Patents
Literature
593results about How to "Prevent atherosclerosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
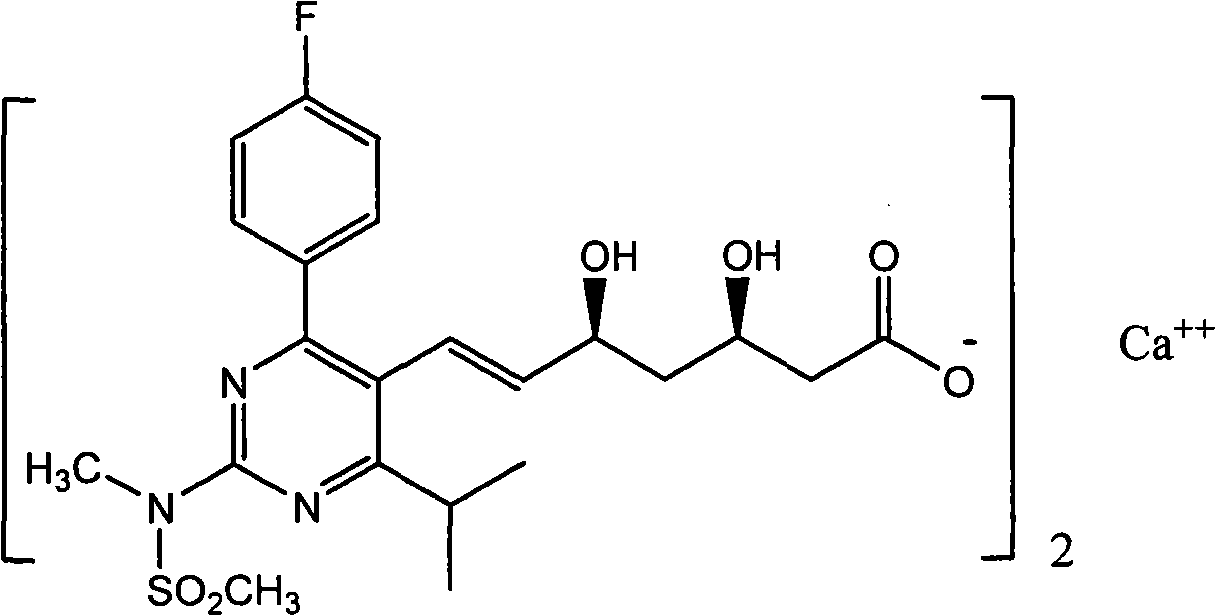
Hydroxy-substituted azetidinone compounds useful as hypocholesterolemic agents
InactiveUSRE37721E1Lowering of total serum cholesterol levelReduce plasma cholesterol levelBiocideOrganic chemistryArylSerum cholesterol
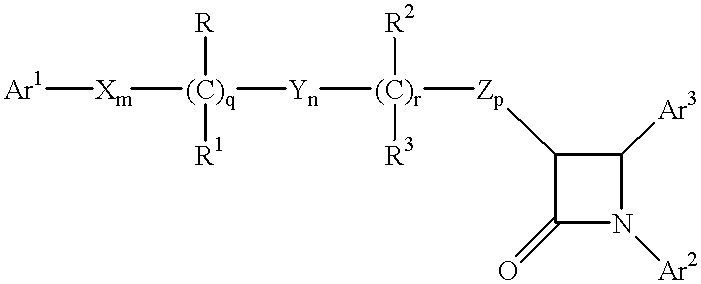
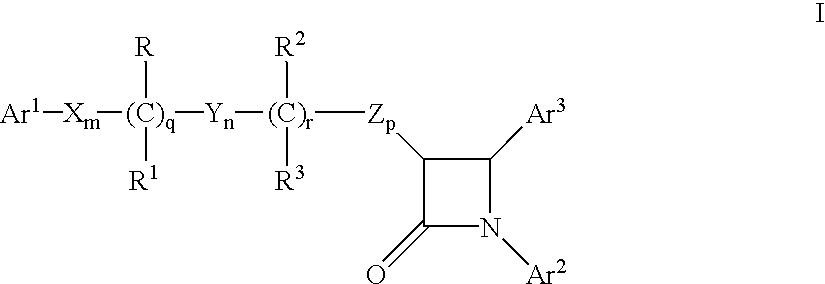
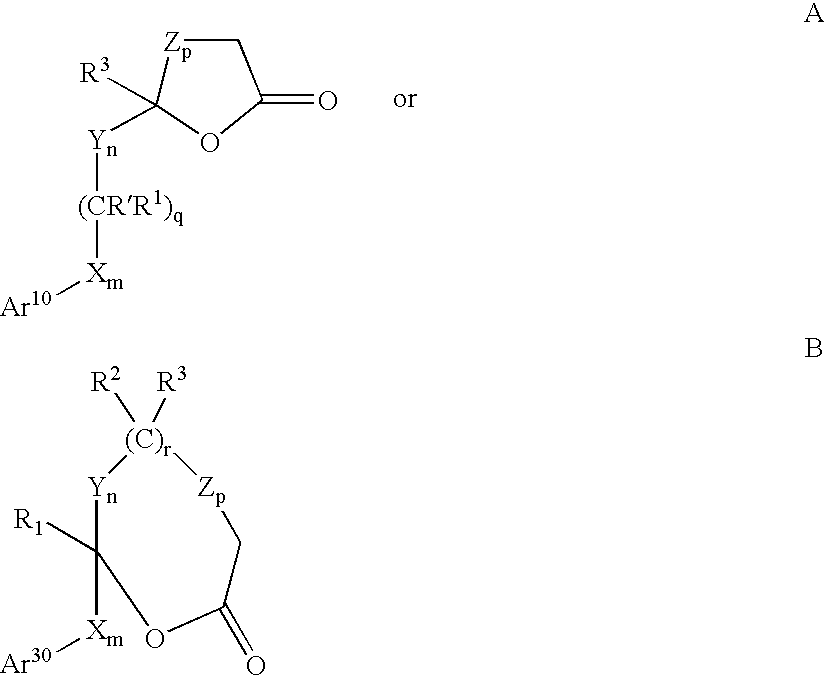
Hydroxy-substituted azetidinone hypocholesterolemic agents of the formulaor a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein:Ar1 and Ar2 are aryl or R4-substituted aryl;Ar3 is aryl or R5-substituted aryl;X, Y and Z are -CH2-, -CH(lower alkyl)- or -C(dilower alkyl)-;R and R2 are -OR6, -O(CO)R6, -O(CO)OR9 or -O(CO)NR6R7;R1 and R3 are H or lower alkyl;q is 0 or 1; r is 0 or 1; m, n and p are 0-4; provided that at least one of q and r is 1, and the sum of m, n, p, q and r is 1-6; and provided that when p is O and r is 1, the sum of m, q and n is 1-5;R4 is selected from lower alkyl, R5, -CF3, -CN, -NO2 and halogen R5 is selected from -OR6, -O(CO)R6, -O(CO)OR9, -O(CH2)1-5OR6, -O(CO)NR6R7, -NR6R7, -NR6(CO)R7, -NR6(CO)OR9, -NR6(CO)NR7R8, -NR6SO2R9, -COOR6, -CONR6R7, -COR6, -SO2NR6R7, S(O)0-2R9, -O(CH2)1-10-COOR6, -O(CH2)1-10CONR6R7, -(lower alkylene)COOR6 and -CH=CH-COOR6;R6, R7 and R8 are H, lower alkyl or aryl-substituted IcR9 is lower alkyl, aryl or aryl-substituted lower alkyl;are disclosed, as well as a method of lowering serum cholesterol by administering said compounds, alone or in combination with a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor, pharmaceutical compositions containing them; and a process for preparing them.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Preparation method of chelate coating with copper ions capable of controllably catalyzing release of nitrogen monoxide and polyphenol complex
ActiveCN104194460ALong-term antibacterialImprove antibacterial propertiesAntifouling/underwater paintsSurgeryBiocompatibility TestingPhenol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a chelate coating with copper ions capable of controllably catalyzing release nitrogen monoxide and a polyphenol complex. The preparation method comprises the following steps: soaking a target modified material or an instrument in a mixed aqueous solution consisting of soluble metal salt, soluble copper salt and a compound having an o-phenol structure; and depositing a layer of chelate coating with copper ions with a function of catalyzing nitrogen monoxide and the polyphenol complex on the surface. The chelate coating with the copper ions and the polyphenol complex, which is obtained by the preparation method disclosed by the invention, not only has excellent biocompatibility and bacterial resistance, but also has a function of inducing catalysis of endogenous nitrogen monoxide to release in a blood environment. In addition, the coating is nearly applicable to surface modification of materials of all textures, complex geometrical shapes and different topological structures.
Owner:GUANGZHOU NANCHUANG EVEREST MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Blend oil with proportional fatty acid prepared by walnut oil and other plant oils
InactiveCN101690526AReduce contentReduce concentrationEdible oils/fatsFood preparationVegetable oilCholesterol
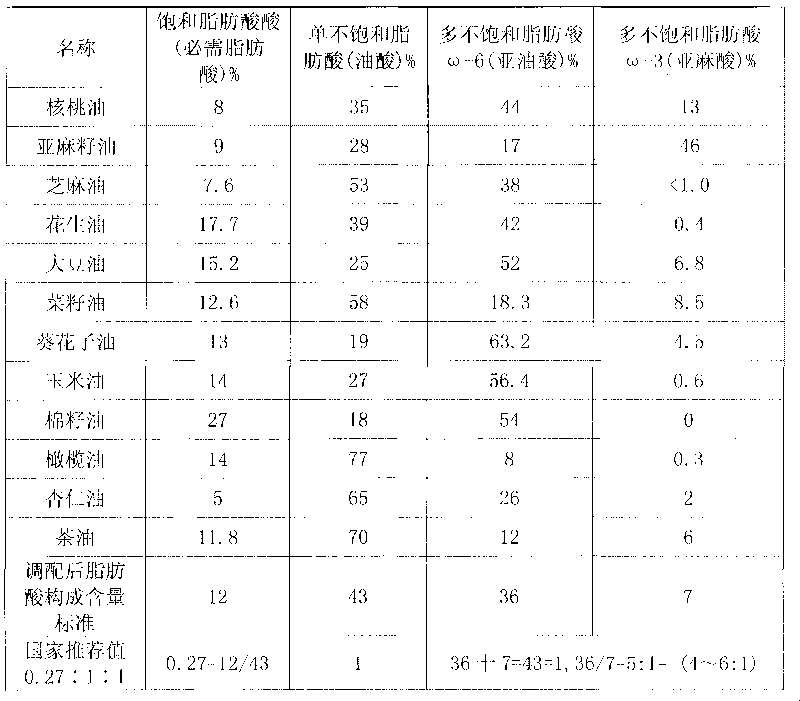
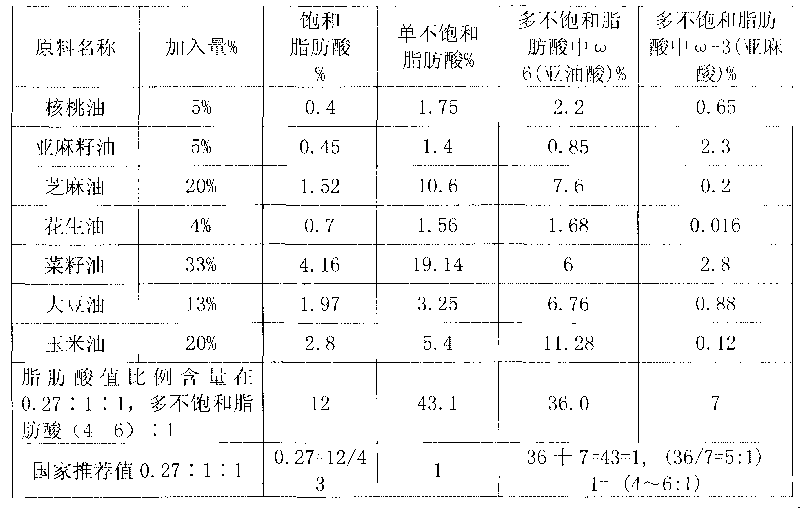
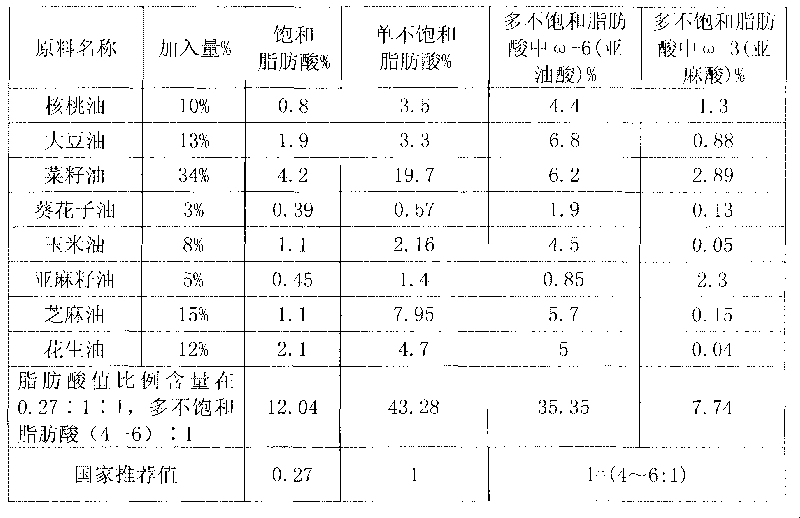
The invention relates to blend oil with proportional fatty acid prepared by walnut oil and other plant oils, which is composed of 5-20% of walnut oil by weight and 80-95% of common plant oils by weight, wherein the common plant oils are selected from any 6 to 11 from peanut oil, soybean oil, sunflower seed oil, teal oil, cotton seed oil, corn oil, almond oil, olive oil, tea oil, linseed oil and colza oil. The ratio of three fatty acids in the blend oil provided by the invention can reach 0.27:1:1, wherein the ratio of omega-6 (linoleic acid) to omega-3 (linolenic acid) in polyunsaturated fatty acids is (4-6):1, and the blend oil in the invention also can overcome the disadvantages that walnut oil is expensive in price and little in market acceptance space while common plant oil has single nutrition and is difficult to supplement fatty acids essential to human body, therefore, by long term administration of the walnut blend oil, cholesterol can be effectively reduced, hyperlipaemia can be reduced, heart cerebrovascular disease can be prevented, and the holistic health level of people can be improved.
Owner:祁景泉
Egg chicken nutrious feed
InactiveCN1620902ALipid stabilizationInhibition formationFood processingAnimal feeding stuffIodine deficiencyVascular disease
The nutritive layer feed is produced with 17 kinds of material, including corn, soybean dreg, shell powder, beer residue, sea weed, etc. The feed has high content of linoleic acid and the egg has obvious preventing and treating effect on iodine deficiency goiter, hyperthyroidosis, etc. It has high content of vitamin E, can stabilize lipoid in egg to inhibit the formation and diffusion of various kinds of cancer cell, and to possess the functions of inhibiting atherosclerosis, improving cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases, etc.
Owner:张明东
Aroniamelanocarpa fruit wine and brewing method thereof
InactiveCN101481643ARaw materials are uniqueFull of nutritionAlcoholic beverage preparationFruit juiceAntioxidant
The invention relates to an aroniamelanocarpa fruit wine and a brewing method thereof. The fruit of aroniamelanocarpa is taken as raw material and is made into fruit juice, fruit wine microzyme is selected for use and put into the fruit juice according to the proportion being 5-10% of the weight of the fruit juice, and the aroniamelanocarpa fruit wine is brewed with the alcohol content of 5-13% (v / v) and the total sugar content of 4.0-80.0g / L. The brewing technique of the invention comprises preparing the fruit juice, inoculation and fermentation, aging and store maturity, purifying wine body as well as filtration and sterilization, and the most advanced fermenting and purifying technique can be adopted by the production. The product of the invention has unique flavor, slightly acerbic and fresh taste, mellow mouthfeel, pleasing aroma and wide applicable people. The fruit wine contains multiple nutritional functional components such as anthocyanin, flavone, polyphenol active substance, vitamins antioxidant, mineral composition, polyoses, organic acid and the like which are rich in the fruit of aroniamelanocarpa, and has good effects of oxidation resistance, ageing prevention, blood pressure regulation, vessel relaxing, blood-fat reduction, anti-inflammation and detoxification, radiation resistance, etc.
Owner:辽宁省干旱地区造林研究所
Culture method and uses of antrodia cinnamomea
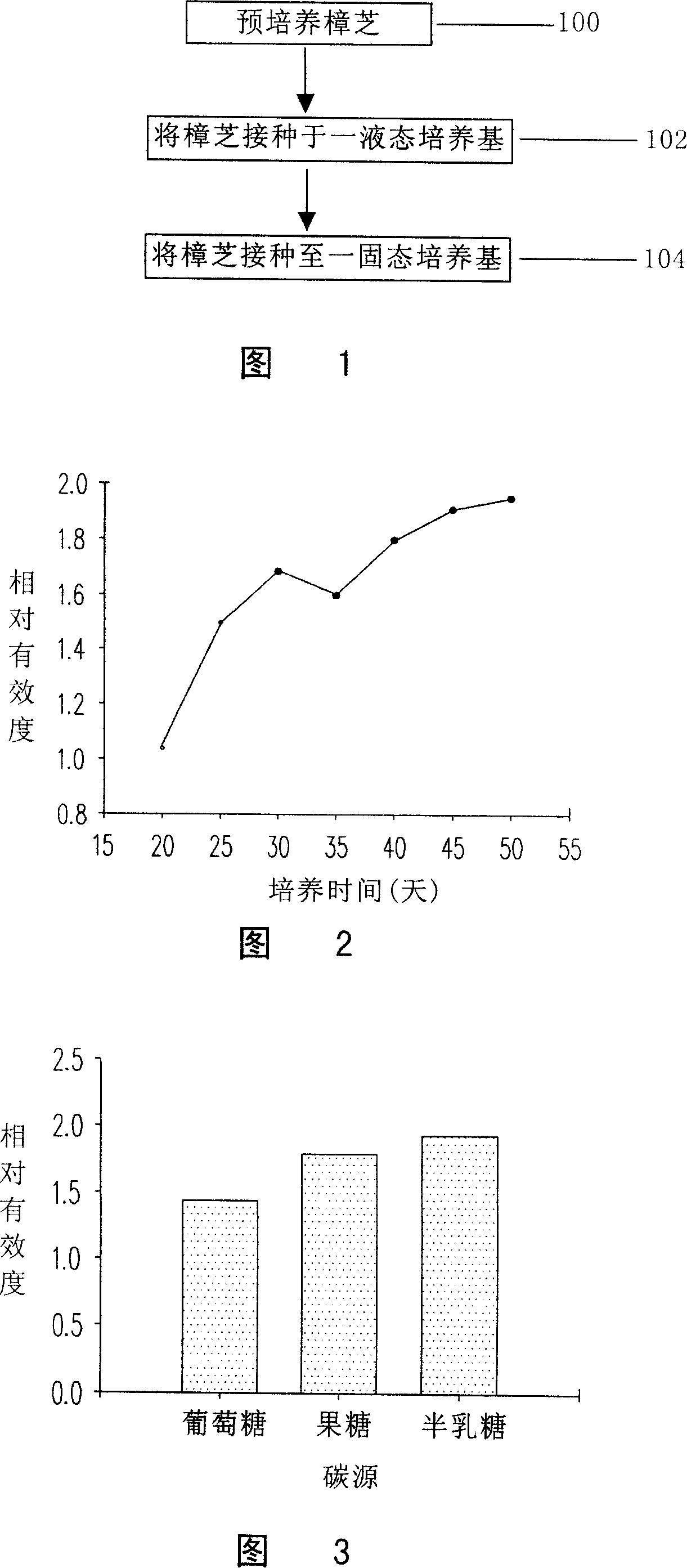
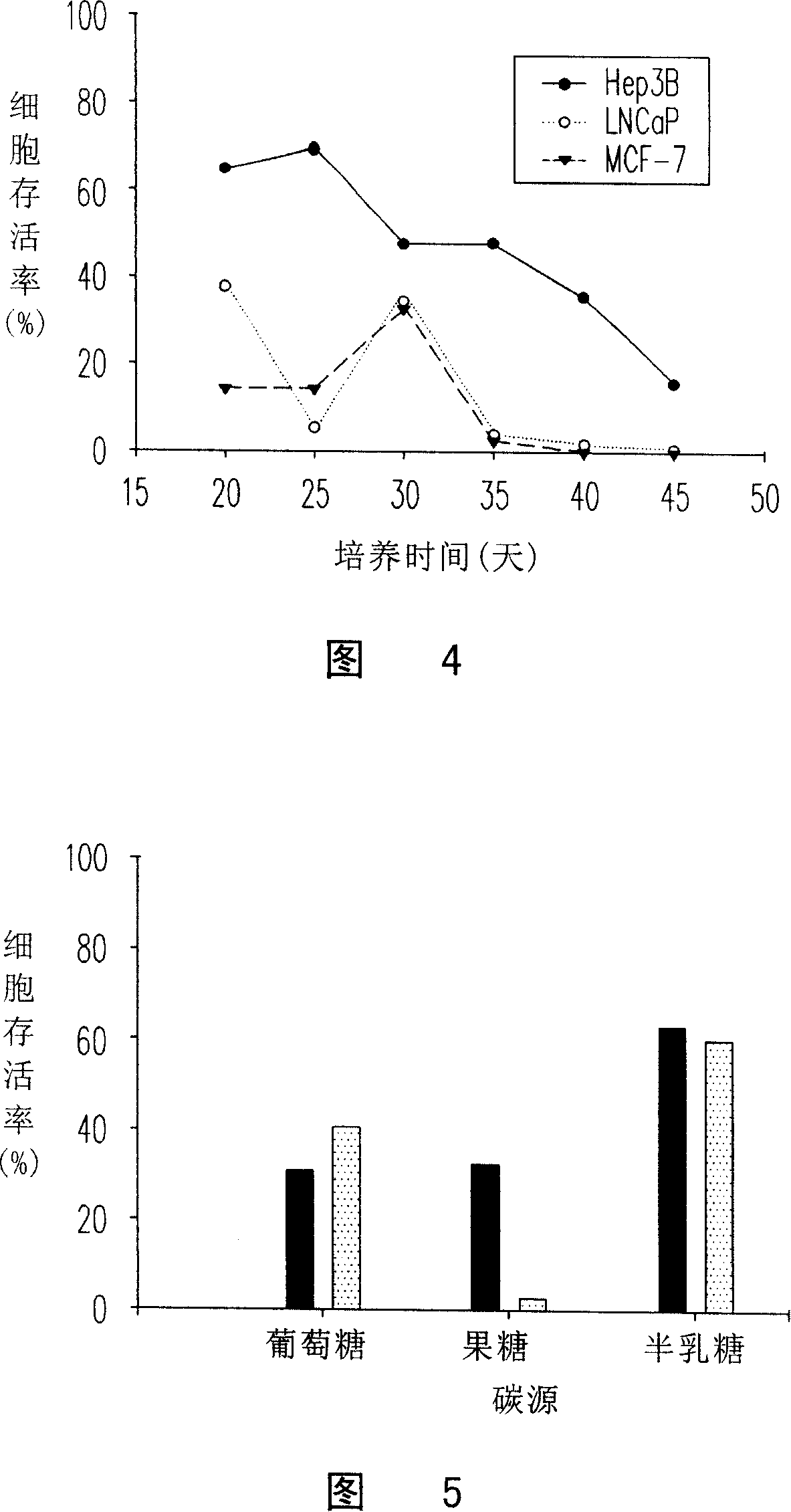
The invention provides an antrodia camphorate cultivation method; firstly, pre-cultivating the antrodia camphorate on a slant culture medium, taking out a part of pre-cultivated antrodia camphorate to inoculate a liquid culture medium, and then inoculating the antrodia camphorate cultivated in the liquid culture medium to a solid culture medium for the cultivation. The antrodia camphorate cultivated in the method has similar effects of wild antrodia camphorate, including effects of restraining growth activity of human cancer cells and cancer auxiliary treatment, also having abilities of restraining human low density lipoprotein oxidation for lowering incidence rates of artery hardening and restoring damaged liver functions.
Owner:GOLDEN BIOTECH
Daily Dosage Regimen for Treating Diabetes, Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
InactiveUS20070015839A1Prevent atherosclerosisEffective treatmentSmall article dispensingOrganic active ingredientsRegimenPhysiology
A daily dosage regimen for treating diabetes, obesity and metabolic syndrome includes a metabolic pill and one or two biguanide hypoglycemic pills packaged together. The package can include a singe day's regiment, or can include multiple days' regimen. This provides an effective method for treating diabetes, obesity and metabolic syndrome, as well as polycystic ovary syndrome.
Owner:FOLLI FRANCO +2
Plants blend oil
ActiveCN101194653AReasonable contentAppropriate compositionEdible oils/fatsFood preparationAdditive ingredientSunflower oil
The invention discloses a plant blend oil, which comprises peanut oil, corn germ oil, sunflower seed oil, tea seed oil, walnut oil, safflower oil and sesame oil, wherein the weight percentage of the peanut oil is 20-40 percent, the weight percentage of the corn germ oil is 20-40 percent, the weight percentage of the sunflower seed oil is 10-20 percent, the weight percentage of the tea seed oil is 3-10 percent, the weight percentage of the walnut oil is 3-10 percent, the weight percentage of the safflower oil is 3-10 percent, and the weight percentage of the sesame oil is 2-6 percent. The invention has the characteristics of high nutritional contents, balanced nutrition and no transgenic ingredients, and meets nutritional requirements of people.
Owner:莱阳齐花特香纯正花生油有限公司
Defatted medical chicken
InactiveCN101108002APrevent obesityPrevent cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseasesFood preparationLiver and kidneyAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a degreasing chick with Chinese herb, which is made with the following method: pack yam, longan pulp, lotus seed, medlar, lily, date, sealwort, cassia seed and black fungus in a gauze cloth bag to form a herb bag; cure a processed chicken of 500g with cooking wine, salt, white sugar, flavor essence, ginger juice and soy sauce for two hours, so that the curing ingredients can fully penetrate into the inside of chicken; cram the herb bag into the chick belly and add spice, galangal, orange peel and angelica dahurica to a pot for cooking with fierce flame; then, fry the chicken to deeply cooked, cool down it and pack it in vacuum package. The invention, in addition to the effects of nourishing the spleen and blood, replenishing the liver and kidney, nourishing and tranquilizing the heart, has the effects of lowering down the fat, blood pressure, blood sugar, preventing obesity and angiocardiopathy. Therefore, the chicken with Chinese herb can be taken as a delicious dish that satisfies people's appetite and prevent the problems of fatty liver and atherosclerosis due to the frequent taking of ordinary chicken meat.
Owner:于洪文
Preparation of Chinese traditional medicine for treating cardiovascular disease, and cerebrovascular disease
InactiveCN1958039AInhibit aggregationSimple preparation processCardiovascular disorderPlant ingredientsCurative effectAtheroma
A Chinese medicine for treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and preventing atherosclerosis is prepared from 28 Chinese-medicinal materials including notoginseng, ginseng, honeysuckle flower, red sage root, etc through immersing, heating, laying aside, and taking supernatant.
Owner:王建兴
Method for extracting dihydroquercetin form larch
InactiveCN101333203AFree radical scavengingLesion hindranceOrganic chemistryConiferophyta medical ingredientsLarchUnit/Kilogram
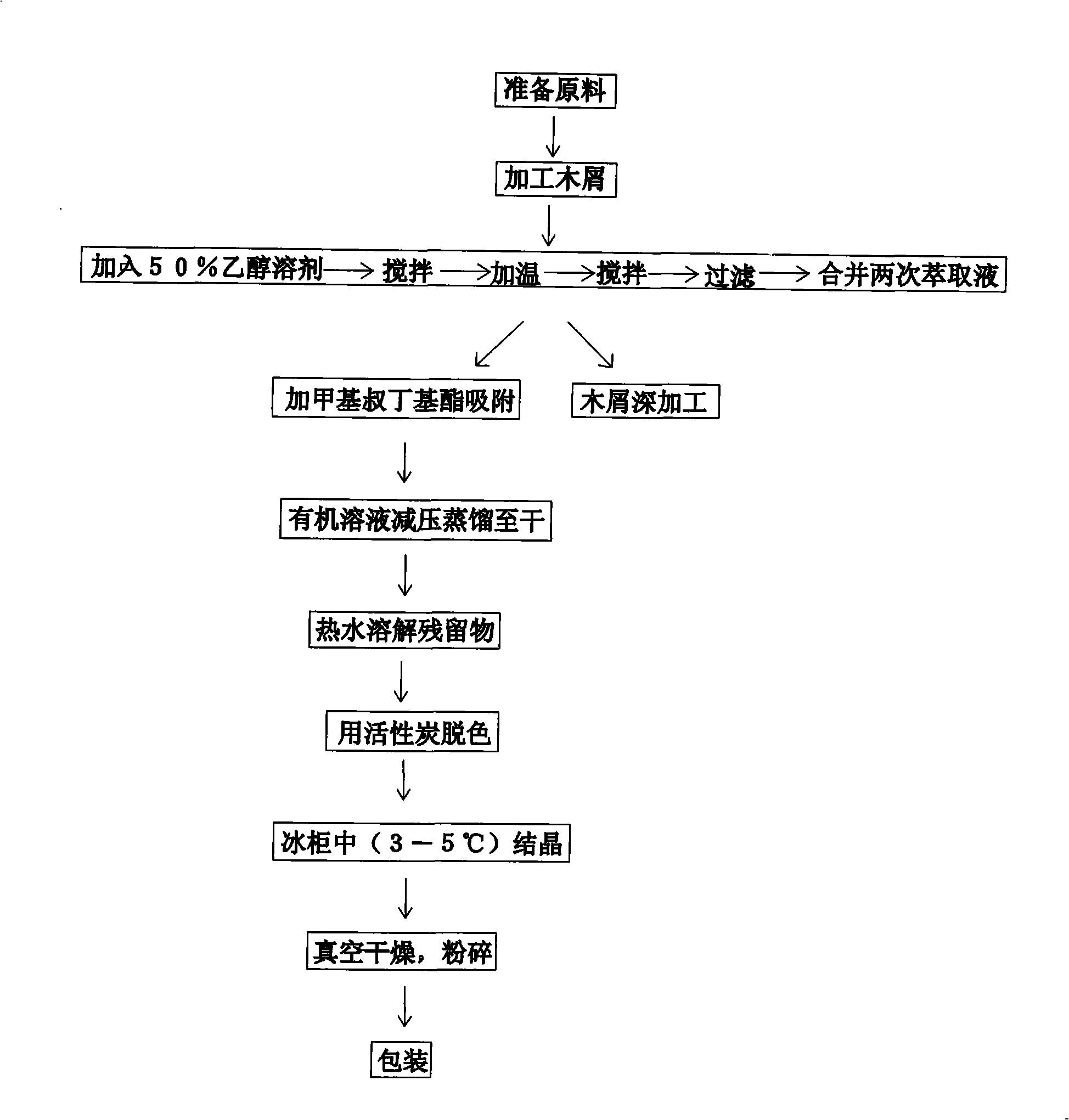
Disclosed is a method for extracting dihydro quercetin from larch. The invention is an improved production method. Due to different production materials and extraction processes, the dihydro quercetin products in U.S. and European markets are very expensive, at a price of 200-1000 euros per gram. Such a high market price economically limits the wide range of practicability of dihydro quercetin products. During the pretreatment of raw materials, 50 kilograms of larch wood chips and 500-800 liters of 50% ethanol solution are added into a reactor to get fully stirred and mixed; then the mixture is extracted and filtered for the second extraction; the filtrates are combined and adsorbed; the organic solvents are collected and dried by a vacuum evaporator through organic phase vacuum distillation; according to a weight proportion of 10:1, the residues are dissolved with hot water, decolorized with activated carbon and then crystallized at a temperature of 3-5 DEG C to precipitate the dihydro quercetin product which is then crushed after vacuum drying to finished product. The invention is used to extract dihydro quercetin from larch.
Owner:黑龙江花旗科技发展有限公司 +2
Combinations of HMG-COA reductase inhibitors and nicotinic acid and methods for treating hyperlipidemia once a day at night
InactiveUS20050255158A1Alter serum lipid levelReduce hyperlipidemiaSalicyclic acid active ingredientsMetabolism disorderLipid formationHMG-CoA reductase
The present invention relates to solid pharmaceutical combinations for oral administration comprising nicotinic acid or a nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof in an extended release form and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, which are useful for altering lipid levels in subjects suffering from, for example, hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis, without causing drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis. The present invention also relates to methods of altering serum lipids in subjects to treat, for example, hyperlipidemia in hyperlipidemics, lipidemia in normolipidemics diagnosed with or predisposed to cardiovascular disease, and atherosclerosis, by administering such oral solid pharmaceutical combinations once per day as a single dose during the evening hours, without causing drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis, or without causing in at least an appreciable number of individuals drug-induced hepatotoxicity, myopathy or rhabdomyolysis to such a level that discontinuation of such therapy would be required. More particularly, the present invention concerns oral solid pharmaceutical combinations comprised of, for example, (1) an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor for immediate or extended release, (2) nicotinic acid, a nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof, and (3) a swelling agent to form a sustained release composition for extended release of the nicotinic acid or nicotinic acid compound or mixtures thereof for nocturnal or evening dosing for reducing serum lipids and increasing HDL-cholesterol. In accordance with the present invention, and by way of example, a composition for oral administration during the evening hours to alter serum lipids comprised of nicotinic acid and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in the form of an extended or sustained release tablet or caplet coated with a coating comprising an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor in immediate release form is disclosed. Also in accordance with the present invention, the pharmaceutical combinations may include a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent for reducing the capacity of nicotinic acid or nicotinic acid compounds to provoke flushing reactions in individuals.
Owner:KOS LIFE SCI
Freeze-dried compound berry superfine powder and production method thereof
ActiveCN103750328ARich in compositionPromote absorptionFood freezingFood shapingFreeze-dryingGranularity
The invention discloses freeze-dried compound berry superfine powder and a production method thereof. The freeze-dried compound berry superfine powder is produced from the following berries in percent by weight: 40-45 percent of raspberry, 25-30 percent of blueberry, 6-8 percent of mulberry, 10-14 percent of sea-buckthorn, 4-6 percent of medlar and 5-7 percent of Lonicera caerulea. The method comprises the following specific steps: weighing and cleaning the berries, and draining for standby; mixing the drained berries under the condition of normal pressure and the temperature of 80 DEG C below zero, freezing for 1-3 hours, and rapidly freezing the fruits; keeping the frozen mixed berries in an environment with the pressure of 50-100Pa for 3-4 hours, controlling additional heating, and returning the temperature to 0 DEG C within 4-5 hours; raising the temperature from 0 DEG C to 45 DEG C within 6-8 hours, wherein the pressure is kept to be 20-50Pa; grinding the berries into the granularity of 5000-10000 meshes at the temperature of 0 DEG C by adopting nitrogen protection; preparing the ground superfine powder into tablets. The berries are reasonably proportioned, so that a health care effect is achieved, the functional ingredients in the product are enriched, the taste characteristics of the product are improved, the product is fresh to drink, contributes to human body absorption and is conveniently prepared into the tablets, and the active substances are well kept.
Owner:山东尚美健康产业技术发展有限公司
Method for processing instant coarse cereal balanced nutritional flour
InactiveCN102160623AMeet dietary recommendationsNutritional balanceFood preparationGramAlpha-amylase
The invention relates to a method for processing instant coarse cereal balanced nutritional flour, which comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing 25 to 30 percent of buckwheat flour, 10 to 15 percent of fagopyrum tataricum flour, 8 to 12 percent of hulless oat flour, 15 to 20 percent of hyacinth bean flour and 30 to 35 percent of pea flour to obtain mixed flour; (2) adding water into the mixed flour and blending to form flour paste, adding solution of CaCl2 to ensure that the pH value of the flour paste is between 6.0 and 6.5, adding 140 to 160u of intermediate-temperature alpha-amylase into each gram of mixed flour, and liquefying at the temperature of between 60 and 65 DEG C to obtain liquefied flour milk; and (3) decoloring the liquefied flour milk, seasoning, and spray-drying to obtain a finished product. The method is simple, easy to operate and master, low in production cost and environment-friendly, the obtained product has high instant and blending performance, is convenient to eat, has an adjuvant therapy effect on senile diseases such as hypertension, hyperlipaemia, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes, obesity and the like, and has better effects of dietetic therapy and health care than rice and wheat flour.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Sweet corn Kefir fermented milk and production method thereof
InactiveCN101708017APromote absorptionDoes not induce acidemiaMilk preparationNutritive valuesAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a sweet corn Kefir fermented milk and a production method thereof; the sweet corn Kefir fermented milk is prepared from the following components: fresh milk, sweet corn juice, white granulated sugar, sweet corn Kefir fermenting agent and a compound stabilizer, wherein, the rate of the components in parts by weight is as follows: 10:(2-4):(0.6-0.8):(0.3-0.5):(0.02-0.03). The production method comprises the following steps: preprocessing the sweet core into juice; activating and domesticating strains to prepare the sweet corn Kefir fermenting agent; preparing the compound stabilizer; blending, homogenizing, inoculating, canning, fermenting and after-ripening. The selected sweet corn Kefir strain can generate amino acid with stronger capacity, generate a large amount of Vitamin B, is restrained on acid generation capacity, has high nutritional value, is easy for human body to absorb, can not induce acidemia of human body after being drunk for a long term, is beneficial to people with poor stomach and intestine function to drink and absorb; compared with other acidic dairy products, the selected sweet corn Kefir strain has no essence ingredient, low acidity and softness, peculiar flavour of the sweet corn, mellow, fine and smooth mouthfeel, is easier to be accepted for people and adds drinking interests.
Owner:王蕊
Medlar composite beverage and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a medlar composite beverage which comprises 55% of medlar leach liquor, 8% of red date leach liquor and 12% of apple leach liquor. According to the invention, medlar with multiple health protection functions, red dates with rich vitamins and apples with special fruit flavor are complemented in nutrition and flavor so as to prepare the composite beverage which has unique flavor, and is sour and tasty, rich in nutrition and stable in property. According to the invention, boiling water is adopted for leaching, and effective ingredients in the raw materials can be utilized fully and effectively, so that on the one hand, the produced medlar composite beverage has functions of medical health protection and immune improvement of the medlar, on the other hand, the mouthfeel and the flavor of the beverage are enriched through the red dates and the apples, and the efficacies and nutritional values of the medlar beverage are improved, Meanwhile, the successful development of the medlar composite beverage provided by the invention not only provides a novel development direction for the research and development of the medlar beverage, but also opens a novel way for the development and utilization of medlar resources.
Owner:宁夏厚生记枸杞饮品股份有限公司
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for preparing woman health-care viscose fiber, prepared health-care viscose fiber and preparation method of health-care viscose fiber
ActiveCN103643333APromote circulationPrevent atherosclerosisArtificial filaments from viscoseWet spinning methodsMotherwortEmulsion
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for preparing a woman health-care viscose fiber, a prepared health-care viscose fiber and a preparation method of the health-care viscose fiber. The traditional Chinese medicine composition comprises the following traditional Chinese medicine components by weight percent: 20-35% of felwort, 15-25% of radix sophorae flavescentis, 15-25% of radix angelicae, 10-20% of flowers carthami and 10-20% of motherwort. The method for preparing the health-care viscose fiber by using the traditional Chinese medicine composition comprises the following steps: dissolving traditional Chinese medicine composition extract powder into an antibacterial health-care solution; heating borneol to melt, and emulsifying into an emulsified liquid; preparing spinning mucilage glue by adopting cellulose pulp as a raw material; adding the antibacterial health-care solution to a viscose solution in any step after yellowing is finished and before spinning is performed, so as to obtain an antibacterial health-care blend viscose solution; spinning and forming, drafting silk and carrying out post-treatment on the antibacterial health-care solution, so as to obtain the health-care viscose fiber; adding a borneol emulsion to the oiling step of after-treatment.
Owner:LINQU XINYUE KNITTING WEAR
Method for manufacturing strawberry jam
InactiveCN101133782APrevent atherosclerosisPrevent high cholesterolFood preparationAdditive ingredientCurative effect
The present invention relates to a preparation method of strawberry jam. It is made up by using 80-100kg of strawberry, 110-115kg of granulated sugar and 0.3kg of citric acid. Said strawberry jam not only contains nutrient components of vitamins and amino acids, etc., but also contains mineral elements of calcium, phosphorus and iron, etc.
Owner:单超
Pure traditional Chinese medicinal female beautifying preparation
InactiveCN103656189APrevention and treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseasesRegulates gastrointestinal and nervous system functionsAnthropod material medical ingredientsDermatological disorderCITRUS MEDICA FRUITRemove blood
The invention belongs to the field of beautifying medicines, and in particular relates to a pure traditional Chinese medicinal female beautifying preparation. The preparation is characterized by comprising the following components in parts by weight: 20-30 parts of bee pollen, 15-20 parts of honeysuckle, 25-35 parts of fingered citron, 15-25 parts of radix polygonati officinalis, 12-17 parts of American ginseng, 30-40 parts of kudzuvine root, 40-50 parts of yam, 30-40 parts of Chinese angelica, 25-35 parts of medlar, 10-15 parts of donkey-hide gelatin, 30-40 parts of hawthorn, 12-17 parts of peach kernel, and 30-40 parts of sealwort. The pure traditional Chinese medicinal female beautifying preparation has the functions of tonifying qi and nourishing blood, clearing and activating the channels and collaterals, removing blood stasis for promoting tissue regeneration, and beautifying and removing speckles, and is safe and efficient.
Owner:TIANJIN XINRUI BIOMEDICAL TECH
Functional health food containing flavone of hawthorn fruit, and preparation method
InactiveCN1759746AHigh nutritional valueEasy to storeFood preparationPlant ingredientsFreeze-dryingHeart disease
A functional health-care food containing crataegolic flavone in the form of capsule, chewing tablet, or powder for decreasing blood fat and preventing heart disease and atherosclerosis is prepared from how through boiling, beating, sieving, mixing it with additives, vacuum freeze-drying, pulverizing, sieving and loading in capsules or tabletting. It features rich nutrients and sure health-care function.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of material with nitric oxide (NO) catalytic activity
The invention discloses a preparation method of a material with nitric oxide (NO) catalytic activity. The preparation method is implemented through the steps that a selenium-containing compound with nitric oxide catalytic activity, a sulfur-containing compound, a soluble copper salt, a compound with an o-phenol structure, a flavonoid compound, and a flavonol compound or a flavanone compound are mixed in a buffer solution and then polymerized. The material with NO catalytic activity not only can be applied to the surface modification of materials which are different in material, geometrical shape and topological structure, and also can be used as a filling material for a controlled release system. Double selenium bonds, double sulfur bonds, copper ions and phenolic hydroxyl groups, which are contained in the prepared material with nitric oxide (NO) catalytic activity, have an excellent free radical removal function; the selenium bonds, the sulfur bonds and the chelate copper ions, which are contained in the material, also have a reduced glutathione (GSH) response function; in addition, the copper ions containing in the material also have an antibacterial function; and the material, besides being used for catalyzing NO release, also can be applied to all related fields of free radical removal and GSH response function.
Owner:GUANGZHOU NANCHUANG EVEREST MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Common yam rhizome dew beverage and production method thereof
The invention relates to a common yam rhizome dew beverage, which is prepared from fresh common yam rhizome serving as a main raw material. The beverage consists of the following components in part by weight: 8 to 20 parts of common yam rhizome, 0.001 to 0.005 part of thermo-stable amylase, 5 to 8 parts of sweetener, 0.10 to 0.15 part of vitamin C, 0.10 to 0.38 part of stabilizer, 0.06 to 0.16 part of acidity regulator and 71.3 to 86.7 parts of purified water. A production method comprises the following steps of: protecting color, coarsely grinding, cooking, pulping, raising the temperature for gelatinization, performing enzymolysis, inactivating at a high temperature, blending, homogenizing, degassing and the like. Common yam rhizome dew furthest keeps the specific active ingredients and flavor of the common yam rhizome, makes the common yam rhizome more easily absorbed and utilized by human bodies, and increases the nutritional value of the common yam rhizome; and the beverage has fragrant and mellow mouthfeel, is tasty and refreshing and has the effects of quenching thirst, moistening the lung, invigorating the spleen, protecting the liver, disintoxicating, tonifying middle-jiao and qi, nourishing the heart, soothing the nerves, preventing atherosclerosis, building the bodies, beautifying and delaying senility. The production method ensures that the common yam rhizome dew beverage is not browned, precipitated and demixed.
Owner:SHENZHEN VIGOR HEALTH CARE PROD CO LTD
Health care preparation for regulating functional balance of organs of bowels in human body and preparing method
InactiveCN1660387APrevent atherosclerosisEnhance metabolic functionUnknown materialsDrug compositionsDiseaseHuman body
A health-care food for preventing and treating atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipemia, hypertension, coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, tumor, etc, and balancing the functions of organs is prepared from 10 Chinese-medicinal materials including anemarrhena rhizome, ginger, wolfberry fruit, yam, etc.
Owner:韦平生
Additive for tea odor type tobacco and method for making same
The invention discloses an additive used for tea fragrant type tobacco and the preparation method thereof. The invention is characterized in that the raw material of the additive used for tobaccos is obtained through reasonably blending the raw materials of jasmine tea, burdock, licorice and bee honey; the extracting solution is prepared through the jasmine tea, burdock as well as the licorice of certain proportion by adopting a solvent refluxing method, is prepared to be medical ointment through being concentrated under reduced pressure, and is formed to be an additive used for tobaccos through being added with a proper amount of bee honey. The use amount is 0.01 to 5 percent of the weight of tobacco thread, in order to cut rolled stem or tobacco thin slice, the additive is dissolved in the mixed solution of distilled water, ethyl alcohol or propylene glycol of certain amount to form an additive used for tea fragrant type tobacco, and is evenly sprayed on the cigarette tobacco thread, the cut rolled stem or the tobacco thin slice and is formed to be cigarettes. The invention can reduce the irritability to the respiratory system generated by the tobacco smoke, has the functions of adjusting tea fragrance, flower fragrance, smoky flavor and medicine fragrance, and can improve the cigarette fragrance, the aftertaste is comfortable, and the tobacco smoke is exquisite and gentle, and thereby the serious irritability to the respiratory system of the smokers is effectively reduced, the respiratory disease is reduced, as well as the harm from smoking is lightened.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGXI IND
Sea cucumber milk, sea cucumber milk beverage and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101015341APrevent atherosclerosisImprove immunityMilk preparationMetabolism disorderFreeze-dryingAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a kind of sea cucumber milk and sea cucumber milk beverage and the preparing method, belonging to food processing technique. It is characterized by high nutritional value and functions of restoring old myocardial infarction, reducing blood pressure, reducing blood fat, anti- oxidation, anti- aging and increasing human immunity. It comprises water- soluble sea cucumber active dry powder, fresh milk and auxiliary agent. Said sea cucumber active powder is produced through following steps: enzymolyzing boiled sea cucumber solution with compound enzyme, purifying with alcohol, filtering, condensing, and freeze drying. The invention takes cooked sea cucumber liquid to produce sea cucumber liquid, which not only makes full use of sea cucumber, but also reduces producttion cost.
Owner:姜玉宝
Beverage for reducing blood sugar, blood pressure and blood fat and production method thereof
InactiveCN102048218ALower blood sugarLower serum cholesterolFood preparationAcute hyperglycaemiaMedicine
The invention discloses a beverage for reducing blood sugar, blood pressure and blood fat, which comprises the following dry materials in part by weight: 3 to 6 parts of bitter gourd, 3 to 6 parts of corn stigma, 2 to 4 parts of raw astragalus, 2 to 4 parts of yam, 2 to 4 parts of Siberian solomonseal rhizome, 5 to 10 parts of bitter buckwheat husk and 100 parts of water. A production method of the beverage comprises the following steps of: cutting the raw materials into small pieces according to the proportion, putting into a ceramic container, adding the water, decocting for two or three times, mixing filtrate, adding an appropriate amount of flavoring agent, and sterilizing to obtain a finished product. The beverage prepared through reasonable compatibility of six natural raw materials is lukewarm in nature, has obvious curative effects on most of patients with hyperglycemia, hypertension and hyperlipidemia, cannot harm intestines and stomach after being drunk, and has a certain health-care effect; and the production process is simple, and the product is convenient to drink.
Owner:常堡同
Stable medicine combination
ActiveCN101336920APrevent hyperlipidemiaPrevent atherosclerosisOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAdjuvantMedicine
The invention relates to a stable oral pharmaceutical composition, particularly to a pharmaceutical composition comprising rosuvastatin calcium, micropowder silica gel and pharmaceutically-acceptable adjuvants, and a preparation method and an application thereof.
Owner:NANJING CHIA TAI TIANQING PHARMA
Health-care cold tea and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101978844AImprove nutrient utilizationEasy to drinkTea substituesAdditive ingredientProtodioscin
The invention provides health-care cold tea prepared mainly from honeysuckle and Camellia nitidissima and a preparation method thereof. The invention adopts a technical scheme that: ingredients of the health-care cold tea comprise 10 to 90 percent of honeysuckle and 90 to 10 percent of Camellia nitidissima; and the preparation method comprises the step of grinding the honeysuckle and Camellia nitidissima into powder respectively or grinding the honeysuckle and Camellia nitidissima into powder by using a supermicron milling technique, stirring uniformly, and packing by 2 to 10 gram bags. In the invention, the honeysuckle and Camellia nitidissima are ground into powder by the supermicron milling technique, so the nutrient utilization rate is high, and the tea is convenient to drink; and the tea has the effects of clearing heat, detoxifying, resisting bacteria and inflammation, regulating immunity, promoting dieresis and diminishing swelling, is rich various natural nutrients such as tea polyphenol, protodioscin, total flavonoids, tea polysaccharide, tea pigment, caffeine, vitamin and amino acid, contains various trace elements such natural organic germanium (Ge), selenium (Se), molybdenum (Mo), zinc (Zn) and the like, and has the health-care functions of preventing cancer, inhibiting tumor growth, reducing blood fat and cholesterol, preventing atherosclerosis, preventing prostatitis, supplying nutrients, in habiting bacteria and resisting aging, and is suitable for all people.
Owner:蒋科罡
Propolis soft capsule and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103637197AEasy to usePrevention and treatment of chronic complicationsOrganic active ingredientsLipidic food ingredientsDiabetes mellitusWheat germ
The invention relates to a propolis soft capsule. The propolis soft capsule comprises a rubber sheet and a capsule content, wherein the capsule content comprises the following components in percent by weight: 20%-60% of propolis supercritical CO2 extract, 30%-70% of wheat-germ oil and 1%-10% of vitamin E; components of the rubber sheet are gelatin, glycerol and purified water in a weight ratio of 100:42:100. The propolis soft capsule is integrated with improving effect of propolis on diabetes mellitus and preventing effect of vitamin E on chronic complication of the diabetes mellitus; moreover, the components are good in synergistic effect. The invention also provides a preparation method of the propolis soft capsule.
Owner:JIANGSU JIANGDAYUAN ECOLOGICAL BIOLOGICAL TECH
Supermicro Tongxinluo Chinese herbal composite and its new usage
ActiveCN1954825AAvoid damageObvious effectPowder deliveryAnthropod material medical ingredientsVascular endotheliumVentricular remodeling
An application of the Chinese medicine 'Superfine Tongxinluo' in relaxing the vascular endothelial injury caused by atherosclerosis, decreasing the cardiac infarction range after AMI reperfusion, preventing hyperlipemia and atherosclerosis, and treating arteria coronaria spasm, pile, thromboangiitis obliterans, platelet coagulation, etc is disclosed.
Owner:HEBEI YILING MEDICINE INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com