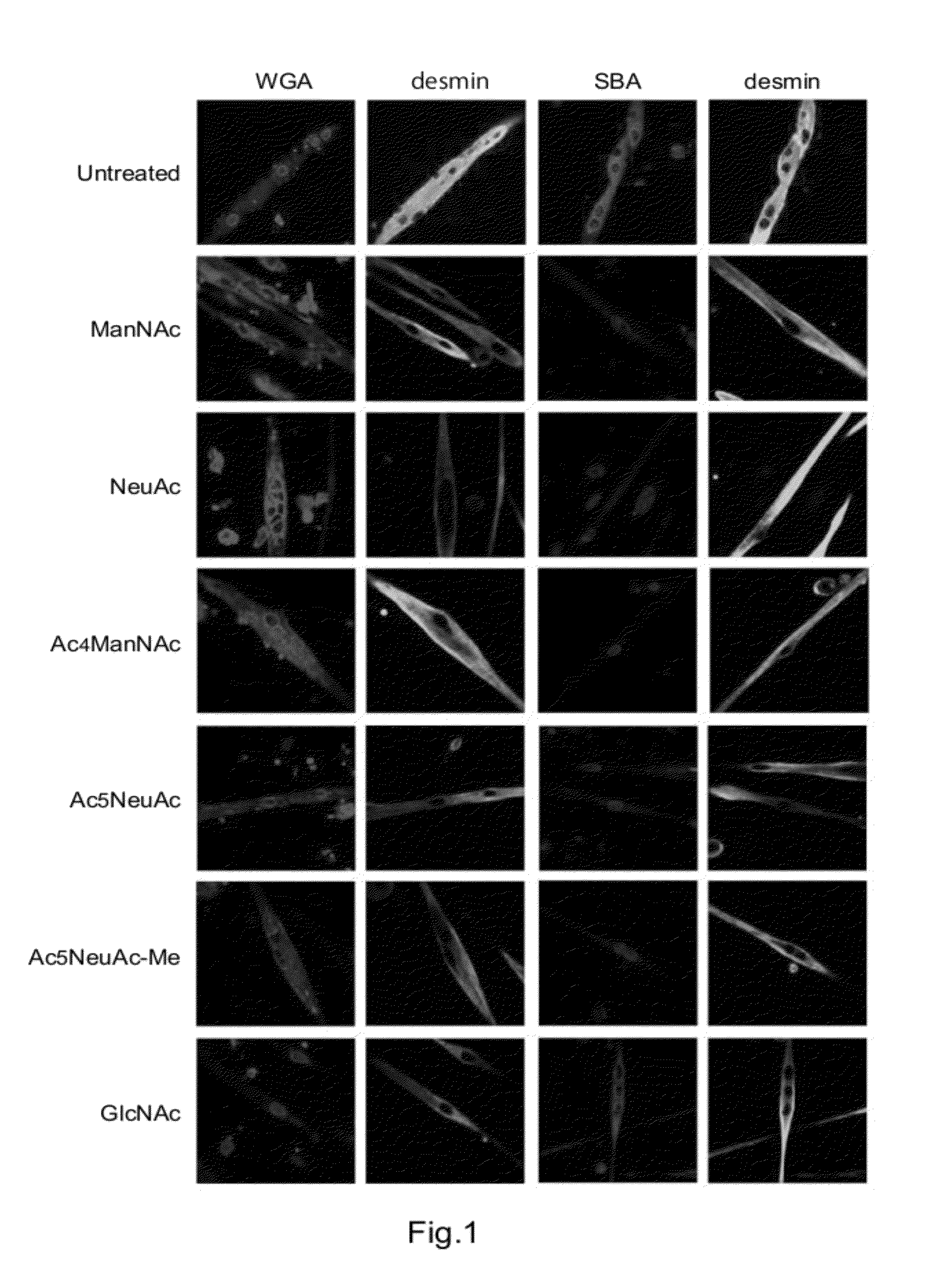
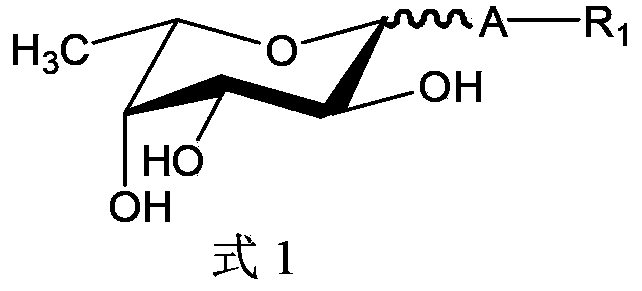
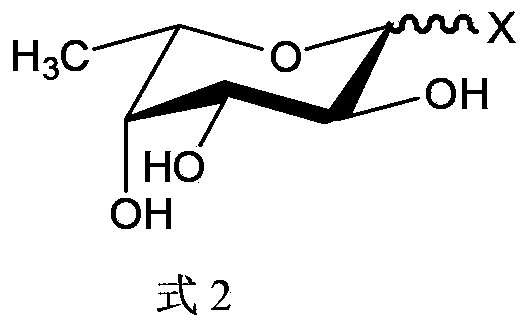
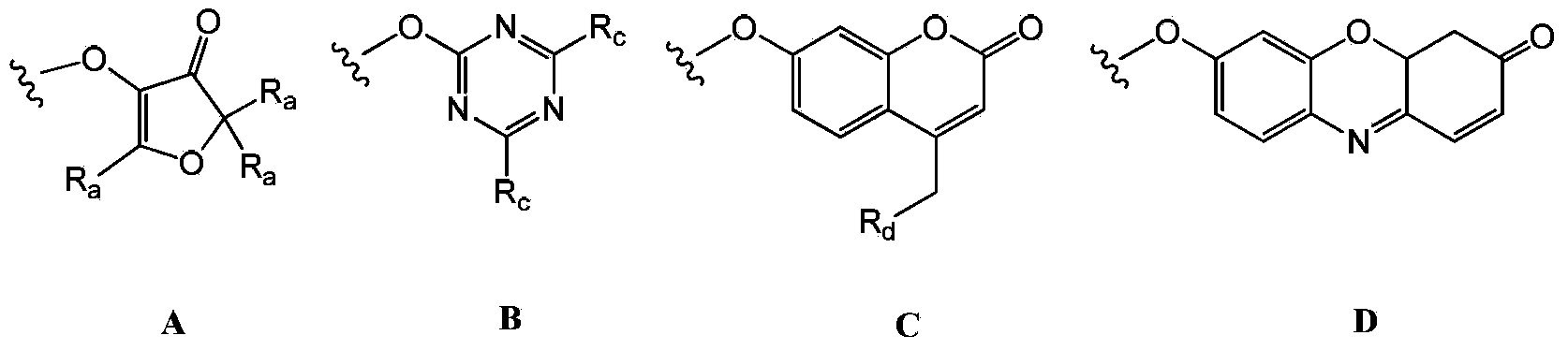
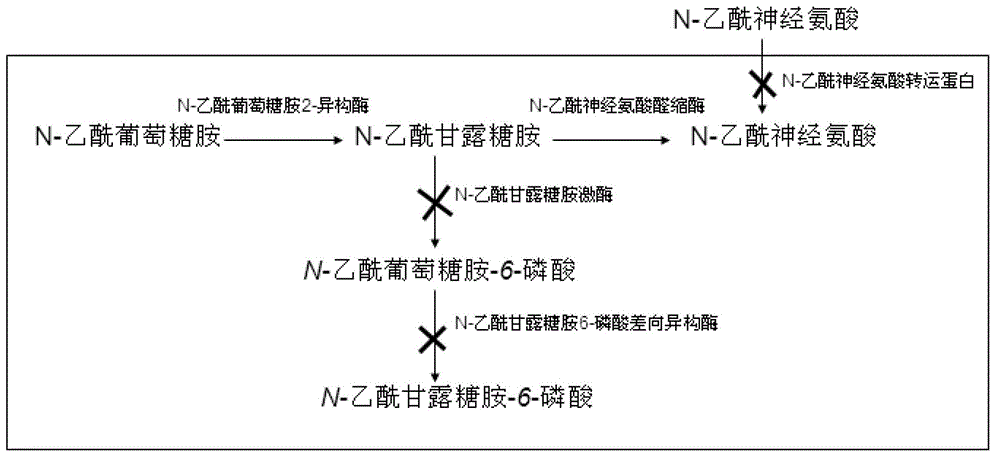
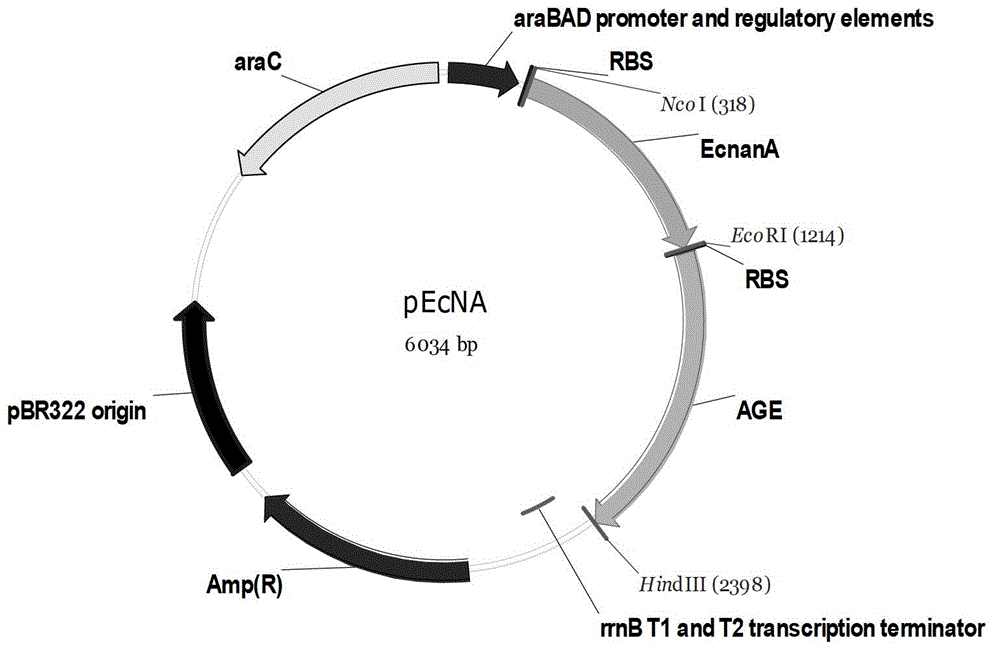
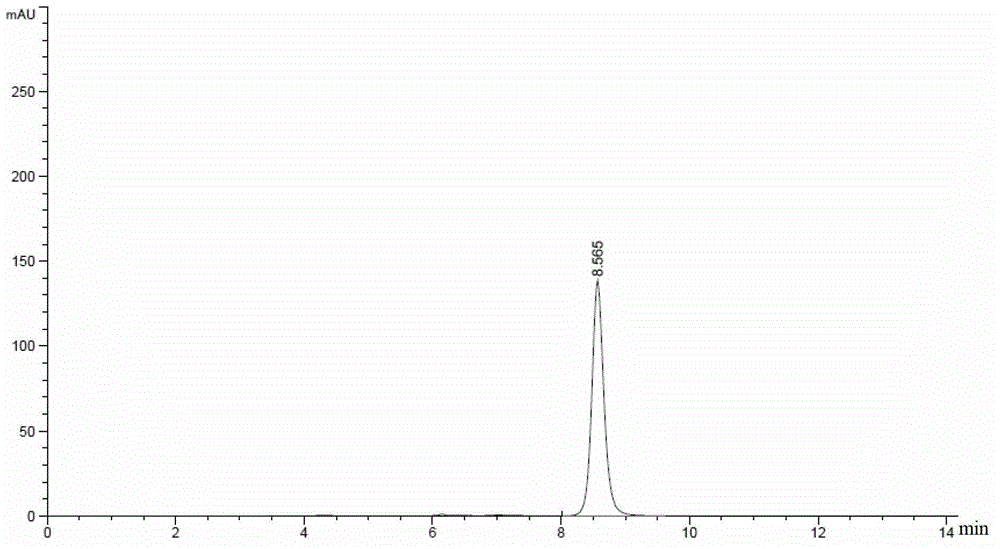
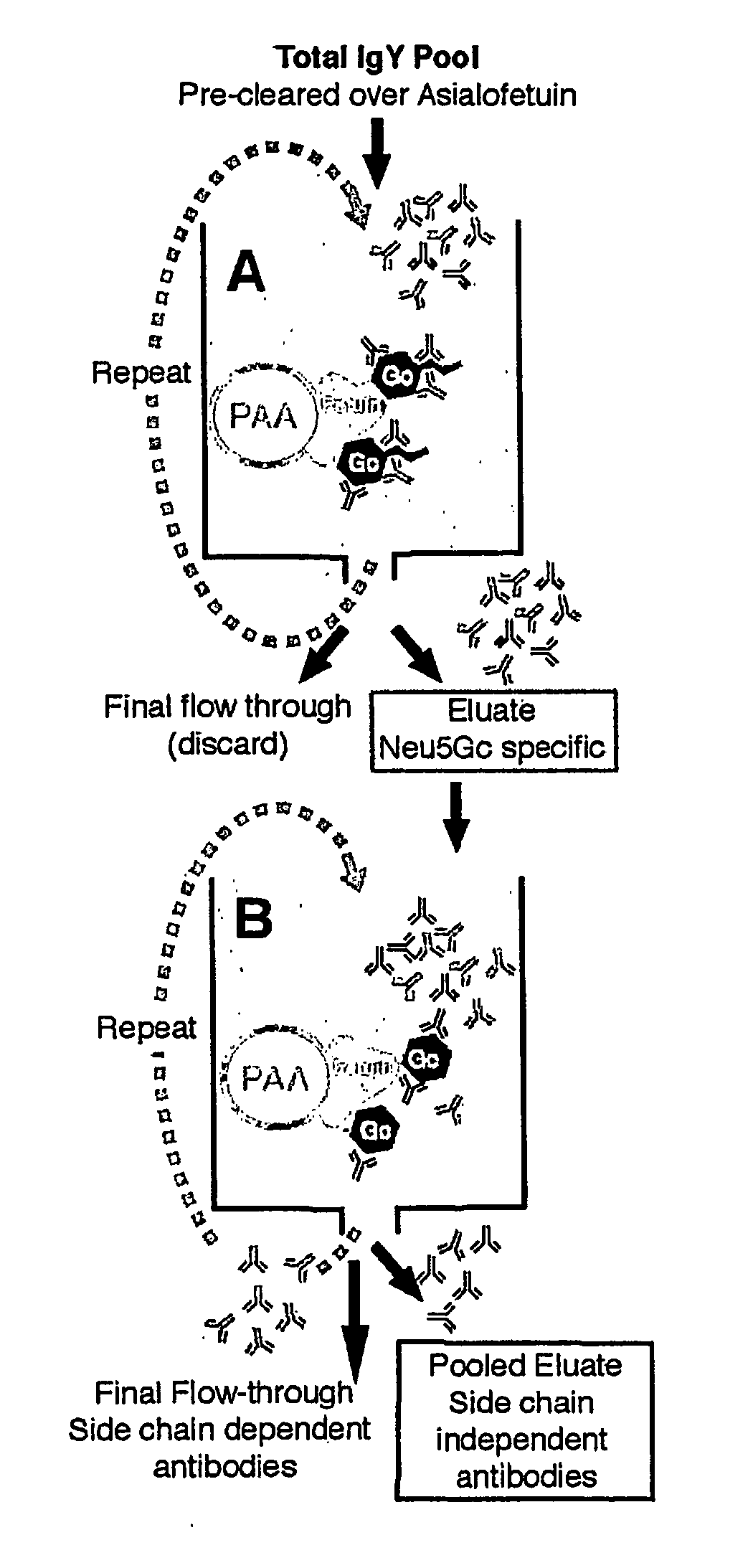
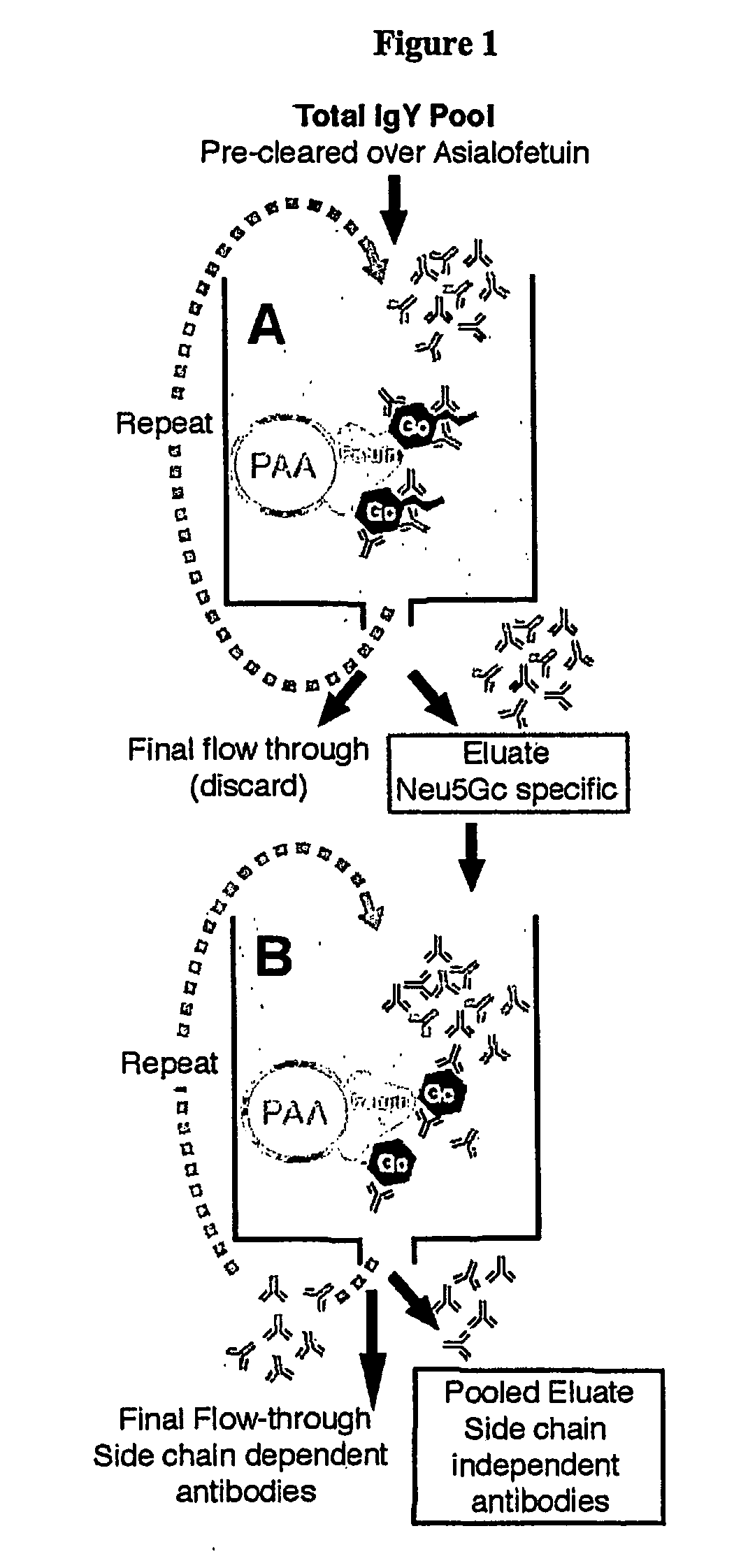
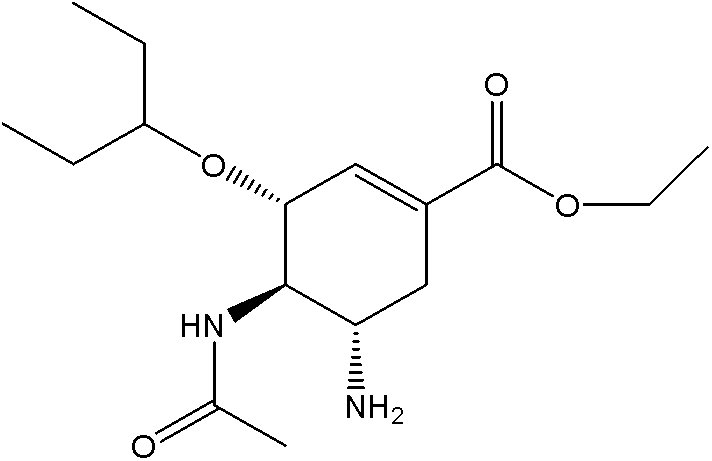
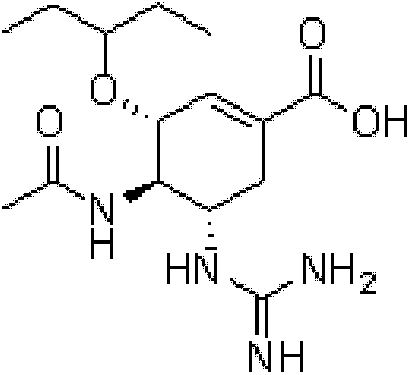
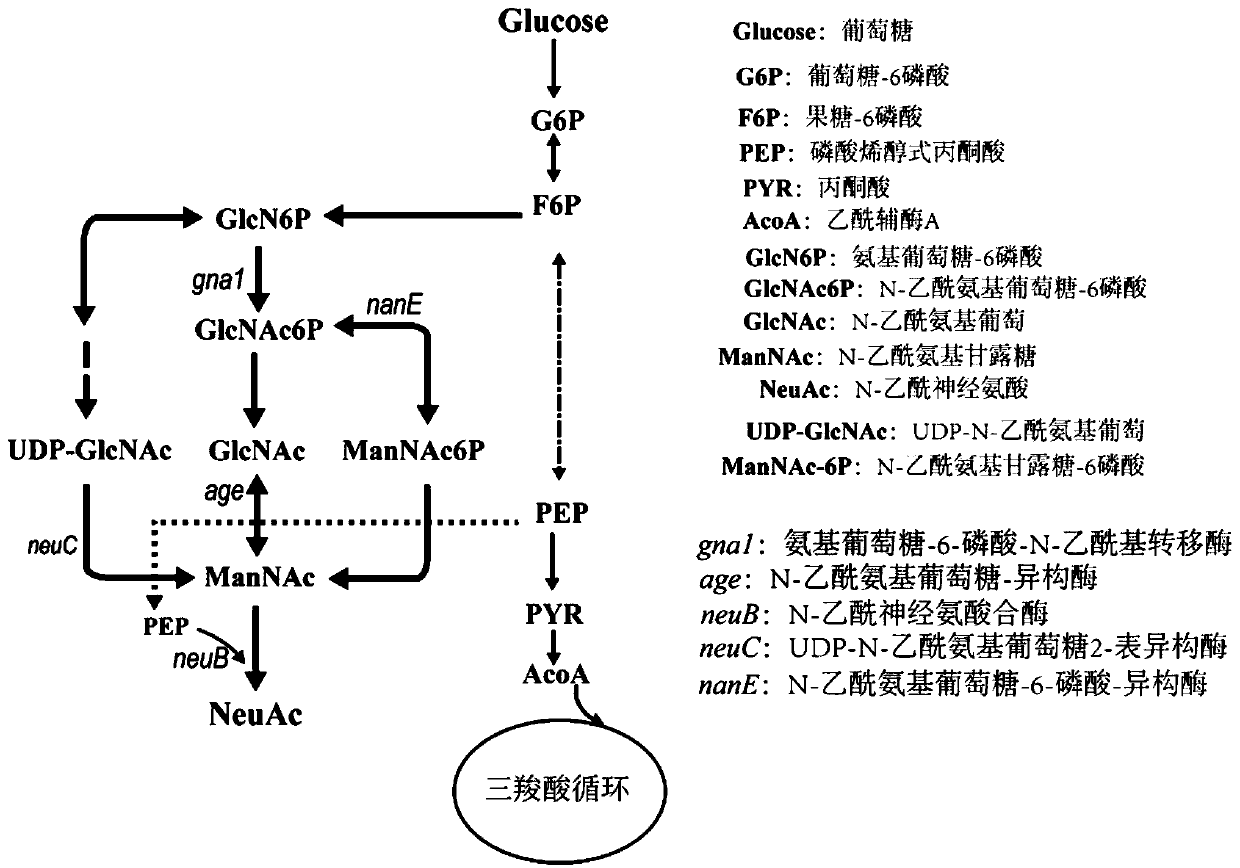
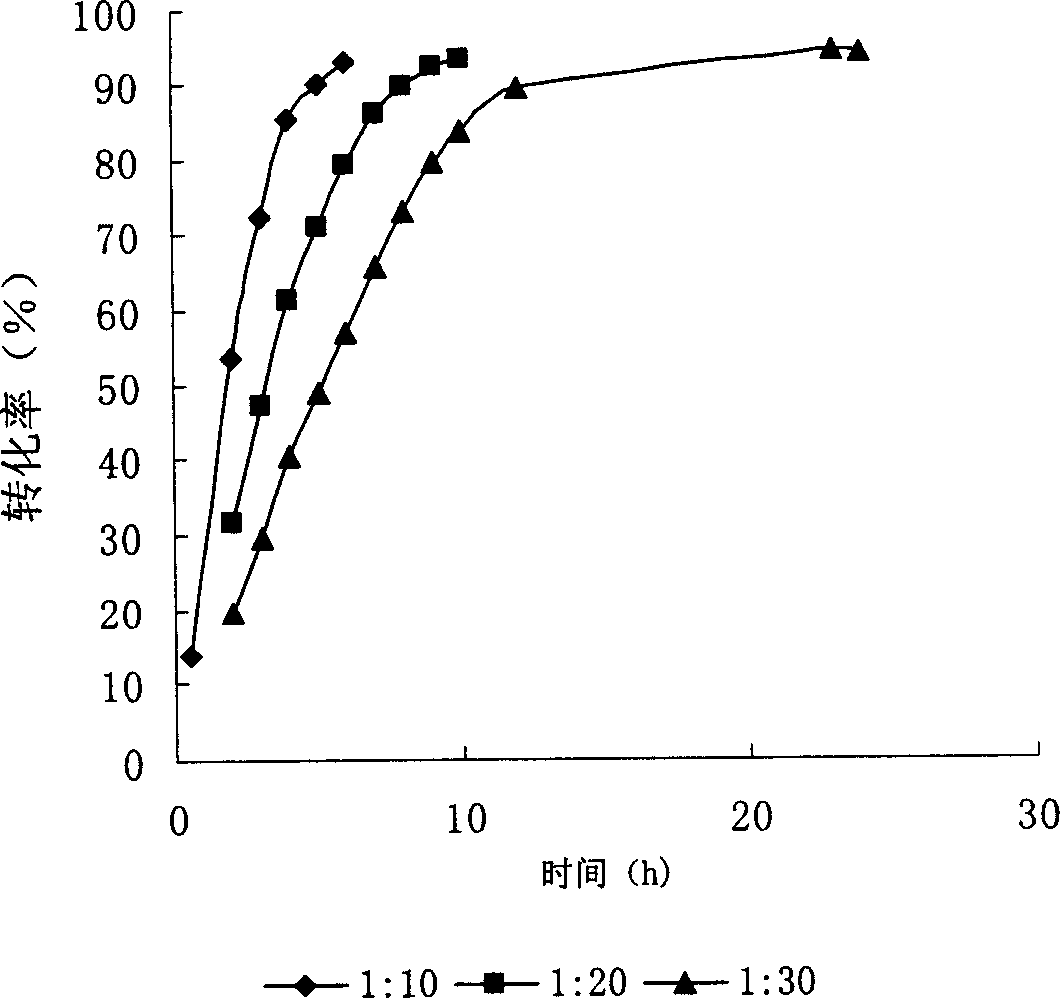
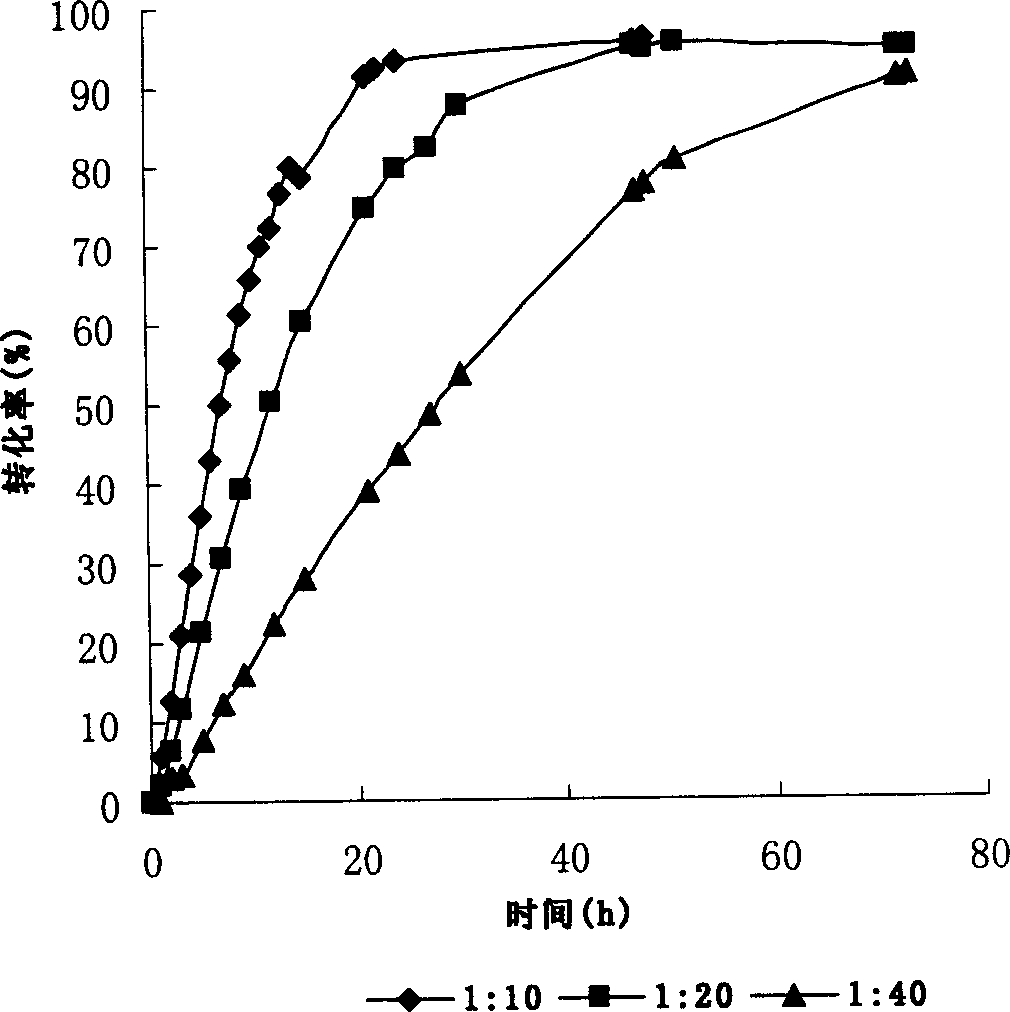
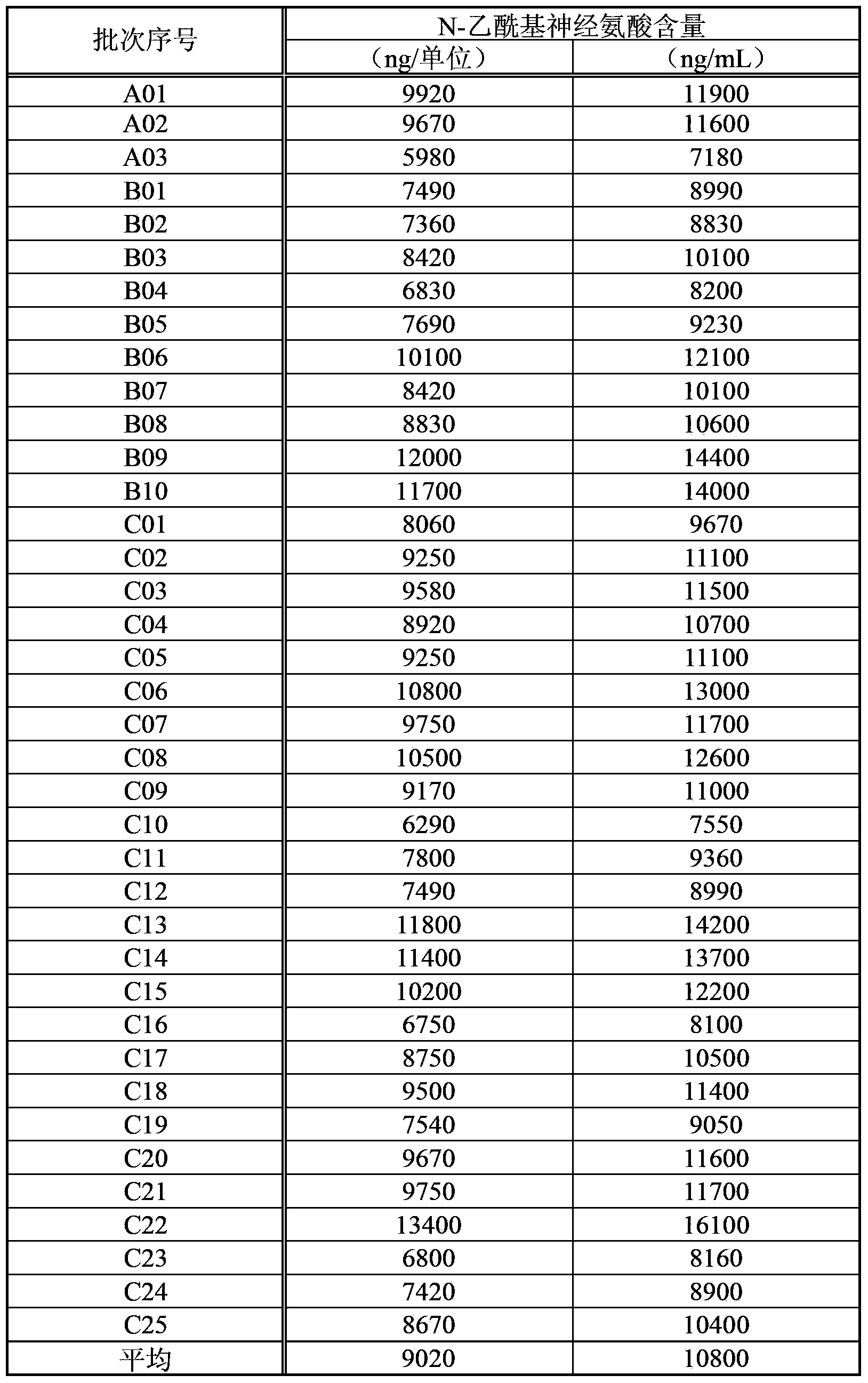
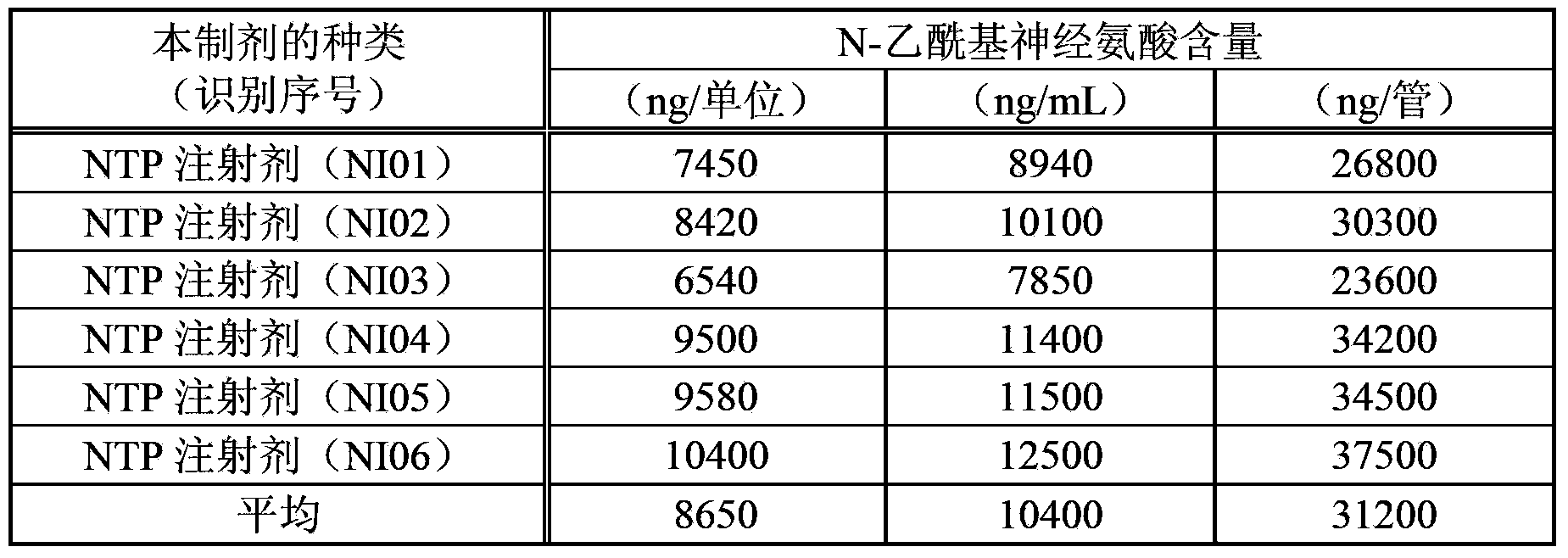
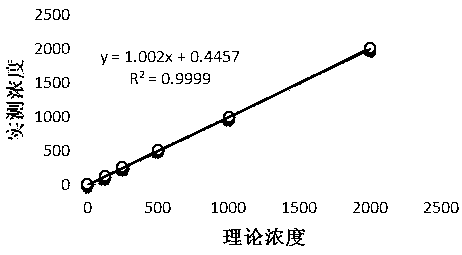
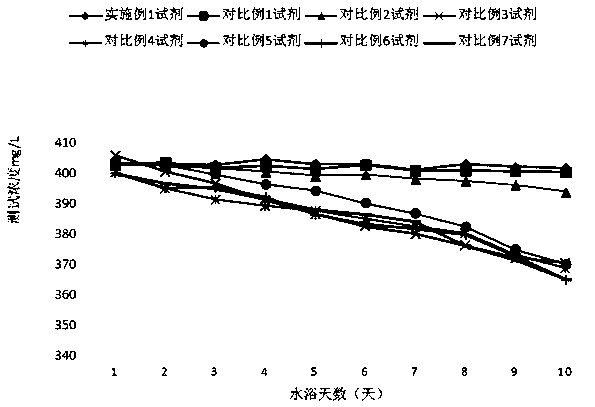
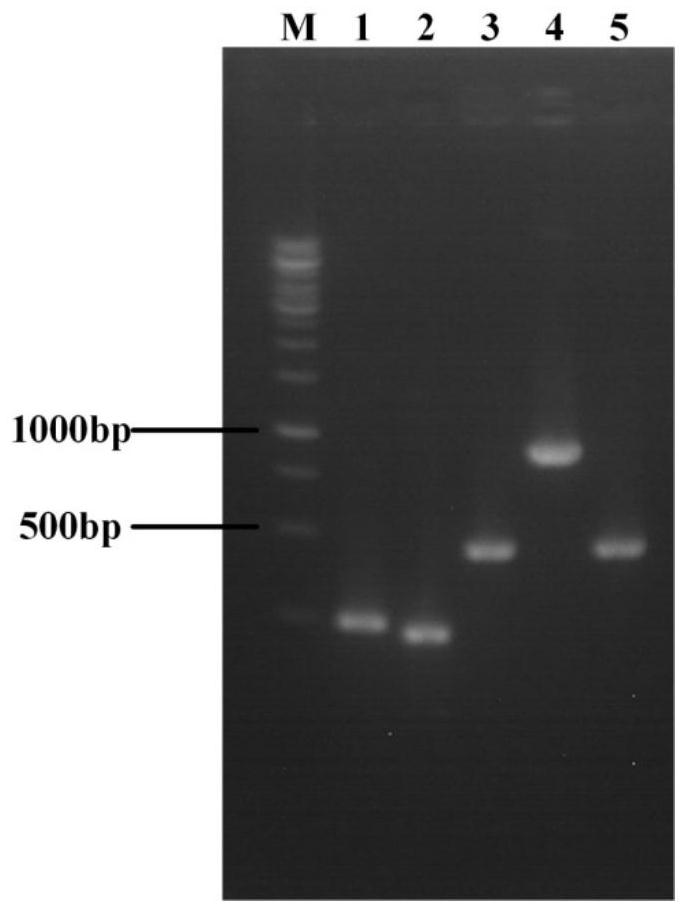
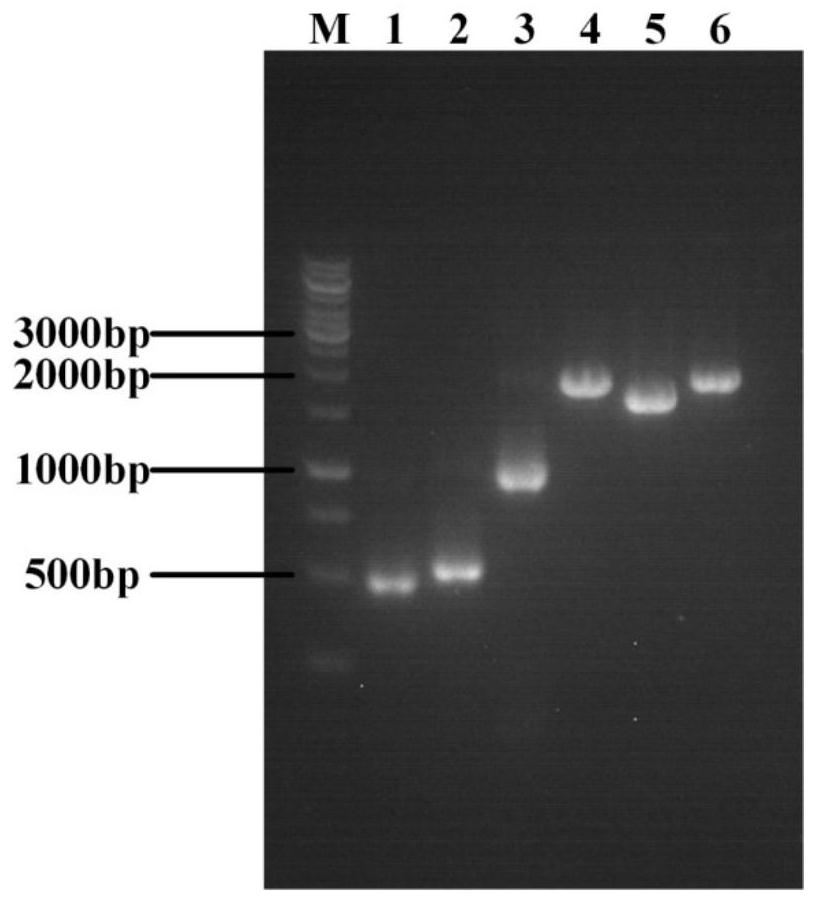
Patents
Literature
124 results about "Neuraminic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
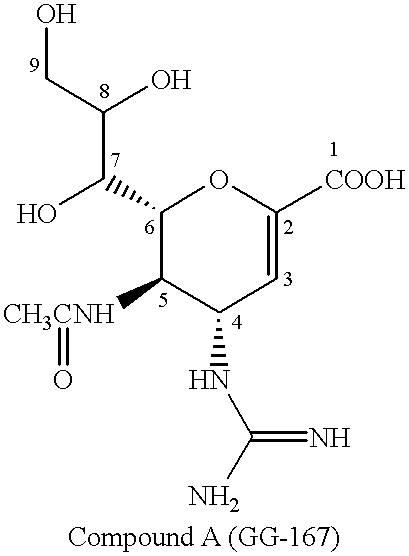
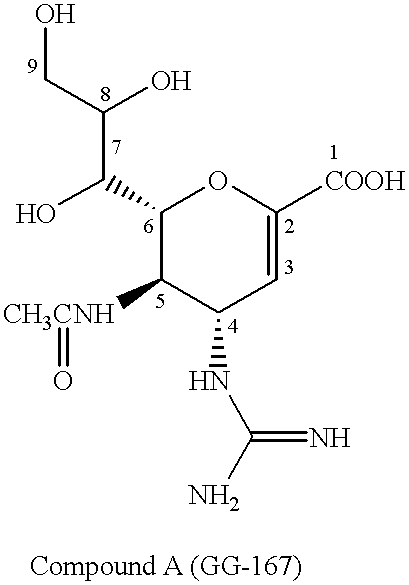
Neuraminic acid (5-amino-3,5-dideoxy-D-glycero-D-galacto-non-2-ulosonic acid) is an acidic amino sugar with a backbone formed by nine carbon atoms. Although 9-carbon sugars do not occur naturally, neuraminic acid may be regarded as a theoretical 9-carbon ketose in which the first link of the chain (the –CH₂OH at position 1) is oxidised into a carboxyl group (–C(=O)OH), the hydroxyl group at position 3 is deoxidised (oxygen is removed from it), and the hydroxyl group at position 5 is substituted with an amino group (–NH₂). Neuraminic acid may also be visualized as the product of an aldol-condensation of pyruvic acid and D-mannosamine (2-amino-2-deoxy-mannose).
Method of using hydroxycarboxylic acids or related compounds for treating skin changes associated with intrinsic and extrinsic aging
A composition comprising an amphoteric or pseudo-amphoteric agent and a polyhydroxy alpha hydroxyacid existing as a free acid, lactone, or salt, and isomeric or non-isomeric forms thereof is provided. The amphoteric or pseudo-amphoteric agent can be selected from amino acids, dipeptides, aminoaldonic acid, aminouronic acid, lauryl aminoproplyglycine, aminoaldaric acid, neuraminic acid desulfated heparin, deacetylated hyaluronic acid, hyalobiuronic acid, chondrosine, deacetylated chondroitin, creatine, creatinine, hydroxyproline, homocysteine, homocystine, homoserine, ornithine, citrulline, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin. The composition may contain other additives, including cosmetic or pharmaceutical agents for topical treatment of dermatological disorders.
Owner:TRISTRATA TECH
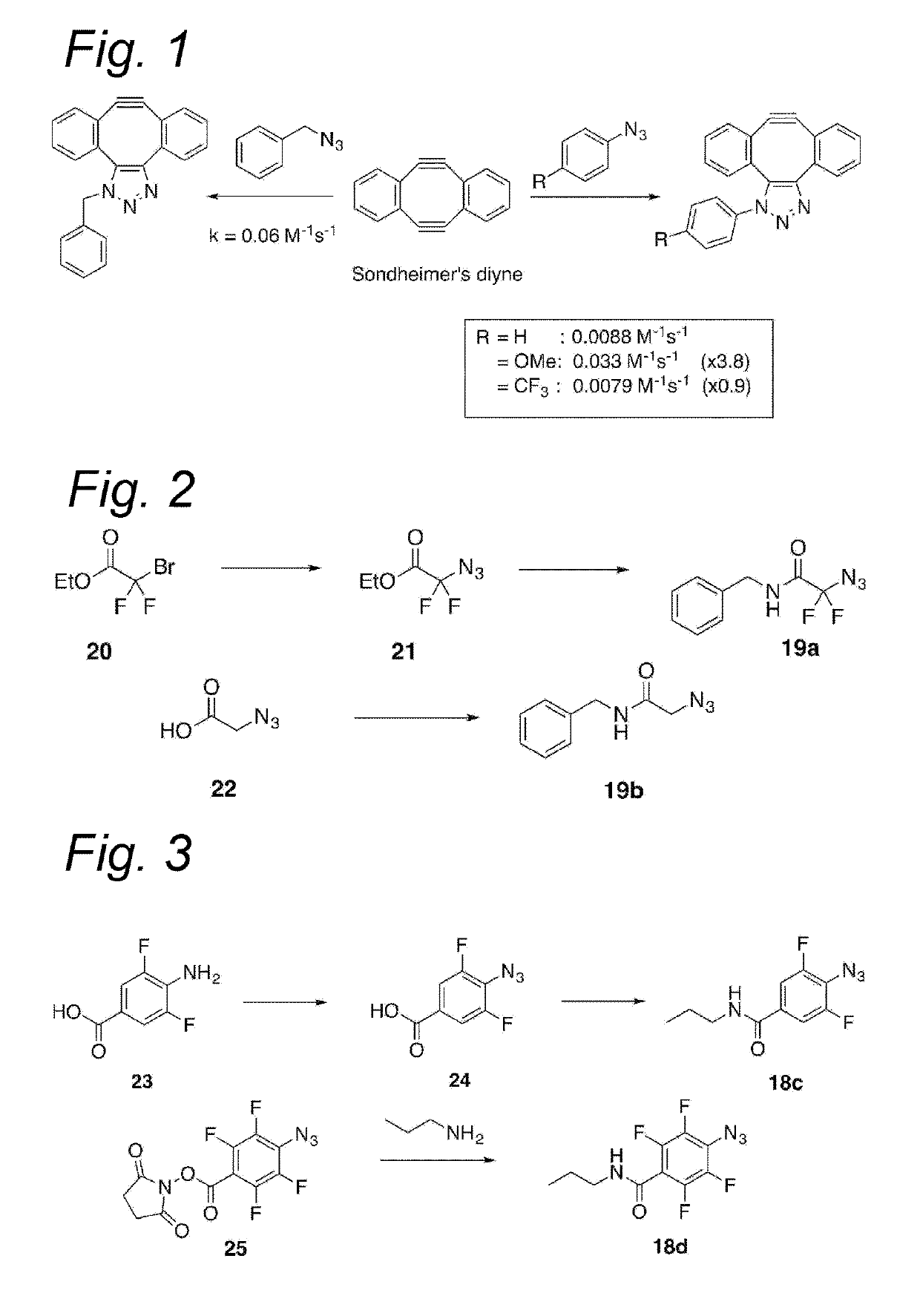
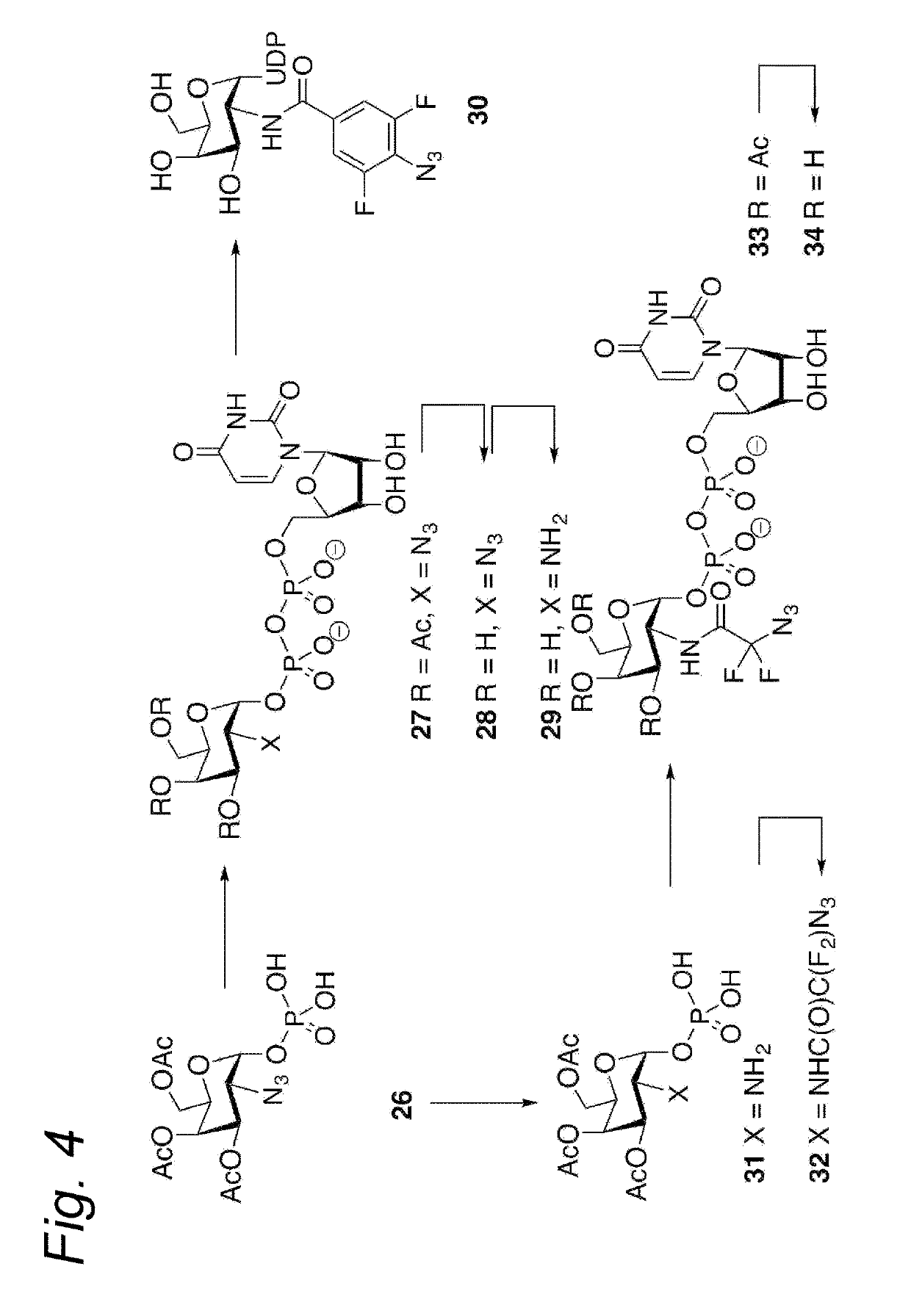
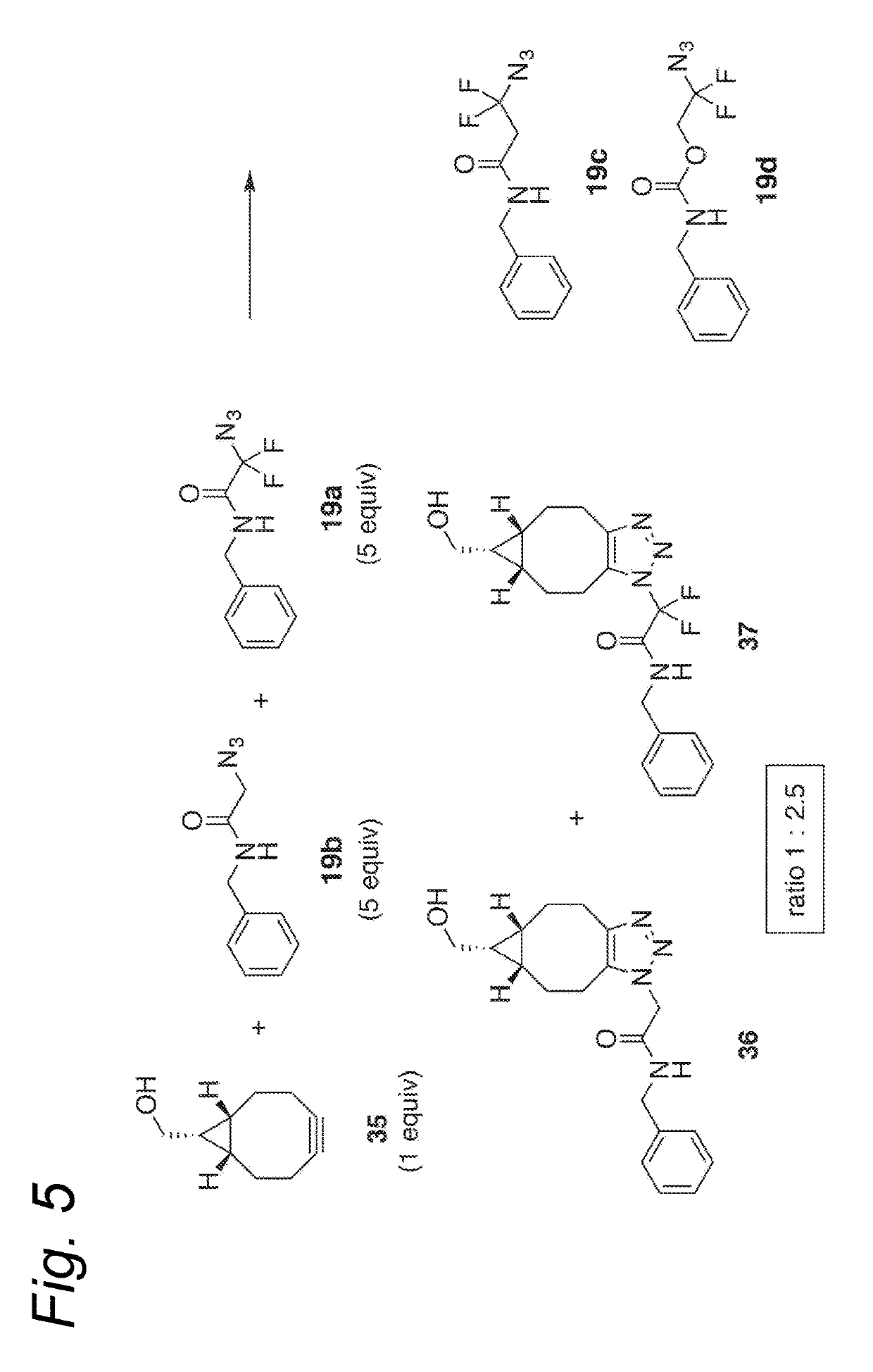
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS10266502B2Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
Owner:SYNAFFIX
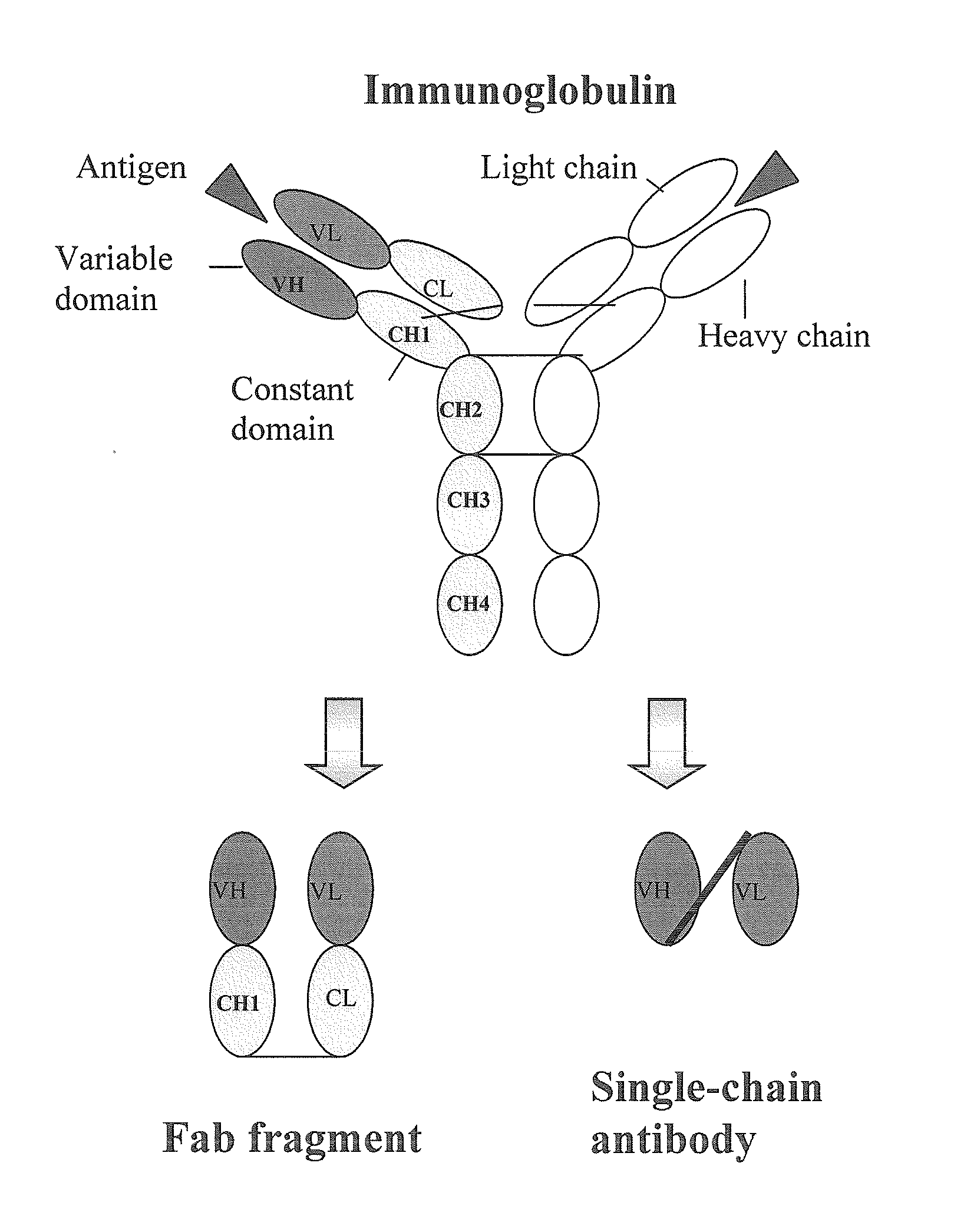
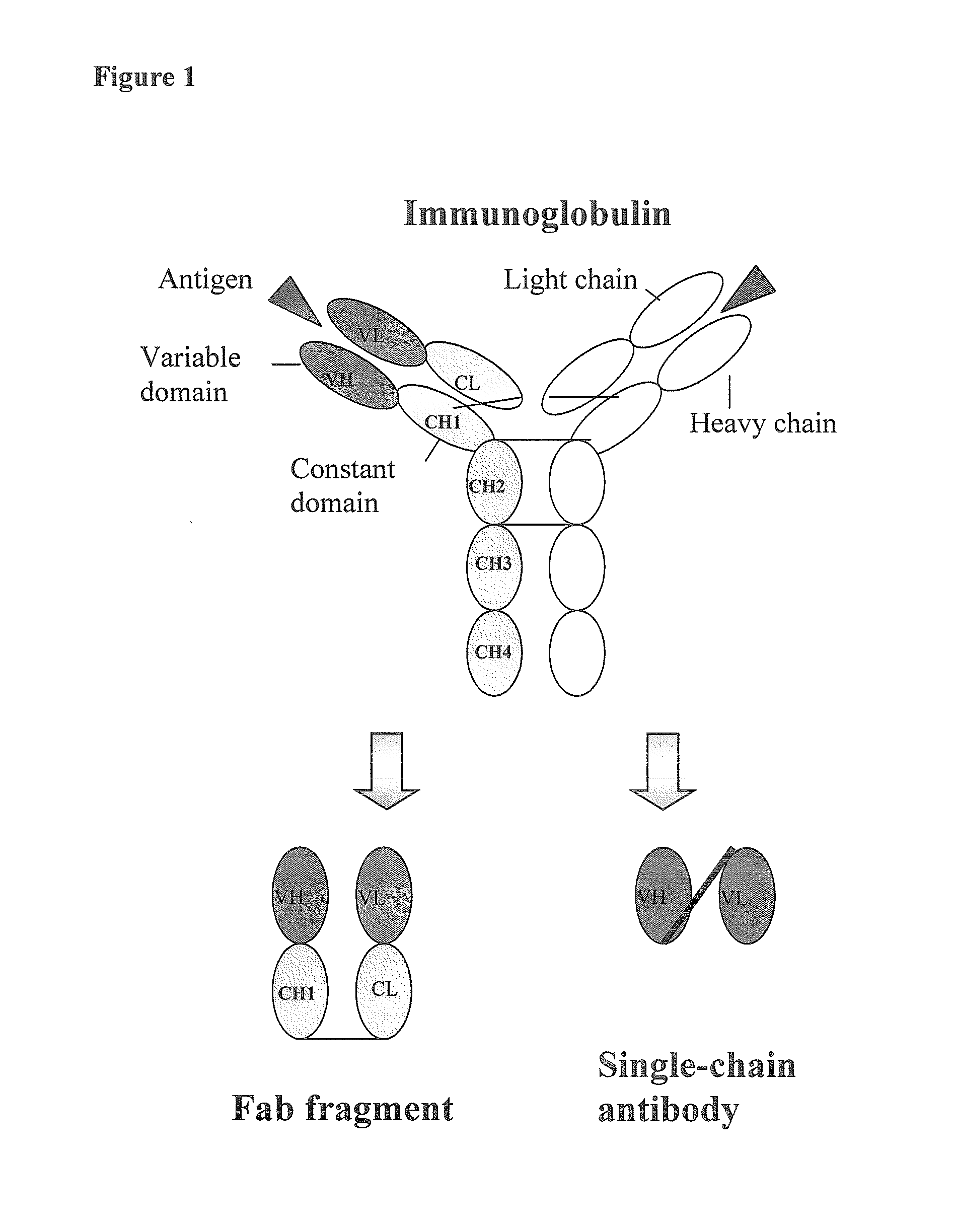
Human monoclonal antibodies directed to sialyl lewis c, sialyl tn and n glycolylneuraminic acid epitopes and a method of analysis of stem cells comprising said epitopes
InactiveUS20100292095A1Eliminate variationSugar derivativesLibrary screeningEpitopeImmunodiagnostics
This invention relates to antibody engineering technology. More particularly, the present invention relates to human IgM antibodies and derivatives thereof, which have novel binding specificity with regard to several oligosaccharide sequences and / or xenoantigenic sialic acid residue. The present invention also relates to processes for making and engineering such novel saccharide and / or NeuGc-binding monoclonal antibodies and to methods for using these antibodies and derivatives thereof in the field of immunodiagnostics, enabling qualitative and quantitative determination of xenoantigenic NeuGc in biological and raw material samples, as well as in immunotherapy, enabling blocking of xenoantigenic NeuGc in patients.
Owner:GLYKOS FINLAND
Therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with decrease in function of gne protein, food composition, and food additive
InactiveUS20120264928A1Easily embodiedEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseFood additive
Disclosed are a therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with the decrease in the function of GNE protein, a food composition, and a food additive. The therapeutic pharmaceutical agent is characterized by comprising a compound capable of increasing the quantity of N-acetylneuraminic acid in cells. Examples of the compound to be contained in the therapeutic pharmaceutical agent include N-acetylneuraminic acid, an intermediate produced downstream from N-acetylmannosamine in an N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis pathway, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative, an N-acetylneuraminic acid-containing compound, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative-containing compound, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylneuraminic acid, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylmannosamine, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for the intermediate, and others.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
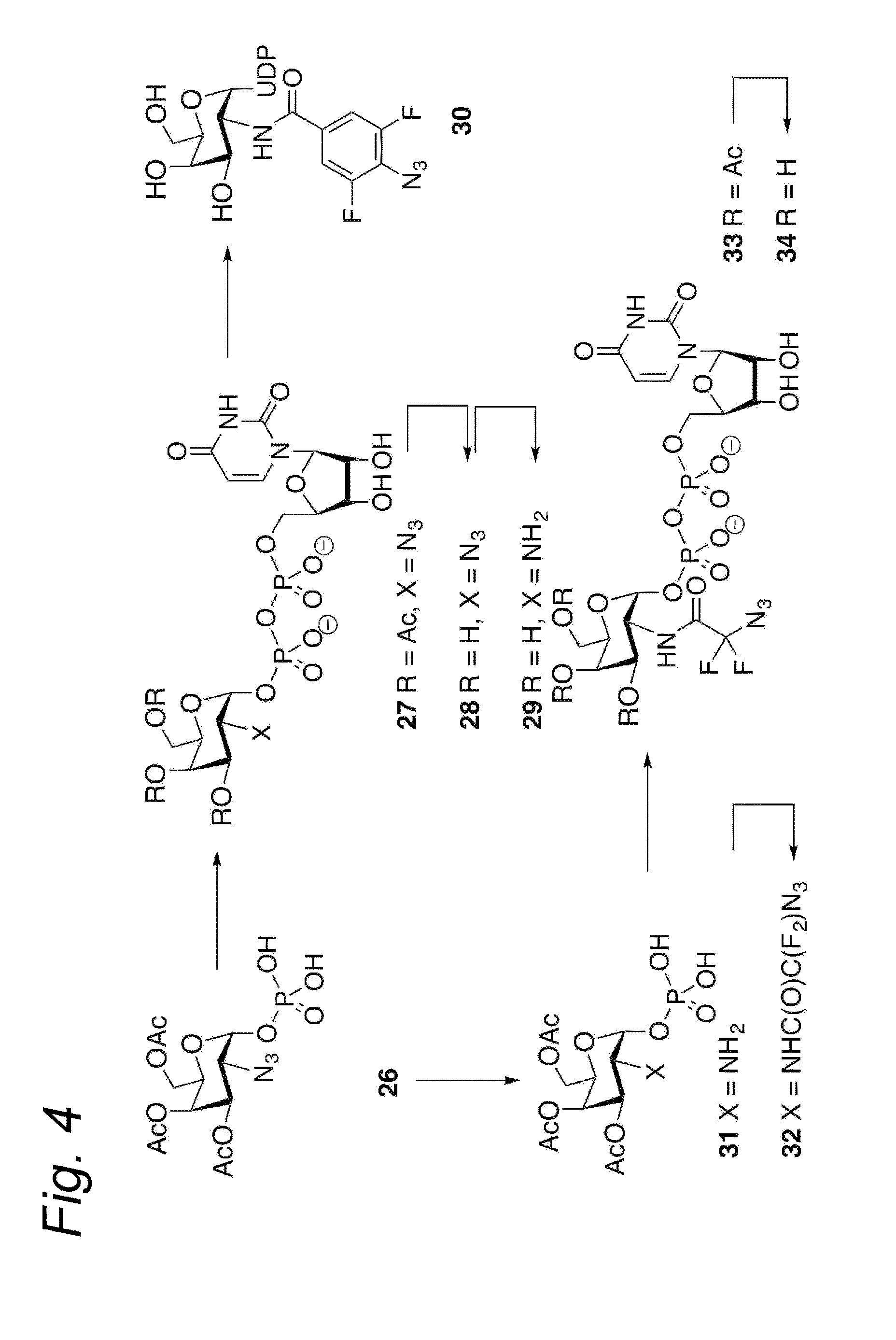
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS20170008858A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention relates to a cycloaddition process comprising the step of reacting a halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1): Preferably, the (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1) is a (hetero)cyclooctyne. The invention also relates to the cycloaddition products obtainable by the process according to the invention. The invention further relates to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds, in particular to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds comprising N-acetylgalactosamine-UDP (GalNAc-UDP), and to halogenated 1,3-dipole compounds comprising (peracylated) N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuNAc).
Owner:SYNAFFIX
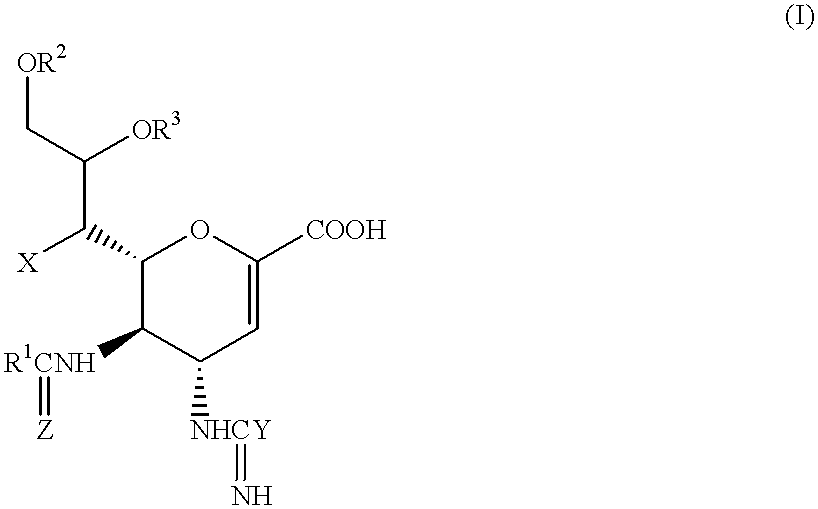
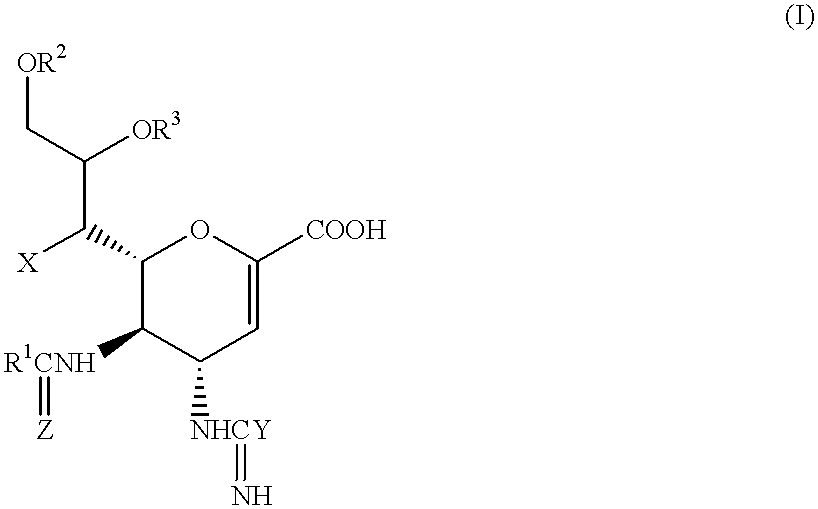
Neuraminic acid derivatives, their preparation and their medical use
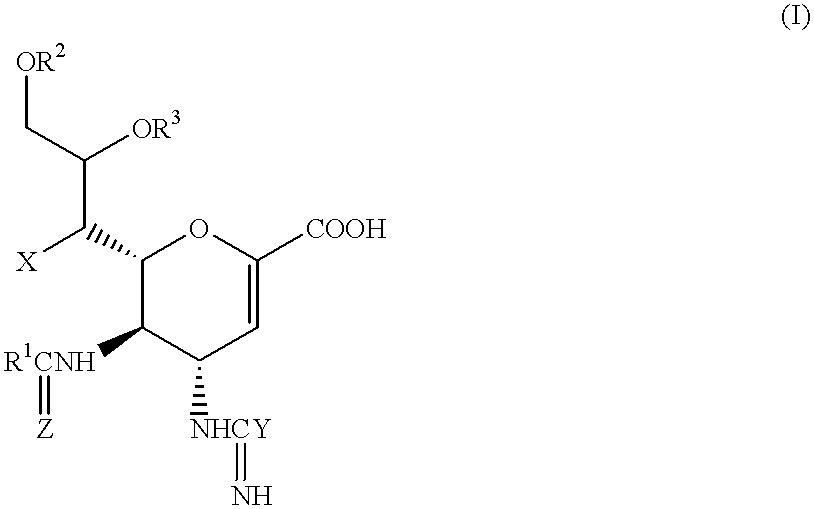
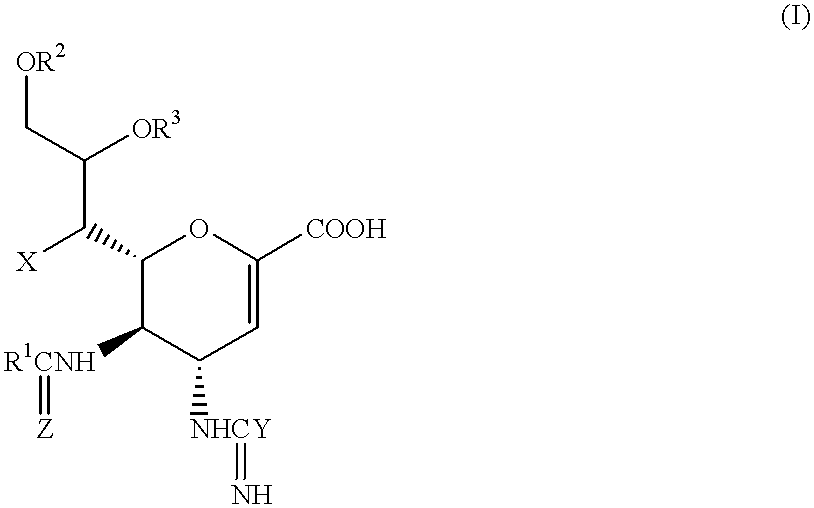
Compounds of formula (I) or their salts or esters:[wherein R1 is alkyl or haloalkyl; R2 and R3 each represents hydrogen or aliphatic acyl; X is hydroxy, halogen, alkoxy, or a group of formula RaO-, where Ra is aliphatic acyl; Y is a group of formula RbRcN- or RbRcN-O-, where Rb and Rc each is hydrogen or alkyl; and Z is oxygen or sulfur] have excellent sialidase inhibitory activity and are therefore useful for the treatment and prevention of influenza and other viral diseases where the replication of the virus is susceptible to sialidase inhibitors.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Method of using hydroxycarboxylic acids or related compounds for treating skin changes asociated with intrinsic and extrinsic aging
A composition comprising an amphoteric or pseudo-amphoteric agent and a polyhydroxy alpha hydroxyacid existing as a free acid, lactone, or salt, and isomeric or non-isomeric forms thereof is provided. The amphoteric or pseudo-amphoteric agent can be selected from amino acids, dipeptides, aminoaldonic acid, aminouronic acid, lauryl aminoproplyglycine, aminoaldaric acid, neuraminic acid desulfated heparin, deacetylated hyaluronic acid, hyalobiuronic acid, chondrosine, deacetylated chondroitin, creatine, creatinine, hydroxyproline, homocysteine, homocystine, homoserine, ornithine, citrulline, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin. The composition may contain other additives, including cosmetic or pharmaceutical agents for topical treatment of dermatological disorders.
Owner:TRISTRATA TECH
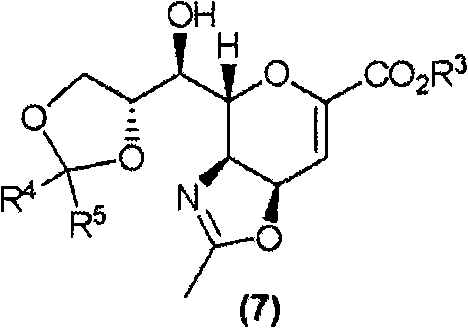
Method for manufacturing neuraminic acid derivatives
ActiveCN101679339AHigh yieldHigh purityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryNeuraminic acidMethyl group
The invention provides a method for manufacturing neuraminic acid derivatives, also synthetic intermediates of the neuraminic acid derivatives and methods for their manufacture, and neuraminic acid derivatives having high purity. A synthetic intermediate compound represented by the formula (7) is provided: wherein R3 represents alkyl; R4 and R5 each represents H, alkyl, phenyl, or together represent tetramethylene, pentamethylene, oxo.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Synthesis of new fucose-containing carbohydrate derivatives
A method for the synthesis of a compound of formula (1) or a salt thereof, wherein A is a carbohydrate linker which is a lactosyl moiety or which consists of a lactosyl moiety and at least one monosaccharide unit selected from the group consisting of: glucose, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, fucose and N-acetyl neuraminic acid; and wherein R1 is one of the following anomeric protecting groups: a) -OR2, wherein R2 is a protecting group removable by catalytic hydrogenolysis; b) -SR3, wherein R3 is an optionally substituted alkyl, an optionally substituted aryl or an optionally substituted benzyl; c) -NH- C(R")=C(R')2, wherein each R' independently is one of the following electron withdrawing groups: -CN, -COOH, -COO-alkyl, -CO-alkyl, -CONH2, -CONH- alkyl or -CON(alkyl)2, or wherein the two R'-groups are linked together and form -CO-(CH2)2-4-CO- and thus form, together with the carbon atom to which they are attached, a 5-7 membered cycloalkan-1,3-dione, in which dione any of the methylene groups is optionally substituted with 1 or 2 alkyl groups, and R" is H or alkyl, in which a fucosyl donor of formula (2) wherein X is selected from the group consisting of: a guanosine diphosphatyl moiety, a lactose moiety, azide, fluoride, optionally substituted phenoxy-, optionally substituted pyridinyloxy-, optionally substituted 3-oxo-furanyloxy- of formula (A), optionally substituted 1,3,5-triazinyloxy- of formula (B), 4-methylumbelliferyloxy-group of formula (C), and a group of formula (D) wherein Ra is independently H or alkyl, or two vicinal Ra groups represent a=C(Rb)2 group, wherein Rb is independently H or alkyl, Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of alkoxy, amino, alkylamino and dialkylamino, Rd is selected from the group consisting of H, alkyl and -C(=O)Re, wherein Re is OH, alkoxy, amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino, hydrazino, alkylhydrazino, dialkylhydrazino or trialkylhydrazino, is reacted with an acceptor of formula H-A-R1 or a salt thereof, wherein A and R1 are as defined above, under the catalysis of an enzyme capable of transferring fucose. A compound of formula 1', its use in manufacture of human milk oligosaccharides, a method of manufacture of human milk oligosaccharides, and a fucosyl donor are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOM AS (DK)
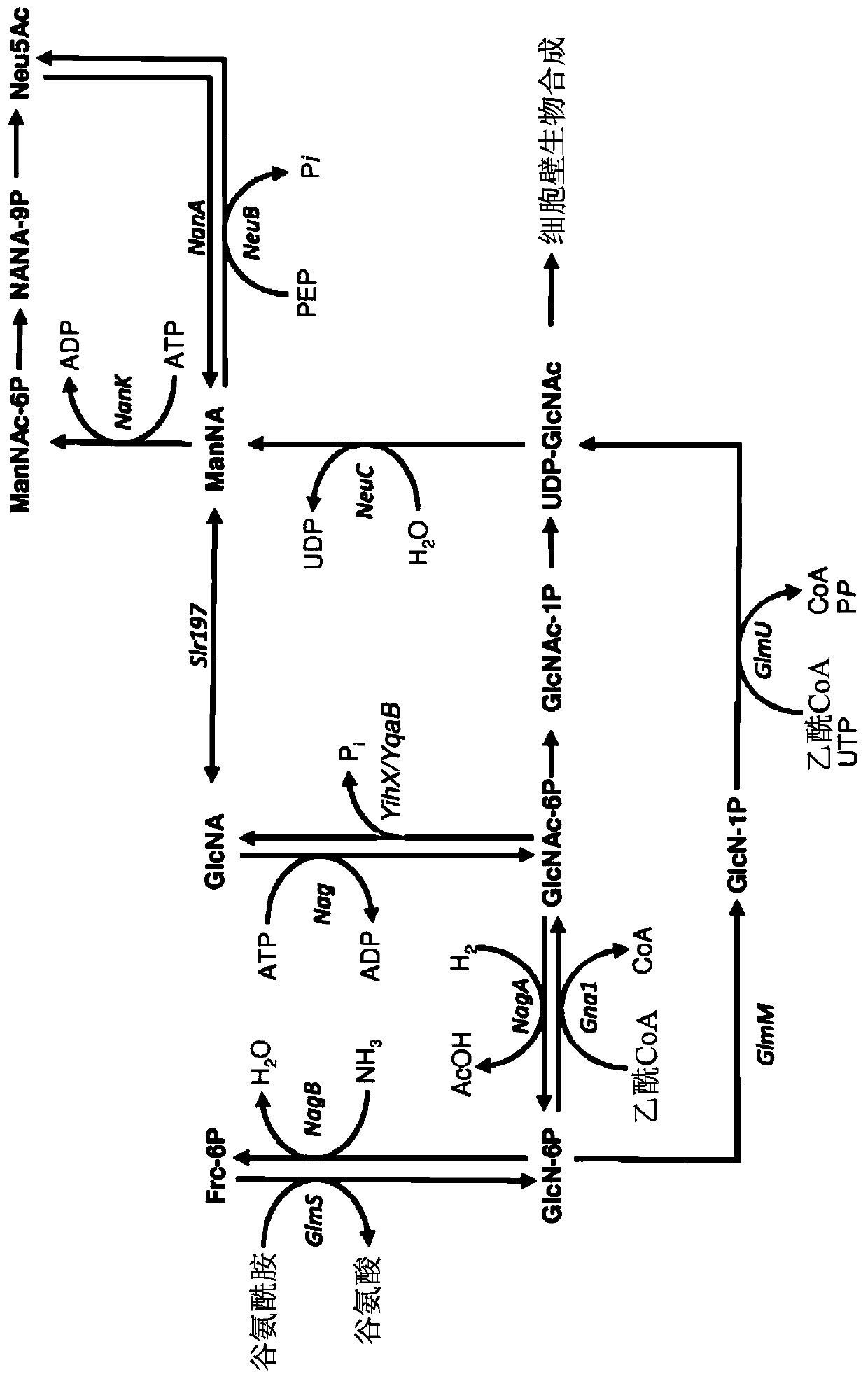
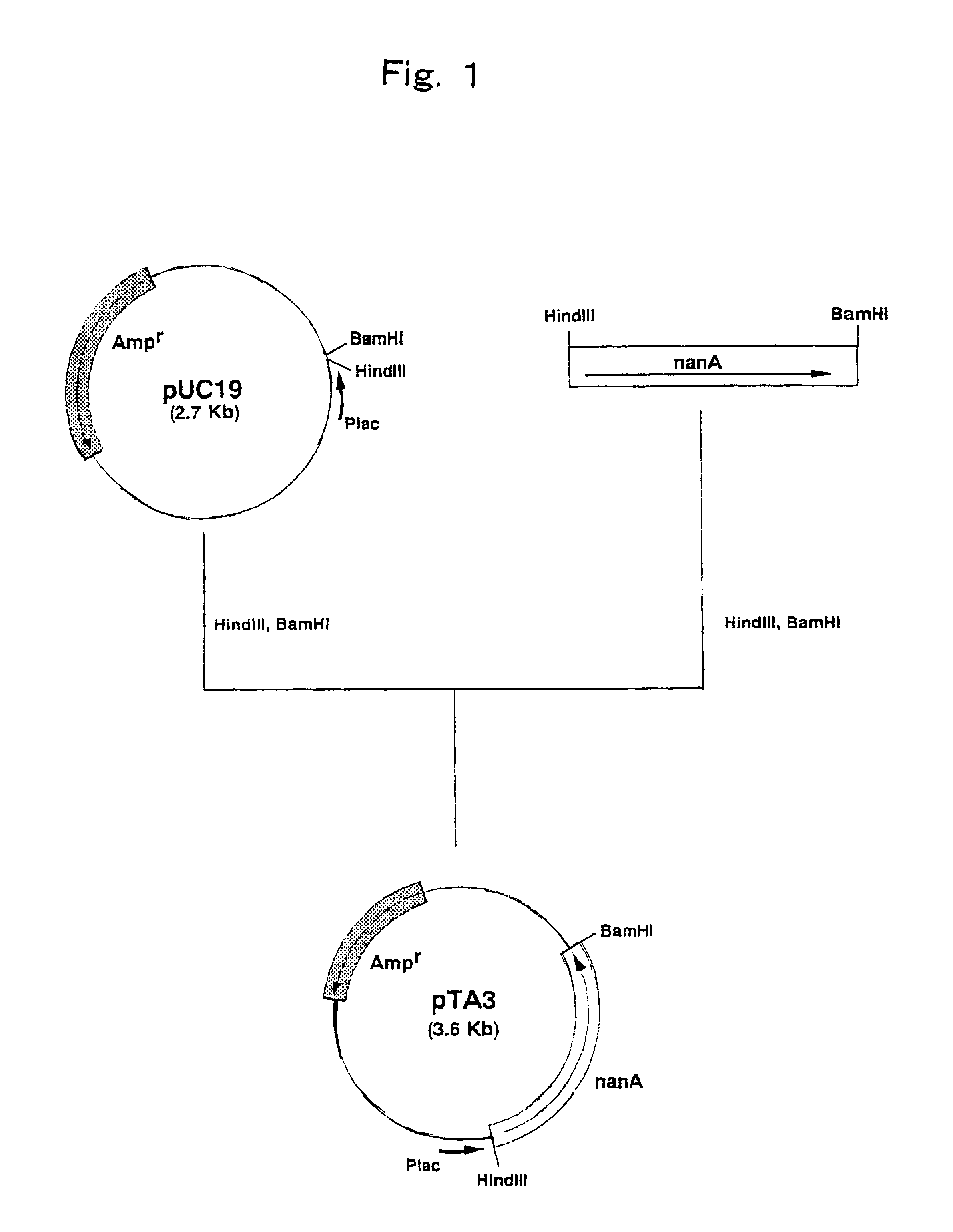
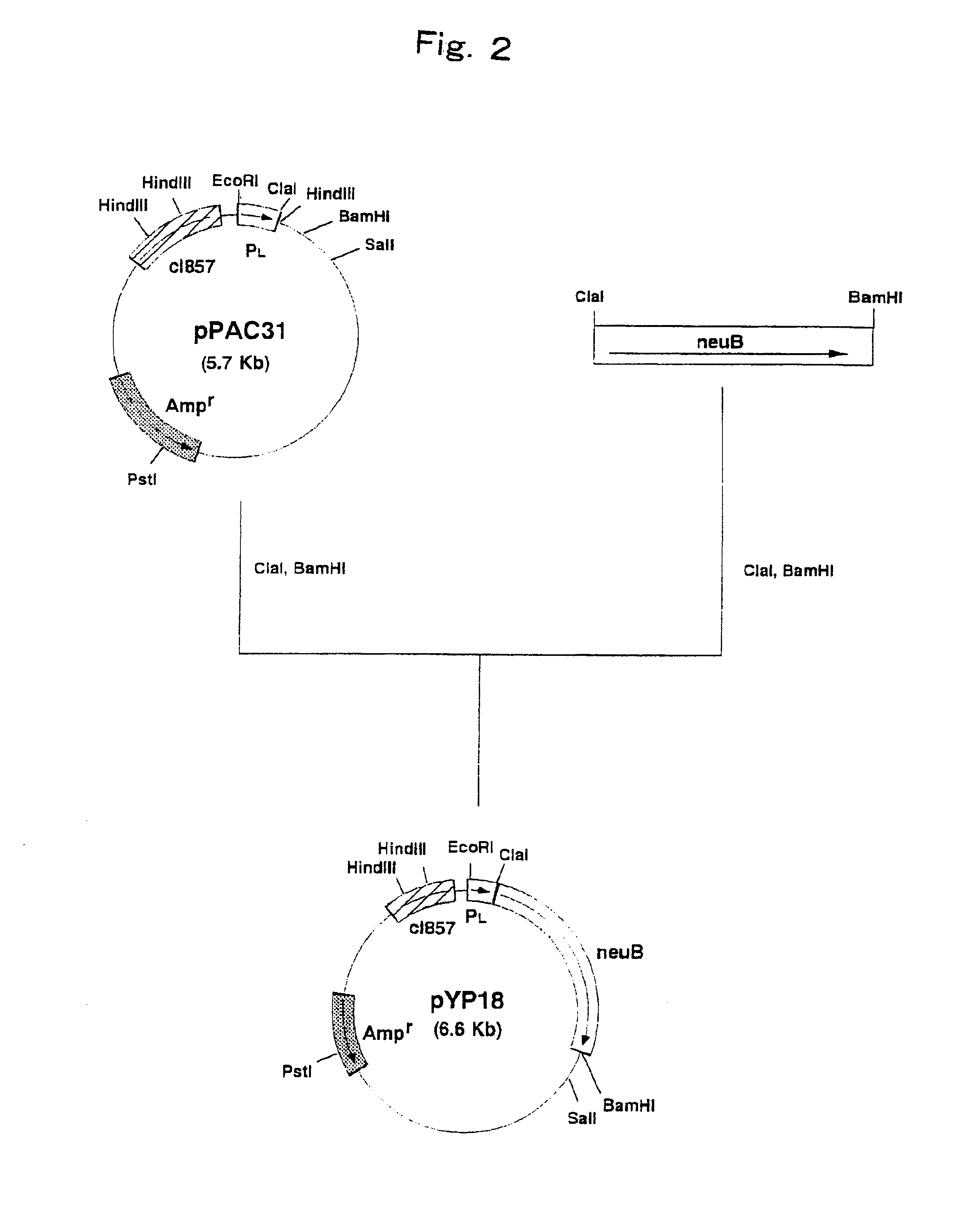
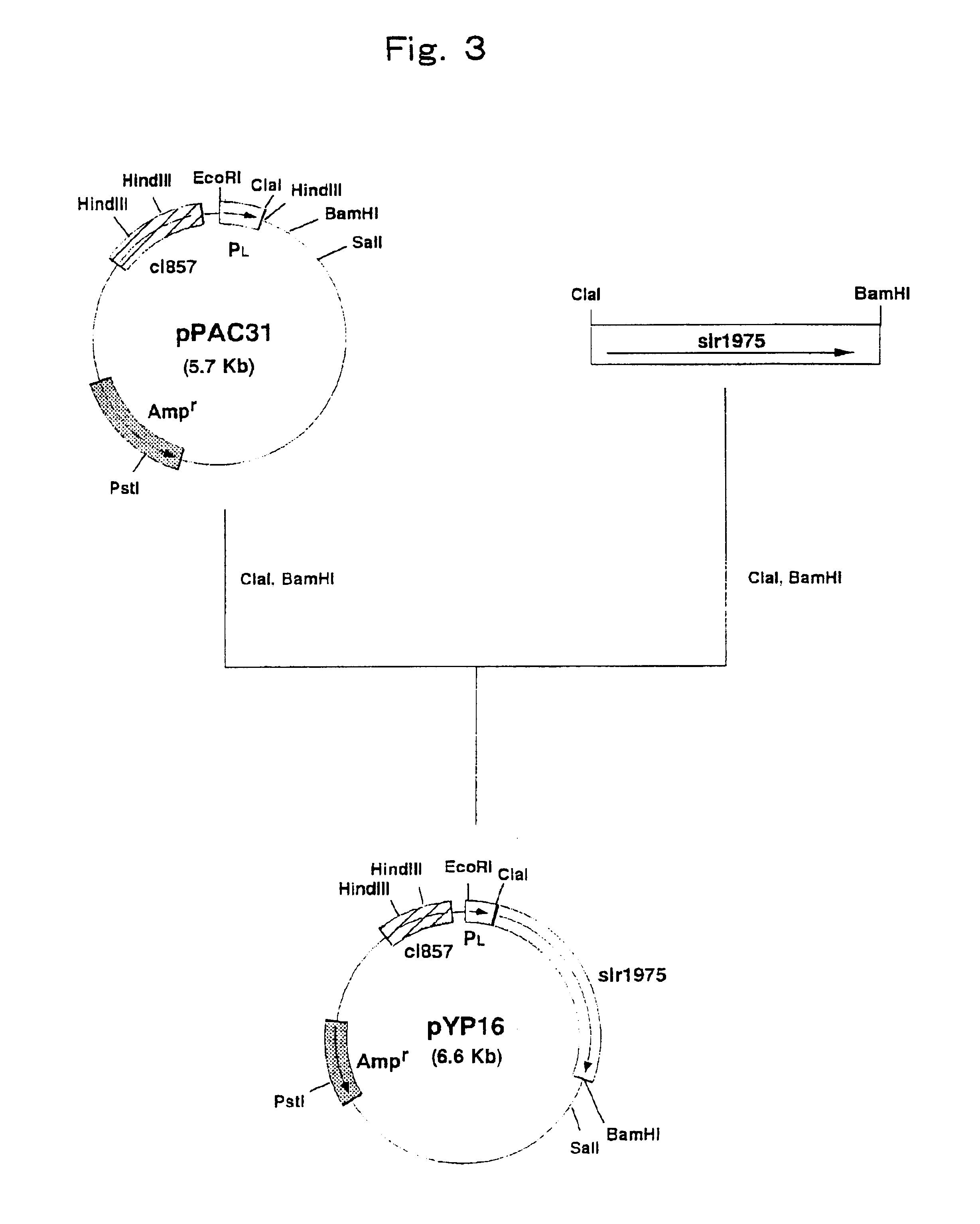
Genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103060358AEliminate degradation pathwaysPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyN-Acetylglucosamine
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. A method for preparing the genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid comprises the following step of: introducing genes associated with the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis into host bacteria so as to obtain recombinant bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid, wherein the genes associated with the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis are coding genes of N-acetylglucosamine and 2-isomerase and a coding gene of N-nacetylneuraminic acid aldolase. The genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid constructed by the invention have the following advantages that the used raw materials are relatively cheap and liable to realize industrial mass product, so that the genetically engineered bacteria play an important role in the production of N-acetylneuraminic acid in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for Detecting and Analyzing N-Glycolynlneuraminic Acid (Neu5Gc) in Biological Materials
InactiveUS20070275409A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesNeuraminic acid
The present application is in the field of sialic acid chemistry, metabolism and antigenicity. More particularly, the present invention relates to the detection and analysis of the non-human sialic acid, N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc) in bio-logical materials, such as food and clinical specimens. Such detection and analysis is facilitated by the use of Neu5Gc specific antibodies. The present invention also relates to the detection of anti Neu5Gc antibodies in clinical samples, as well as the production of anti-Neu5Gc specific antibodies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor and application thereof
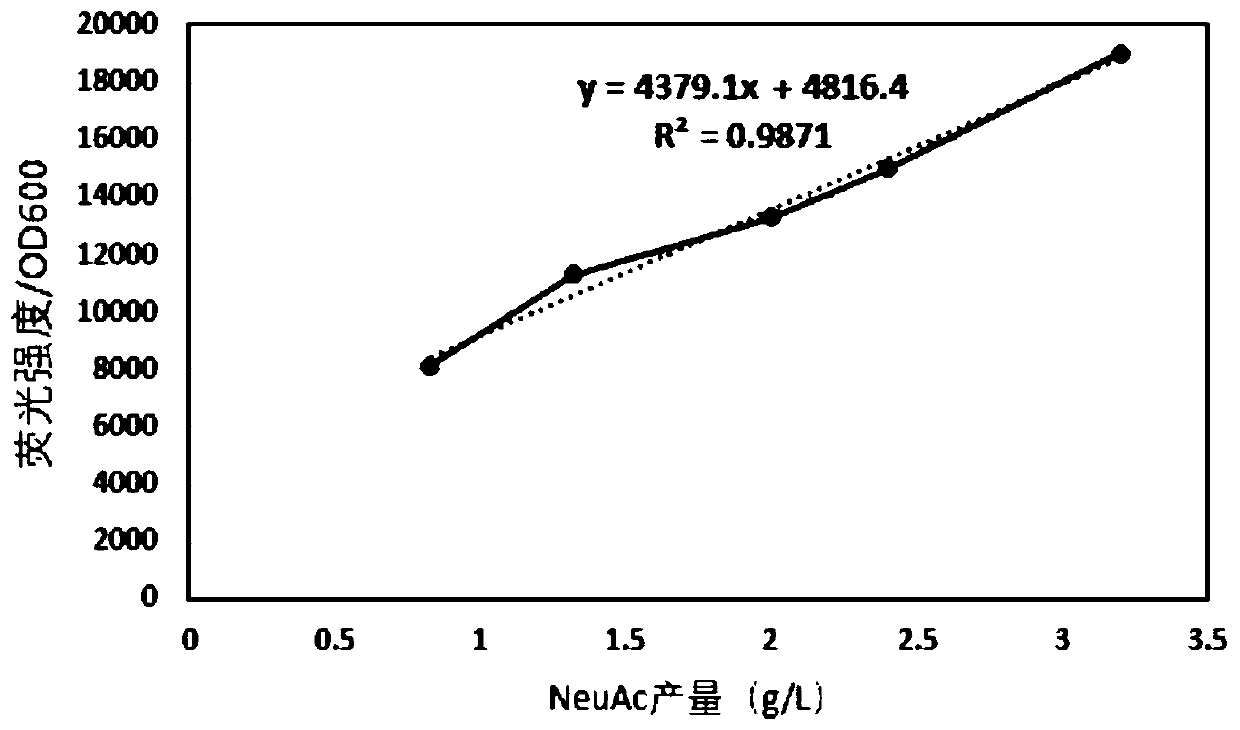
The invention discloses an N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor and application thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor is constructed with transcriptional regulation factor NanR and GFP (green fluorescent protein) gene, from Escherichia coli K12, acting as reporter genes; an effective relationship between N-acetylneuraminic acid and fluorescence intensity is established. The N-acetylneuraminic acid specific biosensor has an important application prospect in screening microorganisms which produce target metabolites.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Sialidase detection reagent
InactiveCN1405562AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNeuraminateSialidase
This invention discloses a sialic acid enzyme test reagent for testing sialic acid enzyme activity in vagina secreta outside the body, containing substrate on the carrier named N-acetyl neuraminate and its salt which can be its derivant or thymolphthaleic N-acetyl neuraminate and its salt, 5-Br-4-Cl-3-indolyl-alpha-D-N-acytylneuraminate and its salt. We can diagnose the bacteriogenic vagina deseases quickly and simple by testing sialic acid enzyme to vagina searate with this sialic acid ester reagent which can be used as an independent diagnosis target with good stability, extremely excellent accuracy and simple operation (one step test).
Owner:肖洪武
Fermentative production of n-acetylneuraminic acid
Disclosed are non-naturally-occurring microorganisms for the production of N-acetylneuraminic acid, a method for the production of N-acetylneuraminic acid by fermentation of the non-naturally-occurring microorganisms, and nutritional compositions containing N-acetylneuraminic acid which has been produced by fermentation of the non-naturally-occurring microorganisms.
Owner:CHR HANSEN HMO GMBH
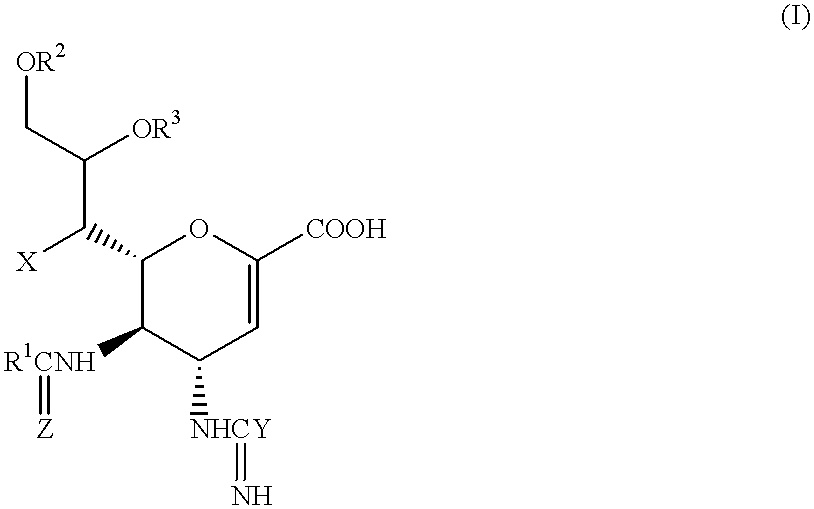
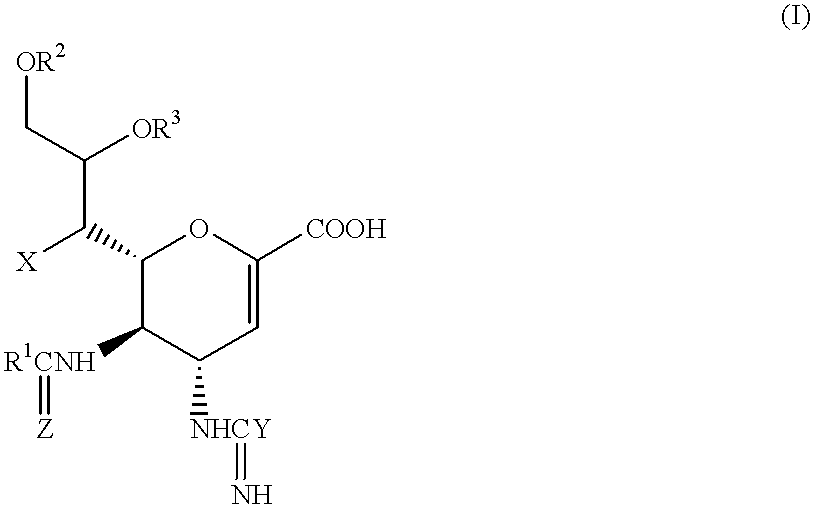
Neuraminic acid derivatives, their preparation and their medical use
Compounds of formula (I) or their salts or esters: [wherein R1 is alkyl or haloalkyl; R2 and R3 each represents hydrogen or aliphatic acyl; X is hydroxy, halogen, alkoxy, or a group of formula RaO-, where Ra is aliphatic acyl; Y is a group of formula RbRcN- or RbRcN-O-, where Rb and Rc each is hydrogen or alkyl; and Z is oxygen or sulfur] have excellent sialidase inhibitory activity and are therefore useful for the treatment and prevention of influenza and other viral diseases where the replication of the virus is susceptible to sialidase inhibitors.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
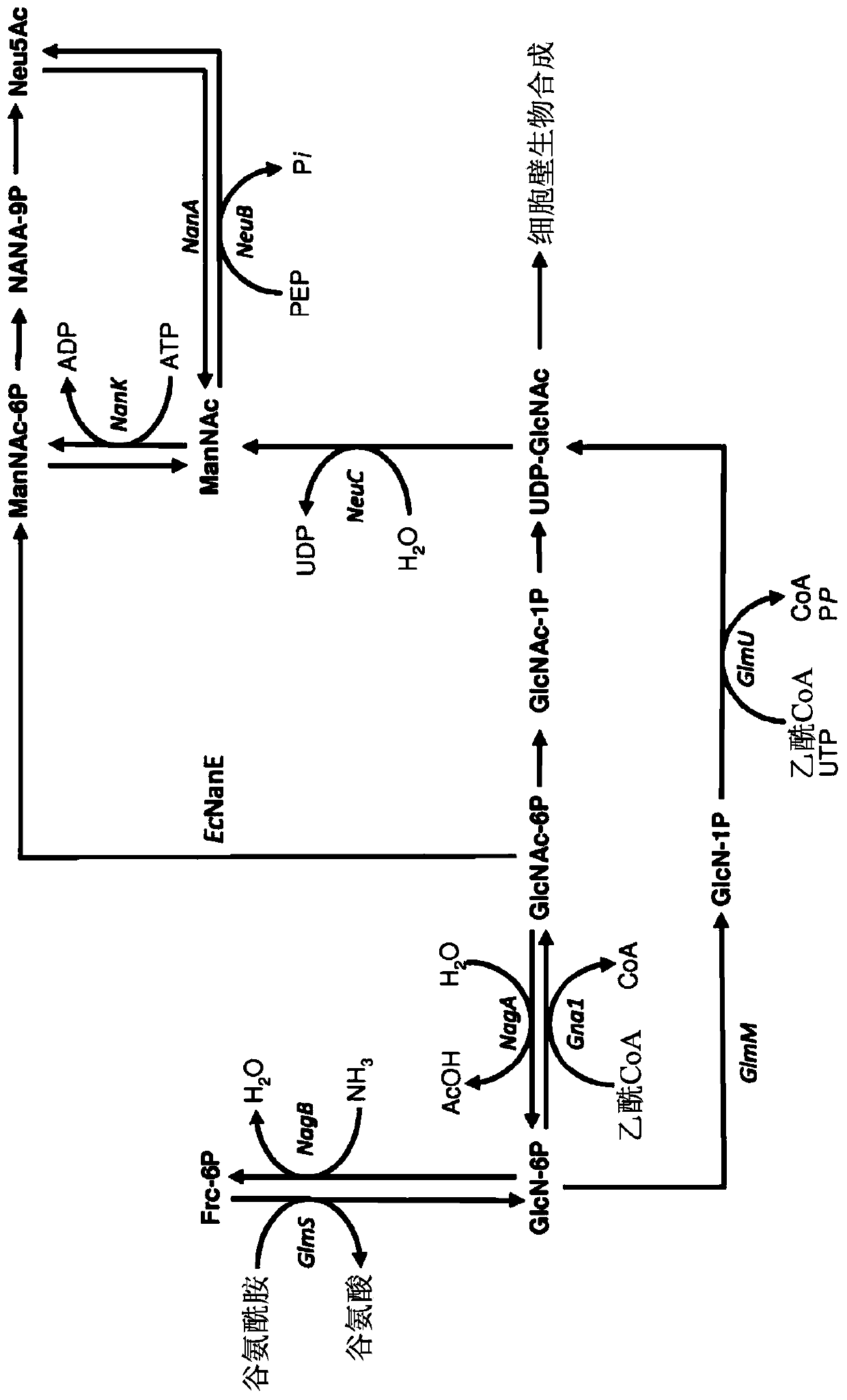
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as construction and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN113817658AIncrease production intensityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid through xylose induction. Escherichia coli is used as a starting strain, an N-acetylglucosamine synthesis pathway is integrated on a genome, an N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene bAGE and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene neuB from collar algae are introduced, an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis pathway is constructed, and a key gene nano ATEK of a catabolism pathway of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is knocked out. Meanwhile, metabolic pathways of precursor substances required by synthesis of the N-acetylneuraminic acid are subjected to multi-copy reinforcement, part of bypass metabolic pathways are knocked out, key enzyme genes for producing GlcNAc and Neu5Ac are optimized according to different copy numbers, the optimal proportion of the key enzyme genes is finally determined, and the high-yield strain of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is obtained. The highest yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach 28g / L, the highest production intensity can reach 0.67 g / (L*h) which is the highest value reported at present, and the N-acetylneuraminic acid has important industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Neuraminidase inhibitor prodrug and its composition and use
ActiveCN103848762AExtended half-lifeOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationEnzyme Inhibitor AgentNeuraminic acid
The invention provides a compound shown as formula Ia, its pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, polymorphs, enantiomer or racemic mixtures. The compound is used as a neuraminidase inhibitor prodrug, and can improve the half-life in the body of a neuraminidase inhibitor. The invention also provides a preparation method of the compound, a pharmaceutical composition containing the compound, and use of the pharmaceutical composition and the compound in preparation of neuraminidase inhibitor drugs and treatment of related diseases.
Owner:BEIJING PRELUDE PHARM SCI & TECH
Multipath composite neuraminic acid producing bacillus subtilis and application thereof
ActiveCN111394292AHigh catalytic activityReduce synthetic pressureBacteriaTransferasesO-Phosphoric AcidGlucosaminephosphate isomerase
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
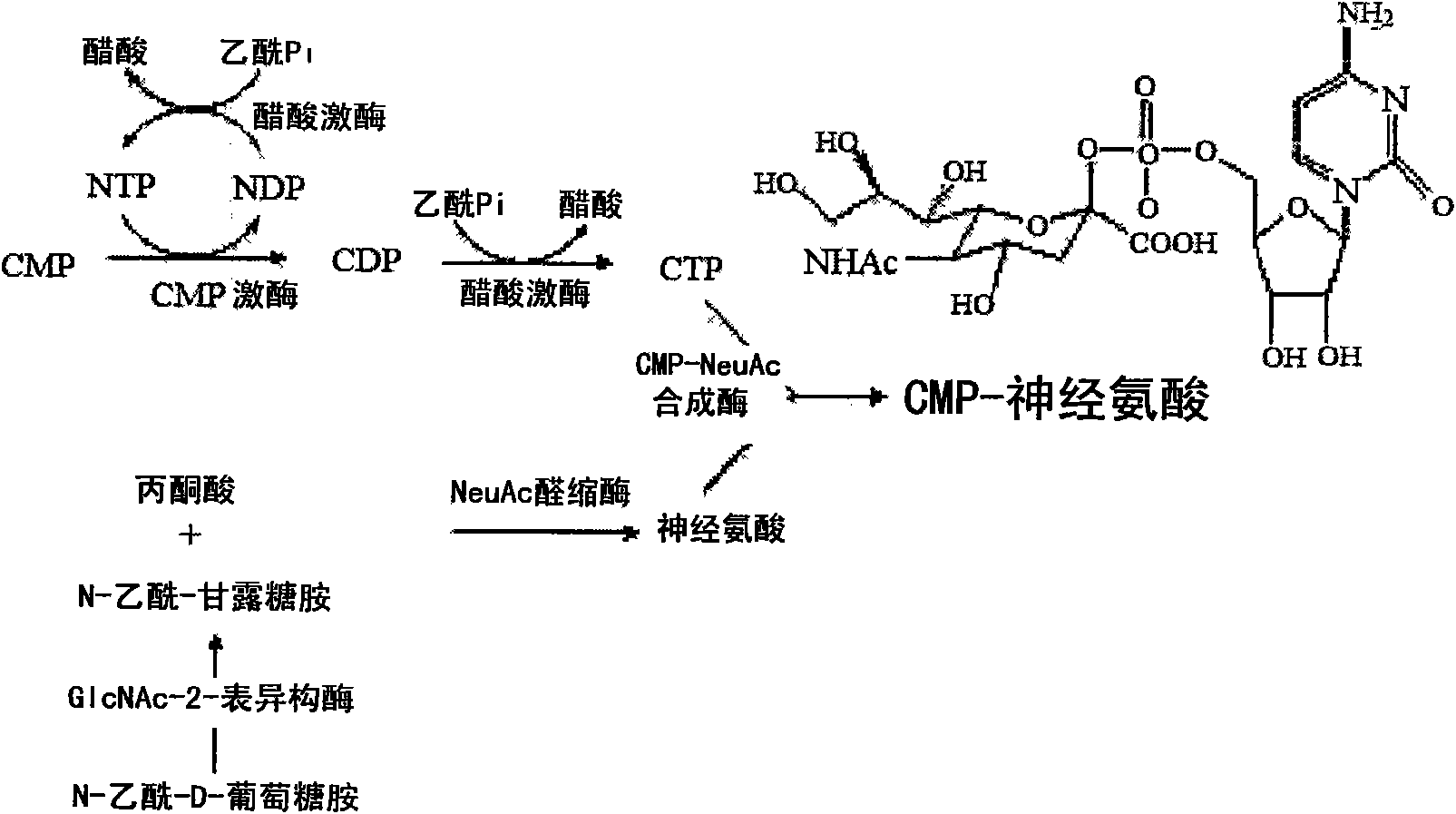
Novel n-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase and method for producing cmp-neuraminic acid using the same
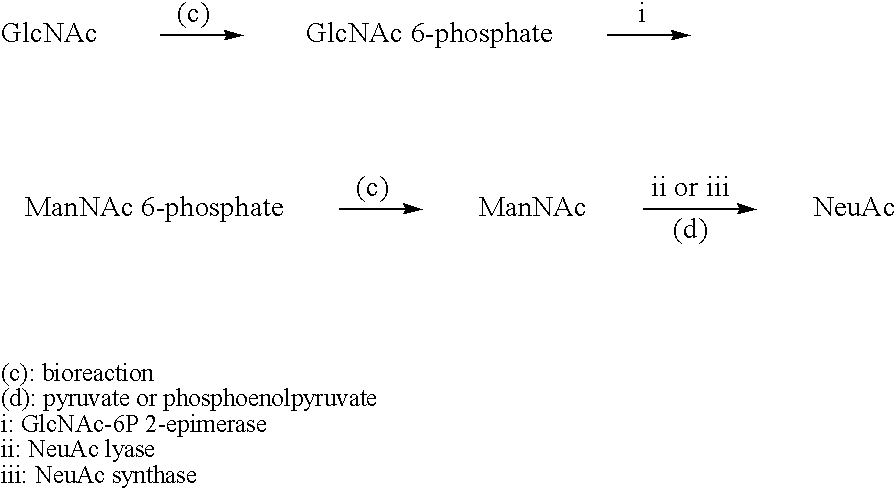
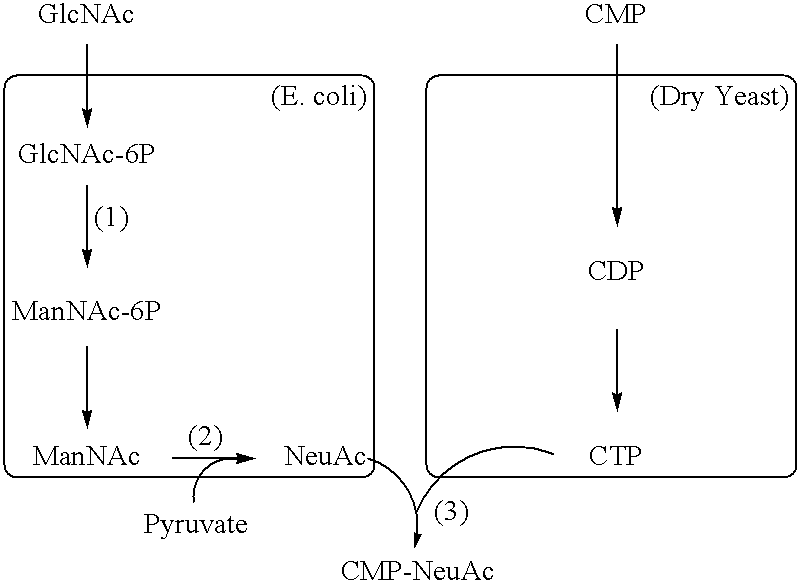
The present invention relates to a novel N-acetylglucosamine-2- epimerase and a method for preparing CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid, more specifically, relates to a N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase derived from Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343, and a method for preparing CMP-N- acetylneuraminic acid using said N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase. According to the present invention, CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid can be produced economically in a large amount through a one-step reaction using cytidine monophosphate and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine which are inexpensive substrates.
Owner:GENECHEM
Preparation of N-aceto-D-neuraminic acid by N-aceto-D-neuraminic acid aldonase immobilizing method
The invention relates to produce the N-acetyl neuraminic acid by the N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid aldolase immobilized enzyme. The process immobilizes the N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid aldolaseby the affinity carrier using the N-acetyl glucosamine and the pyruvic sodium as the substrate.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Separation and extraction method for N-acetylneuraminic acid
ActiveCN111087432AEliminate the solid-liquid separation processImprove adsorption capacitySugar derivativesSaccharide compounds with non-saccharide radicalsPhysical chemistryNeuraminic acid
The invention discloses a separation and extraction method for N-acetylneuraminic acid. The separation and extraction method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out acidolysis on a solution containing polysialic acid so as to obtain an acidolysis solution; (2) allowing the acidolysis solution obtained in the step (1) to pass through a first membrane to remove solid impurities so as to obtain a first permeate, allowing the first permeate to pass through a second membrane to remove macromolecular impurities so as to obtain a second permeate, allowing the second permeate to pass through athird membrane so as to remove monovalent salt, and collecting a trapped fluid; (3) adjusting the pH value of the trapped fluid to an N-acetylneuraminic acid isoelectric point, carrying out electrodialysis to remove multivalent salt, allowing a multivalent salt removed solution to pass through anion exchange resin for impurity washing and elution, collecting an effluent, and carrying out concentrating so as to obtain a concentrated solution; and (4) adjusting the pH value of the concentrated solution obtained in the step (3) to 1-3, adding a reverse solvent, carrying out cooling until a crystal is extracted, and carrying out centrifuging, washing and drying. The whole separation process is simple to operate; the purity of a crystal product is 99% or above; and the yield is greater than 90%.
Owner:NANJING HIGH TECH UNIV BIOLOGICAL TECH RES INST CO LTD
Extractive and preparation containing same
ActiveCN103357006AGuaranteed qualityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderMedicineNeuraminic acid
An objective of the invention is to provide a vaccinia virus inoculation rabbit inflammation skin extractive which is more stable in quality, and a preparation which contains the extractive as an effective constituent, etc. Amount of N-acetyl neuraminic acid which is contained in the vaccinia virus inoculation rabbit inflammation skin extractive and the preparation containing the extractive is used as an index, so that quality of each preparing batch of the extractive and the preparation is more stable. Effectiveness and security of the vaccinia virus inoculation rabbit inflammation skin extractive and the preparation containing the extractive which are made in the method and have more stable quality are ensured strictly, and the extractive and the preparation have very good usefulness.
Owner:NIPPON ZOKI PHARM CO LTD
Recombinant microbe capable of yielding N-acetylneuraminic acid and application of recombinant microbe
ActiveCN113122491AReduce manufacturing costIncrease the level of fermentation productionBacteriaTransferasesNeuraminic acidMicrobiology
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial fermentation and particularly discloses a recombinant microbe capable of yielding N-acetylneuraminic acid and application of the recombinant microbe. According to the recombinant microbe provided by the invention, compared with an original strain, the recombinant microbe has lowered expression of pyruvate kinase and / or enzymatic activity; the pyruvate kinase is pyruvate kinase I and / or pyruvate kinase II; and the original strain is a microbe capable of synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid. Compared with the original strain capable of synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid, the recombinant microbe provided by the invention has lowered expression of the pyruvate kinase and / or enzymatic activity. The recombinant microbe is especially adapted for generating the N-acetylneuraminic acid through carrying out fermentation culture by using a cheap low-carbon raw material, i.e., glucose. According to the recombinant microbe provided by the invention, the fermentation level of synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid is high, the production cost of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is reduced remarkably, and thus, the recombinant microbe has industrialized potentials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Transgenically produced antithrombin III
InactiveUS20080176786A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMonosaccharide compositionPlasma derived
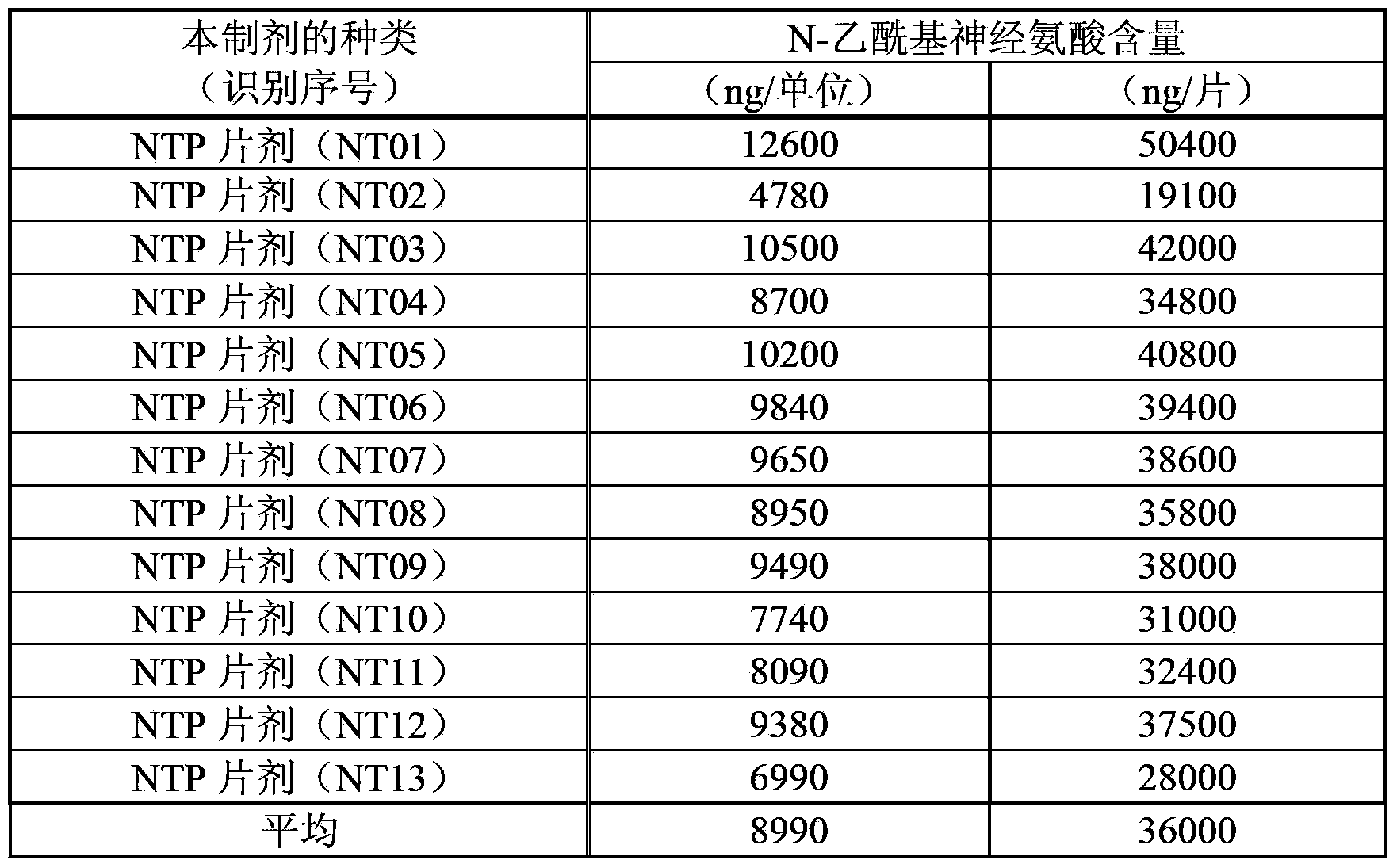
This invention relates to transgenically produced human Antithrombin III (tgATIII). The human ATIII produced by the transgenic process of the present invention has a monosaccharide composition which comprises N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) along with fucose, N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, mannose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid / N-glycolyneuraminic acid. The monosaccharide composition differs with that of plasma derived ATIII (phATIII). It has been found that tgATIII has an increased clearance rate when compared to phATIII.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
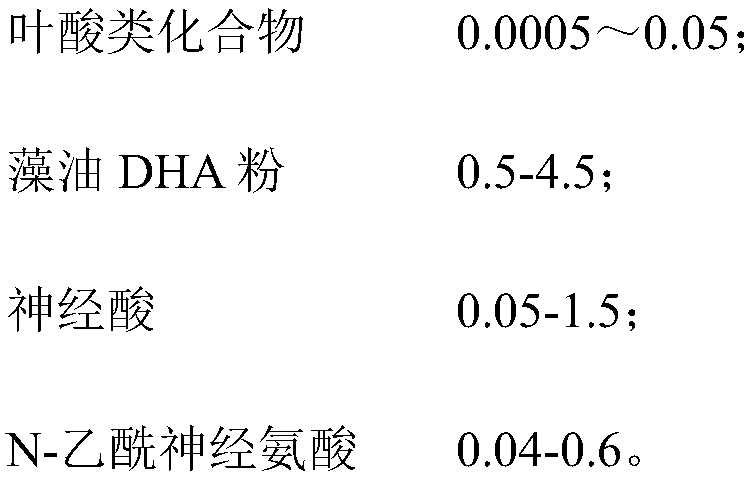
Composition having function of assisting memory improvement, and application and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109288005AImprove reversible memory lossTaste Q bombFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentMemory improvementAntioxidant
The present invention relates to a composition having a function of assisting memory improvement. The composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.0003-0.05 part of a folic acid compound, 0.1-5 parts of algal oil DHA powder, 0.01-2 parts of nervonic acid and 0.01-1 part of N-acetylneuraminic acid. The disclosed composition combines the folic acid compound, algal oil DHA powder, nervonic acid and N-acetylneuraminic acid, controls the weight ratios of the each component, enables each component to achieve synergistic effects and can effectively improve reversible memory loss. Besides, food-acceptable auxiliaries are added into the composition to prepare fruit jelly. The fruit jelly is elastic in mouthfeel, easy to carry and wide in use ranges and can be consumed by pregnant women, the elderly and children. The prepared fruit jelly is free of any preservatives. By controlling pH values of each component and weight ratios of gelling agents and antioxidants in the components, preservation time of the fruit jelly can be effectively increased and the fruit jelly is not deteriorated after being placed for a long time.
Owner:北京斯利安药业有限公司
Process for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid
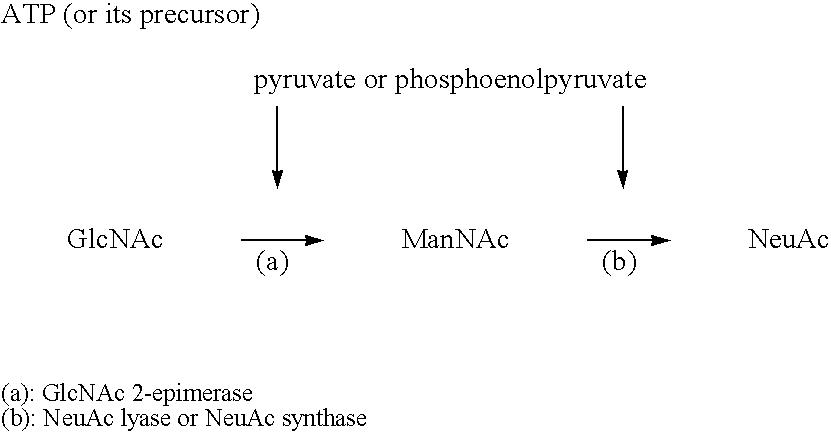
The present invention provides a process for economically producing N-acetylneuraminic acid without using expensive materials such as pyruvic acid and phosphoenolpyruvic acid. The process comprises: allowing (i) a culture of a microorganism having N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase activity or N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase activity, or a treated matter of the culture, (ii) a culture of a microorganism capable of producing pyruvic acid or a treated matter of the culture, or a culture of a microorganism capable of producing phosphoenolpyruvic acid or a treated matter of the culture, (iii) N-acetylmannosamine, and (iv) an energy source which is necessary for the formation of pyruvic acid or phosphoenolpyruvic acid to be present in an aqueous medium to form and accumulate N-acetylneuraminic acid in the aqueous medium; and recovering N-acetylneuraminic acid from the aqueous medium.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
Process for producing cmp-n-acetylneuraminic acid
InactiveUS20050260718A1High yieldEliminate needSugar derivativesTransferasesPhosphoric acidNeuraminic acid
The present invention is directed to a process for producing CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid (CMP-NeuAc), characterized in that the process includes adding yeast cells, N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate 2-epimerase (GlcNAc-6P 2-epimerase), N-acetylneuraminic acid lyase (NeuAc lyase), and CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase (CMP-NeuAc synthase) to a reaction system containing N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), pyruvate, and cytidine 5′-monophosphate (CMP), and inducing reaction of the mixture. The present invention is also directed to a process for producing CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid (CMP-NeuAc), characterized in that the process includes adding yeast cells, N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate 2-epimerase (GlcNAc-6P 2-epimerase), N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase (NeuAc synthase), and CMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase (CMP-NeuAc synthase) to a reaction system containing N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and cytidine 5′-monophosphate (CMP), and inducing reaction of the mixture.
Owner:YAMASA SHOYU KK
Stable serum sialic acid detection kit with high anti-interference capability and production method and application thereof
ActiveCN111334557ANo reconstitution requiredImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementActive agentSurface-active agents
The invention provides a sialic acid detection kit. The kit contains a reagent R1 and a reagent R2; the reagent R1 contains the following components: a tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl aminomethane-hydrochloric acid (Tris-HCL) buffer solution, lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase, a reduced coenzyme I (NADH), a surfactant, a stabilizer, EDTA-Na2 and a preservative; and the reagentR2 contains the following components: a tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl aminomethane-hydrochloric acid (Tris-HCL) buffer solution, neuraminidase, a surfactant, a stabilizer and a preservative. A productionmethod and application of the kit are provided at the same time. The kit is a liquid kit with high stability, high anti-interference capability, high accuracy and good repeatability.
Owner:中拓生物有限公司 +1
Engineering strain for xylose-induced production of N-acetylneuraminic acid and application of engineering strain
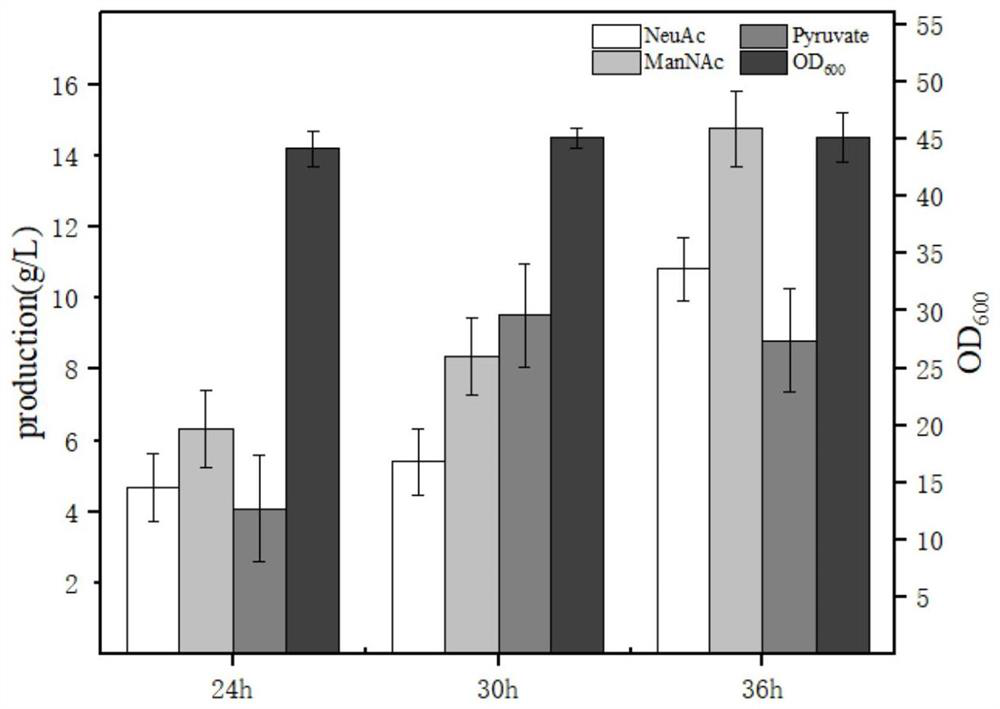
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and particularly relates to construction and application of a genetic engineering strain for xylose-induced production of N-acetylneuraminic acid. According to the construction and the application, a N-acetylglucosamine synthesis way is integrated with a genome, a N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene bAGE and a N-acetylneuraminicacid lyase gene shNAL are introduced, a N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is constructed, and a key gene nanTEK of a catabolism way of the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is knocked out. Meanwhile, metabolic ways of precursor substances required for synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid are subjected to multicopy strengthening, and part of bypath metabolic ways are subjected to knockout, so that the N-acetylneuraminic acid high yielding strain is obtained. In case of shake-flask fermentation for 36h, the yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach 10.8g / L to the maximum, the production intensity can reach 0.3g / (L*h) which is the maximum value reported at present, and thus, the engineering strain has an important industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com