Patents
Literature
5820results about "Optical detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
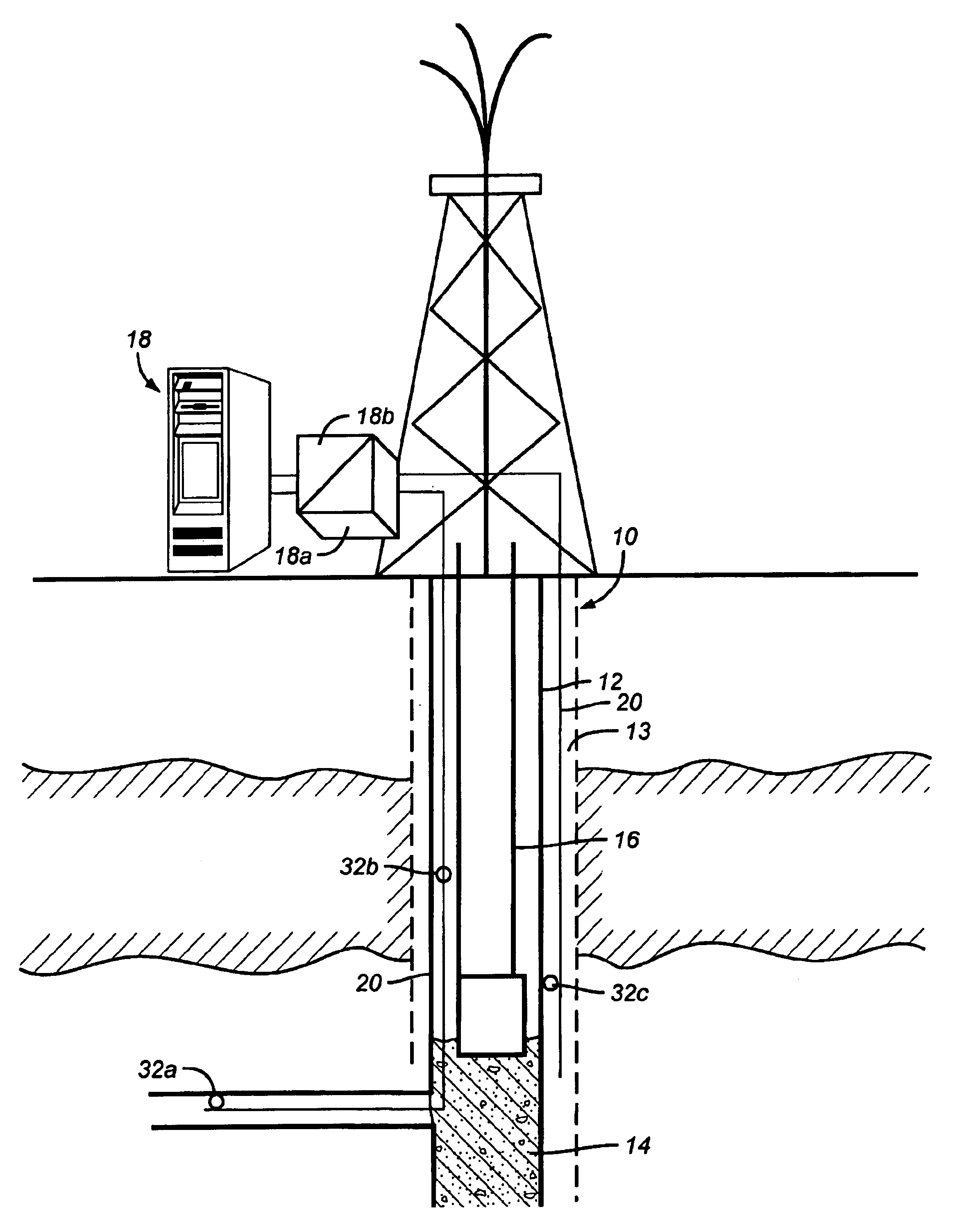
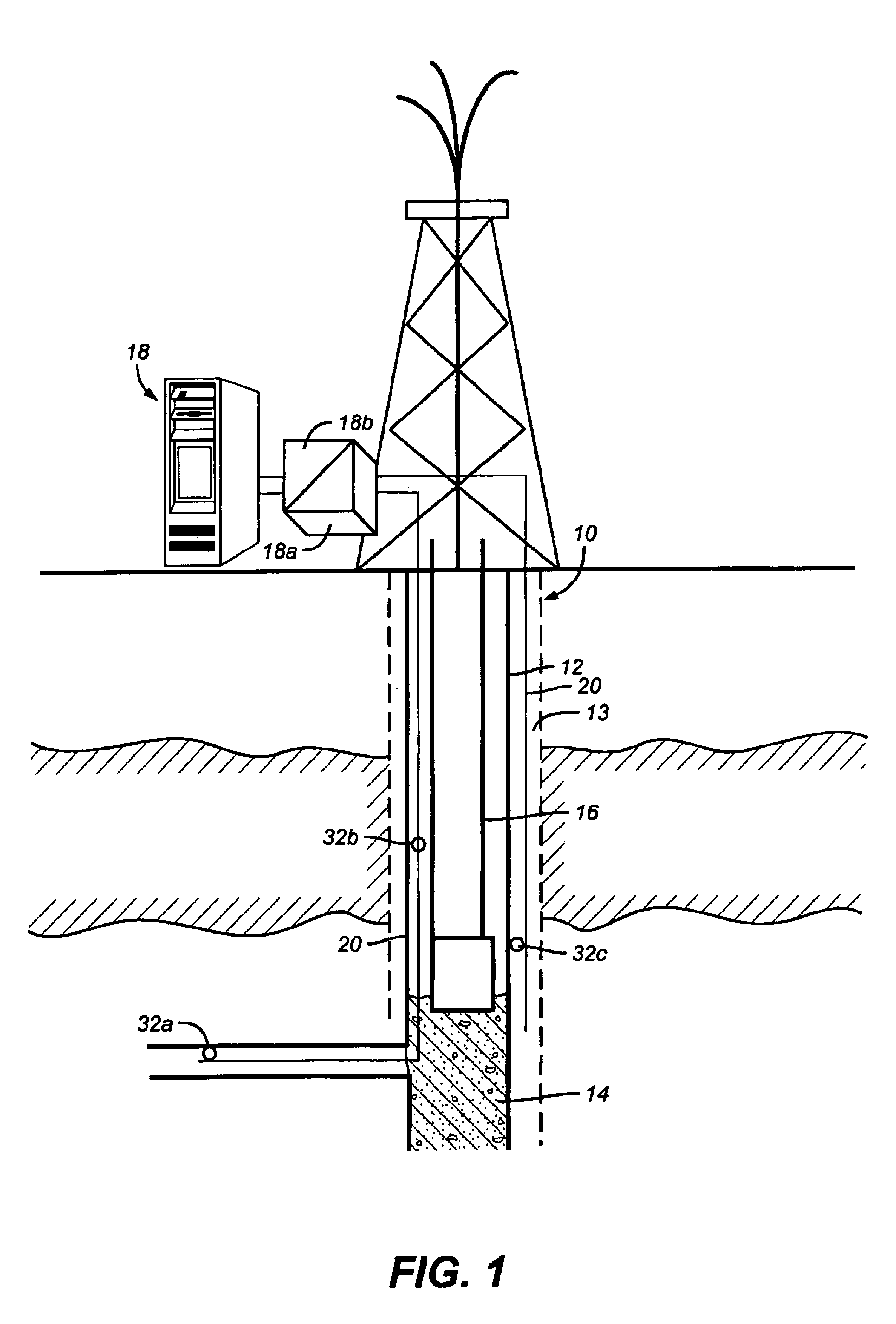
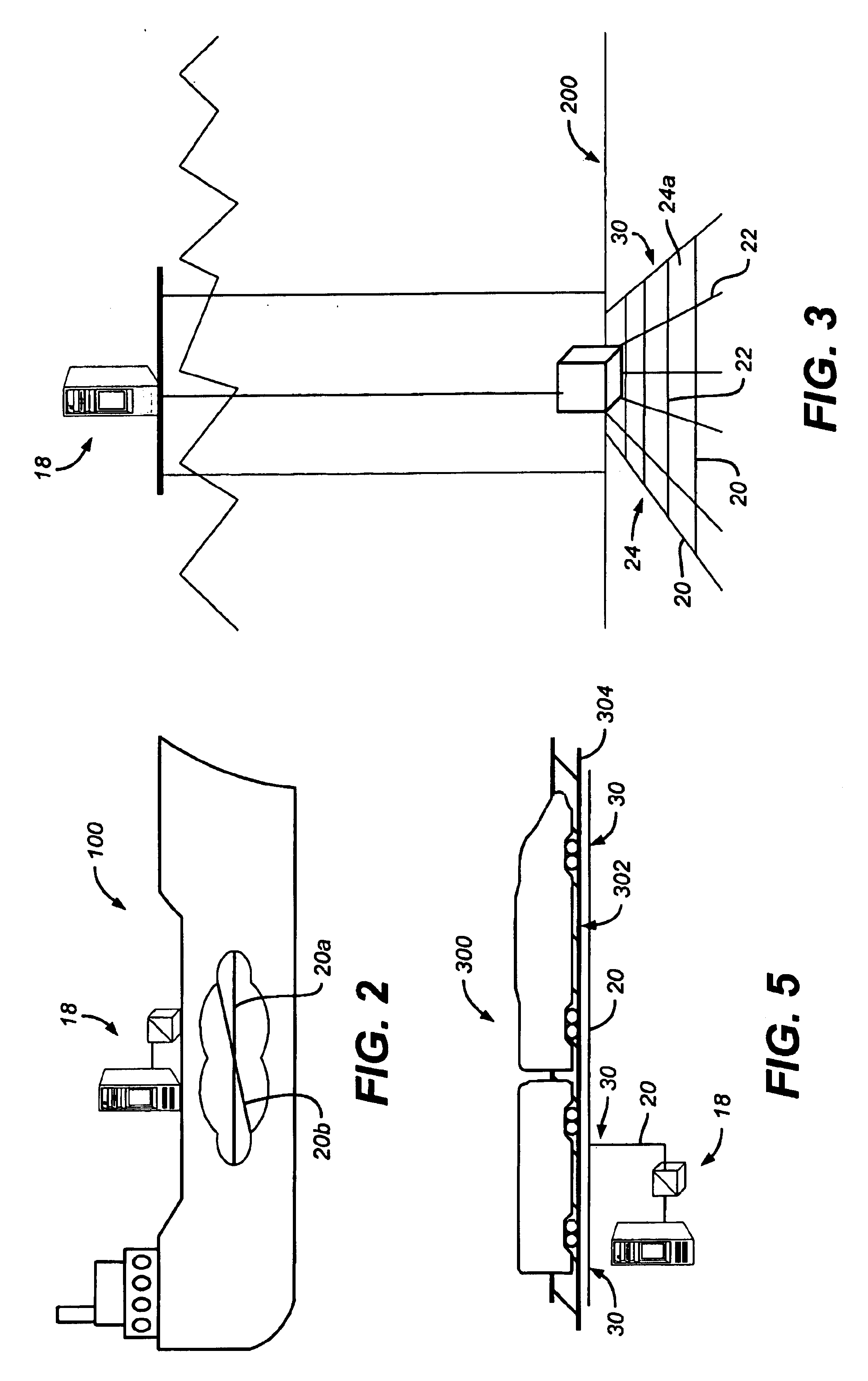
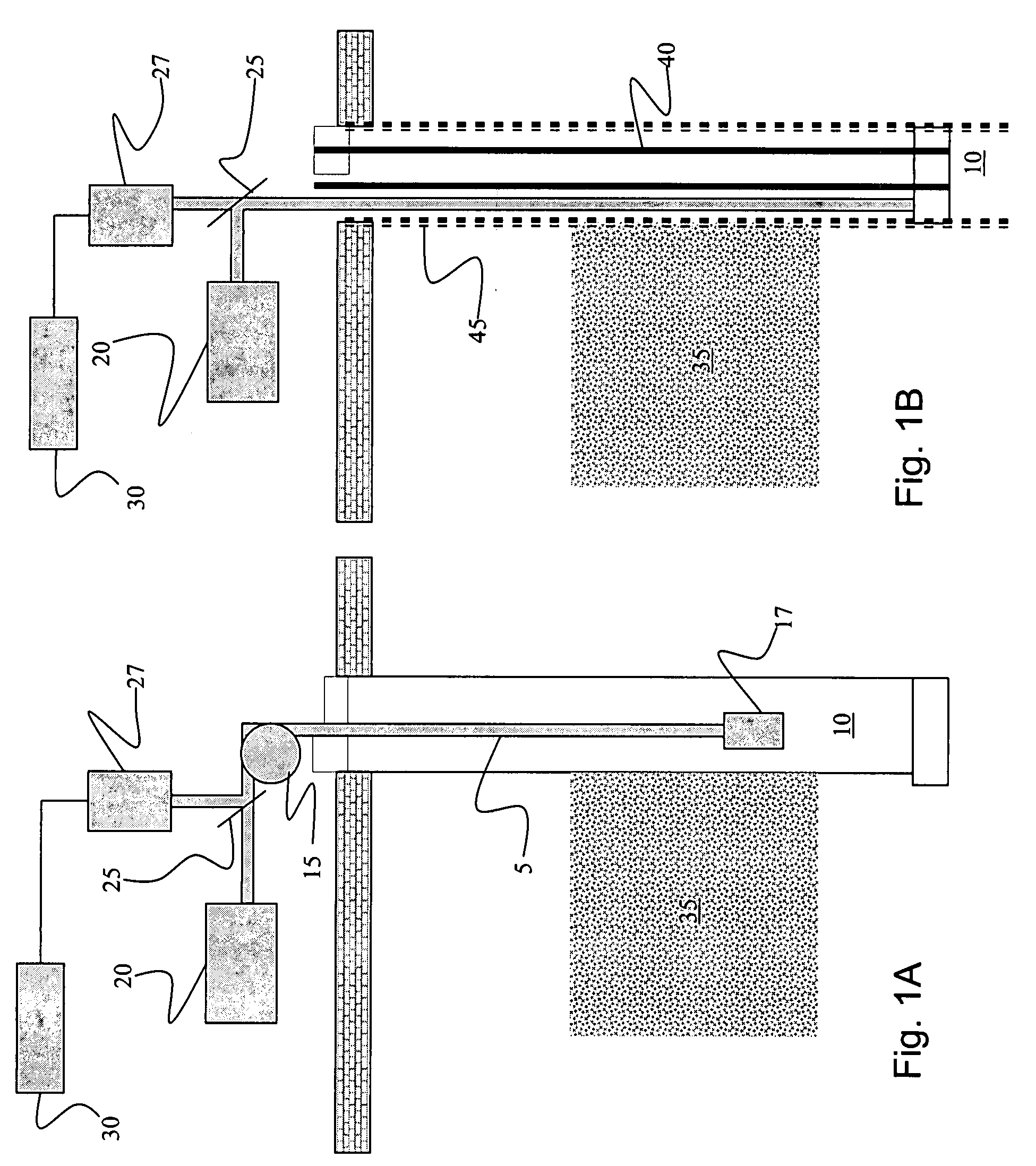
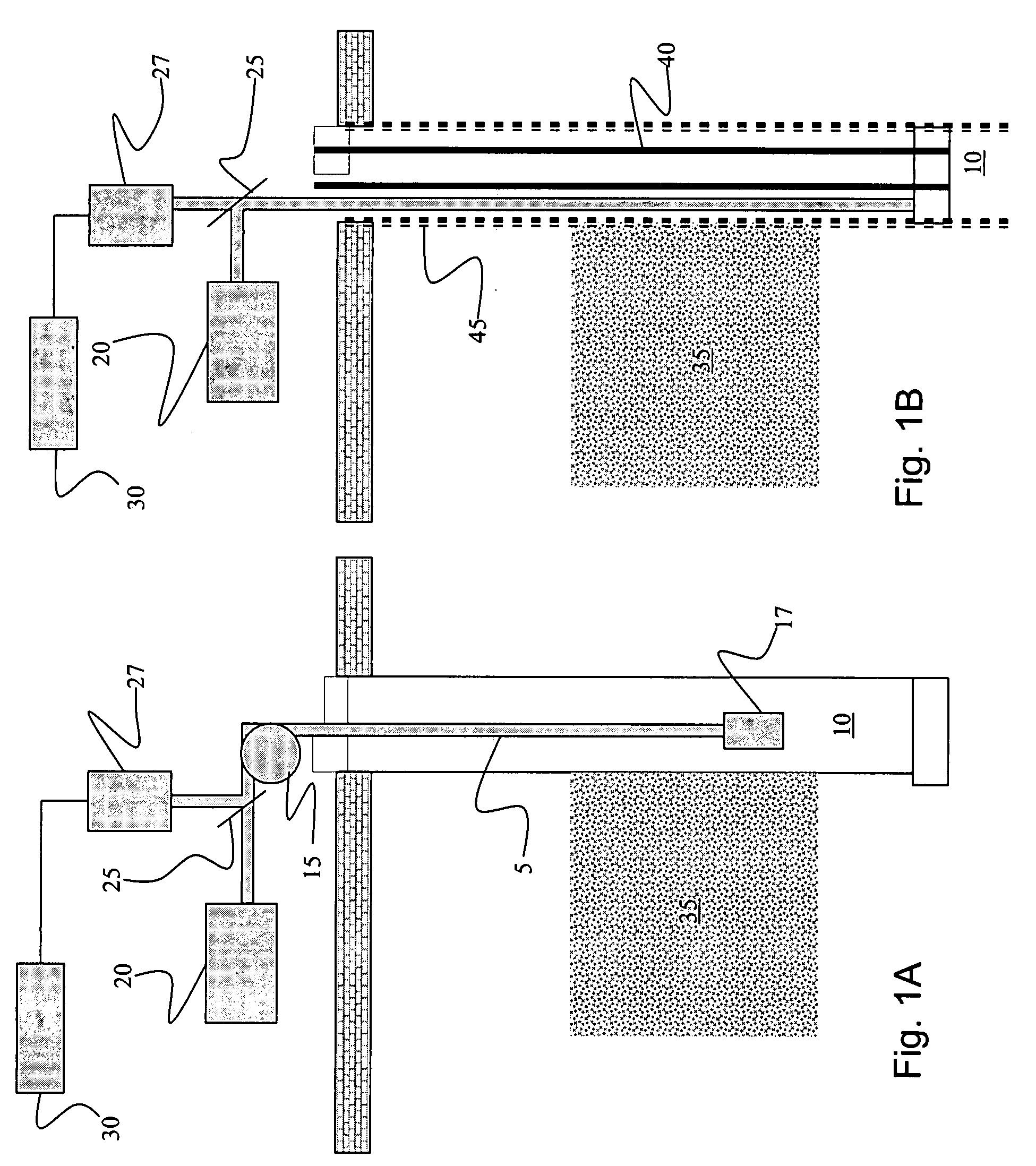
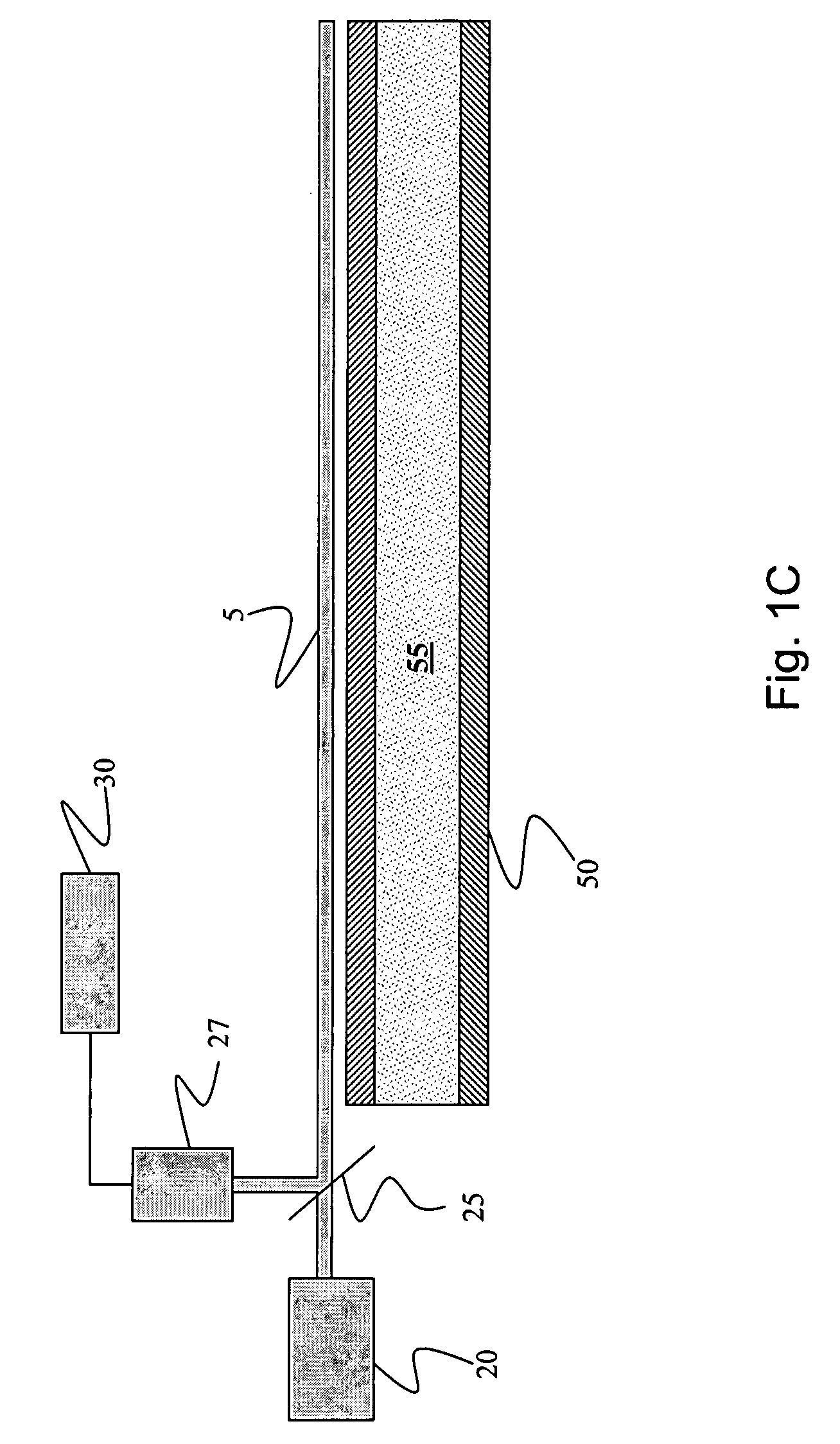
Method and system for monitoring smart structures utilizing distributed optical sensors
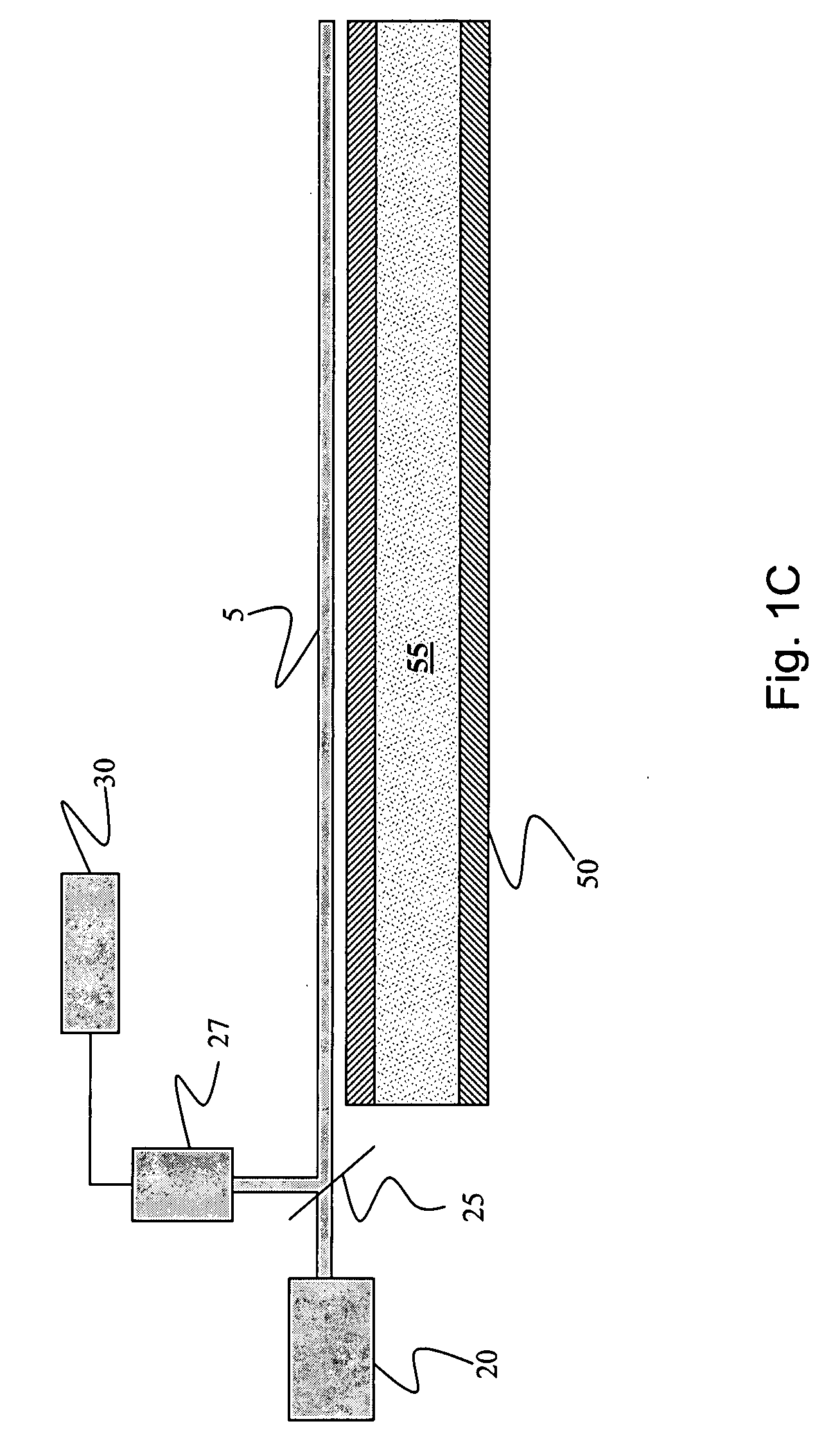
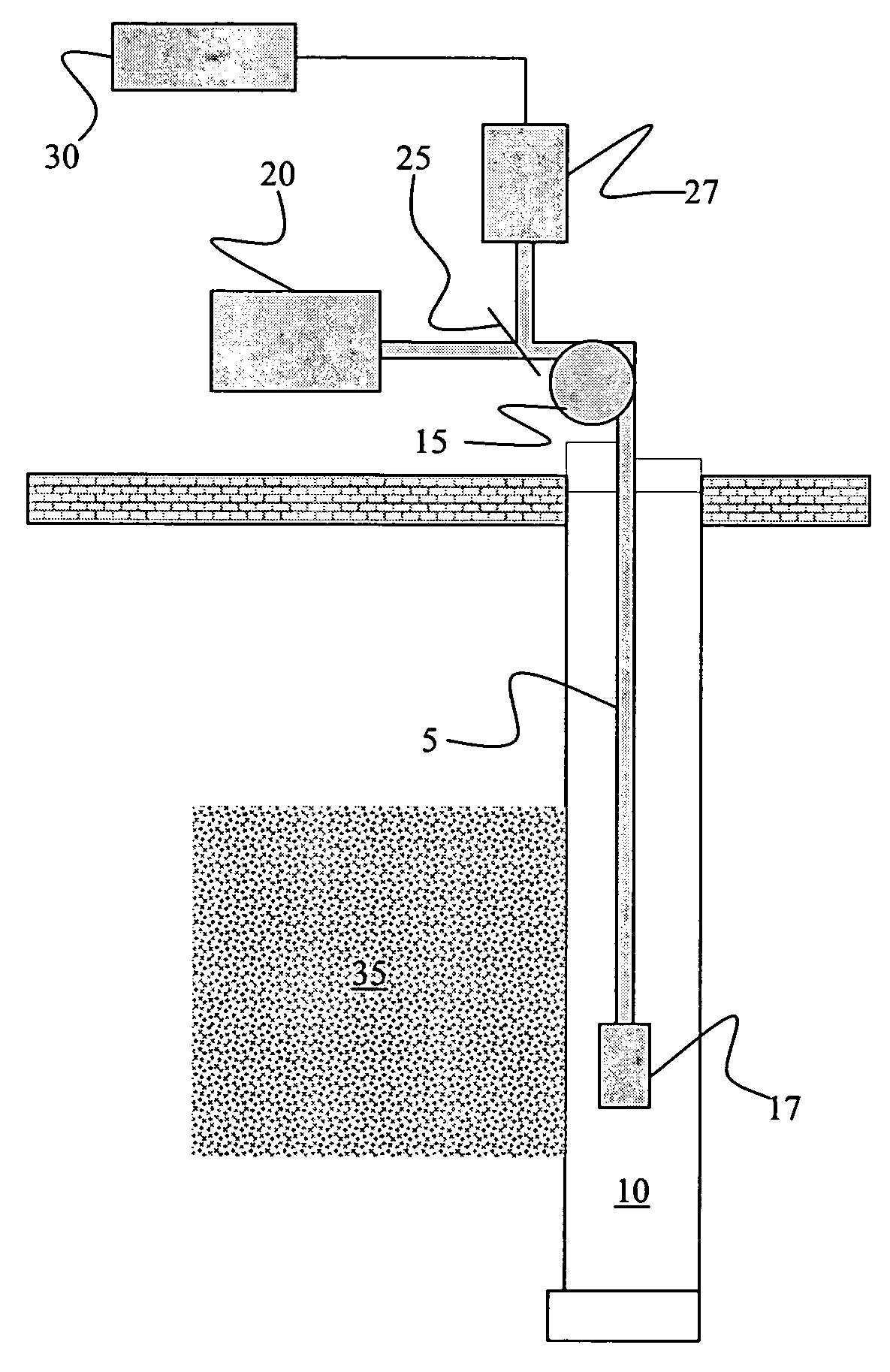
A monitoring system and method for monitoring a predetermined set of physical characteristics associated with a structure using the monitoring system. The system is distributed in the structure and comprises a distributed optical sensing device (30), further comprising a fiber optic cable (20, 22); a light source (18a) operatively in communication with the fiber optic cable (20, 22); a light detection device (18b), operatively in communication with the fiber optic cable (20, 22), for measuring the light received at the light detection device (18b) from the fiber optic cable (20, 22); and a data processor (18) capable of using the light measured to calculate a predetermined set of physical parameters describing the predetermined set of physical characteristics.
Owner:ZIEBEL AS
Systems and methods for distributed interferometric acoustic monitoring
This disclosure relates in general to a method and system for monitoring a conduit, a wellbore or a reservoir associated with hydrocarbon production or transportation and / or carbon dioxide sequestration. More specifically, but not by way of limitation, embodiments of the present invention provide for using an optical fiber as a distributed interferometer that may be used to monitor the conduit, wellbore or reservoir. In certain aspects, the distributed interferometric monitoring provides
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
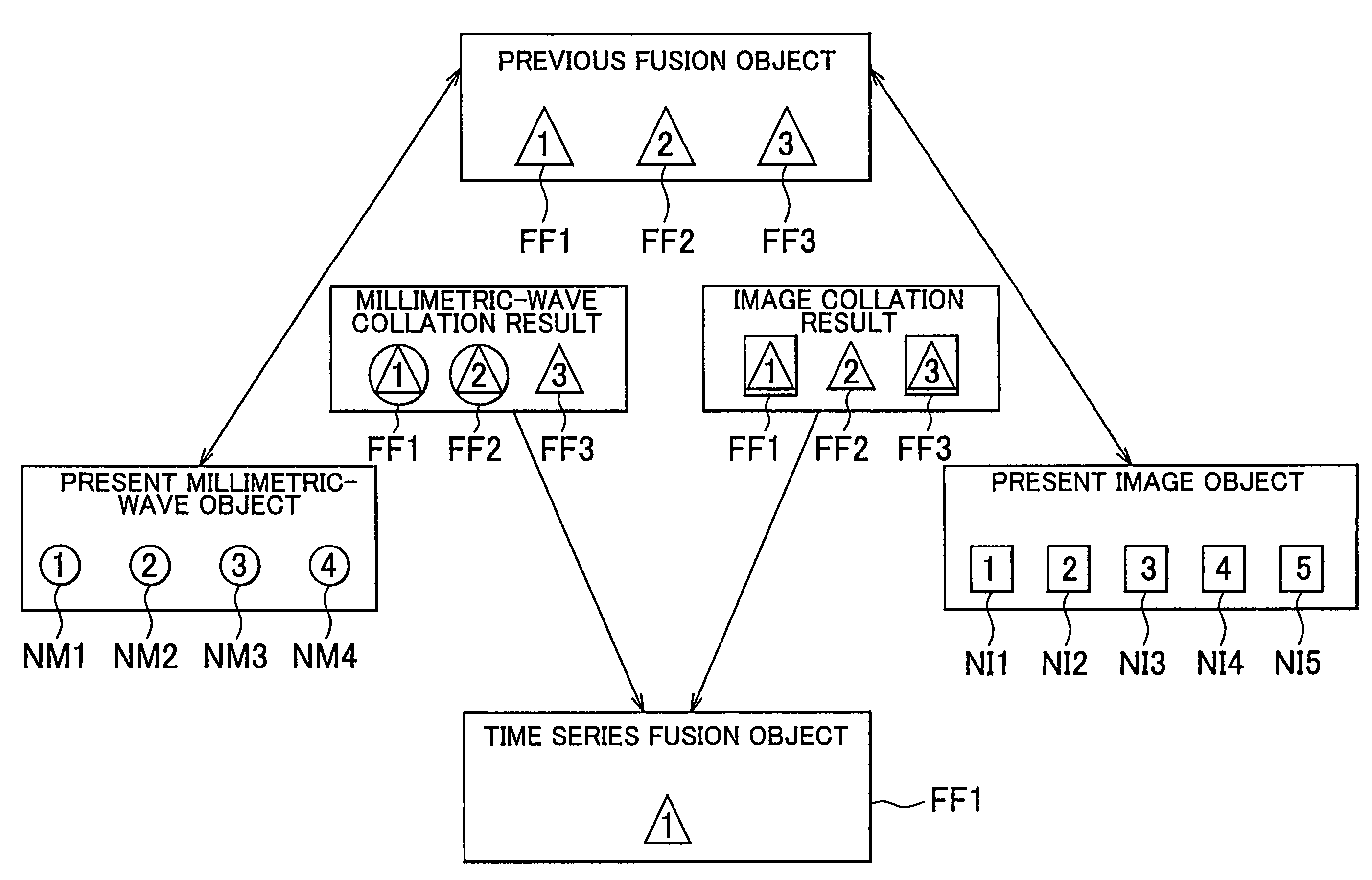
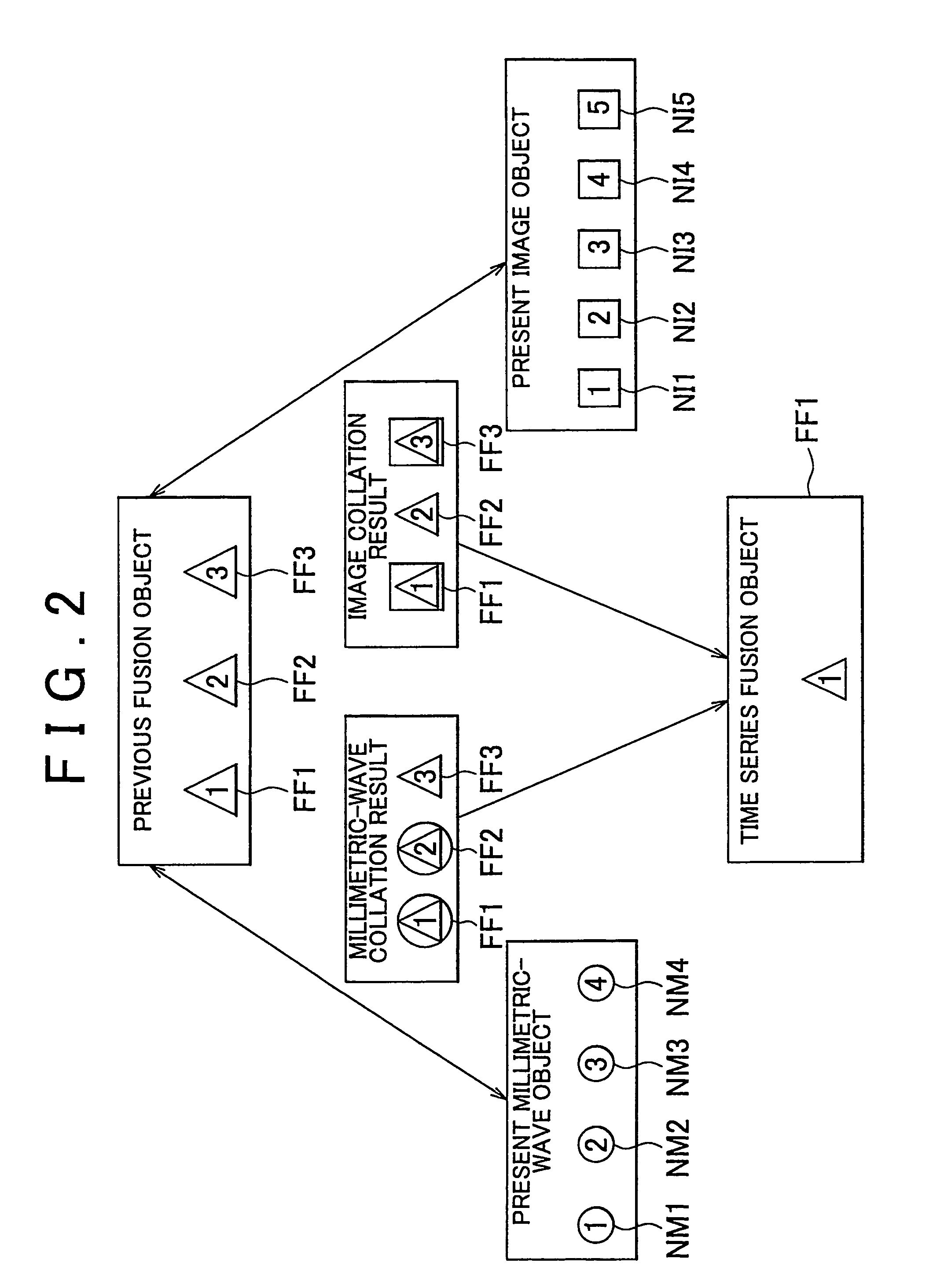
Object detection system and object detection method
ActiveUS7417580B2Easy to organizeImprove detection accuracyPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementOptical detectionObject basedImage detection
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Determination of characteristics of material
InactiveUS6060677ALow costReduce runningSolid waste disposalOptical detectionSolenoid valveLength wave
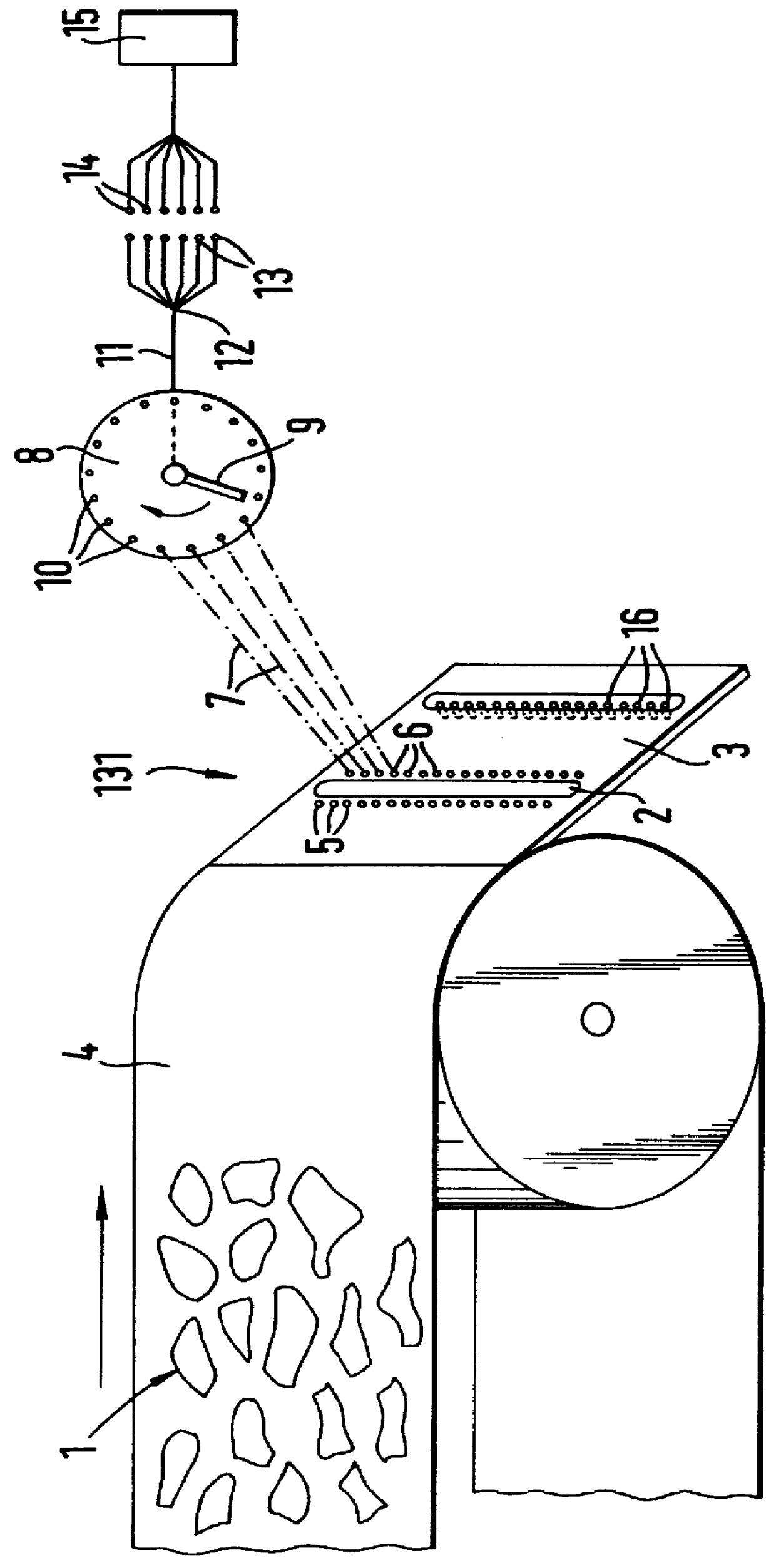
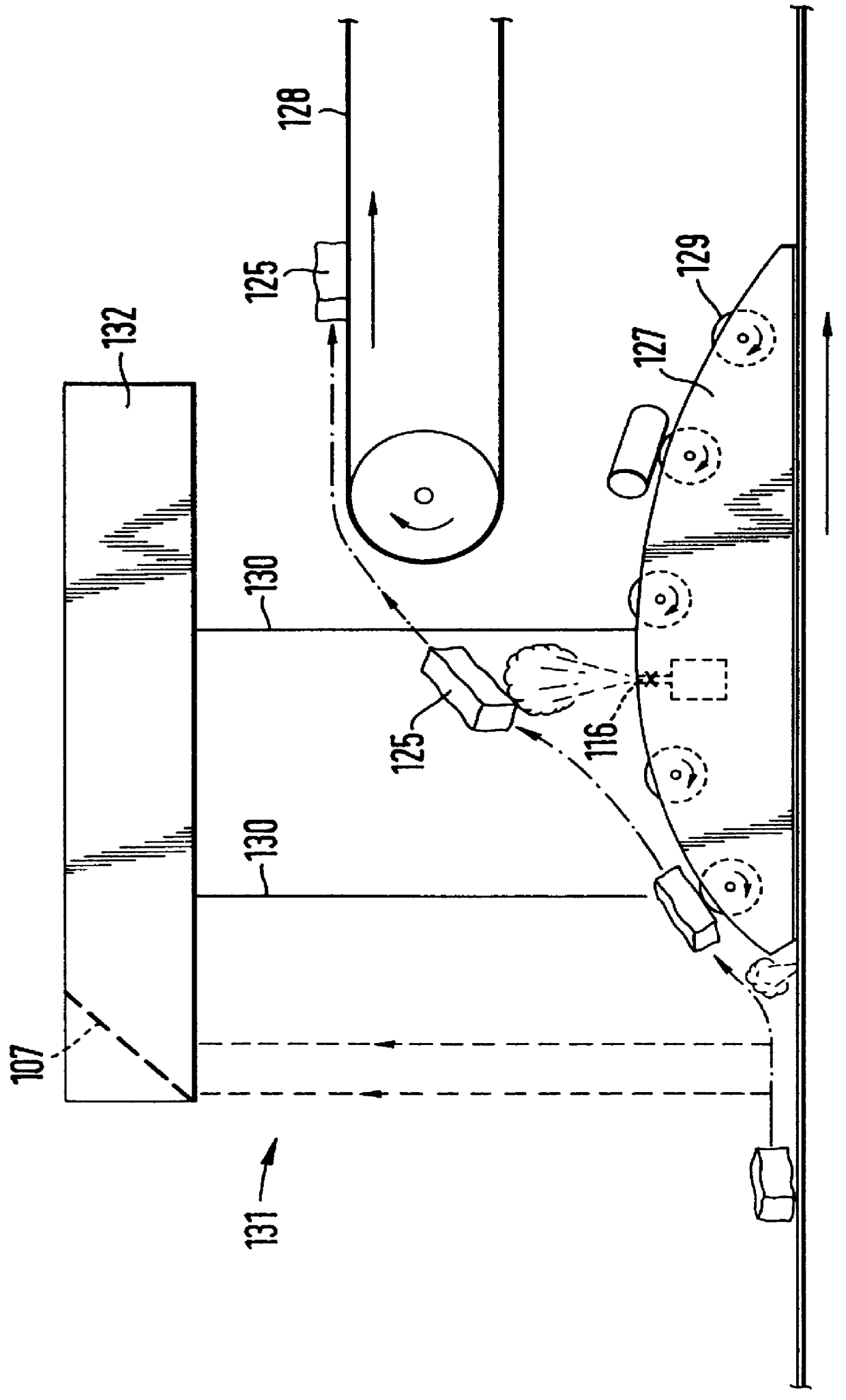
A system for automatically inspecting matter for varying composition comprises one or more detection stations through which one or more streams of matter are advanced and particular materials therein are detected through their diffusely reflected IR spectra, if any, and / or through their variation of an electromagnetic field by their metallic portions, if any. A row of light sources distributed across the overall width of one or more belt conveyors may cause desired portions of the stream to reflect light diffusely onto a part-toroidal mirror extending over that overall width, whence the light is reflected, by a rotating, polygonal mirror through optical filters dedicated to differing IR wavelengths, onto detectors the data output of which is utilized in controlling solenoid valves operating air jet nozzles which separate-out the desired portions. Alternatively or additionally, an oscillator and an antenna which extends over that overall width generate an electromagnetic field through the belt and sensing coils sense variations therein produced by metallic portions of the stream passing through the detection station and the detection data produced by the sensing coils is used to control the solenoid valves operating the nozzles to separate-out the metallic portions.
Owner:TITECH VISIONSORT +1
Systems and methods for distributed interferometric acoustic monitoring
Acoustic monitoring of a conduit, a wellbore or a reservoir associated with hydrocarbon production or transportation and / or carbon dioxide sequestration is carried out using a fibre optic cable extending along or appurtenant to it as a distributed interferometer. Coherent Raleigh noise generated by the transmission of the coherent beam of radiation through the fiber optic is detected and processed to identify an acoustic occurrence.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
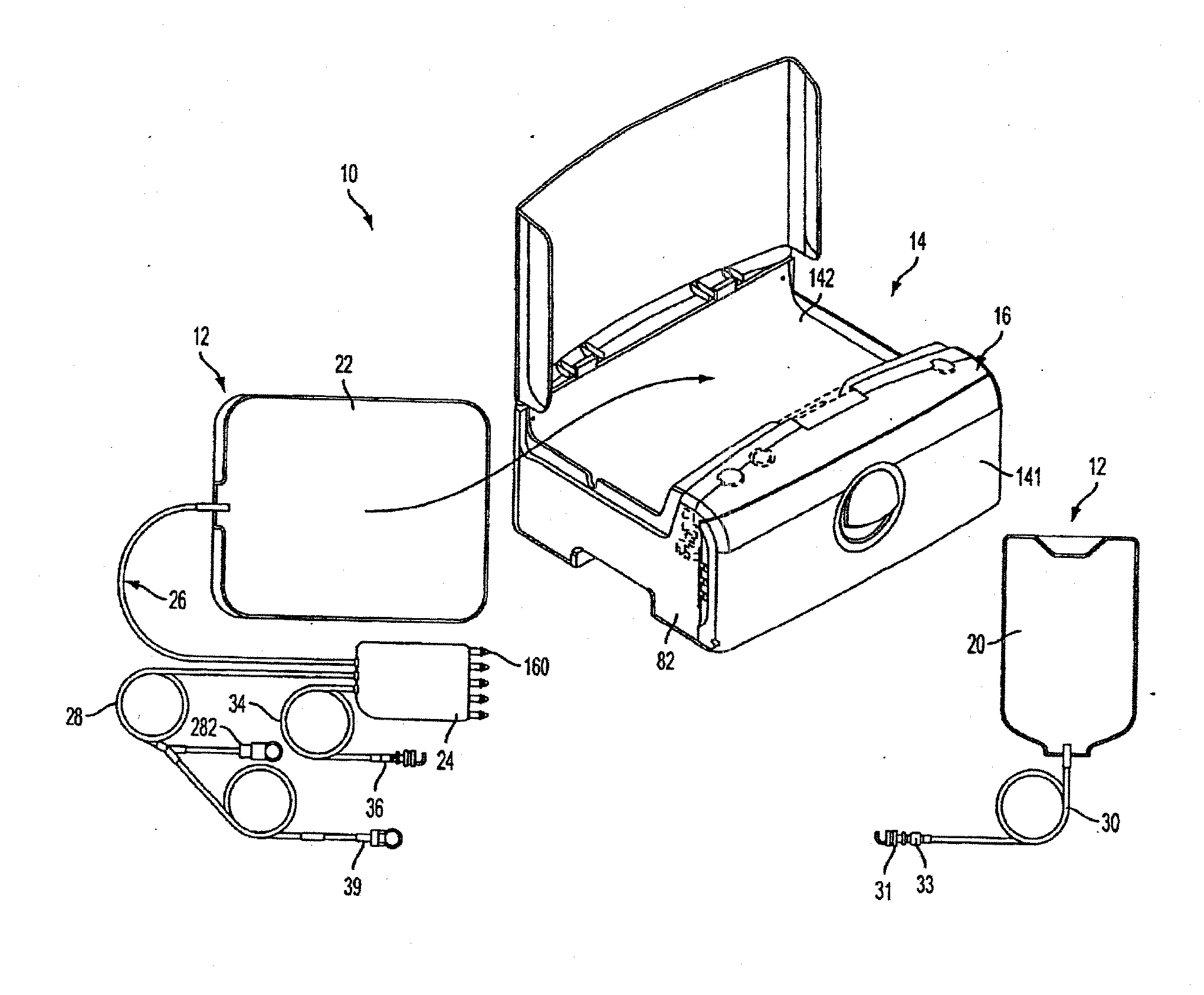
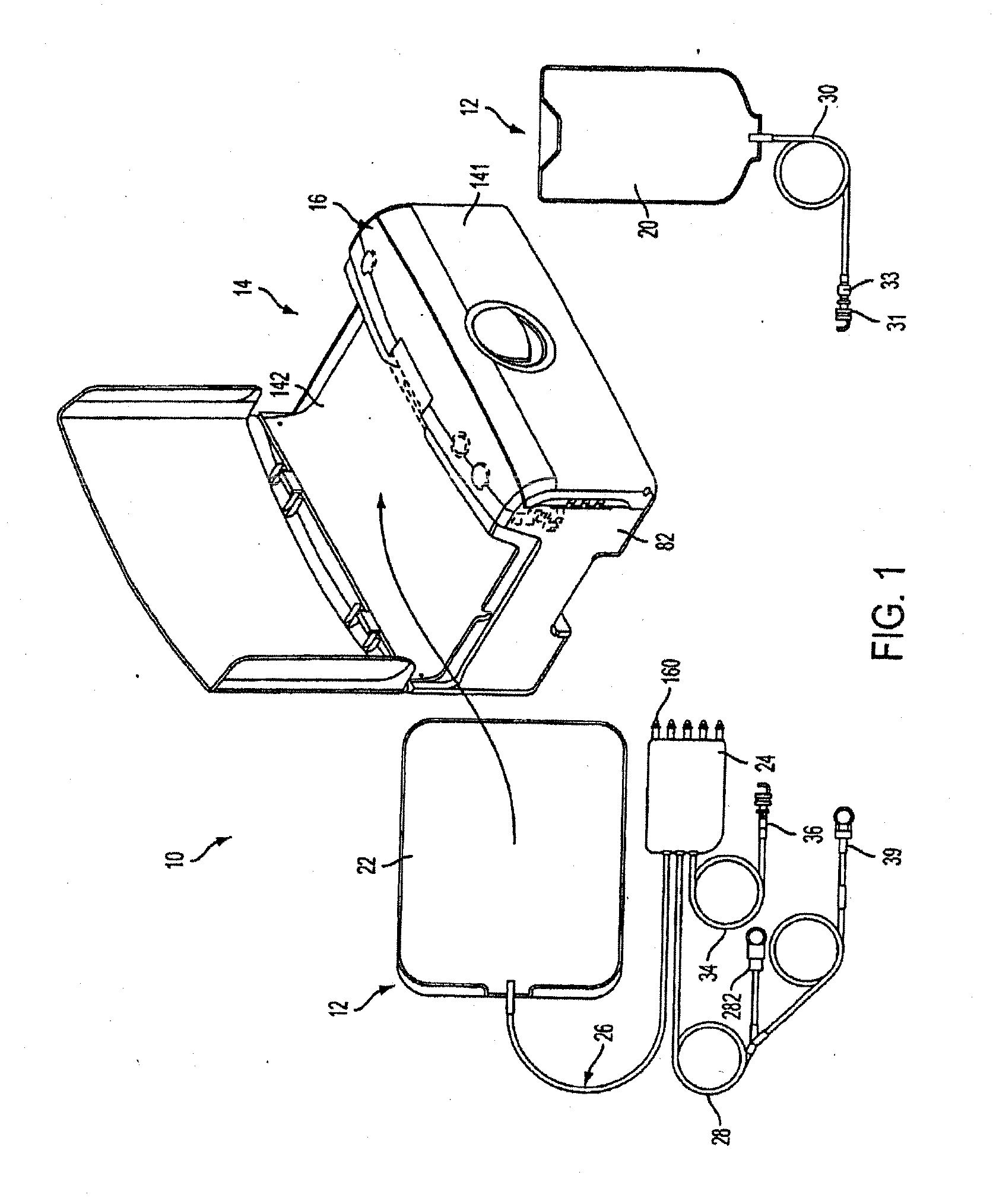
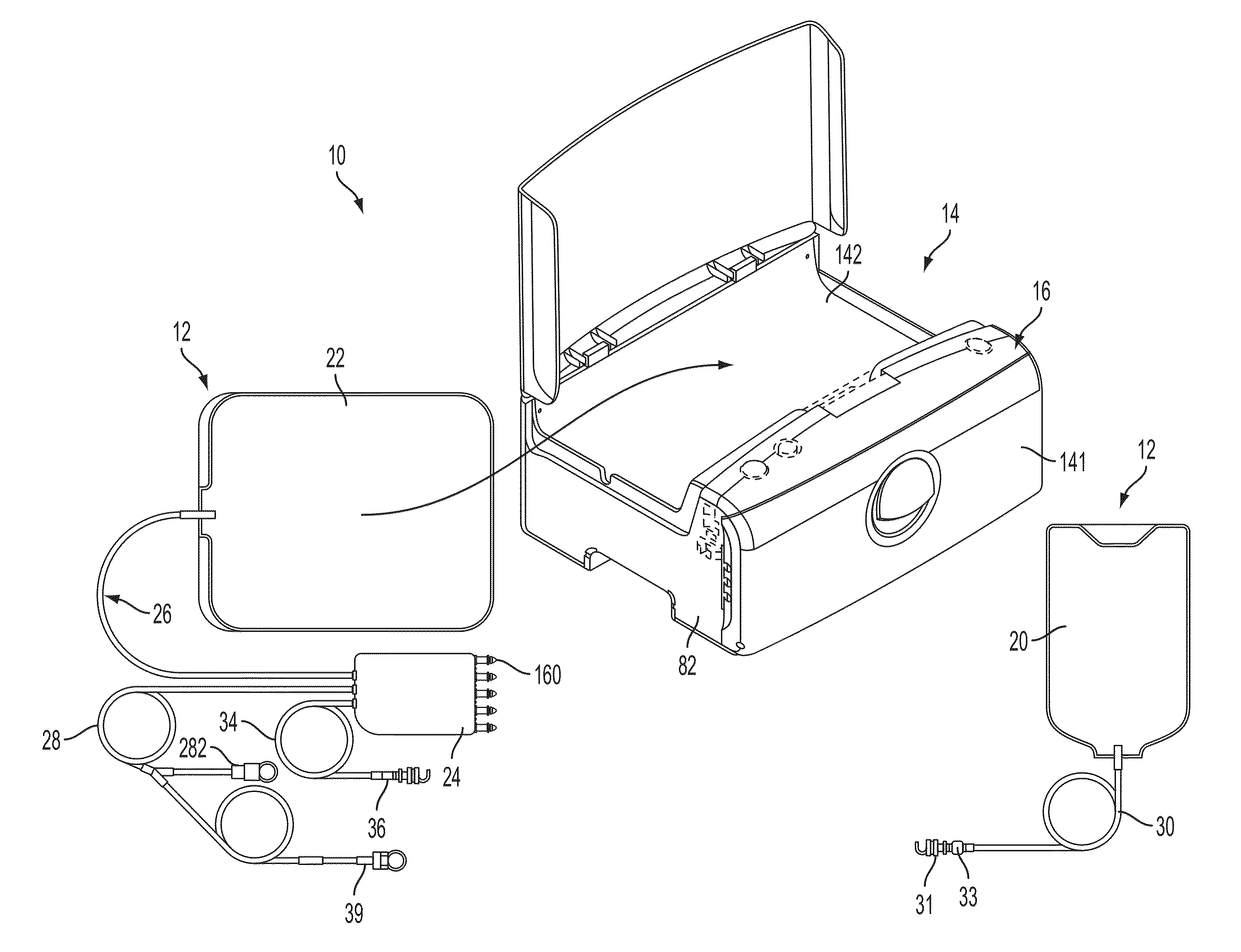
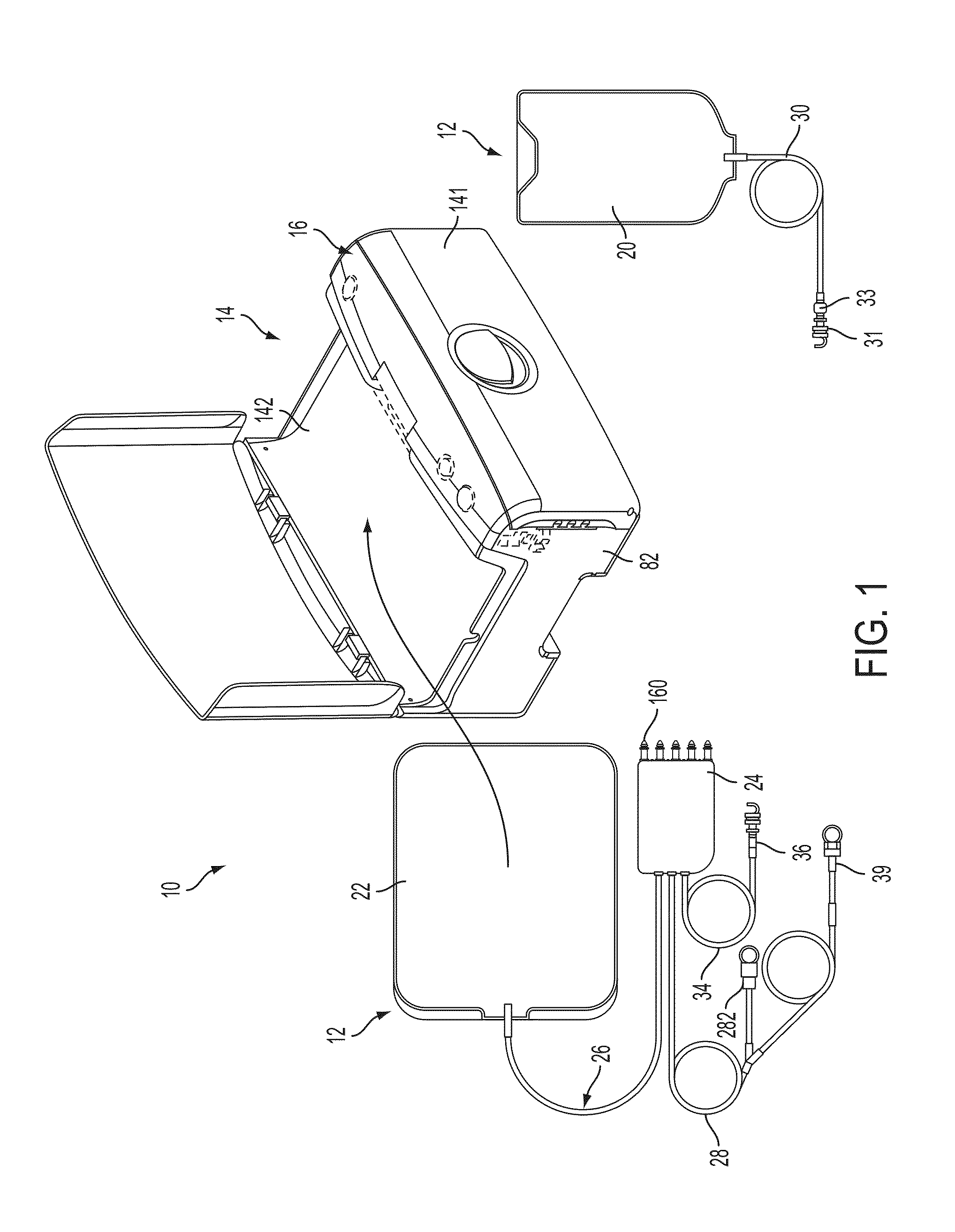
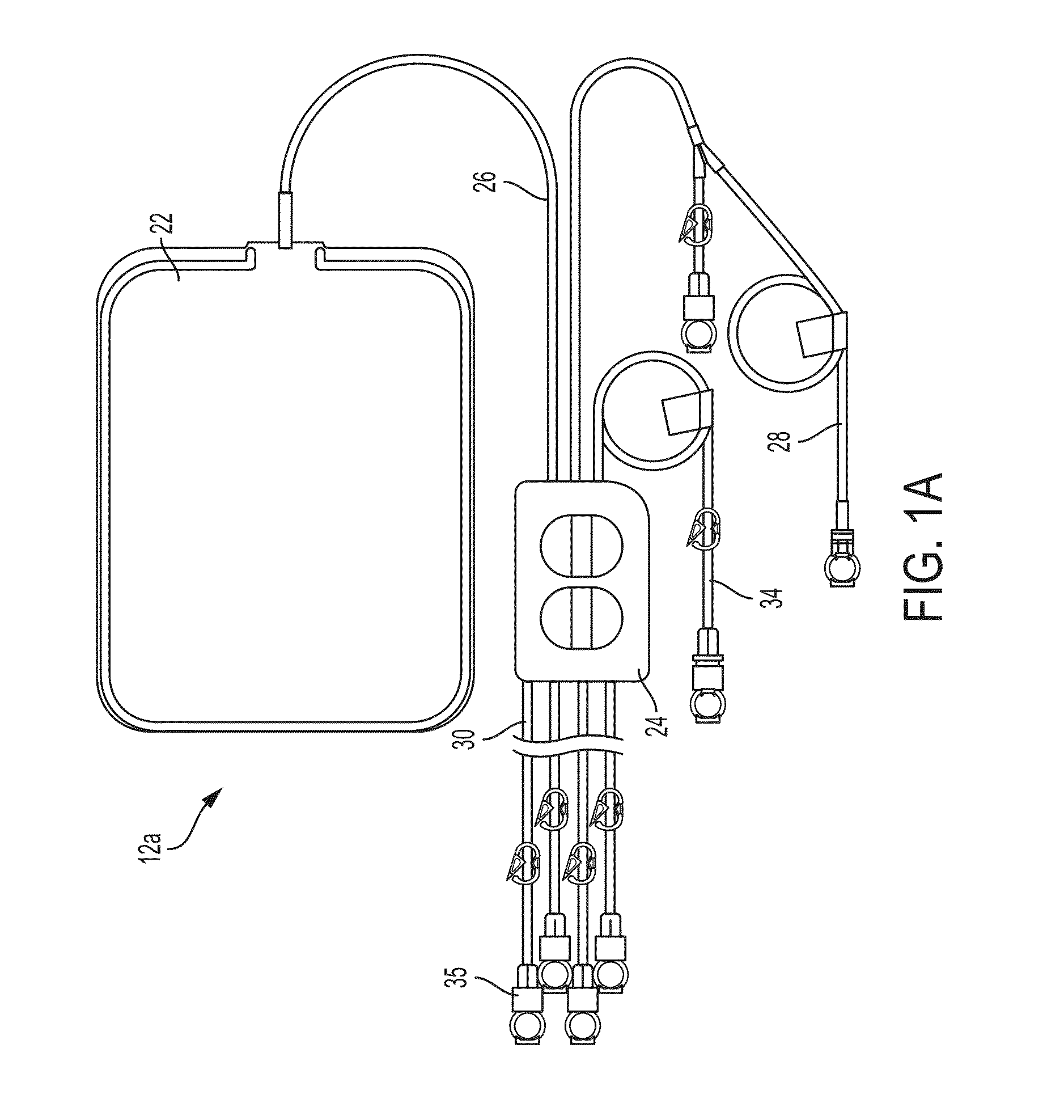
Medical treatment system and methods using a plurality of fluid lines
ActiveUS20130184638A1Reduce trafficIncrease distanceMedical devicesOptical detectionControl systemPeritoneal cavity
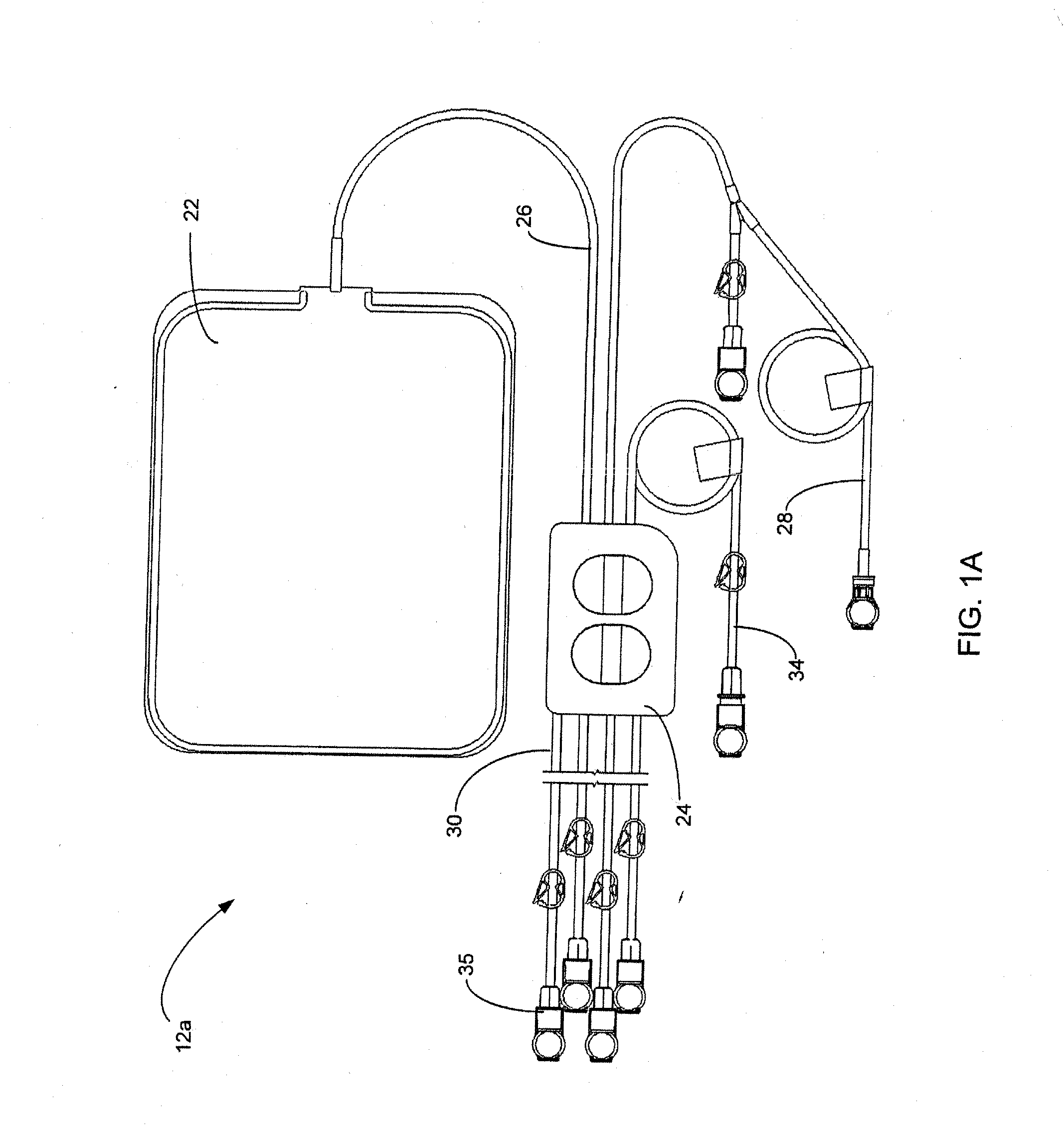
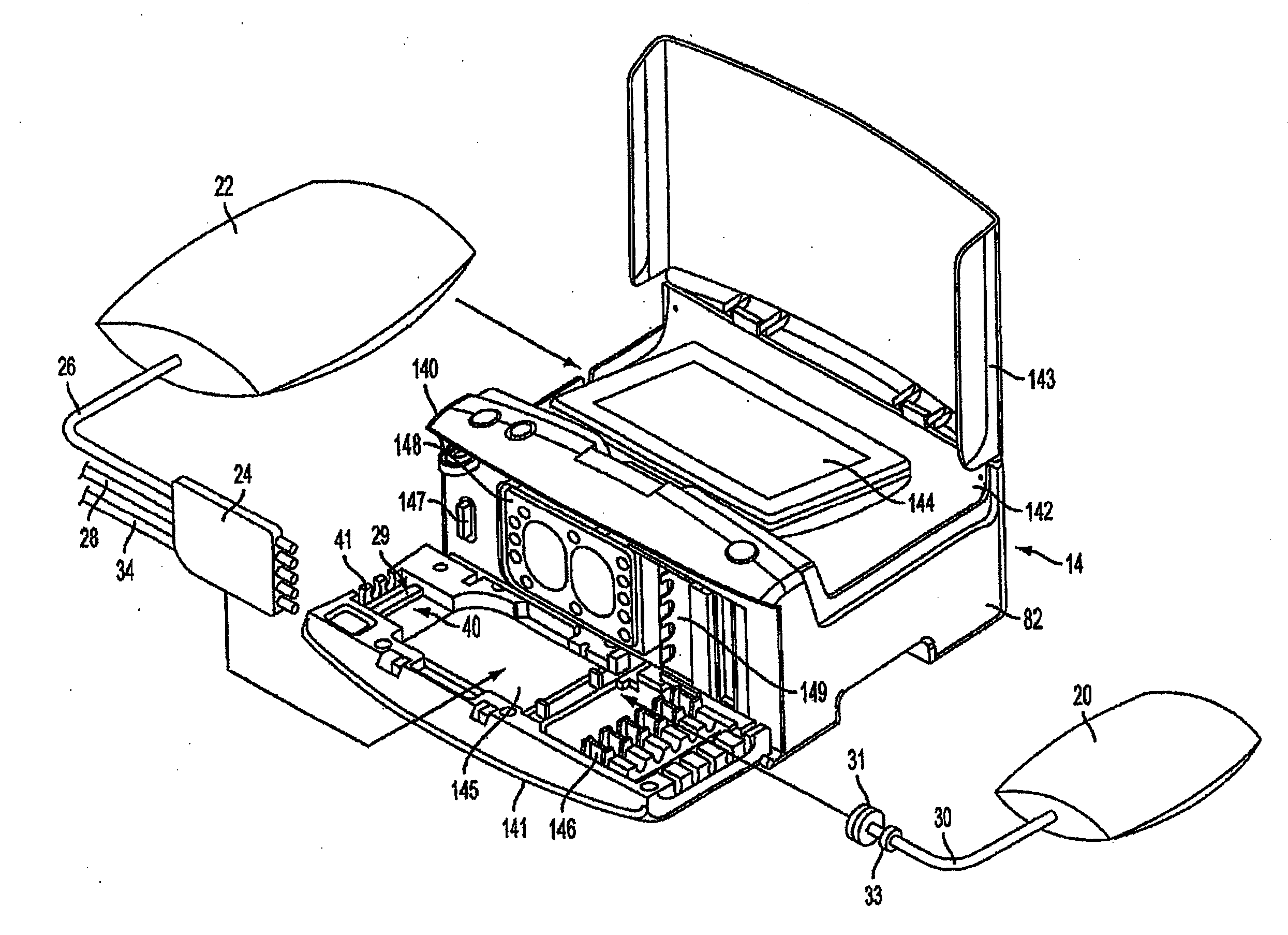
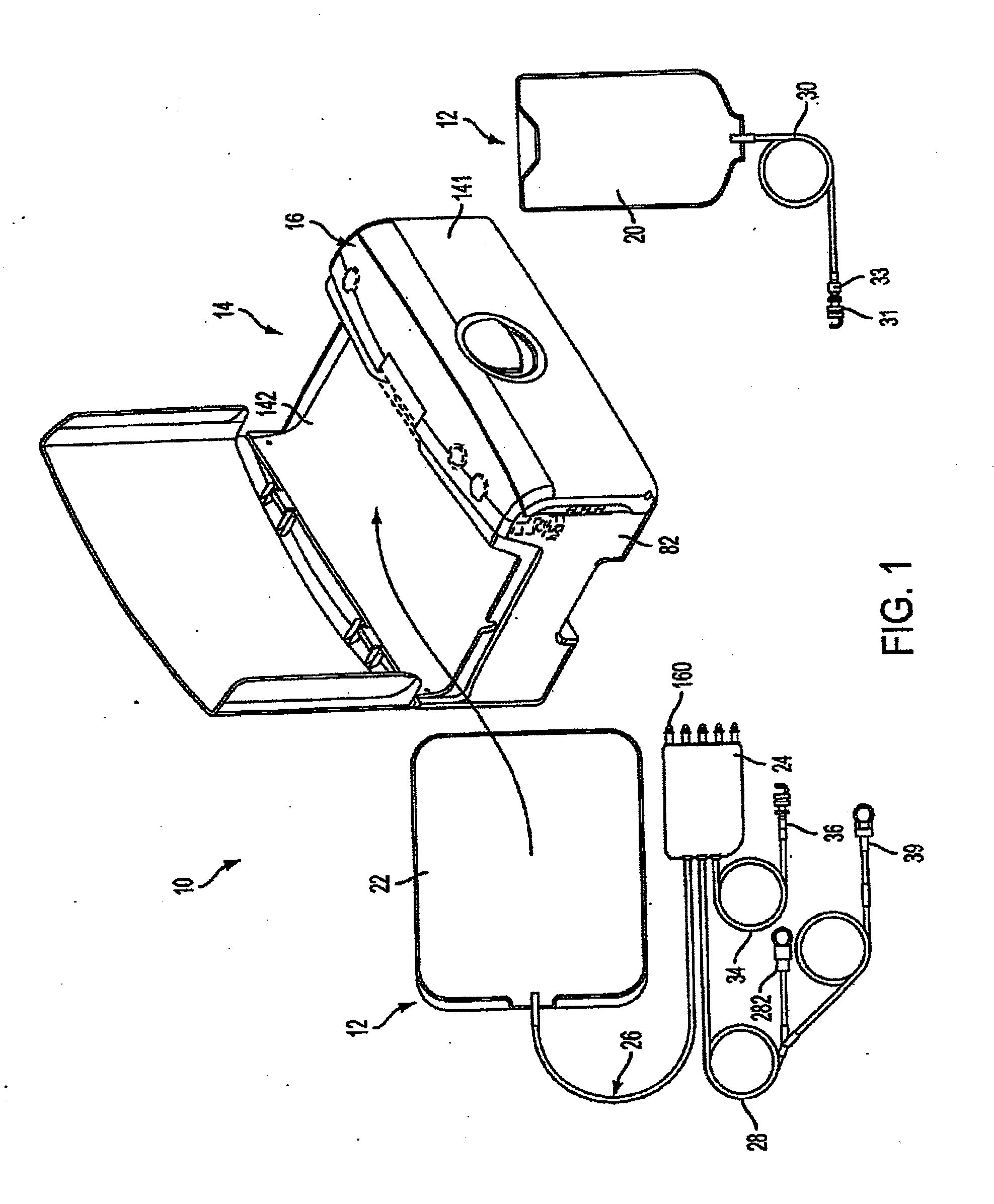
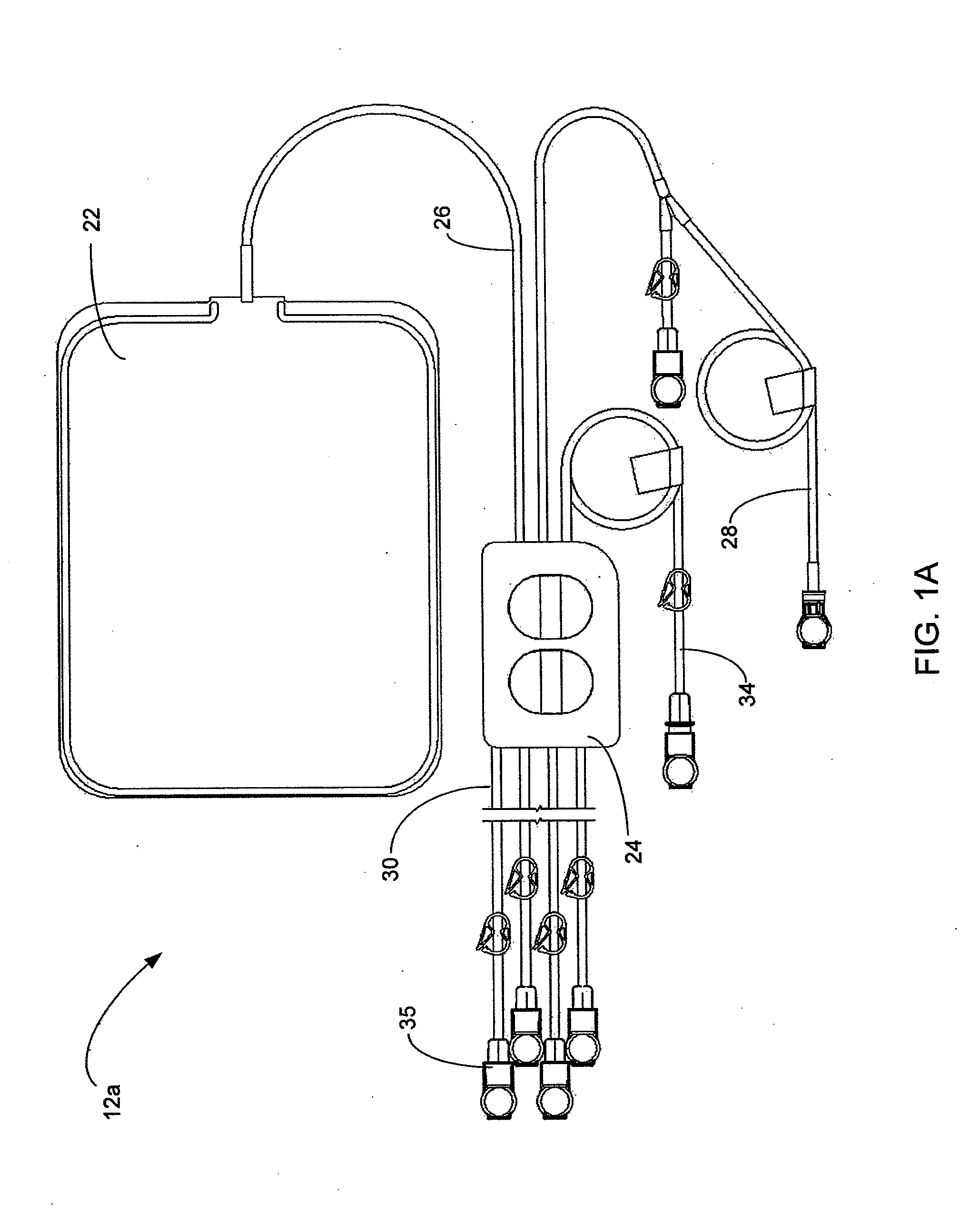
A medical treatment system, such as peritoneal dialysis system, may include control and other features to enhance patient comfort and ease of use. For example, a peritoneal dialysis system may include a control system that can adjust the volume of fluid infused into the peritoneal cavity to prevent the intraperitoneal fluid volume from exceeding a pre-determined amount. The control system can adjust by adding one or more therapy cycles, allowing for fill volumes during each cycle to be reduced. The control system may continue to allow the fluid to drain from the peritoneal cavity as completely as possible before starting the next therapy cycle. The control system may also adjust the dwell time of fluid within the peritoneal cavity during therapy cycles in order to complete a therapy within a scheduled time period. The cycler may also be configured to have a heater control system that monitors both the temperature of a heating tray and the temperature of a bag of dialysis fluid in order to bring the temperature of the dialysis fluid rapidly to a specified temperature, with minimal temperature overshoot.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Medical treatment system and methods using a plurality of fluid lines
ActiveUS20120123322A1Prevent slight movementReduce noiseBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsPatient comfortIntensive care medicine
A medical treatment system, such as peritoneal dialysis system, may include control and other features to enhance patient comfort and ease of use. For example, a peritoneal dialysis system may include patient line state detector for detecting whether a patient line is primed before it is to be connected to the patient. The patient line state detector can also the ability to detect whether a patient line has been properly mounted for priming. Both patient line presence / absence and fill state can be determined using an optical system, e.g., one that employs a single optical sensor.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
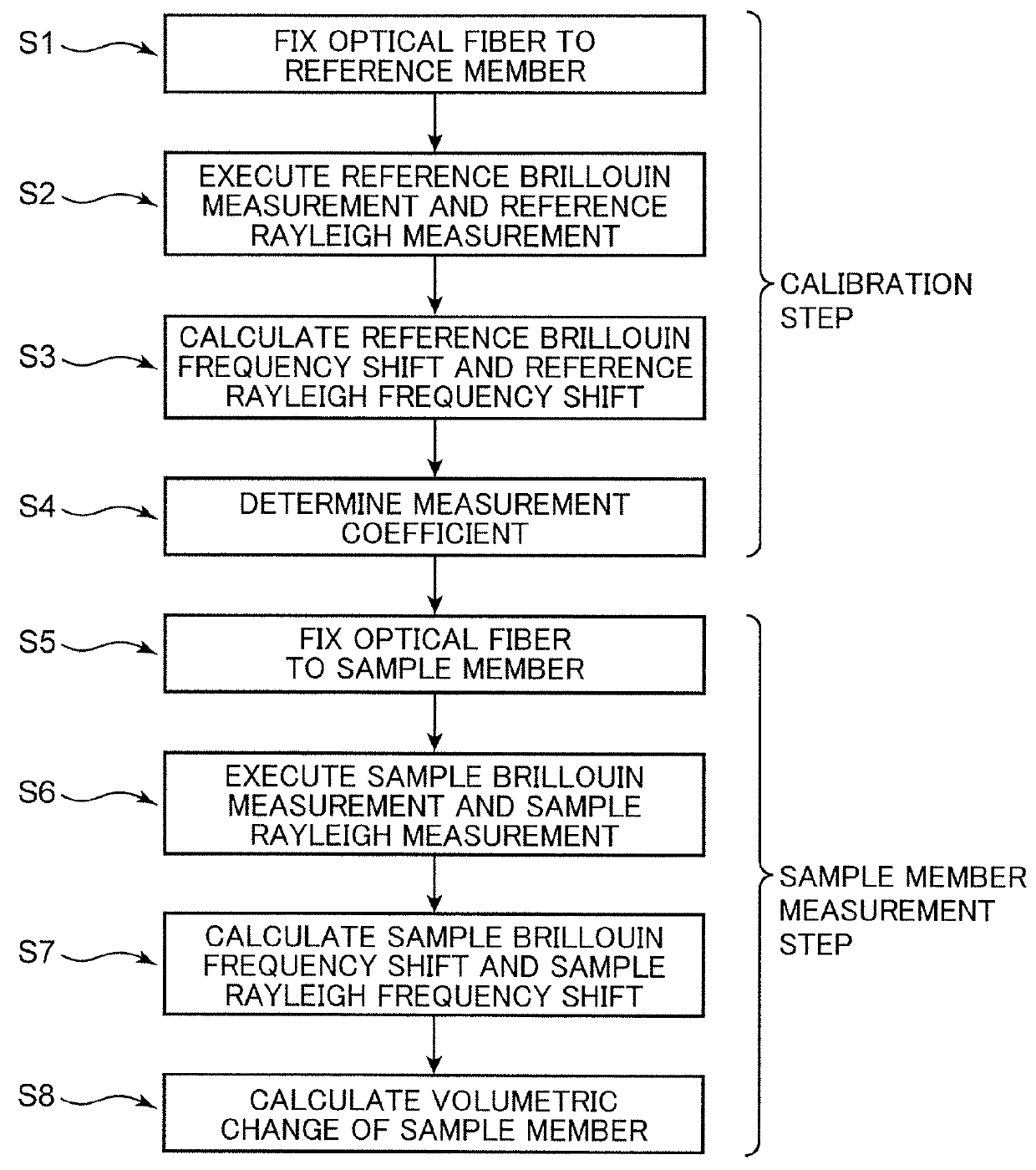
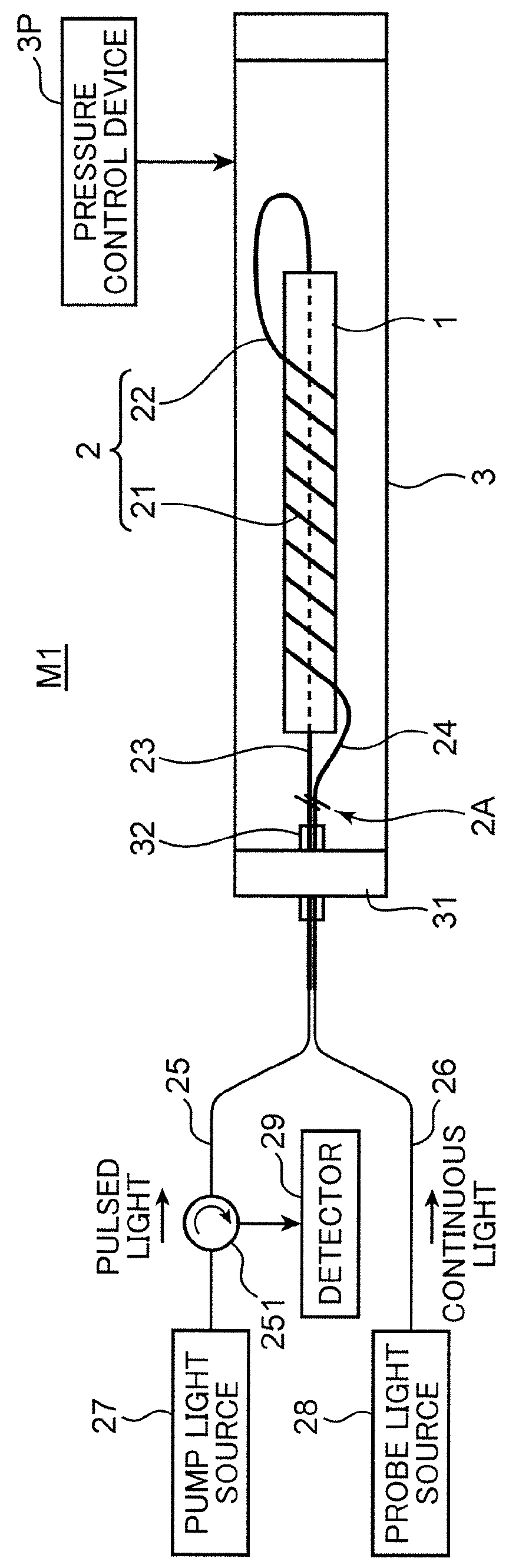
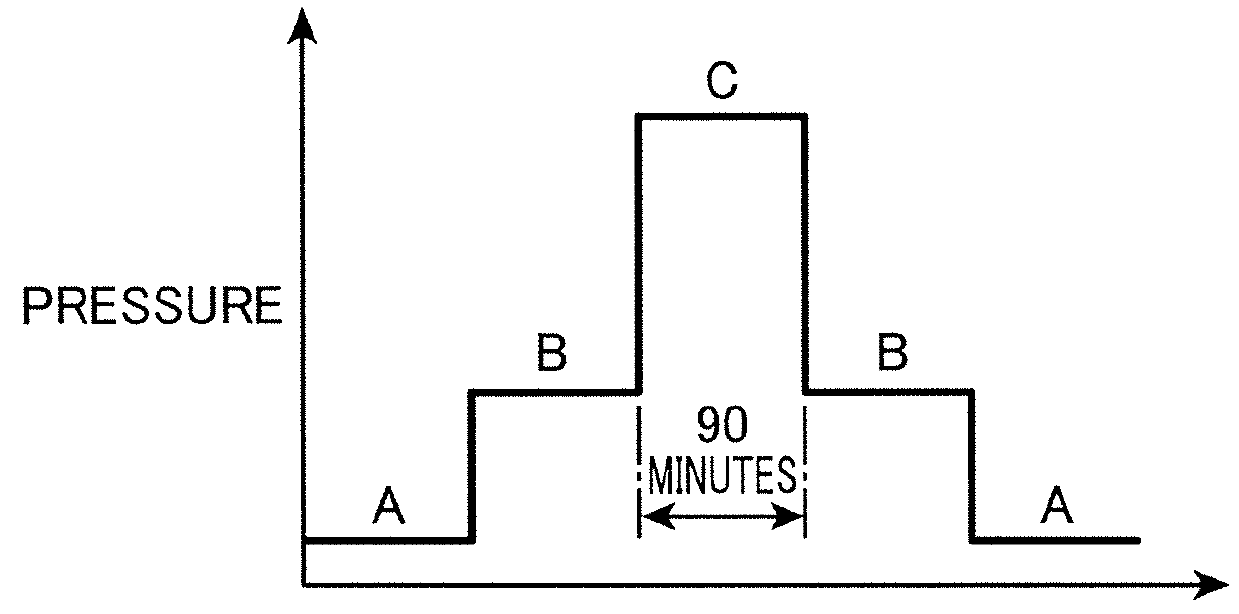
Method for measuring volumetric changes of object
ActiveUS9360304B2Accurate measurementOptical detectionUsing optical meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
Under a known pressure is externally applied to a reference member to which an optical fiber is fixed, test light is allowed to enter the optical fiber, and at least one of a reference Brillouin measurement for determining a reference Brillouin frequency shift amount based on the Brillouin scattering phenomenon, and a reference Rayleigh measurement for determining a reference Rayleigh frequency shift amount based on the Rayleigh scattering phenomenon is performed. A Brillouin measurement coefficient or a Rayleigh measurement coefficient is determined from these calculation results. An optical fiber is fixed to a sample member, the volumetric change of which is unknown, and the same sample Brillouin measurement or sample Rayleigh measurement is performed to determine the frequency shift amount. The volumetric change of the sample member is determined from the sample Brillouin or the sample Rayleigh frequency shift amount, and from the Brillouin or the Rayleigh measurement coefficient.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH +1
Method of detecting object using structured light and robot using the same
ActiveUS20070267570A1Automatic obstacle detectionTravelling automatic controlHeight differenceStructured light
A method of detecting an object using a structured light and a robot using the same are disclosed. The method of detecting a floor object using a structured light includes measuring a height difference of a position onto which a specified structured light is projected with a reference position, and detecting the floor object using the measured height difference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Security sensor having disturbance detecting capability
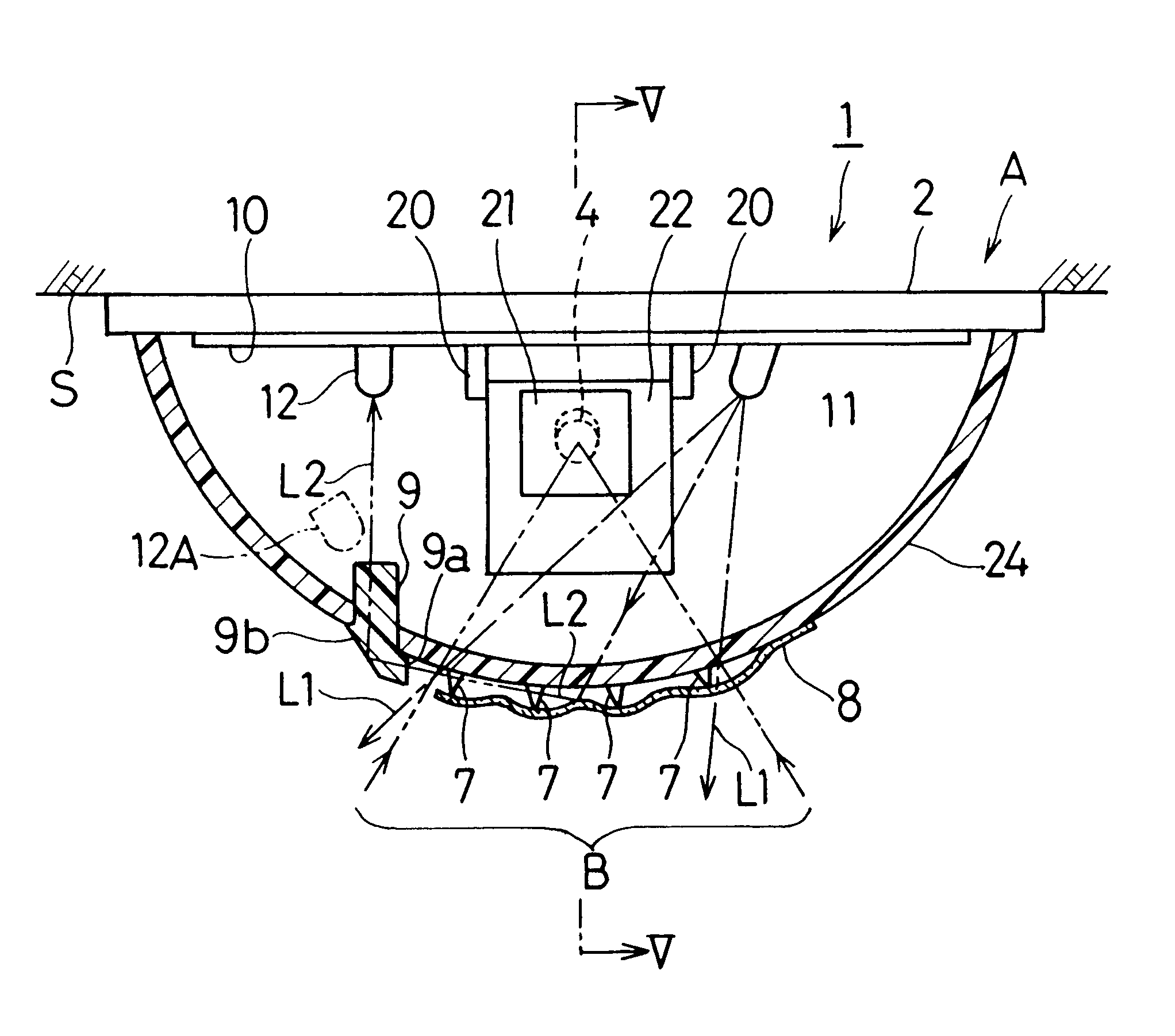
InactiveUS6469625B1Increase freedomReduce disturbance detecting capabilityRadiation pyrometryPhotometryLight beamEngineering
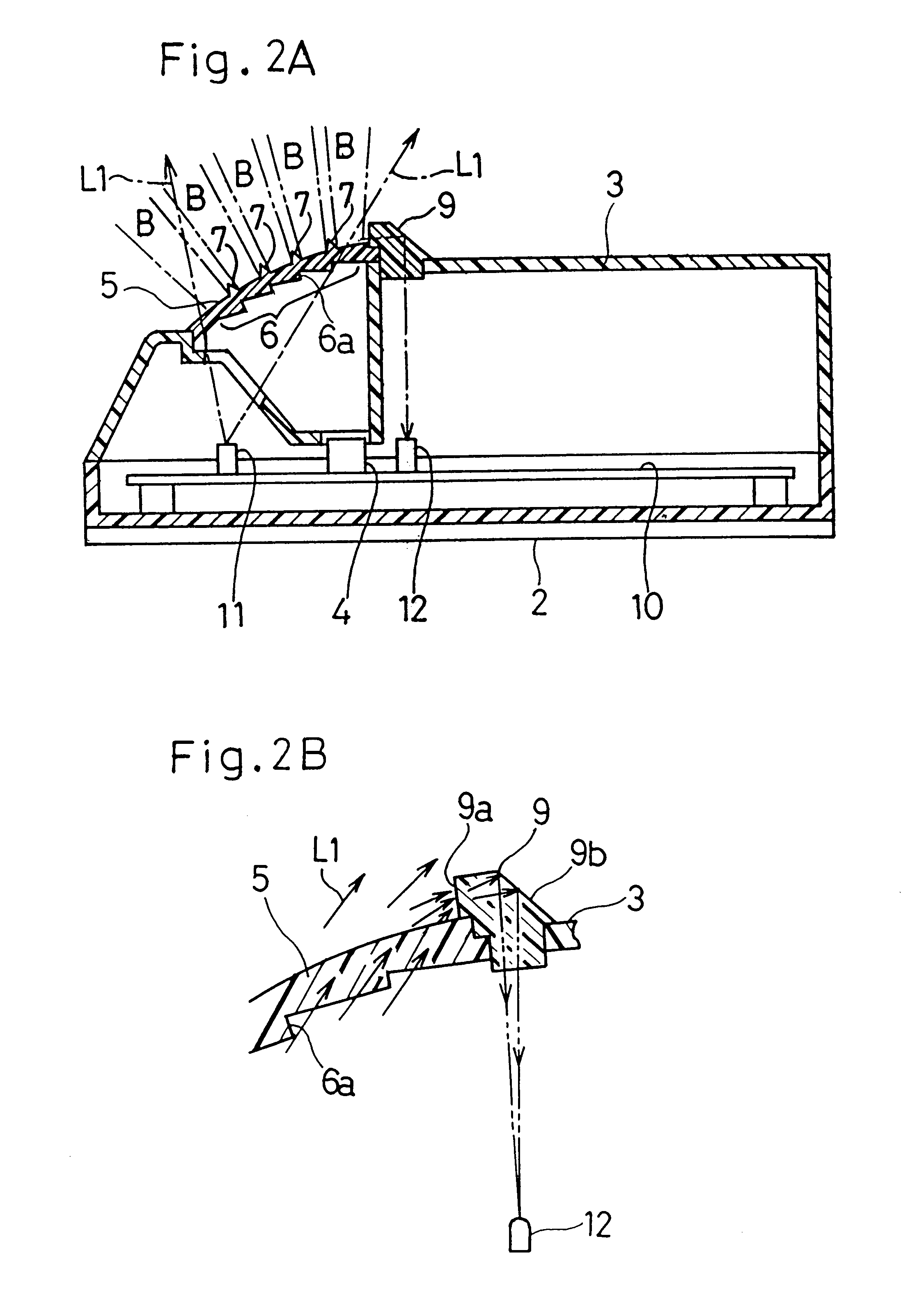
A security sensor 1 having a disturbance detecting capability capable of detecting the presence of an obstacle 8 purposefully applied to the sensor 1 in an attempt to fool or tamper the sensor 1 includes a carrier body A having an infrared sensor element 4, an incident side enclosure 5, such as a lens defining a detection area B, mounted on the carrier body A, a light projecting element 11 for projecting a disturbance detecting beam L1 from inside of the incident side enclosure 5 towards the incident side enclosure 5, a light receiving element 12 for receiving the disturbance detecting beam L1 reflected from the incident side enclosure 5, and a detecting circuit 15 for detecting a presence or absence of the obstacle 8 on the incident side enclosure 5, based on an amount of light received by the light receiving element 12. A multiplicity of projections 7 are formed on an outer surface of the incident side enclosure 5 so as to define a multiplicity of gaps between the obstacle 8 and the outer surface of the incident side enclosure 5, when the obstacle 8 is applied to the outer surface of the incident side enclosure 5.
Owner:OPTEX CO LTD
Millimeter wave imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6353224B1Maximises emissionEmission reductionGeological detection using milimetre wavesMaterial analysis using microwave meansMillimetre waveLength wave
Millimeter wave imaging apparatus for use, in articular, as an indoor security system to identify objects concealed under the clothing of a person in a background scene, including means for generating a millimetric temperature contrast between the person to be imaged and the surroundings in scene. This may be a "hot" or "cold" source for producing a flux, and a relatively smaller flux respectively, of incoherent millimeter wavelength radiation. The apparatus may also include at least one partial ellipsoid reflective enclosure for reflecting millimeter wavelength radiation emitted from the "hot" and "cold" source so as to generate non-localized and uniform illumination of the person. The enclosure may have a metallic inner surface on which a dimpled pattern may be embossed to diffuse the millimeter wavelength radiation reflected from the metallic inner surface. The apparatus also includes one or more millimeter wavelength imaging cameras for detecting the millimeter wavelength radiation at one or more millimeter wave center frequencies, which may be mounted inside or outside the reflective enclosure. An image of the objects may be generated on a television monitor from the detected radiation.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
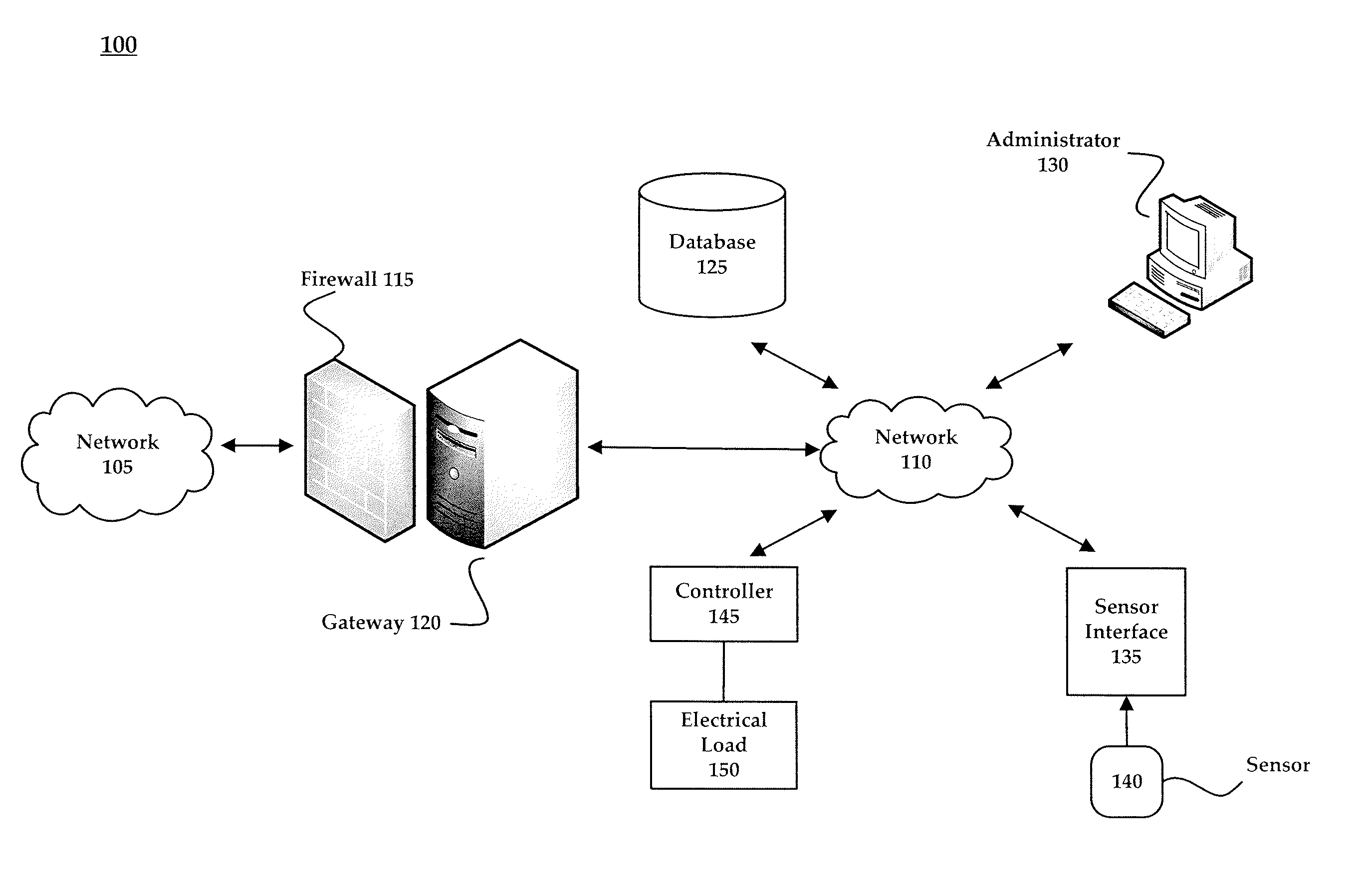
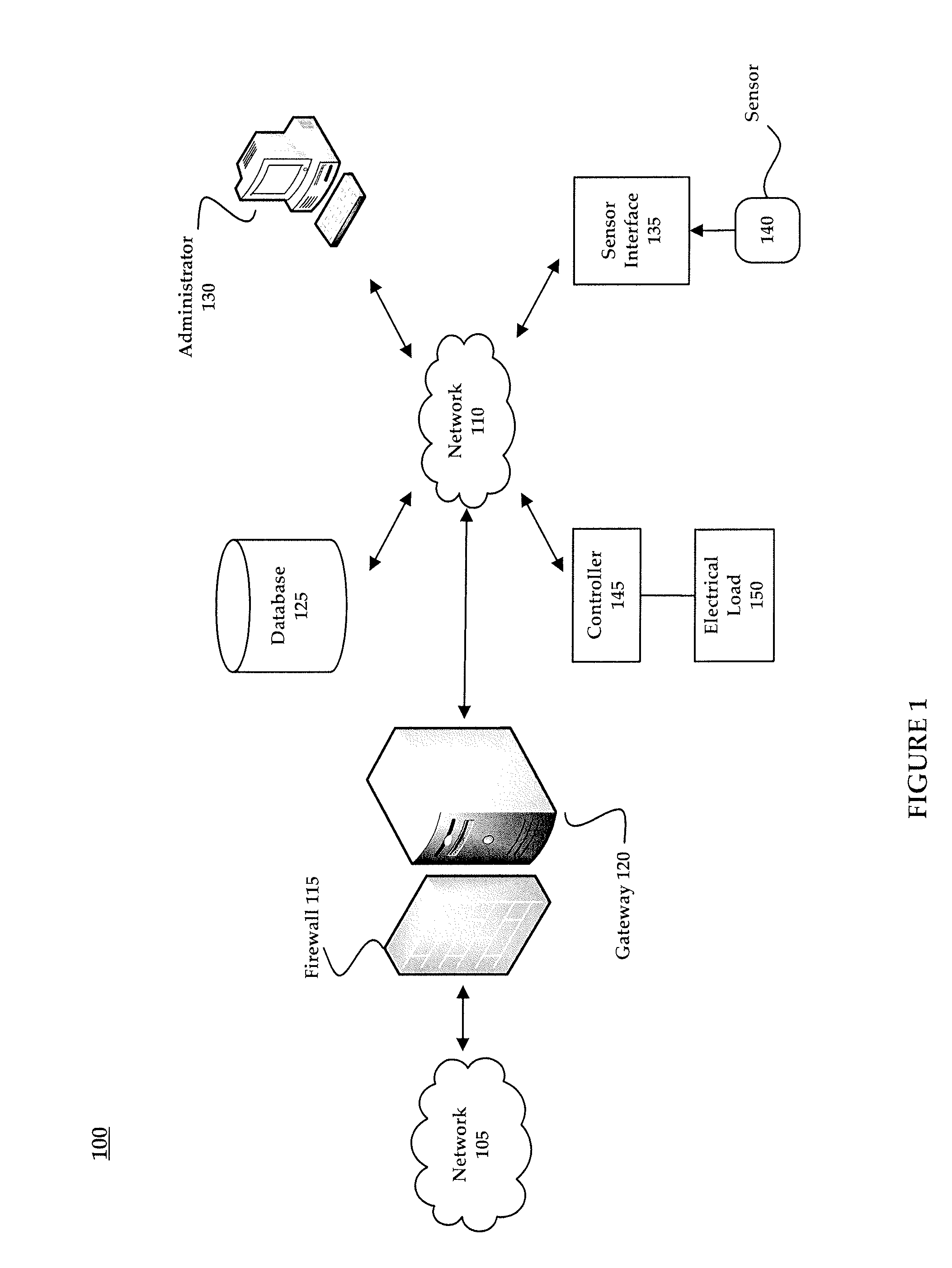
Sensor interface for wireless control
Systems and methods for enabling communication with a wired sensor are provided. A wired sensor may be adapted for wireless communication using a sensor interface. A sensor interface is communicatively coupled with a wired sensor that provides information about a detected environmental condition. The sensor interface wirelessly transmits information received from the wired sensor to a controller that may control an electrical load based on the wirelessly transmitted information.
Owner:ABL IP HLDG
System and method for counting and tracking individuals, animals and objects in defined locations
InactiveUS20080067244A1Inexpensive and reliableOptical detectionCommerceComputer scienceIndividual animal
An automated counting and tracking system for counting the number of individuals, objects or animals having certain common demographics or attributes, located within a defined physical location, which includes a means of determining the composition of persons, items or animals located in such physical location. A method for counting and tracking the number of individuals, objects or animals having certain common demographics or attributes, located within a defined physical location, which includes a method of determining the composition of persons, items or animals located in such physical location.
Owner:MARKS JEFFREY
Systems and methods for intelligent monitoring of thoroughfares using thermal imaging
InactiveUS20140112537A1Television system detailsOptical detectionIntelligent lightingThermal image processing
Various techniques are disclosed for systems and methods using thermal imaging to intelligently monitor thoroughfares. For example, an intelligent monitoring system may include an infrared imaging module, a processor, a communication module, a memory, and an adjustable component. The system may be mounted, installed, or otherwise disposed at various locations along thoroughfares, and capture thermal images of a scene that includes at least a portion of the thoroughfares. Various thermal image processing and analysis operations may be performed on the thermal images to generate comprehensive monitoring information including an indication of detected objects in the scene and at least one attribute associated with the objects. Various actions may be taken, such as generating various alarms and intelligently adjusting operation of various adjustable devices on thoroughfares, based on the monitoring information. The monitoring information may be shared among multiple instances of the system, and may be communicated to external devices.
Owner:FLIR SYST INC
Active infrared presence sensor
InactiveUS20030025082A1Avoid direct couplingLow-cost integrationRadiation pyrometryOptical detectionMicrocontrollerHysteresis
A presence detector includes an optical emitter for emitting optical radiation, an optical detector for detecting a presence of an object based on receiving the optical radiation, and a microcontroller for controlling the optical emitter and processing the optical detector output, such that a range adjustment and range hysteresis based on the object are provided by software in the microcontroller.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
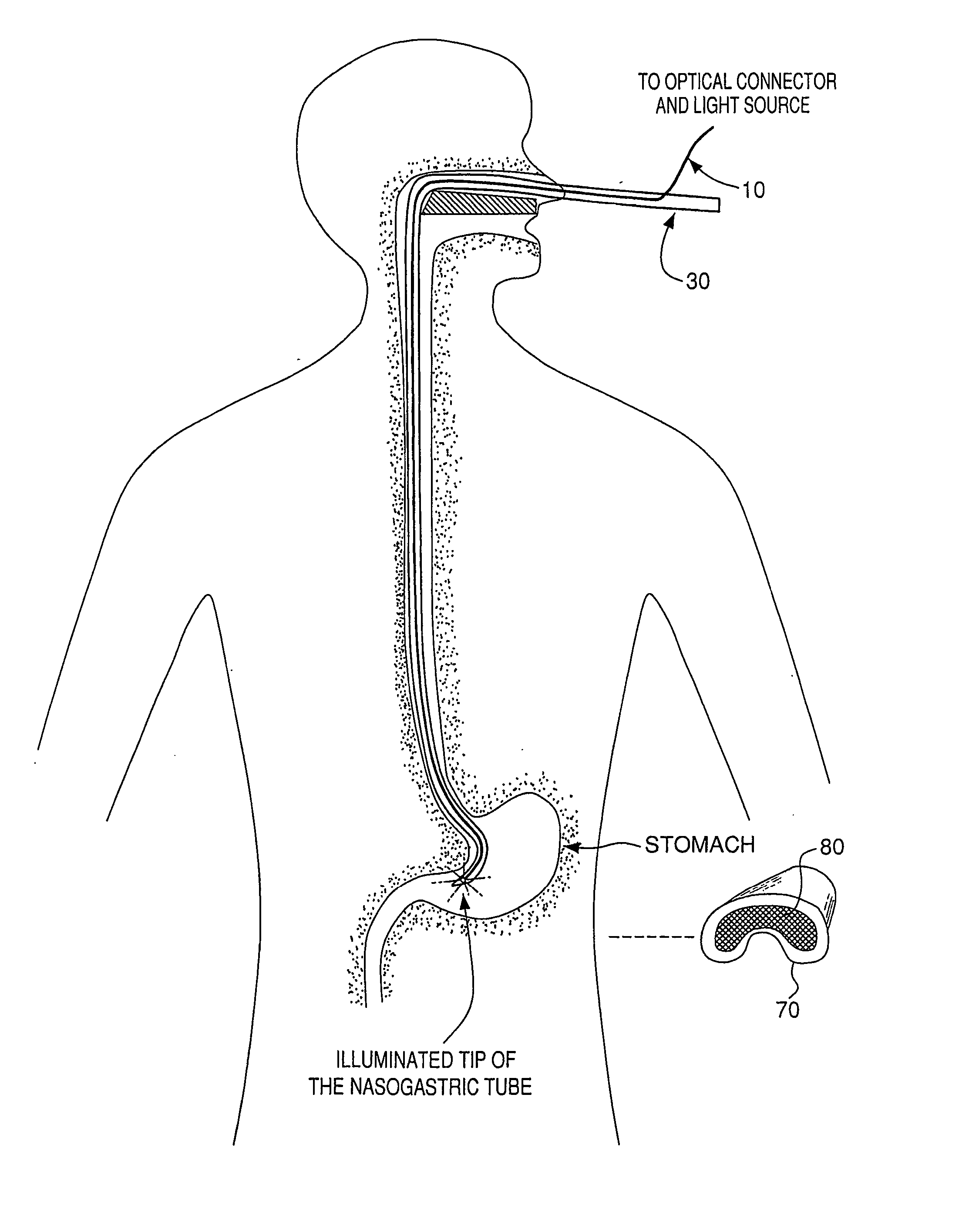
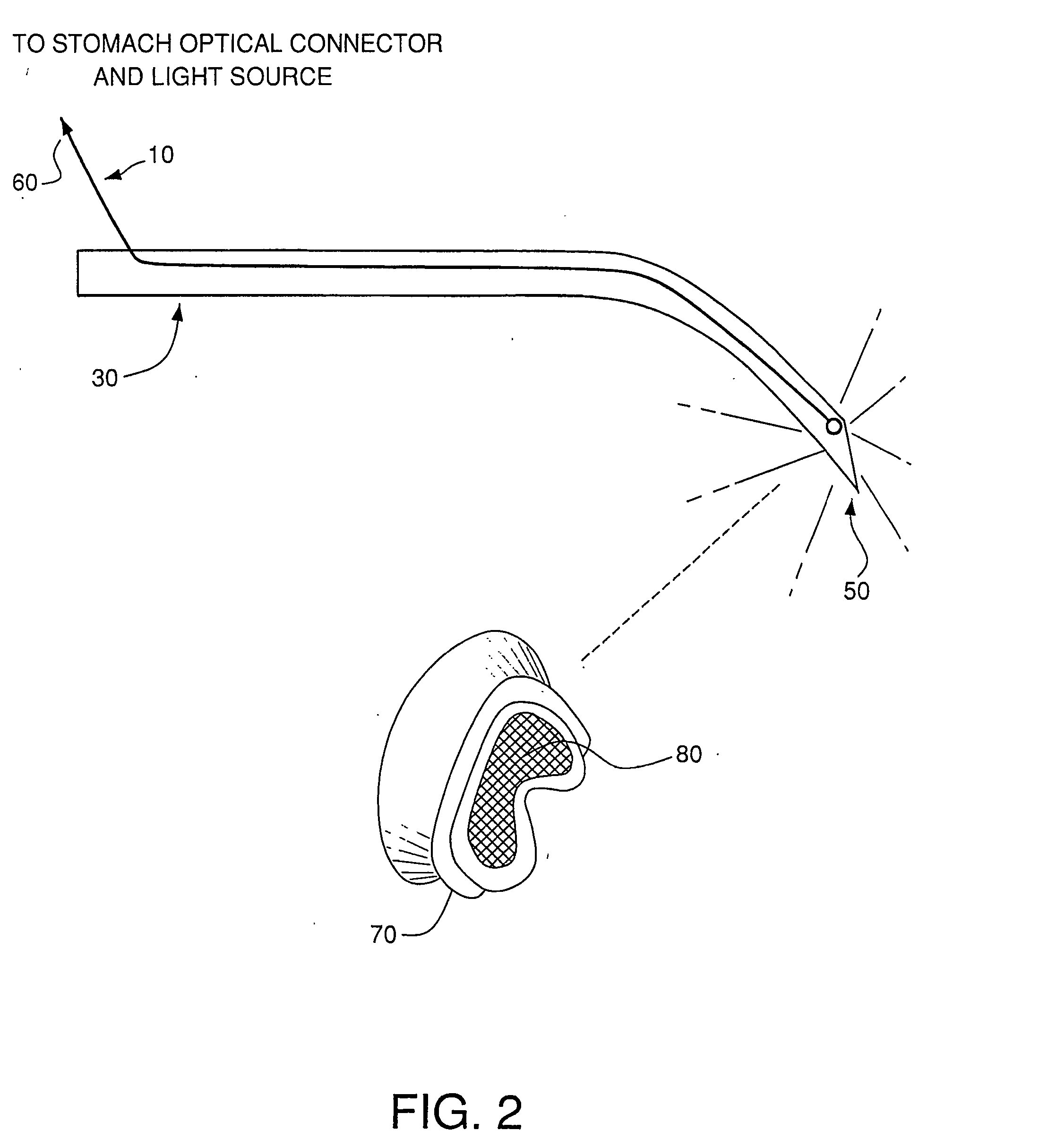
Optical guidance system for invasive catheter placement
Light from a small laser diode is inserted in a distal end of a catheter and passed through an optical fiber that is either included in the lumen or incorporated into the wall of an invasive catheter tube during manufacture. The light is selected to be of a wavelength that is minimally absorbed by tissue, preferably in the range from about 620 nm to 1100 nm. 780 nm is preferably used as this is where the tissue absorption is near a minimum. The light passes out the end of the fiber (at the proximal end of the catheter) and through the tissue to the outside of the patient's skin where it is measured. The light pattern is observed by night vision goggles that filter out other frequencies of light. The detected light permits location of the end of the fiber, the positional accuracy depending on the thickness of tissue between the fiber tip and the exterior of the body. The method is highly accurate for small children and for catheters within a few centimeters of the skin surface of adults.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
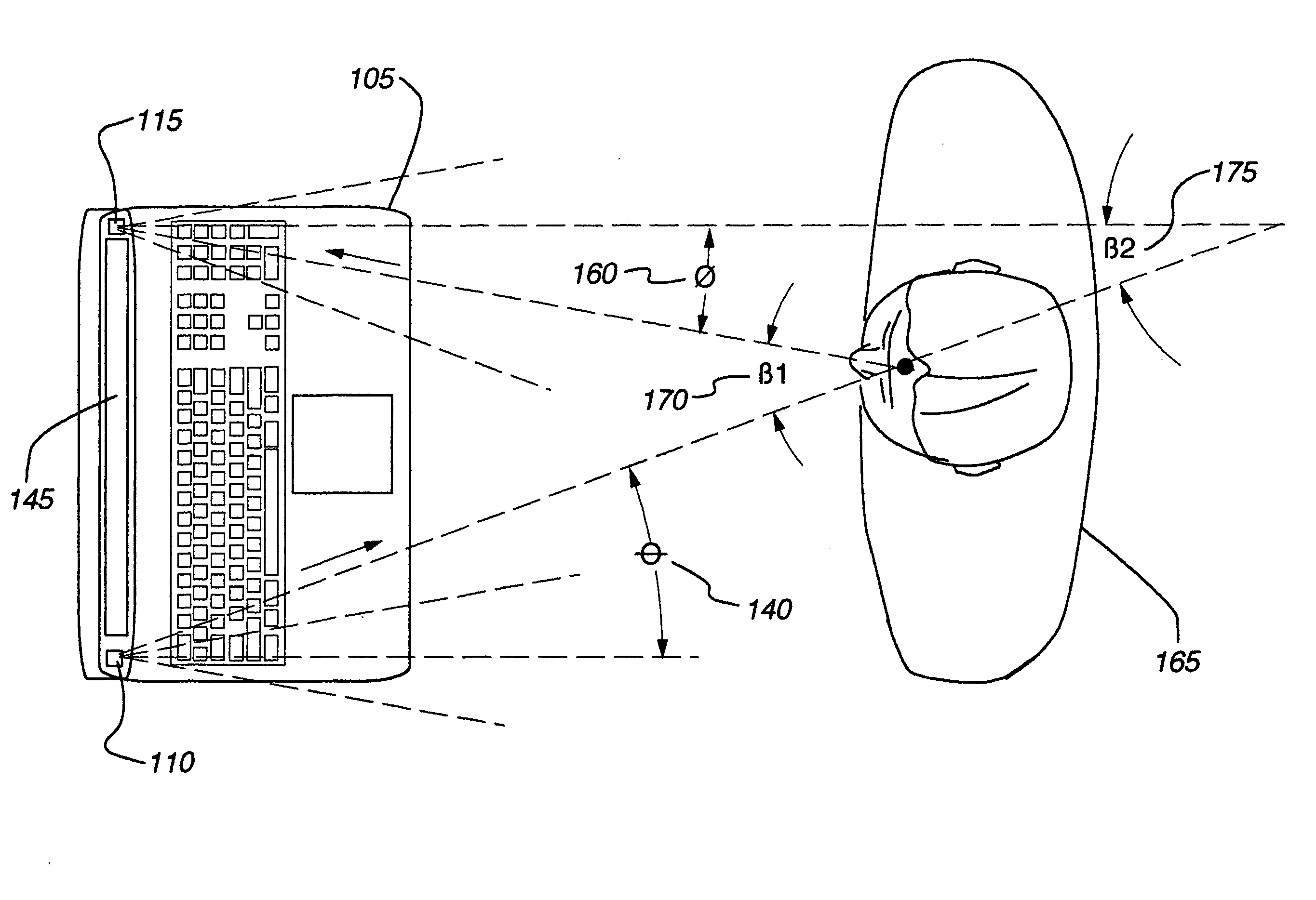
Method and apparatus for remotely detecting presence
ActiveUS20060290921A1Minimize power consumptionImprove user experienceAngle measurementOptical rangefindersElectric forceEngineering
An apparatus for detecting a person's presence without requiring the person to provide auditory or tactile input. The invention may be incorporated into an electronic device, such as a desktop computer or notebook computer. The embodiment may employ a variety of radiation emissions to determine when a person enters the embodiment's field of detection and, in response to the person entering, activate the electronic device. This may prove particularly useful where, for example, the electronic device consumes significant power and / or may suffer deleterious effects if left active for too long.
Owner:APPLE INC
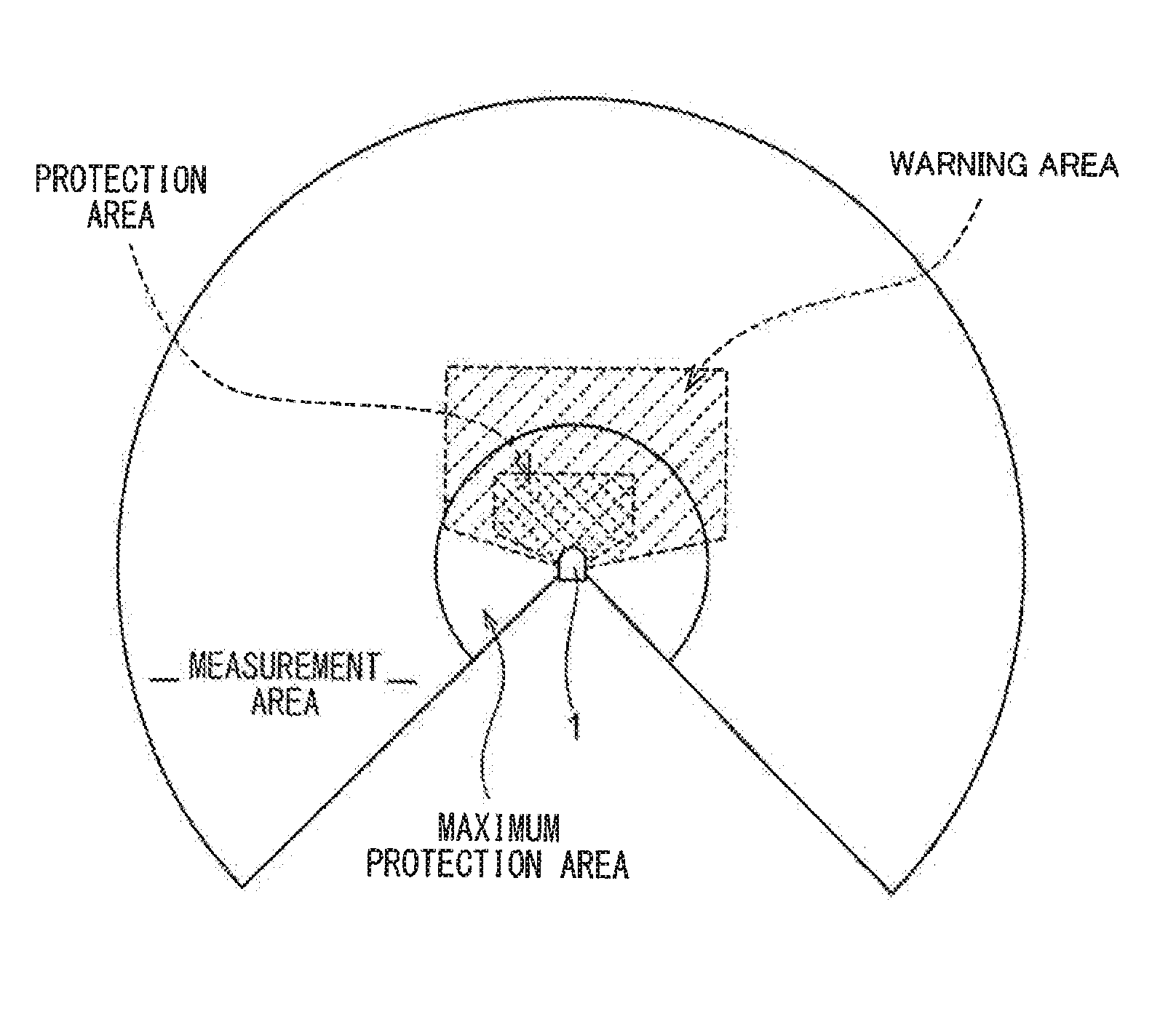
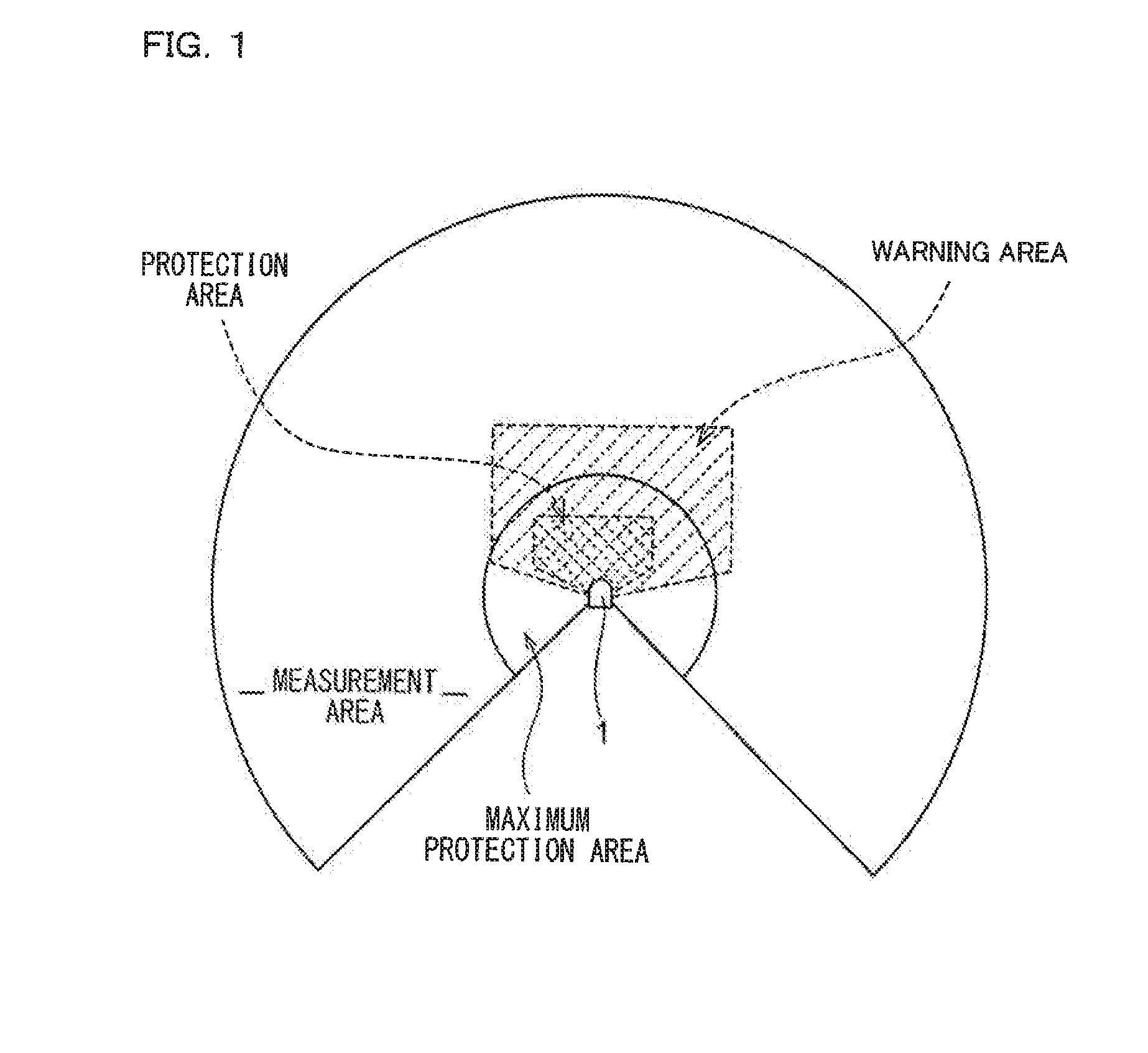
Apparatus and method for monitoring a spatial area, in particular for safeguarding a hazardous area of an automatically operated installation
ActiveUS20080273758A1Increased fail-safetySimple processOptical detectionEngineering safety devicesImage recordingLight signal
An apparatus for monitoring a spatial area, in particular for safeguarding a hazardous area of an automatically operated installation, comprises an illumination device which at least temporarily emits light signals into the spatial area. A first image recording unit records a first image of the spatial area. The first image recording unit comprises an image sensor having a plurality of pixels. An evaluation unit determines a distance value for at least one spatial area point, which is located in the spatial area and is imaged on at least one pixel, by means of a propagation type measurement. The propagation type measurement suffers from a limited unambiguity range. Therefore, a test device is designed to check the distance value by means of a reference distance value determined from a second image of said spatial area.
Owner:PILZ (COMPANY)
Opto-electronic module and devices comprising the same
ActiveUS20130153772A1Safely proximityPredictable and safe operationRadiation pyrometryPhotometryEmission channelingDistribution characteristic
An opto-electronic module includes a detecting channel comprising a detecting member for detecting light and an emission channel comprising an emission member for emitting light generally detectable by said detecting member. Therein, a radiation distribution characteristic for an emission of light from said emission channel is non rotationally symmetric; and / or a sensitivity distribution characteristic for a detection in said detecting channel of light incident on said detection channel is non rotationally symmetric; and / or a central or main emission direction for an emission of light from said emission channel and a central or main detection direction for a detection of light incident on said detection channel are aligned not parallel to each other; and / or at least a first one of the channels comprises one or more passive optical components.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Distributed acoustic sensing with fiber bragg gratings
ActiveUS20100200744A1High sensitivityInexpensive to acquireOptical detectionSeismic signal receiversDistributed acoustic sensingFiber
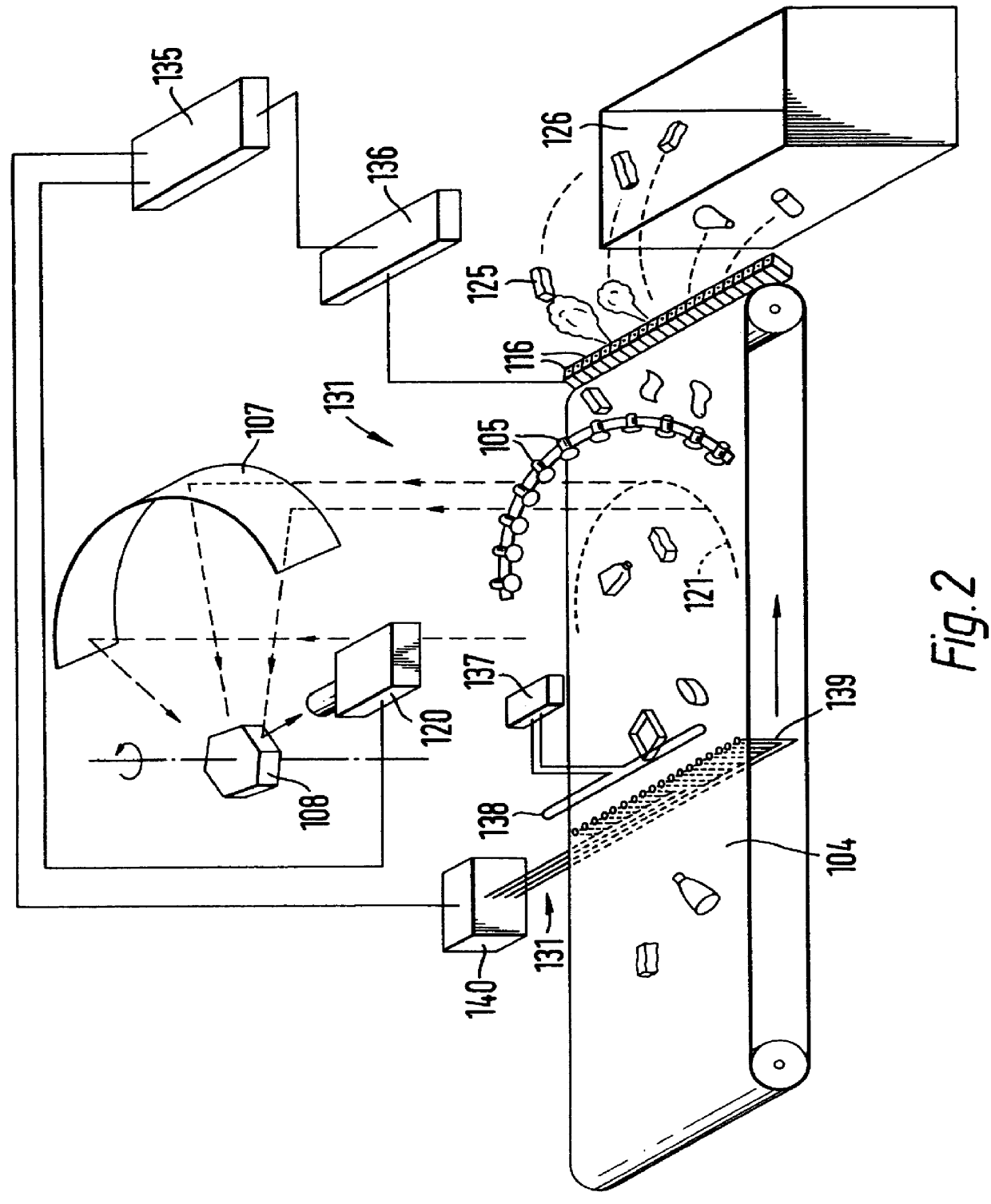
A method for obtaining information about a subsurface formation from acoustic signals that contain information about to the subsurface formation, comprises: providing a fiber optic having a proximal end and a remote end, with the proximal end being coupled to a light source and a proximal photodetector, wherein said fiber optic cable includes randomly spaced impurities and selectively placed Bragg gratings and wherein the fiber optic cable is acoustically coupled to the subsurface formation so as to allow the acoustic signals to affect the physical status of at least one grating: transmitting at least one light pulse into the cable; receiving at the photodetector a first light signal indicative of the physical status of at least one first section of the cable, and outputting at least one item of information to a display.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Hyperspectral remote sensing systems and methods using covariance equalization
InactiveUS7194111B1Reduce decreaseEasy to detectTelevision system detailsOptical detectionAlgorithmCovariance
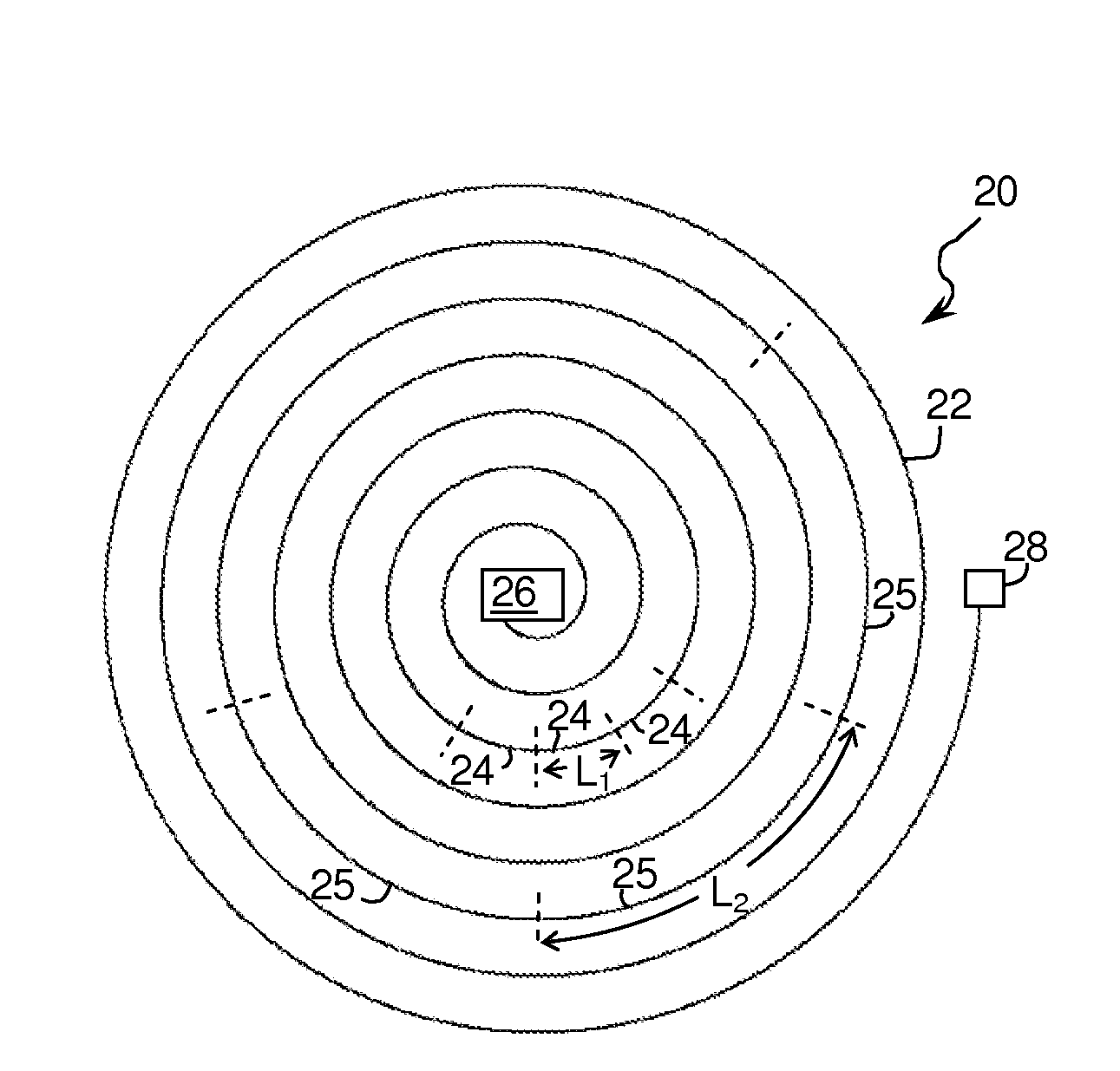
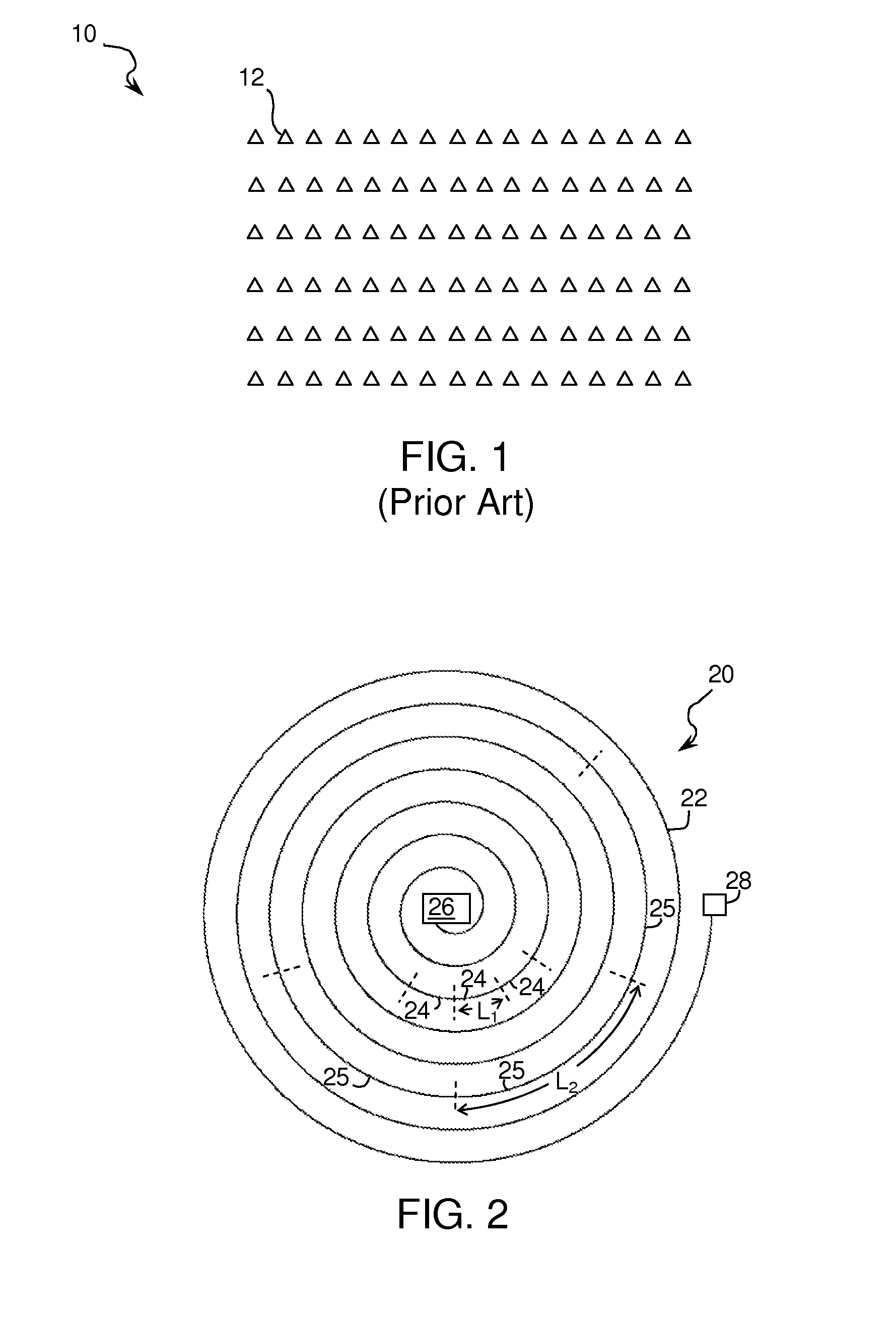
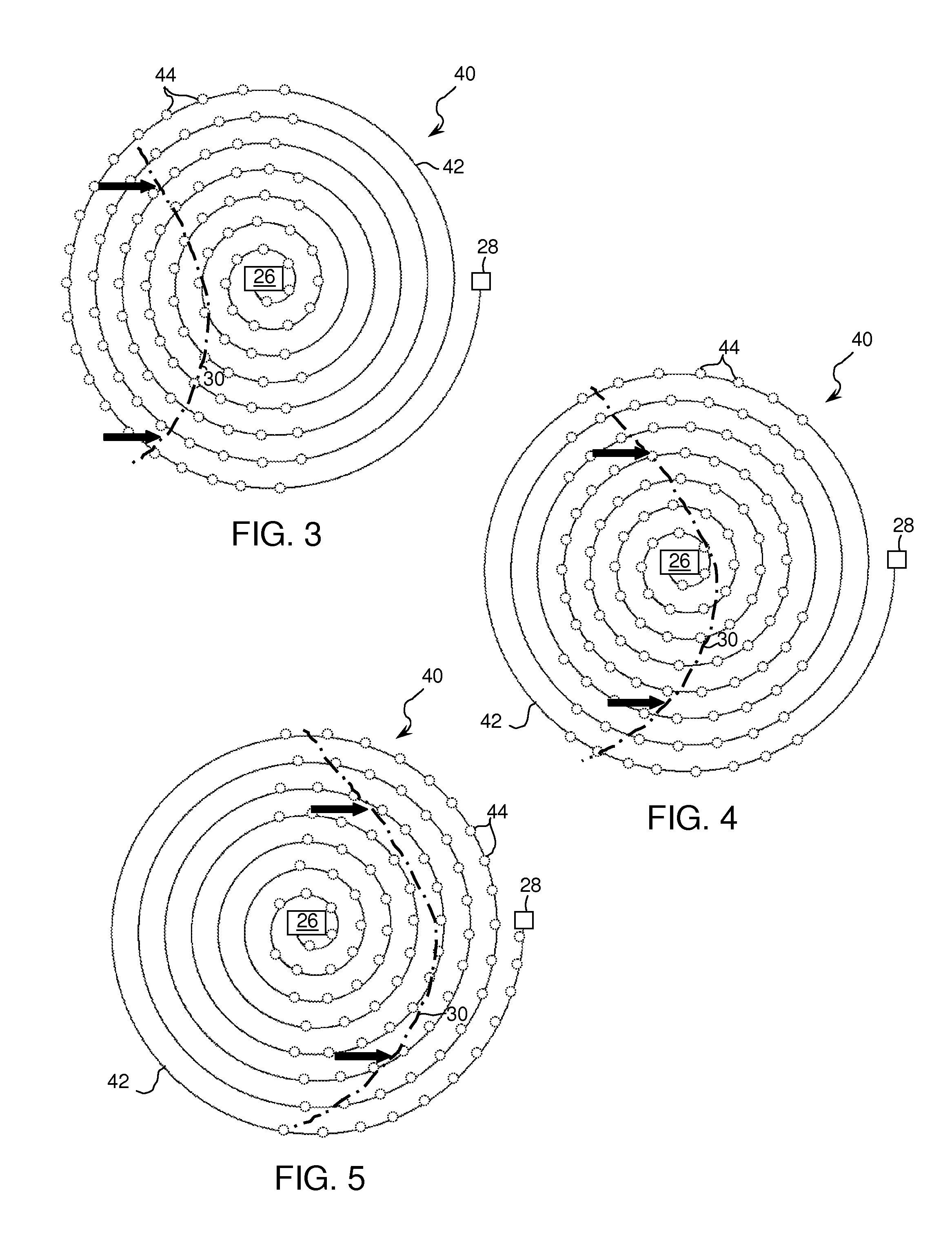
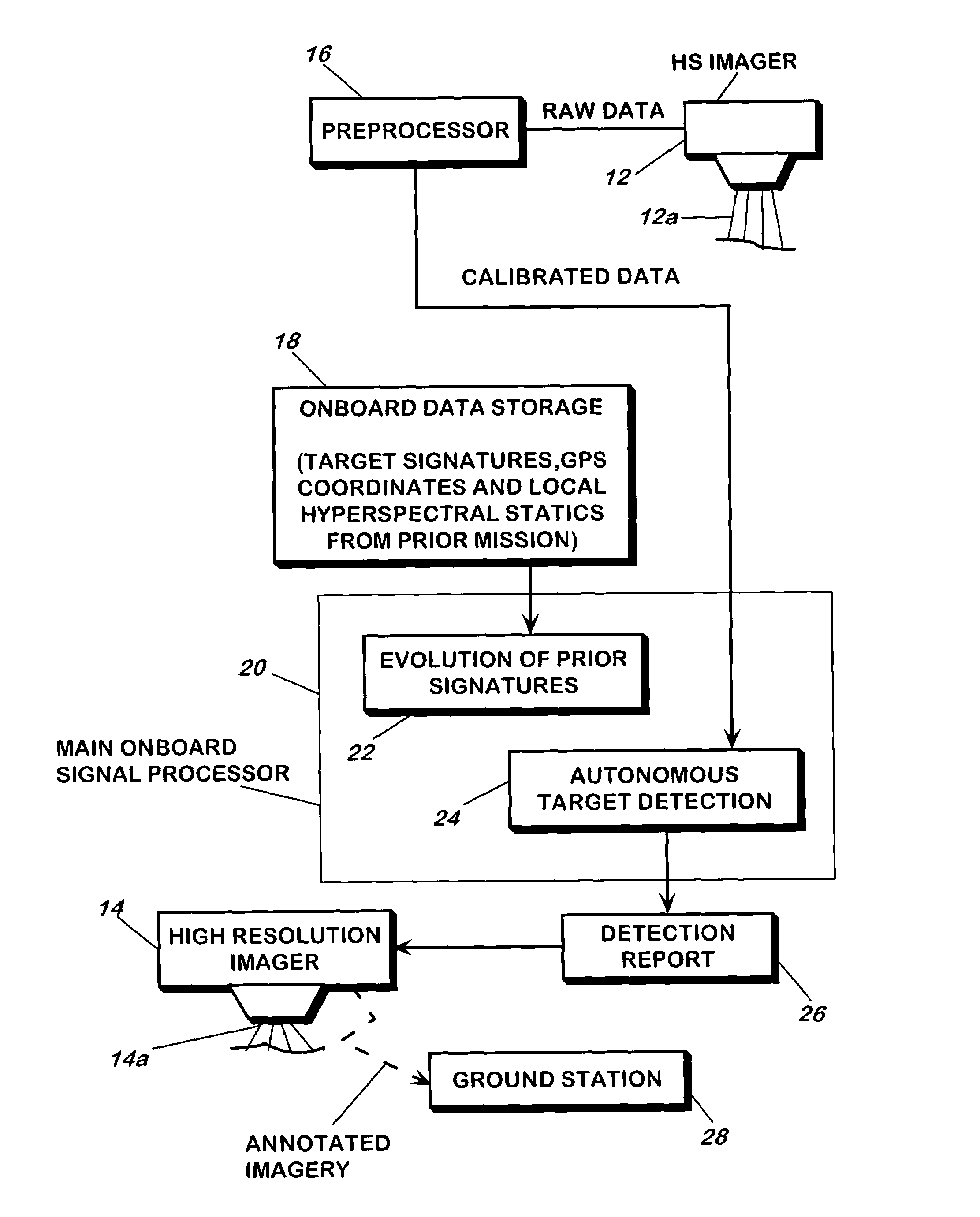
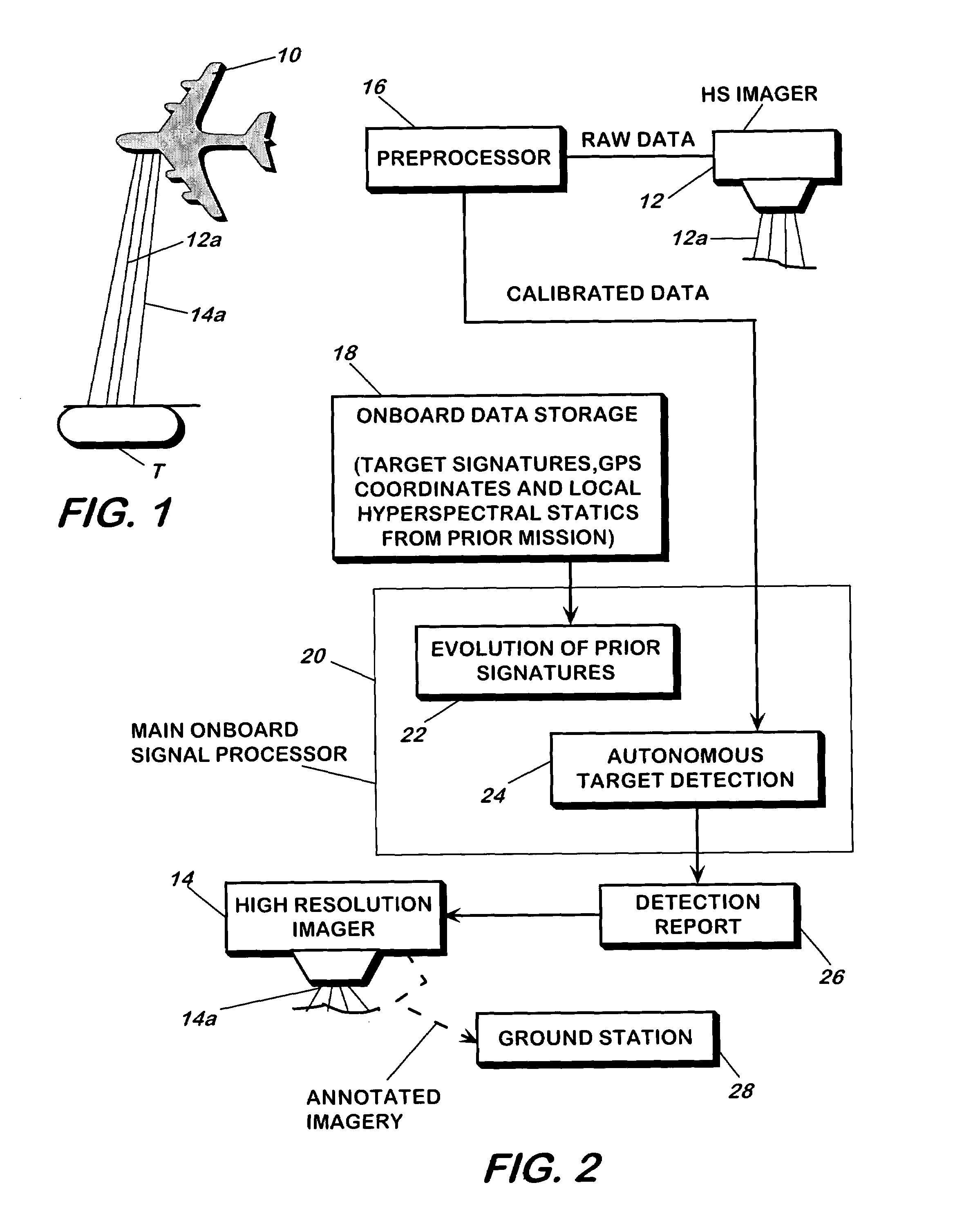
A method and apparatus for detecting a target or targets in a surrounding background locale based on target signatures obtained by a hyperspectral imaging sensor used the hyperspectral imaging sensor to collect raw target signature data and background locale data during a first data collection mission. The data is processed to generate a database including a plurality of target signatures and background data relating to the background locale. The hyperspectral imaging sensor is later used to collect further background data during a further, current data collecting mission so as to provide continuously updated background data, in real time. A covariance equalization algorithm is implemented with respect to the background data contained in the database and the updated background data collected during the current mission to effect transformation of each target signature of the database into a transformed target signature. A detection algorithm which employs the resultant transformed target signature is used to produce detection information related to the target or targets.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Fluid flow measurement using optical fibres
InactiveUS20060214098A1Easy to manufactureConvenient ArrangementSurveyConstructionsFiberElectrical resistance and conductance
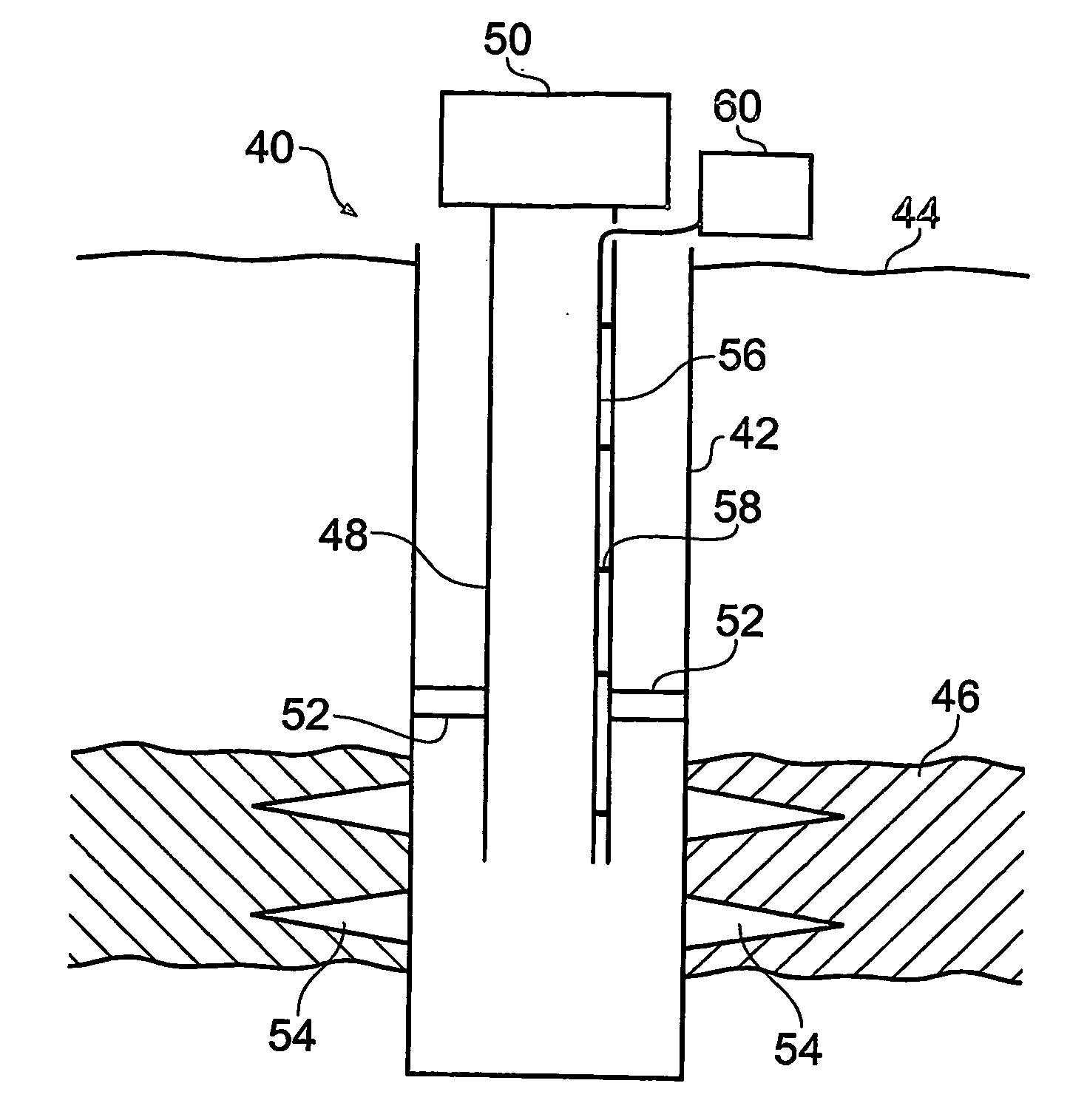
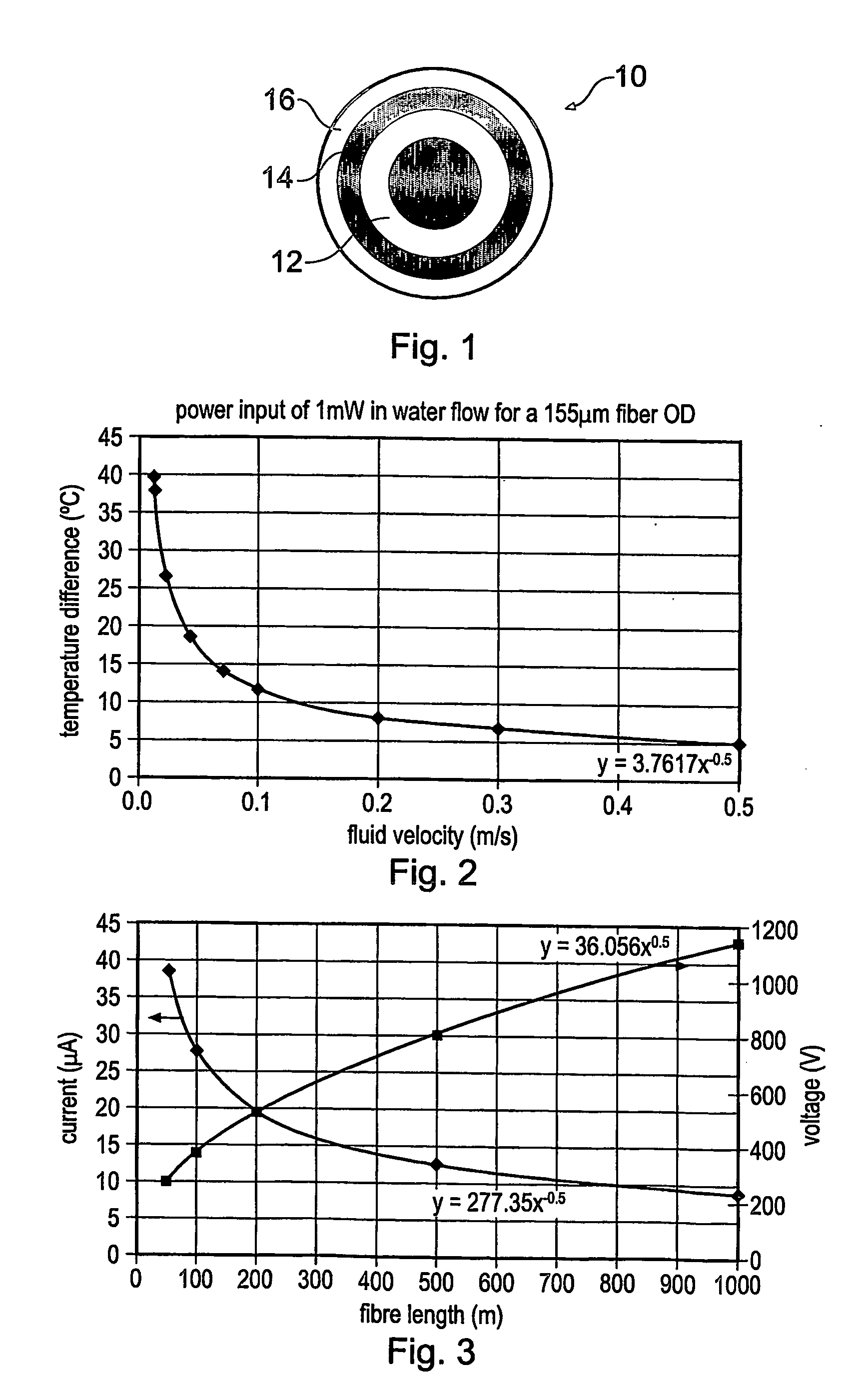
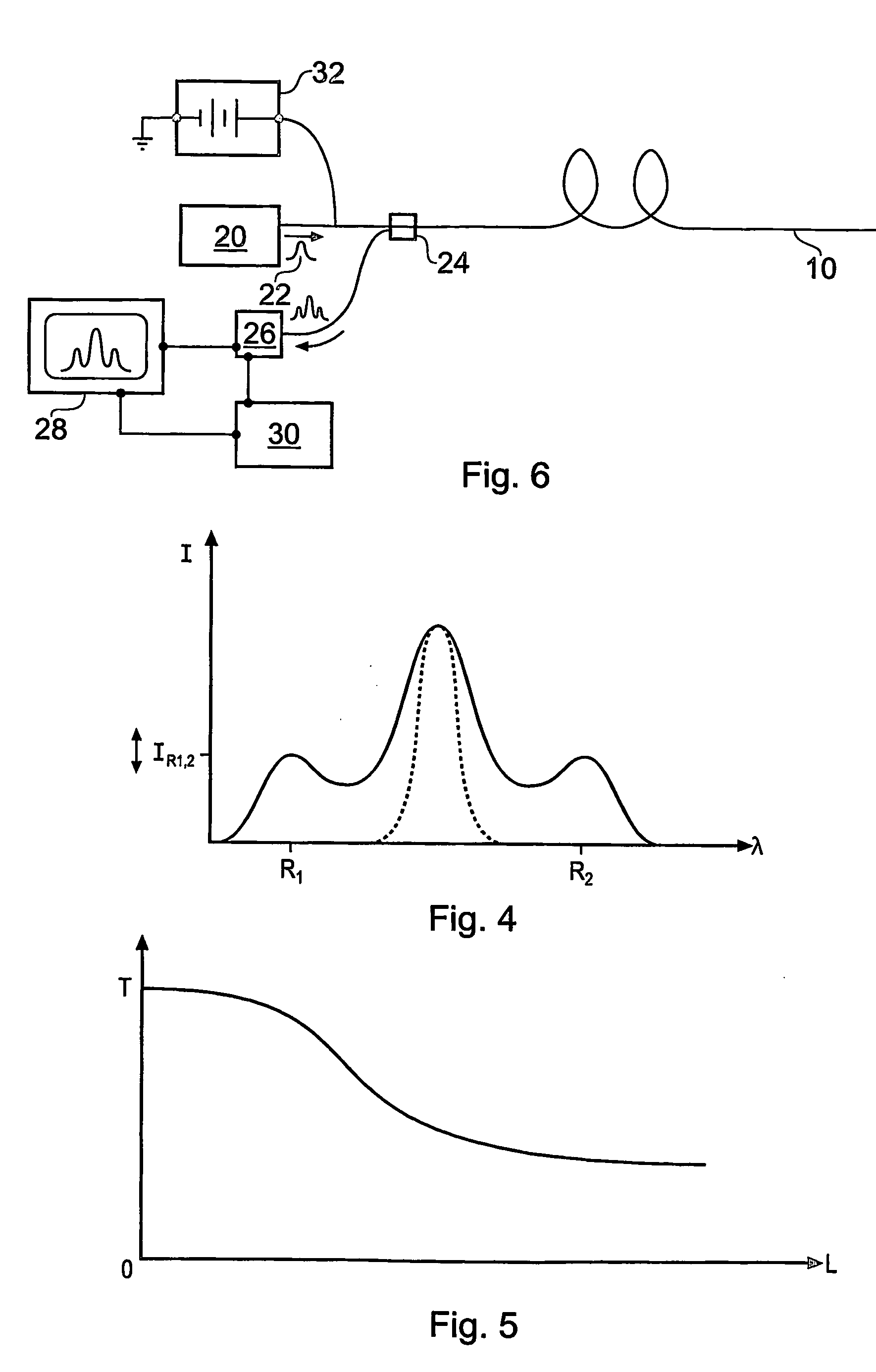
A method of monitoring fluid flow uses an optical fibre having a heatable coating. The fibre is disposed within flowing fluid, and the heatable coating heated so that heat is transferred from the coating to the fluid. Optical measurements of the temperature of the heatable coating are made, where the temperature of the heatable coating depends on the flow velocity of the flowing fluid, and the temperature measurement is used to derive information about the flow. The coating may be an electrically resistive layer on the outer surface of the fibre, that is heated by passing electric current through it. This allows distributed flow measurements to be made. Alternatively, discrete measurements can be made if the coating is provided as a thin film layer on an end facet of the fibre. The coating is heated by directing light at a wavelength absorbed by the thin film material along the fibre.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Systems and methods for high resolution optical touch position systems
InactiveUS20060132454A1High resolutionHigh sensitivityOptical detectionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceOptics
In one embodiment, a touch detection system and method is achieved having high resolution by forming an integrated array of alternating emitters and detectors. Using integration techniques, the detectors can be made much larger than the emitters while the gaps between the emitters and detectors are maintained relatively small. Thus, high resolution is achieved without dramatically increasing the number of emitter / detector pairs. In one embodiment each array is positioned on an edge of a display such that the emitter of one array is lined up (on axis with) a detector of an opposing display. In one embodiment, the touch detection system and method operates to detect the amplitude of signals arriving from opposing arrays so as to precisely determine the location of a touched position. Off-axis scanning can be employed to increase sensitivity.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Apparatus for acquiring 3-dimensional geomatical information of underground pipes and noncontact odometer using optical flow sensor and using the same
InactiveUS20100211354A1Effective maintenanceEffective preservationOptical rangefindersMeasuring wheelsOptical flowOdometer
An apparatus to acquire 3-dimensional geographical information of an underground pipe includes an in-pipe transfer unit which moves along the inside of the underground pipe, a sensing unit which senses 3-dimensional location information of the in-pipe transfer unit, and an information storage unit which stores a value measured by the sensing unit. Accordingly, the depth at which the underground pipe is located as well as 2-dimensional location information of the underground pipe is stored in the information storage unit so that maintenance and repair of the underground pipe can be carried out with greater efficiency.
Owner:WATER RESOURCES ENG +1
Automatic obstacle avoiding method of substation inspection robot
InactiveCN106324619ANot easy to interfereImprove detection accuracyOptical detectionElectromagnetic wave reradiationWalking around obstaclesRadar
The invention relates to an automatic obstacle avoiding method of a substation inspection robot. Obstacle information around the inspection robot is scanned with laser radar, and the types of obstacles are judged through an infrared temperature sensor; if the obstacles are humans or animals, the inspection robot notify the humans to leave or to dispel the animals, and there is no need to avoid the obstacles; if the obstacles remain on a set path of the inspection robot, the inspection robot executes avoiding; obstacle priorities are divided according to 'time distance' that is time that the inspection robot takes to arrive at the obstacles; the inspection robot keeps to the right according to set driving rules; upon contact with an obstacle, the inspection robot moves along the obstacle clockwise from the left of the obstacle and ends avoiding after arriving at the front of the obstacle; if unable to bypass the obstacle from the left, the inspection robot tries to bypass the obstacle anticlockwise from the right of the obstacle. The method is insusceptible to temperature and visible light, and distance and direction information detection precision is higher.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Safety Photoelectric Switch
ActiveUS20100194583A1Solve the real problemAvoid interferenceElectric signal transmission systemsOptical detectionPhotoswitchOptical axis
There is provided an optical scanning type photoelectric switch capable of preventing interference with another photoelectric switch by use of its own capability, wherein, as for light projection pulse periods of the first and second optical scanning type photoelectric switches, the period is set to 30 μs in the first optical scanning type photoelectric switch while the period is set to 33 μs in the second optical scanning type photoelectric switch 1B, the light projection pulses have the same pulse width, and by setting the light projection periods different between the first and second optical scanning type photoelectric switches, even if mutual interference occurs between any optical axes, a phase difference of 36 degrees in rotation period is generated therebetween in a next scan, thereby preventing occurrence of the interference in succession in a plurality of times of scanning.
Owner:KEYENCE
Medical Treatment System and Methods Using a Plurality of Fluid Lines
ActiveUS20160101227A1Reduce touchReduce leakage currentMedical devicesOptical detectionPeritoneal dialysisHemoperitoneum
Improvements in fluid volume measurement systems are disclosed for a pneumatically actuated diaphragm pump in general, and a peritoneal dialysis cycler using a pump cassette in particular. Pump fluid volume measurements are based on pressure measurements in a pump control chamber and a reference chamber in a two-chamber model, with different sections of the apparatus being modeled using a combination of adiabatic, isothermal and polytropic processes. Real time or instantaneous fluid flow measurements in a pump chamber of a diaphragm pump are also disclosed, in this case using a one-chamber ideal gas model and using a high speed processor to obtain and process pump control chamber pressures during fluid flow into or out of the pump chamber. Improved heater control circuitry is also disclosed, to provide added or redundant safety measures, or to reduce current leakage from a heater element during pulse width modulation control of the heater. Improvements are also disclosed in the application of negative pressure during a drain phase in peritoneal dialysis therapy, and to control the amount of intraperitoneal fluid accumulation during a therapy. Improvements in efficiency are also disclosed in the movement of fluid into and out of a two-pump cassette and heater bag of a peritoneal dialysis cycler, and in the synchronization of the operation of two or more pumps in a peritoneal dialysis cycler or other fluid handling devices using a multi-pump arrangement.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
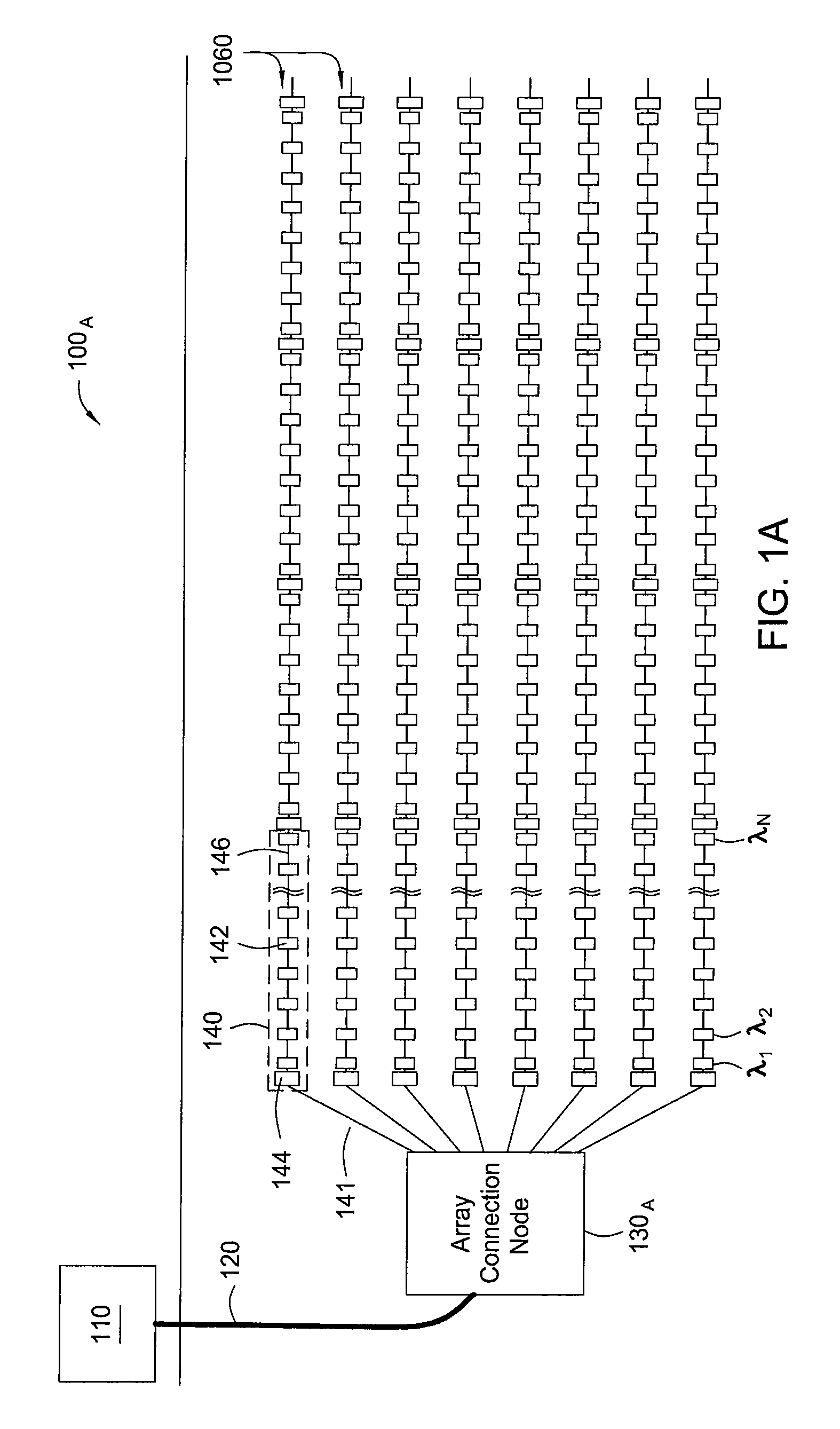
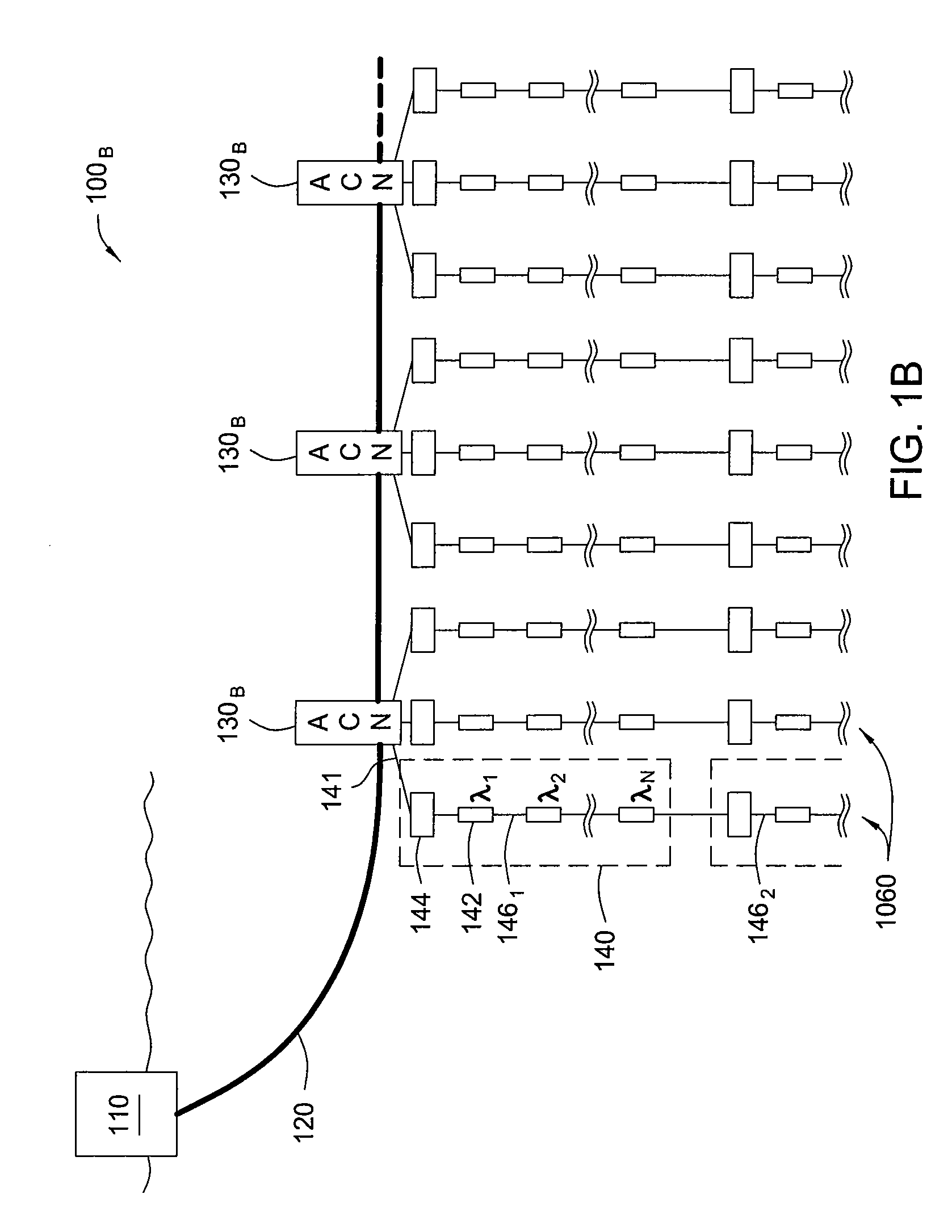
Seismic streamer array
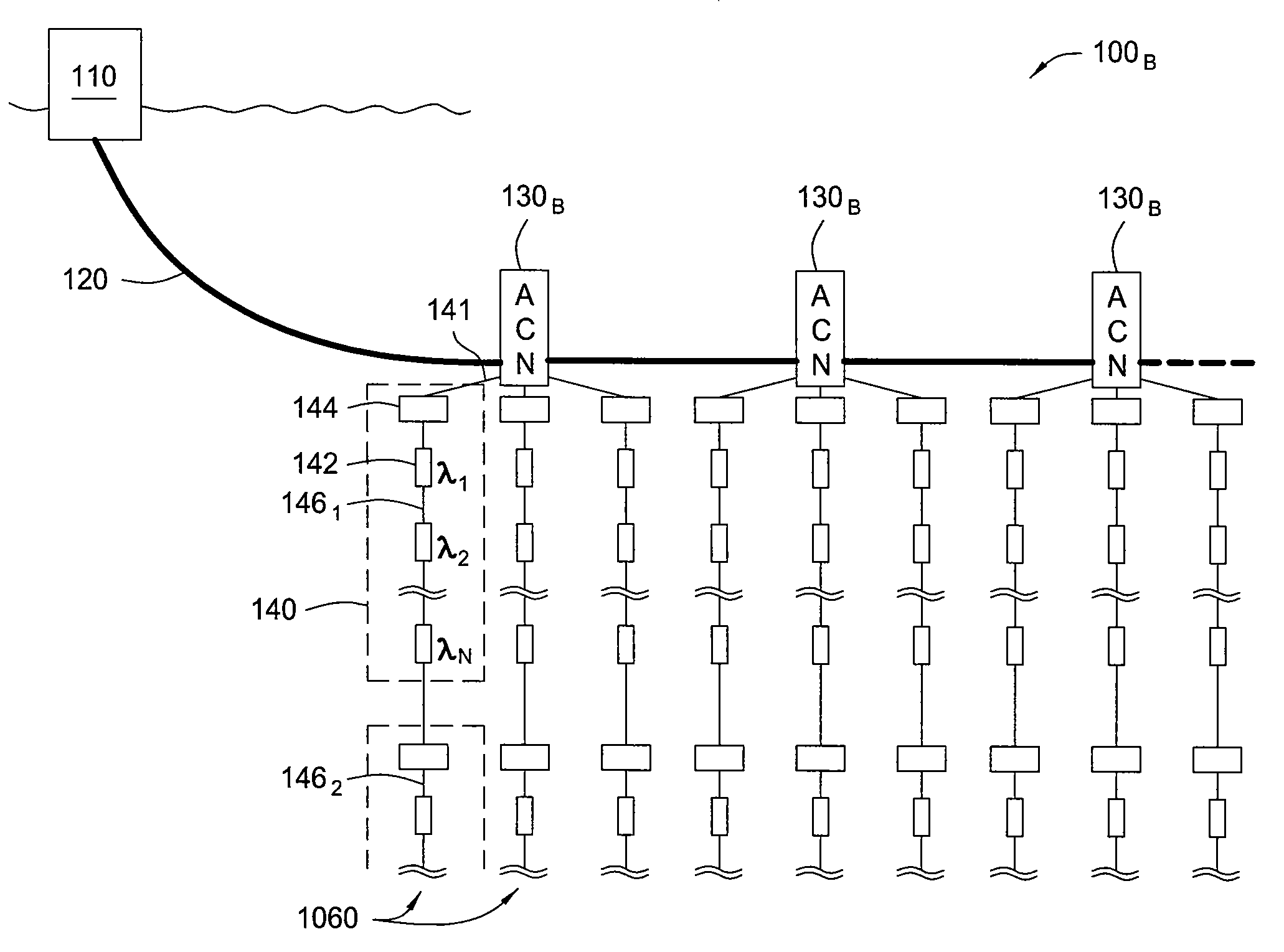
Seismic sensor systems and sensor station topologies, as well as corresponding cable and sensor station components, manufacturing and deployment techniques are provided. For some embodiments, networks of optical ocean bottom seismic (OBS) stations are provided, in which sensor stations are efficiently deployed in a modular fashion as series of array cable modules deployed along a multi-fiber cable.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
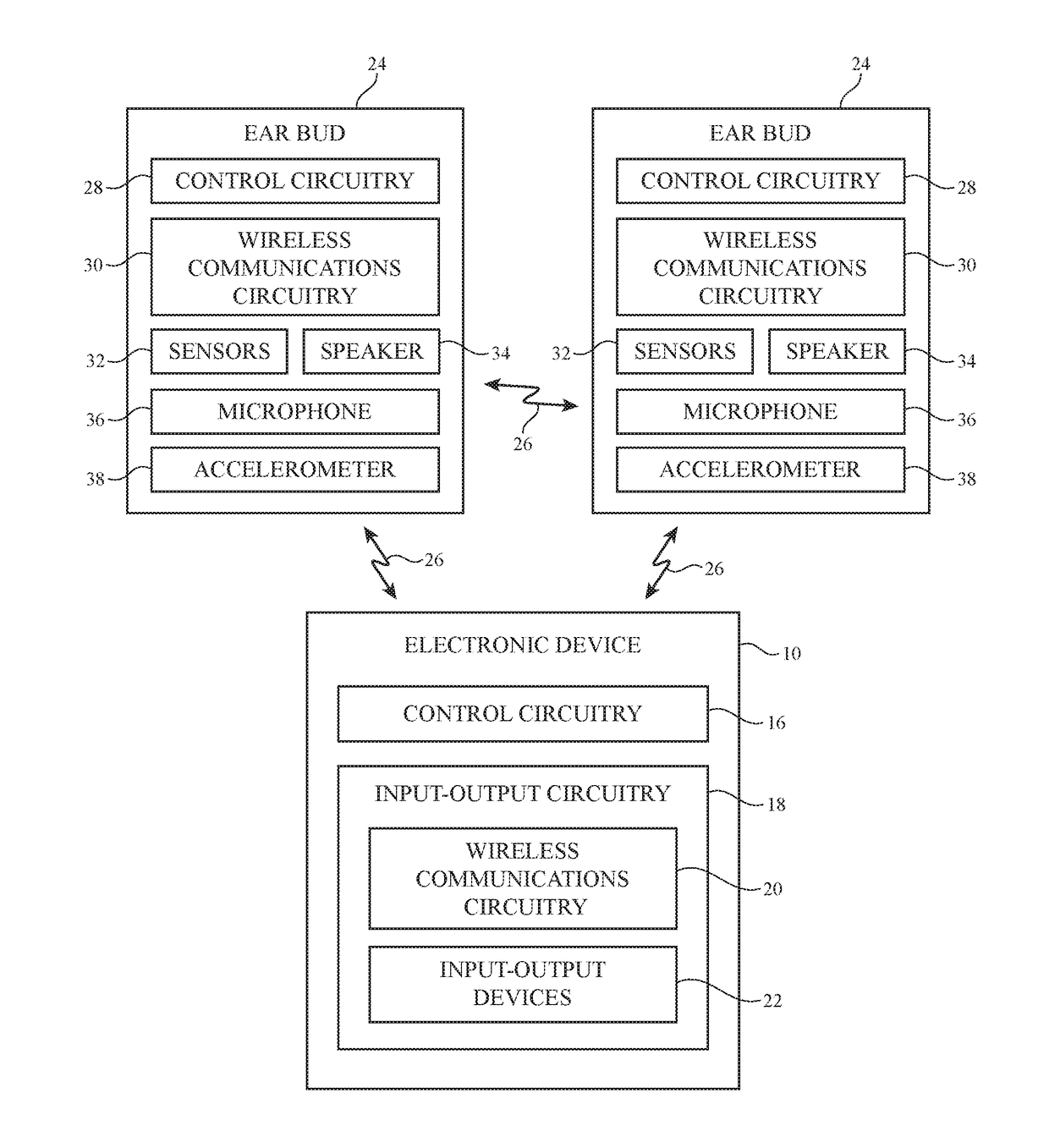
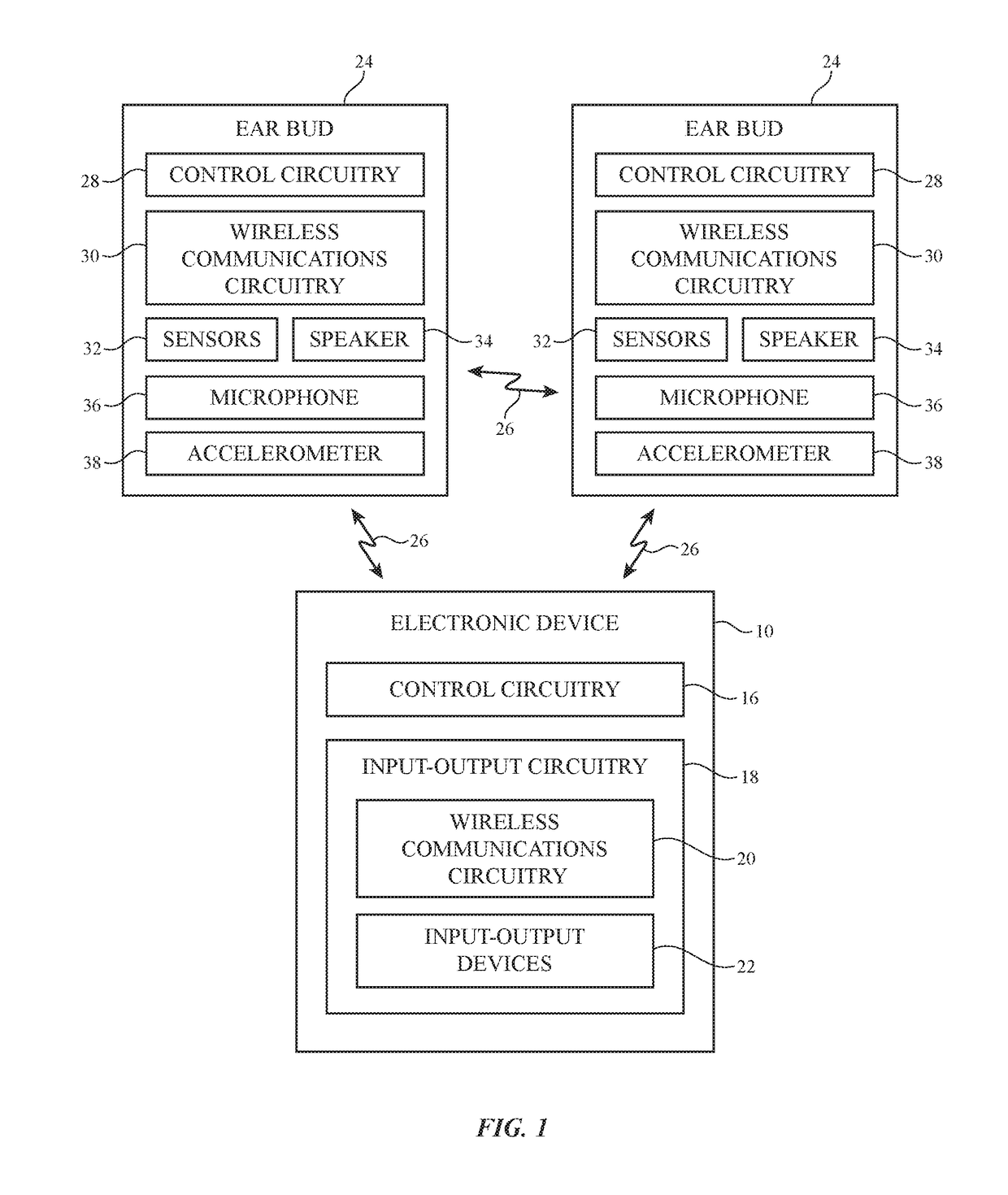
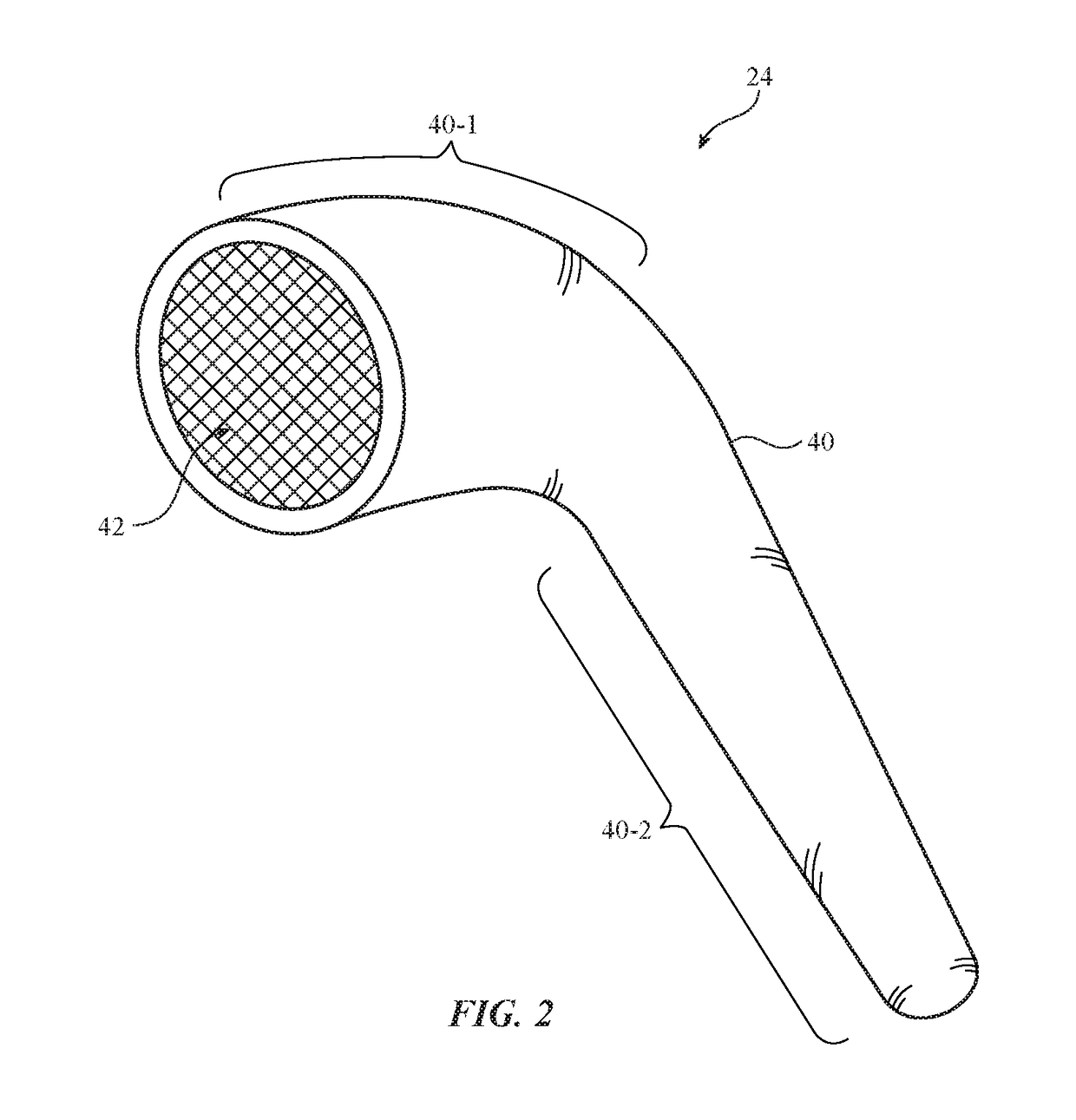
Wireless Ear Buds With Proximity Sensors
Owner:APPLE INC
Perimetric detection system
InactiveUS6974948B1Ambient light fluctuationSimple and inexpensive to produceOptical detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansAutomatic waste containerEngineering
Owner:BRENT MARK R
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com