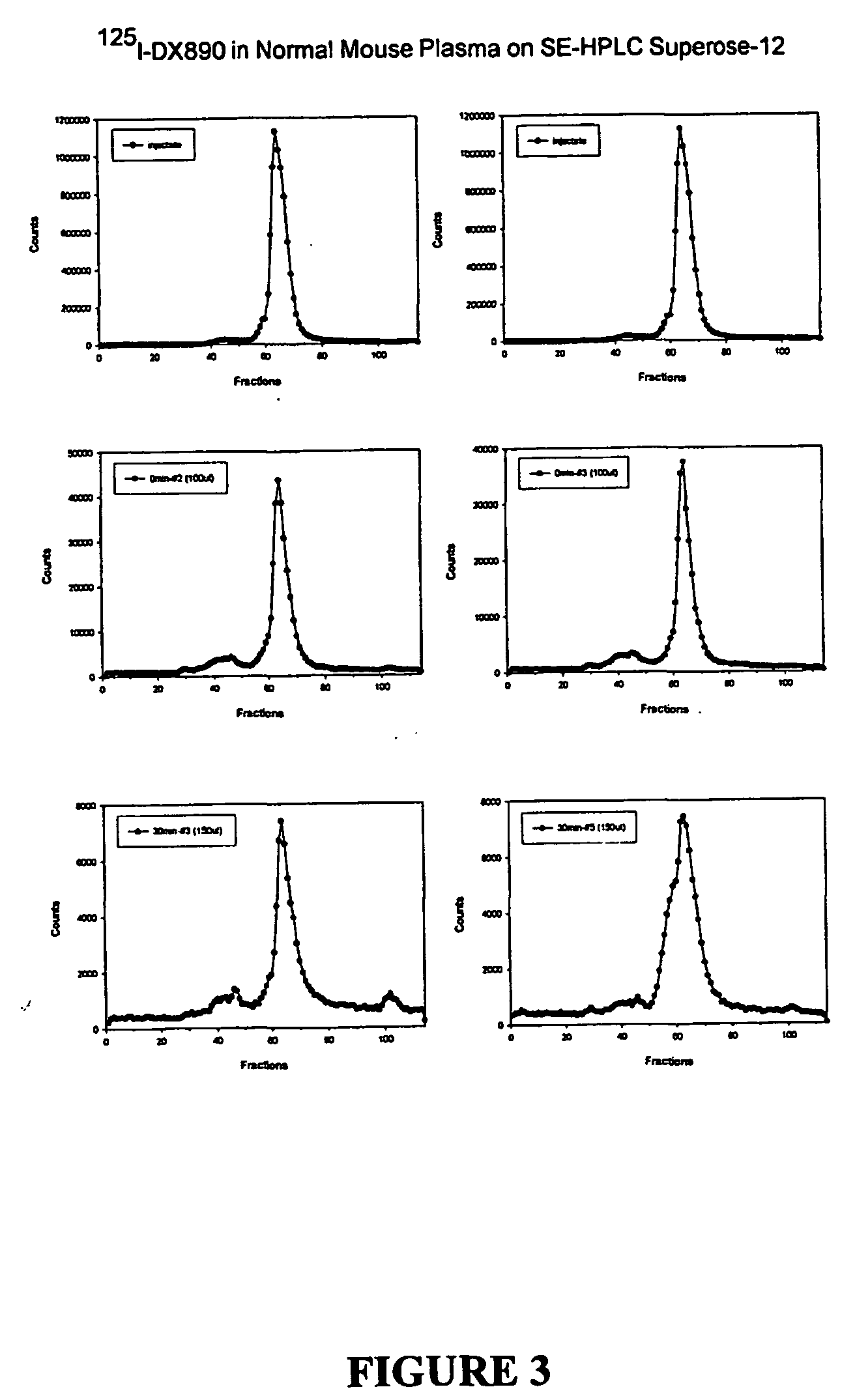
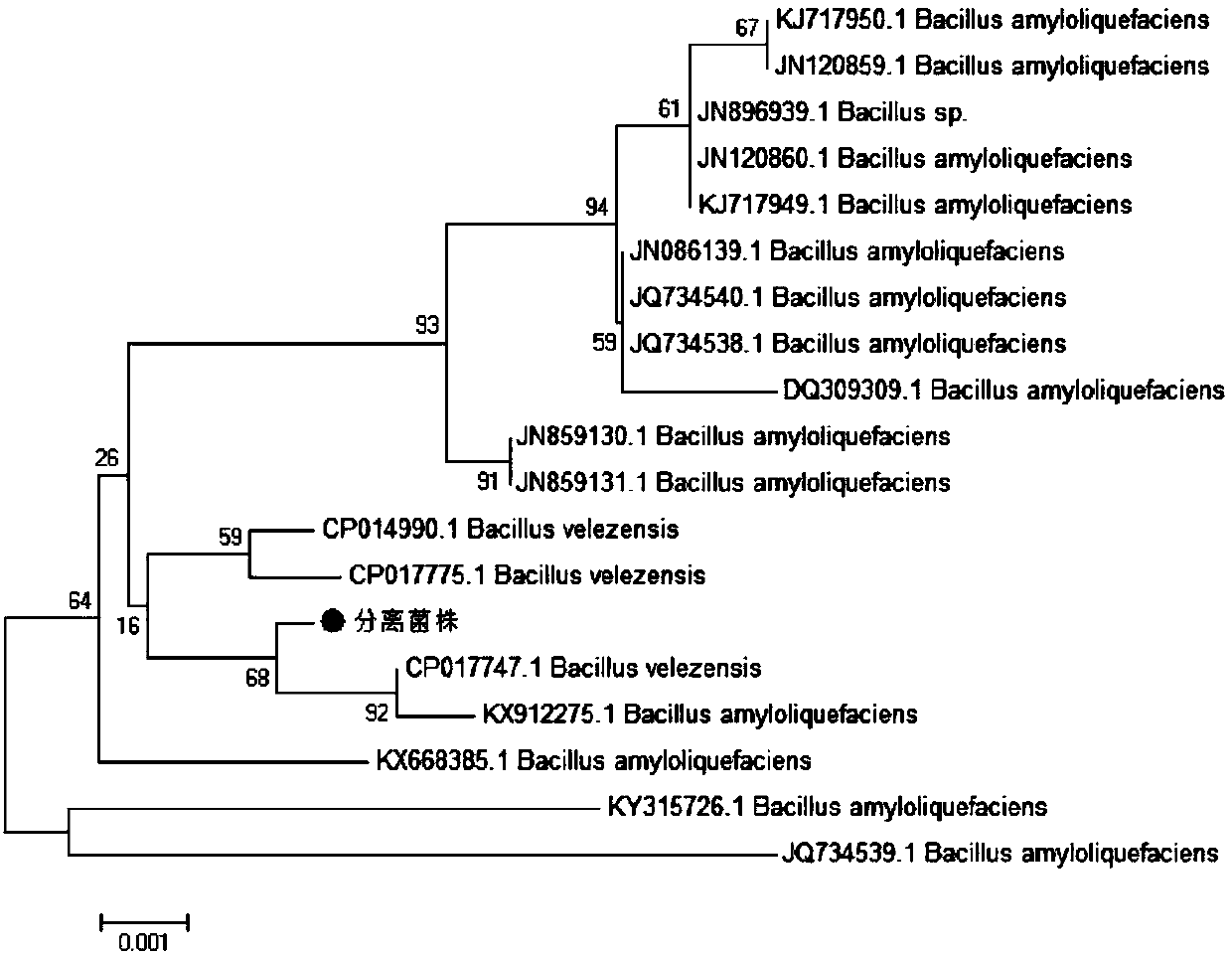
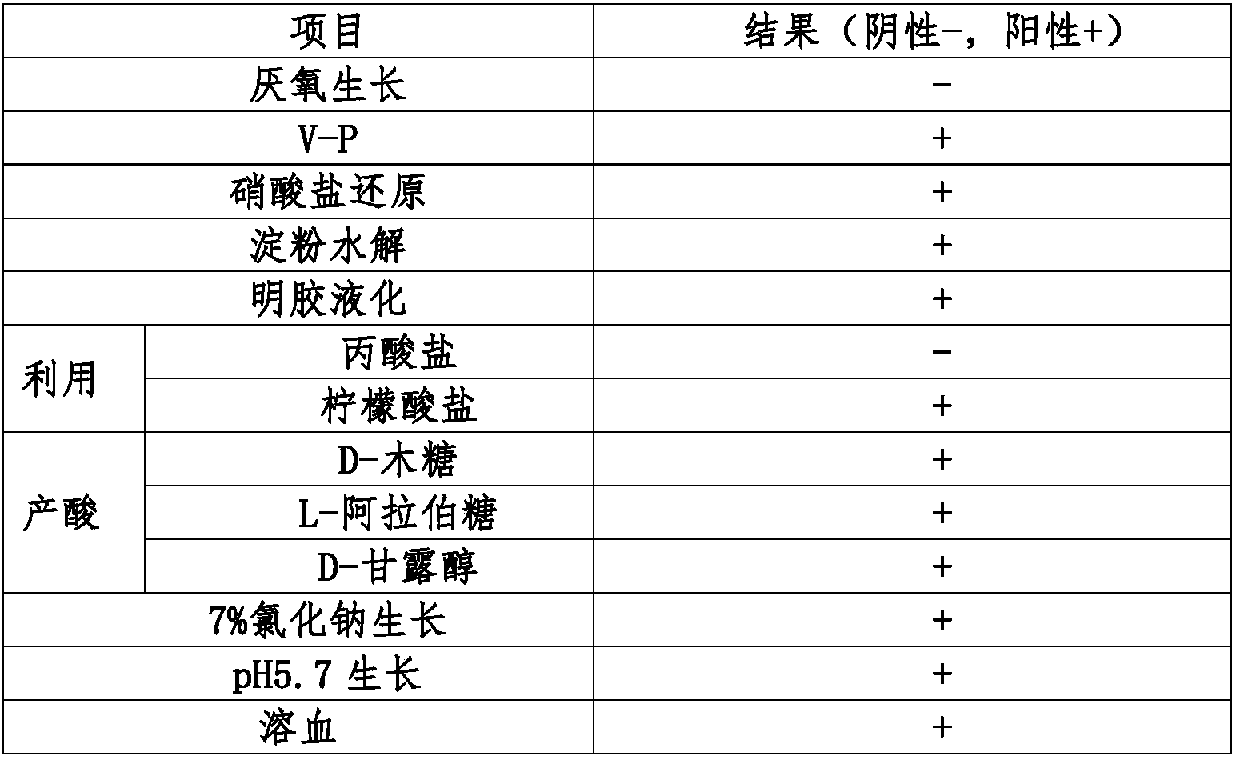
Patents
Literature
174 results about "Plasmin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plasmin is an important enzyme (EC 3.4.21.7) present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein is encoded by the PLG gene.
Novel strain of bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its use
InactiveUS20100143316A1Inhibits pathogenic growthPromote biodegradationAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyAmylase
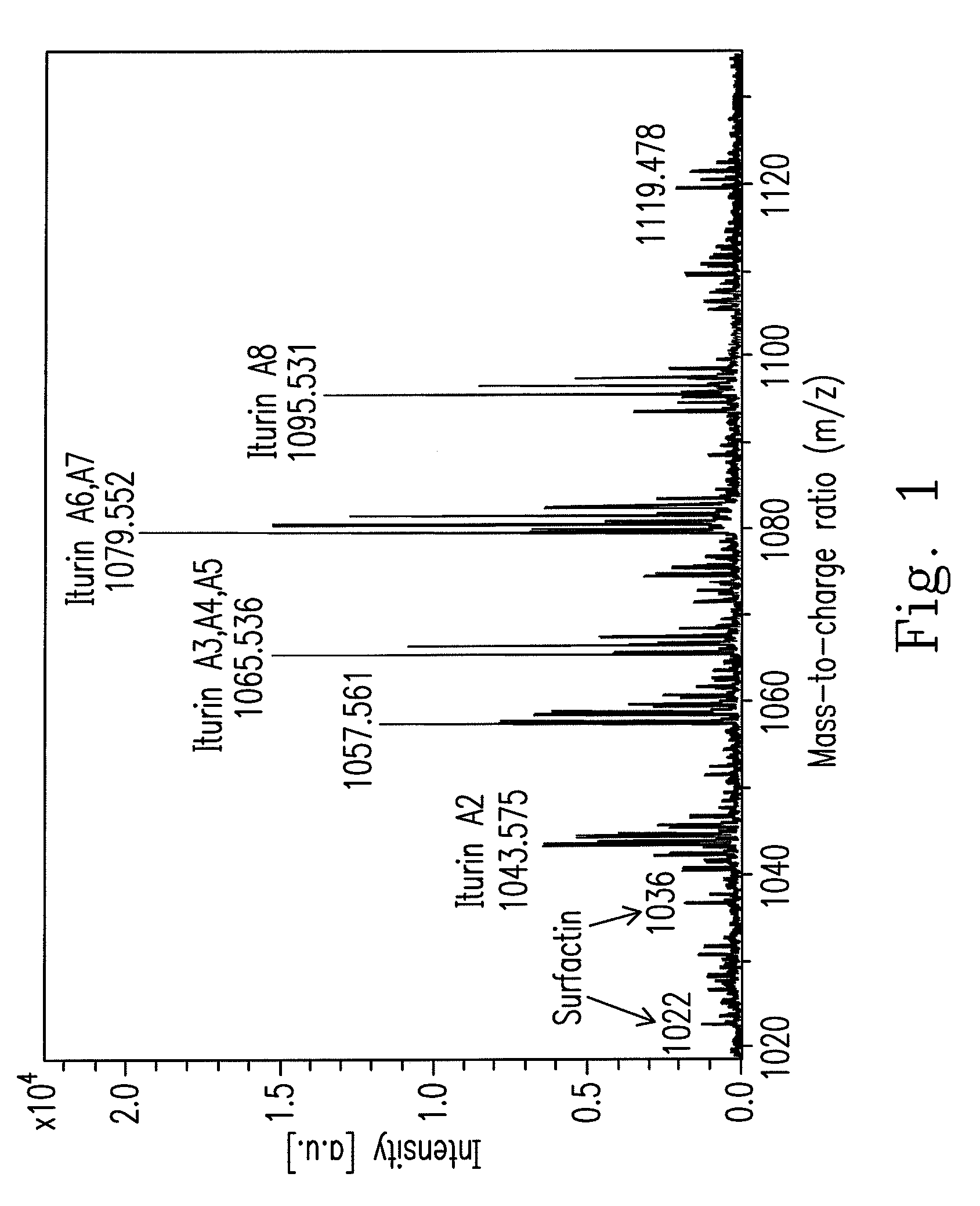
An isolated Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 having an Accession No. of DSM 21836 is provided. This novel strain has unique 16S ribosomal RNA sequenced as SEQ ID NO:1 and produces amylase, protease, cellulase and lipase, fibrinolytic enzyme to show their biodegradation capacities. Further, B. amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 produces the antibiotic substances, such as iturin, fengycin and surfactin, and has antimicrobial capacity for inhibiting the fungal or bacterial growth. In conclusion, the novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba-BPD1 and its products can be applied in agriculture, wastewater treatment, food industry and chemical industry.
Owner:AGRI CHEM & TOXIC SUBSTANCES RES INST COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Compositions and methods for enhancing structural and functional nervous system reorganization and recovery
InactiveUS20060104969A1Improve the degradation problemSimple structurePeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsNervous systemDelivery vehicle
The present invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing recovery in a subject suffering from damage to the nervous system. In particular, the invention includes a method for promoting recovery and / or reorganization in the nervous system of a subject in need of enhancement of recovery and / or reorganization of the nervous system as a result of ischemic, hemorrhagic, neoplastic, degenerative, or traumatic damage by focally administering a composition comprising a proteolysis-enhancing agent such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), plasmin, or a PAI inhibitor to the nervous system of the subject. In some embodiments an additional active agent is also administered. The composition can be delivered using a variety of techniques including injection, via infusion pump, from an implantable microchip, or using a polymeric delivery vehicle. The composition can be administered, for example, to one or more subdivisions or areas of the brain, the spinal cord, or to one or more nerves or nerve tracts innervating diverse regions of the body. The invention also includes a drug delivery device for implantation into the nervous system to promote nervous system reorganization and / or recovery following ischemic, hemorrhagic, neoplastic, traumatic or degenerative damage, the drug delivery device comprising a biocompatible polymer and a proteolysis-enhancing agent such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), plasmin, or a PAI inhibitor, wherein the proteolysis-enhancing agent is released from the polymer in an amount effective to promote structural reorganization of the nervous system. In some embodiments the biocompatible polymer is a hydrogel.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Means and methods for the recruitment and identification of stem cells
InactiveUS20060210532A1Inhibit recruitmentIncreased engraftmentBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsProgenitorHematopoietic cell
Described are methods of modulating stem / progenitor cell recruitment involving molecules that agonize the formation of plasmin stimulating the recruitment of stem / progenitor cells, including hematopoietic and endothelial precursor cells. Conversely, antagonists of plasmin can inhibit recruitment of the stem cells. In addition, the identification of the uPA receptor (uPAR) as a retention signal for stem cells in their niche suggests a novel method for increased engraftment and isolation of multipotent stem cells.
Owner:LIFE SCI RES PARTNERS VZW +1
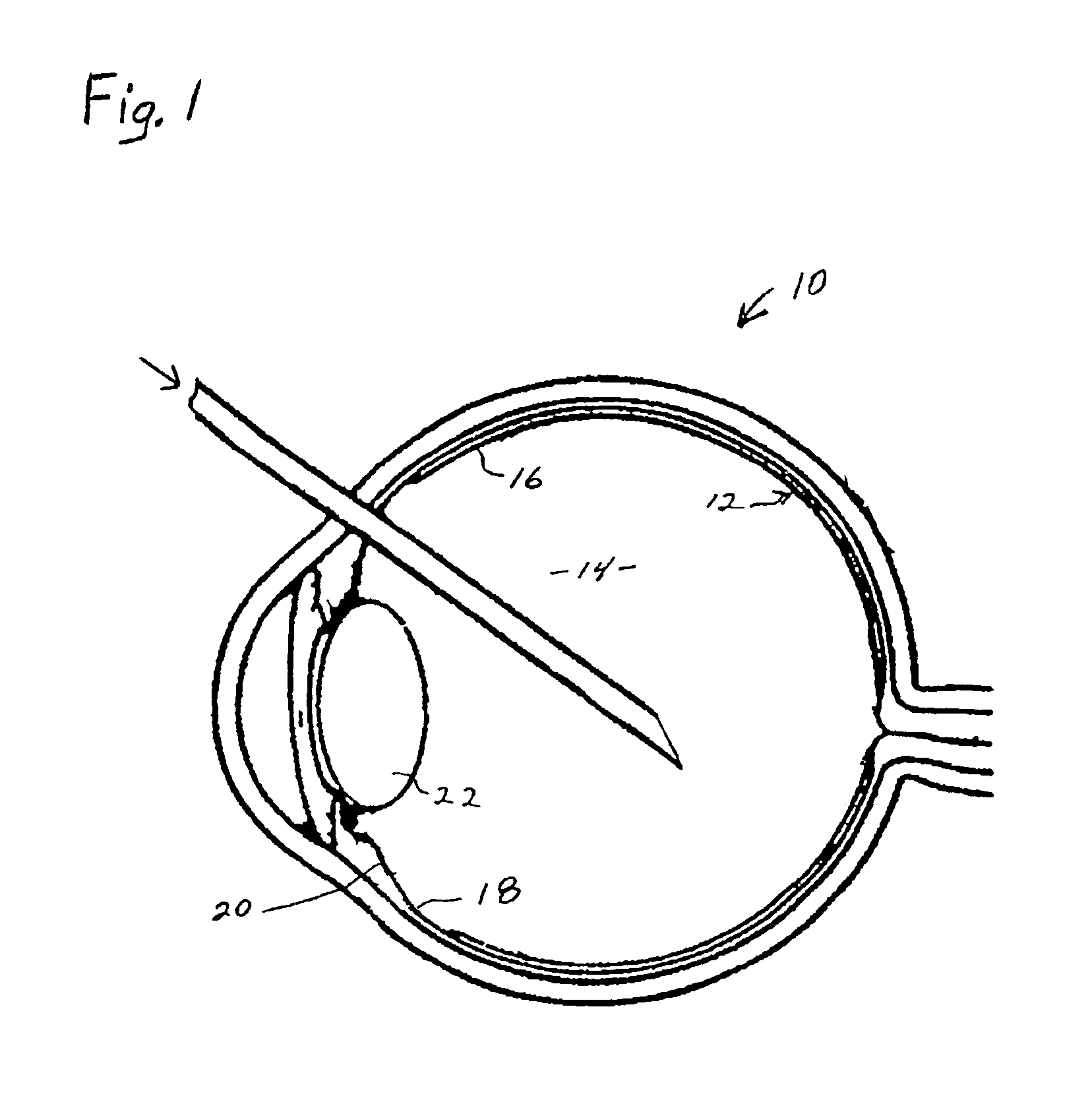
Process for generating plasmin in the vitreous of the eye and inducing separation of the posterior hyaloid from the retina
InactiveUS6899877B2Inhibiting retinal tearReducing and preventing effectSenses disorderEye implantsUrokinase Plasminogen ActivatorVascular proliferation
A process for inhibiting vascular proliferation separately introduces components into the eye to generate plasmin in the eye in amounts to induce complete posterior vitreous detachment where the vitreoretinal interface is devoid of cortical vitreous remnants. The process administers a combination of lysine-plasminogen, at least one recombinant plasminogen activator selected from the group consisting of urokinase, streptokinase, tissue plasminogen activator, chondroitinase, pro-urokinase, retavase, metaloproteinase, and thermolysin and a gaseous adjuvant to form a cavity in the vitreous. The composition is introduced into the vitreous in an amount effective to induce crosslinking of the vitreous and to induce substantially complete posterior vitreous detachment from the retina without causing inflammation of the retina. The gaseous adjuvant material is introduced into the vitreous simultaneously with or after the lysine-plasminogen and recombinant plasminogen activator such as recombinant urokinase to compress the vitreous against the retina while the composition induces the complete posterior vitreous detachment.
Owner:MINU
Inhibitors of human plasmin derived from the kunitz domains
InactiveUS6953674B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPlasminADAMTS Proteins
The invention features novel polypeptides homologous to the first Kunitz domain (K1) of lipoprotein associated coagulation inhibitor (LACI) that are capable of inhibiting plasmin, and nucleic acids encoding these proteins. The invention also features the use of such polypeptides in diagnostic, therapeutic and clinical methods.
Owner:DYAX CORP
Albumin-fused kunitz domain peptides
InactiveUS20050222023A1Extended half-lifeEasy to solvePeptide/protein ingredientsAlbumin peptidesCystic fibrosisFusion protein
The invention relates to proteins comprising serine protease inhibiting peptides, such as Kunitz domain peptides (including, but not limited to, fragments and variants thereof) fused to albumin, or fragments or variants thereof. These fusion proteins are herein collectively referred to as “albumin fusion proteins of the invention.” These fusion proteins exhibit extended shelf-life and / or extended or therapeutic activity in solution. The invention encompasses, therapeutic albumin fusion proteins, compositions, pharmaceutical compositions, formulations and kits. The invention also encompasses nucleic acid molecules encoding the albumin fusion proteins of the invention, as well as vectors containing these nucleic acids, host cells transformed with these nucleic acids and vectors, and methods of making the albumin fusion proteins of the invention using these nucleic acids, vectors, and / or host cells. The invention also relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting neutrophil elastase, kallikrein, and plasmin. The invention further relates to compositions and methods for treating cystic fibrosis and cancer.
Owner:DYAX CORP +1
Bacillus velezensis as well as separation screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN108034617AImprove fermentation effectHigh in free amino acidsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesScreening methodDigestion
The invention provides bacillus velezensis as well as a separation screening method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbe technology and food processing. The invention providesthe bacillus velezensis with high fermentation capability; the bacillus velezensis is obtained through screening; during the fermentation, the capability of high yielding protease, amylase and fermented bean plasmin is realized; the bacillus velezensis can be applied to food fermentation in a large scale when being prepared into a food fermentation strain; fermentation food obtained through fermentation by using the bacillus velezensis, the contents of free amino acid and douchi fibrinolytic enzyme are high; the nutrition is rich; the characteristics of easy digestion, thrombus prevention andthe like are realized.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Fungal fibrinolytic enzyme and cultivating method thereof
ActiveCN101503682AThrombolytic effect is goodNo obvious acute toxicityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesBiotechnologyCordyceps
The invention discloses a fungal fibrinolytic enzyme and a preparation method thereof. The fungal fibrinolytic enzyme is prepared by taking a Cordyceps militaris strain as a strain and performing liquid fermentation culture, separation and purification. The relative molecular weight of the fibrinolytic enzyme is about 21,000. The Cordyceps militaris fibrinolytic enzyme has good thrombolytic performance, is free from obvious acute toxicity, has prospects for clinical trial, development and application, and adds a new member to a rare fibrinolytic enzyme family. Particularly, a preferable fibrinolytic-enzyme Cordyceps militaris strain C.LSG-1 obtained through severe screening is rough in growth conditions, short in enzyme production cycle and capable of harvesting a large amount of Cordyceps militaris mycelium during enzyme production, and is the strain excellent in production performance. The Cordyceps militaris fibrinolytic enzyme is an extracellular enzyme which is particularly beneficial to subsequent separation and purification during preparation. The fungal fibrinolytic enzyme takes corn protein with extensive sources as a main culture medium, thereby having low cost for raw materials and providing a novel way for developing and utilizing the prior resources.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LSSE-62 and application thereof
ActiveCN102533576AInnovativePracticalBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAdditive ingredientBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
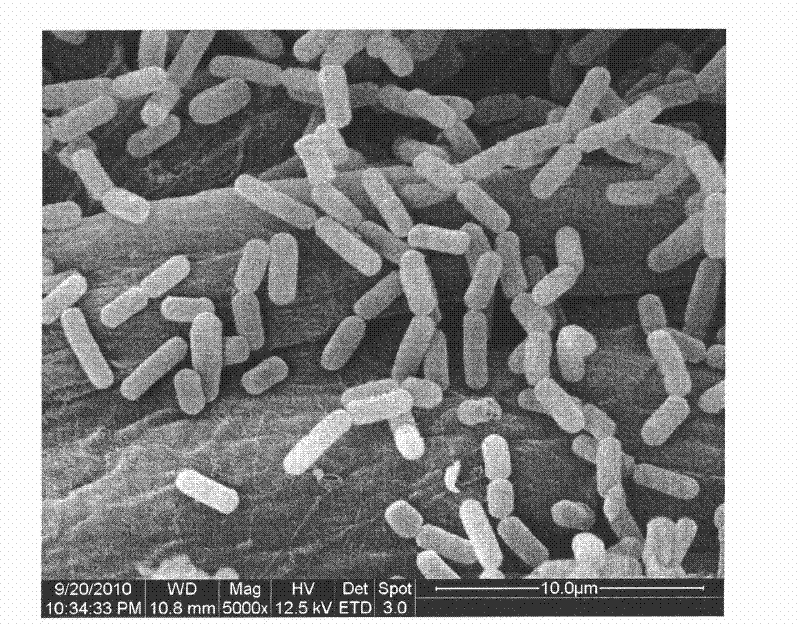
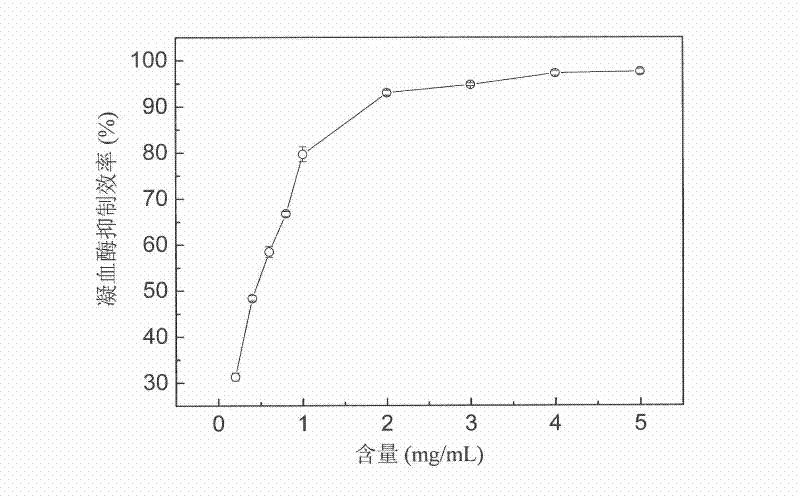
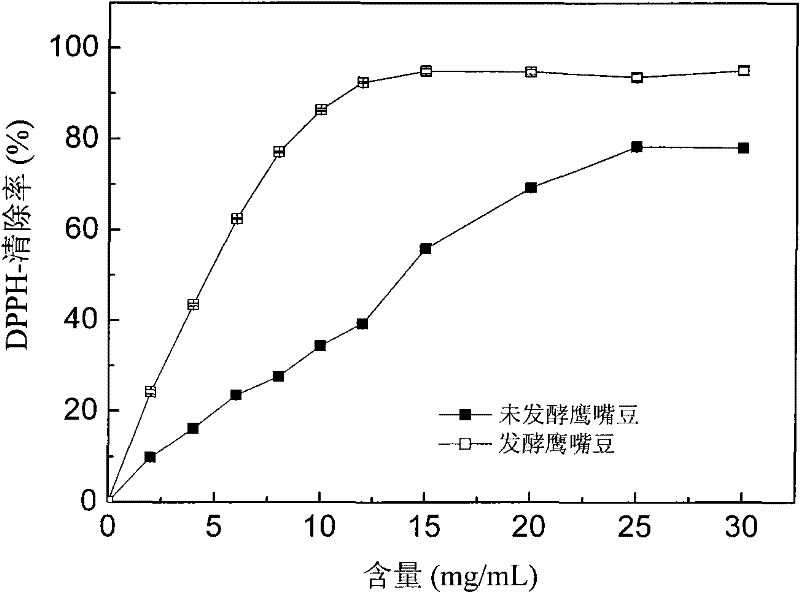
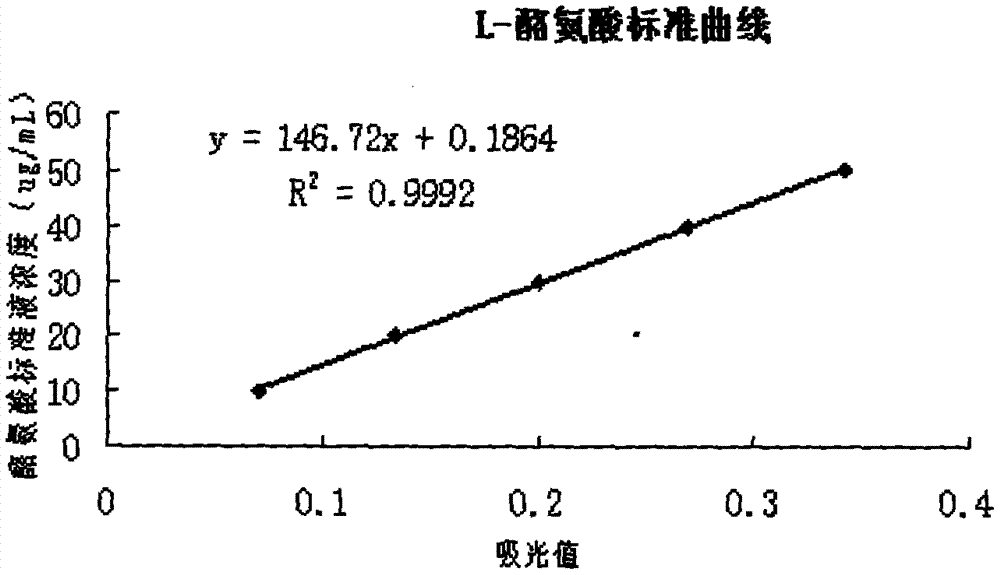
The invention relates to the microbial field, in particular to bacillus amyloliquefaciens LSSE-62 and application thereof. According to the invention, a new bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain is screened, wherein the collection number is CCGMCC No. 4157; and through the strain, plasmin can be prepared by efficiently utilizing fermentation of chickpea, and antithrombin active ingredient can be secreted, so that the total phenol content, the total flavone content and the antioxidant activity of the chickpea are improved. A plasmin health-care food prepared by fermenting the chickpea with the strain has various health-care functions.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for fibrinolytic fermented soya beans
InactiveCN103829166APromote growthProtease content has little effectFood preparationProduction linePlasmin
The invention provides a preparation method for fibrinolytic fermented soya beans. The preparation method comprises the steps of activating strains, preparing a mucor seed solution; preparing a bacillus natto seed solution; processing soya beans; inoculating; culturing and after-ripening. Under the conditions that mucor and bacillus natto produced protease and bacillus natto produced plasmin are used as evaluation indexes, the mucor grows well after bacillus natto is inoculated; influence to protease content is not large; nattokinase activity in the obtained fermented soya beans can reach 823.51 U / g; and protease activity reaches 1983.91 U / g. By seeking optimum conditions for fermentation of the fermented soya beans, the time required by a conventional fermentation process for the fermented soya beans is greatly shortened without influencing the flavor of the fermented soya beans. At the same time, during an operation process, condition control is convenient, thereby facilitating production operations. The preparation method can finish co-fermentation of the bacillus natto and the mucor to the soya beans only by using an original production line of the fermented bean curd blanks, without increasing any equipment, thereby greatly saving production cost.
Owner:CHONGQING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method of promoting healing of a tympanic membrane perforation
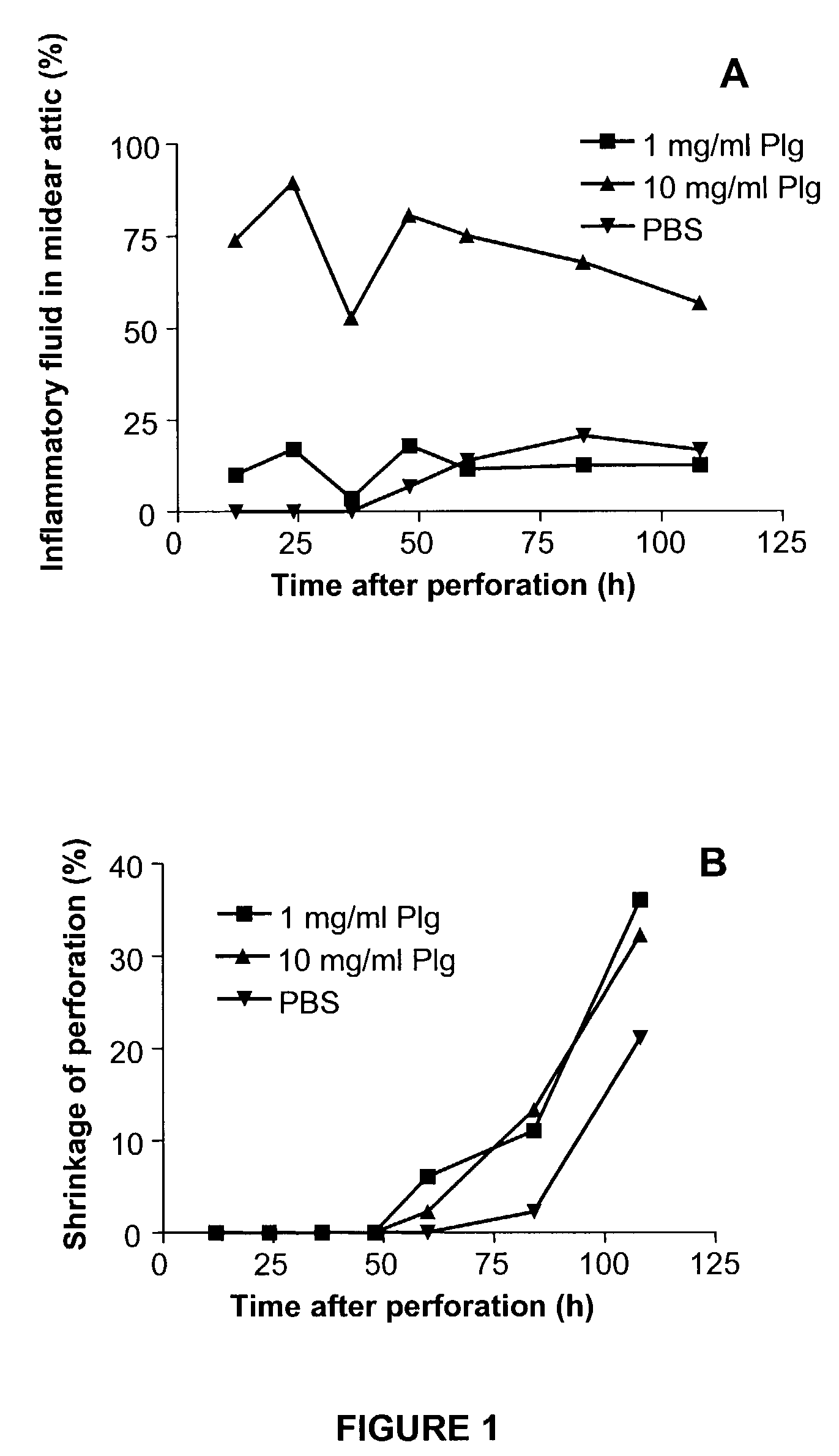
ActiveUS7067492B2Promote healingMinimizing scar formationSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsPlasminTympanic Membrane Perforation
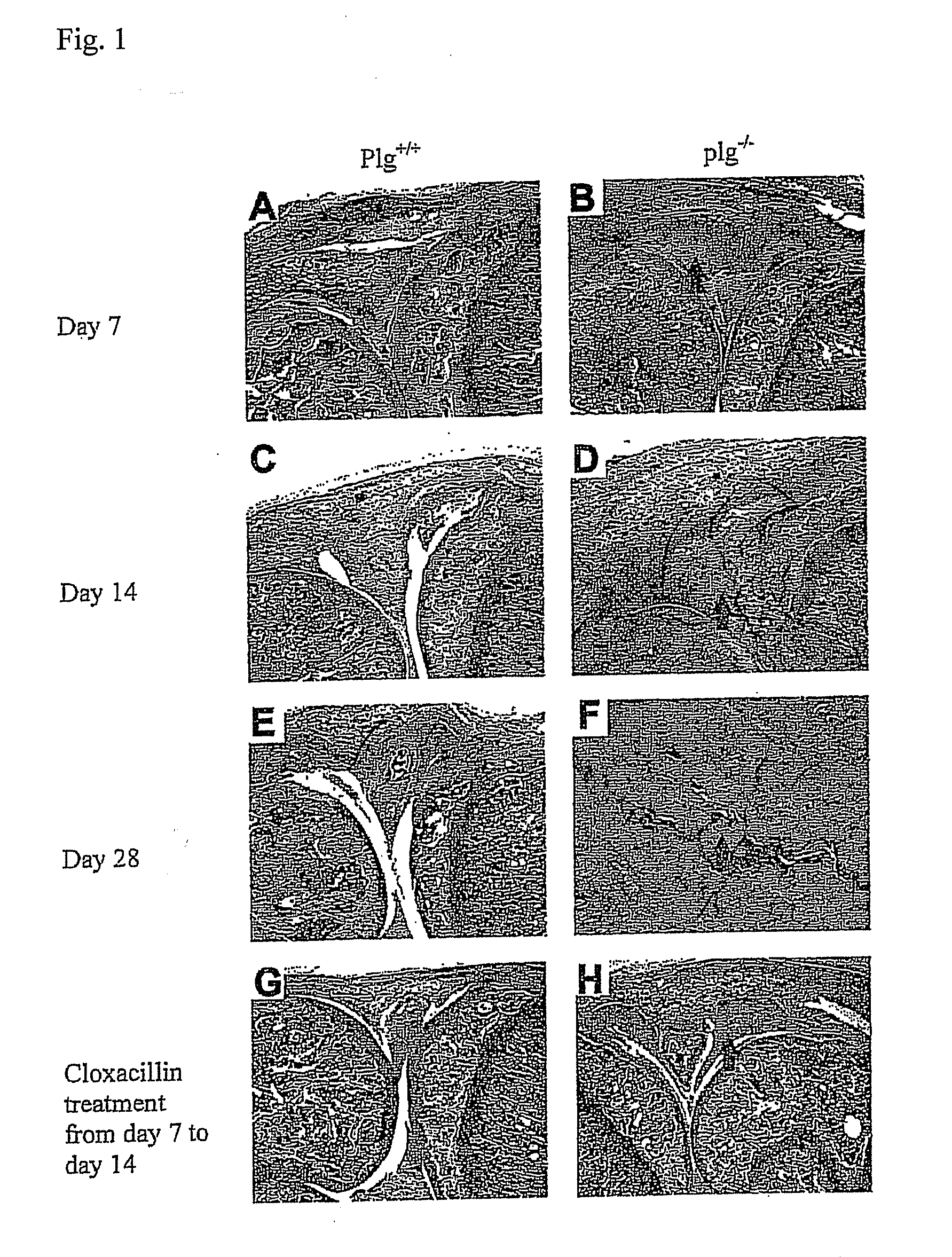
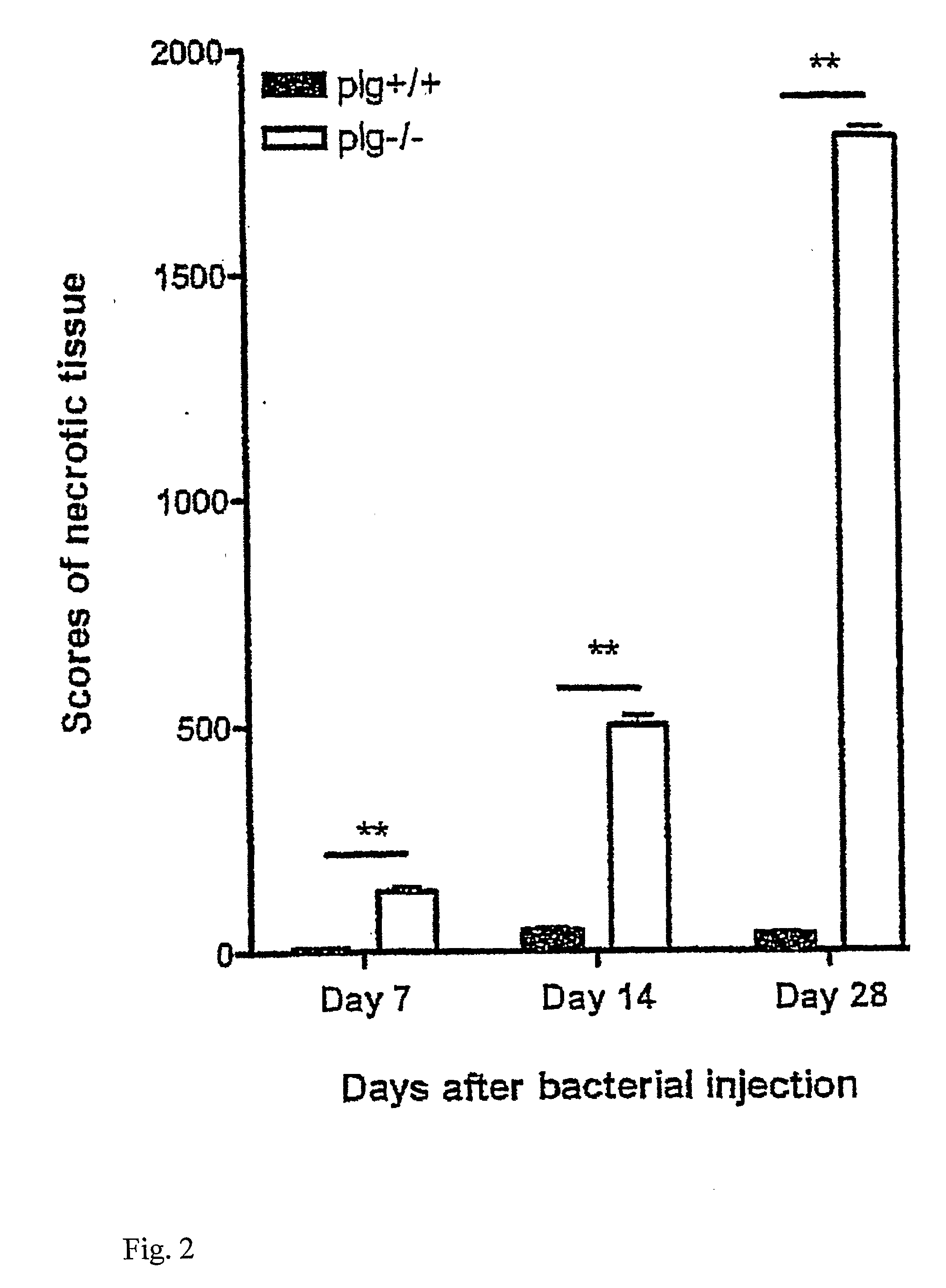
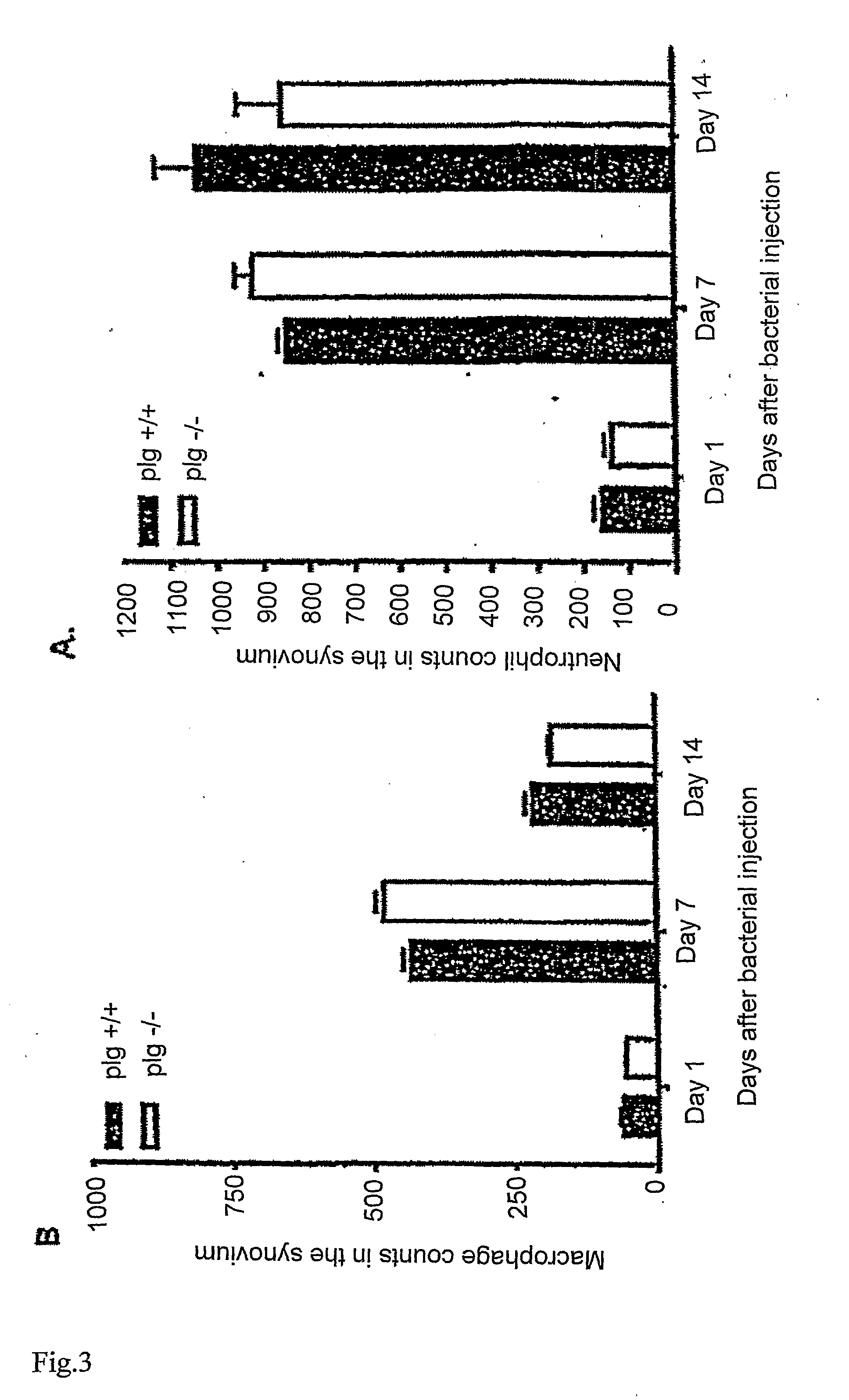
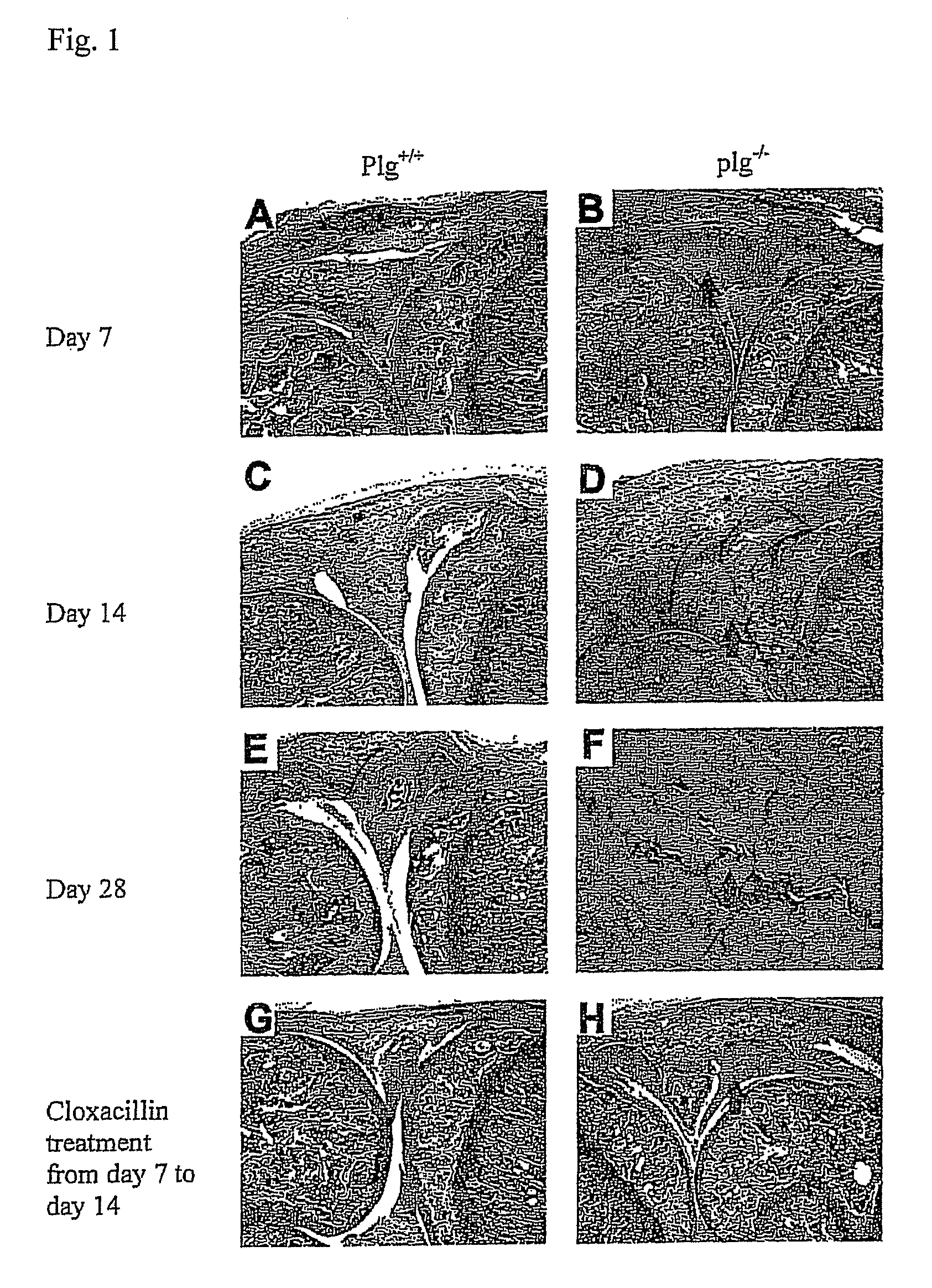
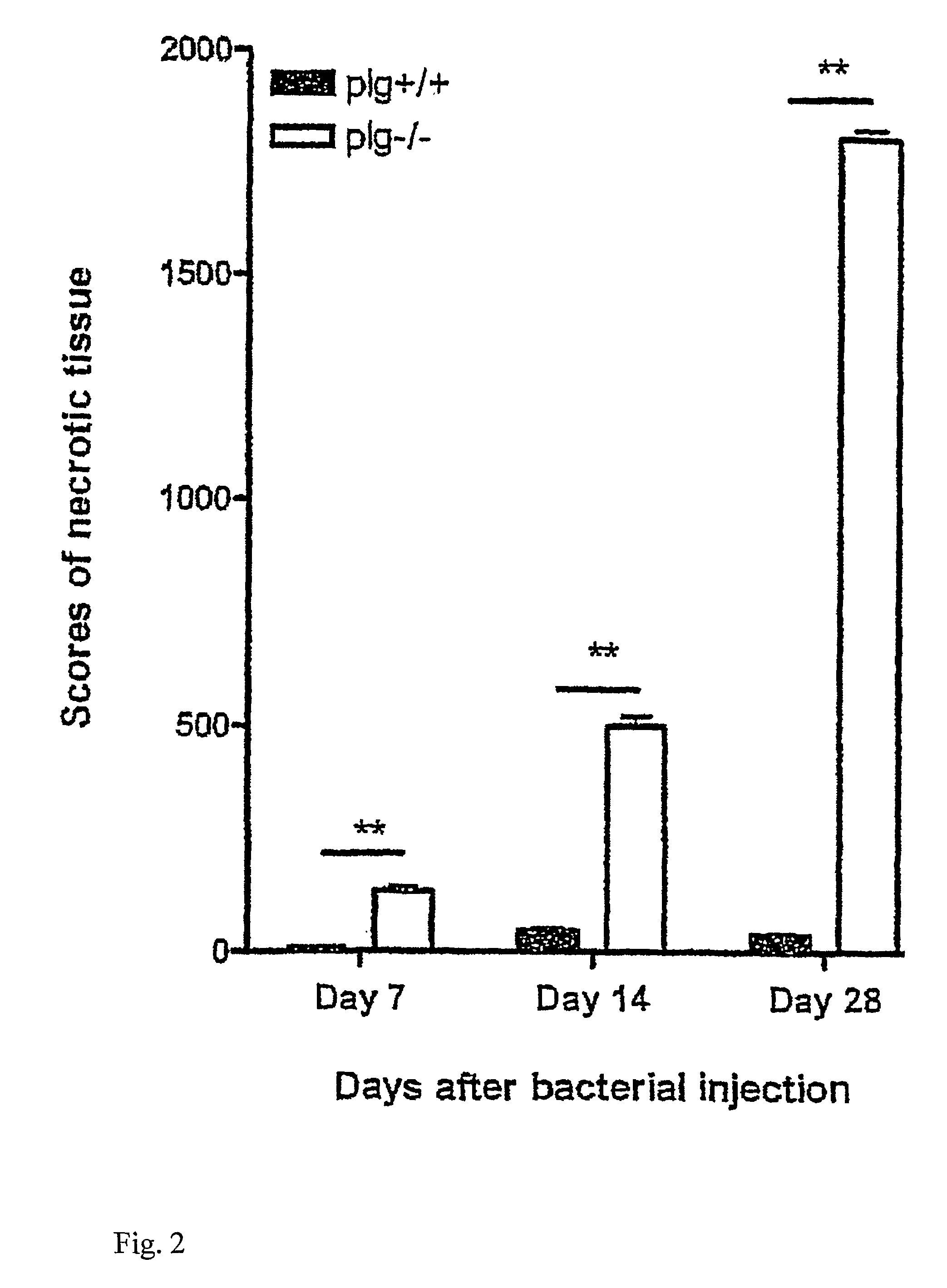
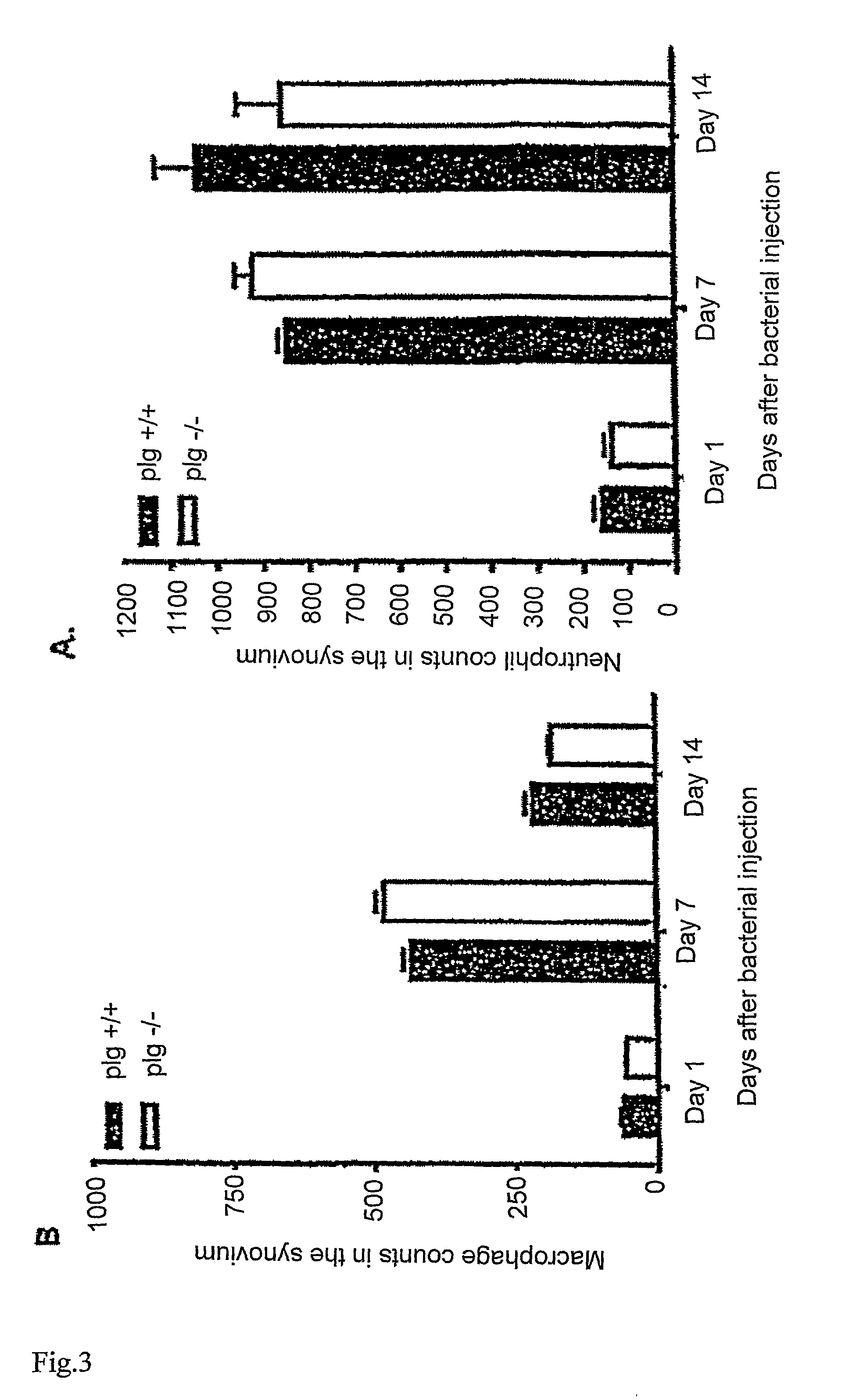
The present invention relates to the use of plasminogen and plasmin as agents for enhancing healing of tympanic membrane perforations or other wounds, and for reducing scars or necrotic tissue forming during wound healing. The invention also relates to a method for screening of compounds which enhance wound healing by evaluating the healing of tympanic membrane perforations in an animal model.
Owner:OMNIO HEALER AB ORG NO 556861 7863
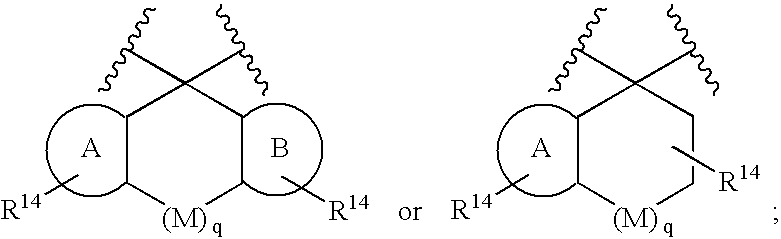
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinW is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—;X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—;U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond;and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification;and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
Substitute for animal protein in cattle feed
InactiveUS20060292205A1Improve performanceIncrease the number ofBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal scienceFeces
A combination one or more species of lactobacillus bacteria and one or more types of fibrolytic enzymes can be used to replace animal protein in cattle feed. The combination results in a better amino acid balance in the digestive tract of cattle resulting in a better utilization of nitrogen. Less water-soluble nitrogen compounds pass through the digestive tract resulting in less pollution. More nitrogen in the feed is converted to water insoluble compounds resulting in better feed utilization and less water-soluble pollution in the manure. The diseases carried by some animal protein additives, such as “mad cow” are not present in the additives of the present invention.
Owner:ROBINSON LEANNE GAIL
Candidates against infection
ActiveUS20100099600A1Reducing and preventing necrosis formationReduce occurrenceAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderPlasminBacterial arthritis
The present invention relates to the use of plasminogen / plasmin and its derivatives as agents for enhancing host defense against infection or other infectious diseases. The invention also relates to a method for screening of compounds which enhance host defense against infection by evaluating the host defense against bacterial arthritis and spontaneous otitis media in an animal model.
Owner:OMNIO HEALER AB
Production process of natural marine organism health food with deep sea clam worm as material
InactiveCN1436490ANo pollution in the processExtraction method scienceCapsule deliveryFood preparationFreeze-dryingPhosphate
The production process of natural marine organism health food includes the process of culturing deep sea clam worm in salt water for 3-4 days to make it spit out content; homogenizing and centrifuging after adding physiological saline or phosphate buffering liquid; salting out, dialysis or column chromatography and ultrafiltration to eliminate impurities and purify solution; spray drying or freezing drying to obtain powder; Co-60 ray irradiatino to sterilize to obtain food powder; and capsulizing. The health food contains rich amino acids, fatty acids, trace elements, vitamines and bioactive enzymes, especially great amount of plasmin. Experiments show that the health food has the health functions of regulating blood pressure and blood fat, preventing thrombus, resisting senility and strengthening immunity.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fibrinolytic-enzyme-producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain separated from traditional fermented black beans
InactiveCN104877936AGrow fastImprove production safetyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetabolitePlasmin
The invention discloses a fibrinolytic-enzyme-producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain separated from traditional fermented black beans, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The strain is separated and purified from traditional fermented black beans, is named Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by taxonomic identification, and is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 10th, 2014; and the collection number is CCTCC M2014638. The fibrinolytic-enzyme-producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain is easy to culture, and has the advantages of high production safety and favorable hereditary stability. The enzyme activity of the strain liquid after fermentation and culture is up to 324.6-410.2 IU / mL. The metabolite fibrinolytic enzyme can be easily separated and purified. The separation of the strain lays foundation for implementing scientific axenic culture in traditional fermented black bean industry.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
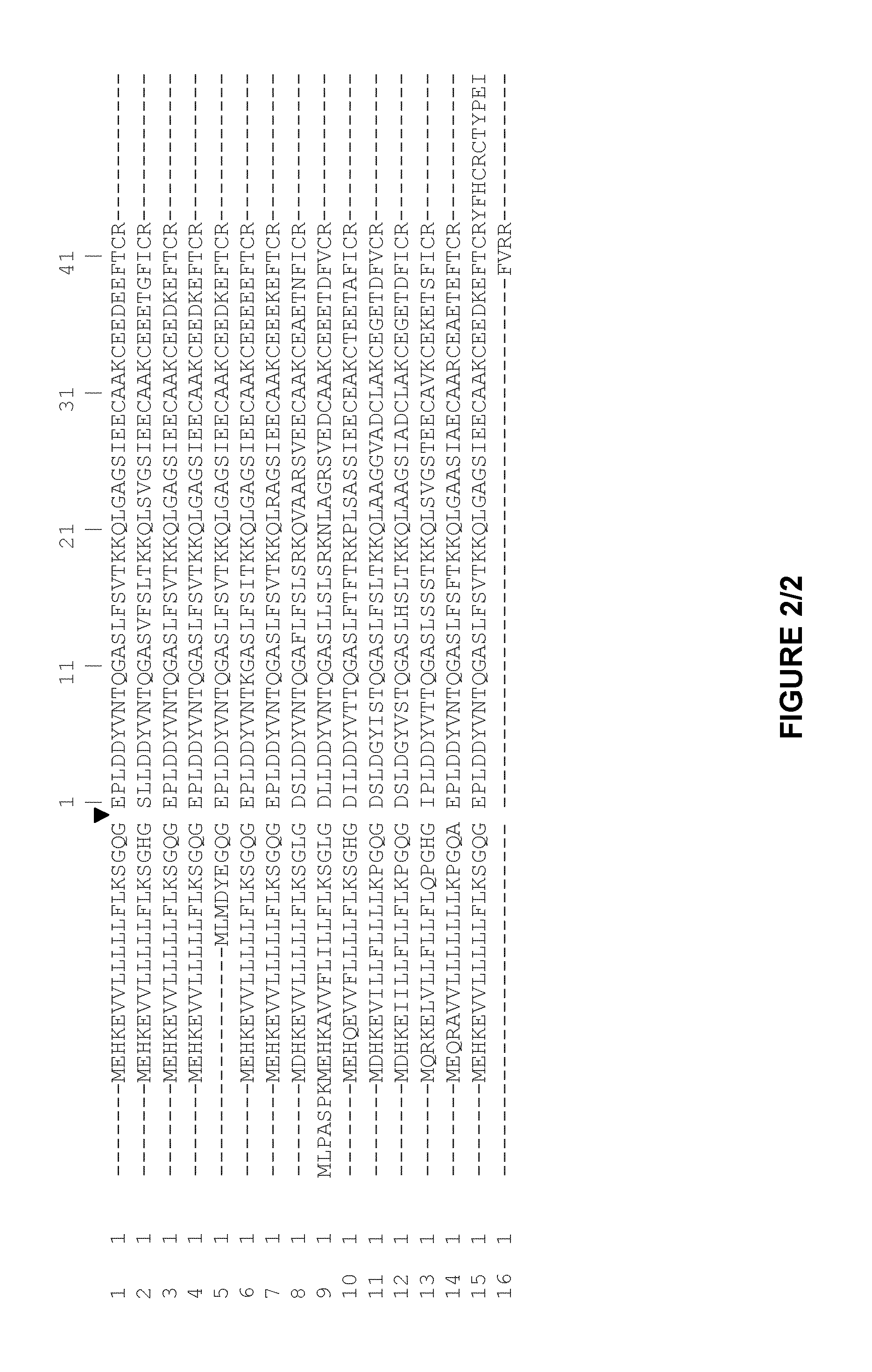
Variants of plasminogen and plasmin
InactiveUS20120114630A1Excellent long-term storage stabilityReducing circulating fibrinogenSenses disorderFungiProteinase activityPlasmin
The invention relates to variants of plasminogen and plasmin comprising one or more point mutations in the catalytic domain which reduce or prevent autocatylic destruction of the protease activity of plasmin. Compositions, uses and methods of using said variants of plasminogen and plasmin are also disclosed.
Owner:THROMBOGENICS NV
TGF-beta activation and use
InactiveUS20050065089A1Improve biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsPlasminChemistry
Proteases are added to Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) along with calcium and thrombin to activate latent TGF-β. The proteases include plasmin, calpin, MMP-9, thrombospondin, transglutaminase, the mannose 6-phosphate receptor (M6PR), furin, substilisin-like endoproteases, and integrins. Dermatopontin can also be added to the PRP to enhance its biologic activity.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
Gene of streptokinase, recombination protein and preparation method
InactiveCN1563378ALow costIncrease fibrinolytic activitySugar derivativesFermentationNucleotideProtein insertion
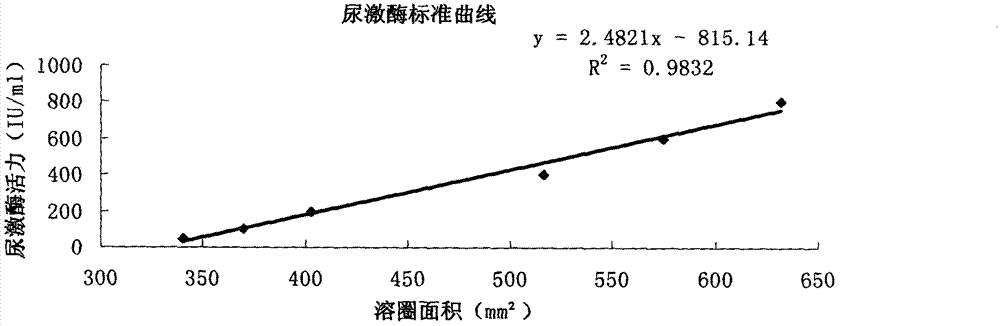
This invention discloses a thrombolytic zyme gene, a recombination protein and its preparation method relating to a thrombus dissolving material, relating to a source strain of thrombus dissolving gene and two reorganized strains containing said gene. Study shows that the zyme is a new plasmin and its vitality is 41000IUmg computed by the fibrin panel method having the function of anti-damage and suppressing protein oxidation arisen from beam, NaNO2 and H2O2.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
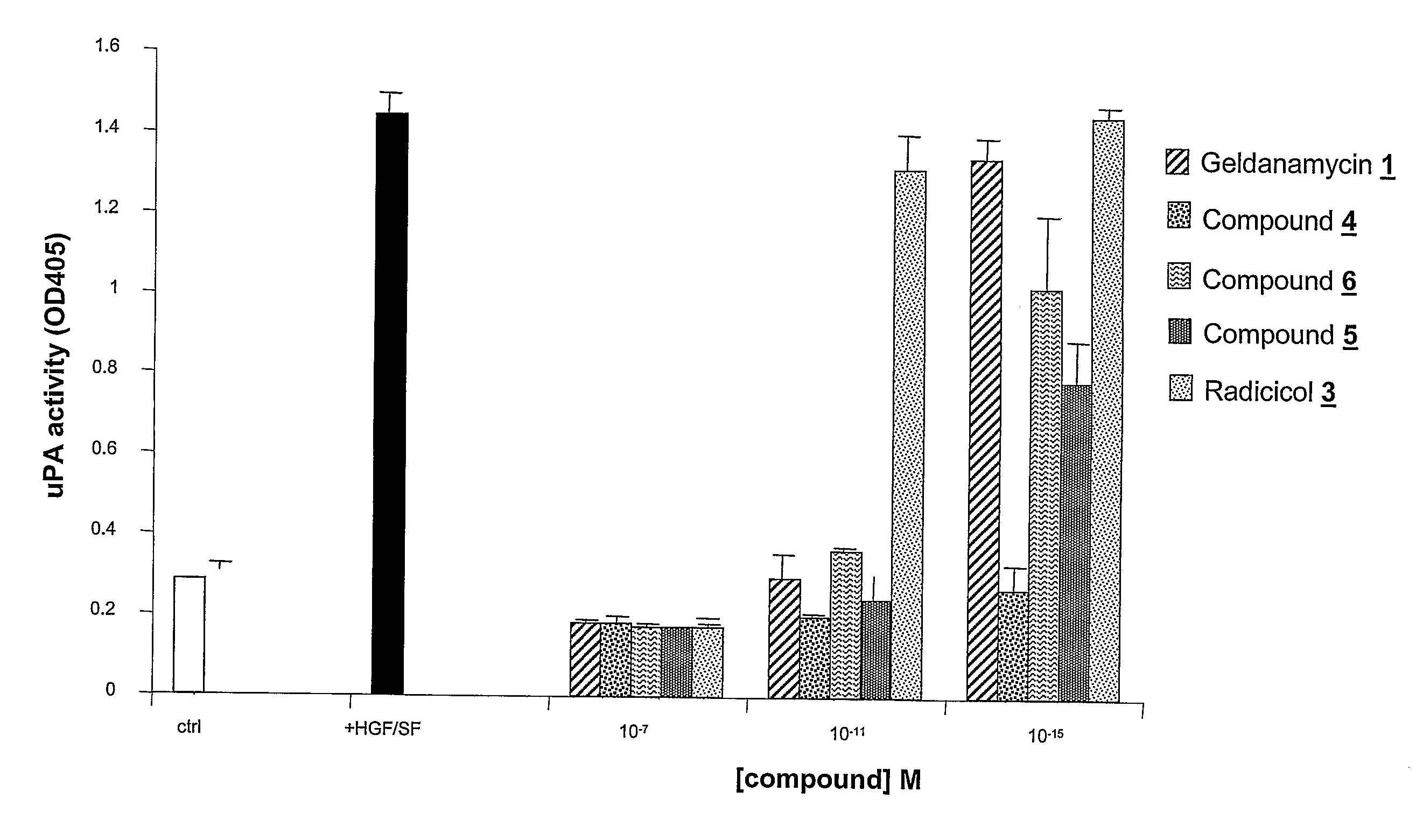
Geldanamycin and Derivatives Inhibit Cancer Invasion and Identify Novel Targets
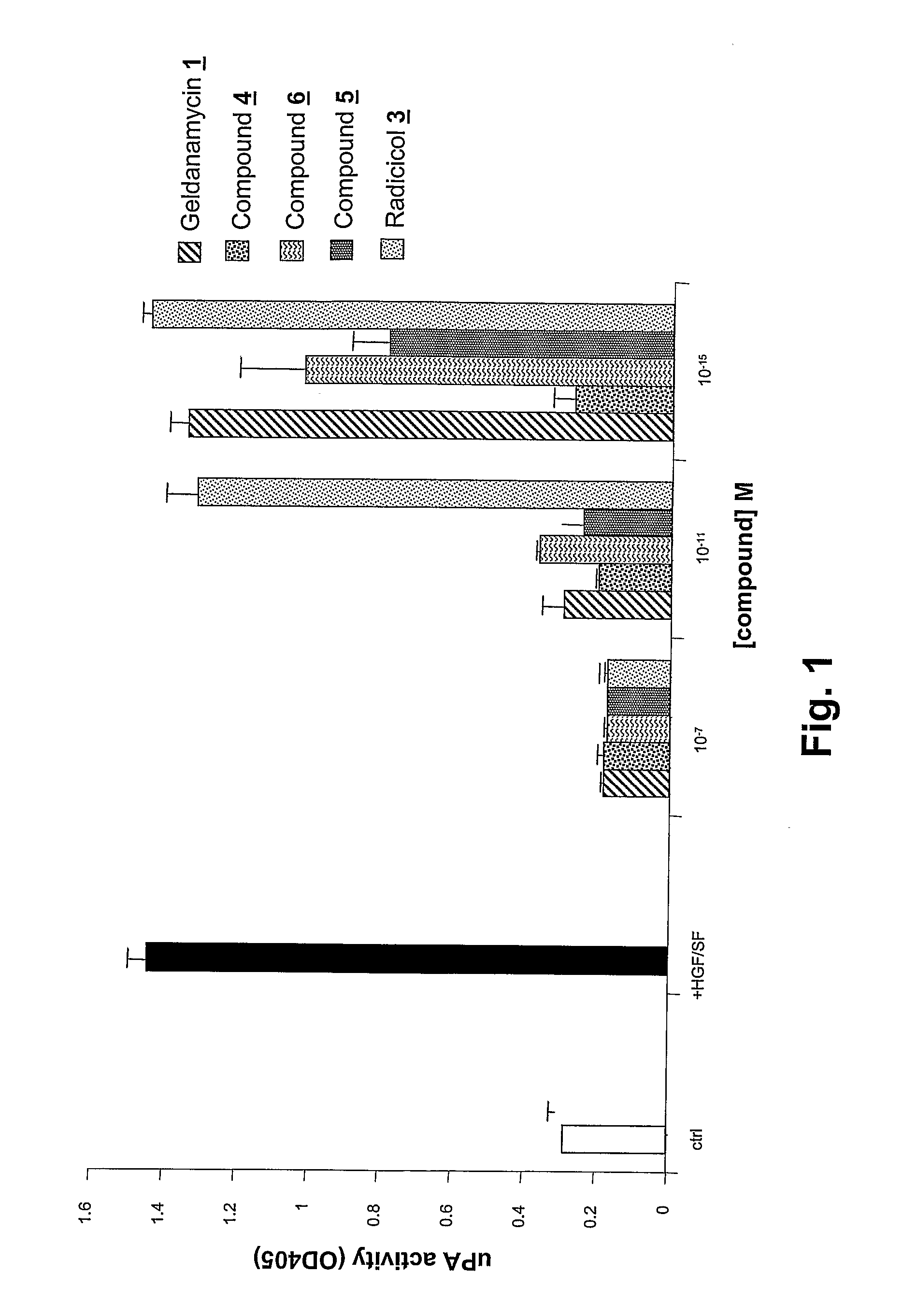
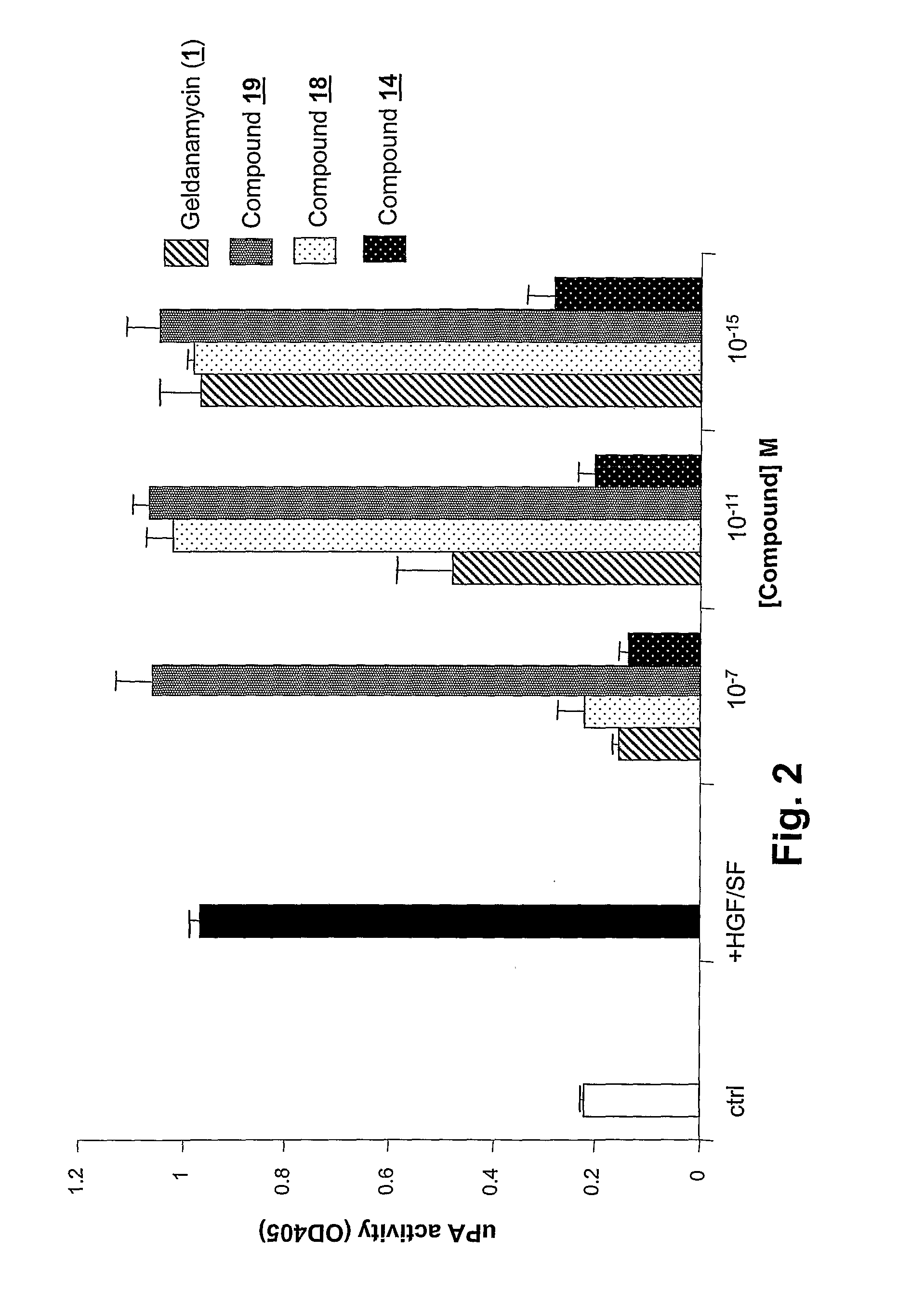
Geldanamycin derivatives that block the uPA-plasmin network and inhibit growth and invasion by glioblastoma cells and other tumors at femtomolar concentrations are potentially highly active anti-cancer drugs. GA and various 17-amino-17-demethoxygelddanamycin derivatives are disclosed that block HGF / SF-mediated Met tyrosine kinase receptor-dependent uPA activation at fM levels. Other ansamycins (macbecins I and II), GA derivatives, and radicicol required concentrations several logs higher (≧nM) to achieve such inhibition. The inhibitory activity of tested compounds was discordant with the known ability of drugs of this class to bind to hsp90, indicating the existence of a novel target(s) for HGF / SF-mediated events in tumor development. Methods of using such compounds to inhibit cancer cell activities and to treat tumors are disclosed. Such treatment with low doses of these highly active compounds provide an option for treating various Met-expressing tumors, in particular invasive brain cancers, either alone or in combination with conventional surgery, chemotherapy, or radiotherapy.
Owner:VAN ANDEL RES INST +1
Method for fermenting and producing plasmin by use of cordyceps militaris liquid
InactiveCN102604919AIncrease liquid fermentation yieldIncrease productionFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyProtein solution
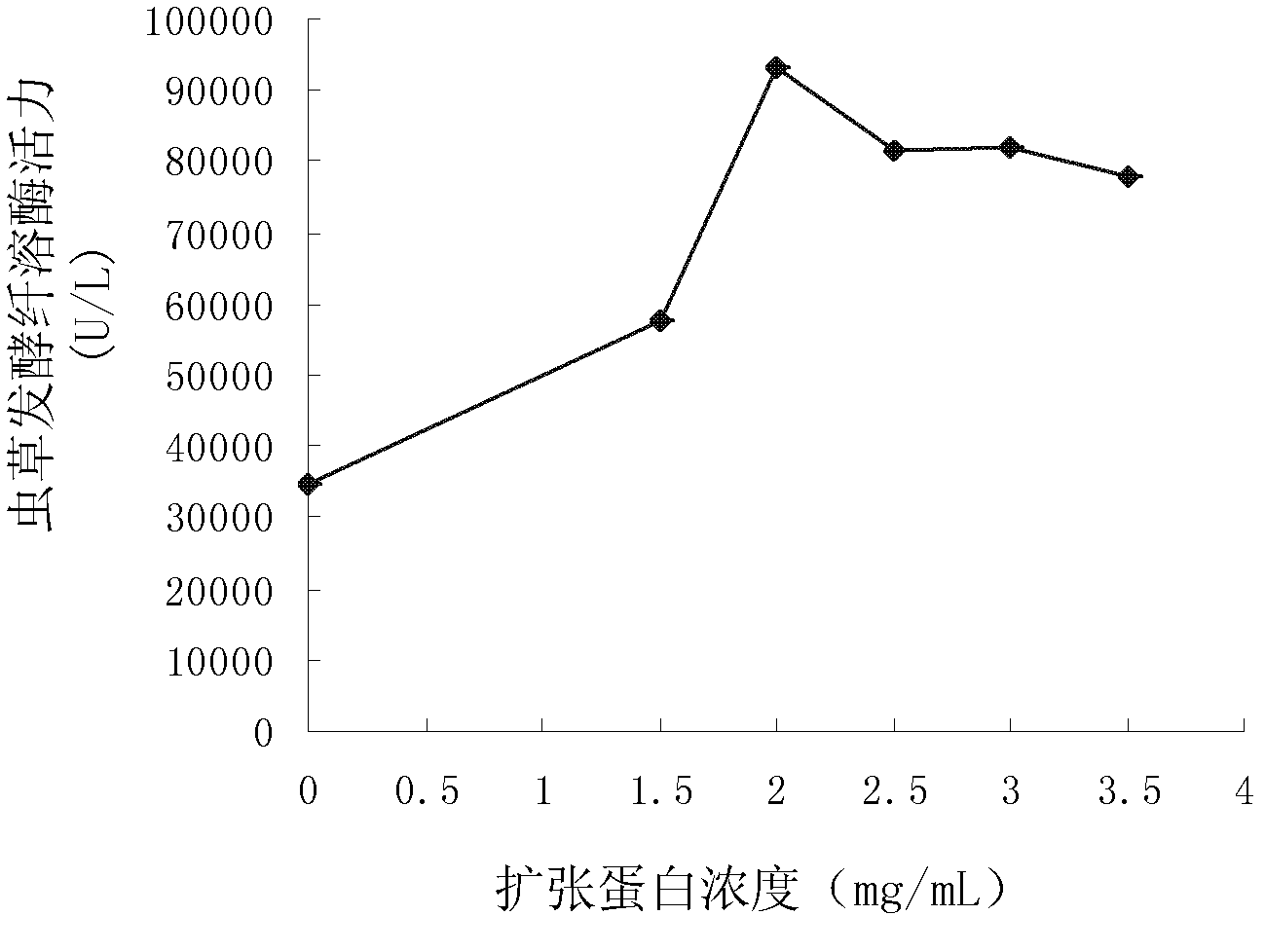
The invention relates to a method for fermenting and producing plasmin by use of cordyceps militaris liquid. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) inoculating the cordyceps militaris strain into the PD liquid fermentation medium to perform activation culture, and transferring to a seed fermentation medium to perform seed culture to obtain seed liquid; (2) inoculating the seed liquid into a liquid fermentation medium according to a volume ratio of 5-15%, and performing liquid fermentation culture for 20-30 hours; adding an expansion protein solution, and continuing culture for 120-168 hours; and separating and removing cordyceps militaris mycelium to obtain plasmin fermentation supernate; and (3) extracting cordyceps militaris extracellular plasmin from the plasmin fermentation supernate to obtain the cordyceps militaris plasmin. According to the invention, the plant expansion protein and the optimized fermentation method are applied to the liquid fermentation production of cordyceps militaris plasmin, and the liquid fermentation output of the cordyceps militaris plasmin is remarkably increased to 93270U per liter of fermentation broth, which is over 2.69 times that of the traditional fermentation production method; and the method has perfect industrial application prospect.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Early detection of pathogens in blood
InactiveUS7993870B2Rapid and efficient analysisSmall proportionSugar derivativesHydrolasesZymogenFIBRINOGEN/THROMBIN
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Production method of thrombolytic fermented soya beans
InactiveCN101305785AIncrease plasmin contentThrombolyticFood preparationBiotechnologyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for preparing thrombolytic black curd beans, which comprises the following steps of: soaking high-quality soybean, cooking, cooling, inoculating to mould starter (Aspergillus), fermenting and culturing for 60-72h to obtain black curd bean semi-product; and soaking at the room temperature for 5h-8h, adding glucose 8.0%-10.0% (W / W), sterilizing, cooling, inoculating to 12.0%-15.0% (V / W) Bacillus subtilis seed solution, and fermenting and culturing at 30 DEG C -35 DEG C for 72h-84h. The thrombolytic black curd beans are rich in nutritive compositions such as soluble nitrogen, soluble sugar, water soluble mineral, and free amino acid and functional components such as black curd bean plasmin, polypeptide, soybean isoflavone, etc., and are prepared by performing two-step solid fermentation, i.e. the primary fermentation of the Aspergillus and the secondary fermentation of the Bacillus subtilis, in combination with the conventional black curd bean production technology. The black curd beans have the effects of resisting oxidation, resisting thrombosis and preventing cardiovascular disease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Early Detection of Pathogens in Blood
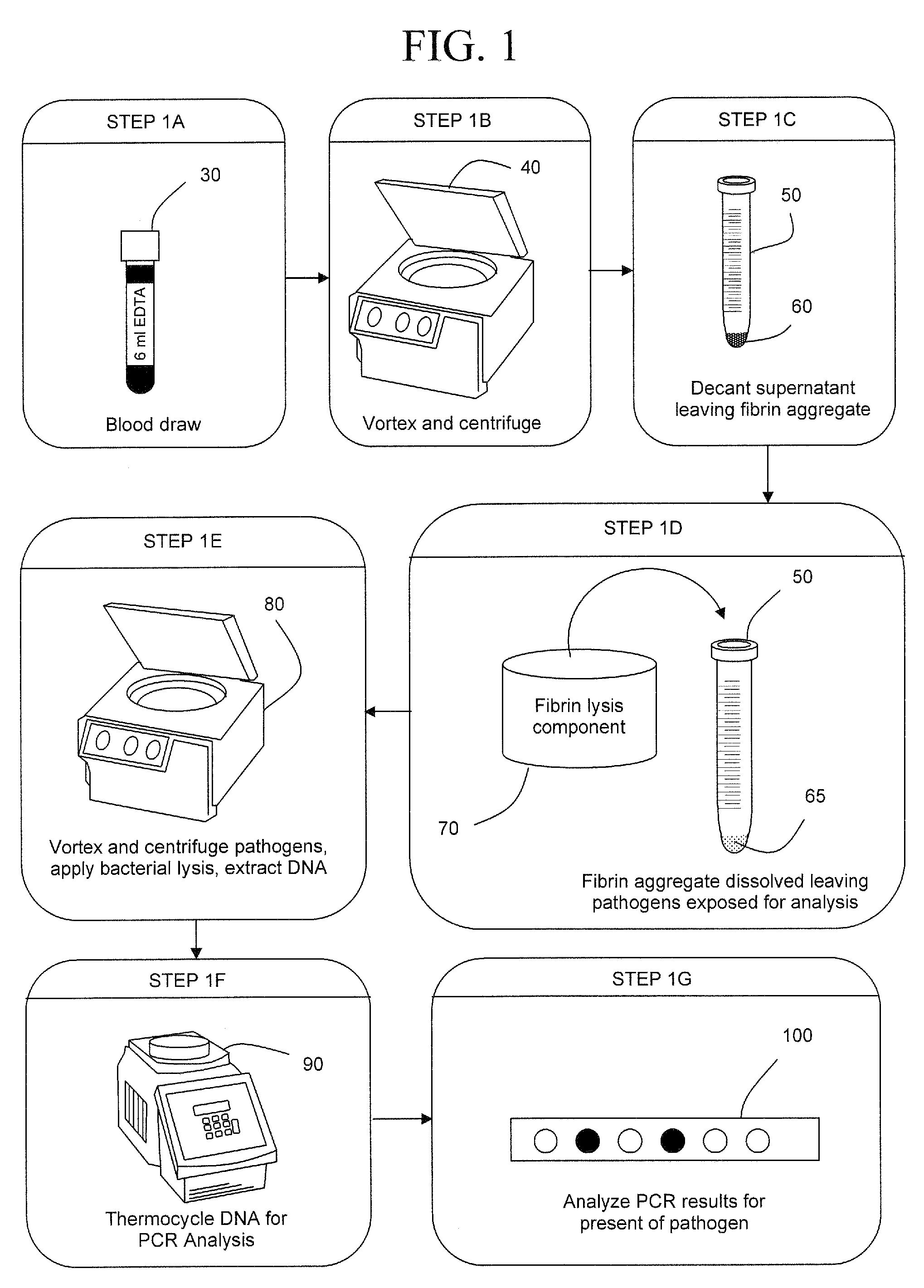
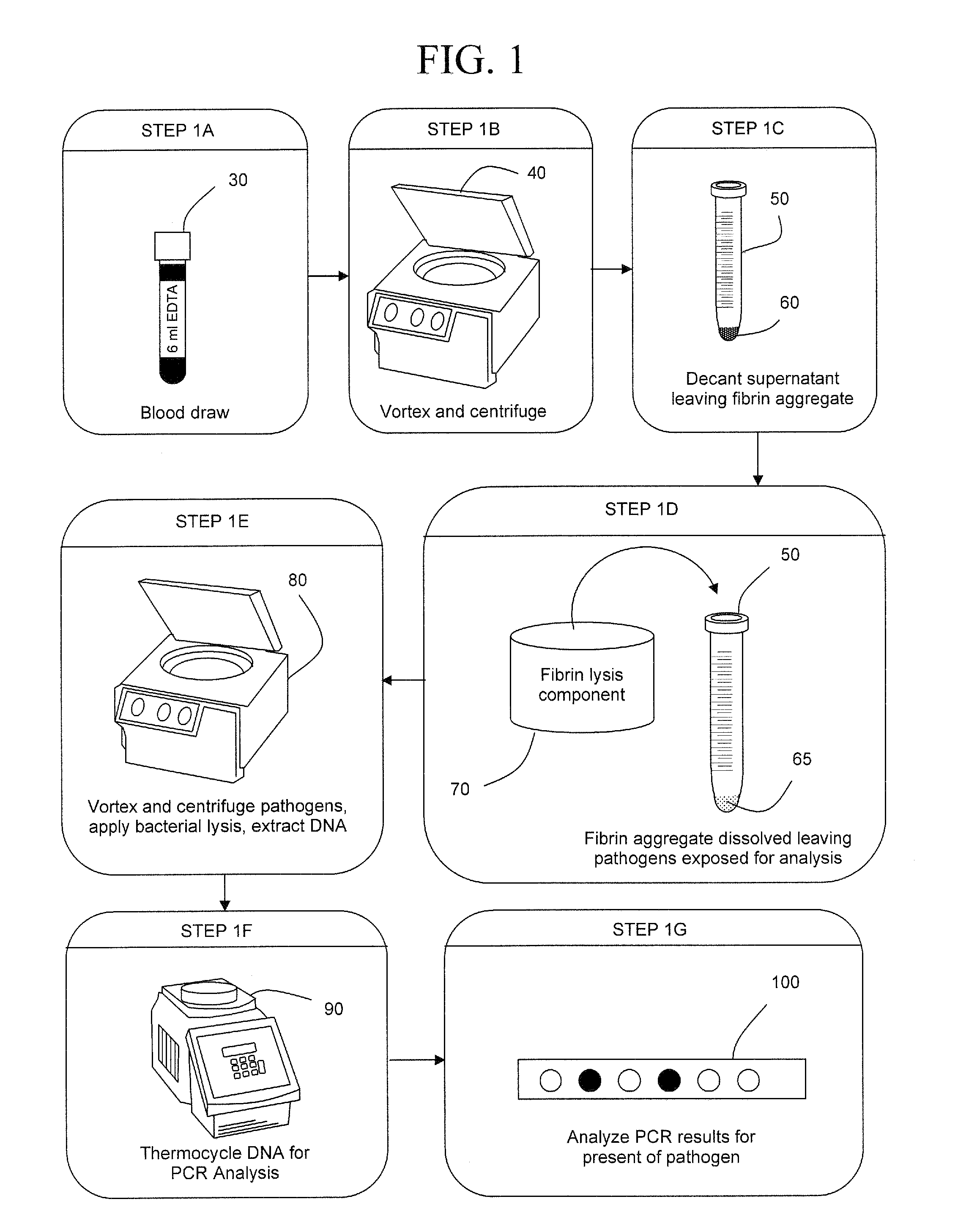
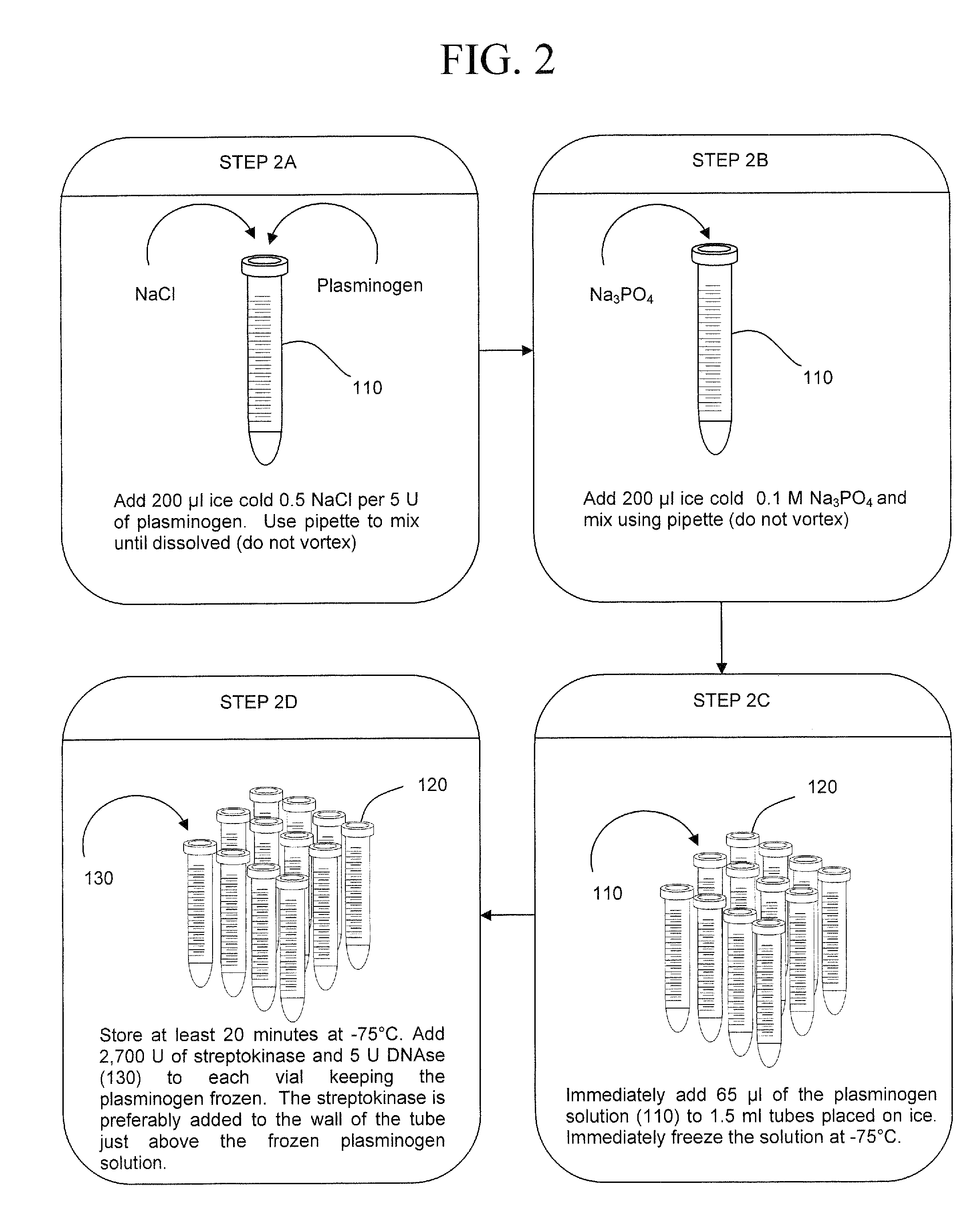
InactiveUS20090305383A1Rapid and efficient analysisSmall proportionSugar derivativesHydrolasesZymogenLysis
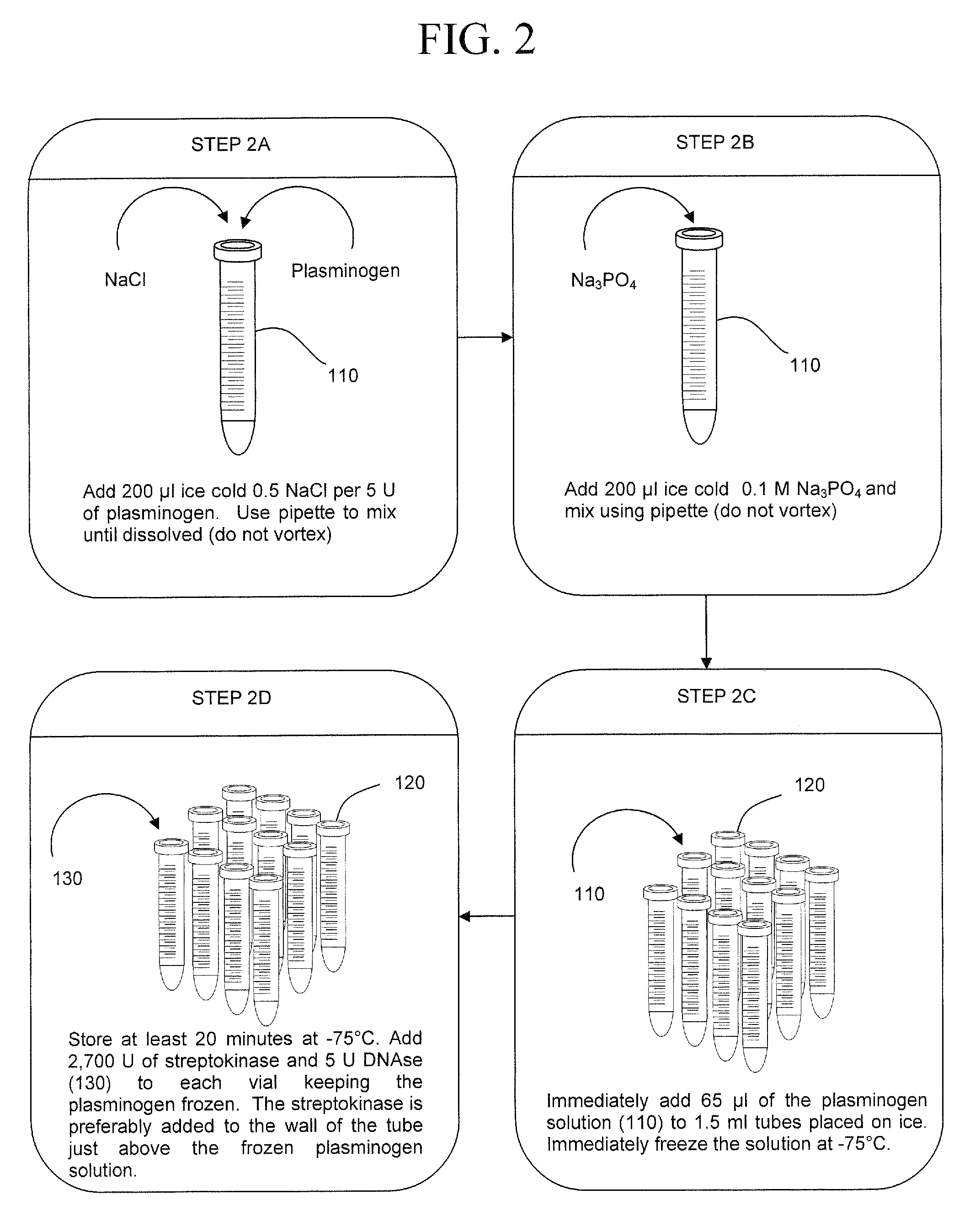
The present invention is a method of extracting infectious pathogens from a volume of blood including the steps of creating a fibrin aggregate confining the pathogens and introducing a fibrin lysis reagent to expose the pathogens for analysis. The fibrin lysis reagent is preferably composed of plasminogen and streptokinase frozen in coincident relation until the fibrin lysis reagent is needed whereby streptokinase enzymatically reacts with plasminogen to form plasmin upon thawing. The plasminogen is suspended in an aqueous salt solution prior to freezing including NaCl and Na3PO4.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
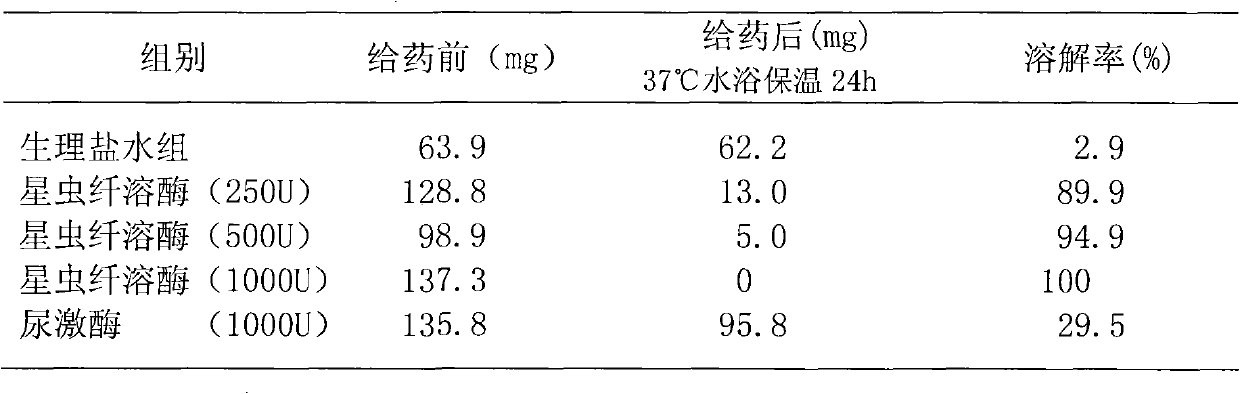
Phascolosoma esculenta plasmin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102002488ASimple extraction processReduce manufacturing costEnzymesArterial occlusionsThrombus
The invention provides phascolosoma esculenta plasmin, which is extracted from phascolosoma esculenta, and has double activities of directly dissolving fibrin and kinase. The phychemical performance of the plasmin is that: the molecular weight is between 28,000 and 32,000, the isoelectric point is between 4.6 and 6.6, the dissolution activity of fibrin does not change greatly under a temperature range between 30 and 70 DEG C, and the stability range to the pH value is between 5.0 and 9.0. The phascolosoma esculenta plasmin has the direct fibrin and kinase dissolving activities, has simple extracting process, low preparation cost and easily obtained raw materials, can be developed into intravenous injection, contains the plasmin capable of directly dissolving thrombus, and is expected to obtain better effect in treating catheter assisted thrombolysis treating peripheral arterial occlusion and deep venous thrombosis.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Production process of preserved beancurd having nutrition and health-care function
InactiveCN101647541AIncrease contentImprove the ability of fermentation to produce proteaseFood preparationMetaboliteProtease preparation
The invention discloses a production process of preserved beancurd having a nutrition and health-care function, comprising the following steps: screening mucor strains; injecting N<+> ions; producinghigh-yield metabolite plasmin; producing the preserved beancurd; and adding a protease preparation. The preserved beancurd has the advantages of rich nutrition, nutrition and health-care function enhancement and low cost. Industrialized low-salt thrombolytic preserved beancurd having a nutrition function and lowering cholesterin can be produced through the invention.
Owner:JIANGSU XINZHONG BREWING
Candidates against infection
ActiveUS8318661B2Effective treatmentReduce occurrence and formationAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderPlasminBacterial arthritis
The present invention relates to the use of plasminogen / plasmin and its derivatives as agents for enhancing host defense against infection or other infectious diseases. The invention also relates to a method for screening of compounds which enhance host defense against infection by evaluating the host defense against bacterial arthritis and spontaneous otitis media in an animal model.
Owner:OMNIO HEALER AB
Plasminogen and plasmin variants
InactiveUS20130273028A1Reduces extent of autoproteolytic degradationPromote lysisSenses disorderBacteriaPlasminProteinase activity
The invention relates to variants of plasminogen and plasmin comprising one or more point mutations in the catalytic domain which reduce or prevent autocatylic destruction of the protease activity plasmin. Compositions, uses and methods of using said variants of plasminogen and plasmin are also disclosed.
Owner:THROMBOGENICS NV
Plasminogen and cultivation method therefor
The present invention relates to one kind of and its culturing and preparing process. The plasmin is prepared with N. sitophila strain No. 17 in the preservation number of CGMCC No. 1836, and through fermentation, separation and purification. It consists of two subunits of molecular weight 30000 and 15500 separately and isoelectric point of 7.9+ / -0.2. The plasmin has high thrombolysis performance, no bleeding activity, no blood coagulating activity and no obvious acute toxicity, and thus possesses clinical test, development and application foreground. The plasmin of the present invention is one kind of extracellular enzyme, and is favorable to post separation and purification. Its preparation adopts wheat bran and soybean residue as main culture medium material, and thus has low material cost.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Sipunculus nudus plasmin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101892210ASimple extraction processReduce manufacturing costPeptide/protein ingredientsEnzymesArterial occlusionsThrombus
The invention relates to sipunculus nudus plasmin which is extracted from sipunculus nudus and has double activities of directly dissolving fibrin and kinase. The sipunculus nudus has the materialization performances that the molecular weight ranges from 27000 to 35000, the isoelectric point ranges from 4.5 to 7.0, the dissolving activity of fibrin varies little within the temperature range of 30 to 70 degrees centigrade, and the stability range of the pH value ranges from 5.0 to 9.0. The sipunculus nudus plasmin has double activities of directly dissolving the fibrin and the kinase, simple extraction process, low preparation cost and easily obtained materials, can be developed into vein injection, contains the plasmin for directly degrading thrombus and is expected to have better effect on treating periphery arterial occlusion and deep vein thrombosis in a conduit-assisted thrombolytic therapy.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com