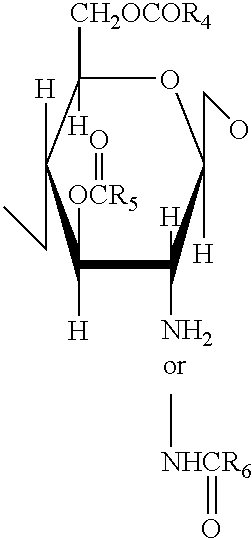
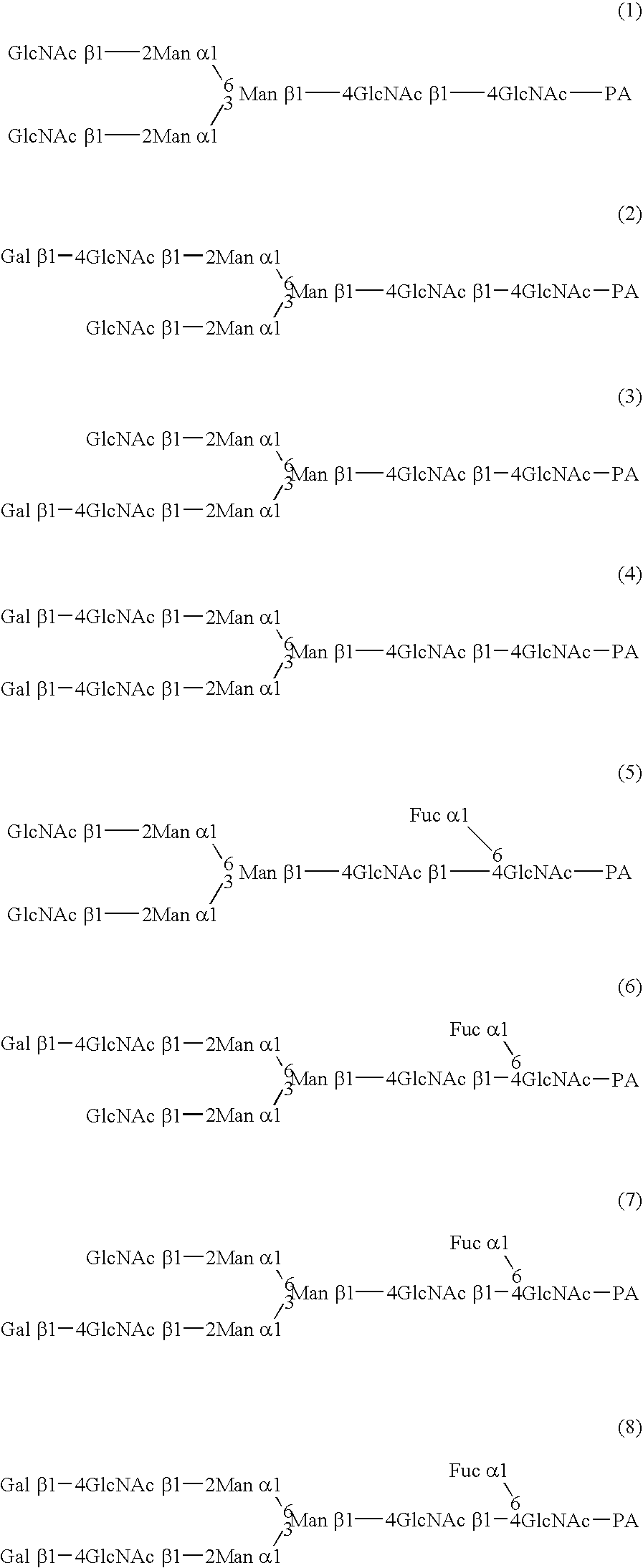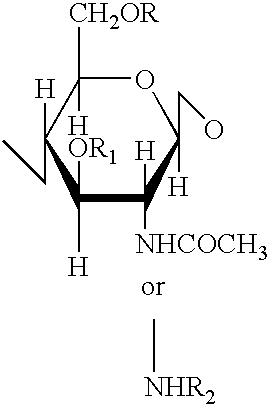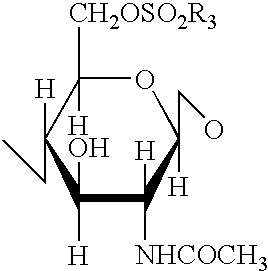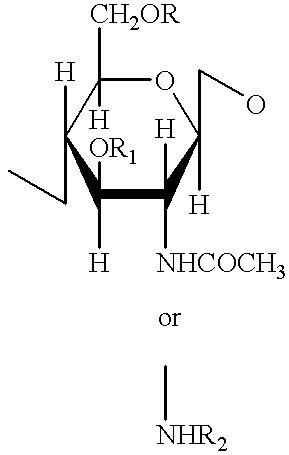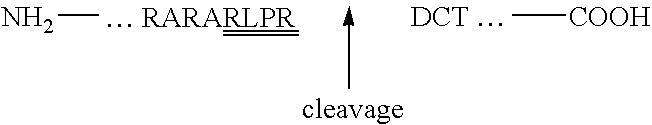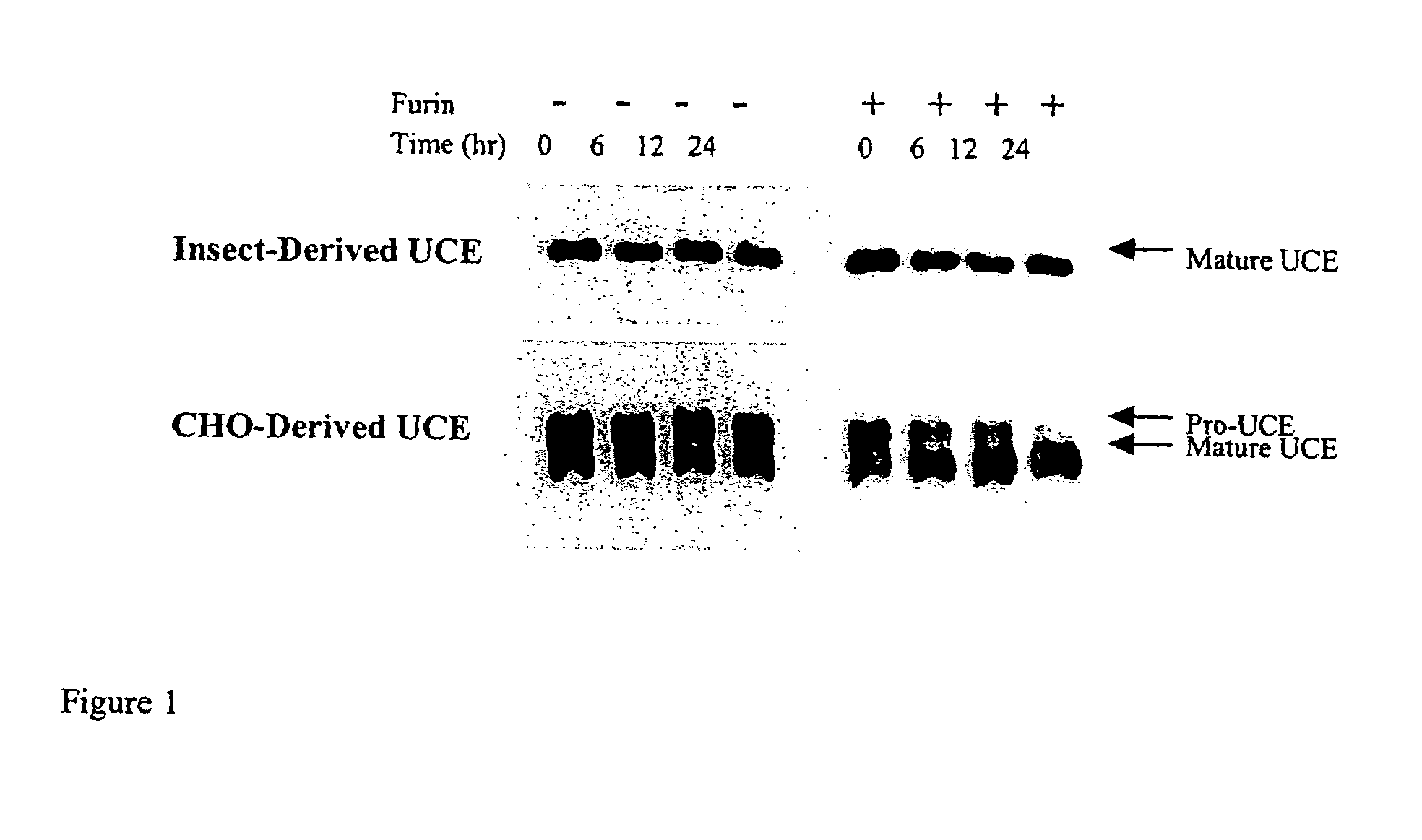Patents
Literature
236 results about "N-Acetylglucosamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
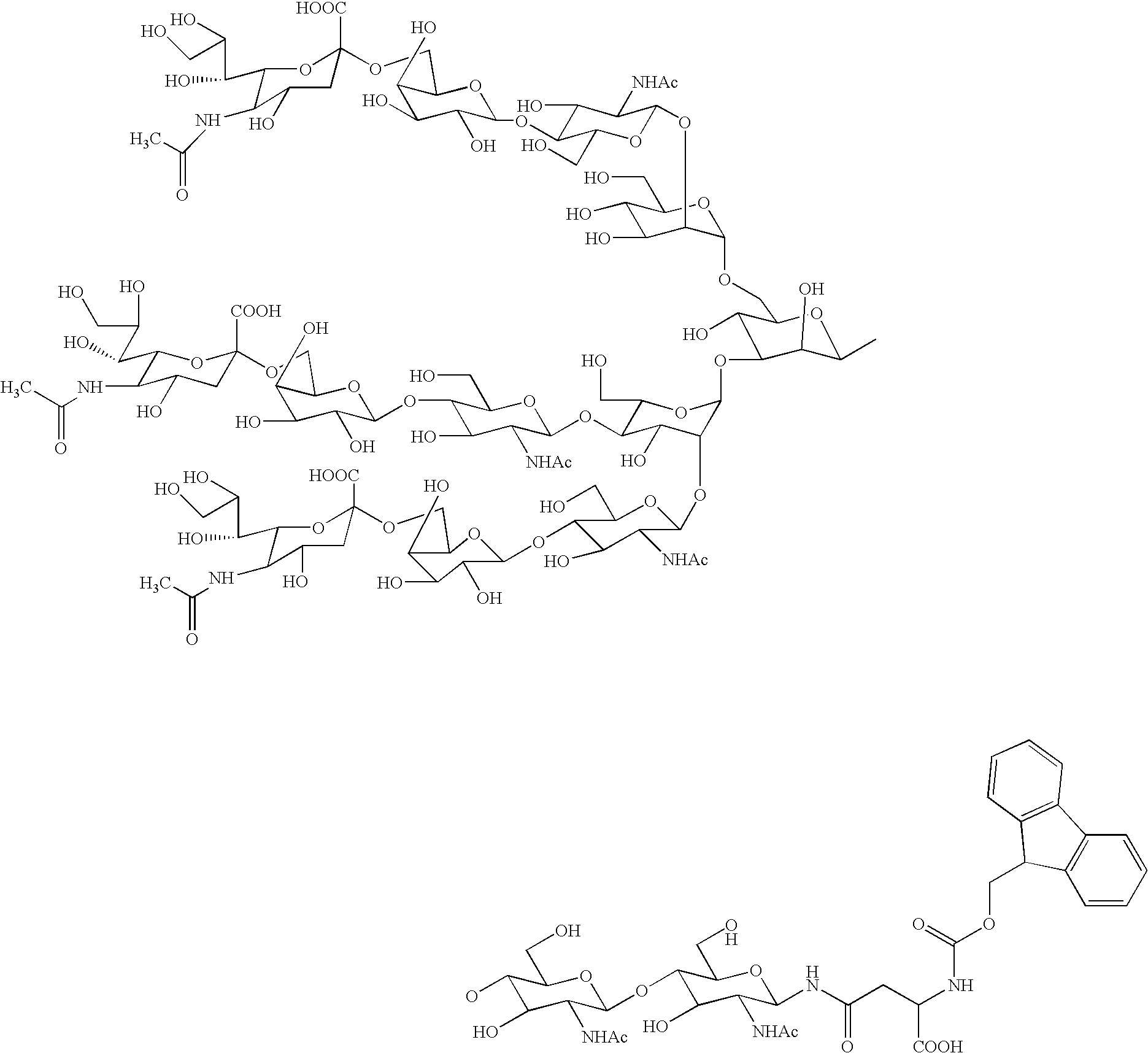
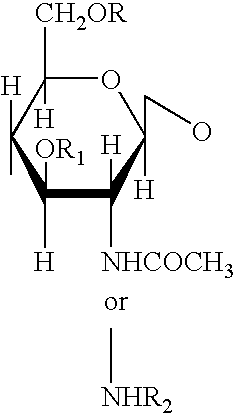
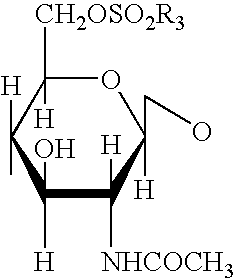
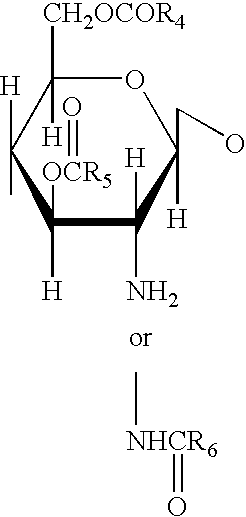
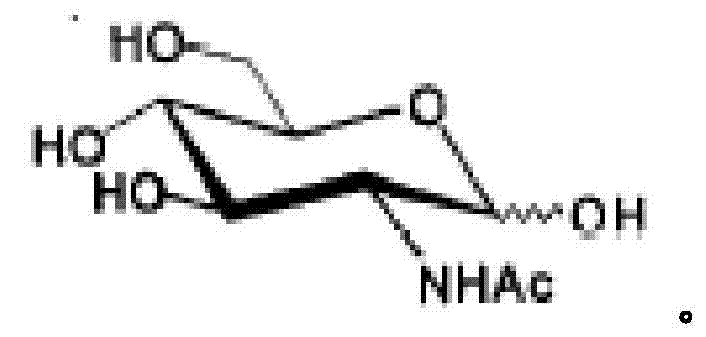
N-Acetylglucosamine an amide derivative of the monosaccharide glucose. It is a secondary amide between glucosamine and acetic acid. It is significant in several biological systems. It is part of a biopolymer in the bacterial cell wall, which is built from alternating units of GlcNAc and N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc), cross-linked with oligopeptides at the lactic acid residue of MurNAc. This layered structure is called peptidoglycan (formerly called murein).
Cells of which genome is modified
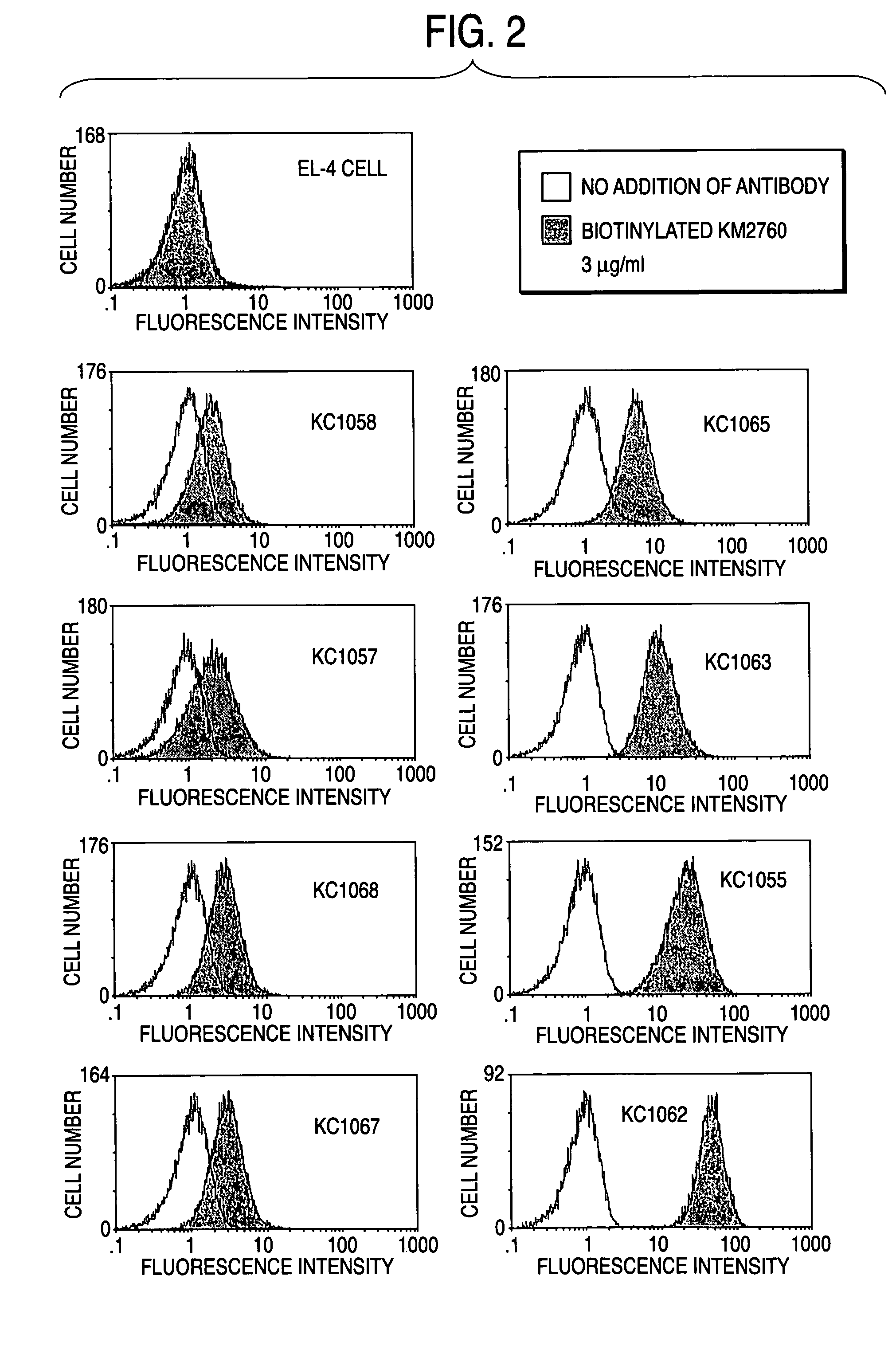
InactiveUS20040110704A1Raise the ratioDecreased and deleted activityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticGlycosideN-Acetylglucosamine
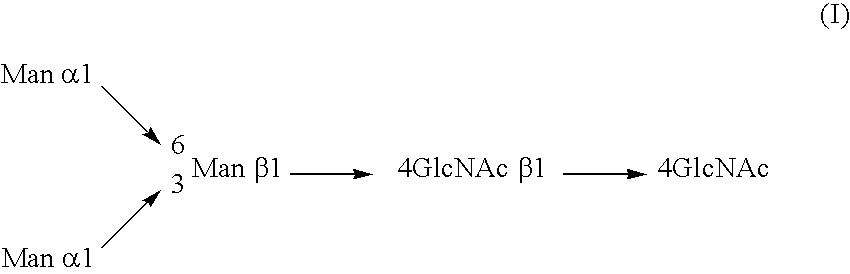
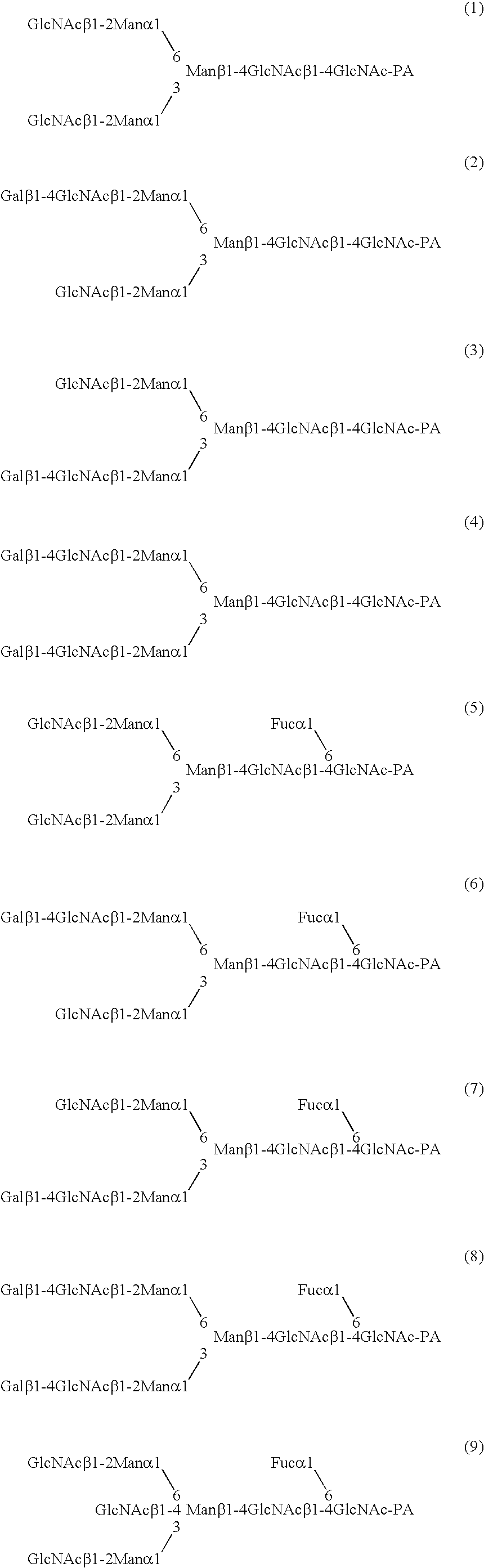
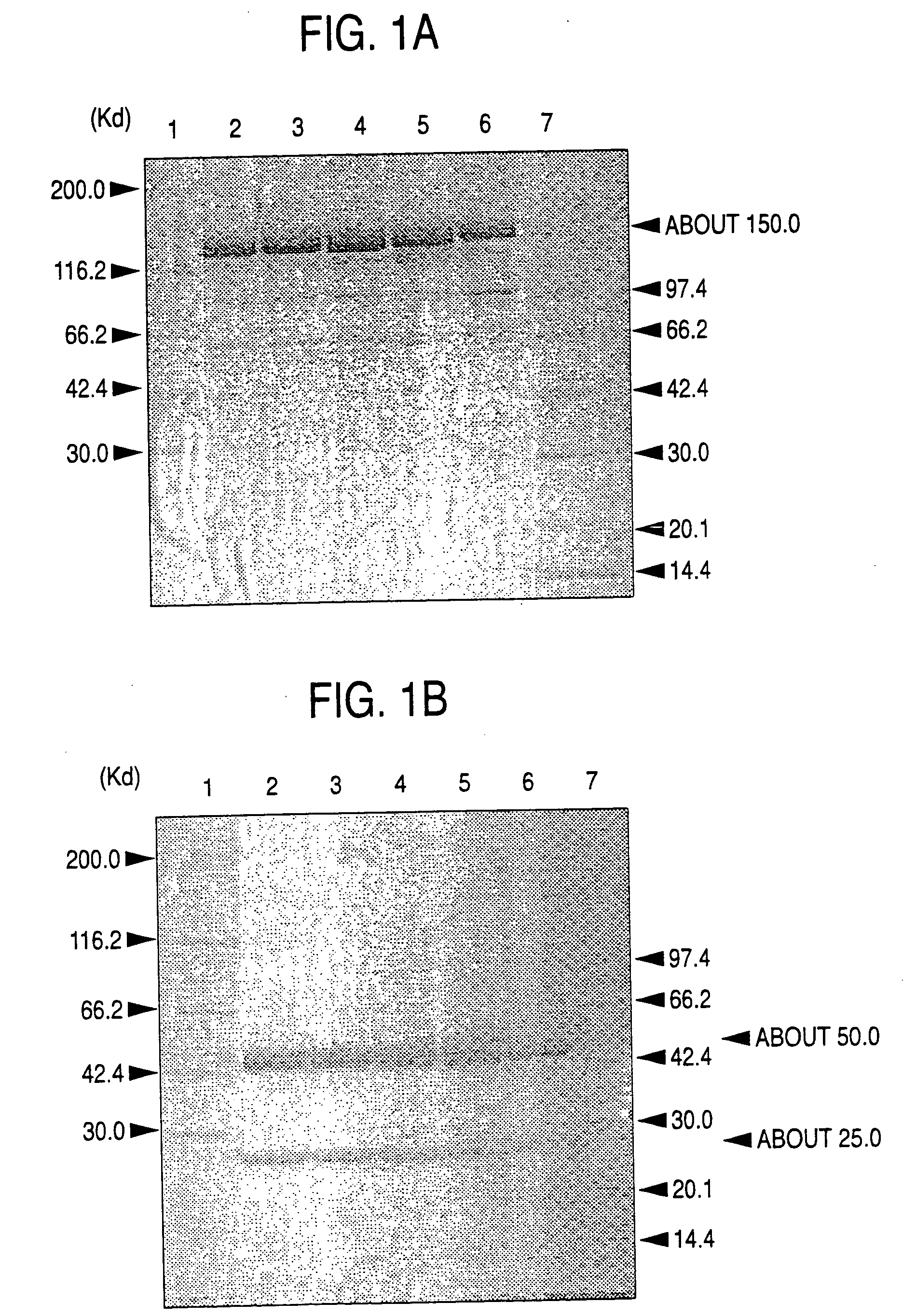
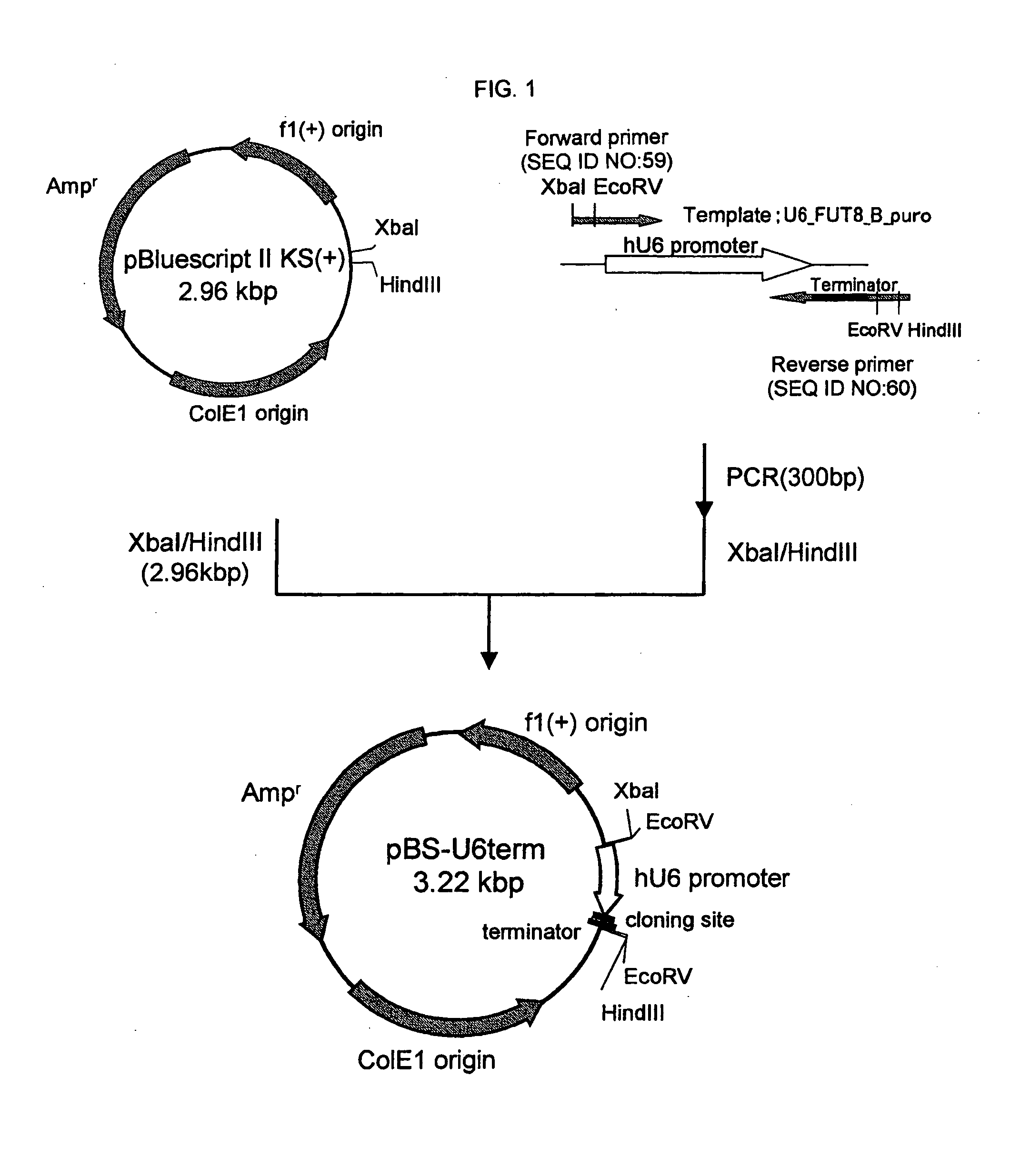
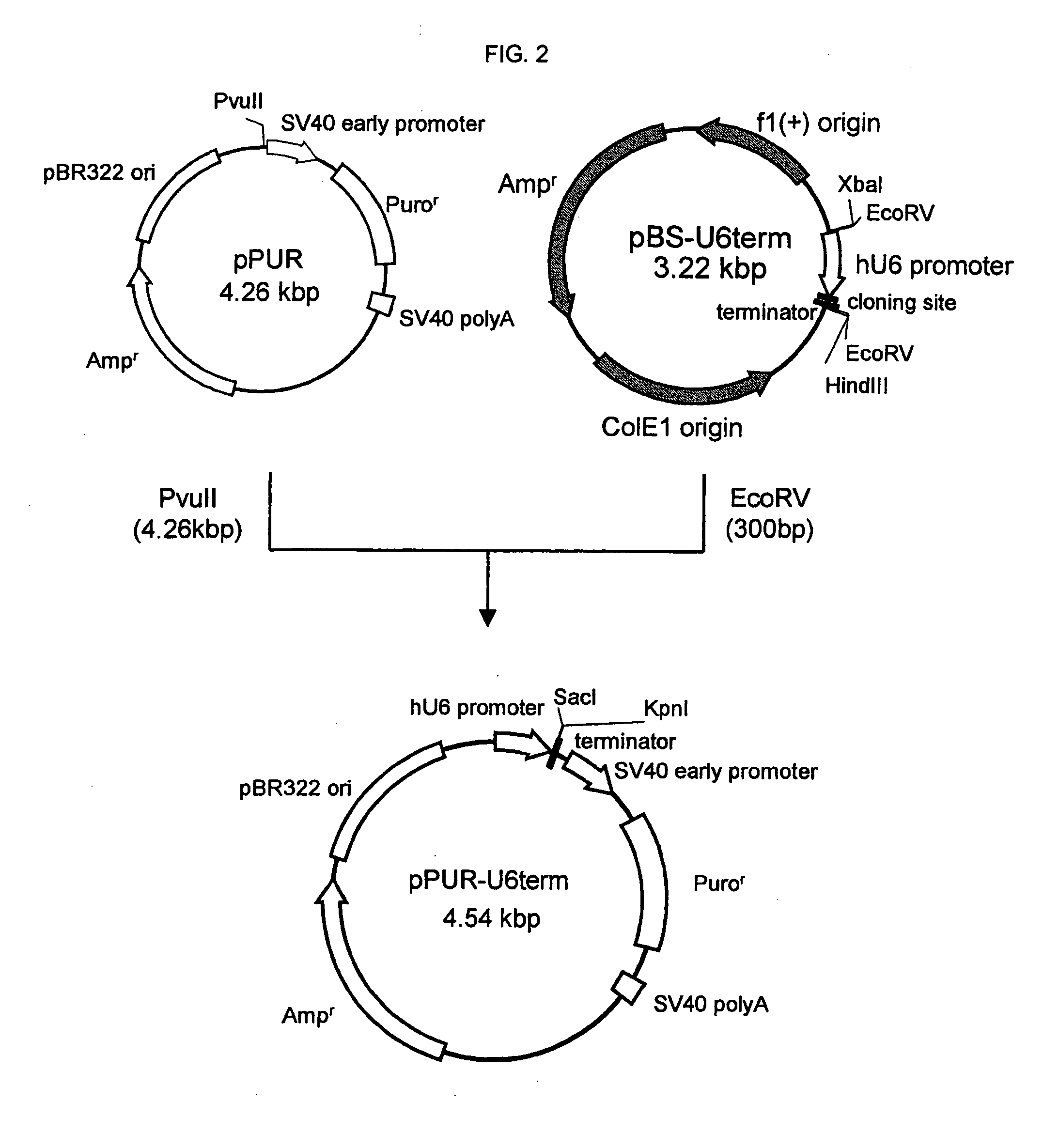
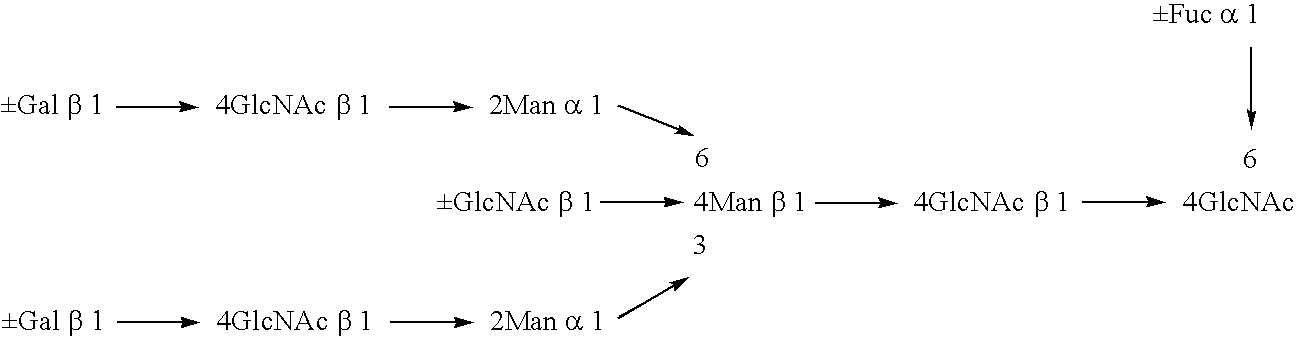
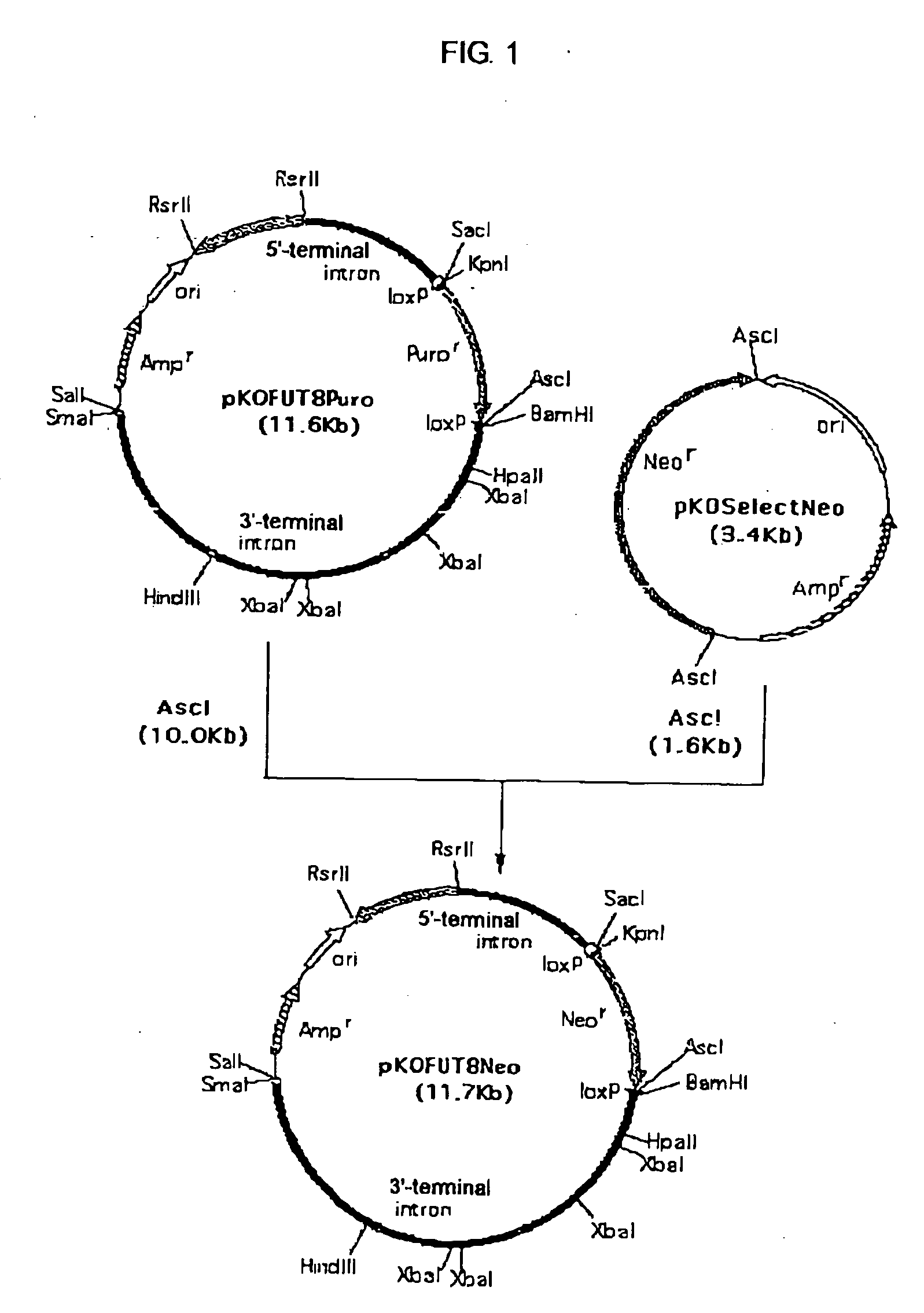
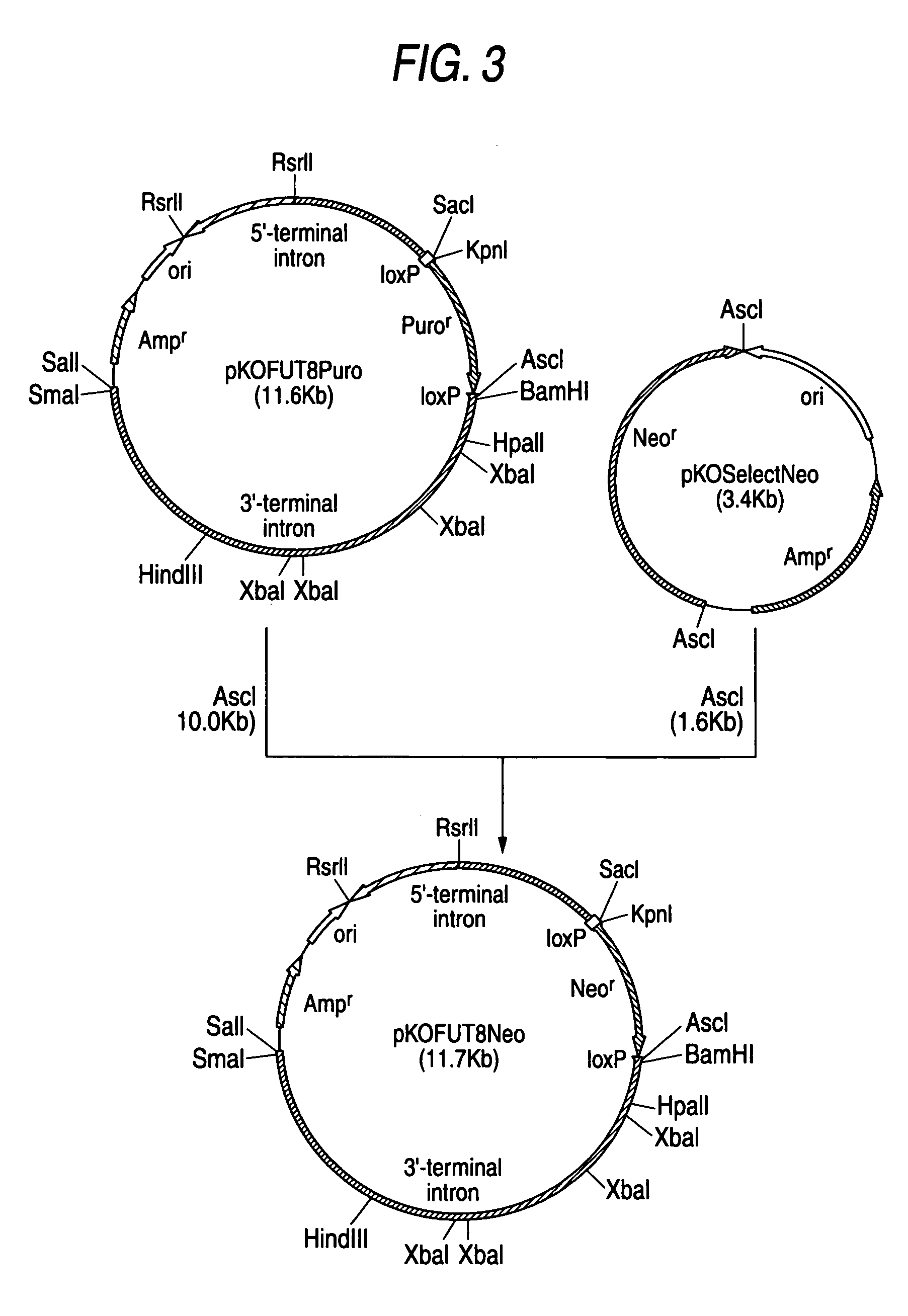
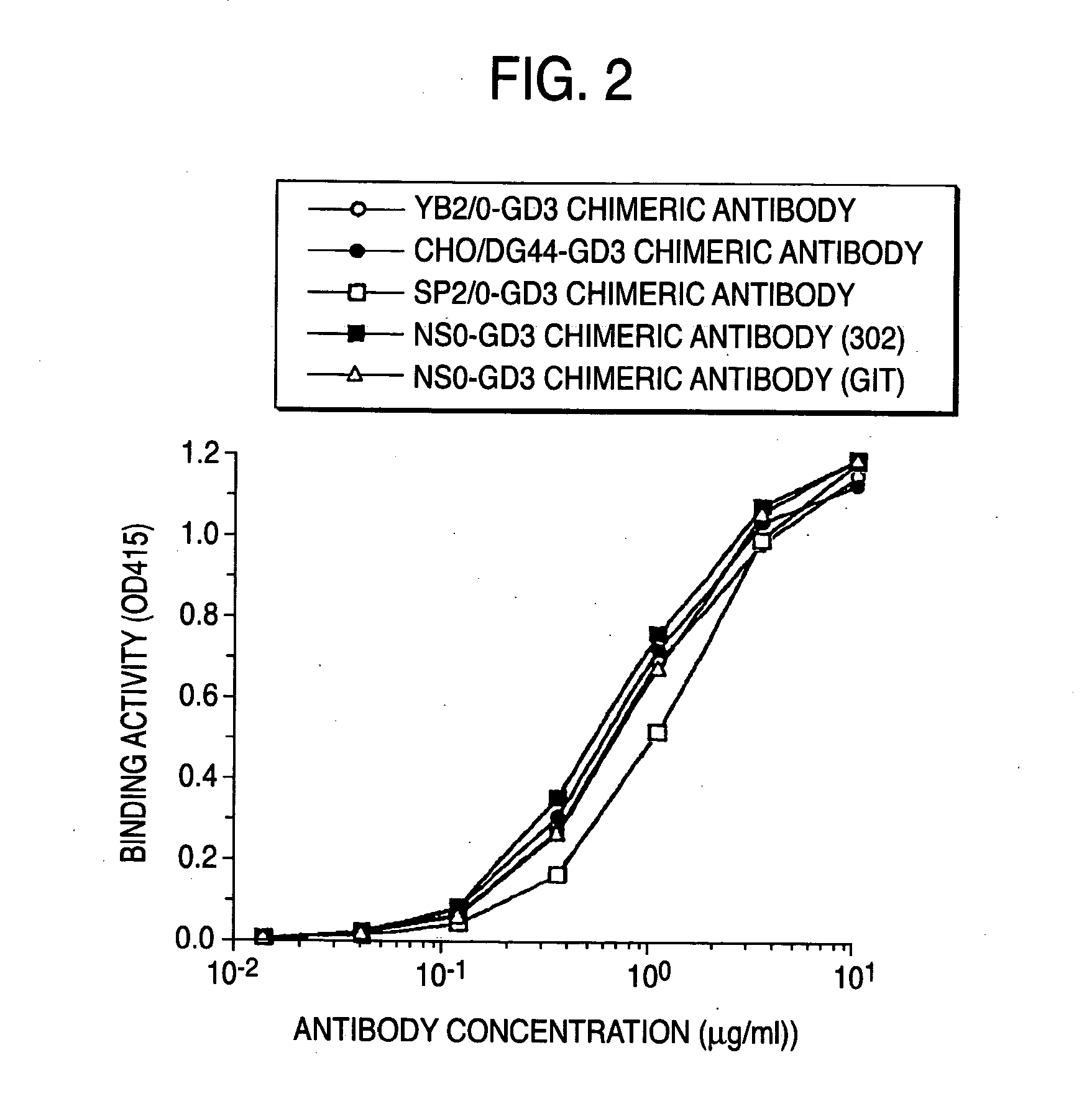
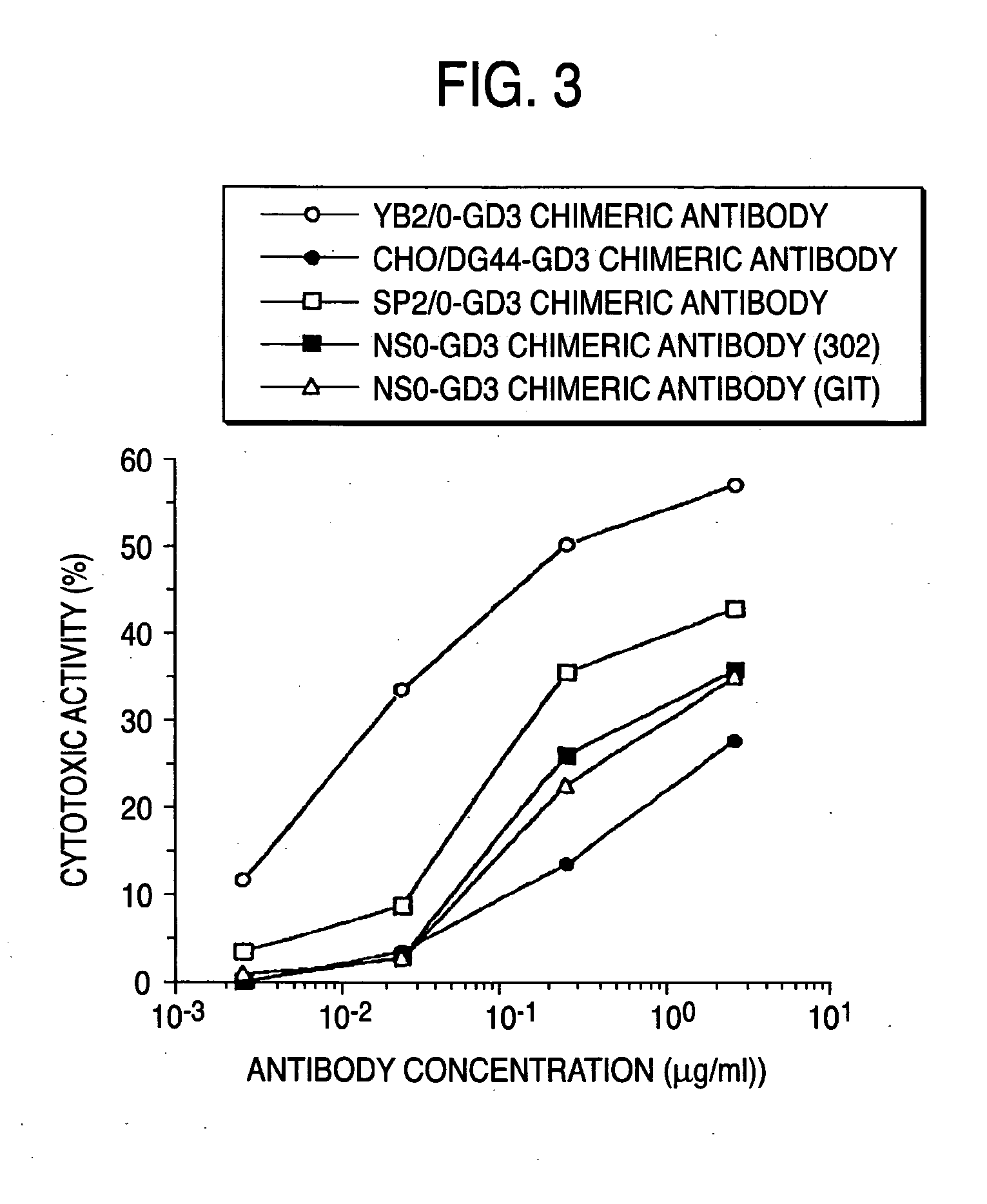
A cell in which genome is modified so as to have a more decreased or deleted activity of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through alpha-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain than its parent cell, and a process for producing an antibody composition using the cell.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
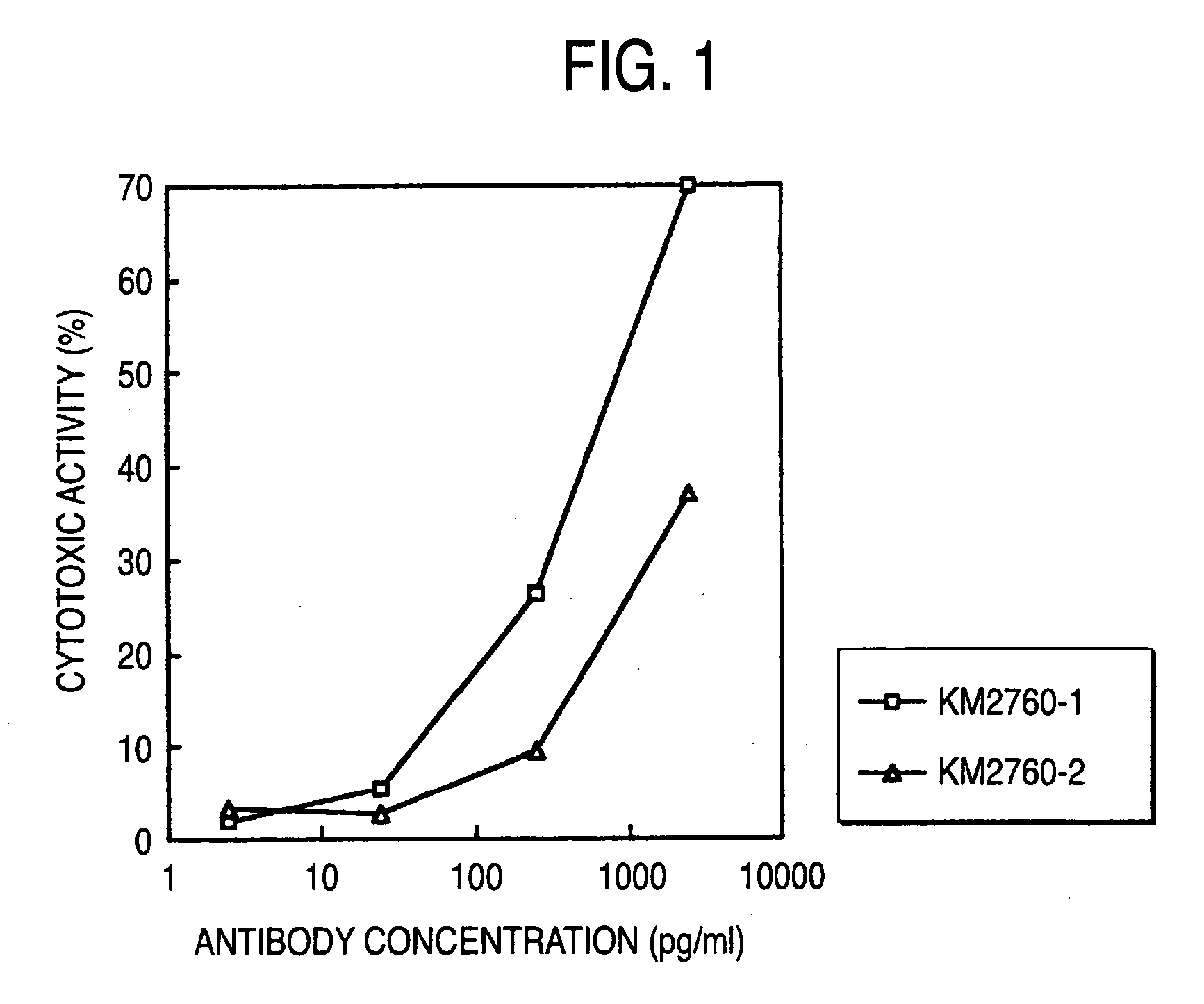
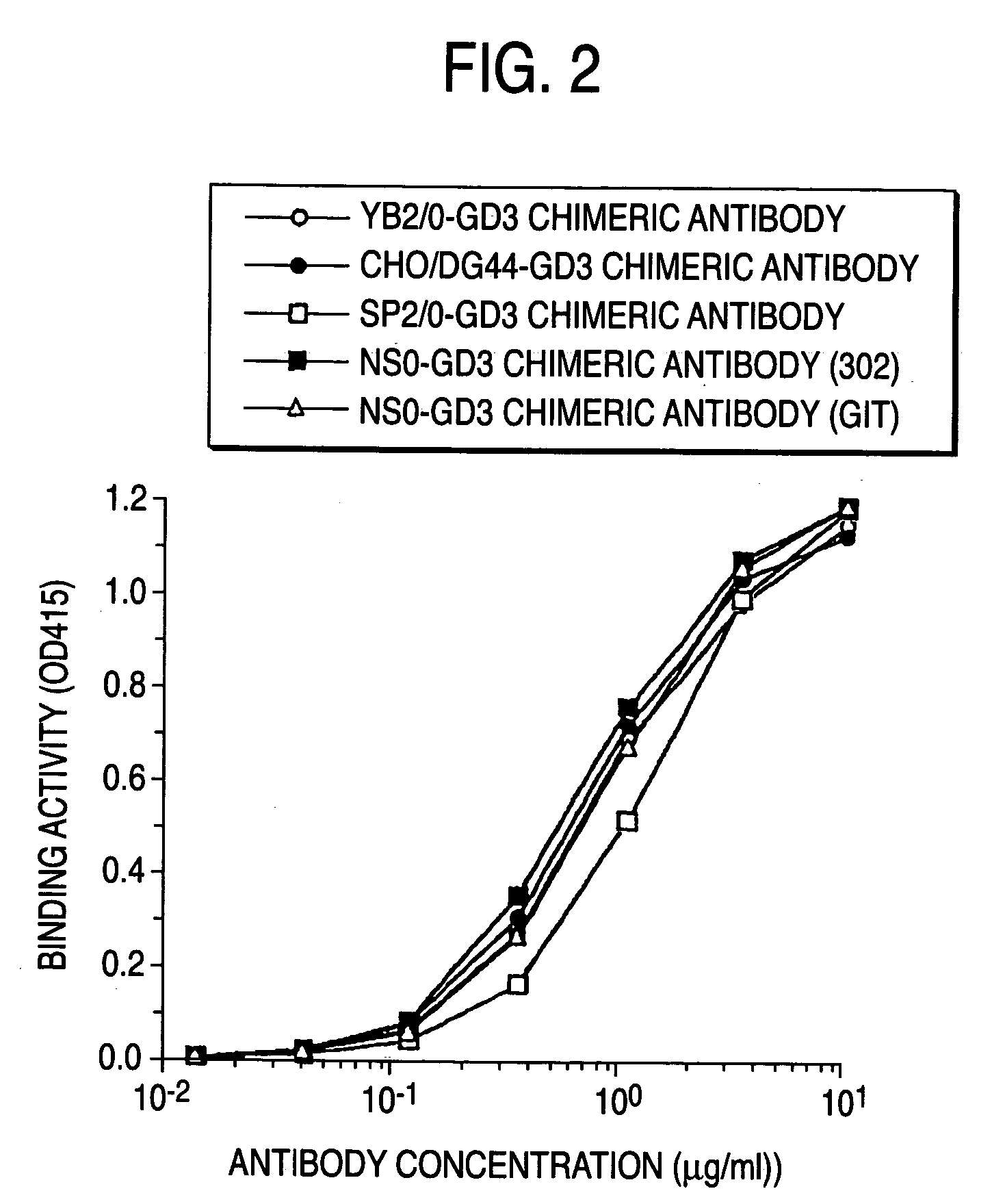
Method of enhancing of binding activity of antibody composition to Fcgamma receptor IIIa
A method for enhancing a binding activity of an antibody composition to Fcgamma receptor IIIa, which comprises modifying a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain which is bound to the Fc region of an antibody molecule; a method for enhancing an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity of an antibody composition; a process for producing an antibody composition having an enhanced binding activity to Fcgamma receptor IIIa; a method for detecting the ratio of a sugar chain in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chain among total complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chains bound to the Fc region in an antibody composition; an Fc fusion protein composition produced by using a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through alpha-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain; and a process for producing the same.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Methods and compositions for treatment of cell proliferative disorders
InactiveUS6063911AImprove efficiencyLow toxicityPowder deliverySugar derivativesChemistryN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention relates to methods and compositions comprising at least one endothelin antagonist, preferably in combination with a poly- beta -1->4-N-acetylglucosamine (p-GlcNAc) polysaccharide matrix, for use in the treatment of cancer and other proliferative diseases. The endothelin antagonist can be a peptide or non-peptide compound, and the p-GlcNAc matrix of the invention is comprised of a polymer of high molecular weight whose constituent monosaccharide sugars are attached in a beta -1->4 conformation, and which is free of proteins, and substantially free of single amino acids, and other organic and inorganic contaminants. The compositions and methods of the invention are useful for inhibiting the growth of tumors and other neoplastic cells and / or for inhibiting the metastasis of neoplastic cells in vivo.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
Cells of which genome is modified
A cell in which genome is modified so as to have a more decreased or deleted activity of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain than its parent cell, and a process for producing an antibody composition using the cell.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Process for producing glycoprotein composition
InactiveUS20060223147A1Raise the ratioAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticComplex typeN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention relates to a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme catalyzing a reaction which converts GDP-mannose into GDP-4-keto,6-deoxy-GDP-mannose is introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein using the cell; a cell into which an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to modification of a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in the complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, and an RNA capable of suppressing the function of an enzyme relating to synthesis of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, or an RNA capable of suppressing the function of a protein relating to transport of an intracellular sugar nucleotide, GDP-fucose, to the Golgi body are introduced; a process for producing a glycoprotein composition using the cell; and the like.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
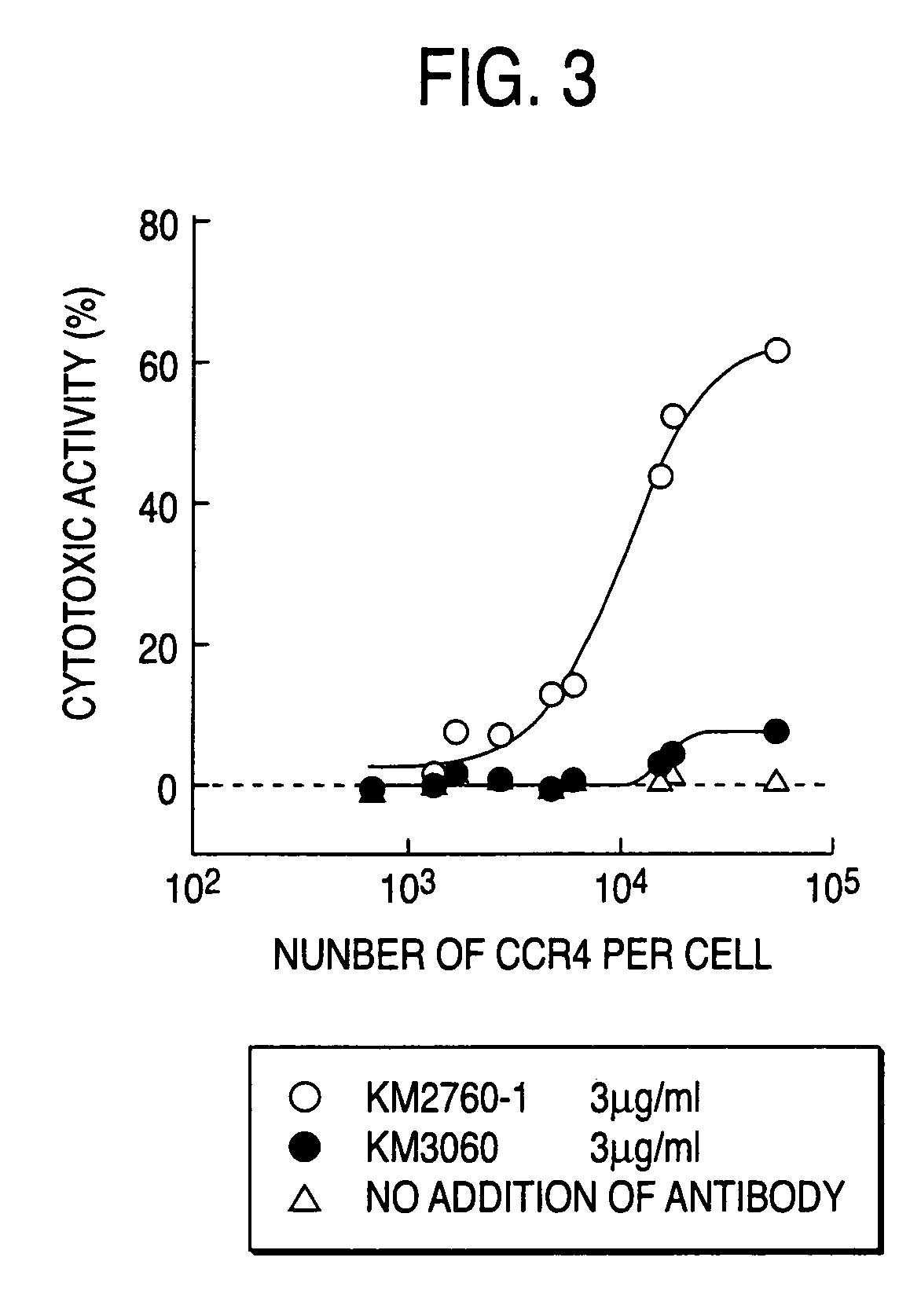
CCR4-specific antibody composition
InactiveUS20050287138A1Enhanced effector functionEffective treatmentImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsGlycosideComplex type
The present invention provides an antibody composition comprising an antibody molecule which specifically binds to human CC chemokine receptor 4 (CCR4) and has complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chains in the Fc region, wherein the complex type N-glycoside-linked sugar chains have a structure in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chains; a transformant which produces the antibody composition; a process for producing the antibody composition; and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the antibody composition.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
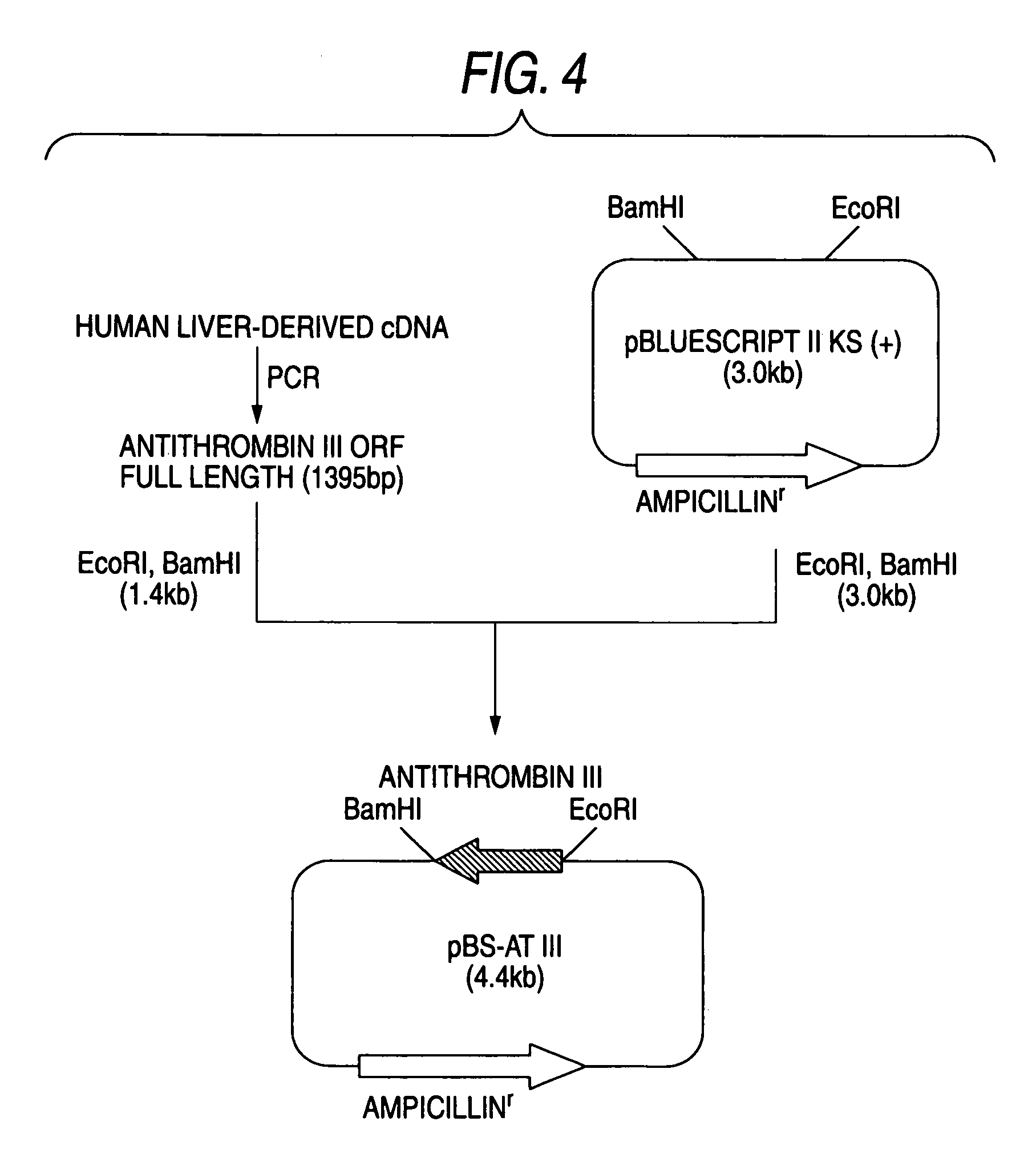
Treatments using transgenic goat produced antithrombin III
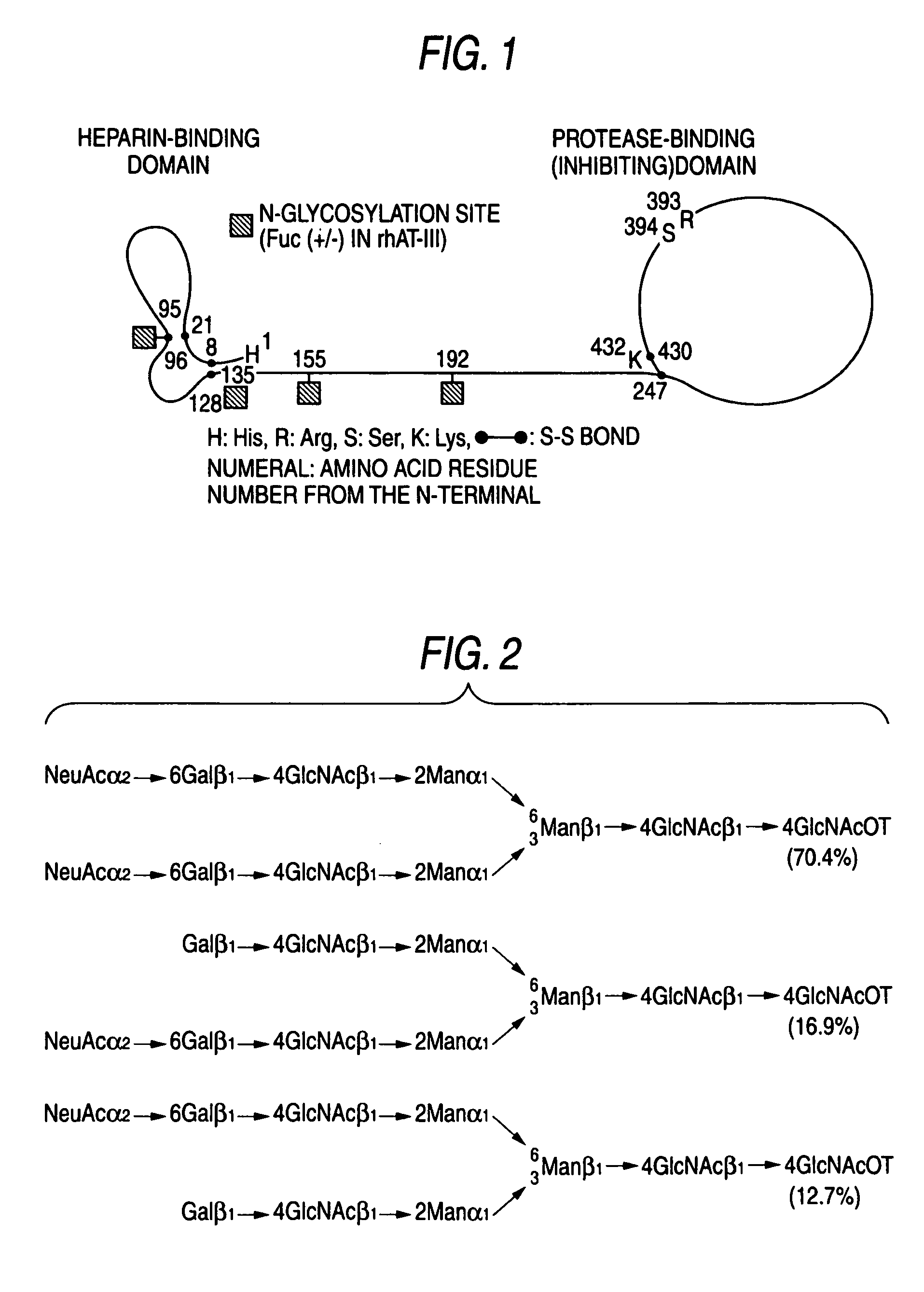
InactiveUS7019193B2Improve clearance ratePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPlasma derivedMonosaccharide composition
This invention relates to transgenically produced human Antithrombin III (tgATIII). The human ATIII produced by the transgenic process of the present invention has a monosaccharide composition which comprises N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) along with fucose, N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, mannose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid / N-glycolyneuraminic acid. The monosaccharide composition differs with that of plasma derived ATIII (phATIII). It has been found that tgATIII has an increased clearance rate when compared to phATIII.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Carbohydrate ligands (myelorollin) that cause E-selectin dependent cell rolling and adhesion under dynamic flow system
InactiveUS6133239AStrong rollingInhibit the inflammatory responseBiocideAntipyreticE-selectinFucosylation
An unbranched polylactosamine comprising at least 6 monosaccharides and having terminal alpha 2->3 sialylation and internal alpha 1->3 fucosylation at various N-acetylglucosamine residues except for solely at the penultimate N-acetylglucosamine residue.
Owner:BIOMEMBRANE INST +1
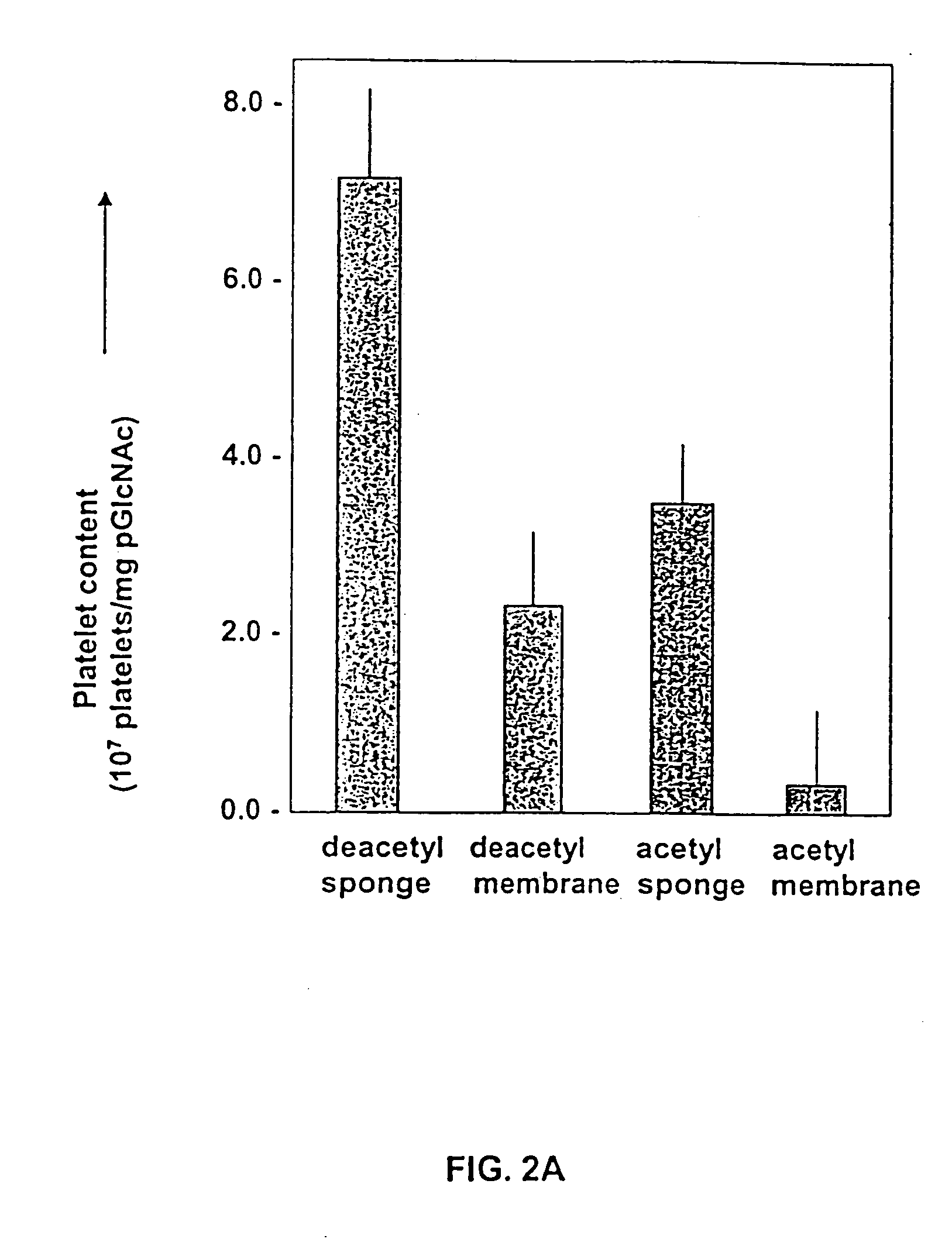
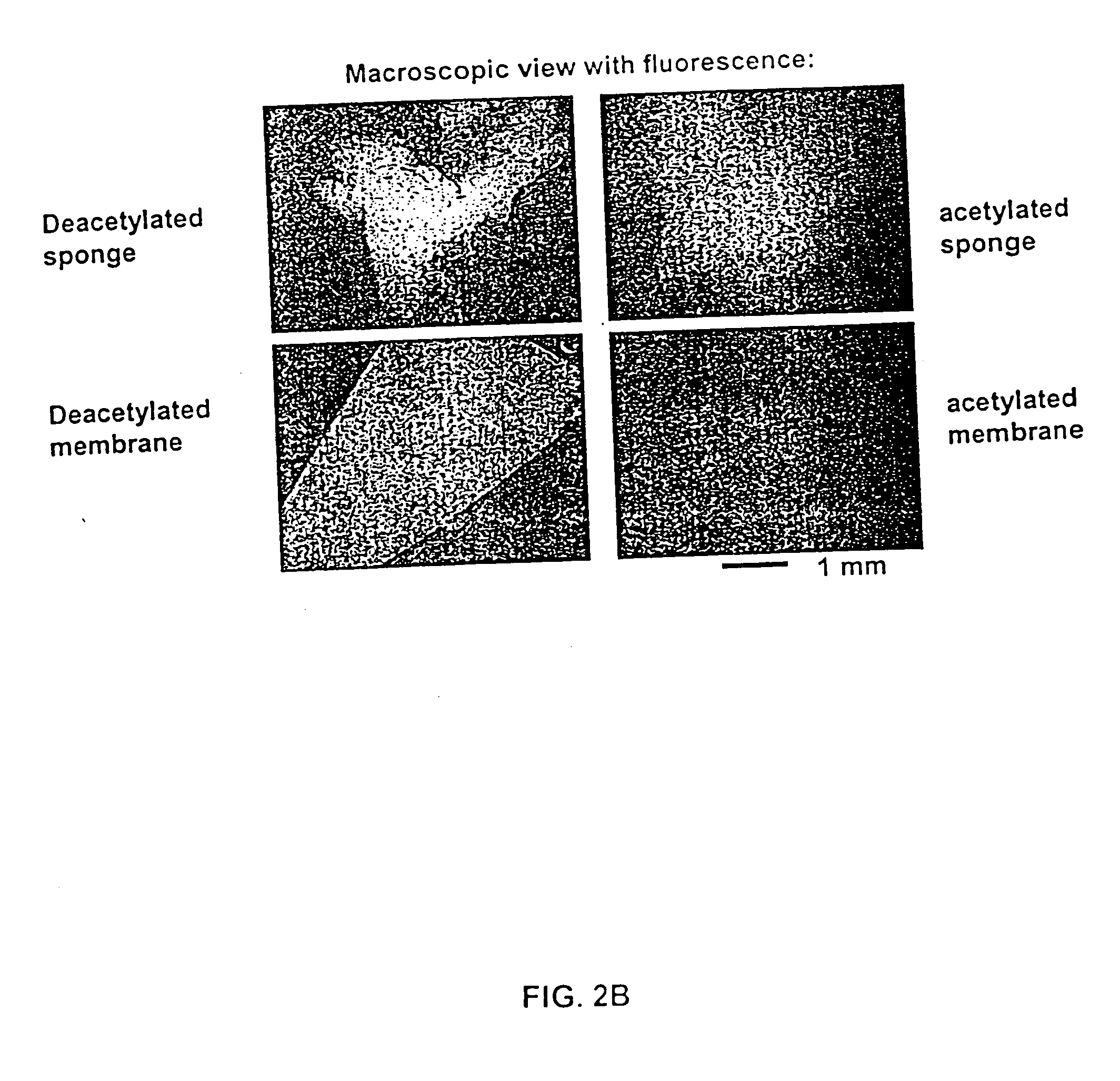
Cell-polymer fiber compositions and uses thereof
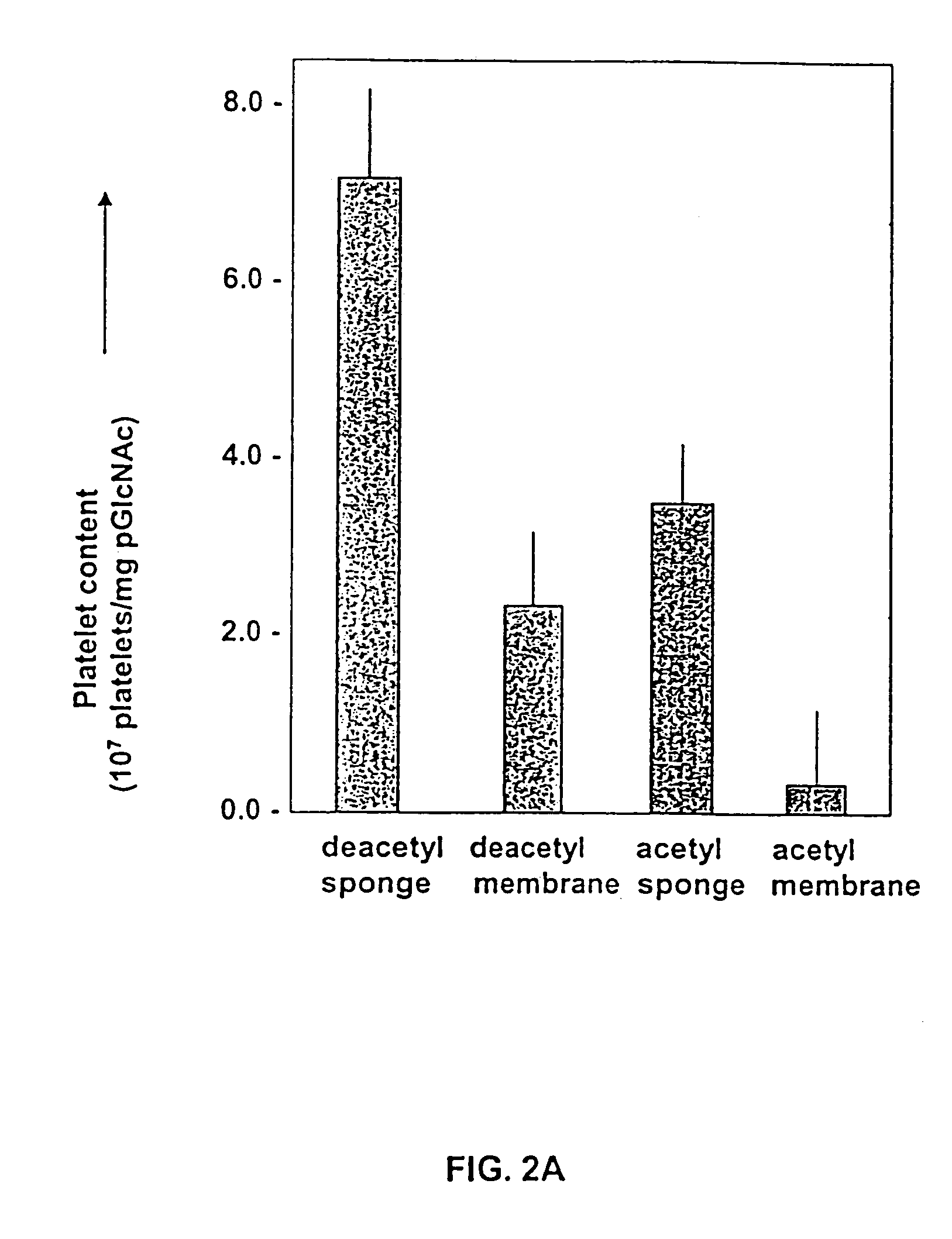
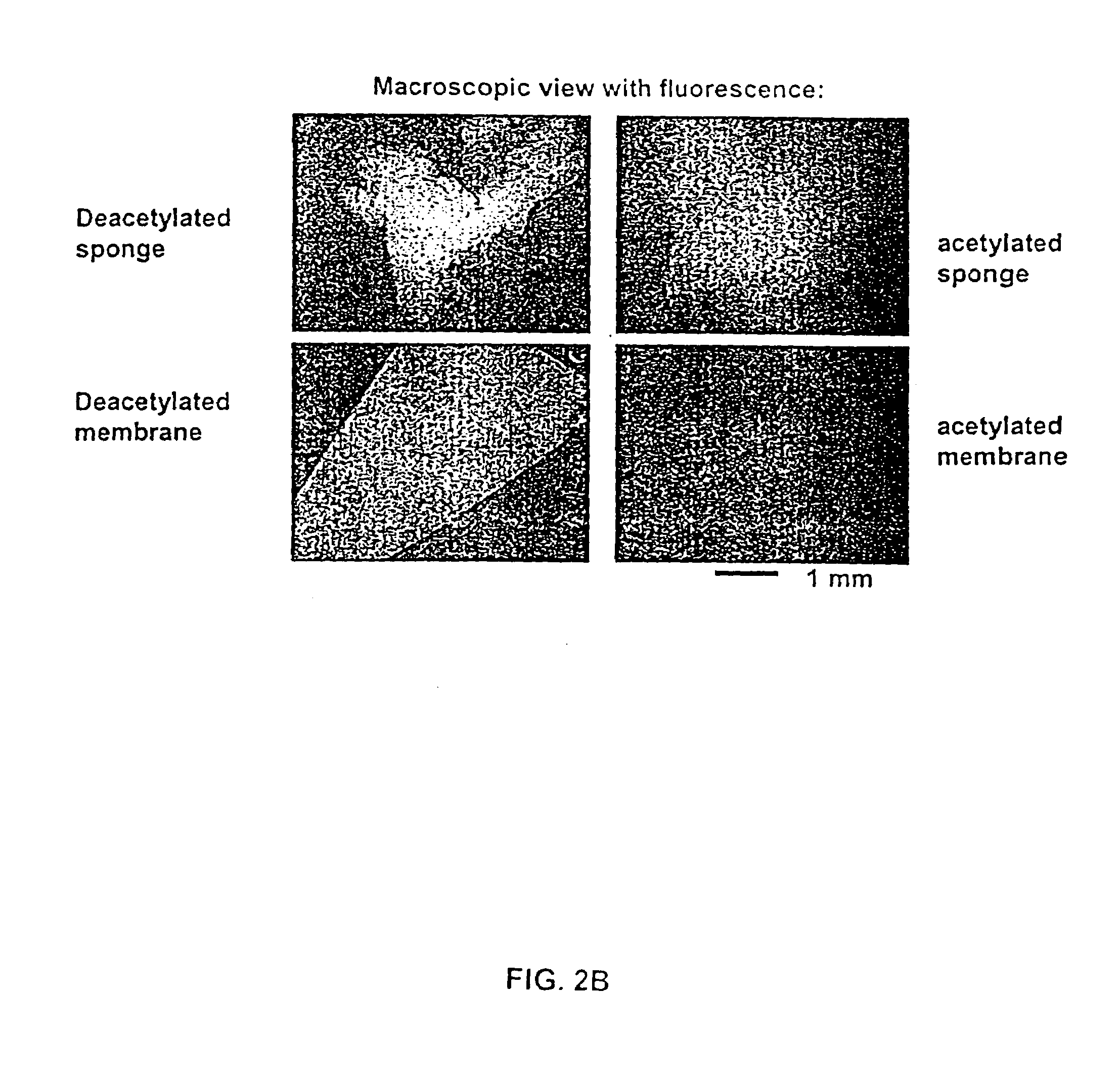
The present invention relates to compositions comprising complexes of human cells and polymer fibers and methods of their use for therapeutic purposes. Methods of making such compositions are also provided. The present invention encompasses compositions comprising poly-β-1→4-N-acetylglucosamine polymers and stored platelets and their use for promoting wound healing and achieving hemostasis.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
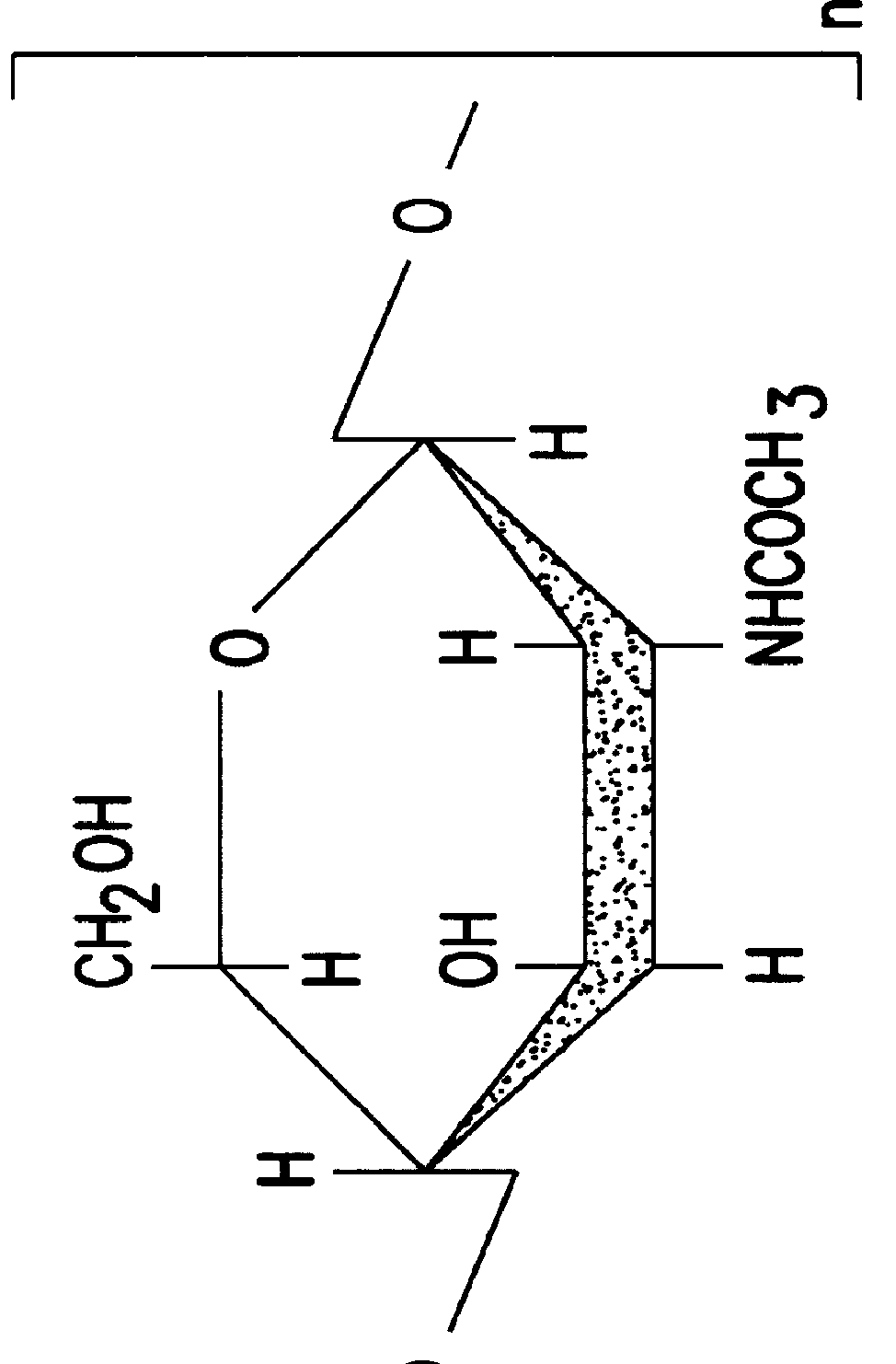
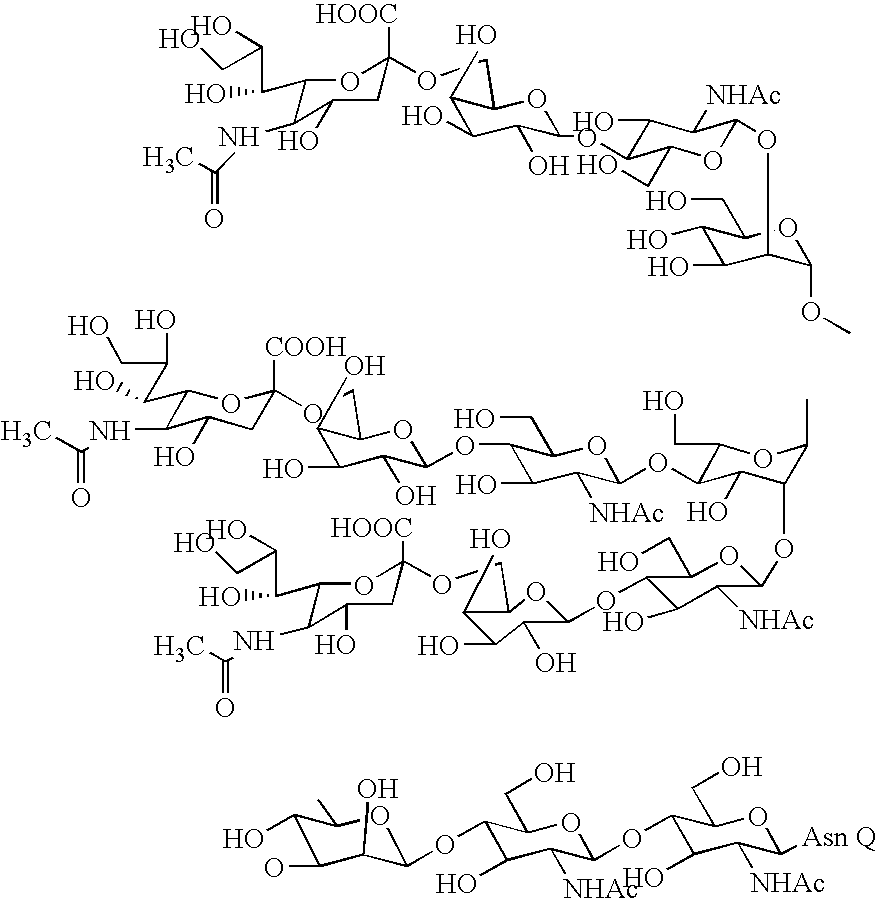
Three-branched sugar-chain asparagine derivatives, the sugar-chain asparagines, the sugar chains, and processes for producing these
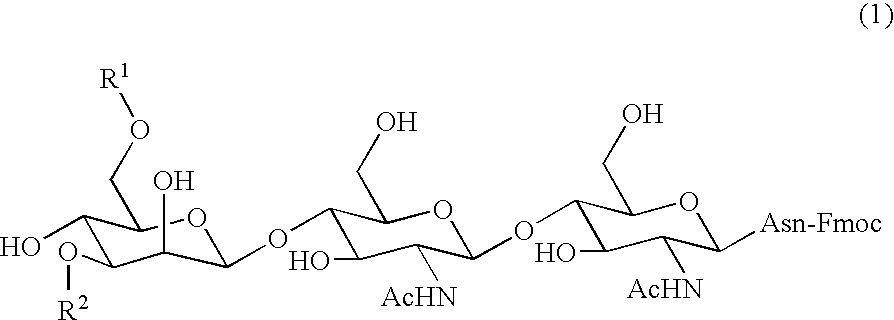
A 3-branched asparagine-linked oligosaccharide derivative of the formula (1) wherein the nitrogen of amino group of asparagine is modified with a lipophilic protective group, biotin group or FITC group; a 3-branched asparagine-linked oligosaccharide derivative which contains at least one fucose in N-acetylglucosamine on the nonreducing terminal side of the asparagine-linked oligosaccharide of the derivative; asparagine-linked oligosaccharides and oligosaccharides thereof wherein Q is a lipophilic protective group, biotin group or FITC group.
Owner:GLYTECH
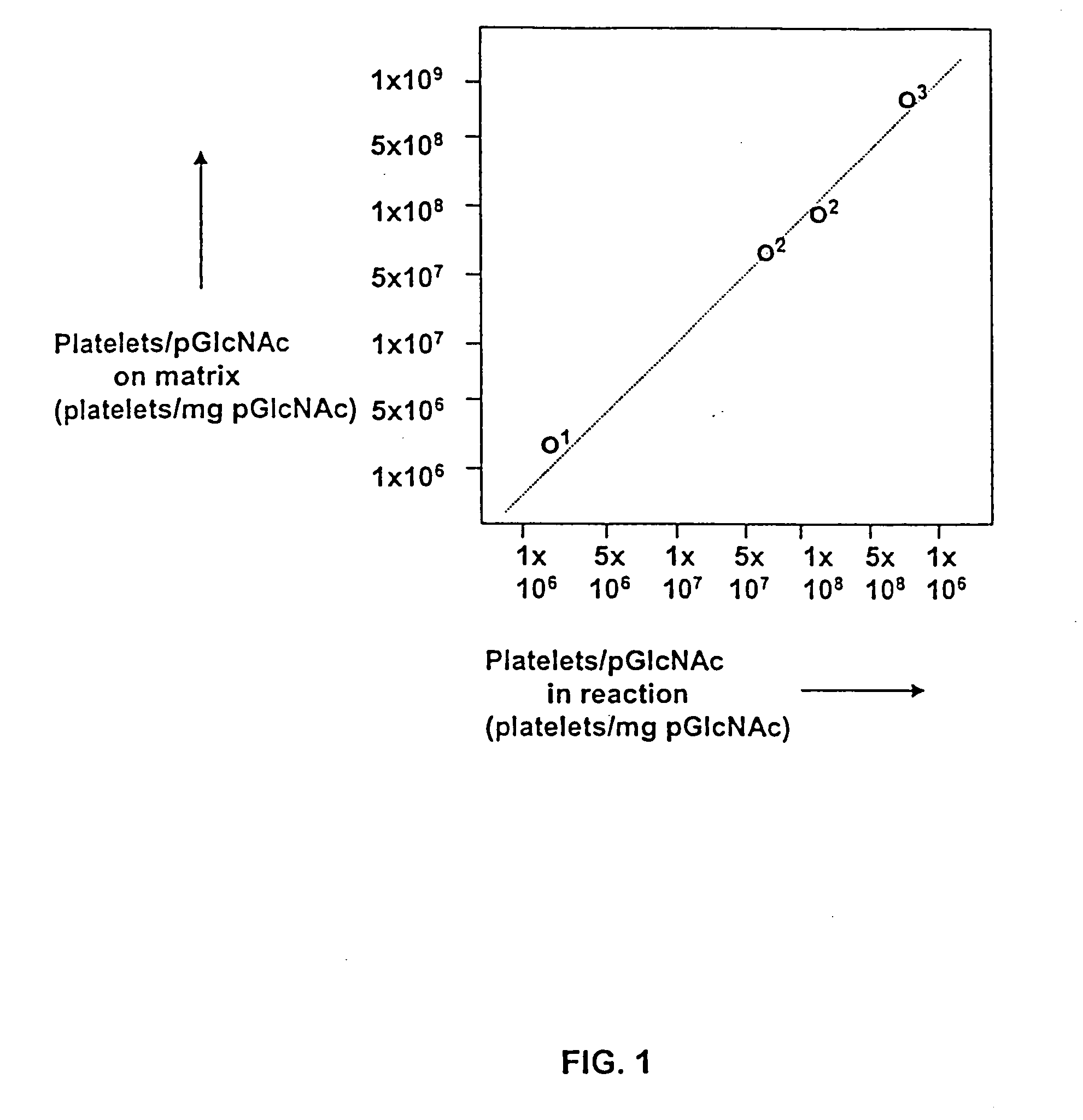
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising poly-beta-1->4-N-acetylglucosamine
InactiveUS6743783B1Easy to produceHigh molecular weightOrganic active ingredientsBiocideN-AcetylglucosamineSugar
The present invention relates to a purified, easily produced poly-beta-1->4-N-acetylglucosamine (p-GlcNAc) polysaccharide species. The p-GlcNAc of the invention is a polymer of high molecular weight whose constituent monosaccharide sugars are attached in a beta-1->4 conformation, and which is free of proteins, and substantially free of single amino acids, and other organic and inorganic contaminants. In addition, derivatives and reformulations of p-GlcNAc are described. The present invention further relates to methods for the purification of the p-GlcNAc of the invention from microalgae, preferably diatom, starting sources. Still further, the invention relates to methods for the derivatization and reformulation of the p-GlcNAc. Additionally, the present invention relates to the uses of pure p-GlcNAc, its derivatives, and / or its reformulations.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
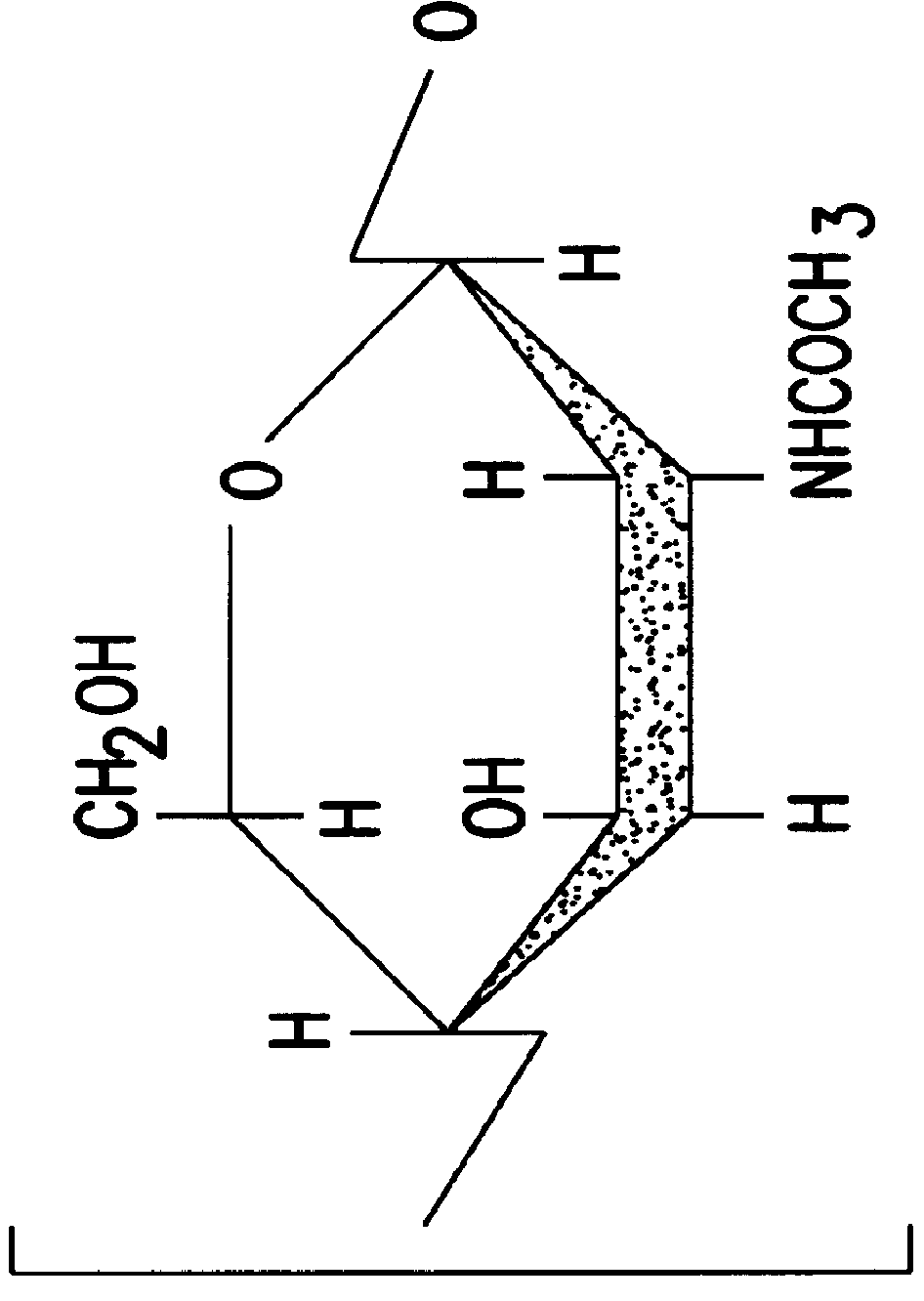
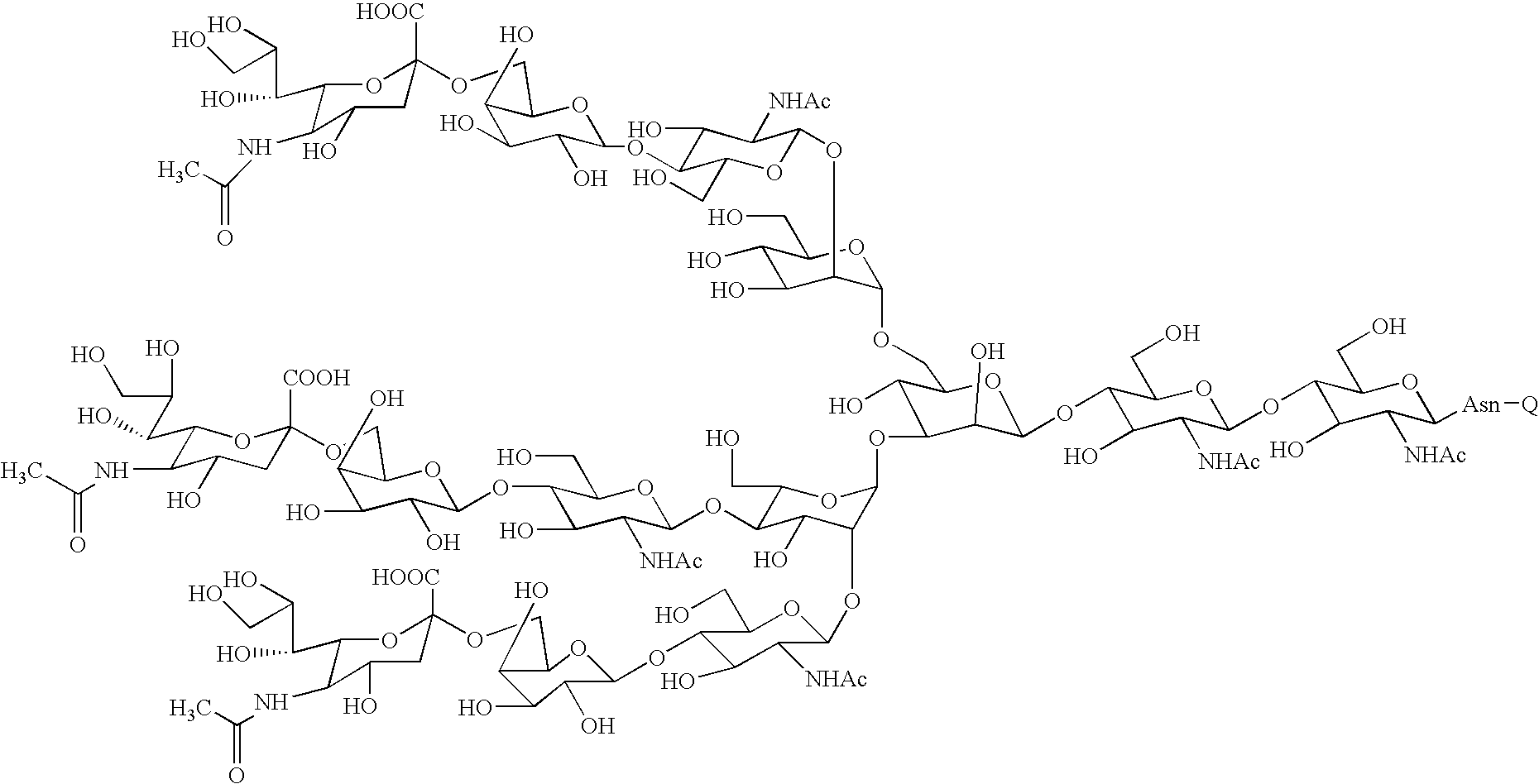
Sugar chain asparagine derivatives, sugar chain asparagine, sugar chain, and processes for producing these
ActiveUS20060228784A1Easy to prepareEfficiently and in large amountOrganic active ingredientsBiocideN-AcetylglucosamineSugar
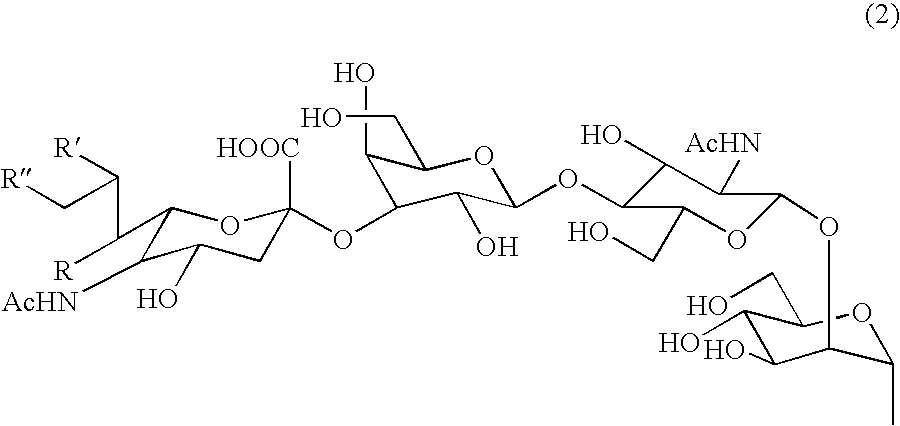
An asparagine-linked α2,3-oligosaccharide having undeca- to hepta-saccharides, an asparagine-linked α2,6-oligosaccharide having undeca- to hepta-saccharides and containing fluorine and an asparagine-linked oligosaccharide derivative containing at least one fucose in N-acetylglucosamine on the nonreducing terminal side of an asparagine-linked oligosaccharide wherein the asparagine has amino group protected with a lipophilic protective group, and a process for producing these compounds.
Owner:GLYTECH
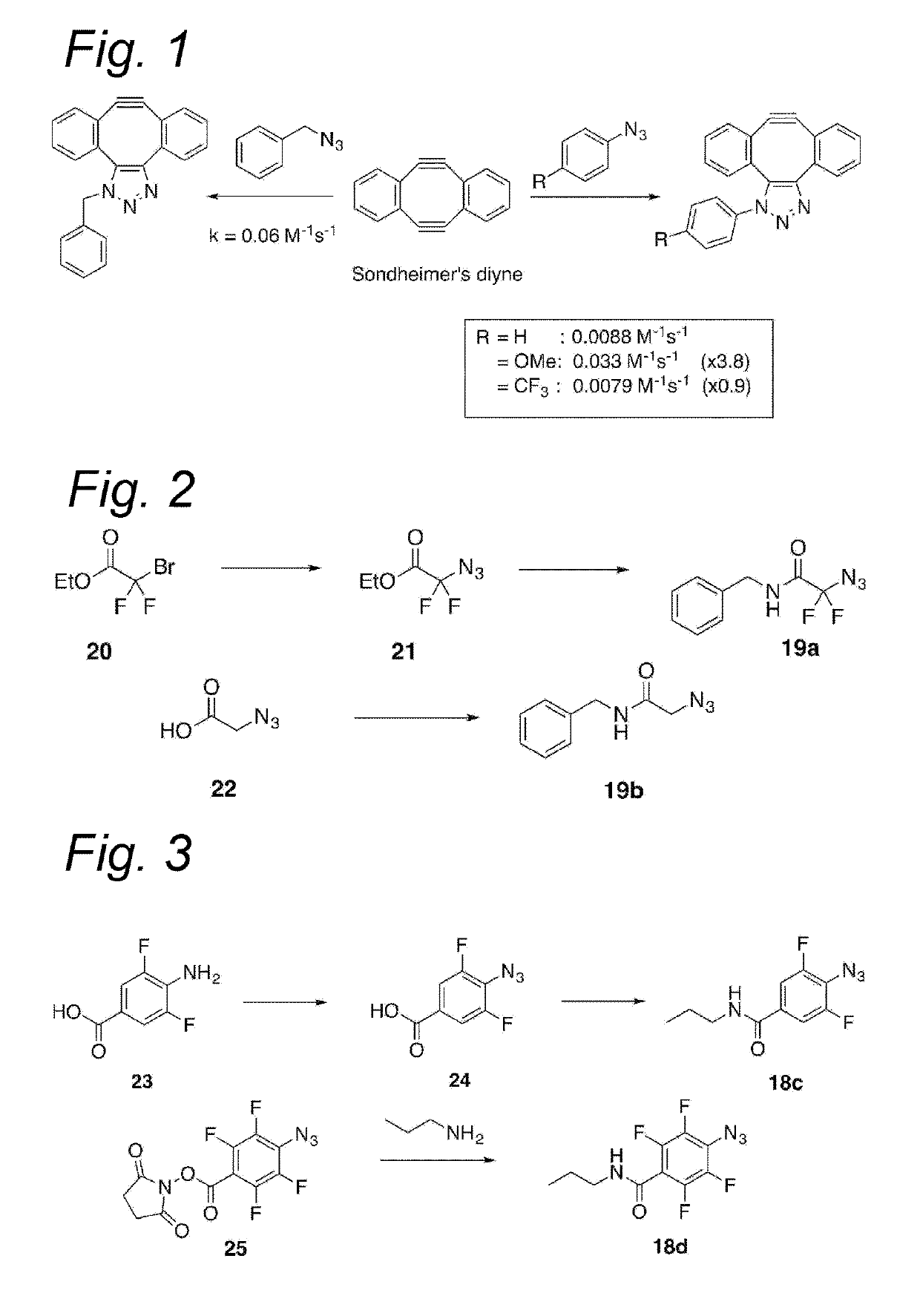
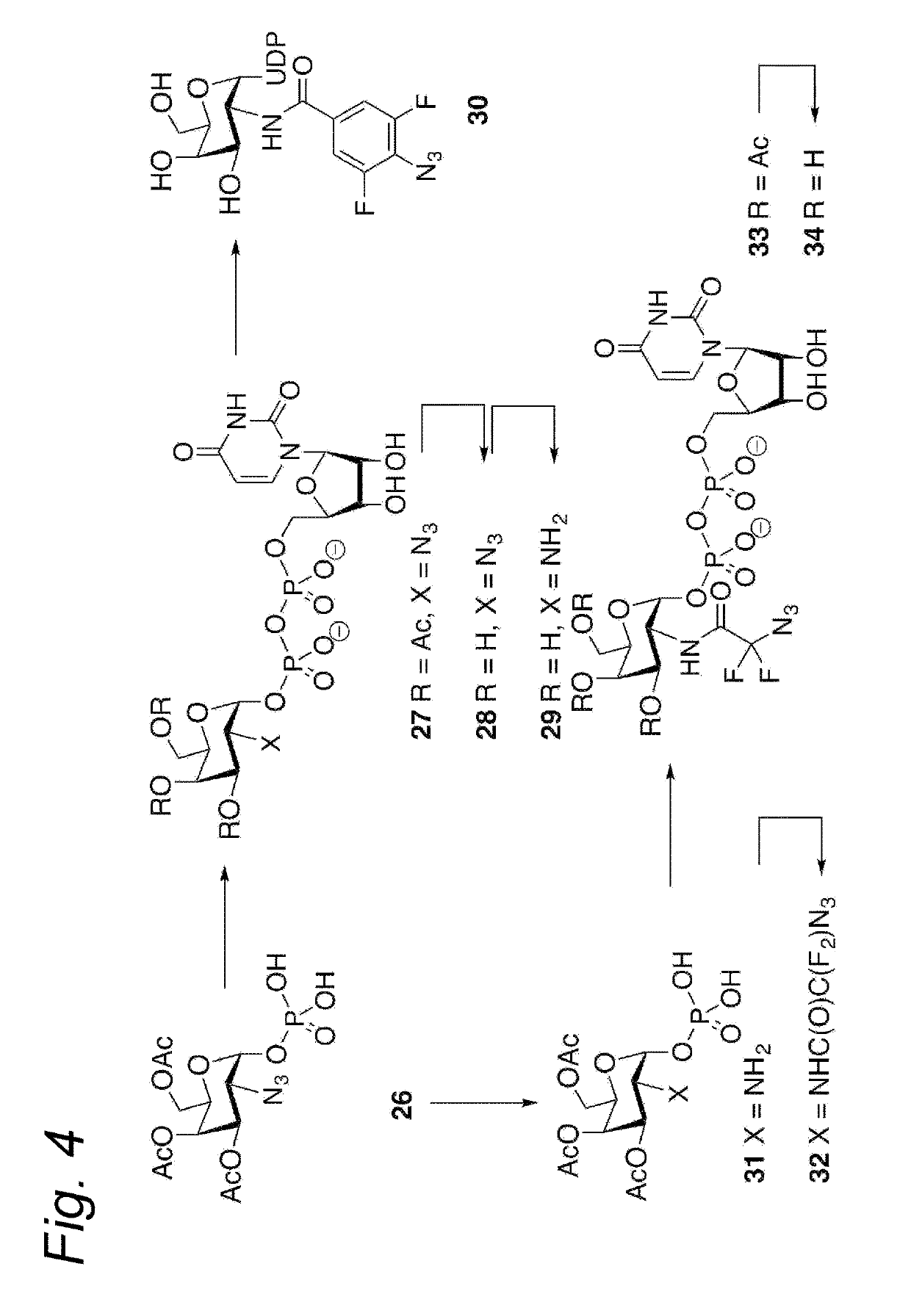
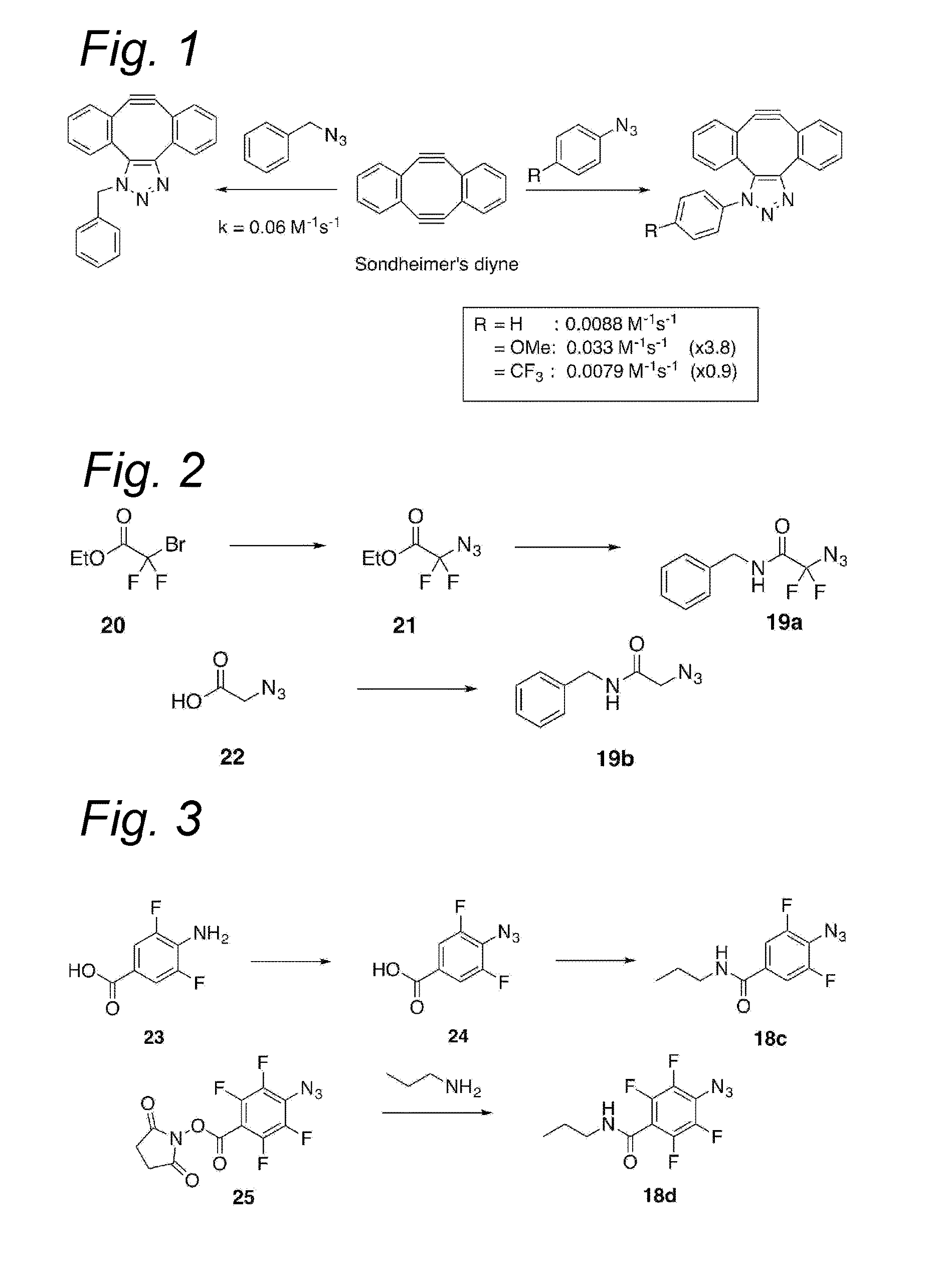
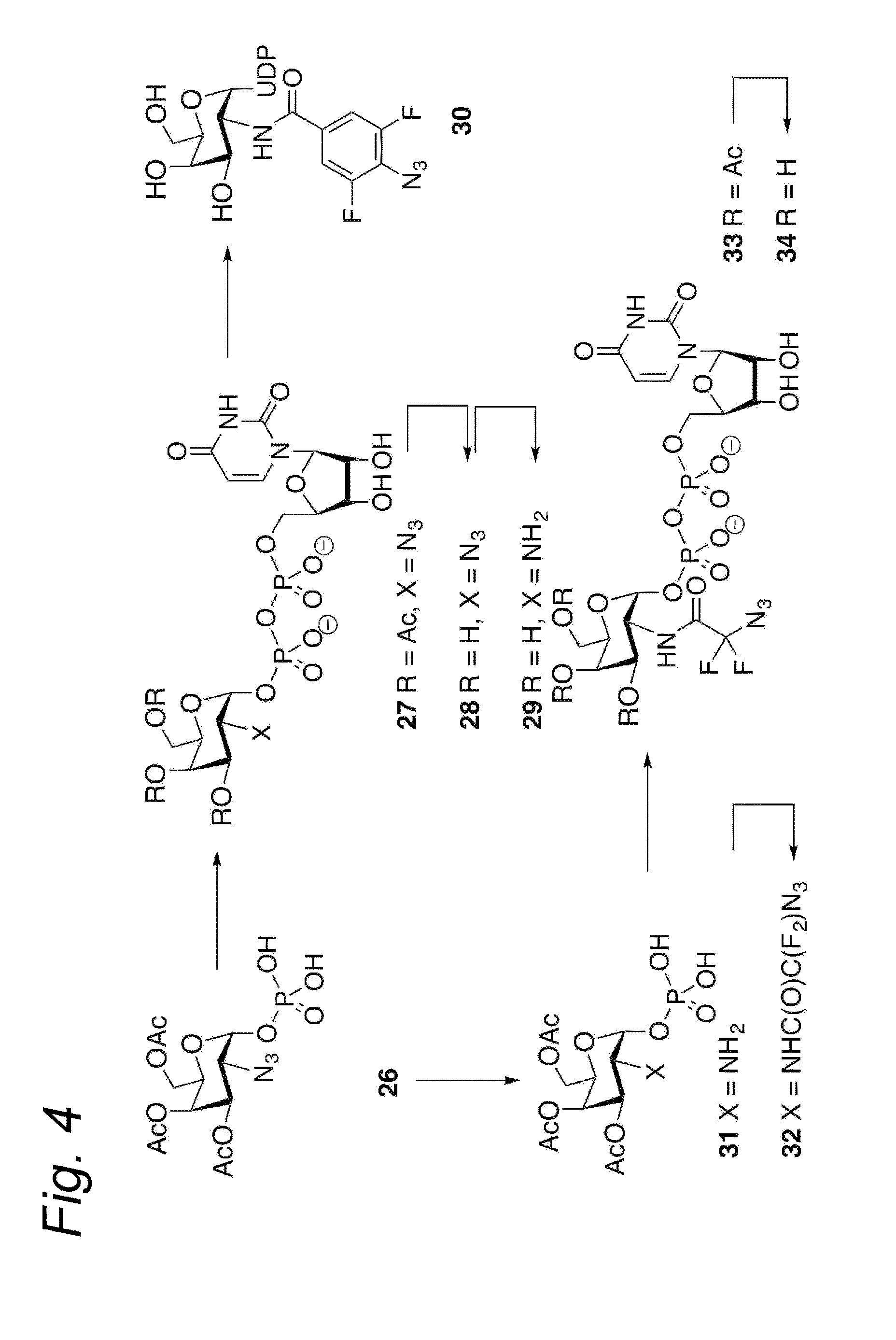
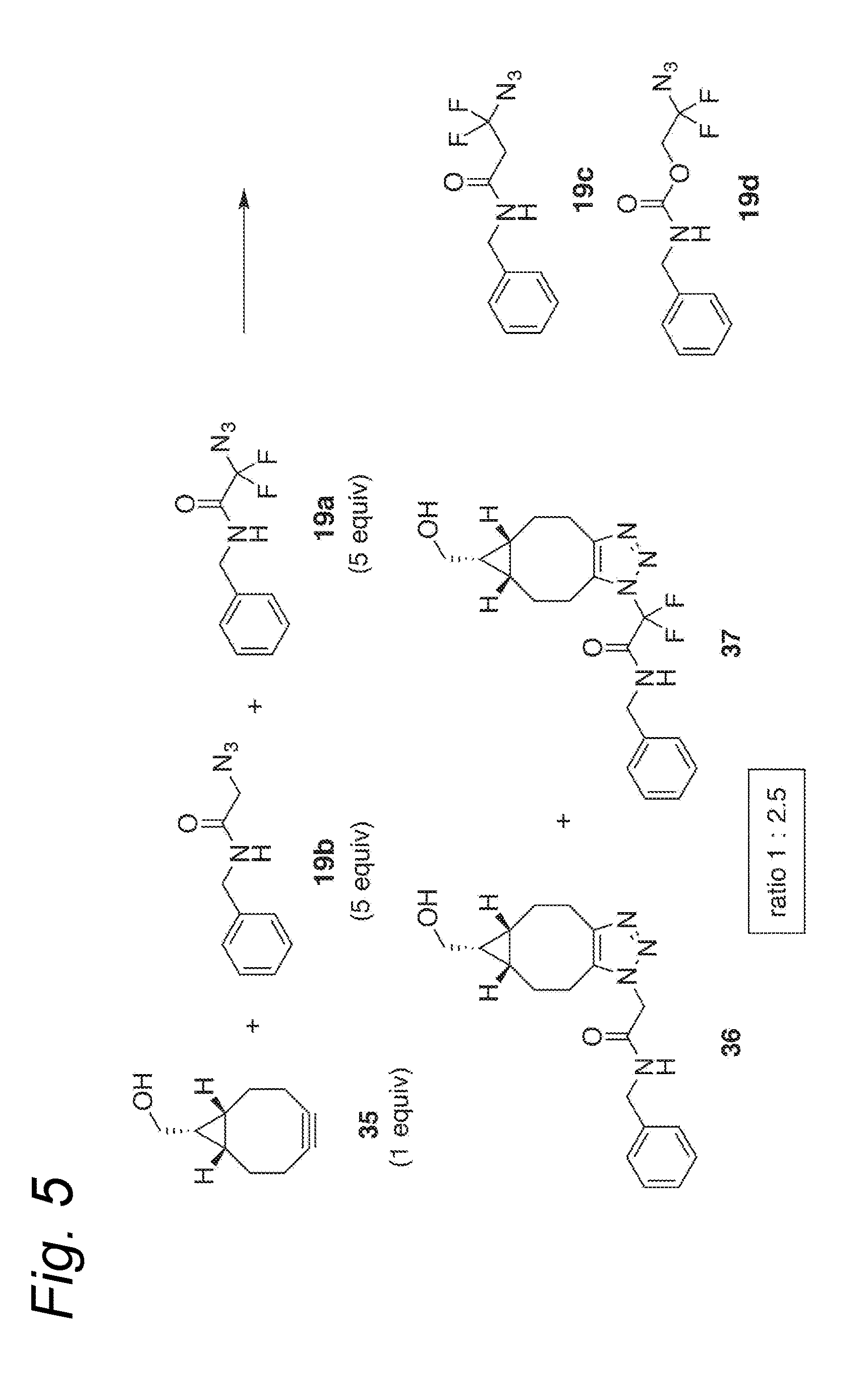
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS10266502B2Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Antibody composition-containing medicament
A medicament for treating a patient who cannot be cured with a medicament comprising as an active ingredient an antibody composition produced by a cell unresistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, which comprises as an active ingredient an antibody composition produced by a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain, and a method for screening the patient by using the medicament.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Cell-polymer fiber compositions and uses thereof
ActiveUS20040220140A1Shorten hemostasis timePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWound healingMedicine
The present invention relates to compositions comprising complexes of human cells and polymer fibers and methods of their use for therapeutic purposes. Methods of making such compositions are also provided. The presen t invention encompasses compositions comprising poly-.beta.-1.fwdarw.4-N-acetylglucosamine polymers and stored platelets and their use for promoting wound healing and achieving hemostasis.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
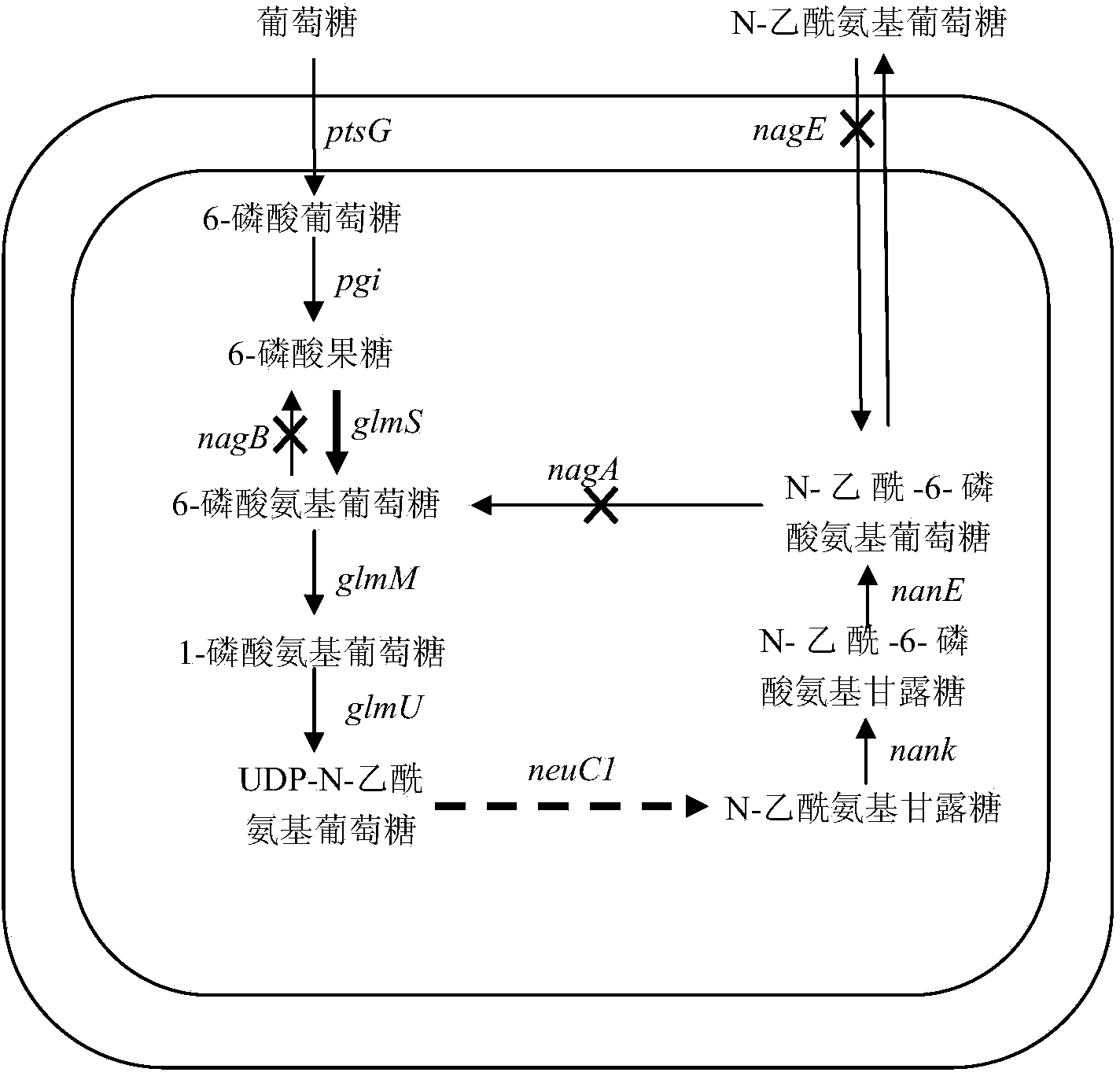
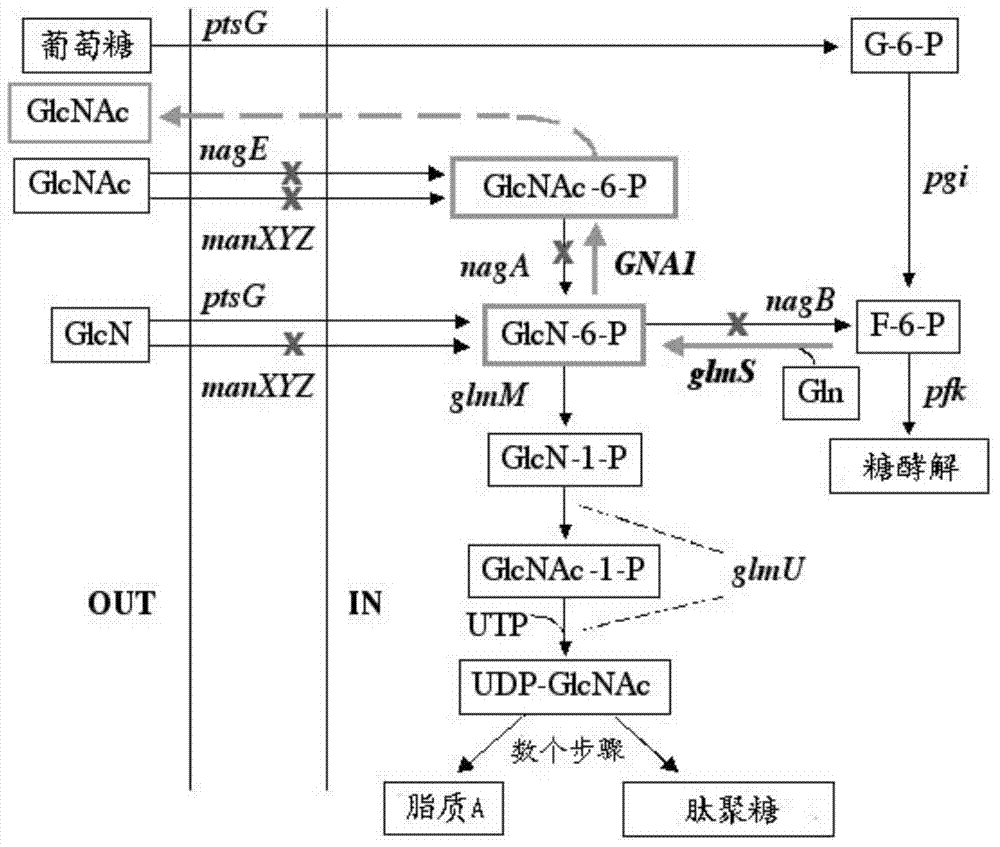
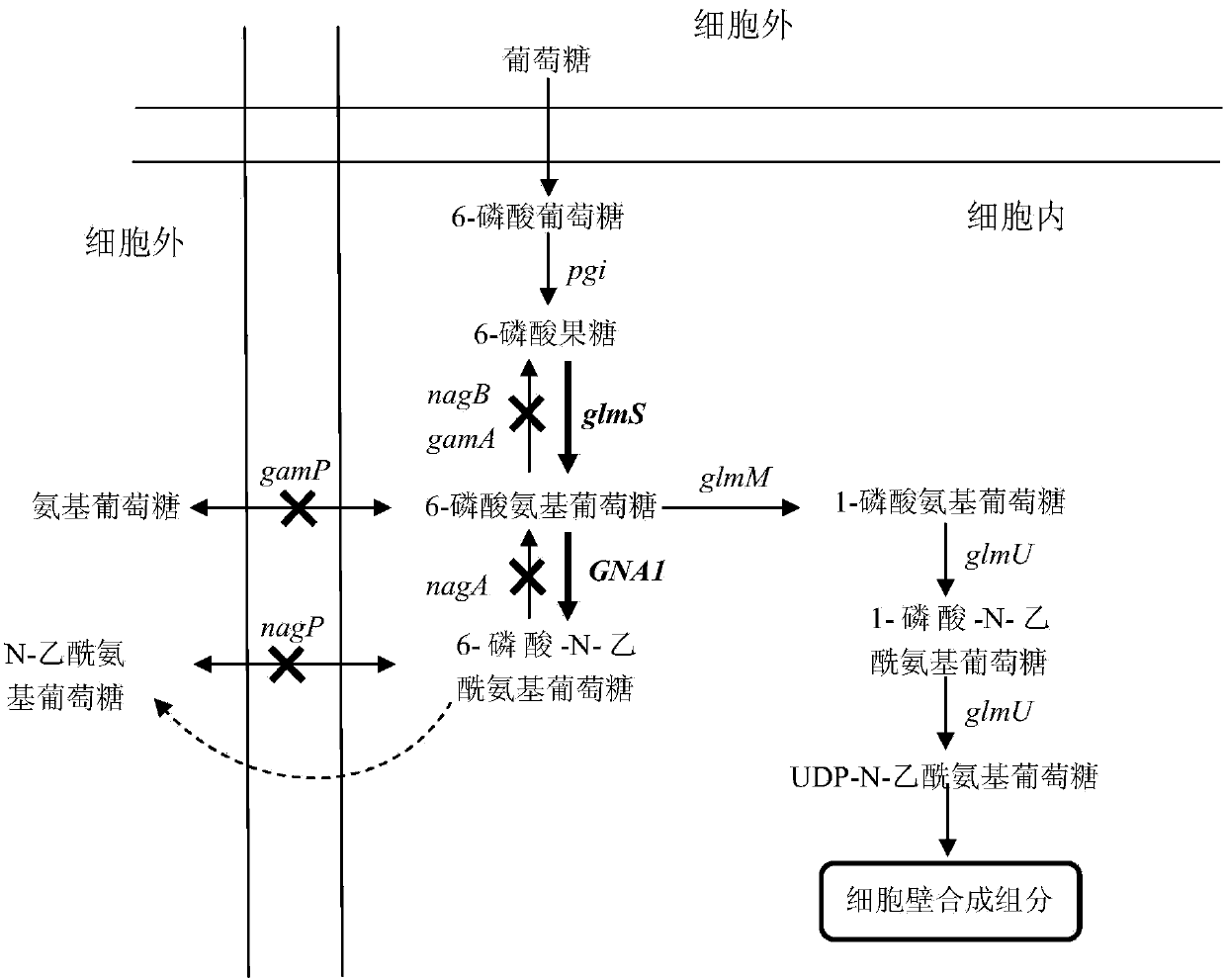
High-yield N-acetylglucosamine metabolic engineering bacterium, as well construction method and applications thereof
The invention discloses a high-yield N-acetylglucosamine metabolic engineering bacterium, as well a construction method and applications thereof. The engineering bacterium is a recombinant Escherichia coli by leading a coded UDP-N-acetylglucosamine epimerase gene and a coded 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase gene into Escherichia coli for expression, and knocking out the gene N-acetylglucosamine in the Escherichia coli to decompose and utilize metabolic pathway enzyme; and the constructed engineering bacterium strain utilizes glucose as a substrate for fermenting and culturing and synthesizing the N-acetylglucosamine. The engineering bacterium is high in the fermenting level of synthesizing the N-acetylglucosamine by utilizing glucose, the accumulation of side products is less, and industrial production potential capability can be achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
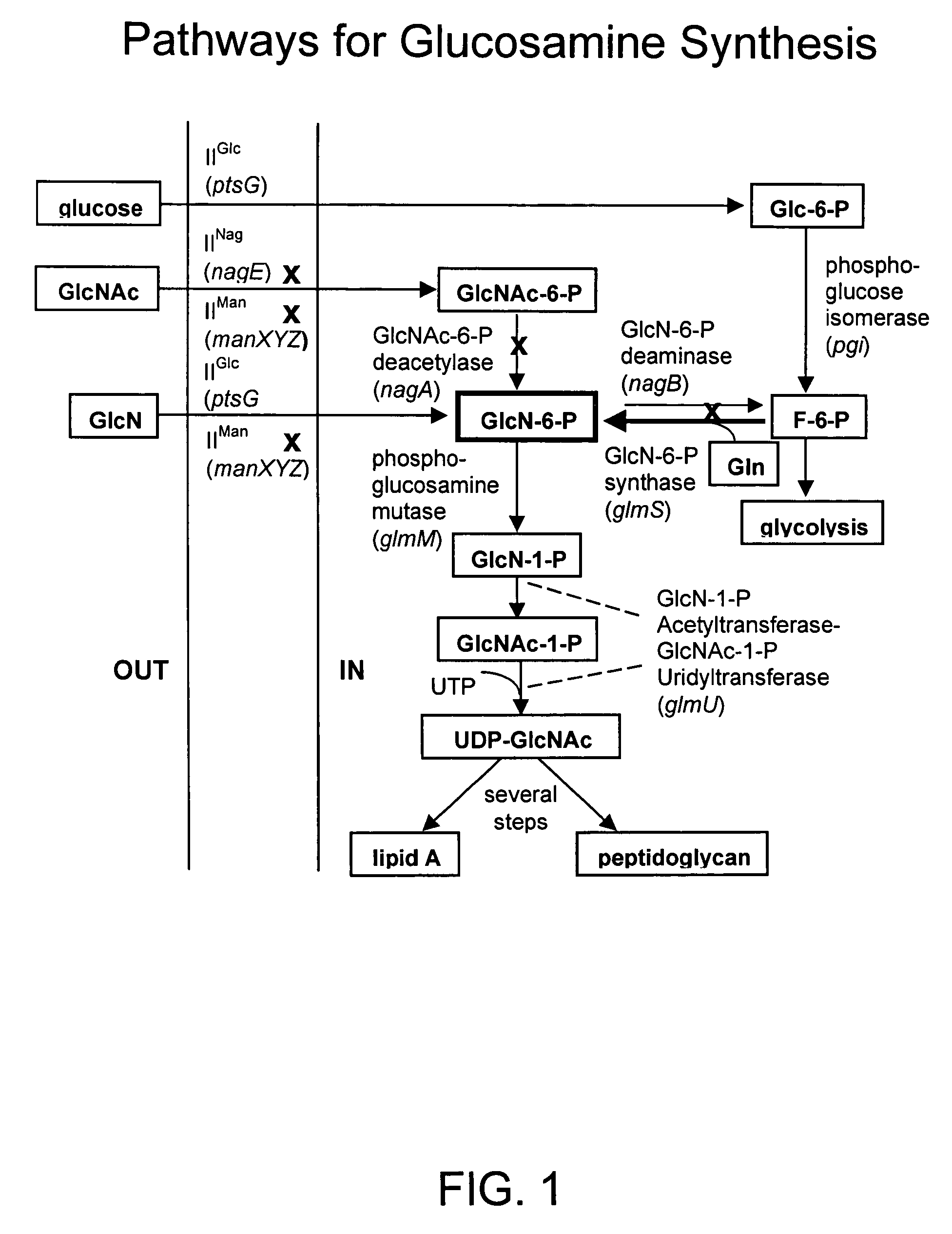
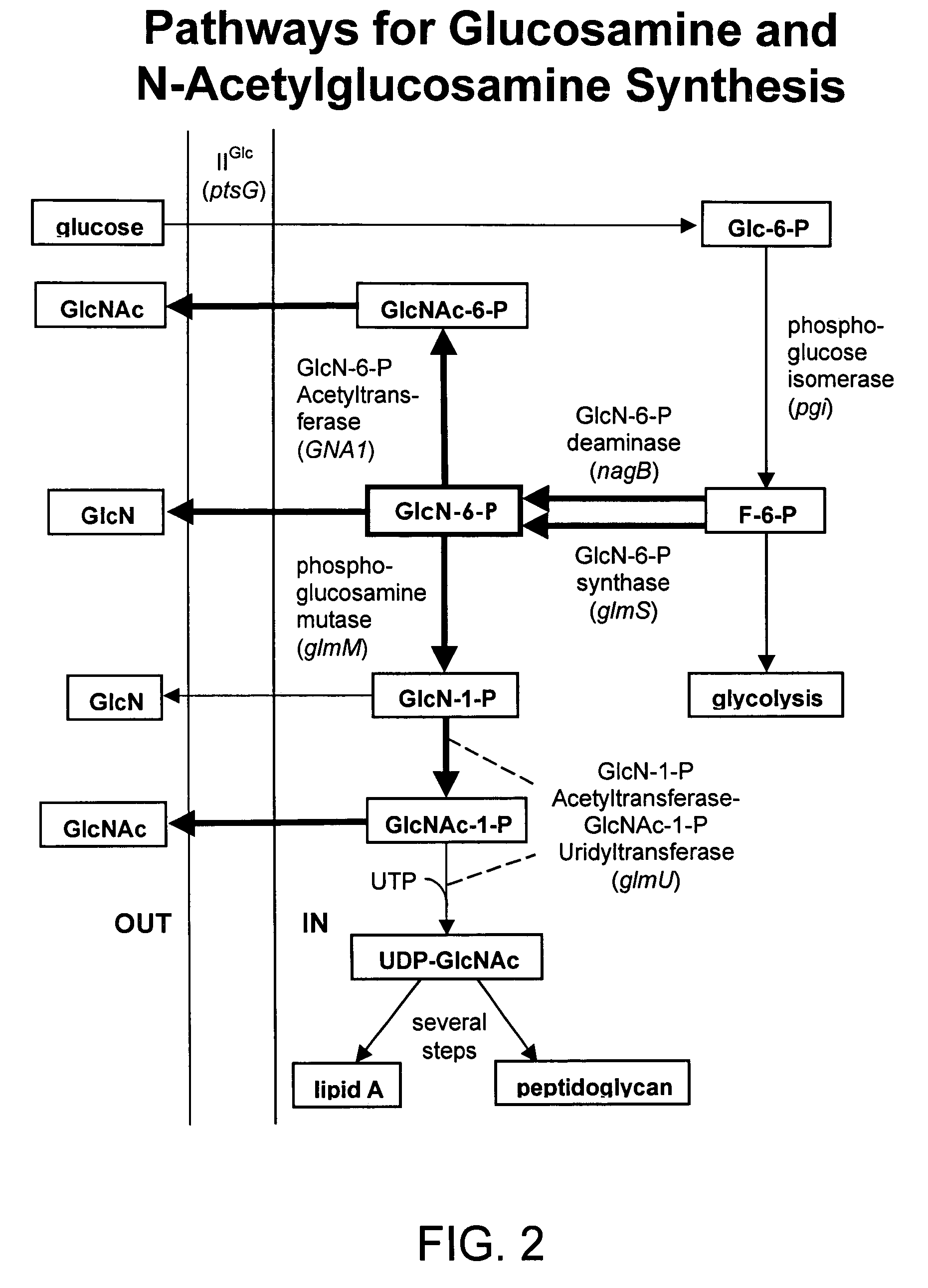
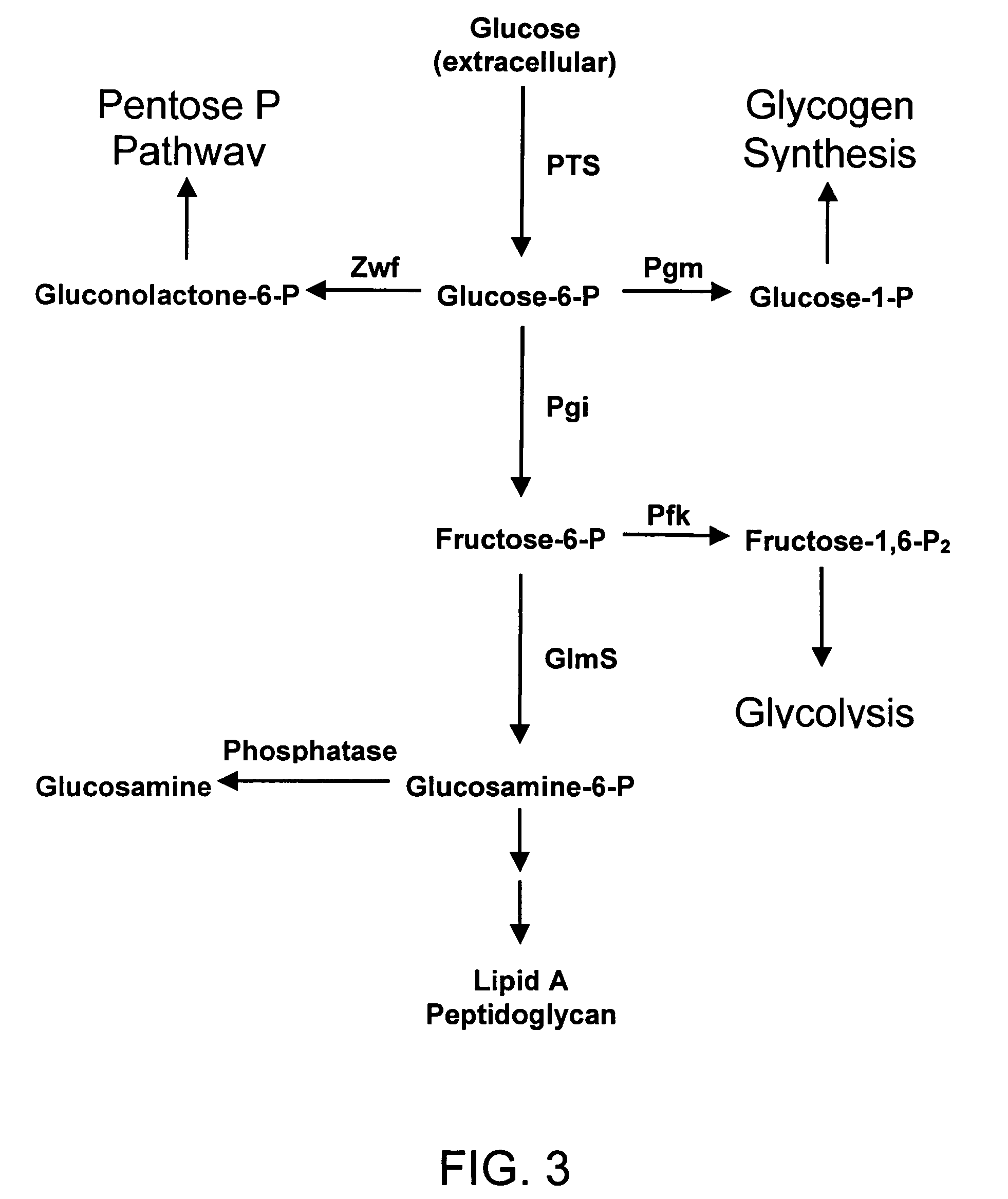
Process and materials for production of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine
A biosynthetic method for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine is disclosed. Such a method includes the fermentation of a genetically modified microorganism to produce glucosamine and / or N-acetylglucosamine. Also disclosed are genetically modified microorganisms that are useful for producing glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine. In addition, methods of recovering N-acetylglucosamine that has been produced by a fermentation process, including methods that result in N-acetylglucosamine of high purity, are described. Also disclosed is a method to produce glucosamine from N-acetylglucosamine.
Owner:ARKION LIFE SCI LLC
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine
InactiveCN104293724AImprove fermentation yieldImprove stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine. The genetically engineered bacteria are prepared by the following steps: integrating chromosome deficiency nag DCABE gene clusters of Escherichia coli, respectively connecting 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes and N-acetylglucosamine transferase genes which are respectively mediated by a T7 promoter and a Trc promoter with a gene expression cassette in series, wherein the 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes are obtained by mutating wild 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase genes from an Escherichia coli W3110 strain source into A38T / R249C / G471S mutants. The genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the invention have the advantages of high N-acetylglucosamine fermentation yield and high strain stability and have wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES & DEV CENT OF INDAL BIOTECH +1
Method of producing recombinant antithrombin III composition
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
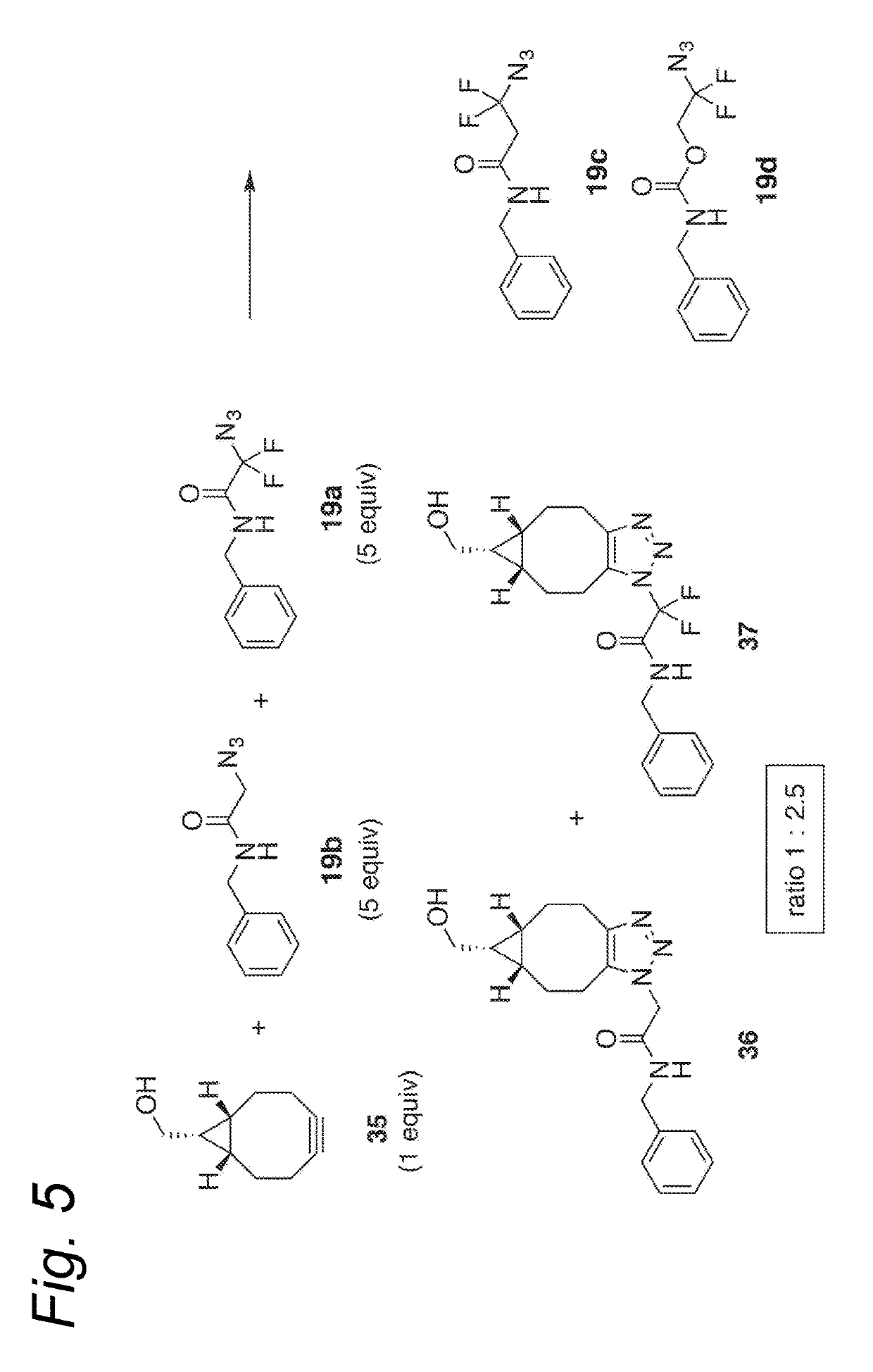
Modified antibody, antibody-conjugate and process for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS20150258210A1Reduced potencyDamage bindingImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFucosylationAntibody conjugate
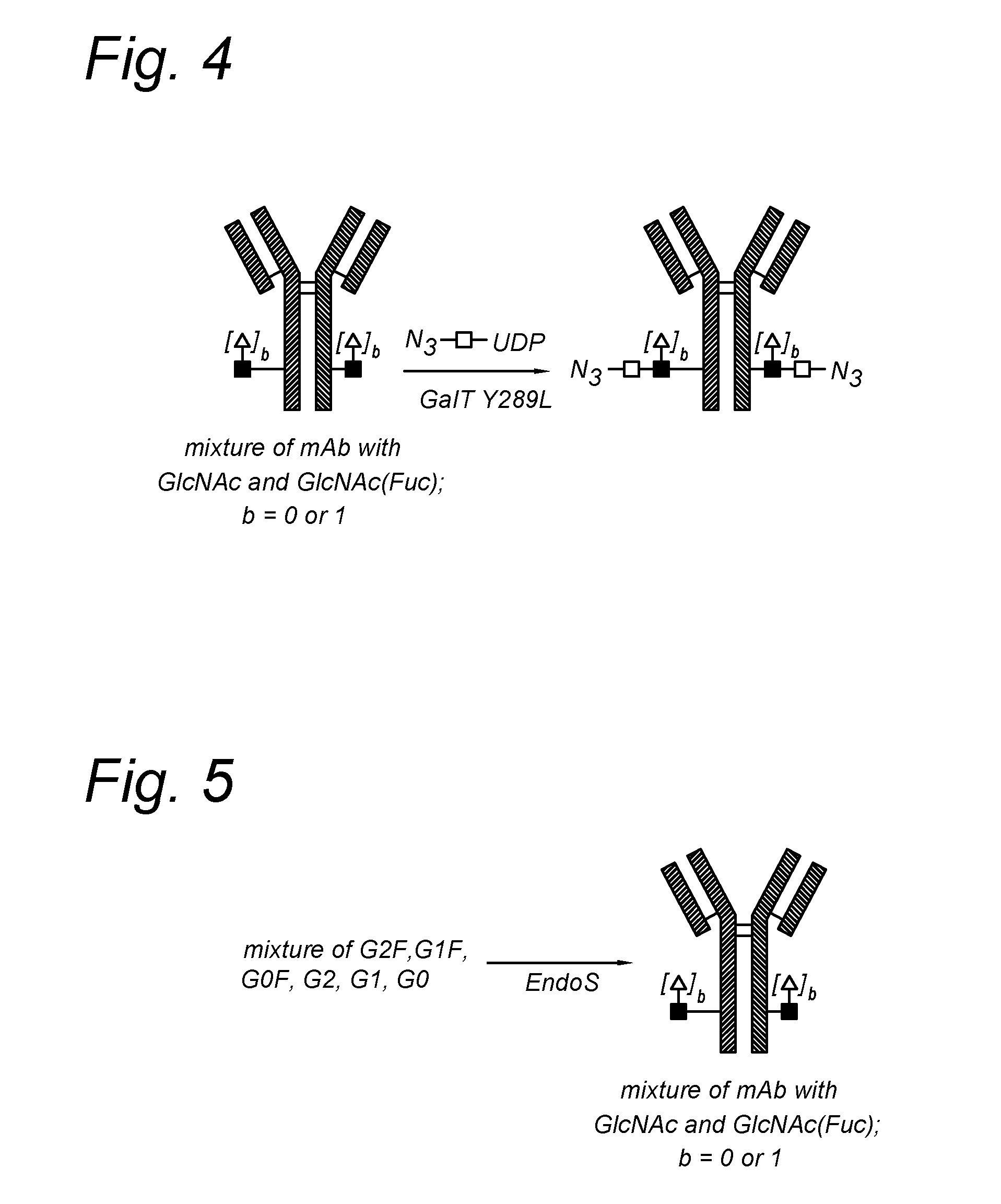
The present invention relates to an antibody comprising a GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent, wherein S(A)x is a sugar derivative comprising x functional groups A wherein A is independently selected from the group consisting of an azido group, a keto group and an alkynyl group and x is 1, 2, 3 or 4, wherein said GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent is bonded to the antibody via CI of the N-acetylglucosamine of said GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent, and wherein said N-acetylglucosamine is optionally fucosylated. The invention also relates to an antibody-conjugate, in particular to an antibody-conjugate according to the Formula (20) or (20b), wherein AB is an antibody, S is a sugar or a sugar derivative, D is a molecule of interest, and wherein said N-acetylglucosamine is optionally fucosylated (b is 0 or 1). The invention further relates to a process for the preparation of a modified antibody, to a process for the preparation of an antibody-conjugate, and to said antibody-conjugate for use as a medicament. In addition, the invention relates to a kit of parts comprising an azide-modified antibody and a linker-conjugate, wherein said linker-conjugate comprises a (hetero)cycloalkynyl group and one or more molecules of interest.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Method for producing l-amino acids using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
InactiveUS20070212764A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationL-threonineArginine
There is disclosed a method for producing an L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of N-acetylglucosamine permease encoded by the nagE gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Methods for treating a breach or puncture in a blood vessel
InactiveUS20030078234A1CessationIncreased riskBiocideSolution deliveryArteriolar VasoconstrictionVascular structure
The present invention relates to compositions comprising semi-crystalline beta-1-4-N-acetylglucosamine polymers (p-GlcNac) and methods utilizing such polymers modulation of vascular structure and / or function. The compositions and methods disclosed are useful for stimulating, in a p-GlcNac concentration-dependent manner, endothelin-1 release, vasoconstriction, and / or reduction in blood flow out of a breached vessel, as well as for contributing to or effecting cessation of bleeding. The methods of the present invention comprise topical administration of materials comprising semi-crystalline p-GlcNac polymers that are free of proteins, and substantially free of single amino acids as well as other organic and inorganic contaminants, and whose constituent monosaccharide sugars are attached in a beta-1-4 conformation.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
Method of Enhancing of Binding Activity of Antibody Composition to FcGamma Receptor IIIa
A method for enhancing a binding activity of an antibody composition to Fcγ receptor IIIa, which comprises modifying a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain which is bound to the Fc region of an antibody molecule; a method for enhancing an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic activity of an antibody composition; a process for producing an antibody composition having an enhanced binding activity to Fcγ receptor IIIa; a method for detecting the ratio of a sugar chain in which fucose is not bound to N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end in the sugar chain among total complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chains bound to the Fc region in an antibody composition; an Fc fusion protein composition produced by using a cell resistant to a lectin which recognizes a sugar chain in which 1-position of fucose is bound to 6-position of N-acetylglucosamine in the reducing end through α-bond in a complex N-glycoside-linked sugar chain; and a process for producing the same.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Bacillus subtilis for producing N-acetylglucosamine as well as construction method and application of bacillus subtilis
InactiveCN104195094APrevent backflowAvoid consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationPhosphate
The invention belongs to the construction and the application of genetically engineered bacterium and particularly relates to bacillus subtilis for producing N-acetylglucosamine as well as a construction method and application of bacillus subtilis. The construction method for the genetically engineered bacterium (bacillus subtilis) comprises the following steps: expressing and coding 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase gene and 6-glucosamine phosphate acetylase gene in bacillus subtilis to form a complete metabolic pathway from glucose to N-acetylglucosamine; knocking out or inactivating glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase genes nagB and gamA, an N-acetylglucosamine 6-phosphate deacetylase gene nagA, a glucosamine transport protein gene gamP and an N-acetylglucosamine transport protein gene nagP in an N-acetylglucosamine catabolism pathway in bacillus subtilis. The construction method can be used for solving the problem that N-acetylglucosamine produced in the prior art is poor in safety, low in yield and high in cost. The constructed genetically engineered bacterium has the advantage that N-acetylglucosamine with relatively high concentration can be accumulated, and the industrial utilization value is relatively high.
Owner:张帆
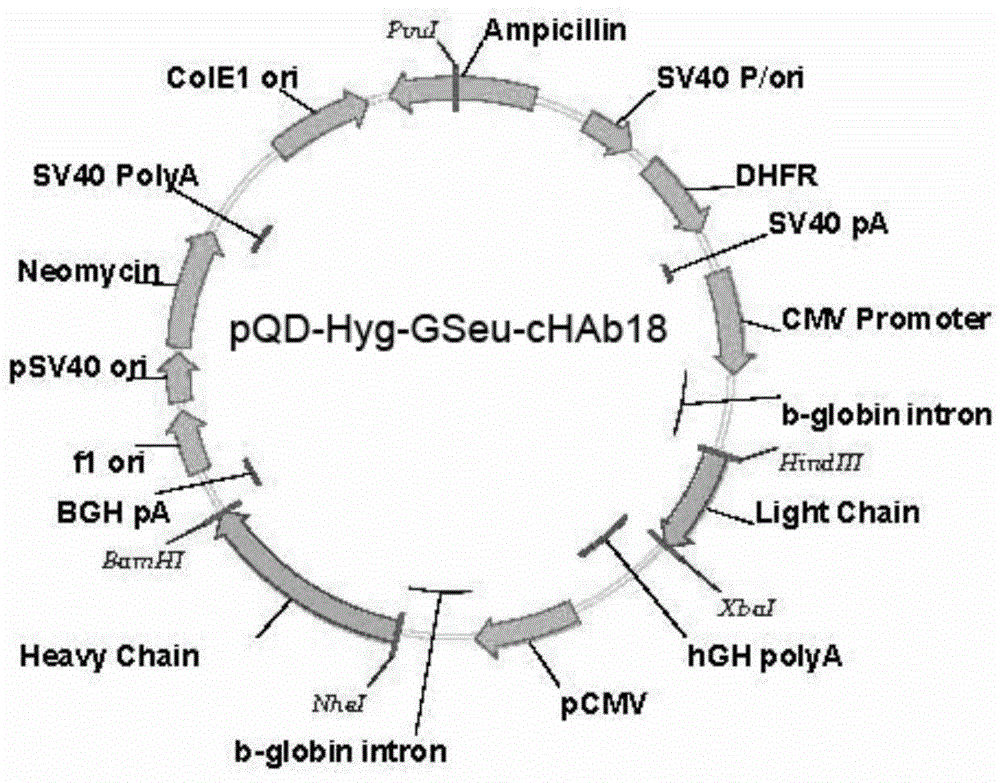
Humanization modified anti-CD147 chimeric antibody HcHAb18 and application thereof
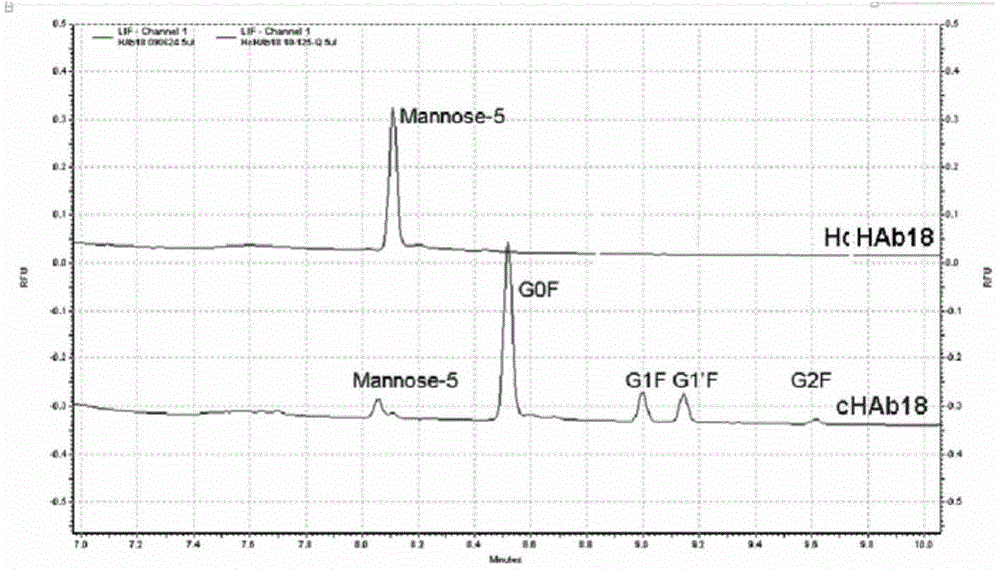
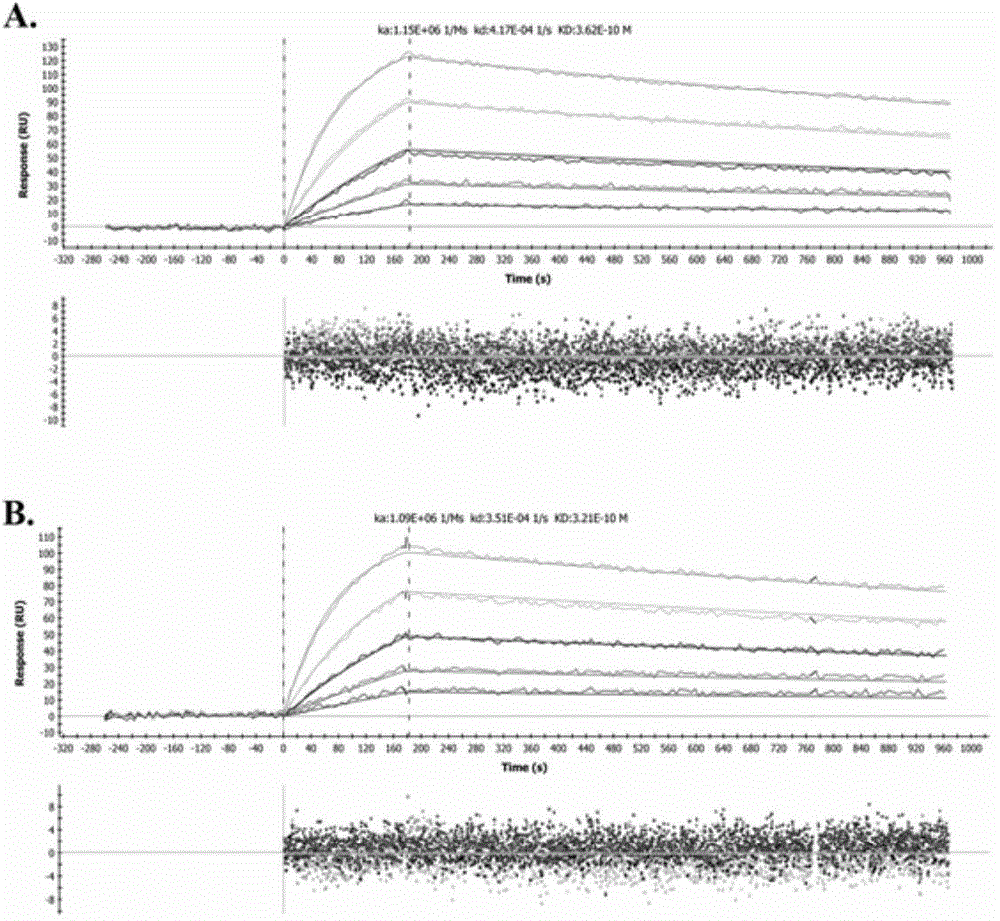
ActiveCN104086654AAbility to inhibit invasion and migrationGrowth inhibitory effectImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicityChimeric antibody
The invention provides a humanized modified anti-CD147 chimeric antibody HcHAb18 and an application thereof. The anti-CD147 human-rat chimeric antibody is prepared on the basis of obtaining hybridoma cells of an anti-human CD147 monoclonal antibody and antibody HcHAb18 genes of the hybridoma cells, wherein the variable region of light chains of the anti-CD147 human-rat chimeric antibody has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1; the variable region of heavy chains of the anti-CD147 human-rat chimeric antibody has the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2; fucose are not combined in N-acetylglucosamine in a reducing end of a carbohydrate chain at a Fc segment of the anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody in a specific host cell; the glycoform of the anti-CD147 monoclonal antibody is of a mannose type (MAN 5); the anti-CD147 chimeric antibody has antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). The invention further provides an expression vector and an engineering cell strain of the anti-CD147 chimeric antibody and the application of the anti-CD147 chimeric antibody taken as a cancer treating medicine.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS20170008858A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention relates to a cycloaddition process comprising the step of reacting a halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1): Preferably, the (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1) is a (hetero)cyclooctyne. The invention also relates to the cycloaddition products obtainable by the process according to the invention. The invention further relates to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds, in particular to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds comprising N-acetylgalactosamine-UDP (GalNAc-UDP), and to halogenated 1,3-dipole compounds comprising (peracylated) N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuNAc).
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Fermentation production method for N-acetylglucosamine
InactiveCN104988196AIncrease contentImprove conversion rateFermentationN-AcetylglucosamineFermentation broth
The invention provides a fermentation production method for N-acetylglucosamine. In the fermentation process, when the residual glucose content of fermentation liquor falls below 0.5 g / L, a glucose solution is flowingly added into the fermentation liquor at the flow acceleration of 5-8 g / L.h, when OD660nm of the fermentation liquor is equal to 28-31, IPTG is added for induction, and then a urea solution is flowingly added into the fermentation liquor at the flow acceleration of 0.5-0.8 g / L.h. According to the fermentation production method for the N-acetylglucosamine, in the fermentation process, induction is performed through the IPTG, the flow adding speed of the glucose solution and the urea solution is optimized when induction is performed, and the N-acetylglucosamine content and the conversion rate at the fermentation end point are significantly improved.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Compositions and methods for modulation of vascular structure and/or function
InactiveUS20020019367A1Minimizing blood lossCessationBiocideSolution deliveryArteriolar VasoconstrictionVascular structure
The present invention relates to compositions comprising semi-crystalline beta-1-4-N-acetylglucosamine polymers (p-GlcNac) and methods utilizing such polymers modulation of vascular structure and / or function. The compositions and methods disclosed are useful for stimulating, in a p-GlcNac concentration-dependent manner, endothelin-1 release, vasoconstriction, and / or reduction in blood flow out of a breached vessel, as well as for contributing to or effecting cessation of bleeding. The methods of the present invention comprise topical administration of materials comprising semi-crystalline p-GlcNac polymers that are free of proteins, and substantially free of single amino acids as well as other organic and inorganic contaminants, and whose constituent monosaccharide sugars are attached in a beta-1-4 conformation.
Owner:MARINE POLYMER TECH
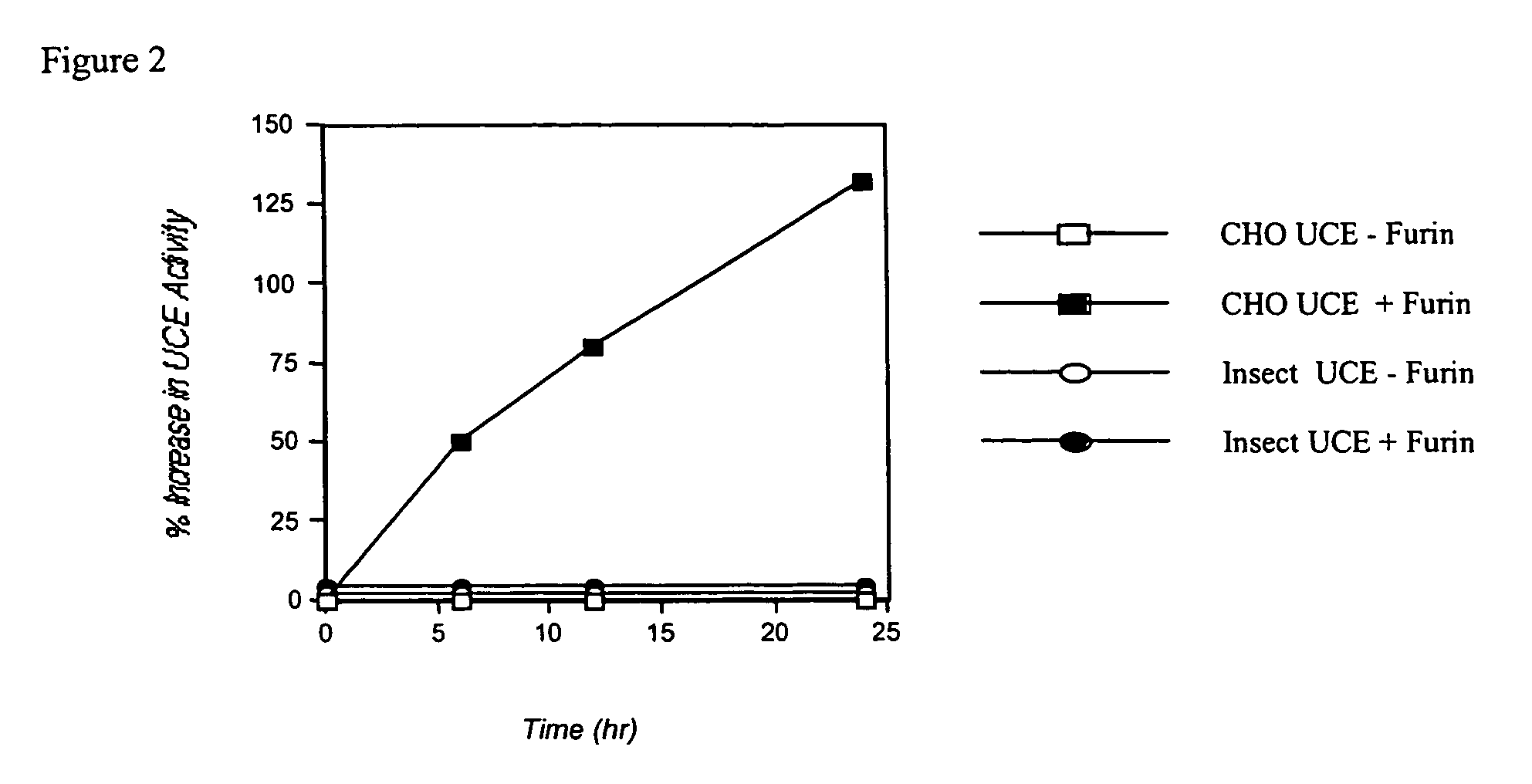
Expression of lysosomal hydrolase in cells expressing pro-N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiester α-N-acetyl glucosimanidase
InactiveUS7135322B2The method is simple and reliableReduce stepsSugar derivativesTissue culturePhosphateLysosome
The present invention provides methods of producing a pro-N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiesterαN-acetyl glucosimanidase (phosphodiester α-GlcNAcase), in mammalian cells deficient in the furin proteolytic enzyme and methods of making lysosomal bydrolases having an N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Culture medium for culturing akkermansia muciniphila and use method thereof
PendingCN109810931ASolve the disadvantages of not being able to growNormal growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismThreonine
The invention provides a culture medium for culturing akkermansia muciniphila and a use method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism culture mediums. Components of the culture medium include soy peptone, threonine, glucose, N-acetylglucosamine, sodium chloride and disodium hydrogen phosphate. By adopting the culture medium, the akkermansia muciniphila quantity required by functional studying of the akkermansia muciniphila can be reached through culture, the components of the culture medium have safe sources, and potential biological hazards do not exist.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGZE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com