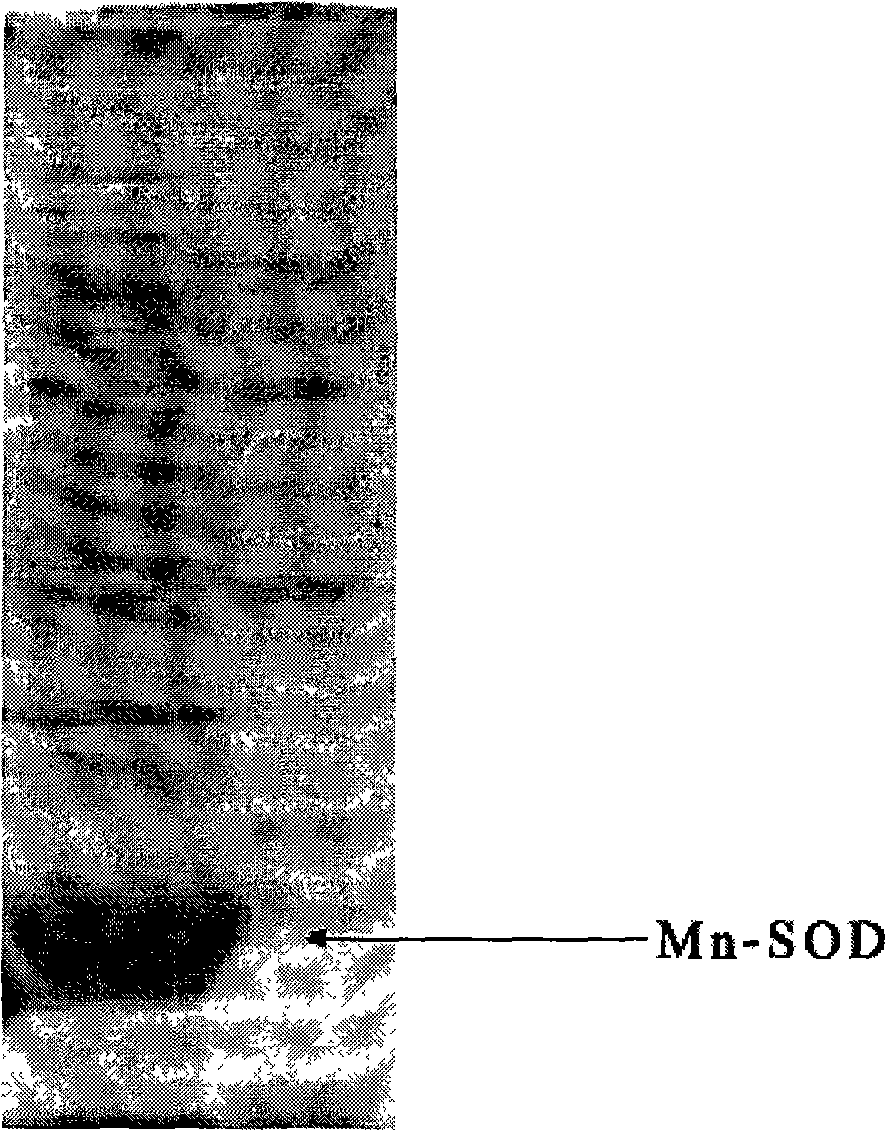High-density fermentation and purification process for recombination high temperature-resistant hyperoxide dismutase
A high-density fermentation and superoxide technology, applied in fermentation, recombinant DNA technology, and microbial-based methods, can solve problems such as difficulty in ensuring SOD yield, SOD production limitation, and low recombinant expression, and achieve high yield , high heat resistance, simple purification process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1. Construction and induced expression of SOD engineering bacteria
[0045] (1) PCR amplify the heat-resistant SOD gene, after double enzyme digestion, connect it to the plasmid vector pET28a after the same digestion treatment to construct a recombinant plasmid, named pSOD. Then the plasmid pSOD was transformed into competent E. coli BL21 (DE3) by chemical transformation method, and after screening, a strain with high SOD production was obtained, and the construction of SOD engineering bacteria was completed.
[0046] (2) Add kanamycin to the LB medium to a final concentration of 30mg / L, inoculate a single colony of SOD engineering bacteria, culture with shaking at 37°C for 2 hours, add 0.5mM IPTG, and continue to culture at 30°C for 8 hours;
[0047] (3) Collect the bacteria by centrifugation and resuspend in 500ml lysis buffer; lysis buffer: 10mM Tris-HCl, pH8.0.
[0048](4) Use an ultrasonic cell disruptor to disrupt the cells, set the power to 400W, working time...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2. High-density fermentation of SOD engineering bacteria
[0051] (1) The basic medium composition of the fermenter is shown in Table 2 and the feed composition is shown in Table 3;
[0052] (2) First-level seed culture: Inoculate 5ul of glycerol bacteria in 20ml LB liquid medium, the final concentration of kana is 50mg / L, 37℃, 220rpm, culture for 10h;
[0053] (3)Secondary seed culture: transfer the cultured bacteria in the previous step to 200ml LB liquid medium, kana final concentration 50mg / L, 37℃, 220rpm, culture for 4h;
[0054] (4) Fermentation in the upper tank: inoculate 200ml of the secondary seed bacteria liquid cultured in the previous step into a fermentation tank with a volume of 6.6L. Fermentation conditions are: dissolved oxygen 30%, temperature 30°C, pH 7.0, and rotation speed is automatically adjusted according to dissolved oxygen between 200 rpm and 800 rpm;
[0055] (5) The fermentation is carried out for 5-6 hours, and the inducer IPTG is added ...
Embodiment 3
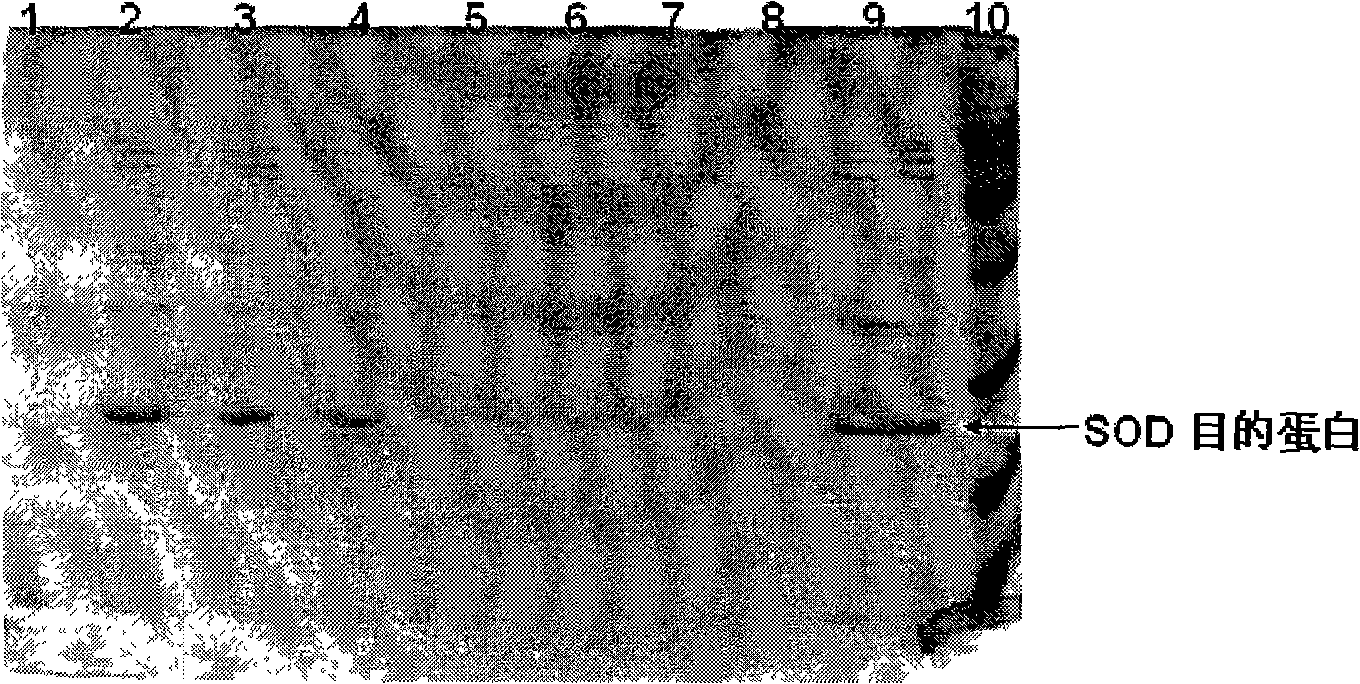
[0056] Example 3: Electrophoresis detection of high-density fermentation products of SOD engineering bacteria
[0057] After the bacterial cells were sonicated under 300W ultrasonic waves, centrifuged at 8000g for 20 minutes, and the supernatant and precipitates were subjected to 12.5% SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. The results are as follows figure 2 . The labels in the figure indicate that they are 1-induction of proschizobacteria supernatant; 2-induction of schizobacteria supernatant for 5 hours; 3-induction of schizobacteria supernatant for 10 hours; 4-induction of schizobacteria supernatant for 14 hours; 5-before induction Cracking bacteria precipitation; 6-induction of 5 hours of cracking bacteria precipitation; 7-inducing of 10 hours of cracking bacteria precipitation; 8-inducing of 14 hours of cracking bacteria precipitation; 9-fermentation broth supernatant; 10-Marker (14400-97000).
[0058] The results showed that no SOD target protein was produced before induction, and al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com