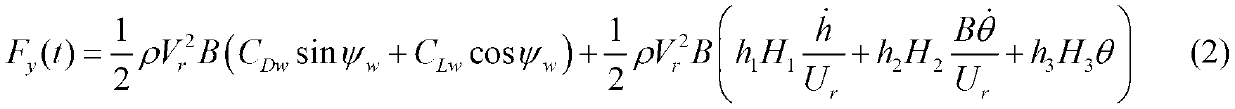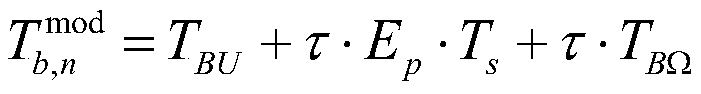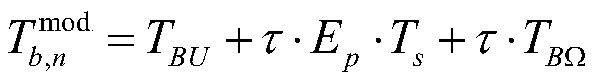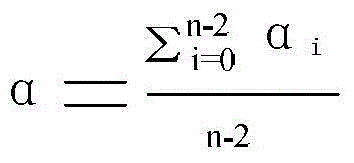Patents
Literature
92 results about "Relative wind" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
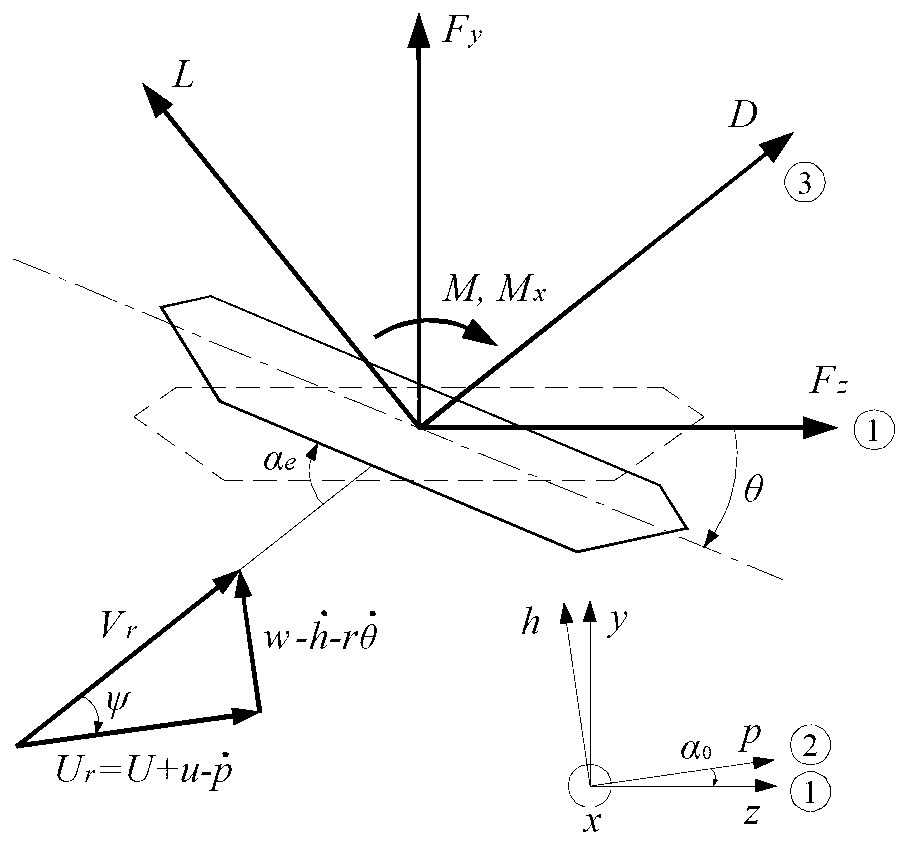
In aeronautics, the relative wind is the direction of movement of the atmosphere relative to an aircraft or an airfoil. It is opposite to the direction of movement of the aircraft or airfoil relative to the atmosphere. Close to any point on the surface of an aircraft or airfoil, the air is moving parallel to the surface; but at a great distance from the aircraft or airfoil the movement of the air can be represented by a single vector. This vector is the relative wind or the free stream velocity vector.
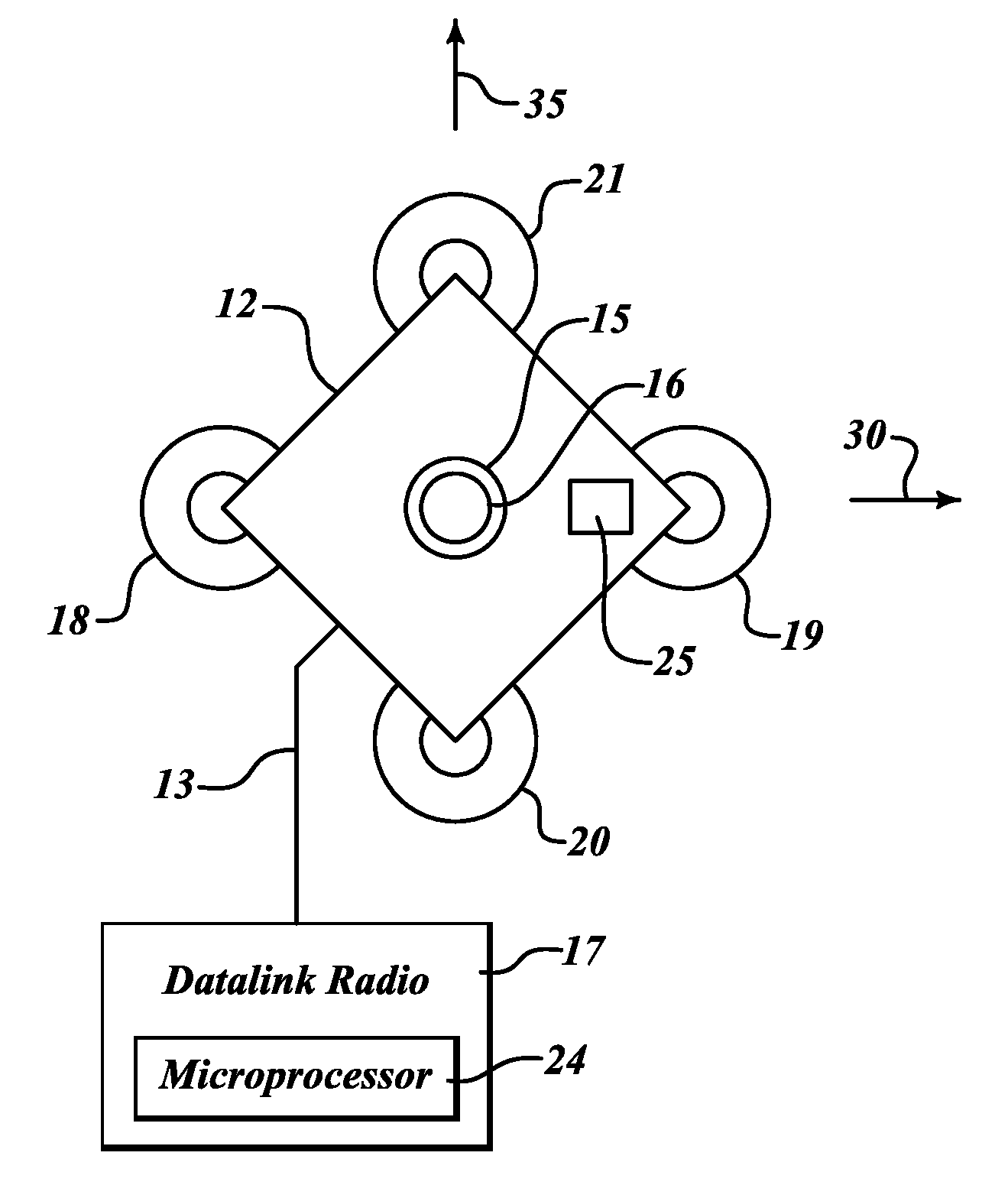
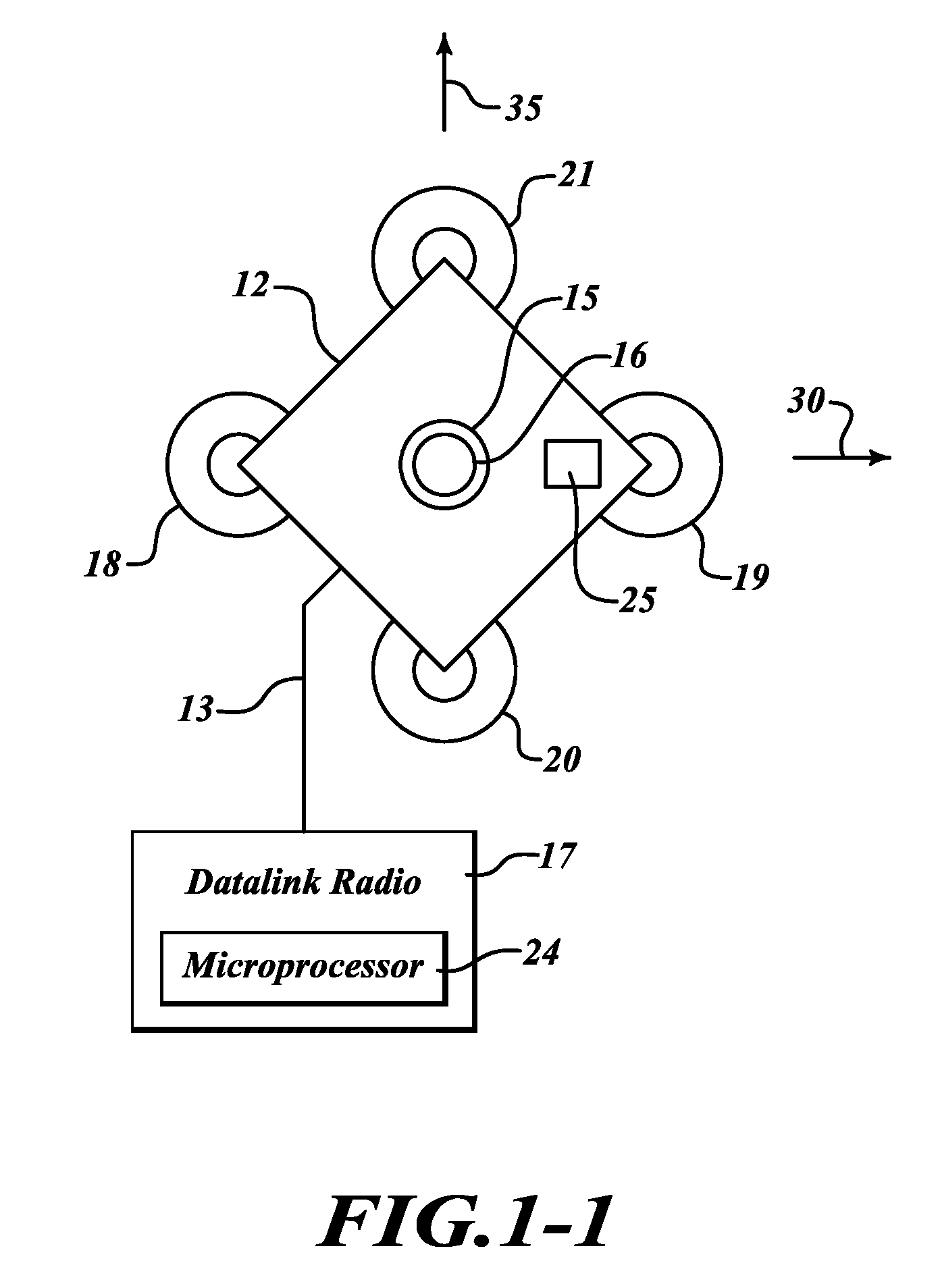
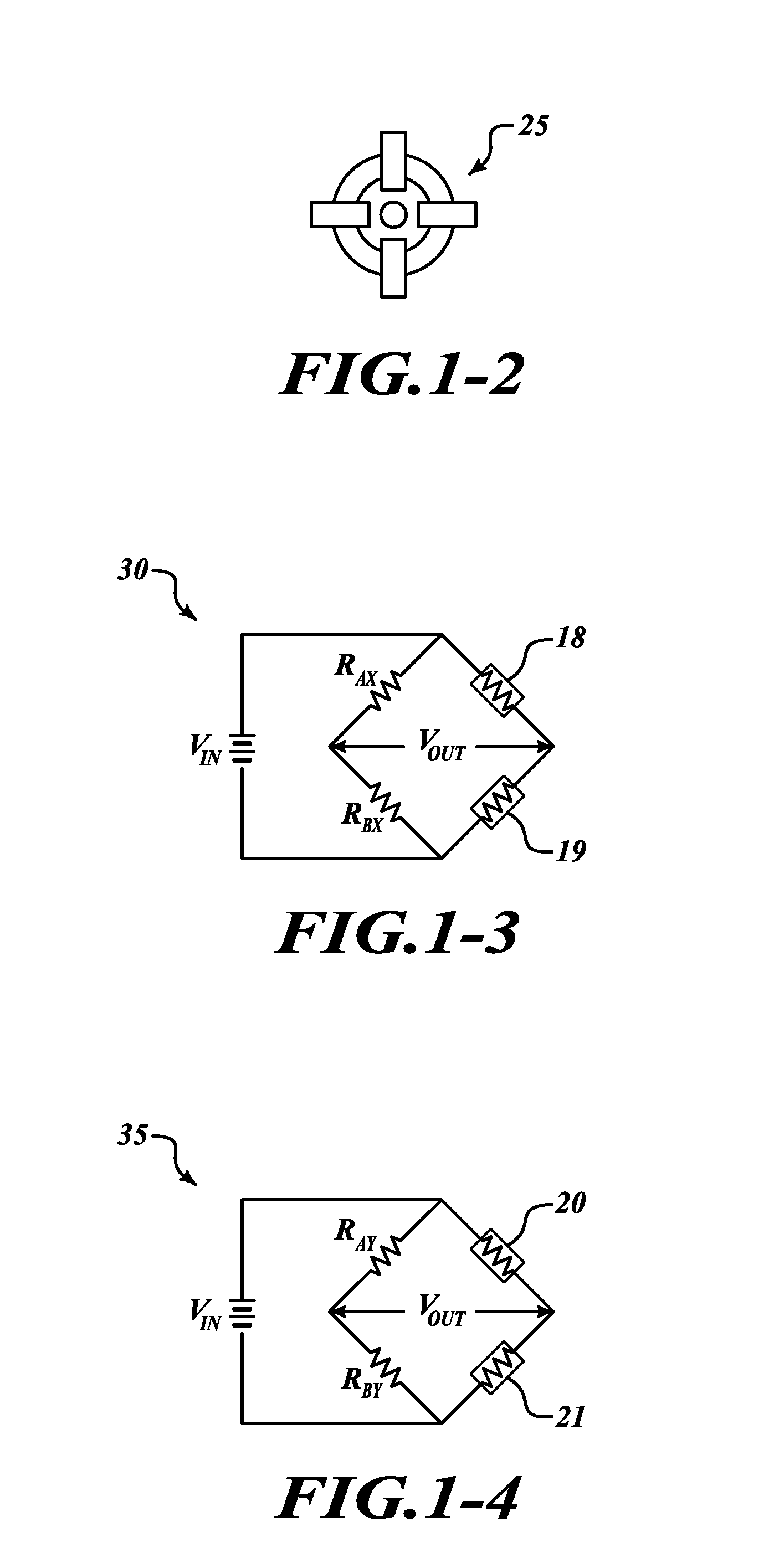
Wiper blade for cleaning screens in particular on motor vehicles
InactiveUS6944905B2Reduce weightSave materialWindow cleanersVehicle cleaningBand shapeMotorized vehicle
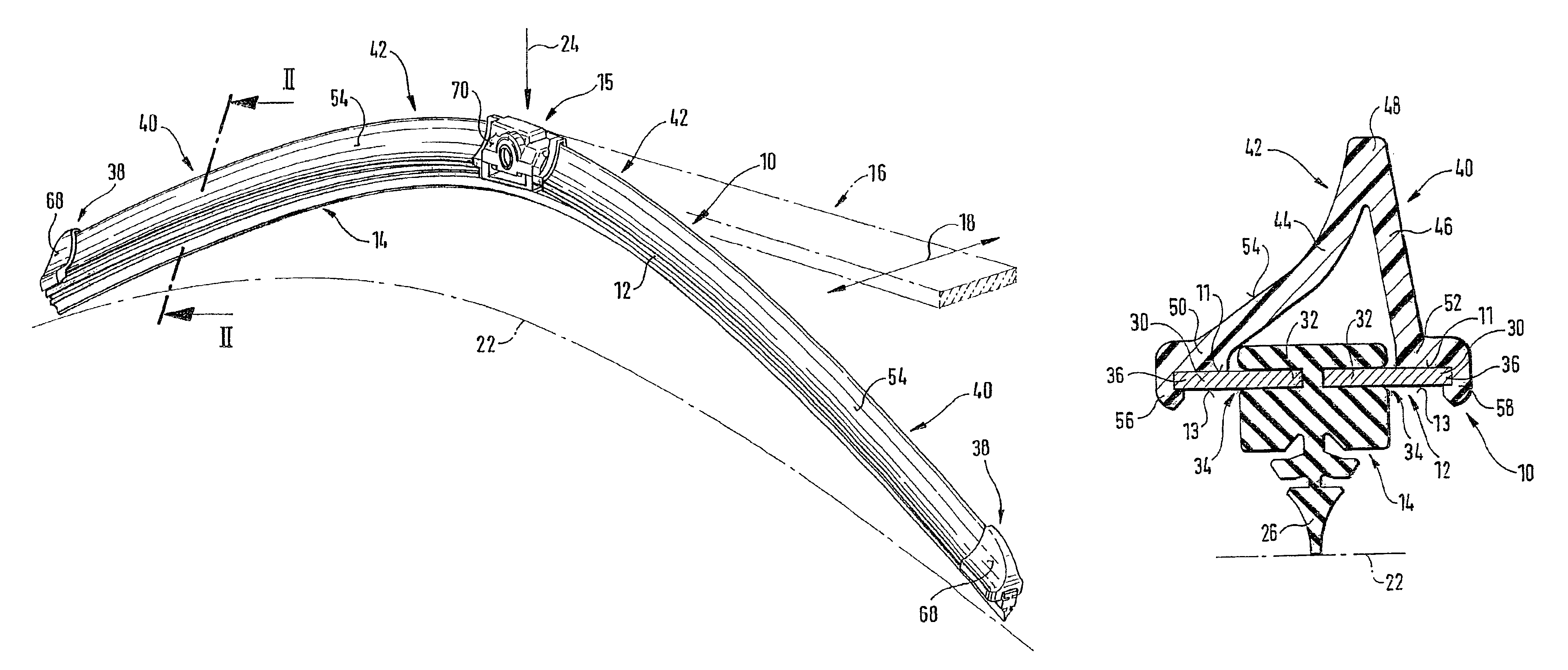
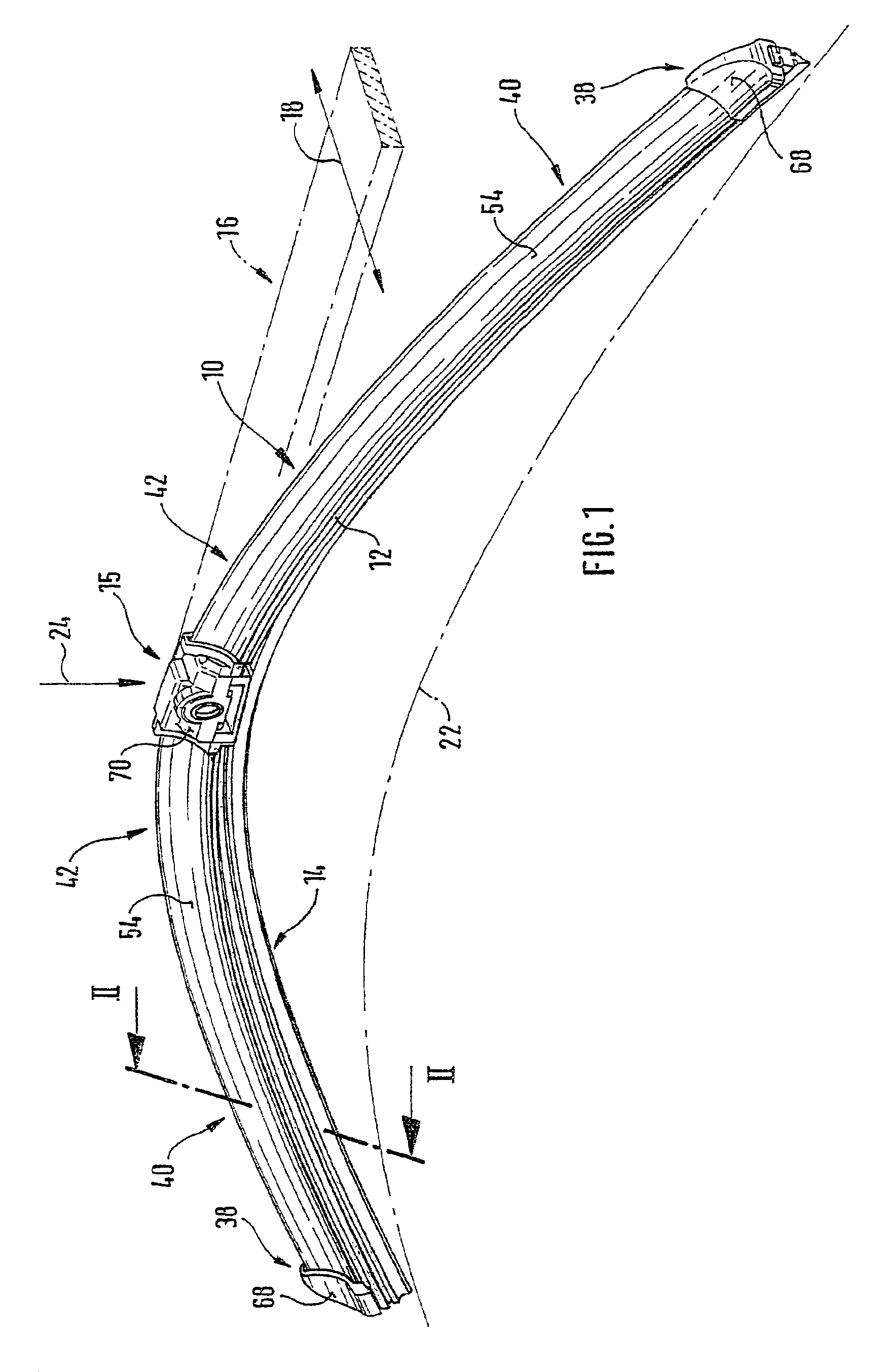
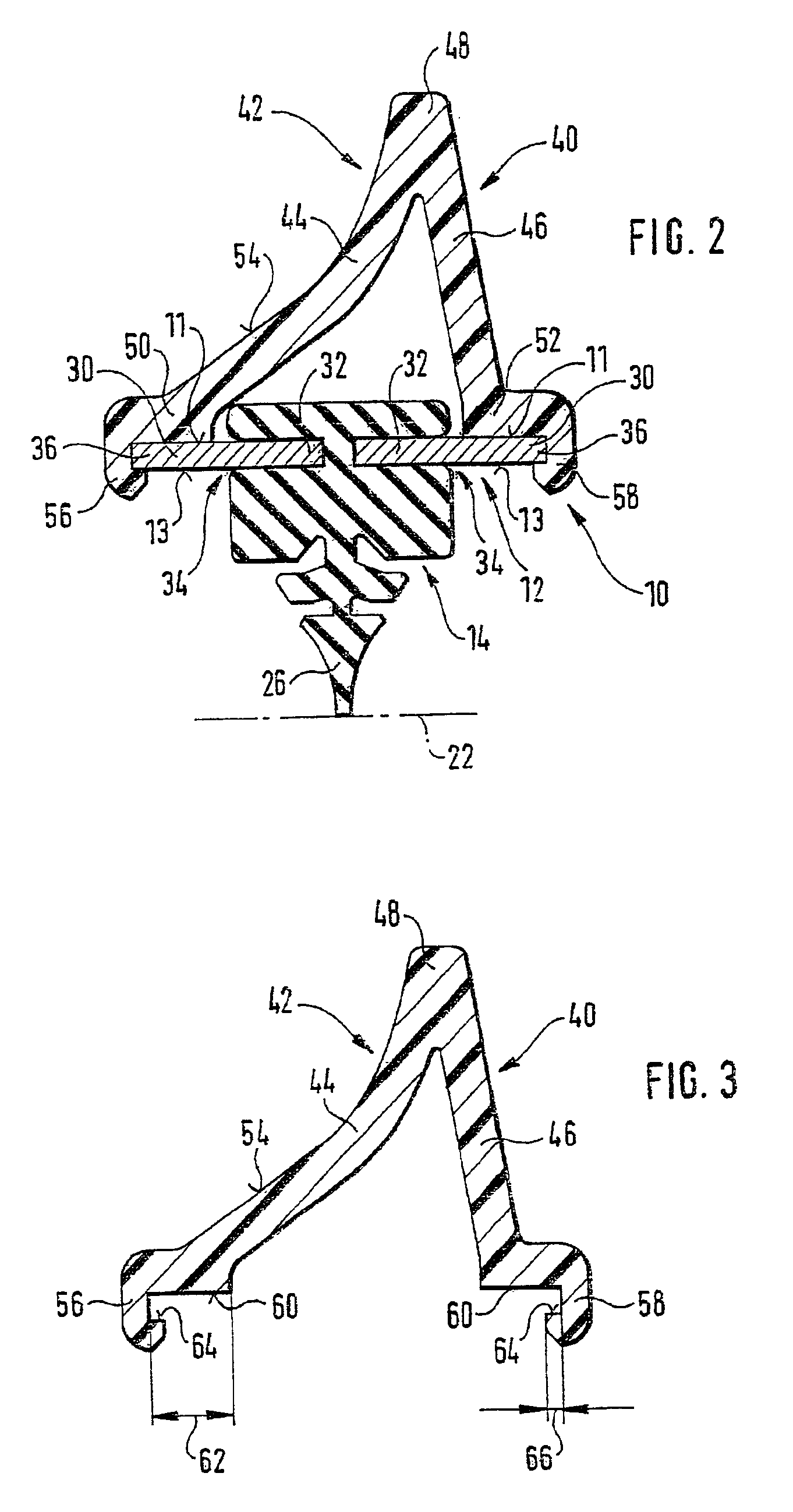
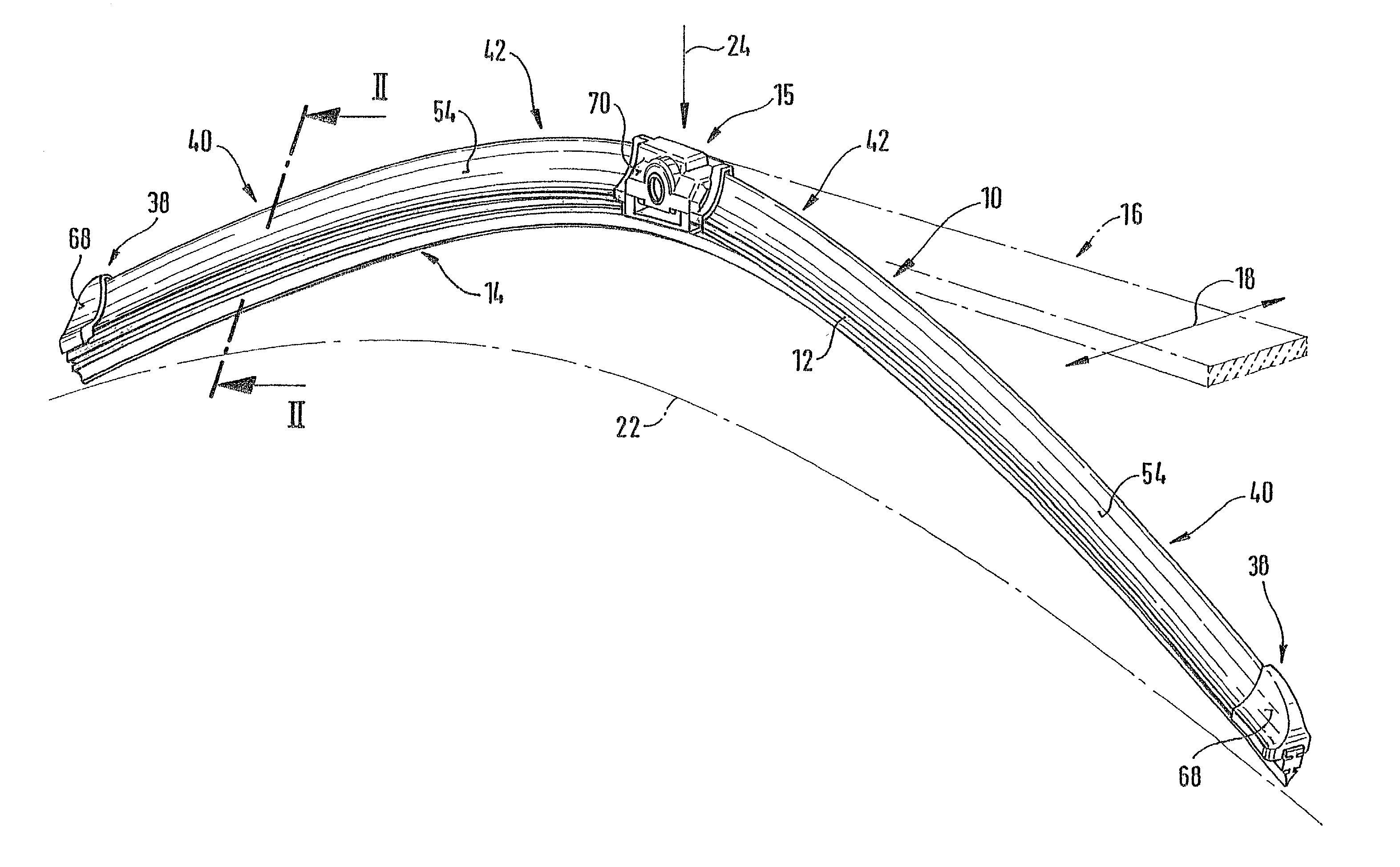
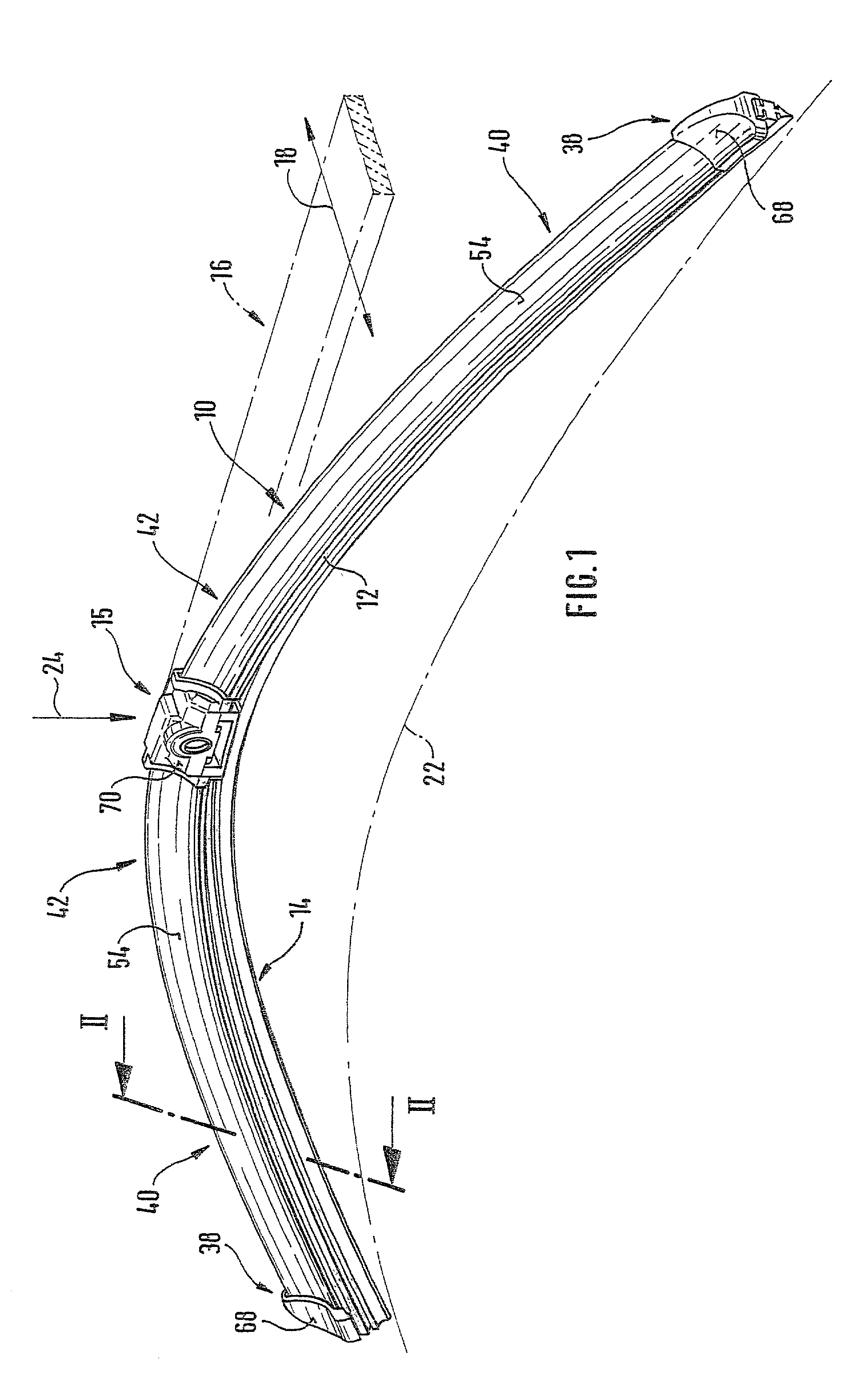
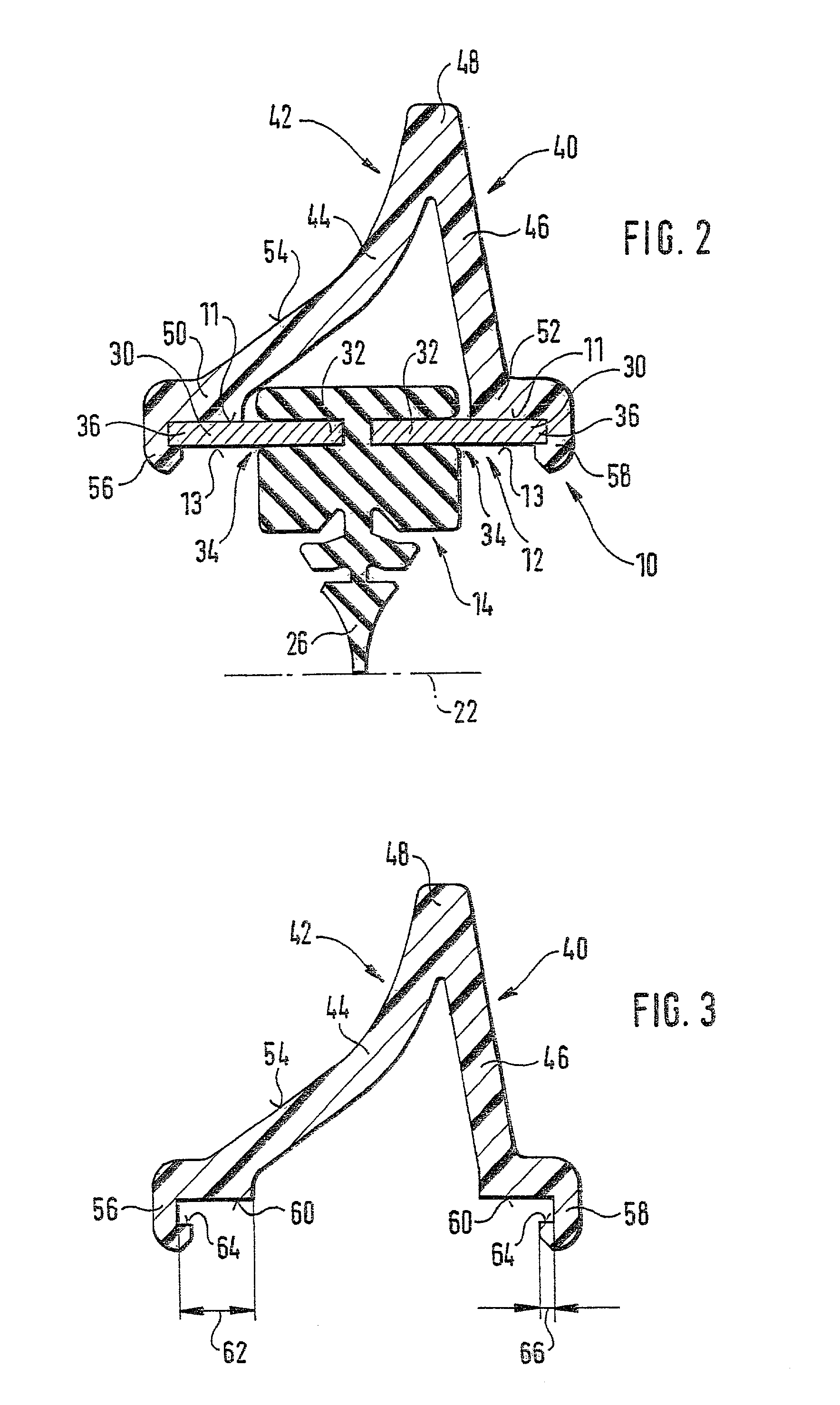
A wiper blade for cleaning motor vehicles is proposed, which is provided with a band-like, elongated, spring-elastic support element (12). The lower band surface (13) of the support element (12) oriented toward the window (22) has an elongated, rubber-elastic wiper strip (14), which can be placed against the window (22), disposed on it so that the longitudinal axes of these two parts are parallel and the upper band surface (11) of the support element (12) has a wind deflection strip (42) disposed on it, which extends in the longitudinal direction of the support element, is provided with an attack surface (54) oriented toward the main flow of the relative wind, and is comprised of an elastic material. A considerable weight savings for the wiper blade is achieved if the wind deflection strip (42, 142, or 242) has two diverging legs (44, 46), viewed in cross section, which are connected to each other at a common base (48) and whose free ends (50, 52) oriented toward the window (22) are supported on the wiper blade (10), and the attack surface (54) is embodied on the outside of the one leg (44).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
Vehicle-mounted generator
InactiveUS7211905B1Improve motor efficiencyExtend battery lifeAuxillary drivesWorking fluid for enginesDrive shaftMechanical energy
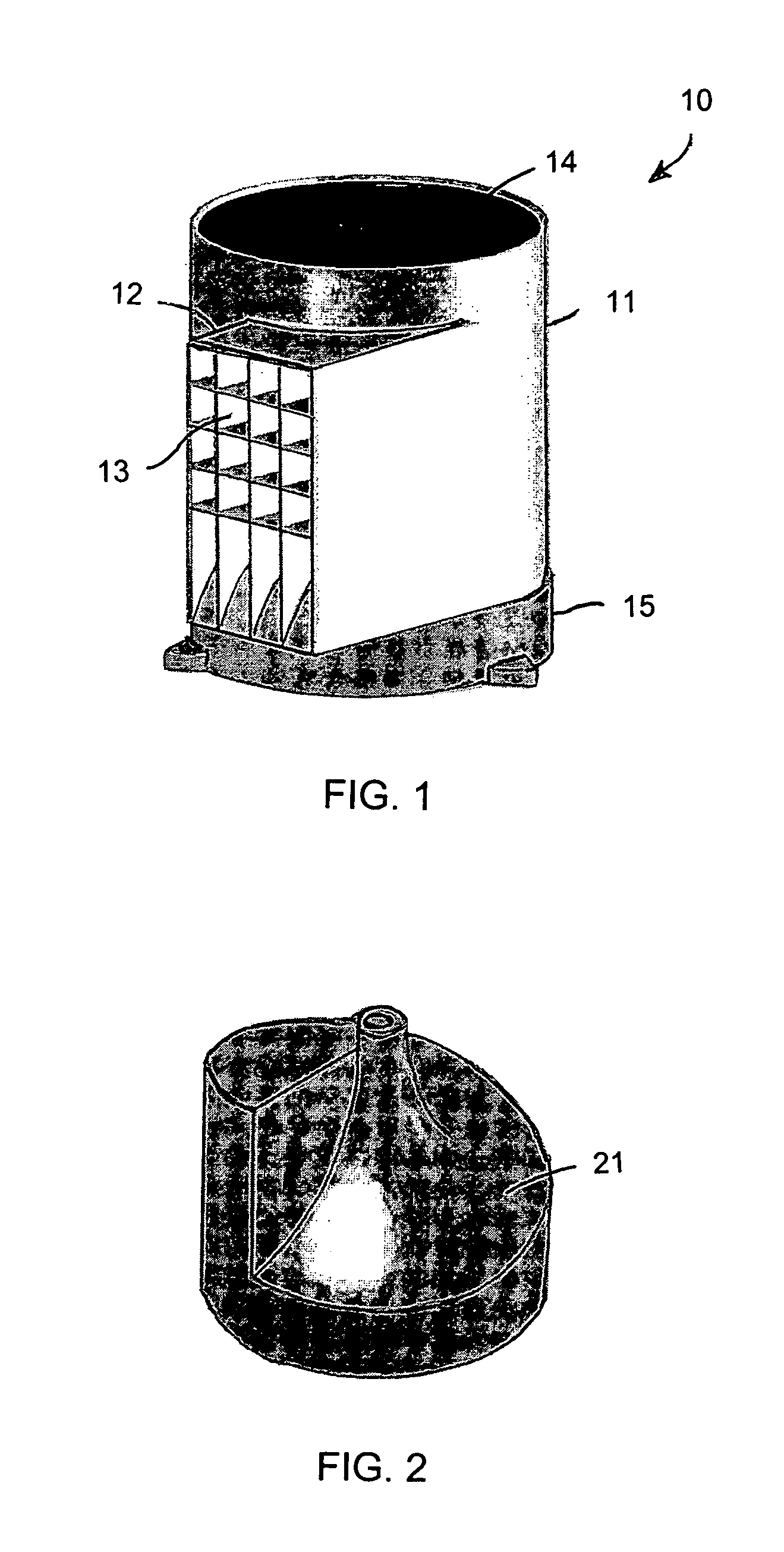
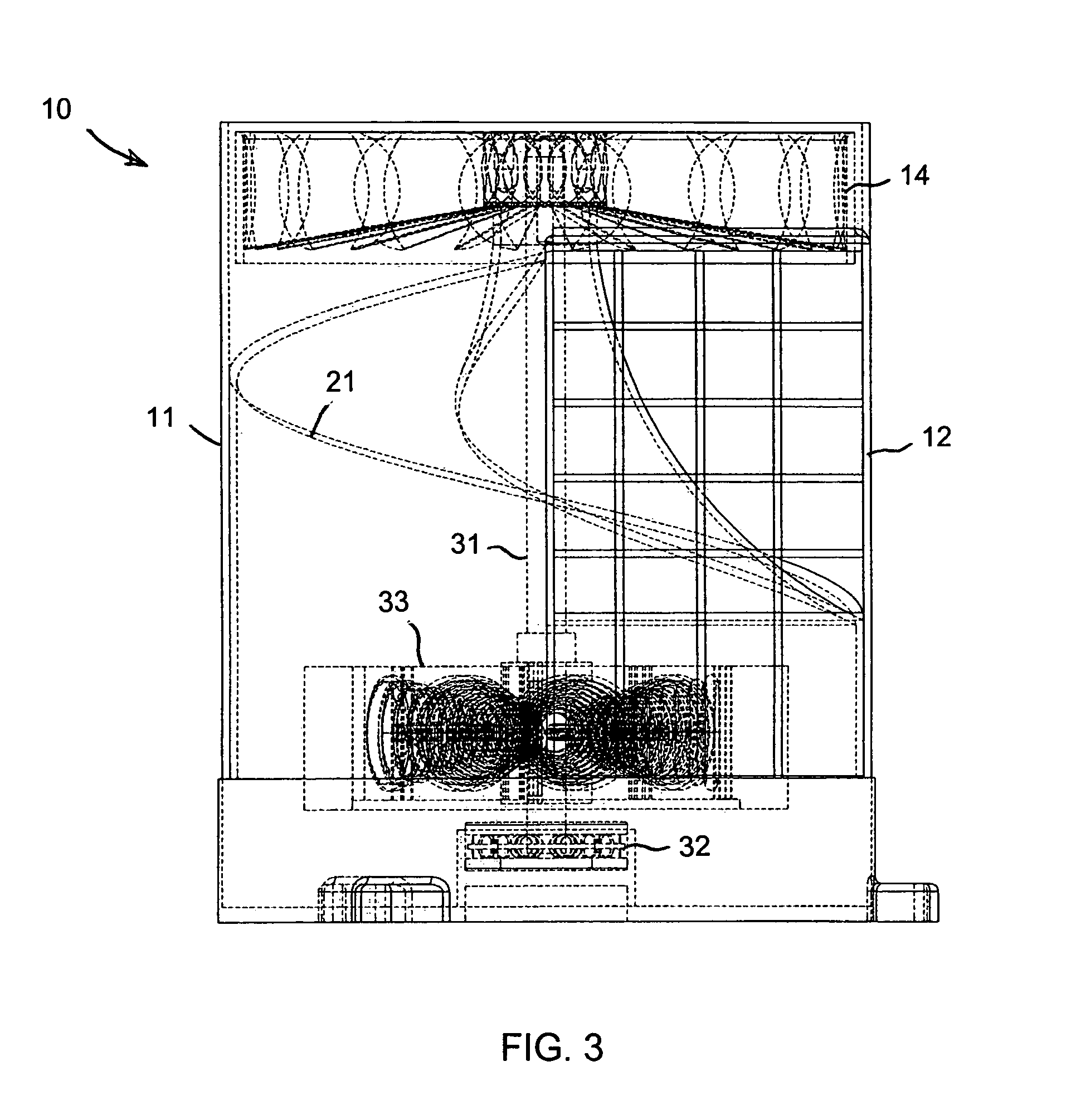
A vehicle-mounted generator is powered by relative wind produced by the combination of ambient wind and motion of the vehicle, or by movement of water when mounted on the hull of a water-borne vehicle. A rigid cylindrical housing forms an enclosed interior chamber. Wind asymmetrically enters the chamber through an inlet located on one side of a central longitudinal drive shaft, and exits through an outlet located at the top of the housing. A spiraling parabolic deck forms a floor of the interior chamber, and spirals around the central longitudinal shaft from the bottom of the housing to the outlet at the top. A turbine mounted on the drive shaft within the outlet converts energy of the exiting wind to mechanical energy. An electrical generator converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy for recharging a battery or powering an electric motor.
Owner:MCDAVID JR WILLIAM K
Wiper blade for cleaning screens in particular on motor vehicles
InactiveUS20020133897A1Reduce weightSave materialWindow cleanersVehicle cleaningCommon baseMobile vehicle
A wiper blade for cleaning motor vehicles is proposed, which is provided with a band-like, elongated, spring-elastic support element (12). The lower band surface (13) of the support element (12) oriented toward the window (22) has an elongated, rubber-elastic wiper strip (14), which can be placed against the window (22), disposed on it so that the longitudinal axes of these two parts are parallel and the upper band surface (11) of the support element (12) has a wind deflection strip (42) disposed on it, which extends in the longitudinal direction of the support element, is provided with an attack surface (54) oriented toward the main flow of the relative wind, and is comprised of an elastic material. A considerable weight savings for the wiper blade is achieved if the wind deflection strip (42, 142, or 242) has two diverging legs (44, 46), viewed in cross section, which are connected to each other at a common base (48) and whose free ends (50, 52) oriented toward the window (22) are supported on the wiper blade (10), and the attack surface (54) is embodied on the outside of the one leg (44).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CORP
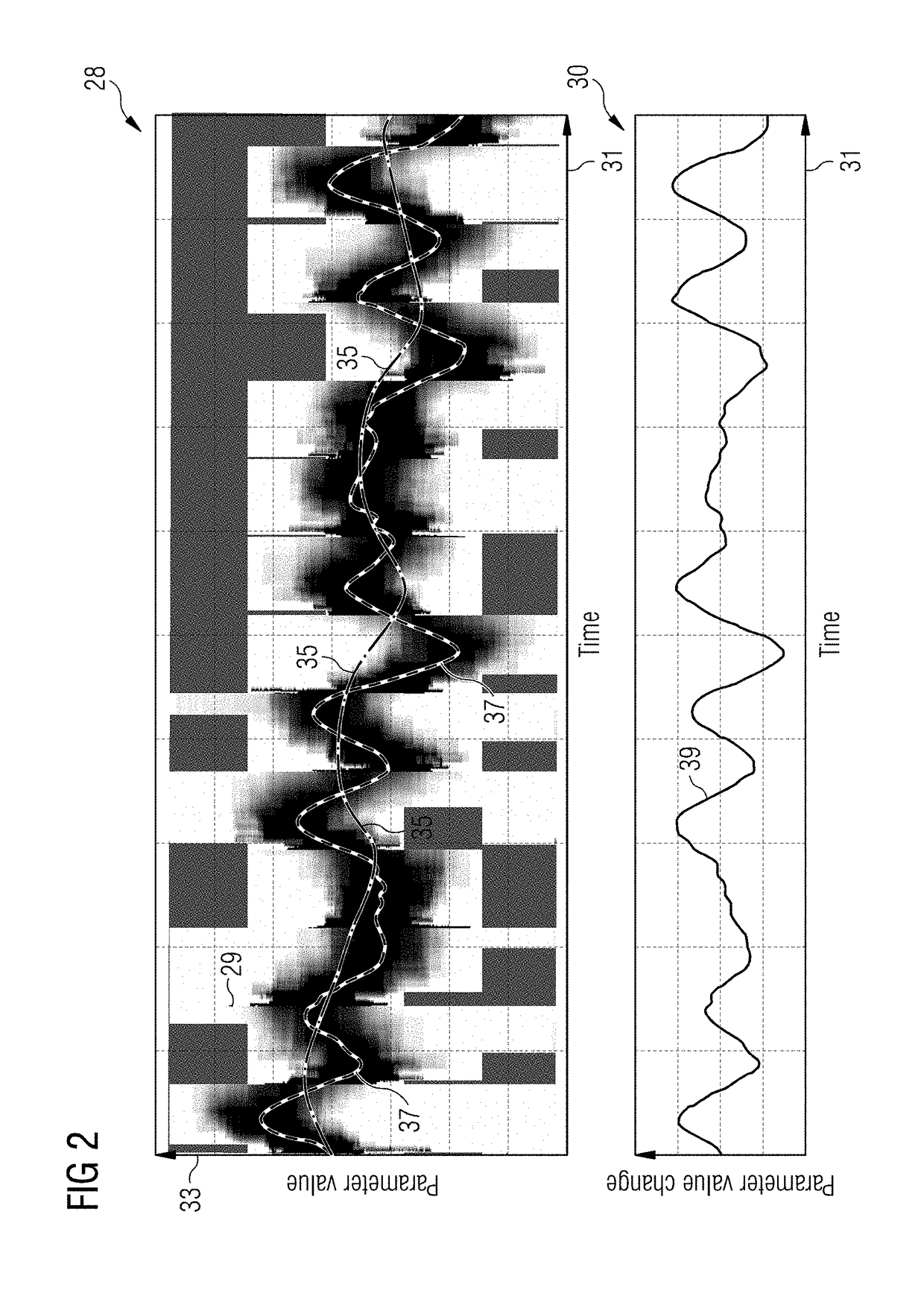
Wind turbine blade fatigue life real-time monitoring method
InactiveCN103063425AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed reliabilityMachine part testingMomentumTurbine blade
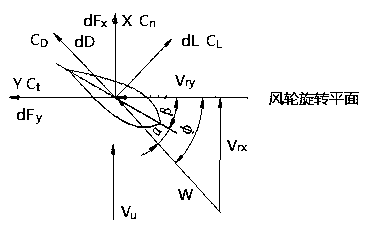
Provided is a wind turbine blade fatigue life real-time monitoring method. The wind turbine blade fatigue life real-time monitoring method real time measures output power, rotating speed and pitch angle of a wind wheel, and reversely pushes out relative wind speed of a random blade element of the blade according to monitoring data, and then apply blade element-momentum (BEM) principle to calculate loading impacted on each blade element, and then calculate loading of the whole blade through integration, form stress spectrum, and eventually use rain-flow counting method to count stress cycle times and accordingly conduct life loss calculation, and obtain fatigue life of wind turbine blade. The power of the wind turbine acts as a monitoring quantity, wind turbine blade fatigue life is obtained by theoretical calculation. The wind turbine blade fatigue life real-time monitoring method has the advantages that not only accuracy of measured data and reliability of monitoring results are guaranteed, but also the whole monitoring process relies on the existing system, and no large quantity sensor is needed to be additionally install. The wind turbine blade fatigue life real-time monitoring method has the advantages of being convenient in implement, low in monitoring cost and the like. The real-time monitoring method of wind turbine blade fatigue life is an ideal method of analyzing and evaluating wind turbine operating safety.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Simulation method of wind-induced disaster whole process of long-span bridge
ActiveCN103218481AColumnar is simple and intuitiveHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelSelf excited
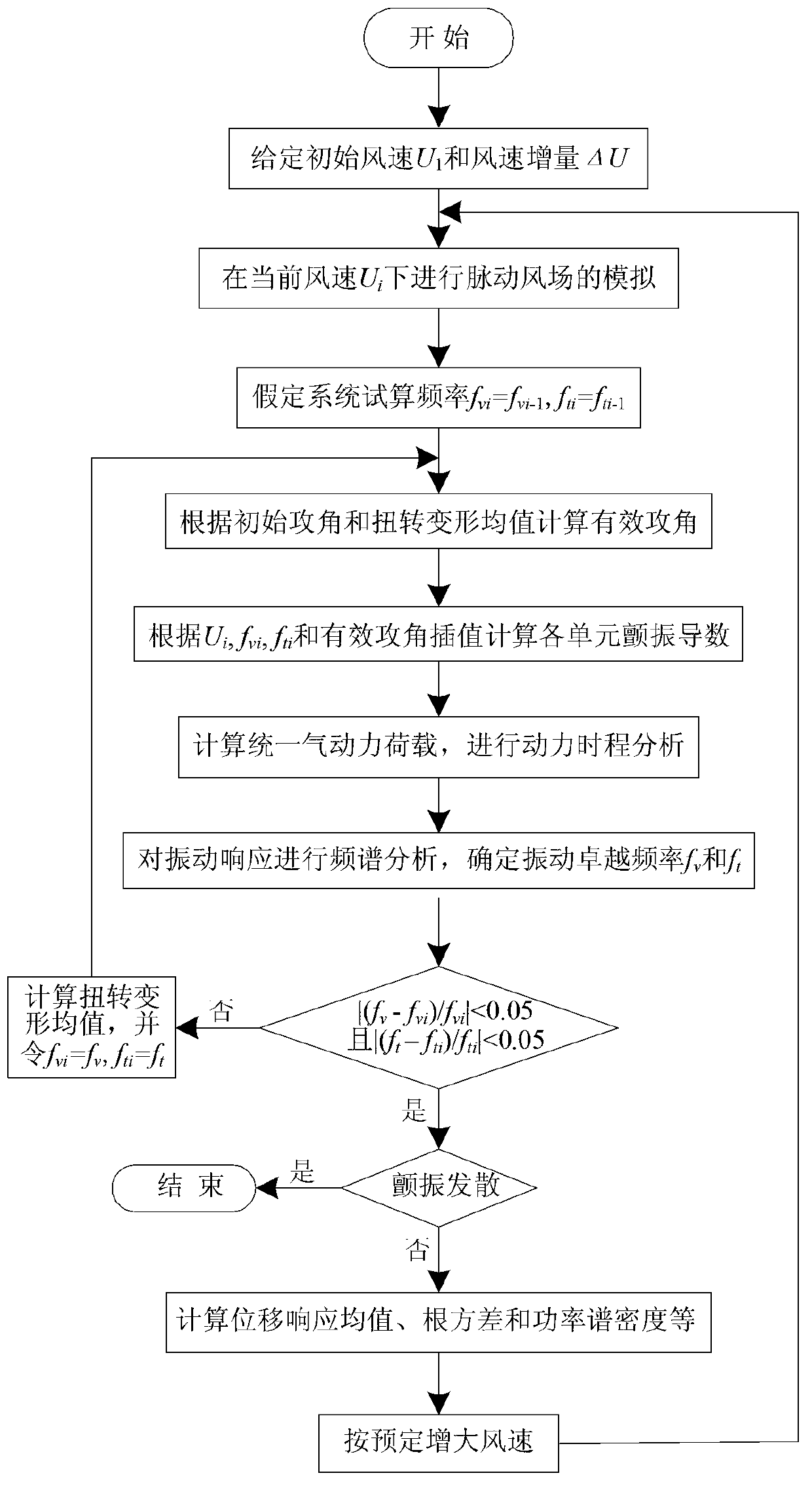
The invention provides a simulation method of a wind-induced disaster whole process of a long-span bridge. The simulation method comprises the steps of making the aerostatic coefficients, an effective instant wind attack angle and the relative wind speed integrally working on an aerodynamic force of a main beam, and then carrying out unsteady correction on self-excited force components in the aerostatic coefficients, the effective instant wind attack angle and the relative wind speed; applying aerodynamic force load to a finite element model for carrying out dynamic-history calculation, and carrying out iteration of torsion base frequency and vertical-curve base frequency in different wind speeds; and judging the steady state of a bridge structure under a certain wind speed according to displacement response. According to the simulation method provided by the invention, the integrated calculation of calm-wind instability, buffering and flutter is realized, the defect of independent calculation in traditional wind vibration calculation is overcome, and the accuracy of bridge wind vibration calculation is increased.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
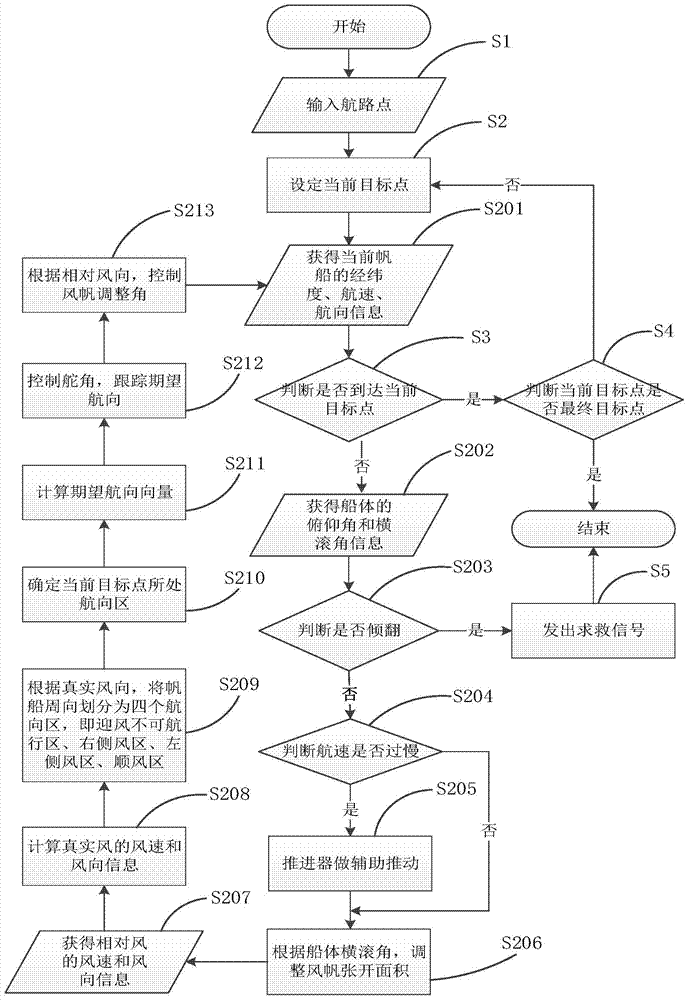
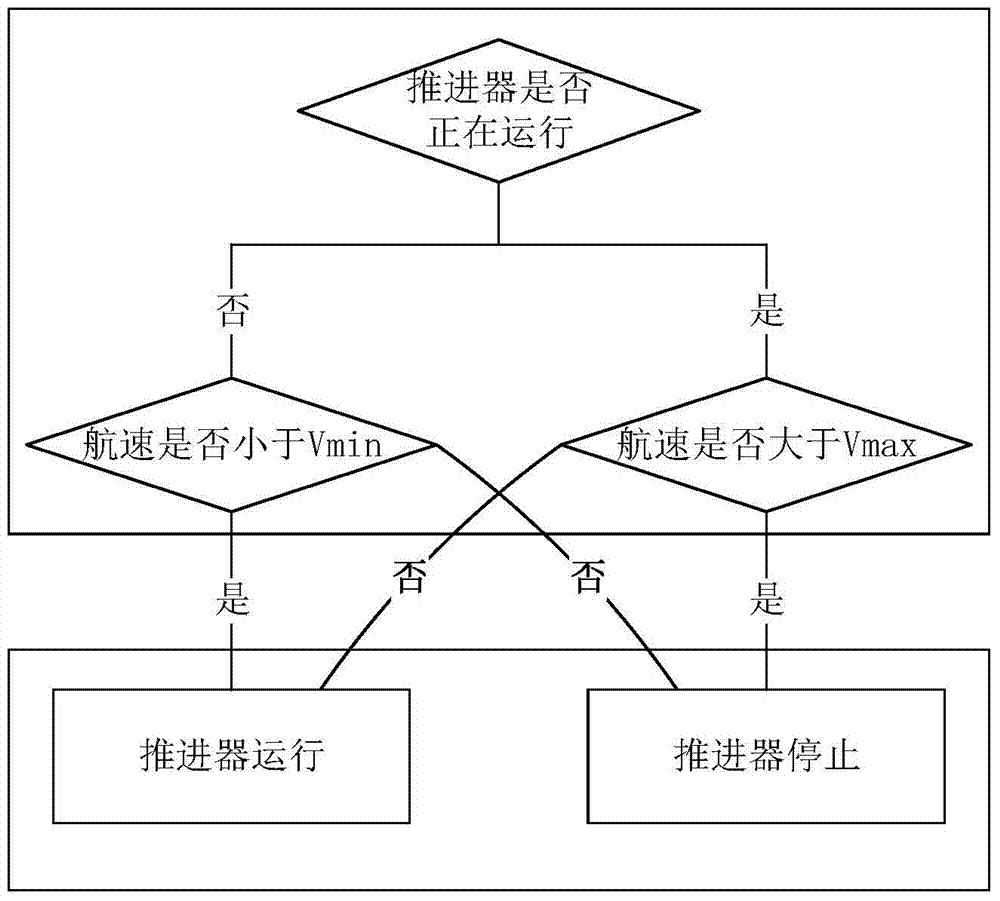
Autonomous control method and device of sailing ship and sailing ship
ActiveCN104267736ARealize automatic generationRealize automatic controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsWind acting propulsive elementsPropellerDirection information
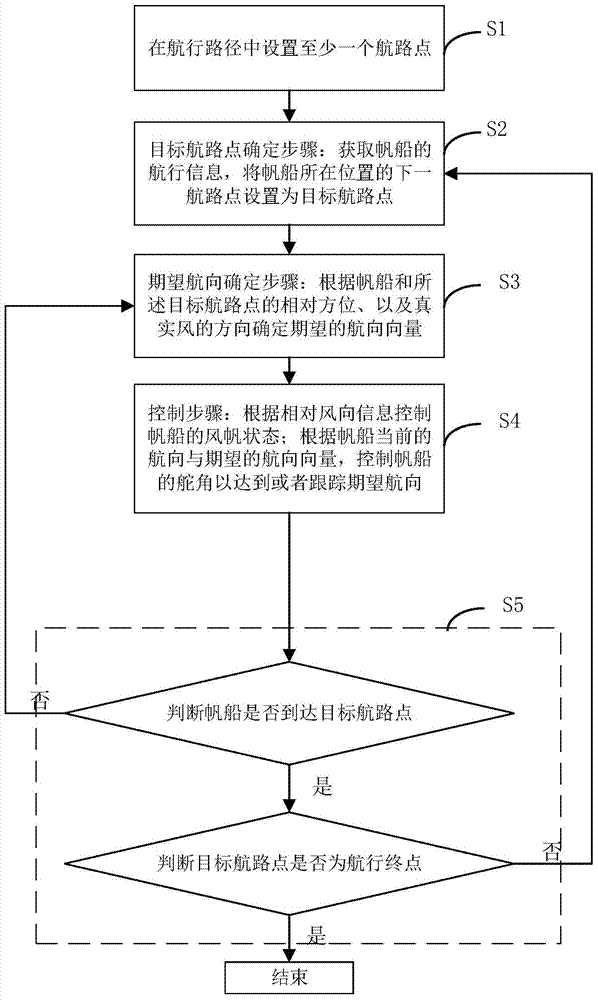
The invention discloses an autonomous control method and device of a sailing ship and the sailing ship. The method includes the steps of setting at least one waypoint; acquiring navigation information of the sailing ship and setting the next waypoint from the position where the sailing ship is located as a target waypoint; determining an expected course vector according to the relative azimuth of the sailing ship and the target waypoint and the true wind direction; controlling the sail state of the sailing ship according to relative wind direction information; controlling the rudder angle according to the current course of the sailing ship and the expected course vector so as to reach or track the expected course; judging whether the sailing ship has reached the target waypoint or not, judging whether the target waypoint is a navigation terminal point if the sailing ship has reached the target waypoint, and ending the process if the target waypoint is the navigation terminal point. According to the autonomous control method and device of the sailing ship and the sailing ship, the complete control method for autonomous navigation of the sailing ship is provided for the autonomous navigation process of the sailing ship, and autonomous control over the sailing ship is systematically achieved through division of a course area, calculation of the expected course vector, control over the rudder angle, control over the unfolding area and the adjustment angle of a sail, assisted propelling of a propeller and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN COSON ELECTRONICS
Cycloidal rotor with non-circular blade orbit
ActiveUS8540485B2Improve efficiencyPowerfulPropellersRotary propellersSpatial OrientationsComputerized system
Owner:OPTIVECTOR LTD
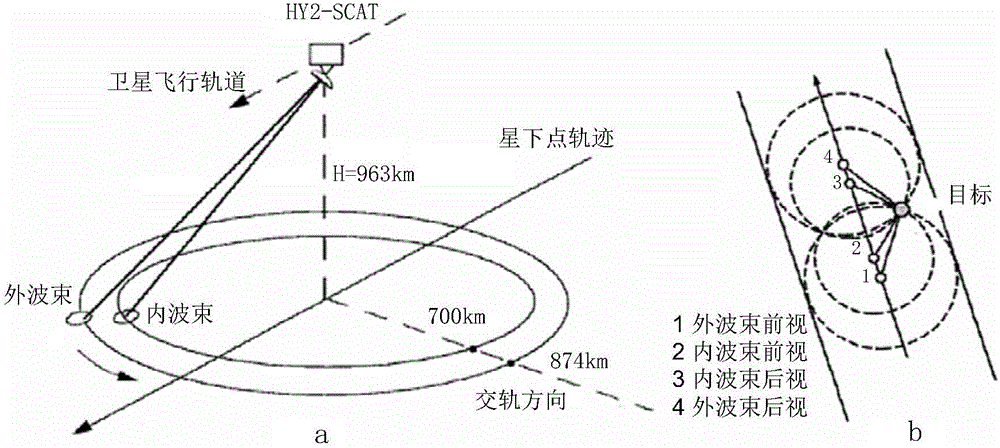
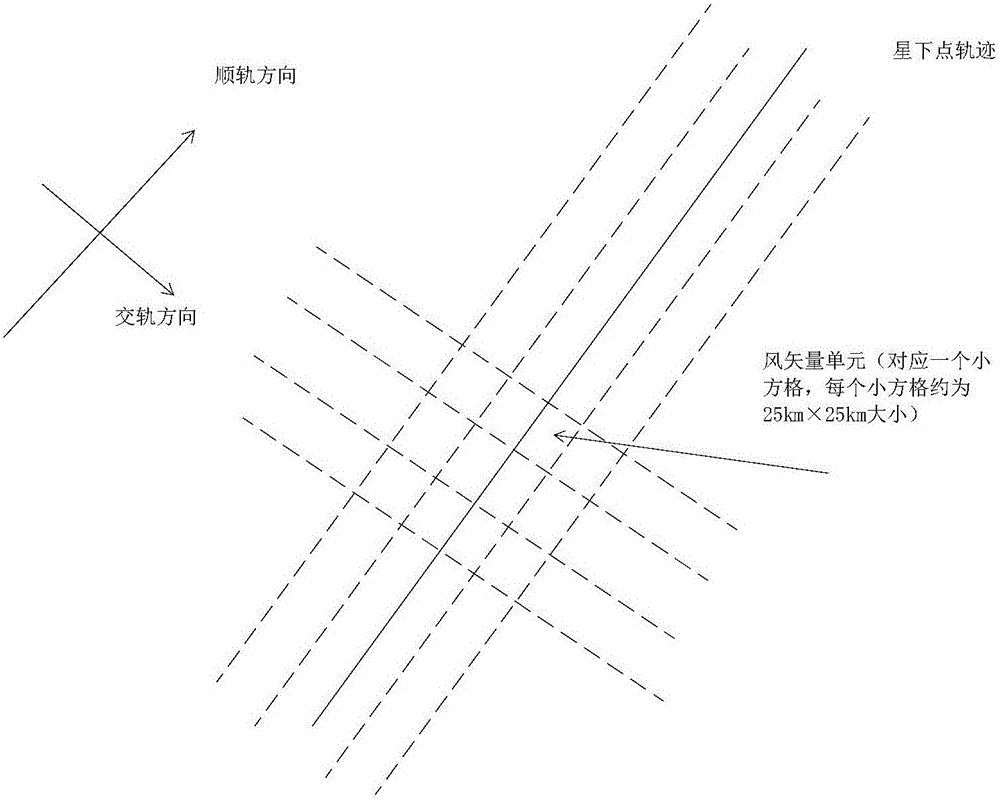
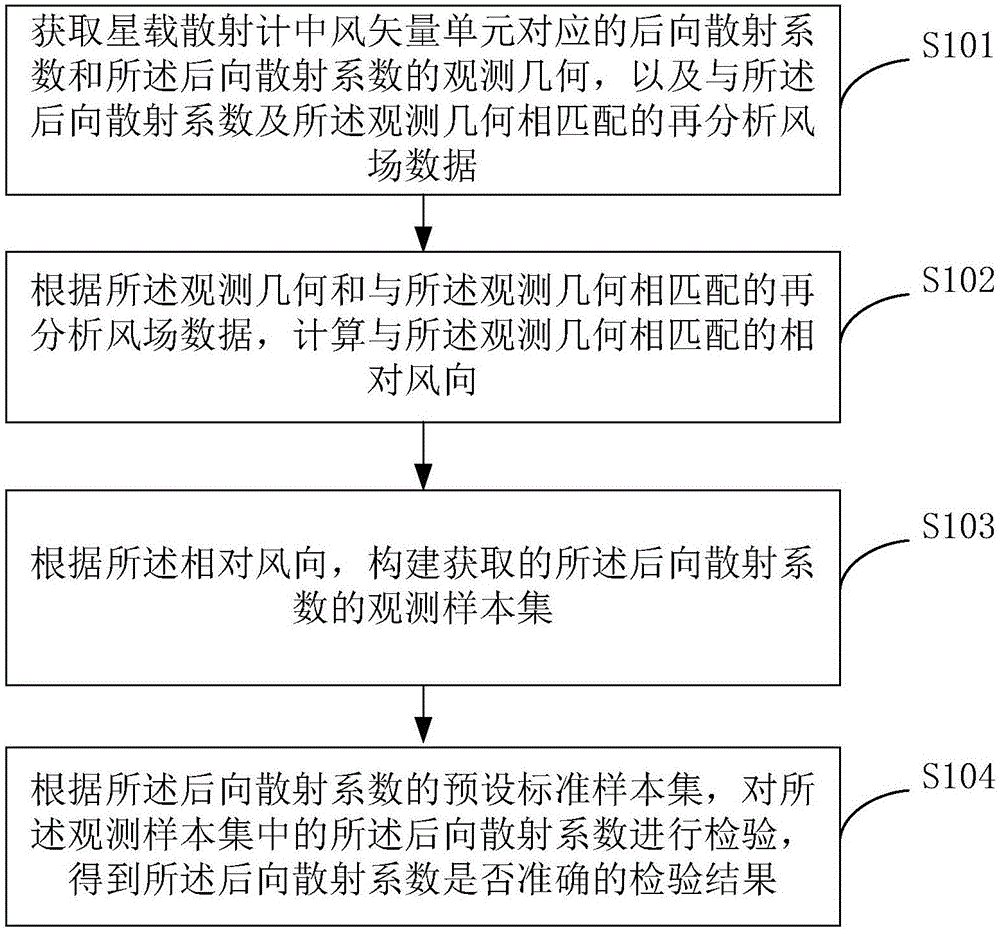
Calibration method and device of back scattering coefficient of space-borne scatterometer
The invention provides a calibration method and device of the back scattering coefficient of a space-borne scatterometer. The calibration method comprises the following steps: obtaining a back scattering coefficient corresponding to a wind vector unit in the space-borne scatterometer, the observation geometry of the back scattering coefficient, and reanalysis wind field data matched with the back scattering coefficient and the observation geometry; according to the observation geometry and the reanalysis wind field data matched with the observation geometry, calculating a relative wind direction matched with the observation geometry; according to the relative wind direction, constructing the observation sample set of the obtained back scattering coefficients; and according to a preset standard sample set, calibrating the observation sample set to obtain a calibration result to show whether the back scattering coefficient measured by the space-borne scatterometer is correct or not. The reanalysis sea surface wind field data is used for developing a quick evaluation method of the back scattering coefficient of the dual-cosine distribution characteristics of the wind direction on the basis of the back scattering coefficient, the quick evaluation of the back scattering coefficient can be realized in short time, evaluation accuracy is high through the reanalysis data, and meanwhile, the evaluation method is high in universality.
Owner:NAT SATELLITE OCEAN APPL SERVICE +1
Vector wind sensor and integrated antenna
InactiveUS7730776B2Ease portabilityEase transportVolume measurement and fluid deliveryIndication/recording movementIntegrated antennaEngineering
An anemometer assembly for sensing and transmitting wind speed and wind direction data. The wind sensor measures relative wind direction and wind speed without the use of moving parts and consumes very little power making it suitable for unattended operation. The main wind sensing member is an elongated vertical member that can be used as radio antenna. The data can be transmitted from a remote location and thus relay data to a central collection repository or network location.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Hybrid free-air gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20120128493A1Raise the combustion temperatureIncrease valuePropellersPump componentsTurbineGas turbines
An alternate means of generating the power to drive the compressor section of gas turbine engines is described. Electric motors embedded within gas turbines would rotate the compressor, and receive the requisite power to perform the compression work from: 1) either a high-capacity APU generator, or 2) from a relative-wind driven turbine in a hybrid power-sharing arrangement. The electric motor provides enhanced control of N1 rpm, assuring greater responsiveness to control inputs.
Owner:SHELLEY RUDOLPH ALLEN
Solid two-dimensional wind speed and direction measuring instrument and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN103630705APressure is less affected by sizeLittle affected by sizeIndication/recording movementFluid speed measurementMeasuring instrumentEngineering
The invention discloses a two-dimensional solid wind speed and direction measuring instrument and a measuring method thereof. The two-dimensional solid wind speed and direction measuring instrument comprises a weather cylinder, pressure pipes and sensors, wherein small holes in the even number are distributed in the cylindrical surface of the weather cylinder; one end of each pressure pipe is communicated with the small holes in the cylindrical surface of the weather cylinder, and the other end of the pressure pipe is communicated with the sensors; and the sensors are used for measuring the pressure-intensity difference between two small holes, whose horizontal distance equals the diameter of the weather cylinder, in the cylindrical surface of the weather cylinder. The measuring method comprises that the measuring instrument is fixed, and the orientation of the measuring instrument is determined; when wind in the horizontal direction acts on the instrument, the pressure-intensity difference between each two points, whose horizontal distance equals the diameter of the weather cylinder, in the cylindrical surface of the weather cylinder of the measuring instrument is measured; according to the relations between wind pressure distribution and wind speed / direction, the wind speed and the wind direction relative to the weather cylinder are calculated via the obtained pressure-intensity differences; and according to the determined orientation of the measuring instrument, the practical wind direction is calculated. Compared with a common wind speed and direction indicator, the two-dimensional solid wind speed and direction measuring instrument disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being small in size, fast in response, and not easy to damage.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
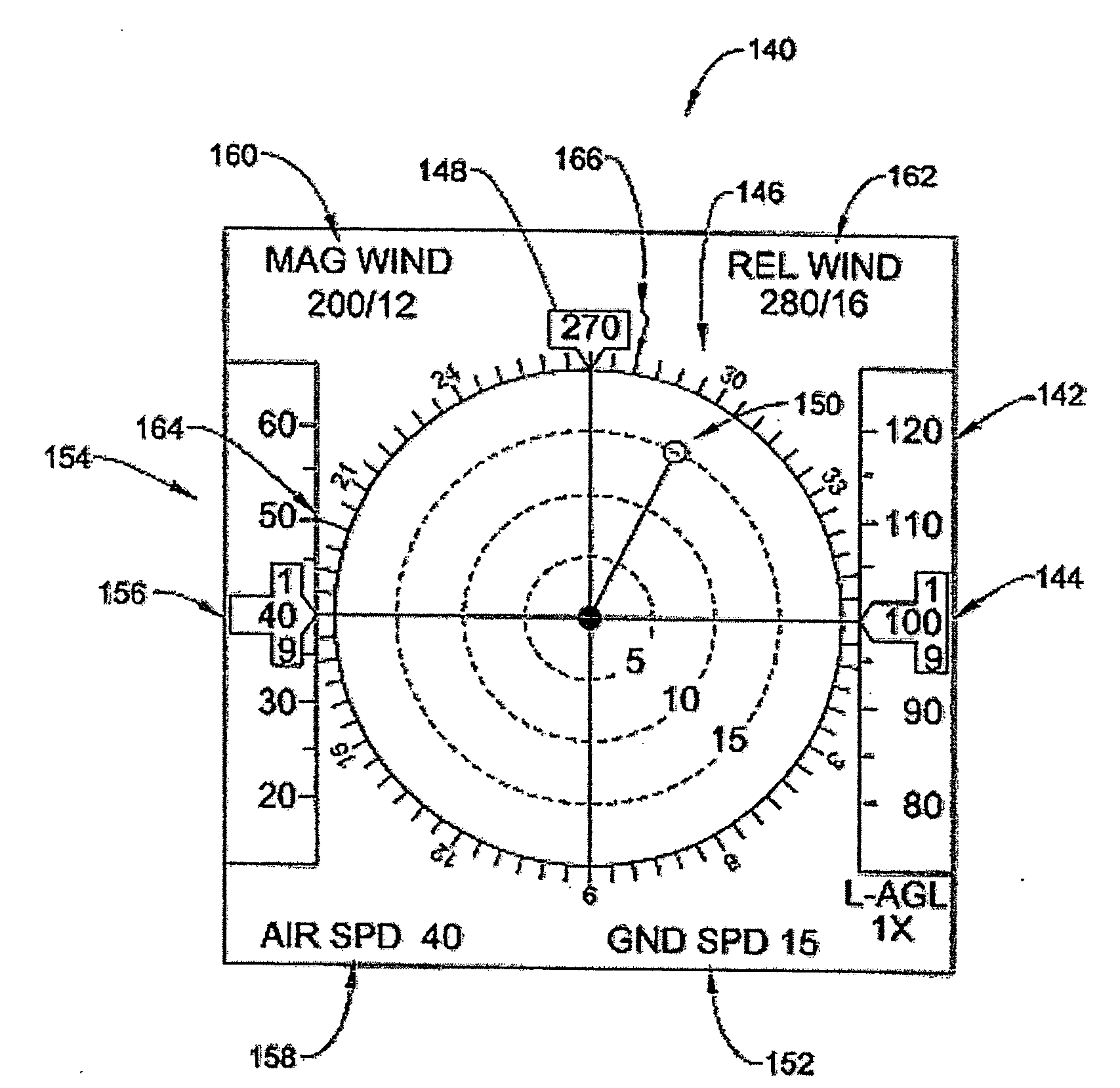
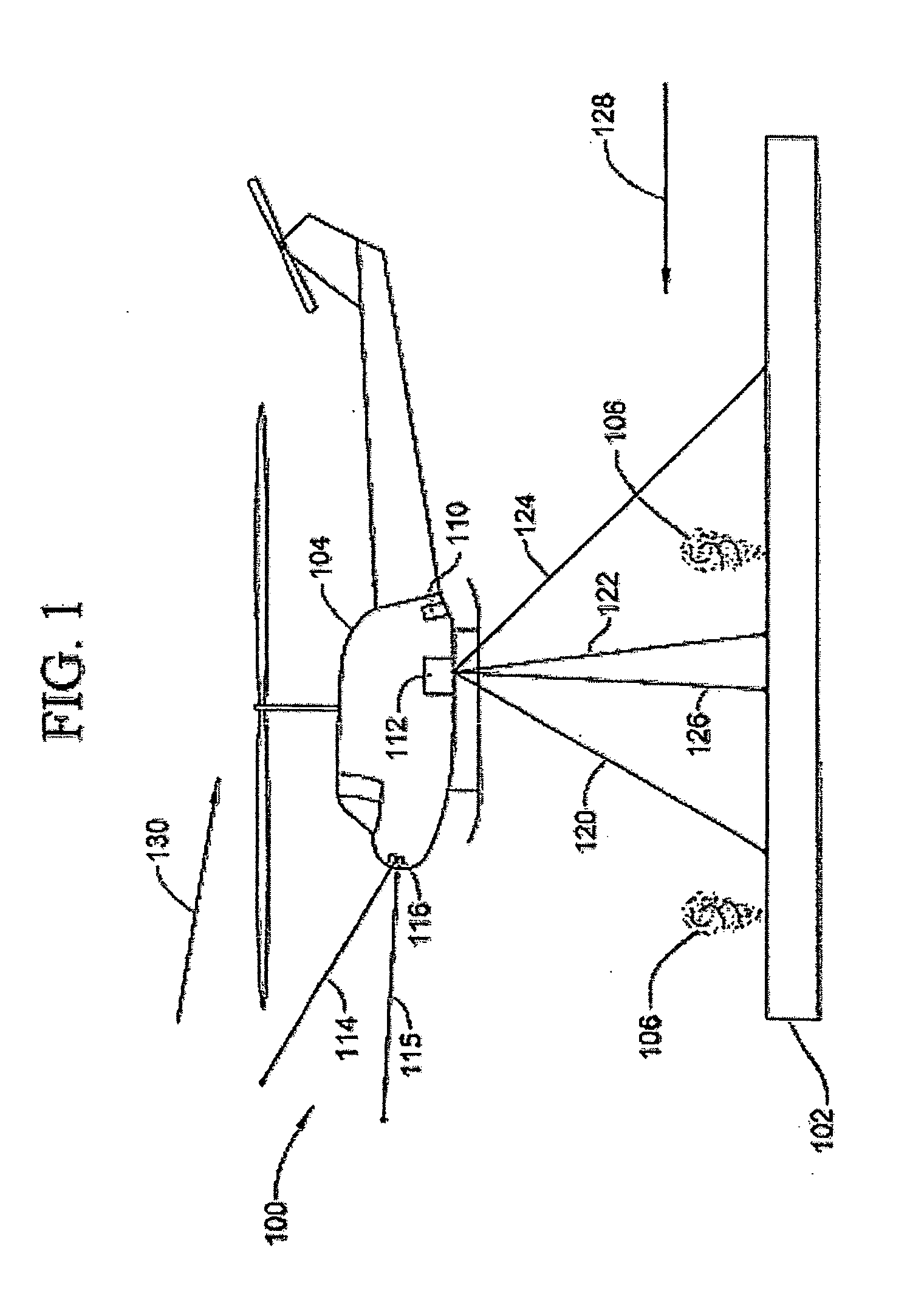
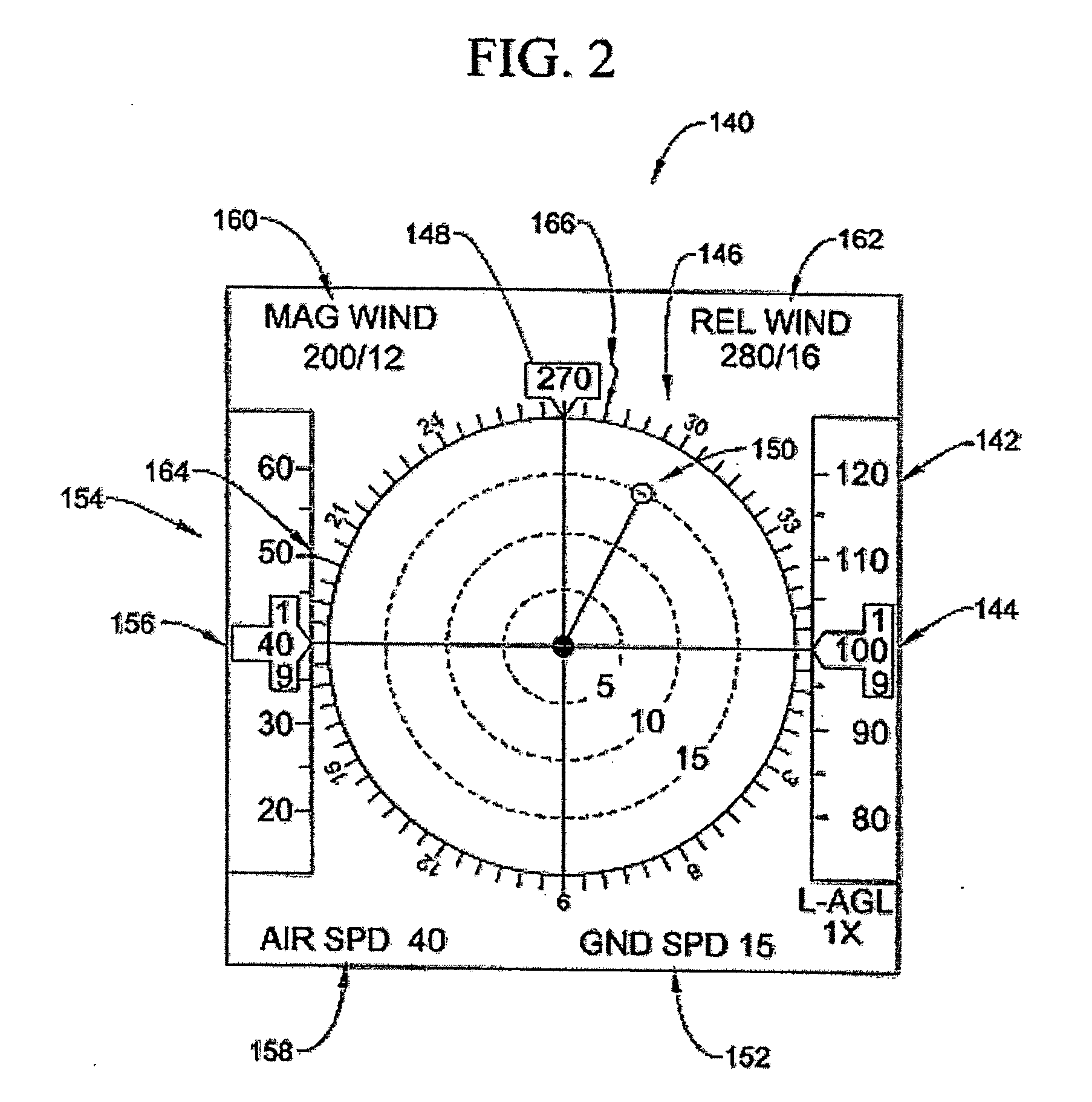
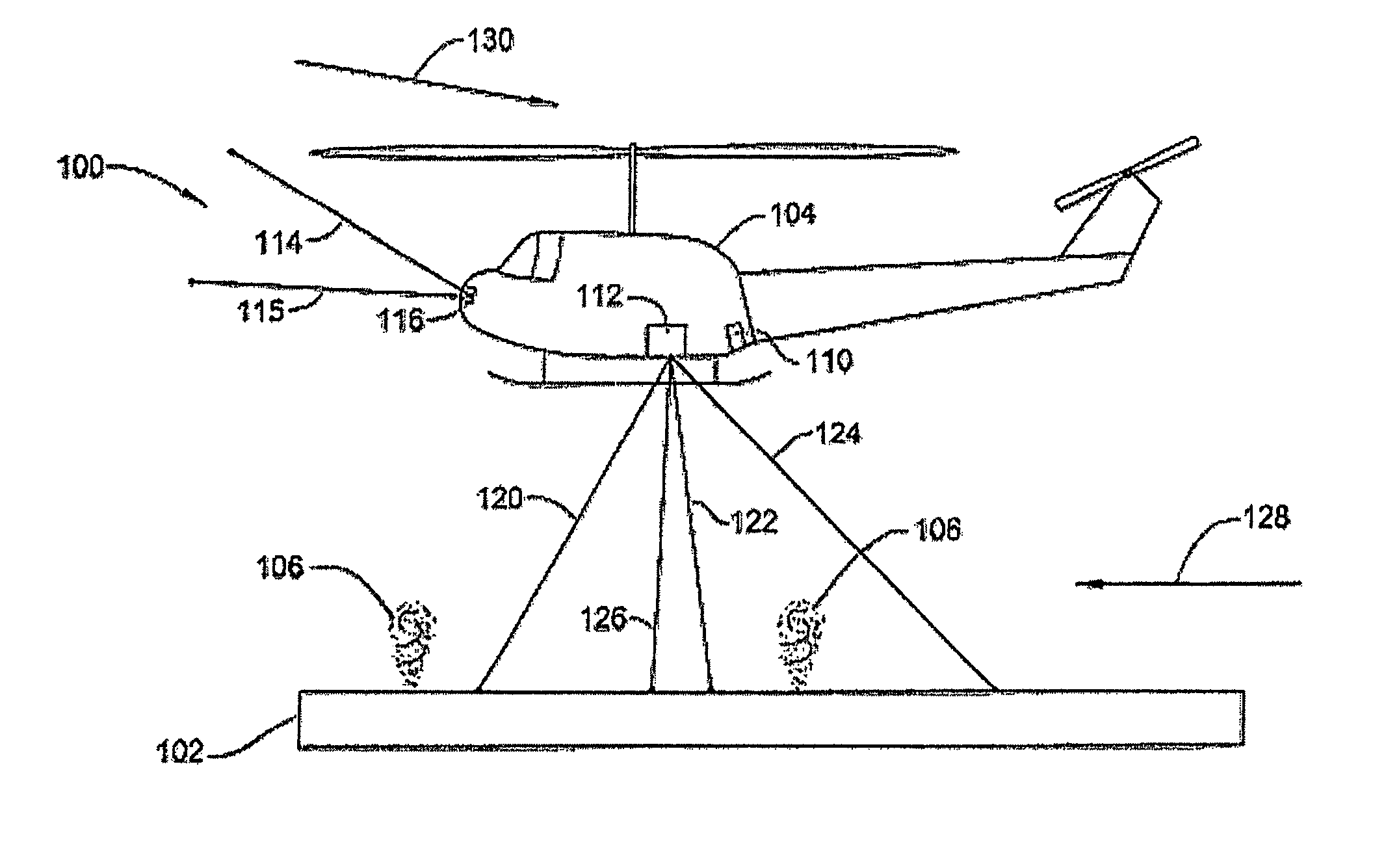
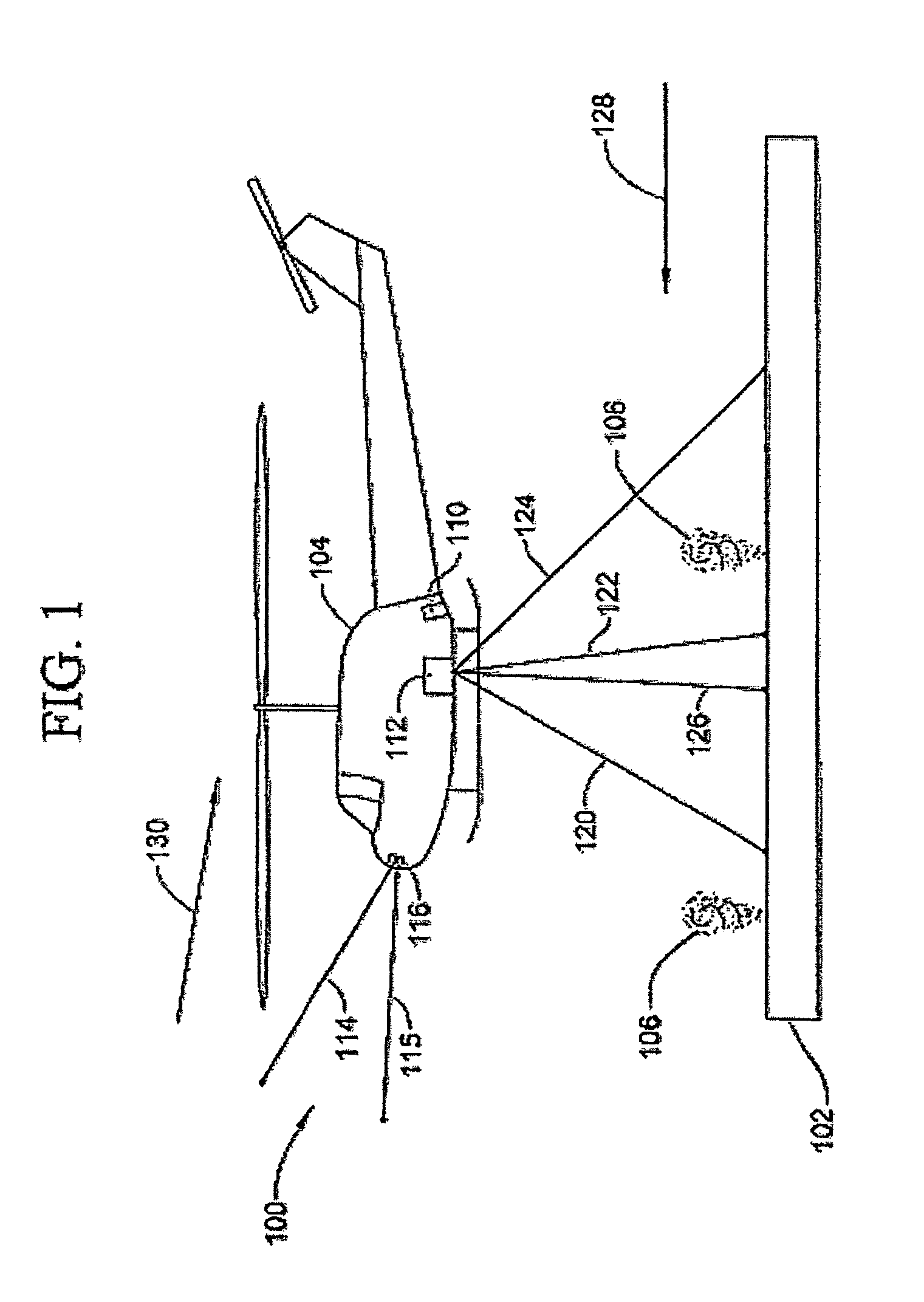
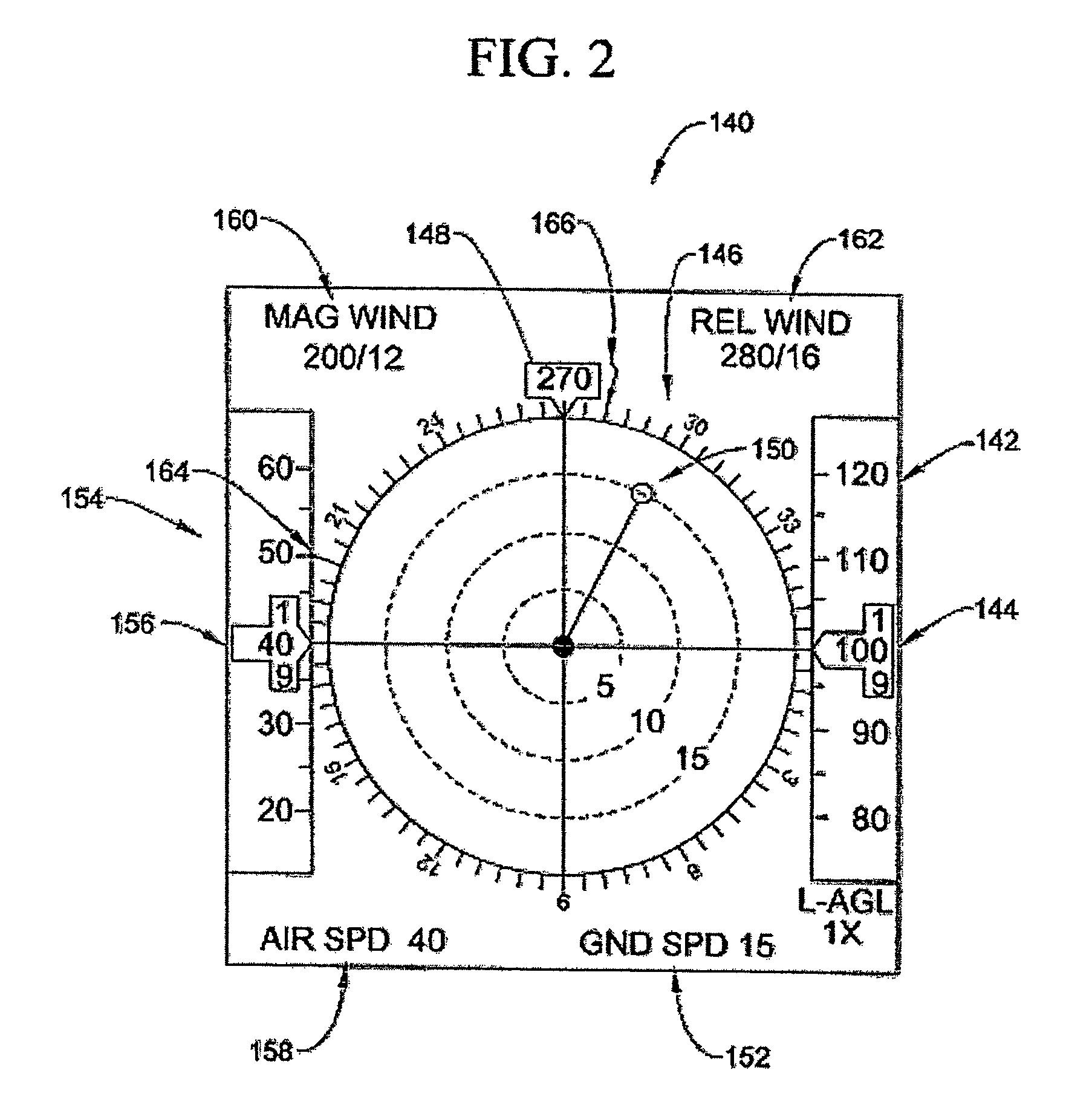
Optical System for Detecting and Displaying Aircraft Position and Environment During Landing and Takeoff
InactiveUS20090140885A1Effective displayReduce the possibilityLanding aidsNavigation instrumentsLow speedVisual perception
A system and method uses light signals to detect and display the position of an airborne vehicle, such as a helicopter, during takeoff or landing or low speed, low altitude operation. A transmitter on the vehicle emits light signals while an optical receiver retrieves reflected light signals. Using light detection and ranging techniques, various parameters, such as altitude, ground speed and relative wind, are calculated based on the Doppler shift within the reflected light signals. The signals are transmitted in three different directions to facilitate the measurements of different Doppler shifts. The parameters are also displayed on a screen or other visual device within the vehicle.
Owner:RD2 LLC
Optical system for detecting and displaying aircraft position and environment during landing and takeoff
InactiveUS7898435B2Flight safetyImprove securityLanding aidsNavigation instrumentsLow speedVisual perception
A system and method uses light signals to detect and display the position of an airborne vehicle, such as a helicopter, during takeoff or landing or low speed, low altitude operation. A transmitter on the vehicle emits light signals while an optical receiver retrieves reflected light signals. Using light detection and ranging techniques, various parameters, such as altitude, ground speed and relative wind, are calculated based on the Doppler shift within the reflected light signals. The signals are transmitted in three different directions to facilitate the measurements of different Doppler shifts. The parameters are also displayed on a screen or other visual device within the vehicle.
Owner:RD2 LLC
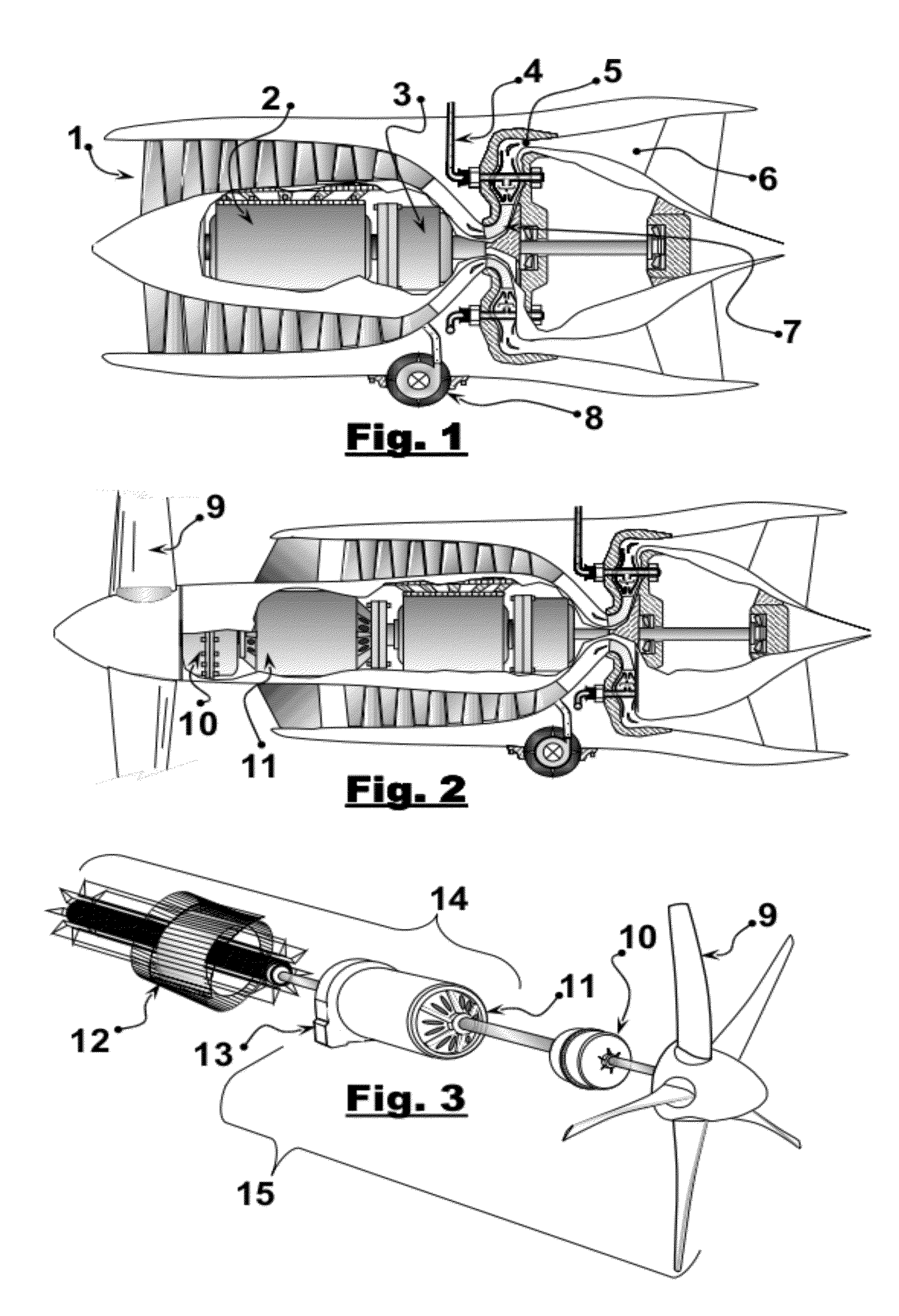
Adjustable angle inlet for turbojet engines
InactiveUS8544793B1Alleviating and preventing engine compressor stallCompensation changesCombustion enginesTurbine/propulsion air intakesJet aeroplaneNacelle
The adjustable angle inlet for turbojet engines provides for the adjustment of the nacelle inlet as the angle of attack of the aircraft changes. The adjustable inlet system thus assures that the nacelle inlet is always oriented directly into the relative wind as the angle of attack of the aircraft changes, e.g., during takeoff, landing, and high-G maneuvers where the aircraft reaches relatively high angles of attack. The adjustable angle inlet is adaptable to most turbojet-powered airplanes, but is particularly well suited for use with aircraft having their engines mounted on lateral pylons on the rear of the fuselage. The system operates according to signals received from an angle of attack sensor. The sensor controls an actuator, which rotates a shaft that is connected to the pivotally mounted inlet of the engine nacelle.
Owner:SHAMMOH ALI A A J
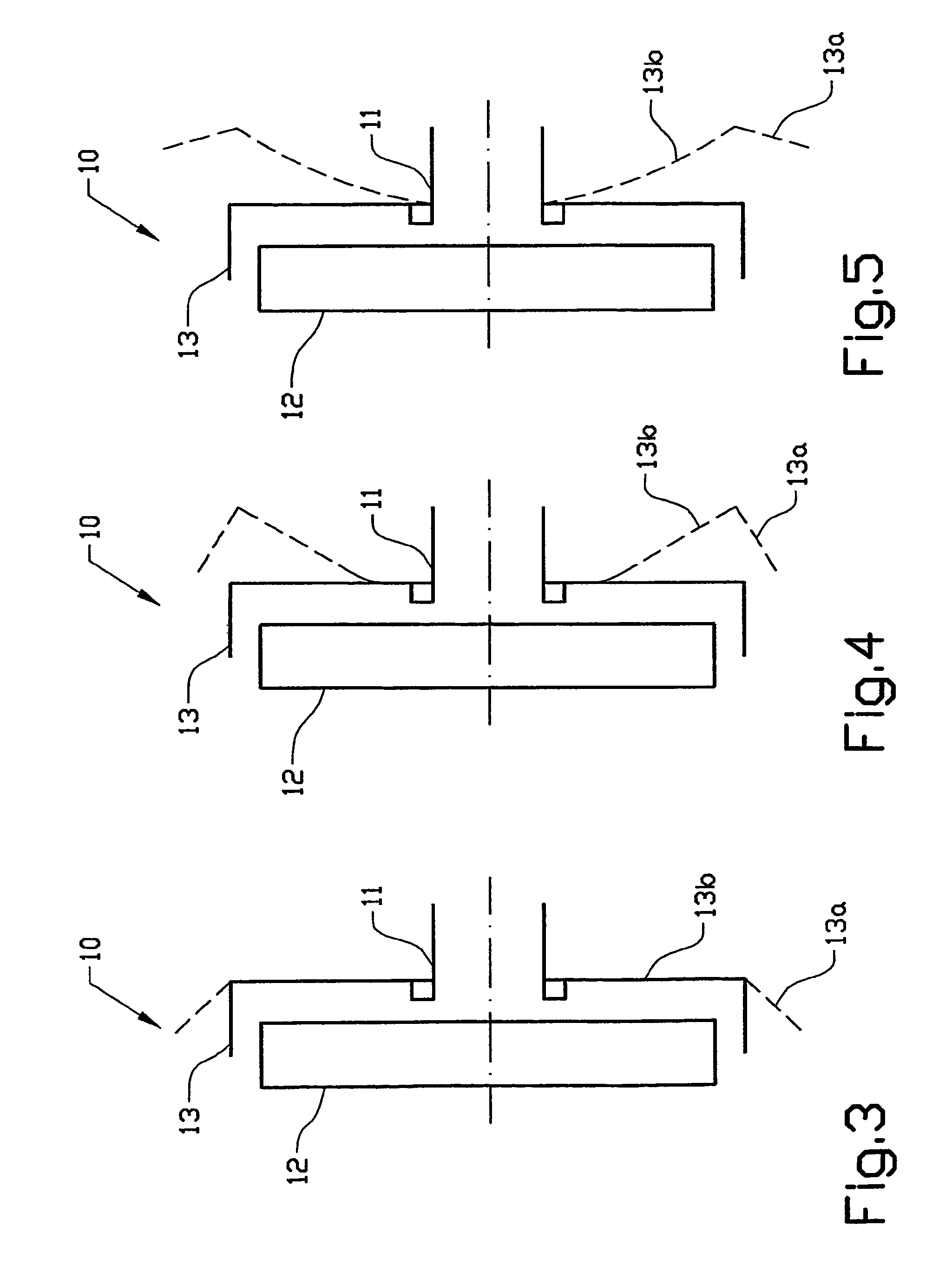
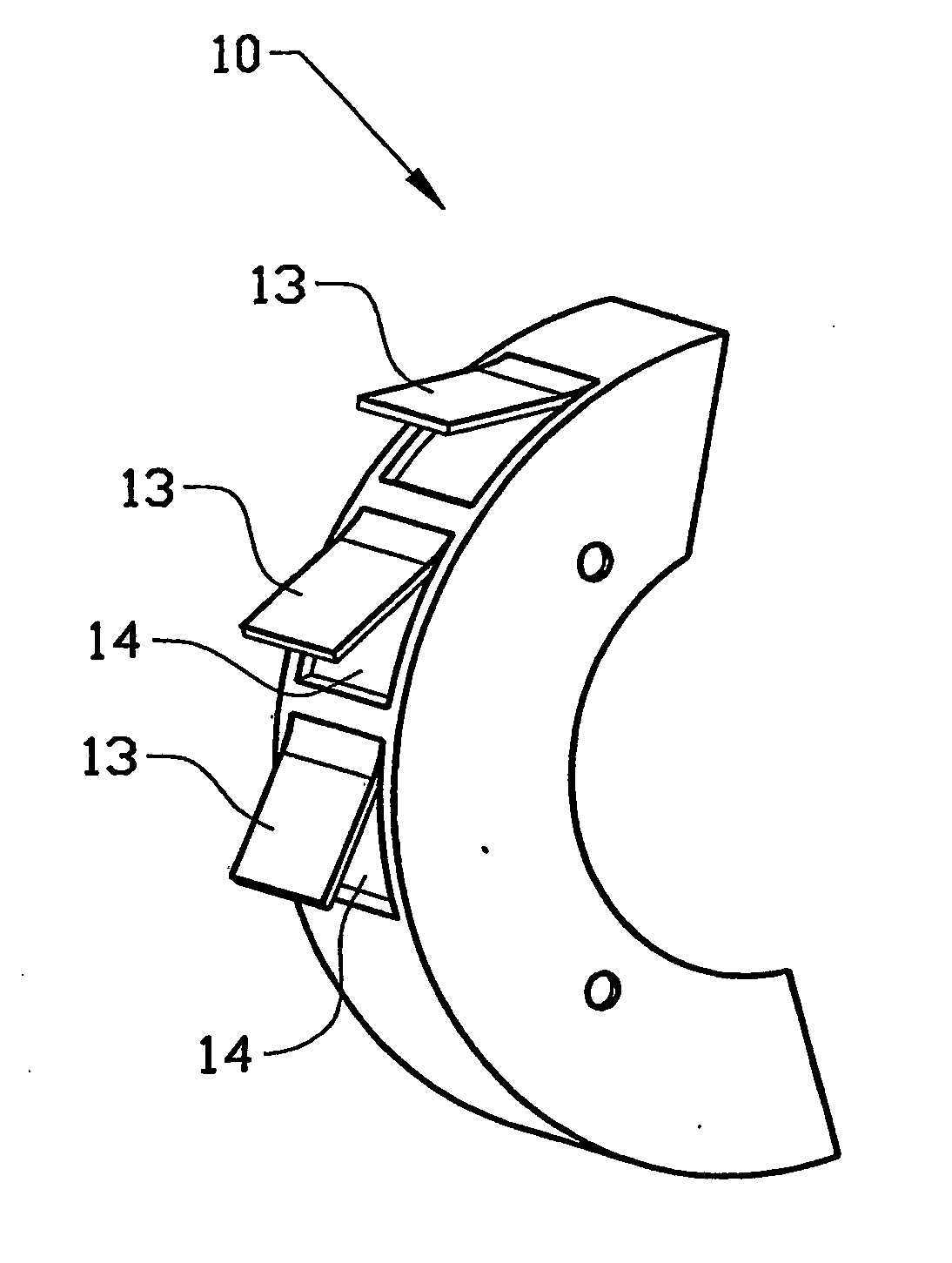
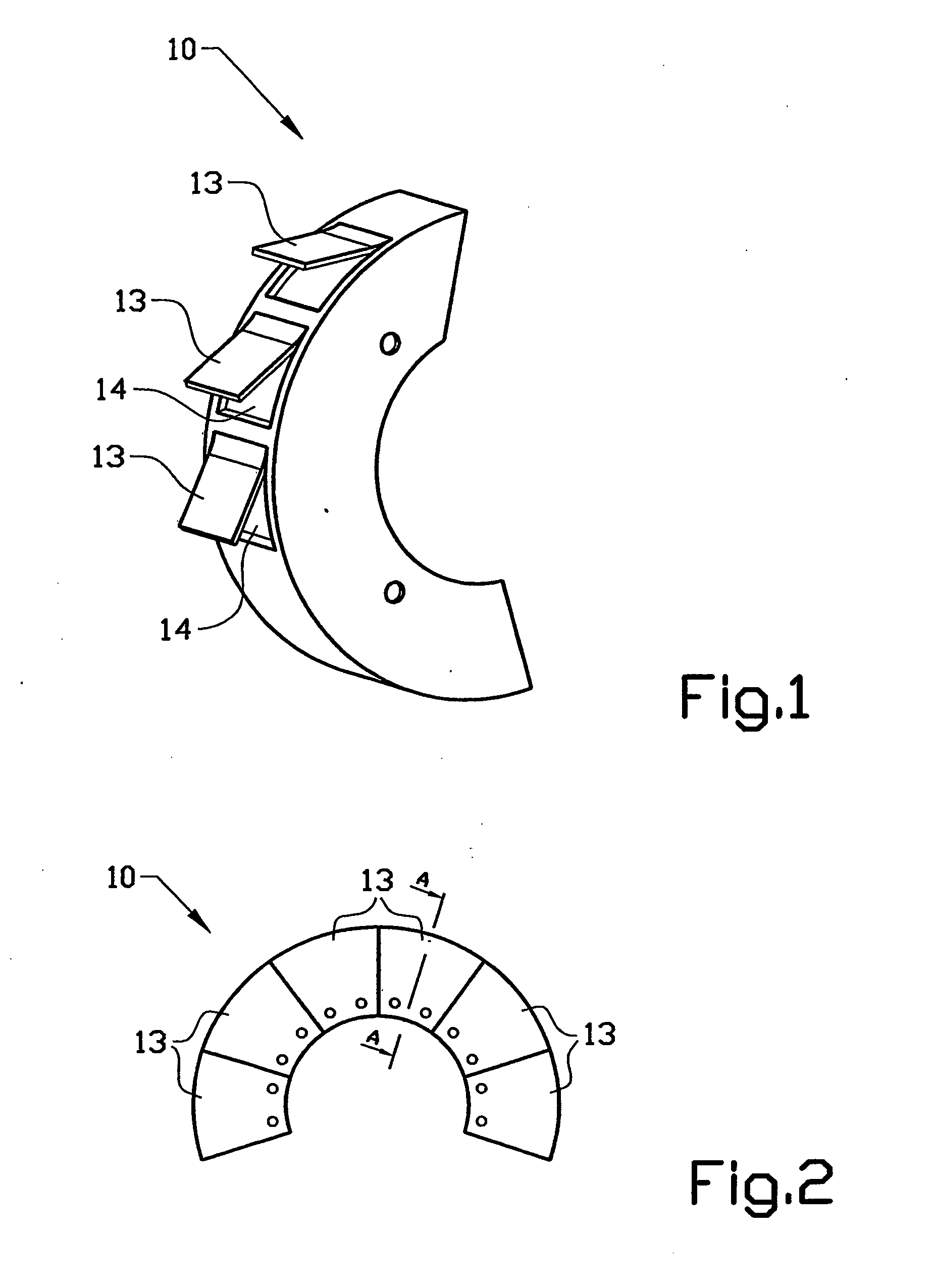
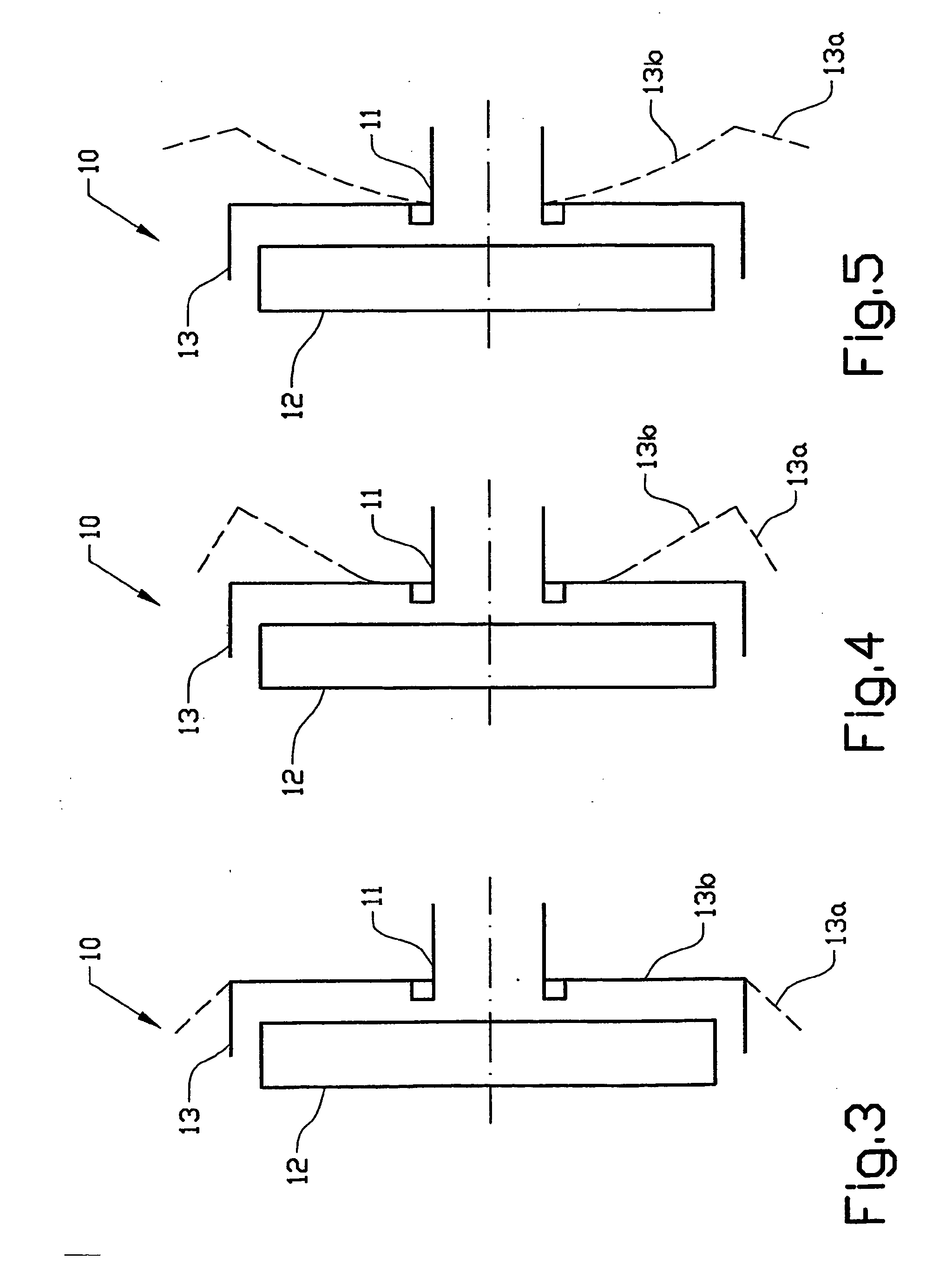
Protection shield for disk brake
InactiveUS7594567B2Simple and reliable processImprove simplicityFluid actuated brakesBraking drumsMechanical engineeringDisc brake
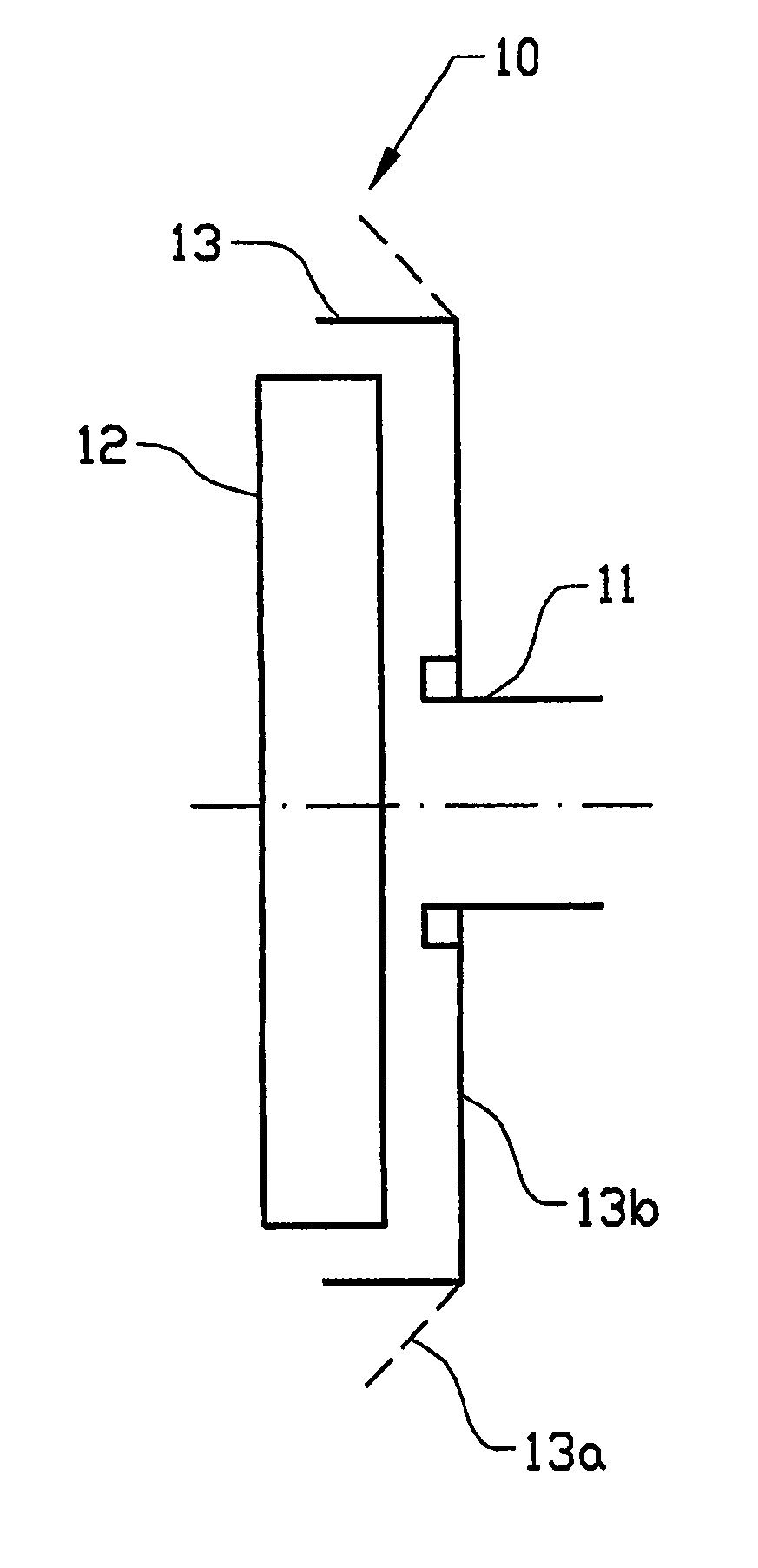
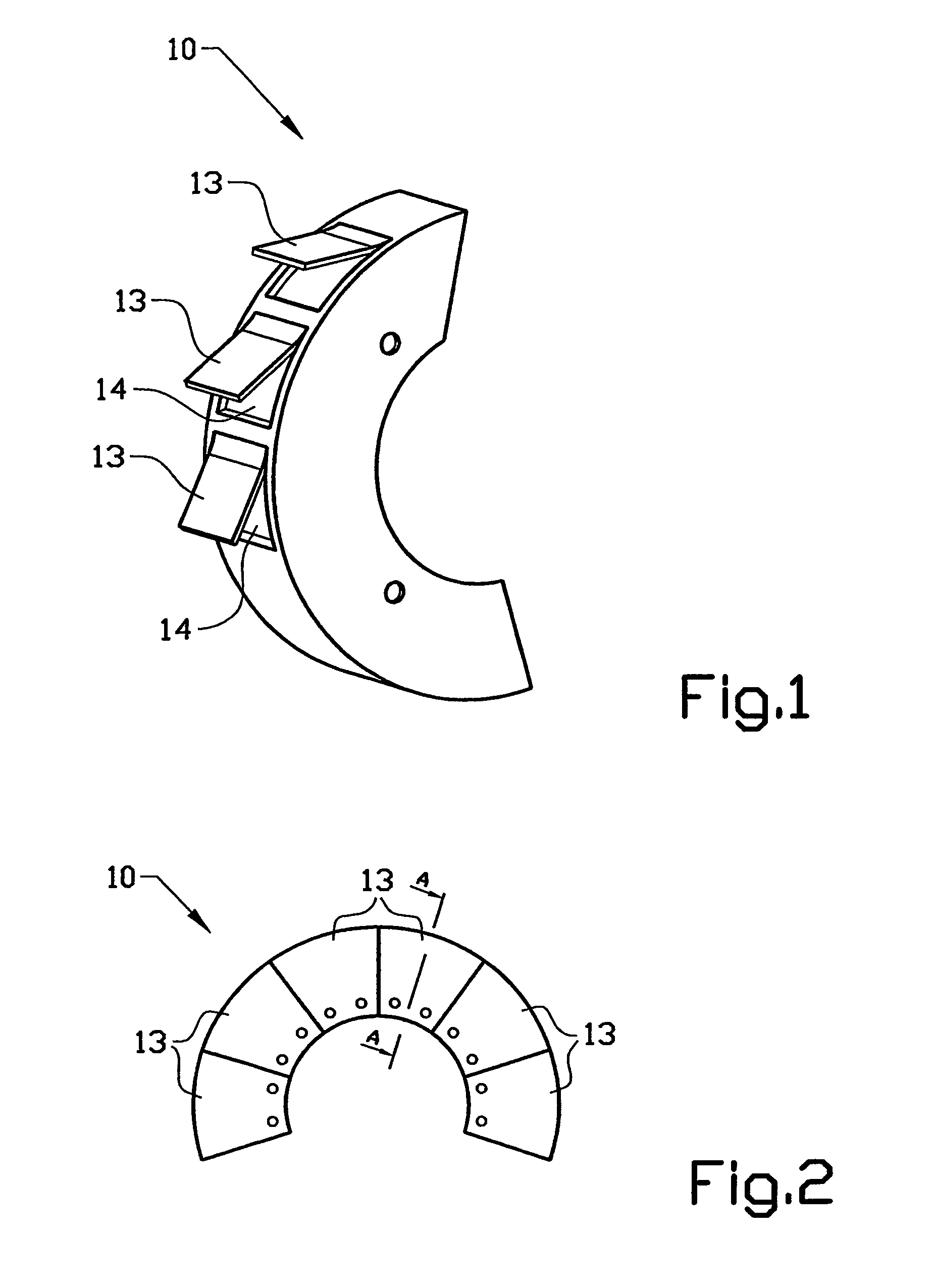
A protection device (10) in a disk brake arrangement for protecting a brake disk (12) from dirt particles. The protection device at least partly surrounds the brake disk (12), and the protection device (10) includes at least one protection assembly (13) that is mounted on the wheel suspension (11) and consists at least partly of a material of which the shape is influenced by heat. The protection assembly has a first end position which prevents dirt particles and relative wind from striking the brake disk directly and a second end position which allows relative wind to strike the brake disk directly so as thus to obtain cooling of the brake disk. The first end position occurs when the temperature of the protection assembly lies below a first temperature and the second end position occurs when the temperature of the protection assembly exceeds a second temperature.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Protection shield for disk brake
InactiveUS20050016798A1Rapid increase in coolingSimple and reliable processAxially engaging brakesBraking elementsEngineeringDisc brake
A protection device (10) in a disk brake arrangement for protecting a brake disk (12) from dirt particles. The protection device at least partly surrounds the brake disk (12), and the protection device (10) includes at least one protection means (13) that is mounted on the wheel suspension 11 and consists at least partly of a material of which the shape is influenced by heat. The protection means has a first end position which prevents dirt particles and relative wind from striking the brake disk directly and a second end position which allows relative wind to strike the brake disk directly so as thus to obtain cooling of the brake disk. The first end position occurs when the temperature of the protection means lies below a first temperature and the second end position occurs when the temperature of the protection means exceeds a second temperature.
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Vector wind sensor and integrated antenna
InactiveUS20090314078A1Ease portabilityEase transportVolume measurement and fluid deliveryIndication/recording movementEngineeringIntegrated antenna
An anemometer assembly for sensing and transmitting wind speed and wind direction data. The wind sensor measures relative wind direction and wind speed without the use of moving parts and consumes very little power making it suitable for unattended operation. The main wind sensing member is an elongated vertical member that can be used as radio antenna. The data can be transmitted from a remote location and thus relay data to a central collection repository or network location.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
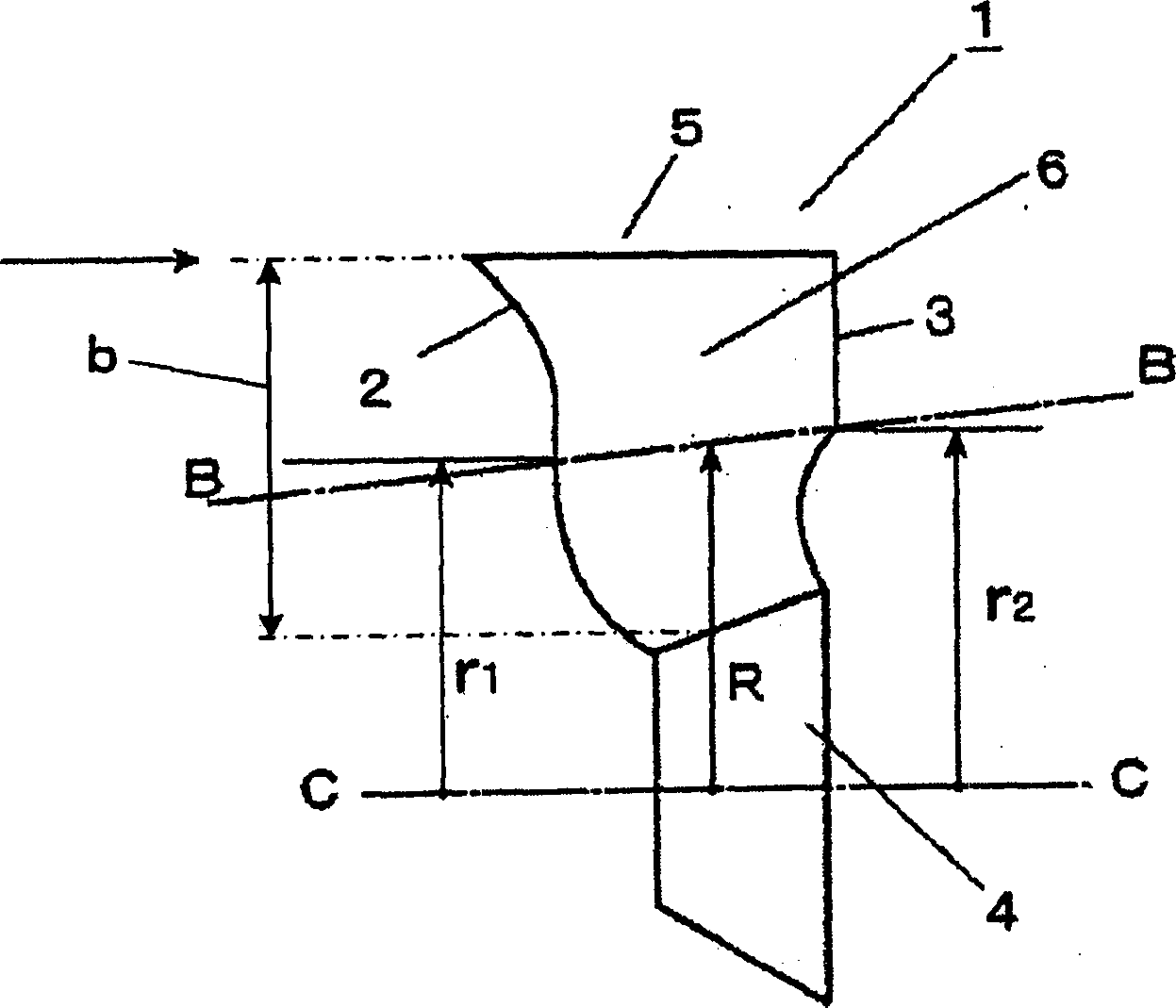
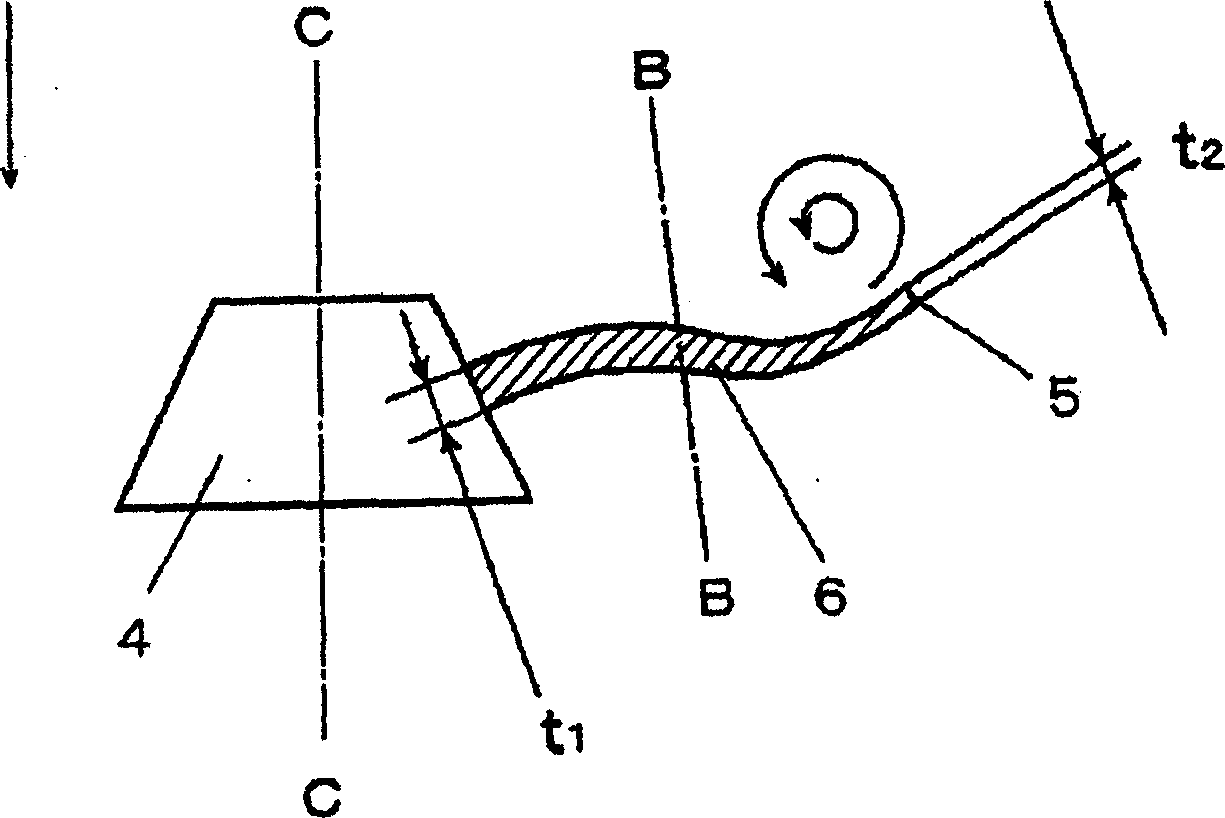
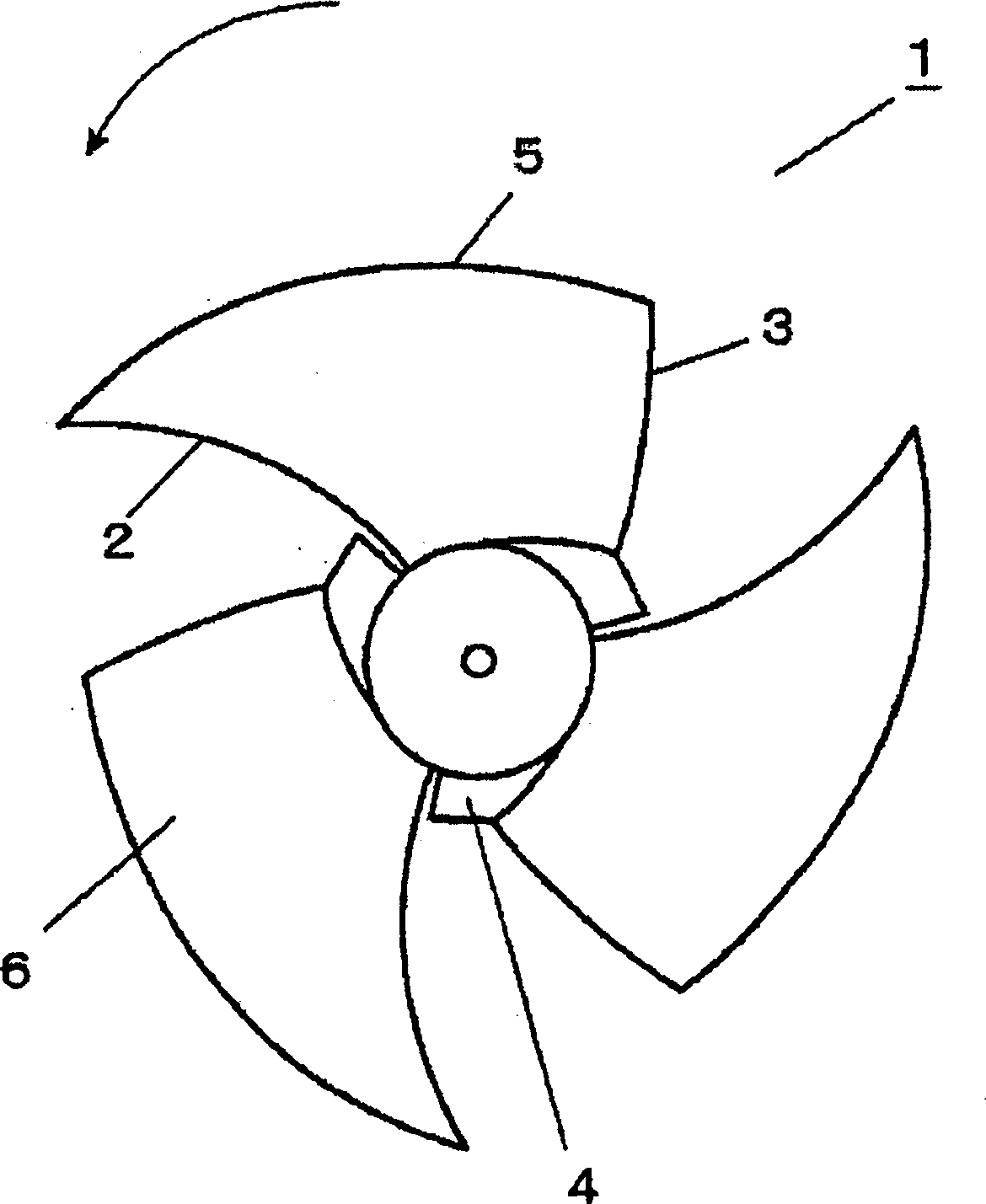
Air feeder vane wheel
The oblique flow blower impeller of the present invention focuses on improving fan efficiency and reducing noise, and improves these performances by improving the structure of the fan. An impeller (1) of a diagonal flow blower is formed by arranging a plurality of thin blades (6) on a roughly truncated cone-shaped hub (4), and the front edge (2) of the blades (6) is formed in the following shape: On the meridian surface of the blade (6), a concave curve is formed on the upper side of the outer peripheral side near the midpoint (BB) of the blade tip (5) of the hub (4) and the blade (6) relative to the wind. The more hub side near the point is formed as a convex curve relative to the upper side of the wind, and the radial cross-sectional shape of the blade (6) is formed as follows: the more blade tip (5) side near the midpoint is formed as a concave curve relative to the upper side of the wind , the more hub (4) side near the midpoint is formed as a convex curve relative to the upper side of the wind. And, the leading edge (2) is formed by a helical curve.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
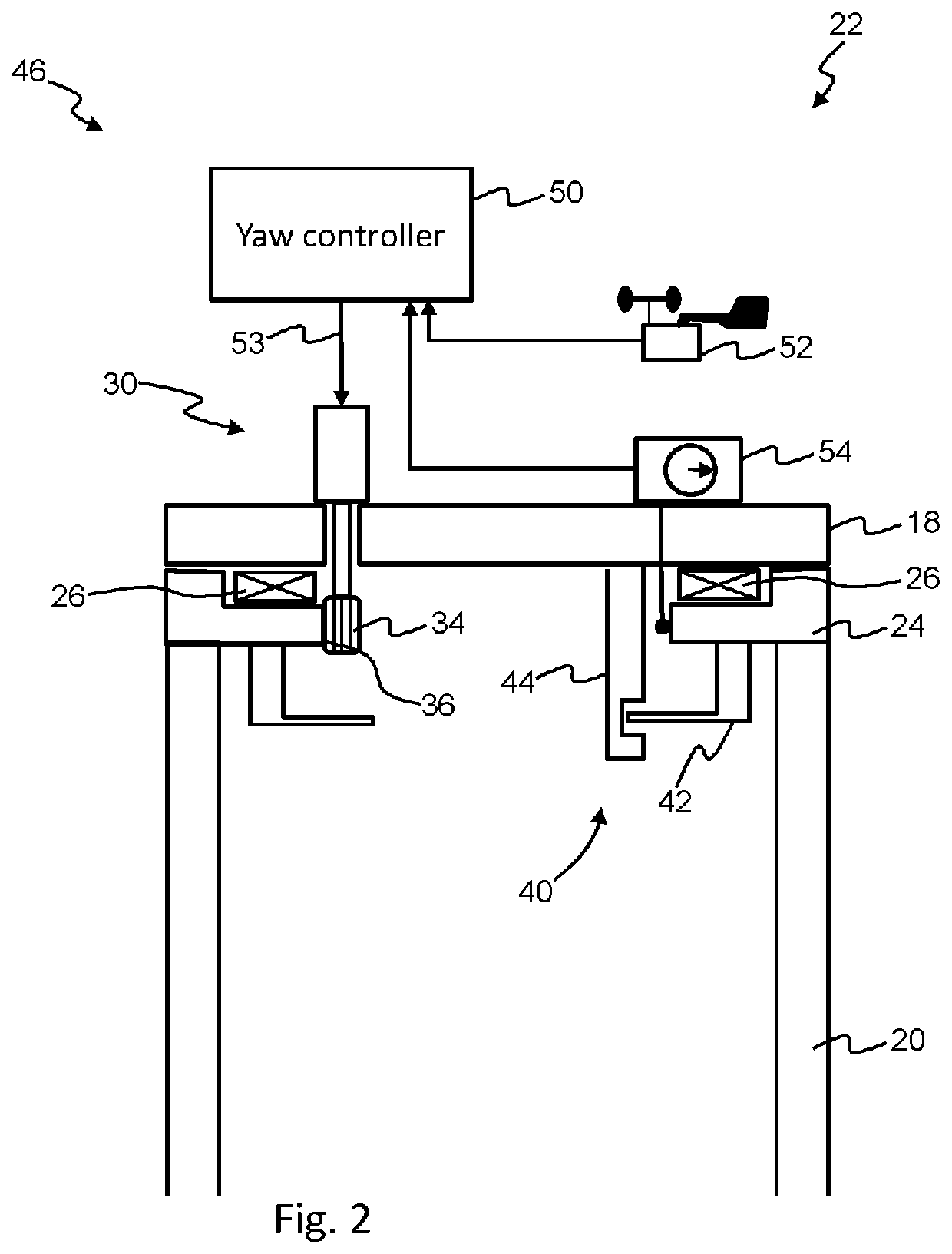
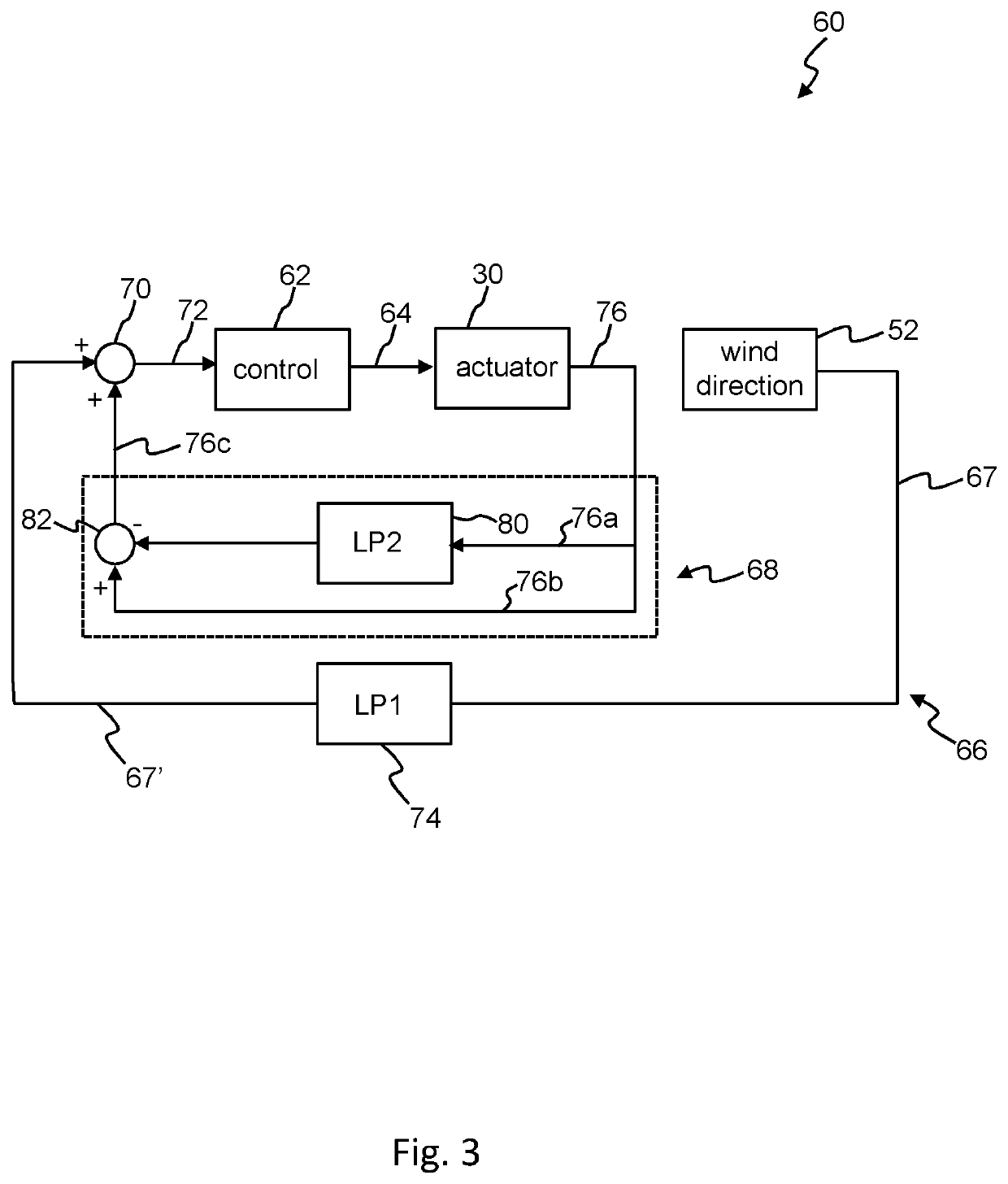
Wind turbine yaw control system with improved wind direction tracking
ActiveUS20200102932A1Improve abilitiesImprove accuracyWind motor controlMachines/enginesNacelleLow-pass filter
A wind turbine including yaw control comprising a controller receiving an input signal, and providing an output control signal to a yaw actuator. The input signal to the controller is based on: a first feedback signal that is indicative of the relative wind direction determined with respect to the wind turbine, wherein the first feedback signal is filtered with a first low pass filter; and a second feedback signal that is indicative of the activity of the yaw actuator. The control technique of the invention significantly improves the ability of a yaw system to maintain a zero degree yaw error during steady state wind conditions, or in other words to maintain an accurate heading of the nacelle pointing into the wind, as well as reducing the maximum yaw error experienced during yaw system activation.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Control method of wind collecting-type vertical-shaft fan and wind generating set thereof
InactiveCN101694205AIncrease wind speedImprove fan efficiencyWind motor controlWind motor combinationsWind drivenPosition angle
The invention discloses a control method of a wind collecting-type vertical-shaft fan and a wind generating set thereof. The method is characterized in that the inflow wind speed, the relative wind speed, the attack angle of blades and the driving force of wind wheels are controlled by adjusting the position angle of a wind collecting system of the wind collecting-type vertical-shaft fan, thus being capable of controlling wind energy efficiency and fan power; a wind collecting-type vertical-shaft wind-driven generator mainly consists of a main shaft, a wind wheel, a tower post, bearings, a pedestal, a gear box, a generator and the wind collecting system, wherein the wind collecting system mainly consists of a wind guiding wing, a wind collecting wing and a driving and controlling component; and the purpose of controlling the wind energy efficiency and the fan power is achieved by adjusting and controlling azimuth angels of the wind guiding wing and the wind collecting wing.
Owner:李锋
Method and arrangement for continuous calibration of a wind direction measurement
ActiveUS20170284375A1Improve accuracyWind motor controlIndication/recording movementTurbineWind force
A method for calibrating a wind direction measurement for a wind turbine is provided. The method including: measuring plural samples of a relative wind direction representing a difference angle between a real wind direction and an orientation of a measurement equipment, in particular a direction orthogonal to a rotor blade plane, to obtain plural measured relative wind directions; deriving a measured relative wind direction change based on the measured relative wind directions; measuring plural samples of a performance parameter indicating a performance of the wind turbine; deriving a performance change based on the plural samples of the performance parameter; determining a correlation value between the measured relative wind direction change and the performance change; measuring further plural samples of the relative wind direction; and correcting the further measured relative wind directions based on the correlation value, to obtain corrected further measured relative wind directions.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
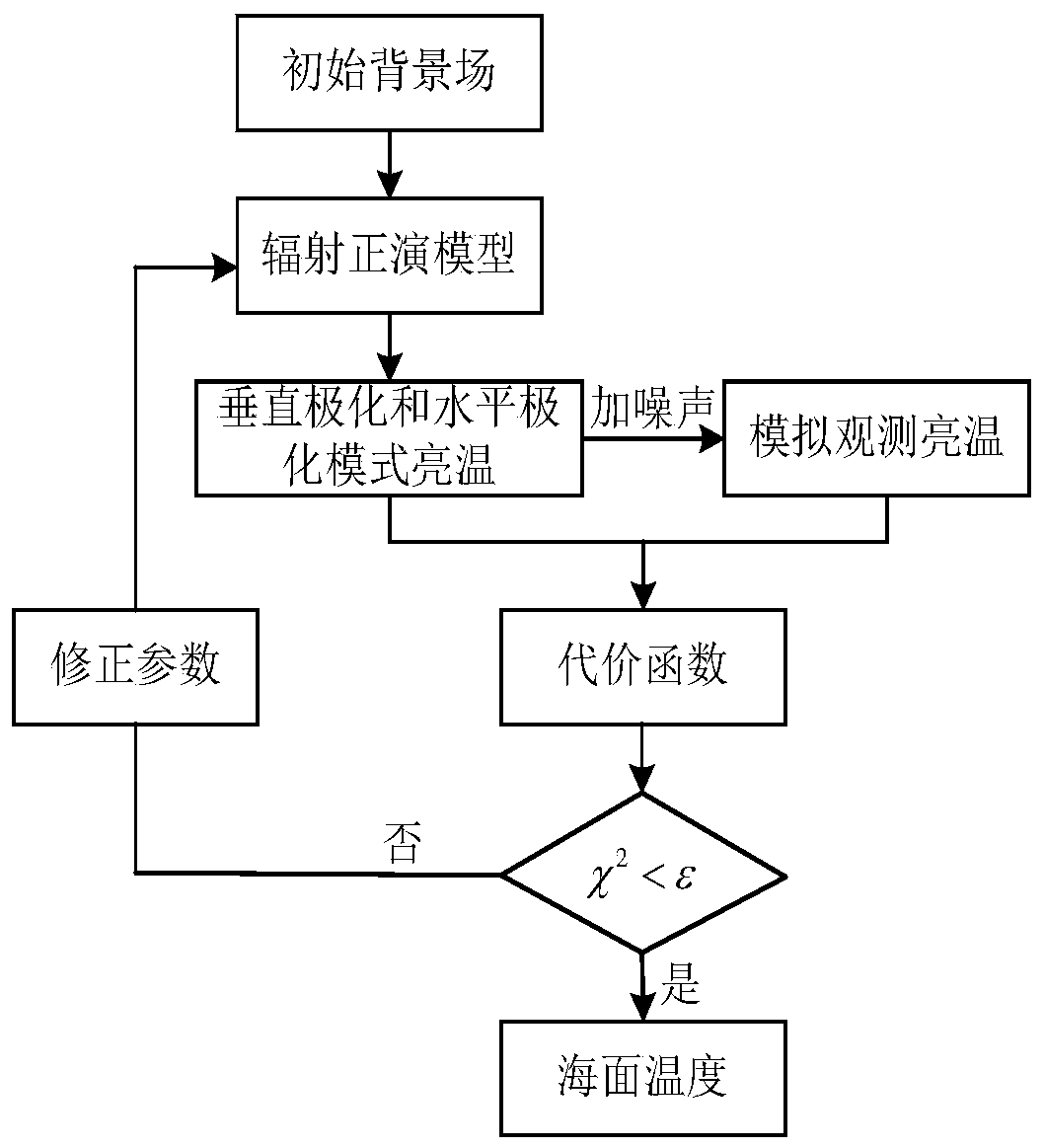
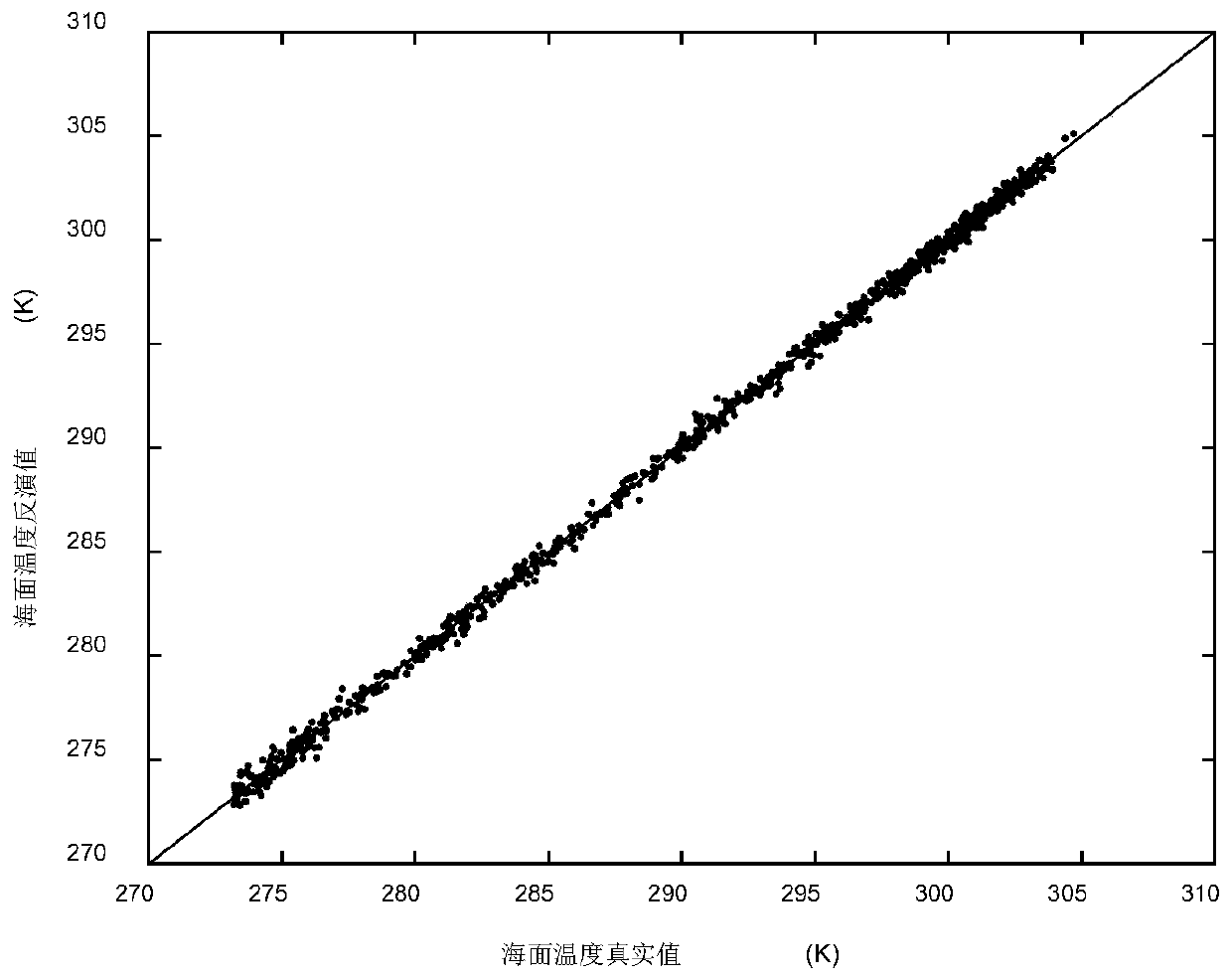
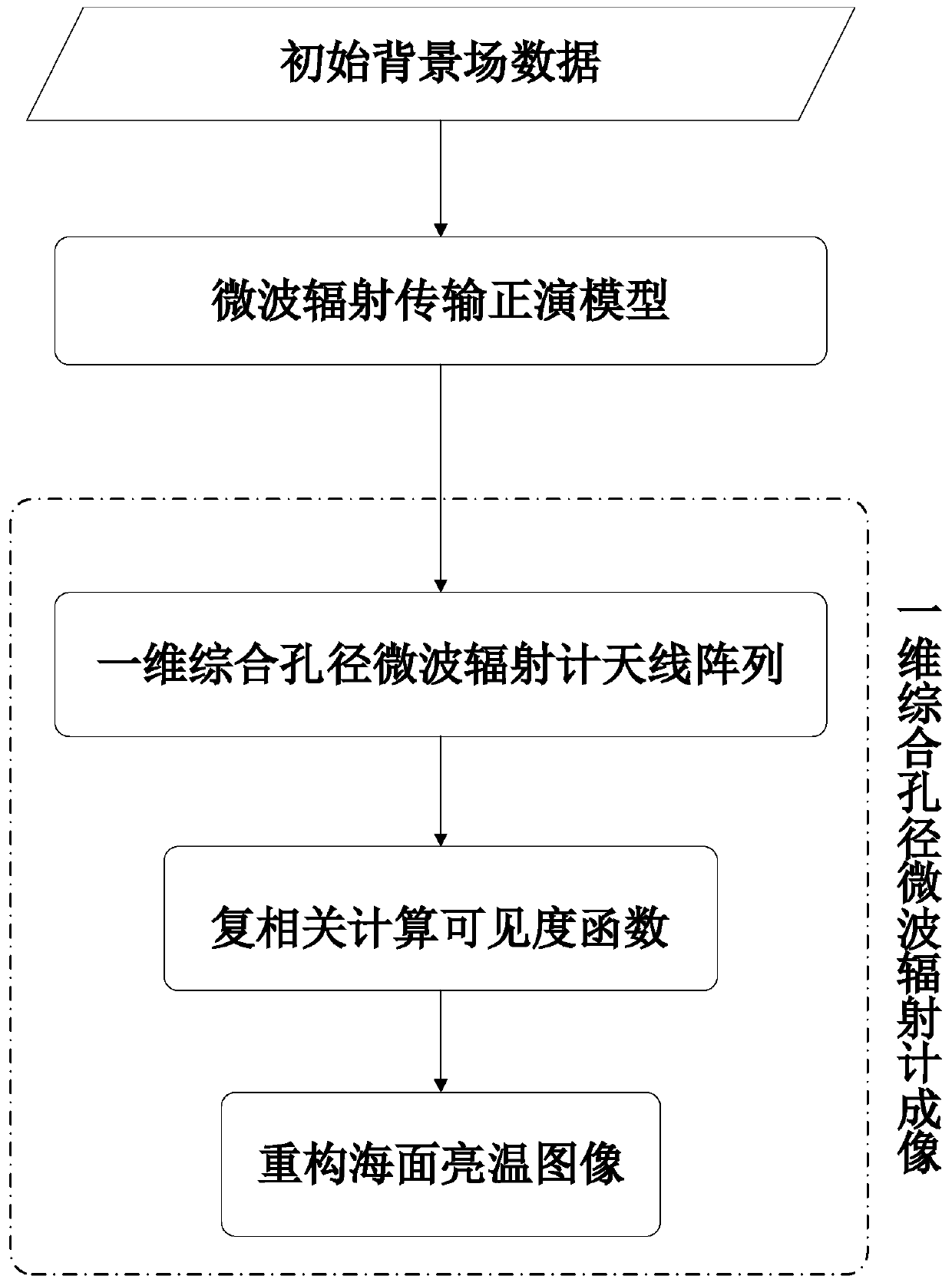
Sea surface temperature physical inversion method based on one-dimensional synthesis aperture microwave radiometer
The invention discloses a sea surface temperature physical inversion method based on one-dimensional synthesis aperture microwave radiometer. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, constructing an initial background field ( frequency f, sea surface temperature Ts, seawater salinity S, incident angle Theta, sea surface wind speed W, sea surface relative wind direction atmospheric water vapor content V, cloud liquid water content L), providing data support for sea surface temperature inversion; secondly, according to the characteristics observed by the one-dimensional comprehensive aperturemicrowave radiometer in multi-incident angle, calculating a mode brightness temperature in an atmospheric top scene at frequency of 6.9 GHz and different incident angles by using a microwave radiation transmission forward model, adding random errors in the mode brightness temperature to simulate the observed brightness temperature of the one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer; and finally, constructing a cost function by using a physical inversion method based on maximum likelihood Bayesian estimation, inverting the sea surface temperature through a minimization cost function. The sea surface temperature physical inversion method provided by the invention solves the problem that the sea surface temperature inversion is difficult in multiple incident angles and improves the sea surface temperature inversion effect.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Resistance and lifting force composite wind pwoer device
ActiveCN1719023AWith resistanceWith lift compounding effectRenewable energy generationMachines/enginesWind forceWind power
Owner:QINGDAO CHENGZHIMEI CREATIVE TECH CO LTD
Sea surface brightness temperature imaging simulation method based on one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer
ActiveCN109725317ARadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationSurface brightnessMicrowave radiometer
The invention discloses a sea surface brightness temperature imaging simulation method based on a one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer. The method comprises the following steps of:constructing initial background field data (frequency f, sea surface temperature Ts, seawater salinity S, incident angle [Theta], sea surface wind speed W, sea surface relative wind direction phi, atmospheric water vapor content V, cloud liquid water content L) to provide data support for sea surface brightness temperature imaging simulation; calculating the brightness temperature of the scene mode at the top of the atmosphere at different incident angles with a frequency of 6.9 GHz by using a microwave radiation transmission forward model according to the observation characteristics of the multi-incident angle of the one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer; receiving a scene brightness temperature signal by the small antenna array of the one-dimensional synthetic aperturemicrowave radiometer to generate an electrical signal, and performing pairwise complex correlation on antenna output voltages to obtain a visibility function; and reconstructing a sea surface brightness temperature image by mathematical operations such as inverse Fourier transform. The method provides technical support for remote sensing sea surface temperature of satellite-bone one-dimensional synthetic aperture microwave radiometer.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
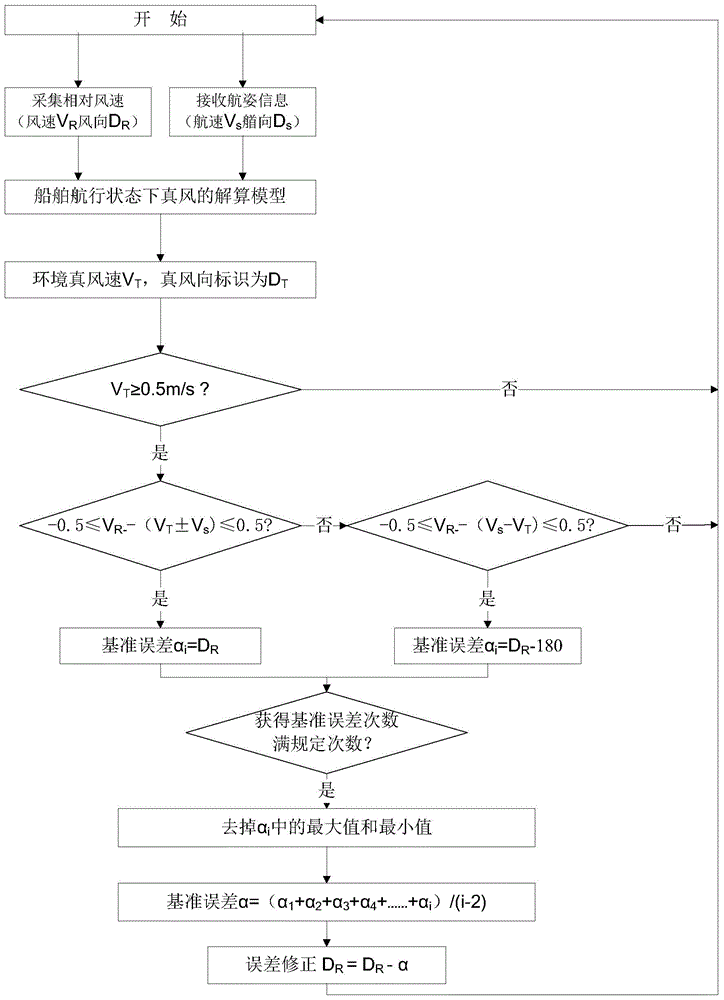
Self-amending method of standard error of ship-based wind speed and direction transducer
InactiveCN104614554AImprove operational safetyHigh measurement accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesTransducerOnline study
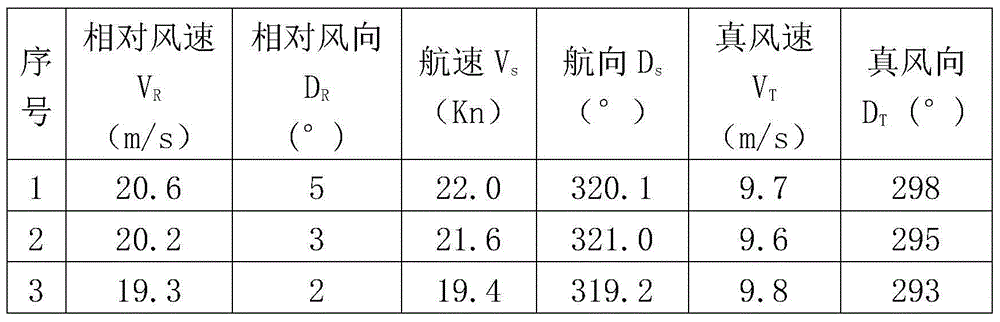
The invention discloses a self-amending method of a standard error of a ship-based wind speed and direction transducer, which can improve the measurement accuracy of a device through online study. The technical scheme is that the self-amending method of the standard error of the ship-based wind speed and direction transducer is characterized by comprising the following steps: when relative wind speed value VR, sailing wind speed Vs and real wind speed VT satisfy 0.5<=VR-(VS+-VT)<=0.5, and the real wind speed VT >= 5.0 m / s, the standard error alpha is equal to DR; when the relative wind speed value VR, sailing wind speed Vs and real wind speed VT satisfy -0.5<=VR-(VT-VS)<= 0.5, and the real wind speed VT >= 5.0 m / s, the standard error alpha is equal to DR-180; when above limit conditions are satisfied, an amending window of the standard error is opened, a standard error value alpha 1 is obtained; along with the ship sailing under different gestures, the n standard error values are obtained and respectively marked as alpha 1, alpha 2, ...alpha n. When the n standard error value is obtained, one maximum value and one minimum value are rejected, and the remaining (n-2) values carry out the arithmetic mean, thus the standard error is obtained; the measurement result of wind speed and direction is amended by using the obtained standard error: DR=DR-alpha, and the record is amended; then the error amending in this turn is completed.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Static pressure calculation from dynamic pressure for rotary air-data system and methodology therefor
ActiveUS6938472B2Accurate calculationImprove abilitiesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsFluid speed measurement using pressure differenceLow speedEngineering
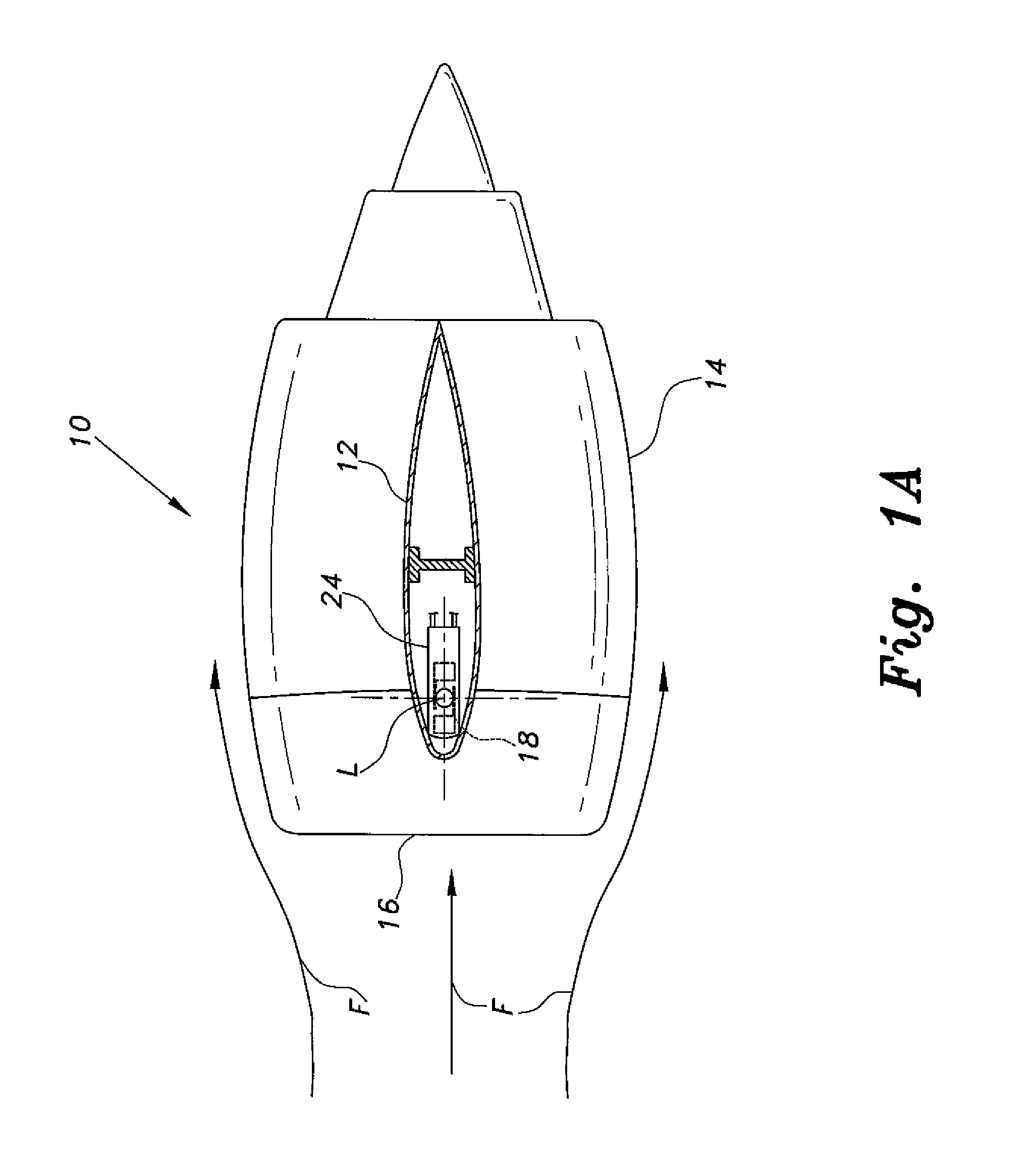
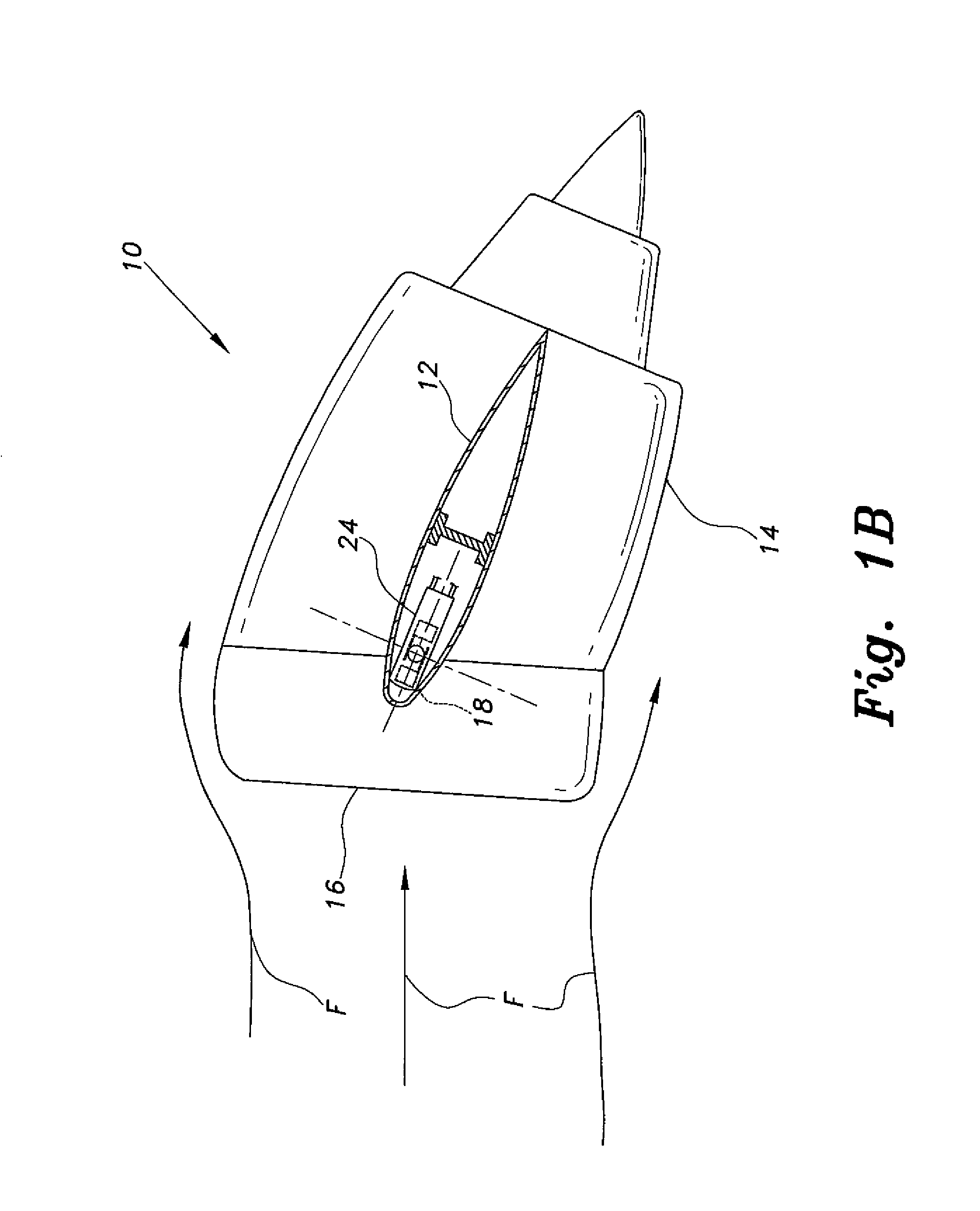
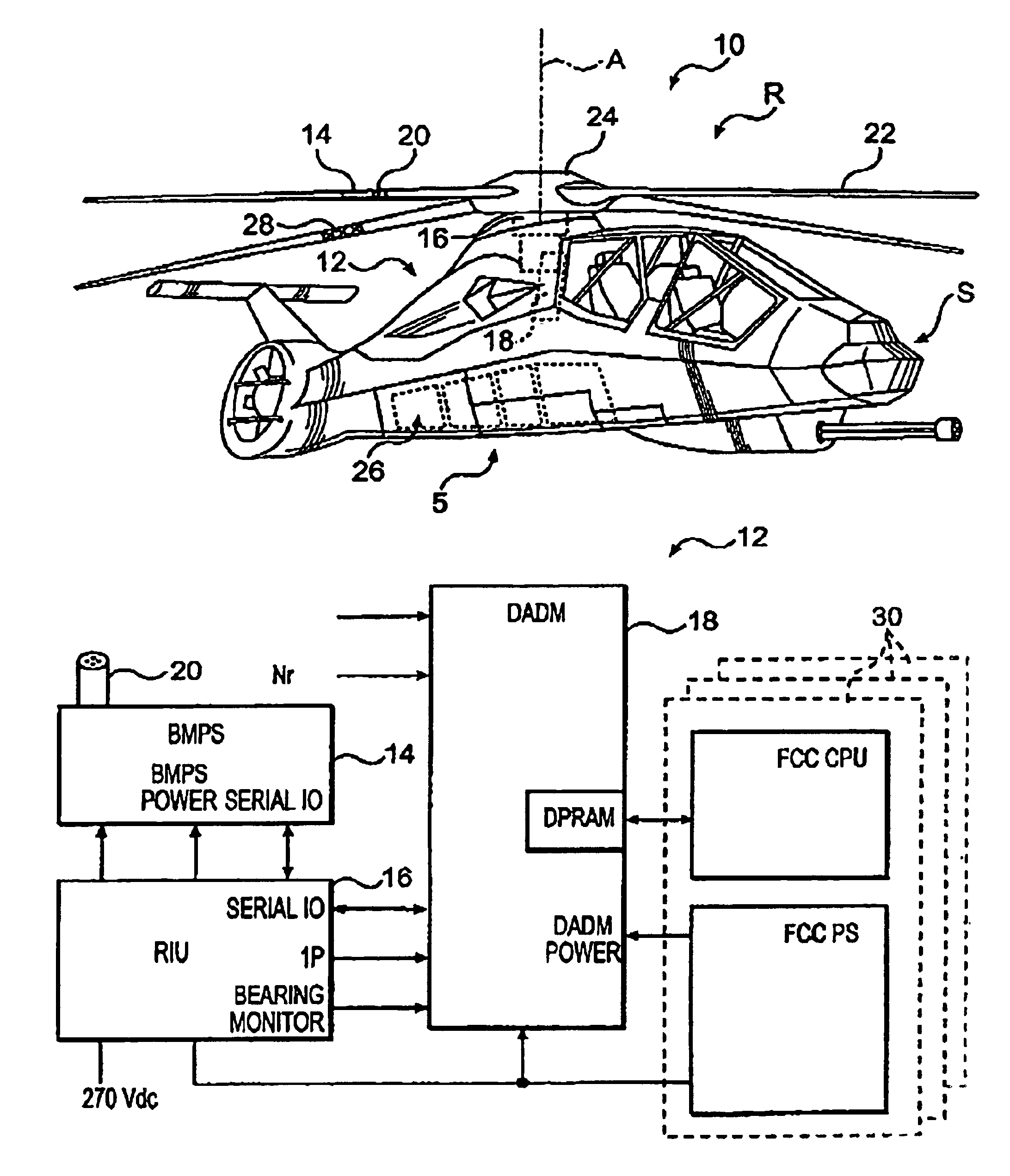
A Rotary Air-data System (RADS) periodically samples pressure data from a main rotor blade mounted pitot-scoop integrated with a high accuracy pressure sensor to compute a velocity vector that is resolvable into the aircraft's coordinate system. Mathematical techniques are employed which provide accurate computations of static pressure without a static pressure sensor. The RADS also computes the direction of the relative wind which is particularly useful when the pilot executes hover or low speed, low altitude maneuvers in restricted visibility. The availability of relative wind velocity information coupled with navigation data enhances the ability of rotary aircraft to perform accurate low altitude hover, fire control and other autopilot maneuvers.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
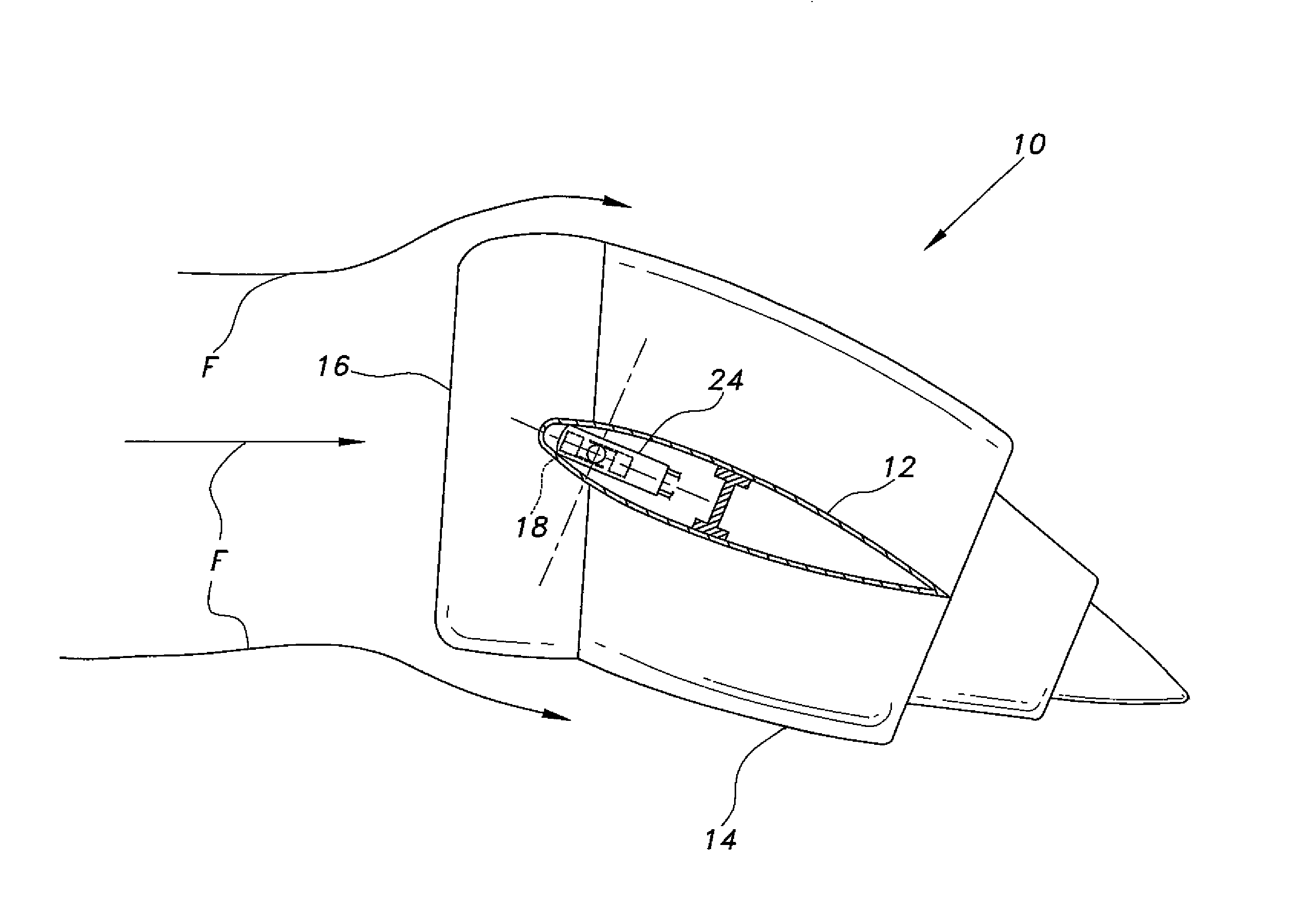
Vehicle having at least one cooling circuit for cooling a fuel cell system
InactiveCN102484270AIncrease surface areaAchieve coolingAir-treating devicesFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsNuclear engineering
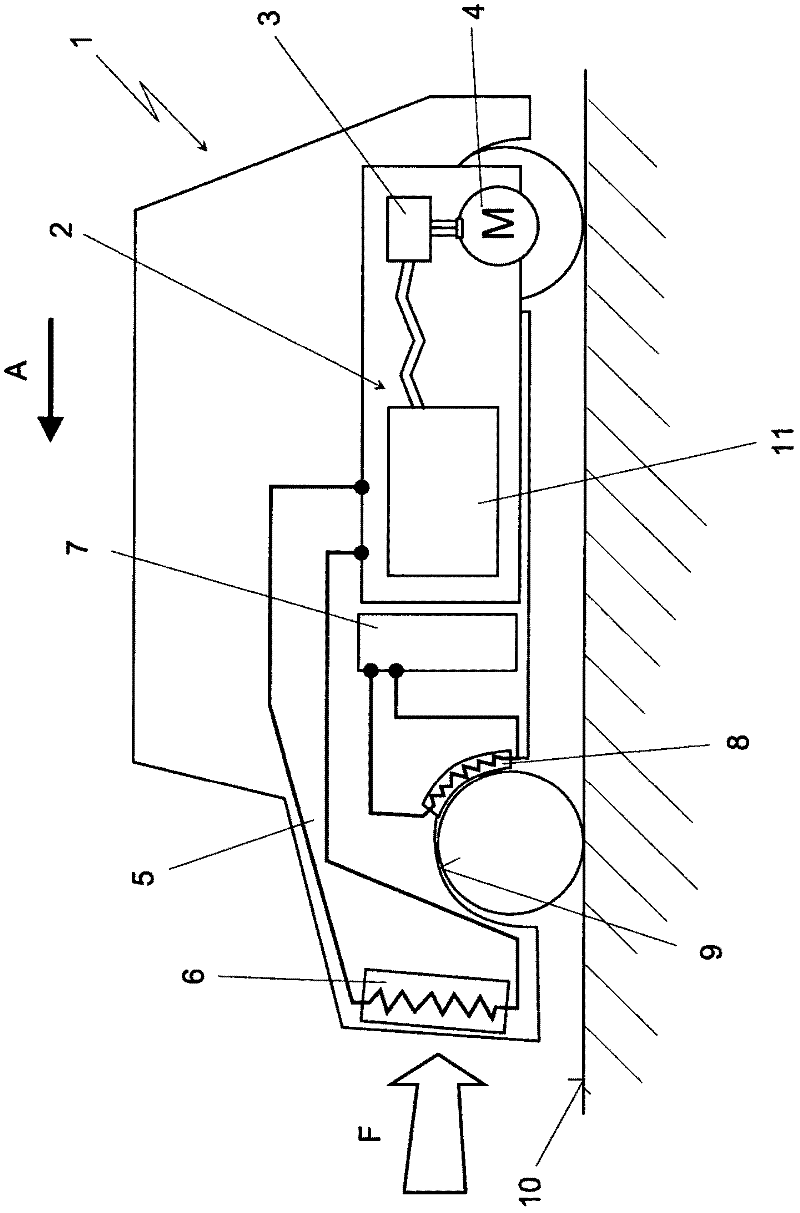
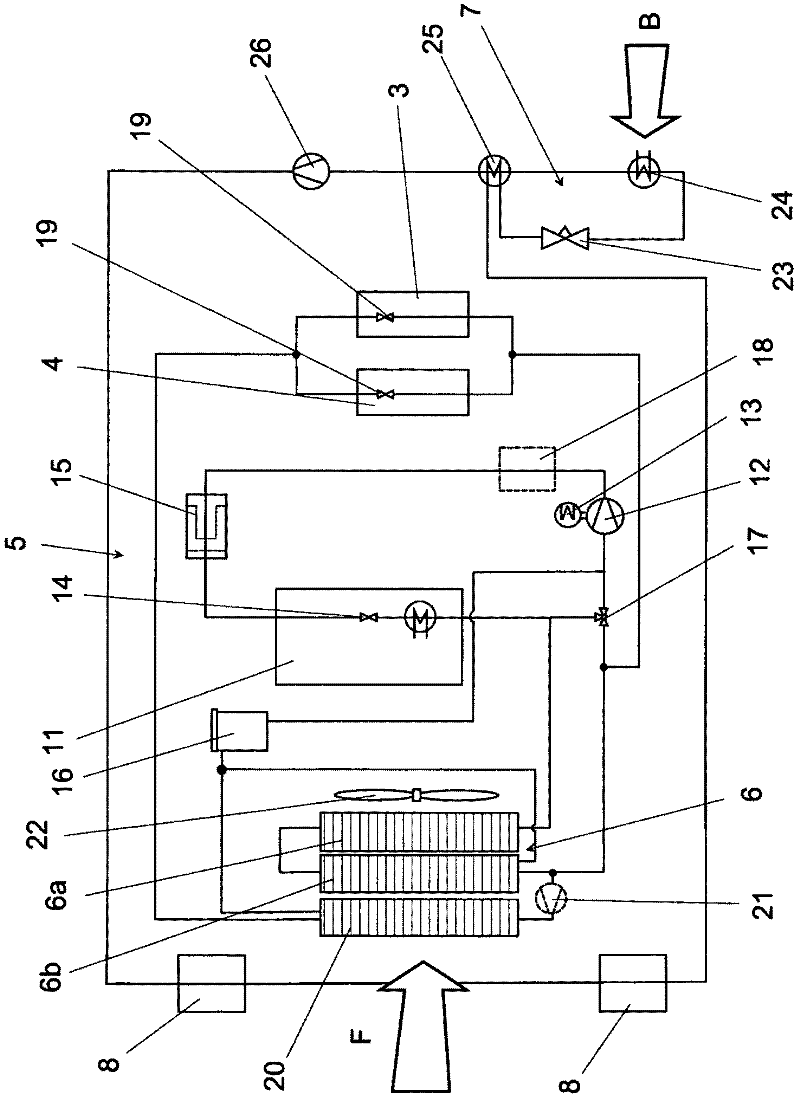
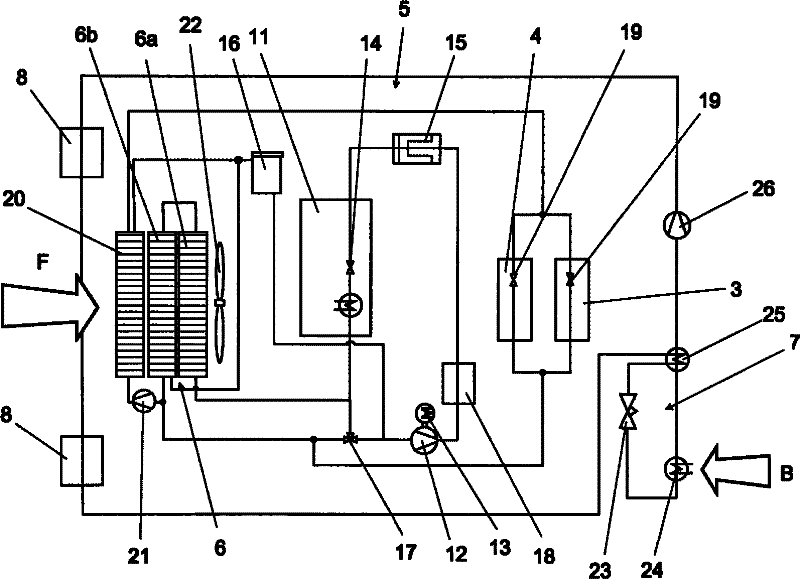
The invention relates to a vehicle, comprising at least one cooling circuit (5) for cooling a fuel cell system (2). The cooling circuit (5) comprises at least one cooling heat exchanger (6), a coolant conveying device (12), and a heat exchanger in a fuel cell stack (11) of the fuel cell system (2). The airstream (F) flows against on the cooling heat exchanger (6) as cooling air. According to the invention, the cooling heat exchanger (6) has at least two stages (6a, 6b), which are designed in such a way that the relative wind (F) flows through the two stages consecutively in series.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Portable Device And Method For The Geolocation And Continuous Location Of An Object Moving In A Constrained Environment
InactiveUS20150296342A1Navigational calculation instrumentsLocation information based serviceAlgorithmGeolocation
The invention includes a portable device and a method for the geolocation and continuous location of an object moving in a constrained environment. This device includes:means to determine the movement speed vector of this object by anemometer reading able to make measurements of relative wind caused by the movement of the object, and to deliver a corresponding signal,means for processing this signal able to calculate the speed vector of this object and its position.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Air guiding element
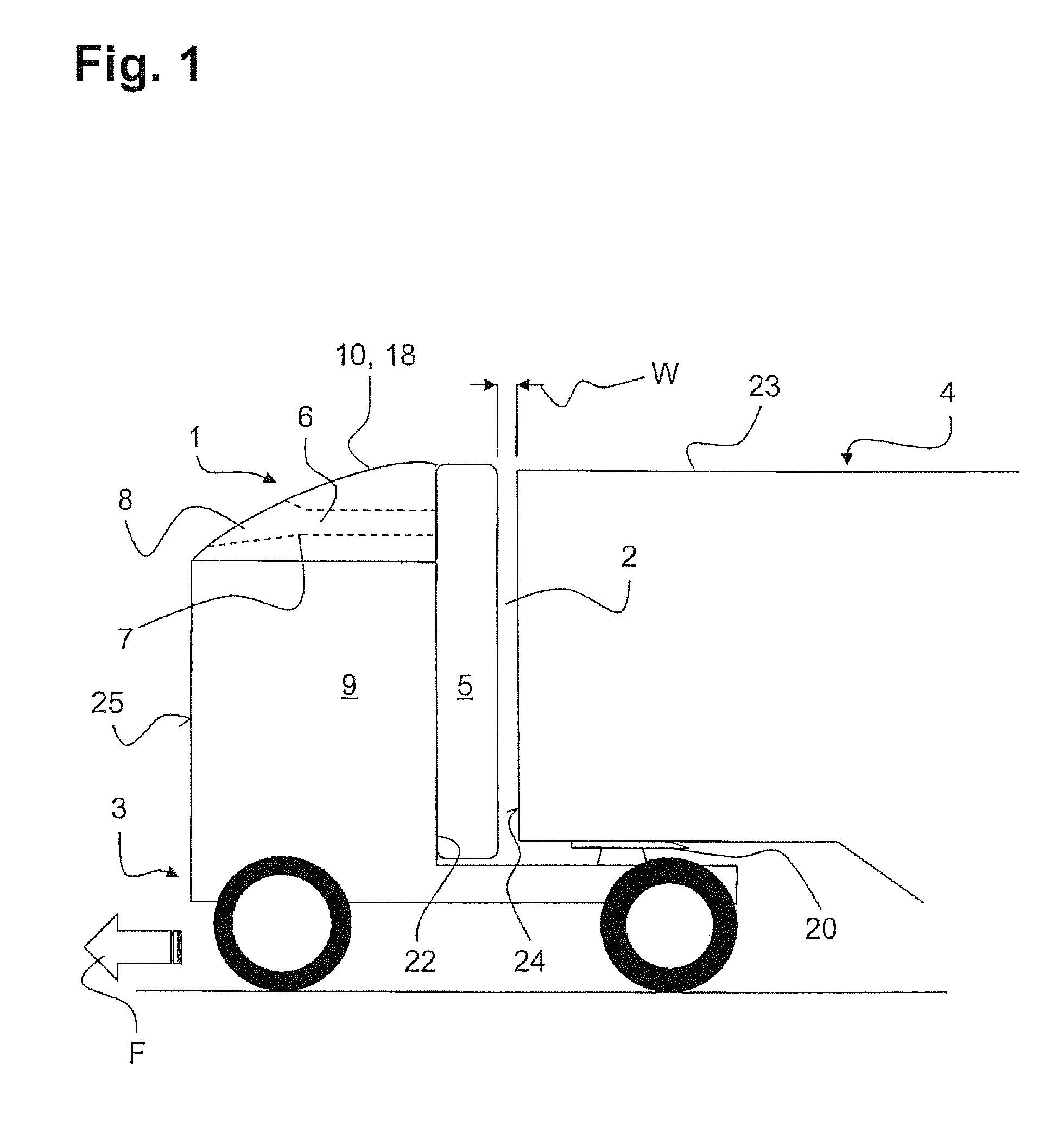
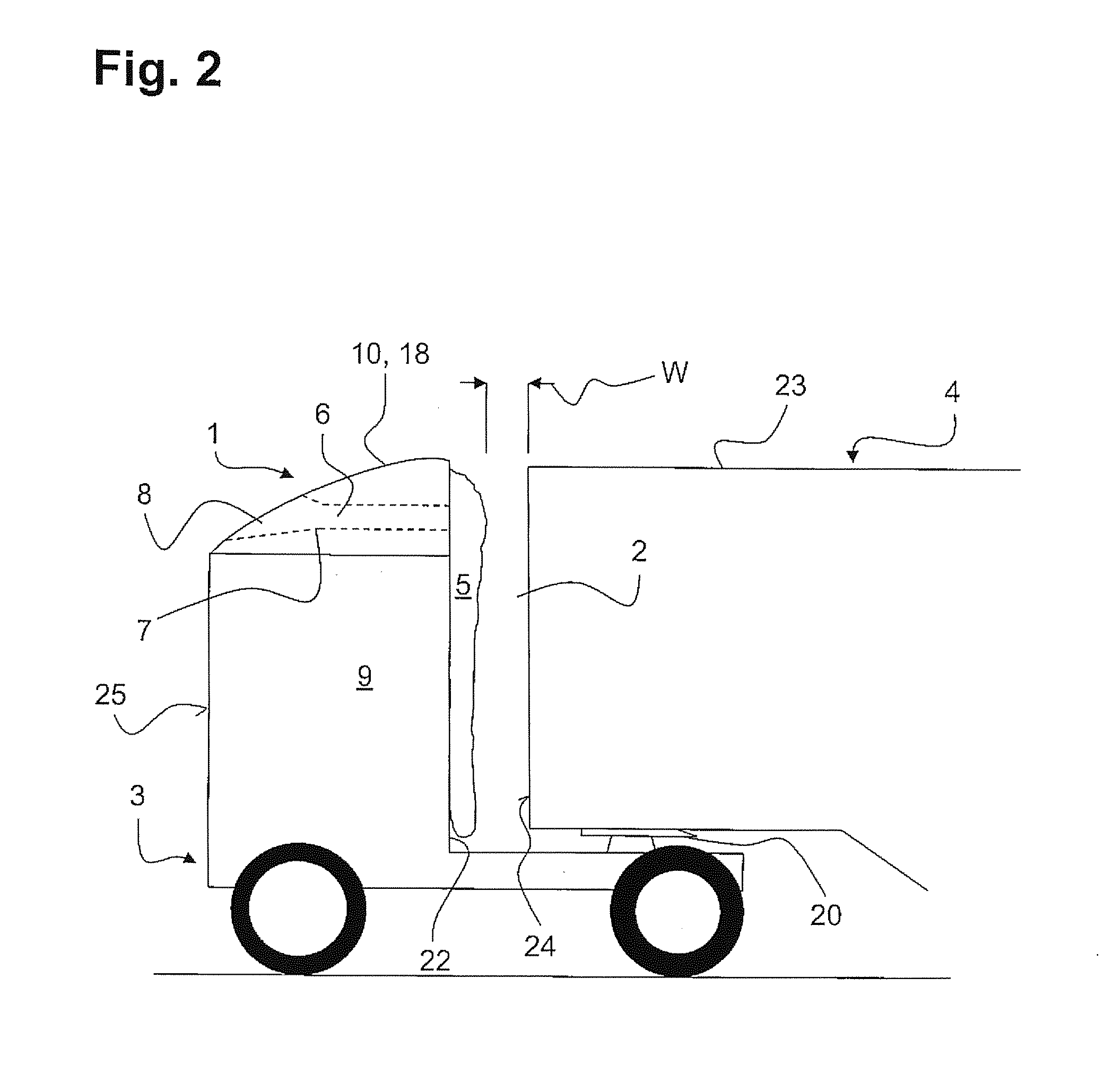
An air guiding element for improved flow over a gap between a tractive vehicle and a trailer vehicle is described, wherein the air guiding element can be mounted on the tractive vehicle or the trailer vehicle and has a flexible and airtight air cushion which is connected to a filling channel. The problem of providing a largely low-maintenance and operationally safe air guiding element, which can be installed independently of the compressed air supply of the tractive vehicle, for improved flow over the gap between a tractive vehicle and a trailer vehicle is addressed. The problem is solved by an air guiding element in which the filling channel has an air entry opening oriented in the direction of travel (F) on the side of the filling channel facing away from the air cushion, the air entry opening being arranged in such a way that the air cushion is filled exclusively by a dynamic pressure of the relative wind.
Owner:JOST WERKE
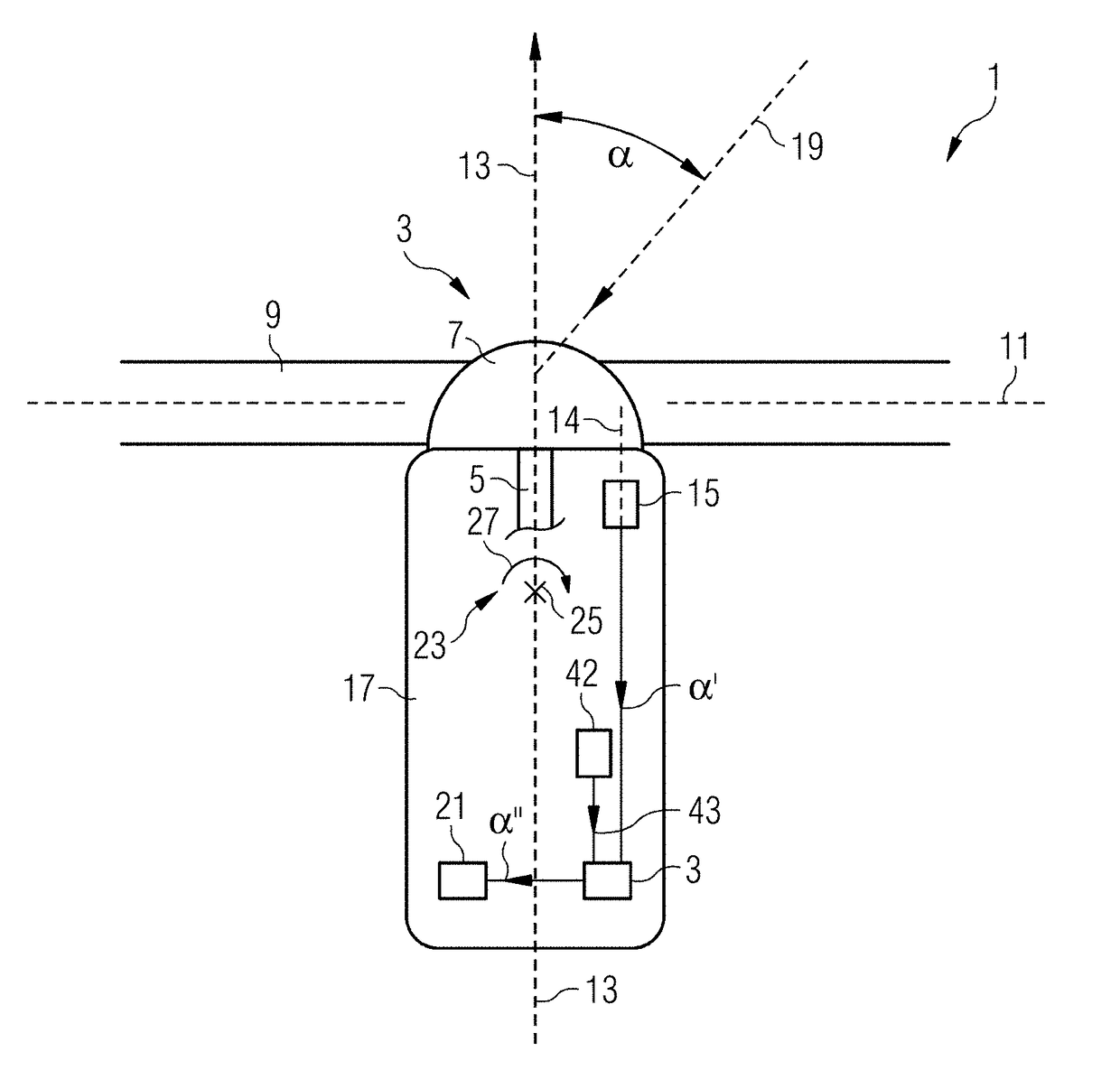
Airship, anchoring device, and landing and mooring method
ActiveUS20140158819A1Easy to liftProcess stabilityNon-rigid airshipsRigid airshipsEngineeringMechanical engineering
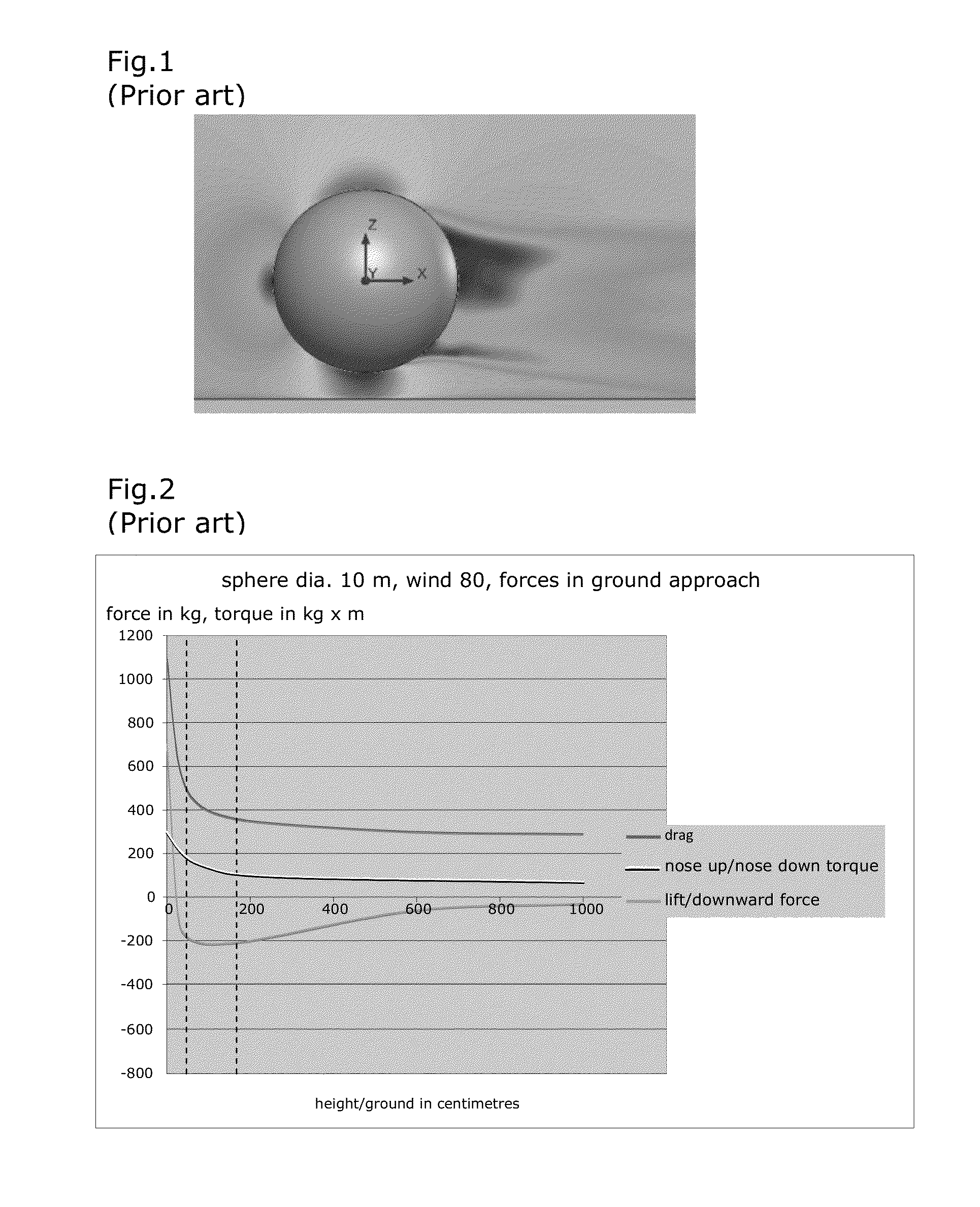
An air vehicle such as an airship is provided, having a rounded top portion, and the bottom portion of which has a substantially planar shape, including a region having a smaller inclination, which is referred to as a bottom surface, and the surface area of which is larger than that of an intermediate region having a greater inclination, referred to as an intermediate surface. The general shape produces, due to relative wind, a resulting overall downward force near the ground. The vehicle also includes a device for anchoring same to the ground, the anchoring device being stationary or controllable from the vehicle, located at the front portion of the vehicle, and projecting downward, in particular a ram including a portion which can be expanded by applying a bar against a translatably movable shoulder. Also included is a landing method implementing such a vehicle.
Owner:DIRISOLAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com