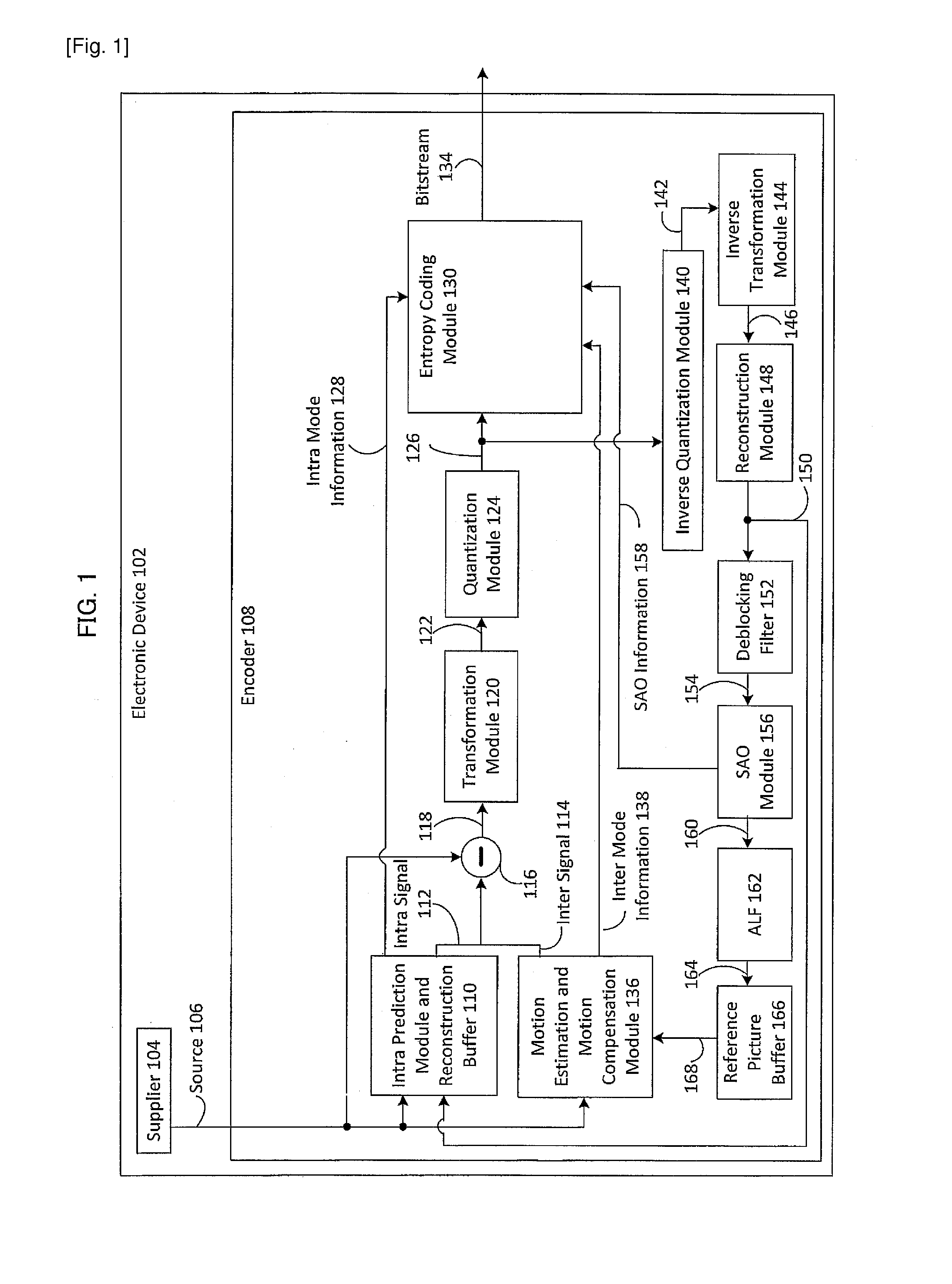
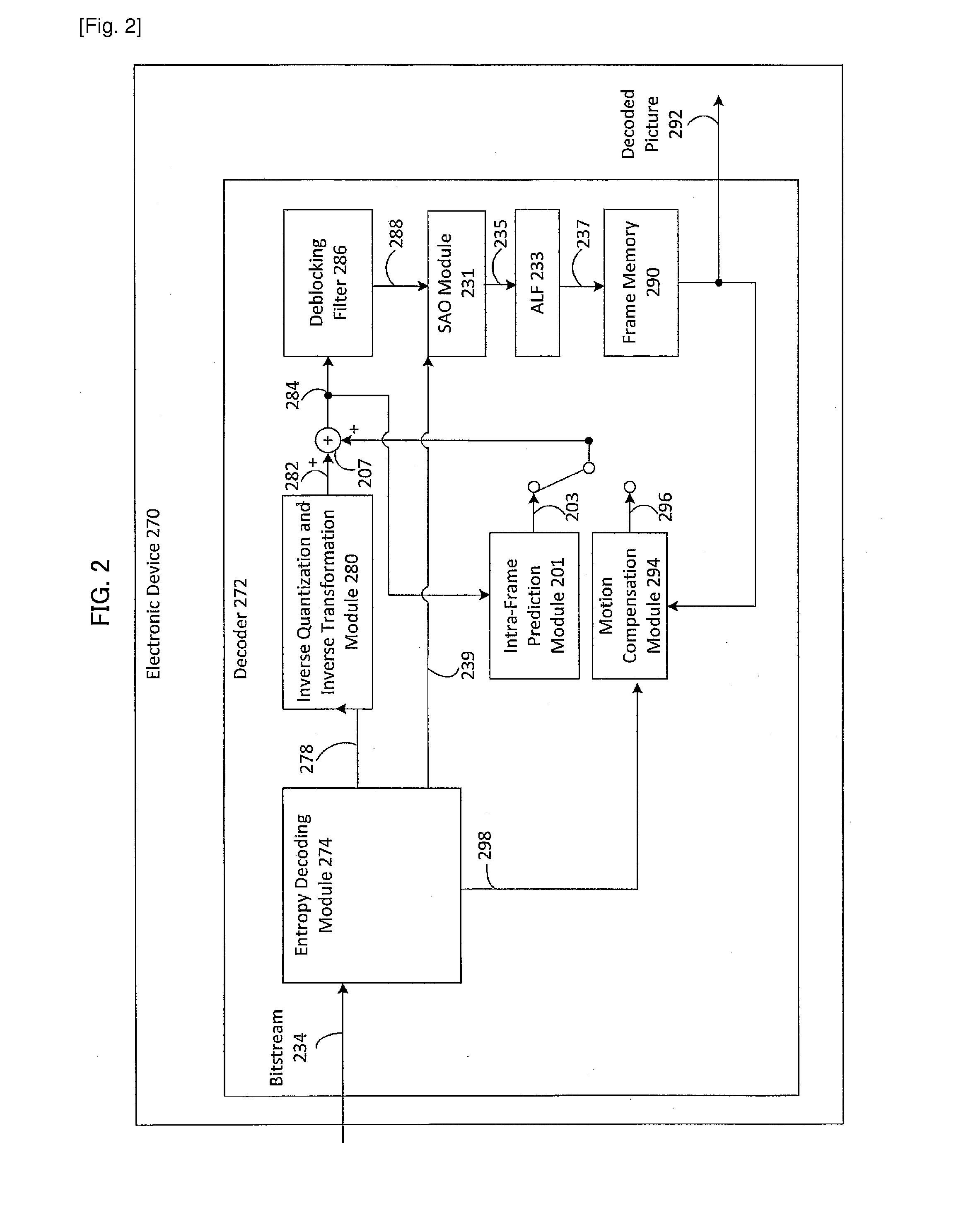
Patents
Literature
163results about How to "Efficient representation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
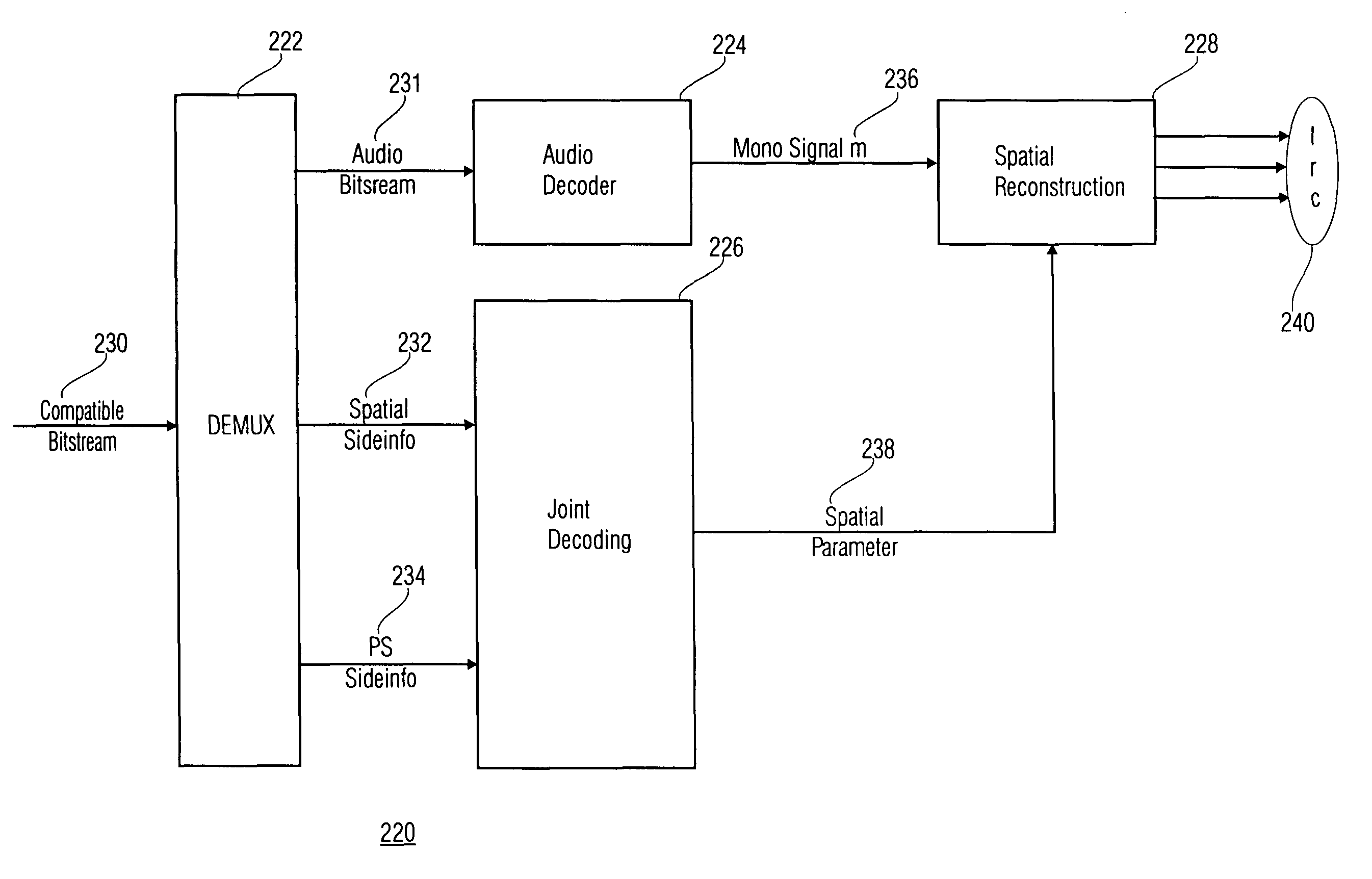
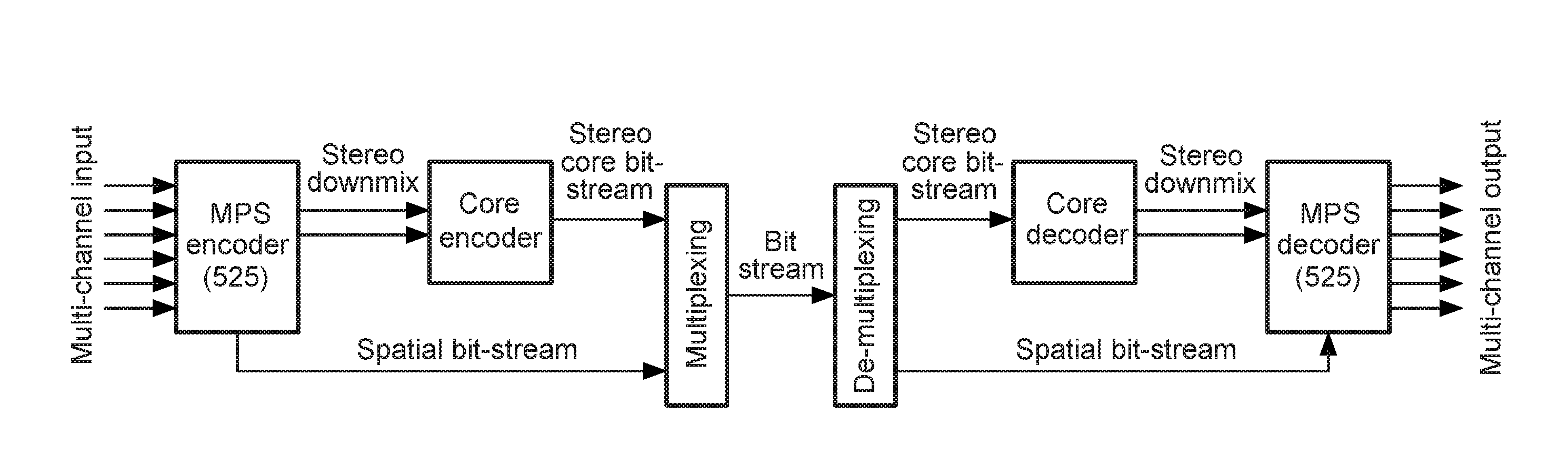
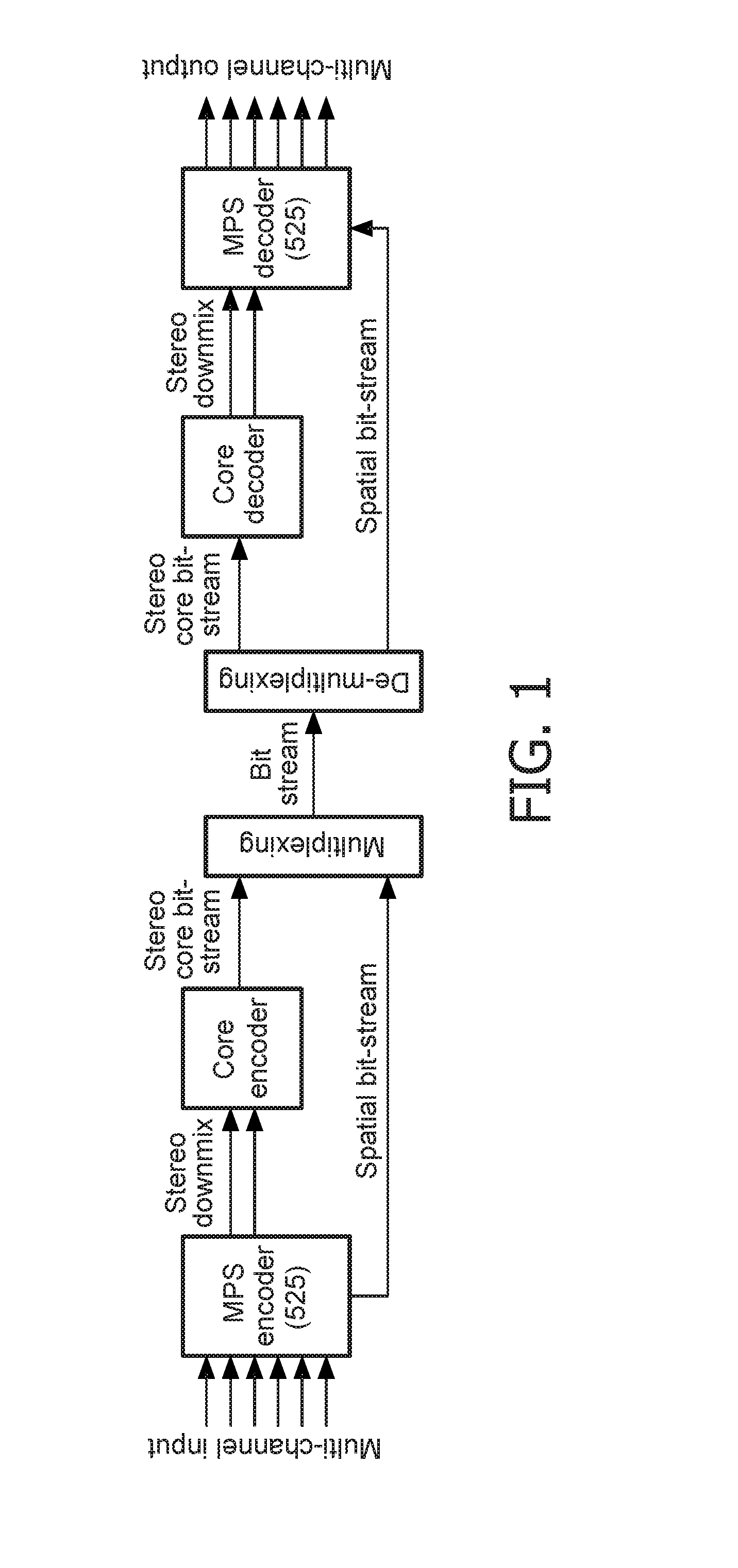
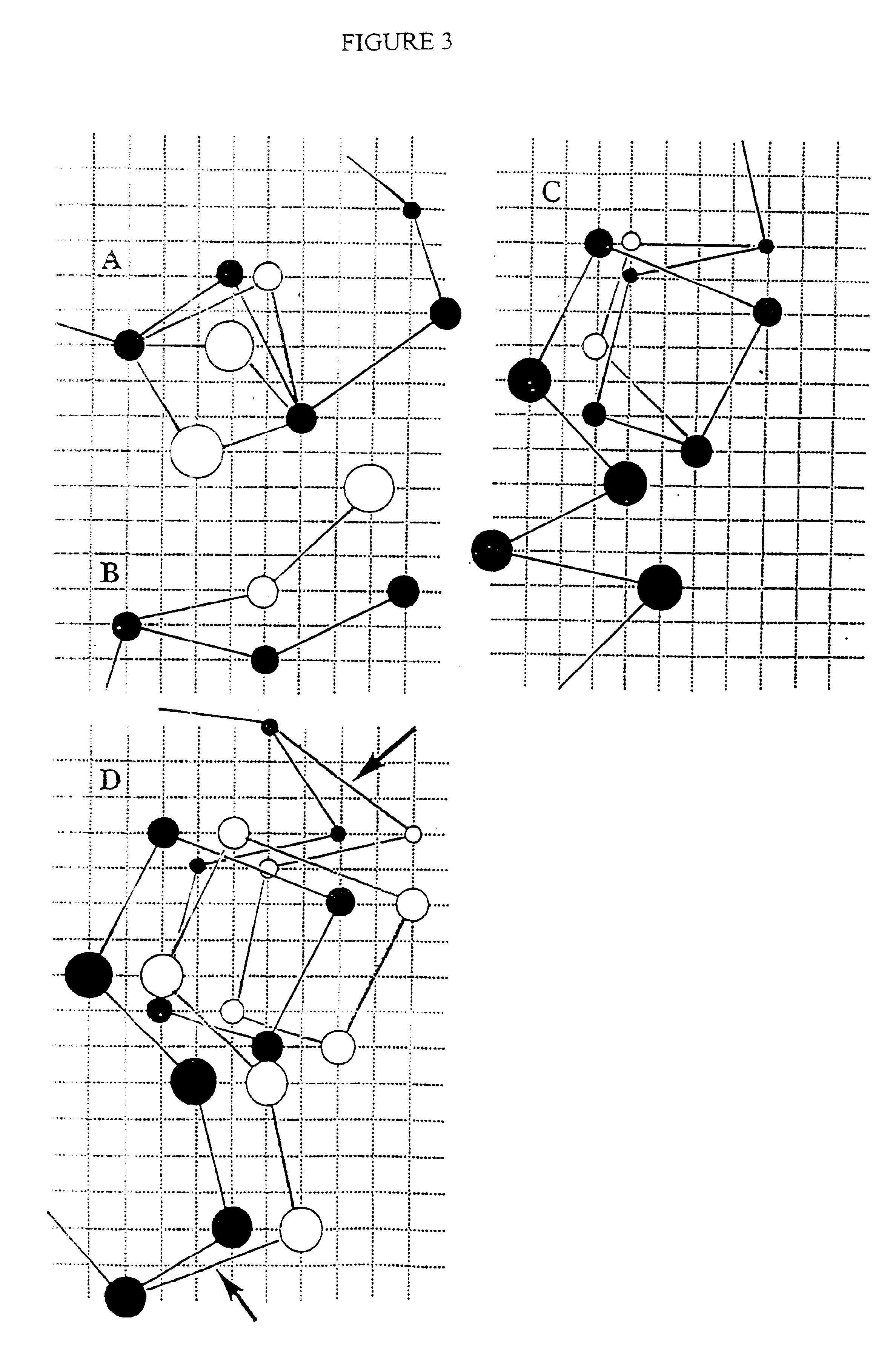
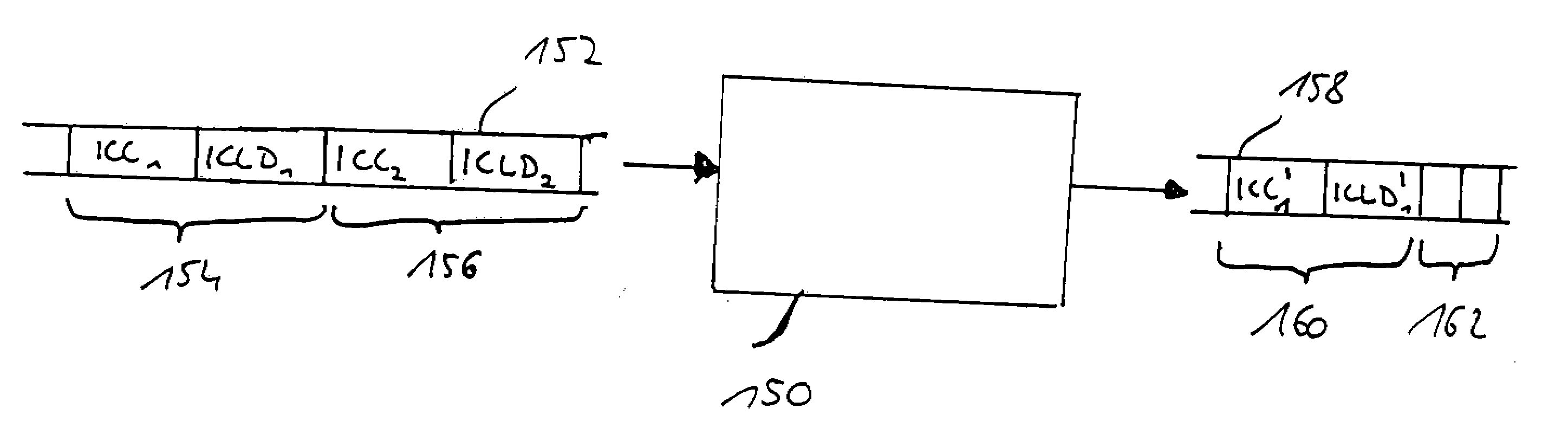
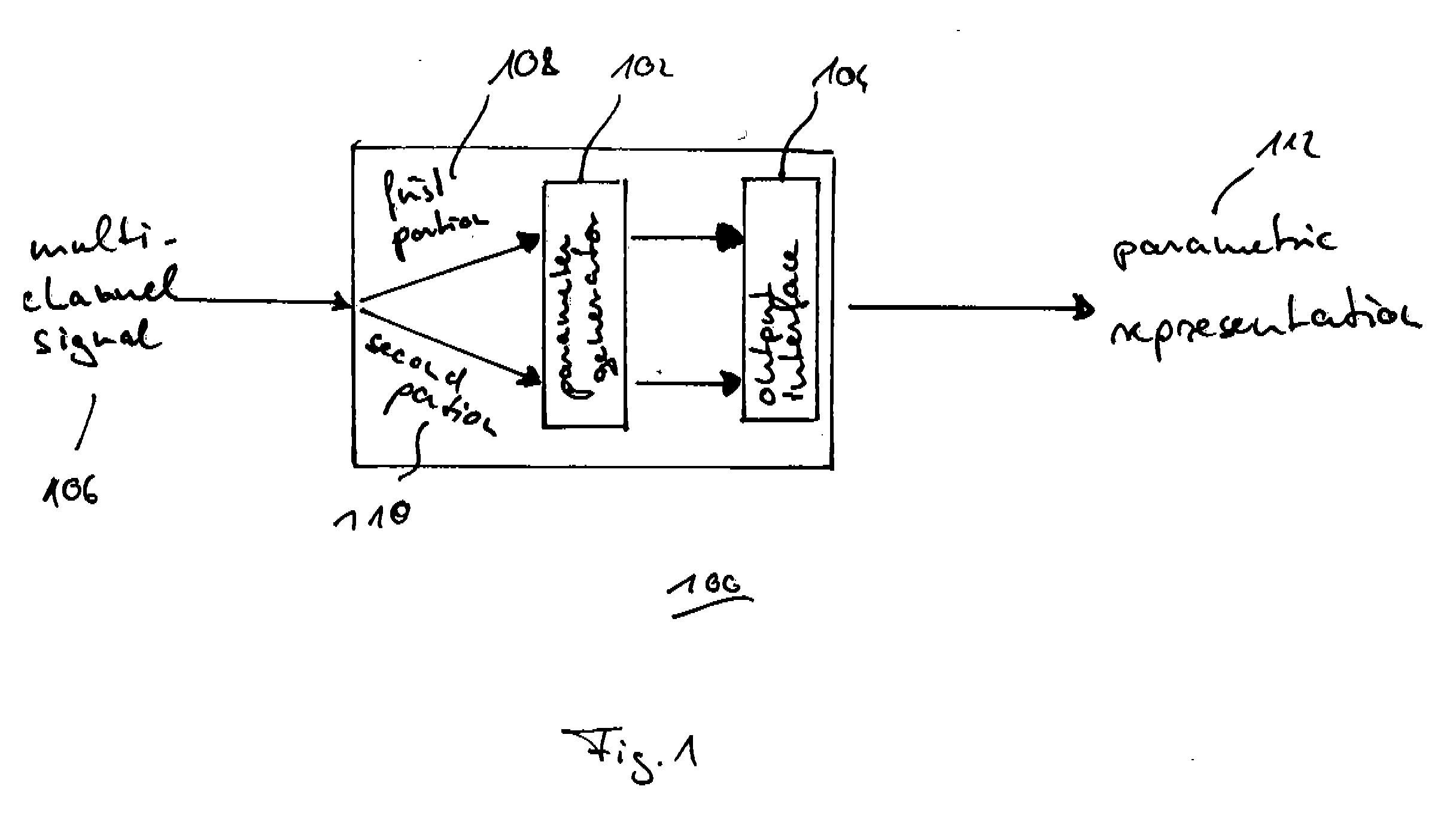
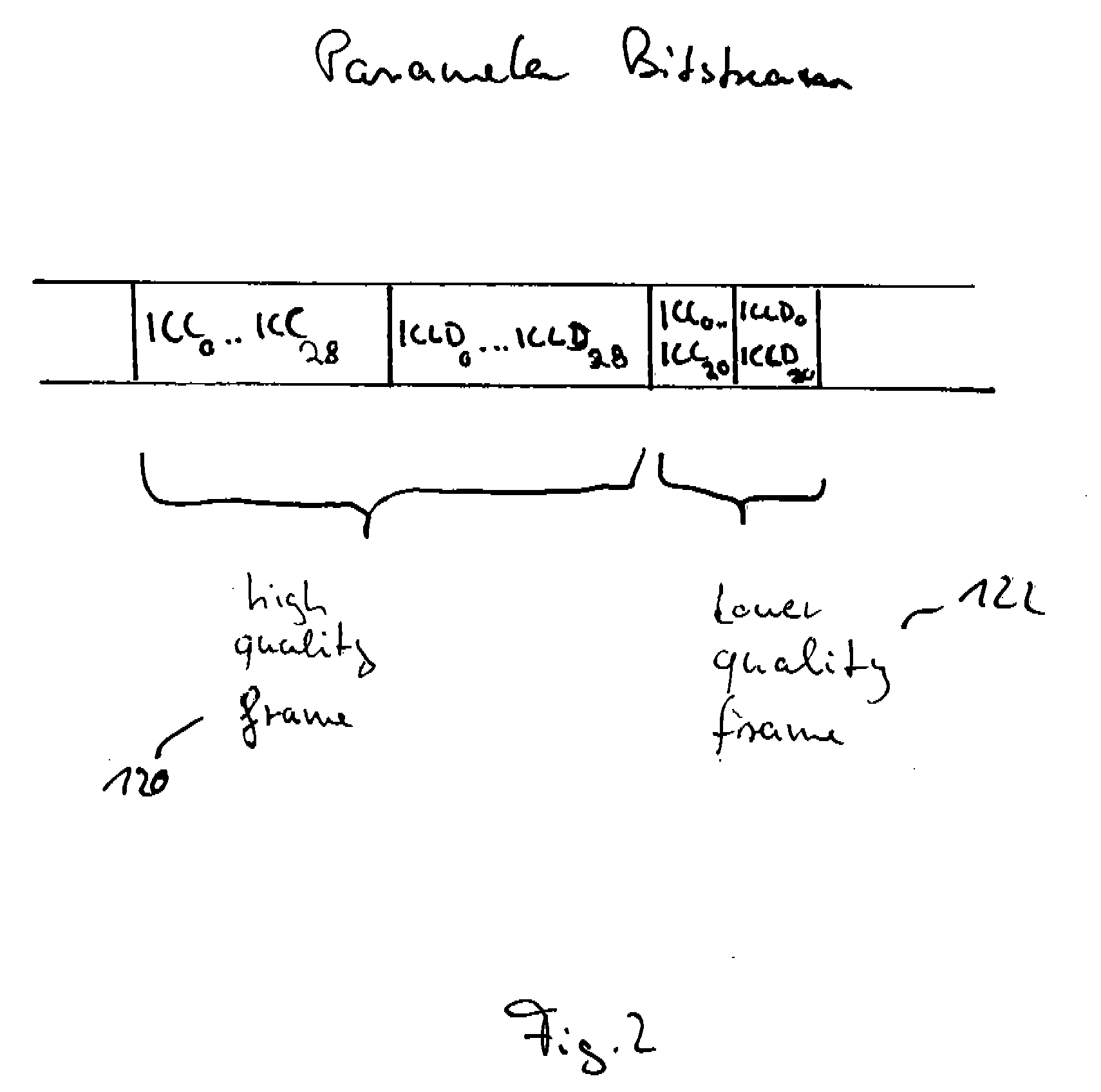
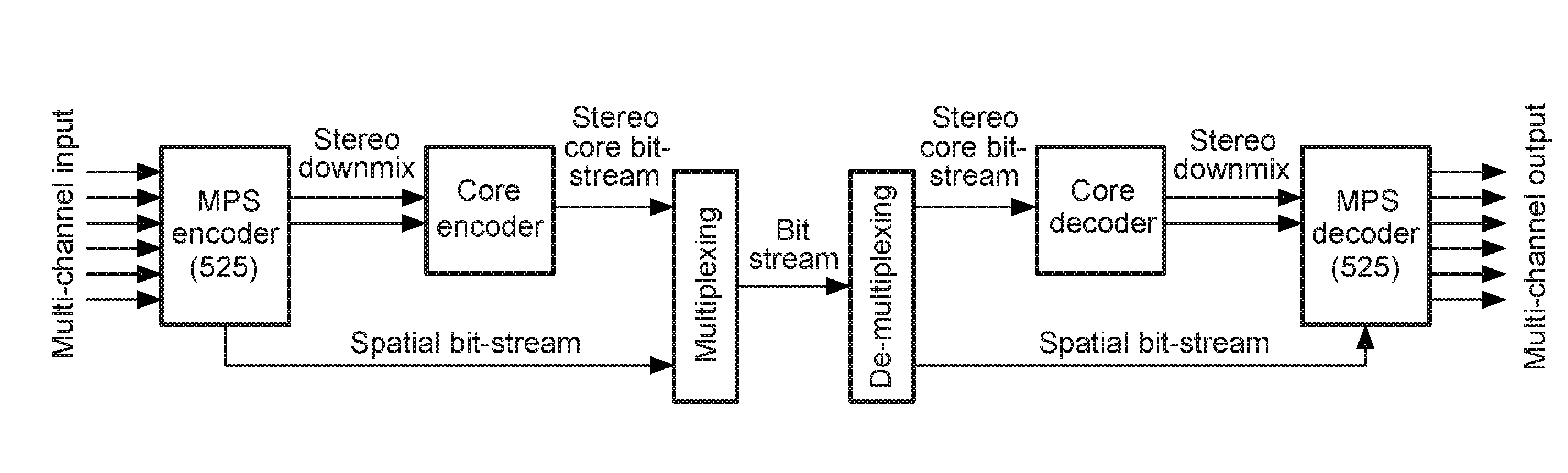
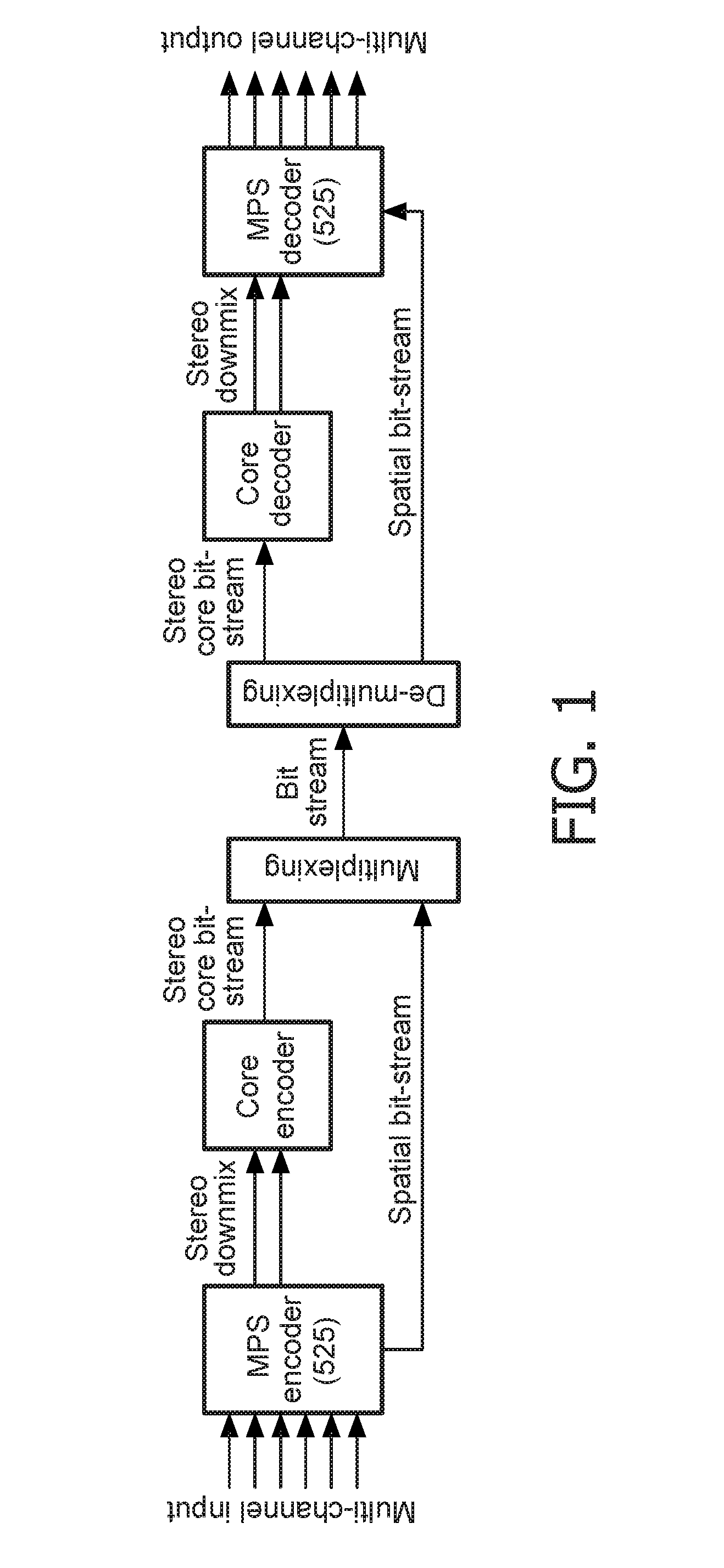
Stereo compatible multi-channel audio coding
ActiveUS20060133618A1High qualityExcellent qualitySpeech analysisCode conversionStereophonic soundAudio signal
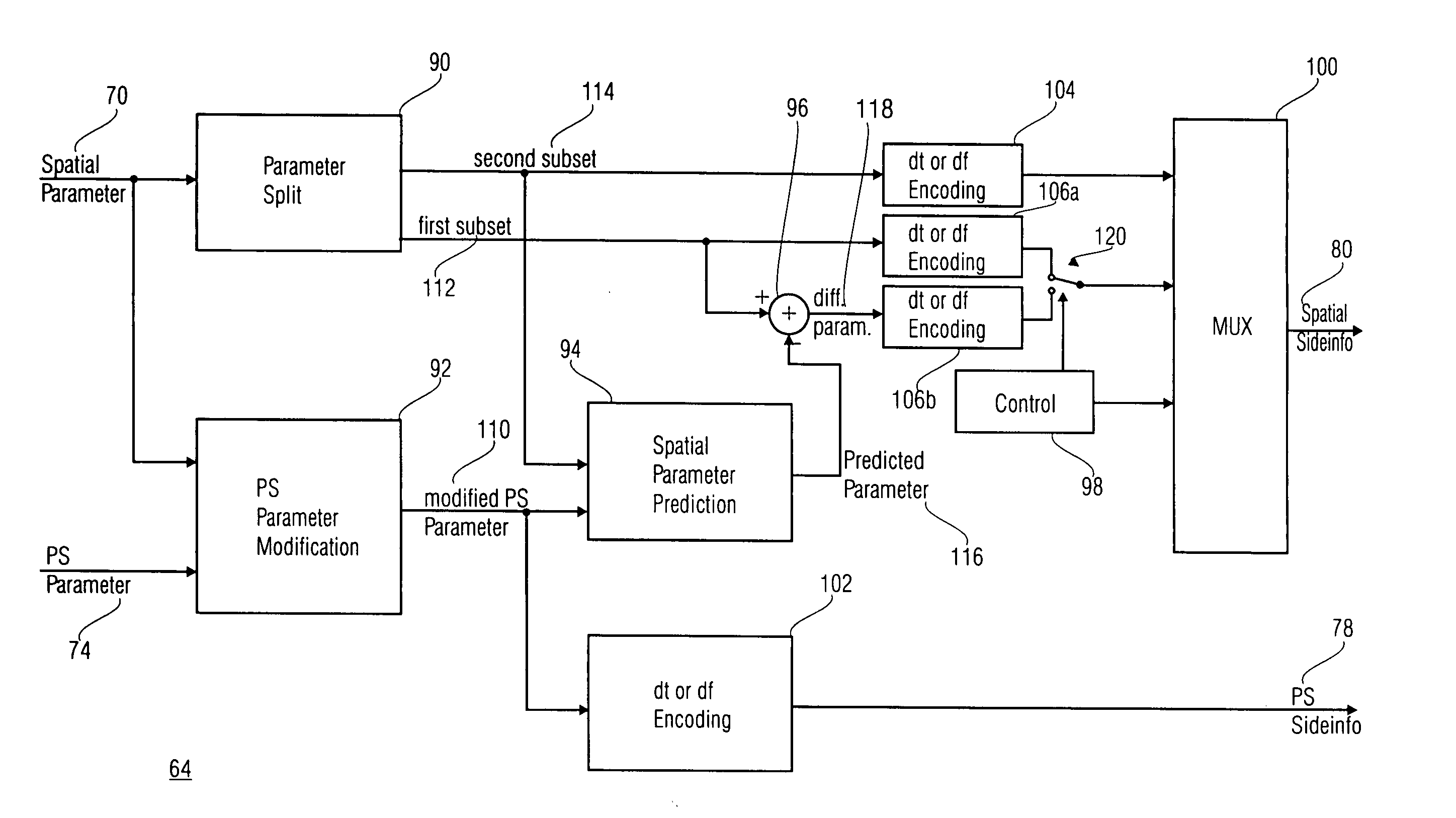
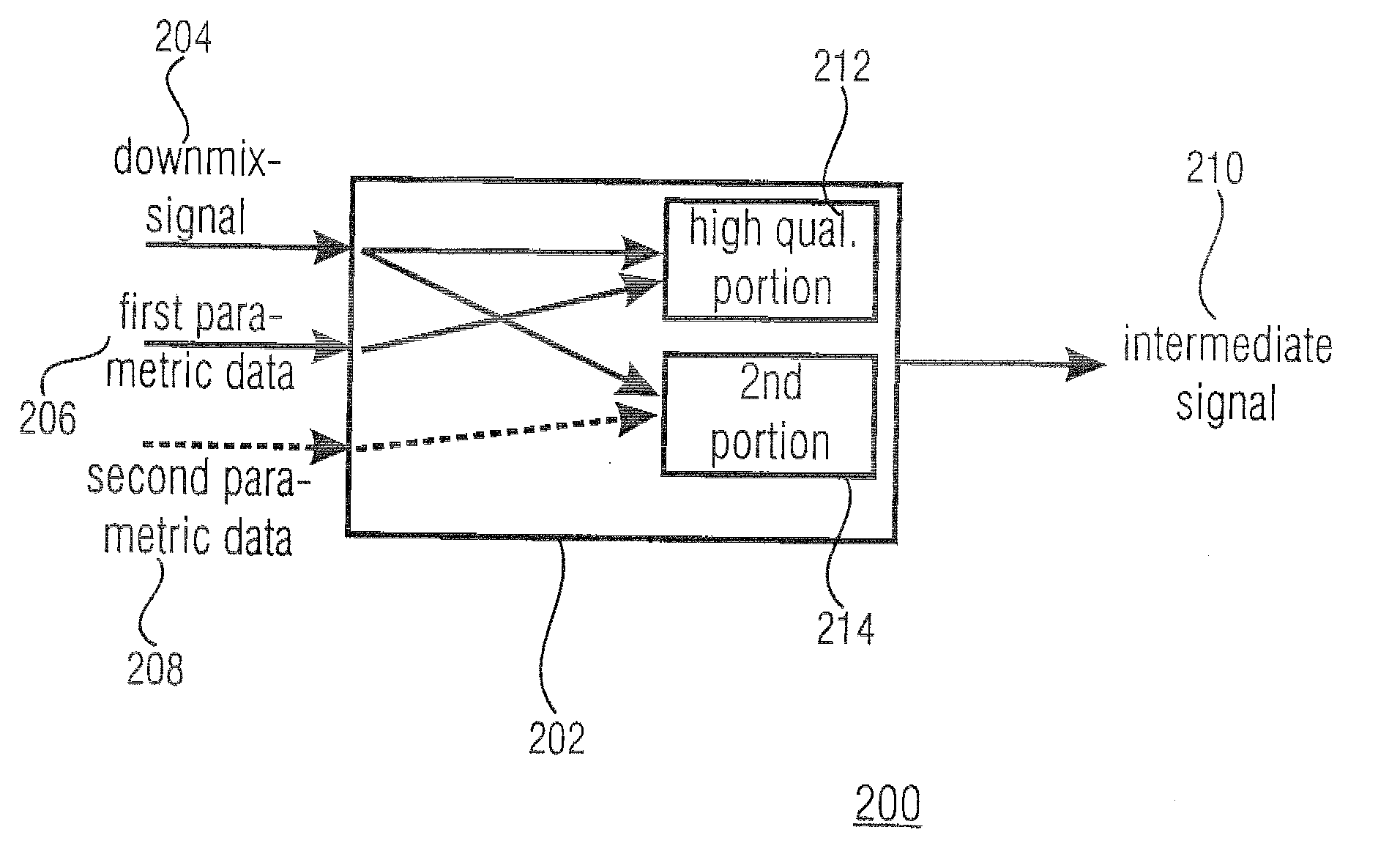
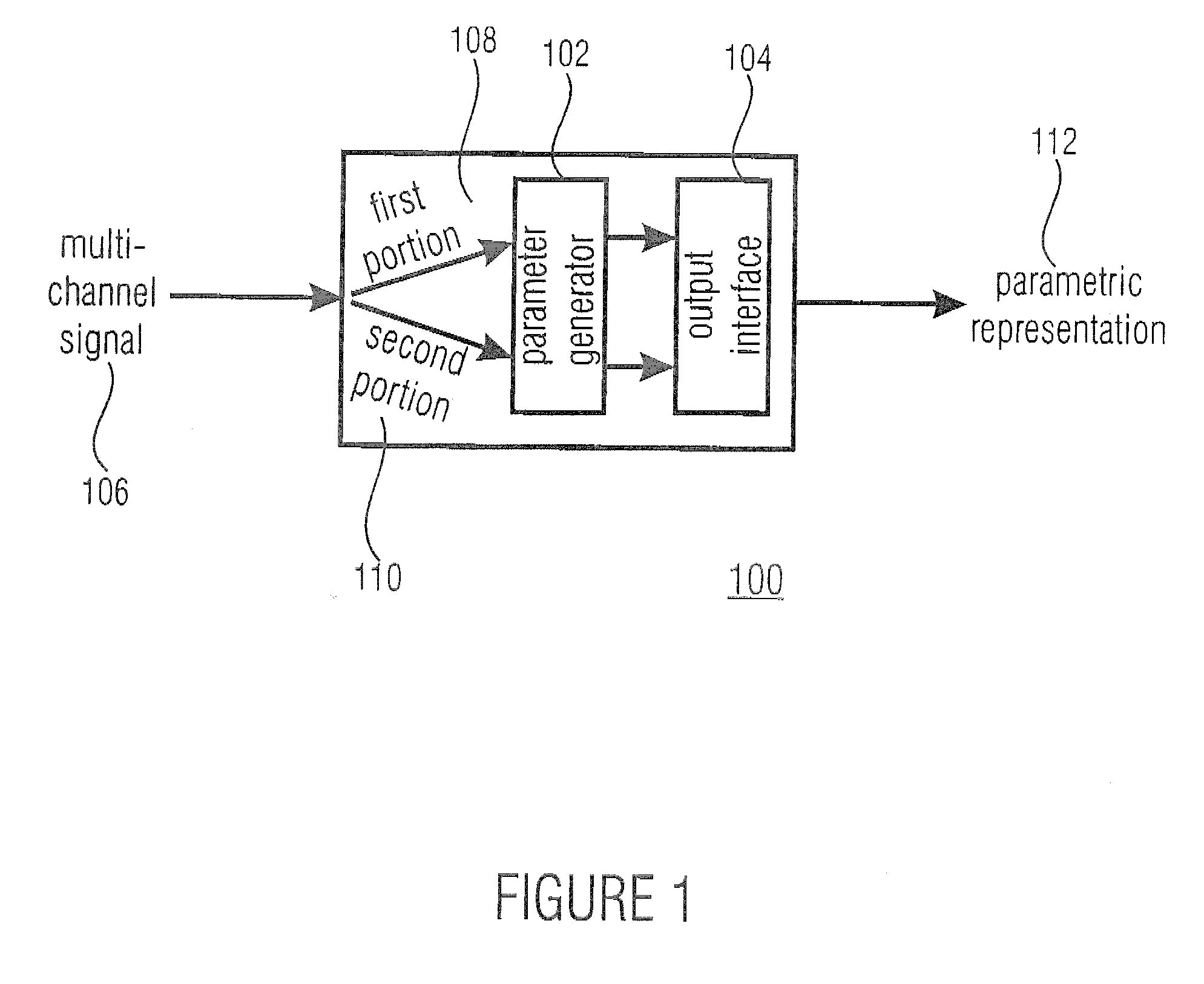
A parametric representation of a multi-channel audio signal having parameters suited to be used together with a monophonic downmix signal to calculate a reconstruction of the multi-channel audio signal can efficiently be derived in a stereo-backwards compatible way when a parameter combiner is used to generate the parametric representation by combining a one or more spatial parameters and a stereo parameter resulting in a parametric representation having a decoder usable stereo parameter and an information on the one or more spatial parameters that represents, together with the decoder usable stereo parameter, the one or more spatial parameters.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +2
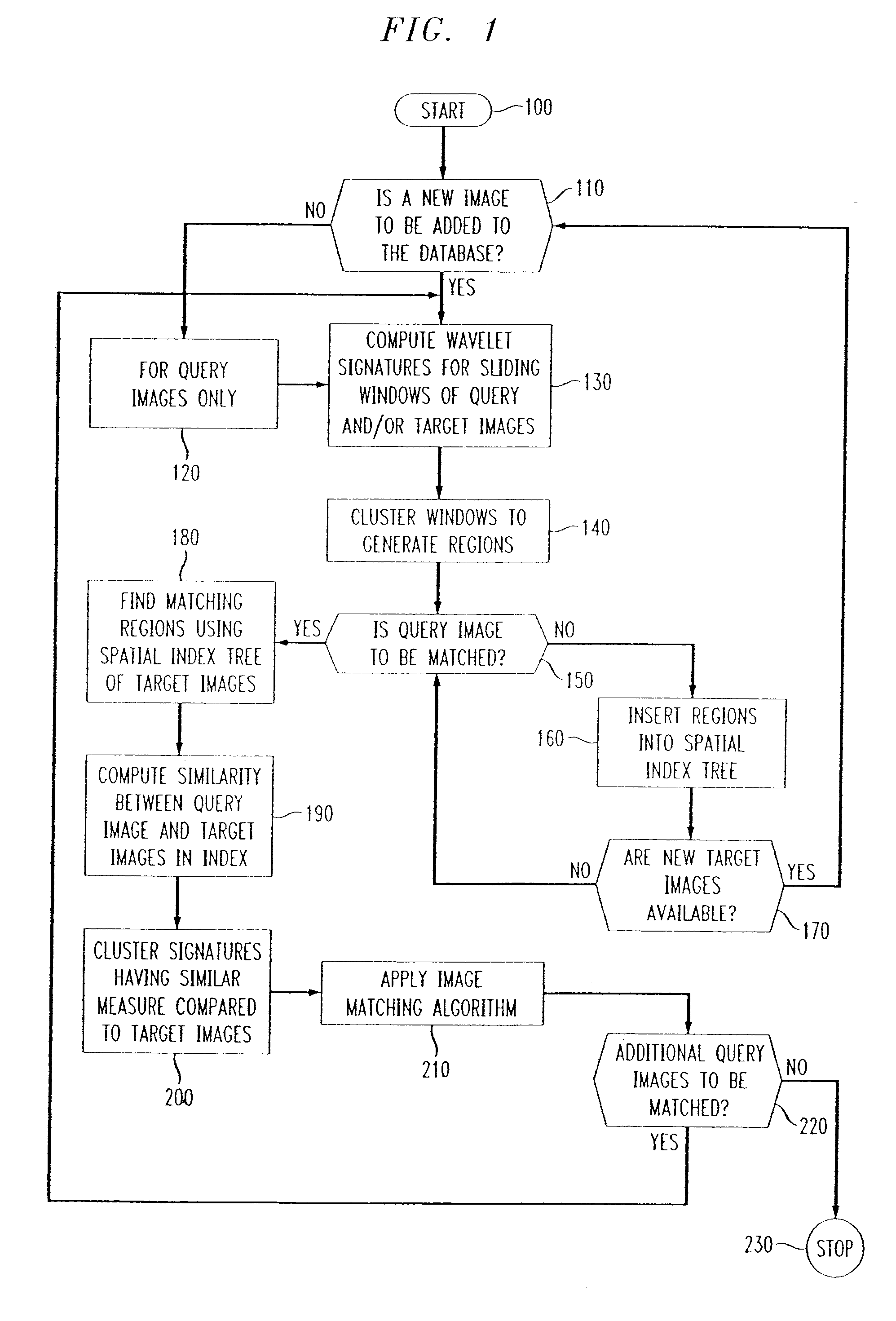
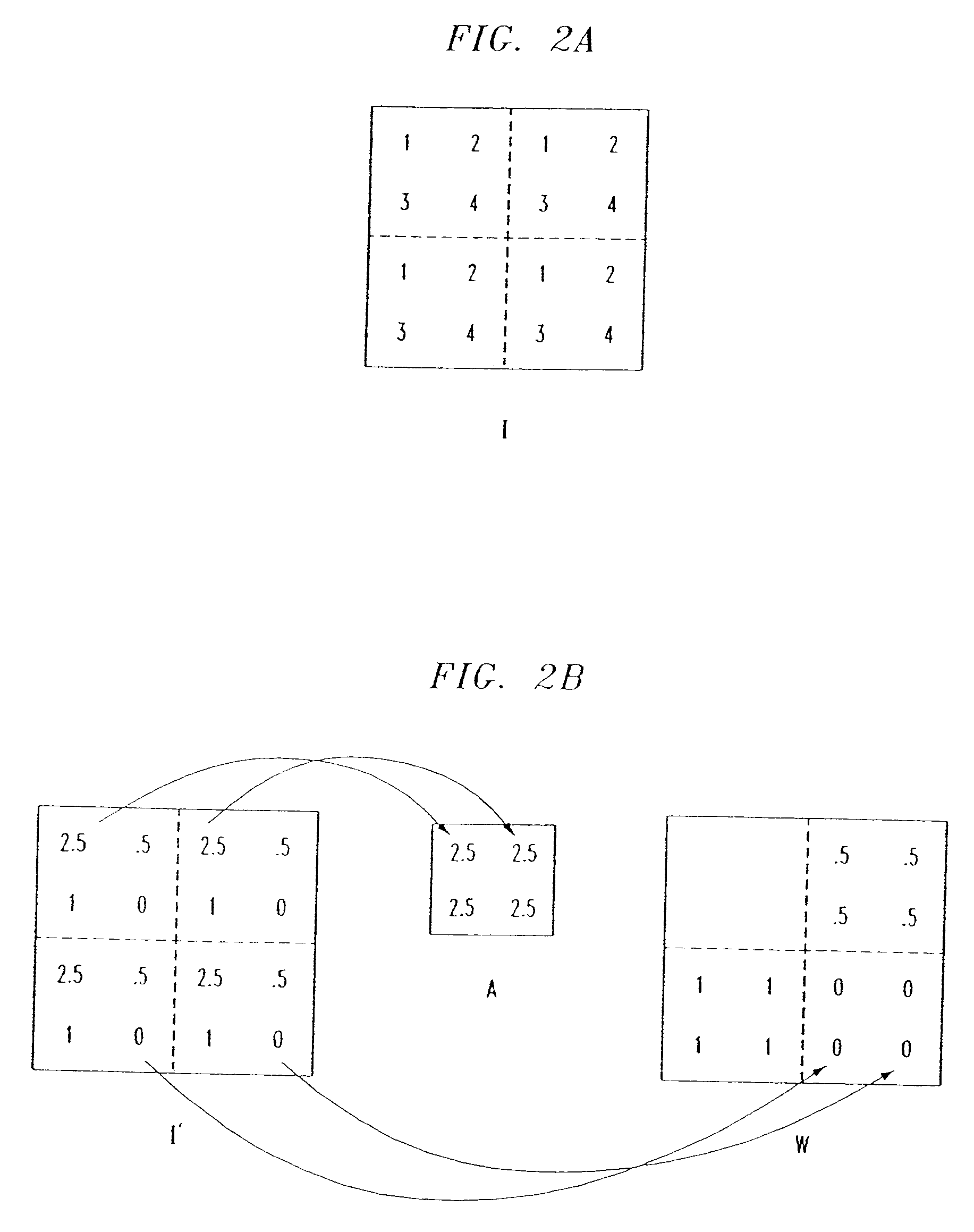
Methods of imaging based on wavelet retrieval of scenes
InactiveUS6751363B1Fast computerComputation taskData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature vectorObject based
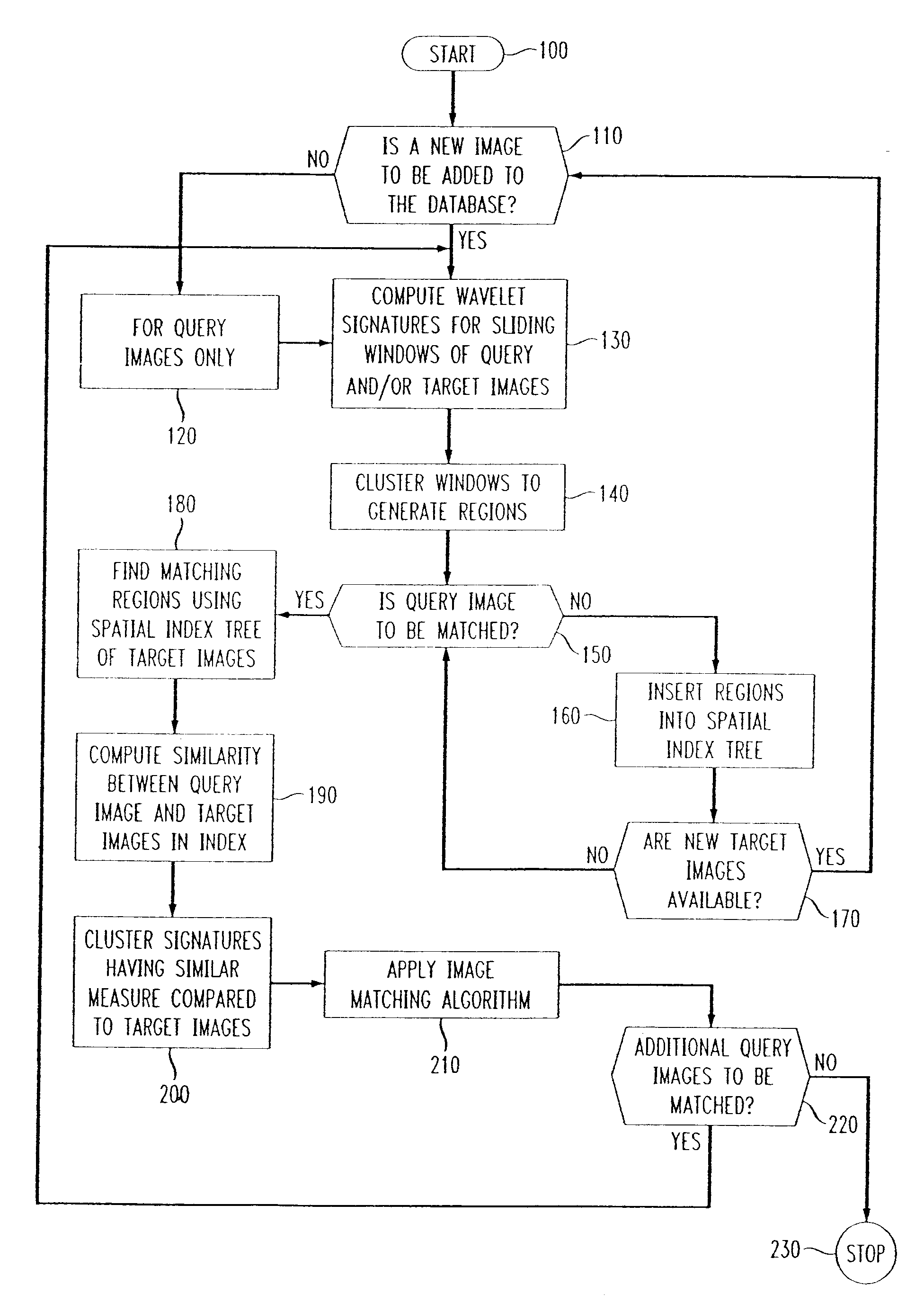
Methods of imaging objects based on wavelet retrieval of scenes utilize wavelet transformation of plural defined regions of a query image. By increasing the granularity of the query image to greater than one region, accurate feature vectors are obtained that allow for robust extraction of corresponding regions from a database of target images. The methods further include the use of sliding windows to decompose the query and target images into regions, and the clustering of the regions utilizing a novel similarity metric that ensures robust image matching in low response times.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
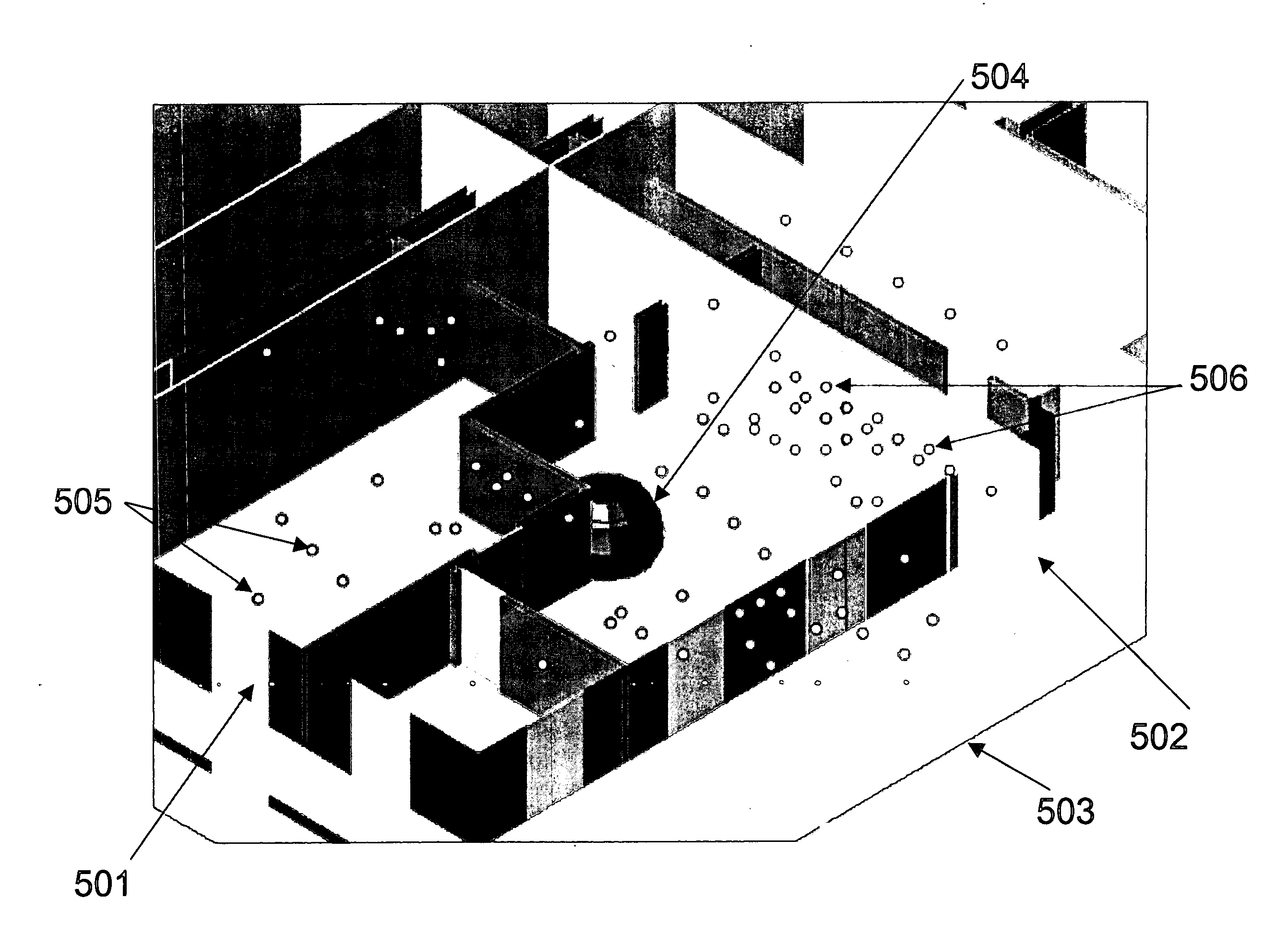
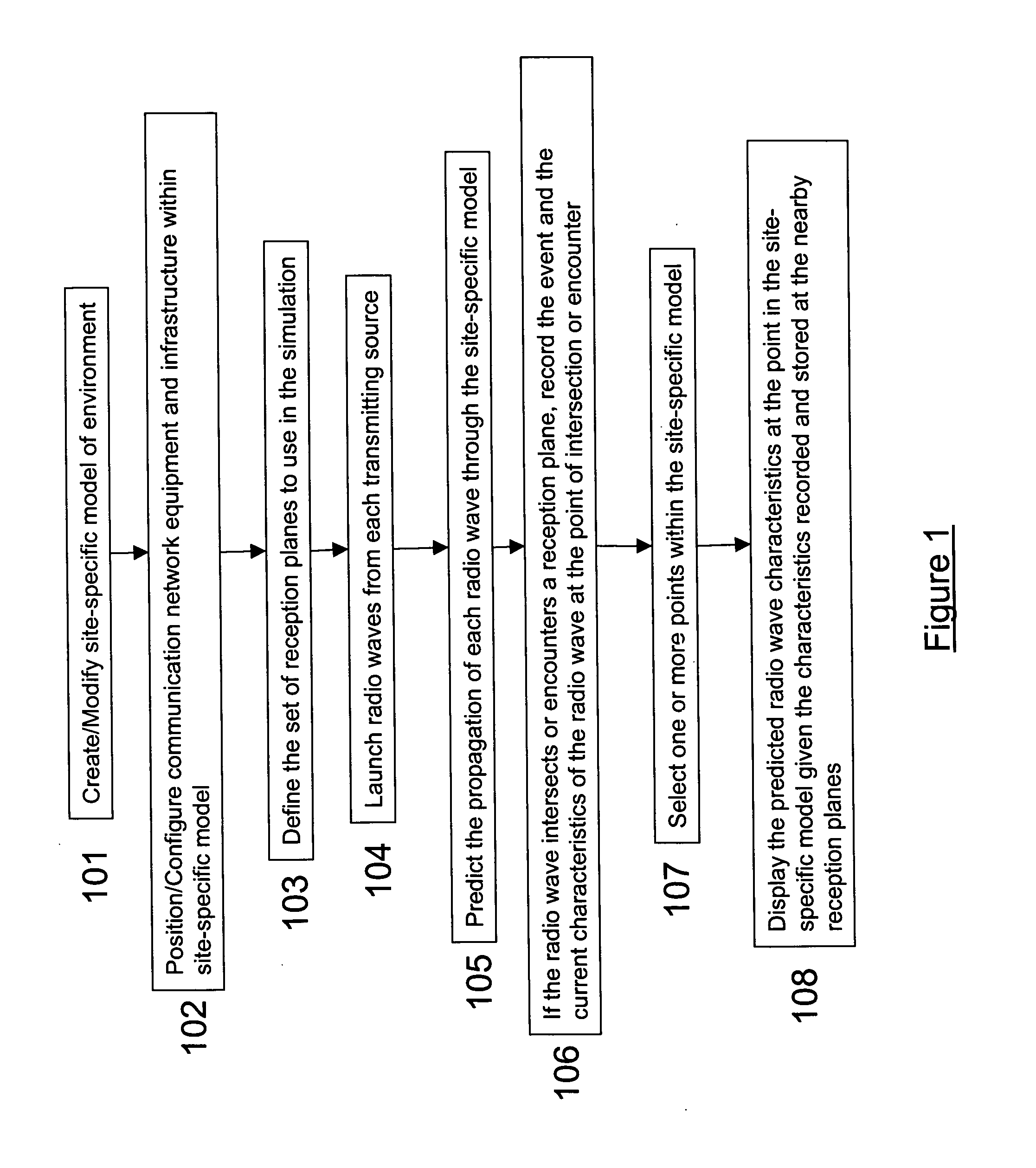
System and method for ray tracing using reception surfaces
InactiveUS20040259554A1Easy to explainQuickly and easily and inexpensivelyAntenna supports/mountingsNetwork planningSpecific modelRadio frequency
This invention provides a system and method for efficient ray tracing propagation prediction and analysis. Given a site-specific model of a physical environment, the present invention places virtual obstructions known as reception surfaces within the environment. As radio waves are predicted to propagate through the environment and intersect with or encounter reception surfaces, the characteristics of the radio wave are captured and stored relative to the location of the interaction with the reception surface. The radio frequency channel environment at any point within the site-specific model can be derived through analysis of the radio wave characteristics captured at nearby reception surfaces.
Owner:WIRELESS VALLEY COMM
Method and apparatus providing a graphical user interface for representing and navigating hierarchical networks
InactiveUS8185824B1Fast and efficientAvoid problemsDigital computer detailsData switching networksGraphical user interfaceGraphical user interface testing
A method and apparatus are provided which present hierarchical data to a user via a graphical user interface. In the interface, hierarchical data is represented by nodes, beginning with one or more top nodes and extending into lower hierarchical levels by the display of child nodes, child's child nodes, and so forth. The arrangement of nodes on the graphical user interface is such that scaling portrays the various hierarchical levels, and nodes do not spatially interfere with one another. Navigation through the hierarchical data is provided by allowing the user to select any visible node, at which point a zoom-in or zoom-out view to the selected node as a centrally located node on the interface is performed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
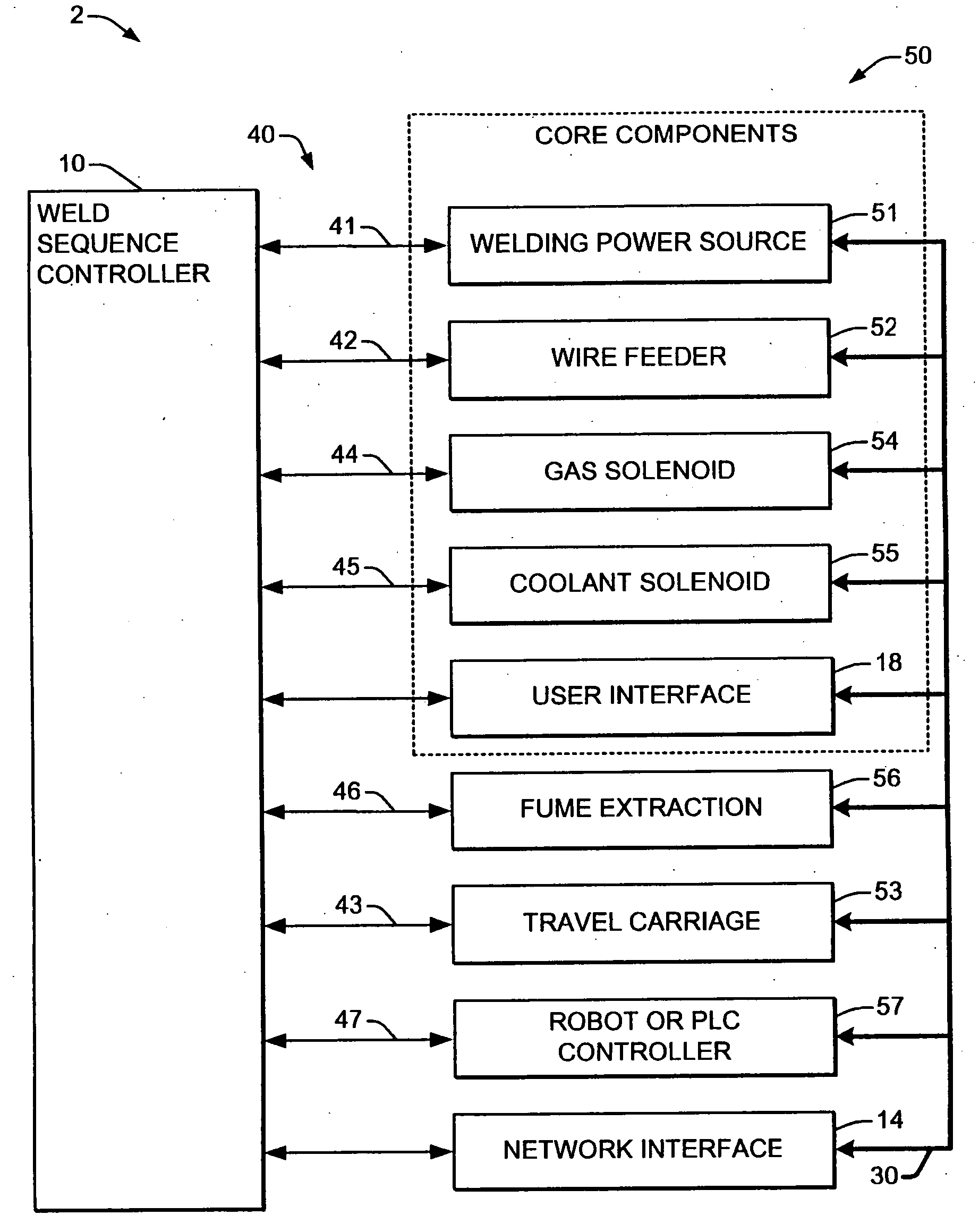
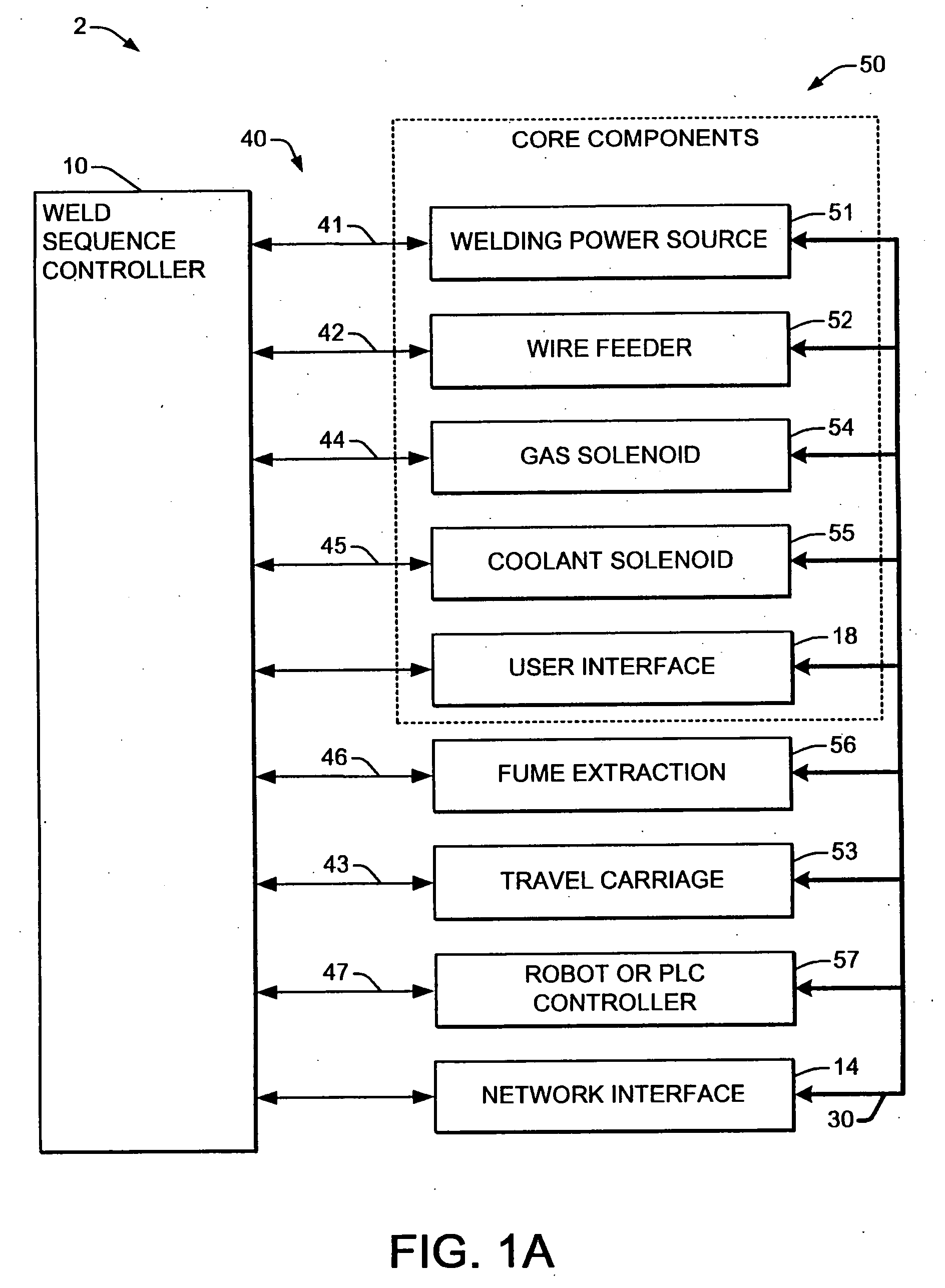
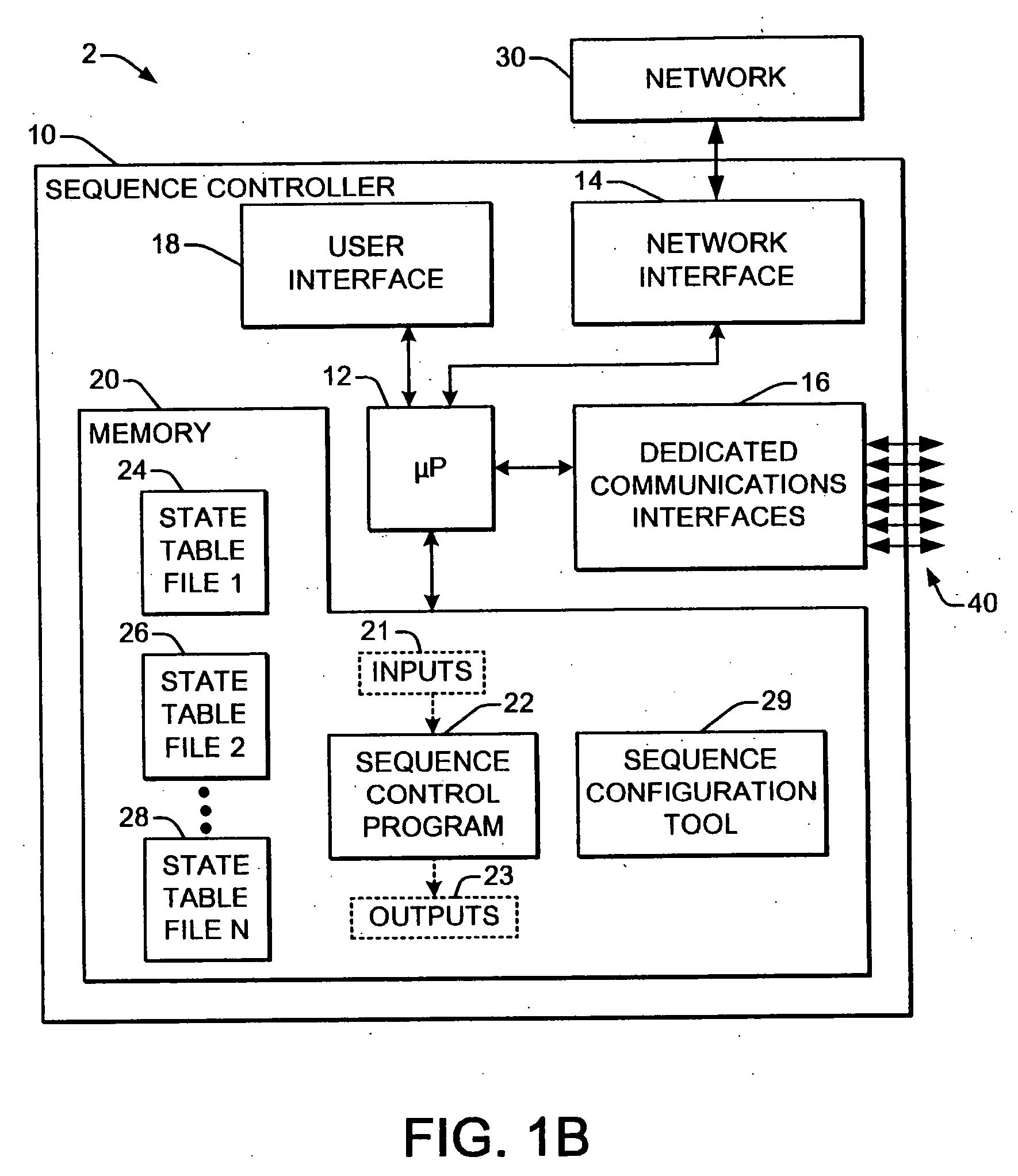
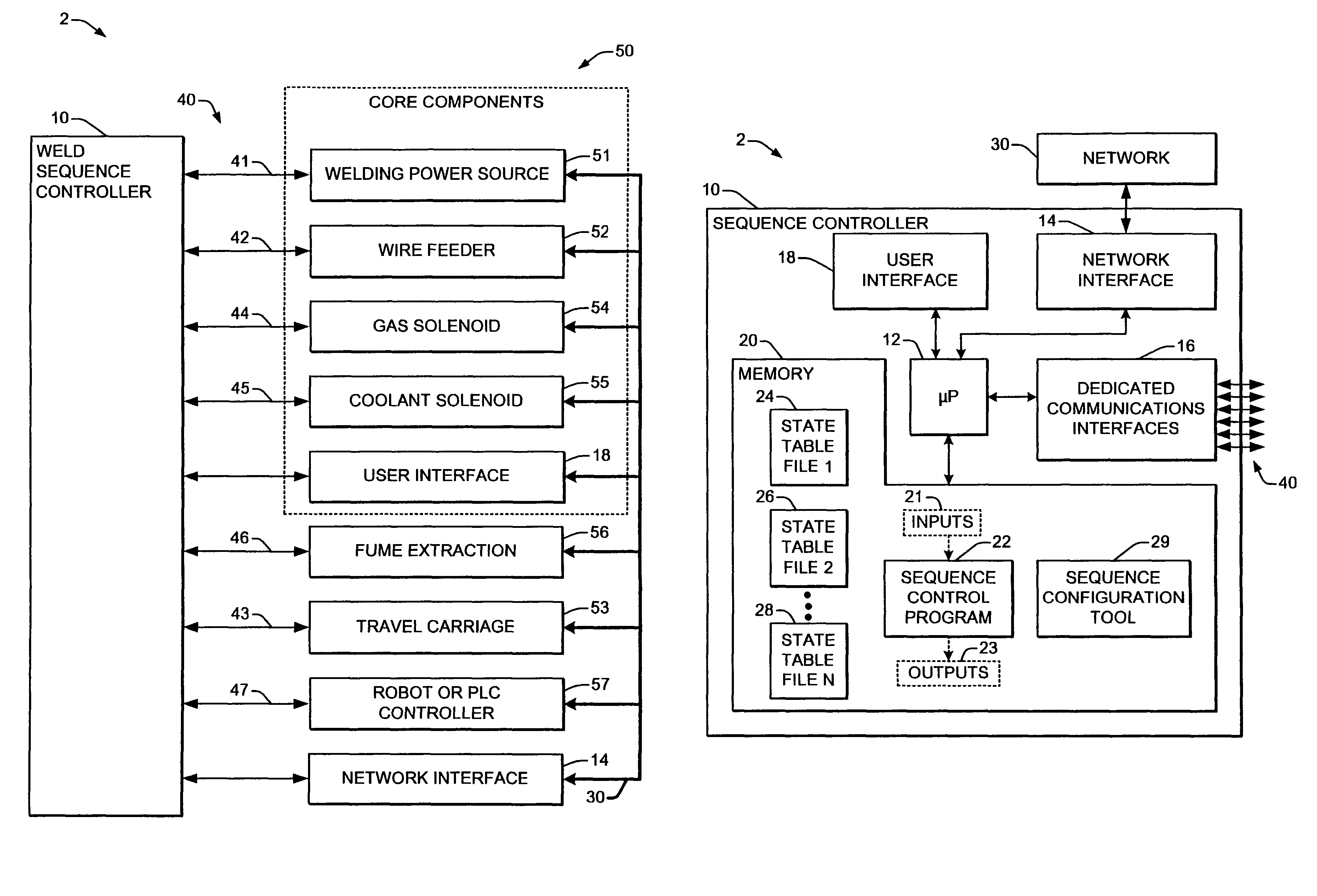
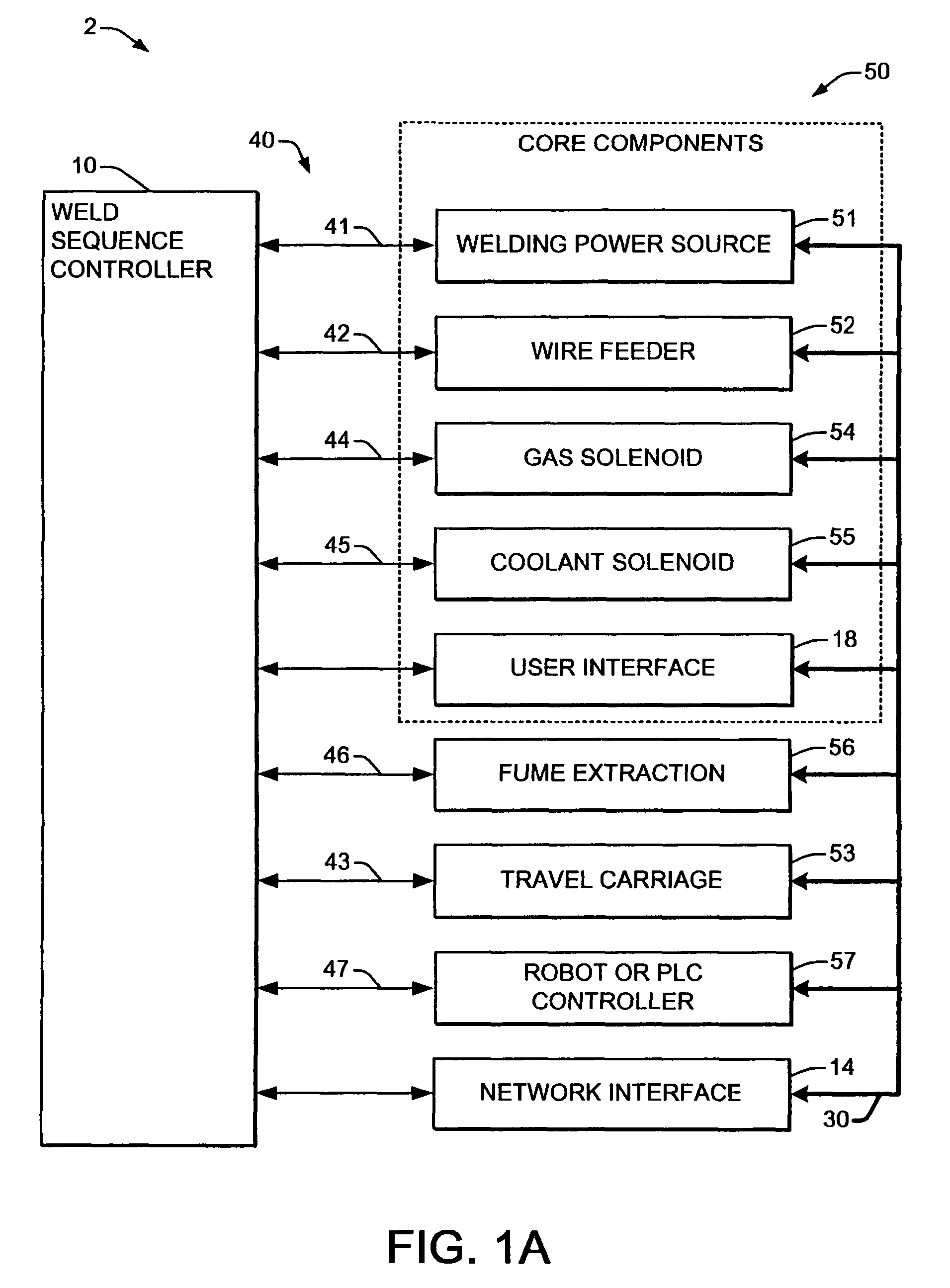
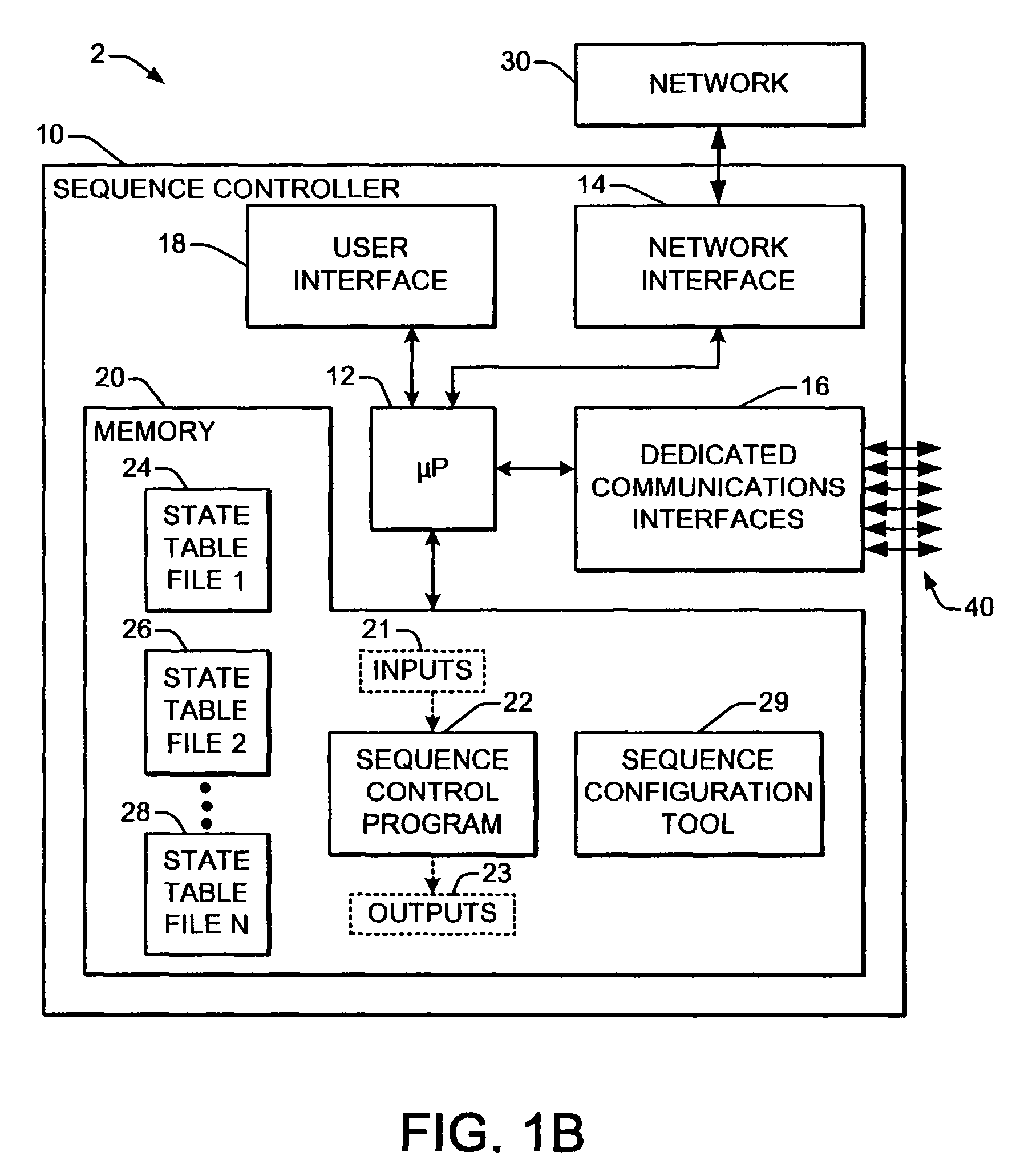
Welding system sequence control apparatus
ActiveUS20070056942A1Reprogram operationEfficient representationArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusSequence controlEngineering
Welding systems and sequence controllers therefor are presented for controlling components of a welding system during a welding operation. The sequence controller receives system inputs and provides control outputs to the system components, and includes a processing component, an executable sequence control program, and a state table file. The sequence control state table file includes a number of entries corresponding to welding operation states, where the individual entries comprise one or more instruction identifiers, instruction parameters, exit condition identifiers and corresponding next state identifiers. The sequence control program is executed according to the sequence controller inputs and according to the state table file to provide the sequence controller outputs, where the state table file can be easily modified or new state table files can be created and downloaded to the sequence controller to facilitate easy reconfiguration of a welding system.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Welding system sequence control apparatus
ActiveUS8692157B2Reprogram operationEfficient representationArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusSequence controlEngineering
Welding systems and sequence controllers therefor are presented for controlling components of a welding system during a welding operation. The sequence controller receives system inputs and provides control outputs to the system components, and includes a processing component, an executable sequence control program, and a state table file. The sequence control state table file includes a number of entries corresponding to welding operation states, where the individual entries comprise one or more instruction identifiers, instruction parameters, exit condition identifiers and corresponding next state identifiers. The sequence control program is executed according to the sequence controller inputs and according to the state table file to provide the sequence controller outputs, where the state table file can be easily modified or new state table files can be created and downloaded to the sequence controller to facilitate easy reconfiguration of a welding system.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
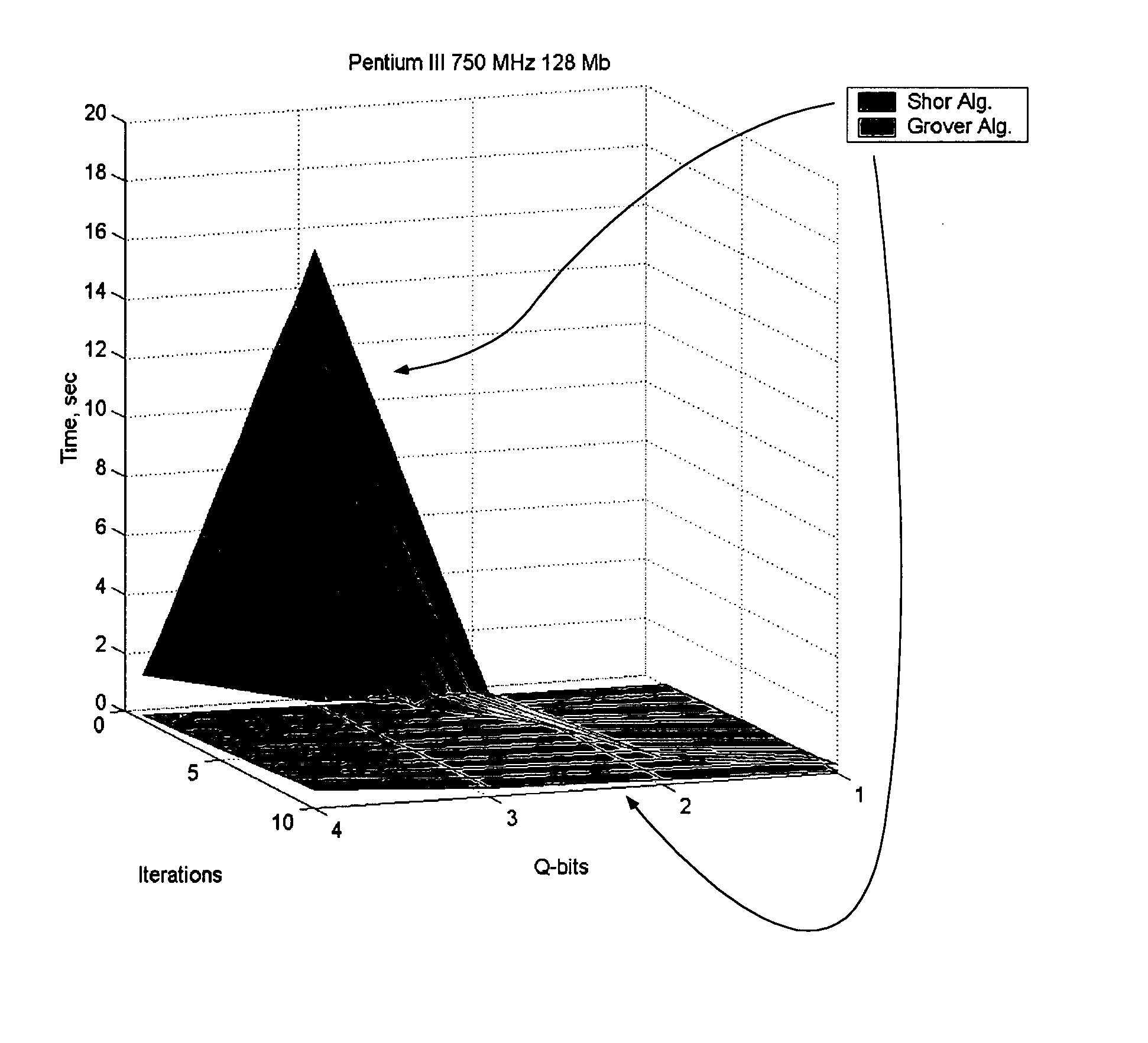
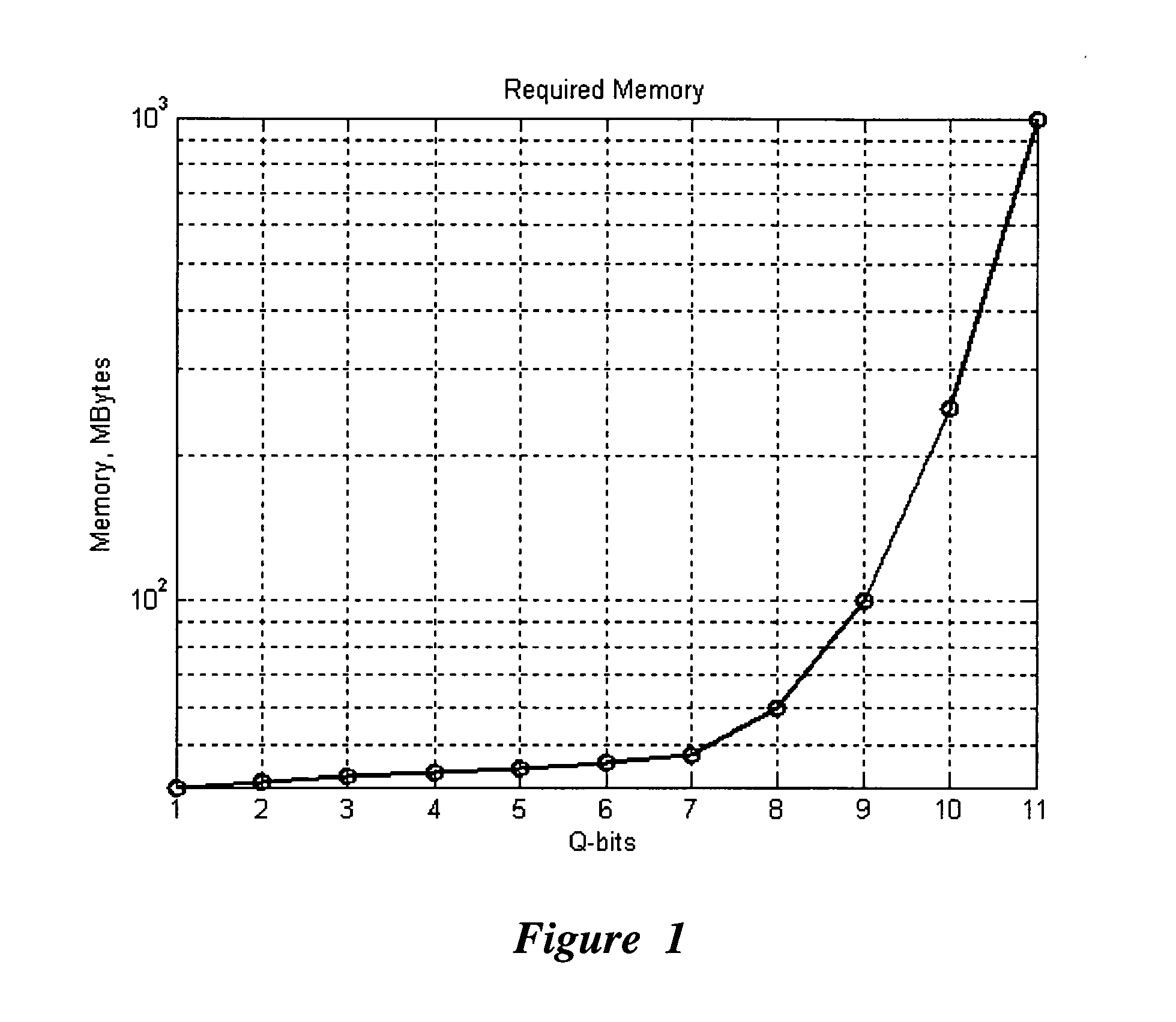
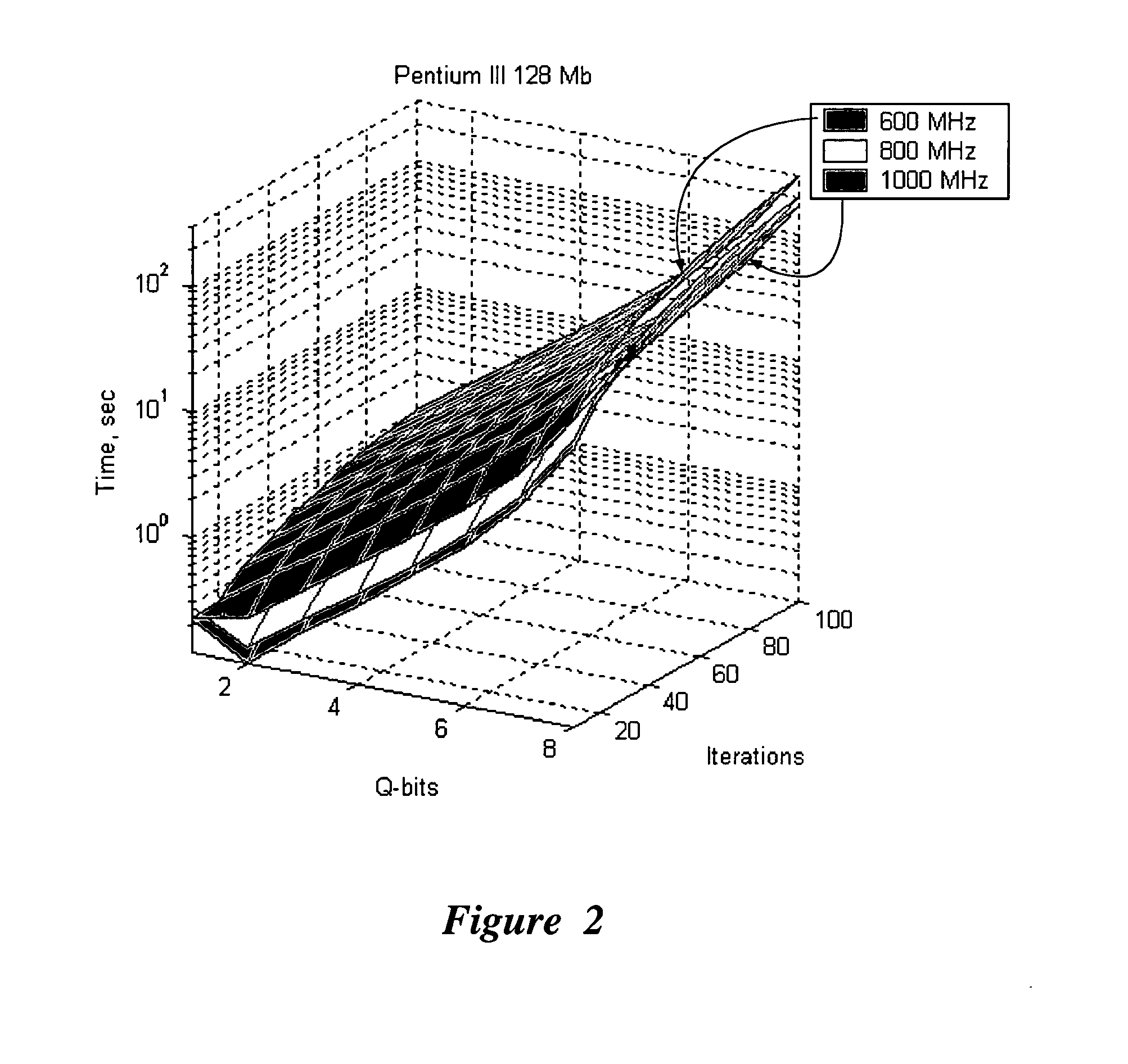
Efficient simulation system of quantum algorithm gates on classical computer based on fast algorithm
InactiveUS20060224547A1Effective simulationReduce in quantityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsFast algorithmMinimum entropy
An efficient simulation system of quantum algorithm gates for classical computers with a Von Neumann architecture is described. In one embodiment, a Quantum Algorithm is solved using an algorithmic-based approach, wherein matrix elements of the quantum gate are calculated on demand. In one embodiment, a problem-oriented approach to implementing Grover's algorithm is provided with a termination condition determined by observation of Shannon minimum entropy. In one embodiment, a Quantum Control Algorithm is solved by using a reduced number of quantum operations.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
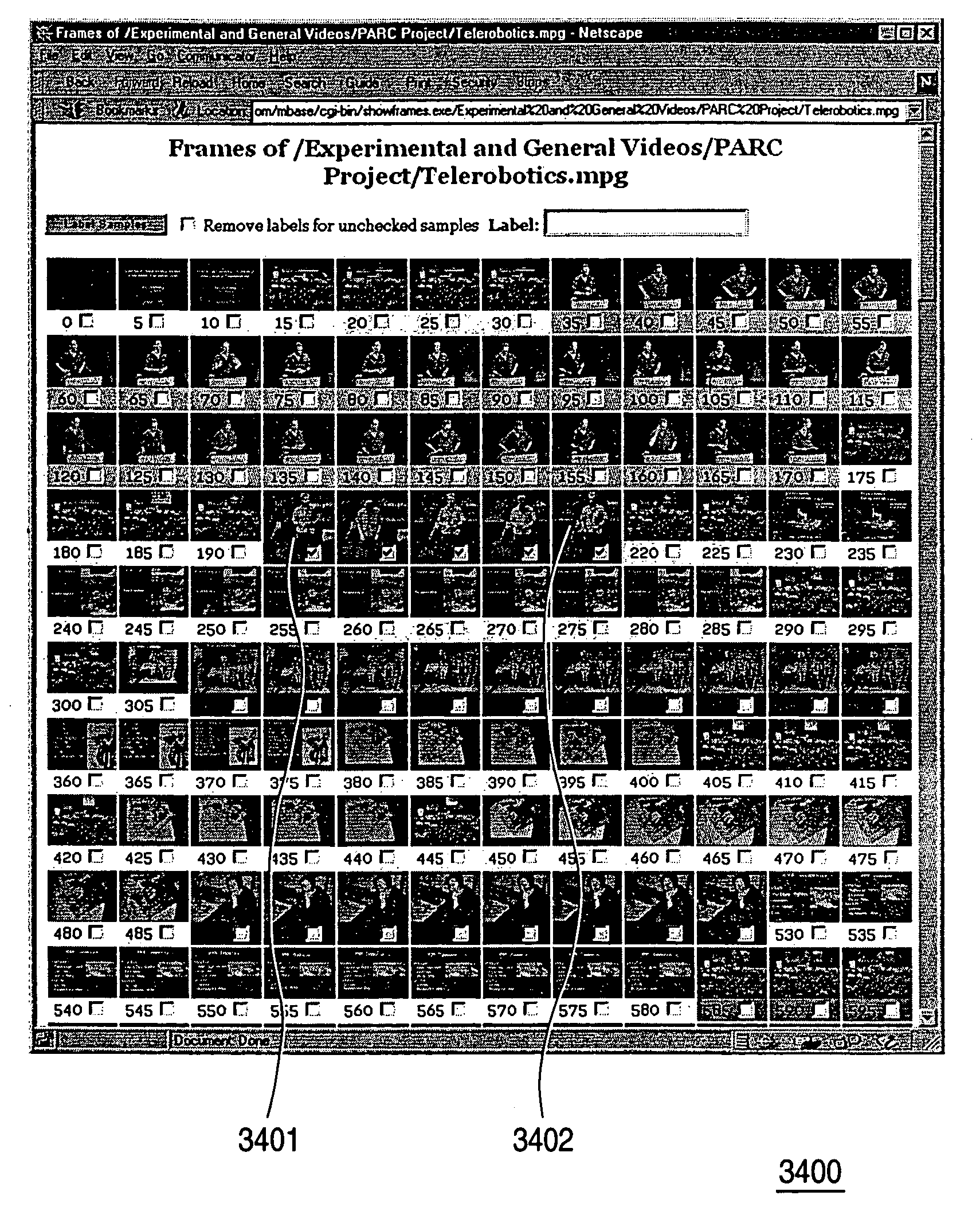
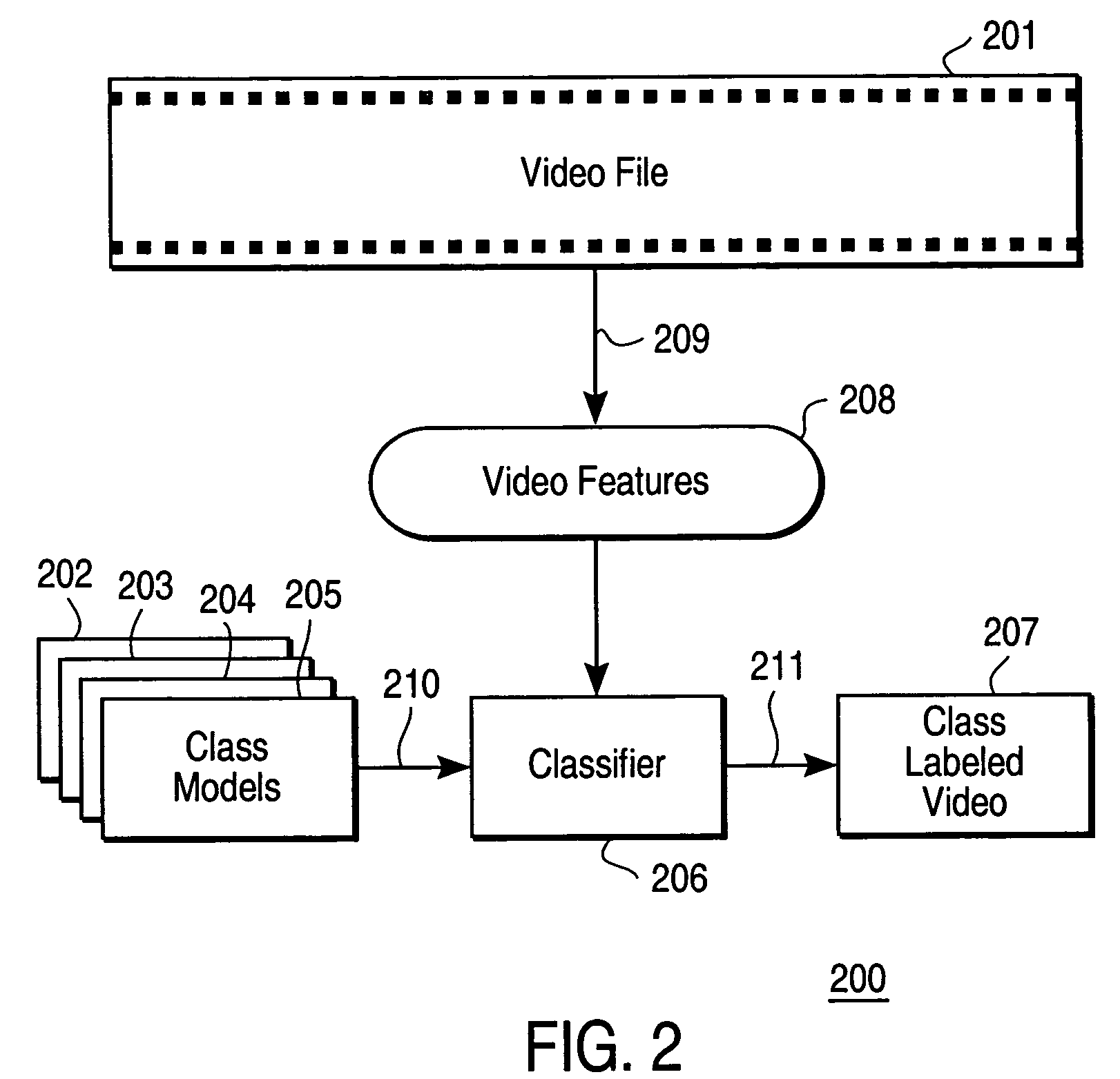
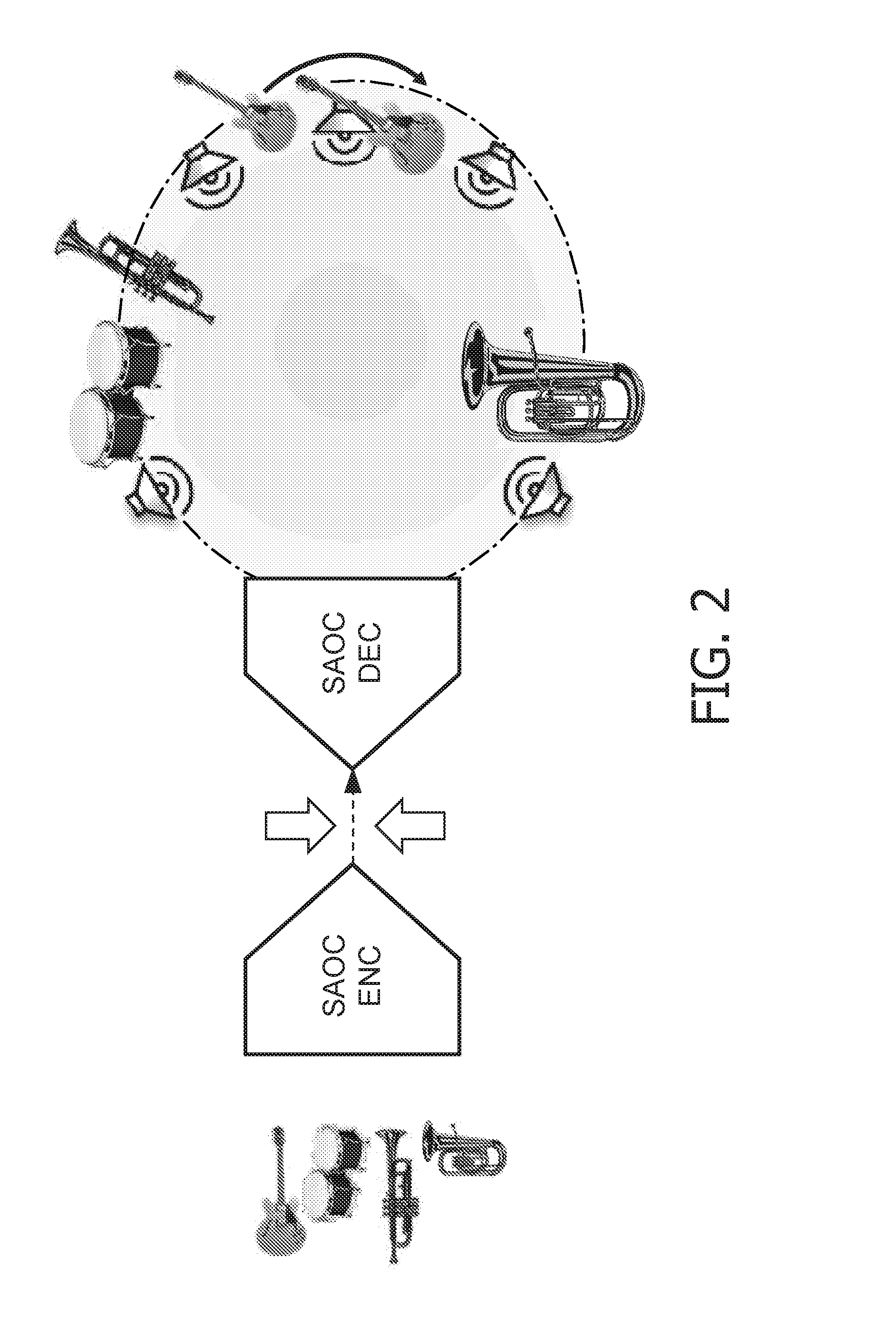
Methods and apparatuses for interactive similarity searching, retrieval and browsing of video
InactiveUS7246314B2Find quicklyQuick calculationTelevision system detailsImage analysisGraphicsFeature vector
Methods for interactive selecting video queries consisting of training images from a video for a video similarity search and for displaying the results of the similarity search are disclosed. The user selects a time interval in the video as a query definition of training images for training an image class statistical model. Time intervals can be as short as one frame or consist of disjoint segments or shots. A statistical model of the image class defined by the training images is calculated on-the-fly from feature vectors extracted from transforms of the training images. For each frame in the video, a feature vector is extracted from the transform of the frame, and a similarity measure is calculated using the feature vector and the image class statistical model. The similarity measure is derived from the likelihood of a Gaussian model producing the frame. The similarity is then presented graphically, which allows the time structure of the video to be visualized and browsed. Similarity can be rapidly calculated for other video files as well, which enables content-based retrieval by example. A content-aware video browser featuring interactive similarity measurement is presented. A method for selecting training segments involves mouse click-and-drag operations over a time bar representing the duration of the video; similarity results are displayed as shades in the time bar. Another method involves selecting periodic frames of the video as endpoints for the training segment.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP +1
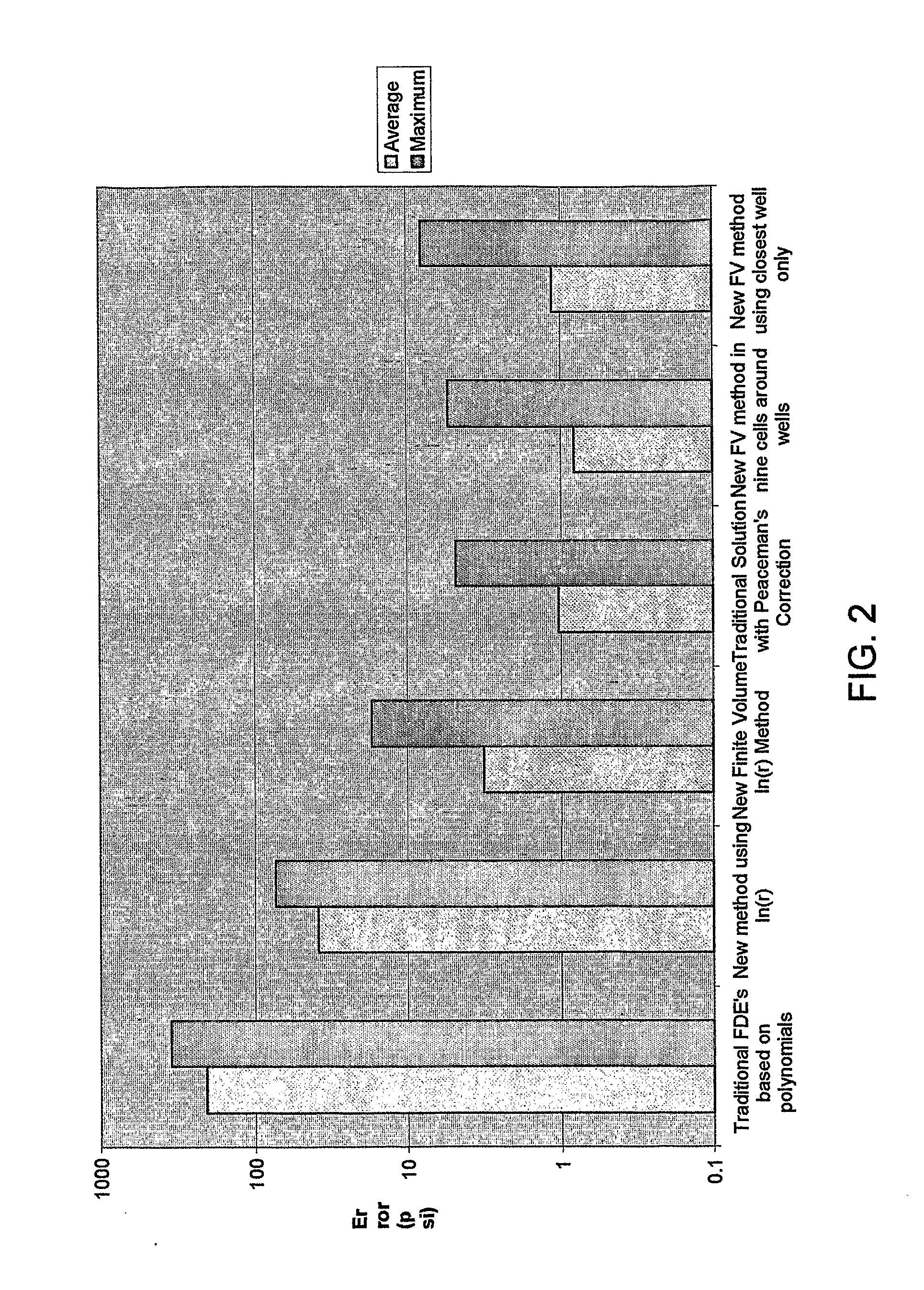
Reservoir Simulation
InactiveUS20080167849A1Easy to predictIncrease speedFluid removalMaterial testing goodsFinite difference methodInjection well
Owner:HALES HUGH
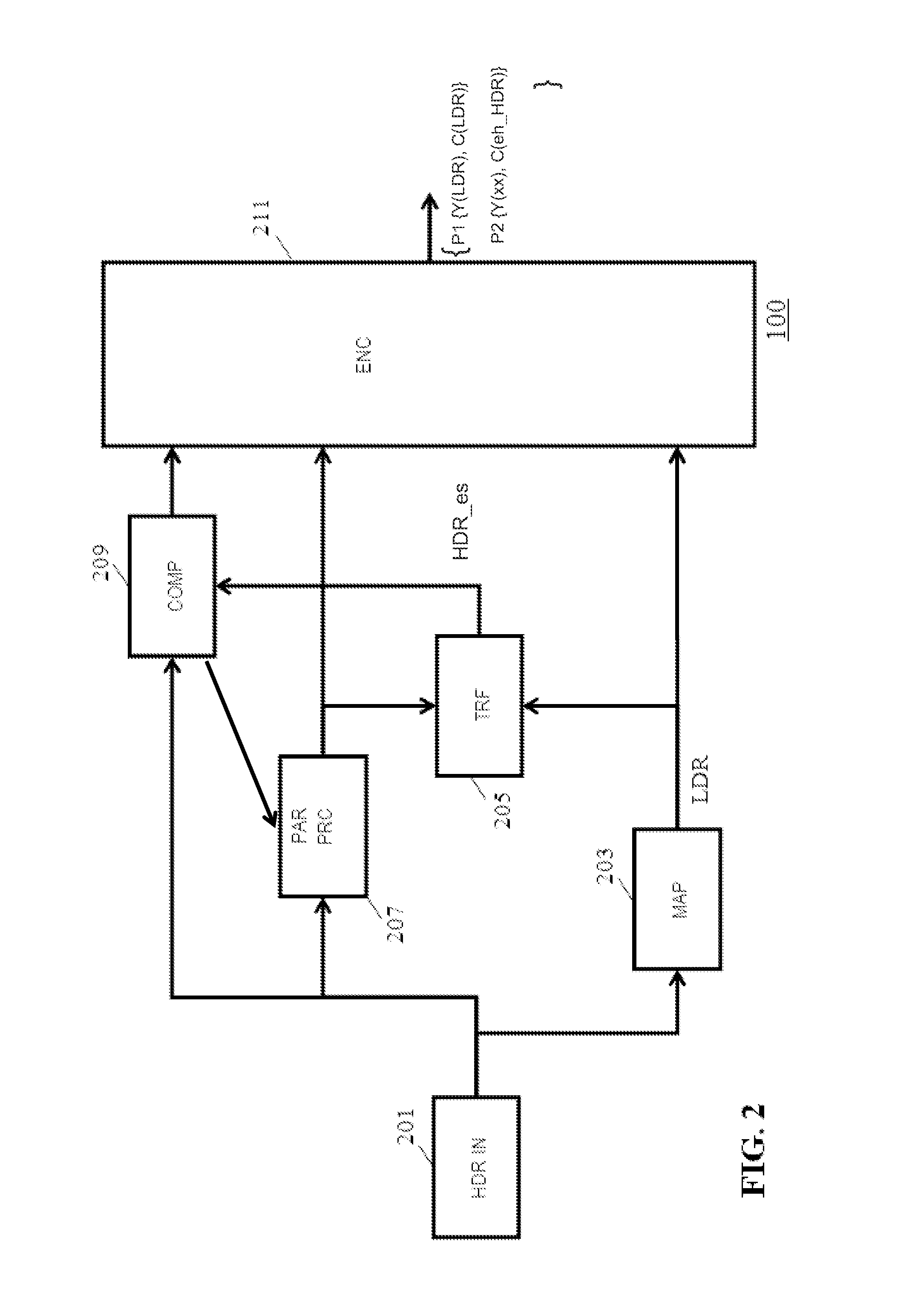
Method and apparatus for generating an image coding signal
InactiveUS20140037206A1Efficient representationImage increaseImage enhancementImage analysisImage codePixelation
An apparatus generates an image coding signal comprising for each image a first pixelised picture and a second pixelised picture having a luminance component and a chroma component. The apparatus comprises a first picture processor (203, 211) which includes image encoding data for an encoded first image in the first pixelised picture. A second picture processor (205, 207, 209, 211) includes dynamic range extension data in the second pixelised picture. The dynamic range extension data may be dynamic range extension data included in a chroma component of the second pixelised picture for generating an increased dynamic range image on the basis of the encoded first image. The compensation data may e.g. be compensation data for correcting another LDR-to-HDR transform, e.g. a prefixed global gamma transformation. The dynamic range extension data may be included in a luminance component and comprise data representing a dynamic range extension transform for generating an increased dynamic range image from the encoded first image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Stereo compatible multi-channel audio coding
A parametric representation of a multi-channel audio signal having parameters suited to be used together with a monophonic downmix signal to calculate a reconstruction of the multi-channel audio signal can efficiently be derived in a stereo-backwards compatible way when a parameter combiner is used to generate the parametric representation by combining a one or more spatial parameters and a stereo parameter resulting in a parametric representation having a decoder usable stereo parameter and an information on the one or more spatial parameters that represents, together with the decoder usable stereo parameter, the one or more spatial parameters.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +2
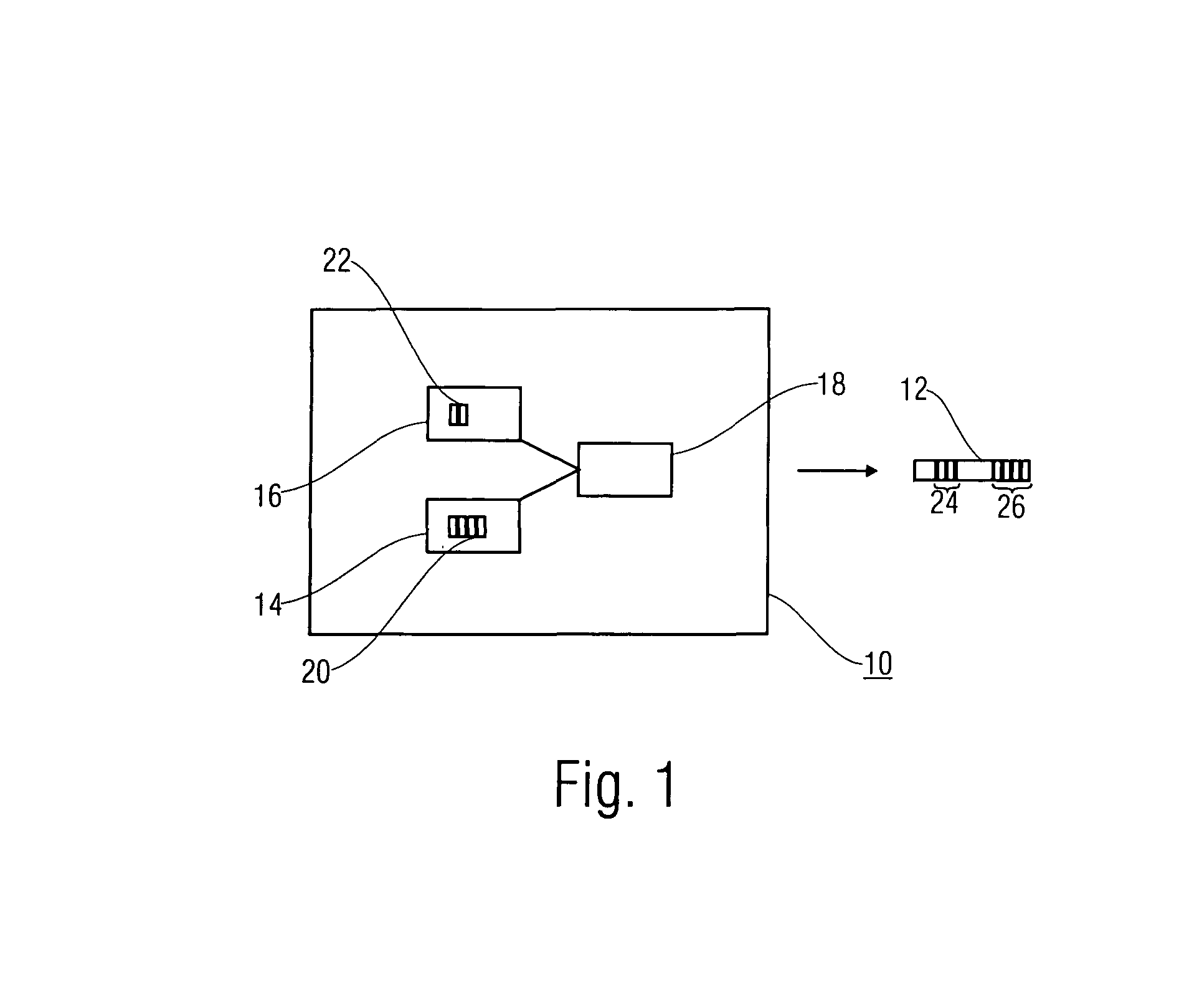
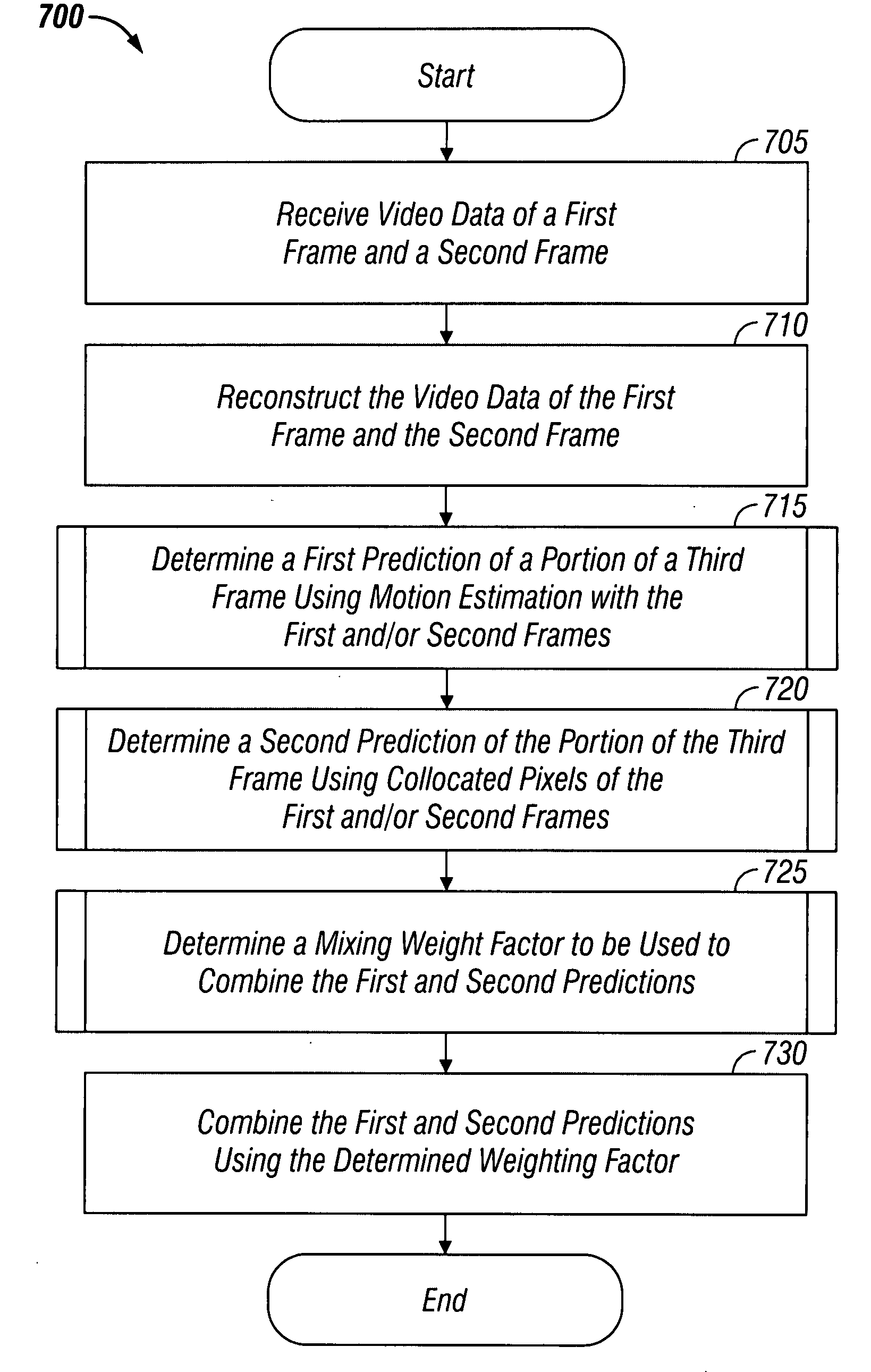
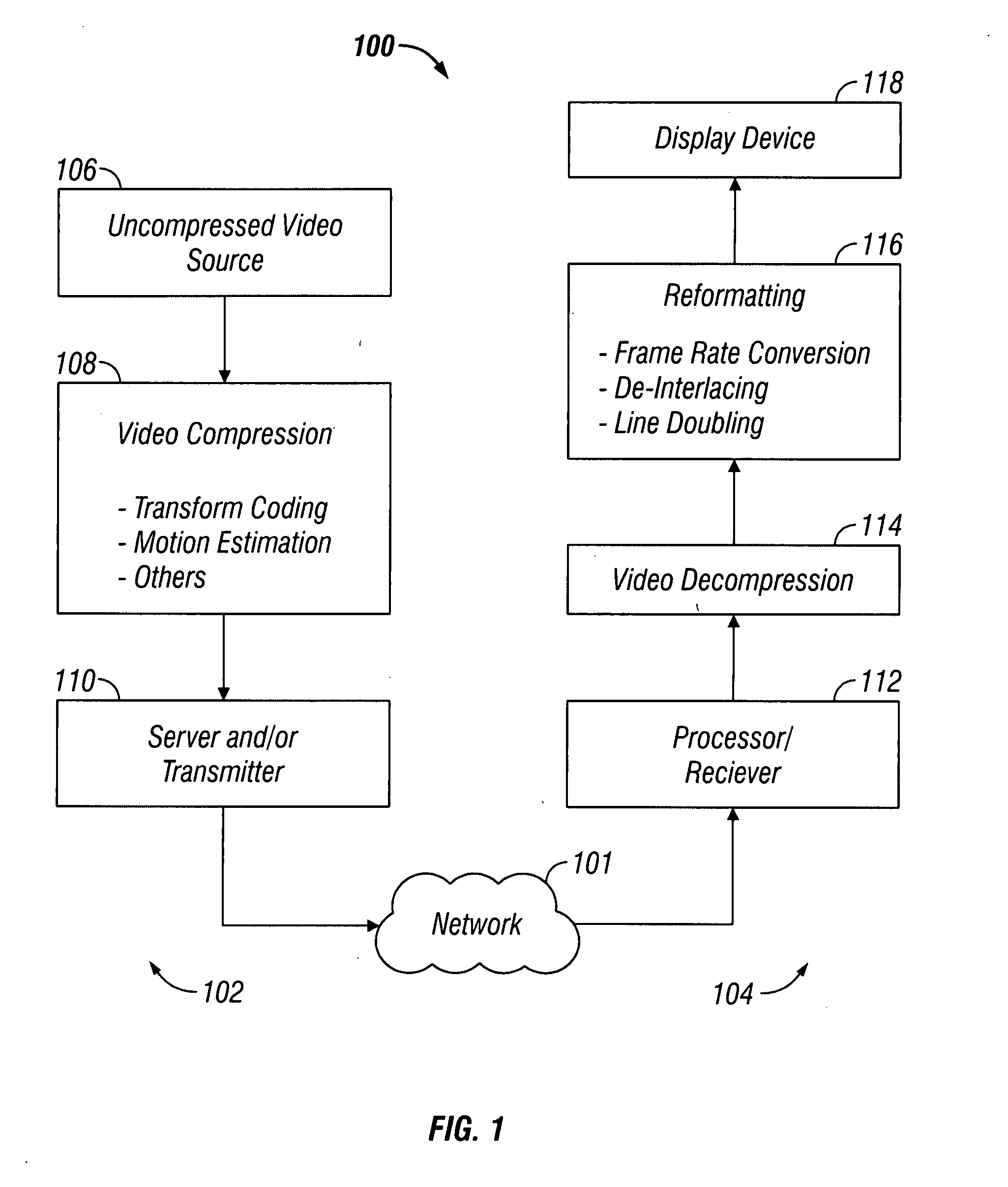
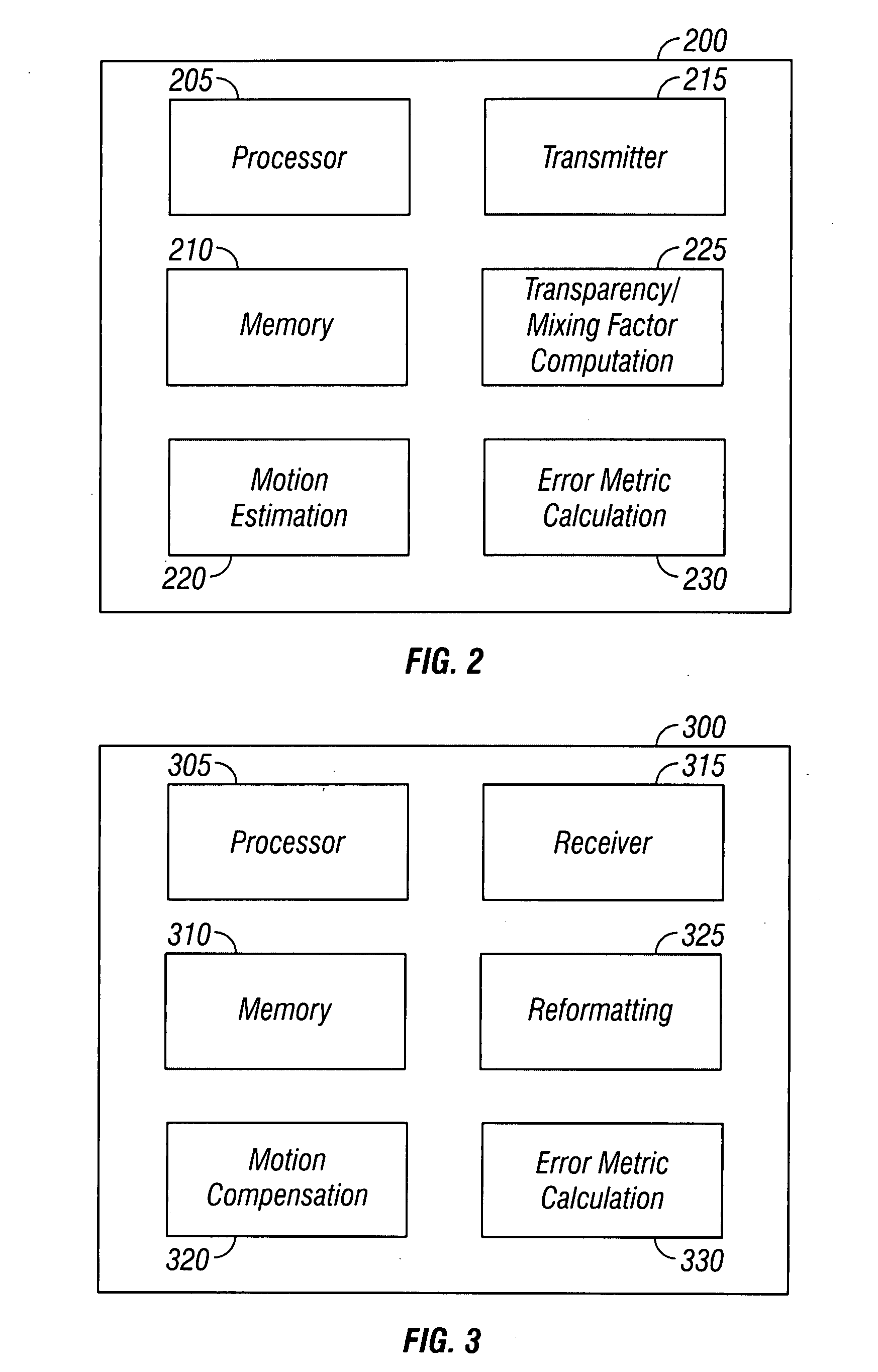
System and method for introducing virtual zero motion vector candidates in areas of a video sequence involving overlays
InactiveUS20080198931A1Stable display of videoEfficient representationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionWeight factorMotion vector
Systems and methods for efficiently encoding and / or reformatting video data including transparent overlay portions are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes using two prediction regions for predicting the portion of the video including the transparent overlay. In one embodiment, a first of the two prediction regions is determined based on motion compensated prediction in reference to another video frame and a second of the two prediction regions is a collocated portion of video in another frame as referenced by a virtual zero motion vector. A mixing weight factor to be used for combining the two predictions is determined. In one embodiment, the mixing weight factor is determined based on the relative values of two error metrics, a first error metric related to the motion compensated prediction and a second error metric related to the collocated prediction of the virtual zero motion vector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
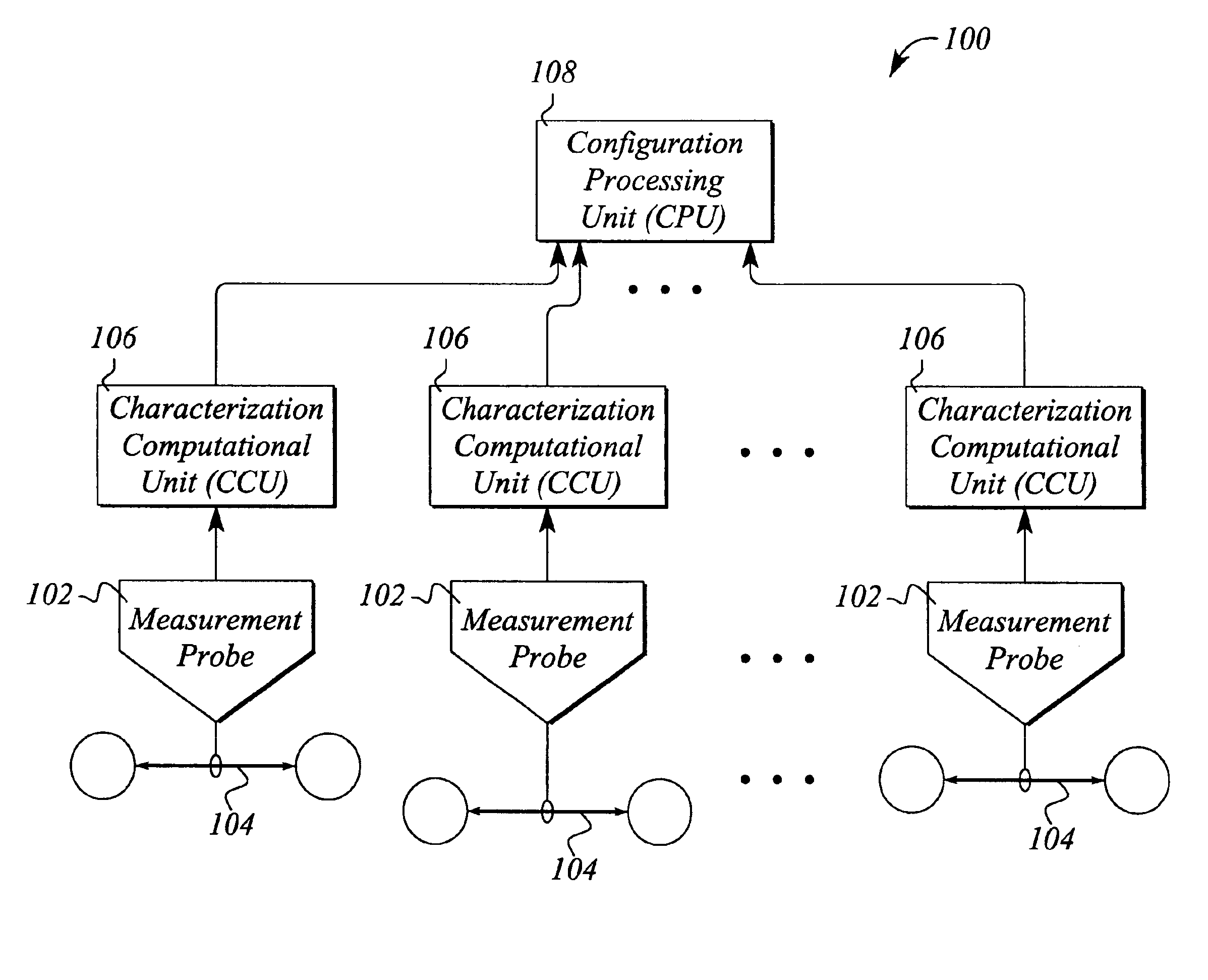
System and method for monitoring communication networks using data stream characterization
InactiveUS6904020B1Efficient representationReduced availabilityError preventionTransmission systemsData streamIndividual data
A system and method for automatically monitoring communications networks and for determining network configuration use data stream characterizations. The system comprises a plurality of measurement probes that passively probe the network and collect data packets carried by data streams in the network. The system further comprises characterization computational units that process the collected data packets and produce data stream characterizations from the collected data packets. The data stream characterizations represent individual data streams in an arbitrarily unique manner. The system still further comprises a configuration processing unit that compares data stream characterizations taken at different points in the network and determines data stream paths through the network based on data stream characterization matching. The method for automatically monitoring communications networks comprises the steps of passively probing the data streams to produce sets of collected data packets from the data streams, determining data stream characterizations from the collected data packets, and comparing the data stream characterizations to one another to identify matching characterizations.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Concept for bridging the gap between parametric multi-channel audio coding and matrixed-surround multi-channel coding
ActiveUS20070019813A1Efficient representationLittle informationSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsTelecommunicationsAudio frequency
The purpose of the invention is to bridge the gap between parametric multi-channel audio coding and matrixed-surround multi-channel coding by gradually improving the sound of an up-mix signal while raising the bit-rate consumed by the side-information starting from 0 up to the bit-rates of the parametric methods. More specifically, it provides a method of flexibly choosing an “operating point” somewhere between matrixed-surround (no side-information, limited audio quality) and fully parametric reconstruction (full side-information rate required, good quality). This operating point can be chosen dynamically (i.e. varying over time) and in response to the permissible side-information rate, as it is dictated by the individual application.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP +1
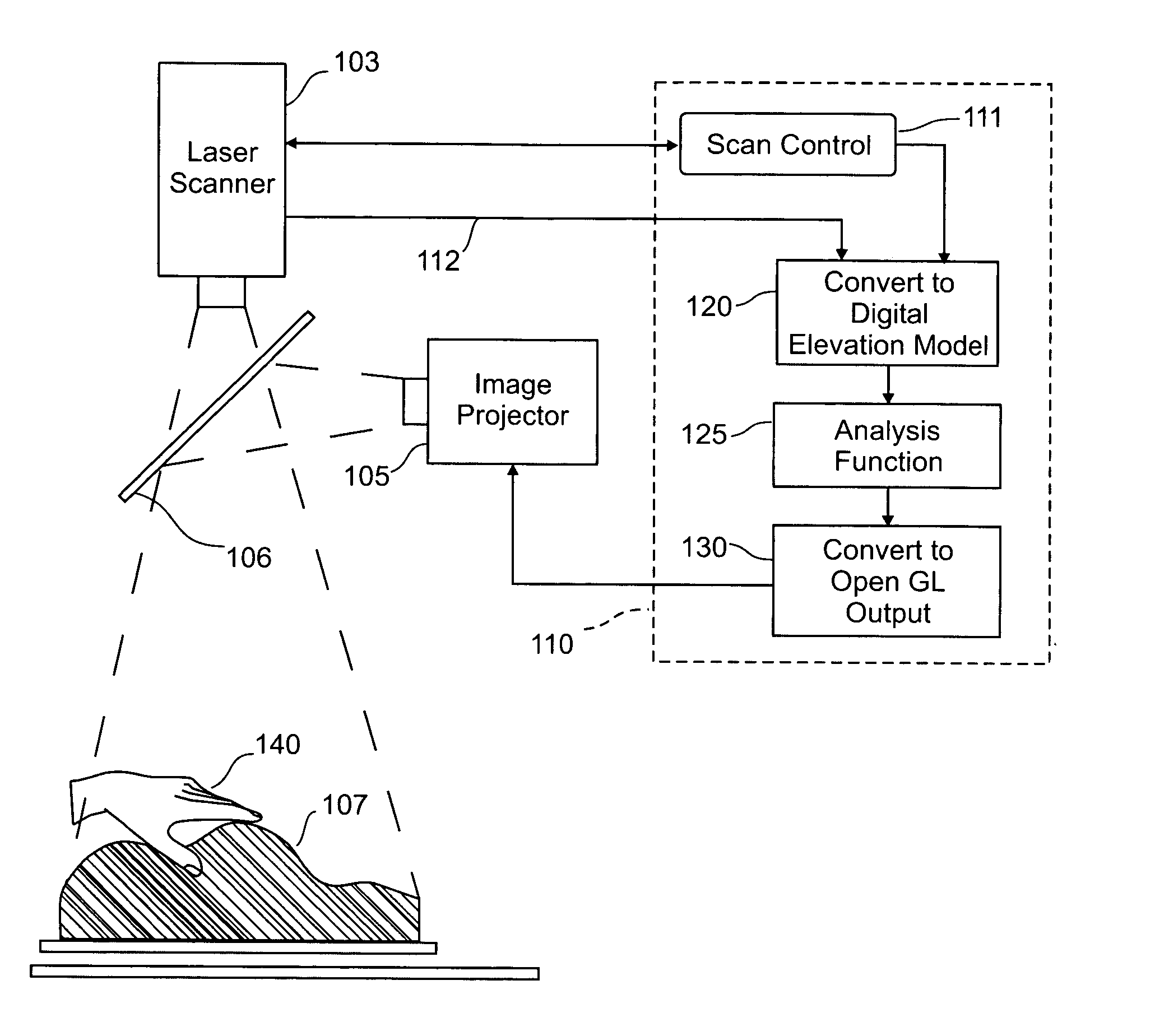
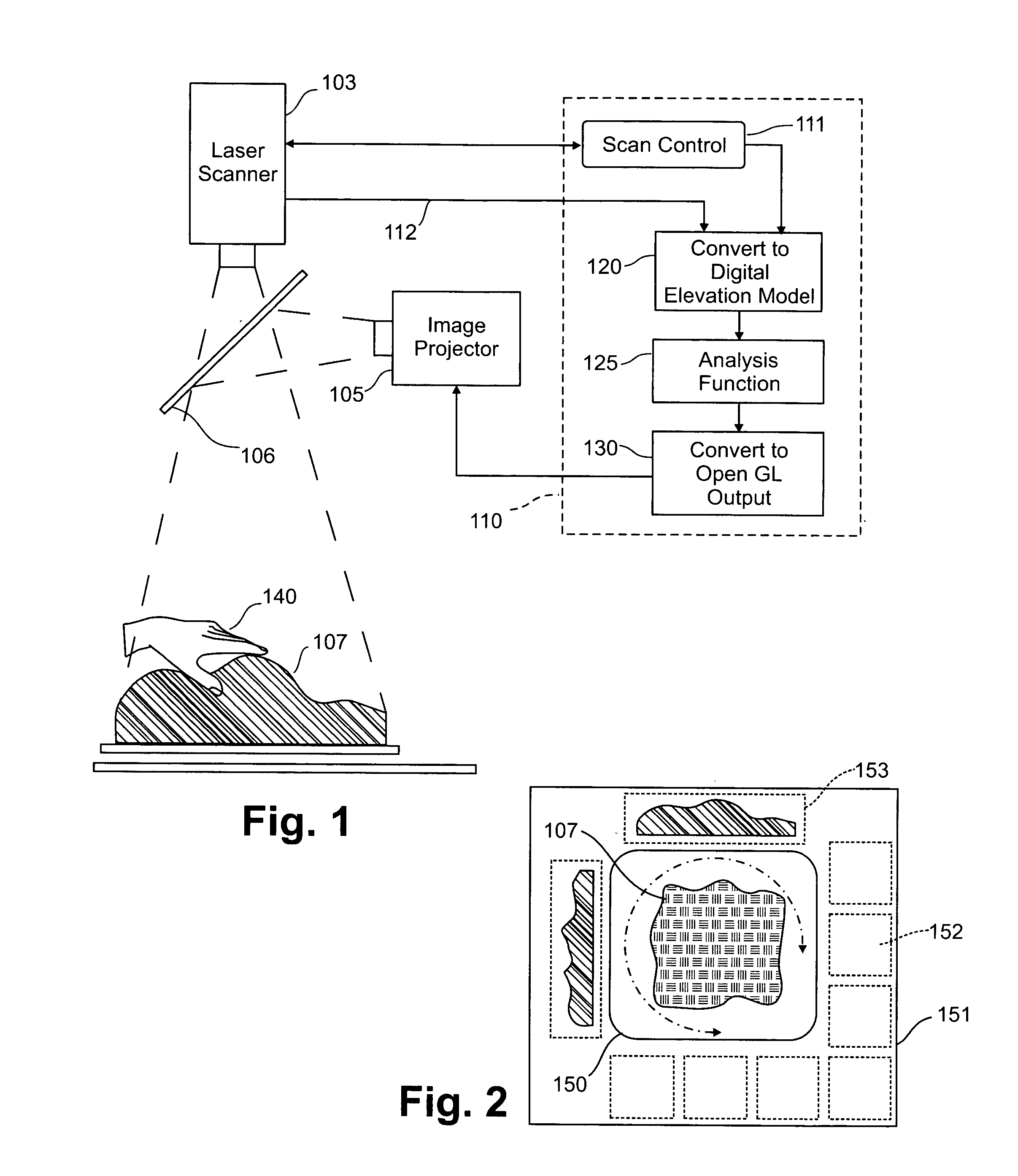
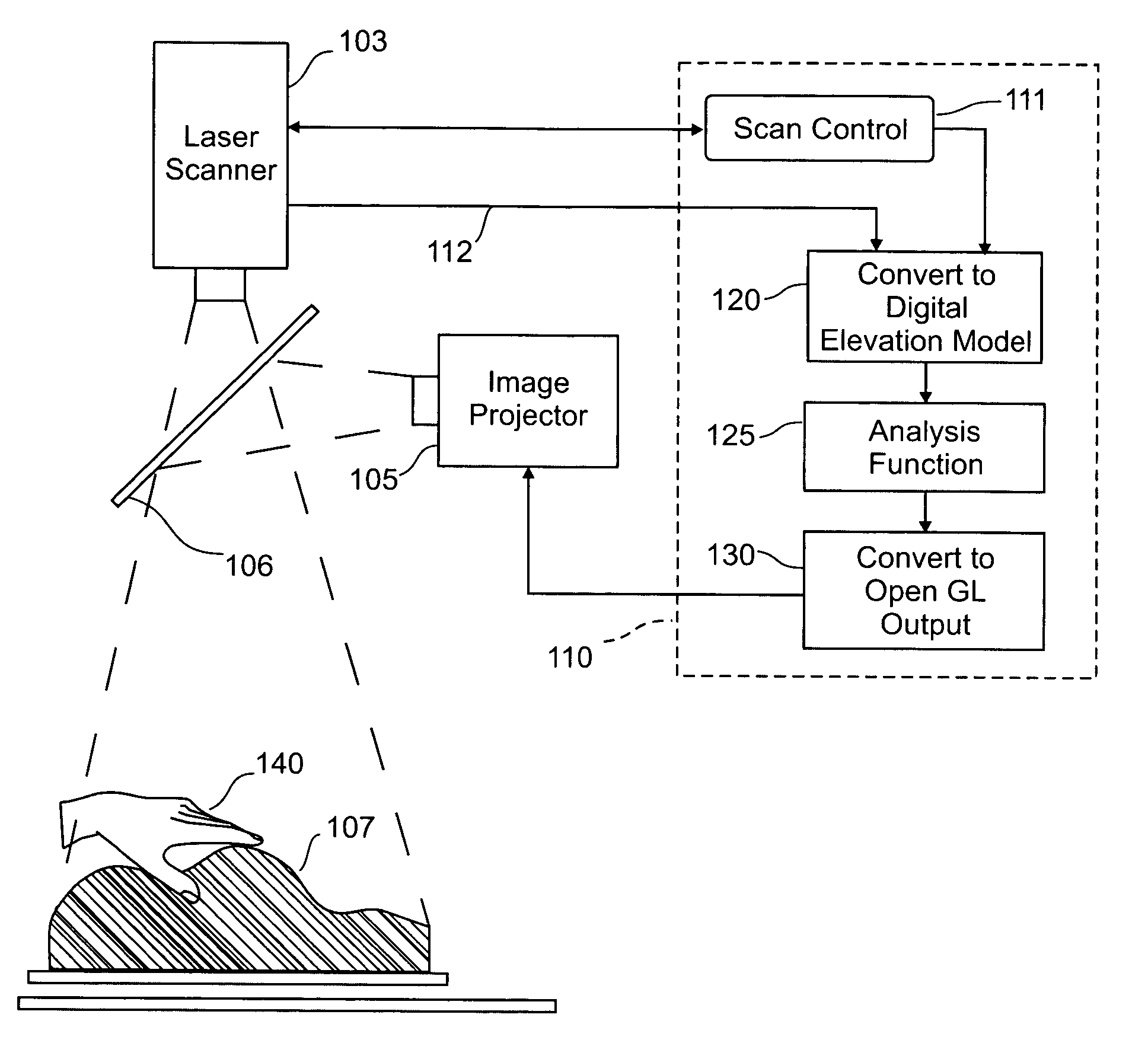
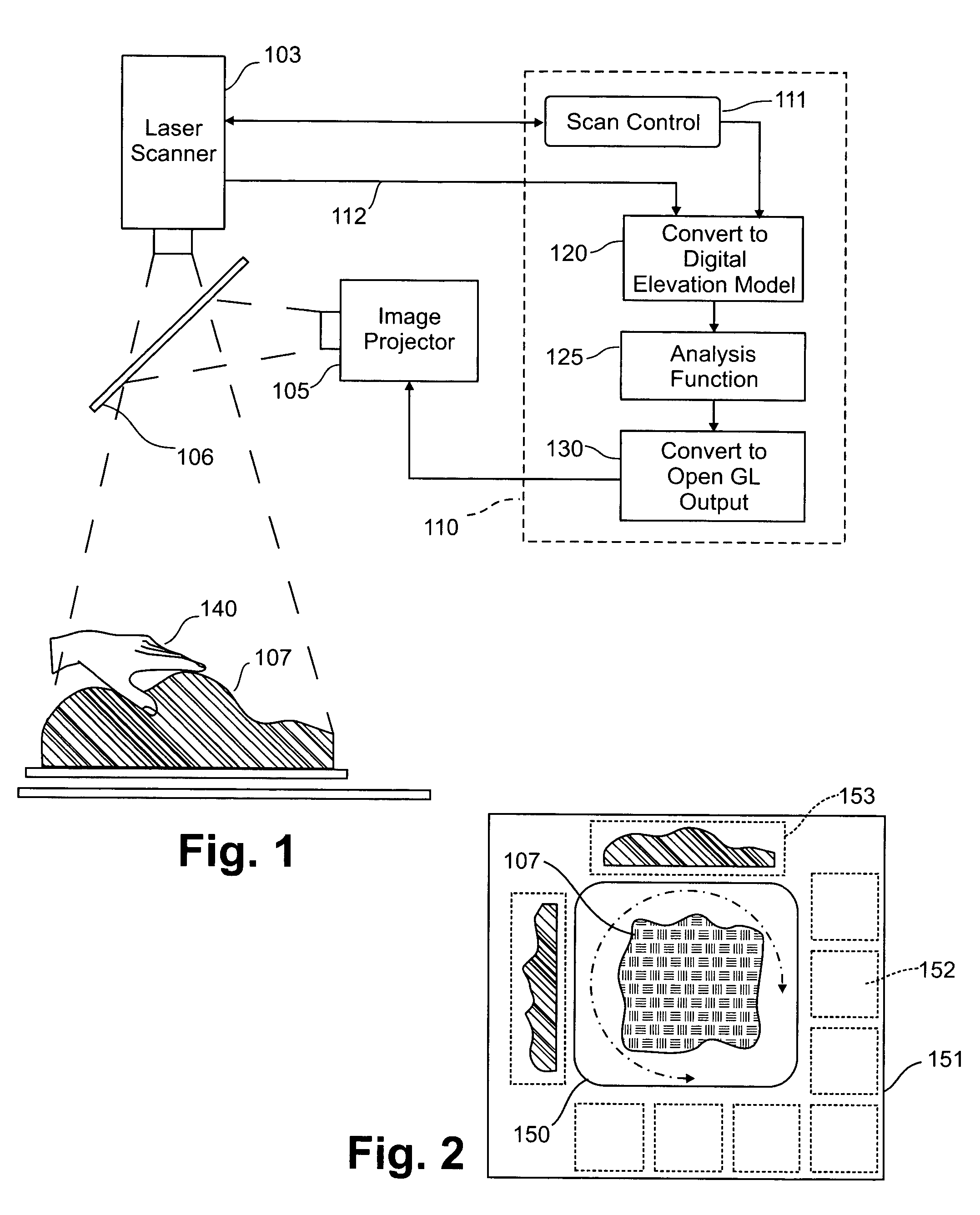
Three dimensional tangible interface for interacting with spatial-temporal data using a laser scanner
InactiveUS20050017967A1Efficient representationQuickly define and understandImage analysisCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Laser scanning
An interface that allows a user to model and analyze the properties of three dimensional surface and the regions surrounding such surfaces. The user manipulates a deformable physical modeling material that defines the geometry of a surface. A position sensor such as a laser scanner captures position data specifying the geometry of the surface. A processor processes the geometry data using a selected analysis function to produce result data representing computed characteristics of the surface or its surrounding region. The result data projected as an image onto the deformable surface. The interface permits the user to modify a surface geometry and directly visualize the characteristics of the modified geometry in real time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
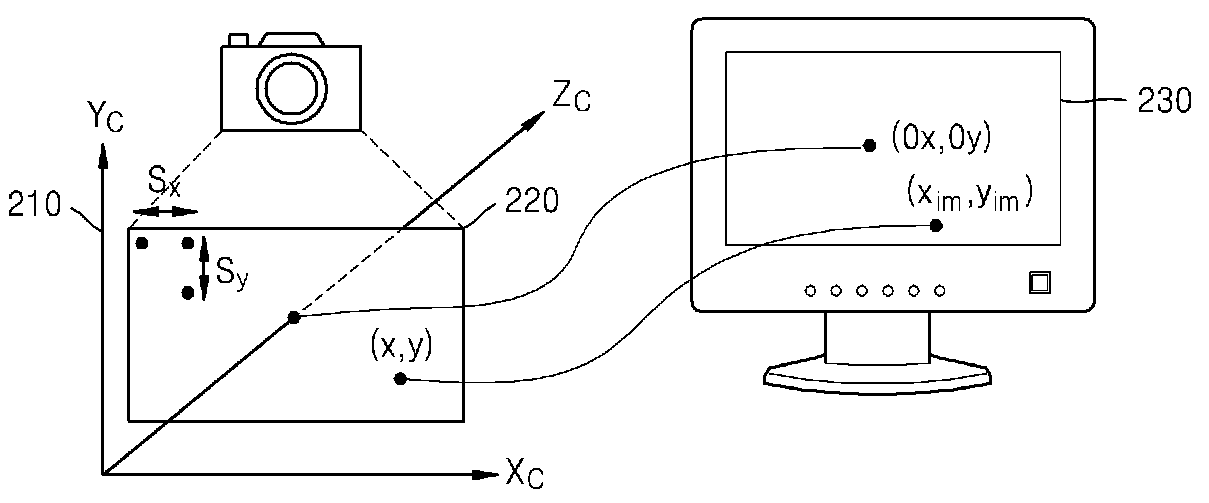
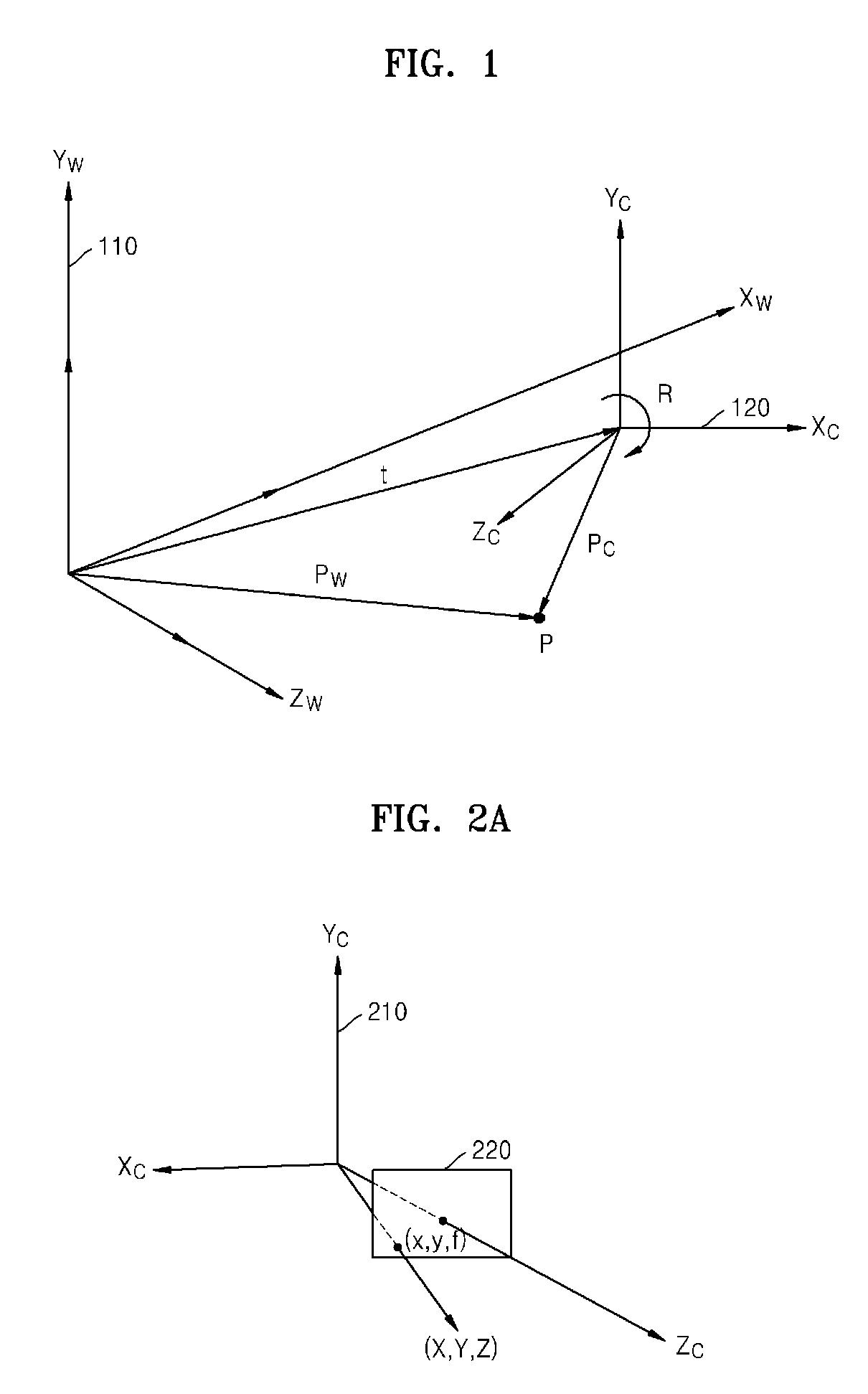
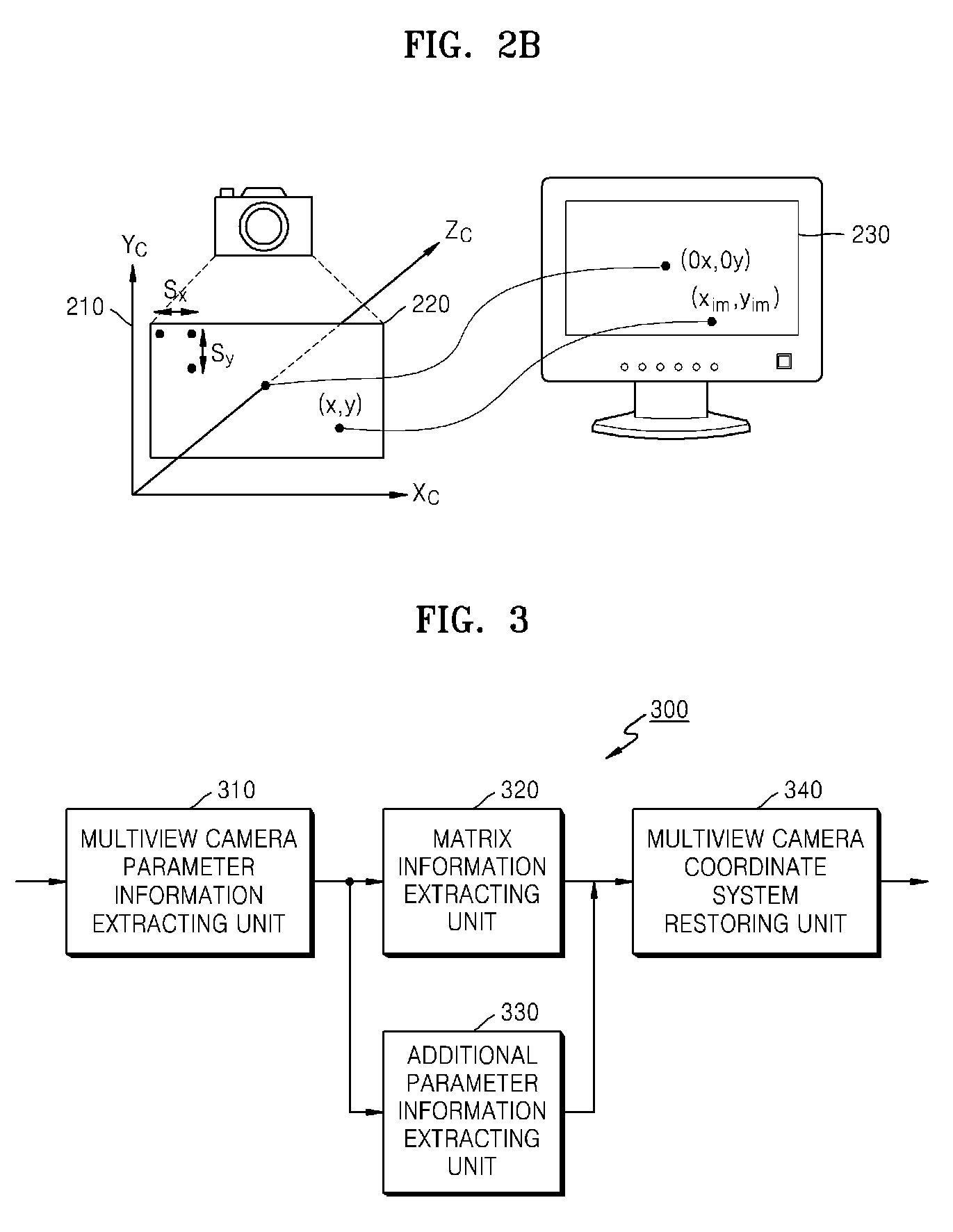
Method and apparatus for receiving multiview camera parameters for stereoscopic image, and method and apparatus for transmitting multiview camera parameters for stereoscopic image
ActiveUS20090092311A1Efficient representationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionData streamComputer vision
Provided is a method of receiving multiview camera parameters for a stereoscopic image. The method includes: extracting multiview camera parameter information for a predetermined data section from a received stereoscopic image data stream; extracting matrix information including at least one of translation matrix information and rotation matrix information for the predetermined data section from the multiview camera parameter information; and restoring coordinate systems of multiview cameras by using the extracted matrix information.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
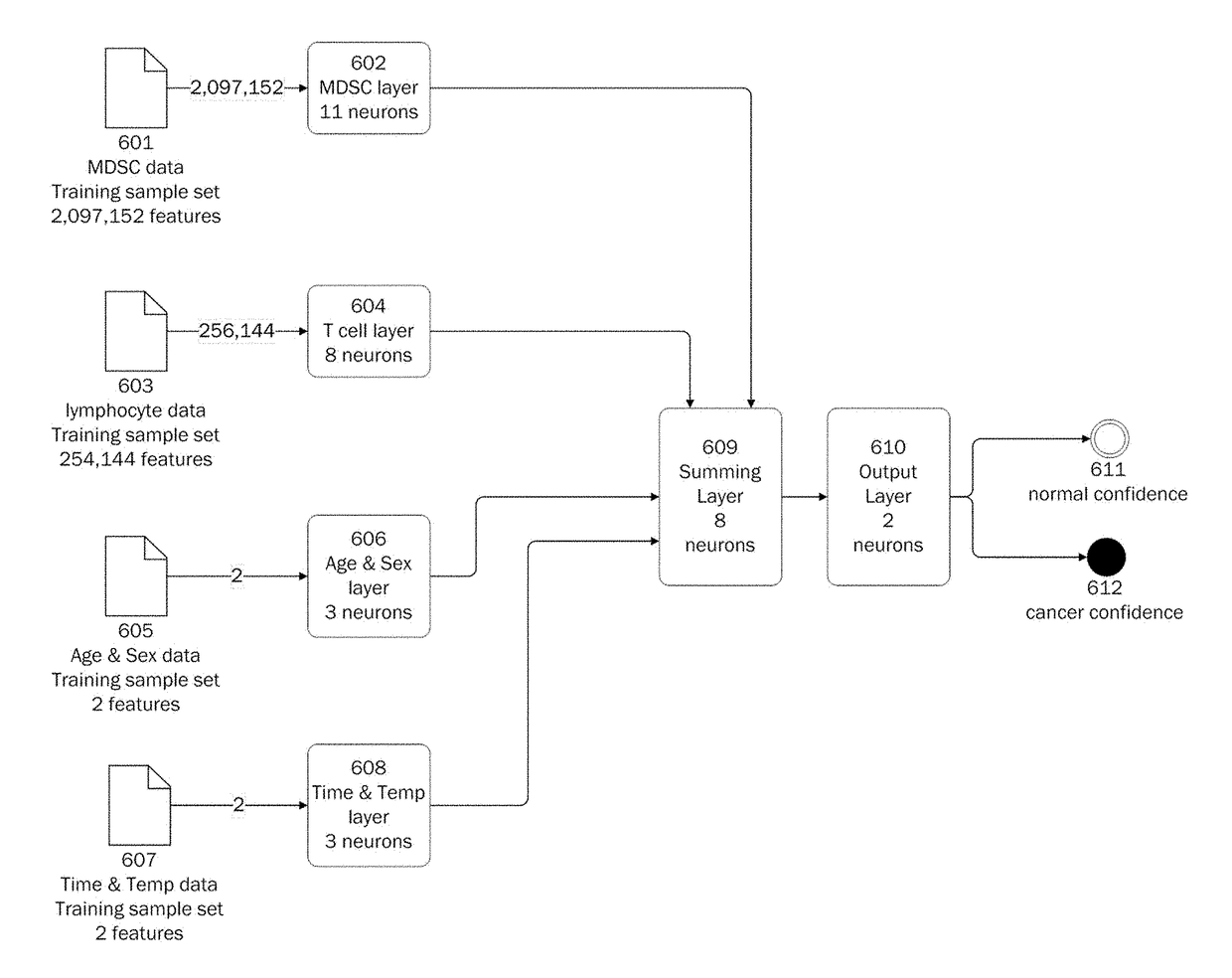
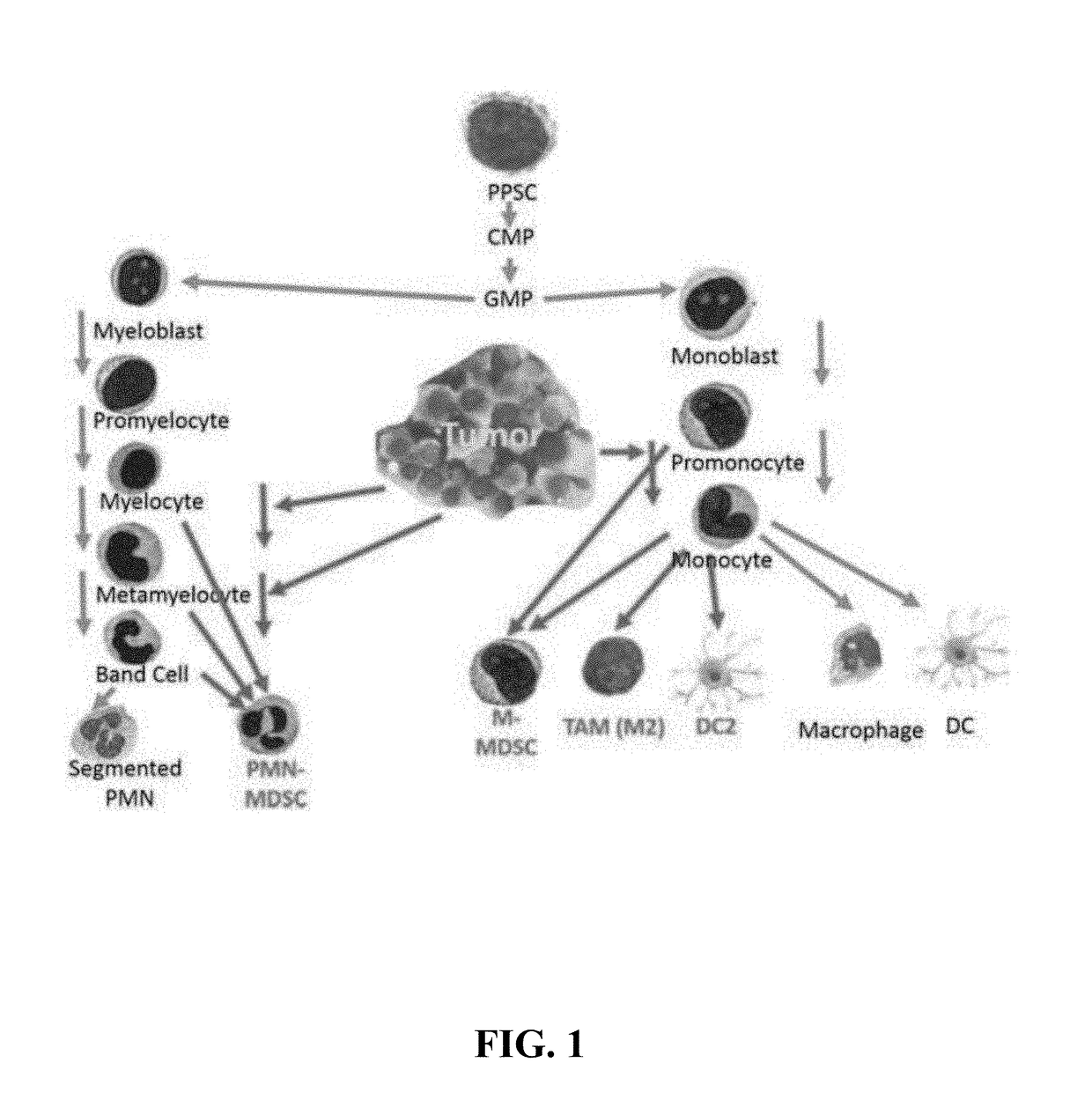
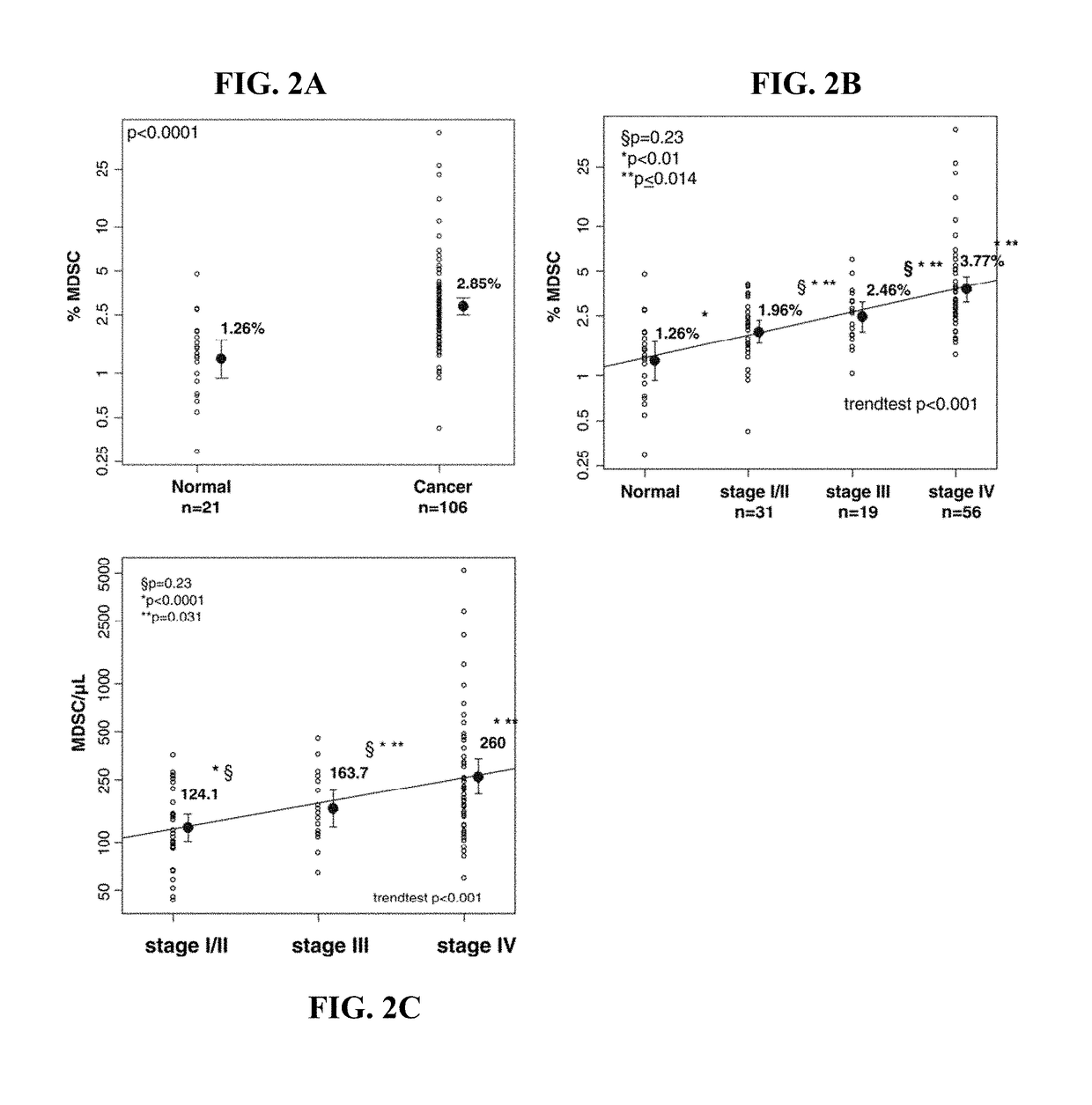
Methods for using artificial neural network analysis on flow cytometry data for cancer diagnosis
The present disclosure provides methods for applying artificial neural networks to flow cytometry data generated from biological samples to diagnose and characterize cancer in a subject. The disclosure also provides methods of training, testing, and validating artificial neural networks.
Owner:ANIXA DIAGNOSTICS CORP
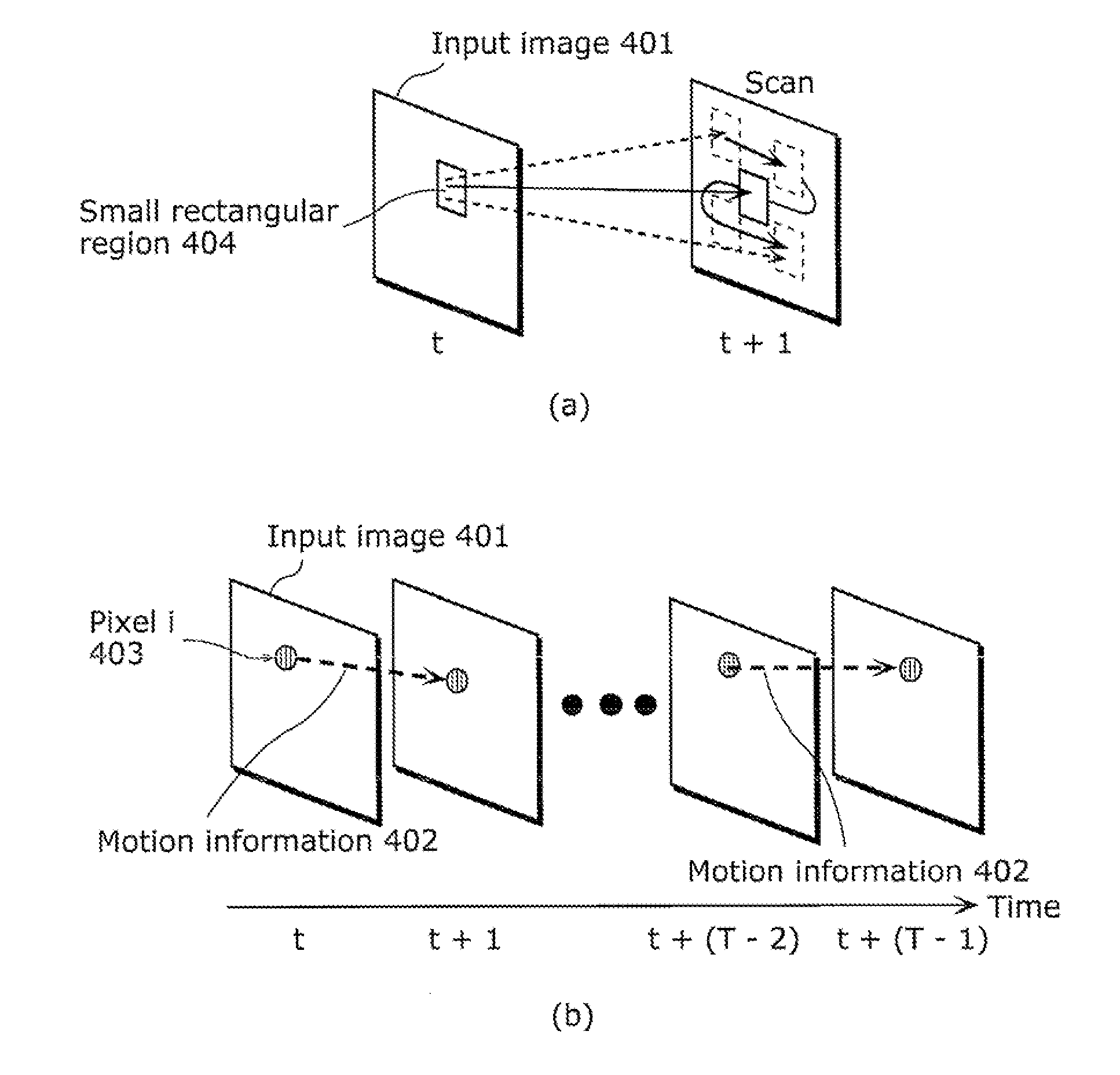
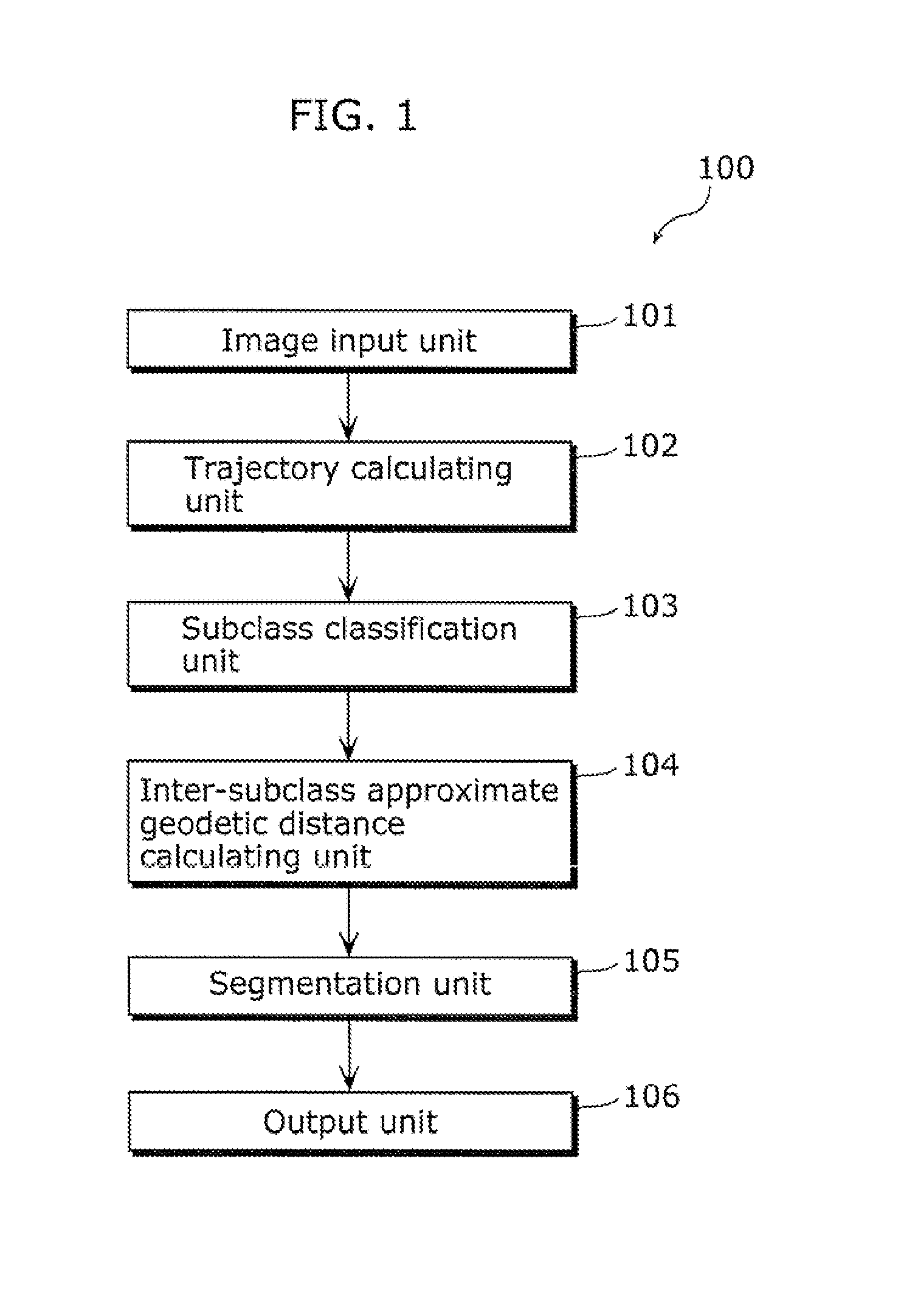
Moving object detection apparatus and moving object detection method
ActiveUS20110255747A1High speedSmall calculation amountImage enhancementImage analysisObject detectionLinear distance
A moving object detection apparatus includes: an image input unit which receives a plurality of pictures included in video; a trajectory calculating unit which calculates a plurality of trajectories from the pictures; a subclass classification unit which classifies the trajectories into a plurality of subclasses; an inter-subclass approximate geodetic distance calculating unit which calculates, for each of the subclasses, an inter-subclass approximate geodetic distance representing similarity between the subclass and another subclass, using an inter-subclass distance that is a distance including a minimum value of a linear distance between each of trajectories belonging to the subclass and one of trajectories belonging to the other subclass; and a segmentation unit which performs segmentation by determining, based on the calculated inter-subclass approximate geodetic distance, a set of subclasses including similar trajectories as one class.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Binaural audio processing
ActiveUS20150350801A1Efficient representationEasy to operateSpeech analysisTwo-channel systemsBinaural processingComputer science
An audio renderer comprises a receiver (801) receiving input data comprising early part data indicative of an early part of a head related binaural transfer function; reverberation data indicative of a reverberation part of the transfer function; and a synchronization indication indicative of a time offset between the early part and the reverberation part. An early part circuit (803) generates an audio component by applying a binaural processing to an audio signal where the processing depends on the early part data. A reverberator (807) generates a second audio component by applying a reverberation processing to the audio signal where the reverberation processing depends on the reverberation data. A combiner (809) generates a signal of a binaural stereo signal by combining the two audio components. The relative timing of the audio components is adjusted based on the synchronization indication by a synchronizer (805) which specifically may be a delay.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Three dimensional tangible interface for interacting with spatial-temporal data using a laser scanner
InactiveUS7181363B2Efficient representationQuickly define and understandImage analysisIncline measurementComputer graphics (images)Laser scanning
An interface that allows a user to model and analyze the properties of three dimensional surface and the regions surrounding such surfaces. The user manipulates a deformable physical modeling material that defines the geometry of a surface. A position sensor such as a laser scanner captures position data specifying the geometry of the surface. A processor processes the geometry data using a selected analysis function to produce result data representing computed characteristics of the surface or its surrounding region. The result data projected as an image onto the deformable surface. The interface permits the user to modify a surface geometry and directly visualize the characteristics of the modified geometry in real time.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
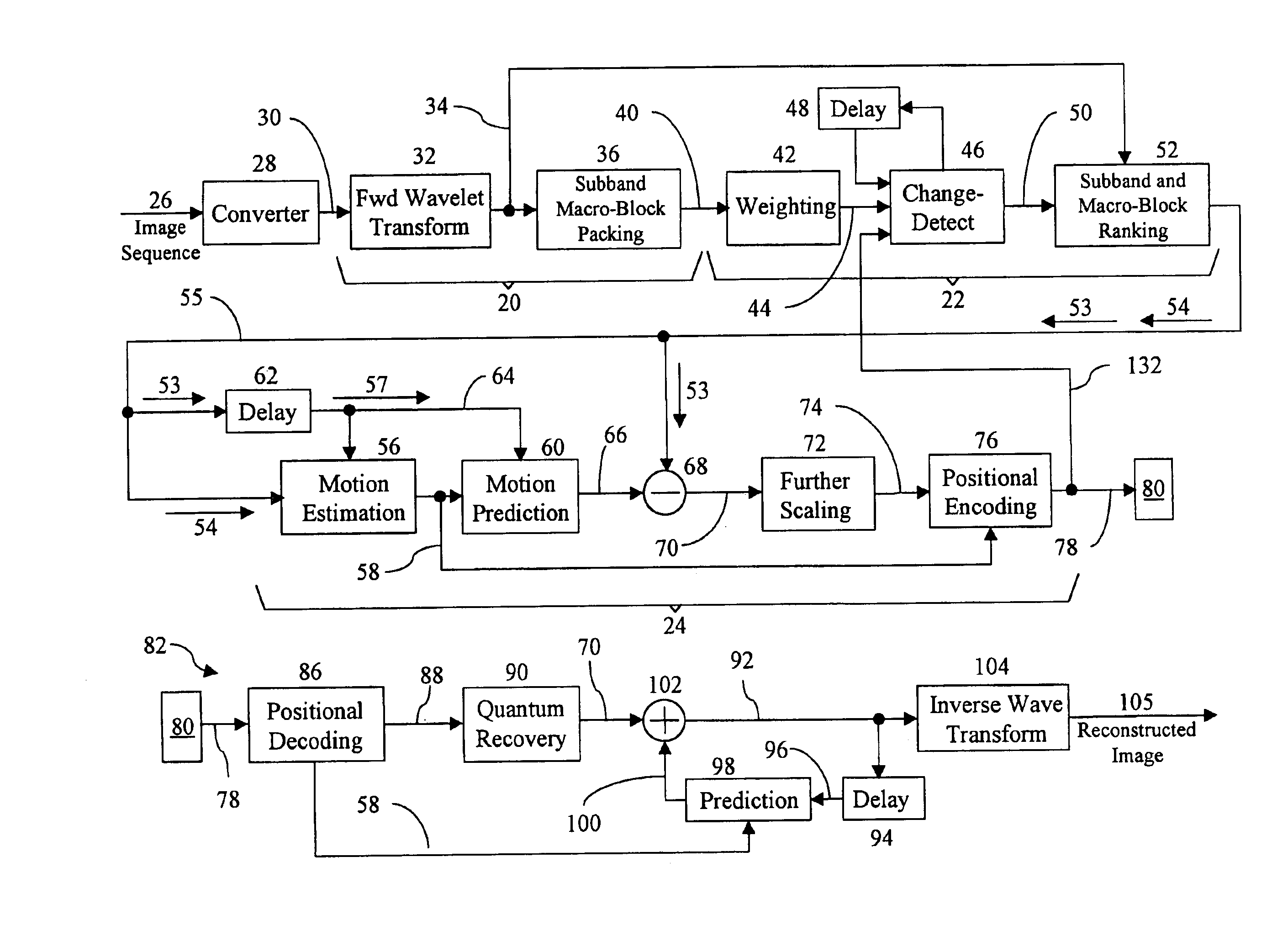
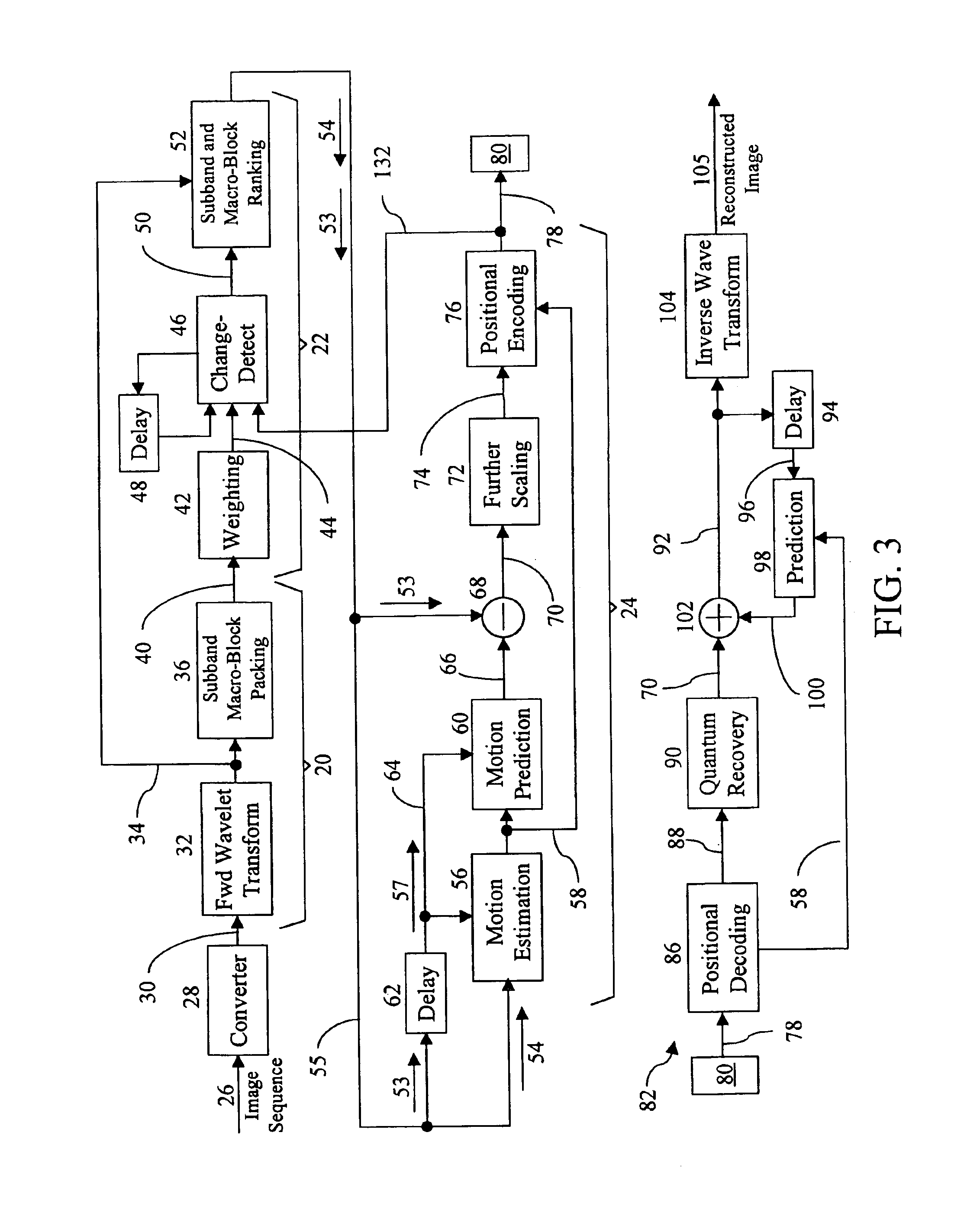
Apparatus and method for compressing video information
InactiveUS6937659B1Efficient codingReduce data volumeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData setMotion vector
A method and apparatus is disclosed for efficiently encoding data representing a video image, thereby reducing the amount of data that must be transferred to a decoder. The method includes transforming data sets utilizing a tensor product wavelet transform which is capable of transmitting remainders from one subband to another. Collections of subbands, in macro-block form, are weighted, detected, and ranked enabling prioritization of the transformed data. A motion compensation technique is performed on the subband data producing motion vectors and prediction errors which are positionally encoded into bit stream packets for transmittal to the decoder. Subband macro-blocks and subband blocks which are equal to zero are identified as such in the bit stream packets to further reduce the amount of data that must be transferred to the decoder.
Owner:GEN DYNAMICS INFORMATION TECH
Methods and apparatus for assessing operational process quality and risk
InactiveUS20080015920A1Sufficient rapidityIdeal overall performanceFinanceMultiprogramming arrangementsProcess qualityHuman decision
Methods and apparatus for assessing operational process quality and risk of an entity or a group of entities. The present invention enables a user to effectively compare one or more events, representing what actually happened, with a reference, which represents ideal performance in terms of operational process quality and risk, and express the corresponding results in quantitative terms. The present invention is capable of presenting results in a form and with sufficient rapidity that a human decision-maker is able to timely observe conditions which represent unacceptable quality or excessive risk and respond appropriately.
Owner:FAWLS ROBERT A +1
Protein modeling tools
InactiveUS20030130797A1Rapid and computationally efficient generationEfficient representationDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsProtein modellingSide chain
The invention provides a new, efficient method for the assembly of protein tertiary structure from known, loosely encoded secondary structure constraints and sparse information about exact side chain contacts. The method is based on a new method for the reduced modeling of protein structure and dynamics, where the protein is described by representing side chain centers of mass rather than alpha-carbons. The model has implicit, built-in multi-body correlations that simulate short- and long-range packing preferences, hydrogen bonding cooperativity, and a mean force potential describing hydrophobic interactions. Due to the simplicity of the protein representation and definition of the model force field, the Monte Carlo algorithm is at least an order of magnitude faster than previously published Monte Carlo algorithms for three-dimensional structure assembly. In contrast to existing algorithms, the new method requires a smaller number of tertiary constraints for successful fold assembly; on average, one for every seven residues as compared to one for every four residues. The reliability and robustness of the invention make it useful for routine application in model building protocols based on various (and even very sparse) experimentally-derived structural constraints.
Owner:SKOLNICK JEFFREY +1
Concept for bridging the gap between parametric multi-channel audio coding and matrixed-surround multi-channel coding
InactiveUS20070055510A1Efficient representationLittle informationSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsOperating pointSide information
The purpose of the invention is to bridge the gap between parametric multi-channel audio coding and matrixed-surround multi-channel coding by gradually improving the sound of an up-mix signal while raising the bit-rate consumed by the side-information starting from 0 up to the bit-rates of the parametric methods. More specifically, it provides a method of flexibly choosing an “operating point” somewhere between matrixed-surround (no side-information, limited audio quality) and fully parametric reconstruction (full side-information rate required, good quality). This operating point can be chosen dynamically (i.e. varying over time) and in response to the permissible side-information rate, as it is dictated by the individual application.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Binaural audio processing
ActiveUS20150358754A1Easy to operateEfficient representationSpeech analysisTwo-channel systemsData setVirtual position
A transmitting device comprises a binaural circuit (601) which provides a plurality of binaural rendering data sets, each binaural rendering data set comprising data representing parameters for a virtual position binaural rendering. Specifically, head related binaural transfer function data may be included in the data sets. A representation circuit (603) provides a representation indication for each of the data sets. The representation indication for a data set is indicative of the representation used by the data set. An output circuit (605) generates a bitstream comprising the data sets and the representation indications. The bitstream is received by a receiver (701) in a receiving device. A selector (703) selects a selected binaural rendering data set based on the representation indications and a capability of the apparatus, and an audio processor (707) processes the audio signal in response to data of the selected binaural rendering data set.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Subsurface scattering approximation methods and apparatus
A method for determining illumination of surface points of an object in a scene from lighting sources includes determining a first thickness map for a first lighting source for the scene, wherein the first thickness map includes a first plurality of thickness values of the object with respect to distance from the first lighting source, determining a surface point on the object, determining a first plurality of thickness values associated with the surface point on the object in response to the first thickness map, determining a first filtered thickness value associated with the surface point on the object in response to the first plurality of thickness values, and determining an illumination contribution from the first lighting source at the surface point in response to the first filtered thickness value.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Method and system for restructuring a visualization graph so that entities linked to a common node are replaced by the common node in response to a predetermined stimulus
ActiveUS7549309B2Efficient representationImprove distributionDigital data information retrievalBuilding locksData mining
A visualization graph is provided on a computer. Data is stored corresponding to a plurality of entities, wherein a semantic net includes the entities and wherein the entities are linked to each other by a plurality of relations. In response to a query with respect to an entity selected from the plurality of entities, a visualization graph representing the results of the query is provided. Entities are selected from the plurality of entities having at least one common relation and storing the selected entities as a plurality of groups.
Owner:SAP AG
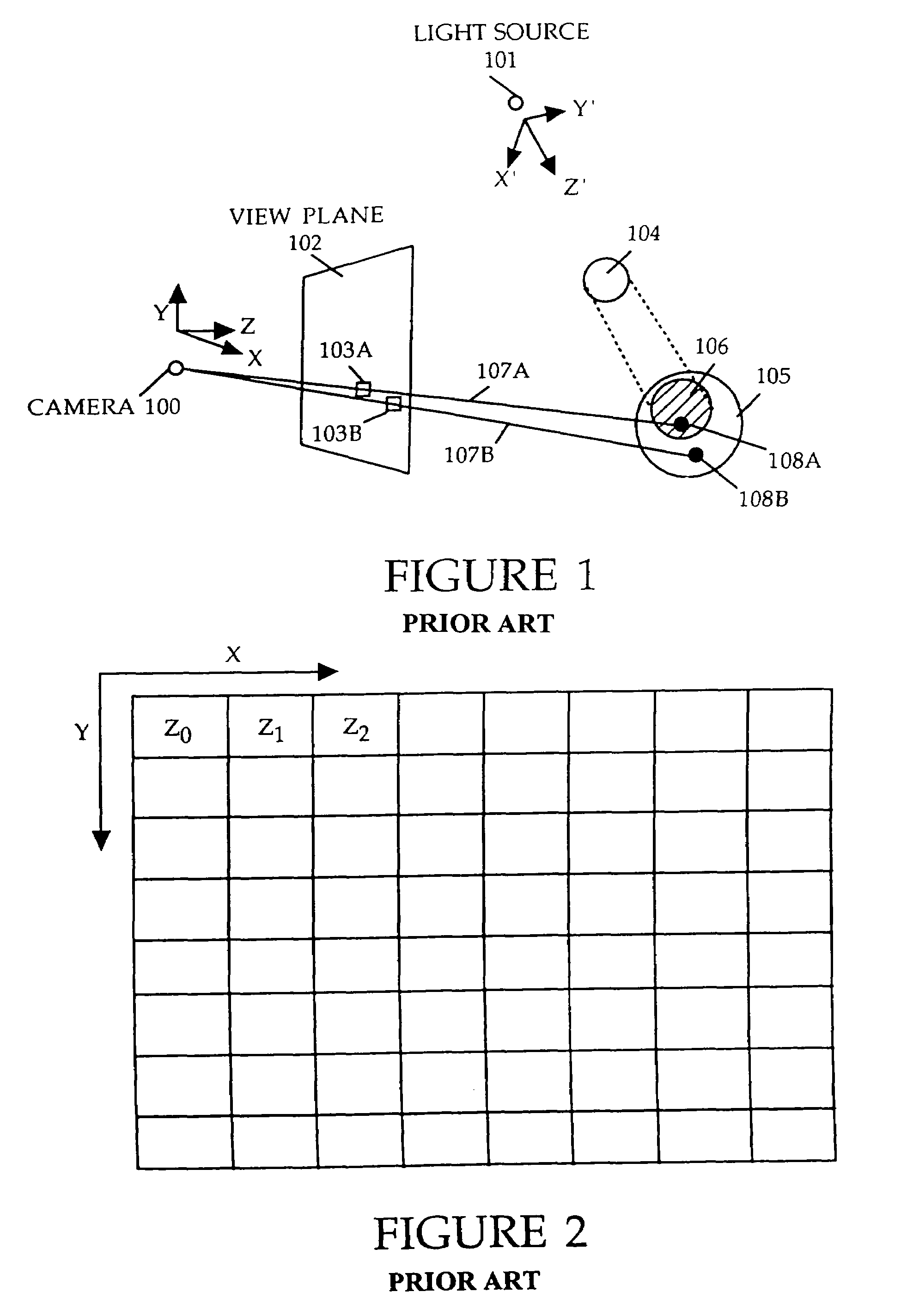
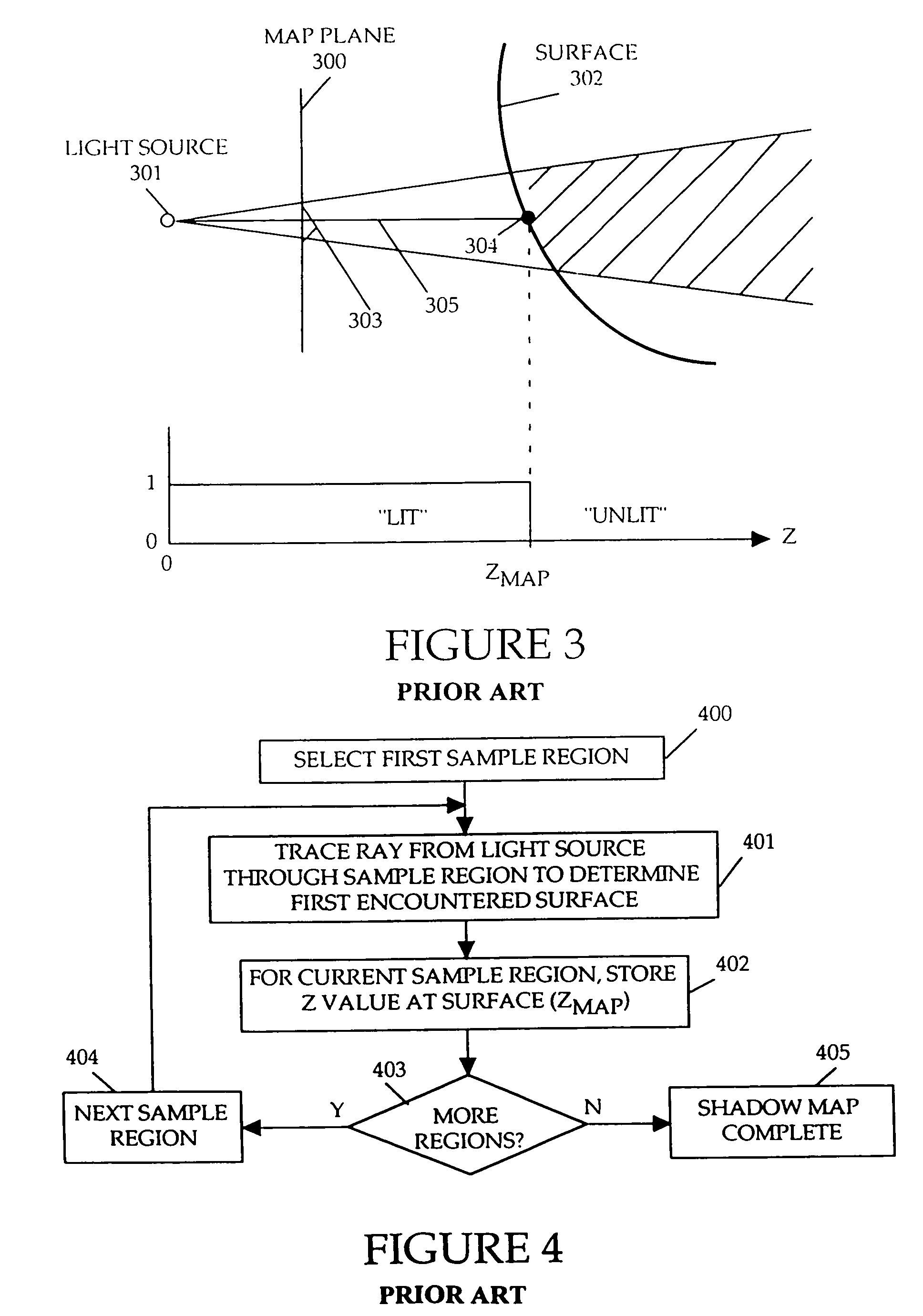
Method and apparatus for rendering shadows
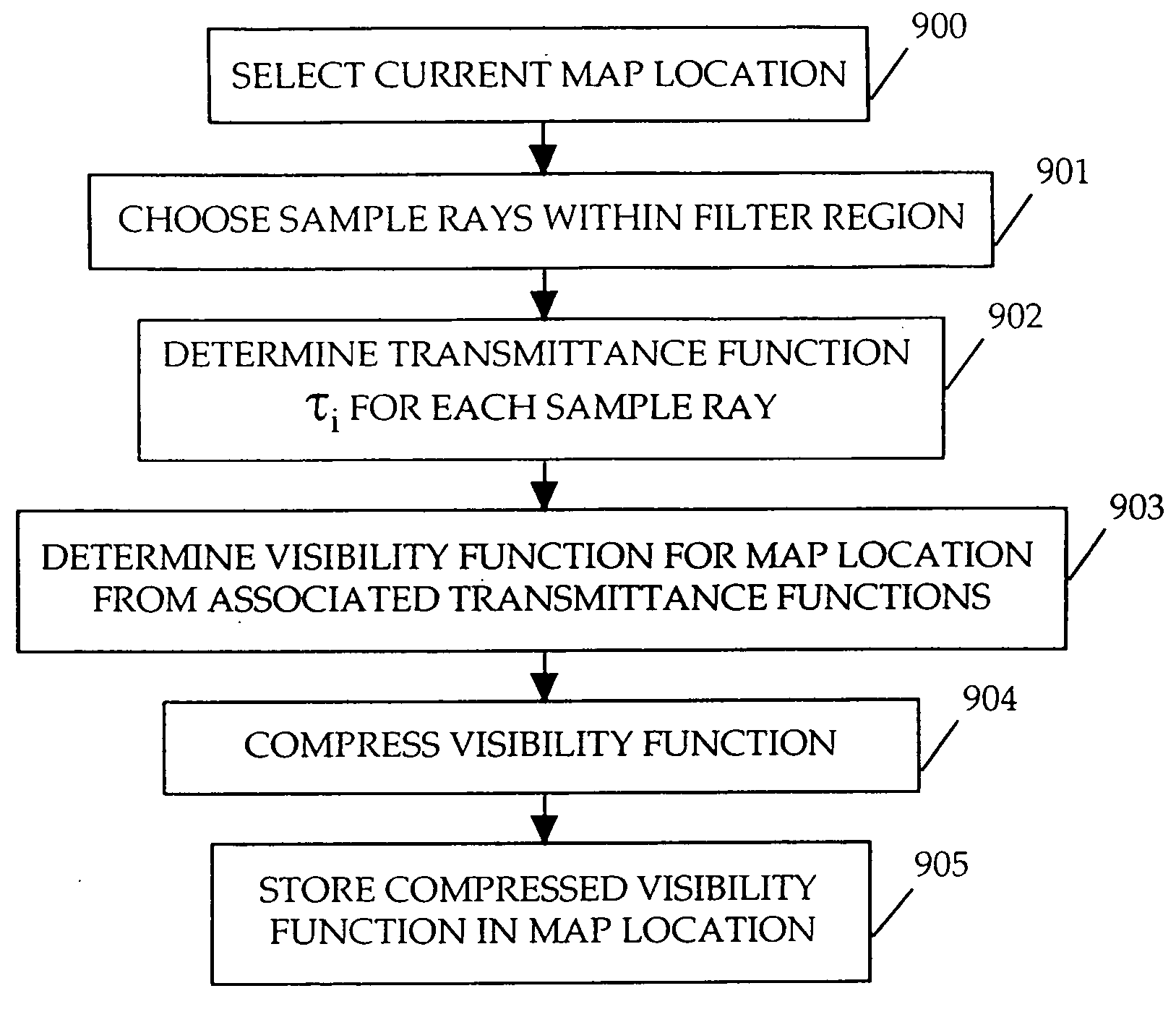
InactiveUS20060119600A1Efficiently determinedAccurate modelingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Transmittance
A method and apparatus for rendering shadows. A pre-rendering process implements a two dimensional array or map of depth-based functions, such as a visibility function in z. During rendering of an object scene, these functions are accessed via lookup operations to efficiently determine the function value for a sample point at a given depth. The use of visibility functions allows for partial light attenuation effects. Each visibility function is computed by filtering multiple transmittance functions obtained by casting sample rays from a light source onto an object scene. The visibility function is implemented as a sequence of vertices. Colored shadows are modeled by vertices comprising a depth value and separate visibility function values for red, green, and blue light at a given depth value. Compression is achieved by minimizing the number of vertices needed to represent a visibility function within a desired error tolerance.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
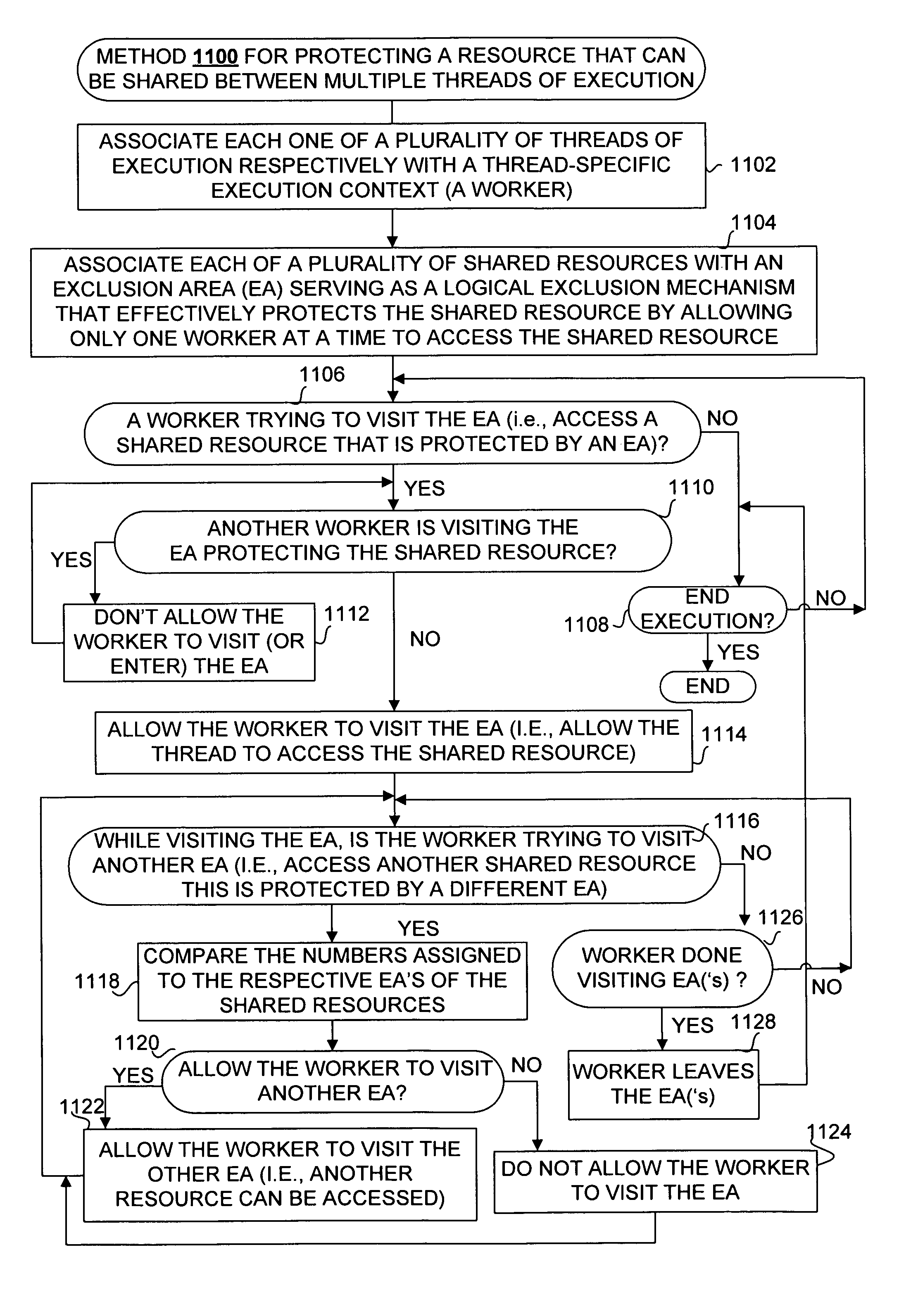
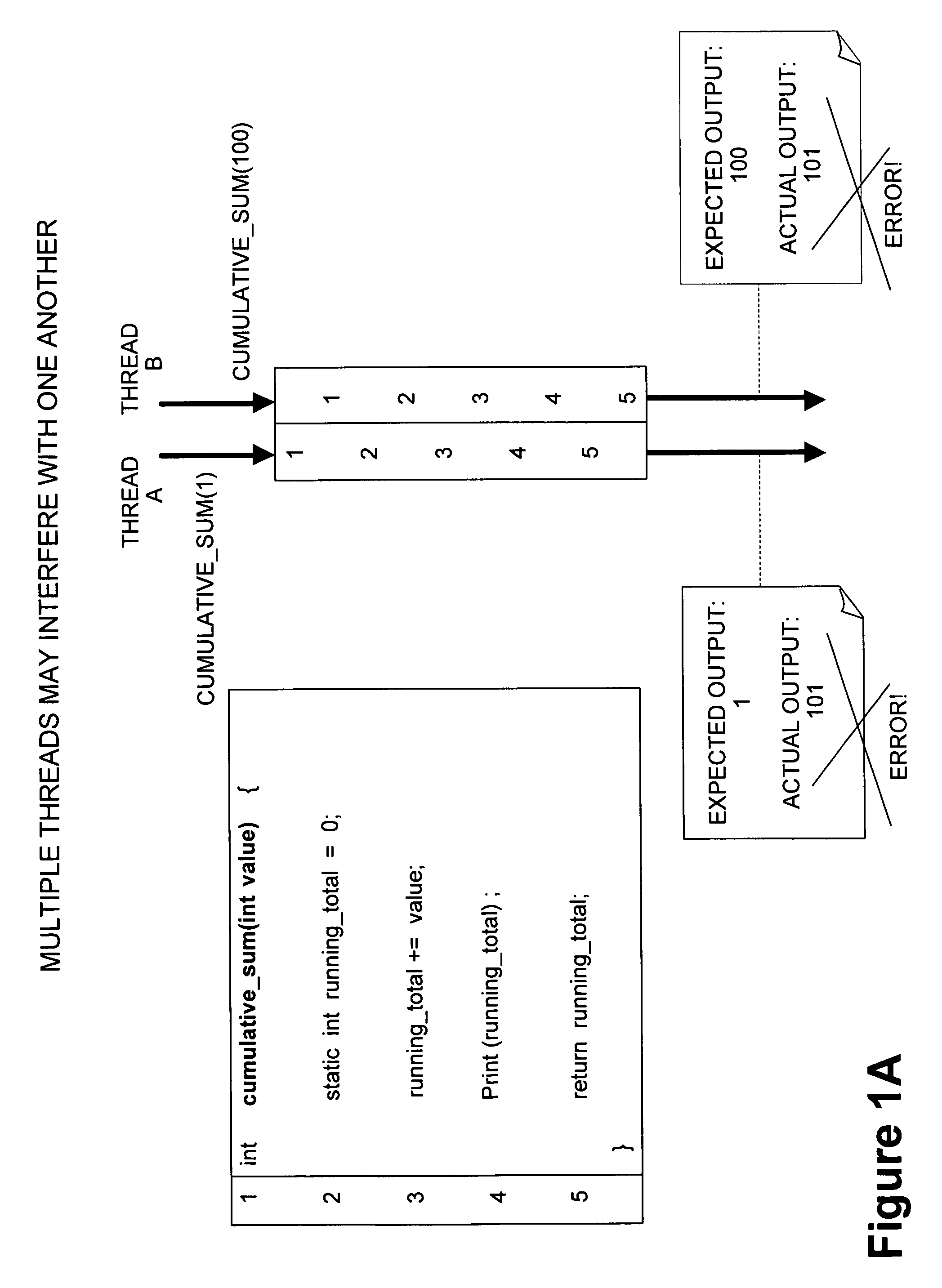
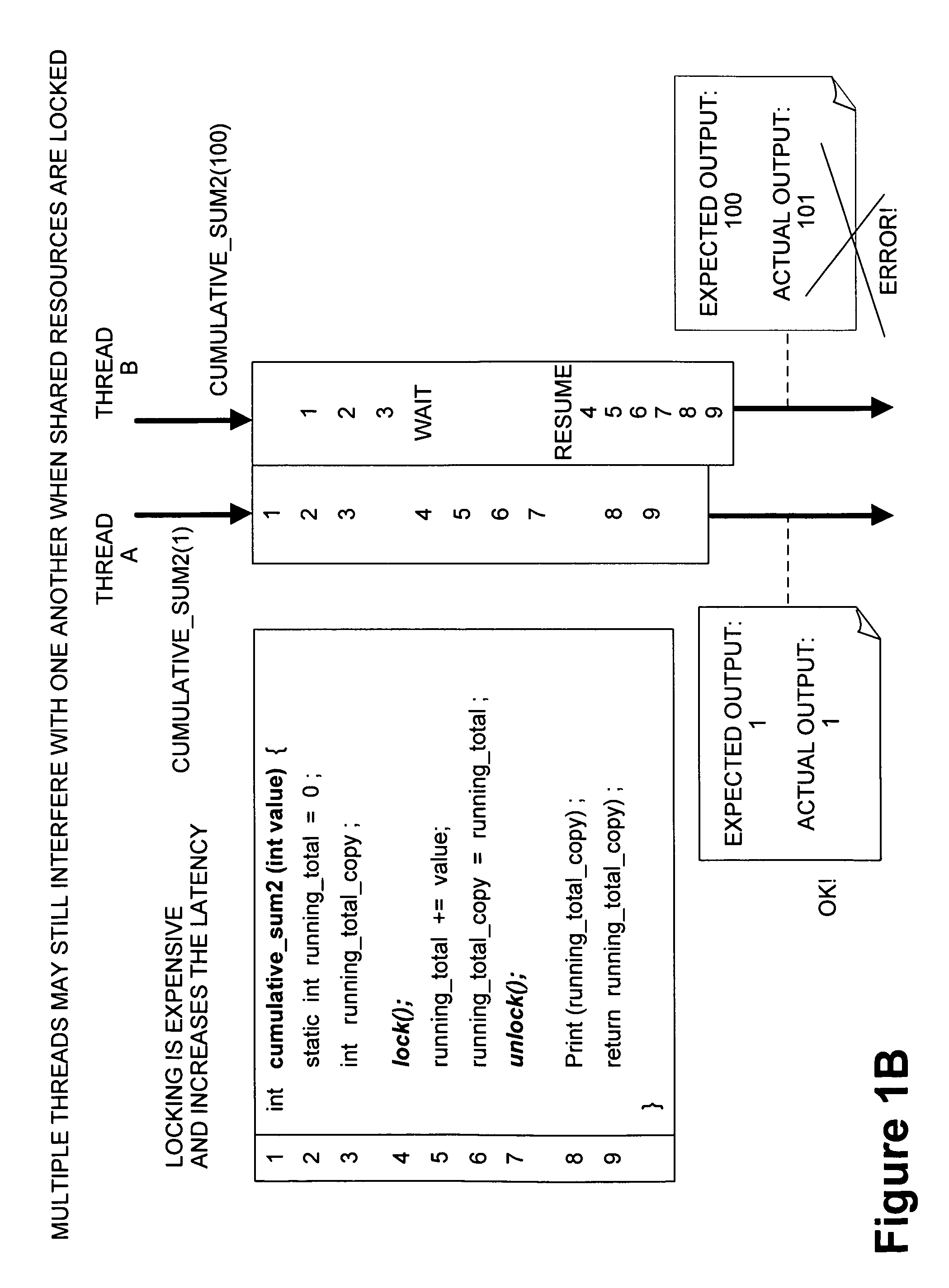
Framework for executing multiple threads and sharing resources in a multithreaded computer programming environment
ActiveUS7827559B1Efficient mappingLatency experiencedMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingDelayed time
Techniques for execution of multiple threads in a multithreaded computing programming environment are disclosed. The techniques are especially well suited for environments that use multilayered programming architecture where a higher layer can build on the functions provided by a lower layer where the delay time is an important consideration. In one aspect, the conceptual notion of a “Worker” effectively serves to represent the thread-specific execution context for a thread of execution (“thread”) in a multithreaded computing environment. Another aspect, provides the notion of an Exclusion Area (EA) as logical lock that serves to protect shared resources in a multithreaded environment. The combination of the worker and EA are used to provide a powerful framework that, among other things, allows minimizing of the delay time.
Owner:REAL TIME INNOVATIONS
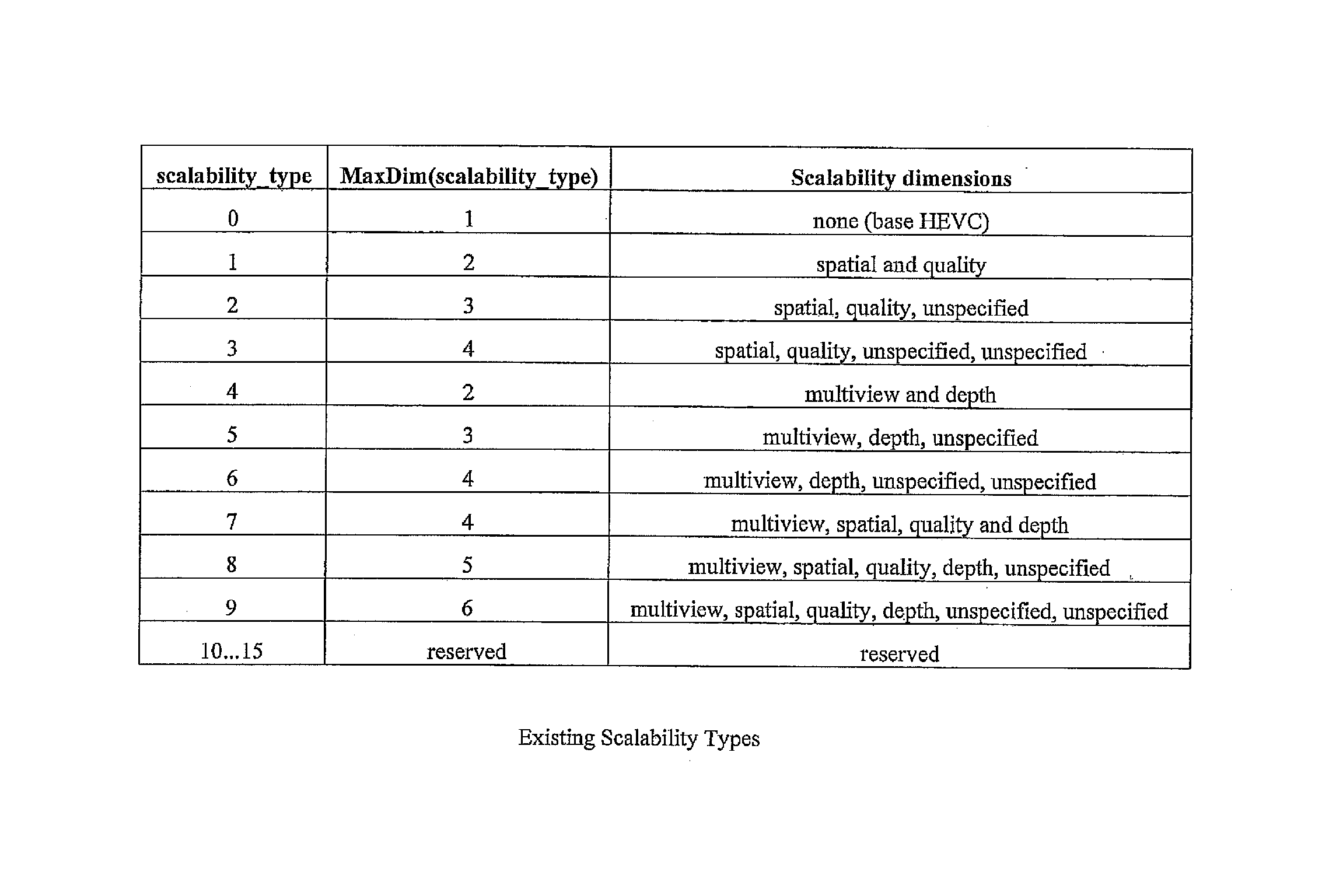
Signaling scalability information in a parameter set
InactiveUS20150256838A1Efficient representationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer engineeringScalability
A method for signaling scalability information in a video parameter set is described. A modified video parameter set extension includes a scalability mask that is used in combination with a scalability dimension. The scalability mask indicates whether or not a scalability dimension is present in each layer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com