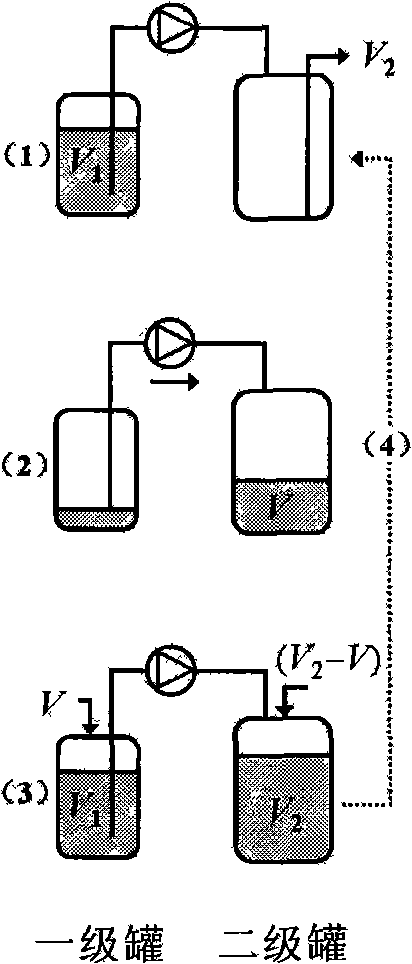
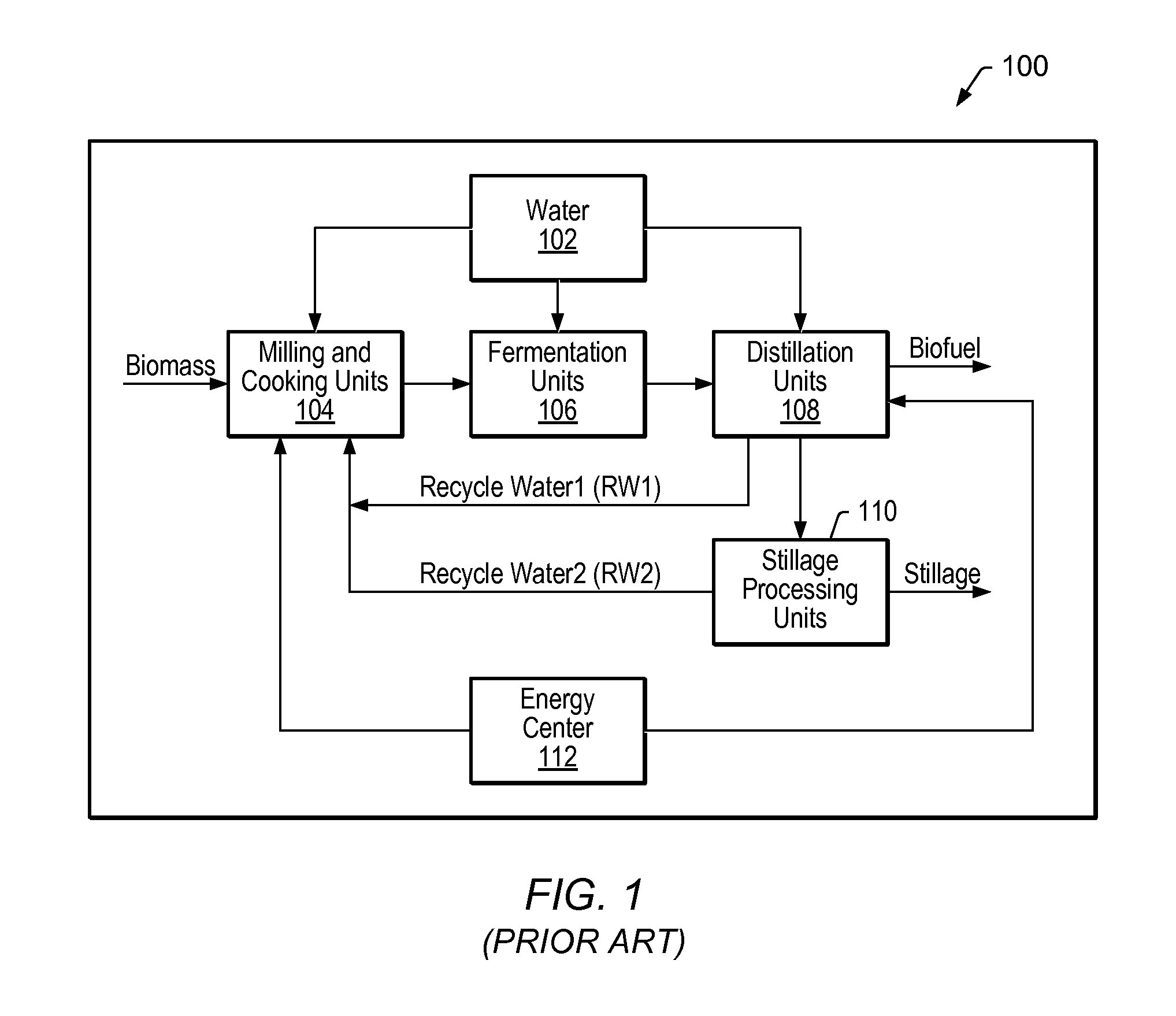
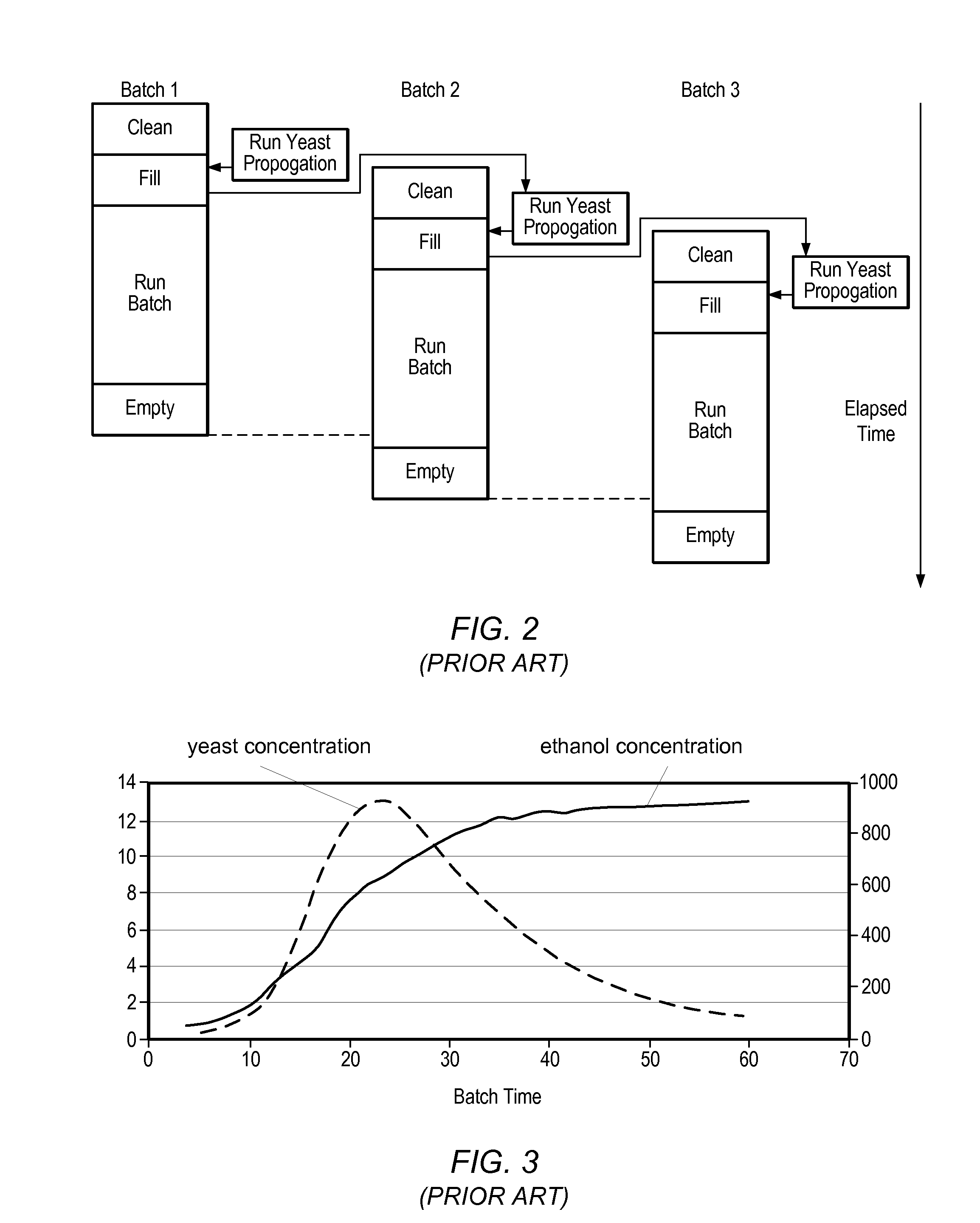
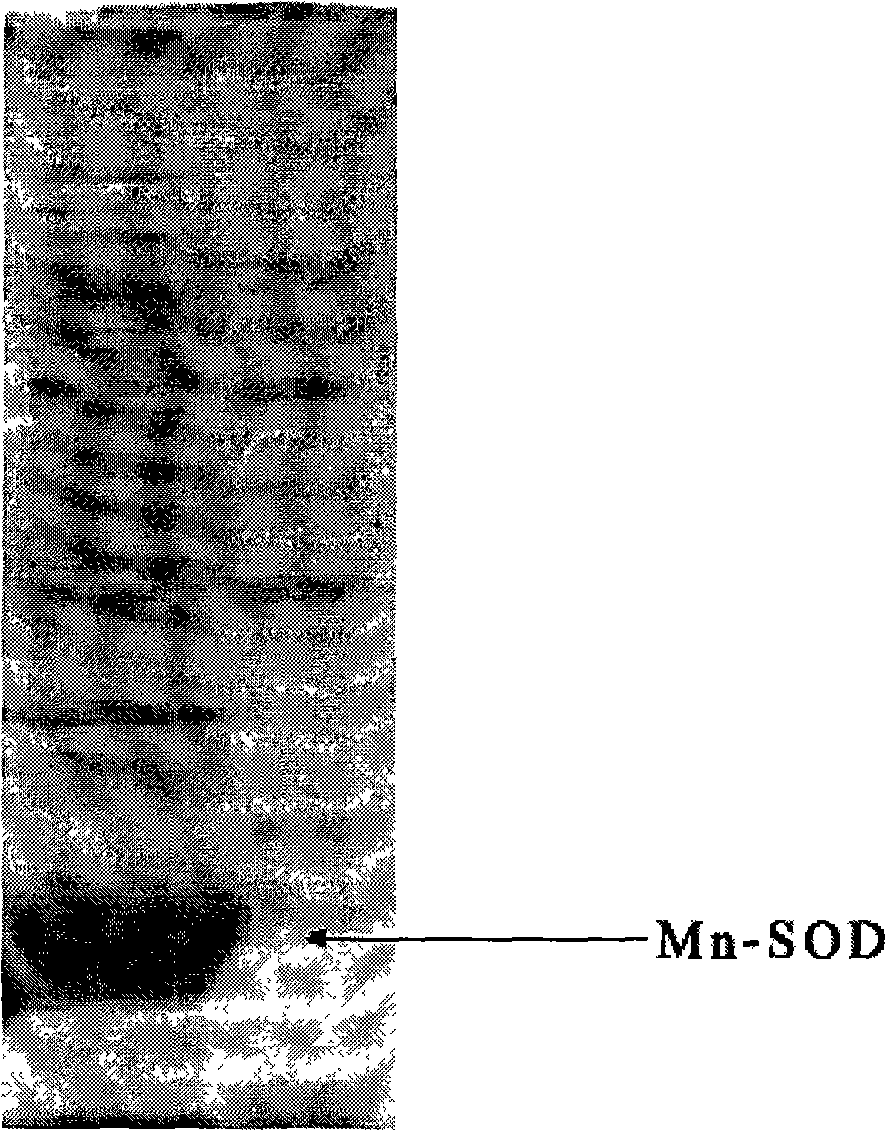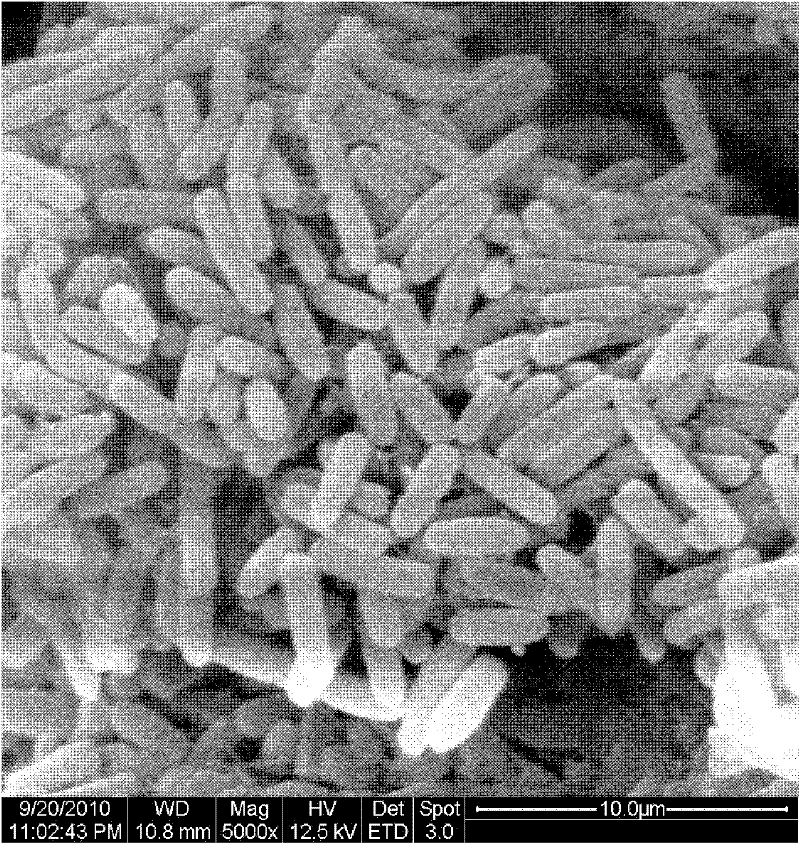Patents
Literature
610 results about "Batch fermentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
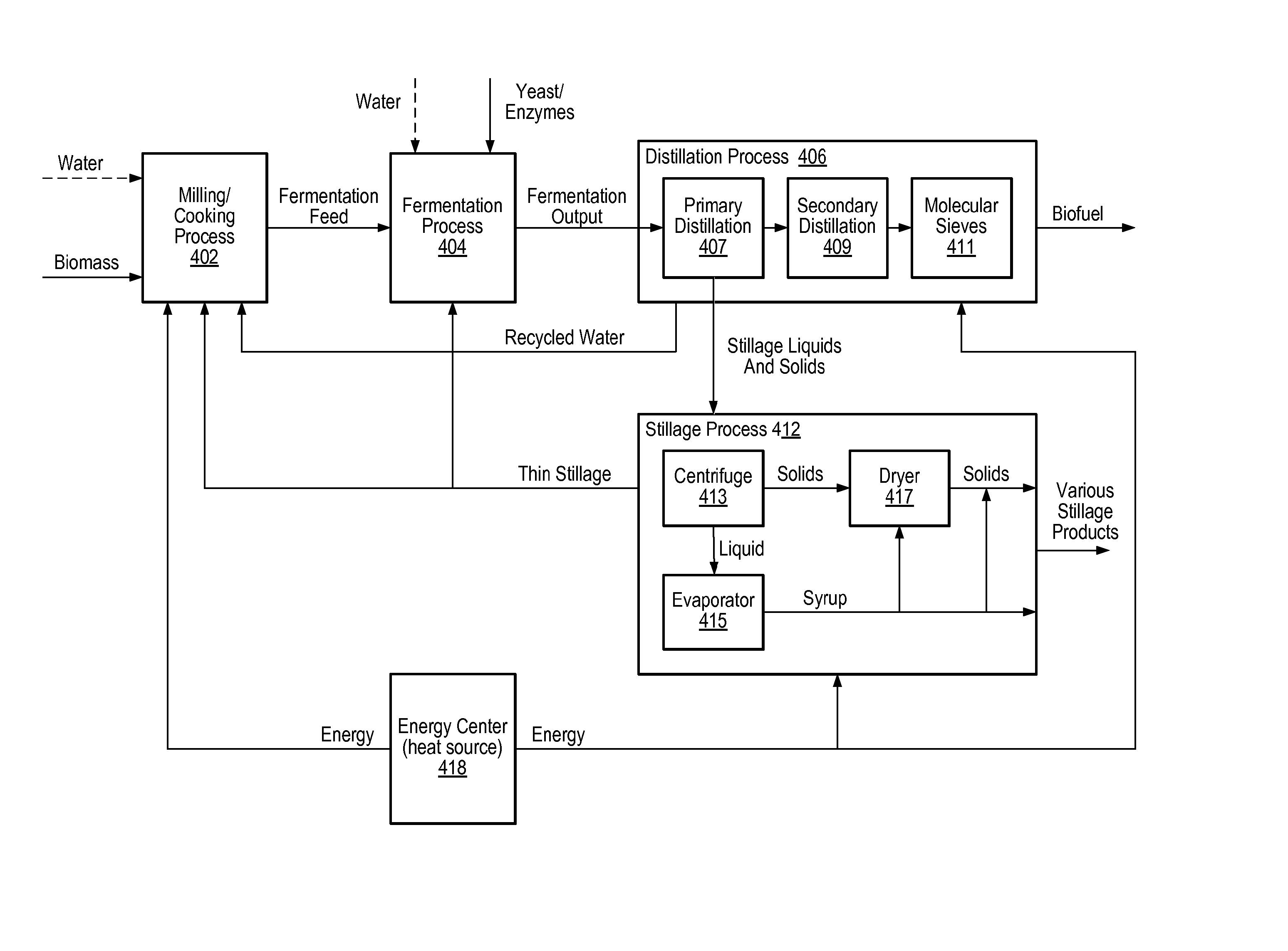
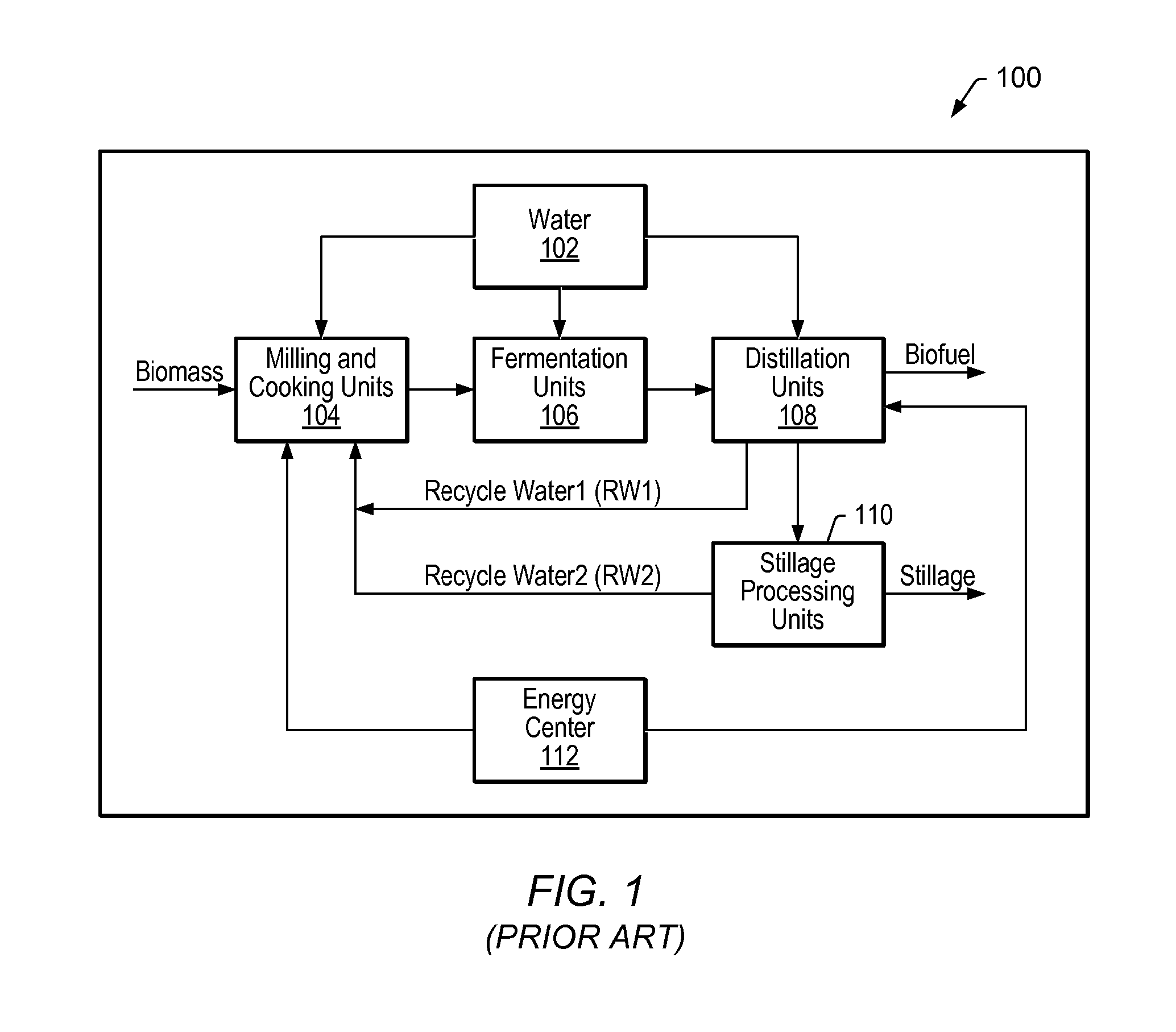
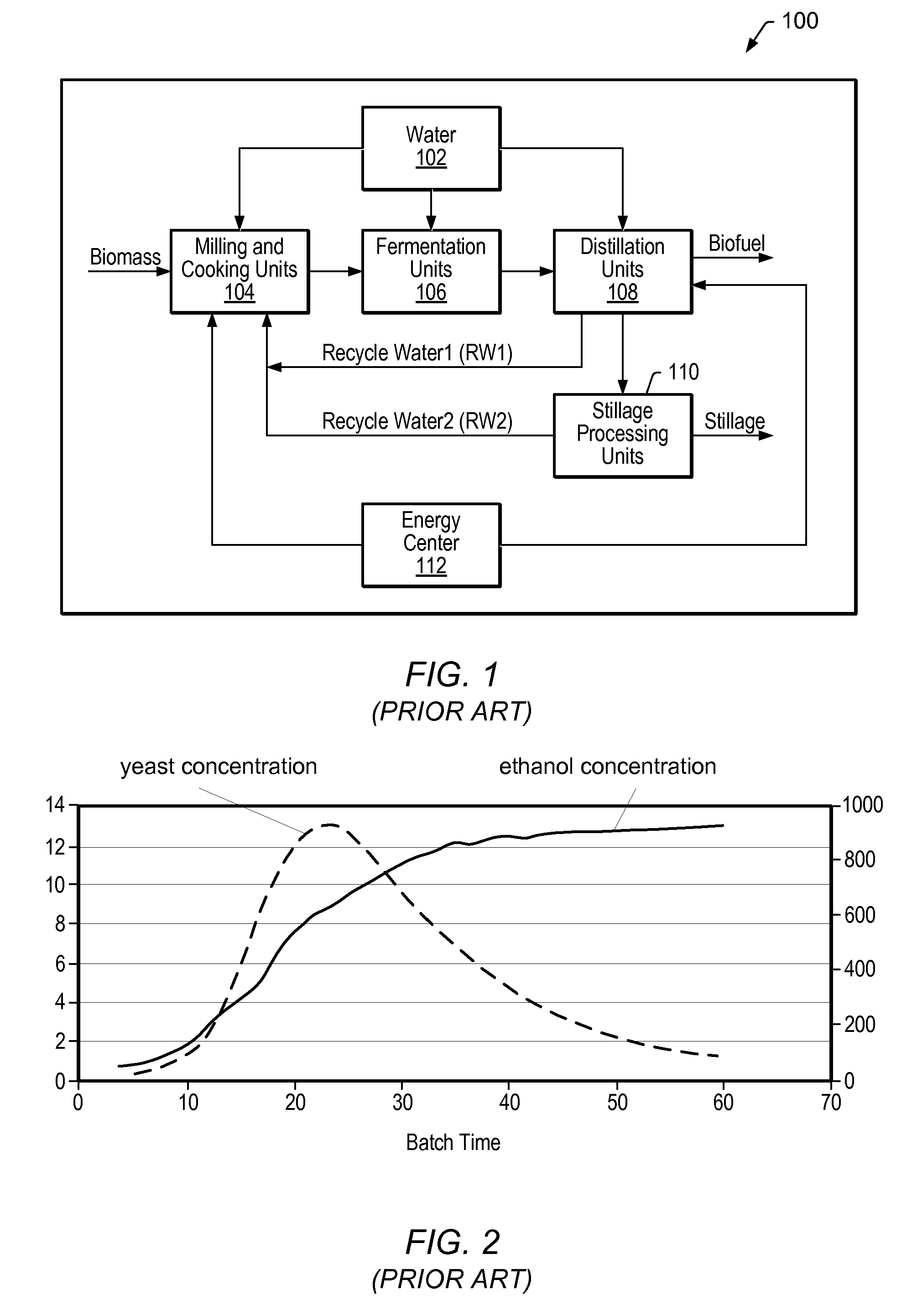
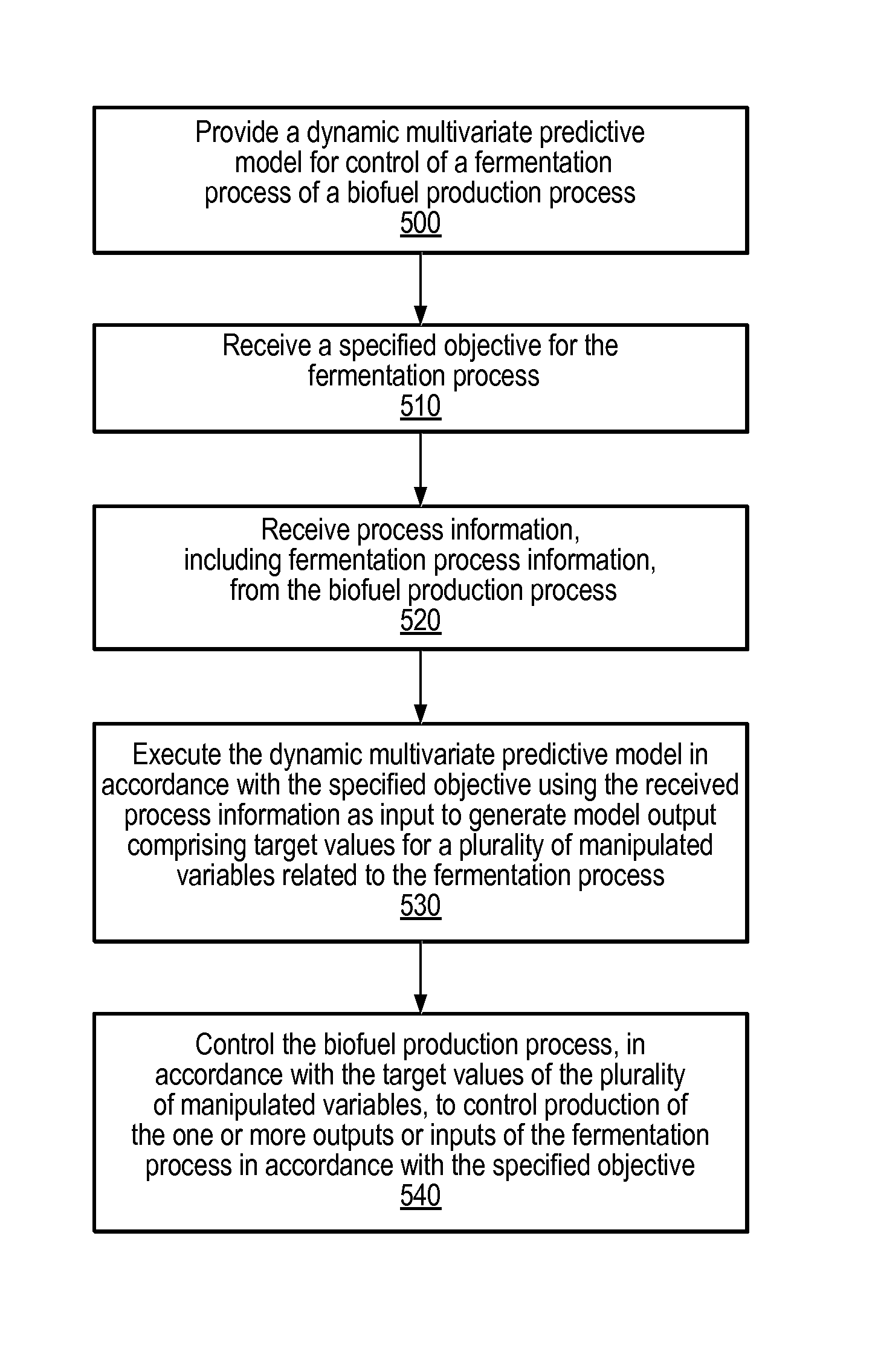
Model predictive control of fermentation in biofuel production
ActiveUS20080109100A1Easy to controlImprovement in biofuel yieldBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperatue controlHorizonBiofuel
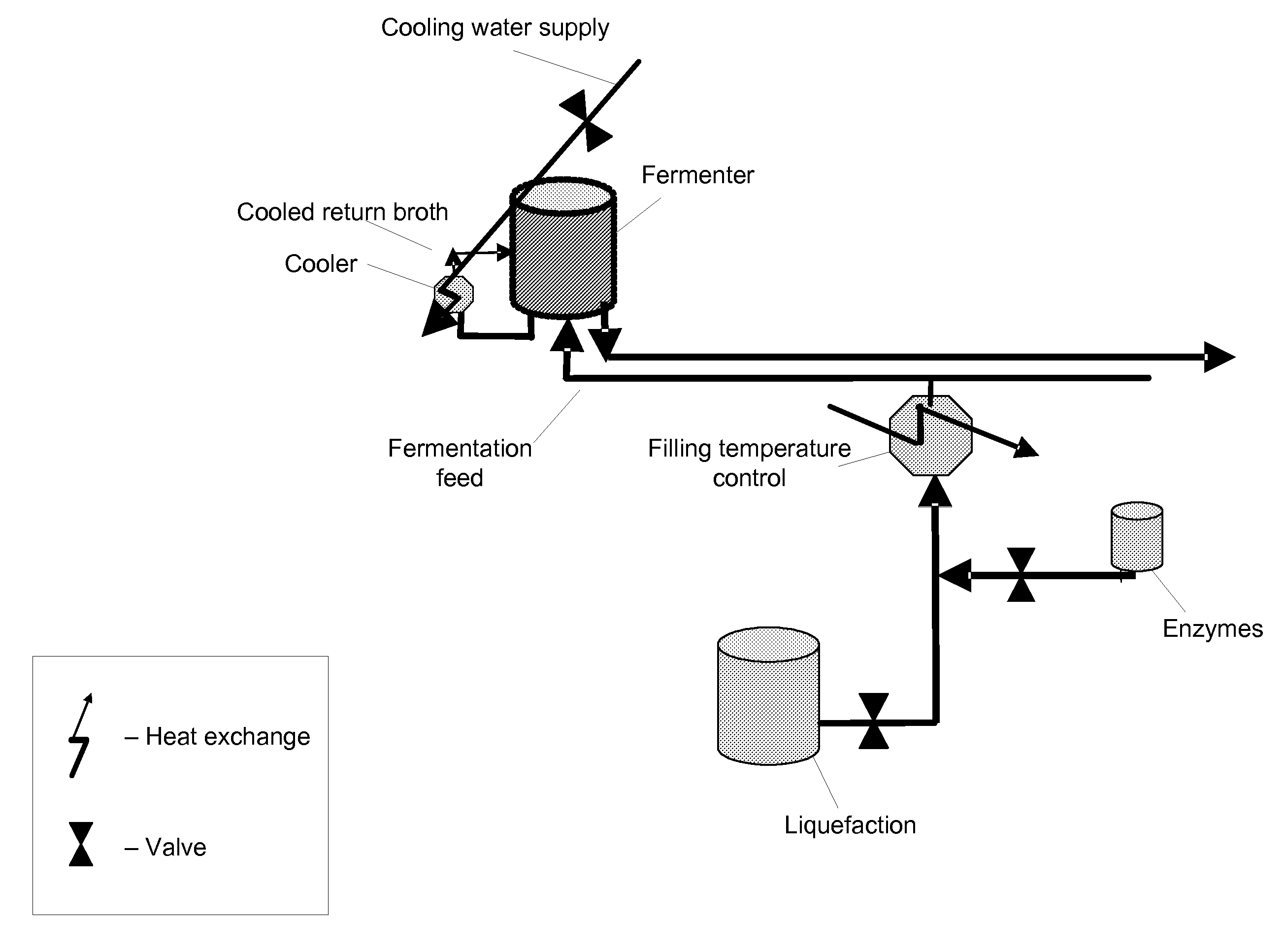
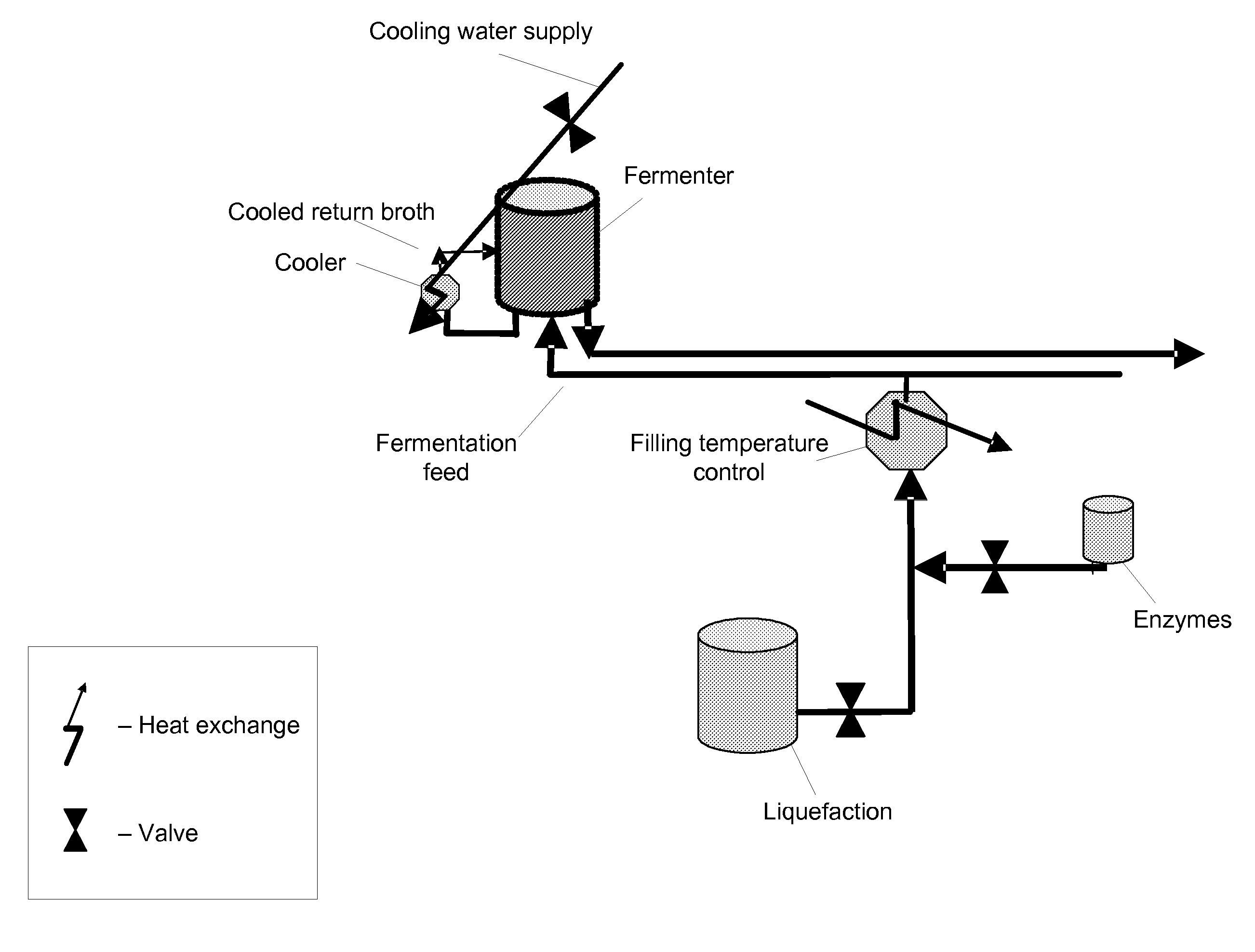
System and method for managing batch fermentation in biofuel production. An optimizer executes a nonlinear multivariate predictive model of a batch fermentation process in accordance with an end of batch objective specifying a target end of batch biofuel concentration to determine an optimal batch trajectory over a temporal control horizon specifying a biofuel and / or sugar concentration trajectory over the batch fermentation process. A nonlinear control model for the batch fermentation process that includes the temporal control horizon driven by biofuel concentration during the batch fermentation process is executed per the determined optimal batch trajectory using received process information as input, thereby generating model output including target values for manipulated variables for the batch fermentation process, including batch fermentation temperature. The batch fermentation process is controlled per the target values to produce biofuel in accordance with the determined optimal batch trajectory, to substantially optimize the end of batch biofuel yield.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of a Biofuel Fermentation Process
ActiveUS20080167852A1Maximizing yeast growthMaximize productionBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperatue controlBiotechnologyLinear control
System and method for managing batch fermentation in a biofuel production process. A nonlinear control model of yeast growth and fermentable sugar concentration for biofuel (e.g., fuel ethanol) production in a batch fermentation process (pure and / or fed-batch fermentation) of a biofuel production process is provided. Process information for the batch fermentation process is received, and the nonlinear control model executed using the process information as input to determine values of one or more fermentation process variables for the batch fermentation process, e.g., fermentation temperature and / or enzyme flow, for substantially maximizing yeast growth and achieving target fermentable sugar concentrations. The batch fermentation process is then controlled in accordance with the determined values for the one or more fermentation process variables to substantially maximize yeast growth and achieve target fermentable sugar concentrations, where substantially maximizing yeast growth and achieving target fermentable sugar concentrations substantially maximizes biofuel production in the batch fermentation process.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Method of making alcohol concentrate
ActiveUS20100047386A1Efficient extractionBeer fermentationWine preparationContinuous fermentationAlcohol
One embodiment of the present invention is method for making an alcohol concentrate using a nested batch fermentation process, wherein multiple rounds of wort fermentation, distillation and refortification, is described. The rounds are repeated until the desired concentration of fermented wort is obtained. Another embodiment of the present invention is a method for a continuous fermentation process, wherein portions of the fermentation are distilled and the remaining wort is returned to the active fermentation. This process is repeated until the desired concentration of the fermented wort is obtained. Yet another embodiment of the present invention is a method for extraction of hops compounds, wherein the distilled alcohol from the nested or continuous fermentation process is used.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE BEVERAGE TECH INC
Model predictive control of fermentation temperature in biofuel production
InactiveUS20080108048A1Easy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiofuelBatch fermentation
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Model predictive control of fermentation temperature in biofuel production
InactiveUS7831318B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiofuelBatch fermentation
A system and method are provided for controlling temperature of a batch fermenter in a biofuel production process. A nonlinear predictive integrating temperature model for a batch fermentation process is provided that is a function of fermenter level. An objective for the batch fermentation process specifying a target fermenter temperature for the batch fermentation process is received, as is process information for the batch fermentation process, including fermenter level and fermenter temperature. The nonlinear predictive integrating temperature model is executed in accordance with the objective using the process information as input to determine target values for manipulated variables for controlling fermenter temperature of the batch fermentation process. The fermenter temperature for the batch fermentation process is controlled in accordance with the target values to produce biofuel in accordance with the objective, to substantially optimize the end of batch biofuel yield.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Yarrowia lipolytica strain and method thereof for synthesizing erythritol
ActiveCN103374534AHigh ability to synthesize erythritolImprove conversion rateFungiMicroorganism based processesContinuous fermentationInorganic salts
The invention discloses a yarrowia lipolytica strain and a method thereof for synthesizing erythritol. The yarrowia lipolytica strain is yarrowia lipolytica BLC13 CGMCC NO. 7326. The method for synthesizing the erythritol by the yarrowia lipolytica strain comprises the following steps of: taking a carbon source with an initial fermentation concentration of 100-400g / L, a nitrogen source with an initial fermentation concentration of 2-35g / L and inorganic salt as raw materials, treating for 30 minutes at 80-90 DEG C, cooling down and subsequently inoculating the yarrowia lipolytica strain, carrying out continuous fermentation or in-batch fed-batch fermentation under an aerobic condition, and after the fermentation is accomplished, purifying the erythritol from a fermentation liquid. The yarrowia lipolytica strain disclosed by the invention is used for synthesizing the erythritol from glucose, the conversion rate is high, and the Chinese erythritol standard is met.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
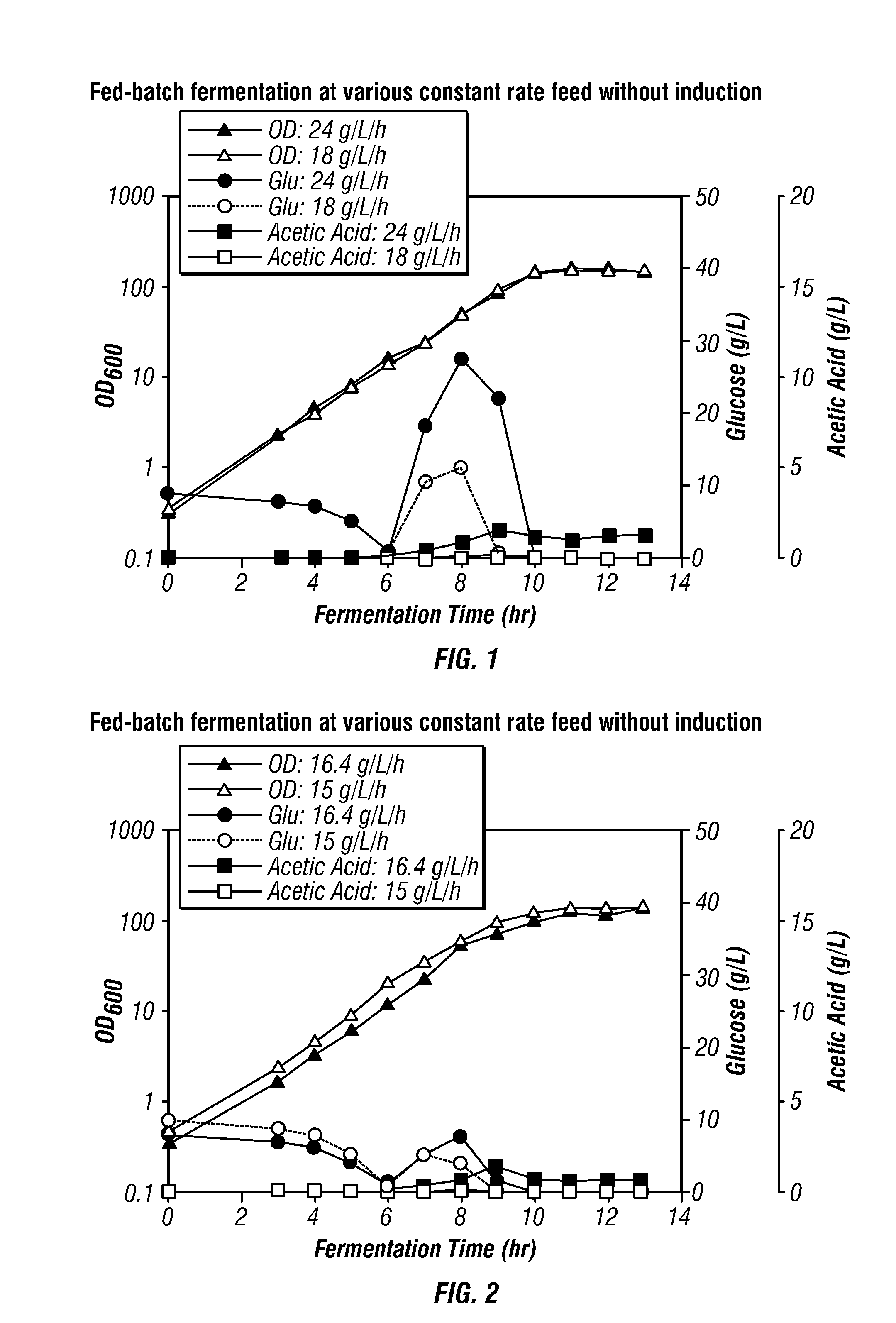
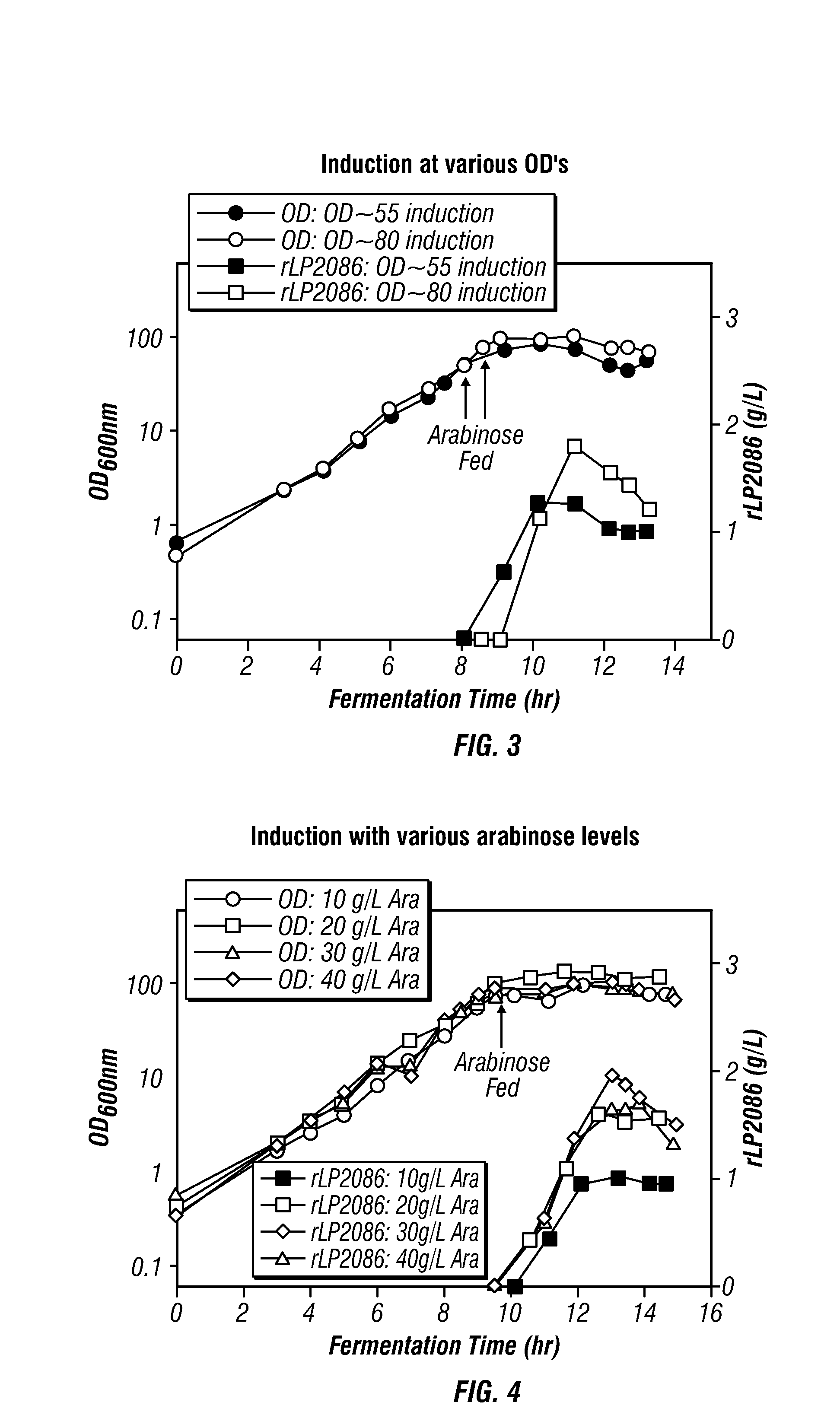
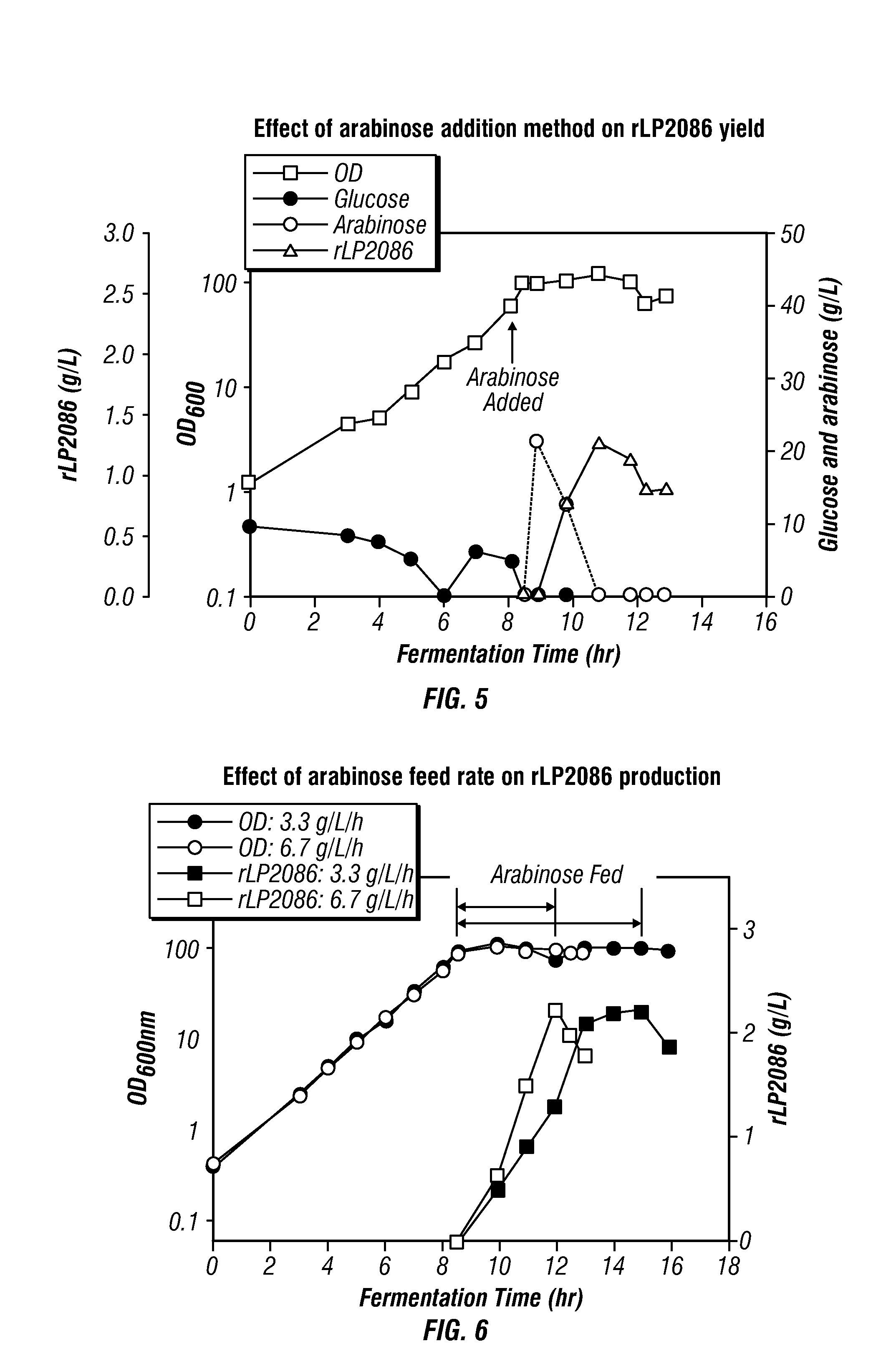
High-cell density fed-batch fermentation process for producing recombinant protein
Methods for producing proteins, for example, recombinant meningococcal 2086 proteins, using fed-batch fermentation with continuous input of an inducer after achieving a threshold parameter, and optionally continuous input of a carbon source, for example, a constant rate input, to improve protein yields, as well as high density protein compositions and compositions for use in the methods of the present invention, are provided.
Owner:WYETH LLC
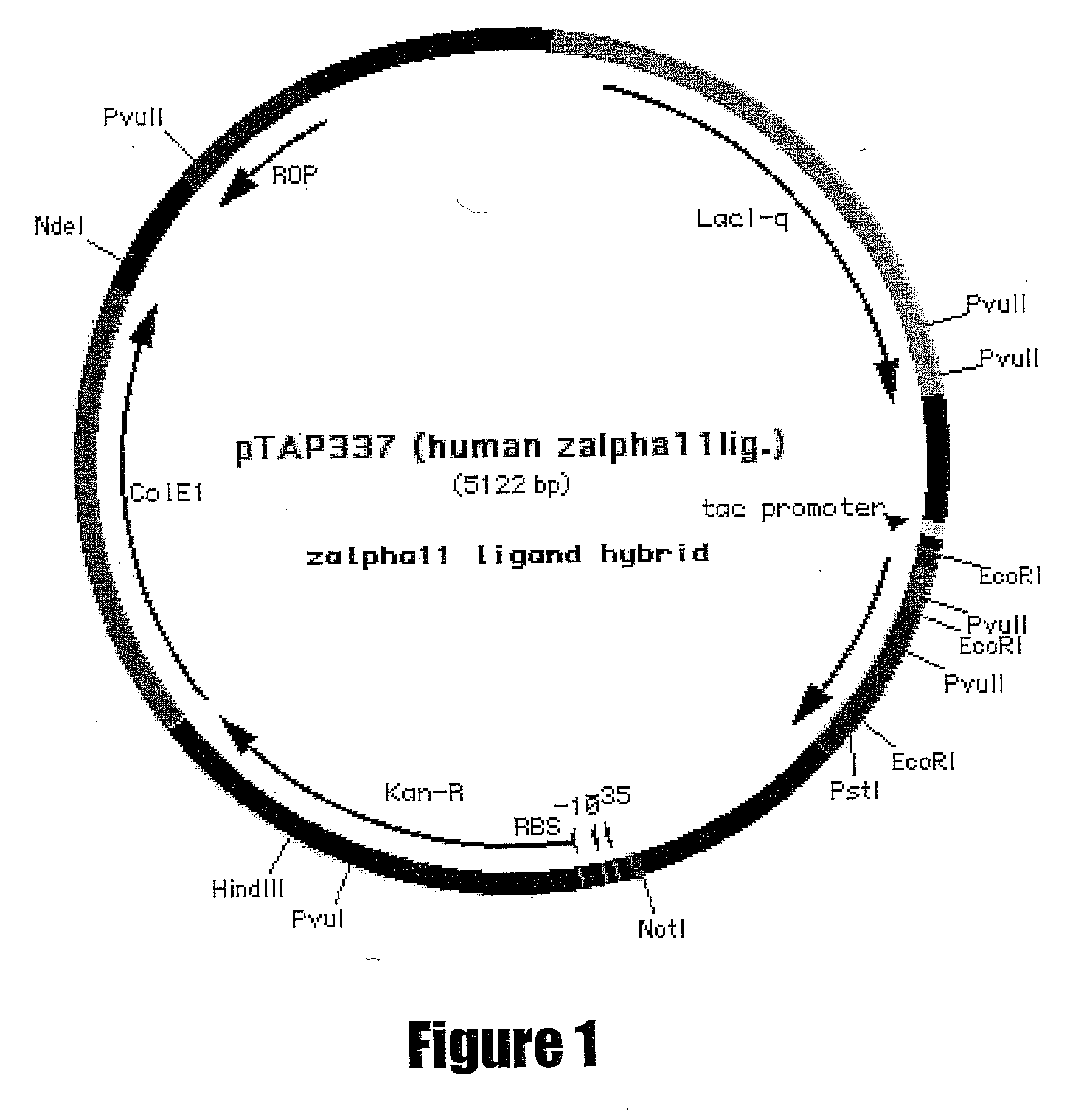
IL-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-21 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
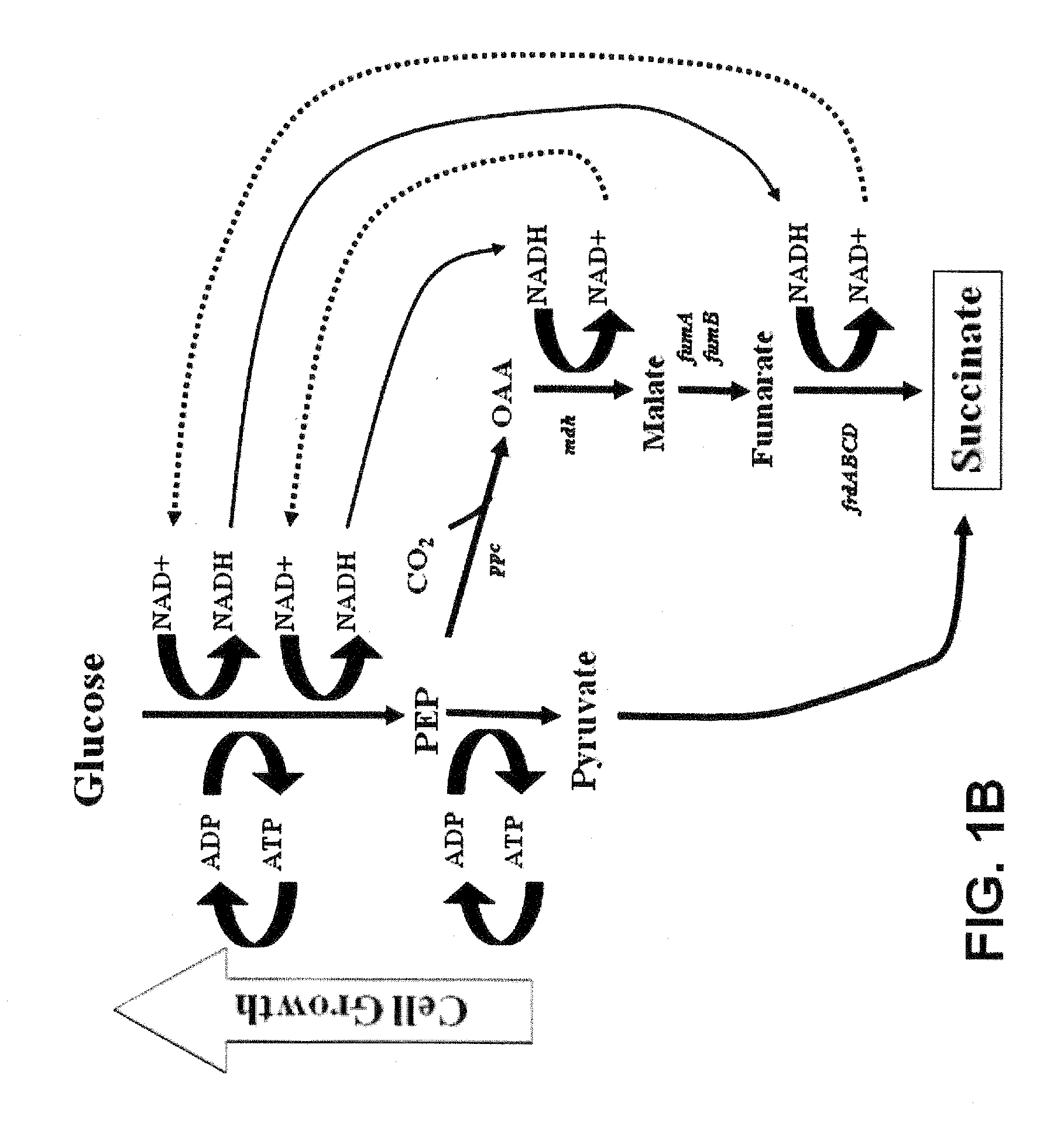
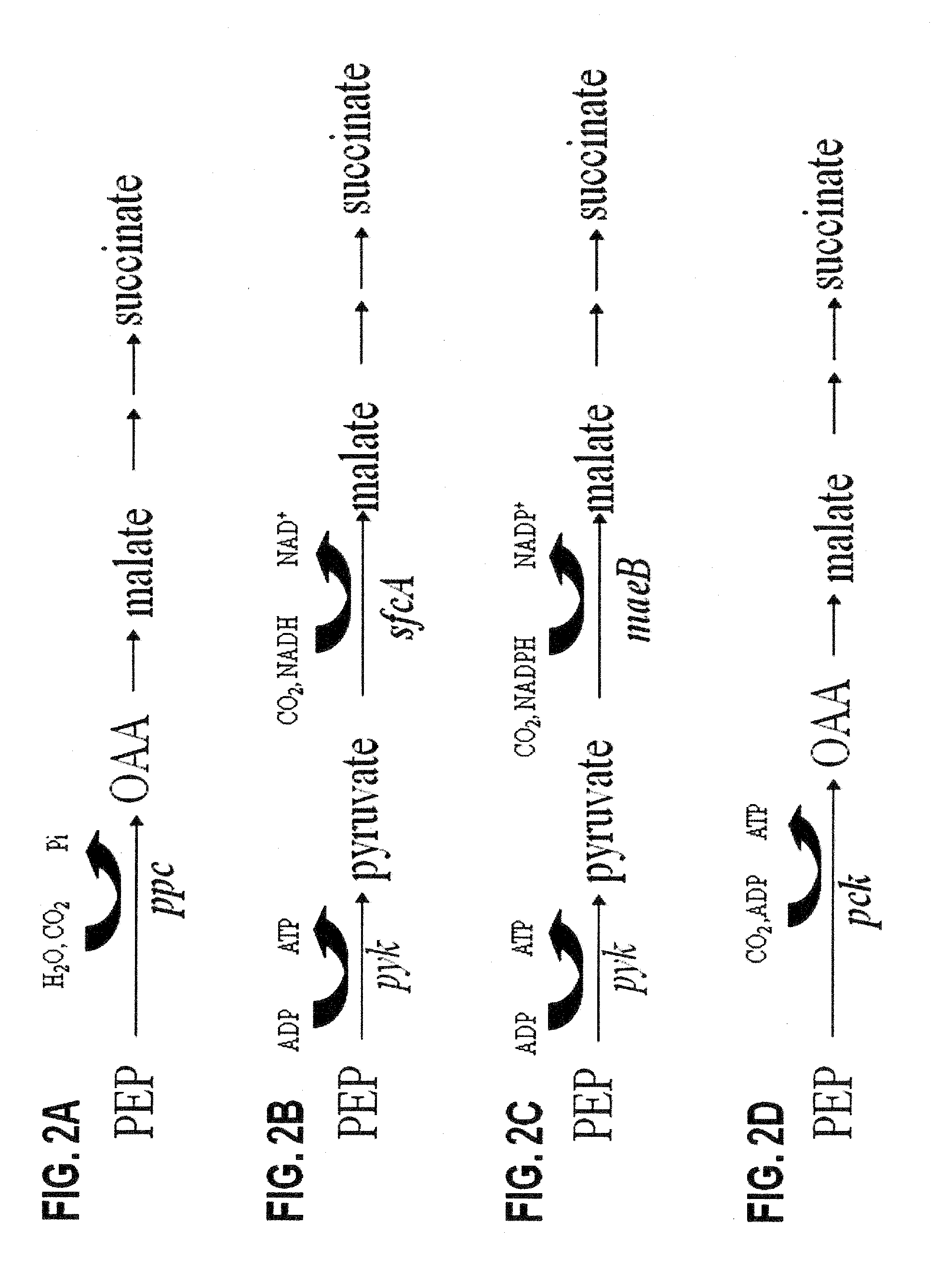
Engineering the pathway for succinate production
InactiveUS20120058530A1Increase overall carbon flowHigh expressionVectorsBacteriaMannheimiaPh control
This invention relates to the biocatalysts for the efficient production of succinic acid and / or other products from renewable biological feedstocks. The biocatalysts have a very high efficiency for the growth-coupled production of succinic acid and / or other products from carbohydrate feed stocks as a result of both genetic manipulations and metabolic evolution. More specifically, certain biocatalysts of the present invention produce succinic acid at high titers and yield in mineral salts media during simple pH-controlled, batch fermentation without the addition of any exogenous genetic material. The genetic manipulations of the present invention are concerned with the energy-conserving strategies coupled with the elimination of alternative routes for NADH oxidation other than the routes for succinic acid production. The biocatalysts contain glucose-repressed gluconeogenic phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (pck) depressed by genetic modifications and a genetically-inactivated phosphotransferase system. In terms of succinic acid production efficiency, the biocatalysts of the present invention are functionally equivalent to succinate producing rumen bacteria such as Actinobacillus succinogens and Mannheimia succiniproducens with one difference that the biocatalysts are able to achieve this high level of succinic acid production in a minimal salt medium with carbohydrate source as opposed to the requirement for a rich media for succinic acid production by rumen bacteria.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
FQ15 enterococcus faecalis and method for producing somatotrophic feed additive with the bacteria
The invention discloses an FQ15 enterococcus faecalis and a method of a feed additive which uses the bacteria production for promoting the growth: an MRS culture medium is taken as a seed culture medium, and the FQ15 enterococcus faecalis is cultured under the aerobic or facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C for 4 to 24 hours, so as to become a grade one seed; the grade one seed liquid is inoculated in a seed tank for amplification culture, the MRS culture medium is adopted as the seed culture medium, and the culture is carried out for 4 to 24 hours under the aerobic or the facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C to become a grade two seed; the grade two seed liquid is inoculated in a fermentation tank for fermentation culture, an improved MRS culture medium is adopted as the fermentation culture medium, and the culture is carried out for 8 to 36 hours by using timing or continuous fed-batch fermentation mode under the aerobic or the facultative condition at 30 to 45 DEG C; the obtained fermentation liquid is sub-packaged or the fermentation liquid which is obtained by step c is separated, 1 to 25 percent drying protector is added in the bacterial sludge, and the granulation at 20 - 80 DEG C, freeze-drying or spray drying are adopted. The invention has the advantages that the invention can substitute the feed antibiotics and improve the high efficient weight increase of livestock and poultry; the production process is simple; the cost is low, etc.
Owner:DALIAN SANYI ANIMAL MEDICINE CO LTD +2
Il-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-2 1 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
High-density fermentation and purification process for recombination high temperature-resistant hyperoxide dismutase
InactiveCN101275144AAvoid pollutionSimple purification processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDismutase
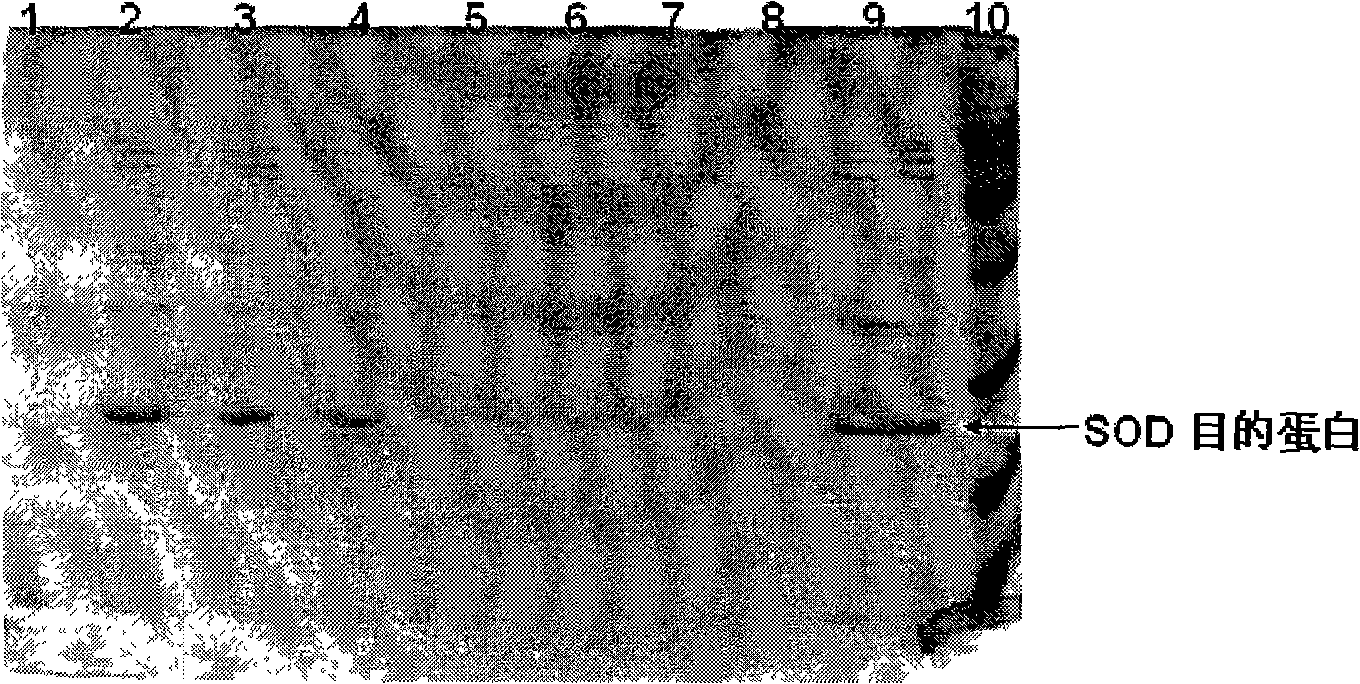
The present invention provides a high density fermentation and a purification process of a recombination high temperature resistance superoxide dismutase, the construction method of the invention includes: using gene coded for SOD in a thermophilic bacteria as a template, designing specific primer amplification target gene having restriction enzyme sites, after double digestion, connecting to plasmid vector pET28a after the same double digestion, constructing a recombinant plasmid, named for pSOD, transforming plasmid pSOD to competence escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by chemical transformation method, obtaining strain having high SOD yield after screening, completing the construction of SOD engineering bacteria; the fermentation process includes four steps of first order seed culture, secondary order feed culture, batch fermentation and induced expression, fermentation product SOD is finally obtained; the fermentation process realizes high level expression of SOD, the expression of the target protein is more than 60% of the bacterial protein total; SOD has excellent thermal stability and heat resistance, the expression product accounts for more than 60% of the whole proteins, and fully soluble protein, avoiding any trouble in the course of inclusion body renaturation; the purification process is simple, having high yield, lower cost, the final product SOD has high purification, high activity and strength stability.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF TSINGHUA UNIV ZHEJIANG +1
Fed-batch fermentation preparation of lysine
ActiveCN102234666AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyCulture fluid
The invention provides a method for fed-batch fermentation of L-lysine, which comprises the following steps of: introducing engineering bacteria for expressing pyridine nucleotide transhydrogenase variants into a first fermentation tank for culturing, and inoculating the obtained culture solution to a second fermentation tank for culturing; then, continuously feeding sugar in batches to the second fermentation tank; and then, continuously feeding sugar and nitrogen sources in batches to the second fermentation tank.
Owner:NINGXIA EPPEN BIOTECH +1
Il-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-21 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
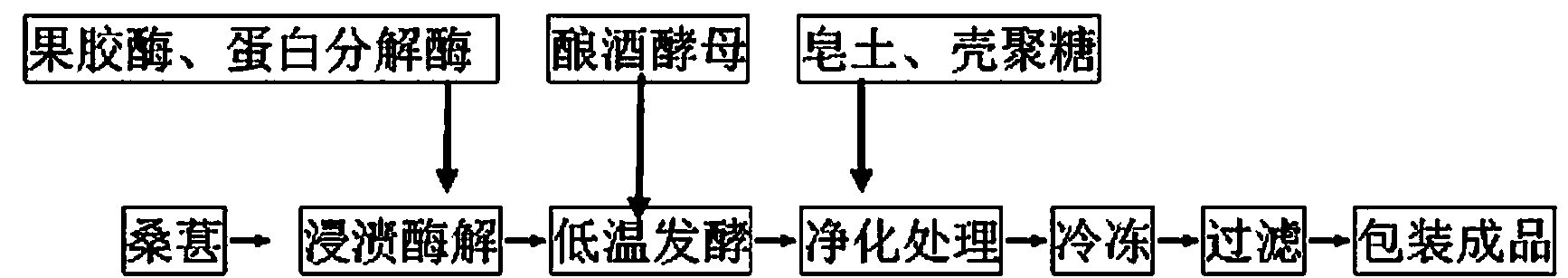
Production method for completely-fermented mulberry wine and product
InactiveCN103642635AComposite enzymatic hydrolysis effect is goodGood enzymatic effectMicroorganism based processesAlcoholic beverage preparationPectinaseFlavor
The invention discloses a production method for completely-fermented mulberry wine and a product. The method comprises the following steps of performing composite enzymatic hydrolysis on a raw material mulberry flesh by using pectinase and proteinase, performing primary fermentation for 16 to 25 days and performing after fermentation for 12 to 22 days at 15 to 21 DEG C by using 165 to 215mg / L alcohol-fermentation dry yeasts until the alcohol strength is finally 11.5 percent Vol, clarifying a product by taking a 420 to 650g / L bentonite solution and a 200 to 320g / L chitosan solution as clarifying agents, performing aging for 3 months at 18 DEG C, performing freezing treatment for 5 days at -5.8 to -6.2 DEG C, performing preliminary filtering, and performing filtering disinfection twice by using a sheet filter and a membrane filter. According to the production method, good composite enzymatic hydrolysis and low-temperature batch fermentation effects are achieved, the stability of the wine is further improved by composite fining, and the stability and flavor of the wine are improved by low-temperature freezing. The production method is applied to the production of the completely-fermented mulberry wine.
Owner:YUNFU HUANAN LIQUOR
Il-21 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-21 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-21 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the IL-21 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains transformed with an IL-21 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
FGF18 production in prokaryotic hosts
The expression vectors and methods using an E. coli expression system for the large scale production of FGF18 are described. The vectors utilize the FGF18 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Using the expression vectors, the FGF18 gene was produced in E. coli to a level of greater than 1 g / L in fed batch fermentation. Also included are OmpT deficient E. coli strains, as well as OmpT and fhuA negative strains transformed with an FGF18 expression vector.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Antimicrobial compound and preparation method and application thereof
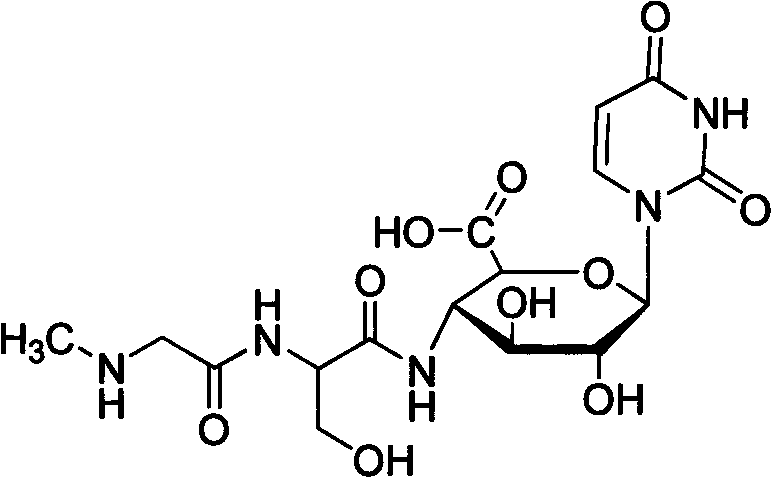
InactiveCN101967182AIncrease synthesis rateIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsBiocideDipeptideD-Glucopyranose
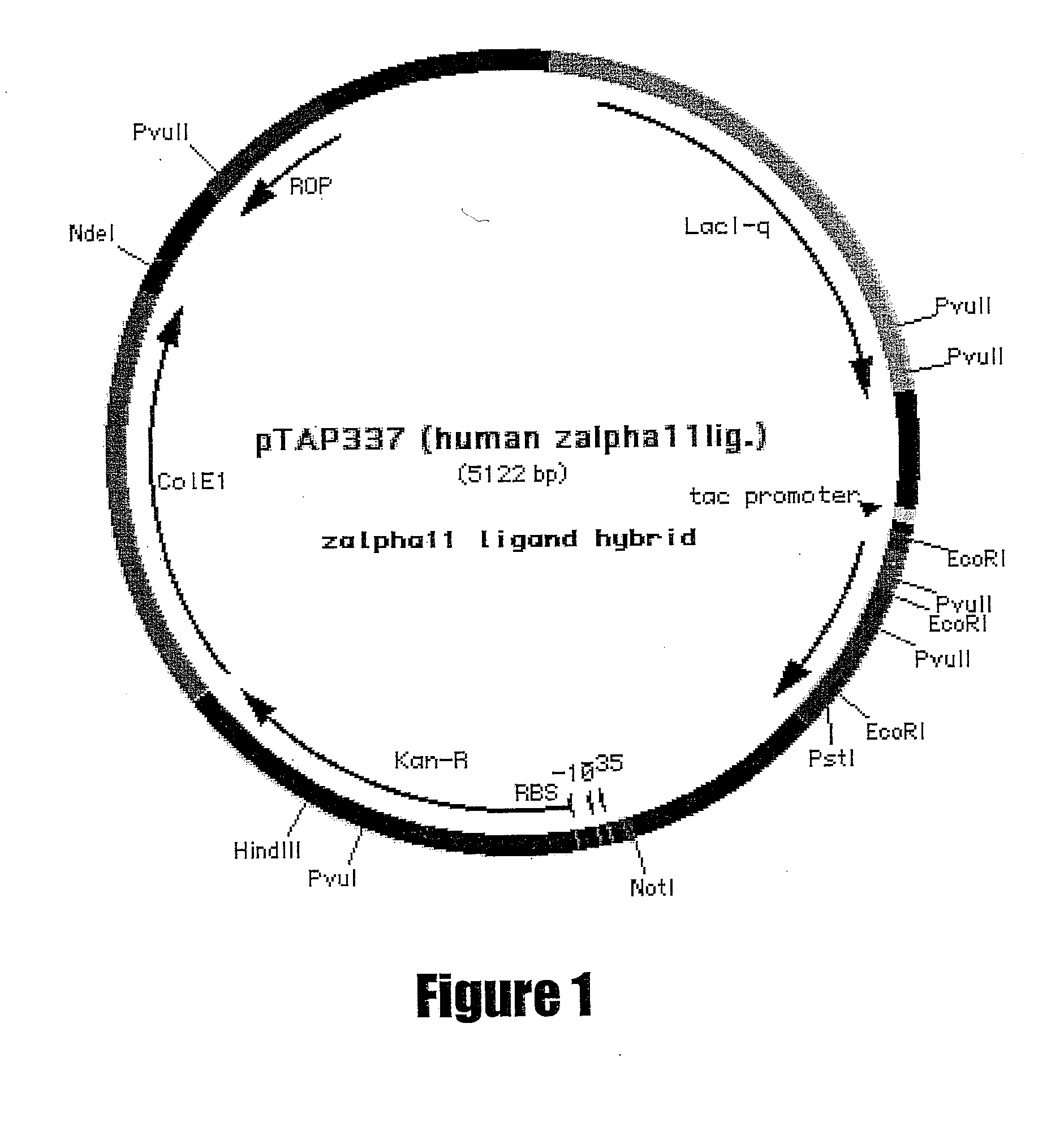
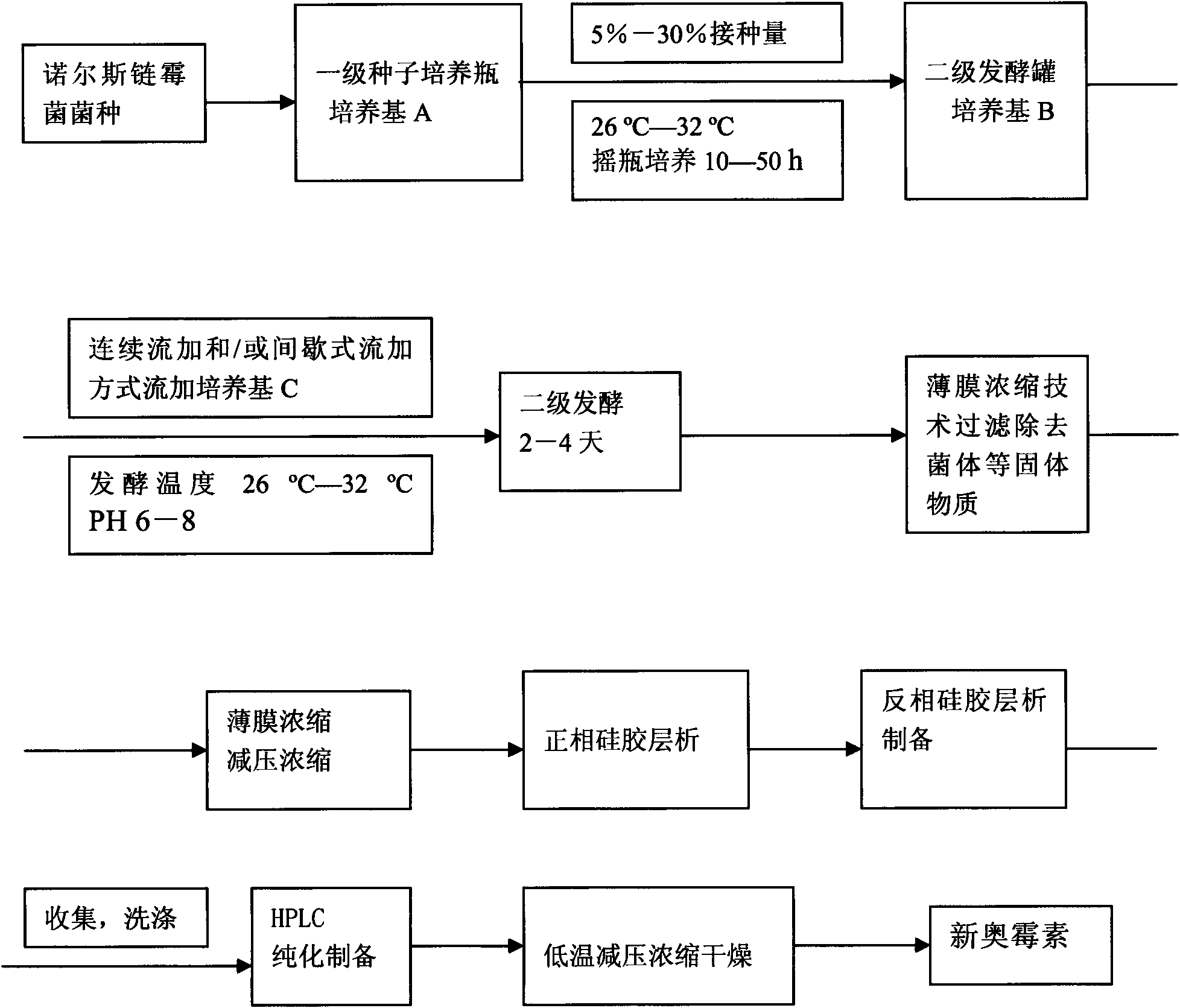
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes, and in particular relates to an antimicrobial compound and a fermenting preparation method and application thereof. The molecular weight of the antimicrobial compound of the invention is 445, the molecular formula of the antimicrobial compound is C16H23N5O10, the chemical name of the antimicrobial compound is 1-uracil-4-sarkosyl-serylamido-1,4-dideoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl acid, and the antimicrobial compound belongs to uracil hexose dipeptide and is named xin'aomycin. The preparation method adopts actinomycetes Streptomyces noursei and genetically improved strains thereof, and comprises the following steps: culturing in a primary liquid culture medium as a seed liquid; inoculating the cultured seed liquid to a secondary liquid culture medium B for culturing, and carrying out fed-batch fermentation culture of fed-batch liquid C; and after fermentation is finished, separating and purifying the structural compound from the fermentation culture liquid. The antimicrobial compound is used for manufacturing pesticide or medicine products. The invention has the characteristics of high yield, simple process and easy industrialization.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Bacillus licheniformis and applications thereof
InactiveCN102367431AImprove performanceShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisMicroorganism
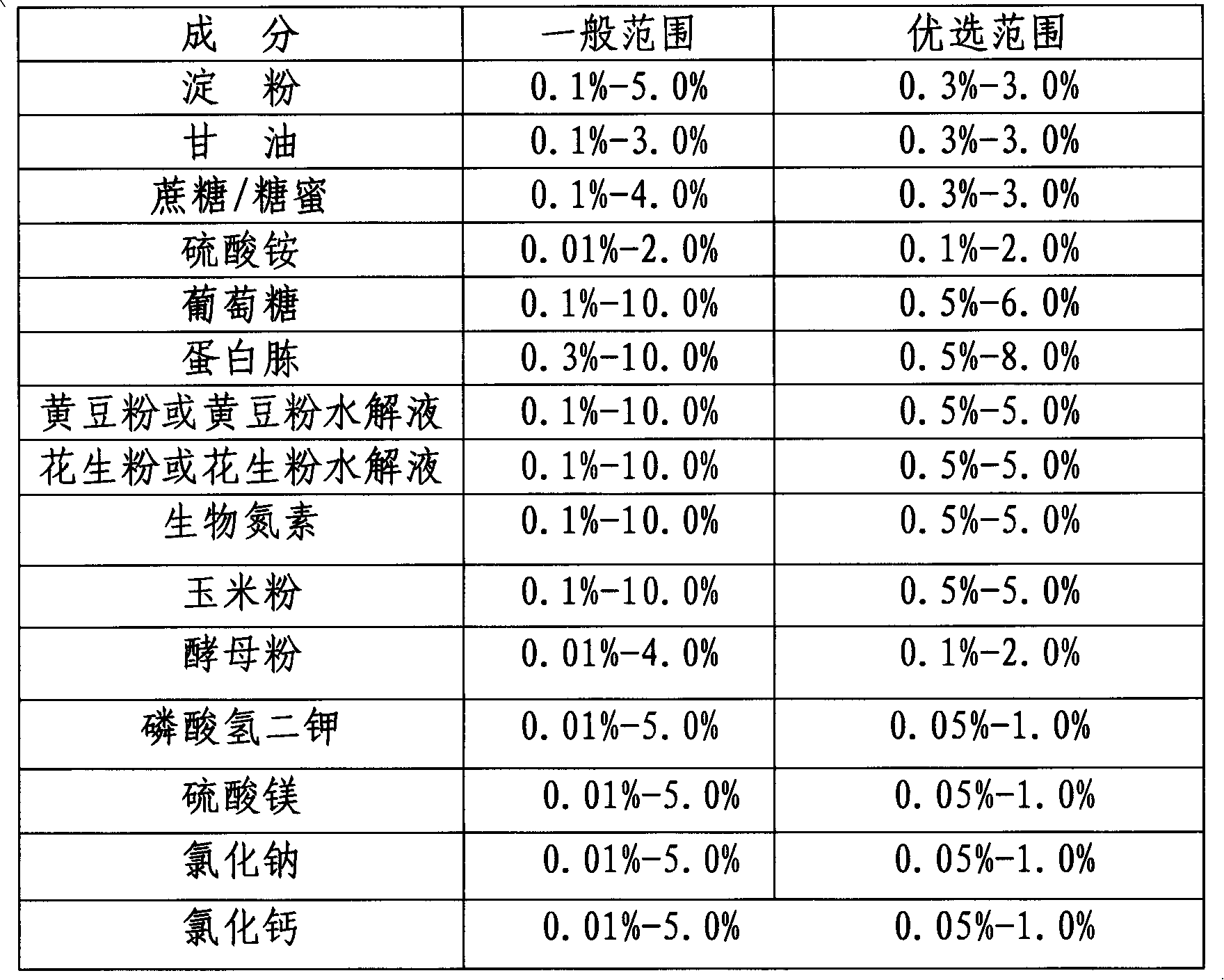
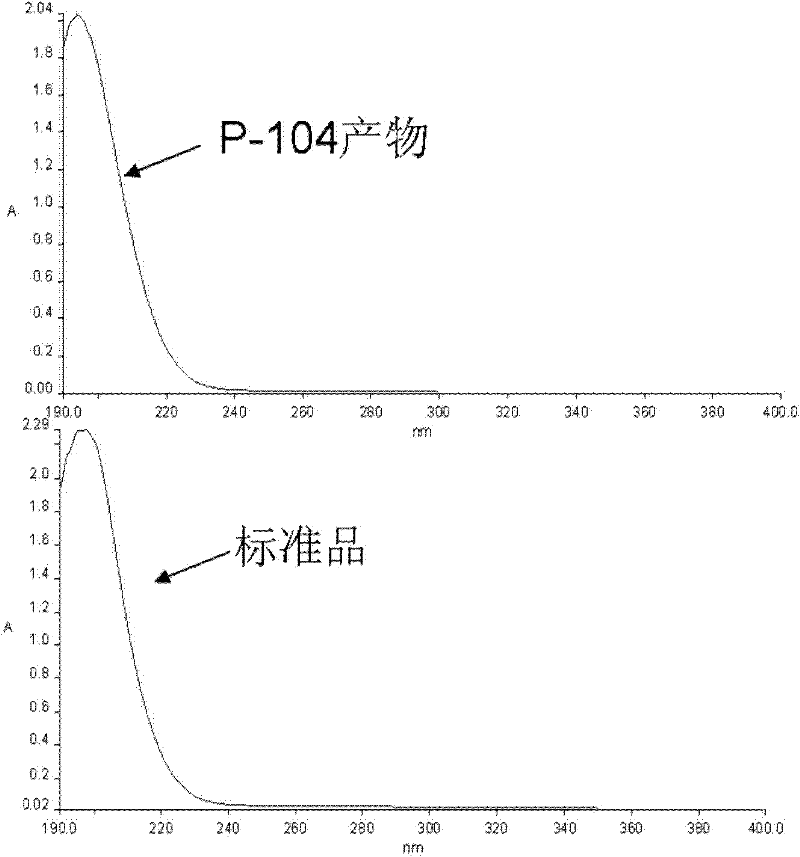
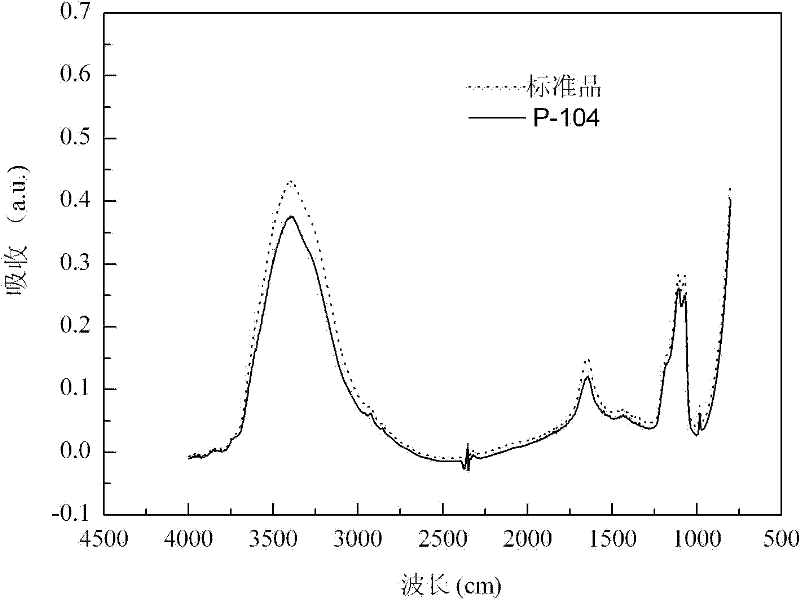
The invention relates to Bacillus licheniformis P-104 for gamma-PGA (gamma-polyglutamic acid) fermentation production and applications thereof. The Bacillus licheniformis P-104 is conserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on September 14, 2010 with the conservation number of CGMCC NO.4156. The Bacillus licheniformis P-104 is obtained by screening and separating the Chinese traditional fermented bean paste product, and has the advantages of short production period, high production efficiency and low production cost. By using the strain and fermentation method thereof provided by the invention, the output of a 7 L fermentation tank of gamma-PGA can reach 32 g / L, and the fed-batch fermentation yield reaches 41.6 g / L.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing bacterial strain of Pediococcus acidilactici, and bacterin of Pediococcus acidilactici
InactiveCN101050437AIncrease growth rateIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationSynechococcusCoccidia
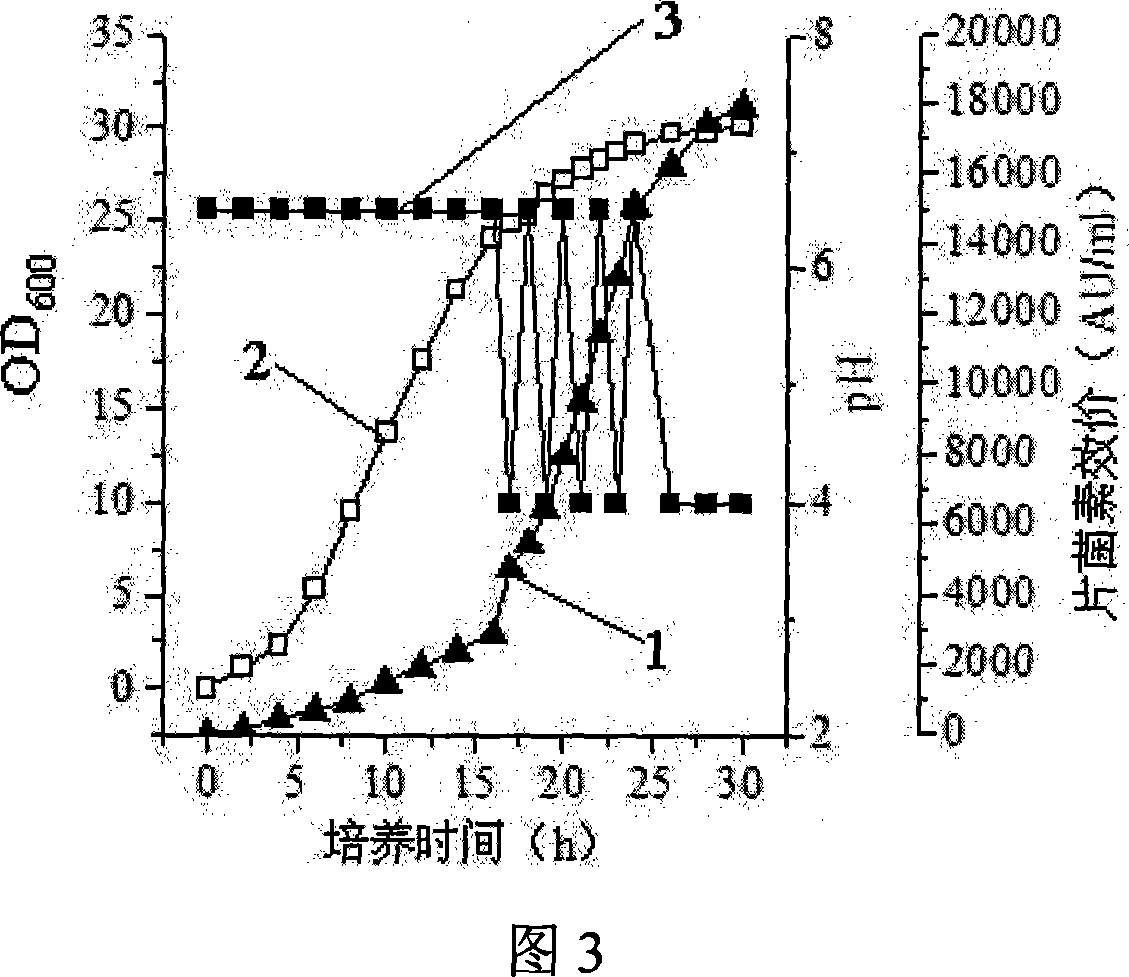
This invention discloses Pediococcus acidilactici LH31 (CCTCC M207013), and a method for producing pediocin from it. The method comprises: inoculating Pediococcus acidilactici LH31 in modified MRS liquid medium, culturing, activating, inoculating activated Pediococcus acidilactici LH31 in a fermentation tank, and performing feed-batch fermentation with three stages. Pediococcus acidilactici LH31 is proliferated in stages 1 and 2. The maximal bacterial density (OD600 nm) can reach 30. Pediocin is accumulated in stages 2 and 3. The maximal titer can reach 18000 AU / mL. The method is suitable for industrialization.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing amber acid by continuous fermentation or semi-continuous fermentation
InactiveCN101302546AIncrease production intensityLess investmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBatch fermentationSweet sorghum
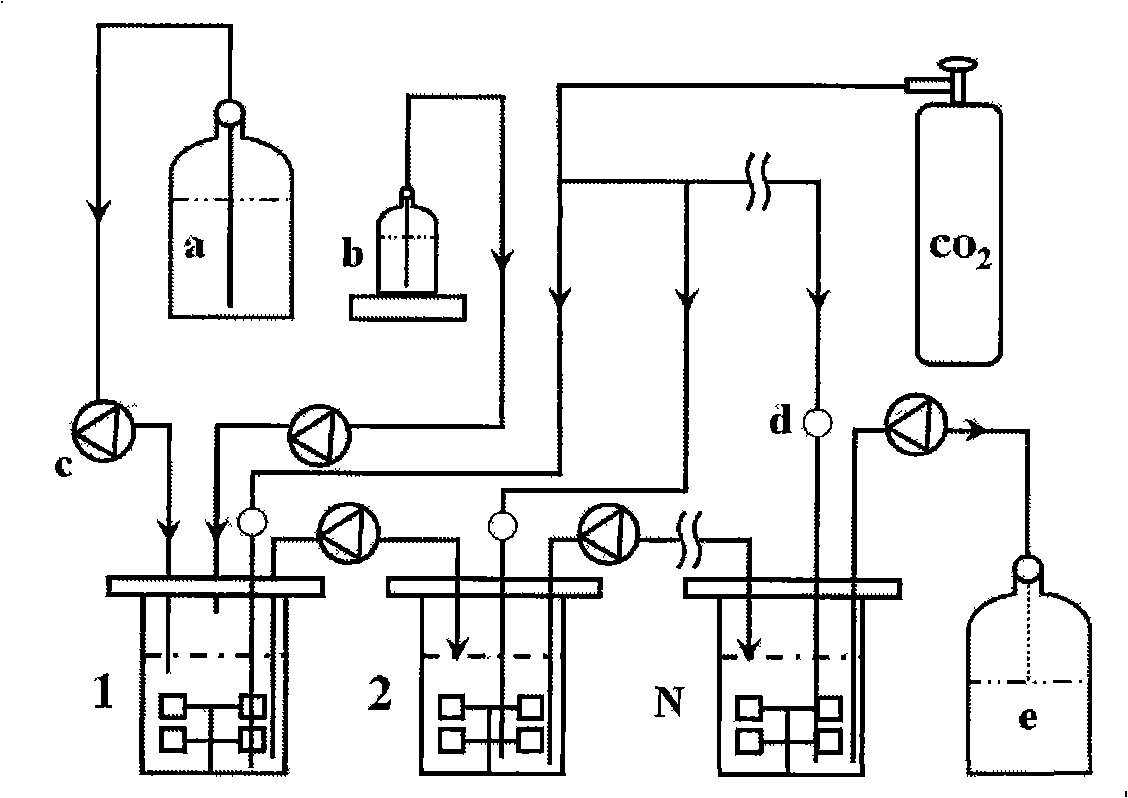
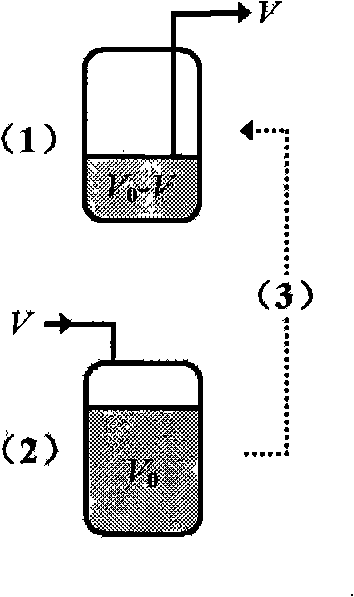
The invention discloses a method for producing butane diacid through continuous fermentation or semi-continuous fermentation, which belongs to the bioengineering technical field. The invention provides application of Actinobacillus succinogenes in the method for continuously or semi-continuously preparing the butane diacid by utilizing carbohydrate raw materials such as cane molasses, corn starch syrup, Jerusalem artichoke hydrolysis syrup, sweet sorghum straw syrup, and lignocellulose hydrolysis syrup and so on. The method utilizes multi-step continuous fermentation or two-step semi-continuous fermentation, which can improve germ concentration and cell activity and can obtain high butane diacid output and high butane diacid production intensity; the method is easy to realize automatic and continuous operation; compared with batch fermentation, the method can save non-fermentation time such as repeated tank cleaning, sterilization and so on, so the production efficiency can be greatly improved; the semi-continuous fermentation for producing the butane diacid is easier to control fermentation parameters than the continuous fermentation, has high sugar utilization rate, target product yield and target product output, has simple and easy equipment and operation, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Model predictive control of fermentation in biofuel production
ActiveUS8571689B2Increase productionEasy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHorizonBiofuel
System and method for managing batch fermentation in biofuel production. An optimizer executes a nonlinear multivariate predictive model of a batch fermentation process in accordance with an end of batch objective specifying a target end of batch biofuel concentration to determine an optimal batch trajectory over a temporal control horizon specifying a biofuel and / or sugar concentration trajectory over the batch fermentation process. A nonlinear control model for the batch fermentation process that includes the temporal control horizon driven by biofuel concentration during the batch fermentation process is executed per the determined optimal batch trajectory using received process information as input, thereby generating model output including target values for manipulated variables for the batch fermentation process, including batch fermentation temperature. The batch fermentation process is controlled per the target values to produce biofuel in accordance with the determined optimal batch trajectory, to substantially optimize the end of batch biofuel yield.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Antrodia camphorate quick liquid fermentation process based on asexual spores
ActiveCN102172174AShorten the fermentation cycleQuality improvementHorticultureBiotechnologyBatch fermentation
The invention provides an Antrodia camphorate quick liquid fermentation process based on asexual spores. The process is characterized by comprising the following steps of: fermenting Antrodia camphorate serving as parent strains in a fermentation tank to generate the asexual spores; and taking a part of fermentation broth containing the Antrodia camphorate asexual spores to another fermentation tank provided with fresh fermentation media to continuously ferment after the completion of fermentation, wherein material removing and feeding, re-fermentation and circulation can be repeated several times according to requirements. Compared with a batch fermentation process, the quick fermentation process can shorten the fermentation period of the Antrodia camphorate by at least 40 percent and has the characteristics of improvement on production strength, reduction in the probability of bacterial contamination, stabilization of fermentation quality of an Antrodia camphorate product and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing mannitol by taking jerusalem artichoke as raw materials through biotransformation
InactiveCN101736058AGreat tasteAvoid raising blood sugar levelsMicroorganism based processesFermentationHigh concentrationLactarius
The invention relates to saccharification processing technology of jerusalem artichoke by utilizing high-quality fructose biomass as a raw material and strain selection and technology optimization for producing mannitol by taking jerusalem artichoke as carbon source through fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: 1) crushing jerusalem artichoke tuber into coarse particles, filtering after water leaching and enzymolysis for 6 hours, supernating at 42 DEG C, rotating, evaporating and concentrating to obtain saccharification jerusalem artichoke juice with high concentration of fructose; 2) establishing high performance liquid chromatography analysis and detection conditions which can synchronously analyze the content of fermentation liquor substrate (glucose and fructose) and products (mannitol); and 3) inspecting the capacity for producing lactic acid and mannitol through fermentation by seven lactic acid bacteria by utilizing saccharification jerusalem artichoke juice with different concentration of total sugar, thus determining lactic acid bacteria with high transformation rate and production intensity of fructose, and optimizing production fermentation conditions and the highest concentration of tolerant substrate. Through feed-batch fermentation, production efficiency can be improved and mannitol can be continuously produced in large scale. The method not only generates no byproduct of sorbitol, but also has low production cost, wide raw material sources, simple technology, and mature technical route and can be implemented in industrialization.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
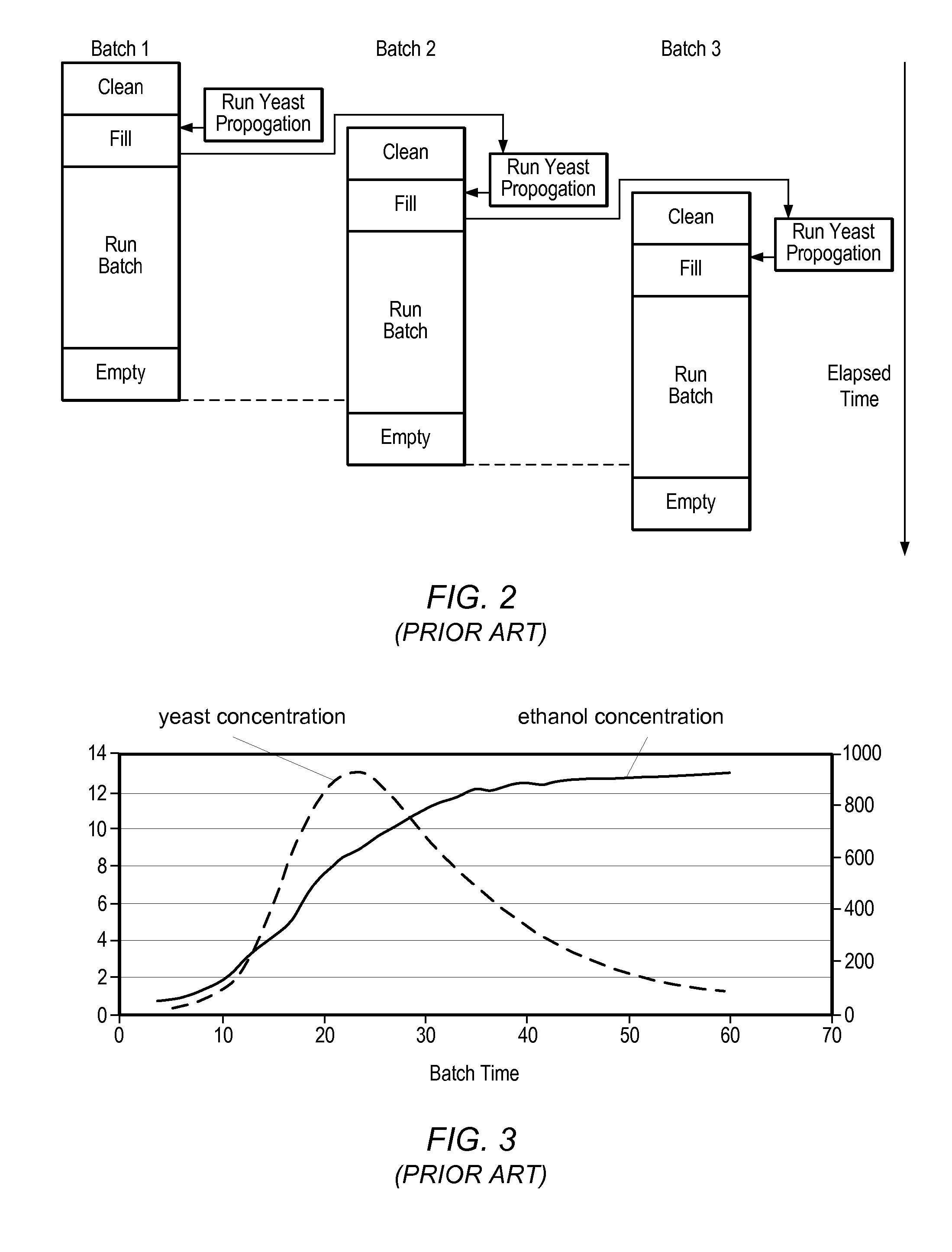
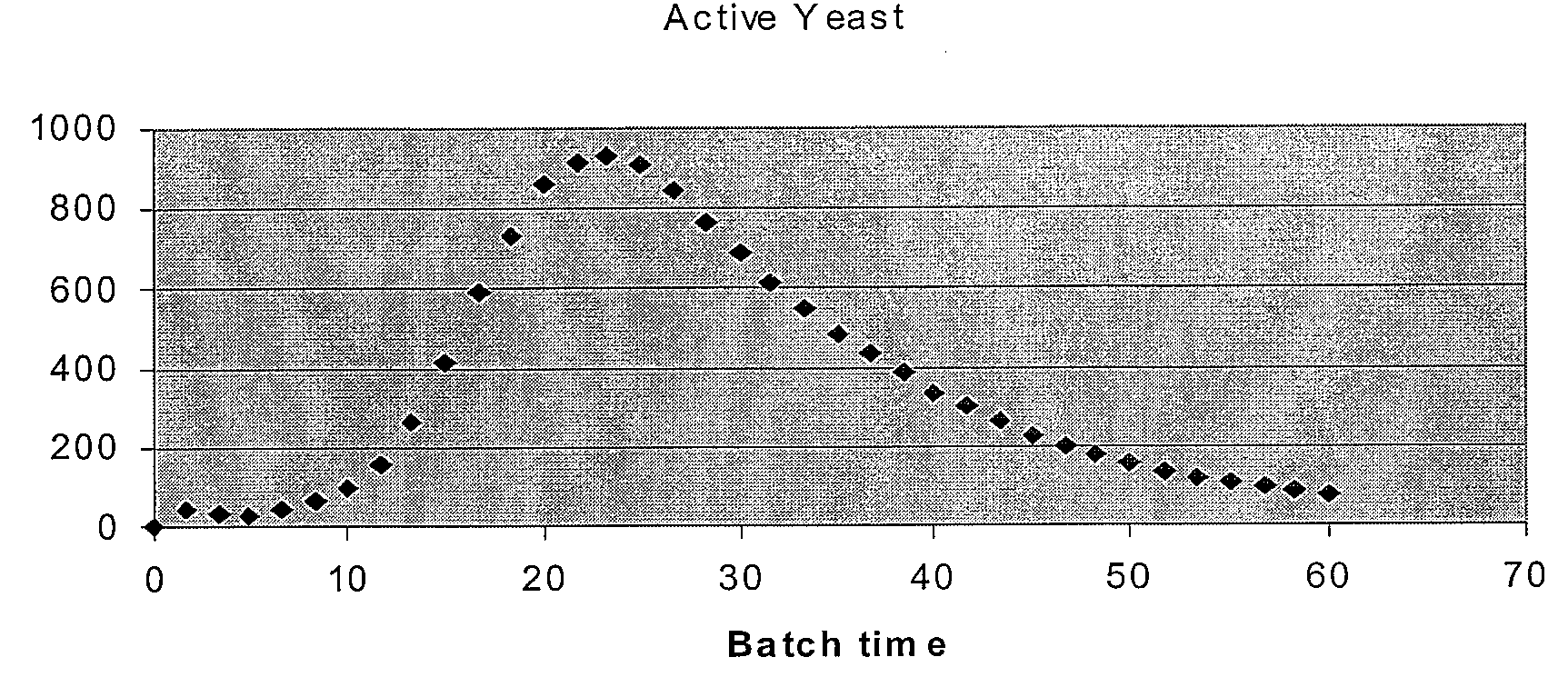
Method for on-line prediction of future performance of a fermentation unit
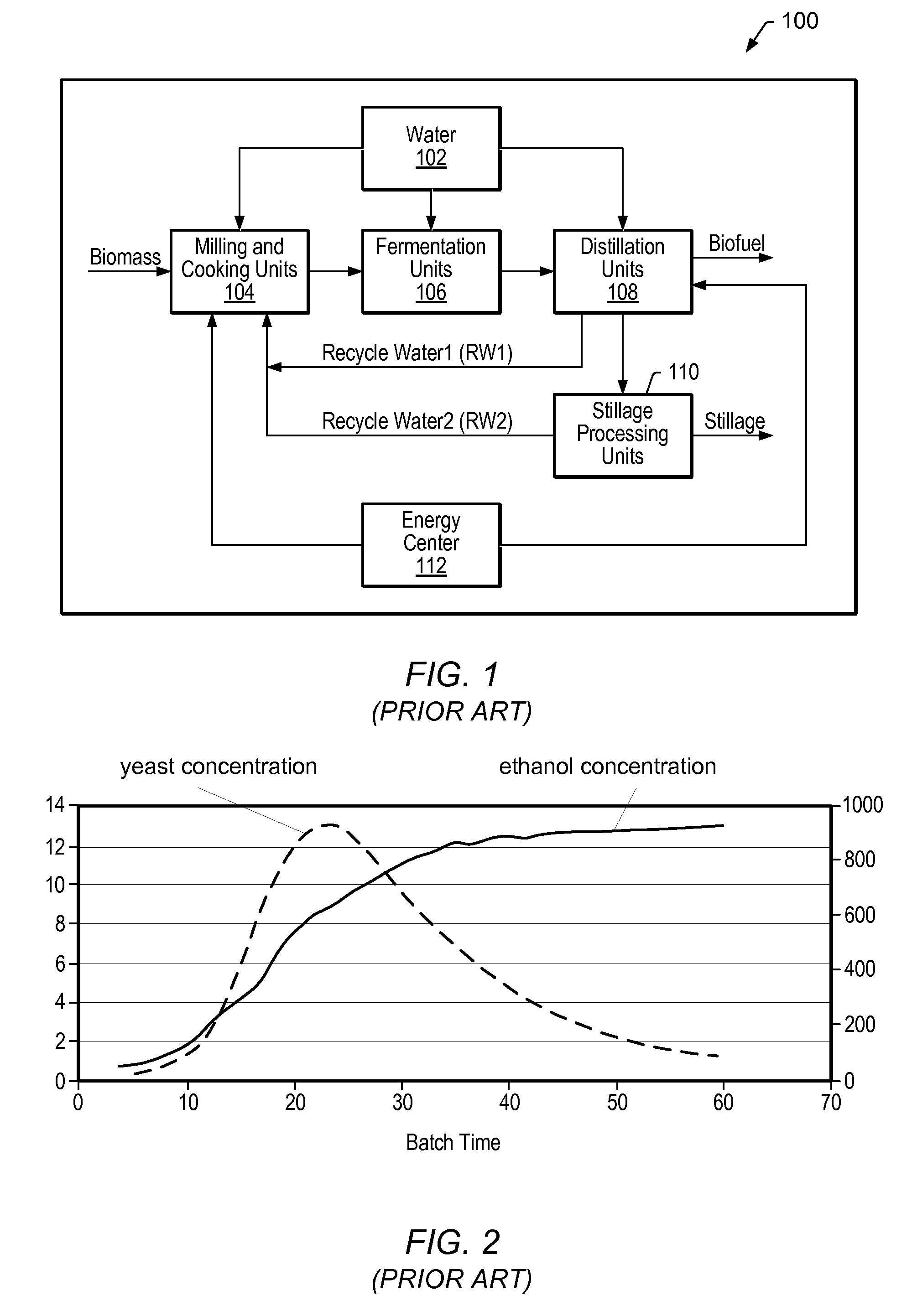
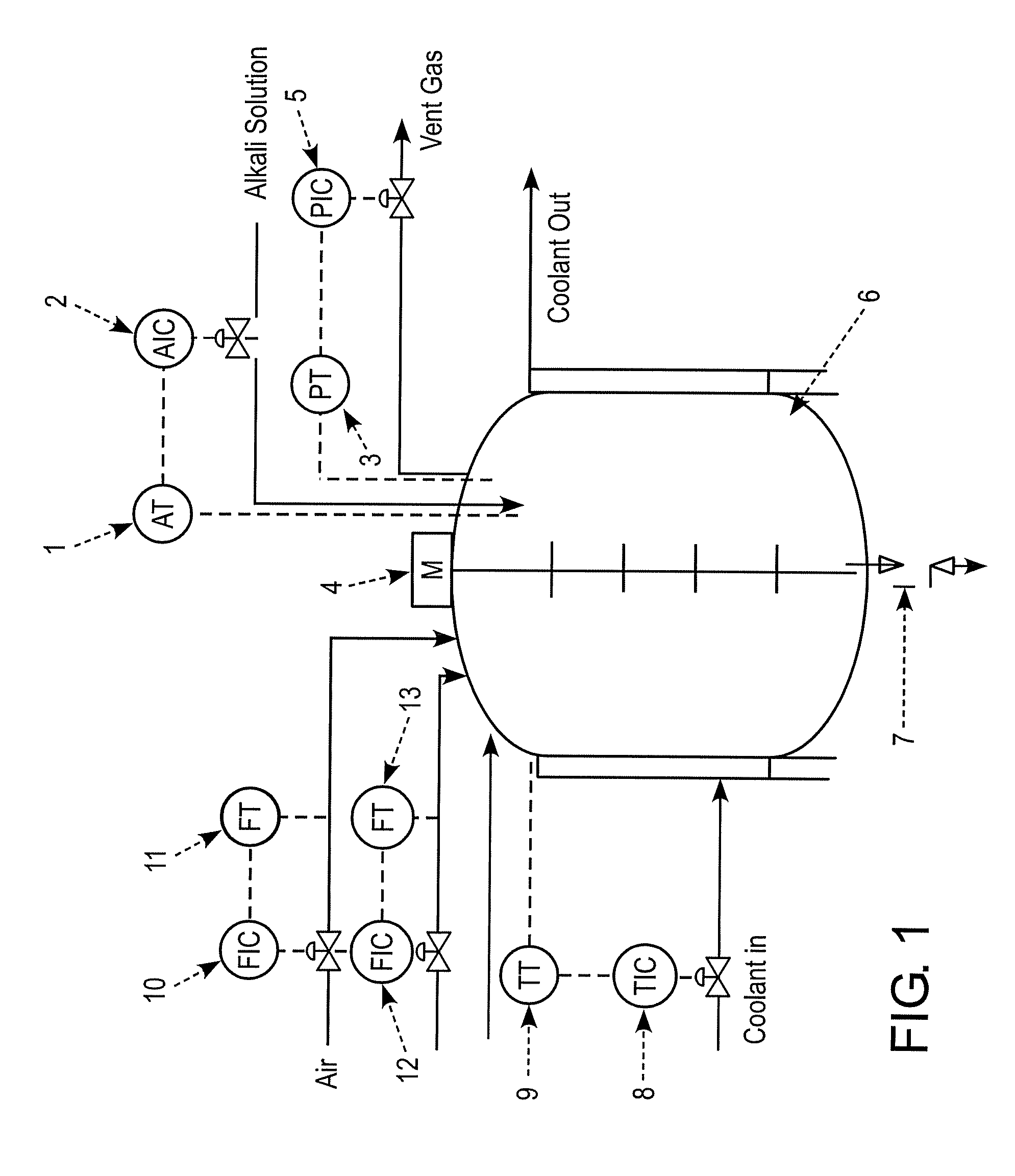
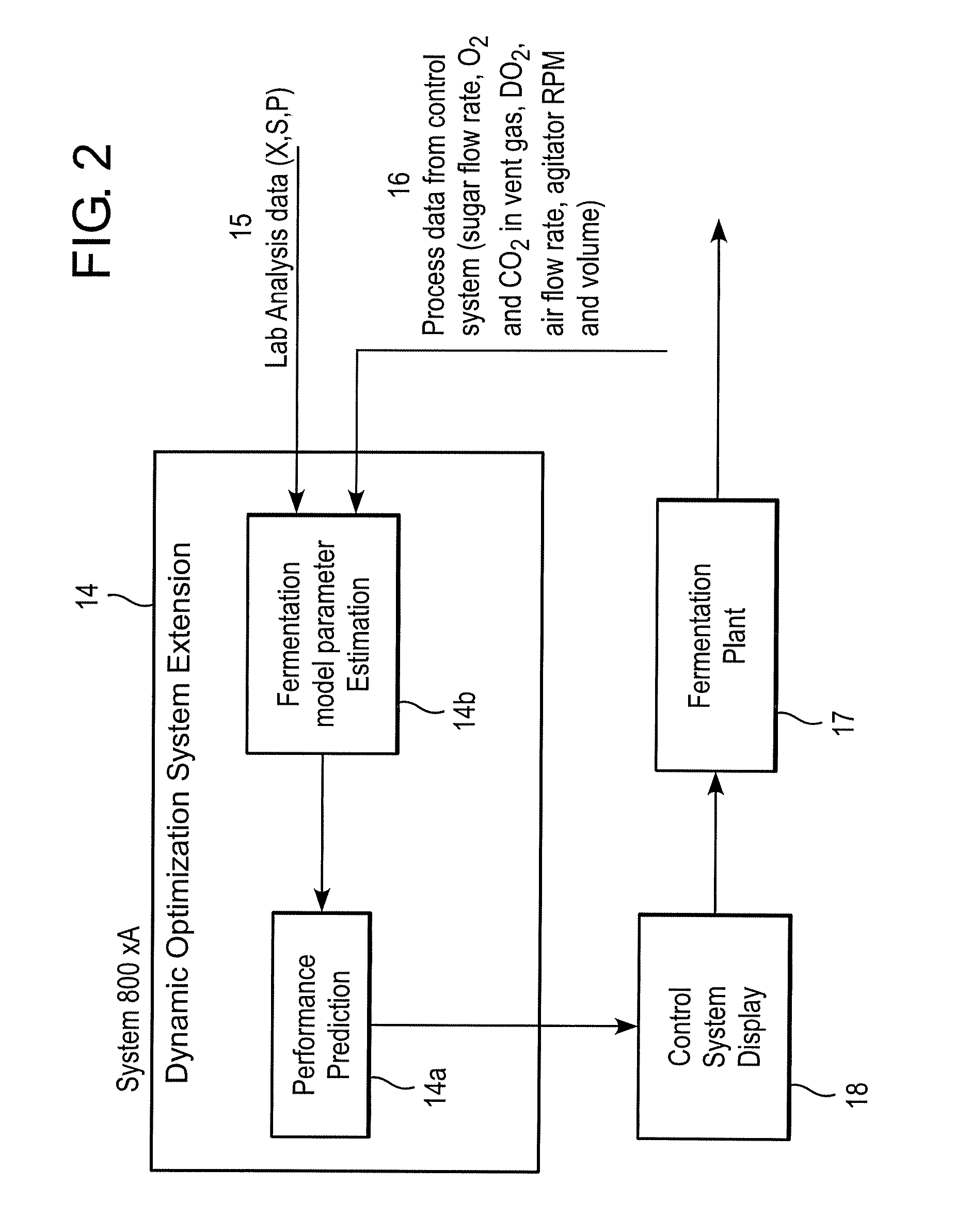
InactiveUS20090048816A1Minimize plant model mismatchImprove business performanceBiochemistry apparatusAnalogue computers for chemical processesControl systemBatch fermentation
A method is disclosed for on-line prediction of performance of a fermentation unit, such as prediction of performance parameters like concentration of product, biomass, or sugar in the broth of a batch / fed-batch fermentation unit containing bacteria and nutrients. A computer model predicts a future product concentration based on current plant data. While a batch is in progress, model parameters are adjusted on-line based on plant data to reduce a mismatch between the plant data and model data. A method / fermenter model can be implemented as a software program in a PC that can be interfaced to a plant control system for on-line deployment in an actual plant environment. An on-line performance monitoring system can be used by plant operating personnel, to know the performance of the batch in advance for implementing corrective measures in advance to improve / maintain performance at desired level.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
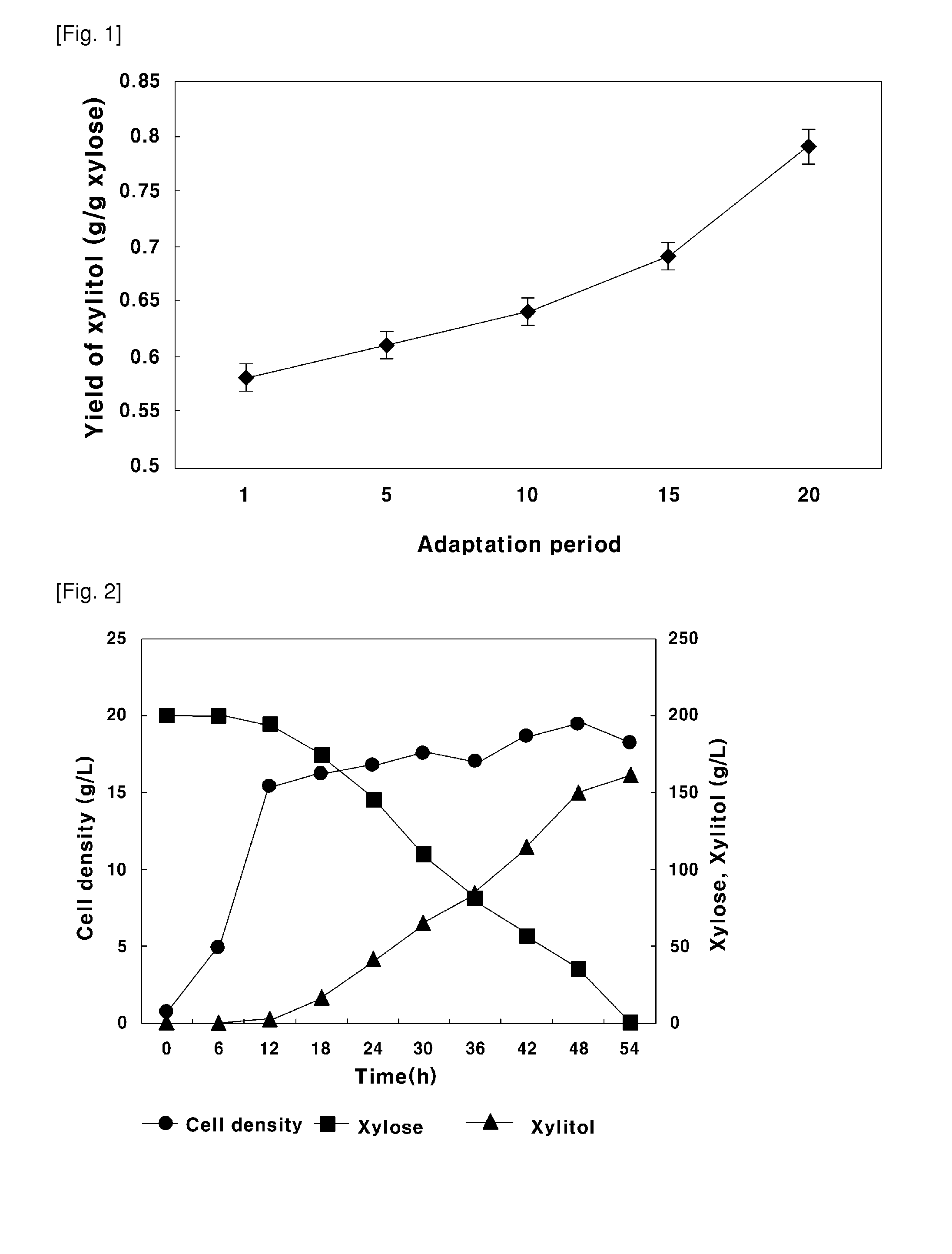
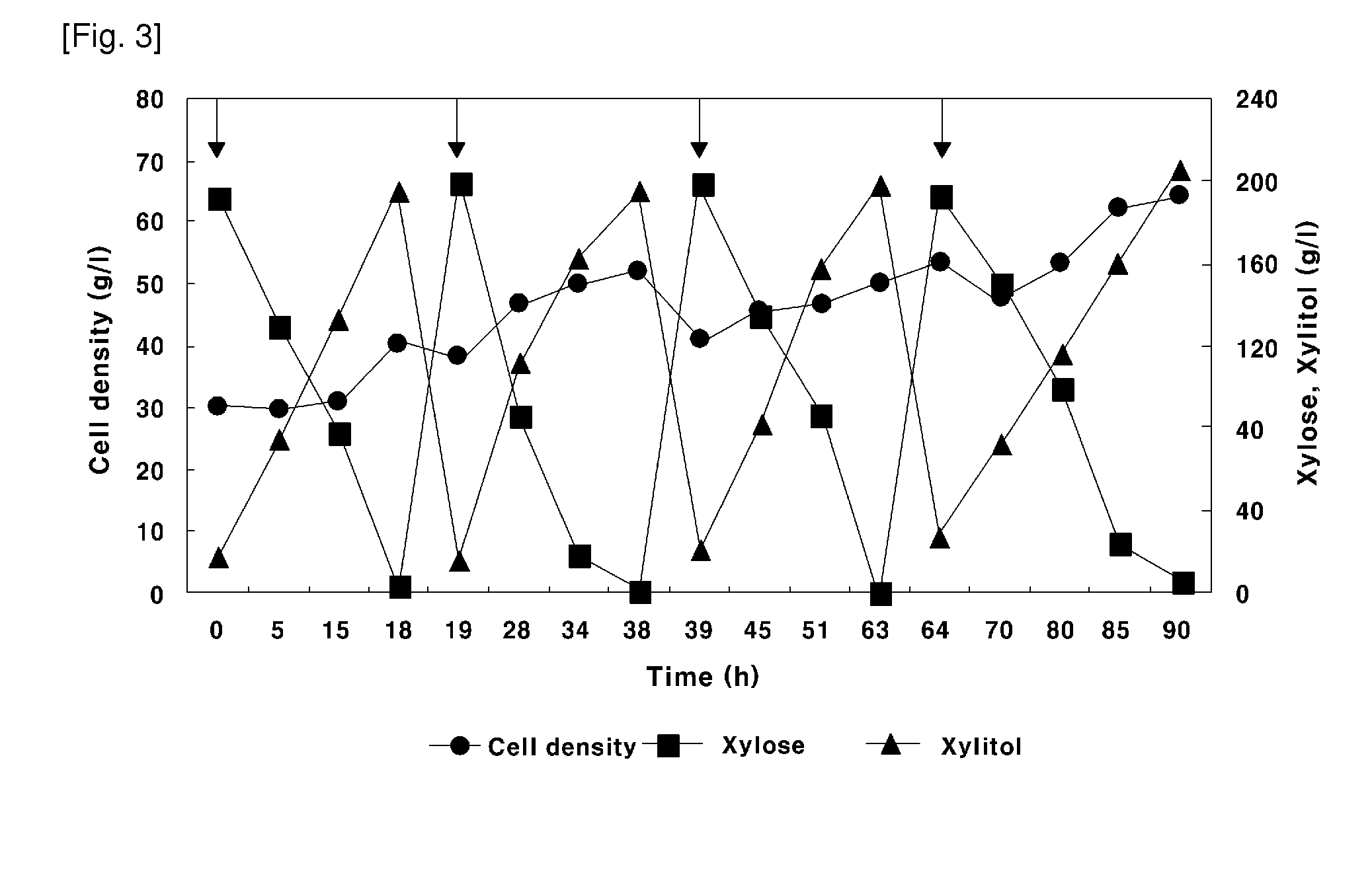
Method of Producing Xylitol Using Hydrolysate Containing Xylose and Arabinose Prepared from Byproduct of Tropical Fruit Biomass
ActiveUS20100068121A1Easy to useDecrease productivitySemi-permeable membranesCarbon compoundsHydrolysateCarbonization
Disclosed is a method of producing xylitol using a hydrolysate containing xylose and arabinose prepared from byproducts of tropical fruit biomass and more precisely, a method of producing xylitol which includes the steps of producing xylose and arabinose by the pretreatment of tropical fruit biomass byproducts including coconut shell, palm shell and oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB) via acid (0.2-5%) hydrolysis and an electrodialysis and an ionic purification; and producing xylitol with high yield based on repeated batch fermentation using a hydrolysate containing xylose and arabinose as a carbon source. In addition, the present invention relates to an active carbon produced by carbonization and activation of a hydrolysate remainder of a tropical fruit shell, the byproduct of xylose and arabinose production, at a certain temperature and a preparation method of the same.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Bacillus subtillis and method for preparing raw powder of each gram of bacillus subtillis with 1 trillion live germs
ActiveCN101935624AEffective dispersionAccurate detectionAntibacterial agentsBacteriaTrace elementGram
The invention discloses bacillus subtillis and a method for preparing raw powder of each gram of bacillus subtillis with 1 trillion live germs. The bacillus subtillis is CCTCC: No. M209317. The method comprises the following steps of: A, screening of a Bs strain: collecting a sample from soil and water, adding sterile water into the sample and standing the sample; B, confirmation of the Bs strain: together measuring 1,244 effective basic groups in 16SrDNA of the stain; C, screening of Bs culture medium: determining an optimal factor from numerous carbon sources, nitrogen sources and trace element factors by adopting a response surface experiment of Box-Behken design and using the germ number as a screening index; D, improving the quantity of fermentation organisms, and performing batch fermentation by using the culture medium screened by a response surface method; E, extracting and reclaiming the germs; and F, detecting the number of the live germs, namely accurately detecting the number of the effective live germs in the product. The method has the advantages of good repeatability, low cost, capability of simultaneously detecting 7 to 8 samples and simple operation. The produced bacillus subtillis has the advantages of clean and safe raw medicament, high reclamation rate, stable germ number of the product, capability of reaching 1 trillion live germs in each gram and the like.
Owner:WUHAN KERNEL BIO-TECH CO LTD
Seabuckthorn-snow daisy fruit vinegar beverage and preparation method thereof
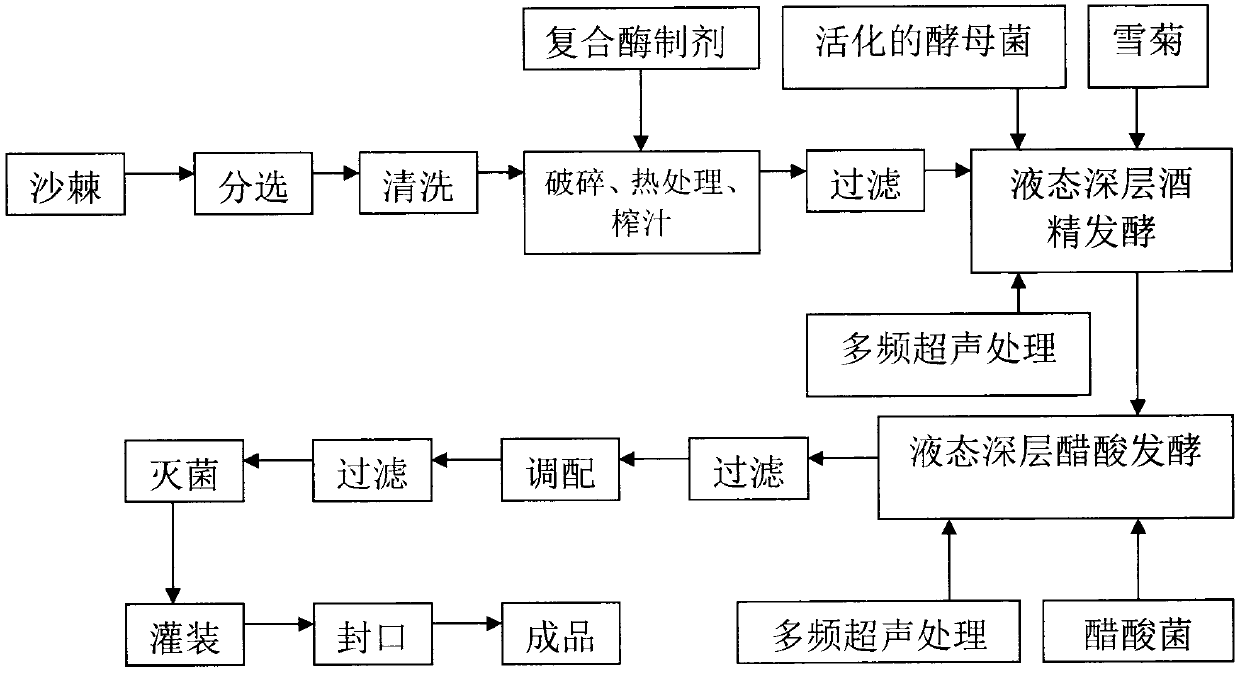
InactiveCN103385518AIncrease varietyEnhance the added value of characteristic resourcesVinegar preparationFood preparationAcetic acidSucrose
The invention discloses a seabuckthorn-snow daisy fruit vinegar beverage and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting, cleaning, crushing, performing heat treatment, enzyme treatment, juicing and filtering seabuckthorn fruits, respectively performing ultrasound-enhanced liquid deep alcohol and ultrasound-enhanced liquid deep acetic acid for batch fermentation on seabuckthorn pulp and snow daisy, filtering and blending, evenly mixing 1-40wt% of seabuckthorn-snow daisy acetic acid fermentation undiluted liquid, 5-10% of honey, 5-10% of sucrose, 10-30% of clear seabuckthorn juice and 10-70% of purified water, filtering, sterilizing and filling to obtain the seabuckthorn-snow daisy fruit vinegar beverage. According to the invention, key technologies such as composite enzymatic hydrolysis juicing technology, multifrequency ultrasound-enhanced efficient liquid batch fermentation technology and fermentation synchronous extraction technology are used to prepare the natural seabuckthorn-snow daisy fruit vinegar fermentation beverage which has wide practicability.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Bacillus mucilaginosus and culture method and culture medium thereof
InactiveCN101967456AOvercoming craftOvercoming complexityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDipotassium hydrogen phosphate
The invention relates to a kind of Bacillus mucilaginosus and a culture method and culture medium thereof, belonging to the microbiological technical field. The Bacillus mucilaginosus P.muc3016 has the functions of nitrogen fixation, phosphorus-dissolving and potassium-releasing and belongs to the Paenibacillus group. The batch fermentation method is adopted to ferment and culture the Bacillus mucilaginosus and the concentrations of carbon source and dissolved oxygen are monitored and regulated. The culture medium contains carbon source, soybean meal powder, ammonium sulfate, magnesium sulfate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, calcium sulfate and calcium carbonate, and the pH value of the culture medium is 7.5-7.0. The Bacillus mucilaginosus of the invention has three functions of nitrogen fixation, phosphorus-dissolving and potassium-releasing simultaneously, has higher function activity and can obviously increase the crop yield; and by adopting the culture method and culture medium of the invention, the fermentation density can be increased and the fermentation time can be shortened.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
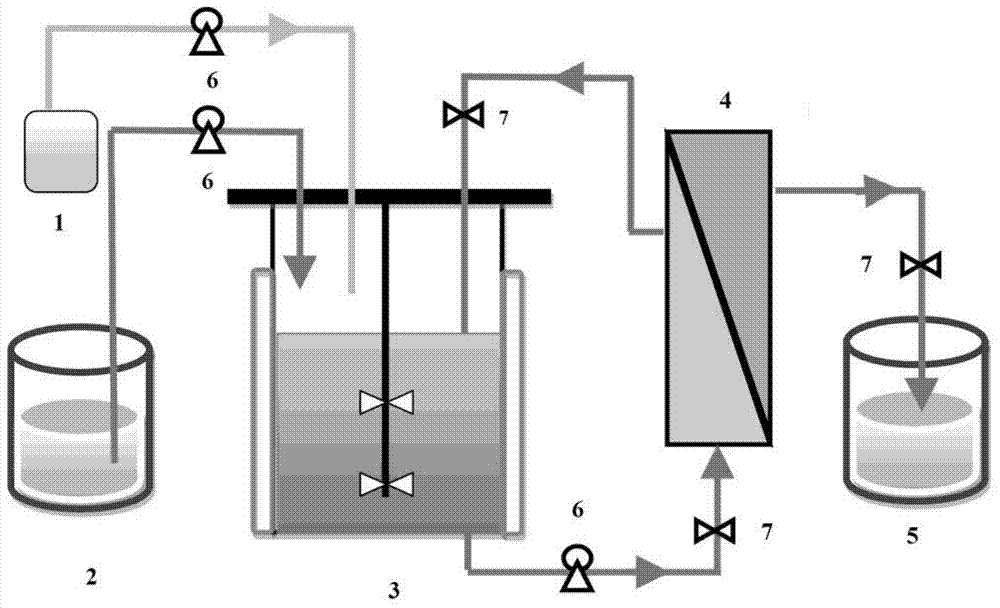
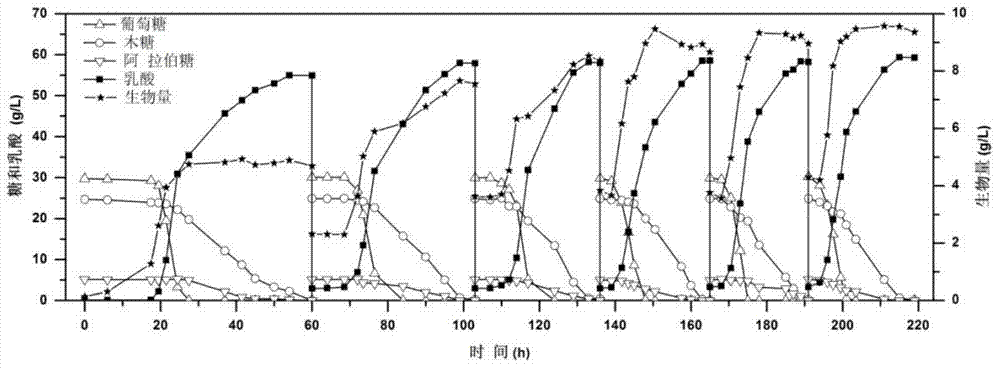
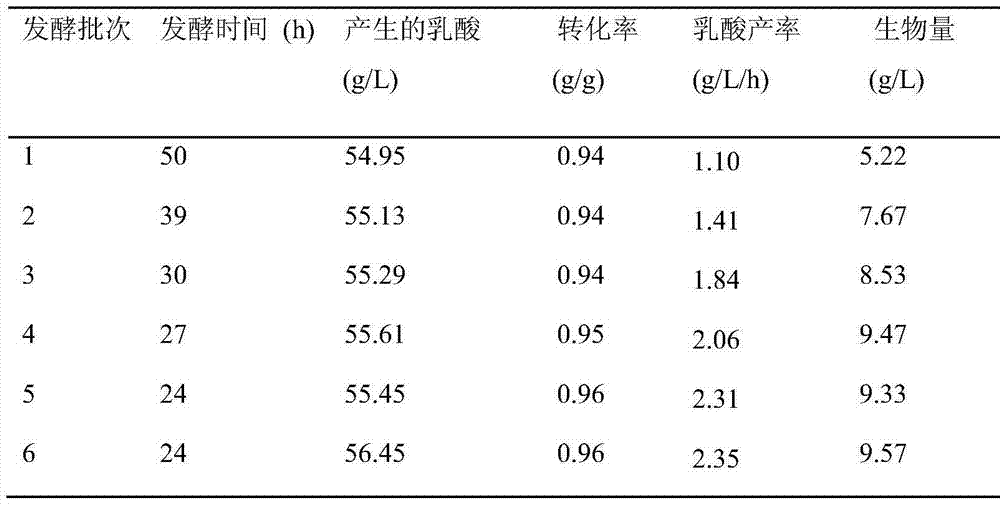
Method for producing lactic acid through continuously fermenting batches of lignocellulose hydrolysate by coupling fermenting and membrane separation
ActiveCN103834696AReduce manufacturing costReduce productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseFiltration
The invention discloses a method for producing lactic acid through continuously fermenting batches of lignocellulose hydrolysate by coupling fermenting and membrane separation. According to the method, bacillus coagulans CGMCCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 7635 is taken as the fermented culture, and mixed sugar in the lignocellulose hydrolysate is taken as the carbon source. Aiming at the defects in the fermentation process that unsynchronized utilization of hexose and pentose by microorganism results in longer fermentation period and low yield, the invention provides a method for cell recycling and continuous batch fermentation through coupling of membrane separation units and fermentation, and the method comprises steps of activation of culture, seed culture, fermentation cultivation, filtration of ultrafiltration membrane, cell recycling and batch fermentation. By adopting the method, the fermentation period can be effectively shortened, and the utilization efficiency of the mixed carbon source of hexose and pentonse by the thallus is improved. The method has mild operation conditions, has good stability, has general guiding significance in production of biochemical products through fermenting by the microorganism using the mixed sugar in the lignocellulose hydrolysate, and has wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com