Fungal fibrinolytic enzyme and cultivating method thereof
A technology of fibrinolytic enzyme and fungus, applied in the field of cultivation of the fungal fibrinolytic enzyme, can solve the problems of limited popularization and application, limited resources, etc., and achieve the effects of good thrombolytic performance, short enzyme production cycle, and low raw material cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] 1. Strain: Cordyceps militaris strain C.LSG-1, the preservation number is CGMCC N 0 .2577
[0021] 2. Medium and culture conditions:
[0022] (1) Incline medium: glucose 1%, agar 2.5%, potato juice 20%, peptone 0.5%, KH 2 PO 4 0.1%, MgSO 4 0.05%, pH natural. Culture conditions: culture at a constant temperature of 23°C for 10 days. (Preparation of 20% potato juice: Weigh 200g of peeled potatoes, cut into pieces, add 1000ml of distilled water, boil for 30min, filter with double gauze to get the juice for later use)
[0023] (2) Plate medium: glucose 1%, agar 2.5%, potato juice 20%, peptone 0.5%, KH 2 PO 4 0.1%, MgSO 4 0.05%, pH natural. Culture conditions: culture at a constant temperature of 23°C for 10 days.
[0024] (3) Liquid fermentation medium: 1.25% sucrose, 5% zein, KH 2 PO 4 0.01%, KCl0.005%, MgSO 4 0.001%, CuSO 4 0.001%, the filling volume is 40mL / 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, and the initial pH value of the fermentation medium is natural. Liquid fer...
Embodiment 2
[0026] 1. Incline cultivation is the same as in Example 1
[0027] 2, liquid fermentation culture is the same as embodiment 1
[0028] 3. Separation and purification of cordyceps militaris fibrinolytic enzyme: the liquid fermentation product was subjected to 20% saturation ammonium sulfate salting out, Phenyl Sepharose HP hydrophobic interaction chromatography, and Superdex75 gel filtration chromatography to collect fibrinolytic active components.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Proof of fibrinolytic activity of Cordyceps militaris fibrinolytic enzyme:
[0031] The solubility of the enzyme to fibrin was tested by the fibrin plate method.
[0032] fibrin plate method
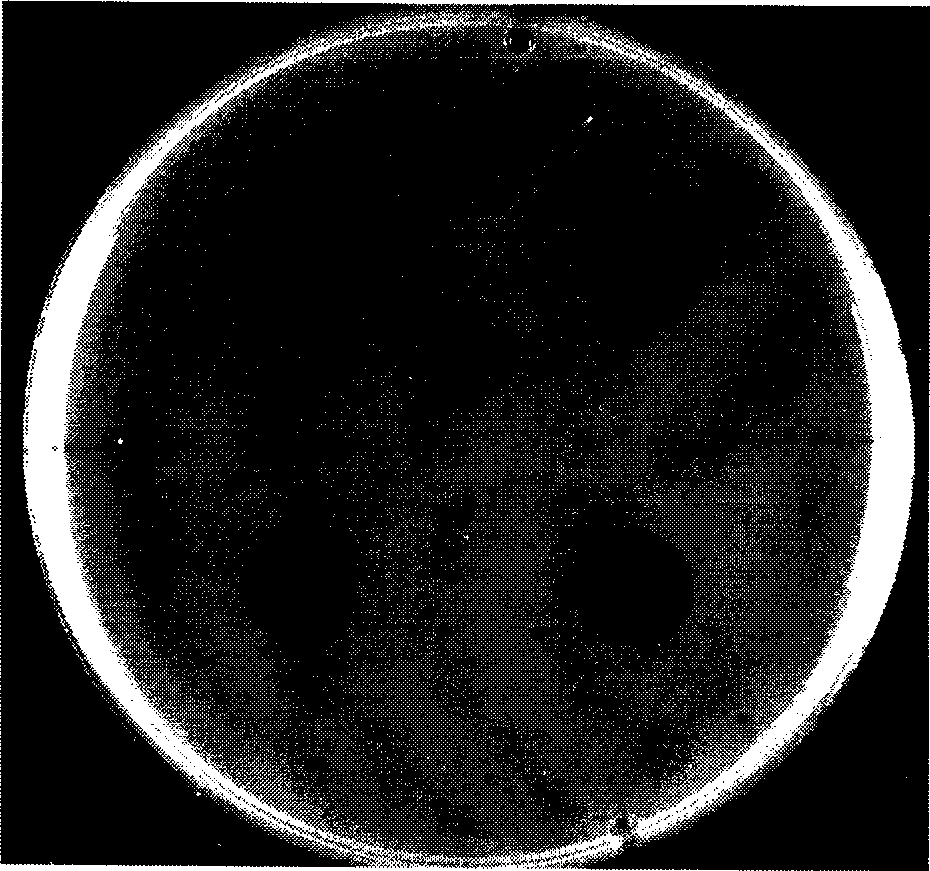
[0033] The fibrin plate contains fibrinogen (commercially available fibrinogen may contain fibrin) and thrombin. The soluble fibrinogen forms fibrin monomers under the action of thrombin, and the fibrin monomers spontaneously associate. Polymerization forms a visible fibrin gel, and the plasminase solution is added to the surface of the slab gel. After a short period of incubation, the enzyme dissolves the fibrin, forming a transparent circle visible to the naked eye on the surface of the slab gel. See figure 1 .
[0034] Bacterial strains used in the present invention can use existing commercially available products, and the high-yield fibrinolytic enzyme Cordyceps militaris bacterial strain C.LSG-1 that preferably uses through strict screening obtains, and its growth conditio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com