Fermentative production of n-acetylneuraminic acid
A kind of fermentation broth and microorganism technology, applied in the product field of N-acetylneuraminic acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0201] Example 1: Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) strain producing N-acetylneuraminic acid
[0202] Metabolic engineering is achieved through mutagenesis and deletion of specific endogenous genes and genomic integration of heterologous genes. The genes lacZ and araA were inactivated by mutagenesis using mismatched oligonucleotides as described by Ellis et al. (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:6742-6746 (2001)).
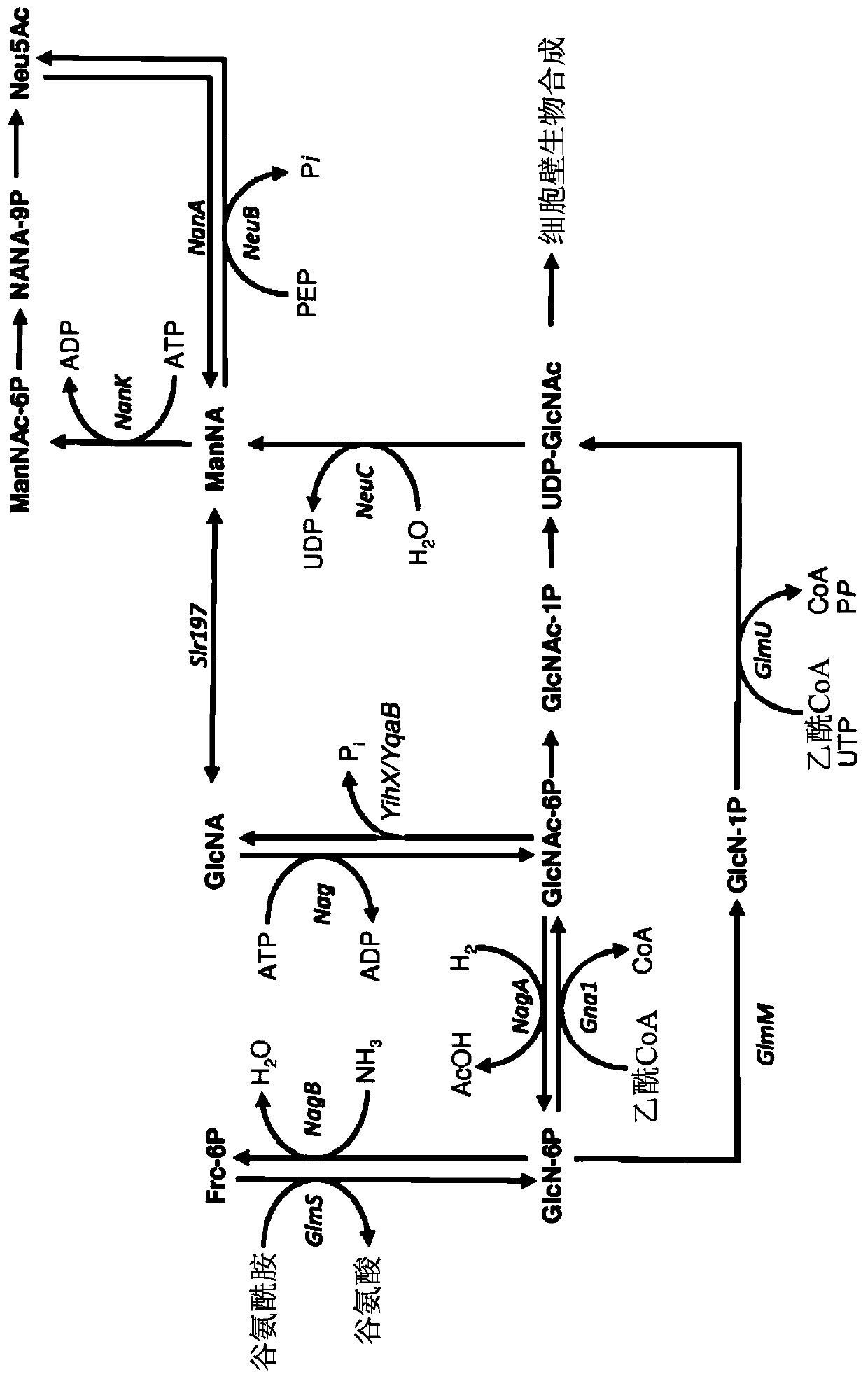
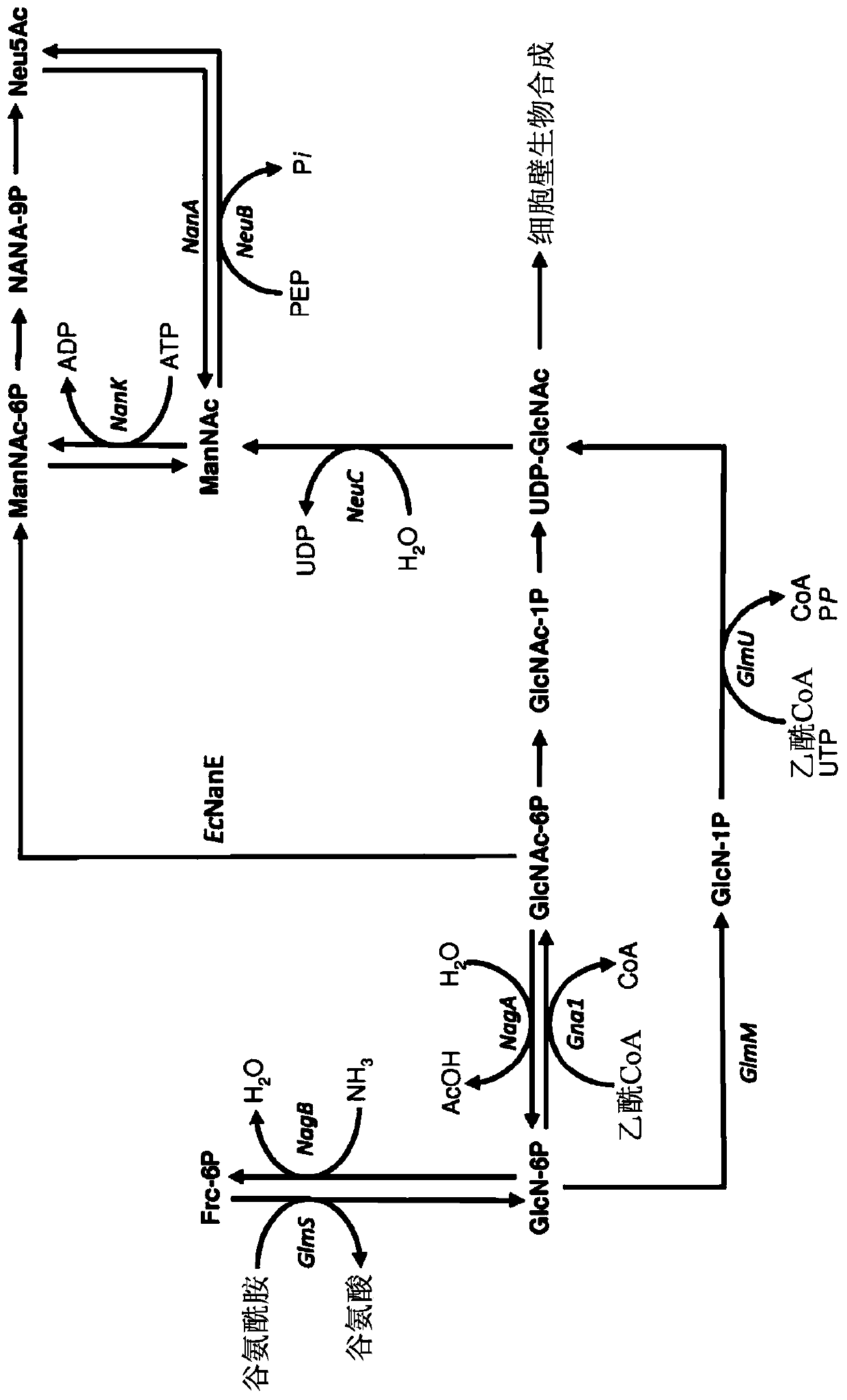
[0203] Genomic deletions were generated according to the method of Datsenko and Wanner (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:6640-6645 (2000)). To prevent the degradation of N-acetylglucosamine, the following genes were deleted from the genome of E. coli strain BL21(DE3): N-acetylglucosamine-specific PTS enzyme II (nagE), N-acetylglucosamine-6 - Phosphate deacetylase (nagA) and glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase (nagB). Also deleted are N-acetylmannosamine kinase (nanK), N-acetylmannosamine-6-phosphate epimerase (nanE), N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase (na...
Embodiment 2
[0213] Example 2: Production of N-acetylneuraminic acid in a batch fermentation process
[0214] Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) strain #NANA1 was cultured in a 3L fermenter (New Brunswick, Edison, USA) at 30°C, initially using 1000 mL of mineral salt medium containing 7 g L -1 NH 4 h 2 PO 4 , 7g·L - 1 K 2 HPO 4 , 2g·L -1 KOH, 0.3g·L -1 Citric acid, 2g·L -1 MgSO 4 x7·H 2 O, 5g·L -1 NH 4 Cl 2 and 0.015g·L - 1 CaCl 2 x6·H 2 O, add 1mL·L -1 Trace element solution (54.4g L -1 Ferric ammonium citrate, 9.8g·L -1 MnCl 2 ×4·H 2 O, 1.6g·L -1 CoCl 2 x6·H 2 O, 1g L -1 CuCl 2 x2·H 2 O, 1.9g·L -1 h 3 BO 3 , 9g·L -1 ZnSO 4 x7·H 2 O, 1.1g L -1 Na 2 MoO 4 x2·H 2 O, 1.5g·L -1 Na 2 SeO 3 , 1.5 L -1 NiSO 4 x6·H 2 O), and containing 2% (m / v) sucrose as carbon source and the antibiotic bleomycin (10 μg·mL -1 ). Cultures were initiated using a 2.5% (v / v) inoculum from a preculture grown in the same sucrose-containing medium. The end of the batch phase is c...
Embodiment 3
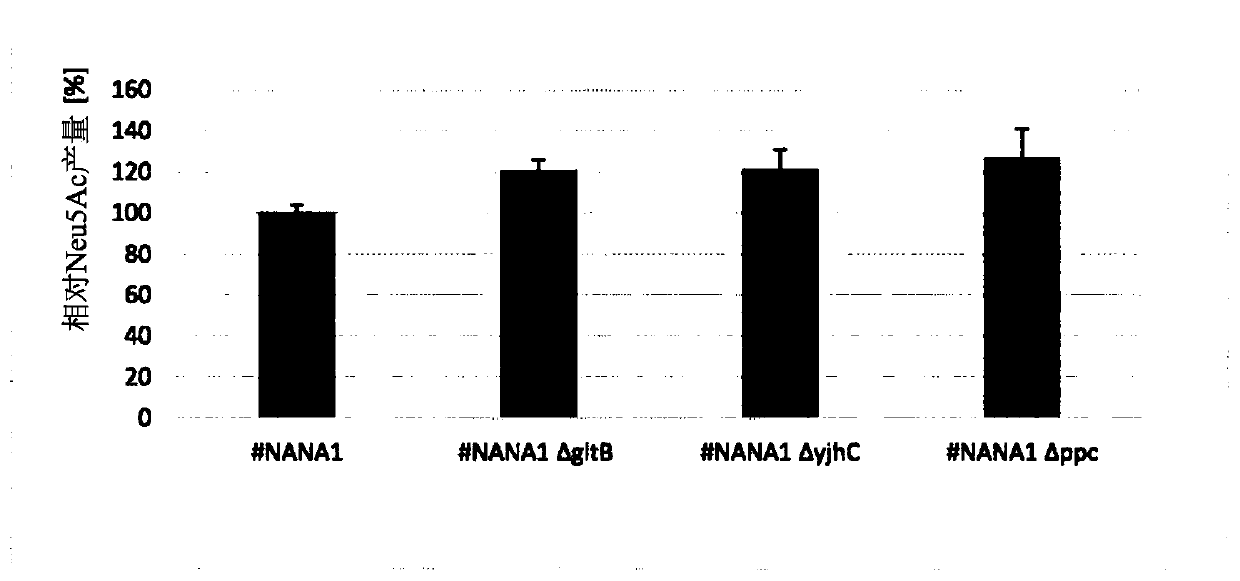
[0216] Example 3: Generation and cultivation of a single gene knockout mutant of E. coli strain #NANA1 exhibiting increased Neu5Ac production capacity
[0217] E. coli BL21(DE3) strain #NANA1 was further modified to generate deletion mutants that removed or disrupted the genes gltB, yjhC and ppC. Strains #NANA1, #NANA1△gltB, #NANA1△yjhC and #NANA1△ppc were grown in 96-well plates. Therefore, a single colony of the strain was transferred from the agar plate to a microtiter plate containing 200 μL of the minimal medium described in Example 2 and incubated at 30° C. for about 20 h with vigorous shaking. Subsequently, 50 μL of the culture solution was transferred to a deep-well 96-well plate (2.0 mL), each well containing 400 μL of minimal medium.
[0218] After further incubation for 48 hours, the culture was stopped, and the content of N-acetylneuraminic acid in the supernatant was determined by mass spectrometry using an LC triple quadrupole MS detection system in multiple rea...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com