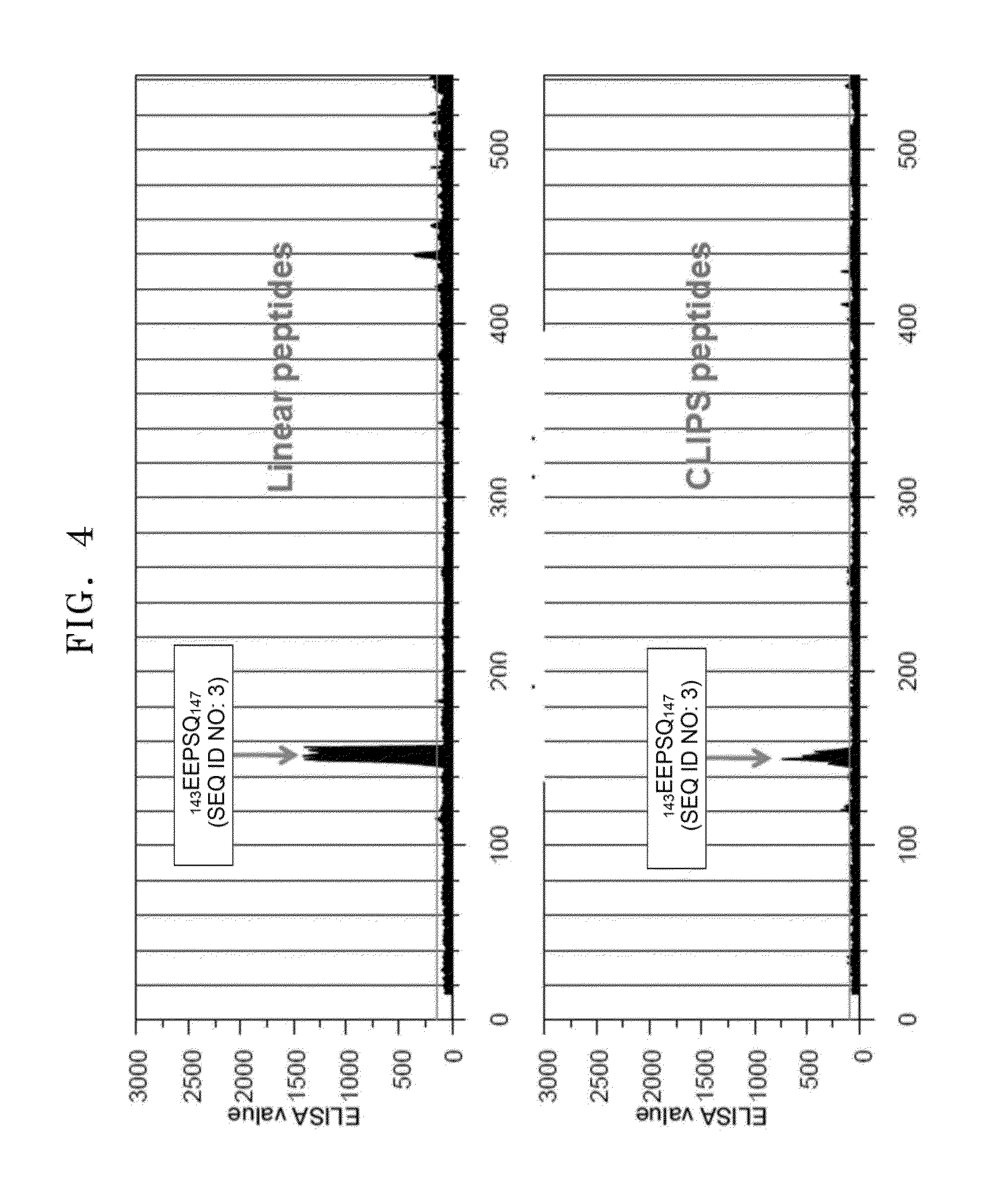
Patents
Literature
118 results about "Epitope specificity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
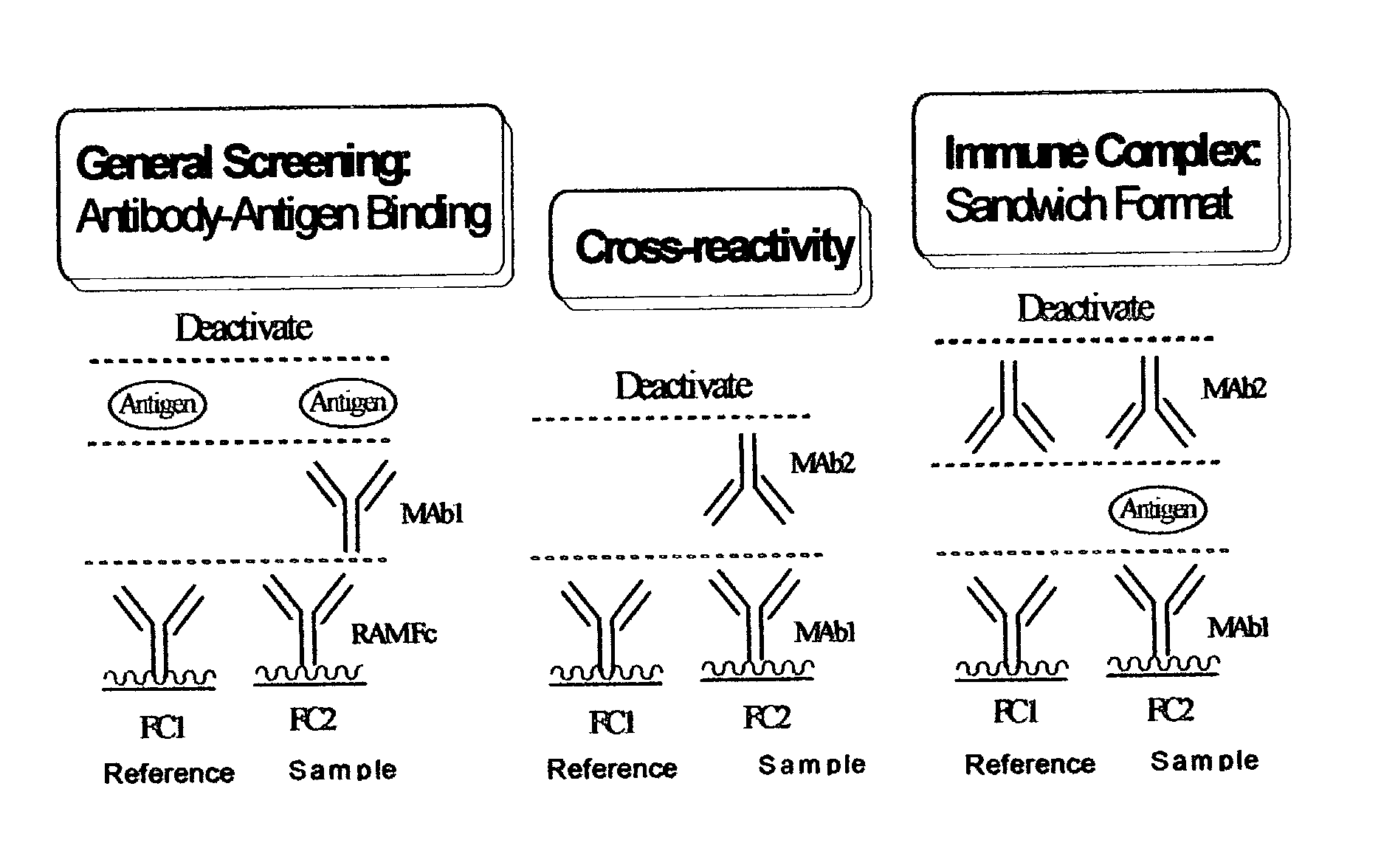
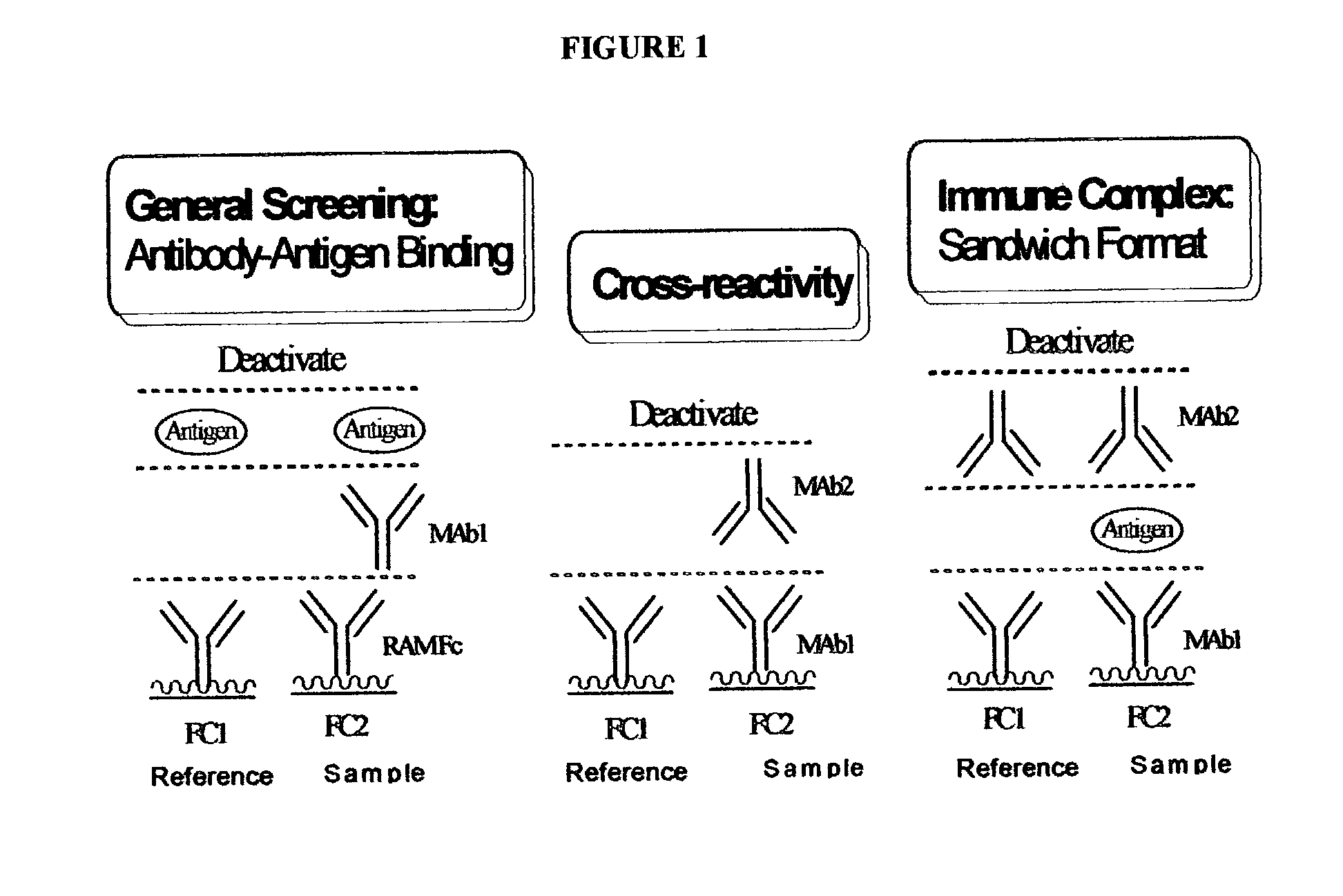
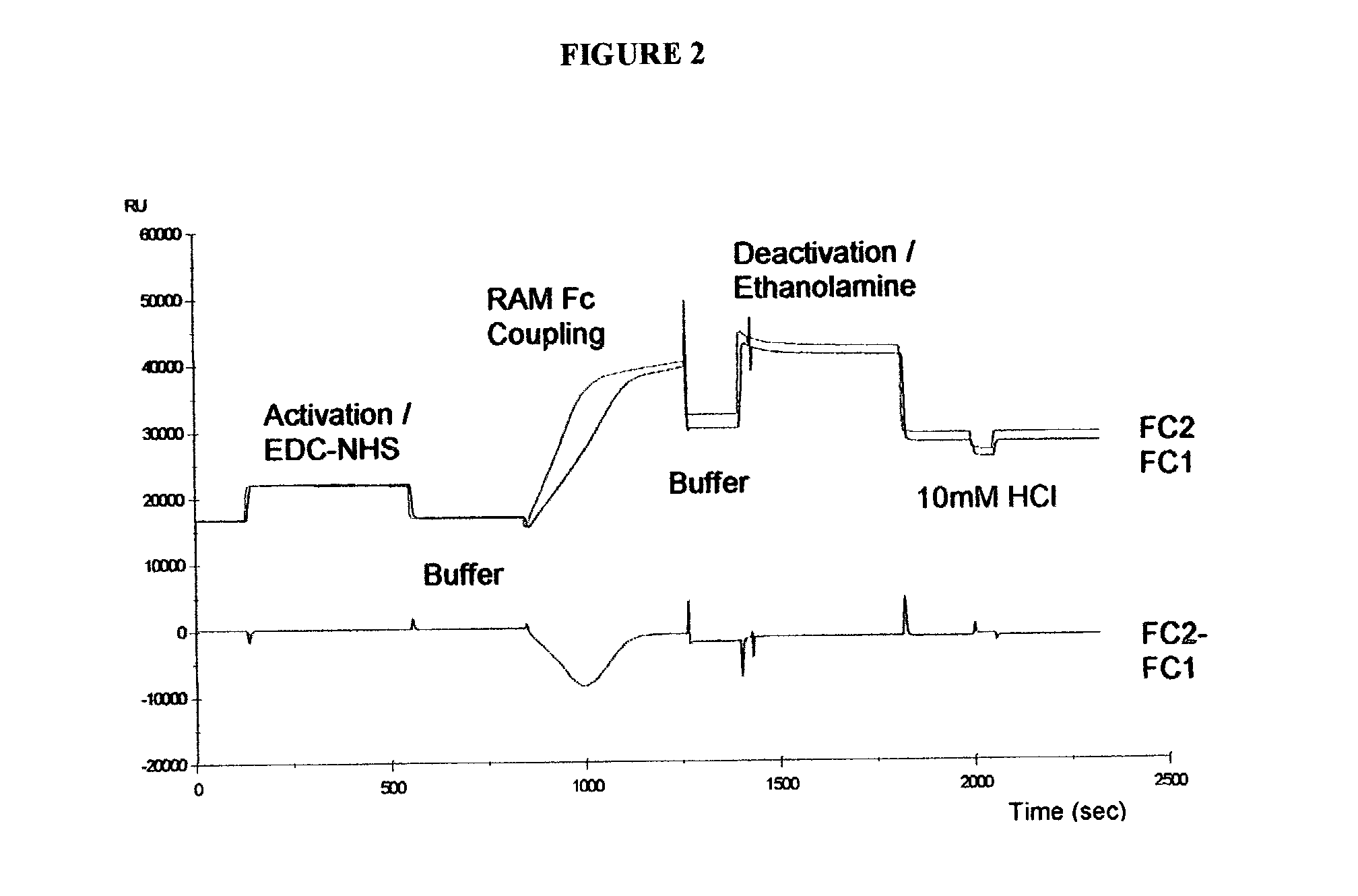
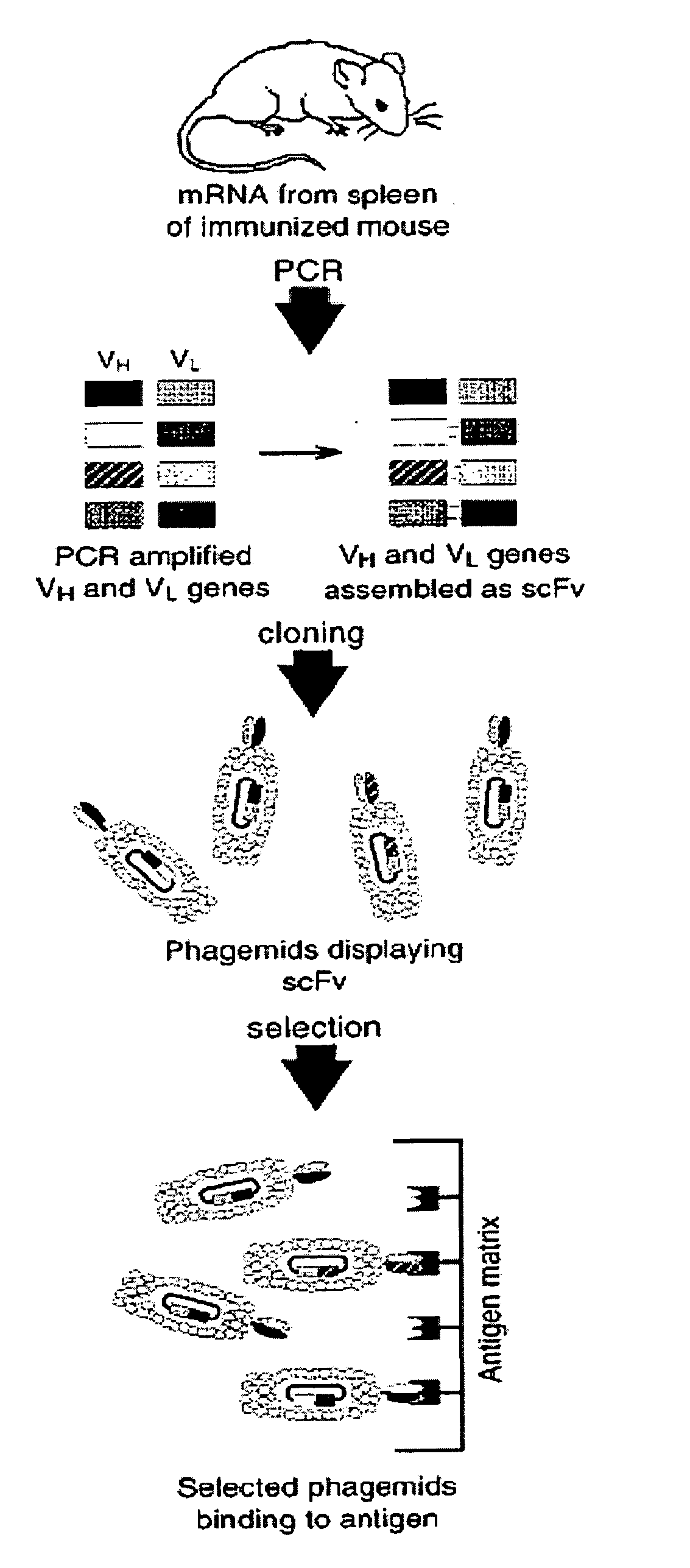
Determination of epitope specificity is an important part of MAb characterization for both investigative work and medical and industrial applications. The epitope specificity of a panel of MAbs is most easily determined by testing the ability of pairs of MAbs to bind simultaneously to the antigen.
Antibodies recognizing a carbohydrate containing epitope on CD-43 and CEA expressed on cancer cells and methods using same
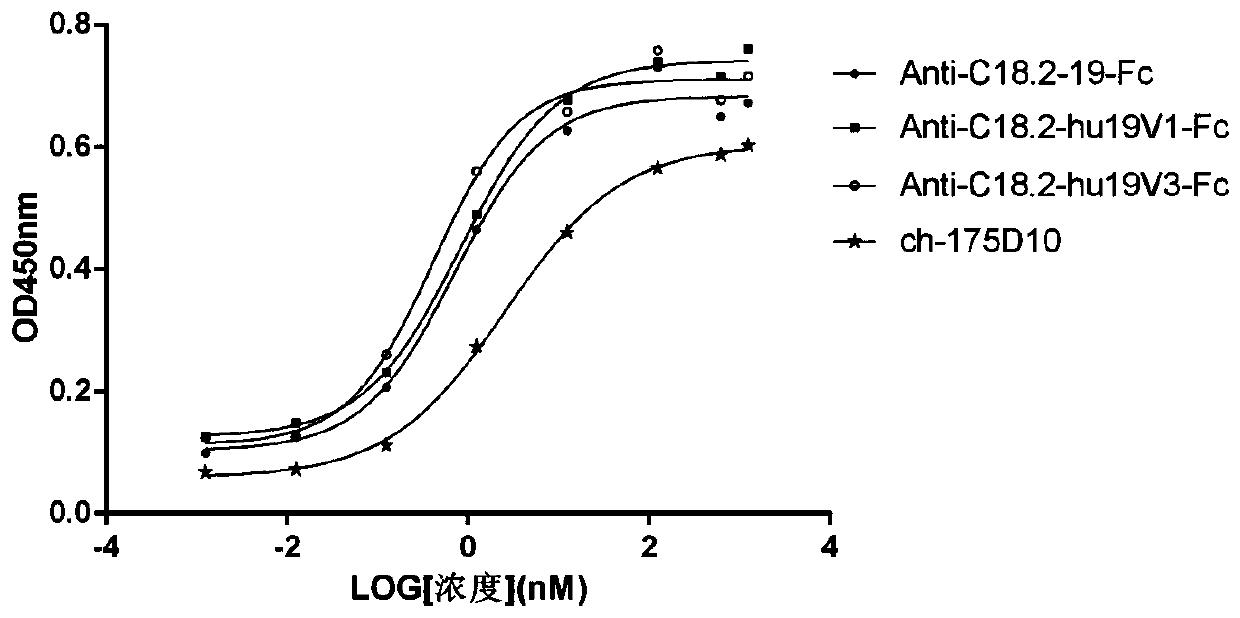
The present invention provides antibodies (such as chimeric and humanized antibodies) specifically bind to an epitope on CD43 and CEA expressed on nonhematopoietic cancer cells. In addition, the present invention also provides use of the antibodies described herein for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Owner:BIOALLIANCE CV
Antibodies recognizing a carbohydrate containing epitope on CD-43 and CEA expressed on cancer cells and methods using same
ActiveUS7674605B2Reduce in quantityInhibit growth and proliferationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationHematopoietic cellCancer cell
The present invention provides novel antibodies specifically bind to an epitope on CD43 and CEA expressed on nonhematopoietic cancer cells, but do not specifically bind to a CD43 expressed by a leukocyte or by a Jurkat cell, and is capable of inducing apoptosis of the nonhematopoietic cancer cell after binding to the epitope on cell surface of the nonhematopoietic cancer cell in the absence of cytotoxin conjugation and immune effector function, wherein the epitope comprises a carbohydrate structure and the binding of the antibody to the epitope is inhibited by a carbohydrate comprising a Lea structure, a Lea-lactose structure, a LNDFH II structure, or a LNT structure. In addition, the present invention also provides use of the antibodies described herein for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Owner:ALTRUBIO INC
Antibody pair screening methods
The invention provides methods for identifying antibody preparations that can form a pair of antibodies that optimally detect a target antigen, for example, in a sandwich immunoassay. These methods provide high affinity and epitope-specific antibodies.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Test device and method for colored particle immunoassay
InactiveUS20060040405A1Minimize false positiveEasy to useEnzymologyLaboratory glasswaresEpitope specificityCell space
Disclosed is a test cell and a method for detection of a preselected ligand in a liquid sample such as a body fluid. The test cell includes an elongate outer casing which houses an interior permeable material capable of transporting an aqueous solution and defining a sample inlet, a test volume, and a reservoir volume. The reservoir volume is disposed in a section of the test cell spaced apart from the inlet and is filled with sorbent material. The reservoir acts to receive liquid transported along a flow path defined by the permeable material and extending from the inlet and through the test volume. In the test volume is a test site which includes a first protein having a binding site specific to a first epitope of the ligand immobilized in fluid communication with the flow path. The test site can be observed through a window of the casing.
Owner:CHARLTON DAVID E +1
Methods for identifying multiple epitopes in selected sub-populations of cells
InactiveUS20180320241A1Maximize probabilityInhibition formationMicrobiological testing/measurementAssay labelsEpitope specificitySub populations
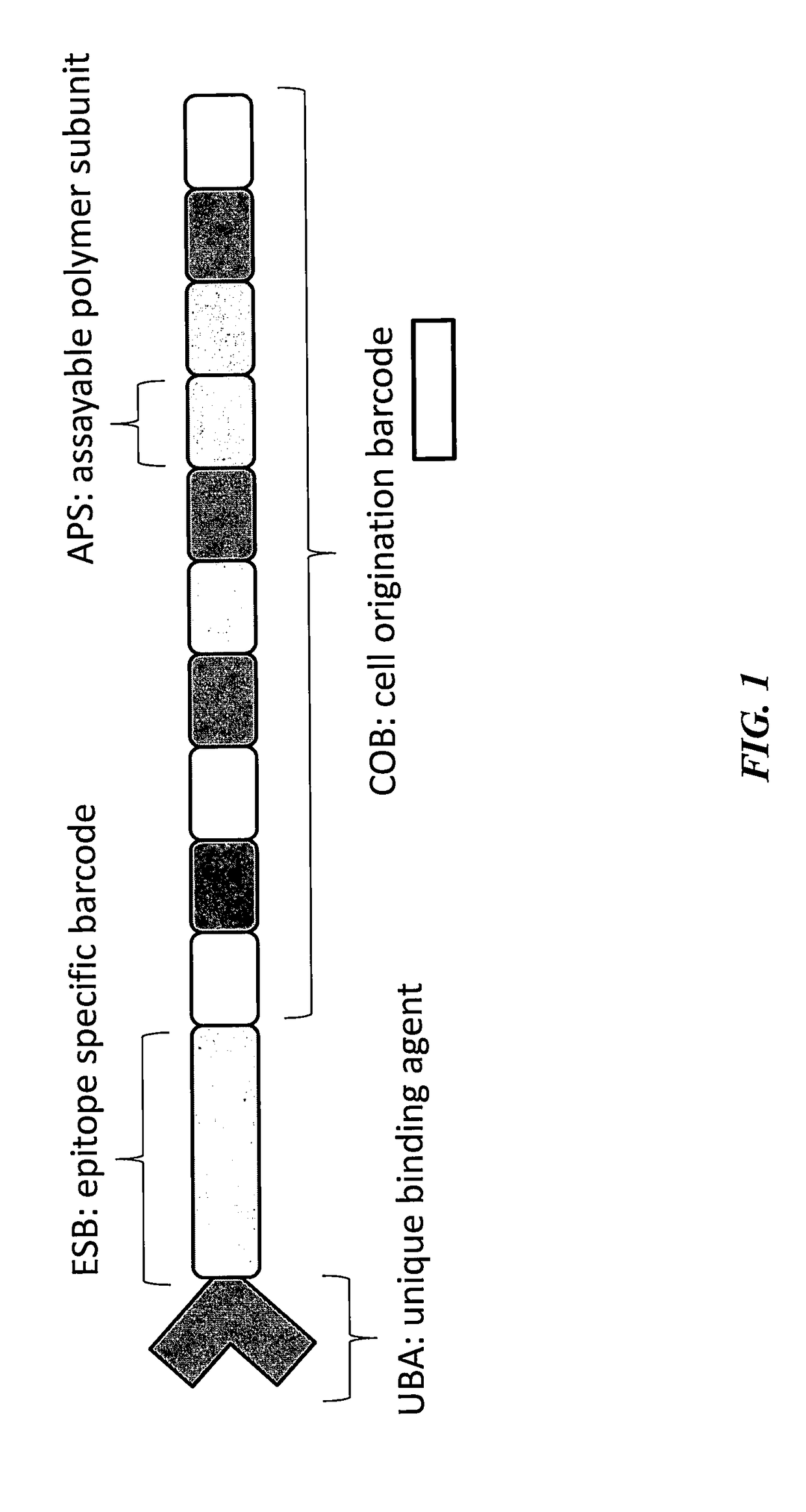
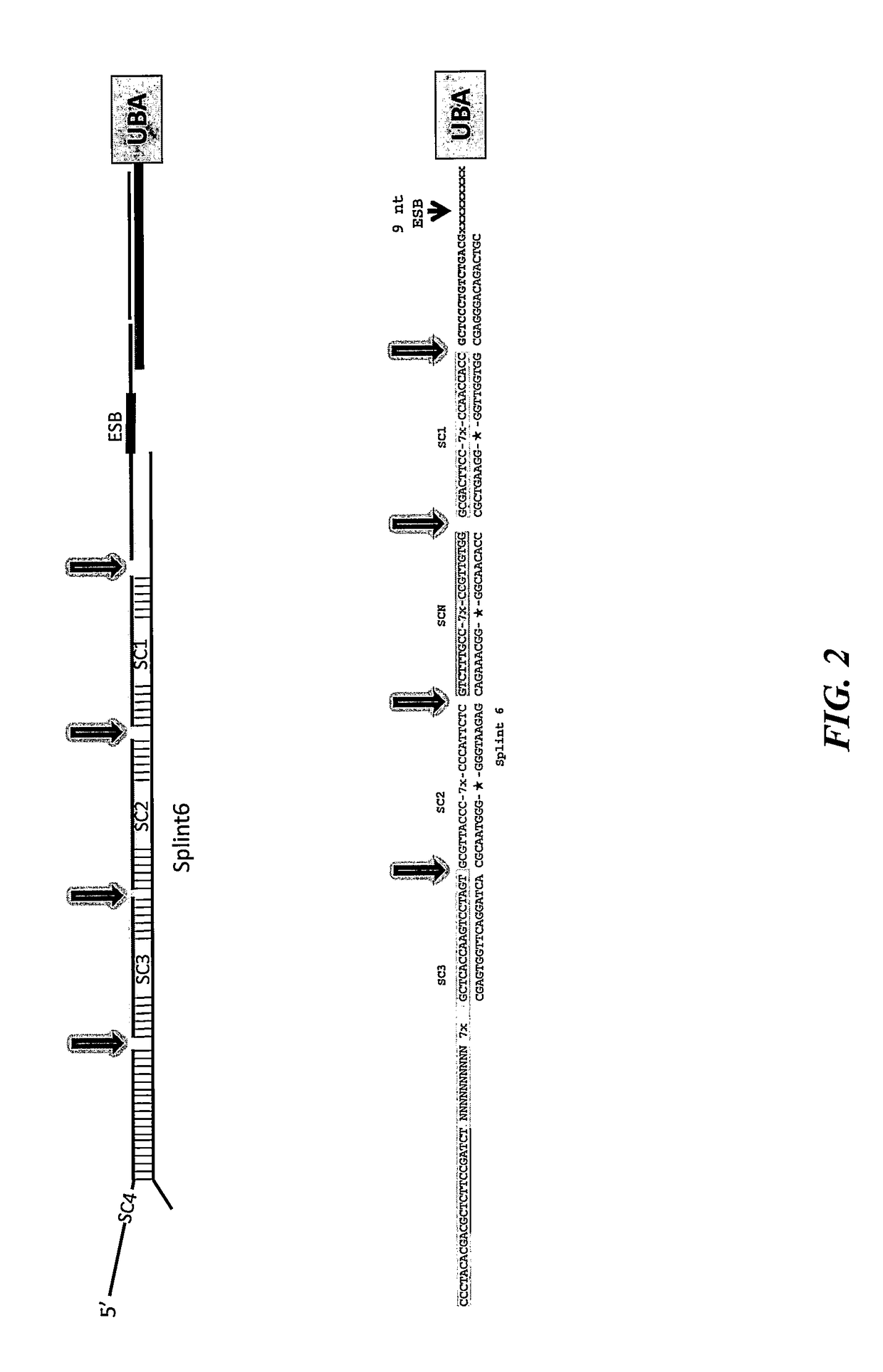
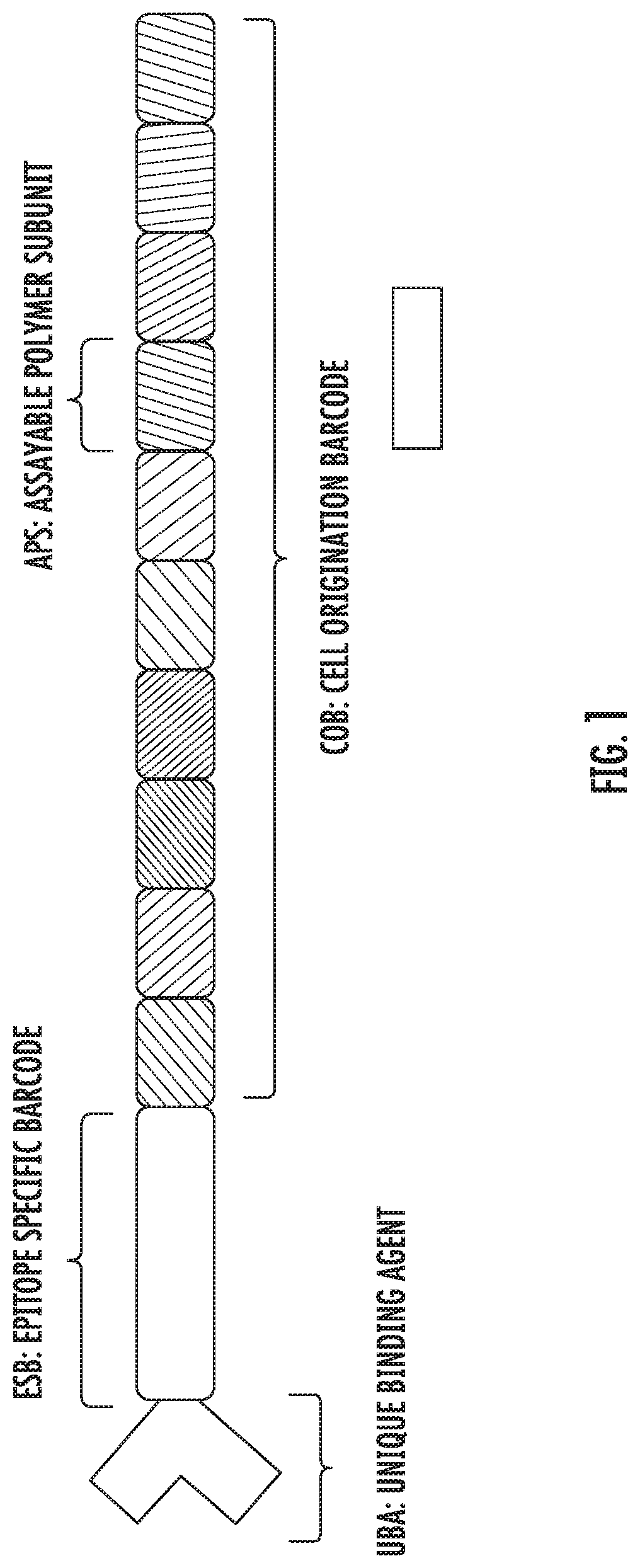
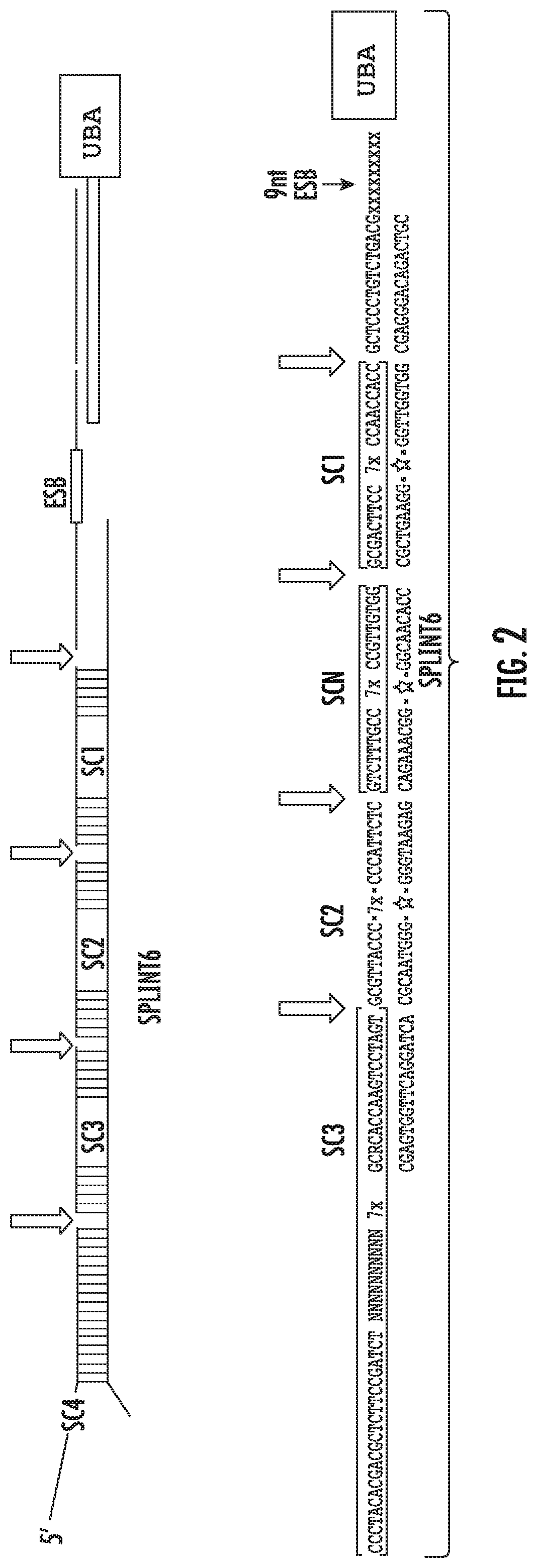
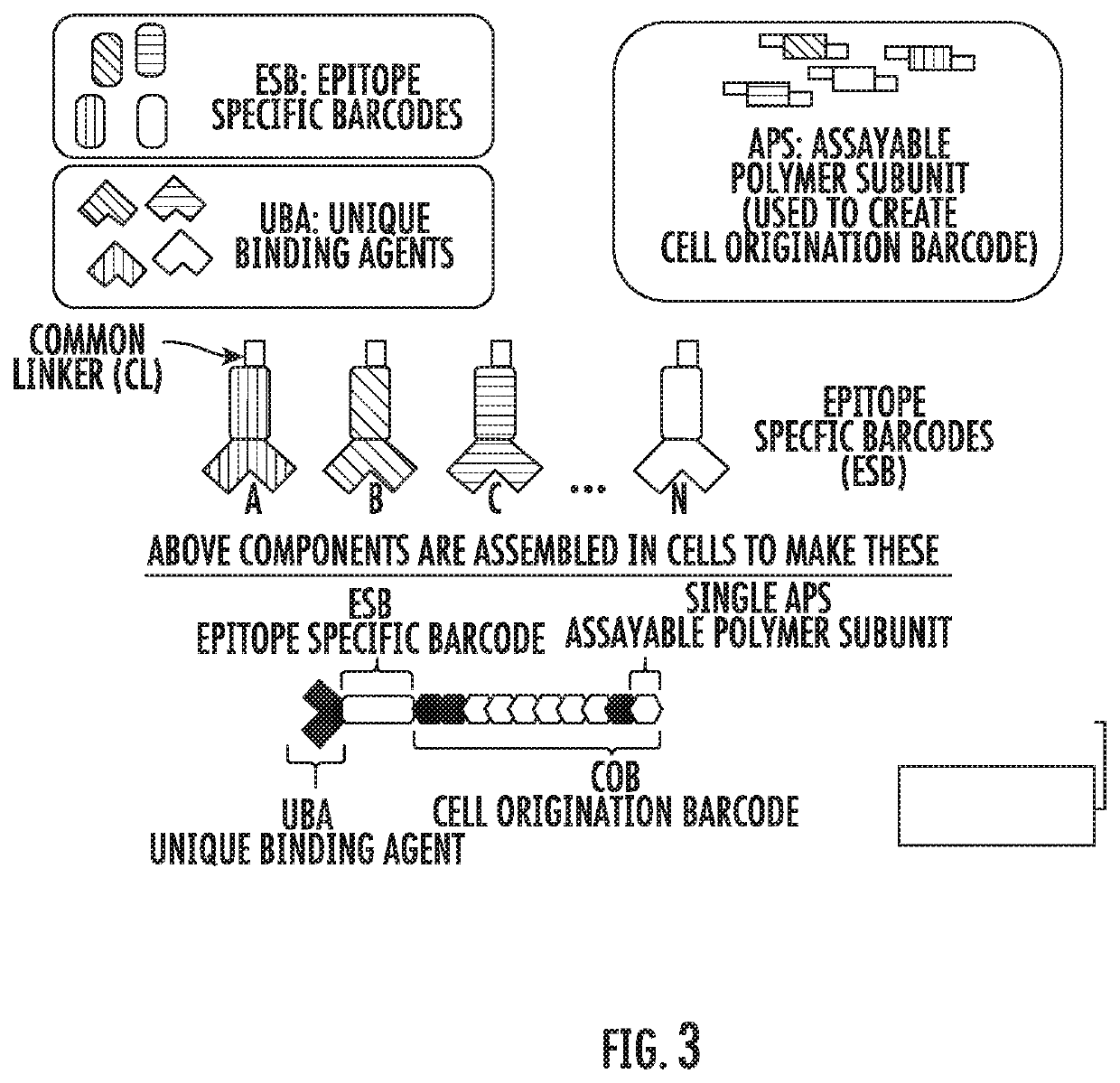
A method for identifying a sub-population within a mixed population of cells is disclosed. The method involves contacting the mixed population of cells with at least one unique binding agent, wherein the at least one unique binding agent is designed to bind to a target molecule present in the sub-population, and wherein the at least one unique binding agent is attached to an epitope specific barcode that represents the identity of the target molecule. The method further involves sequentially attaching two or more assayable polymer subunits to the epitope specific barcode to create unique cell origination barcodes that represent the identities of individual cells to which the at least one unique binding agent has bound; and decoding the epitope specific barcode and cell origination barcodes, thereby identifying the sub-population within the mixed population of cells.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
Human monoclonal antibody
InactiveUS20050175986A1Increase concentrationReduce the amount requiredAnimal cellsSugar derivativesEpitope specificityProphylactic treatment
This invention relates to novel human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and to the genes encoding same. More specifically, this invention relates to human monoclonal antibodies specifically reactive with an epitope of the fusion (F) protein of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). Such antibodies are useful for the therapeutic and / or prophylactic treatment of RSV infection in human patients, particularly infants and young children.
Owner:SMIT KLINE BEECHAM +1
Reagents and treatment methods for autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20080118505A1Clinical improvementImprove curing speedSenses disorderAntipyreticDiseaseEpitope
The invention concerns treatment methods using anti-CD22 monoclonal antibodies with unique physiologic properties. In particular, the invention concerns methods for the treatment of B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases by administering an effective amount of a blocking anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody specifically binding to the first two Ig-like domains, or to an epitope within the first two Ig-like domains of native human CD22 (hCD22).
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies that neutralize botulinum neurotoxins
ActiveUS20100166773A1Low toxicityExtension of timeAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaMedicineNeutralizing epitope
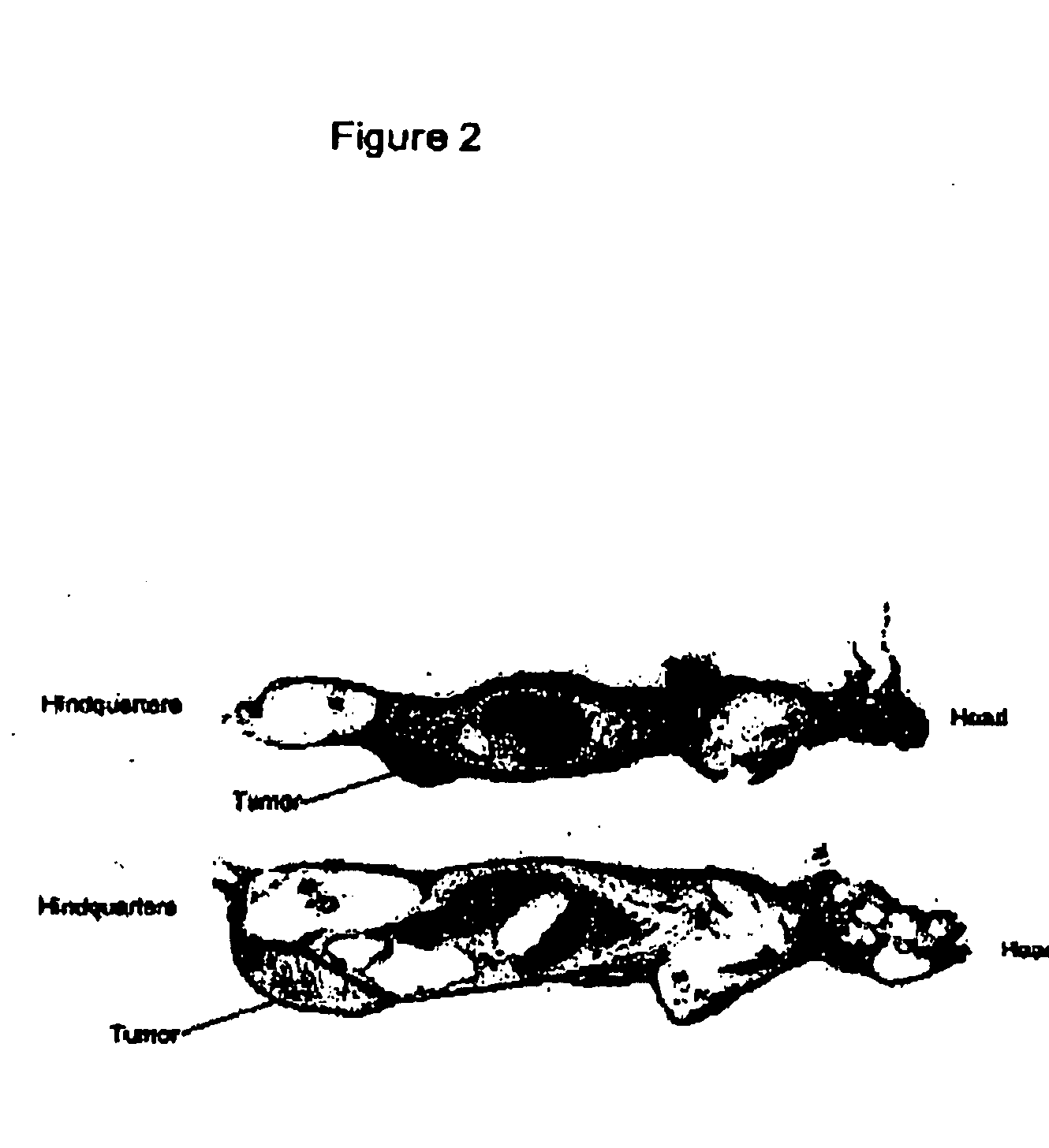
This invention provides antibodies that specifically bind to and typically neutralize botulinum neurotoxins (e.g., BoNT / A, BoNT / B, BoNT / E, etc.) and the epitopes bound by those antibodies. The antibodies and derivatives thereof and / or other antibodies that specifically bind to the neutralizing epitopes provided herein can be used to neutralize botulinum neurotoxin and are therefore also useful in the treatment of botulism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Immunogenic compositions and diagnostic and therapeutic uses thereof
ActiveUS20060147476A1Improve diseasePreventing itBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMicroorganismEpitope specificity
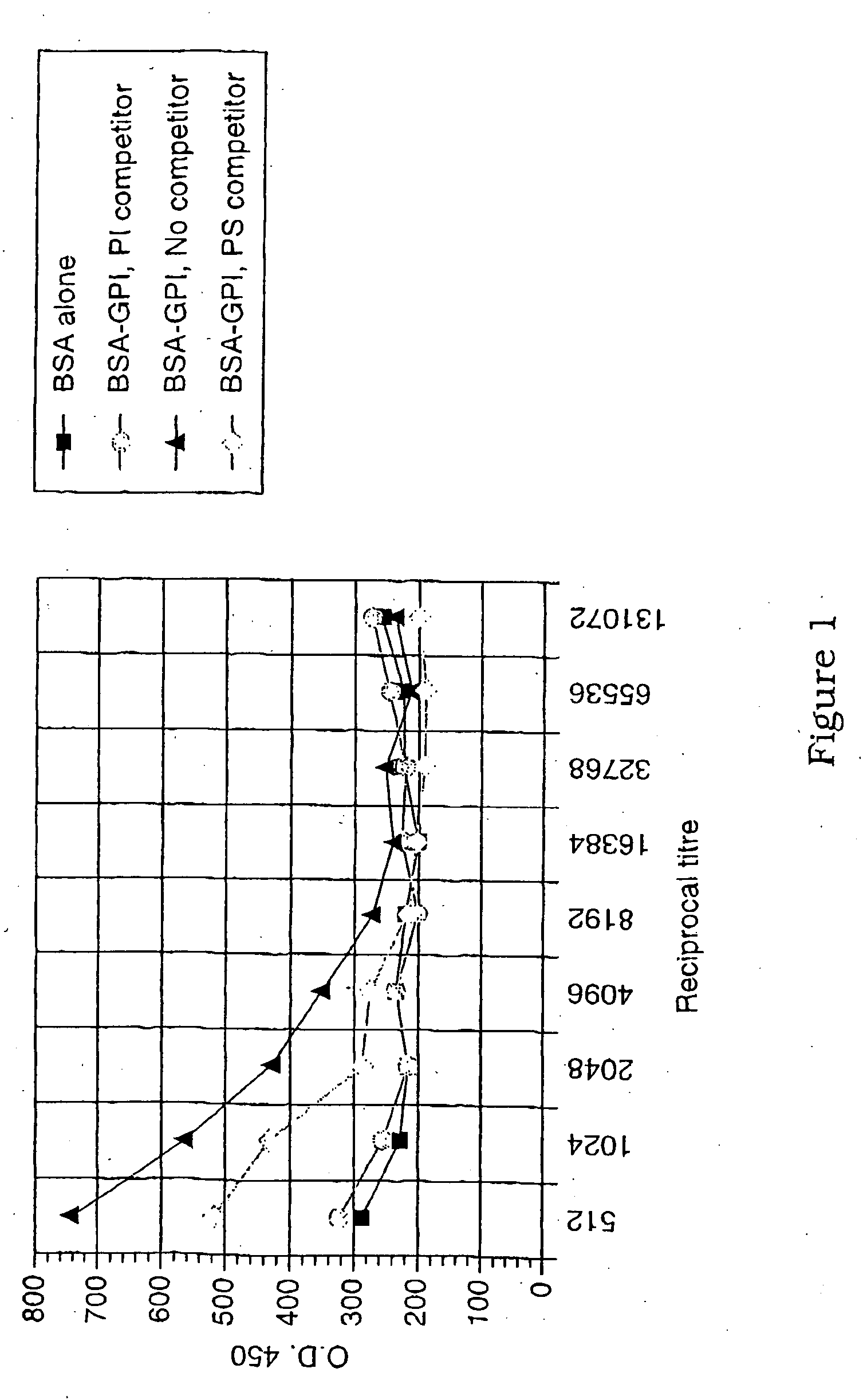
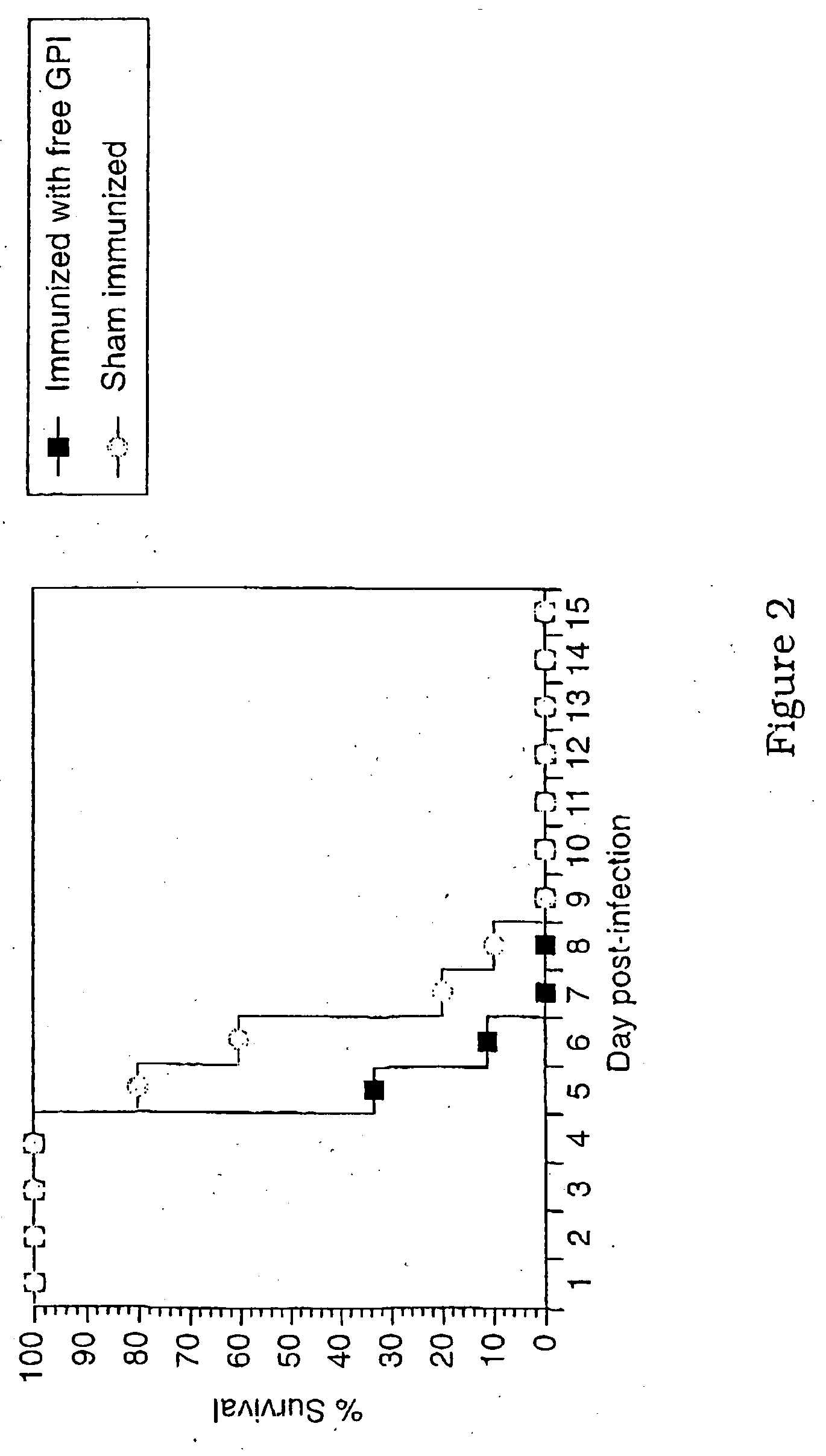
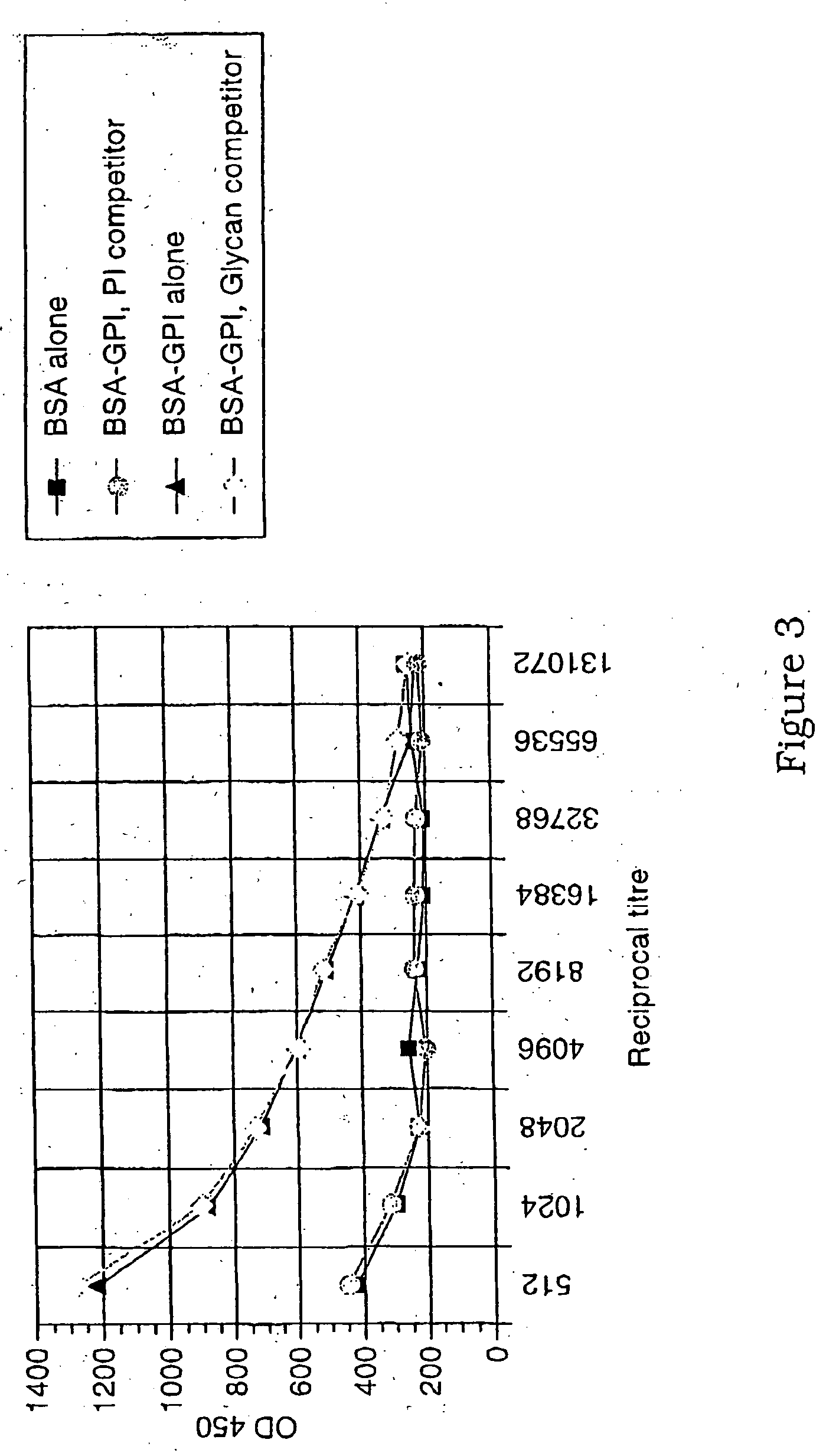
The present invention relates generally to a method of eliciting or otherwise inducing an immune response to a microorganism and compositions for use therein. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method of inducing an immune response to a parasite utilising an immunogenic composition comprising a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (referred to herein as “GPI”) inositolglycan domain or its derivative or equivalent. The present invention is useful, inter alia, as a prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment for microorganism infections of mammals such as, for example, parasite infections and in particular infection by Plasmodium species. In another aspect the invention provides a method of diagnosing, monitoring, screening for or otherwise qualitatively or quantitatively assessing an immune response to a microorganism and, in particular, a parasite. More particularly, this aspect of the present invention is directed to assessing said immune response utilising a GPI inositoglycan domain or its derivative or equivalent. The development of this aspect of the present invention facilitates, inter alia, the qualitative and / or quantitative analysis of anti-GPI antibodies in a biological sample, the identification and / or isolation of unique specificities of antibodies (such as those which bind a parasite derived toxin or the parasite itself), epitope specific screening or the rational design of immunogenic molecules and the generation, thereby, of functionally effective immunointeractive molecules.
Owner:WALTER & ELIZA HALL INST OF MEDICAL RES
Alpaca-derived nanobody binding to SARS-CoV-2 RBD
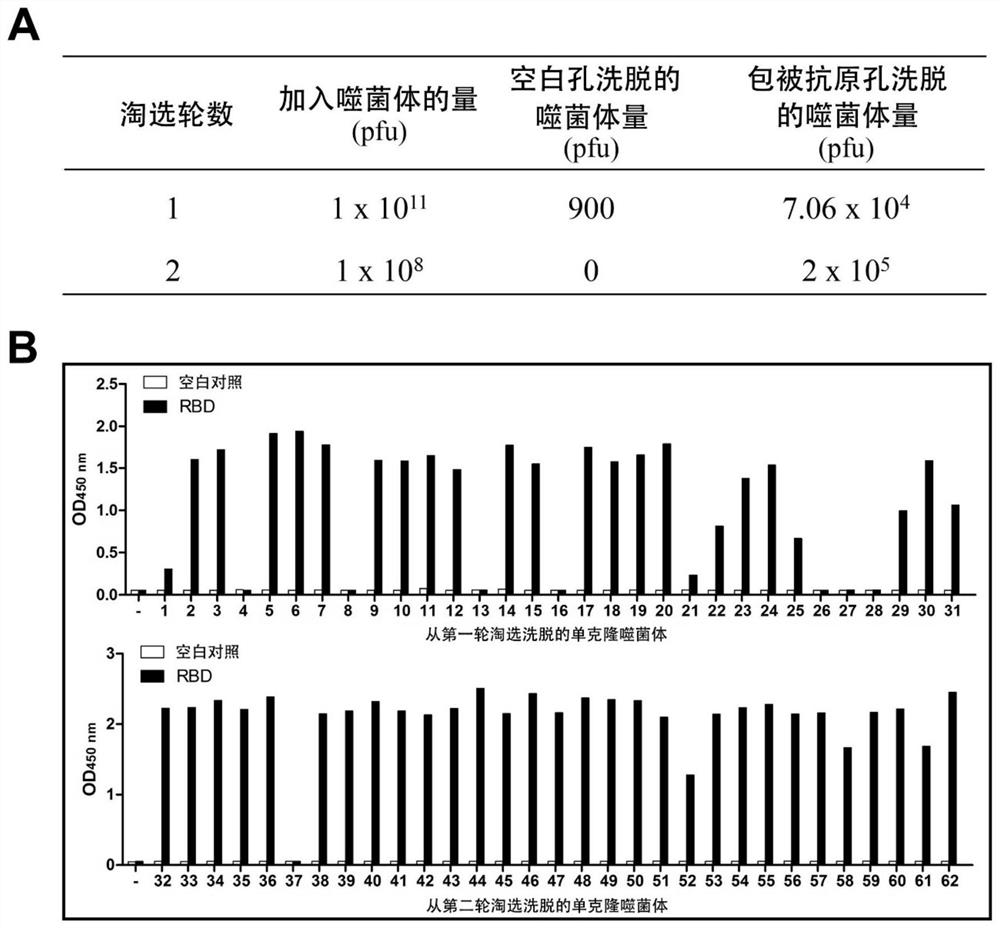
ActiveCN112094342AImprove stabilityHigh expressionHybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against virusesViral ReceptorEpitope specificity
The present invention relates to an alpaca-derived nanobody binding to SARS-CoV-2 RBD or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, and particularly relates to an alpaca-derived nanobody capable of bindingto a neocoronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) receptor binding Region (RBD) with high affinity or a double epitope-specific antibody composed thereof or an antigen-binding fragment thereof, which can be used for preventing, treating and / or diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Monoclonal antibody with liver cancer resisting activity and application thereof
ActiveCN102180969AStrong specificityImprove bindingMicroorganism based processesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigen epitopeAntigen
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody with a liver cancer resisting activity and application thereof. The monoclonal antibody can perform specific binding with glypican-3 (GPC3) antigen epitope; and the amino acid sequence of the GPC3 antigen epitope is 359th-580th amino acid residue from an amino terminal with Gen Bank accession Number of AAA98132.1. In the invention, a high-valence high-specificity mouse-anti-human GPC3-C monoclonal antibody with an immunological activity and a cancer cell poisoning activity is prepared, thereby establishing an experimental foundation for studying expression and distribution of GPC3 in tissues and cells, deeply studying biological function of GPC3 protein and early detecting liver cancer in clinic and providing a non-toxicity auxiliary medicament.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Method for detecting pig plague virus specific antibody and its ELISA reagent kit
InactiveCN101144818AGuaranteed specificityGuaranteed Differential DiagnosisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElisa kitSwine Fever Virus
The invention discloses a method for detecting the specific antibody of classical swine fever virus and a special ELISA kit thereof. The kit includes a classical swine fever virus antigen and an enzyme-labeled classical swine fever virus single-epitope specific antibody; the said swine fever virus antigen is a polypeptide containing one or more than one amino acid residue sequence described in sequence 1. The detection reagent of the classical swine fever virus specific antibody of the present invention can carry out effective detection to the classical swine fever virus specific antibody by solid-phase antigen competition ELISA (blocking method); The B cell epitope ensures the differential diagnosis, and the high degree of conservation of the epitope among various strains ensures the specificity of detection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
Antibodies recognizing a carbohydrate containing epitope on CD-43 and CEA expressed on cancer cells and methods using same
ActiveUS20080171043A1Reduce in quantityInhibit growthImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFermentationCancer cellHematopoietic cell
The present invention provides novel antibodies specifically bind to an epitope on CD43 and CEA expressed on nonhematopoietic cancer cells, but do not specifically bind to a CD43 expressed by a leukocyte or by a Jurkat cell, and is capable of inducing apoptosis of the nonhematopoietic cancer cell after binding to the epitope on cell surface of the nonhematopoietic cancer cell in the absence of cytotoxin conjugation and immune effector function, wherein the epitope comprises a carbohydrate structure and the binding of the antibody to the epitope is inhibited by a carbohydrate comprising a Lea structure, a Lea-lactose structure, a LNDFH II structure, or a LNT structure. In addition, the present invention also provides use of the antibodies described herein for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
Owner:ALTRUBIO INC
Identification of gene sequences and proteins involved in vaccinia virus dominant T cell epitopes
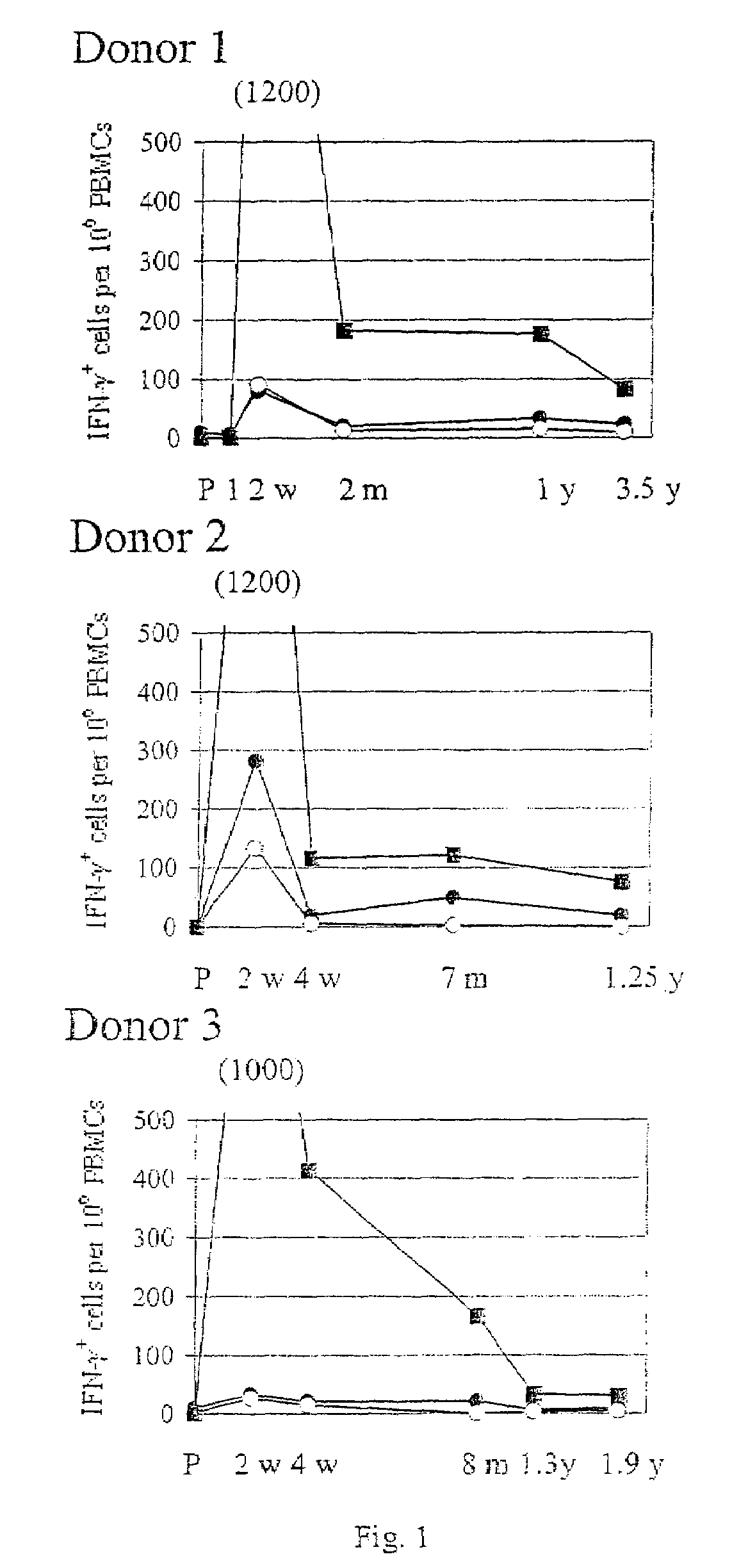
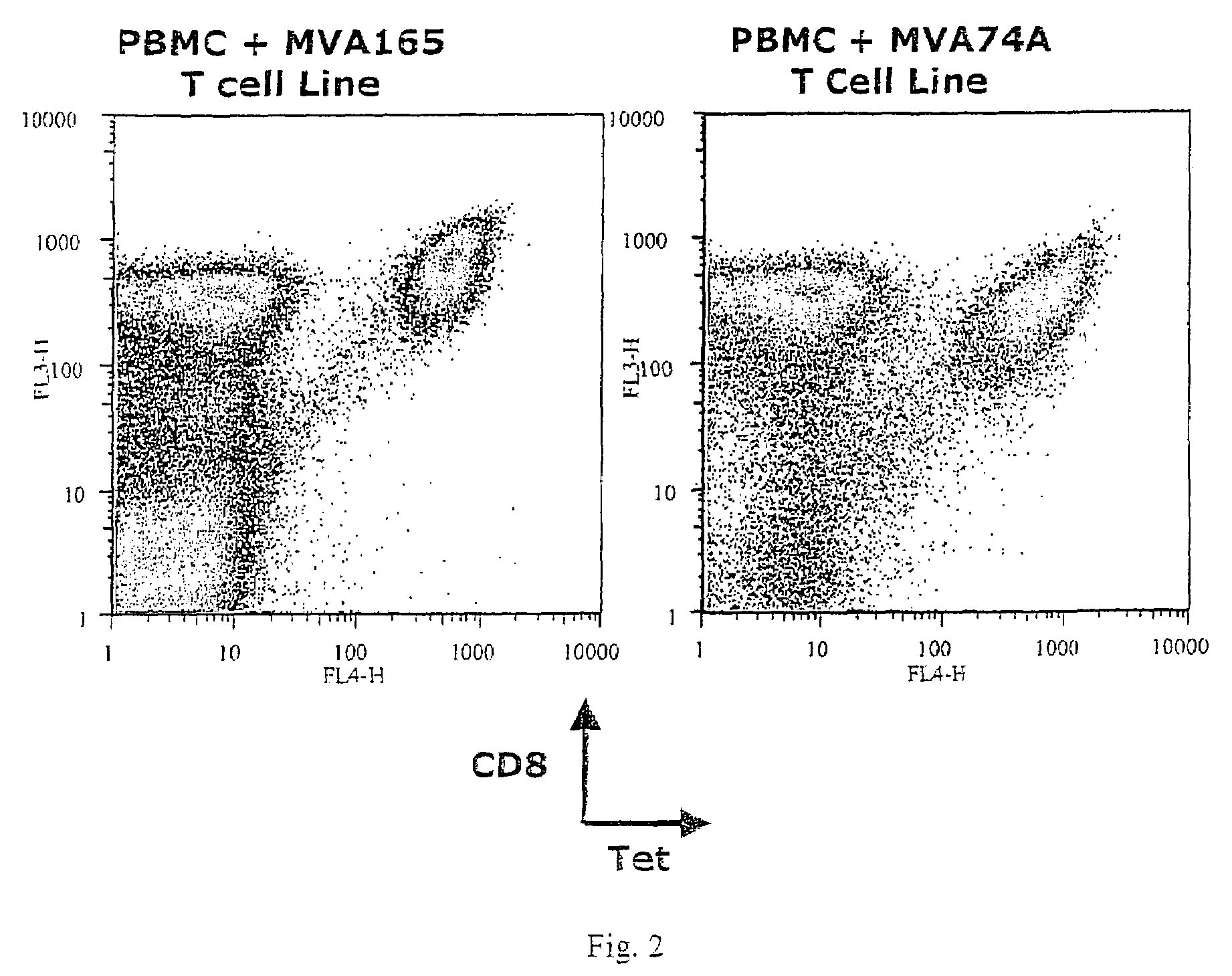
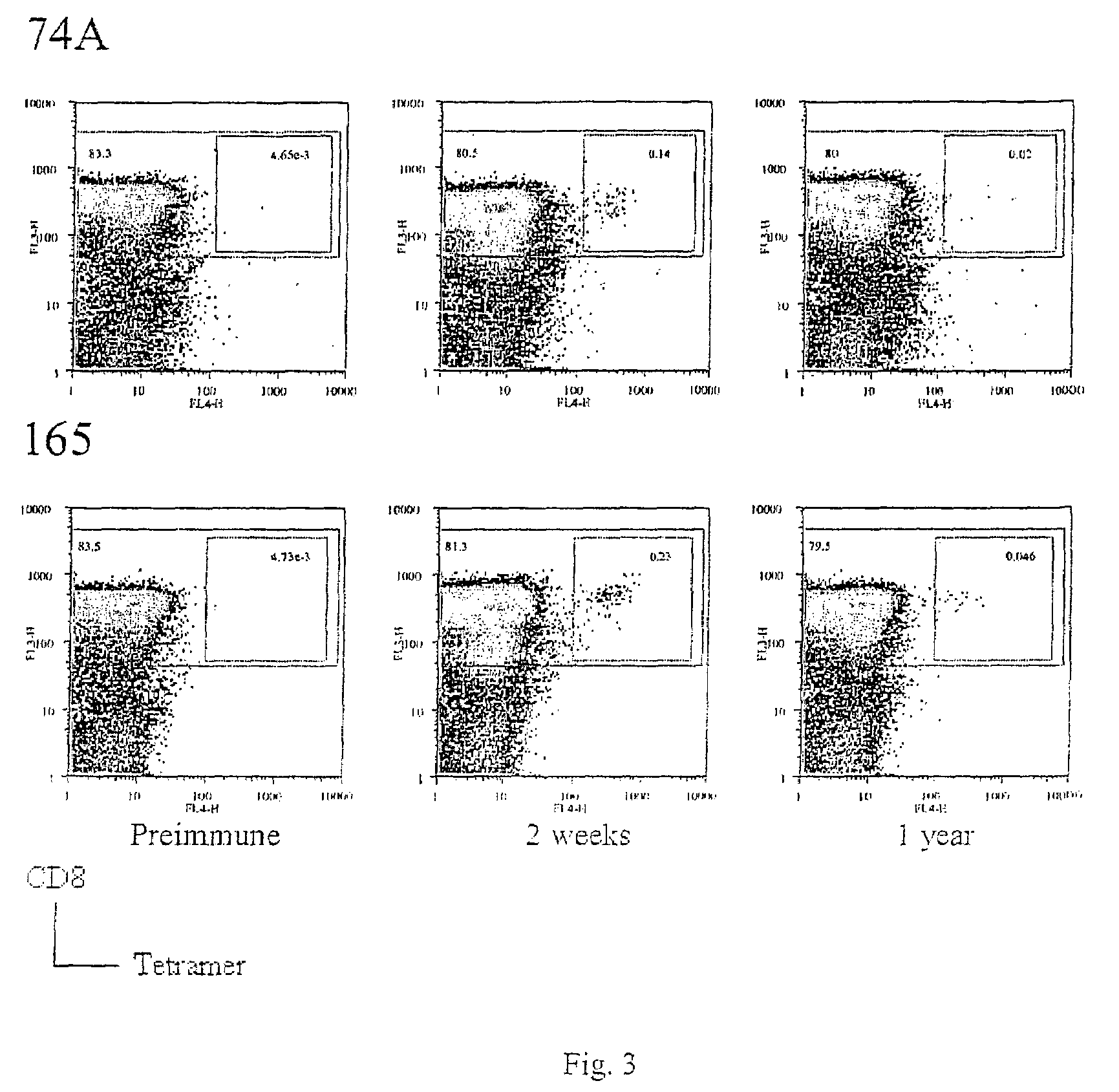
The present invention relates to the identification of gene sequences and proteins involved in vaccinia virus dominant T cell epitopes. Two vaccinia virus CD8+ T cell epitopes restricted by the most common human MHC class I allele, HLA-A0201 have been identified. Both epitopes are highly conserved in vaccinia and variola viruses. The induction of the T cell responses following primary vaccination is demonstrated by the kinetics of epitope specific CD8+ T cells in 3 HLA-A0201 individuals. This information will be useful for the design and analyses of the immunogenicity of experimental vaccinia vaccines, and for basic studies of human T cell memory.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL SCHOOL
Anti-CLD18A2 nanobody and application thereof
ActiveCN111434692AAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPill deliveryEpitope specificityComplementarity determining region
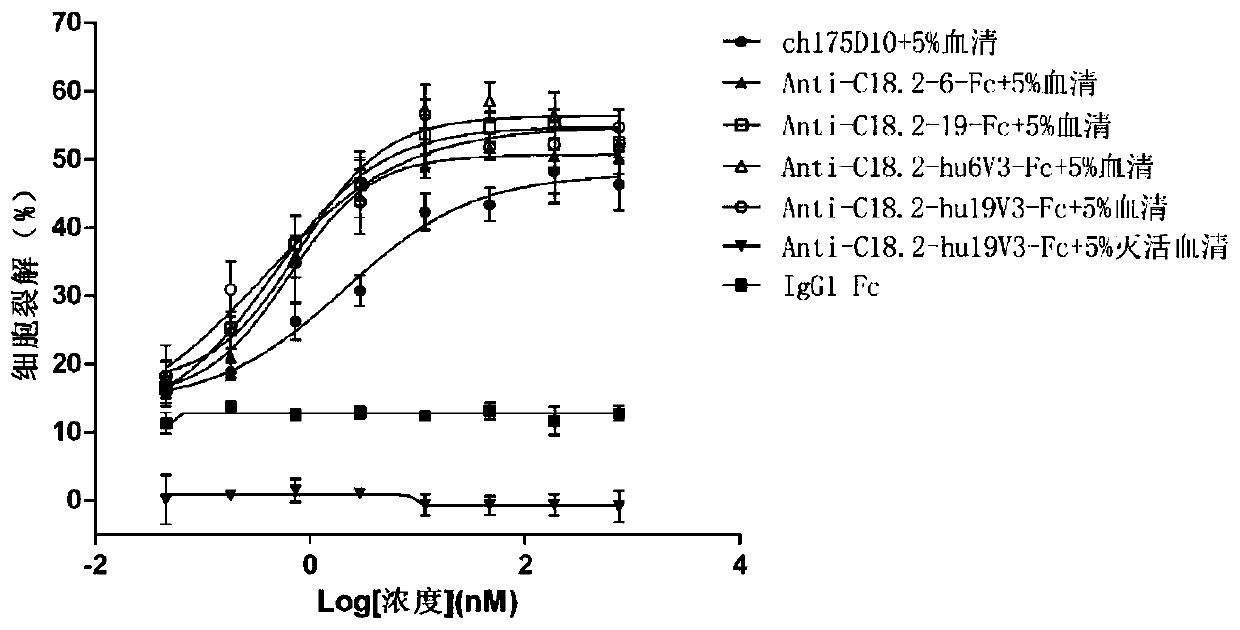
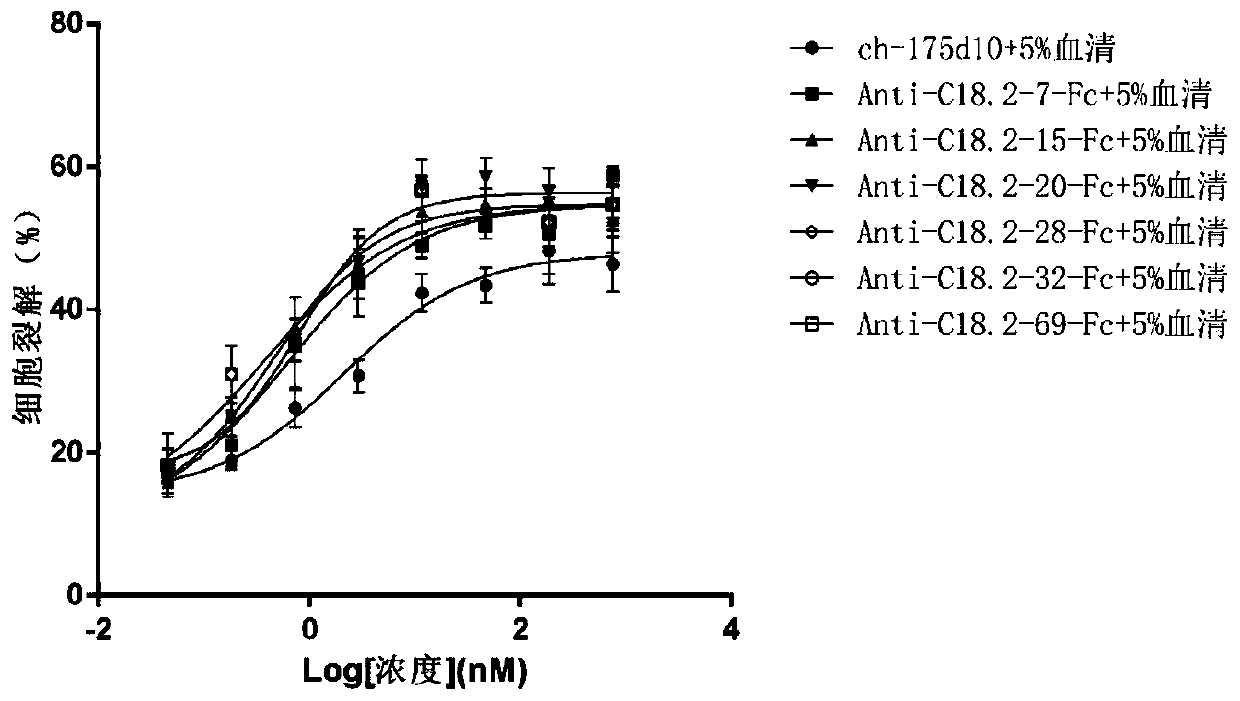
The invention relates to the field of biology, in particular to an anti-CLD18A2 nanobody. According to the anti-CLD18A2 nanobody provided by the invention, a complementary determining region (CDR) ofthe anti-CLD18A2 nanobody includes CDR1-CDR3 of which the amino acid sequences are shown as follows: CDR1 of which the amino acid sequence is shown by one of SEQ ID NO.4-11, CDR2 of which the amino acid sequence is shown by one of SEQ ID NO.19-26 and CDR3 of which the amino acid sequence is shown by one of SEQ ID NO.33-39. The anti-CLD18A2 nanobody provided by the invention can be specifically bound to an epitope present on CLD18A2, and fusion protein corresponding to the nanobody has good specificity and affinity on CLD18A2, and has an obvious tumor suppression effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DOER BIOLOGICS CO LTD
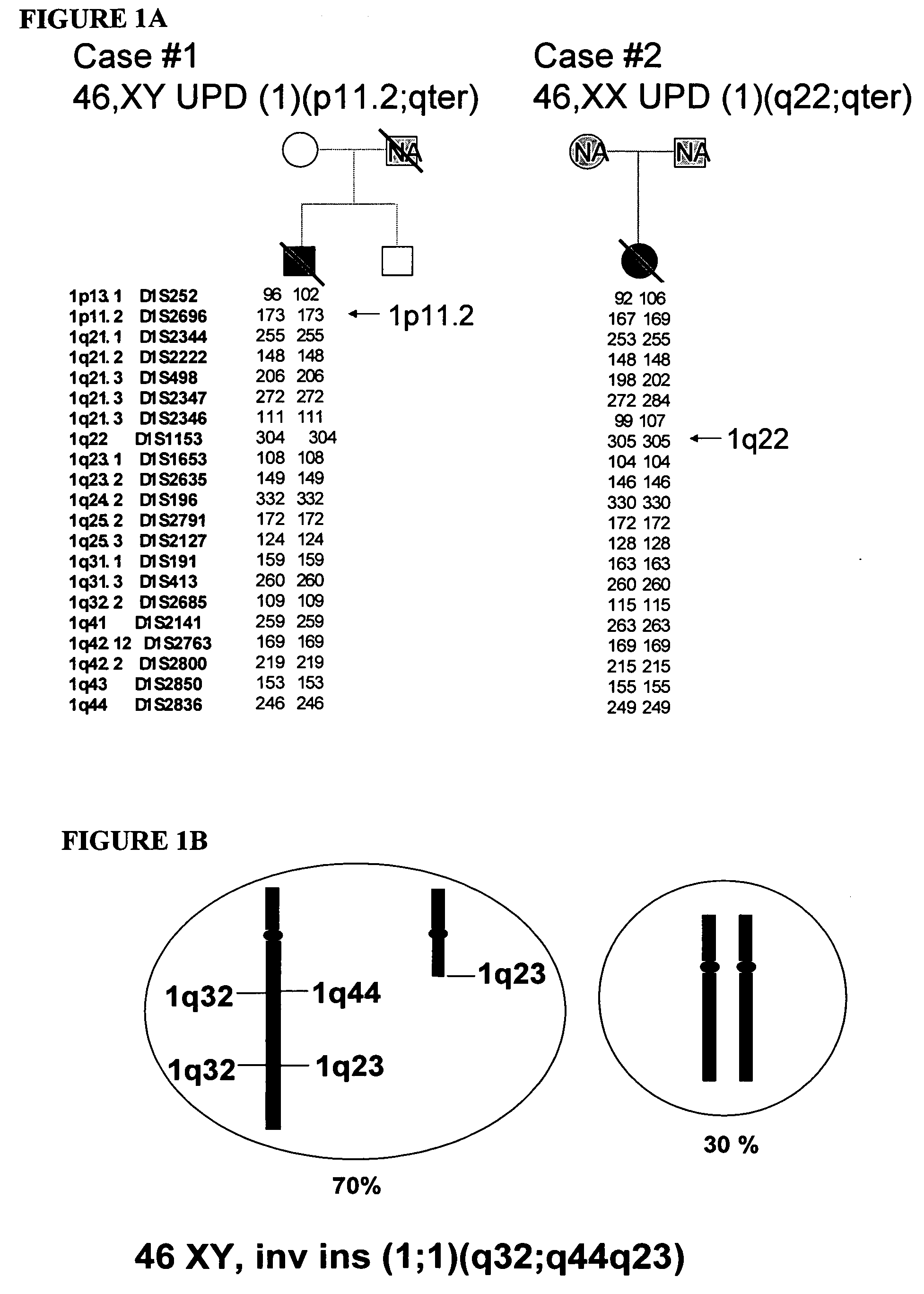
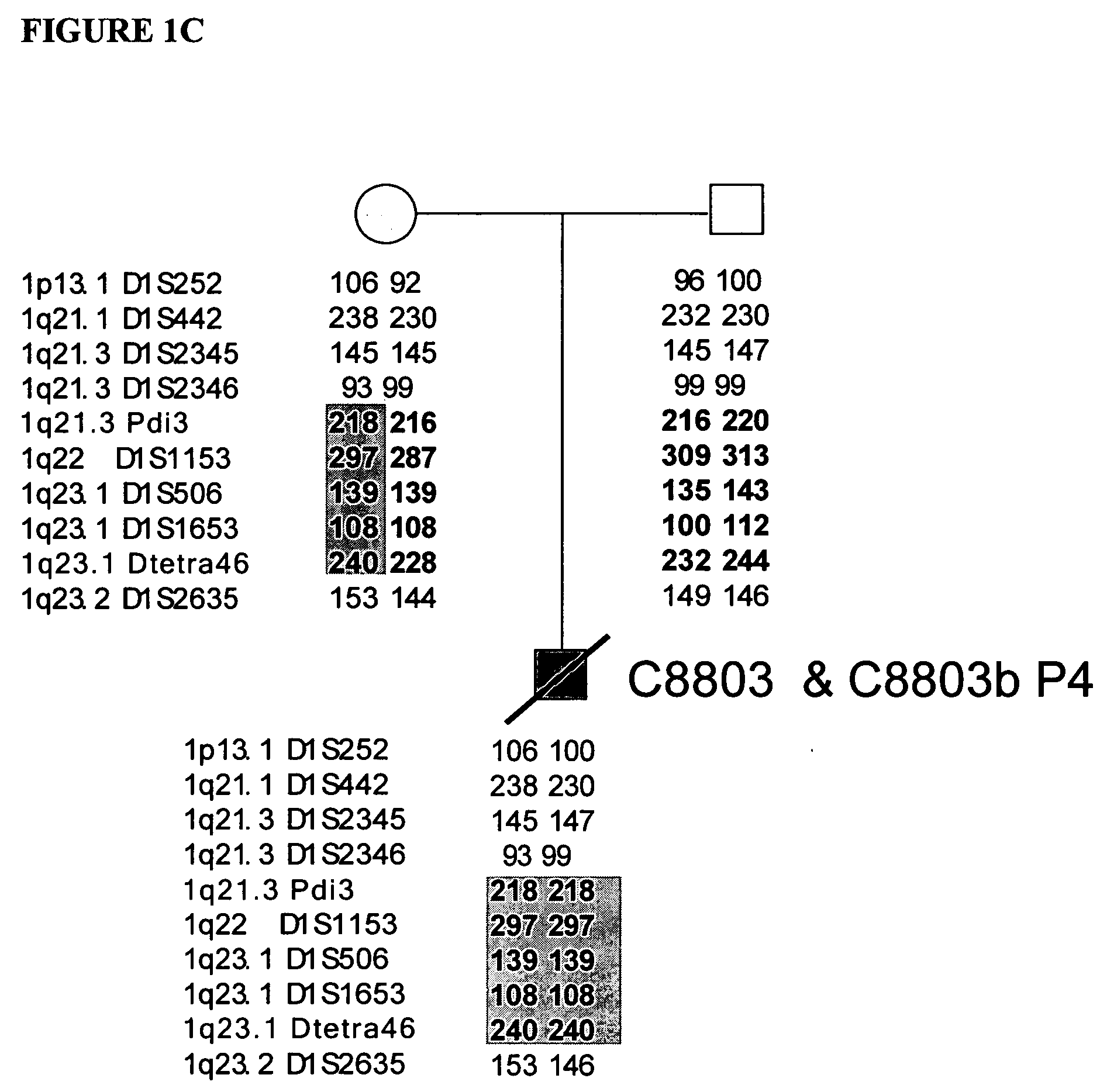
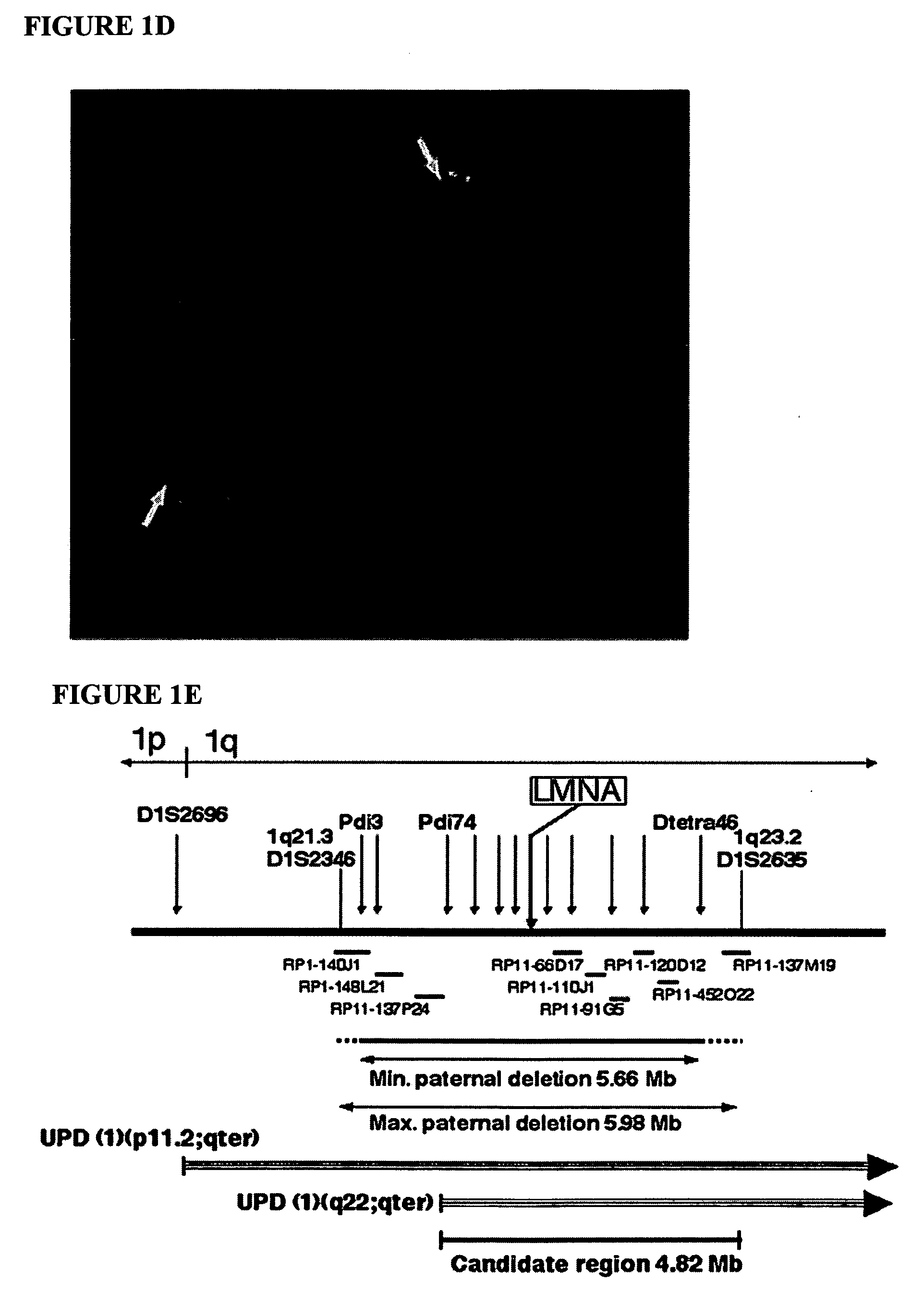
LMNA gene and its involvement in hutchinson-gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS) and arteriosclerosis
Disclosed herein are point mutations in the LMNA gene that cause HGPS. These mutations activate a cryptic splice site within the LMNA gene, which leads to deletion of part of exon 11 and generation of a mutant Lamin A protein product that is 50 amino acids shorter than the normal protein. In addition to the novel Lamin A variant protein and nucleic acids encoding this variant, methods of using these molecules in detecting biological conditions associated with a LMNA mutation in a subject (e.g., HGPS, arteriosclerosis, and other age-related diseases), methods of treating such conditions, methods of selecting treatments, methods of screening for compounds that influence Lamin A activity, and methods of influencing the expression of LMNA or LMNA variants are also described. Oligonucleotides and other compounds for use in examples of the described methods are also provided, as are protein-specific binding agents, such as antibodies, that bind specifically to at least one epitope of a Lamin A variant protein preferentially compared to wildtype Lamin A, and methods of using such antibodies in diagnosis, treatment, and screening. Also provided are kits for carrying out the methods described herein.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES +2
Vaccine for preventing and curing tumor
InactiveCN101920009AGenetic material ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsReverse transcriptaseNucleotide
The invention belongs to vaccine and preparation thereof, in particular to a vaccine for preventing and curing tumor and preparation thereof. The vaccine is prepared by steps of: choosing a telomerase reverse transcriptase epitope sequence, serially connecting nucleotides the telomerase reverse transcriptase with multi-epitope, preparing the DNA vaccine of the telomerase reverse transcriptase with multi-epitope, and preparing the multi-epitope vaccine of the telomerase reverse transcriptase with multi-epitope. The invention overcomes the shortcomings that a single peptide vaccine only has a clinical effect in several tumor patients. After the vaccine has an immune body, the epitope specific CD4+T cells and the CD8+T cells can be activated. Under the assistance of the Th1 cell factor excreted from the CD4+T cells, the CD8+CTL can kill the tumor cell presenting TERT so as to prevent and cure tumor.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for identifying multiple epitopes in selected sub-populations of cells
InactiveUS20210002733A1Microbiological testing/measurementAssay labelsEpitope specificityCellular origin
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
Prevention or Treatment of Cancer Using Integrin alphavbeta3 Antagonists in Combination with Other Agents
InactiveUS20090148459A1Improve efficiencyImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer preventionOncology
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management or prevention of cancer. The methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of one or more antagonists of Integrin αVβ3 alone or in combination with the administration of an effective amount of one or more other agents useful for cancer therapy. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more antagonists of Integrin αVβ3 and / or one or more other agents useful for cancer therapy. In particular, the invention is directed to methods of treatment and prevention of cancer by the administration of a therapeutically or prophylactically effective amount of one or more antagonists of Integrin αVβ3 alone or in combination with standard and experimental therapies for treatment or prevention of cancer. Also included are methods for screening for epitope-specific Integrin αVβ3 antagonists which can be used according to the methods of the invention. In addition, methods for facilitating the use of Integrin αVβ3 antagonists in the analysis of Integrin αVβ3 expression in biopsies of animal model and clinical study samples are also contemplated.
Owner:WOESSNER RICHARD +4
Binary epitope antibodies and B cell superantigen immune stimulants
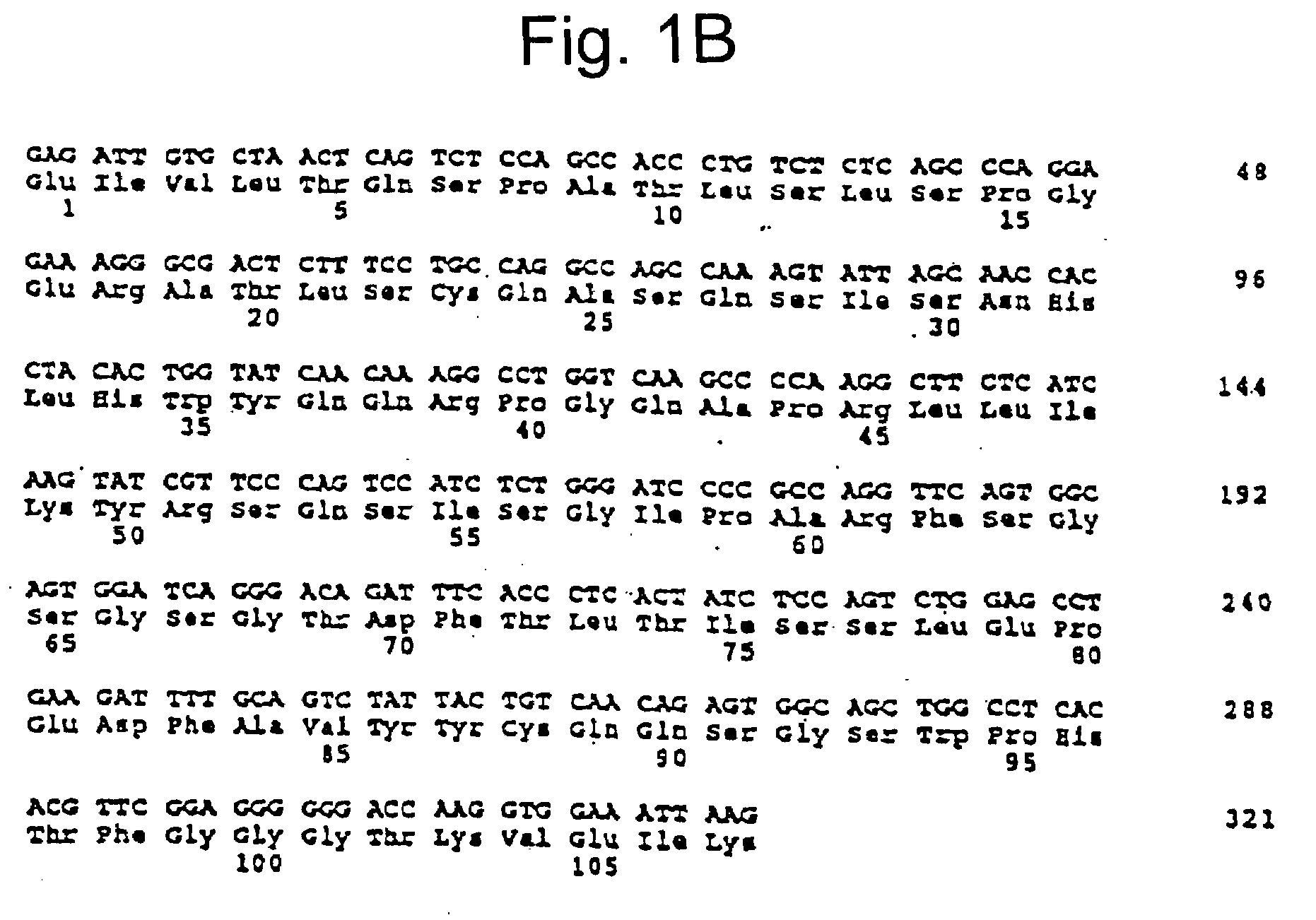
InactiveUS20090117115A1Enhanced nucleophilic reactivityEnhances antibody potencyAntiviralsPeptide preparation methodsIMMUNE STIMULANTSLipid formation
Provided herein are dual epitope polypeptides and electrophilic analogs thereof having a superantigenic epitope and at least one other epitope effective to induce the production of antibodies with binary specificity for the epitopes on a polypeptide antigen. Also, provided are electrophilic analogs of polyclonal B cell stimulants or lipids, polysaccharides and lipopolysaccharides or nucleotides. In addition, provided herein are methods for increasing production of binary epitope specific antibodies recognizing B cell polypeptide antigens, for stimulating production of antibodies using one or more of the polypeptides or electrophilic analogs and for isolating binary epitope specific antibodies or fragments thereof. Further provided are the antibodies so produced and methods of treating HIV using the same.
Owner:PAUL SUDHIR PHD +1
Therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20190002521A1Improve stabilityReduce riskPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyEpitope specificityTransmembrane domain
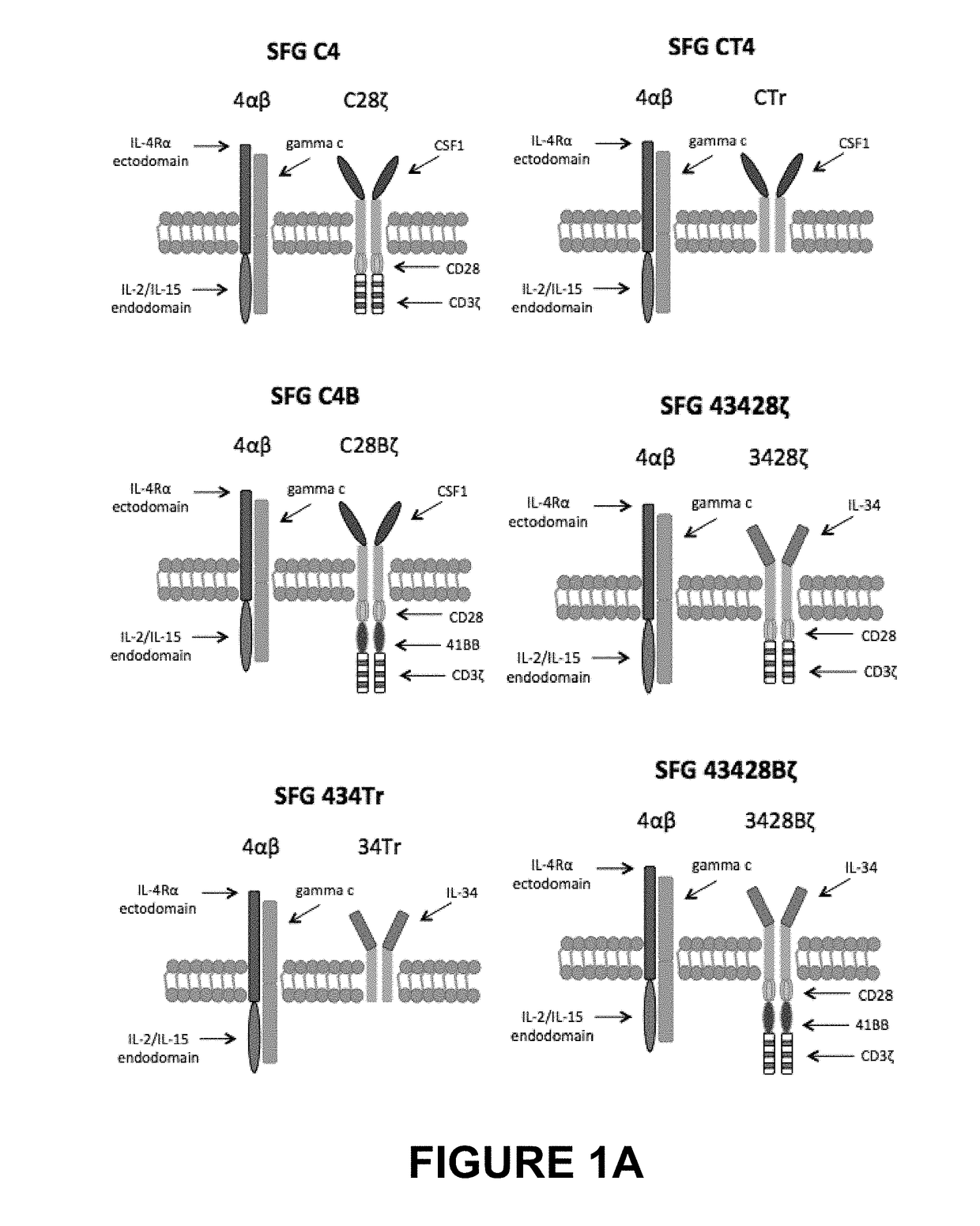
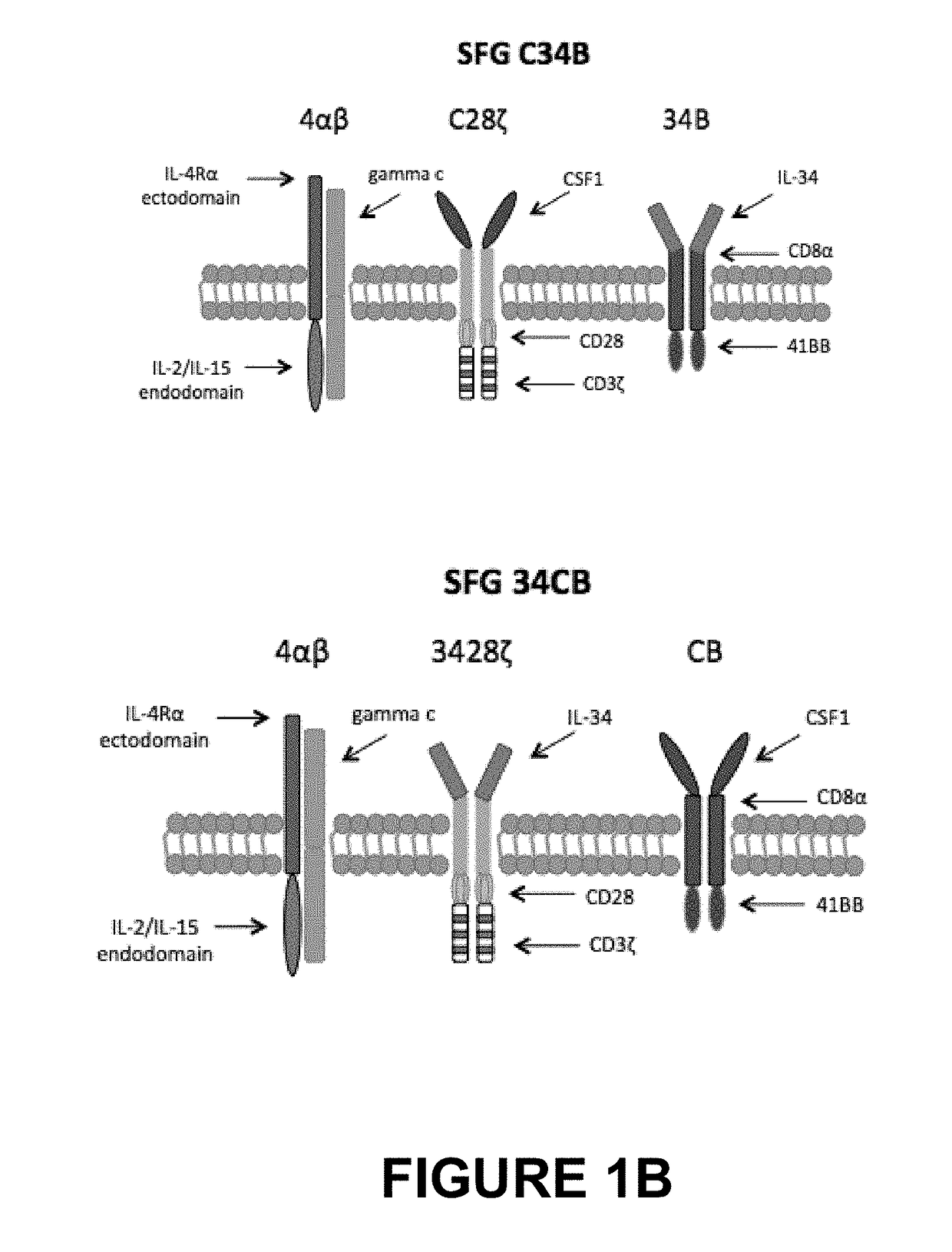
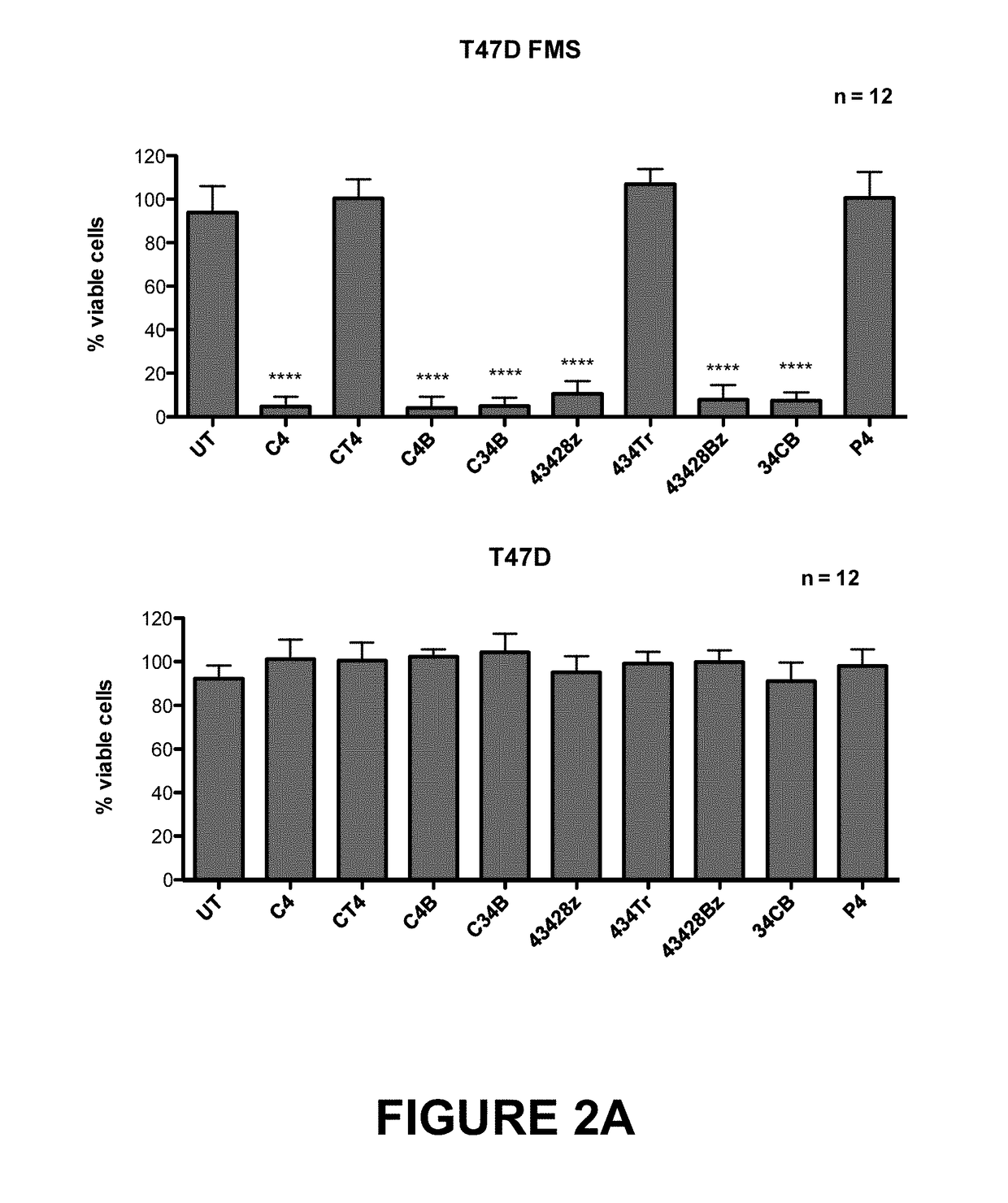
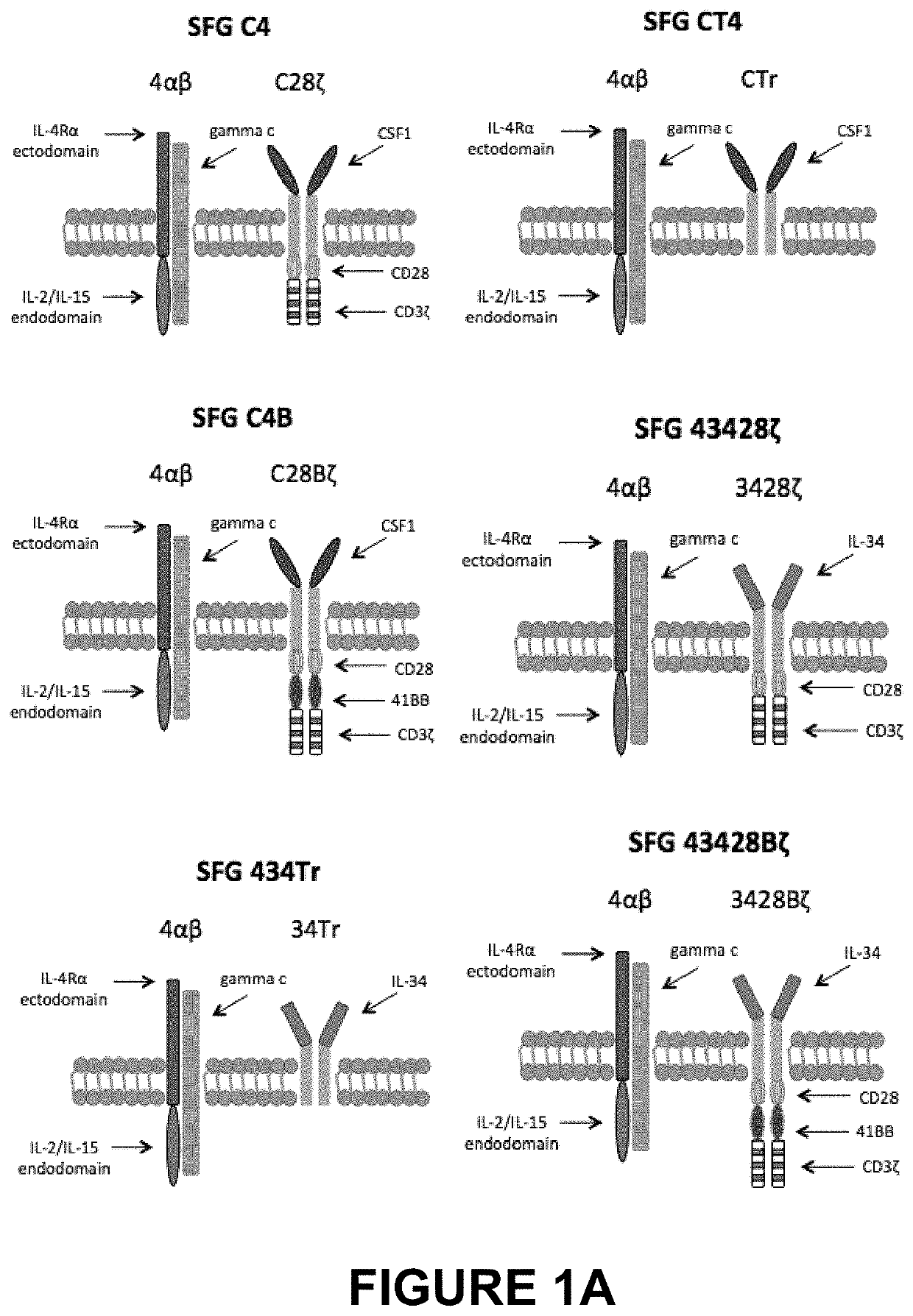
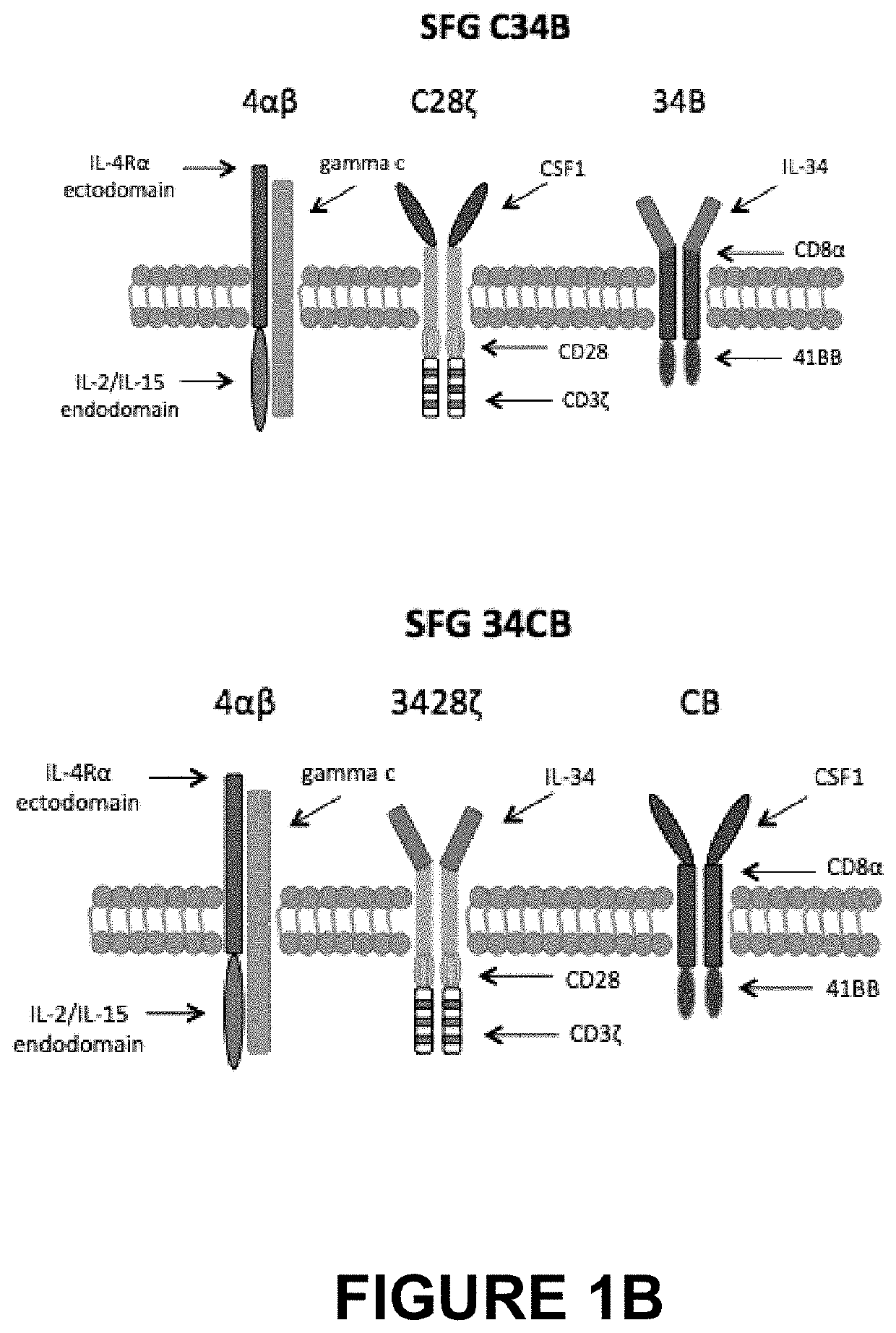
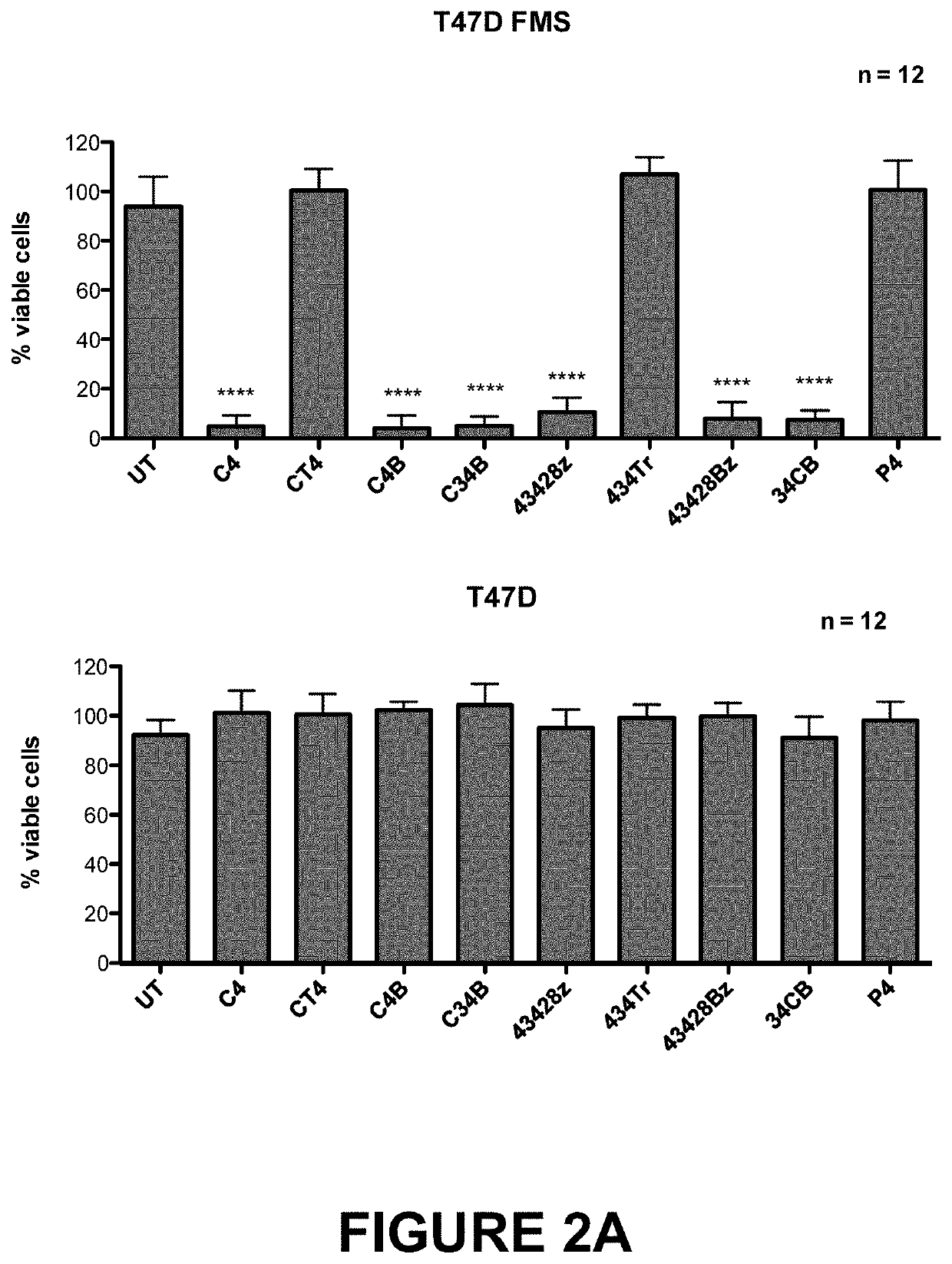
An immunoresponsive cell, such as a T-cell expressing(i) a second generation chimeric antigen receptor comprising:(a) a signalling region;(b) a co-stimulatory signalling region;(c) a transmembrane domain; and(d) a binding element that specifically interacts with a first epitope on a target antigen; and(ii) a chimeric costimulatory receptor comprising(e) a co-stimulatory signalling region which is different to that of (b);(f) a transmembrane domain; and(g) a binding element that specifically interacts with a second epitope on a target antigen.This arrangement is referred to as parallel chimeric activating receptors (pCAR). Cells of this type are useful in therapy, and kits and methods for using them as well as methods for preparing them are described and claimed.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
Bispecific binding molecules that are capable of binding cd137 and tumor antigens, and uses thereof
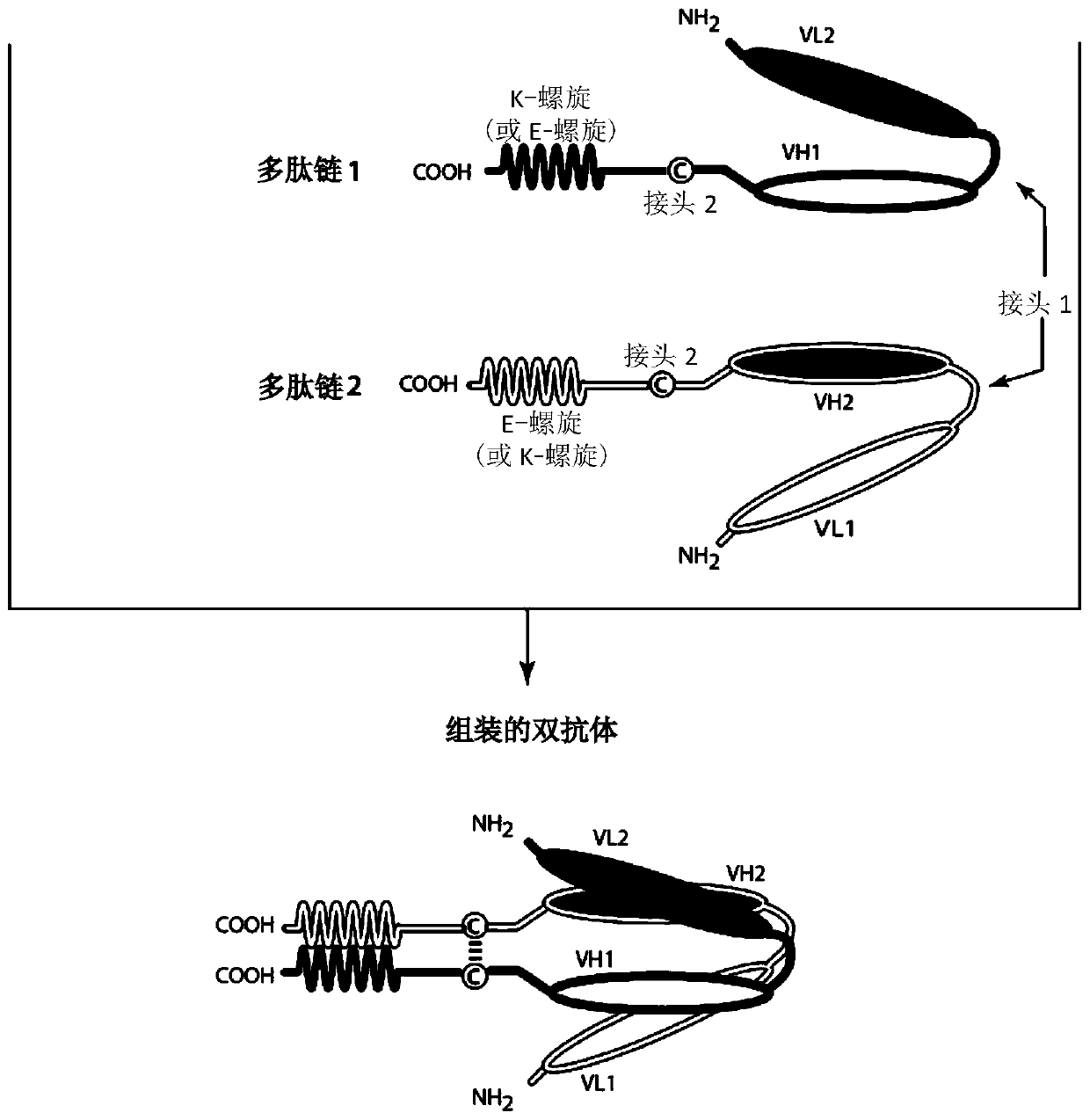
The present invention is directed to binding molecules that possess one or more epitope-binding sites specific for an epitope of CD137 and one or more epitope-binding sites specific for an epitope ofa tumor antigen ("TA") (e.g., a "CD137 x TA Binding Molecule"). In one embodiment, such CD137 x TA Binding Molecules will be bispecific molecules, especially bispecific tetravalent diabodies. Alternatively, such CD137 x TA Binding molecules will be bispecific trivalent binding molecules. The CD137 x TA Binding Molecules of the invention are capable of simultaneous binding to CD137, and a TA. The invention is directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the CD137 x TA Binding Molecules, methods of using the same to treat cancer and other disease and conditions. The invention also providesnovel CD137-binding molecules, and HER2 / neu-binding molecules, as well as derivatives thereof and uses thereof.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
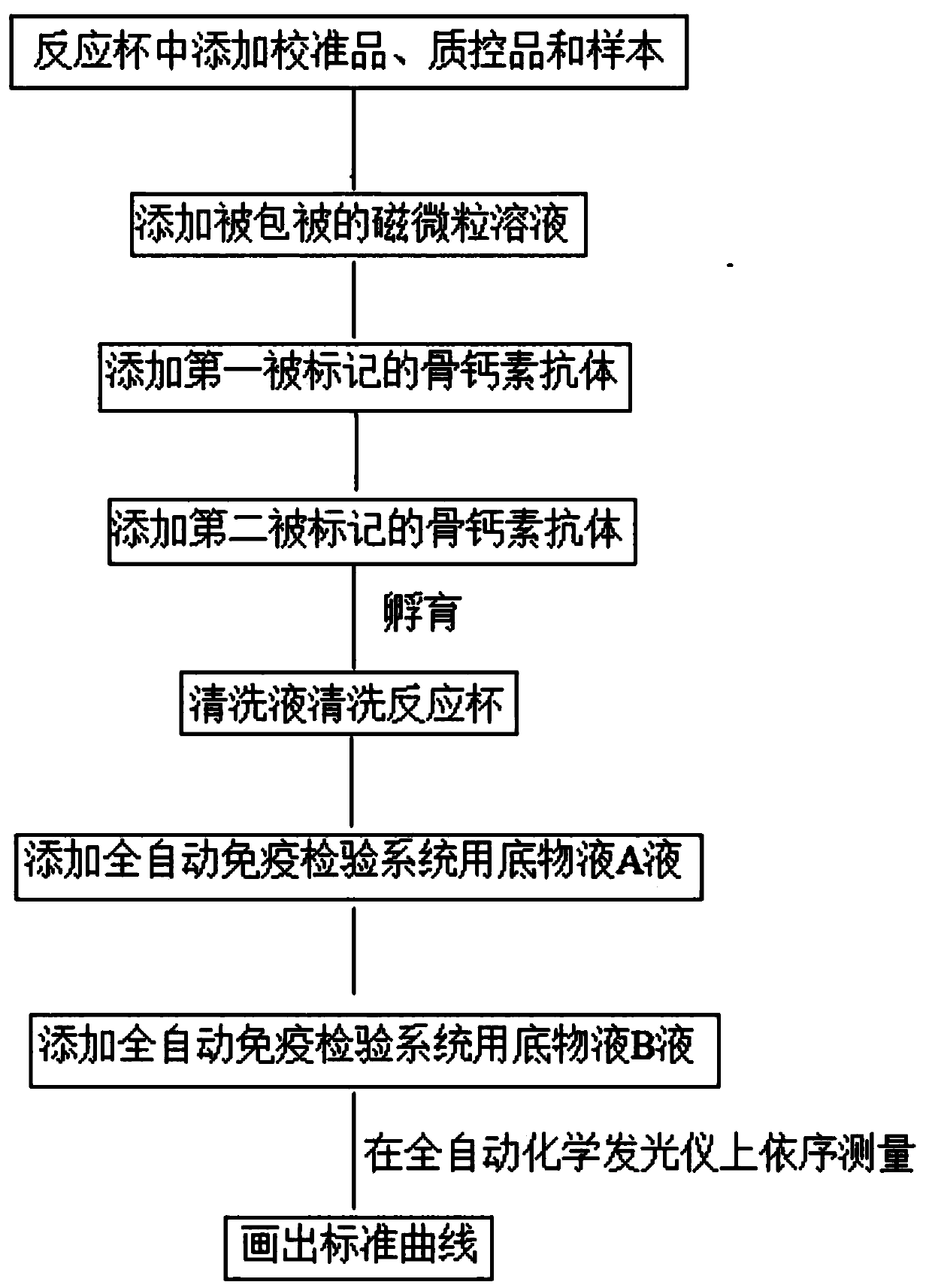
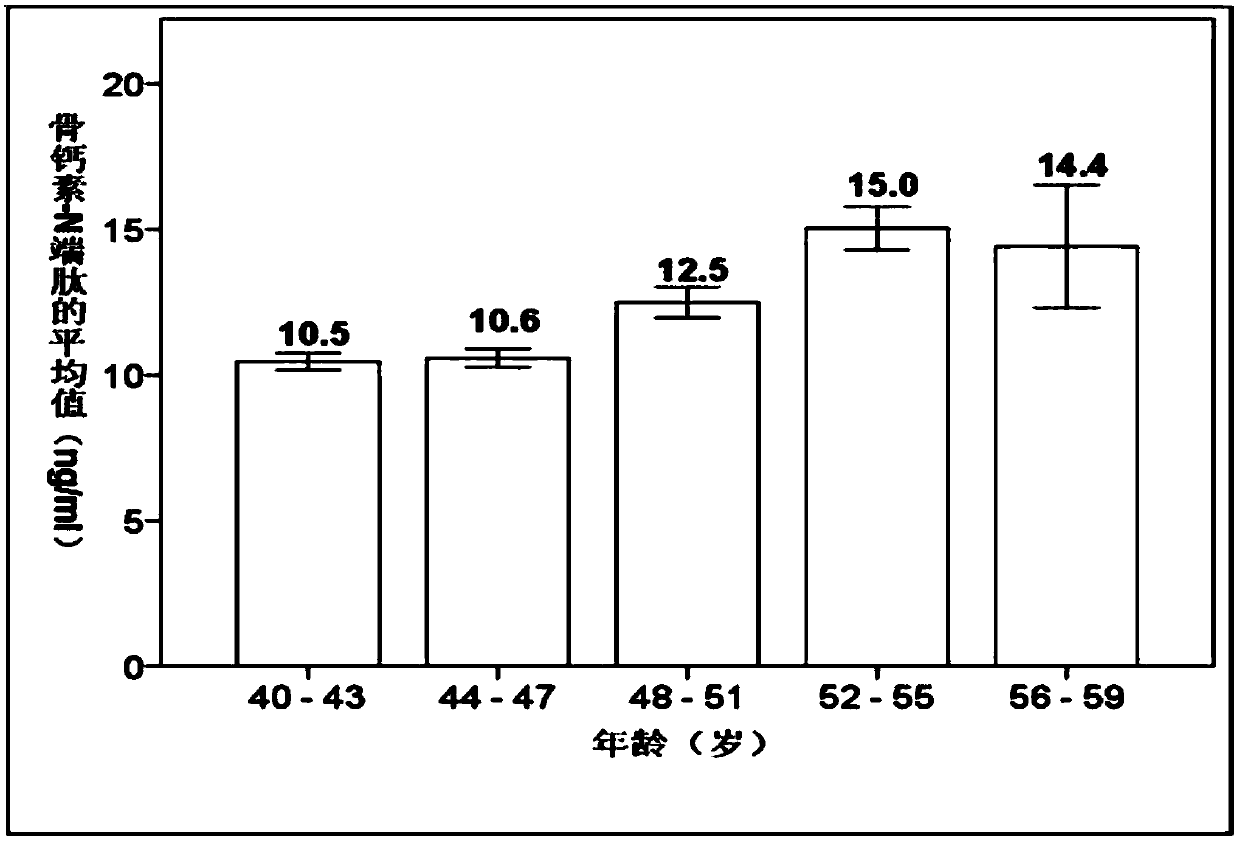
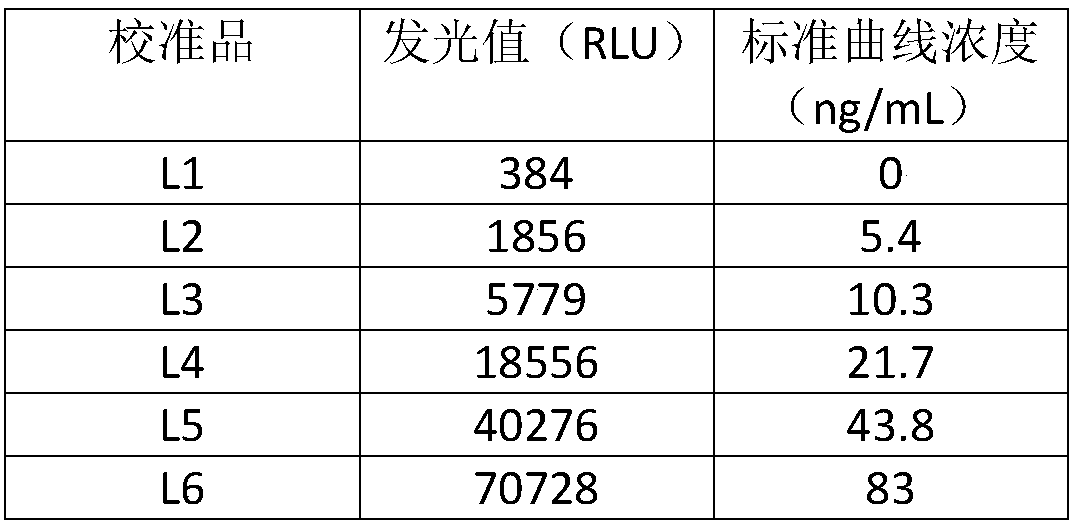
Osteocalcin-N terminal peptide detecting reagent, detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN109633178AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityBiological testingEpitope specificityImmune complex deposition
The invention discloses an osteocalcin-N terminal peptide detecting reagent, a detection method and an application thereof. The detecting reagent comprises an immune complex and an antibody detectionsystem. The immune complex uses a first labeled specific antibody, a second labeled specific antibody, an osteocalcin calibration product, an osteocalcin quality control product, and a sample to be tested to compositely form a first labeled specific antibody-osteocalcin-N terminal peptide-second labeled specific antibody. One of the first specific antibody and the second specific antibody is specifically combined with the epitope of an amino acid in an osteocalcin-N terminal peptide amino acid sequence, and the other antibody is specifically combined with the epitope of the amino acid in the osteocalcin-N terminal peptide amino acid sequence. The detecting reagent can specifically detect a completely-carboxylated osteocalcin molecule whole section and a degraded amino terminal N-terminal macromolecule fragment and has the advantages of high sensitivity, good stability and the like. A bone mass loss and a bone conversion rate can be well reflected.
Owner:EPITOPE BIOTECH
Multi-T cell epitope tuberculosis gene vaccine with HSP65 as epitope scaffold
InactiveCN104127883AEfficient removalImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsTreating tuberculosisTGE VACCINE
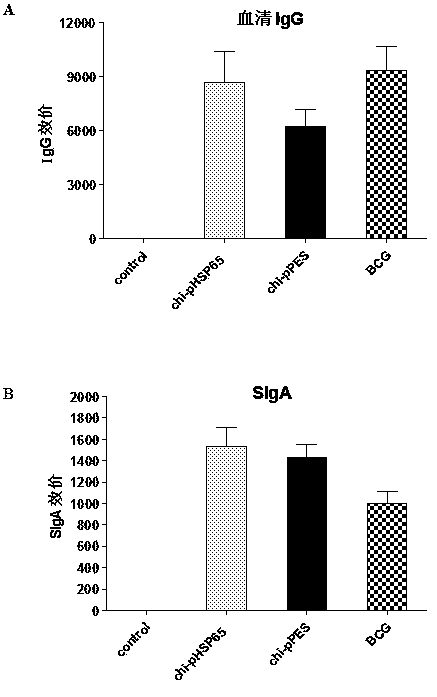
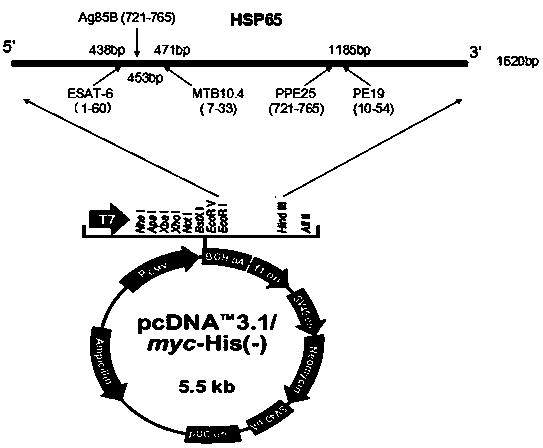
The invention discloses a multi-T cell epitope tuberculosis gene vaccine with HSP65 as an epitope scaffold. The full-length gene of HSP65 protein in which 5 T cell epitope polypeptide genes originated from mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen are embedded is inserted into a vector. A preparation method for the vaccine comprises a step of inserting the 5 T cell epitope genes originated from mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen into the HSP65 full-length gene, wherein the 5 T cell epitope genes comprise EAST-61-60, Ag85B721-765, MTB10.47-33, PPE25721-765 and PE1910-54. It is proved that the tuberculosis gene vaccine can induce response of serum IgG and lung SIgA to the HSP65 vector and induce cellular immunologic response of specific strong secretion of high-level IFN gamma to multiple tuberculosis antigen epitopes through intranasal immunization of mice with a nanometer granular compound formed by the gene vaccine and deacetylated chitosan, so the tuberculosis gene vaccine is a potential vaccine for prevention and treatment of tuberculosis.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Compositions and methods for the identification and isolation of cell-membrane protein specific binding moieties
ActiveUS20150322150A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide preparation methodsCell membraneRapid identification
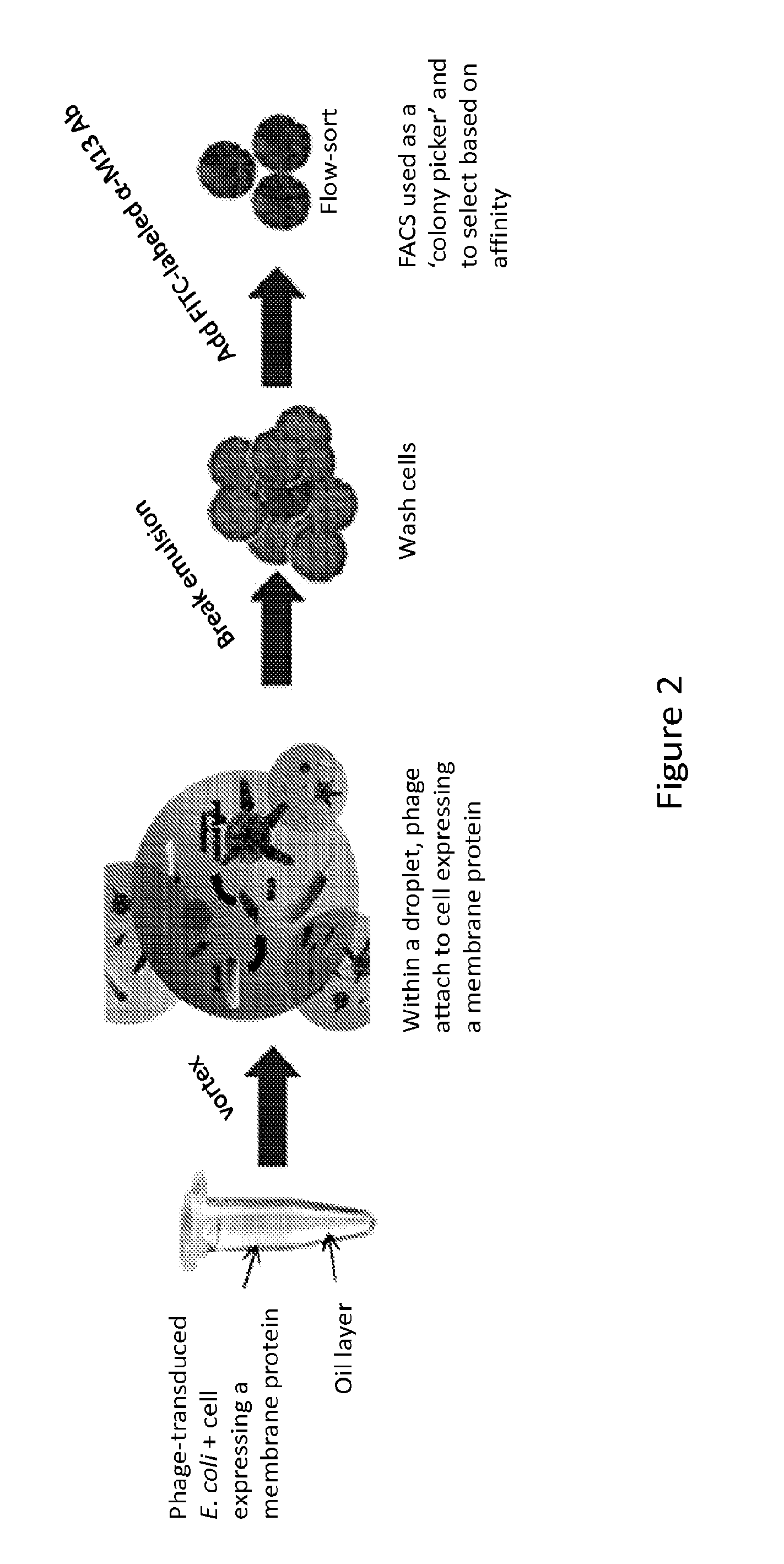
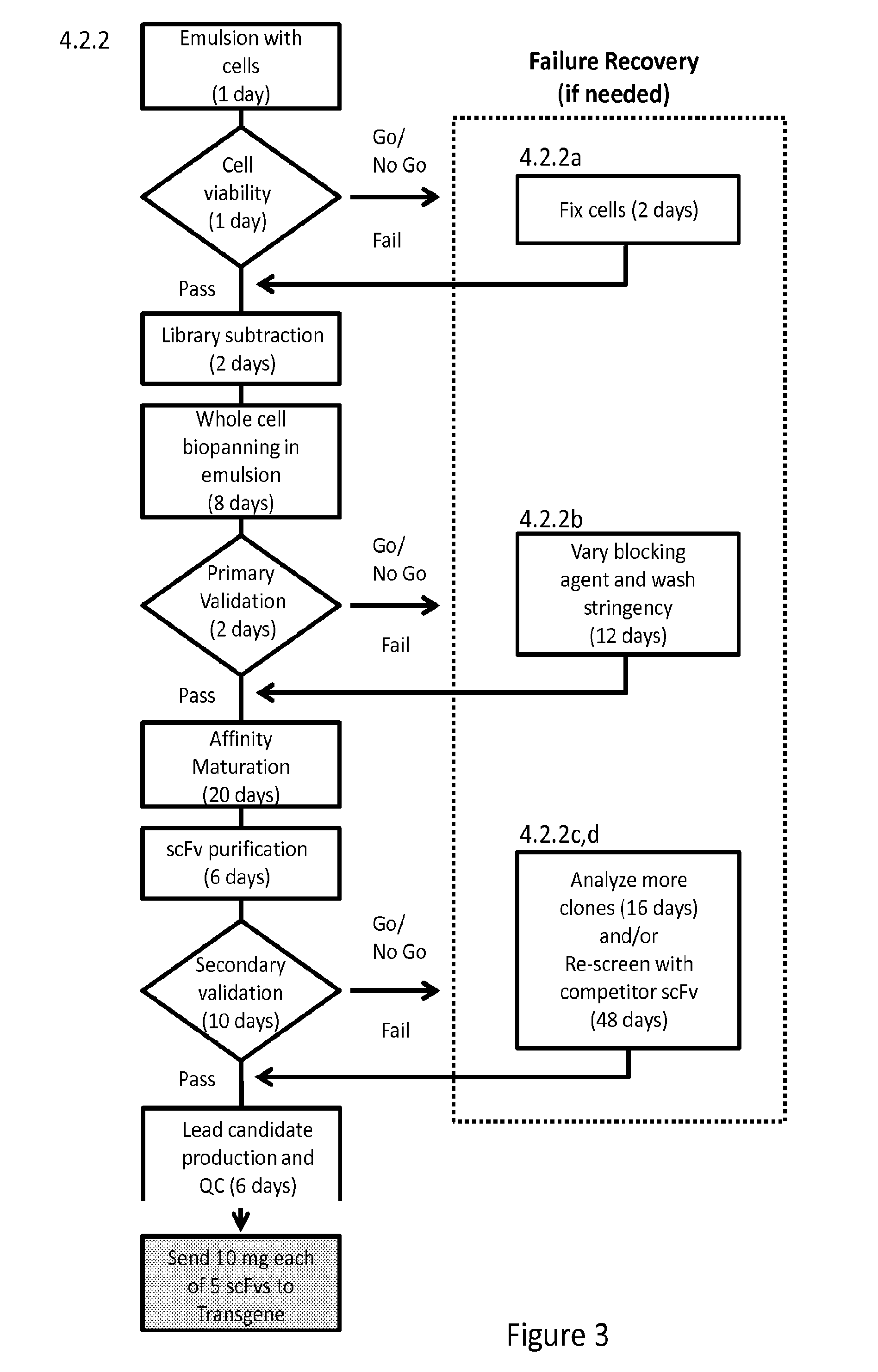
Disclosed are methods of identifying binding moieties that recognize antigens displayed on cells, such as membrane proteins or recombinant proteins that display eptiopes on the surface of cells. Binding moieties capable of binding membrane proteins can be difficult to obtain because these proteins can depend on their native environments for structural integrity. In some methods scFv phage display libraries are panned against whole cells expressing a membrane protein in an emulsion. Certain methods further permit discrimination of binding moieties according to their affinity or avidity for a target. This approach allows rapid identification of cell surface epitope specific antibodies for research, diagnostics, and immunotherapeutics.
Owner:AXIOMX
Therapeutic agents
ActiveUS10703794B2Improve stabilityReduce riskBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorEpitope specificity
An immunoresponsive cell, such as a T-cell expressing(i) a second generation chimeric antigen receptor comprising:(a) a signalling region;(b) a co-stimulatory signalling region;(c) a transmembrane domain; and(d) a binding element that specifically interacts with a first epitope on a target antigen; and(ii) a chimeric costimulatory receptor comprising(e) a co-stimulatory signalling region which is different to that of (b);(f) a transmembrane domain; and(g) a binding element that specifically interacts with a second epitope on a target antigen.This arrangement is referred to as parallel chimeric activating receptors (pCAR). Cells of this type are useful in therapy, and kits and methods for using them as well as methods for preparing them are described and claimed.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
Immunoaffinity chromatography using epitope tags to polyol-responsive monoclonal antibodies
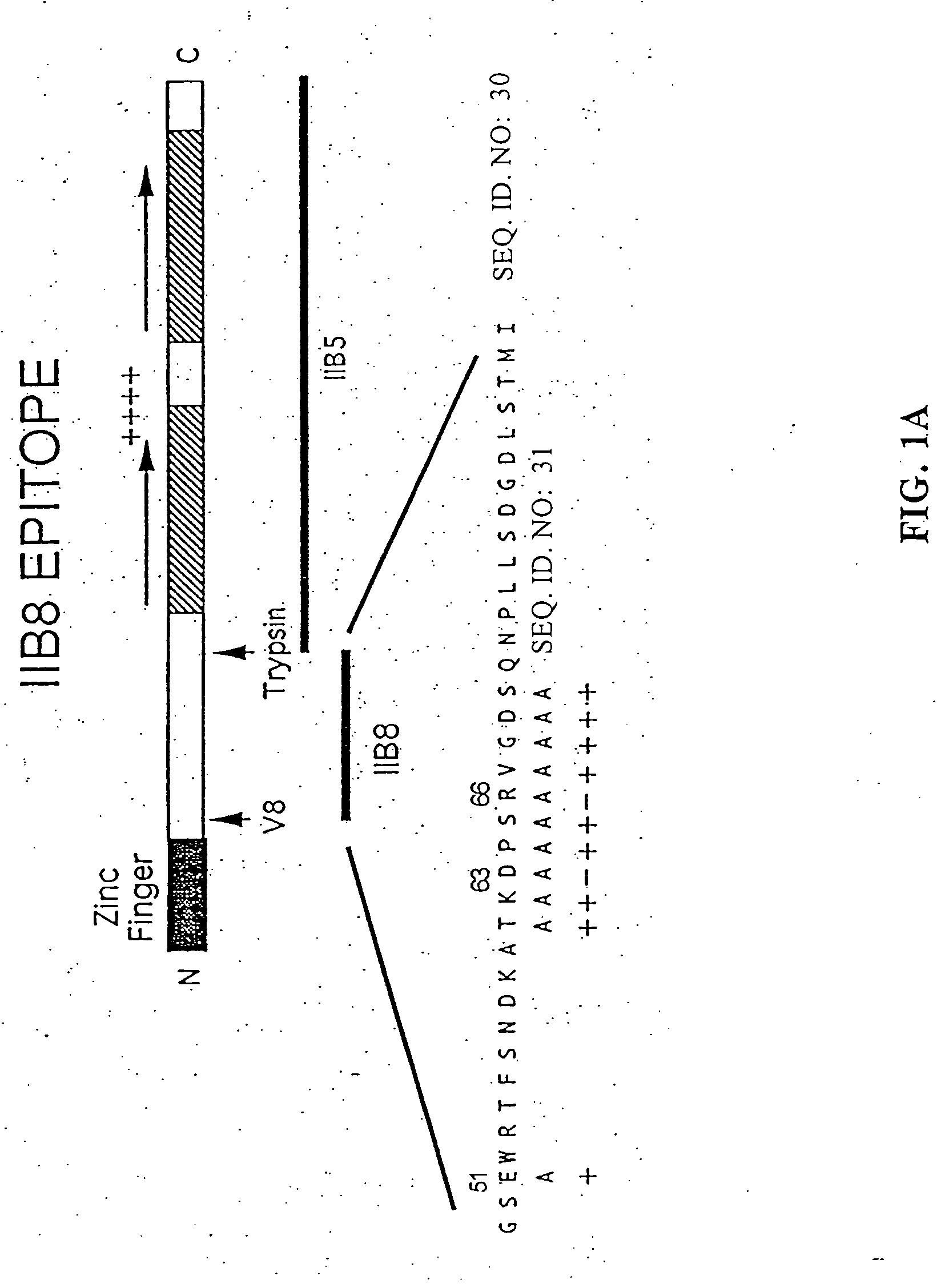
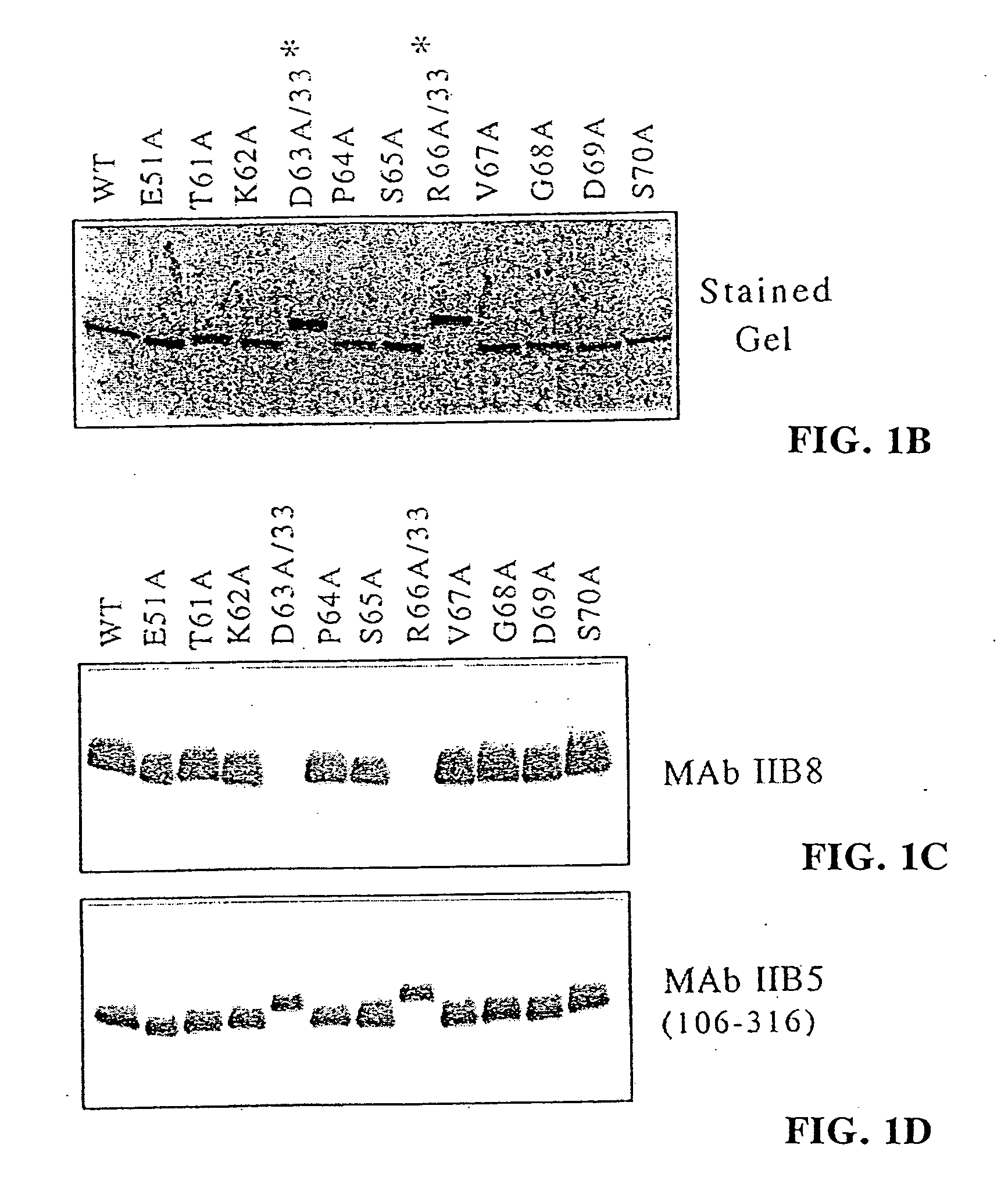
Disclosed is a method of isolating, purifying, or concentrating a target compound. The method includes the steps of onjugating the target compound to an epitope for a polyol-responsive monoclonal antibody (PR-mAb) to yield a conjugate; and then contacting the conjugate to an immunoaffinity matrix comprising a PR-mAb specifically reactive with the PR-mAb epitope. Preferred epitopes for use in the method include amino acids of from 4 to about 30 amino acids, wherein the amino acid sequence comprises the sub-sequence D-X-S-R, (where X is any natural or unnatural amino acid), such as TKDPSRVG and TQDPSRVG. Additional epitopes for use in the method include SLAELLNGLGGS and PTSPSYSPTSPSYS. The method enables the rapid isolation of desired target compounds under gentle purification conditions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Antibodies against n-acetylgucosamine and n-acetyl-galactosamine
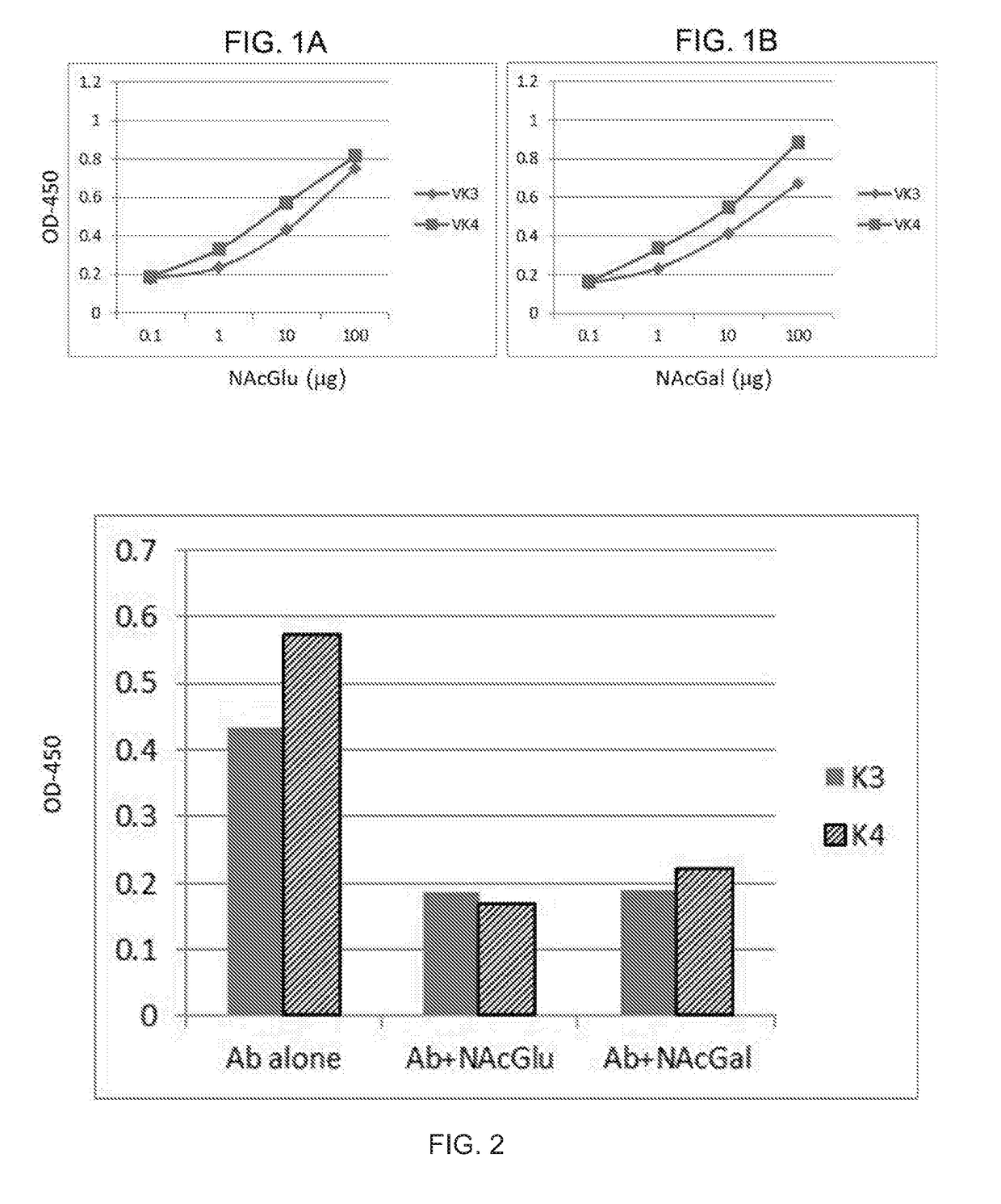
ActiveUS20190038669A1Reduce growth rateHigh levelPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyN-AcetylglucosamineInflammatory cell
It provides antibodies and chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that specifically bind to an epitope containing N-acetyl-glucosamine and / or N-acetyl-galactosamine, e.g., expressed by a cancer cell or an inflammatory cell. Also provided are compositions including these antibodies and / or CARs, as well as polynucleotides, vectors, host cells, methods, and kits related thereto. Further provided are methods and kits for treating or preventing cancer in an individual by administering to the individual an antibody that specifically binds to an epitope containing N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetyl-galactosamine, or a T cell comprising a CAR that specifically binds to an epitope containing N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetyl-galactosamine, optionally in combination with another anti-cancer agent.
Owner:B&H BIOTECH LLC
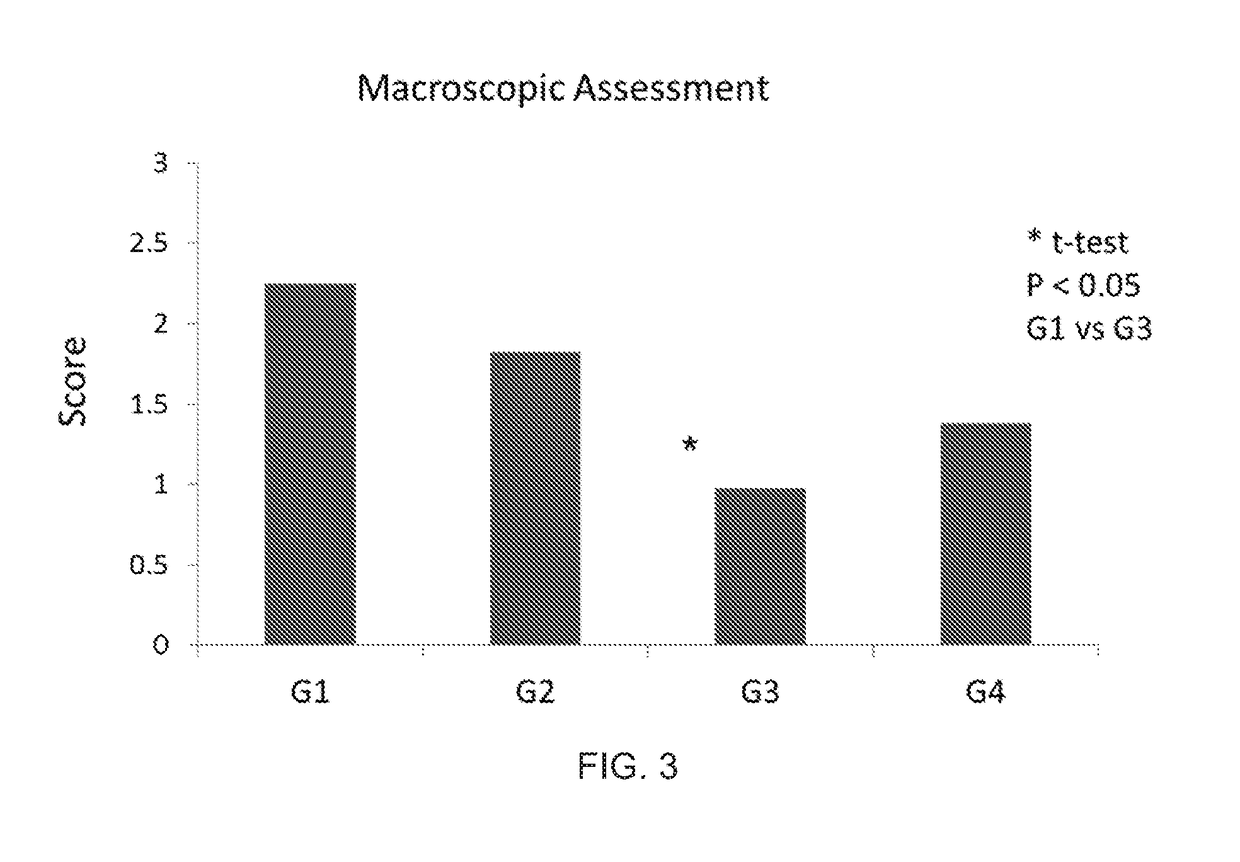
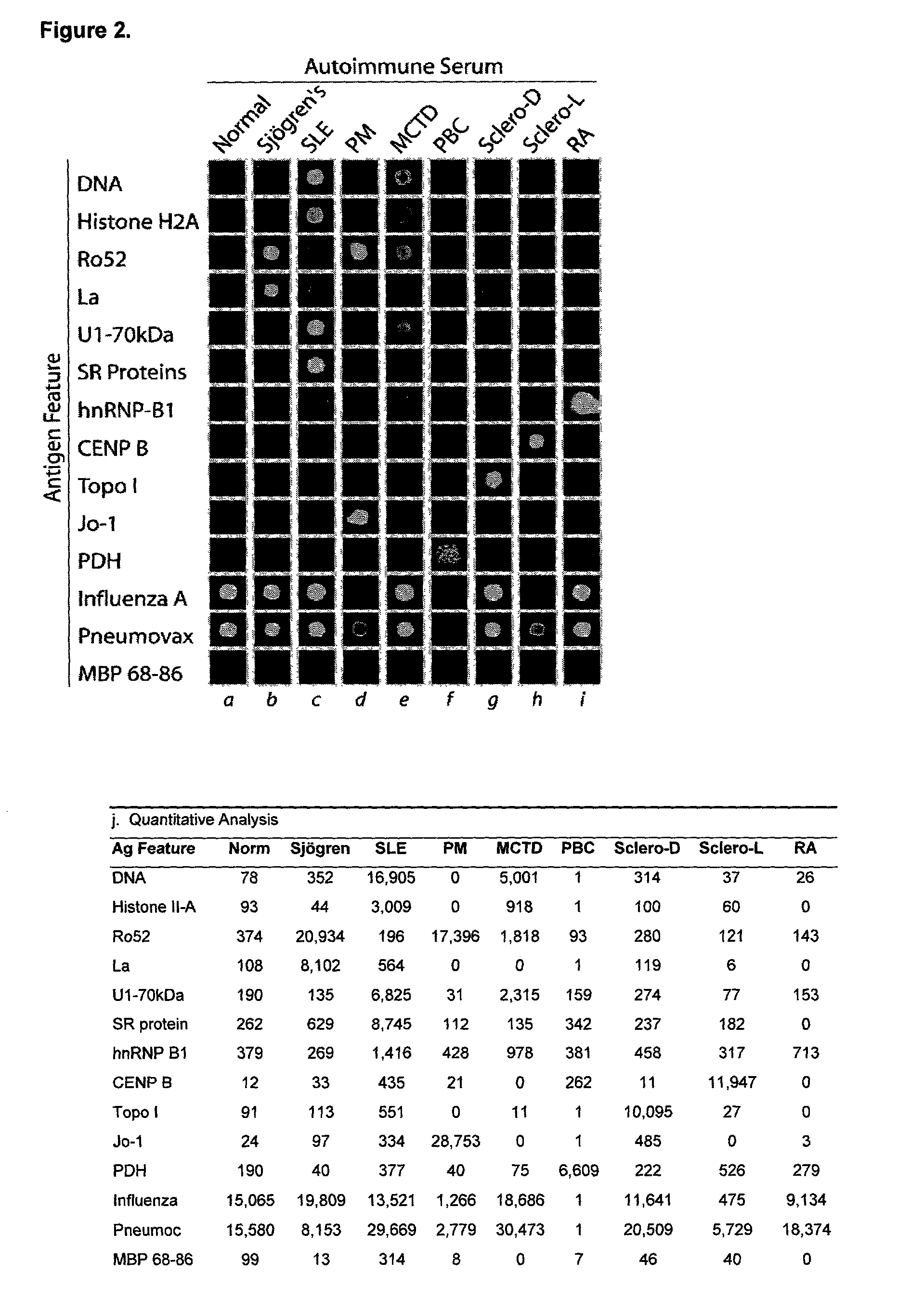
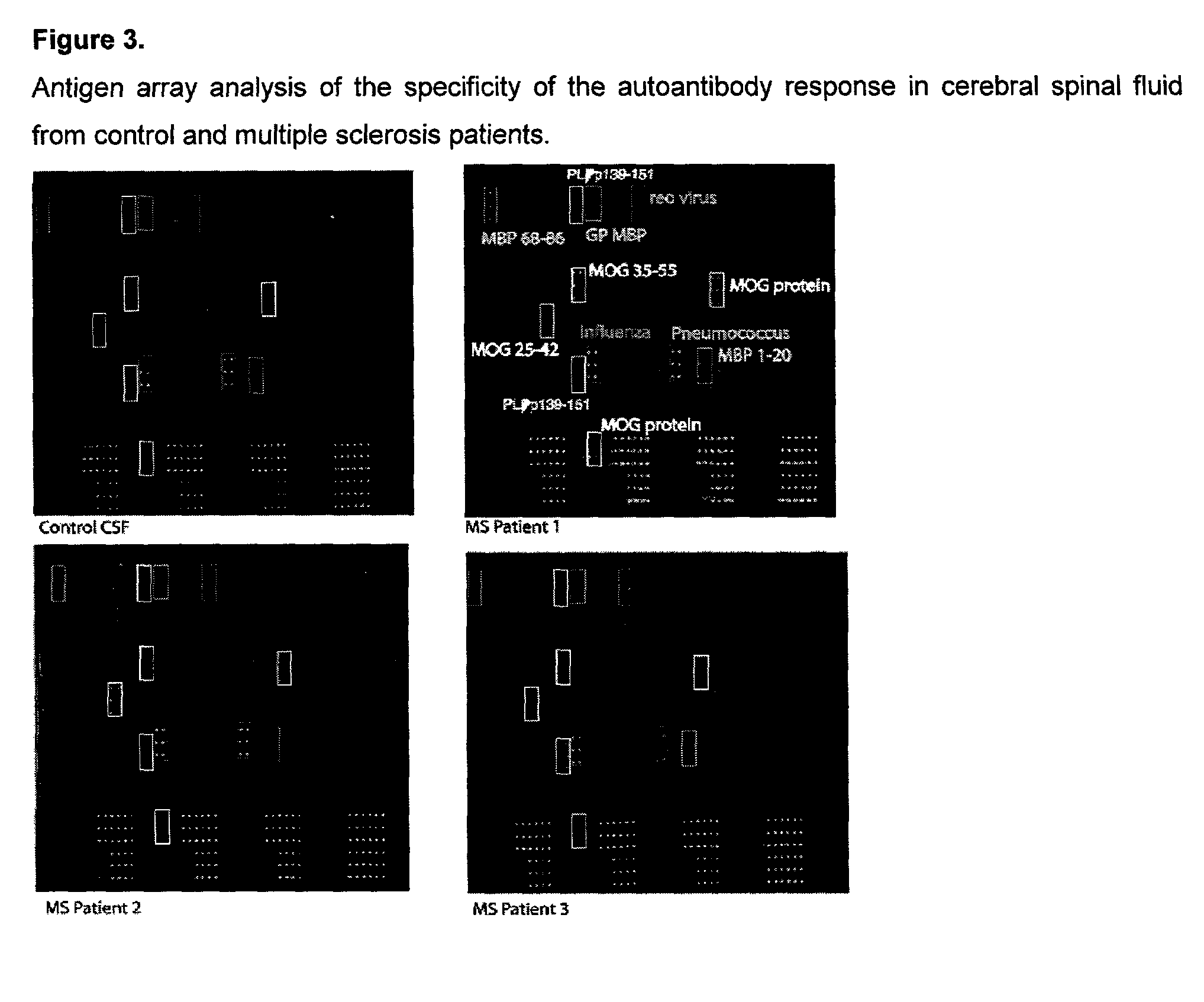
Therapeutic and diagnostic uses of antibody specificity profiles
This invention provides a method for determining the antibody specificity profile in an individual. This specificity profile reveals the individual's immune response to multiple antigens and / or epitopes of autoantigens, allergens, graft antigens, etc. The antibody specificity profile is determined through the binding of patient samples comprising antibodies to the arrays. The array can comprises antigens and epitopes. The invention also provides the means and methods for determining antigen or epitope specificity profiles that can be used in the development of either generic and individualized diagnosis and treatment for immune related diseases, including autoimmune disease, allergy and graft rejection.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com