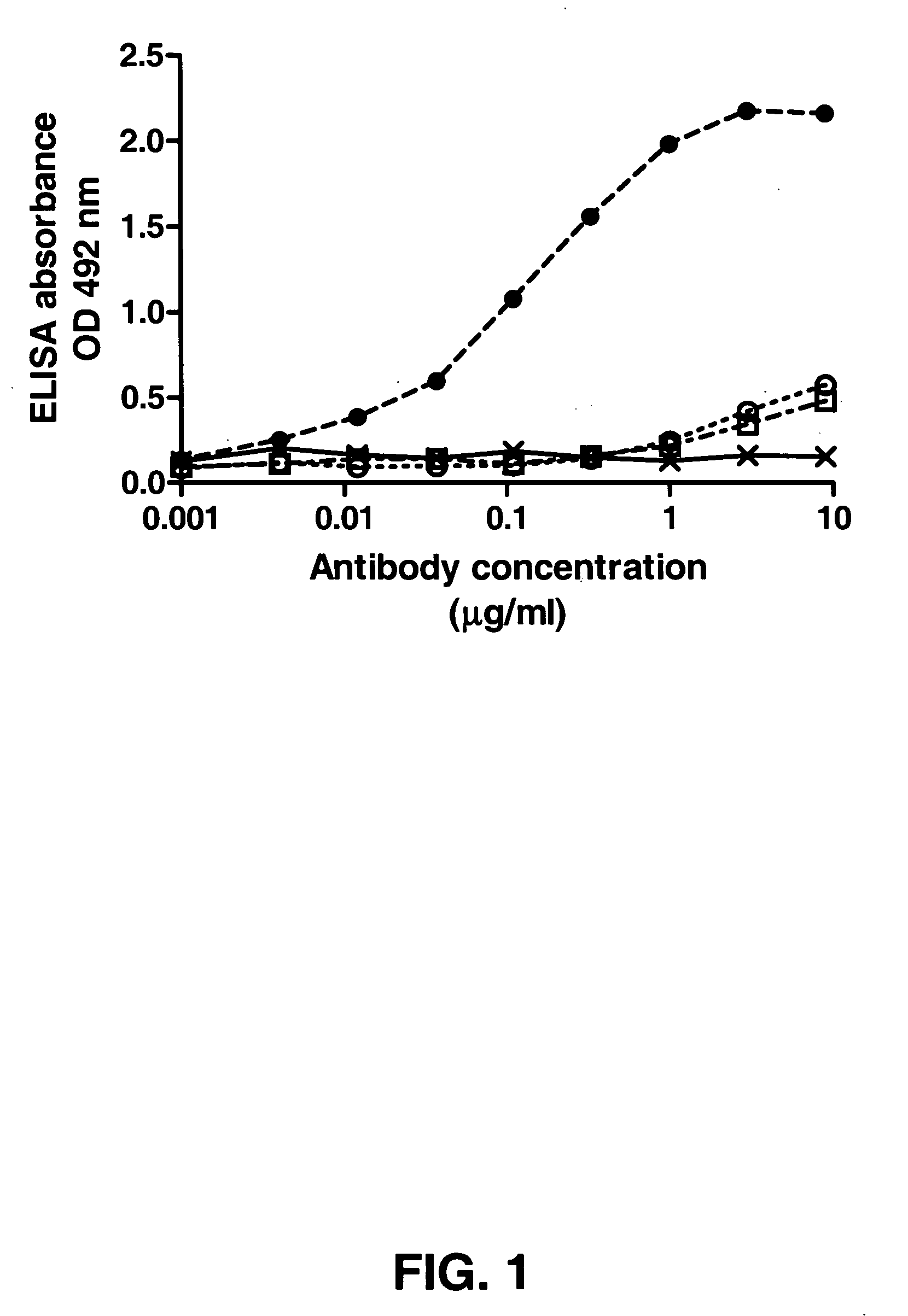
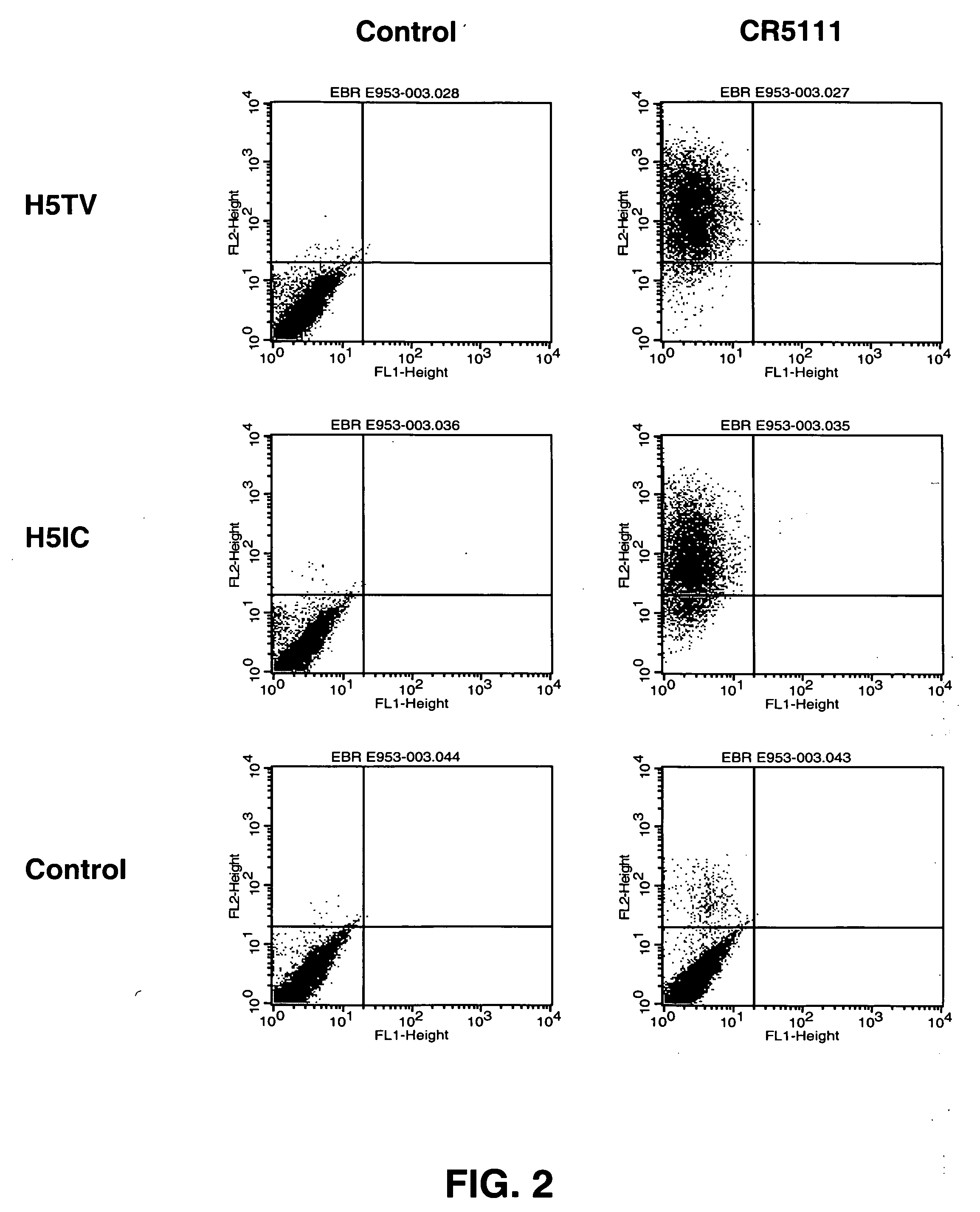
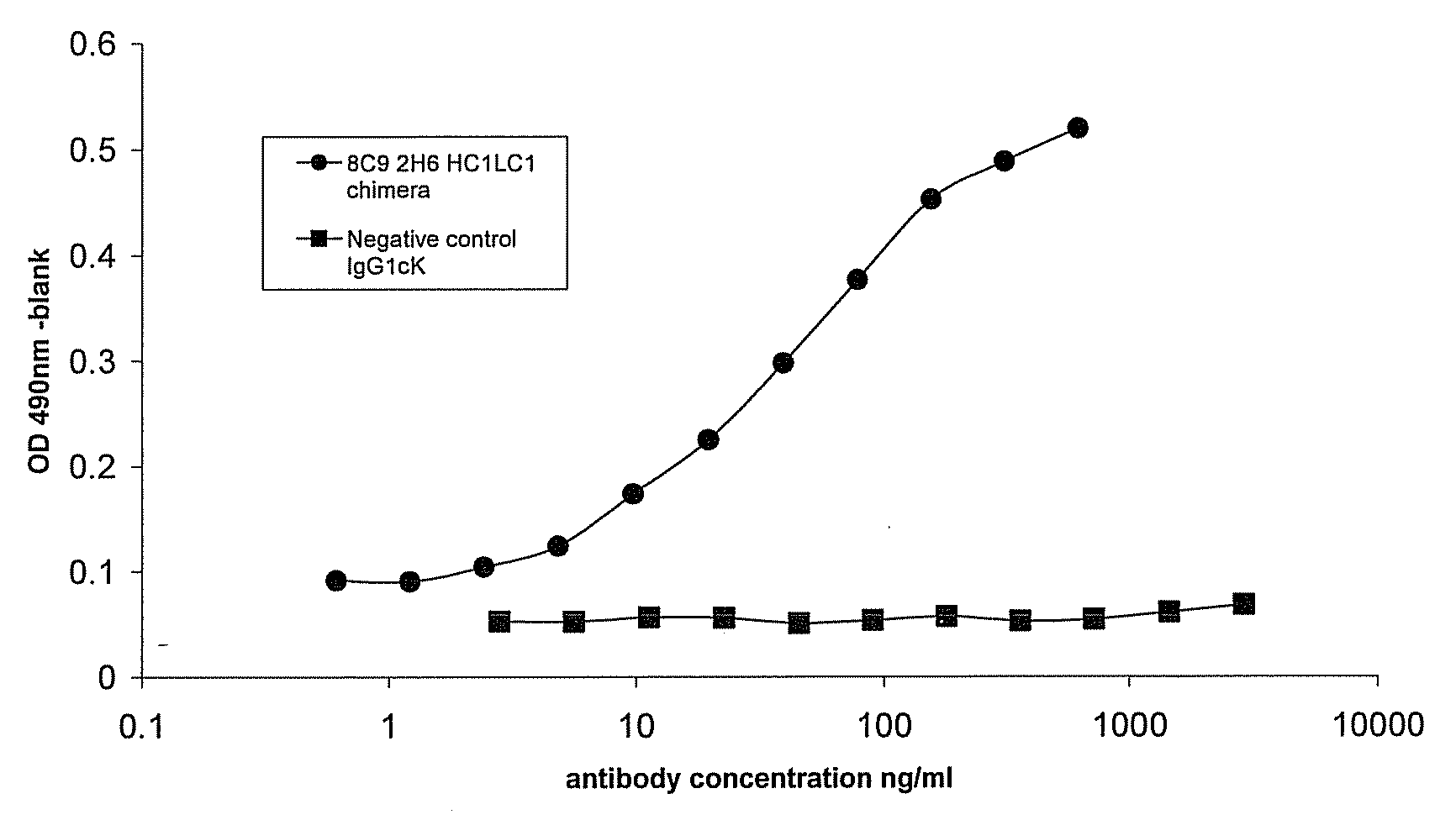
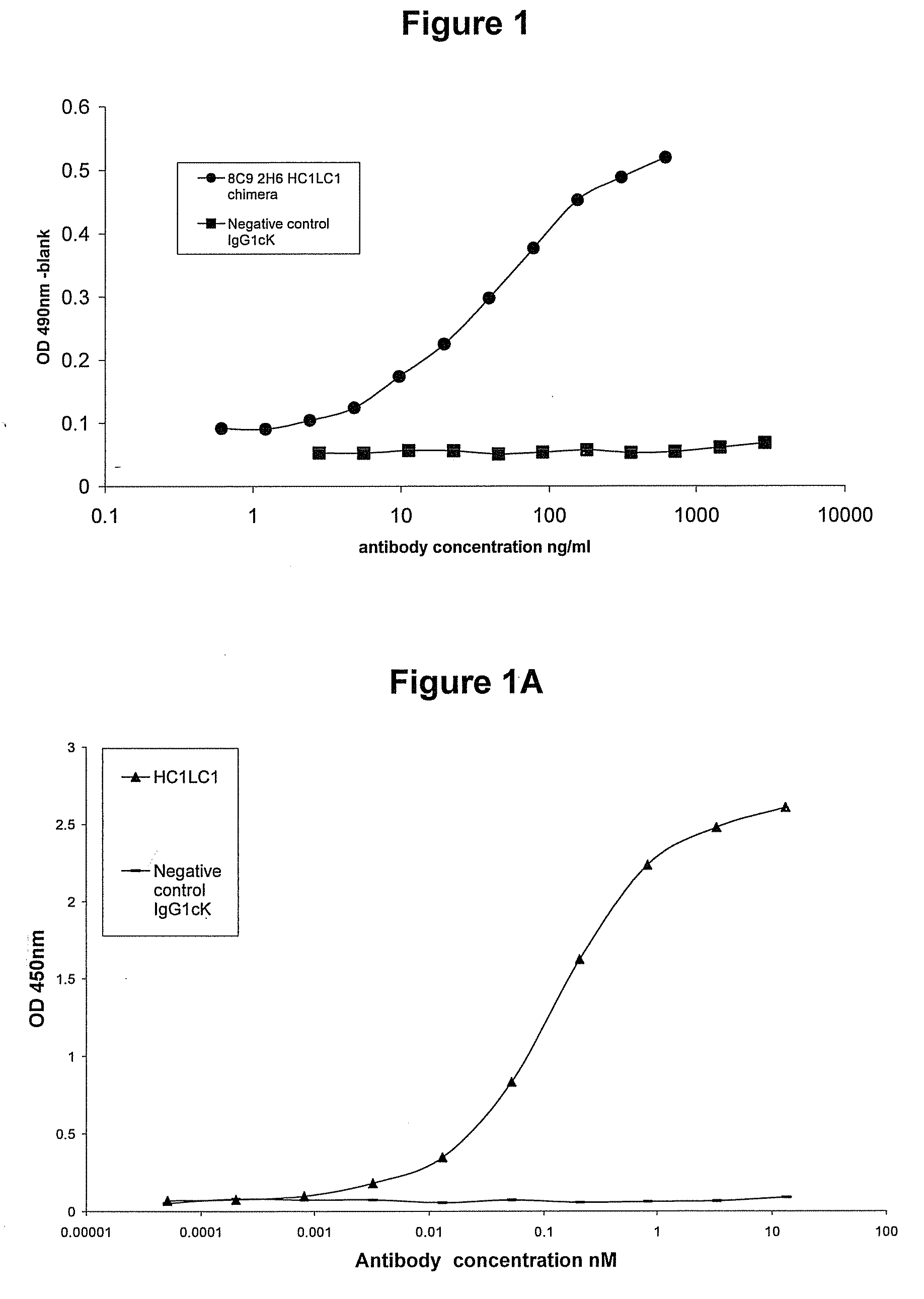
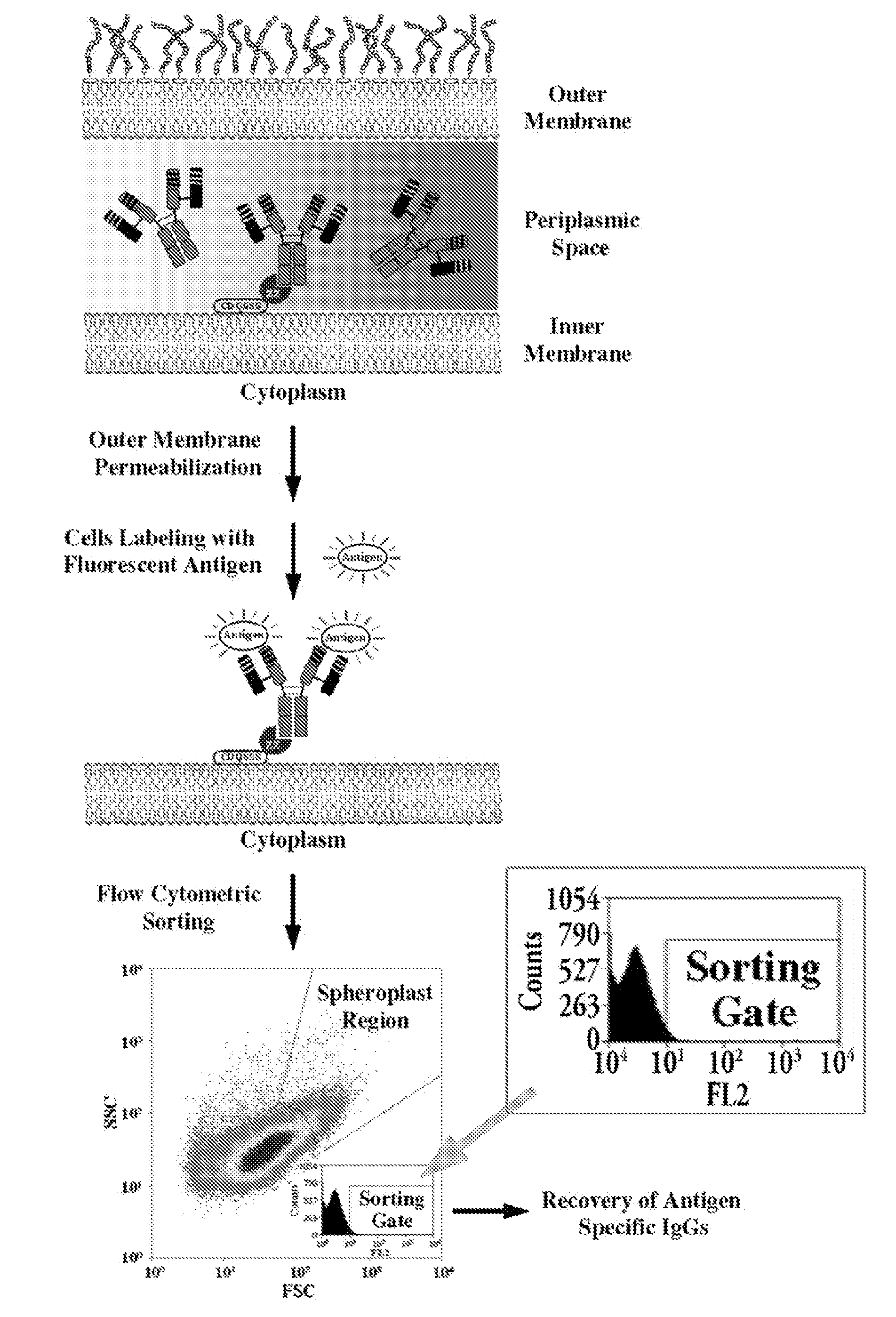
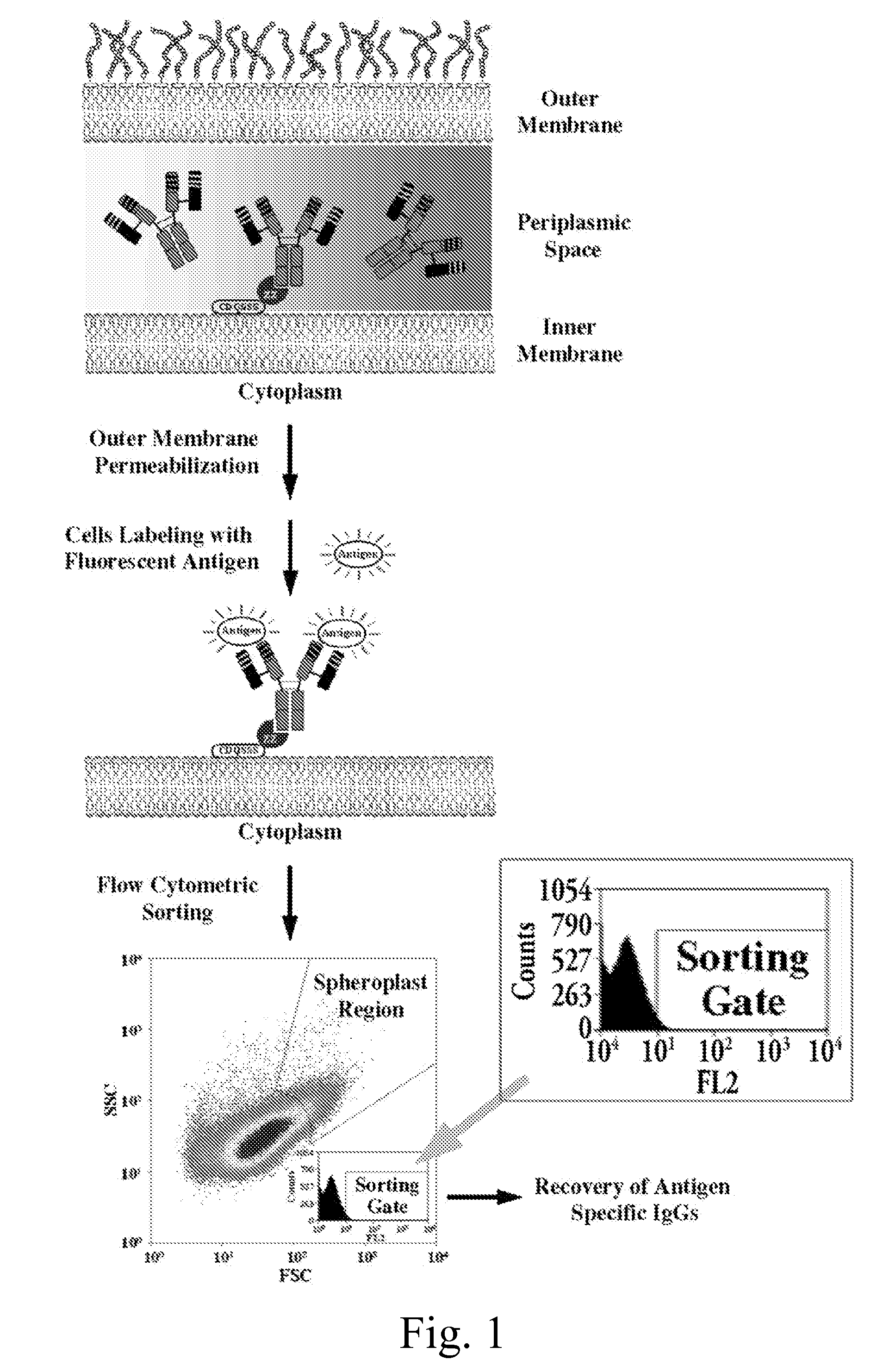
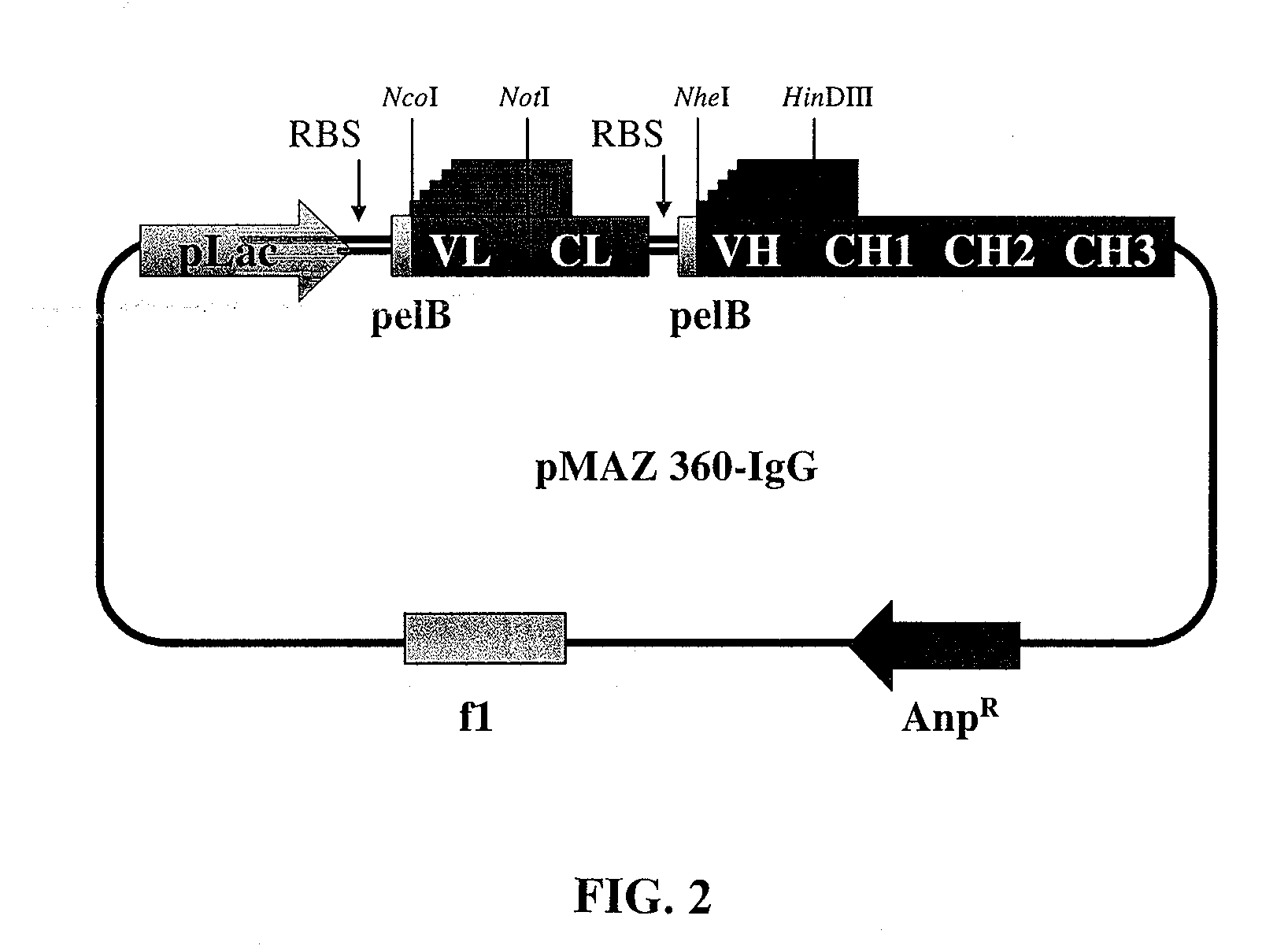
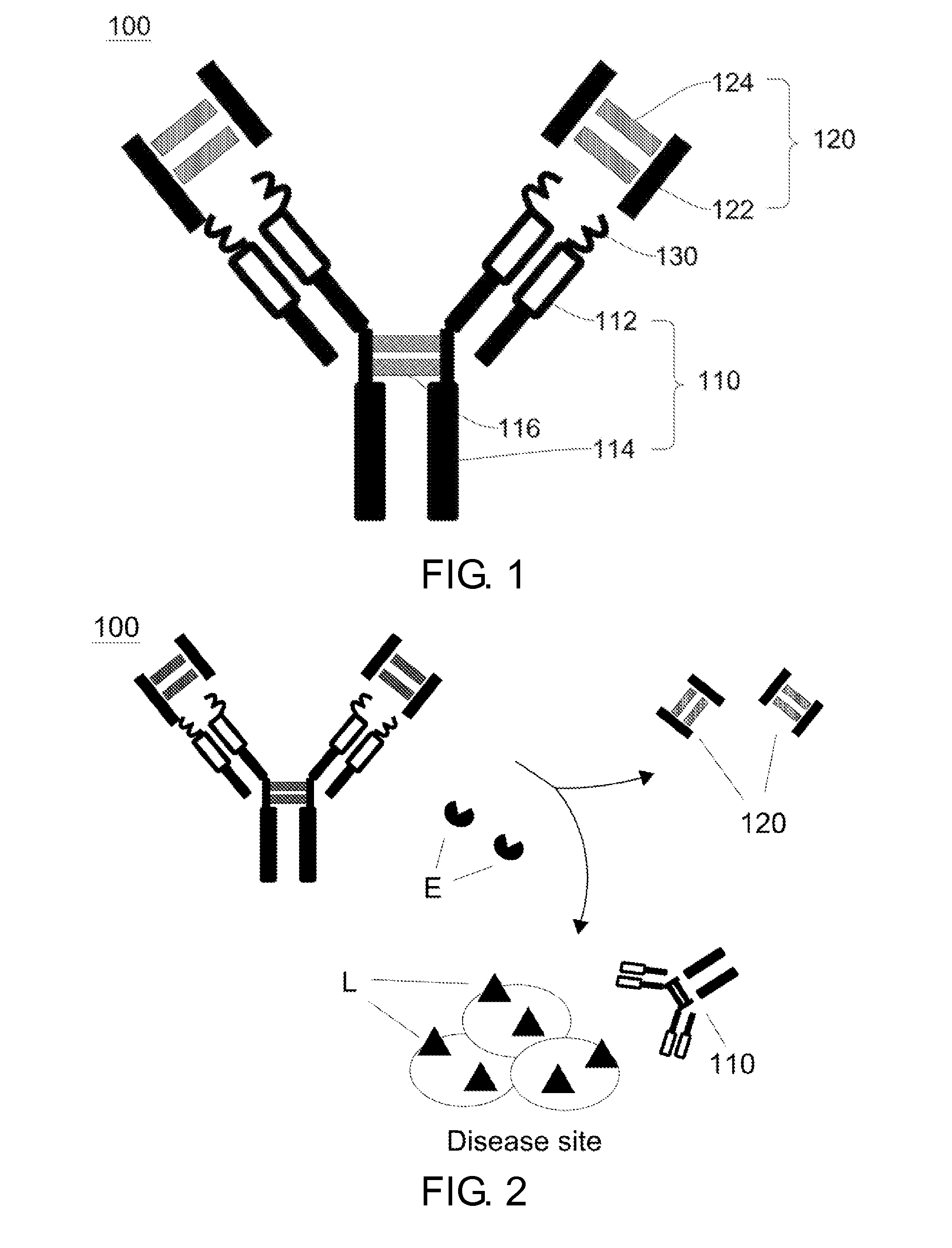
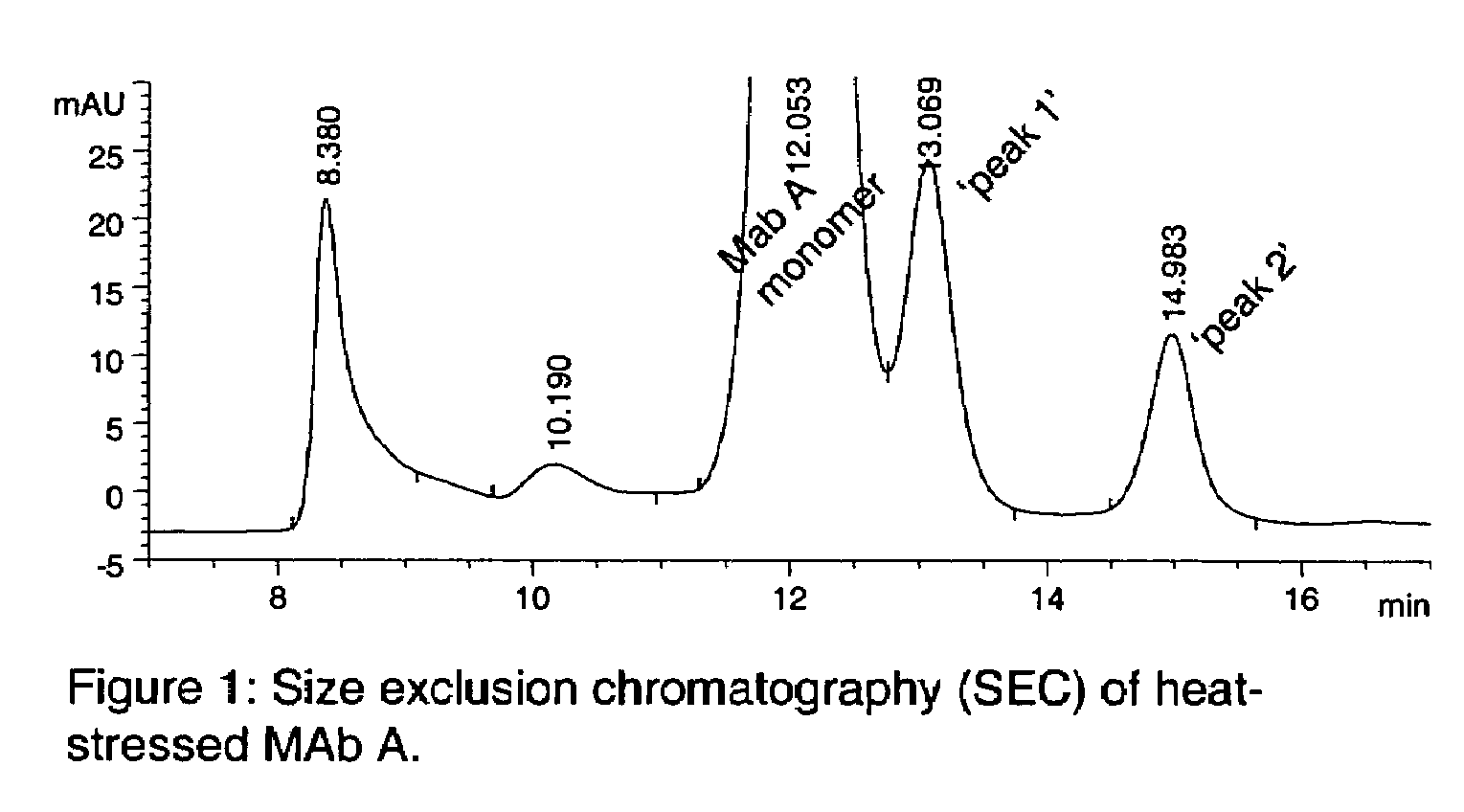
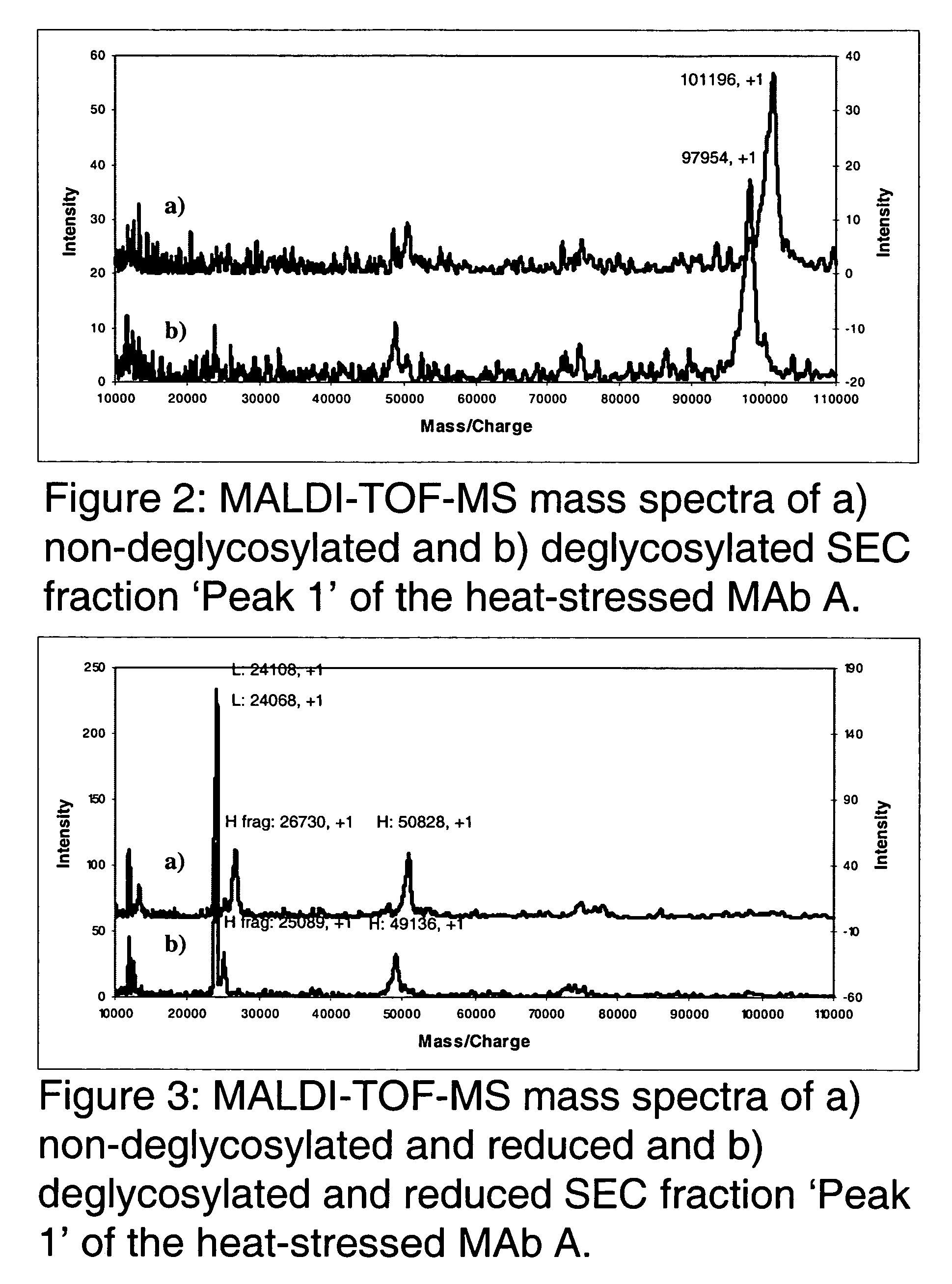
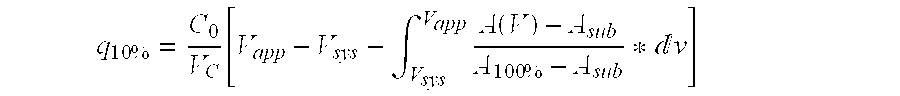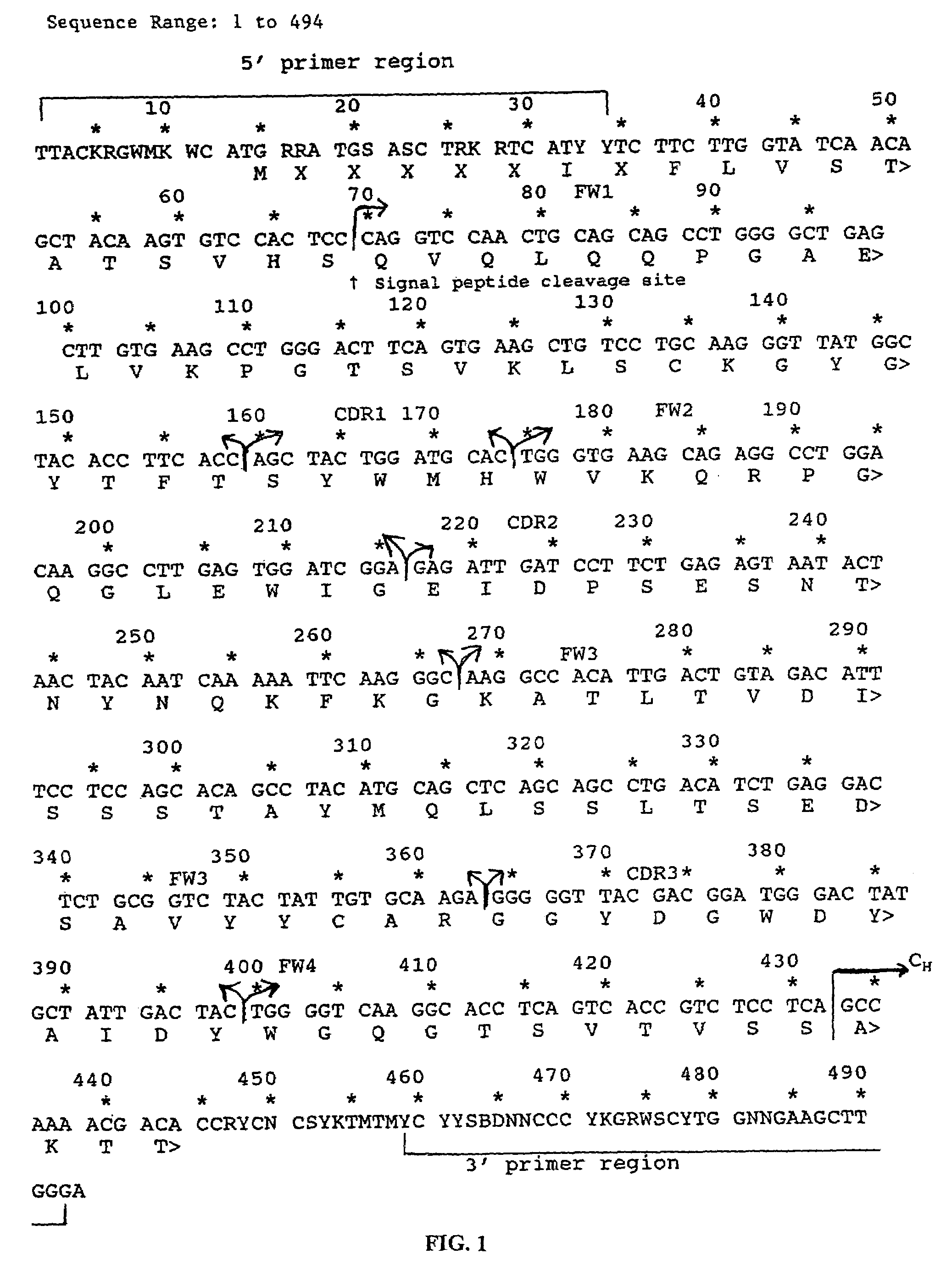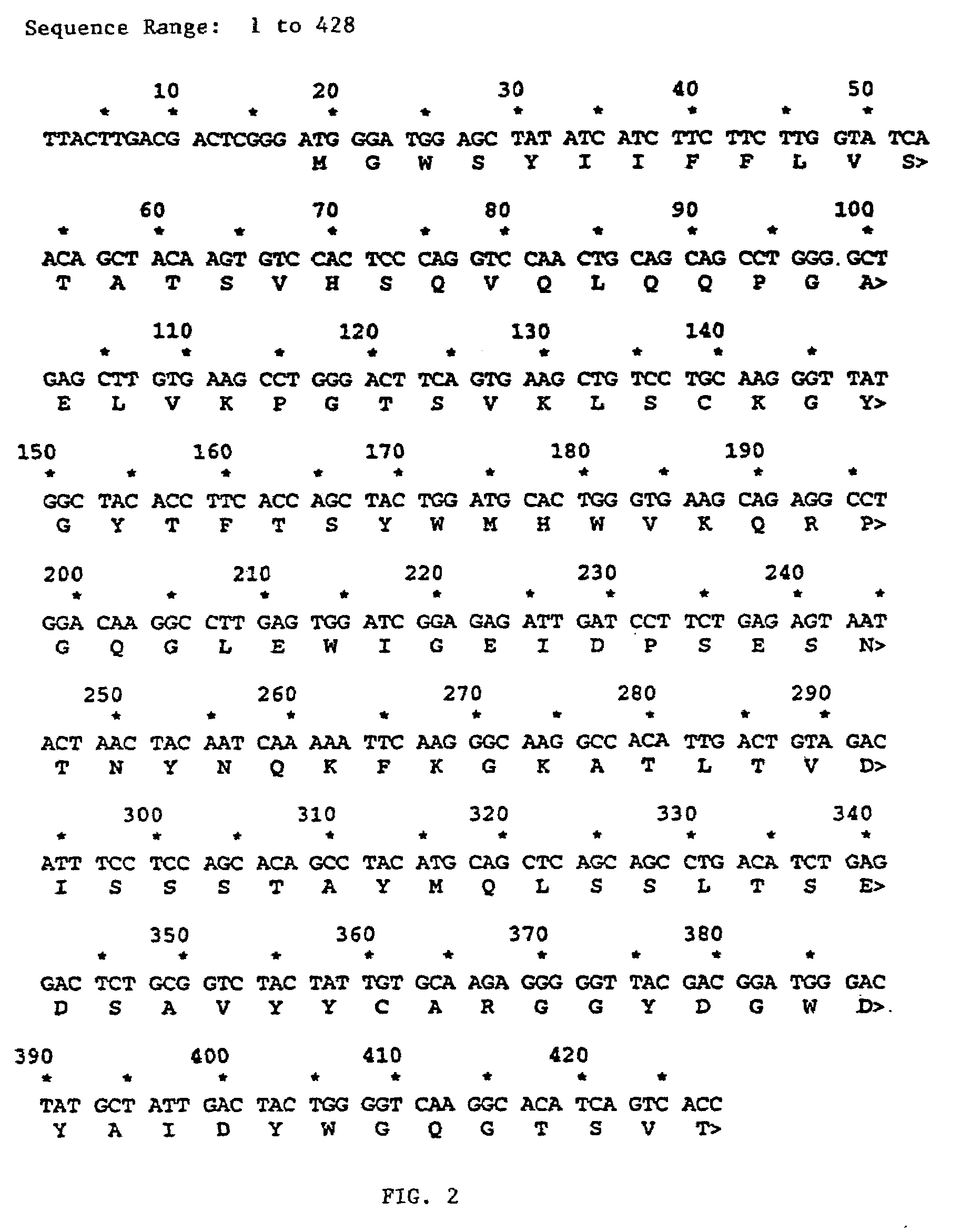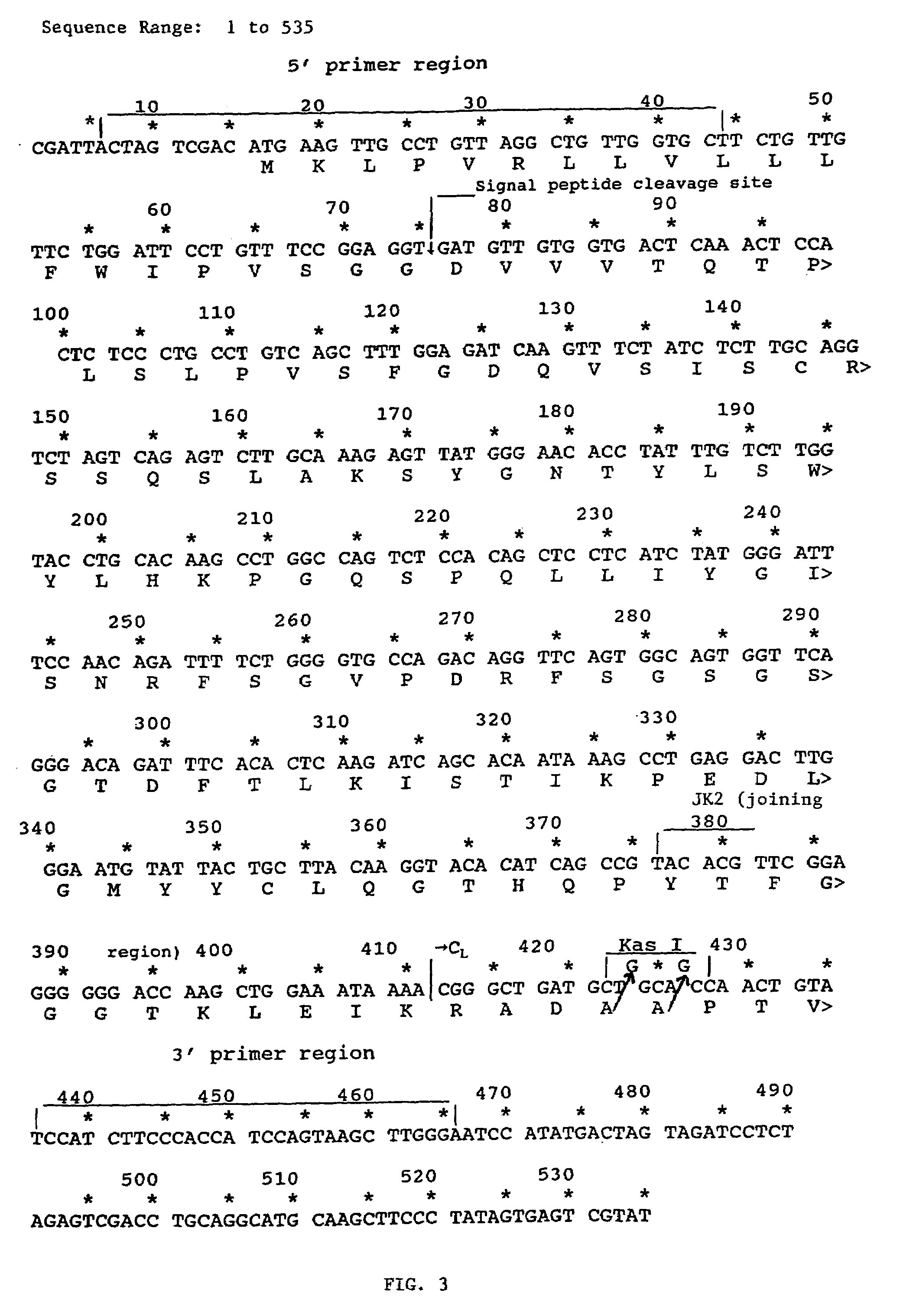Patents
Literature
131 results about "Immunoglobulin class" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
There are five immunoglobulin classes (isotypes) of antibody molecules found in serum: IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. They are distinguished by the type of heavy chain they contain.
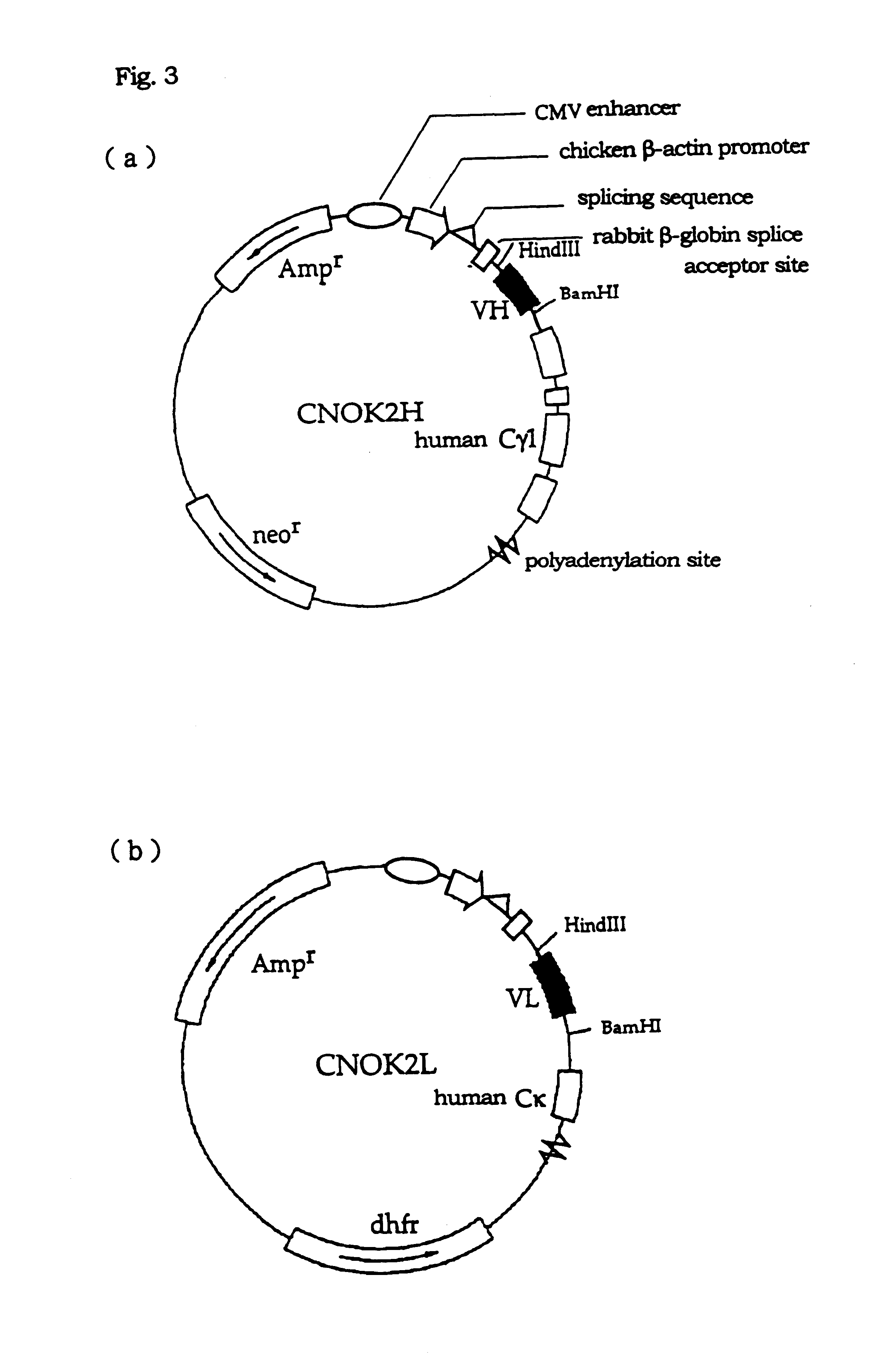
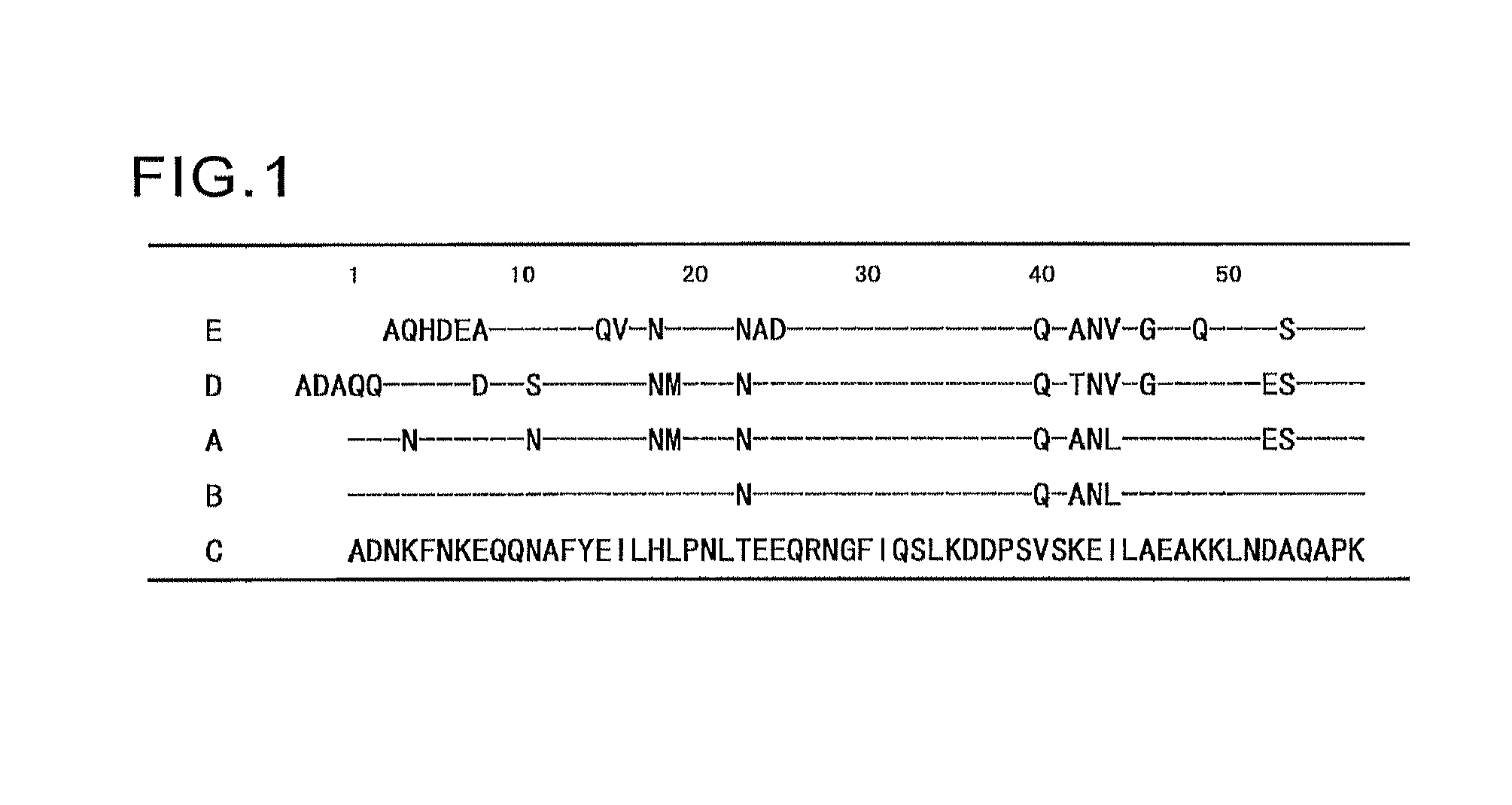
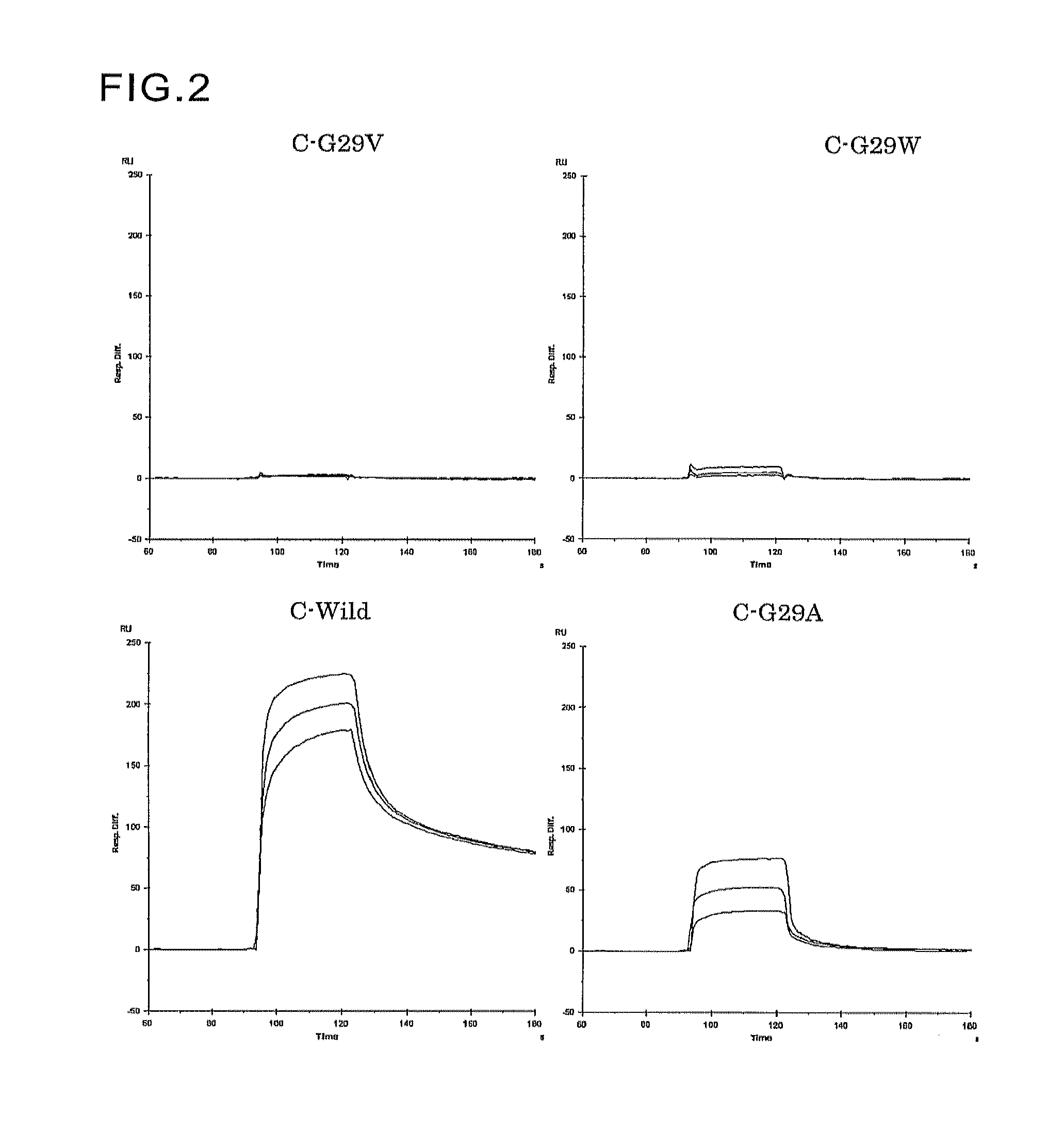
Humanized immunoglobulins
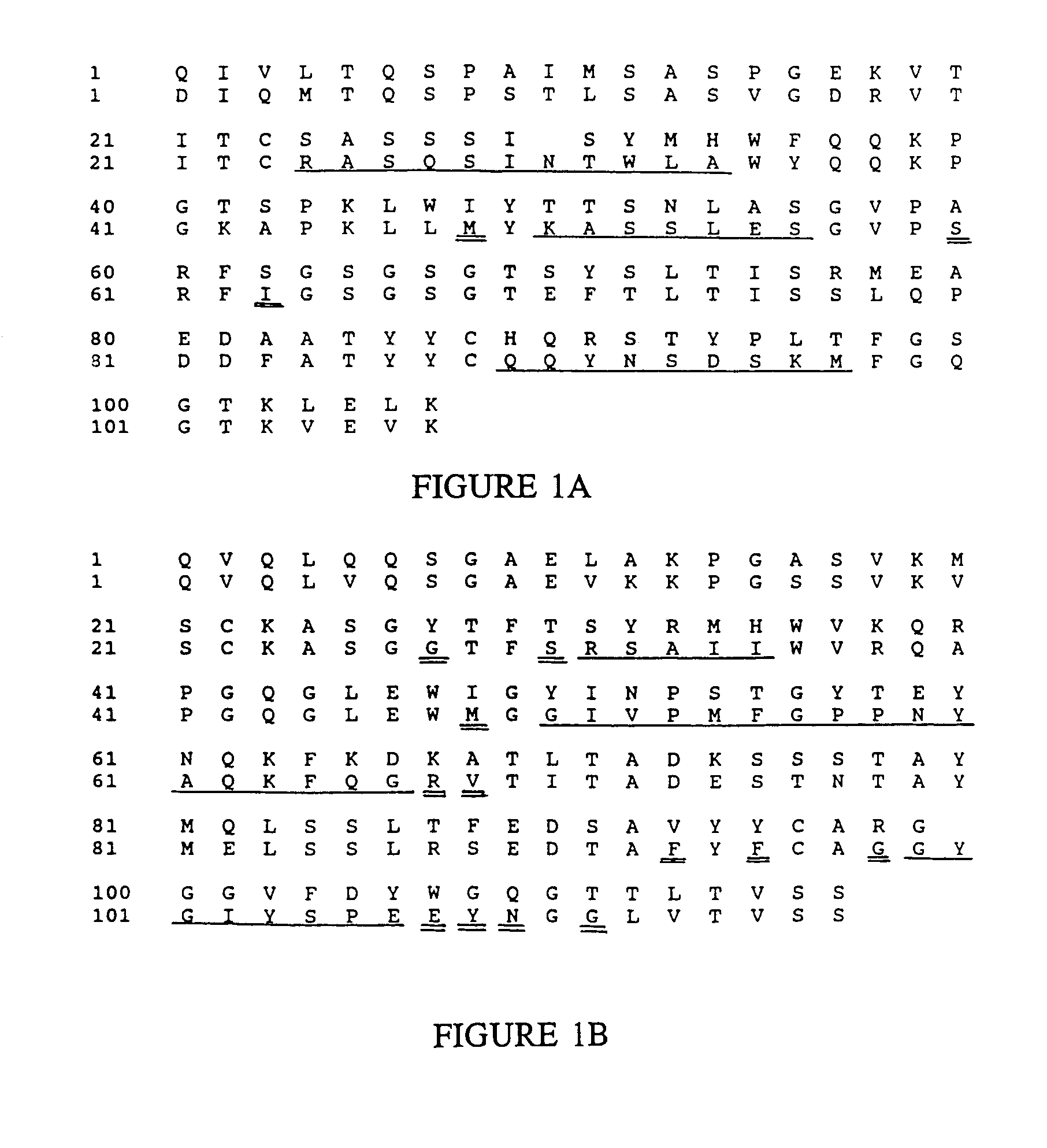
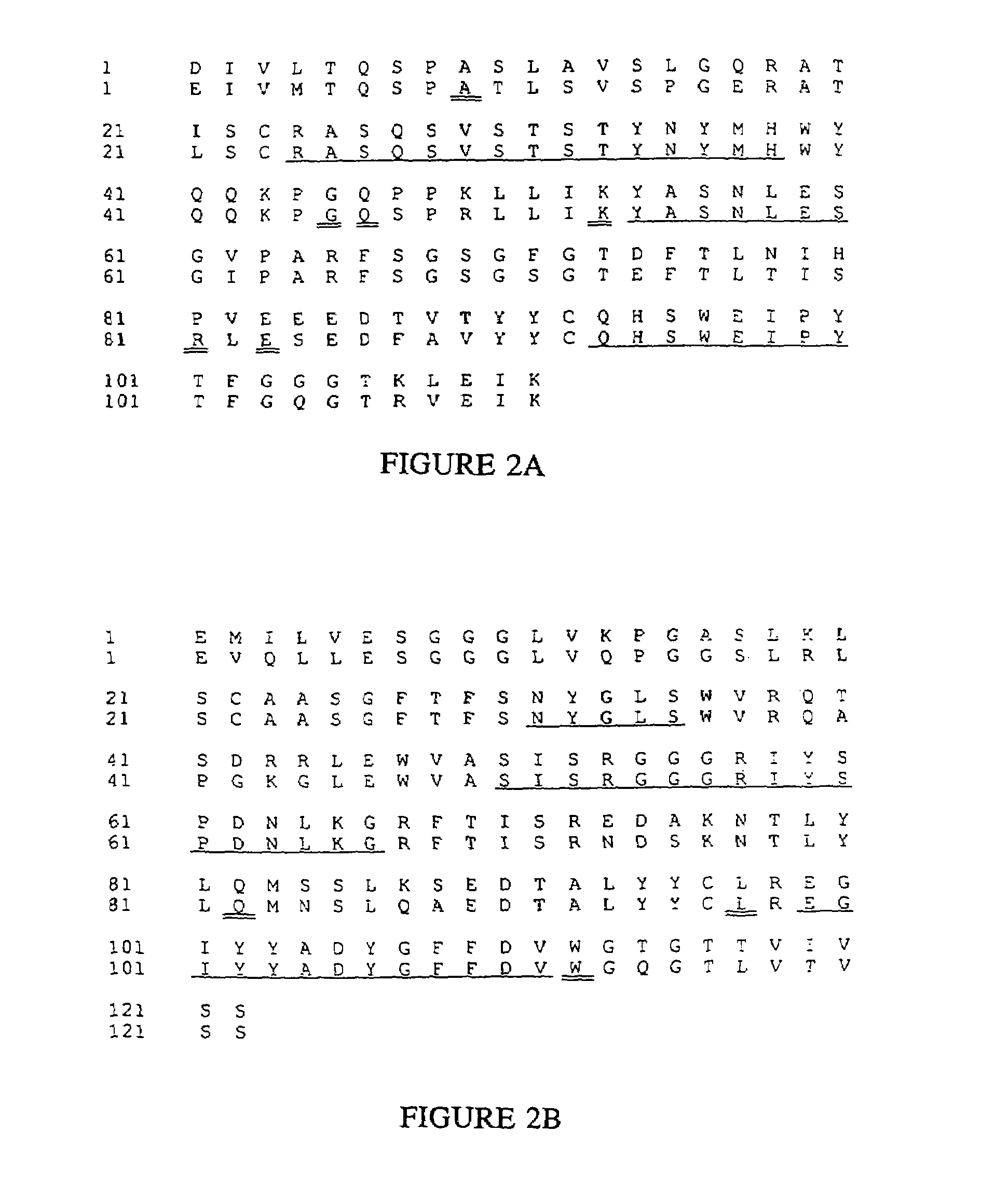
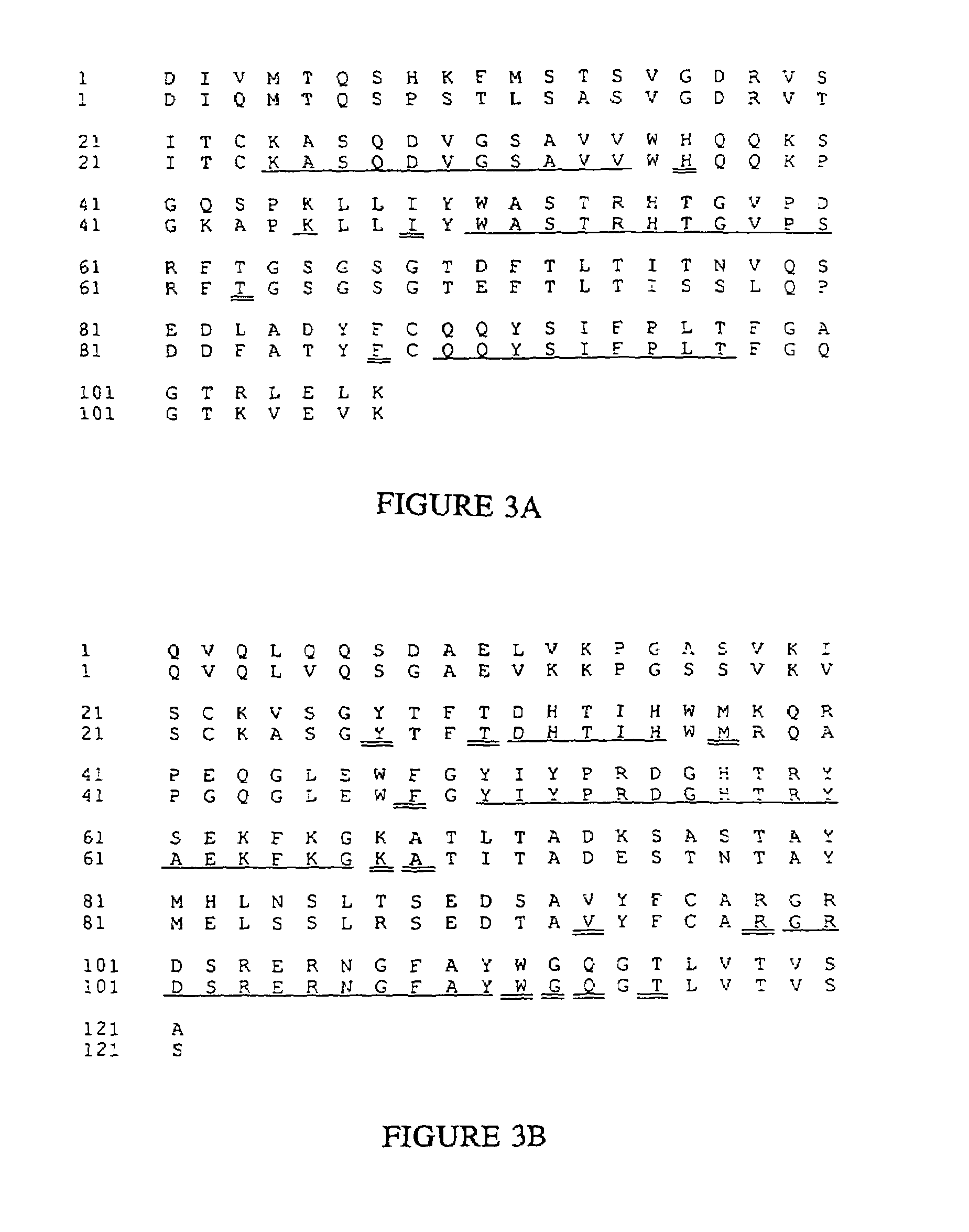
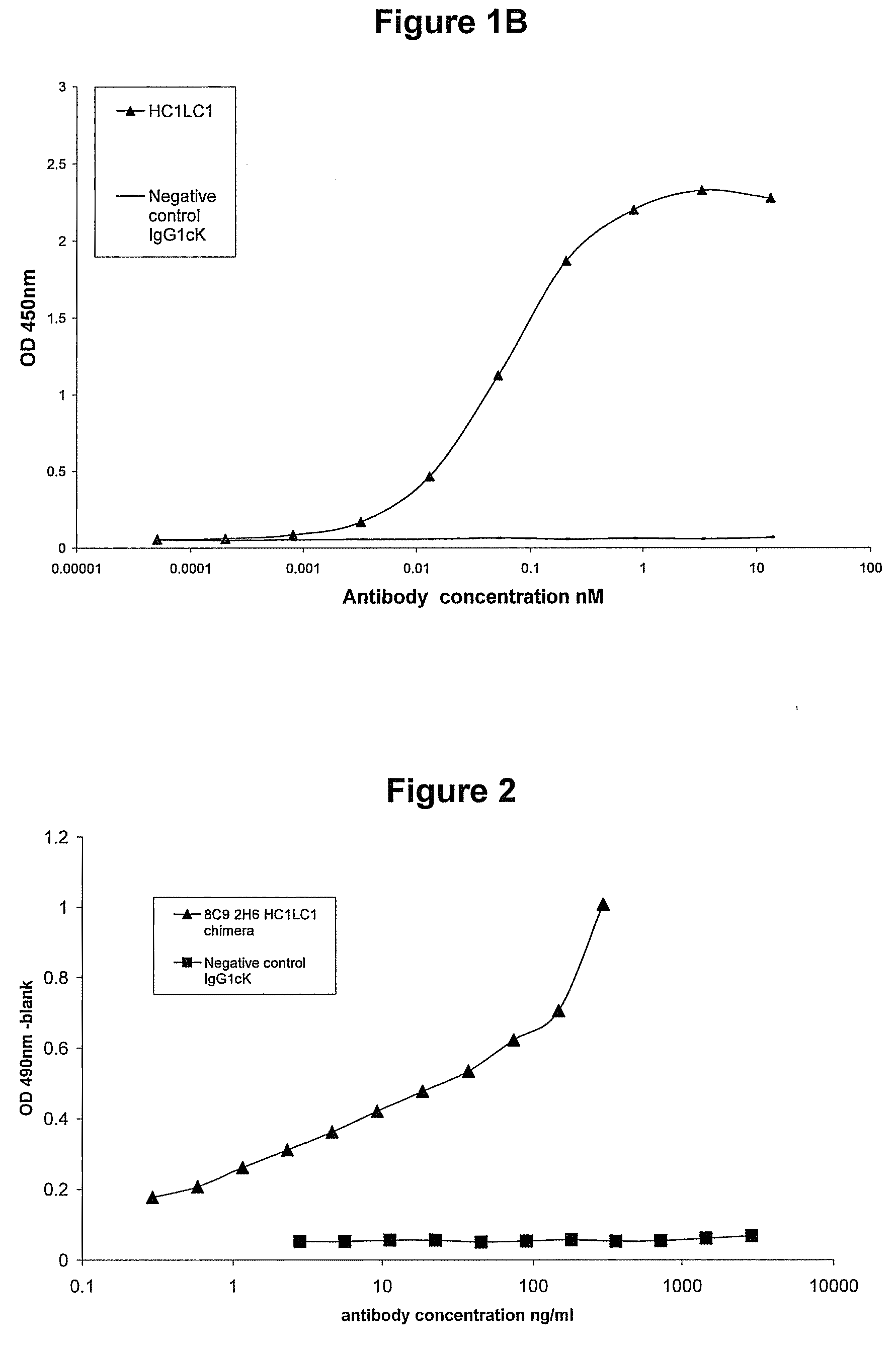
Novel methods for producing, and compositions of, humanized immunoglobulins having one or more complementarity determining regions (CDR's) and possible additional amino acids from a donor immunoglobulin and a framework region from an accepting human immunoglobulin are provided. Each humanized immunoglobulin chain will usually comprise, in addition to the CDR's, amino acids from the donor immunoglobulin framework that are, e.g., capable of interacting with the CDR's to effect binding affinity, such as one or more amino acids which are immediately adjacent to a CDR in the donor immunoglobulin or those within about about 3Å as predicted by molecular modeling. The heavy and light chains may each be designed by using any one or all of various position criteria. When combined into an intact antibody, the humanized immunoglobulins of the present invention will be substantially non-immunogenic in humans and retain substantially the same affinity as the donor immunoglobulin to the antigen, such as a protein or other compound containing an epitope.
Owner:PDL BIOPHARMA INCORPORATED
Glycosylation engineering of antibodies for improving antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
InactiveUS20040072290A1Increase healing valueStrong cytotoxicityFungiNanotechAntibody fragmentsADAMTS Proteins
The present invention relates to the field glycosylation engineering of proteins. More particular, the present invention is directed to the glycosylation engineering of proteins to provide proteins with improved therapeutic properties, e.g., antibodies, antibody fragments, or a fusion protein that includes a region equivalent to the Fc region of an immunoglobulin, with enhanced Fc-mediated cellular cytotoxicity.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
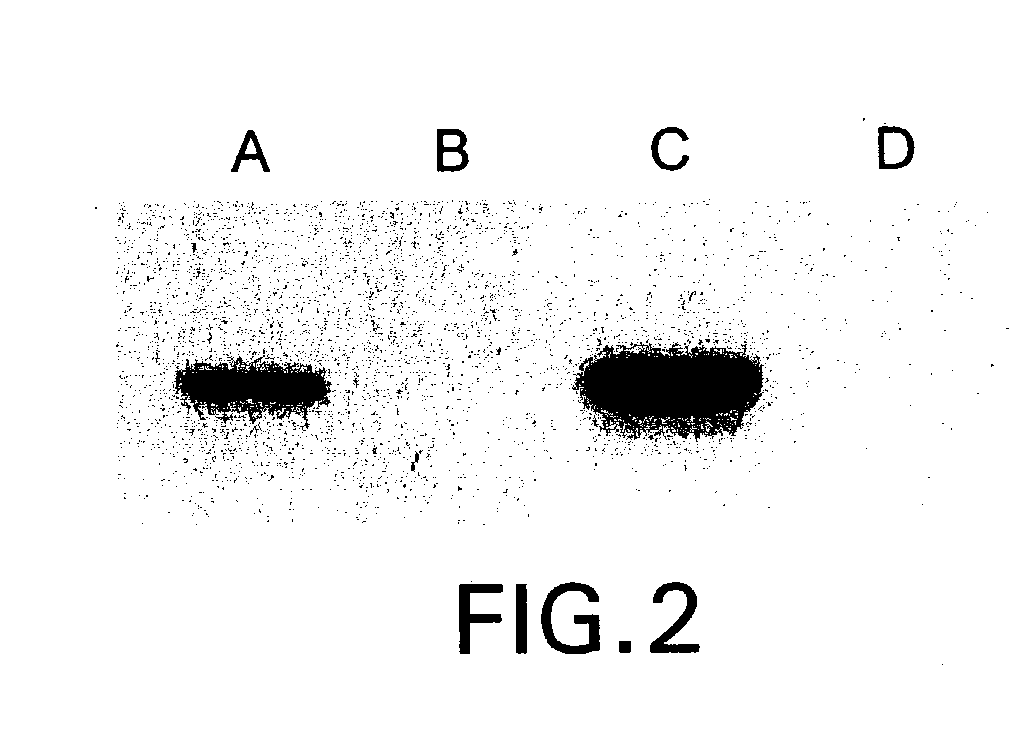
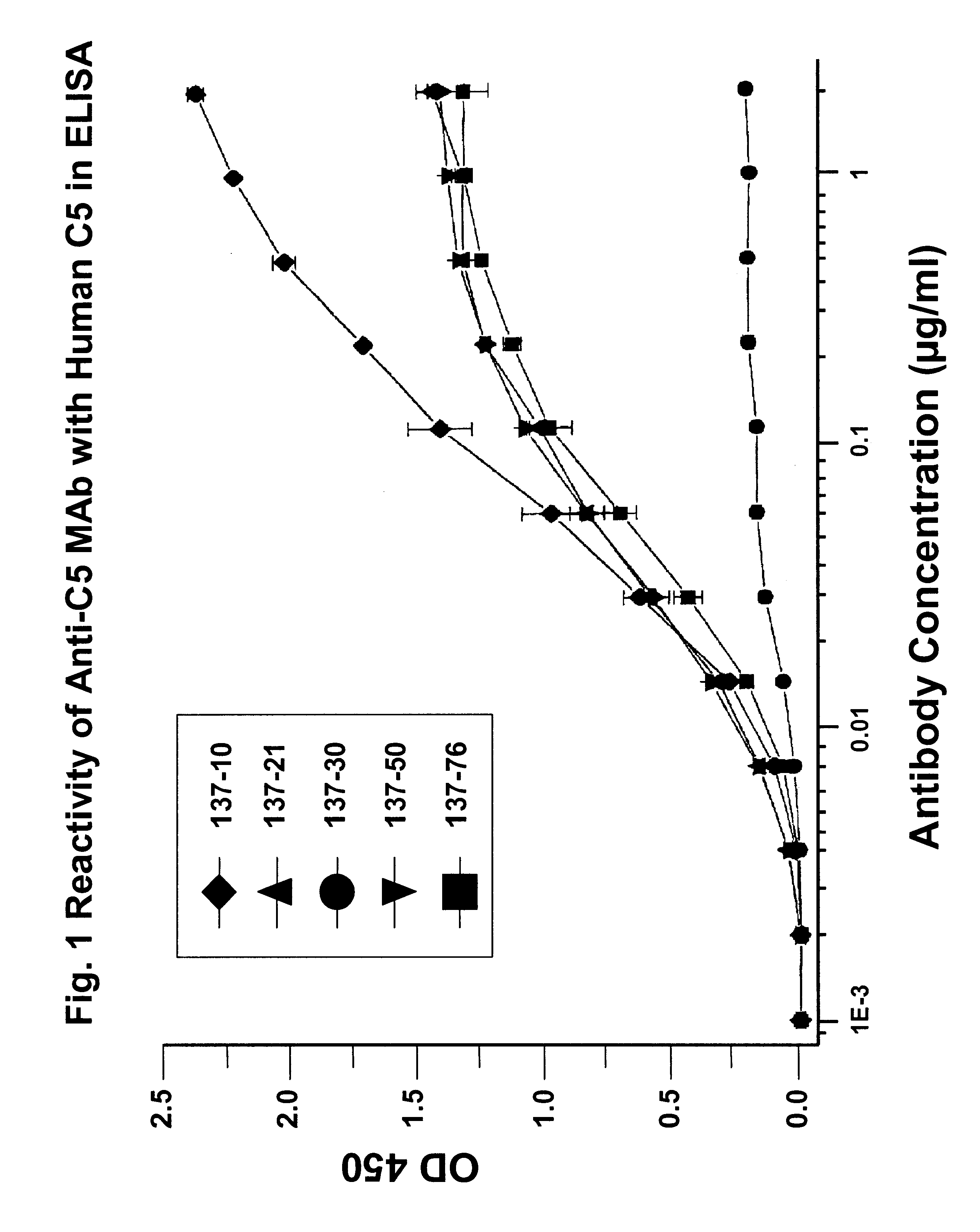
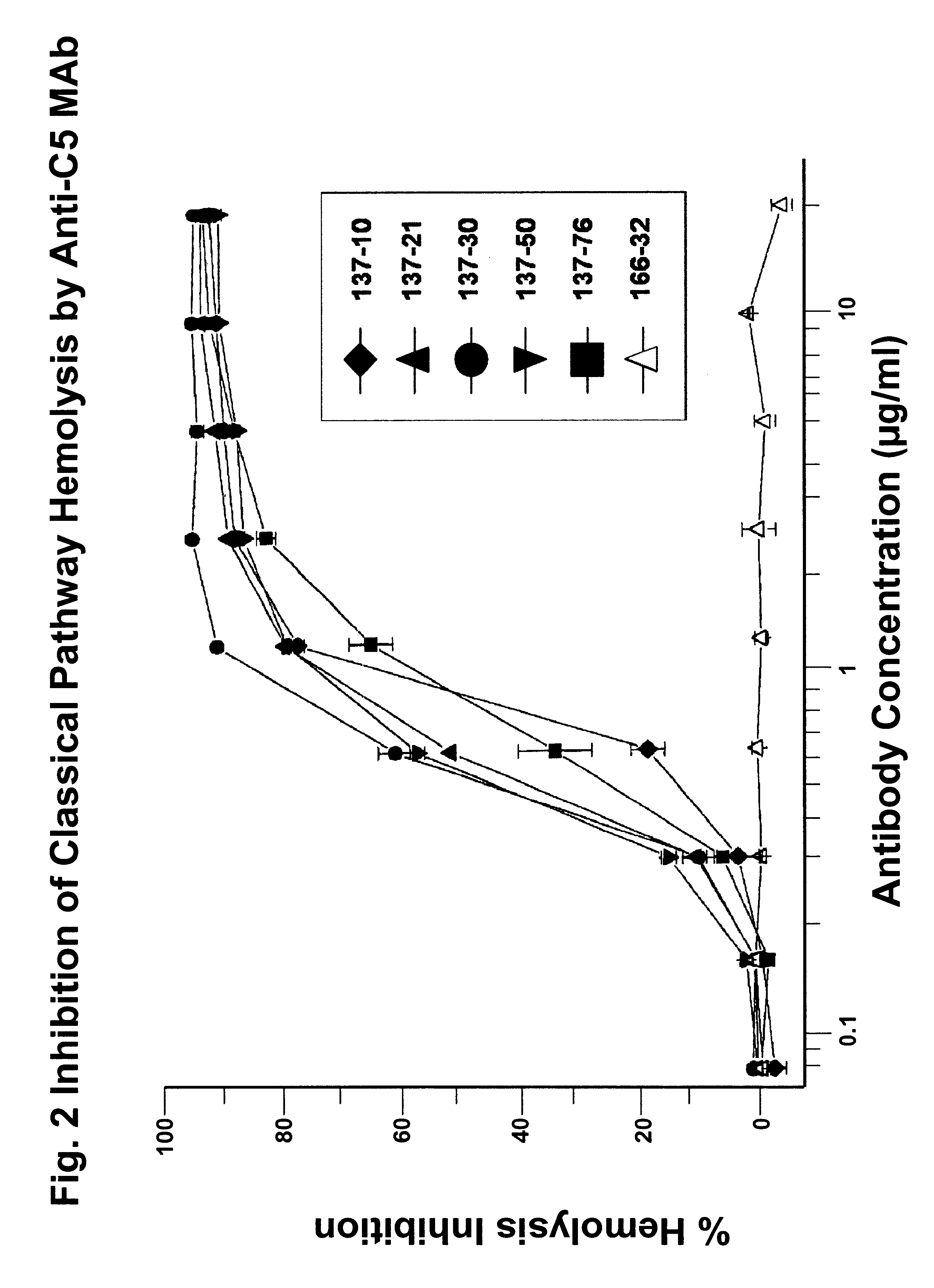
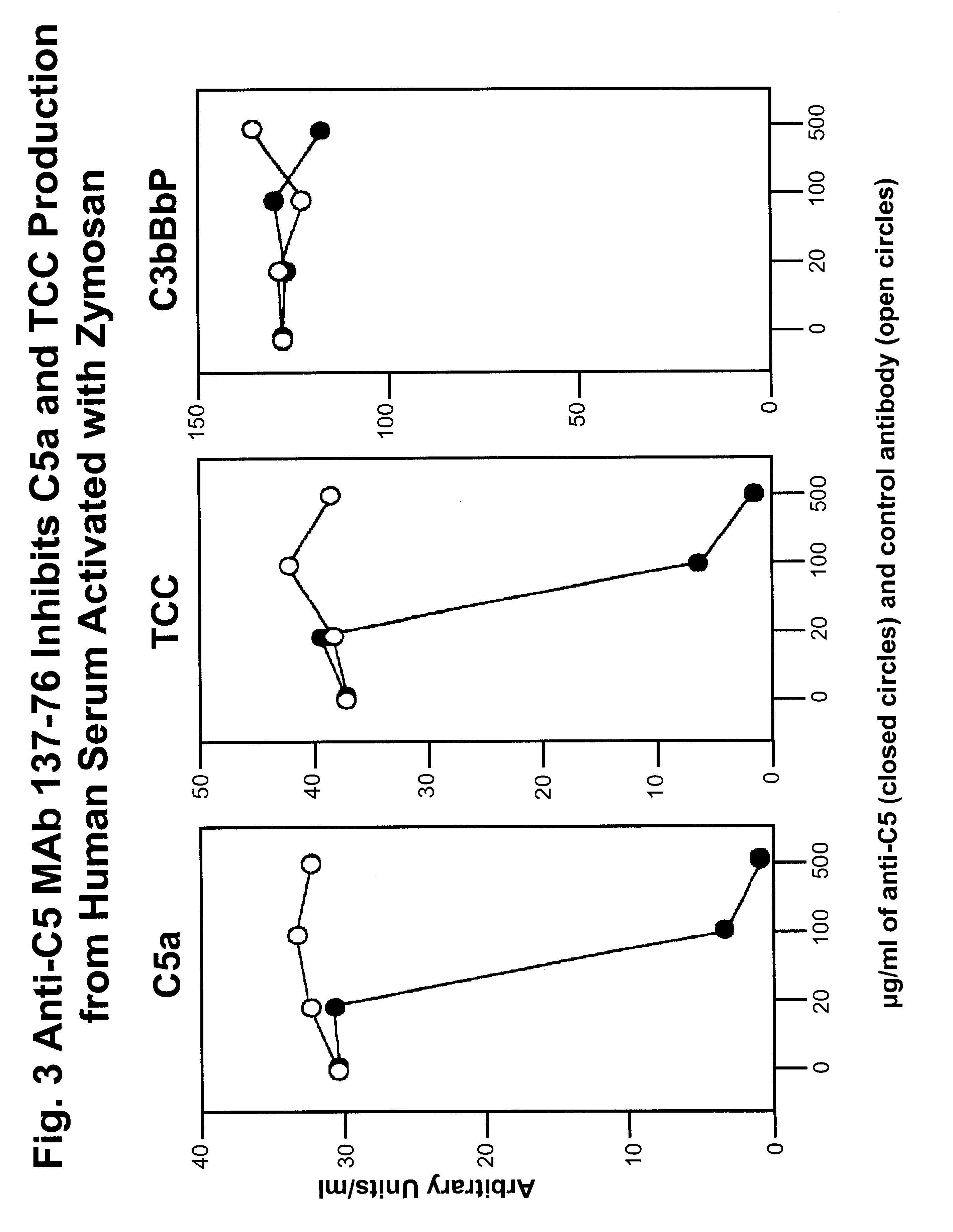
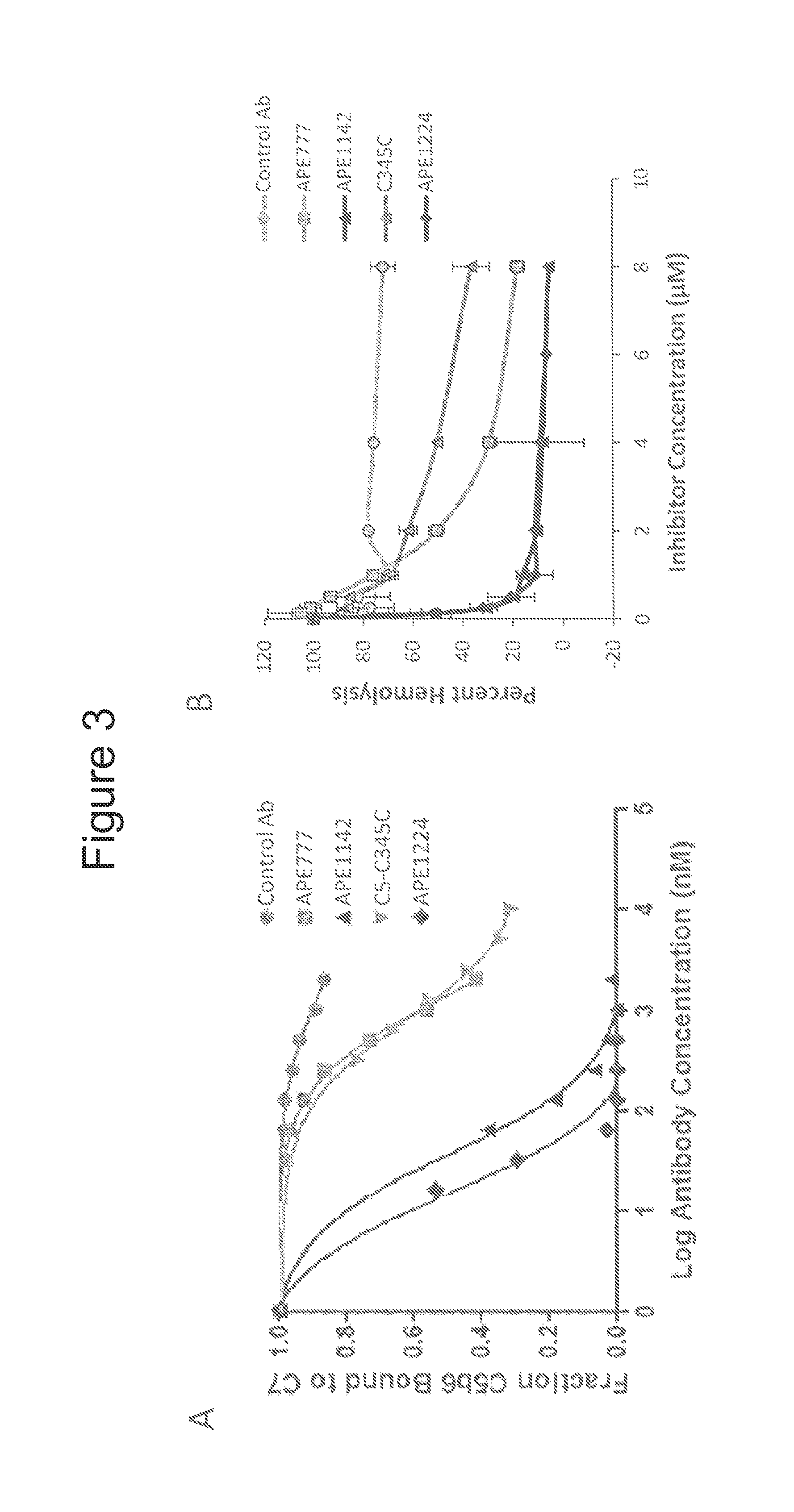
Anti-C5 monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS6534058B2High affinityMaximizing characteristicImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAnimal cellsAcute vascular rejectionOligonucleotide
The invention relates to C5 inhibitors, which inhibit type II endothelial cell activation, wherein the inhibition is manifested by the suppression of E-selectin. These inhibitors are useful in treatment of delayed xenograft rejection or acute vascular rejection. The inhibitors include antibody molecules, as well as homologues, analogues and modified or derived forms thereof, including immunoglobulin fragments like Fab, F(ab')2 and Fv, small molecules, including peptides, oligonucleotides, peptidomimetics and organic compounds. Examples of monoclonal antibodies, which bind to and inhibit C5, were generated and are designated MAb 137-76 and MAb 137-30.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
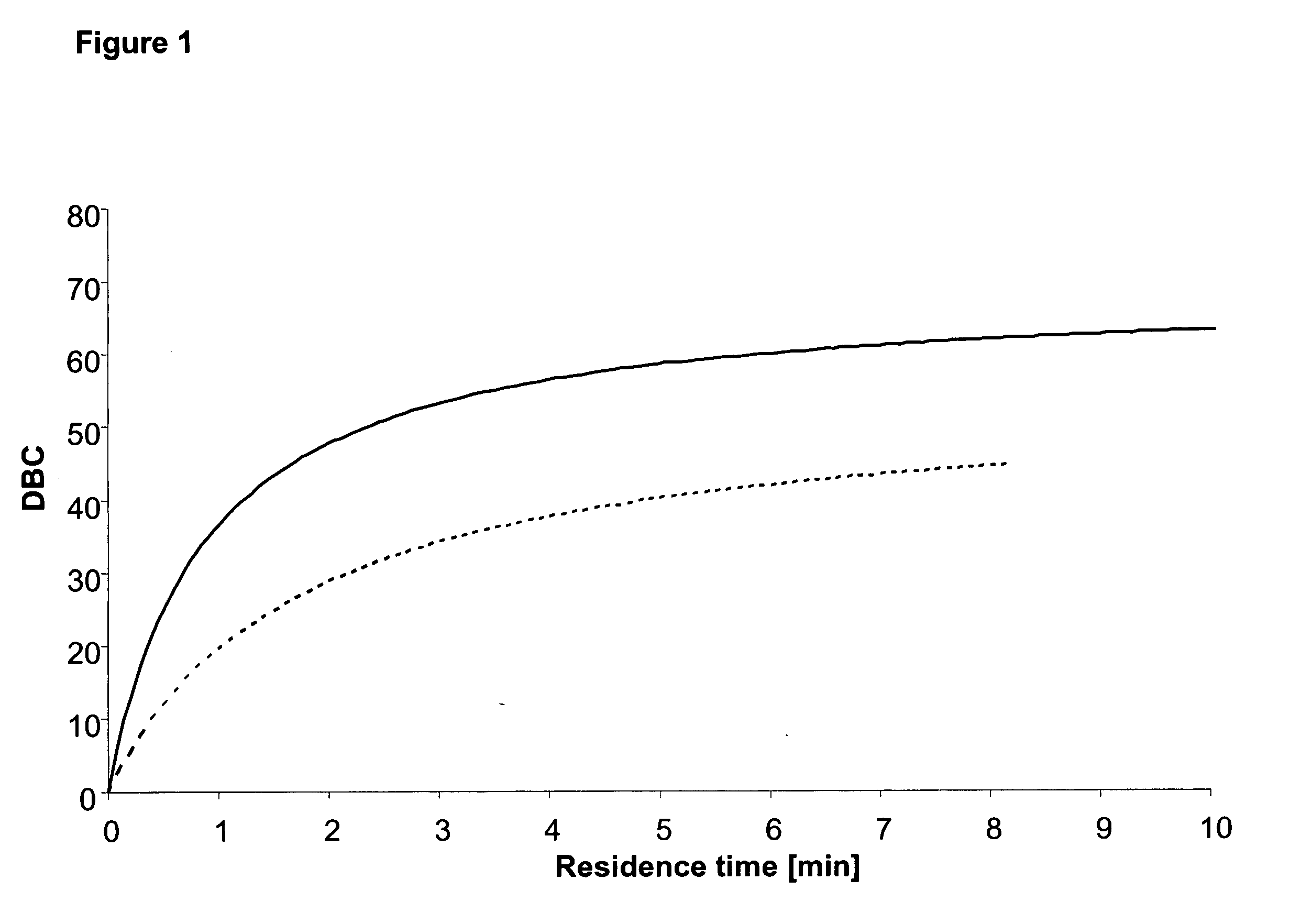
Purification of immunoglobulins
ActiveUS20060134805A1Faster and economic purificationIncrease capacitySolid sorbent liquid separationImmunoassaysCross-linkChemical physics
The present invention relates to a separation matrix comprised of porous particles to which antibody-binding protein ligands have been immobilised, wherein the ligand density is in the range of 5.0-10 mg / ml; the gel phase distribution coefficient of the particles expressed as Kav for a dextran of size 110 kDa is above 0.65 and the median particle diameter is between 65-84 μm. The carbohydrate material is preferably highly cross-linked agarose.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
Humanized immunoglobulin reactive with α4β7 integrin
InactiveUS7147851B1Reduce inflammationLess immunogenicFungiBacteriaComplementarity determining regionAntigen binding
The present invention relates to humanized immunoglobulins having binding specificity for α4β7 integrin, comprising an antigen binding region of nonhuman origin (e.g., rodent) and at least a portion of an immunoglobulin of human origin (e.g., a human framework region, a human constant region). In one embodiment, the humanized immunoglobulin can compete with murine Act-1 for binding to human α4β7 integrin. In a preferred embodiment, the antigen binding region of the humanized immunoglobulin comprises each of the complementarity determining regions of the light and heavy chains of the murine Act-1 antibody.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC
Antibodies to c-Met
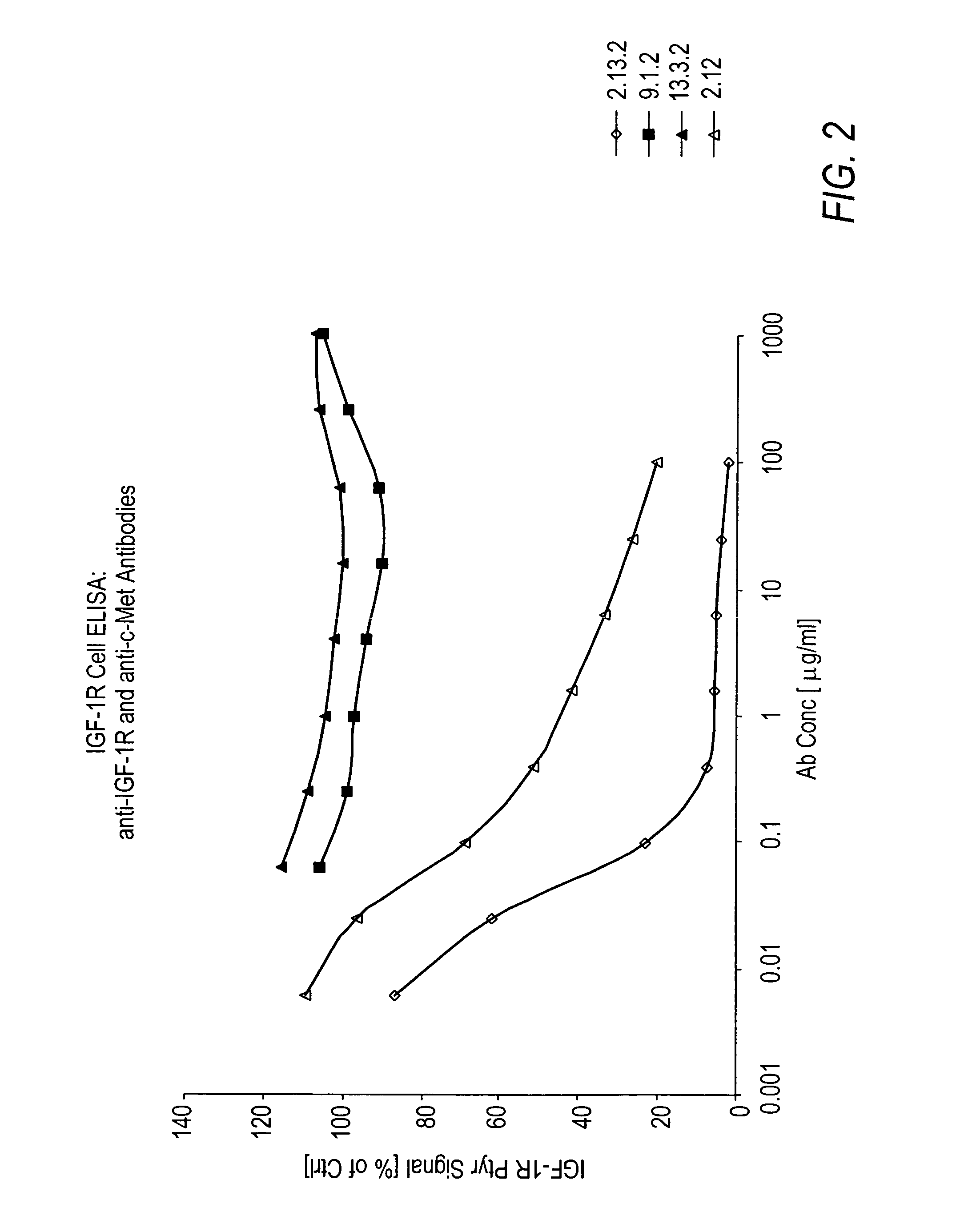
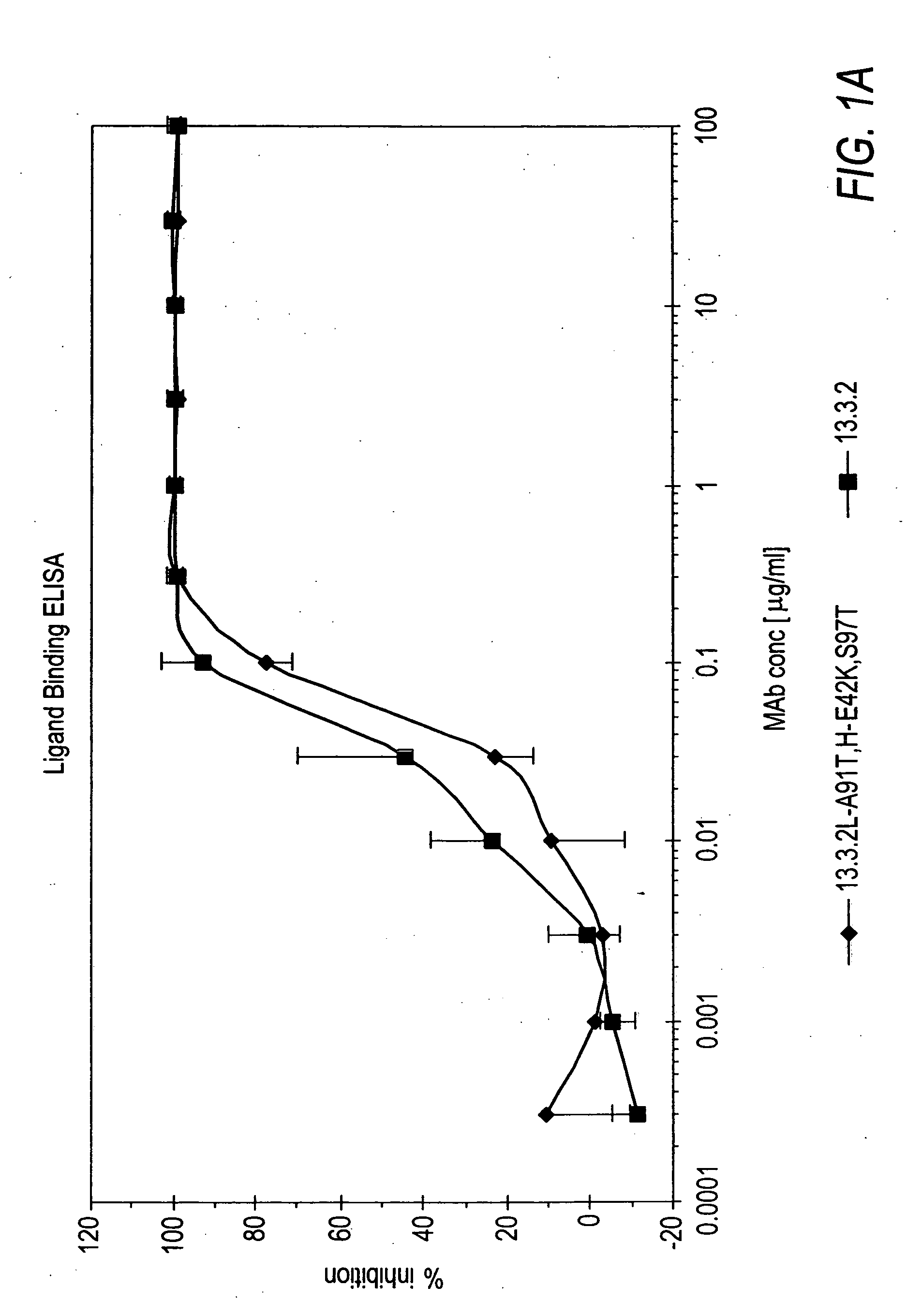
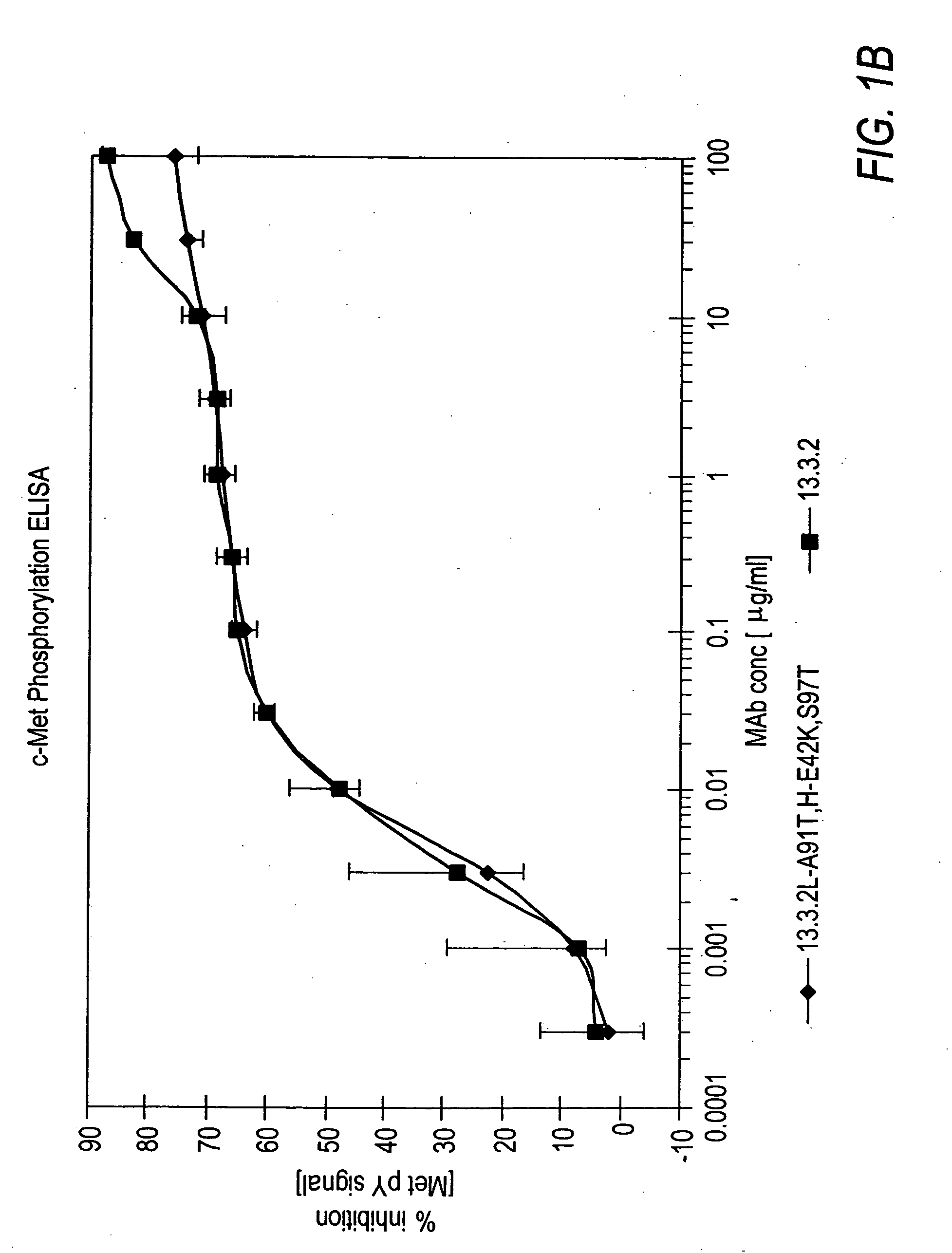
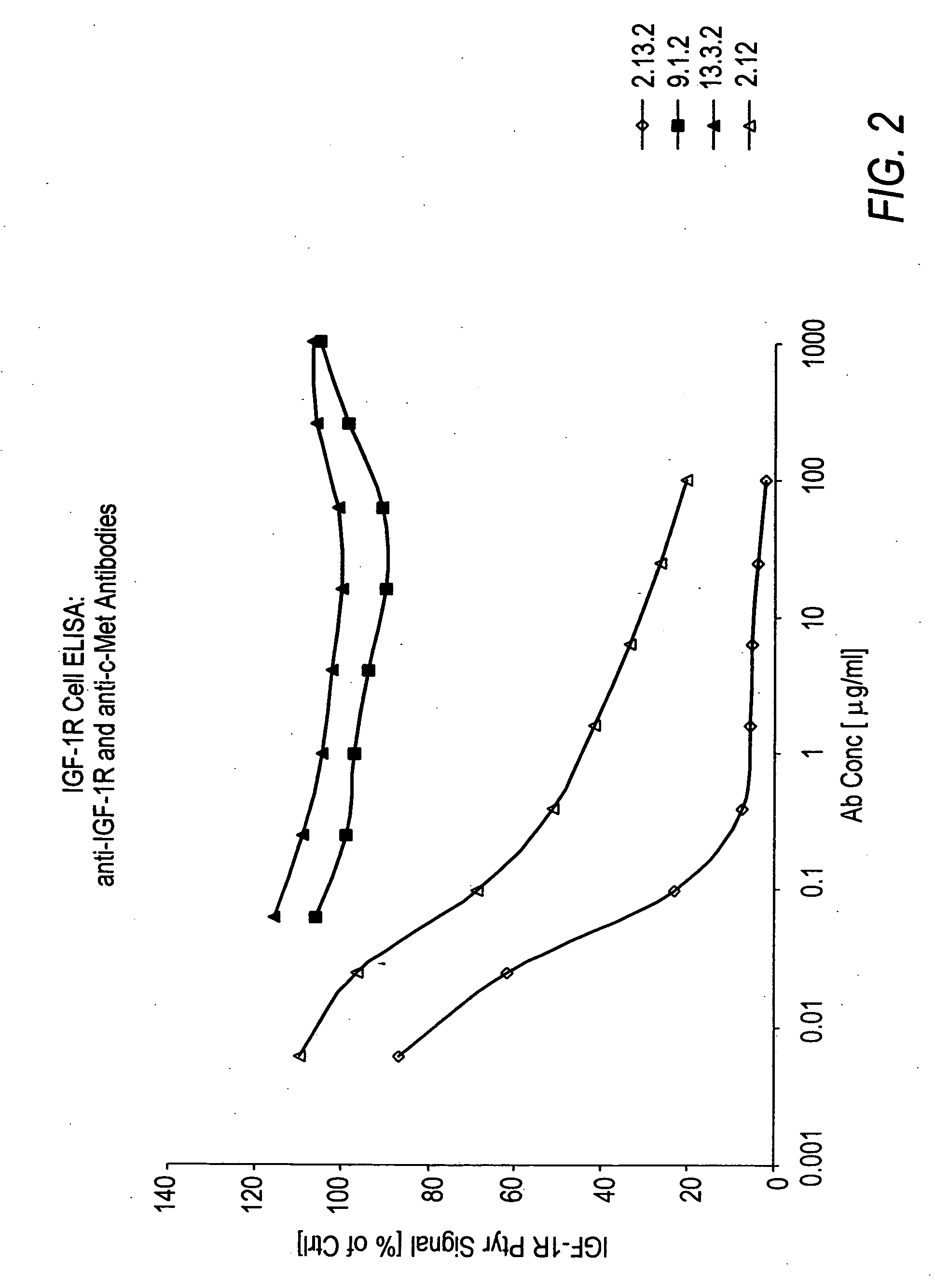
ActiveUS7498420B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesHeavy chain
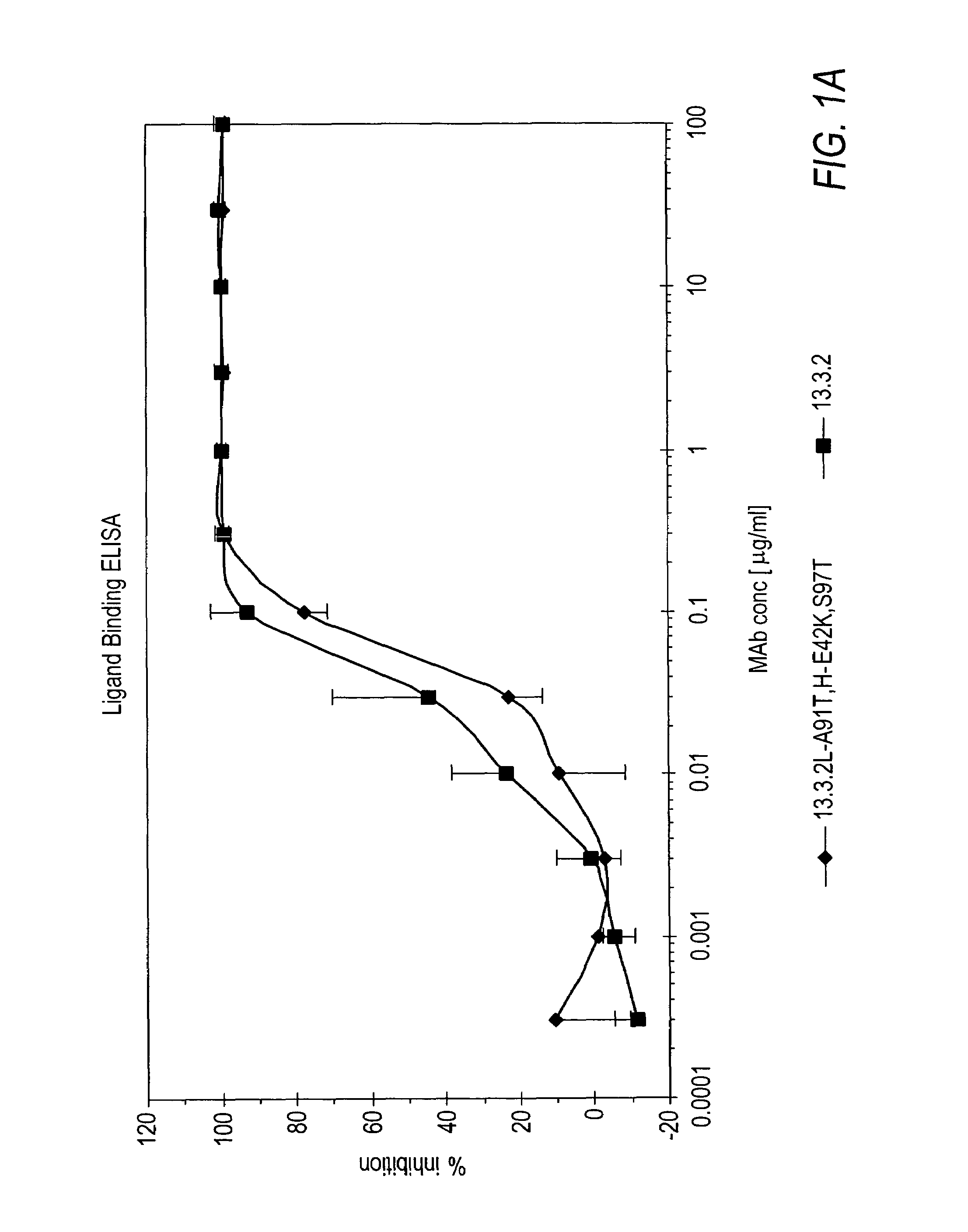
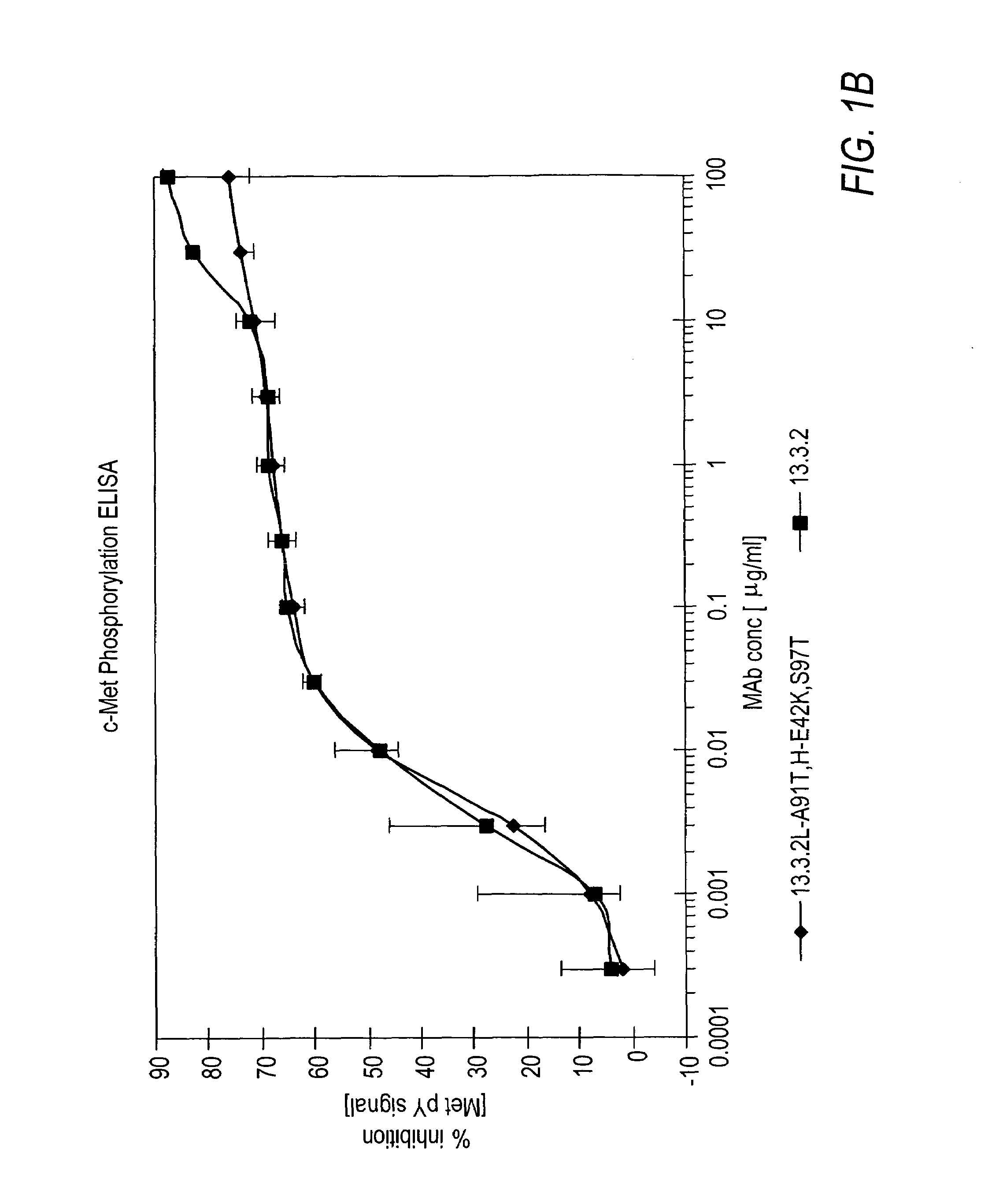
The present invention relates to antibodies including human antibodies and antigen-binding portions thereof that specifically bind to c-Met, preferably human c-Met, and that function to inhibit c-Met. The invention also relates to human anti-c-Met antibodies and antigen-binding portions thereof. The invention also relates to antibodies that are chimeric, bispecific, derivatized, single chain antibodies or portions of fusion proteins. The invention also relates to isolated heavy and light chain immunoglobulins derived from human anti-c-Met antibodies and nucleic acid molecules encoding such immunoglobulins. The present invention also relates to methods of making human anti-c-Met antibodies, compositions comprising these antibodies and methods of using the antibodies and compositions for diagnosis and treatment. The invention also provides gene therapy methods using nucleic acid molecules encoding the heavy and / or light immunoglobulin molecules that comprise the human anti-c-Met antibodies. The invention also relates to transgenic animals or plants comprising nucleic acid molecules of the present invention.
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC +1
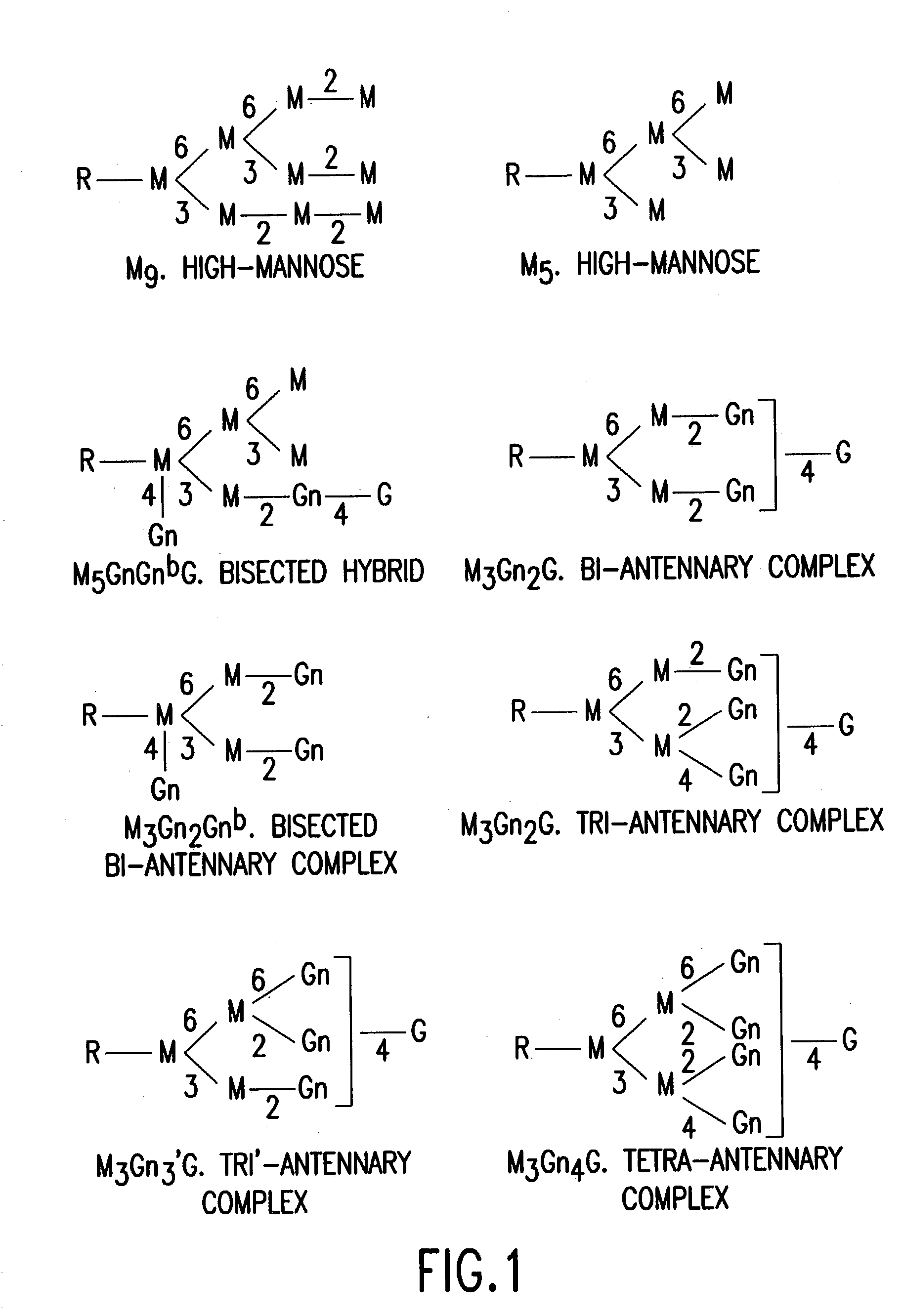
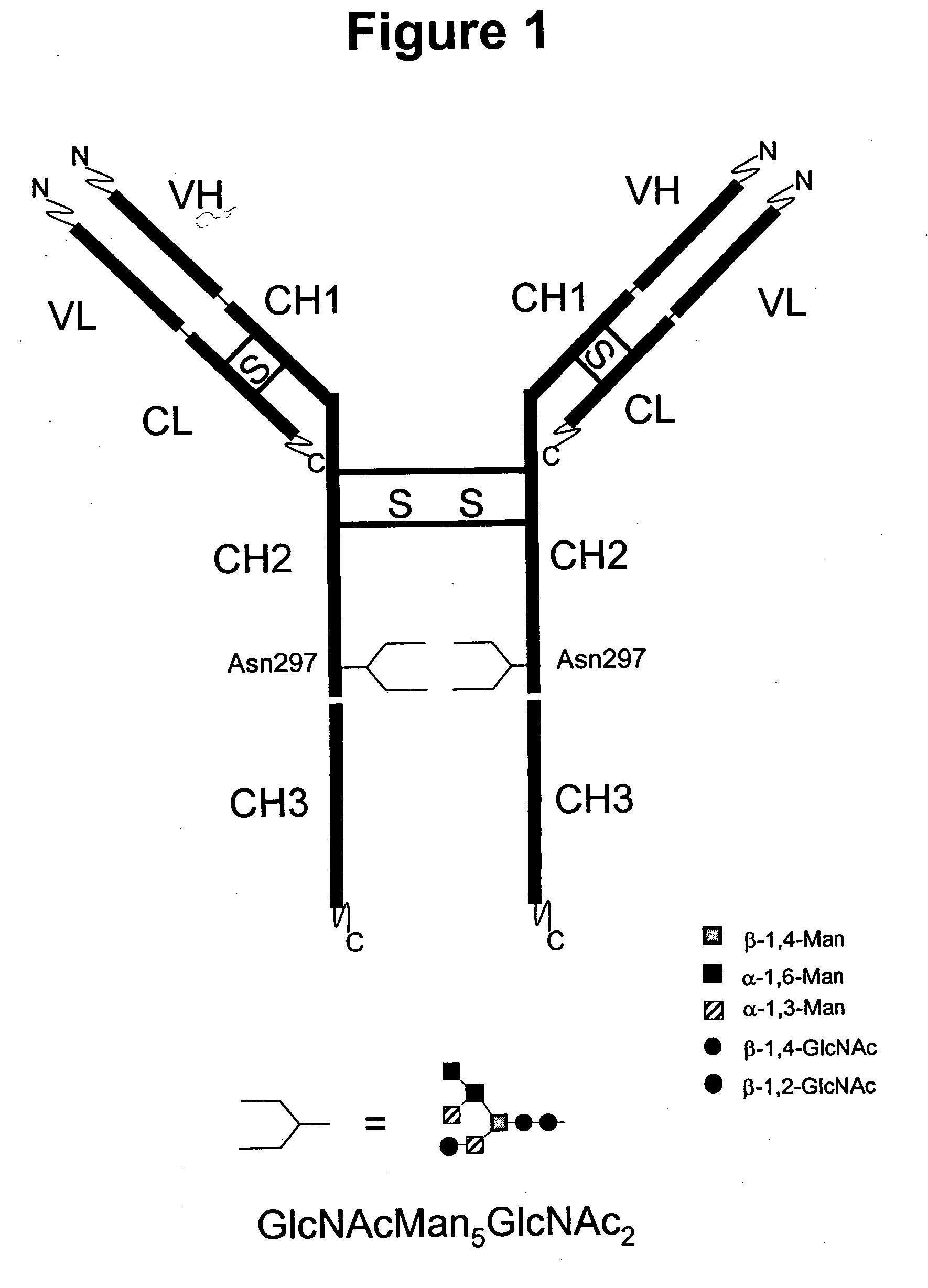
Immunoglobulins comprising predominantly a GlcNAcMAN5GLCNAC2 glycoform
InactiveUS20060034828A1Adverse effect can be minimized and avoidedEasily reproducibleAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGlycoproteinImmunoglobulin class
The present invention relates to immunoglobulin glycoprotein compositions having predominant N-glycan structures on an immunoglobulin glycoprotein which confer a specific effector function. Additionally, the present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising an antibody having a particular enriched N-glycan structure, wherein said N-glycan structure is GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Antibodies to c-Met
ActiveUS20100040629A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsSingle-Chain AntibodiesHeavy chain
Owner:AMGEN FREMONT INC +1
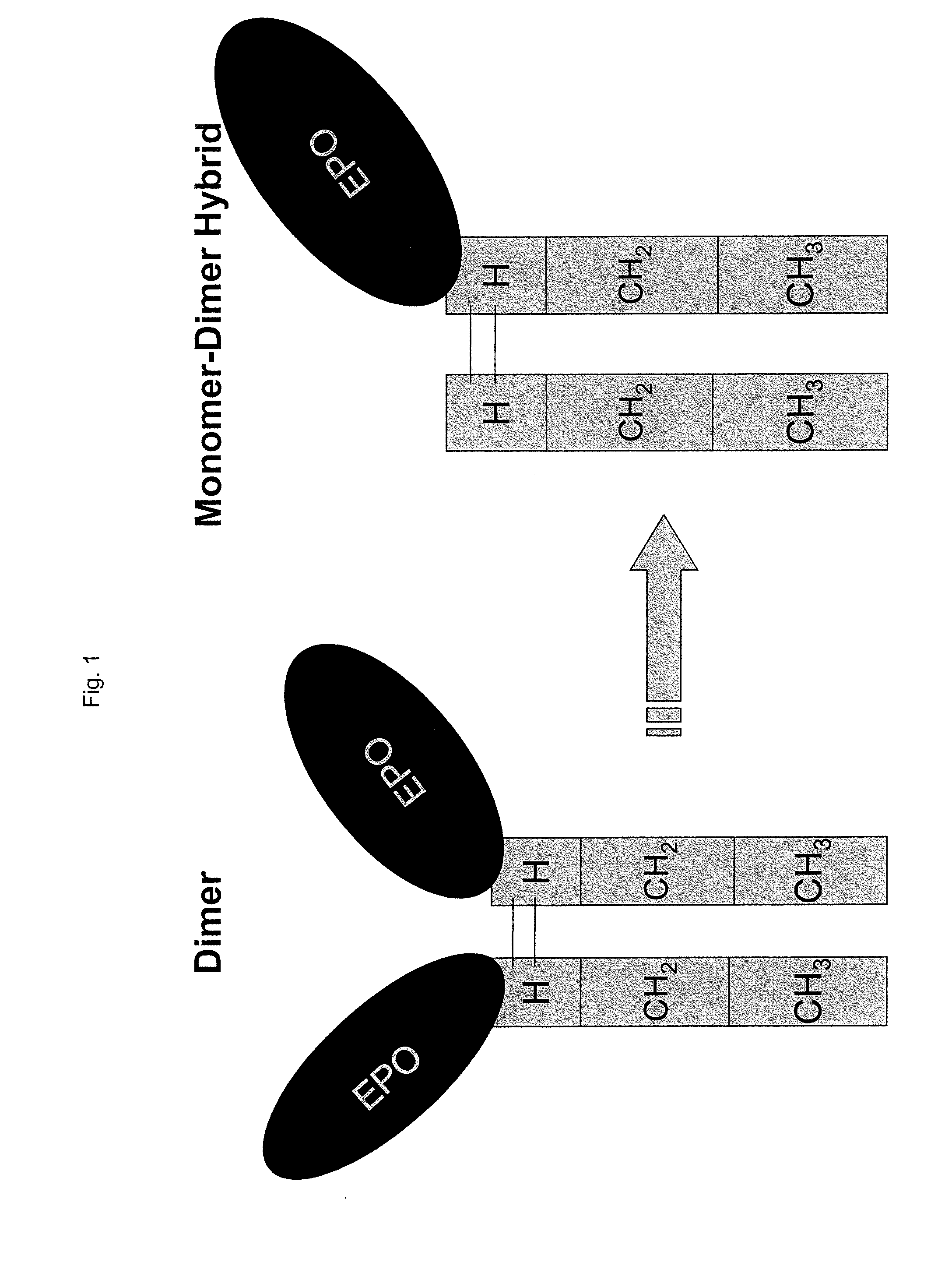
Heterodimeric proteins
ActiveUS9605084B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsBiologyImmunoglobulin class
The present invention describes novel immunoglobulin compositions that co-engage at least two antigens, e.g. a first and second antigen, or, as outlined herein, three or four antigens can be bound, in some of the scaffold formats described herein. First and second antigens of the invention are herein referred to as antigen-1 and antigen-2 respectively (or antigen-3 and antigen-4, if applicable. As outlined herein, a number of different formats can be used, with some scaffolds relying combinations of monovalent and bivalent bindings.
Owner:XENCOR INC
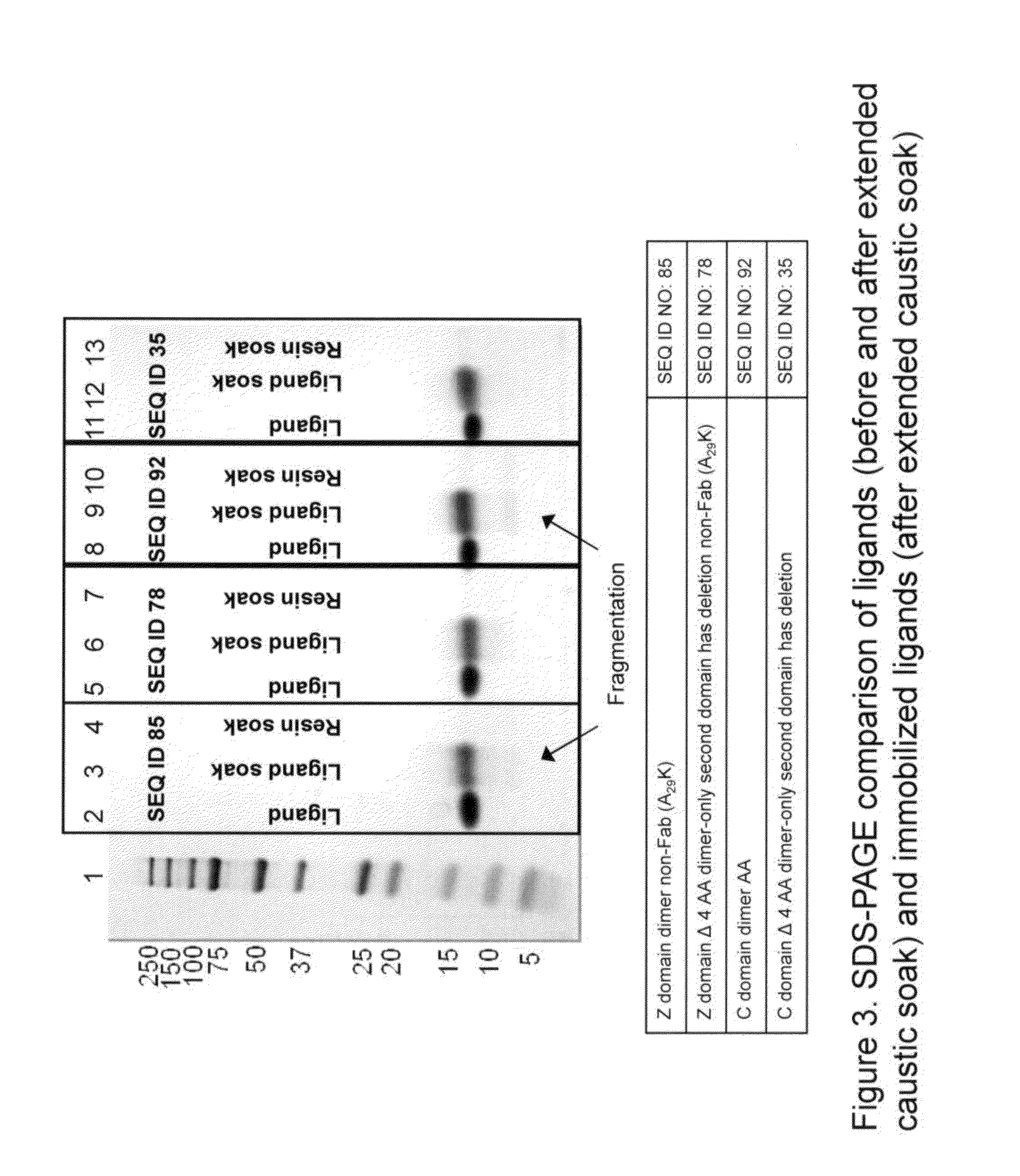
Chromatography matrices including novel staphylococcus aureus protein a based ligands
ActiveUS20130046056A1Reduce lossesLarge degree of fragmentationSolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus aureus protein A
The present invention relates to chromatography matrices including ligands based on one or more domains of immunoglobulin-binding proteins such as, Staphylococcus aureus Protein A (SpA), as well as methods of using the same.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Method for Preparing Immunoglobulin Libraries
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Immunoglobulins
The present invention relates to antigen binding proteins to human IL-23, pharmaceutical formulations containing them and to the use of such antigen binding proteins in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of inflammatory diseases such as Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
Method for mass humanization of non-human antibodies
The present invention relates to a method for producing a population of nucleic acids encoding at least one protein comprising at least one immunoglobulin variable domain having a non-human-derived CDR3 amino acid sequence embedded in essentially human framework sequences, as well as to a population of nucleic acids and a population of proteins relates thereto and uses thereof.
Owner:CHARLES RIVER LAB INC
Antigen-binding proteins specific for hla-a2-restricted wilms tumor 1 peptide
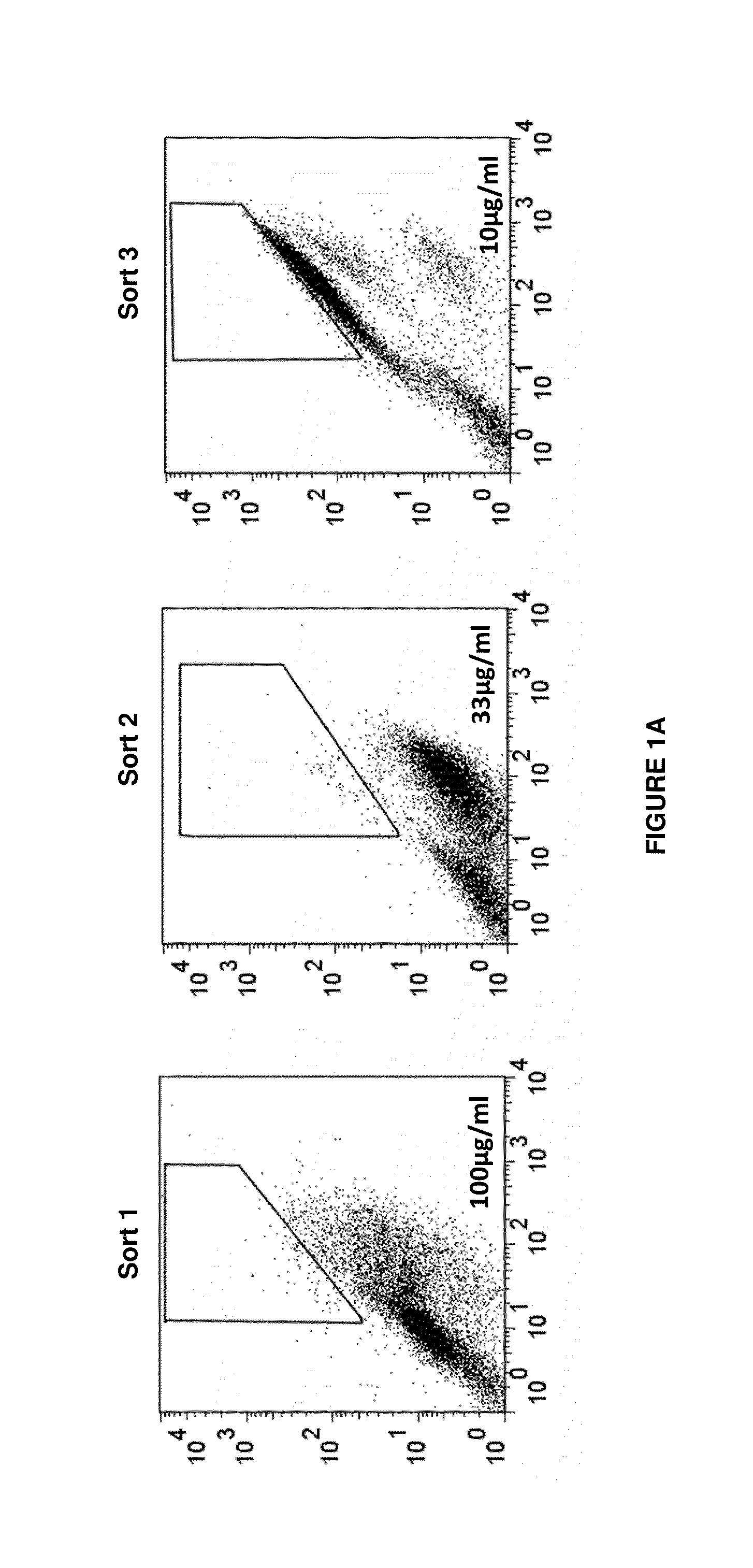
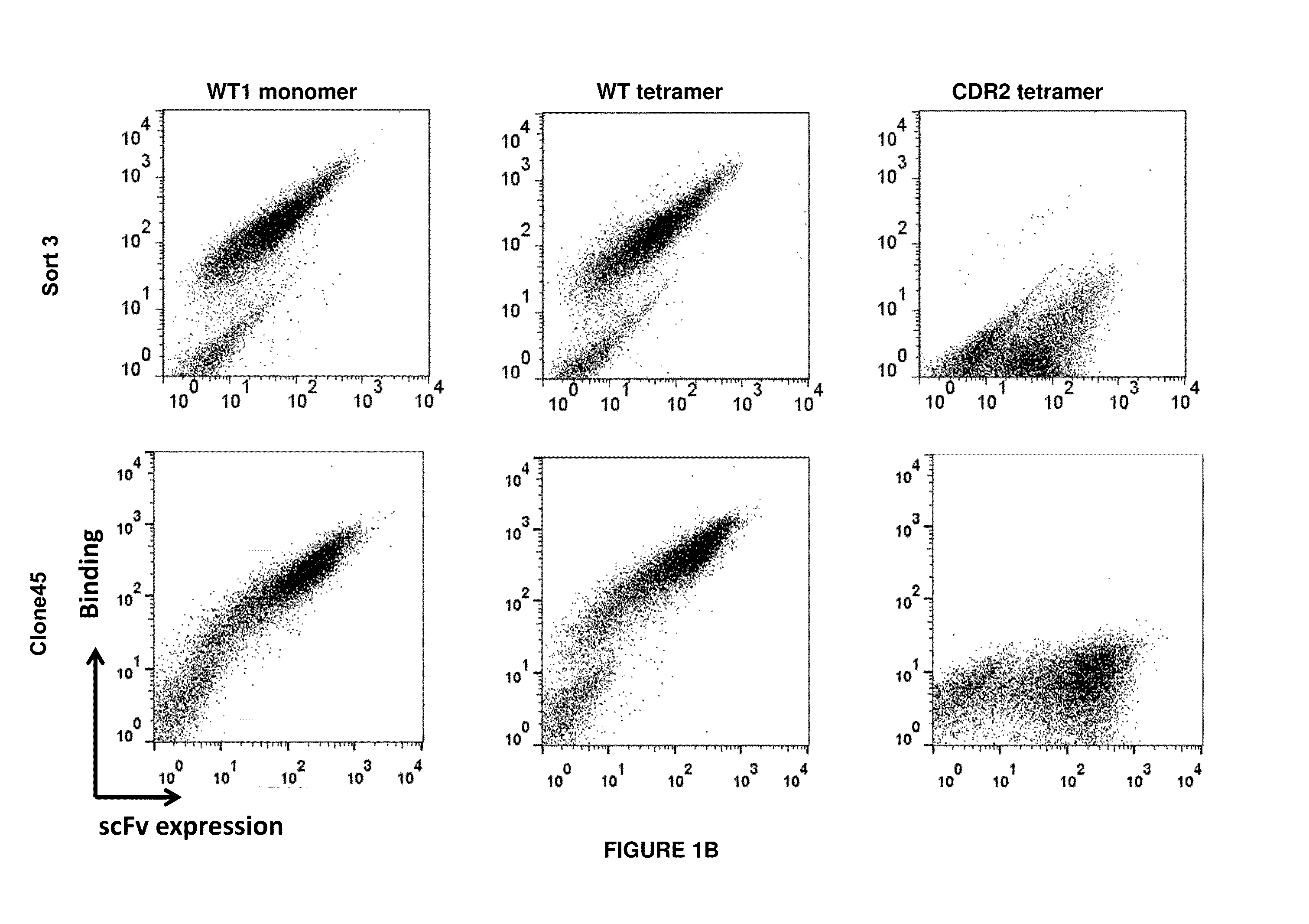
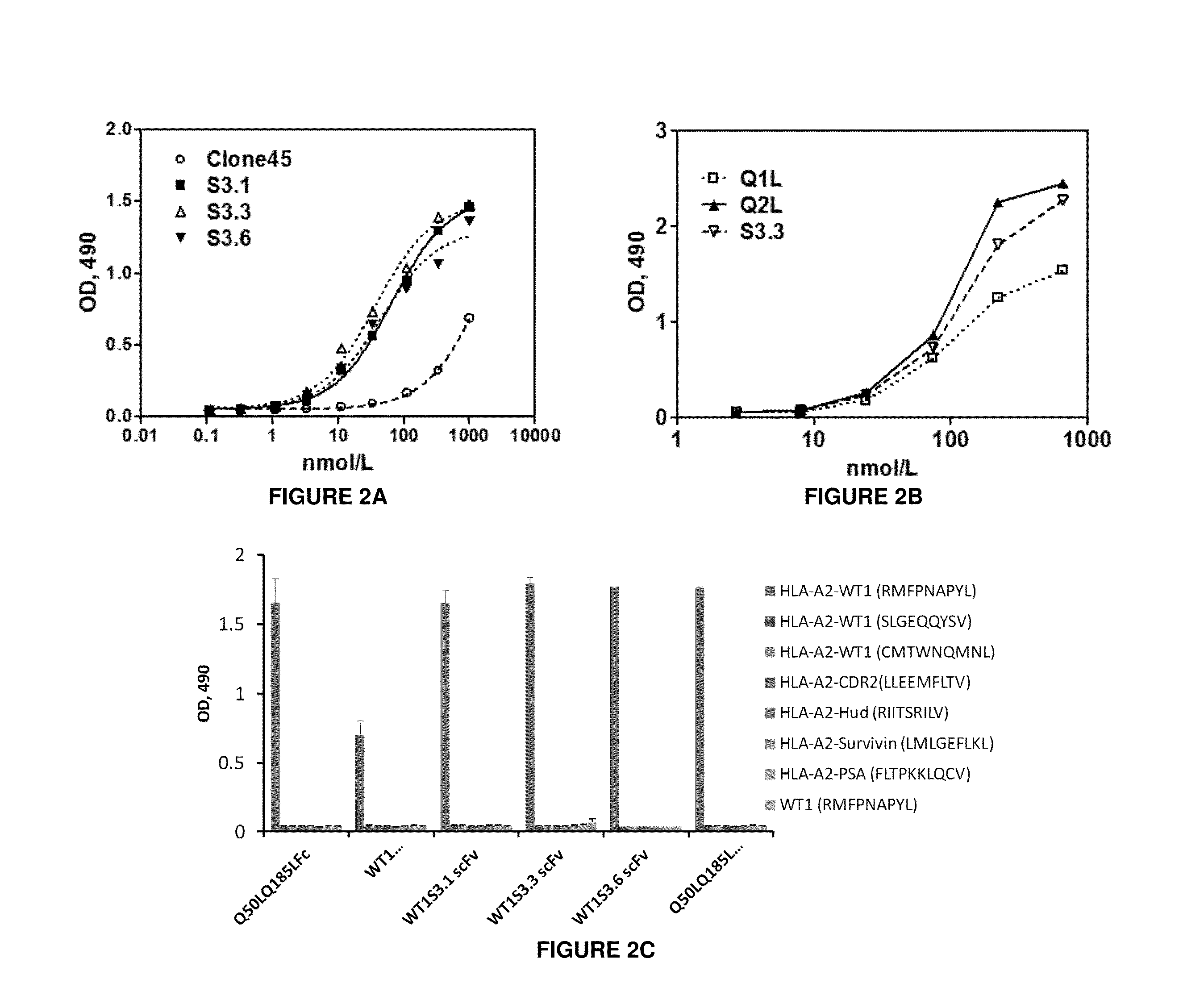
InactiveUS20160152725A1Inhibit tumor growthAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide antigenDisease
Antigen-binding proteins specific for HLA-A2-restricted Wilms tumor 1 peptide are disclosed. The antigen-binding proteins encompass antibodies in a variety of forms, including full-length antibodies, substantially intact antibodies, Fab fragments, F(ab′)2 fragments, and single chain Fv (scFv) fragments, as well as chimeric antigen receptors. Fusion proteins, such as scFv fusions with immunoglobulin or T-cell receptor domains, incorporating the antigen-binding proteins are provided. Methods of using the antigen-binding proteins in the treatment of hyperproliferative diseases such as cancer are also disclosed.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Humanized immunoglobulin reacting specifically with Fas ligand or active fragments thereof and region inducing apoptosis originating in Fas ligand
InactiveUS6777540B1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyDiagnostic agentMonoclonal antibody
Novel humanized immunoglobulins and active fragments thereof which are specifically reactive to Fas ligand are provided, and a site on Fas ligand which is important to inhibit apoptosis induced by the Fas-Fas ligand interaction against Fas-expressing cells is demonstrated. The novel humanized immunoglobulins and active fragments thereof which are specifically reactive to Fas ligand are prepared from hybridomas which produce monoclonal antibodies specifically reactive to Fas ligand, via recombinant DNA techniques. The humanized immunoglobulins can inhibit the physiological reactions between Fas ligand and Fas such as apoptosis. Further, identification of the site which is on Fas ligand and responsible for apoptosis induction allows creation of recombinant proteins or peptides which are specifically reactive to the amino acids within the site so as to inhibit apoptosis, and to find new therapeutic or diagnostic agents.
Owner:OKUMURA KO
Immunoglobulin libraries
Methods and compositions for the screening and isolation of ligand-binding polypeptides, such as antibodies. In some aspects, methods of the invention enable the isolation of intact soluble antibodies comprising a constant domain. Screening methods that employ genetic packages such as bacteria and bacteriophages enable high through-put identification of ligand binding molecules.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Antibody locker for the inactivation of protein drug
ActiveUS20160185875A1Sugar derivativesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsPeptide substrateHeavy chain
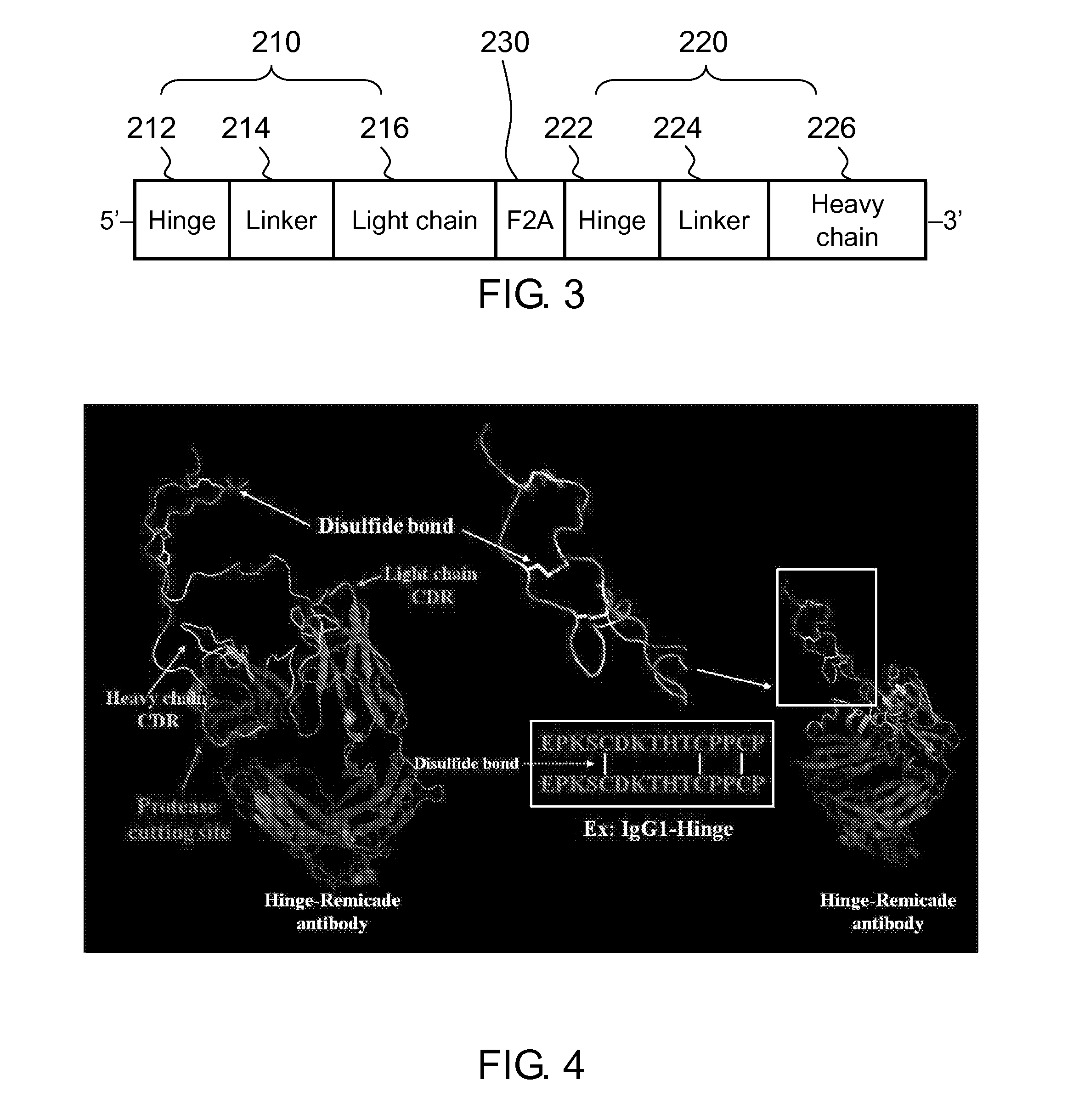
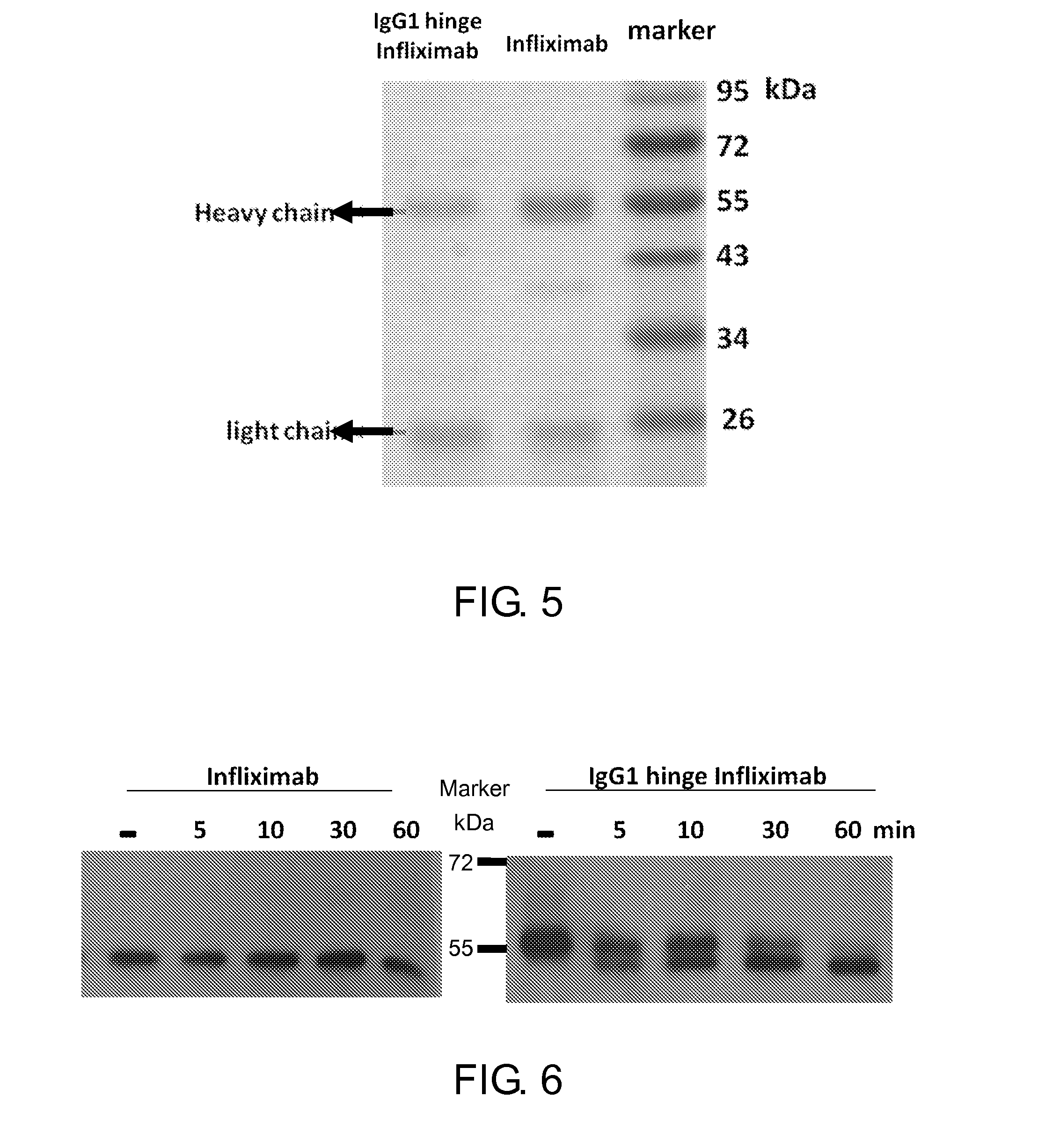
Disclosed herein is a hinge antibody capable of being selectively activated in a target cell or tissue to treat a condition therein. The hinge antibody includes a functional antibody, two inhibitory domains and four cleavable linkers. The functional antibody is capable of treating the condition in an activated state, and has two light chains and two heavy chains. Each inhibitory domain includes a hinge domain of an immunoglobulin and consists of two peptide arms. Each cleavable linker includes a peptide substrate cleavable by an enzyme specifically or highly expressed in the target cell or tissue, and connects one of the peptide arms of the inhibitory domains to the N-terminal of one of the light chains and heavy chains of the functional antibody. Also disclosed herein are methods for preparing and using this hinge antibody.
Owner:DCB USA +1
Nested primer sets for amplifying mouse immunoglobulin variable gene segments
ActiveUS8143007B2Minimal cross-reactivityLow degeneracySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellImmunoglobulin Gene Rearrangement
The present invention provides oligonucleotides for detection of rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes for identifying clonality of cells, cancer cells, hypermutation in immunoglobulin gene, antibody isotype producing cell and / or assaying B cell repertoire in a sample. The oligonucleotides disclosed in the present invention are very specific to the immunoglobulin genes.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTUTUTE OF IMMUNOLOGY
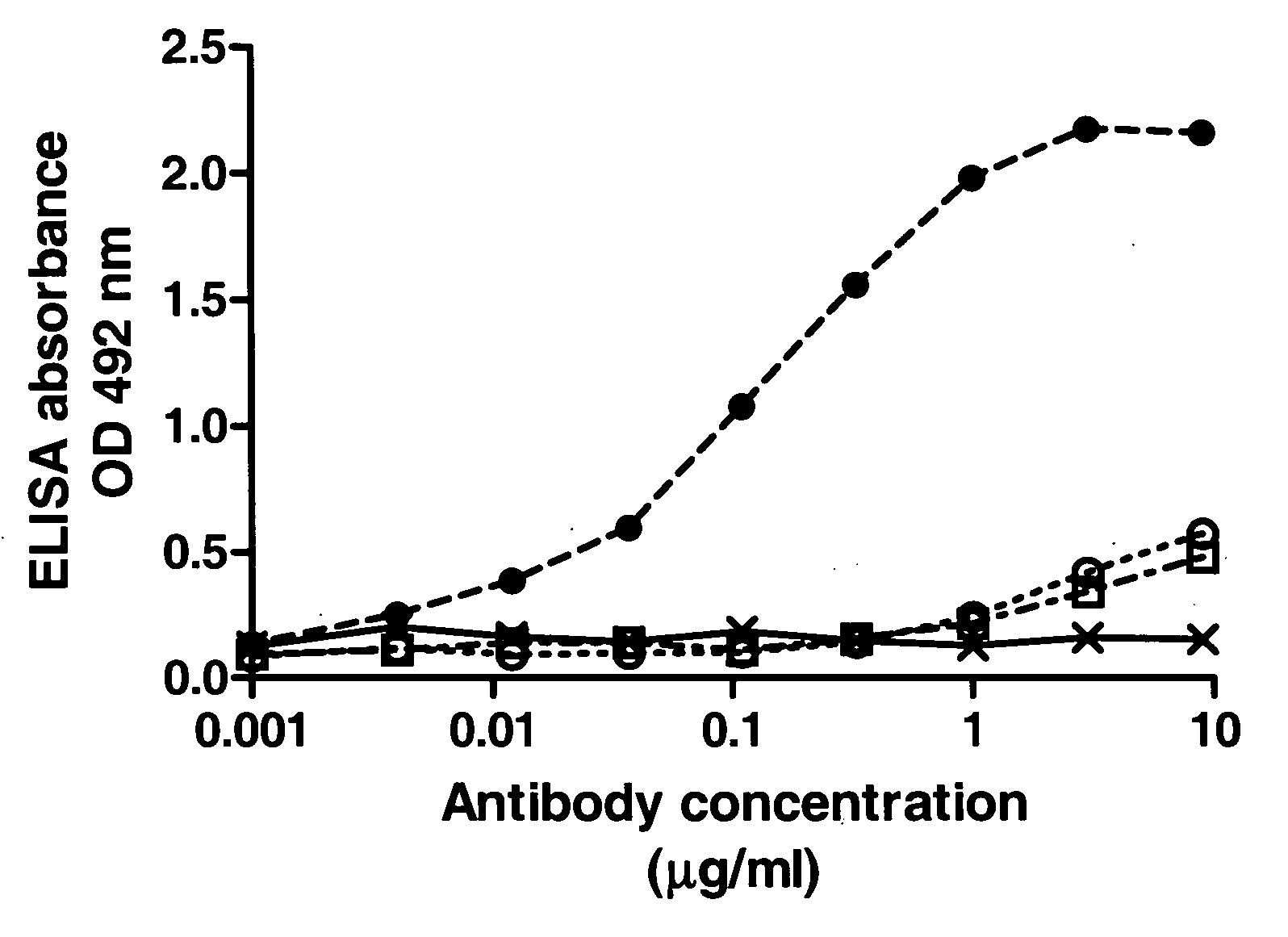
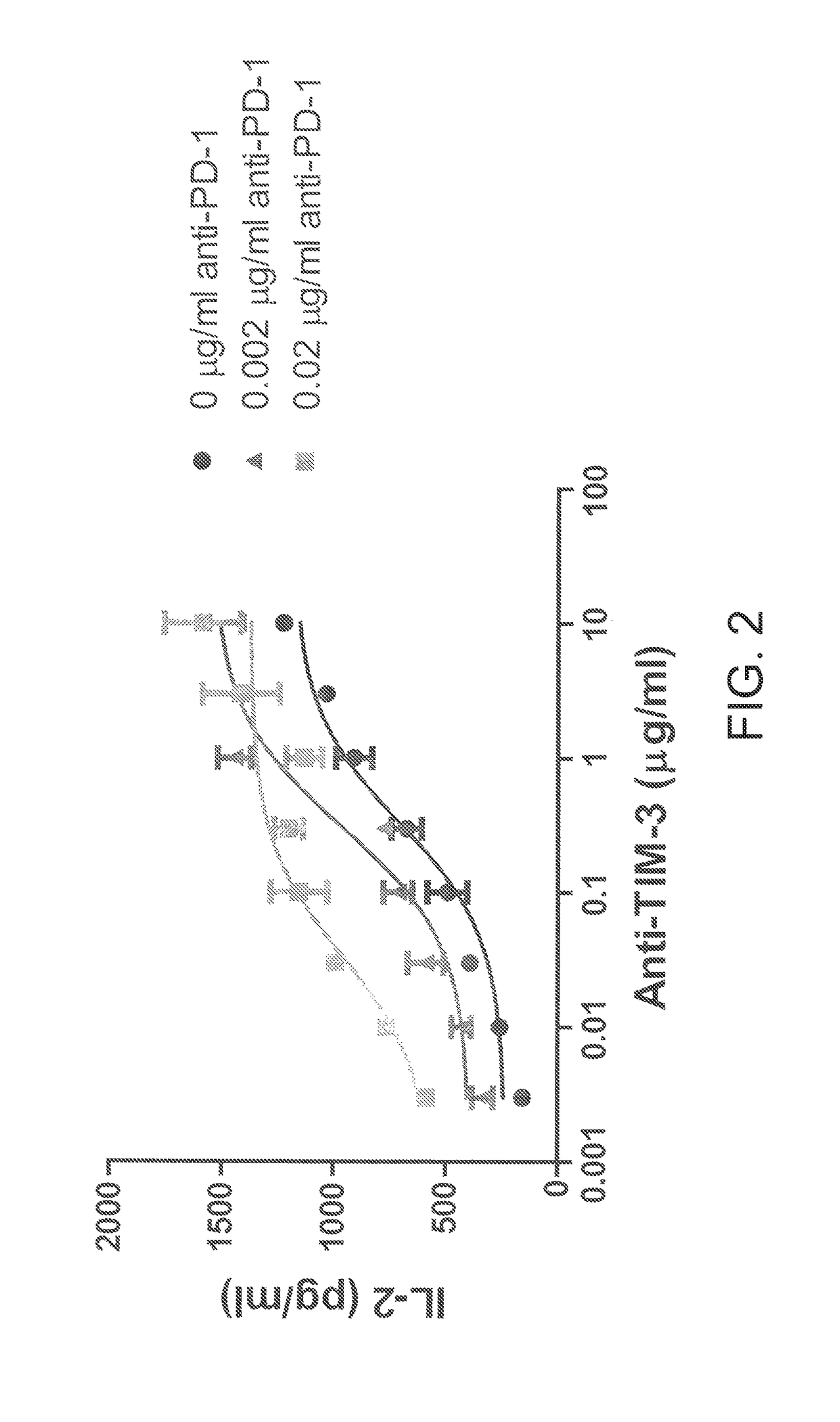
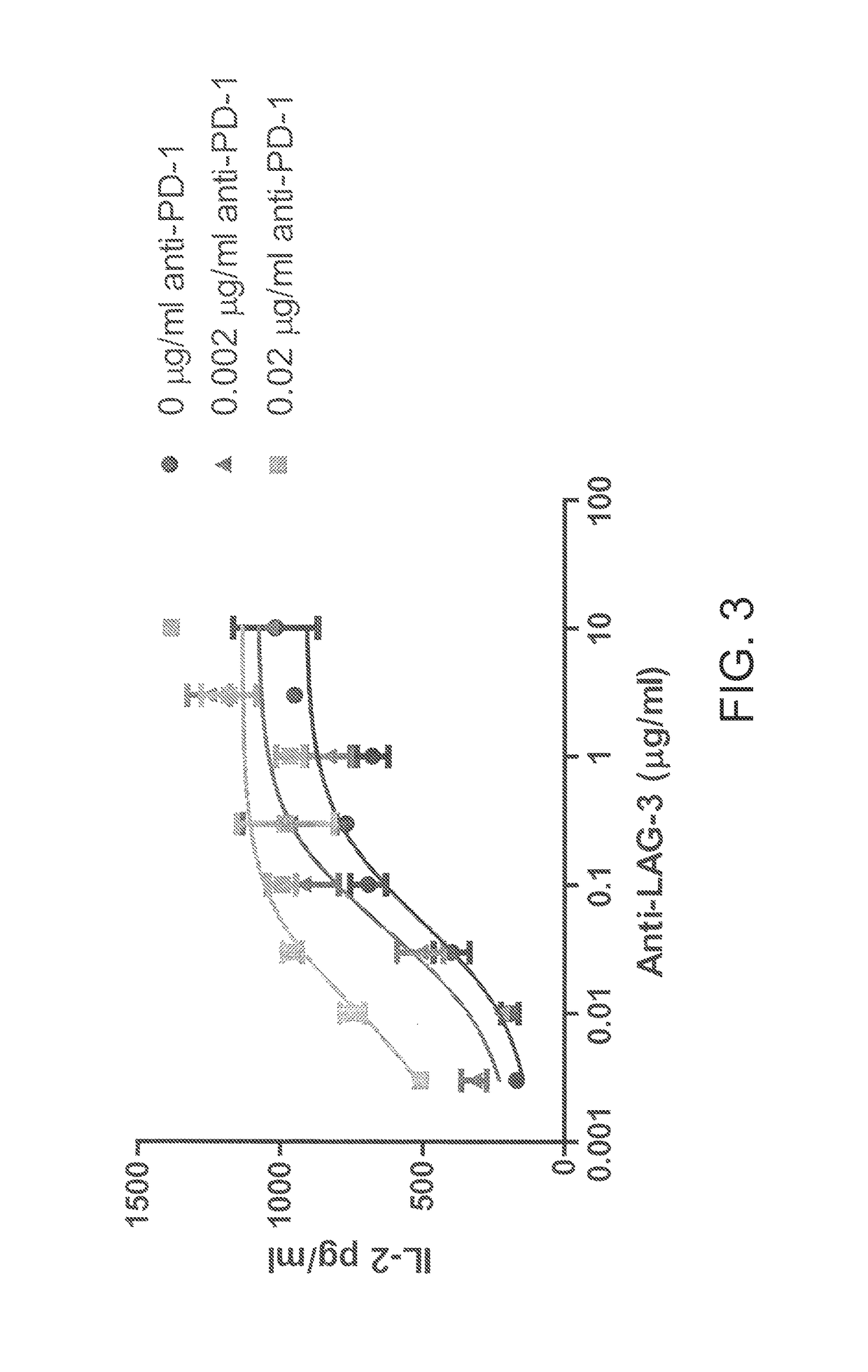
Antibodies directed against programmed death-1 (PD-1)
The invention relates to an isolated immunoglobulin heavy chain polypeptide and an isolated immunoglobulin light chain polypeptide that bind to a programmed death-1 (PD-1) protein. The invention provides a PD-1-binding agent that comprises the aforementioned immunoglobulin heavy chain polypeptide and immunoglobulin light chain polypeptide. The invention also provides related vectors, compositions, and methods of using the PD-1-binding agent to treat a cancer or an infectious disease.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
Protein having affinity for immunoglobulin, and immunoglobulin-binding affinity ligand
ActiveUS9403883B2Good chemical stabilityImprove identityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityLower affinity
Owner:KANEKA CORP
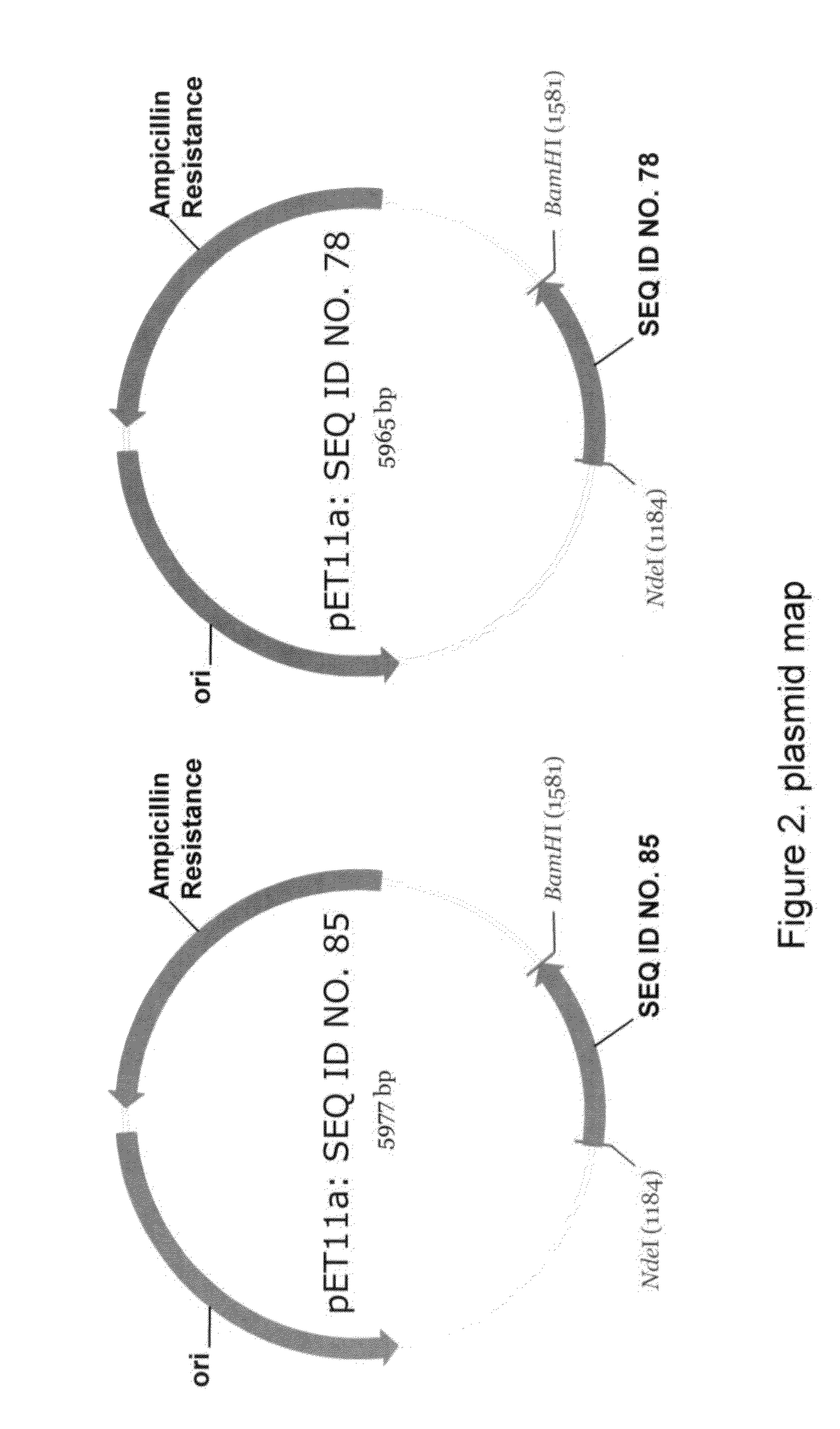
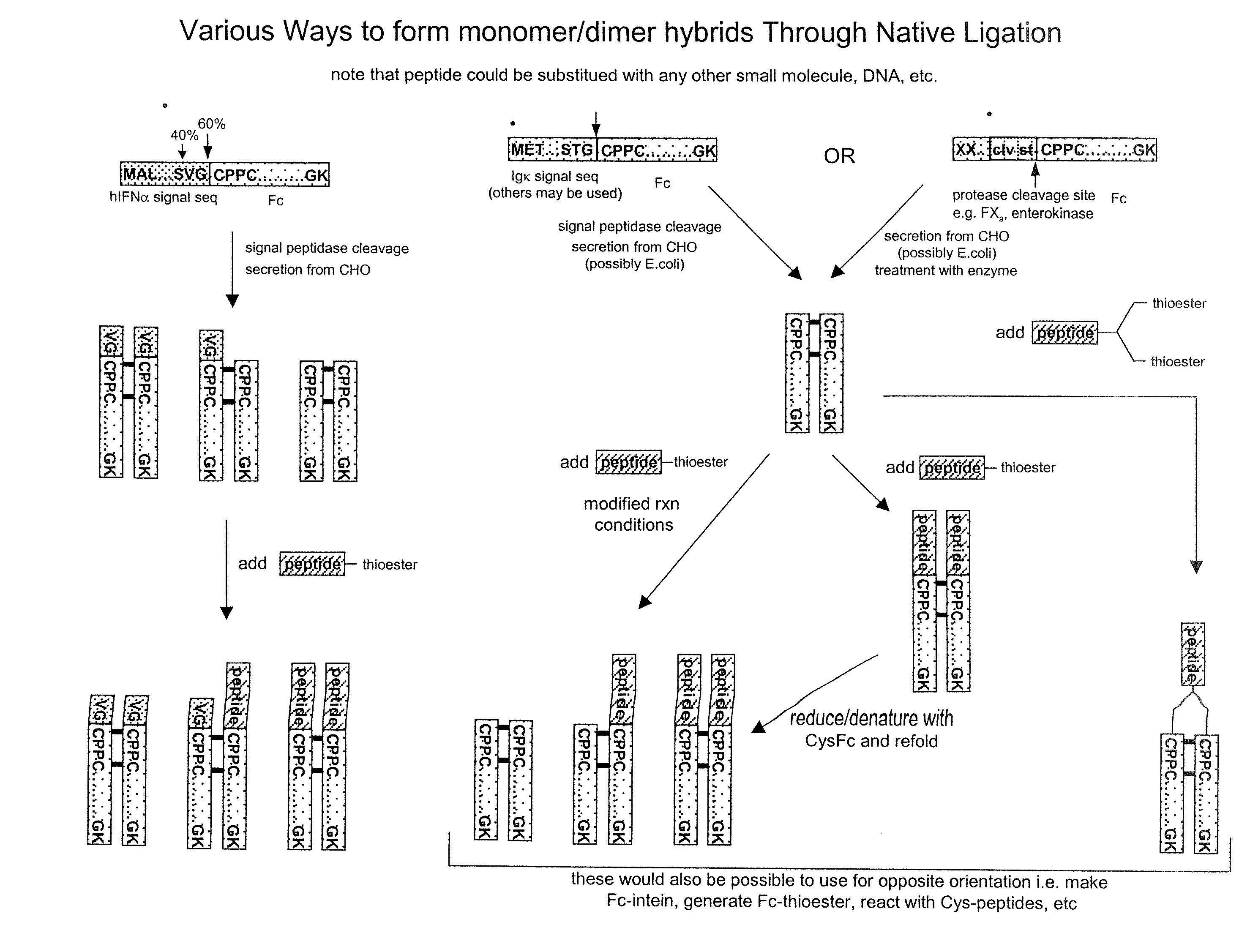
Methods for Chemically Synthesizing Immunoglobulin Chimeric Proteins
ActiveUS20080249288A1Longer in vivo halflifeEasy to purifyHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisImmunoglobulin Constant Region
The invention provides methods of chemically synthesizing chimeric proteins comprising at least a portion of an immunoglobulin constant region and a biologically active molecule.
Owner:BIOVERATIV THERAPEUTICS INC
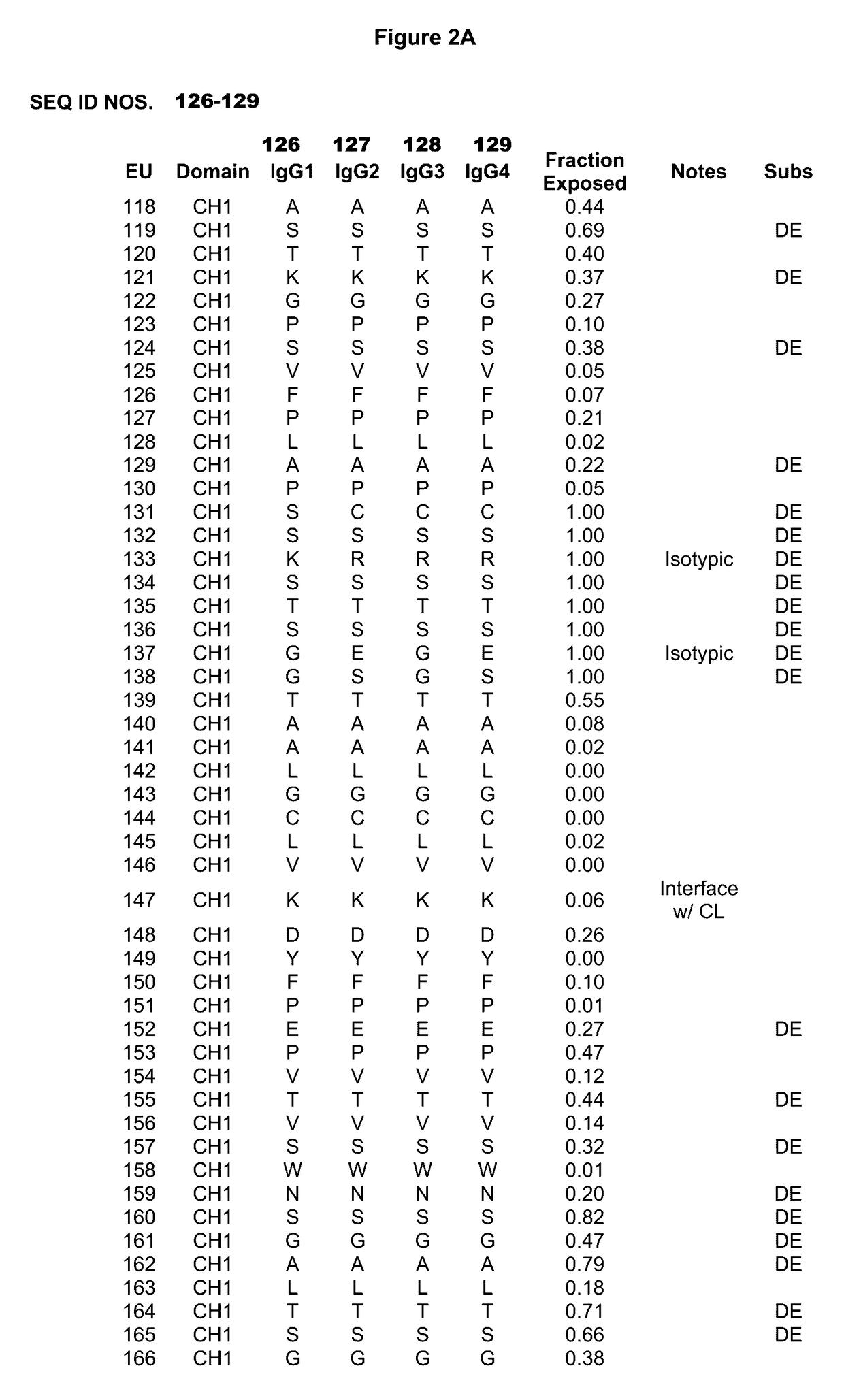
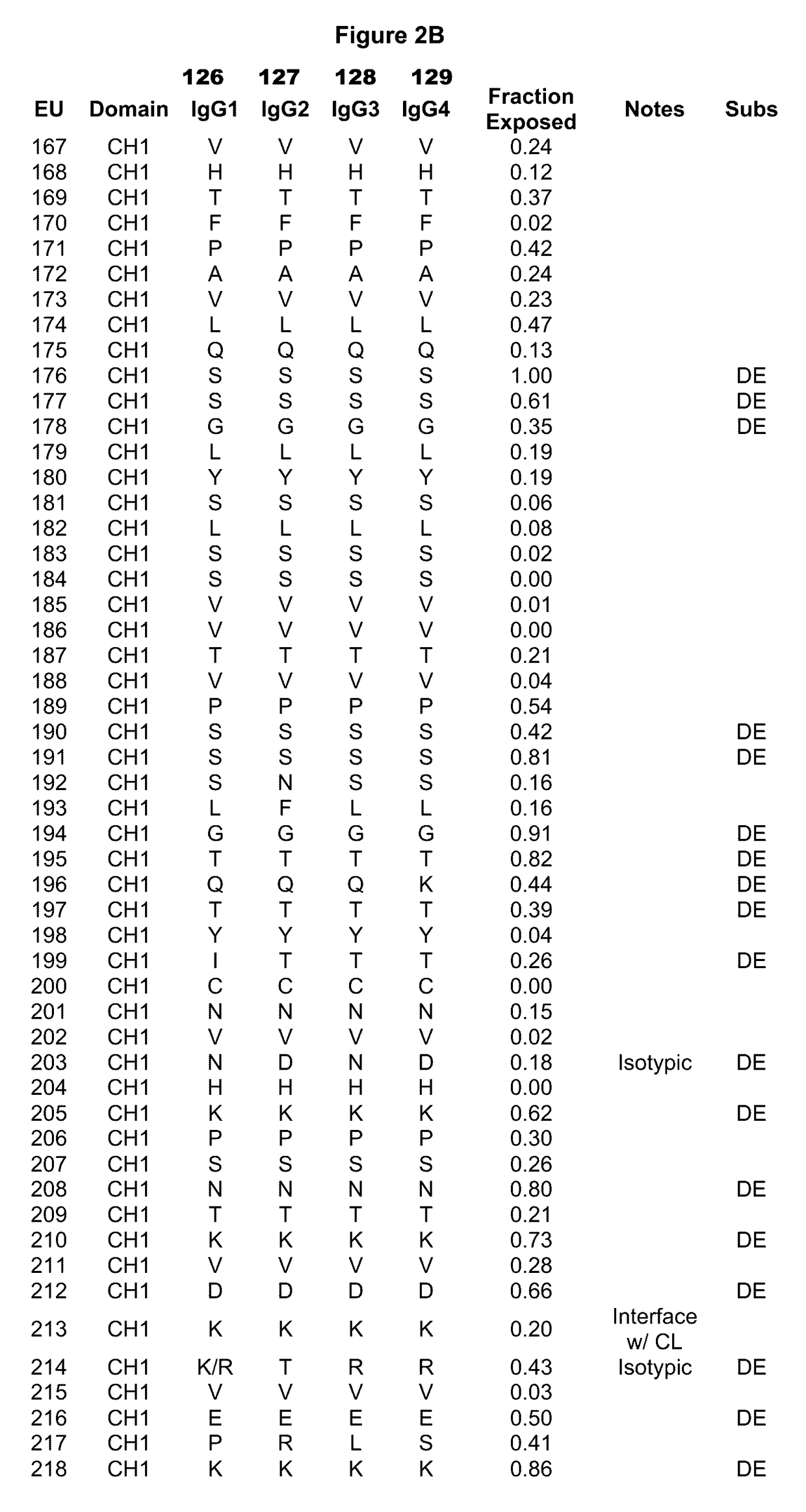
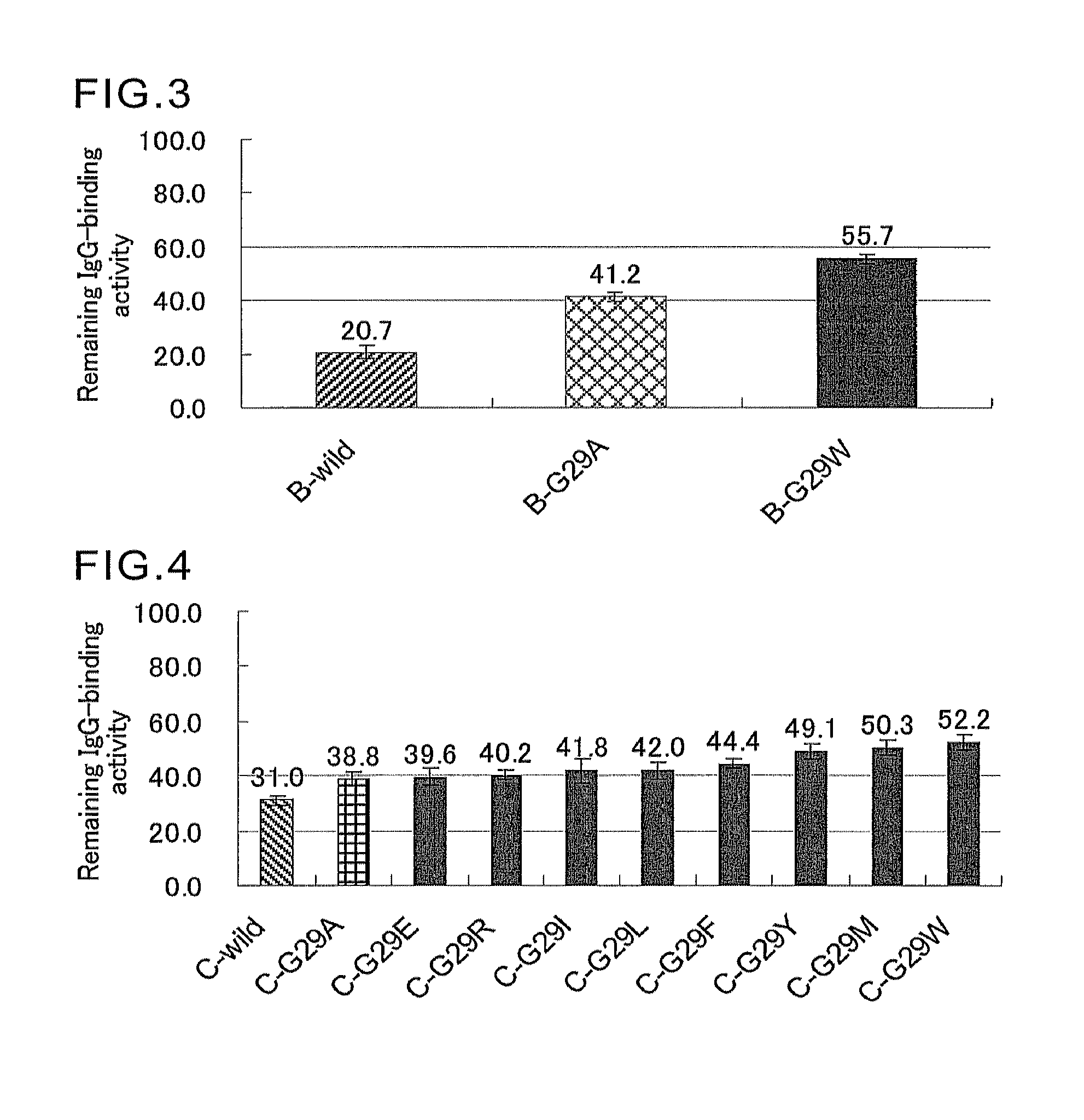
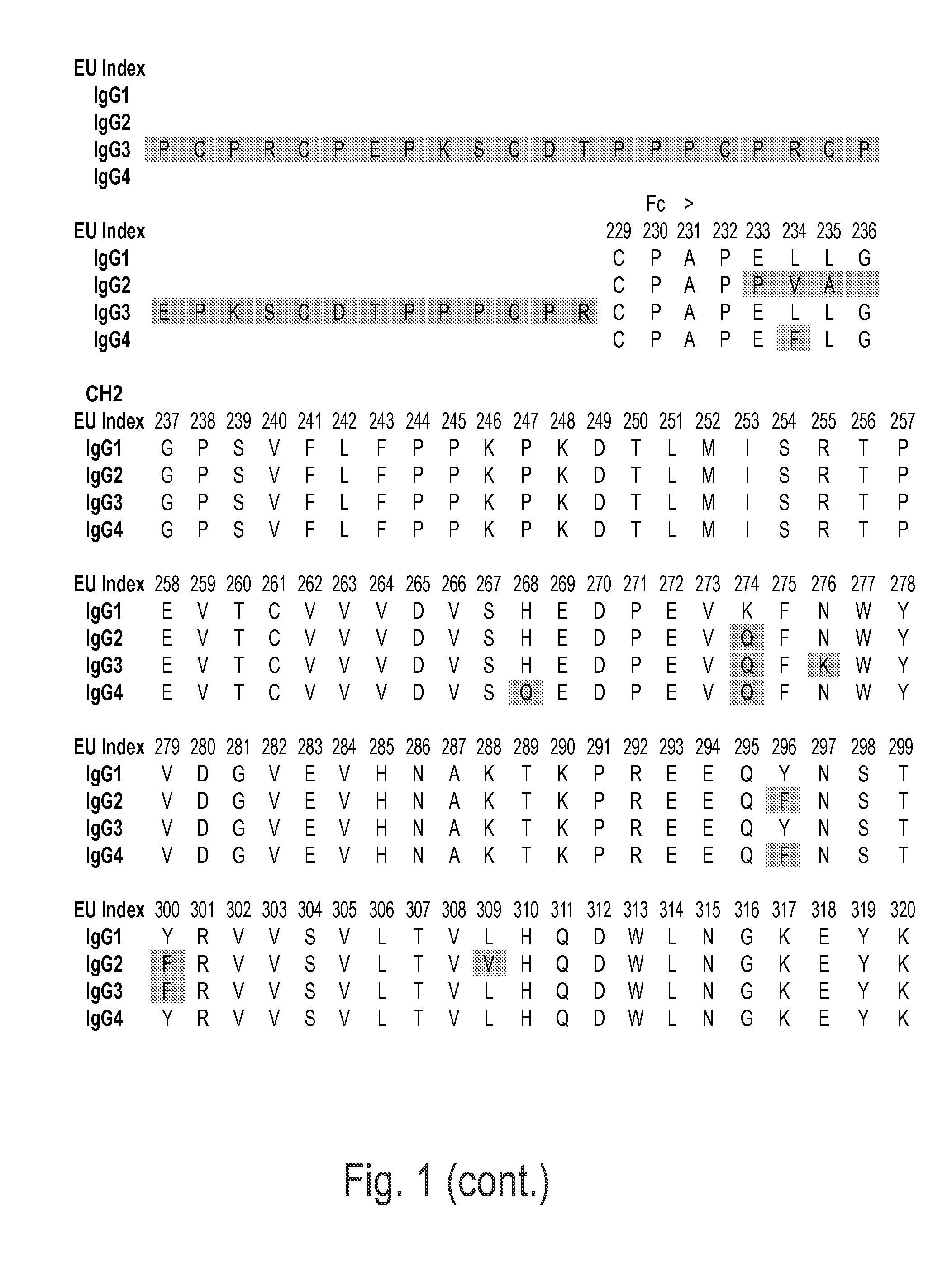
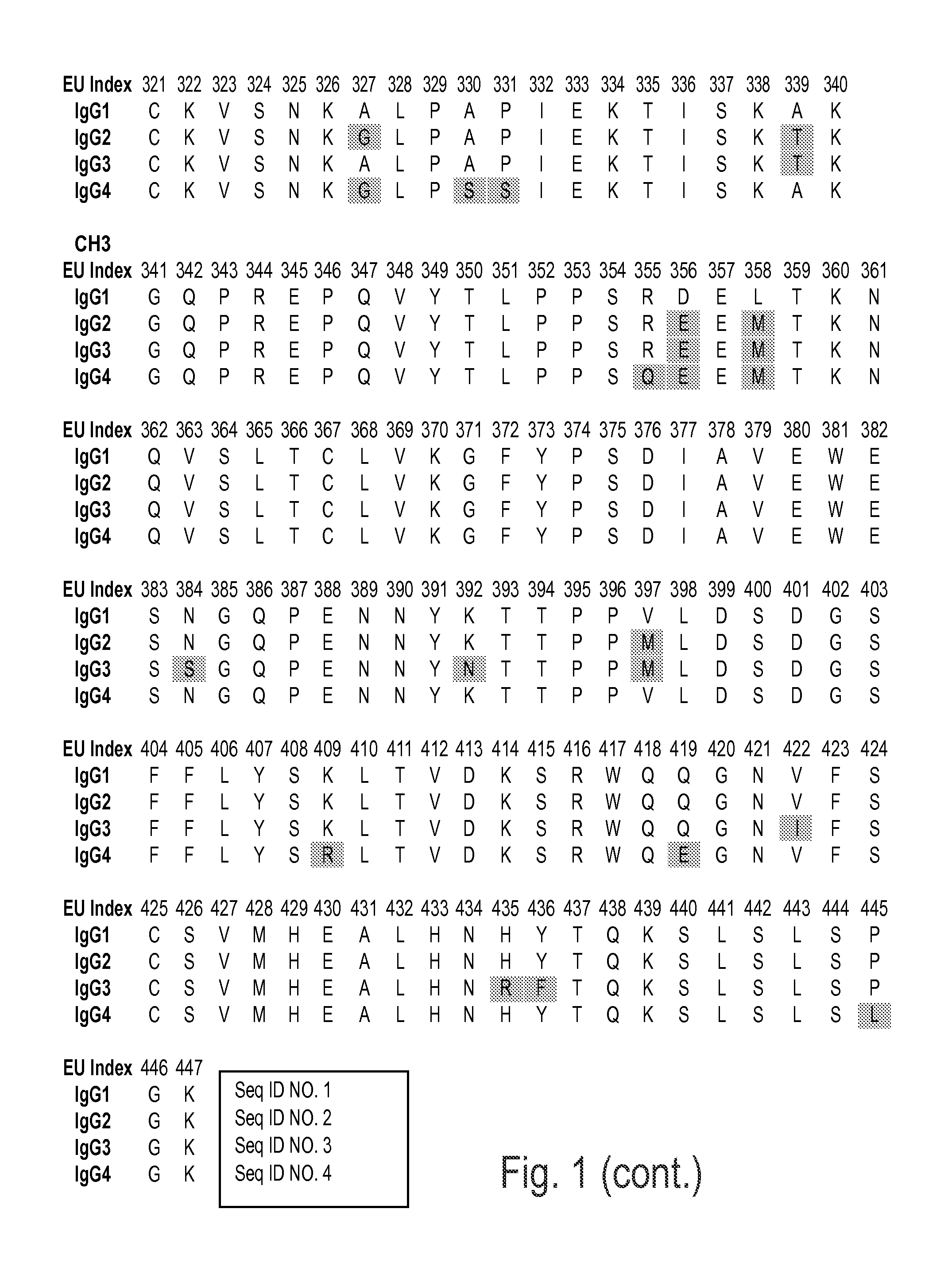
Immunoglobulins insertions, deletions, and substitutions
ActiveUS8883147B2Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulin classChemistry
An Fc variant of a parent Fc polypeptide, wherein said Fc variant exhibits altered binding to one or more FcγRs, wherein said Fc variant comprises at least one amino acid insertion in the Fc region of said parent Fc polypeptide.
Owner:XENCOR INC
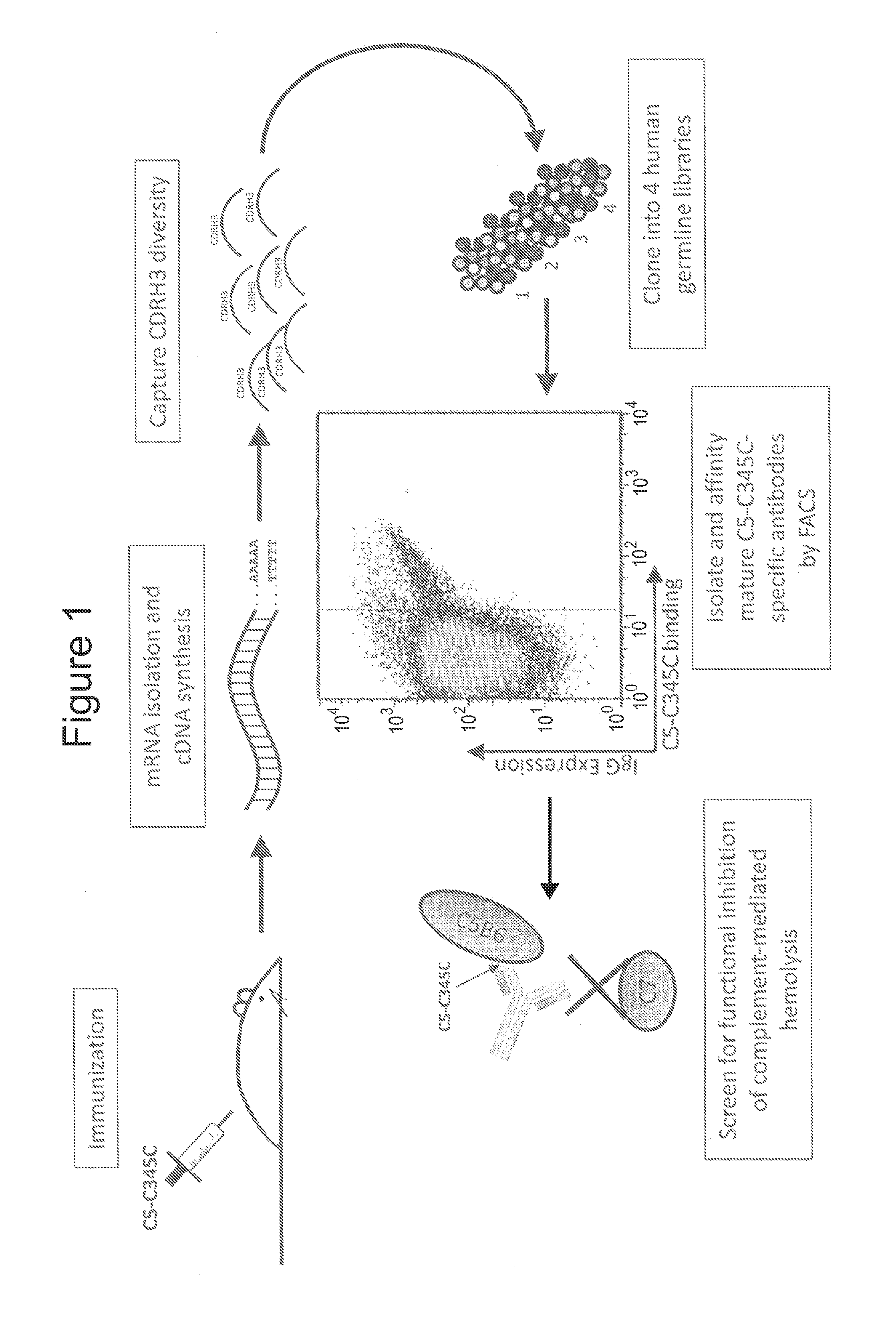
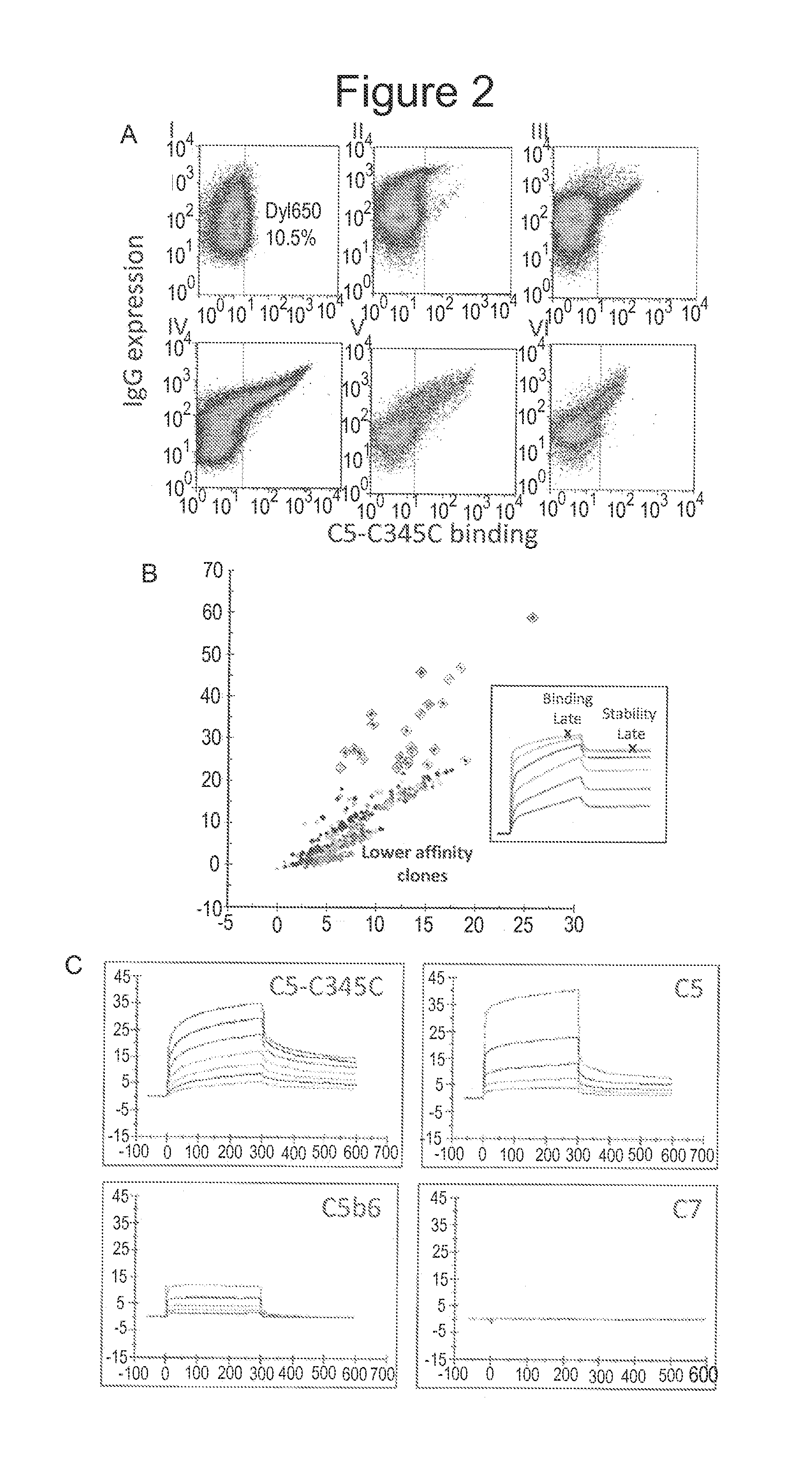
Humanized antibodies directed against complement protein C5
ActiveUS9133269B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsImmunoglobulin heavy chainDisease
The invention relates to an isolated immunoglobulin heavy chain polypeptide and an isolated immunoglobulin light chain polypeptide that binds to complement protein C5. The invention provides a C5-binding agent that comprises the aforementioned immunoglobulin heavy chain polypeptide and immunoglobulin light chain polypeptide. The invention provides an isolated complement protein C5 epitope. The invention also provides related vectors, compositions, and methods of using the C5-binding agent to treat an C5-mediated disease.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
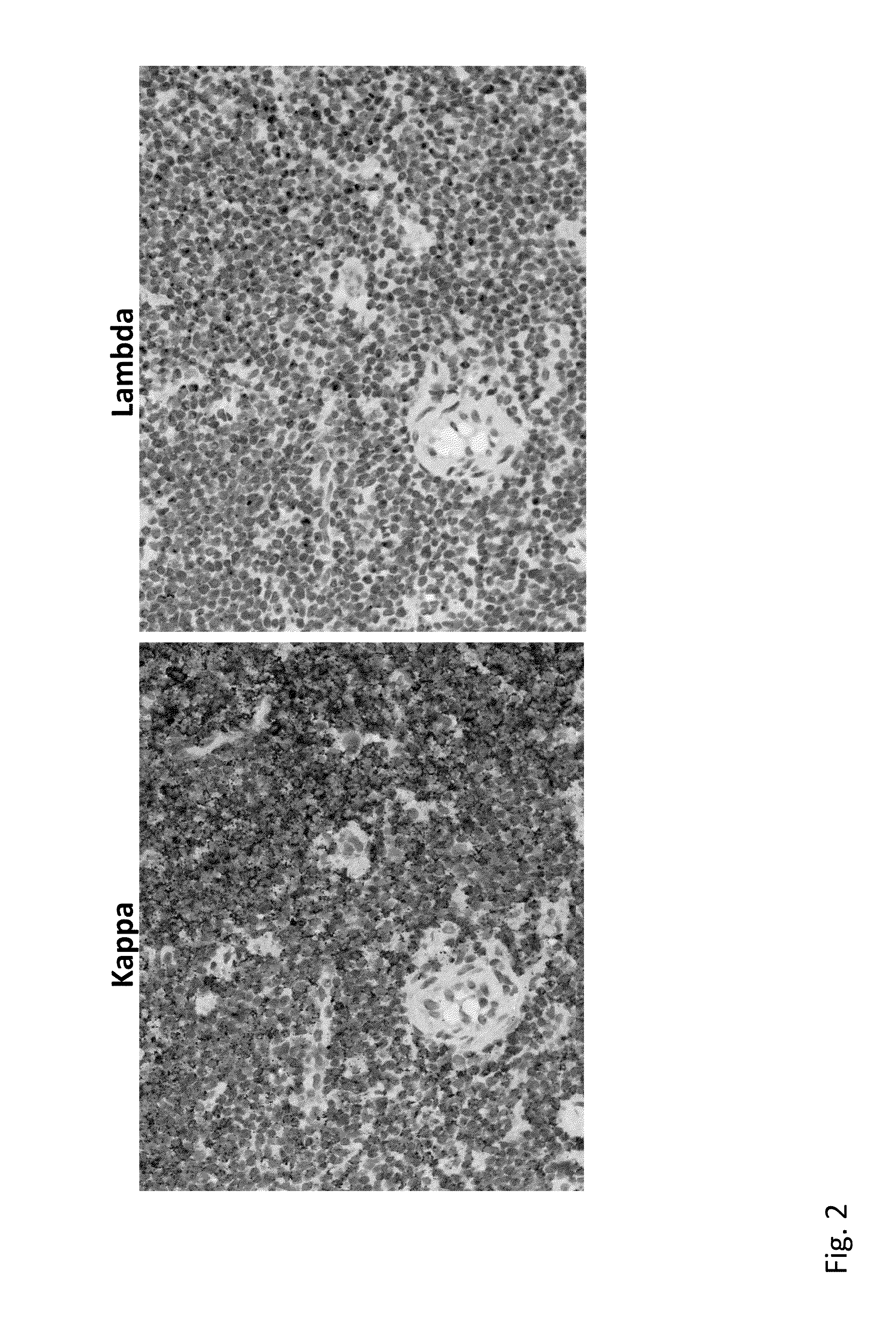
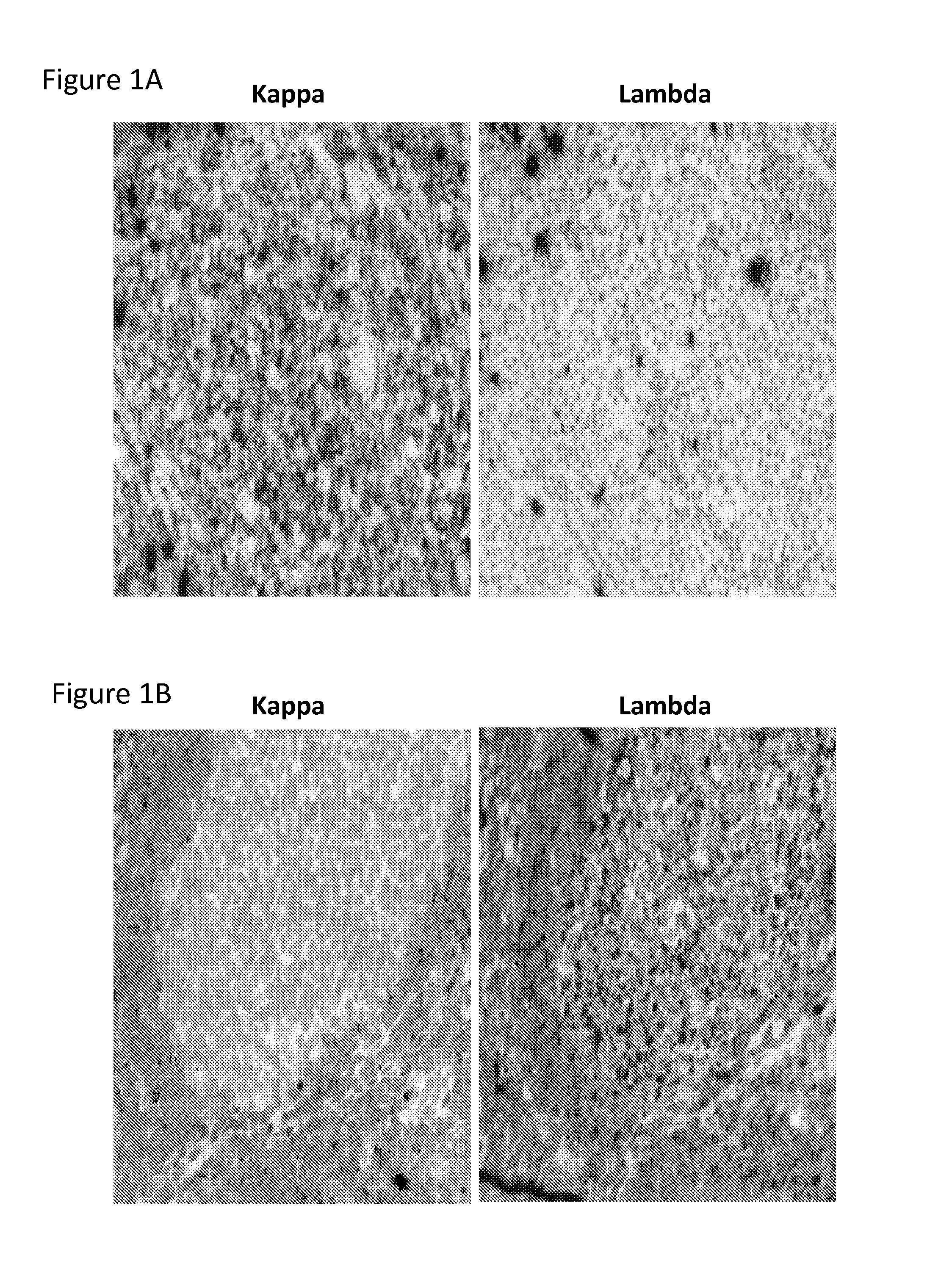
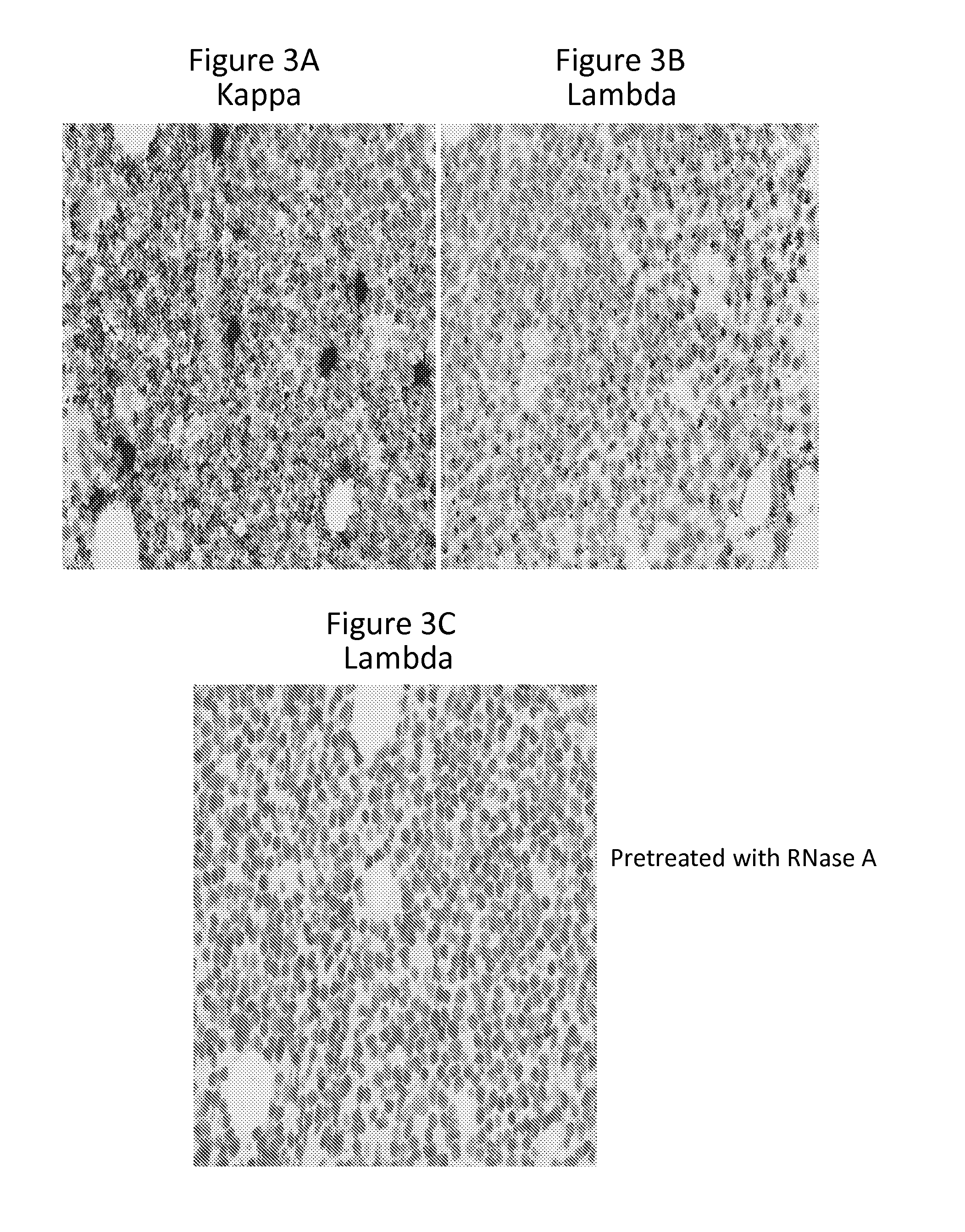
Detection of immunoglobulin light chain restriction by RNA in situ hybridization
InactiveUS20140178869A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin kappa-ChainsIn situ hybridisation
The invention provides a method for detecting immunoglobulin light chain restriction and clonality in B cells by obtaining a sample of B cells from a subject; conducting a duplex in situ hybridization assay on the sample using (i) at least one probe set which is designed to specifically hybridize to immunoglobulin kappa chain constant region (IGKCR) RNA; and (ii) at least one probe set which is designed to specifically hybridize to immunoglobulin lambda chain constant region (IGLCR) RNA; detecting signal associated with hybridized IGKCR probe and signal associated with hybridized IGLCR probe in a population of B cells in the sample; and determining a pattern of signal associated with hybridized IGKCR probe and hybridized IGLCR probe within individual cells in the B cell population, wherein the pattern of signal within individual cells indicates the presence or absence of light chain restriction and clonality of the B cells.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
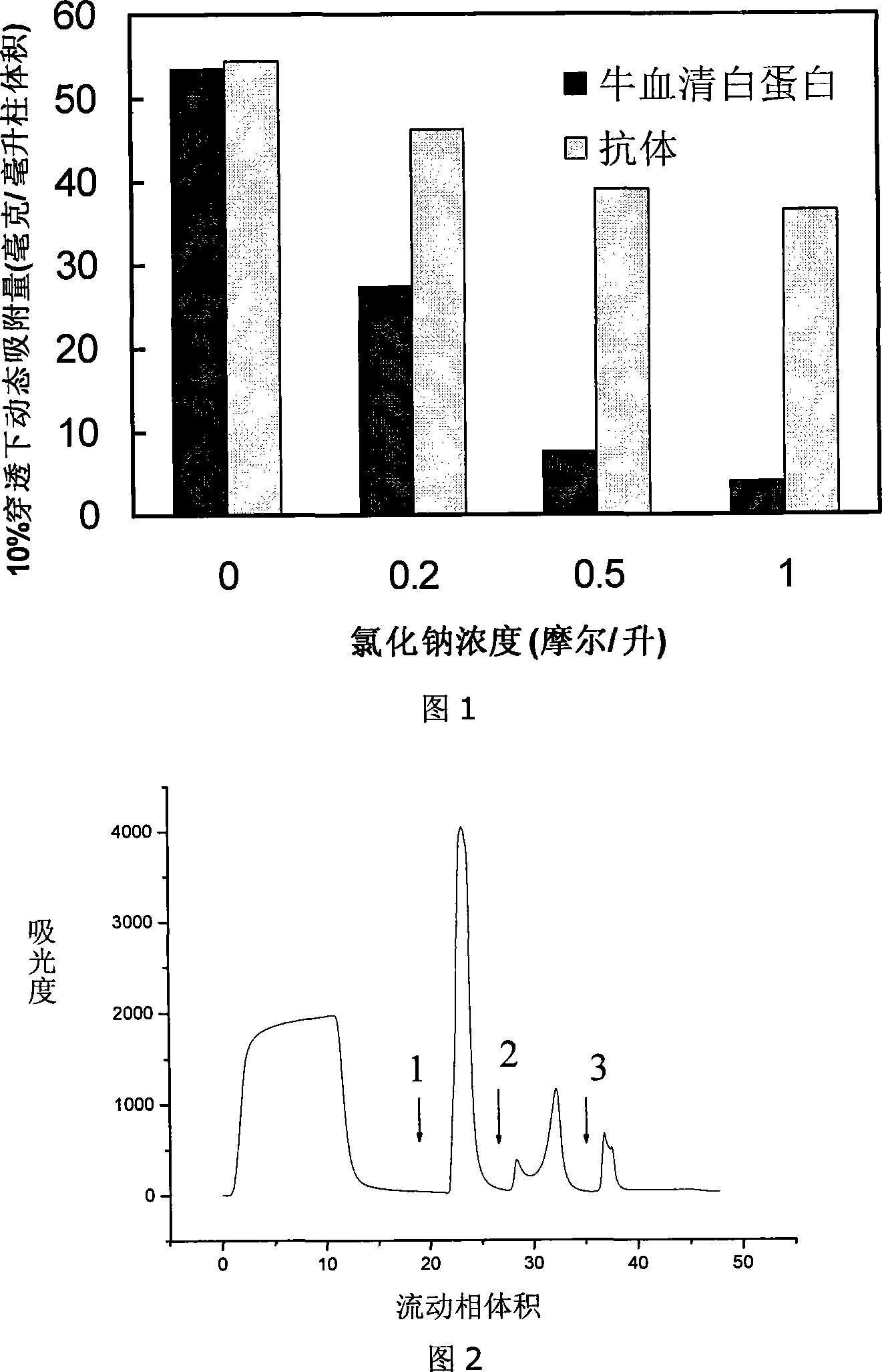
Chromatogram medium for immunoglobulin class protein separation purification and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101185881AImprove adsorption capacityHigh purityOther chemical processesPeptide preparation methodsCell culture supernatantChromatography column
The invention relates to a chromatography which is used for isolating and purifying immunoglobulin protein and a preparation method and belongs to the preparation technology of isolating and purifying a chromatography medium of the immunoglobulin. The chromatography medium refers to the end of a space arm that is coupled with a double-loop compound molecular which has an imidazol group and a benzene ring as a chromatography medium matrix. The preparation method uses an allylic chromatography medium and a bromide alchoholization reaction of N-bromosuccinimide to get an activated chromatography medium which reacts with the amino of the double-loop compound to complete the coupling of the matrix in dimethyl sulfoxide solution. The chromatography medium has higher dynamic adsorption capacity to the antibody within the ionic strength scope from 0.02 mol / L to 2.0 mol / L and is directly applied to the recycling of the antibody in the solid to liquid; at he same time, the medium has more moderate elution condition and can purify the antibody from serum, ascites, cell culture supernatant and other solid to liquid having the antibody. The chromatography medium has the wide application prospect in the process of antibody preparation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Monoclonal antibody of immunoglobulin of anti lymphocyst vitos of Pacific fluke, and preparation method
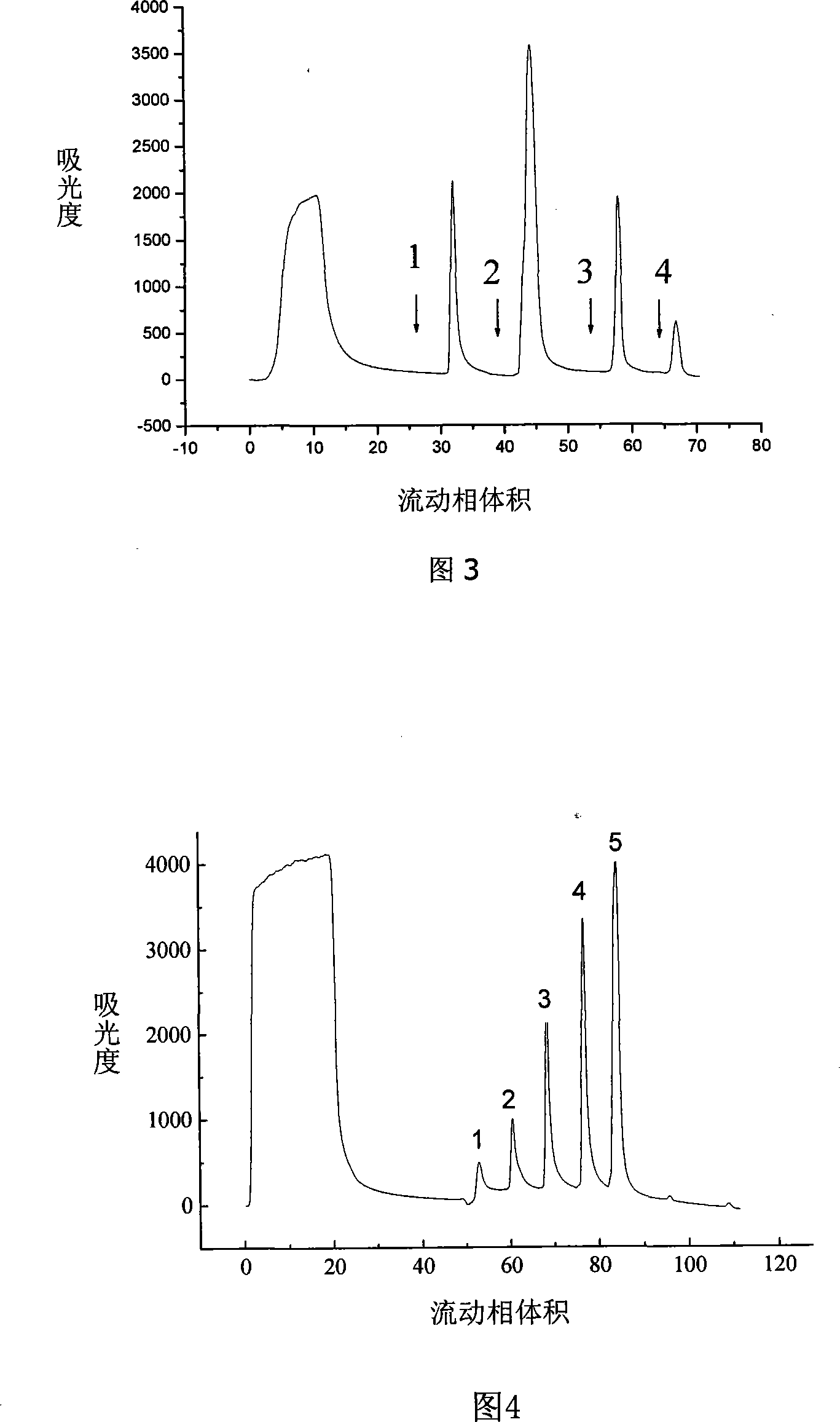
ActiveCN101003572AInnovative designAchieve purificationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingBALB/cCell engineering
This invention discloses monoclonal antibody against anti-LCDV immunoglobulin of Paralichthys olivaceus, which is excreted by hybridoma JF-lgM-H (CCTCC-C200631). The method comprises: immunizing Paralichthys olivaceus with LCDV inactivated by formalin to prepare antiserum, purifying Paralichthys olivaceus immunoglobulin, immunizing Balb / c mice as antigen, preparing hybridoma cells by cell engineering method, and screening the monoclonal antibody by immunoassay. Indirect ELISA and indirect immunofluorescent antibody assay show that this monoclonal antibody is located on the heavy chain (7-80 kDa) of the anti-LCDV immunoglobulin. The monoclonal antibody can be used for preparing reagents for detecting LCDV infection in early stage, and evaluating the immune effects of LCDV vaccine inactivated by formalin.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
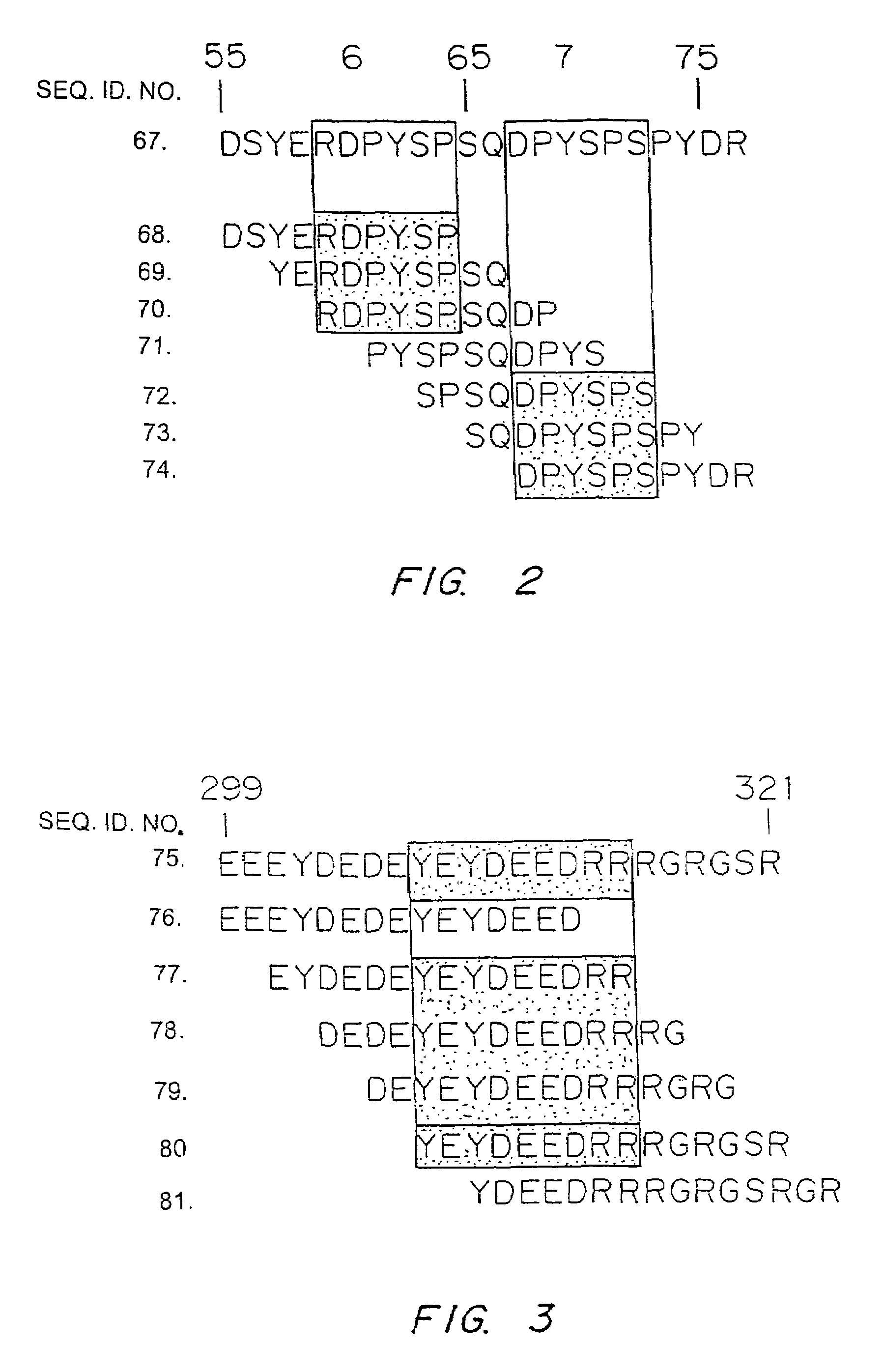
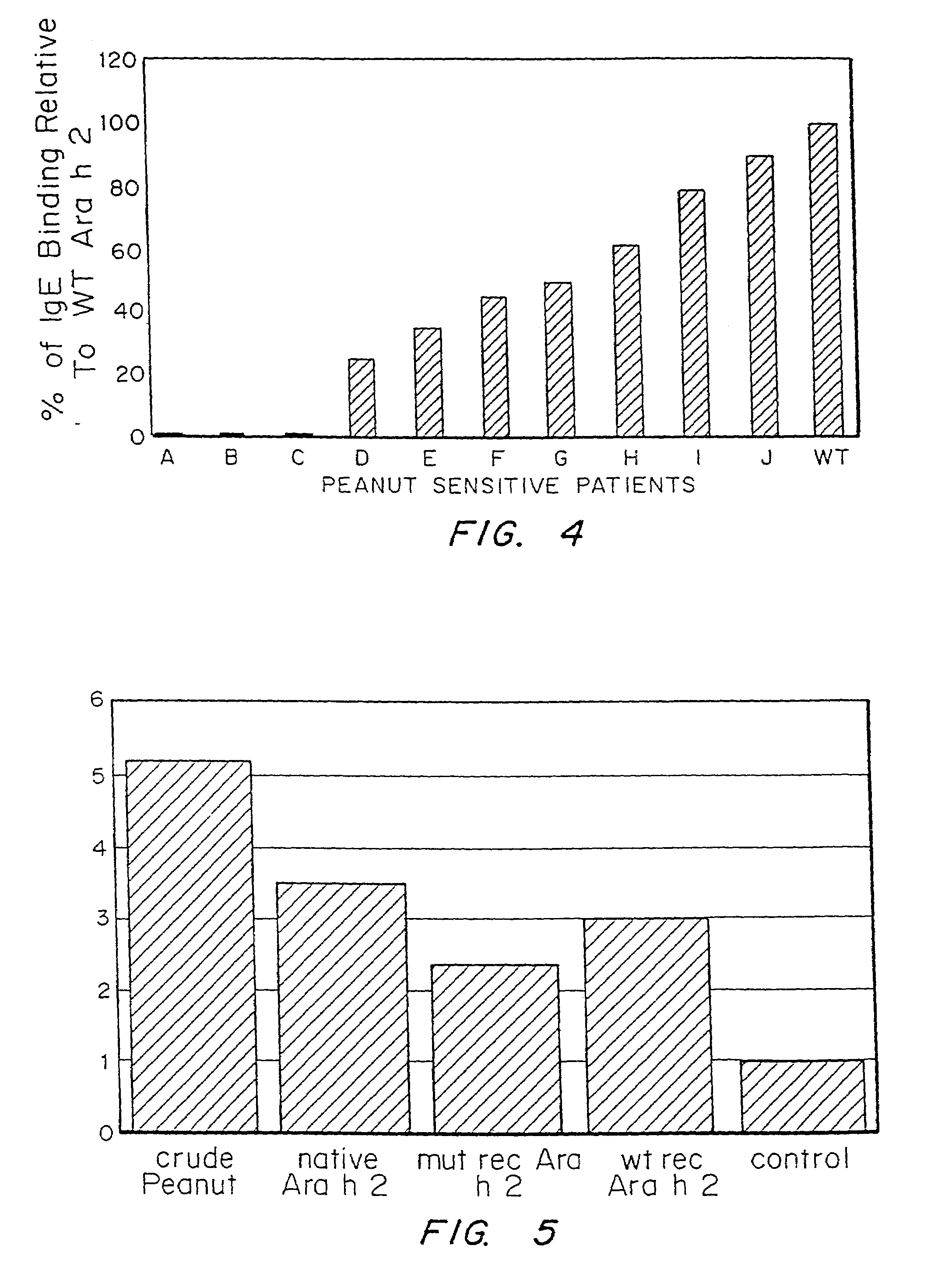
Nucleic acids encoding ara h 3 polypeptides
It has been determined that allergens, which are characterized by both humoral (IgE) and cellular (T cell) binding sites, can be modified to be less allergenic by modifying the IgE binding sites. The IgE binding sites can be converted to non-IgE binding sites by masking the site with a compound that prevents IgE binding or by altering as little as a single amino acid within the protein, most typically a hydrophobic residue towards the center of the IgE binding epitope, to eliminate IgE binding. The method allows the protein to be altered as minimally as possible, other than within the IgE-binding sites, while retaining the ability of the protein to activate T cells, and, in some embodiments by not significantly altering or decreasing IgG binding capacity. The examples use peanut allergens to demonstrate alteration of IgE binding sites. The critical amino acids within each of the IgE binding epitopes of the peanut protein that are important to immunoglobulin binding have been determined. Substitution of even a single amino acid within each of the epitopes led to loss of IgE binding. Although the epitopes shared no common amino acid sequence motif, the hydrophobic residues located in the center of the epitope appeared to be most critical to IgE binding.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
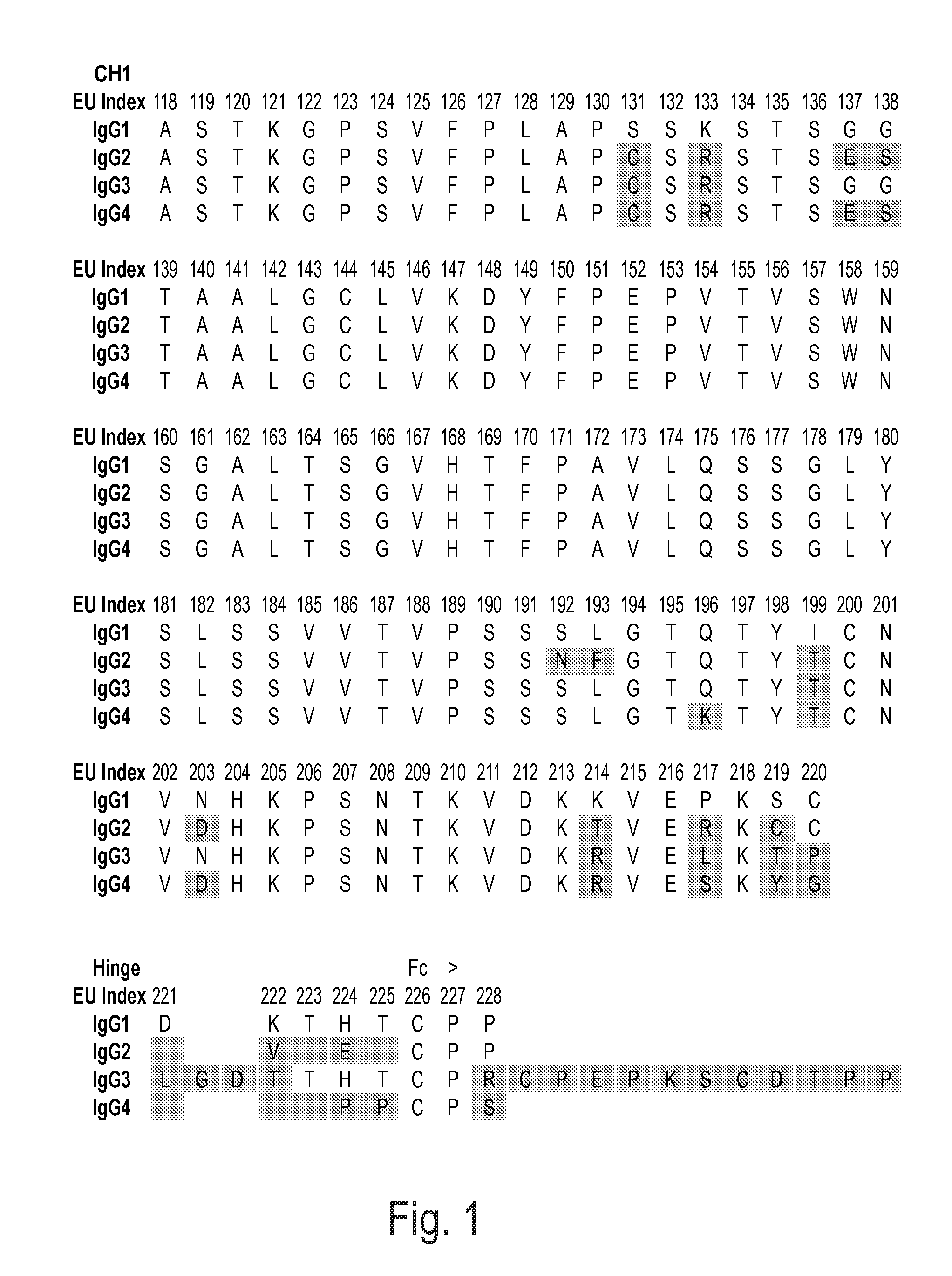
Stabilized immunoglobulins
ActiveUS7608260B2Prolong lifeImprove stabilitySnake antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeavy chainHinge region
The present invention provides stabilized immunoglobulin molecules that have increased storage stability and / or in vivo half-lives due to the mutation of one or more amino acids that would otherwise render the immunoglobulin molecules susceptible to degradation. In a preferred embodiment, the stabilized immunoglobulins of the invention have mutations at the heavy chain constant domain hinge region. Such stabilized immunoglobulin molecules, i.e., immunoglobulin molecules with increased storage stability have one or more of the following advantages they are more readily transported and / storable for longer periods and / or less stringent conditions than non-stabilized counterparts; that smaller amounts and or less frequent dosing is required in the therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic use of such stabilized molecules.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
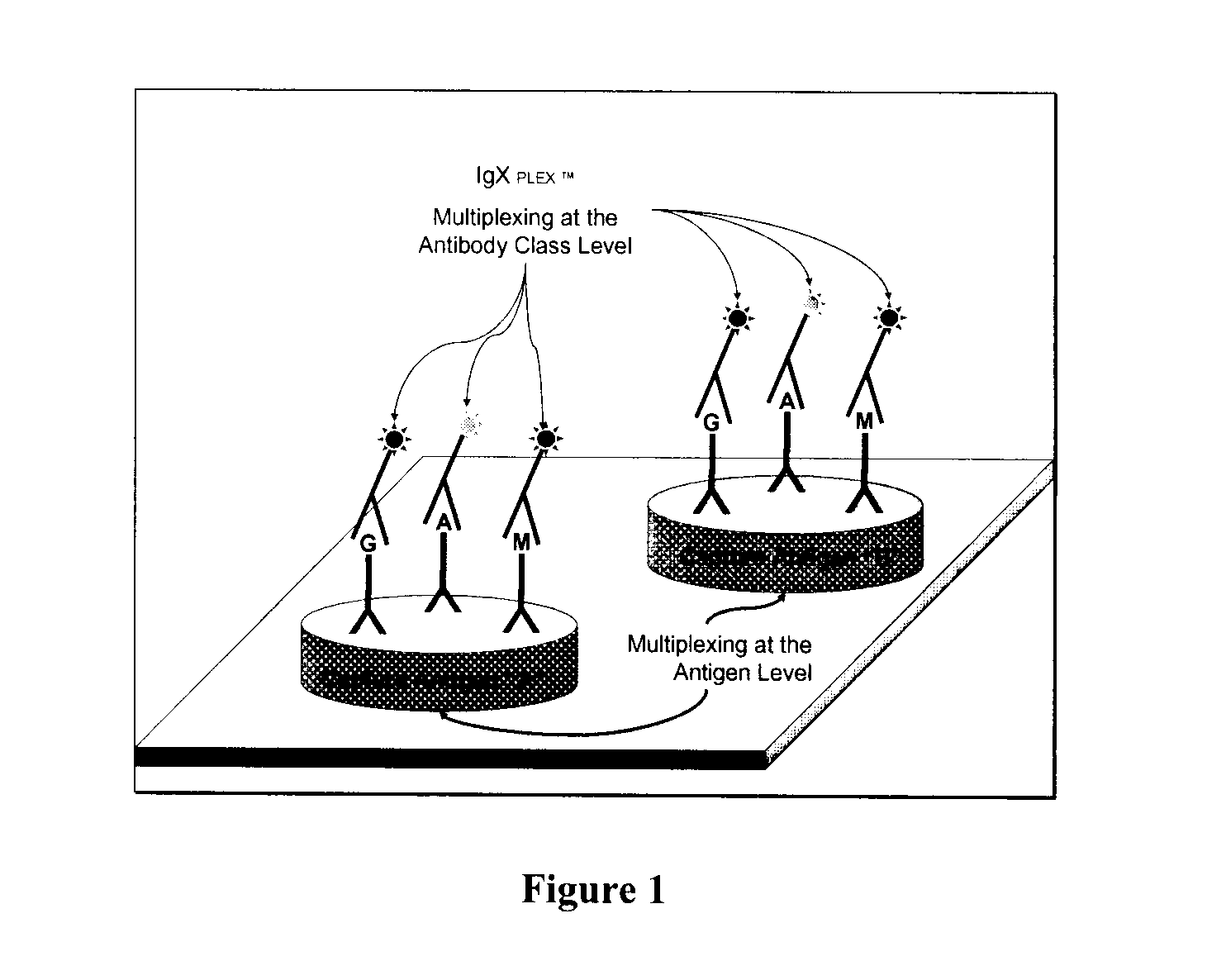
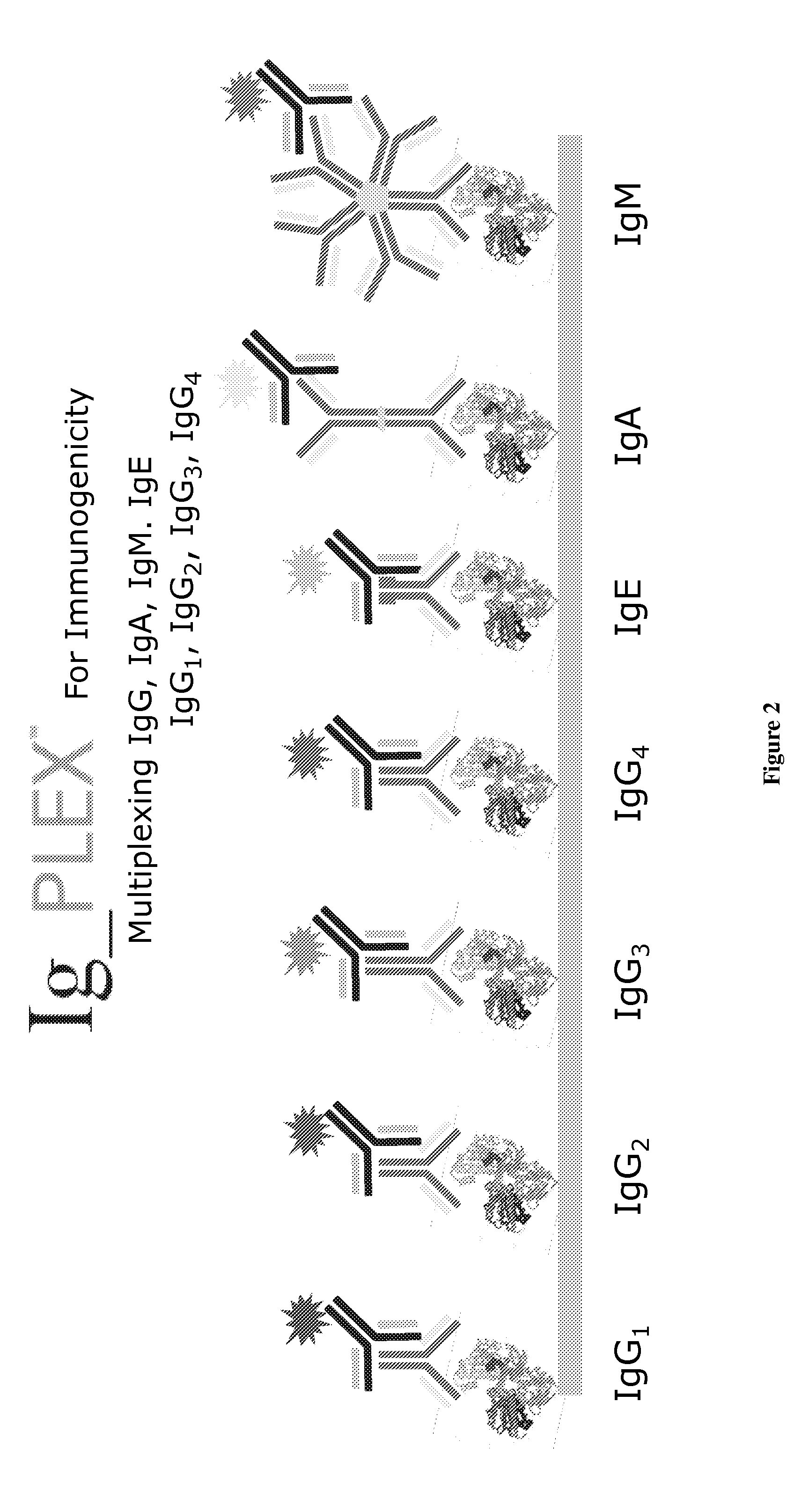
Multiplex measure of isotype antigen response
InactiveUS20130165335A1Fast and cost-effective methodLibrary screeningFluorescence/phosphorescenceImmunoglobulin isotypeTherapeutic protein
The application discloses methods for simultaneous detection and quantifying multiple target analytes, including immunoglobulin isotypes and sub-classes, single and multiple protein antibodies within a test sample in a single reaction vessel. The method uses reaction wells as on a multi-well plate, each single well comprising microarrays of: calibration spots, having a predetermined quantity of a target analyte; and capture spots, having multiple agent antibodies, including isotypes and subclasses that specifically bind the target analytes. The captured analytes and the calibration spots are detected with fluorescently labeled antibodies specific for each analyte. The application also discloses methods for detecting and quantifying biomarkers, therapeutic proteins and patient derived antibodies; the use of secondary reagents to determine immunoglobulin classes Ig G, A, M, E and sub-classes including IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4 and IgA. The intensity of each fluorescent signal allows measurement of a specific immune response to a therapeutic protein and associated analytes.
Owner:SQI DIAGNOSTICS SYST
Immune complex-specific antibodies for increased sensitivity in immunoassay array tests
The invention concerns a method for determining antigen-specific antibodies of a particular immunoglobulin class in a sample by means of an immunoassay in an array format in which various binding partners Bnx are bound on different discrete areas on a support where Bnx in each case contain the various antigens that are able to specifically bind to the antibodies to be detected, by incubating the support with the sample and a binding partner B2 which carries a label and subsequently detecting the label on the respective discrete areas wherein B2 specifically binds antibodies of a certain immunoglobulin class that have been bound in an antigen-specific manner.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com