Antibodies and methods for generating genetically altered antibodies with enhanced effector function
a technology of effector function and antibody, which is applied in the field of mutagenesis, can solve the problems of loss of binding affinity due to conformational changes in the 3-, inability to restore the affinity of the hab, and very time-consuming process, and achieves enhanced mutability in cells and beneficial pharmacokinetic profiles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Stable Expression of Dominant Negative MMR Genes in Hybridoma Cells
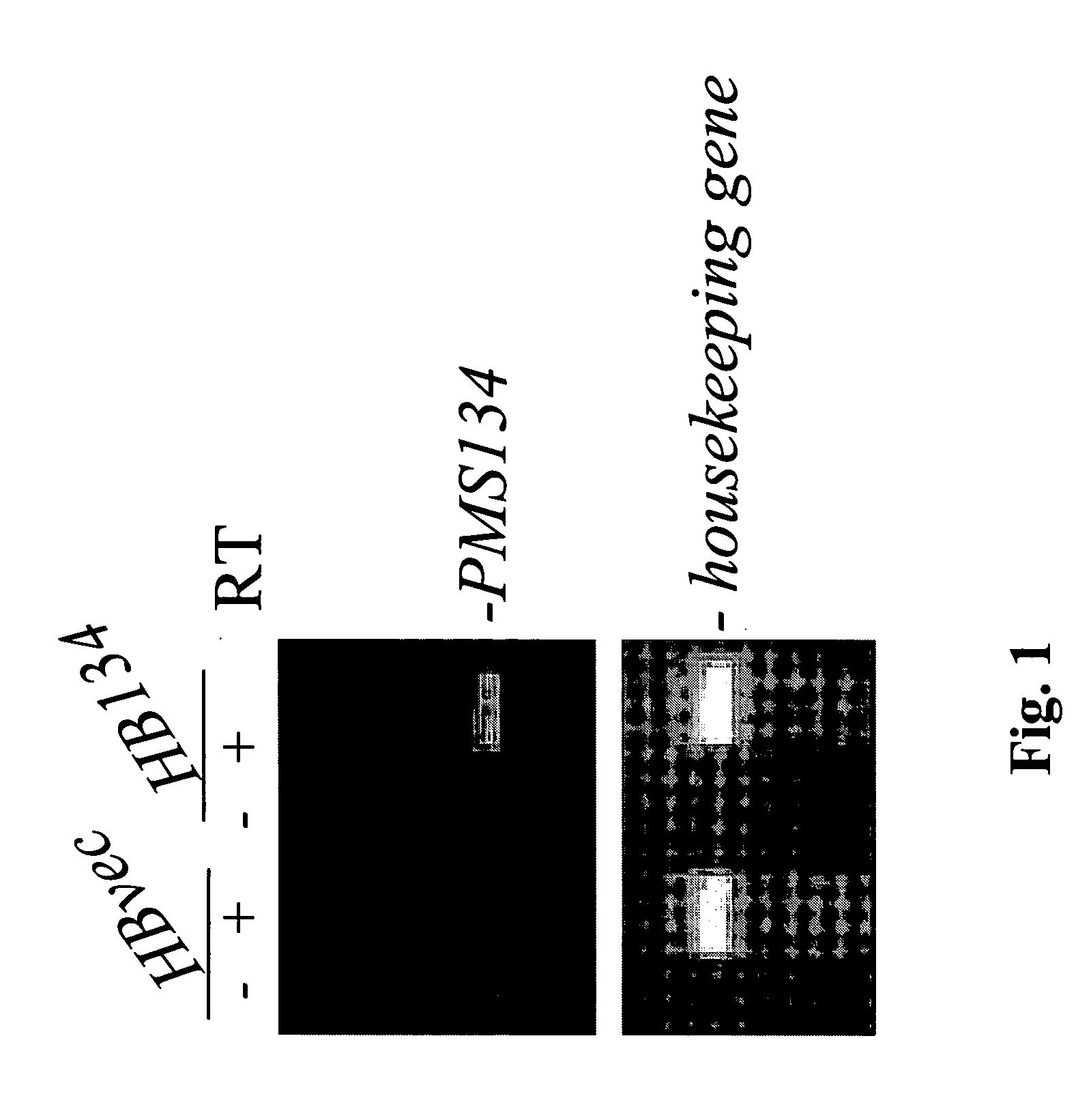
[0102] It has been previously shown by Nicolaides et al. (Nicolaides et al. (1998) A Naturally Occurring hPMS2 Mutation Can Confer a Dominant Negative Mutator Phenotype Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:1635-1641) that the expression of a dominant negative allele in an otherwise MMR proficient cell could render these host cells MMR deficient. The creation of MMR deficient cells can lead to the generation of genetic alterations throughout the entire genome of a host organisms offspring, yielding a population of genetically altered offspring or siblings that may produce biochemicals with altered properties. This patent application teaches of the use of dominant negative MMR genes in antibody-producing cells, including but not limited to rodent hybridomas, human hybridomas, chimeric rodent cells producing human immunoglobulin gene products, human cells expressing immunoglobulin genes, mammalian cells producing single chain antibodie...
example 2
hPMS134 Causes a Defect in MMR Activity and Hypermutability in Hybridoma Cells
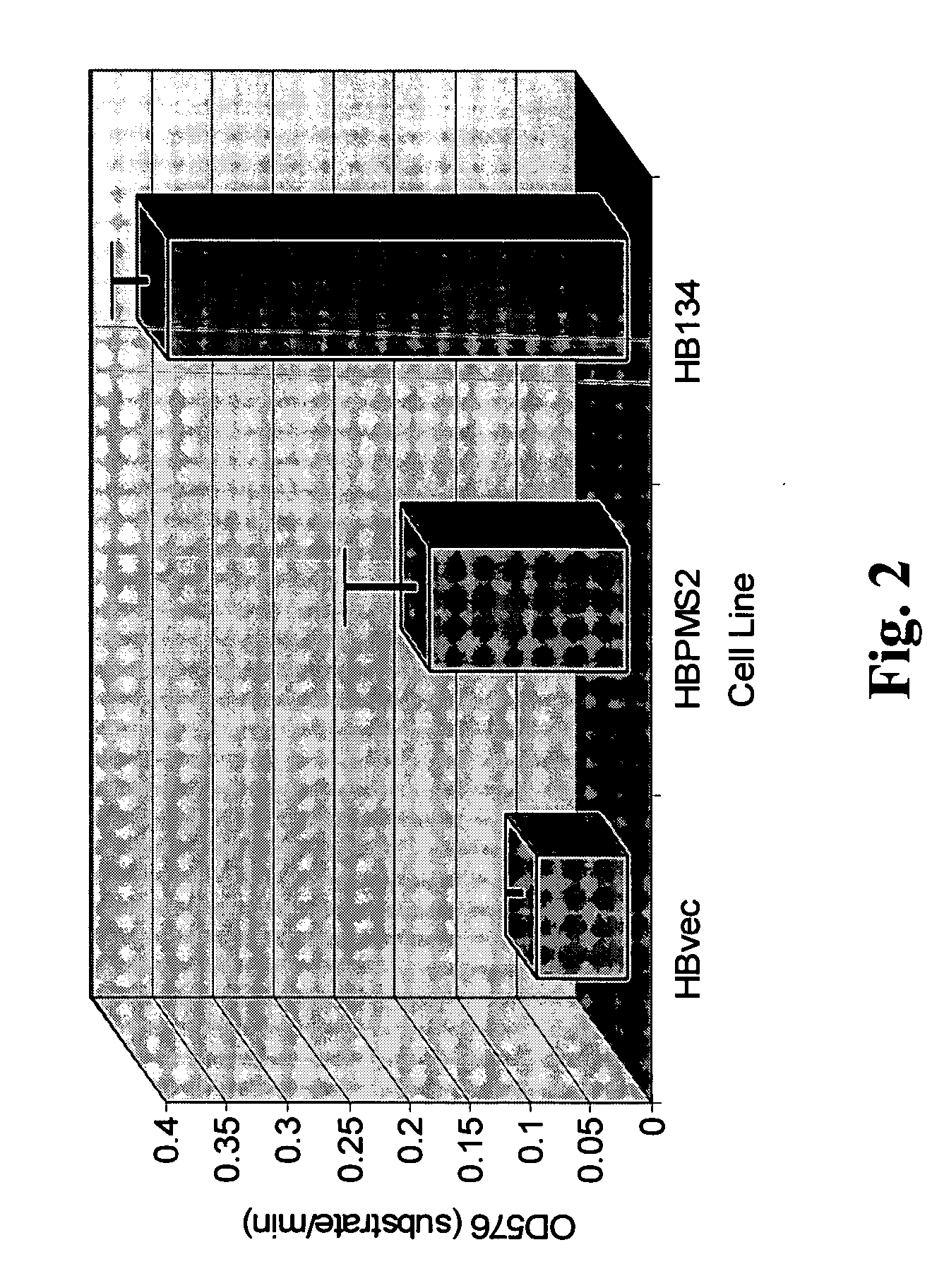
[0106] A hallmark of MMR deficiency is the generation of unstable microsatellite repeats in the genome of host cells. This phenotype is referred to as microsatellite instability (MI) (Modrich, P. (1994) Mismatch repair, genetic stability, and cancer. Science 266:1959-1960; Palombo, F., et al. (1994) Mismatch repair and cancer. Nature 36:4 17). MI consists of deletions and / or insertions within repetitive mono-, di-, and / or tri-nucleotide repetitive sequences throughout the entire genome of a host cell. Extensive genetic analyses of eukaryotic cells have found that the only biochemical defect that is capable of producing MI is defective MMR (Strand, M., et al. (1993) Destabilization of tracts of simple repetitive DNA in yeast by mutations affecting DNA mismatch repair. Nature 365:274-276; Perucho, M. (1996) Cancer of the microsatellite mutator phenotype. Biol Chem. 377:675-684; Eshleman J. R., and Markowitz...
example 3
Screening Strategy to Identify Hybridoma Clones Producing Antibodies with Higher Binding Affinities and / or Increased Immunoglobulin Production.
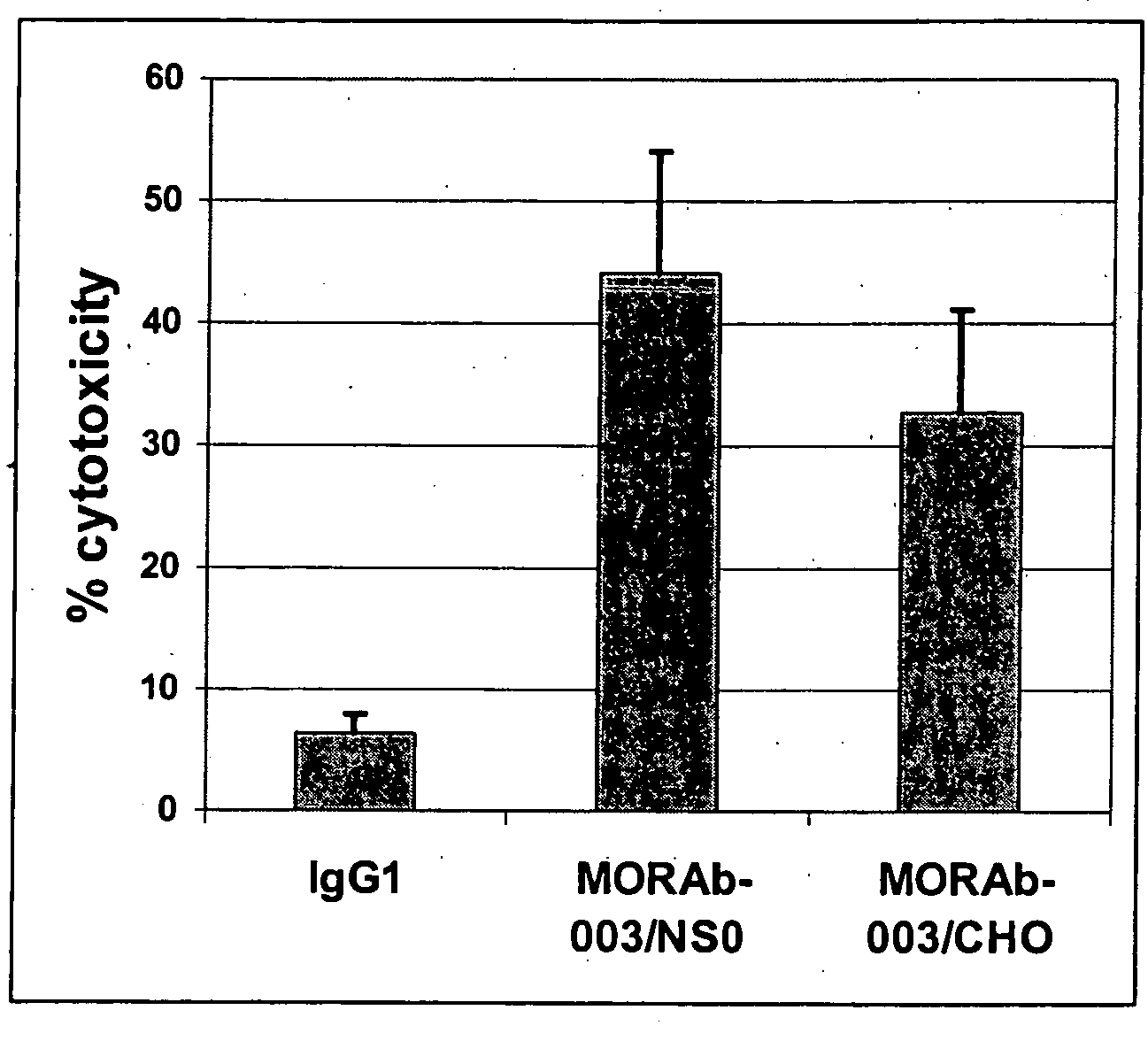
[0109] An application of the methods presented within this document is the use of MMR deficient hybridomas or other immunoglobulin producing cells to create genetic alterations within an immunoglobulin gene that will yield antibodies with altered biochemical properties. An illustration of this application is demonstrated within this example whereby the HB134 hybridoma (Example 1), which is a MMR-defective cell line that produces an anti-human immunoglobulin type E (hIgE) MAb, is grown for 20 generations and clones are isolated in 96-well plates and screened for hIgE binding. FIG. 3 outlines the screening procedure to identify clones that produce high affinity MAbs, which is presumed to be due to an alteration within the light or heavy chain variable region of the protein. The assay employs the use of a plate Enzyme Linked Immunosorbant Assay...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Stability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Cytotoxicity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com