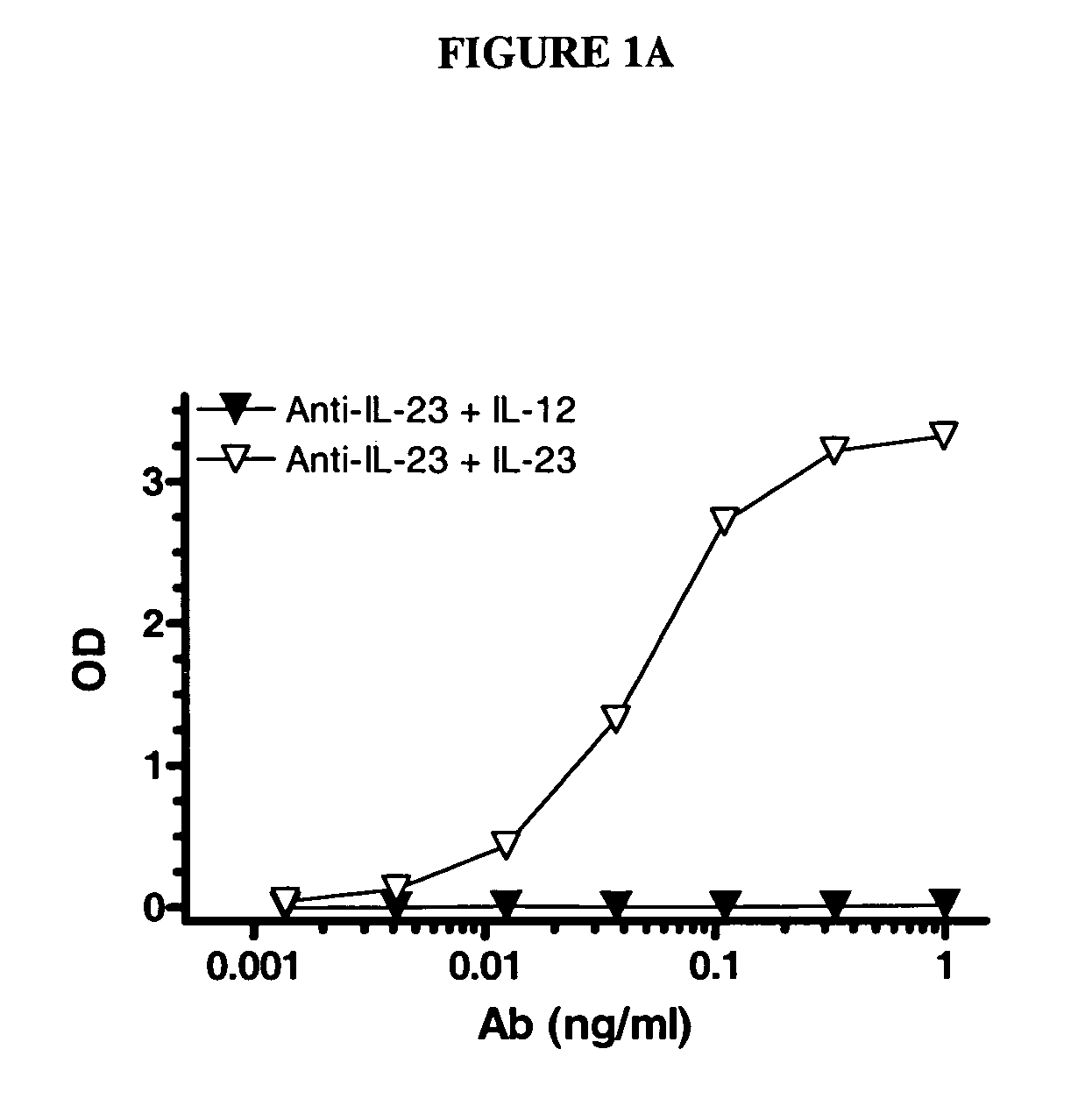
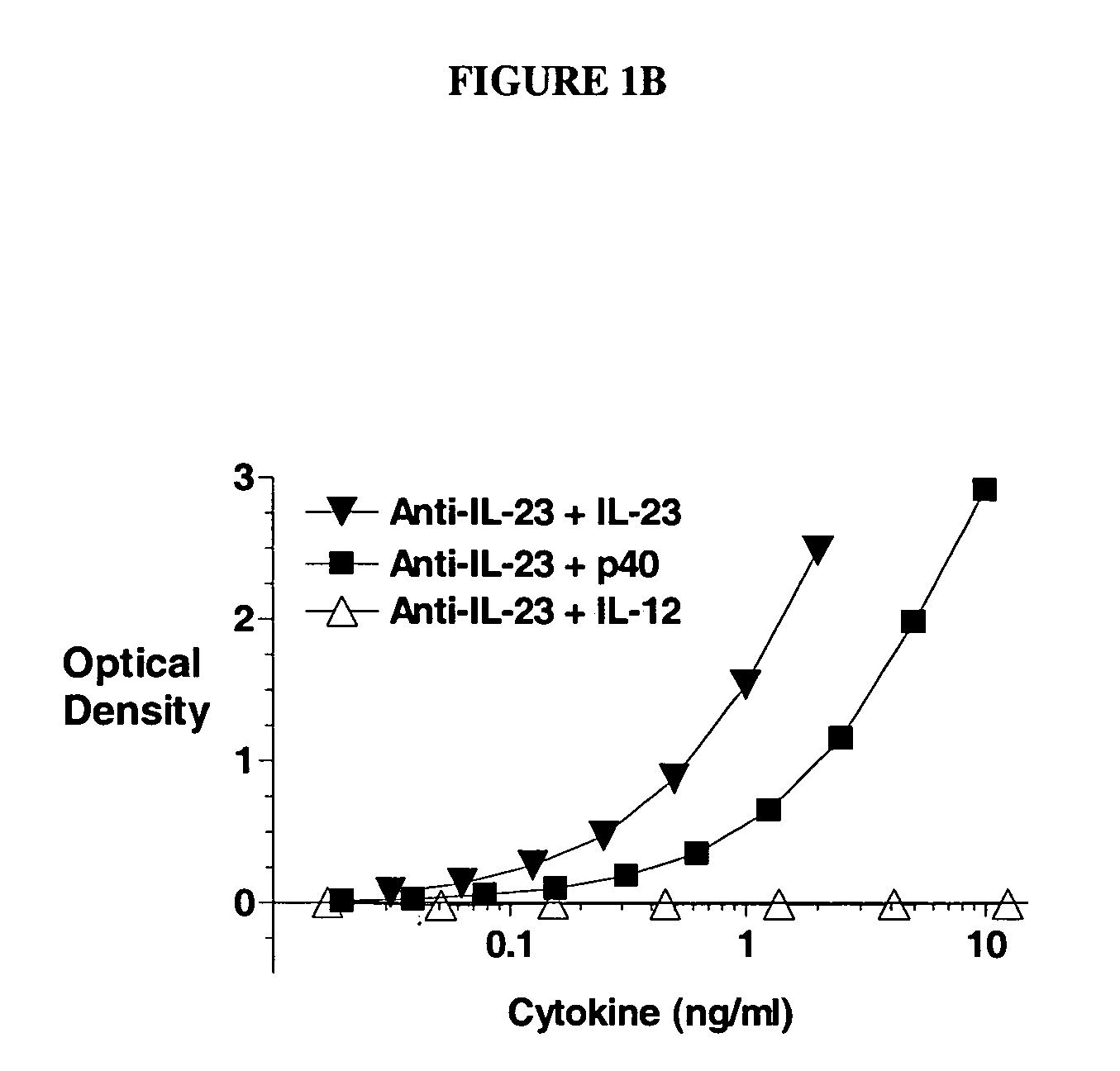
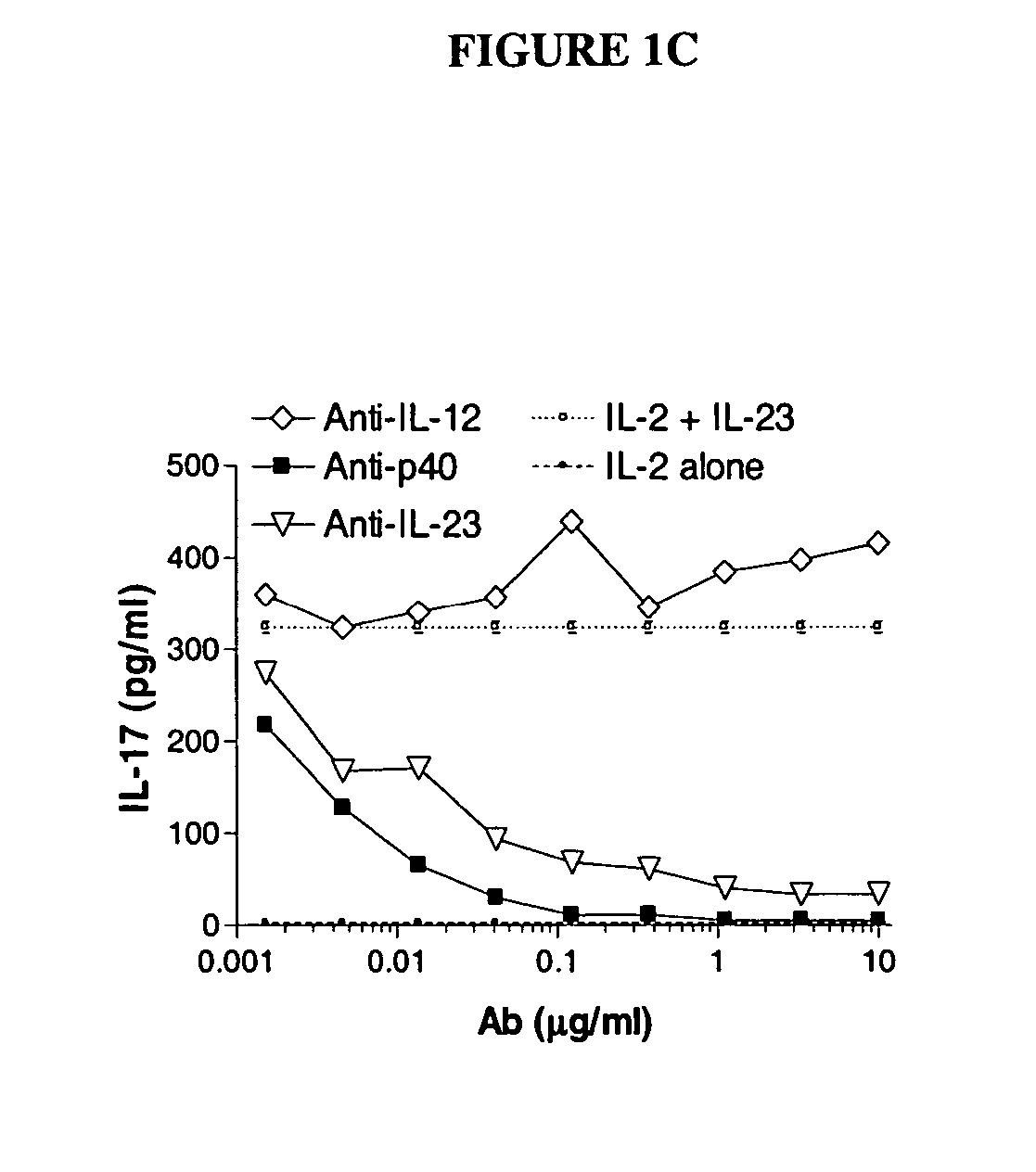
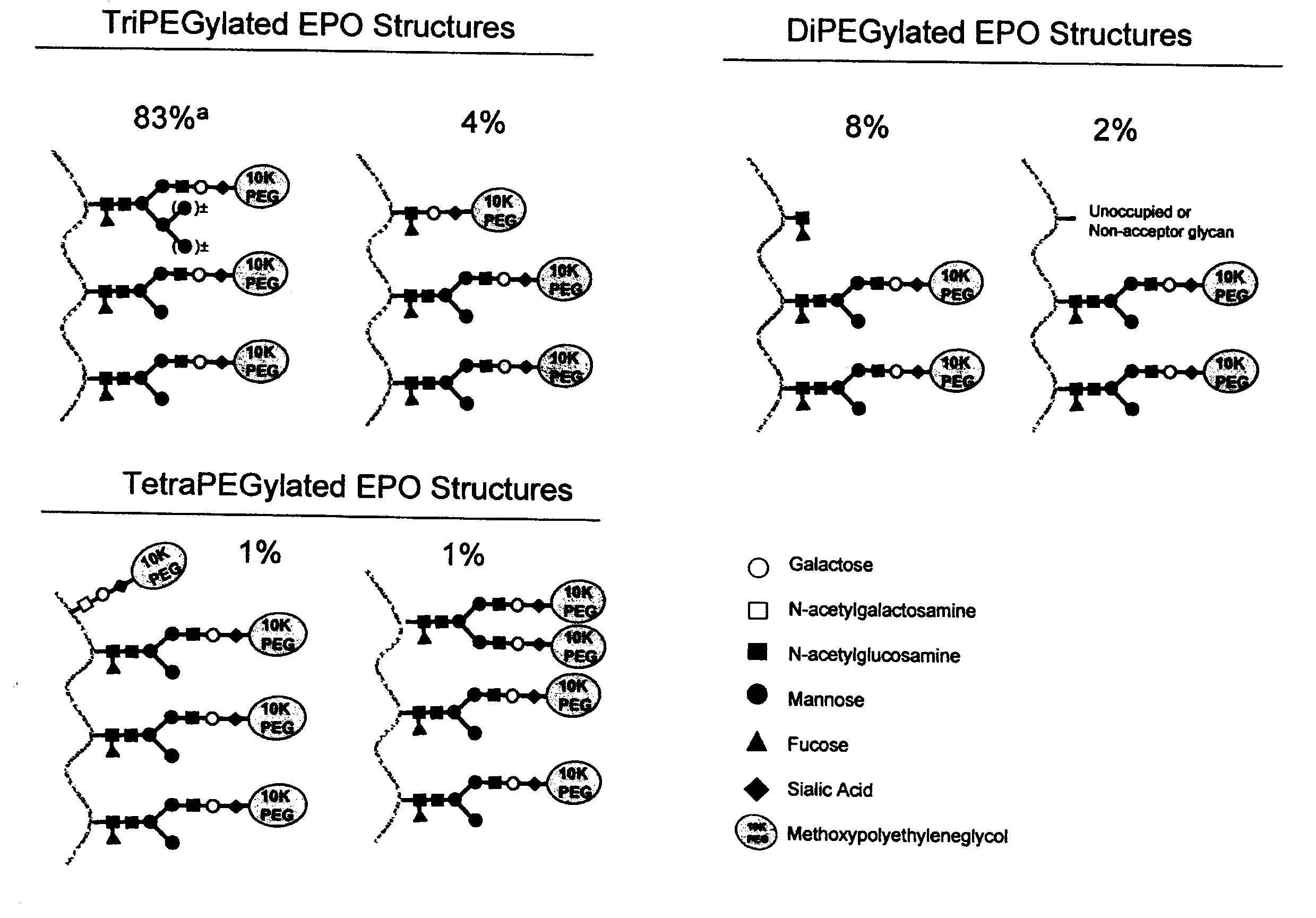
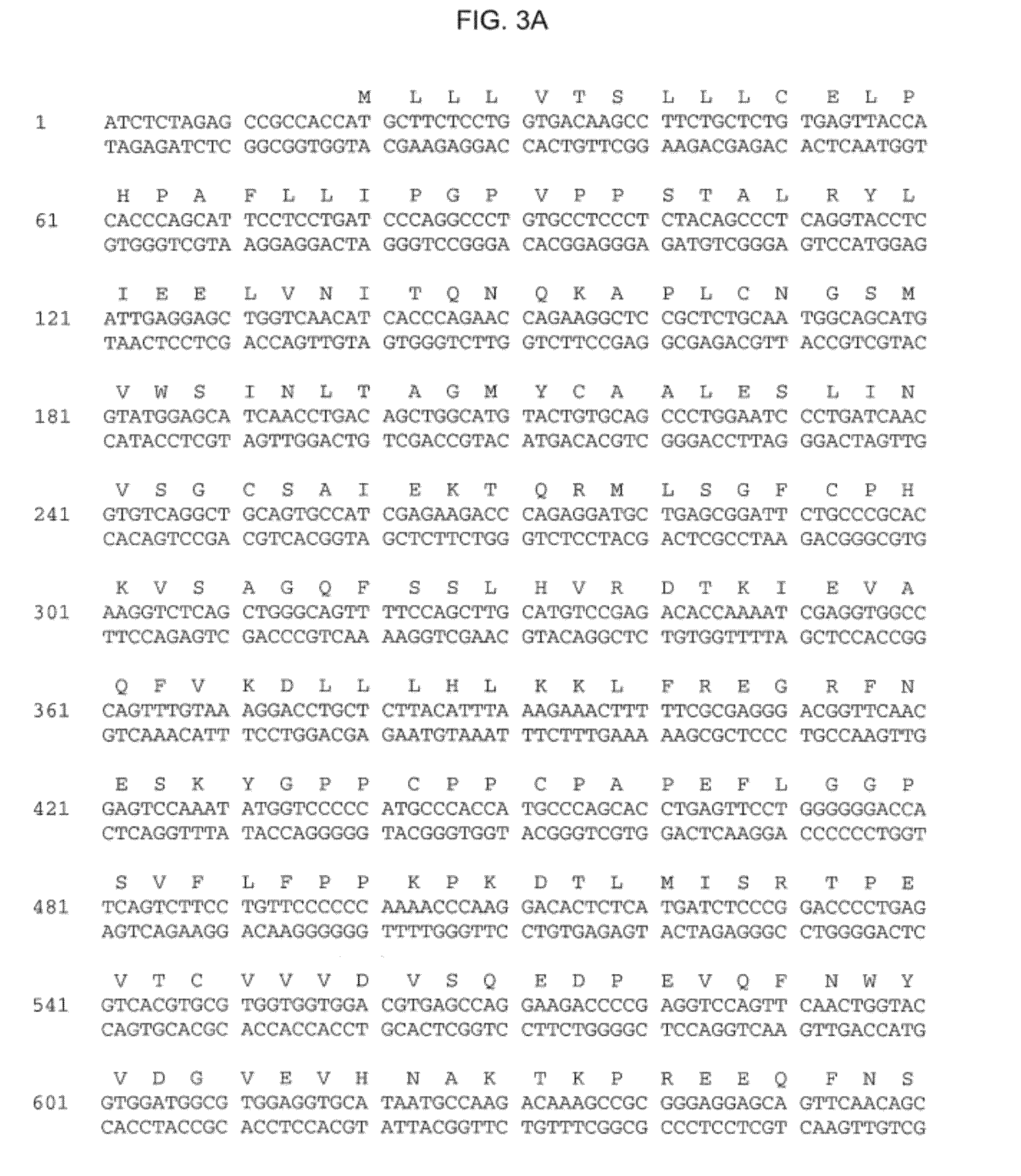Patents
Literature
1422results about "Interleukins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
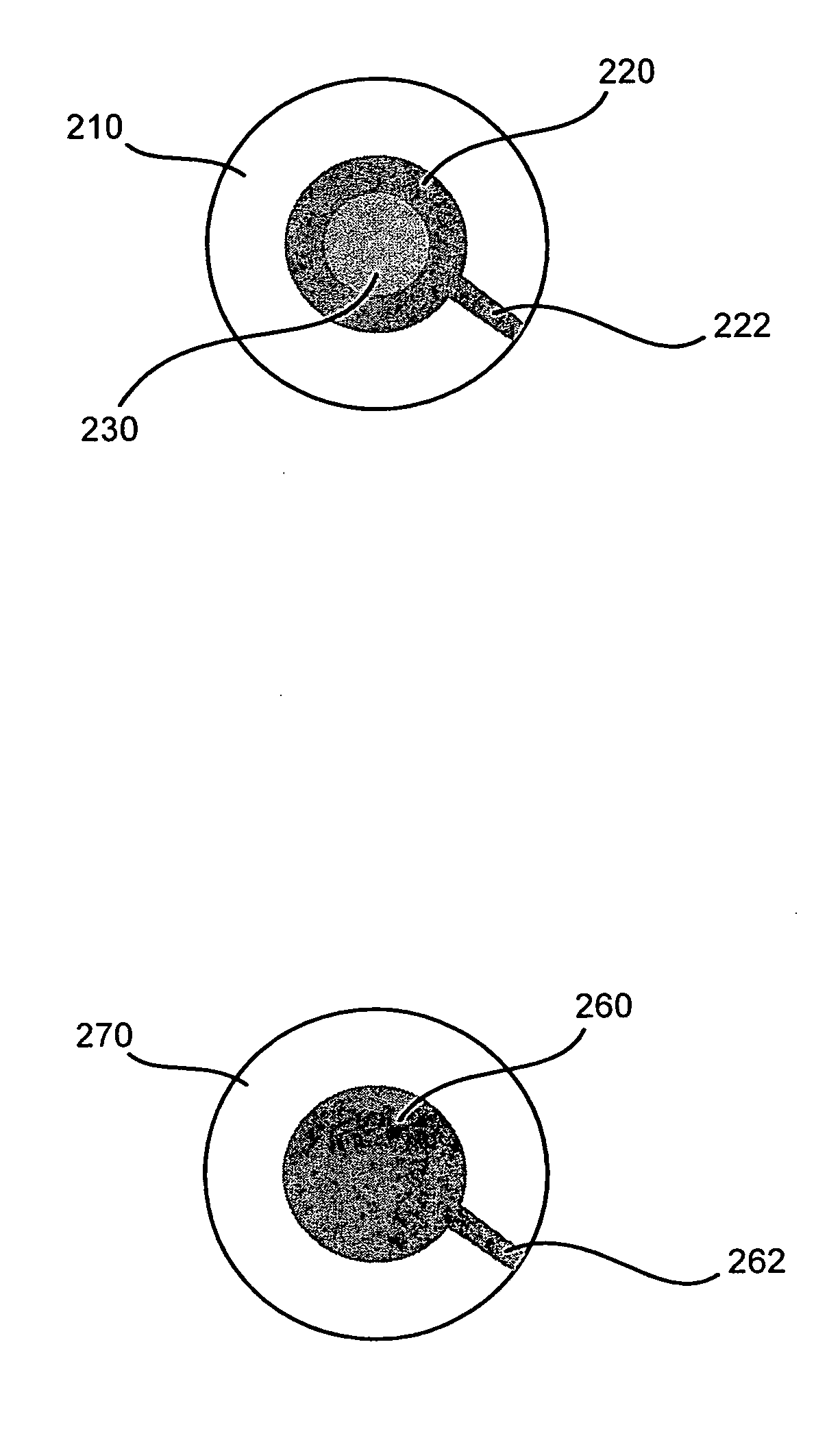
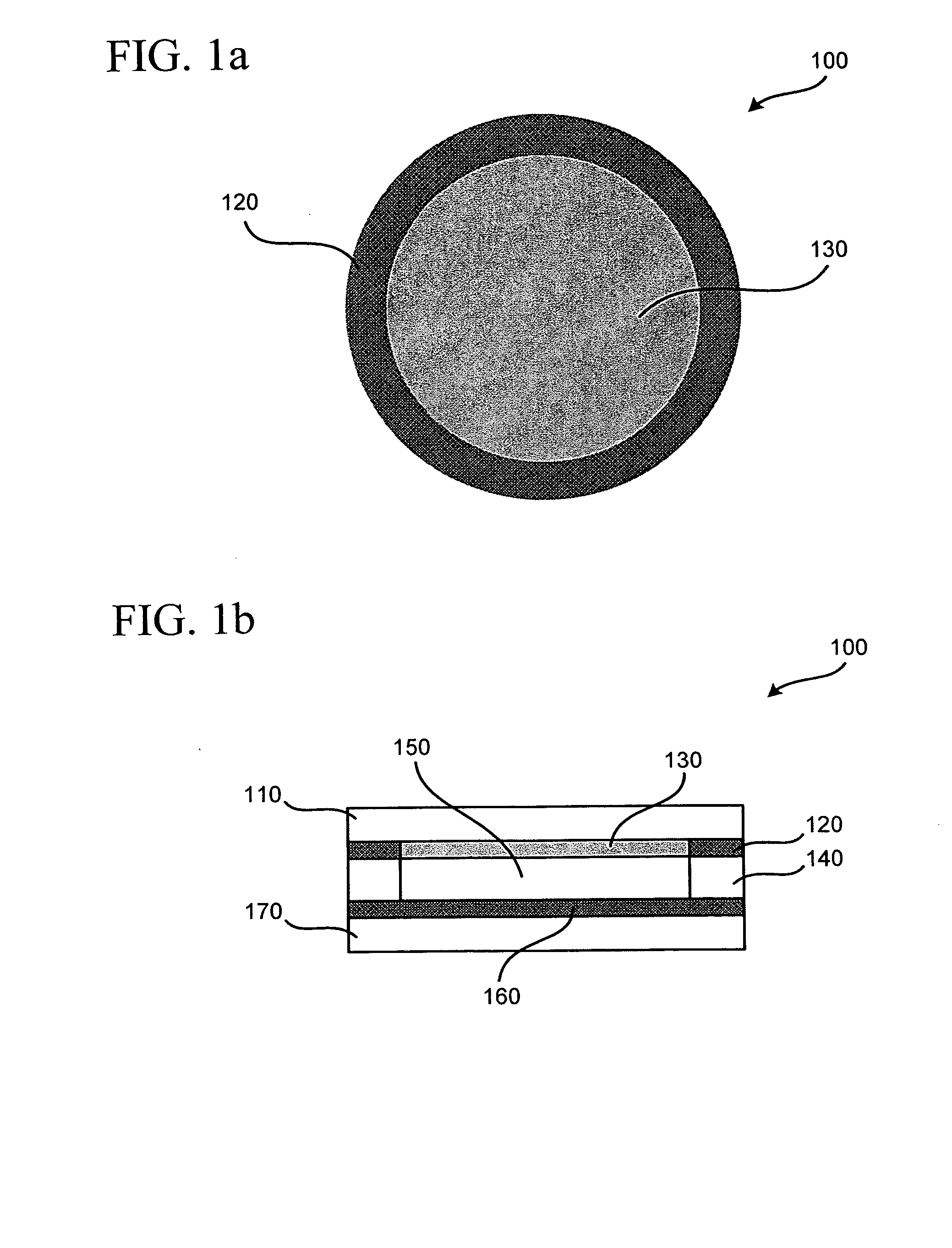
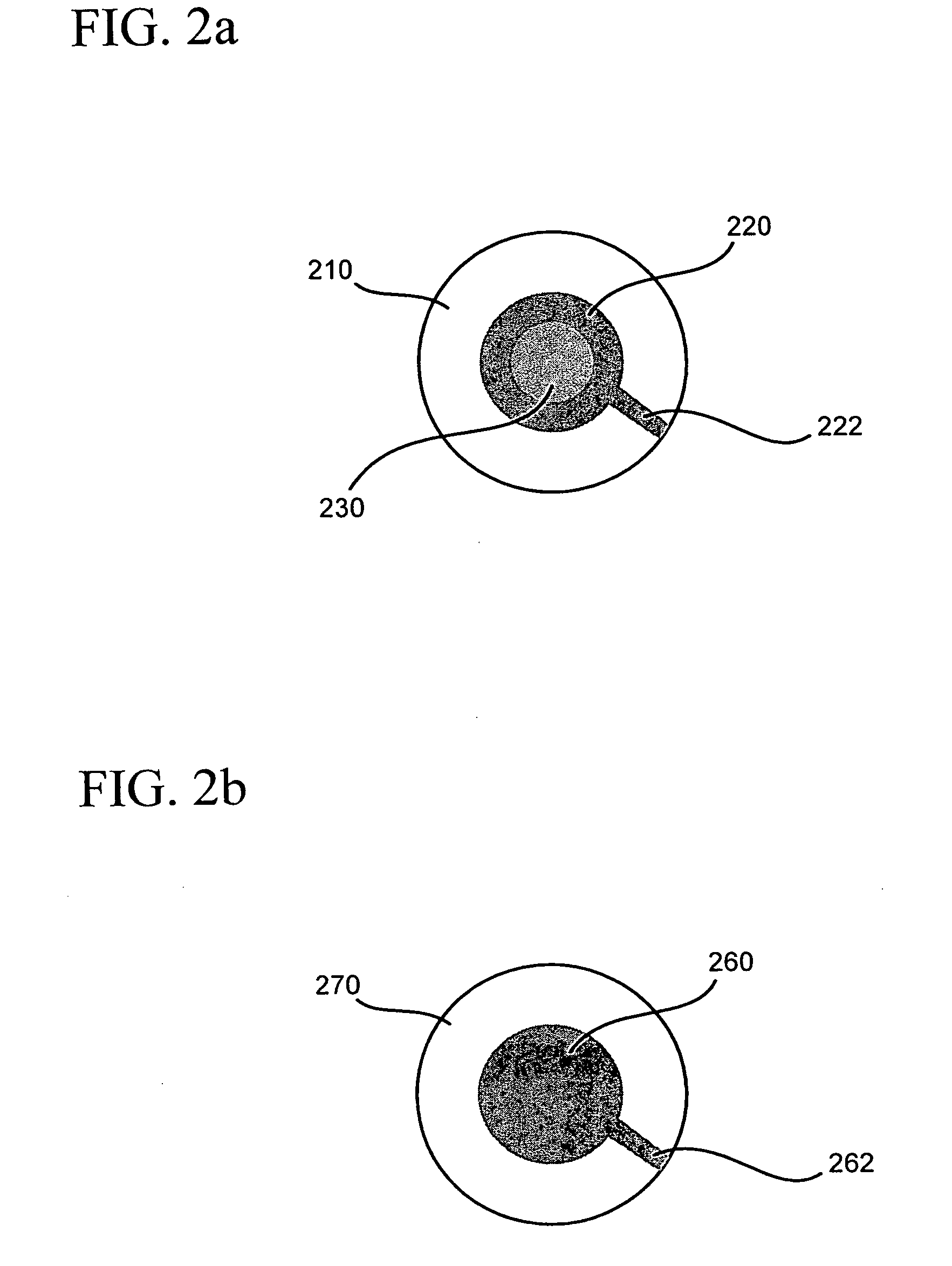
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
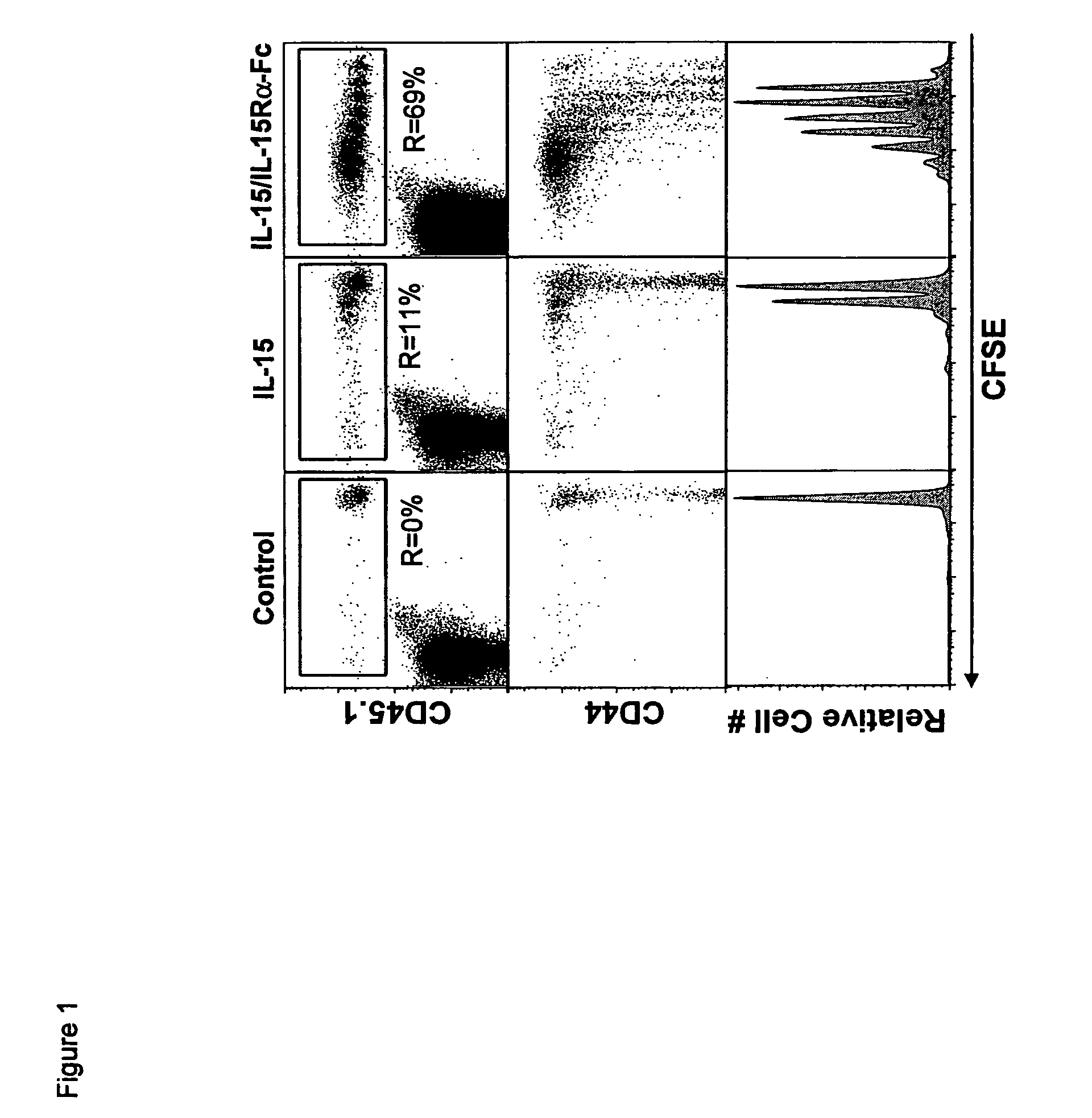
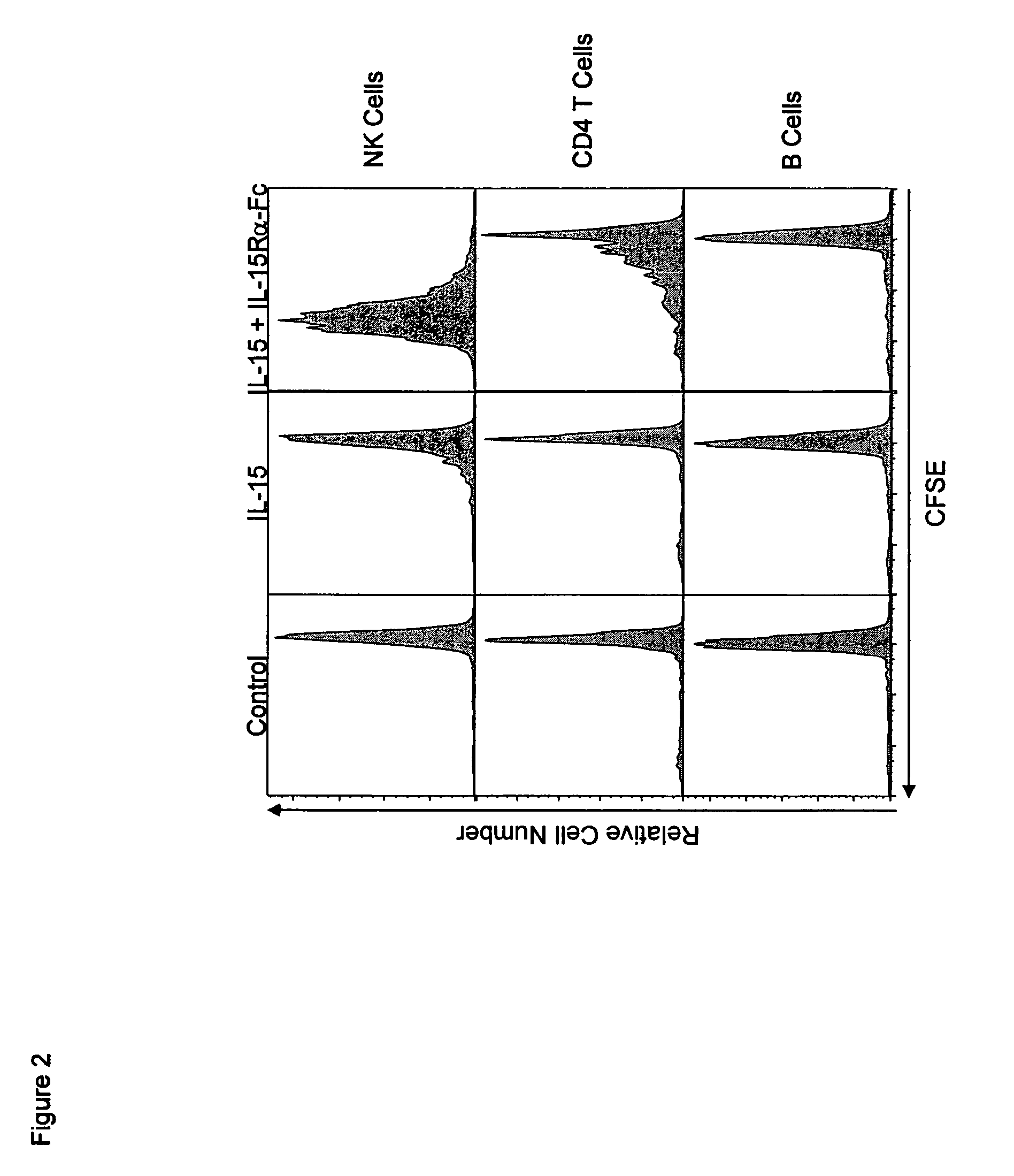
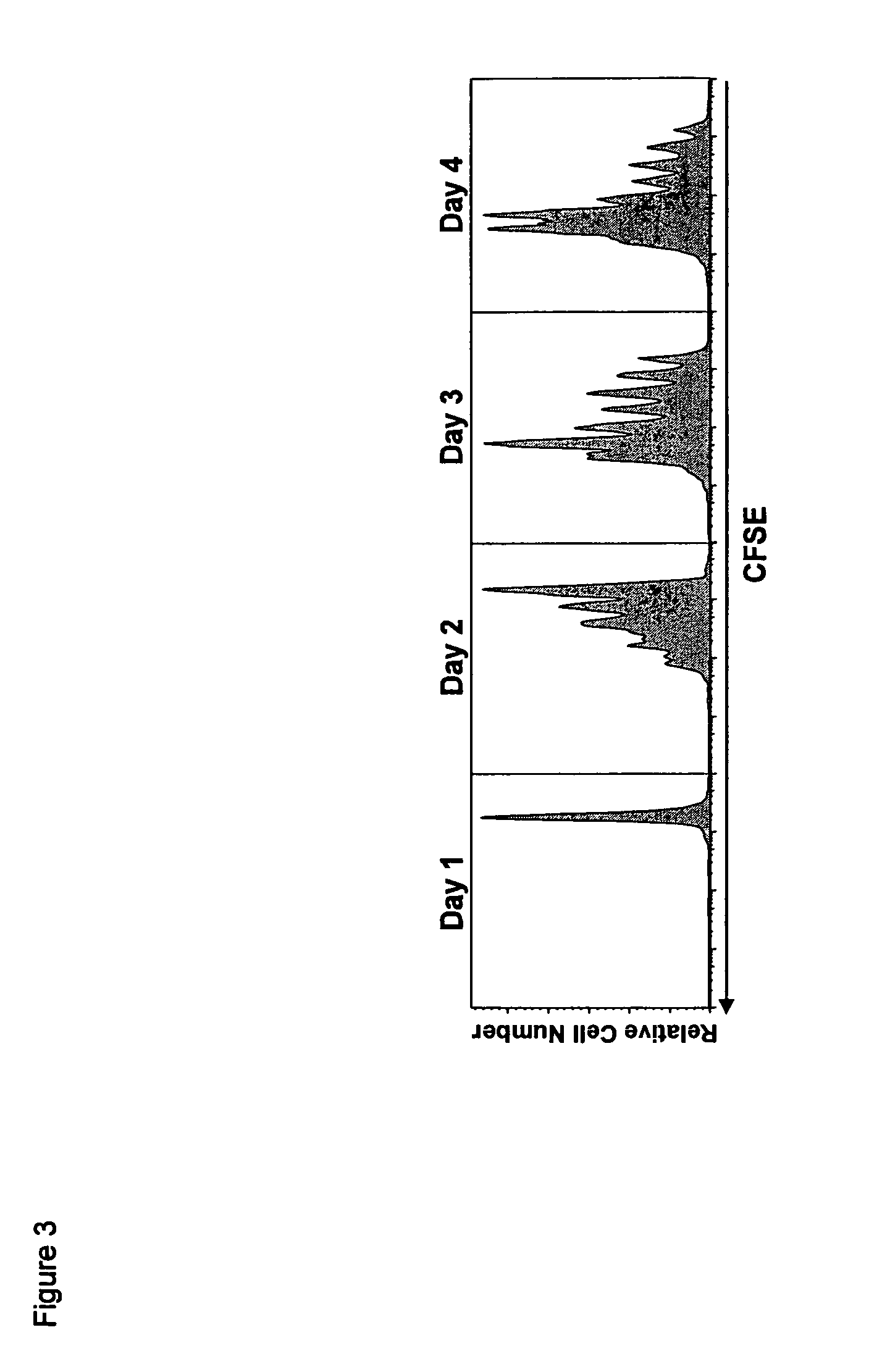
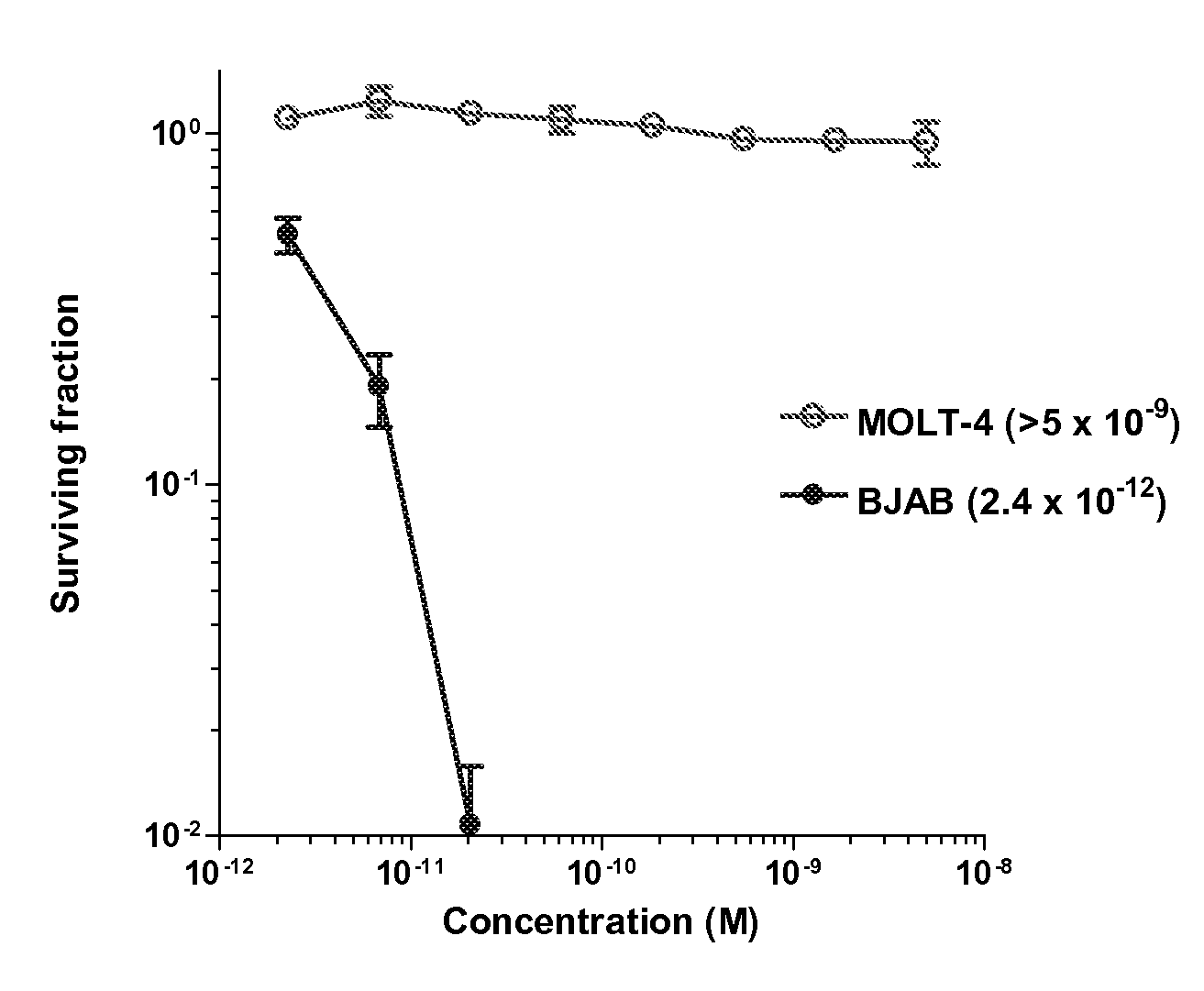
Compositions and methods for immunomodulation in an organism using IL-15 and soluble IL-15Ra
ActiveUS8124084B2Extended half-lifeImprove bioavailabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological bodyVaccination
The present invention relates to a therapeutic polypeptide and methods for its creation and use for modulating an immune response in a host organism in need thereof. In particular, the invention relates to the administration to an organism in need thereof, of an effective amount of a pre-coupled polypeptide complex comprising a lymphokine polypeptide portion, for example IL-15 (SEQ ID NO: 5, 6), IL-2 (SEQ ID NO: 10, 12) or combinations of both, and an interleukin receptor polypeptide portion, for example IL-15Ra (SEQ ID NO: 7, 8), IL-2Ra (SEQ ID NO: 9, 11) or combinations of both, for augmenting the immune system in, for example, cancer, SCID, AIDS, or vaccination; or inhibiting the immune system in, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, or Lupus. The therapeutic complex of the invention surprisingly demonstrates increased half-life, and efficacy in vivo.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Cytotoxic Agents Comprising New Tomaymycin Derivatives
ActiveUS20090036431A1Easy to useHighly toxicBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCytotoxicityTreatment use
Owner:SANOFI SA
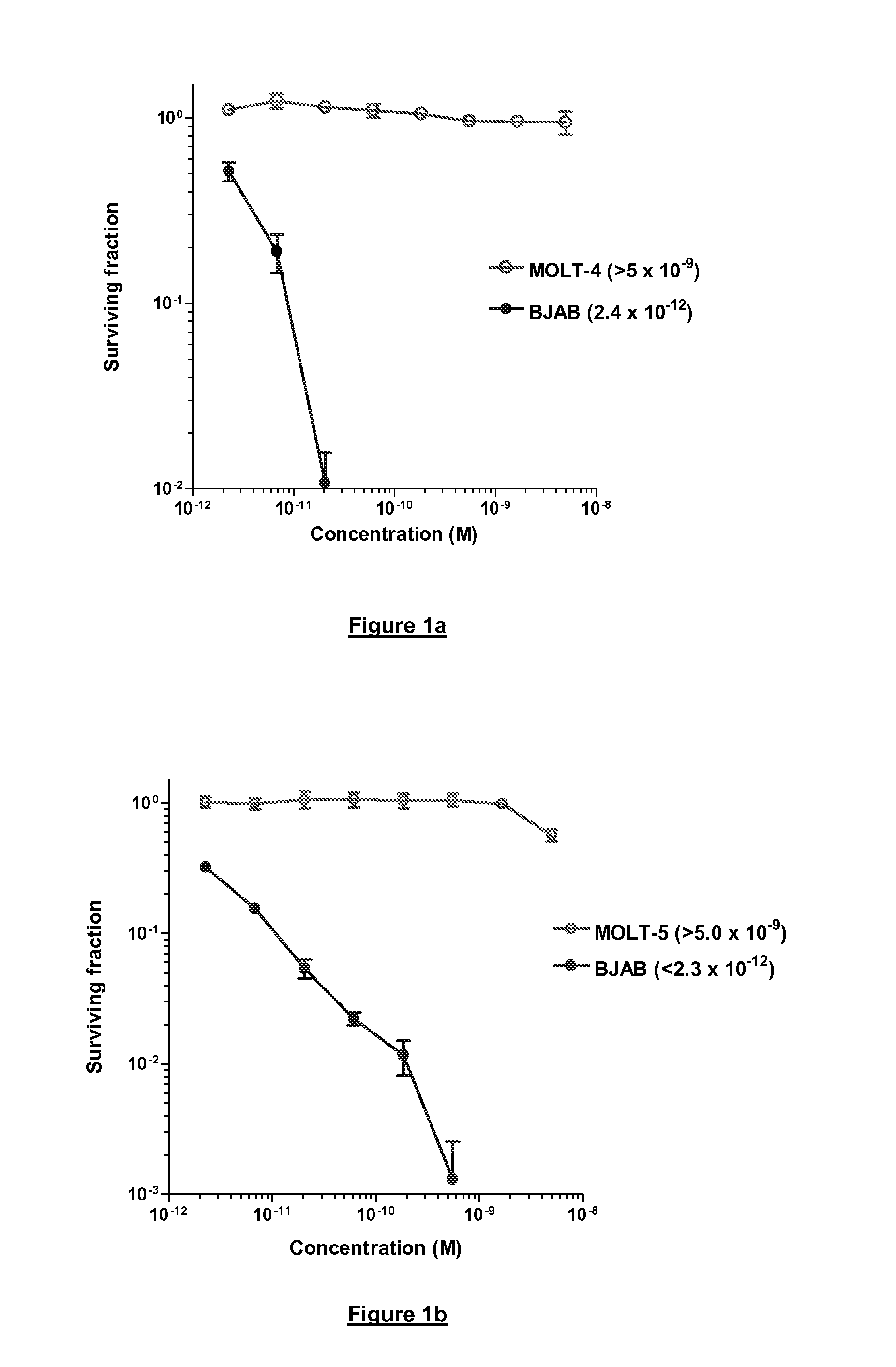
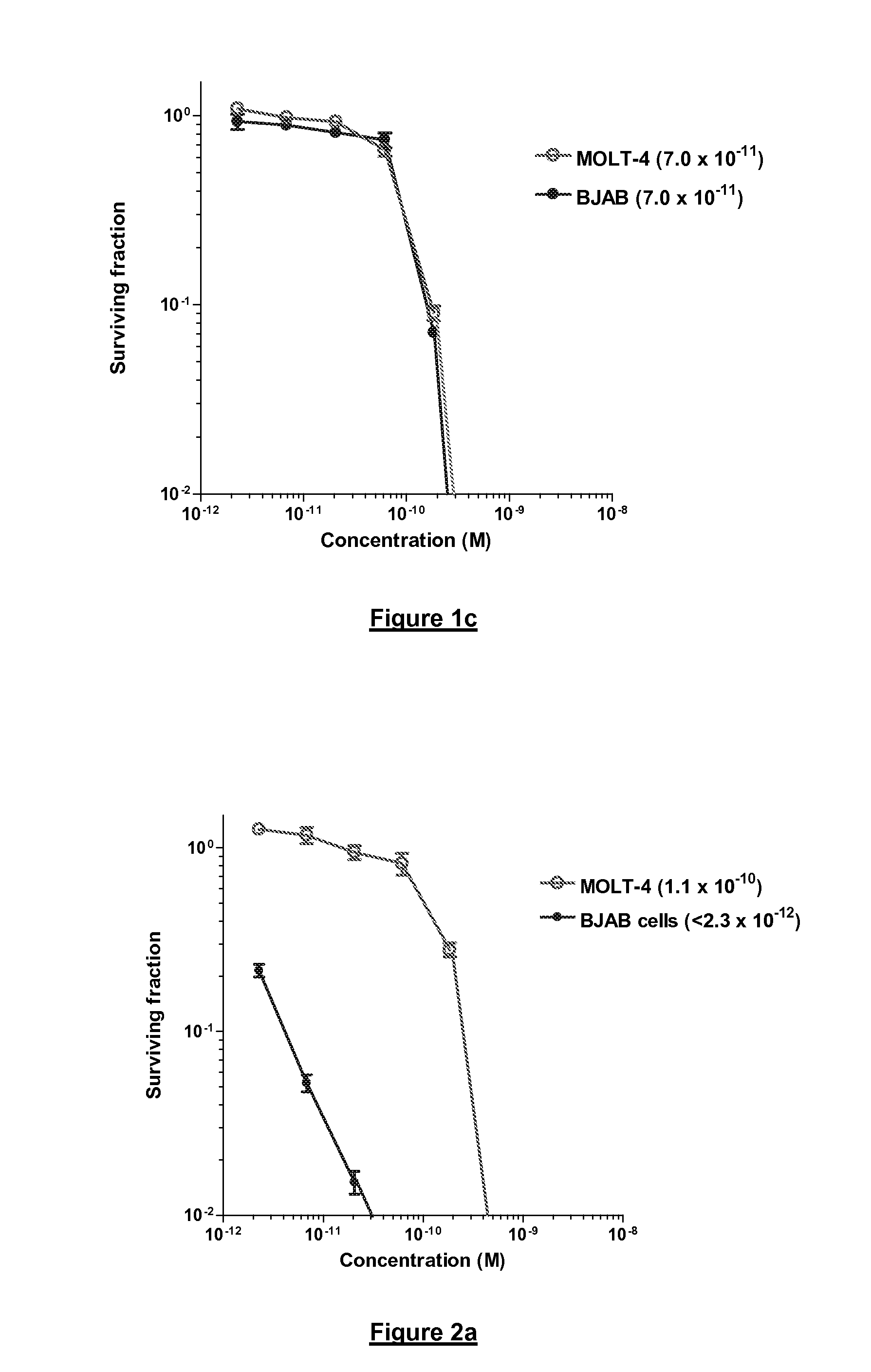
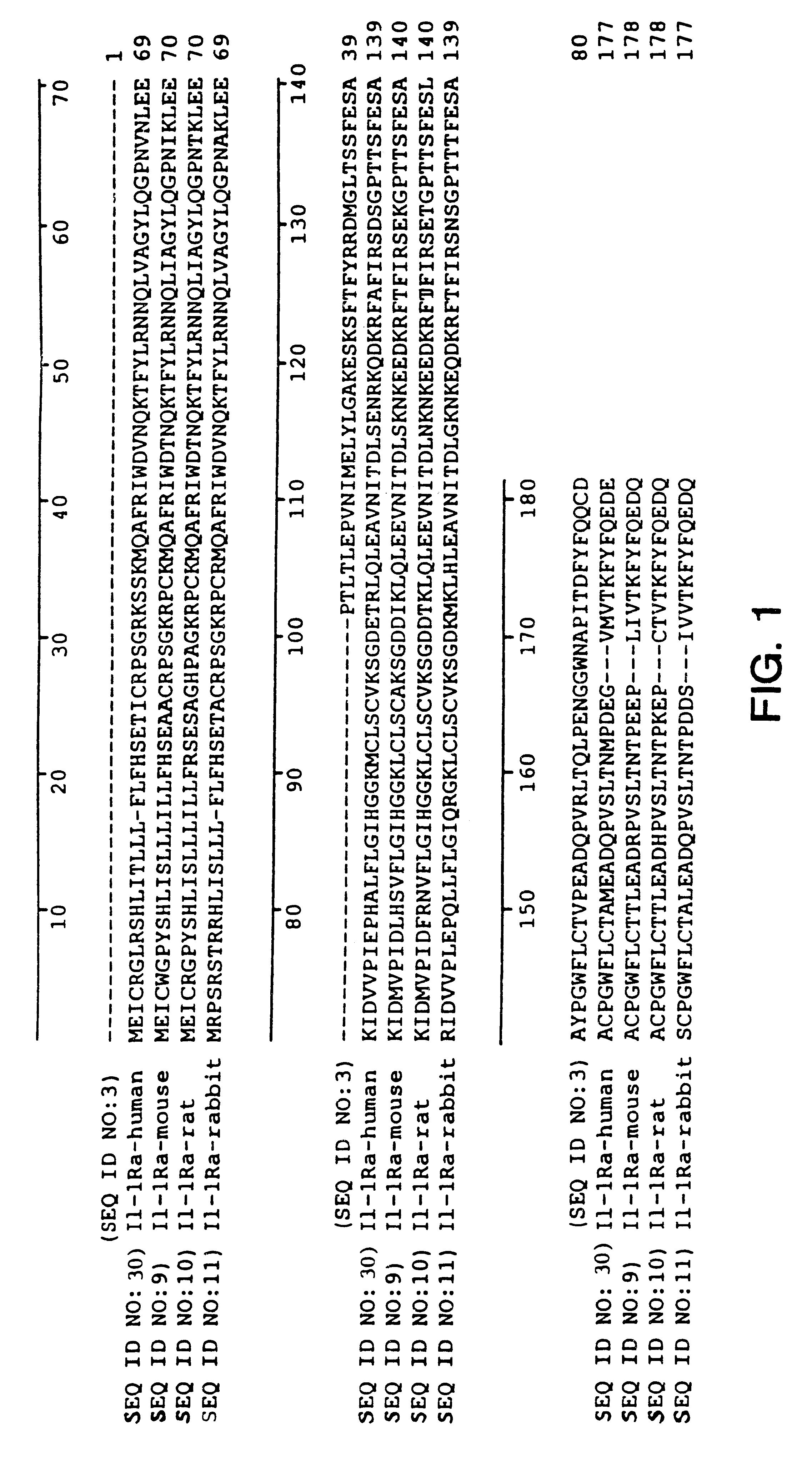
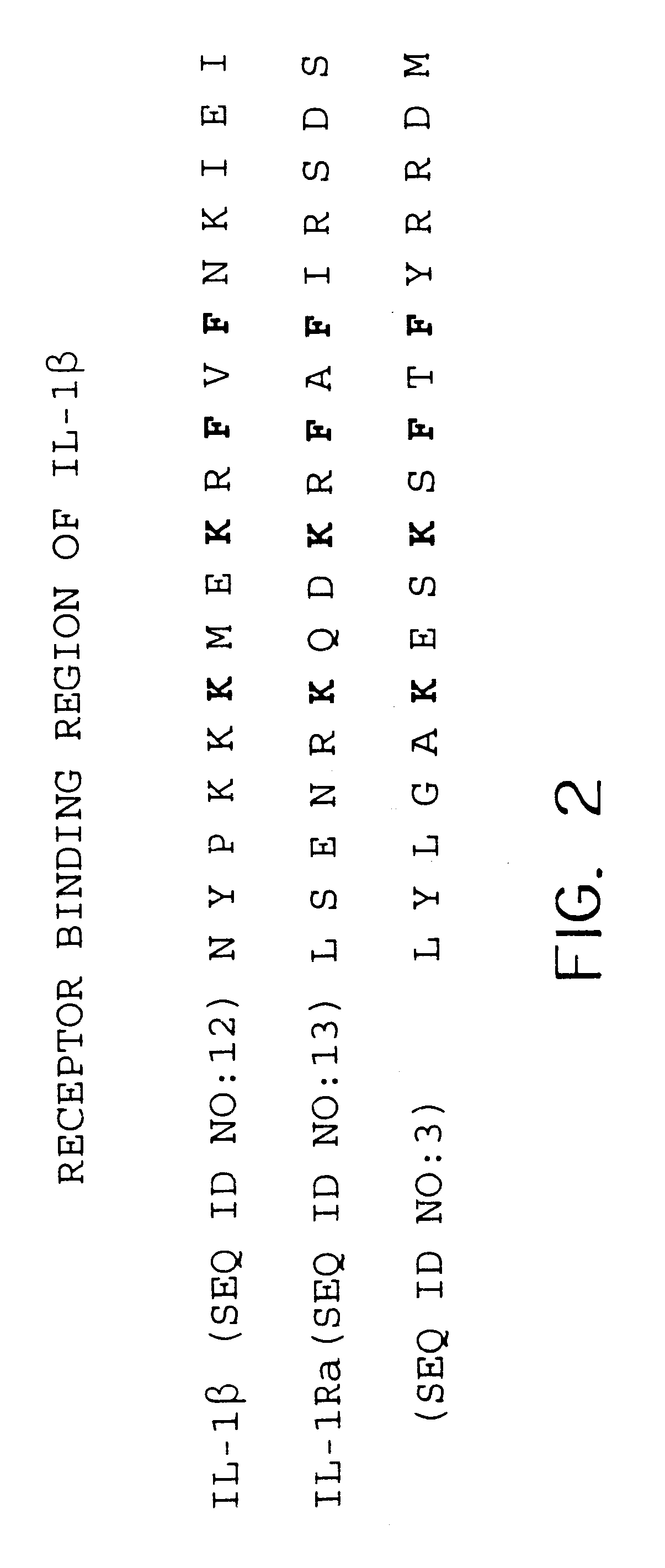
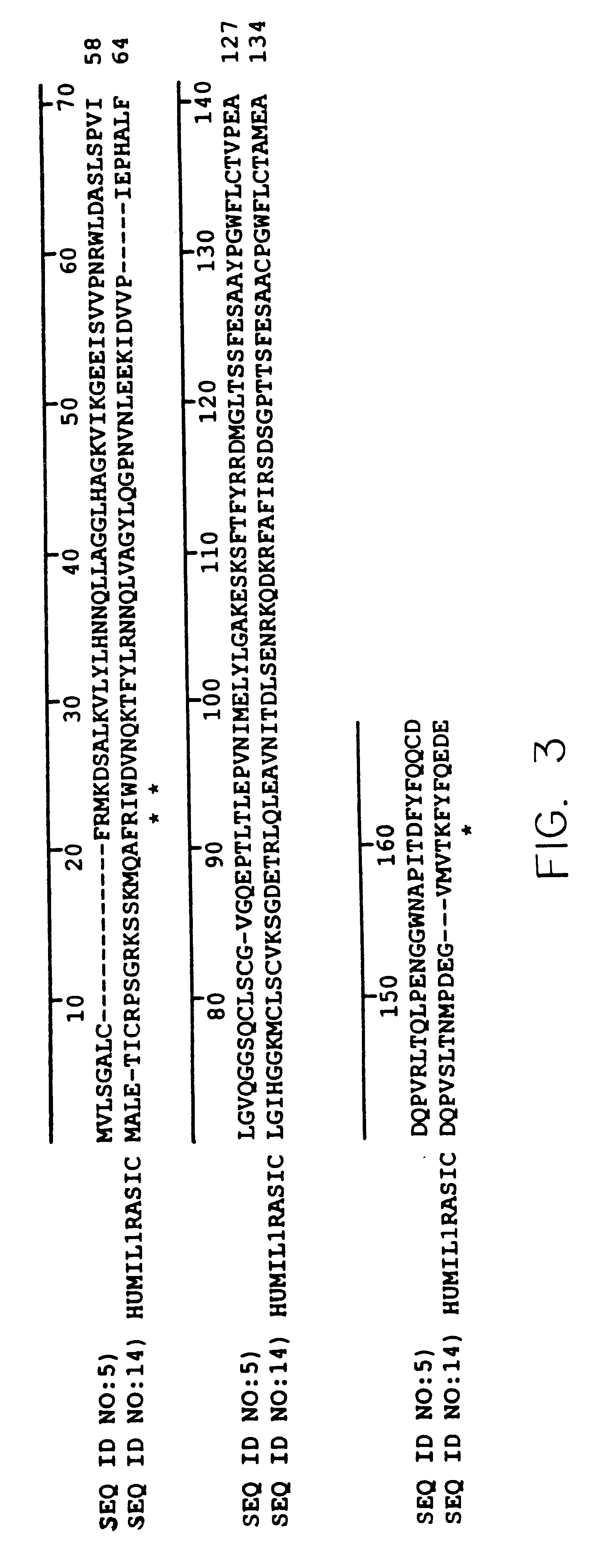
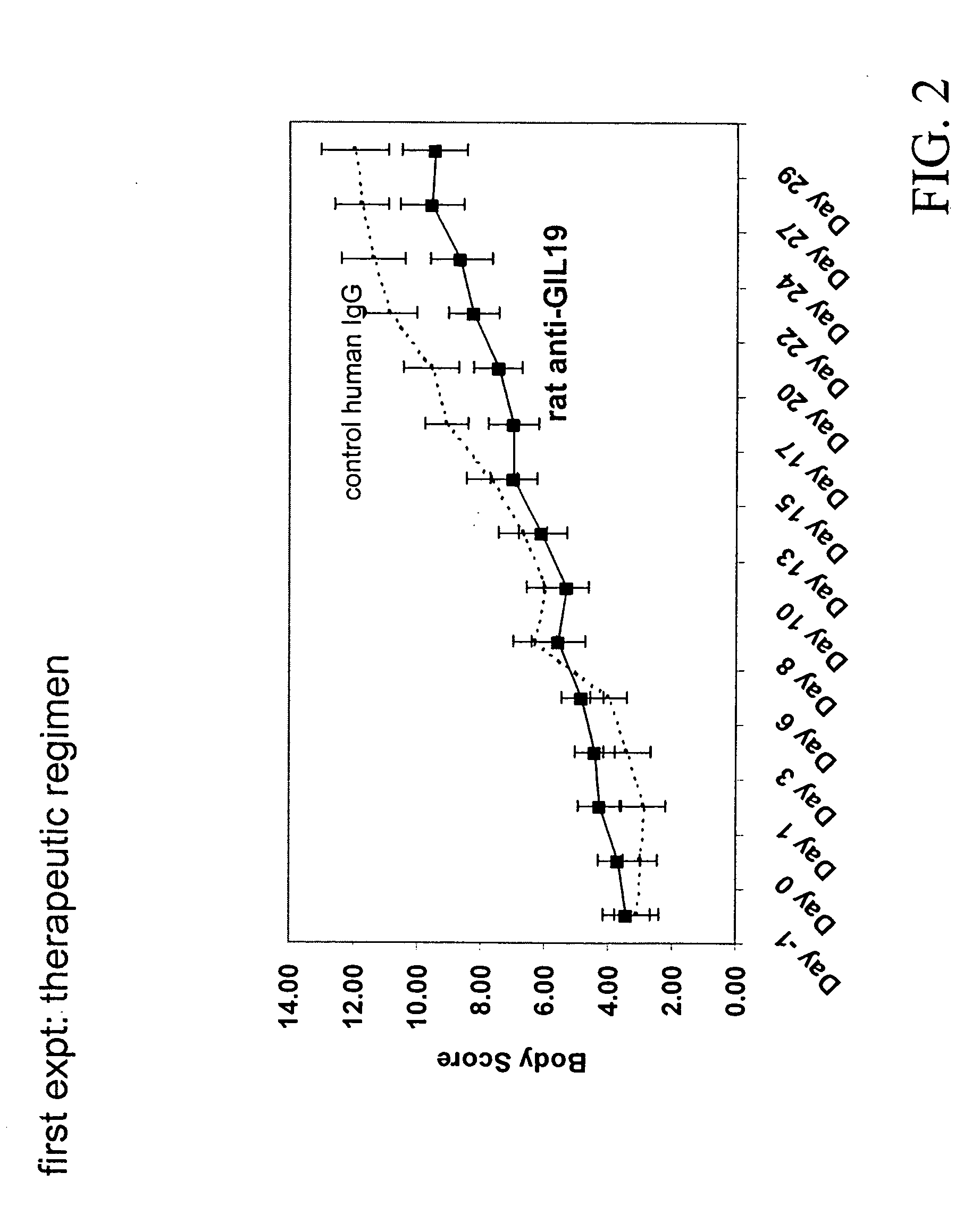
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and recombinant production thereof
The present invention provides novel nucleic acids, the novel polypeptide sequences encoded by these nucleic acids and uses thereof. These novel polynucleotide and polypeptide sequences were determined to be a novel Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist.
Owner:NUVELO INC
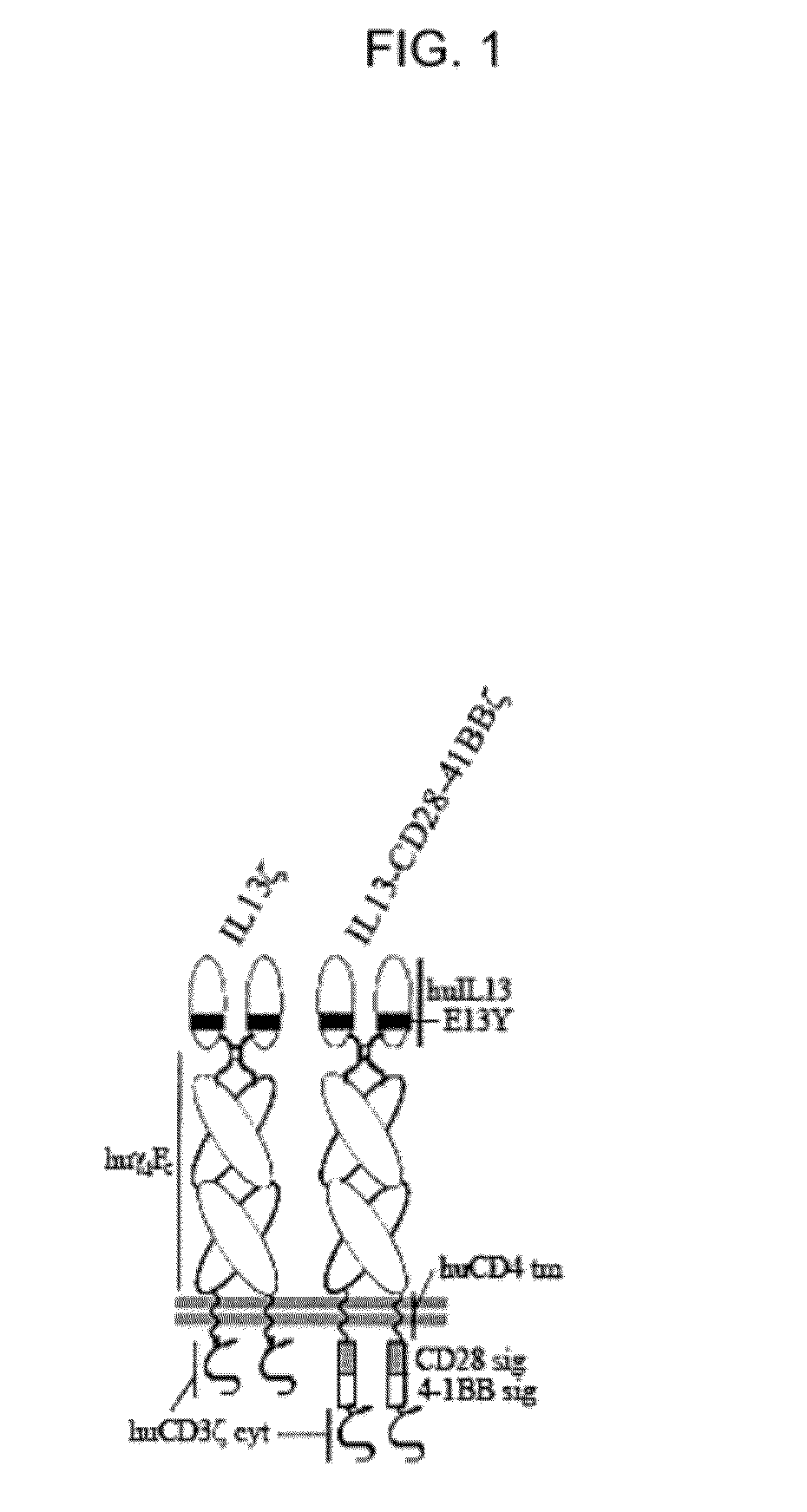
Method and compositions for enhanced Anti-tumor effector functioning of t cells
ActiveUS20120148552A1Function increaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTumor targetChimeric antigen receptor
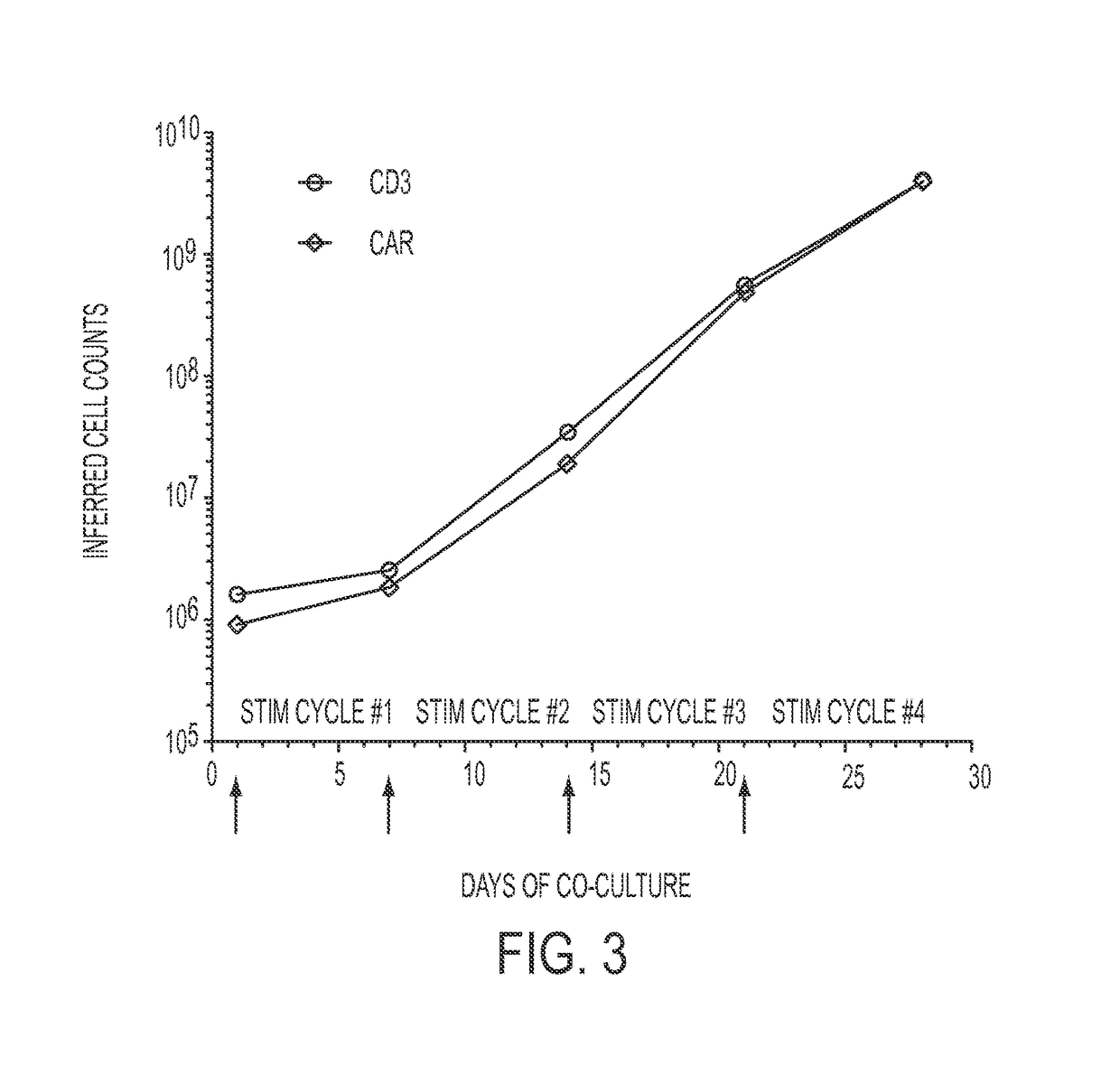
Integration of costimulatory signaling domains within a tumor targeting chimeric antigen receptor (CAR), such as the IL13Rα2 specific IL13-zetakine (IL13ζ), enhances T cell-mediated responses against tumors even in the absence of expressed ligands for costimulatory receptors.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Composition and method for trating inflammatory disorders
Owner:GENETICS INST LLC
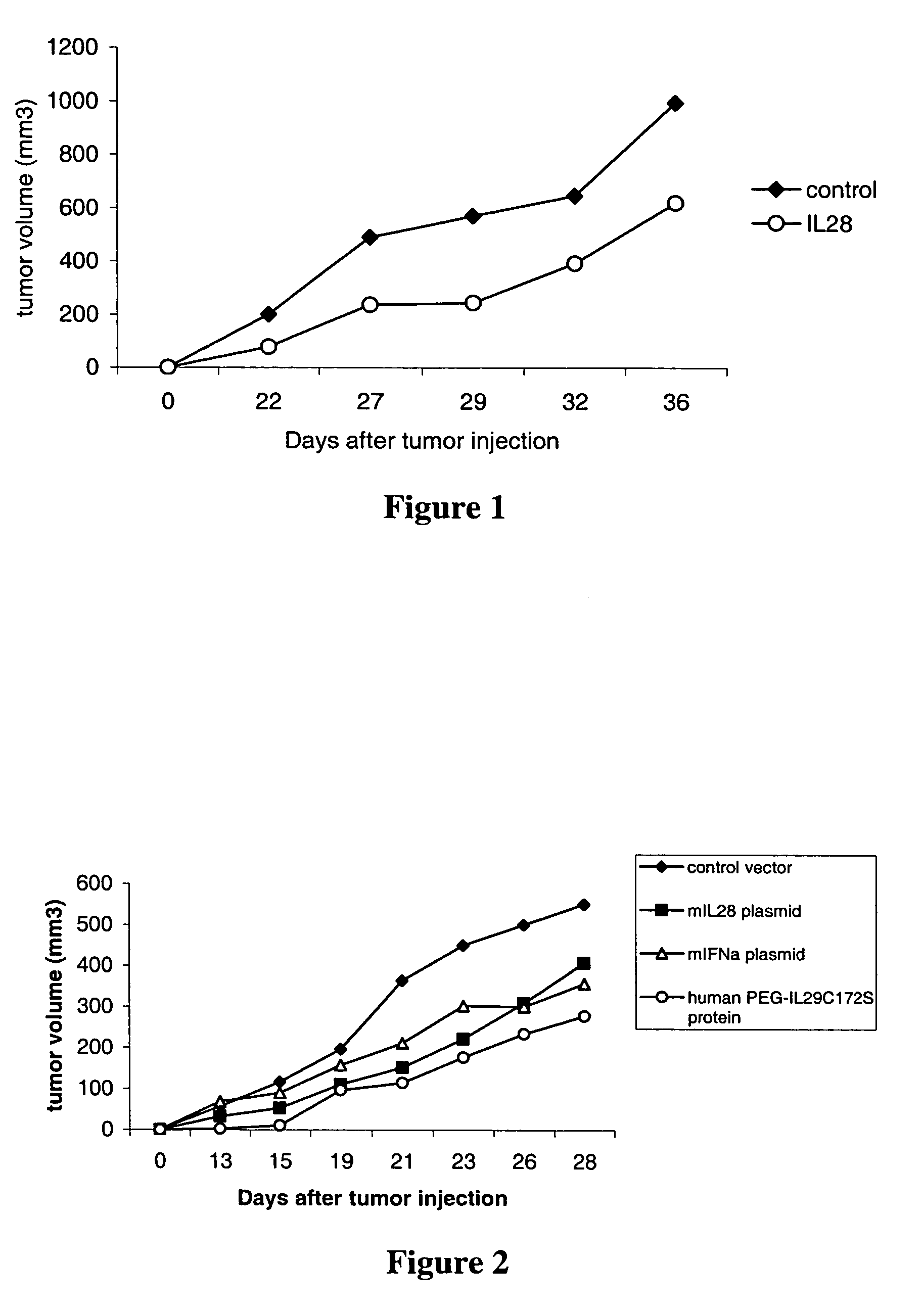
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28 and IL-29
ActiveUS7157559B2Improve expression levelIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 have been produced by mutating one or more of the cysteine residues in the polynucleotide sequences encoding the mature proteins. The cysteine mutant proteins can be shown to either bind to their cognate receptor or exhibit biological activity. One type of biological activity that is shown is an antiviral activity.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Method for Purifying Antibodies
ActiveUS20130171095A1Increased serum half-lifeMinimize the possibilityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsIsoelectric pointAntibody
The invention relates generally to compositions and methods for purifying the desired species from a mixture of desired heterodimer and contaminating homodimer immunoglobulin variants by modifying the isoelectric point(s) of the individual chains.
Owner:XENCOR
Pegylated interleukin-10
InactiveUS7052686B2Minimize disruptionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticInterleukin 10White blood cell
Interleukin-10 (IL-10) conjugated via a linker to one or more polyethylene glycol (PEG) molecules at a single amino acid residue of the IL-10, and a method for preparing the same, are provided. The method produces a stable mono-pegylated IL-10, which retains IL-10 activity, where pegylation is selective for the N-terminus on one subunit of IL-10 with little or no formation of monomeric IL-10. The method also provides a substantially homogenous population of mono-PEG-IL-10.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Methods for treating viral infection using IL-28 and IL-29
ActiveUS7135170B2Reduction in viral infection levelReduce viral infectionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon therapyHematopoietic cell
IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and certain mutants thereof have been shown to have antiviral activity on a spectrum of viral species. Of particular interest is the antiviral activity demonstrated on viruses that infect liver, such as hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. In addition, IL-28A, IL-28B, IL-29, and mutants thereof do not exhibit some of the antiproliferative activity on hematopoietic cells that is observed with interferon treatment. Without the immunosuppressive effects accompanying interferon treatment, IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 will be useful in treating immunocompromised patients for viral infections.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Reducing the immunogenicity of fusion proteins
InactiveUS6992174B2Low immunogenicityHigh expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IIVaccine Immunogenicity
Disclosed are compositions and methods for producing fusion proteins with reduced immunogenicity. Fusion proteins of the invention include a junction region having an amino acid change that reduces the ability of a junctional epitope to bind to MHC Class II, thereby reducing its interaction with a T-cell receptor. Methods of the invention involve analyzing, changing, or modifying one or more amino acids in the junction region of a fusion protein in order to identify a T-cell epitope and reduce its ability to interact with a T cell receptor. Compositions and methods of the invention are useful in therapy.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Electro-active spectacle employing modal liquid crystal lenses
An electro-active spectacle lens is disclosed. The spectacle lens comprises a first substrate having a first outer region and first inner region, a first electrode layer disposed adjacent to the first inner region, the first electrode layer including an outer electrode region having a first conductivity and an inner electrode region having a second conductivity, the first conductivity being greater than the second conductivity, a second substrate having a second outer region and second inner region, a second electrode layer disposed adjacent to the second inner region, the second electrode layer having a third conductivity, and an electro-active cell disposed between the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer, the electro-active cell containing an electro-active material. The first outer region and second outer region are configurable for fitting the spectacle lens within a lens frame without altering the electro-active cell.
Owner:E VISION LLC
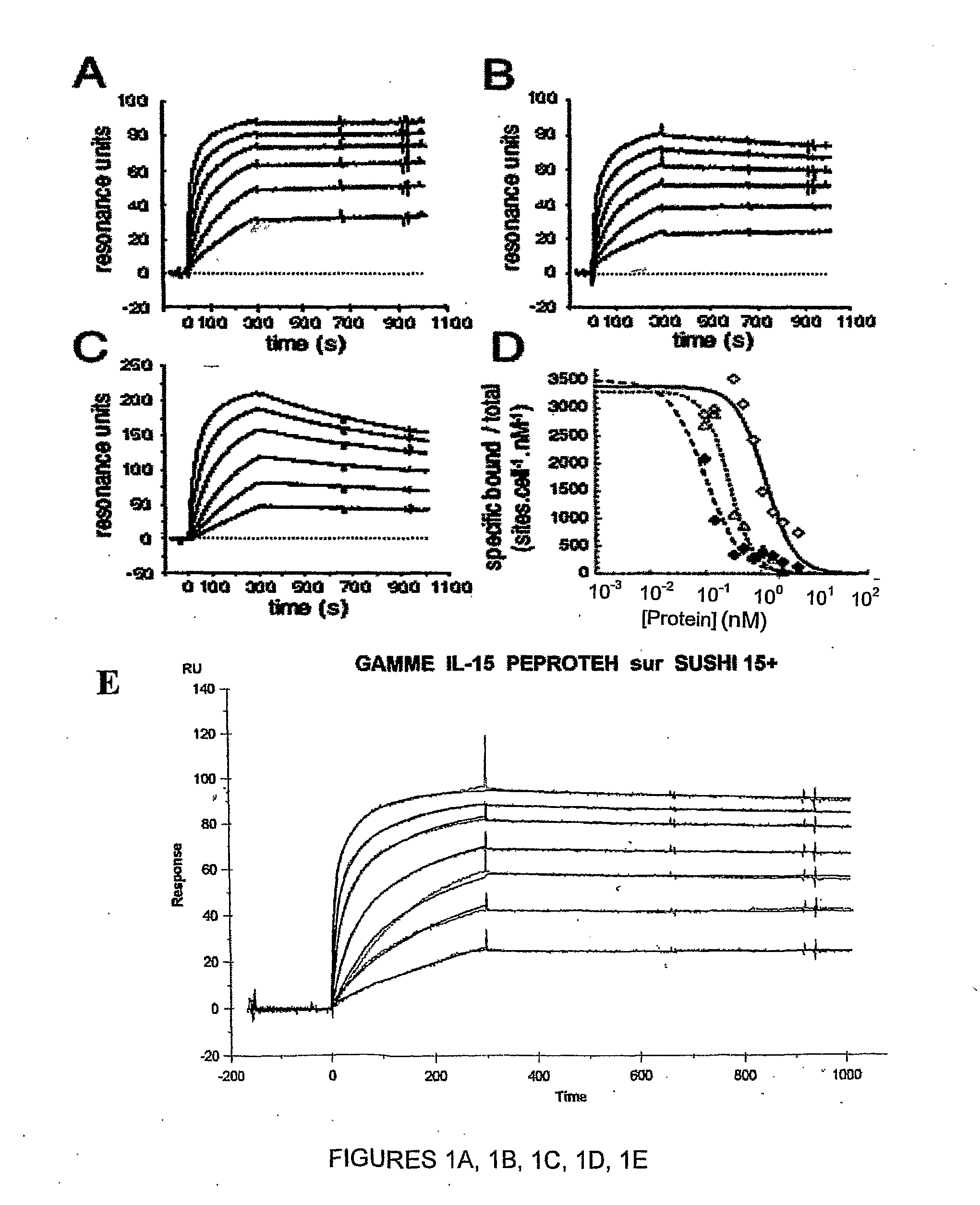
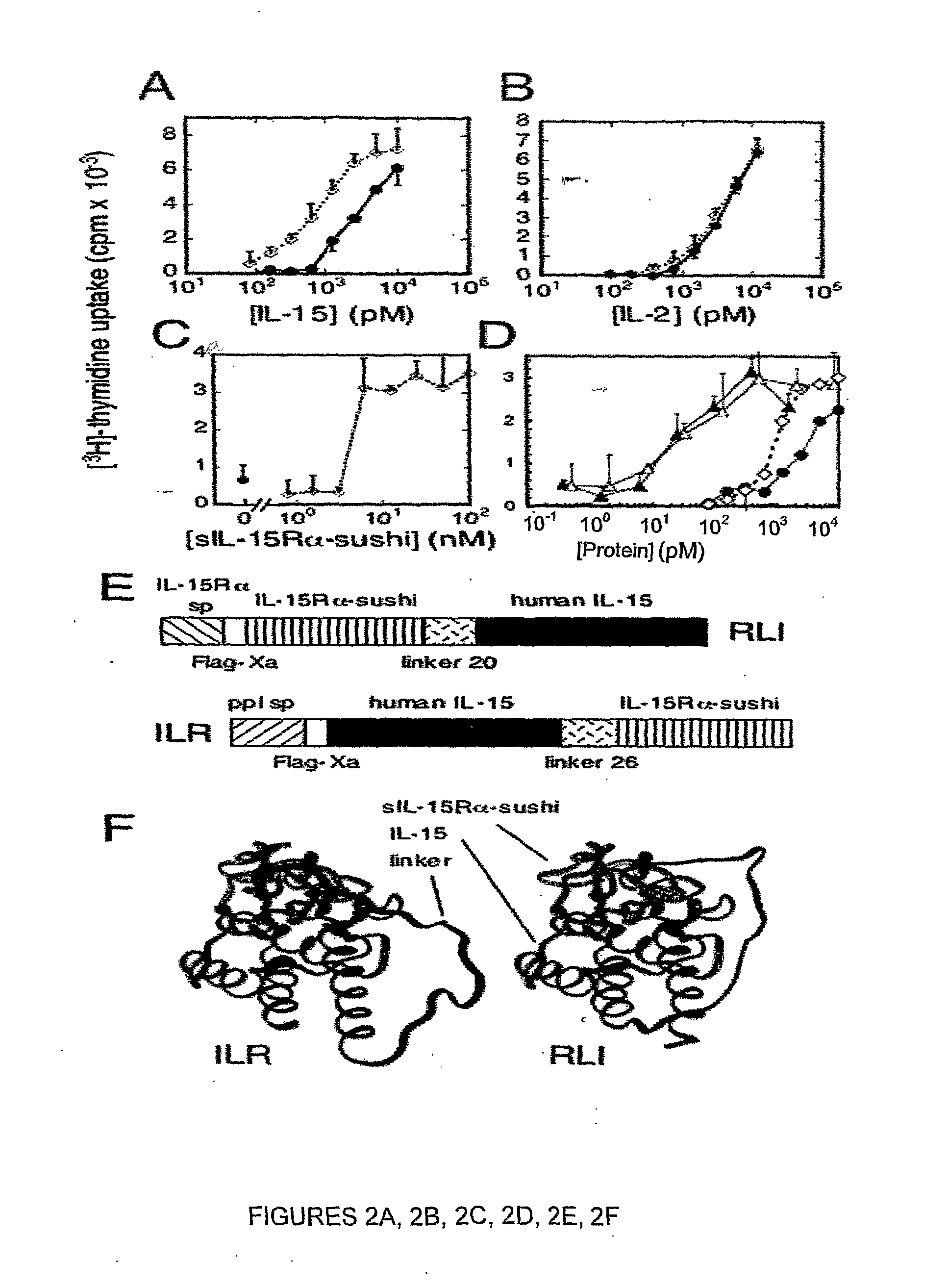
Il-15ralpha sushi domain as a selective and potent enhancer of il-15 action through il-15beta/gamma, and hyperagonist (il-15ralpha sushi - il-15) fusion proteins
ActiveUS20090238791A1Improve efficiencyAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsSushi domainBiological activation
The present invention relates to the stimulation of the IL-15R beta / gamma signalling pathway, to thereby induce and / or stimulate the activation and / or proliferation of IL-15Rbeta / gamma-positive cells, such as NK and / or T cells. Appropriate compounds include compounds comprising at least one IL-15Rbeta / gamma binding entity, directly or indirectly linked by covalence to at least one polypeptide which contains the sushi domain of the extracellular region of an IL-15Ralpha.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
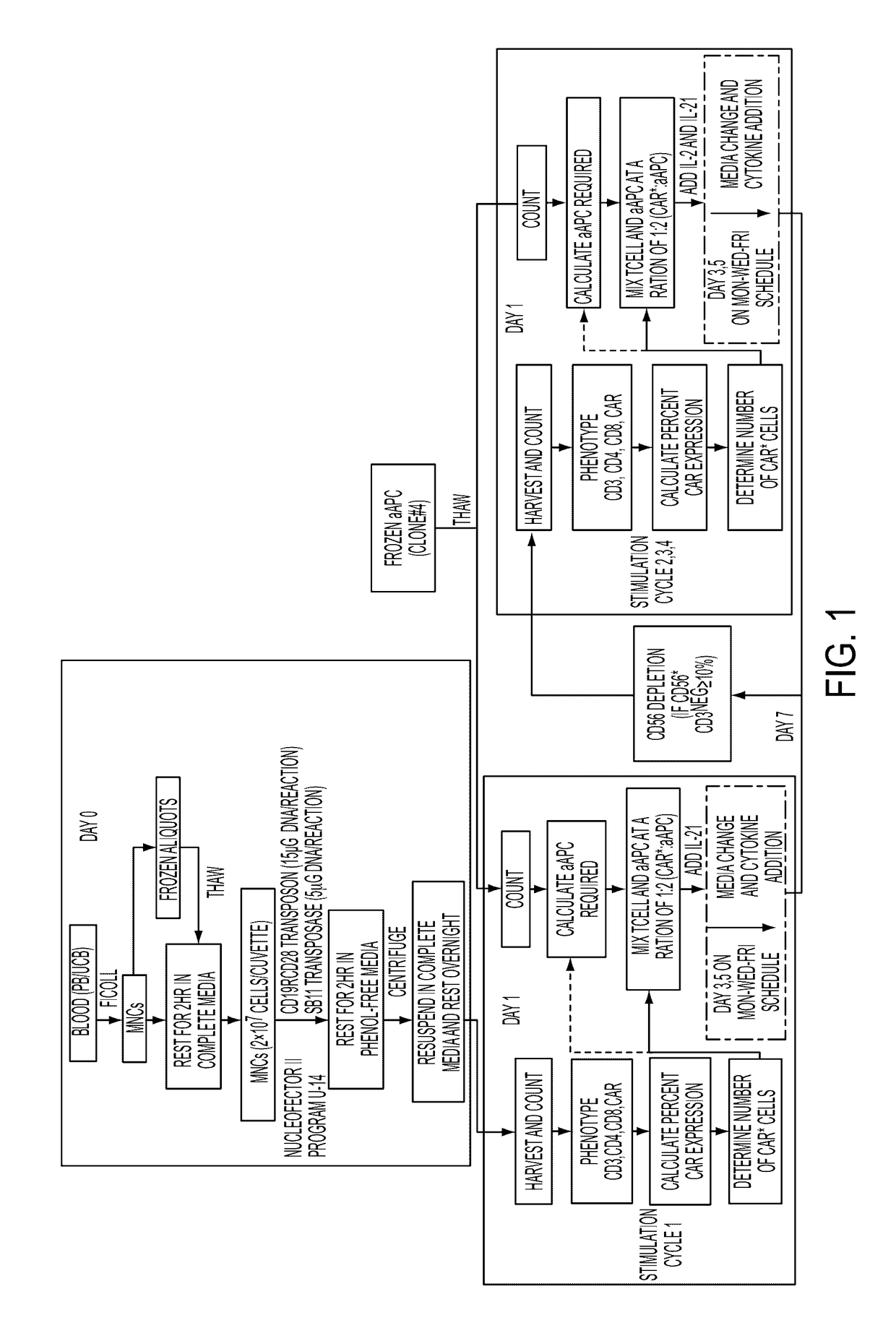
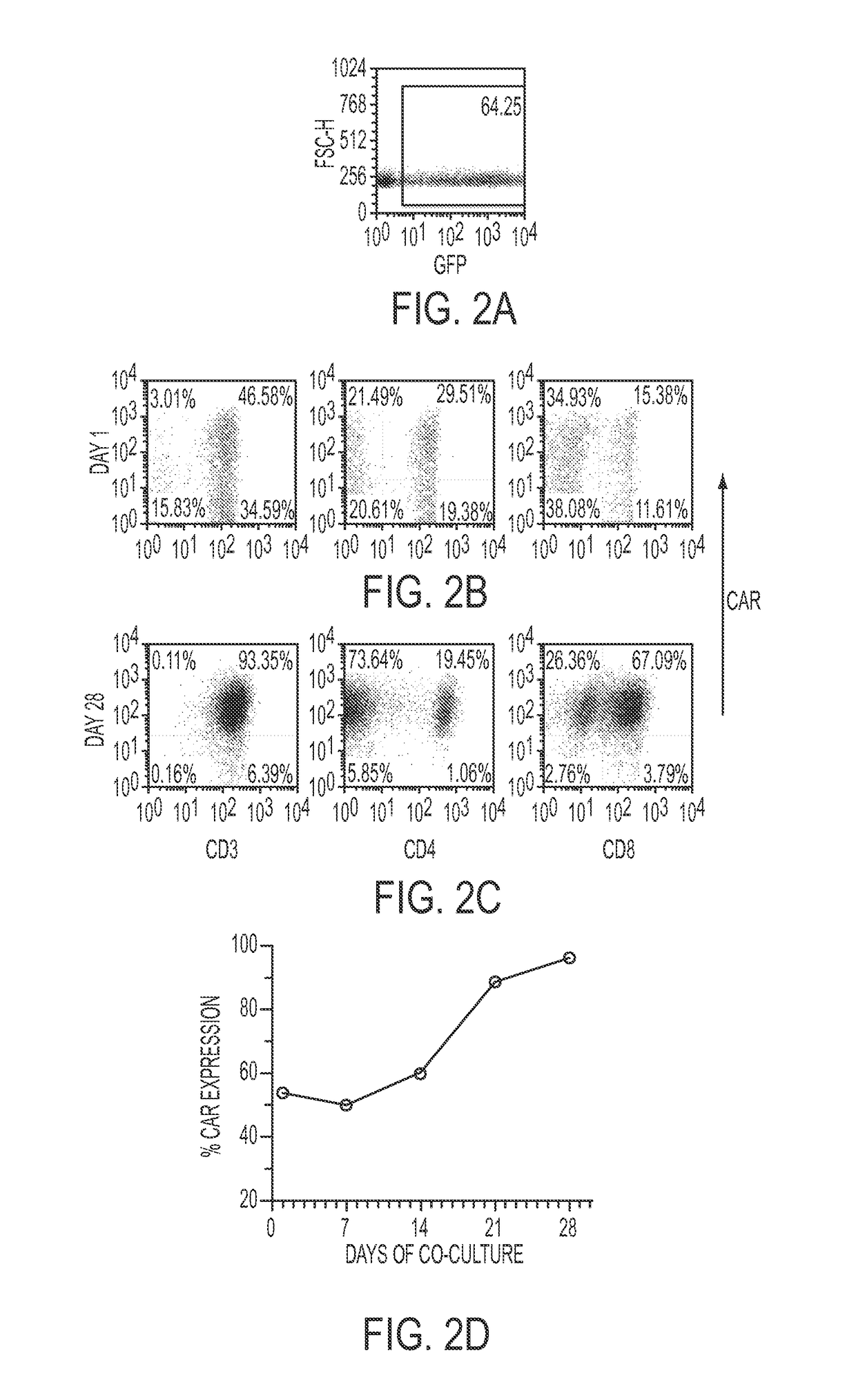
Human application of engineered chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells
ActiveUS9629877B2Promote proliferation and survivalInhibit expressionImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsMammal material medical ingredientsHuman bodyElectroporation
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for immunotherapy employing a modified T cell comprising a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). In particular aspects, CAR-expressing T-cells are producing using electroporation in conjunction with a transposon-based integration system to produce a population of CAR-expressing cells that require minimal ex vivo expansion or that can be directly administered to patients for disease (e.g., cancer) treatment.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Homogeneous preparations of IL-31
Homogeneous preparations of human and murine IL-31 have been produced by mutating one or more of the cysteine residues in the polynucleotide sequences encoding the mature proteins. The cysteine mutant proteins can be shown to either bind to their cognate receptor or exhibit biological activity.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Production and purification of il-29
InactiveUS20080096252A1DepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliMrna secondary structure
The expression vectors and methods using an E. Coli expression system for the large scale production of IL-29 are described. The vectors utilize the IL-29 coding sequence with specific changes in nucleotides in order to optimize codons and mRNA secondary structure for translation in E. coli. Also included are methods of producing, purifying and pegylating an IL-29 polypeptide.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Conjugation methods
ActiveUS20110003969A1Reduce potential steric hindrancePeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsBiochemistryAntibody
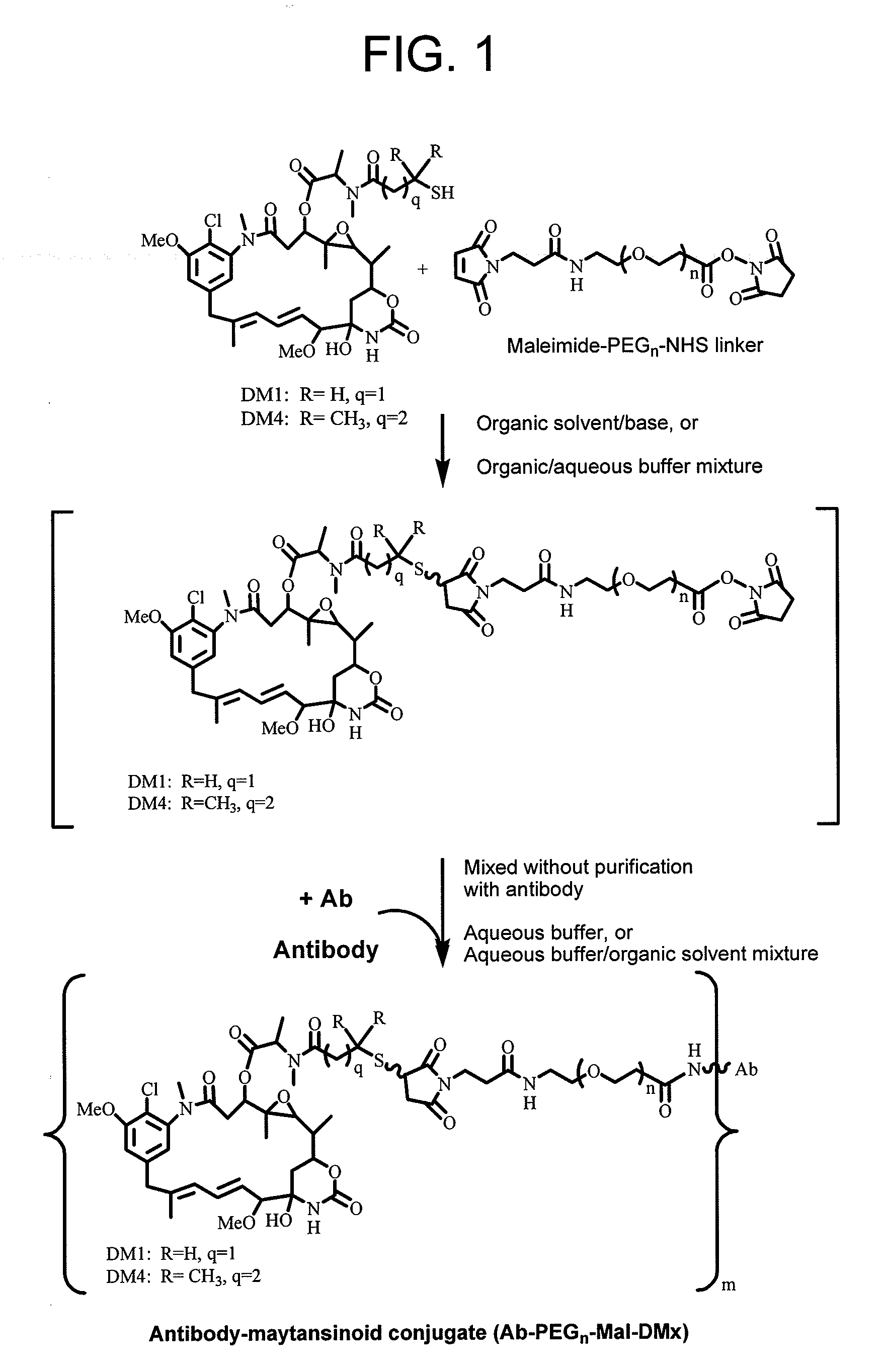
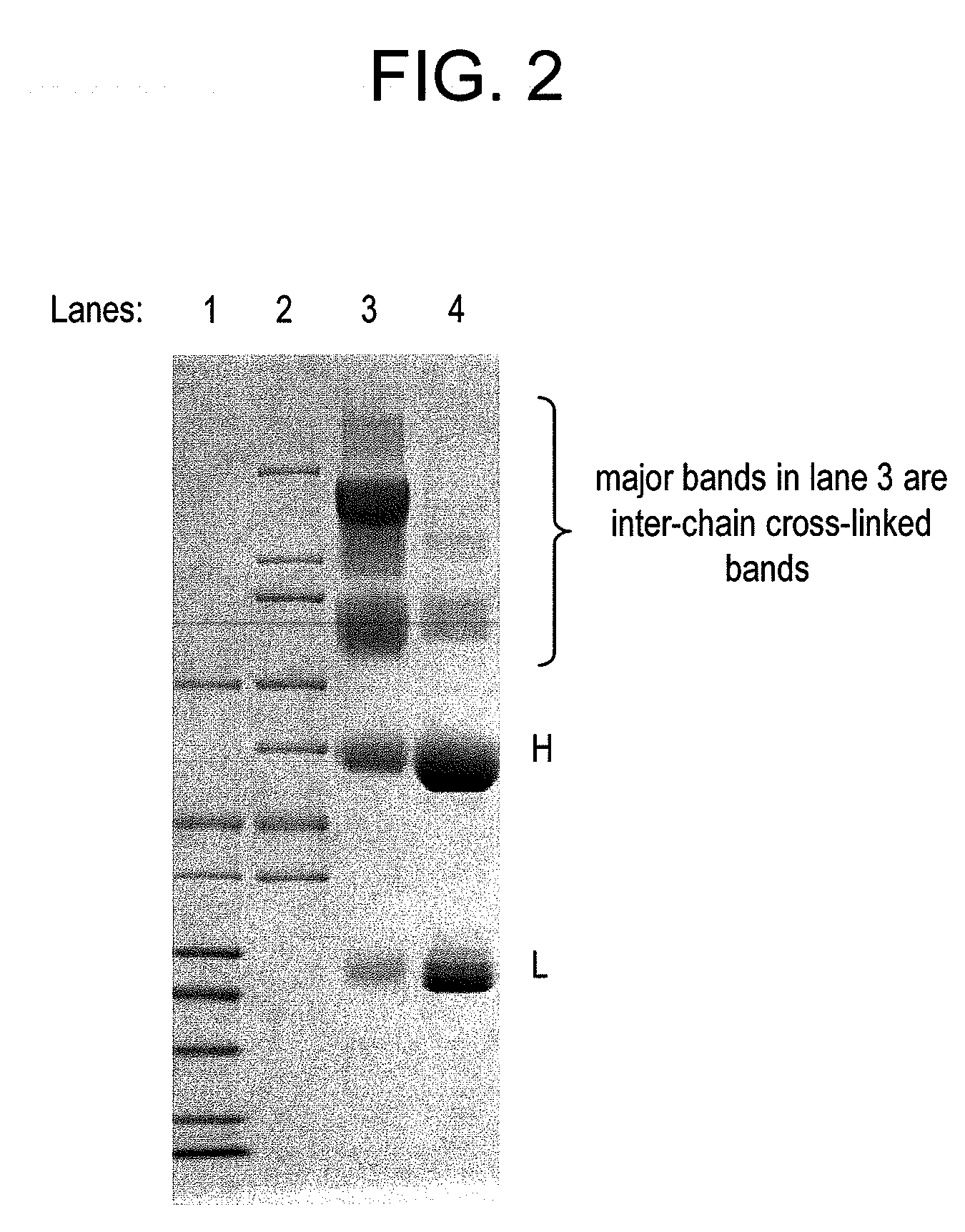
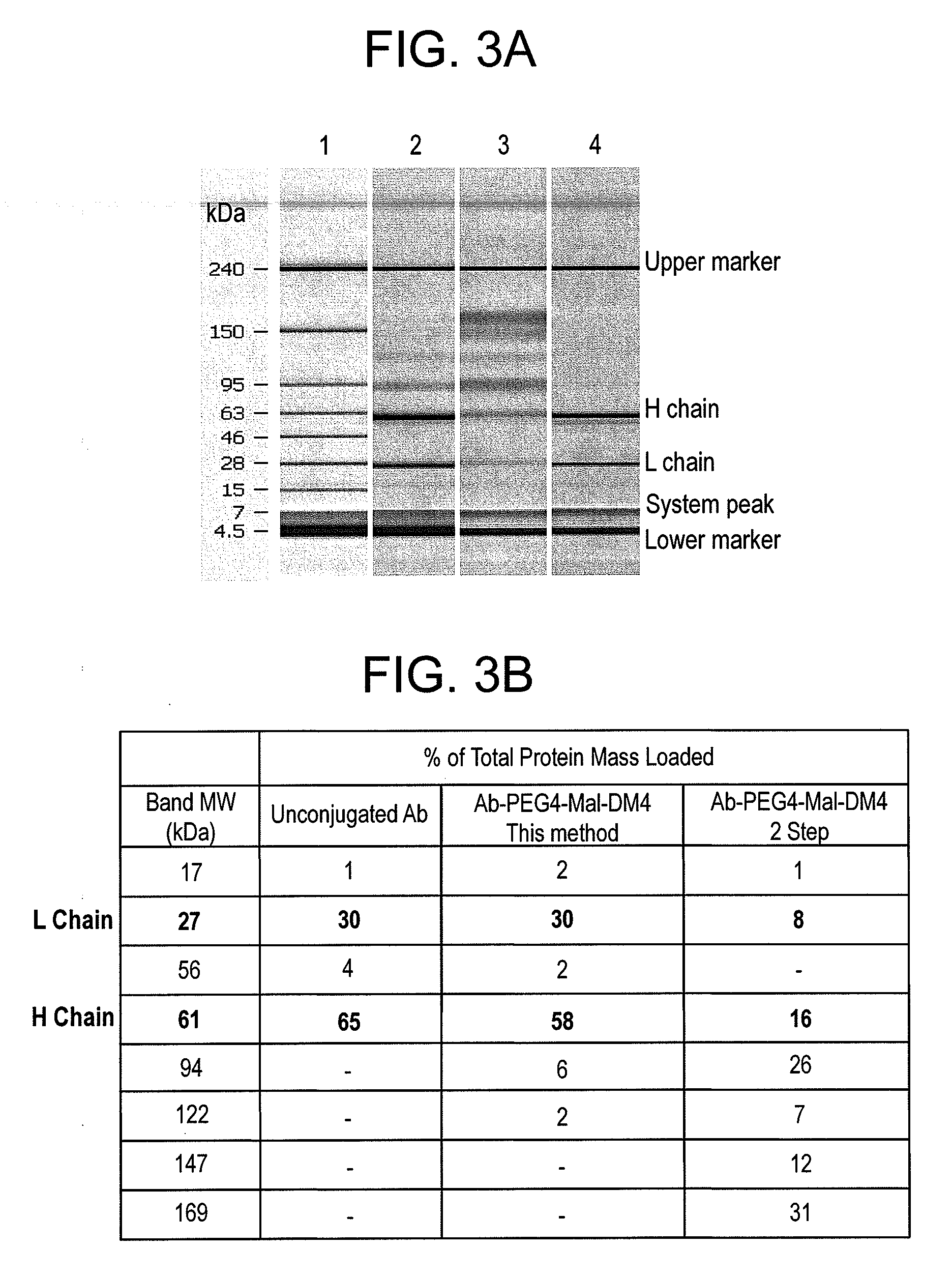
This invention describes a method of conjugating a cell binding agent such as an antibody with an effector group (e.g., a cytotoxic agent) or a reporter group (e.g., a radionuclide), whereby the reporter or effector group is first reacted with a bifunctional linker and the mixture is then used without purification for the conjugation reaction with the cell binding agent. The method described in this invention is advantageous for preparation of stably-linked conjugates of cell binding agents, such as antibodies with effector or reporter groups. This conjugation method provides in high yields conjugates of high purity and homogeneity that are without inter-chain cross-linking and inactivated linker residues
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Methods for the purification of polypeptide conjugates
InactiveUS20100035299A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsPolymer sciencePolypropylene glycol
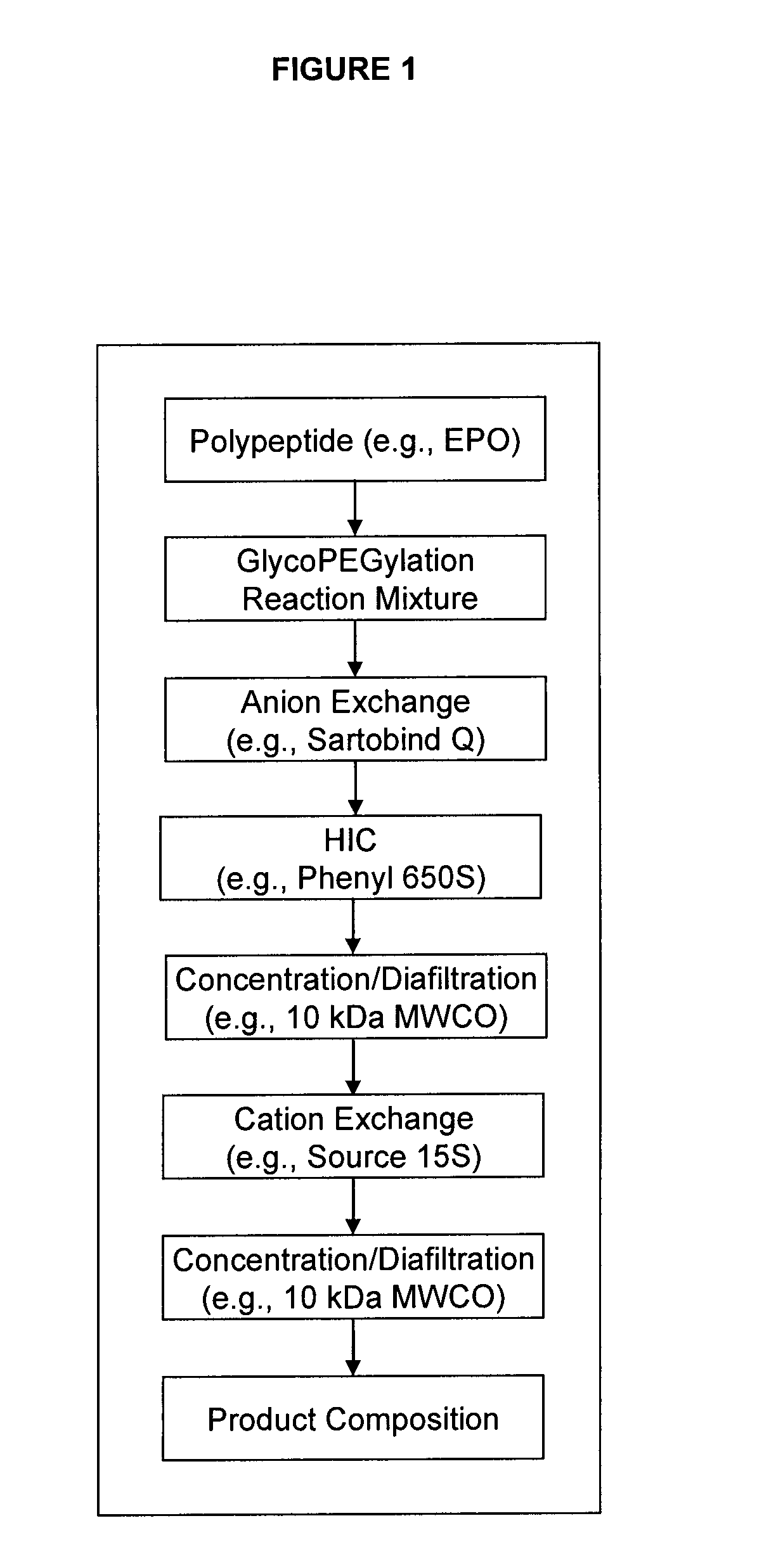
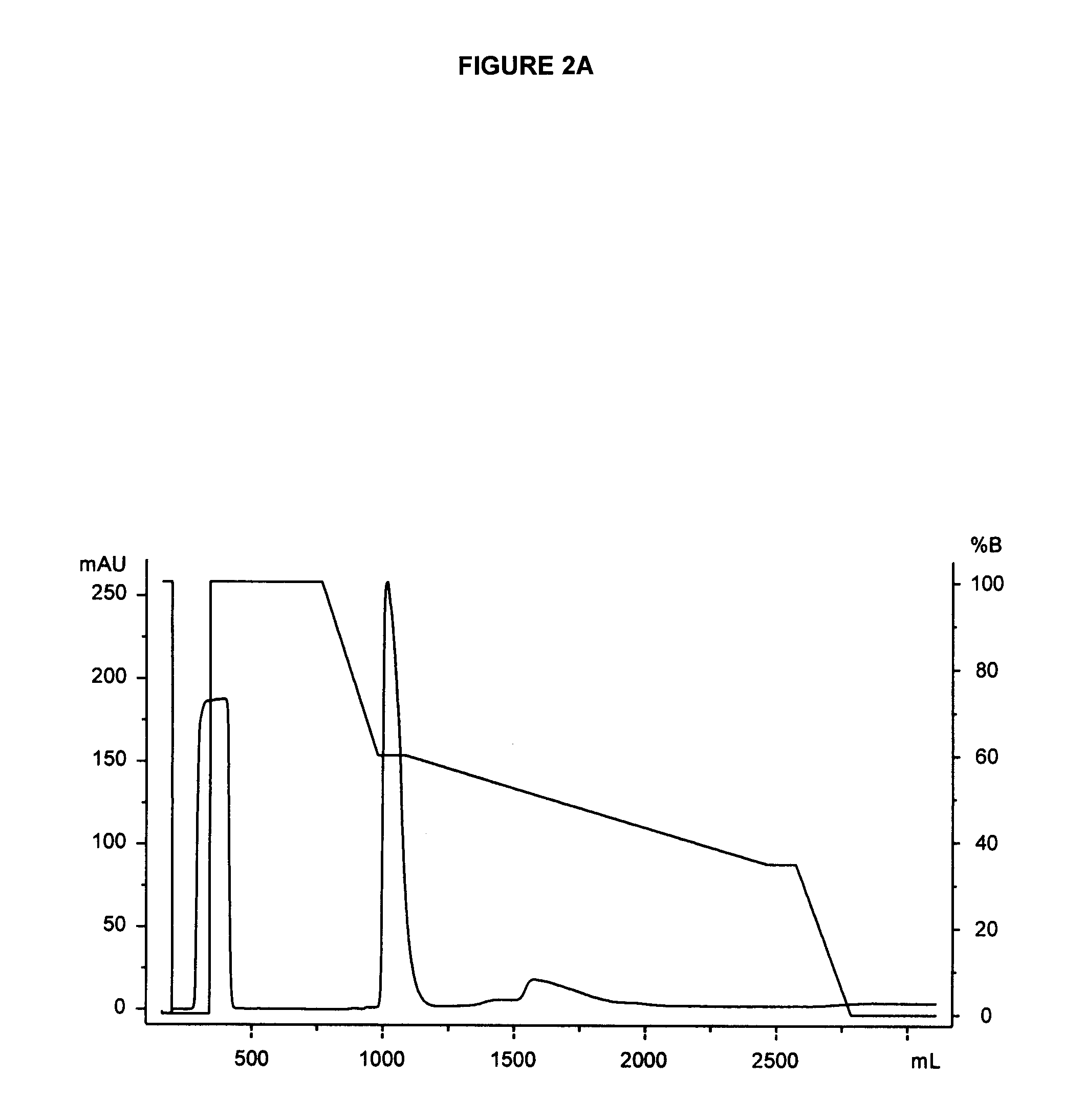
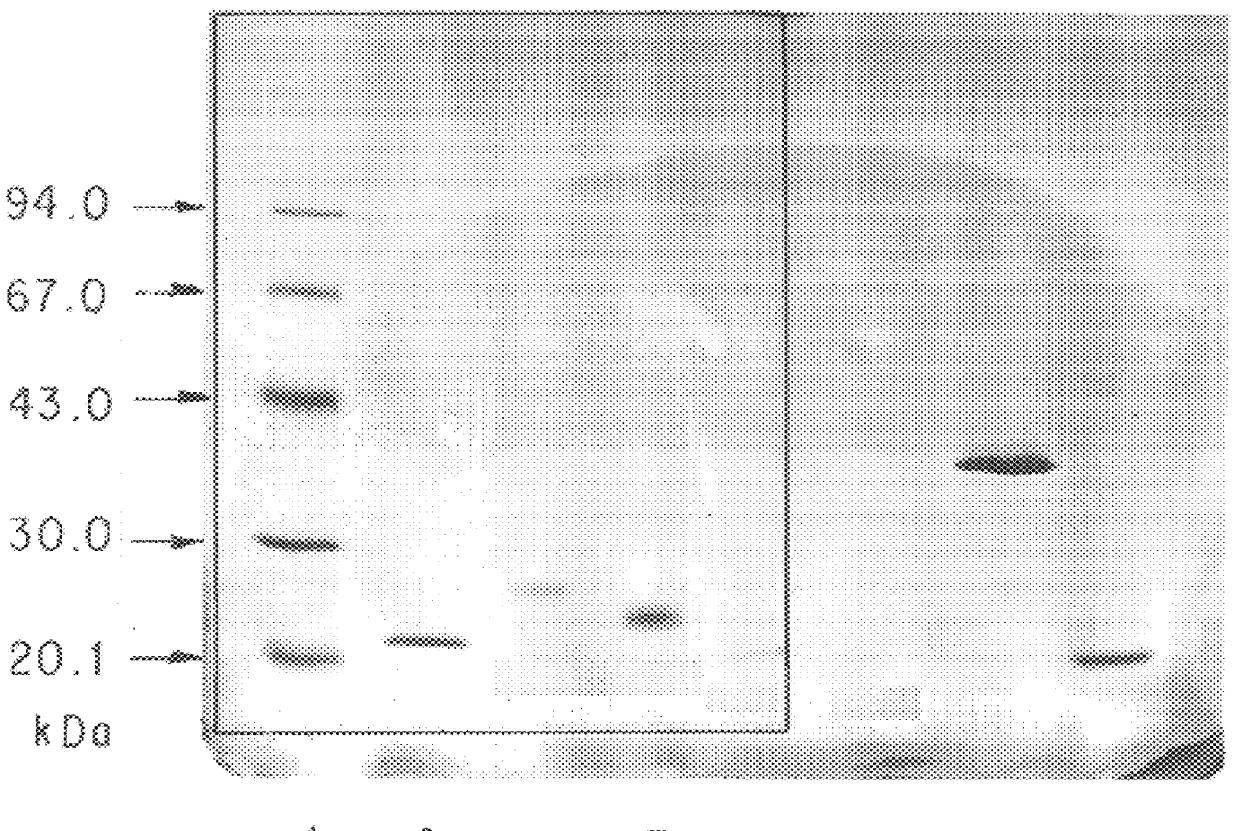
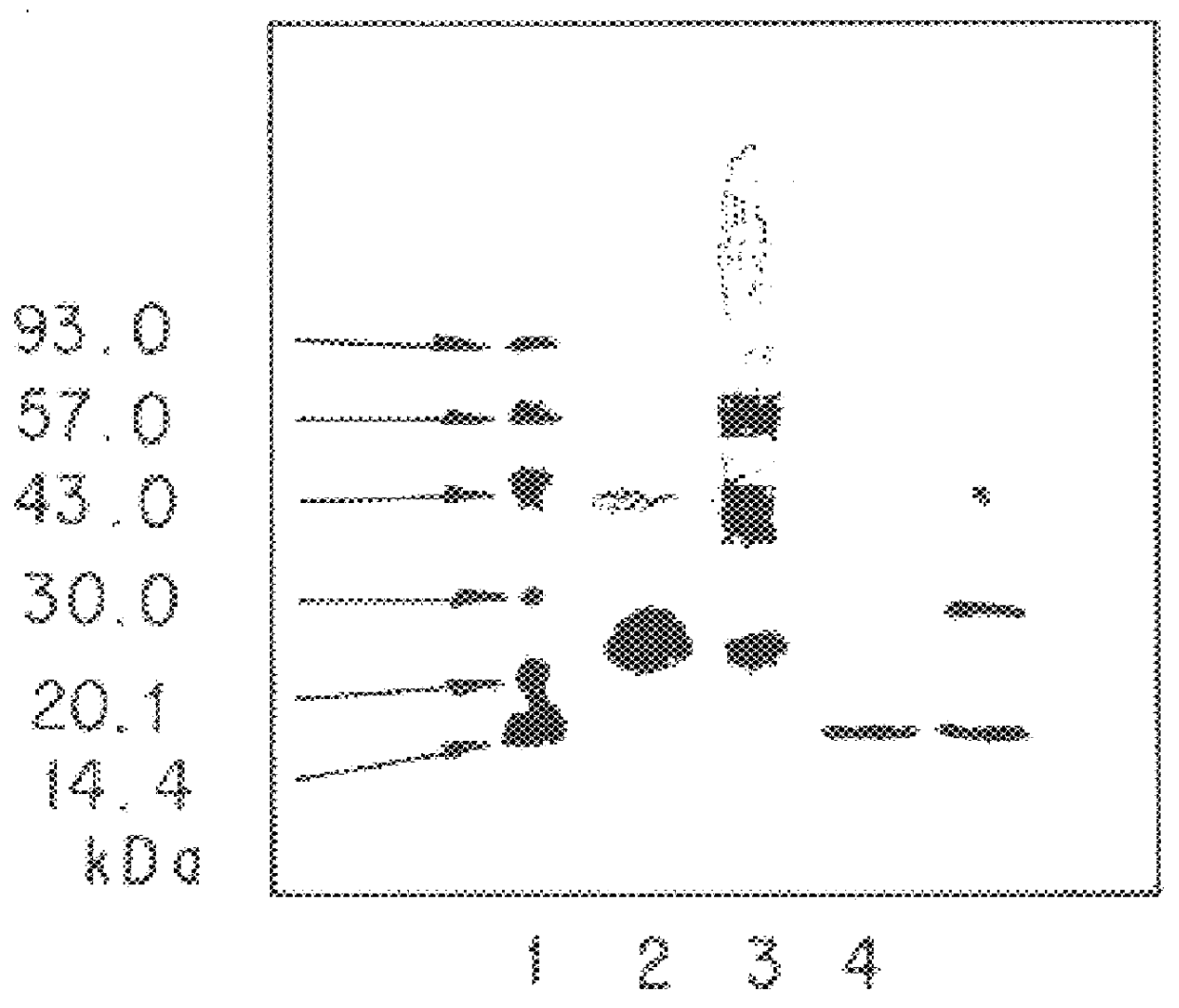
The present invention provides processes for the manufacturing of polypeptide conjugates. In particular, the invention provides methods for the purification of polypeptide conjugates, which include at least one polymeric modifying groups, such as a poly(alkylene oxide) moiety. Exemplary poly(alkylene oxide) moieties include poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and poly(propylene glycol). In an exemplary process, hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC) is used to resolve different glycoforms of glycoPEGylated polypeptides.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Modification of peptide and protein
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 01994 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 8, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 8, 1997 PCT Filed Sep. 29, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 10089 PCT Pub. Date Apr. 4, 1996A process for modifying a physiologically active peptide or a physiologically active protein which comprises reacting a physiologically active peptide or a physiologically active protein having at least a glutamine residue with a substance having an amino donor in the presence of a transglutaminase originating in a microorganism to thereby form an acid amide bond at the gamma -position acid amide group of the glutamine residue with the amino group of the amino donor; and the product of modification obtained thereby.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
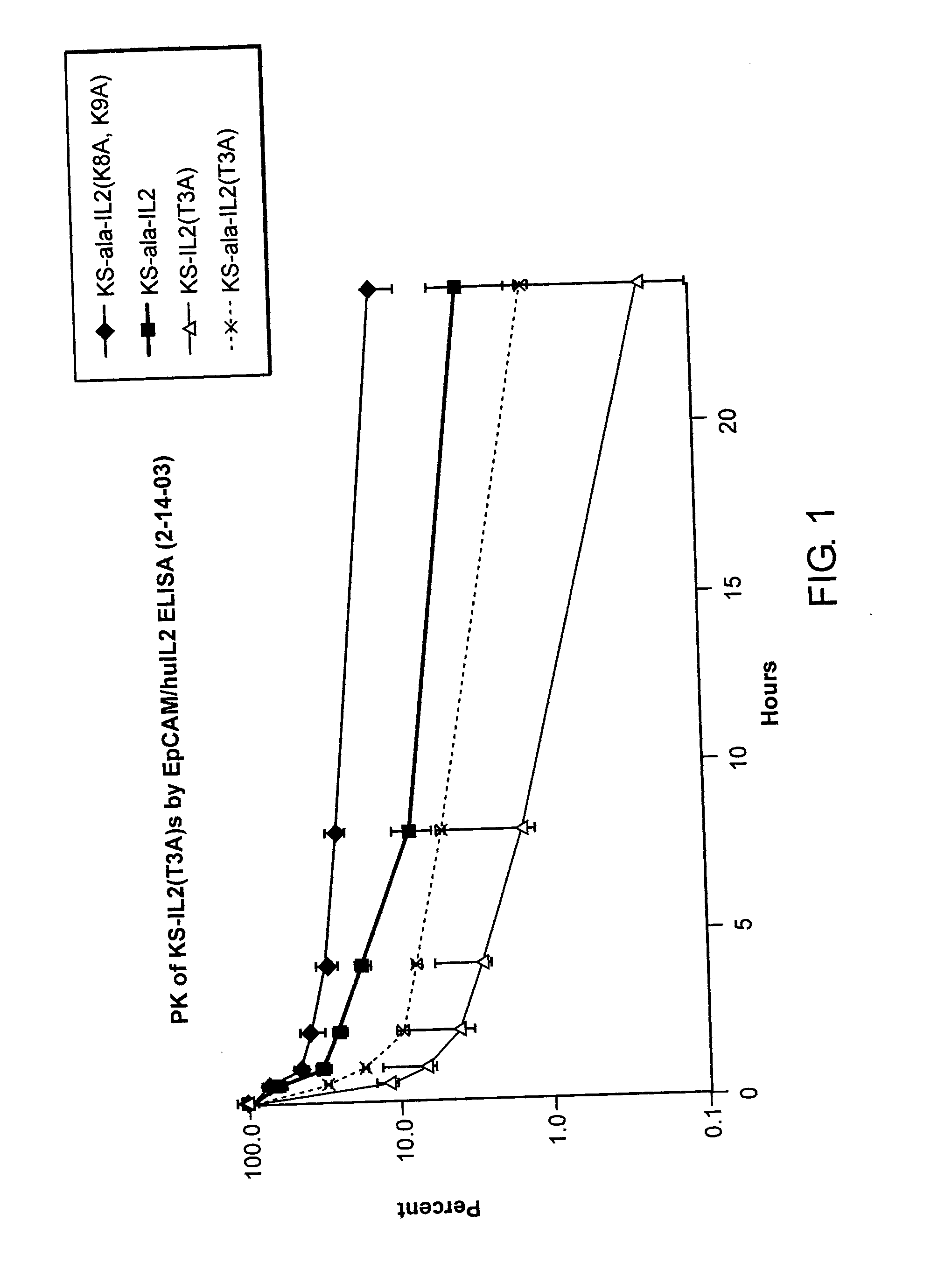
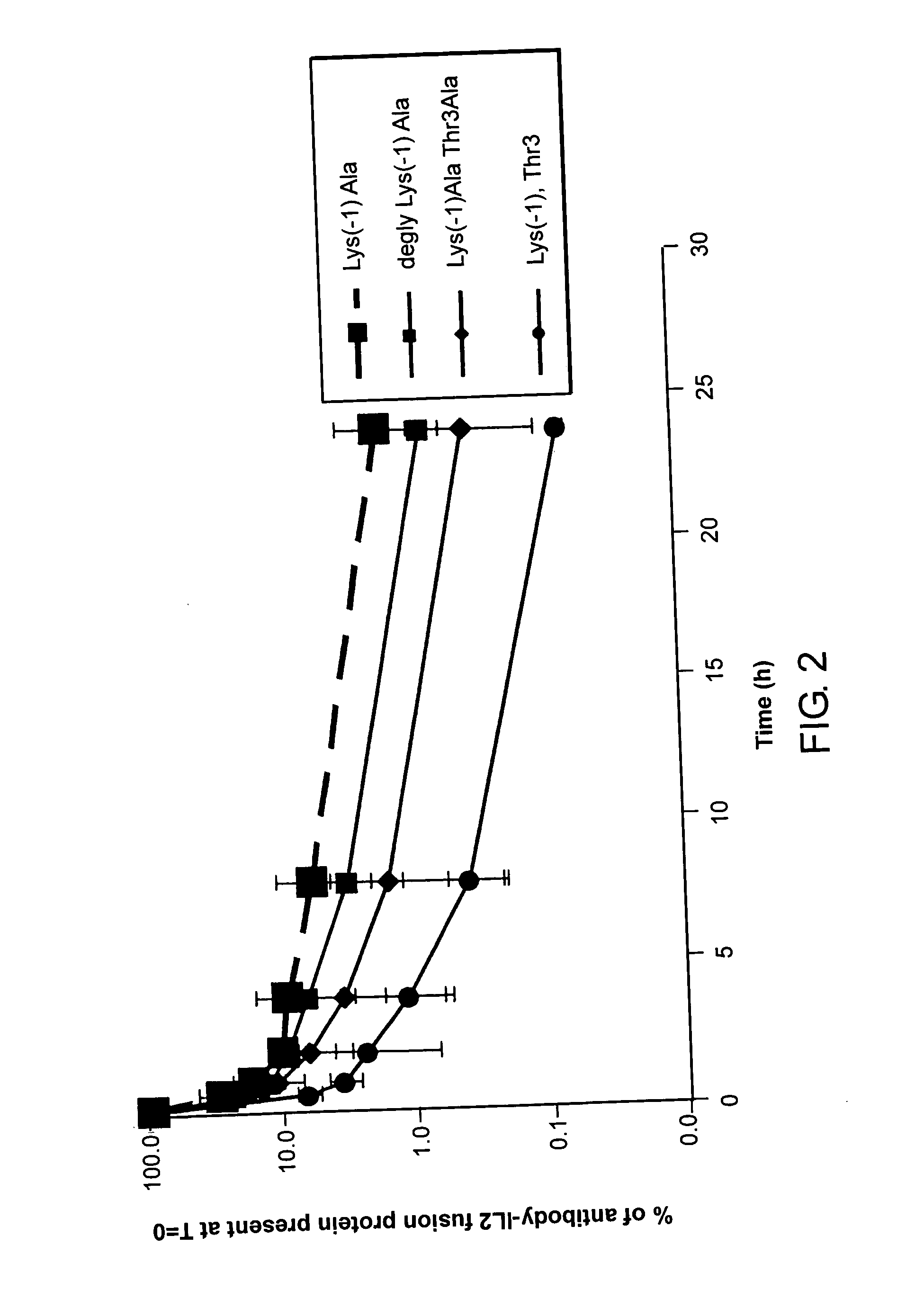
Enhancing the circulating half-life of interleukin-2 proteins
InactiveUS20050069521A1Enhance growth (and proliferation)Increased serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeInterleukin II
Disclosed are compositions and methods for enhancing the circulating half-life of interleukin-2 proteins.
Owner:EMD SERONO RES CENT
Use of IL-28 and IL-29 to treat cancer and autoimmune disorders
ActiveUS7351689B2Improve expression levelIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseFunctional activity
Methods for treating patients with cancer and autoimmune disorders using IL-28 and IL-29 molecules. The IL-28 and IL-29 molecules include polypeptides that have homology to the human IL-28 or IL-29 polypeptide sequence and proteins fused to a polypeptide with IL-28 and IL-29 functional activity. The molecules can be used as a monotherapy or in combination with other known cancer and / or autoimmune therapeutics.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Novel synthetic chimeric fusion transgene with immuno-therapeutic uses
InactiveUS20050053579A1Reducing tumorigenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsInterferon alphaWilms' tumor
The present invention relates to an immuno-therapy conjugate which comprises A-c-B wherein: A and B are different and are compounds selected from the group consisting of cytokines, chemokines, interferons, their respective receptors or a functional fragment thereof; and c is a linker consisting of a bond or an amino acid sequence containing from 1 to 100 residues. The present invention also relates to a vaccine adjuvant comprising the immuno-therapy conjugate of the present invention. The present invention further relates to a method of reducing tumor growth, for inhibiting a viral infection and for improving immune response in a patient.
Owner:GALIPEAU JACQUES +1
Interleukin-6 antagonists
InactiveUS20070178098A1Avoid interactionPromote formationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsInterleukin 6Antagonist
The present invention provides an isolated IL-6 antagonist including an antibody variable region that prevents IL-6 from binding to gp130. The present invention also provides compositions and methods for treating IL-6 related diseases based on the IL-6 antagonists of the invention.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
IL-7 fusion proteins
ActiveUS20050164352A1Good biological propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulin chainInterleukin I
The invention is directed to a fusion protein which includes a first portion including an immunoglobulin (Ig) chain and a second portion including interleukin-7 (IL-7).
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
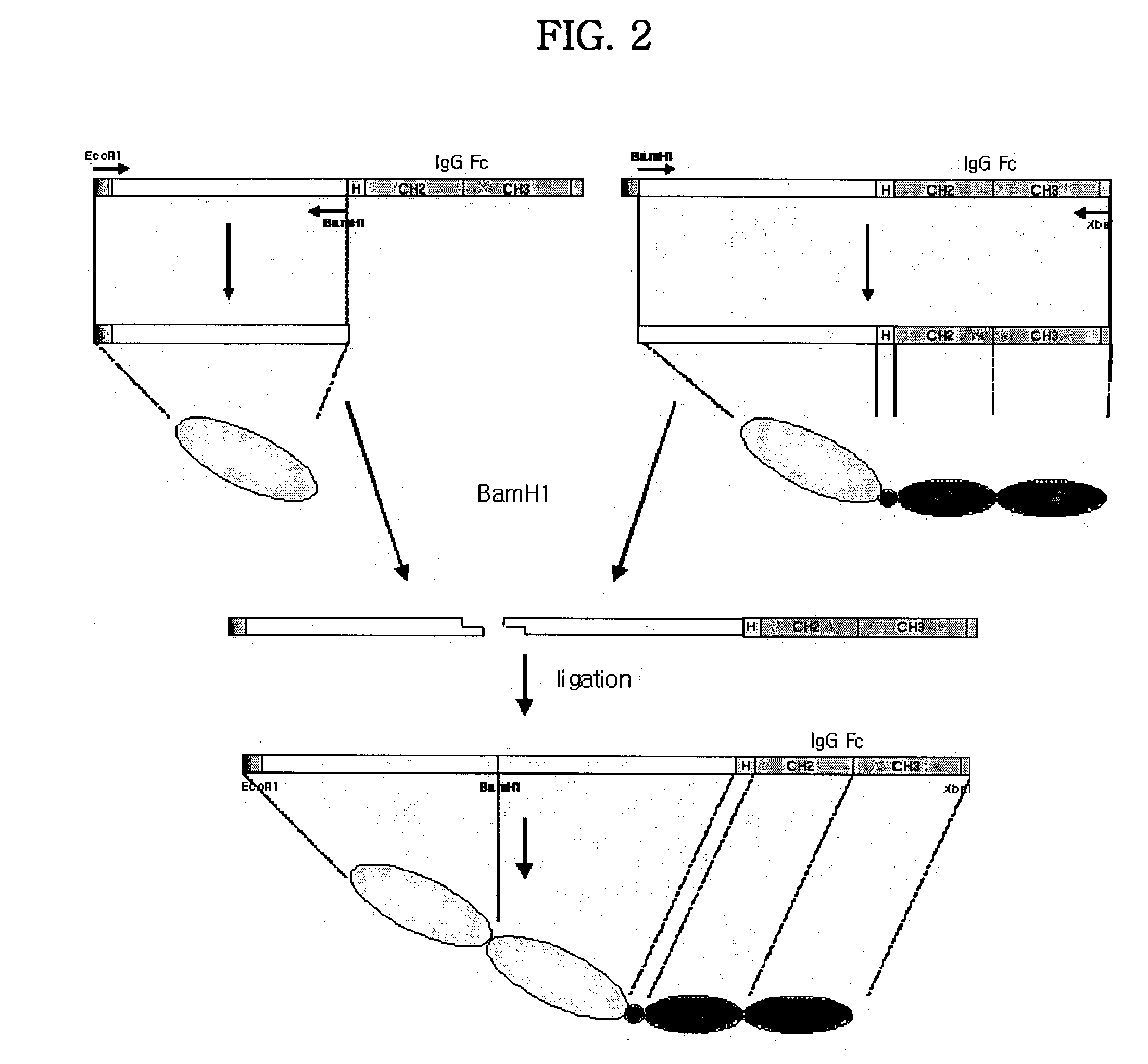
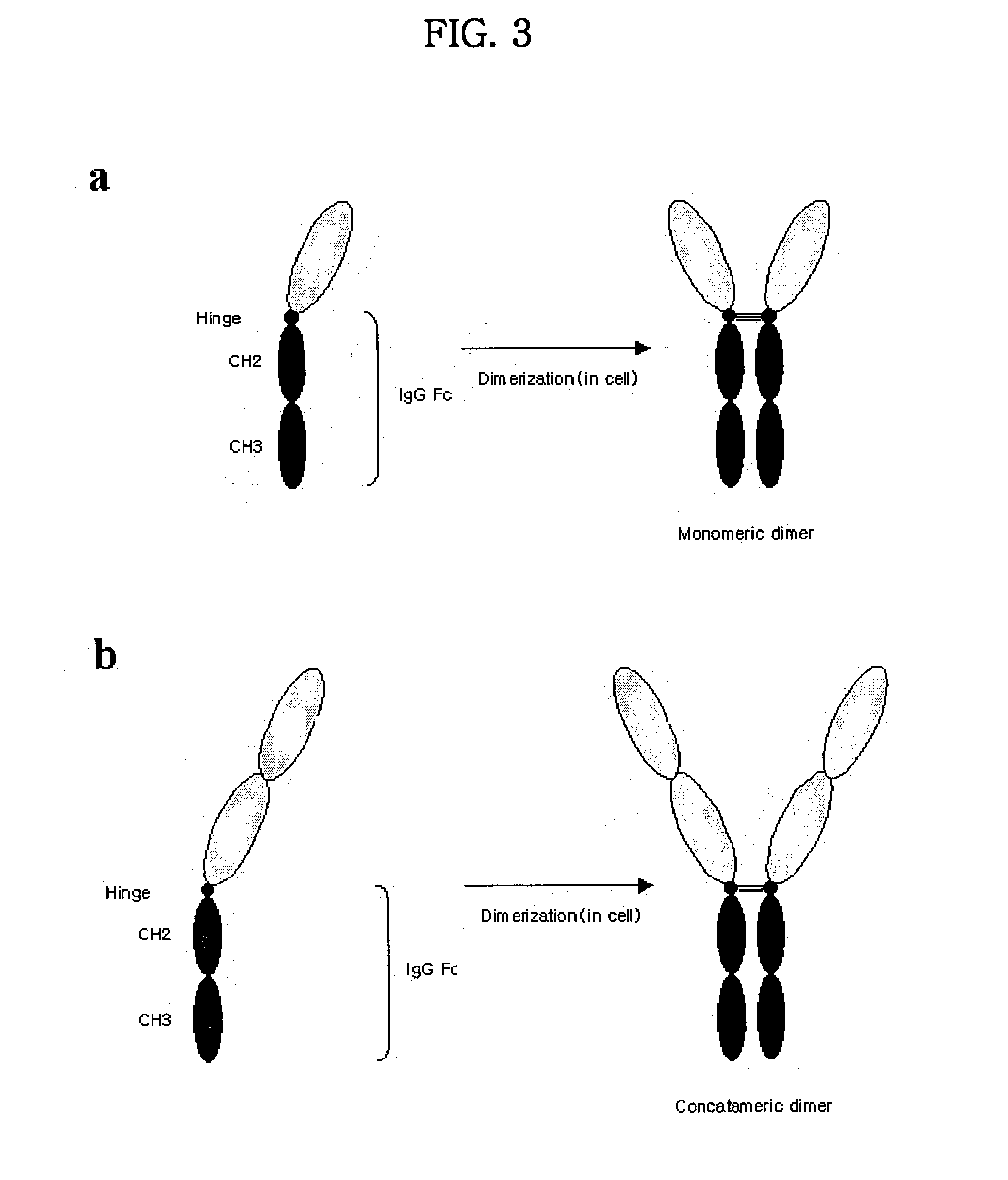
Concatameric immunoadhesion
ActiveUS20030195338A1Improve efficacyImprove stabilityAntipyreticAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA constructActive protein
Disclosed are concatameric proteins comprising two soluble domains, in which the C-terminus of a soluble domain of a biologically active protein is linked to the N-terminus of an identical soluble domain or a distinct soluble domain of a biologically active protein. Also, the present invention discloses dimeric proteins formed by formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds at the hinge region of two monomeric proteins formed by linkage of a concatamer of two identical soluble extracellular regions of proteins involving immune response to an Fc fragment of an immunoglobulin molecule, their glycosylated proteins, DNA constructs encoding the monomeric proteins, recombinant expression plasmids containing the DNA construct, host cells transformed or transfected with the recombinant expression plasmids, and a method of preparing the dimeric proteins by culturing the host cells. Further, the present invention discloses pharmaceutical or diagnostic compositions comprising the dimeric protein or its glycosylated form.
Owner:MEDEXGEN
Atherosclerosis genes and related reagents and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20070253901A1Prevent atherosclerosisDelaying onset of atherosclerorisHybrid immunoglobulinsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsImaging agentCancer research
The invention provides genes (DEA genes) that are differentially expressed in atherosclerotic lesions and polypeptides encoded by these genes. The invention provides compositions comprising a targeting agent conjugated to a functional moiety, wherein the targeting agent selectively binds to a polypeptide encoded by one a DEA gene. The functional moiety can be an imaging agent, therapeutic agent, etc. The invention further provides methods for providing diagnostic or prognostic information related to atherosclerosis involving detecting expression or activity of an expression product of one or more of the DEA genes. The invention further provides therapeutic methods comprising administering to a subject a composition comprising a targeting agent conjugated to a functional moiety that binds selectively binds to a polypeptide encoded by a DEA gene.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Gene transfer for studying and treating a connective tissue of a mammalian host
InactiveUS7037492B2Reducing at least one deleterious joint pathologyCompounds screening/testingBiocideConnective tissue fiberMammal
Methods for introducing at least one gene encoding a product into at least one target cell of a mammalian host for use in treating the mammalian host are disclosed. These methods include employing recombinant techniques to produce a vector molecule that contains the gene encoding for the product, and infecting the target cells of the mammalian host using the DNA vector molecule. A method to produce an animal model for the study of connective tissue pathology is also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Conjugates comprising human IL-18 and substitution mutants thereof
Human interleukin-18 (IL-18) polypeptides and substitution mutants thereof were conjugated to water-soluble polymers at specific sites on the human IL-18 protein. These conjugated human IL-18 and substitution mutants thereof retain biological activity. These conjugated cytokines demonstrate enhanced and unexpected biological properties when compared to the corresponding unconjugated cytokines.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com