Patents
Literature
137results about How to "Efficient mapping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
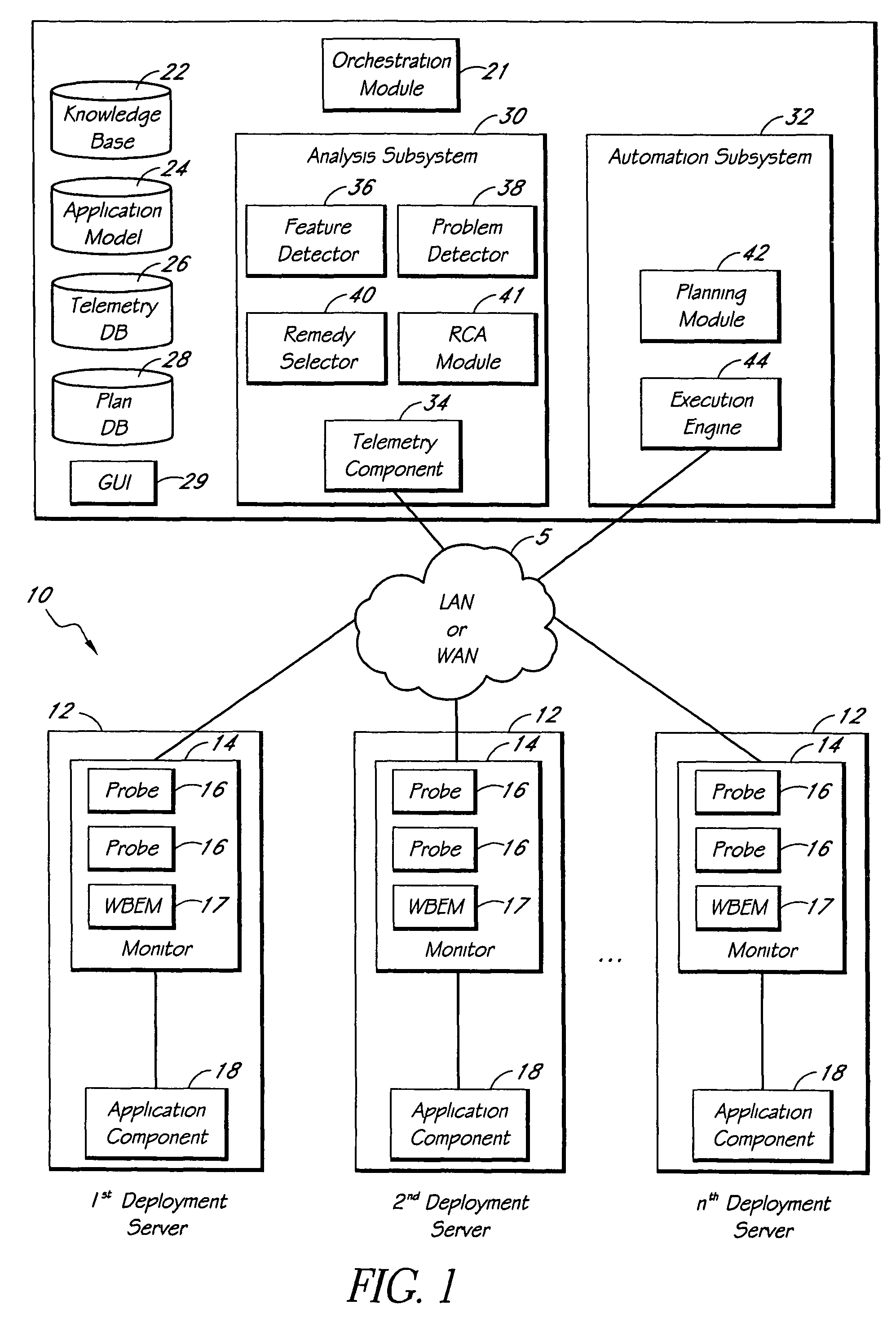
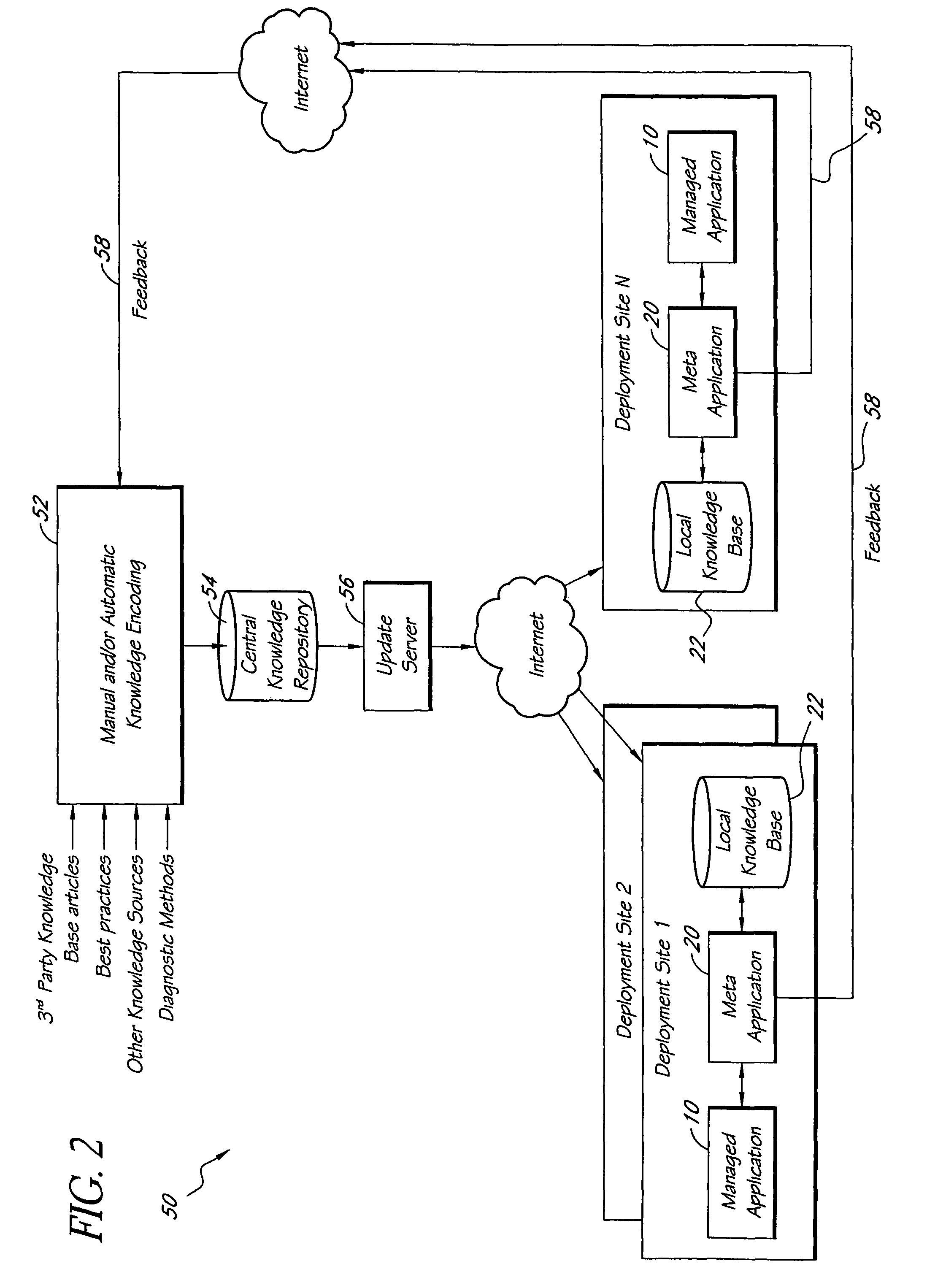
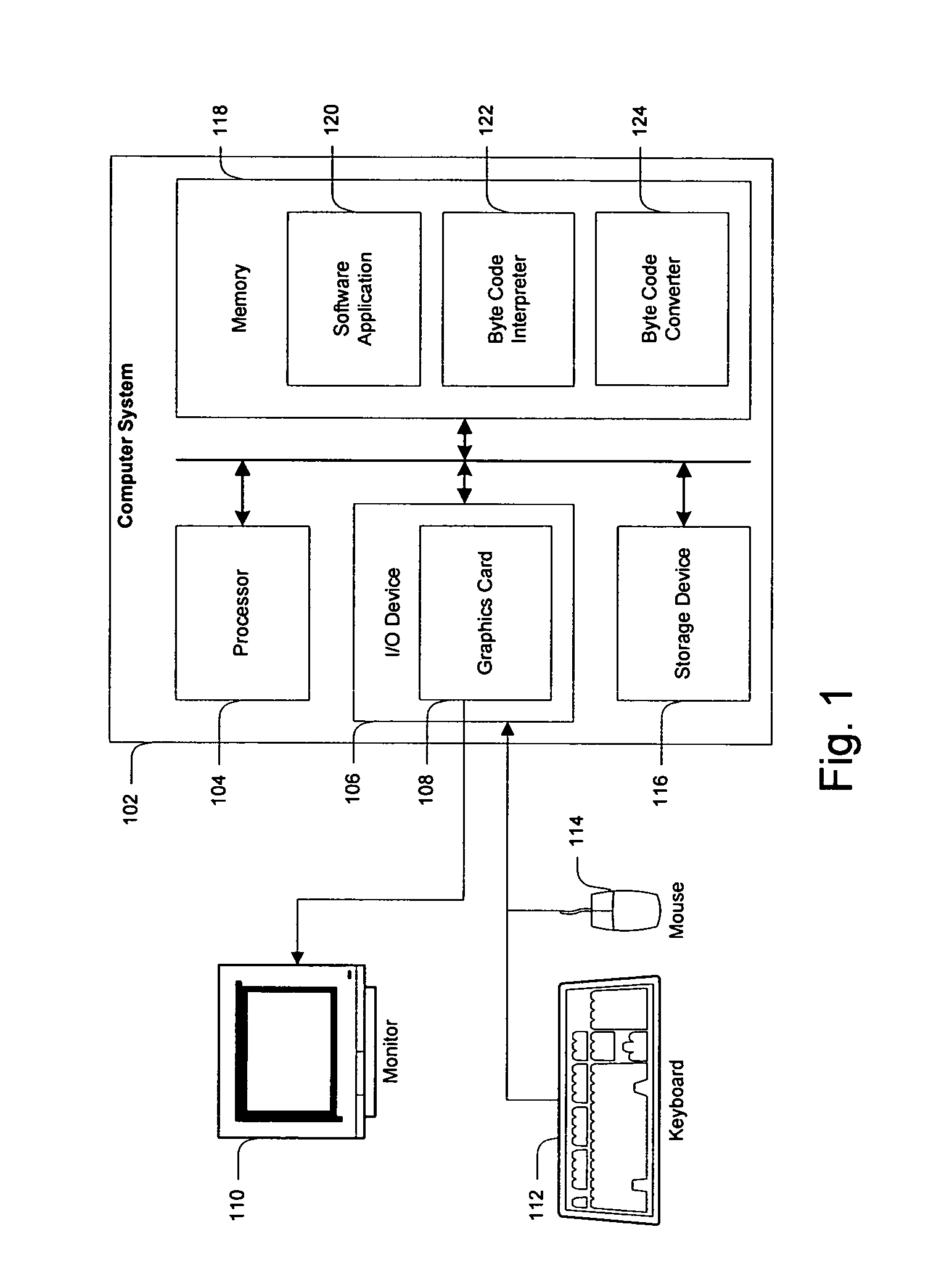
Systems and methods for encoding knowledge for automated management of software application deployments
ActiveUS7490073B1Efficient mappingGreat leverageError detection/correctionChaos modelsKnowledge sourcesSoftware
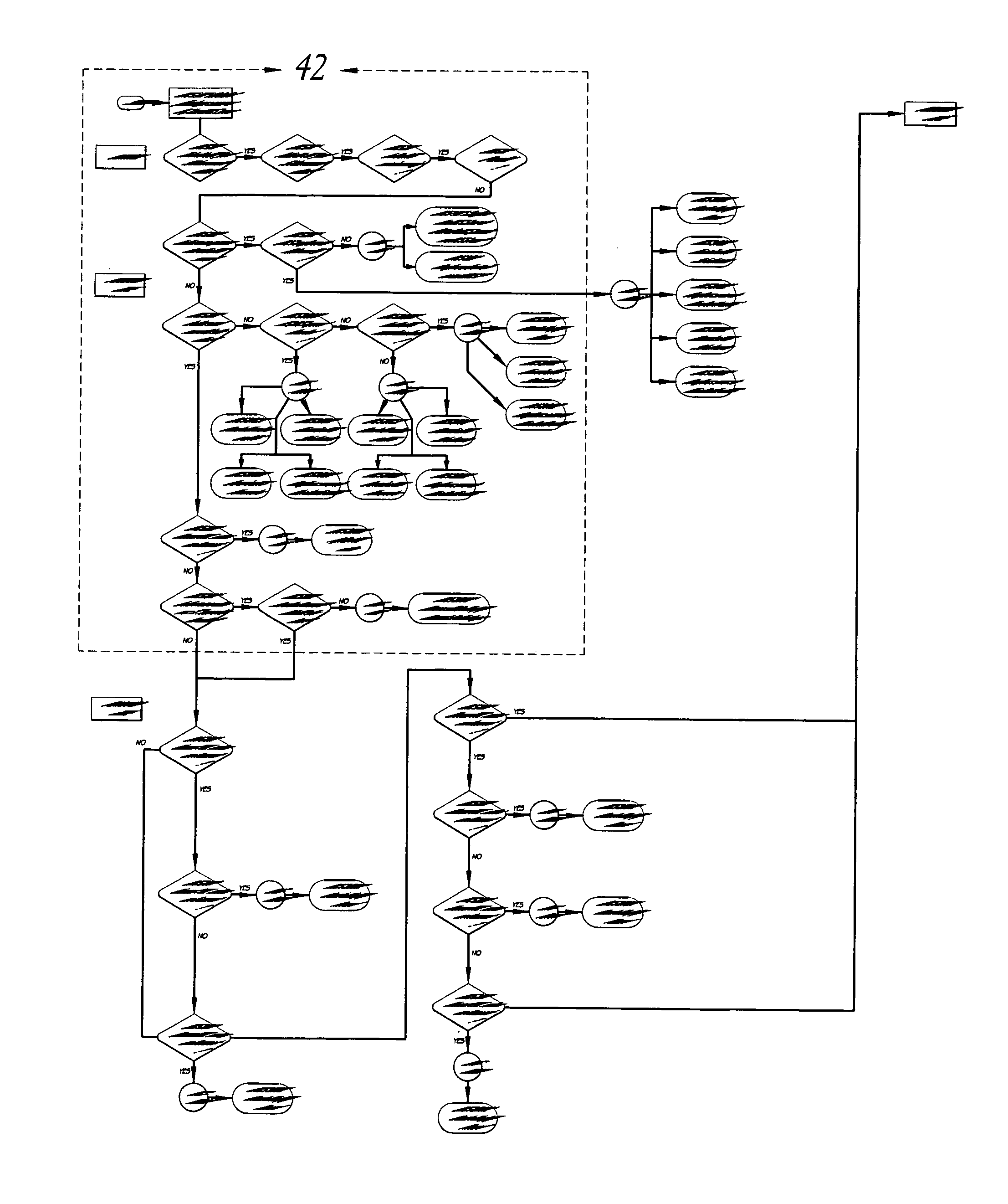
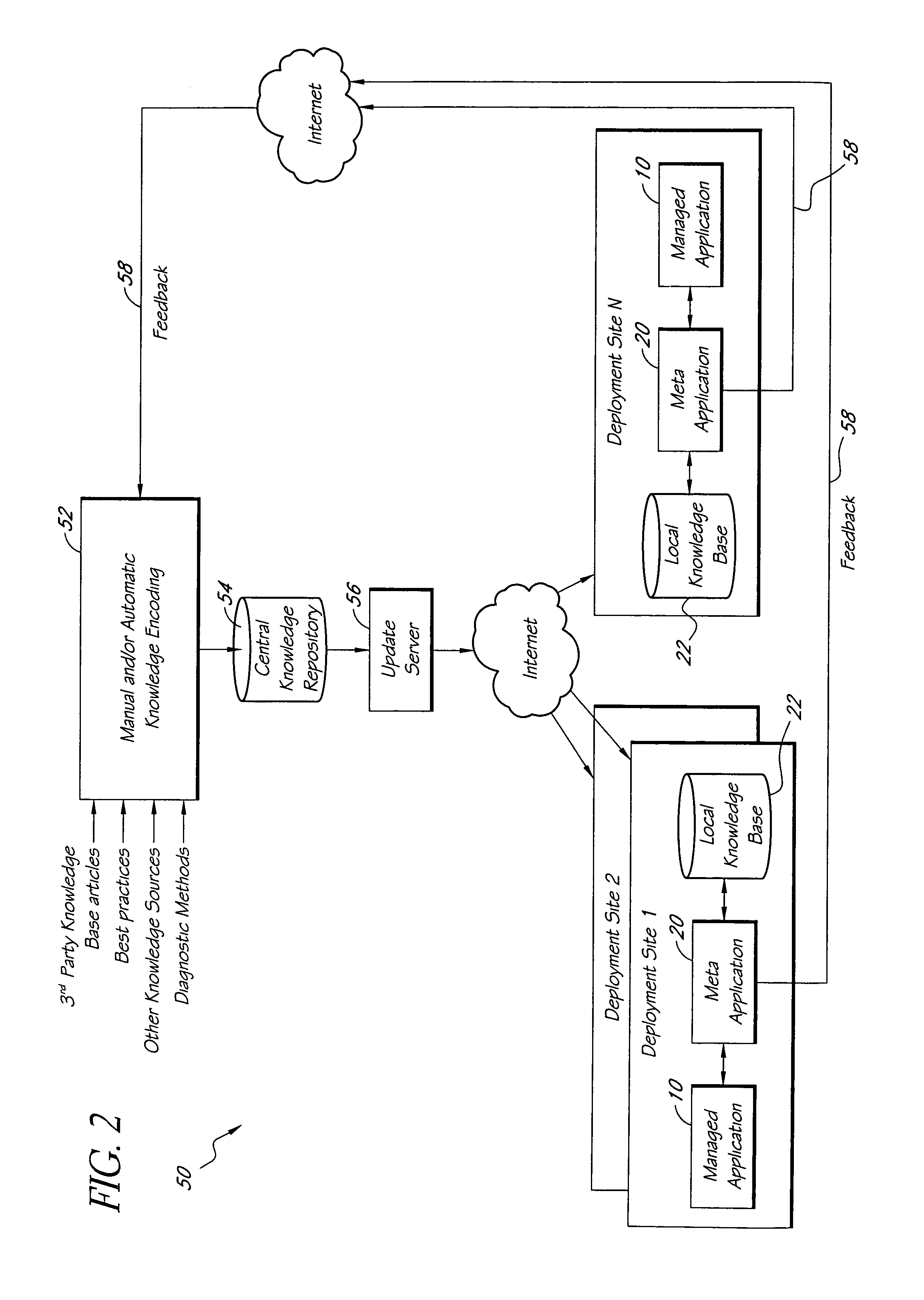
A method of encoding knowledge is disclosed, which can be used to automatically detect problems in software application deployments. The method includes accessing a source of knowledge describing a problem known to occur in deployments of a particular software application, and which identifies a plurality of conditions associated with the problem. An encoded representation of the knowledge source is generated according to a predefined knowledge encoding methodology. The encoded representation is adapted to be applied automatically by a computer to analyze data representing a current state of a monitored deployment of the software application to detect whether the conditions and the problem exist therein. In various implementations, the encoded representation of the knowledge can include queries for deployment information, information concerning the relative importance of the conditions to a detection of the problem, and / or logical constructs for computing a confidence value in the existence of the problem and for determining whether to report the problem if some of the conditions are not true. The knowledge source can comprise a text document (such as a knowledge base article), a flowchart of a diagnostic troubleshooting method, and the like. Also disclosed are methods of at least partially automating the encoding process.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Automated detection of problems in software application deployments
ActiveUS7788536B1Efficient mappingGreat leverageError detection/correctionInference methodsData miningData value
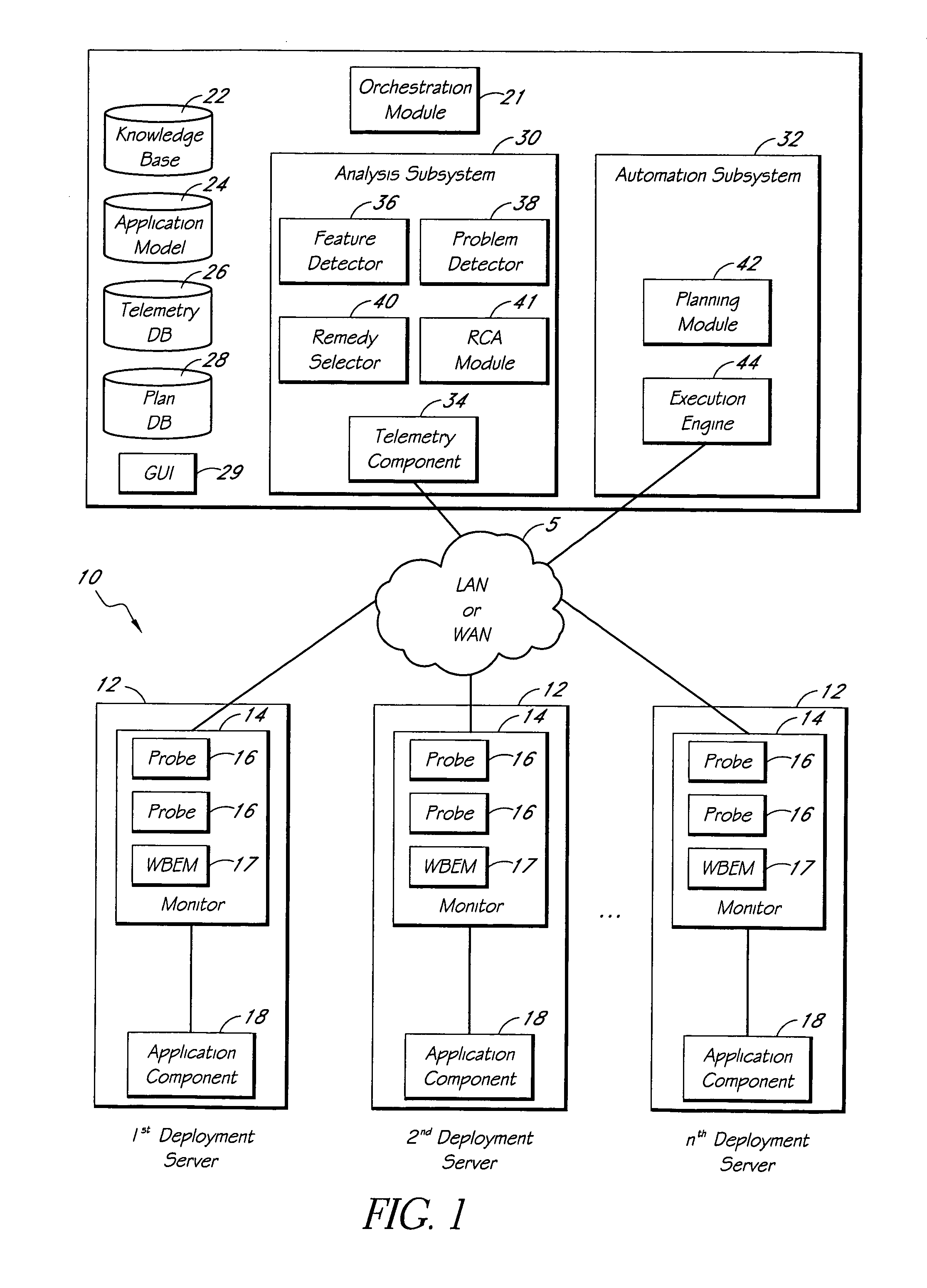
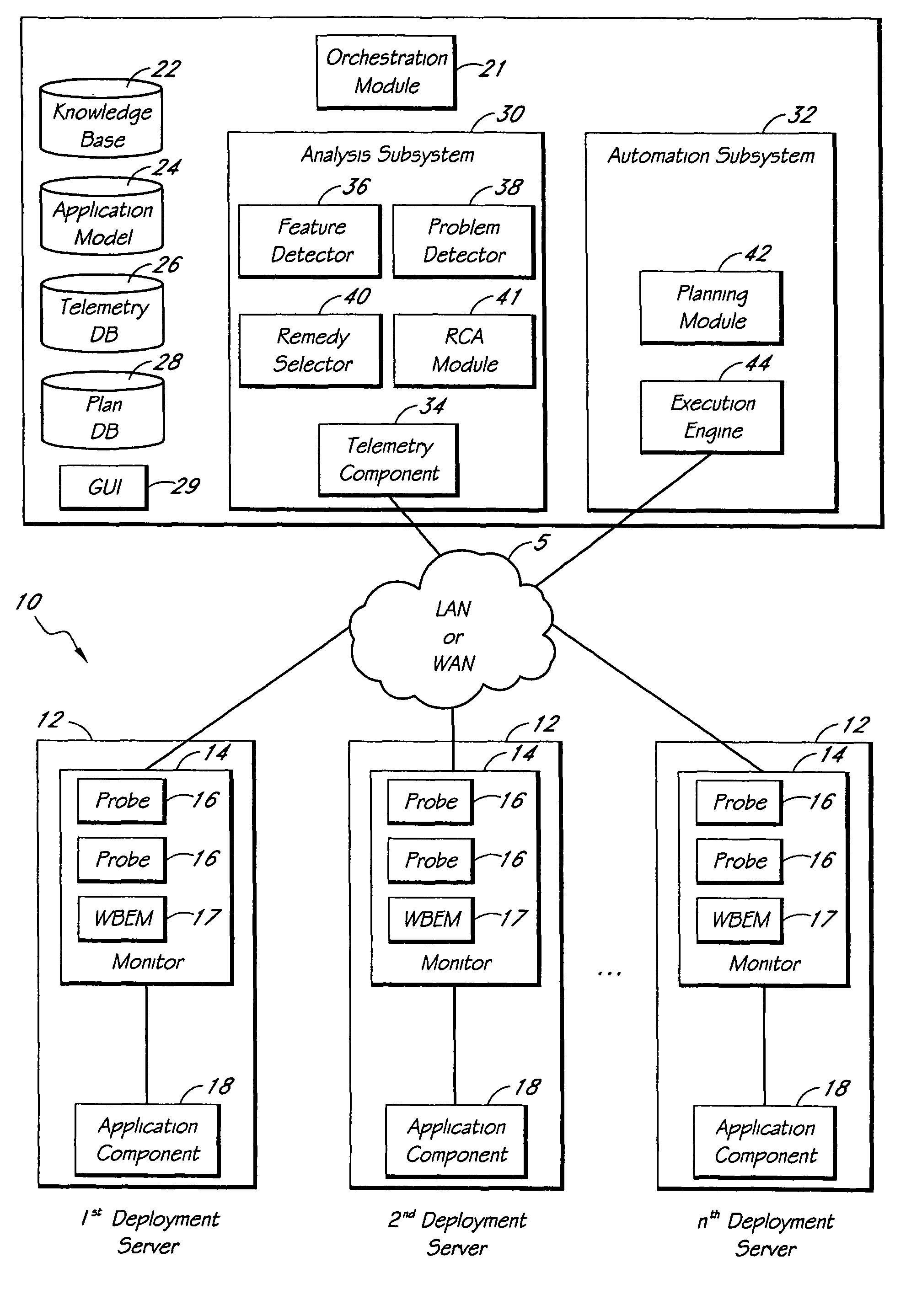
A system for monitoring and analyzing the operation of a deployment of a software application is disclosed. The system includes a monitoring component, a repository that stores a plurality of rules, and an analysis engine. The monitoring component collects data values of each of a plurality of state metrics associated with the deployment of the software application. At least some of the rules in the repository map respective combinations of states associated with the state metrics to corresponding problems. The analysis engine programmatically detects instances of said problems, at least in-part, by using the rules to analyze the state metric data values collected by the monitoring component. The rules can also include remedies associated with the detected problems, and the system may include remedy selection and execution modules.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
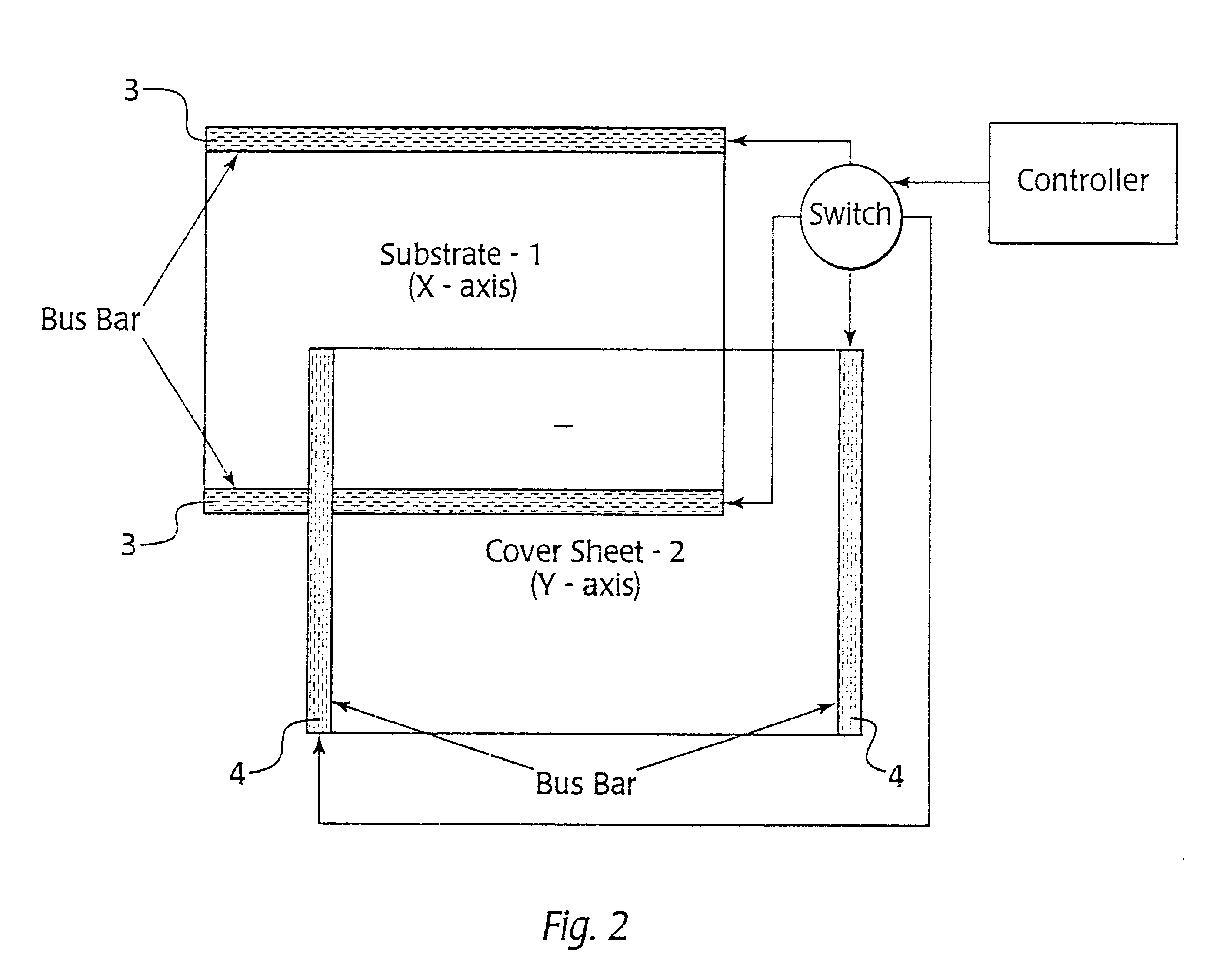
Algorithmic compensation system and method therefor for a touch sensor panel
InactiveUS6506983B1Efficient mappingEfficient polynomial coefficient storageTransmission systemsUsing electrical meansCurve fittingTouchscreen
A general method is described for producing an inexpensive touchscreen system that provides accurate positional information and compensates for manufacturing variations without complicated sensor arrangements. Utilizing a set of sensed signals that are unique to each location on the touchscreen sensor, equations for X and Y are derived via curve fitting methods. The coefficients of the equations are stored with the sensor. During touchscreen operation the coefficients are used to calculate X and Y to the desired accuracy directly and independently.
Owner:ELO TOUCH SOLUTIONS INC
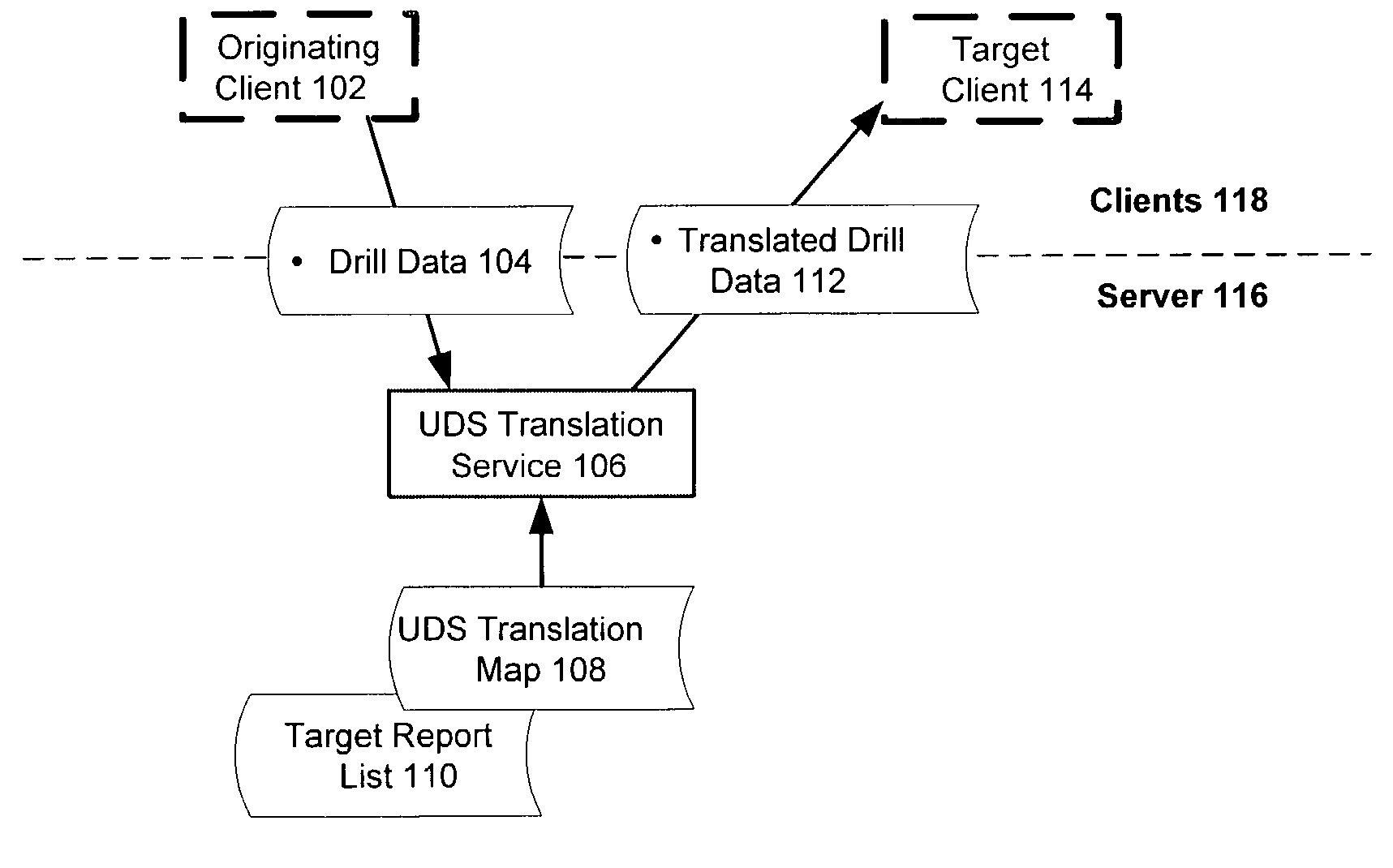
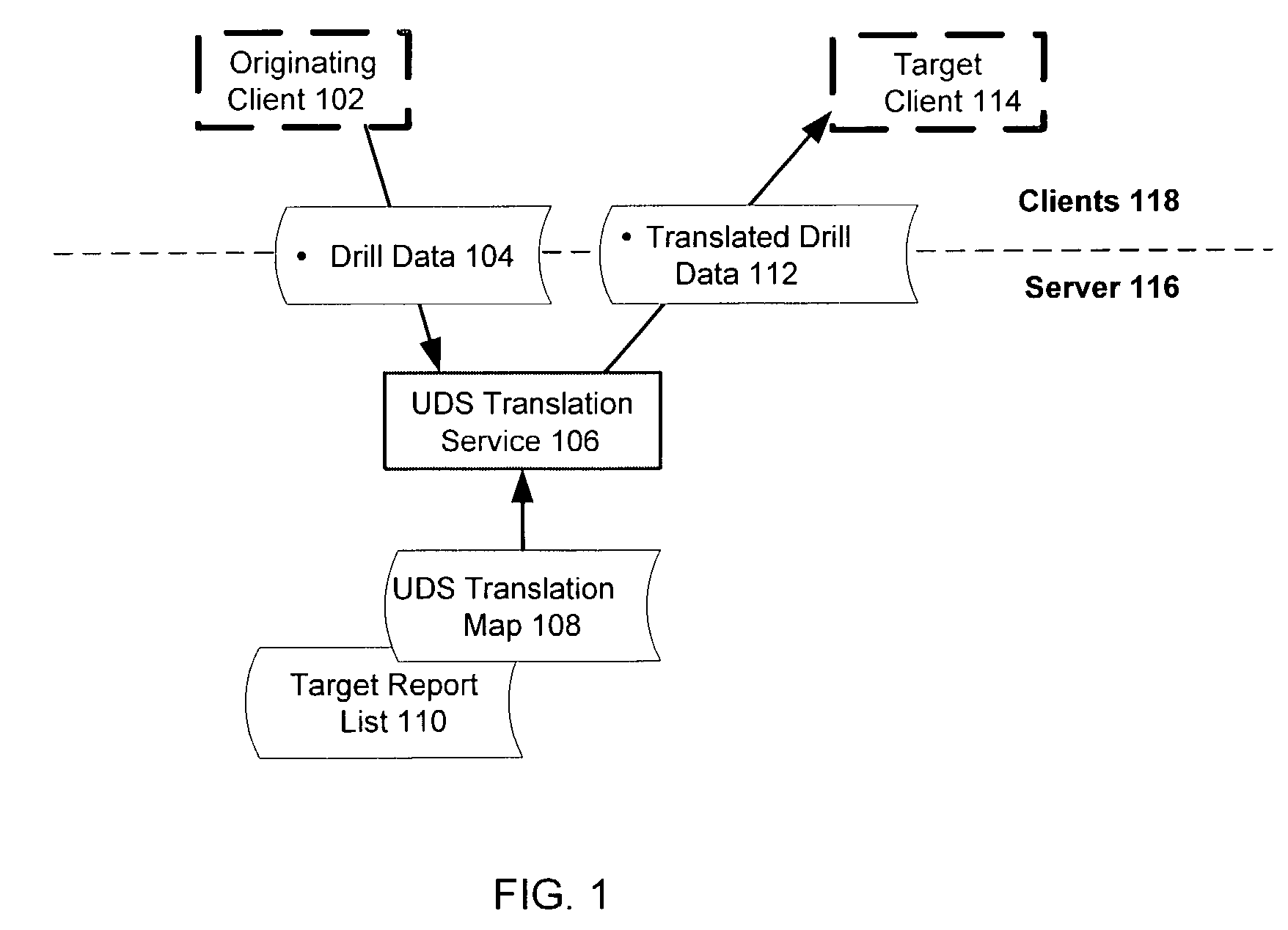
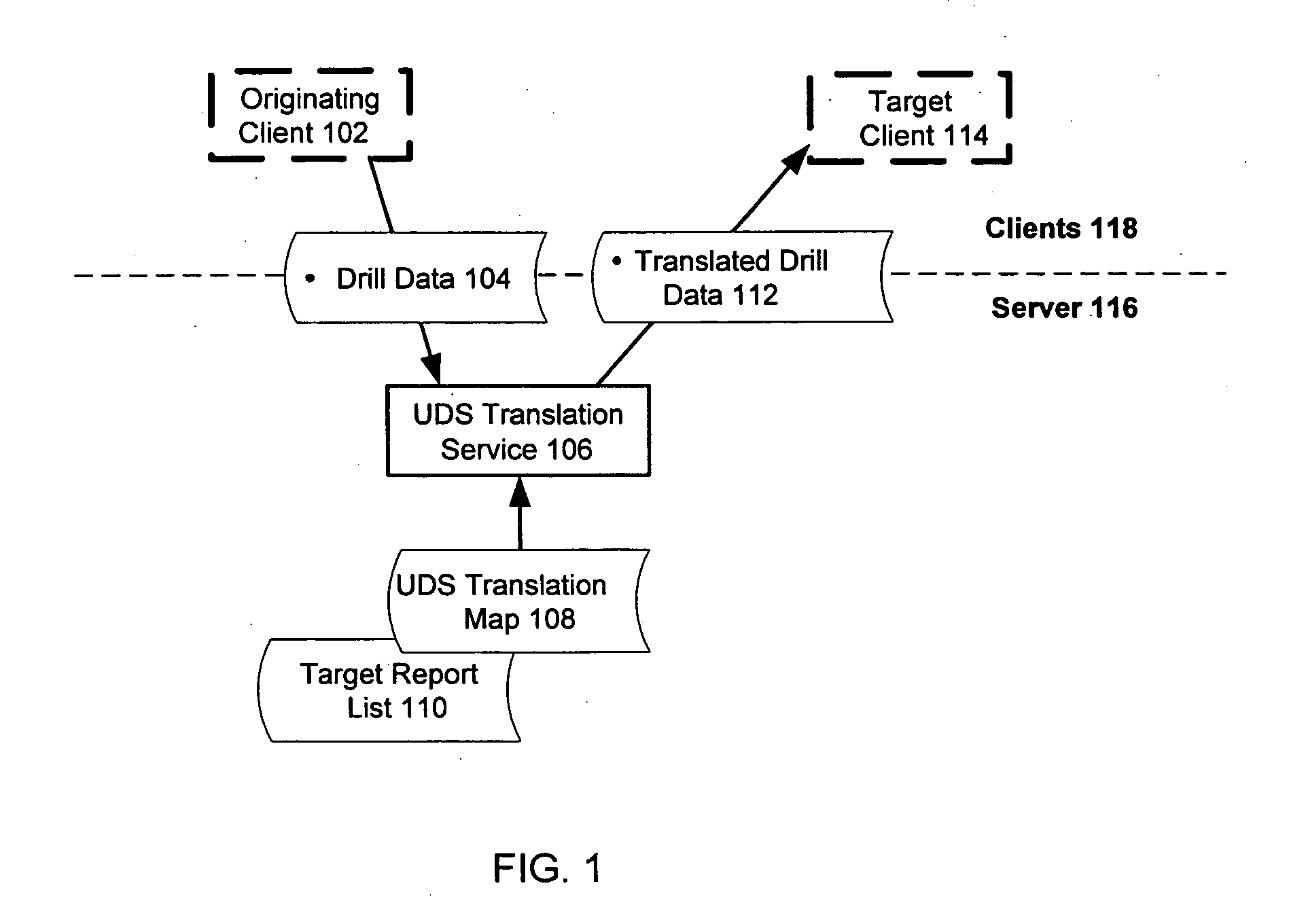
Universal drill-down system for coordinated presentation of items in different databases
ActiveUS7139766B2Accurate mappingEfficient mappingData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDrill downData source
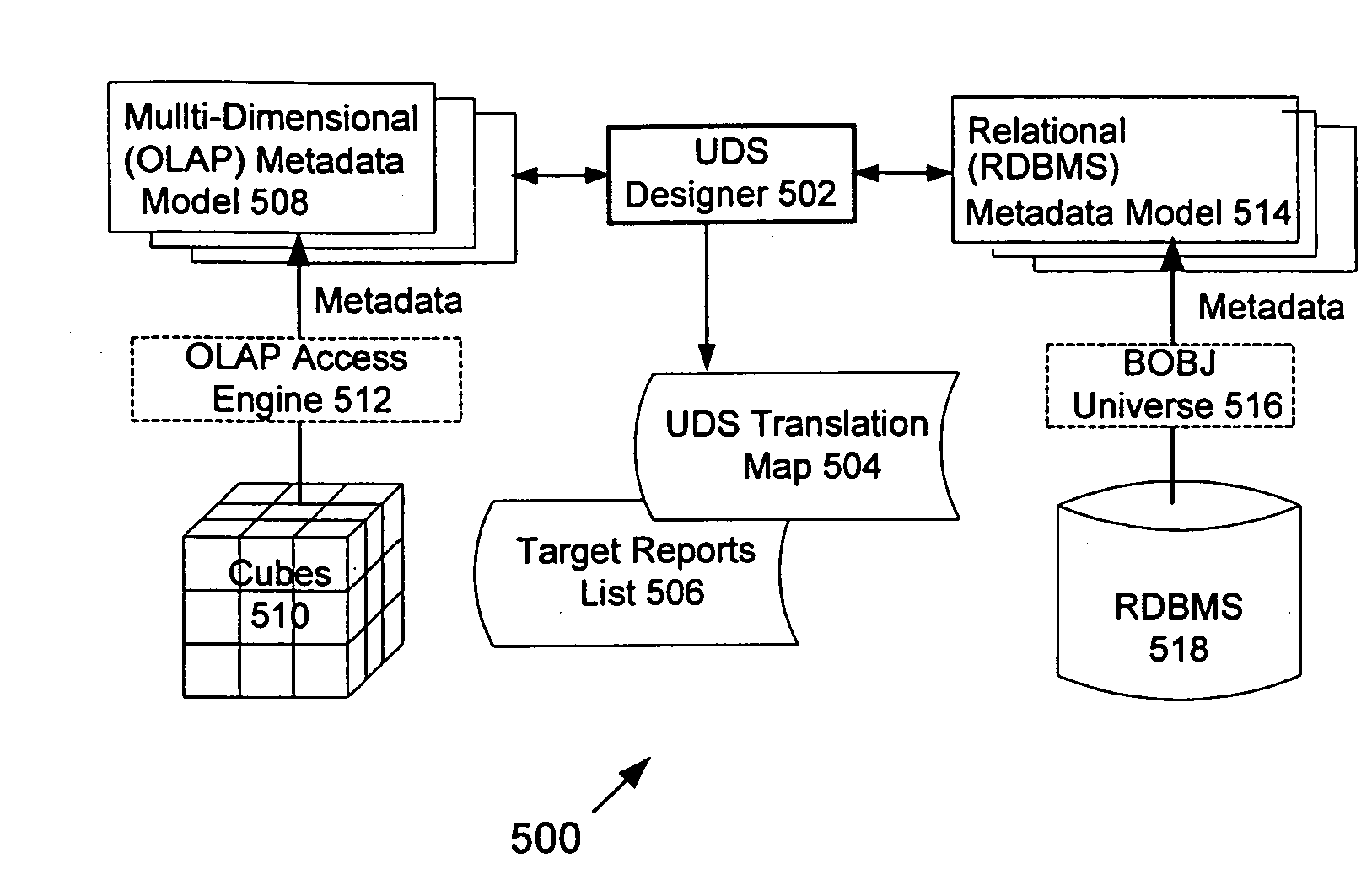
A computer implemented method for mapping data from one presentation to another includes capturing and transmitting the context of an original report based on an originating data source such that it preserves the organization of the query and variable levels of context “fidelity”. The context of the originating report is translated in terms of the originating data source to a target context for presentation of a target report based on a target data source. The translation of different mapping scenarios is controlled in accordance with a translation model with a translation map.
Owner:BUSINESS OBJECTS SOFTWARE
Methods and apparatus for storage virtualization
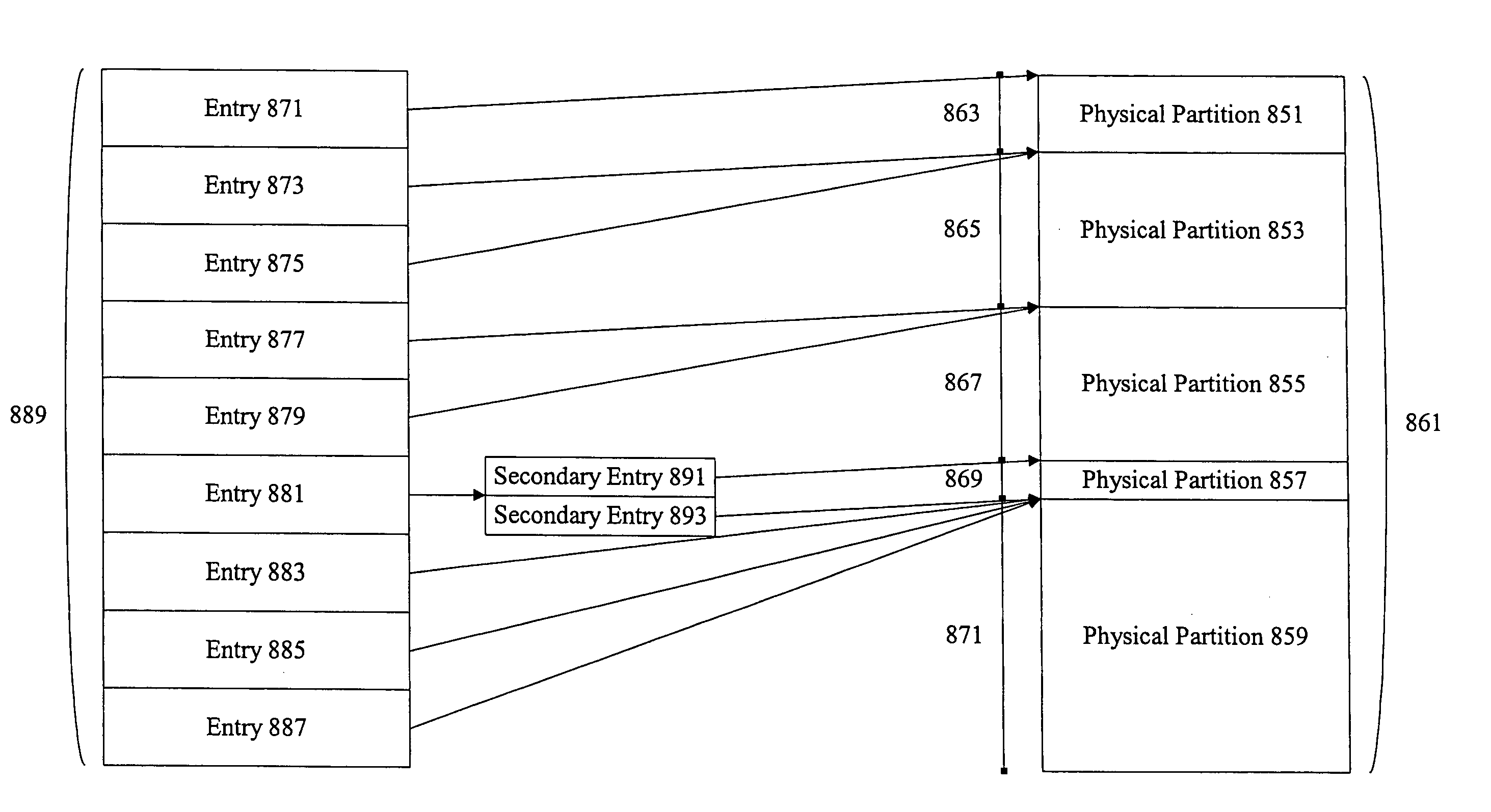
InactiveUS6948044B1Improve data access efficiencyEfficient mappingInput/output to record carriersError preventionStorage area networkData access
Methods and apparatus are provided improving data access efficiency in a storage area network. Mechanisms are provided to allow a virtual disk address to be efficiently mapped to a particular physical partition in a virtual disk while recognizing the mirroring, striping, and concatenation characteristics associated with the virtual disk. A variety of indices are used to allow direct access of a physical partition upon identification of a virtual disk address.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Data extensibility using external database tables
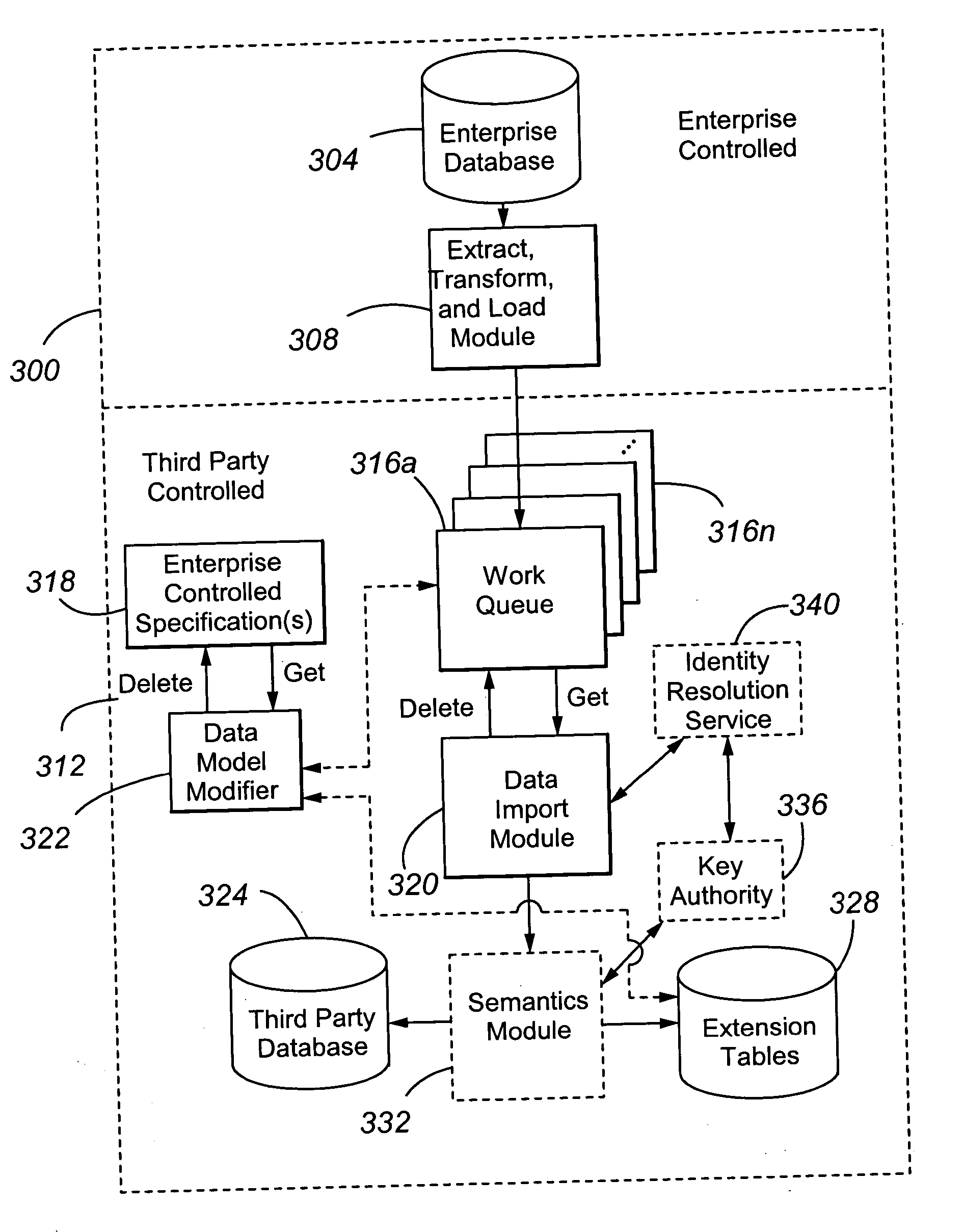
ActiveUS20070083572A1Efficient mappingProvide protectionDatabase updatingDigital data protectionExtensibilityData processing system
In one embodiment, a data processing system includes: (a) a first database 304 maintained by a first party; (b) a second database 324, 328 maintained by a second party different from the first party; (c) a work queue 316 operable to specify data to be added to the second database; (d) an extract, transform and load module 308 operable to write data from the first database to the work queue; and (e) a data import module operable 320 to import data from the work queue to the second database. In the system, the first party is not privileged to write the data directly to the second database.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method and apparatus for prioritizing information protection in high order modulation symbol mapping
InactiveUS6476734B2Increase chanceImprove performanceCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareHigher-order modulation
Owner:APPLE INC
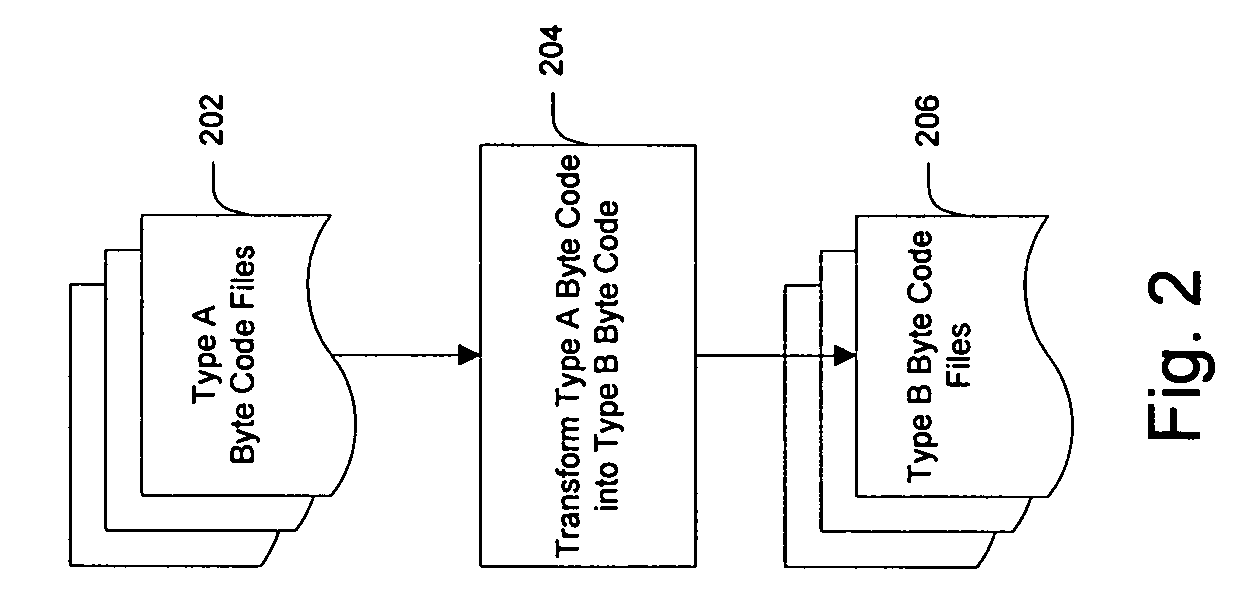
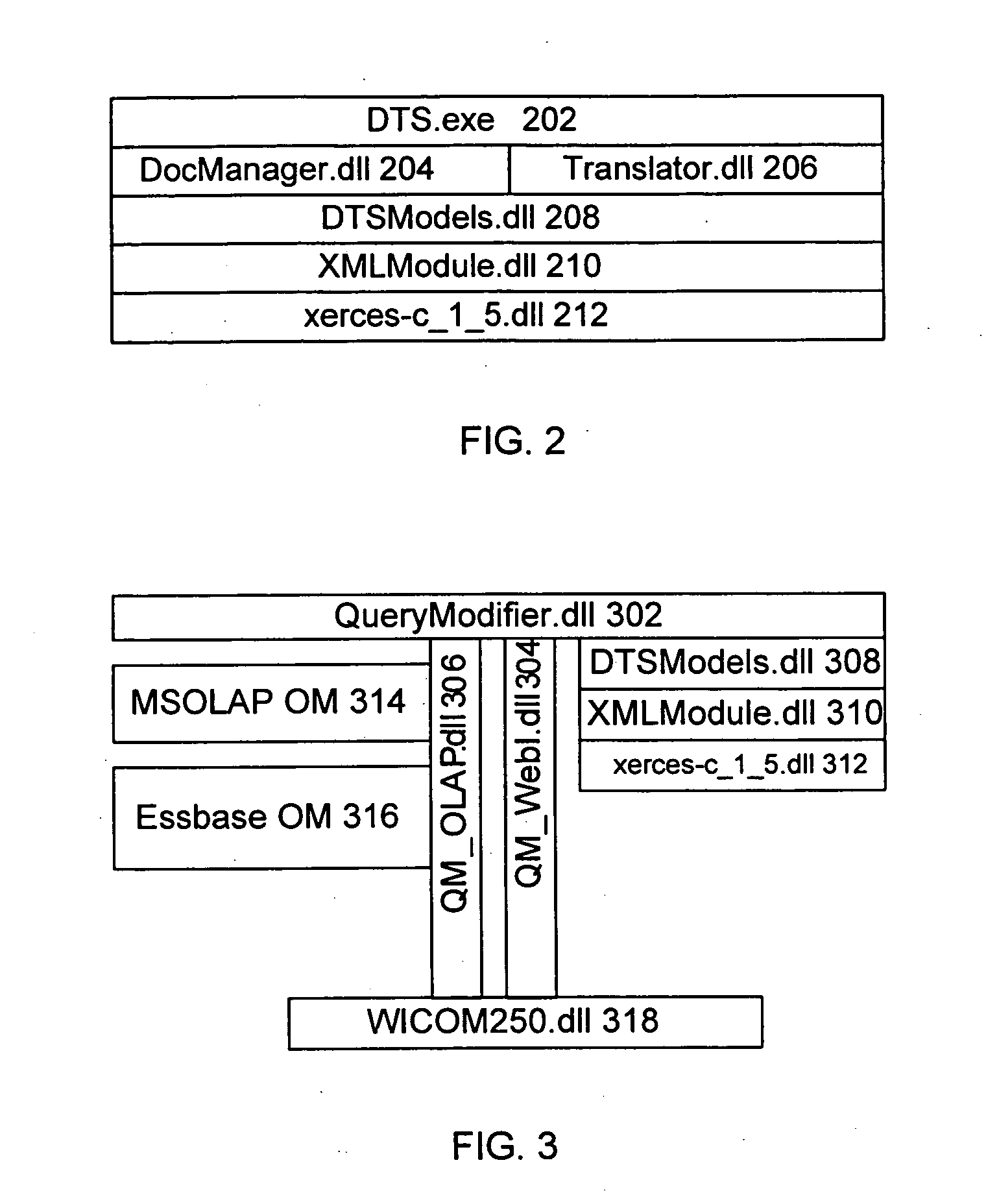
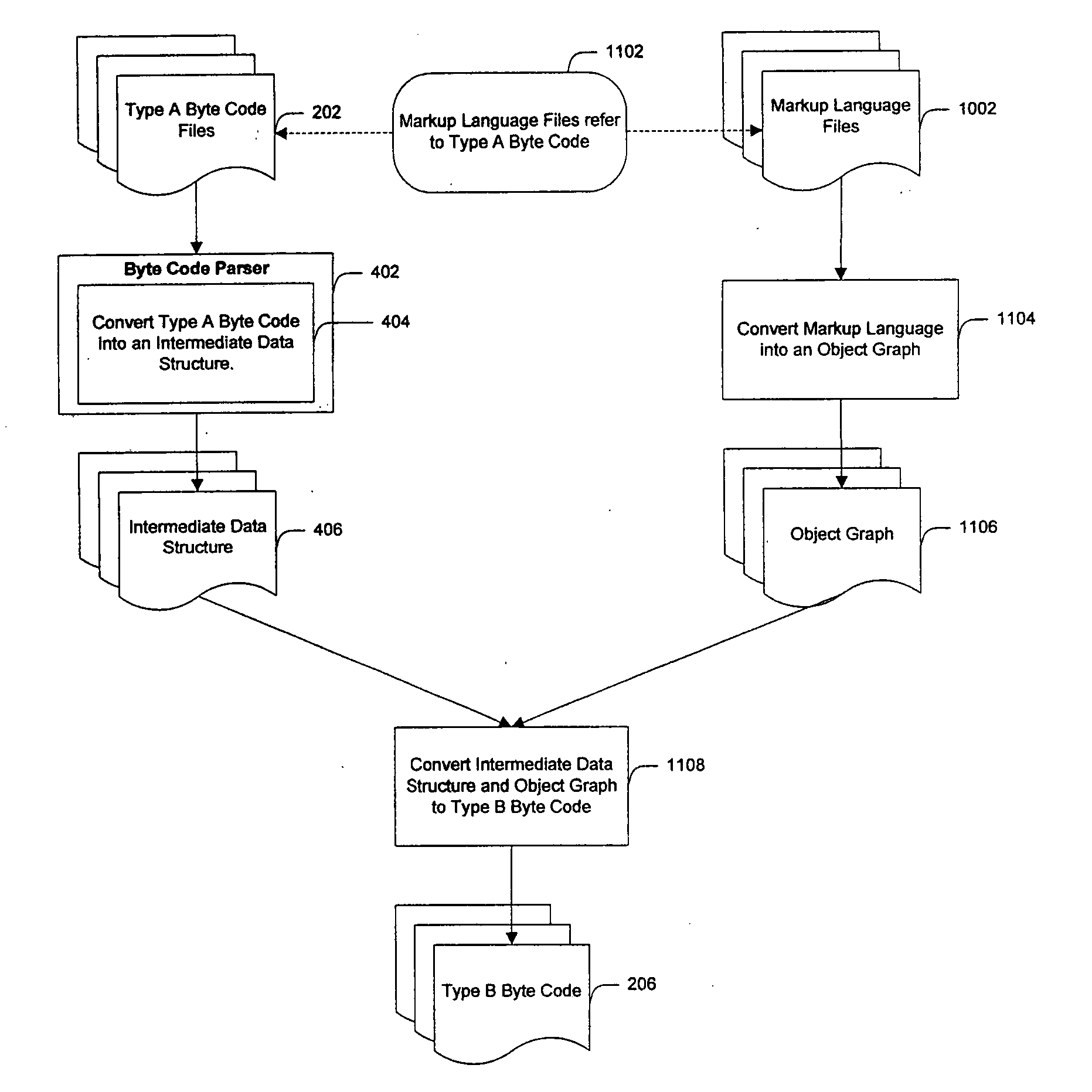
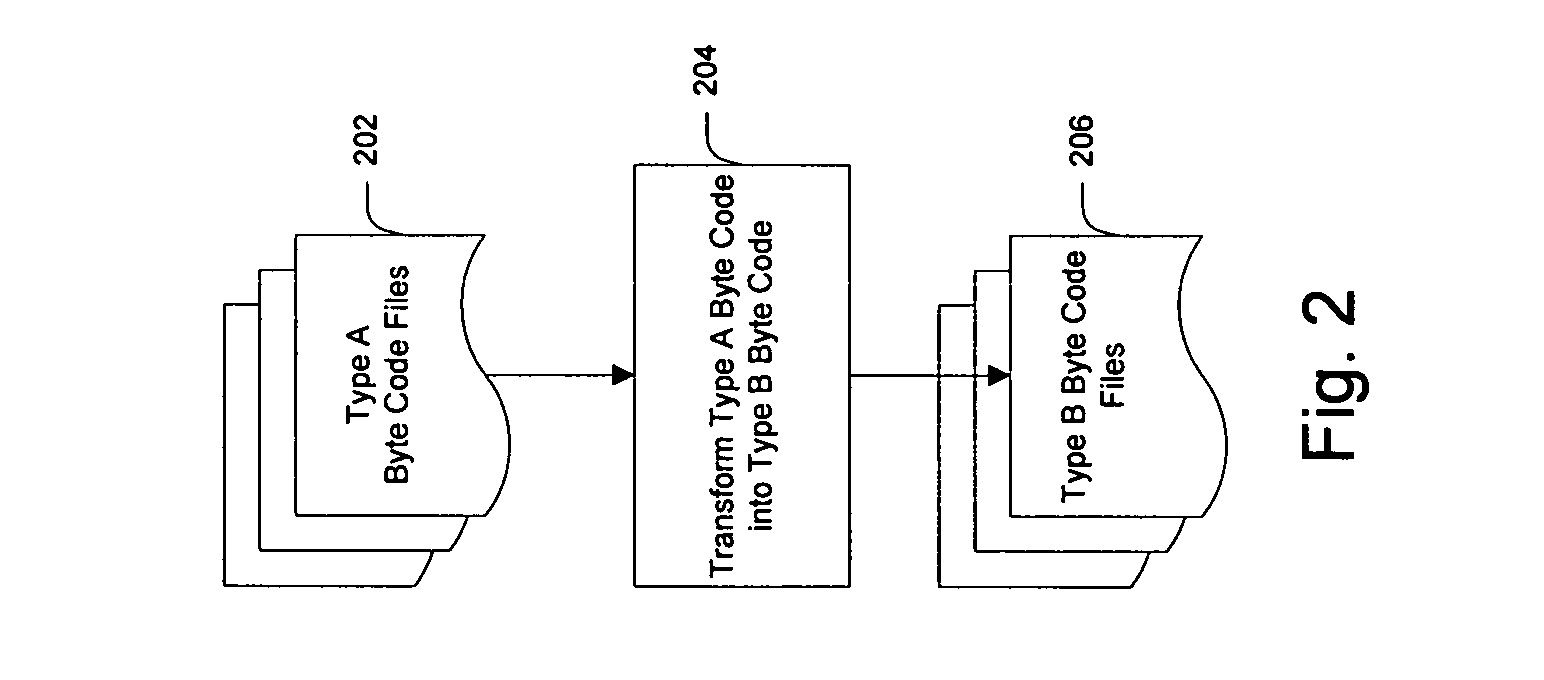
System and method for creating target byte code
InactiveUS7707547B2Efficient mappingSmaller and faster byte code of a second typeBinary to binaryDigital data processing detailsData elementByte
Owner:APPCELERATOR
Peer-to-peer semantic indexing
InactiveUS20070112803A1Efficient mappingData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData objectsPeer-to-peer
An index data structure comprises a plurality of index keys for uniquely identifying potential data object context nodes. Each index key is, in turn, associated with one or more potential context nodes. Moreover, the index key has a label that provides semantic content to a user. The index data structure further comprises one or more routing tables associated with each index key that generally include a plurality of path references.
Owner:PETTOVELLO PRIMO M
Method for content-aware redirection and content renaming
InactiveUS6954456B2Efficient mappingEfficiently mappedTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsContent discoveryInformation retrieval
The present invention is directed to mechanisms for content-aware redirection and content exchange / content discovery that permit a request for content to be redirected to a particular advantageous server that can serve the content.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
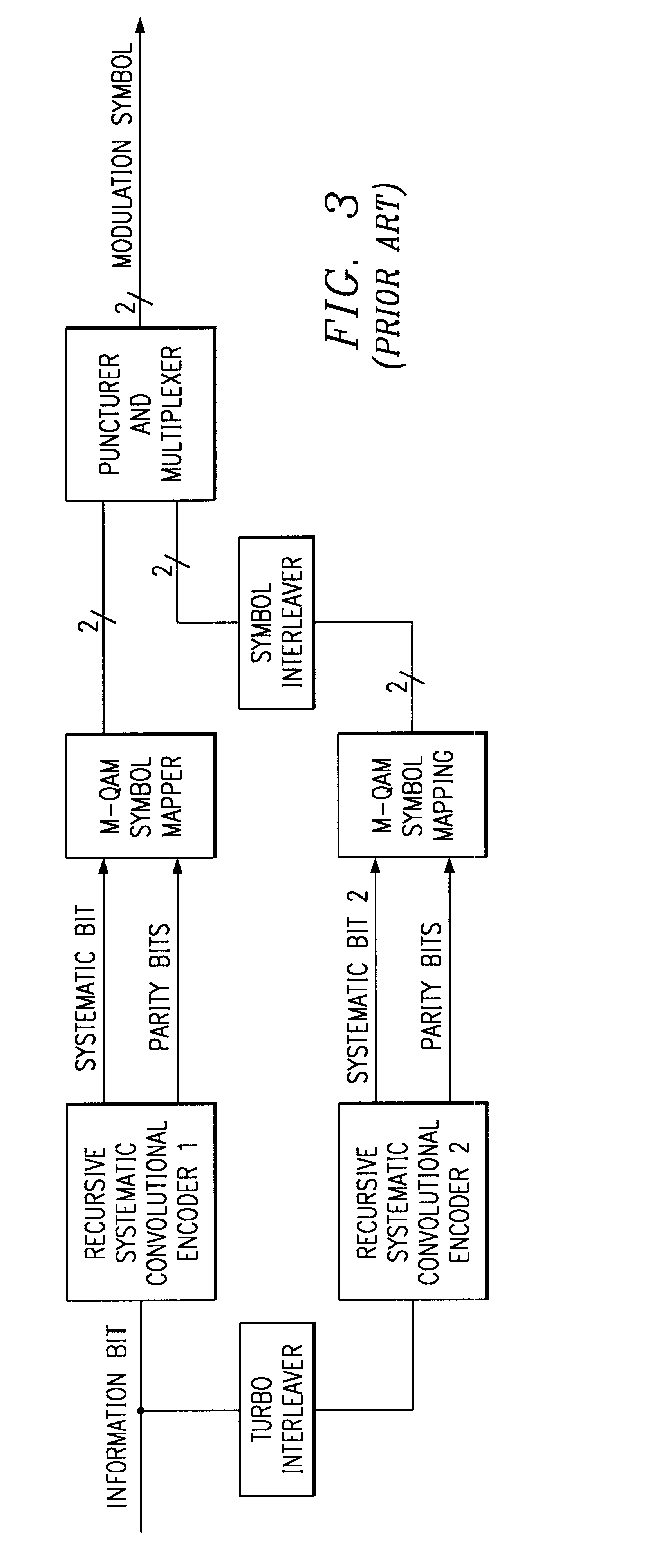
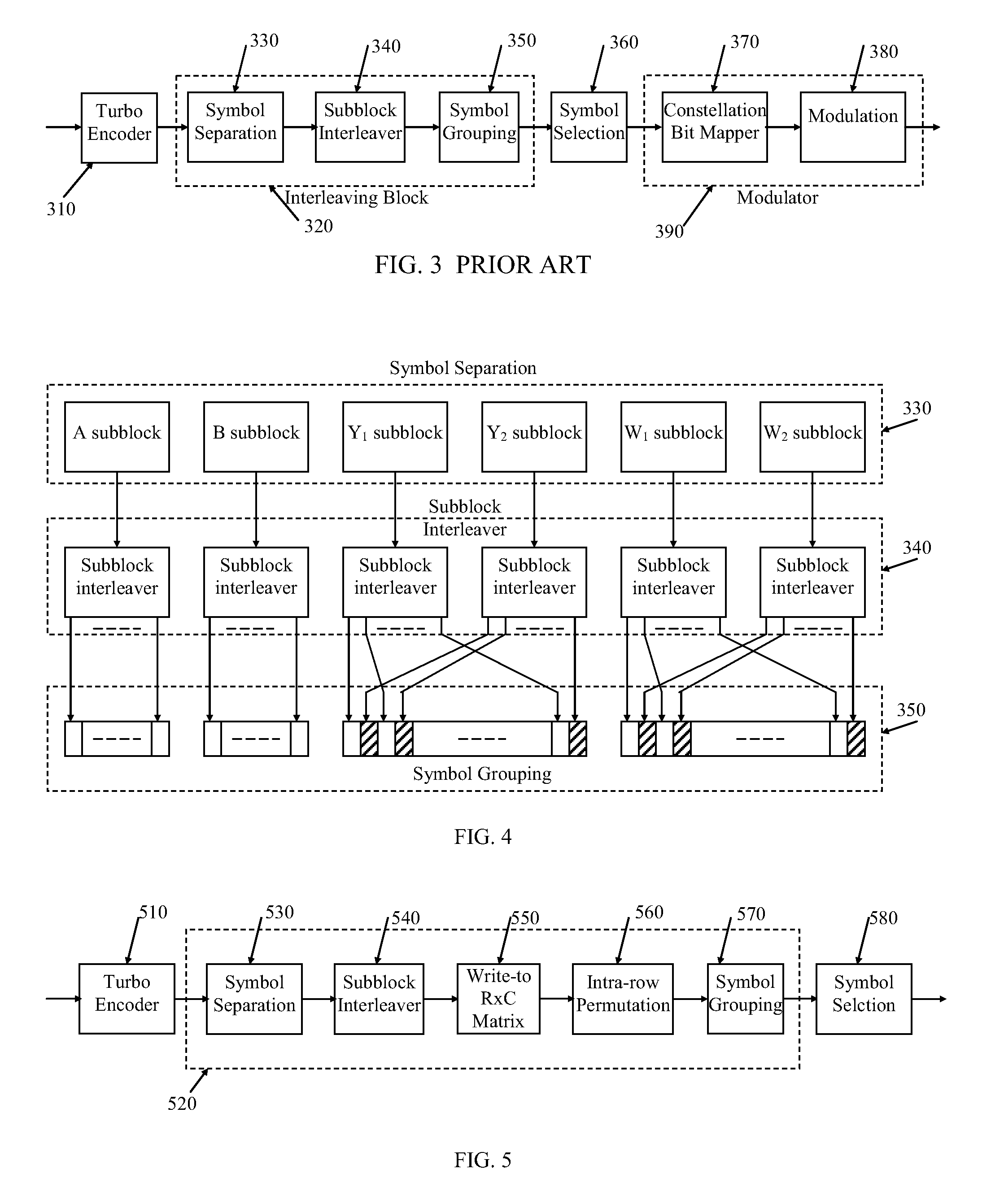
Bit Reverse Interleaving Methods for QAM Modulation in a Wireless Communication System
ActiveUS20090113274A1Efficient mappingEasy to operateError detection/correctionCode conversionCommunications systemQam modulation
In a communication method, a sequence of information bits is encoded into systematic bits and parity bits. The systematic bits and the parity bits are grouped in output blocks, each output block to be assigned to an address of a constellation scheme. The addresses include addresses that are more prone to error and address that are less prone to error so that the symbols are grouped such that bits in groups of consecutive bits of the sequence of information bits are not all assigned to addresses that are more prone to error.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Method and applications for rasterization of non-simple polygons and curved boundary representations
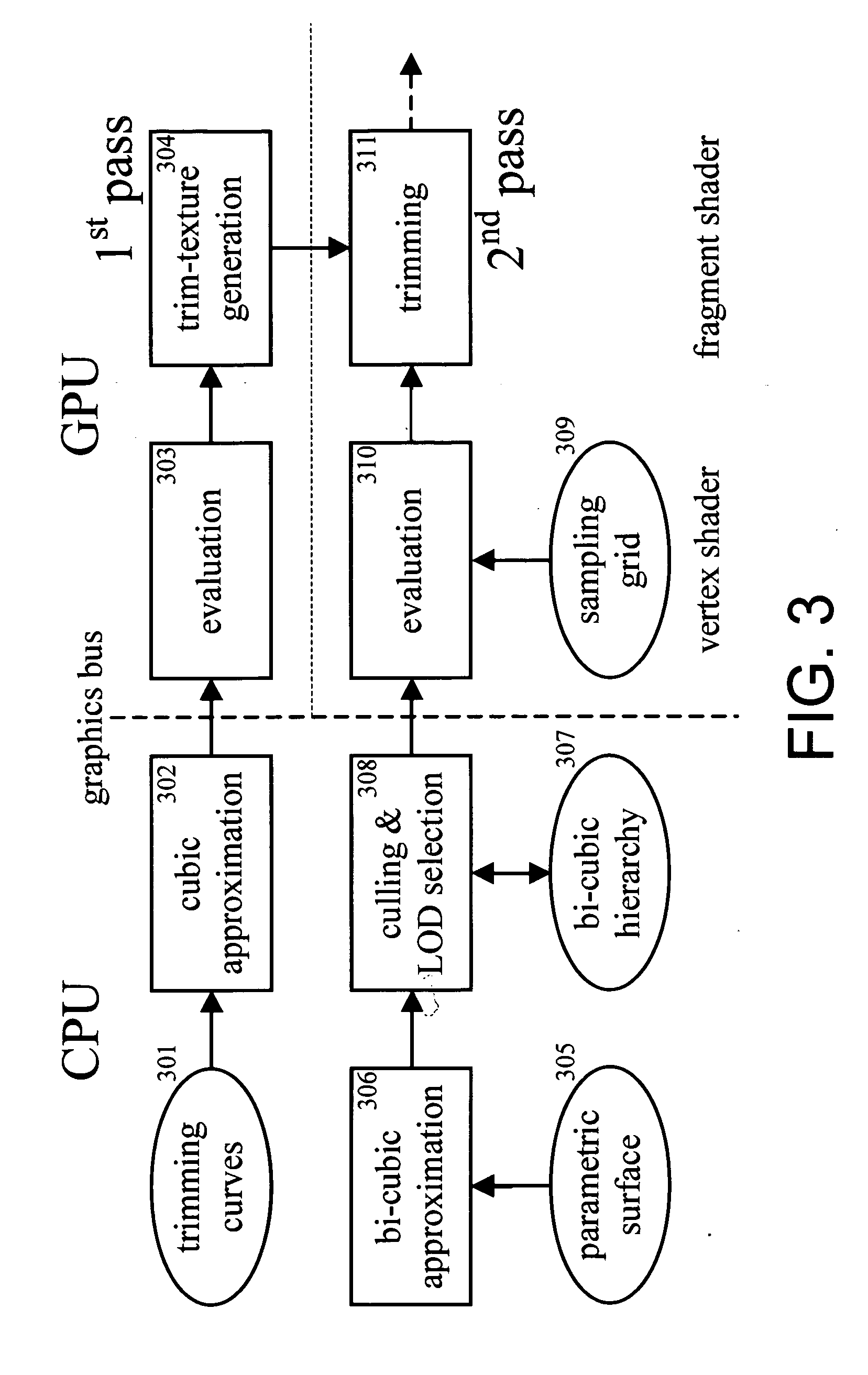
A hardware-accelerated method for the rasterization of non-simple polygons is used to generate a trim-texture that is dynamically adapted to the required resolution. This method is combined with a GPU-based tessellation of parametric surfaces and a method to generate non-simple polygons with the required resolution from the parametric trimming curves on the GPU. This way trimming and tessellation of parametric surfaces like rational Bézier and Spline surfaces can be performed on the GPU. The method can also be used for the visualization of 2D boundary data on arbitrary parametric surfaces.
Owner:GUTHE MICHAEL
Method and system for efficient emulation of multiprocessor address translation on a multiprocessor host
ActiveUS20040054518A1Efficient mappingEfficiently maps the shared memoryError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtual memoryMemory address
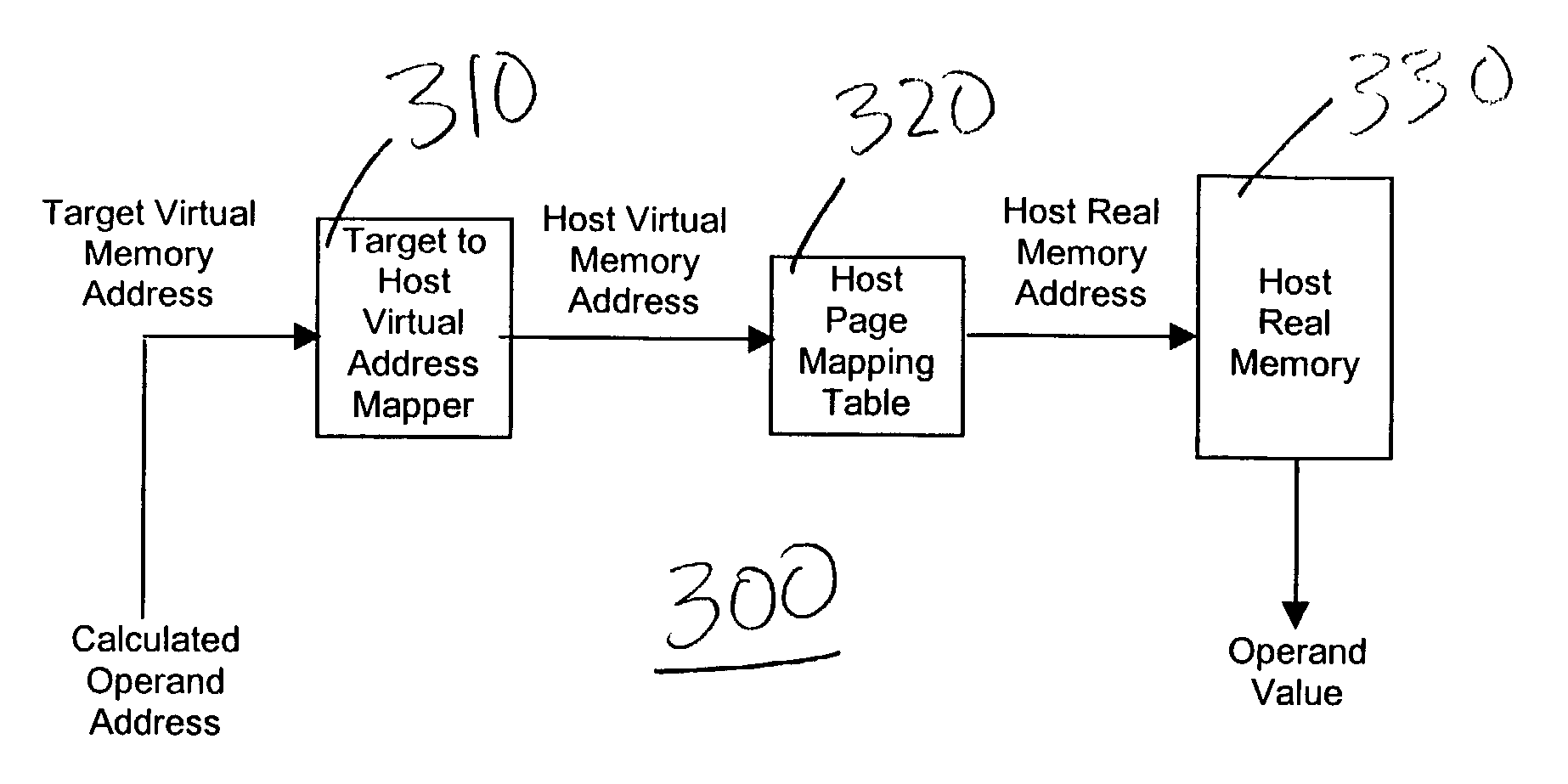
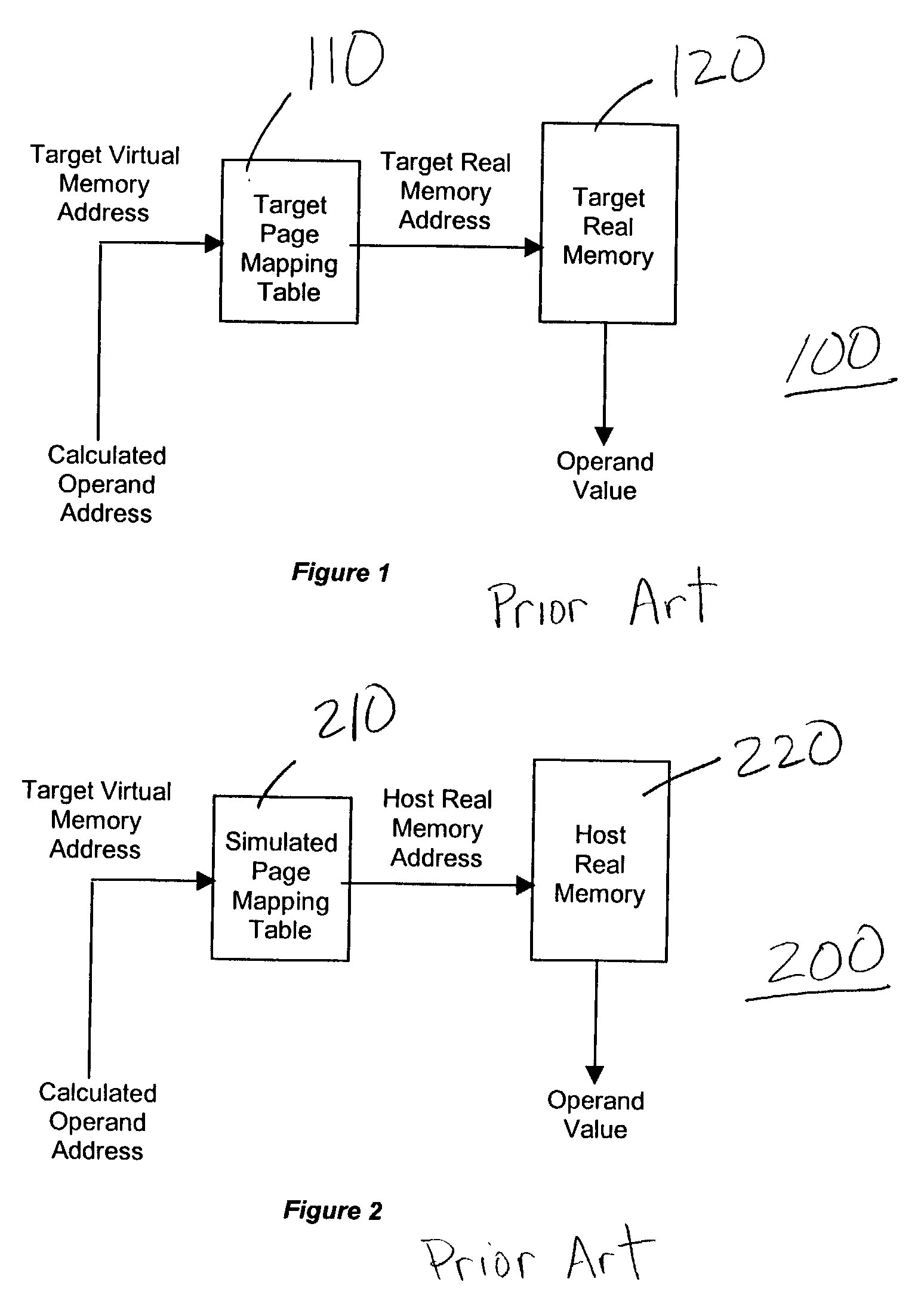
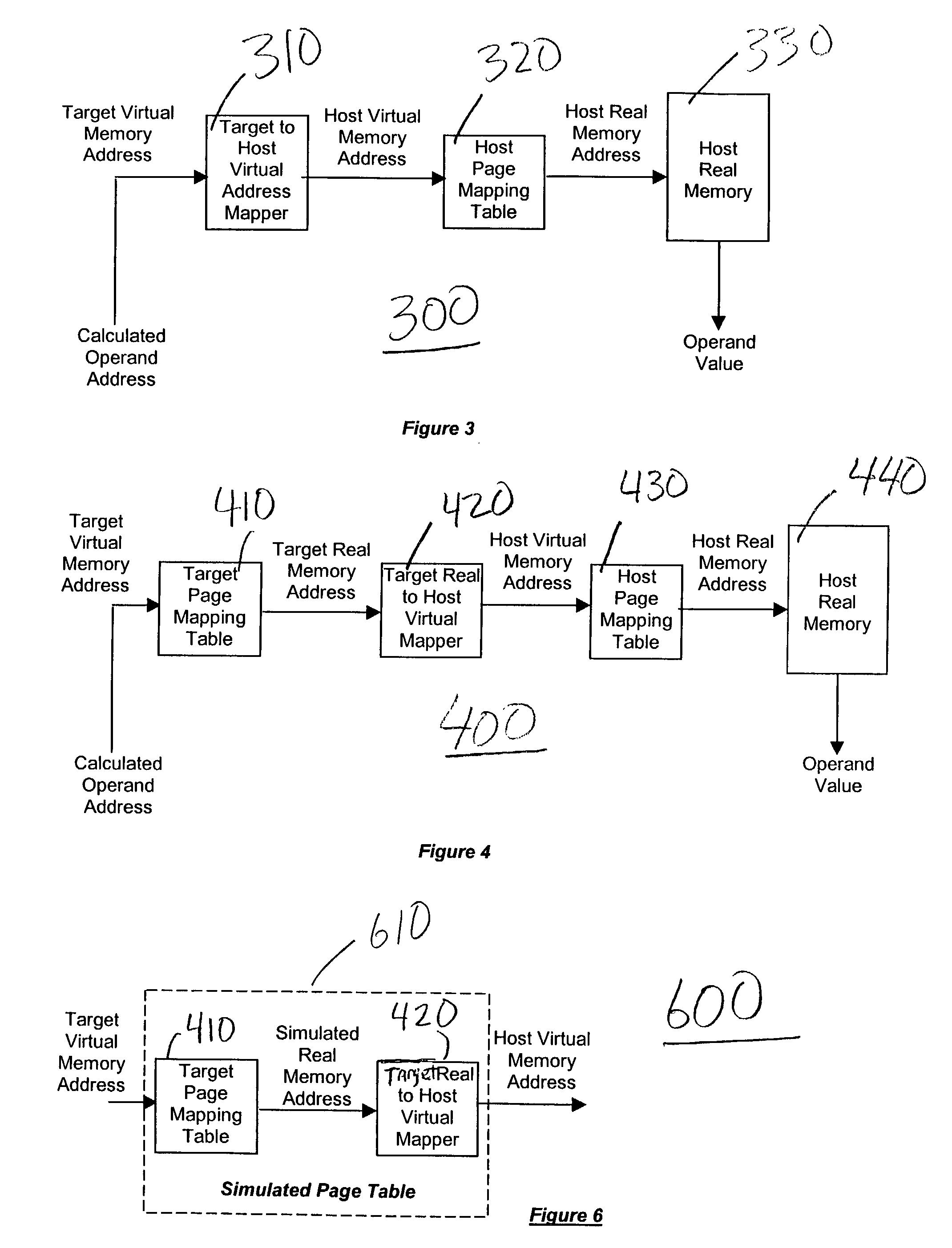
A method (and system) for emulating a target system's memory addressing using a virtual-to-real memory mapping mechanism of a host multiprocessor system's operating system, includes inputting a target virtual memory address into a simulated page table to obtain a host virtual memory address. The target system is oblivious to the software it is running on.
Owner:IBM CORP
Universal drill-down system for coordinated presentation of items in different databases
InactiveUS20060294098A1Accurate mappingEfficient mappingData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDrill downData source
A system for capturing the context of, and translating, or mapping, from data in an originating database presentation, or in an originating format, to data in a target database presentation, or target format. The translation uses the context of the originating report / query in terms of the originating database as a basis for the translation. The originating context is translated to the target context and is used to accurately map data from one presentation to another. By using a context and a translation map, which define specifics of the translation between contexts against different data sources, the invention is able to achieve a mapping engine that can efficiently map data between databases of different types. The translation map includes rules set automatically by the system, or set by a human administrator. The rules permit special treatment of different mapping scenarios. For example, specified types of mappings can be prevented so that selected users will be denied the ability to access restricted target information. Member exceptions are used that permit mapping between different data models, as, for example, where rows or columns in an originating data source (e.g. OLAP) are not present in a target data source (e.g. Relational). Other aspects of the invention include using supplemental member translations, translating items in an OLAP level to more than one translation object, delegating data items in cases where there is little or no correspondence between data models, translating a data item to a plurality of data items, translating a data item to a range, and additional aspects. An administrator interface is provided to create, modify, monitor and manage a mapping system.
Owner:BUSINESS OBJECTS SOFTWARE
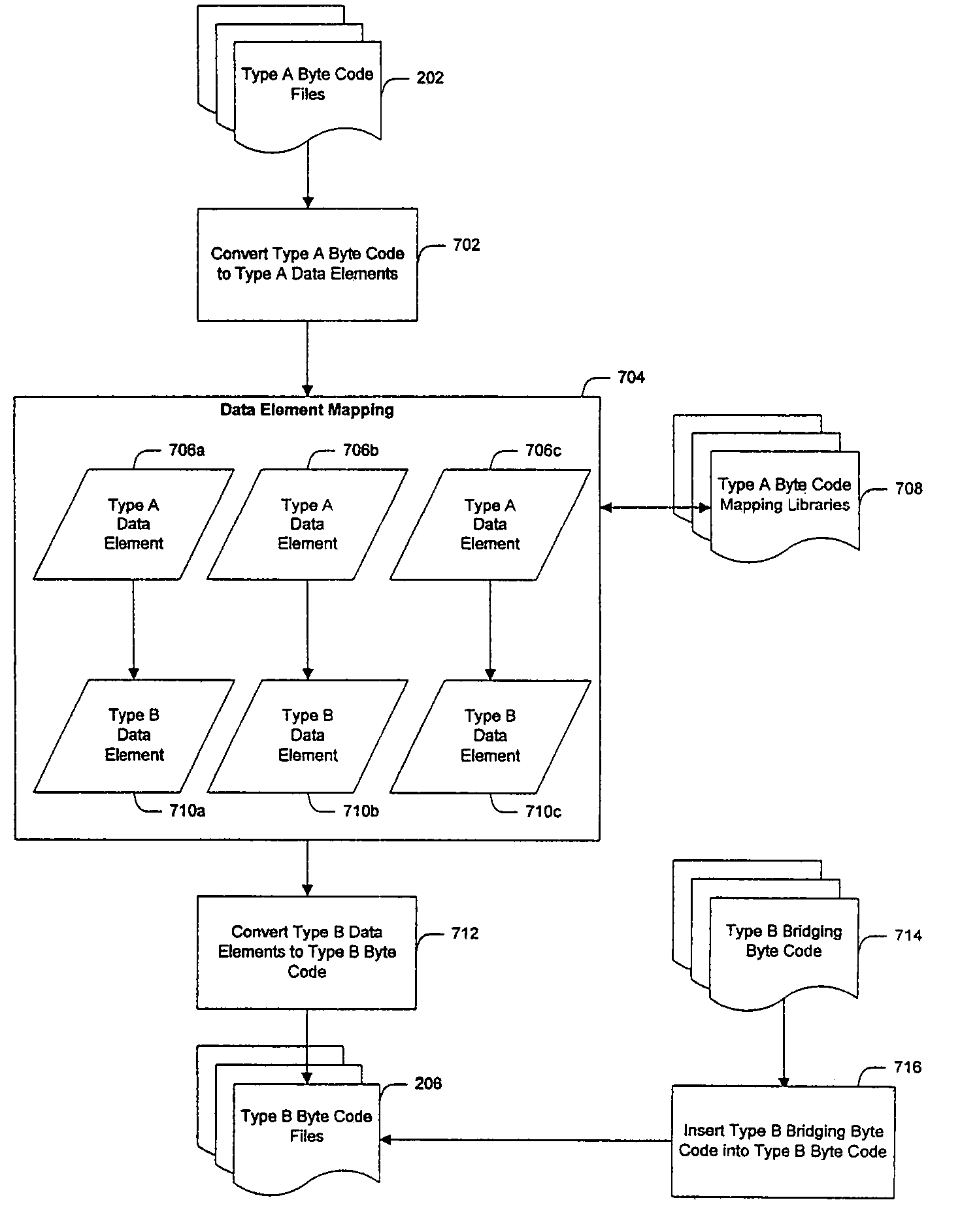
System and method for creating target byte code
InactiveUS20060230070A1Improve developmentEfficient mappingBinary to binaryDigital data processing detailsSoftwareByte
A system and method for converting byte code of a first type into byte code of a second type. Byte code of a first type is received as input. The first byte code is converted into constituent byte code data elements that can comprise any logical unit or grouping of at least a portion of a software application. The first byte code data elements are mapped to data elements of a second byte code type. The second byte code data elements are assembled into a resulting second byte code.
Owner:APPCELERATOR
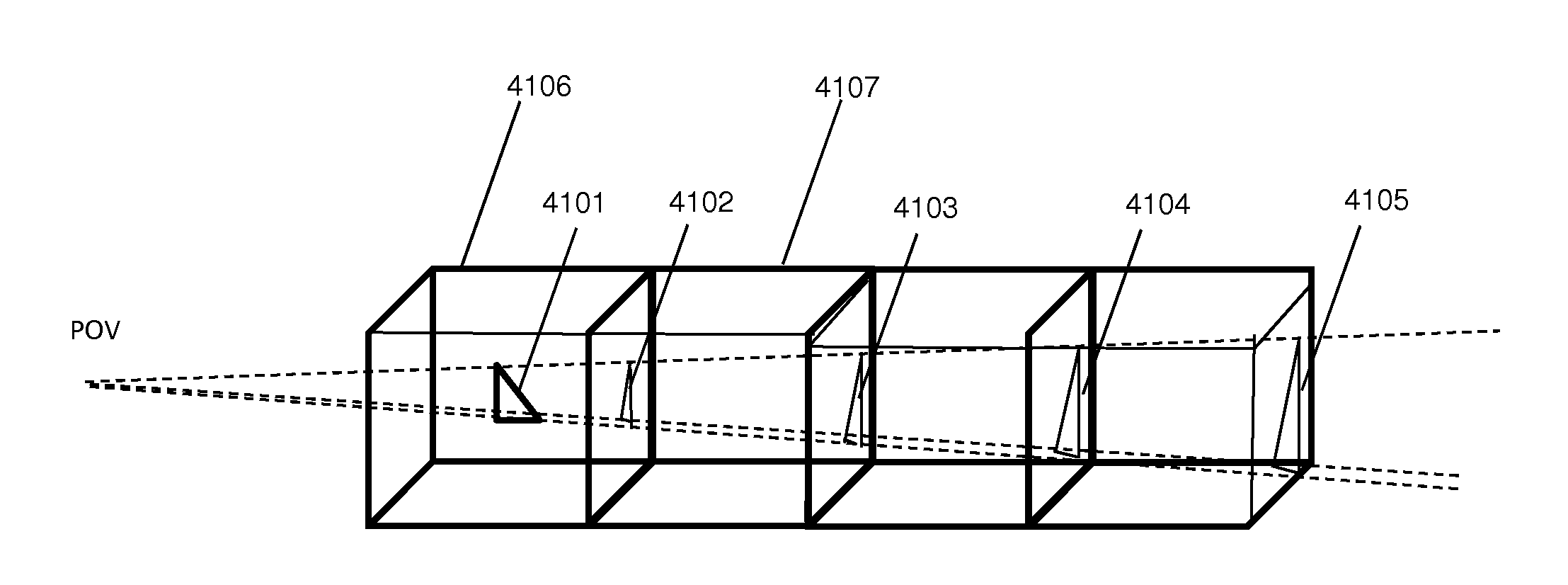
Ray shooting method utilizing geometrical stencils
ActiveUS20140375641A1Effective trackingCut down high traversalDetails involving 3D image dataProgram controlVisibilityViewpoints
Aspects comprise a ray shooting method based on the data structure of a uniform grid of cells, and on local stencils in cells. The high traversal and construction costs of accelerating structures are cut down. The object's visibility from the viewpoint and from light sources, as well as the primary workload and its distribution among cells, are gained in the preprocessing stage and cached in stencils for runtime use. In runtime, the use of stencils allows a complete locality at each cell, for load balanced parallel processing.
Owner:SNAP INC
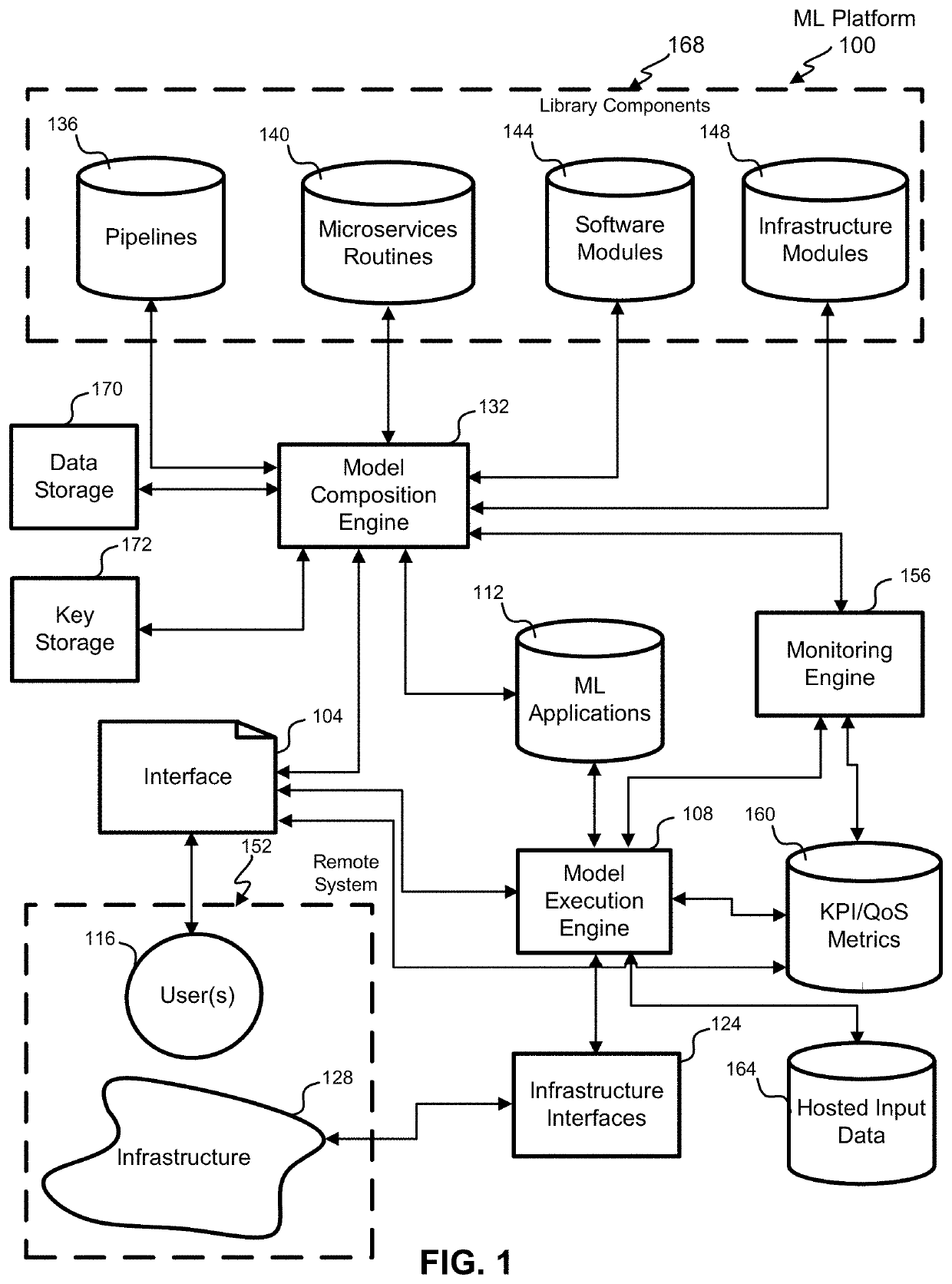
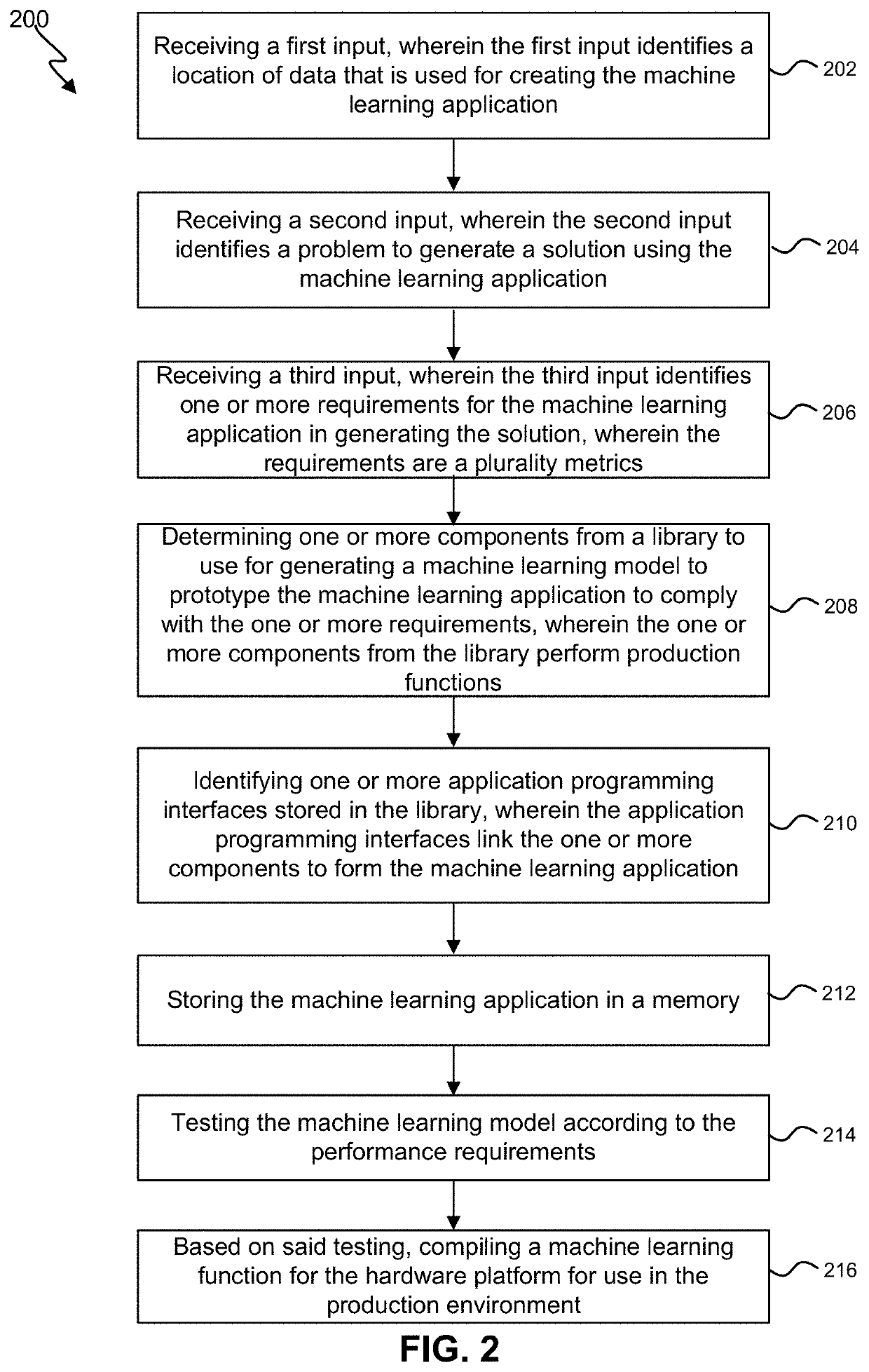
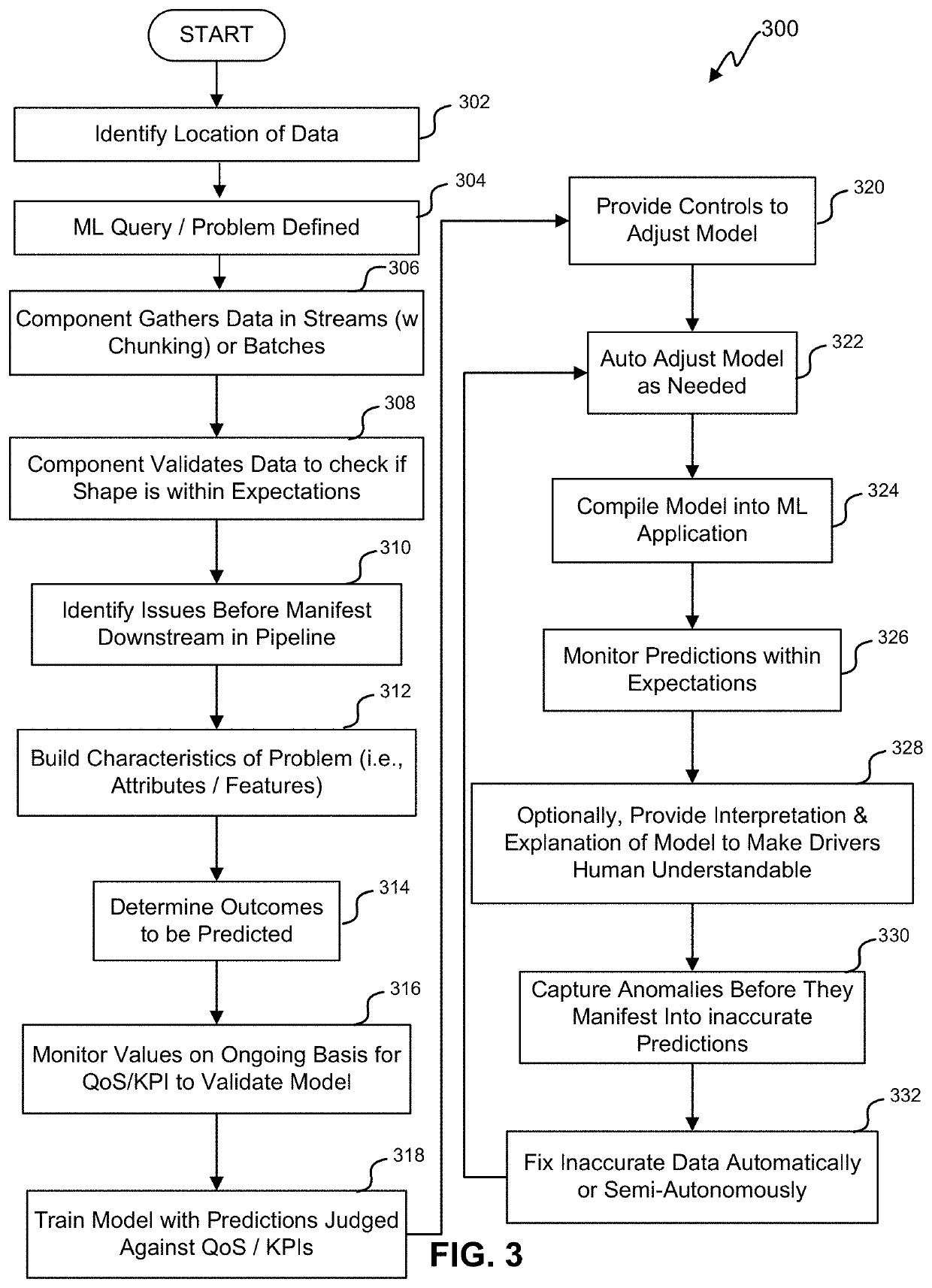
Machine learning (ML) infrastructure techniques
ActiveUS20210081837A1Simple interfaceData efficientEnsemble learningInterprogram communicationEngineeringData mining
The present disclosure relates to systems and methods for a machine learning platform that generates a library of components to generate machine learning models and machine learning applications. The machine learning infrastructure system allows a user (i.e., a data scientist) to generate machine learning applications without having detailed knowledge of the cloud-based network infrastructure or knowledge of how to generate code for building the model. The machine learning platform can analyze the identified data and the user provided desired prediction and performance characteristics to select one or more library components and associated API to generate a machine learning application. The machine learning can monitor and evaluate the outputs of the machine learning model to allow for feedbacks and adjustments to the model. The machine learning application can be trained, tested, and compiled for export as stand-alone executable code.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
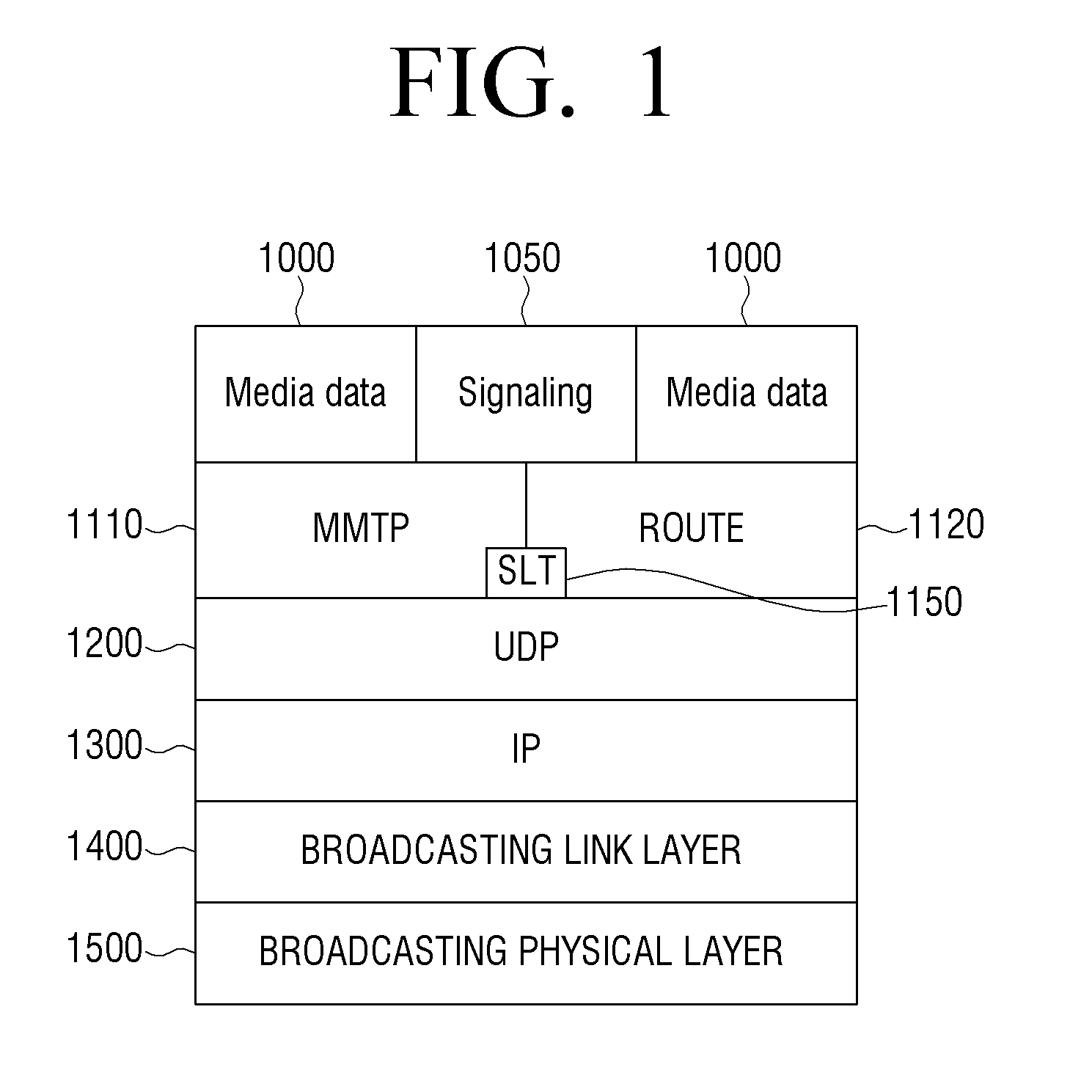
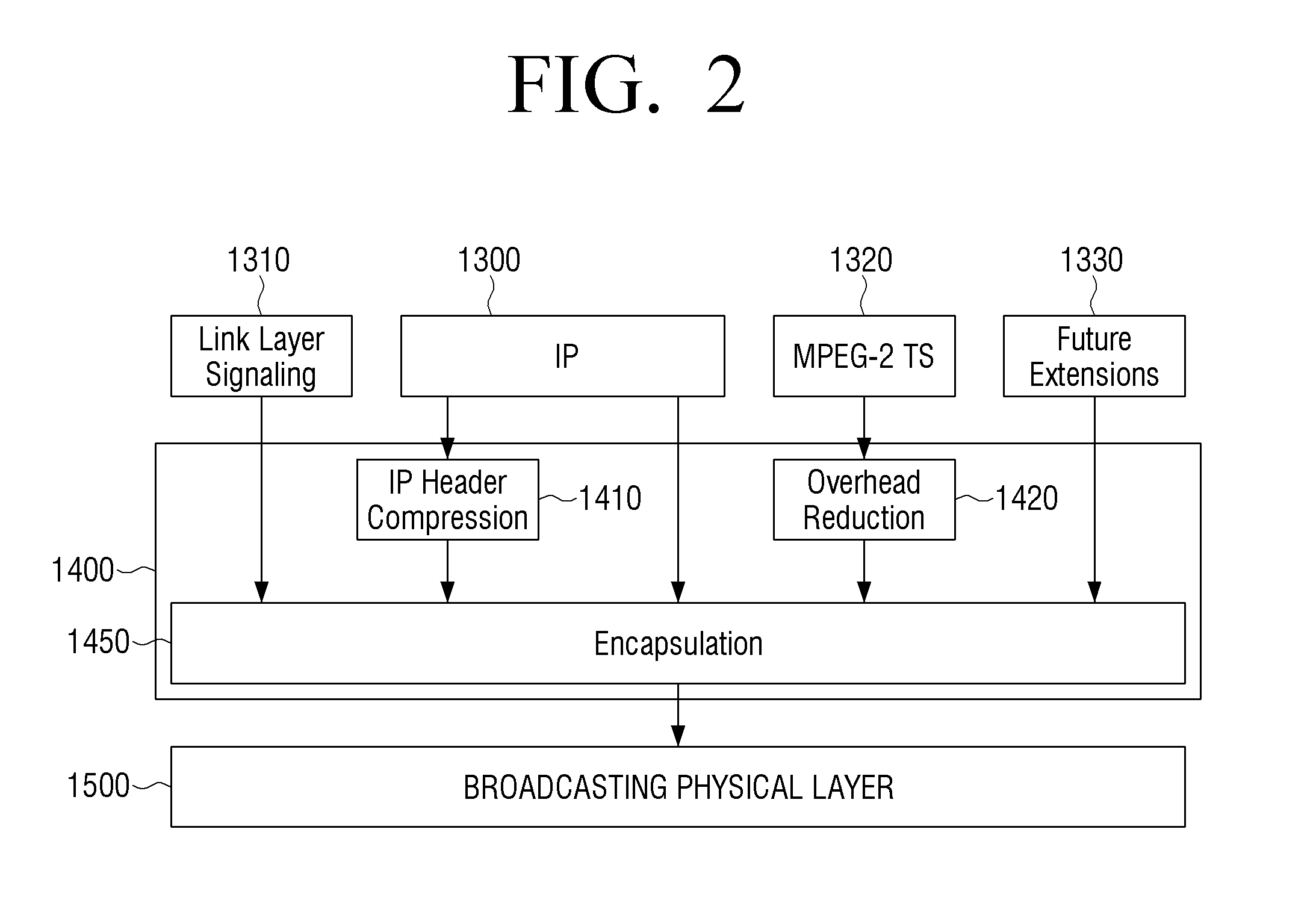
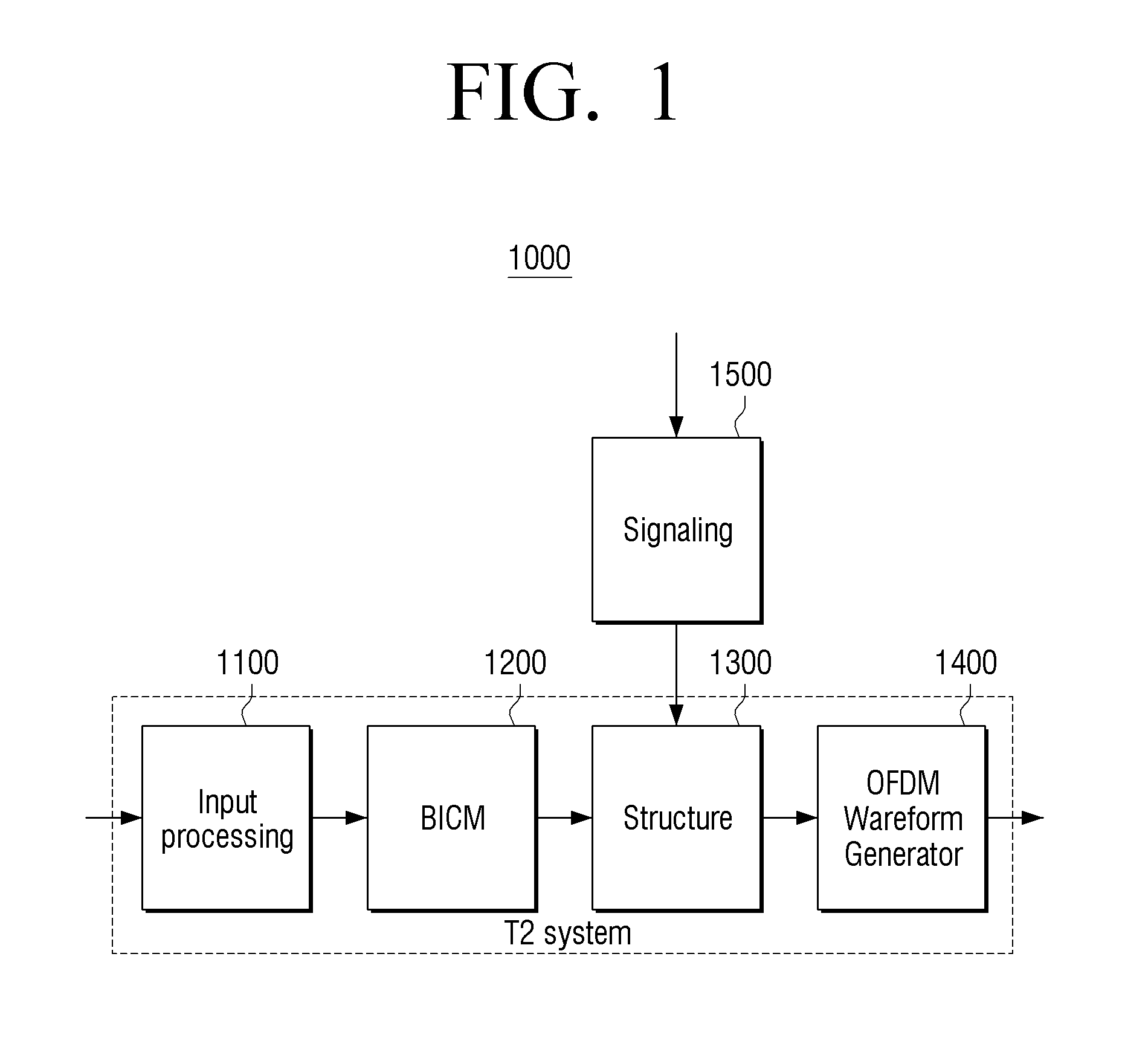
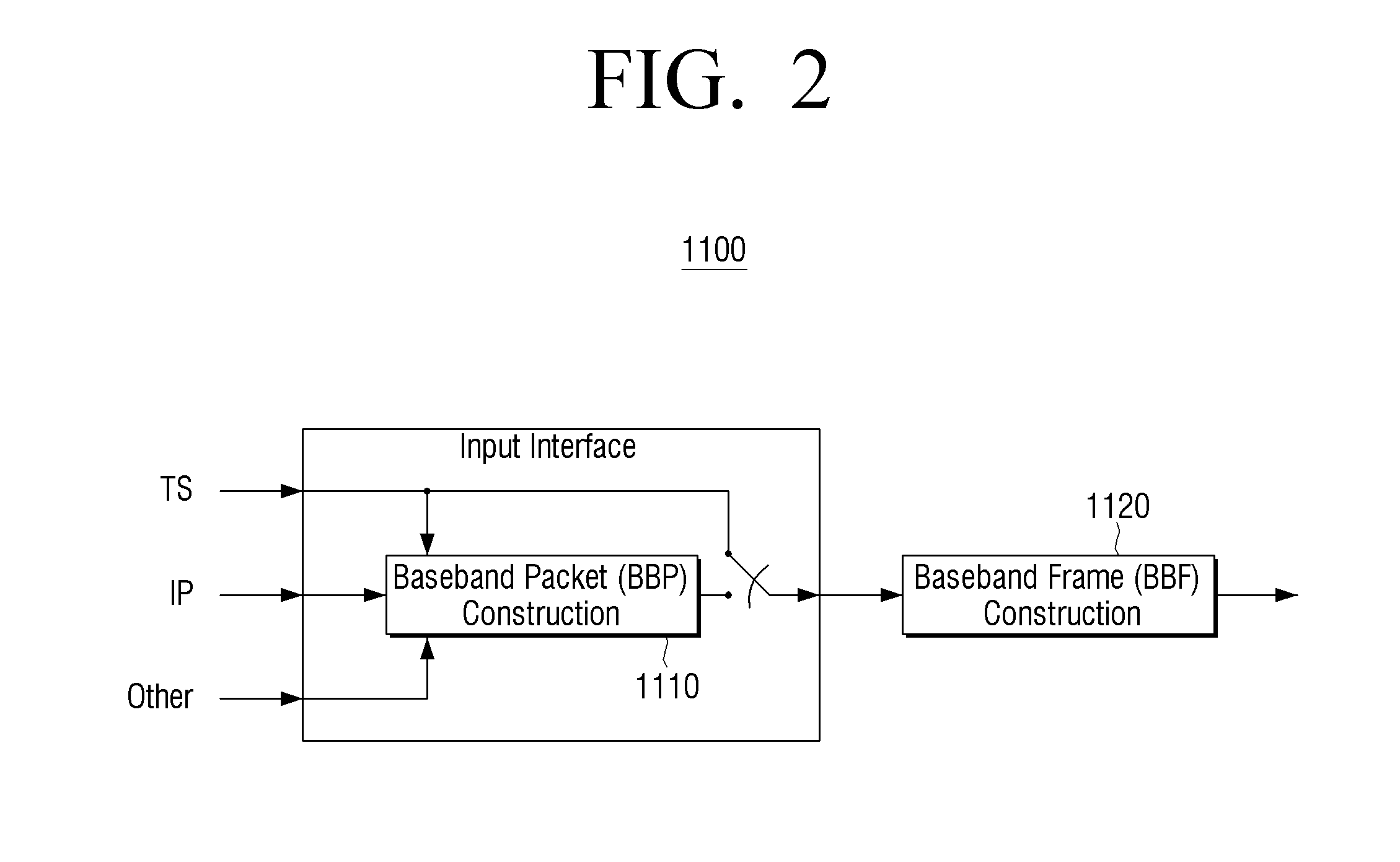
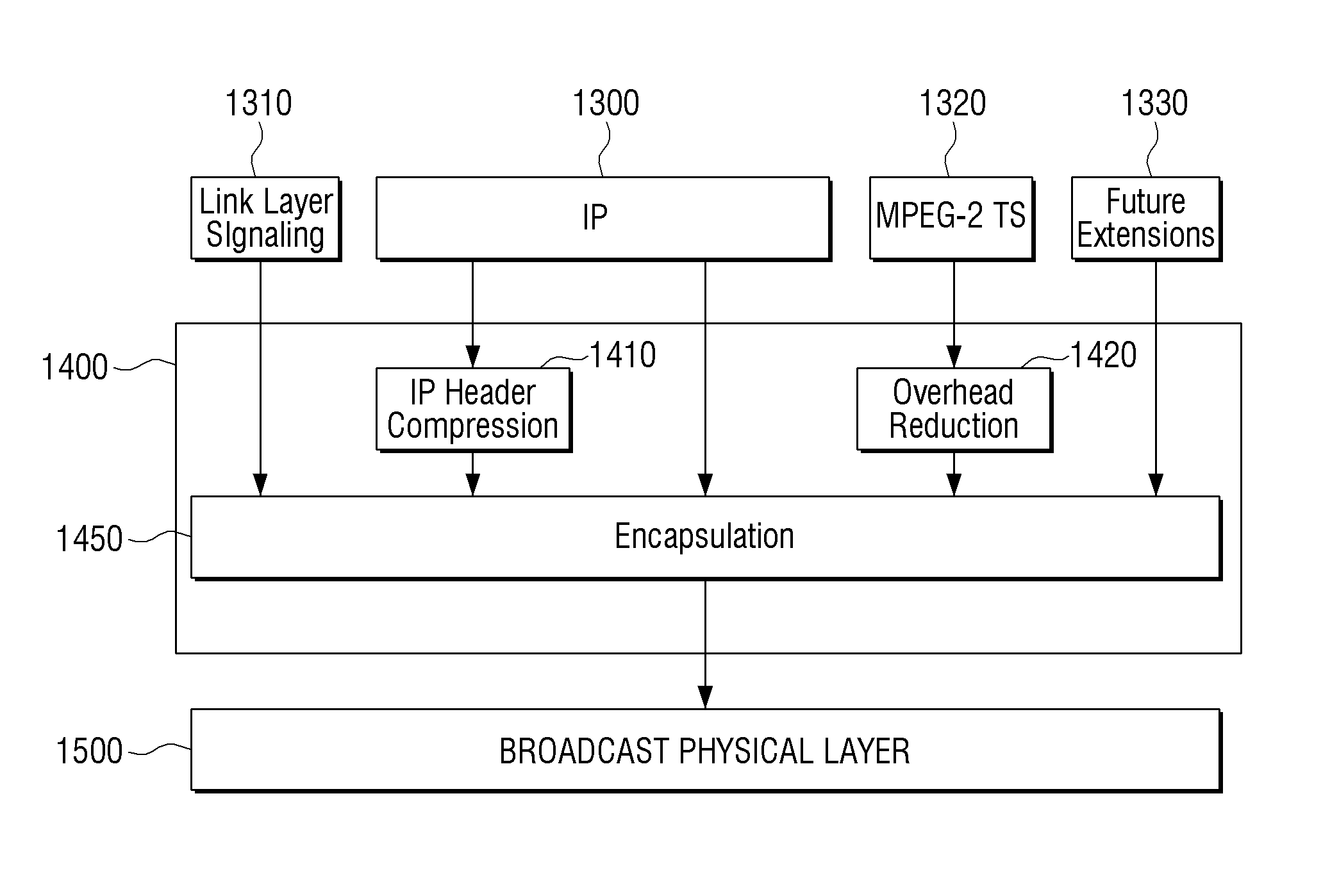
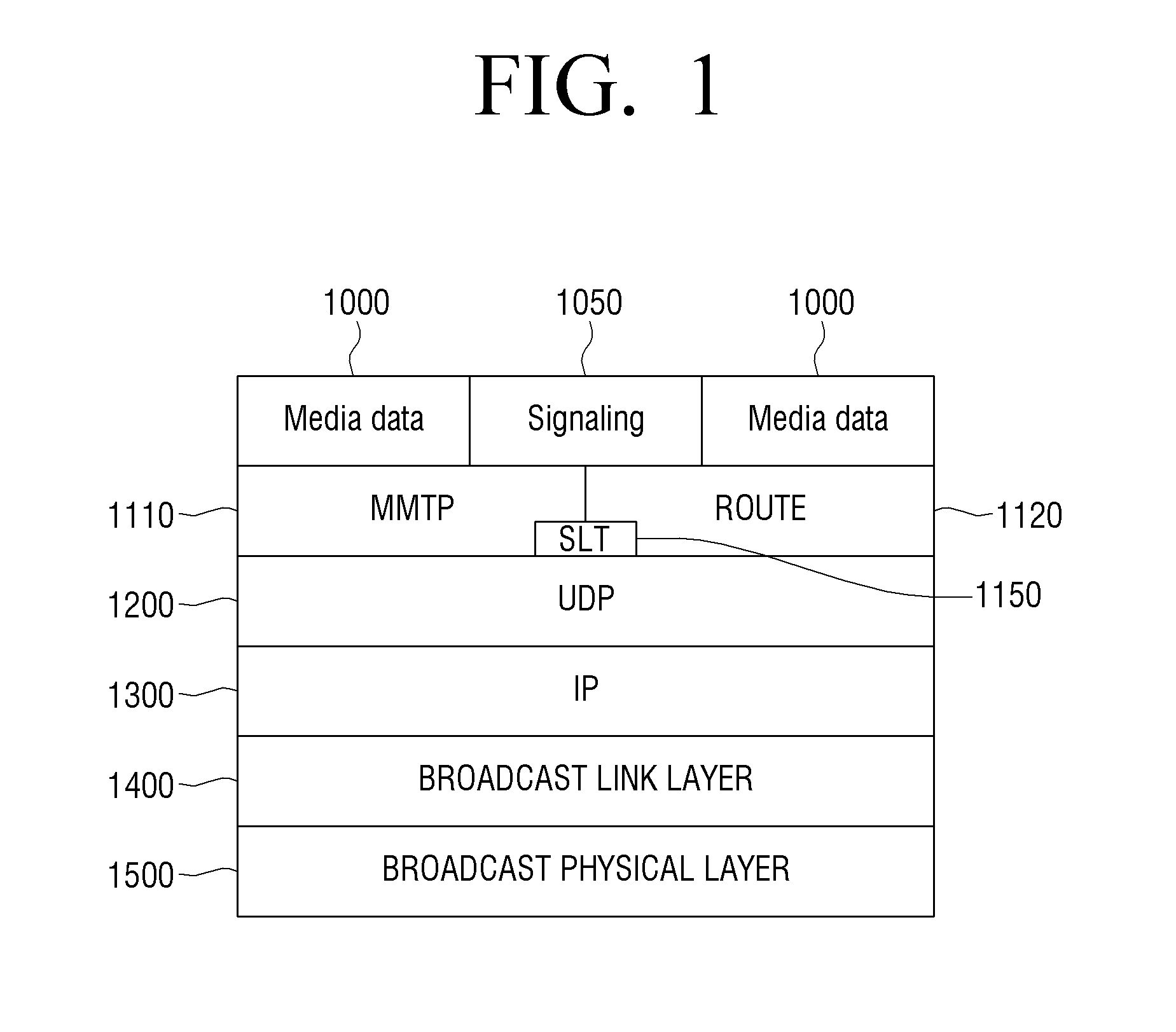
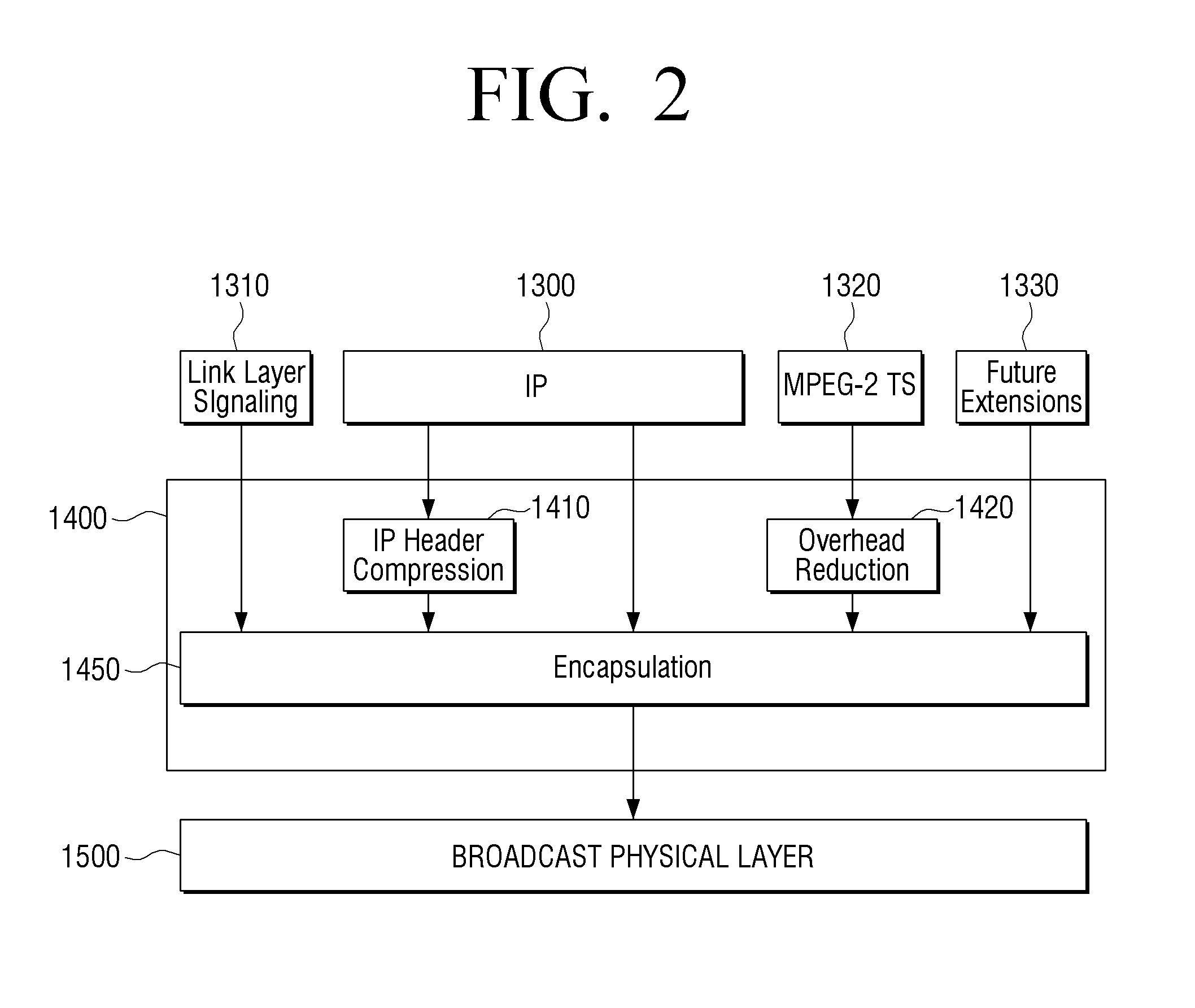
Transmitting apparatus and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20160127522A1Improve data processing efficiencyEfficient mappingData switching by path configurationPacket generatorComputer science
A transmitting apparatus, a receiving apparatus, and a method of signal processing are provided. The transmitting apparatus includes at least one processor configured to implement: a packet generator which generates a packet including a header and a payload, based on an input stream; and a signal processor which signal-processes the generated packet. The header includes a base header, and the base header includes various fields indicating at least one of a packet type, and a value indicating that the packet transmits one single complete input packet, a segment of an input packet, or a plurality of input packets. The fields included in the base header may also indicate presence of an additional header and a substream identifier.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
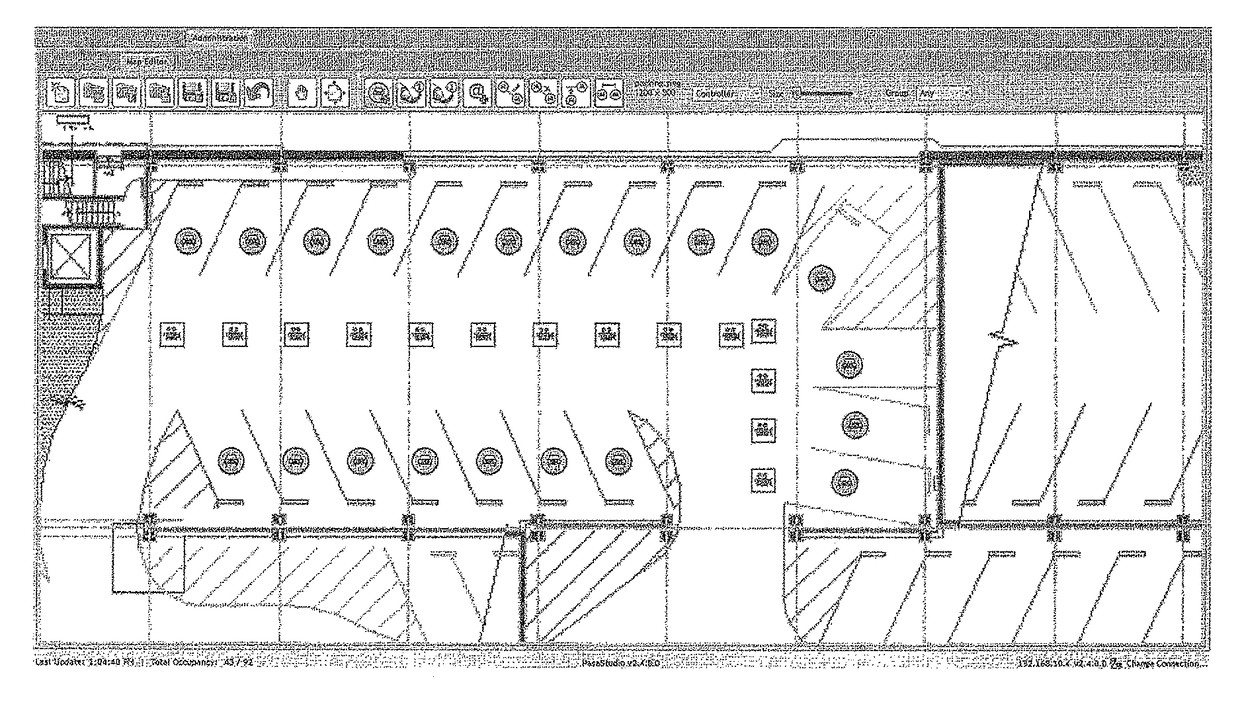
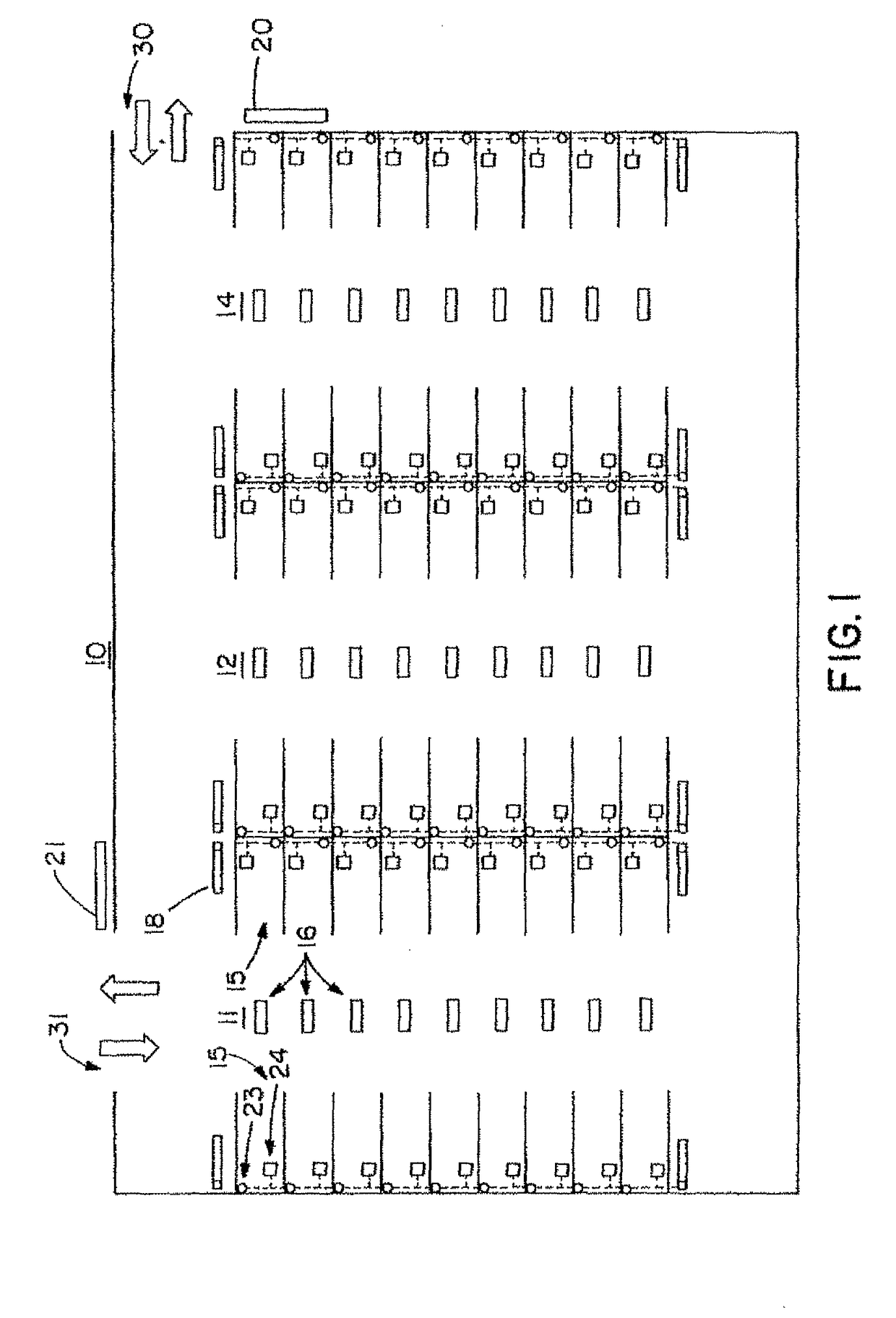
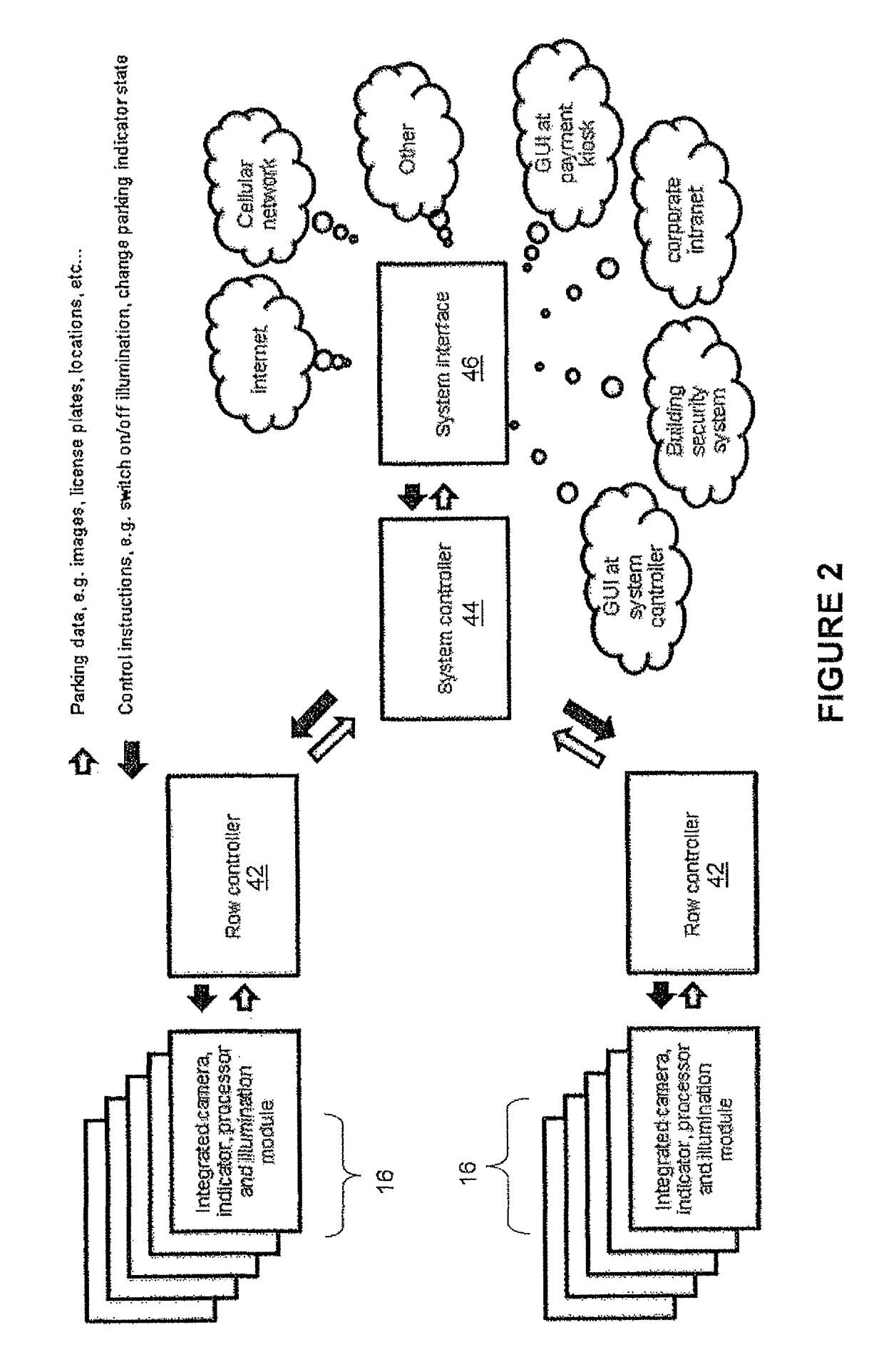
Method and system for managing a parking lot based on intelligent imaging
ActiveUS9594956B2Efficiently findIncrease enforcementTicket-issuing apparatusIndication of parksing free spacesParking spaceIntelligent agent
Owner:TKH SECURITY LLC
Transmitting apparatus, receiving apparatus and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20150023249A1Improve data processing efficiencyEfficient mappingModulated-carrier systemsNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket generatorBaseband
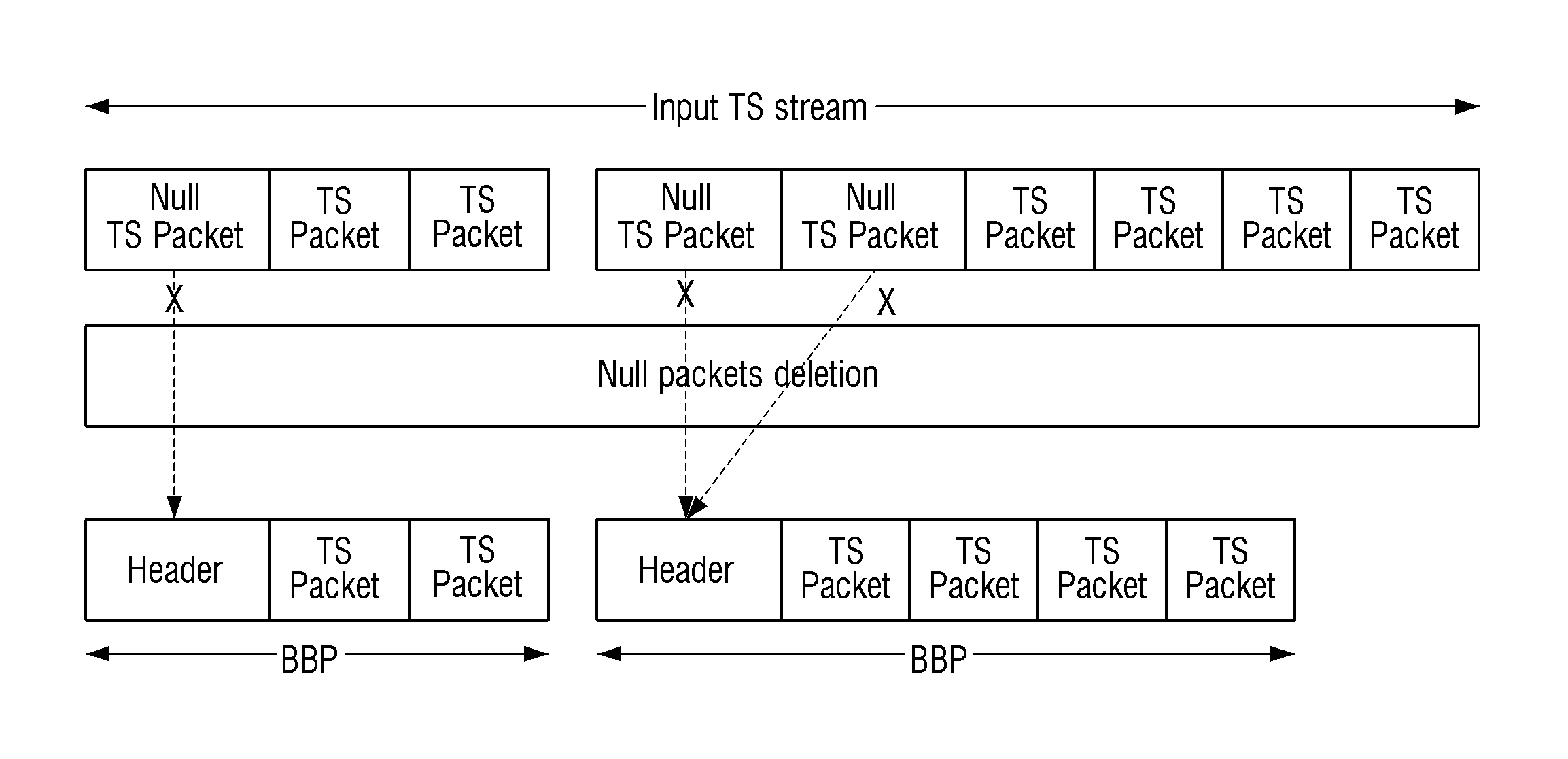
A transmitting apparatus includes: a baseband packet generator configured to generate a baseband packet including a header and payload data corresponding to an input stream; a frame generator configured to generate a frame including the baseband packet; a signal processor configured to process the generated frame; and a transmitter configured to transmit the processed frame, wherein the header includes information about whether a number of null packets deleted when generating the baseband packet is more than a predetermined number, information about a number of packets within the baseband packet, and information about a number of the deleted null packets.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
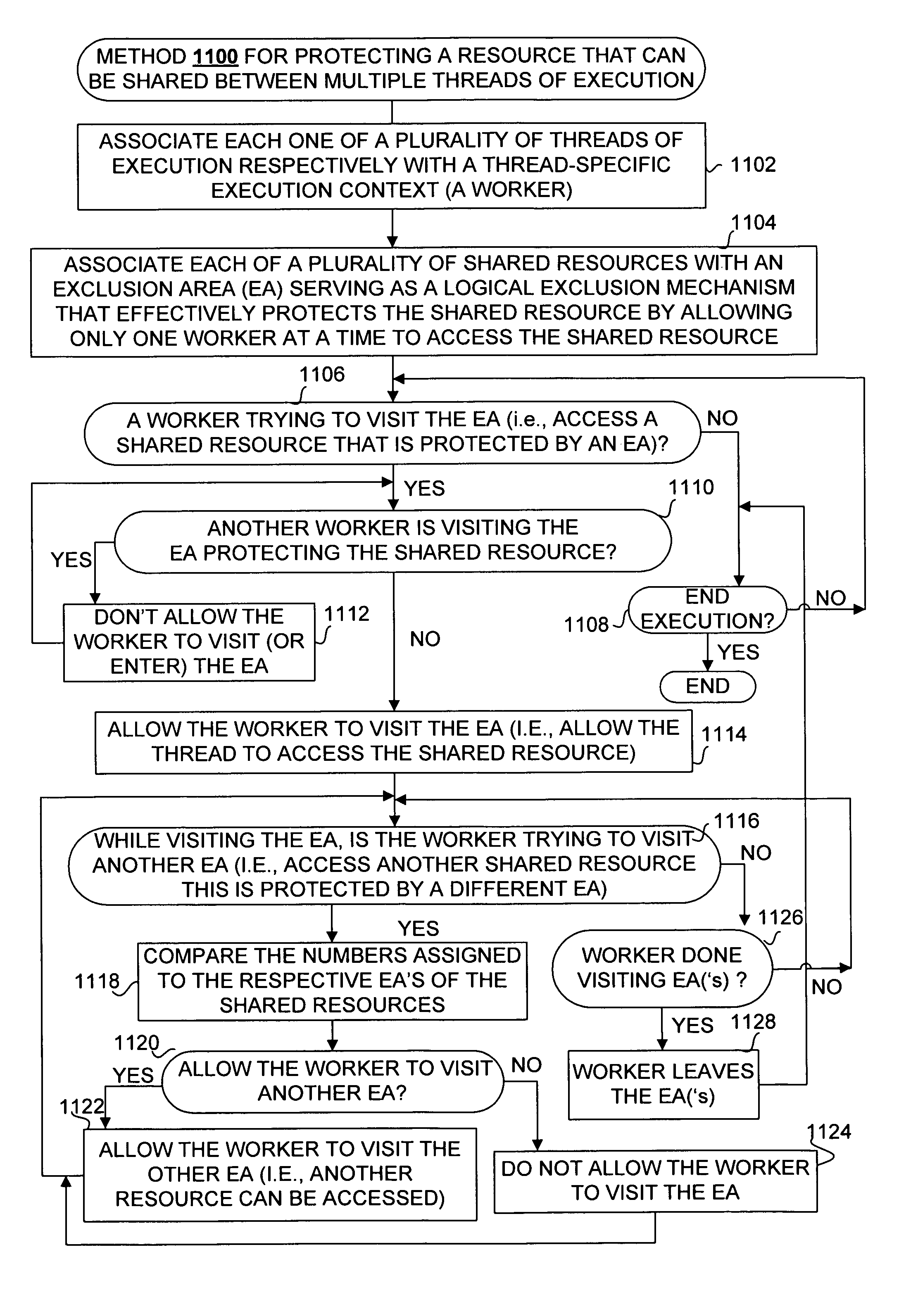
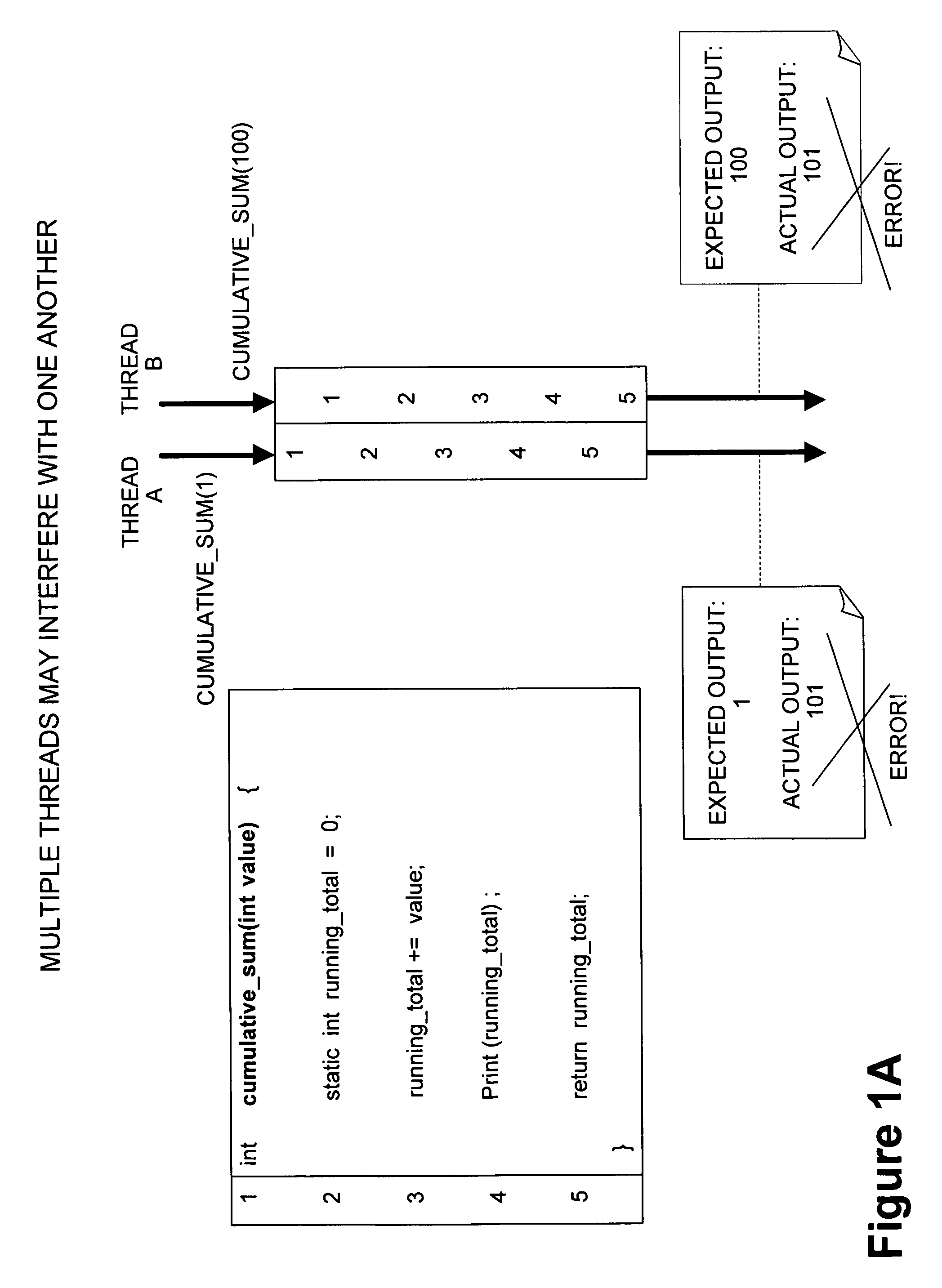
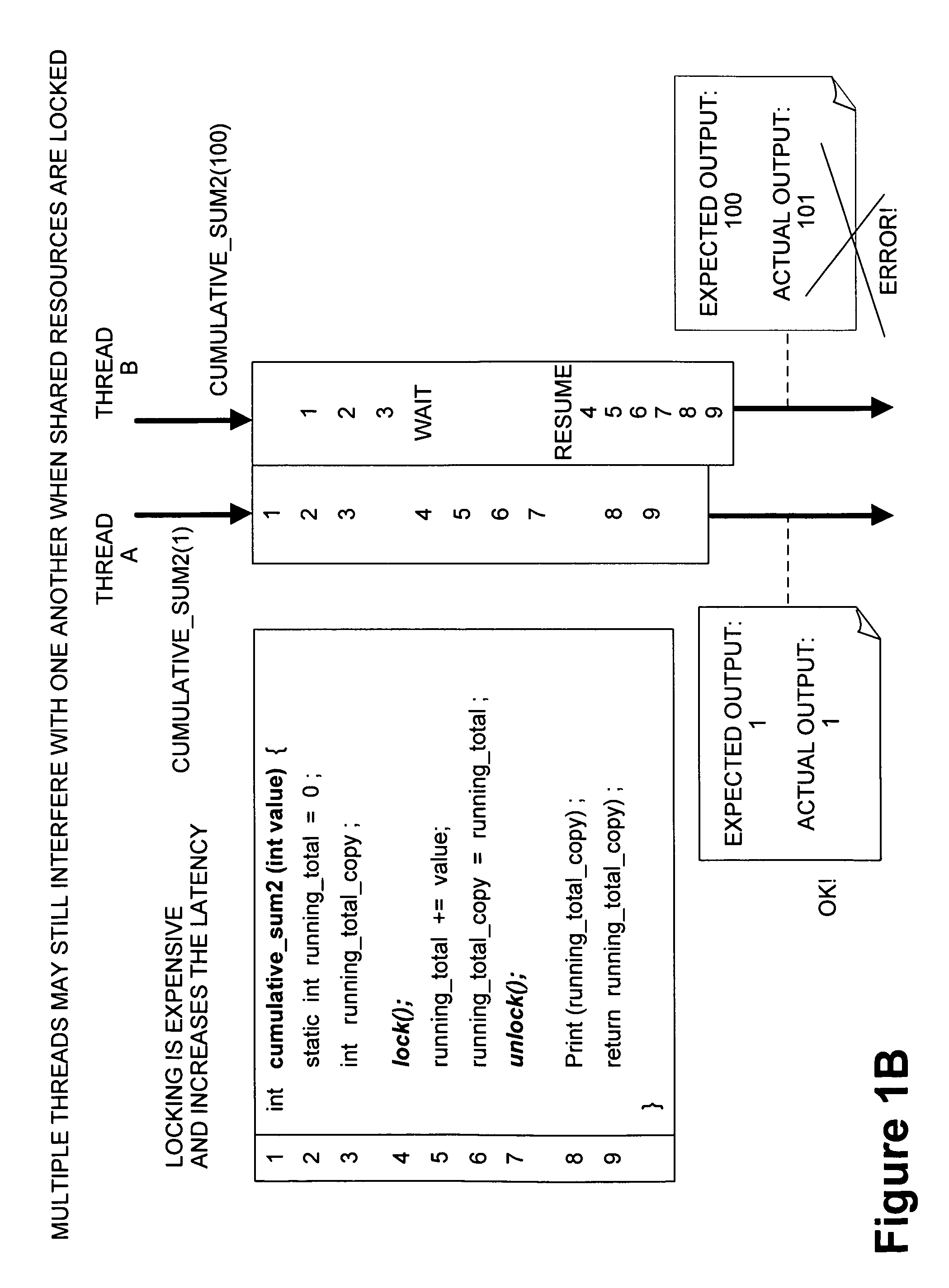
Framework for executing multiple threads and sharing resources in a multithreaded computer programming environment
ActiveUS7827559B1Efficient mappingLatency experiencedMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationParallel computingDelayed time
Techniques for execution of multiple threads in a multithreaded computing programming environment are disclosed. The techniques are especially well suited for environments that use multilayered programming architecture where a higher layer can build on the functions provided by a lower layer where the delay time is an important consideration. In one aspect, the conceptual notion of a “Worker” effectively serves to represent the thread-specific execution context for a thread of execution (“thread”) in a multithreaded computing environment. Another aspect, provides the notion of an Exclusion Area (EA) as logical lock that serves to protect shared resources in a multithreaded environment. The combination of the worker and EA are used to provide a powerful framework that, among other things, allows minimizing of the delay time.
Owner:REAL TIME INNOVATIONS
Search space for non-interleaved relay physical downlink control channel r-pdcch
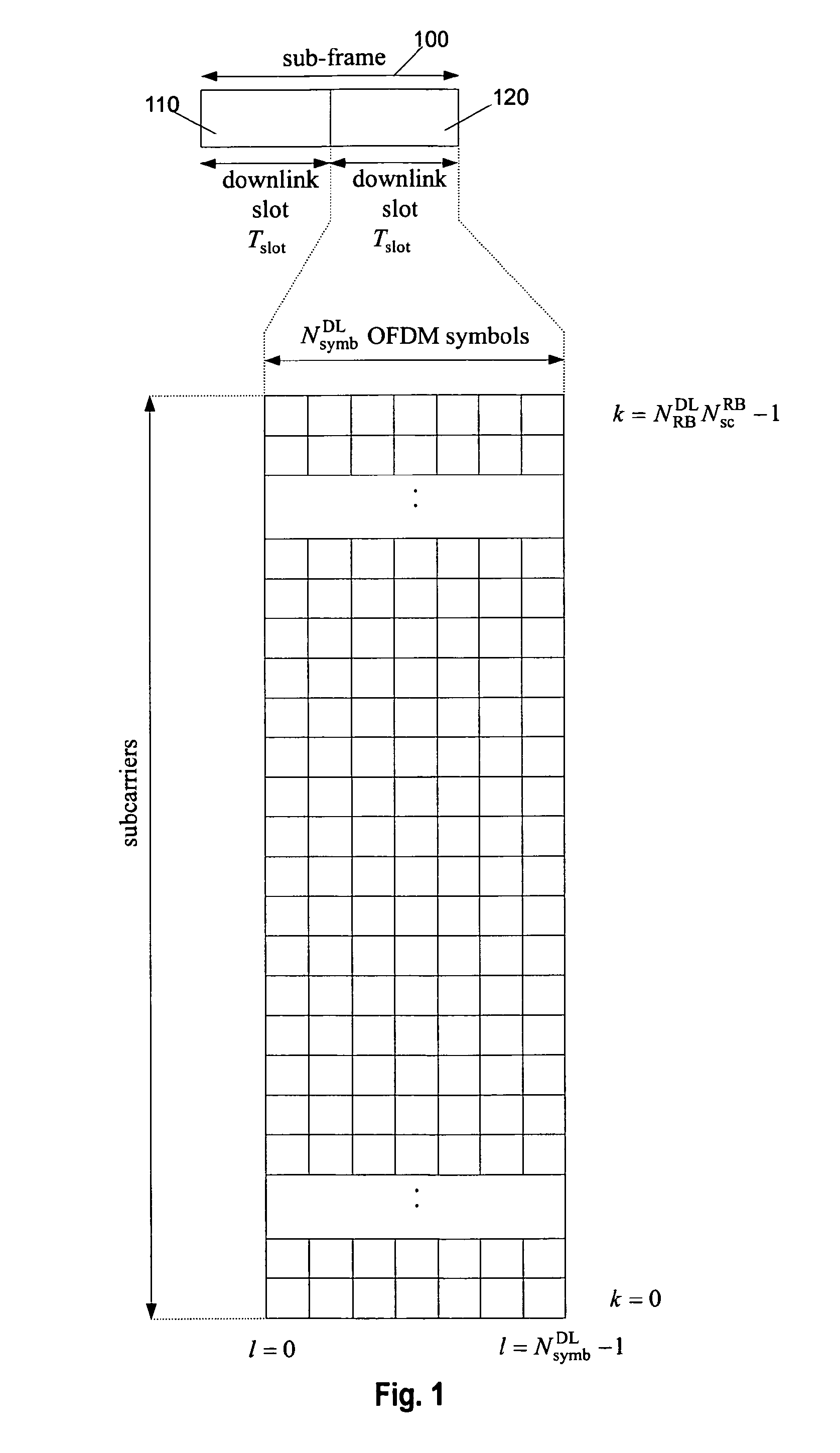
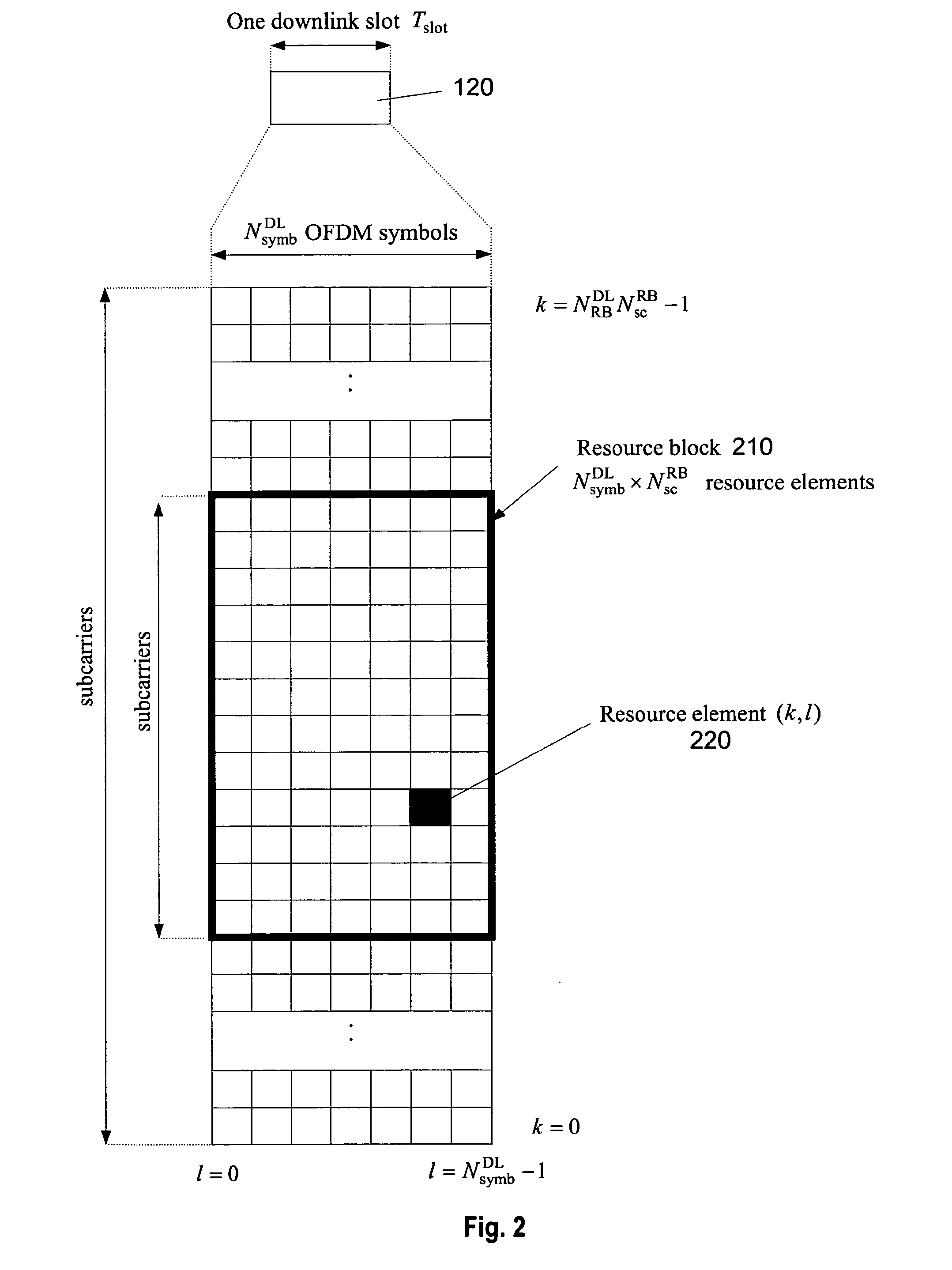
ActiveUS20130250906A1Efficient mappingEfficient use of resourcesModulated-carrier systemsReceiver specific arrangementsCommunications systemControl channel
The present invention relates to providing control information within a search space for blind decoding in a multi-carrier communication system. In particular, the control information is carried within a sub-frame of the communication system, the sub-frame including a plurality of control channel elements. The control channel elements may be aggregated into candidates for blind decoding. The number of control channel elements in a candidate is called aggregation level. In accordance with the present invention, the candidates of lower aggregation levels are localised, meaning that the control channel elements of one candidate are located adjacently to each other in the frequency domain. Some candidates of the higher aggregation level(s) are distributed in the frequency.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
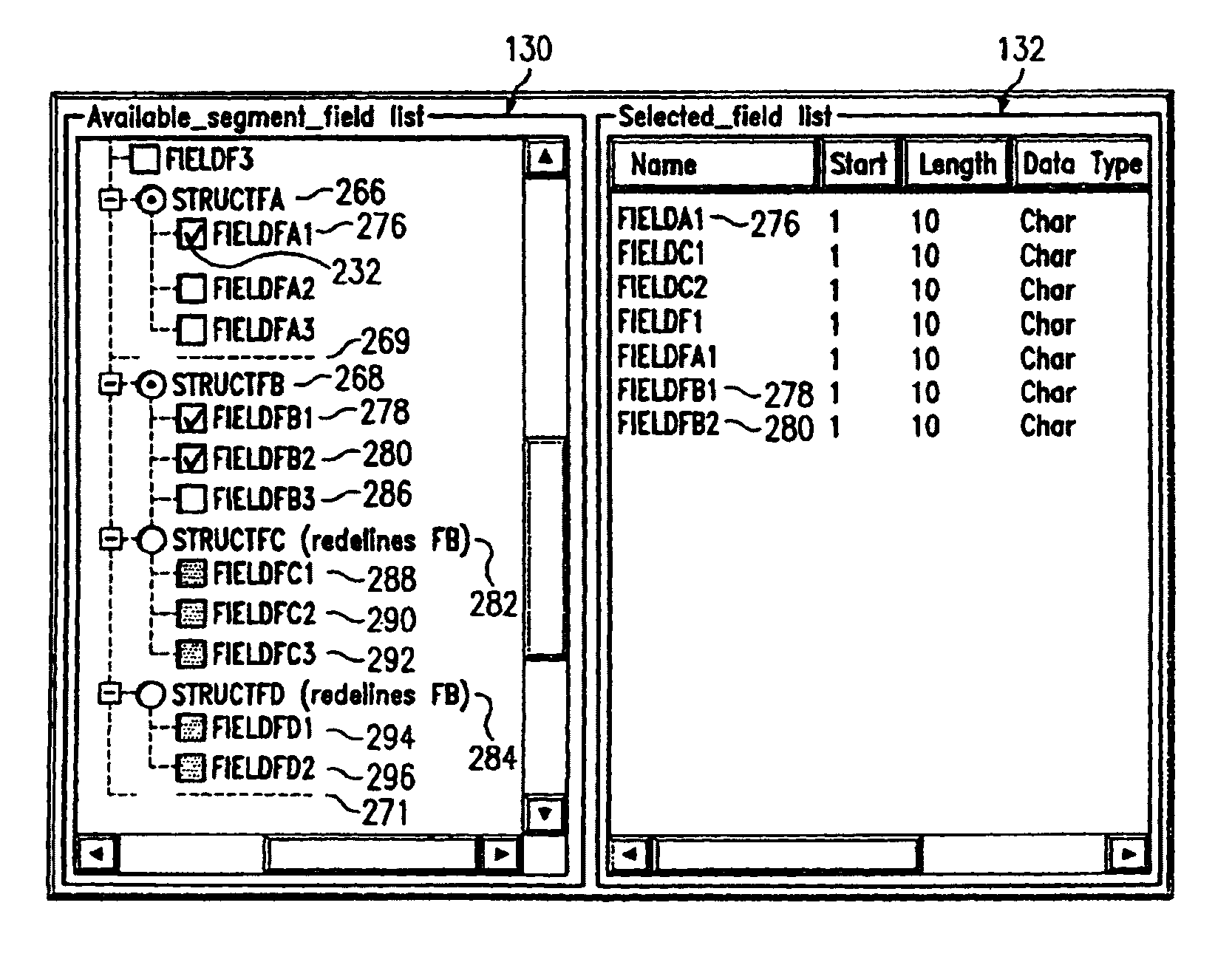
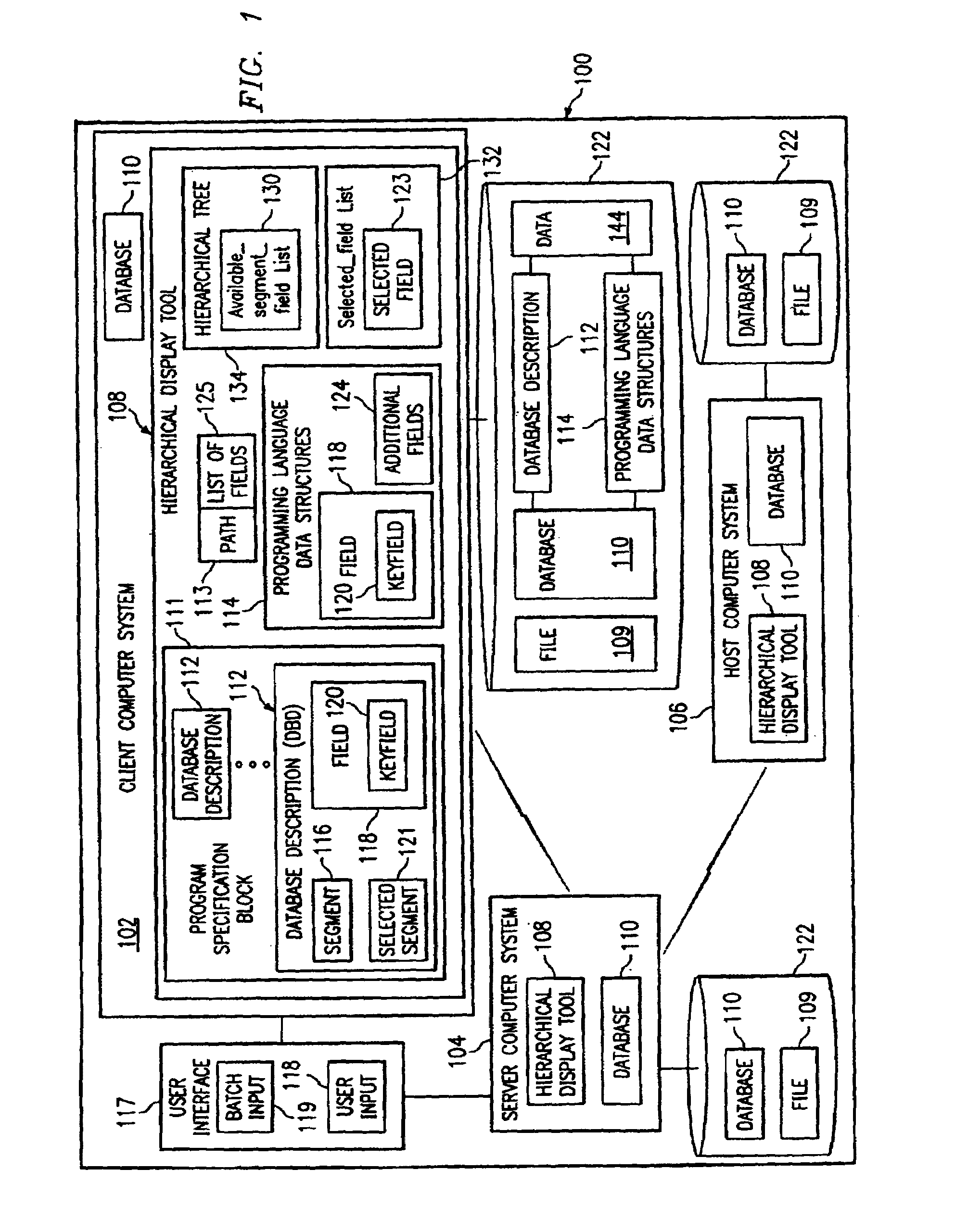
Systems, methods, and computer program products to display and select hierarchical database segments and fields
InactiveUS7197517B2Efficient sharingEffective movementData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Systems, methods, and computer products that efficiently share and move data between different types of data storage formats. More particularly, the preferred embodiment of the present invention provides an easy to use graphical user interface (GUI) for displaying, navigating, and selecting hierarchical database segments and fields. The preferred embodiment of the present invention novelly uses a hierarchical tree structure that clearly represents the structures of a database and their mutual exclusivity, for easy understanding of and navigation through the various database structures. The user is prevented from selecting segments and fields that are not valid for the selected path thereby ensuring accuracy in the representation of the database data structures. Also, the user may select a path from the top of the hierarchical tree, the root, to a specific segment or field.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transmitting apparatus, receiving apparatus and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20160134532A1Improve data processing efficiencyEfficient mappingModulated-carrier systemsData switching by path configurationPacket generatorTransmitter
Provided are a transmitting apparatus, a receiving apparatus and controlling methods thereof. The transmitting apparatus includes: at least one processor configured to implement a packet generator which generates a packet including a header and a payload based on a plurality of input packets; and a signal processor which signal-processes the generated packet, and a transmitter configured to transmit the signal-processed packet. A base field included in the header includes a first field set to a first value representing that the base field is a first length or a second value representing that the base field is a second length.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Index data structure for a peer-to-peer network
InactiveUS7664742B2Efficient mappingData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRouting tableDatabase
An index data structure has a plurality of index keys for uniquely identifying potential data object context nodes. Each index key is, in turn, associated with one or more potential context nodes. Moreover, the index key has a label that provides semantic content to a user. The index data structure further includes one or more routing tables associated with each index key that generally include a plurality of path references.
Owner:PETTOVELLO PRIMO M
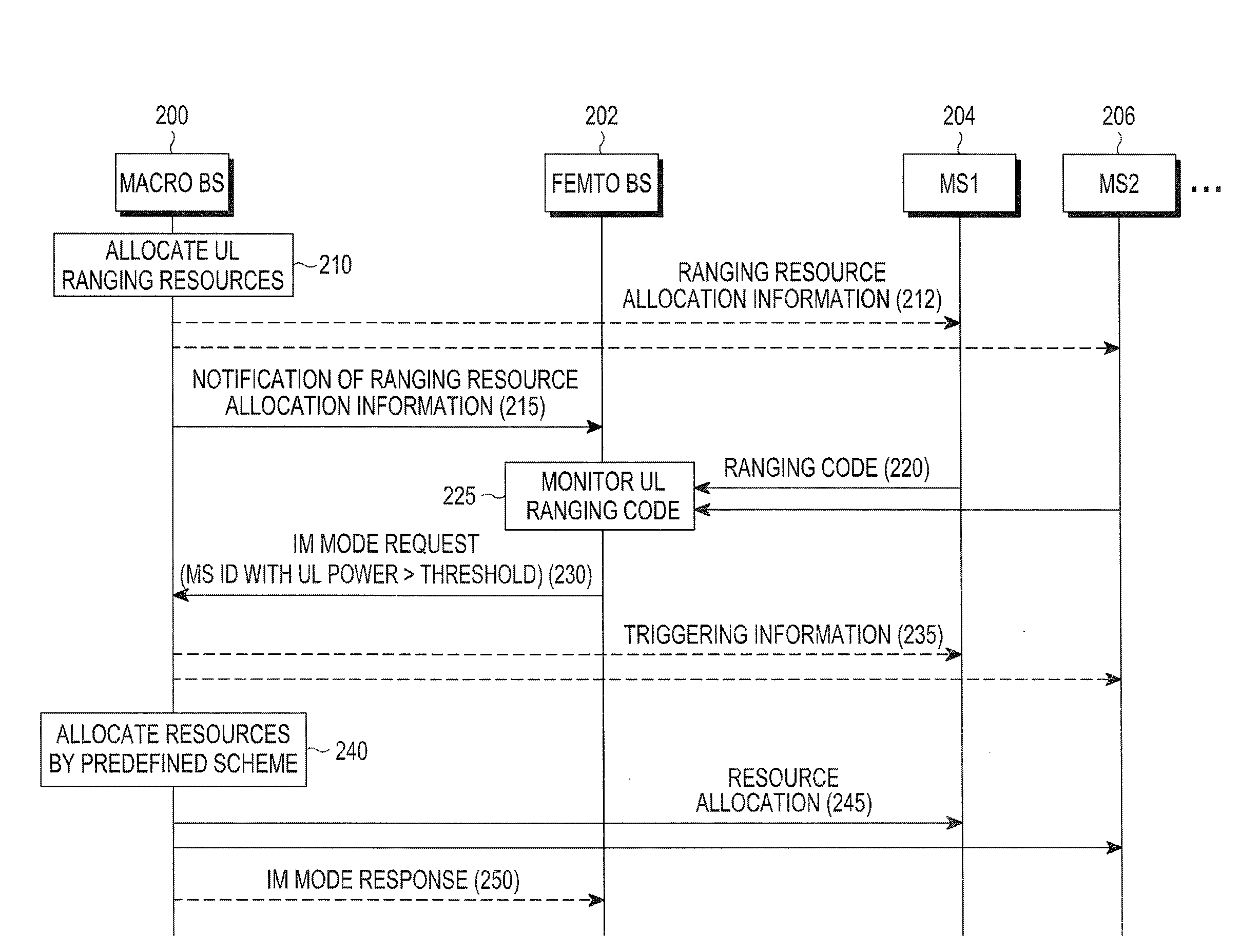
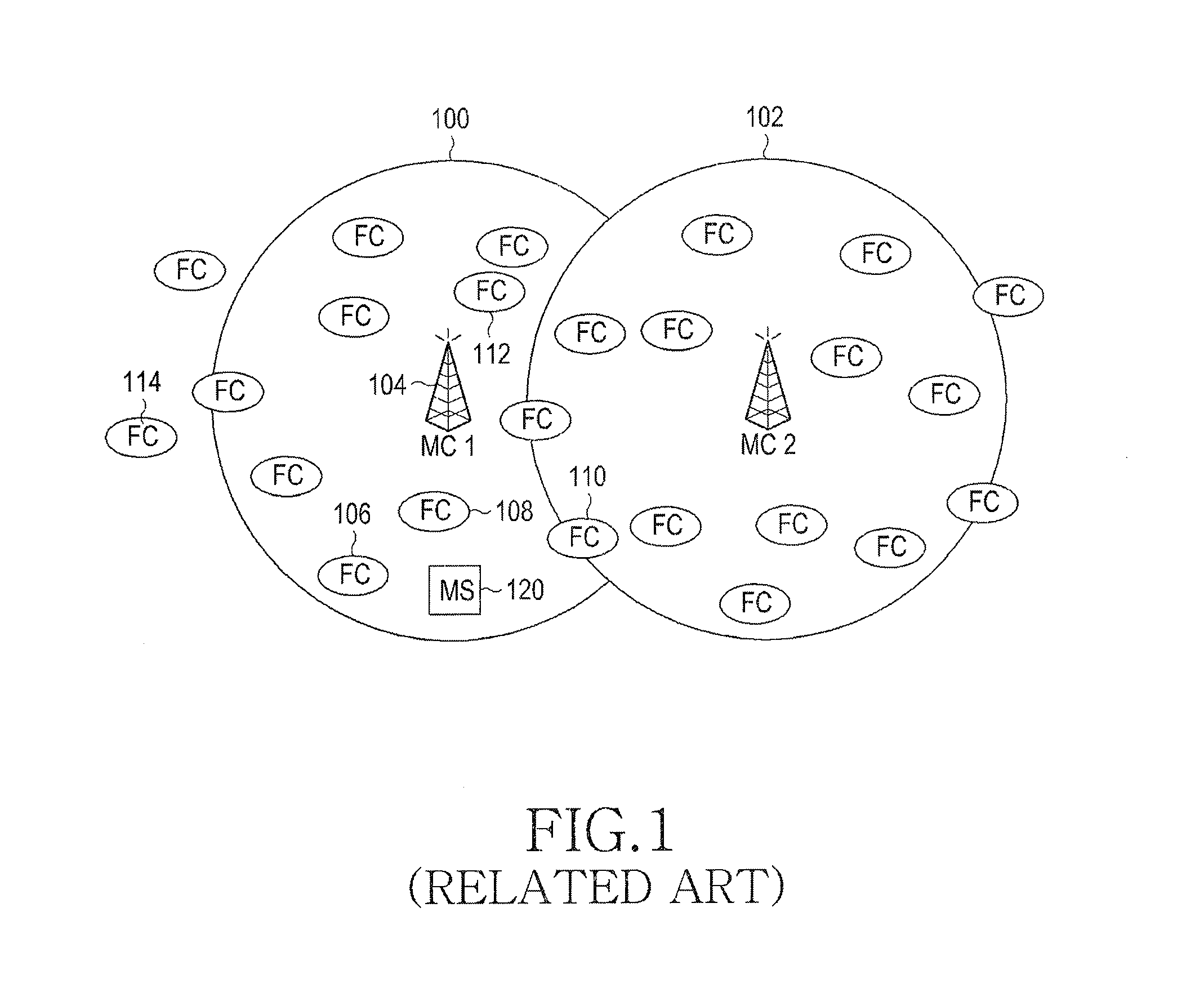
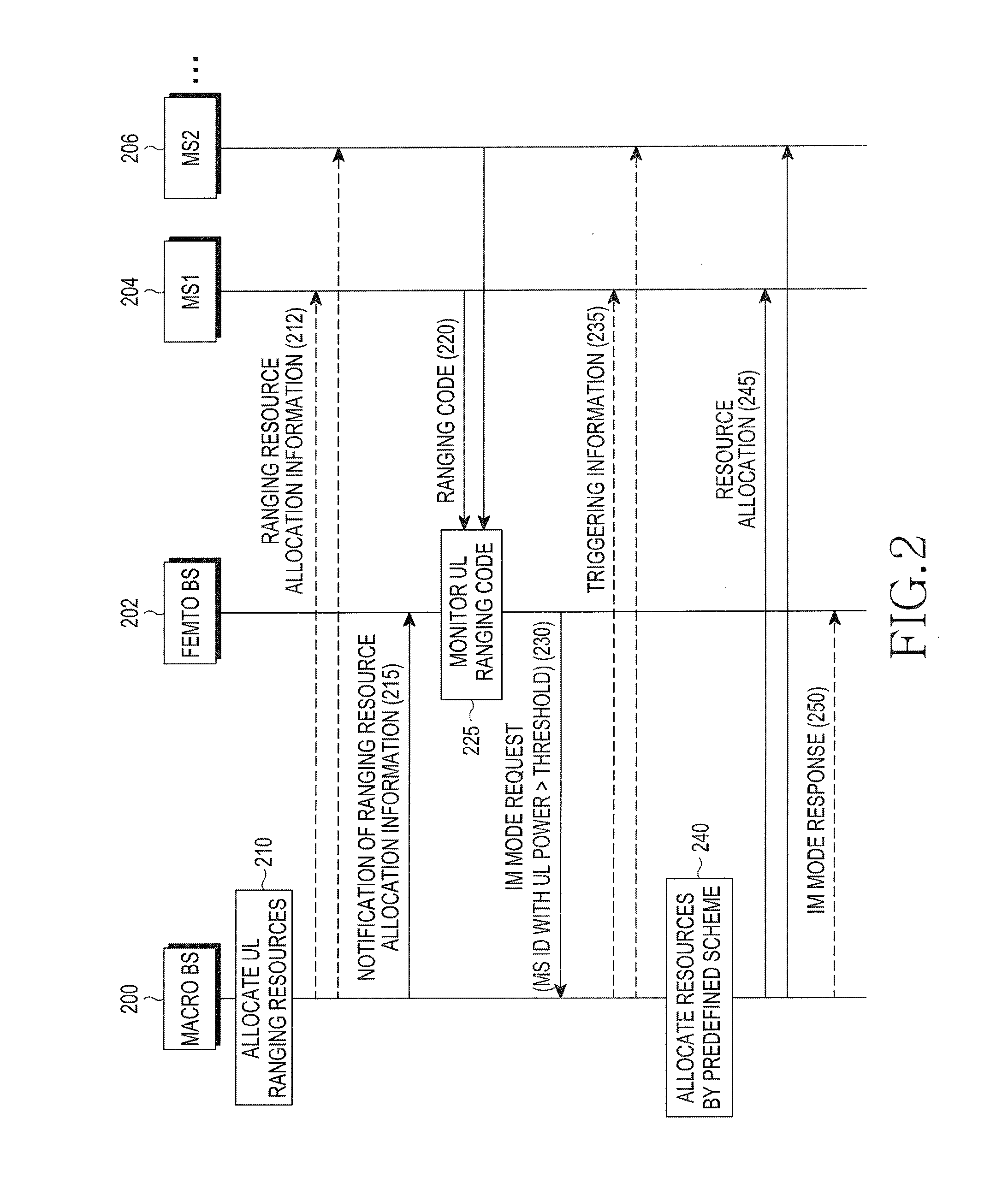
Method and apparatus for mitigating interference in femto cell in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20120015664A1Reduce uplink interferenceEffective resourcesNetwork topologiesNetwork data managementCommunications systemMobile station
A method for mitigating interference by a femto Base Station (BS) in a wireless communication system including a macro BS is provided. The method includes receiving information about resources allocated for a channel measurement signal from the macro BS, measuring an UpLink (UL) power by detecting a channel measurement signal transmitted from at least one Mobile Station (MS) to the macro BS based on the received information, determining MSs whose UL powers are greater than or equal to a threshold, and transmitting identification information for the MSs to the macro BS.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
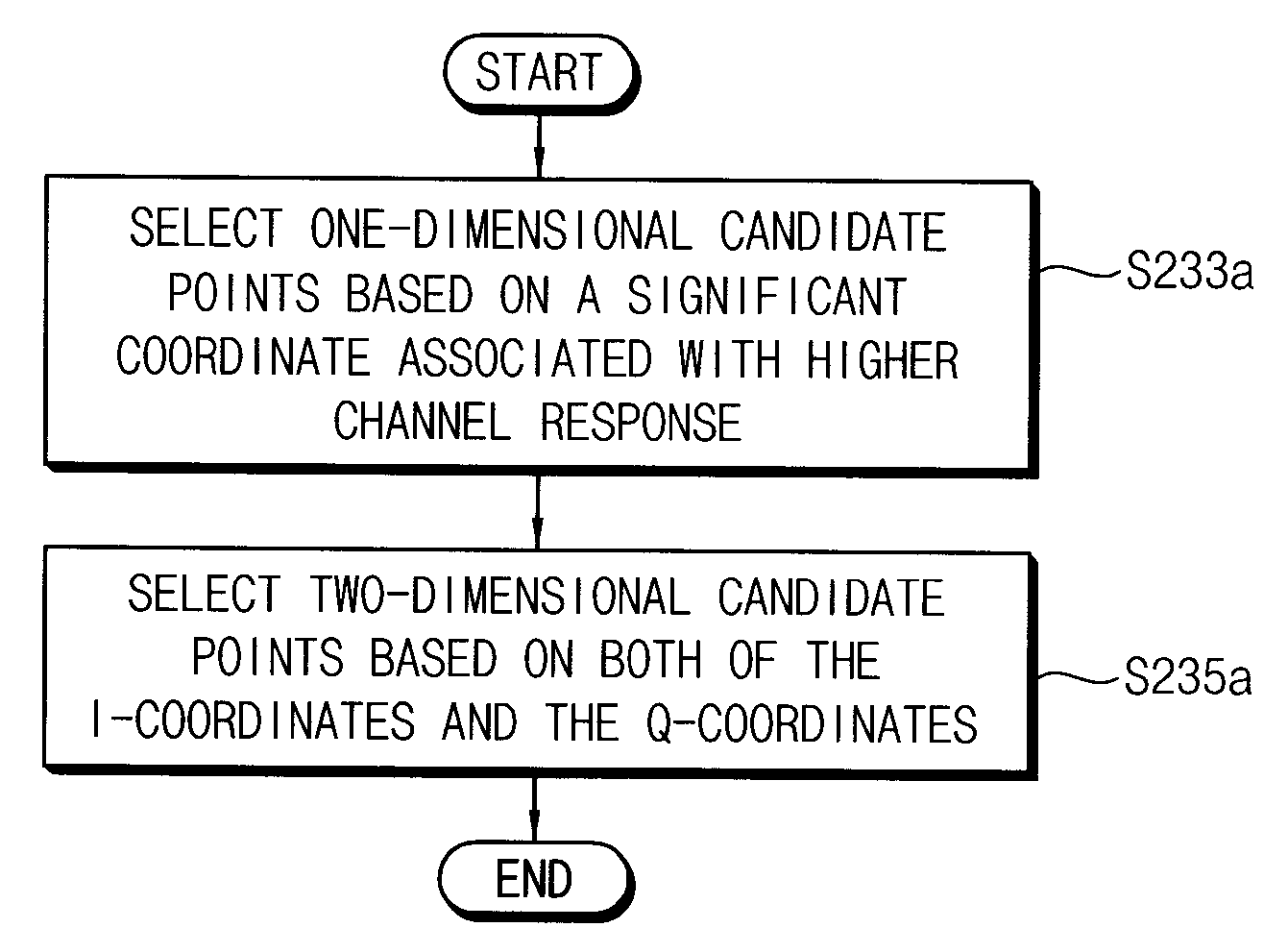
Method of demodulating a quadrature amplitude modulation signal and method of data communication
ActiveUS20120250805A1Efficient mappingError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsOrthogonal coordinatesLog likelihood
To demodulate a quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) signal, a reception point is determined corresponding to a symbol in the QAM signal that is received where the symbol is mapped to one reference point of a plurality of reference points in a rotated constellation and the plurality of reference points are represented by an in-phase (I) coordinate and a quadrature-phase (Q) coordinate. A plurality of candidate points corresponding to a portion of the plurality of reference points are selected based on distances between the reception point and the respective reference points. The reception point is demapped by calculating a plurality of log-likelihood ratios based on the plurality of candidate points, the plurality of log-likelihood ratios corresponding to bits of data represented by the reception point.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Efficient mapping of signal elements to a limited range of identifiers
InactiveUS7197622B2Reduce riskIncrease profitMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSecuring communicationVirtual spaceUser identifier
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Apparatus, system, and method for efficient mapping of virtual and physical addresses
ActiveUS8195912B2Efficiently mappedEfficient identificationMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram synchronisationData segmentData store
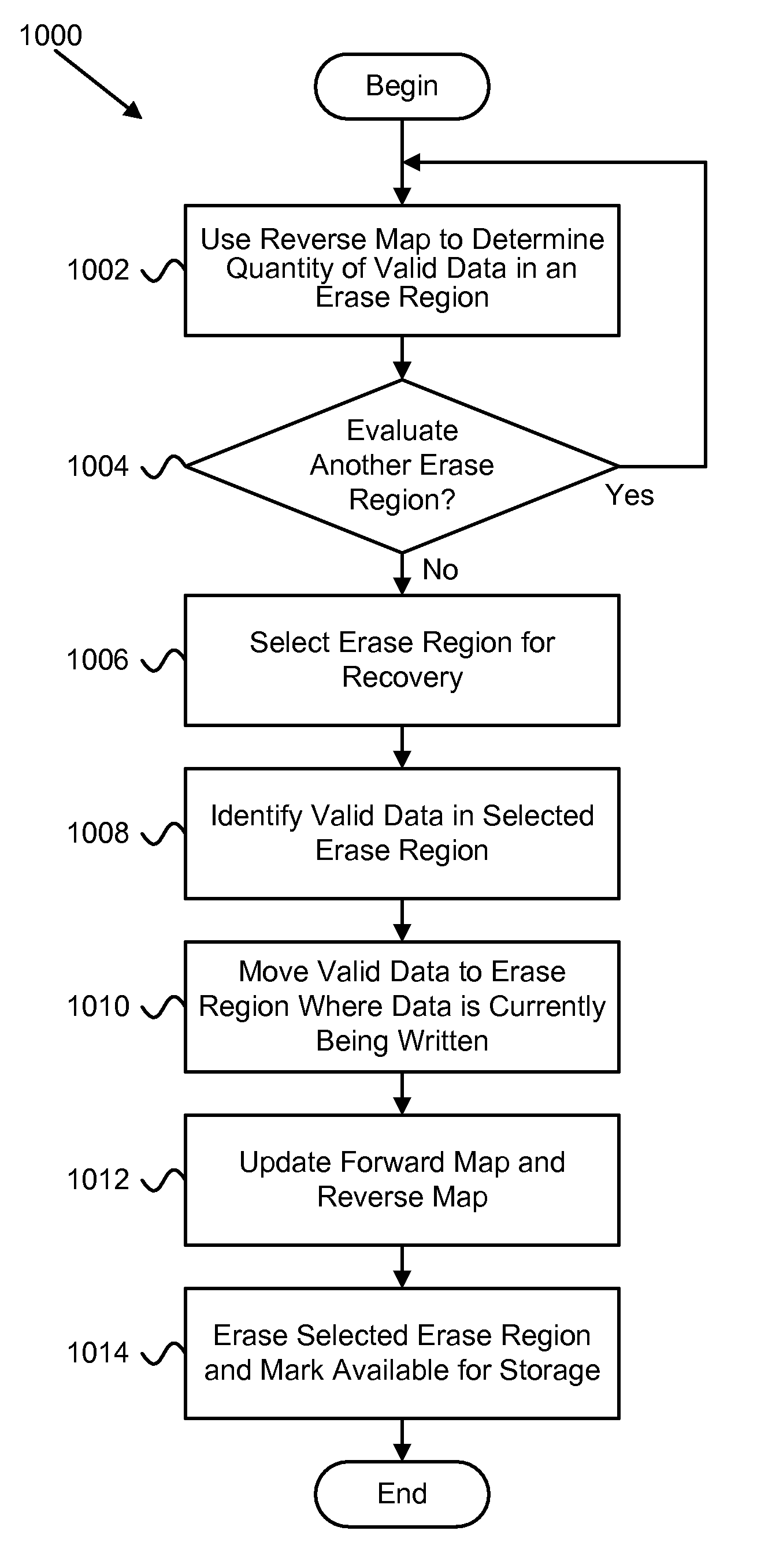
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for efficiently mapping virtual and physical addresses. A forward mapping module uses a forward map to identify physical addresses of data of a data segment from a virtual address. The data segment is identified in a storage request. The virtual addresses include discrete addresses within a virtual address space where the virtual addresses sparsely populate the virtual address space. A reverse mapping module uses a reverse map to determine a virtual address of a data segment from a physical address. The reverse map maps the data storage device into erase regions such that a portion of the reverse map spans an erase region of the data storage device erased together during a storage space recovery operation. A storage space recovery module uses the reverse map to identify valid data in an erase region prior to an operation to recover the erase region.
Owner:UNIFICATION TECH LLC
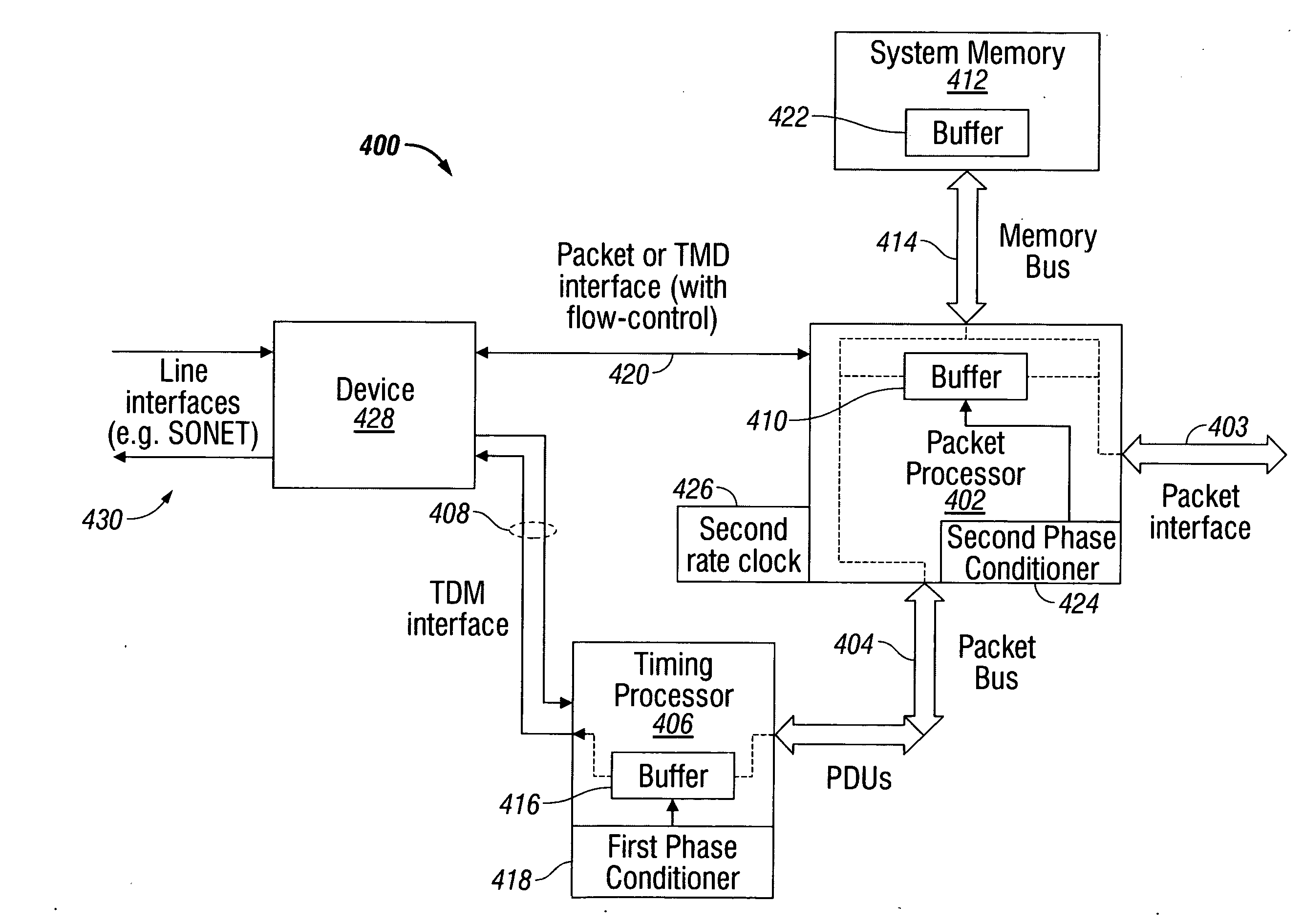
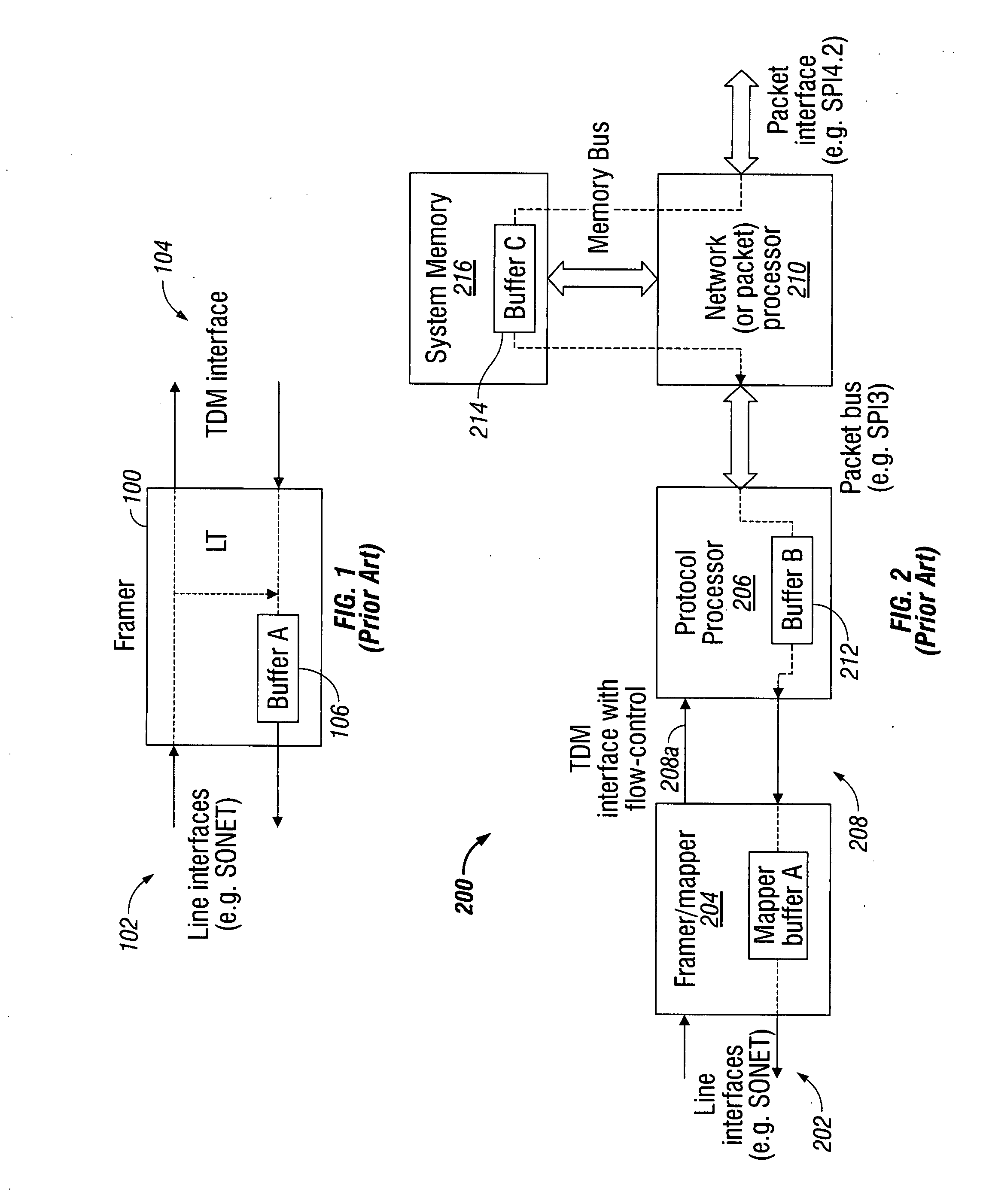
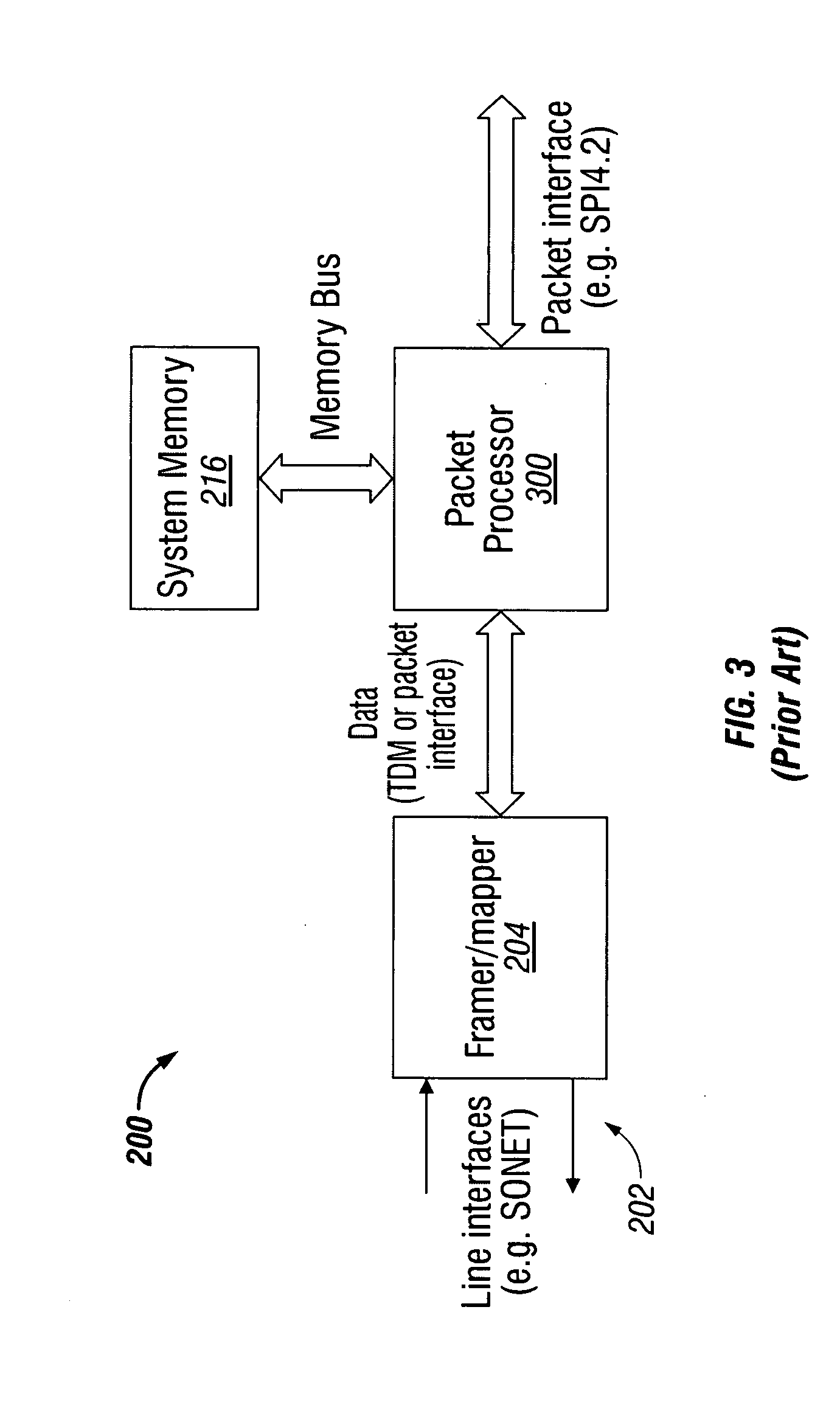
Multiservice system and method for packet and time division multiplexed transport
InactiveUS20090097506A1Lower latencyReduce data rateTime-division multiplexTransmissionCommunication interfaceTime sensitive
A system and method are presented for providing packet and time division multiplex (TDM) services in a data communication interface. The method accepts packets at a first rate over a packet interface, and transfers time-sensitive data in the packets as packet data units (PDUs) having a smaller number of bits than a packet and a second rate, faster than the first rate. The method transforms the PDUs into frames in a first TDM protocol. Typically, the PDUs are transformed into units having a smaller number of bits than the PDU and a third rate, faster than the second rate. Then, the TDM frames are transmitted over a line interface.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com