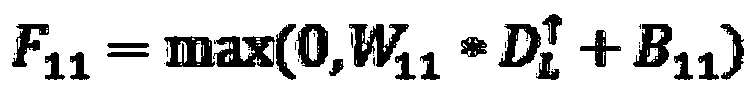Patents
Literature
159 results about "Color edge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
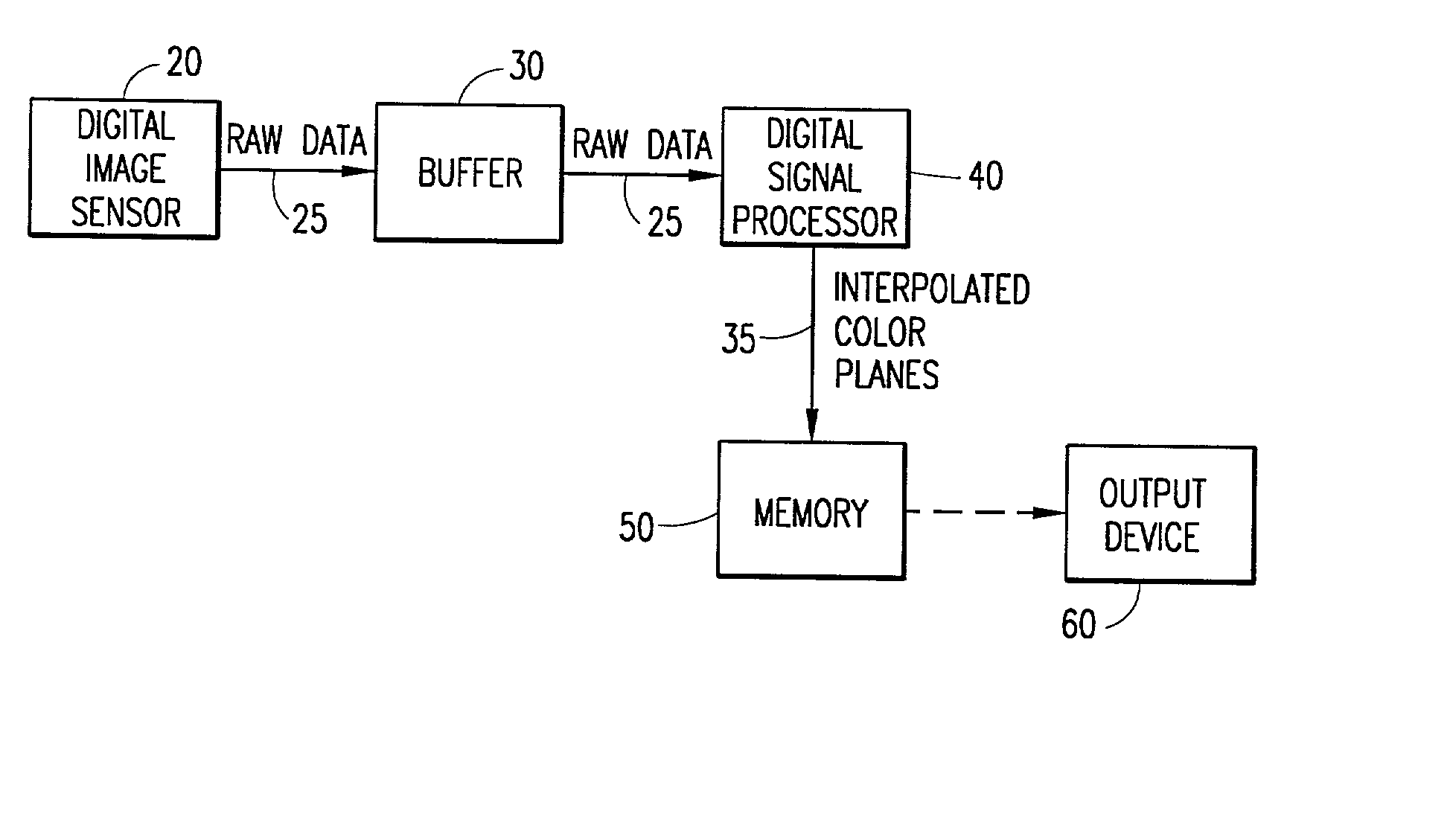
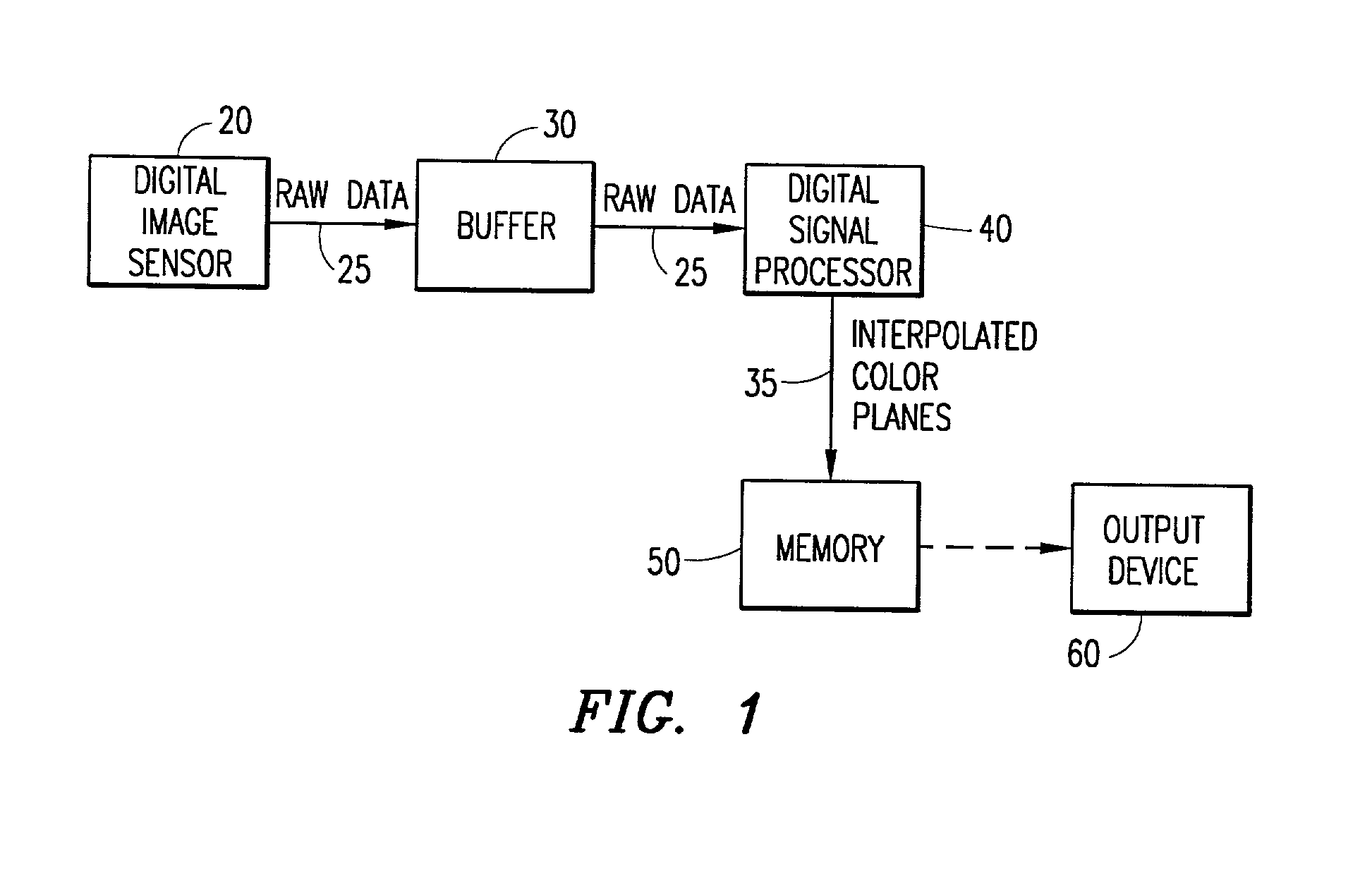
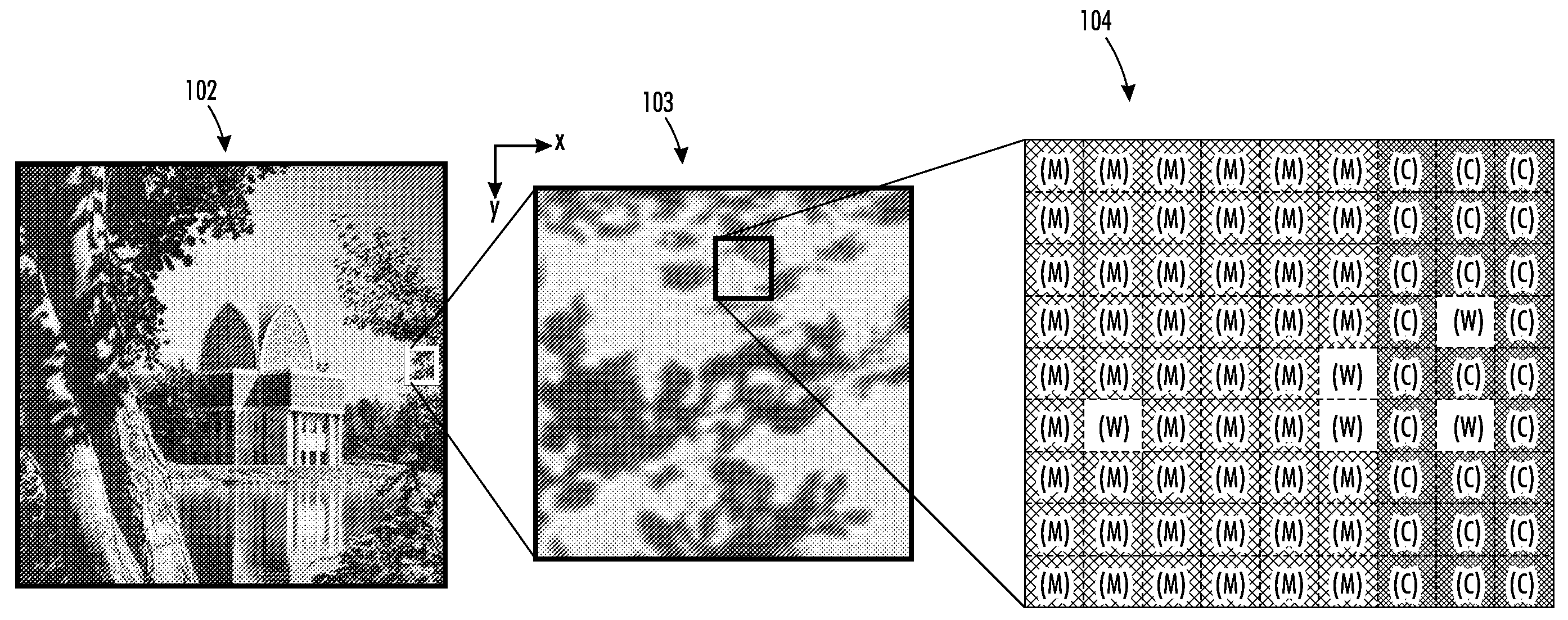
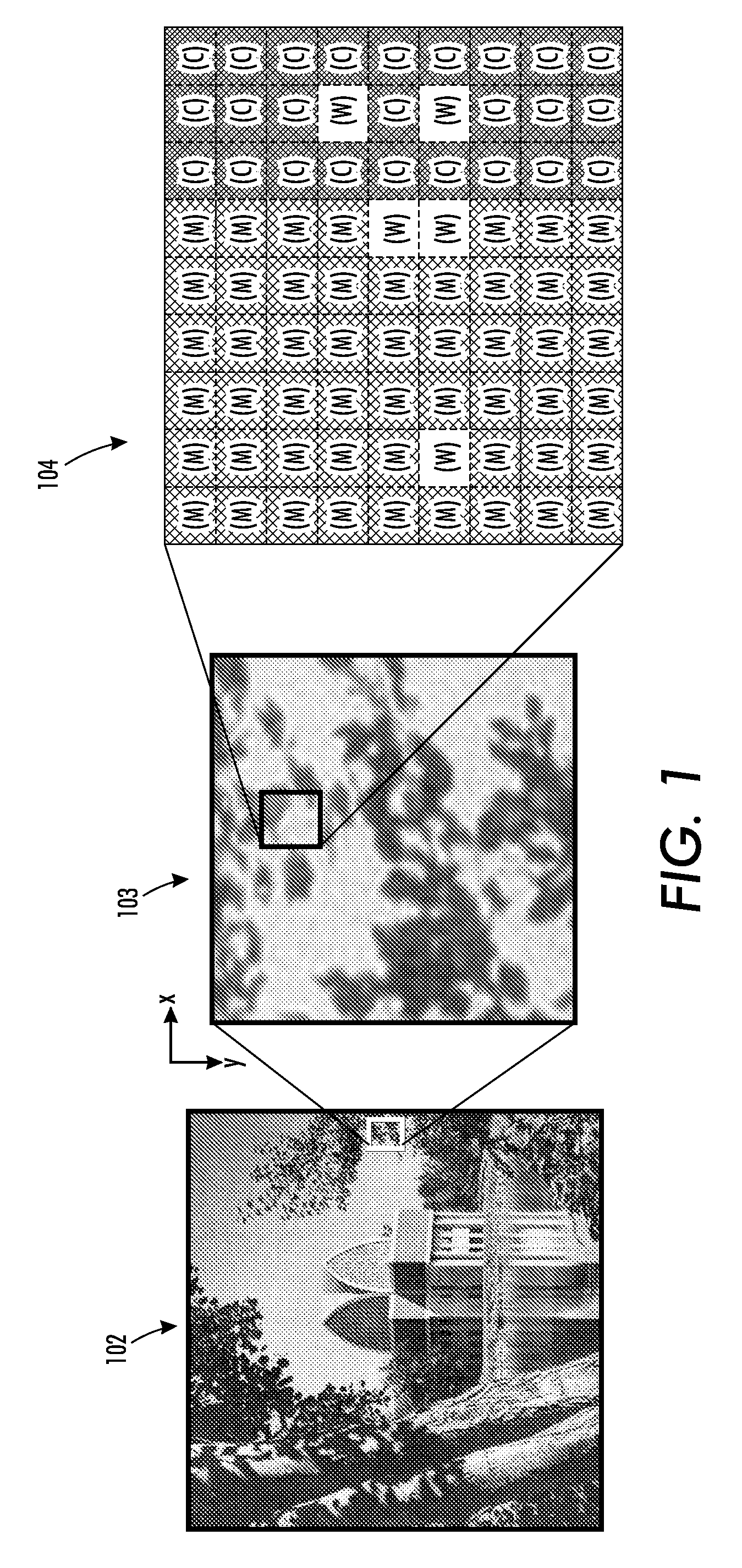
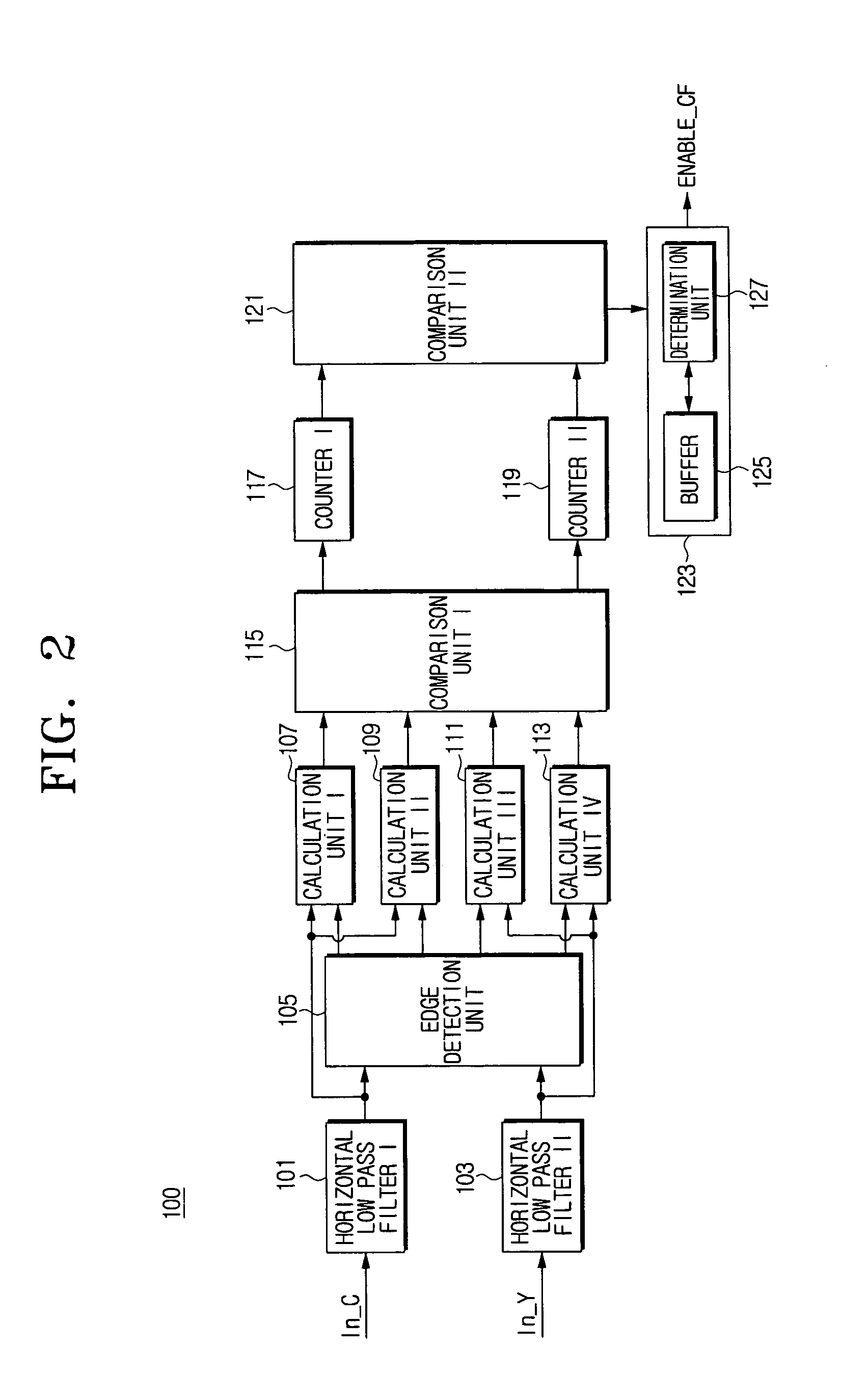
Digital image system and method for implementing an adaptive demosaicing method
InactiveUS7088392B2Reduce imbalanceAdaptive smoothingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSharpening
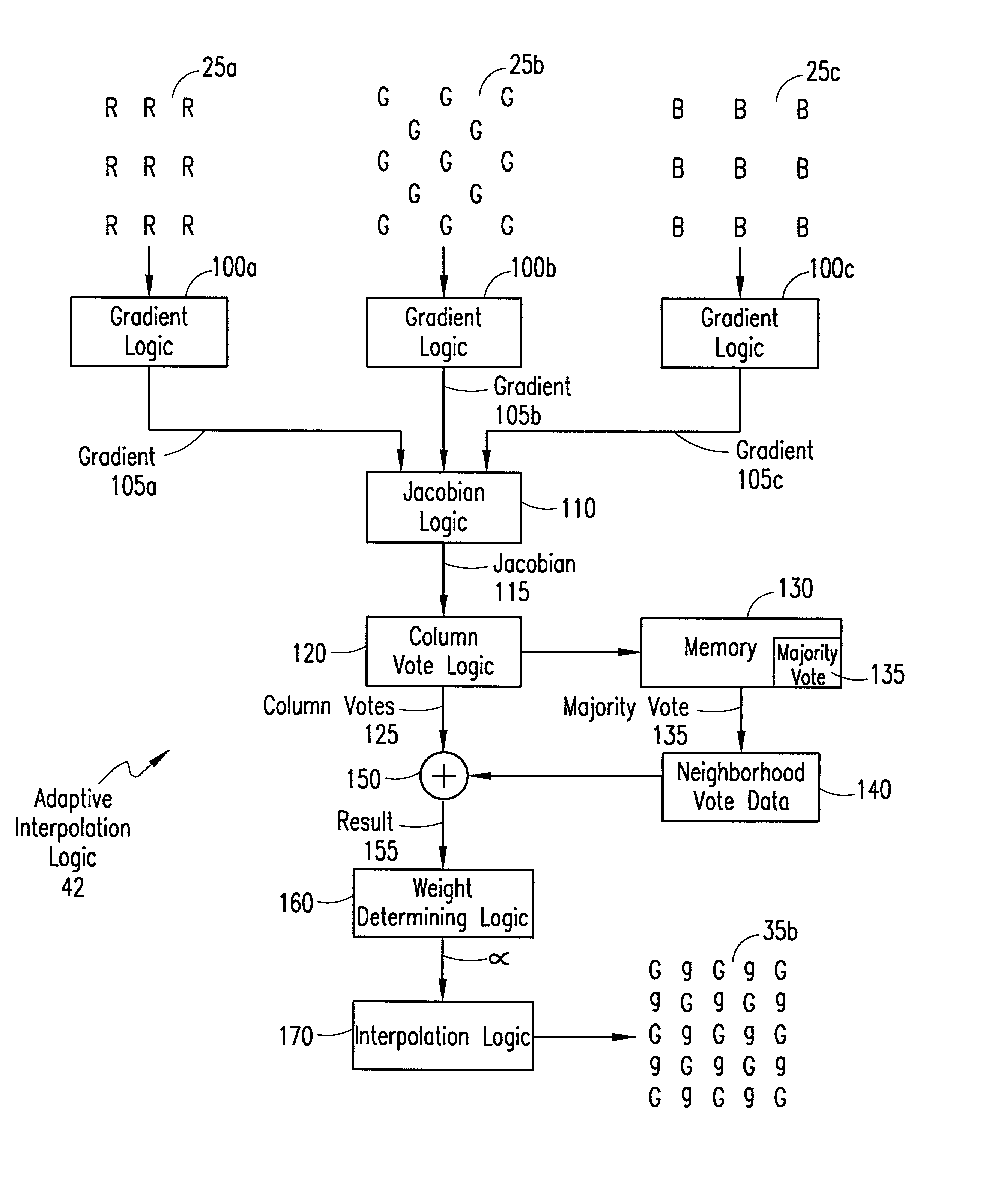
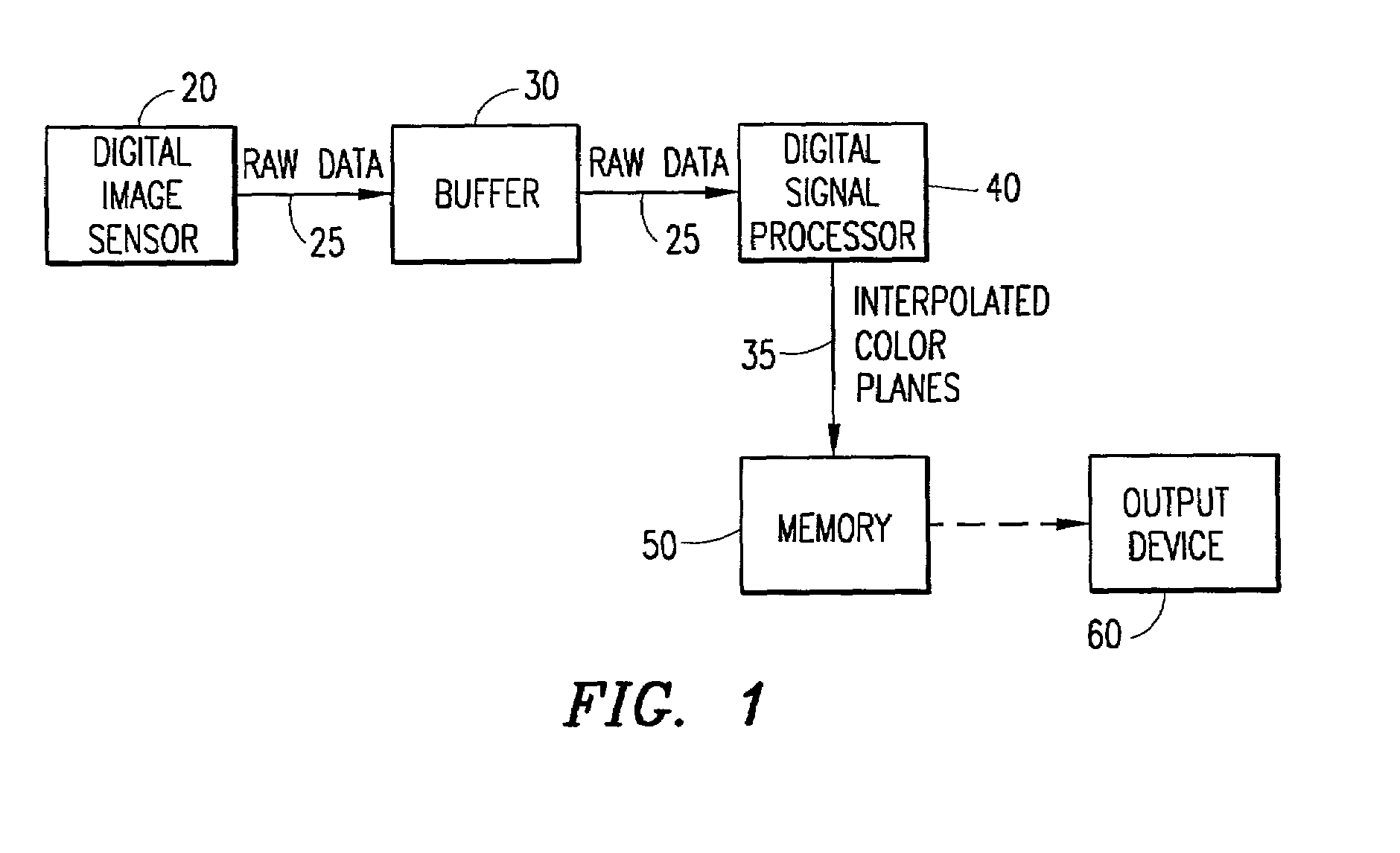
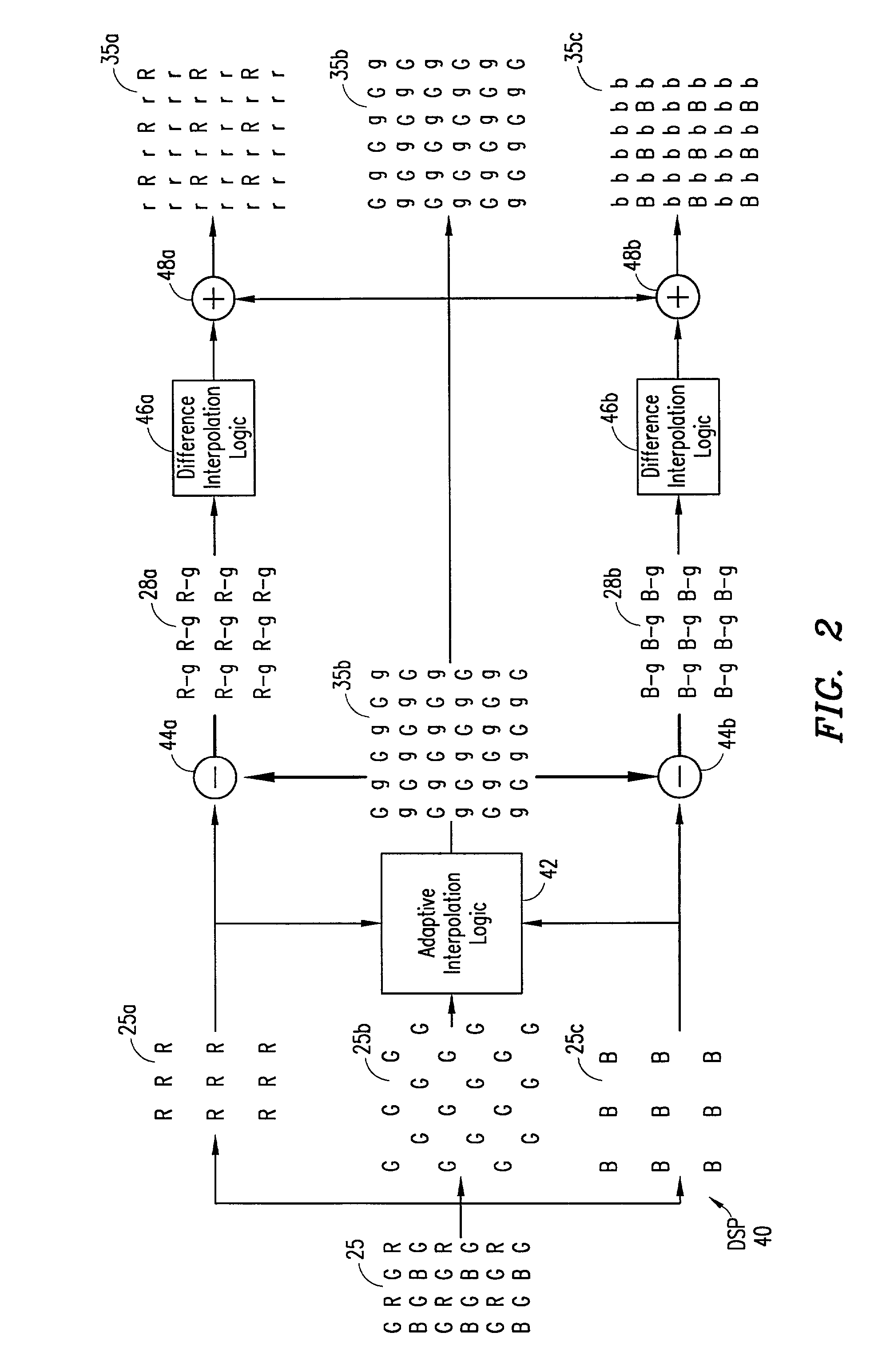
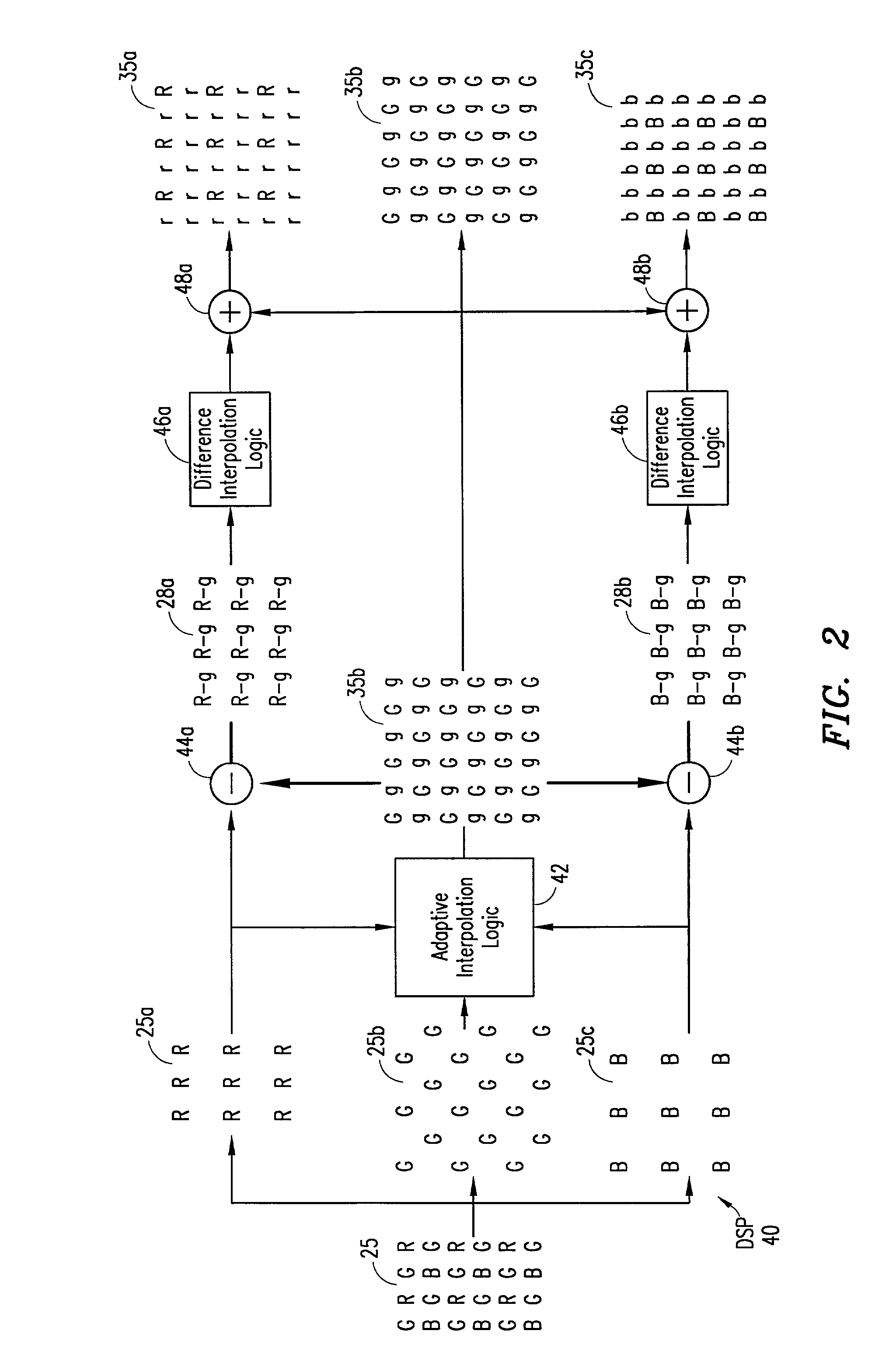
An adaptive demosaicing method interpolates images based on color edge detection and neighborhood voting. The adaptive demosaicing algorithm uses a voting scheme to determine the direction of interpolation at each missing luminance pixel location. Each color plane votes either horizontal or vertical based on a comparison between the horizontal and vertical components of the degree of change (i.e., gradient, Laplacian or other measure of the degree of change) in that color plane. Votes are counted from the neighborhood pixels as well as from measurements taken at the pixel location itself. Once the luminance plane is fully interpolated, the chrominance planes are filled in by simple bilinear or median interpolation of difference chrominance values. Enhancements to the adaptive demosaicing algorithm permit adaptive smoothing and sharpening.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
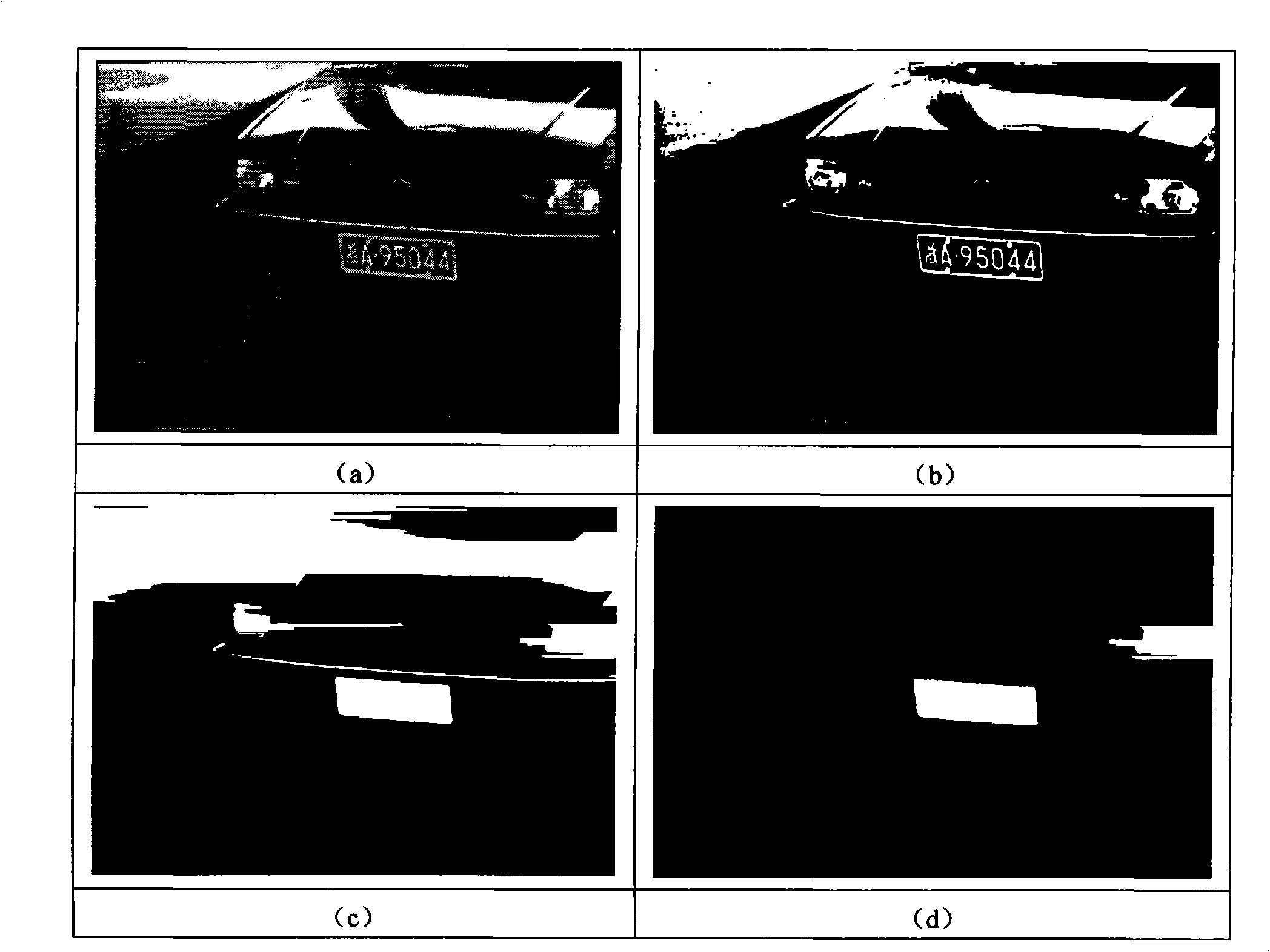
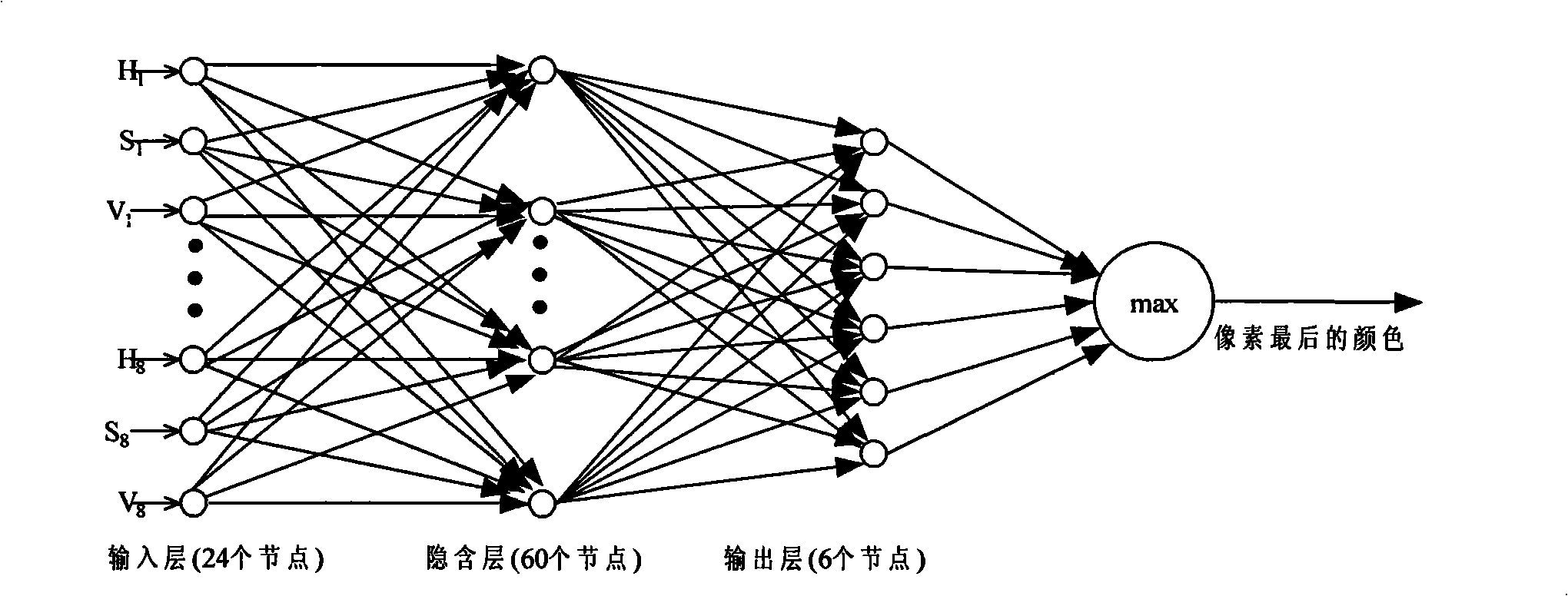
Method for locating license plate under a complicated background
InactiveCN101408942AReduce distractionsReduce complexityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionColor recognition
The invention discloses a method for locating a vehicle license plate in complex background. The method comprises the following steps: (1). Differentiating a gray scale mean of a fixed-size region and extracting a vehicle body image from a video; (2). preprocessing the vehicle body image such as gradation, gradient information enhancing, binarization and the like; (3). performing mathematical morphology operation on the processed vehicle body image, and performing primary screening by combining structural features of the vehicle license plate to obtain a plurality of candidate vehicle license plate regions; (4). converting the obtained candidate vehicle license plate regions into an HSV color spatial image; (5). adopting a BP neural network to perform color identification on the HSV color spatial candidate vehicle license plate image, and performing color edge detection by computing the mean color distance between two adjacent regions of a certain pixel; (6). judging edge color pair of an edge point, and eliminating the false vehicle license plate edge; and (7). performing final vehicle license plate location by the texture feature of the vehicle license plate. The method is suitable for complex background, and has higher location accuracy rate and higher robustness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Digital image system and method for implementing an adaptive demosaicing method
InactiveUS20030052981A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSharpening
An adaptive demosaicing method is disclosed that interpolates images based on color edge detection and neighborhood voting. The adaptive demosaicing algorithm uses a voting scheme to determine the direction of interpolation at each missing luminance pixel location. Each color plane votes either horizontal or vertical based on a comparison between the vertical and horizontal components of the degree of change (i.e., gradient, Laplacian or other measure of the degree of change) in that color plane. Votes are counted from the neighborhood pixels as well as from measurements taken at the pixel location itself. Once the luminance plane is fully interpolated, the chrominance planes are filled in by a simple bilinear or median interpolation of difference chrominance values. Enhancements to the adaptive demosaicing algorithm permit adaptive smoothing and sharpening.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
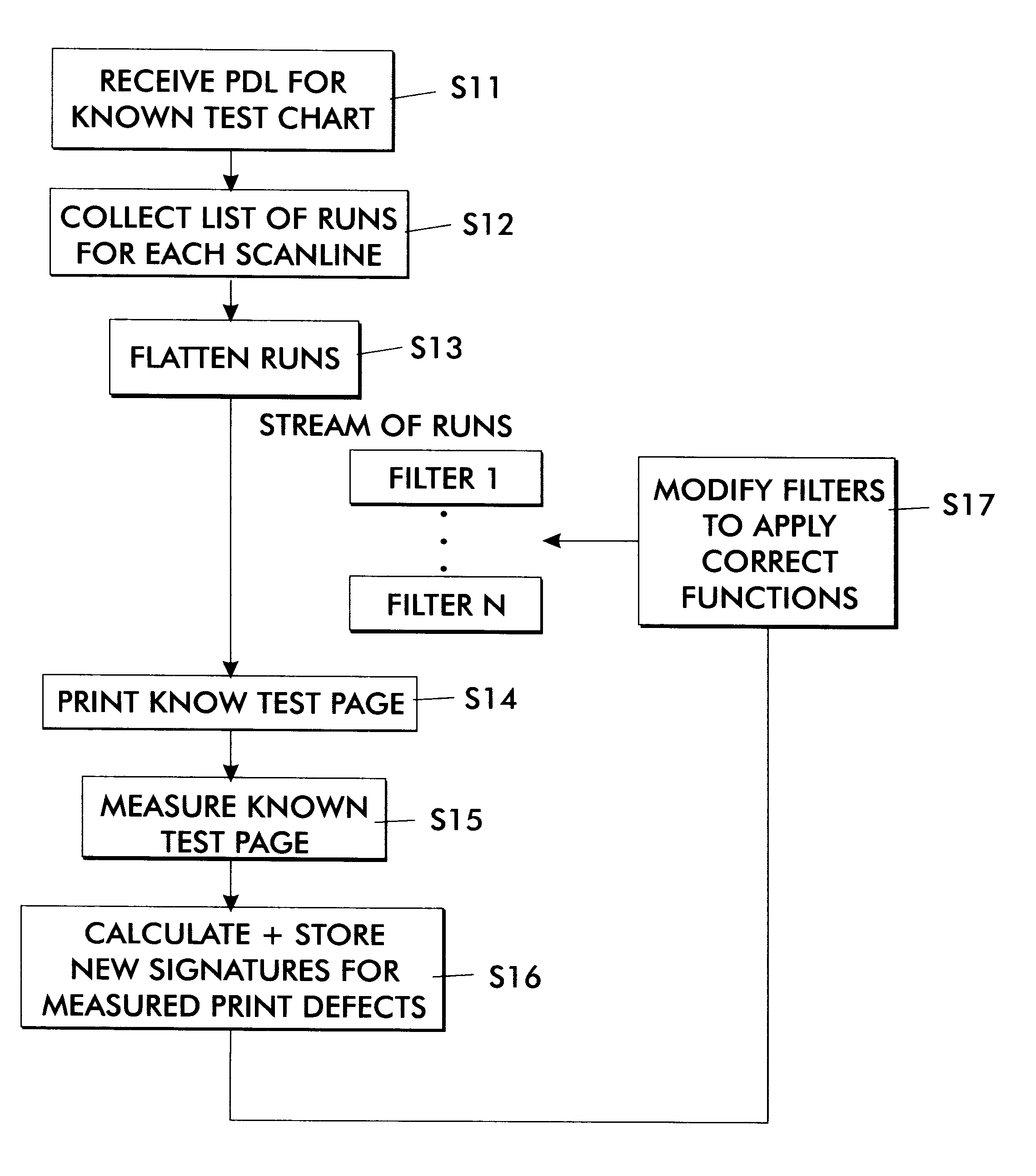
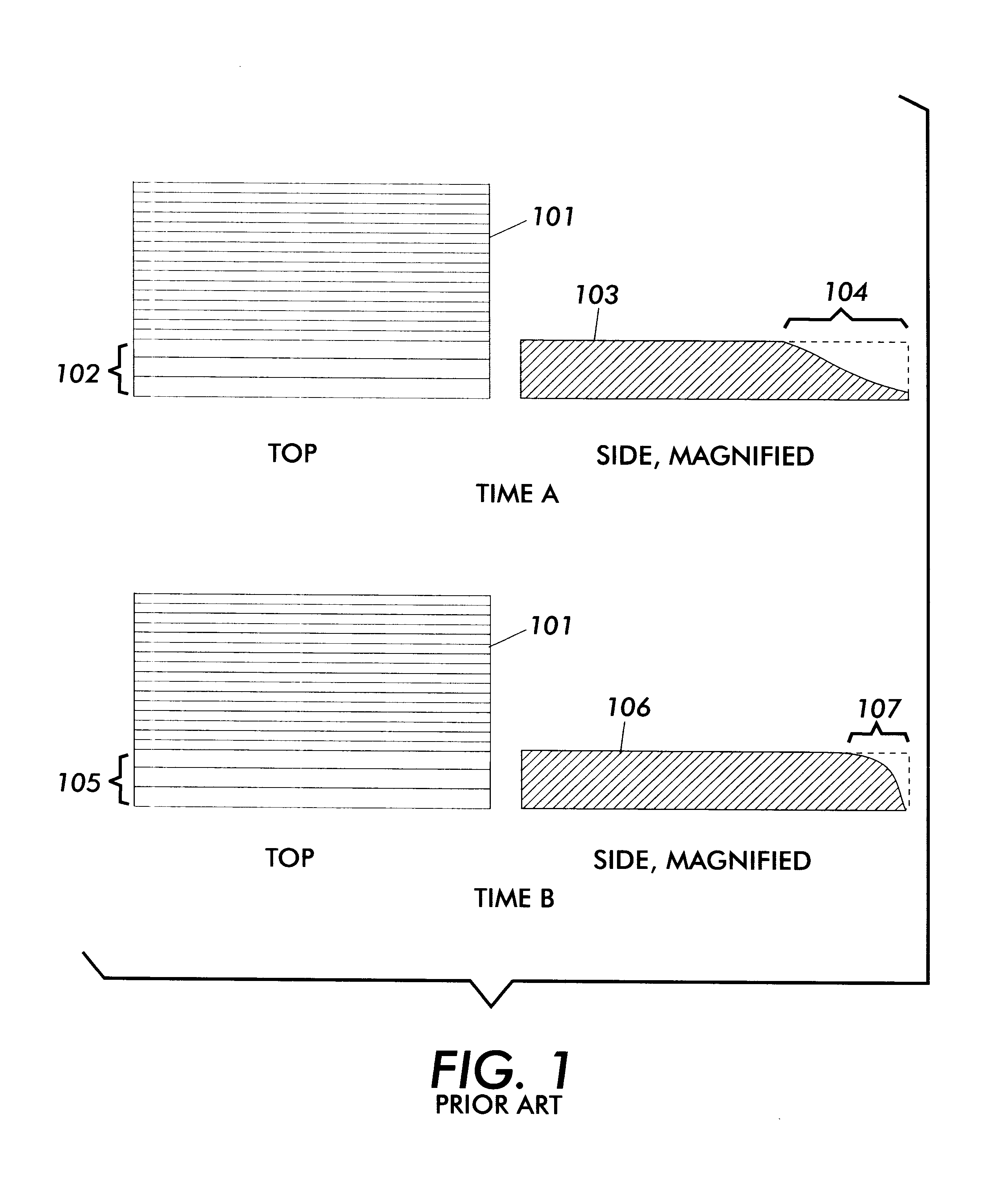
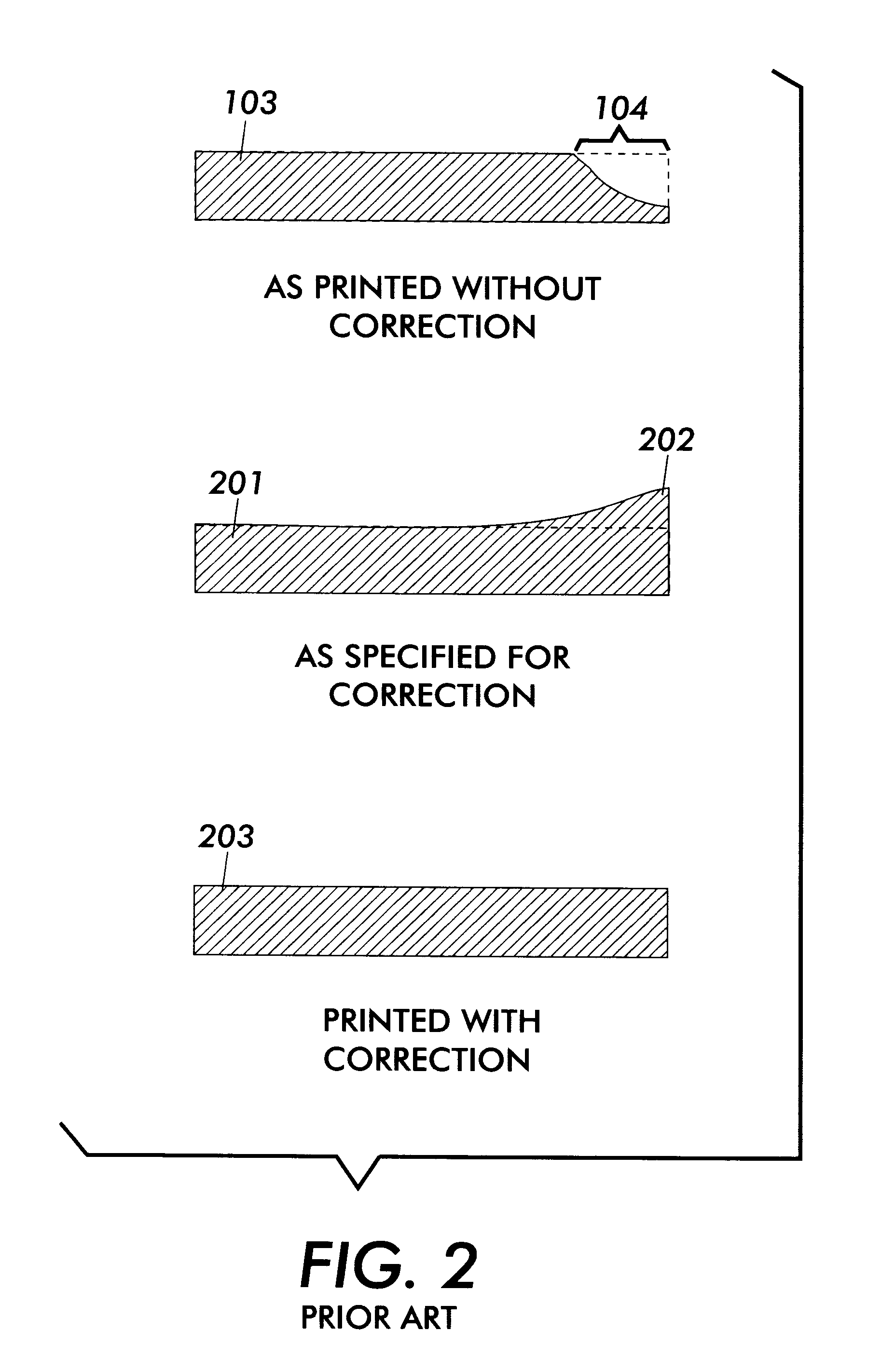
Anamorphic object optimized function application for printer defect pre-compensation
InactiveUS6341020B1Better addressImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersDigital dataHead movements
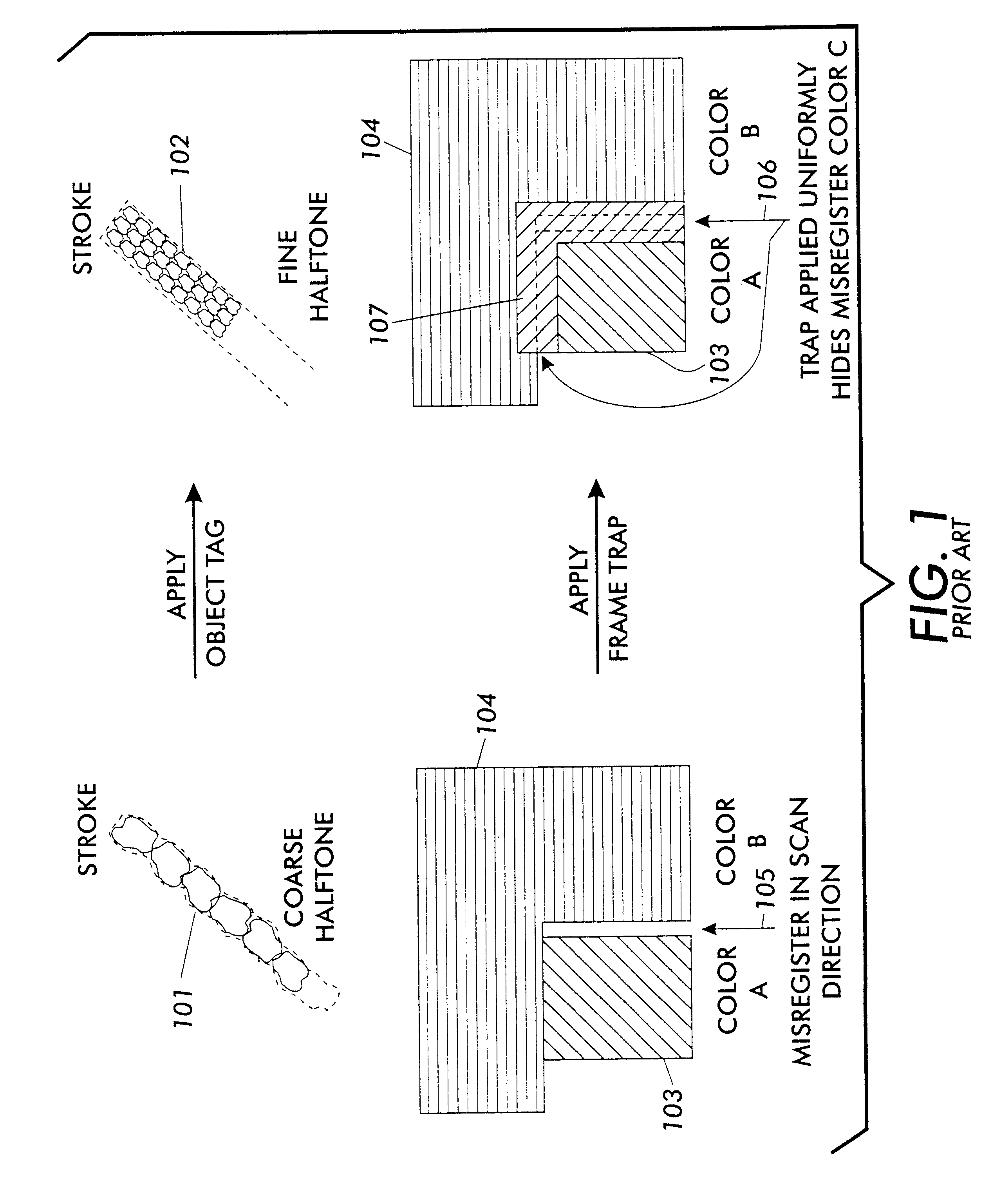
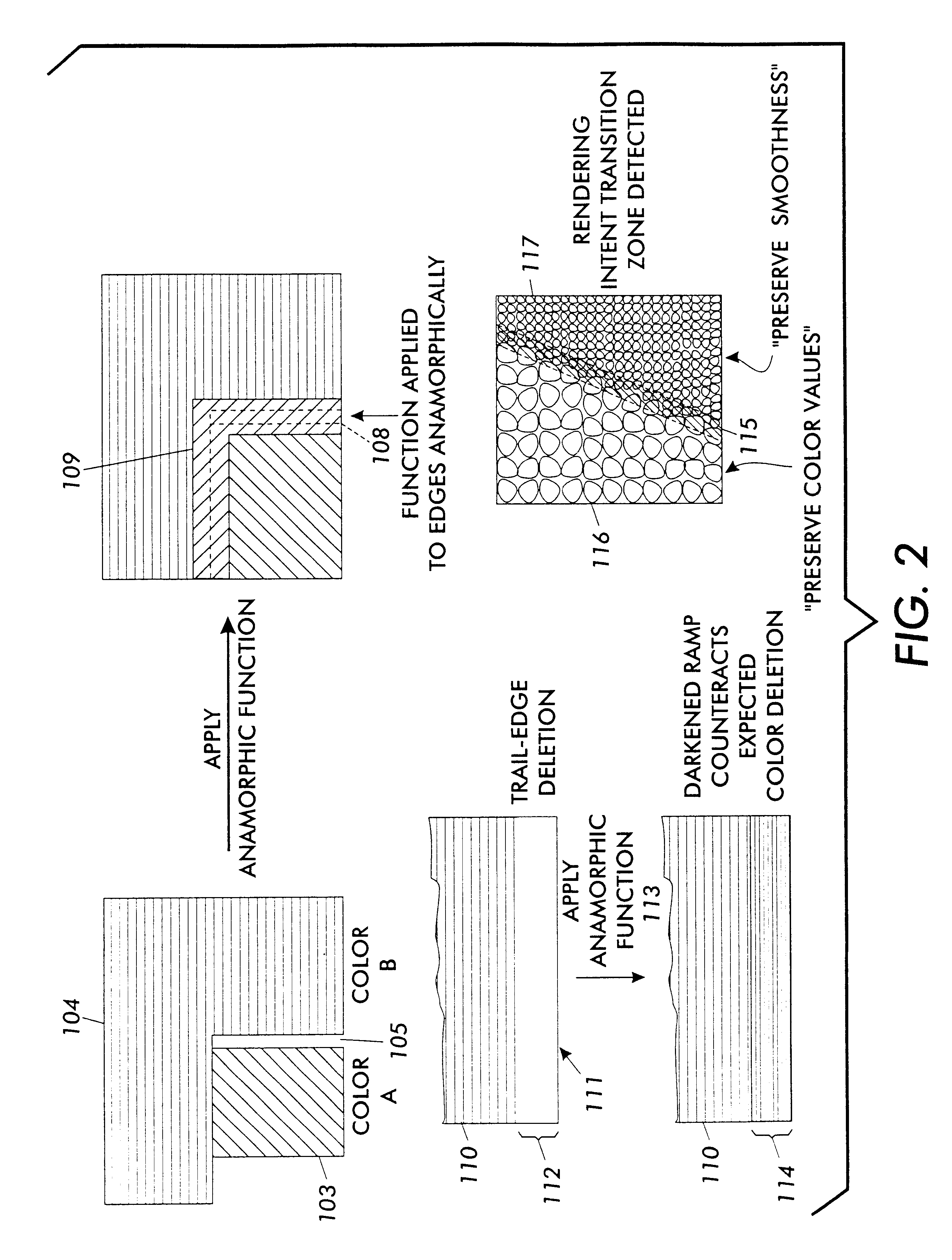
Every printing system has characteristic defects which detract from high quality printing. Xerographic printing systems show defects such as banding, mottled colors in large fill areas, trail-edge deletion and starvation where toner concentrations drop at certain color edges, misregistration, and so on. Ink jet printing systems can show ink bleeding, streaking in the direction of head movement, and so on. One approach to reducing printer defects is to refine the electro-mechanics for more precise printing. Another approach which works for predictable defects is to modify the digital data being sent to the printer to pre-compensate for the defect. The prior art does this to a limited extent for individual object types (strokes, fills, images, text, etc.) and for misregistered color edges (trapping). This invention extends the range of edge-related defects that can be both predicted and pre-compensated for. An embodiment of the invention is described which pre-compensates for defects such as trail-edge deletion, starvation, misregistration, halo, etc. by identifying runs of color which meet the criteria likely to cause the effect and applying a function f(edge-distance, object-type) to such runs to modify them appropriately. Both the prediction criteria and the functions applied are anamorphic (the scan direction and process direction are treated differently) and object-optimized (object attributes are taken into account). Further, both prediction criteria and applied correction functions allow user-settable input.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Organic light emitting display panel and display device
ActiveCN107123394AImproved aliasing effectImprove color fringing effectStatic indicating devicesIdentification meansCapacitanceDisplay device
The invention discloses an organic light emitting display panel and a display device. A part, near a non-display area, in a display area for light emitting display is defined as a display area edge, and a pixel on the display area edge is provided with a first capacitor related to a grid of a driving transistor in the pixel; a part, except the display area edge, in the display area is defined as a display area remainder, and a pixel on the display area remainder is provided with a second capacitor related to a grid of a driving transistor in the pixel; a capacitance value of the first capacitor is set to be different from that of the second capacitor, namely, the first capacitor in the pixel on the display area edge and the second capacitor in the pixel on the display area remainder are designed differently; the brightness of the pixel on the display area edge is lower than that of the pixel on the display area remainder, then the color contrast between the display area edge and the non-display area can be reduced, and a sawtooth effect and a color edge effect of the organic light emitting display panel can be relieved.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Color edge based system and method for determination of 3d surface topology
InactiveUS20070085849A1Television system scanning detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSingle image3d surfaces
A method and system for determining surface topology of a three-dimensional (3D) structure, based on a structured pattern that is projected onto the surface structure, and images of the pattern superposed on the structured surface are analysed to provide surface coordinates of the structure. The pattern comprises a plurality of unique color edges defined between pairs of differently-colored stripes, which substantially overcomes ambiguity problems. In one embodiment, a calibration method is provided enabling the surface coordinates to be obtained from a single image of the structure.
Owner:C M D CONTROLLED MICRO DEVICES +1
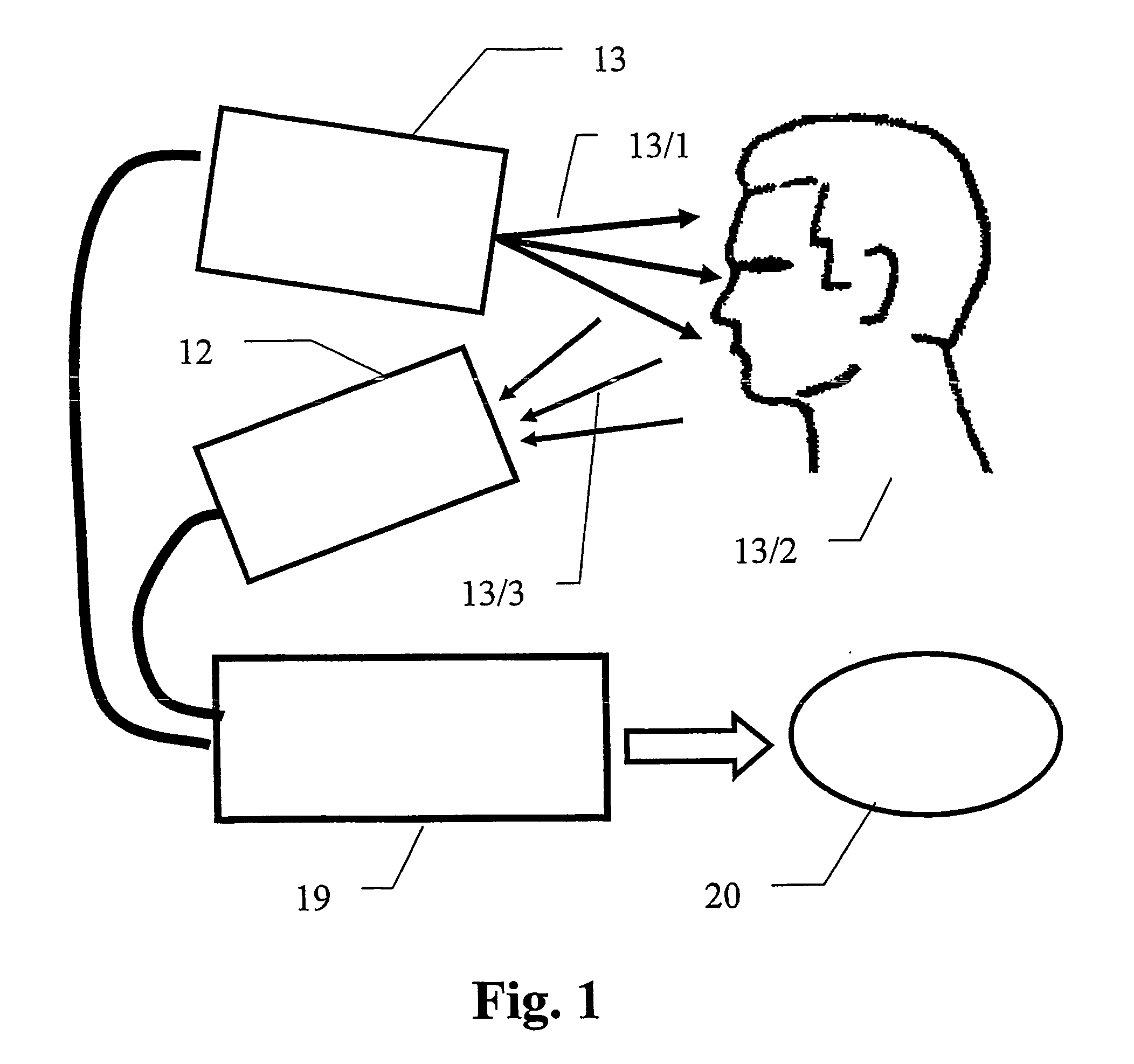
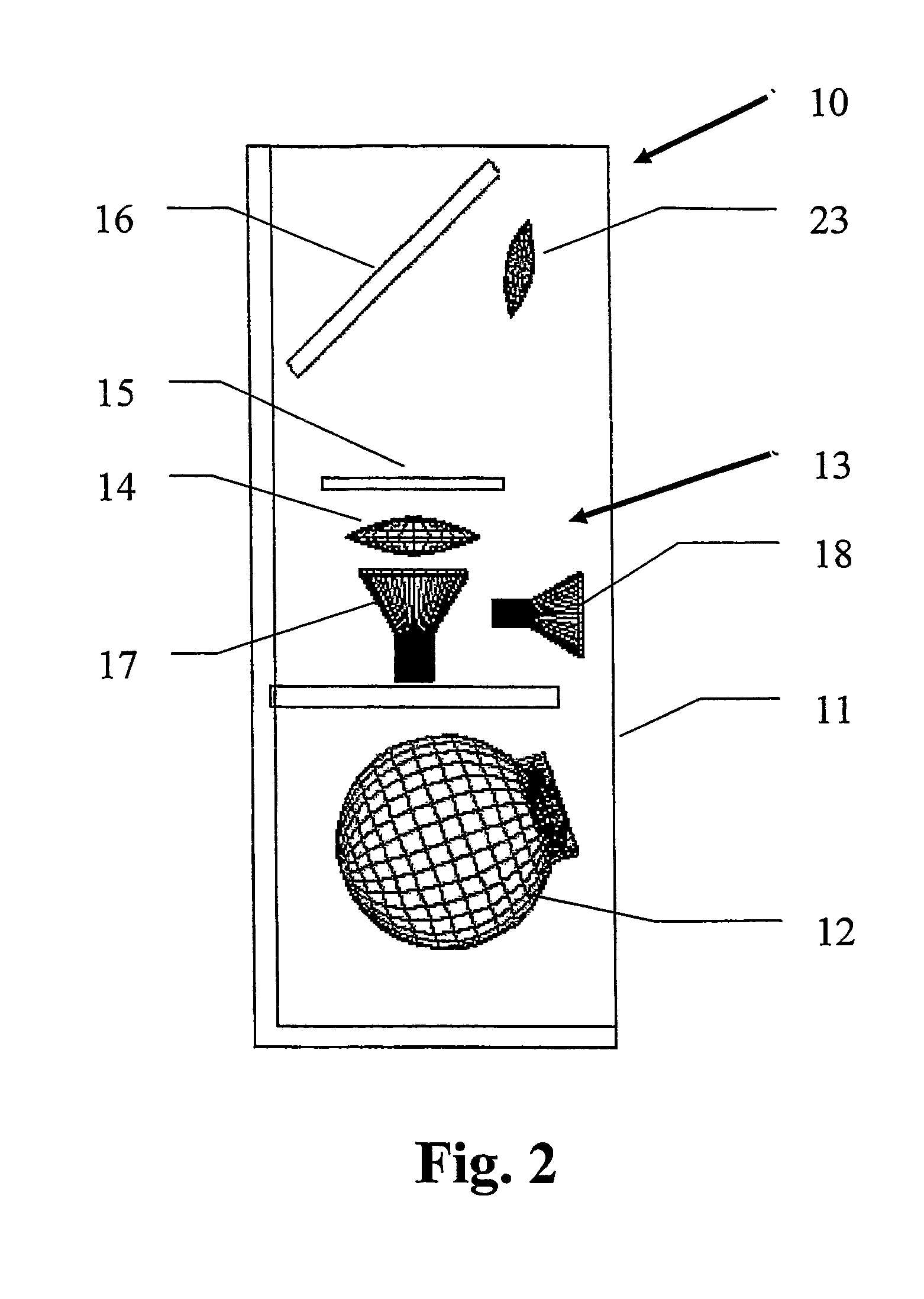
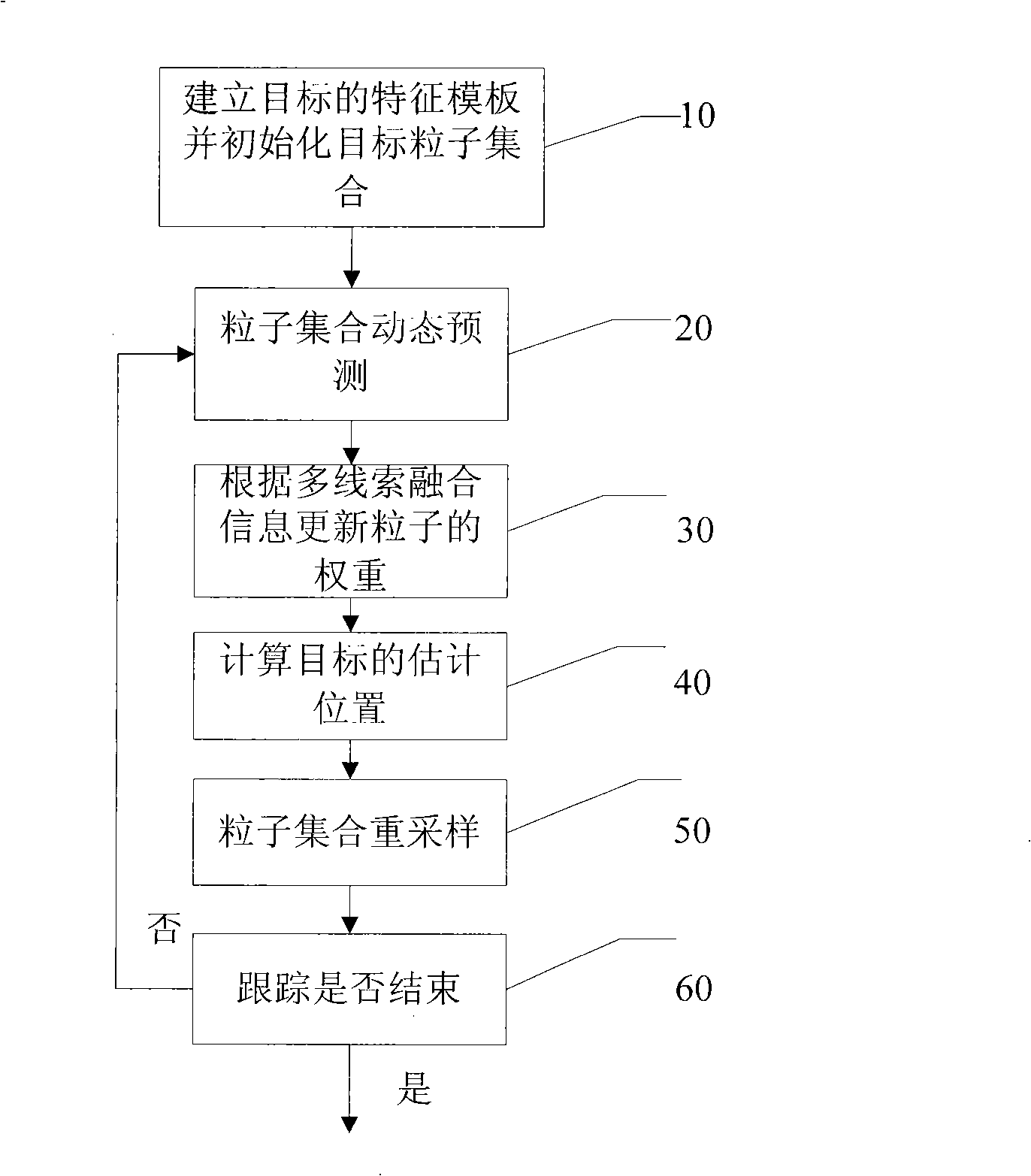
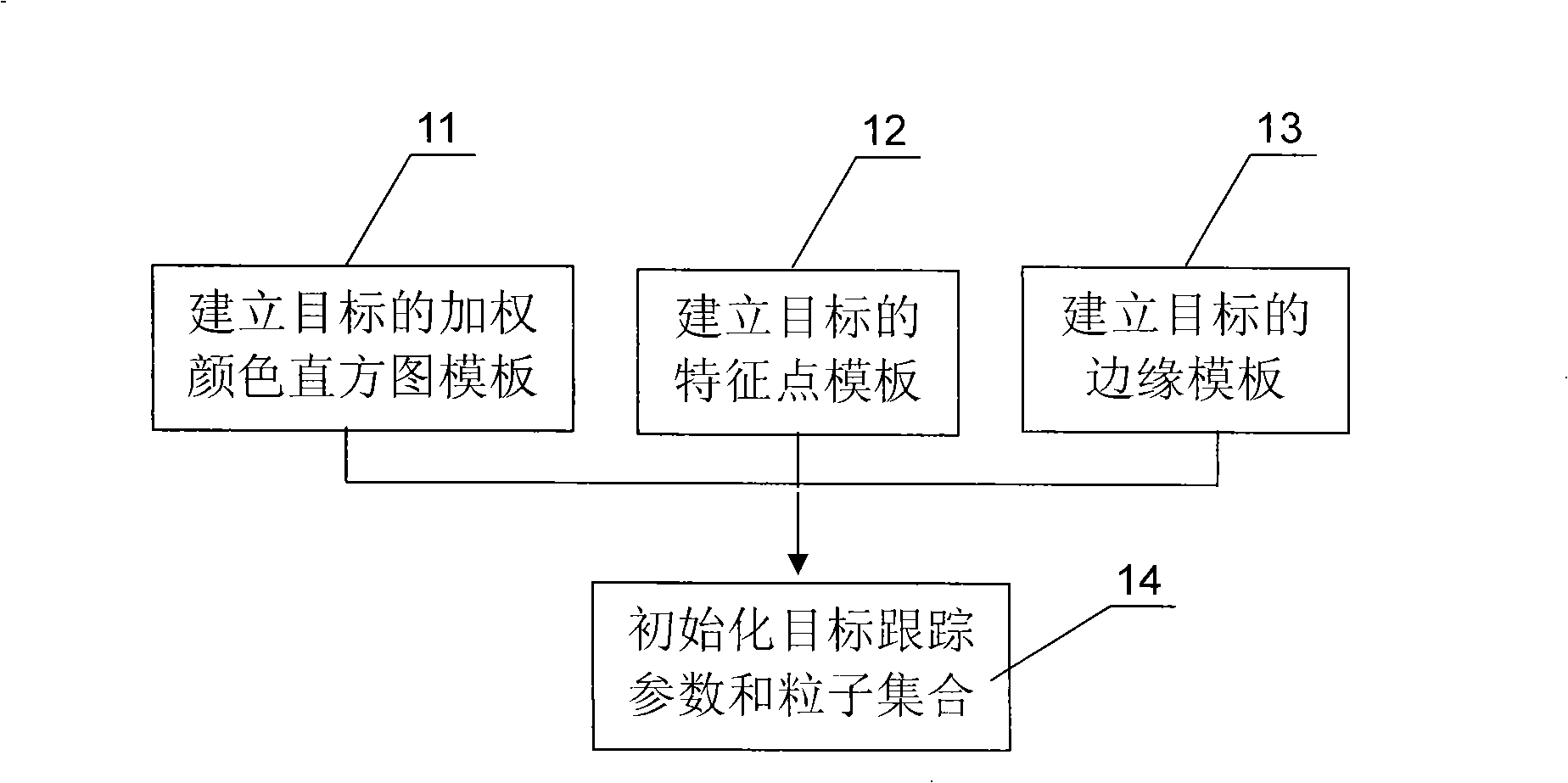
Target tracking method and device based on video
InactiveCN101404086AThe description is validEffectively deal with "multi-peak" phenomenonImage analysisRadiologyNuclear medicine
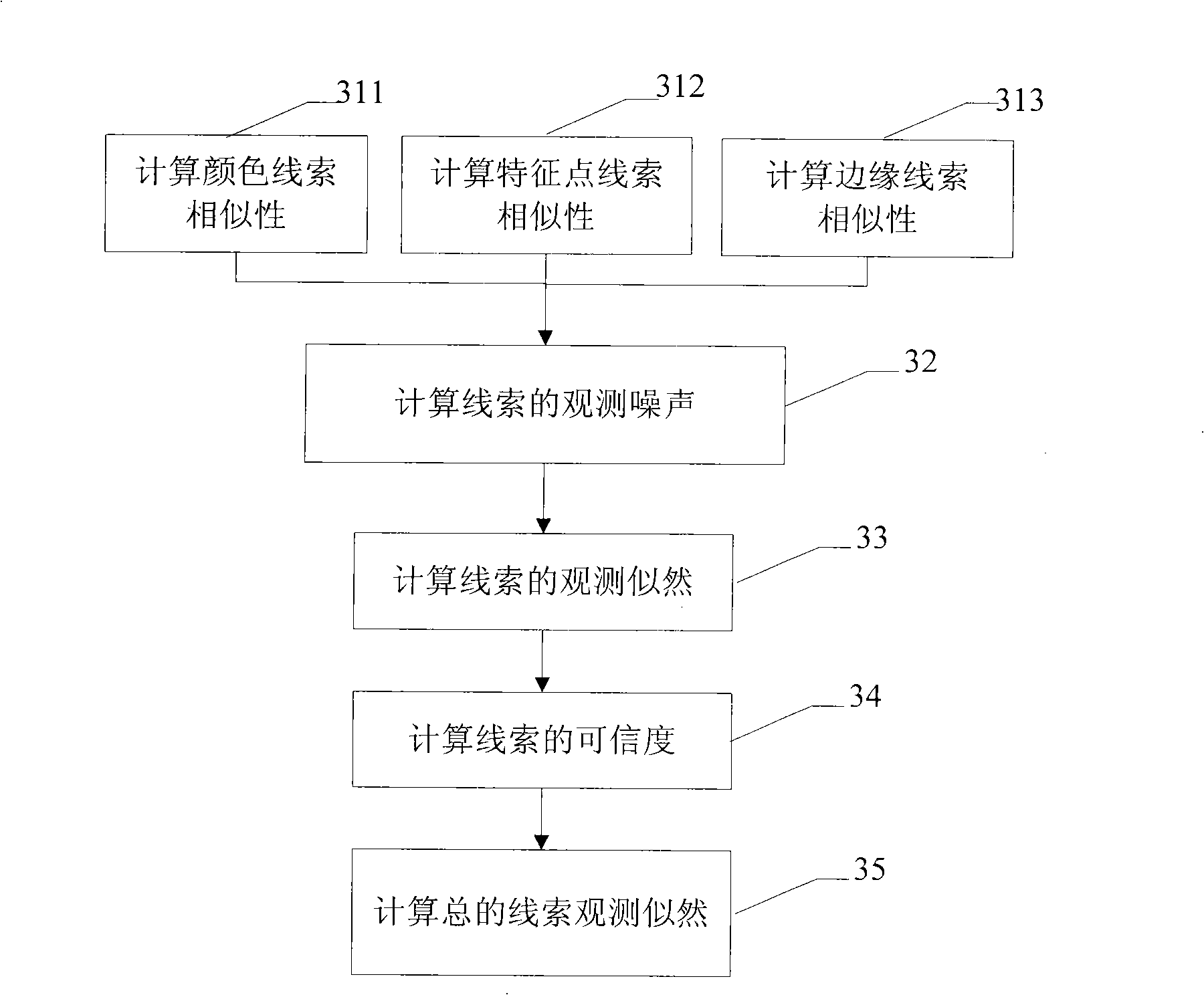
The invention discloses a video target tracking method which is based on multi-cue integration and particle filtration and a device thereof. The method carries out the self-adaptive integration according to three cues of color, edge and feature points to obtain target observation information, then the particle filtration technology is used for updating the target state, and the specific steps comprise: A. a target template is extracted and target parameters are initialized; B. dynamic prediction is carried out on a particle set according to a motion model; C. the particle weight is updated according to multi-cue integration information; D. the motion state of a target is updated. The video target tracking method and the device can improve the tracking effect and the tracking stability of the moving target under the complex environment and the tracked target can comprise human heads, pedestrians, cars, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Color filter and LCD
InactiveCN101782697AImprove the display effectSmooth transitionOptical filtersNon-linear opticsLight filterColor filter array
The invention provides a color filter and an LCD. The invention relates to a color filer applied to an LCD with arc-shaped display edge. The color edge comprises a color filter area which comprises an edge display area close to the arc-shaped display edge; the edge display area comprises at least one first pixel block, areas of photo-permeable parts of sub-pixel units of the first pixel block are the same and the photo-permeable parts are arranged in a terraced manner along the arc-shaped display edge. In the embodiment of the invention, the color filter is free from mixed color and large sawtooth edge formed due to terraced arrangement of the pixel block in the prior art is greatly weakened, so that the arch-shaped edge of the edge display area features smooth transition, thus improving display effect of the edge display area.
Owner:TRULY SEMICON
Color edge based system and method for determination of 3D surface topology
InactiveUS7456842B2Television system scanning detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A method and system for determining surface topology of a three-dimensional (3D) structure, based on a structured pattern that is projected onto the surface structure, and images of the pattern superposed on the structured surface are analysed to provide surface coordinates of the structure. The pattern comprises a plurality of unique color edges defined between pairs of differently-colored stripes, which substantially overcomes ambiguity problems. In one embodiment, a calibration method is provided enabling the surface coordinates to be obtained from a single image of the structure.
Owner:C M D CONTROLLED MICRO DEVICES +1
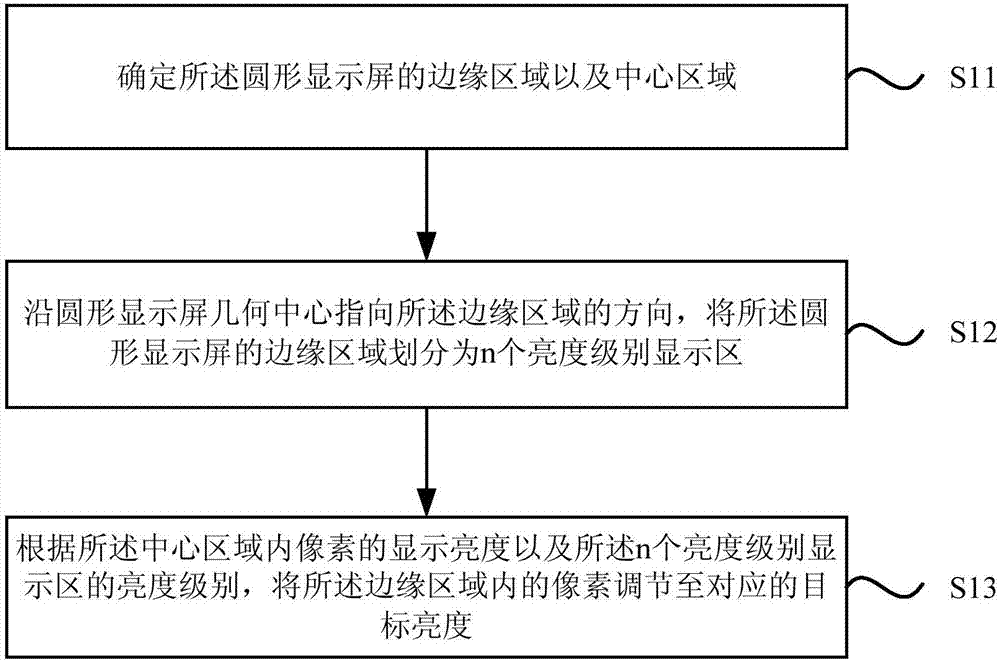
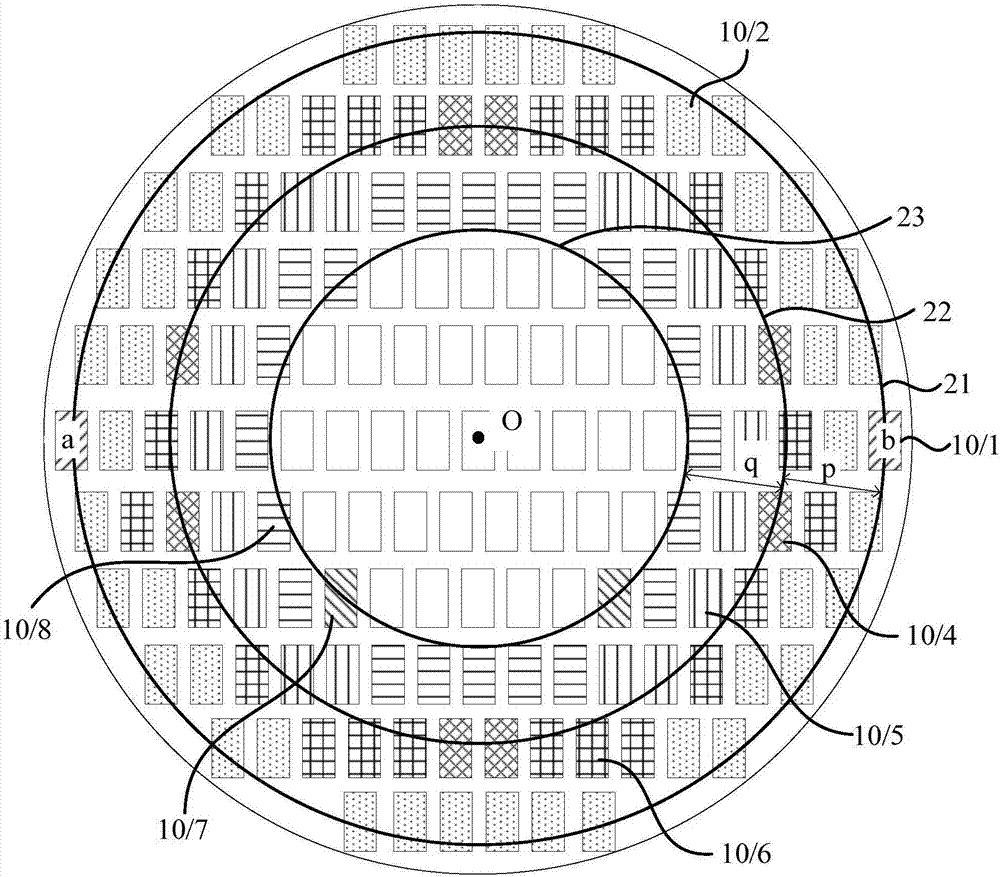
Method for improving edge display effect of circular display screen
ActiveCN107103893AReduce brightnessCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Pixel brightness
The invention discloses a method for improving the edge display effect of a circular display screen. The method includes: determining the edge area and the central area of the circular display screen; dividing the edge area of the circular display screen into display areas of n brightness levels along a direction pointing from the geometrical center to the edge area; adjusting pixels in the edge area to corresponding target brightness according to the display brightness of pixels in the central area and the brightness levels of the display areas. By the method, the brightness of the pixels in the edge area is allowed to be lower than that of the central area, the brightness of the pixels in the display areas in the edge area sequentially decreases along the direction pointing from the central area to the edge area, and the problems of edge aliasing, color edges and bright edges of the circular display screen are improved.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Achieving system stability in anamorphic printer defect pre-compensation
InactiveUS6304278B1Easy to trackChange trackOther printing apparatusPictoral communicationHead movementsDigital data
Every printing system has characteristic defects which detract from high quality printing. Xerographic printing systems show defects such as banding, mottled colors in large fill areas, trail-edge deletion and starvation where toner concentrations deplete at certain color edges, misregistration, and so on. Ink jet printing systems can show ink bleeding, streaking in the direction of head movement, and so on. If a printer defect occurs predictably, it is possible to pre-compensate for the defect by modifying the digital signal in such a way that the modifications cancel out or hide the expected defect. However, most printing defects, while statistically predictable, vary over time in the severity and extent of the defect. Some defects, such as misregistration, may vary in severity and direction with each print, because the defect is caused in part by paper feeding and shifting during printing. Other defects, such as trail-edge deletion, starvation, halo, tenting, etc. may change more slowly because they are controlled in part by environmental conditions such as humidity or definable printing conditions like paper type. The invention proposes a method whereby defects that vary sufficiently slowly in a particular printing system are measured for extent and severity at appropriate intervals, and the measurements are used to modify correction functions applied to the digital data to pre-compensate for these defects. In this way, the corrections applied will track more precisely the current extent and direction of the defects they are correcting.
Owner:XEROX CORP
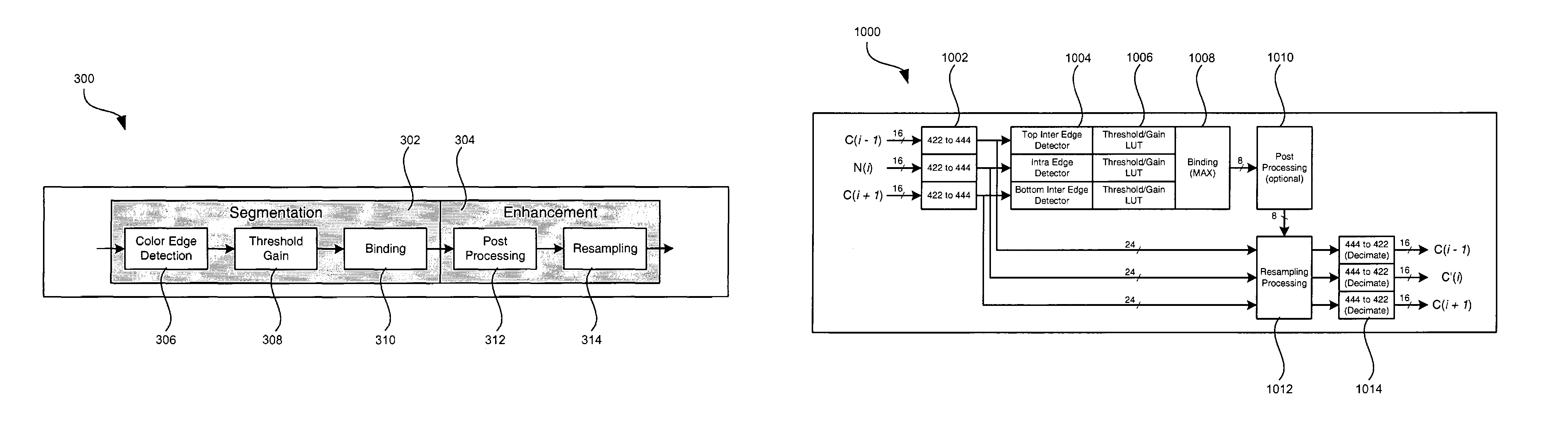
Method and system for converting interlaced formatted video to progressive scan video using a color edge detection scheme
InactiveUS7057664B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsProgressive scanInterlaced video
Aspects of the invention for converting interlace formatted video to progressive scan video, may include a color edge detector block (306) adapted to determined edges in interlaced formatted video. A threshold and gain processor block (308) coupled to the color edge detector block (306) may be adapted to quantify a likelihood of motion for each pixel comprising at least a portion of the interlaced scanned video using a motion value. A binder block (310) coupled to the threshold and gain processor block (308) may be configured to combine the motion value for each component of a luminance and chrominance of each of the pixels. A resampler block (314) may be coupled to the binder to determine an actual pixel value. The resampler block (314) may include at least one of a vertical and a horizontal filter adapted to determine an actual value of each of the pixels in at least a portion of the interlaced scanned video. A post-processor block (312) may be coupled to the binder block (310) and the resampler block (314) and adapted to remove unwanted signals such as noise from signals generated by the binder block (310).
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Detecting and compensating for color misregistration produced by a color scanner
InactiveUS20050069220A1Character and pattern recognitionColour-separation/tonal-correctionComputer visionComputer science
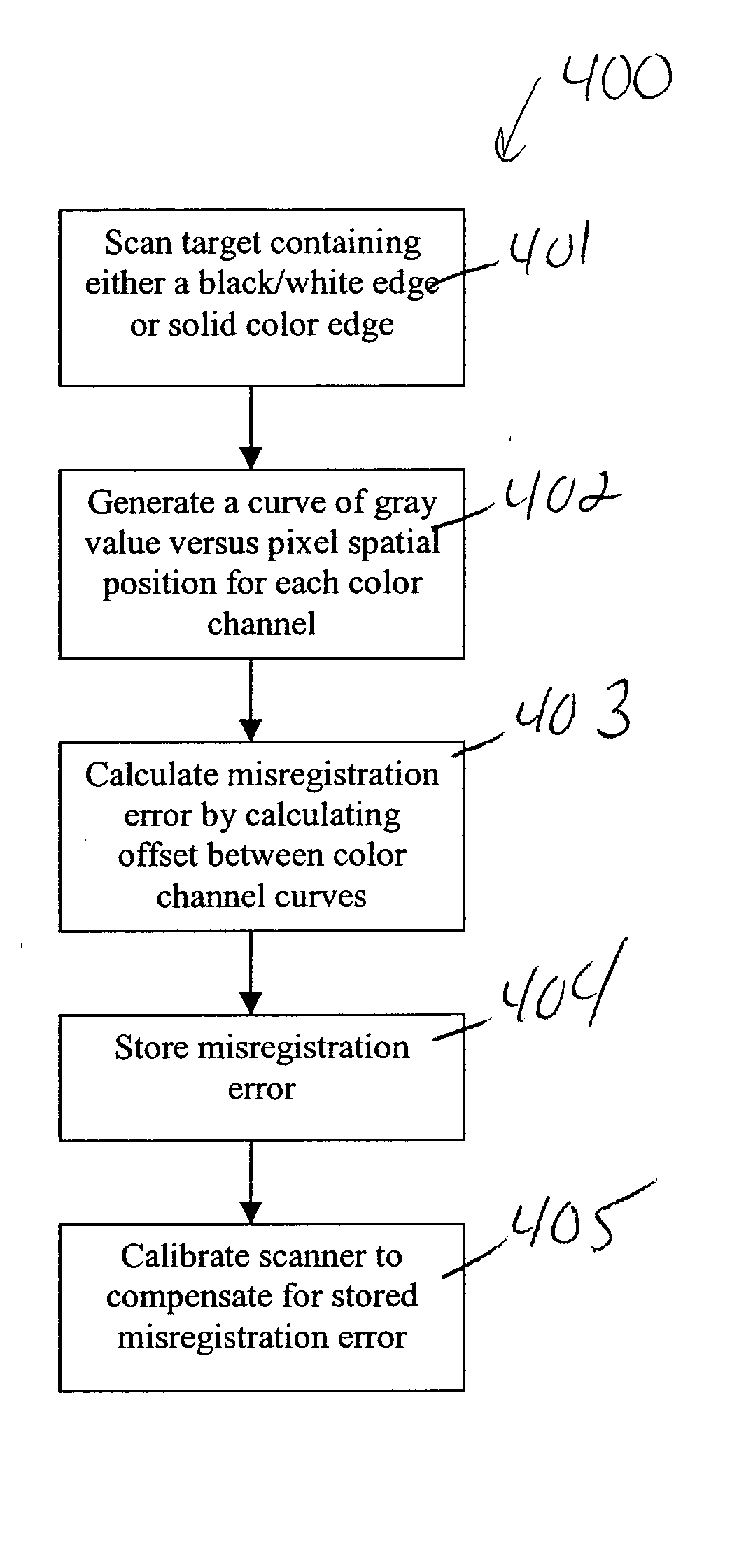
A method, computer program product and system for detecting and compensating for color misregistration. A black / white edge or a solid color edge on a target may be scanned. A black / white edge may refer to a black image, e.g., black text, on a white surrounding background having a rapid spatial transition from black to white. A solid color edge may refer to a solid color image, e.g., solid color text, on a white surrounding background having a rapid spatial transition from color to white. A curve of gray values versus spatial pixel positions for each color channel, e.g., red, green and blue color channels, may be generated. A misregistration error may then be calculated by calculating the offset between the color channel curves. The misregistration error may then be used to calibrate the scanner to compensate for the detected color misregistration.
Owner:RICOH KK
Systems and methods for object detection
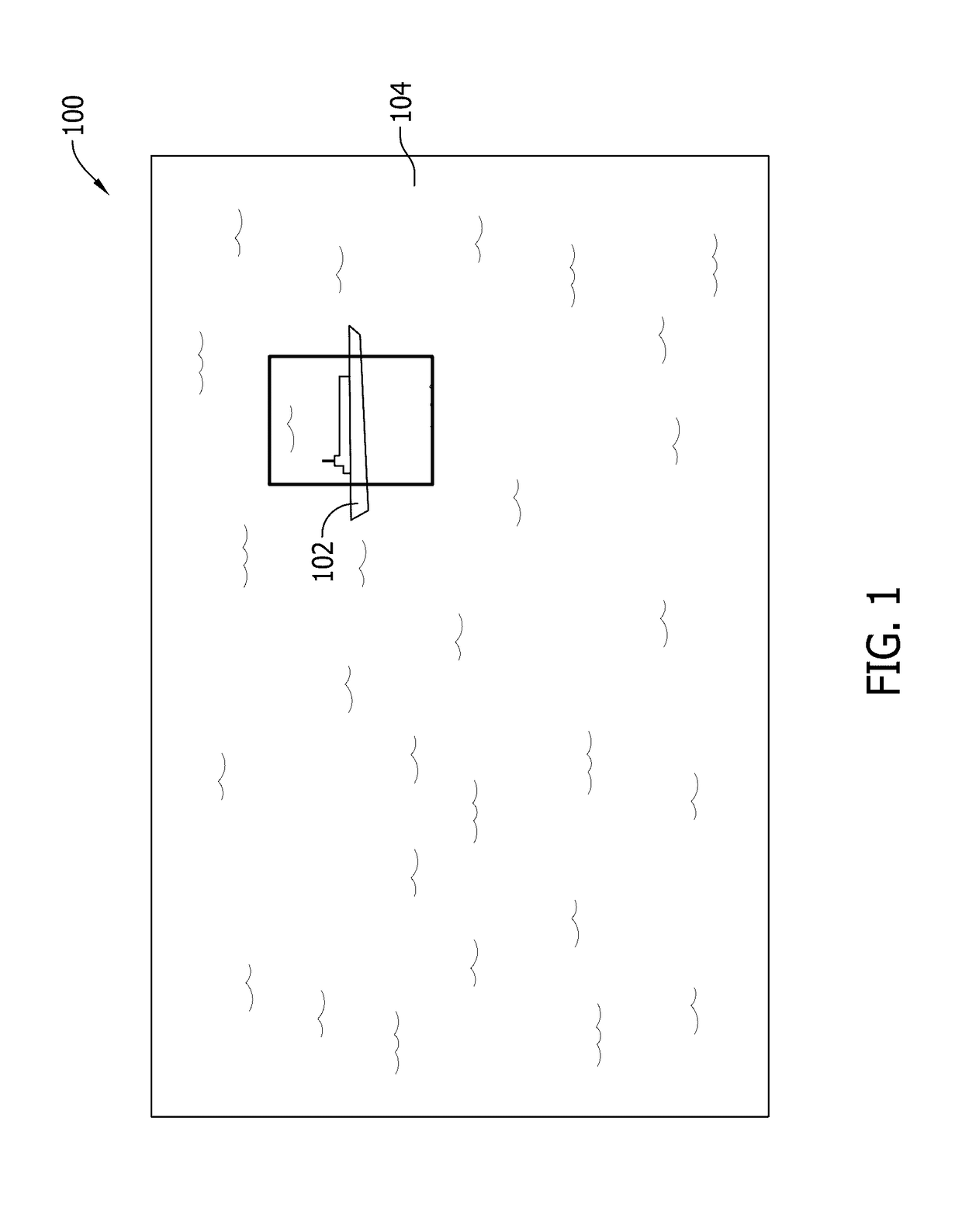
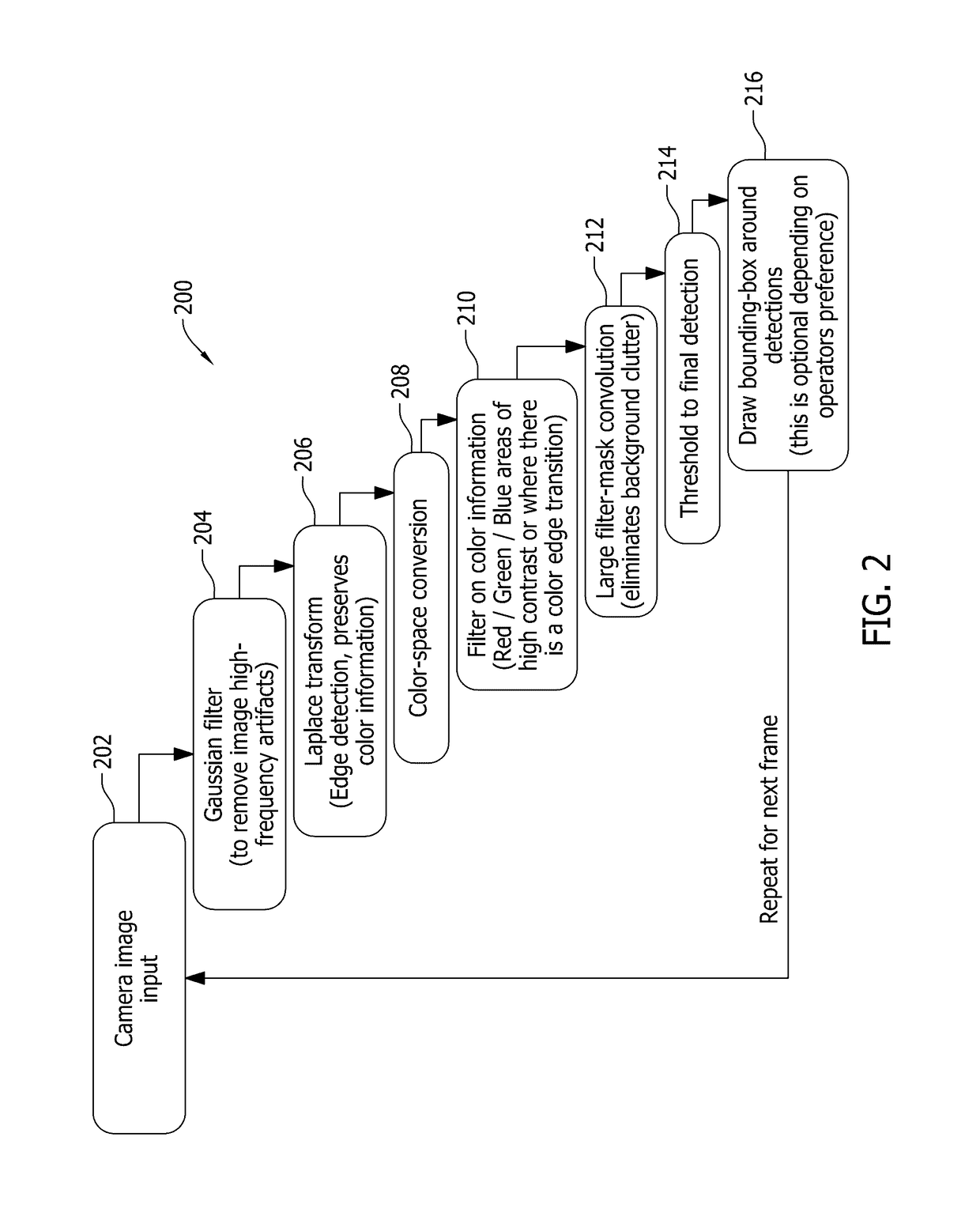
A computing device for detecting an object of interest in an image is provided. The computing device includes a memory device and a processor to process image data by evaluating pixel contrast to facilitate detecting an edge transition in an image, by identifying neighboring pixels that are above a predetermined contrast value, which represent a potential object of interest, filtering the pixels based on color information to identify areas where there is a color edge transition, applying a convolution filter mask to yield regions of pixels having a localized concentration of contrast and color changes, applying a threshold filter for identifying those pixel regions having values that are greater than a predetermined threshold value and grouping the identified pixel regions into one or more groups representing an object of interest, and generating an alert to notify an operator that the object of interest in the image has been detected.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
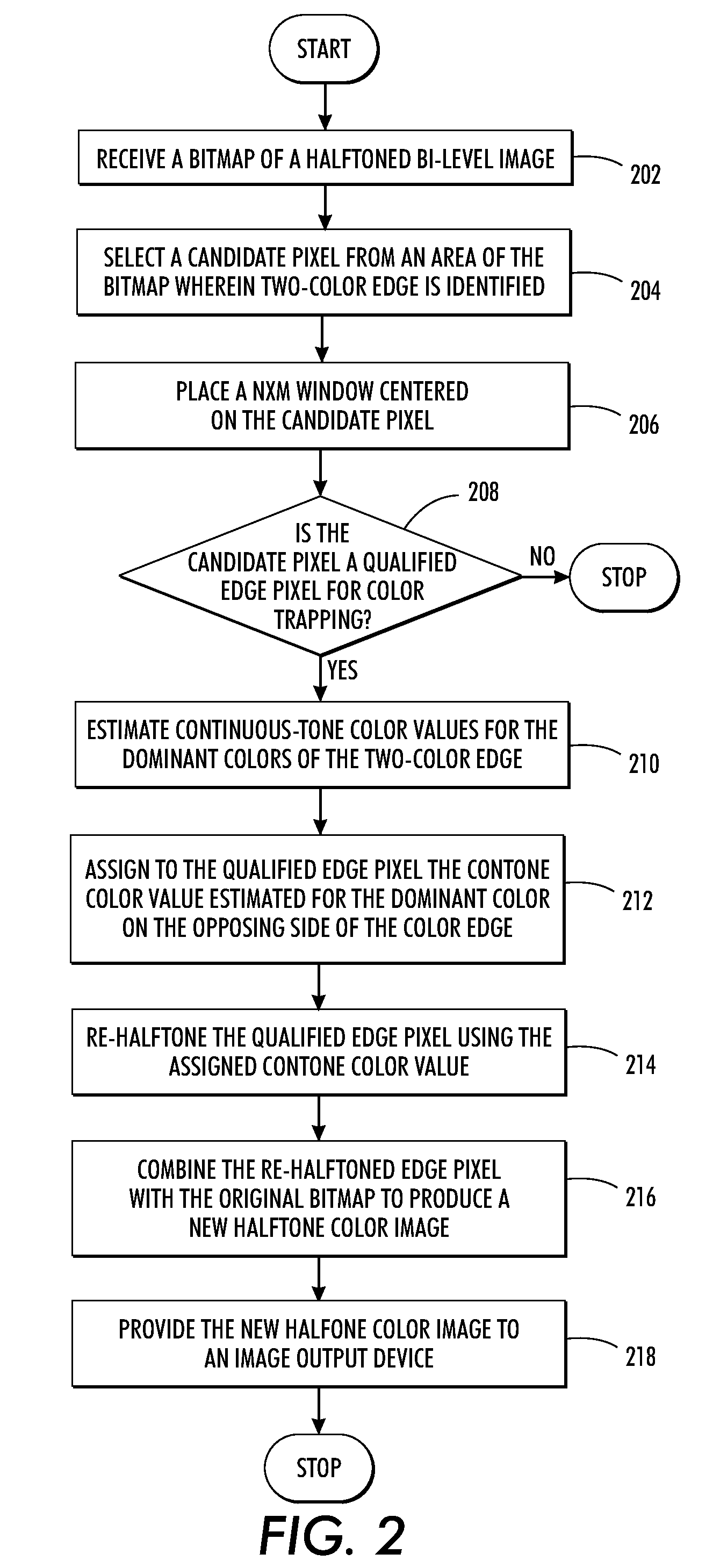
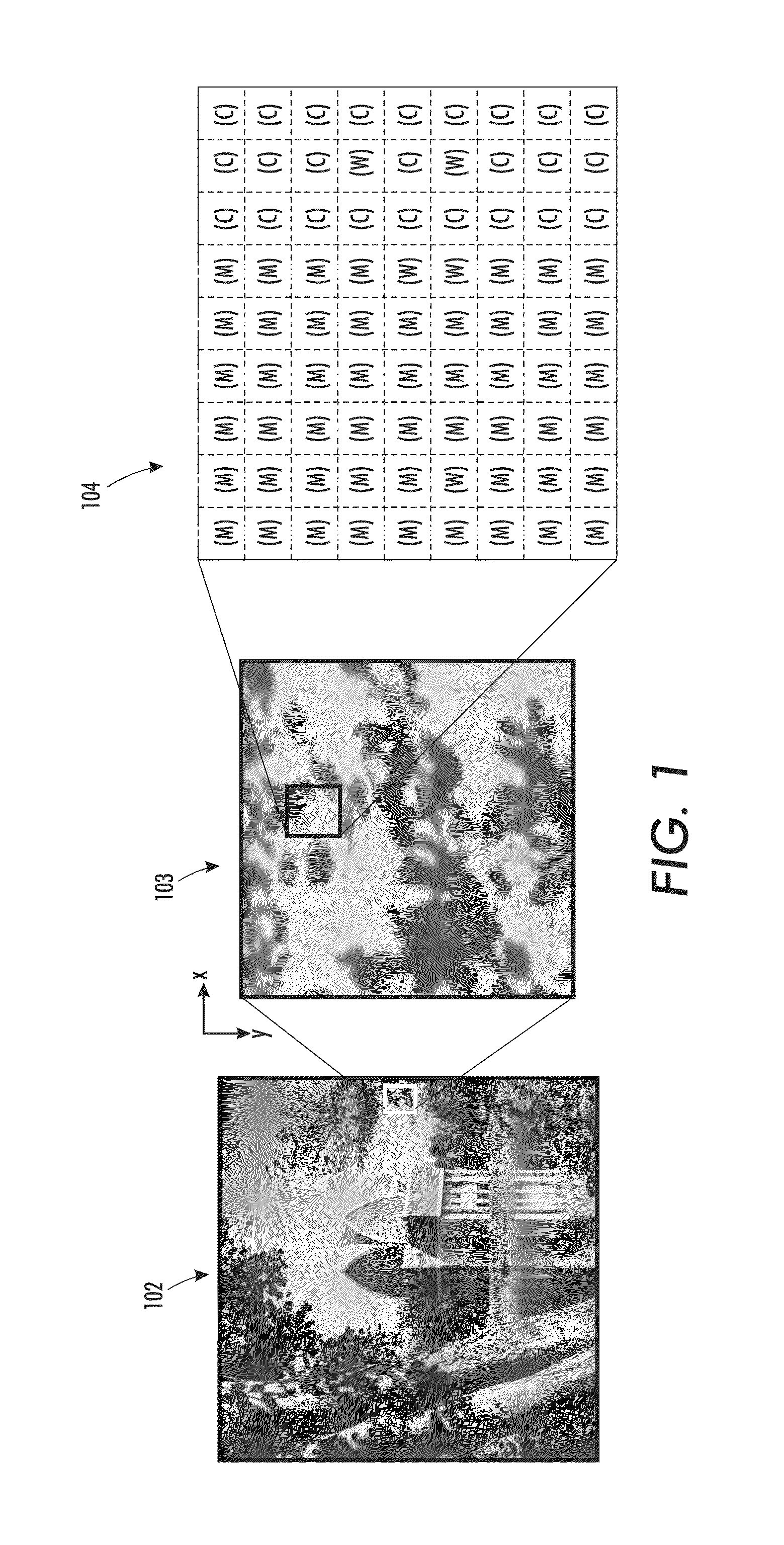
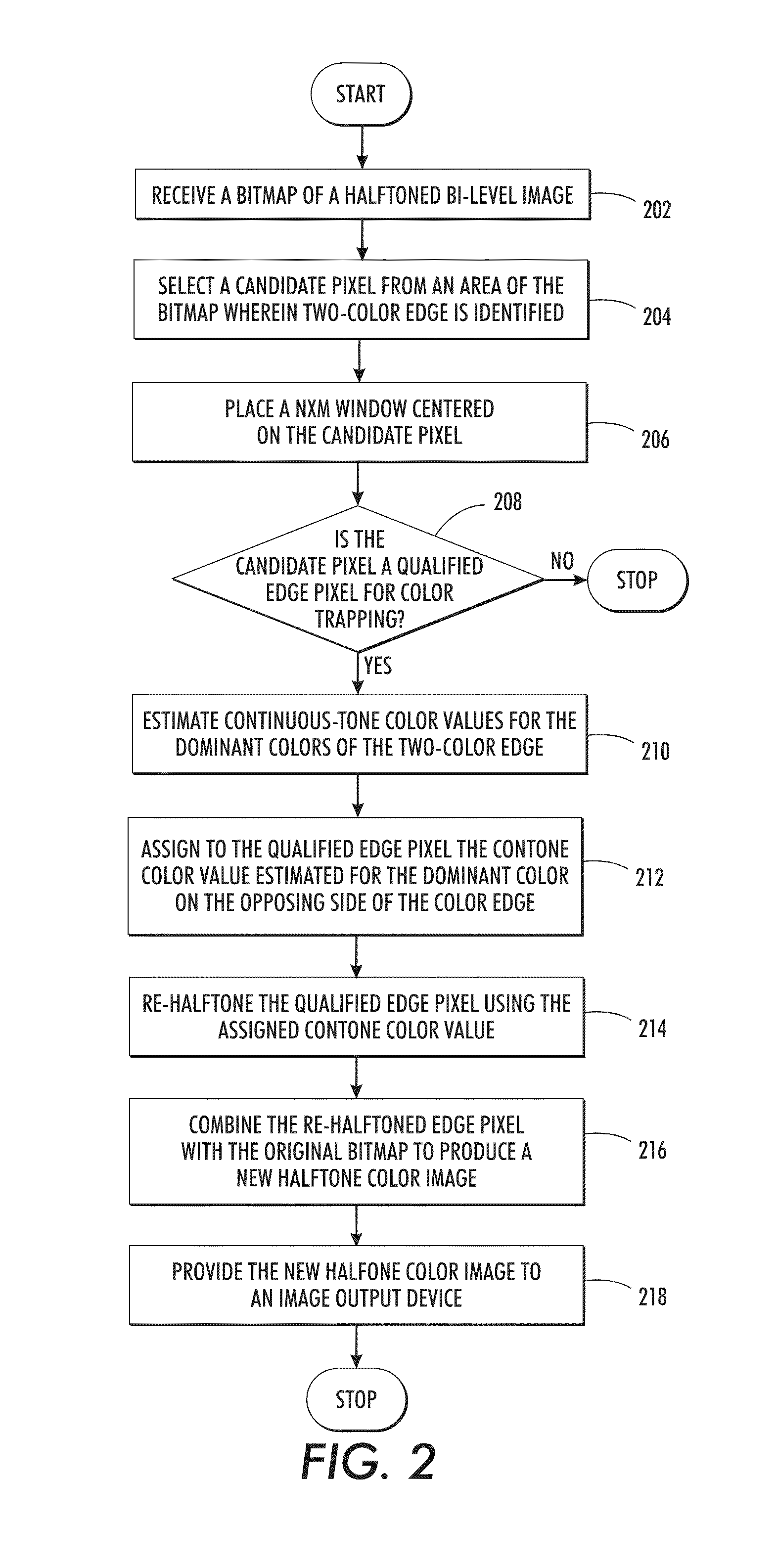
Color trapping on a halftoned bi-level bitmap
ActiveUS20100277770A1Digitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsContinuous toneOutput device
What is disclosed is a novel system and method for color trapping on halftoned bi-level bitmaps. Color edges are detected and edge pixels that need to be trapped are identified. The number of pixels qualified as edge pixels eligible for color trapping can be up to a pre-determined number of pixels away from the color edge. Estimates for the continuous-tone values are obtained for the dominant colors on each side of the two-color edge. The contone value of the dominant color on the opposing side of the two-color edge is assigned to the qualified edge pixels. Qualified edge pixels are re-halftoned using their assigned contone value so that halftones for one color are extended beyond the edge into the other color. The re-halftoned edge pixels are combined with the original bitmap to produce a new bitmap for the image. The new bitmap is then provided to an image output device.
Owner:XEROX CORP
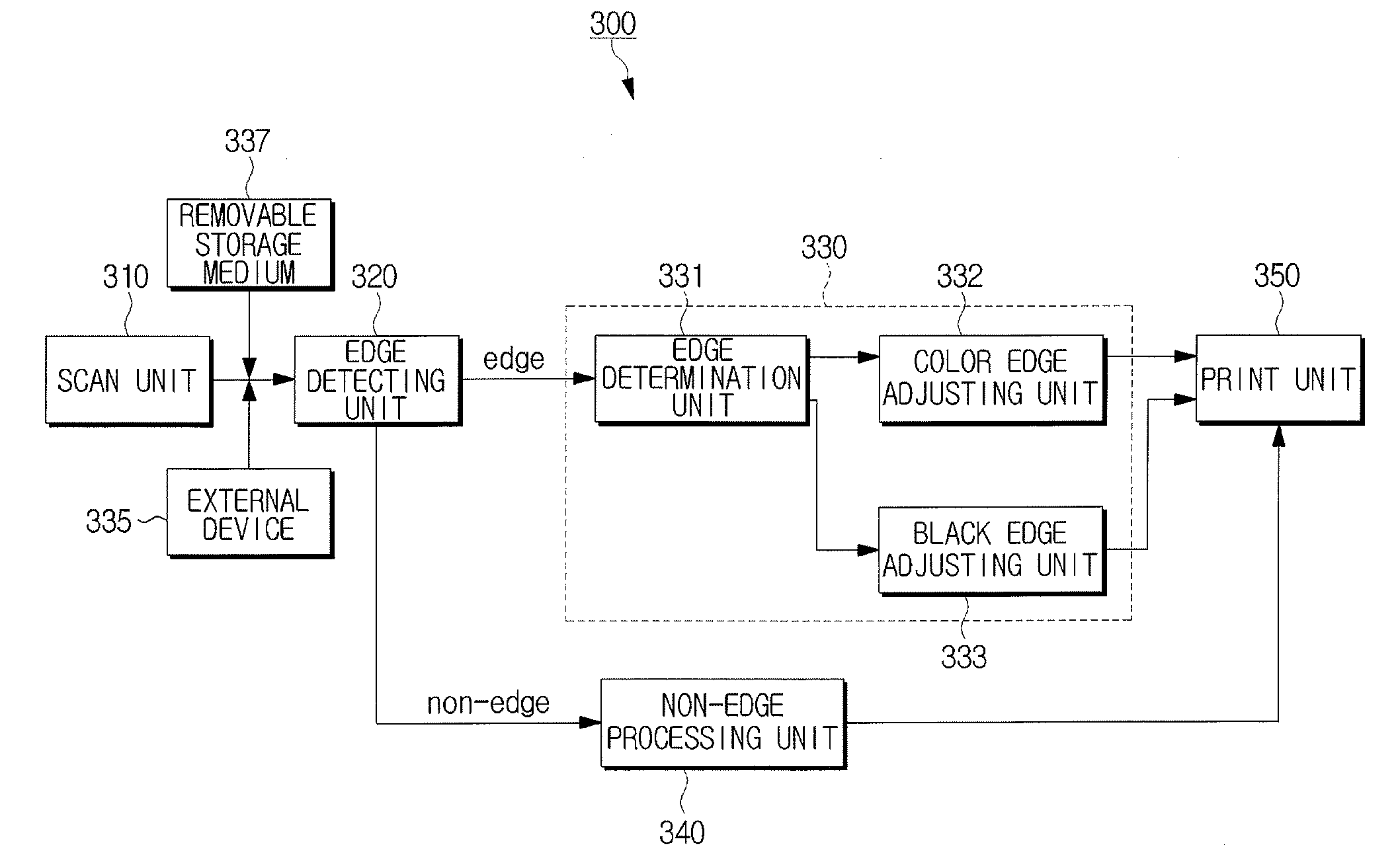
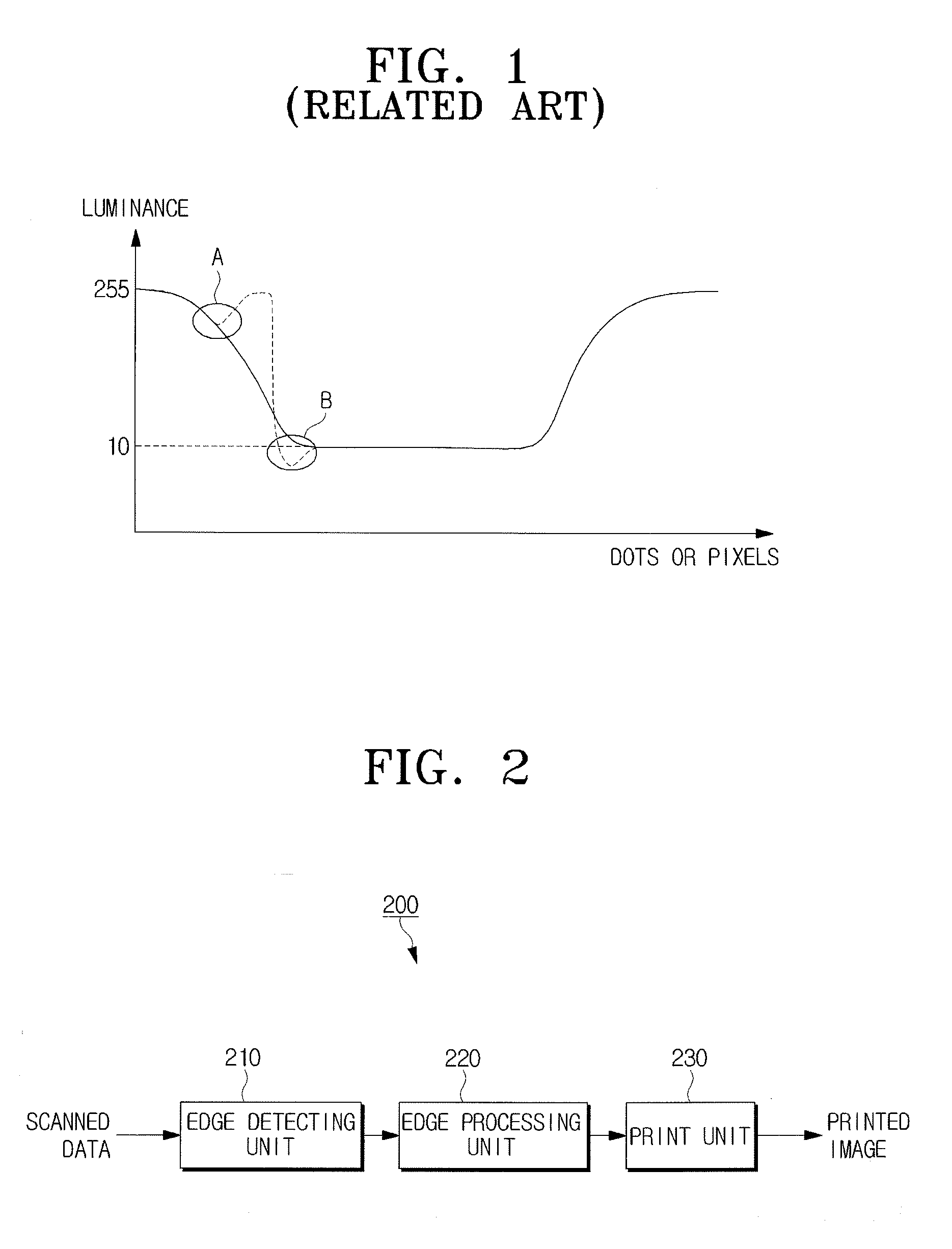
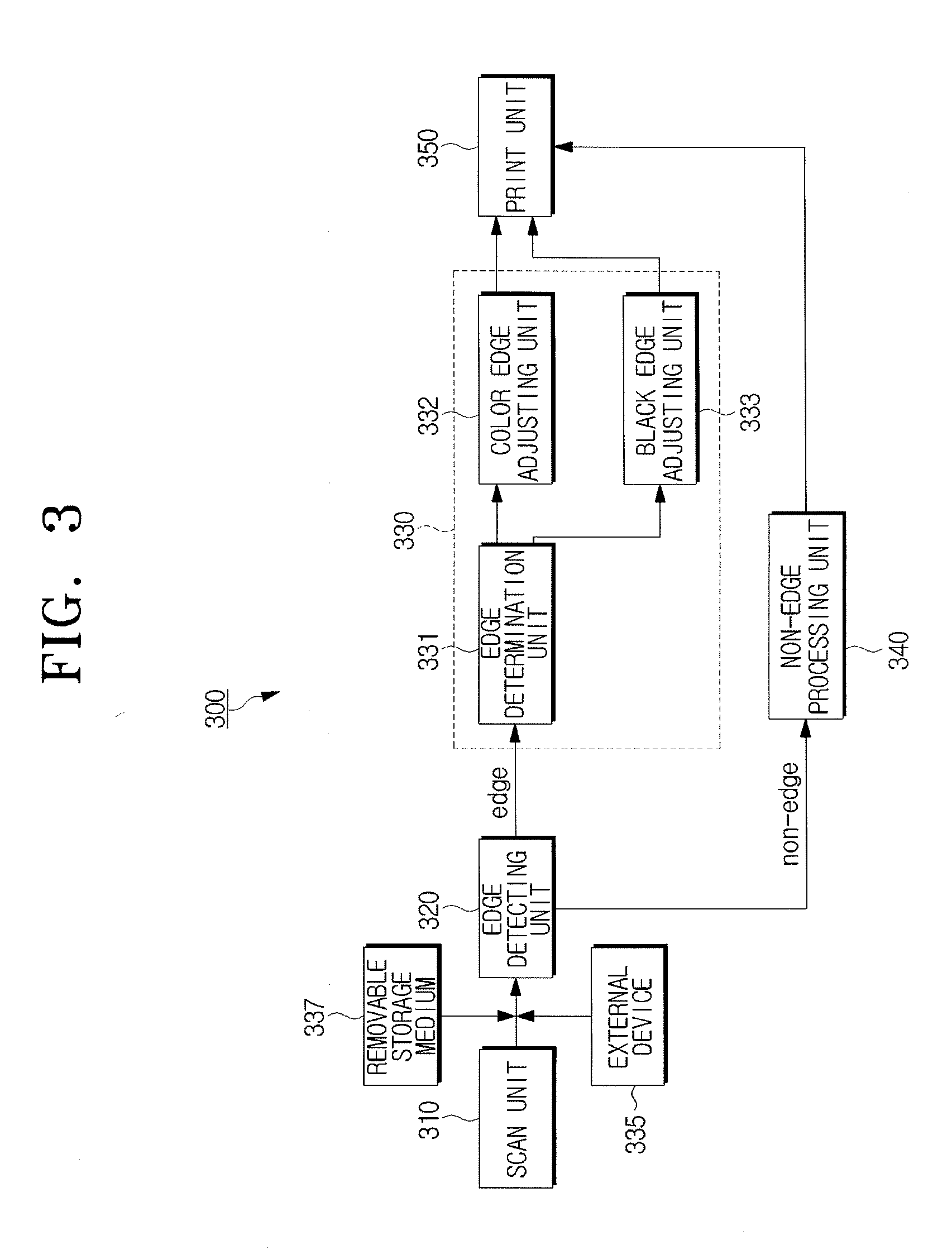
Image forming apparatus and a control method to improve image quality
ActiveUS20090009779A1Improve image qualityReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersImaging qualityImage formation
An image forming apparatus and a control method to improve image quality. In the image forming apparatus, an edge detecting unit detects an edge pixel from scanned image data, an edge processing unit determines whether the edge pixel is a color edge pixel or a black edge pixel and applies independent edge processing methods to the color edge pixel and the black edge pixel, and a print unit prints the scanned image data using the processed edge pixel.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Pixel arrangement of organic light-emitting display panel and organic light-emitting display panel
ActiveCN109713027AIncrease opening ratioReduce the risk of vapor deposition color mixingStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesEvaporationComputer science
The embodiment of the invention provides pixel arrangement of an organic light-emitting display panel. The pixel arrangement of the organic light-emitting display panel comprises repetitive units arranged in an array mode. The repetitive units comprise a first pixel row to a sixth pixel column, wherein the first pixel column comprises a first sub-pixel located in an i-th pixel row and a second sub-pixel located in an (i+2)-th pixel row; the second pixel column comprises a third sub-pixel located in a j-th pixel row and a (j+2)-th pixel row; the third pixel column comprises a second sub-pixel located in an i-th pixel row and a first sub-pixel located in the (i+2)-th pixel row; the fourth pixel column comprises a second sub-pixel located in a j-th pixel row and a first sub-pixel located in a(j+2)-th pixel row; the fifth pixel column comprises a third sub-pixel located in an i-th pixel row and an (i+2)-th pixel row; the sixth pixel column comprises a first sub-pixel located in an j-th pixel row and a second sub-pixel located in a (j+2)-th pixel row, wherein i = 1, j = 2, or j = 1, i = 2. According to the scheme, the evaporation color mixing risk can be reduced, the mask plate manufacturing difficulty is reduced, the aperture opening ratio is increased, and the color edge phenomenon can be improved.
Owner:WUHAN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
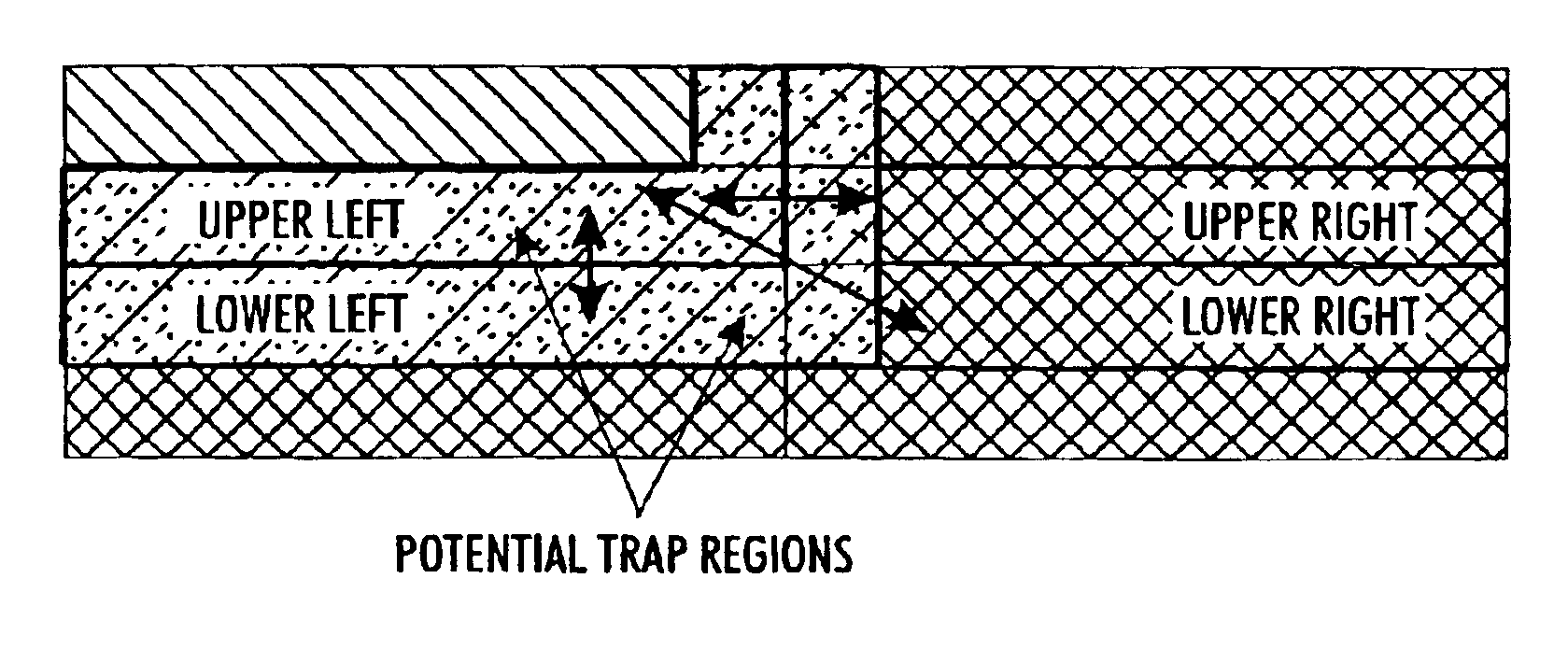
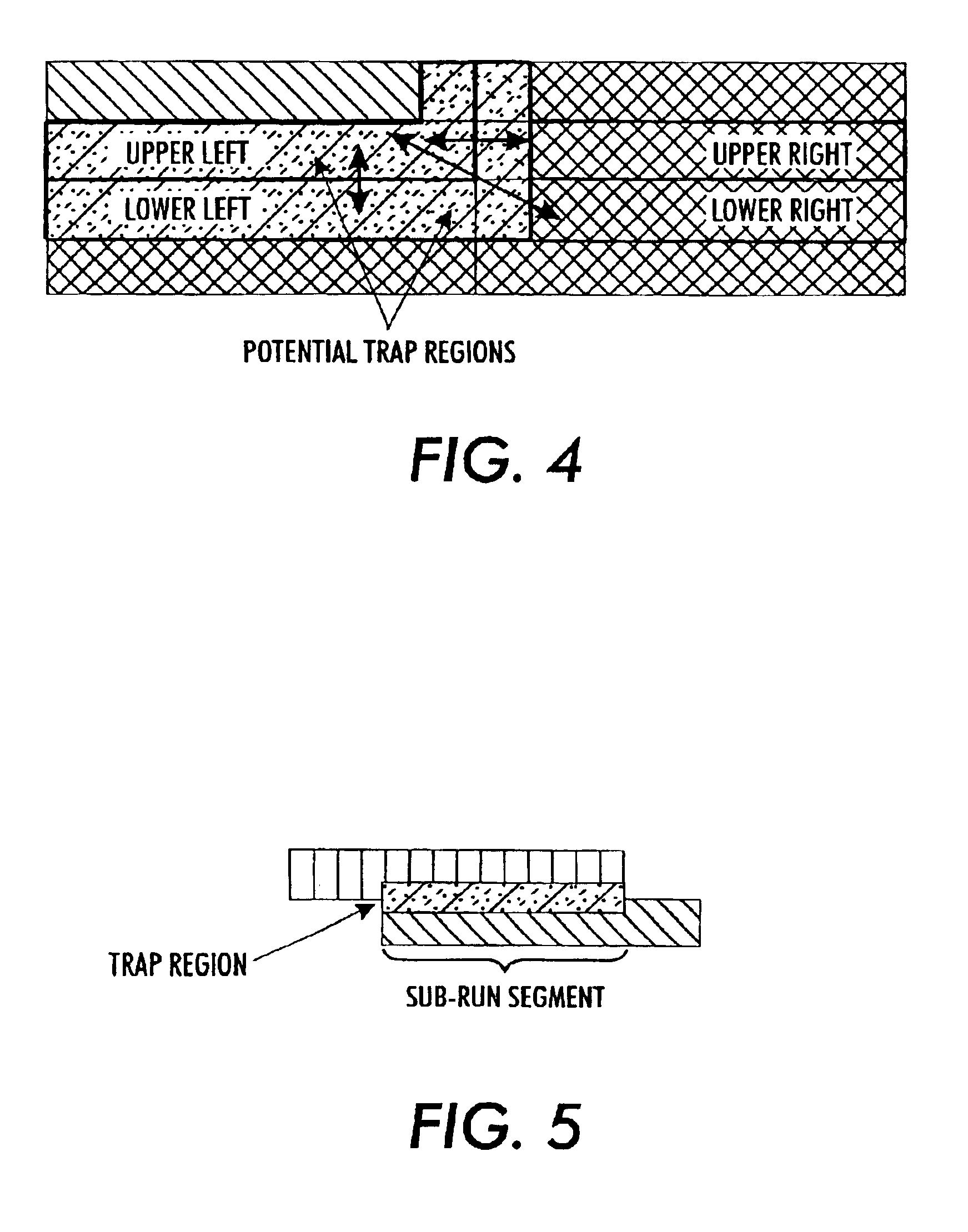
Color trapping on a halftoned bi-level bitmap
ActiveUS8340396B2True colorReduce artifactsDigitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersHueBitmap
What is disclosed is a novel system and method for determining whether a pixel resides along a two-color edge in a halftoned bi-level bitmap. In one embodiment, a bitmap having a plurality of colored pixels is received. For each pixel in the bitmap, a window of size n×m is defined centered on the current pixel. The window is partitioned into a plurality of regions with each region having an orientation direction with each orientation direction having an associated numeric value. A number of pixels are counted for each of the first and second colors in each of the associated orientation directions. A determination is made as to the respective orientation direction having the maximum and minimum pixel counts for each of the first and second colors. Thereafter, a determination is made whether the pixel resides along a two color edge based upon the max / min counts and each associated orientation direction.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Tire with color pattern and production method thereof
ActiveCN103182908AImprove appearance qualityClear color edgesTyresTyre sidewallsVulcanizationColor film
The invention aims to provide a tire with a color pattern and a production method thereof. The lateral surface of the tire can have various colors and patterns. the production method comprises the following main process that in the forming process, a color film is adhered to glue at a tire side, wherein the position on a vulcanization die, which corresponds to the tire side, is provided with a ring-shaped groove; a bulge corresponding to a preset pattern is arranged in the ring-shaped groove; and the bulge corresponds to the position of the color film in a tire blank. The position of the tire side of the formed tire is provided with a boss higher than the outline of a normal tire side; the upper surface of the boss is provided with a sucken pattern; and the sucken part at least has one color different from the basic color of the tire. According to the invention, appearance quality of the tire is improved; the lateral surface of the tire can have various colors and patterns; the tire is provided with a clear color edge and is of a regular shape; safety of the tire is not influenced; the process is simple; and the tire is convenient to produce.
Owner:SAILUN GRP CO LTD
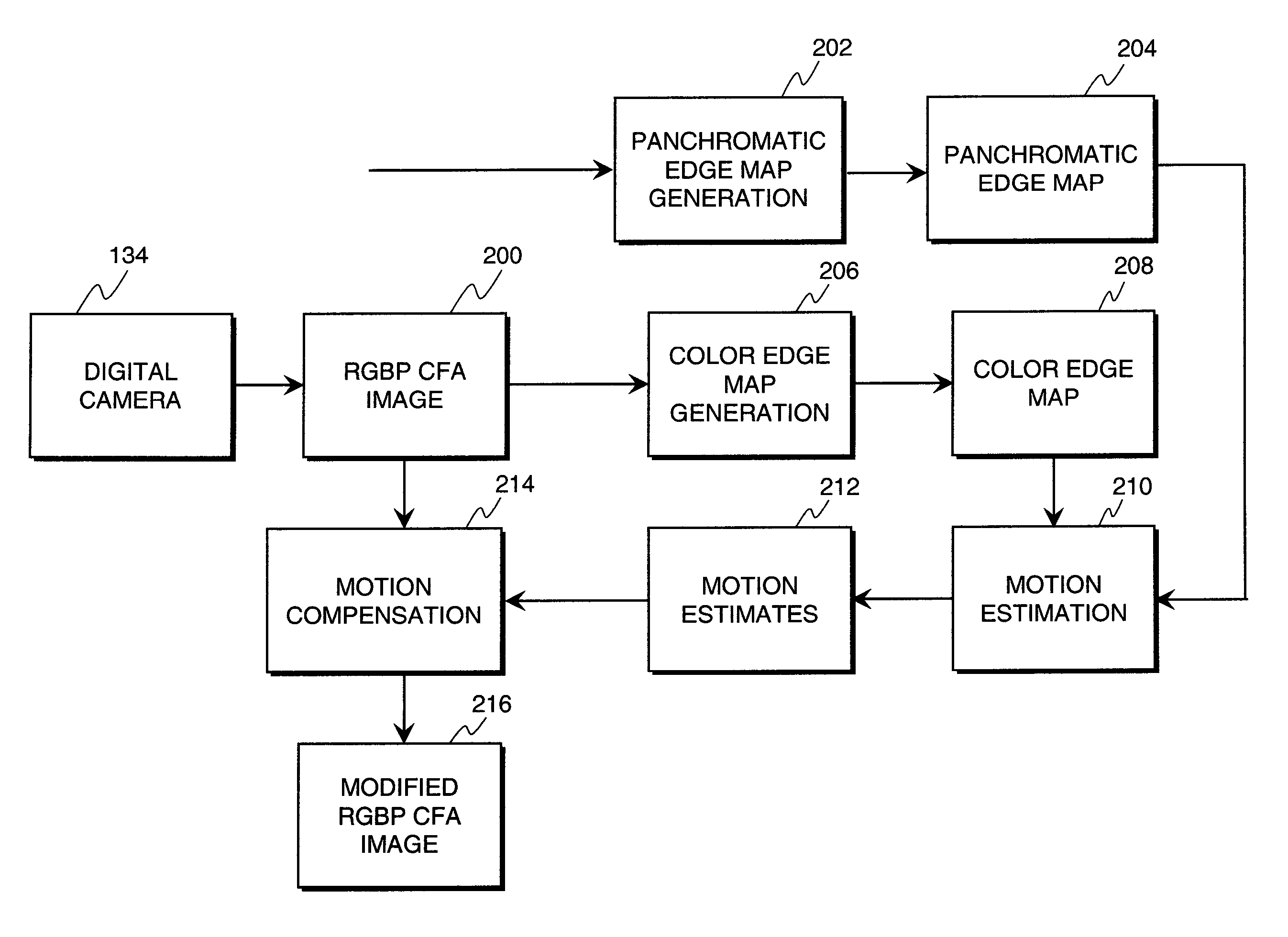
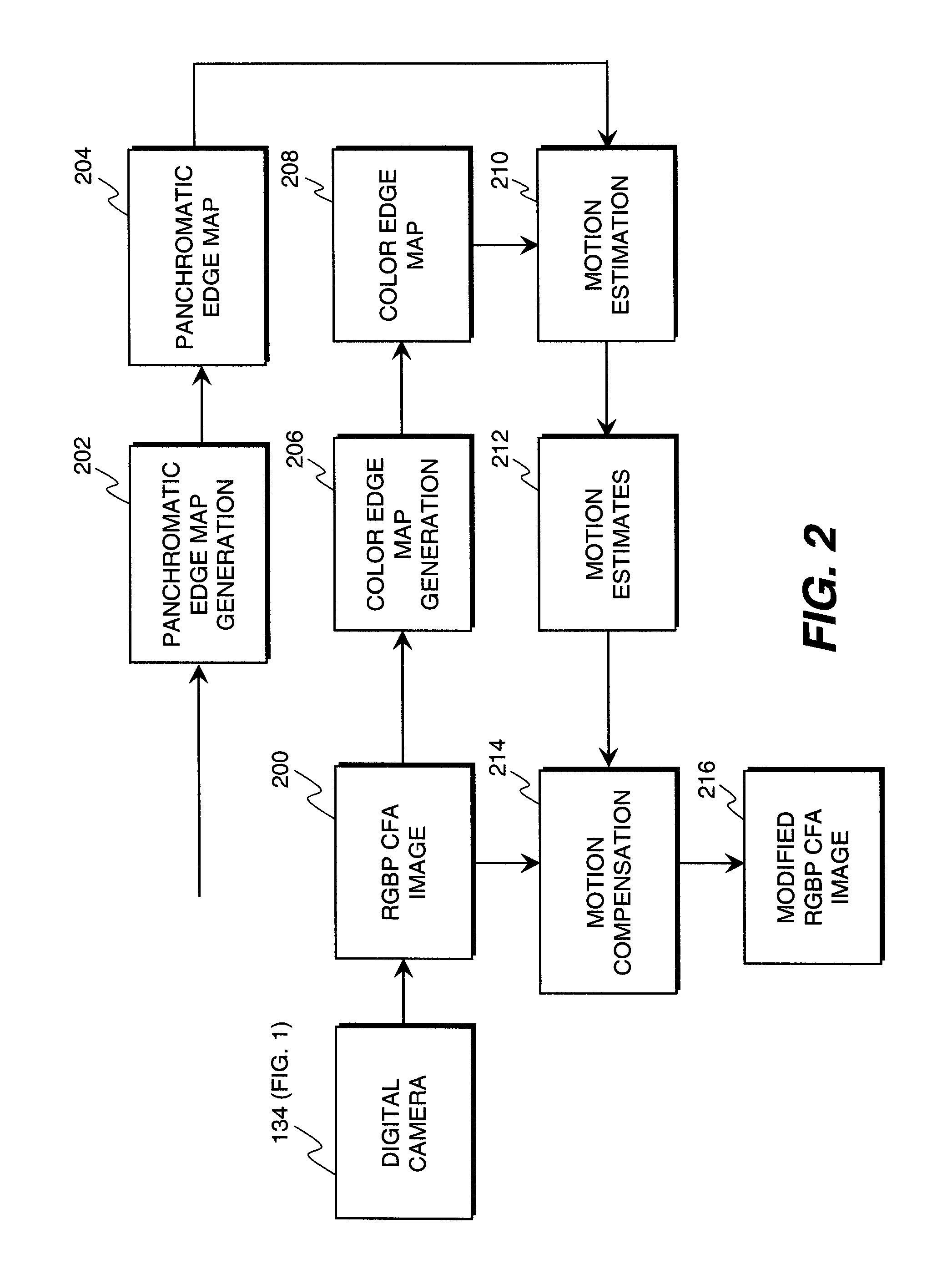
Modifying color and panchromatic channel cfa image
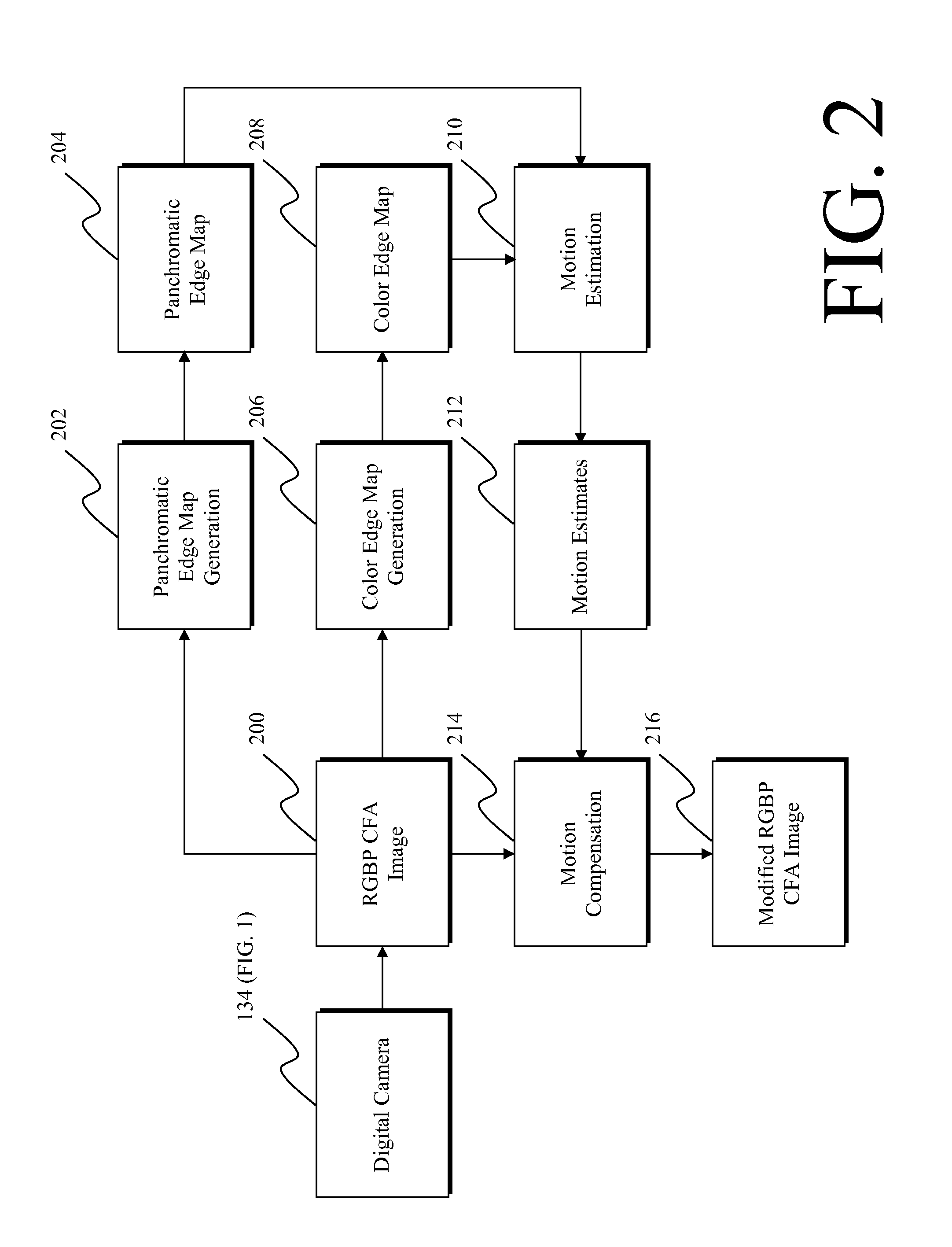
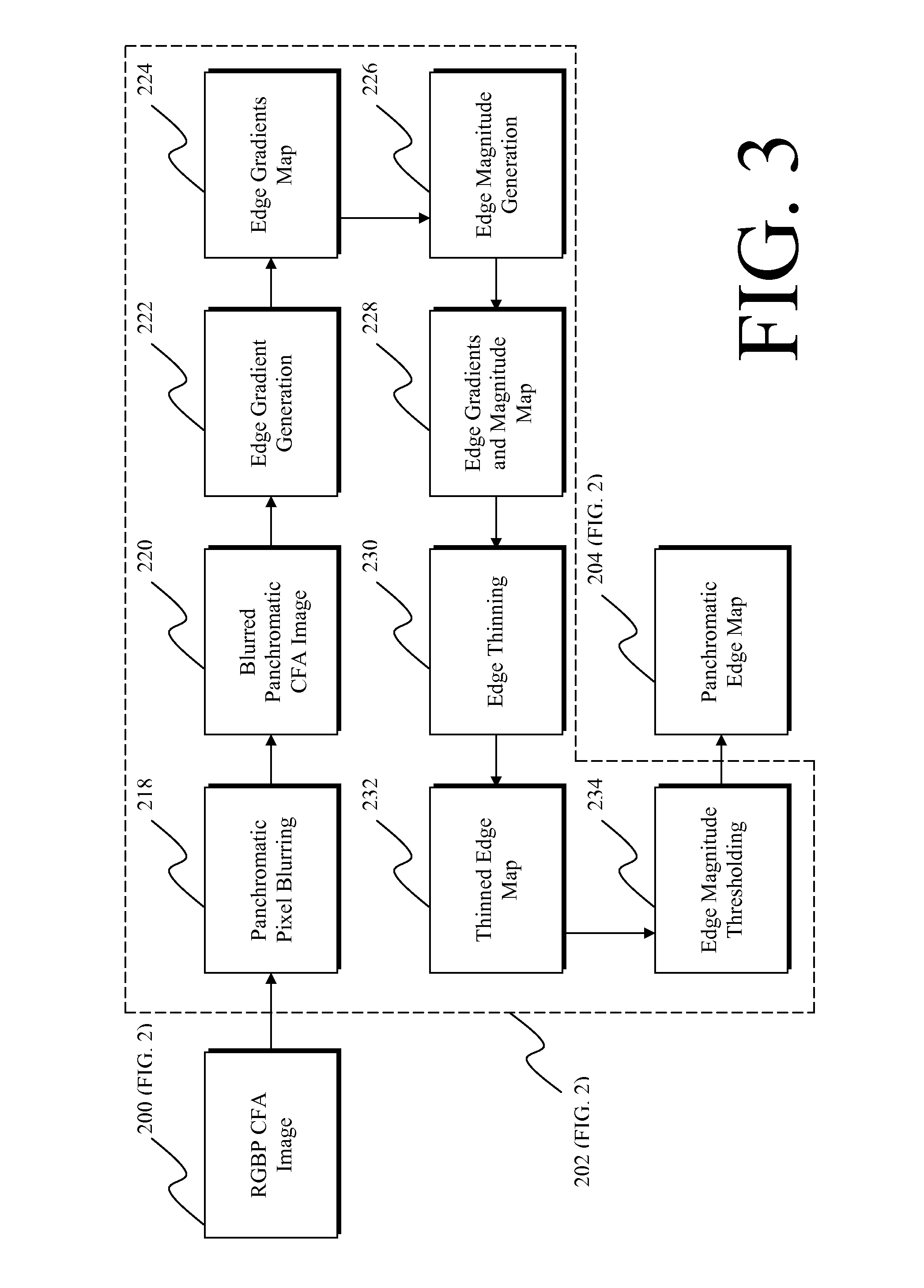
ActiveUS20100119148A1Improved color filter array imageReduce blurTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionEdge mapsMotion estimate
A method of modifying a CFA image or full-color image having a plurality of color channels and a panchromatic channel, includes capturing the panchromatic channel at a different exposure time than at least one of the color image channels with the CFA sensor within one image; producing a panchromatic edge map and a color edge map from the CFA image; using the panchromatic edge map and the color edge map to provide motion estimates; and using the motion estimates to modify at least one of the channels of the CFA image or full-color image.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
A depth map super-resolution method
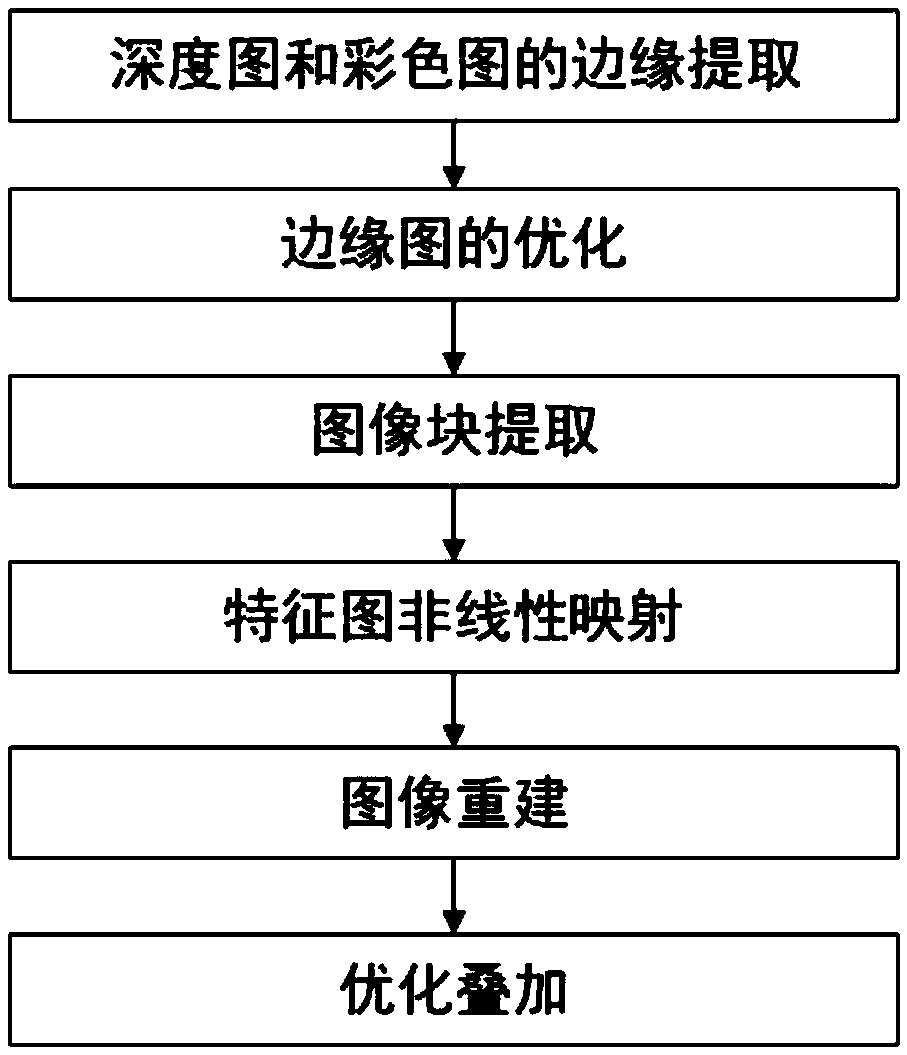
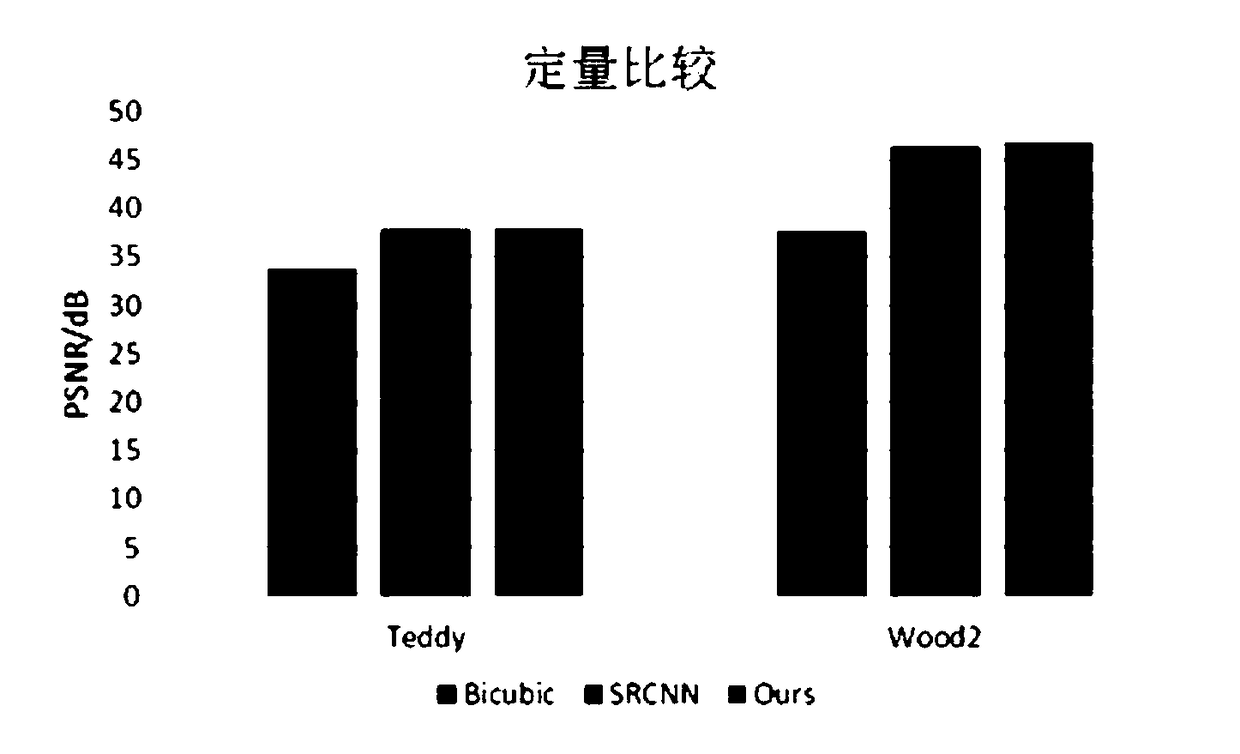
InactiveCN109272447ADepth pixel values are accurateSuppress ringing effectImage enhancementImage analysisStochastic gradient descentMean square
The invention discloses a depth map super-resolution method. The method comprises the following steps: color map edges and depth map edges after initial upsampling are extracted respectively by usingedge detection operators; the edge map is optimized by 'AND' operation of expanded color edge and depth edge. The super-resolution network is constructed by four steps: image block extraction, featuremap nonlinear mapping, image reconstruction and optimization and superposition, and then the super-resolution network is constructed. Driven by mean square error and optimized by stochastic gradientdescent, the super-resolution network is trained to update the learning parameters of the network. The method not only improves the image resolution, but also makes the depth pixel value of the imagemore accurate and the image clearer, and effectively suppresses the ringing effect, so that the reconstructed depth edge is sharper.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Robot vision locating method based on round road sign imaging analysis
The invention discloses a robot vision locating method based on round road sign imaging analysis, belonging to the technical field of robot vision location. The robot vision locating method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: designing and placing a circular road sign; identifying the circular road sign, wherein the step of identifying the circular road sign comprises the three procedures of fitting edges with specific colors, fitting RANSAC (Random Sampling Consensus) ellipse and checking the sign; and finally, locating a mobile robot. The robot vision locating method has the advantages of location completion by using only one road sign, simple road sign mode, short detection process, capability of being used in outdoor light conditions and simpleness and rapidness in location.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
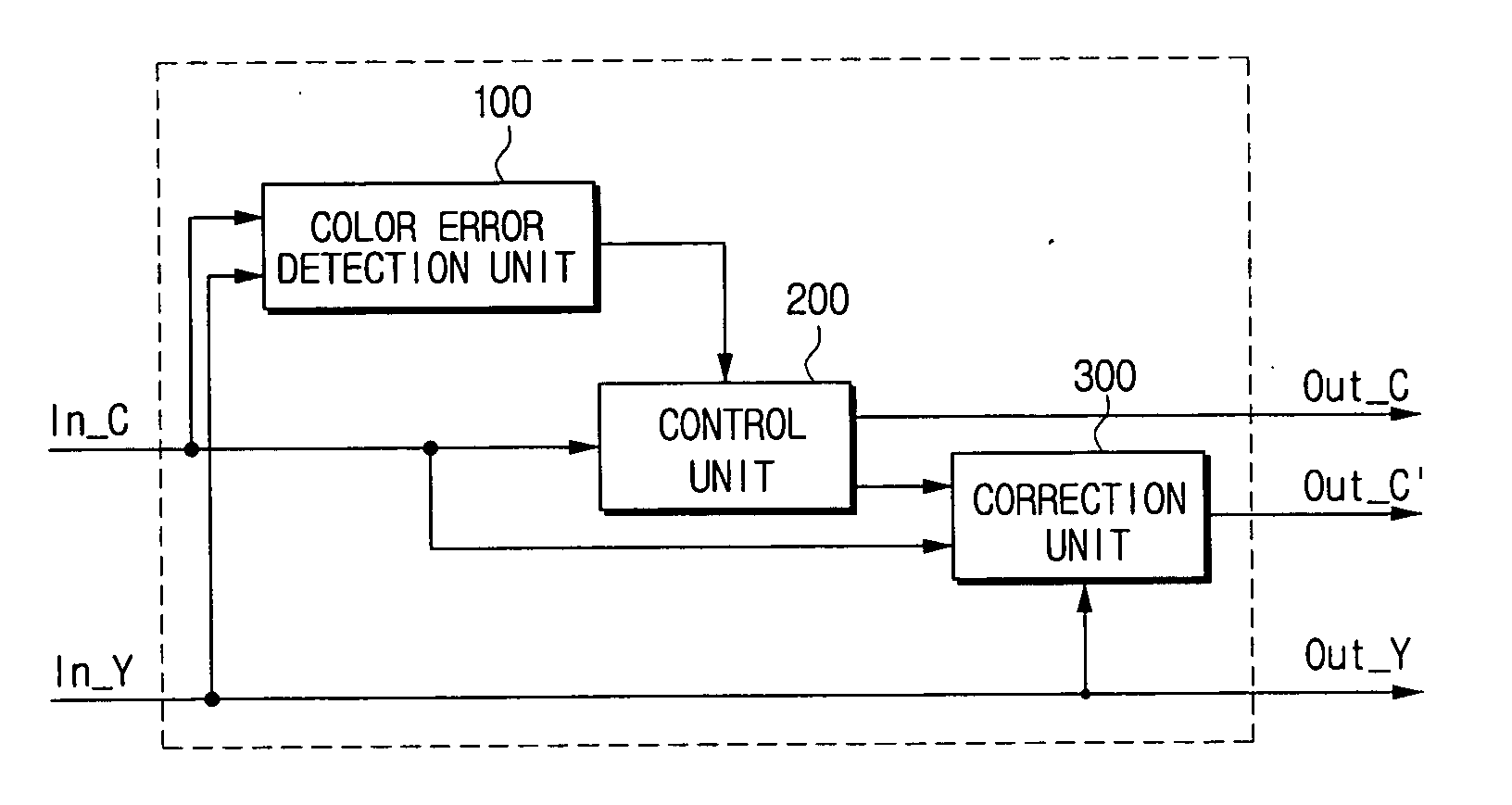
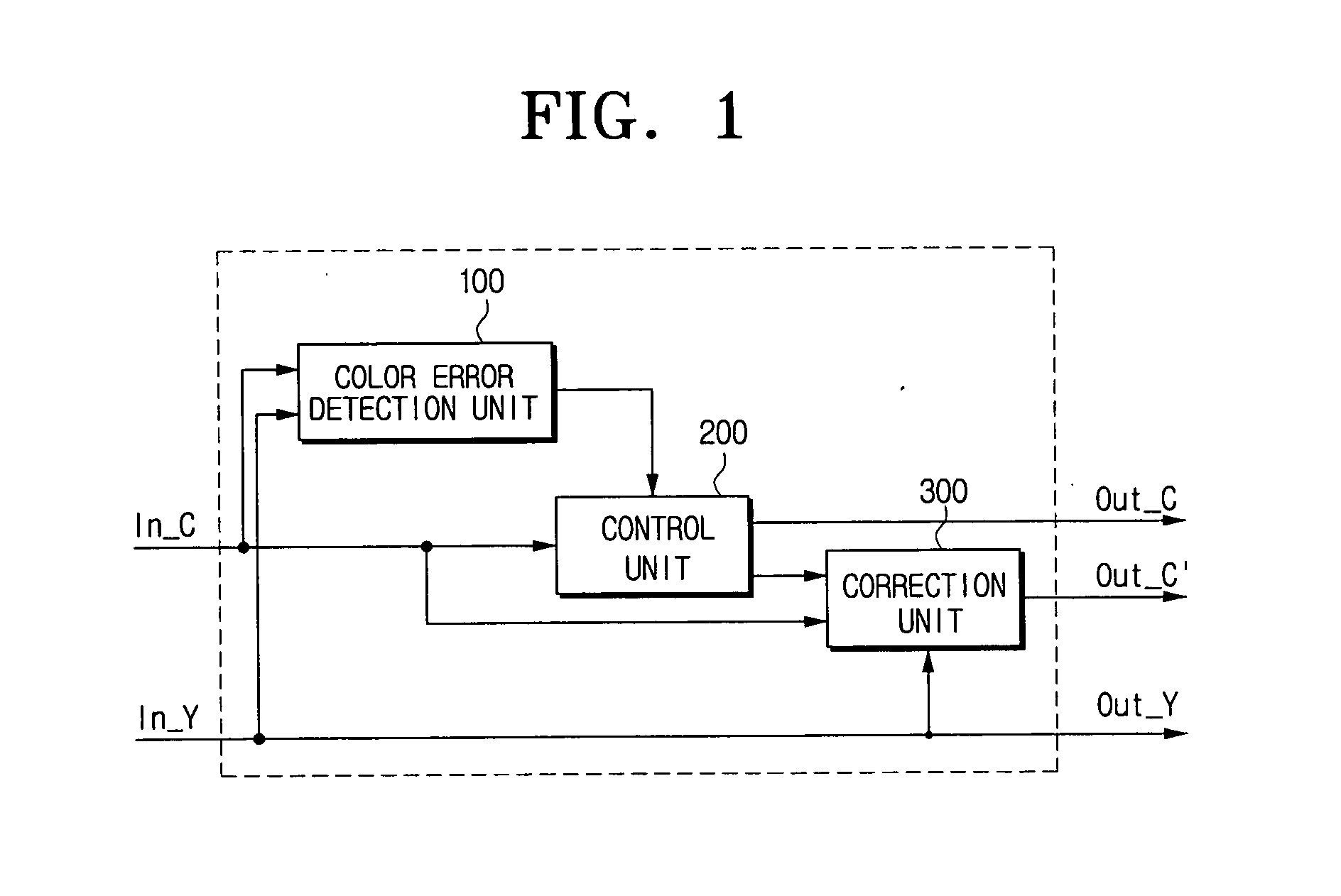
Apparatus and method for correcting color error by adaptively filtering chrominance signals
InactiveUS20070040944A1Improve picture qualityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsInterlaced videoLevel line
An apparatus for correcting a color error, including: a color error detection unit for detecting the presence or absence of a color error in an edge region of an input video, based on a relation between difference values between interlaced horizontal lines and difference values between non-interlaced horizontal lines of chrominance and luminance signals, respectively; a correction unit for correcting the color error by performing chroma filtering on the chrominance signals of the input video, if the color edge is present in the edge region; and a control unit for controlling the chrominance signals to be outputted after being corrected if the color error is present in the edge region, and for controlling the input chrominance signals to be outputted as they are if the color error is not present in the edge region.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
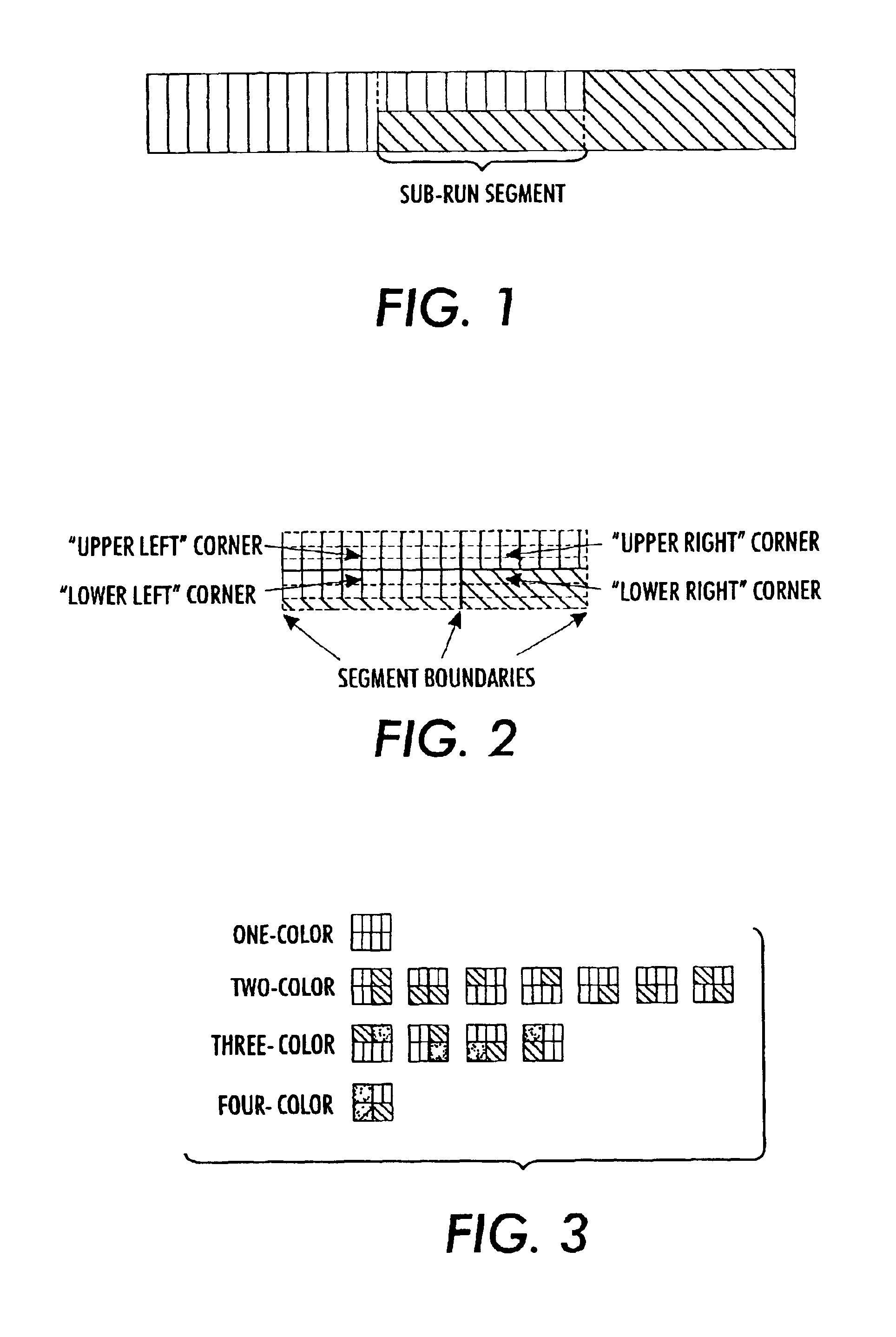
Method for trapping raster data in a run-length encoded form
A method of correction for toner misregistration in color printing systems, specifically for run length encoded image data. This method, called “trapping”, usually involves extending the color separations one or more pixels to overlay the edge. The color of the “trap zone” is chosen such that it is nearly imperceptible in the presence of the two initial colors. Our approach assumes the existence of a “trap generator”, which provides a trap color given two input colors.In run length encoded image format, the image is comprised of an array of “scanlines”, consisting of a string of “runs” that are specified by a minimum position in the fast (horizontal) direction, a length, and a color. We describe a method of trapping involving the following steps: 1) inspecting the run lengths in each scanline to determine the color edges of the image; 2) sending the colors at the boundaries to the trap generator to determine the trap color; and 3) modifying the intersecting runs with the trap color. The result is an efficient elimination of the edge defects at color boundaries, which is enabled by the run length encoded image format.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Modifying color and panchromatic channel CFA image
ActiveUS8073246B2Reduce blurLower captureTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMotion estimateFull color
A method of modifying a CFA image or full-color image having a plurality of color channels and a panchromatic channel, includes capturing the panchromatic channel at a different exposure time than at least one of the color image channels with the CFA sensor within one image; producing a panchromatic edge map and a color edge map from the CFA image; using the panchromatic edge map and the color edge map to provide motion estimates; and using the motion estimates to modify at least one of the channels of the CFA image or full-color image.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
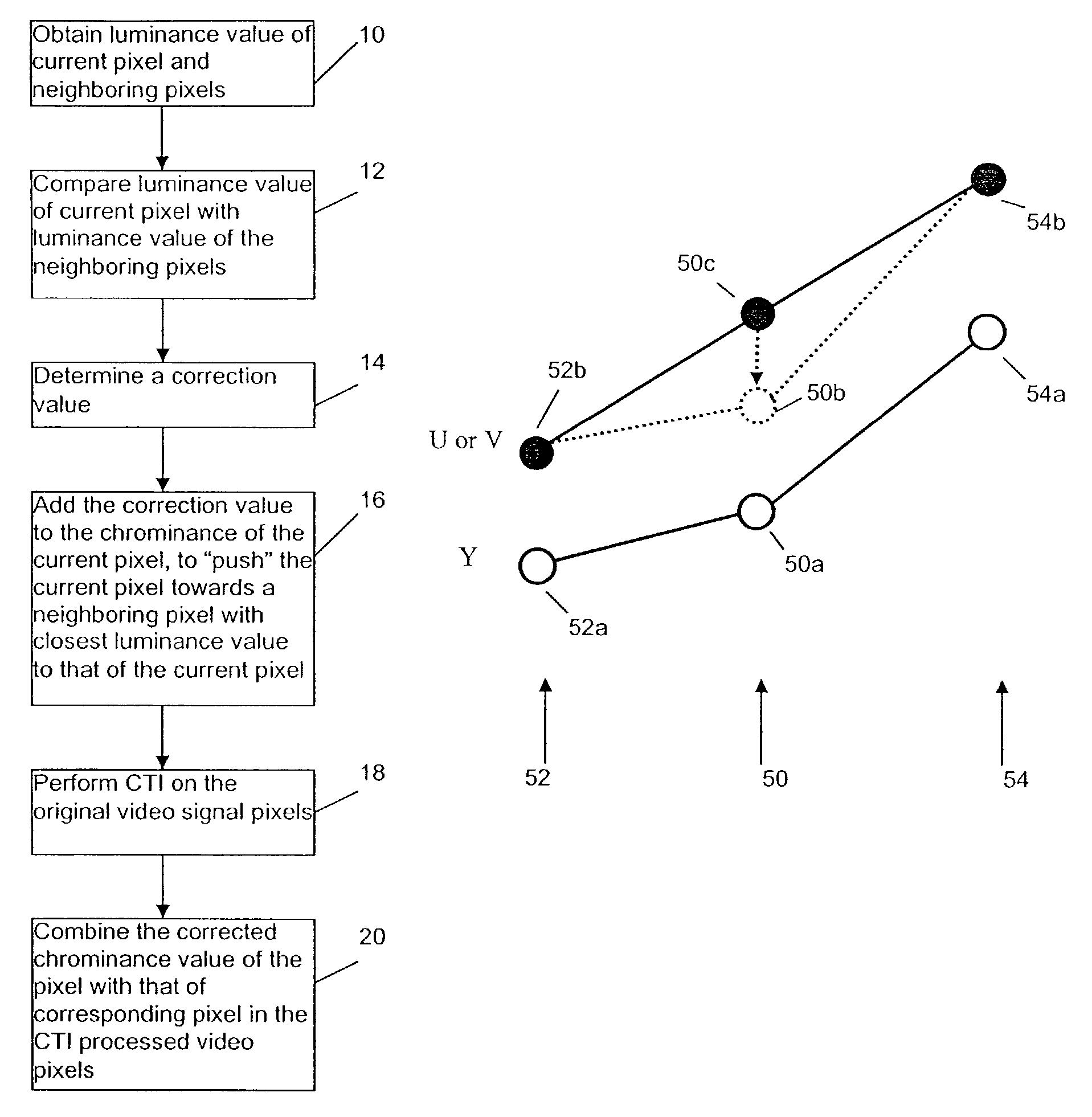
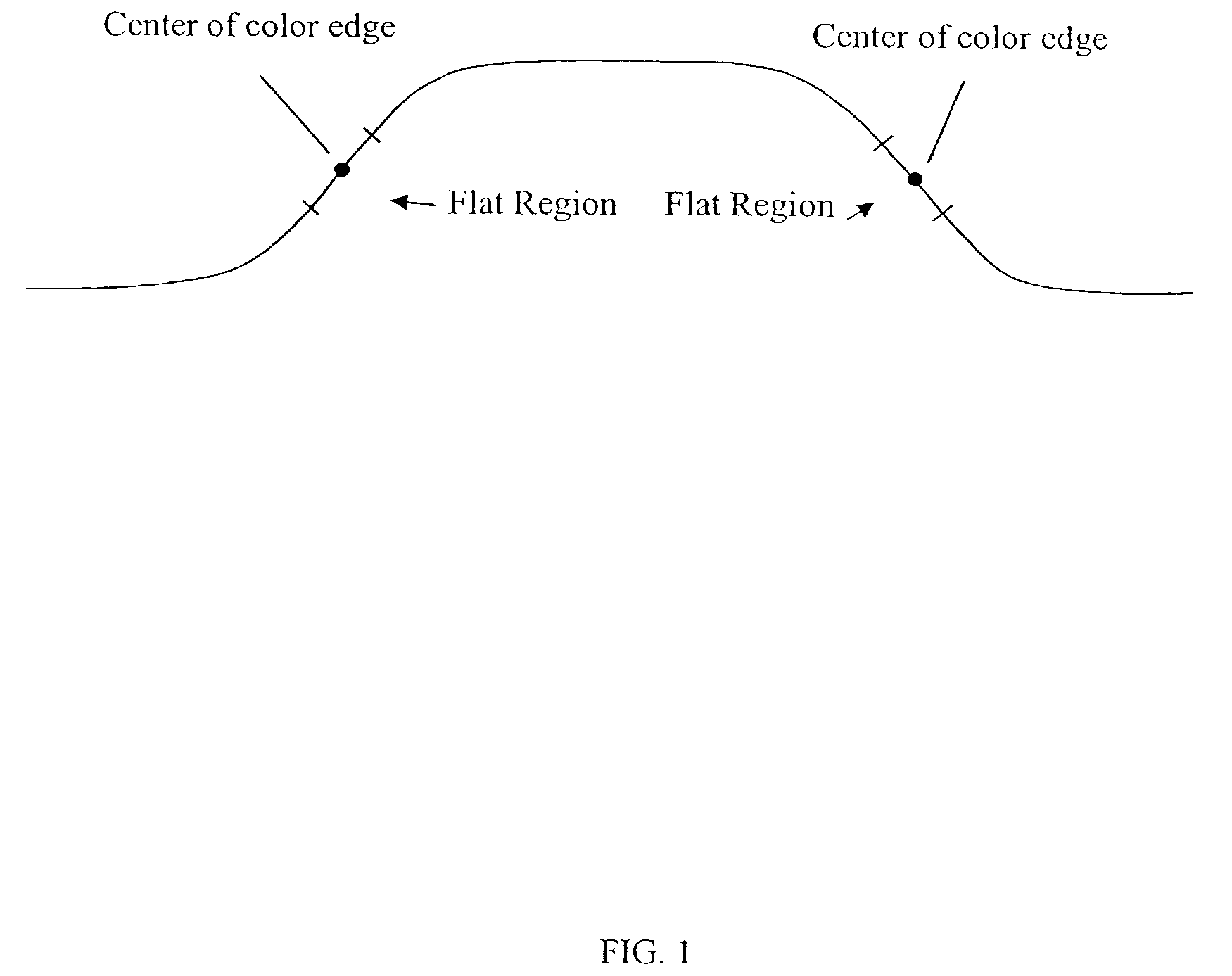
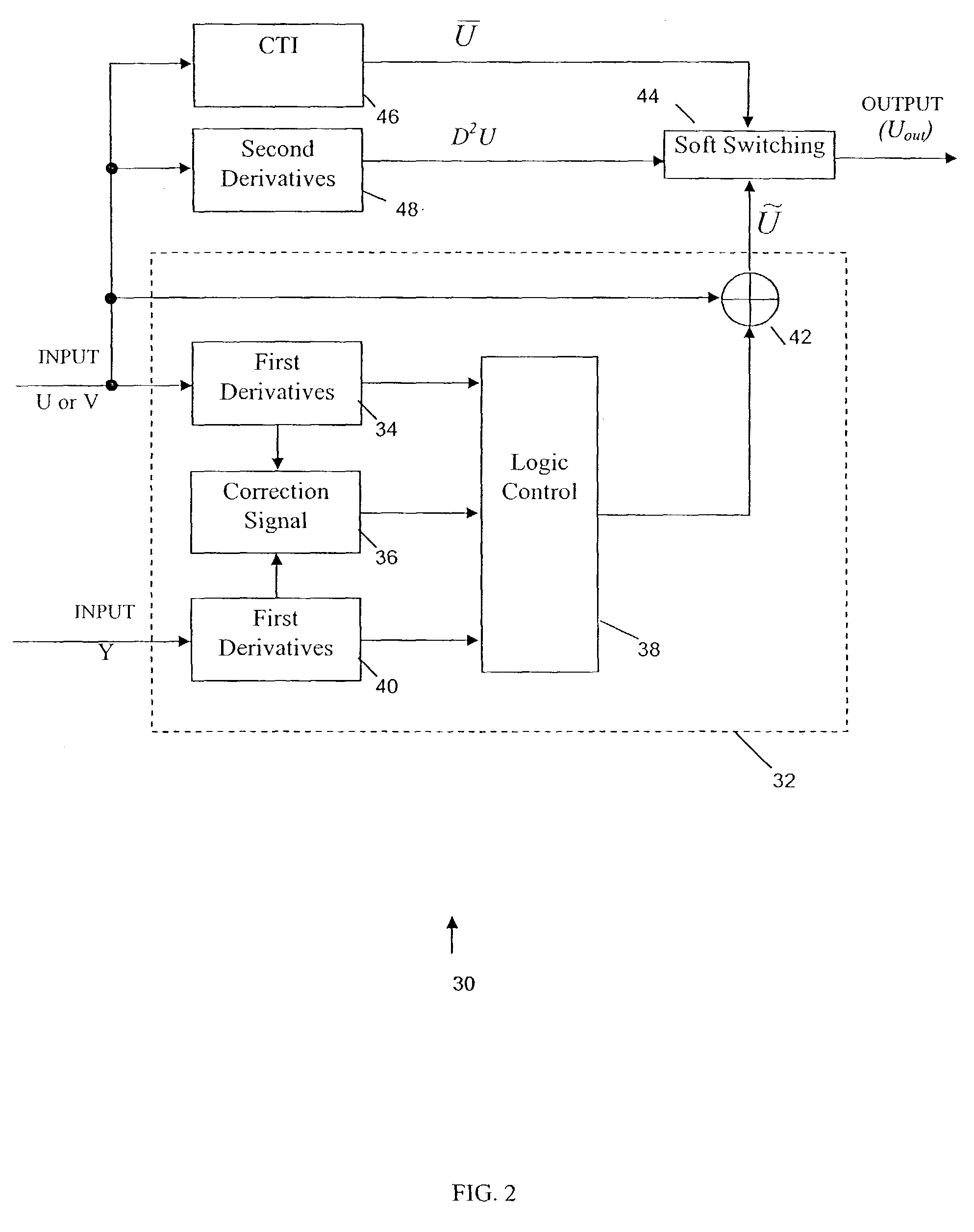
Method and apparatus for adjusting color edge center in color transient improvement
InactiveUS7289163B2Component can be lostEnhance color transientImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSoft switchImproved method
An improved method for color transient enhancement in an input video frame of pixels. The luminance value of a current pixel is compared to that of neighboring pixels. A correction value is determined and the chrominance value of the current pixel is “pushed” towards the neighboring pixel that has a luminance value closest to that of the current pixel, by adding the correction value to the current pixel's chrominance value. The original video frame is also separately processed using a CTI method, and the current pixel's corrected chrominance value is combined with the corresponding pixel in the output of the CTI processing by soft switching unit to generate an output video frame that is an enhanced version of the input video frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
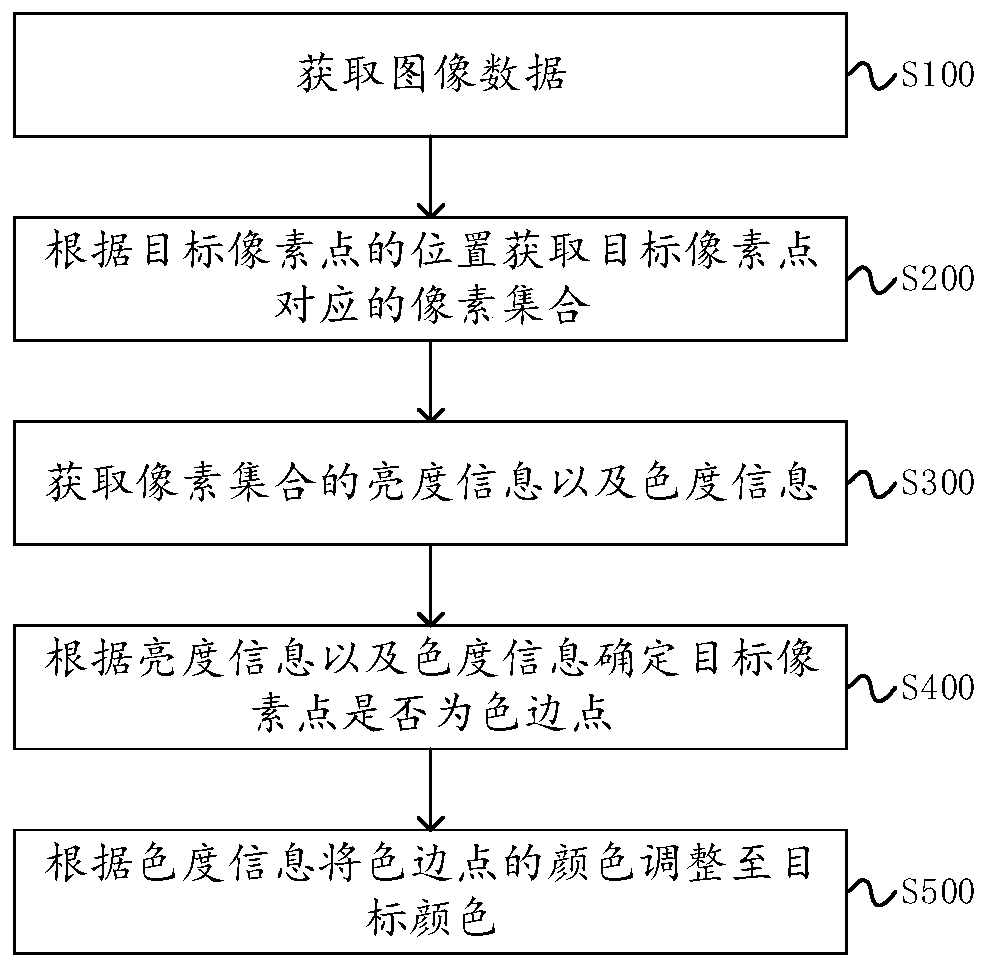
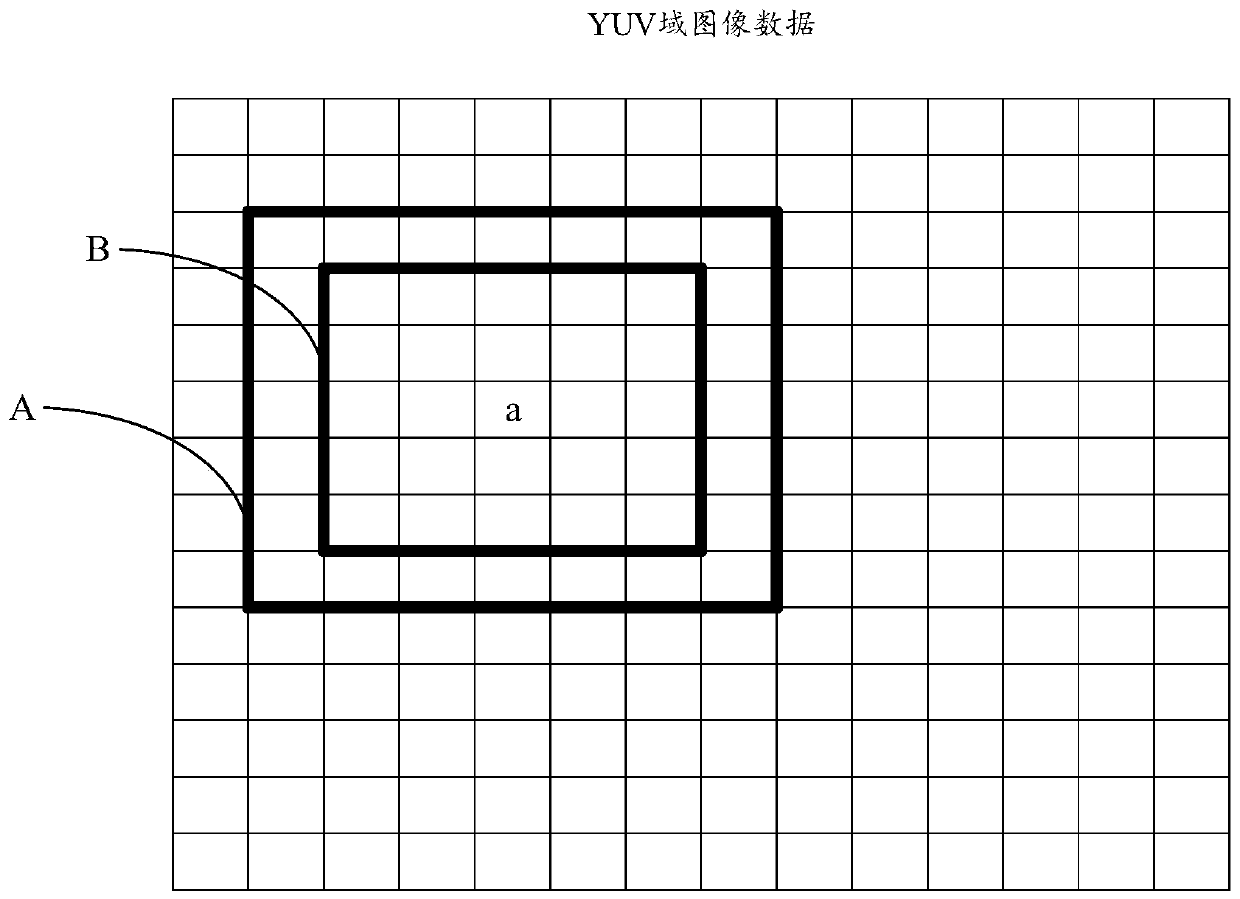
Image color edge eliminating method and device and electronic device
ActiveCN109978961AReduce consumptionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging dataBrightness perception
The embodiment of the invention provides an image color edge elimination method and device and an electronic device, and relates to the field of image data processing. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring image data comprising a plurality of pixel points; obtaining a pixel set corresponding to the target pixel point according to the position of the target pixel point; brightness information and chrominance information of the pixel set are acquired, the brightness information comprises Y-domain data of each pixel in the pixel set, and the chrominance information comprises U-domain and V-domain data of each pixel in the pixel set; determining whether the target pixel point is a color edge point according to the brightness information and the chromaticity information; and adjusting the color of the color edge point to a target color according to the chromaticity information, the target color being a color satisfying a color edge disappearance condition. In the YUV domain ofthe image data, the color edge points are determined according to the brightness information and the chromaticity information, and the colors of the color edge points are adjusted by adopting a point-to-point replacement mode, so that compared with other color edge removing algorithms, the consumption of hardware resources is effectively reduced, and more accuracy is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN GOKE MICROELECTRONICS
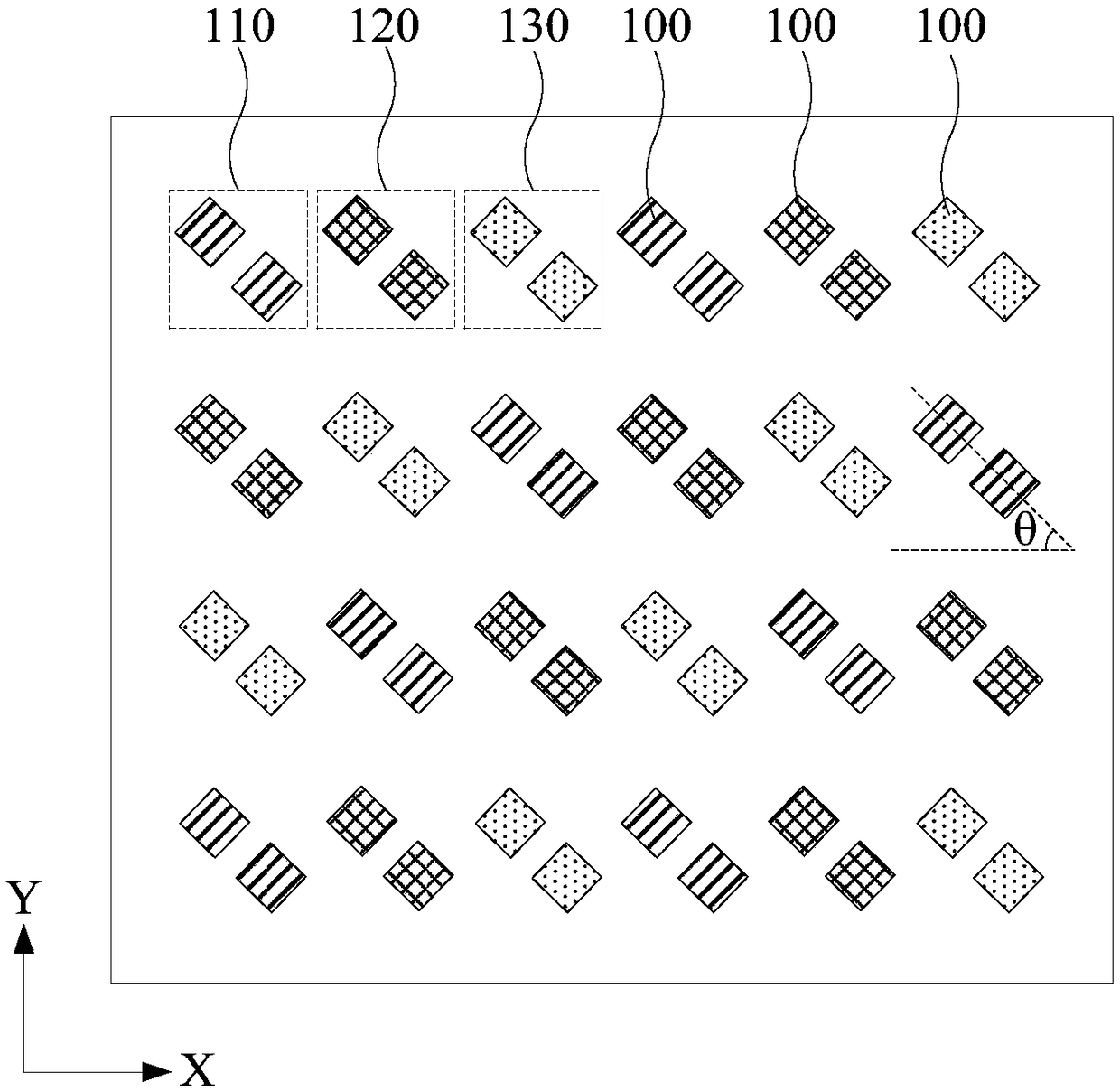
Pixel arrangement structure, display panel and display device
ActiveCN112436031AImprove the color fringing problemSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesComputer graphics (images)Display device
The invention relates to a pixel arrangement structure. The pixel arrangement structure comprises a first sub-pixel, a second sub-pixel, a third sub-pixel and a fourth sub-pixel, the centers of the two first sub-pixels arranged in an aligned mode and the centers of the two second sub-pixels arranged in an aligned mode serve as vertex connecting lines to form a virtual quadrangle, the virtual quadrangle comprises two opposite equilateral sides, a short side and a long side, the short side and the long side are arranged oppositely and connected with the vertexes of the equilateral sides; the short sides of the virtual quadrangle are not parallel to the long sides of the virtual quadrangle; and the third sub-pixel or the fourth sub-pixel is arranged in the virtual quadrangle, and the third sub-pixel and the fourth sub-pixel are the same in light emitting color. According to the pixel arrangement structure, the sub-pixels are arranged in a staggered mode due to the limiting conditions, thesituation that the sub-pixels emitting light of the same color are independently arranged in a column is avoided, and the color edge problem of the display edge is solved. The invention further provides a display panel and a display device.
Owner:KUNSHAN GO VISIONOX OPTO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display substrate, display panel and display device
ActiveCN109300936AImprove edge aliasingComplete red, green and blue sub-pixelsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesAcute angleDisplay device
The invention discloses a display substrate, a display panel and a display device. The display substrate comprises multiple first sub-pixel groups, multiple second sub-pixel groups and multiple thirdsub-pixel groups which are arranged in a matrix; along the row direction and the column direction of the matrix, the first sub-pixel groups, the second sub-pixel groups and the third sub-pixel groupsare sequentially and cyclically arranged; the first sub-pixel groups, the second sub-pixel groups and the third sub-pixel groups all comprise two sub-pixels with the same color, sub-pixels in the first sub-pixel groups, the second sub-pixel groups or the third sub-pixel groups have different colors, and two sub-pixels in the same sub-pixel group are arranged along a direction with an acute angle formed with the matrix row direction. According to the technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention, the gradient of the edge step of the pixel arrays of a circular display screen adopting the above-mentioned pixel arrangement mode is reduced, the edge sawtooth problem is effectively improved, the edge of the circular display screen can have complete red, green and blue sub-pixels,and a color edge phenomenon is eliminated.
Owner:EVERDISPLAY OPTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Method and system for processing color noise in image, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN111882504AImprove deficienciesReduce color bleedingImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionChannel data
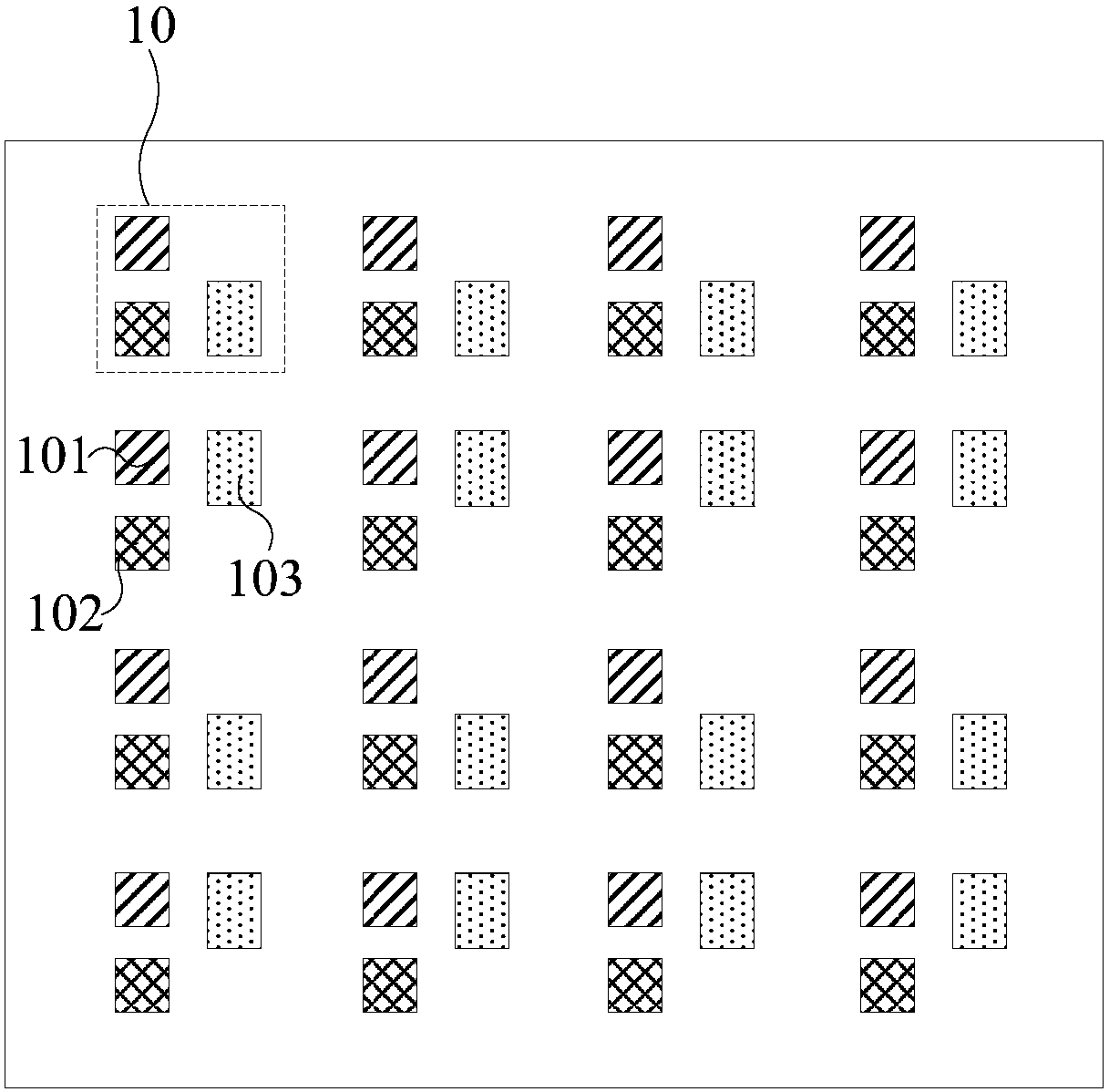
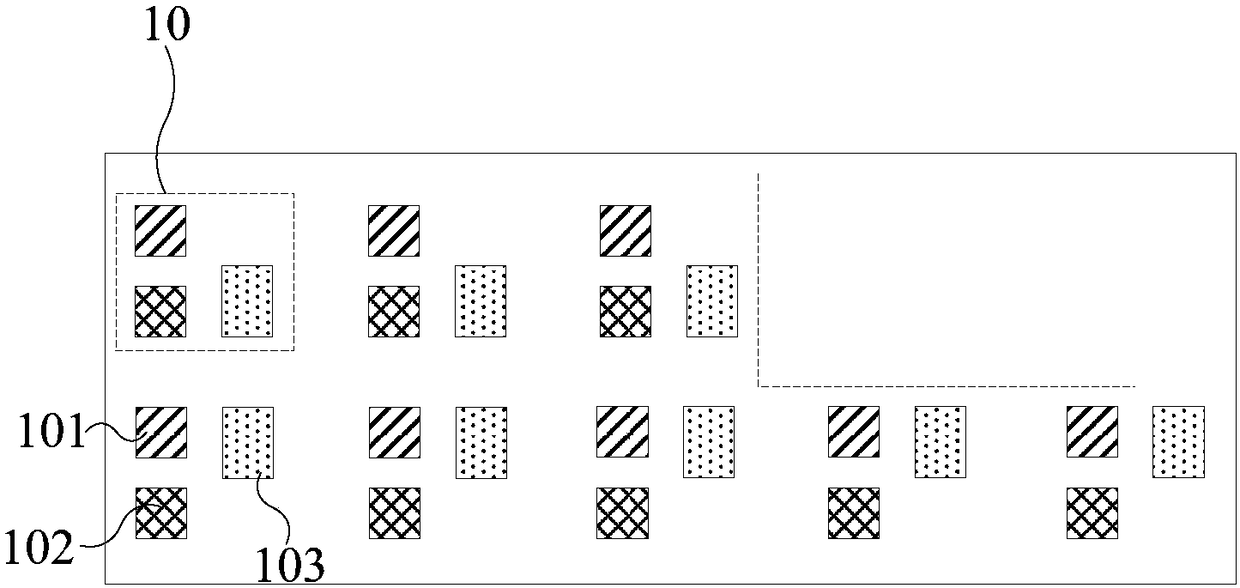
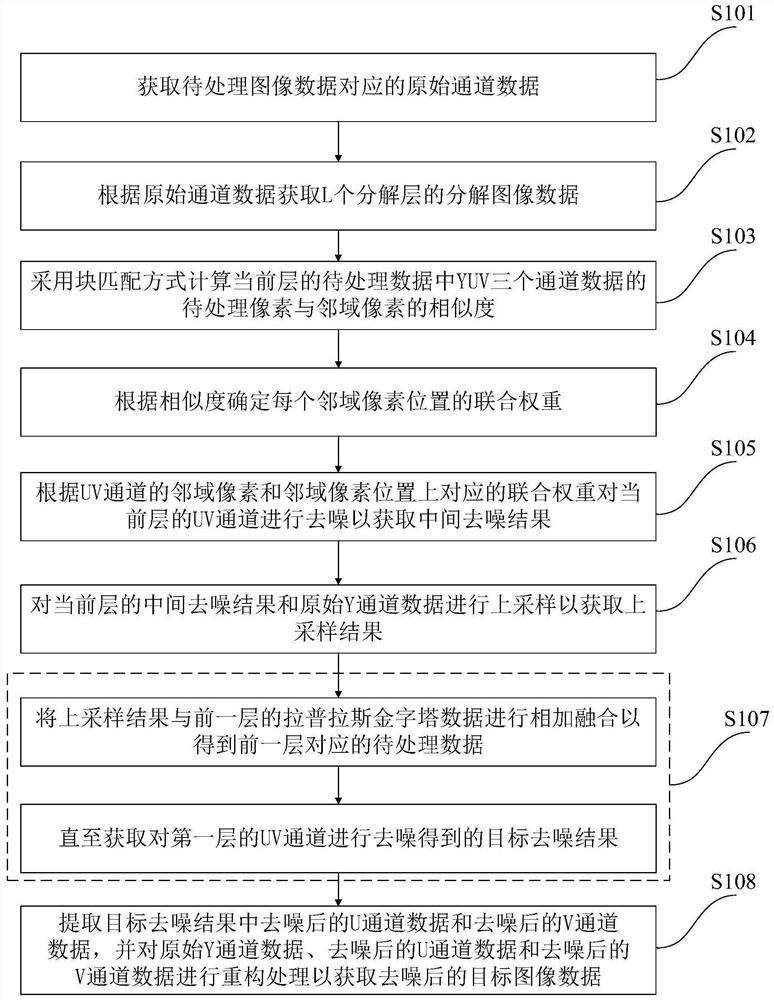
The invention discloses a method and a system for processing color noise in an image, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring original channel data; obtaining decomposed image data of the L decomposition layers; calculating the similarity between to-be-processed pixels and neighborhood pixels of the YUV three-channel data in the to-be-processed data of the Lth layer, determining the joint weight of each neighborhood pixel position, and denoising the UV channel according to the neighborhood pixels of the UV channel and the joint weights atthe neighborhood pixel positions; and performing up-sampling on the denoising result of the Lth layer, combining the denoising result of the Lth layer with the Laplace pyramid data of the L1th layer to obtain data of the L1th layer, performing operation similar to that of the Lth layer on the data, performing circulation in sequence until the data of the first layer is obtained, and performing filtering and denoising on the data to finally obtain denoised image data. According to the invention, large-size color noise and small-particle noise points can be suppressed at the same time, the coloredge retention characteristic is good, and the color overflow phenomenon can be effectively reduced.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com