Method for extracting dihydroquercetin form larch
A technology for extracting dihydroquercetin and larch, which is applied in the direction of organic chemistry and medical raw materials derived from gymnosperms, can solve the problems of limited practicality and high price of dihydroquercetin, and achieve the treatment of ischemia heart disease, improve coronary blood flow, increase the inhibitory effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
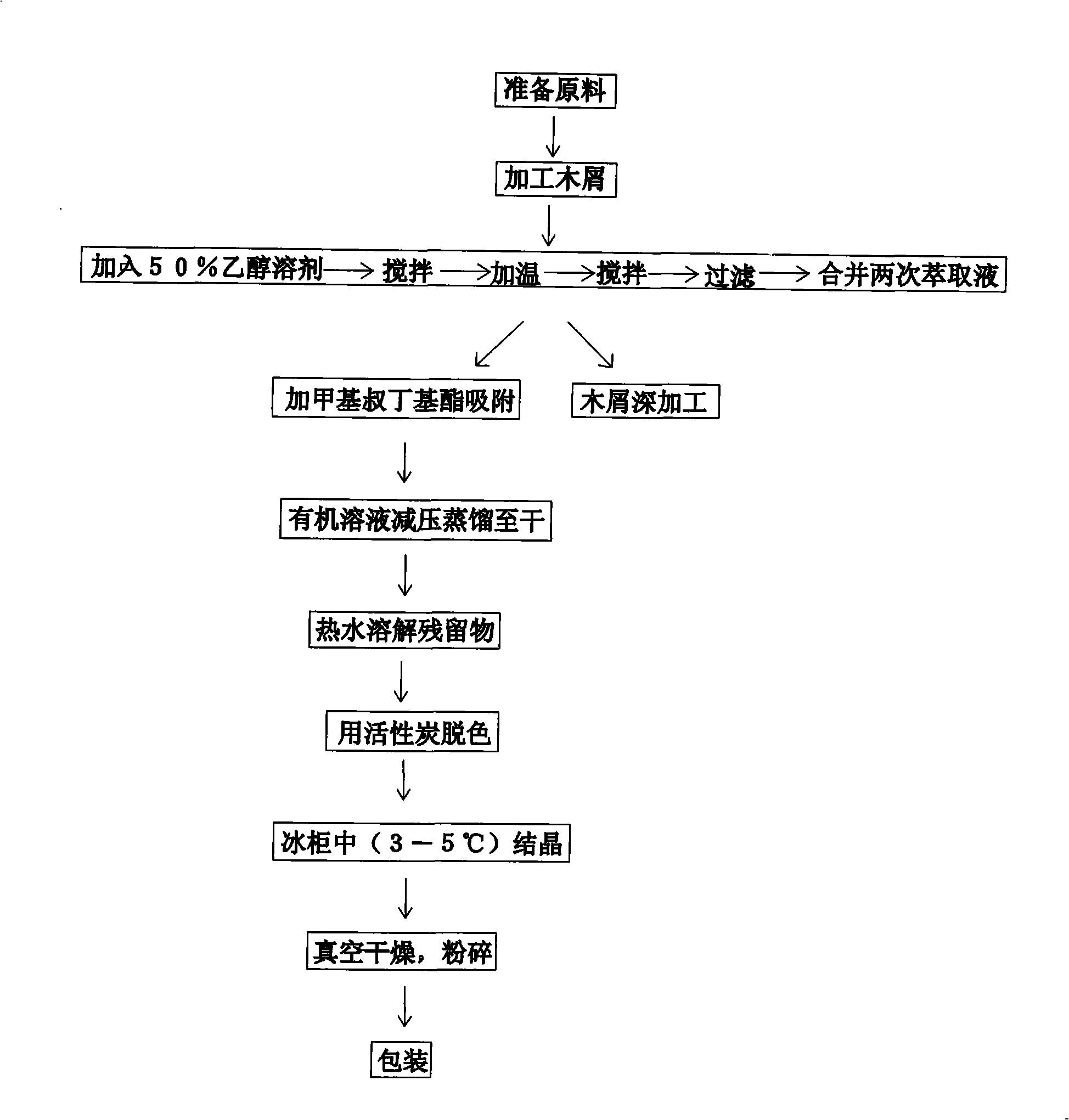
[0029] The method for extracting dihydroquercetin from larch: select larch rhizomes, saw sections of raw materials, peel them, process them into sawdust, weigh 50 grams of larch sawdust, and place them in a reaction kettle. Use a measuring cylinder to measure 500-800ml of 50% ethanol solution, add it to the reaction kettle, stir and mix it with larch sawdust, soak for 1 hour, stir twice in between, each time for 10 minutes, and then start heating to 65-75°C, The temperature was kept at constant temperature for 1 hour, during which time it was stirred twice for 10 minutes each time. Close the reaction kettle, the mixture presents a yellowish-brown slightly oily turbid liquid, filter, collect the filtrate, perform secondary extraction on the raw material, remove sawdust, and combine the filtrate after two extractions. Under the condition of a temperature of 30-40° C., the filtrate was adsorbed twice with methyl tert-butyl ether at a ratio of 1:10, and the organic mixed solution ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] In the process of extracting dihydroquercetin, it is affected by many factors. Among them, the ratio of larch sawdust mass to ethanol solution, cooking time, amount of filtrate adsorbent, adsorption time, adsorption times and pH value are the main influencing factors. After several experiments and the quality of the obtained products, the optimal process route for extracting dihydroquercetin from larch was determined. The reaction kettle is kept at a constant temperature of 65-75°C.
[0032] 1. Change the solid-liquid ratio and compare the experimental results with other conditions unchanged:
[0033] solid to liquid ratio
cooking time
Adsorbent dosage
Adsorption time
Adsorption times
PH value
Extraction %
1 / 8
60 minutes
1 / 10
1 hour
2
5
1.30
1 / 10
60 minutes
1 / 10
1 hour
2
5
2.20
[0034] 1 / 12
60 minutes
1 / 10
1 hour
...
Embodiment 3
[0052] 1. Physical and chemical indicators of the product:
[0053] Appearance Powder
[0054] Color white-yellow
[0055] Odor No smell
[0056] Taste No special taste
[0057] Solubility 0.001mg / kg water
[0058] Moisture ≤8
[0059] Purity ≥90%
[0060] Melting point 230°C
[0061] Mineral ≤0.3
[0062] 2. Comparison of melting points:
[0063] Compare with a melting point analyzer.
[0064] 3. Infrared spectrum detection:
[0065] The product dihydroquercetin was tested by an infrared spectrometer.
[0066] 4. Liquid chromatographic detection of products:
[0067] Put 0.1 g of the reference standard dihydroquercetin into a drying oven at 120° C. to dry. Then dissolve in 10 ml of acetone solution.
[0068] Add 700 ml of 2% acetic acid solution into 300 ml of acetone solution, and stir well.
[0069] Fill 19 milliliters of 2% acetic acid solution into a measuring beaker with a capacity of one liter, add distilled water to one liter, and stir well.
[0070] Dis...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| relative humidity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com