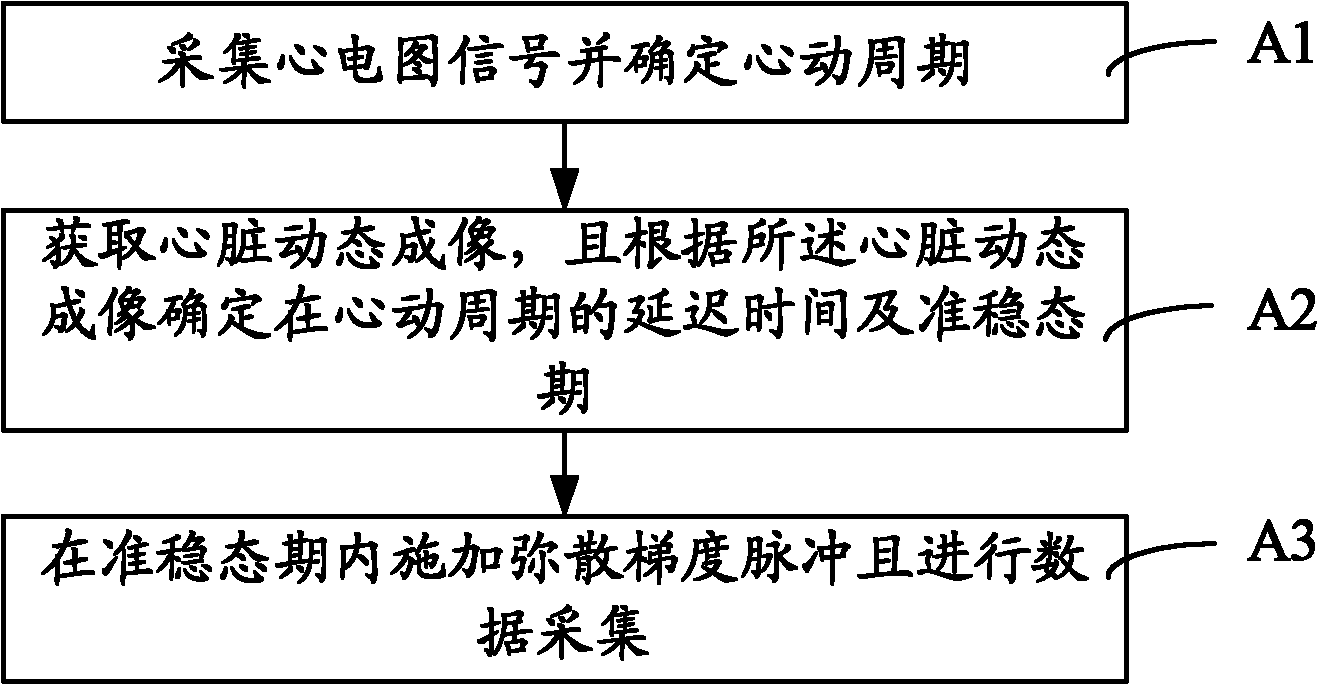
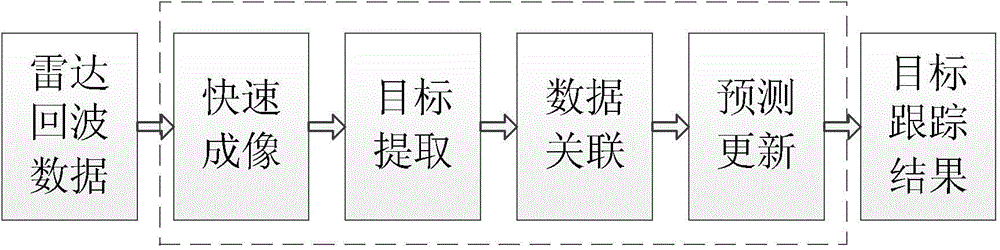
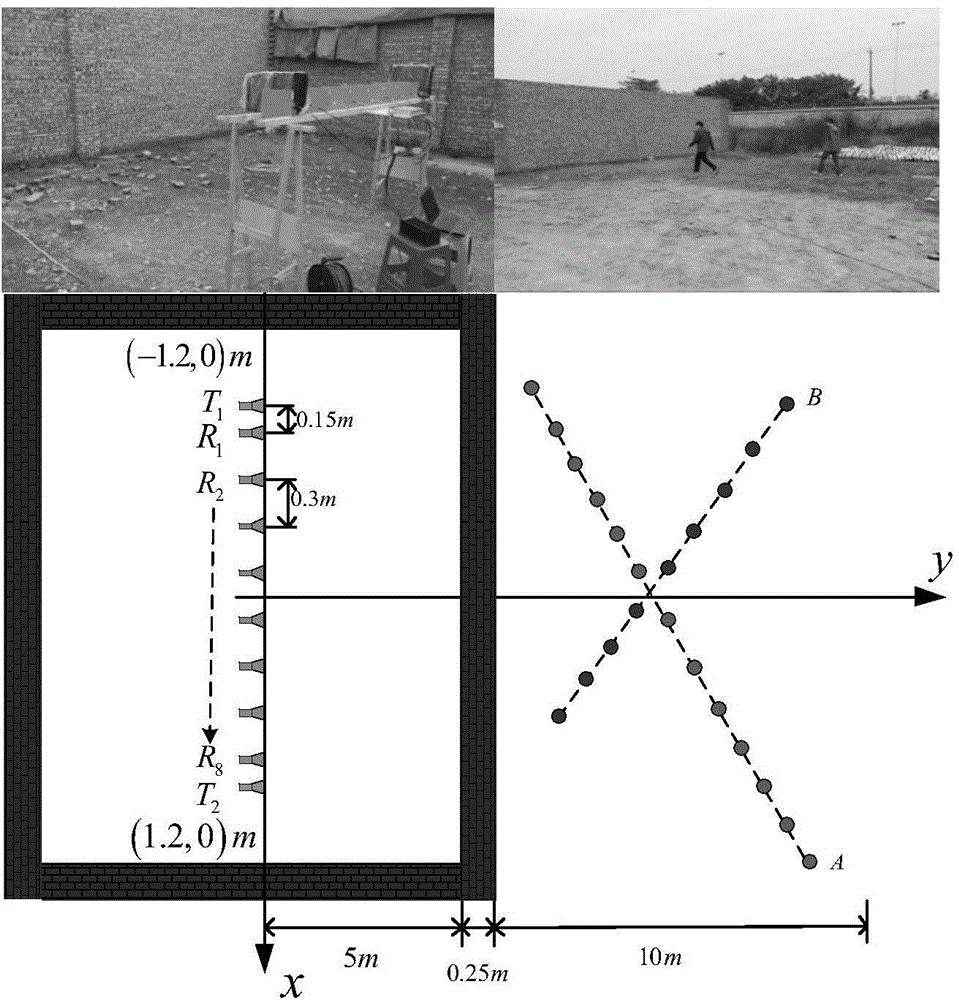
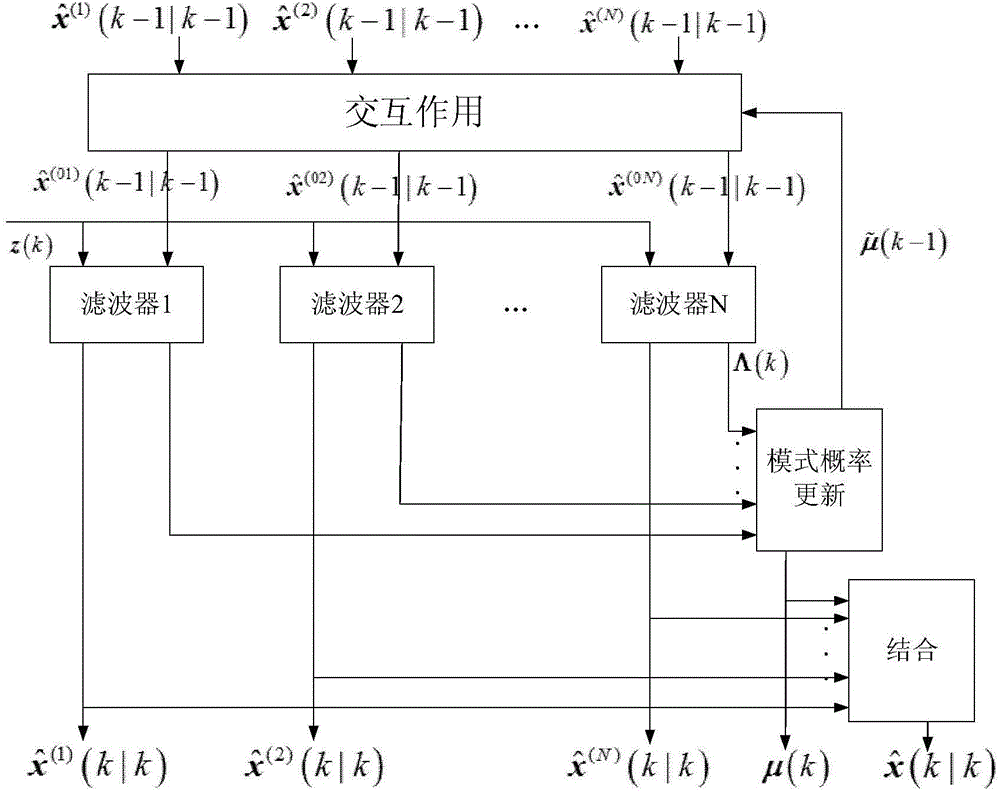
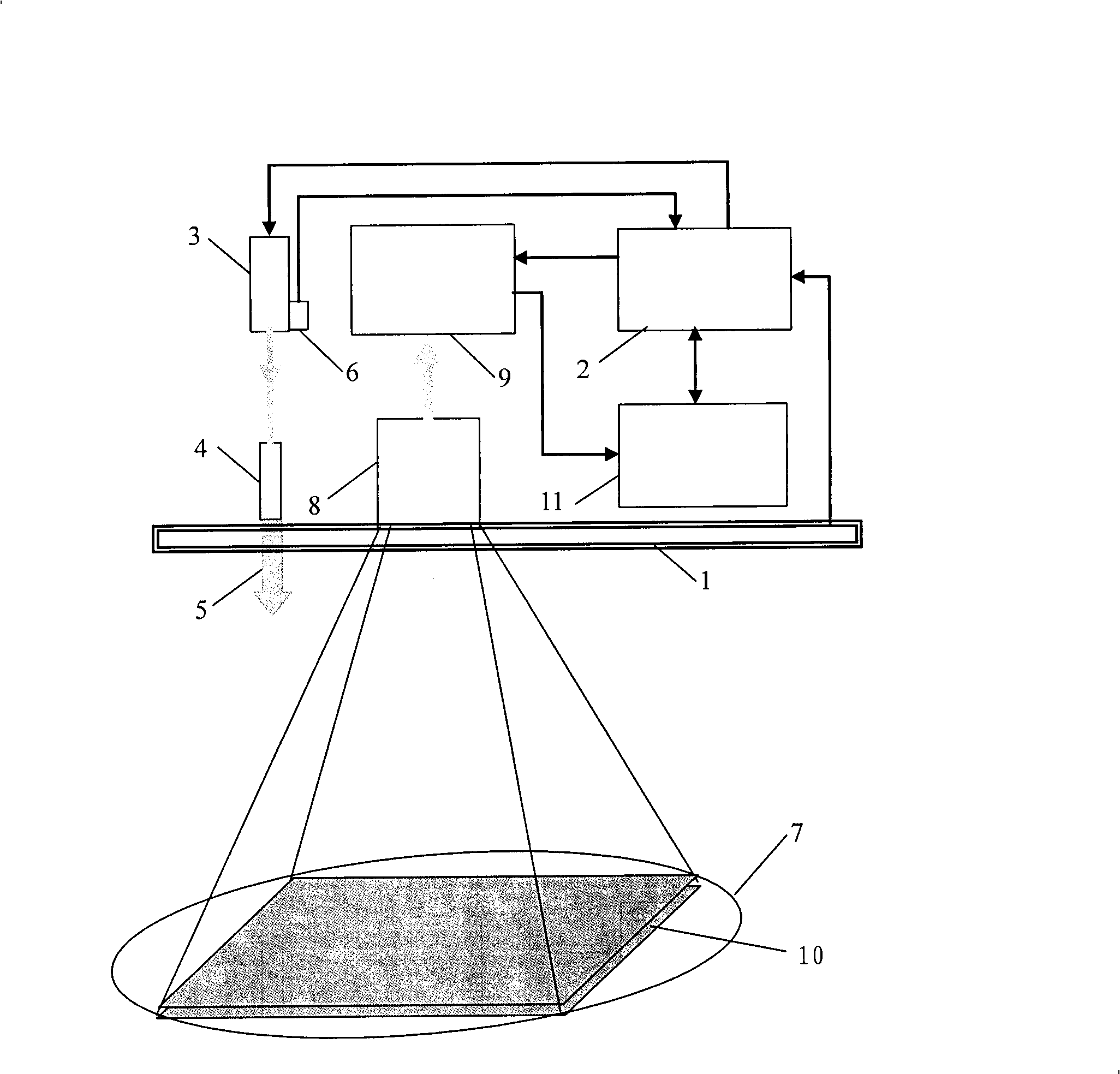
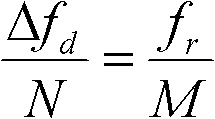Patents
Literature
441 results about "Rapid imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Efficient optical coherence tomography (OCT) system and method for rapid imaging in three dimensions
InactiveUS20050140984A1Enhanced OCT channel sensitivityImprove accuracyScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansRapid imagingData set
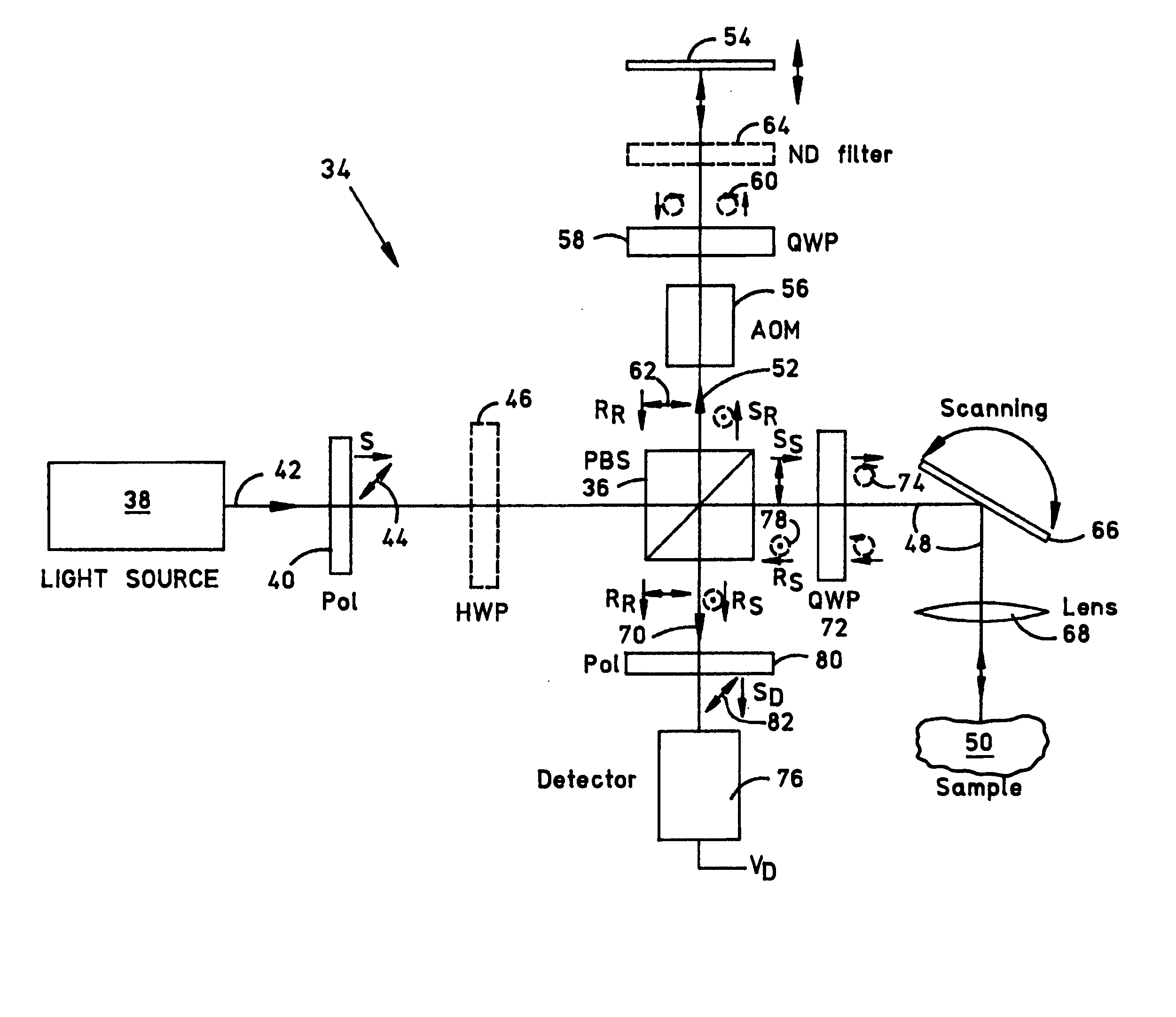
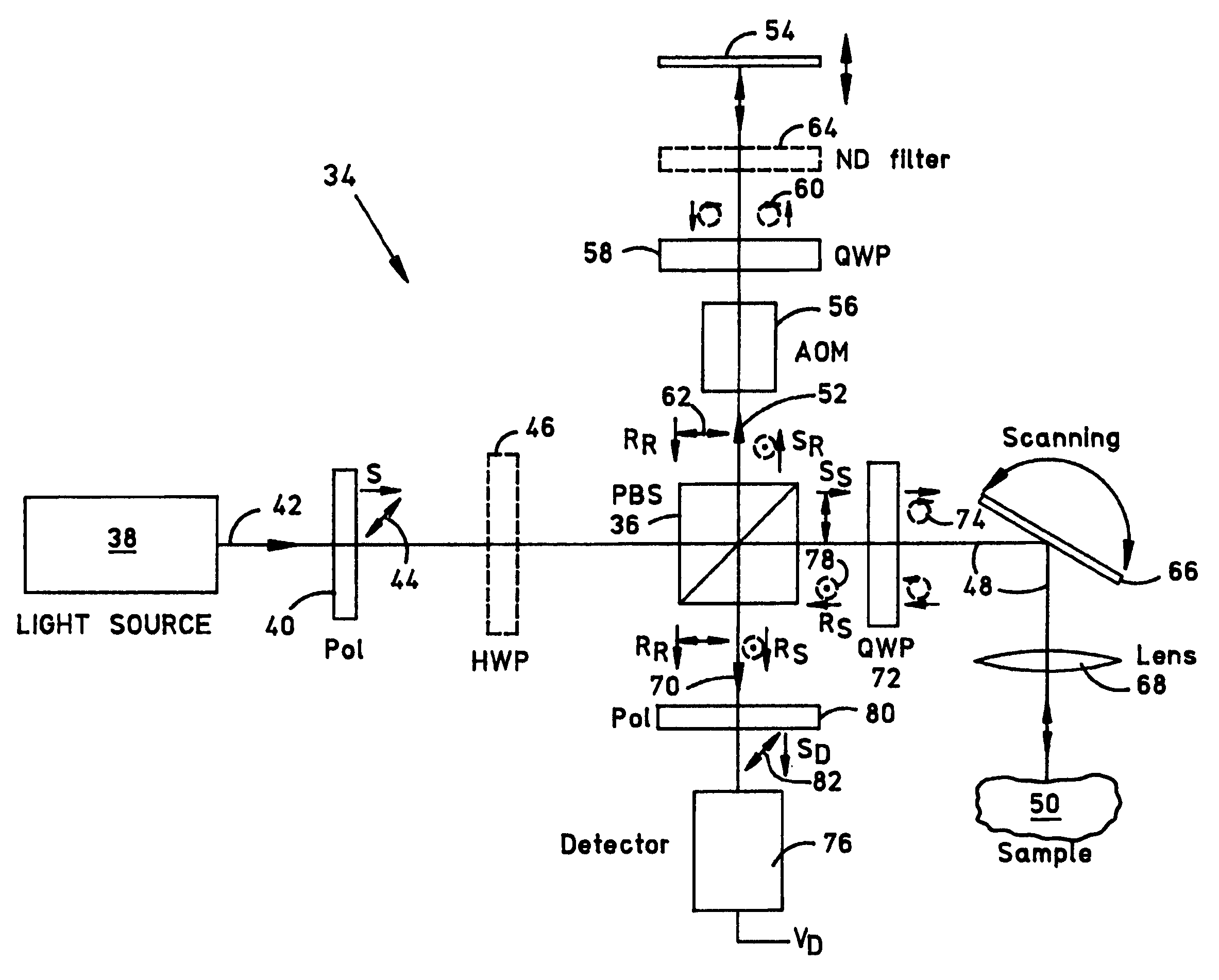
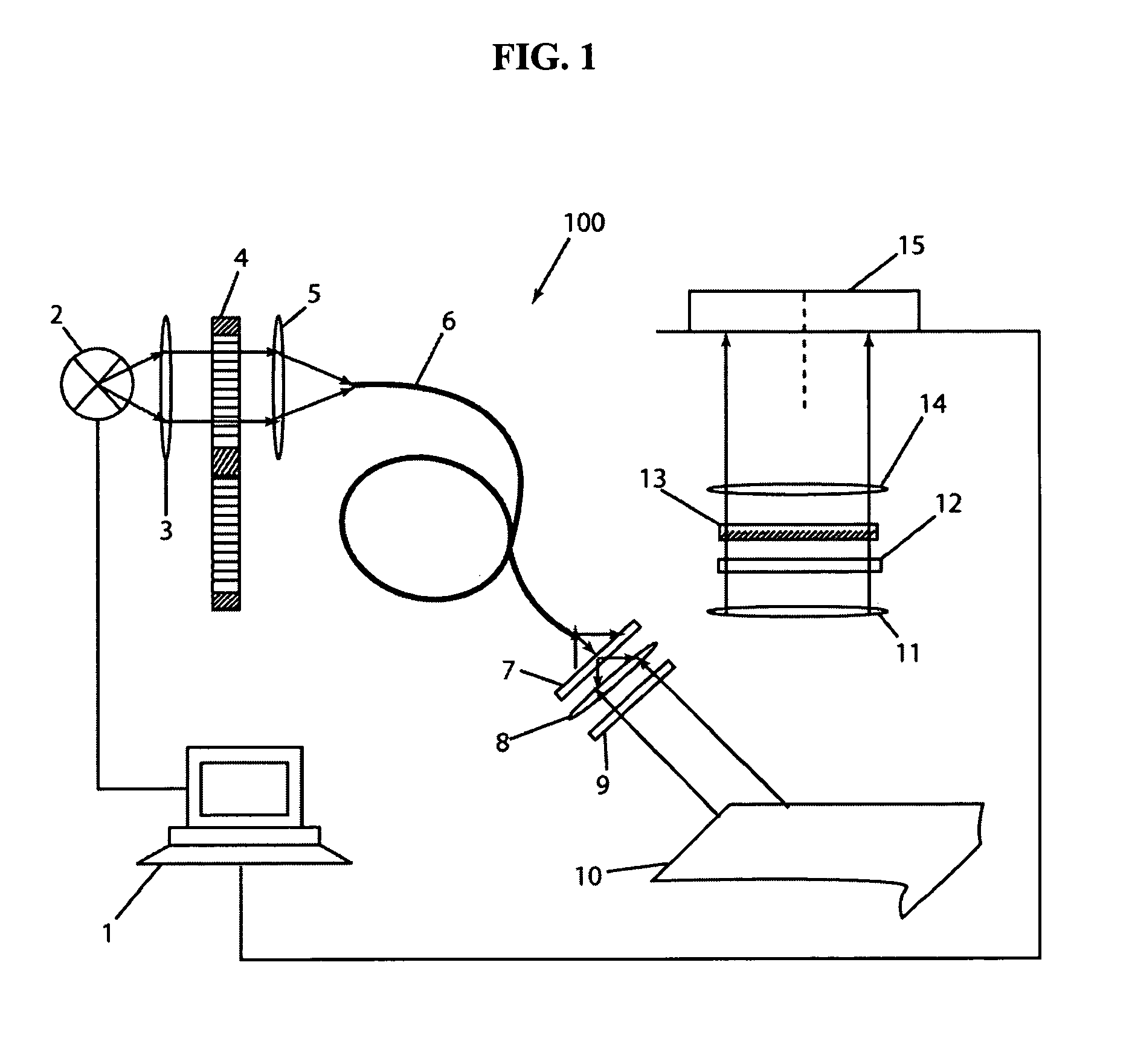
An optical coherence tomography (OCT) system including a polarizing splitter disposed to direct light in an interferometer such that the OCT detector operates in a noise-optimized regime. When scanning an eye, the system detector simultaneously produces a low-frequency component representing a scanning laser ophthalmoscope-like (SLO-like) image pixel and a high frequency component representing a two-dimensional (2D) OCT en face image pixel of each point. The SLO-like image is unchanging with depth, so that the pixels in each SLO-like image may be quickly realigned with the previous SLO-like image by consulting prominent image features (e.g., vessels) should lateral eye motion shift an OCT en face image during recording. Because of the pixel-to-pixel correspondence between the simultaneous OCT and SLO-like images, the OCT image pixels may be remapped on the fly according to the corresponding SLO-like image pixel remapping to create an undistorted 3D image data set for the scanned region.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Efficient optical coherence tomography (OCT) system and method for rapid imaging in three dimensions
InactiveUS7145661B2Remove Motion ArtifactsRaise the ratioScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansRapid imagingData set
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Vehicle underbody imaging system
InactiveUS7102665B1Increase the number ofCost effectiveMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionRapid imagingMobile vehicle
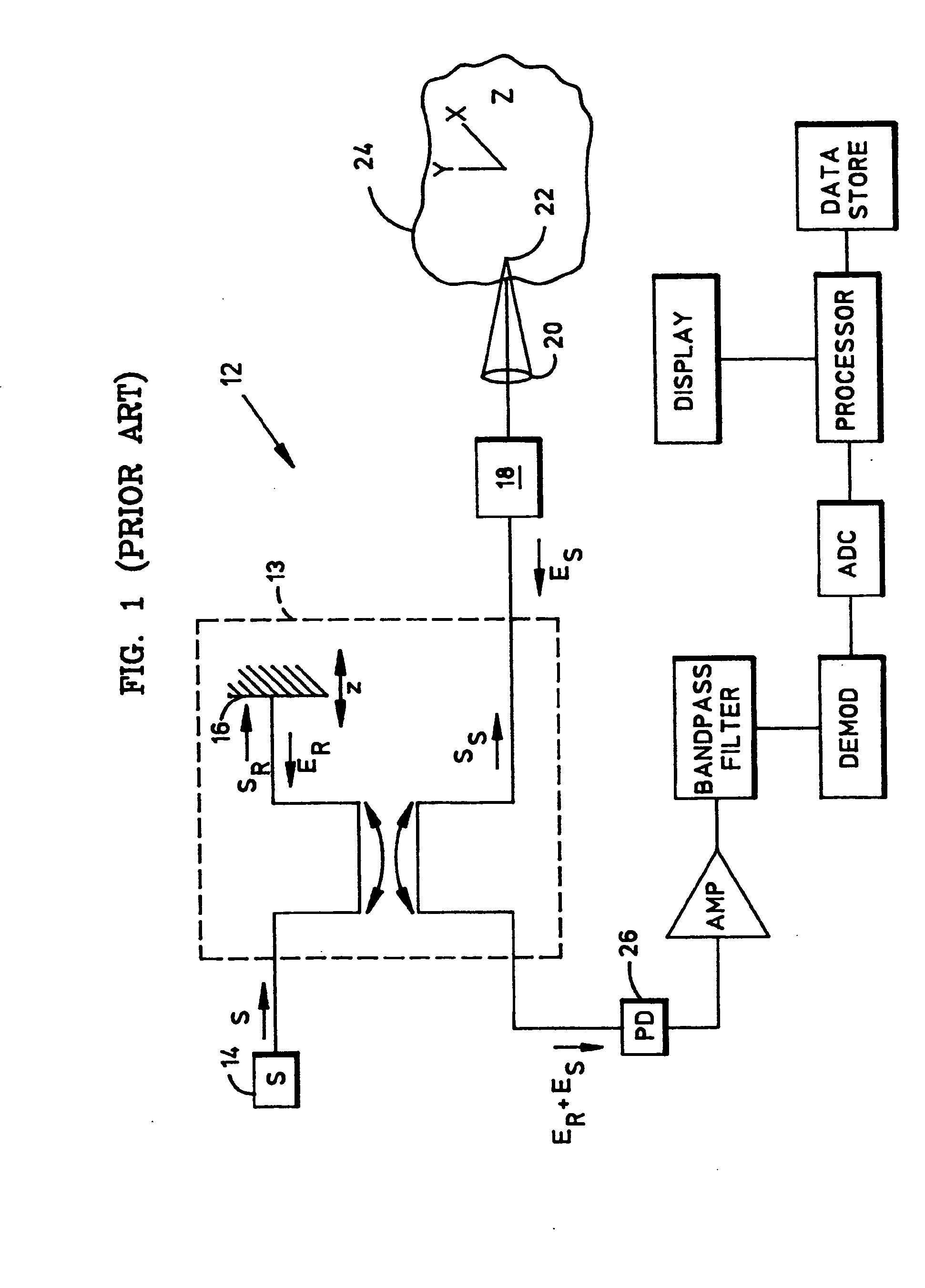
A system and method for imaging underbodies of moving vehicles have a stationary source of radiation to radiate energy upwardly on underbodies of moving vehicles. A stationary video camera adjacent the radiation source on a roadway has an upwardly facing field of view for creating image signals representative of sequential portions of each underbody as each moving vehicle passes overhead. A control station activates the camera and radiation source to create the image signals and creates mosaic signals of all of each underbody from the image signals. A display screen provides a mosaic image of each underbody from its mosaic signals. A virtually real-time inspection or a comparison can be made with previously taken underbody images of the same moving vehicle or with vehicle manufacturers' data for the same vehicular models. Moving cars, trucks, marine vessels, aircraft, can be quickly imaged for inspection and / or comparison by fewer security personnel.
Owner:NAVY THE UNITED SATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Method and system for high resolution, ultra fast 3-D imaging
InactiveUS20080031513A1Add depthHigh displacement accuracyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRapid imagingImage resolution
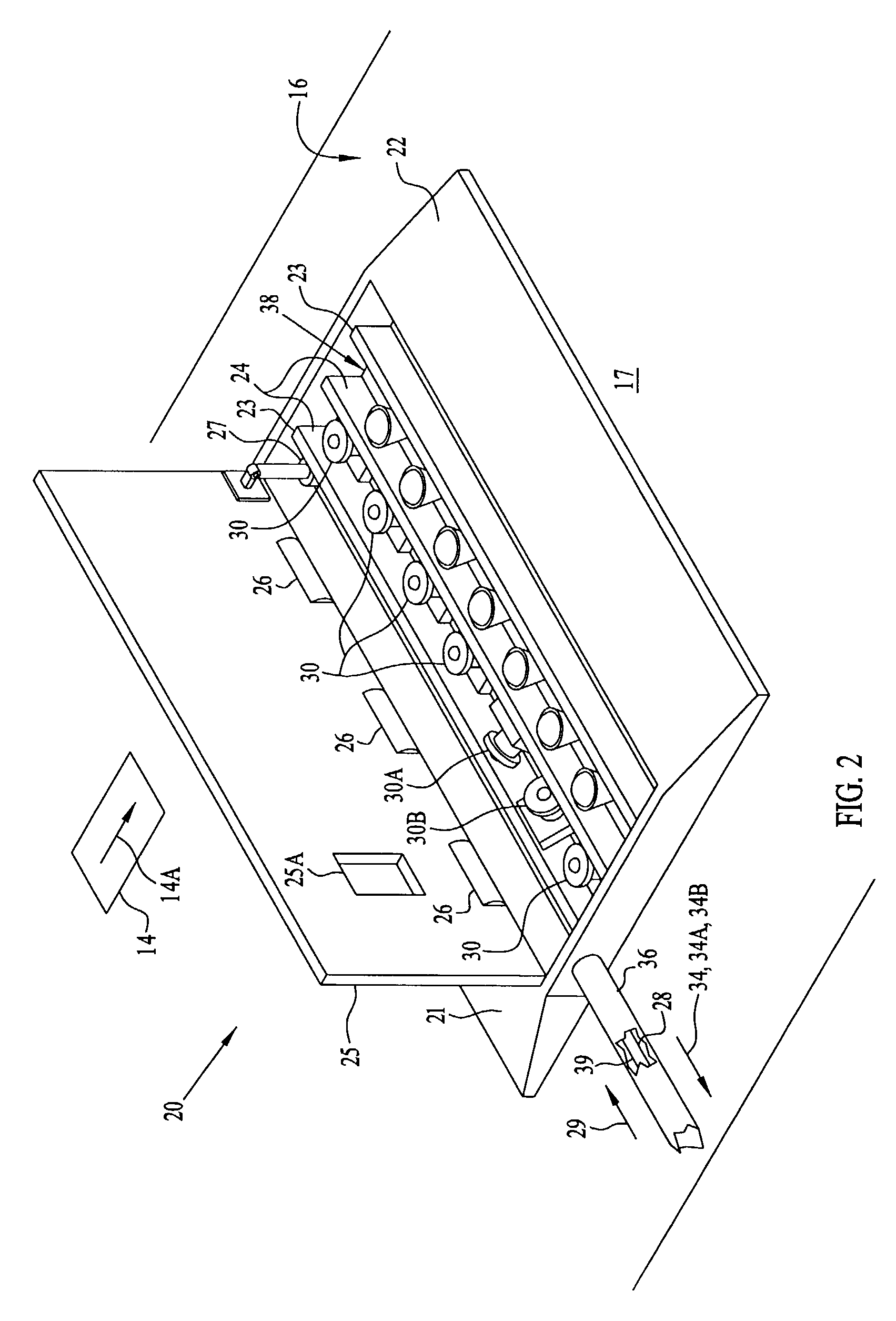
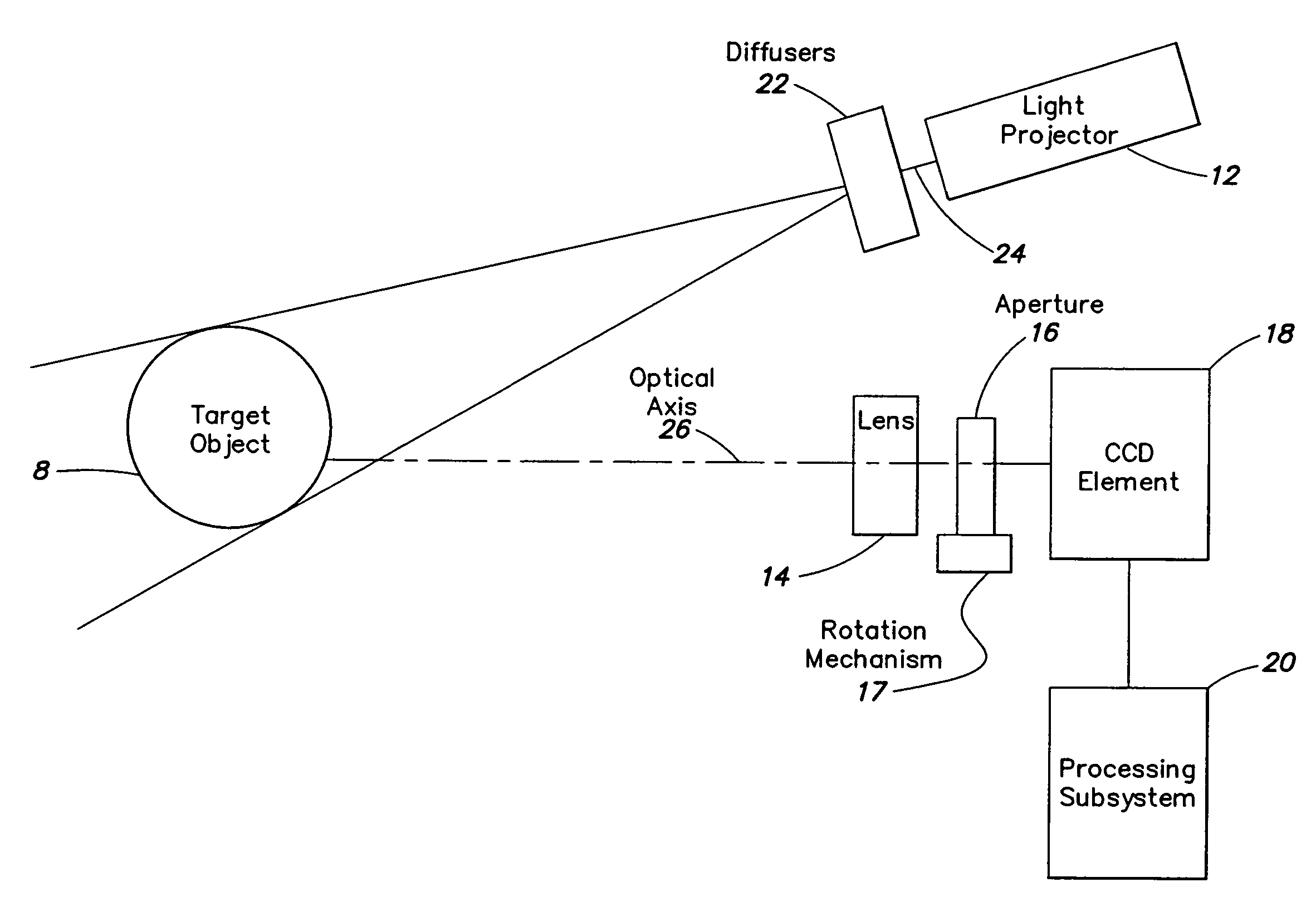
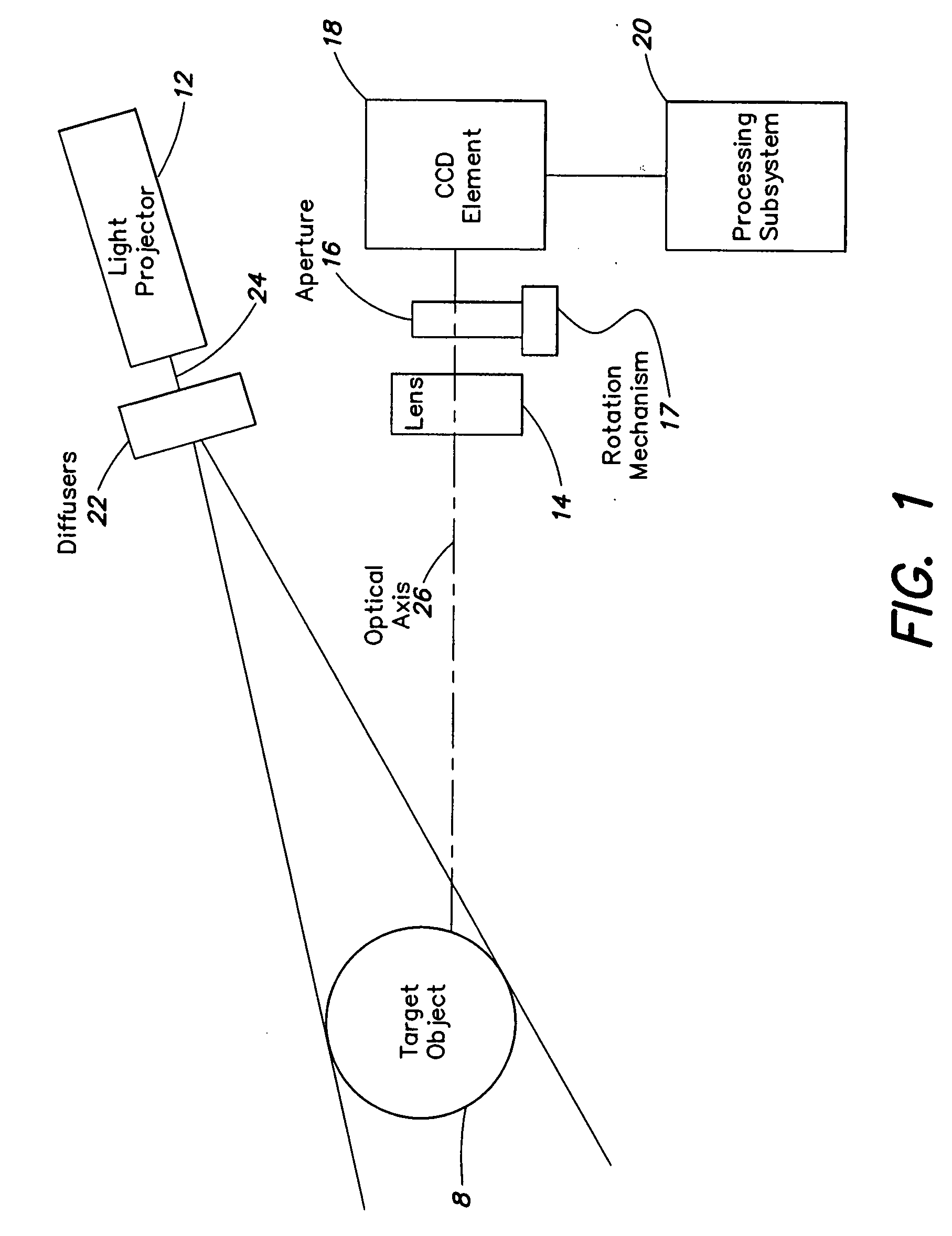
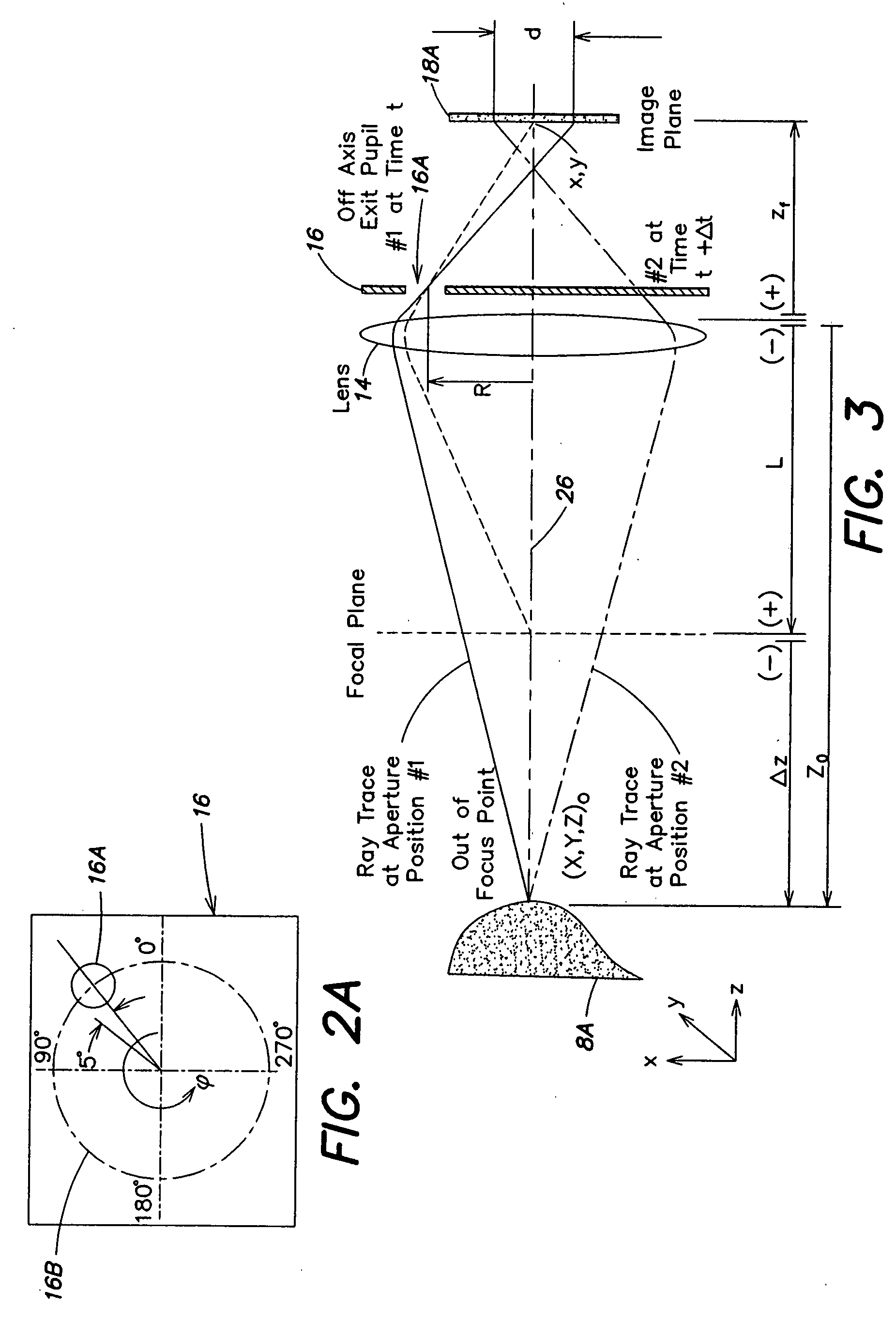
A high-speed three-dimensional imaging system includes a single lens camera subsystem with an active imaging element and CCD element, and a correlation processing subsystem. The active imaging element can be a rotating aperture which allows adjustable non-equilateral spacing between defocused images to achieve greater depth of field and higher sub-pixel displacement accuracy. A speckle pattern is projected onto an object and images of the resulting pattern are acquired from multiple angles. The images are locally cross-correlated using a sparse array image correlation technique and the surface is resolved by using relative camera position information to calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of each locally correlated region. Increased resolution and accuracy are provided by recursively correlating the images down to the level of individual points of light and using the Gaussian nature of the projected speckle pattern to determine subpixel displacement between images. Processing is done at very high-speeds by compressing the images before they are correlated. Correlation errors are eliminated during processing by a technique based on the multiplication of correlation table elements from one or more adjacent regions.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fluorescence polarization imaging devices and methods
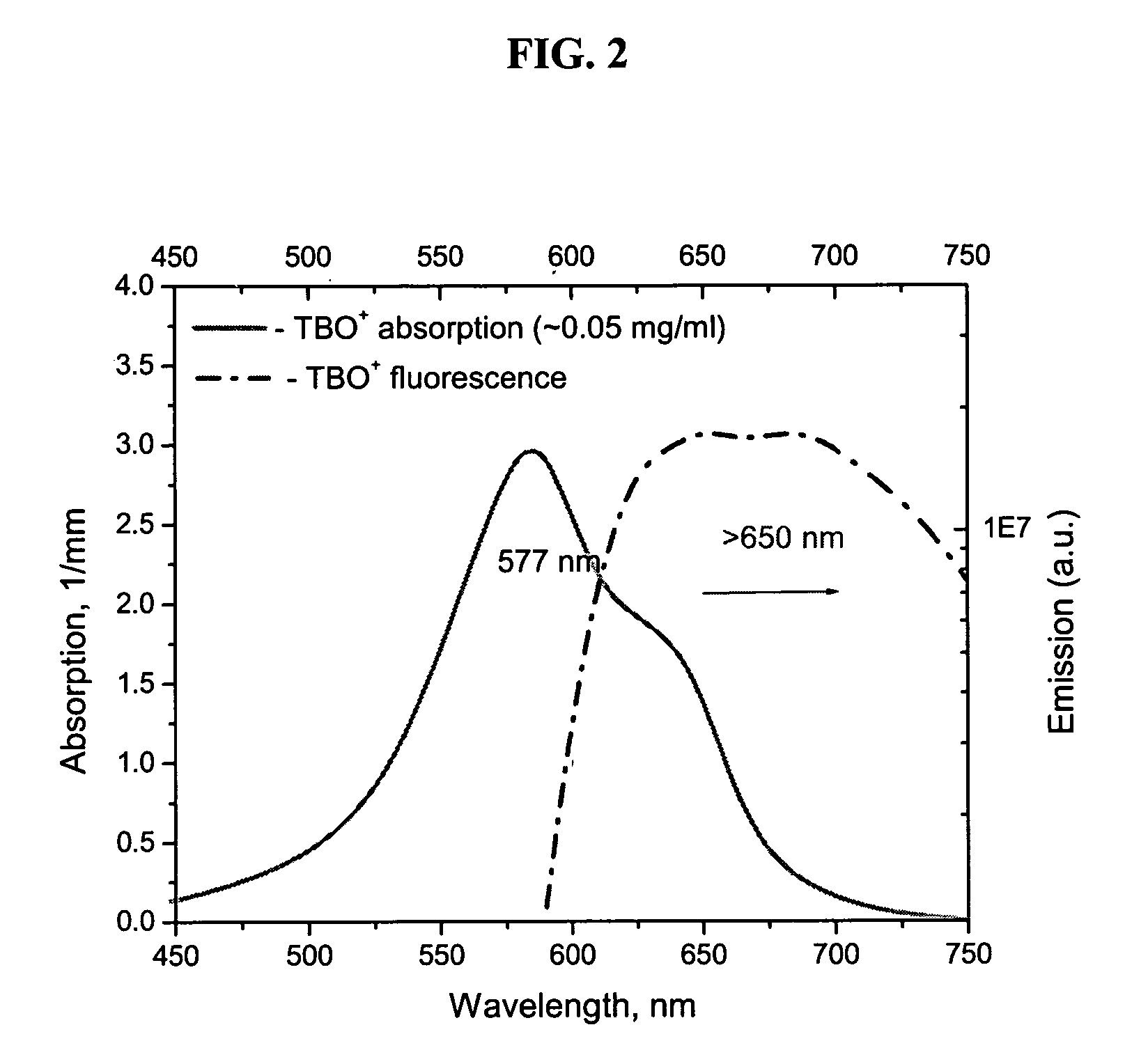
InactiveUS7289205B2Improvements in standard cancer surgeryIncrease the number ofRaman/scattering spectroscopyLuminescent dosimetersRapid imagingFluorescence
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
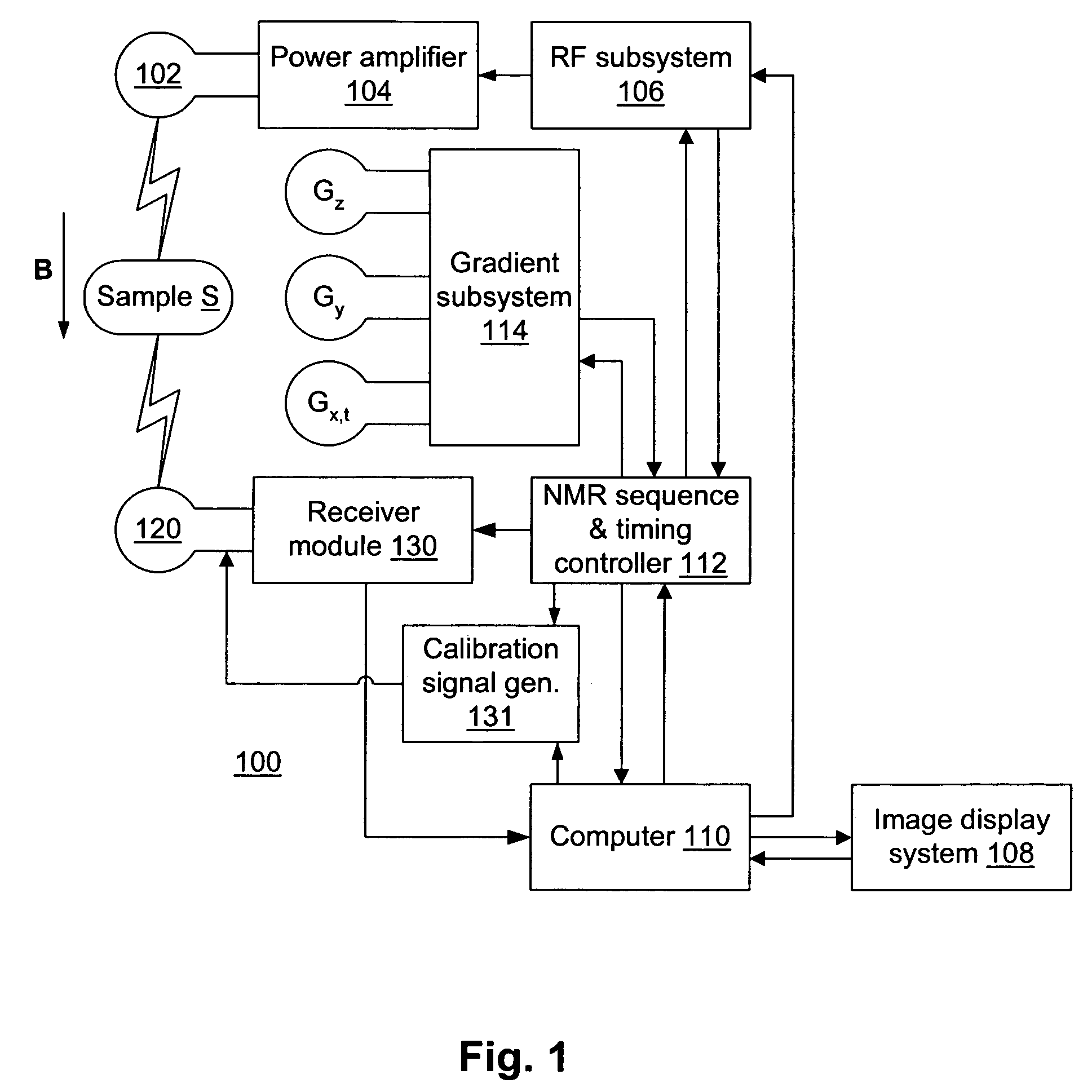
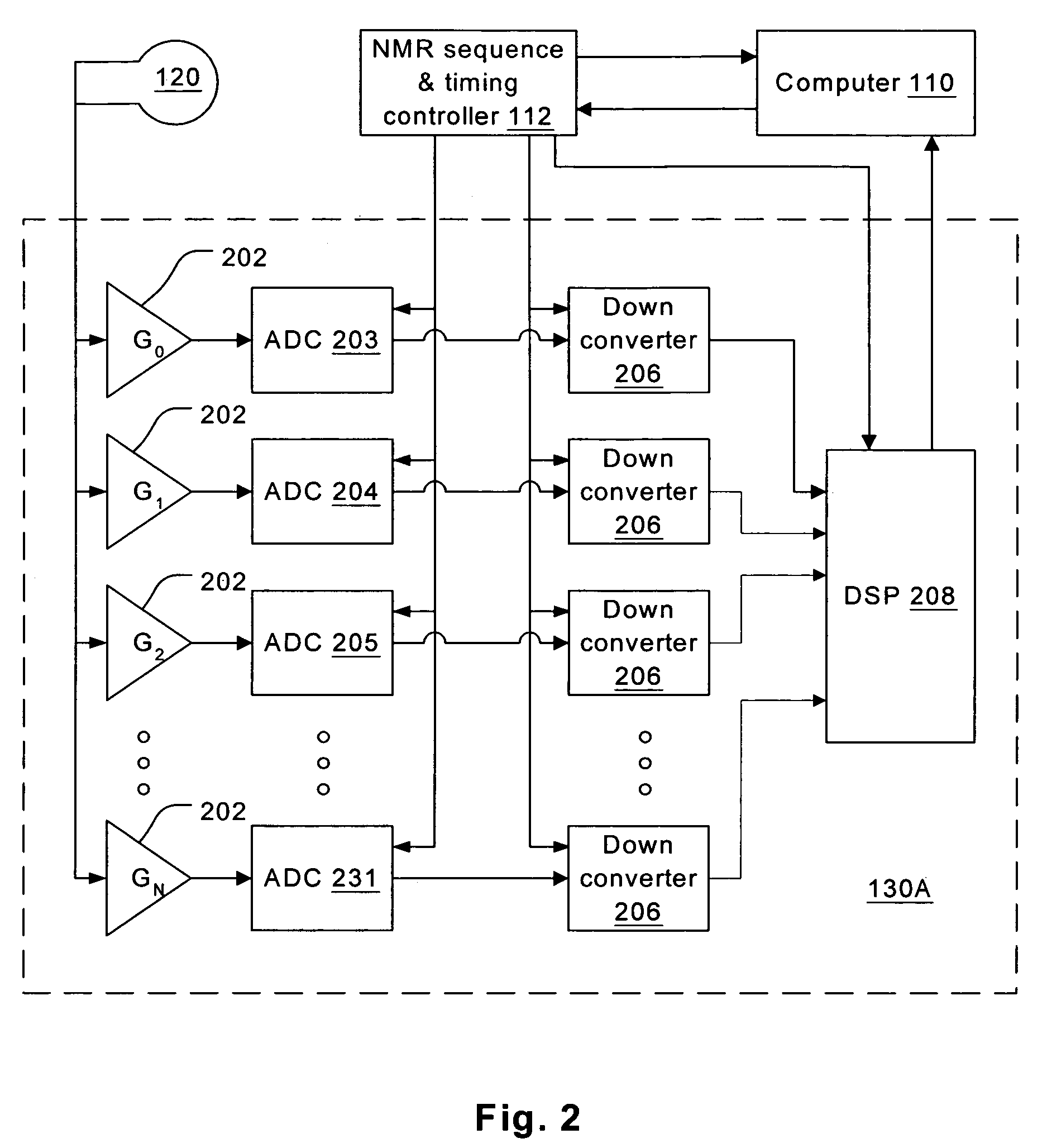
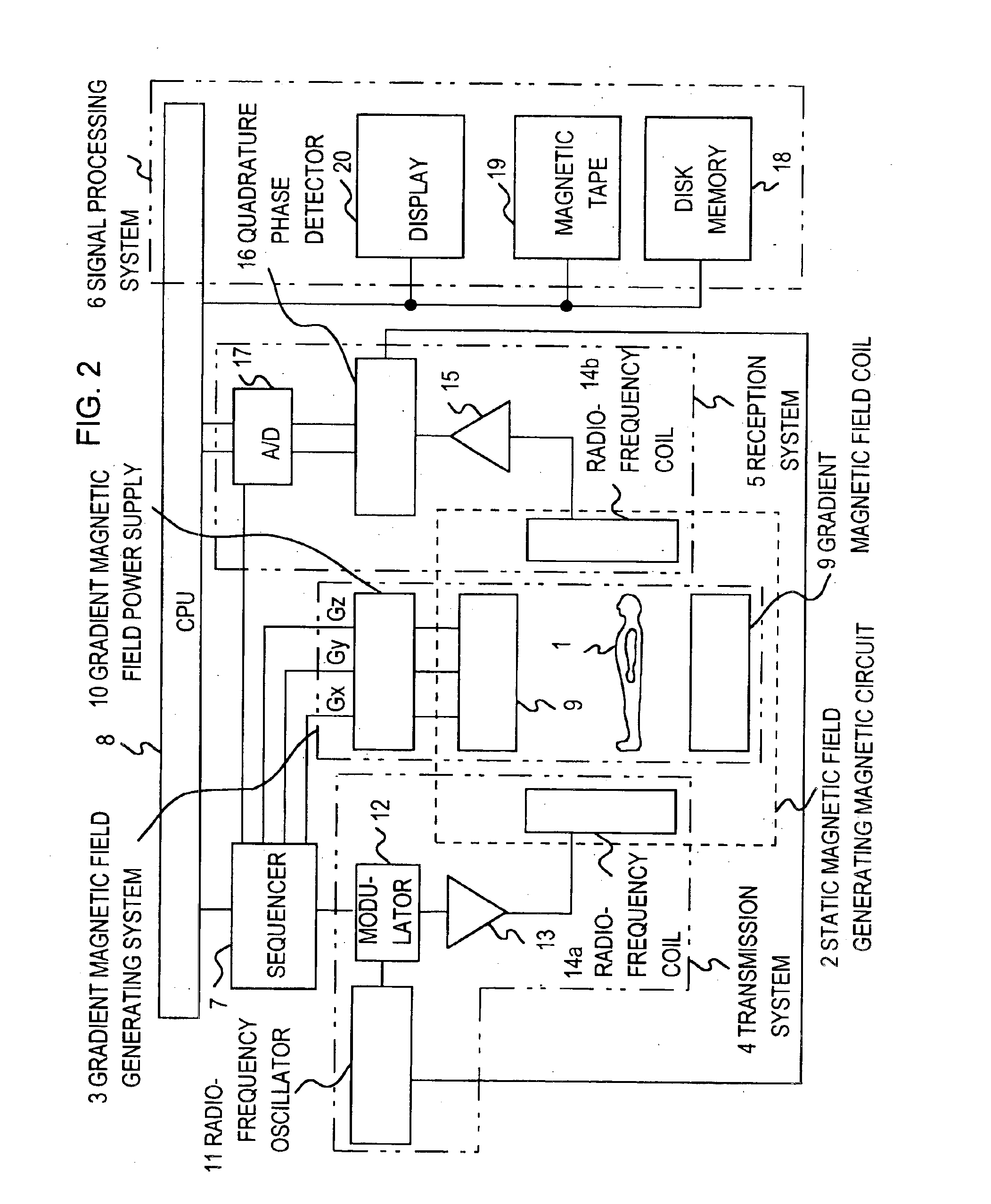
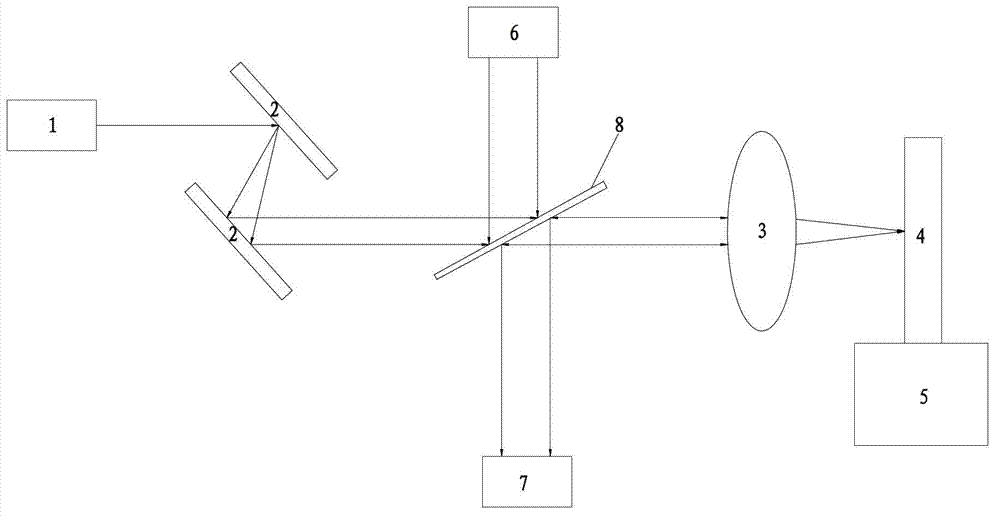
Adaptive dynamic range receiver for MRI
InactiveUS7403010B1Avoid the needLimited dynamic rangeElectric signal transmission systemsMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoRapid imaging
A receiver for a resonance signal of a magnetic resonance imaging system generates a baseband signal for image processing by dividing a raw resonance signal among multiple parallel channels, each amplified at a respective gain. A digital channel selector determines, at any given moment, a lowest-distortion channel to be further processed. Amplitude and phase error compensation are handled digitally using complex multipliers, which are derived by a calibration, based on a simple Larmor oscillator, which can be done without the need for a sample and without repeating when measurement conditions are changed. One of the important benefits of the invention is that it provides for gain selection without repeated calibration steps. This is particularly important in systems that employ fast imaging techniques such as fast spin echo, where the invention can speed imaging substantially.
Owner:FONAR
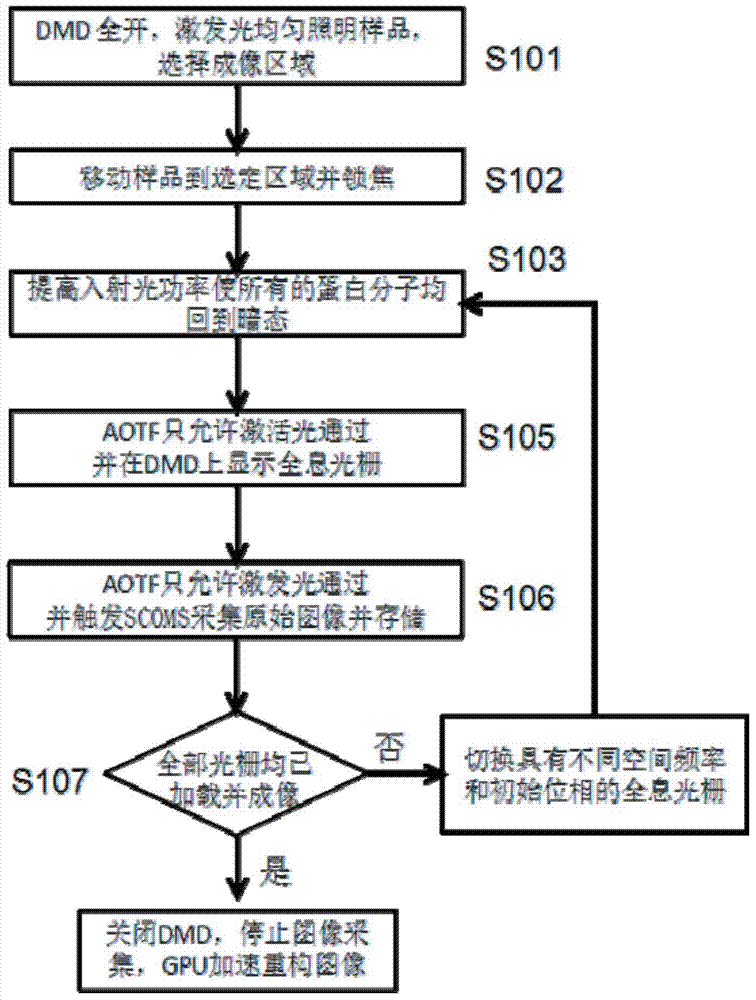
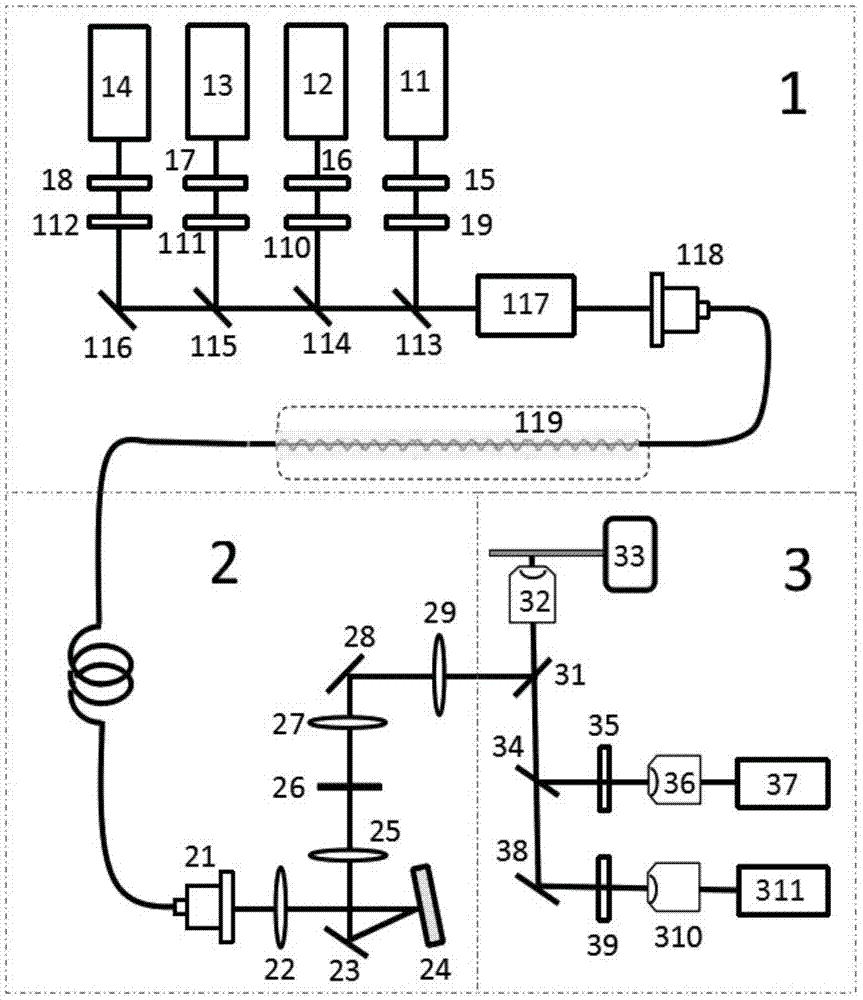
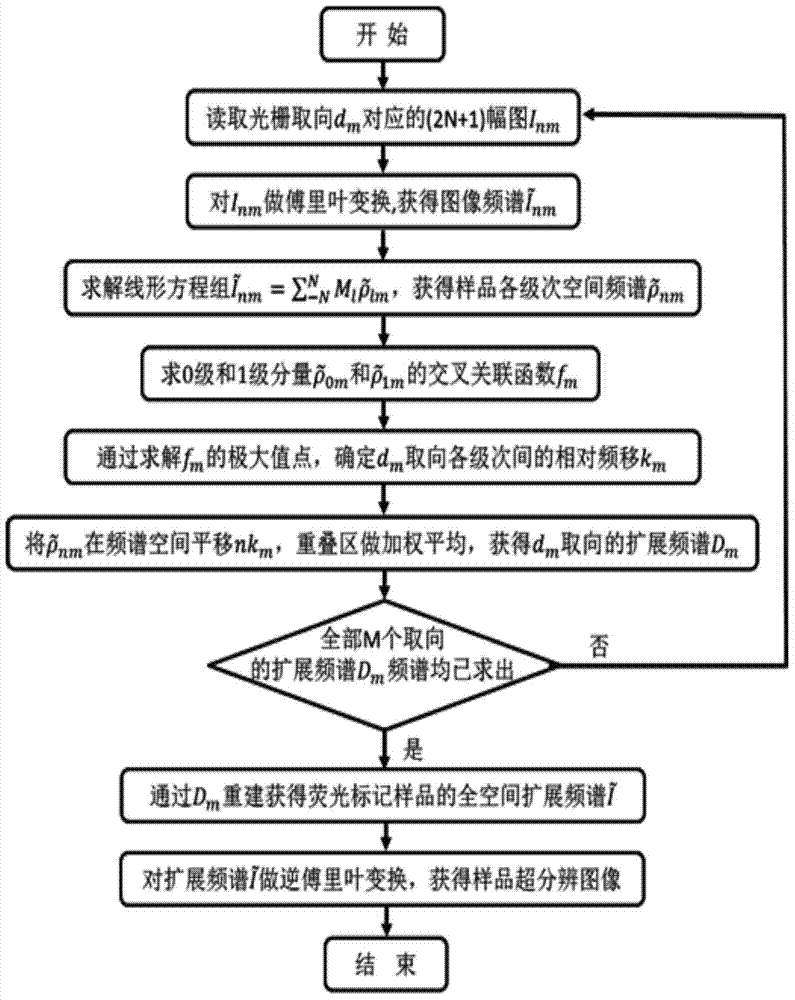
Non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method and system
ActiveCN104515759AImprove imaging resolutionReduce bleaching effectFluorescence/phosphorescenceRapid imagingFluorescence
The invention discloses a non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method which comprises the following steps: 1) loading a computed hologram on a digital microscopic array; 2) generating a first spatial structure light field which meets sine distribution and is used for activating fluorescent protein, and radiating the first spatial structure light field to the surface of a sample, so as to convert a part of protein to be in an illuminated state from a dark state; 3) radiating the sample in a second spatial structure light field so as to enable fluorescent protein in the bright state to emit fluorescent light, collecting the fluorescent light, and imaging in a photoelectric detector; 4) repeating the step 2) and the step 3), acquiring a plurality of spatial frequencies, acquiring a plurality of initial phases in each direction to obtain a plurality of original images, and reestablishing a super-resolution image according to a GPU acceleration algorithm. The invention further discloses a non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging system. The non-linear structure light illumination microscopic imaging method has the advantages of relatively high system imaging resolution, high fluorescent drifting resistance, low phototoxicity and rapid imaging.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
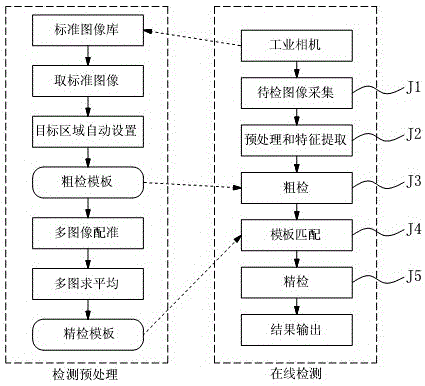
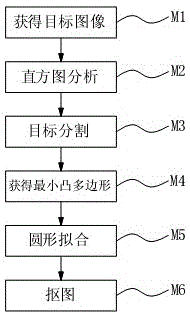
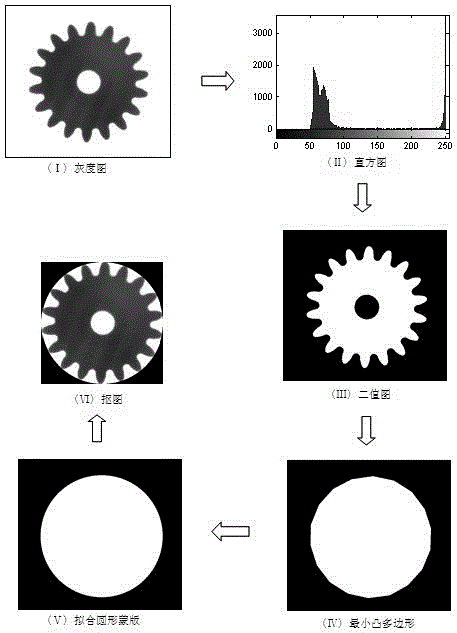
Rapid imaging detection method for gear appearance defect
ActiveCN105069790AAvoid dependencyImprove detection efficiencyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRapid imagingTemplate matching
The invention relates to a rapid imaging detection method for gear appearance defects. The rapid imaging detection method comprises two stages including a pre-processing stage and an online detection stage. The pre-processing stage comprises three procedures including automatically setting a target region, generating a coarse detection template and generating a fine detection template. The online detection stage comprises the steps of: J1) acquiring an image; J2) preprocessing and extracting features; J3) carrying out area difference value calculation on the image to be detected and an image of the coarse detection template for coarse detection judgment; J4) registering the image to be detected and an image of the fine detection template so that gear tooth directions of the two images are coincided; J5) and carrying out exclusive-or operation on the image to be detected and the image of the fine detection template to obtain a differential image, and acquiring defect region area in the differential image for fine detection judgment. The rapid imaging detection method for gear appearance defects acquires images by utilizing machine vision, performs coarse and fine judgment by utilizing template matching and image exclusive-or operation, and is high in detection precision and fast in speed.
Owner:WEIFANG UNIVERSITY
Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method and system
ActiveCN102018514AAcquisition speed is fastFast imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsComplete dataRapid imaging
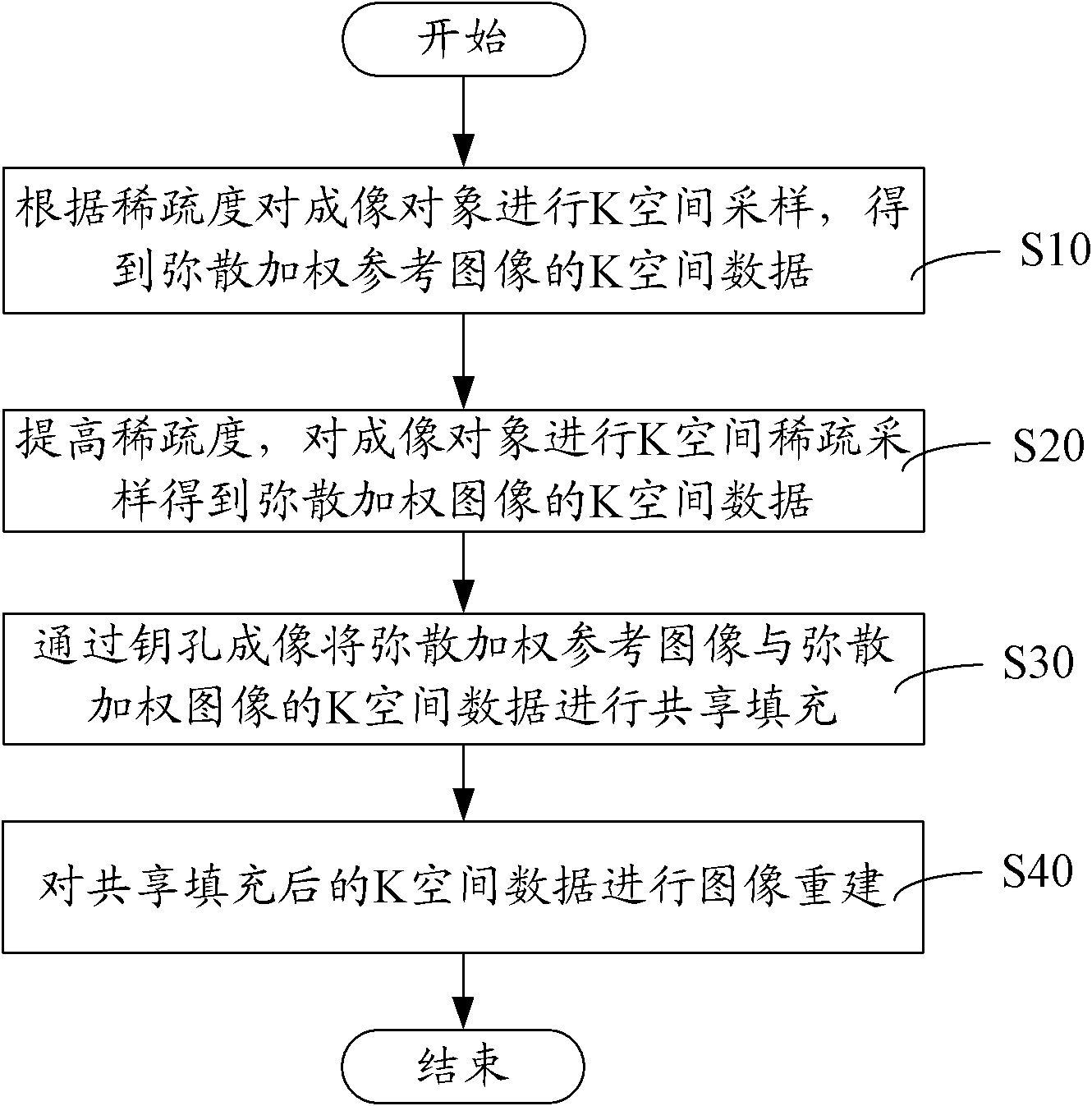
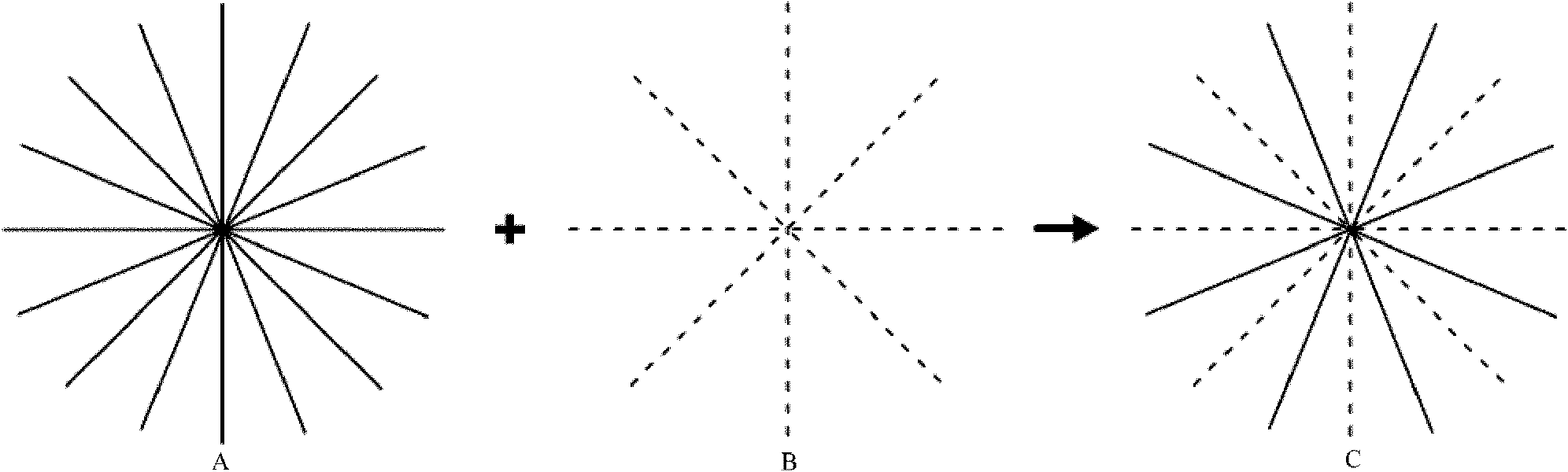
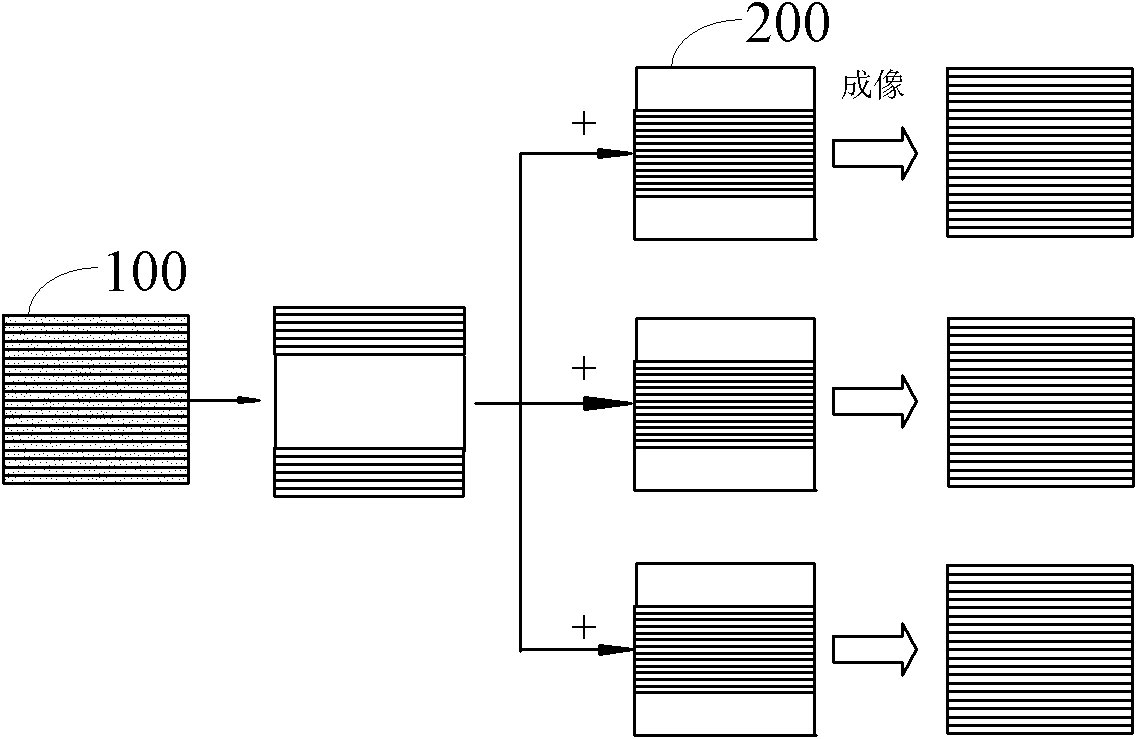
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method which comprises the following steps: performing K space sparse sampling on an imaging object to obtain K space data of a diffusion weighted reference image; performing K space sparse sampling on the imaging object to obtain the K space data of a diffusion weighted image; performing share filling on the K space data of the diffusion weighted reference image and the diffusion weighted image by keyhole imaging; and performing image reconstruction on the K space data after share filling. The magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method and system provided by the invention have the advantages of reconstructing complete data, shortening the scanning time, improving the data acquiring speed and achieving rapid imaging by adopting sparse sampling rapidly and continuously to acquire K space data and performing share filling under the action of the keyhole imaging technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescence polarization imaging devices and methods
InactiveUS20050094147A1Increase the number ofImprovements in standard cancer surgeryRaman/scattering spectroscopyLuminescent dosimetersRapid imagingFluorescence
The present invention is directed to a novel multi-spectral exogenous fluorescence polarization imaging technique that enables rapid imaging of large tissue fields. The imaging device includes a tunable monochromatic light source and a CCD camera. Linear polarizers are placed into both the incident and collected light pathways in order to obtain fluorescence polarization or / and anisotropy image. To acquire exogenous fluorescence image, fluorescent contrast agents are delivered to a target tissue.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Parallel MR imaging using high-precision coil sensitivity map
InactiveUS6949928B2Improve accuracyHigh precision estimationDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRapid imagingSensitivity distribution
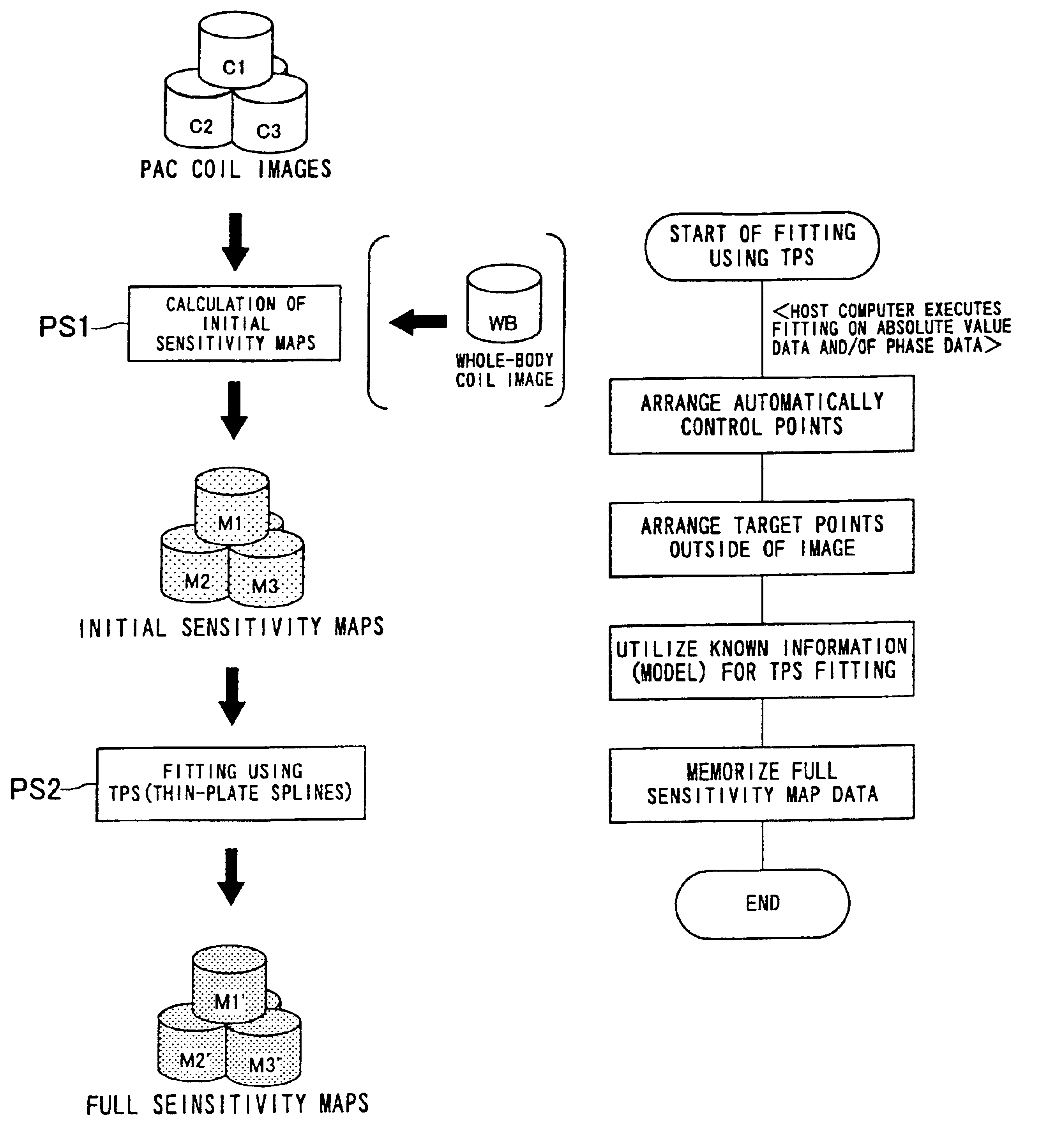
A sensitivity distribution is estimated for a multicoil used in multicoil fast imaging. Initial sensitivity maps M1 to M3 are produced respectively from images C1 to C3 acquired from the plurality of RF coils in the multicoil. By fitting TPS (thin-plate splines) to the initial sensitivity maps M1 to M3 used as target data, sensitivity maps M1′ to M3′ for unfolding are estimated. In fitting the TPS, functions are activated, such as automatic arrangement of control points, addition of target points to the outside of an image, use of a known model, and fitting to at least either absolute value components of MR data or phase components of the MR data. Thus, even if only coarse echo data is acquired from the region to be imaged, a sensitivity map of each element coil of the multicoil is estimated with high precision.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Non-contact type electric impedance sensor and image rebuilding method based on the sensor
InactiveCN101241094AQuick responseLow costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRapid imagingBreakdown strength
The present invention provides a non-contact impedance sensor which is mounted on measuring region, the radial section structure of the sensor comprises of four layers, metal tube layer, insulation material layer, electrode array layer and insulation ring layer from outside to inside in turn. At least two electrodes are distributed in one circle on the insulation ring layer whose thickness is less than 1% of external diameter, and electric field intensity between electrode array and metal tube layer is less than breakdown strength of insulation layer. The electrode array is separated with measuring region by insulation ring layer. Two image reconstruction algorithms to realize electrical impedance tomography based on the said sensor are also provided. The present invention provides analytical medel, corresponding sensitivity distribution expression and two rapid imaging methods, the sensor can measuring synchronous same-positional dual-mode impedance, advance mutual fusion of real parts and imaginary part information of impedance distribution, predigest the design and implement of software and hardware of dual-mode measuring system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
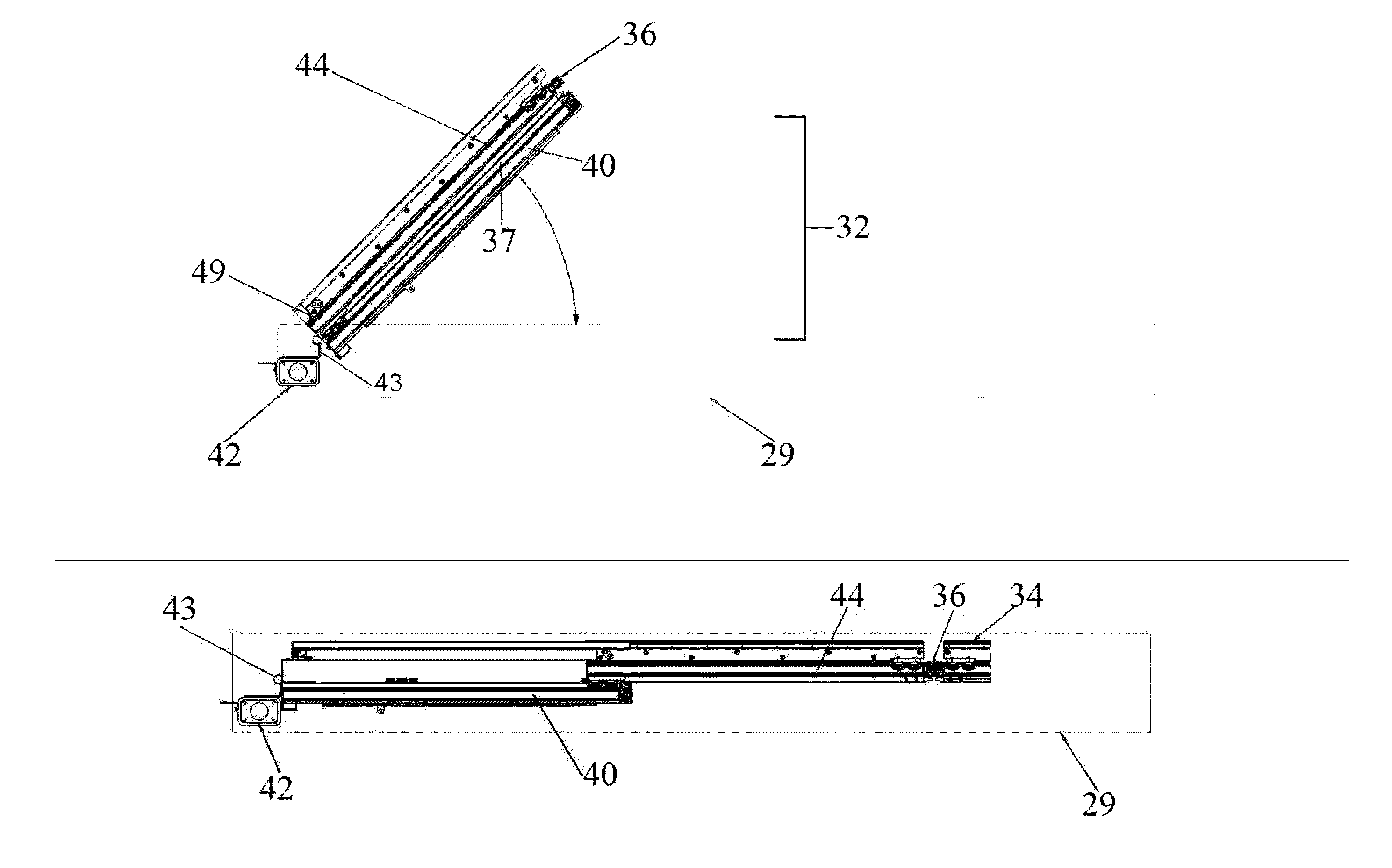
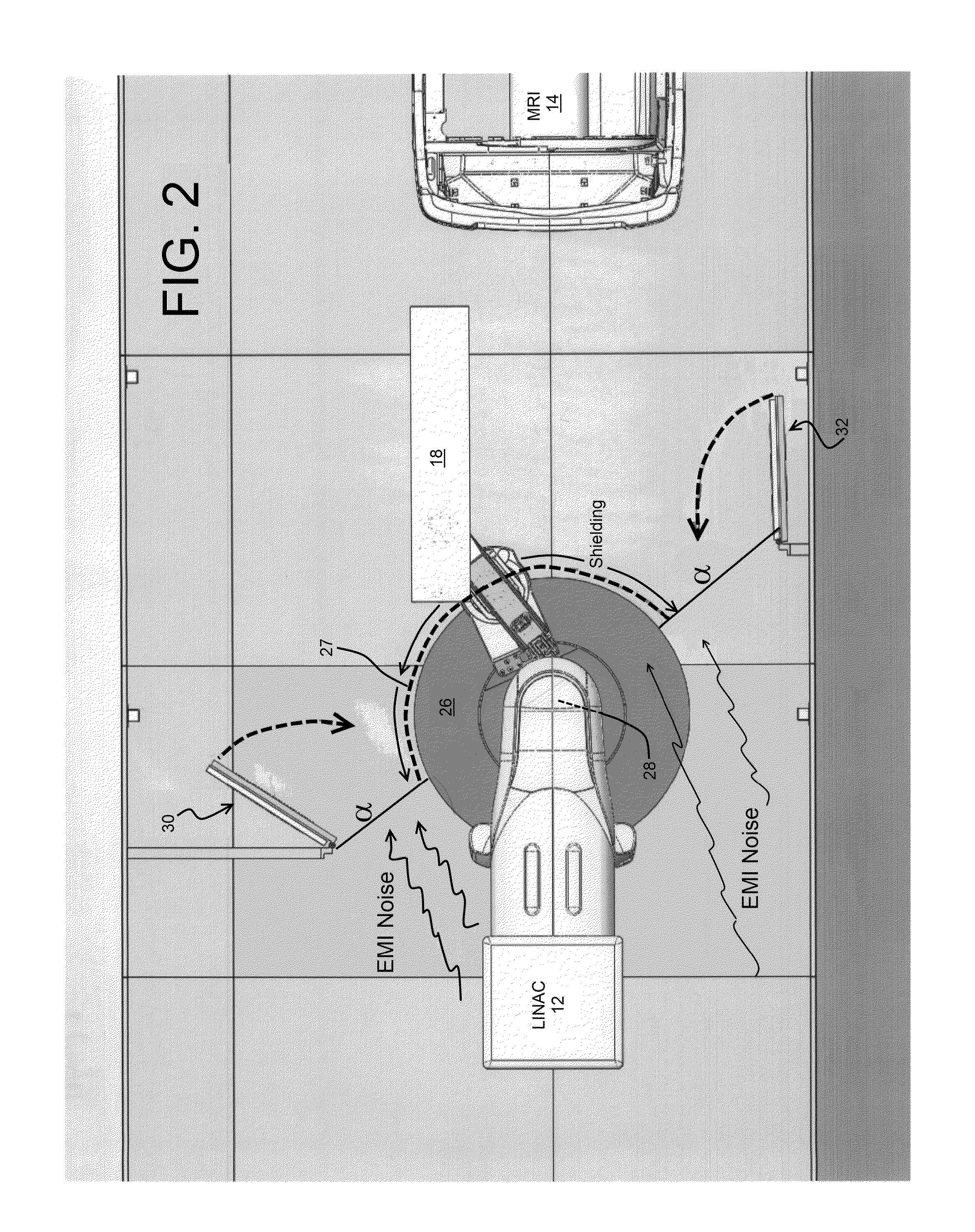
Movable EMF shield, method for facilitating rapid imaging and treatment of patient
ActiveUS8993898B2Screening rooms/chambersElectrically conductive connectionsRapid imagingLeading edge
A radio frequency shield which reversibly transects an electromagnetic frequency enclosure is provided. The shield includes first a number of panels attached to a first surface of the enclosure. The panels are adapted to move through a first arc relative to the first surface. Shield also includes a first panel from the number of panels having a first leading edge capable of transecting the first arc. The shield further includes a second number of panels attached to a second surface of the enclosure. The second set of panels is adapted to move through an arc relative to the second surface of the enclosure. Also a second panel from said second set of panels has a second leading edge capable of transecting the second arc so as to oppose the first leading edge. Finally, the shield includes a means for reversibly attaching the first leading edge to the second leading edge while simultaneously establishing electrical communication between the first and second plurality of panels.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
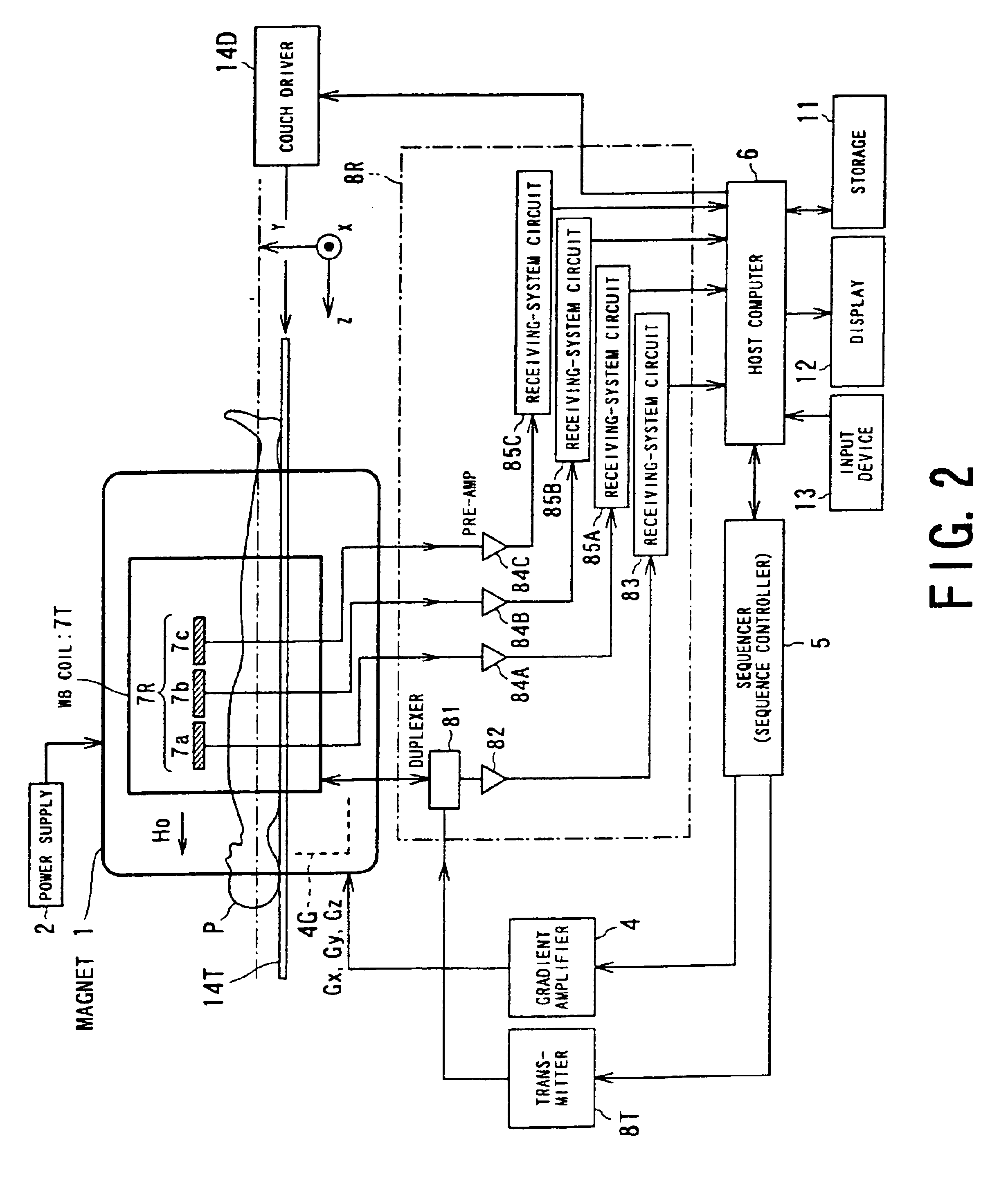
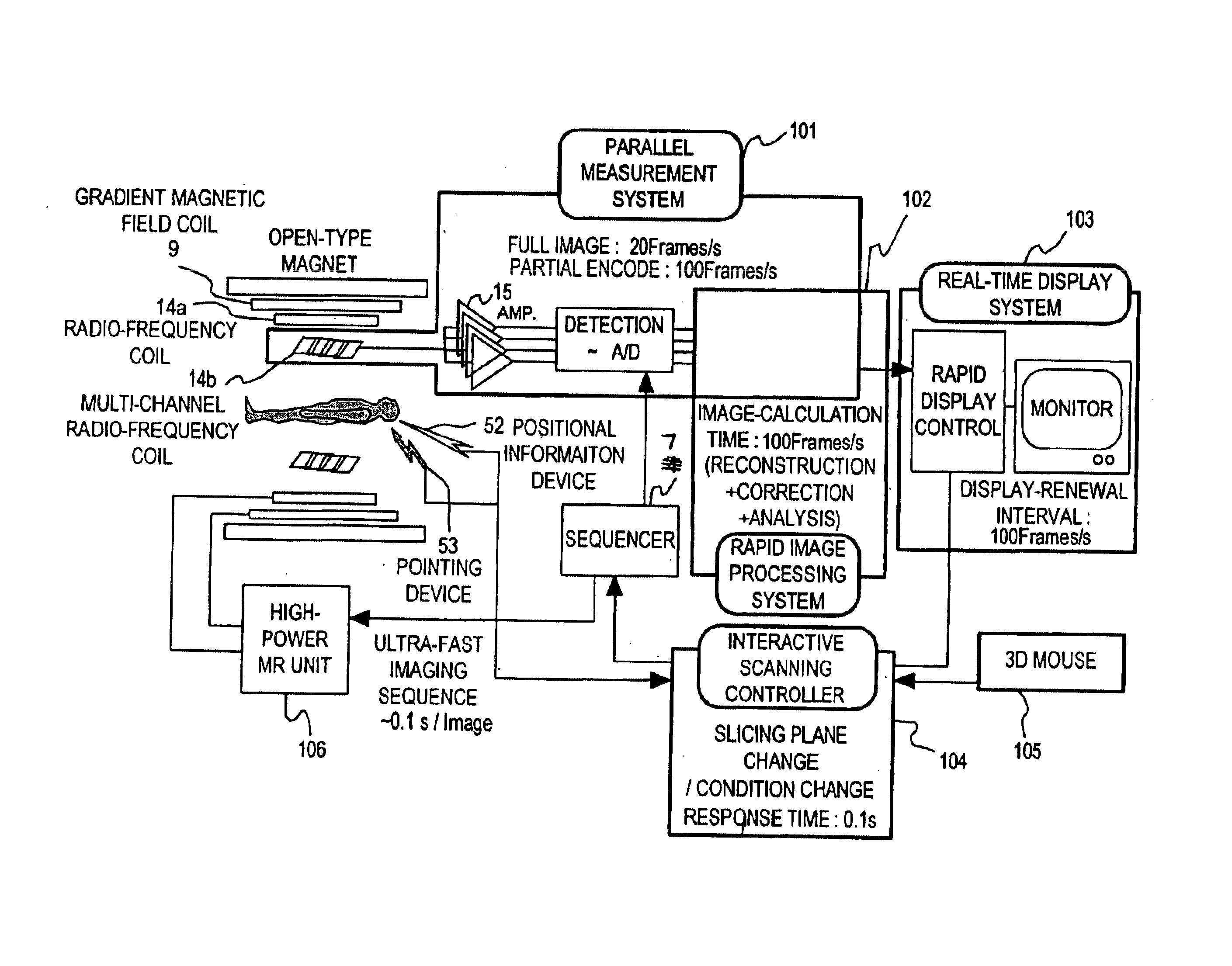
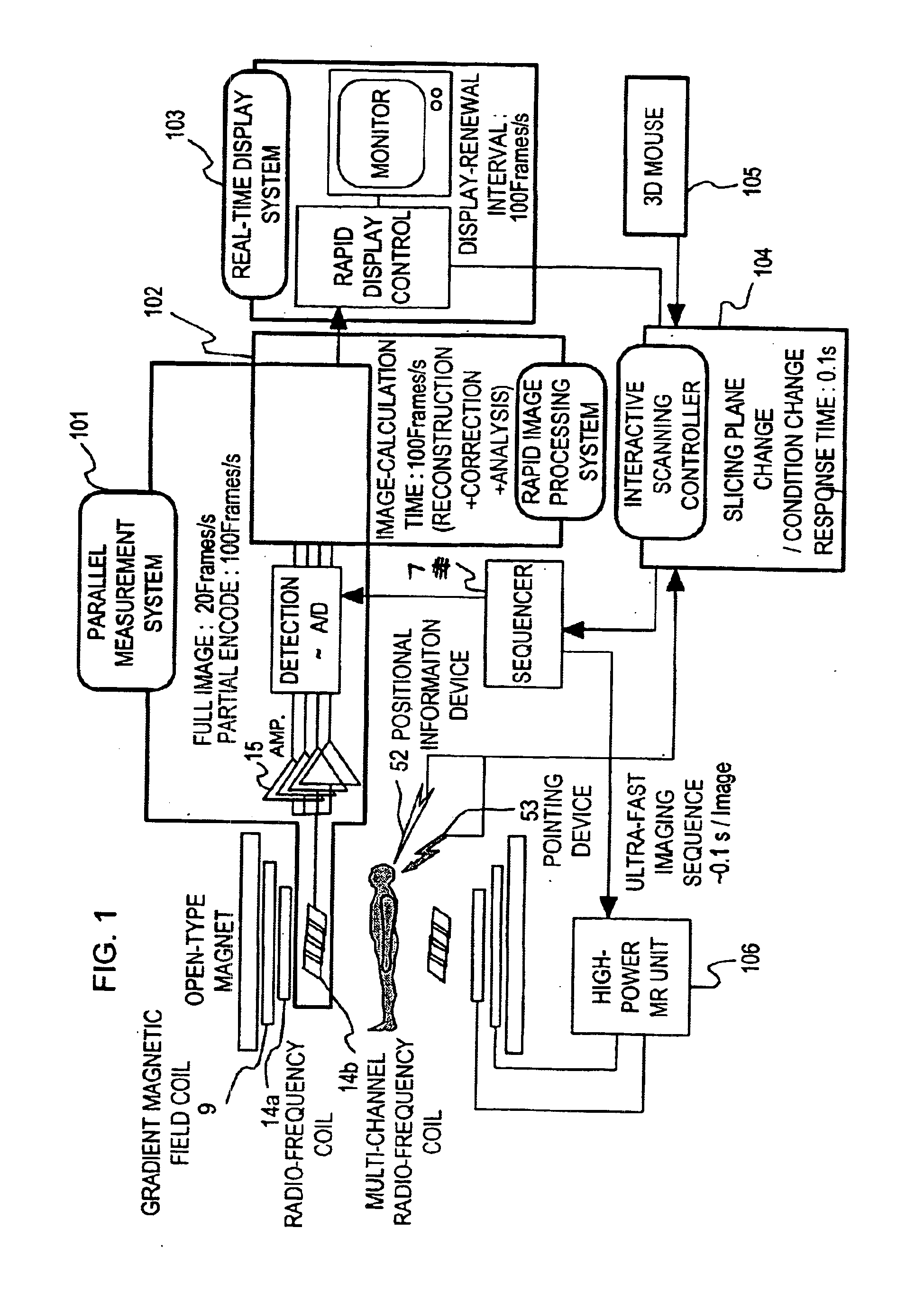
Magnetic resonance imaging system
InactiveUS6876198B2Reduce in quantityUltra-rapid imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRapid imagingImaging processing
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus is provided with a sequencer for executing a rapid imaging sequence of up to 100 ms at a full scan, a parallel measurement system for executing a partial encoding measurement in which the number of phase encoding operations performed for the measurement is reduced, an image processing system for reconstructing images from the information obtained though parallel measurements and composing reconstructed images of a plurality of areas to make one image, a display system for displaying the obtained images at a rate of 50 frame / second or more, and an image renewal system for taking in coordinate information of the cross-section to be imaged from position and pointing devices at intervals of about 0.1 second, and renewing the cross-section to be imaged in real time. Thus, imaging on the cross-sections indicated by a device can be performed in real time with high spatial and high time resolution.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Method for rapid imaging of biologic fluid samples
A method for analyzing a biologic fluid sample is provided. The method includes the steps of: a) disposing the biologic fluid sample within a chamber; b) imaging the biologic fluid sample at a first resolution, and producing first image signals representative of a low resolution image of the sample; c) analyzing the first image signals to identify one or more first characteristics of the sample, and determining a position of each first characteristic within the chamber using a map of the chamber; d) imaging a portion of the biologic fluid sample at a second resolution and producing second image signals, which portion of the sample is determined using the first characteristics and the map, and wherein the second resolution is greater than the first resolution; and e) analyzing the biologic fluid sample using the second image signals.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Terahertz wave fast imaging scanner
InactiveCN101832912AFast imagingReduce volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical elementsRapid imagingImaging modalities
The invention relates to an imaging device for performing large field of view and fast scanning on terahertz waves by using a fast scanning device. The terahertz wave fast imaging scanner is used for scanning objects to be scanned, and comprises a frame scanning lens group, a row scanning lens group, a concave mirror and a terahertz wave detector. The frame scanning lens group is positioned behind the objects to be scanned and is used for longitudinally scanning the objects to be scanned; the row scanning lens group is arranged on a light path behind the frame scanning lens group and is used for transversely scanning the objects to be scanned; the concave mirror is positioned on the light path behind the row scanning lens group and is used for converging the terahertz waves; and the terahertz wave detector is positioned on the light path behind the concave mirror and is used for receiving scanning signals. Due to the adoption of the imaging mode of single point light machine scanning, the terahertz wave fast imaging scanner can realize fast imaging of the field of view, and make the whole imaging system have small volume, low cost and relatively easy manufacture and debugging. The terahertz wave fast imaging scanner can be applied to passive imaging modes, and also can be applied to active imaging modes.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
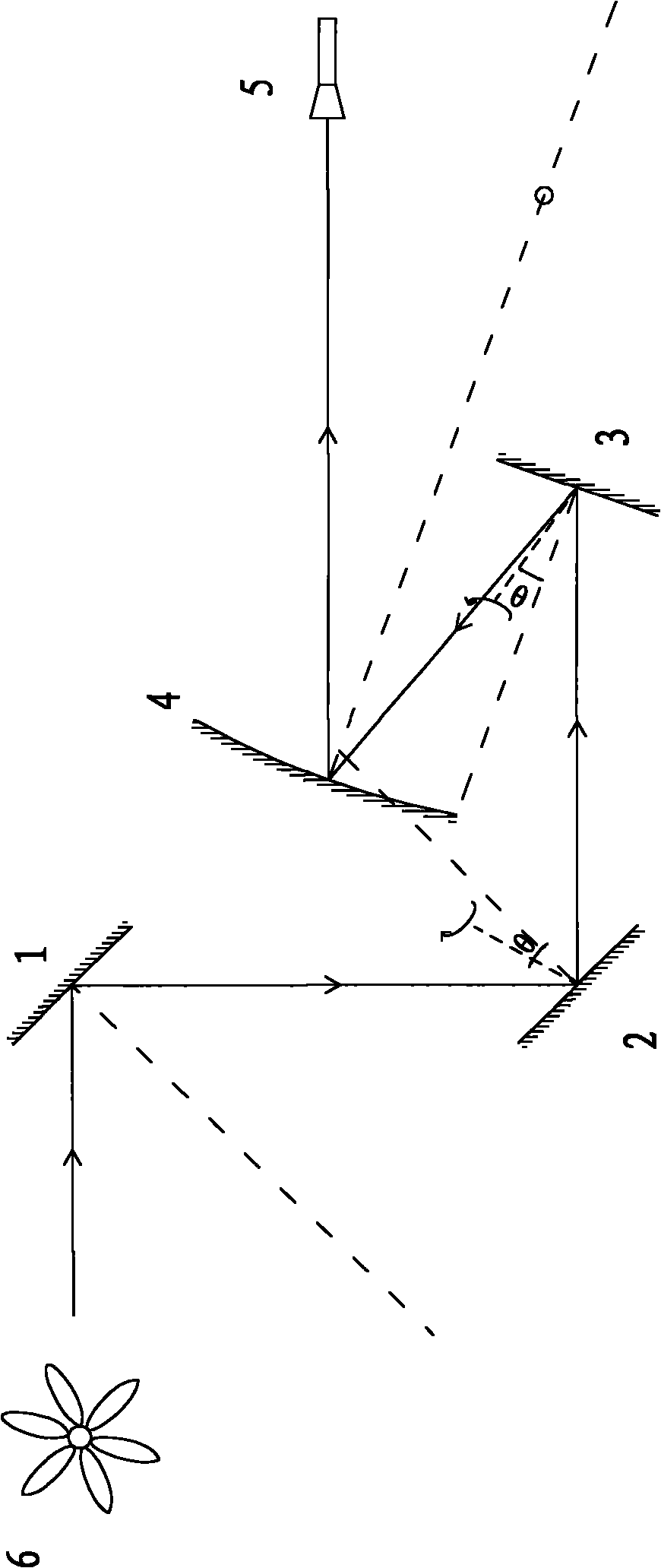
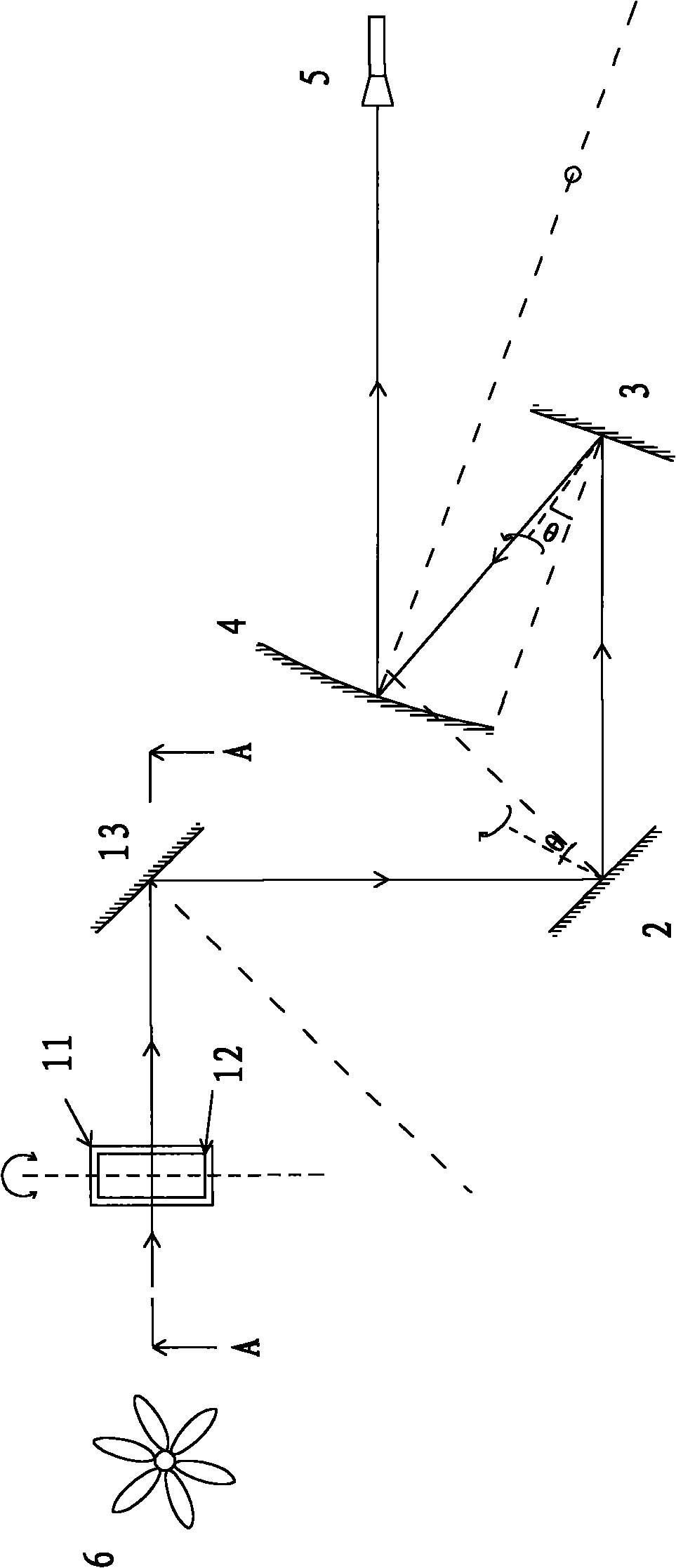
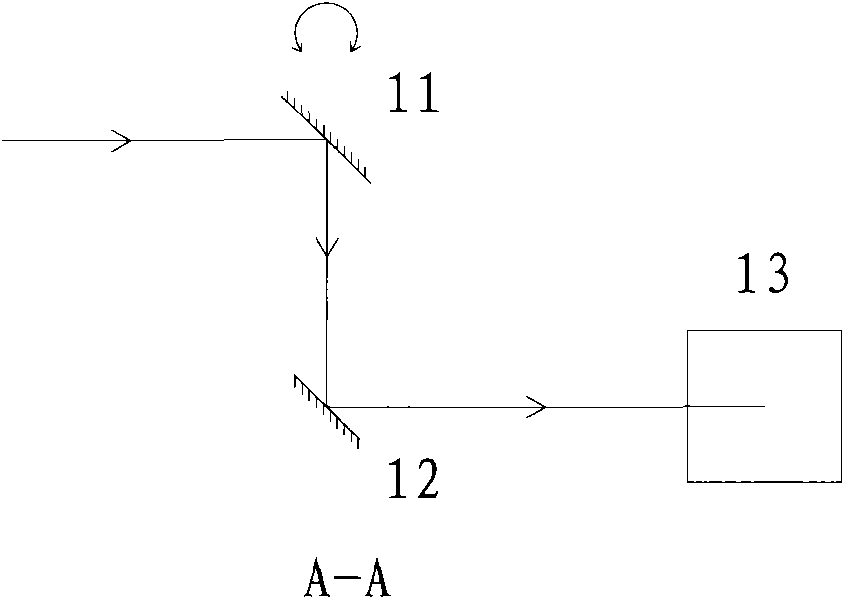
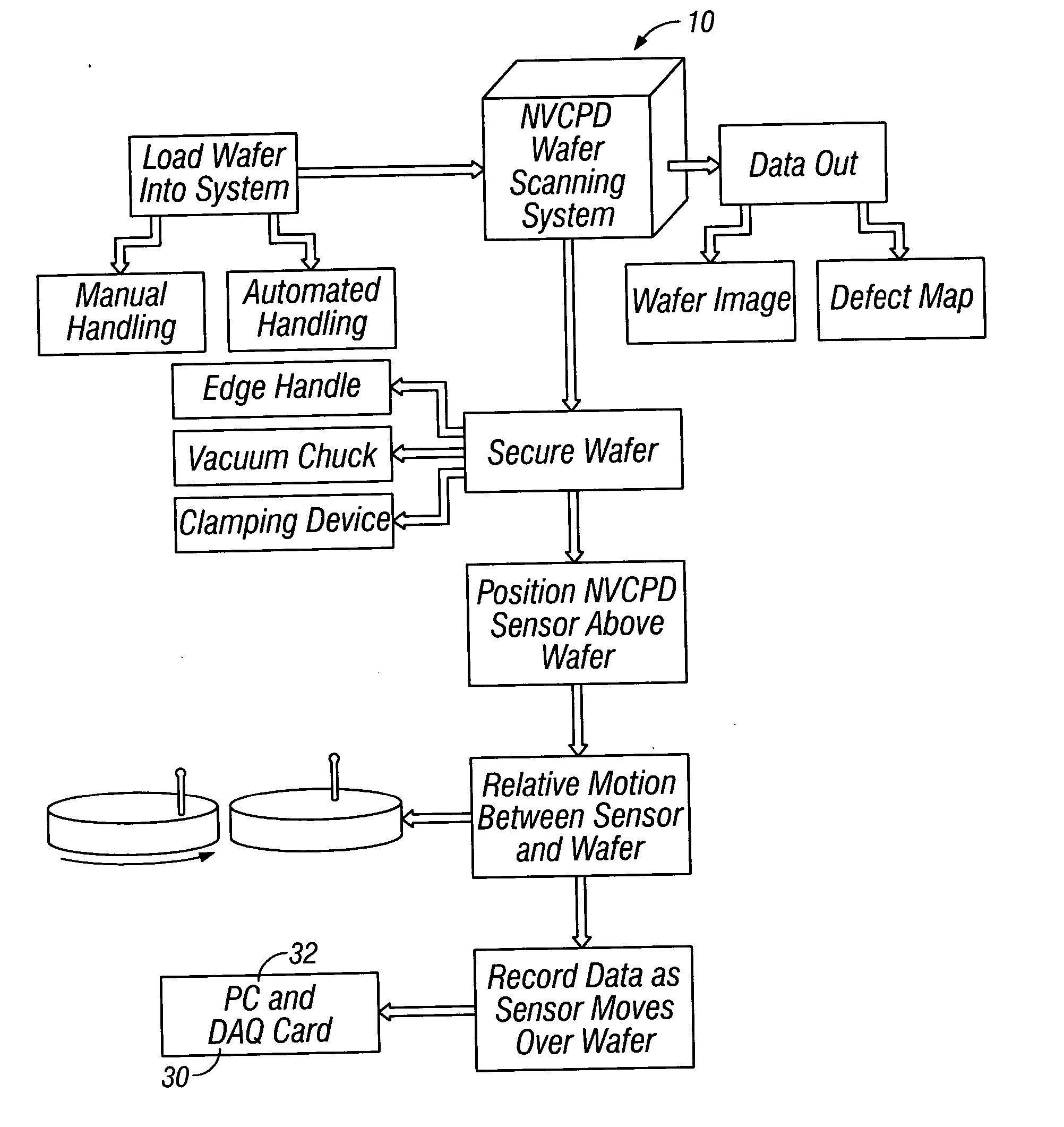
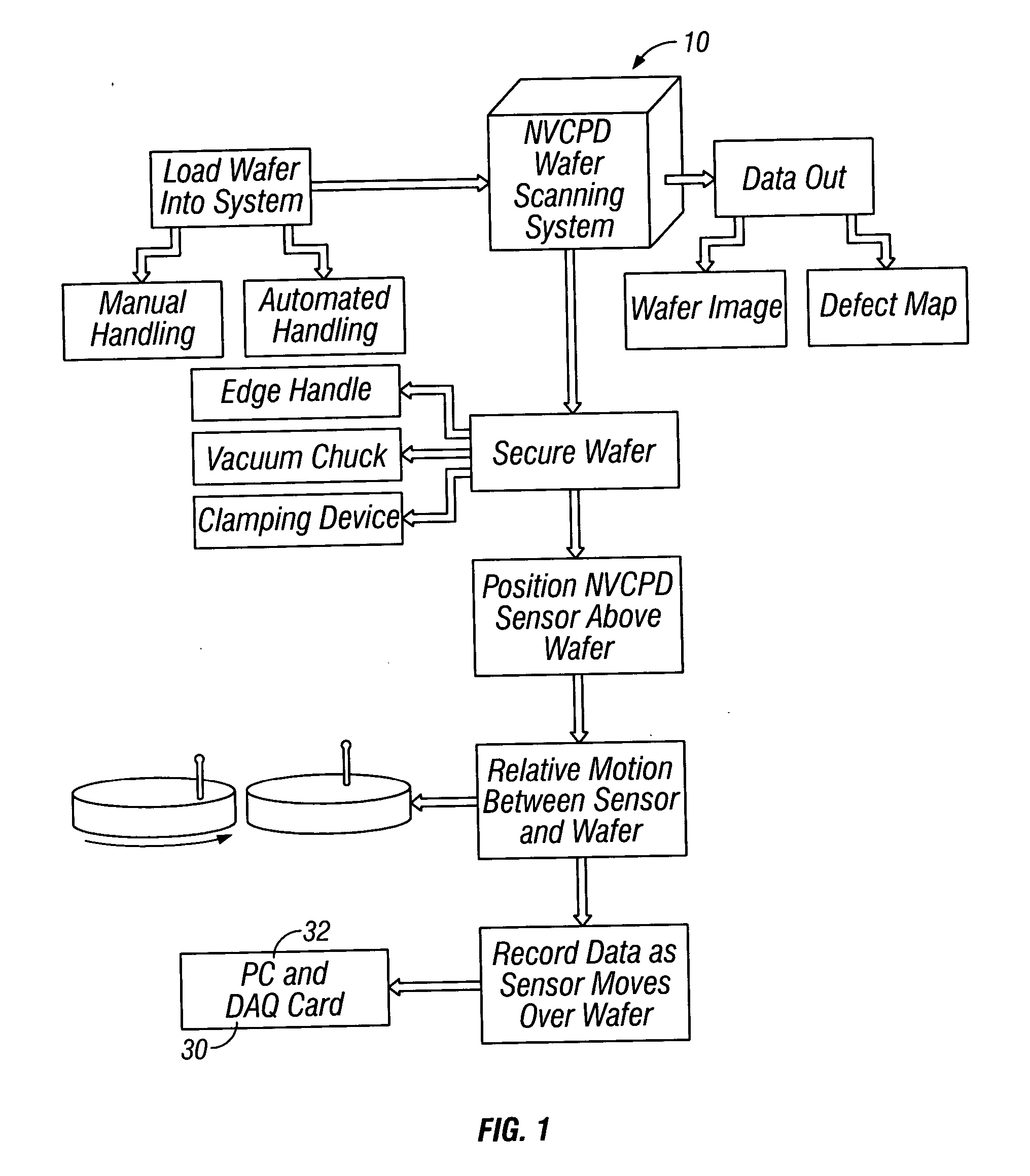
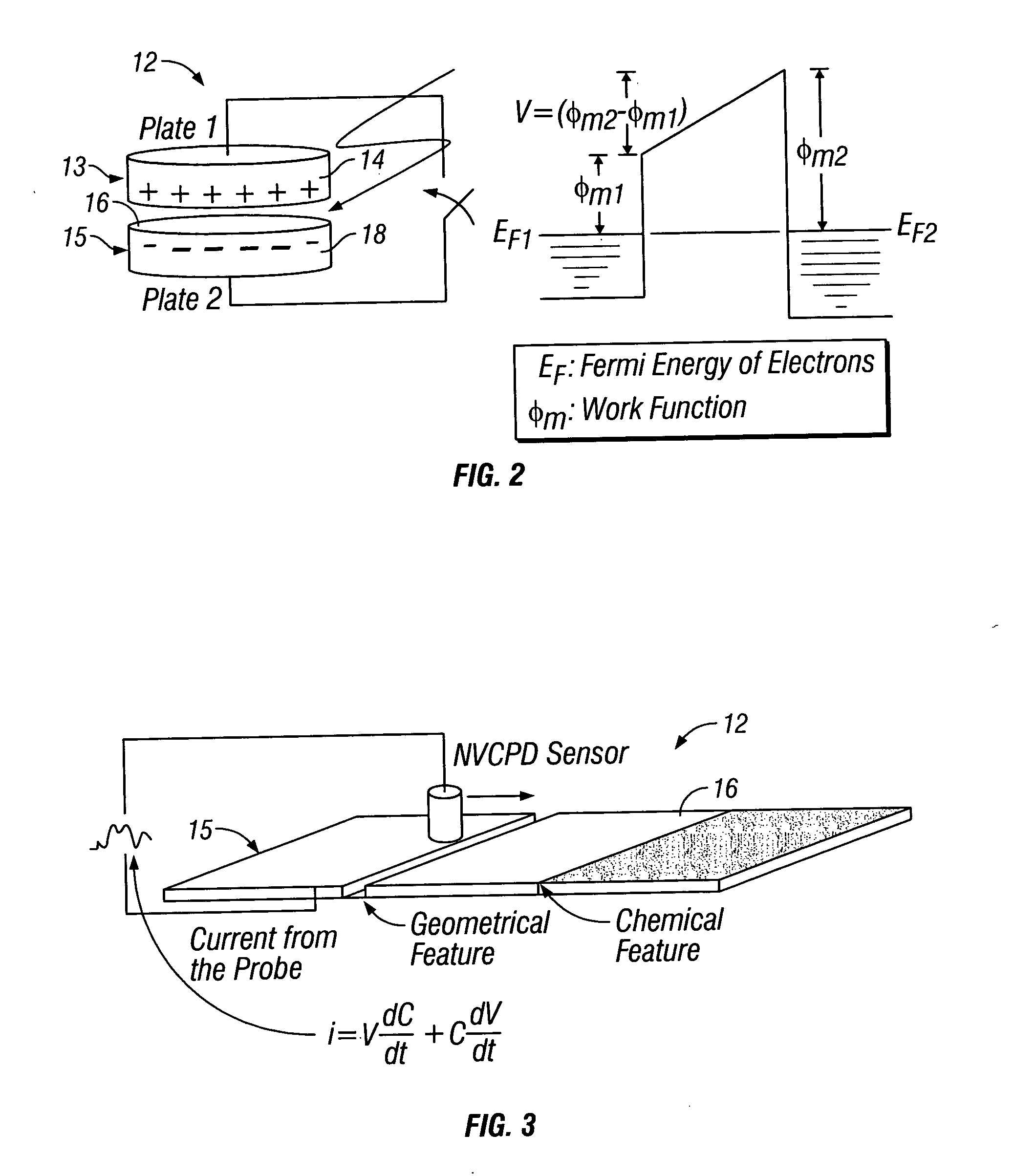
Inspection system and apparatus
InactiveUS20050162178A1Minimize complexitySimple signal processingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRapid imagingPotential difference
A method and system for identifying a defect or contamination on a surface of a sample. The system operates by detecting changes in work function across a surface via both vCPD and nvCPD. It utilizes a non-vibrating contact potential difference (nvCPD) sensor for imaging work function variations over an entire sample. The data is differential in that it represents changes in the work function (or geometry or surface voltage) across the surface of a sample. A vCPD probe is used to determine absolute CPD data for specific points on the surface of the sample. The combination of vibrating and non-vibrating CPD measurement modes allows the rapid imaging of whole-sample uniformity, and the ability to detect the absolute work function at one or more points.
Owner:QCEPT INVESTMENTS LLC
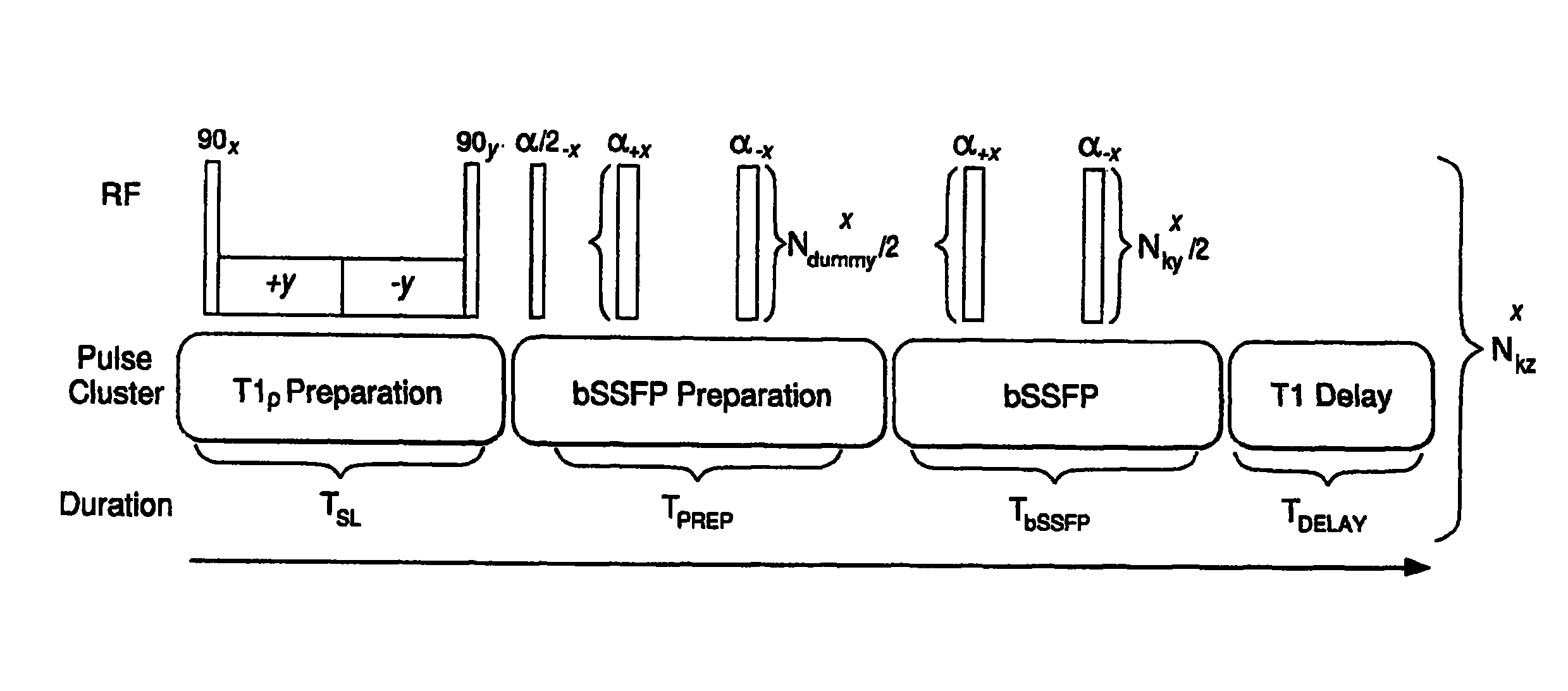
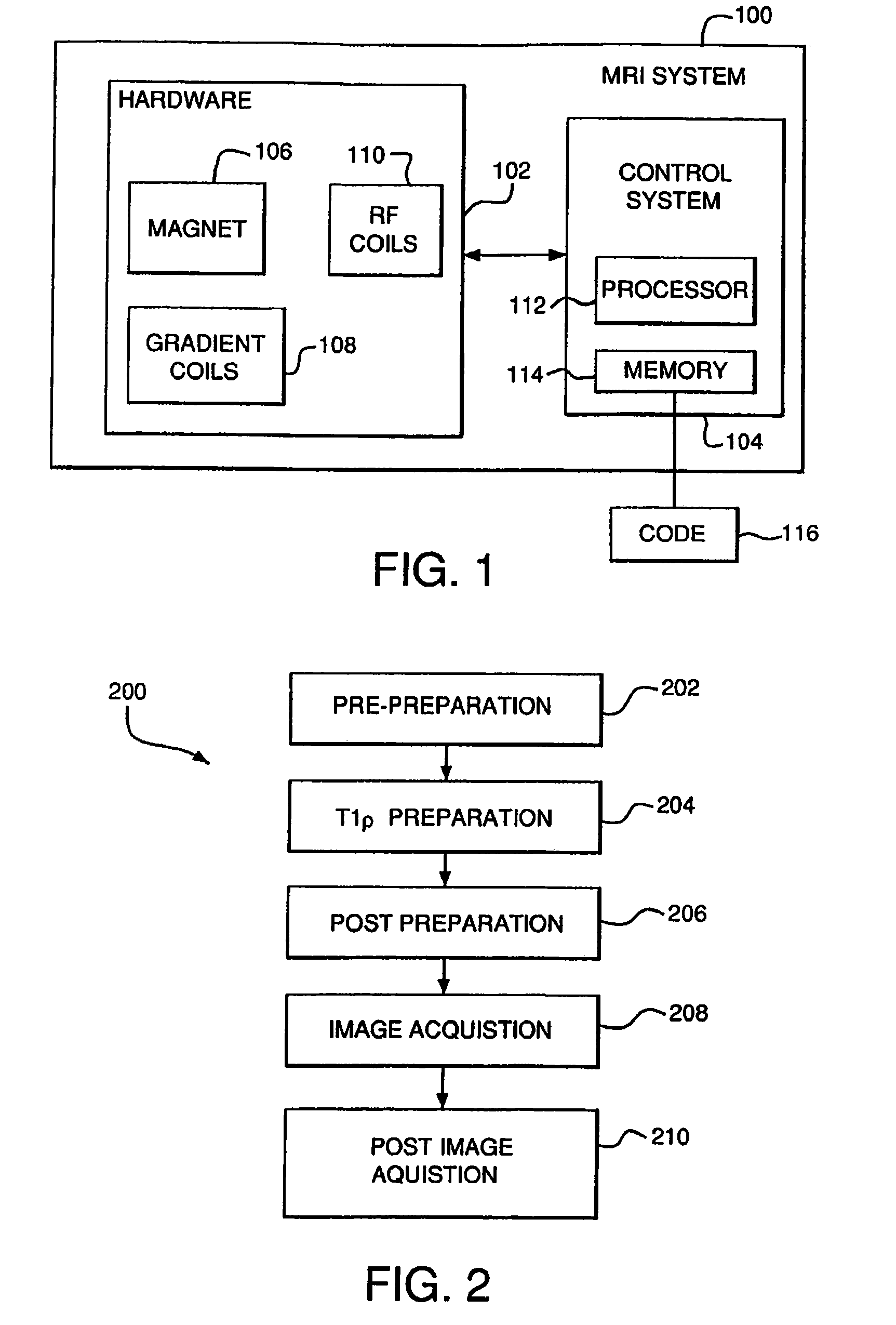
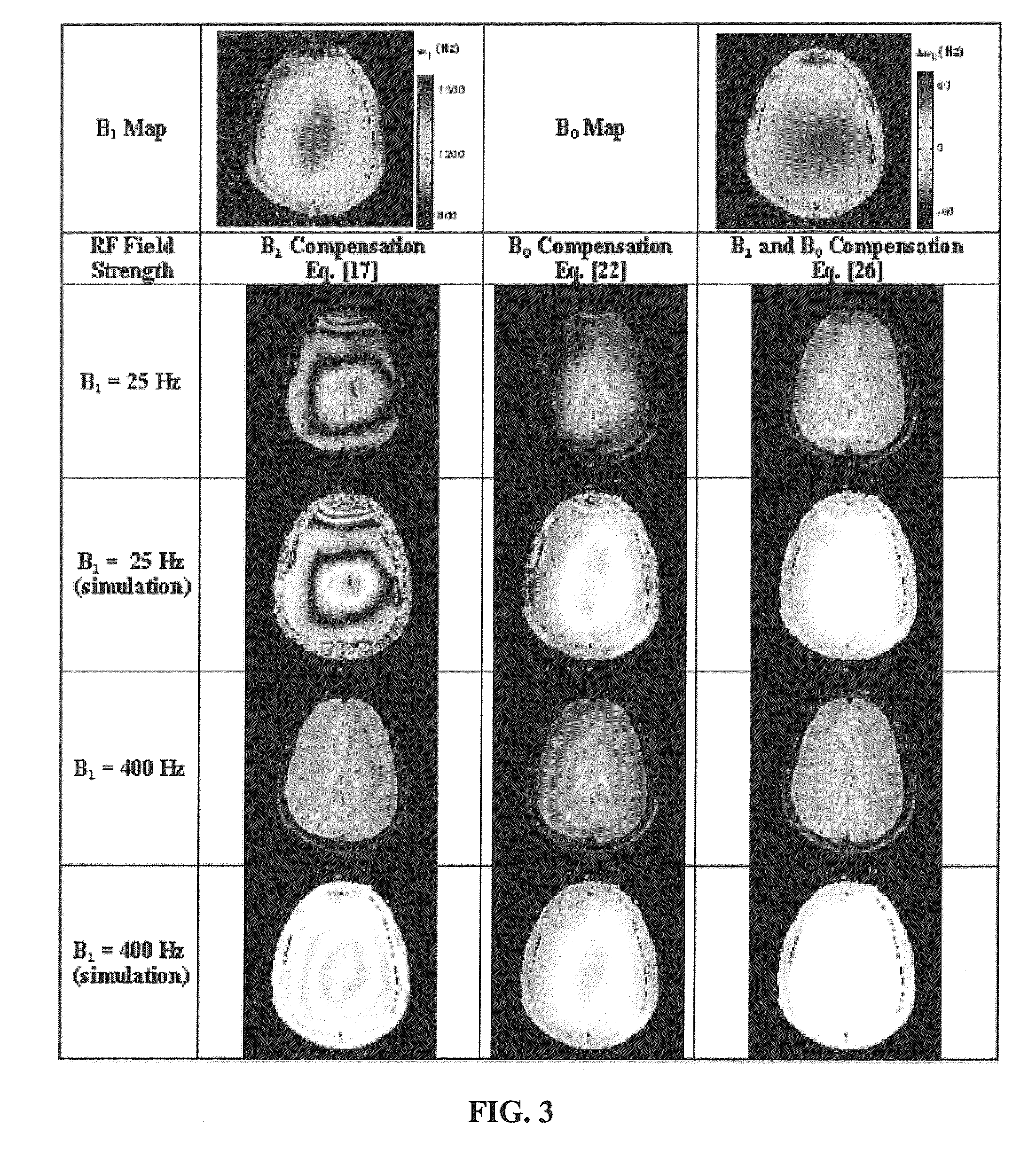
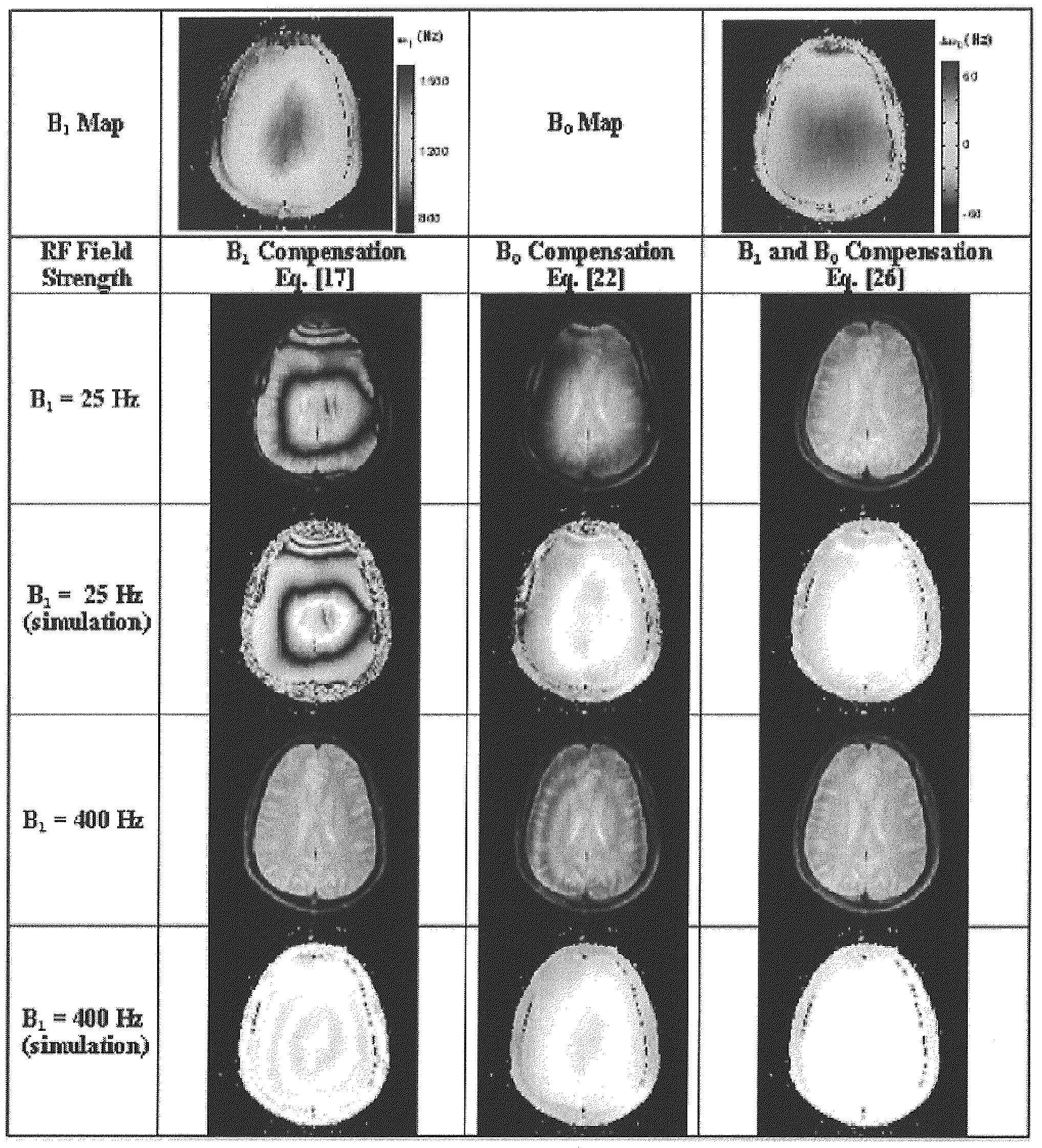
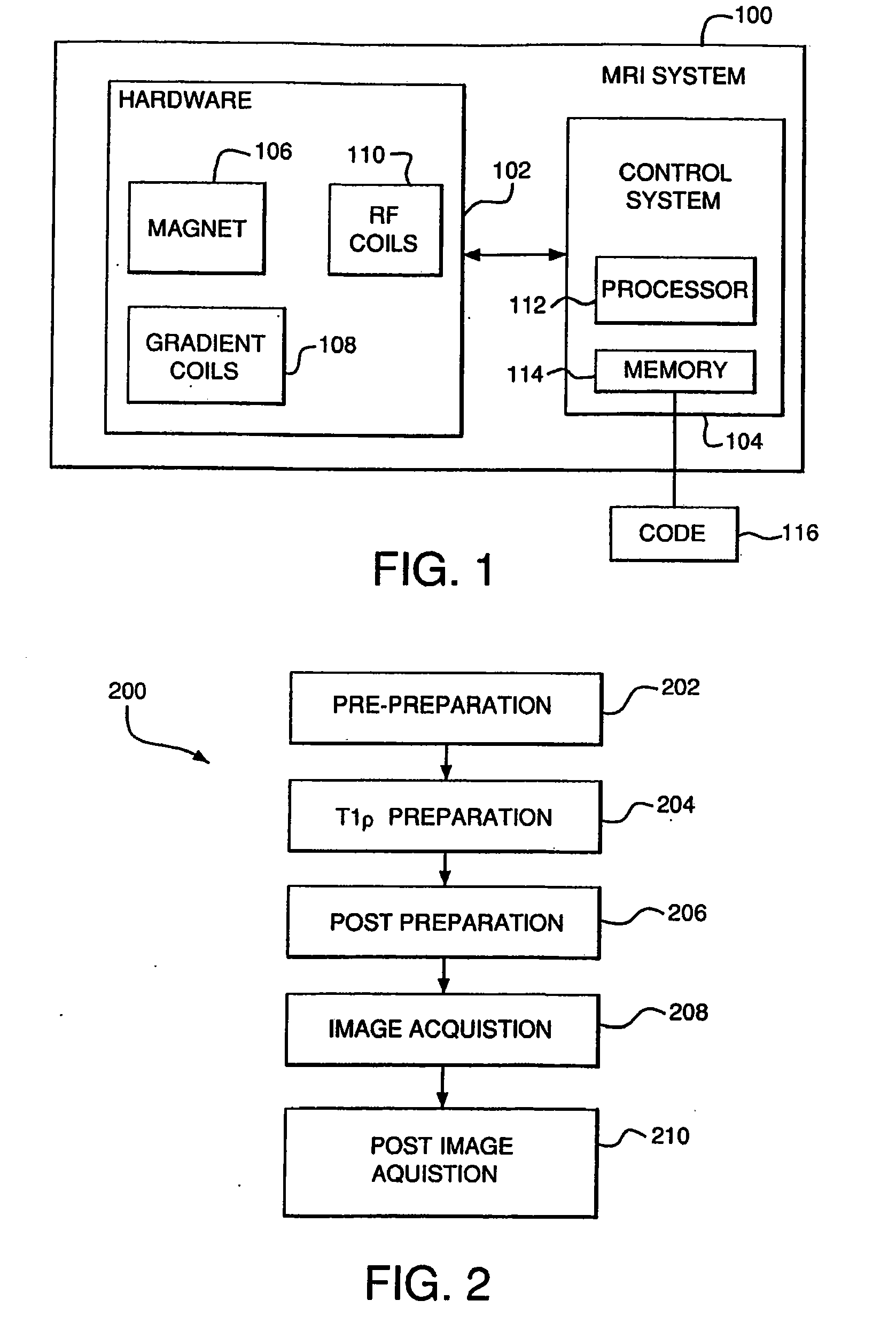
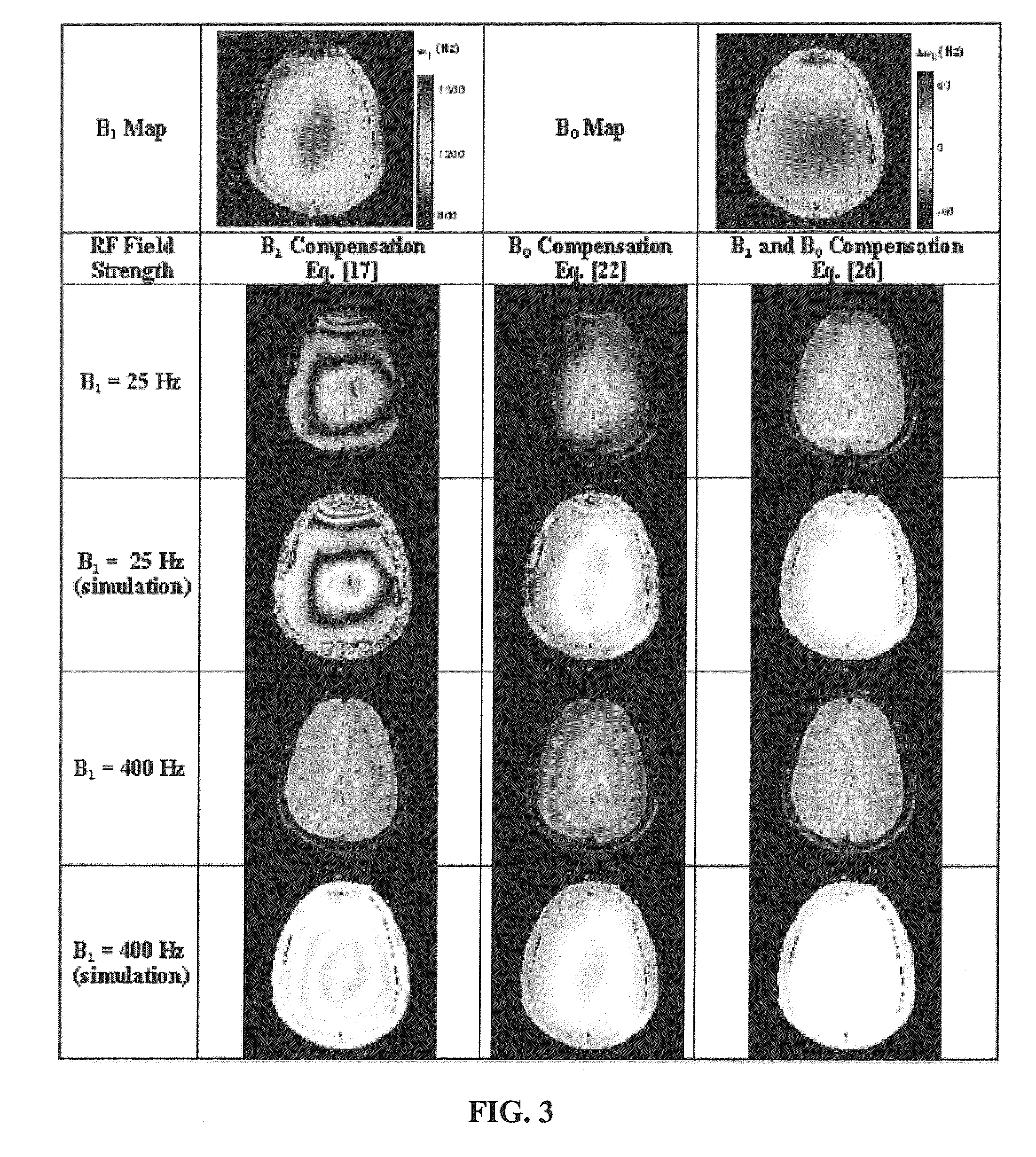
Reducing imaging-scan times for MRI systems
ActiveUS8076936B2Exceeding SAR limitImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringRapid imagingPulse sequence
Provided are methods and systems for rapid MRI imaging-scanning that provides 2D or 3D coverage, high precision, and high-temporal efficiency, without exceeding SAR limits. In one embodiment, a pulse sequence process is performed that includes a T1ρ preparation period, followed by a very rapid image acquisition process, which acquires multiple lines of k-space data. The combination of T1ρ preparation and acquisition of multiple lines of k-space, allows scan times to be shortened by as much as 3- or 4-fold or more, over conventional MRI scanning methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Reducing imaging-scan times for MRI systems
ActiveUS20090273343A1Improve accuracyExceeding SAR limitCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringPulse sequenceFast mri
Provided are methods and systems for rapid MRI imaging-scanning that provides 2D or 3D coverage, high precision, and high-temporal efficiency, without exceeding SAR limits. In one embodiment, a pulse sequence process is performed that includes a T1ρ preparation period, followed by a very rapid image acquisition process, which acquires multiple lines of k-space data. The combination of T1ρ preparation and acquisition of multiple lines of k-space, allows scan times to be shortened by as much as 3- or 4-fold or more, over conventional MRI scanning methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Tera-hertz two-dimensional area array scanning imaging method and imaging system for implementing same
The invention discloses a tera-hertz two-dimensional area array scanning imaging method and an imaging system for implementing the same, which relate to a tera-hertz scanning imaging method and an imaging system. The method and the system solve the problem of overlong imaging time caused by the point-by-point scanning imaging which can only process single data points in the prior art and the problem that the area array canning imaging can only image small objects in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: scanning and imaging a two-dimensional area array by using a tera-hertz laser, an optical system, an area array detector, a two-dimensional translation stage, a stepper motor controller, a data acquisition card and a computer; under the condition that an imaging light source is fixed, moving the a two-dimension translation stage to a proper initial position and completely scanning a target in an imaging process, wherein a certain area of the imaging object is imaged at each time, and all sub-graphs are stitched together finally. An image of the imaging target is obtained by controlling the two-dimensional translation stage and the data acquisition card and processing and storing data. The method and the system are suitable for large-size and high-speed target imaging.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
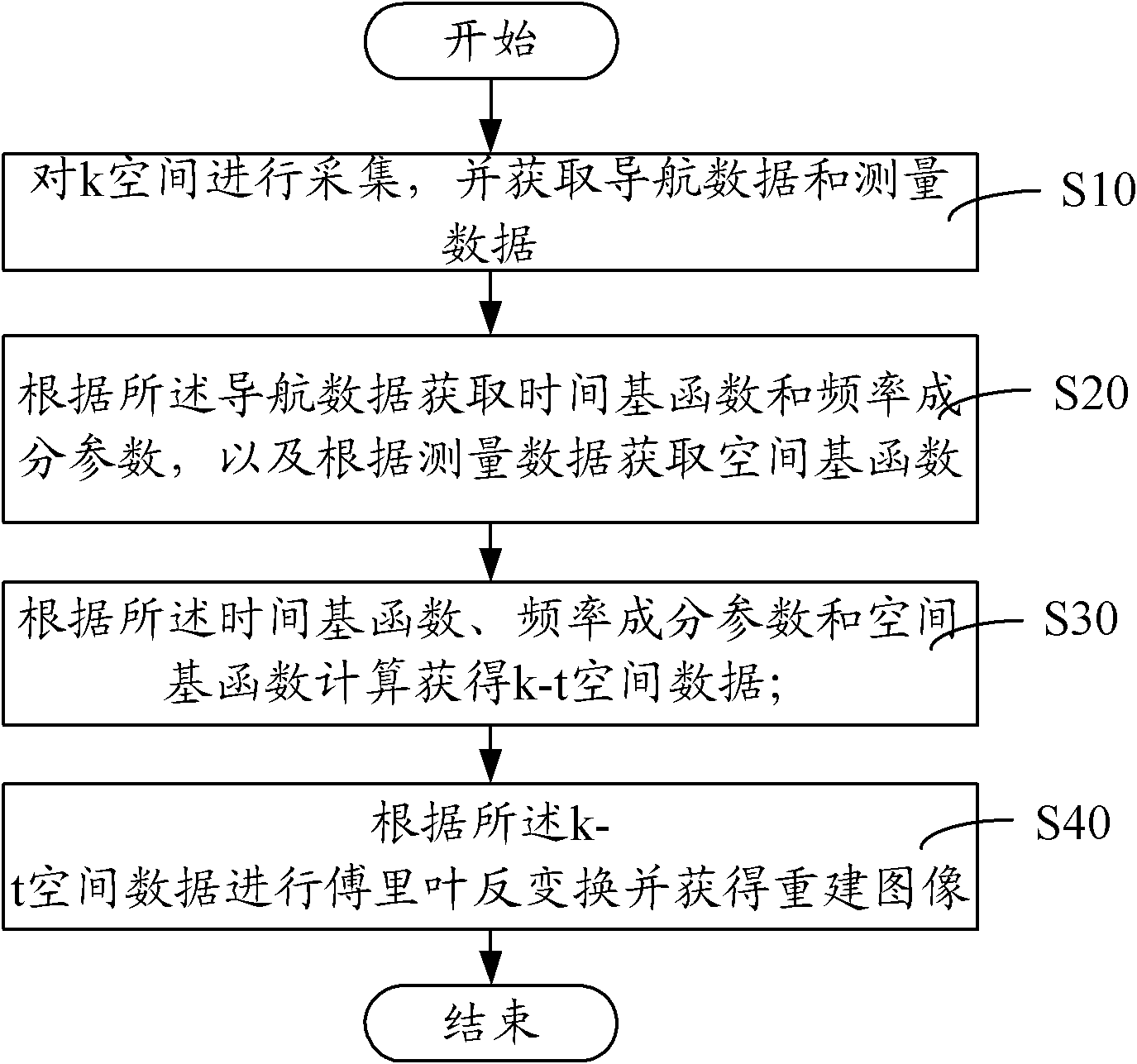
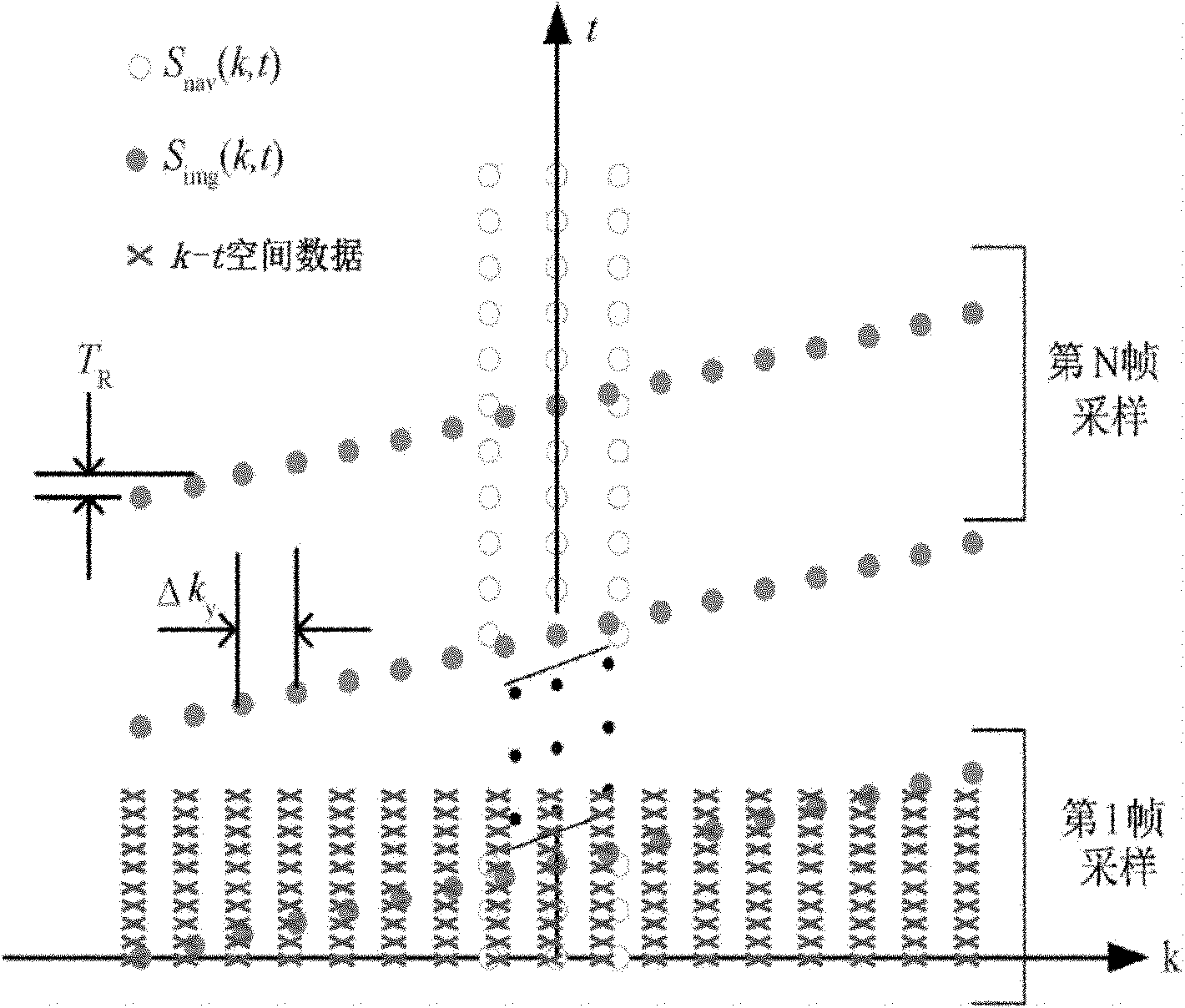
Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method and system
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging method, comprising the following steps: acquisition is carried out on k space, and navigation data and measured data are acquired; a time base function and a frequency component parameter are acquired according to the navigation data, and a space base function is acquired according to the measured data; k-t spatial data is obtained by computation according to the time base function, the frequency component parameter and the space base function; and Fourier inversion is carried out according to the k-t spatial data, and a reconstructed image is obtained. Based on the partial separable function technology, the scanning data acquisition speed is quickened, and imaging information of moving object is rapidly acquired, thus achieving rapid imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
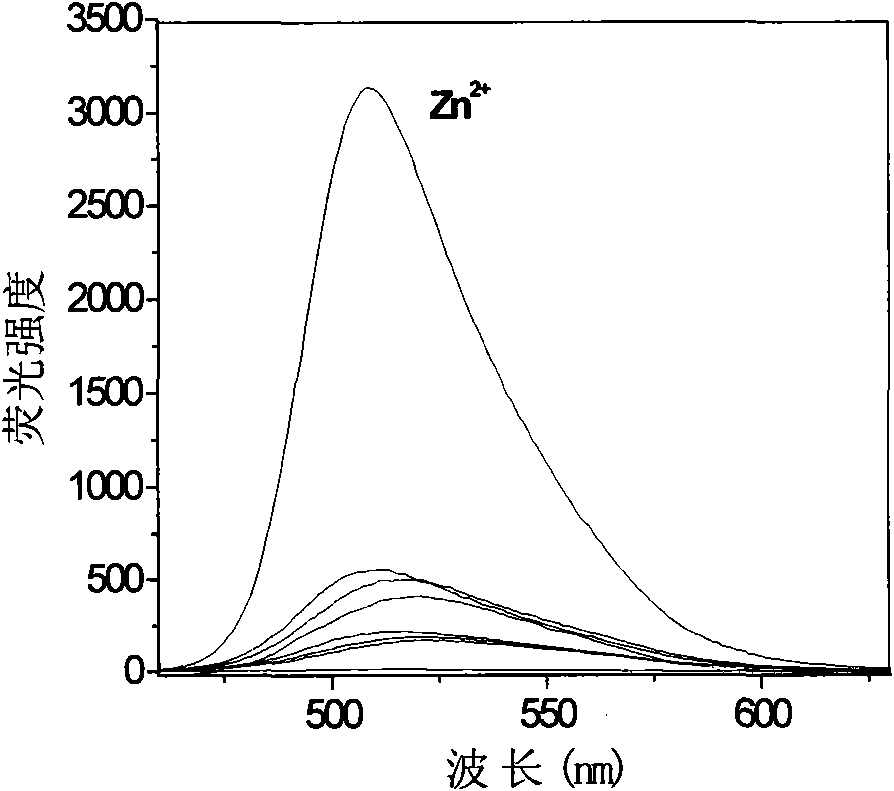
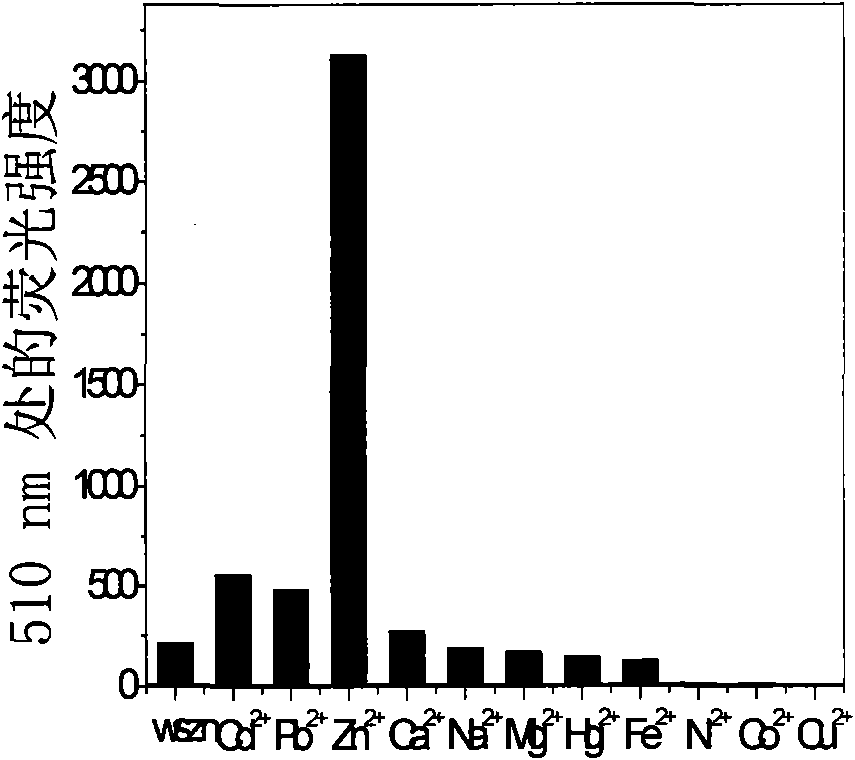
Fluorescent probe for selectively detecting zinc ions in cells, synthesizing method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN101613344AGood choiceSimple structureOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by optical meansRapid imagingOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe for selectively detecting zinc ions in cells, a synthesizing method thereof and application thereof. The fluorescent probe has good selectivity for the zinc ions in vitro, and can be used for quick imaging of the zinc ions in the cells. The synthesizing method comprises the following steps: dissolving a coumarin-3-carbonyl compound with R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 substituted groups into a drying organic solvent, slowing dropping 2-hydrazopyridine with R6 substituted group into the solution under refluxing and stirring, filtering the mixture after refluxing and stirring reaction, and removing the organic solvent to obtain the fluorescent probe (1) for selectively detecting the zinc ions in the cells. The fluorescent probe can be used for analysis detection and fluorescent imaging detection for the zinc ions in biological living cells and living tissues and detection for the zinc ions in pathological tissues in clinical medicine.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
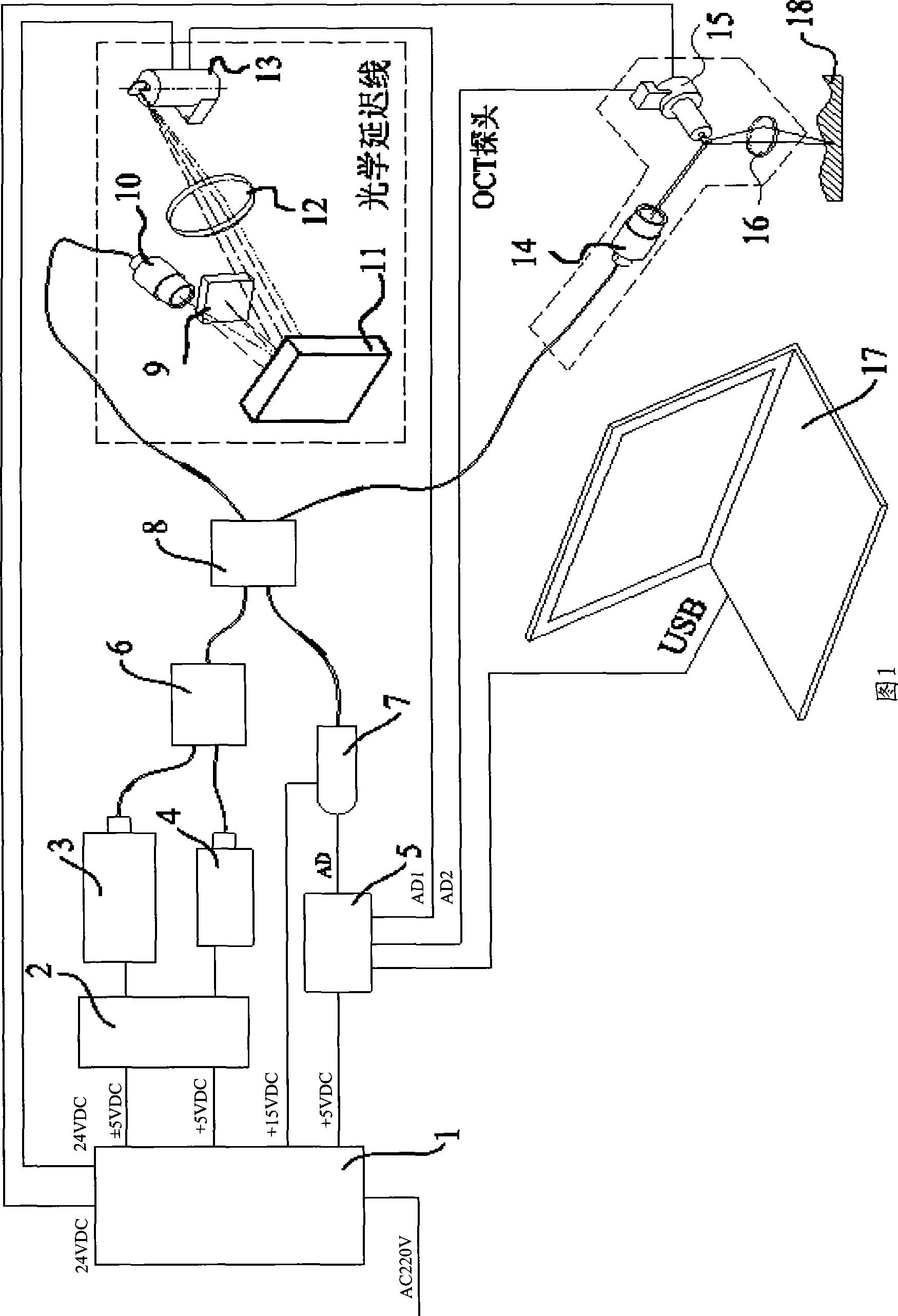
Real-time imaging optical coherent chromatography skin diagnostic device
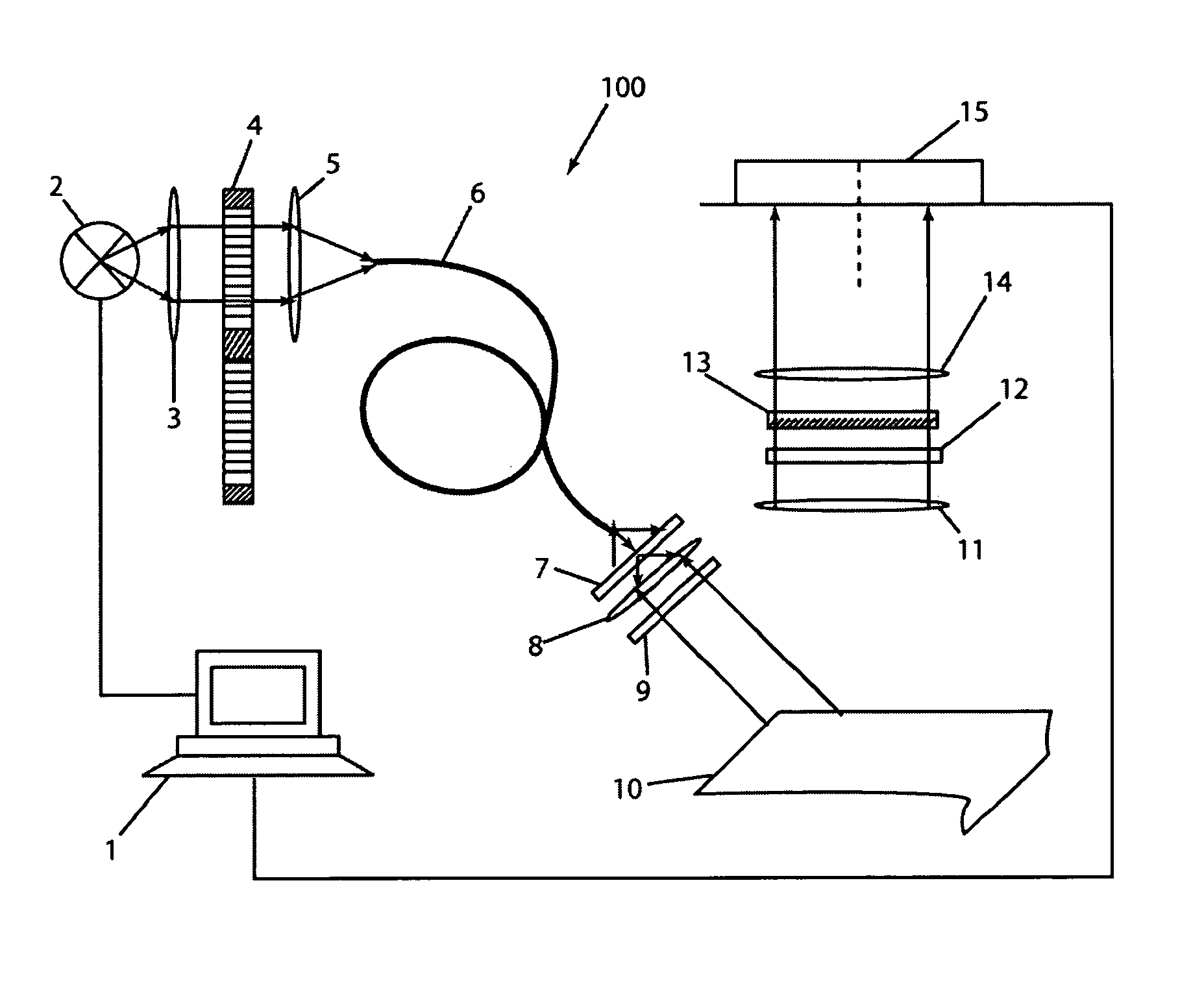
InactiveCN101458212AQuick scanHigh-resolutionPhase-affecting property measurementsRapid imagingDisplay device
The invention discloses real-time imaging skin diagnosis equipment by optical coherence tomography, and belongs to the field of optical imaging equipment. The equipment comprises a power supply, a light source control circuit, a light source, an indicating light source, a first optical fiber coupler, a second optical fiber coupler, an OCT probe, an optical delay line, a photo detector, a signal processing and control circuit, and a computation processing and display device. The imaging equipment takes the optical coherence tomography (OCT probe) as a core, processes signals rapidly by the signal processing and control circuit, and improves the imaging speed and image resolution by cooperating with the computation processing and display device; designs of a wideband light source and a duckbill-shaped probe applicable to skin scanning cause the equipment to be applicable to scanning human skin, and real-time and rapid imaging can be realized by cooperation of the signal processing and control circuit with the computation processing and display device.
Owner:BEIJING NEWRAYSING LASER TECH
Head PET device for rapid imaging and imaging method
InactiveCN107595316AHigh sensitivityEliminate claustrophobiaComputerised tomographsTomographyRapid imagingDetector array
The invention discloses a head PET device for rapid imaging and an imaging method. A detector of the PET device comprises multiple detector modules, and the detector modules are aligned on a quasi-capsule curve face of an opening; removable eye detectors are arranged on the detector array so as to facilitate the visual study and elimination of claustrophobia of a scanned object; the detector arrayis a separable structure; before the head imaging, the detector is separated; after the head part of the scanned object enters the detector, the detector is closed and scanning is completed.
Owner:SHANDONG MADIC TECH CO LTD
Method for measuring object surface topography
InactiveCN102967274AHigh imaging sensitivityImprove resolution accuracyUsing optical meansRapid imagingFrequency spectrum
Owner:广东华快光子科技有限公司
Magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7230424B1Improve magnetic efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionRapid imagingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Through advancing the phase of radio frequency (RF) excitation with each phase-encoding level, a method and apparatus increases the effectiveness of a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) device by correcting for main magnetic field inhomogeneities without noticeably decreasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The present invention also increases the effectiveness of fast imaging with steady precession (FISP) scans and allows FISP scans to image multiple slices. In an MRI device, a patient is subjected to a constant magnetic field, and RF pulses are used to excite the nuclei in the patient's body. The nuclei release a corresponding RF signal as the nuclei relax, which can be measured and mapped into a visual display. The RF pulses used to excite the nuclei in the body cooperate with a slice select gradient and a phase-encoding gradient. When the RF pulse is phase shifted with each phase-encoding gradient level, improved signal-to-noise ratios are observed.
Owner:FONAR
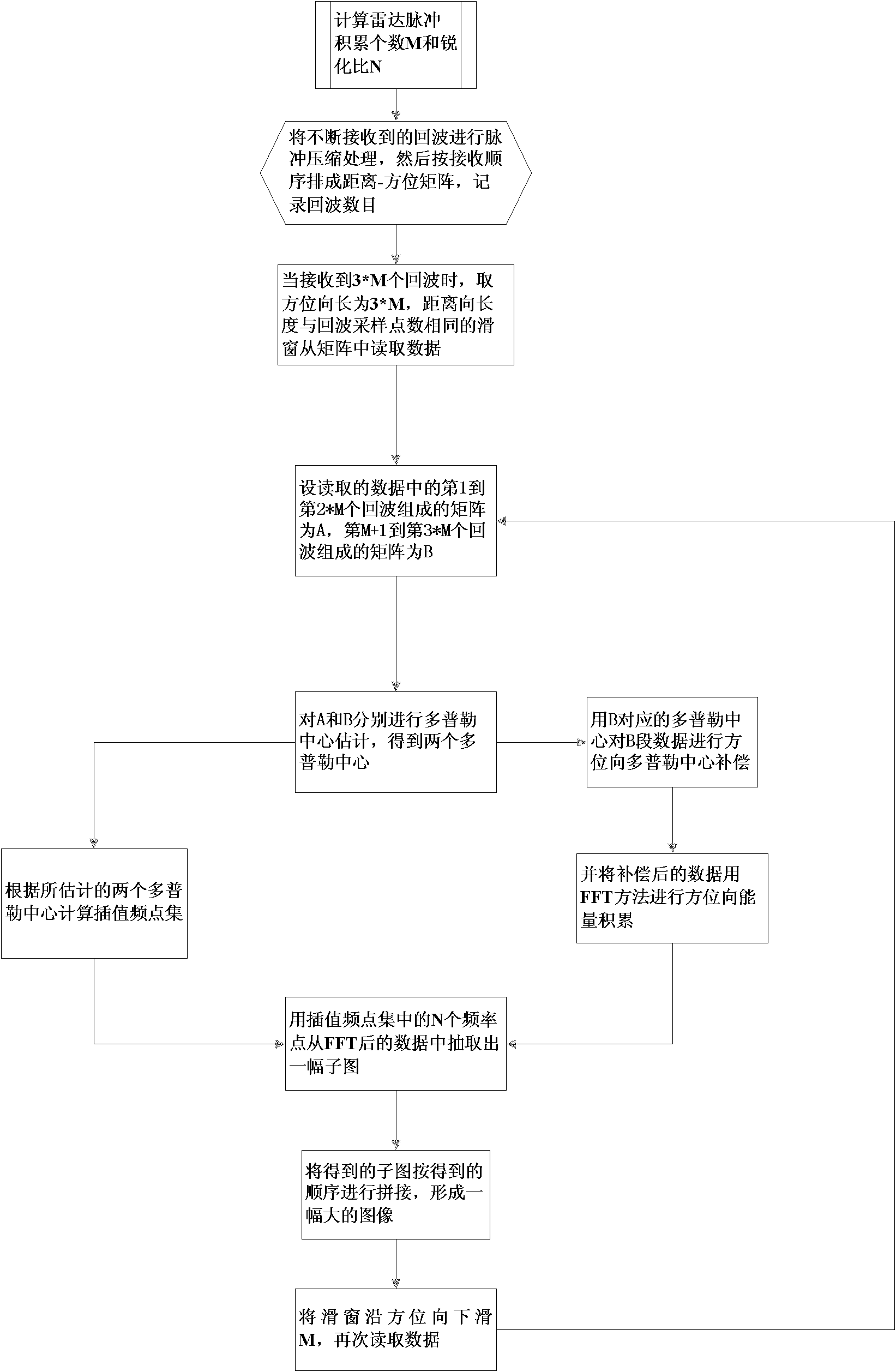
Doppler wave beam sharpening rapid imaging method of mechanical scanning radar
InactiveCN102176018AIncrease scan rateProcessing speedRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRapid imagingFast Fourier transform
The invention discloses a Doppler wave beam sharpening rapid imaging method of a mechanical scanning radar, which mainly solves the problem that the prior art cannot be applied to a mechanical scanning radar. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly determining a pulse accumulation number M and a sharpening ratio N, arranging echoes after the pulse compression into a distance-direction matrix according to a receiving order; taking out two small matrixes which has directional length of 2*M and are mutually overlapped M from the matrix according to the receiving order; respectively performing the Doppler central estimation on the two small matrixes; using two Doppler centers to compute an interpolation frequency point; meanwhile, using the latter Doppler centre to perform the directional Doppler central compensation on the latter small matrix; then performing the directional FFT (Fast Fourier Transform), using the interpolation frequency point to extract a sub-image from thedata behind the FFT, splicing the sub-image according to the receiving order to obtain a large image. Compared with the traditional DBS (direct broadcasting by satellite) imaging method, the Doppler wave beam sharpening rapid imaging method has low computation, and low requirement on the radar performance, and can be applied to the traditional mechanical scanning radar DBS imaging.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multi-target tracking method after through-wall radar imaging
InactiveCN104898115AEfficient extractionHigh Quality Imaging ResultsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRapid imagingEtching
The present invention provides a multi-target tracking method after through-wall radar imaging, the rapid imaging can be achieved in a certain error, and a high quality imaging result can be obtained. According to the target targeting algorithm based on two-dimensional low-pass filtering and image etching, measurement position information and amplitude information can be effectively extracted, and finally a nearest area data association algorithm is used to carry out target tracking. At the same time, according to an interacting multiple model tracking algorithm, the high mobility of the target is fully considered, and the target tracking accuracy is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wide light beam illumination three-dimensional gating imaging system of airborne laser radar
InactiveCN101408618AAvoid pointing errorsReduce complexityElectromagnetic wave reradiationRapid imaging3d image
The invention relates to a broad beam illumination 3D gated imaging system of an airborne laser radar and belongs to the image communication field. In the system, flight data are transmitted to a system control mechanism, the mechanism automatically generates working time-sequence data of various parts of the mechanism, and controls the working time sequence as well as hardware and software; a laser transmits a pulse laser beam according to a laser emission command sent by the system control mechanism, a target is illuminated by an homogeneous beam expander, meanwhile, a laser pulse emission time detection mechanism transmits the detected emission time data to the system control mechanism; a large-aperture telescope receives the reflected light from the target to the illumination laser, an ICCD camera performs gated imaging on a light signal received by the large-aperture telescope according to the time sequence and the gated imaging command, and transmits the data to a signal processing mechanism; and the signal processing mechanism processes the imaging information and generates 3D image information of the target. The imaging system has the advantages of rapid imaging speed, broad detection range, high reliability of measurement data and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Equipment and method for quick-speed image-forming checking mobile target
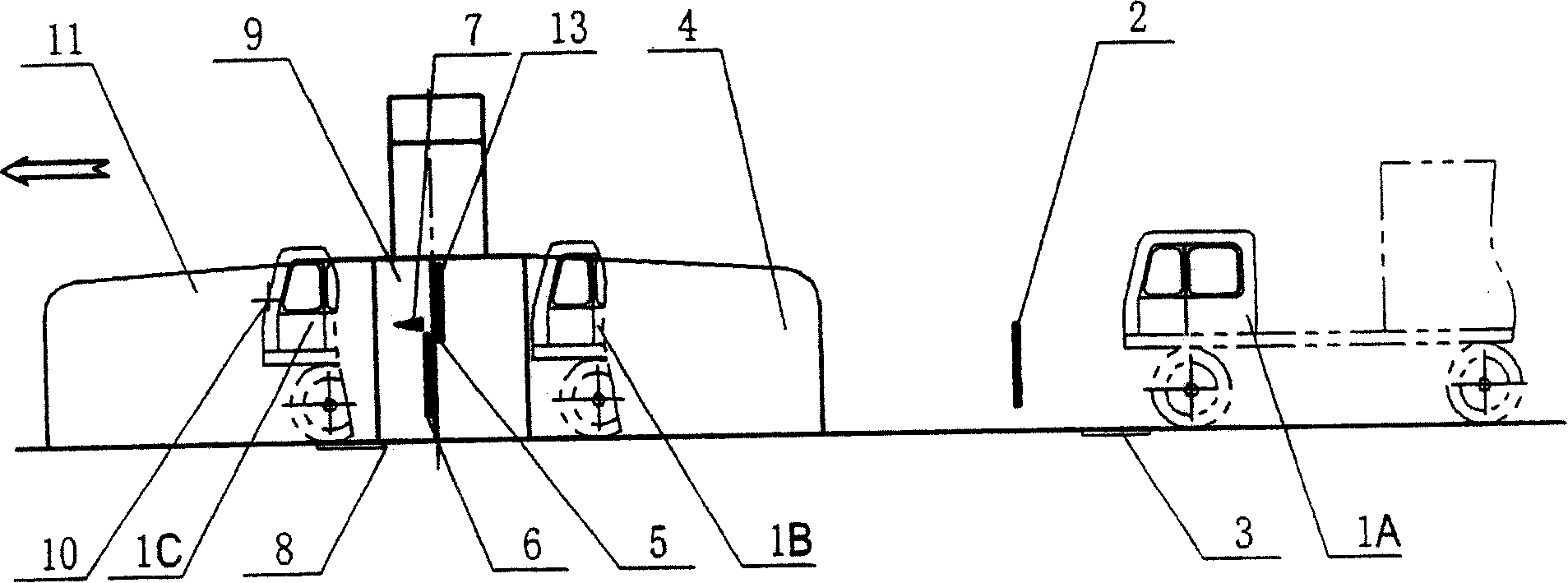
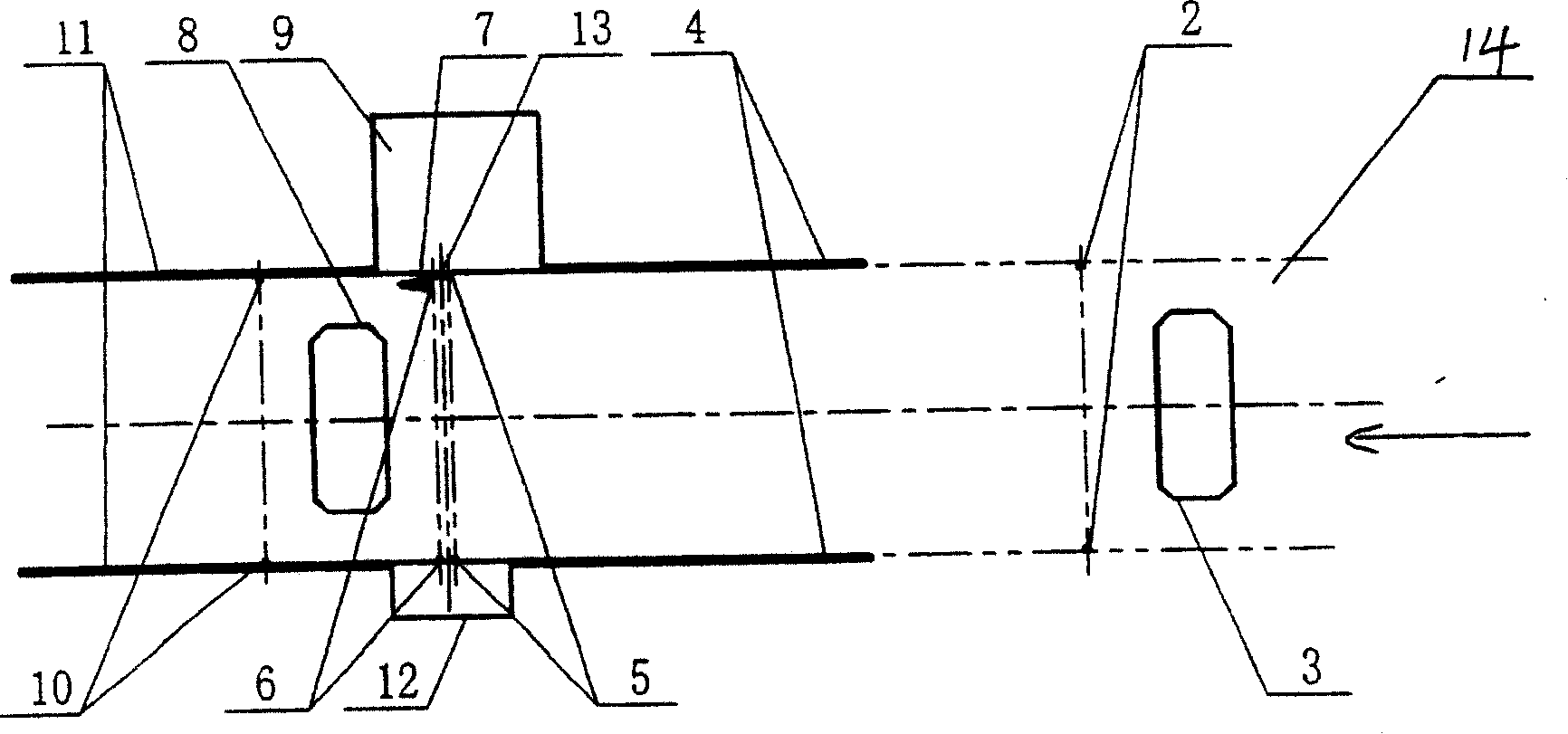
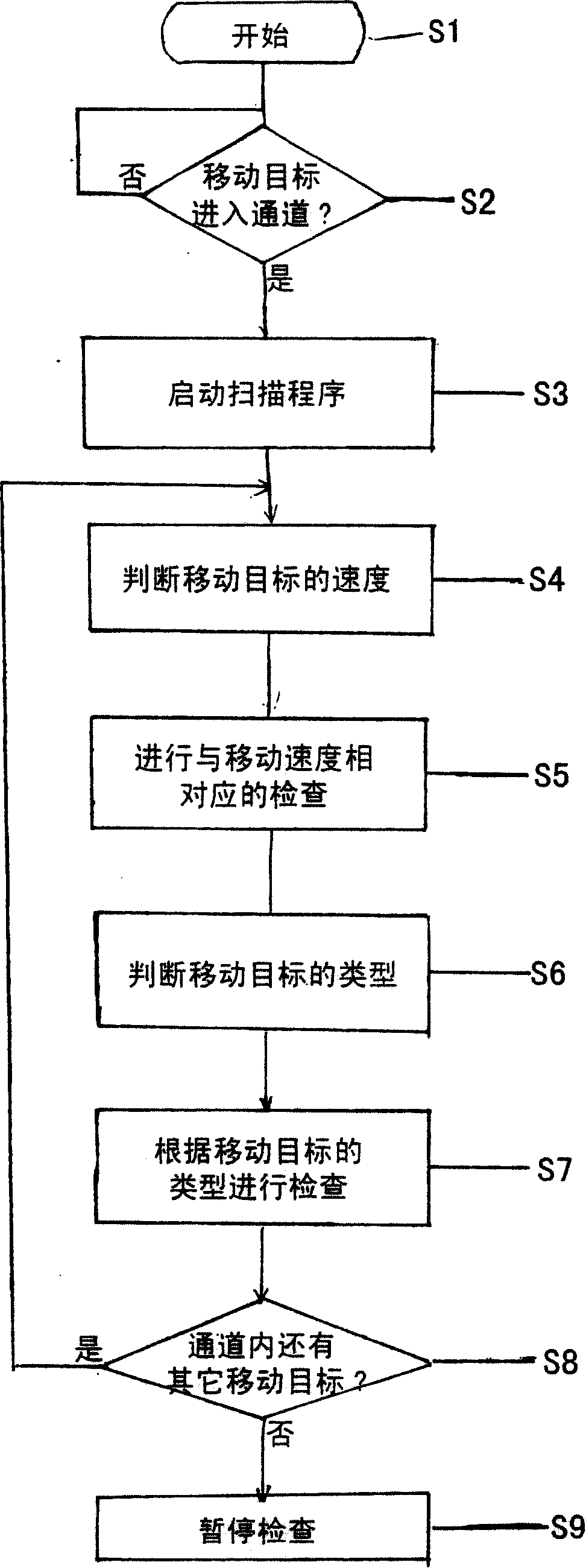
ActiveCN101162209AImprove pass rateShorten inspection timeX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRapid imagingComputer science
The invention discloses a device used for the imaging and checking to a moving target rapidly, comprising a channel for the moving target to pass through; a scan imaging device which images the moving target by emitting radiant flux to the moving target passing through the channel and then checks the moving target; a first detecting unit which is used for judging whether the moving target enters the channel and counting the number of the moving target entering the channel; a second detecting unit which is used for measuring the moving speed of the moving target in the channel; and a control unit which controls the second detecting unit to detect the moving speed of the moving target according to the detecting signals received from the first detecting unit about the moving target entering the channel, and controls the scan imaging device according to the measuring result of the second detecting unit, so that the scan imaging device emits radiant flux at a frequency corresponding to the speed of the moving target, thereby checking the moving target.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com