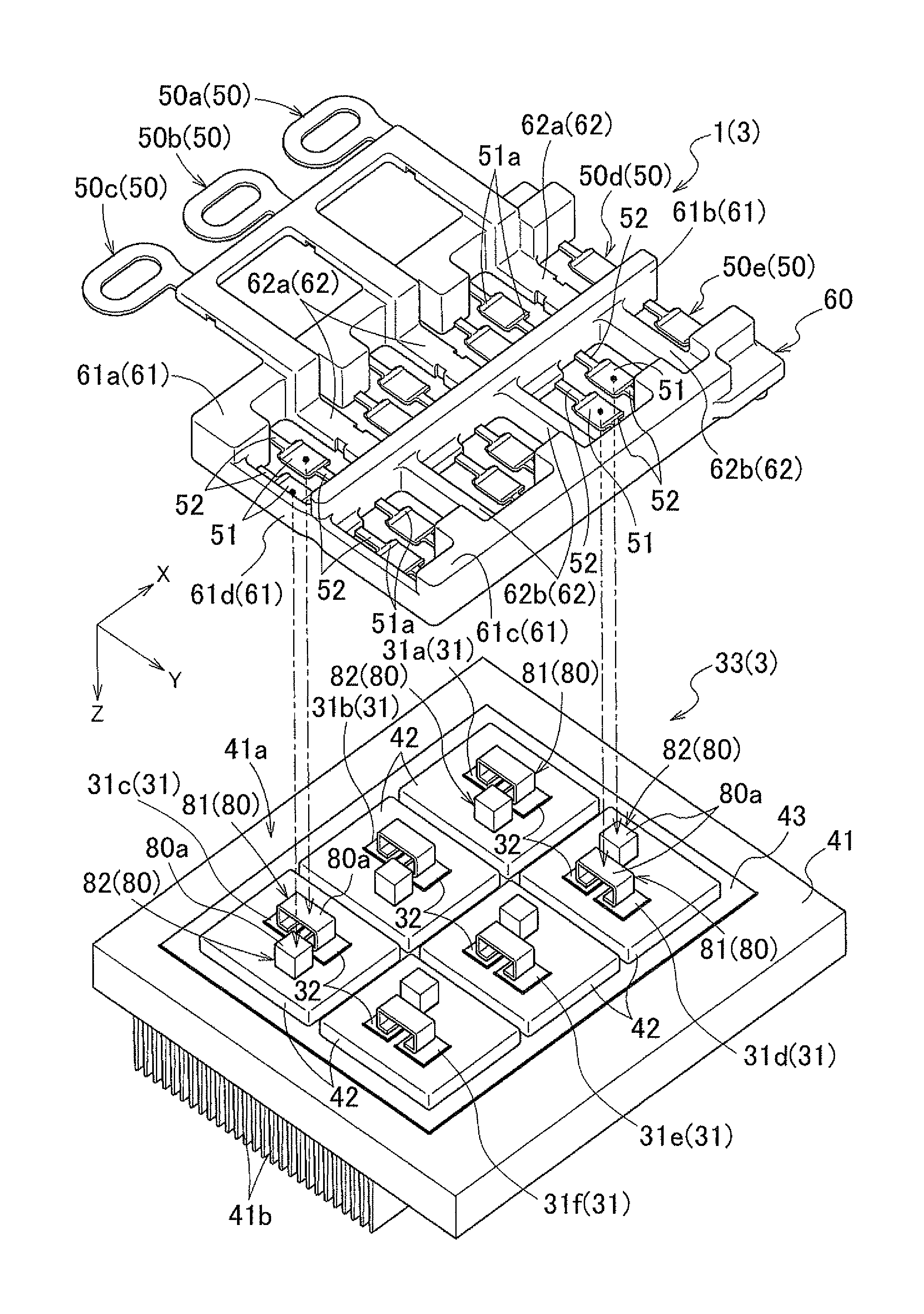
Electrical connection device
InactiveUS8500491B2Enhanced surface contactEasy to pressConversion constructional detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical connectionEngineering
An electrical connection device configured with a conductive connection member having a joint portion joined to an electrode member while being pressed against the electrode member in a pressing direction. An insulating support body supports the connection member such that the connection member includes the joint portion which is formed in a flat plate shape and is brought into surface contact with a joint surface of the electrode member. Crossover portions sandwich the joint portion and extend toward both sides along a predetermined extending direction. Supported portions are provided at respective end portions, opposite the joint portion, of the crossover portions on both sides. The support body is disposed at least on both sides of the joint portion in the extending direction and spaced apart from the joint portion, and formed to integrally support the supported portions on both sides of the joint portion.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com