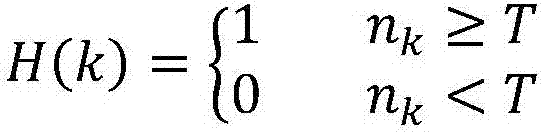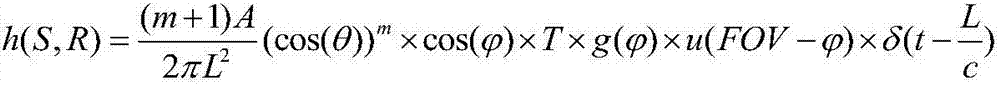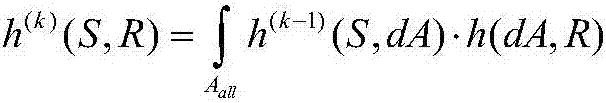Patents
Literature
89 results about "Visibility function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
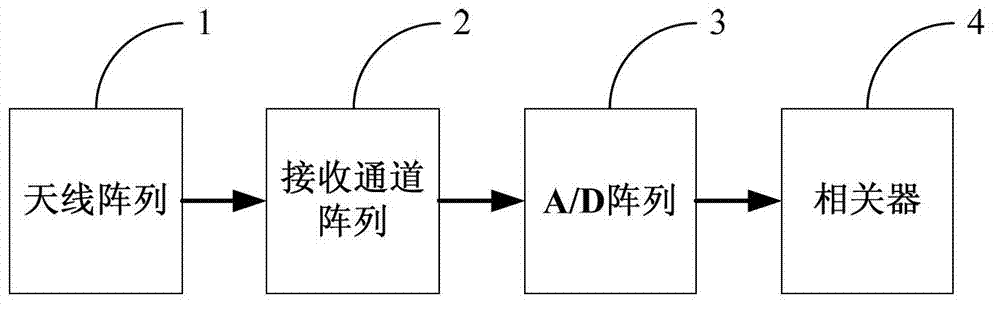
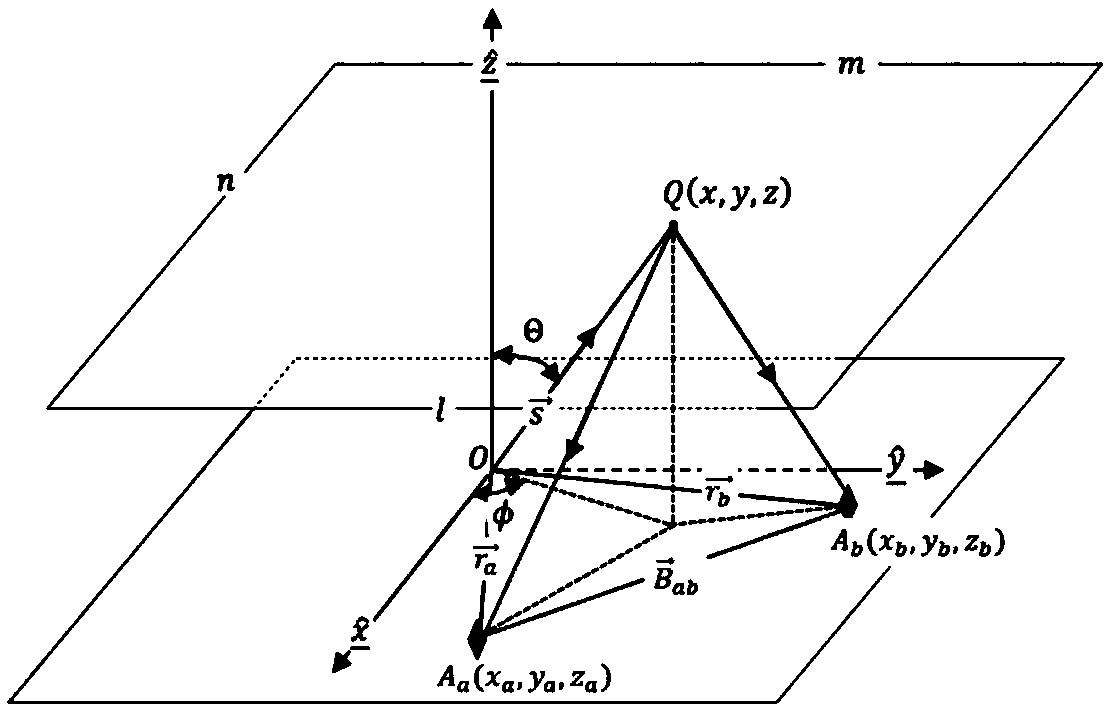
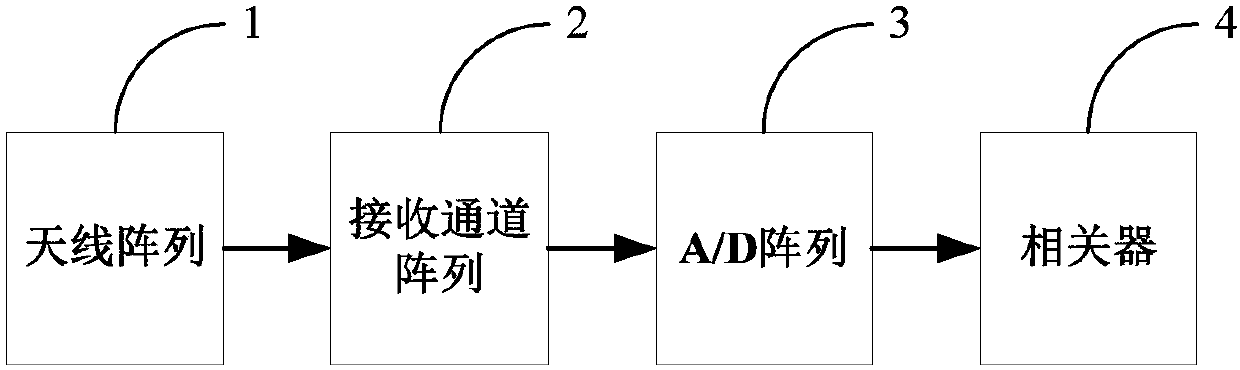
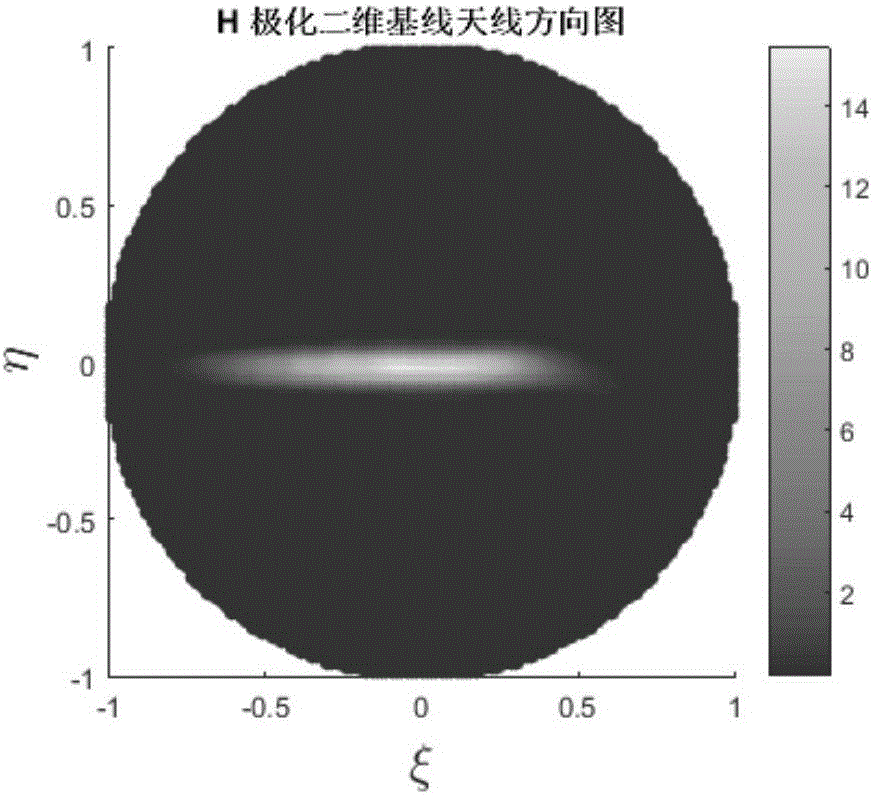
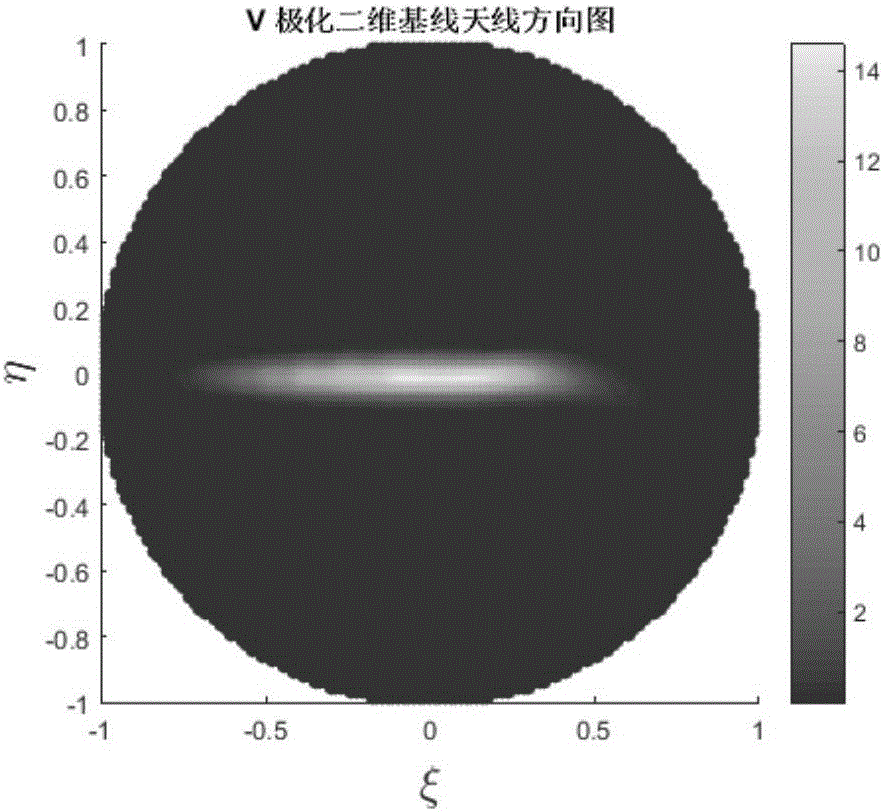
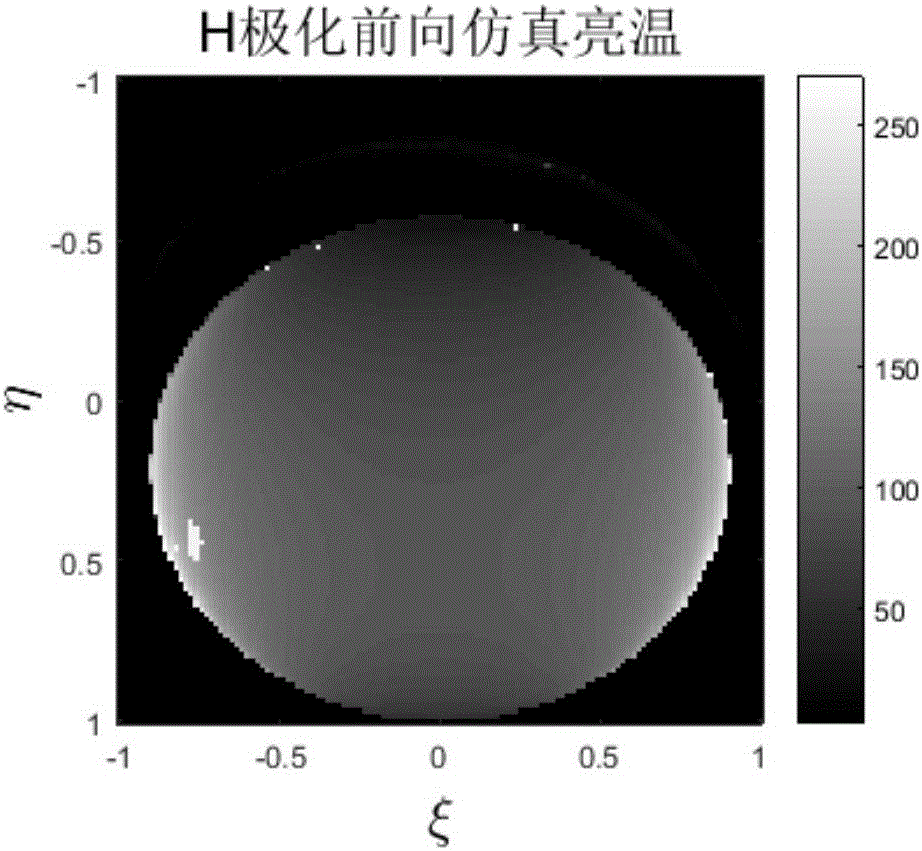
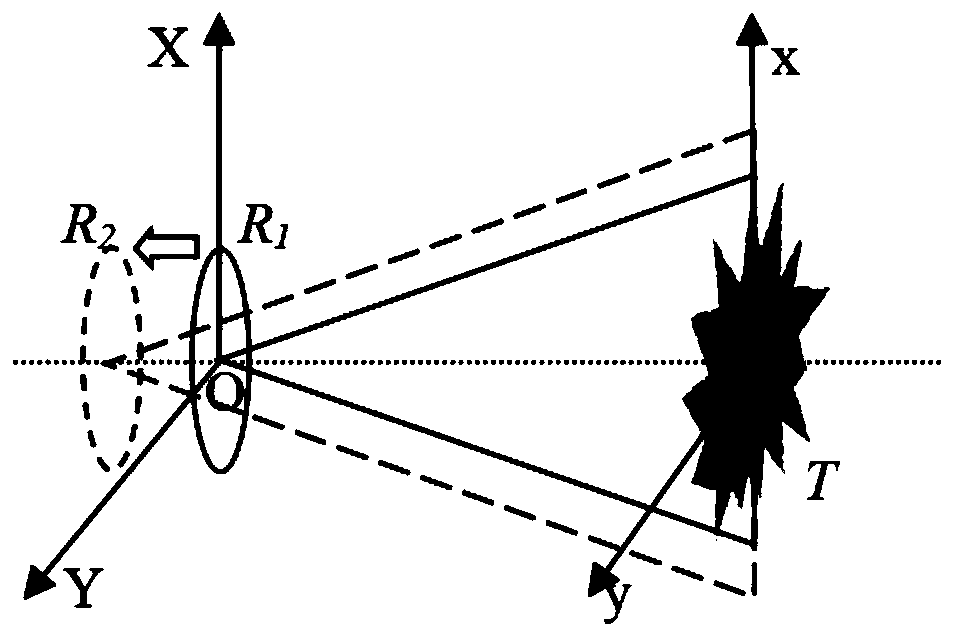
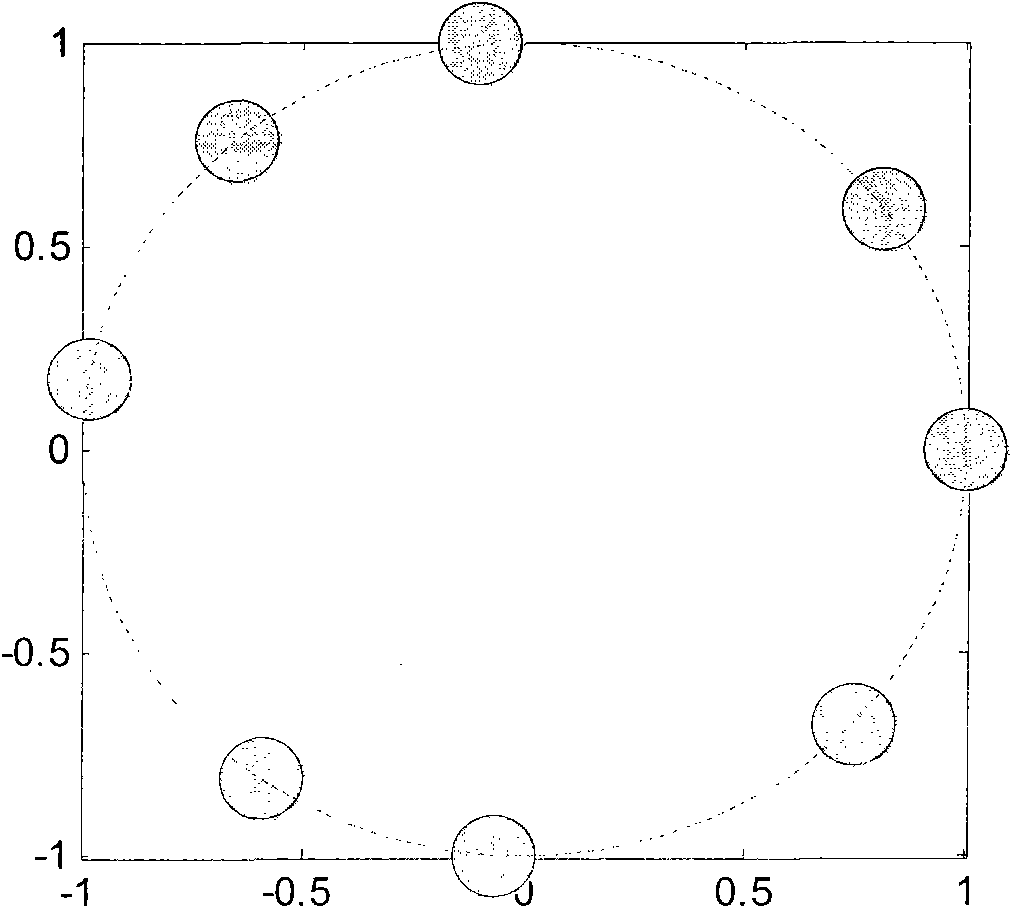
The visibility function should be formulated as a vector due to the fact that the visibilities lie naturally in random locations for the circular arrays. The digital signal processing subsystem is used to calculate the visibility function samples and reconstruct the millimeter-wave image in real-time.
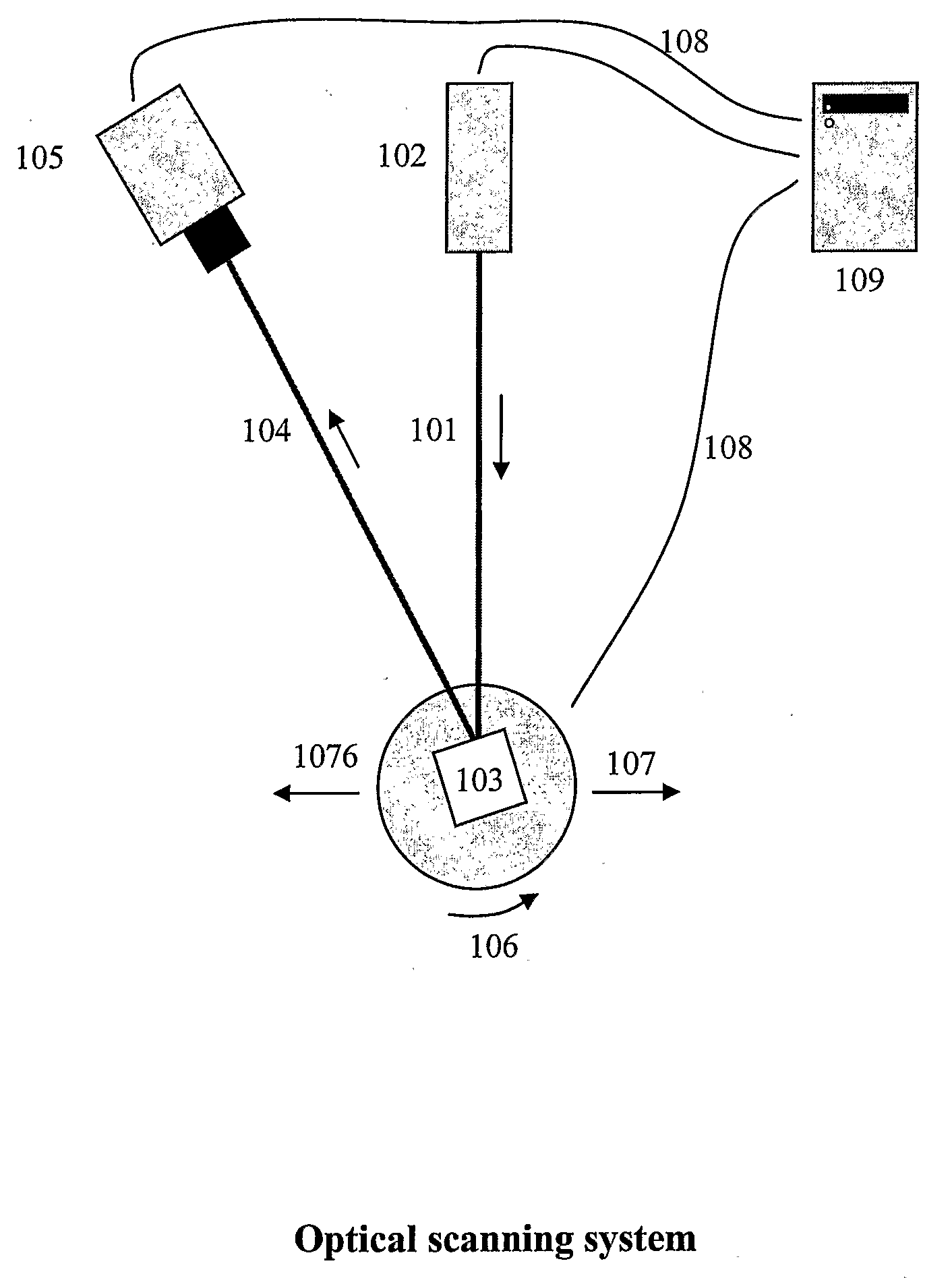
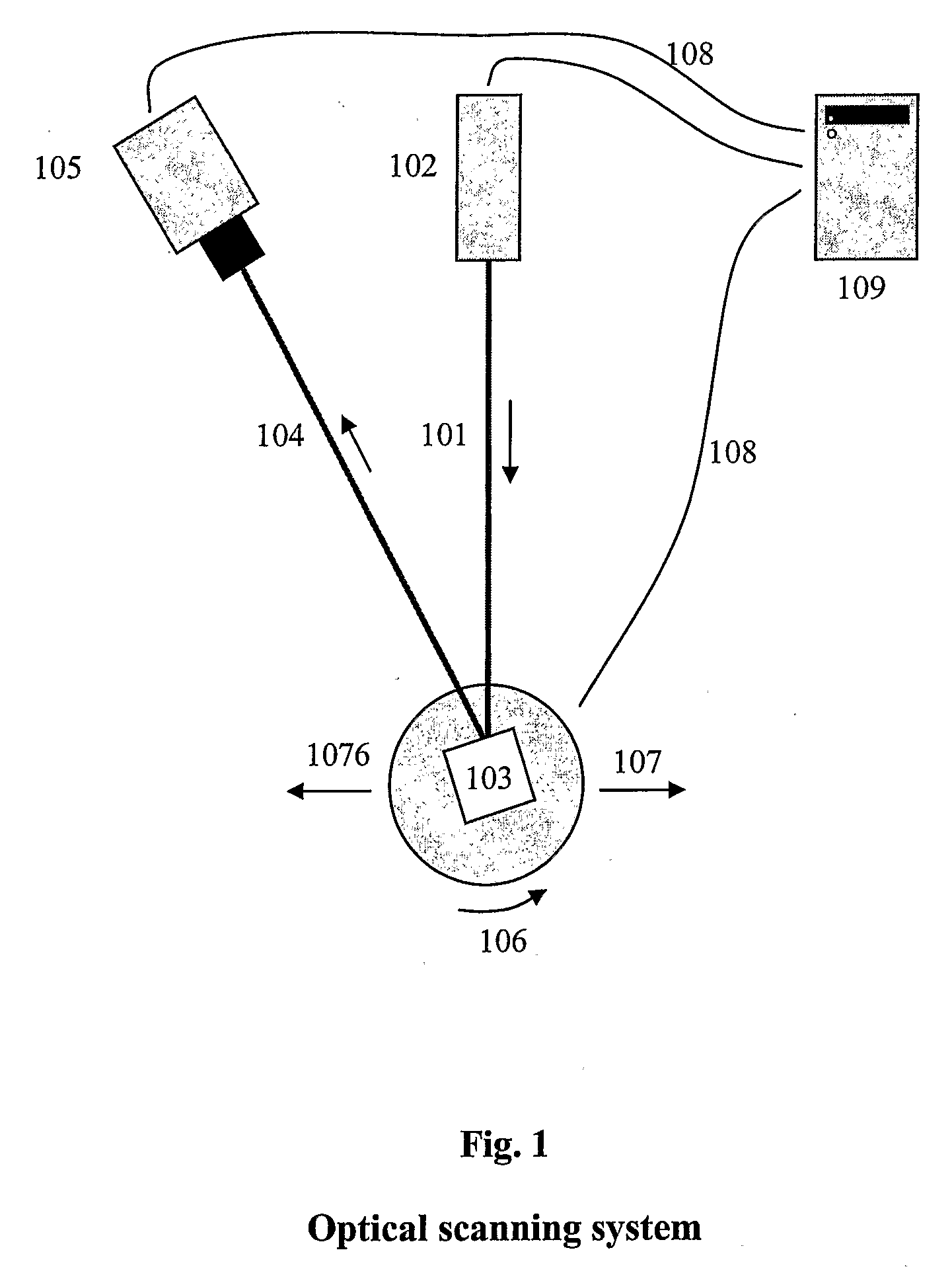
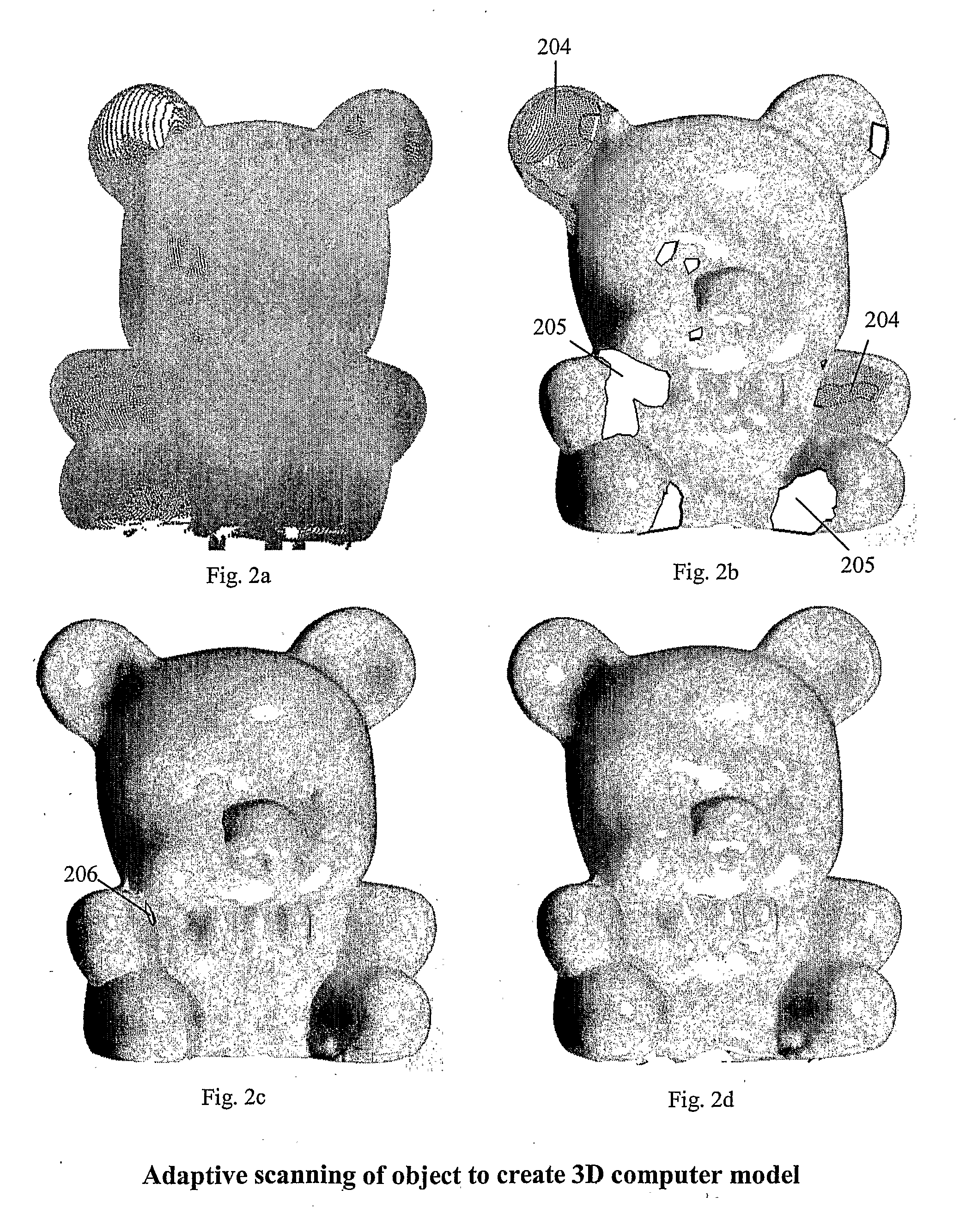
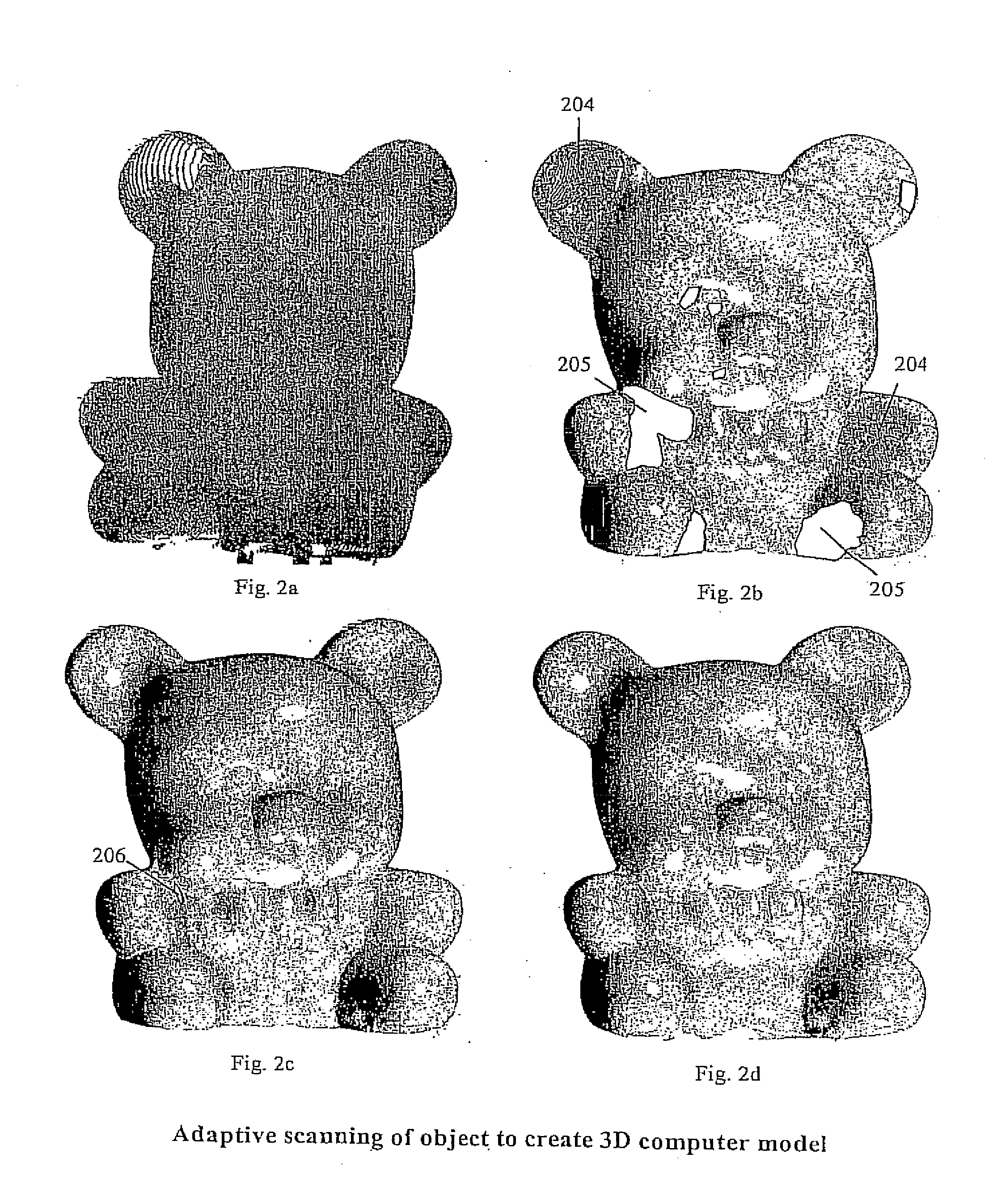
Adaptive 3D Scanning
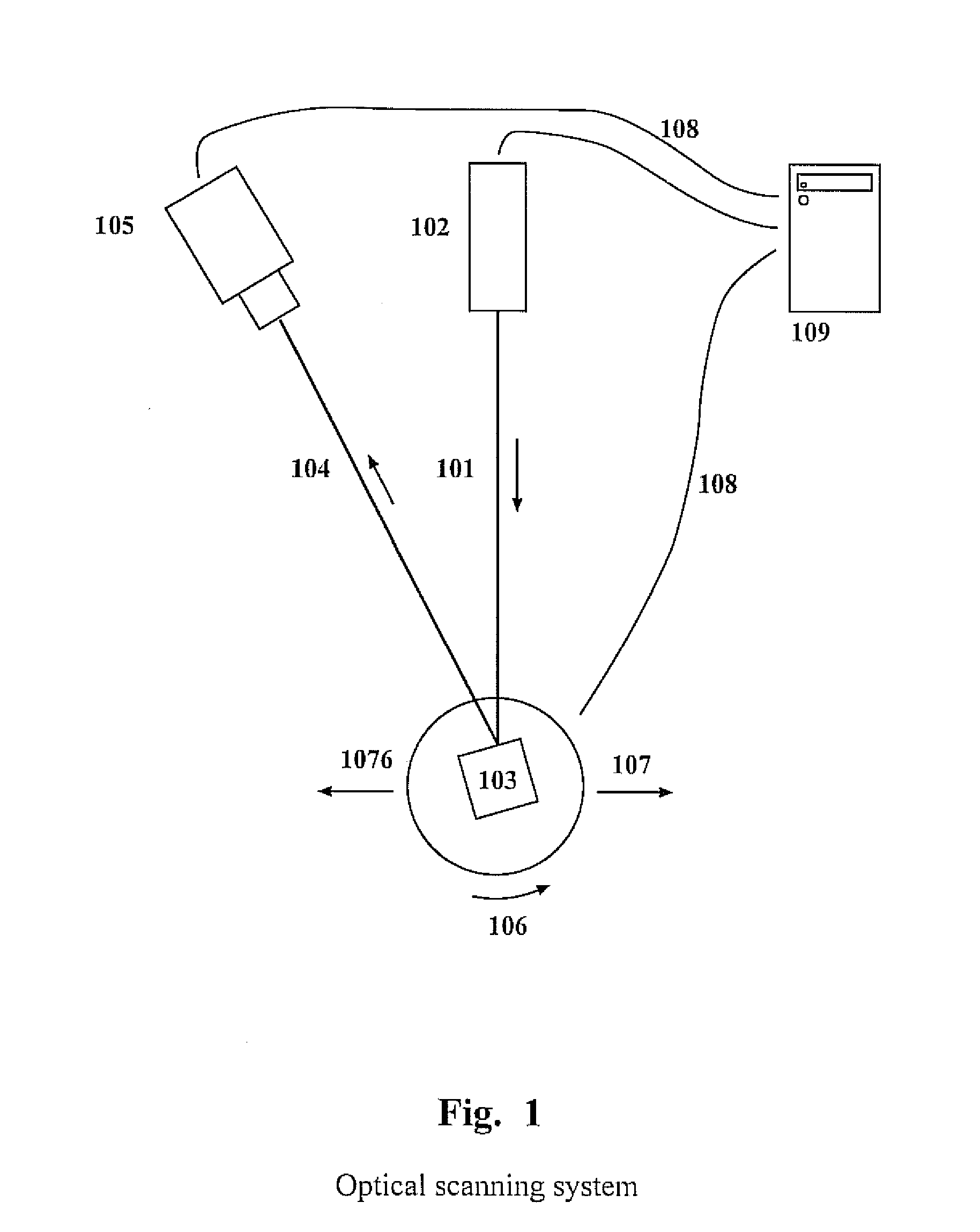
ActiveUS20080306709A1Feeler-pin gaugesMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsComputer graphics (images)3d scanning
The present invention relates to adaptive 3D scanning wherein a scan sequence for obtaining full geometrical coverage of a physical object are created automatically and specifically for the physical object, by using a method and a system for producing a 3D computer model of a physical object, wherein the method comprises the following steps providing a scanner system, said scanner system comprising a scanner, and a computer connectable to and / or integrated in said scanner, said computer comprising a virtual model of said scanner, entering shape information of the physical object into the computer, creating in said computer a visibility function based on said virtual model and the shape information, said visibility function being capable of evaluating the coverage of areas of interest of the physical object by at least one predetermined scan sequence, establishing at least one scan sequence based on the evaluation of the visibility function, performing a scan of the physical object using said at least one scan sequence, and obtaining a 3D computer model of the physical object.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
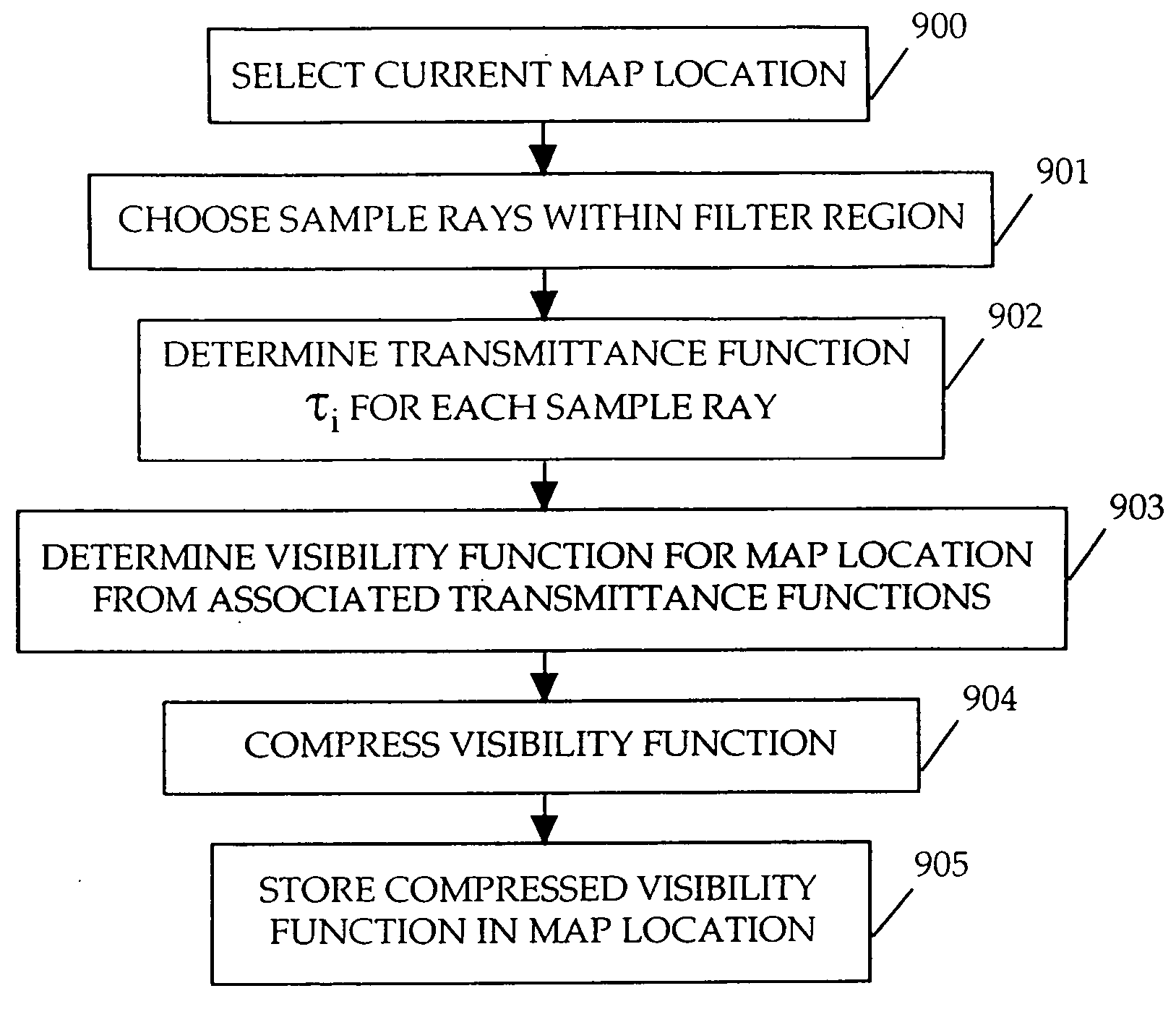
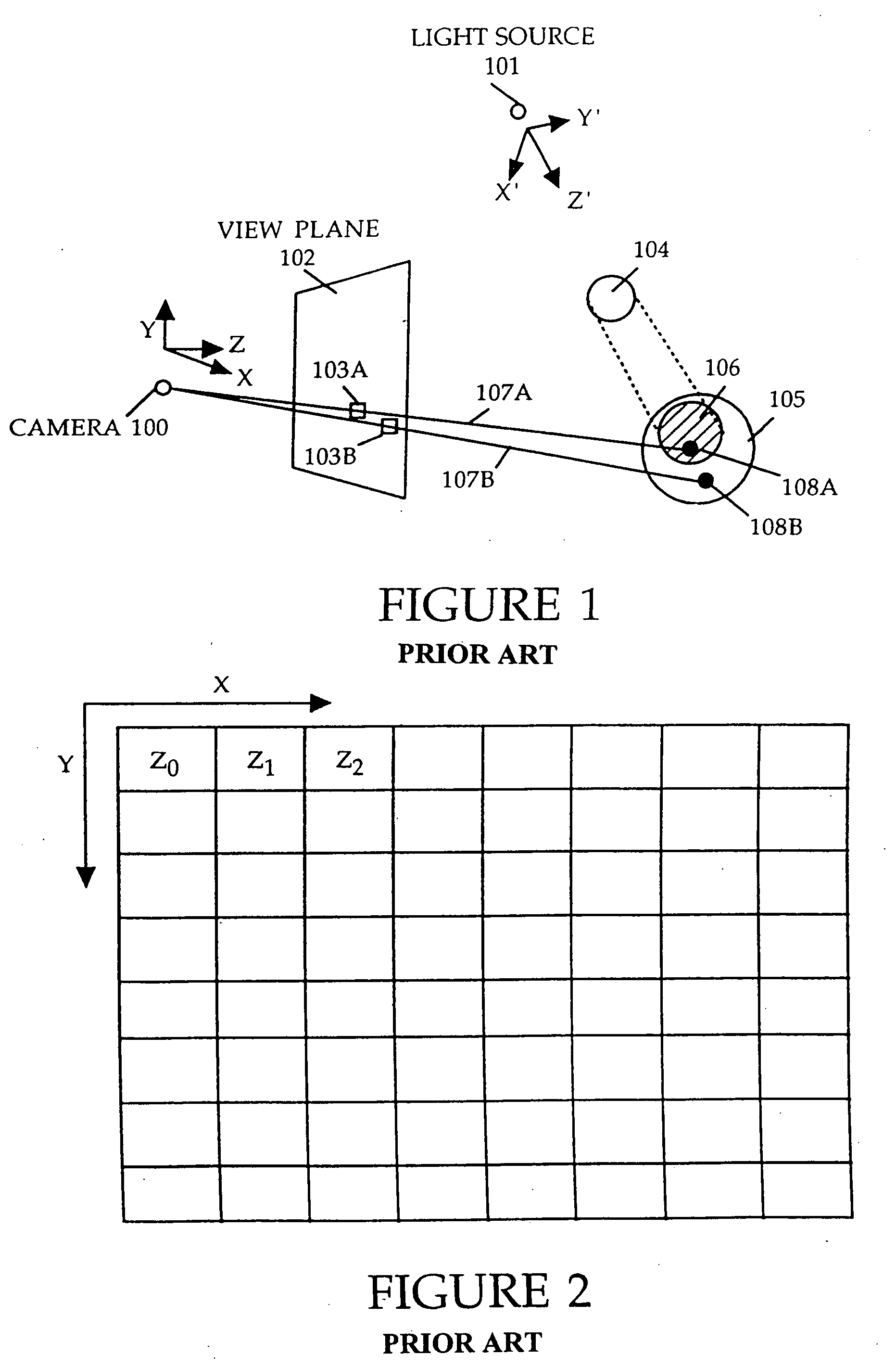
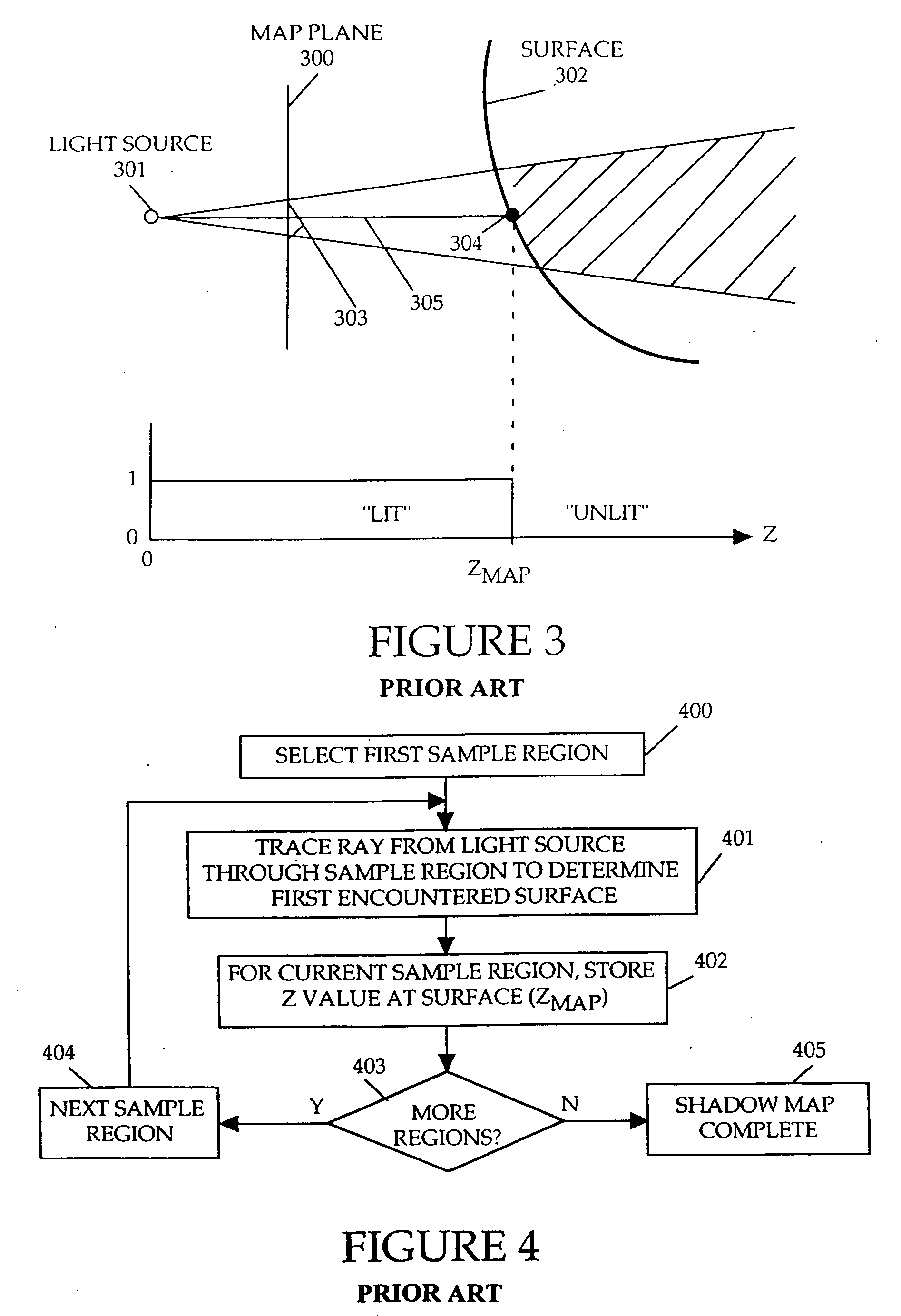
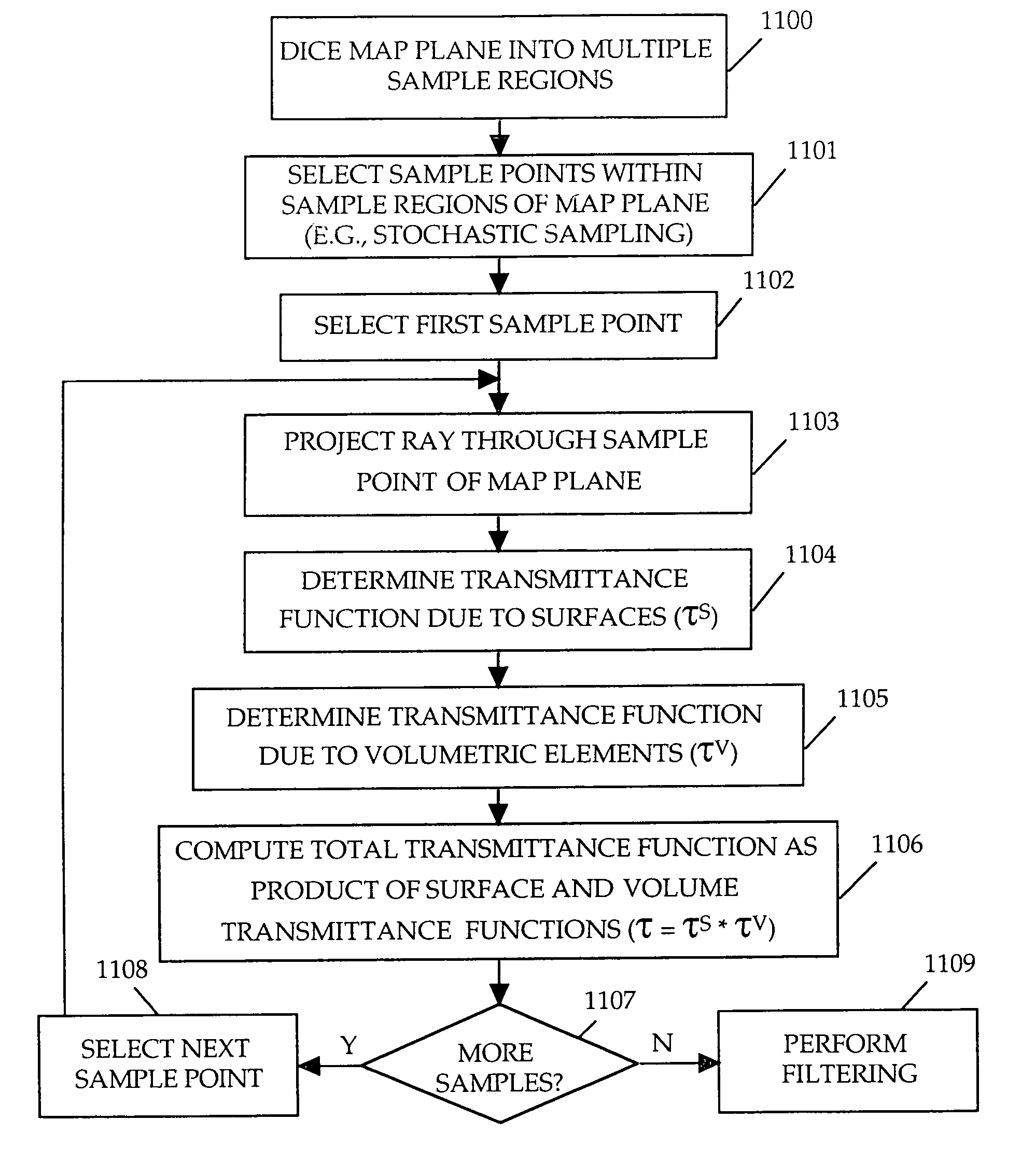
Method and apparatus for rendering shadows
InactiveUS20060119600A1Efficiently determinedAccurate modelingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Transmittance
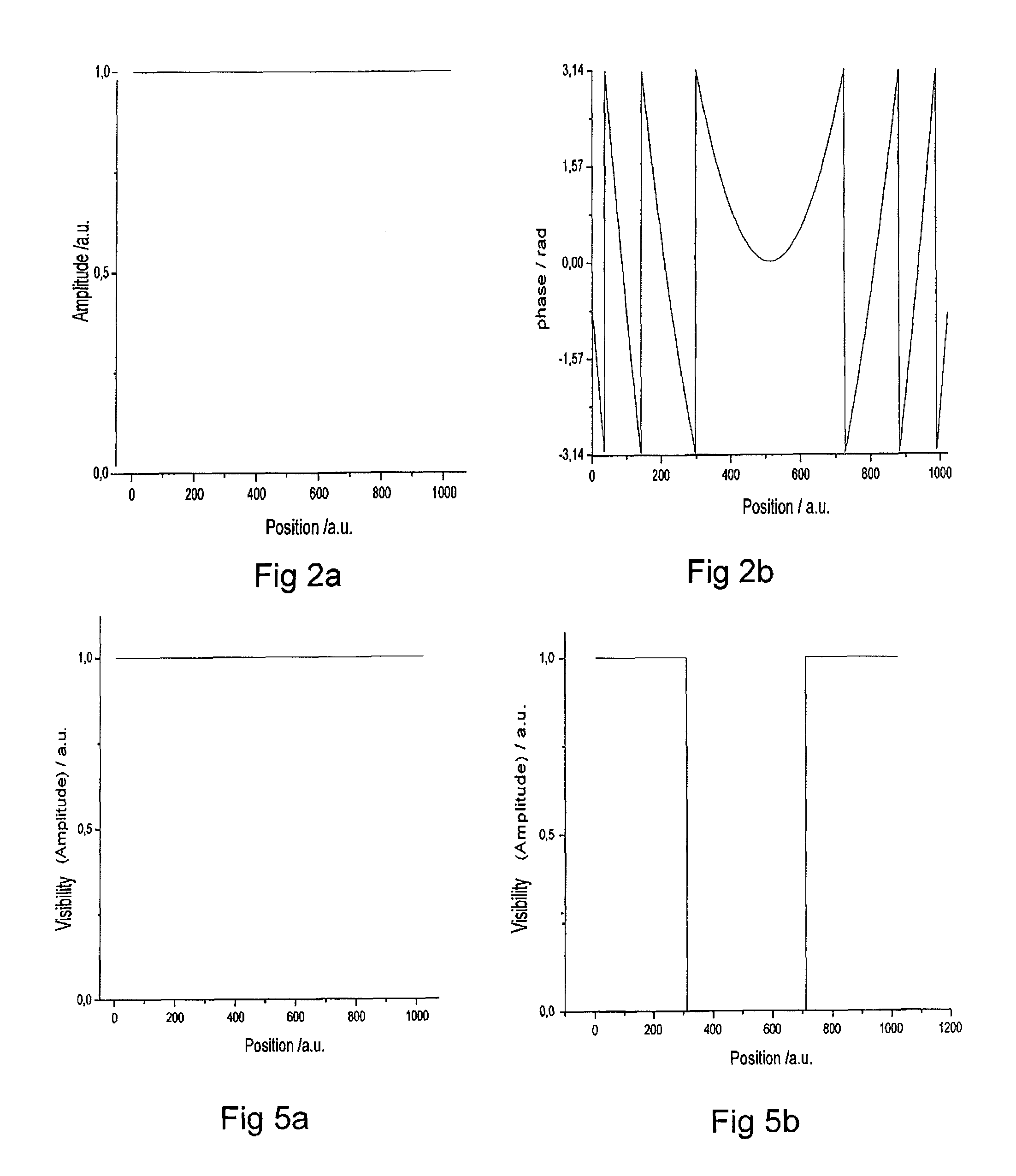
A method and apparatus for rendering shadows. A pre-rendering process implements a two dimensional array or map of depth-based functions, such as a visibility function in z. During rendering of an object scene, these functions are accessed via lookup operations to efficiently determine the function value for a sample point at a given depth. The use of visibility functions allows for partial light attenuation effects. Each visibility function is computed by filtering multiple transmittance functions obtained by casting sample rays from a light source onto an object scene. The visibility function is implemented as a sequence of vertices. Colored shadows are modeled by vertices comprising a depth value and separate visibility function values for red, green, and blue light at a given depth value. Compression is achieved by minimizing the number of vertices needed to represent a visibility function within a desired error tolerance.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
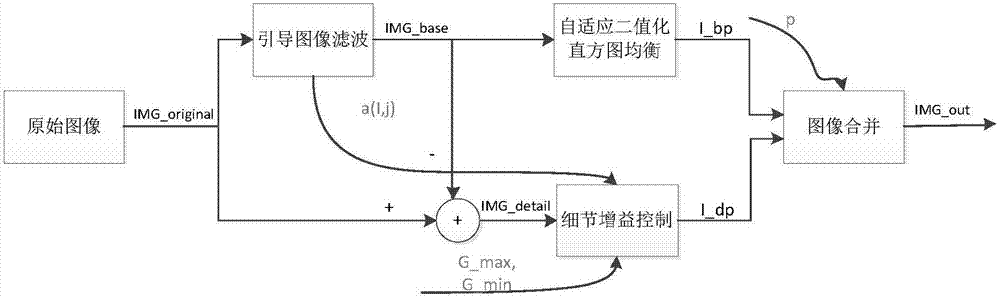
Guide image filtering based adaptive infrared image detail enhancement method
InactiveCN107016654AGood local contrastFree from lossImage enhancementImage analysisImage contrastSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a guide image filtering based adaptive infrared image detail enhancement method, which comprises the steps of firstly dividing an original image into a basic layer containing a low-frequency background and a detail layer containing high-frequency details by adopting a guide filter; then processing the basic layer by adopting an improved adaptive histogram projection algorithm so as to realize improvement for the image contrast and improve the scene adaptability of the algorithm; meanwhile, processing the detail layer by adopting a method based on a noise visibility function so as to enhance image details and suppress image noise; and finally building a final output image by using the processed basic layer and the processed detail layer. According to the invention, true infrared image data under multiple scenes can be effectively improved by adopting an adaptive threshold parameter selecting method and a simpler detail layer processing process, the output image is good in contrast and rich in detail and has good visual effects, and the real-time performance of the algorithm is also good.
Owner:EZHOU INST OF IND TECH HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
AS-OCT-SD (Anterior Segment-Optical Coherence Tomography-Spectrum Domain) imaging system and AS-OCT-SD imaging method based on visibility function regulation
ActiveCN102670172AEnable Independent ImagingHigh sensitivityEye diagnosticsGratingOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses an AS-OCT-SD (Anterior Segment-Optical Coherence Tomography-Spectrum Domain) imaging system and an AS-OCT-SD imaging method based on the visibility function regulation. Low coherent light emitted by a broadband light source can respectively enter into a sample arm and a reference arm after being split by an optical fiber coupler, light returned from the sample arm and the reference arm can respectively enter into a detection arm through a circulator, different light paths can be respectively selected by the light through light switches, the light can irradiate in different areas of a grating, and thus the switching between the reference arm position and the maximum sensitivity position corresponding to the reference arm position can be realized; different light spectrum components after the dispersion by the grating can be gathered on different pixels of a CCD (Charge Coupled Device), interference can be generated, and an OCT image of a sample can be reconstructed after an interference spectrum signal is transmitted to a computer; and two OCT images corresponding to two states of the light switches can be split-jointed, and thus an OCT image with double measuring range can be obtained. According to the AS-OCT-SD imaging system and the AS-OCT-SD imaging method, disclosed by the invention, the AS-OCT-SD imaging can be realized under a high sensitivity premise.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and apparatus for rendering shadows
InactiveUS7023438B2Efficiently determinedAccurate modelingCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingComputer graphics (images)Transmittance
A method and apparatus for rendering shadows. A pre-rendering process implements a two dimensional array or map of depth-based functions, such as a visibility function in z. During rendering of an object scene, these functions are accessed via lookup operations to efficiently determine the function value for a sample point at a given depth. The use of visibility functions allows for partial light attenuation effects. Each visibility function is computed by filtering multiple transmittance functions obtained by casting sample rays from a light source onto an object scene. The visibility function is implemented as a sequence of vertices. Colored shadows are modeled by vertices comprising a depth value and separate visibility function values for red, green, and blue light at a given depth value. Compression is achieved by minimizing the number of vertices needed to represent a visibility function within a desired error tolerance.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Adaptive 3D scanning
InactiveUS20100332196A1Special data processing applications3D modellingComputer graphics (images)3d scanning
The present invention relates to adaptive 3D scanning wherein a scan sequence for obtaining full geometrical coverage of a physical object are created automatically and specifically for the physical object, by using a method and a system for producing a 3D computer model of a physical object, wherein the method comprises the following steps providing a scanner system, said scanner system comprising a scanner, and a computer connectable to and / or integrated in said scanner, said computer comprising a virtual model of said scanner, entering shape information of the physical object into the computer, creating in said computer a visibility function based on said virtual model and the shape information, said visibility function being capable of evaluating the coverage of areas of interest of the physical object by at least one predetermined scan sequence, establishing at least one scan sequence based on the evaluation of the visibility function, performing a scan of the physical object using said at least one scan sequence, and obtaining a 3D computer model of the physical object.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
Blocking effect analysis method and system
InactiveCN101605257AAccurate evaluationSubjective feelingTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSubjective refractionBlock effect
The invention discloses a blocking effect analysis method. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a decoded image; calculating brightness differences on boundaries among pixel blocks; utilizing a blocking effect visibility function to process the brightness differences on the boundaries among the pixel blocks; utilizing a Weber-Fick inner law to calculate the subjective sensation of a human vision system to visible blocking effects; and integrating the blocking effects on all the boundaries in the image to obtain the blocking effect evaluation analysis results of the whole image. The blocking effect analysis method and the system can accurately realize the blocking effect evaluation so that results can more suit the subjective sensation of the eyes.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGCHUANG TELECOM TEST
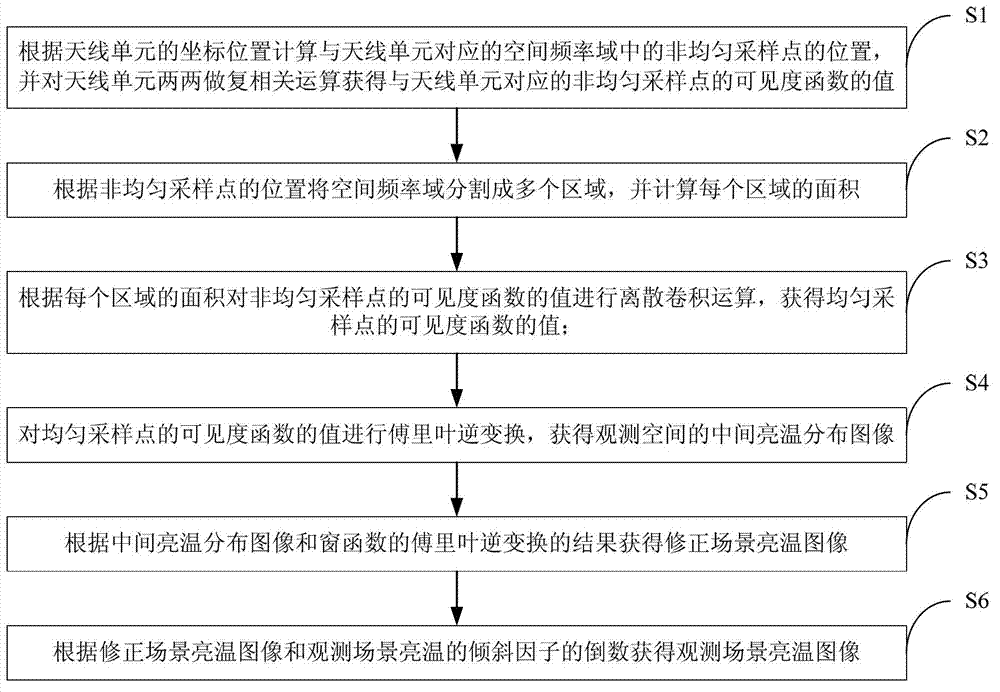
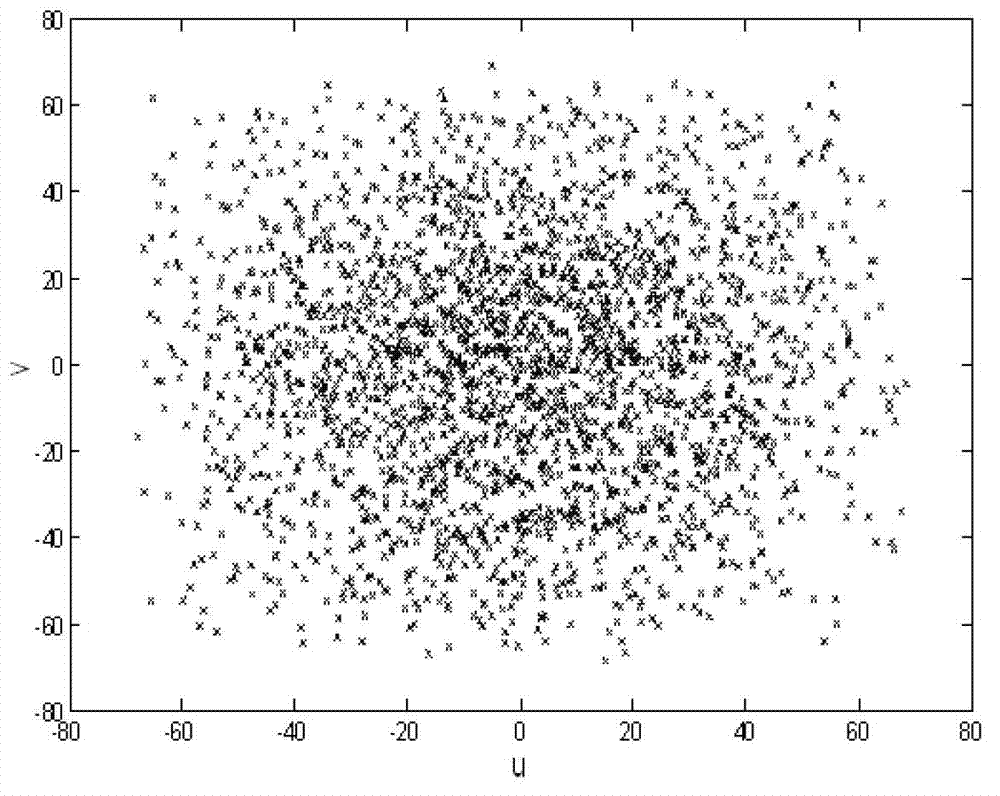
Image inversion method of non-uniform sampling comprehensive bore diameter radiometer
ActiveCN103323845AFast inversionEfficient inversionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBrightness temperatureRadiometer
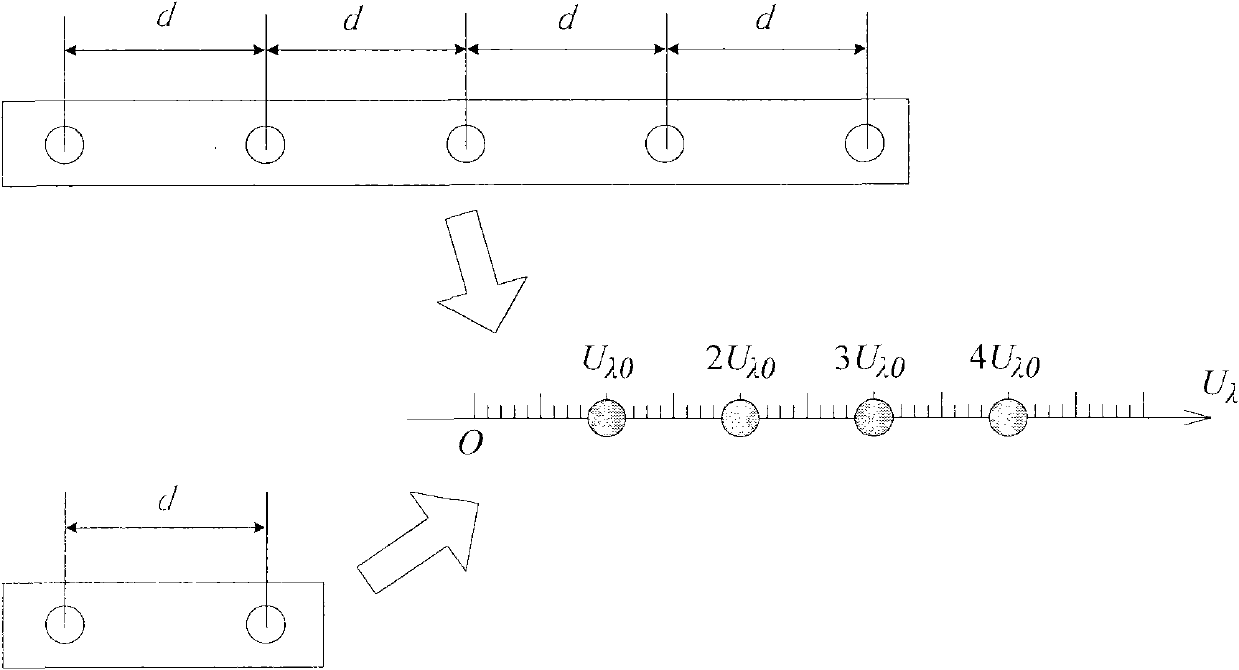
The invention discloses an image inversion method of a non-uniform sampling comprehensive bore diameter radiometer. The image inversion method comprises the steps that the positions of non-uniform sampling points are calculated according to position coordinates of antenna units, and the values of the visibility functions of the non-uniform sampling points are obtained; according to the positions of the non-uniform sampling points, a spatial frequency domain is divided into a plurality of regions, and the area of each region is calculated; according to the area of each region, discrete convolution operation is conducted on the values of the visibility functions of the non-uniform sampling points, and the values of the visibility functions of uniform sampling points are obtained; inverse Fourier transformation is conducted on the values of the visibility functions of the uniform sampling points, and a middle brightness temperature distribution image of an observation space is obtained; according to the middle brightness temperature distribution image and the result of inverse Fourier transformation of a window function, a correction scene brightness temperature image is obtained; according to the correction scene brightness temperature image and the reciprocal of an inclination factor of the observation scene brightness temperature, an observation scene brightness temperature image is obtained. The image inversion method can rapidly, efficiently and accurately achieve inversion of a scene brightness temperature distribution image of the non-uniform sampling comprehensive bore diameter radiometer.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
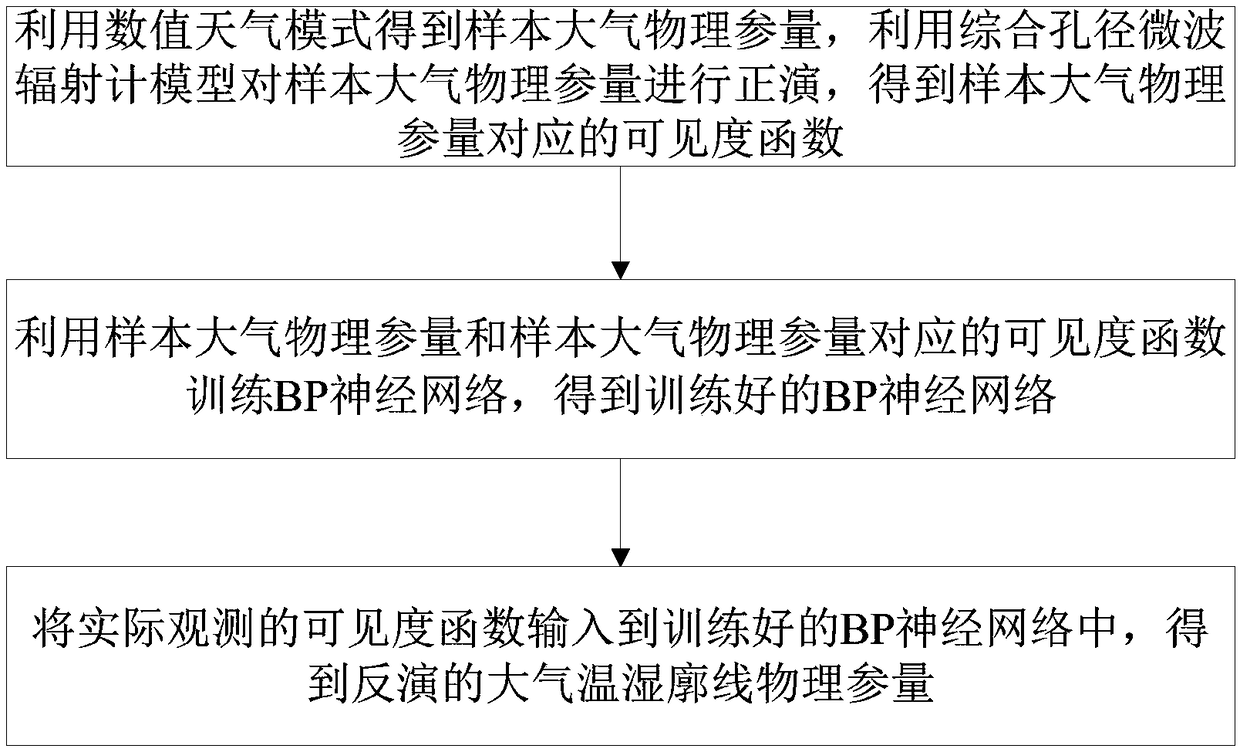
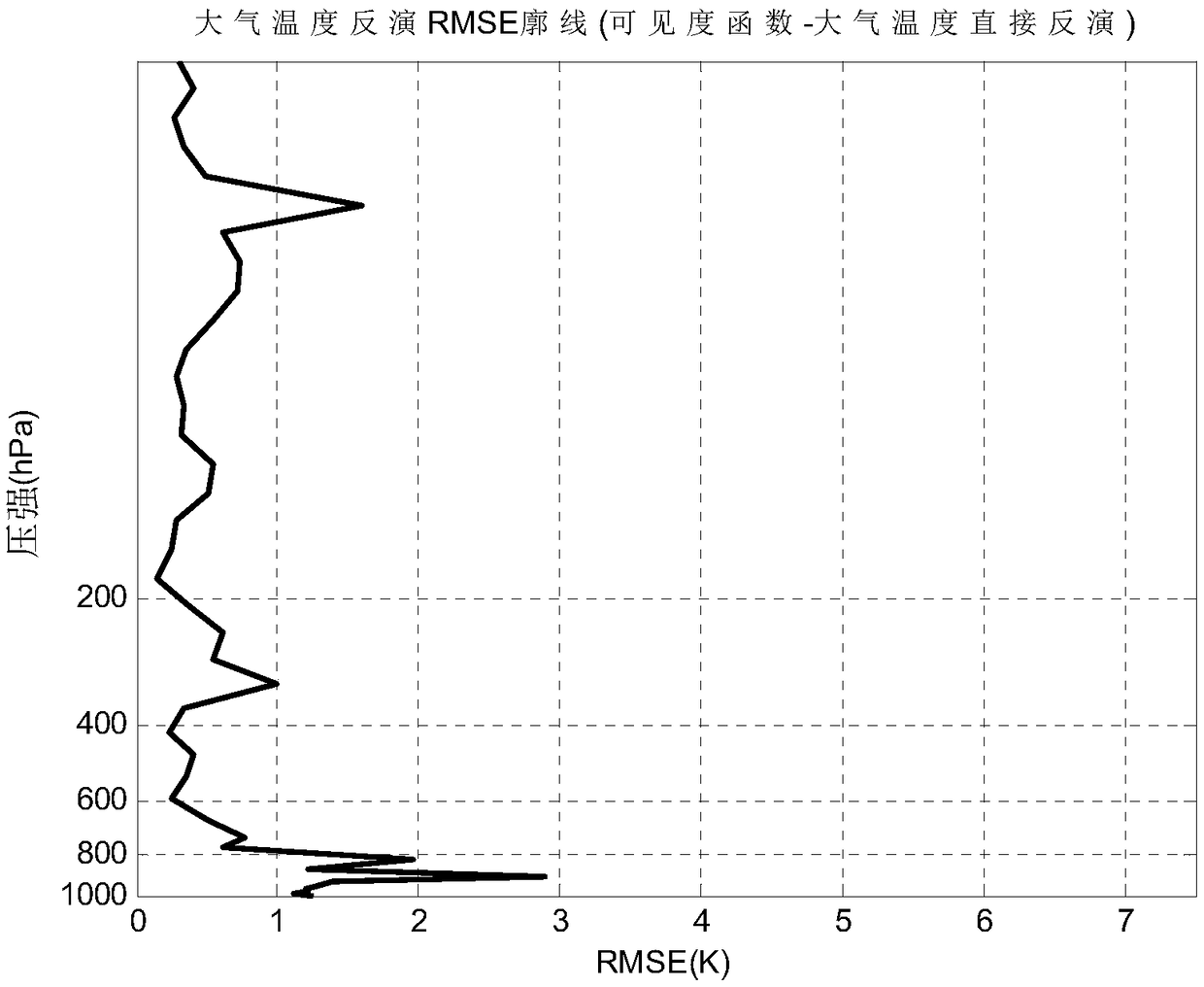
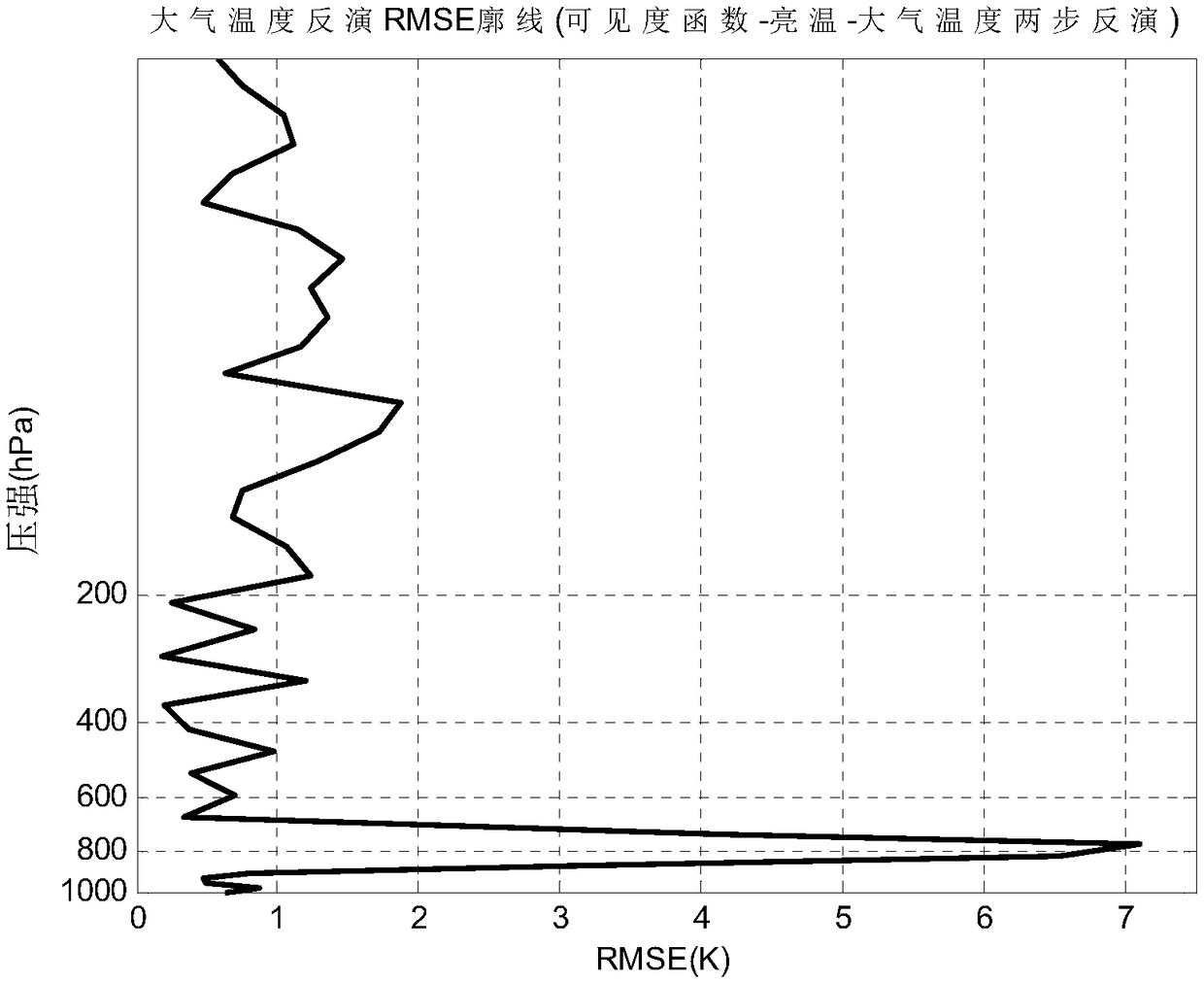
Visibility function direct inversion method of atmospheric temperature and humidity profile
ActiveCN108875905AEasy to handleReduce inversion errorIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesNeural architecturesBrightness temperatureAtmospheric temperature
The invention discloses a visibility function direct inversion method of an atmospheric temperature and humidity profile. The method comprises the following steps: inputting an actual observed visibility function into a trained BP neural network, so as to obtain an inversed atmospheric temperature and humidity profile physical parameter, wherein the training of the BP neural network comprises: using a numerical weather mode to obtain a sample atmospheric physical parameter, and using an aperture synthesis microwave radiometer model to carry out forward modeling on the sample atmospheric physical parameter to obtain a visibility function corresponding to the sample atmospheric physical parameter; and using the sample atmospheric physical parameter and the visibility function corresponding to the sample atmospheric physical parameter to train the BP neural network, so as to obtain the trained BP neural network. The invention changes a two-step inversion method of visibility-brightness temperature-atmospheric physical parameters required for remote sensing atmospheric physical parameters of a current aperture synthesis microwave radiometer, and proposes a direct inversion method of visibility-atmospheric physical parameters, which simplifies the data processing flow and reduces inversion errors, so as to obtain more accurate atmospheric physical parameters.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
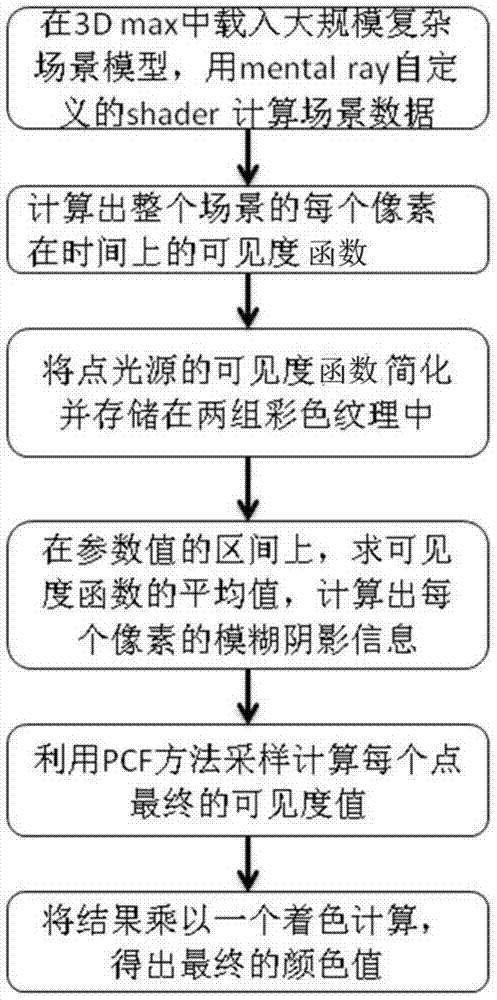
Three-dimensional vector model real-time shadow deferred shading method based on controllable texture baking
InactiveCN103700134AOvercoming the aliasing problemMeet application requirements3D-image renderingCooking & bakingTime domain
The invention relates to a computer application technology and the field of computer vision, and particularly relates to a three-dimensional vector model real-time light and shadow deferred shading method based on controllable texture baking. The method comprises the following steps: loading a whole large-scale complex model scene into a 3Dmax; calculating a visibility function of each pixel of the whole scene in terms of time, simplifying the visibility functions and then storing the simplified visibility functions into two colourful texture groups; calculating the average illumination of the time period in time domain; generating a faint shadow by utilizing shadows shaded by light source points on the time period; calculating light sources in the shadow information by virtue of a PCF (Photonic Crystal Fiber) method so as to obtain characteristics such as final visibility value. An offline shading method based on ray tracing and adjacent region sampling filtration blocking interval mapping technology are combined, the shadow generated according to the algorithm is more real, the sawtooth problem generated by a shadow mapping algorithm is overcome, and the application requirement of virtual reality is met.
Owner:WISESOFT CO LTD +1
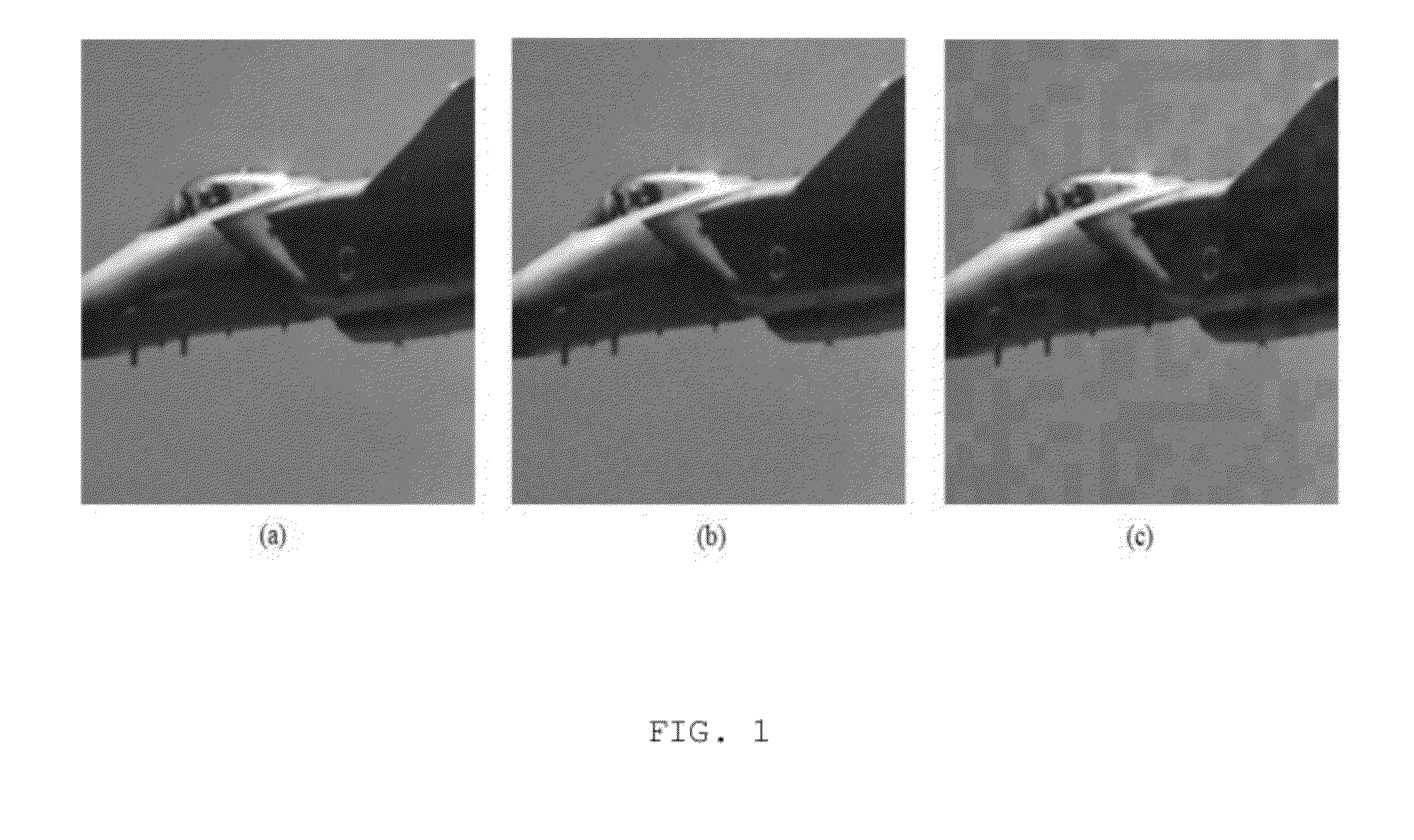
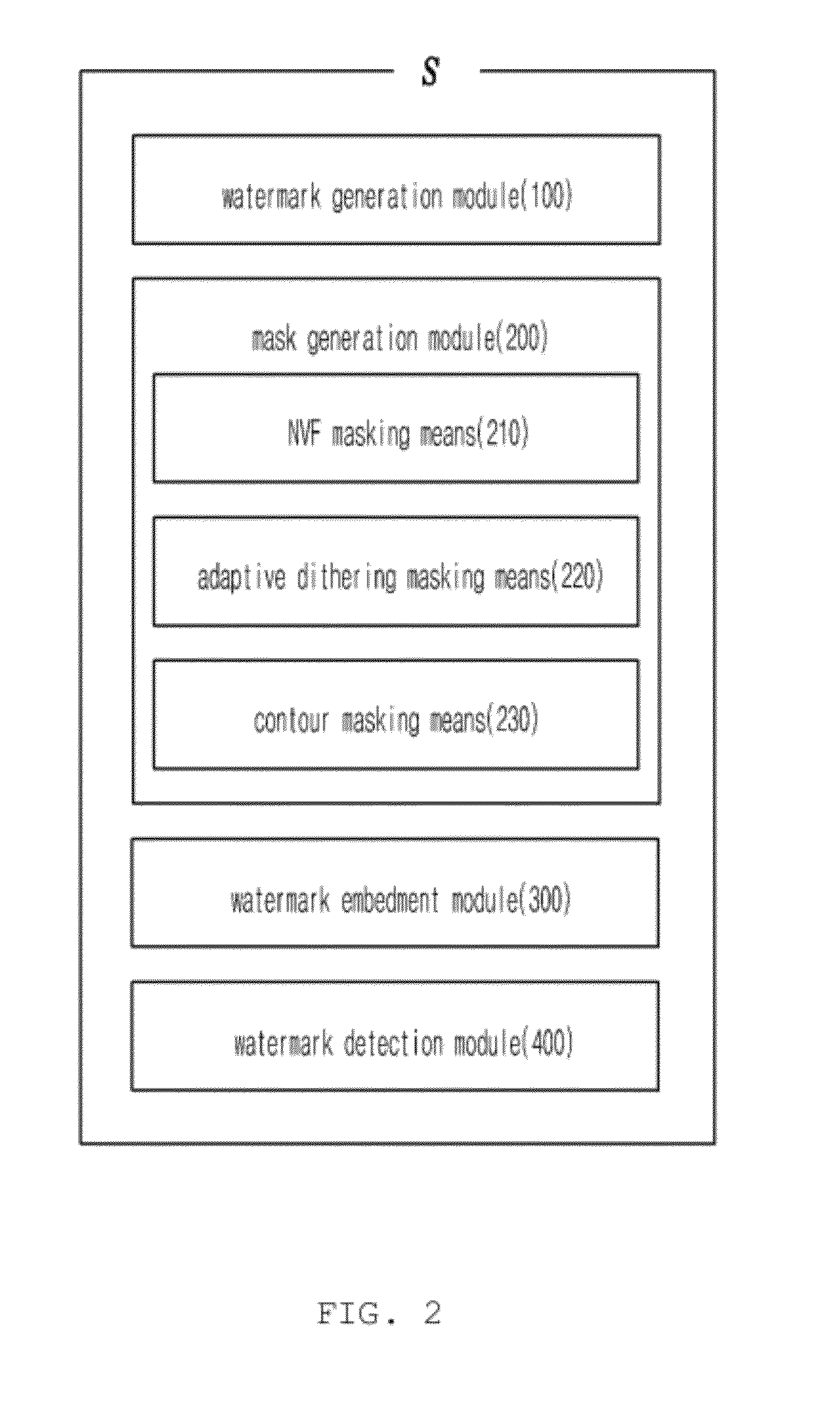
Composite masking system and method for improving invisibility of high-definition video watermarking
ActiveUS20120027207A1Improve stealth performanceAvoid problemsCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsInvisibilityHigh-definition video
A composite masking system and method for improving the invisibility of high-definition video watermarking. The composite masking system includes a watermark generation module, a mask generation module, and watermark embedment means. The watermark generation module generates a basic watermark pattern using a private key, and generate a watermark pattern by repeatedly extending the basic watermark pattern. The mask generation module generates a Noise Visibility Function (NVF) mask using NVF masking means, an adaptive dithering mask using adaptive dithering masking means, and a contour mask using contour masking means. The watermark embedment means generates a composite mask by multiplying the NVF mask, the adaptive dithering mask and the contour mask together, multiplying the composite mask and the extended watermark pattern together, and embedding the result of the second multiplication in the luminance channel of an original image.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
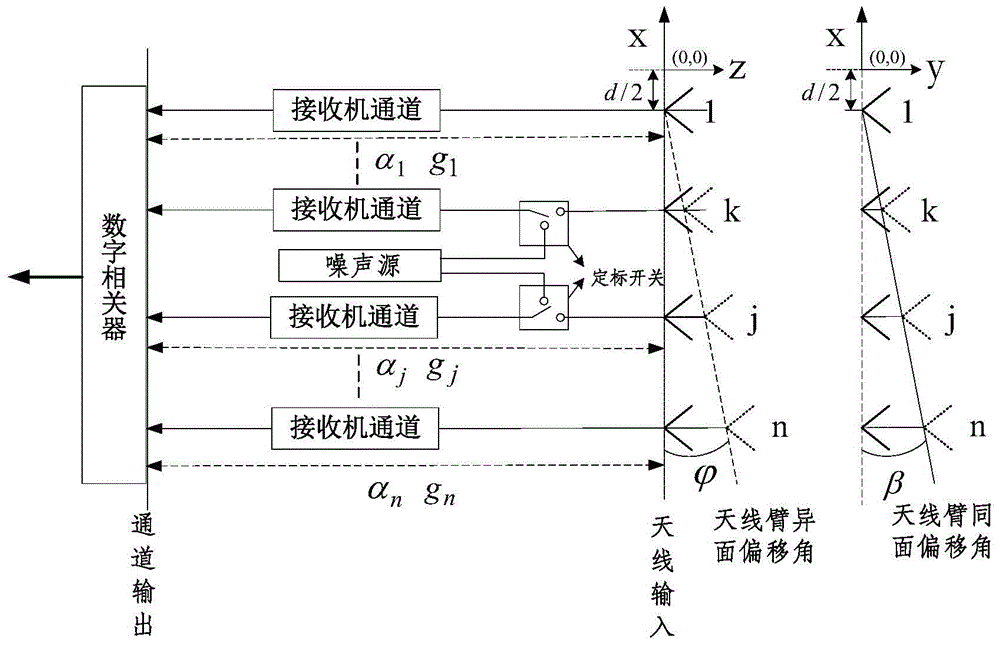
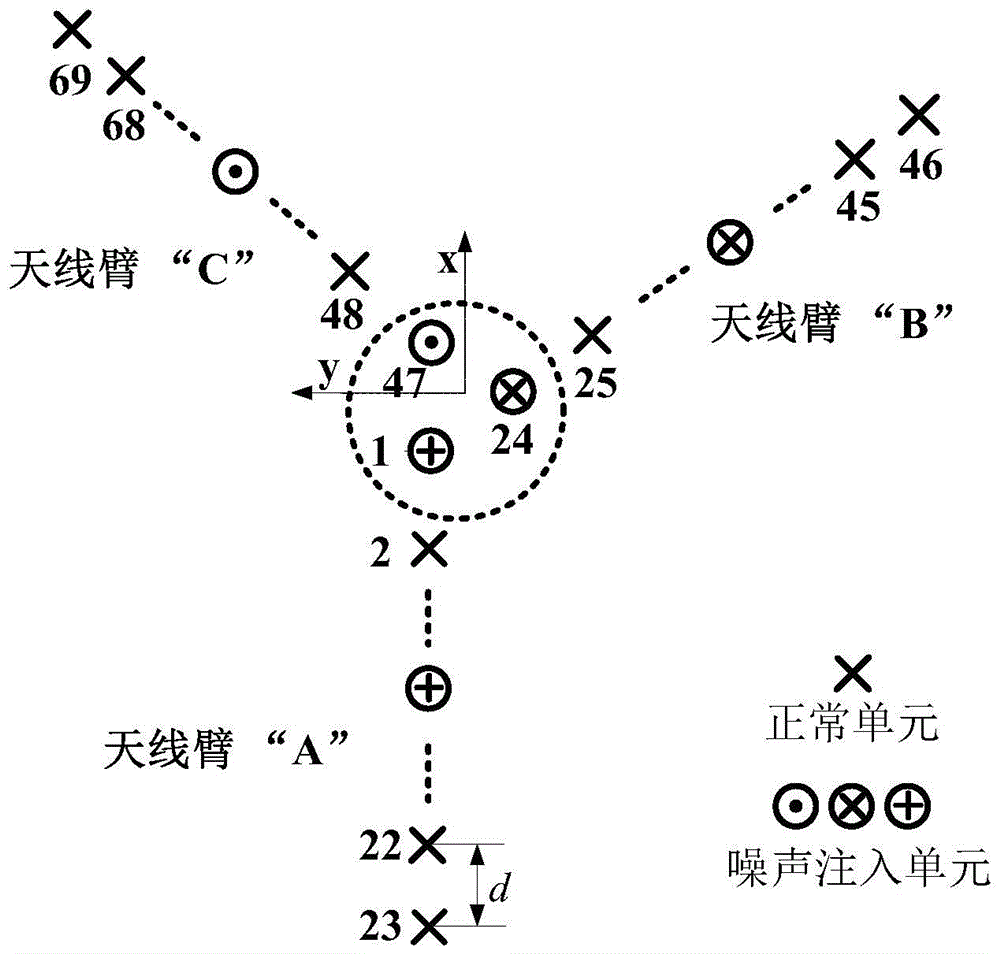
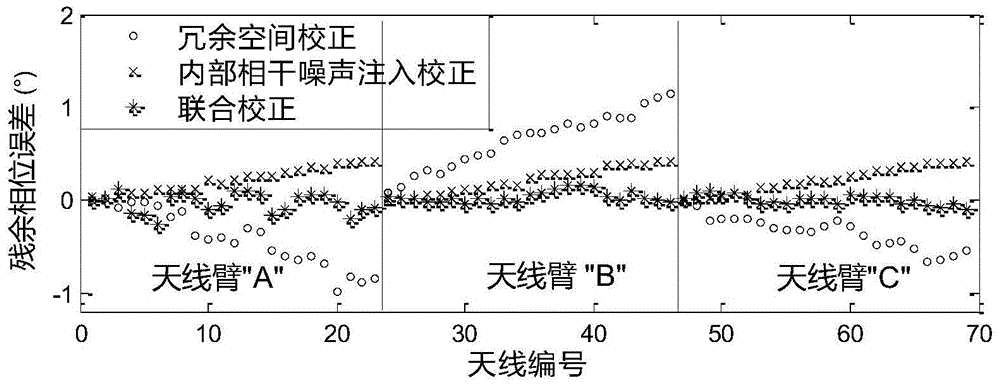
Synthetic aperture microwave radiometer combined correction method
ActiveCN105738851AReduce volumeReduce weightElectrical measurementsBrightness temperatureClassical mechanics
The invention provides a synthetic aperture microwave radiometer combined correction method comprising the steps that (1) the shortest baseline is selected to act as a redundant baseline, and all the related calibration equations are constructed; (2) a few receiver units are selected to act as internal coherent noise injection units, the amplitude and phase error are acquired through a noise injection correction method, and the calibration equations related to the noise injection units are constructed; (3) all the calibration equations of (1) and (2) form simultaneous equations so that a combined calibration equation group based on redundant space and internal coherent noise injection is formed; (4) the constructed combined calibration equation group is solved so that the amplitude and phase error of all the receivers and the out-of-plane displacement angle of an antenna arm are acquired; and (5) the measured visibility function is corrected according to the amplitude and phase error and the out-of-plane displacement angle of the antenna arm which are acquired in the step (4), and the corrected brightness temperature image is acquired by adopting a brightness temperature inversion method.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
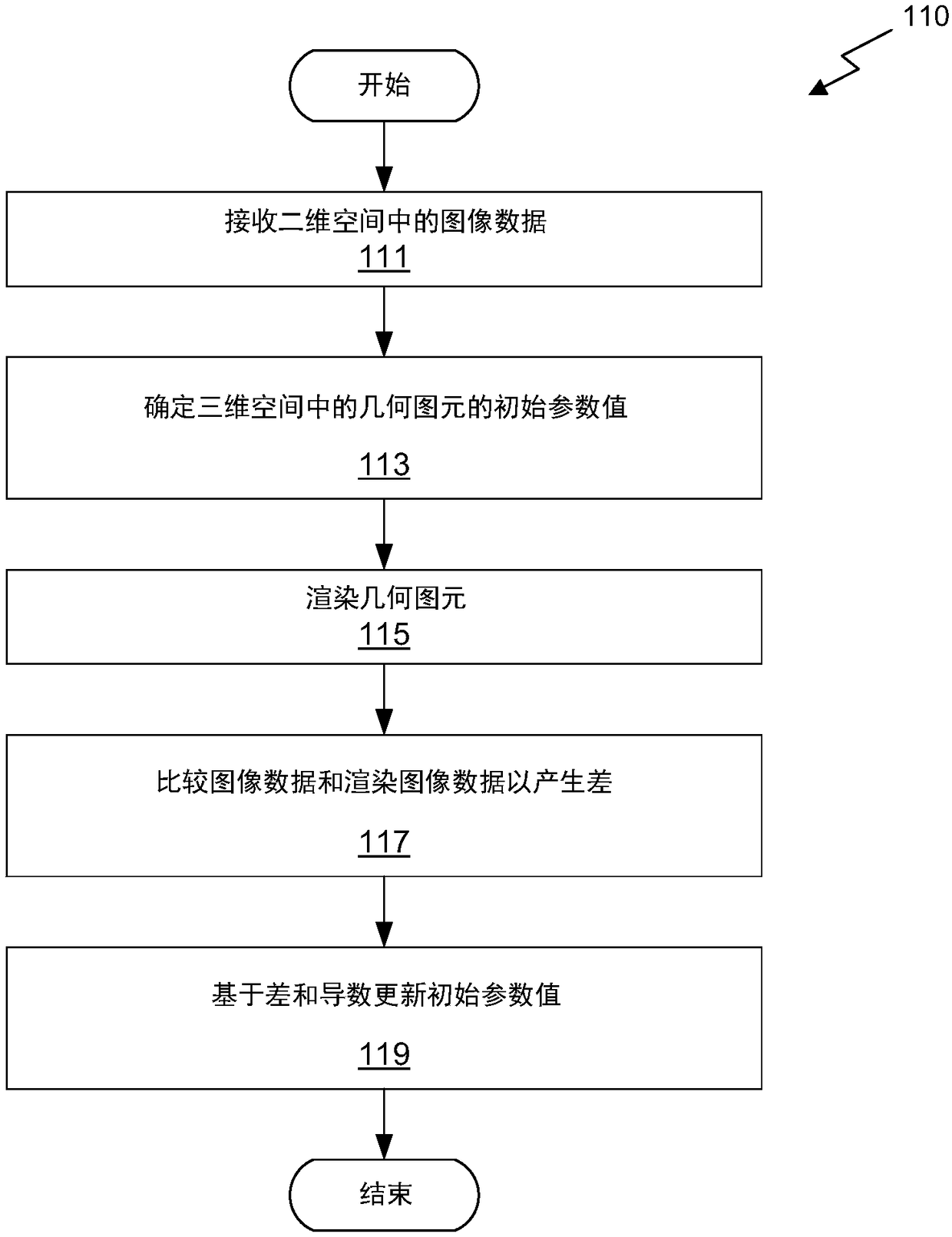
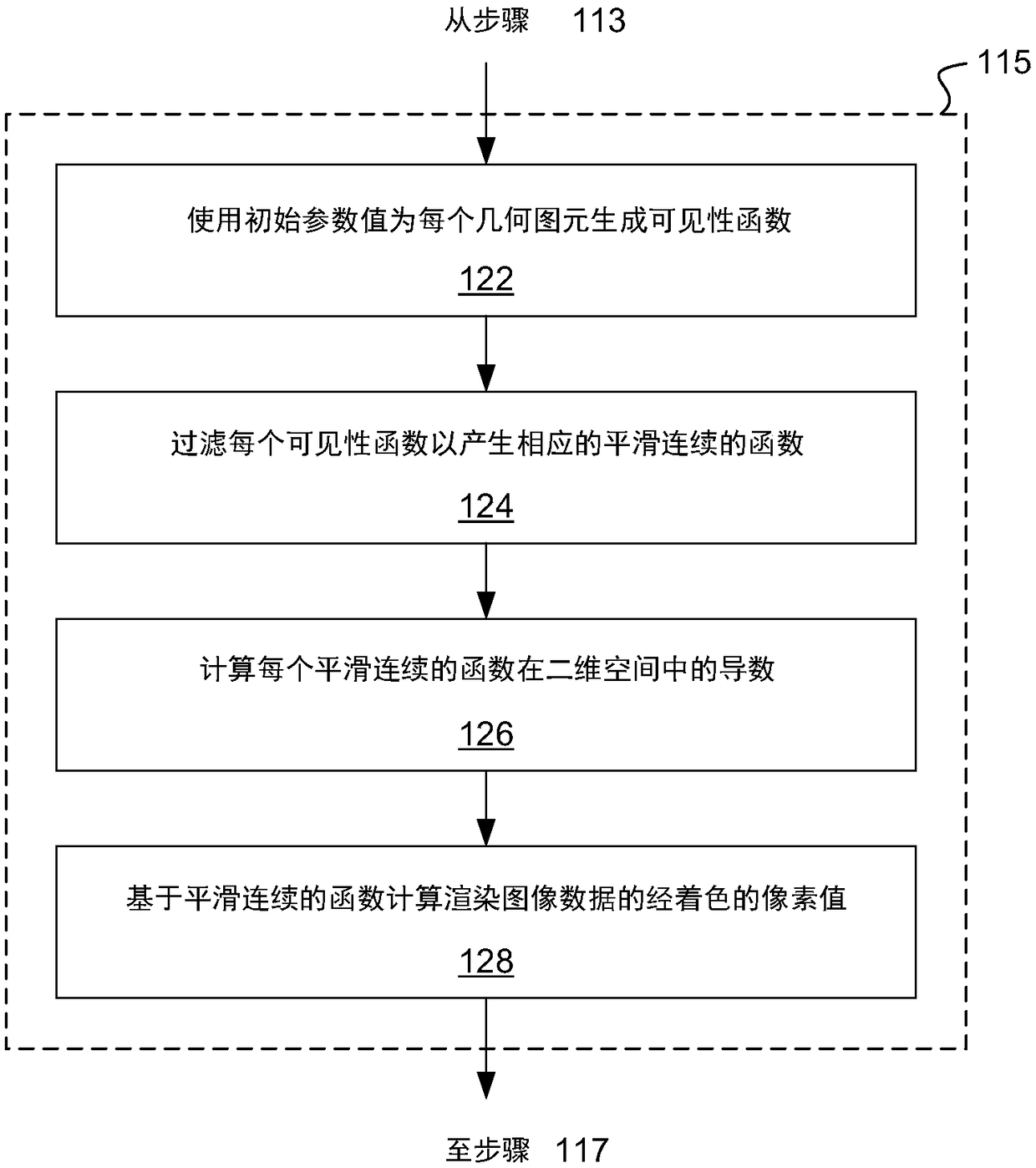
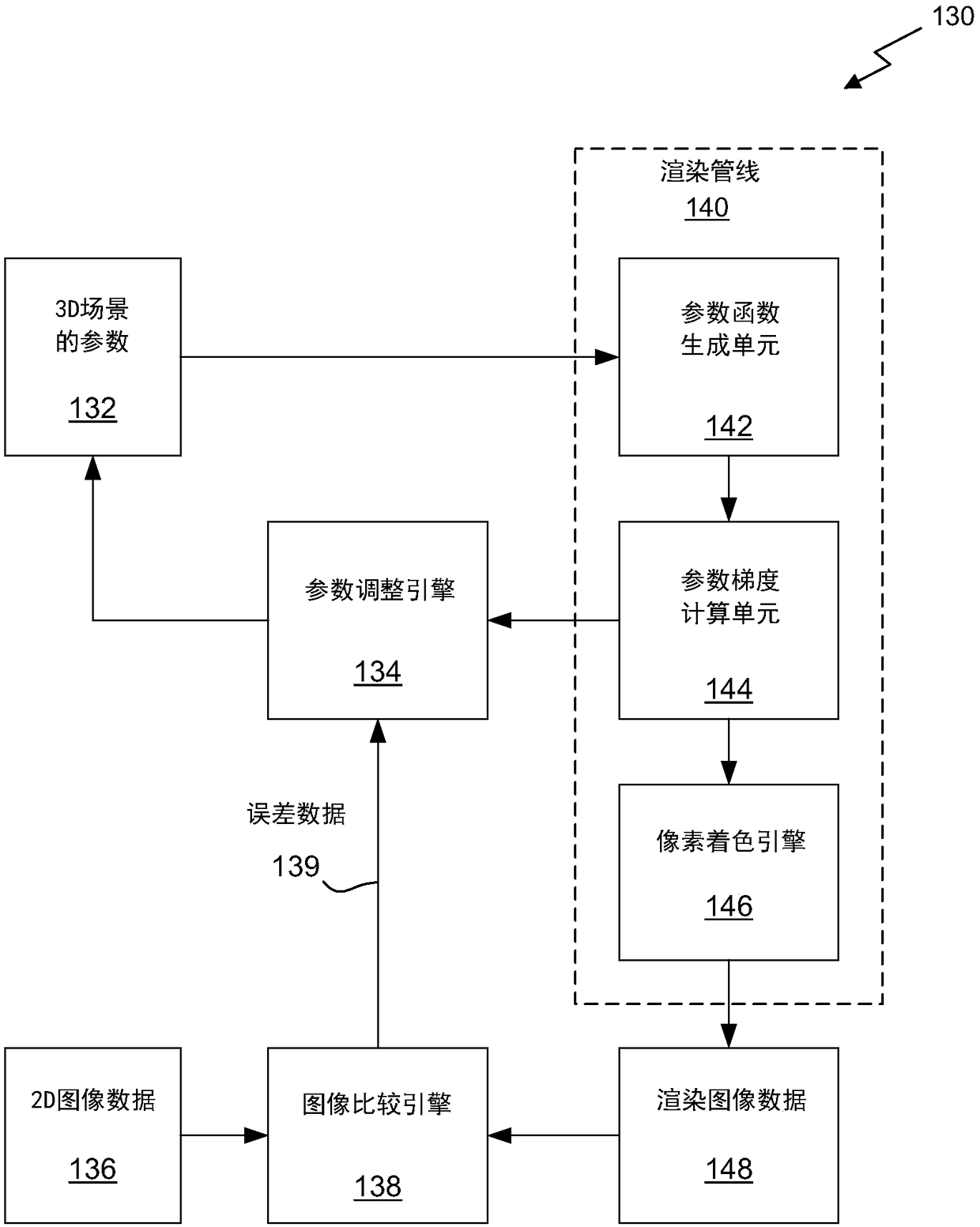
Differentiable rendering pipeline for inverse graphics
ActiveCN109472858AReconstruction from projectionProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsVisibility function
Provided is a system, a method, and a computer readable medium for inverse graphics rendering. The system comprises a differentiable rendering pipeline and a gradient descent optimization engine. A given scene is described using scene parameters. Visibility functions, and other rendered functions, are constructed to be continuous and differentiable, allowing the optimization engine and the rendering pipeline to efficiently iterate through increasingly refined scene models.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
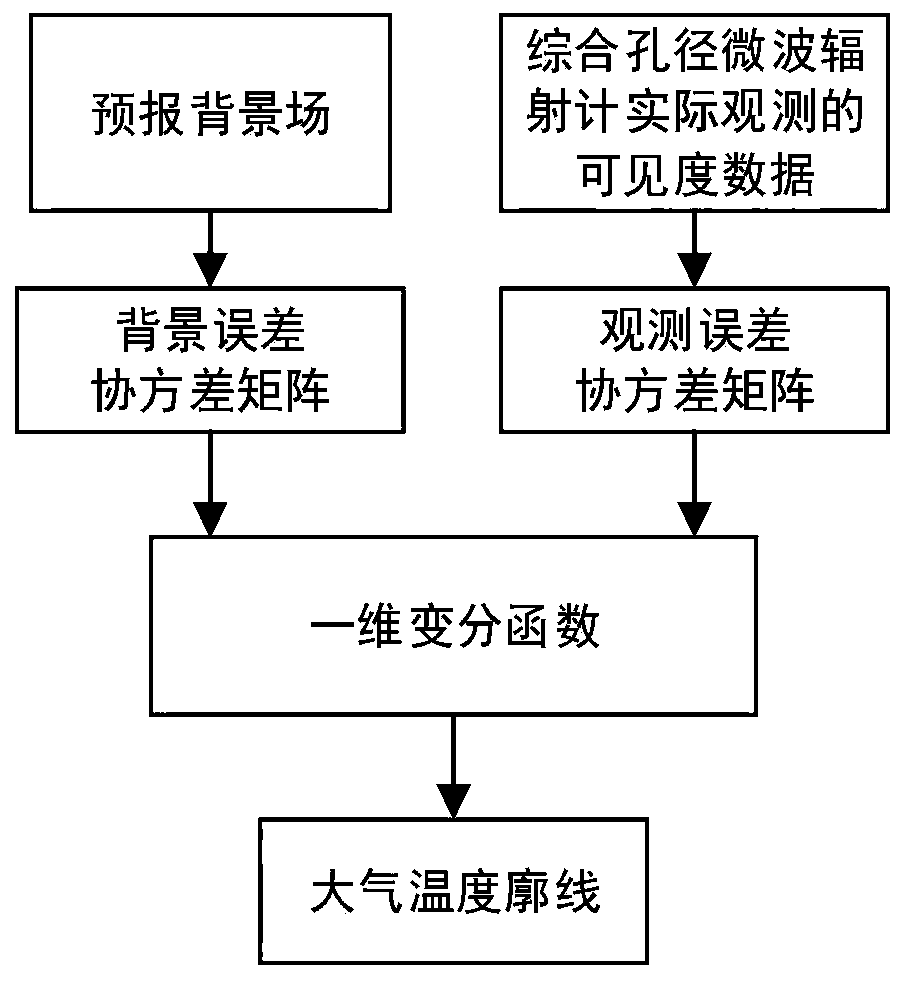
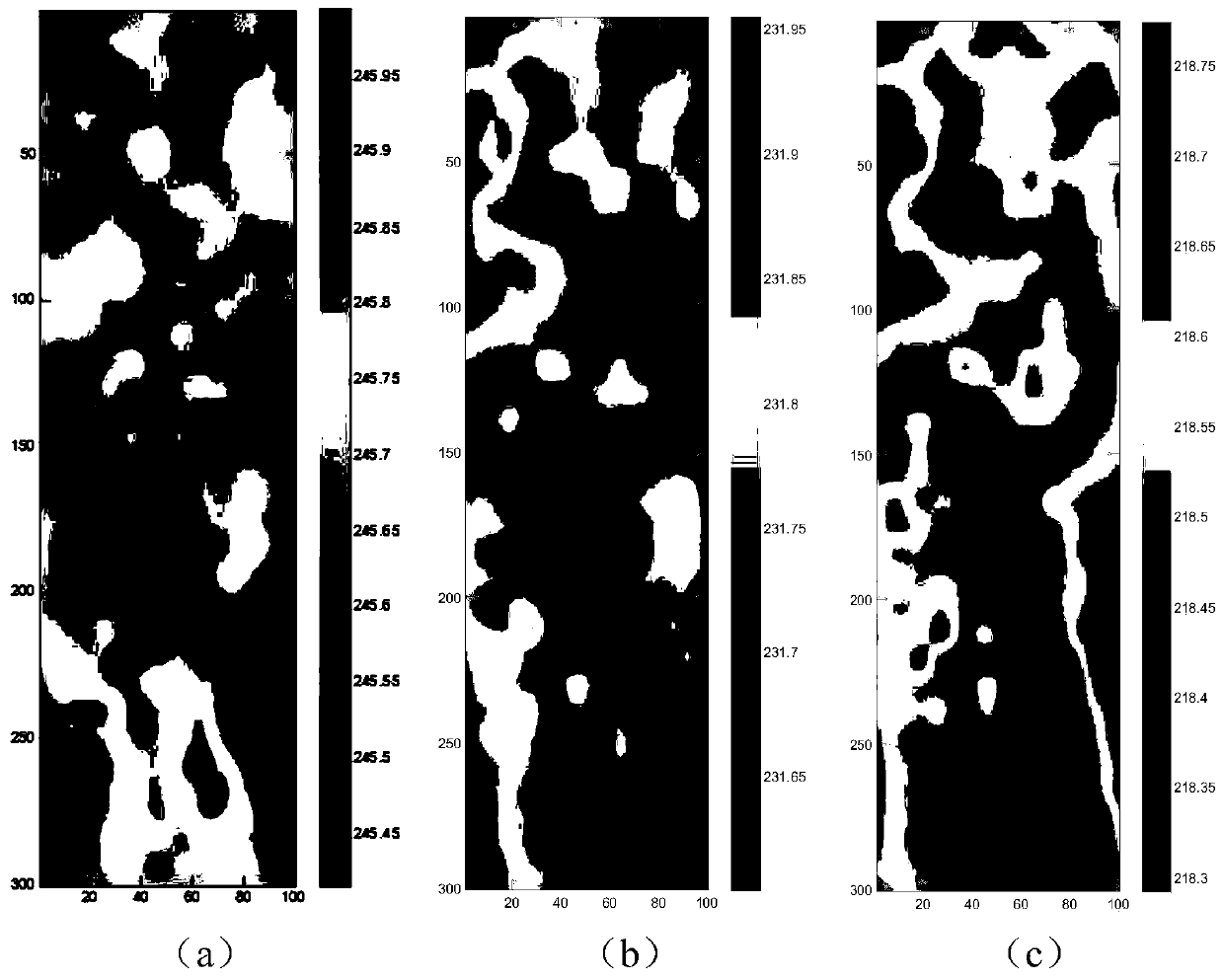
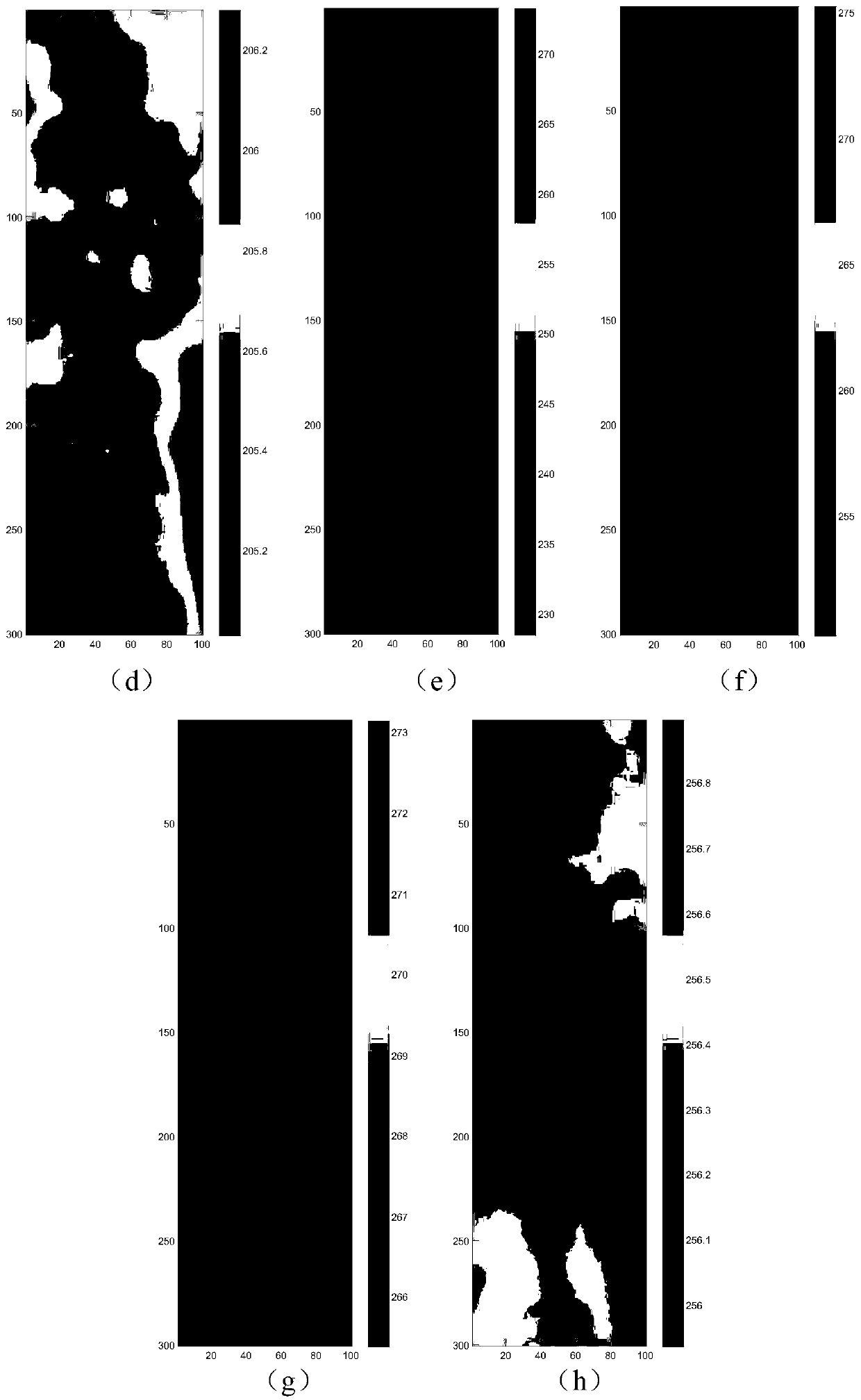
Atmospheric temperature profile direct inversion method and system
InactiveCN110632599AData processing is simpleImprove inversion accuracyICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBrightness temperatureAtmospheric temperature
The invention discloses an atmospheric temperature profile direct inversion method and system. The method comprises the following steps that: S1, a background error covariance matrix is calculated based on a real atmospheric temperature profile and a forecast background field; S2, an observation error covariance matrix is calculated based on ideal visibility data and visibility data observed by asynthetic aperture microwave radiometer; and S3, the forecast background field and the actually observed visibility function are substituted into a one-dimensional variational function, so that an objective function can be obtained, and the minimum value of the objective function is solved based on the obtained observation error covariance matrix and the background error covariance matrix, so thata to-be-inverted atmospheric temperature profile can be obtained. According to the atmospheric temperature profile direct inversion method and system of the invention, the visibility function data ofthe remote sensing measurement of the synthetic aperture microwave radiometer can be inputted into the variational objective function; atmospheric temperature profile physical parameters are obtainedthrough iterative solution; a step of reconstructing brightness temperature in an existing method can be omitted; and therefore, direct inversion from the visibility function to the atmospheric temperature profile is achieved, and higher inversion precision is achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
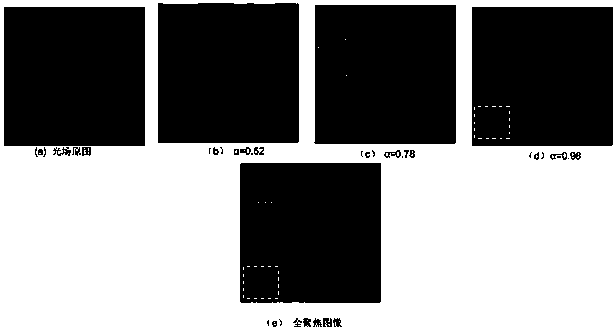
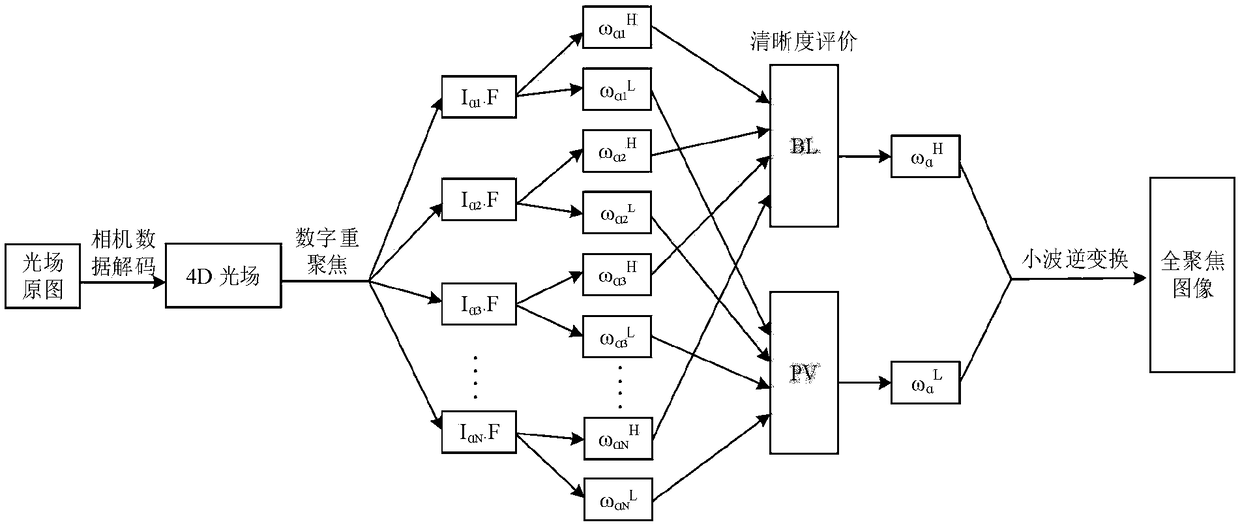
Wavelet domain light field full-focus image generation algorithm
ActiveCN109447930AQuality improvementAvoid block effectImage enhancementImage analysisOriginal dataLight-field camera
A wavelet domain light field full-focus image generation algorithm belongs to the field of full-focus image fusion, the invention effectively avoids the block effect of the traditional spatial light field image fusion algorithm, high quality fully focused image of light field is obtained. Through spatial transformation and projection of 4D light field data obtained by microlens array light field camera, a multi-focus image for full-focus image fusion is obtained, a wavelet decomposition method for extracting multi-focus images of each frame is high, low frequency sub-image set. A domain equilibrium Laplace operator is proposed, the pixel visibility function constructs the high of the fusion image respectively, low-frequency wavelet coefficients realize image fusion, Its performance is superior to the traditional region definition evaluation function, and the experiment verifies the correctness and effectiveness of the method provided by the invention, and adopts the original data of the Lytro light field camera to calculate the fused fully-focused image. Compared with the traditional image fusion algorithm, the human visual effect is better, and the objective image index is also improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
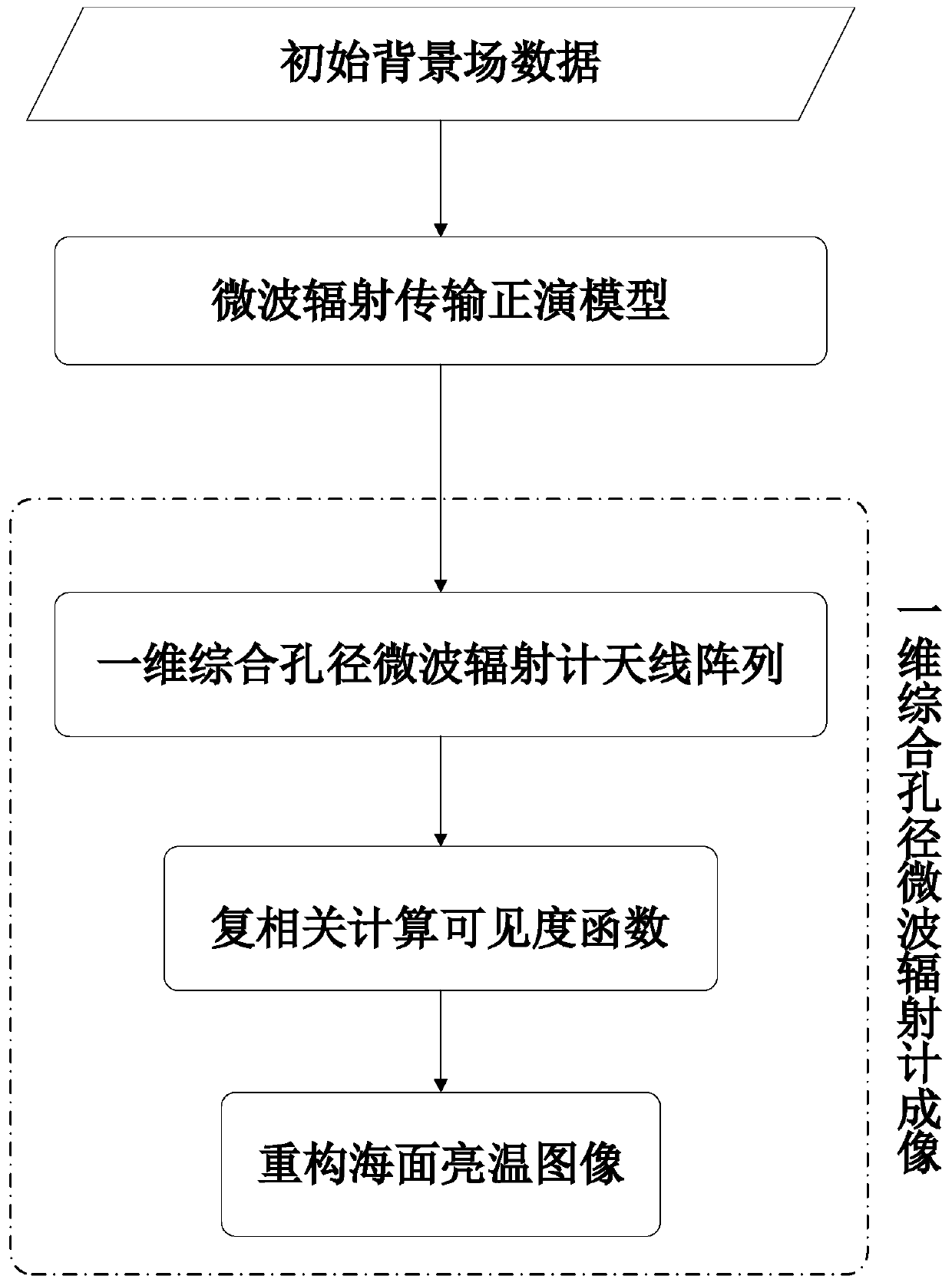
Sea surface brightness temperature imaging simulation method based on one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer
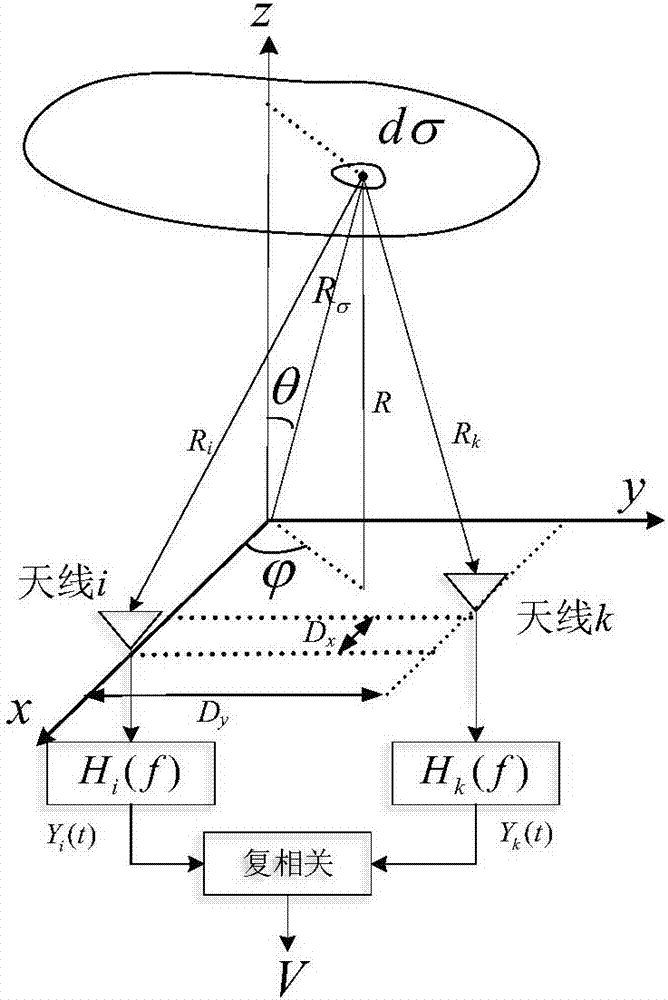
ActiveCN109725317ARadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationSurface brightnessMicrowave radiometer
The invention discloses a sea surface brightness temperature imaging simulation method based on a one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer. The method comprises the following steps of:constructing initial background field data (frequency f, sea surface temperature Ts, seawater salinity S, incident angle [Theta], sea surface wind speed W, sea surface relative wind direction phi, atmospheric water vapor content V, cloud liquid water content L) to provide data support for sea surface brightness temperature imaging simulation; calculating the brightness temperature of the scene mode at the top of the atmosphere at different incident angles with a frequency of 6.9 GHz by using a microwave radiation transmission forward model according to the observation characteristics of the multi-incident angle of the one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer; receiving a scene brightness temperature signal by the small antenna array of the one-dimensional synthetic aperturemicrowave radiometer to generate an electrical signal, and performing pairwise complex correlation on antenna output voltages to obtain a visibility function; and reconstructing a sea surface brightness temperature image by mathematical operations such as inverse Fourier transform. The method provides technical support for remote sensing sea surface temperature of satellite-bone one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Holographic microwave rapid imaging method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN109188431ALow costReduce scan timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRapid imagingMicrowave signals
The invention relates to a holographic microwave rapid imaging method based on compressed sensing. The holographic microwave rapid imaging method comprises the steps that a system for imaging is configured, the system comprises a signal transmitting module, a signal receiving module and a signal processing module, the signal transmitting module comprises a transmitting antenna, and the signal receiving module comprises at least three receiving antennas which are not uniformly arranged; the signal transmitting module continuously transmits a microwave signal of a single frequency to a target area as an incident electric field; at least part of the microwave signal is reflected by different parts in a target object to form a scattered electric field in the target area after the microwave signal penetrates the target object located in the target area, and the scattered electric field is detected by the at least three receiving antennas to obtain scattered electric field echo signals; andthe signal processing module performs pairwise comparison on the scattered electric field signals detected by any two of the at least three receiving antennas, and a visibility function obtained by the pairwise comparison is combined with a compressed sensing signal processing method to be used for constructing a two-dimensional image of the target object in an arbitrary shape.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Real-time order-independent transparent rendering
ActiveUS20130314431A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsImage generationPattern recognitionVisibility function
A method and system for producing an image to be displayed are disclosed herein. The image includes a plurality of pixels. An example of the method includes dedicating a fixed amount of memory to store a data structure for a pixel of plurality of pixels. The method also includes building a visibility function and determining a partial color sum for each fragment of the plurality of fragments. A pixel color is determined using the visibility function and the partial color sums.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and device for reconstructing a three-dimensional scene with corrected visibility
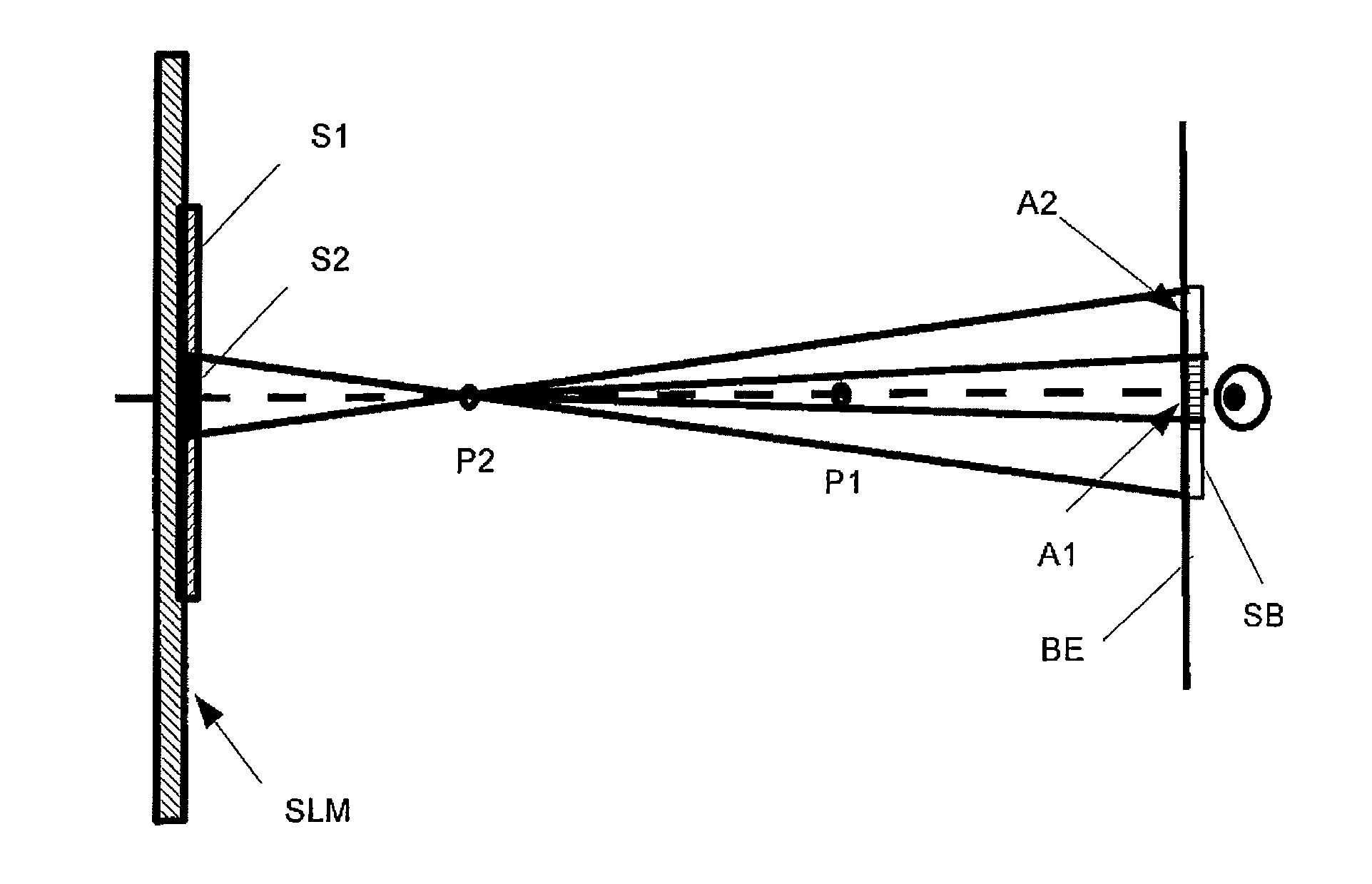
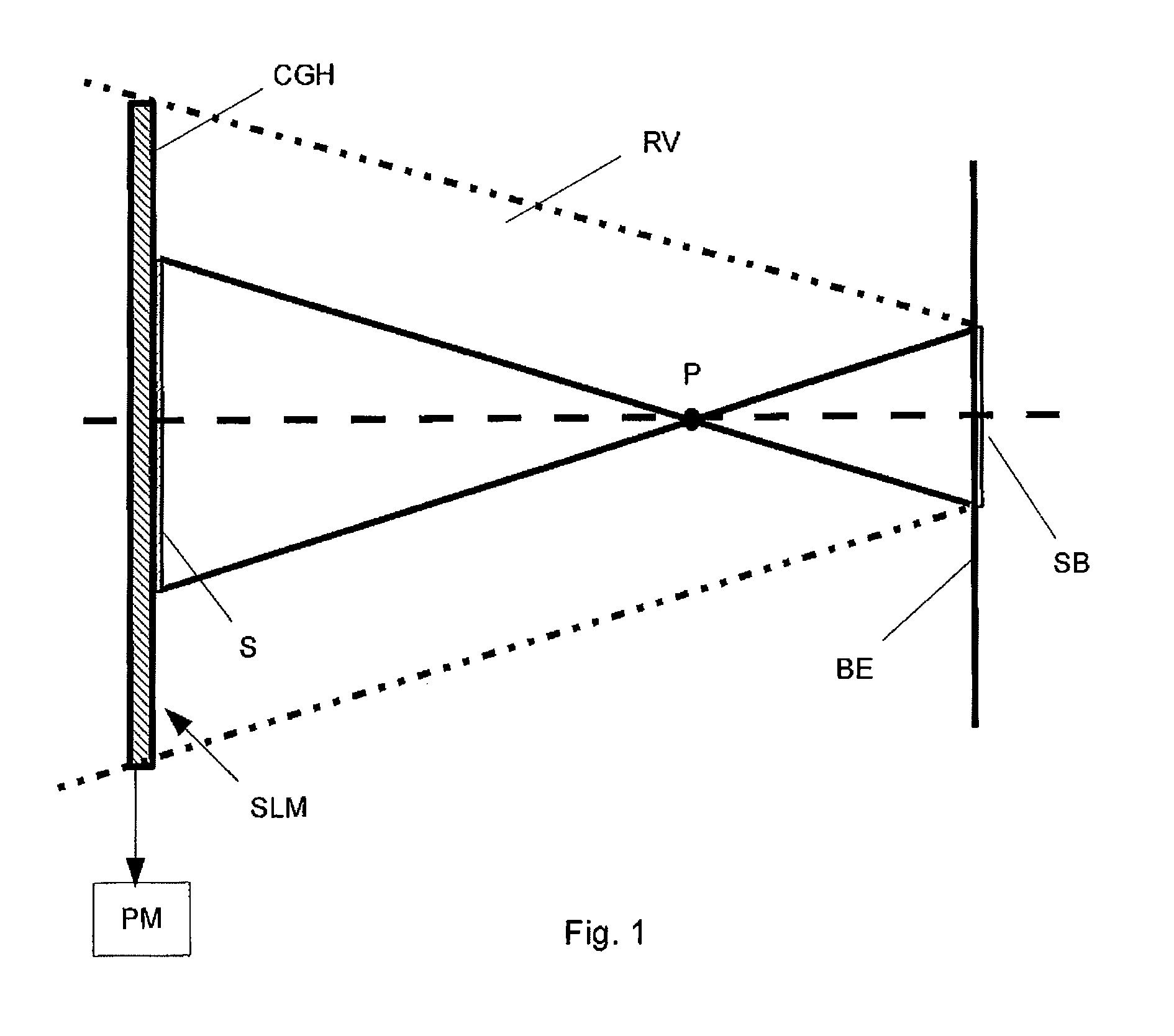
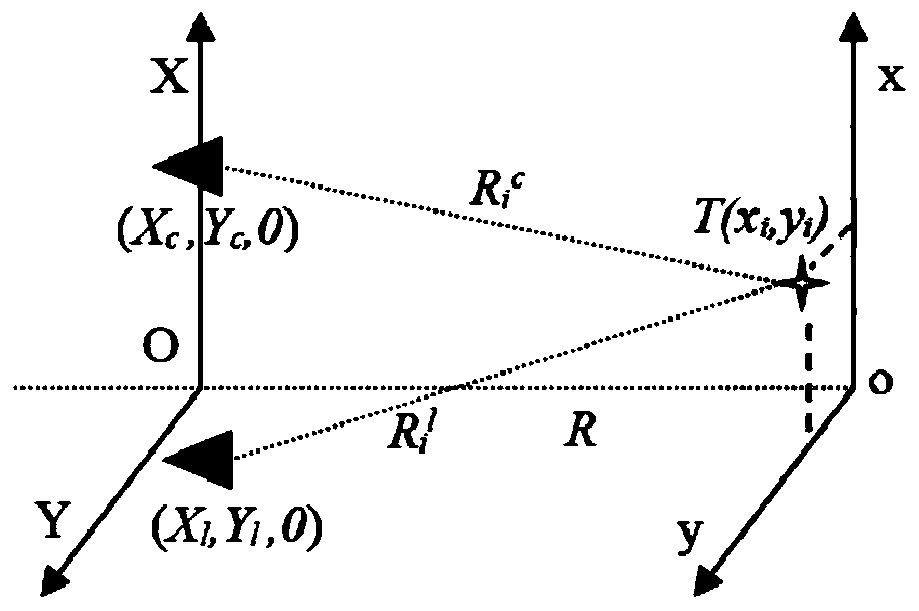
ActiveUS8384973B2Simple methodSave computing powerHolographic object characteristics3D-image renderingObject pointVisibility function
A method is disclosed for reconstructing a 3D scene made of object points in a holographic display, wherein the reconstruction is visible from a visibility region. Visibility and / or covering of parts of the 3D scene corresponding to the real parameters is realized, with the reconstruction, for a viewer from every place of the visibility region. Processor means generate a spatial point matrix for defining the positions of individual object points, which are assigned predetermined intensity and phase values. Within the visibility region, a complex-value wave front for each single object point is calculated. The intensity values of the object points are multiplied with the associated visibility function, to determine a common modified wave front of the object points, transformed into the plane of a light modulator to calculate modified control values for the object points.
Owner:SEEREAL TECHNOLOGIES
Three-dimensional base line integration aperture imaging method based on array factor integration
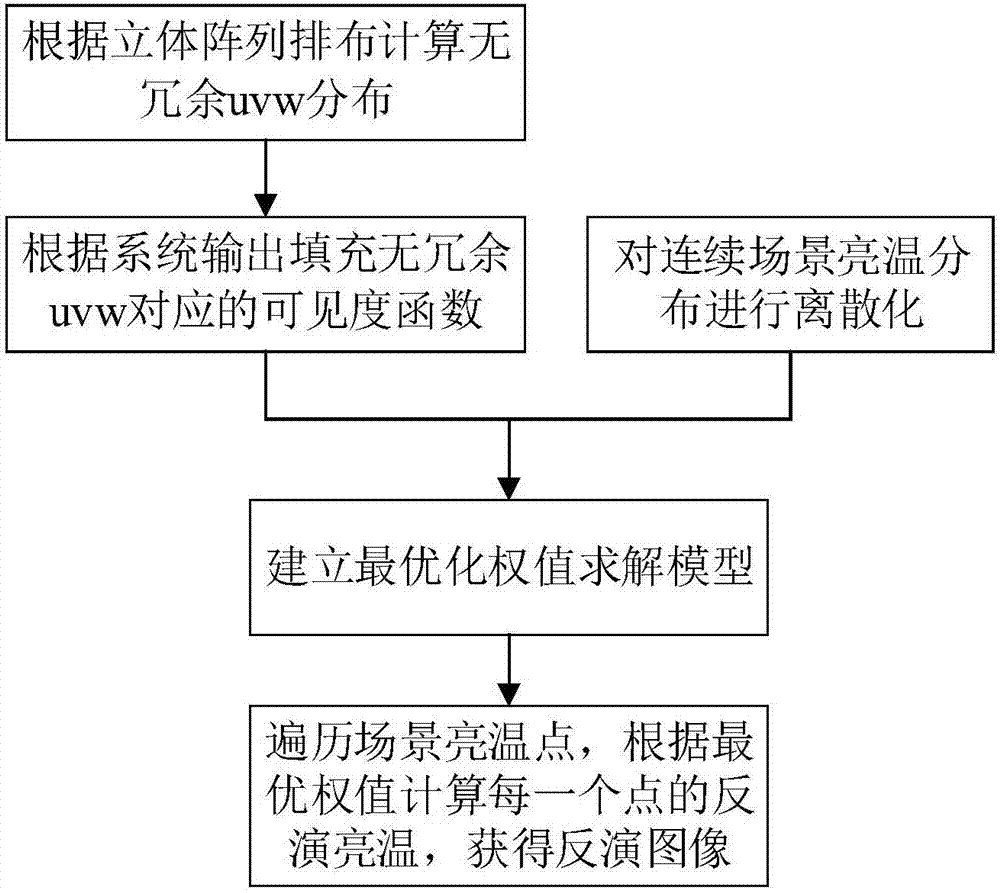
ActiveCN107037431AFast imagingTakes up little storage spaceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionExtinctionObservation point
The present invention discloses a three-dimensional base line integration aperture imaging method based on array factor integration. The method comprises: calculating a base line vector coordinate sequence and removing redundant base lines wherein to form integrated aperture array non-redundancy uvw distribution; filling a visibility function corresponding to non-redundancy uvw according to the multiple correlation output through system output, obtaining a non-redundancy visibility function vector, and performing discretization of scene brightness temperature distribution; establishing an integration aperture forward model according to the redundancy average visibility function, the non-redundancy uvw distribution, the scene discretization distribution and an extinction fringe function, and establishing an optimal weight solution model according to the inversion image noise minimization and the array directional diagram major lobe pointing observation direction; and traversing object scene observation points, calculating the brightness temperature of each observation point according to an optimal weight, and obtaining an inversion image. Compared to a traditional inversion method based on a G matrix, the three-dimensional base line integration aperture imaging method based on array factor integration is equivalent in prevision, but is better in inversion efficiency and storage space occupation.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
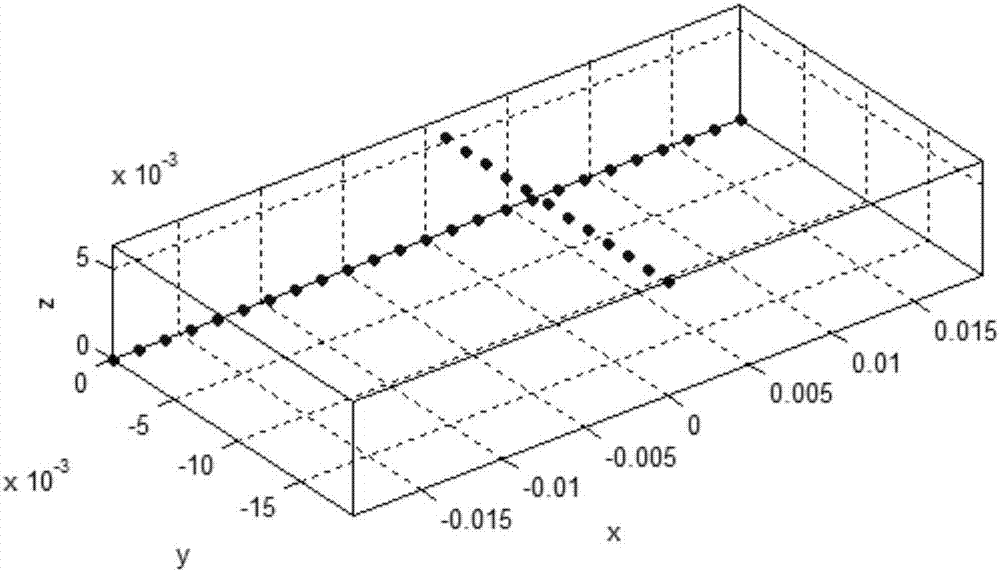
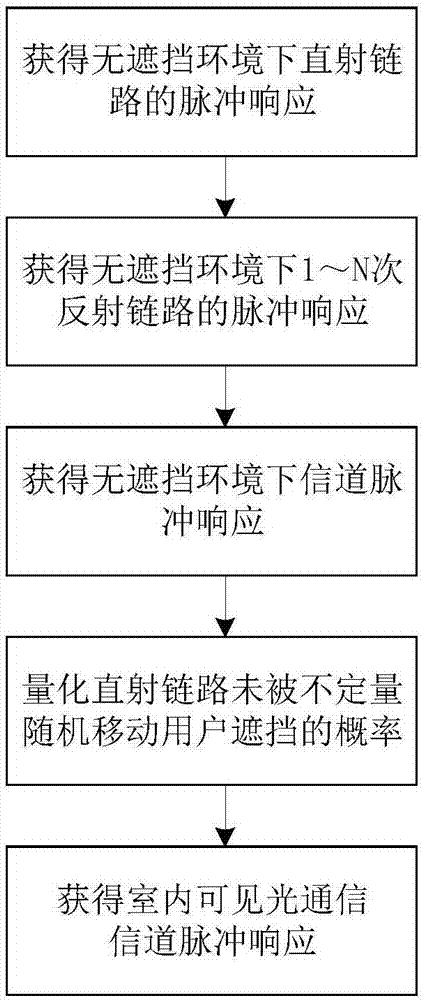
Method of acquiring characteristics of indoor visible light communication channel
ActiveCN107017943AAccurate descriptionImprove practicalityClose-range type systemsImpulse responseComputer science
Disclosed in the invention is a method of acquiring characteristics of an indoor visible light communication channel, which mainly solves problems that the current indoor visible light communication channel model is only based on open rooms but does not consider the shielding effect, and only 0 or 1 can be taken as the value of a visibility function. The technical core of the method is as follow: the quantity of nonquantitative random mobile users entering an indoor region is described by introducing a Poisson count process; the widths and heights of the nonquantitative random mobile users and joint distribution of abscissas and ordinates of the indoor region are described by introducing a probability intensity function; a probability of not shielding a direct beam link of the visible light communication channel by the nonquantitative random mobile users is quantized; and an impulse response and a received signal power value describing channel characteristics are obtained through impulse responses of direct beam links of a classic indoor visible light communication channel model multiplied by the probability of not shielding a direct beam link of the visible light communication channel by the nonquantitative random mobile users. The method can be utilized in the indoor visible light communication environment with multiple mobile users.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Opening labeling machine and cigarette packaging production system
ActiveCN106240983AHigh degree of automationIngenious structural designLabelling deformable materialsLabelling machinesProduction lineVisibility function
The invention relates to the technical field of cigarette packaging, in particular to an opening labeling machine and a cigarette packaging production system. The opening labeling machine comprises a feeding mechanism, a die-cutting machine, the labeling machine body and a collection mechanism which are sequentially arranged on a production line. The feeding mechanism, the die-cutting machine, the labeling machine body and the collection mechanism are in mutual collaboration to form a stable labeling system. The labeling system is high in automation degree, capable of producing lined paper with moisturizing, aroma conservation and visibility functions, the structural design is ingenious, and application and popularization are facilitated.
Owner:JIANGSU KINGHENG PACKAGE MATERIAL CO LTD
Three-dimensional antenna array synthetic aperture radiometer segmented image inversion method
InactiveCN107167807ASolve the problem of poor inversion accuracyHigh precisionDirection finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadiometerVisibility function
The invention discloses a three-dimensional antenna array synthetic aperture radiometer segmented image inversion method. The method includes diving an observation view field interval into N subintervals; putting an external correction source in each of the divided N view field intervals; sequentially measuring visibility functions of the external correction sources output by the three-dimensional antenna array synthetic aperture radiometer in the N view field subintervals, and obtaining phase angles of the visibility functions; performing simulation calculation on the phase of the visibility function under the condition that the three-dimensional antenna array synthetic aperture radiometer only has two-dimensional coordinates; sequentially subtracting the phase angle obtained by simulation from the phase angles measured in the N view field subintervals to obtain phase compensation angle of the nth view field subinterval; using the three-dimensional antenna array synthetic aperture radiometer to observe a target scene, and sequentially performing image inversion on the divided N view field subintervals; and splicing inversion images in the N view field subintervals into an inversion image in the whole view field. The method is relatively high in precision, and has relatively good application prospects.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
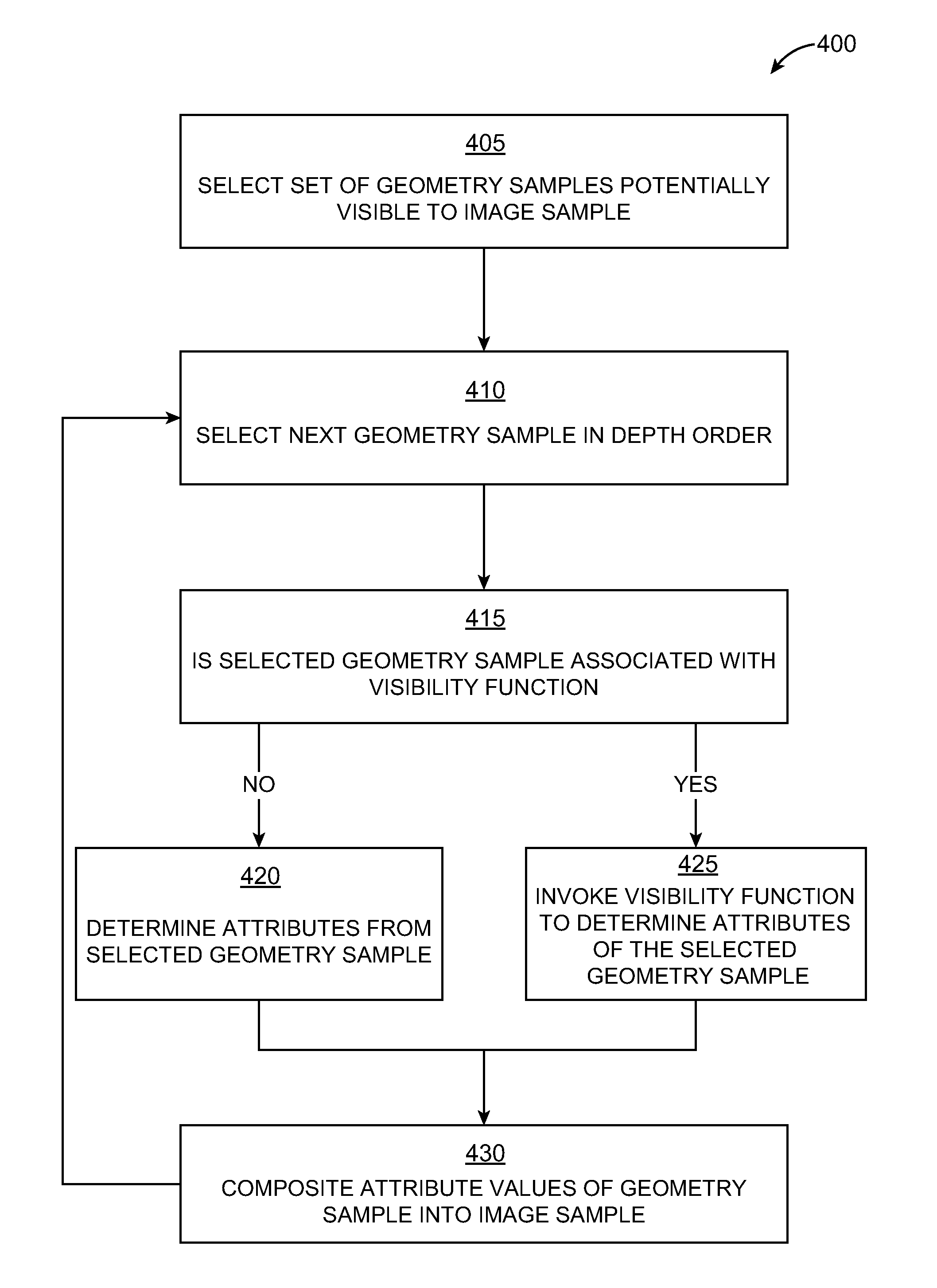
Programmable visible surface compositing
InactiveUS8026915B1Drawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVisible surfaceVisibility function
Programmable or user-defined visibility functions can be defined to achieve rendering effects and eliminate rendering errors. A renderer traverses the set of geometry samples potentially visible to an image sample. Rather than accumulate opacity and color in strict depth order, the renderer can invoke visibility functions associated with some or all of the geometry samples. Each geometry sample's visibility function can access attributes of any other geometry sample associated with the image sample. Furthermore, each geometry sample's visibility function can identify the position of its associated geometry sample and any other geometry samples in the depth sequence of geometry samples associated with an image sample. A visibility function can return any arbitrary value based on attributes of its associated geometry sample, attributes of other geometry samples associated with the image sample, and / or the position of geometry samples in the depth sequence associated with the image sample.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
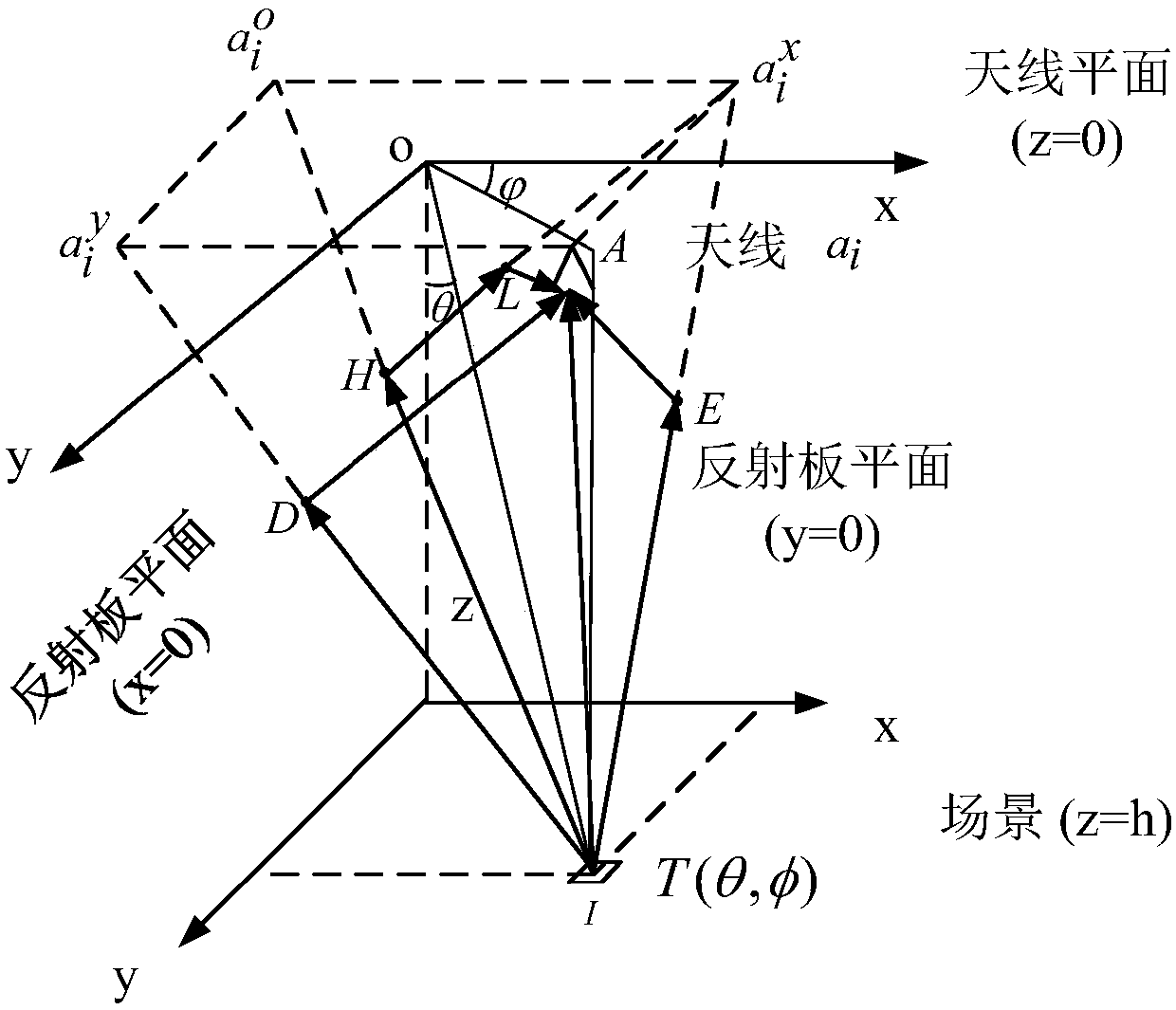
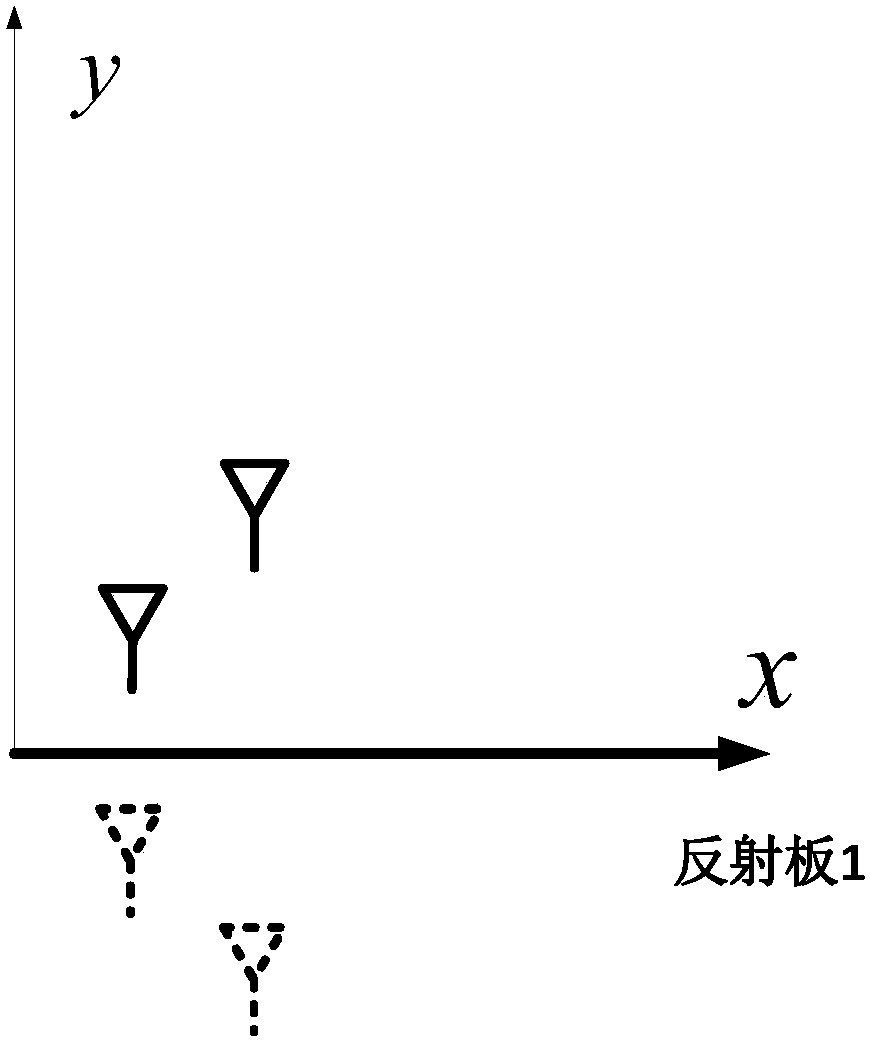
Reflection-board-combination-based imaging method of mirror-image synthetic aperture radiometer
ActiveCN108375767ASolving the rank deficit problemImprove accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadiometerImaging quality
The invention discloses a reflection-board-combination-based imaging method of a mirror-image synthetic aperture radiometer. The method comprises: according to an antenna array and an x-direction reflection board, a first linear equation group formed by first correlation functions outputted by an antenna array; on the basis of the antenna array and reflection boards in the x direction and y direction, a second linear equation group formed by second correlation functions outputted by the antenna array is obtained; on the basis of the antenna array and the reflection board in the y direction, athird linear equation formed by third correlation functions outputted by the antenna array; the three linear equation groups are combined to obtain a target linear equation group including scene brightness temperature image information; the target linear equation group including scene brightness temperature image information is calculated to obtain a cosine visibility function; and with the cosinevisibility function, inverse cosine transform is carried out to rebuild a scene brightness temperature image. Therefore, the accuracy of the cosine visibility function is improved and thus the imaging quality is enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
One-dimensional interference-type microwave radiometer image reconstruction method
ActiveCN106092336AHigh precisionAvoid brightness temperature inversion errorsRadiation pyrometryThermometers using physical/chemical changesBrightness temperatureReconstruction method
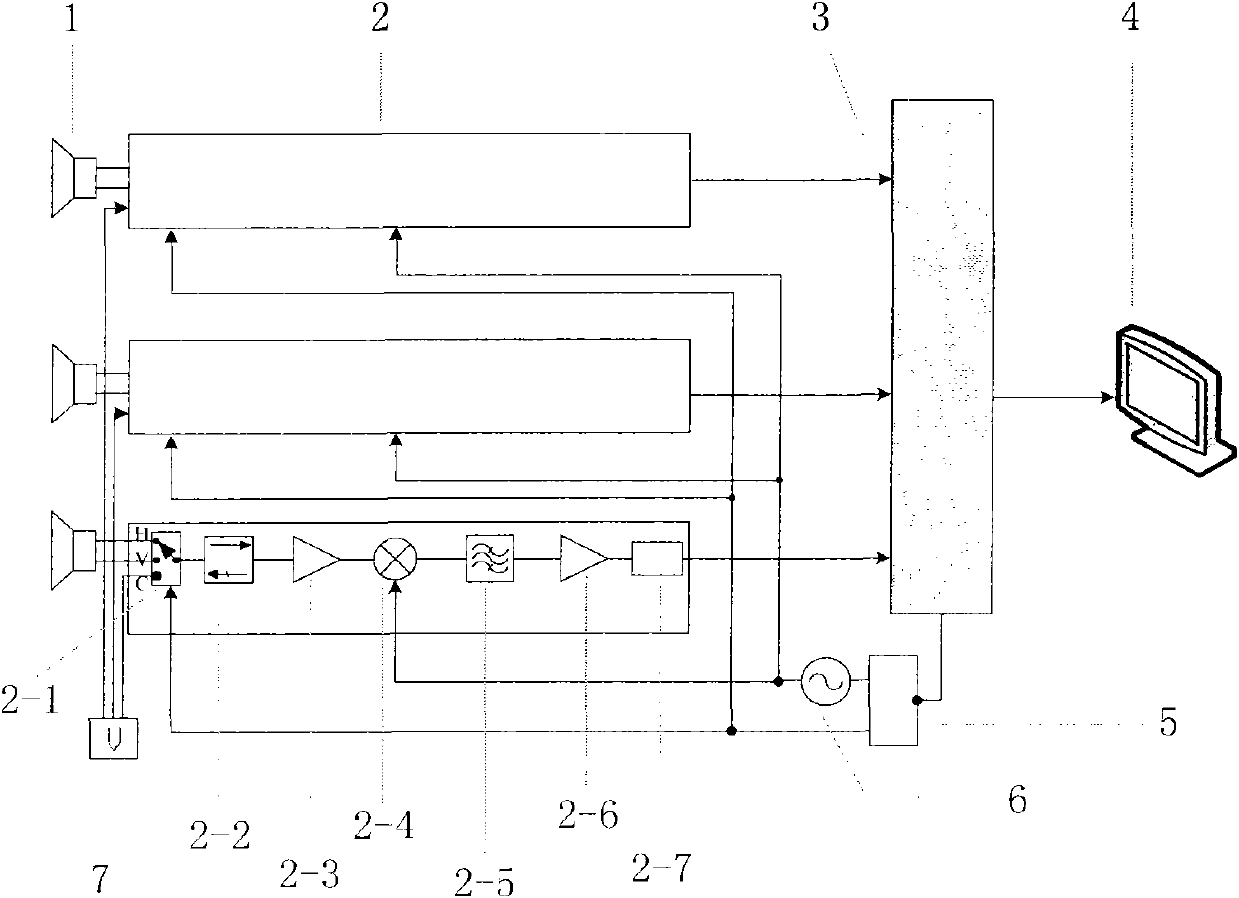
The invention relates to a one-dimensional interference-type microwave radiometer image reconstruction method. The method comprises steps: a two-dimensional antenna pattern of each unit antenna in the one-dimensional interference-type microwave radiometer is measured, and sparse arrangement is carried out on an antenna unit array to form baseline coverage meeting imaging requirements; the two-dimensional antenna pattern is converted to a one-dimensional antenna pattern, and the one-dimensional antenna pattern obtained through conversion is used for calculating and acquiring a measurement system response matrix for the one-dimensional interference-type microwave radiometer; and according to the measurement system response matrix for the one-dimensional interference-type microwave radiometer and a visibility function after measurement and calibration by the system, image reconstruction is carried out to obtain a high-precision brightness temperature image.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Multiscale fusion-based synthetic aperture imaging method
ActiveCN110231625AHigh precisionLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPattern recognitionRadiometer
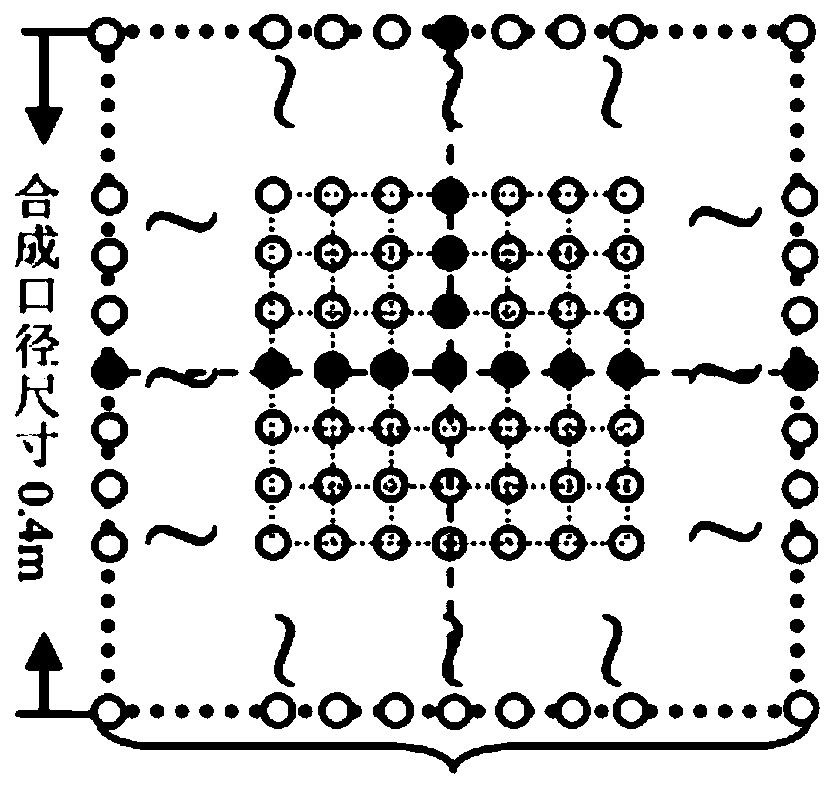
The invention discloses a multiscale fusion-based synthetic aperture imaging method. The method comprises the steps of carrying out multiscale detection on a target scene under the premise of not changing the system structure, so as to obtain visibility function sampling values under different scales; combining the obtained multiscale visibility function values into a fused visibility function set, and constructing a multiscale sensing matrix model matched with the fused visibility function set; and carrying out rapid solution on the multiscale sensing model through an FGP method, so as to reconstruct a high-precision millimeter wave image. According to the method, a super-resolution fusion thought is used for reference; and a proposed MsF method is higher in reconstruction precision whenbeing compared with the traditional image fusion method which firstly carries out inversion and then carries out fusion, and is capable of effectively improving the imaging detection precision of thesynthetic aperture radiometers.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multiband passive synthetic aperture imaging system
InactiveCN102004248AReduce the numberMulti-field spatial frequency sampling pointsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionUltra-widebandIntermediate frequency
The invention provides a new multiband passive synthetic aperture imaging system. Spatial frequency sampling coverage of the imaging system is greatly improved by a multiband technology, thereby realizing high-resolution and high-quality imaging in real time while working in a radio-frequency microwave band. In the invention, signals radiated and scattered by a target are received by a multiband antenna array, and enters an array receiver; the signals are mixed with local oscillation signals output by an ultra wideband tunable YIG (yttrium iron garnet) oscillator; the mixed output signals are filtered to acquire intermediate frequency signals; the intermediate frequency signals are output after intermediate frequency amplification; and finally, after passing through an analog-to-digital conversion acquisition card, the signals are input into a signal processor for carrying out pairwise correlation calculation to acquire spatial frequency sampling of a field of view. By tuning the YIG oscillator by using the multiband antenna array, visibility functions of different frequency bands can be acquired, thereby greatly improving the coverage effect of target spatial frequency sampling and the imaging quality.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
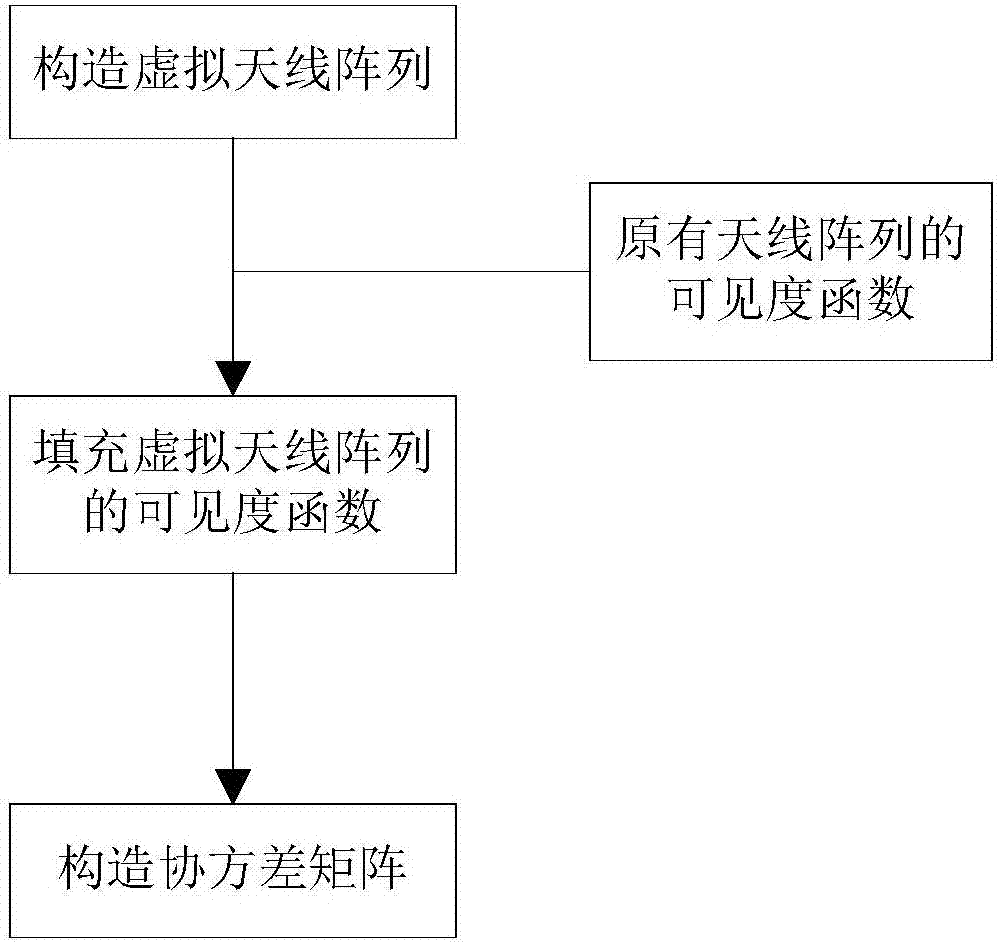
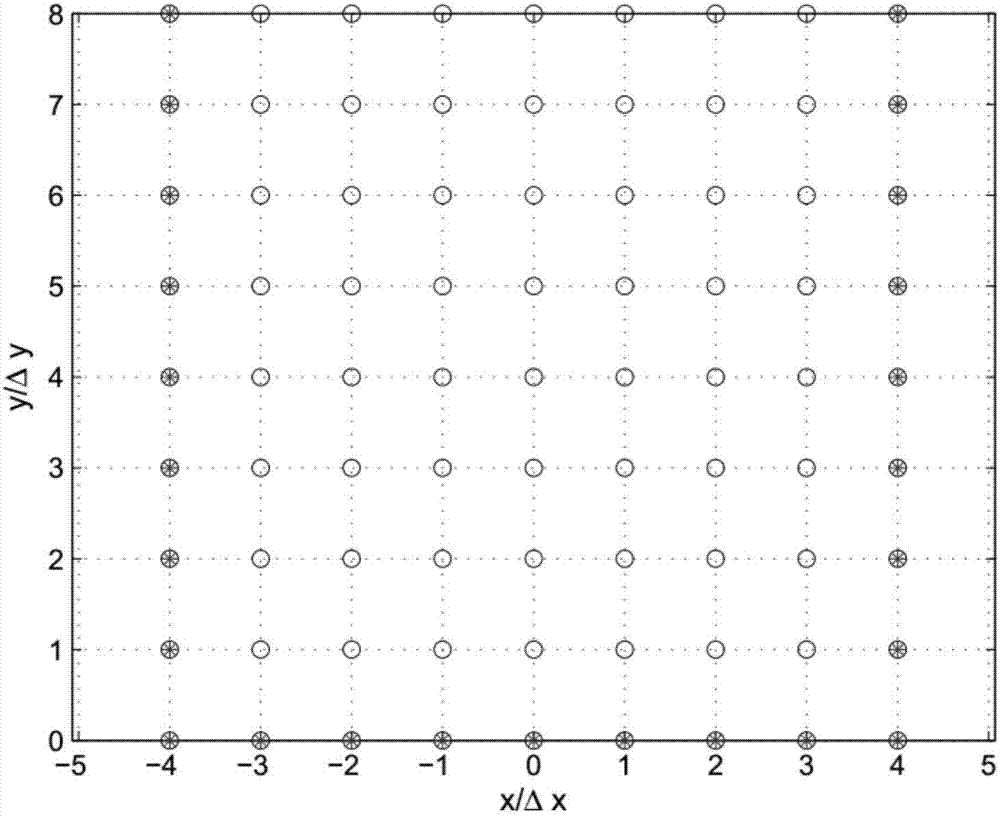
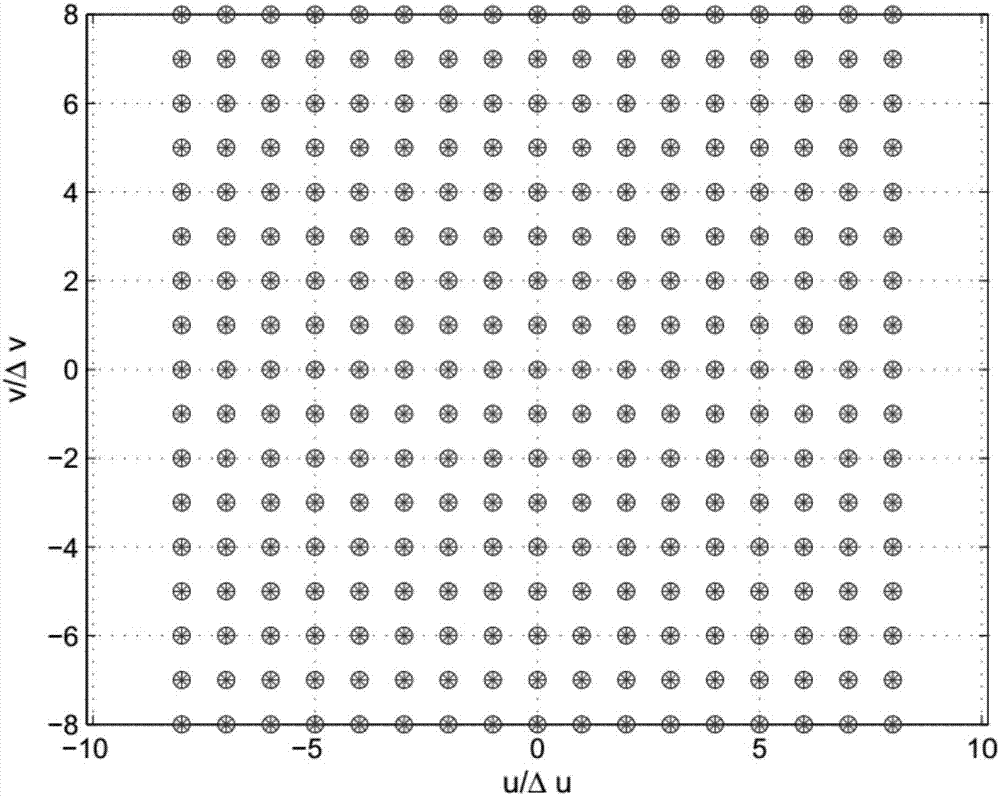
Antenna array augmented covariance matrix-based radio frequency interference source positioning method
ActiveCN107167765APrecise positioningImprove orderPosition fixationBrightness temperatureEstimation methods
The invention discloses an antenna array augmented covariance matrix-based radio frequency interference source positioning method. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) a virtual filling antenna array is constructed according to the UV distribution of an antenna array; (2) visibility assignment is performed on the virtual filling antenna array according to the visibility function of the antenna array, so that visibilities corresponding to the UV points of the antenna pairs of the virtual filling antenna array are obtained; (3) an augmented covariance matrix is constructed according to the visibilities corresponding to the UV points of the antenna pairs of the virtual filling antenna array; and (4) on the basis of the constructed augmented covariance matrix, a spatial spectrum estimation method is used to position of a radio frequency interference source. The antenna array augmented covariance matrix-based radio frequency interference source positioning method of the invention is greatly improved in distinguishing the number of radio frequency interference sources and distinguishing the clarity degrees of the radio frequency interference sources compared with Fourier transform algorithm-based radio frequency interference source positioning performance and direct covariance matrix-based radio frequency interference source positioning performance. The augmented covariance matrix constructed by the method can significantly improve the quality of a brightness temperature image.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Brightness temperature inversion imaging method for uniform circular array synthetic aperture radiometer
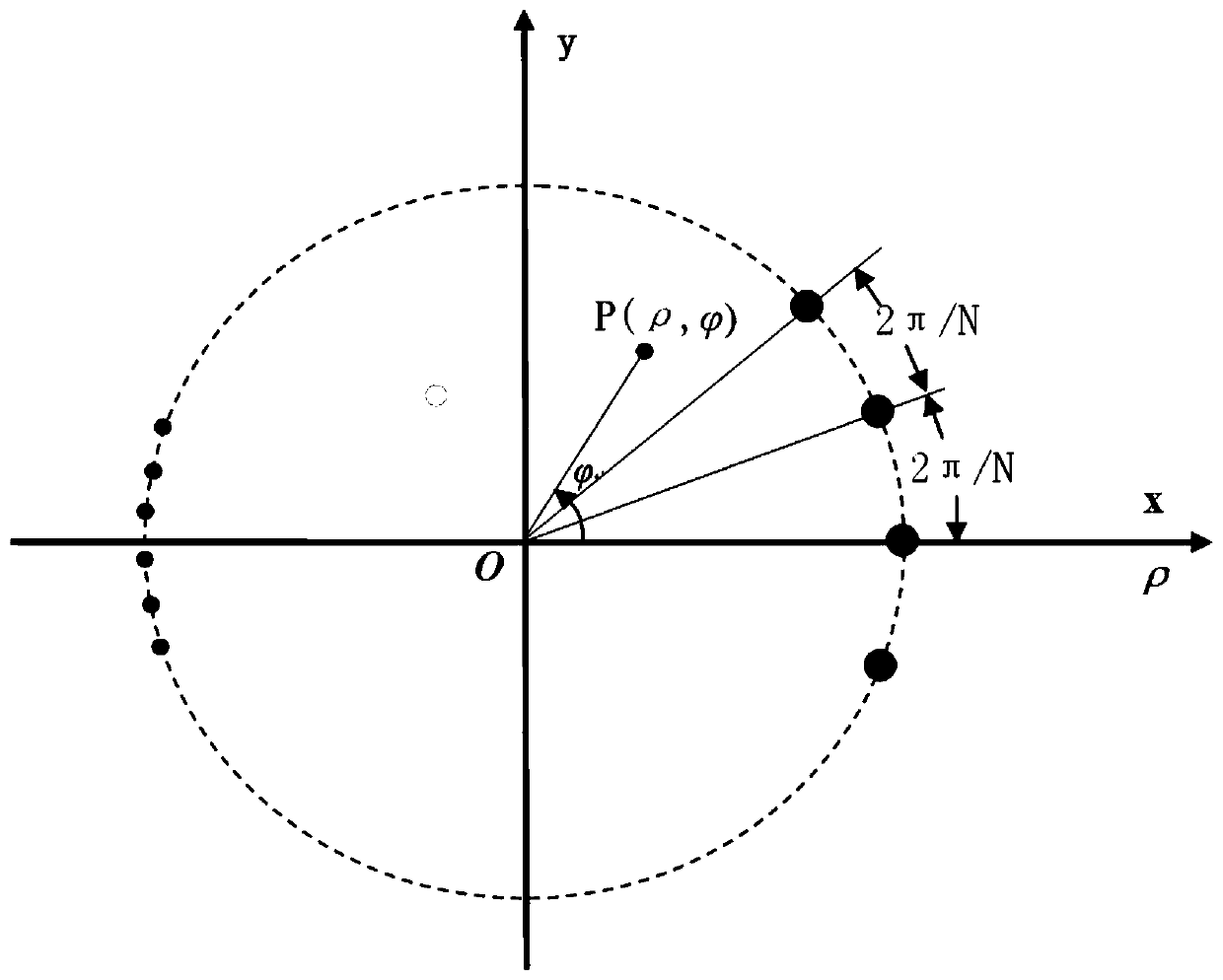
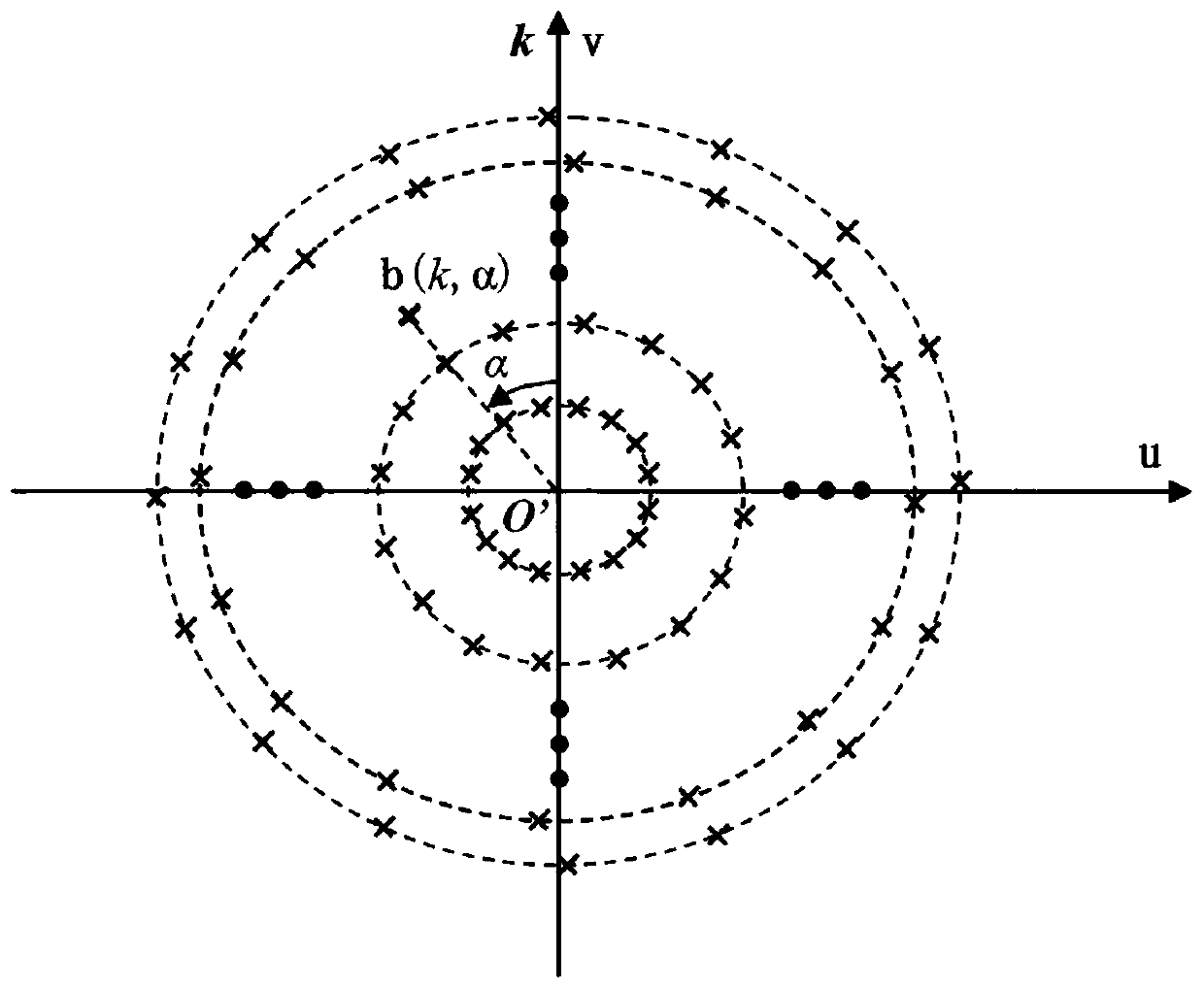
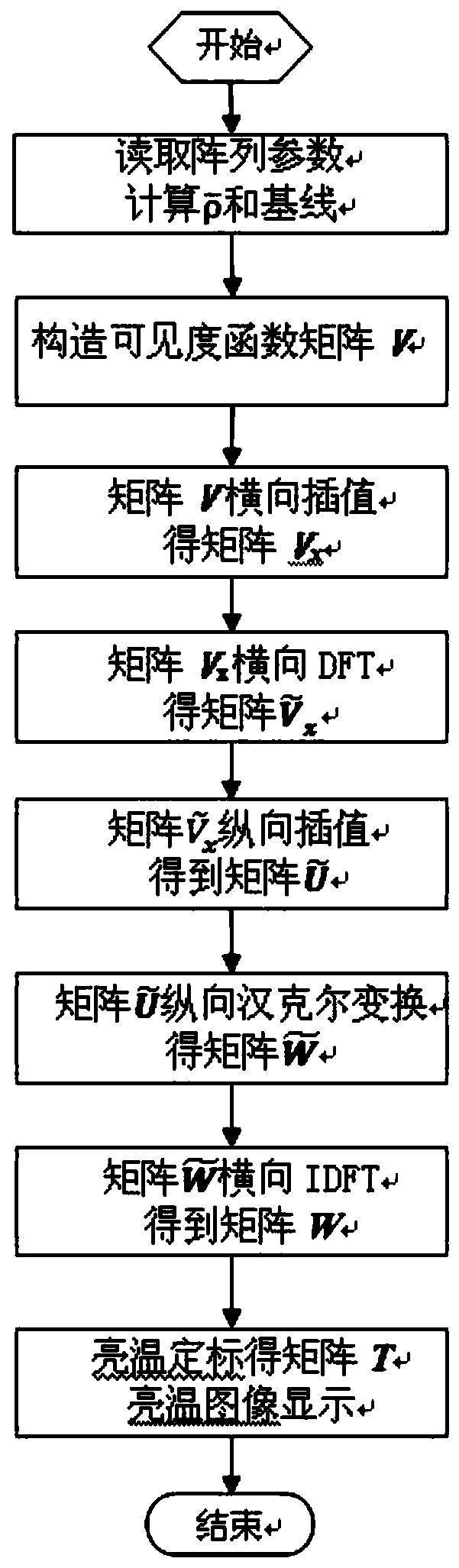
ActiveCN111538000AImproving the imaging performance of brightness temperature retrievalReduce the impactRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDistribution matrixBrightness temperature
The invention discloses a brightness temperature inversion imaging method for a uniform circular array synthetic aperture radiometer, and aims to provide a UCSAIR brightness temperature inversion imaging method which is high in inversion precision and capable of shortening inversion calculation time. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises: under the condition of establishing a spectral domain polar coordinate system, arranging corresponding visibility functions into a visibility function matrix form by taking UCSAIR baseline spectral domain polar diameters from small to largeas a row sequence and baseline spectral domain polar angles from small to large as a column sequence; carrying out one-dimensional transverse interpolation and transverse FFT; carrying out one-dimensional longitudinal interpolation; calculating a numerical value corresponding to a fast Hankel transformation lattice point; carrying out longitudinal Hankel transformation, then carrying out transverse one-dimensional inverse Fourier transformation, and carrying out brightness temperature calibration on the transformed matrix to obtain brightness temperature distribution matrixes of each point inan observation space under the spatial polar coordinate; and displaying a brightness temperature image according to a corresponding relationship between a brightness temperature distribution matrix element position and a spatial direction to realize brightness temperature inversion imaging.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com