Preparative regimen for engraftment, growth and differentiation of non-hematopoeitic cells in vivo after transplantation
a non-hematopoeitic cell and engraftment technology, applied in the field of cell transplantation therapy, can solve the problems of cell transplantation, inability to engraft, and inability to fully utilize donor organs, so as to increase the intrinsic proliferation capacity or survival of donor cells, the effect of increasing the proliferation capacity of donor cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
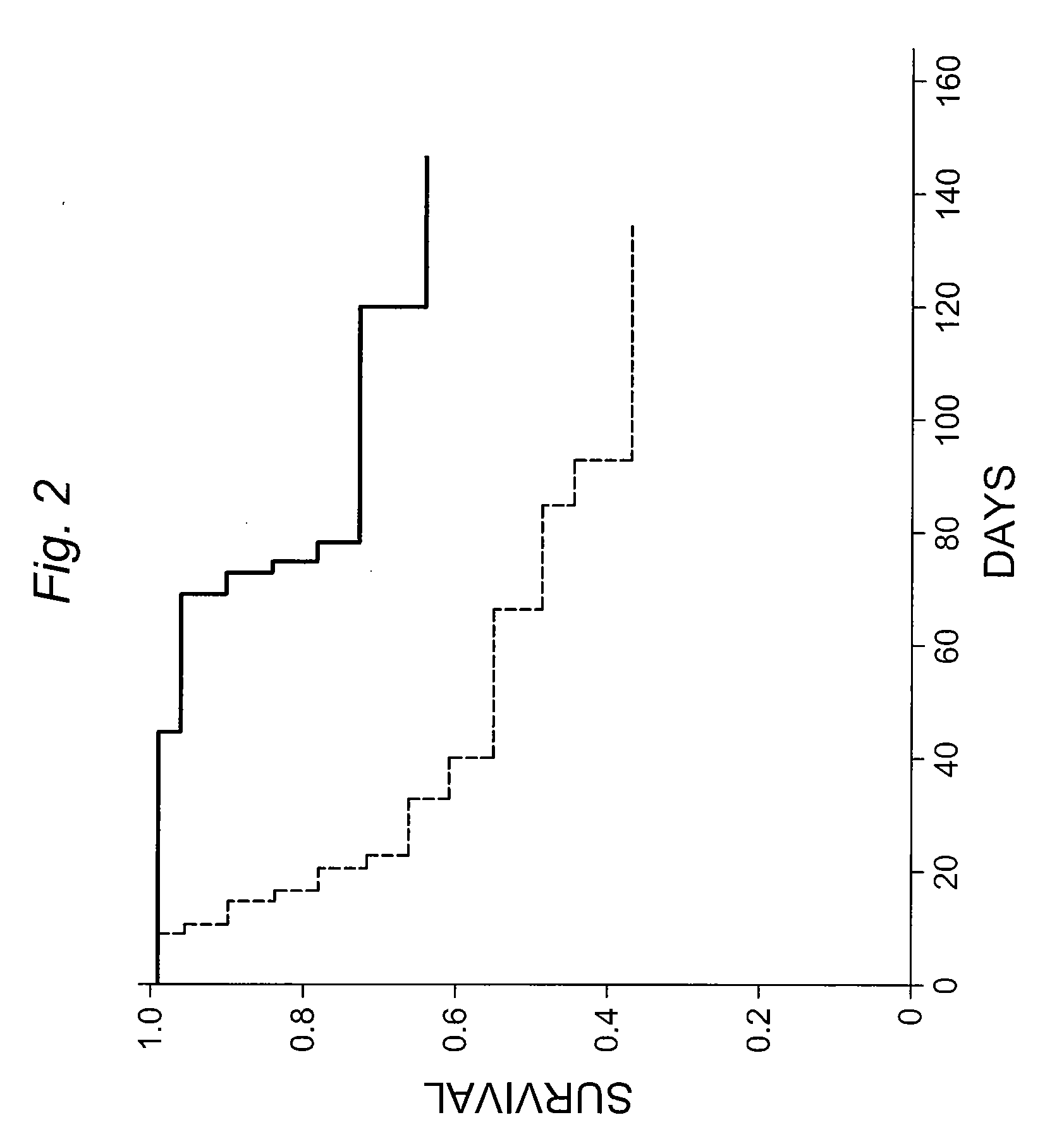
Hepatocyte Transplantation (HT) Ameliorates Radiation-Induced Liver Damage (RILD) and Increases Survival After Partial Hepatic Resection and Irradiation (12)
[0175]Liver cancer is the sixth most common cancer worldwide in terms of number of cases (626,00 / yr) but because of very poor prognosis, the number of deaths is almost the same as its incidence (598,000 / yr). Besides primary liver cancer, metastatic liver cancer, arising from abdominal malignancies, remains a vexing and commonly encountered problem. Although, surgery is the only curative therapy, most patients with liver tumors are unresectable and chemotherapy fails to cure patients. This is rather unfortunate because a significant proportion of these patients have limited hepatic metastases (oligometastases), without harboring tumor deposits in extrahepatic sites. Failure to control the hepatic oligometastases results in eventual systemic progression of the cancer. In many cancers, such as head and neck, esophagus, lung, cervix...
example 2
PH+HIR as a Preparative Regimen for Liver Repopulation by Transplanted Hepatocytes
Guha, C. et al., Hepatology, 36:354-362 (2002)
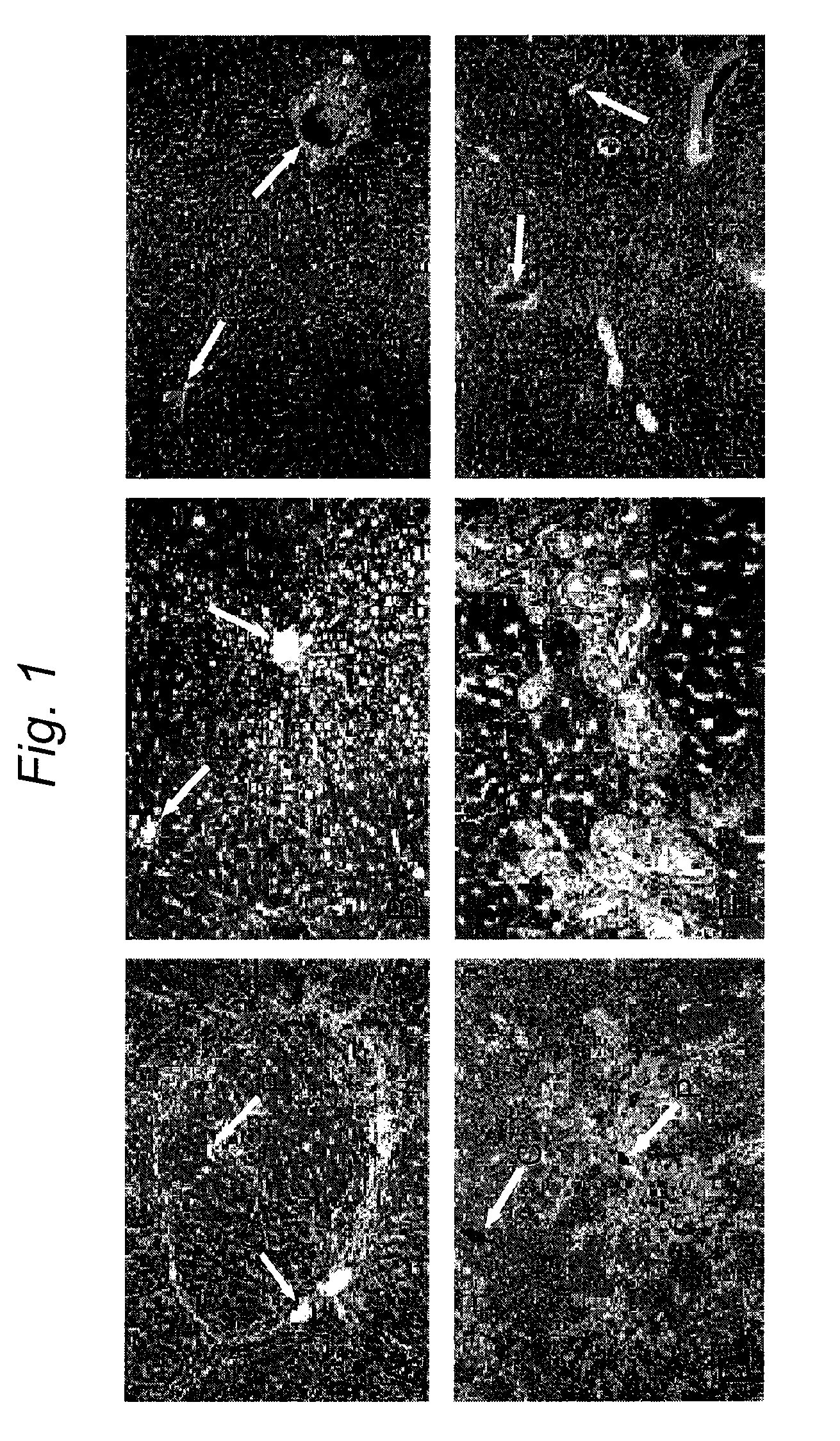
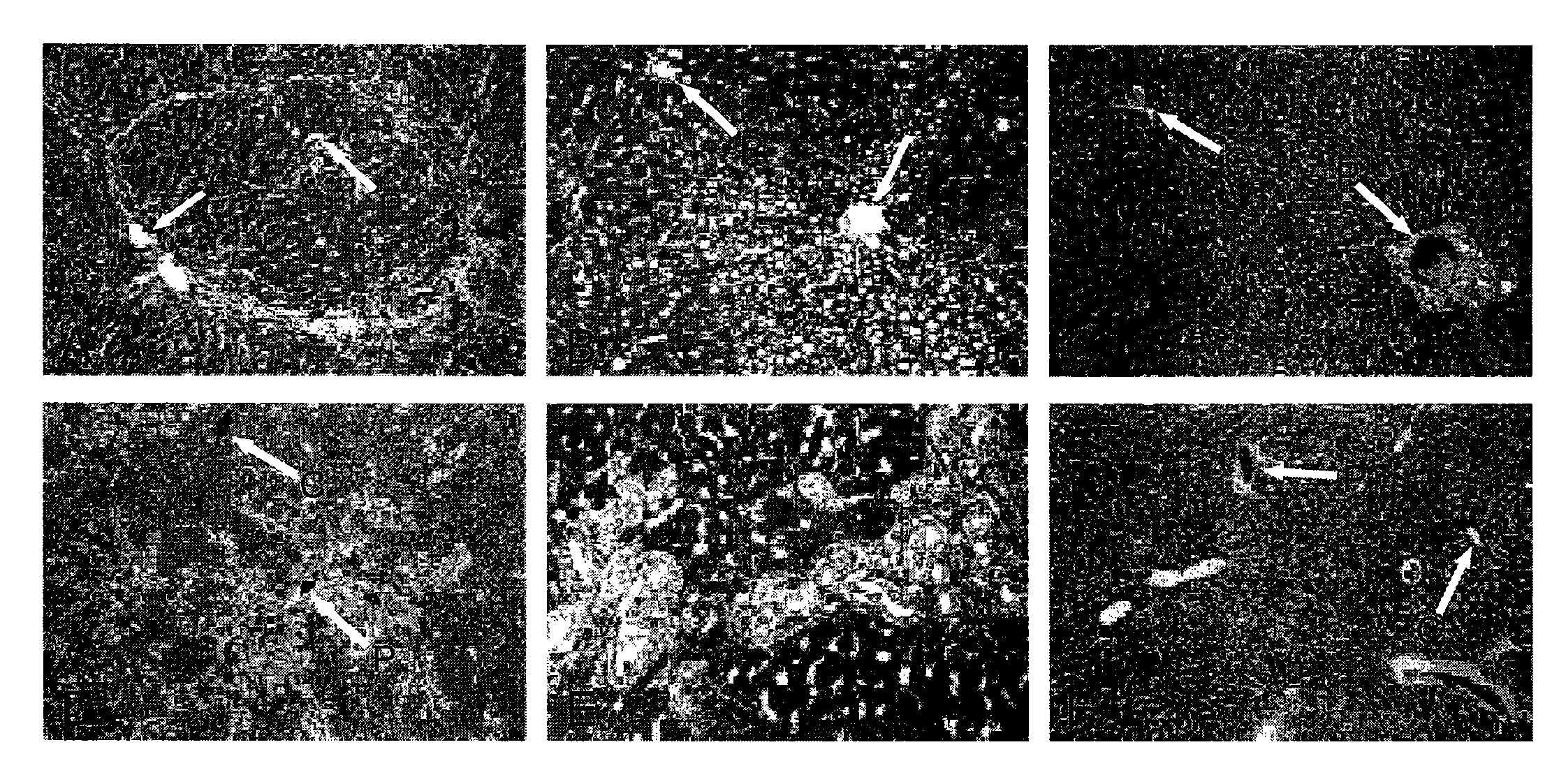
[0177]Encouraged by our findings, we examined whether PH+HIR could be used as a preparative regimen of HT for amelioration of inherited metabolic liver diseases. Gunn rat is an animal model for bilirubin-uridinediphosphoglucuronate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A1) deficiency, which causes Crigler-Najjar syndrome type 1 in humans. UGT1A1 deficiency results in the lack of glucuronidation of bilirubin, resulting in the accumulation of unconjugated bilirubin in plasma and consequent bilirubin encephalopathy. We transplanted congeneic UGT1A1-proficient, Wistar-RHA hepatocytes in jaundiced Gunn rats, 4 days after PH+HIR. Five months after HT, there was 60-80% repopulation of the host liver by the engrafted UGT1A1+ve, transplanted hepatocytes (FIG. 4B-D). HPLC of bile collected 5 months after PH+HIR+HT showed complete normalization of the pigment profile, with exc...
example 3
Noninvasive Substitutes to PH in the Preparative Regimen of HT
[0178]The success of PH+HIR as a preparative regimen for HT depends on HIR suppressing the host hepatocellular proliferation and inducing mitotic catastrophe in host cells, while PH providing the mitotic stimuli and a selective growth advantage for transplanted hepatocytes. Although PH provides a very strong mitotic stimulus to the hepatocytes, it is invasive and is not desirable in clinical protocols of liver repopulation of transplanted hepatocytes for patients with metabolic disorders. We, therefore, examined noninvasive alternatives to PH (Table 2) (Takahashi, M. et al., Gene Ther, 10:304-313 (2003); Deb, N. et al., Hepatology, 34 (4):153A., 34:153A (2001); Parashar, B. et al., Hepatology, 32:206A (2000); Guha, C. et al., Am J Nephrol, 25:161-170 (2005); Malhi, H. et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 99:13114-13119 (2002)).
TABLE 2HIR-BASED PREPARATIVE REGIMENS OF LIVERREPOPULATION (SUBSTITUTES TO PH)MECHANISM OFPREPARATIVE...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com