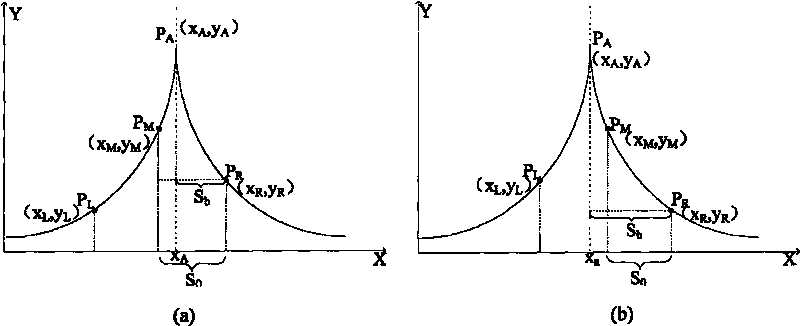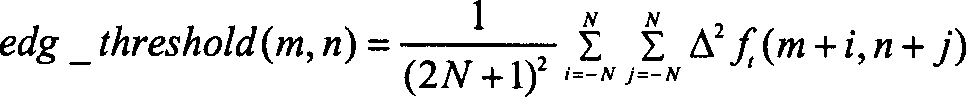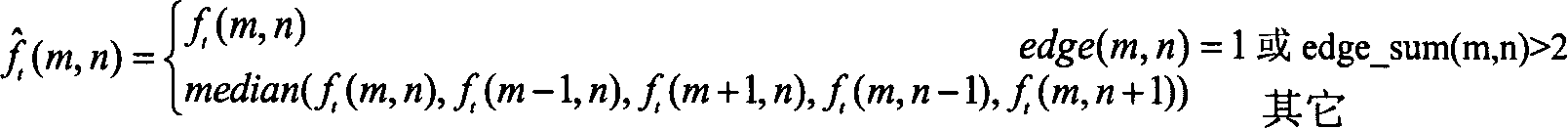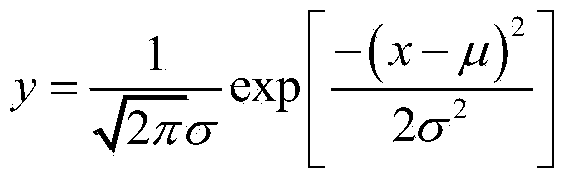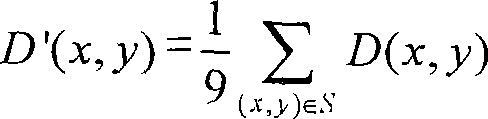Patents
Literature
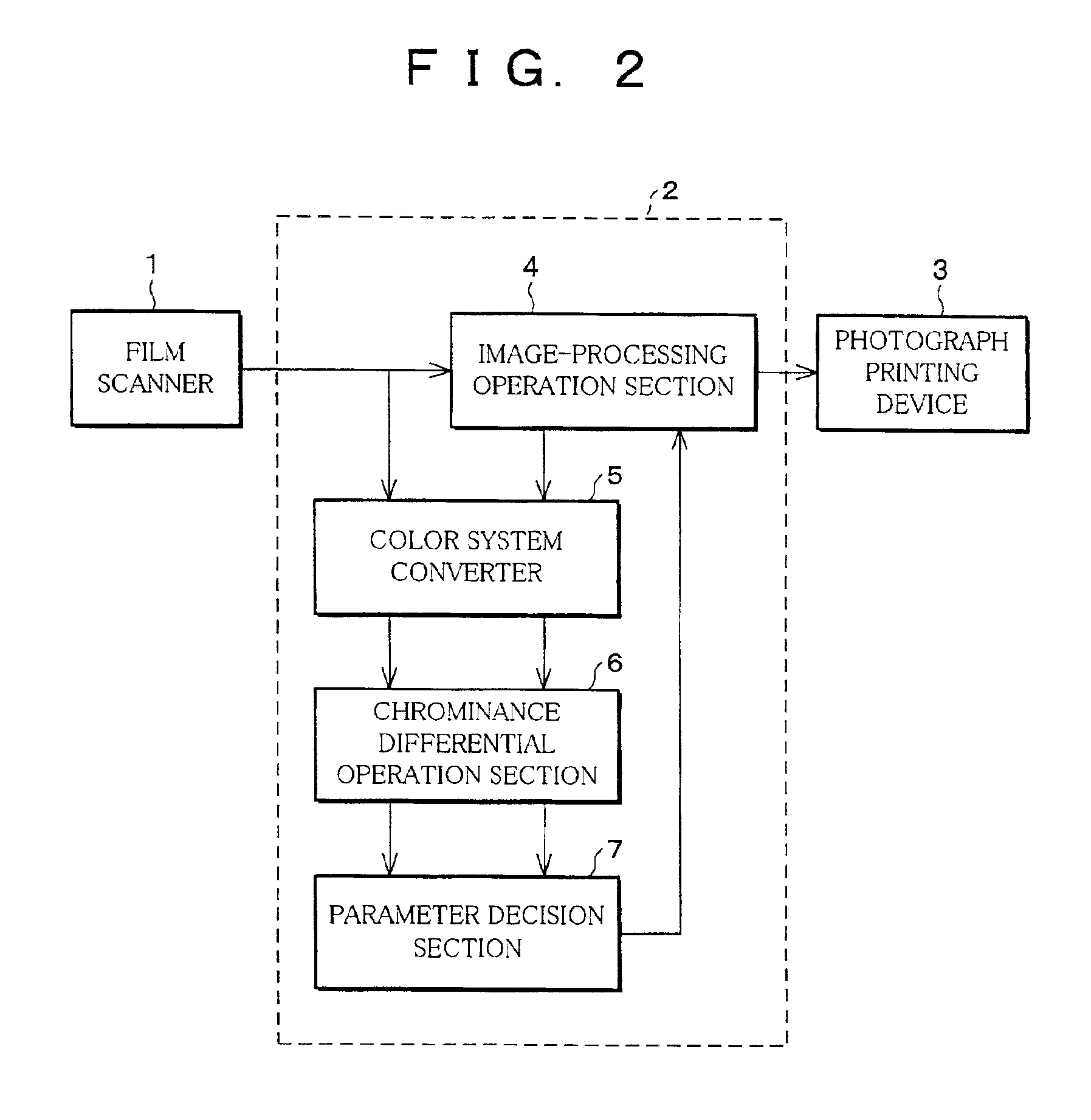
214 results about "Laplace operator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, the Laplace operator or Laplacian is a differential operator given by the divergence of the gradient of a function on Euclidean space. It is usually denoted by the symbols ∇·∇, ∇². The Laplacian ∇·∇f(p) of a function f at a point p, is (up to a factor) the rate at which the average value of f over spheres centered at p deviates from f(p) as the radius of the sphere shrinks towards 0. In a Cartesian coordinate system, the Laplacian is given by the sum of second partial derivatives of the function with respect to each independent variable. In other coordinate systems such as cylindrical and spherical coordinates, the Laplacian also has a useful form.
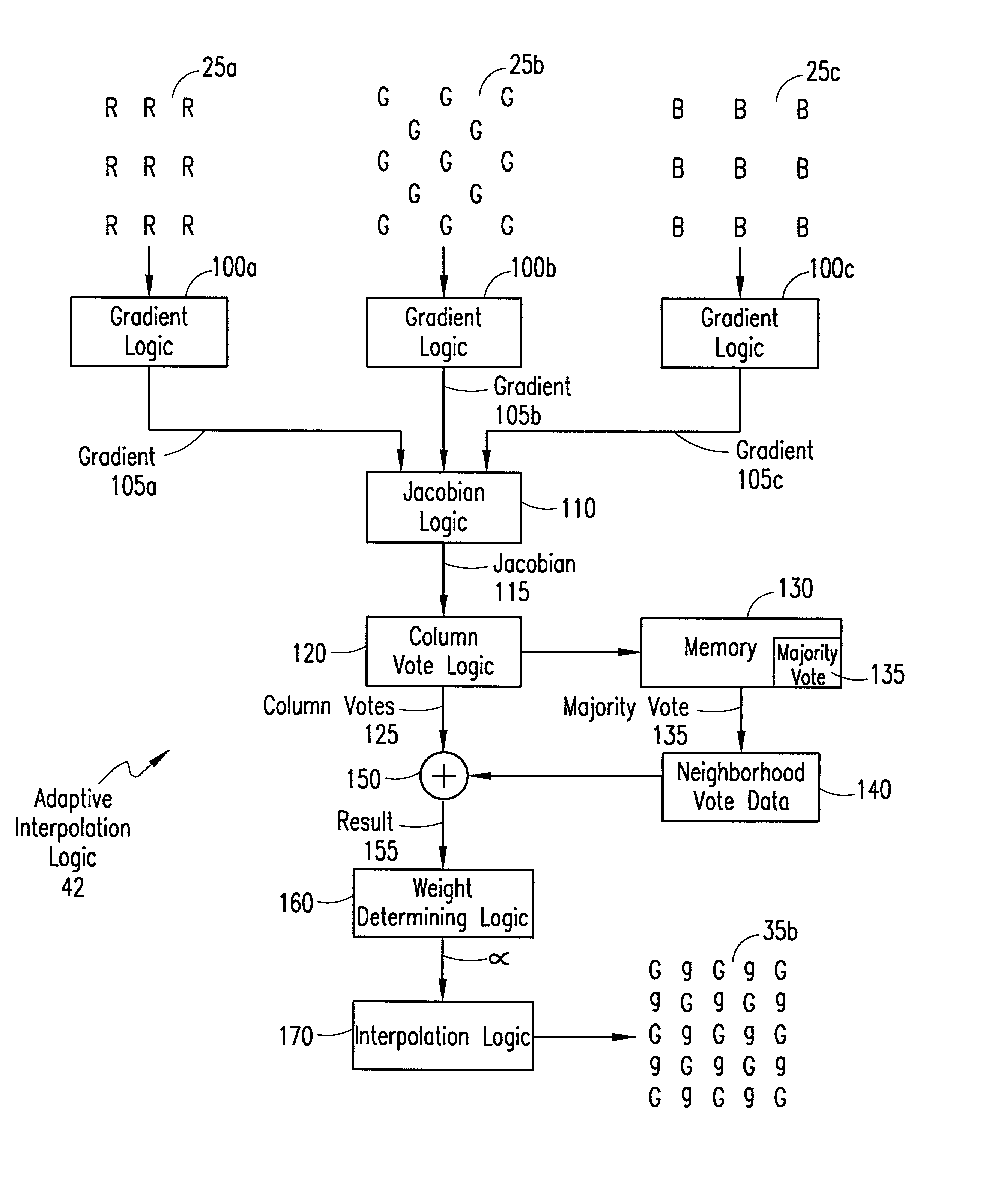
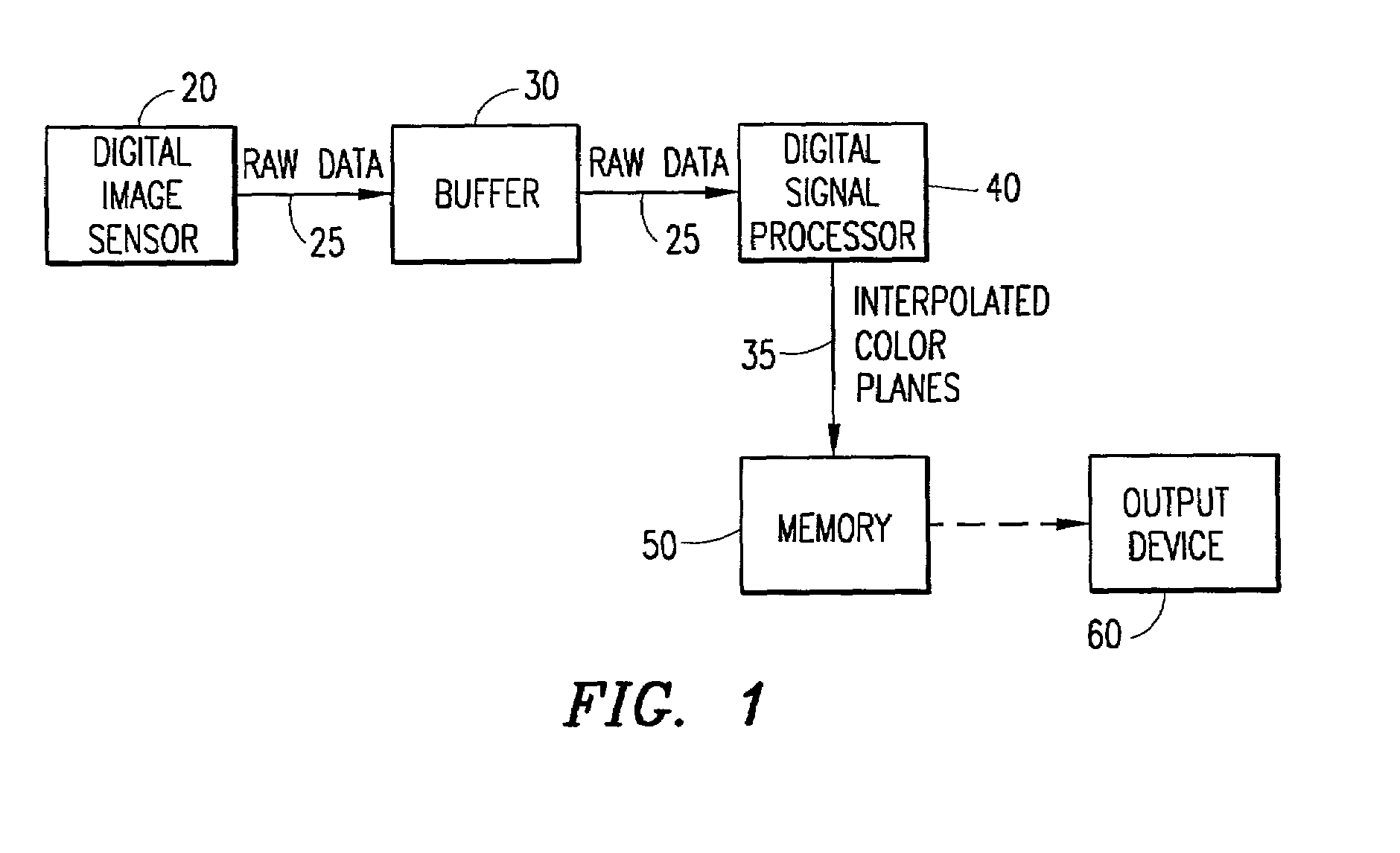
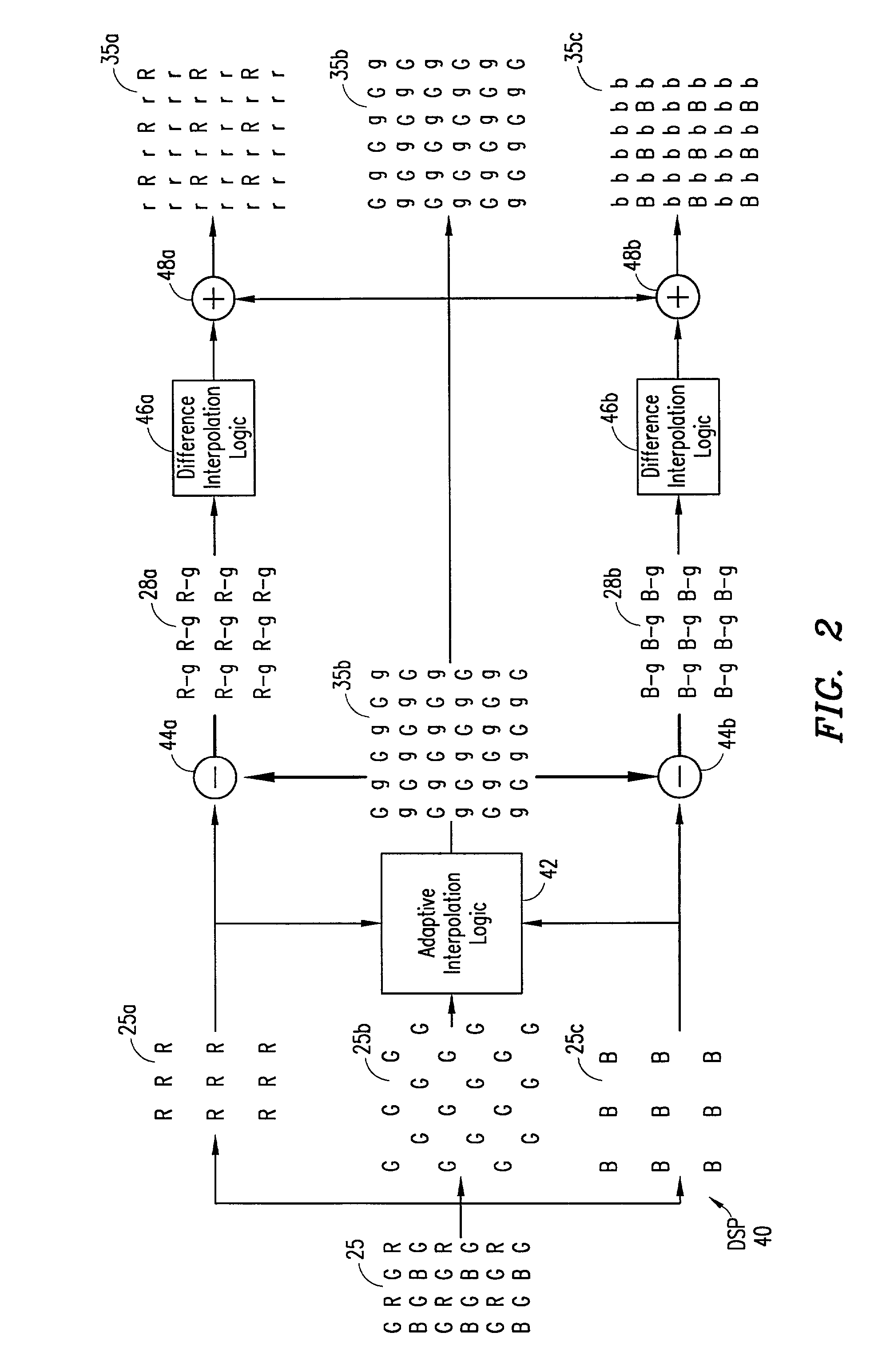
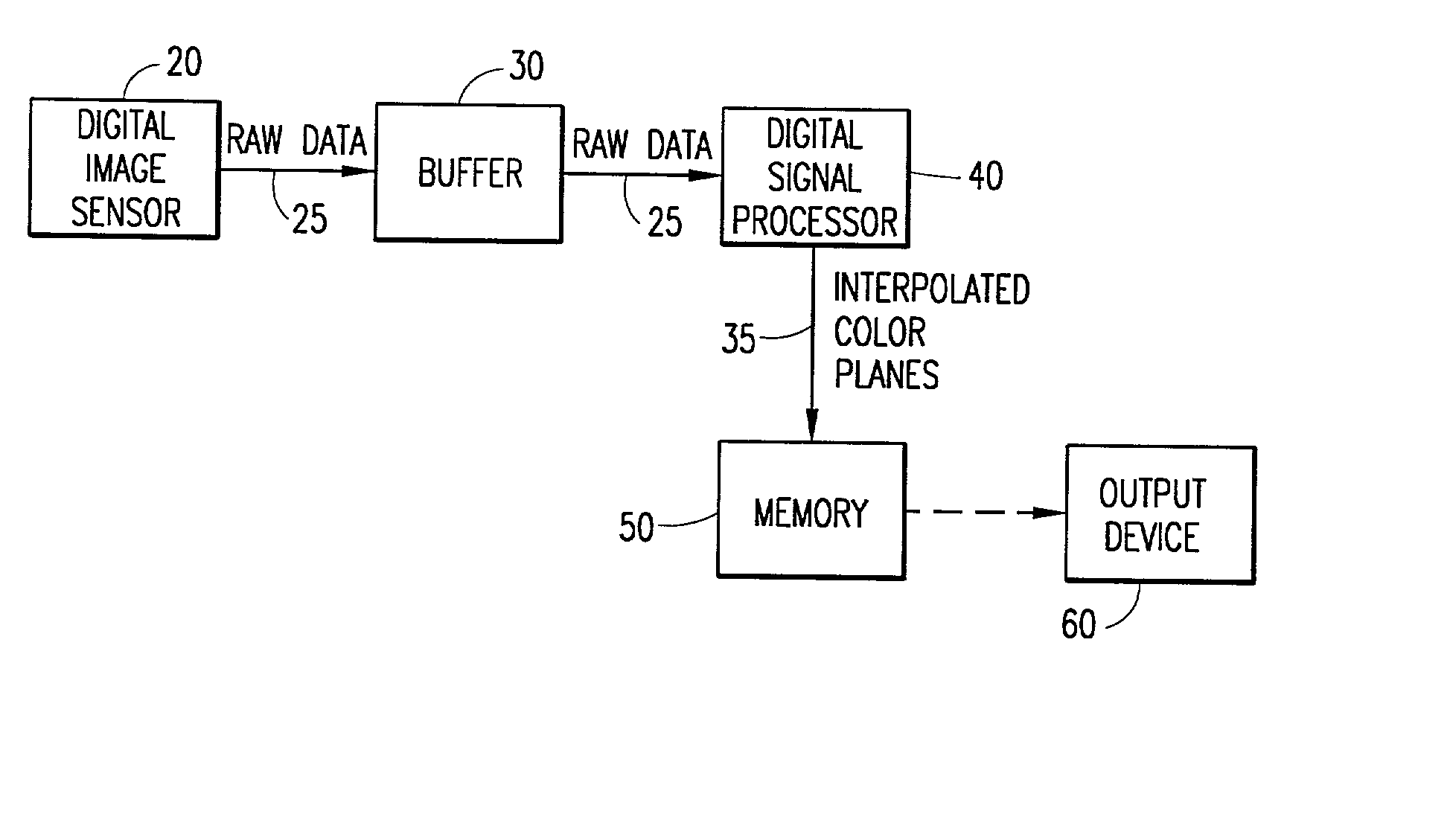
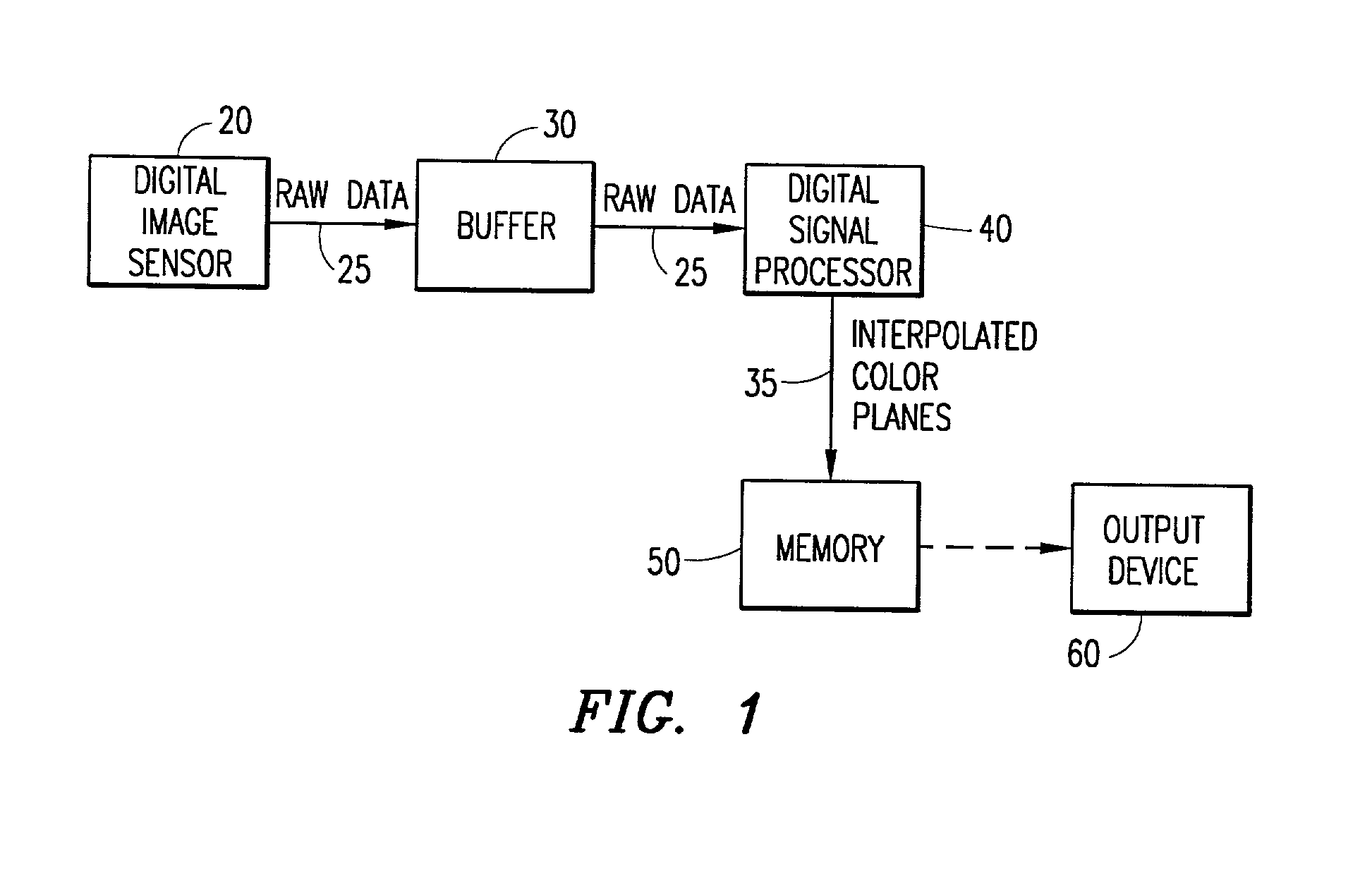
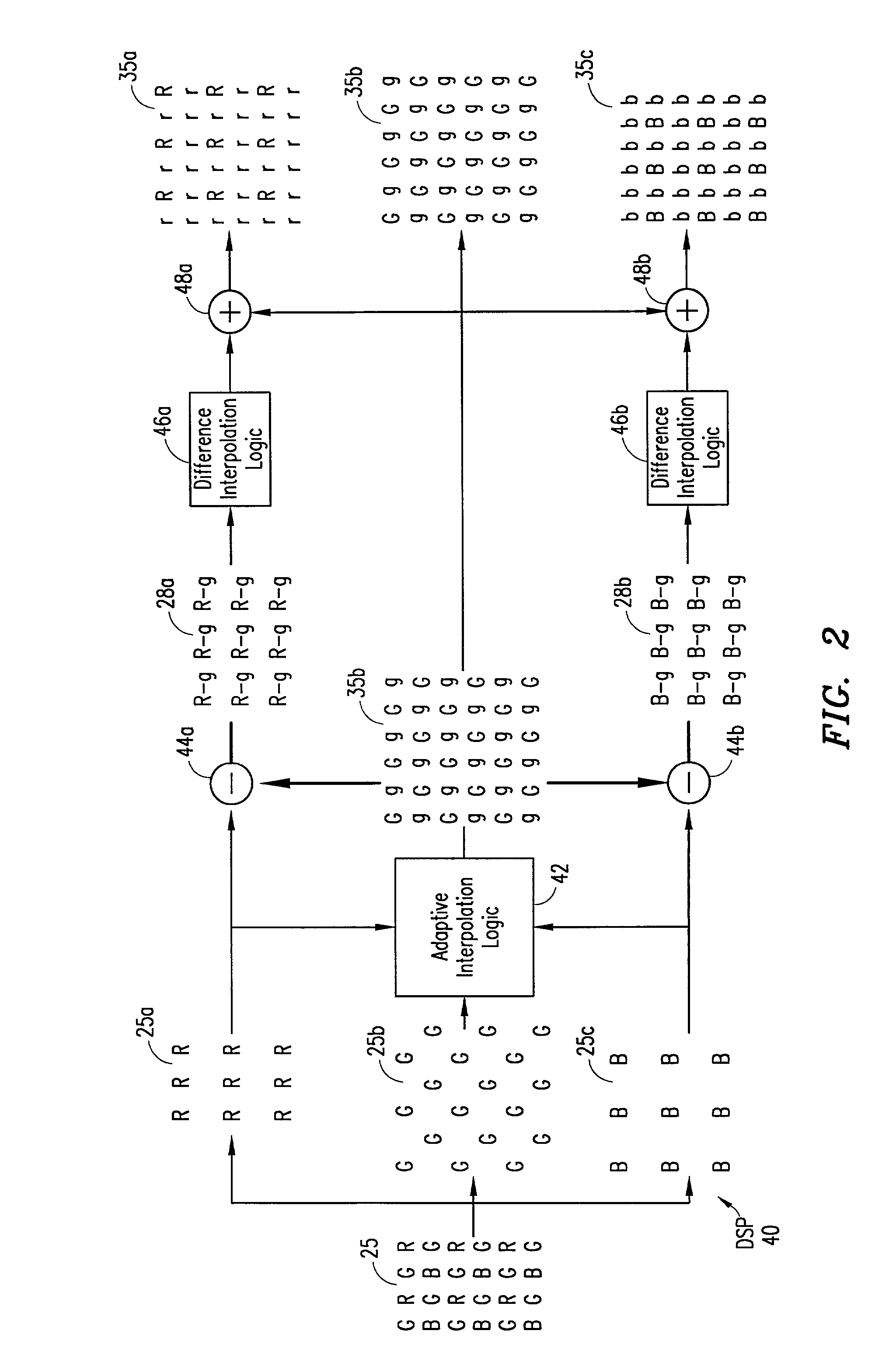
Digital image system and method for implementing an adaptive demosaicing method
InactiveUS7088392B2Reduce imbalanceAdaptive smoothingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSharpening
An adaptive demosaicing method interpolates images based on color edge detection and neighborhood voting. The adaptive demosaicing algorithm uses a voting scheme to determine the direction of interpolation at each missing luminance pixel location. Each color plane votes either horizontal or vertical based on a comparison between the horizontal and vertical components of the degree of change (i.e., gradient, Laplacian or other measure of the degree of change) in that color plane. Votes are counted from the neighborhood pixels as well as from measurements taken at the pixel location itself. Once the luminance plane is fully interpolated, the chrominance planes are filled in by simple bilinear or median interpolation of difference chrominance values. Enhancements to the adaptive demosaicing algorithm permit adaptive smoothing and sharpening.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Digital image system and method for implementing an adaptive demosaicing method
InactiveUS20030052981A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSharpening
An adaptive demosaicing method is disclosed that interpolates images based on color edge detection and neighborhood voting. The adaptive demosaicing algorithm uses a voting scheme to determine the direction of interpolation at each missing luminance pixel location. Each color plane votes either horizontal or vertical based on a comparison between the vertical and horizontal components of the degree of change (i.e., gradient, Laplacian or other measure of the degree of change) in that color plane. Votes are counted from the neighborhood pixels as well as from measurements taken at the pixel location itself. Once the luminance plane is fully interpolated, the chrominance planes are filled in by a simple bilinear or median interpolation of difference chrominance values. Enhancements to the adaptive demosaicing algorithm permit adaptive smoothing and sharpening.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
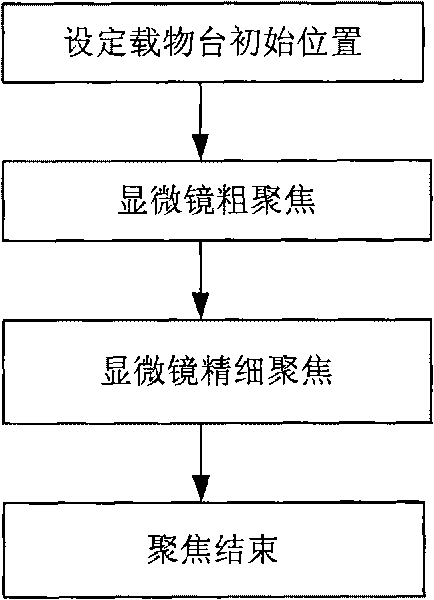
Image processing based fast automatic focusing method of microscope
InactiveCN101706609AImprove real-time performanceImprove reliabilityMicroscopesImaging processingLaplace operator
The invention relates to the technical field of automatic focusing of microscopes, in particular to an image processing based fast automatic focusing method of a microscope. In the method, the automatic focusing process is divided into a coarse focusing stage and a fine focusing stage; different focusing evaluation functions and different extremum searching strategies are adopted on different stages, specifically, on the coarse focusing stage, the gray scale different evaluation function and a fast hill-climbing backtracking search algorithm are adopted, and decision-making factors are introduced to prevent the search algorithm from falling into local extrema; and on the fine focusing stage, the Laplace operator based evaluation function and the small-step searching strategy are adopted. The method provided by the invention better solves the problem that the traditional algorithm is slow in focusing speed, easily falls into local extrema and is not high in focusing accuracy, and has strong real-time property and high reliability and practicability.
Owner:常州超媒体与感知技术研究所有限公司 +1
Image reinforcement method for self-adaptive regulation according to edge and brightness
InactiveCN101101669AEasy to filterIncrease brightnessImage enhancementPictoral communicationOutput deviceLaplace transform
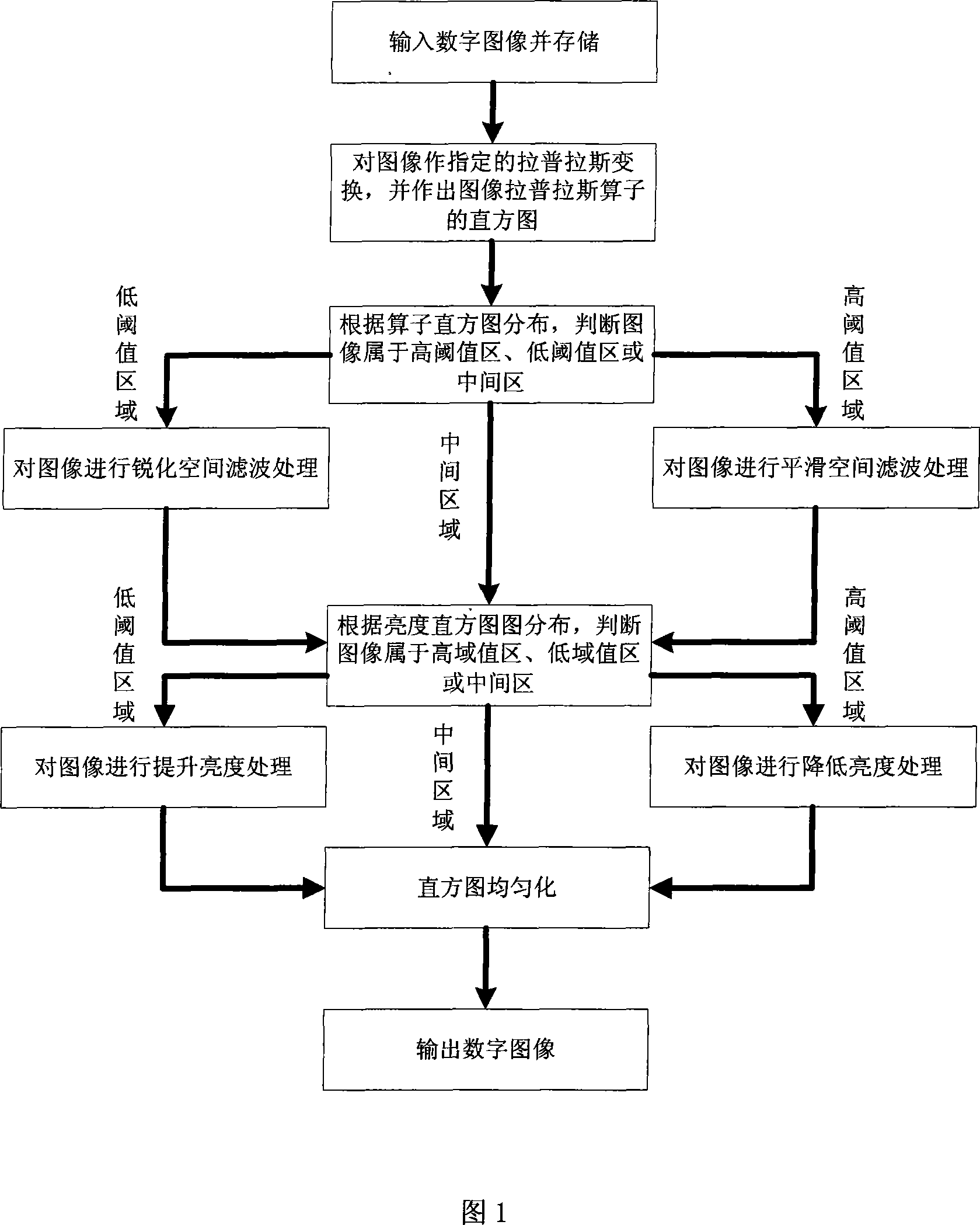
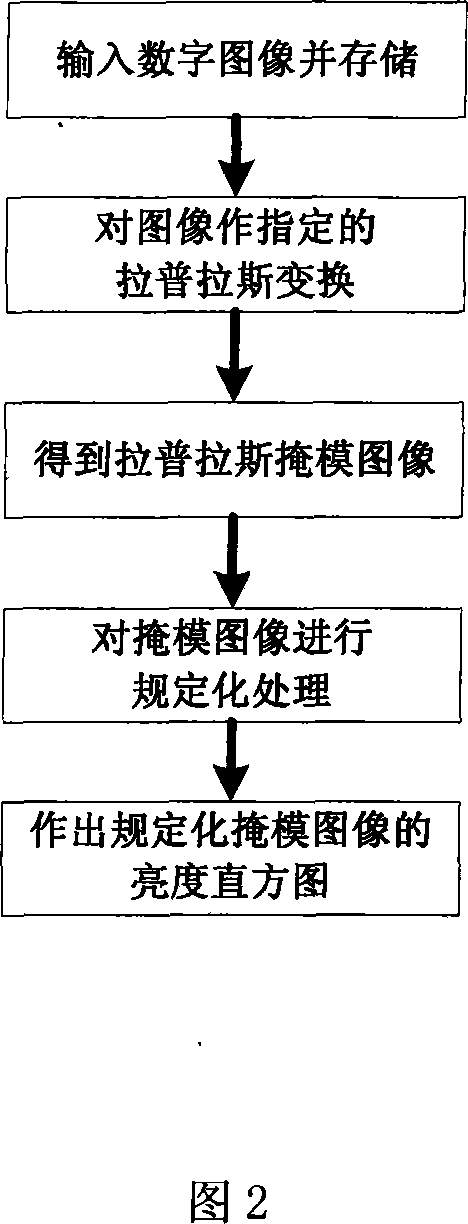
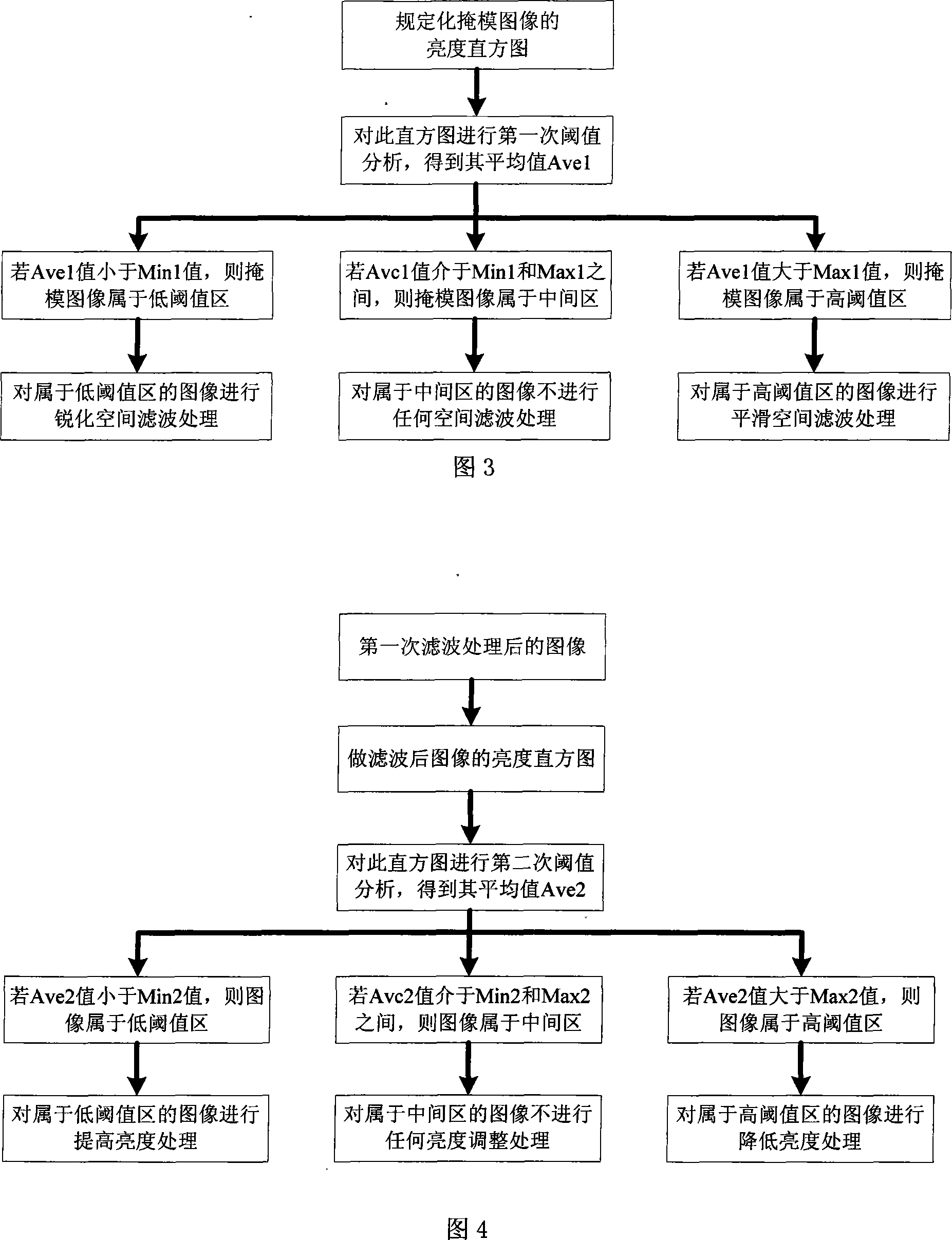
This method (1) makes scattered Laplacian conversion against the input digit images to obtain the Laplacian operator mask images (MI); (2) analyzes the converted MI on the brightness rectangle graph (RG) and classifies images according to RG character; (3) makes different space filtering against the classified different images depending on images' characters; (4) analyzes the filtered images on the obtained RG and re-classifies images according to RG character; (5) makes different brightness regulation against the re-classified different images depending on images' characters; (6) makes RG equalizing against the finally obtained images and sends to the output device. This invention (1) can filter and improve brightness via different means against the input images with different margin characters and brightness characters; (2) can effectively filter-boost and regulate brightness against more images in a larger range.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
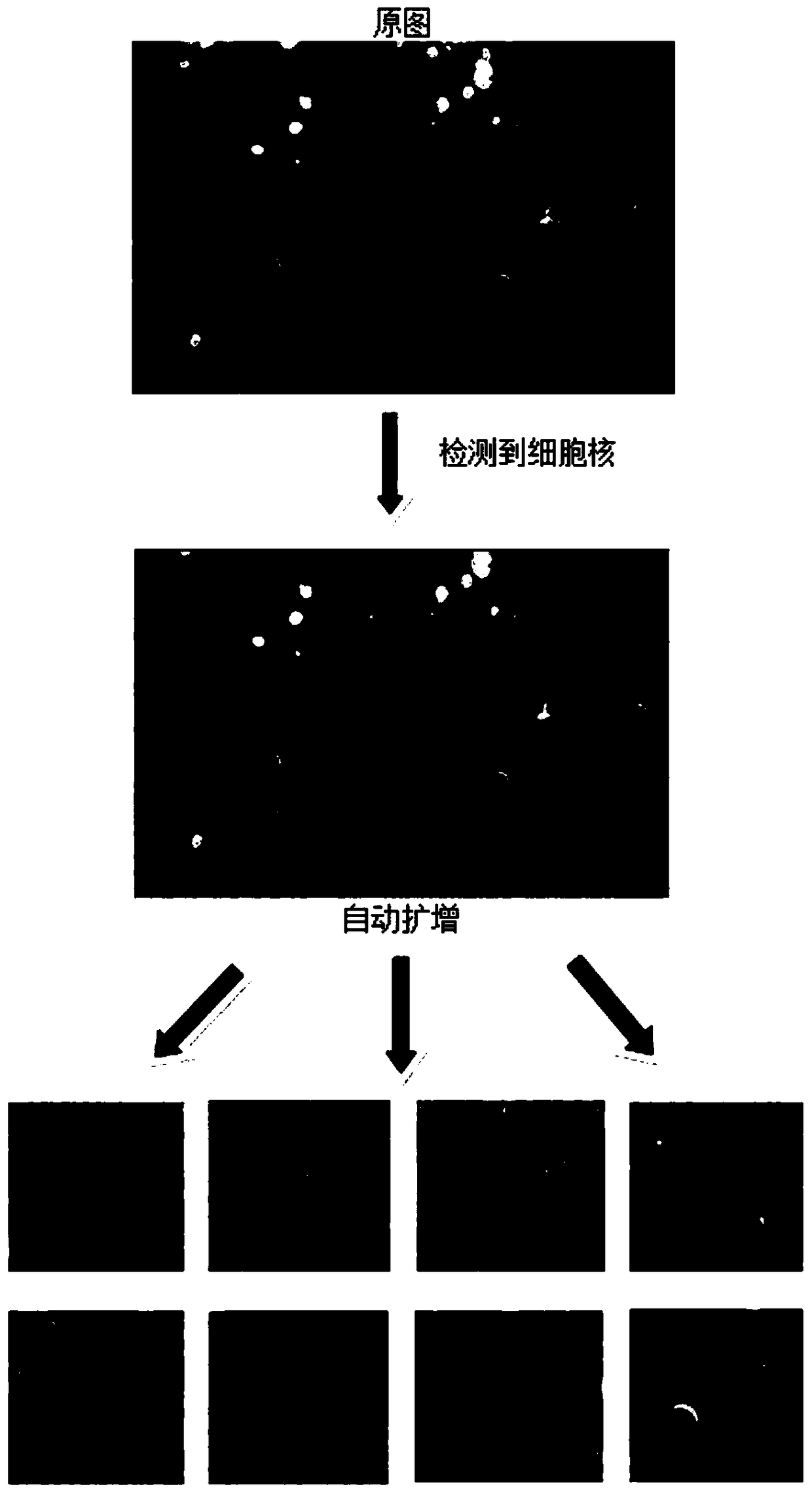
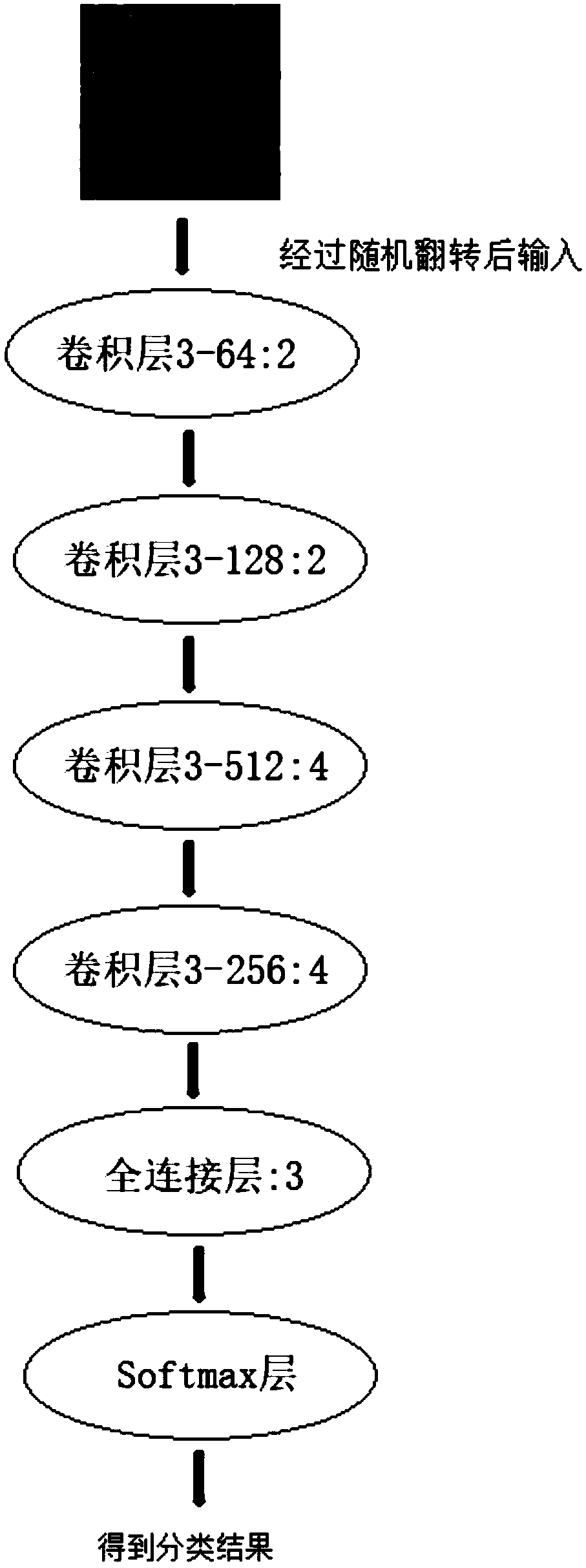
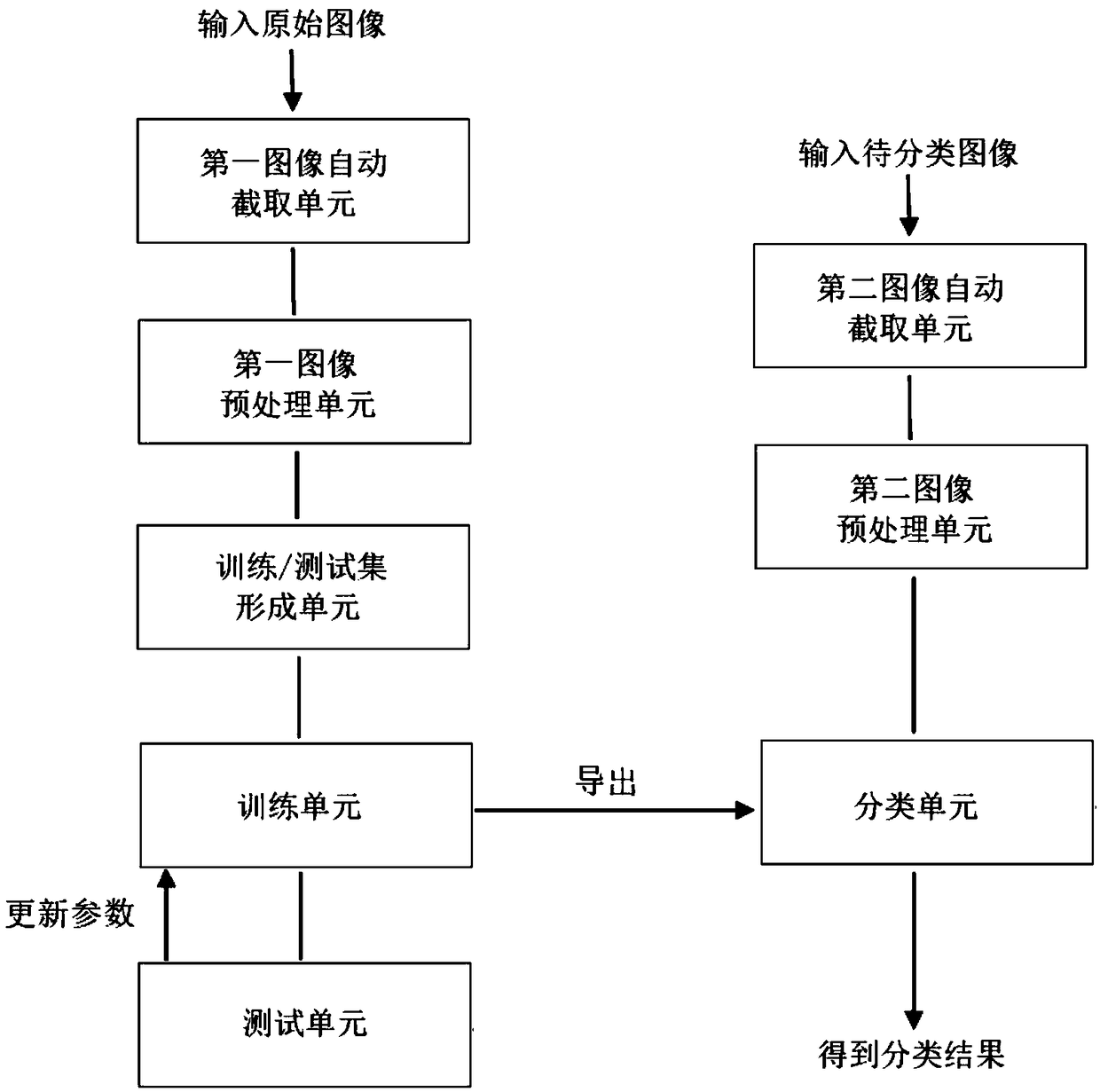
Thyroid tumor pathological tissue section image classification method and device
InactiveCN108717554AReduce workloadEasy to assistImage enhancementImage analysisCancers diagnosisClassification methods
The invention discloses a thyroid tumor pathological tissue section image classification method and a thyroid tumor pathological tissue section image classification device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring an original image set of classified thyroid tumor pathological tissue sections; automatically intercepting multiple area images including cells from each original image to serve as asub-image set; using the total or partial sub-image set as a training set; building a preliminary convolutional neural network model; training the preliminary convolutional neural network model by using the training set to acquire a mature convolutional neural network model; and classifying the classified thyroid tumor pathological tissue section images by using the mature convolutional neural network model. Cell nucleuses in the thyroid tumor pathological tissue sections are matched by using Gaussian laplace operator characteristics to find positions of cells, automatic image interception isimplemented in the area with many cells, so that the full-automatic cell image classification and cancer diagnosis are achieved, the workload of a doctor when in checking of the tissue section image can be greatly reduced, and the diagnosis accuracy is improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT +1
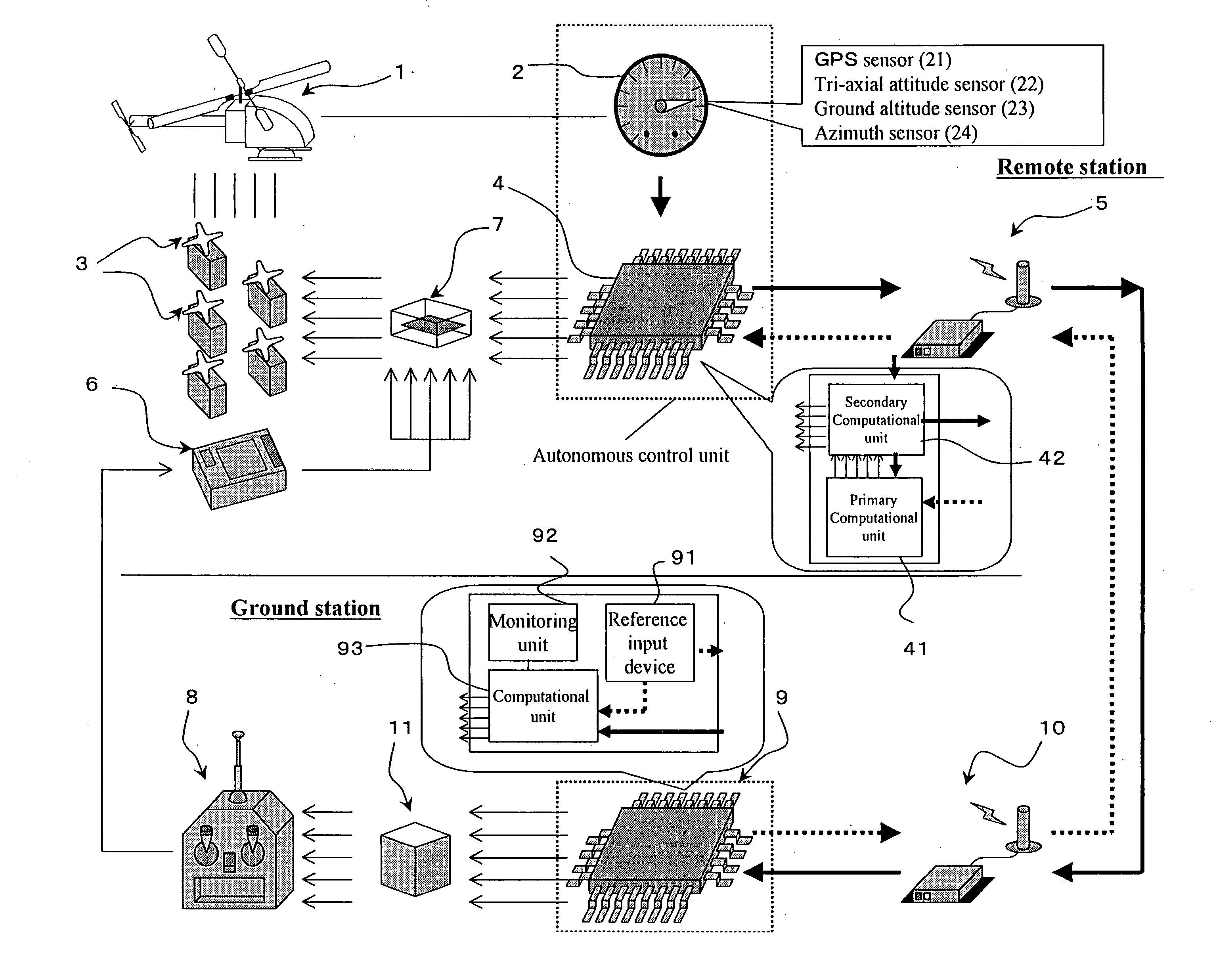
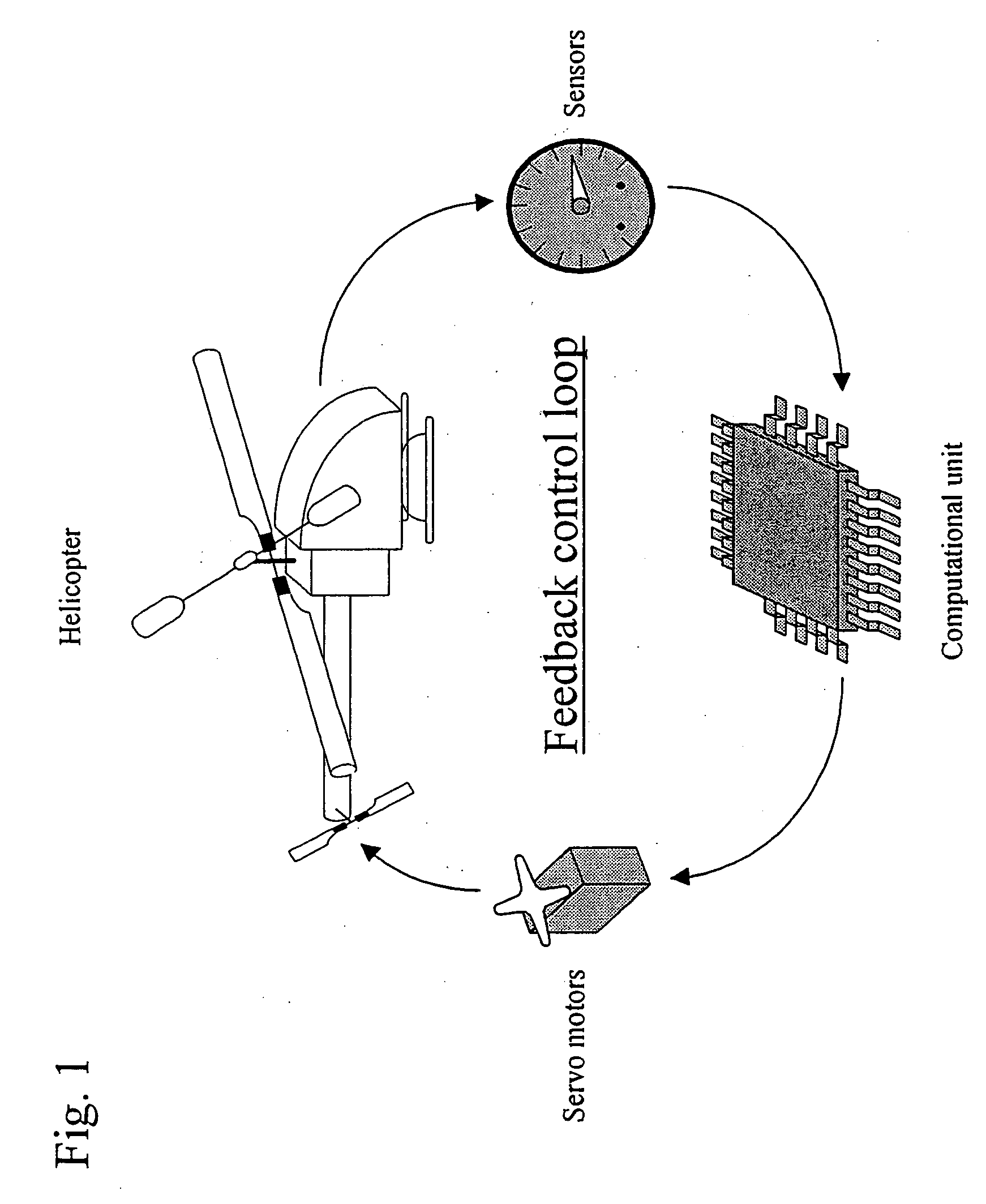
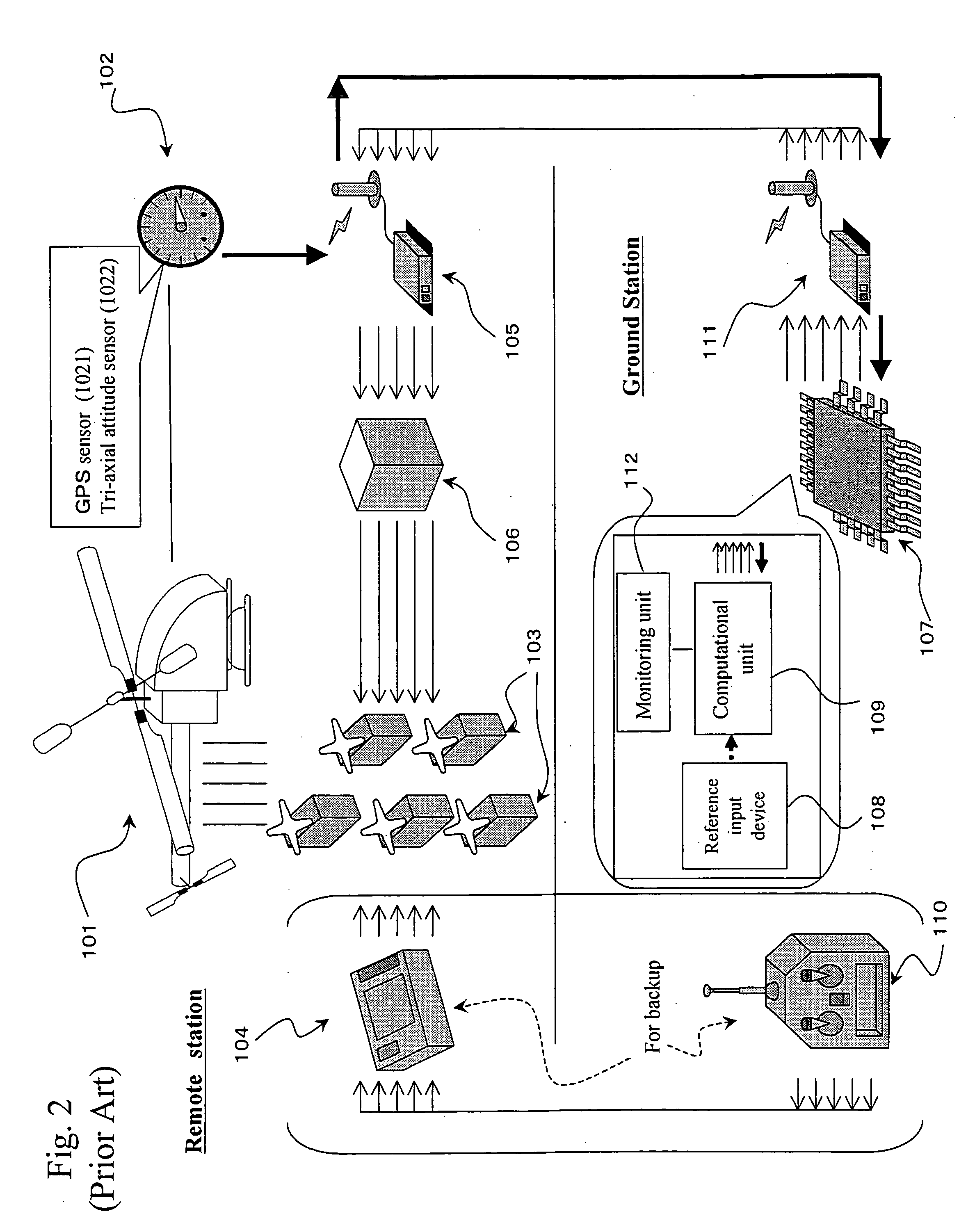
Autonomous control method for small unmanned helicopter
InactiveUS20060060694A1Easy to carryBroaden applicationPropellersDigital data processing detailsDead timeControl signal
An objective of the present invention is to provide an autonomous control method that autonomously controls a small unmanned helicopter toward target values, such as a set position and velocity, by deriving model formulas that are well suited for the autonomous control of small unmanned helicopters, by designing an autonomous control algorithm based on the model formulas, and by calculating the autonomous control algorithm. The autonomous control system for a small unmanned helicopter of the present invention comprises: sensors that detect the current position, the attitude angle, the altitude relative to the ground, and the absolute azimuth of the nose of the aforementioned small unmanned helicopter; a primary computational unit that calculates optimal control reference values for driving the servo motors that move five rudders on the helicopter from target position or velocity values that are set by the ground station and the aforementioned current position and attitude angle of the small unmanned helicopter that are detected by the aforementioned sensors; an autonomous control system equipped with a secondary computational unit that converts the data collected by said sensors and the computational results as numeric values that are output by said primary computational unit into pulse signals that can be accepted by the servo motors, such that these components are assembled into a small frame box, thereby achieving both size and weight reductions; a ground station host computer that can also be used as the aforementioned computational unit for the aforementioned autonomous control system; if the aforementioned ground station host computer is used as the aforementioned computational unit for the aforementioned autonomous control system, in the process of directing the computational results that are output from said ground station host computer to said servo motors through a manual operation transmitter, a radio control generator that converts said computational results as numerical values into pulse signals that said manual operation transmitter can accept; a servo pulse mixing / switching apparatus, on all said servo motors for said small unmanned helicopter, that permits the switching of manual operation signals and said control signals that are output from said autonomous control system or mixing thereof in any ratio; an autonomous control algorithm wherein the mathematical model for transfer function representation encompassing pitching operation input through pitch axis attitude angles in the tri-axis orientation control for said small unmanned helicopter is defined as Gθ(s)=e-LsKθωns2(s2+2sωn ss+ωn s2)(Tθs+1)swherein Gθ: parameter e−Ls: dead time element Kθ: model gain Tθ: model gain ωns: natural frequency s: laplace operator ξs: damped ratio such that the aforementioned small unmanned helicopter is controlled autonomously based on the aforementioned mathematical model.
Owner:NONAMI KENZO +4
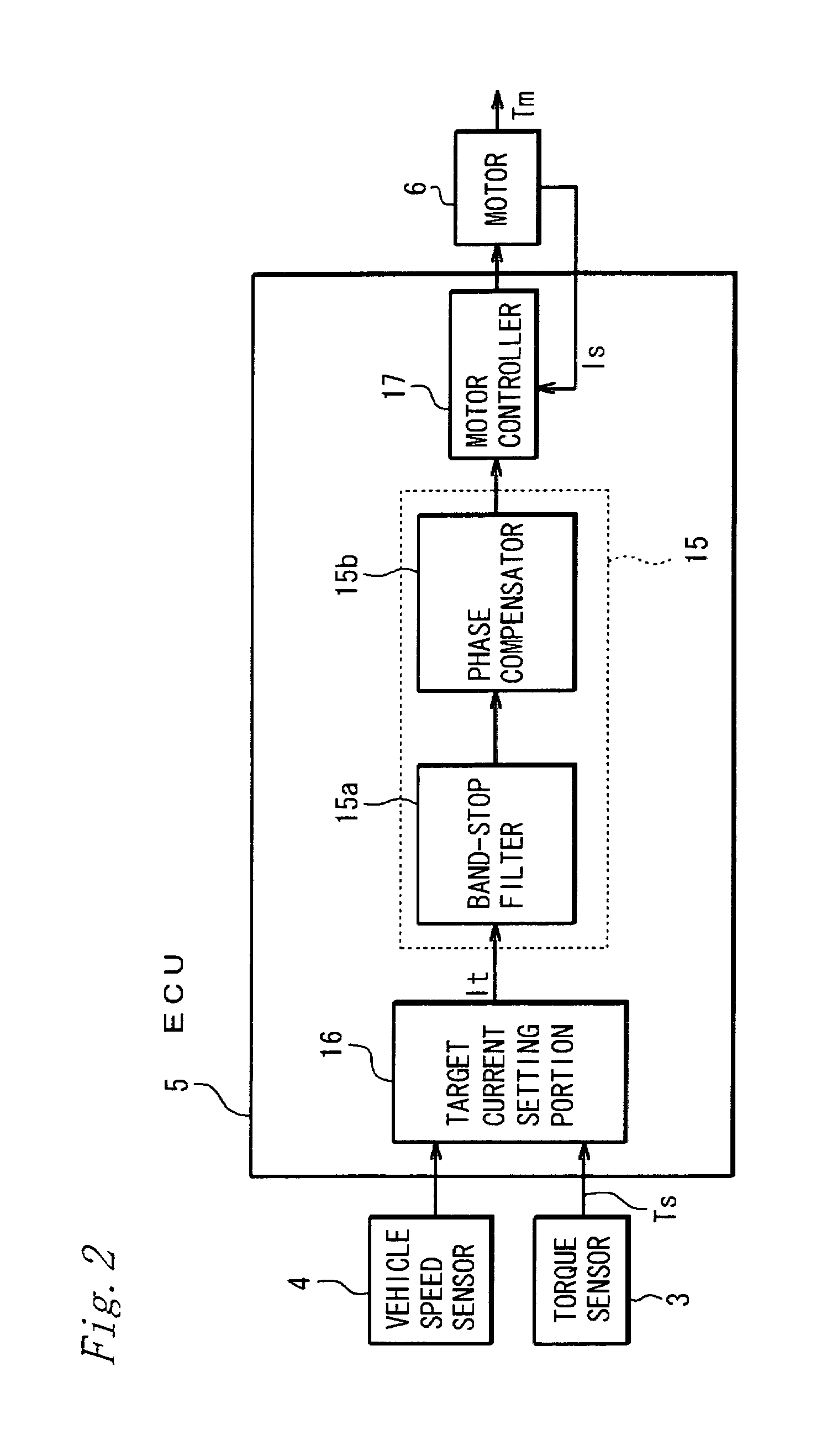
Electric power steering system
InactiveUS20070198153A1Reducing arithmetic loadEasy to getDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsElectric power steeringResonance
An electric power steering system includes: a band-stop filter 15a having a transfer function G1(s) for suppressing resonance, and a phase compensator 15b having a transfer function G2(s). The above function G1(s) is represented by an expression G1(s)=(s2+2ζ11ω1+ω12) / (s2+2ζ12ω1+ω12), where s: a Laplace operator, ζ11: a damping coefficient, ζ12: a damping coefficient, and ω1: an angular frequency. On the other hand, the above function G2(s) is represented by an expression G2(s)=(s2+2ζ21ω2+ω22) / (s2+2ζ22ω2+ω22), where s: a Laplace operator, ζ21: a damping coefficient, ζ22: a damping coefficient, and ω1: an angular frequency. Furthermore, the above damping coefficients ζ21, ζ22 satisfy an expression ζ2124 ζ22≧1. Thus, a filter such as a phase compensator may attain a design freedom while preventing the increase of arithmetic load, whereby both the suppression of resonance and a good assist response in a normal steering speed region, for example, may be achieved.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
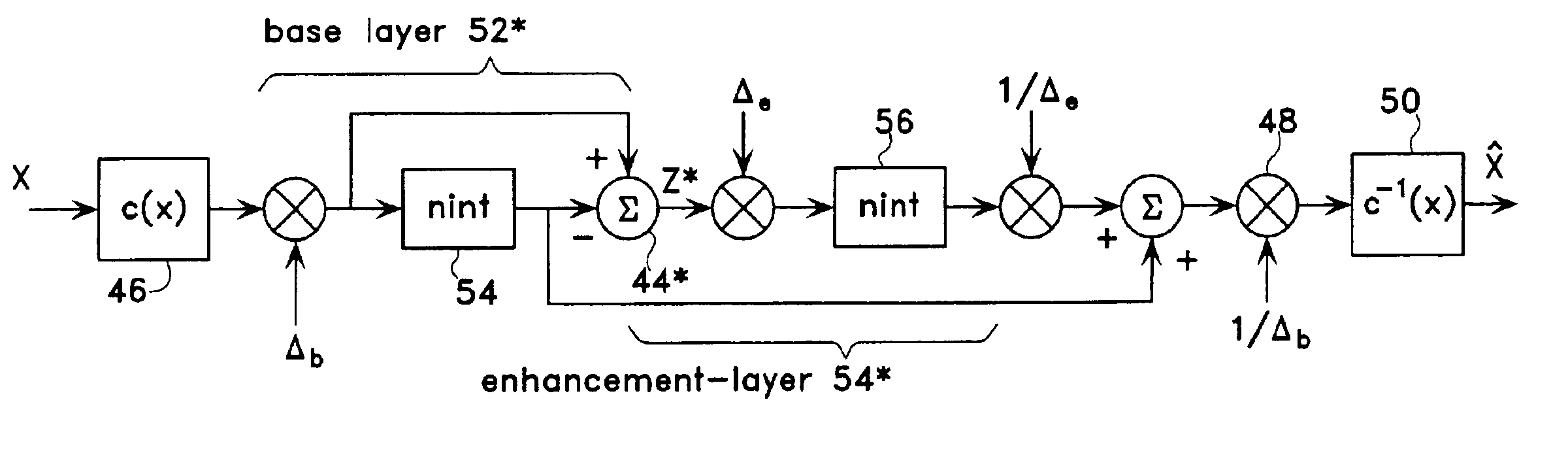
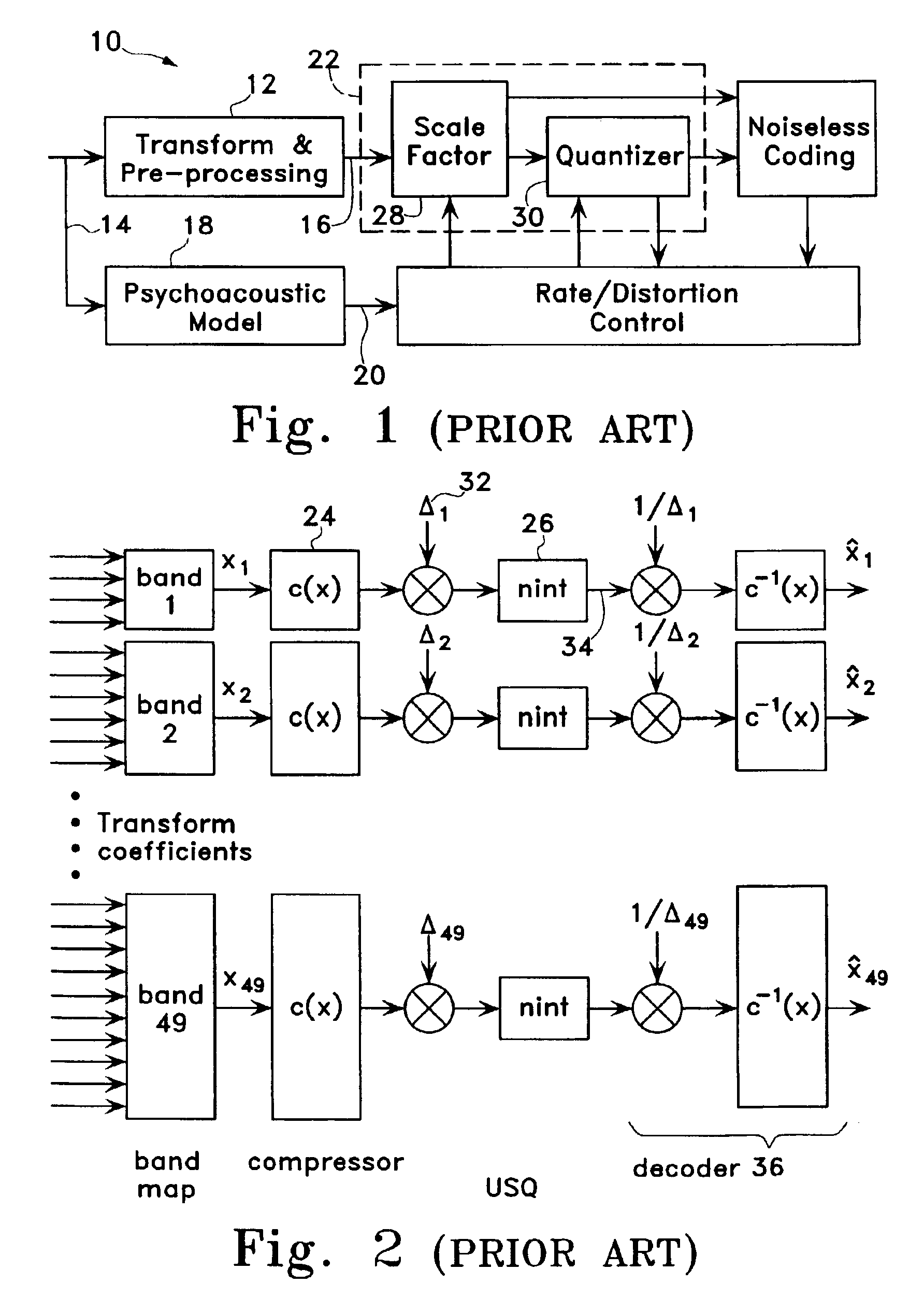
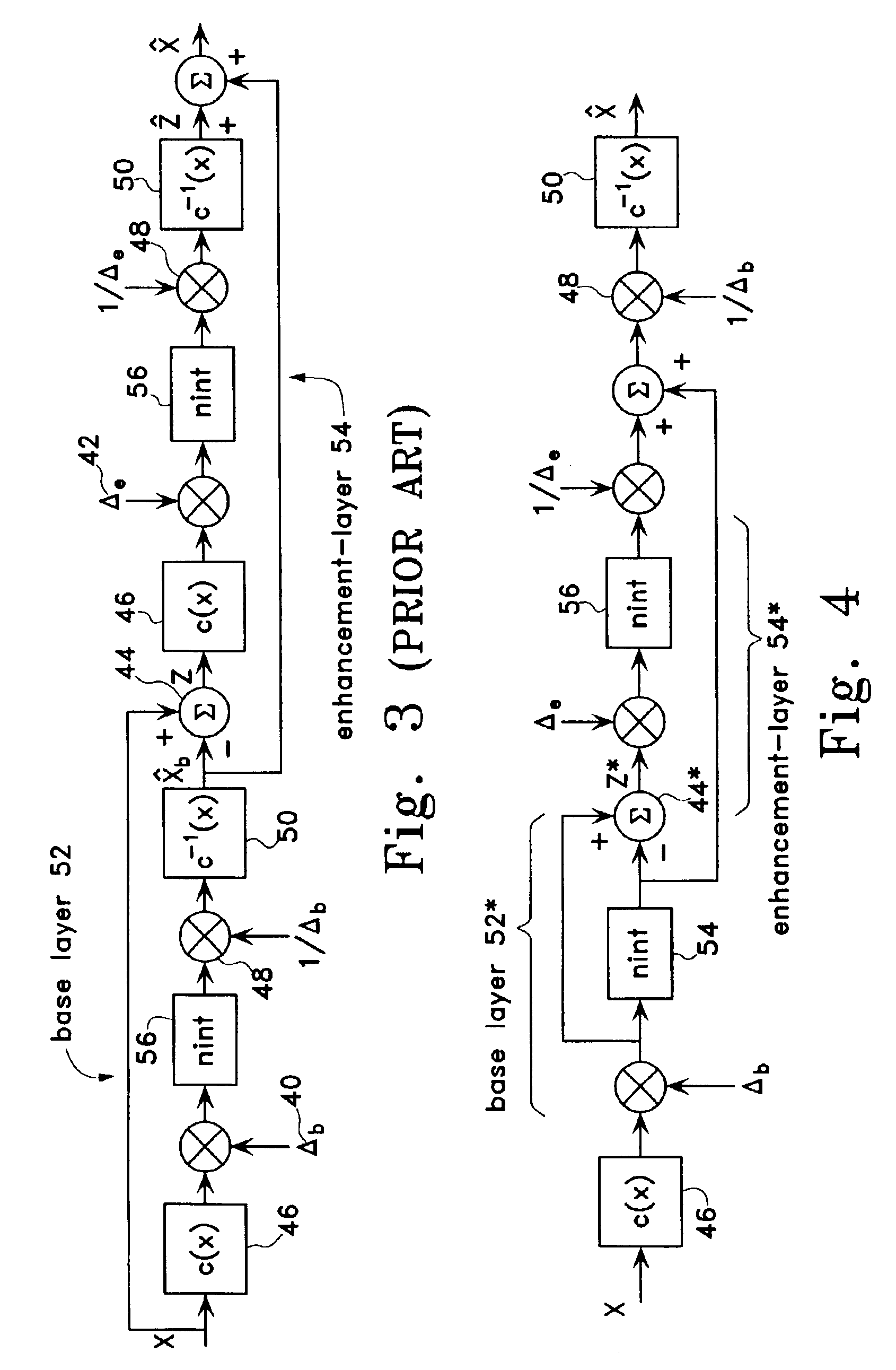
Scalable compression of audio and other signals
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
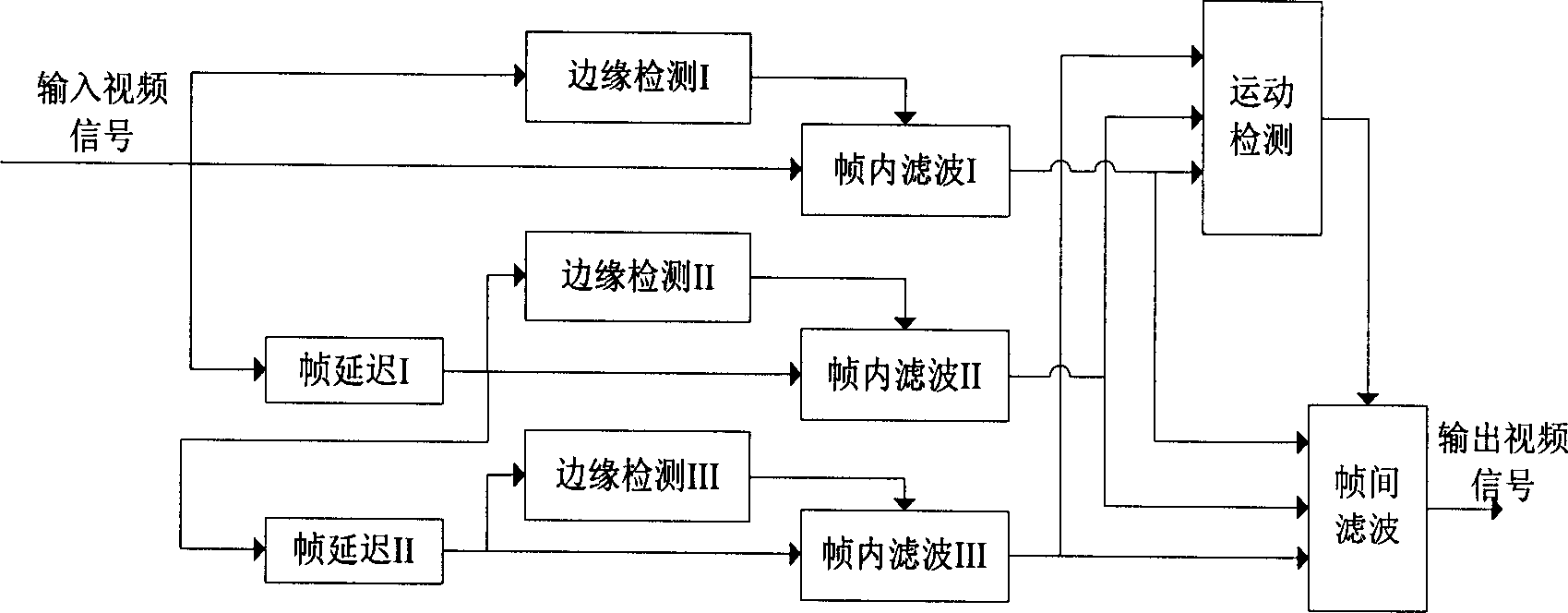
Method for detecting movement detection by using edge detection, and for removing ripple noise through medium filtering
InactiveCN1761286AProtection detailsImprove clarityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInter frameVisual perception
The invention carries out process in frame for image; then carries out process inter frame for continuous three frames of image, which are processed in frame. The method includes following steps: using Laplace operator to carry out edge detection for image so as to obtain edge information of each pixel; if a pixel is an edge pixel or its more than two neighbor pixels in four pixels around are as edge pixels, then value of the pixel is saved; otherwise, carrying out filtering process for the pixel by using median filter; based on difference between adjacent frames, movement detection is carried out to determine whether pixel in the current frame is moved; if yes, the value is saved; if no, then result of median filter for corresponding points in three frames is as result of filtering the pixel. The invention protects details of image and sharpness furthest so as to raise vision quality of output image.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
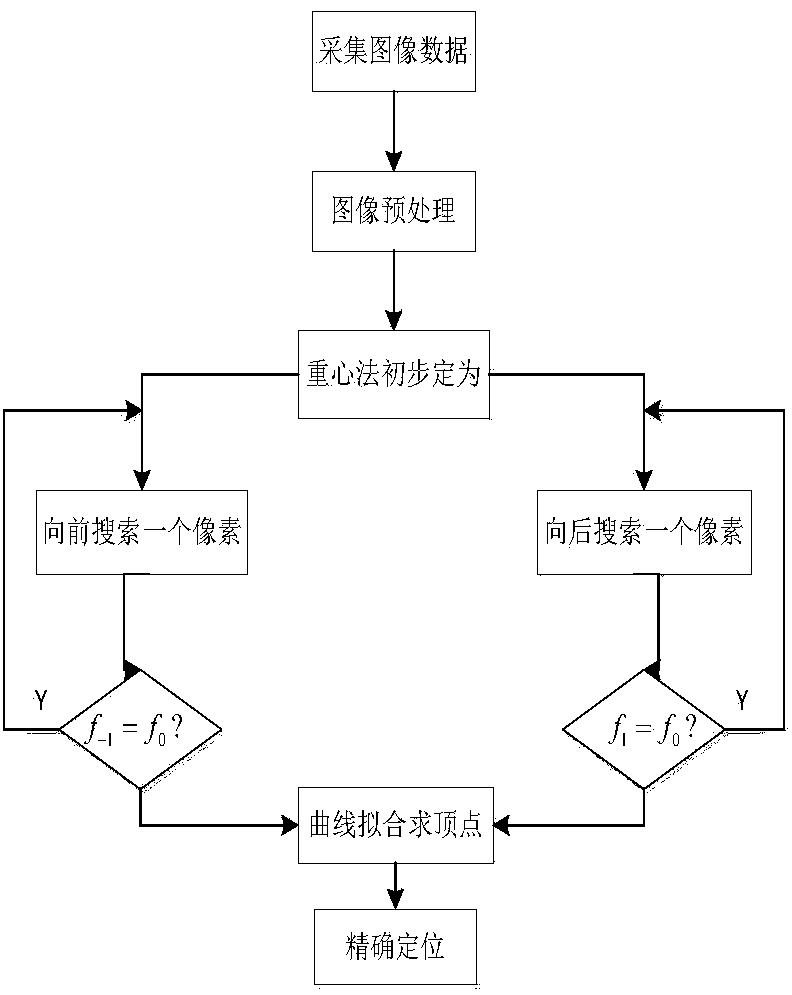
Method for facula center positioning of CCD image measurement system
InactiveCN103455813AEffective filteringEasy to implementCharacter and pattern recognitionInterference resistanceGray level
The invention provides a method for facula center positioning of a CCD image measurement system. According to the method, a facula image generated by a CCD sensor is simulated by means of software, denoising is carried out on a laser facula generated by simulation by means of median filtering, binarization is then carried out on the denoised image, edge extraction is carried out on the image treated with binarization by means of the Gauss-Laplace operator, then primary positioning is carried out by means of the gray level gravity method, and finally accurate positioning is carried out on the primarily positioned image by means of the Gaussian curvefitting algorithm. According to the method, due to the introduction of the image pre-processing step, noise in the image can be effectively filtered, and interference resistance is improved; due to the fact that only useful data points in the image are calculated and analyzed, the calculated amount is small, and then realization of the software is easy and resources of the system are saved greatly.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
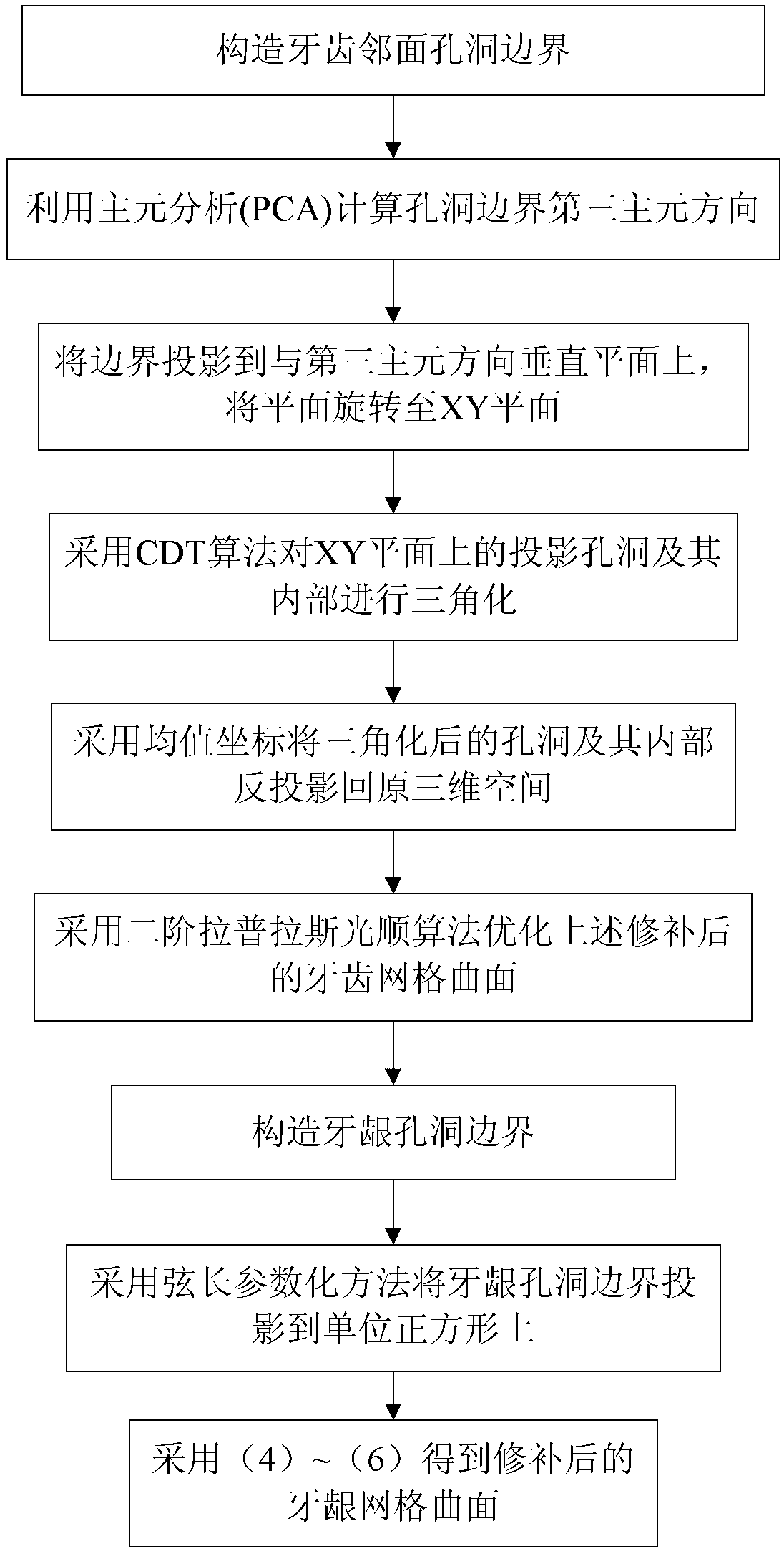
Tooth-and-gum-oriented high-efficiency mesh repairing method
ActiveCN102930091AReduce deformationShorten the timeSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmThree-dimensional space
The invention discloses a tooth-and-gum-oriented high-efficiency mesh repairing method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, constructing a hole boundary of tooth and gum information loss parts, and projecting the hole boundary to a two-dimensional plane; secondly, triangularizing the interior of the projected hole boundary by employing a constrained Delaunay triangularization algorithm; thirdly. projecting the triangularized mesh back to an original three-dimensional space by employing a mean value coordinate principle; and finally, optimizing the repaired curved mesh surface by employing a second-order Laplace operator. A projection plane of the tooth hole boundary is calculated by employing a principal component analysis (PCA) algorithm, a gum hole boundary is projected to a unit square by employing a chord length parameterization method, the deformation degree of the hole boundary is reduced, the dimension of the triangularized operation is reduced, the triangularization time is greatly shortened, the quality of a triangular mesh is guaranteed by employing the mean value coordinate principle and back projection, and finally the mesh is faired by employing the second-order Laplace operator, the first-order continuity of the hole boundary is guaranteed, and the method is simple in algorithm and highly efficient.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Point cloud feature point detection method and cloud point feature extraction method
ActiveCN108010116AExtract orderlyImprove estimation accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionPoint cloud
The invention provides a point cloud feature point detection method and a cloud point feature extraction method. The checking method comprises the following steps that: taking one data point in pointcloud data as a sphere center to establish a local spherical coordinate frame, and finding k pieces of neighbourhoods through a k nearest neighbor algorithm; independently connecting the sphere centerwith each nearest neighbor point to obtain k pieces of line segment groups; according to the horizontal projection included angles of the line segment groups, sorting k pieces of line segment groups,checking each line segment group through a Laplace operator, and determining whether the data point is a feature point or not; and according to the above steps, processing each data point in the cloud point data, and obtaining all feature points of the cloud point data. The point cloud feature extraction method comprises the following steps that: according to the above detection method, determining feature points, and recording the regional connection information of each feature point; and determining a sequential connection relationship between the feature points, connecting the feature points, and forming a segmented feature polygon to realize region segmentation. The amount of labeled feature points is small, feature points are extracted orderly, and feature lines are conveniently reconstructed.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for detecting far-field laser spot image
InactiveCN110246115AImprove detection efficiencyEnsure real-time unimpededImage enhancementImage analysisTelecommunications linkLight spot
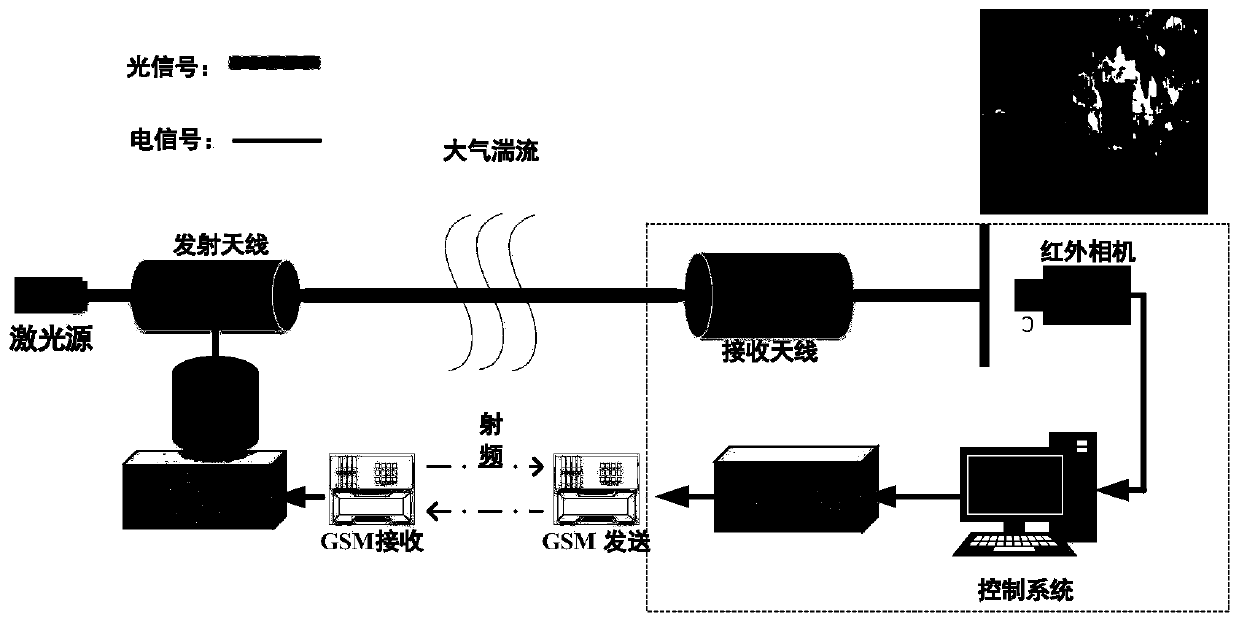
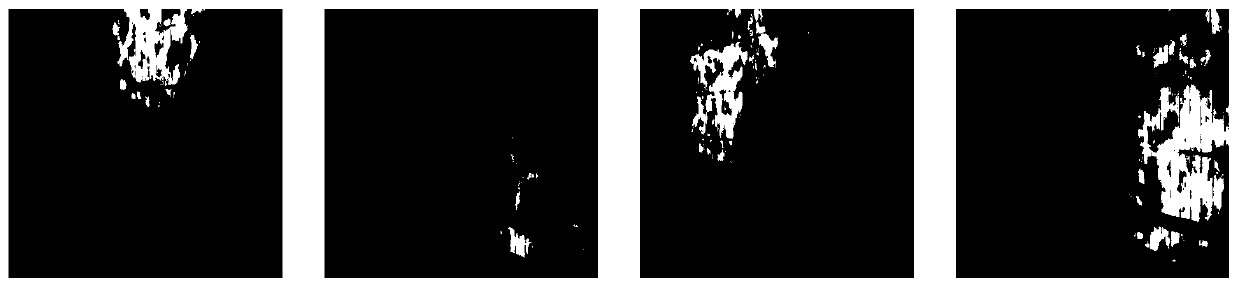
The invention discloses a method for detecting a far-field laser spot image, which is specifically implemented according to the following steps: 1, performing interval sampling by using a Xenics infrared camera, and outputting a standard video signal by using a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) detector; 2, comparing the light spots under different transmitting powers and distances; 3, preprocessing the irregular far-field laser spot image; 4, extracting a target light spot; and 5, calculating a gradient through a Laplace operator to extract a light spot target, carrying out simulation analysis on a far-field laser light spot, designing and applying an algorithm, finally detecting a position coordinate center of the light spot, detecting a difference value of the coordinate center of the light spot, and realizing re-alignment and tracking of the light beam. The invention discloses a method for detecting a far-field laser spot image, which effectively improves the detection precision, improves the detection efficiency of a far-field laser spot, and ensures that a communication link is smooth in real time.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
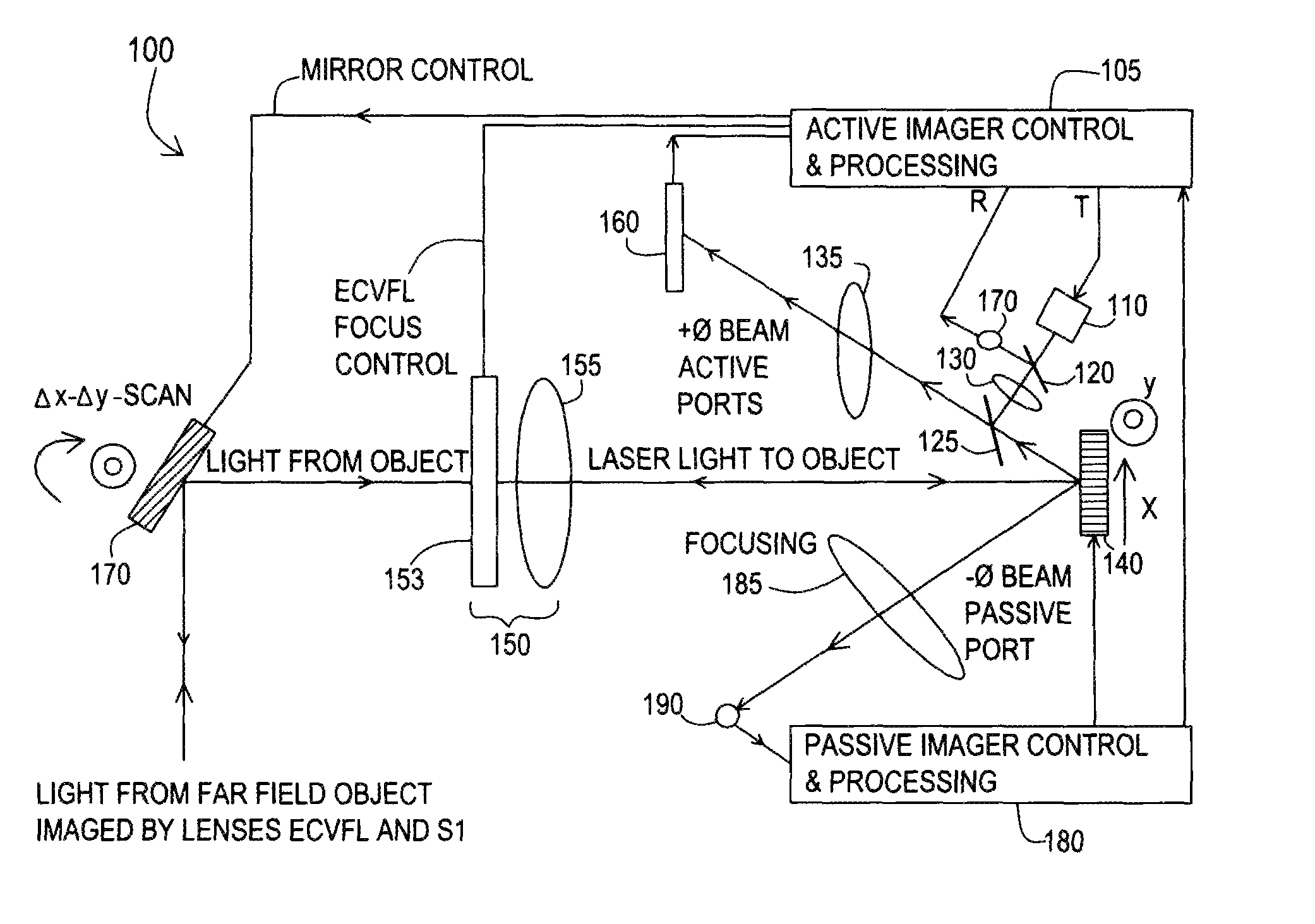
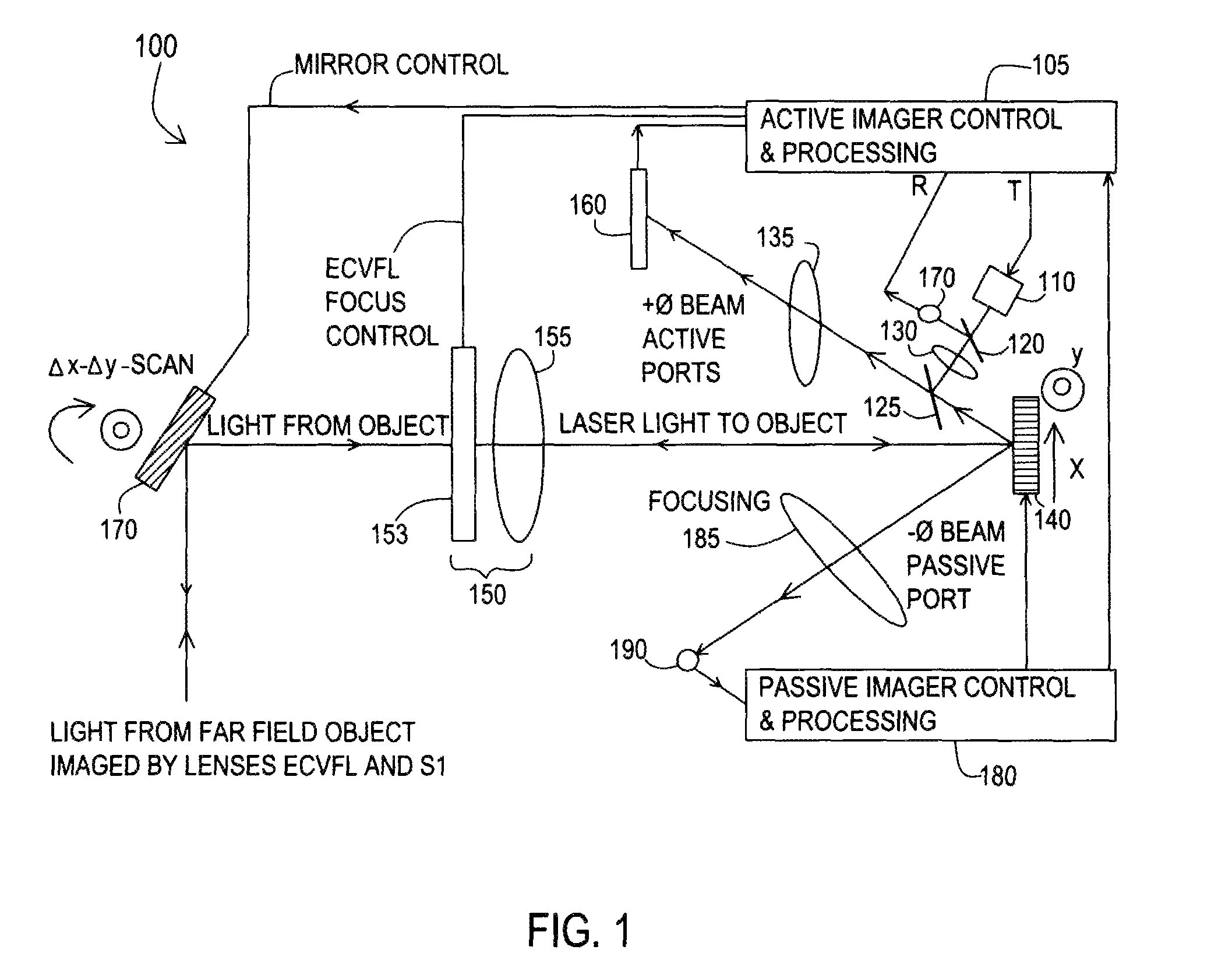
Hybrid differential optical sensing imager
InactiveUS8587686B1Reduce needTelevision system detailsColor television detailsThree-dimensional spaceOptical sensing
Methods and systems for a differential compressed sensor to form a smart optical imager that uses both active (laser) and passive (ambient light) to sample the direct image information within a three-dimensional spatial frame. The lens-based distance sensor is produces smart sampling of target by adjusting the size of the laser beam spot on the target sampling grid to produce a boundary outline by a light flooding. This target dependent direct sampling of the target results in direct compressed sensing. A passive light acquisition pin-hole sampling optical sensor design is proposed that produces the pixel-basis Laplacian to determine the compressed sensed pixels in the incident image.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
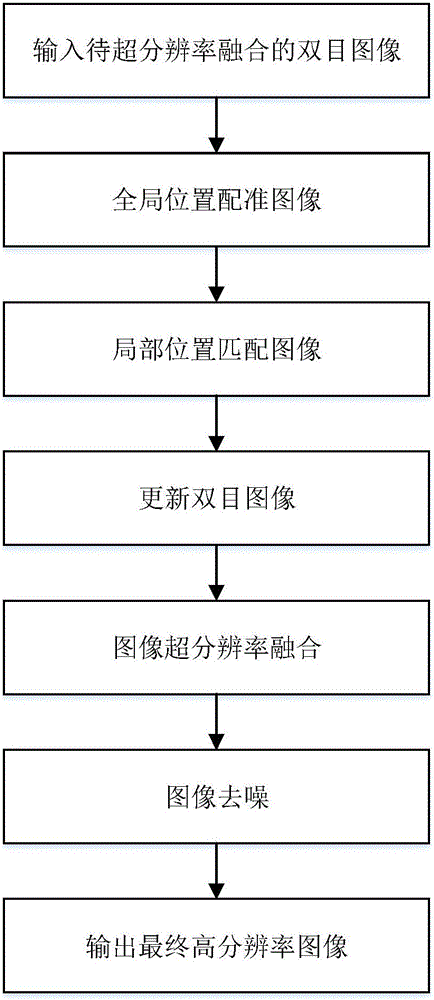
Binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method
ActiveCN105844630AConducive to super-resolution fusion processingOvercome the local position mismatchImage enhancementImage analysisHigh resolution imageImage matching
The invention discloses a binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method, comprising steps of (1) inputting a binocular image to be subjected to super-resolution fusion, (2) performing global position image registration, (3) performing local position image matching, (4) updating the binocular image, (5) performing image super-resolution fusion, (6) performing image de-noising, and (7) outputting a final high resolution image. In the image registration process, a local position registration method is added, a Laplace operator is applied to the image super resolution fusion, and a non-local mean value filtering method is employed to perform de-noising on the fusion image. The binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method overcomes the deficiencies in the prior art that image local positions are not matched, detail enhancement is not enough and the function of noise inhibition is absent. The binocular visual image super-resolution fusion de-noising method obtains a super resolution fusion image which has enhanced image details and reduced noise.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
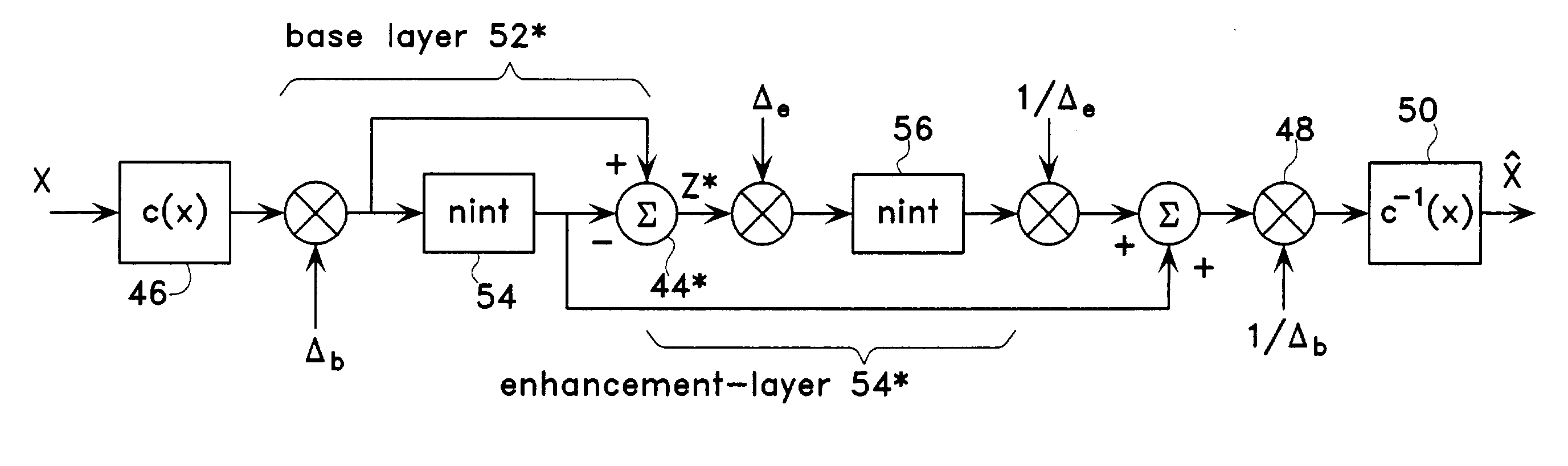
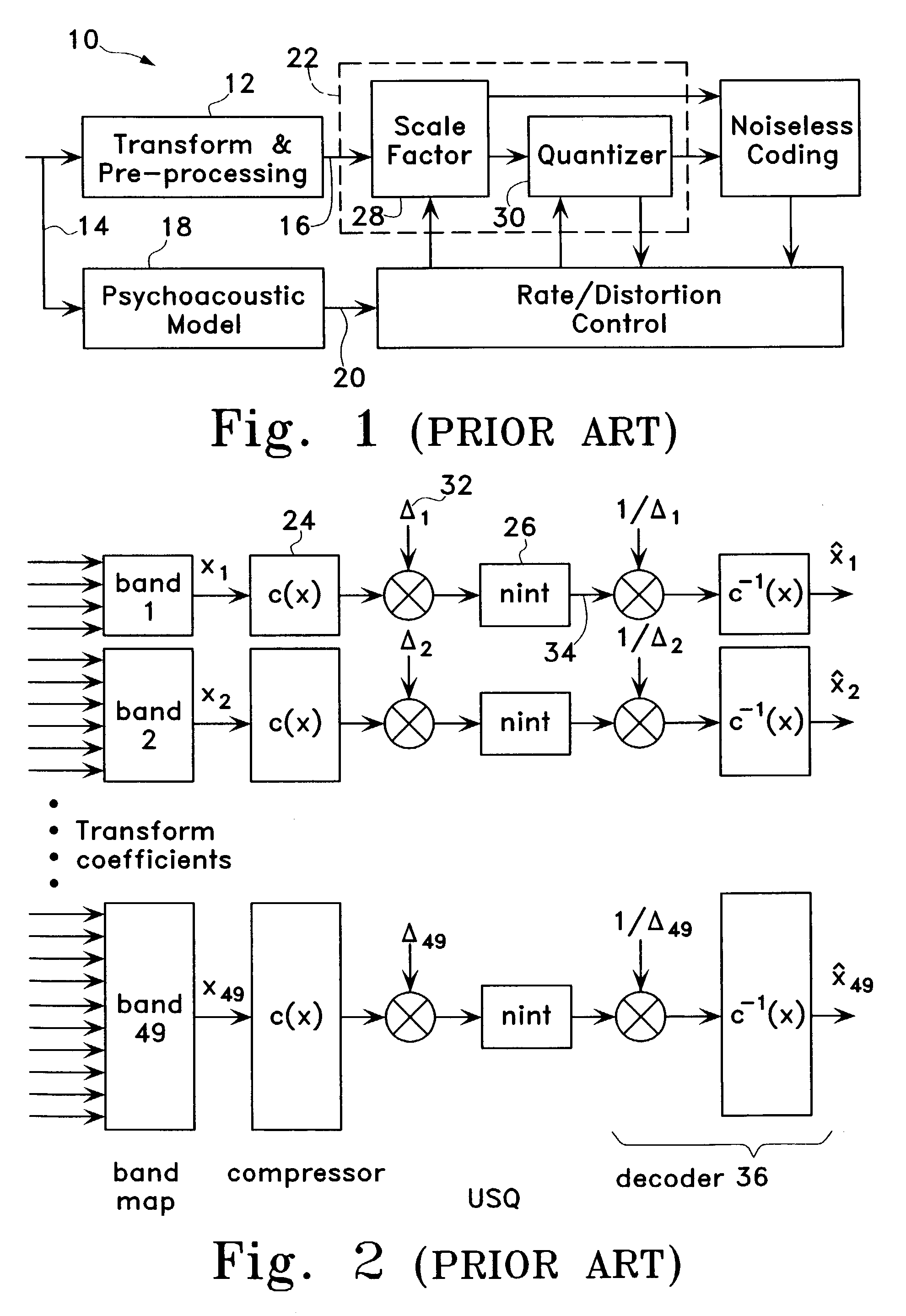
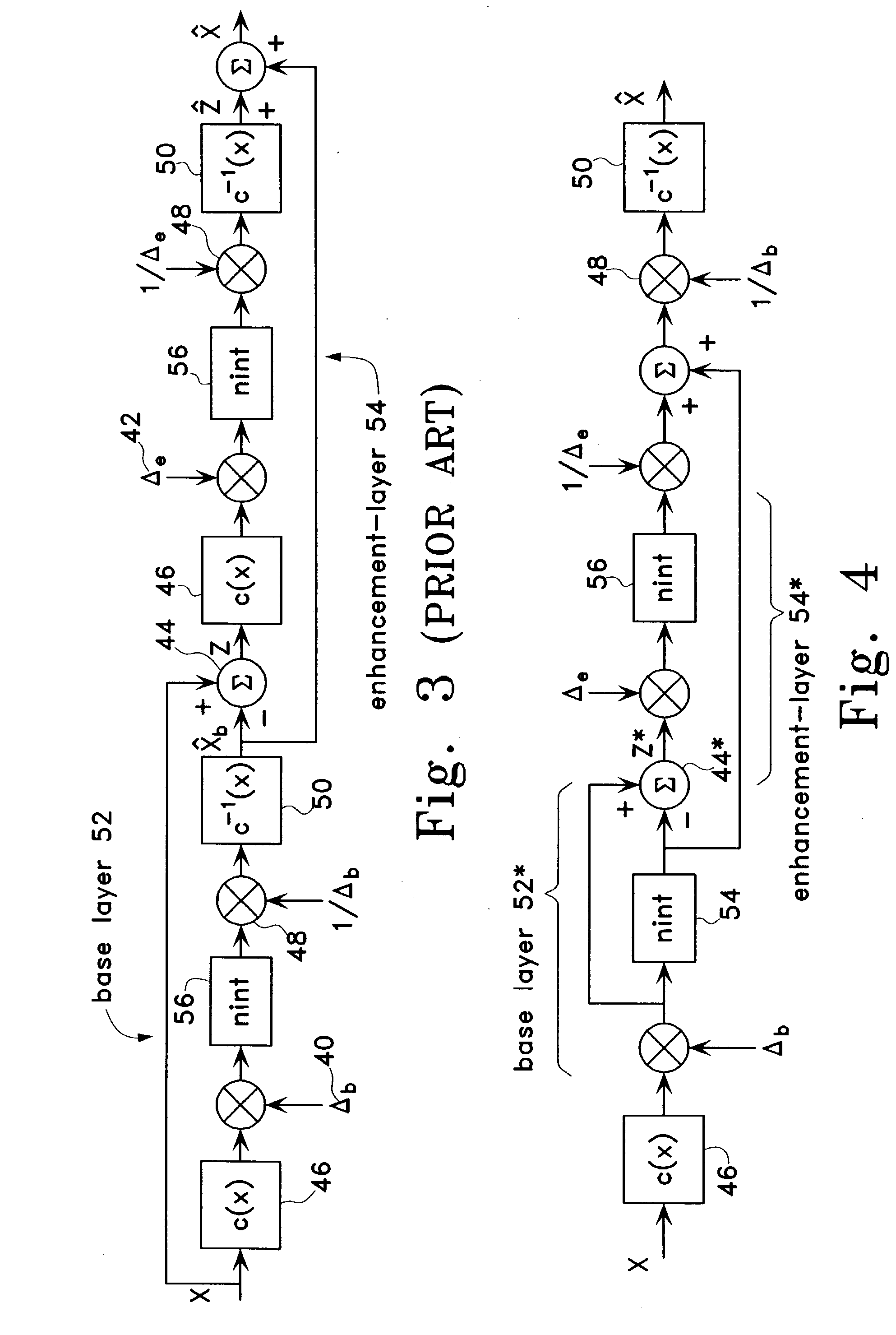
Scalable compression of audio and other signals
ActiveUS6947886B2Improve signal qualityComparable distortionSpeech analysisTransmissionScalable compressionSignal on
Disclosed are scalable quantizers for audio and other signals characterized by a non-uniform, perception-based distortion metric, that operate in a common companded domain which includes both the base-layer and one or more enhancement-layers. The common companded domain is designed to permit use of the same unweighted MSE metric for optimal quantization parameter selection in multiple layers, exploiting the statistical dependence of the enhancement-layer signal on the quantization parameters used in the preceding layer. One embodiment features an asymptotically optimal entropy coded uniform scalar quantizer. Another embodiment is an improved bit rate scalable multi-layer Advanced Audio Coder (AAC) which extends the scalability of the asymptotically optimal entropy coded uniform scalar quantizer to systems with non-uniform base-layer quantization, selecting the enhancement-layer quantization methodology to be used in a particular band based on the preceding layer quantization coefficients. In the important case that the source is well modeled as Laplacian, the optimal conditional quantizer is implementable by only two distinct switchable quantizers depending on whether or not the previous quantizer identified the band in question as a so-called “zero dead-zone:” Hence, major savings in bit rate are recouped at virtually no additional computational cost. For example, the proposed four layer scalable coder consisting of 16 kbps layers achieves performance close to a 60 kbps non-scalable coder on the standard test database of 44.1 kHz audio.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
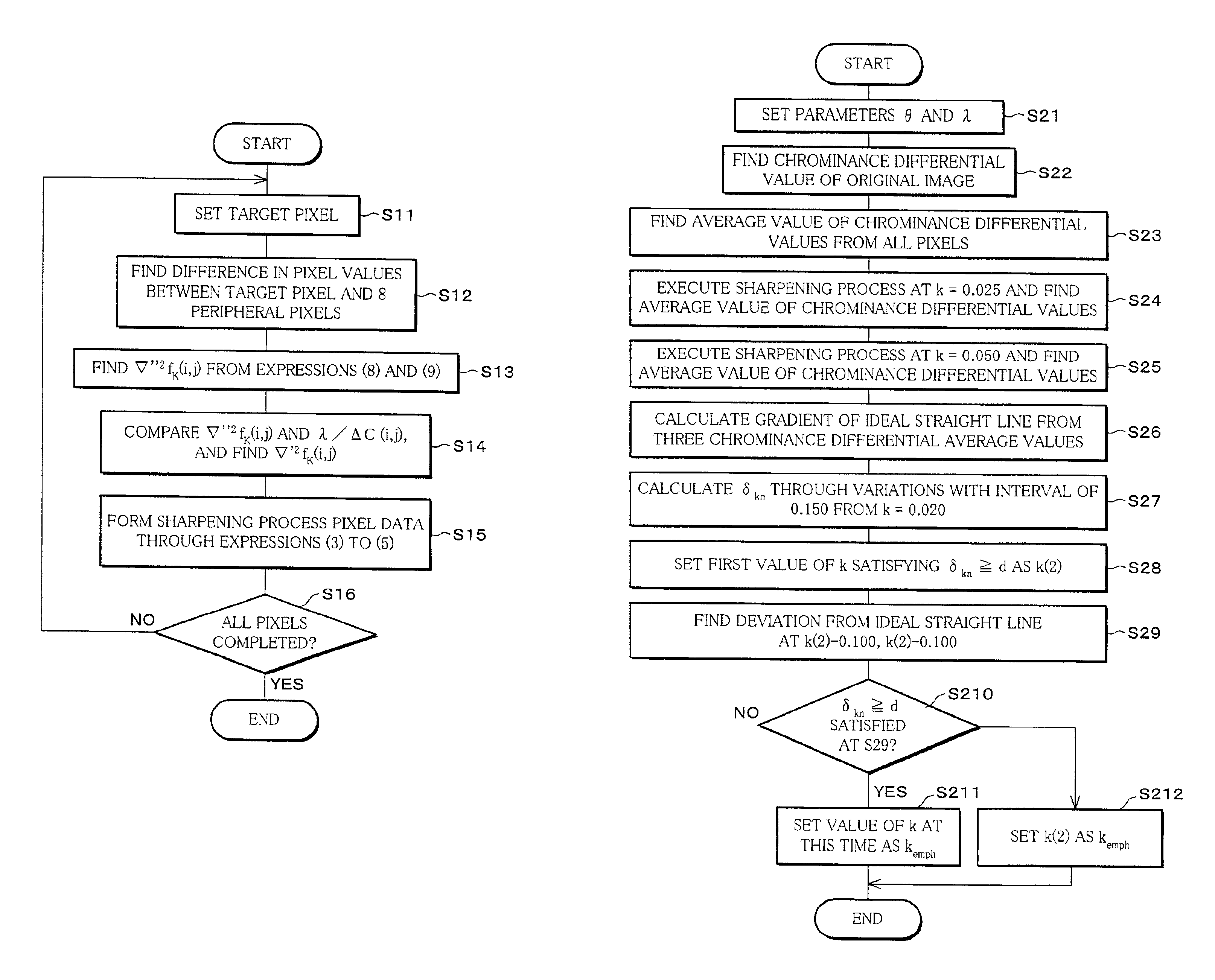
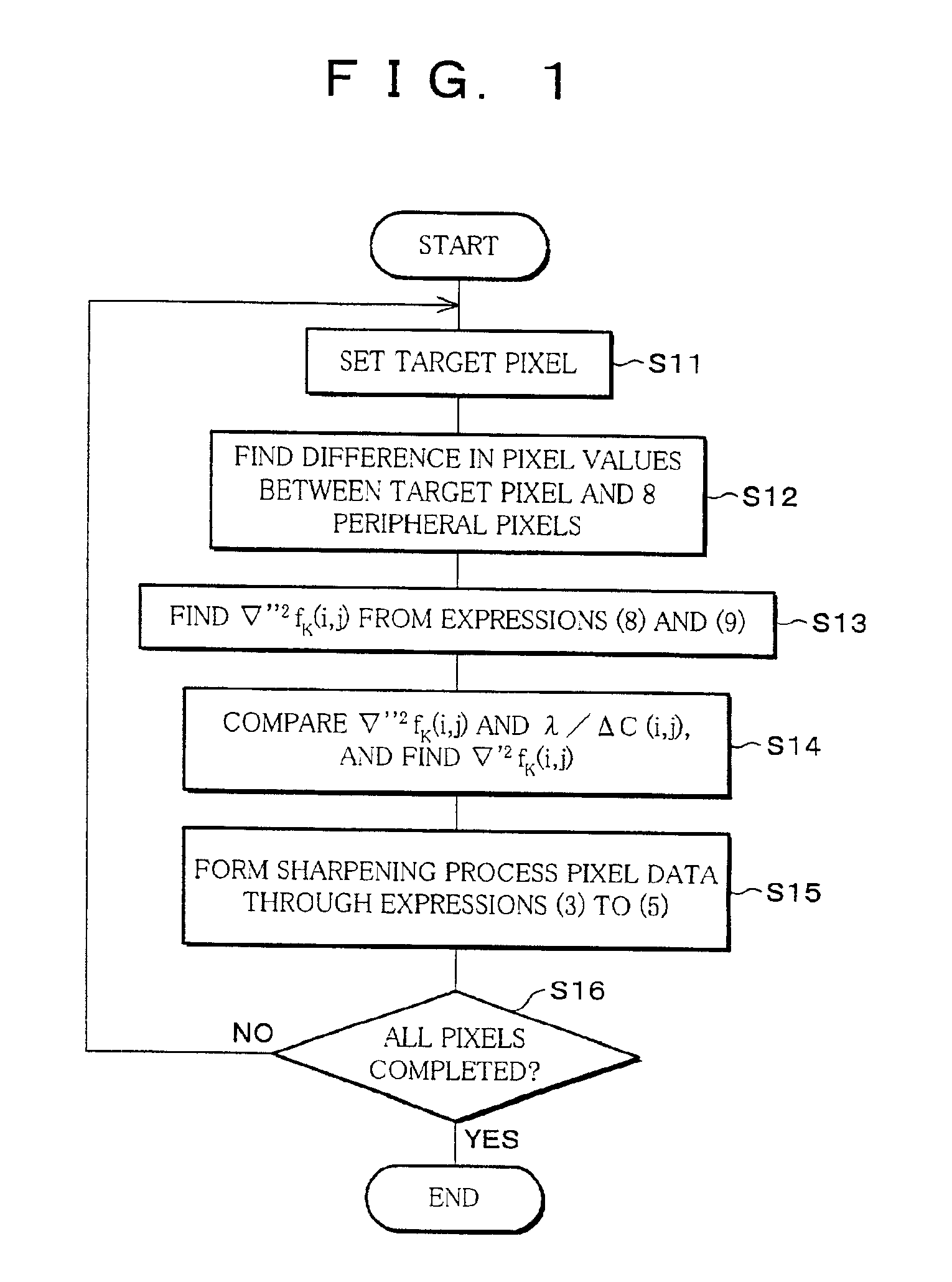
Image-processing method and recording medium in which such an image-processing method is recorded
InactiveUS6924839B2Problem noiseProblem occurrenceTelevision system detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionImaging processing
In a sharpening process of image data using a Laplacian operation, a parameter k for controlling the size of a Laplacian to be subtracted from an original image, a parameter θ for suppressing influences of noise and a parameter λ for suppressing an overshoot and an undershoot are respectively provided, and these parameters are altered in accordance with the state of an original image. Thus, it becomes possible to carry out the sharpening process on the image data without causing emphasized noise and occurrences of an overshoot and an undershoot.
Owner:NORITSU PRECISION CO LTD
Camera source evidence obtaining method based on mode noise big component
ActiveCN102819831AEnhance high frequency mode noise componentsEliminate the influence of other low-frequency factors such as scene noiseImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputation complexity
The invention discloses a camera source evidence obtaining method based on a mode noise big component, which is divided into two parts of mode noise big component extraction and relevancy detection. The camera source evidence obtaining method based on the mode noise big component specifically comprises the following steps of: selecting a picture; sharpening an image; carrying out filtering processing; extracting a big component; calculating a relevant coefficient; and distinguishing a source. According to the camera source evidence obtaining method based on the mode noise big component, the image is preprocessed by a Laplace operator, a high-frequency mode noise ingredient is effectively enhanced, and the influence of other low-frequency factors, such as scene noise and the like is eliminated. While the detection accuracy is guaranteed, the computation complexity of an algorithm is lowered to a large extent. Detection is carried out by a photoresponse sensitive spot set in mode noise, and a new concept of image source identification based on mode identification is opened up. The camera source evidence obtaining method based on the mode noise big component has the advantages of simpleness, convenience and strong robustness in practical application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
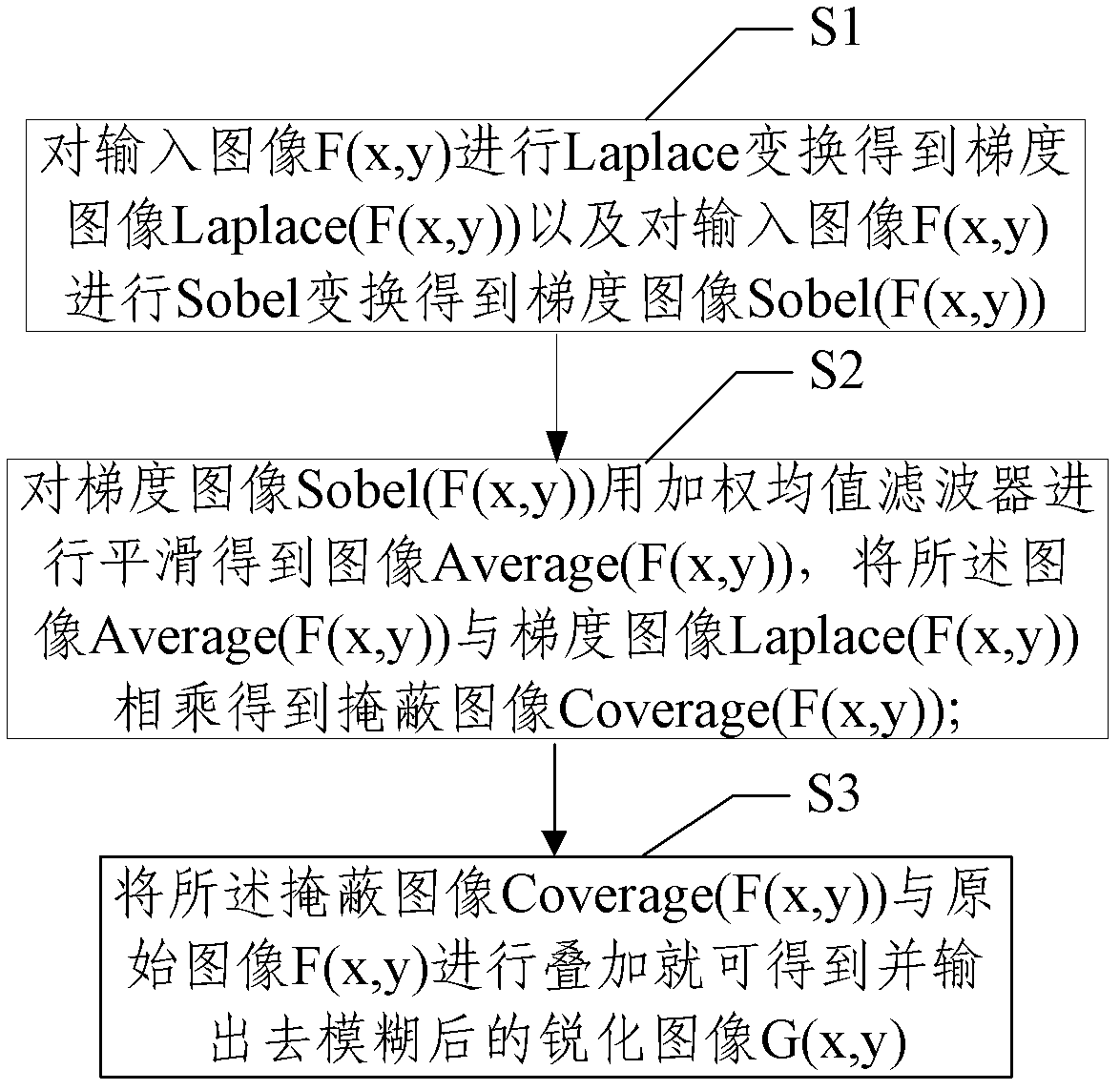
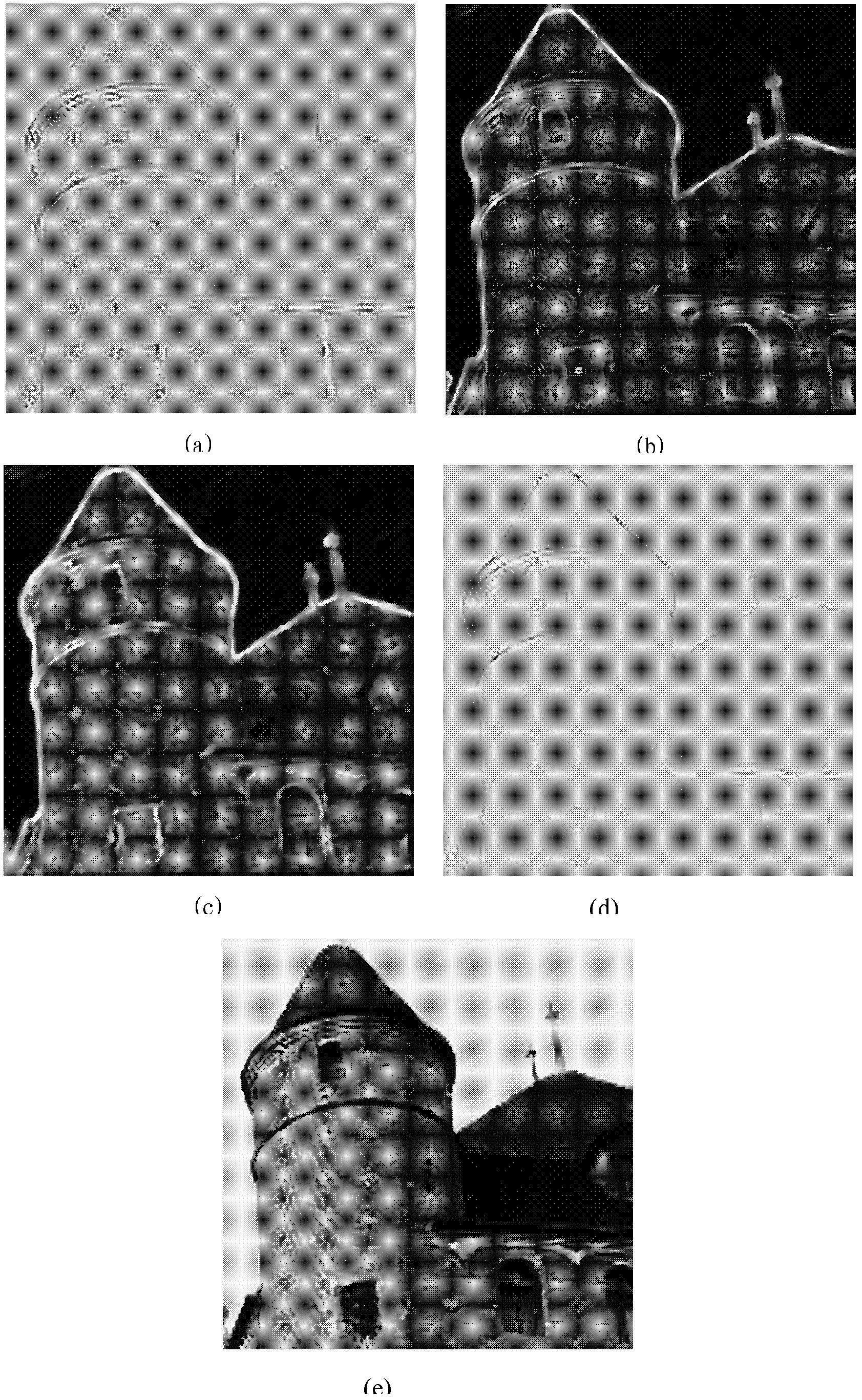
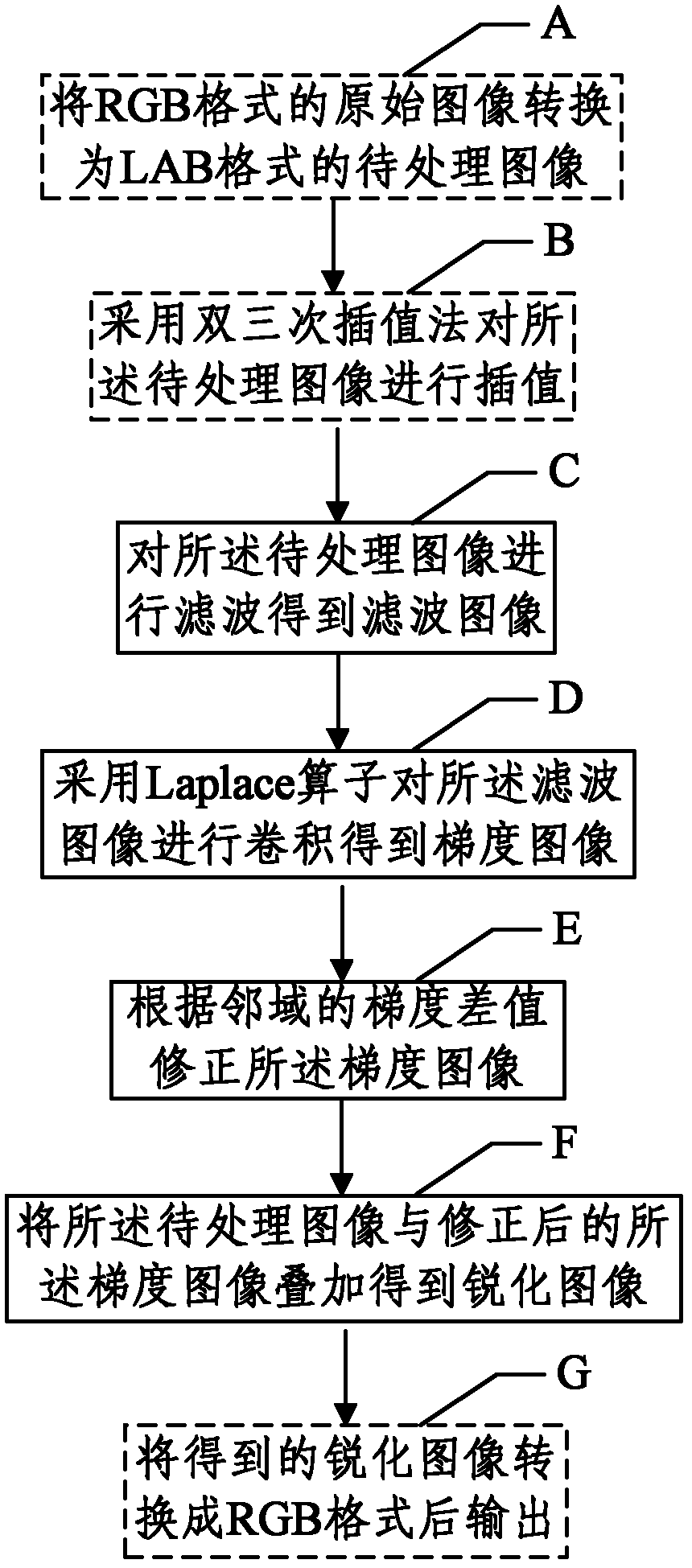
Method and device for deblurring images based on single low resolution
The invention provides a method and a device for deblurring an image based on single low resolution, relating to the technical field of image processing. The method for deblurring the image based on single low resolution comprises the following steps of: filtering an image to be processed to obtain a filter image; convoluting the filtered image by means of a Laplace operator to obtain a gradient image; correcting the gradient image based on the gradient difference value of a neighbourhood; and overlapping the image to be processed with the corrected gradient image to obtain a sharpened image.By adopting the method and the device for deblurring the image based on single low resolution of the invention, the noise of a smooth region in the gradient image is reduced and the profile and detail losses of an object are lessened during the sharpening process of the single low-resolution image, so that the visual effect of the image is greatly improved.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Non-reference image objective quality evaluation method
The invention discloses a non-reference image objective quality evaluation method. The non-reference image objective quality evaluation method comprises the following steps: respectively applying Gaussian smoothing gradient filter and laplace operator Gaussian filter to a distorted image by deeply excavating perception characteristic of human vision to image structure to correspondingly obtain a Gaussian smoothing gradient filter image and a laplace operator Gaussian filter image, then respectively carrying out local binaryzation mode operation on the two filter images to obtain respective local binaryzation mode feature images, then calculating respective marginal probability feature and conditional probability feature of the two local binaryzation mode feature images, and finally forecasting on objective quality evaluation predicted value of the to-be-evaluated distorted images by adopting support vector regression according to the marginal probability feature and conditional probability feature. The obtained objective quality evaluation predicted value can accurately reflect subjective perceived quality of human vision and can be used for effectively improving correlation between objective evaluation result and subjective perception.
Owner:四川济舟信息科技有限公司
Method of detecting single moving target under complex background
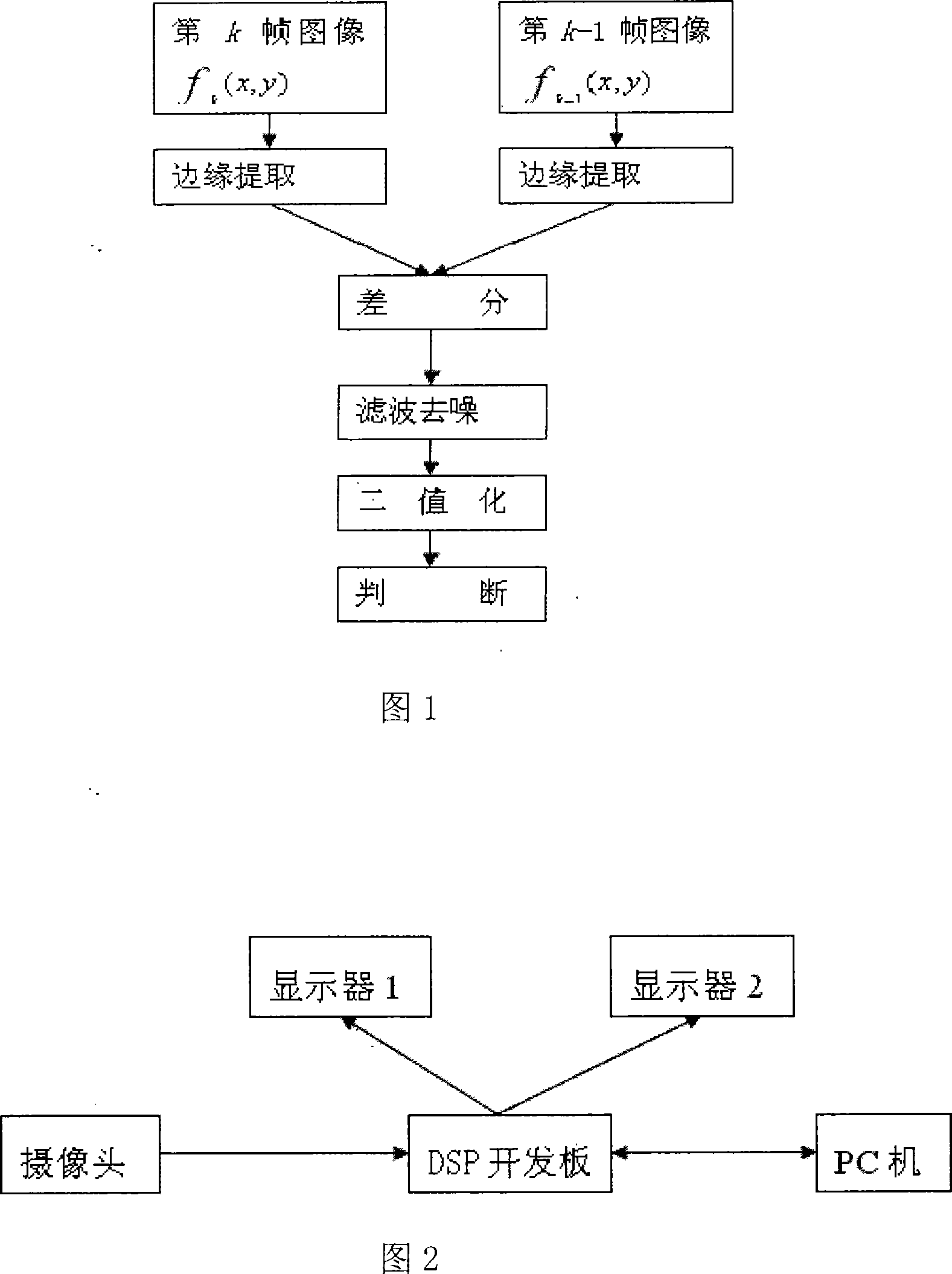
InactiveCN101179713AEasy to detectImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsComputer visionLaplace operator
A measurement method for a single moving target under a complex background belongs to the field of digital image processing. Firstly, edge extracting is conducted with a laplace operator for a k frame image of fk(x, y) and a k-1 frame image of fk-1(x, y) collected by a camera; secondly, difference calculus is conducted for images of two frames whose edge is extracted, and a difference image of D (x, y) is obtained; thirdly, average filtering and binary processing is conducted for the difference image of D (x, y), fourthly, the image which is processed of binary is judged, i.e. when the difference of a pixel in the difference image is more than the set threshold value, the pixel is confirmed as a target pixel; otherwise, the pixel is a static background pixel. The invention is capable of detecting the moving target in large noise well and has a wide application prospect in the fields such as monitoring and intelligent traffic.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
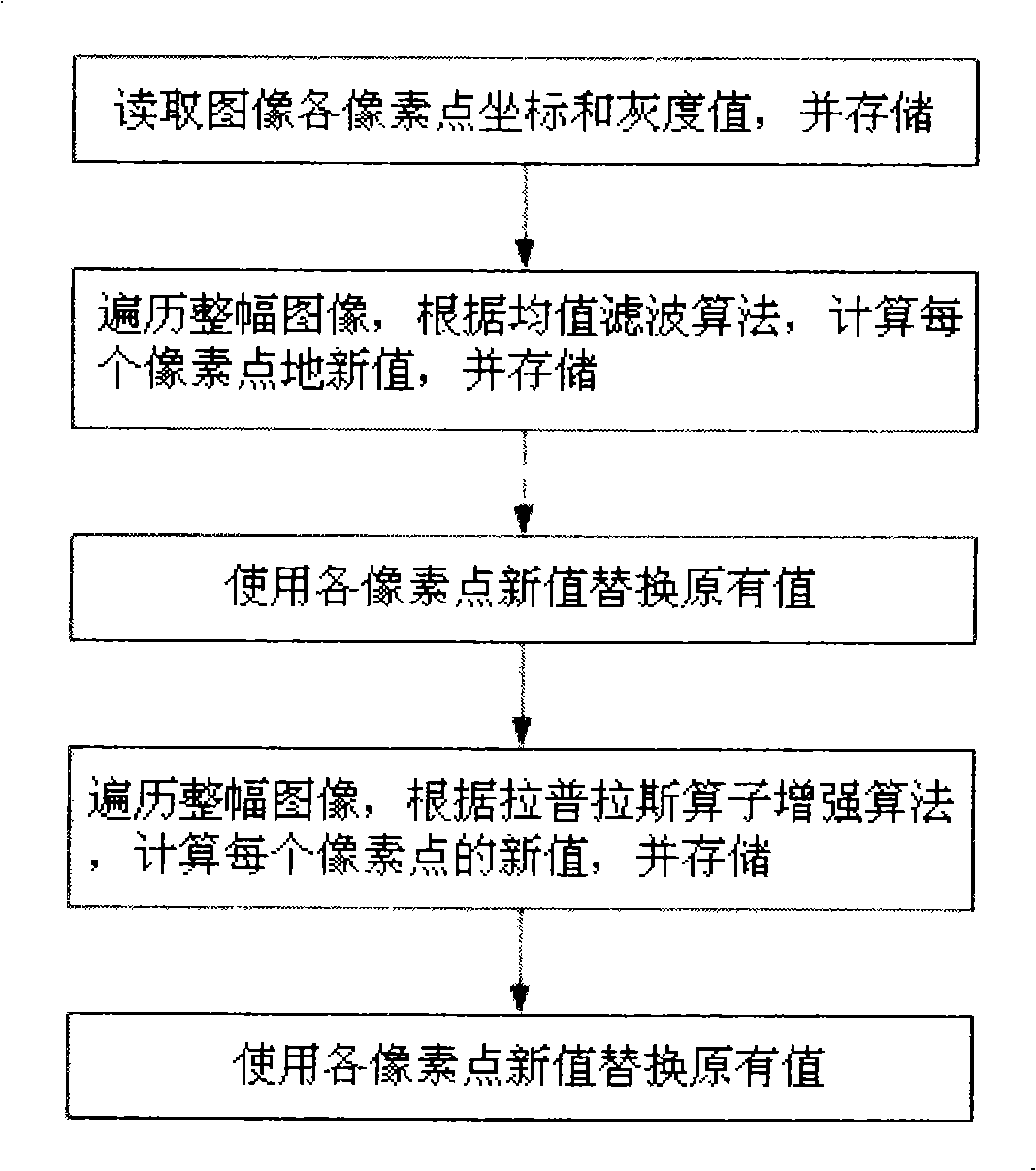
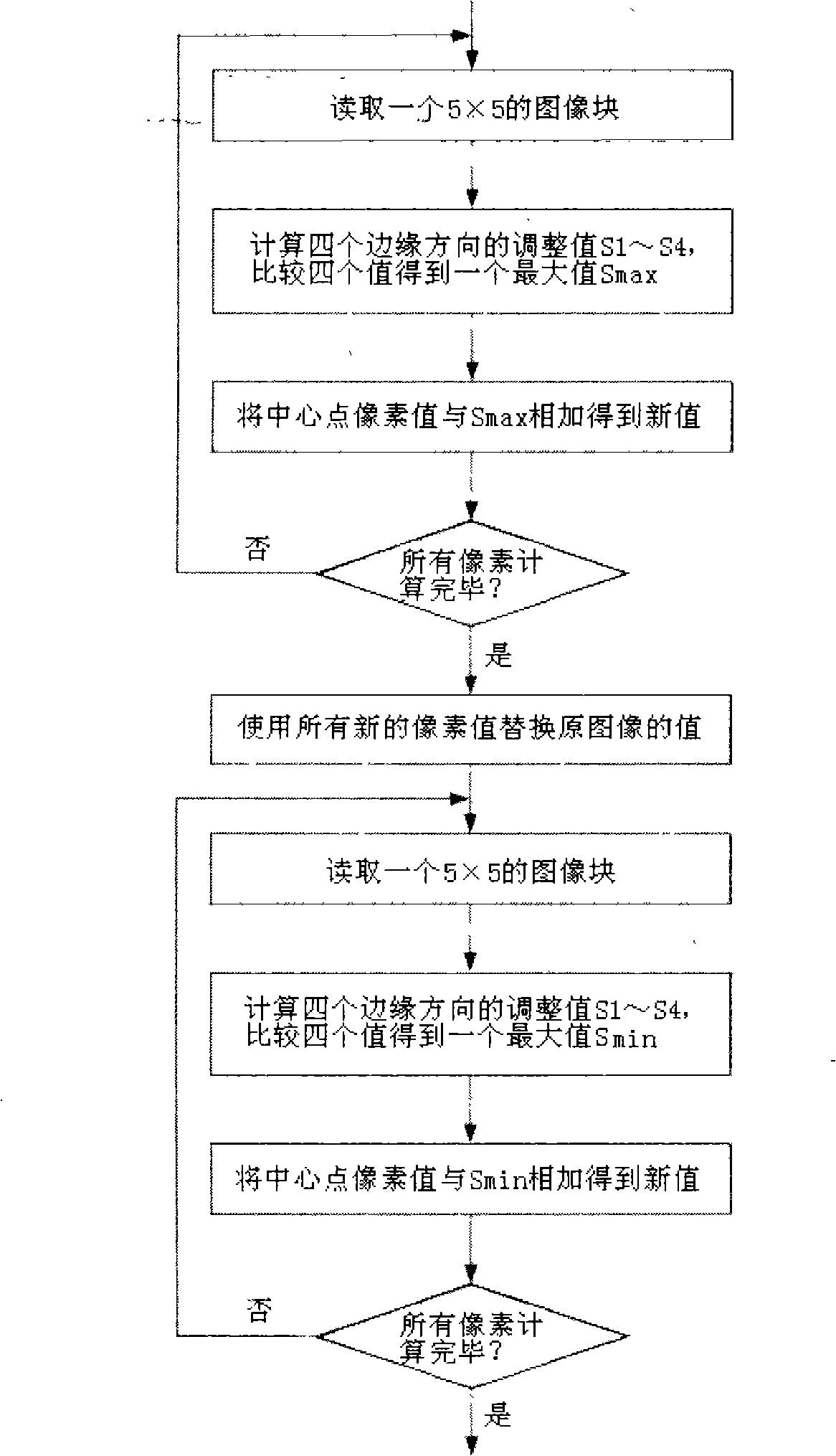
Method for reducing image noise and enhancing image
InactiveCN101355648AOvercoming ambiguityReduce noiseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionImage denoising
The invention relates to a method for reducing noise of an image and intensifying the image, comprising the following steps that: (1) the coordinate and a grey level value of each pixel point of the image are read; (2) the whole image is traversed, an improved image noise reducing algorithm is adopted to calculate each pixel point so as to obtain a novel pixel value after the noise reduction; (3) the novel pixel value after the noise reduction is adopted to replace the value of each pixel of the prior image so as to obtain the image after the noise is reduced; (4) the image after the noise reduction is traversed, an improved Laplacian operator enhancing algorithm is adopted to calculate each pixel point so as to obtain a novel enhanced pixel value; and (5) a novel enhanced pixel value is adopted to replace the prior pixel value so as to obtain the finally enhanced image. The method performs the noise reduction and enhancement on the image by the improved image noise reduction algorithm and the improved Laplacian operator enhancing algorithm, has good image processing effect and meets the monitoring requirement.
Owner:TIANJIN YAAN TECH CO LTD
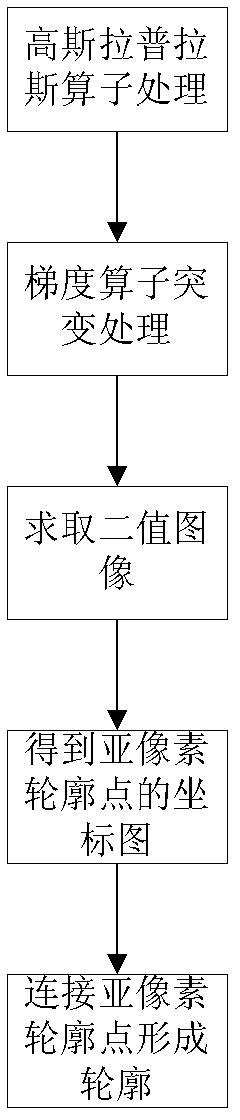
Method for extracting contour of image of printed circuit board (PCB)
ActiveCN102496161ALess interventionImprove stabilityImage analysisPattern recognitionGradient operators
The invention aims to provide a method for extracting a contour of an image of a printed circuit board (PCB). By the method, the defect of inaccuracy in extraction of the contour of the image of the PCB in the conventional contour extraction method is overcome, the accuracy and stability of contour detection are improved, and working efficiency is improved. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquisition of an original image of the PCB; 2) Gaussian Laplacian operator processing: processing the original image by using a Gaussian Laplacian operator to obtain a processed Gaussian Laplacian image; 3) gradient operator mutant processing: processing the original image by using a gradient operator to obtain a gradient image which is subjected to mutant processing through the gradientoperator; 4) processing the original image by using high and low threshold values to obtain a binary image; 5) establishing coordinate graphs of sub-pixel contour points, determining the pixel position of the contour according to the boundary of the binary image, and thus obtaining the coordinates of the sub-pixel contour points according to a Gaussian Laplacian value, a pixel value and a gradient value in the corresponding direction of the contour; and 6) connecting the sub-pixel contour points to form the contour, and connecting the sub-pixel contour points into a set in a certain sequence according to the coordinates of the sub-pixel contour points, wherein the coordinates are obtained in the step 5).
Owner:浙江欧威科技有限公司
Grid rebuilding method based on scattered-point cloud feature
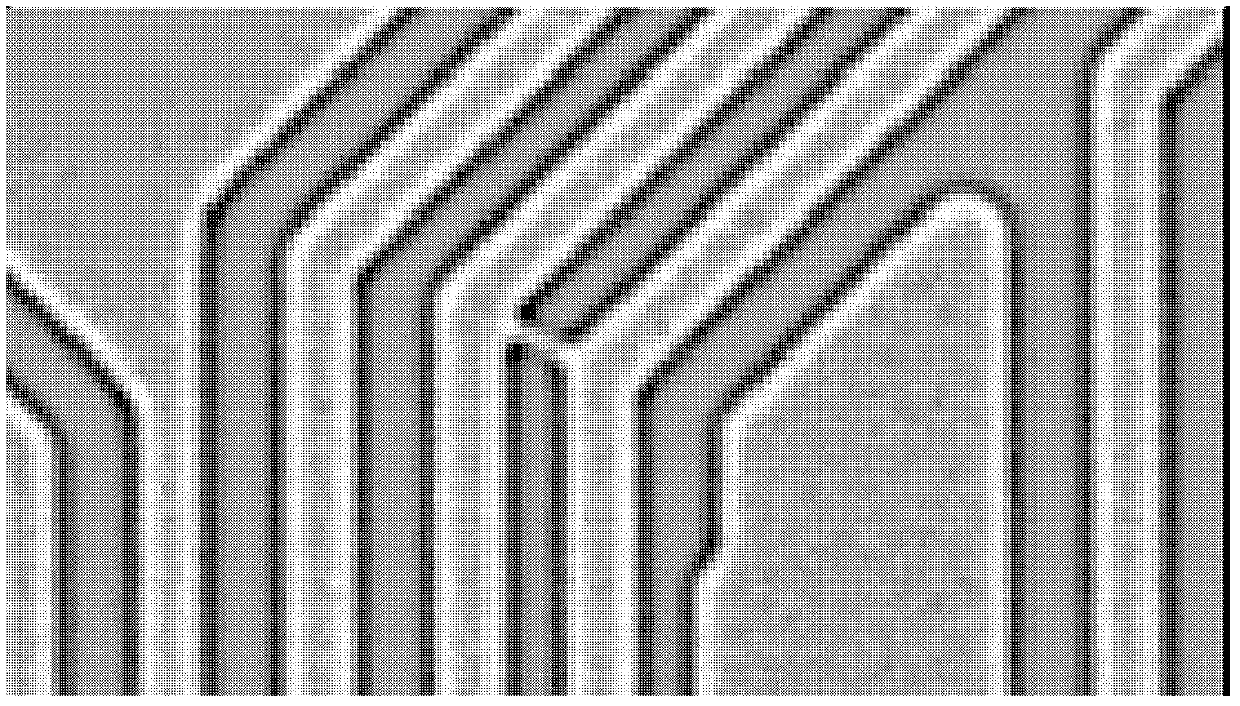
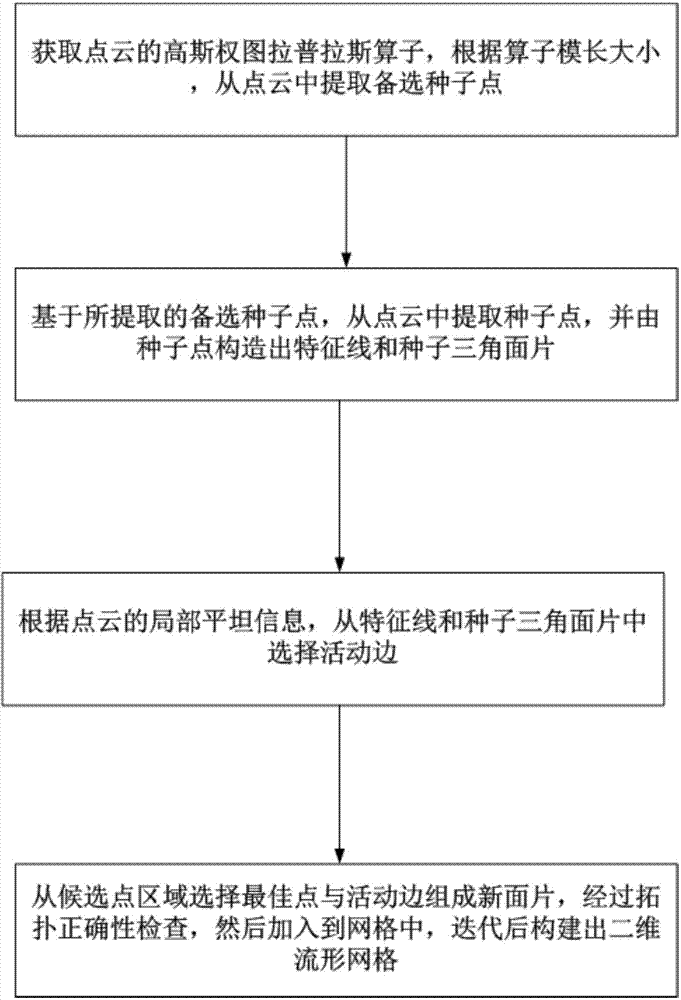
The invention discloses a grid rebuilding method based on a scattered-point cloud feature. The method includes the following steps that a point cloud Gaussian weight graph laplace operator is obtained, and alternative seed points are extracted from the point cloud according to the length and size of the operator; based on the extracted alternative seed points, seed points are extracted from the point cloud, and a characteristic line and a seed triangular patch are constructed through the seed points; according to the local flat information of the point cloud, an active edge is selected from the characteristic line and the seed triangular patch; an optimum point selected from a candidate point region and the active edge form a new patch, the new patch is added into a grid after topology correctness checking is conducted on the new patch, and a two-dimensional manifold grid is built after iteration. By means of the grid rebuilding method, the original shape, especially the sharp feature, of an object is well maintained, the method is suitable for the point cloud with unevenly distributed points, sealed reconstitution with boundaries is conducted, and finally the output result is a two-dimensional manifold triangularization grid.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
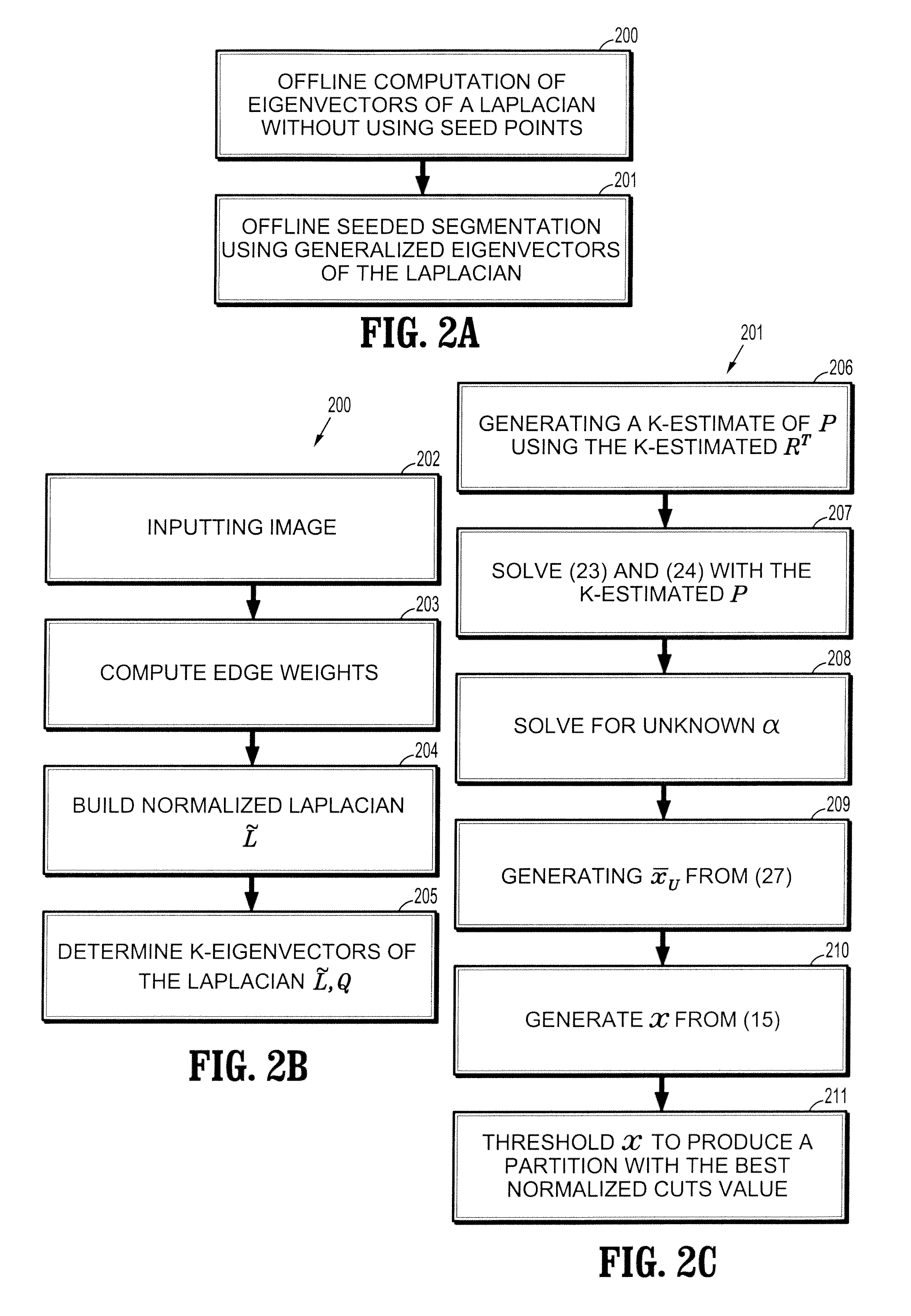
Interactive image segmentation by precomputation
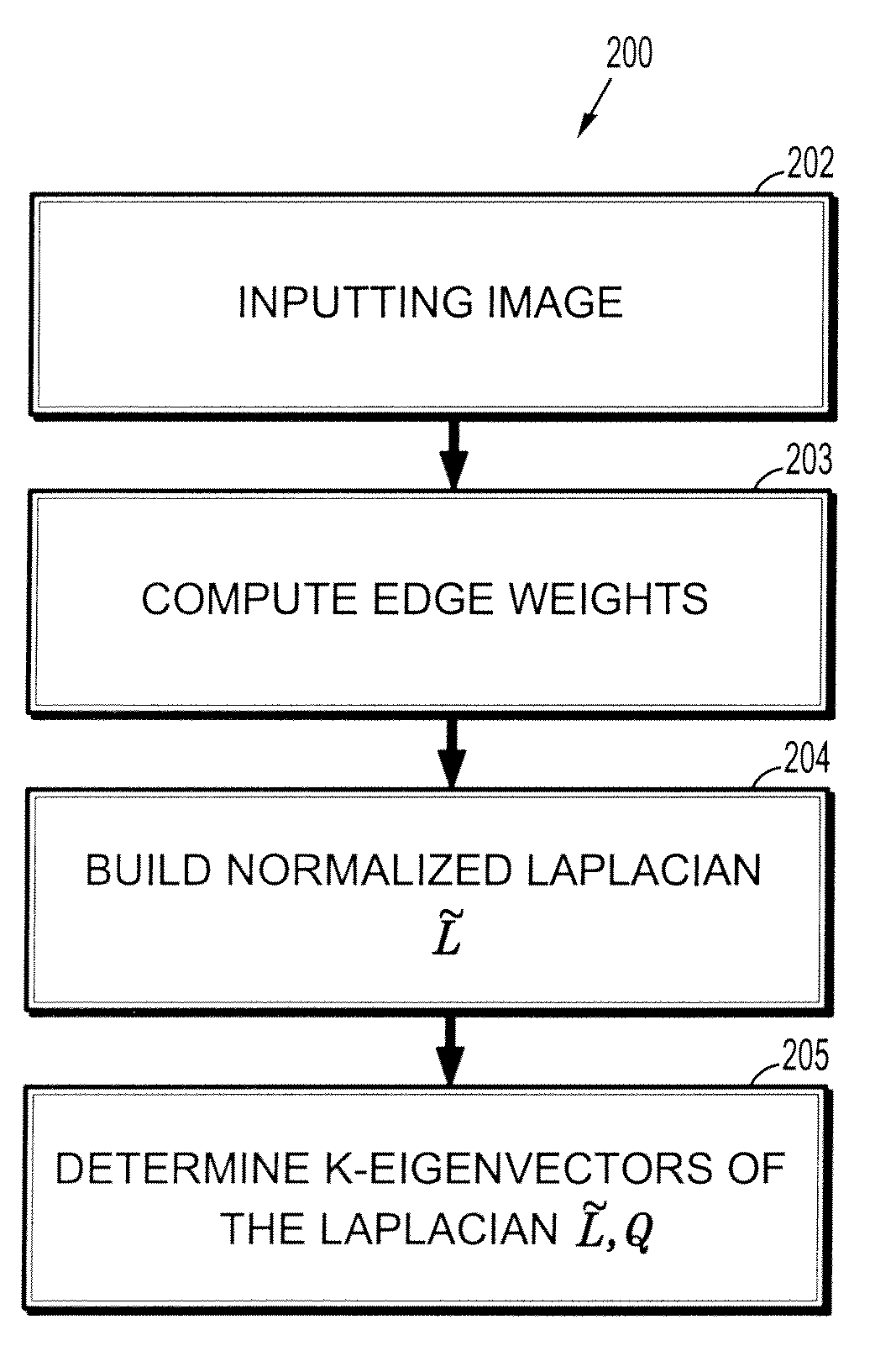
A method for interactive image segmentation includes receiving an image to be segmented, performing an offline computation of eigenvectors of a Laplacian of the image without using seed points, receiving seed points, and performing an online segmentation taking the seed points and the eigenvectors of the Laplacian as input and outputting a partition of the image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Visual detection method and system for pasting quality of FPC reinforcing pieces
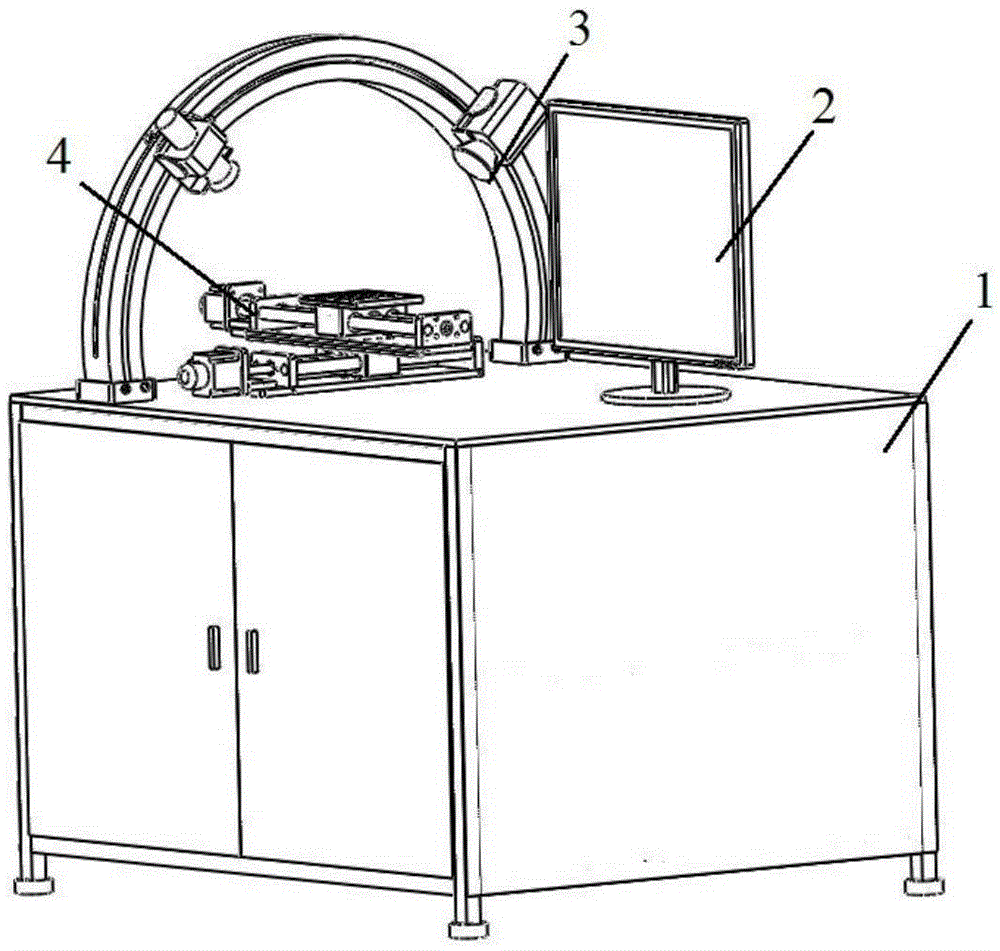
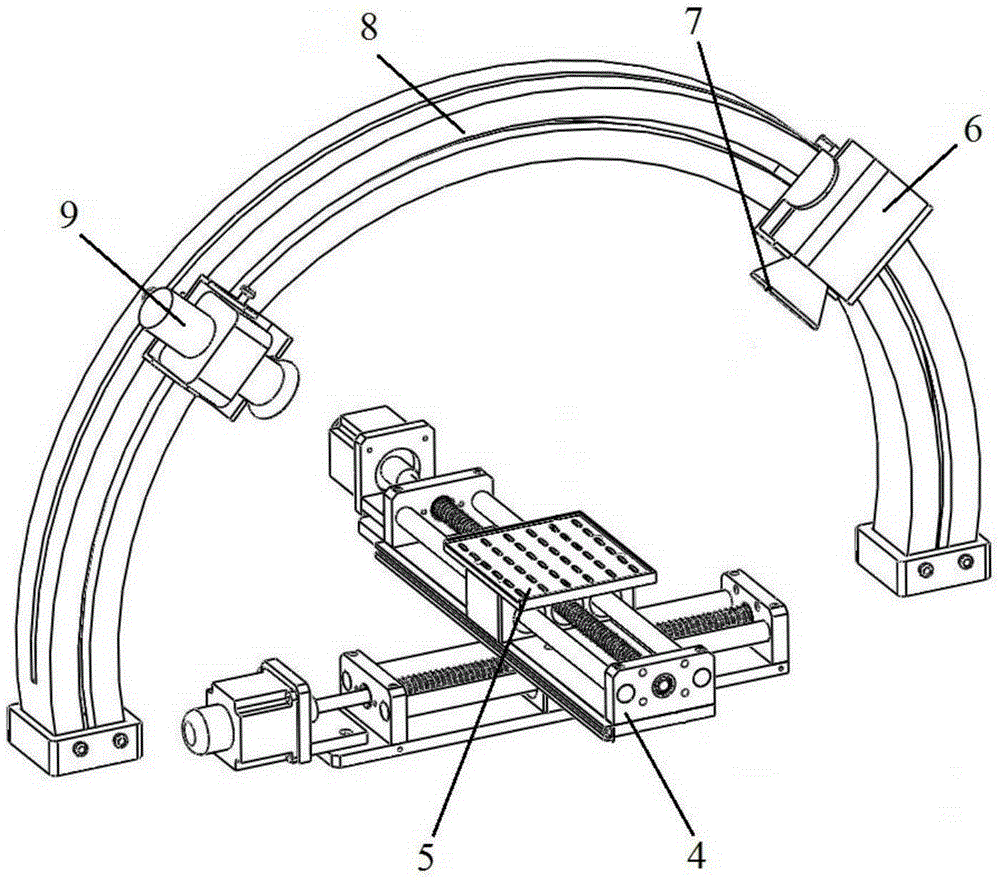
ActiveCN105334231AImprove detection efficiencyHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisLaser transmitterEllipse
The invention discloses a visual detection method and system for the pasting quality of FPC reinforcing pieces. The visual detection system comprises a control cabinet, a display screen, an image collection device, a cross-shaped precision worktable and a tray. The image collection device comprises a camera, a lens, an arc-shaped rack and a laser transmitter. According to the visual detection method and system, the arc-shaped rack is adopted for simplifying the calibration process and reducing the influences of hardware equipment on image collection, Guass-Laplacian operators are utilized on the basis of a laser triangulation method, limit type threshold segmentation is introduced, and meanwhile morphological close operation is adopted for separating out the optical center areas of laser spots; the invariance of moment is utilized for performing ellipse fitting, variation of the center position of an ellipse is converted into variation of the thickness of the reinforcing pieces, and therefore observation is easier. By means of the visual detection method and system, the pasting quality of the reinforcing pieces is automatically detected, detection precision is high, detection efficiency is improved, working intensity is relieved, manual operation can be completely replaced, and the arc-shaped rack can also be applied to stereoscopic visional detection.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Mel frequency cepstrum coefficient (MFCC) underwater target feature extraction and recognition method
ActiveCN102799892AImprove recognition rateFeature refinementCharacter and pattern recognitionMel-frequency cepstrumFeature set
The invention discloses a Mel frequency cepstrum coefficient (MFCC) underwater target feature extraction and recognition method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring a data sequence x(n); 2) framing to obtain xi(n); 3) obtaining yi(n) through windowing operation; 4) calculating the one-sided power spectrum density pi(l) of a framed and windowed signal; 5) solving a transfer function Hm(f) of a triangular filter bank, and obtaining Q by using the triangular filter bank; 6) performing logarithmic transformation to obtain E; 7) performing 3*3 template block operation of a Sobel operator and a Laplace operator in a t direction and a f direction respectively to obtain A, B and C; 8) performing discrete cosine transform (DCT) respectively to obtain feature sets, namely CA, CB and CC, and combining features; and 9) performing underwater target identification by using a clustering classifier of an expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm-based Gaussian mixture model. The method is favorable for improving the recognition rate of underwater targets.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System and method for using graph transduction techniques to make relational classifications on a single connected network
InactiveUS20140258196A1Efficient and accurateEfficient leveragingMathematical modelsDigital computer detailsGraphicsLabeled data
A system and method for extending partially labeled data graphs to unlabeled nodes in a single network classification by weighting the data with a weight matrix that uses a modified graph Laplacian based regularization framework and applying graph transduction methods to the weighted data. The technique may be applied to data graphs that are directed or undirected, that may or may not have attributes and that may be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Owner:IBM CORP
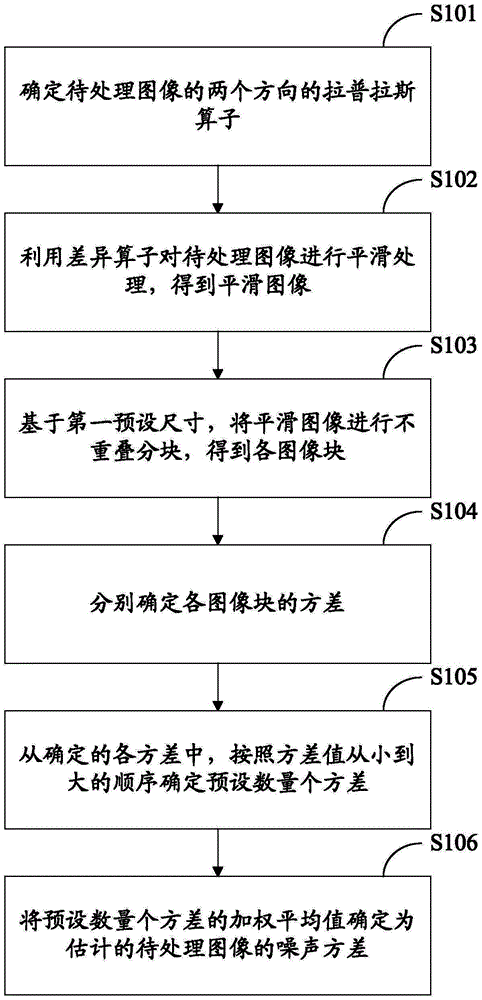
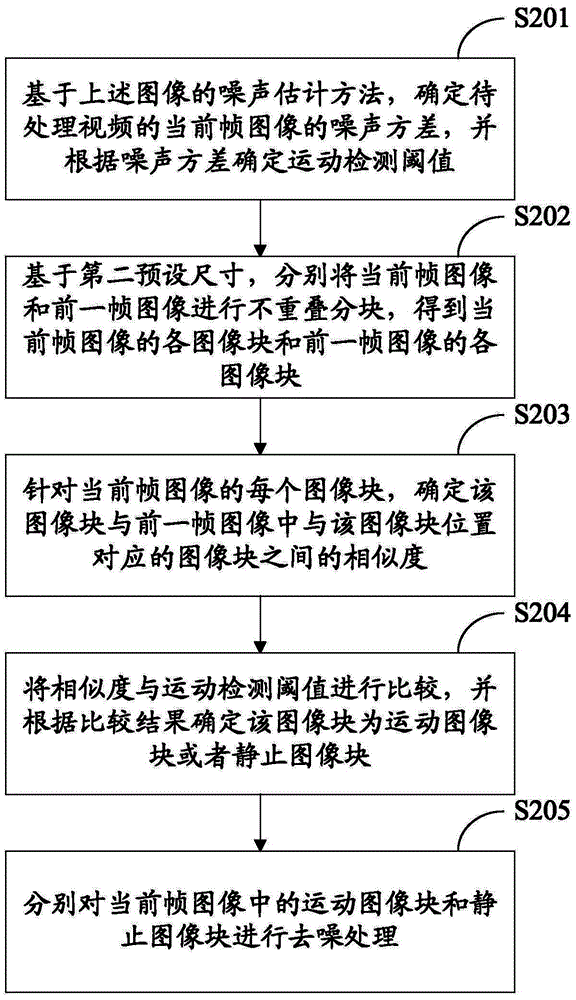
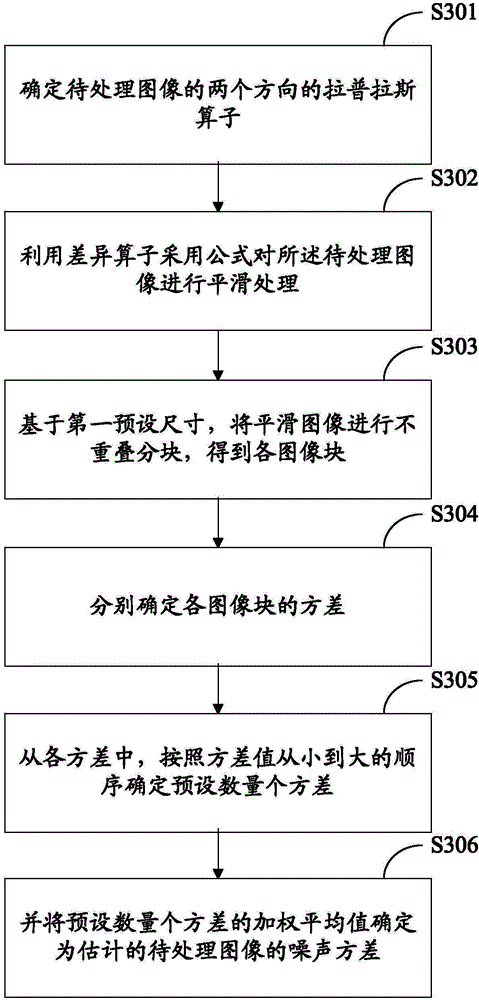
Image noise estimating method, video image de-noising method, image noise estimating device, and video image de-noising device
ActiveCN104680483AAccurate Noise EstimationImprove denoising effectImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImaging processing
The embodiment of the invention provides an image noise estimating method, a video image de-noising method, an image noise estimating device, and a video image de-noising device. The image noise estimating method comprises the following steps: determining the Laplasse operators of an image to be processed in two directions, wherein, among difference operators obtained through default linear operation on the Laplasse operators in two directions, the sum of numerical values in all rows and the sum of numerical values in all columns are zero, and the absolute value of the numerical value in the center is larger than the absolute value of a numerical value not in the center; smoothing the image to be processed by use of the difference operators to obtain a smooth image; partitioning the smooth image in a non-overlapping way based on a first preset size to obtain image blocks; and determining the variance of each image block, determining a preset number of variances according to the order of the variances from small to large, and determining the weighted average of the preset number of variances as an estimated noise variance of the image to be processed. The problem that image noise estimation is inaccurate in the prior art is solved. The invention relates to the field of image processing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting defect in material and system for the method
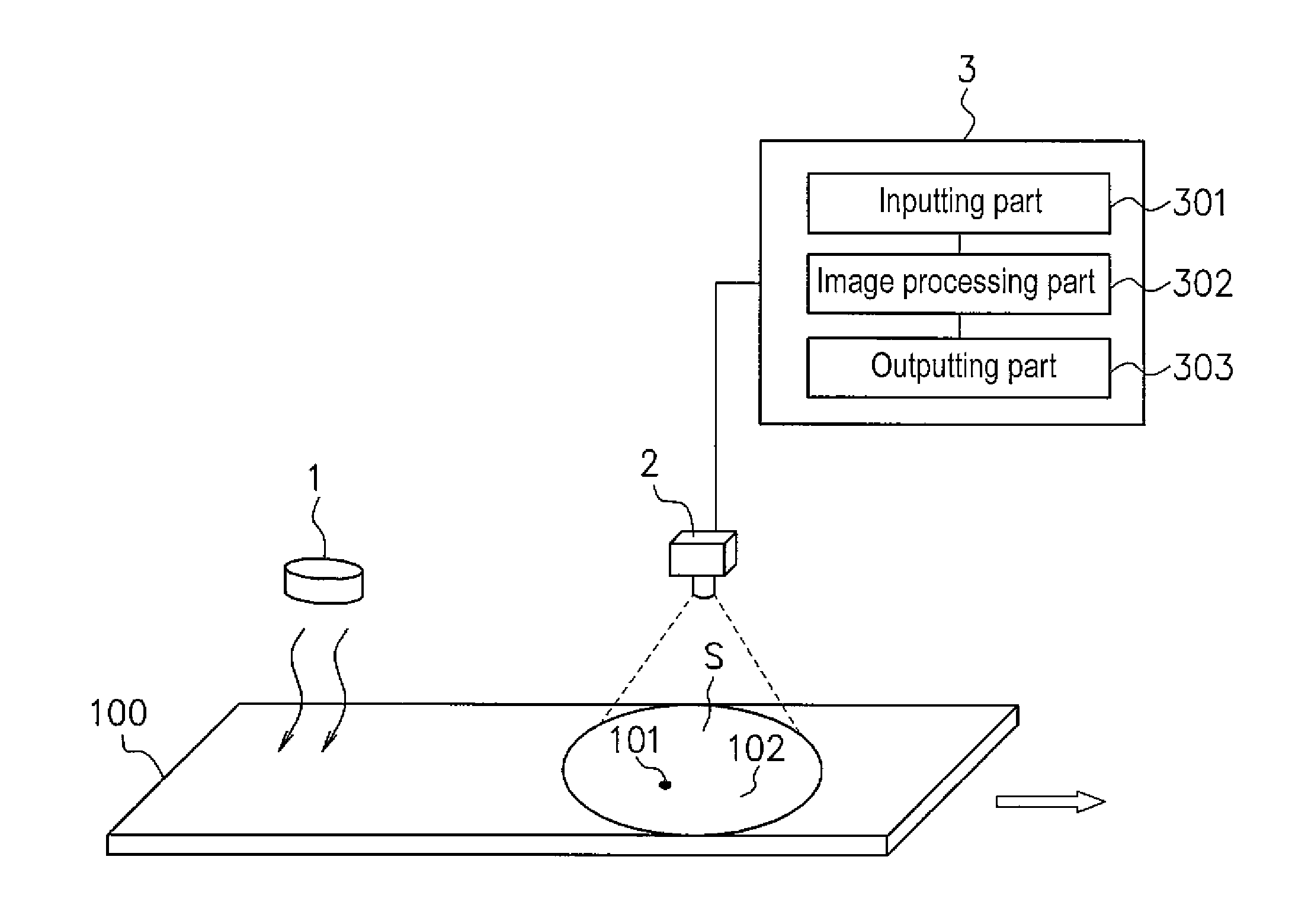
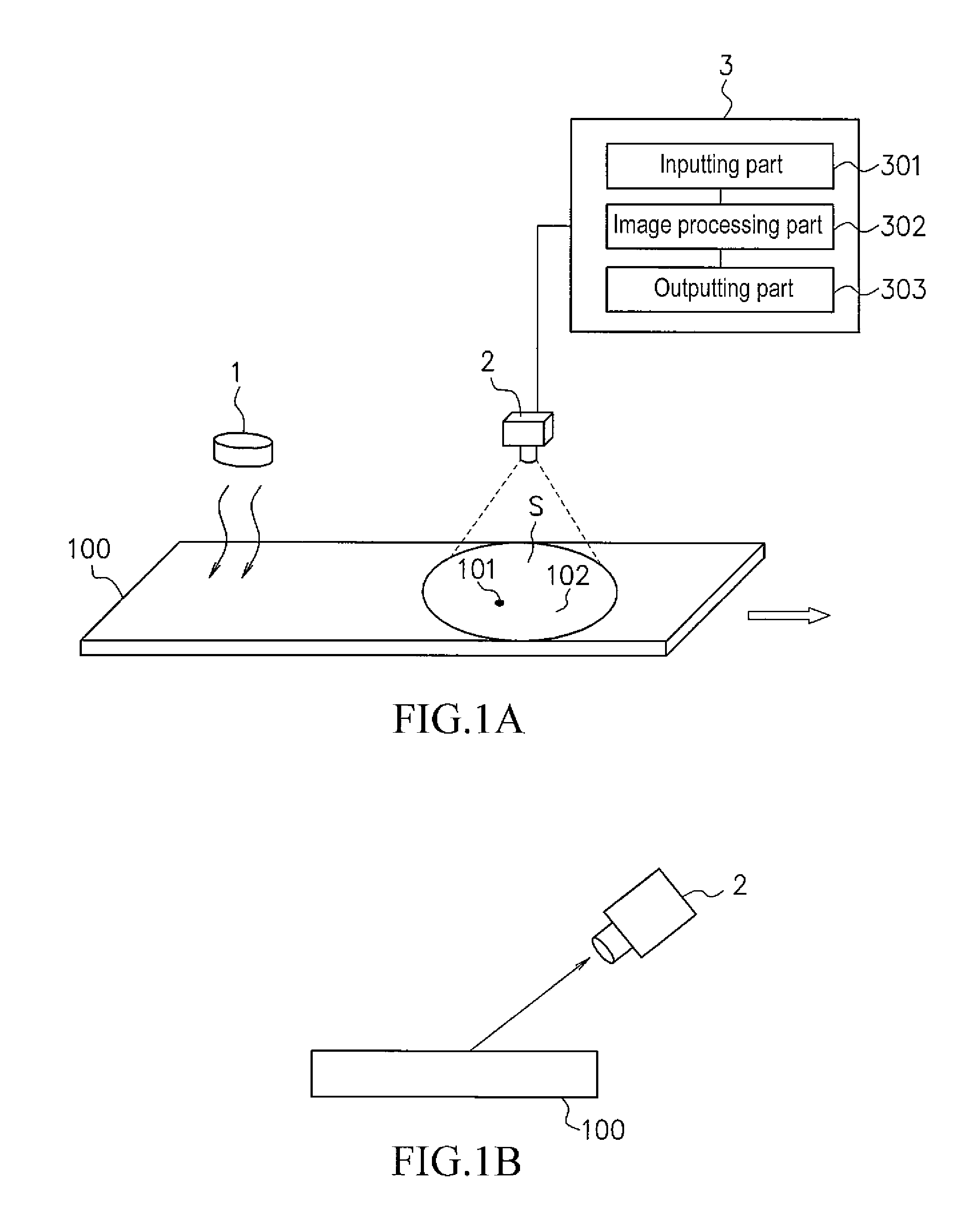
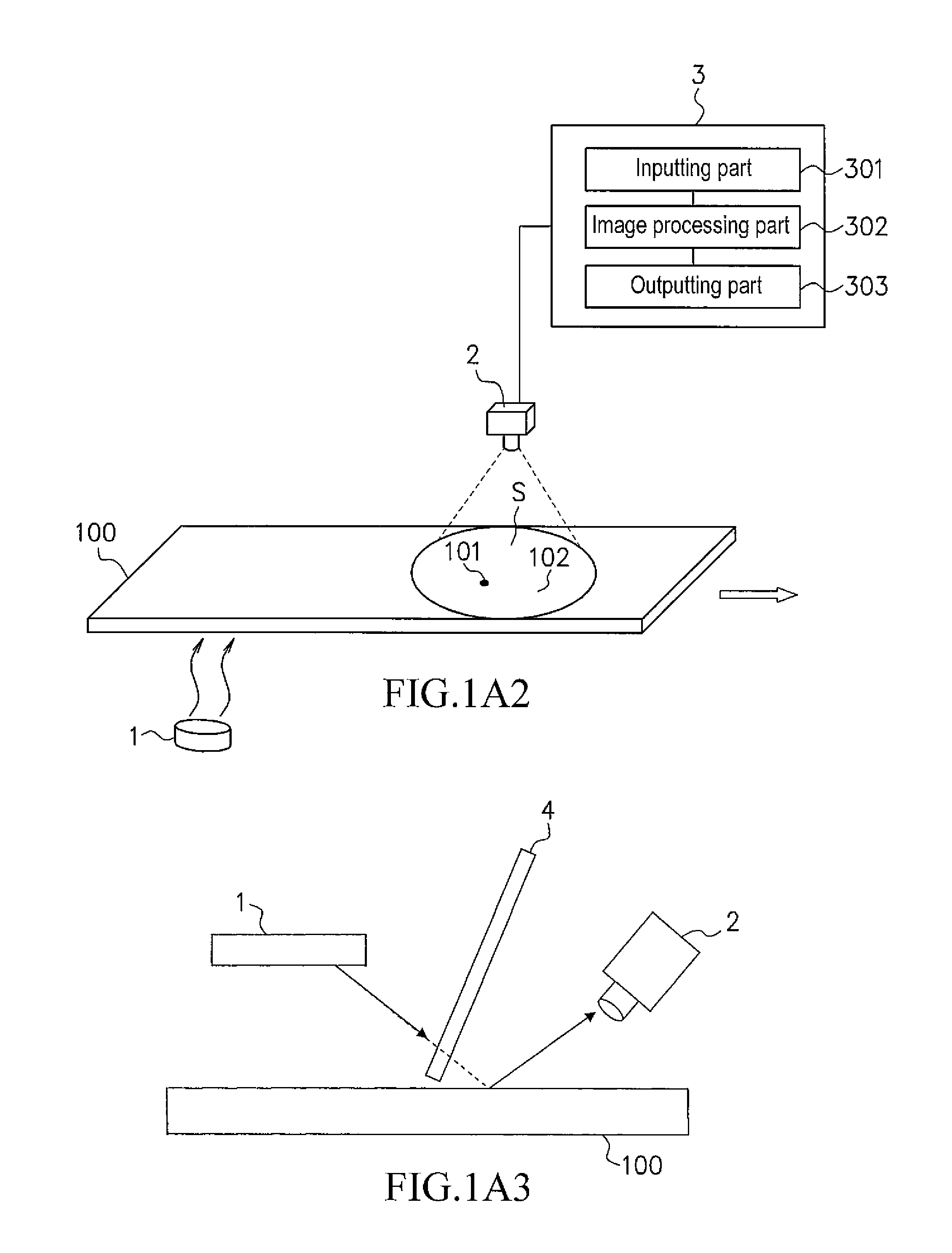
ActiveUS20110249700A1Improve accuracyRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansThermal energySurface layer
A defect on the surface or in the surface layer of a moving material can be detected by using a method comprising steps of: heating the surface of the material, obtaining thermal image data of the surface of the material using an infrared thermography camera while the surface of the material is being heated up at the heating step or being cooled down after heating, and detecting the defect by calculating Laplacian with respect to temperature of the surface represented by the thermal image data. When the thermal image data is obtained while the material is being heated up, a heating device and the camera is arranged so that thermal energy emitted from the heating device is reflected by the material to come into the camera.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com