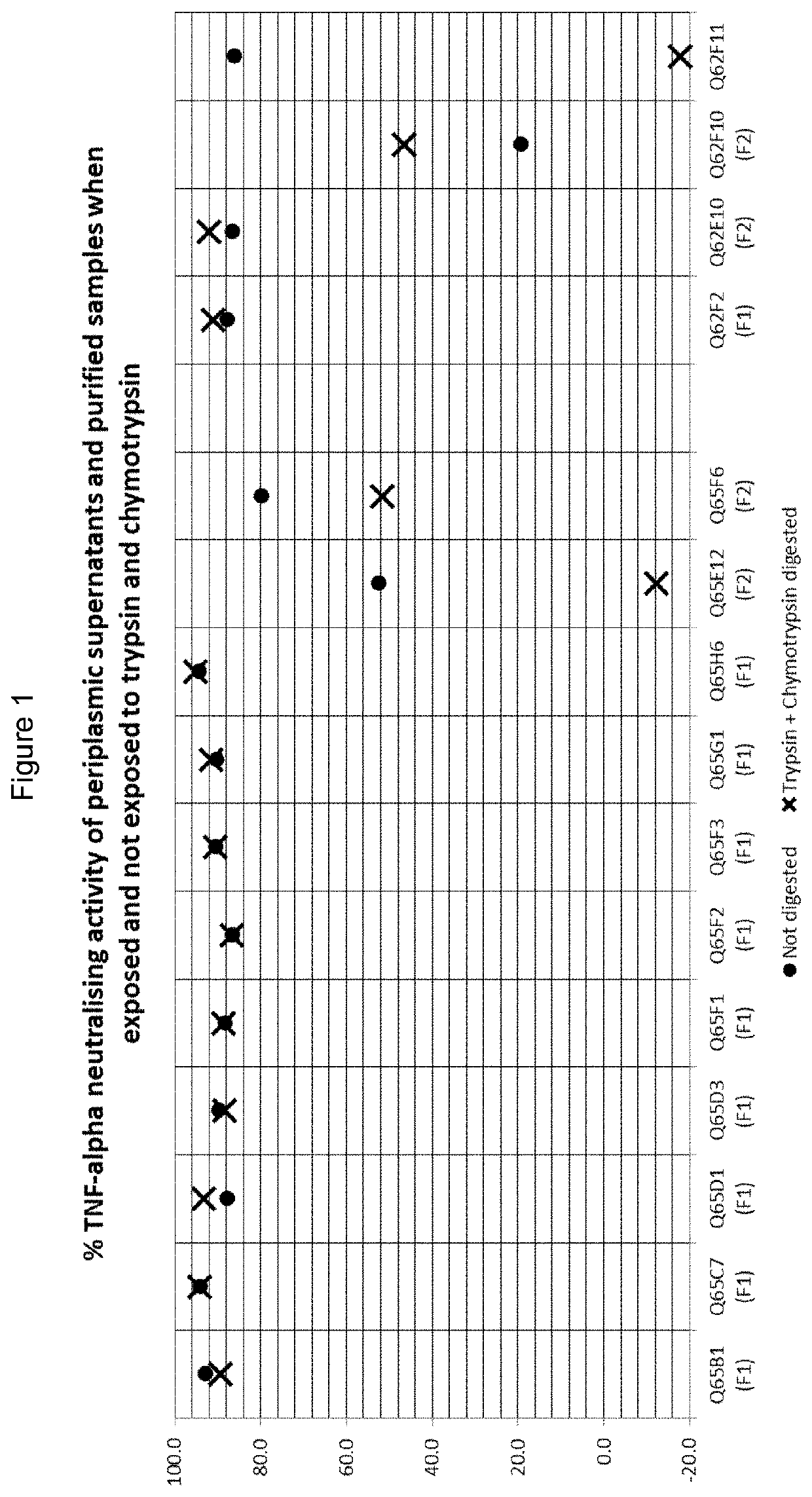
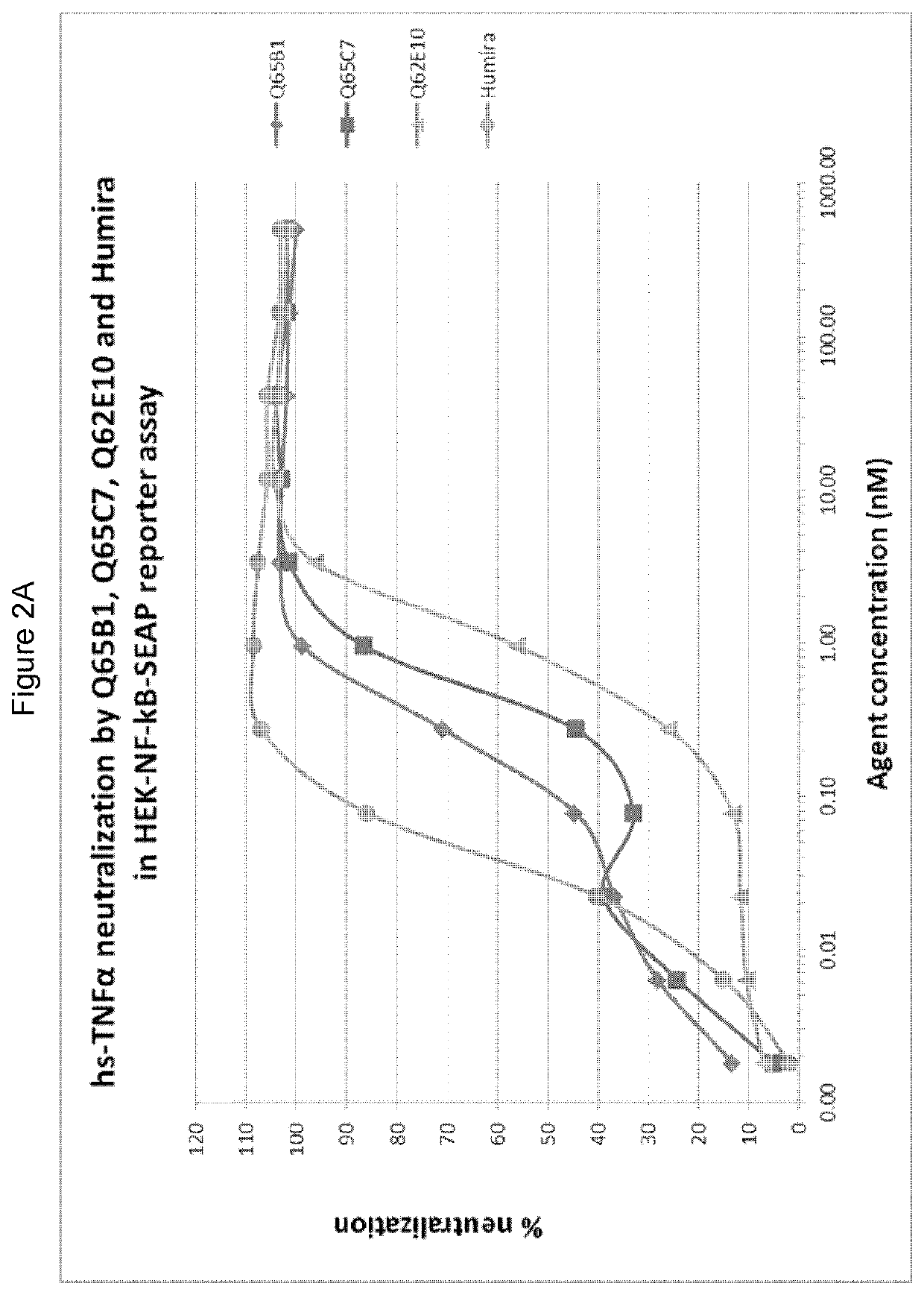
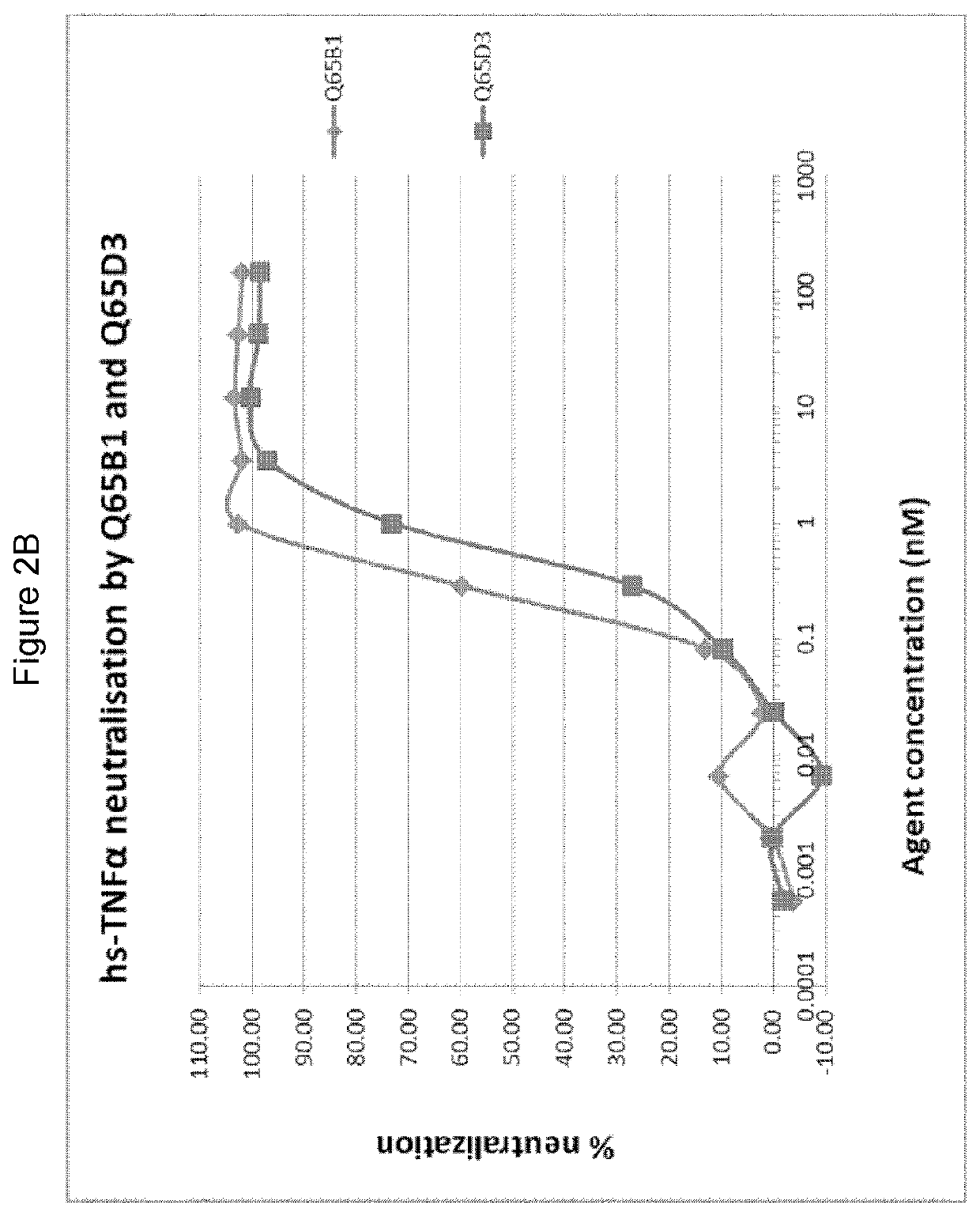
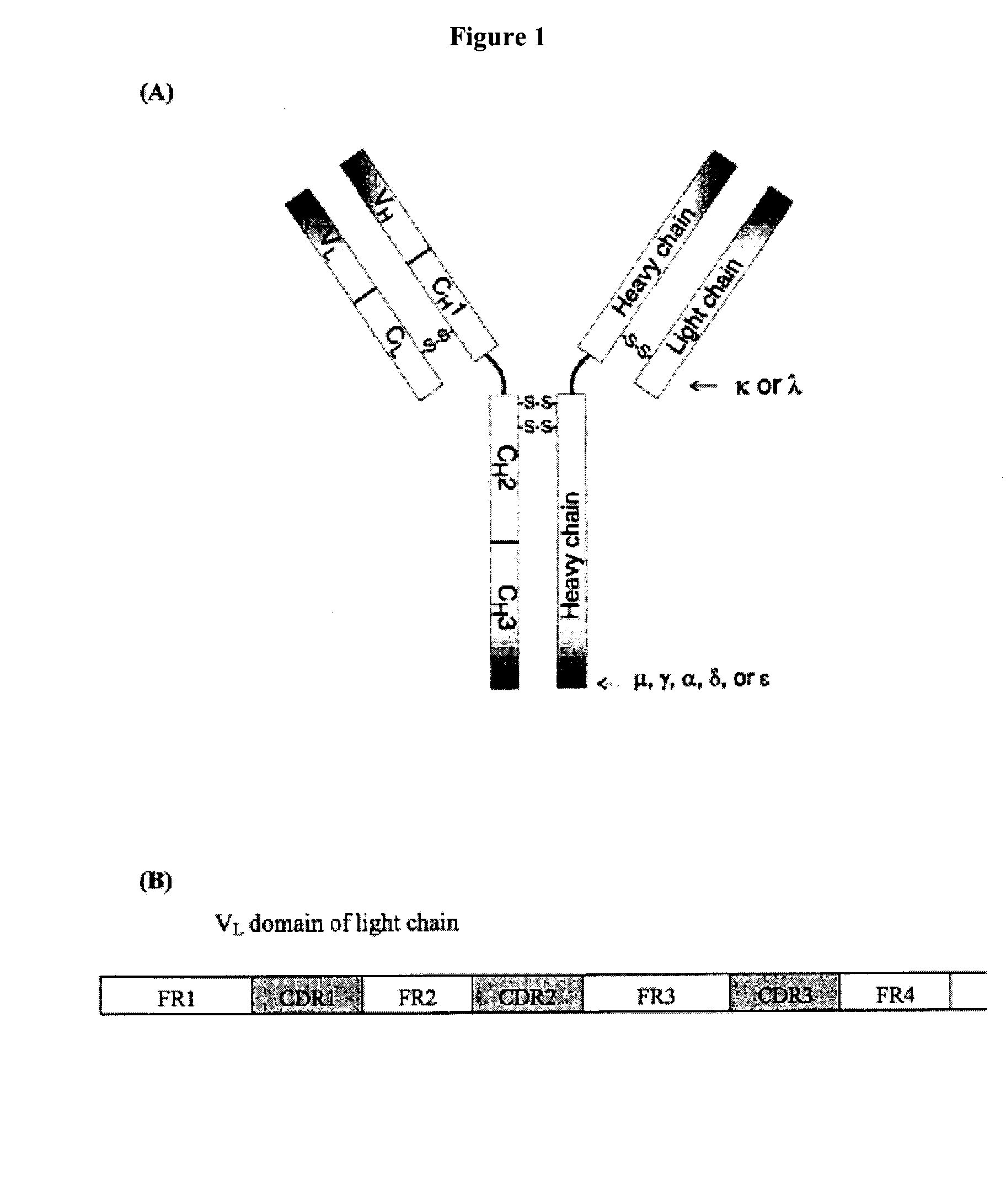
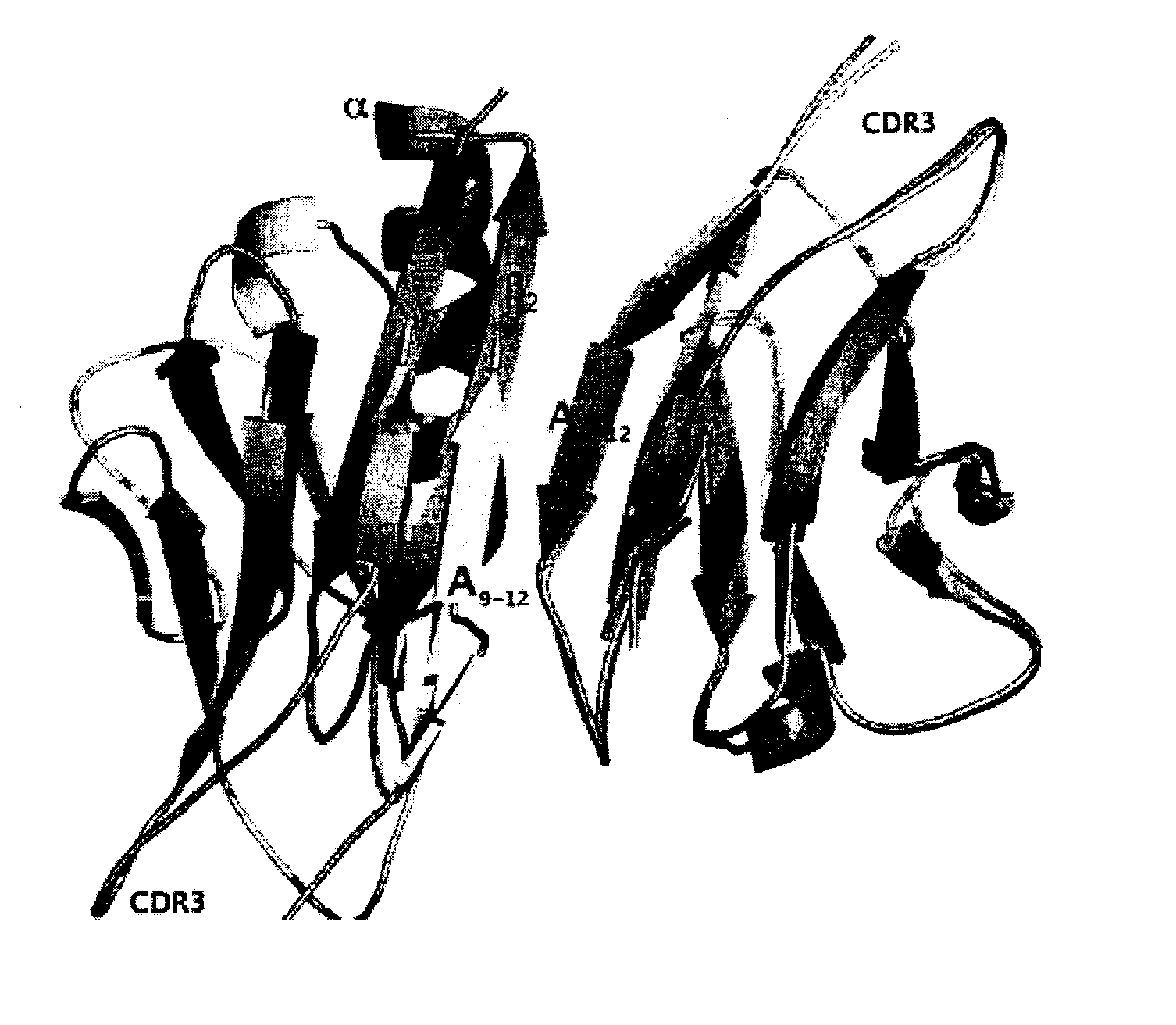Patents
Literature
51 results about "Immunoglobulin chain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Humanized immunoglobulins
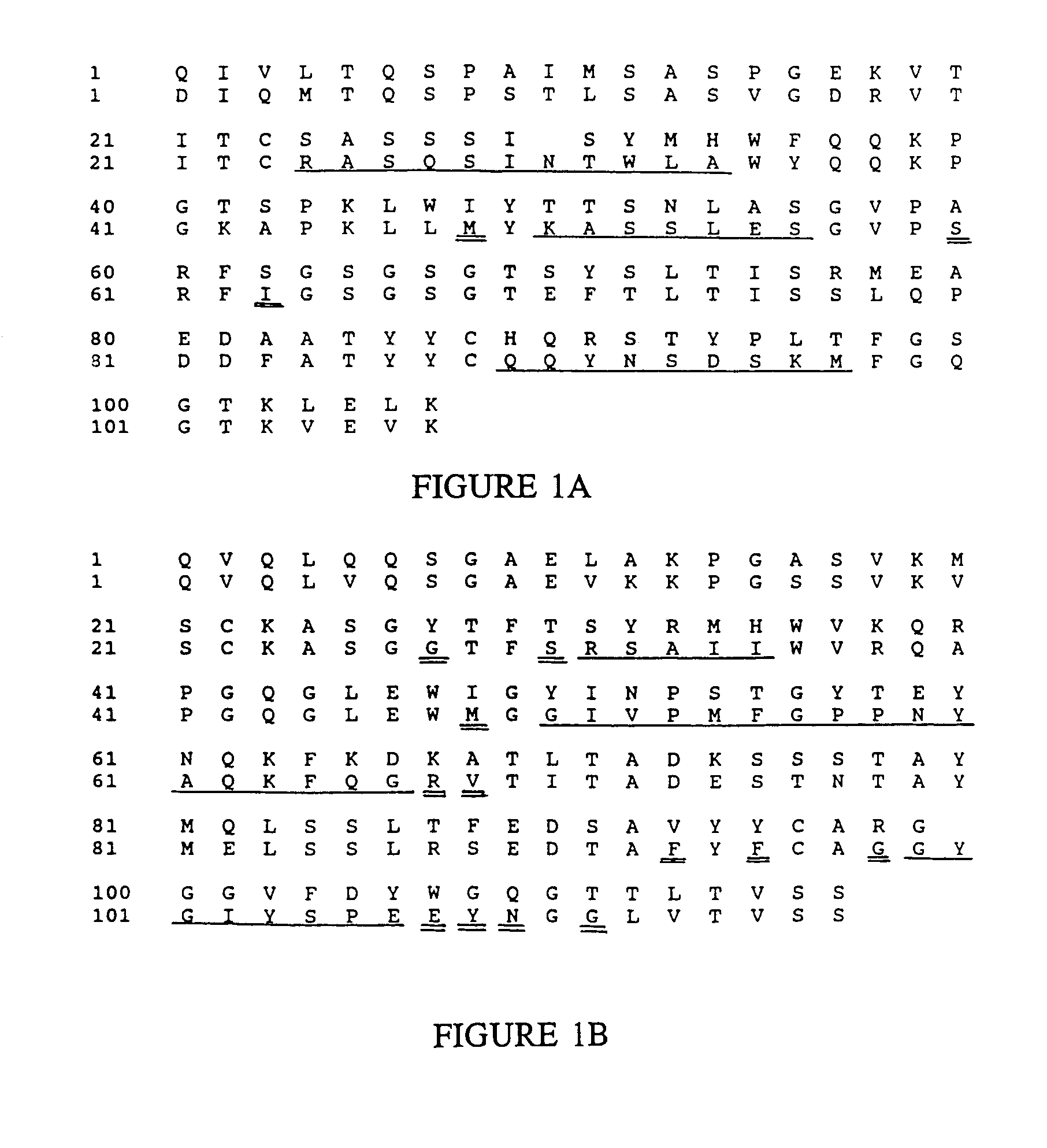
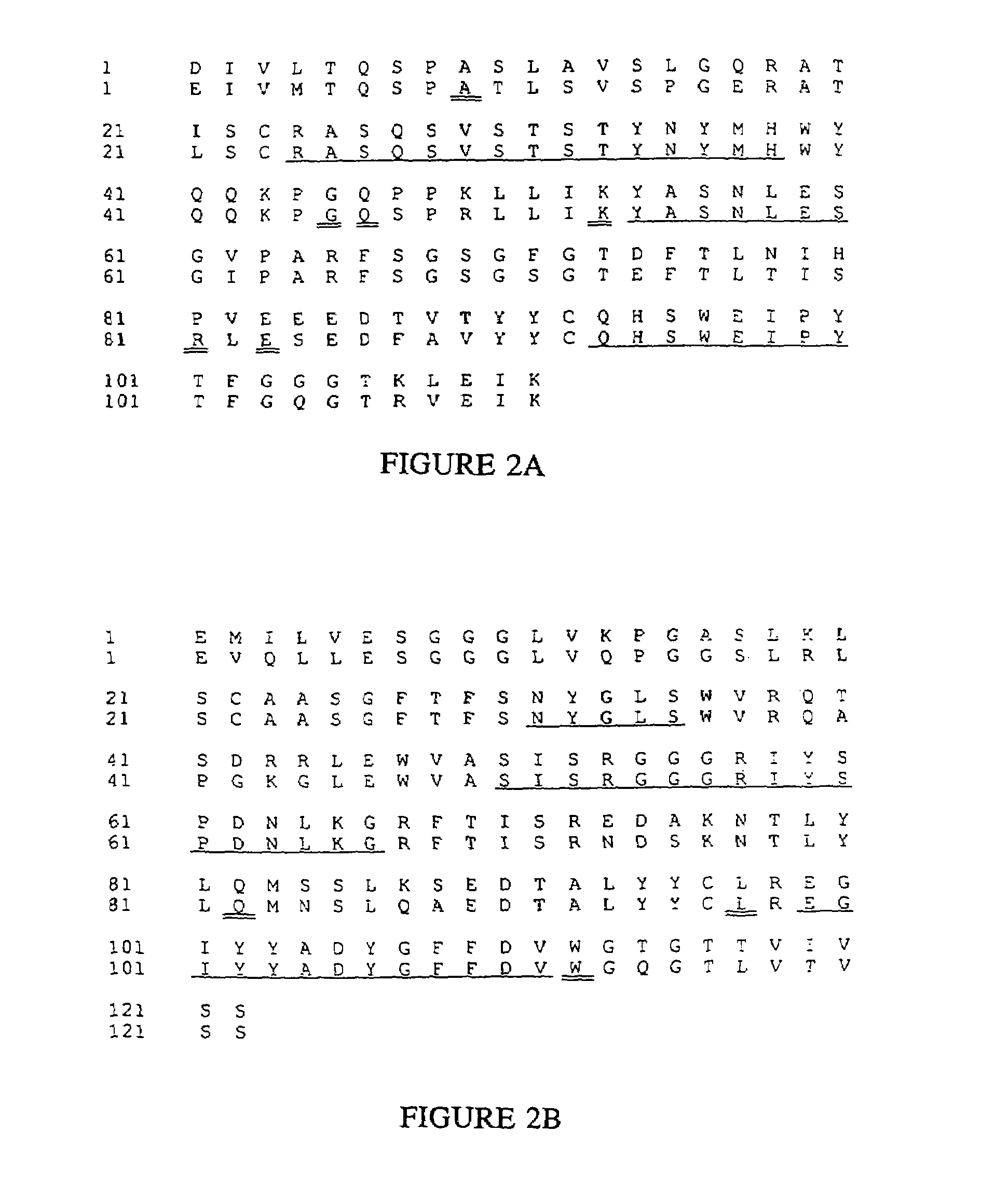
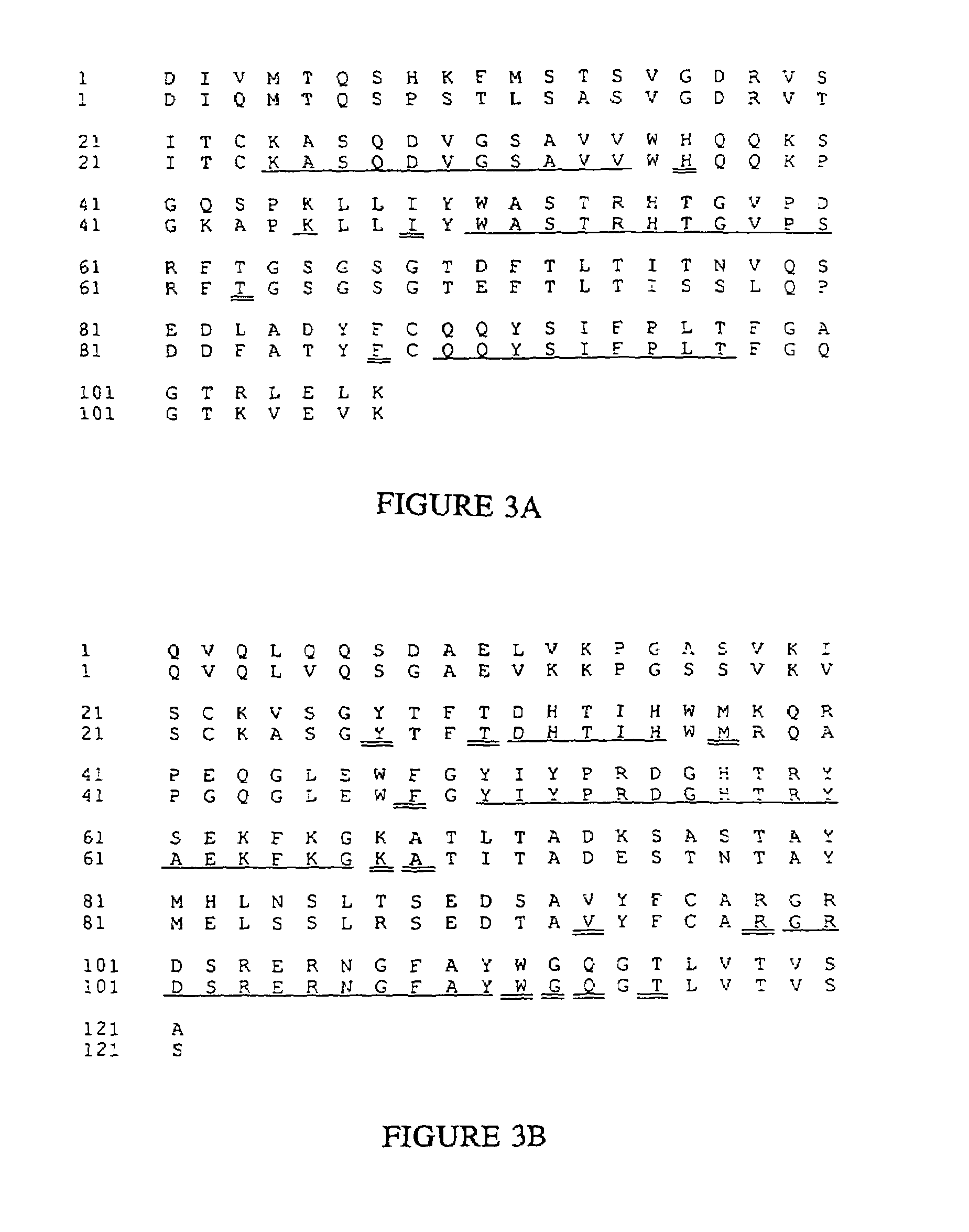
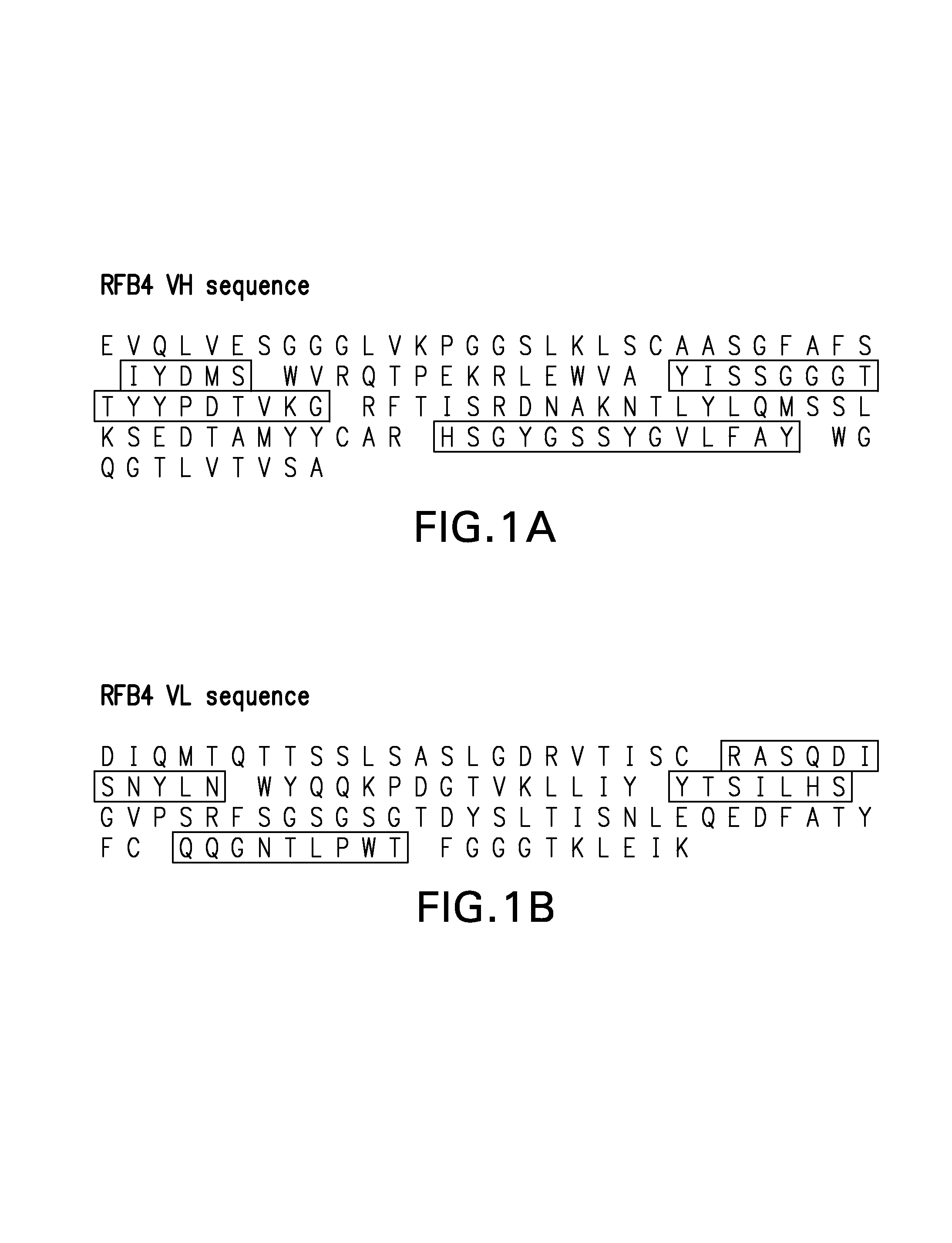
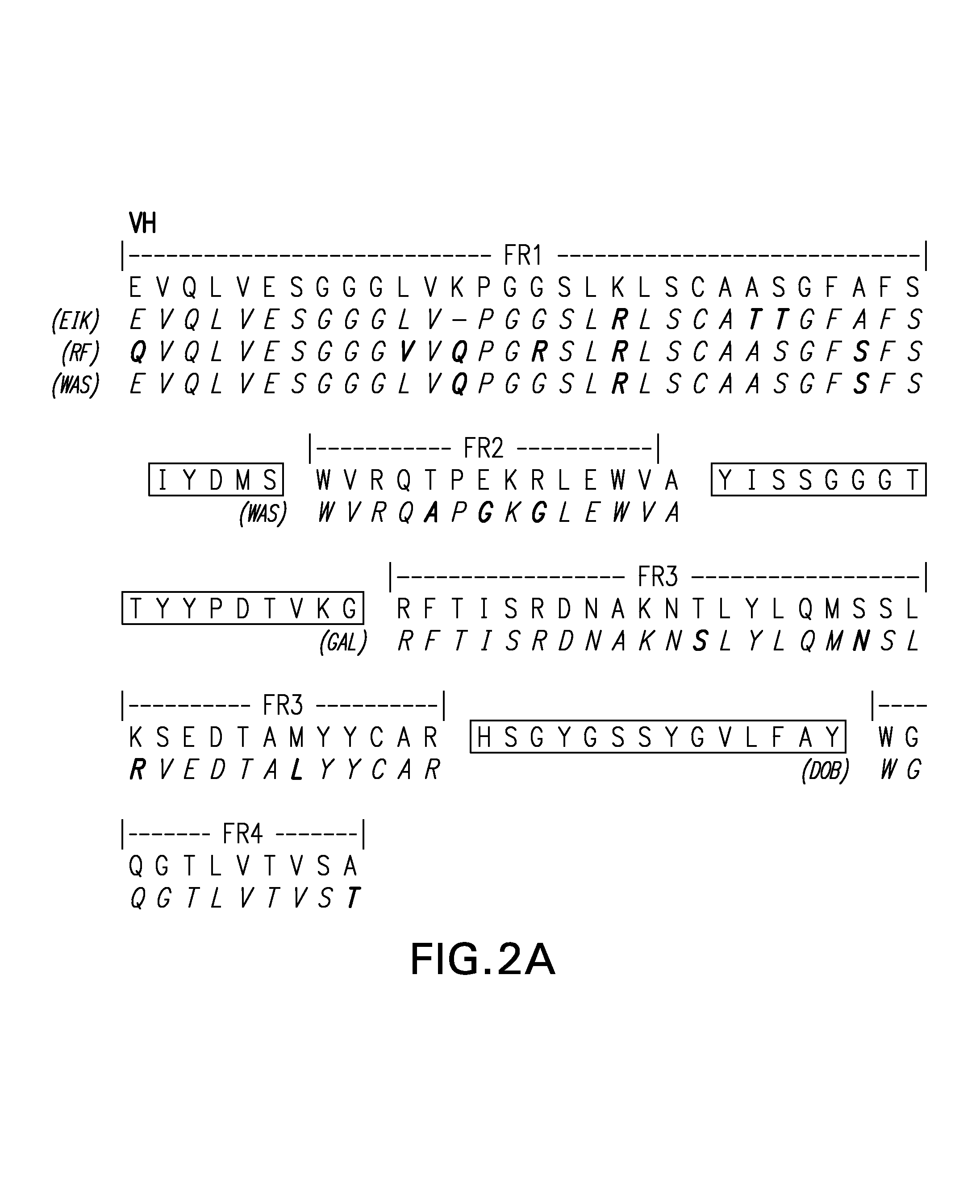
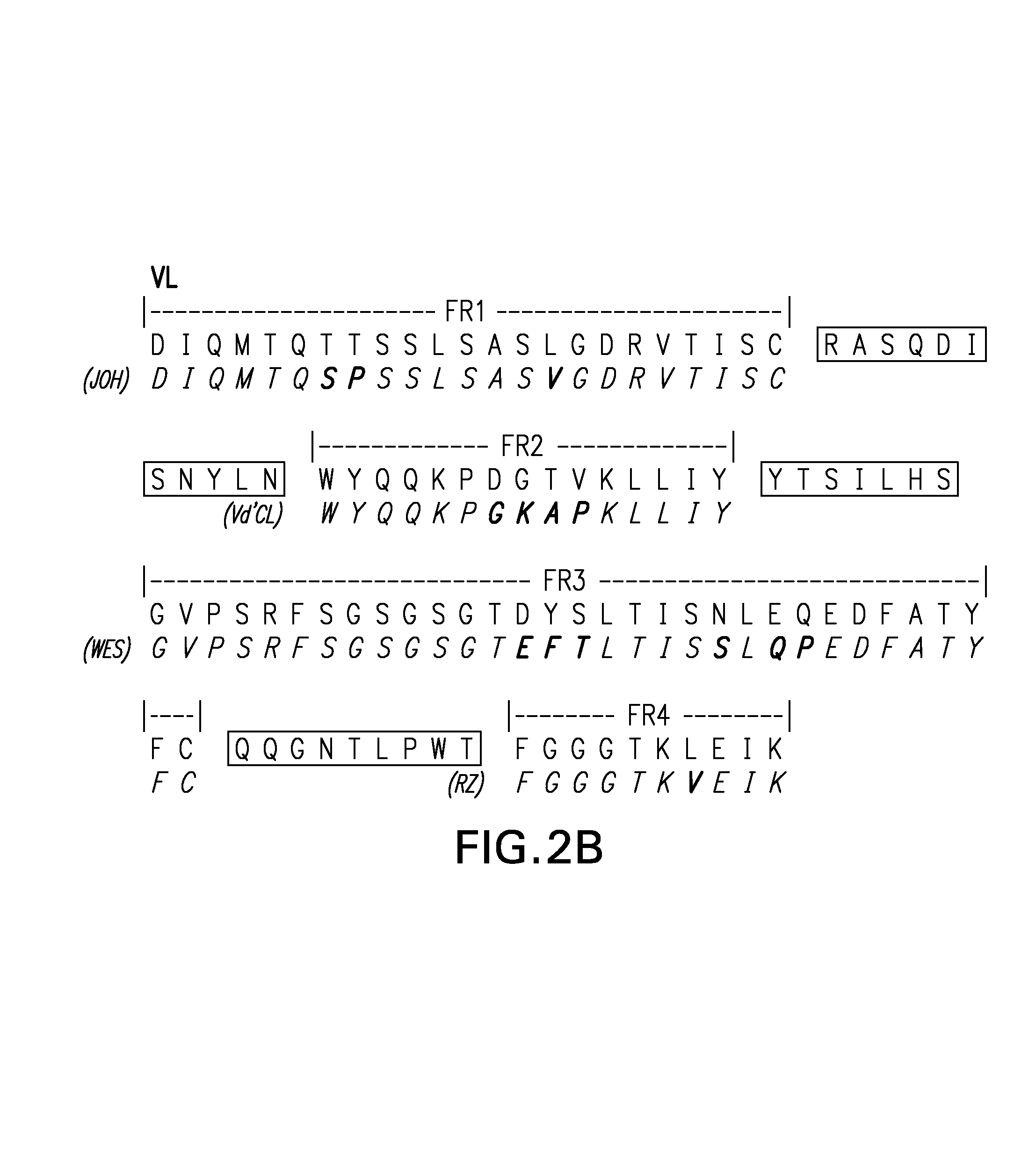
Novel methods for producing, and compositions of, humanized immunoglobulins having one or more complementarity determining regions (CDR's) and possible additional amino acids from a donor immunoglobulin and a framework region from an accepting human immunoglobulin are provided. Each humanized immunoglobulin chain will usually comprise, in addition to the CDR's, amino acids from the donor immunoglobulin framework that are, e.g., capable of interacting with the CDR's to effect binding affinity, such as one or more amino acids which are immediately adjacent to a CDR in the donor immunoglobulin or those within about about 3Å as predicted by molecular modeling. The heavy and light chains may each be designed by using any one or all of various position criteria. When combined into an intact antibody, the humanized immunoglobulins of the present invention will be substantially non-immunogenic in humans and retain substantially the same affinity as the donor immunoglobulin to the antigen, such as a protein or other compound containing an epitope.
Owner:PDL BIOPHARMA INCORPORATED
Human Anti-Tau Antibodies
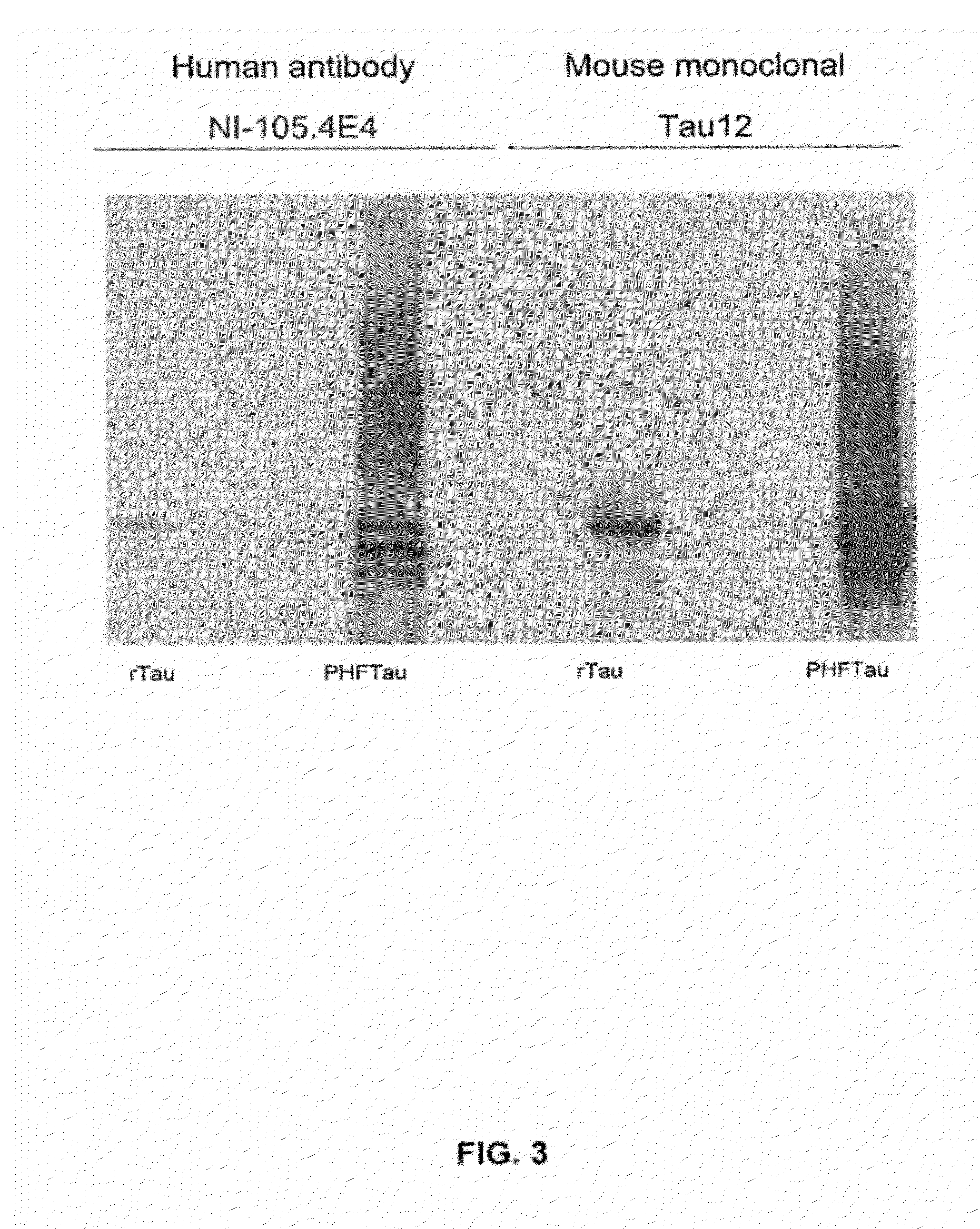
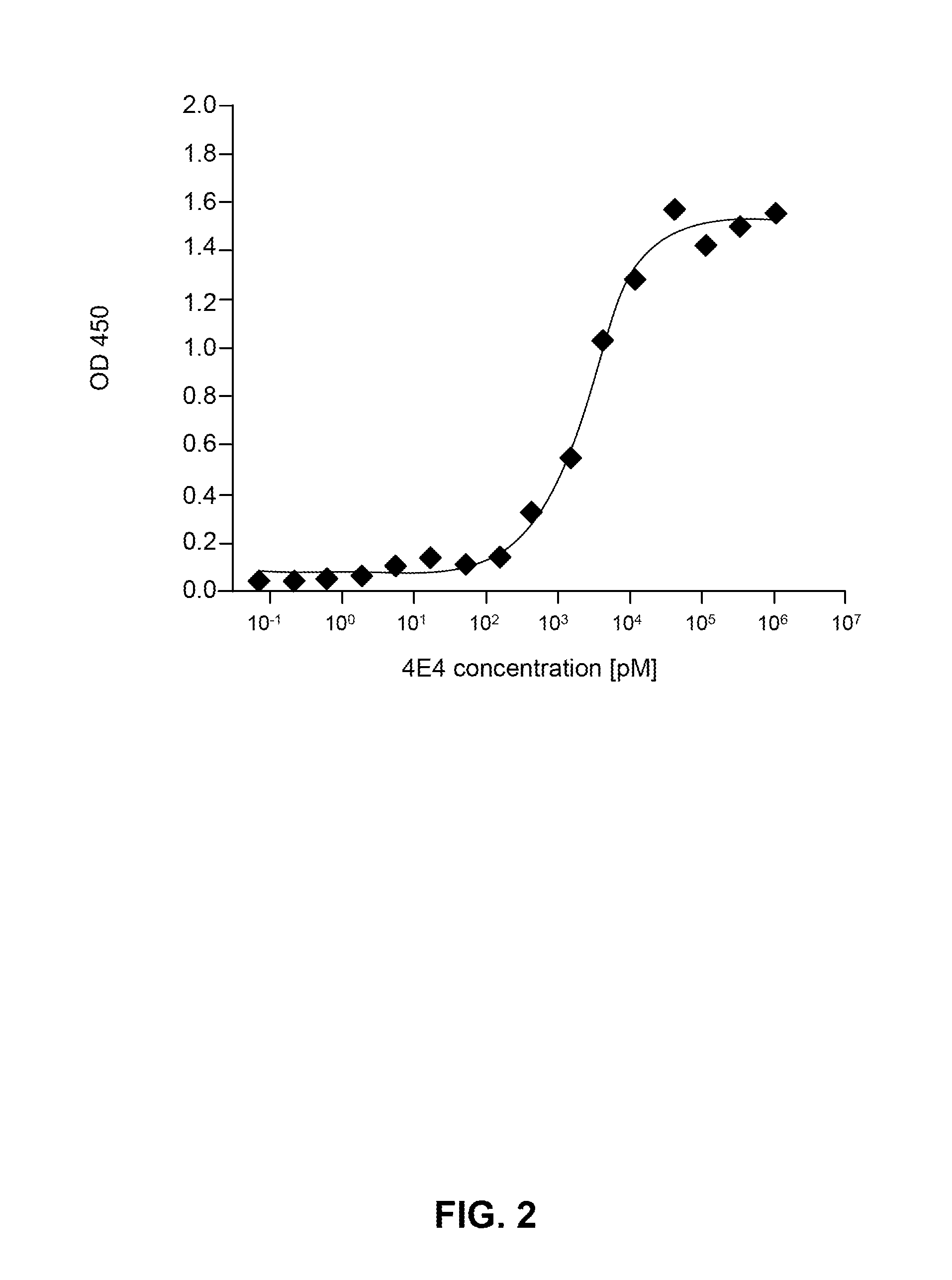
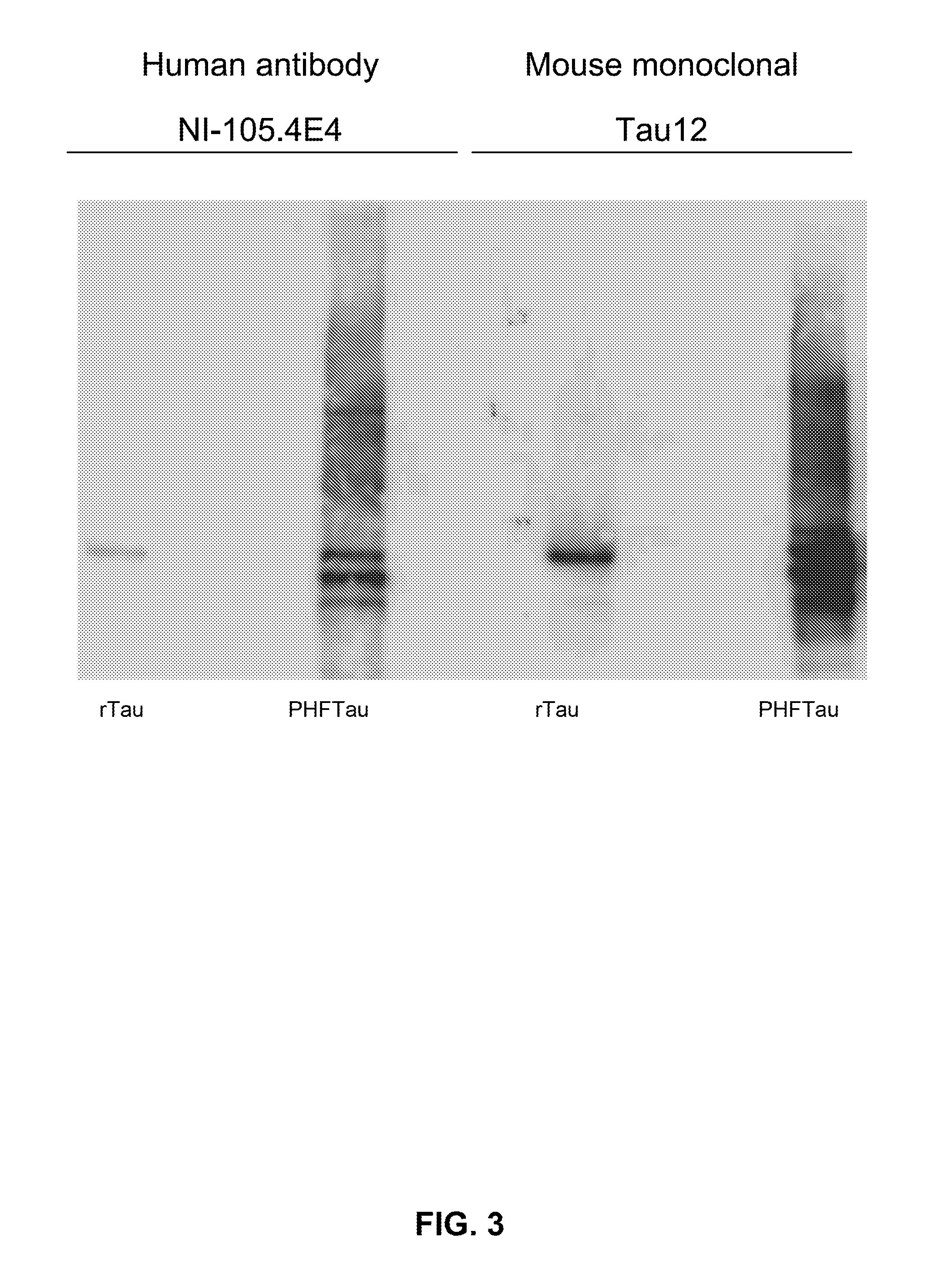
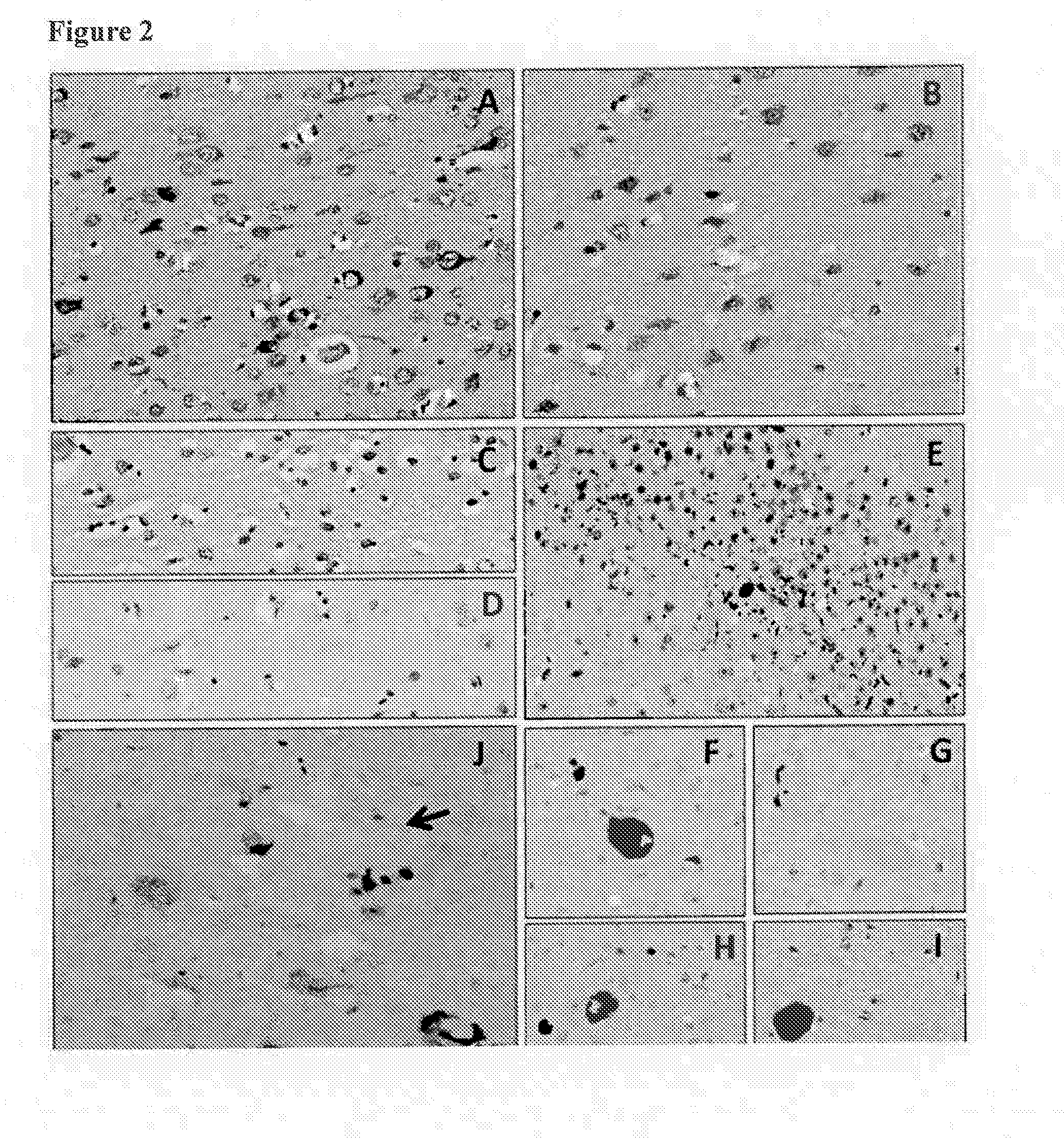
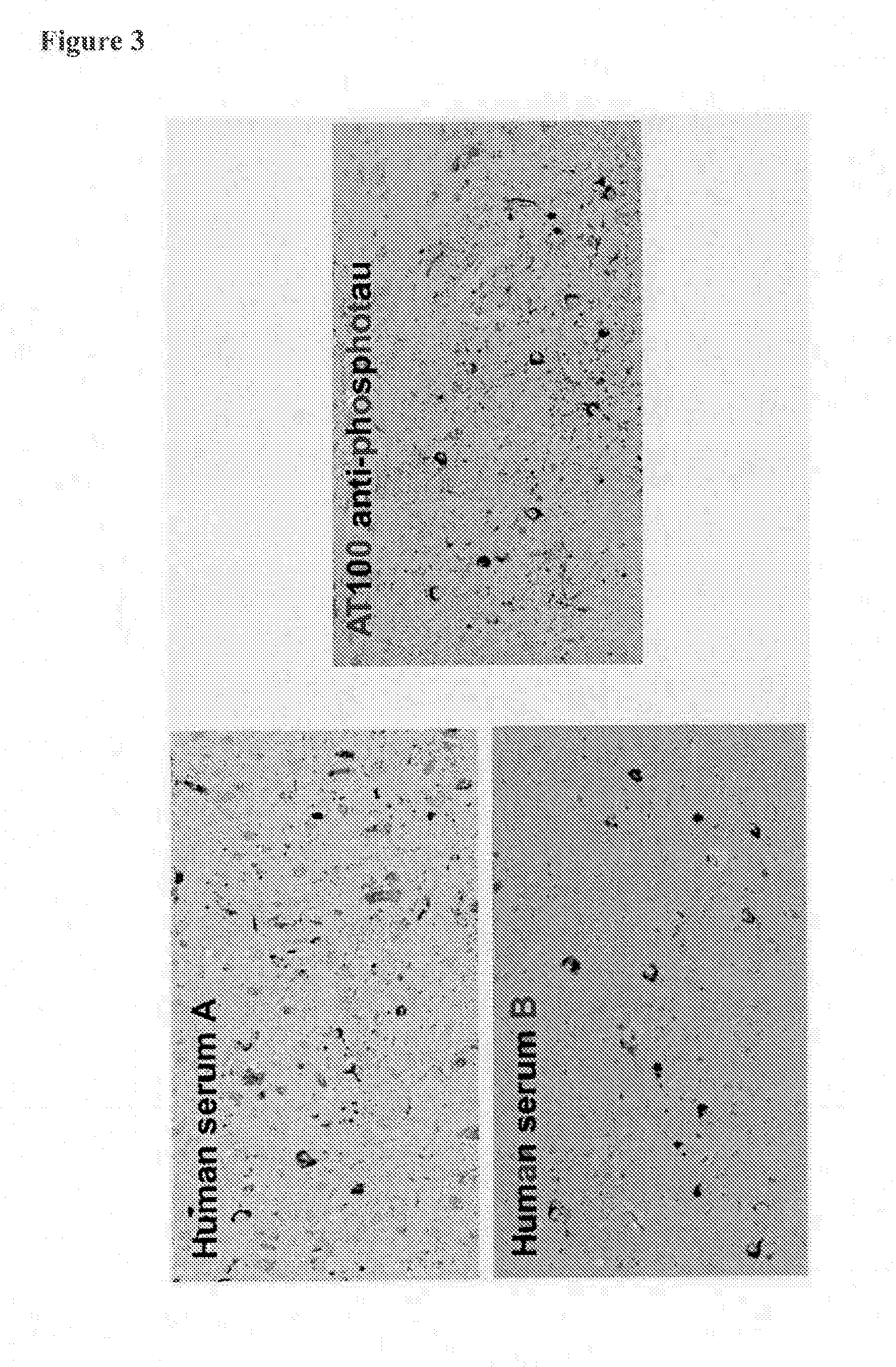
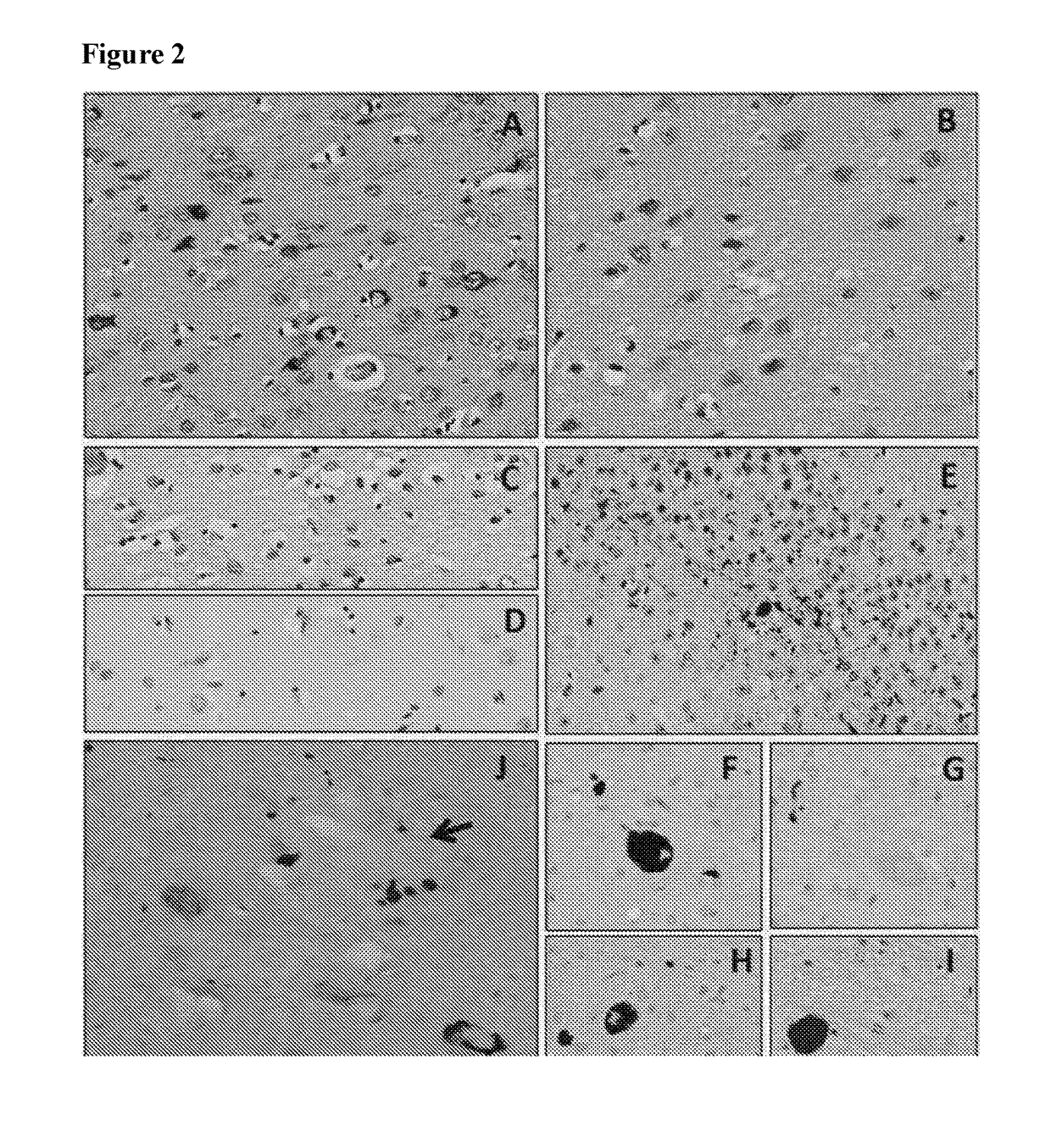
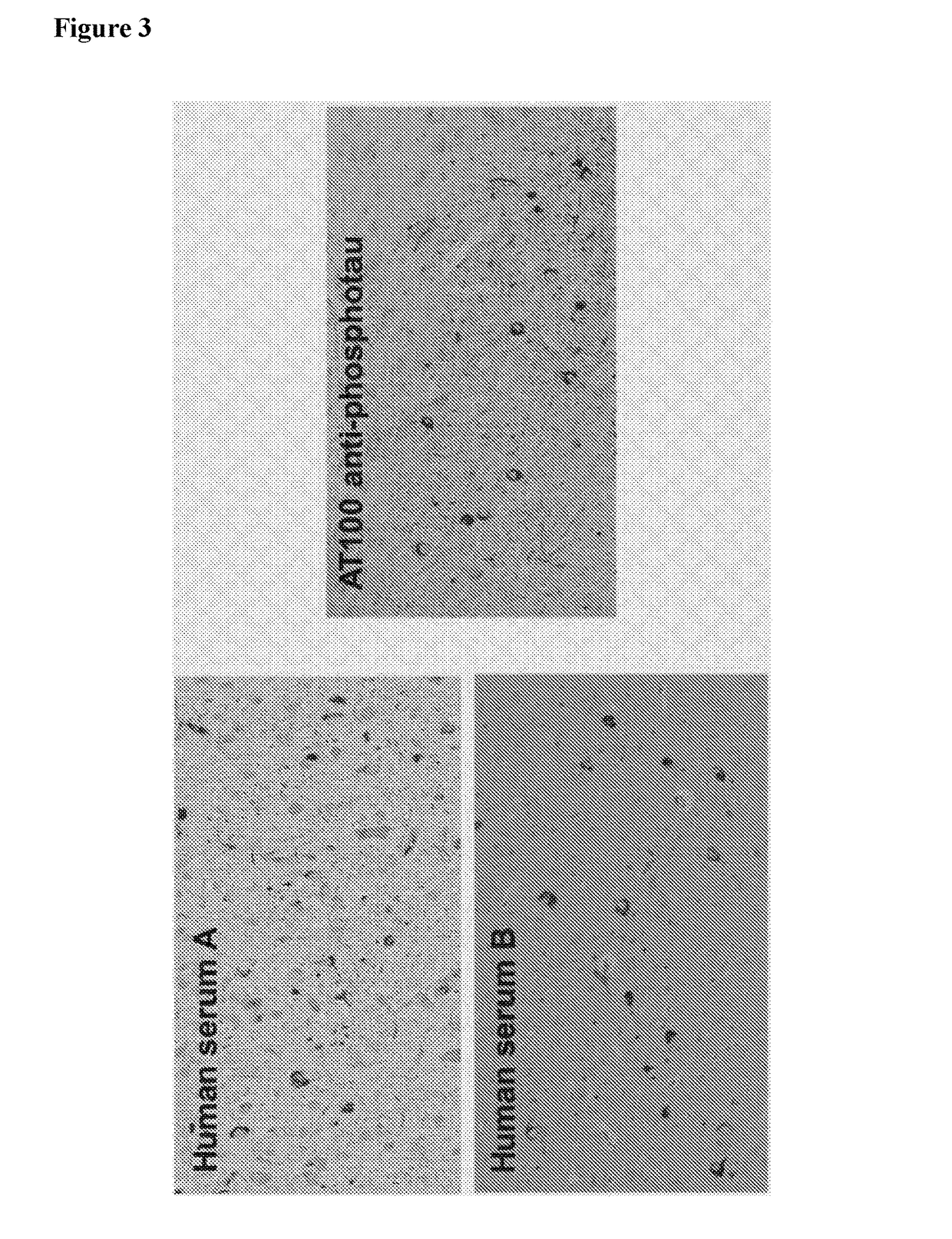
Provided are novel human tau-specific antibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for tau are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for tau targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Framework-patched immunoglobulins
InactiveUS7321026B2Reduced and eliminated immunogenicityIncrease flexibilityAntipyreticAnalgesicsB-Cell EpitopesVaccine Immunogenicity
Framework (FR)-patching is a novel approach to modify immunoglobulin for reducing potential immunogenicity without significant alterations in specificity and affinity. Unlike previous described methods of humanization, which graft CDRs from a donor onto the frameworks of a single acceptor immunoglobulin, we patch segments of framework (FR1, FR2, FR3, and FR4), or FRs, to replace the corresponding FRs of the parent immunoglobulin. Free assortment of these FRs from different immunoglobulins and from different species can be mixed and matched into forming the final immunoglobulin chain. A set of criteria in the choice of these FRs to minimize or eliminate the need to reintroduce framework amino acids from the parent immunoglobulin for patching is described. The approach gives greater flexibility in the choice of framework sequences, minimizes the need to include parent framework amino acids, and, most importantly, reduces the chances of creating new T- and B-cell epitopes in the resultant immunoglobulin.
Owner:SKYTECH TECH
IL-7 fusion proteins
ActiveUS20050164352A1Good biological propertiesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulin chainInterleukin I
The invention is directed to a fusion protein which includes a first portion including an immunoglobulin (Ig) chain and a second portion including interleukin-7 (IL-7).
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Human Anti-tau antibodies
InactiveUS20130295021A1Reduce riskSlow onsetBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsTargeted immunotherapySpecific antibody
Provided are human tau-specific antibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for tau are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for tau targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN INT NEUROSCI +1
Single chain antibody with cleavable linker
InactiveUS20060252096A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiSingle-Chain AntibodiesConstant region
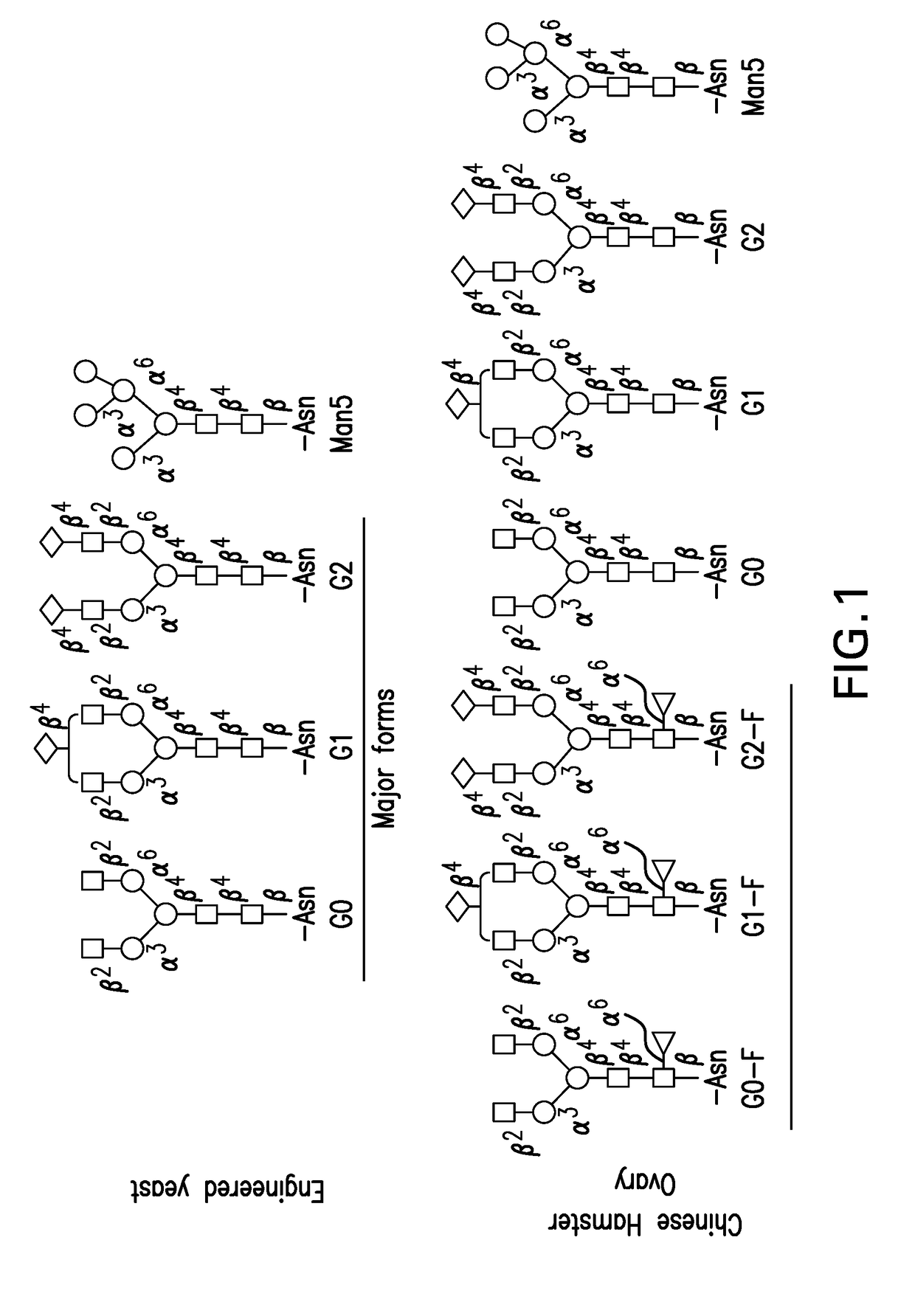
Disclosed are antibodies and methods for making antibodies with desired glycosylation and efficient production. Host cells transformed with a nucleic acid encoding a fusion protein comprising a signal sequence, light and heavy immunoglobulin chains, each comprising a variable region and a constant region and separated by a spacer peptide comprising at least one proteolytic cleavage site are cultured to express the nucleic acids and are cleaved by appropriate proteases to produce antibodies.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Human anti-tau antibodies
ActiveUS8940272B2Reduce riskSlow onsetBacteriaLibrary screeningTargeted immunotherapySpecific antibody
Provided are novel human tau-specific antibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for tau are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for tau targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
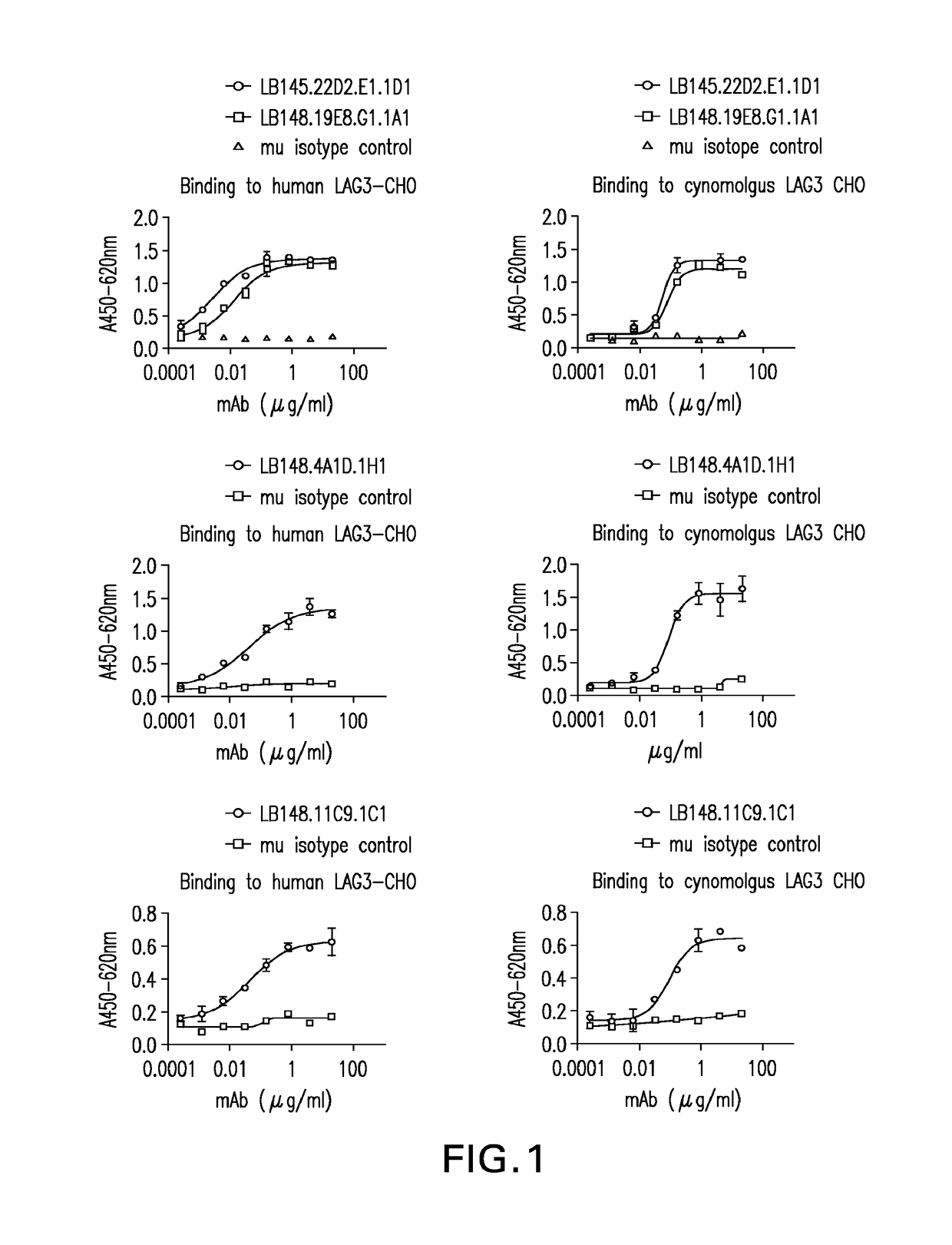
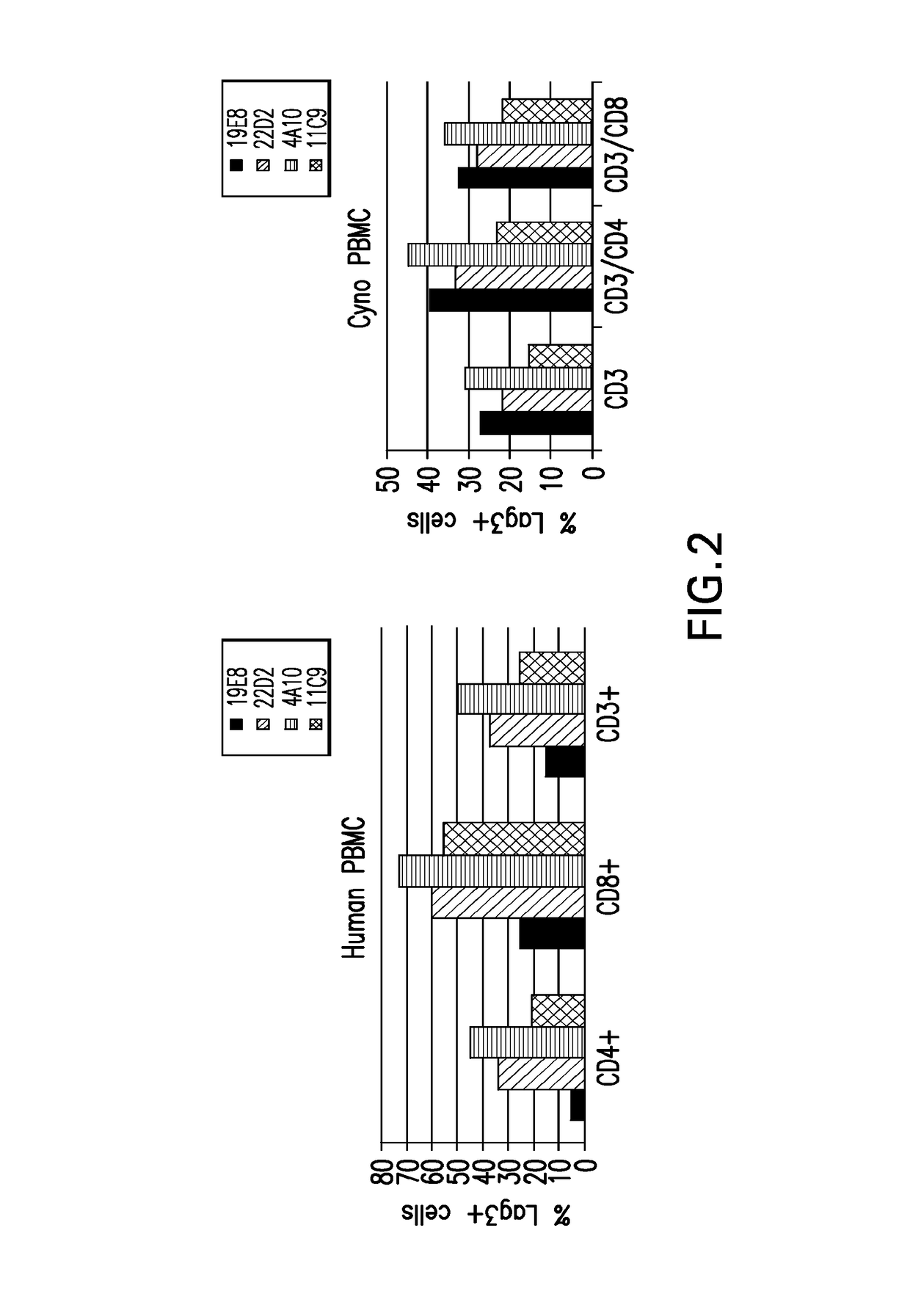
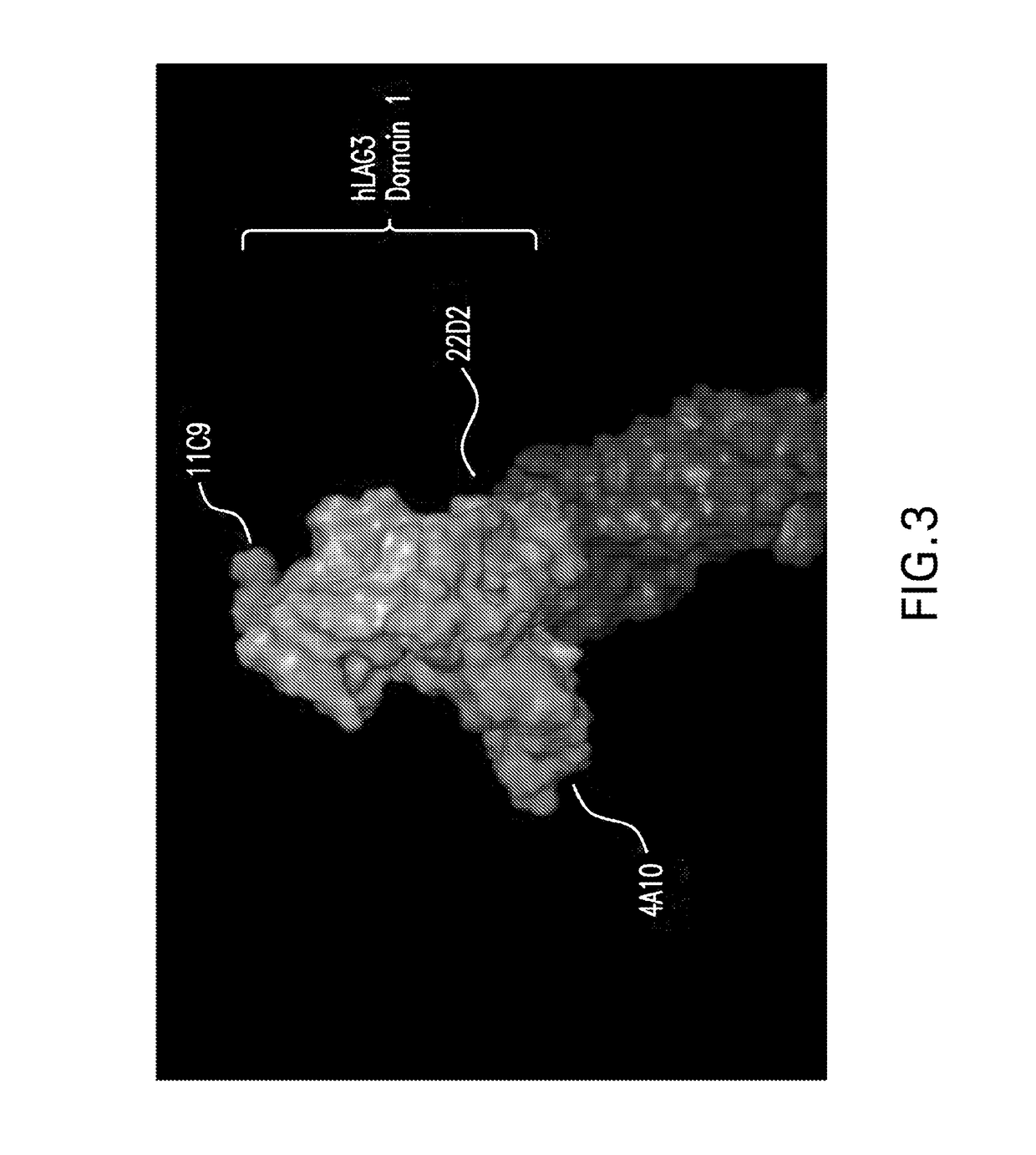
Anti-LAG3 antibodies and antigen-binding fragments
ActiveUS10188730B2Biological material analysisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
The present invention includes antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof that specifically bind to human or cynomolgous monkey LAGS as well as immunoglobulin chains thereof and polynucleotides encoding the same along with injection devices comprising such antibodies or fragments. Vaccines including such antibodies and fragments as well as compositions comprising the antibodies and fragments (e.g., including anti-PD1 antibodies) are included in the invention. Methods for treating or preventing cancer or infection using such compositions are also provided. In addition, methods for recombinant expression of the antibodies and fragments are part of the present invention.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Human anti-alpha-synuclein antibodies
Provided are human alpha-synuclein-specific autoantibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for α-synuclein are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for α-synuclein targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN INT NEUROSCI +1
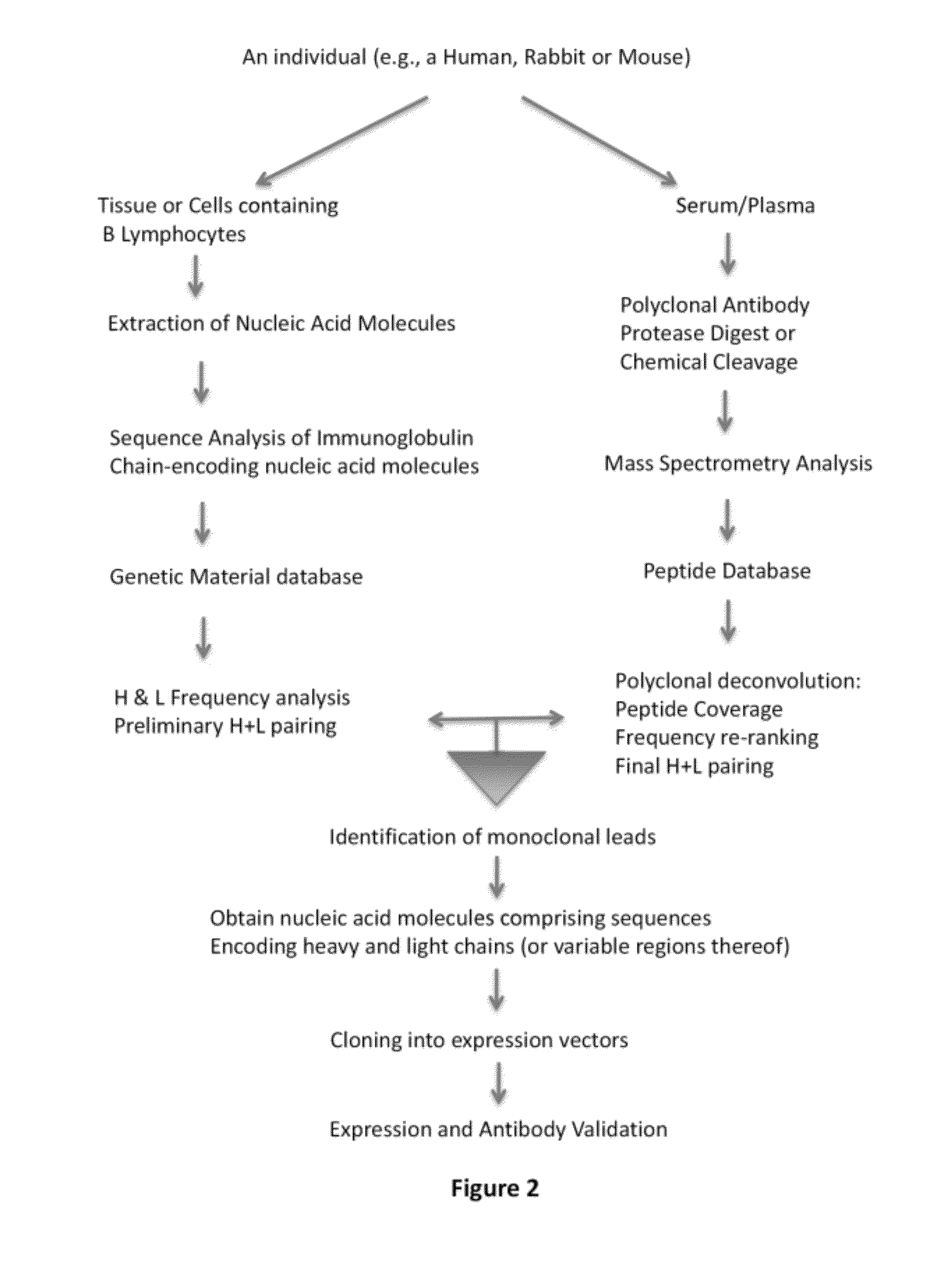
Methods and reagents for creating monoclonal antibodies
ActiveUS20120308555A1Reduce the likelihood of occurrenceImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansHeavy chainMonoclonal antibody
In some embodiments, the invention relates to methods for creating a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to antigen. The method may start from a polyclonal population of antibodies such as a non-specific polyclonal population or a polyclonal population of antibodies that specifically bind to the antigen. The method includes obtaining nucleic acid molecules encoding heavy and light immunoglobulin chains (or variable regions thereof) of multiple immunoglobulins from an animal; obtaining mass spectra information of peptide fragments of a population of polyclonal immunoglobulins that specifically bind to an antigen of choice; comparing and / or correlating the mass spectra information of the peptide fragments of the polyclonal immunoglobulins with predicted mass spectra information of predicted amino acid sequences encoded by the nucleic acid molecules, and then assembling the heavy and light chains to create an antibody (or variable region thereof) that specifically binds to the antigen.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Anti-psgl-1 antibodies
InactiveUS20090198044A1Induced deathAntipyreticAnalgesicsComplementarity determining regionHeavy chain
Immunoglobulin chains or antibodies having light or heavy chain complementarity determining regions of antibodies that bind to P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1. Also disclosed are methods of inducing death of an activated T-cell and of modulating a T cell-mediated immune response in a subject.
Owner:ABGENOMICS COOPERATIEF U A
Human Anti-Alpha-Synuclein Antibodies
Provided are human alpha-synuclein-specific autoantibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for α-synuclein are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for α-synuclein targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN INT NEUROSCI +1
Human Anti-tau antibodies
ActiveUS20150344553A1Reduce riskSlow onsetNervous disorderBacteriaTargeted immunotherapySpecific antibody
Provided are novel human tau-specific antibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for tau are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for tau targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Human anti-tau antibodies
ActiveUS9598484B2Reduce riskSlow onsetNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansTargeted immunotherapySpecific antibody
Provided are human tau-specific antibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for tau are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for tau targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Human anti-SOD1 antibodies
ActiveCN103380145AMonitor disease progressionMonitor therapeuticMuscular disorderVertebrate antigen ingredientsDismutaseSuperoxide dismutases
Provided are novel human copper-zinc superoxide dismutase, also known as superoxide dismutase 1 or SOD1, specific antibodies as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof as well as methods related thereto. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to antibodies specific for SOD1 are also disclosed. The antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for SOD1 targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:NEURIMMUNE HLDG +1
Tdp-43 specific binding molecules
Provided are novel TDP-43-specific binding molecules including polypeptides such as human antibodies, as well as fragments, derivatives and variants thereof. Also provided are methods related to these TDP-43 specific binding molecules. Assays, kits, and solid supports related to TDP-43-specific binding molecules, including polypeptides such as, human antibodies are also disclosed. The TDP-43-specific binding molecule, antibody, immunoglobulin chain(s), as well as binding fragments, derivatives and variants thereof can be used in pharmaceutical and diagnostic compositions for TDP-43 targeted immunotherapy and diagnosis, respectively.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Polypeptides
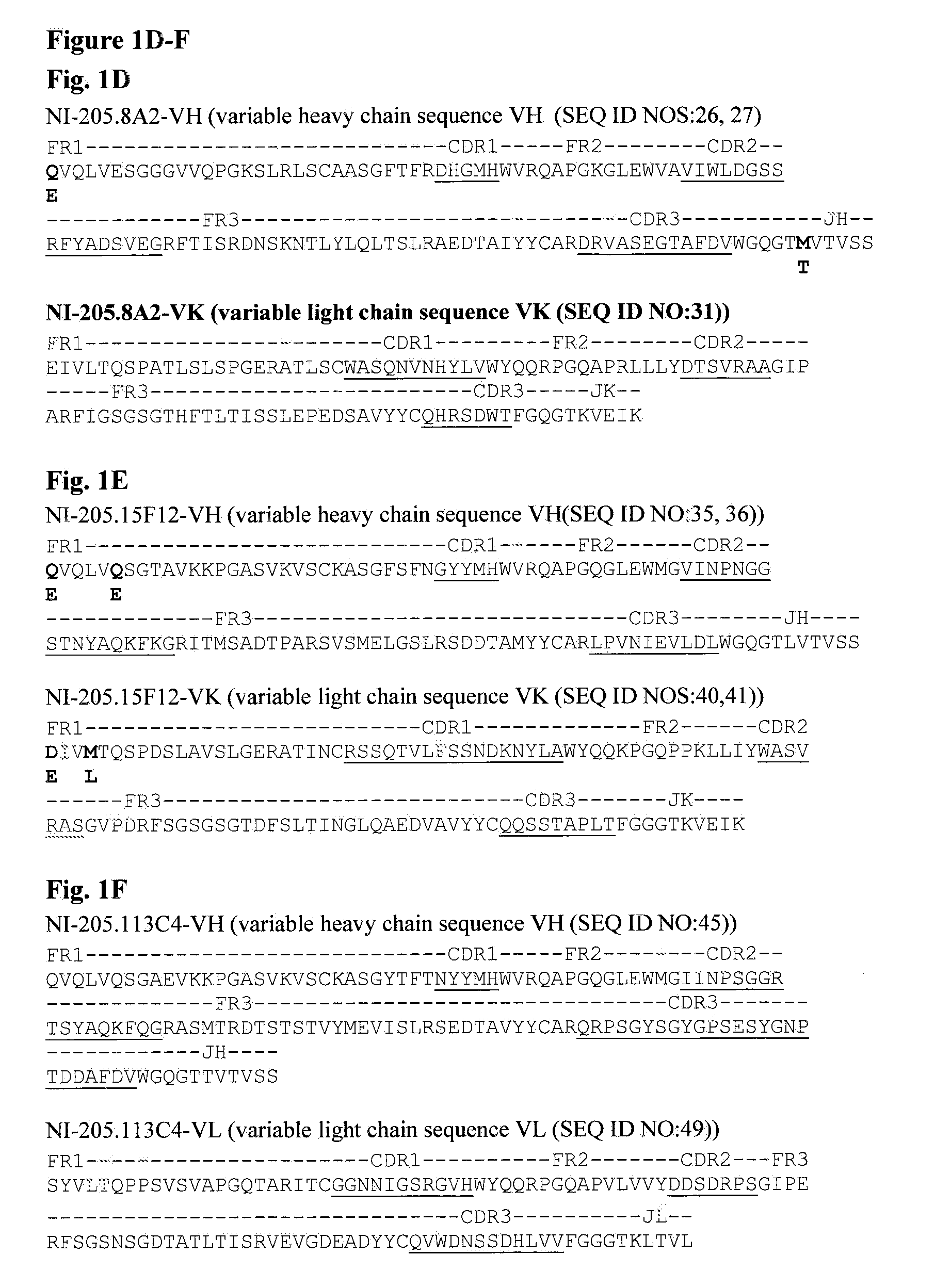
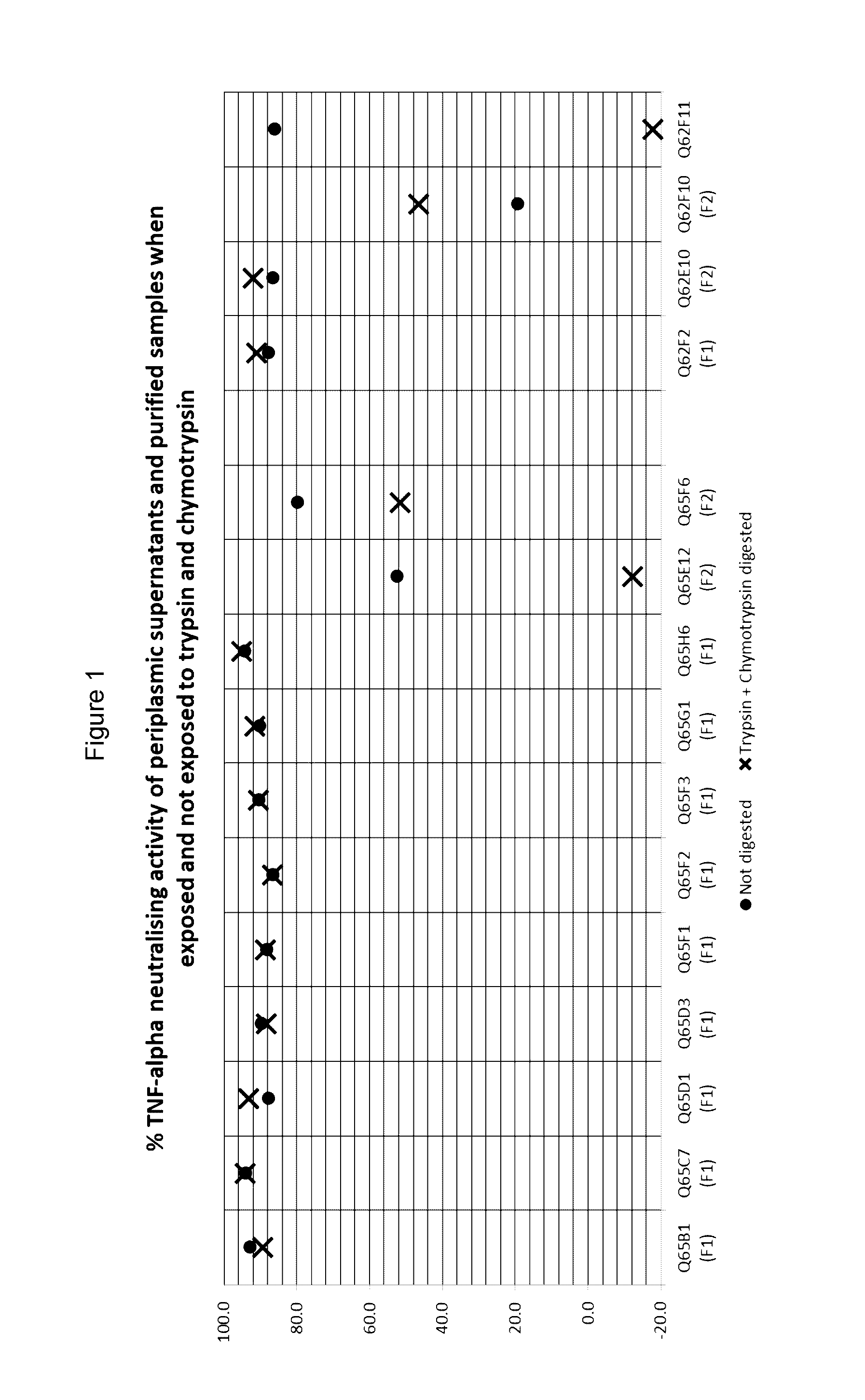
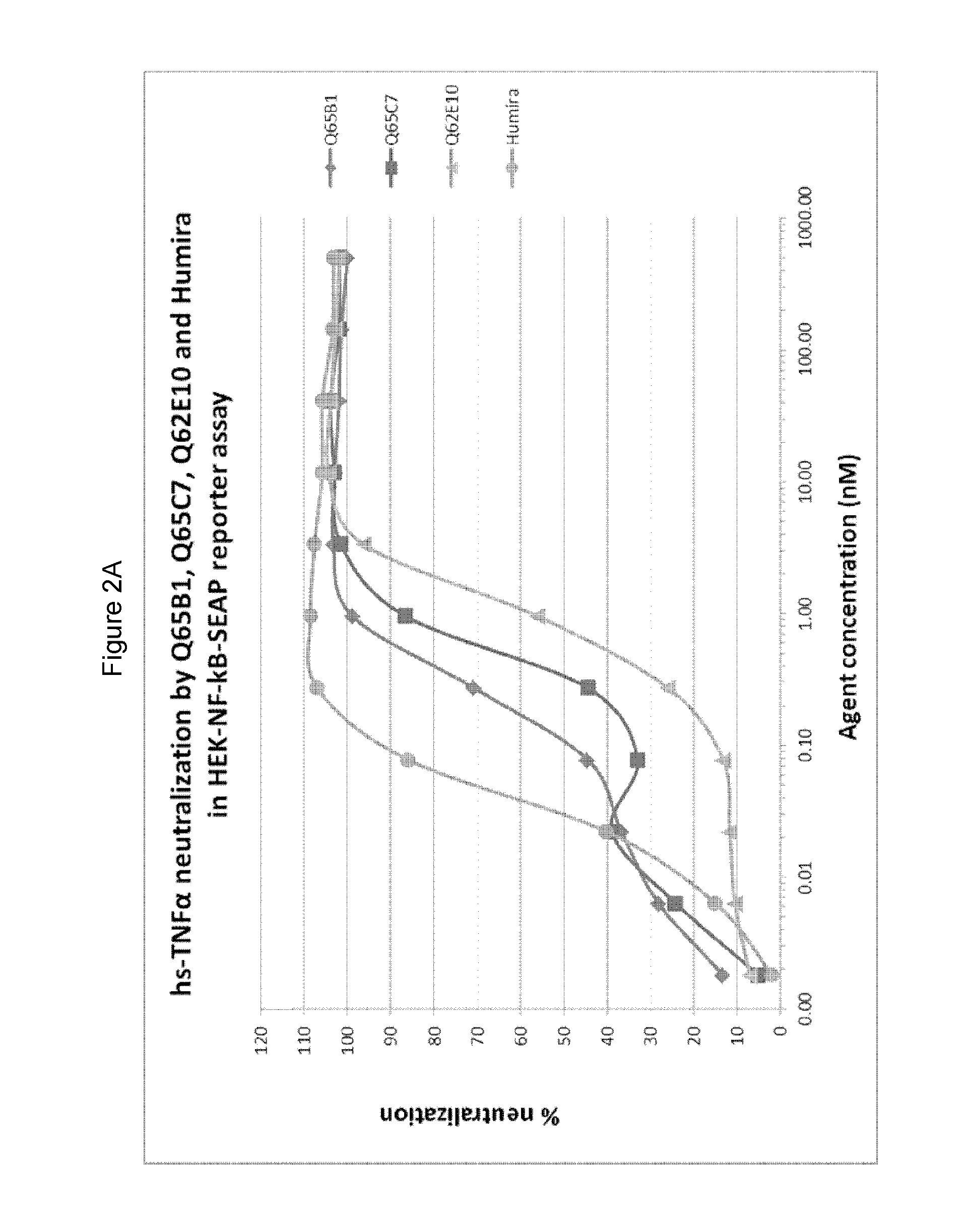
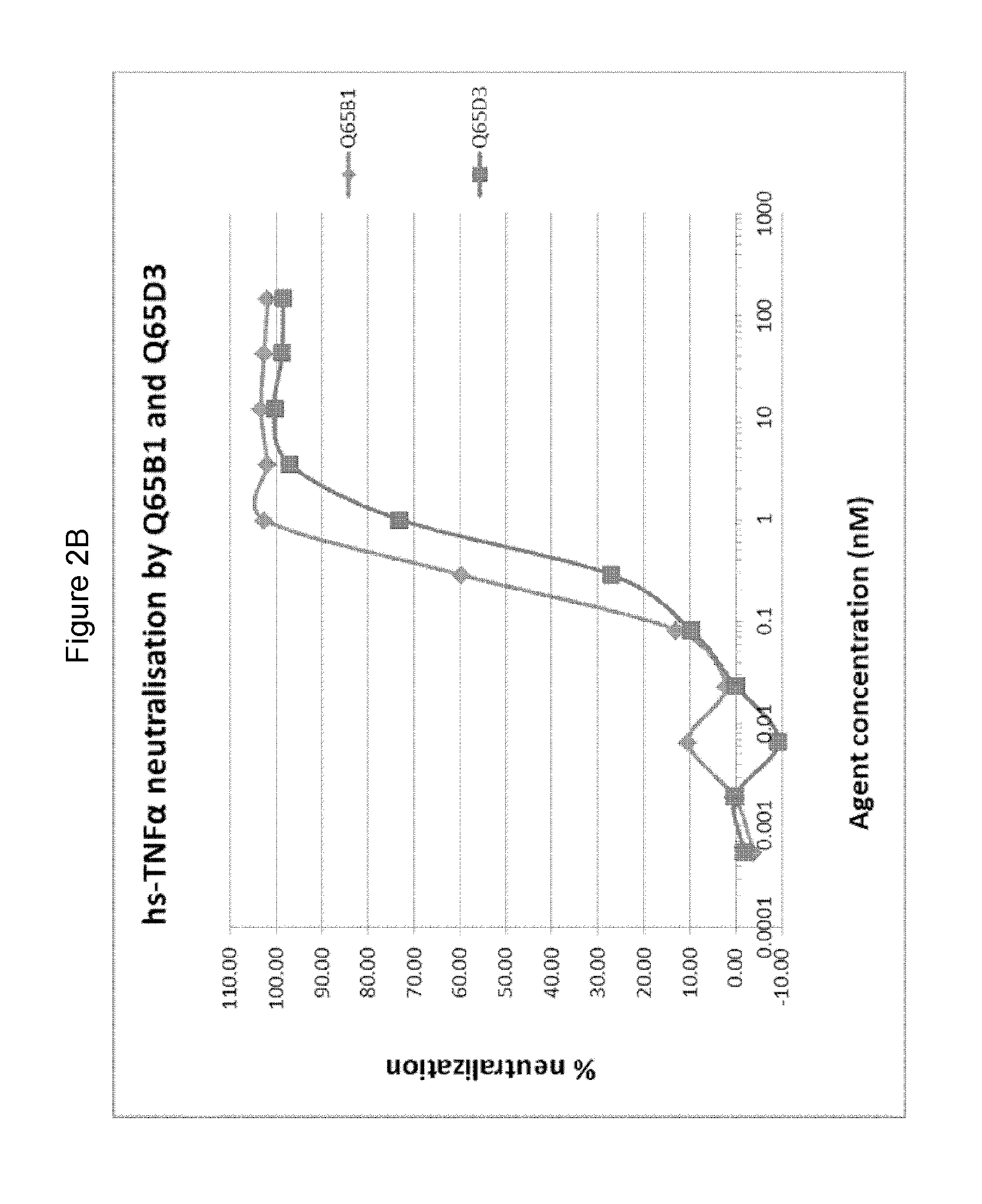
ActiveUS20170002069A1Improve performanceResist degradation and inactivationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsComplementarity determining regionVariable domain
There is provided inter alia a polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain which binds to TNF-alpha, wherein the immunoglobulin chain variable domain comprises three complementarity determining regions (CDR1-CDR3) and four framework regions (FR1-FR4), wherein CDR1-CDR3 and FR1-FR4 are as defined in the specification.
Owner:SORRISO PHARM INC
Anti-lag3 antibodies and antigen-binding fragments
ActiveUS20180369375A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
The present invention includes antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof that specifically bind to human or cynomolgous monkey LAG3 as well as immunoglobulin chains thereof and polynucleotides encoding the same along with injection devices comprising such antibodies or fragments. Vaccines including such antibodies and fragments as well as compositions comprising the antibodies and fragments (e.g., including anti-PD1 antibodies) are included in the invention. Methods for treating or preventing cancer or infection using such compositions are also provided. In addition, methods for recombinant expression of the antibodies and fragments are part of the present invention.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Anti-blys antibodies
InactiveUS20170101466A1Boron compound active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntigen Binding FragmentAntigen binding
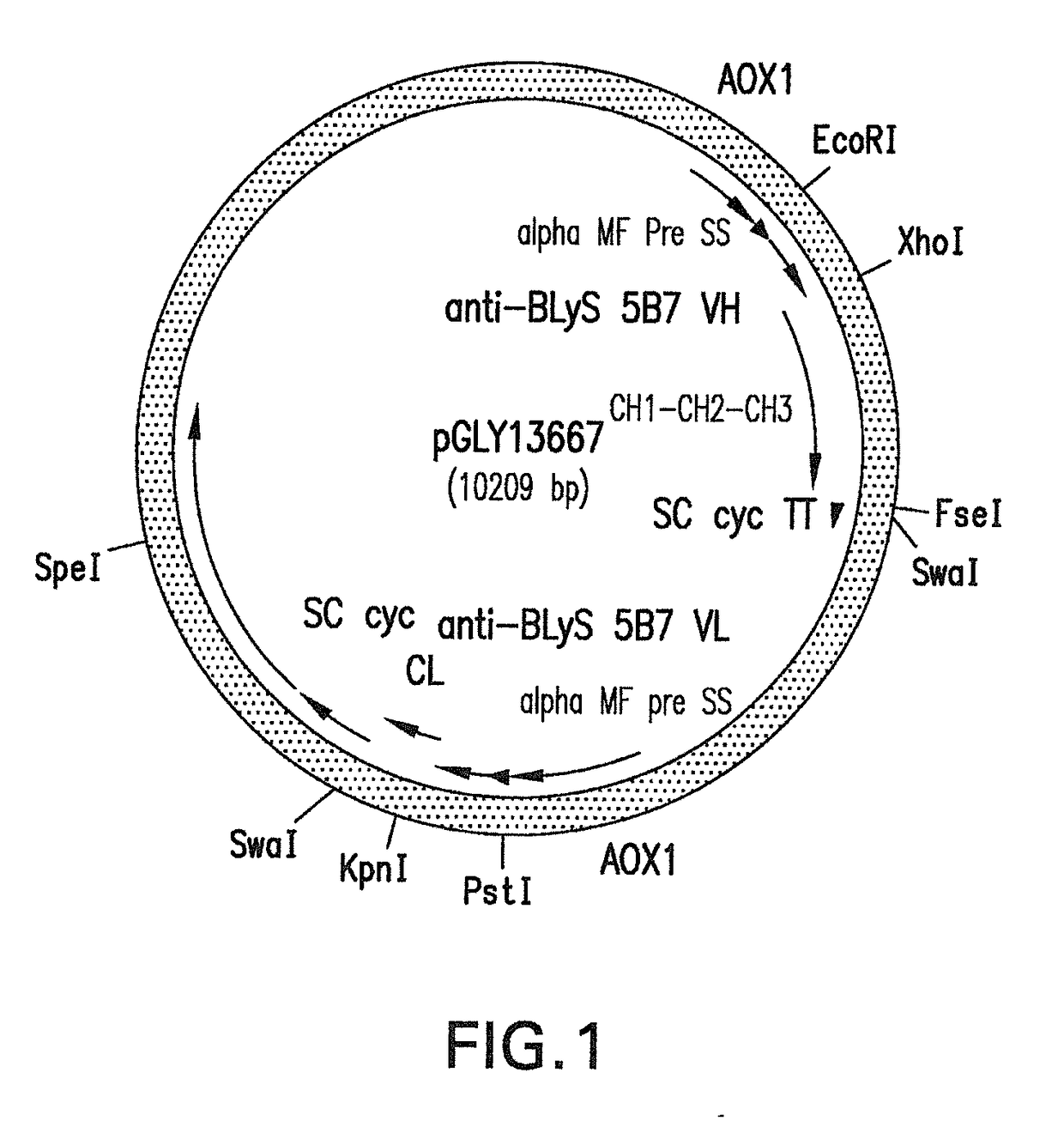
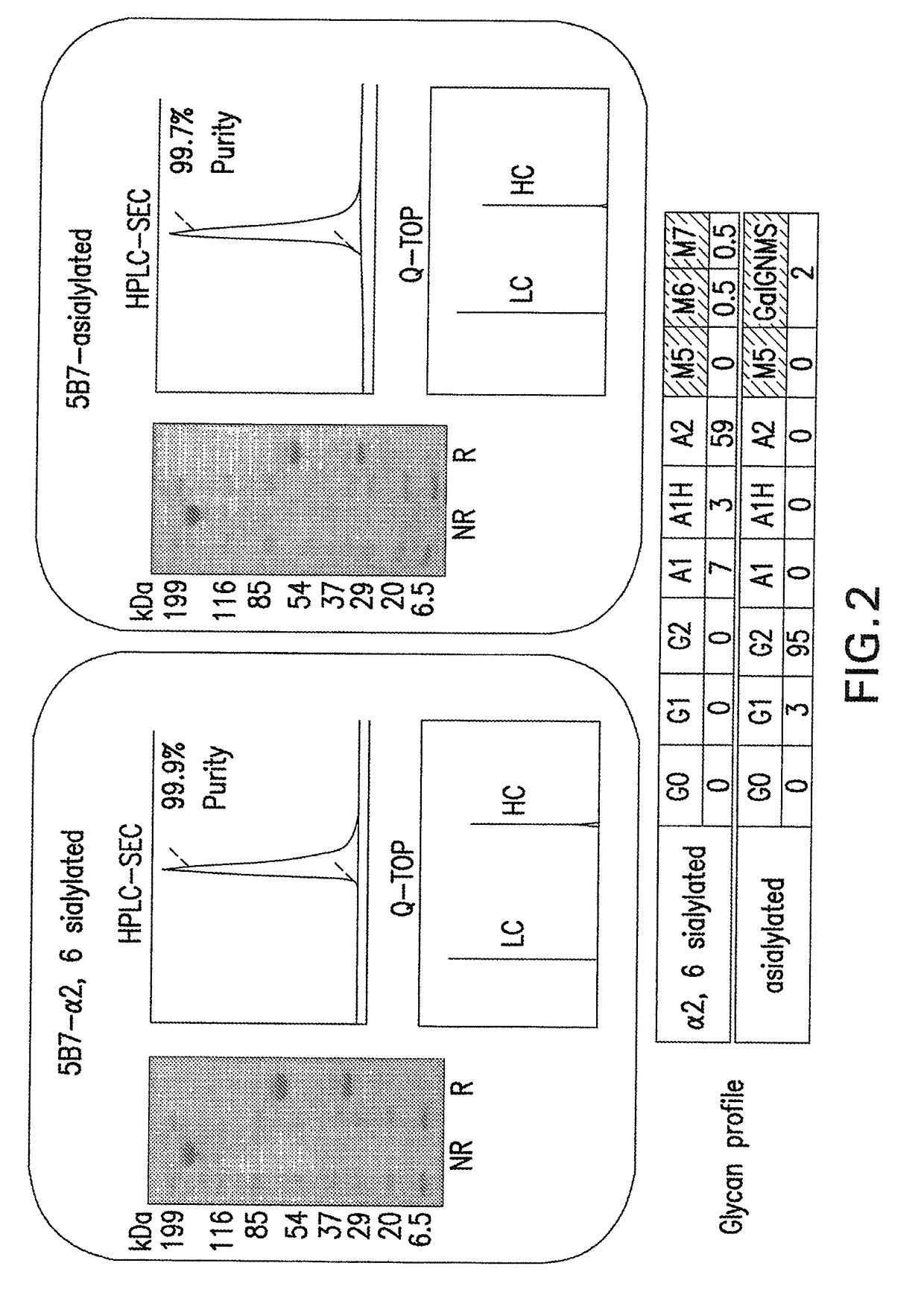
The present invention provides antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof that bind specifically to BlyS, immunoglobulin chains thereof, variants thereof; and method of use thereof, e.g., for the treatment or prevention of inflammatory and / or immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythramatous; as well as polynucleotides encoding the immunoglobulin chains of such antibodies and fragments. Methods for the recombinant expression of immunoglobulin chains are also part of the present invention.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Polypeptides
ActiveUS10633438B2Improve performanceResist degradation and inactivationPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsComplementarity determining regionBiochemistry
There is provided inter alia a polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain which binds to TNF-alpha, wherein the immunoglobulin chain variable domain comprises three complementarity determining regions (CDR1-CDR3) and four framework regions (FR1-FR4), wherein CDR1-CDR3 and FR1-FR4 are as defined in the specification.
Owner:SORRISO PHARM INC
Prevention of aggregation of immunoglobulin light or heavy chains
ActiveUS20100047237A1Reduce and prevent likelihoodInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderAntigenImmunglobulin e
The present invention provides an inhibitor of the aggregation of immunoglobulin chains (or immunoglobulin VL or CH1 domains). In preferred embodiments, the inhibitor comprises or consists of a polypeptide which comprises or consists of (a) an amino acid sequence corresponding to the amino acid sequence of the FR1 region of an immunoglobulin light chain variable domain, or part thereof which includes amino acid residue 12, (b) an amino acid sequence corresponding to the amino acid sequence of the immunoglobulin-binding domain of bacterial superantigen Protein L, or part thereof, and / or (c) an amino acid sequence corresponding to the amino acid sequence of the immunoglobulin-binding domain of streptococcal protein G (SpG), or part thereof, or a variant, fusion or derivative thereof, or a fusion of a said variant or derivative thereof which retains the ability of the parent polypeptide to inhibit aggregation of immunoglobulin chains, or domains thereof. The invention further provides a non-naturally occurring antibody, or antigen-binding fragment, fusion or derivative thereof comprising a light chain variable domain, or a fusion of said fragment or derivative, wherein the FR1 region of the light chain variable domain is modified (e.g., mutated) so as to inhibit, at least in part, the ability of the antibody, fragment, fusion or derivative to form aggregates. Most preferably, the light chain variable domain is modified at position 12 of the FR1 region by replacing the naturally occurring amino acid (e.g., serine in K light chains) with proline.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Polypeptides
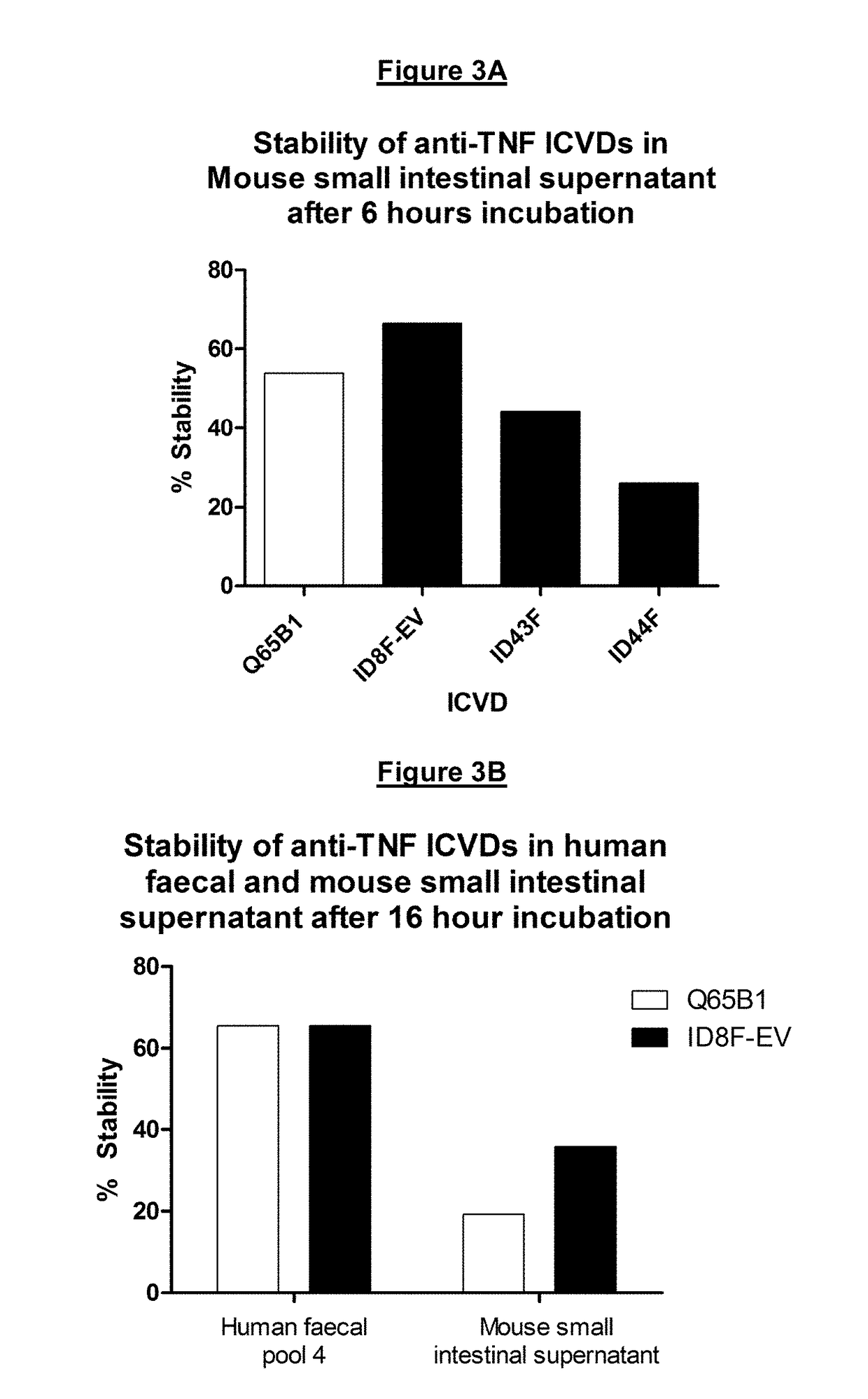
InactiveUS20180009881A1Increased intestinal stabilityImprove stabilityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticComplementarity determining regionArginine
There is provided inter alia a polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain comprising three complementarity determining regions (CDR1-CDR3) and four framework regions, wherein: (a) at least one lysine residue in CDR1, CDR2 and / or CDR3 has been substituted with at least one histidine residue, and / or (b) at least one arginine residue in CDR1, CDR2 and / or CDR3 has been substituted with at least one histidine residue; wherein the polypeptide has increased intestinal stability relative to a corresponding polypeptide not having said histidine substitutions.
Owner:VHSQUARED
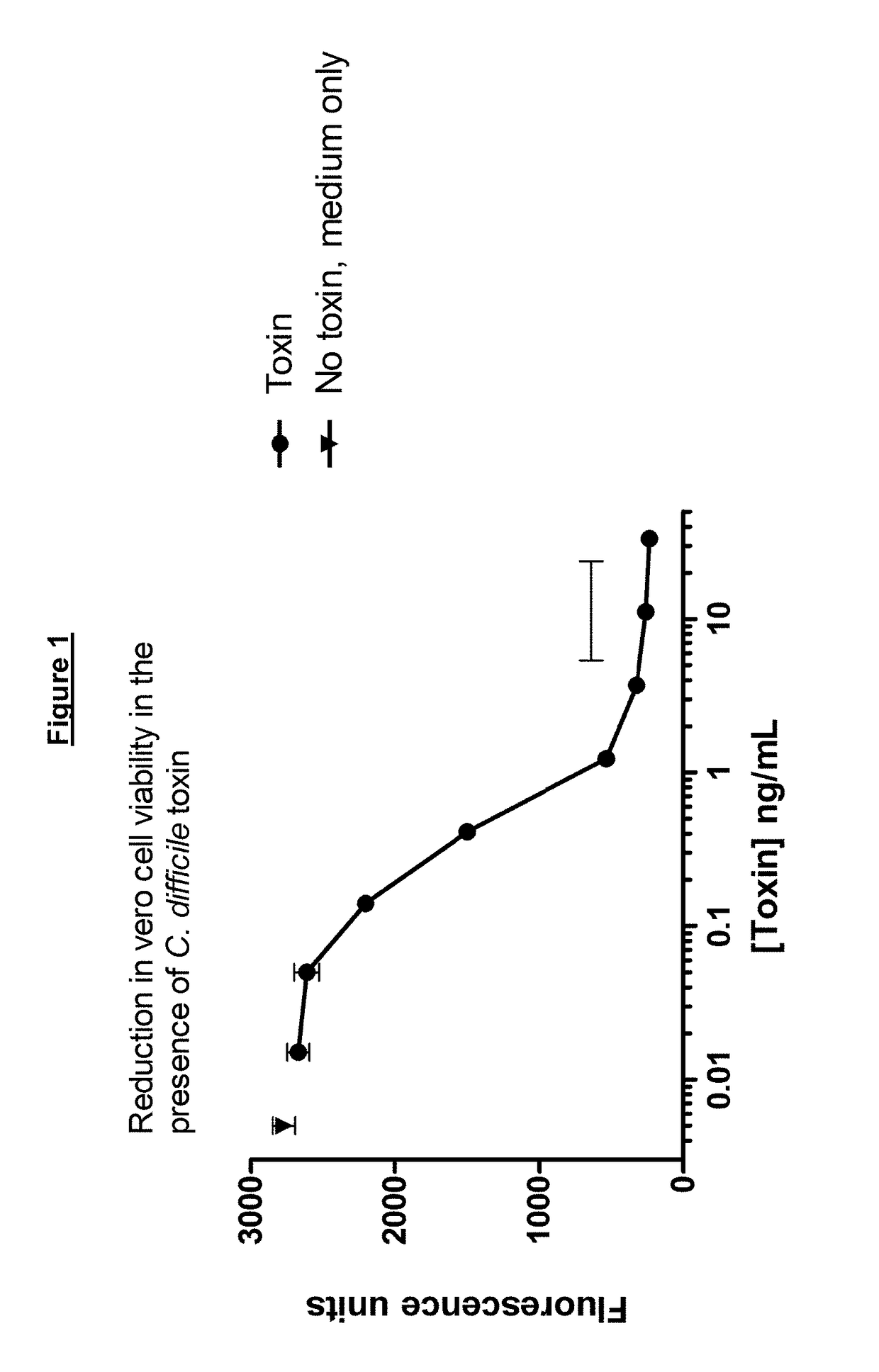
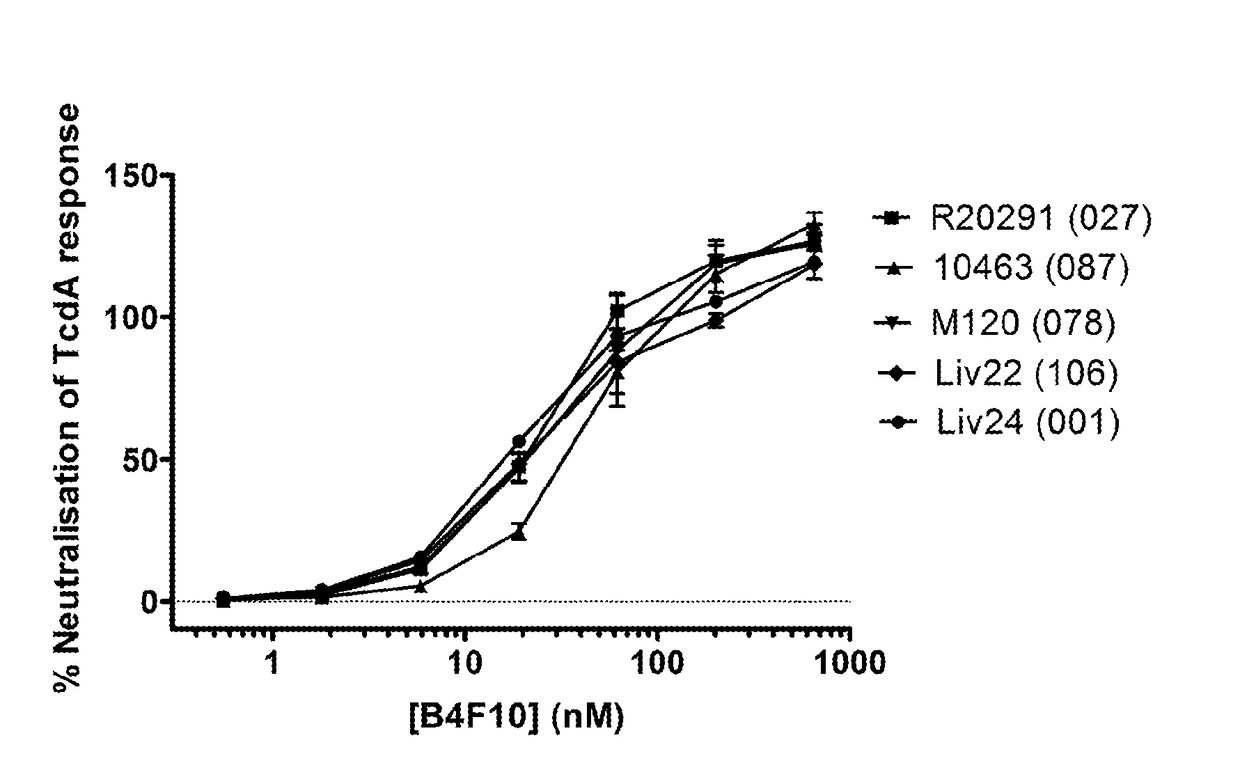
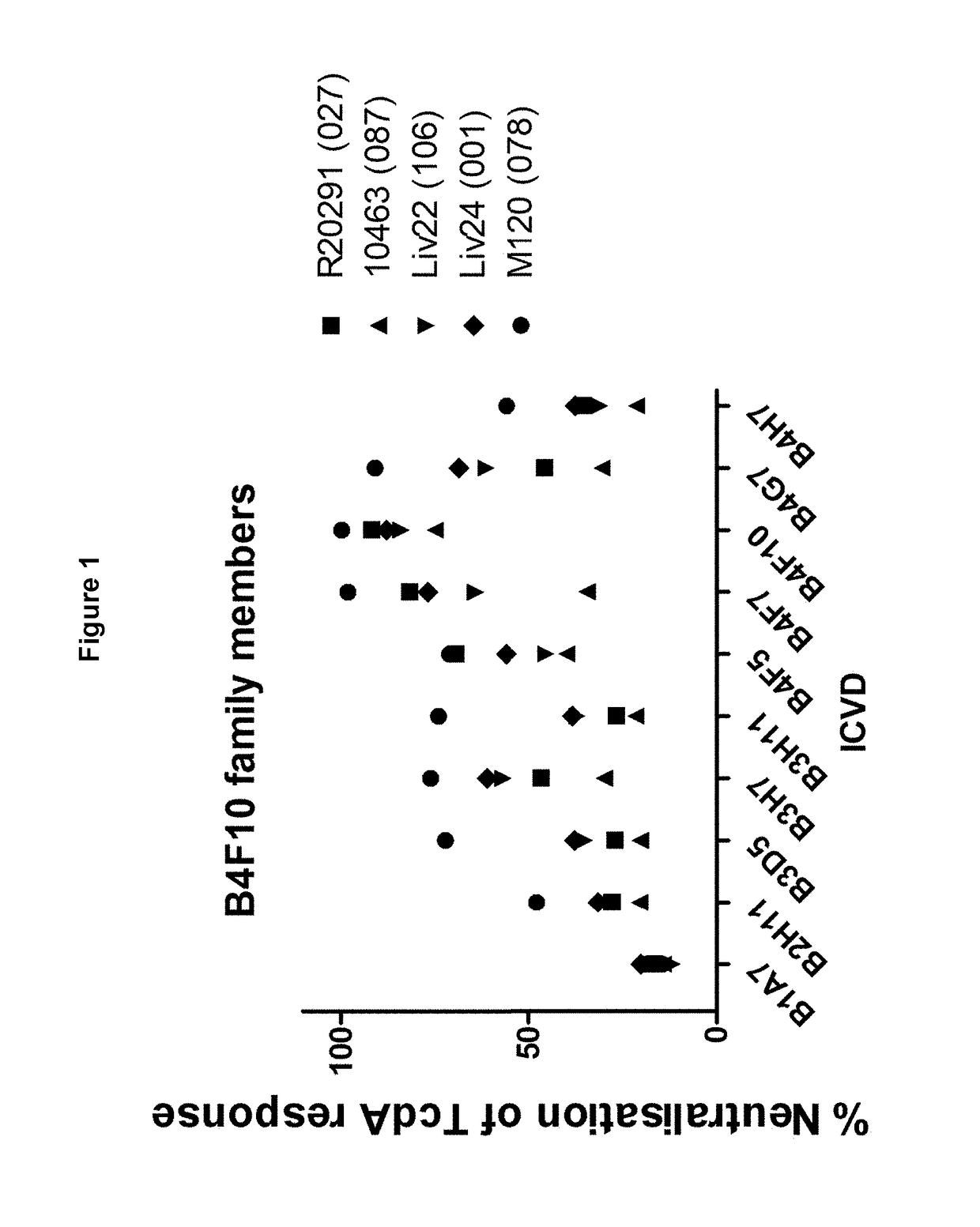
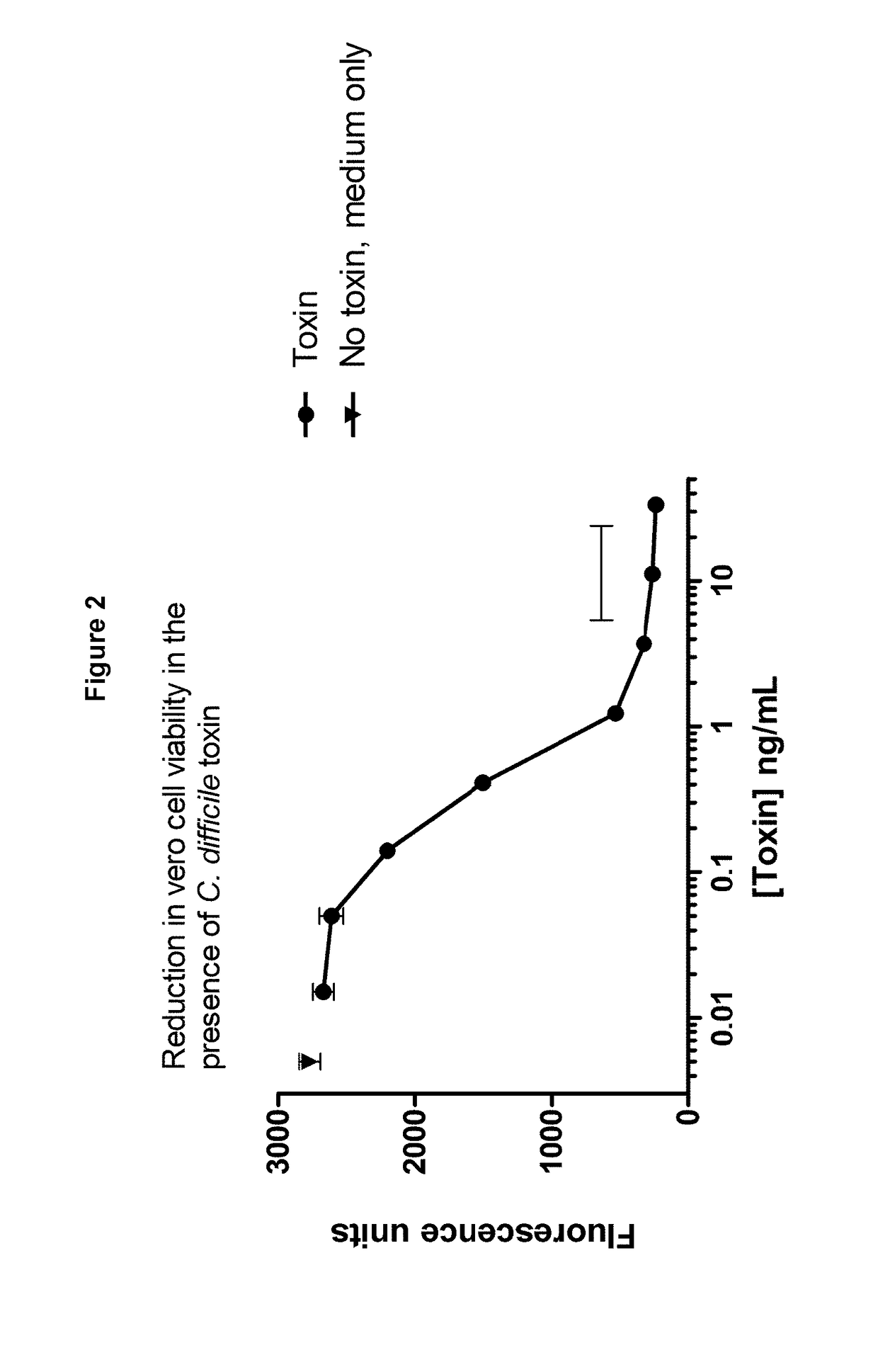
Polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain which binds to clostridium difficile toxin a
InactiveUS20180100009A1High potency against TcdAResistance to degradationImmunoglobulins against bacteriaDepsipeptidesClostridial toxinClostridium difficile toxin A
There is provided inter alia a polypeptide comprising an immunoglobulin chain variable domain which binds to Clostridium difficile toxin A.
Owner:VHSQUARED +1
Epsilon immunoglobulin chain derived peptides for induction of anti-IgE antibodies
The present invention relates to identification of polypeptides useful for generating antibodies specific for non-human IgE, particularly equine IgE. The invention, therefore, also relates to antibodies that specifically bind to IgE and methods to detect IgE using the antibodies. The invention also provides a kit for detection of IgE.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Reducing imunogenicities of immunoglobulins by framework-patching
InactiveUS20070298035A1Reduced and eliminated immunogenicityIncrease flexibilityHybrid immunoglobulinsAntipyreticB-Cell EpitopesBiology
Framework (FR)-patching is a novel approach to modify immunoglobulin for reducing potential immunogenicity without significant alterations in specificity and affinity. Unlike previous described methods of humanization, which graft CDRs from a donor onto the frameworks of a single acceptor immunoglobulin, we patch segments of framework (FR1, FR2, FR3 and FR4), or FRs, to replace the corresponding FRs of the parent immunoglobulin. Free assortment of these FRs from different immunoglobulins and from different species can be mixed and matched into forming the final immunoglobulin chain. A set of criteria in the choice of these FRs to minimize or eliminate the need to reintroduce framework amino acids from the parent immunoglobulin for patching is described. The approach gives greater flexibility in the choice of framework sequences, minimizes the need to include parent framework amino acids, and, most importantly, reduces the chances of creating new T- and B-cell epitopes in the resultant immunoglobulin.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
TDP-43 specific binding molecules
ActiveUS9587014B2Reduce riskSlow onsetNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAssayPharmaceutical drug
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Humanized immunoglobulins
InactiveUS20080160018A1Maximize likelihoodHigh binding affinityFungiBacteriaImmunoglobulin heavy chainHuman immunoglobulins
Novel methods for producing, and compositions of, humanized immunoglobulins having one or more complementarity determining regions (CDR's) and possible additional amino acids from a donor immunoglobulin and a framework region from an accepting human immunoglobulin are provided. Each humanized immunoglobulin chain will usually comprise, in addition to the CDR's, amino acids from the donor immunoglobulin framework that are, e.g., capable of interacting with the CDR's to effect binding affinity, such as one or more amino acids which are immediately adjacent to a CDR in the donor immunoglobulin or those within about 3 Å as predicted by molecular modeling. The heavy and light chains may each be designed by using any one or all of various position criteria. When combined into an intact antibody, the humanized immunoglobulins of the present invention will be substantially non-immunogenic in humans and retain substantially the same affinity as the donor immunoglobulin to the antigen, such as a protein or other compound containing an epitope.
Owner:PDL BIOPHARMA INCORPORATED
Single chain antibody with cleavable linker
InactiveCN101166755APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiSingle-Chain AntibodiesProtein C
Disclosed are antibodies and methods for making antibodies with desired glycosylation and efficient production. Host cells transformed with a nucleic acid encoding a fusion protein comprising a signal sequence, light and heavy immunoglobulin chains, each comprising a variable region and a constant region and separated by a spacer peptide comprising at least one proteolytic cleavage site are cultured to express the nucleic acids and are cleaved by appropriate proteases to produce antibodies.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Novel bifunctional antibody and application thereof
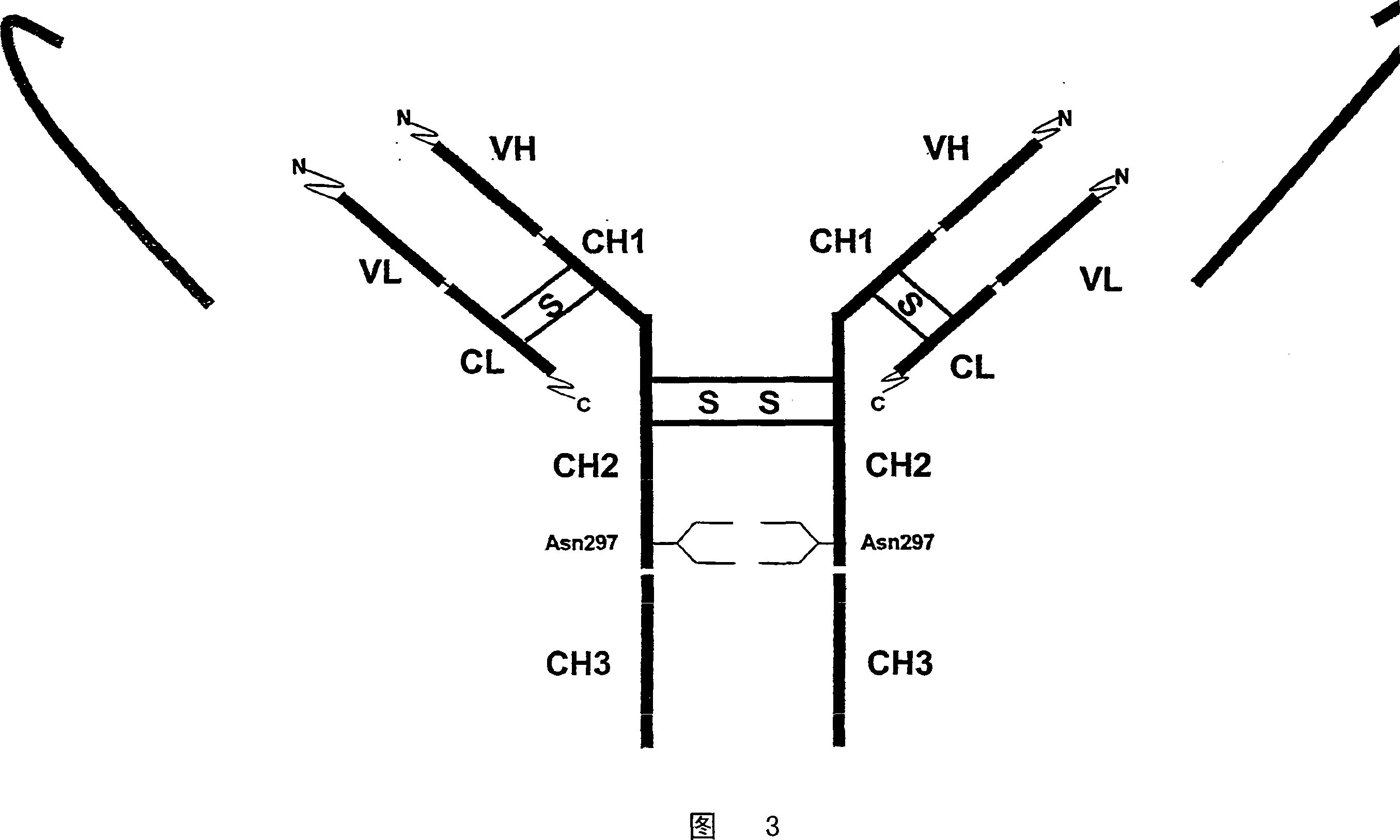
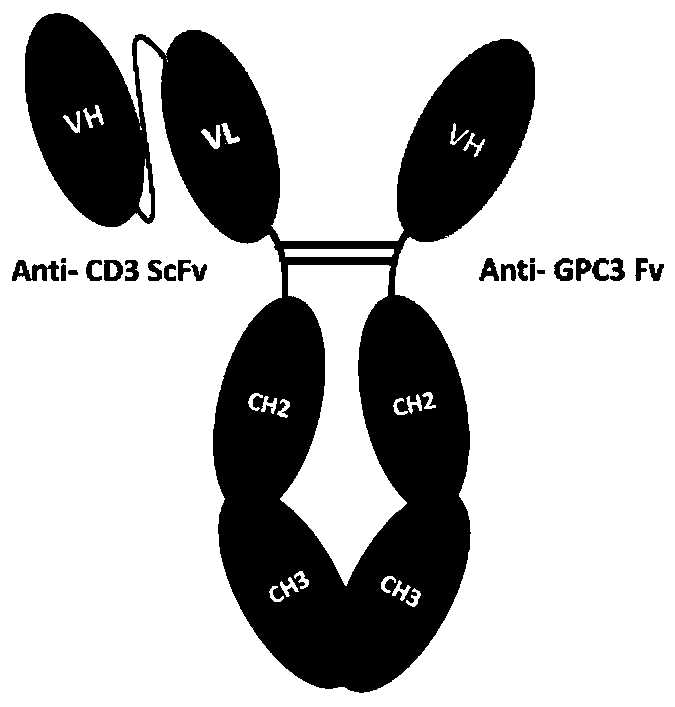
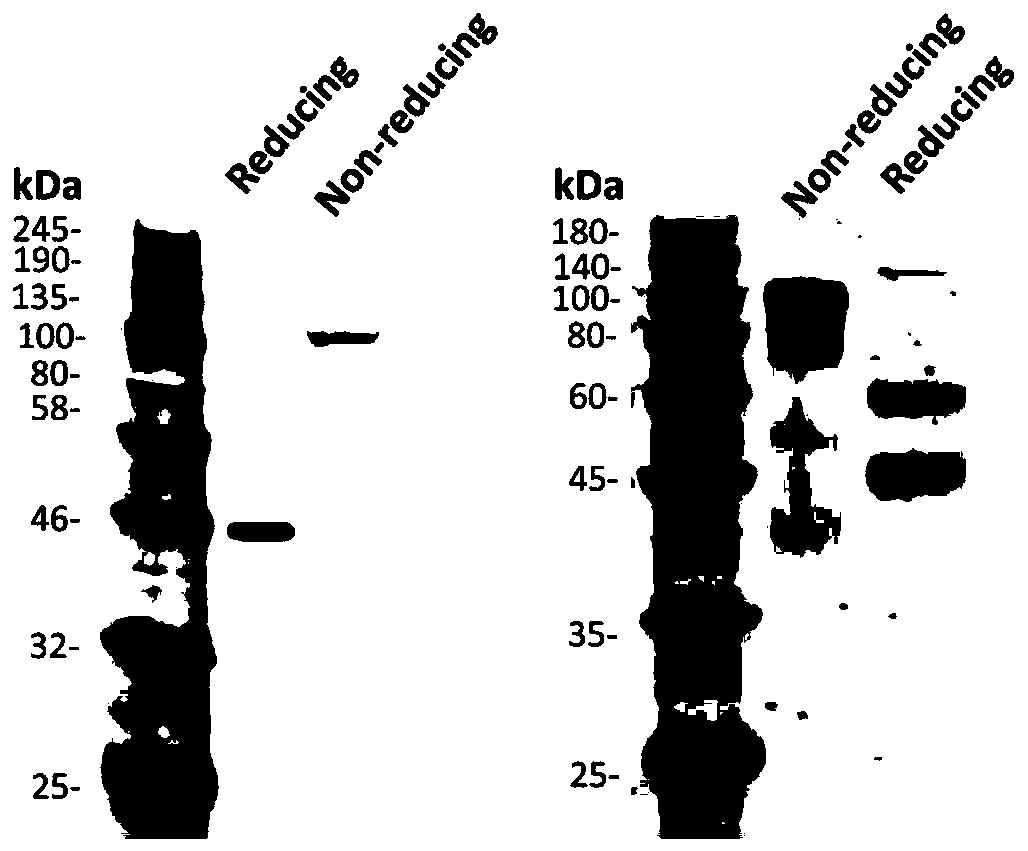
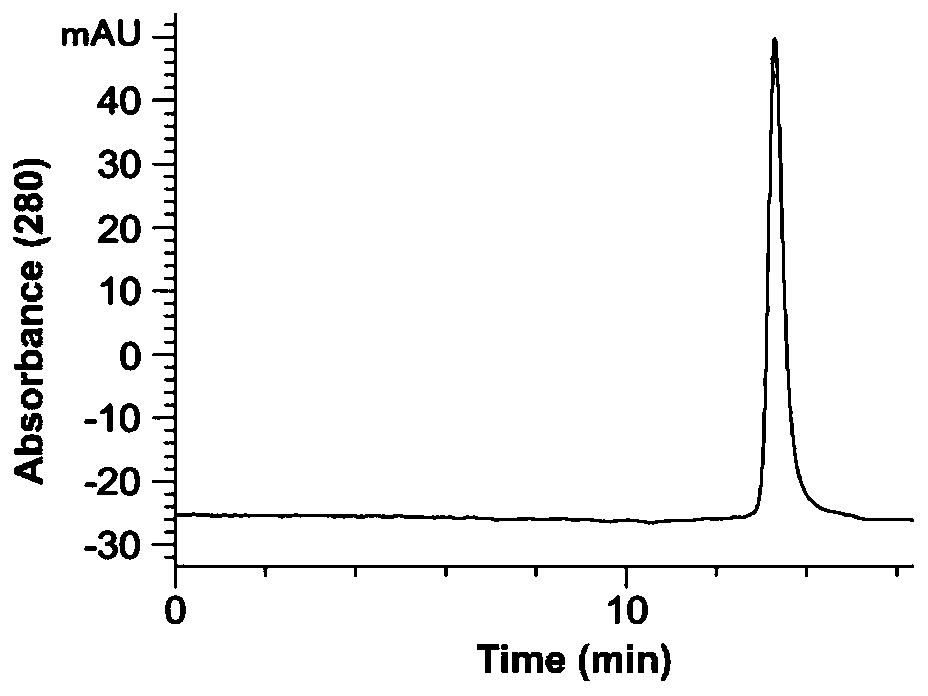
ActiveCN110551222AIndustrial Application LimitationsEfficient purificationHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeavy chainAntibody combining site
The invention provides an antibody. The antibody comprises a protein dimer, wherein the protein dimer comprises a first functional domain including an immunoglobulin chain or an antibody combining site of a specifically-recognized specific antigen and a second functional domain including an immunoglobulin chain or an antibody combining site of a specifically-recognized specific antigen. The antibody is characterized in that the first functional domain consists of a first VH structural domain and a first VL structural domain, and the second functional domain consists of a second VH structural domain. The VH is a heavy chain variable zone, and the VL is a light chain variable zone. The bifunctional antibody provided by the invention has the advantages that a half-life period is greatly prolonged; and a homodimer is extremely less, so that identification and removal can be carried out only through primary purification even if aggregates occur.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF ANIMAL SCI +1
Assay for diabetes
InactiveUS20070105149A1ApolipeptidesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiabetes mellitusInter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor
An assay for testing a subject for diabetes or a predisposition to diabetes including analysing a biological fluid from a subject for the presence of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of Alpha 2 macroglobulin, Apolipoprotein All, Immunoglobulin alpha heavy chain constant region, Immunoglobulin mu chain C region, Chain A of Human IgA1, Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain H4 precursor, and Apolipoprotein B100; wherein detection of the protein is indicative of diabetes or a predisposition to diabetes in the subject
Owner:MINOMIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com