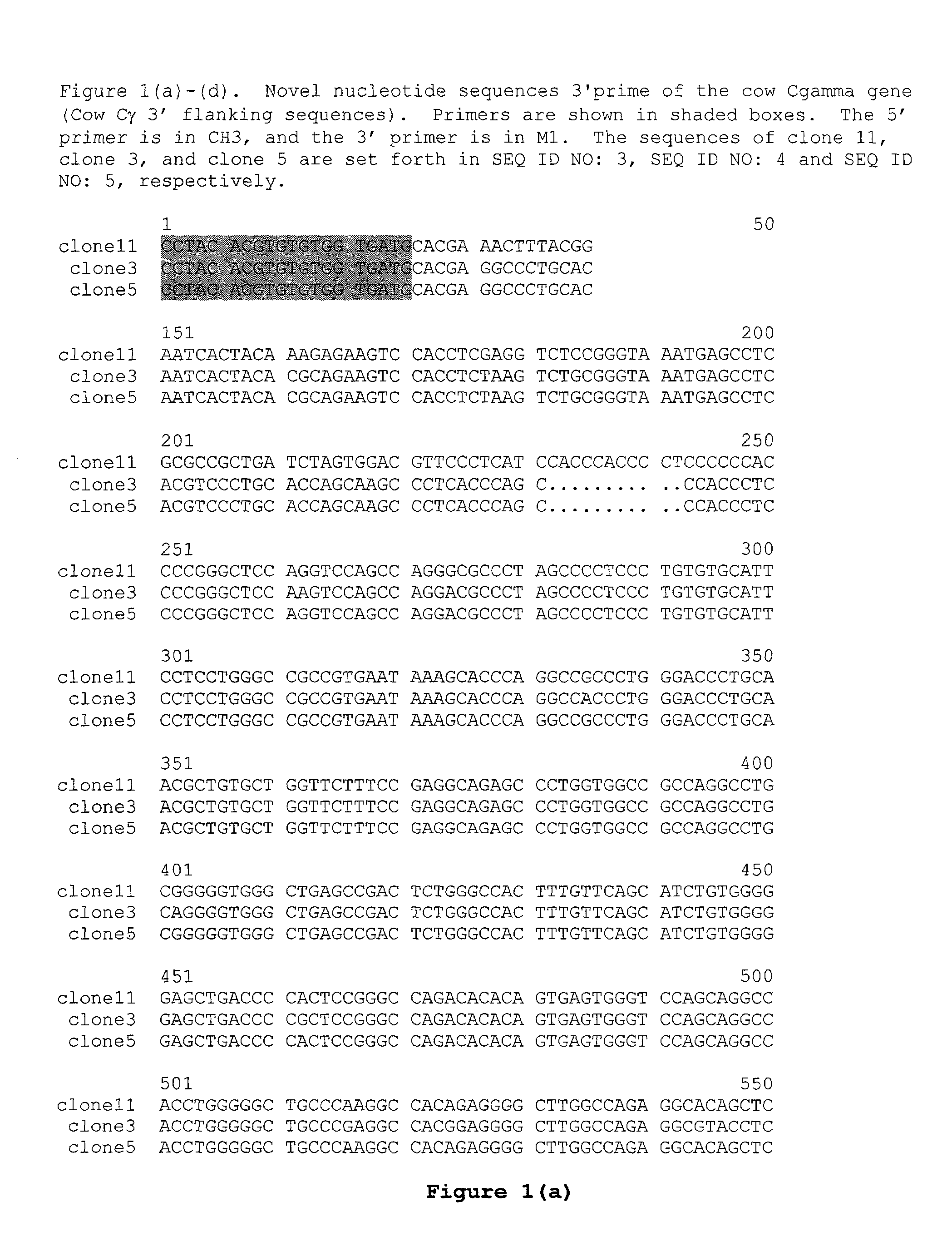
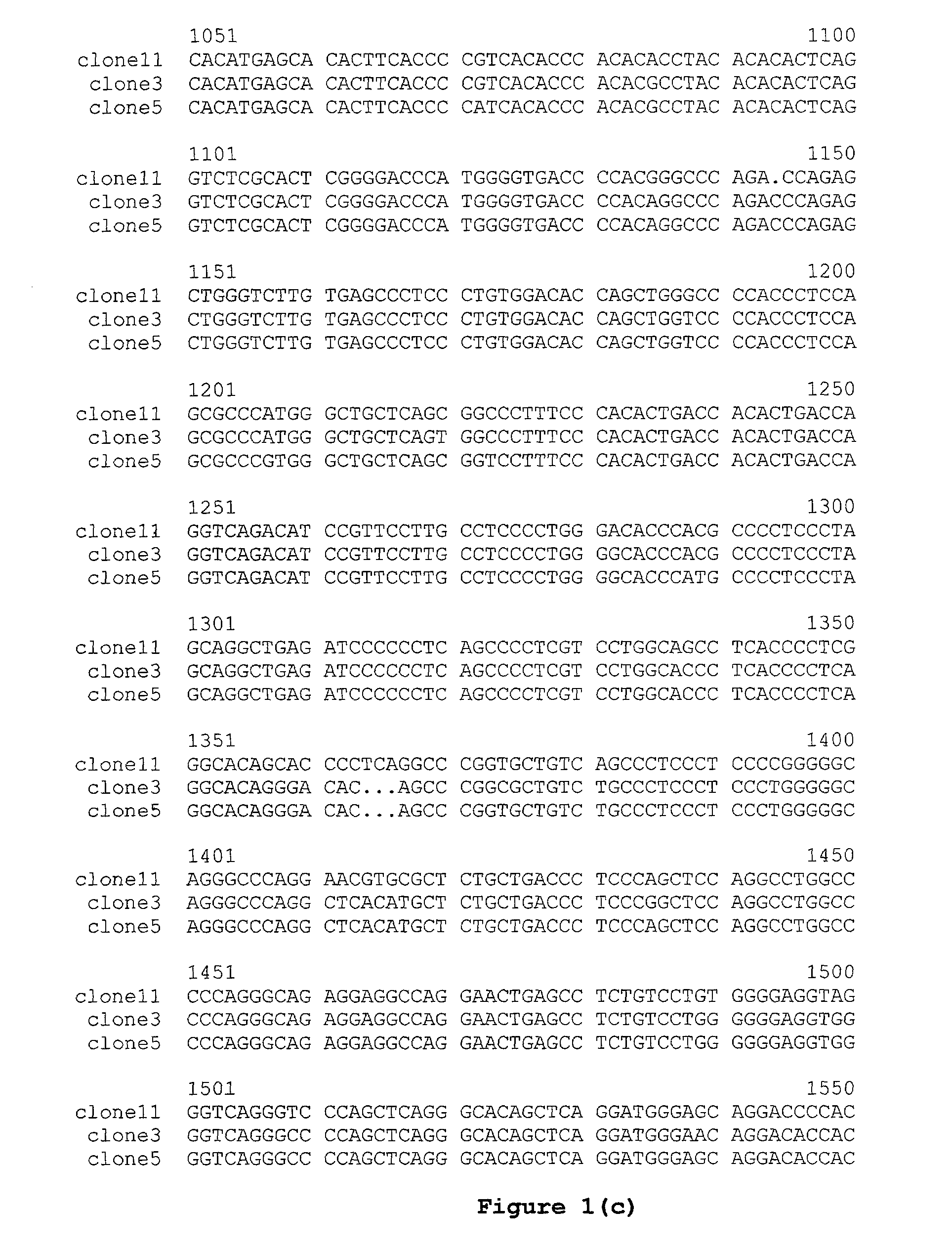
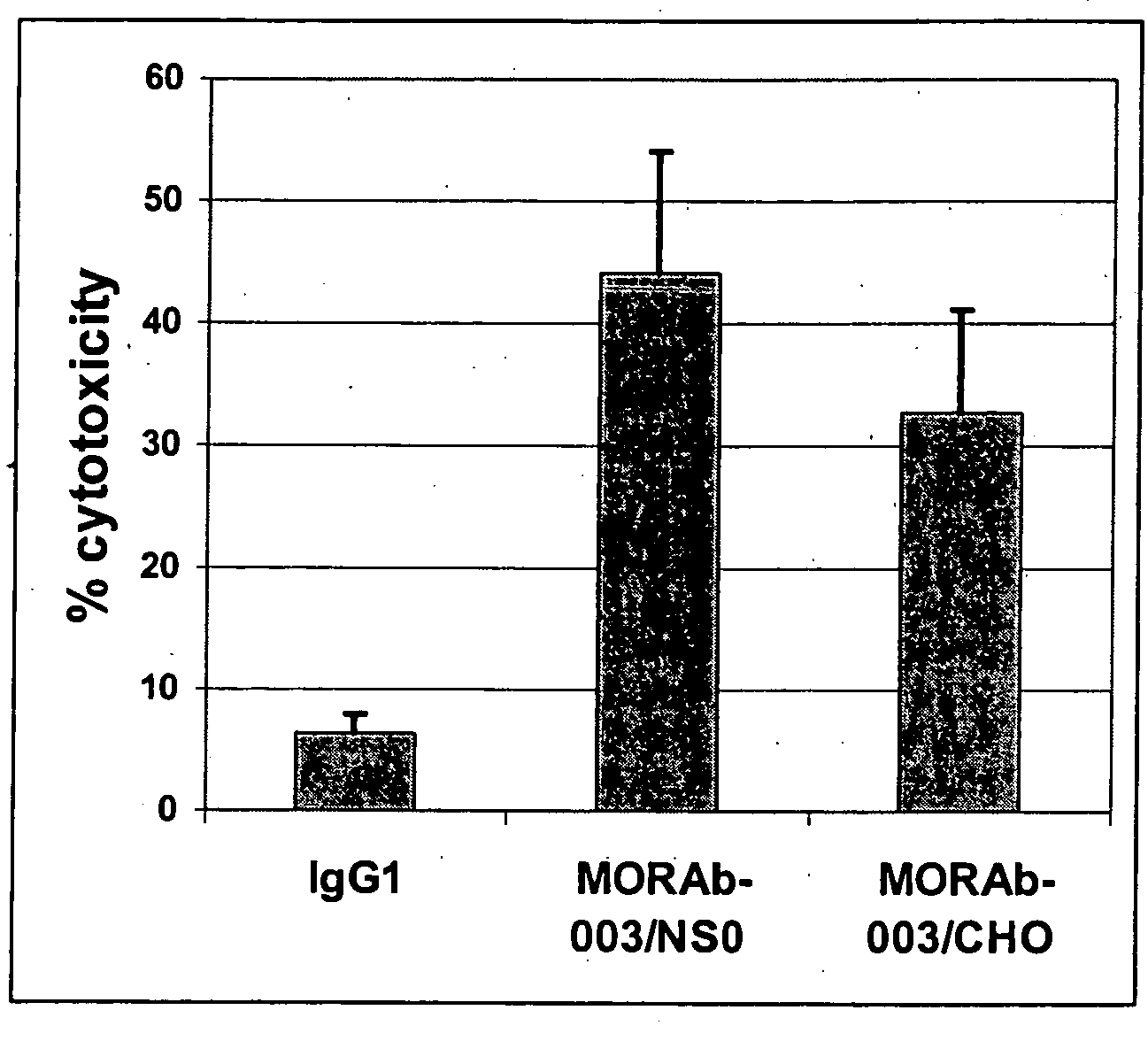
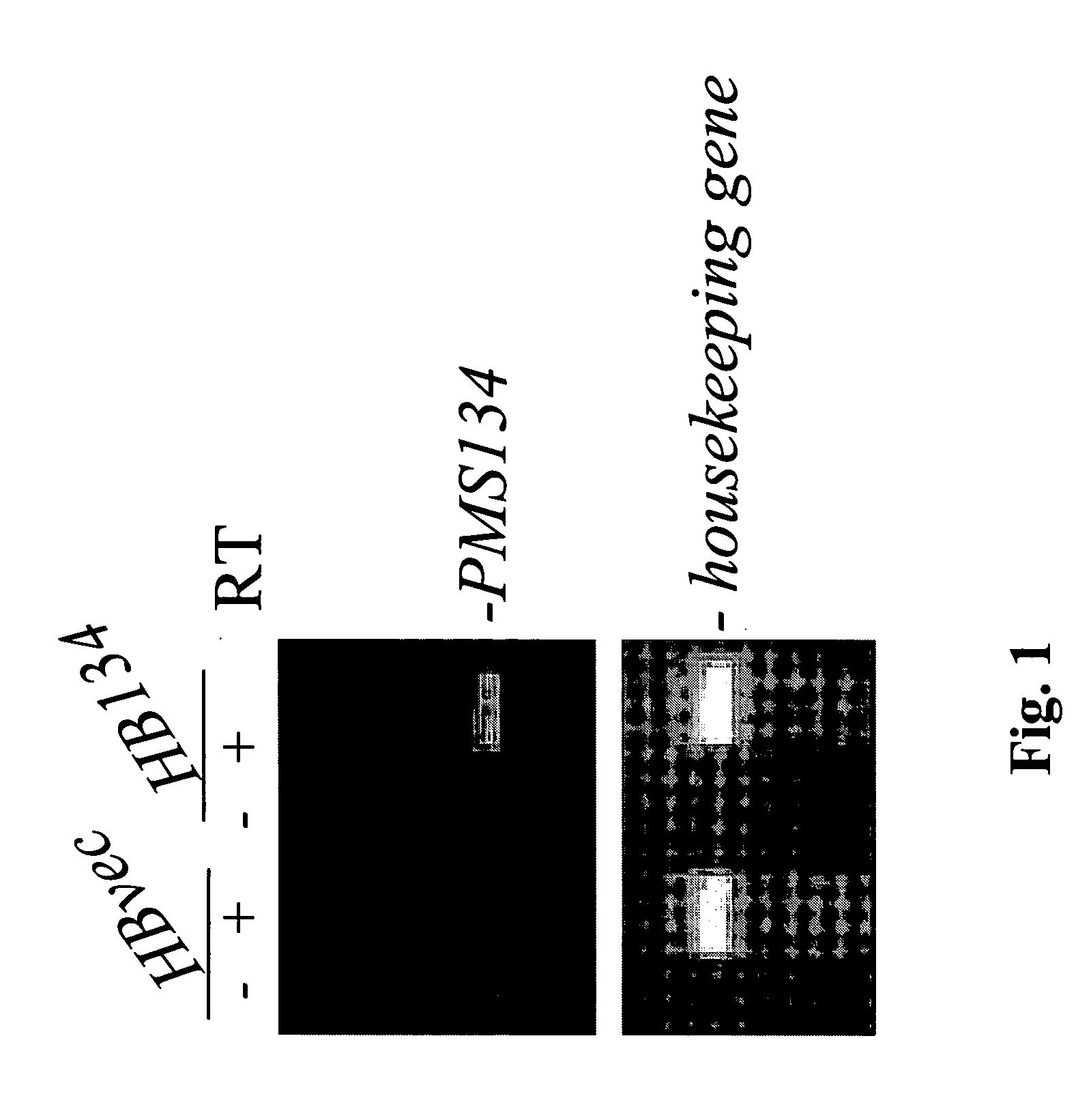
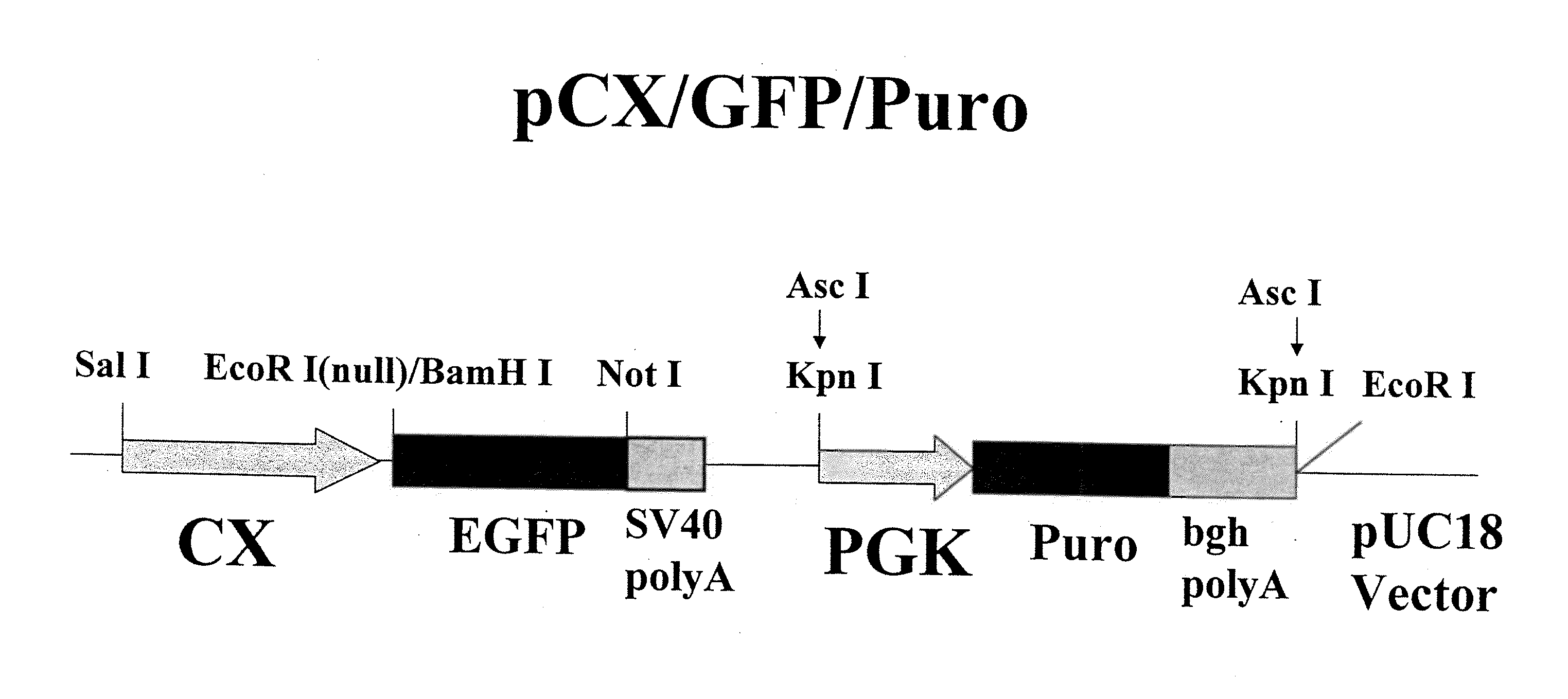
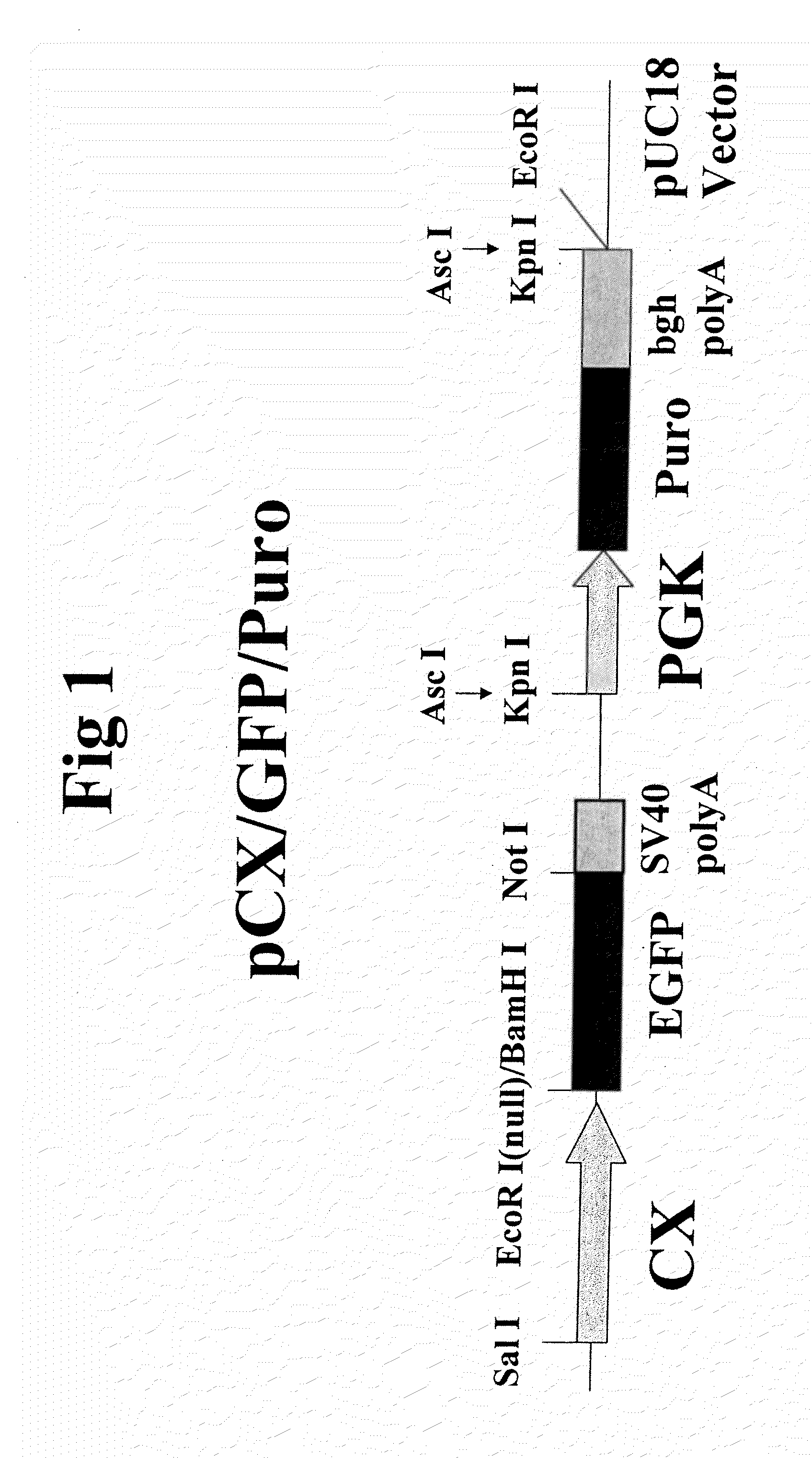
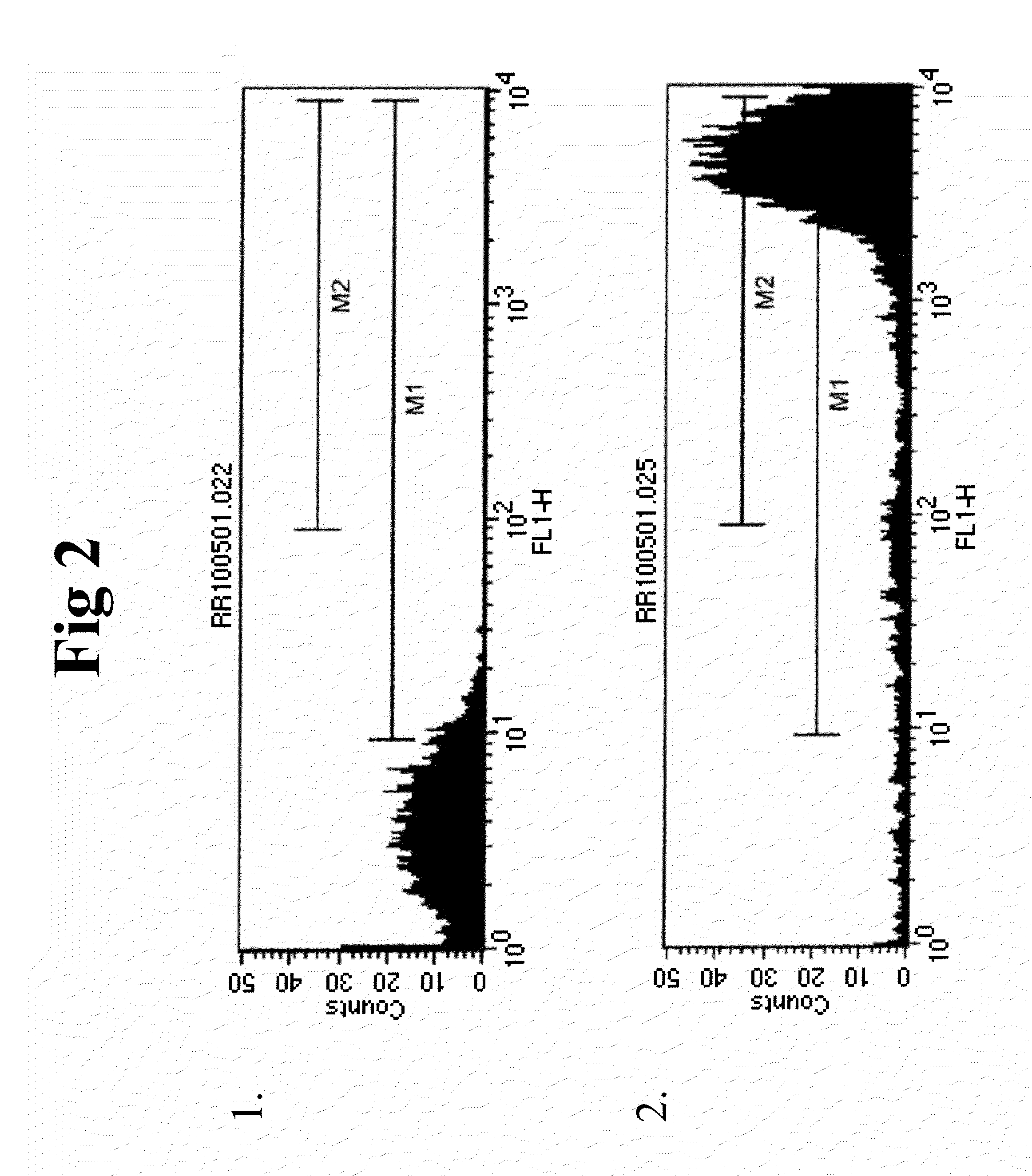
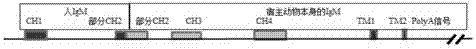
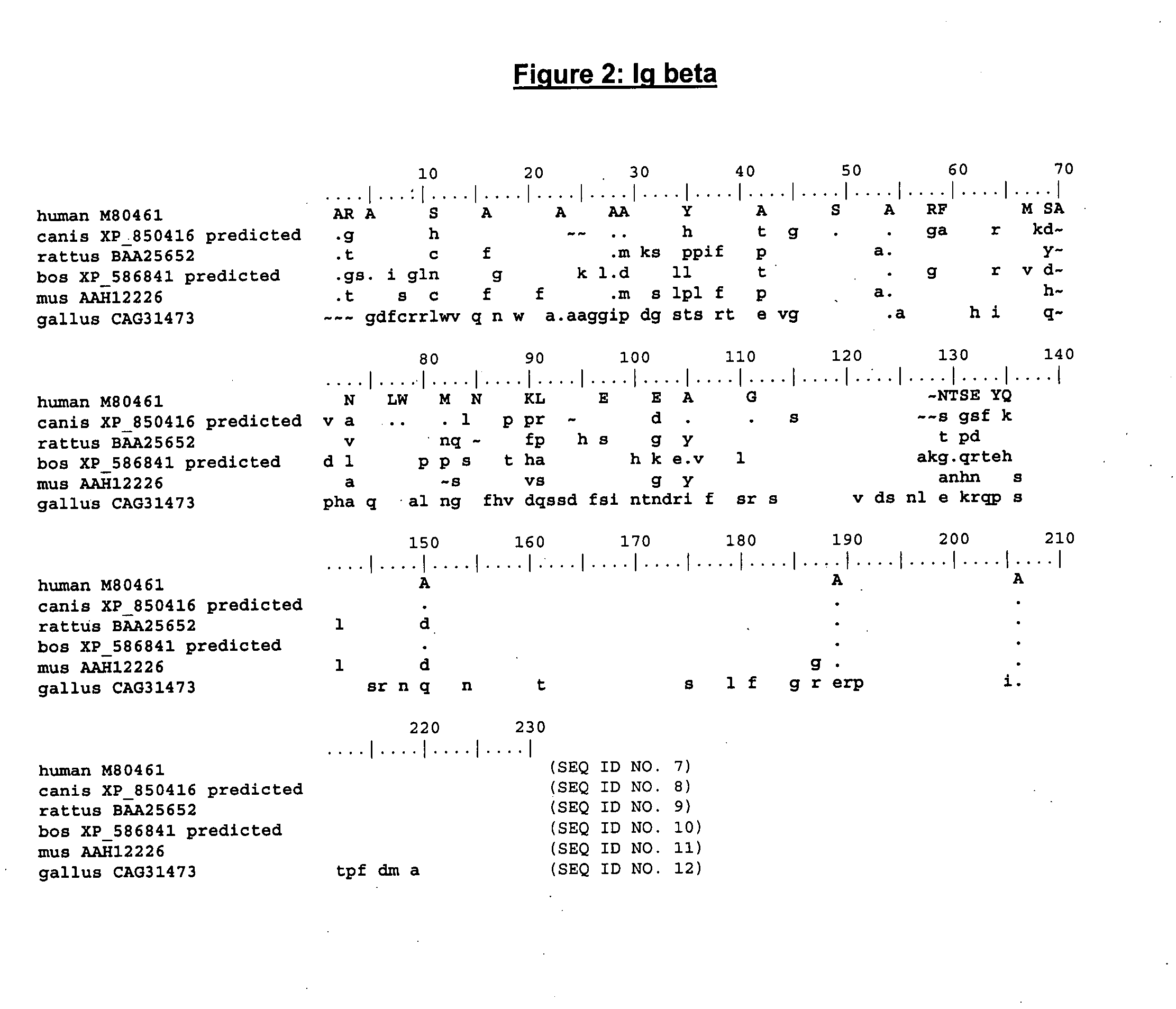
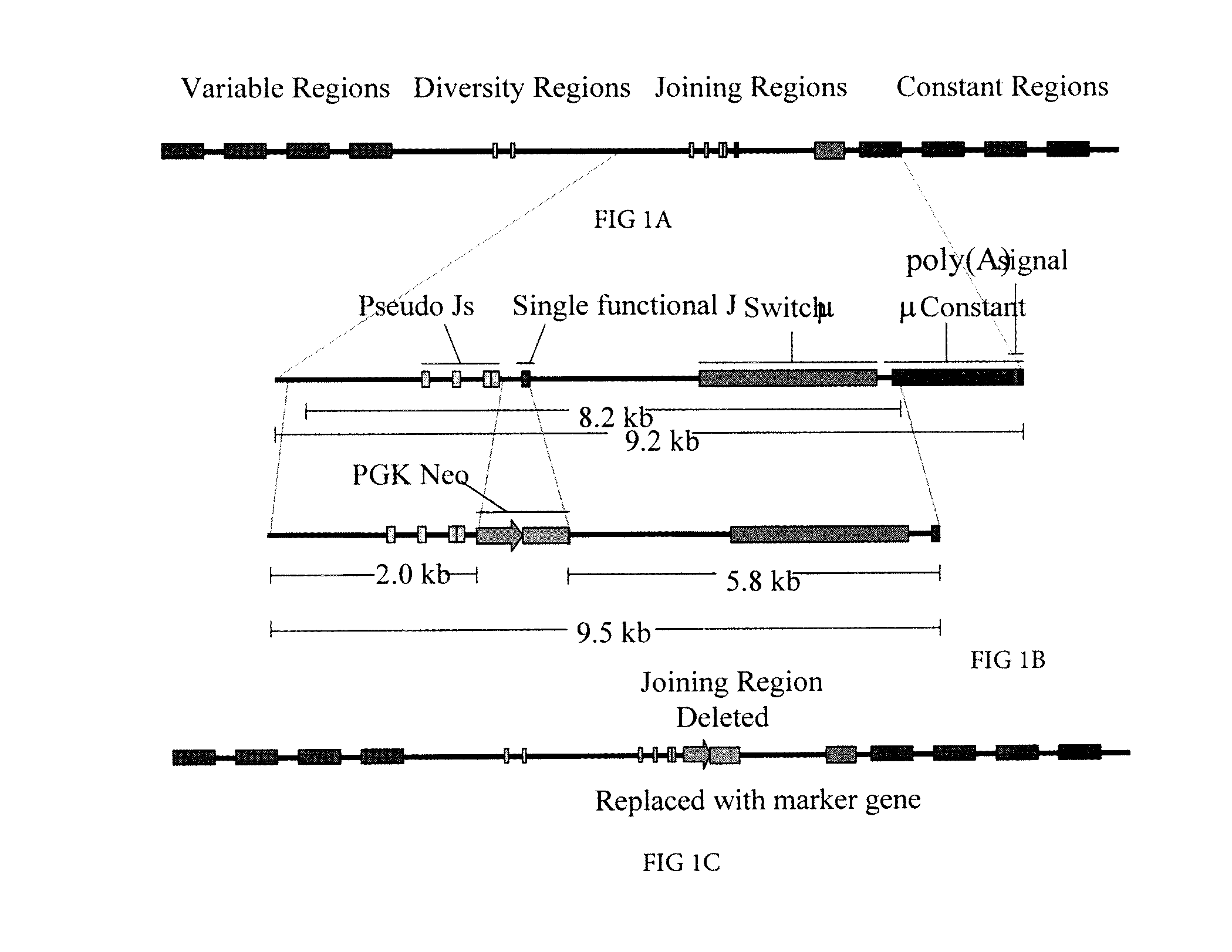
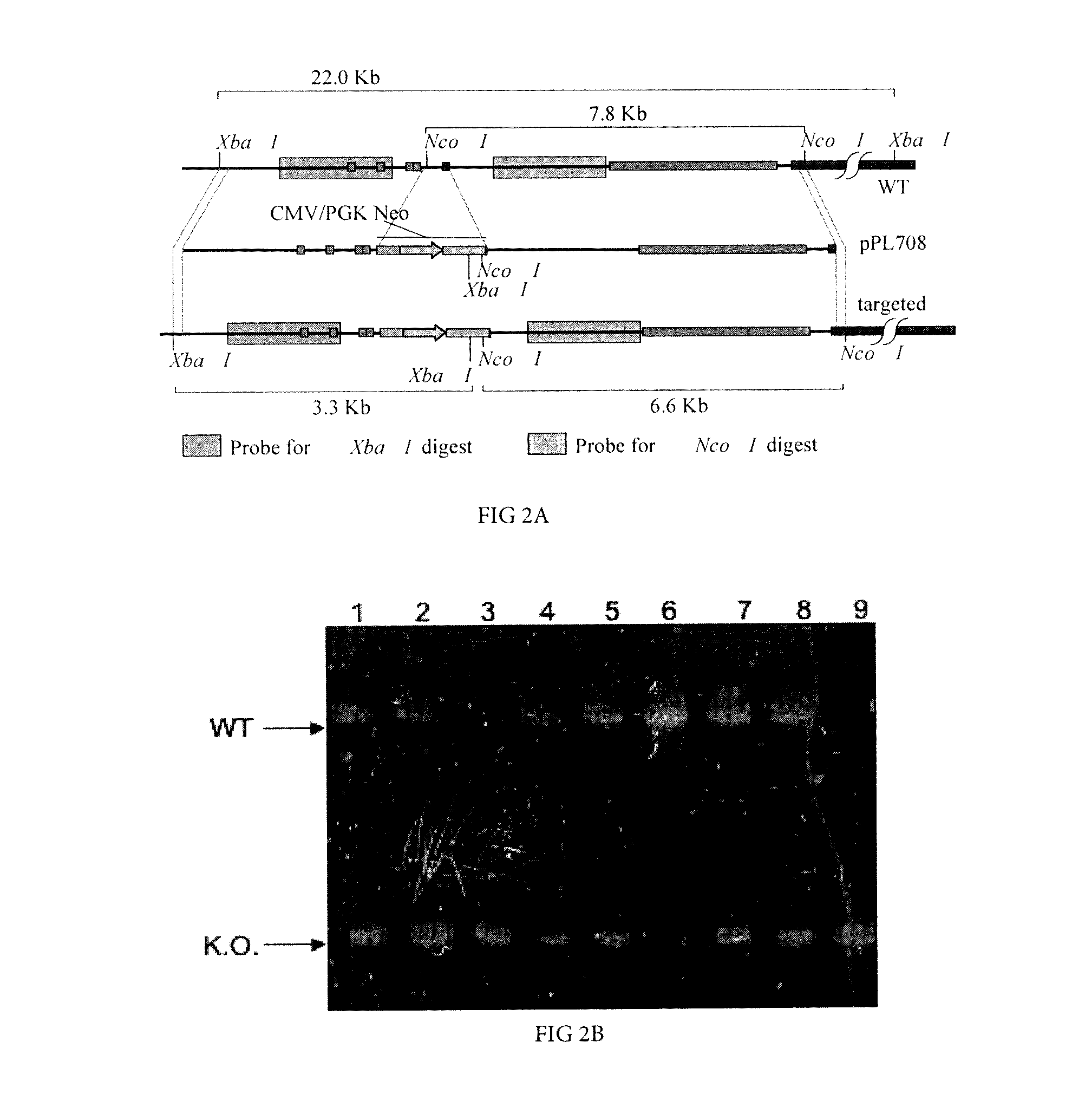
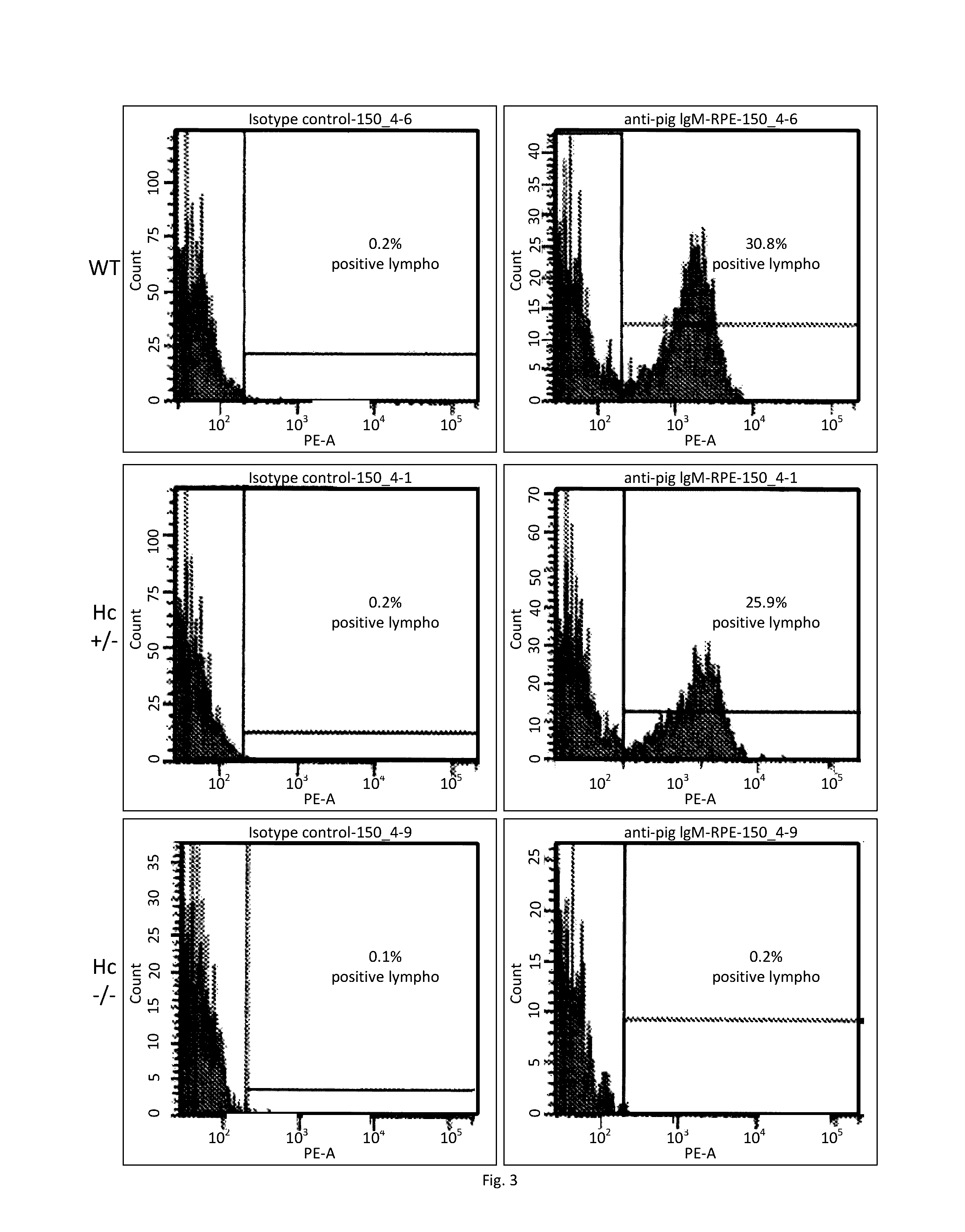
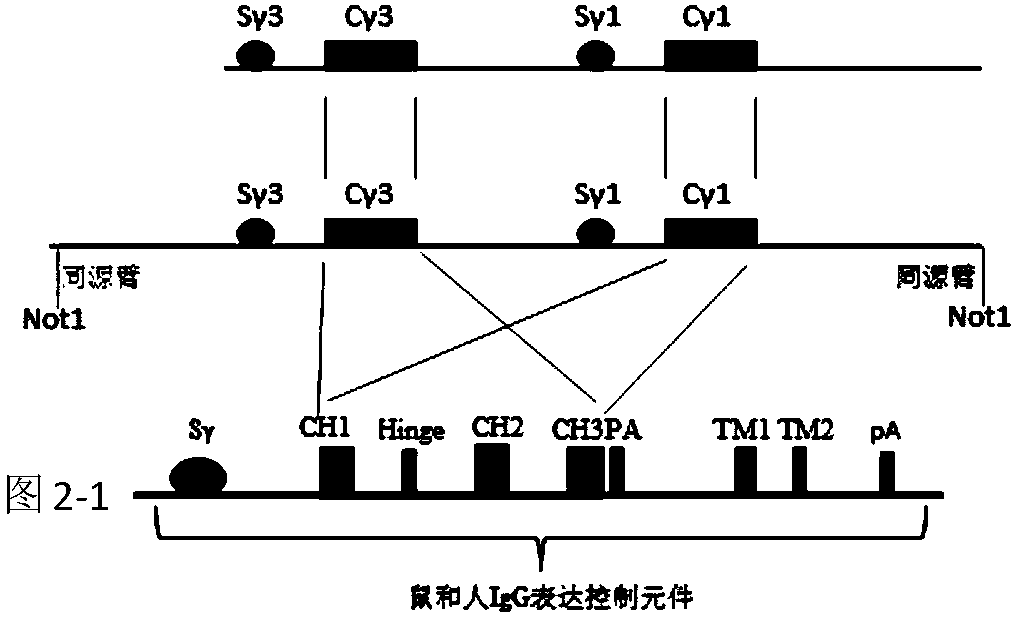
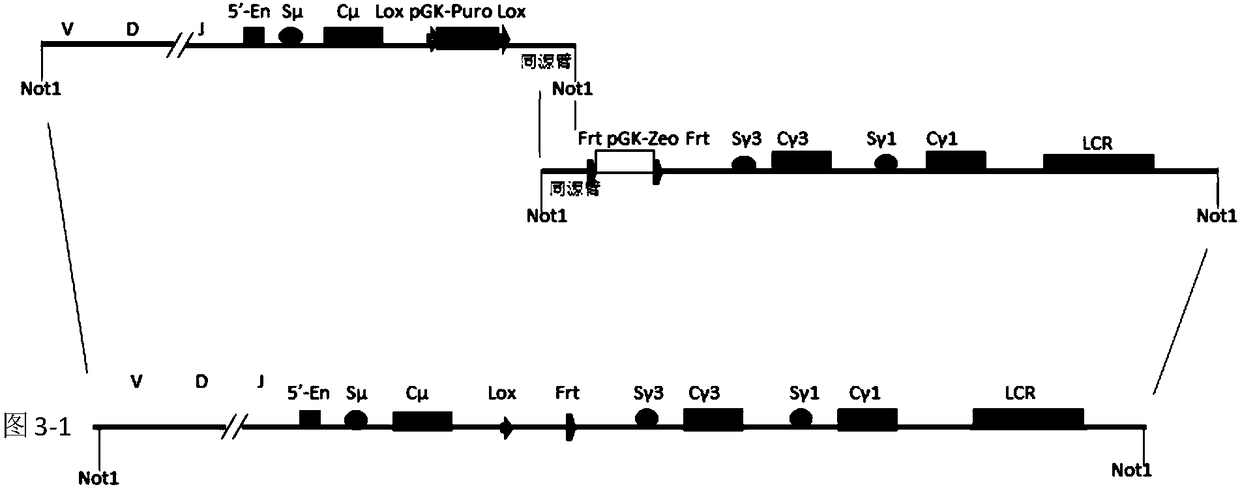
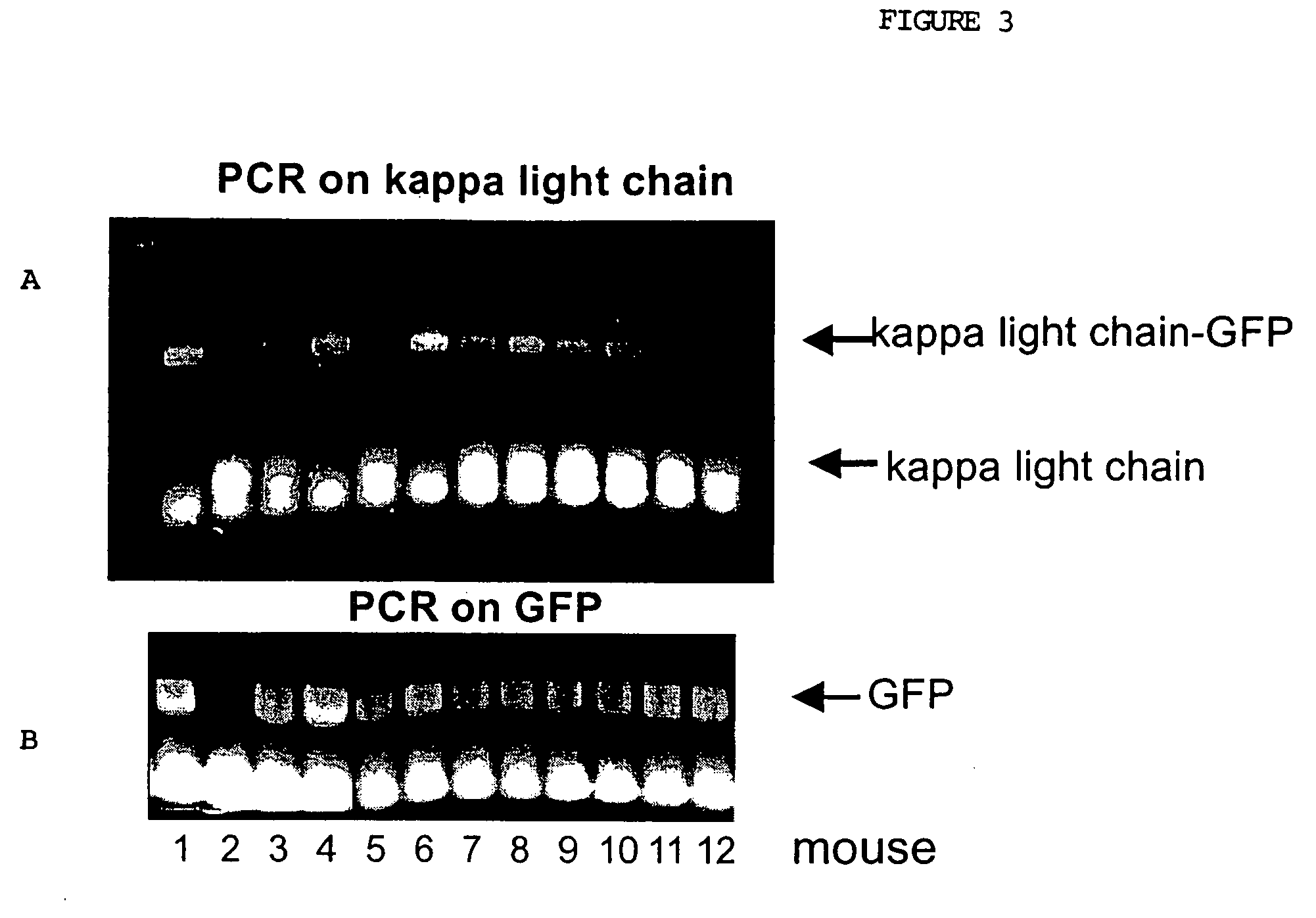
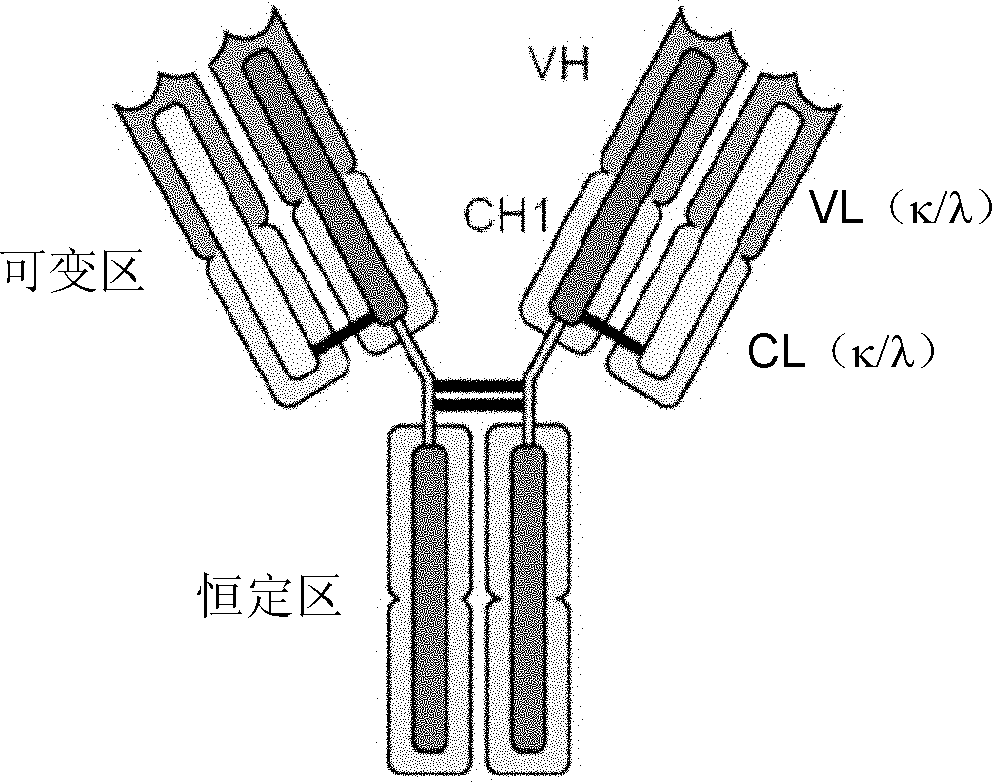
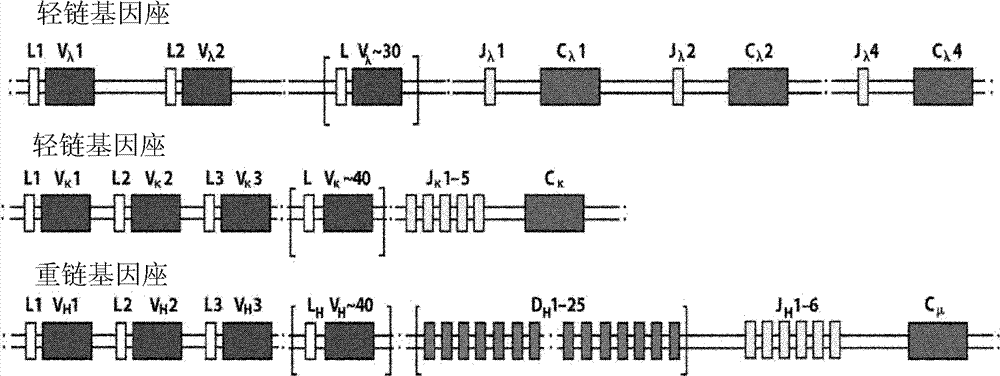
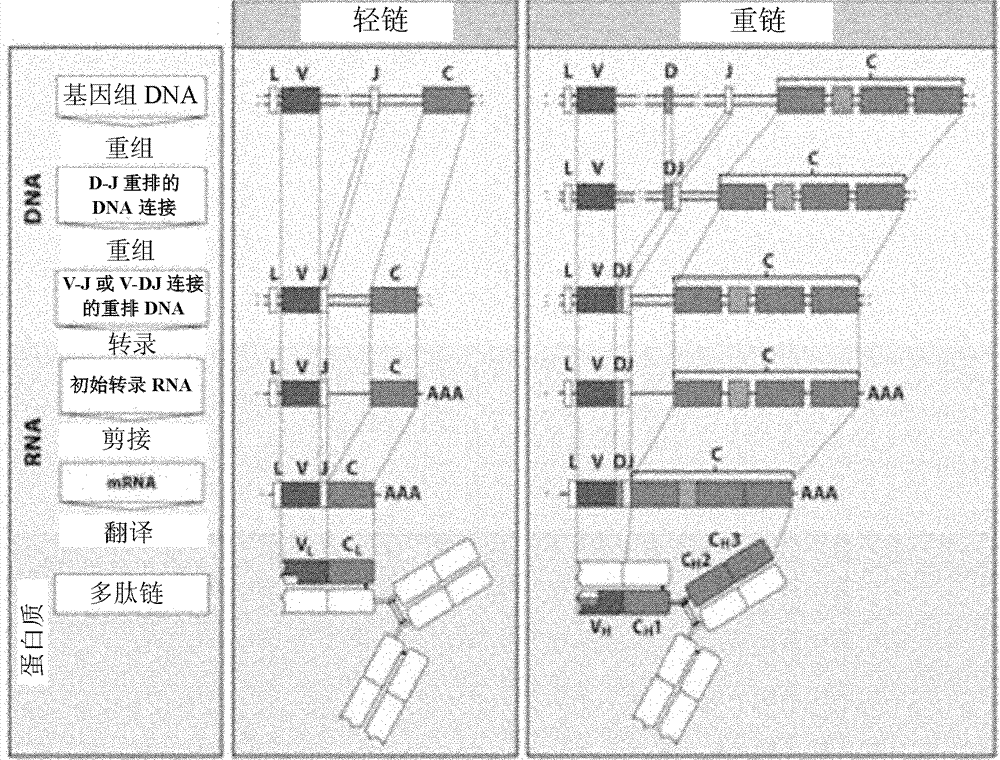
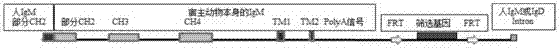Patents
Literature
36 results about "Immunoglobulin gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
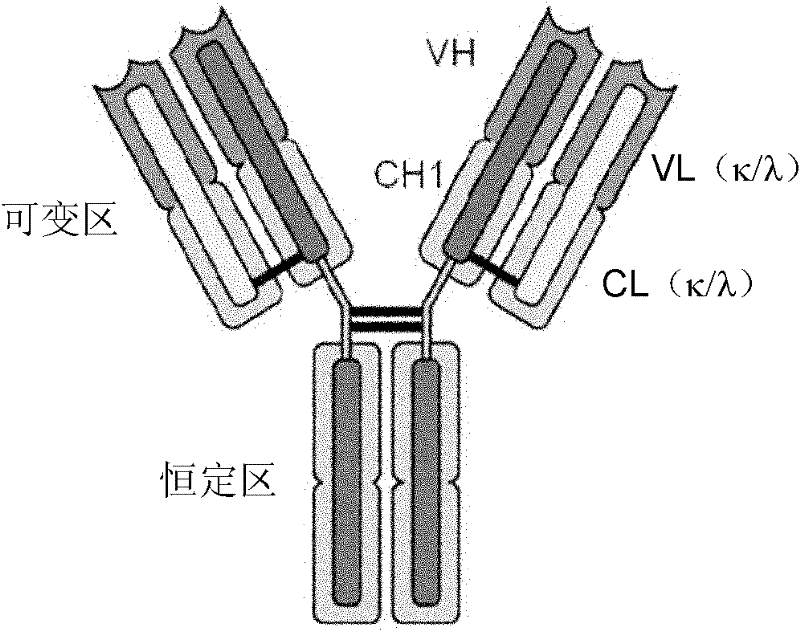
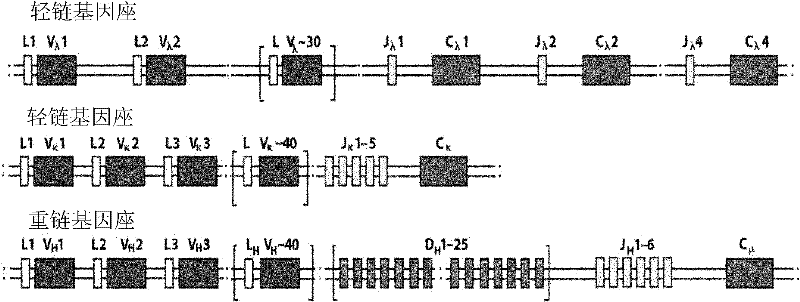
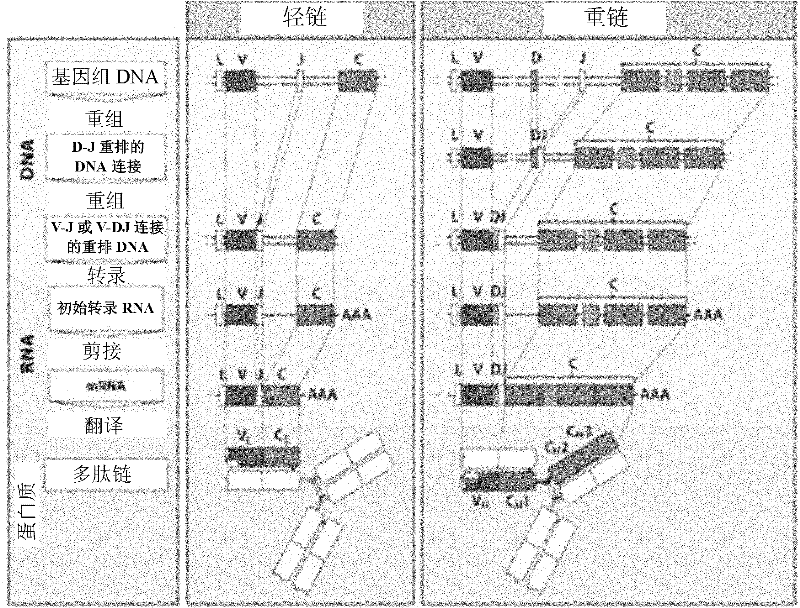
The immunoglobulin gene complex is responsible for generating an extraordinarily wide range of antibodies, each possessing a unique antigen specificity. The Second Edition of Immunoglobulin Genes brings the reader up to date with the rapid progress in our understanding of this system.
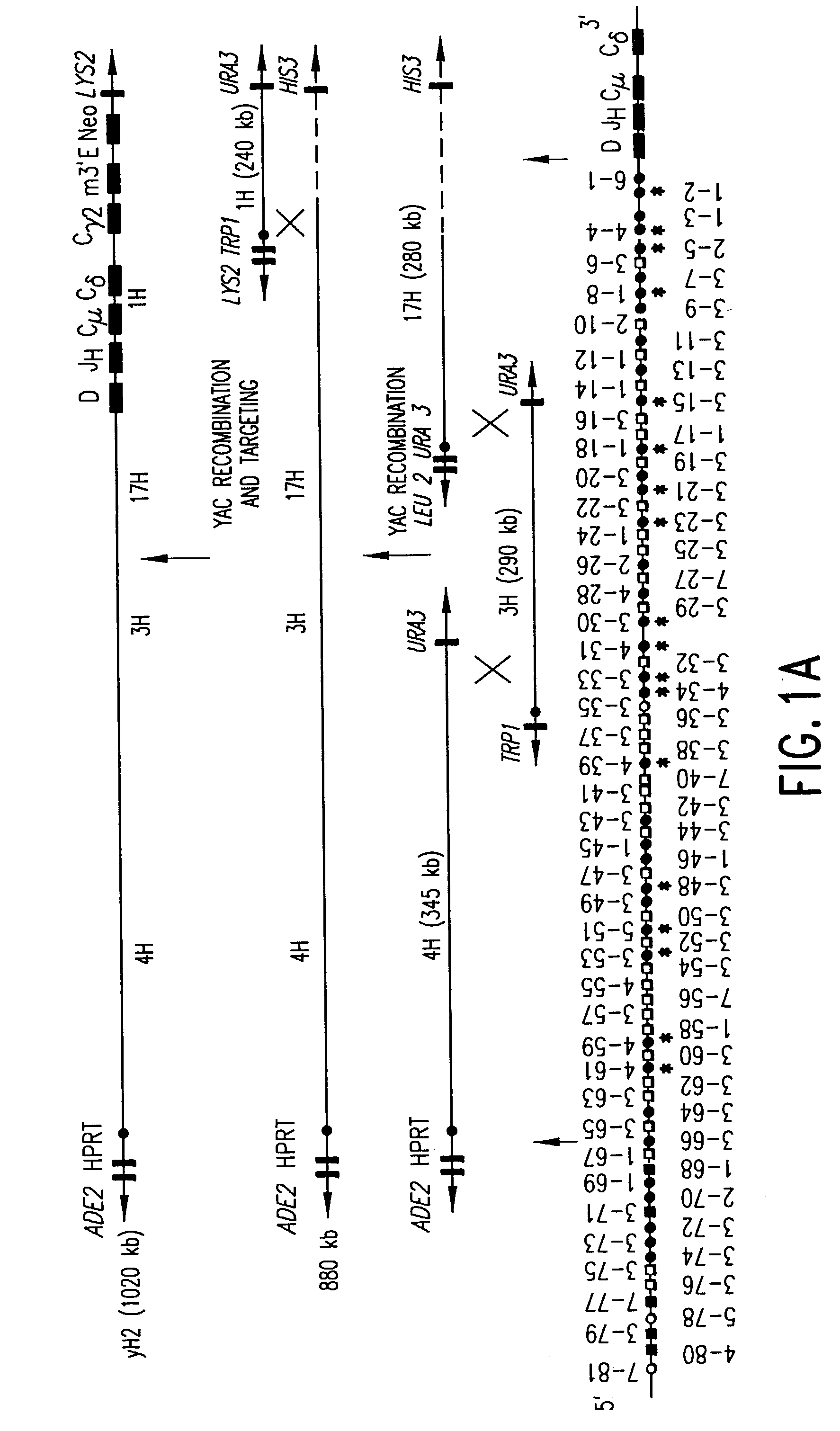
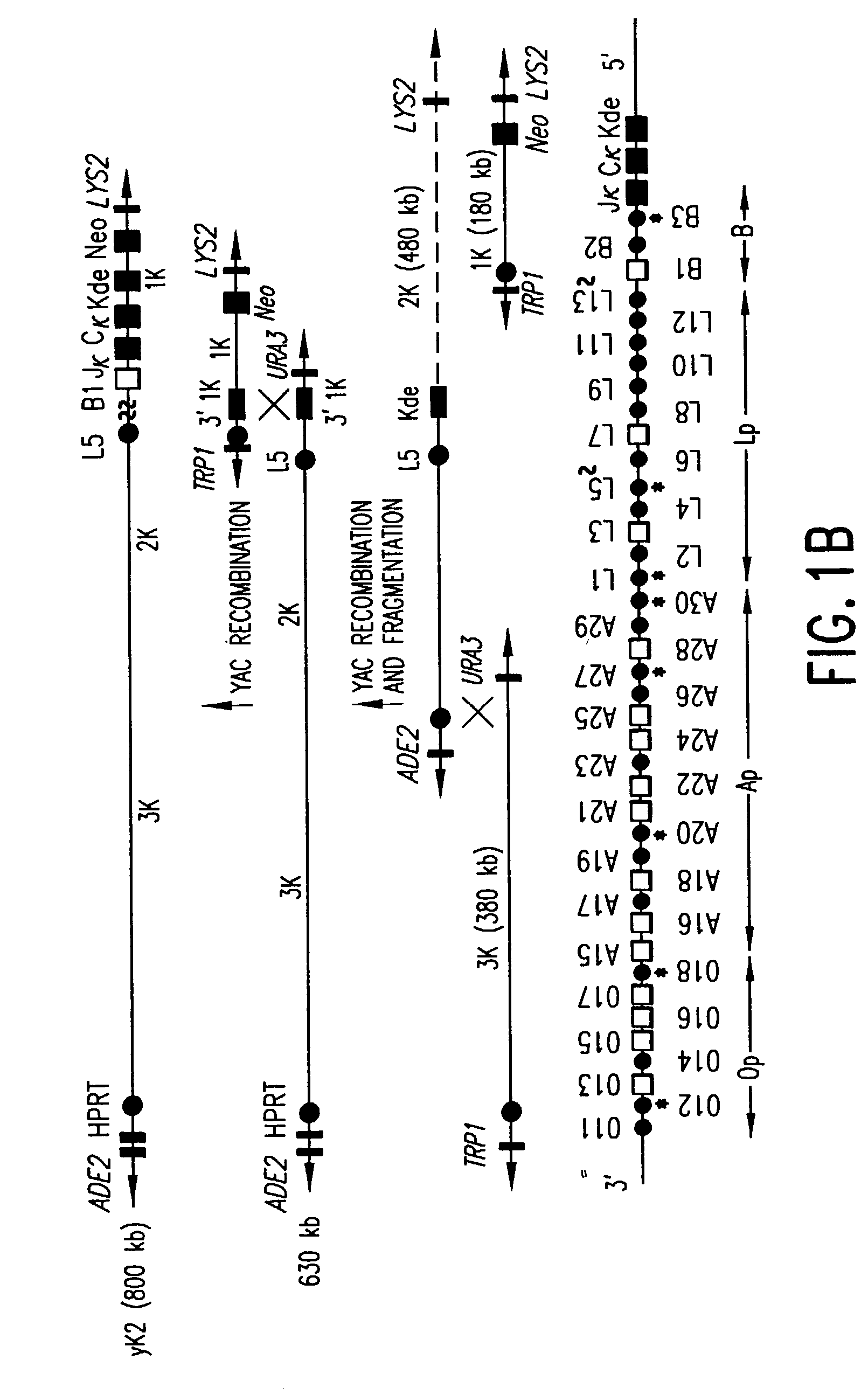
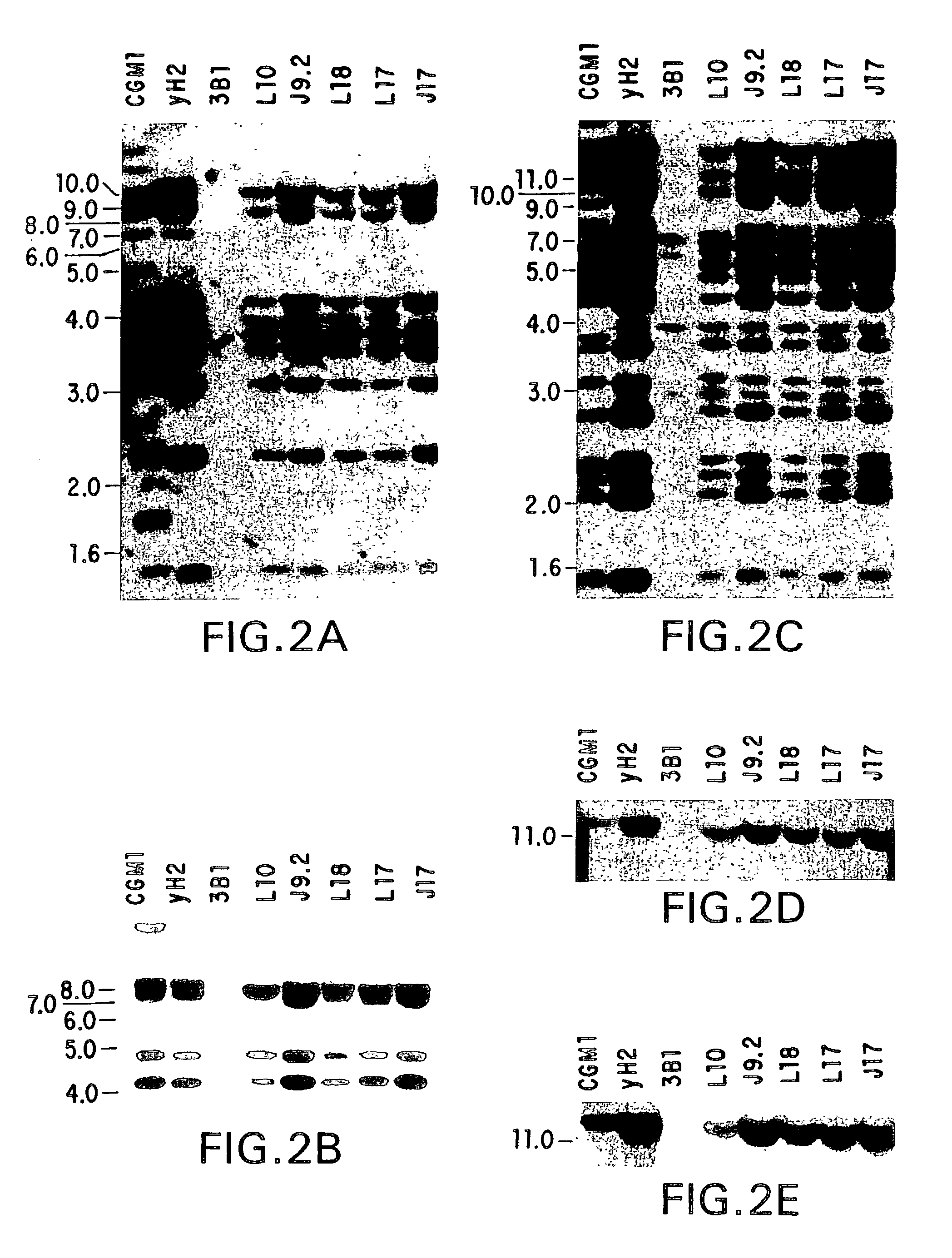
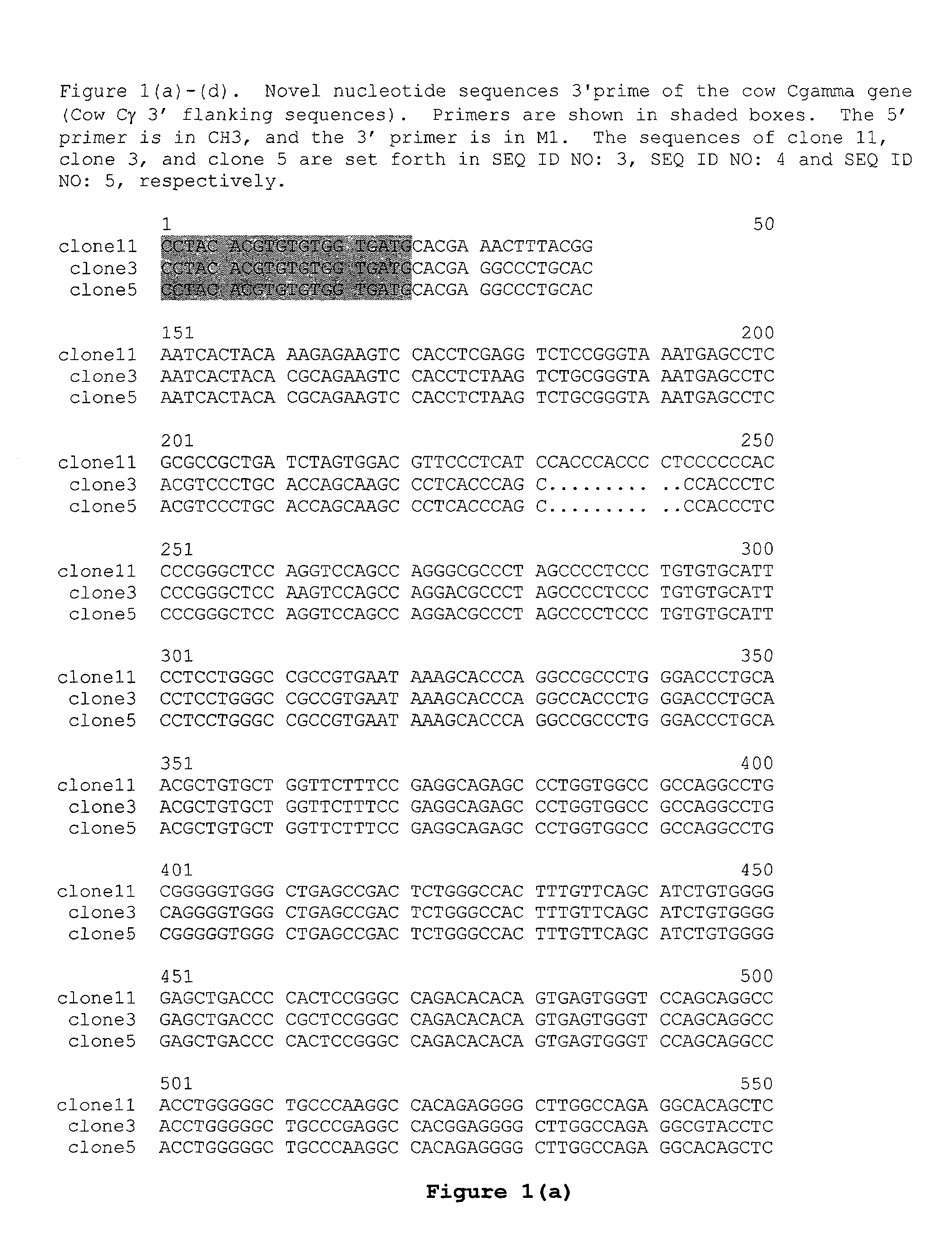
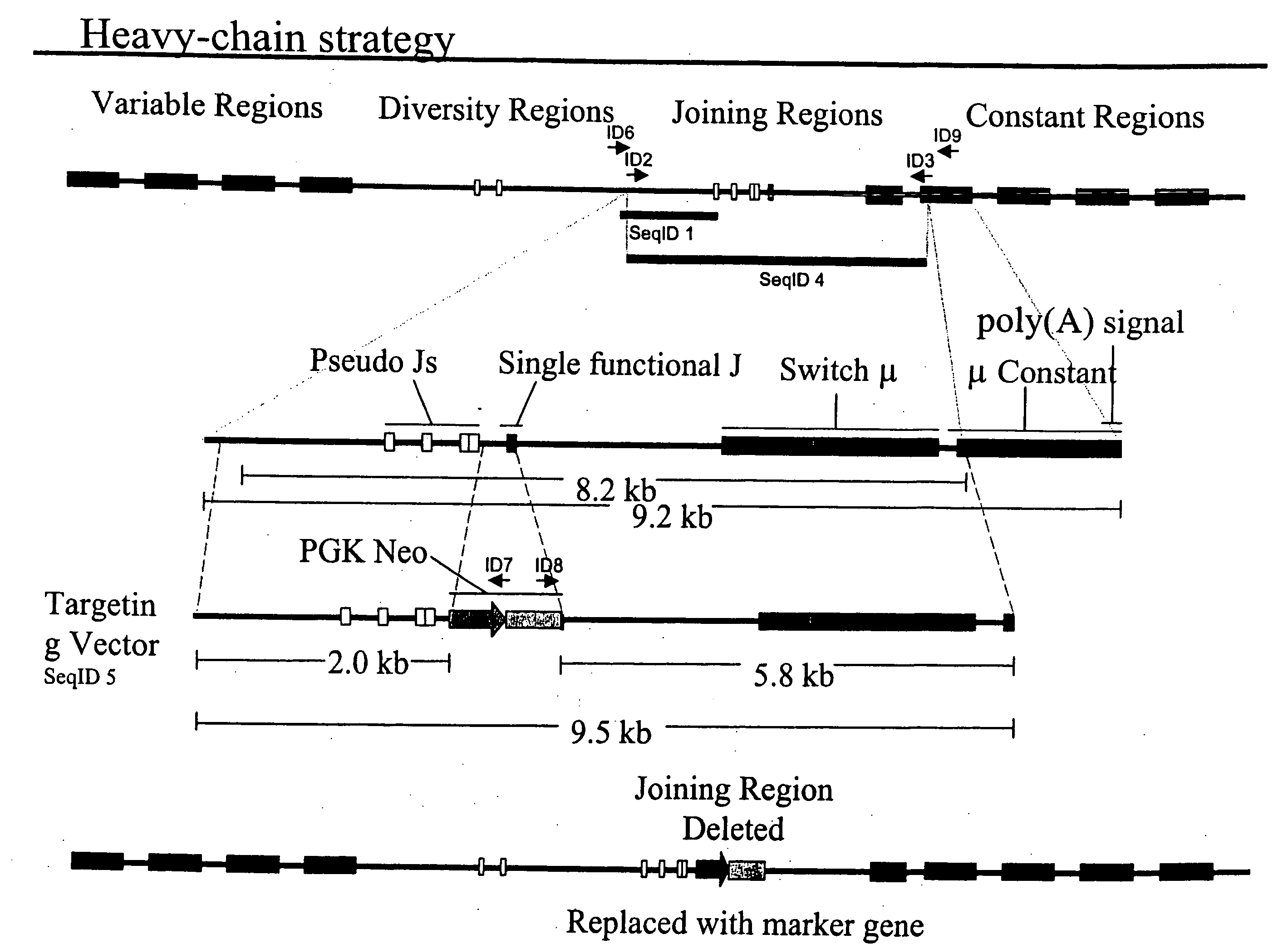
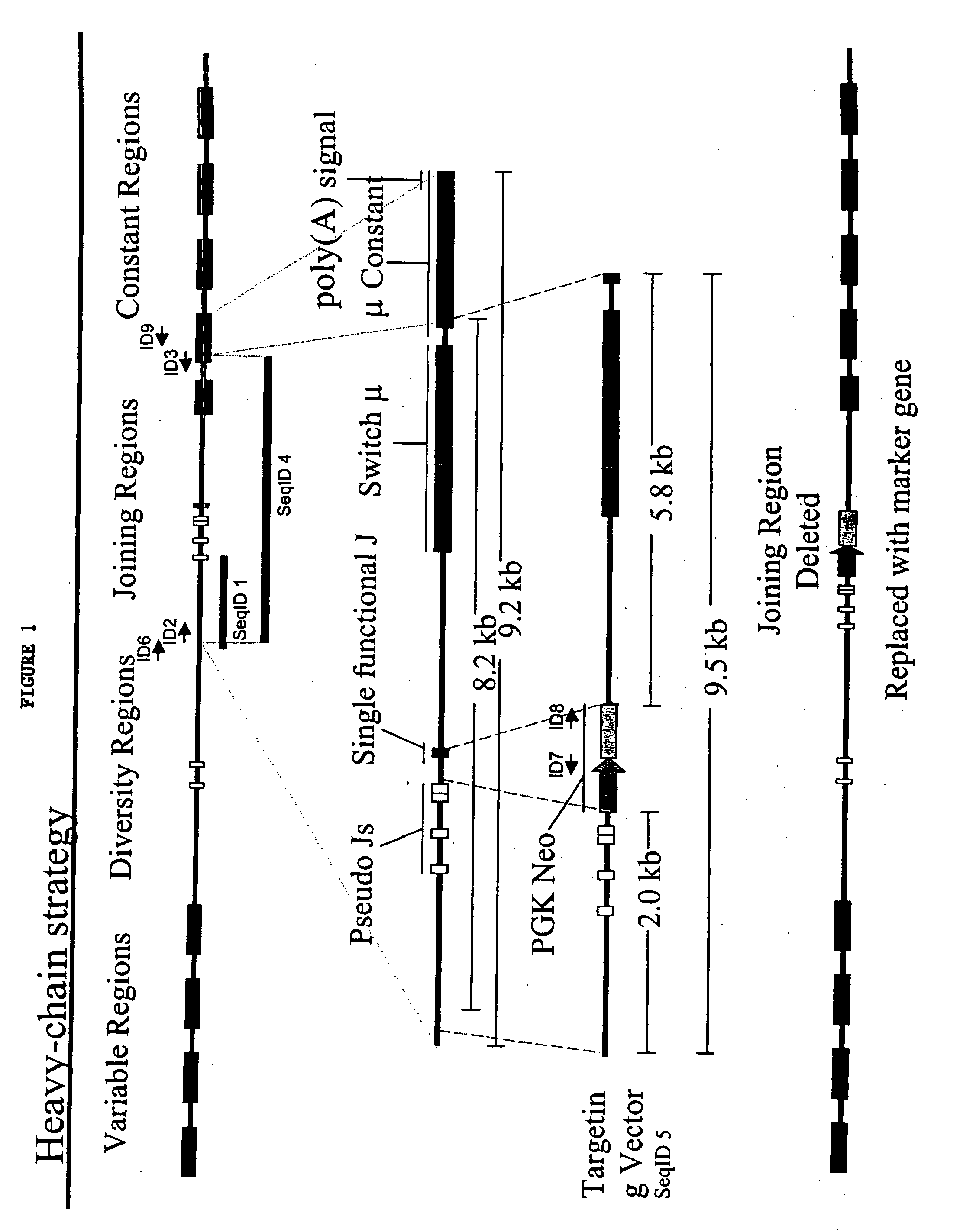
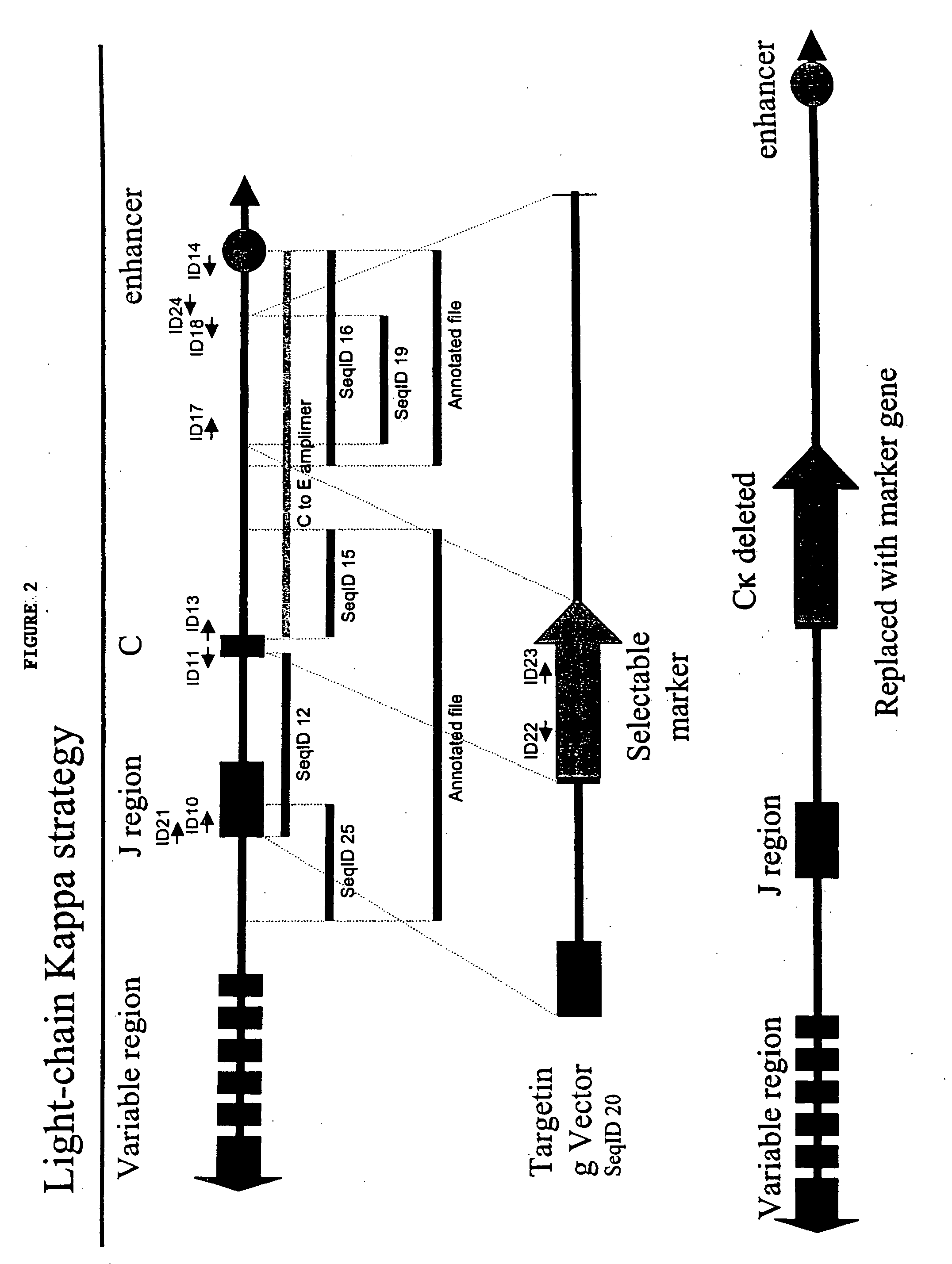
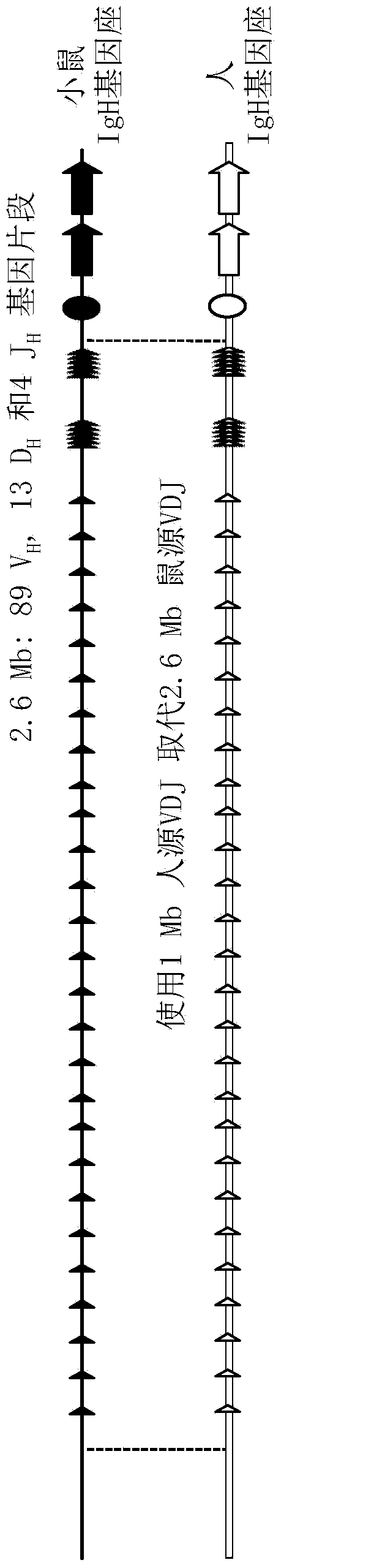
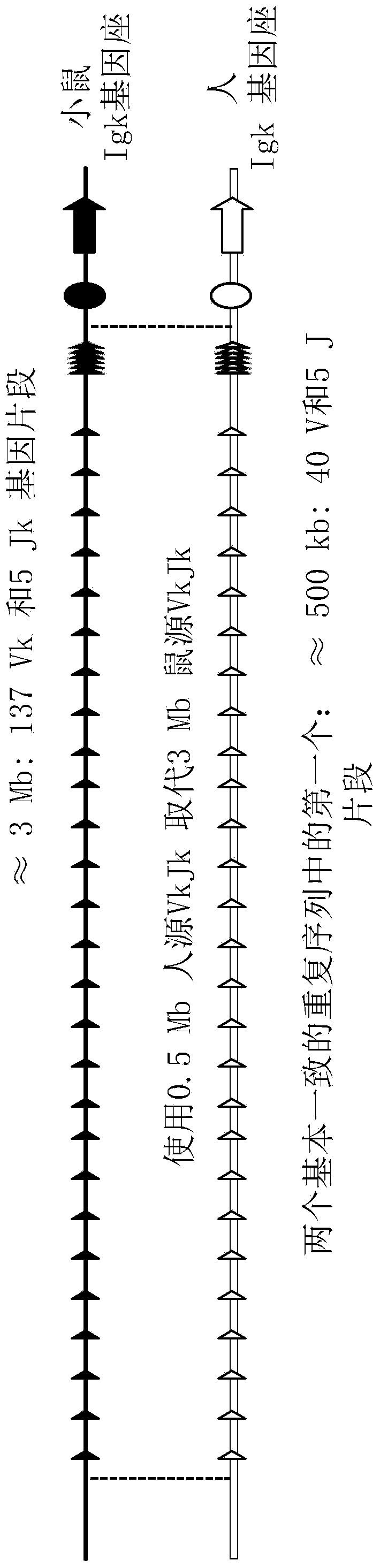
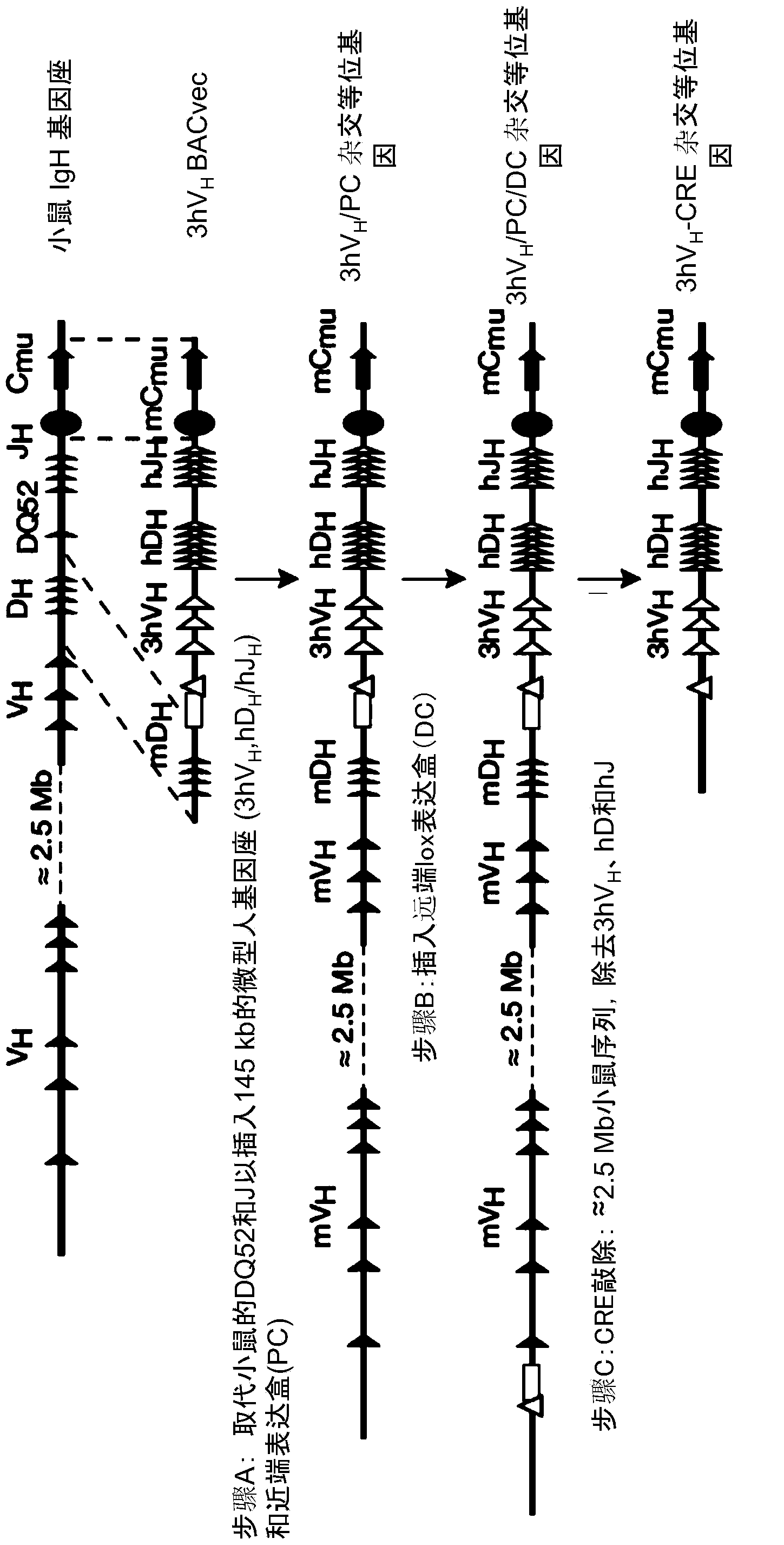
Transgenic mammals having human Ig loci including plural VH and VK regions and antibodies produced therefrom
InactiveUS7064244B2Reduced development and maturation of B-cellsEfficient productionAntipyreticAnalgesicsHuman animalMammal
The present invention relates to transgenic non-human animals that are engineered to contain human immunoglobulin gene loci. In particular, animals in accordance with the invention possess human Ig loci that include plural variable (VH and Vκ) gene regions. Advantageously, the inclusion of plural variable region genes enhances the specificity and diversity of human antibodies produced by the animal. Further, the inclusion of such regions enhances and reconstitutes B-cell development to the animals, such that the animals possess abundant mature B-cells secreting extremely high affinity antibodies.
Owner:ABQENIX INC
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS20030017534A1Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS7129084B2Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Antibodies and methods for generating genetically altered antibodies with enhanced effector function
InactiveUS20050054048A1Increase variabilityBetter pharmacokinetic profileAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGenetic diversityMonoclonal antibody
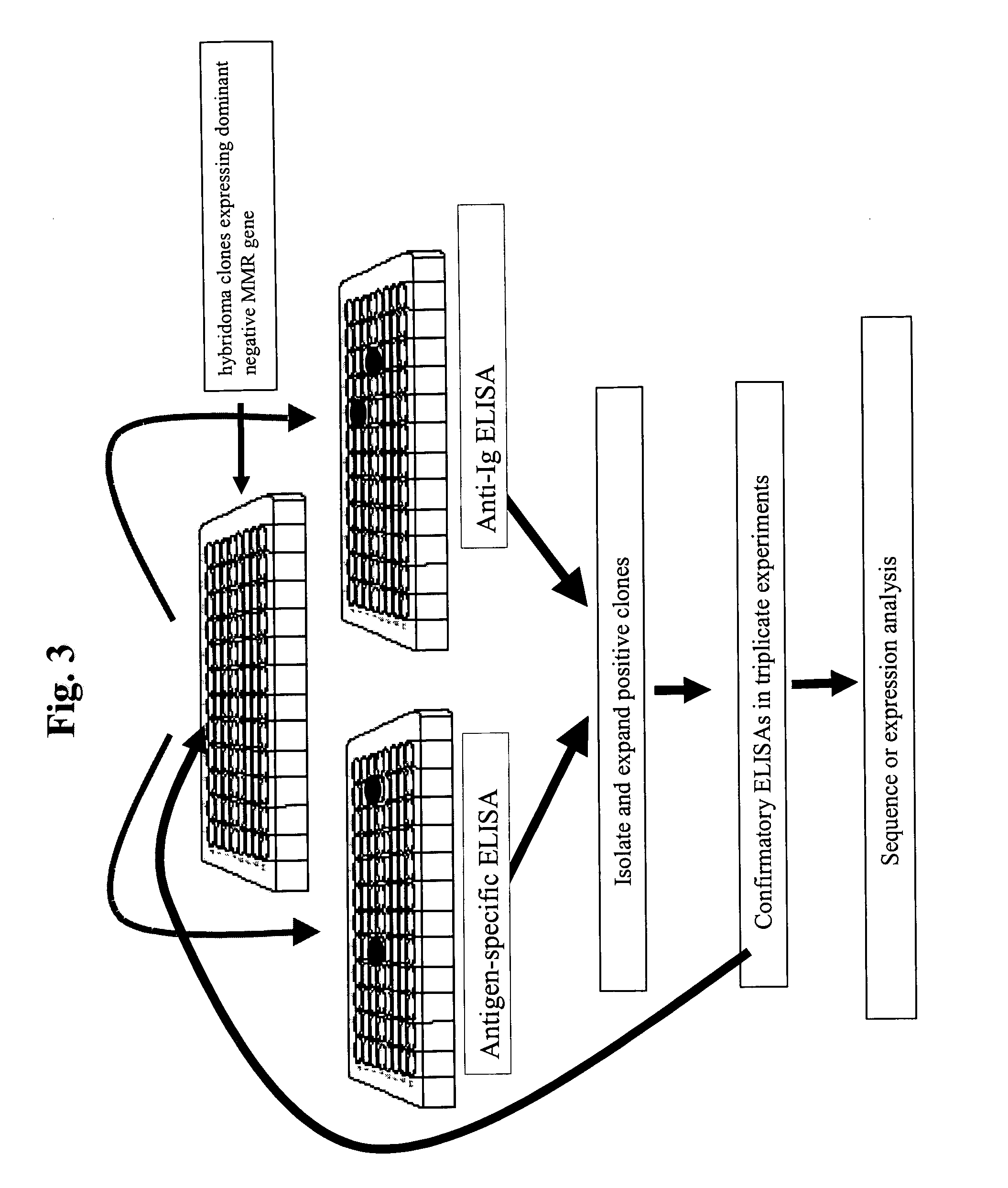
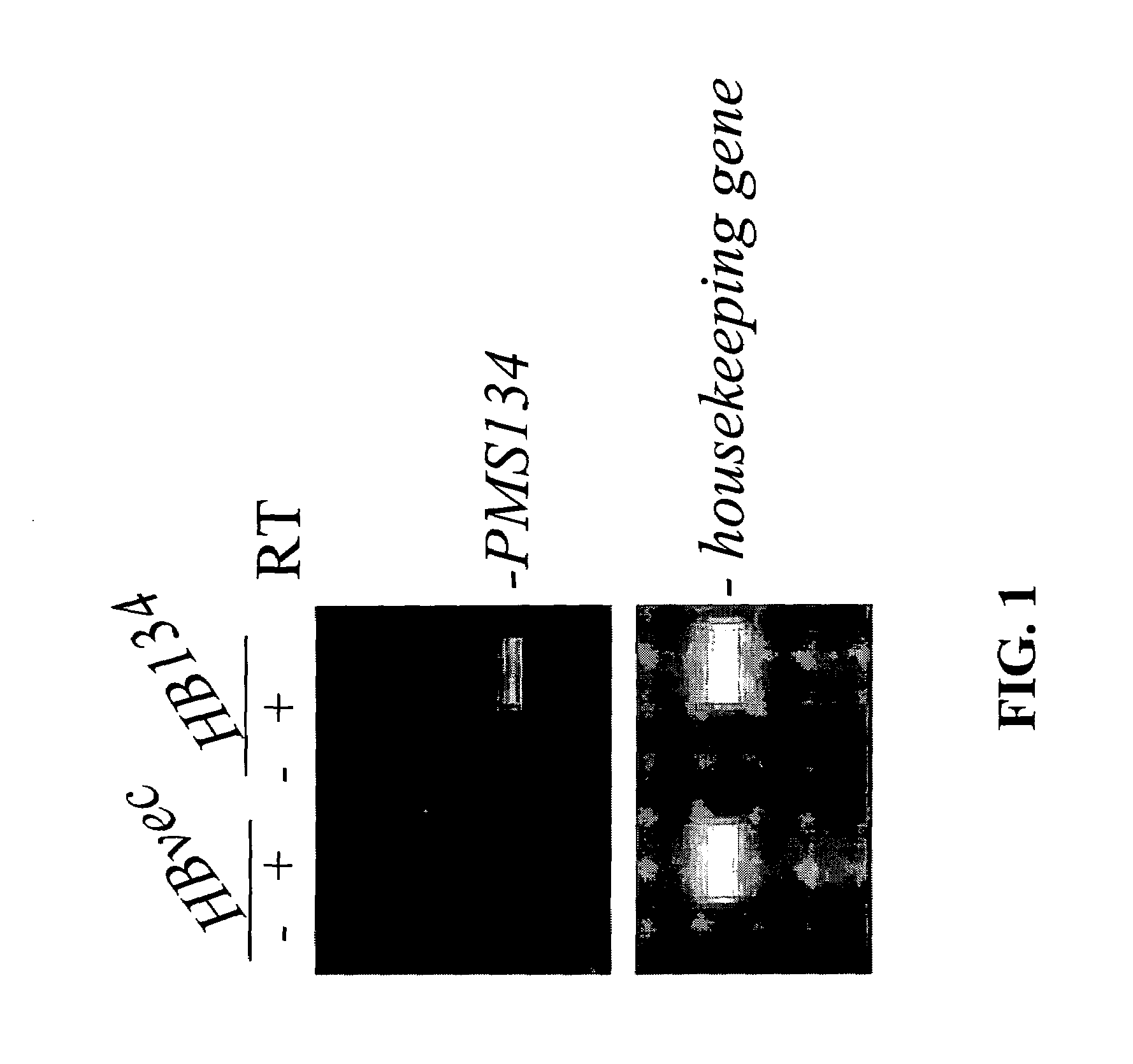
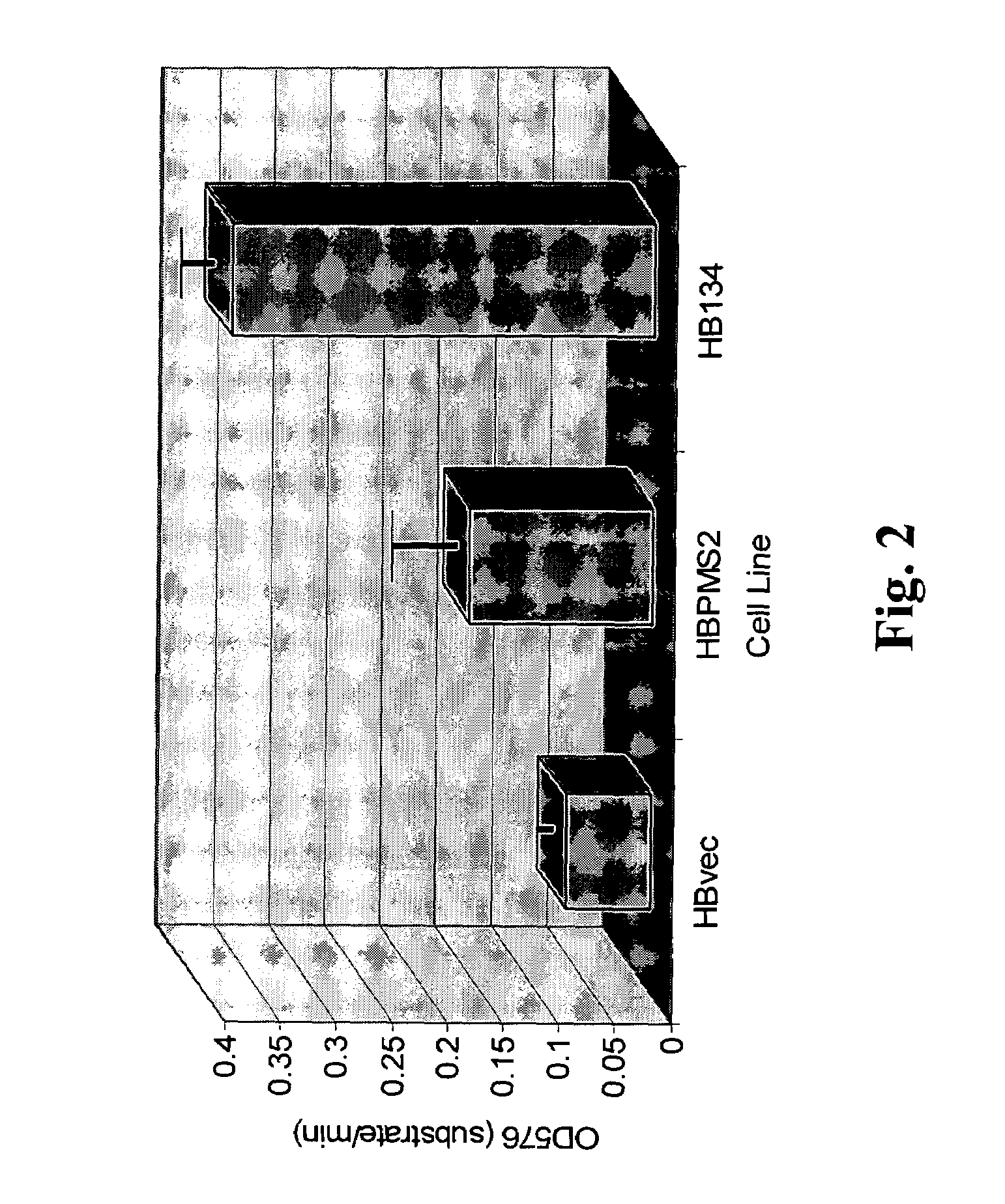
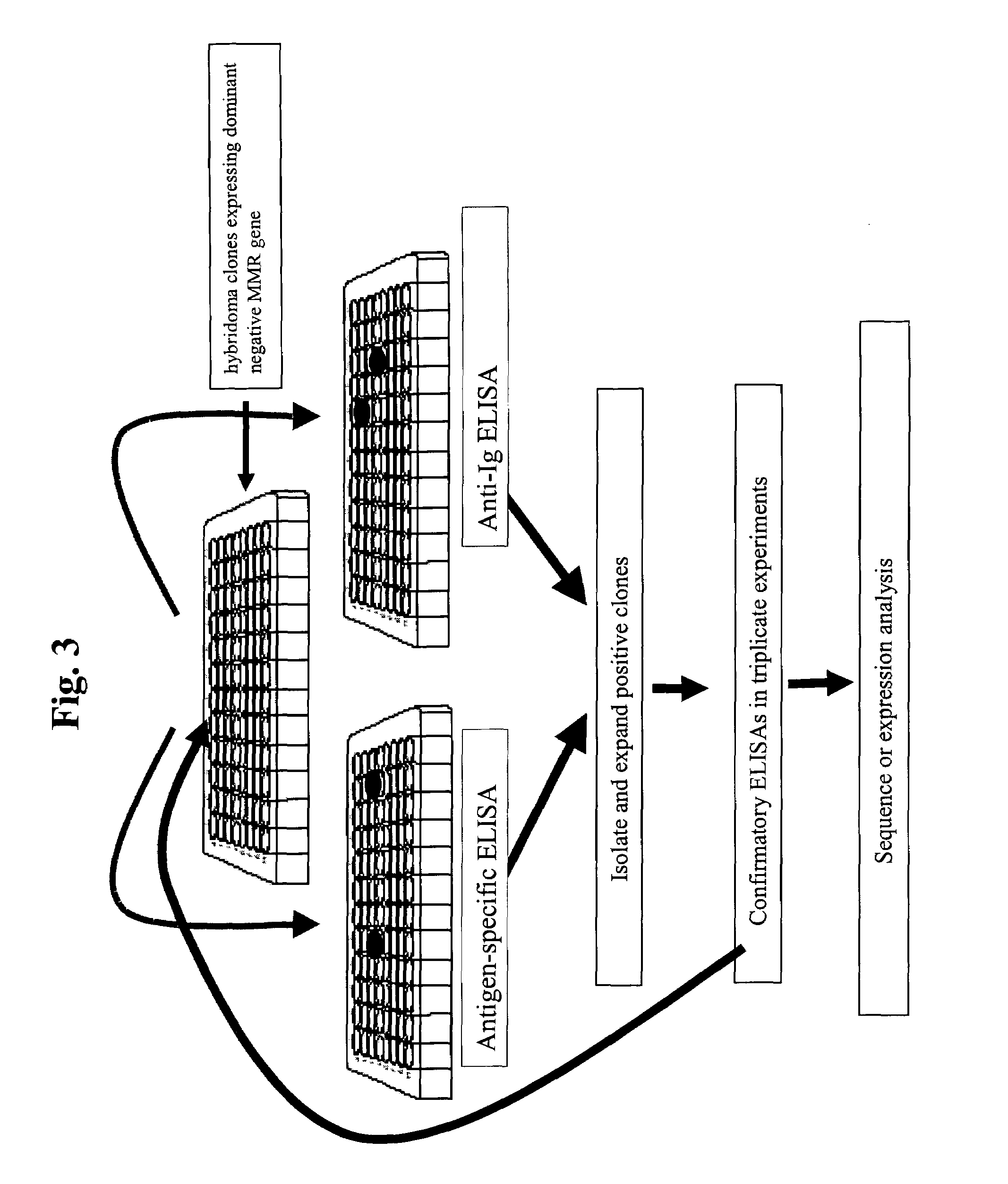
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. By introducing these genes into cells and transgenic animals, new cell lines and animal varieties with novel and useful properties can be prepared more efficiently than by relying on the natural rate of mutation. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production. The invention also provides methods for increasing the effector function of monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibodies with increased effector function.
Owner:EISAI INC
Production of antibodies using cre-mediated site-specific recombination
InactiveUS7145056B2Improve recombination efficiencyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationAntibody-Producing Cells
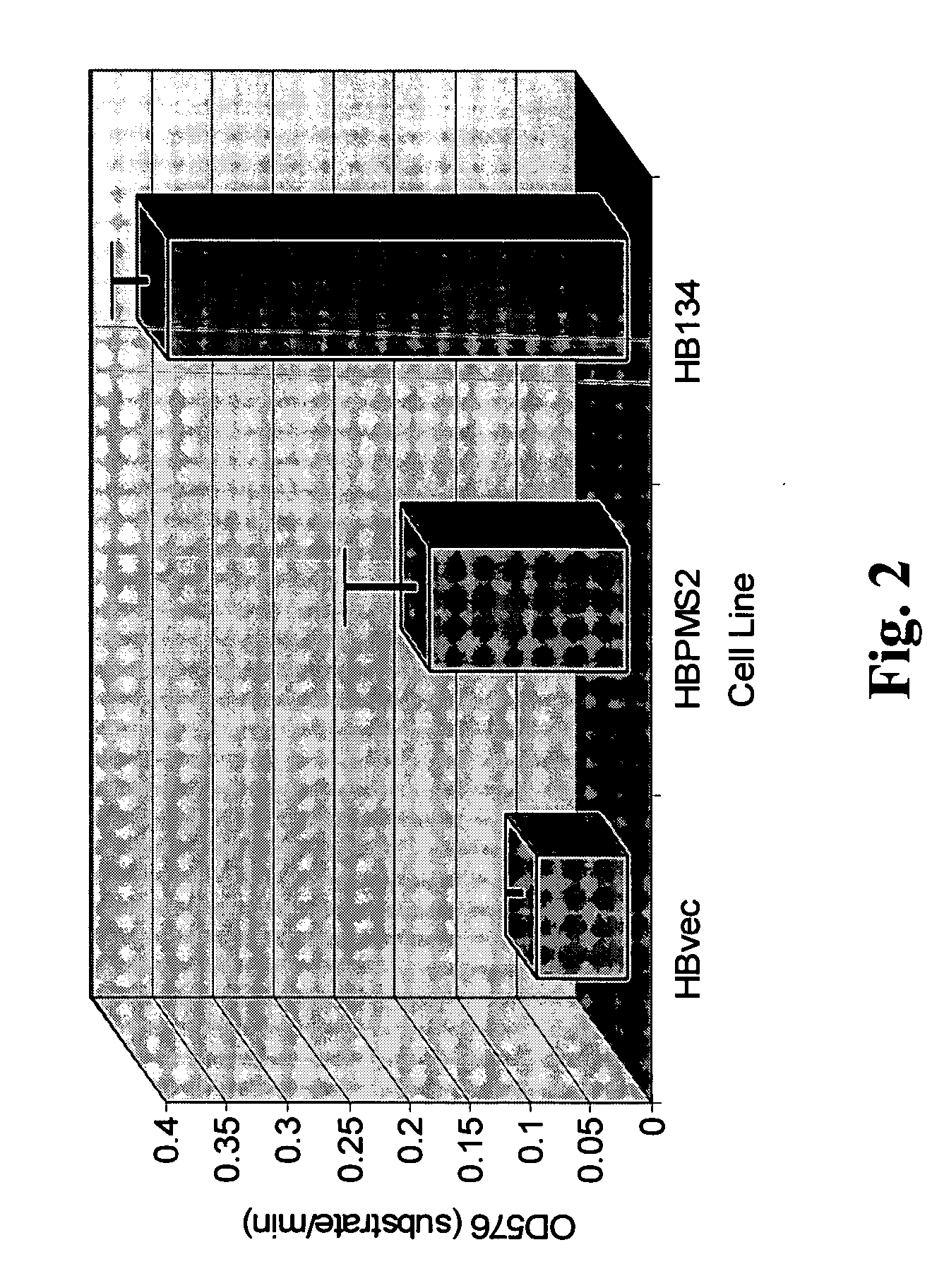
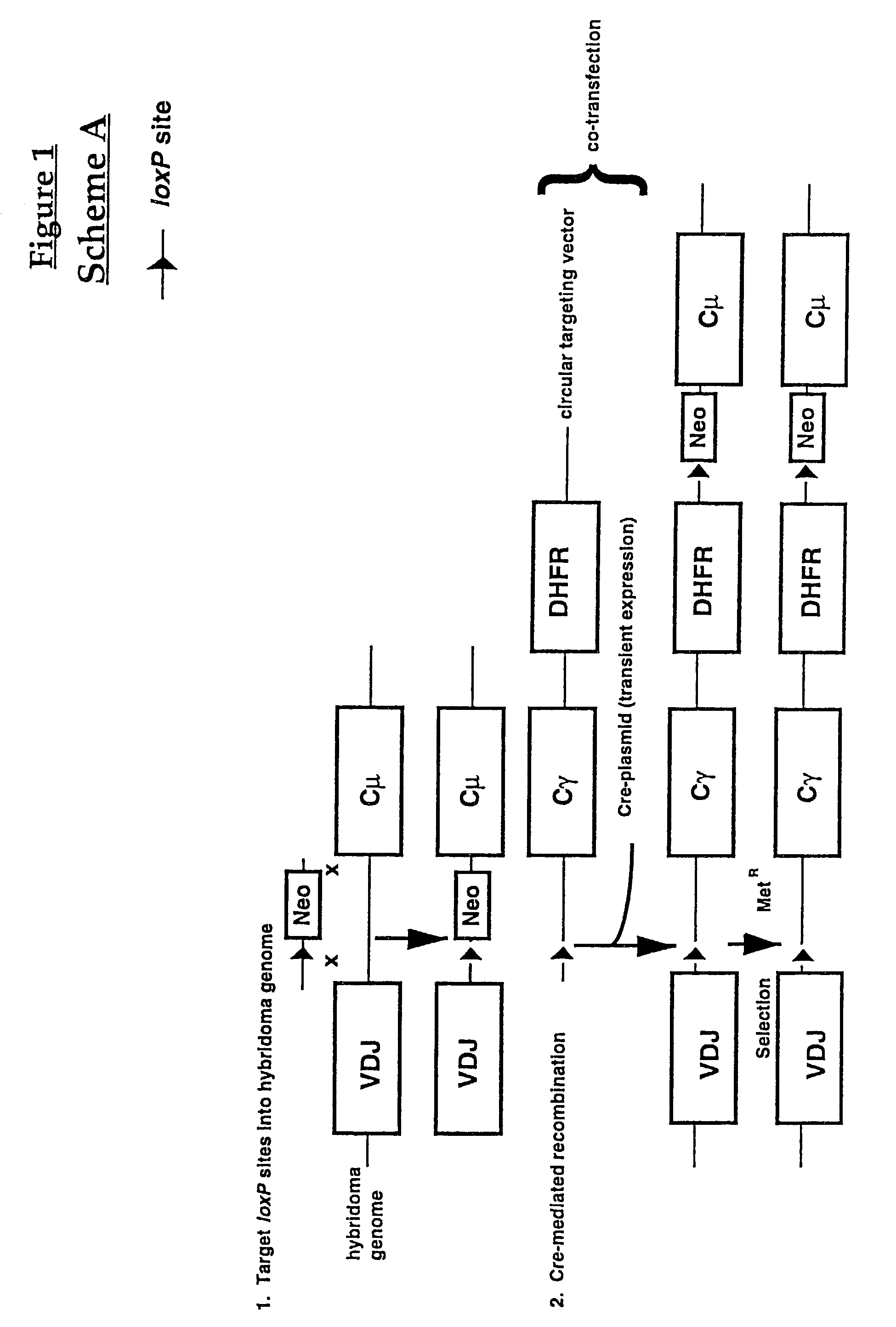
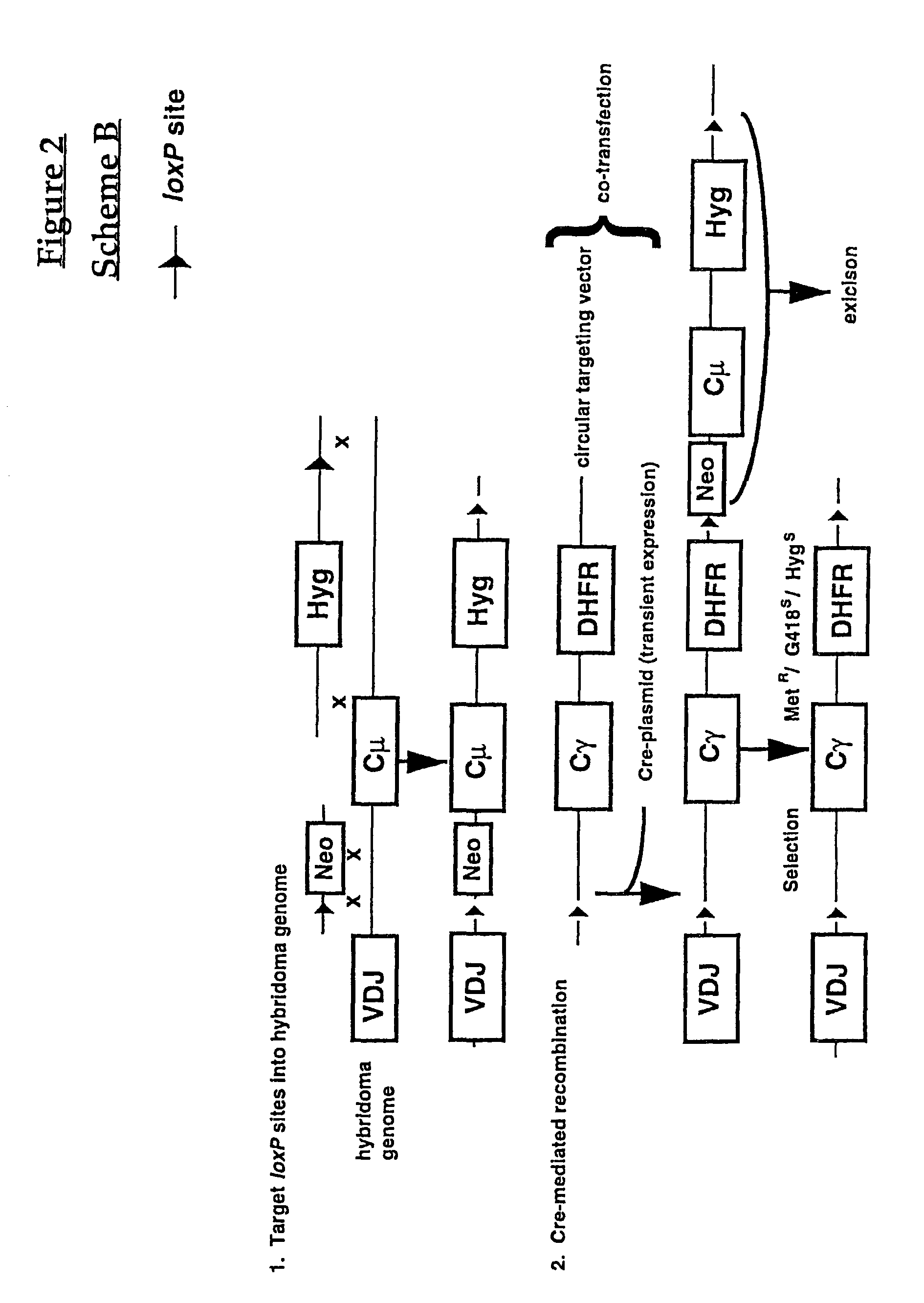
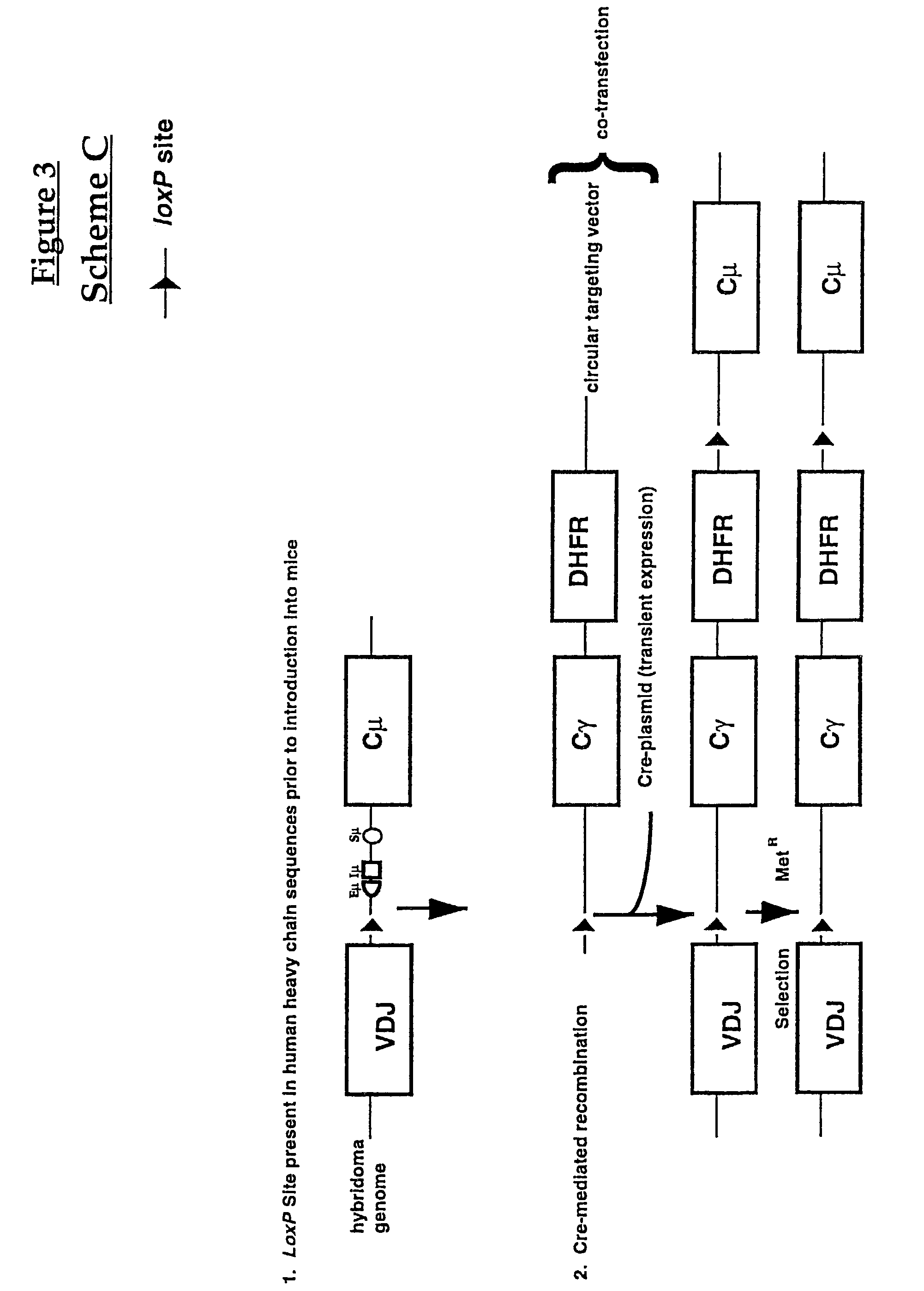
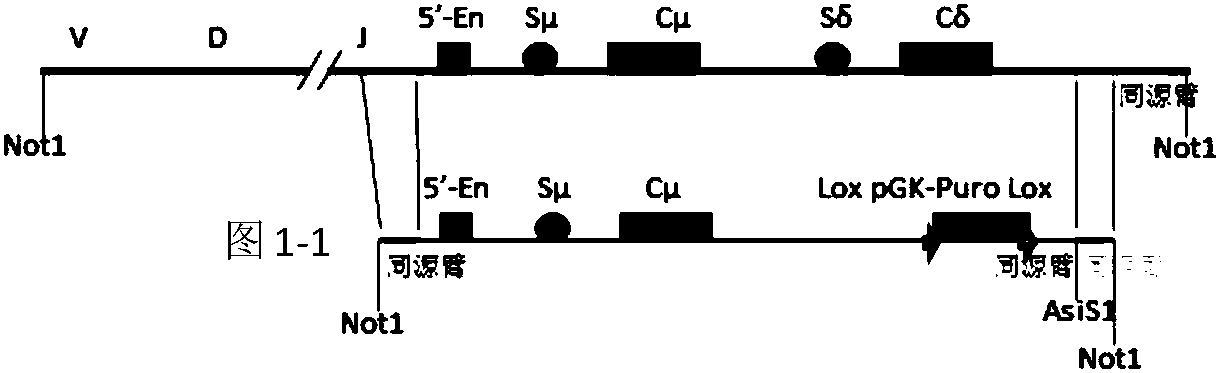
A method to produce a cell expressing an antibody from a genomic sequence of the cell comprising a modified immunoglobulin locus using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination is disclosed. The method involves first transfecting an antibody-producing cell with a homology-targeting vector comprising a lox site and a targeting sequence homologous to a first DNA sequence adjacent to the region of the immunoglobulin loci of the genomic sequence which is to be converted to a modified region, so the first lox site is inserted into the genomic sequence via site-specific homologous recombination. Then the cell is transfected with a lox-targeting vector comprising a second lox site suitable for Cre-mediated recombination with the integrated lox site and a modifying sequence to convert the region of the immunoglobulin loci to the modified region. This conversion is performed by interacting the lox sites with Cre in vivo, so that the modifying sequence inserts into the genomic sequence via Cre-mediated site-specific recombination of the lox sites. Also disclosed are a form of the method used to produce a cell expressing a modified antibody molecule using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination, and antibody-producing cells obtainable by the disclosed methods. Class-switching modifications of human antibodies produced in murine hybridoma cells are exemplified.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC +1
Human antibodies
InactiveUS7135287B1Organic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulin IgEGenetically modified animal
The invention uses the power of display selection methods to screen libraries of human immunoglobulin genes from nonhuman transgenic animals expressing human immunoglobulins. Such screening produces unlimited numbers of high affinity human antibodies to any target of interest.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
Genetically altered antibody-producing cell lines with improved antibody characteristics
InactiveUS20050048621A1Increase variabilityBetter pharmacokinetic profileAnimal cellsSugar derivativesBiological bodyGenetic diversity
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. Cells may be selected for expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), stimulated to produce AID, or manipulated to express AID for further enhancement of hypermutability. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production.
Owner:EISAI INC
Ungulates with genetically modified immune systems
The present invention provides ungulate animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which lack expression of functional endogenous immunoglobulin loci. The present invention also provides ungulate animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which express xenogenous, such as human, immunoglobulin loci. The present invention further provides ungulate, such as porcine genomic DNA sequence of porcine heavy and light chain immunogobulins. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and medical therapy. In addition, methods are provided to prepare such animals, organs, tissues, and cells.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Transgenic Aves Producing Human Polyclonal Antibodies
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
Chimeric nucleic acid molecule and application thereof to humanized antibody preparation
ActiveCN105441455AHigh affinityImprove rearrangement efficiencyHybrid immunoglobulinsFermentationHumanized antibodyImmunoglobulin M
The invention provides a nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule comprises human immunoglobulin genes or segments thereof and is characterized by also comprising gene segments in a host animal IgM (immunoglobulin M) constant region. The nucleic acid molecule can be used for efficiently preparing full humanized antibodies and has the effect of solving the problem of incompatibility of the interactions between BCRs (B cell receptors) of different species and Ig alpha and Ig beta. Meanwhile, the humanized antibodies expressed by the nucleic acid molecule are unnecessary to undergo second modification.
Owner:CHONGQING JINMAIBO BIOTEC CO LTD
Ungulates with genetically modified immune systems
The present invention provides ungulate animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which lack expression of functional endogenous immunoglobulin loci. The present invention also provides ungulate animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which express xenogenous, such as human, immunoglobulin loci. The present invention further provides ungulate, such as porcine genomic DNA sequence of porcine heavy and light chain immunogobulins. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and medical therapy. In addition, methods are provided to prepare such animals, organs, tissues, and cells.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
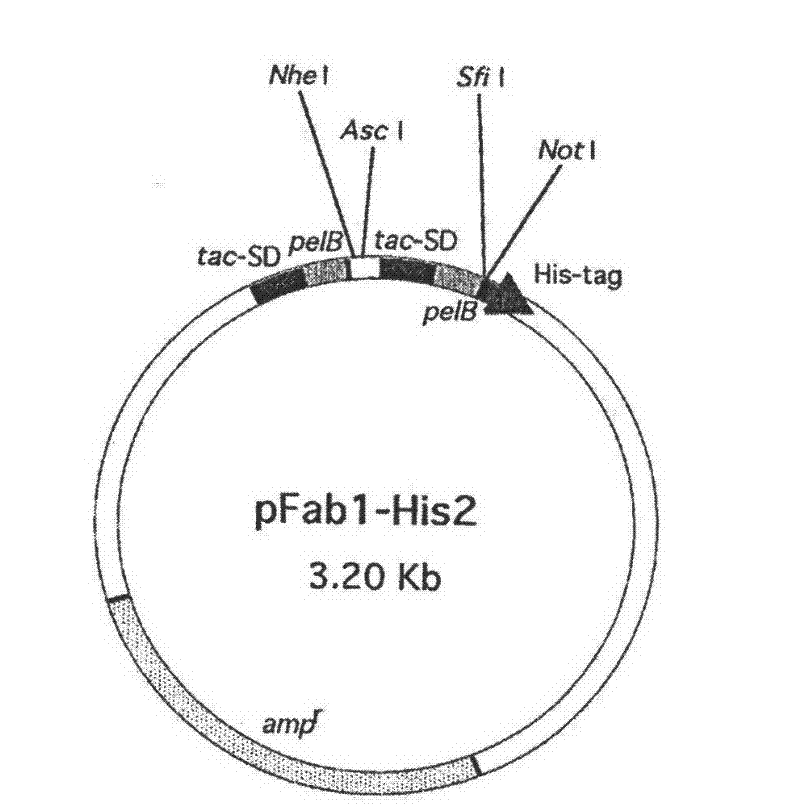
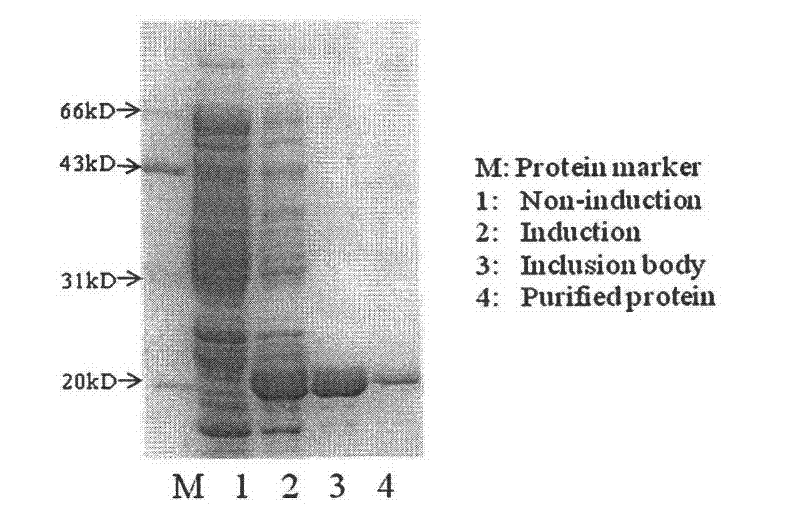
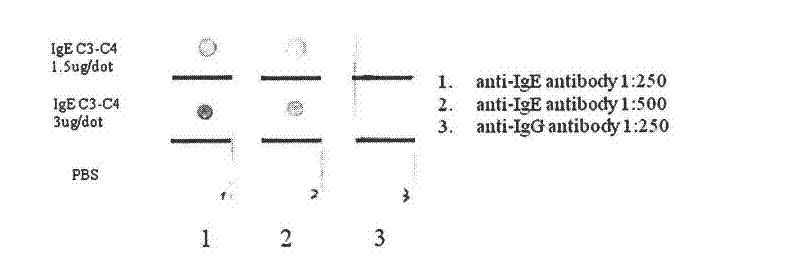
Human IgE (immunoglobulin E) Fab (fragment ab) against human and coding gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and relates to a human IgE (immunoglobulin E) Fab (fragment ab) against human and a coding gene and application thereof. In the invention, a recombined IgE C3-C4 protein is used for screening a natural human immunoglobulin gene library, and a human antibody Fab of IgE against human is screened from the library through ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) sequencing analysis and the like; extensive expression purification and further identification prove that the antibody Fab of human IgE against human is fully human and without Fc (fragment c), has an effect of inhibiting IgE mediated anaphylaxis without activating complements or causing human immune response or other pathological lesions and can be used for preparing antibody drugs for treating allergic diseases caused by IgE.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Enhanced expression of human or humanized immunoglobulin in non-human transgenic animals
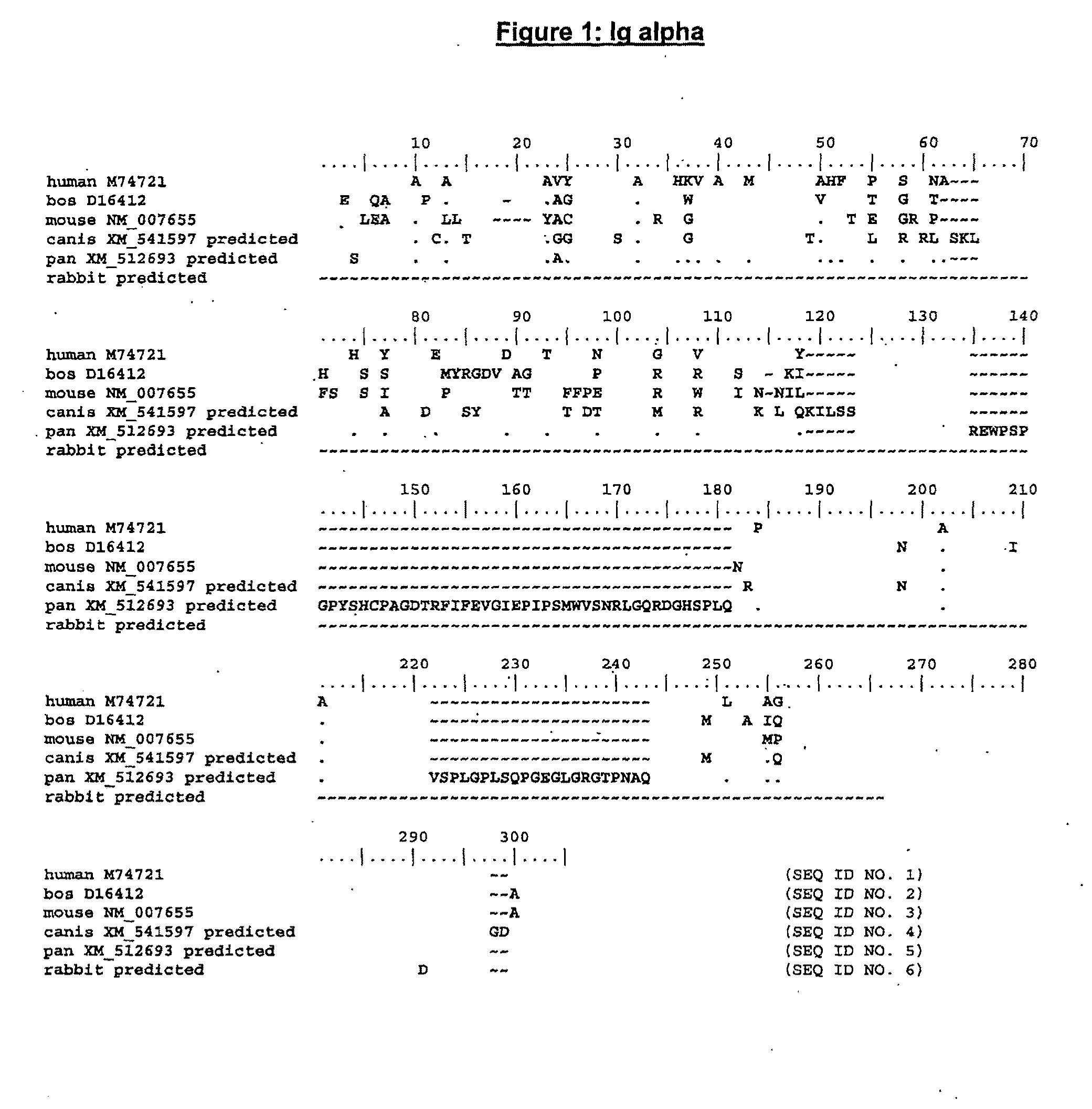
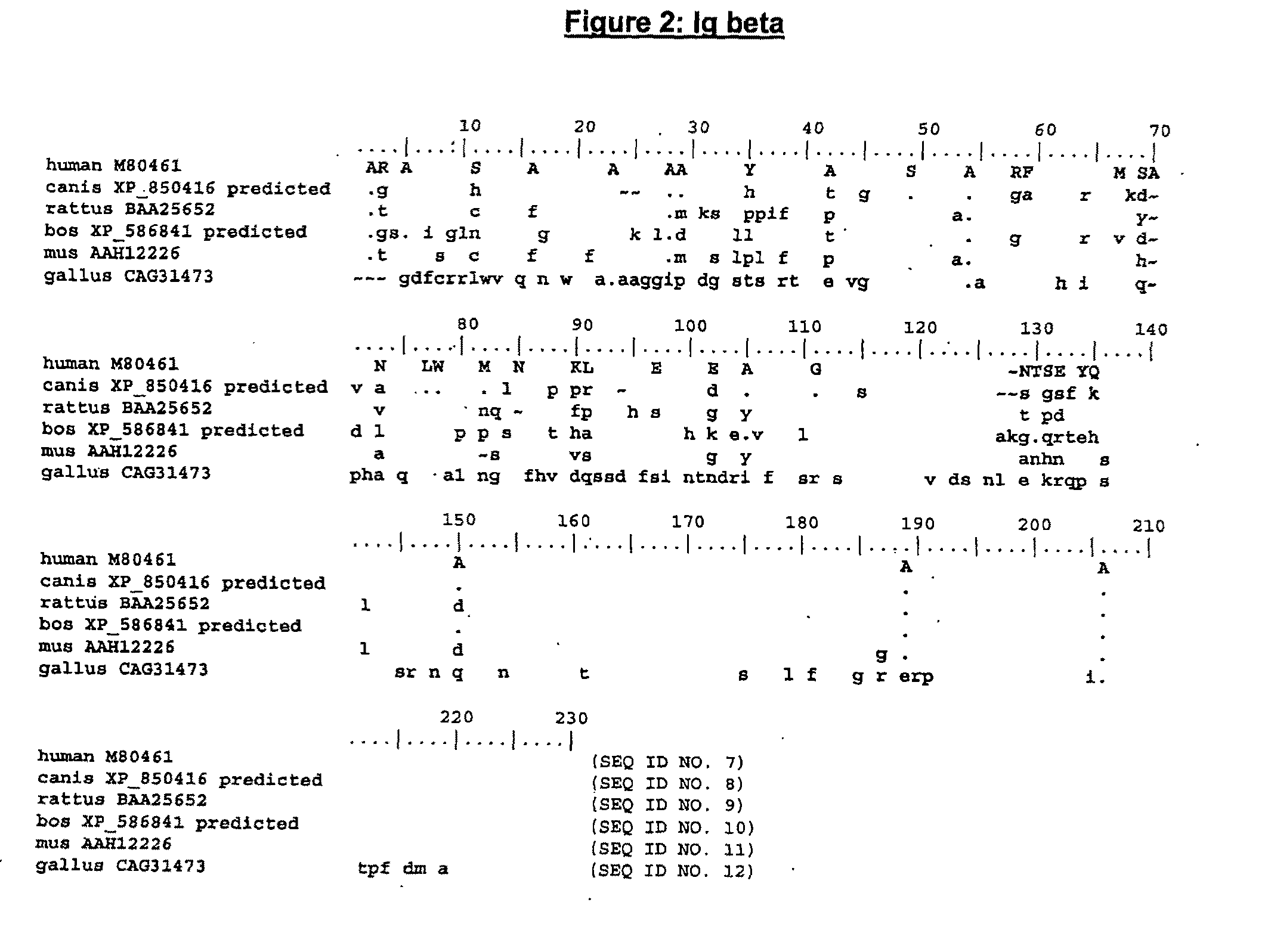
The present invention describes transgenic animals with human(ized) immunoglobulin loci and transgenes encoding human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ sequences. Of particular interest are animals with transgenic heavy and light chain immunoglobulin loci capable of producing a diversified human(ized) antibody repertoire that have their endogenous production of Ig and / or endogenous Igα and / or Igβ sequences suppressed. Simultaneous expression of human(ized) immunoglobulin and human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ results in normal B-cell development, affinity maturation and efficient expression of human(ized) antibodies.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Immunocompromised Ungulates
ActiveUS20160278349A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsVector-based foreign material introductionModel systemBiological agent
Porcine animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals are provided that lack functional endogenous immunoglobulin loci and are deficient in immunoglobulin expression and B-cells. These animals are useful as model systems for research and for development of new pharmaceutical and biological agents. In addition, methods are provided to prepare such animals.
Owner:REVIVICOR INC
Artificial antibody library with super-repertory
ActiveUS8178320B2Improve stabilityProvide stableCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCDNA libraryPcr method
Owner:SHIMIZU NOBUYOSHI +1
Nucleic acid for preparation of humanized antibody and application of nucleic acid
ActiveCN105274116AHigh affinityImprove rearrangement efficiencyImmunoglobulinsFermentationHumanized antibodyGene sequence
The invention provides a nucleic acid. The nucleic acid comprises a human immunoglobulin gene or fragments thereof and is characterized by further comprising a human CD79 gene sequence. By the nucleic acid, the problem of incompatibility between BCR and each of Ig alpha and Ig beta of the human immunoglobulin gene in different species is solved, and secondary modification of a humanized antibody expressed by the nucleic acid is not needed.
Owner:CHONGQING JINMAIBO BIOTEC CO LTD
Enhanced Expression of Human or Humanized Immunoglobulin in Non-Human Transgenic Animals
The present invention describes transgenic animals with human(ized) immunoglobulin loci and transgenes encoding human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ sequences. Of particular interest are animals with transgenic heavy and light chain immunoglobulin loci capable of producing a diversified human(ized) antibody repertoire that have their endogenous production of Ig and / or endogenous Igα and / or Igβ sequences suppressed. Simultaneous expression of human(ized) immunoglobulin and human(ized) Igα and / or Igβ results in normal B-cell development, affinity maturation and efficient expression of human(ized) antibodies.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Surface antigen 1 of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment and encoded gene thereof
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and relates to a surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment, encoded gene and use thereof. According to the invention, the surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is filtered from a base through establishing a Toxoplasma gondii human immunoglobulin, ELISA, diluting the prothrombin time, sequencing analysis, etc. Through expression purifying and authenticating, the human antigen Fab fragment is authenticated to specifically identify the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii and have higher affinity with the tachyzoite-bradyzoite recombination SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii, for being identified with the specificity of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite. The human antigen Fab fragment of the invention does not contain Fc segment and does not activate the alexin or cause the histopathological damages of human immune response, etc. when the function of restricting the invasion of Toxoplasma gondii to the host cell is exerted. The surface antigen 1 (SAG1) of Toxoplasma gondii human antibody Fab fragment is safe and reliable when applied for the human body. The antigen medicine for treating toxoplasmosis or the antigen targeted medicine can be prepared.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Genetically altered antibody-producing cell lines with improved antibody characteristics
InactiveUS7604994B2Altering the hypermutability of an antibody-producing cellGenetic stabilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGenetic diversityActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminase
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. Cells may be selected for expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), stimulated to produce AID, or manipulated to express AID for further enhancement of hypermutability. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production.
Owner:EISAI INC
Nucleic acid molecule and application to humanized antibody
PendingCN108486126AGuarantee normal developmentEnsure antibody maturationImmunoglobulins against animals/humansFermentationTherapeutic antibodyHumanized antibody
The invention provides a nucleic acid molecule. The nucleic acid molecule comprises an immune globulin gene or a fragment of the immune globulin gene. The nucleic acid molecule is characterized by comprising an IgM gene (IgHCmu) and an IgM transduction element (switch region, Smu), and the Smu and the IgHCmu are host animal sequences. The humanoral antibody is directly acquired, the artificial modification in the later period is reduced, and the druggability of the antibody is improved. The development and the maturation of the transgenic B-cells and the number of the B-cells are completely consistent with those of the normal mouse, thereby being favorable for the differentiation of the B-cells; the specificity and the diversity of the produced antibody are improved; and the efficiency ofscreening the therapeutic antibody is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING JINMAIBO BIOTEC CO LTD
Characterization of adaptive immune response to vaccination or infection using immunosequencing
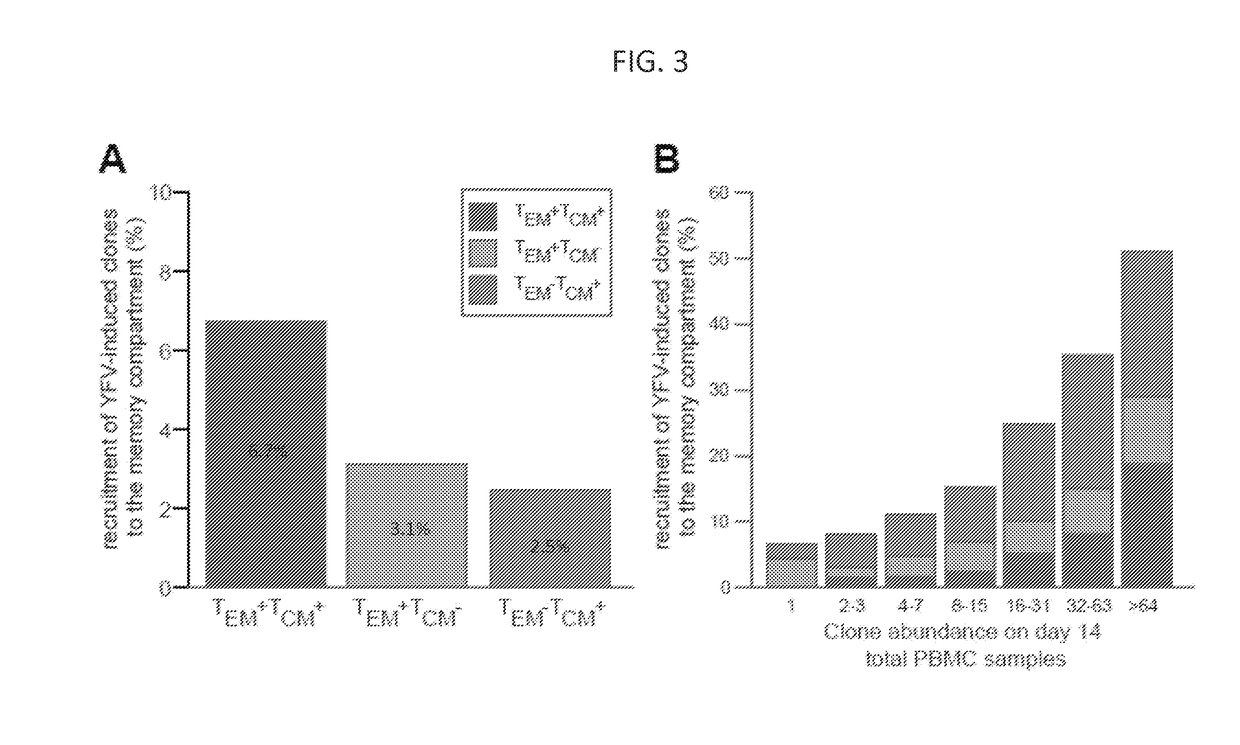
ActiveUS20170362653A1High proportional abundanceMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunological memoryVaccination
Methods of monitoring and measuring dynamic adaptive immune cell responses are provided. High-throughput sequencing of T cell receptor and immunoglobulin loci is used to characterize the breadth of an effector cell response to a stimulus, such as a vaccine or infection. Unique responding effector cell clones and abundance thereof can be determined. Additionally, methods for determining the contribution of responding effector cells to the immunological memory compartment are provided.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT +1
Artificial antibody library with super-repertory
ActiveUS20060057632A1Quality improvementEasy to introduceCompound screeningPeptide librariesCDNA libraryPcr method
An artificial antibody library with a super-repertory (1011 or more) is constructed by: using a cDNA library as a template, amplifying a fragment containing the CDR1 and CDR2s regions of the VH or VL region of immunoglobulin gene and a fragment containing the CDR3 region each by the PCR method; integrating the VH library and the VL library, which are little contaiminated with unexpressionable repertory and have high safety, into an nono-expression vector; transferring it into a host; and then shuffling the VH region in the VH library with the VL region in the VL library.
Owner:SHIMIZU NOBUYOSHI +1
Humanized universal light chain mice
Mice, tissues, cells, and genetic material are provided that comprise a humanized heavy chain immunoglobulin locus, a humanized light chain locus that expresses a universal light chain, and a gene encoding an ADAM6 or ortholog or homolog or functional fragment thereof. Mice are provided that express humanized heavy chains comprising human variable domains, and that express humanized light chains comprising human variable domains wherein the light chains are derived from no more than one, or no more than two, light chain V and J or rearranged V / J sequences. Fertile male mice that express antibodies with universal light chains and humanized heavy chains are provided. Methods and compositions for making bispecific binding proteins are provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
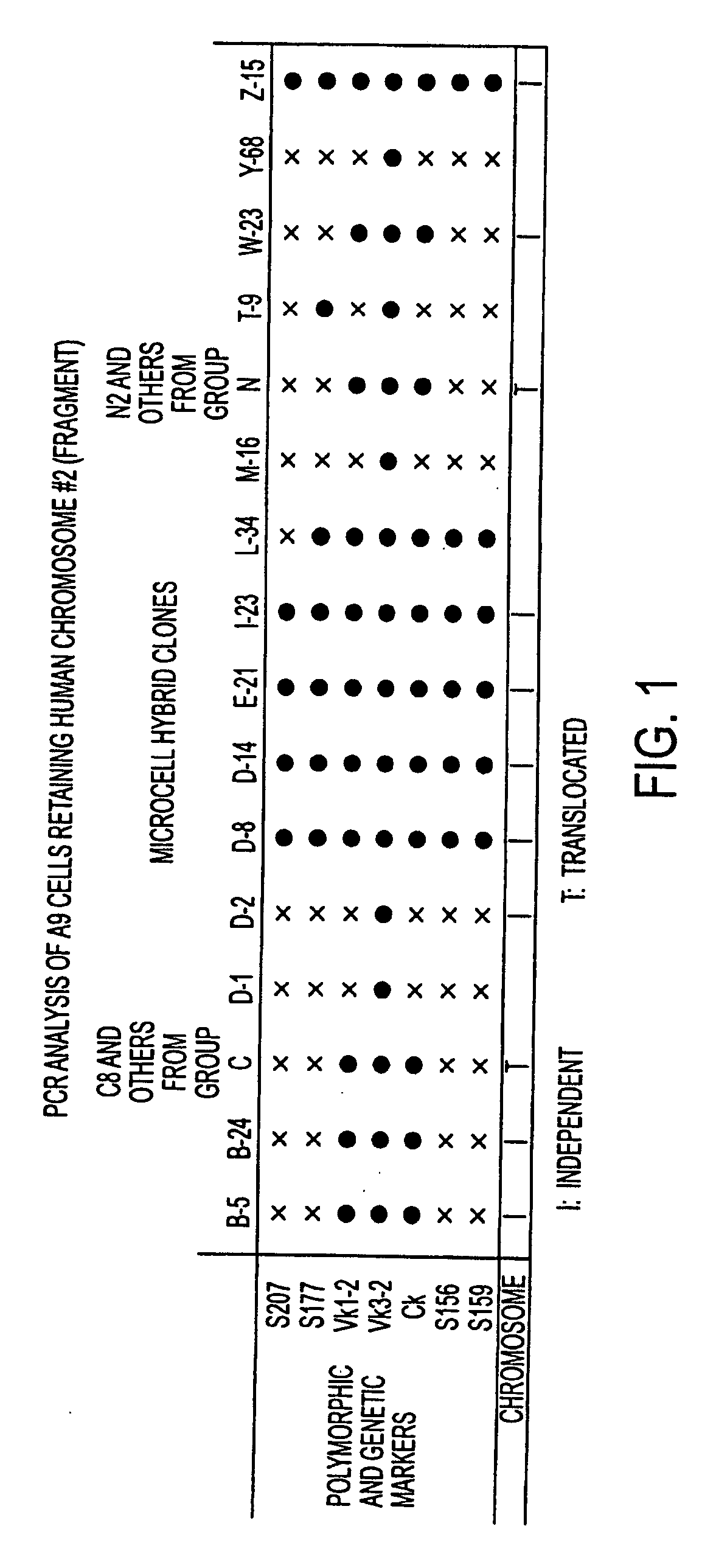
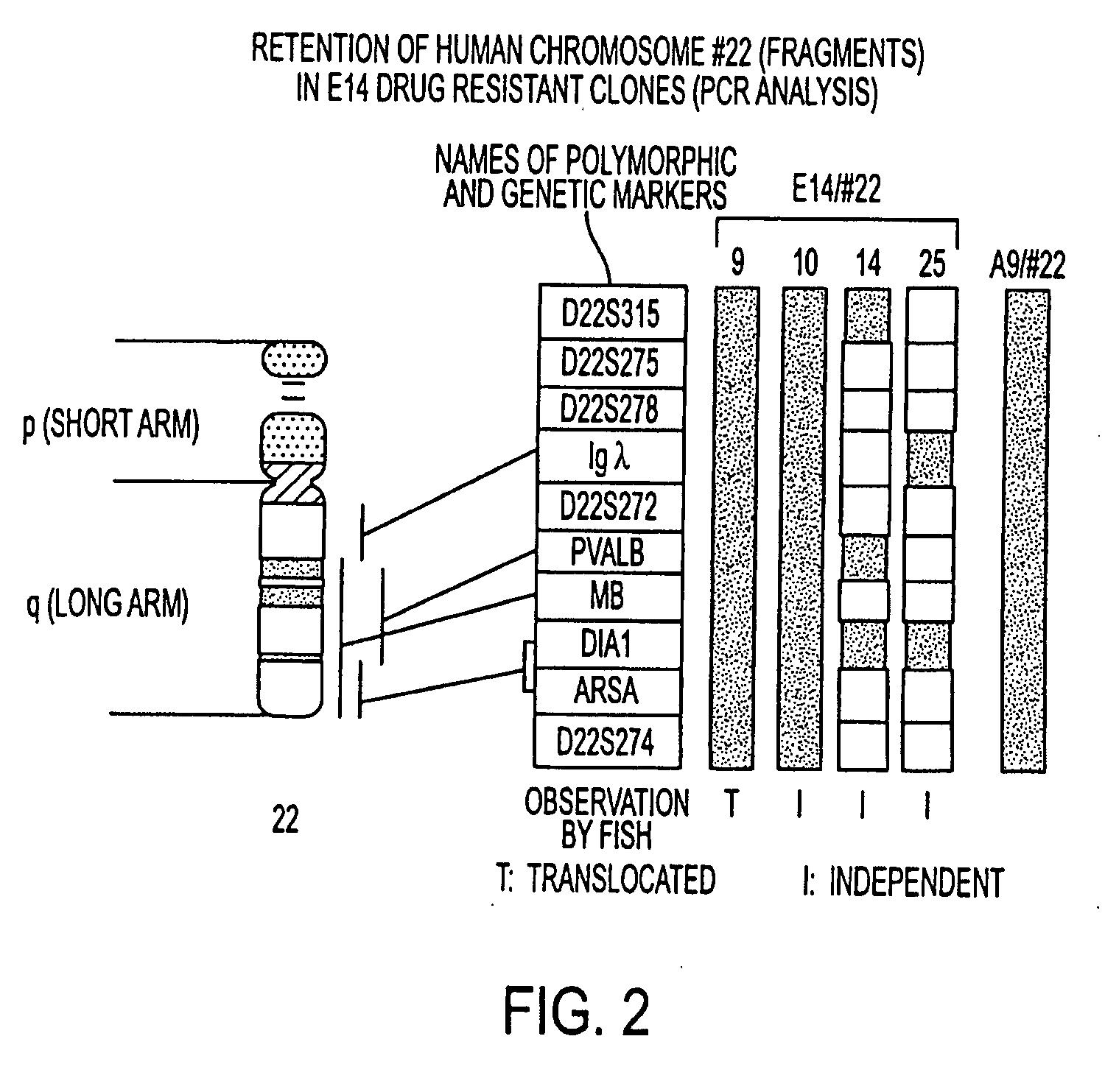
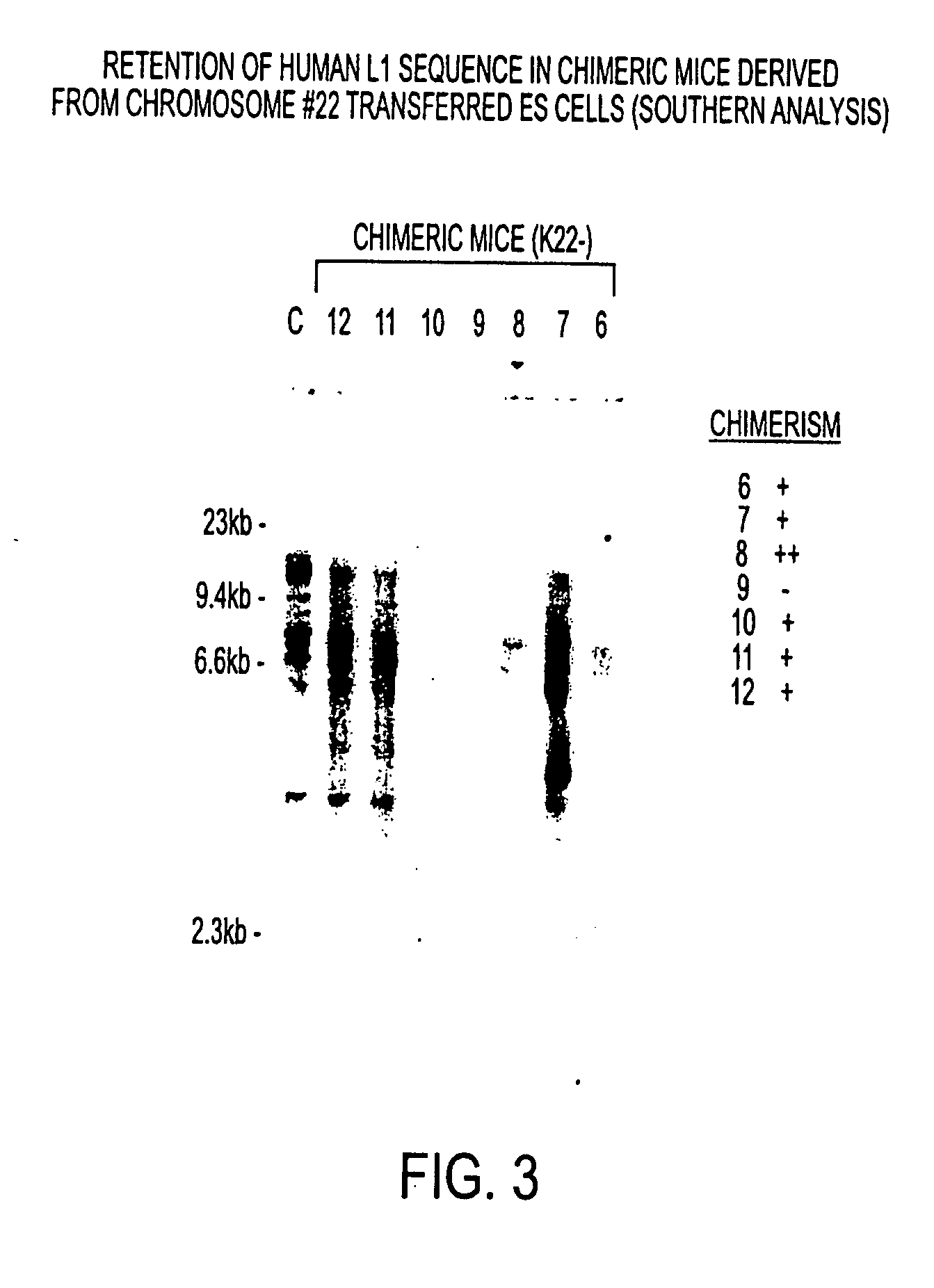
Isolation of a rearranged human immunoglobulin gene from a chimeric mouse and recombinant production of the encoded immunoglobulin
InactiveUS20090253902A1Retention stabilitySugar derivativesNew breed animal cellsHuman animalAlien chromosome
The specification relates to a method for producing a chimeric non-human animal, which comprises preparing a microcell containing a foreign chromosome(s) or a fragment(s) thereof and transferring the foreign chromosome(s) or fragment(s) thereof into a pluripotent cell by fusion with the microcell; a chimeric non-human animal which can be produced by the above method and its progeny; tissues and cells derived therefrom; and a method for using the same. Further, a pluripotent cell containing a foreign chromosome(s) or a fragment(s) thereof, a method for producing the same, and a method for using the same are also provided. Moreover, a pluripotent cell in which at least two endogenous genes are disrupted, and a method for producing the same by homologous recombination are provided.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
Humanized anti-plasmodium falciparum antibody and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and relates to a humanized anti-plasmodium falciparum antibody as well as a coding gene and application thereof. According to the invention, an anti-plasmodium falciparum human immunoglobulin gene library is constructed; the humanized anti-plasmodium falciparum antibody is screened from the library through ELISA, sequencing analysis and the like;expression, purification and identification are carried out to prove that the humanized anti-plasmodium falciparum antibody can specifically recognize and has high affinity to a plasmodium falciparummerozoite recombinant surface antigen MSP1, and also can be specifically recognized with plasmodium falciparum merozoite; the humanized anti-plasmodium falciparum antibody plays a role of preventingplasmodium falciparum from invading erythrocytes, and also plays roles of activating complements, causing immune response of a human body and the like so as to enhance a treatment effect and be applied to the human body safely and reliably; the humanized anti-plasmodium falciparum antibody can be used for preparing antibody drugs against malaria and antibody targeting drugs.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Mammalian cell line for protein production and library generation
According to a first aspect of the invention, a method for the generation of a cell line is provided, comprising the steps of (a) providing a plurality of mammalian B cells, wherein each of the plurality of B cells comprises a transgenic genomic DNA sequence encoding a marker protein inserted into an endogenous immunoglobulin locus comprised in said B cell, and wherein the transgenic genomic DNA sequence is amenable to cleavage by a site directed nuclease, particularly Cas9; (b) replacing the transgenic genomic DNA sequence encoding a marker protein with a second transgenic DNA sequence encoding a protein of interest; (c) sorting B cells based on the presence or absence of the marker protein; and (d) collecting B cells in which the marker protein is absent.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Method for rearranging immunoglobulin and producing antibody through MDA-PCR (Multiple Displacement Amplification-Polymerase Chain Reaction) enriched genome
ActiveCN102676532AAvoid the disadvantages of instabilitySimple stepsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeavy chainMature B-Cell
The invention provides a method for rearranging immunoglobulin by specifically amplifying a genome. The method comprises the following steps of: cracking mature B cells; amplifying genome genes of the B cells through a primer capable of specifically amplifying a variable region of a heavy chain and / or a light chain of an antibody by using a multiple displacement amplification method, thereby amplifying a sequence of the variable region comprising the heavy chain and / or light chain from the genome relatively and specifically; and performing PCR amplification by using the primer for specifically combining the variable region of the heavy chain and / or the light chain of the antibody by taking reaction solution obtained by multiple displacement amplification as a substrate, thereby obtaining a gene sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain and / or the light chain of the antibody; sequencing an obtained PCR product to determine the gene sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain and / or the light chain of the antibody obtained by PCR amplification. Through the method provided by the invention, rearranged immunoglobulin is obtained and the gene is utilized to product the antibody.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
Humanized immunoglobulin loci
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Animals, cells and methods for production of detectably-labeled antibodies
Genetically-modified mammals and immune cells are provided which are capable of producing or secreting detectably-labeled immunoglobulin molecules as a result of genetic modifications of at least one immunoglobulin gene in the genome thereof, such that a fusion polynucleotide encoding a detectable protein or peptide and an immunoglobulin component molecule is present.
Owner:SIMON SANFORD +1
Method for rearranging immunoglobulin and producing antibody through MDA-PCR (Multiple Displacement Amplification-Polymerase Chain Reaction) enriched genome
ActiveCN102676532BAvoid the disadvantages of instabilitySimple stepsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeavy chainMature B-Cell
The invention provides a method for rearranging immunoglobulin by specifically amplifying a genome. The method comprises the following steps of: cracking mature B cells; amplifying genome genes of the B cells through a primer capable of specifically amplifying a variable region of a heavy chain and / or a light chain of an antibody by using a multiple displacement amplification method, thereby amplifying a sequence of the variable region comprising the heavy chain and / or light chain from the genome relatively and specifically; and performing PCR amplification by using the primer for specifically combining the variable region of the heavy chain and / or the light chain of the antibody by taking reaction solution obtained by multiple displacement amplification as a substrate, thereby obtaining a gene sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain and / or the light chain of the antibody; sequencing an obtained PCR product to determine the gene sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain and / or the light chain of the antibody obtained by PCR amplification. Through the method provided by the invention, rearranged immunoglobulin is obtained and the gene is utilized to product the antibody.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com