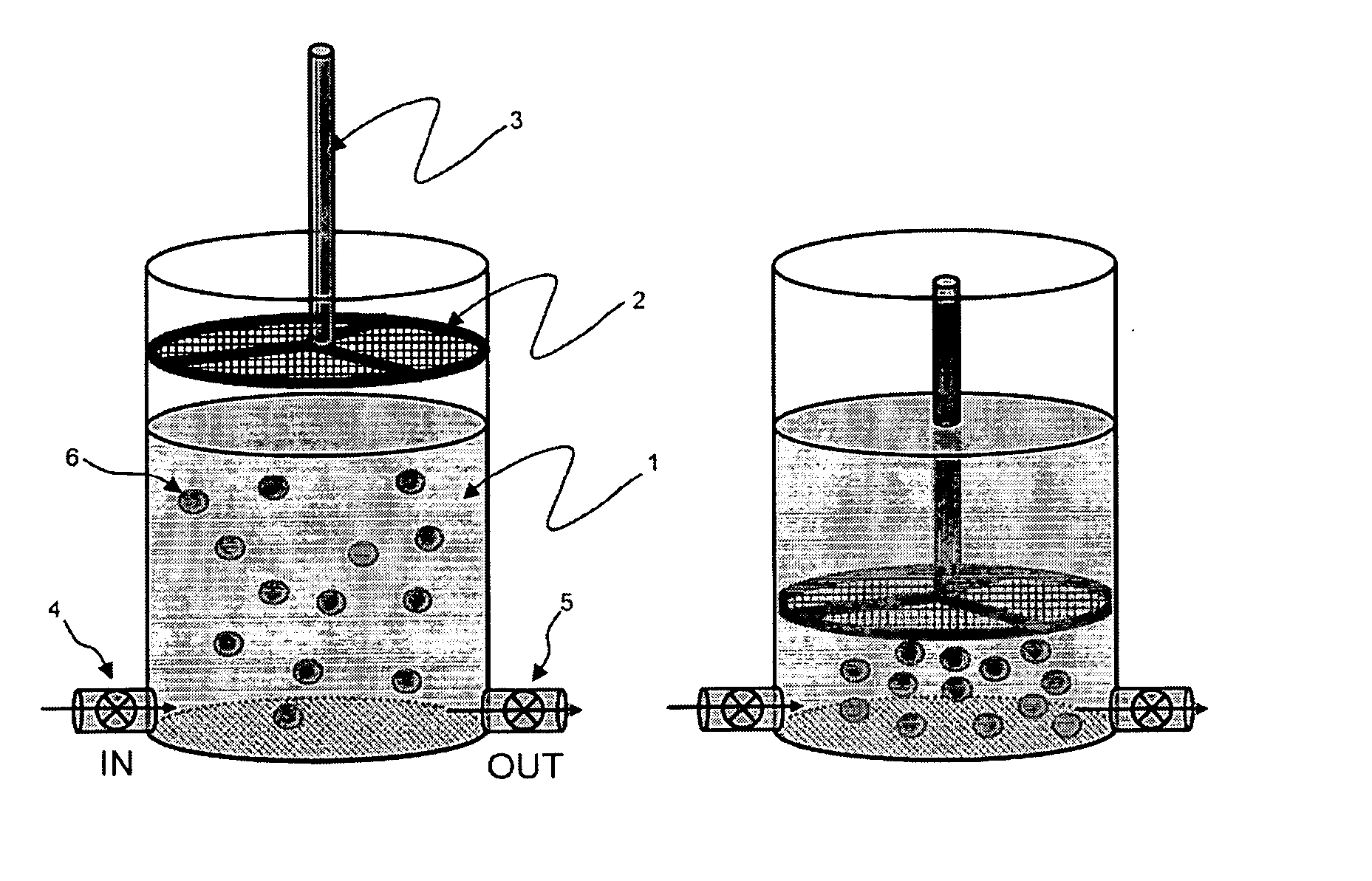
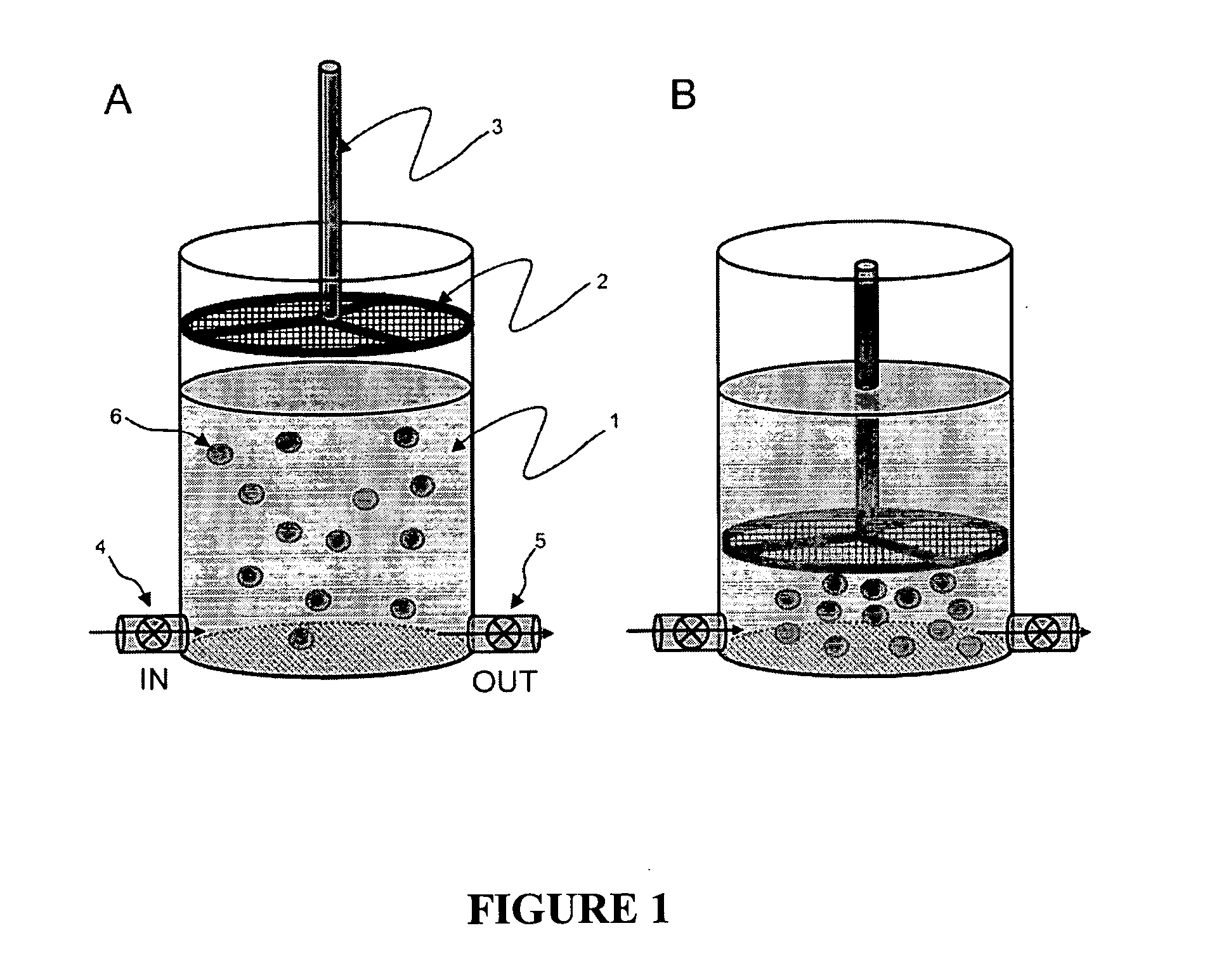
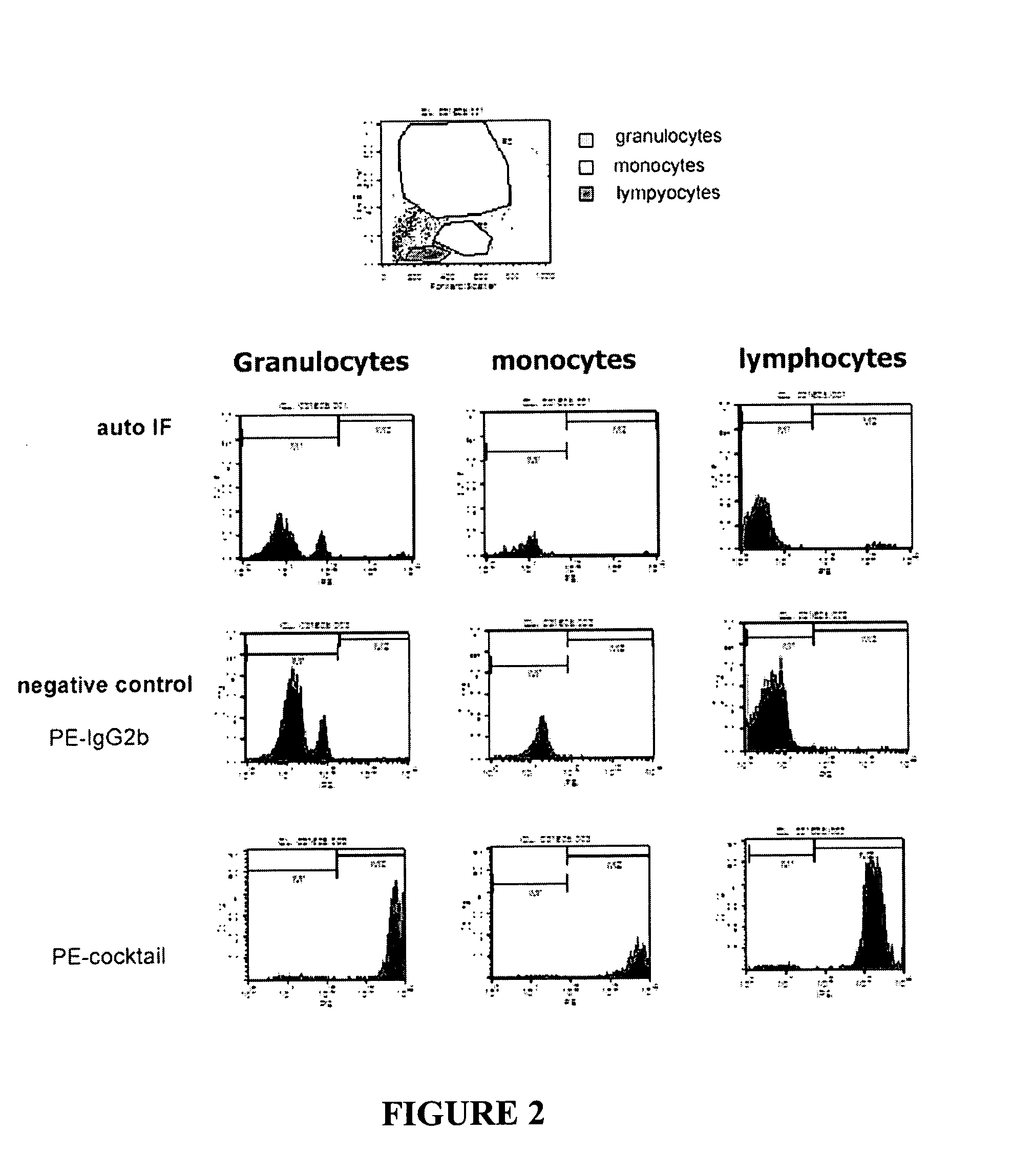
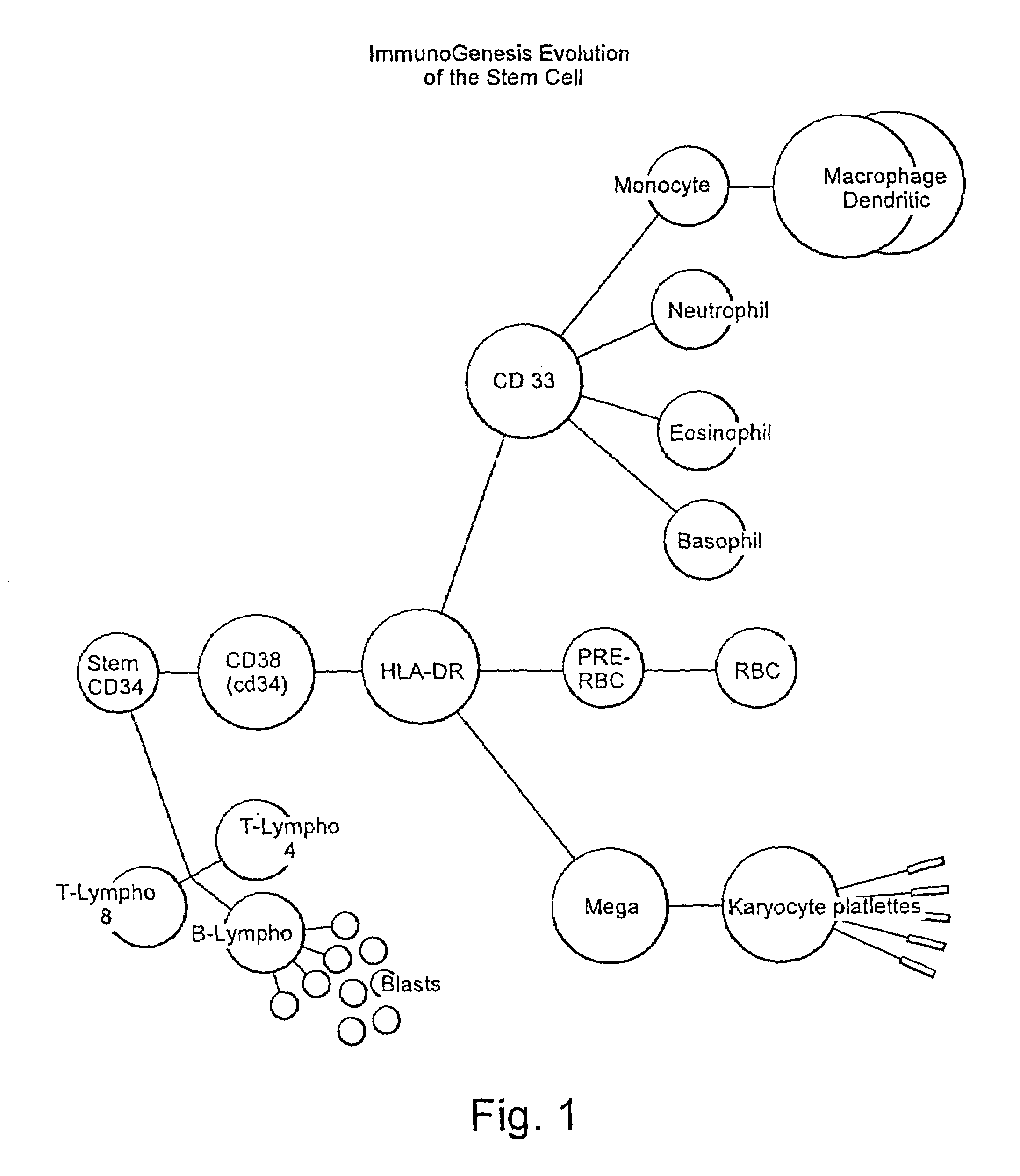
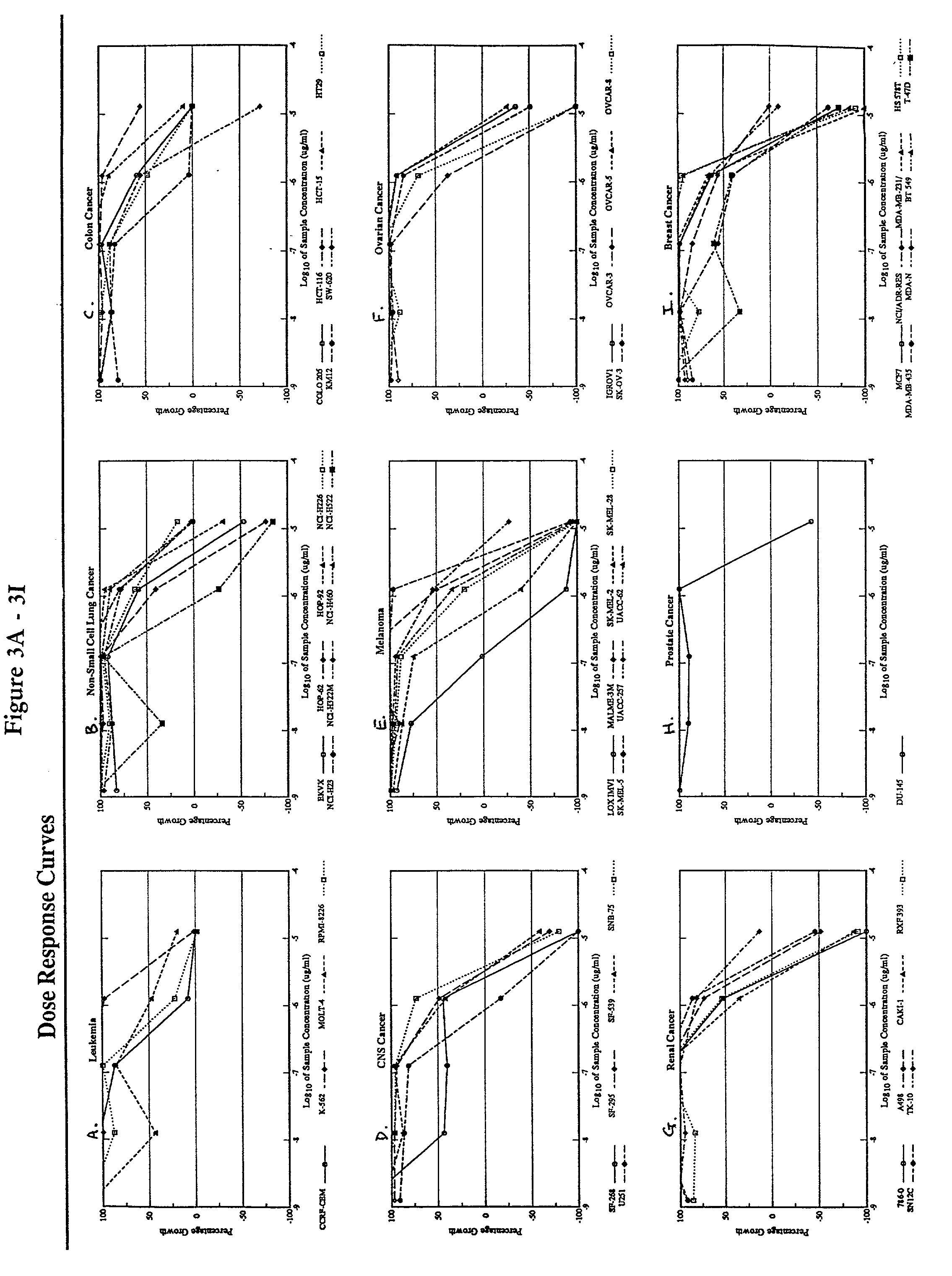
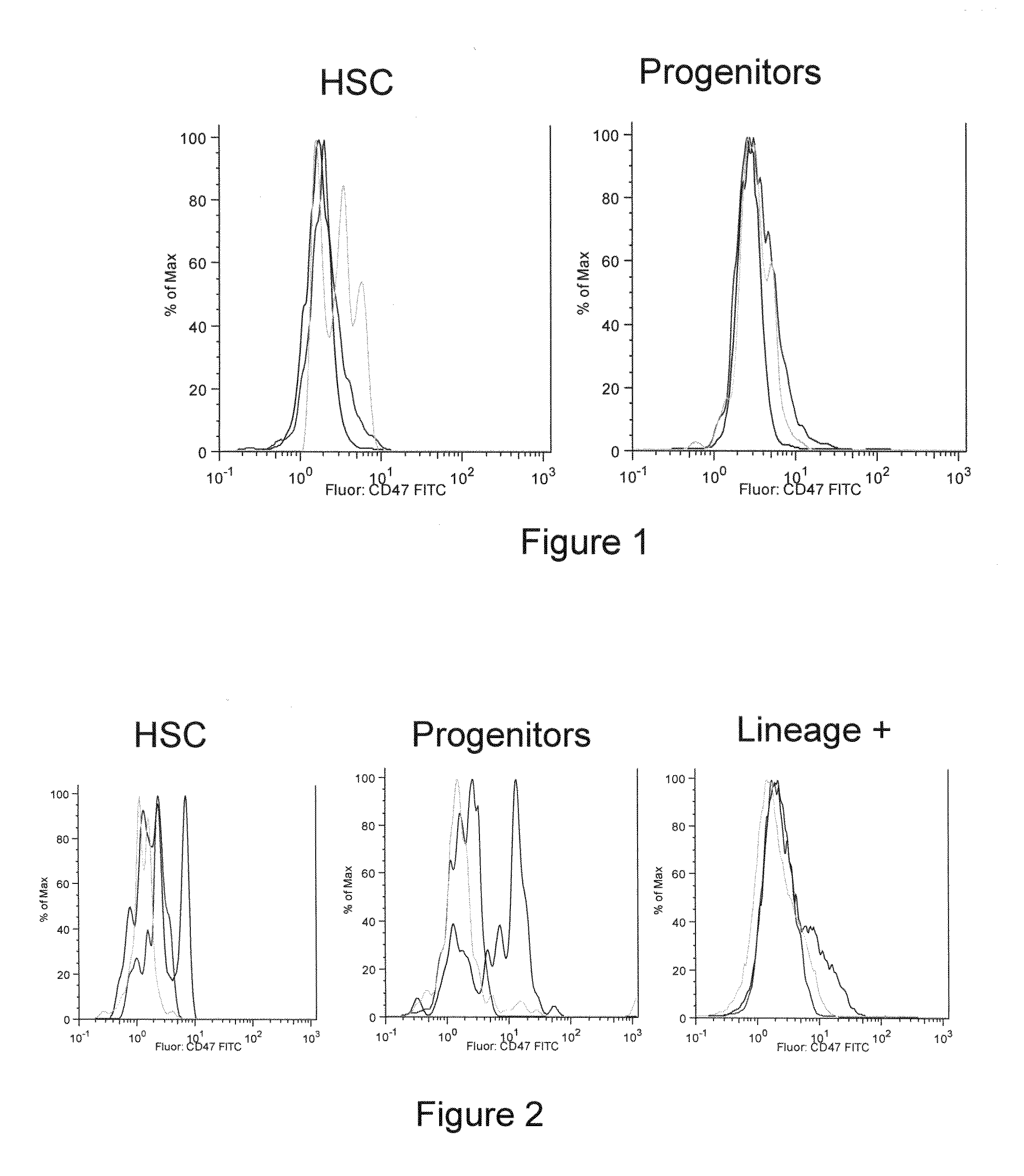
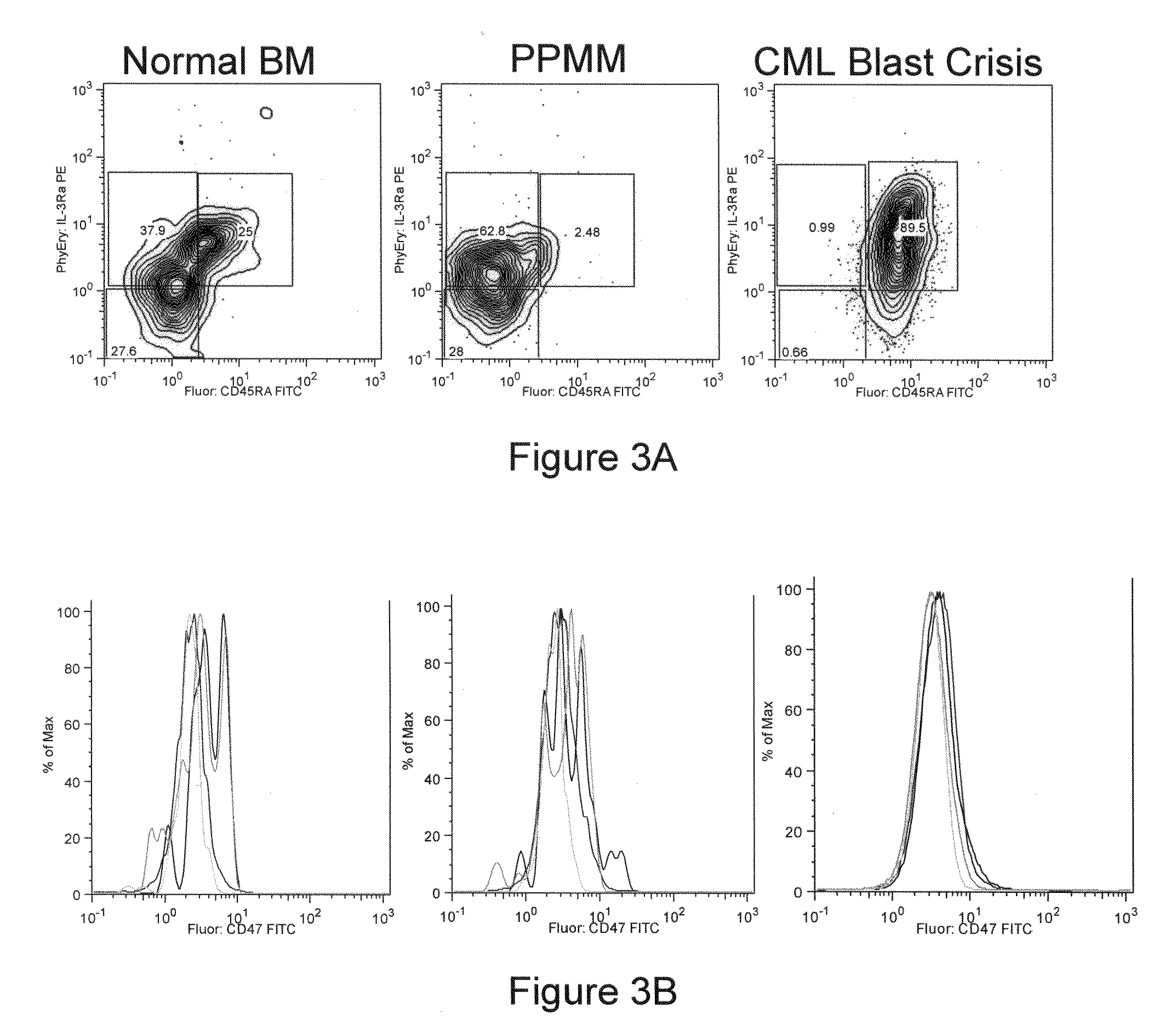
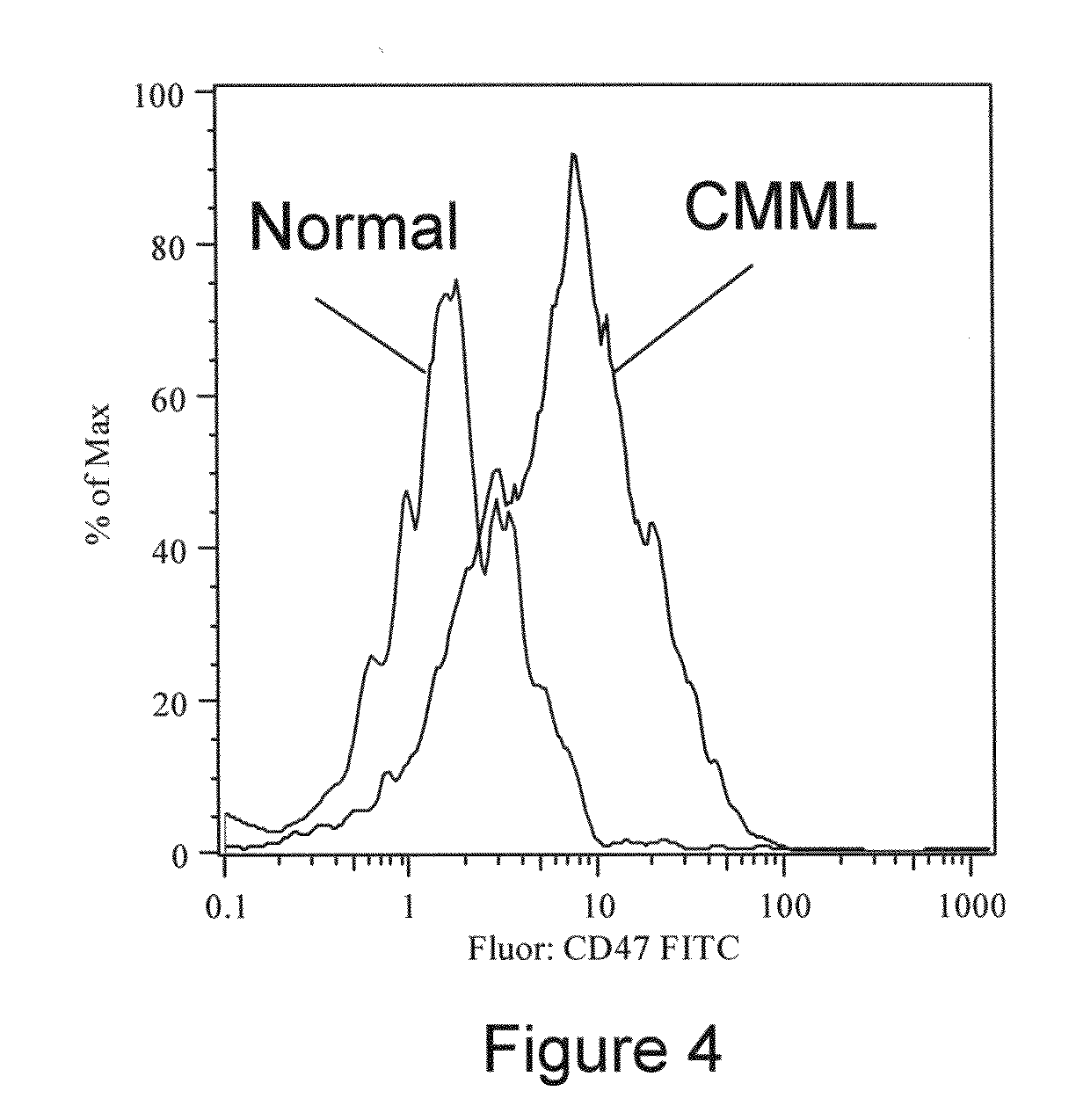
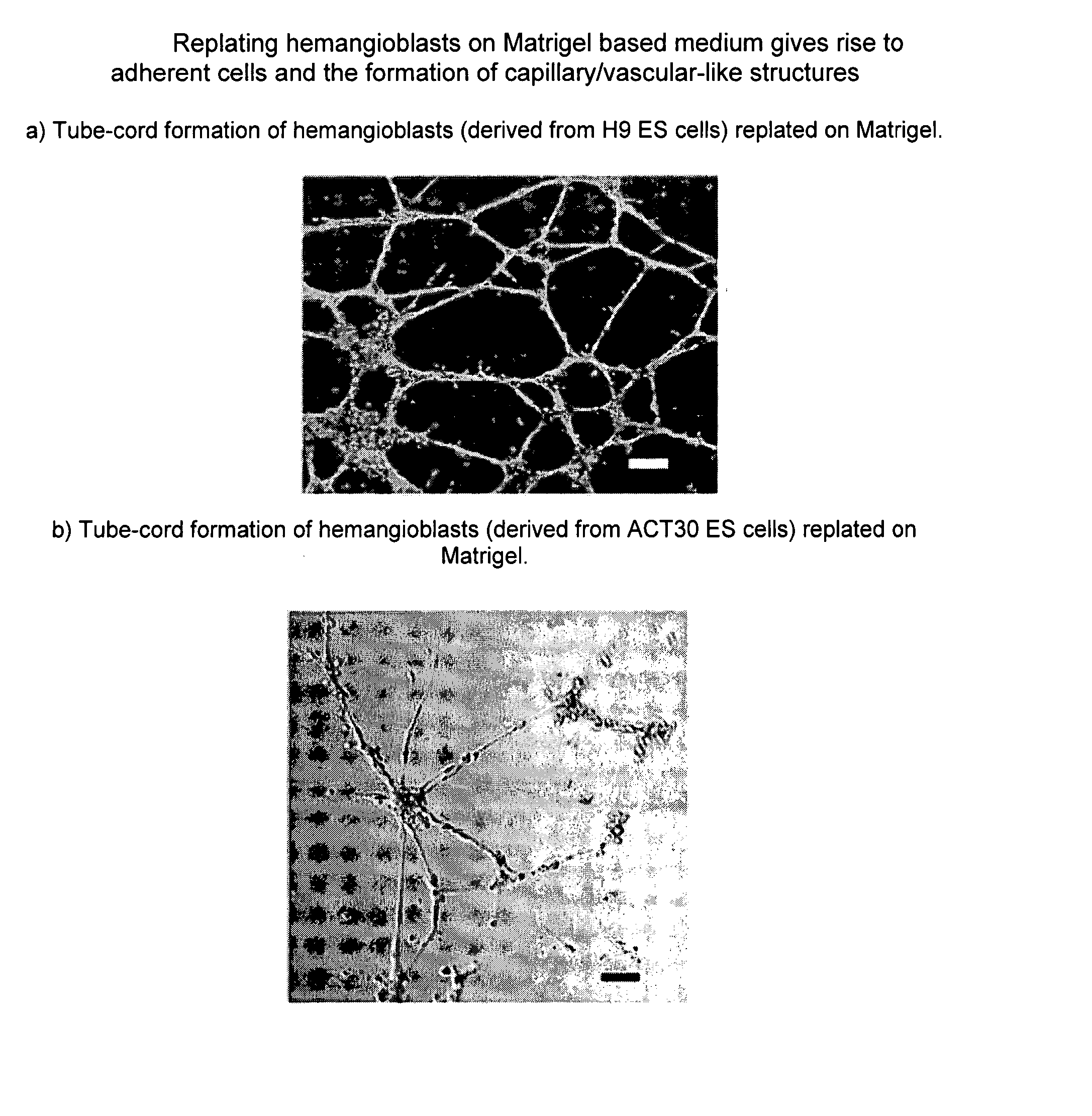
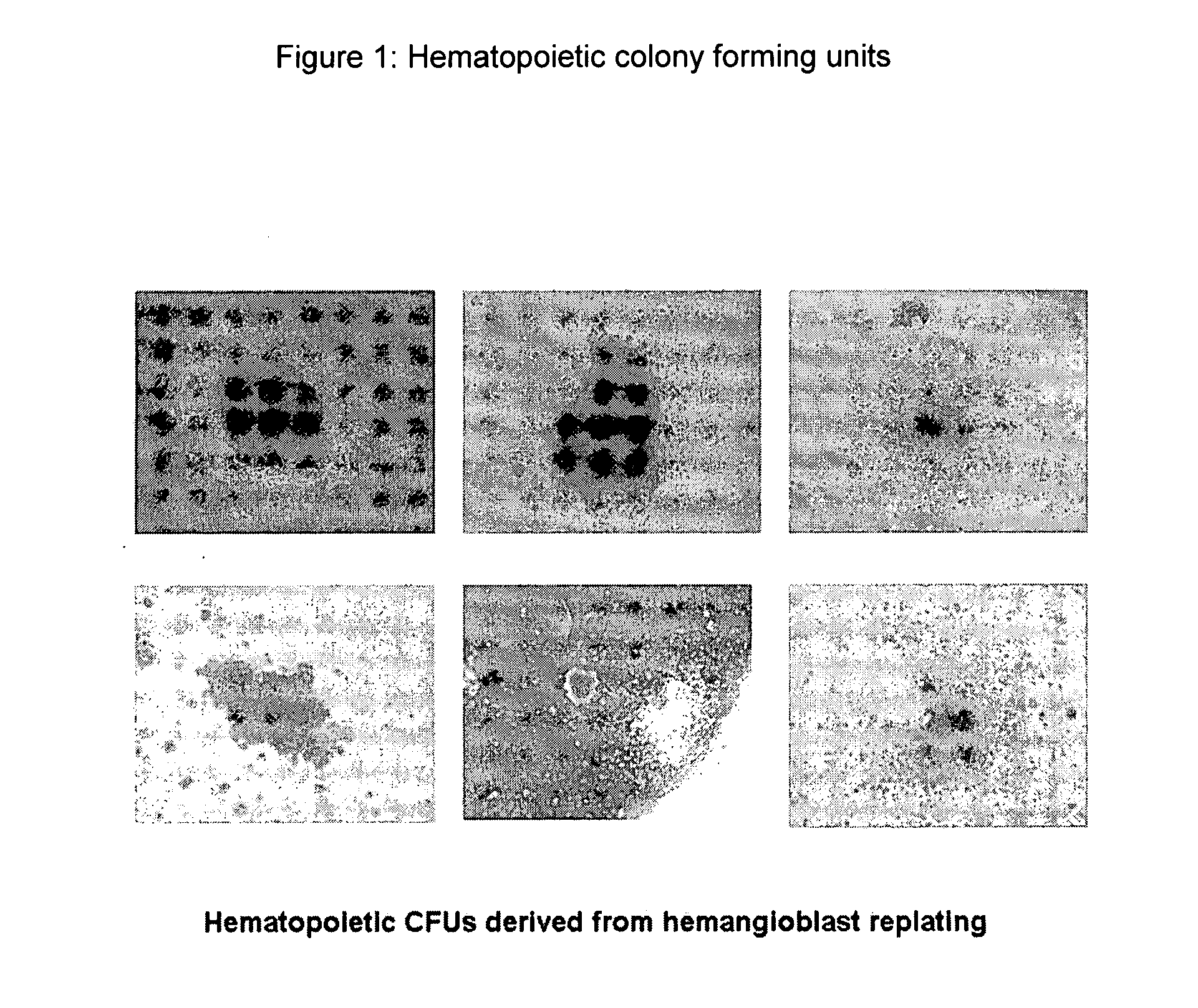
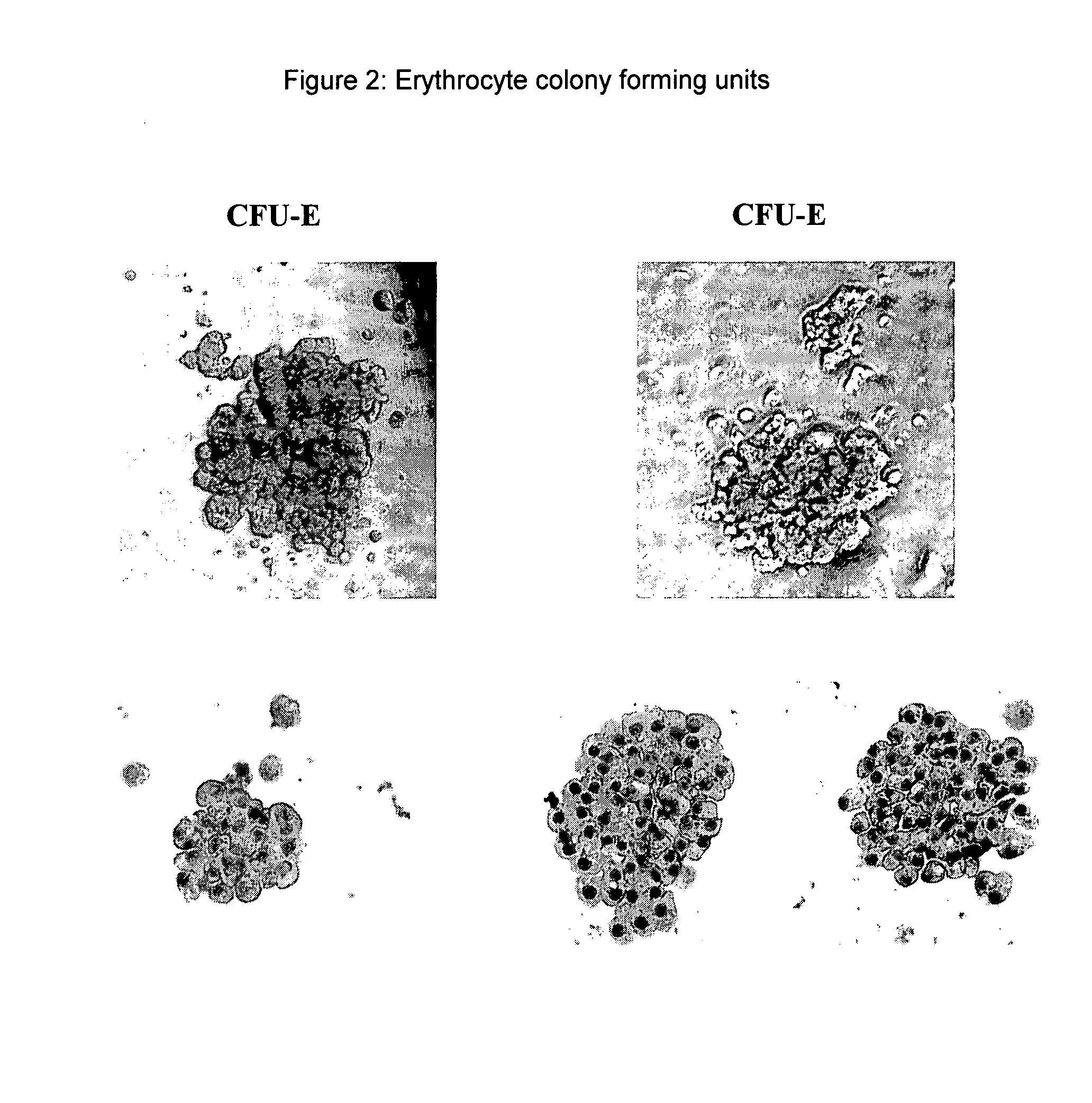
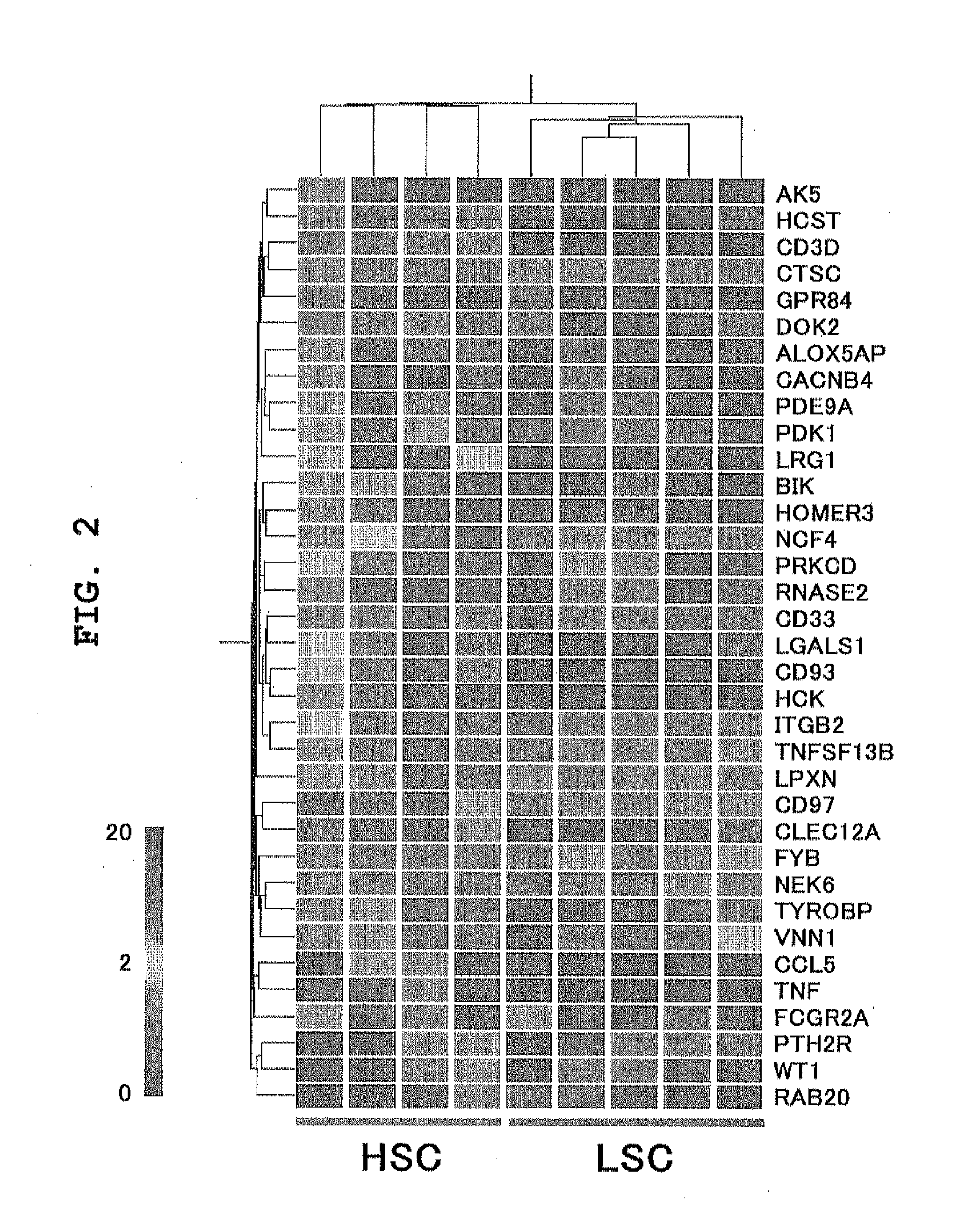
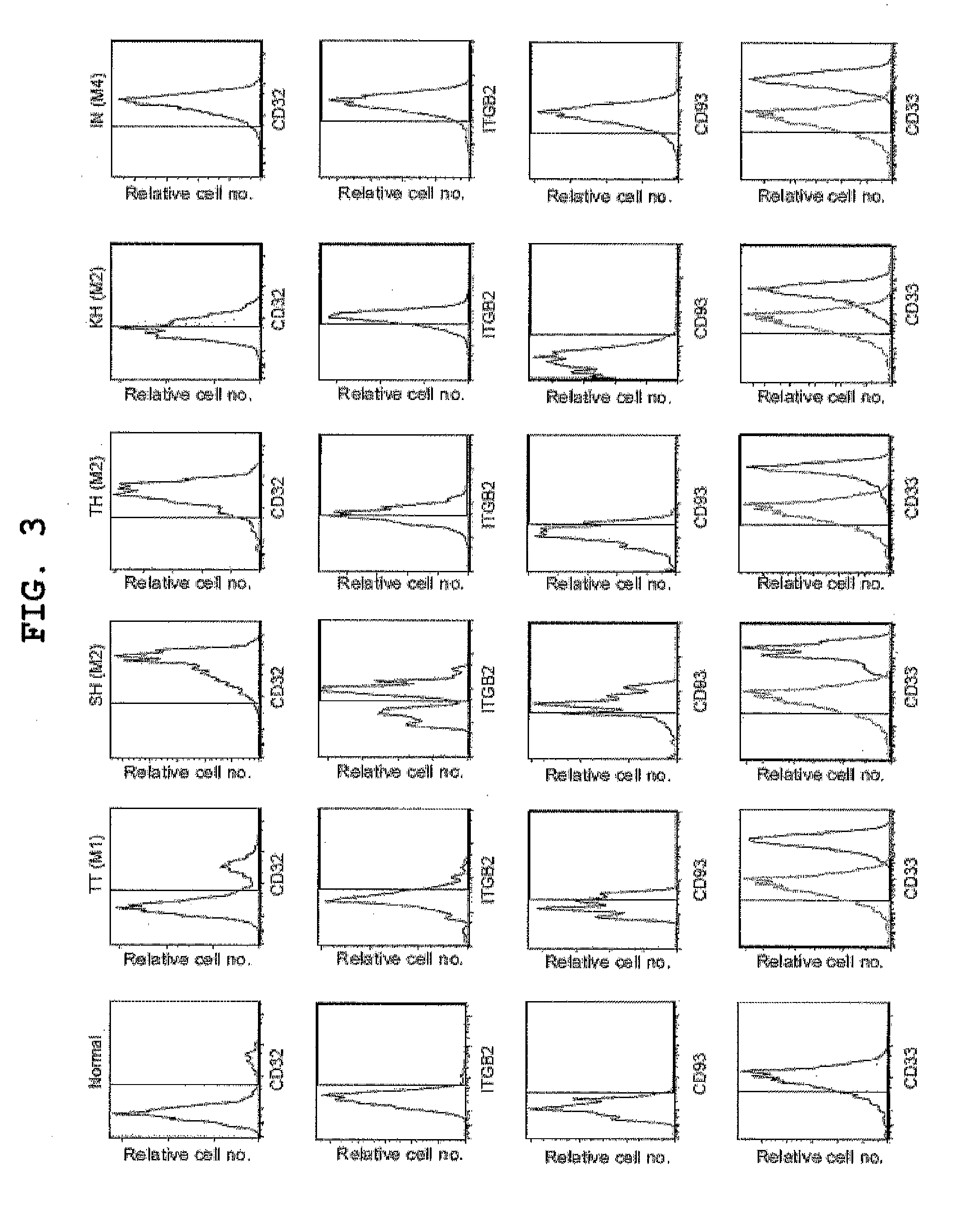
Patents
Literature
572 results about "Hematopoietic cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hematopoietic cells. Those cells that are lodged within the bone marrow, and which are responsible for producing the cells which circulate in the blood (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets). Mentioned in: Aplastic Anemia.
Cellular compositions and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS20050074435A1Increase the number ofEasy to collectPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug screeningProgenitorHematopoietic cell
The invention relates to cellular compositions comprising hematopoietic cells with the potential or increased potential to form non-hematopoietic cells; methods for producing such cellular compositions; methods for differeentitation of cells of cellular compositions of the invention into cells that exhibit morphological, physiological, functional, and / or immunological features of non-hematopoietic cells; and uses of the cellular compositions. The invention also relates to a method for the expansion of hemtopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
Owner:MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL
Methods for treating and/or preventing aberrant proliferation of hematopoietic cells
The invention relates generally to methods for treating and / or preventing aberrant proliferation of hematopoietic cells. More particularly, the invention relates to methods for treating and / or preventing aberrant proliferation of hematopoietic cells comprising selectively inhibiting phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta (PI3Kδ) activity in hematopoietic cells. The methods may be used to treat any indication involving aberrant proliferation of hematopoietic cells.
Owner:ICOS CORP
Methods and compositions for detecting non-hematopoietic cells from a blood sample
InactiveUS20060252054A1Aid in diagnosis and prognosisPromote recoveryMembranesOther blood circulation devicesRare cellHematopoietic cell
The present invention recognizes that diagnosis and prognosis of many conditions can depend on the enrichment of rare cells, especially tumor cells, from a complex fluid sample such as a blood sample. In particular, the present invention is directed to methods and compositions for detecting a non-hematopoietic cell, e.g., a non-hematopoietic tumor cell, in a blood sample via, inter alia, removing red blood cells (RBCs) from a blood sample using a non-centrifugation procedure, removing white blood cells (WBCs) from said blood sample to enrich a non-hematopoietic cell, if any, from said blood sample; and assessing the presence, absence and / or amount of said enriched non-hematopoietic cell.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Methods for treating viral infection using IL-28 and IL-29
ActiveUS7135170B2Reduction in viral infection levelReduce viral infectionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon therapyHematopoietic cell
IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and certain mutants thereof have been shown to have antiviral activity on a spectrum of viral species. Of particular interest is the antiviral activity demonstrated on viruses that infect liver, such as hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. In addition, IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and mutants thereof do not exhibit some of the antiproliferative activity on hematopoietic cells that is observed with interferon treatment. Without the immunosuppressive effects accompanying interferon treatment, IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 will be useful in treating immunocompromised patients for viral infections.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Cytotoxicity mediation of cells evidencing surface expression of TROP-2
InactiveUS7420040B2Reduce the likelihood of problemsProlong survival timeImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationDiseaseHematopoietic cell
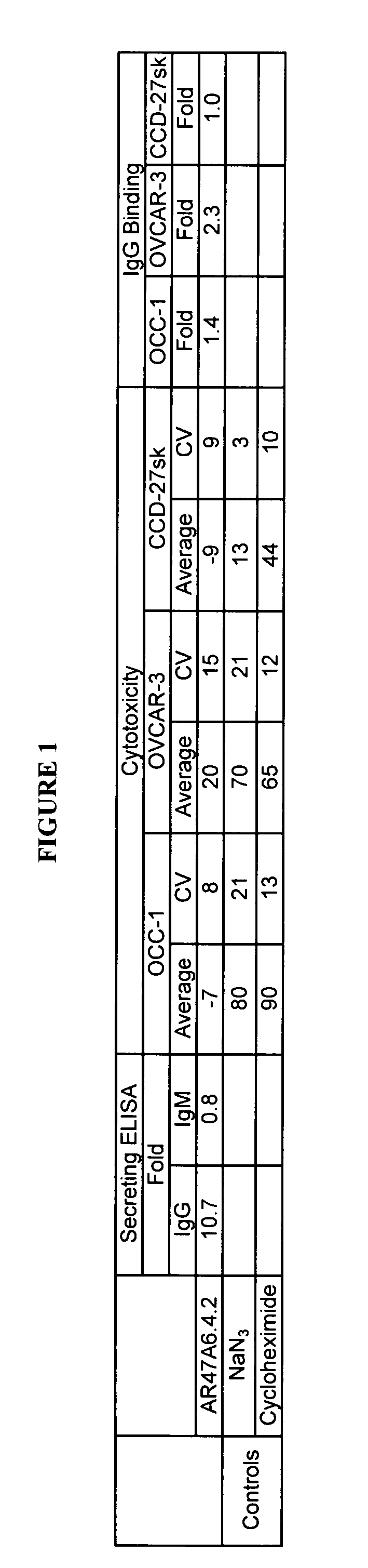
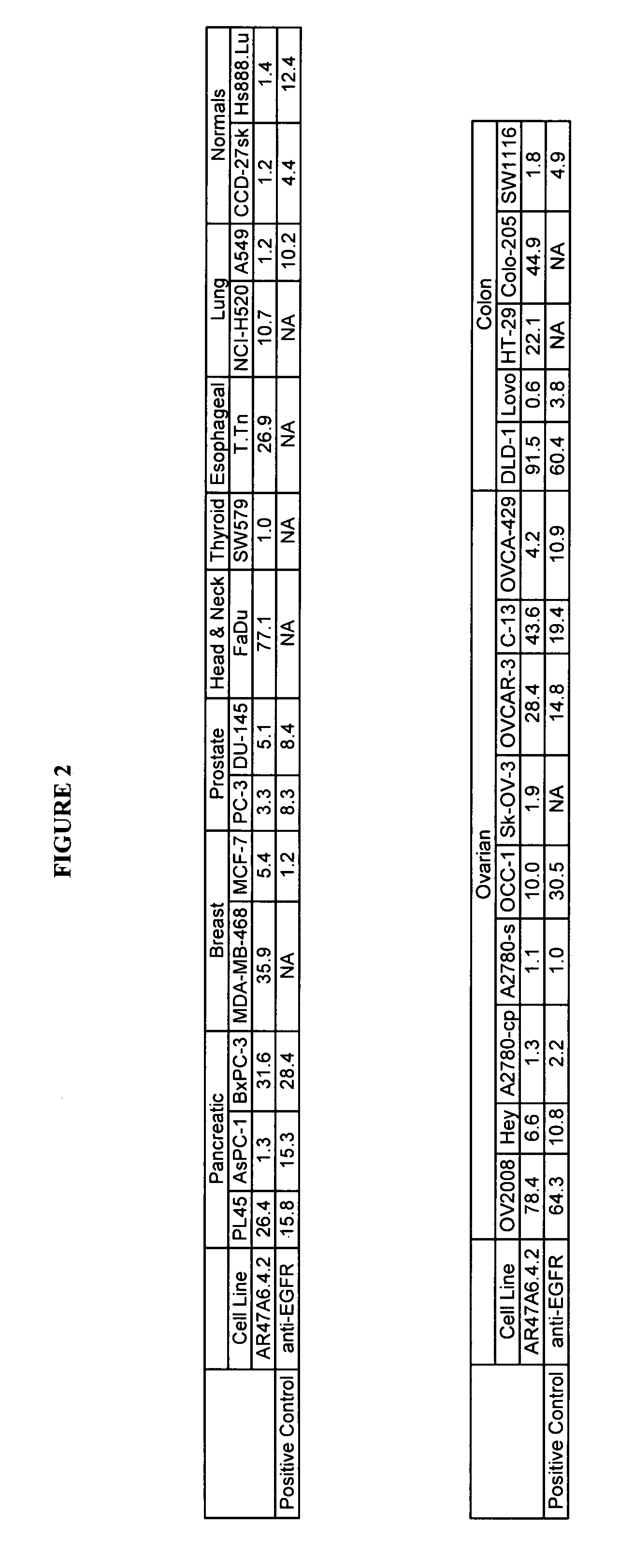
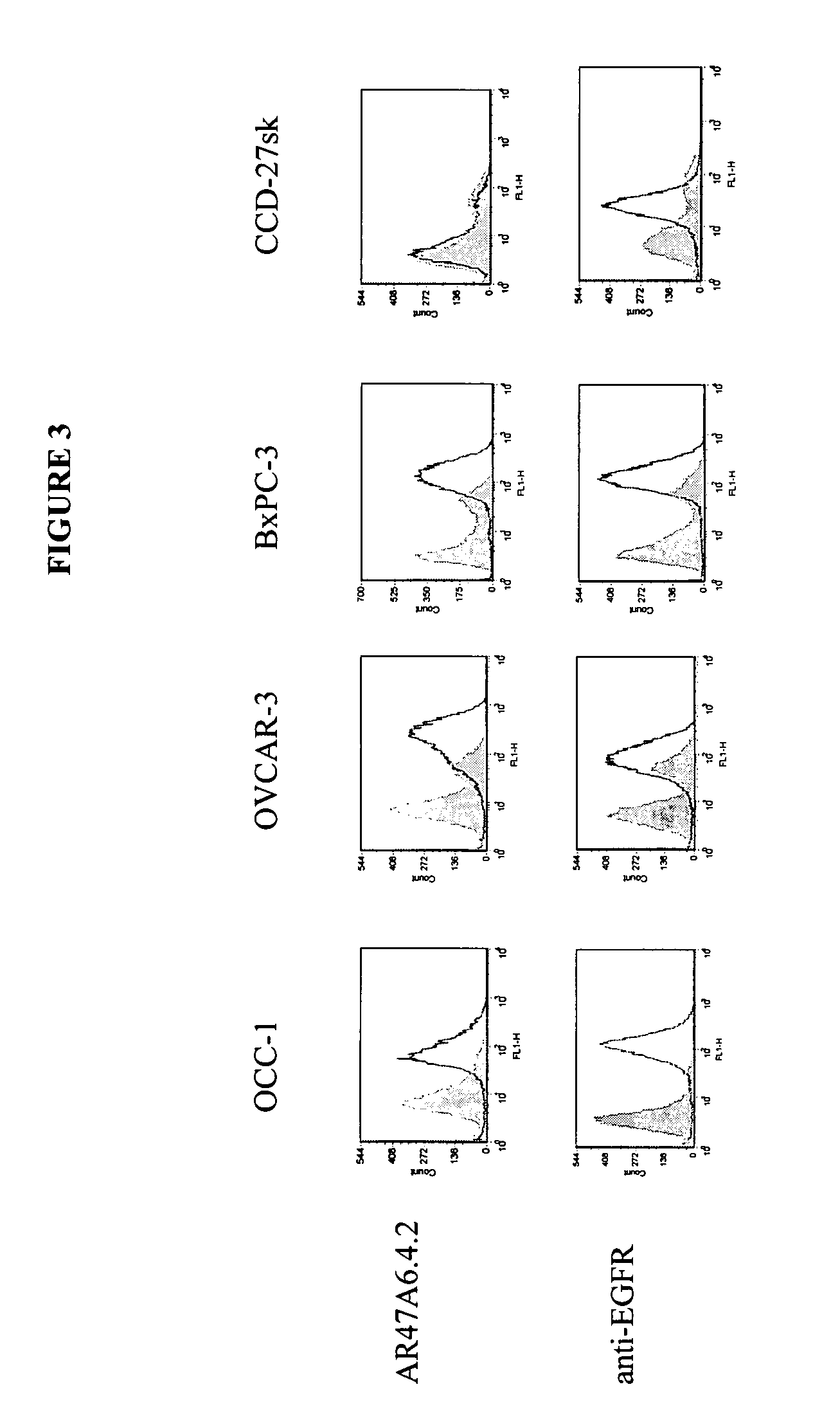
The present invention relates to a method for producing cancerous disease modifying antibodies using a novel paradigm of screening. By segregating the anti-cancer antibodies using cancer cell cytotoxicity as an end point, the process makes possible the production of anti-cancer antibodies for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. The antibodies can be used in aid of staging and diagnosis of a cancer, and can be used to treat primary tumors and tumor metastases. The anti-cancer antibodies can be conjugated to toxins, enzymes, radioactive compounds, cytokines, interferons, target or reporter moieties and hematogenous cells.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Hematopoietic stem cells and methods of treatment of neovascular eye diseases therewith
InactiveUS20050063961A1Stably incorporated into neovasculature of the eyePromote repairBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseProgenitor
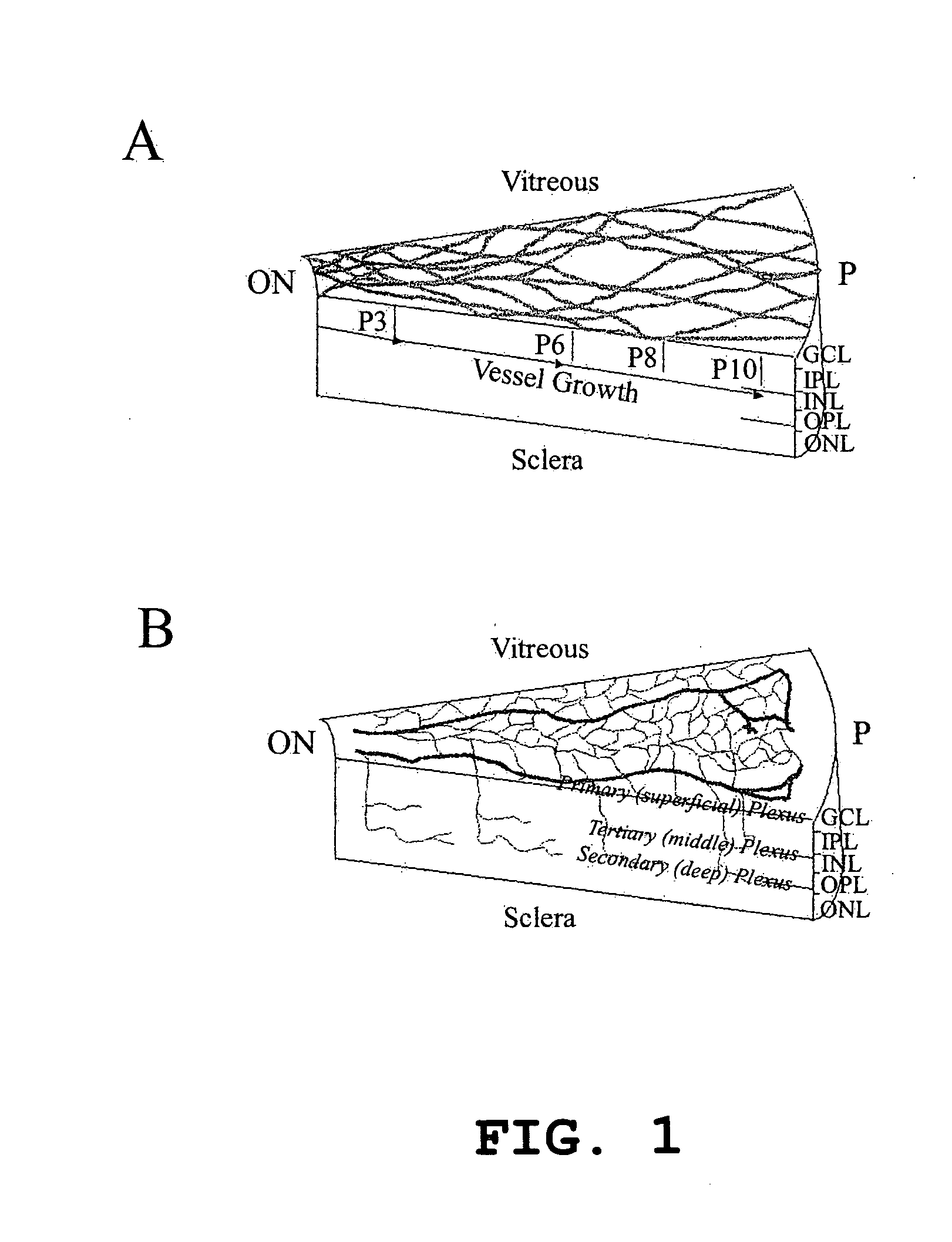
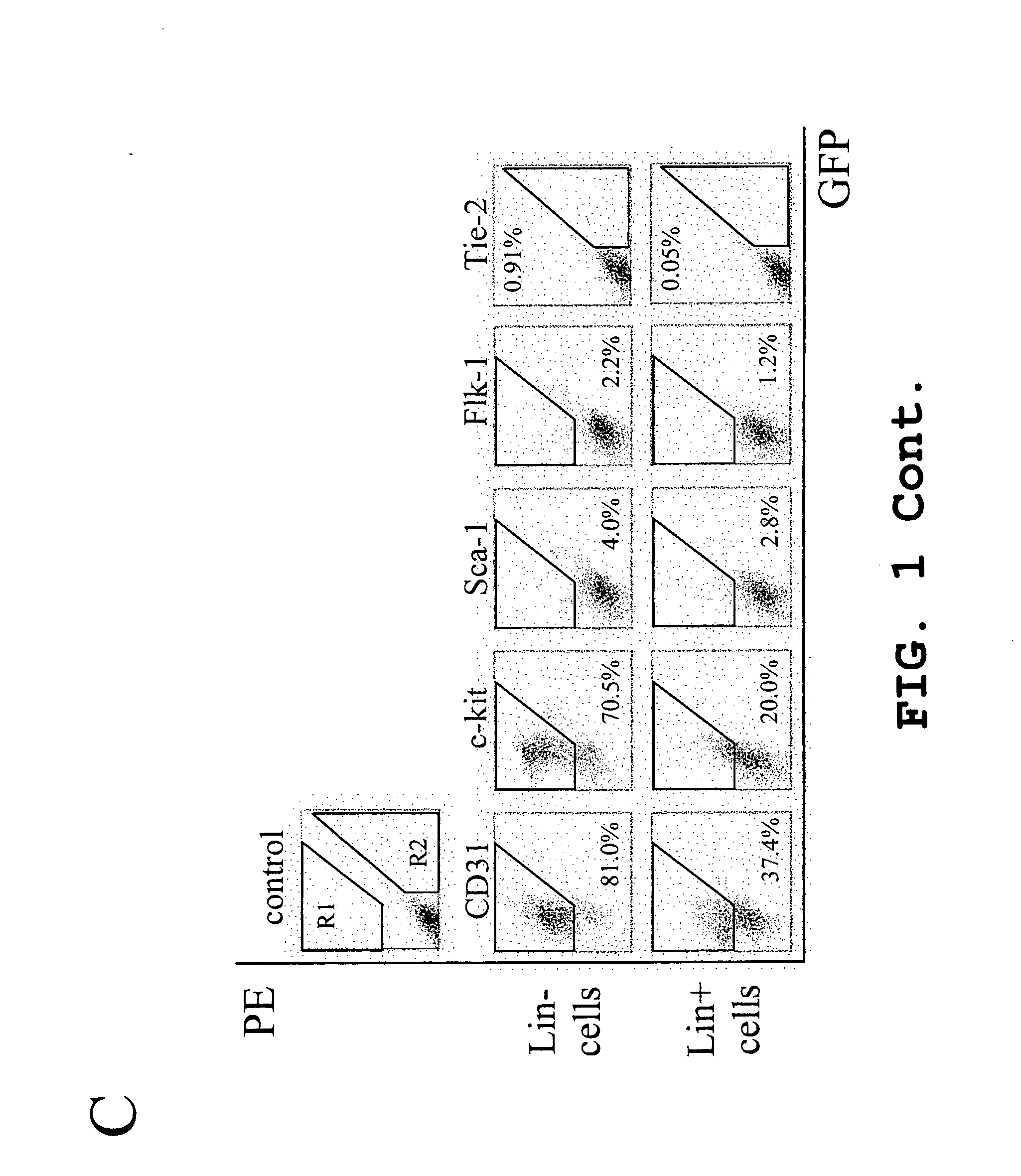
Isolated, mammalian, adult bone marrow-derived, lineage negative hematopoietic stem cell populations (Lin− HSCs) contain endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) capable of rescuing retinal blood vessels and neuronal networks in the eye. Preferably at least about 20% of the cells in the isolated Lin− HSCs express the cell surface antigen CD31. The isolated Lin− HSC populations are useful for treatment of ocular vascular diseases. In a preferred embodiment, the Lin− HSCs are isolated by extracting bone marrow from an adult mammal; separating a plurality of monocytes from the bone marrow; labeling the monocytes with biotin-conjugated lineage panel antibodies to one or more lineage surface antigens; removing of monocytes that are positive for the lineage surface antigens from the plurality of monocytes, and recovering a Lin− HSC population containing EPCs. Isolated Lin− HSCs that have been transfected with therapeutically useful genes are also provided, and are useful for delivering genes to the eye for cell-based gene therapy. Methods of preparing isolated stem cell populations of the invention, and methods of treating ocular diseases and injury are also described.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method for establishing hematopoietic stem cells bank by extracting hematopoietic cells from placenta tissues
InactiveCN1407088AIncrease the number ofSave livesMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsHigh concentrationHematopoietic cell
A process for extracting hemopoietic stem cells from the placenta of healthy puerperant to create hemopoistic stem cell bank features that the mechanical, enzyme digestive and monoclonal antibody-magnetic bead method is used to extract blood stem cells from placenta, and concentrate and purify them. Its advantages are high activity and high concentration.
Owner:上海厚东生物科技有限公司
Antibodies recognizing a carbohydrate containing epitope on CD-43 and CEA expressed on cancer cells and methods using same
The present invention provides antibodies (such as chimeric and humanized antibodies) specifically bind to an epitope on CD43 and CEA expressed on nonhematopoietic cancer cells. In addition, the present invention also provides use of the antibodies described herein for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Owner:BIOALLIANCE CV
Antibodies recognizing a carbohydrate containing epitope on CD-43 and CEA expressed on cancer cells and methods using same
ActiveUS7674605B2Reduce in quantityInhibit growth and proliferationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationHematopoietic cellCancer cell
The present invention provides novel antibodies specifically bind to an epitope on CD43 and CEA expressed on nonhematopoietic cancer cells, but do not specifically bind to a CD43 expressed by a leukocyte or by a Jurkat cell, and is capable of inducing apoptosis of the nonhematopoietic cancer cell after binding to the epitope on cell surface of the nonhematopoietic cancer cell in the absence of cytotoxin conjugation and immune effector function, wherein the epitope comprises a carbohydrate structure and the binding of the antibody to the epitope is inhibited by a carbohydrate comprising a Lea structure, a Lea-lactose structure, a LNDFH II structure, or a LNT structure. In addition, the present invention also provides use of the antibodies described herein for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Owner:ALTRUBIO INC
Methods and compositions for detecting rare cells from a biological sample
InactiveUS20080057505A1Strong specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentHematopoietic cellWhite blood cell
The present invention provides methods and compositions for isolating and detecting rare cells from a biological sample containing other types of cells. In particular, the present invention includes a debulking step that uses a microfabricated filters for filtering fluid samples and the enriched rare cells can be used in a downstream process such as identifies, characterizes or even grown in culture or used in other ways. The invention also include a method of determining the aggressiveness of the tumor or of the number or proportion of cancer cells in the enriched sample by detecting the presence or amount of telomerase activity or telomerase nucleic acid or telomerase expression after enrichment of rare cells. This invention further provides an efficient and rapid method to specifically remove red blood cells as well as white blood cells from a biological sample containing at least one of each of red blood cells and white blood cells, resulting in the enrichment of rare target cells including circulating tumor cells (CTC), stromal cells, mesenchymal cells, endothelial cells, fetal cells, stem cells, non-hematopoietic cells etc from a blood sample. The method is based upon combination of immuno-microparticles (antibody coated microparticles) and density-based separation. The final enriched target cells can be subjected to a variety of analysis and manipulations, such as flowcytometry, PCR, immunofluorescence, immunocytochemistry, image analysis, enzymatic assays, gene expression profiling analysis, efficacy tests of therapeutics, culturing of enriched rare cells, and therapeutic use of enriched rare cells. In addition, depleted plasma protein and white blood cells can be optionally recovered, and subjected to other analysis such as inflammation studies, gene expression profiling, etc.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
Method for stimulating an immune response
InactiveUS6977073B1Stimulating directed immune responseStimulate immune responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsAbnormal tissue growthHematopoietic cell
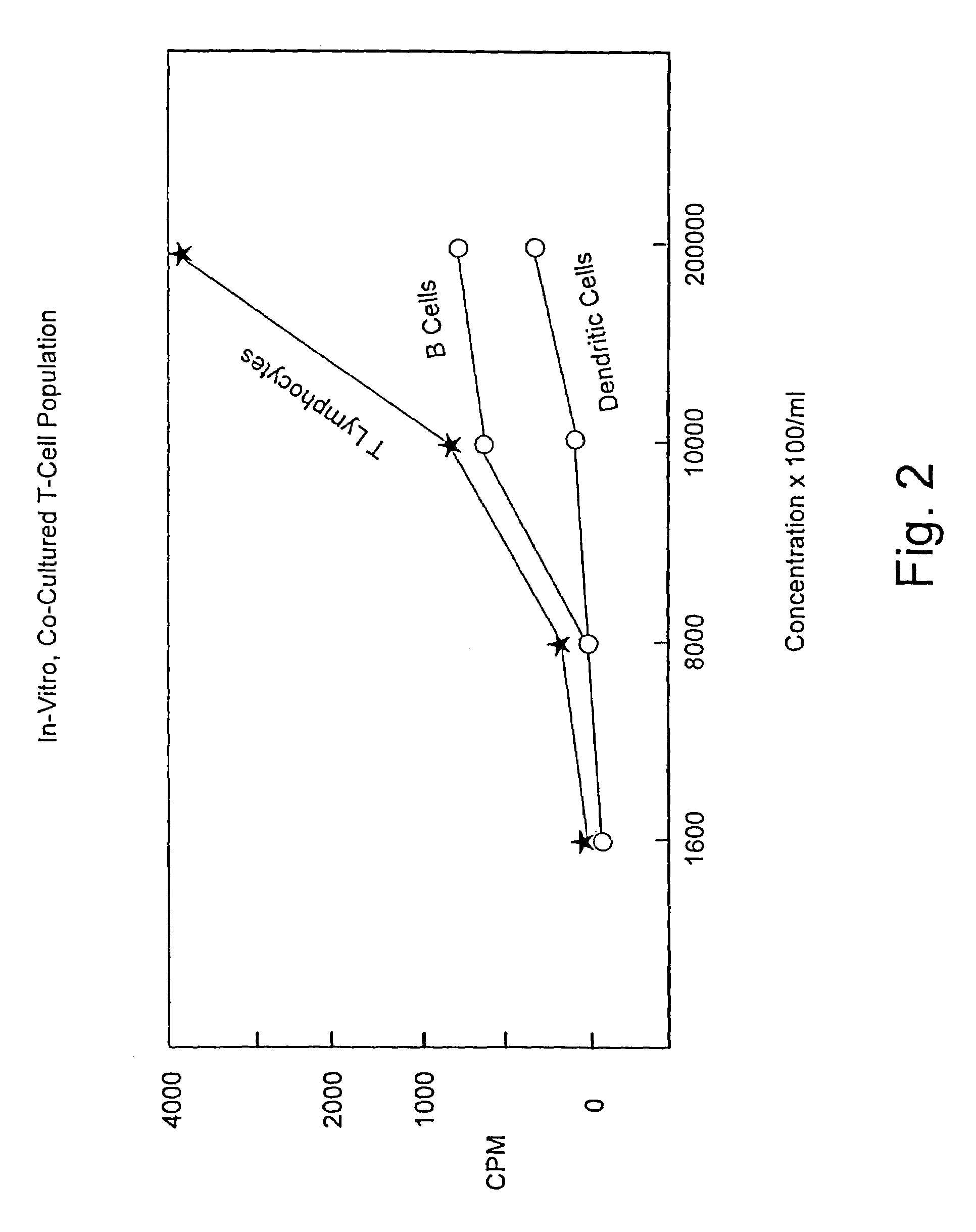
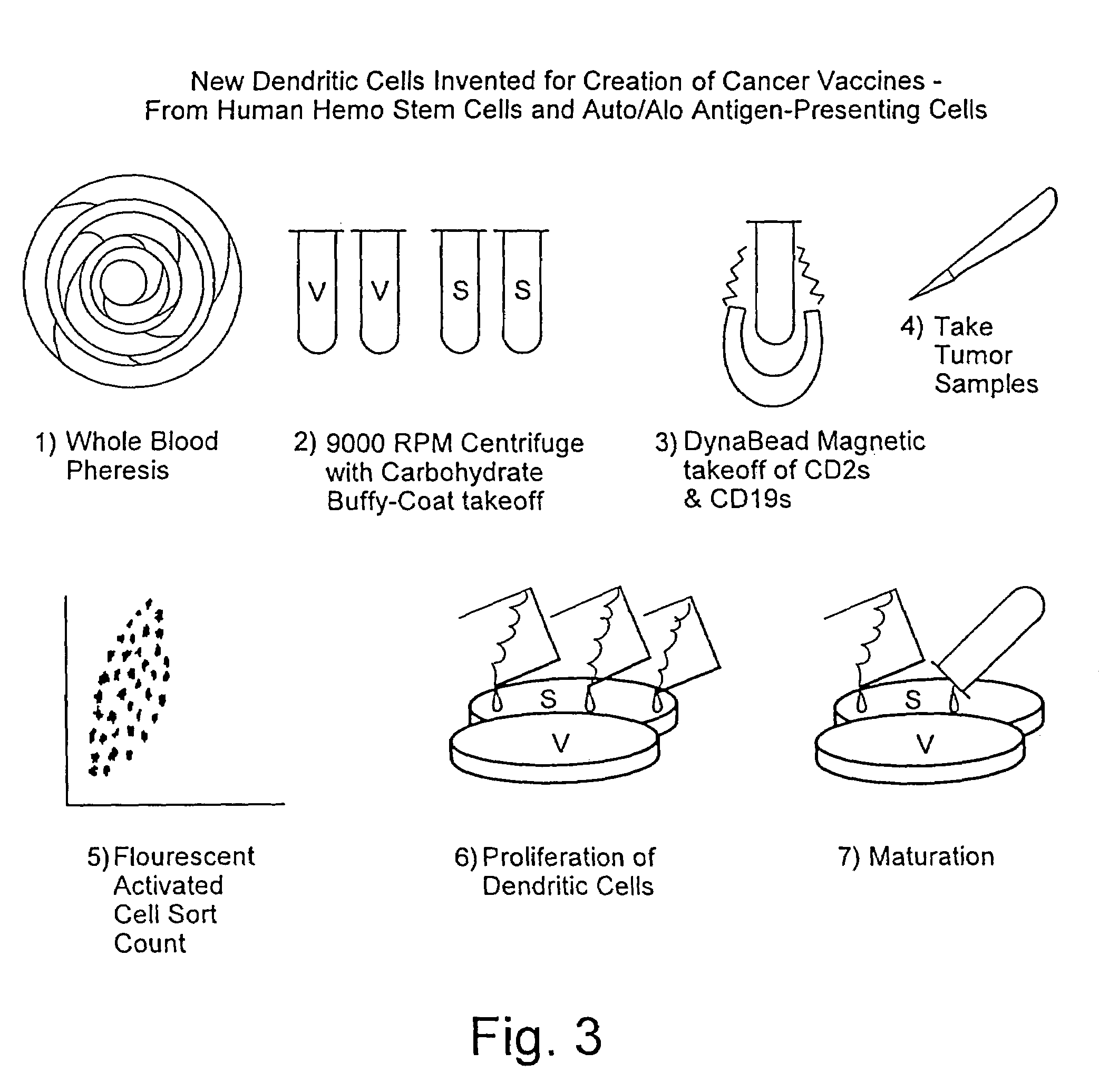
A method is described whereby dendritic cells derived from the CD34+ and CD 34−hematopoietic cell lineages are directed to become programmable antigen presenting cells. The programmed cells may be pulsed with tumor cell RNA or tumor cell RNA expression products. The protocol provides for directing the maturation of dendritic cells to become antigen presenting cells. The protocol further provides for isolating tumor cell RNA from biopsy material that has been prepared in paraffin block storage. The directed dendritic cell is provided with a plurality of tumor markers by using tumor RNA in toto, the poly A+RNA fraction or the expression product of such RNA. Once activated the dendritic cells are incubated with T4 and T8 lymphocytes to stimulate and sensitize the T lymphocytes which upon introduction either into a donor host or a nondonor recipient will provide immune response protection.
Owner:CEZAYIRLI CEM
Compositions and methods for the treatment of primary and metastatic neoplastic diseases using arsenic compounds
InactiveUS20020183385A1Improve the quality of lifeRestricted blood flowHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The invention relates to the use of arsenic compounds to treat a variety of neoplastic diseases. The present invention encompasses the administration to a mammal of arsenic in the form of a salt, complex, organic compound or ionic solution to treat tumors of epithelial tissue, connective tissue, central nervous system, lymphoid tissue, hematopoietic cells and tumors associated with oncogenic viruses. This invention also encompasses the treatment of hematopoietic disorders in mammals by the administration of one or more arsenic compounds to said mammal. Further, the arsenic compounds may be used to treat metastatic neoplastic diseases.
Owner:POLARX BIOPHARM
Methods for manipulating phagocytosis mediated by CD47
InactiveUS20090191202A1Enhance phagocytosisPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsHematopoietic cellSolid tumor
Methods are provided to manipulate phagocytosis of cells, including hematopoietic cells, e.g. circulating hematopoietic cells, bone marrow cells, etc.; and solid tumor cells. In some embodiments of the invention the circulating cells are hematopoietic stem cells, or hematopoietic progenitor cells, particularly in a transplantation context, where protection from phagocytosis is desirable. In other embodiments the circulating cells are leukemia cells, particularly acute myeloid leukemia (AML), where increased phagocytosis is desirable.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Optimizing culture medium for CD34<+> hematopoietic cell expansion
InactiveUS20050032122A1Simple compositionCulture processBlood/immune system cellsHematopoietic cellSerum free
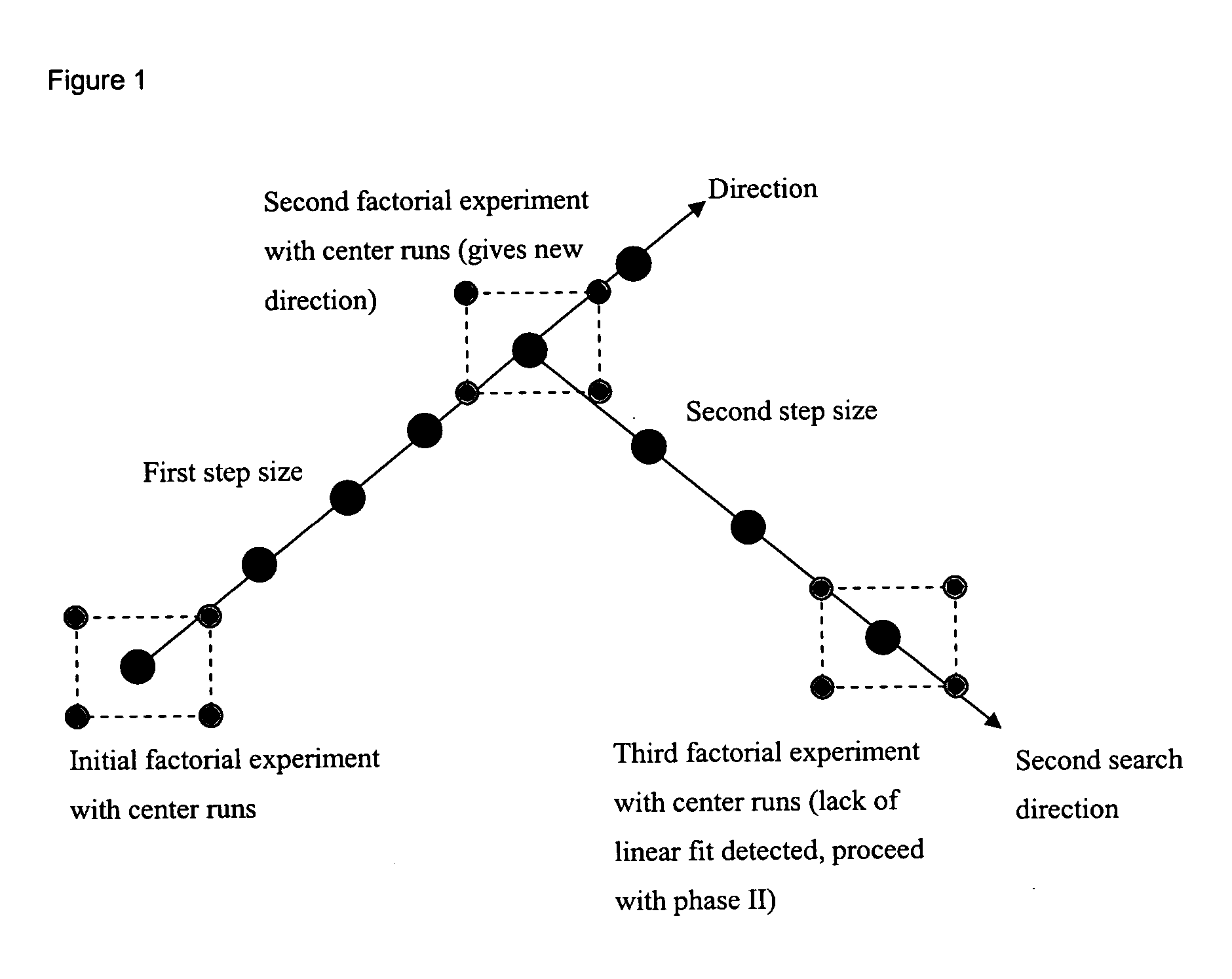
The present invention provides a method of determining the optimal composition of a serum-free, eukaryotic cell culture medium supplement, using 2-level factorial design and the deepest ascent method. The invention further provides a method of making a serum-free eukaryotic cell culture medium supplement and the generated thereof. The invention further provides a method of making a serum-free, eukaryotic cell culture medium and the medium generated thereof. The invention further provides a kit containing the medium of the invention. The invention also provides a method of expanding CD34<+> hematopoietic cells and a composition comprising CD34<+> hematopoietic cells in a serum-free, eukaryotic cell culture medium of the invention.
Owner:SINO CELL TECH
Reprogramming T cells and hematopoietic cells
ActiveUS8741648B2Increase capacityGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsProgenitorHematopoietic cell
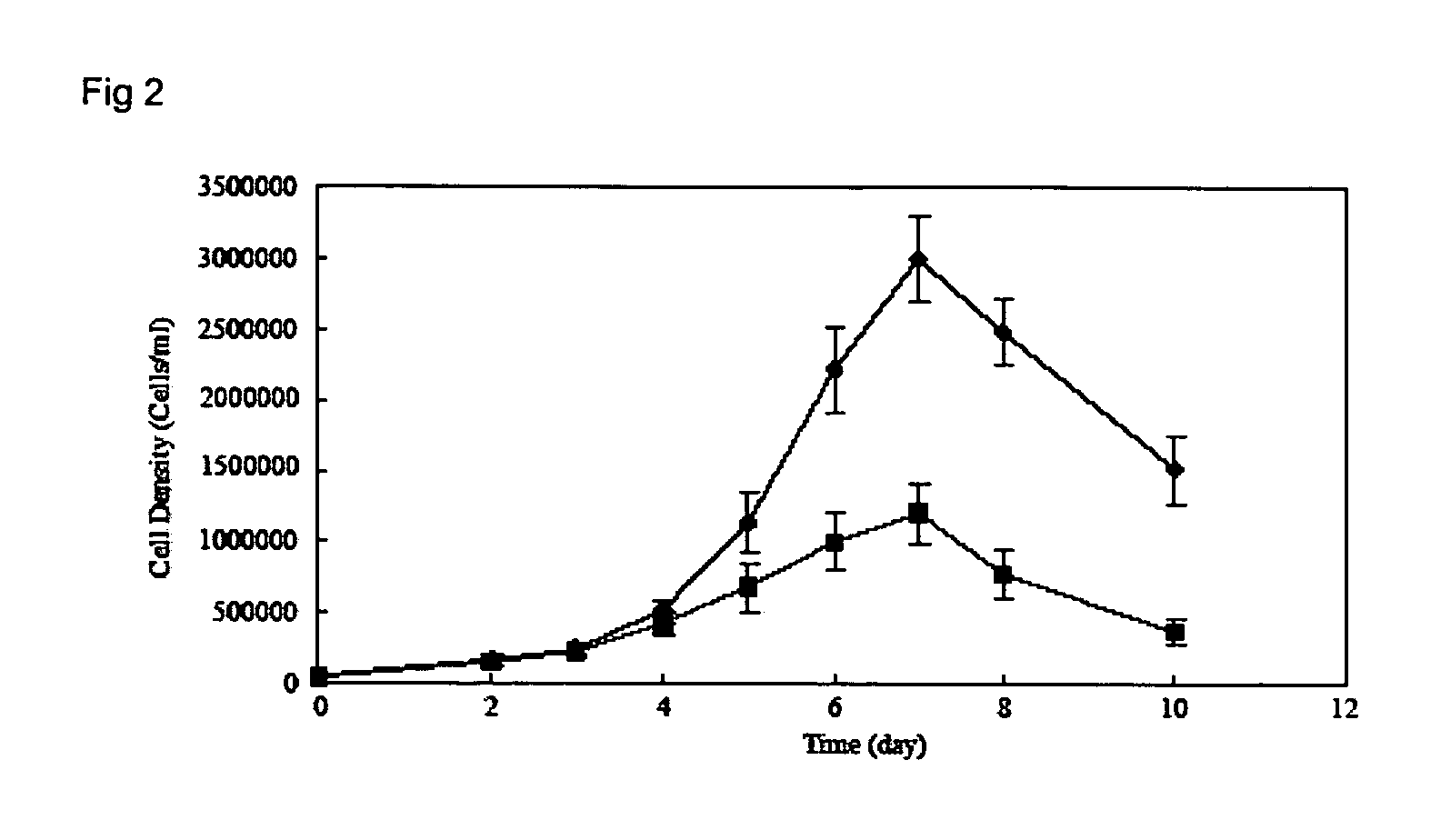
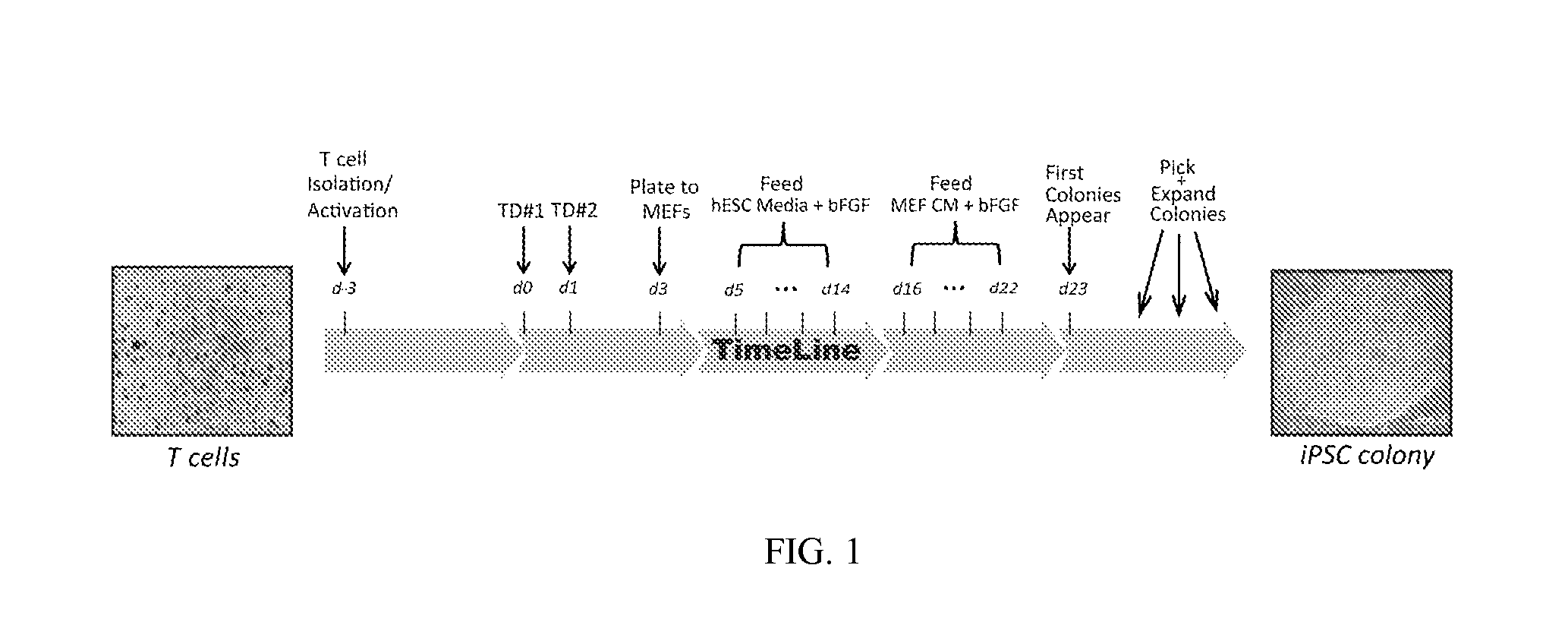
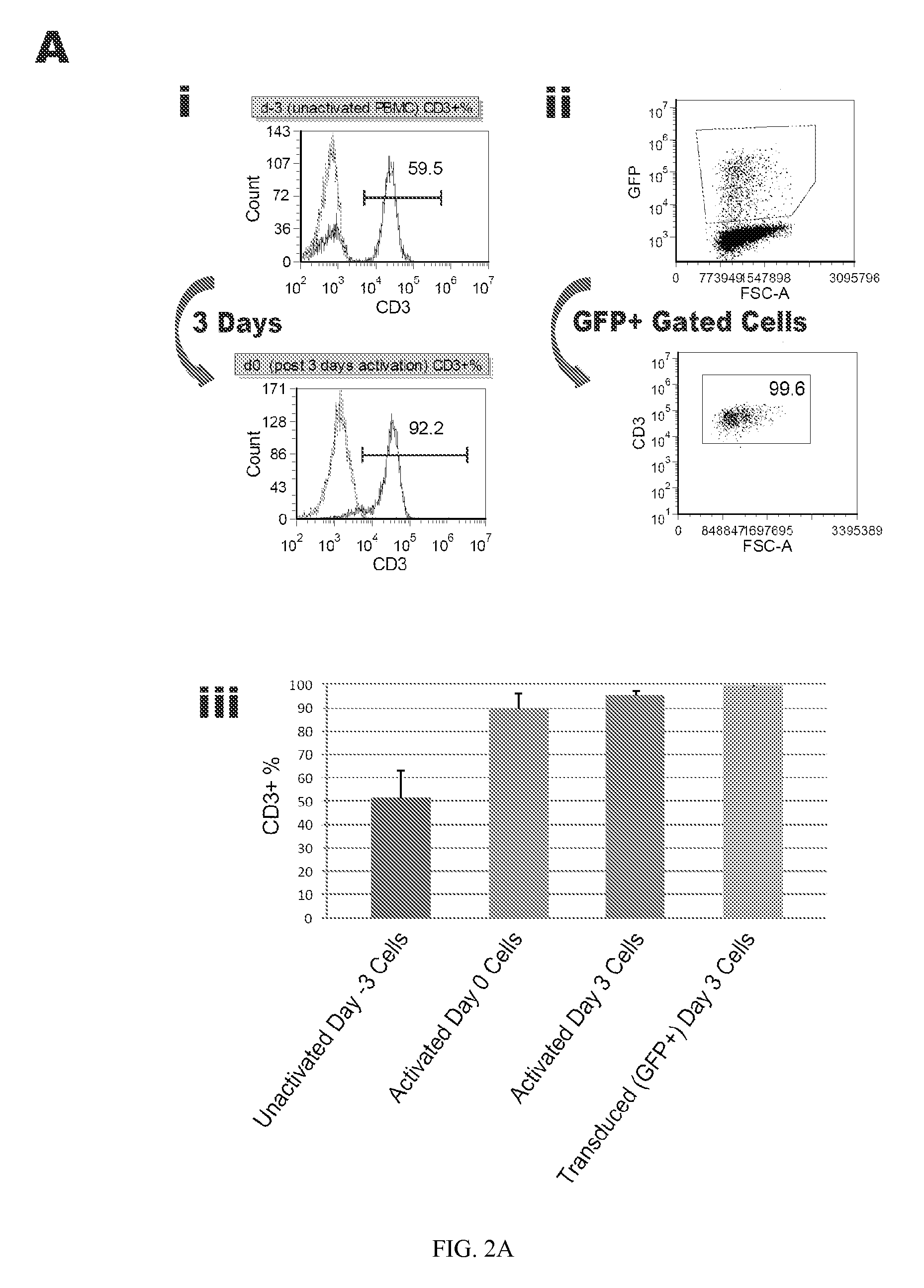
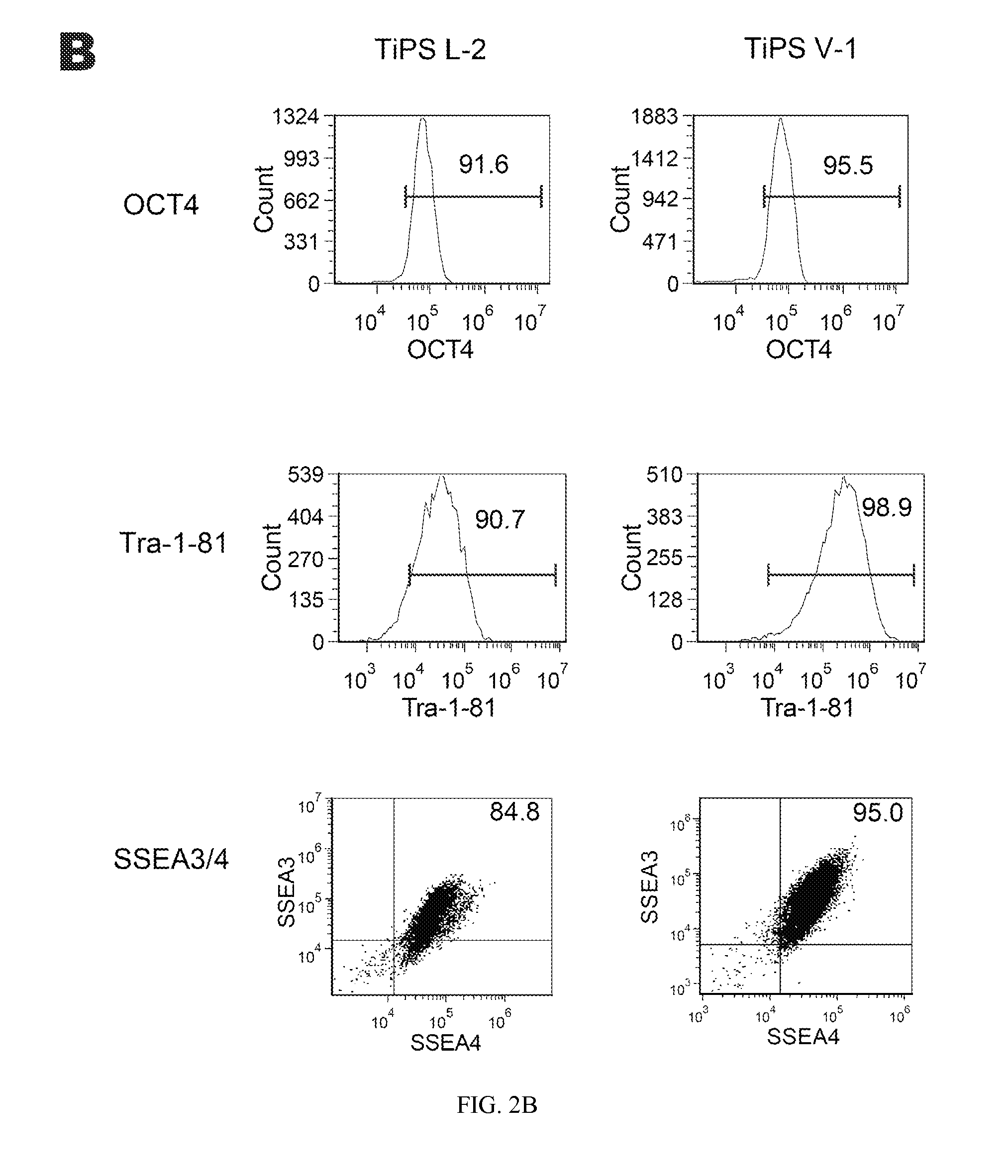
Methods and compositions relating to the production of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) are disclosed. For example, induced pluripotent stem cells may be generated from CD34+ hematopoietic cells, such as human CD34+ blood progenitor cells, or T cells. Various iPS cell lines are also provided. In certain embodiments, the invention provides novel induced pluripotent stem cells with a genome comprising genetic rearrangement of T cell receptors.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Methods of identifying and isolating stem cells and cancer stem cells
InactiveUS7217568B2AlterationEasy to analyze and useMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsHematopoietic cellCancer cell
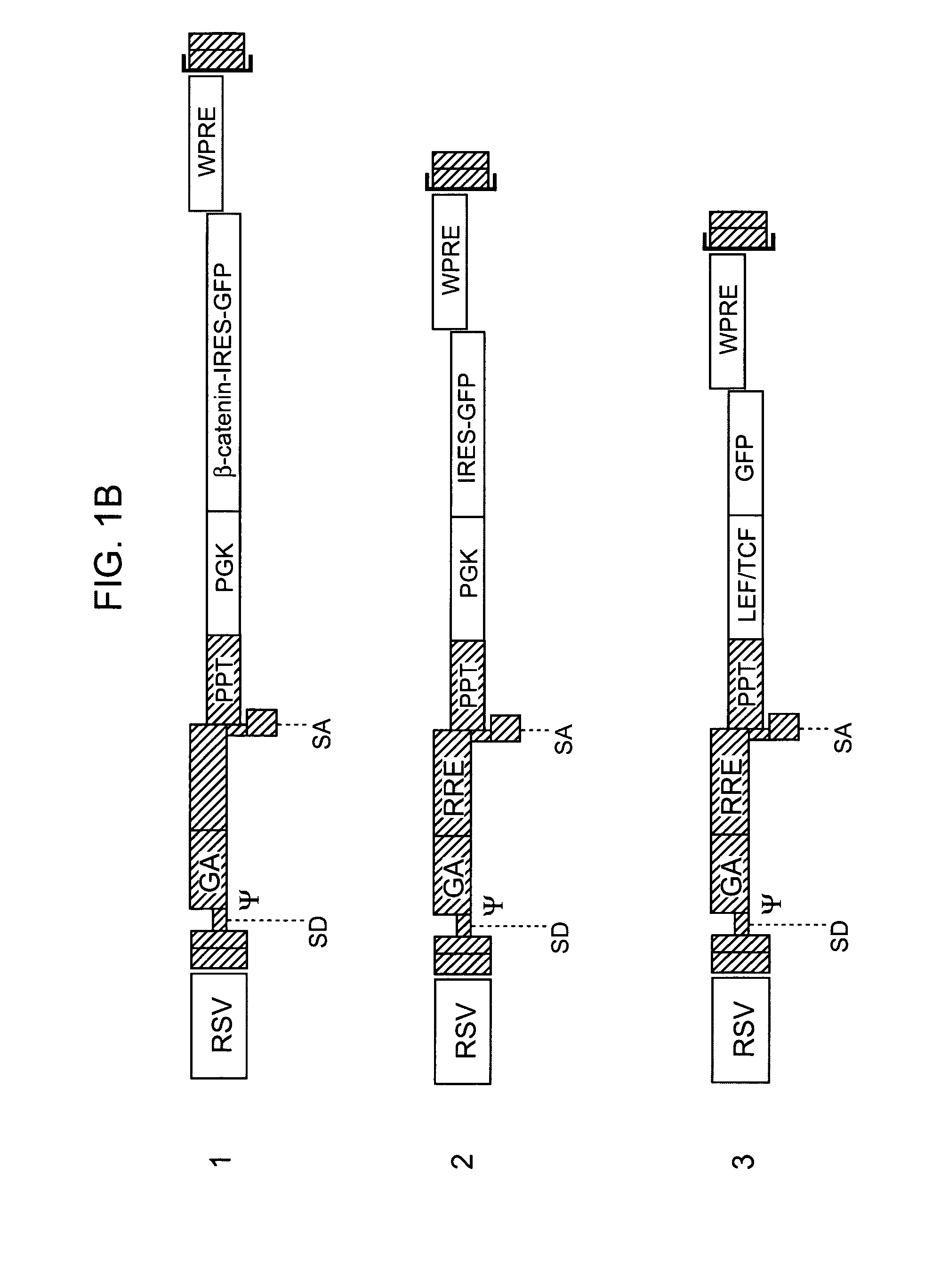
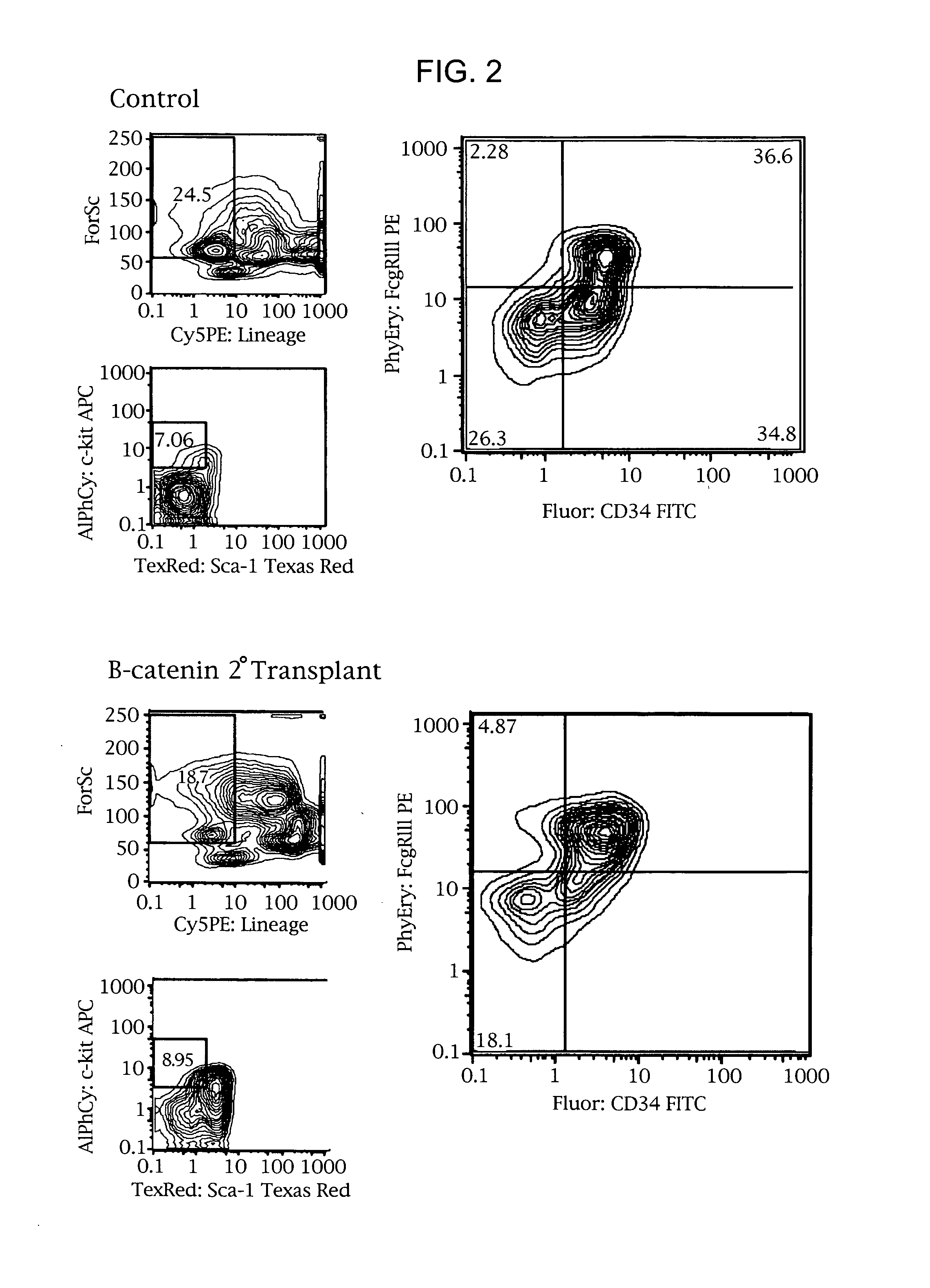
Methods and compositions are provided for the identification of stem cells and cancer stem cells. β-catenin is also identified as a target for the development of therapeutic moieties against hematopoietic tumors, i.e. leukemia and lymphoma cells, which may include screening assays directed at β-catenin, or members of the β-catenin signaling pathway. Cellular proliferation in hematopoietic cells can be altered by introducing stabilized β-catenin into a hematopoietic cell that is altered in its ability to undergo apoptosis but which is not fully transformed. The immortalized cells are useful in screening assays, and in the analysis of pathways by which hematopoietic cells undergo transformation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
IL28 and IL29 TRUNCATED CYSTEINE MUTANTS AND ANTIVIRAL METHODS OF USING SAME
InactiveUS20070053933A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon therapyHematopoietic cell
IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and certain mutants thereof have been shown to have antiviral activity on a spectrum of viral species. Of particular interest is the antiviral activity demonstrated on viruses that infect liver, such as hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. In addition, IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and mutants thereof do not exhibit some of the antiproliferative activity on hematopoietic cells that is observed with interferon treatment. Without the immunosuppressive effects accompanying interferon treatment, IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 will be useful in treating immunocompromised patients for viral infections.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
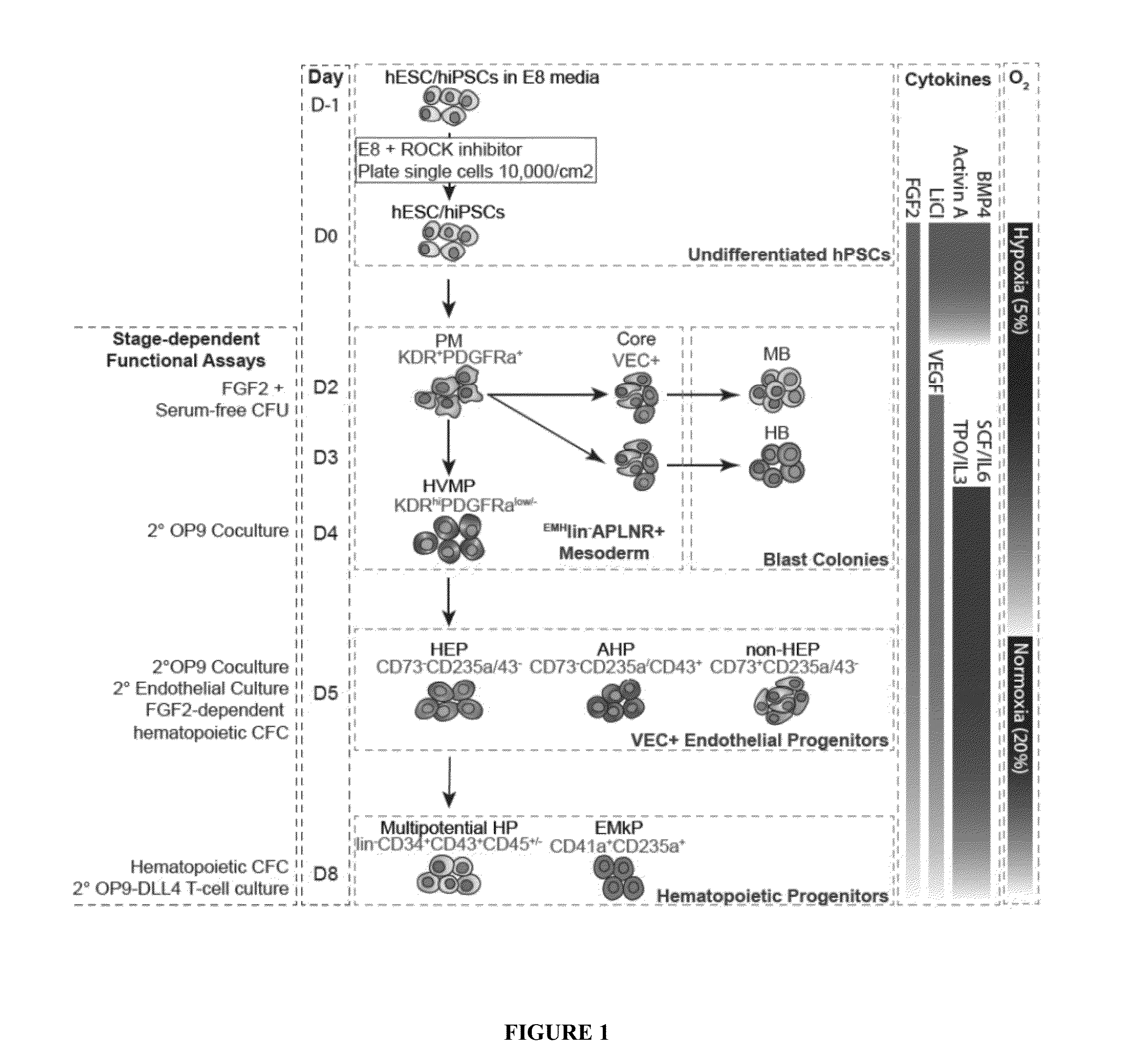
Methods and Materials for Hematoendothelial Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Under Defined Conditions
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Cancer Metastasis Inhibitor
InactiveUS20120183539A1Promoted angiogenesisPromoted tumor growthImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsHematopoietic cellLymphatic Spread
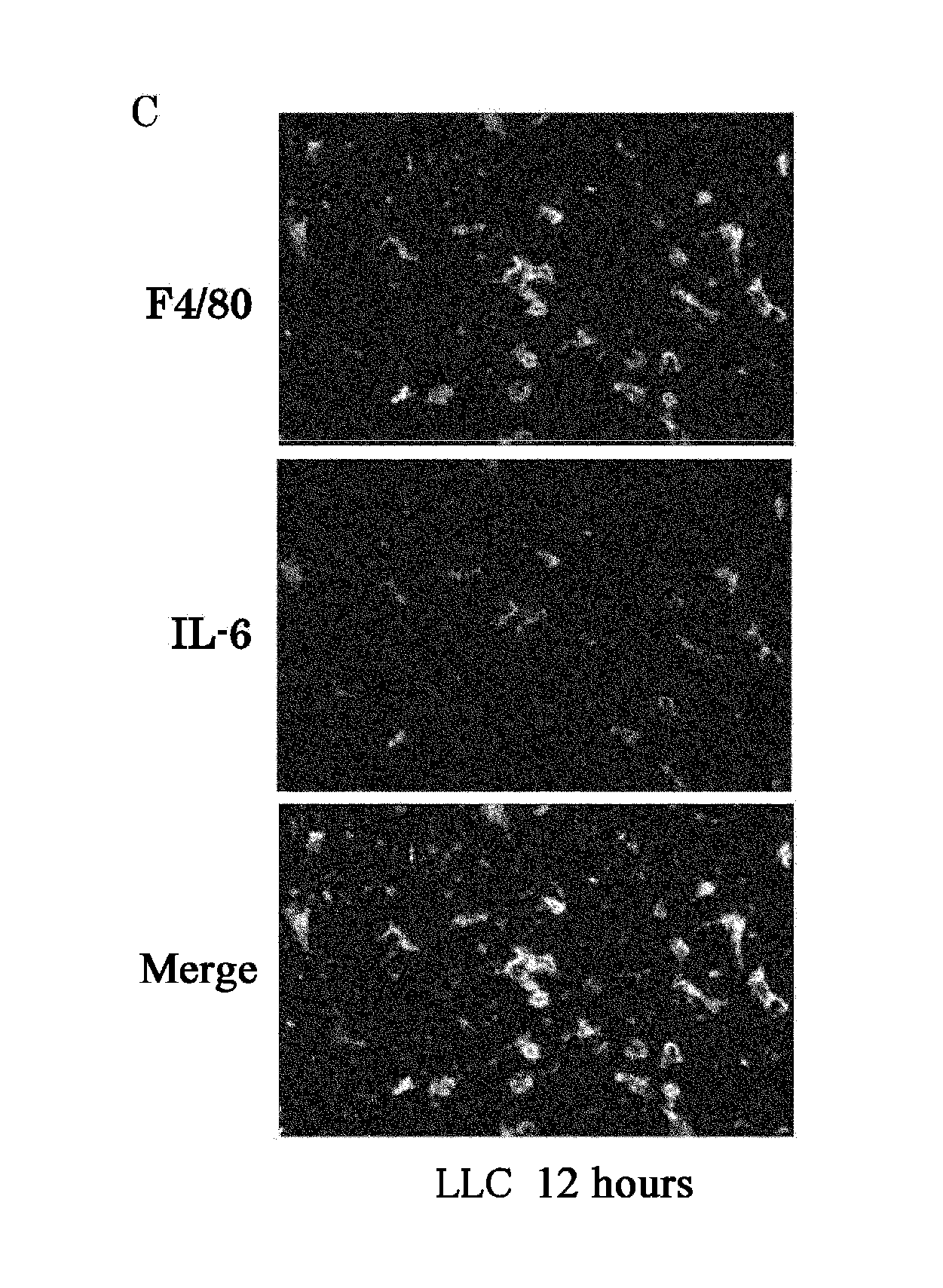
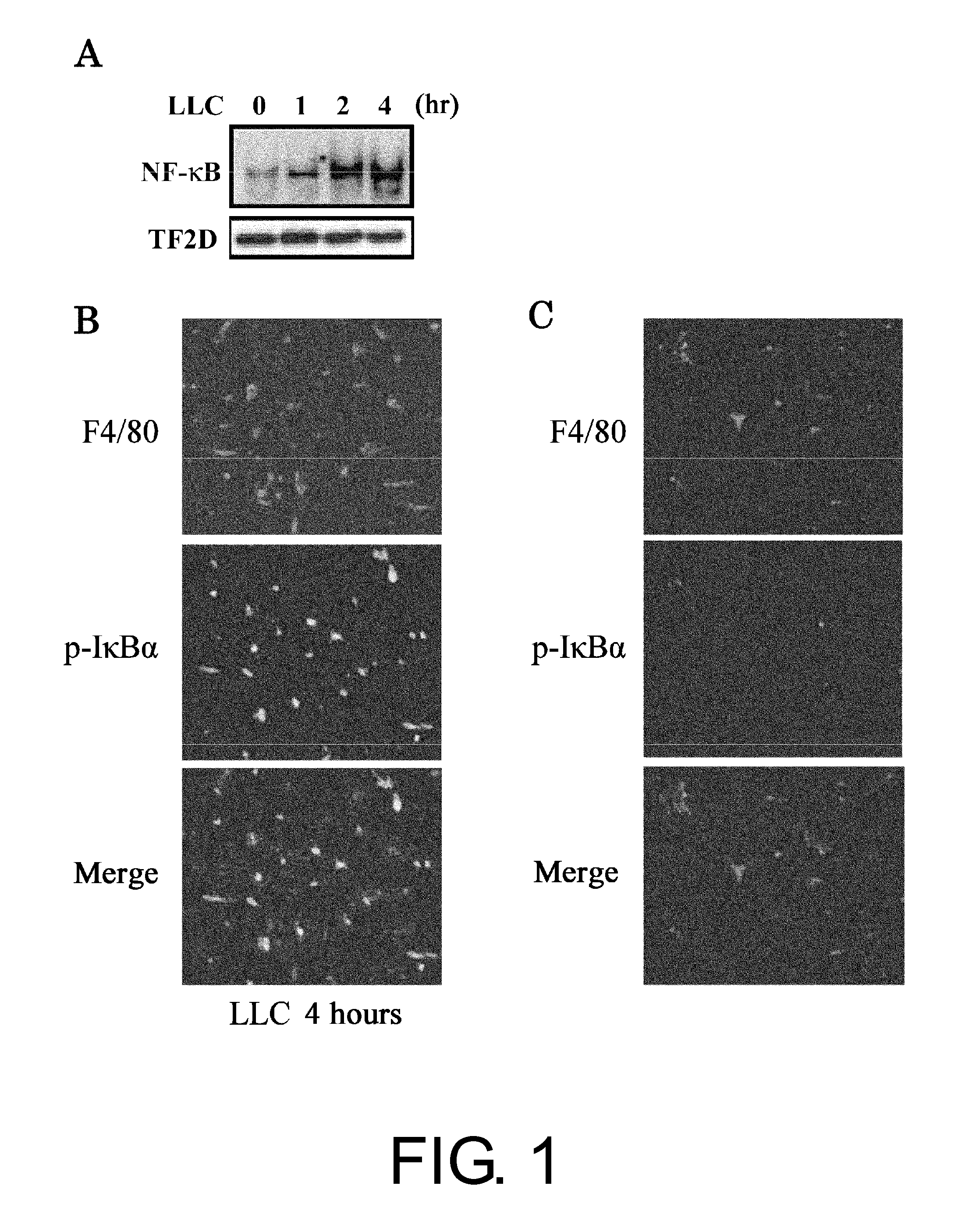
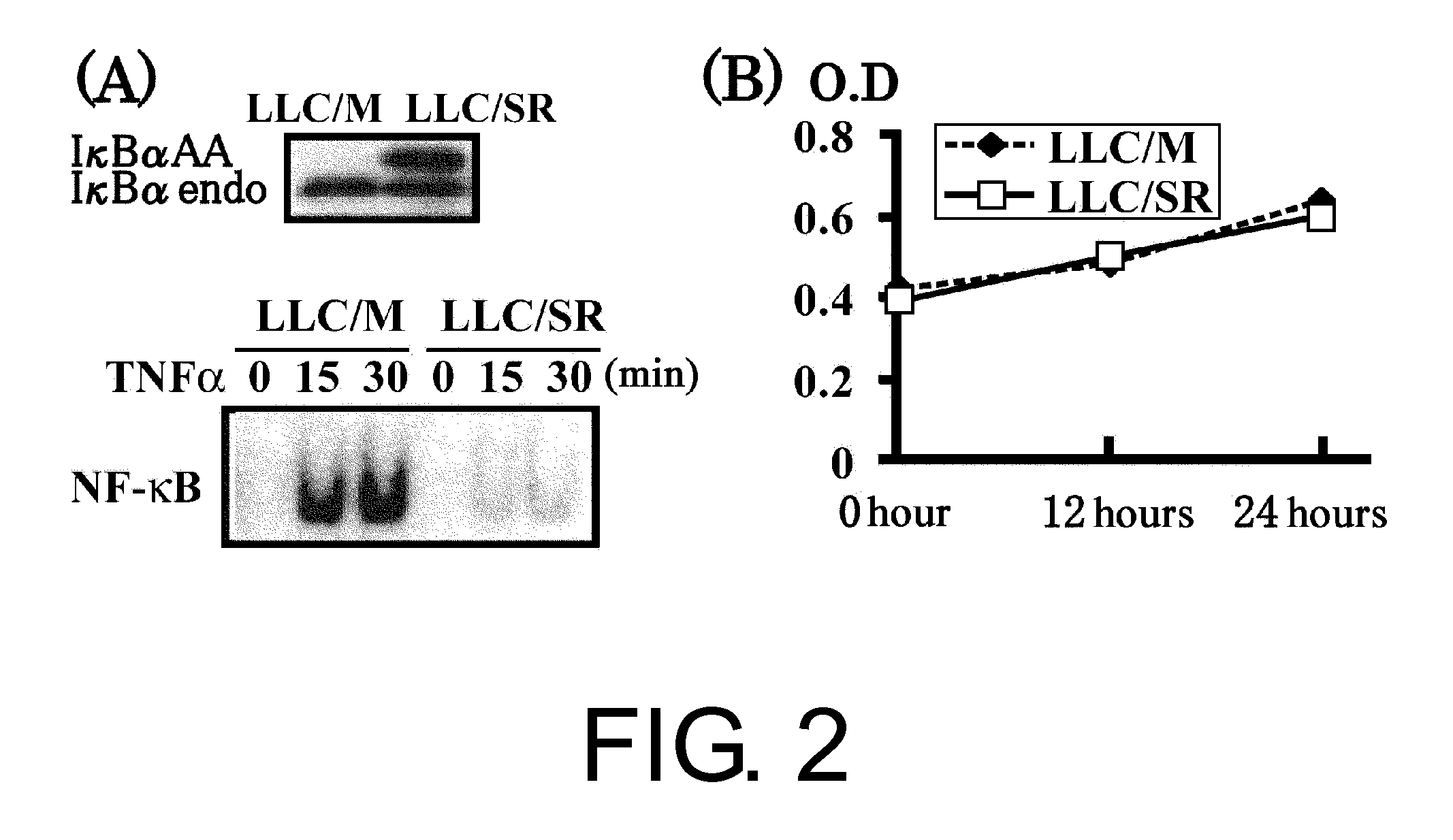
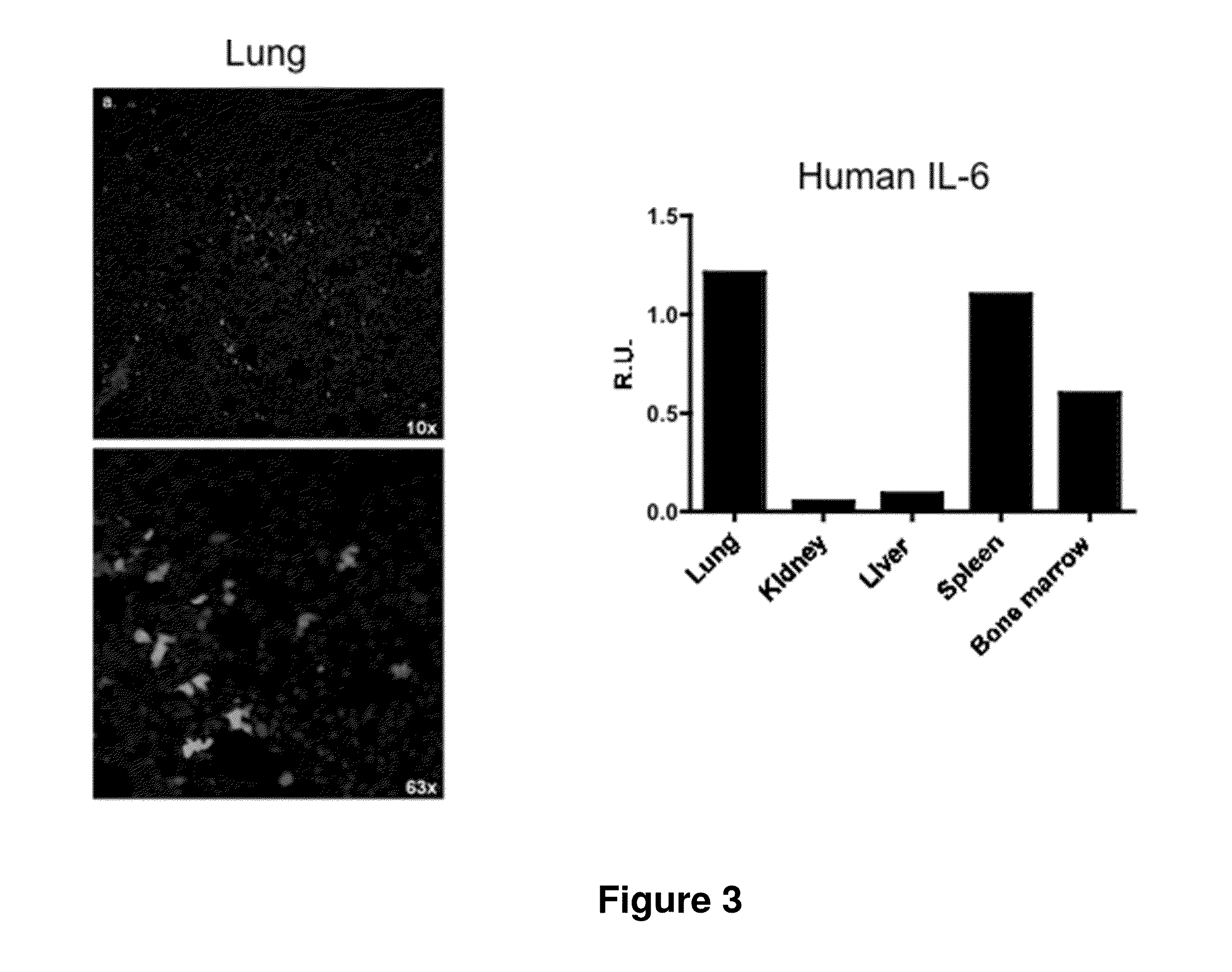
The present inventors used a model of intrasplenically induced liver metastasis to determine whether or not NF-κB activation in the liver is involved in the onset of metastatic tumors. When IKKβ was deleted from both liver cells and hematopoietically-derived cells, the onset of tumors was reduced remarkably. Tumor cells activated neighboring bone marrow cells (Kupffer cells) and produced mitogens such as interleukin (IL)-6, and this promoted angiogenesis and growth of tumors. The mitogen production depended on NF-κB in hematopoietically-derived Kupffer cells. Furthermore, treatment with an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody decreased the degree of metastatic tumor development. That is, the present inventors showed that tumor metastasis depends on inflammation, and proinflammatory intervention that targets Kupffer cells is useful for chemical prevention of metastatic tumors. Furthermore, it was shown that inhibition of the IKKβ / NF-κB signal transduction pathway, in particular IL-6 inhibition, can be utilized for anti-metastasis agents.
Owner:MAEDA CORPORATION
Mammalian common lymphoid progenitor cell
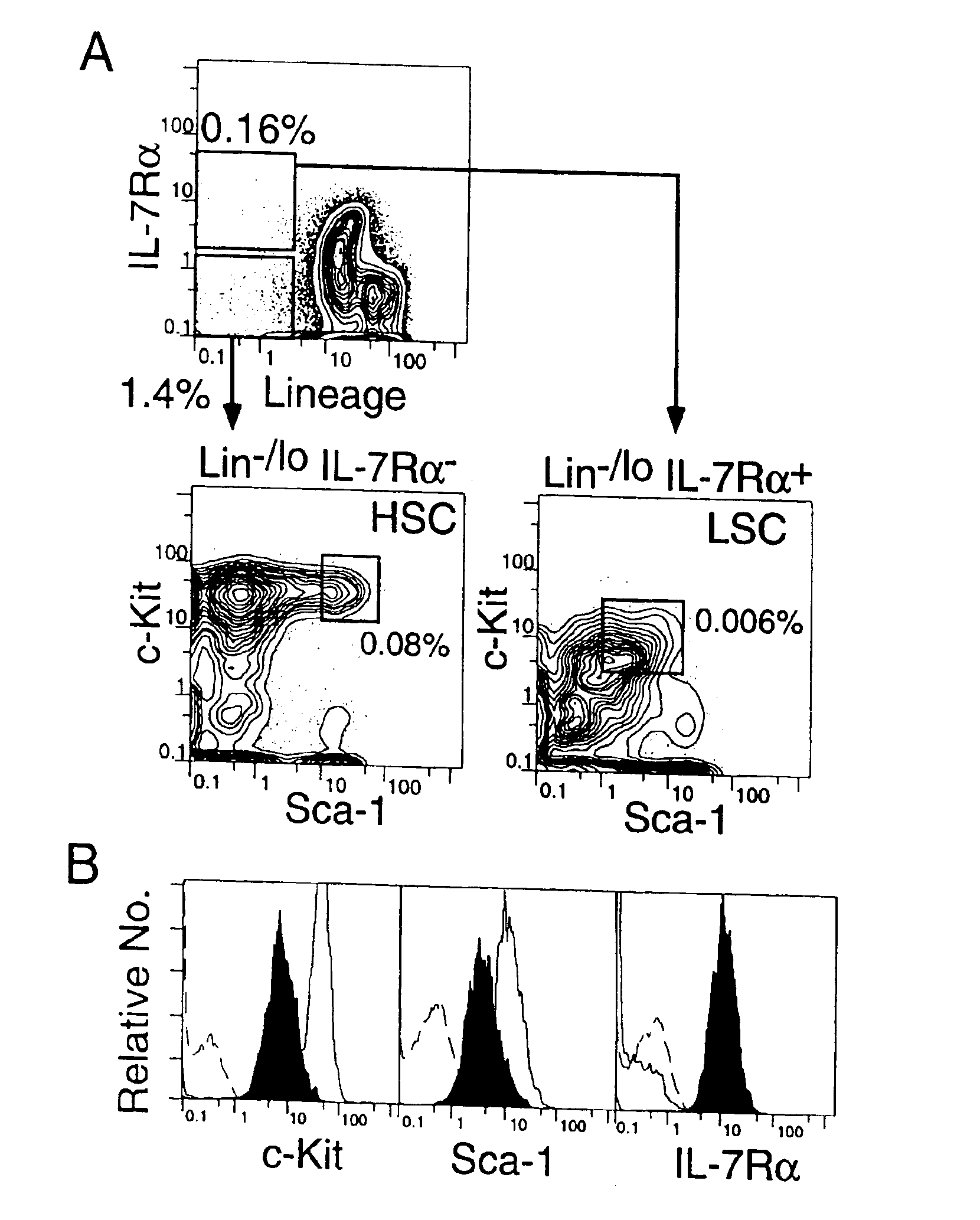
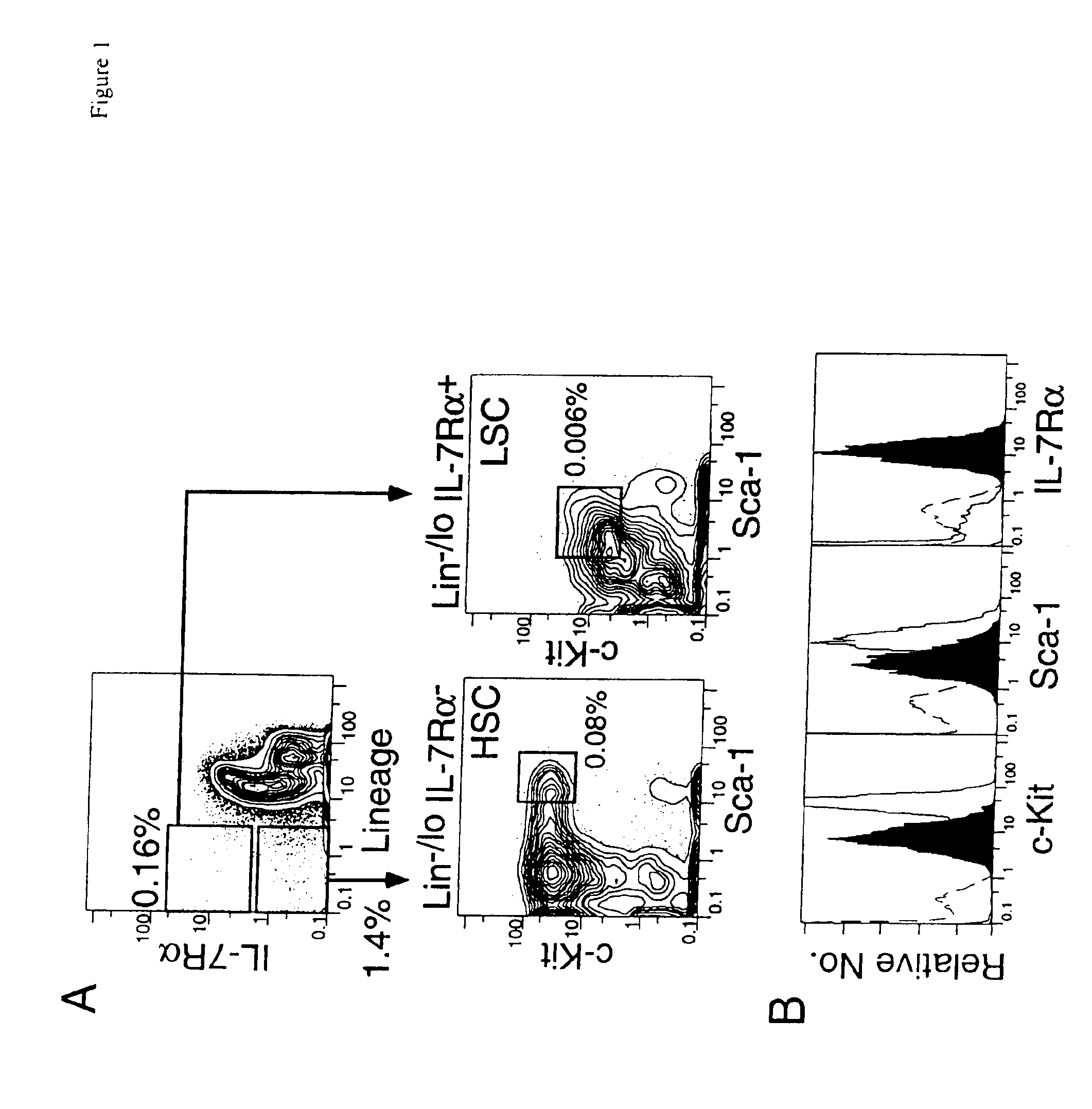
A substantially enriched mammalian hematopoietic cell subpopulation is provided, which is characterized by progenitor cell activity for lymphoid lineages, but lacking the potential to differentiate into myeloid and erythroid lineages. Methods are provided for the isolation and culture of this common lymphoid progenitor cell (CLP). The cell enrichment methods employ reagents that specifically recognize CDw127 (IL-7 receptor α); CD117 (c-kit) protein, in conjunction with other markers expressed on lineage committed cells. The murine cells are also characterized as expressing low levels of sca-1 (Ly-6E and Ly-6A). The CLPs are predominantly cycling, blast cells. These cells give rise to B cells, T cells and natural killer cells, as evidenced by their growth and differentiation in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
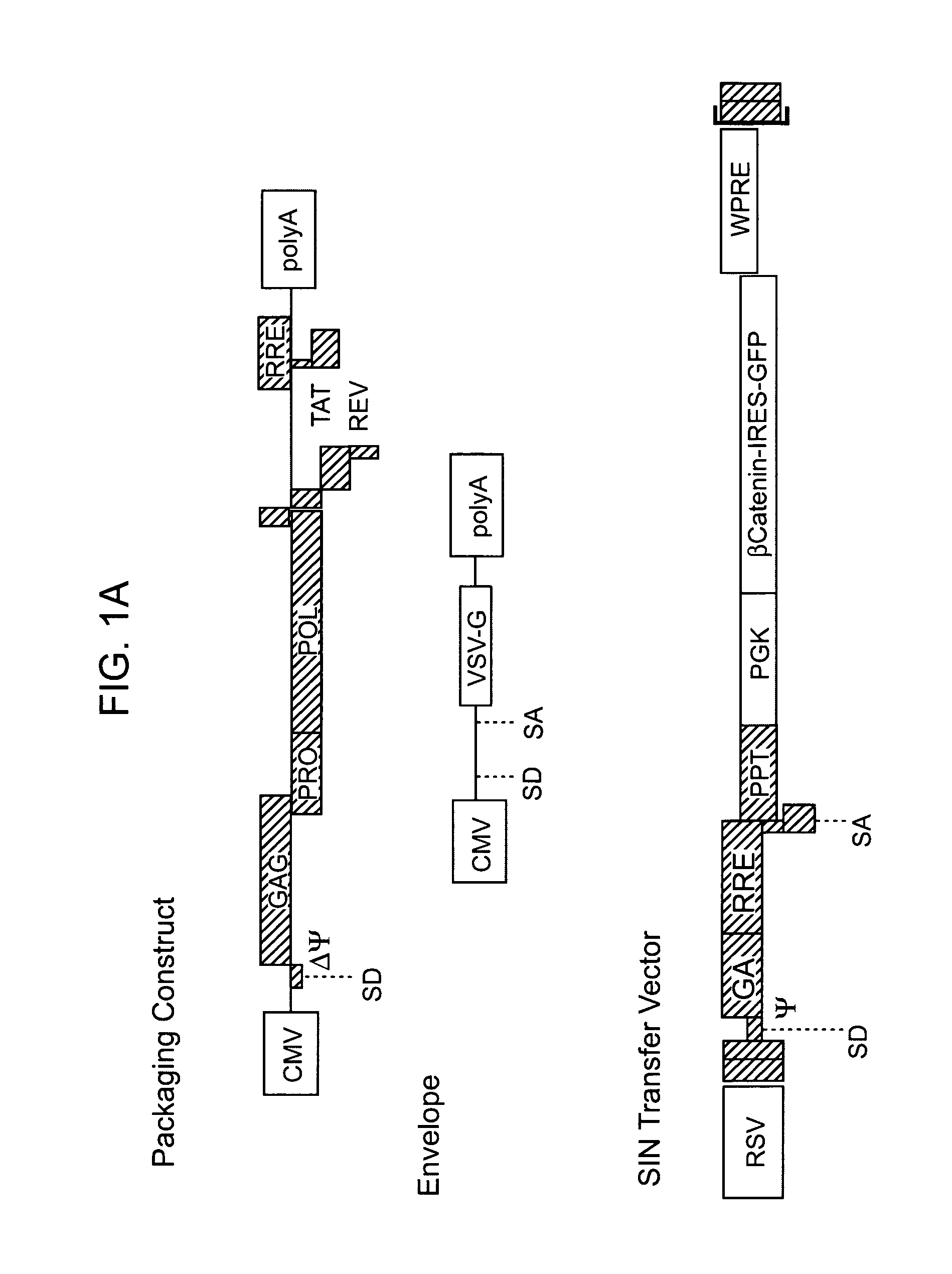
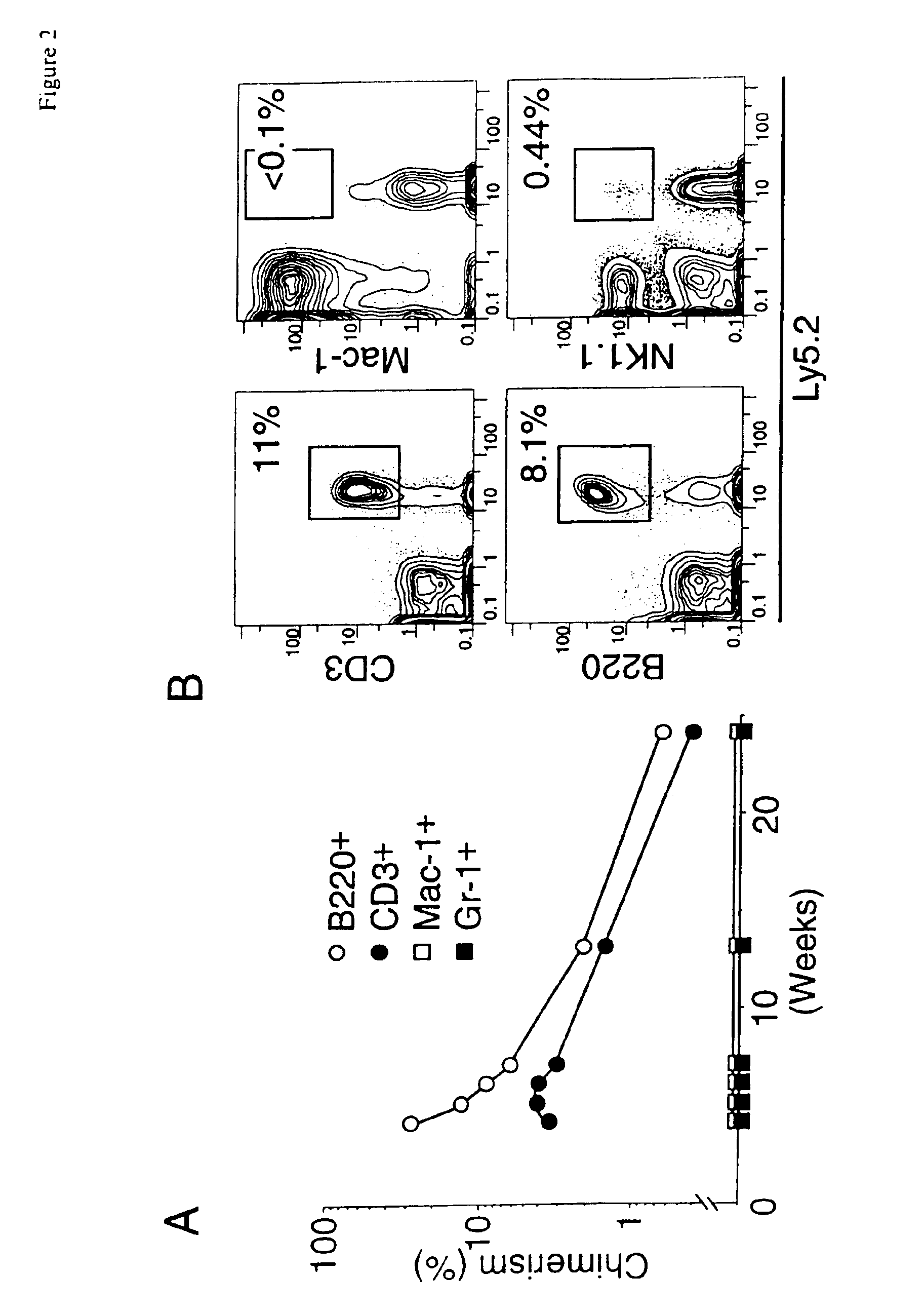
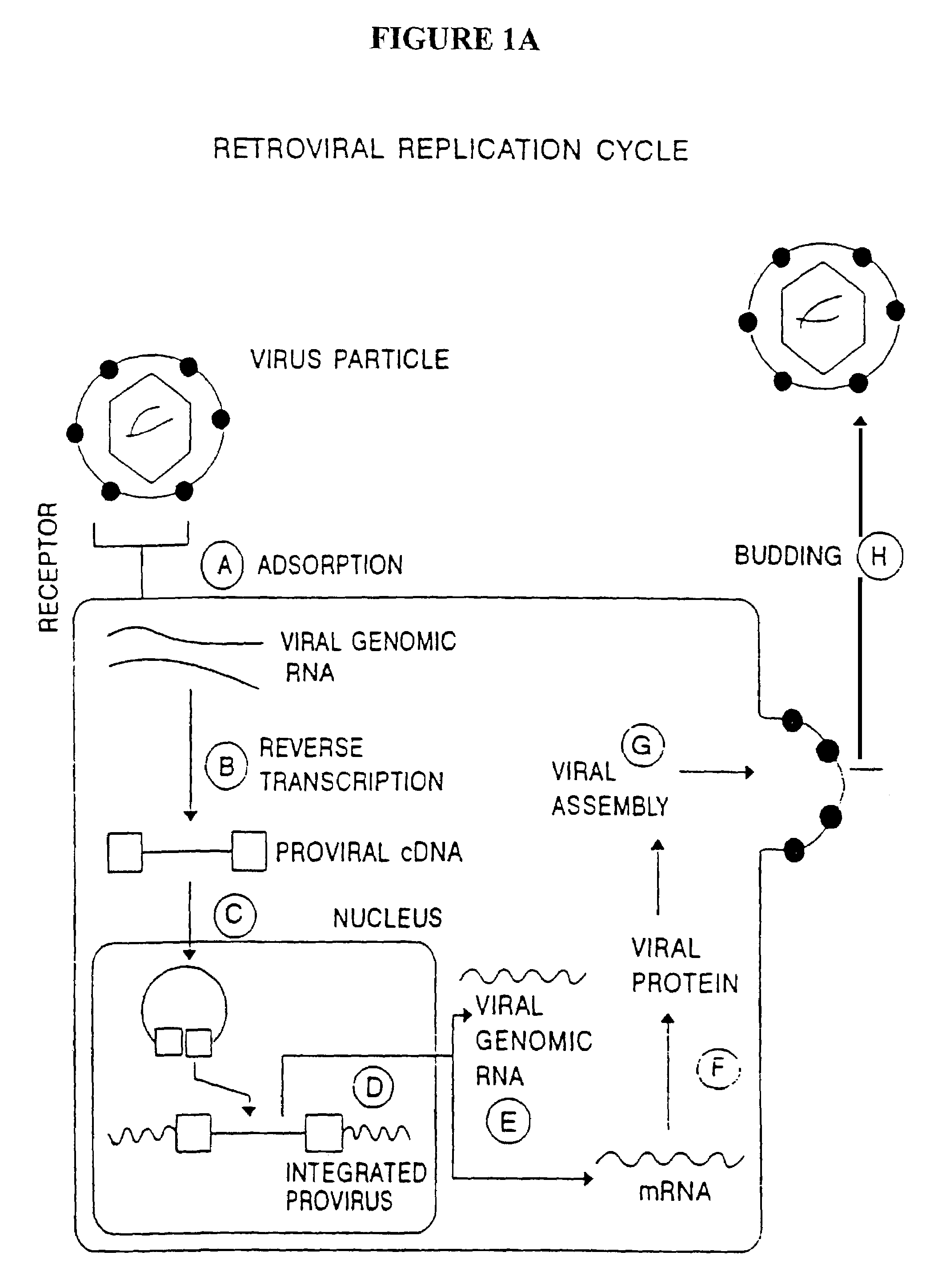
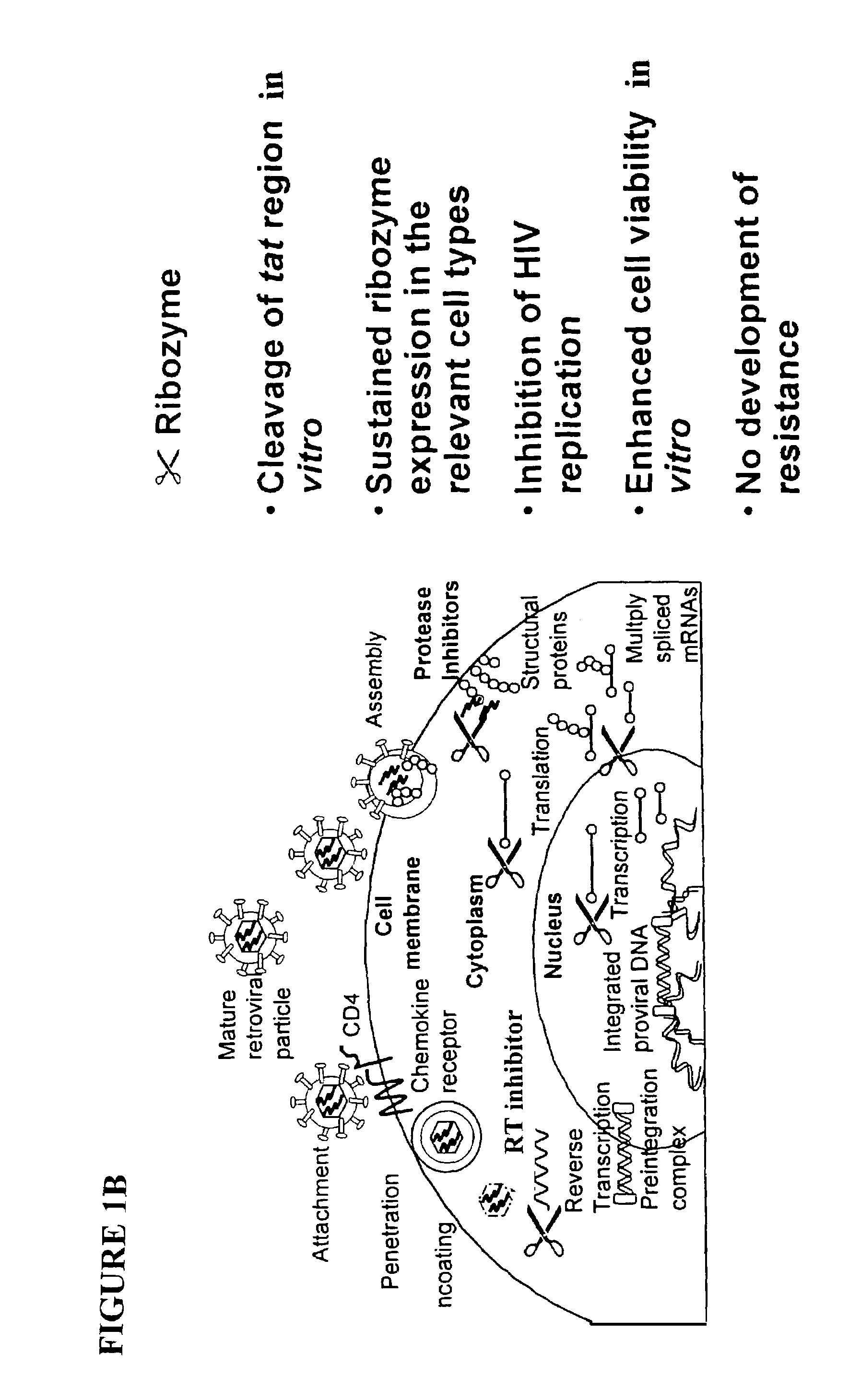
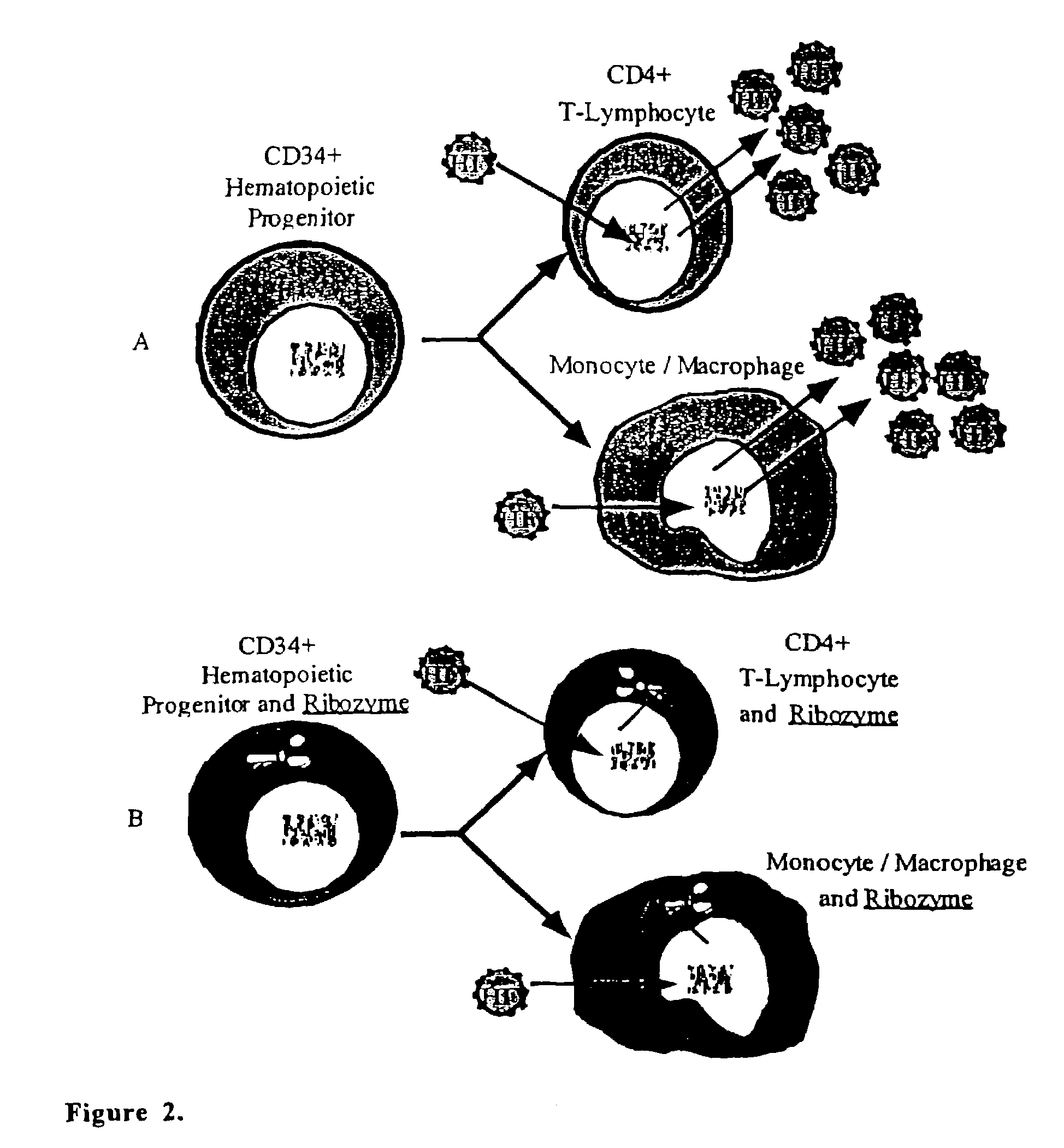
Methods for genetic modification of hematopoietic progenitor cells and uses of the modified cells
Described are compositions and methods relating to gene therapy, particularly as applied to hematopoietic progenitor (HP) cells, to transduced cells and methods of obtaining them, and to methods of using them to provide prolonged engraftment of modified hematopoietic cells in human subjects. The invention particularly relates to ex vivo gene therapy of HP cells for treatment or prevention of HIV infection.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON RES PTY LTD
Hemangio-colony forming cells
ActiveUS20080014180A1Reduce riskInduce toleranceBiocideBlood/immune system cellsHematopoietic cellCell biology
Methods of generating and expanding human hemangio-colony forming cells in vitro and methods of expanding and using such cells are disclosed. The methods permit the production of large numbers of hemangio-colony forming cells as well as derivative cells, such as hematopoietic and endothelial cells. The cells obtained by the methods disclosed may be used for a variety of research, clinical, and therapeutic applications.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL TECH INC
Methods for treating viral infection using il-28 and il-29 cysteine mutants
InactiveUS20080075693A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeLow immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticInterferon therapyHematopoietic cell
IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and certain mutants thereof have been shown to have antiviral activity on a spectrum of viral species. Of particular interest is the antiviral activity demonstrated on viruses that infect liver, such as hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. In addition, IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and mutants thereof do not exhibit some of the antiproliferative activity on hematopoietic cells that is observed with interferon treatment. Without the immunosuppressive effects accompanying interferon treatment, IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 will be useful in treating immunocompromised patients for viral infections.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
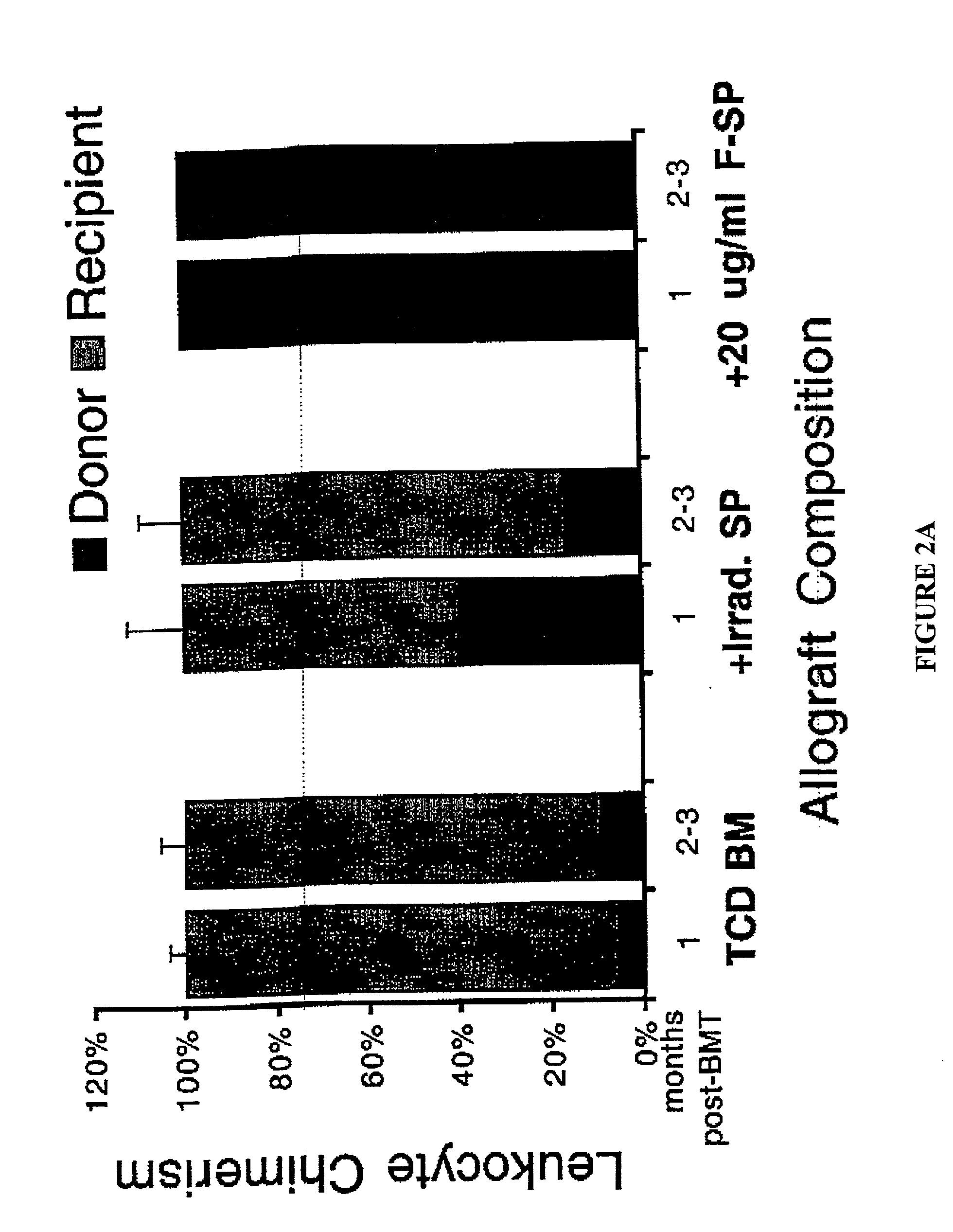
Method of transplantation using chemotherapy-treated allogeneic cells that enhance immune responses without graft versus host disease
InactiveUS20020127208A1Effective in treating and preventing infectionReduce capacityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAllogeneic cellHematopoietic cell
The present invention provides a method of transplanting hematopoietic cells between genetically unrelated individuals, comprising administering to the recipient, in combination with the administration of the hematopoietic cells, an amount of mononuclear cells which are treated so as to substantially reduce their ability to cause graft versus host disease while they retain their ability to proliferate in the recipient. The treated mononuclear cells can facilitate engraftment of hematopoietic cells when transplanted in combination with hematopoietic cells, treat or prevent infections, and treat cancer.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Genetically modified non-human animals and methods of use thereof
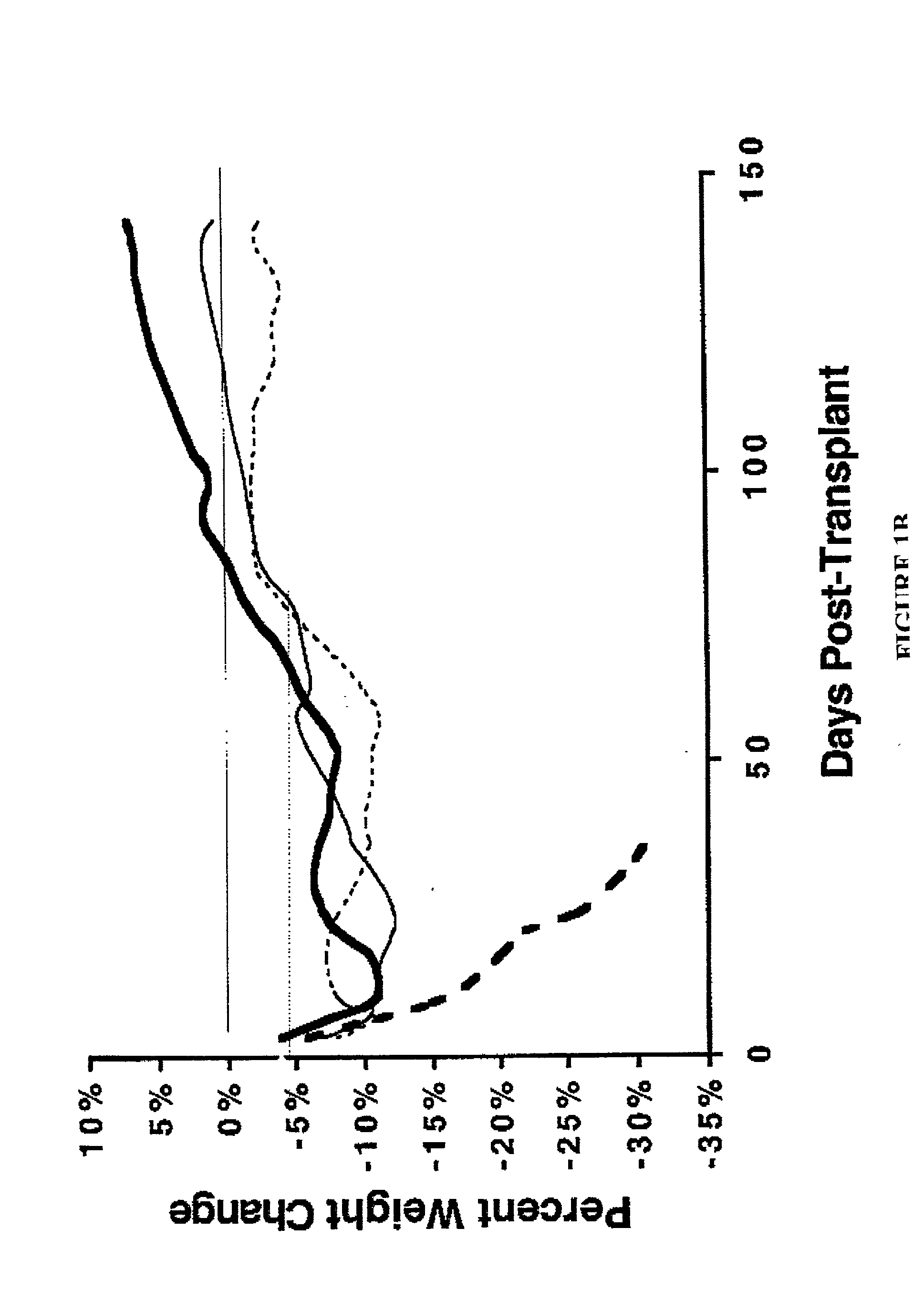
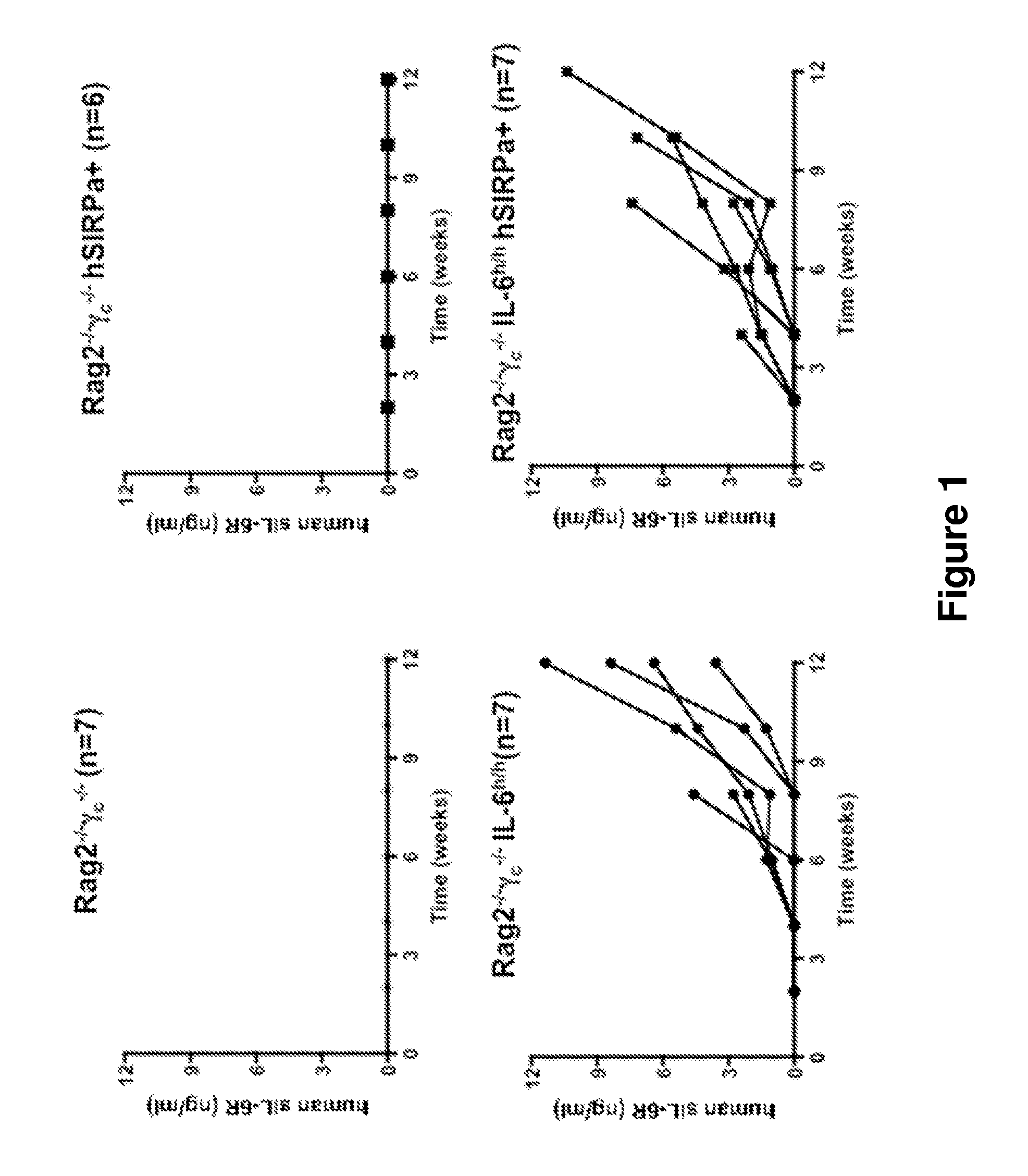
ActiveUS20140134662A1Reduce rateReduced viabilityCompounds screening/testingThrombopoietinDiseaseHematopoietic cell
Genetically modified non-human animals are provided that may be used to model human hematopoietic cell development, function, or disease. The genetically modified non-human animals comprise a nucleic acid encoding human IL-6 operably linked to an IL-6 promoter. In some instances, the genetically modified non-human animal expressing human IL-6 also expresses at least one of human M-CSF, human IL-3, human GM-CSF, human SIRPa or human TPO. In some instances, the genetically modified non-human animal is immunodeficient. In some such instances, the genetically modified non-human animal is engrafted with healthy or diseased human hematopoietic cells. Also provided are methods for using the subject genetically modified non-human animals in modeling human hematopoietic cell development, function, and / or disease, as well as reagents and kits thereof that find use in making the subject genetically modified non-human animals and / or practicing the subject methods.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC +3
Multiple mechanisms for modulation of jak/stat activity
InactiveUS20100209929A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionGain of function mutationHematopoietic cell
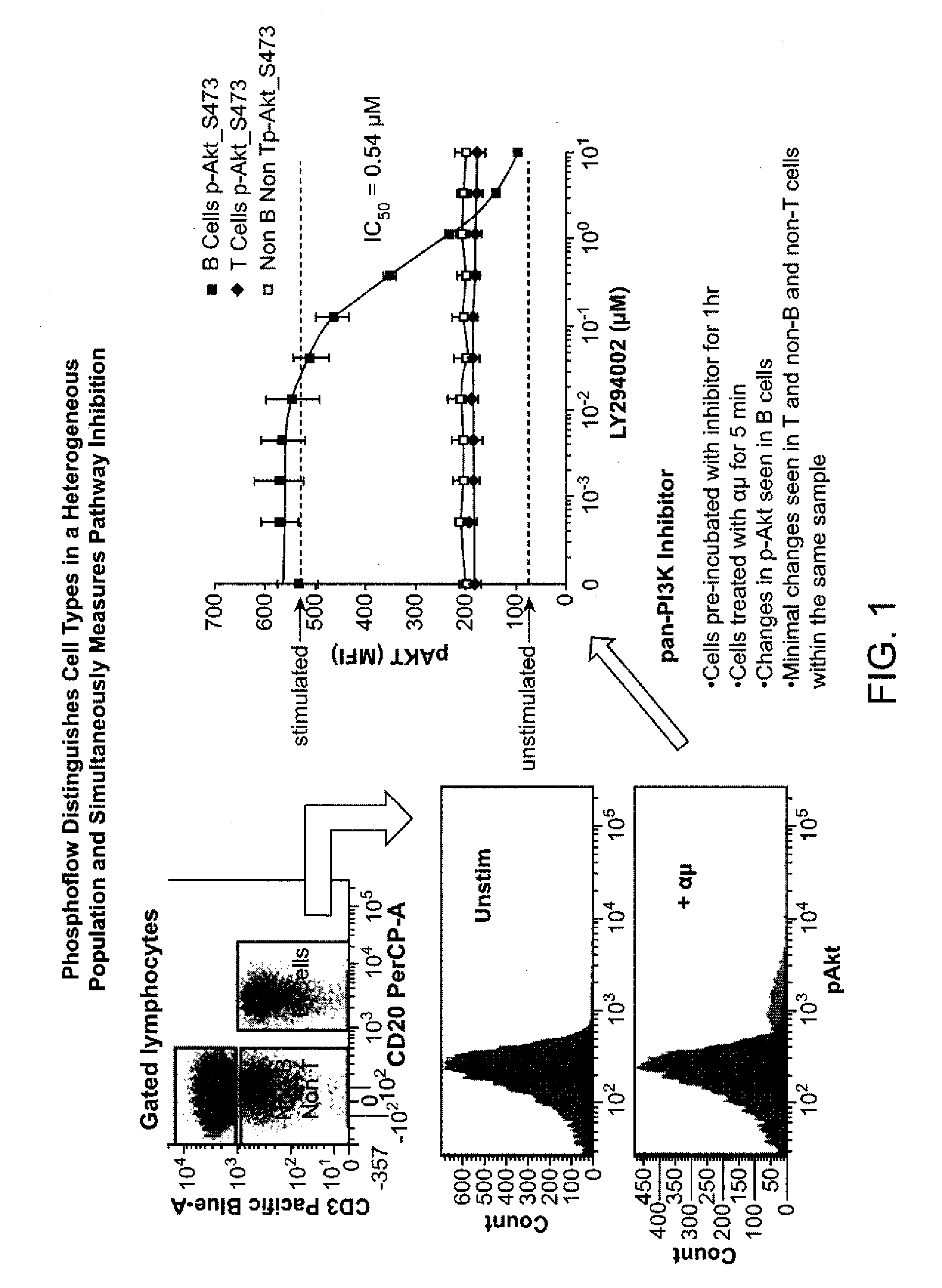
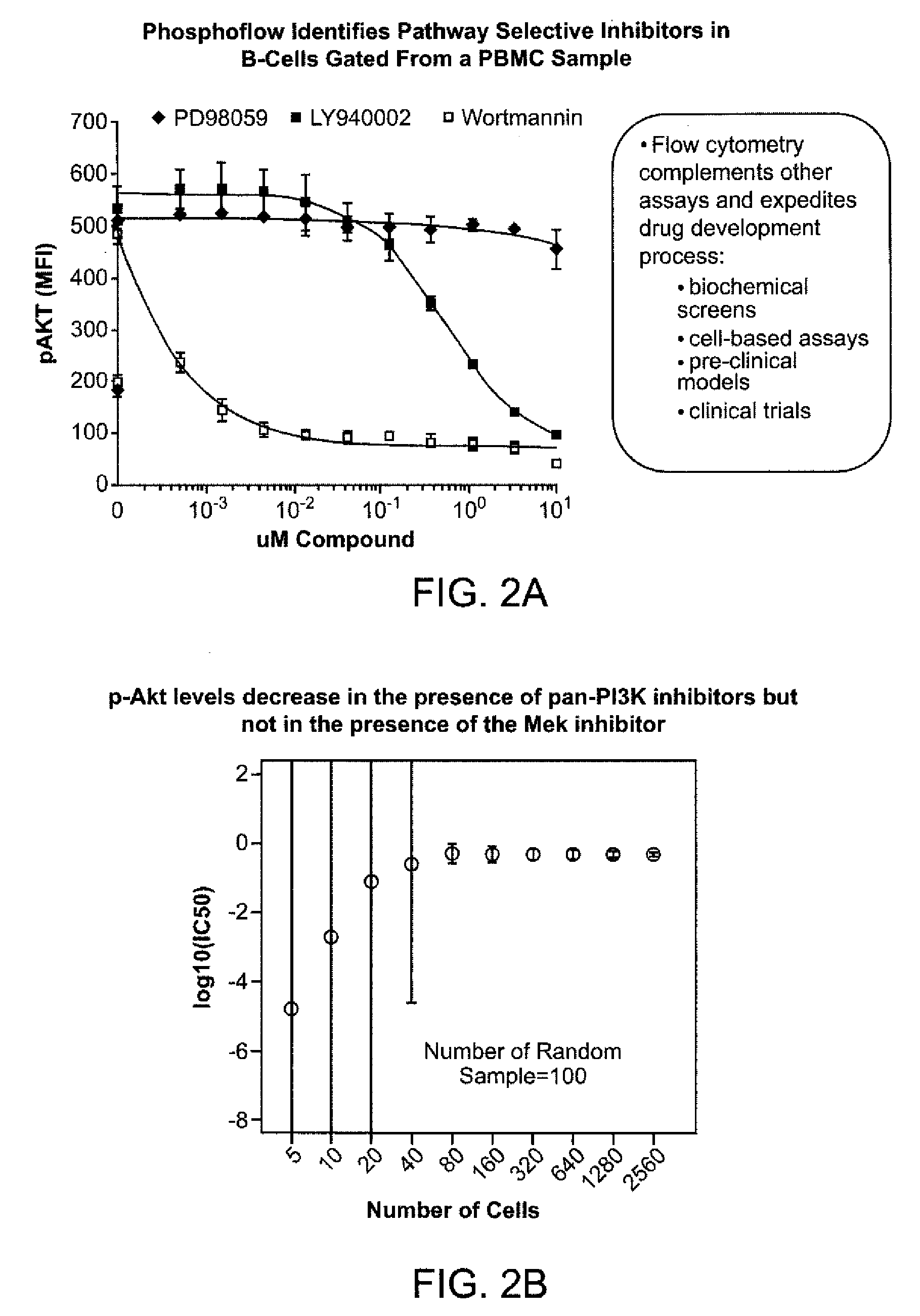
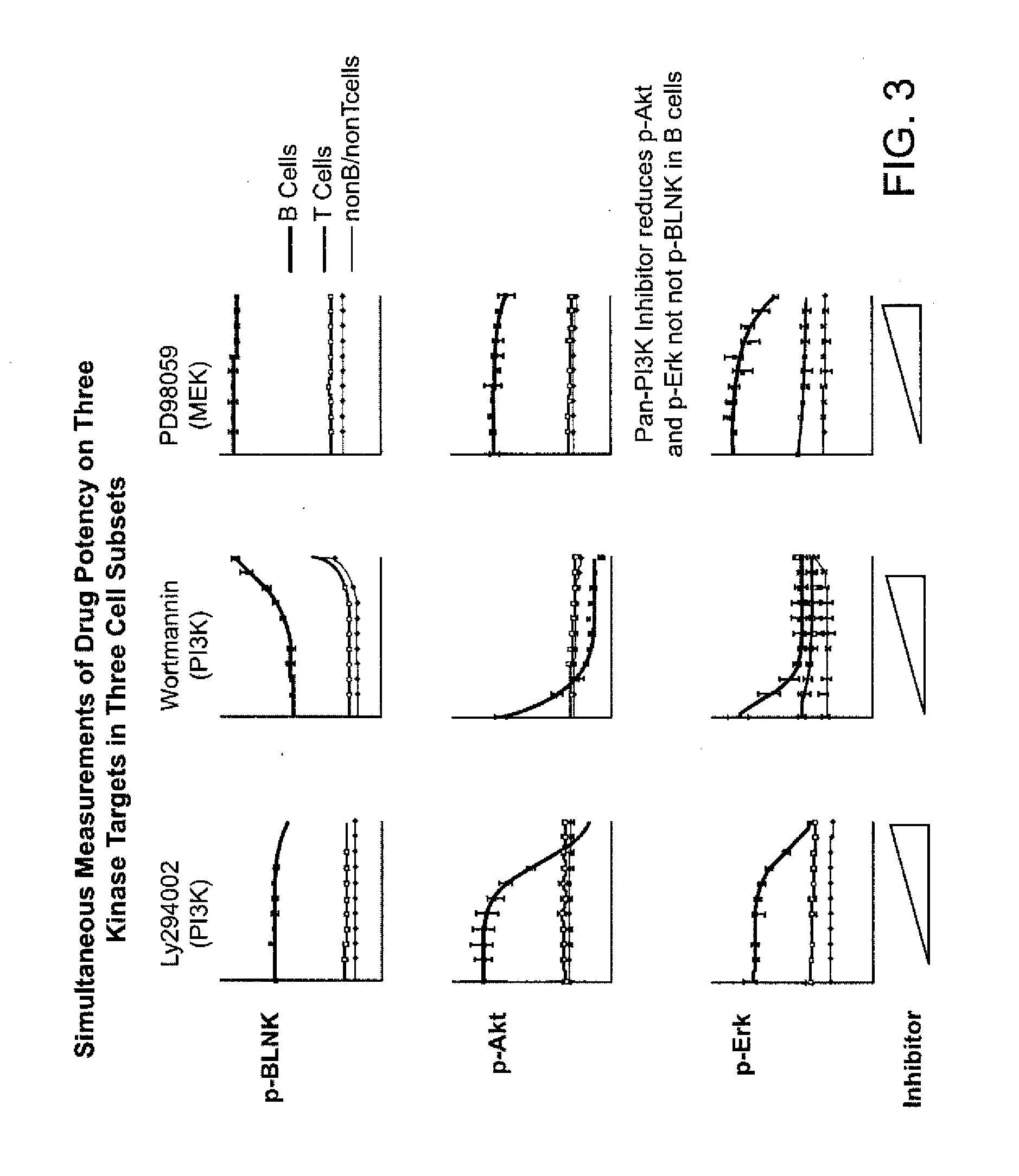
An embodiment of the present invention is a method for subjecting a hematopoetic cell to a JAK / STAT inhibitor, determining the activity of gain-of-function mutations of a Jak family kinase, determining the expression levels and activity of JAK / STAT regulatory proteins, correlating the expression levels and the activity of JAK / STAT regulatory proteins with the activity of gain-of-function mutations of a Jak family kinase and with a response to the JAK / STAT inhibitor, and then classifying the cells. A further embodiment of the invention includes determining the clinical outcome based on the cell classification, determining a method of treatment, determining dosing and scheduling of at least one of the JAK / STAT inhibitors or other compounds.
Owner:NODALITY
Therapeutic compositions containing glutathione analogs
InactiveUS7029695B2Improve bioavailabilityPromote absorptionTripeptide ingredientsImmunoglobulinsLipid formationHematopoietic cell
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of using them. Lipid formulations of a glutathione analog and methods of manufacturing them. Their use to stimulate hematopoiesis, protect hematopoietic cells from damage caused by radiation or chemotherapy, or potentiate the stimulatory action of one or a combination of cytokines on colony formation by hematopoietic progenitor cells, protect a subject from a destructive effect of a chemotherapeutic agent or irradiation, or to potentiate the effect of a chemotherapeutic agent.
Owner:TELIK INC
Leukemia stem cell markers
InactiveUS20120070450A1Prevent relapseAnimal cellsOrganic active ingredientsHematopoietic cellAnalyte
The invention provides a test method for predicting the initial onset or a recurrence of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) comprising (1) measuring the expression level of human leukemic stem cell (LSC) marker genes in a biological sample collected from a subject for a transcription product or translation product of the gene as an analyte and (2) comparing the expression level with a reference value; an LSC-targeting therapeutic agent for AML capable of suppressing the expression of a gene selected from among LSC marker genes or a substance capable of suppressing the activity of a translation product of the gene; a method for producing a sample containing hematopoietic cells for autologous transplantation or allogeneic transplantation for AML patients comprising obtaining an LSC-purged sample with at least 1 kind of LSC marker as an index; and a method of preventing or treating AML.
Owner:RIKEN
Surrogate tolerogenesis for the development of tolerance to xenografts
InactiveUS6060049AIncrease differentiationIncreased proliferationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHematopoietic cellTolerability
PCT No. PCT / US94 / 05844 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 6, 1995 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 6, 1995 PCT Filed May 24, 1994 PCT Pub. No. WO94 / 27622 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 8, 1993This invention provides a method for developing immune tolerance in xenogeneic organ graft recipients, in which lympho-hematopoietic cells from an intended organ graft recipient are differentiated within a xenogeneic surrogate, such as a fetal animal. After birth of the surrogate, the matured lympho-hematopoietic cells containing antigen specific regulatory cells, including suppressor cells, veto cells, select B cells, anti-idiotype antibodies, and other related factors responsible for antigen specific tolerance in a surrogate animal are reintroduced into the intended organ graft recipient, in conjunction with an organ transplant or a tissue transplant from the xenograft surrogate. The invention also provides an organ graft repopulated with cells from the intended organ graft recipient produced in a surrogate animal.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Preparative regimen for engraftment, growth and differentiation of non-hematopoeitic cells in vivo after transplantation
InactiveUS20080233088A1Improve proliferative abilityEnhanced signalBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHematopoietic cellInjury brain
The invention relates to methods of obtaining an expanded population of mammalian ex vivo cells and / or for treating a mammalian subject by (a) administering to a subject an effective amount of an agent that confers a growth disadvantage to at least a subset of endogenous cells at the site of engraftment; (b) administering to the subject an effective amount of a mitogenic stimulus for the ex vivo cells; and (c) administering the ex vivo cells to the subject, wherein the ex vivo cells engraft at the site and proliferate to a greater extent than the subset of endogenous cells, to repopulate at least a portion of the engraftment site with the ex vivo cells. The repopulated cells can be harvested for further use or be left at the engraftment site of a subject to be treated. The invention also provides methods of treating brain injury in a subject by engrafting ex vivo cells at the site of injury.
Owner:MONTEFIORE MEDICAL CENT INC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com