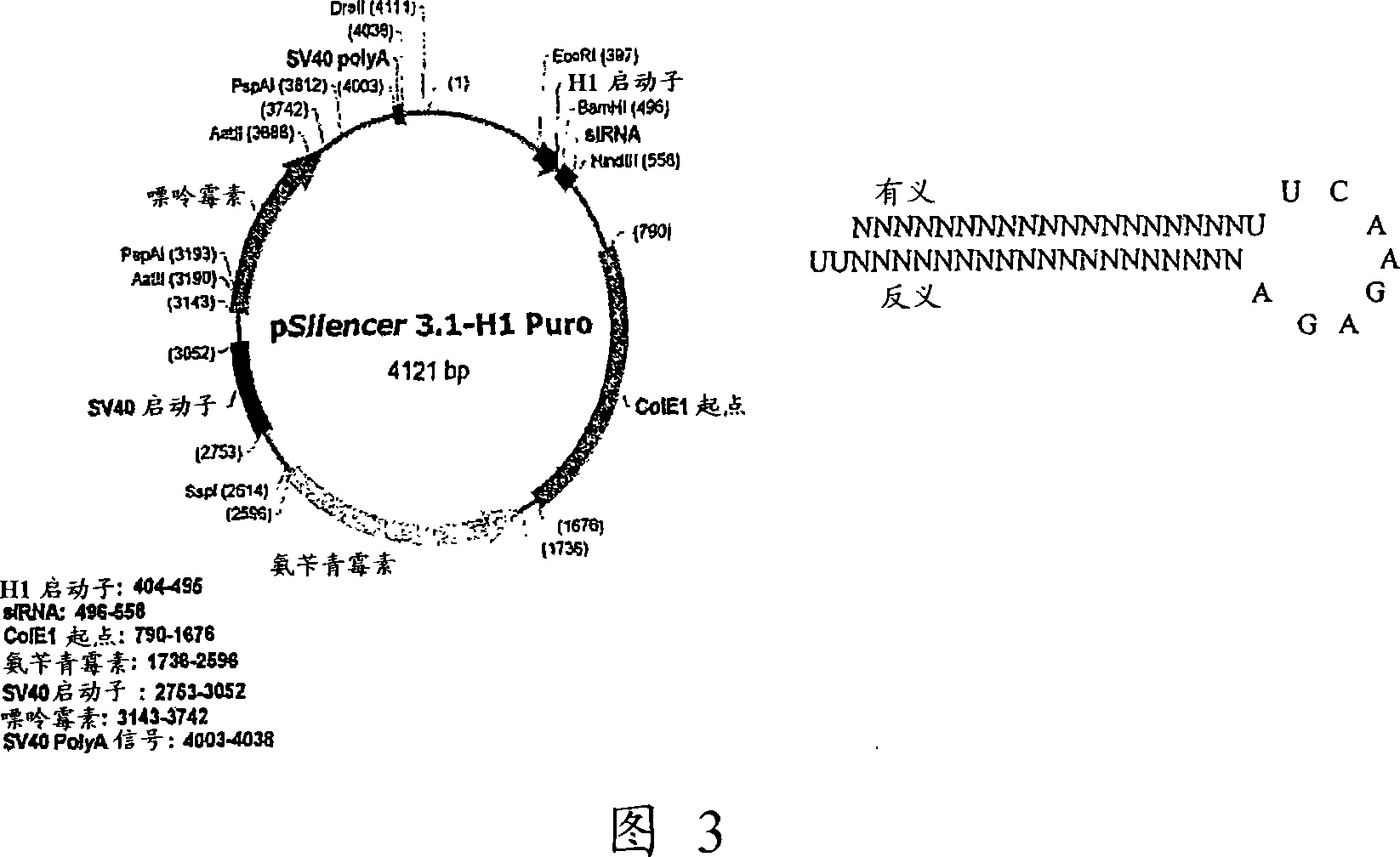
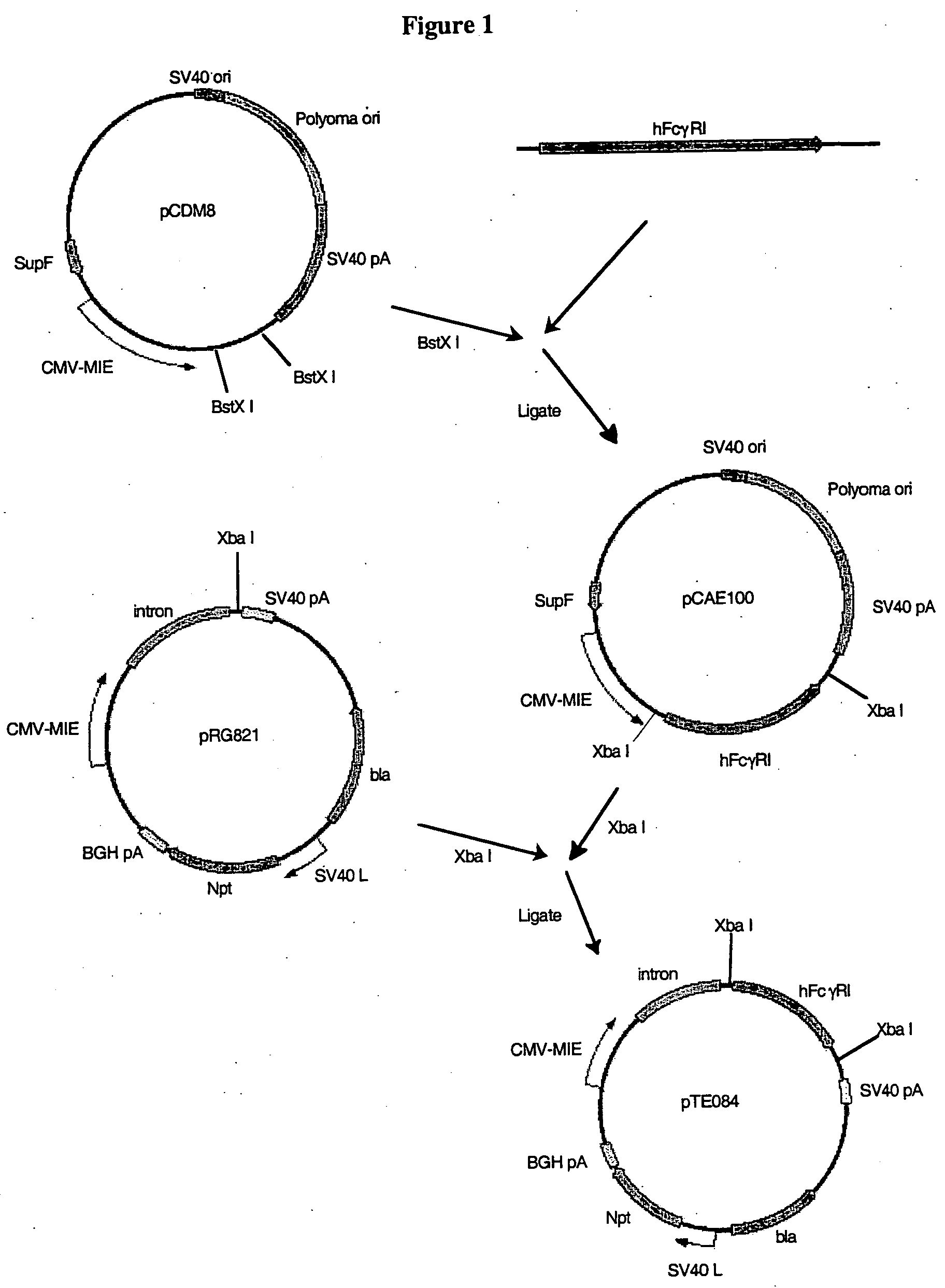
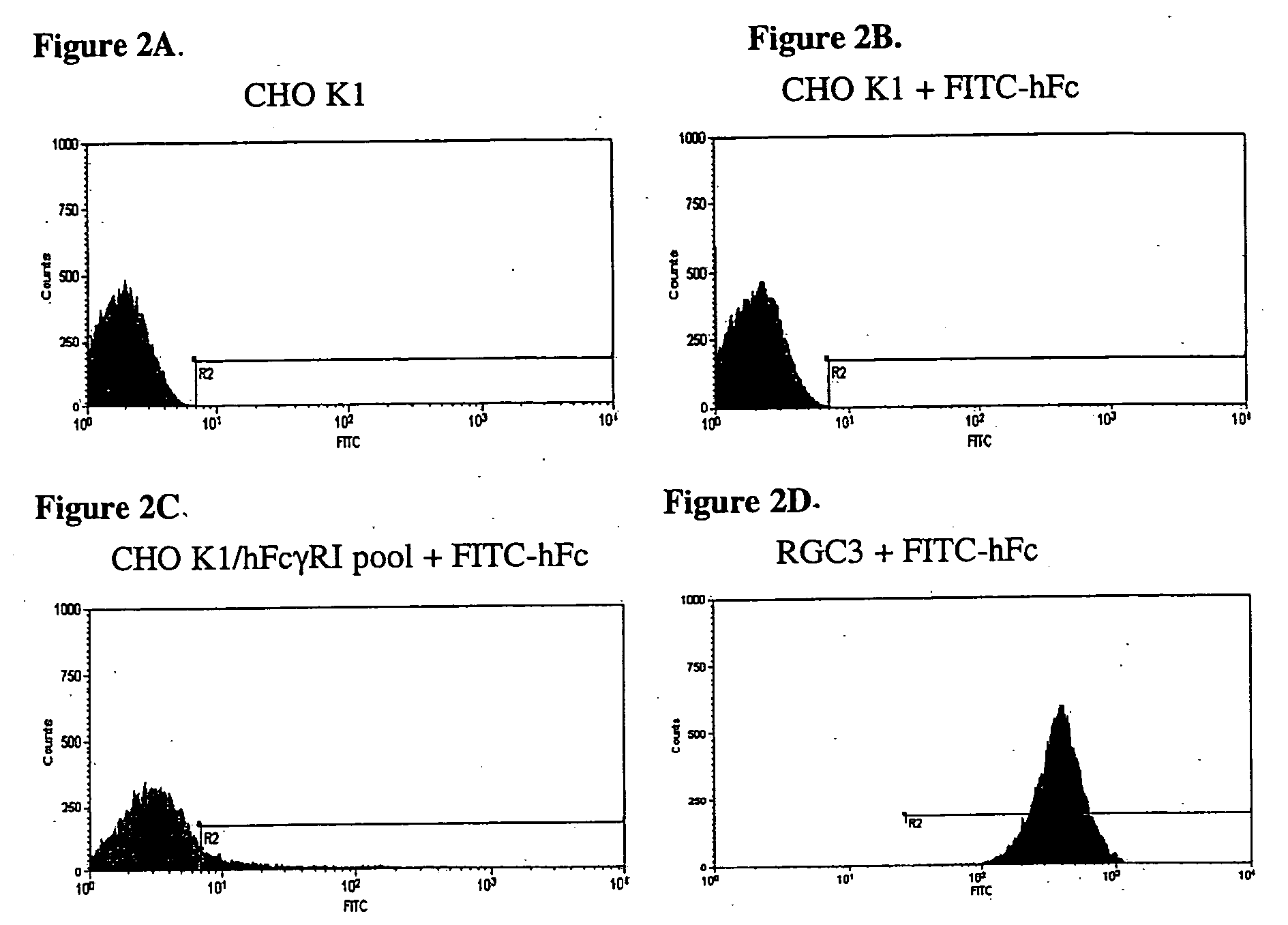
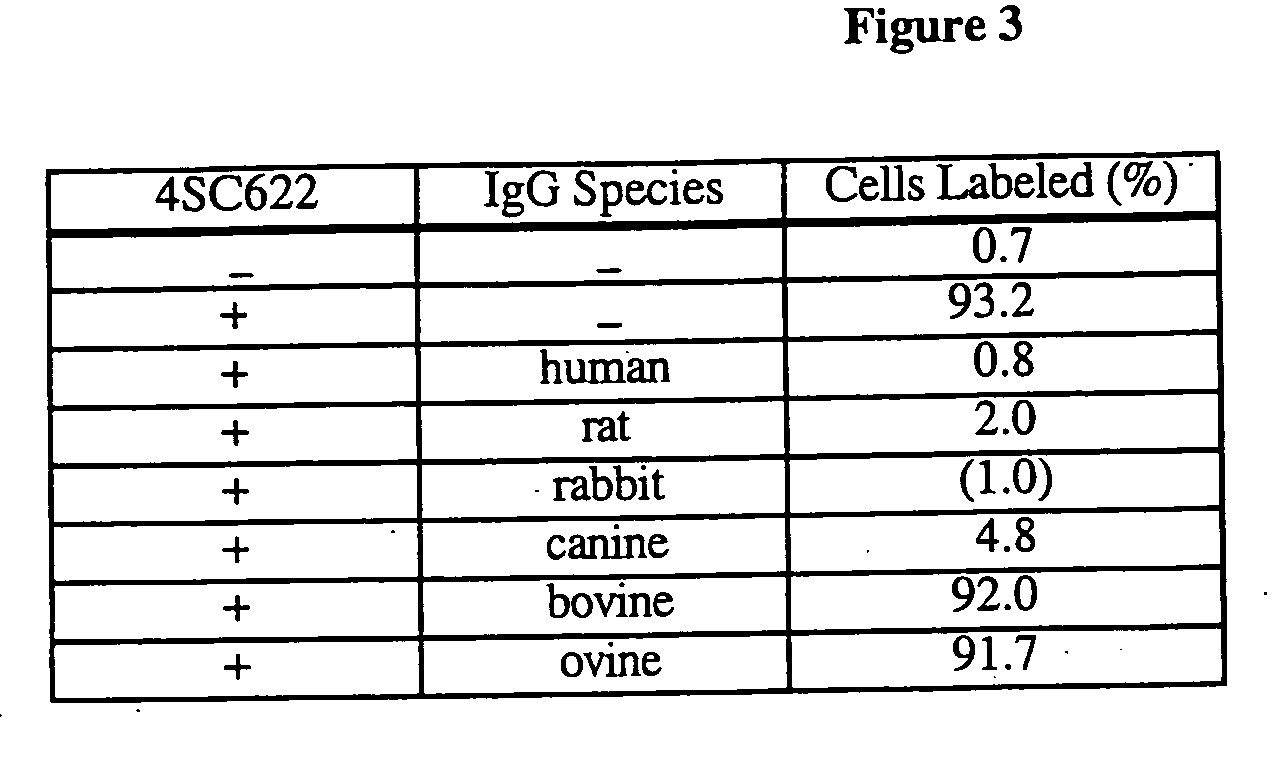
Patents
Literature
84 results about "Antibody-Producing Cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
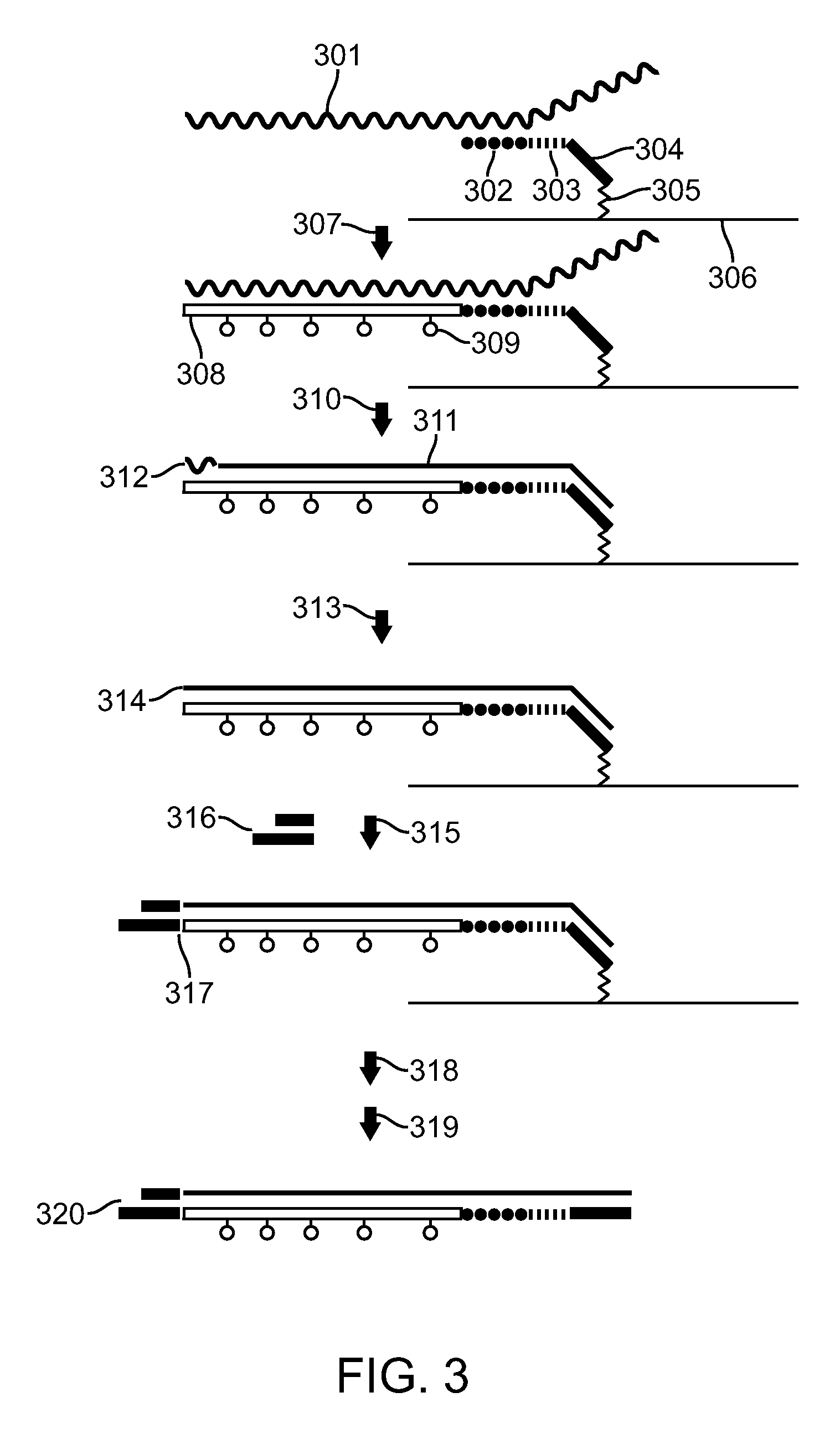
Antibodies and methods for generating genetically altered antibodies with enhanced effector function
InactiveUS20050054048A1Increase variabilityBetter pharmacokinetic profileAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGenetic diversityMonoclonal antibody
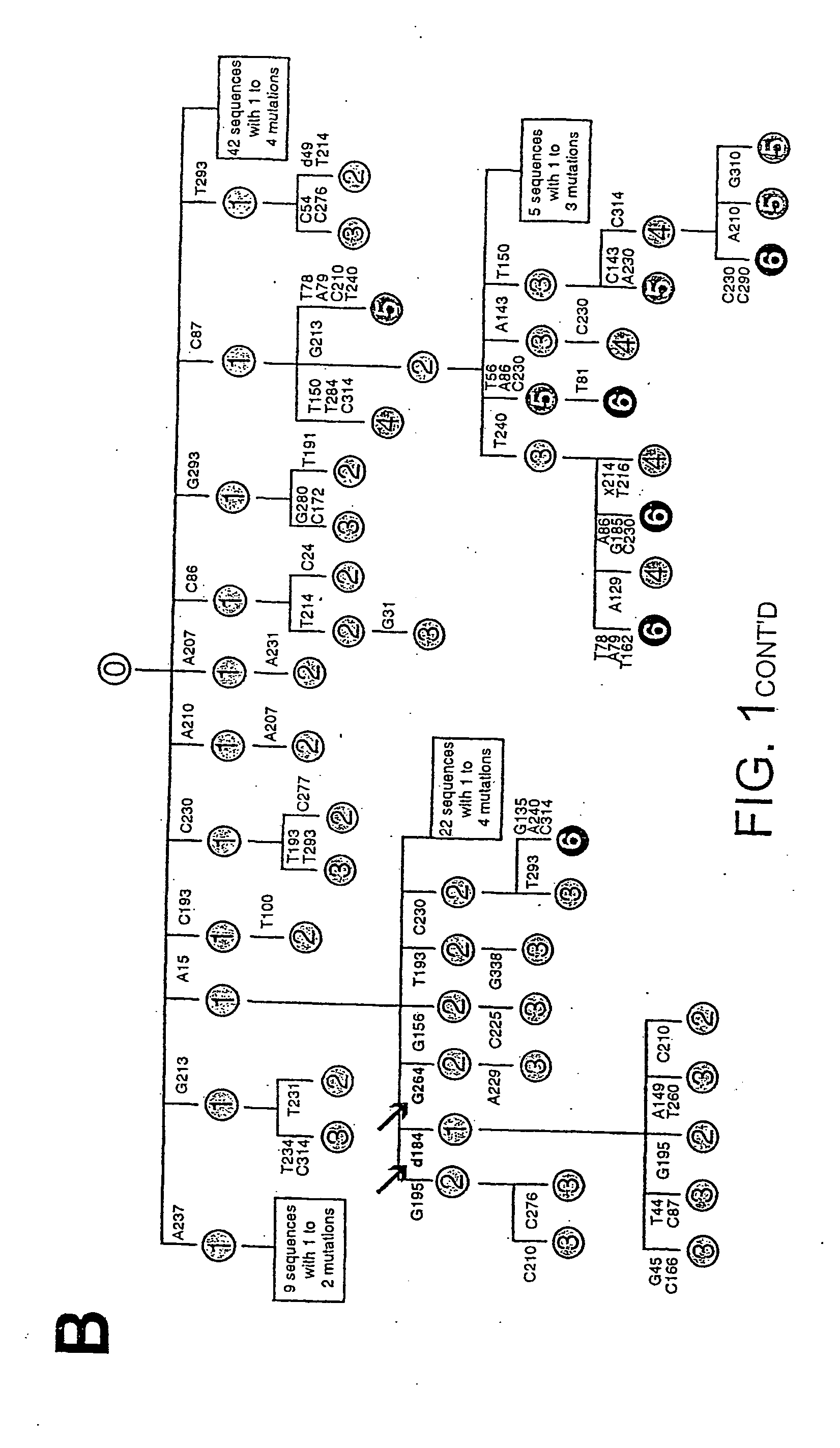
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. By introducing these genes into cells and transgenic animals, new cell lines and animal varieties with novel and useful properties can be prepared more efficiently than by relying on the natural rate of mutation. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production. The invention also provides methods for increasing the effector function of monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibodies with increased effector function.
Owner:EISAI INC
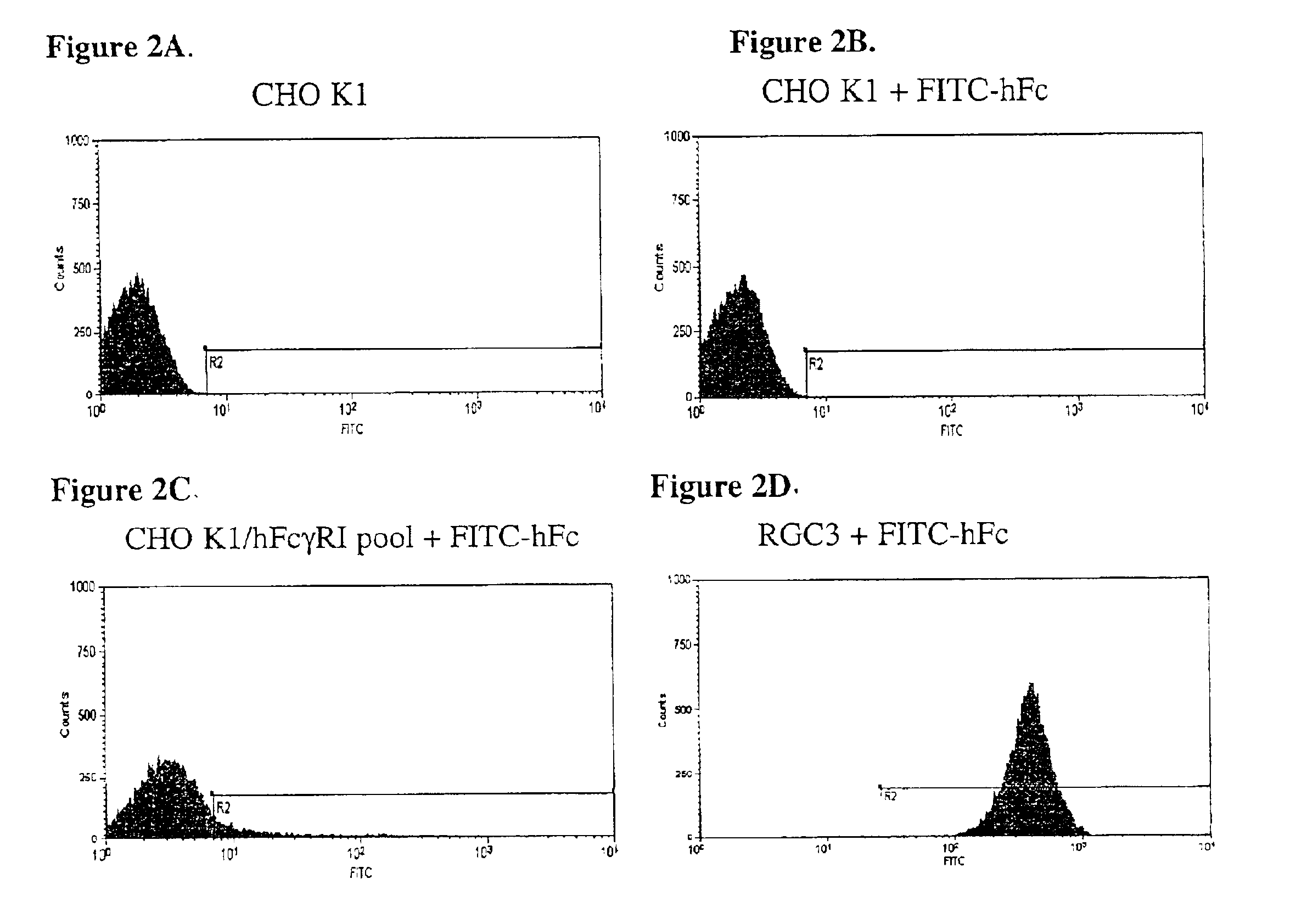
Isolating cells expressing secreted proteins
InactiveUS6919183B2Easy to detectImprove isolationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSecretory proteinCell sheet
A method for identifying and isolating cells which produce secreted proteins. This method is based upon a specific characteristic or the expression level of the secreted protein by transiently capturing the secreted protein on the surface of an individual cell, allowing selection of rare cell clones from a heterogeneous population. Also provided is the use of this method to generate cells which produce a desired level of secreted protein or secreted protein of a particular characteristic(s), and organisms which possess such cells. In particular, the method allows rapid isolation of high expression recombinant antibody-producing cell lines, or may be applied directly to rapid isolation of specific hybridomas, or to the isolation of antibody-producing transgenic animals. This method is applicable for any cell which secretes protein.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
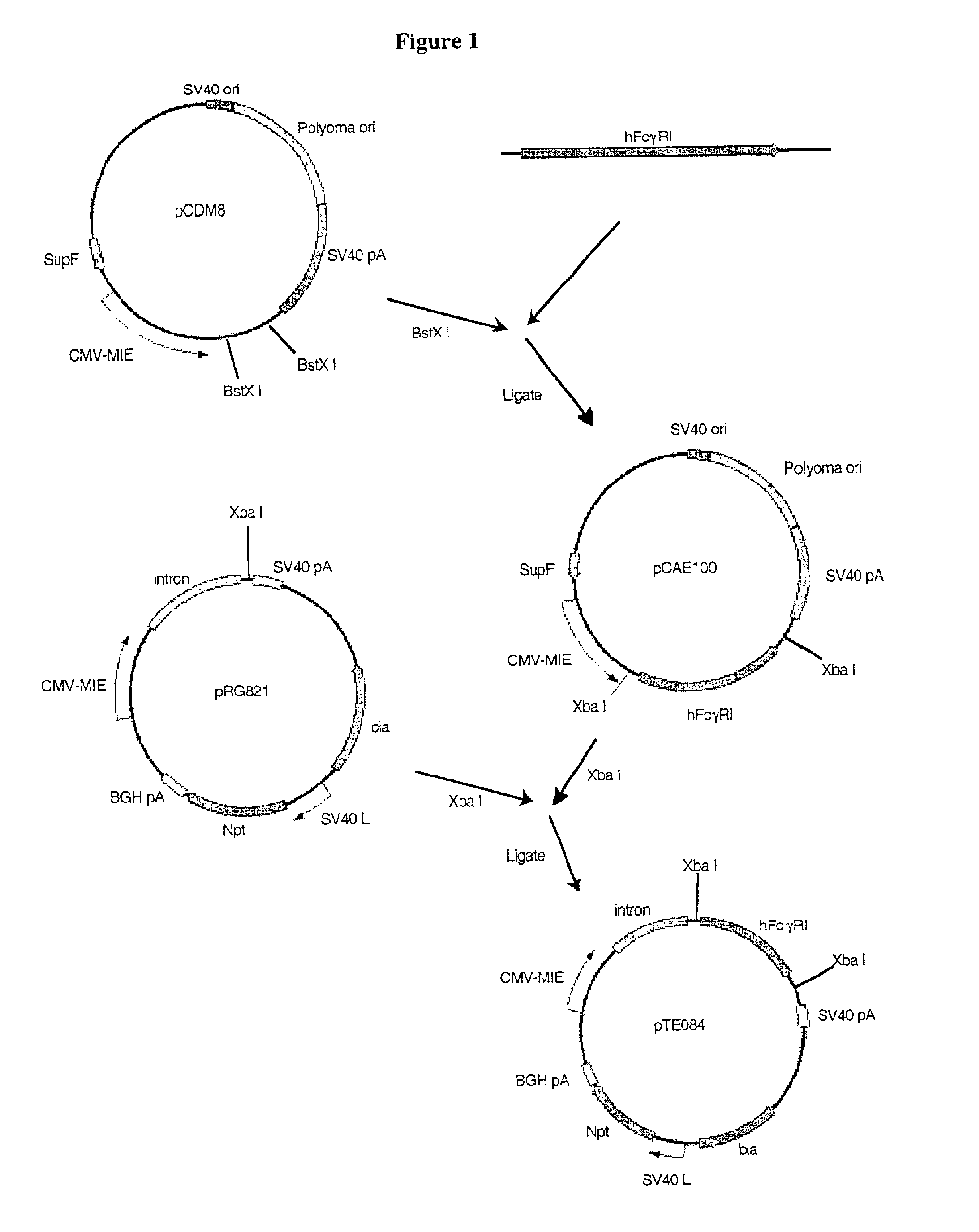
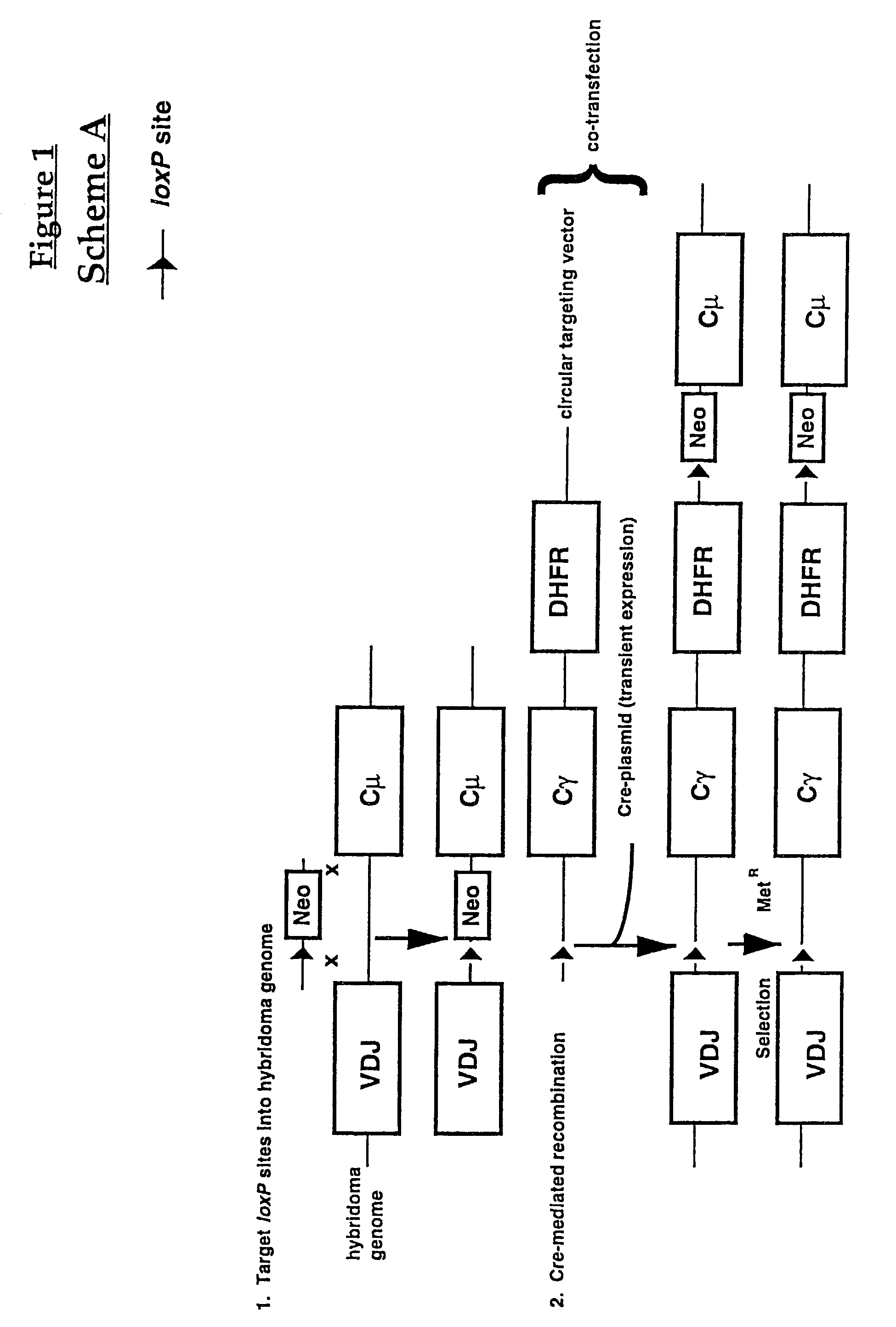
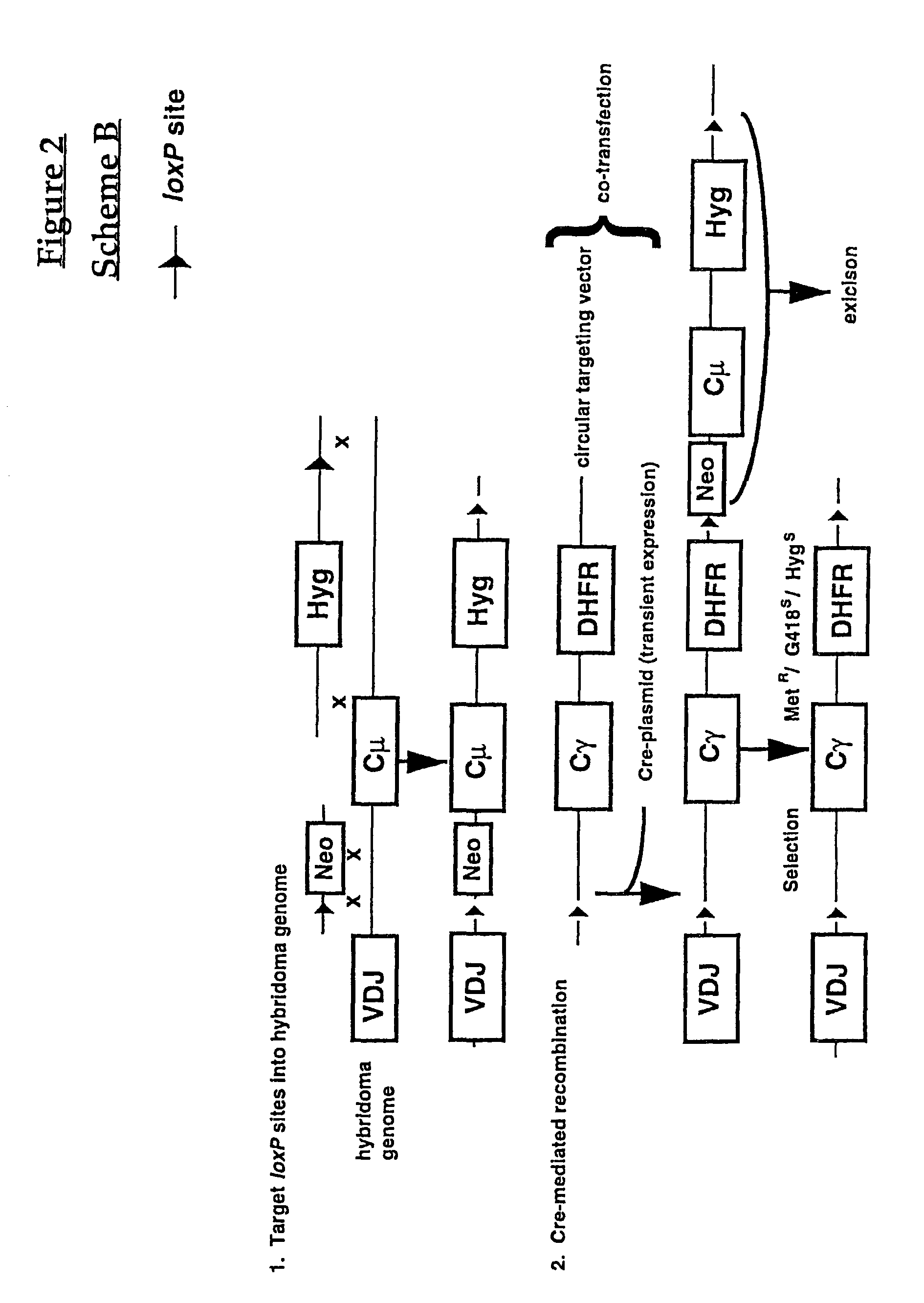
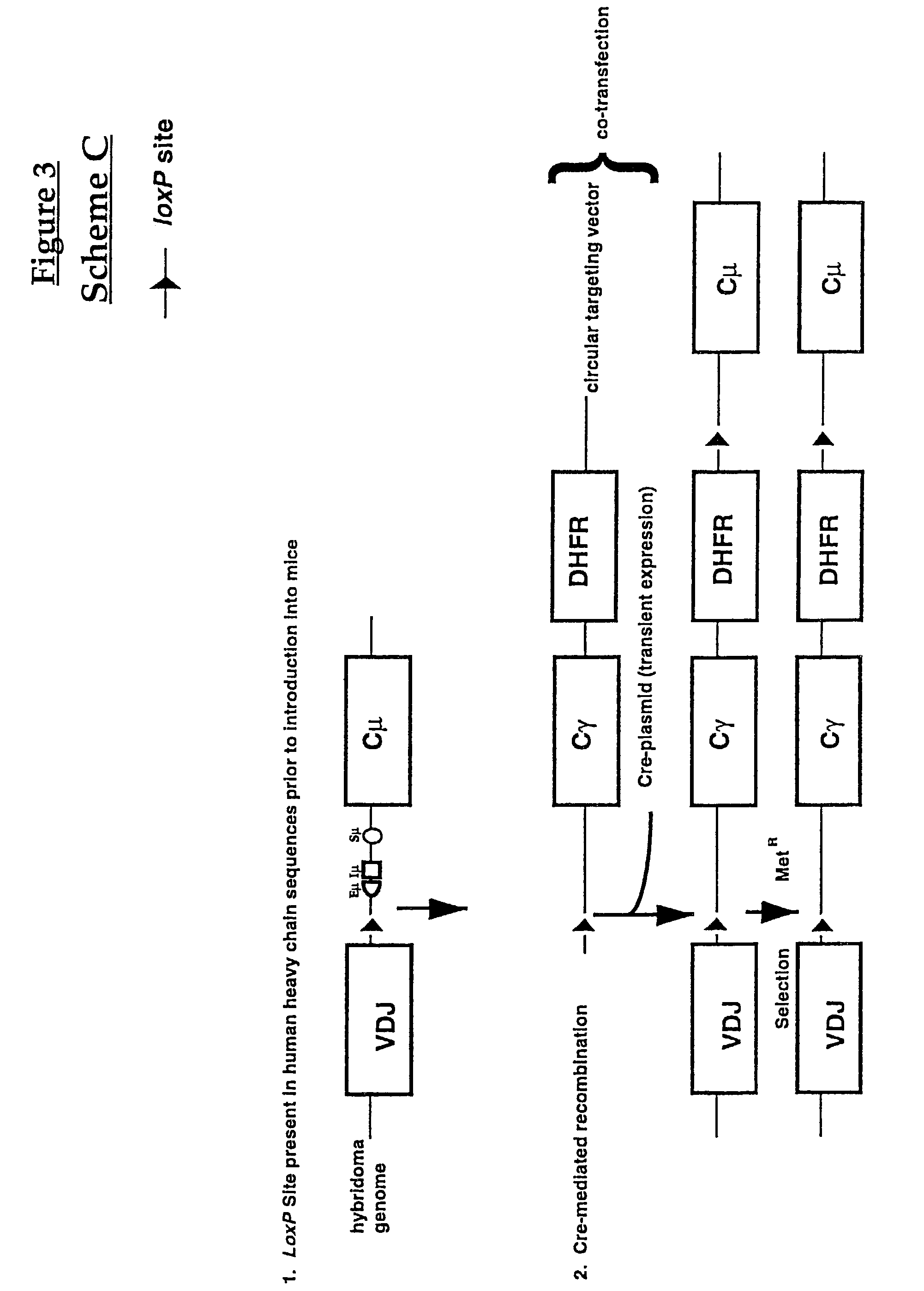
Production of antibodies using cre-mediated site-specific recombination
InactiveUS7145056B2Improve recombination efficiencyAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationAntibody-Producing Cells
A method to produce a cell expressing an antibody from a genomic sequence of the cell comprising a modified immunoglobulin locus using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination is disclosed. The method involves first transfecting an antibody-producing cell with a homology-targeting vector comprising a lox site and a targeting sequence homologous to a first DNA sequence adjacent to the region of the immunoglobulin loci of the genomic sequence which is to be converted to a modified region, so the first lox site is inserted into the genomic sequence via site-specific homologous recombination. Then the cell is transfected with a lox-targeting vector comprising a second lox site suitable for Cre-mediated recombination with the integrated lox site and a modifying sequence to convert the region of the immunoglobulin loci to the modified region. This conversion is performed by interacting the lox sites with Cre in vivo, so that the modifying sequence inserts into the genomic sequence via Cre-mediated site-specific recombination of the lox sites. Also disclosed are a form of the method used to produce a cell expressing a modified antibody molecule using Cre-mediated site-specific recombination, and antibody-producing cells obtainable by the disclosed methods. Class-switching modifications of human antibodies produced in murine hybridoma cells are exemplified.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC +1
Genetically altered antibody-producing cell lines with improved antibody characteristics
InactiveUS20050048621A1Increase variabilityBetter pharmacokinetic profileAnimal cellsSugar derivativesBiological bodyGenetic diversity
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. Cells may be selected for expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), stimulated to produce AID, or manipulated to express AID for further enhancement of hypermutability. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production.
Owner:EISAI INC
Methods and compounds for raising antibodies and for screening antibody repertoires
InactiveUS20060222654A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansSnake antigen ingredientsAntibody-Producing CellsImmunogenicity
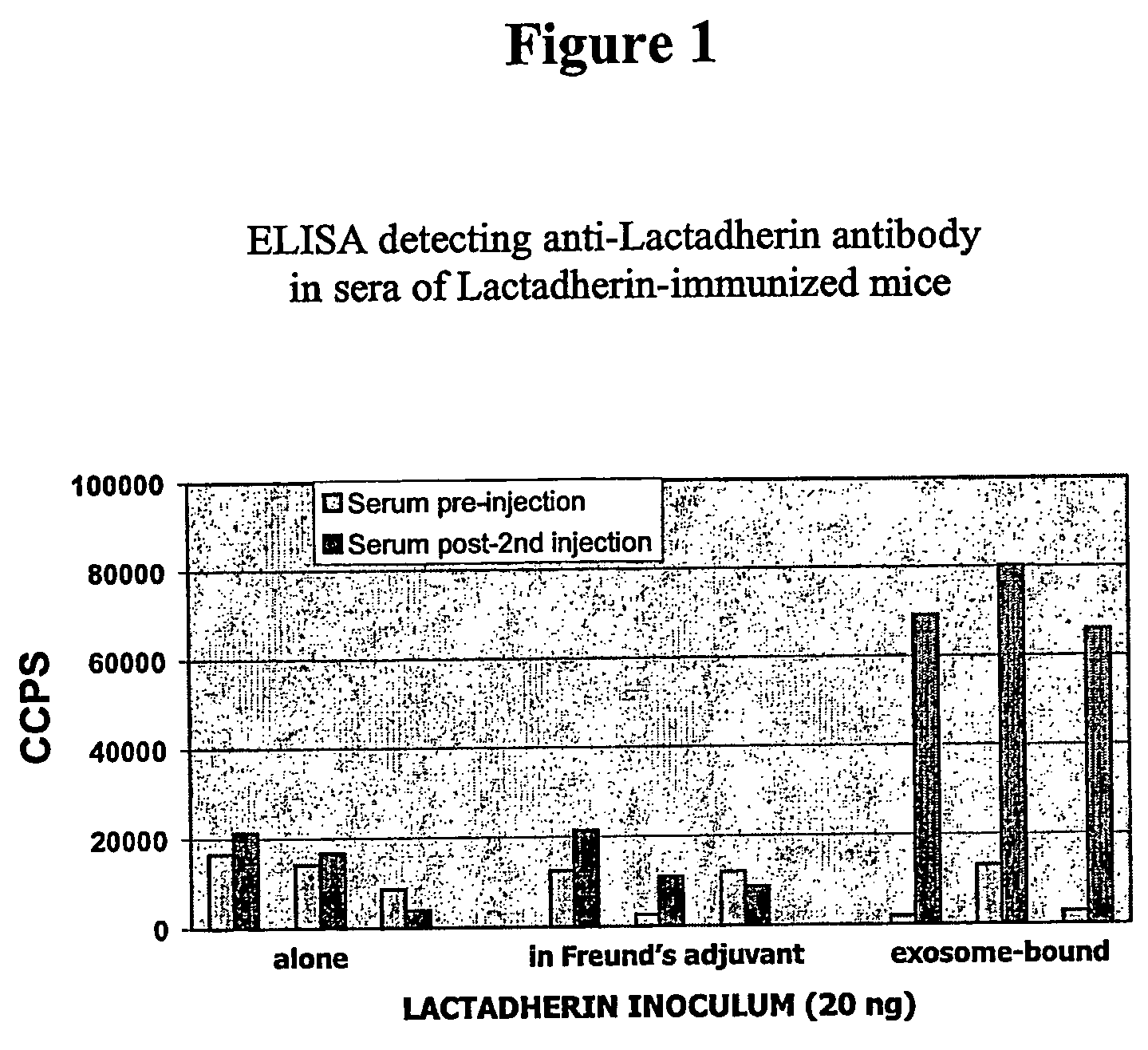
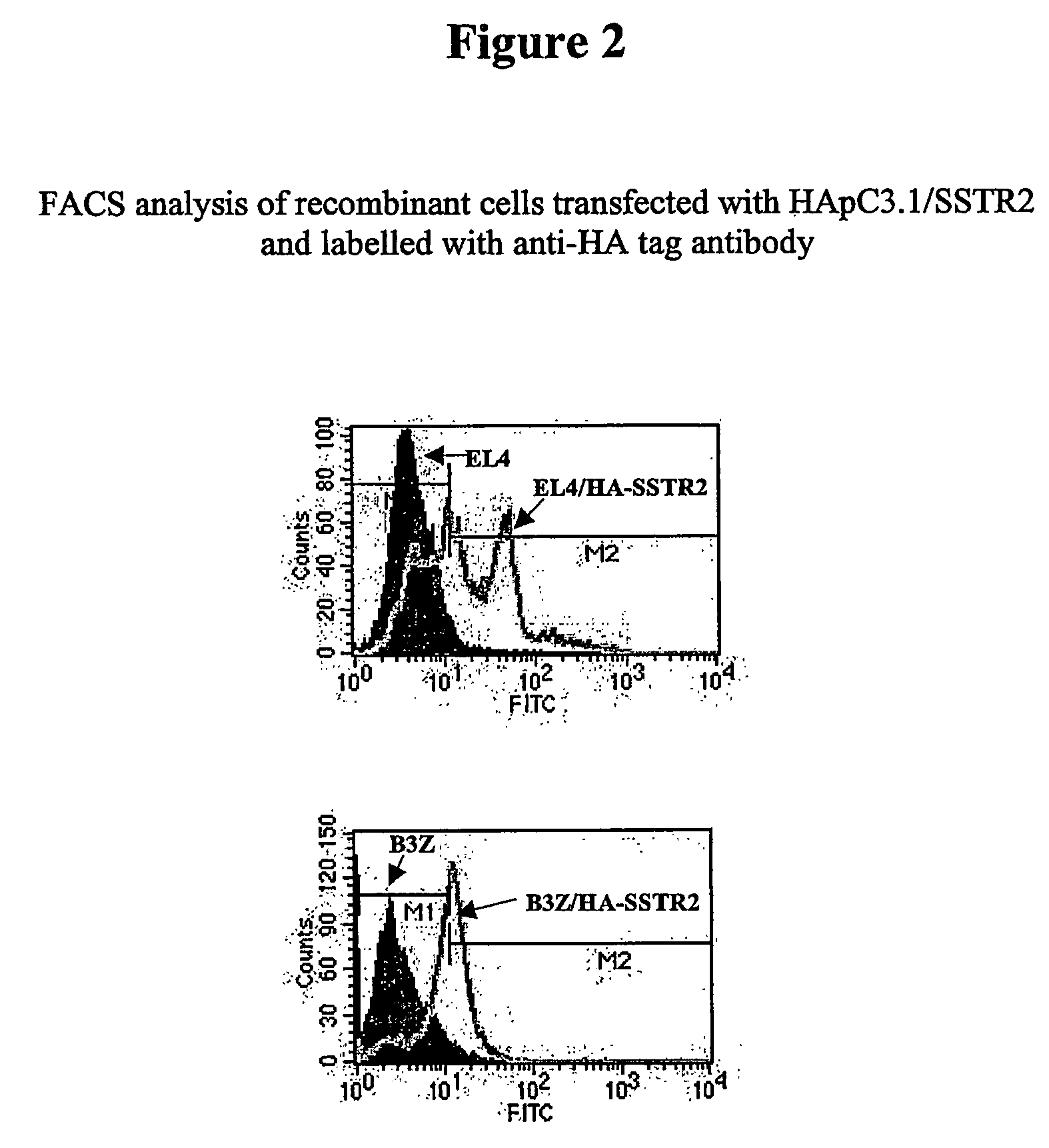
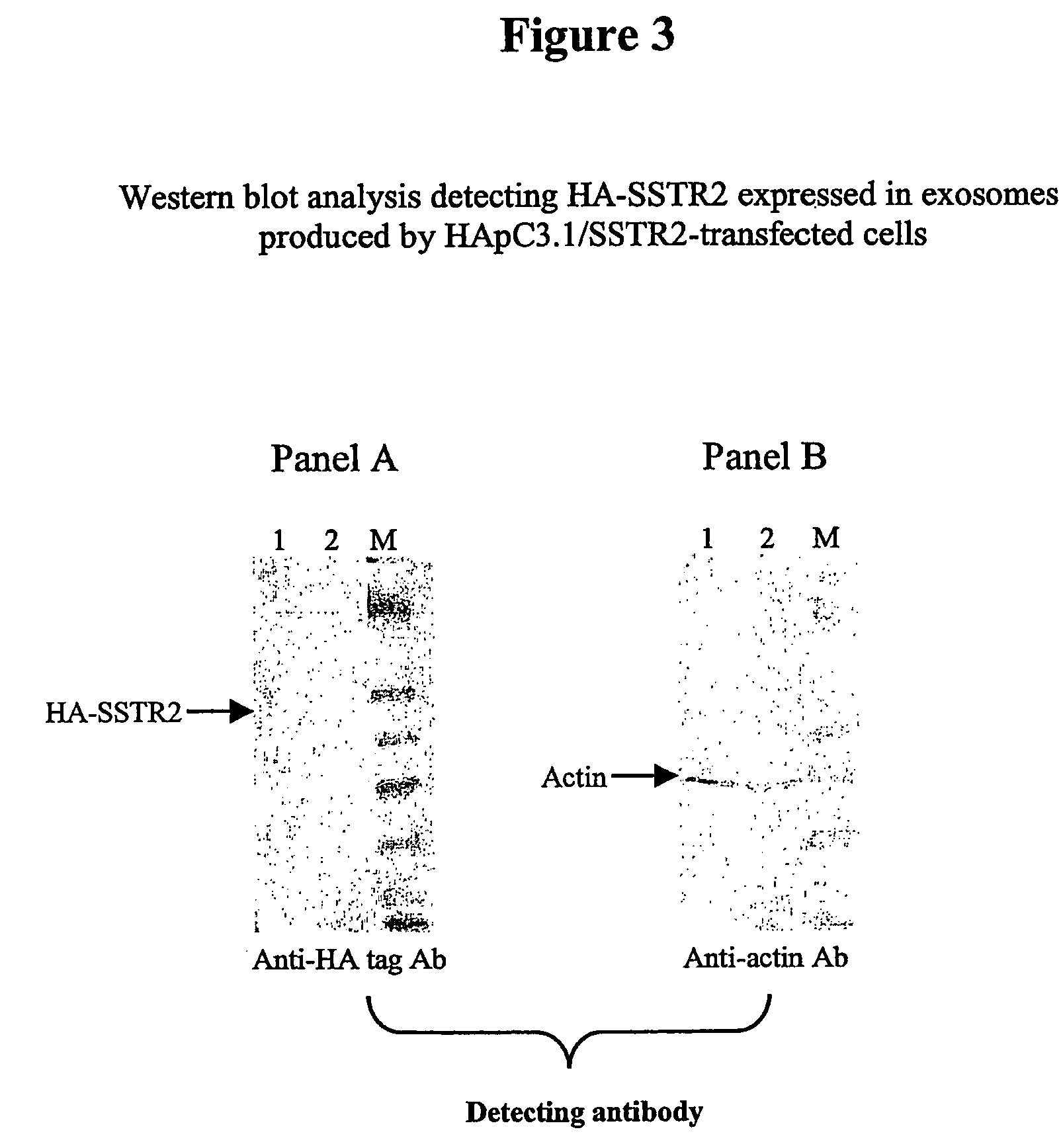
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for raising antibodies generally comprising 1) providing highly immunogenic vesicles bearing at least one target antigen and 2) immunizing animals with the said antigen-bearing vesicles to induce antigen-specific antibody responses. The invention also relates to methods of screening antibody repertoires comprising 1) providing vesicles bearing at least one target antigen and one marker and 2) isolating antibody-producing cells or particles with defined antigen specificity using the said antigen- and marker-bearing vesicles. Antibodies with defined antigen specificity can then be prepared from isolated antibody-producing cells using known methods of the art. This invention can be used in experimental, research, therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic areas.
Owner:EXOTHERA
Antibodies and processes for preparing the same
ActiveUS20090291094A1Shorten the timeOrganic active ingredientsAnimal cellsAntibody-Producing CellsOrganism
Provided herein are various processes for the improved production of antibody producing organisms, antibody producing tissues, antibody producing cells and antibodies. In certain embodiments, provided herein are methods for rapidly producing antibody producing organisms, tissues, cells and antibodies derived from humans, organisms, plants or cells that are genetically altered to over-express certain proteins.
Owner:TAIGA BIOTECH
Method for Generation of Antibodies
ActiveUS20100279351A1Promotes cell survivalPromotes proliferationSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsAntigenAntibody-Producing Cells
This invention generally relates to methods for the production of antibody producing cells and antibodies in protooncogene expressing animals. The invention also relates to methods for the efficient production of antibodies specific for antigens that are normally subject to immunological constraints such as self tolerance. The invention further relates to the production of antibody producing cells and antibodies without the need for the conventional fusing of antibody producing B cells with a myeloma fusion partner.
Owner:REFAELI YOSEF +2
Method for Accelerating Somatic Mutations and use Thereof in Proteomics
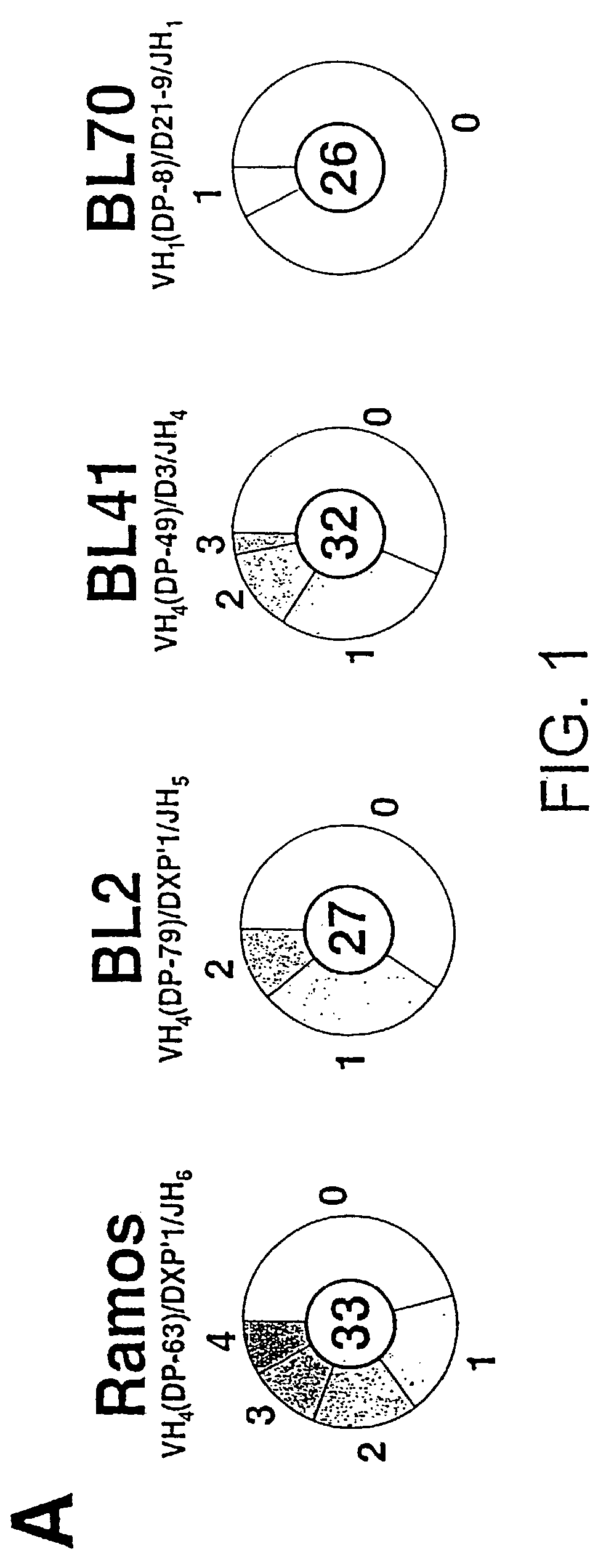
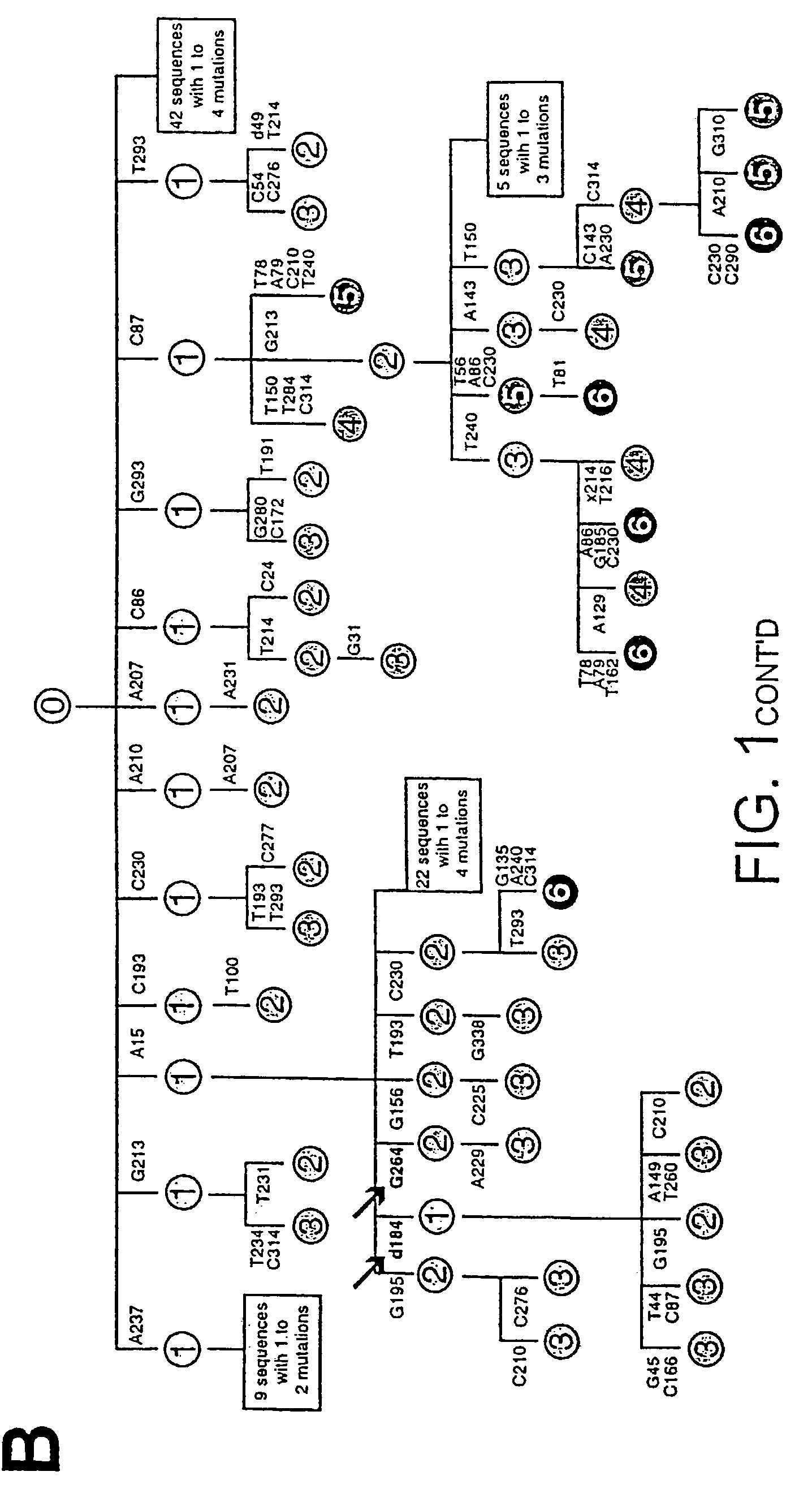
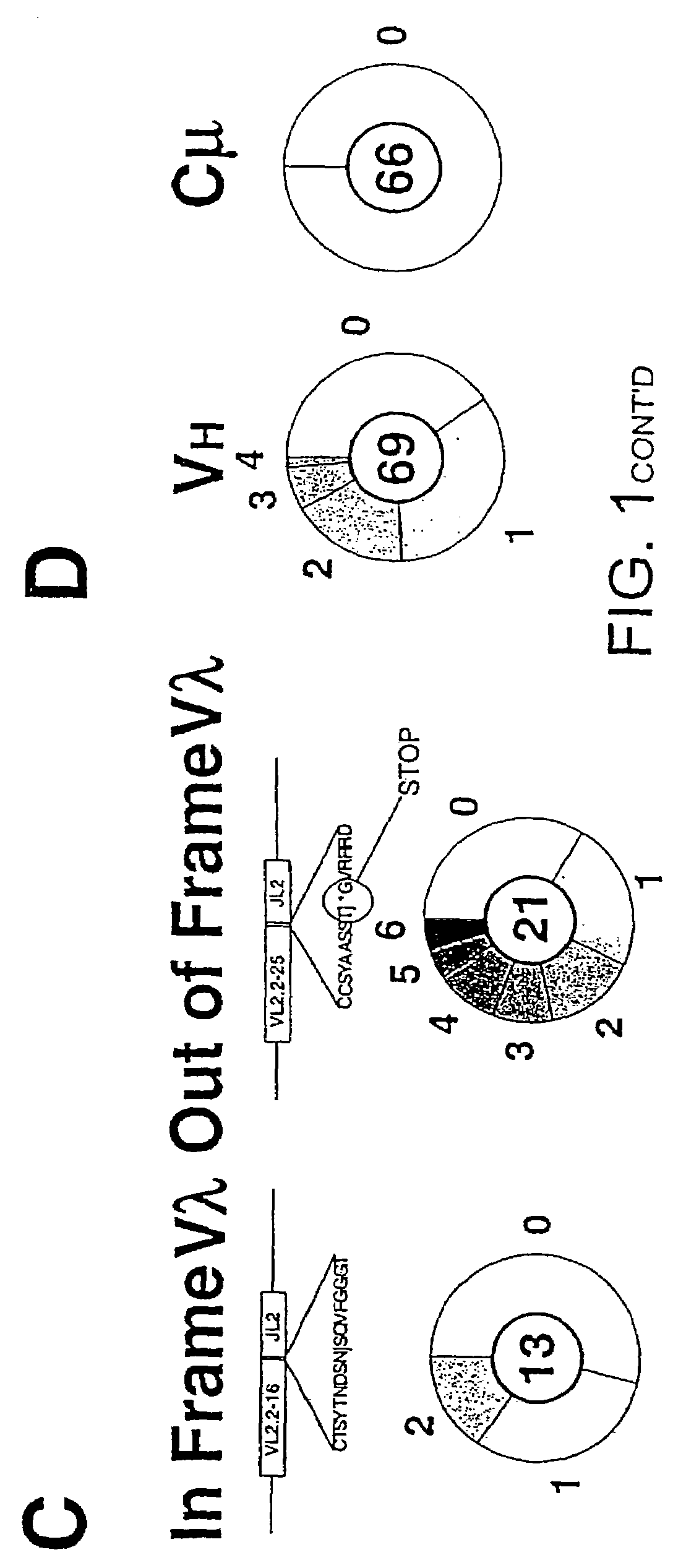
The invention relates to a method of accelerating the induction of somatic mutations in vitro. The inventive method comprises the expression of at least one cDNA expressing a modified version of the AID gene in the cells to be mutated, in culture conditions and a medium that are suited thereto, said modified version resulting from an AID gene in which the three hydrophobic amino acids, leu189, phe193 and leu196, have been replaced by means of alanine mutations in each case. The invention can be used to induce mutations in Burkitt's lymphoma BL2. The invention can also be used to induce mutations in the immunoglobulin genes of immortalised antibody-producing cells, such as mouse hybridoma cells, human hybridoma cells or human B-cell lines immortalised by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Owner:INST NECKER
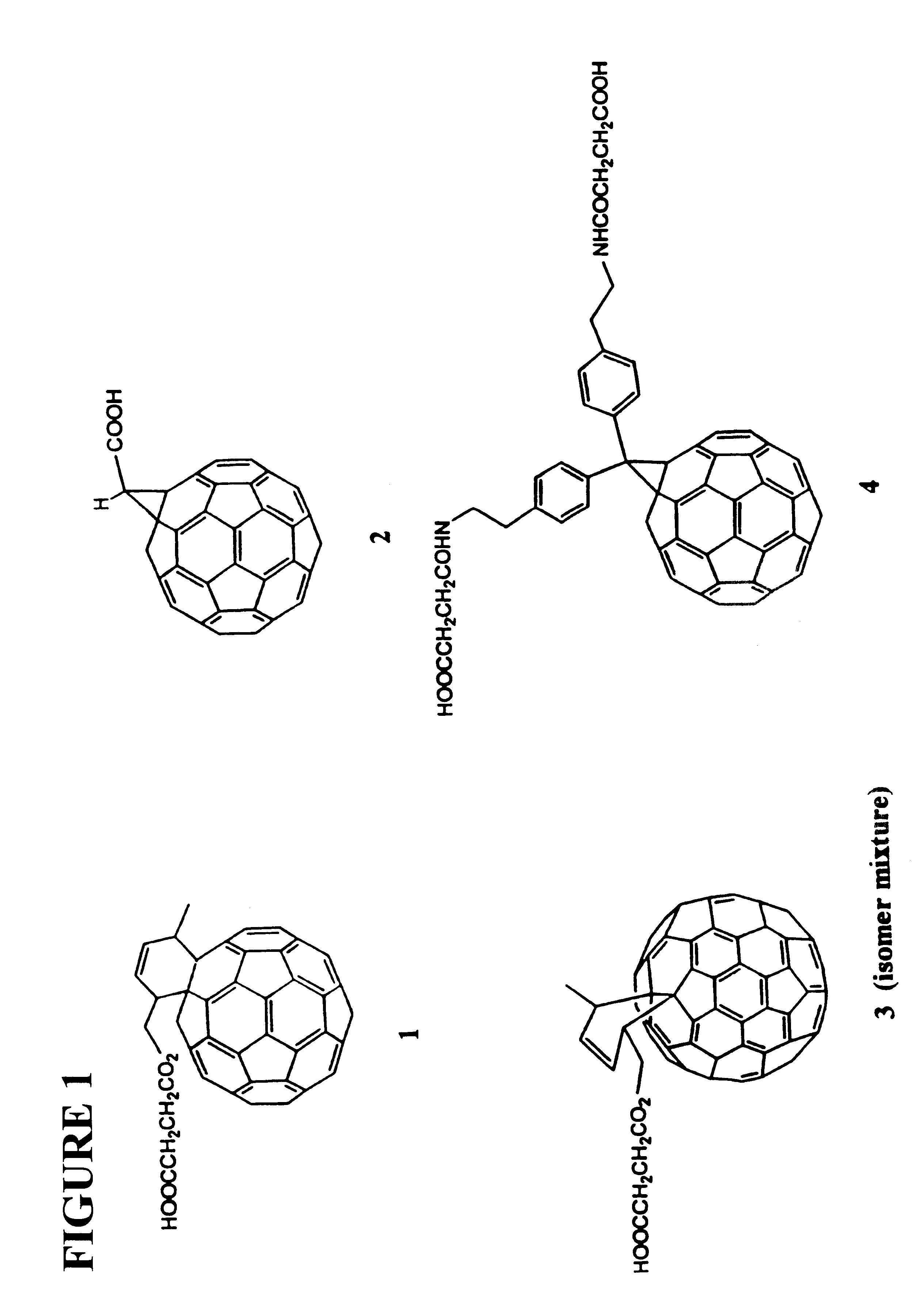
Antibodies specific for fullerenes
This invention provides a hybridoma produced by the fusion of a mouse antibody-producing cell and a mouse myeloma which is designated 1-10F-8A and deposited with the ATCC under Accession Number PTA-279, said hybridoma producing a monoclonal antibody which binds to fullerene C60. This invention provides a mouse monoclonal antibody specific for a fullerene-C60 and produced by the mouse monoclonal antibody-producing hybridoma designated 1-10F-8A. The invention provides the amino acid and encoding nucleic acid sequences of the heavy and light chains of the 1-10F-8A monoclonal antibody. This invention also provides methods of determining a serum concentration of a fullerene in a subject and of purifying a fullerene from a sample.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
P-terphenyl compounds
InactiveUS7101915B1Enhanced inhibitory effectLiquid crystal compositionsBiocideBenzeneB cells differentiation
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Para-terphenyl compounds
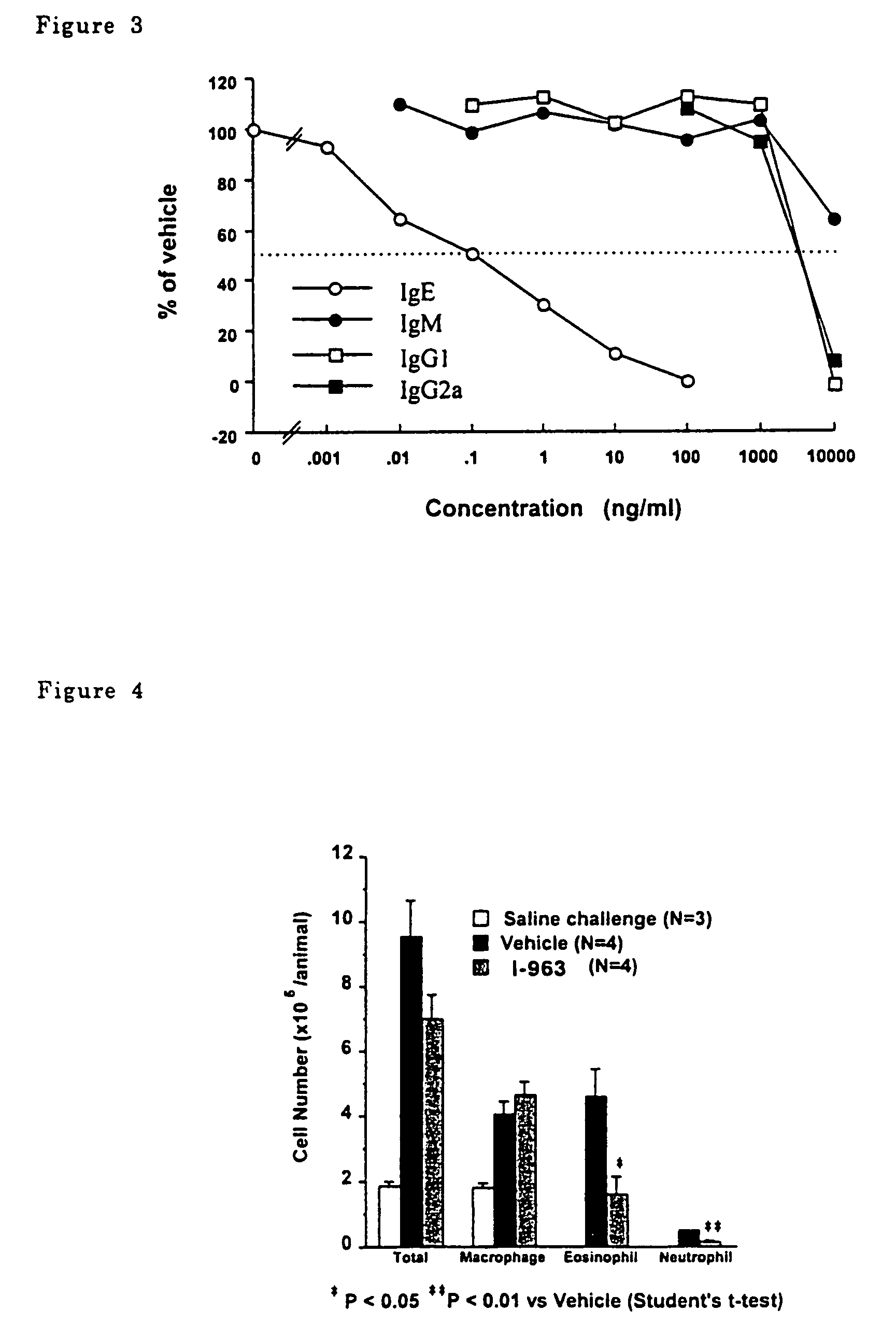
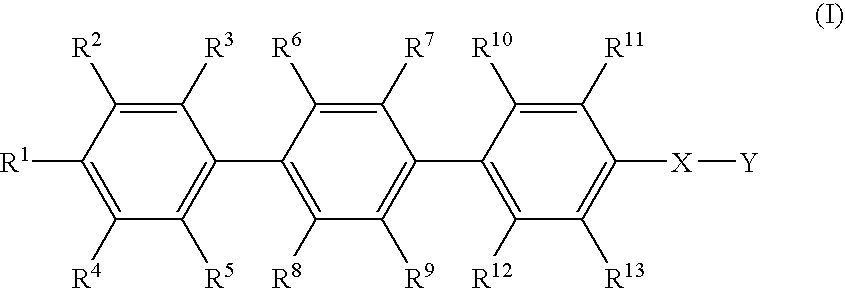
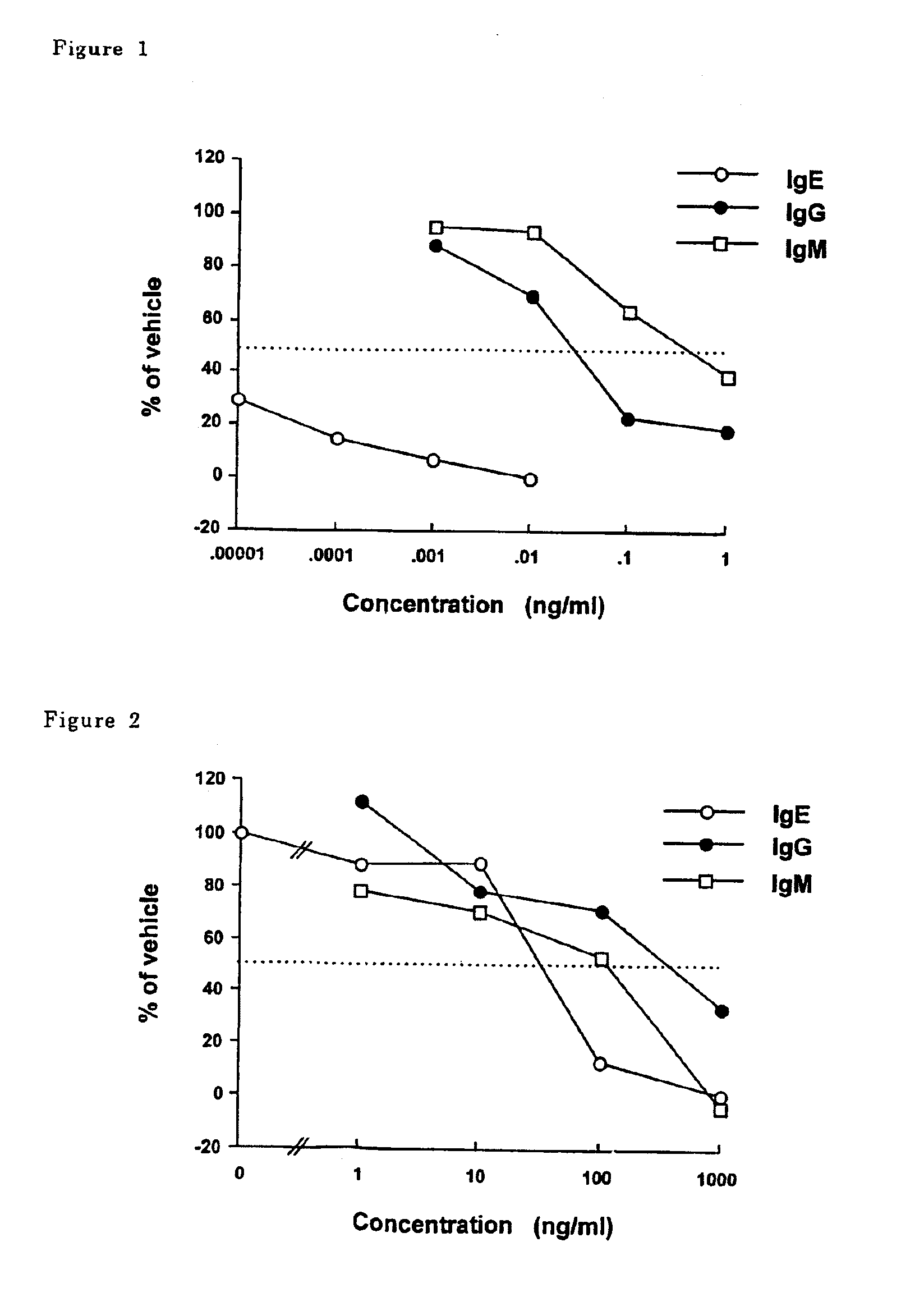
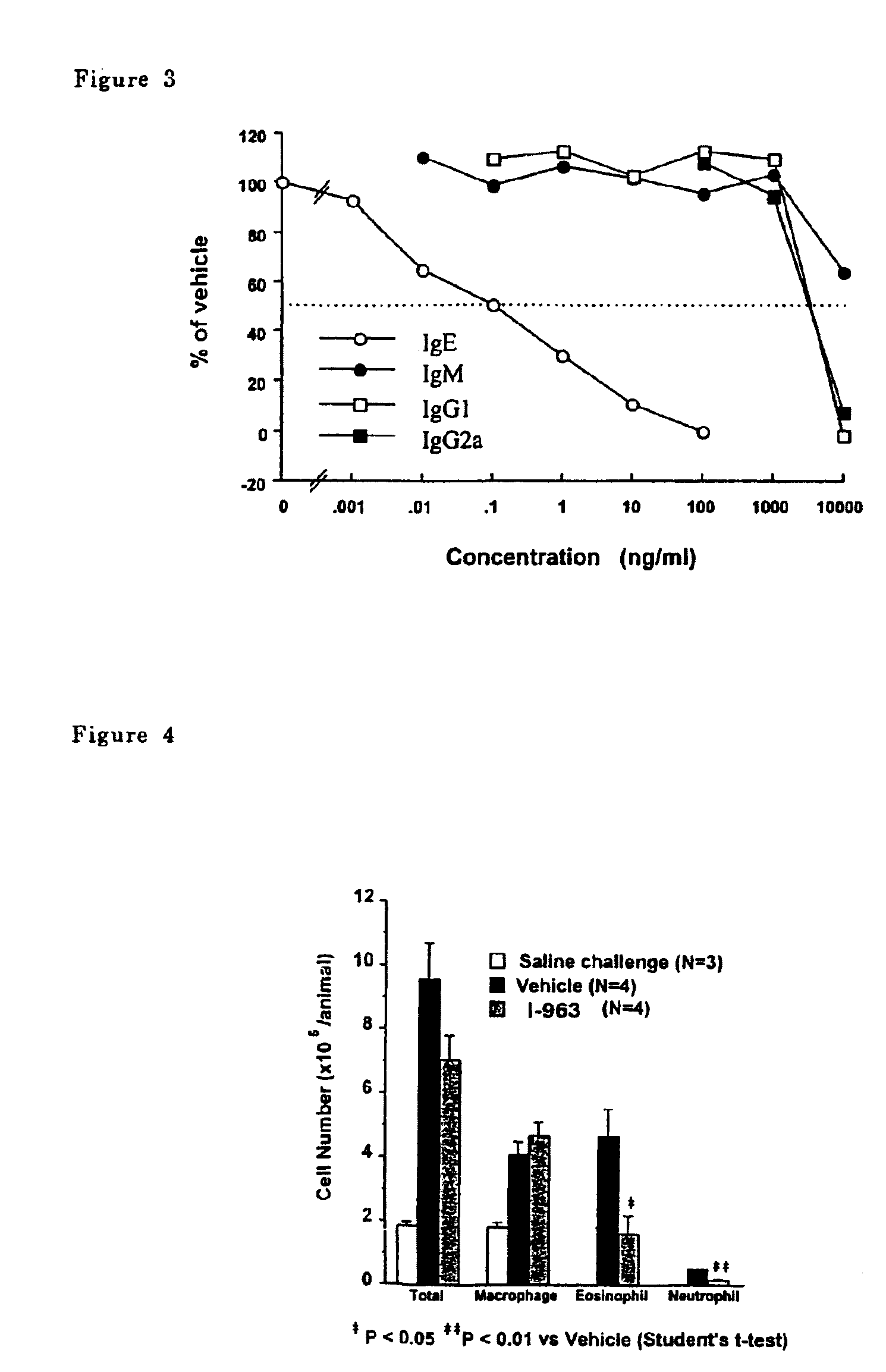
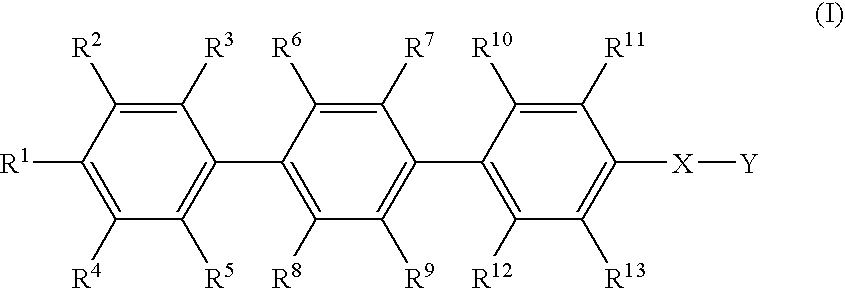
The present invention provides a selective suppressor of the IgE production comprising a compound which suppresses the IgE production in a process from a differentiation of a mature B cell into an antibody-producing cell to the production of an antibody and which does not suppress or weakly suppresses the production of IgG, IgM and / or IgA which are produced at the same time, a compound of the formula (I):wherein R1–R13 are hydrogen, halogen, lower alkyl, lower alkoxy or the like, X is —O—, —CH2—, —NR14— or —S(O)p- and Y is lower alkyl, lower alkenyl or the like, a process for producing the same and a pharmaceutical composition comprising the same.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
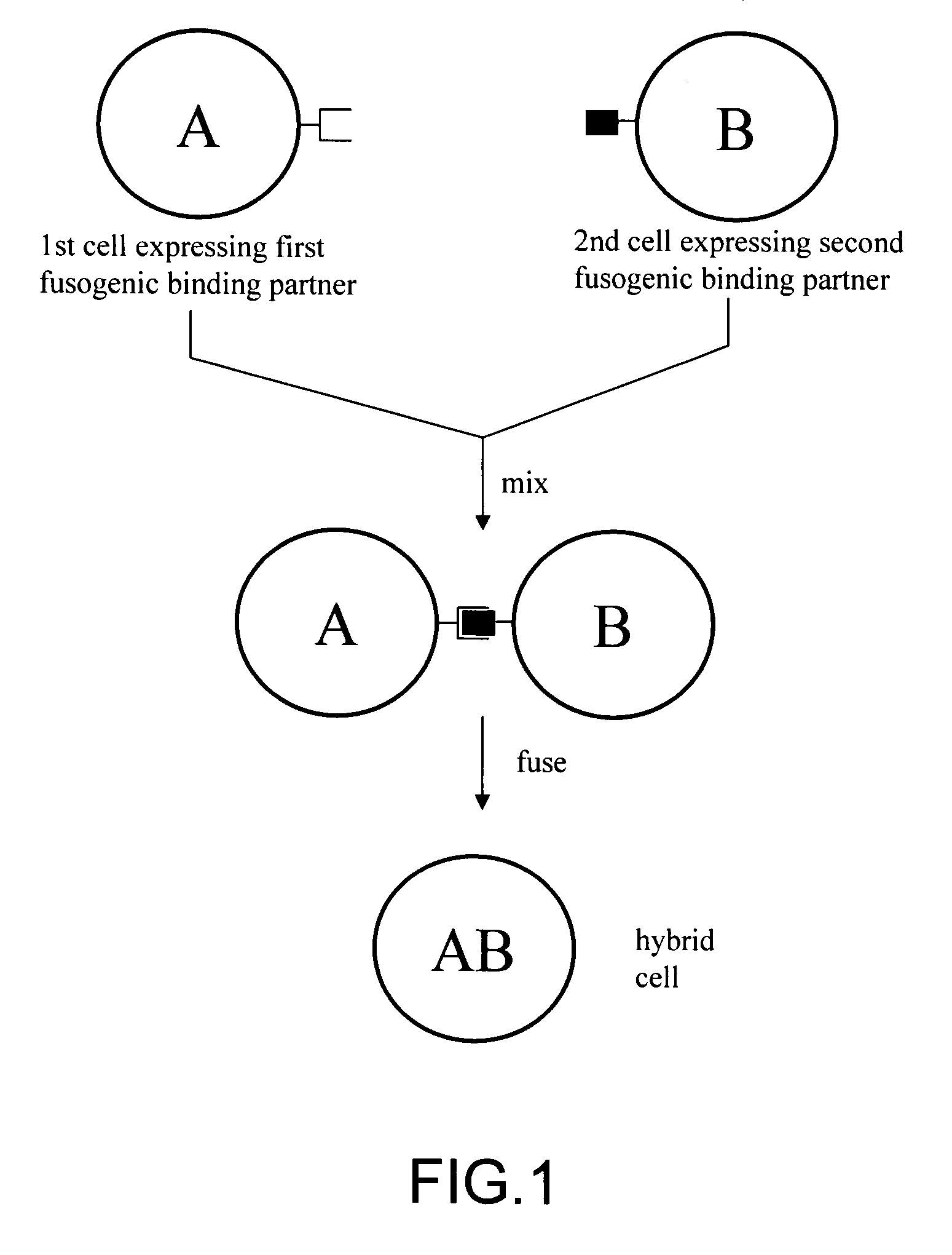
Cell fusion method
ActiveUS7402409B2Increase ratingsAnimal cellsSugar derivativesPolyethylene glycolAntibody-Producing Cells
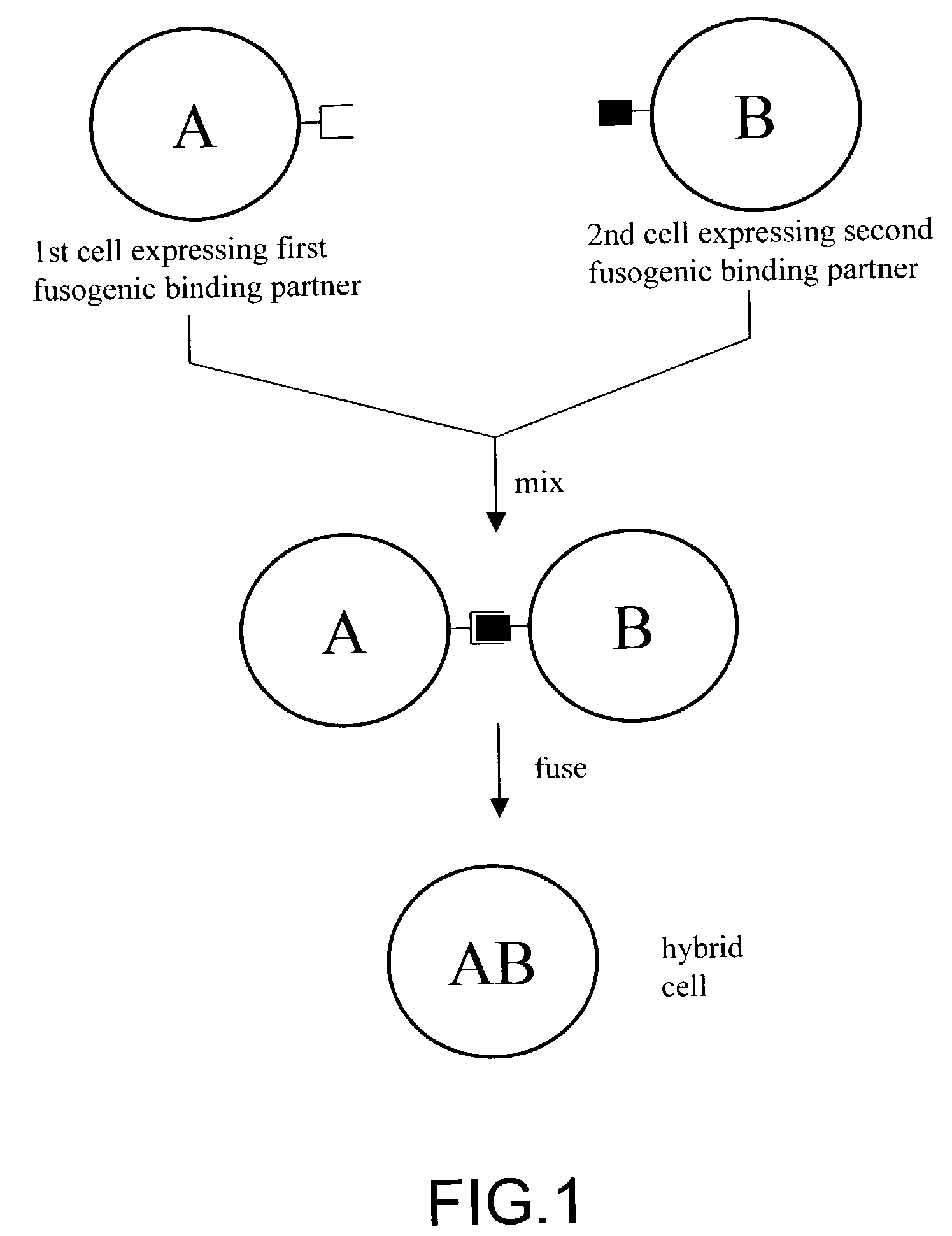
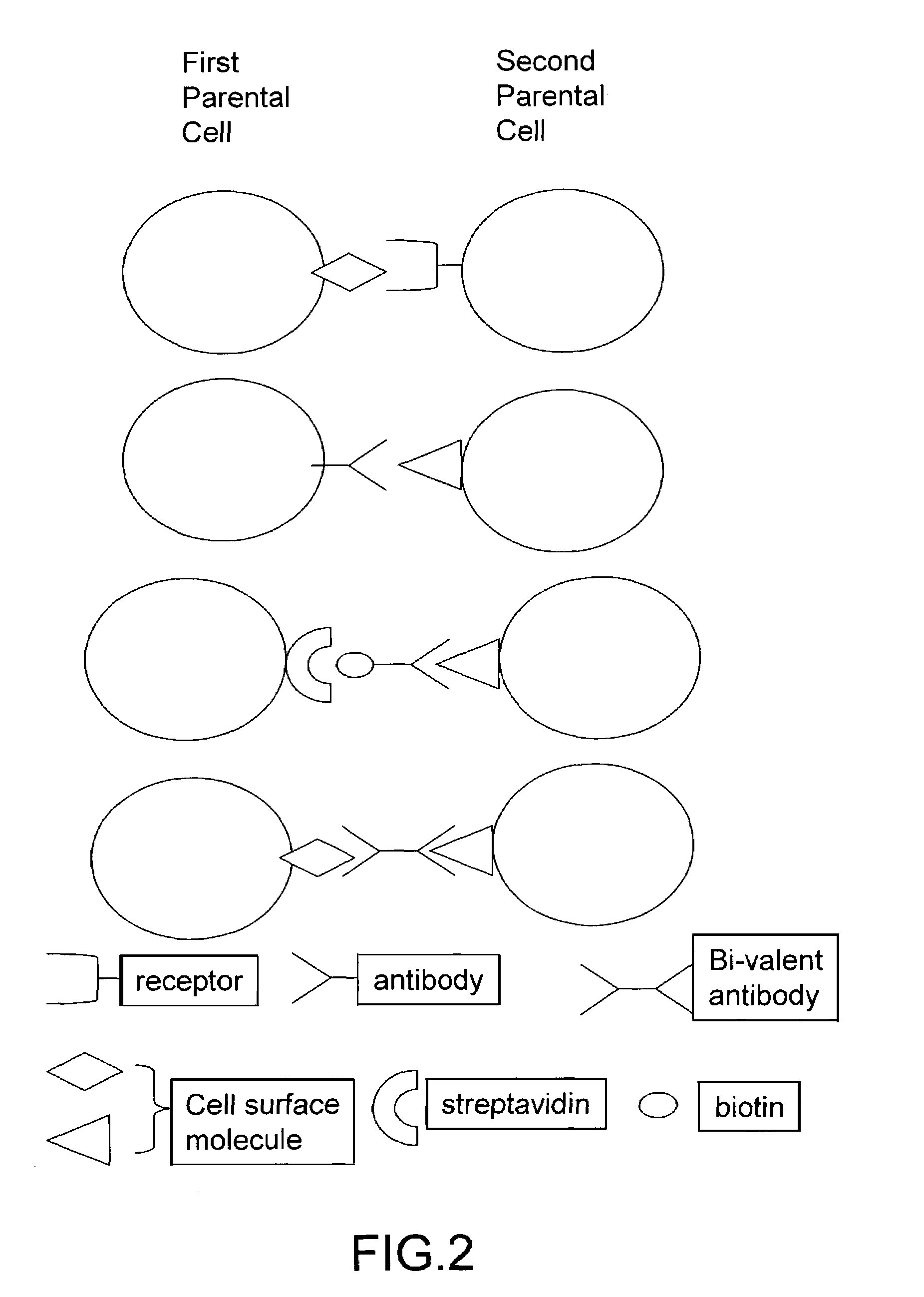
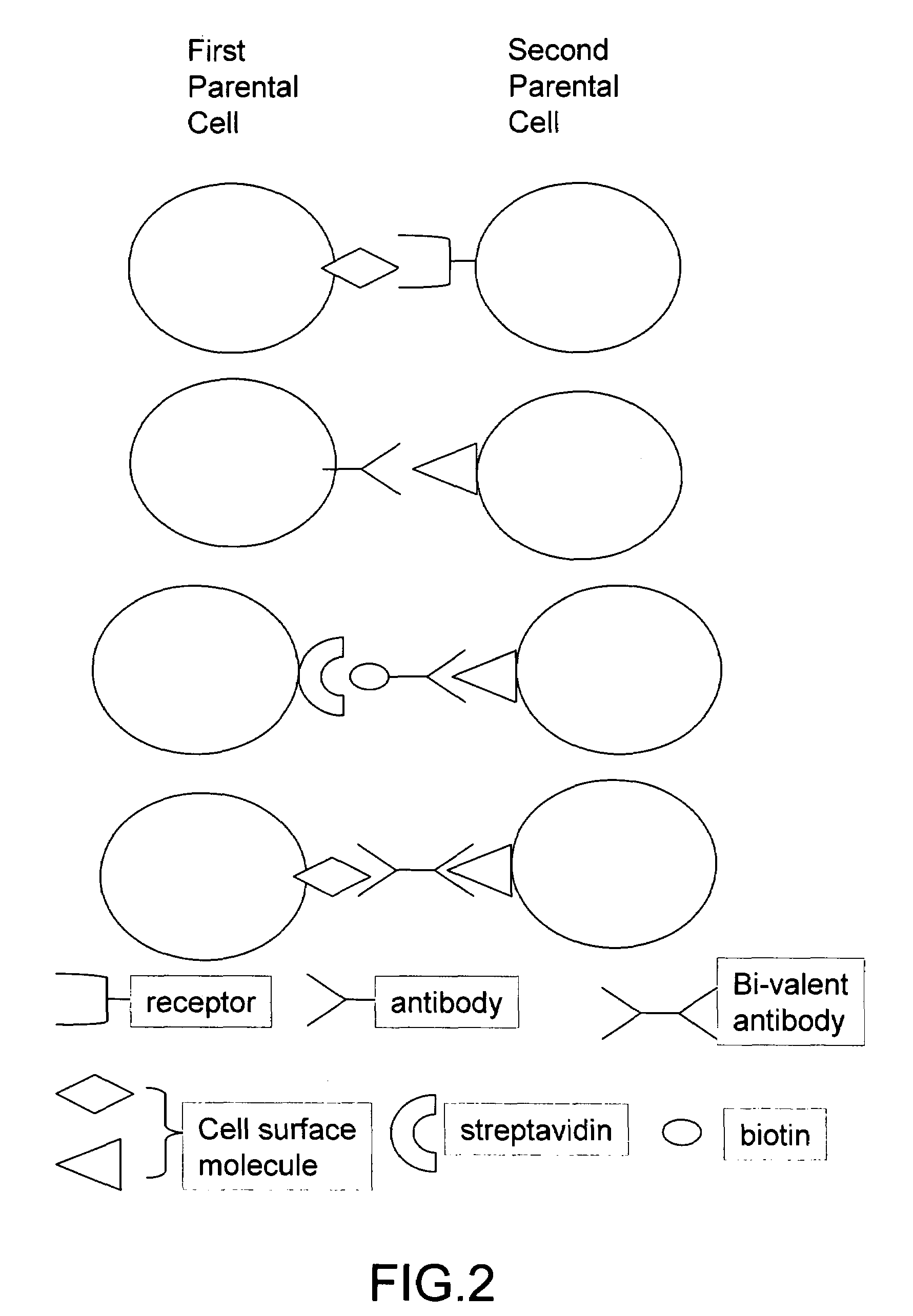
The invention provides methods for fusing a first cell with a second cell to form a hybrid cell. The methods involve incubating a first parental cell producing a first partner of a fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface with a second parental cell producing a second partner of the fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface. In certain embodiments, the parental cells are incubated with a known fusogen such as polyethylene glycol and the fusogenic binding partner pair increases the rate of cell fusion. In many embodiments, the first cell is an antibody producing cell, the second cell is an immortal cell, and the hybrid cell is a hybridoma cell that produces a monoclonal antibody. Also provided by the invention are methods for producing hybridoma cells, and methods for screening those cells for production of a monoclonal antibody of interest. The invention further provides systems and kits for carrying out the subject methods. The subject methods, systems, and kits find use in a variety of different industrial, medical and research applications.
Owner:EPITOMICS INC
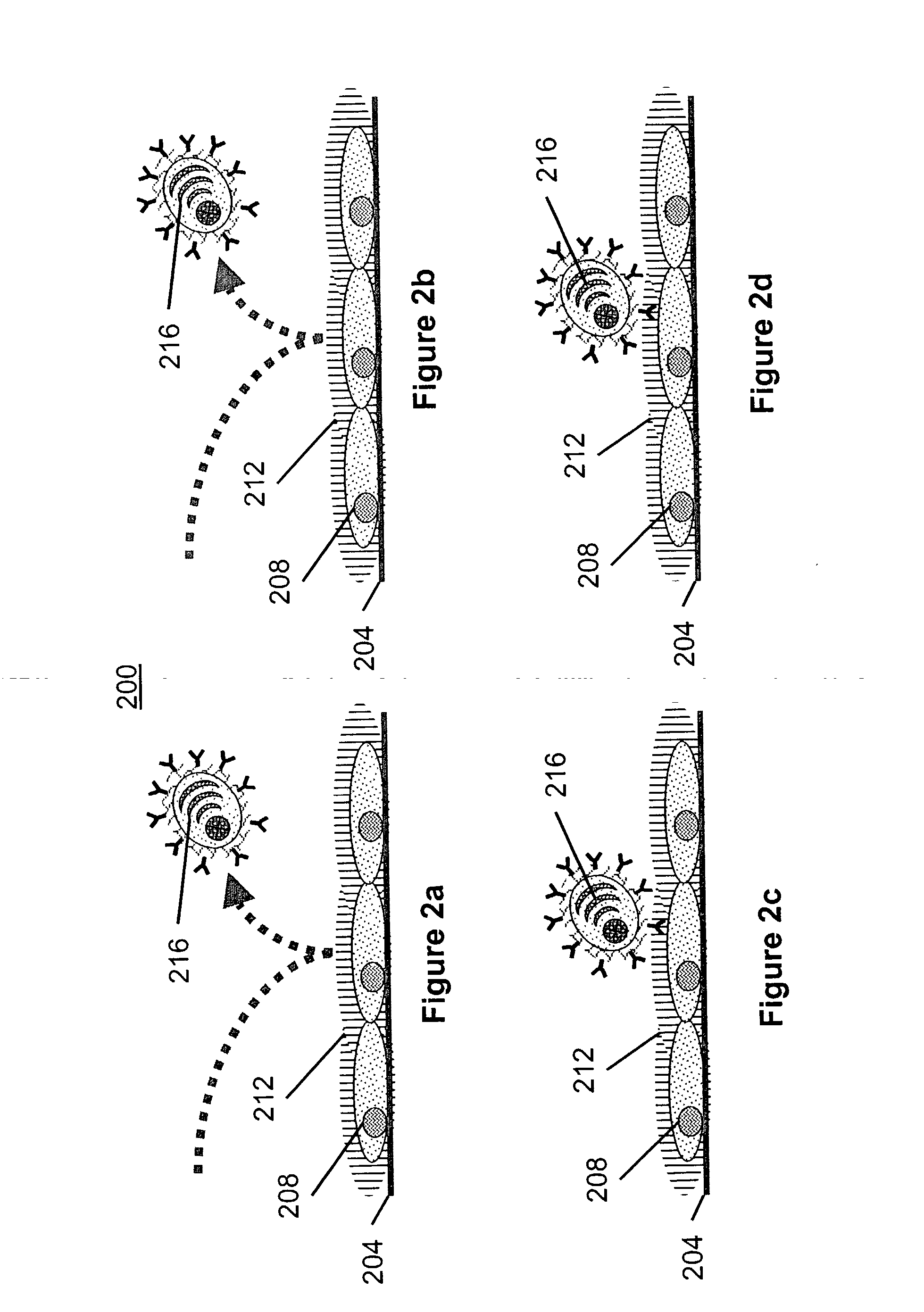
Methods for screening antibody-producing cells on heterogeneous antigen substrates
InactiveUS20060073095A1Reduce complexityShorten the timeAnimal cellsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsEpitopeMonoclonal antibody
Methods and compounds are disclosed that relate to screening and selection of monoclonal antibodies specific for antigens in heterogeneous antigen mixtures. Antibody-secreting cells such as hybridomas are modified to make them capable of directly binding antigens by capturing their secreted antibody products onto their surface membranes in appropriate binding density and orientation. Selectivity of binding to novel or desired antigens is achieved by first reacting the antigen mixtures affixed to a solid substrate with a polyclonal antibody library that prevents access to the majority of antigens or epitopes other than those that are novel or desired.
Owner:KESSLER STEVEN
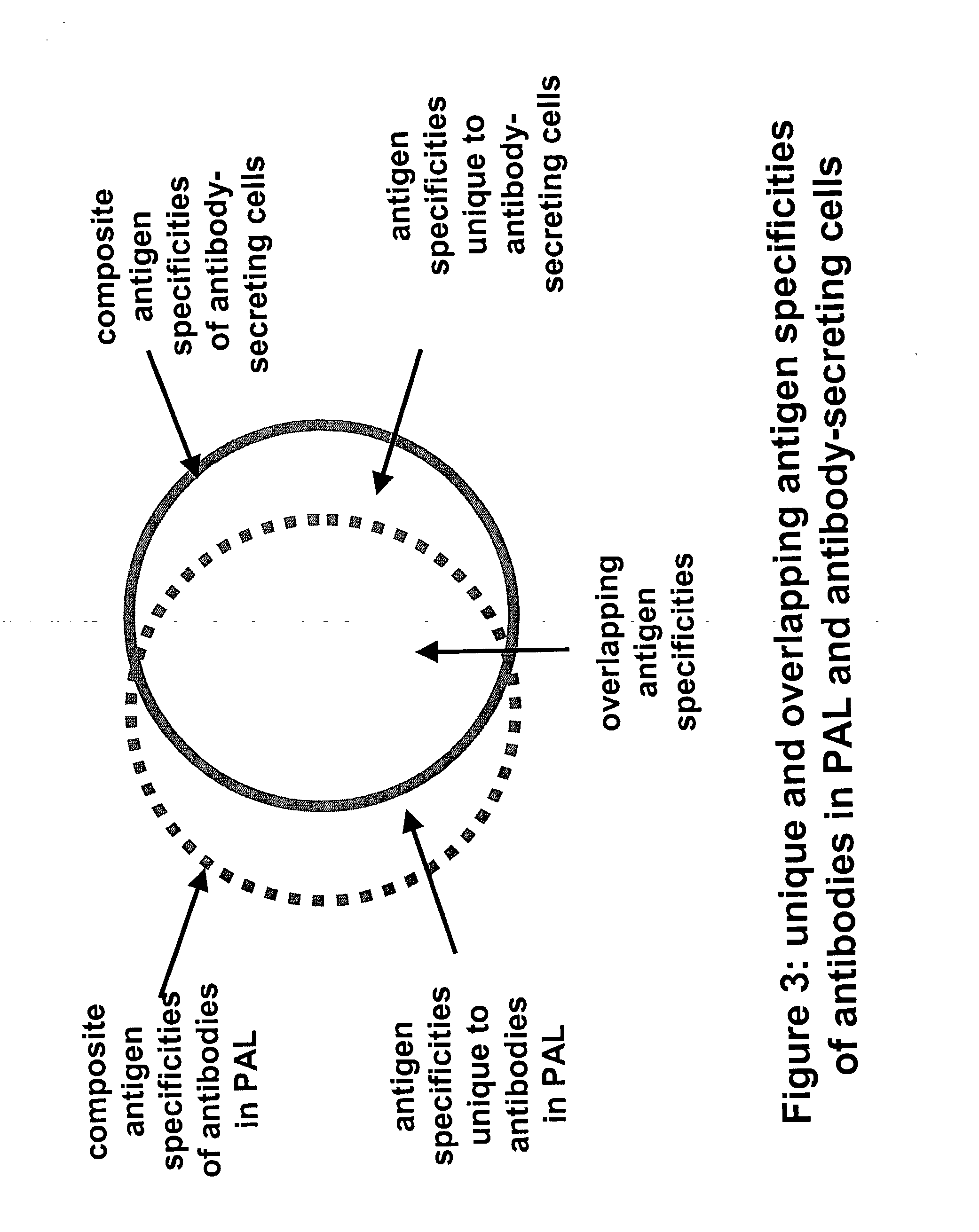
Method for generating diversity
InactiveUS20050026246A1Increase probabilityAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGenes mutationAntibody-Producing Cells
The invention relates to a method for preparing an antibody-producing cell line capable of directed constitutive hypermutation of a specific nucleic acid region, comprising the steps of: a) screening a clonal cell population for V gene diversity; b) isolating one or more cells which display V gene diversity and comparing the rate of accumulation of mutations in the V genes and other genes of the selected cells; and c) selecting a cell in which the rate of V gene mutation exceeds that of other gene mutation.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Antibodies and methods for generating genetically altered antibodies with high affinity
InactiveUS7235643B2Increase variabilityBetter pharmacokinetic profileAnimal cellsSugar derivativesGenetic diversityMonoclonal antibody
Dominant negative alleles of human mismatch repair genes can be used to generate hypermutable cells and organisms. By introducing these genes into cells and transgenic animals, new cell lines and animal varieties with novel and useful properties can be prepared more efficiently than by relying on the natural rate of mutation. These methods are useful for generating genetic diversity within immunoglobulin genes directed against an antigen of interest to produce altered antibodies with enhanced biochemical activity. Moreover, these methods are useful for generating antibody-producing cells with increased level of antibody production. The invention also provides methods for increasing the affinity of monoclonal antibodies and monoclonal antibodies with increased affinity.
Owner:EISAI INC
Method for generating diversity
InactiveUS7122339B2Increase probabilityAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody-Producing CellsAntibody
The invention relates to a method for preparing an antibody-producing cell line capable of directed constitutive hypermutation of a specific nucleic acid region, comprising the steps of: a) screening a clonal cell population for V gene diversity; b) isolating one or more cells which display V gene diversity and comparing the rate of accumulation of mutations in the V genes and other genes of the selected cells; and c) selecting a cell in which the rate of V gene mutation exceeds that of other gene mutation.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Method of obtaining antibodies of interest and nucleotides encoding same
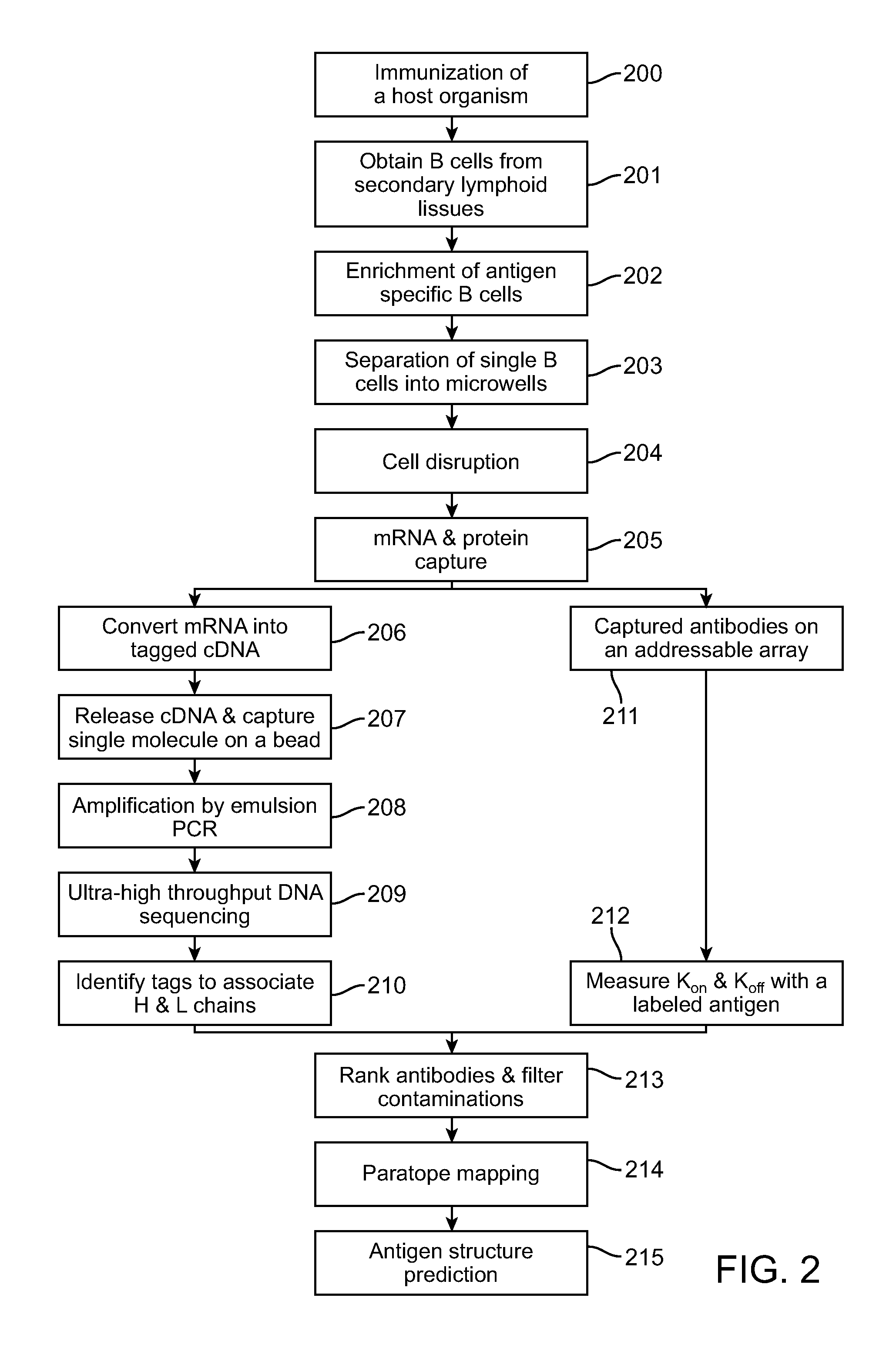
ActiveUS20110190148A1Limited effectivenessImprove efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlasma cellAntigen binding
The invention is a methodology which makes it possible to select from a very large number of cells, a single cell or cells of interest and obtain specific information from those cells in a rapid and efficient manner. As an example of the methodology, a large number of antibody producing cells such as plasma cells are separated so that these individual antibody producing plasma cells are placed in individual wells. The cells are allowed to produce antibodies and the antibodies in the wells are then contacted with a protein bound to a solid surface such as a well top. The protein universally and specifically binds antibodies in the wells. The surface or well tray top includes addresses configured such that each address is specifically related to one of the individual wells containing a cell producing antibodies.
Owner:SINGLE CELL TECH INC
Encapsulated cells producing antibodies
InactiveUS6426088B1Facilitating antibody uptakeIncrease supplyBiocideGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoAntibody-Producing Cells
The present invention relates to capsules encapsulating antibody-producing cells, and to use of such capsules and encapsulated cells, respectively, for implantation in vivo for long term delivery or sustained delivery of antibodies of therapeutic interest.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS +1
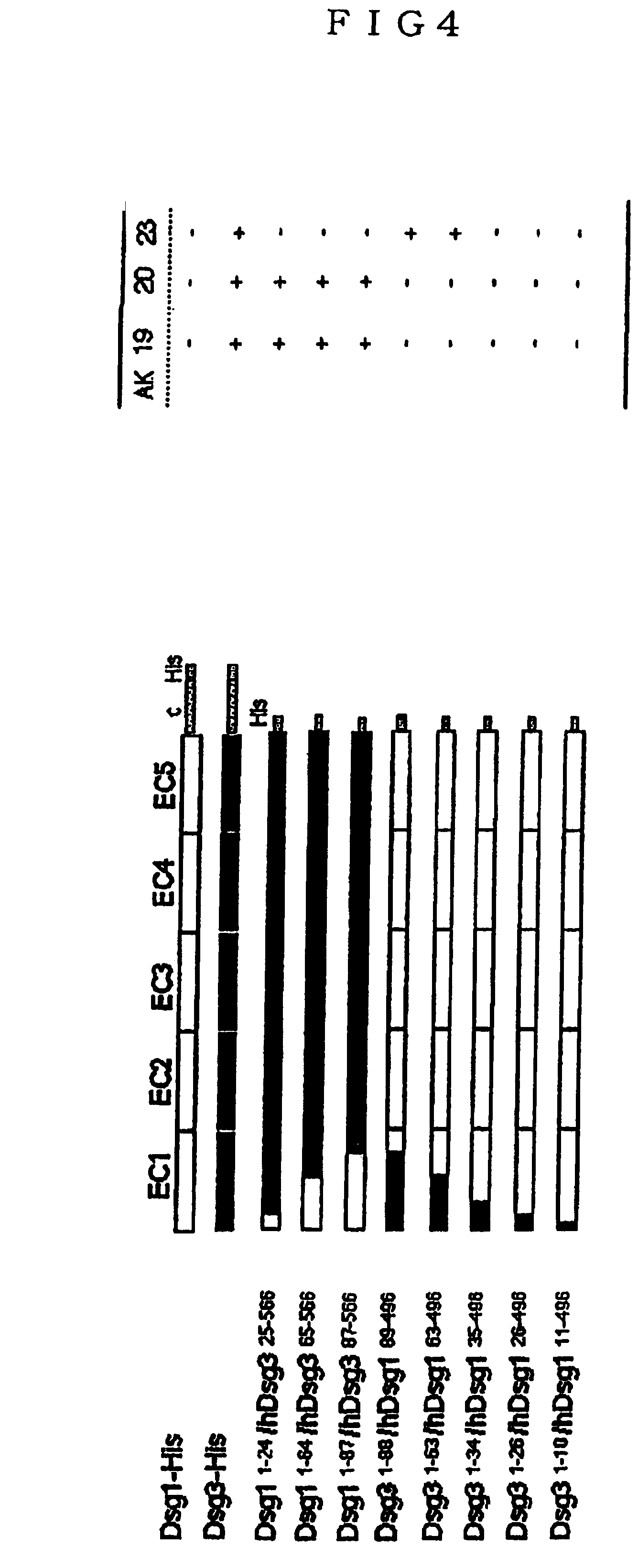
Pemphigus monoclonal antibody
The present invention provides a monoclonal antibody having a pathogenic activity that can induce pemphigus lesion, a peptide specifically recognized by the monoclonal antibody and useful as a therapeutic drug for pemphigus autoimmune disease, etc. As anti-mouse Dsg3 antibody-producing cells are present in the splenocytes of pemphigus vulgaris mouse model constructed by using autoantigen knockout mouse, cell fusion was conducted with the splenocytes of said mouse model and mouse myeloma cells using polyethyleneglycol, hybridomas were constructed, and monoclonal antibodies against Dsg3 were constructed. Among them, a monoclonal antibody having a pathological activity that can induce pemphigus lesions was screened, the base sequence and amino acid sequence in its variable region (heavy chain, light chain) was determined, and the specific epitope part was identified.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Cell fusion method
InactiveUS7575896B2Increase ratingsAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyethylene glycolAntibody-Producing Cells
The invention provides methods for fusing a first cell with a second cell to form a hybrid cell. The methods involve incubating a first parental cell producing a first partner of a fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface with a second parental cell producing a second partner of the fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface. In certain embodiments, the parental cells are incubated with a known fusogen such as polyethylene glycol and the fusogenic binding partner pair increases the rate of cell fusion. In many embodiments, the first cell is an antibody producing cell, the second cell is an immortal cell, and the hybrid cell is a hybridoma cell that produces a monoclonal antibody. Also provided by the invention are methods for producing hybridoma cells, and methods for screening those cells for production of a monoclonal antibody of interest. The invention further provides systems and kits for carrying out the subject methods. The subject methods, systems, and kits find use in a variety of different industrial, medical and research applications.
Owner:EPITOMICS INC
Method of Antibody Production
InactiveUS20070269436A1Easy to demonstrateAnimal cellsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody-Producing CellsIn vitro
The present invention relates to a method for the in vitro production of antibody in an antigen specific manner and, more particularly, to the in vitro production of human antibody in an antigen specific manner. The present invention further extends to the antibody produced therefrom and to the antibody producing cells produced in accordance with the methods disclosed herein. The antibodies and antibody producing cells of the present invention are useful, inter alia, in a range of therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:APOLLO LIFE SCI
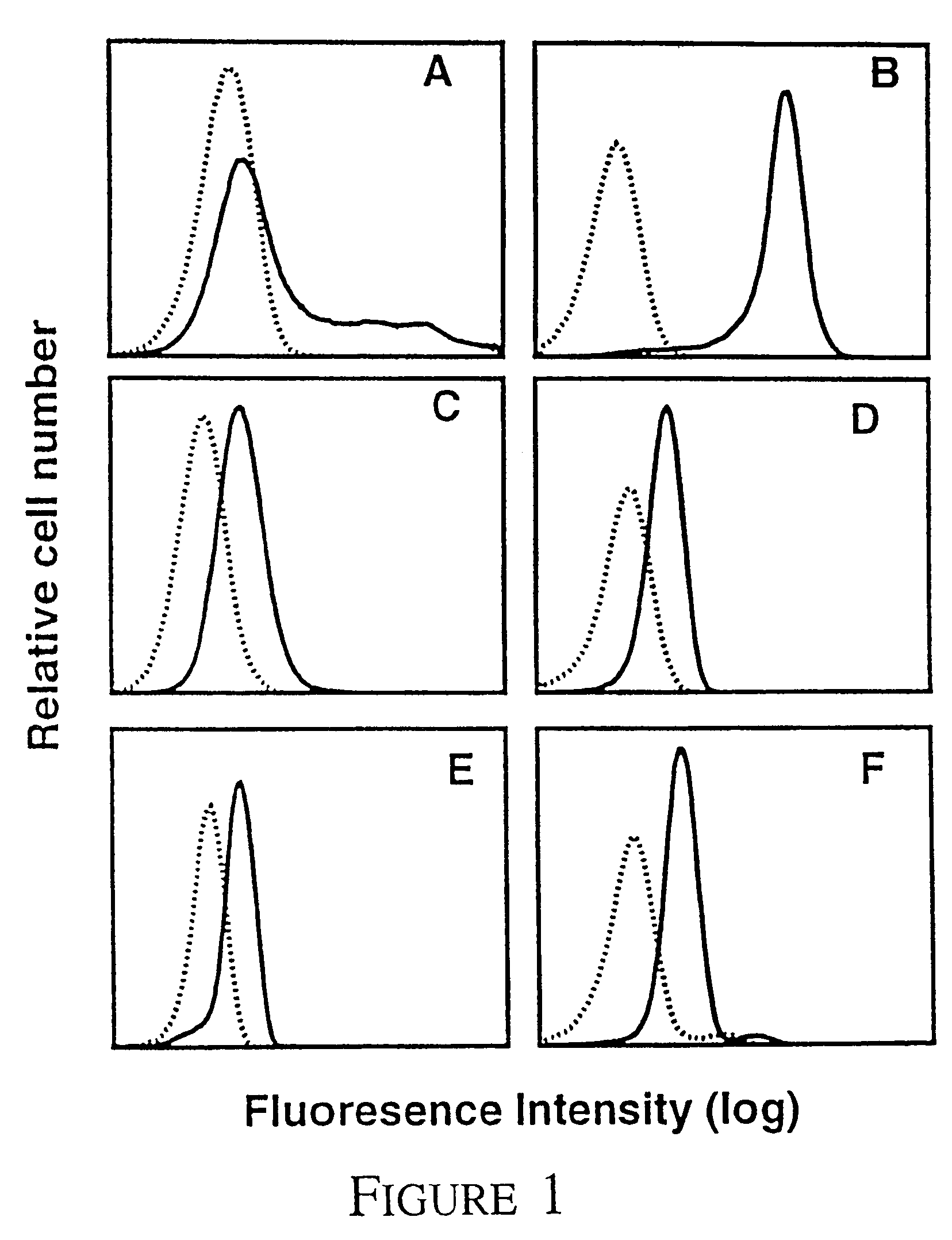
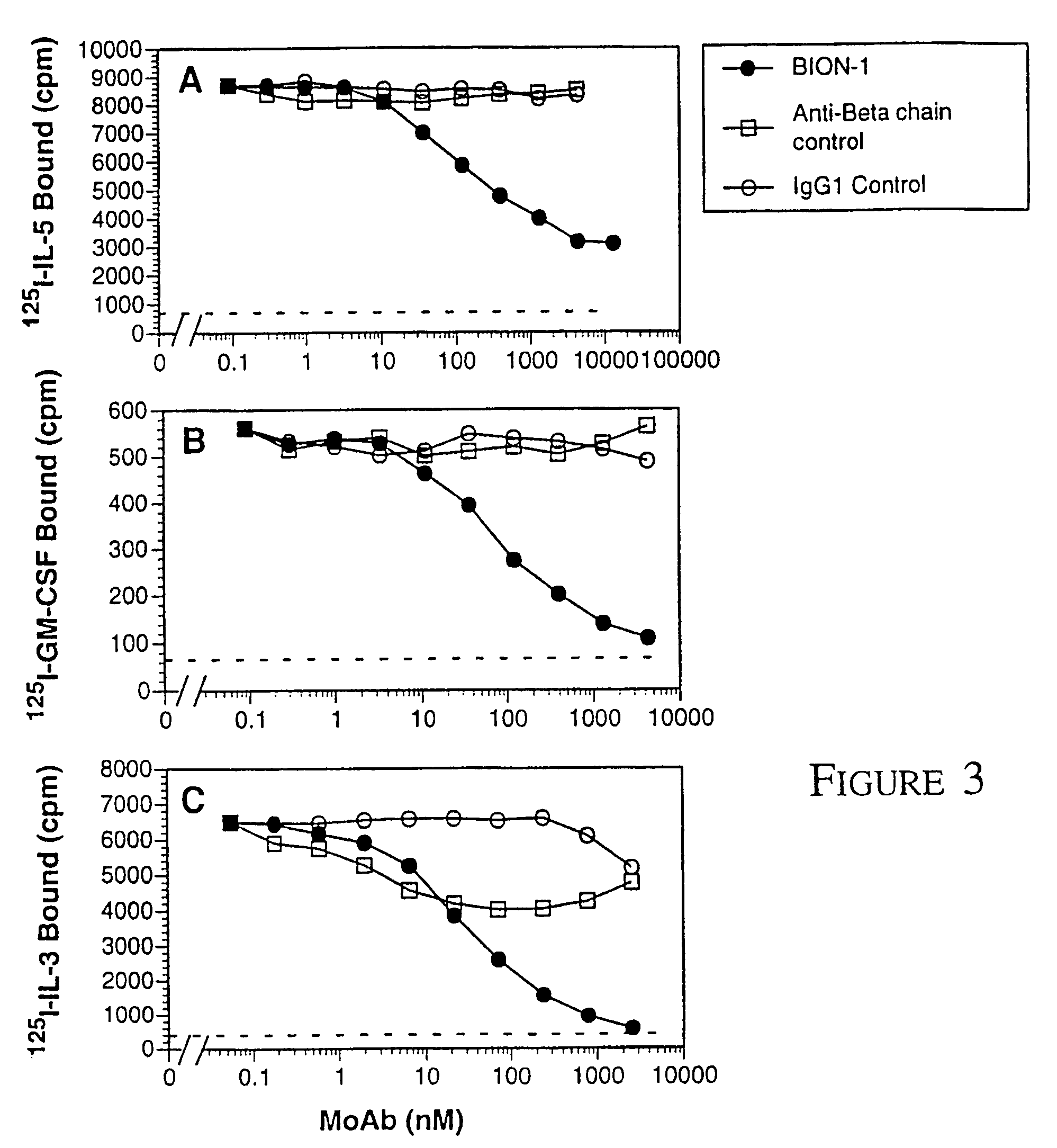
Method of modulating leukemic cell and eosinphil activity with monoclonal antibodies
InactiveUS7427401B2Block high affinity bindingInhibition of activationImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsBinding siteEosinophil
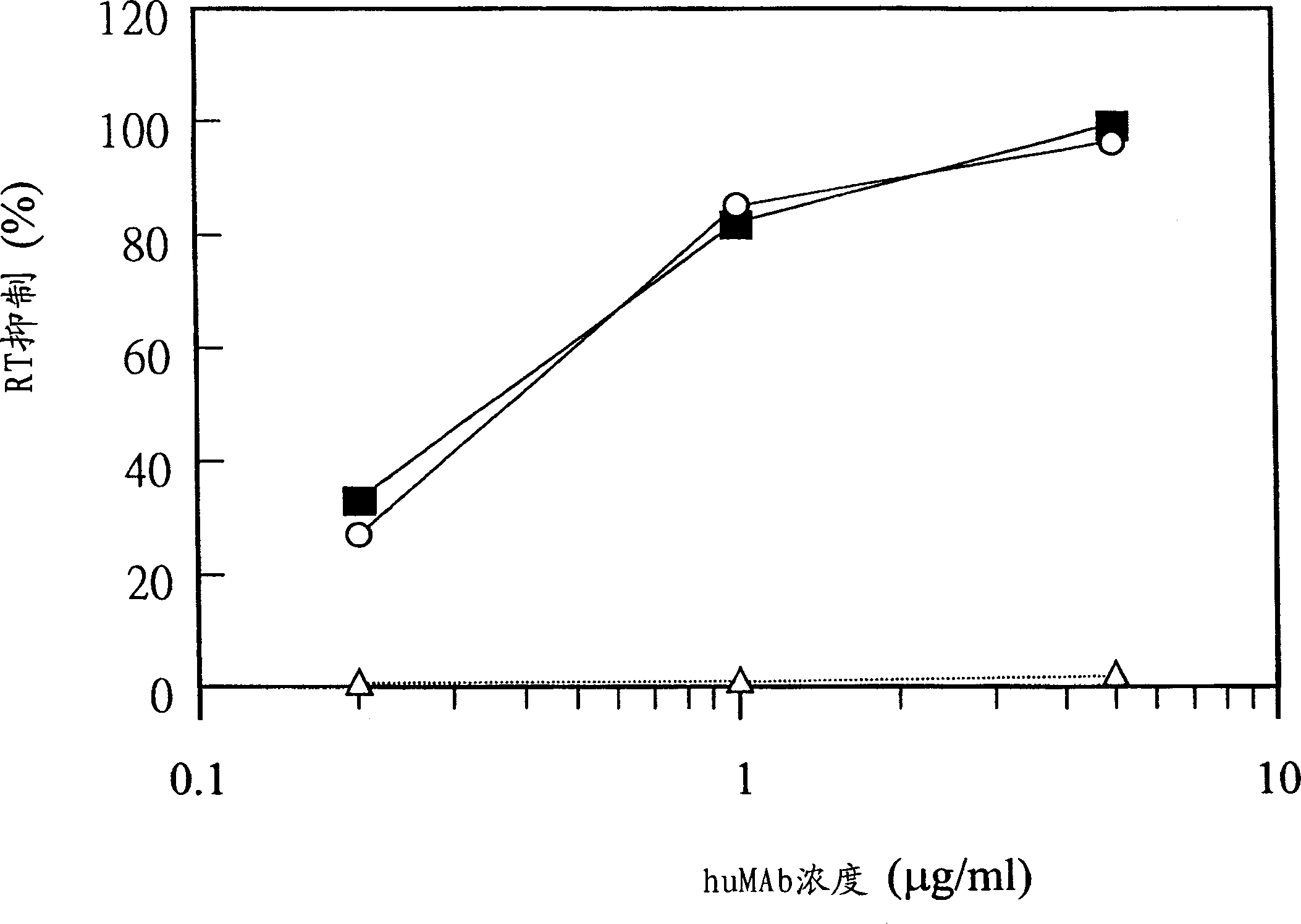
A method of isolating a monoclonal antibody capable of inhibiting any one of IL-3, GM-CSF and IL-5 binding to the common receptor βc, or a monoclonal antibody capable of inhibiting the cytokines binding to a receptor analogous to βc. The method includes the steps of immunizing an animal with a cytokine receptor or portion of a cytokine containing the critical binding site which portion includes the extracellular domain 4 or analogous domain in the analogous common receptor or part thereof. Antibodies producing cells from the animal are then isolated and fused with a myeloma cell line and then screened for a cell line that produces an antibody of the desired type. A monoclonal antibody, or fragments thereof capable of inhibiting the binding of the cytokines IL-3, GM-CSF and IL-5 to the βc receptor, and a hybridoma cell line producing the antibody are also claimed.
Owner:MEDVET SCI
Method of producing antibodies with modified fucosylation level
InactiveCN101238148ATransferasesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFucosylationAntibody-Producing Cells
The present invention provides methods for controlling the level of fucosylation and enhancing ADCC activity in antibodies by inhibiting FUT8 expression in antibody-producing cells.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Isolating cells expressing secreted proteins
InactiveUS20050186623A1DifferentiateImprove the level ofCompound screeningApoptosis detectionBiological bodyRare cell
A method for identifying and isolating cells which produce secreted proteins. This method is based upon a specific characteristic or the expression level of the secreted protein by transiently capturing the secreted protein on the surface of an individual cell, allowing selection of rare cell clones from a heterogeneous population. Also provided is the use of this method to generate cells which produce a desired level of secreted protein or secreted protein of a particular characteristic(s), and organisms which possess such cells. In particular, the method allows rapid isolation of high expression recombinant antibody-producing cell lines, or may be applied directly to rapid isolation of specific hybridomas, or to the isolation of antibody-producing transgenic animals. This method is applicable for any cell which secretes protein.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
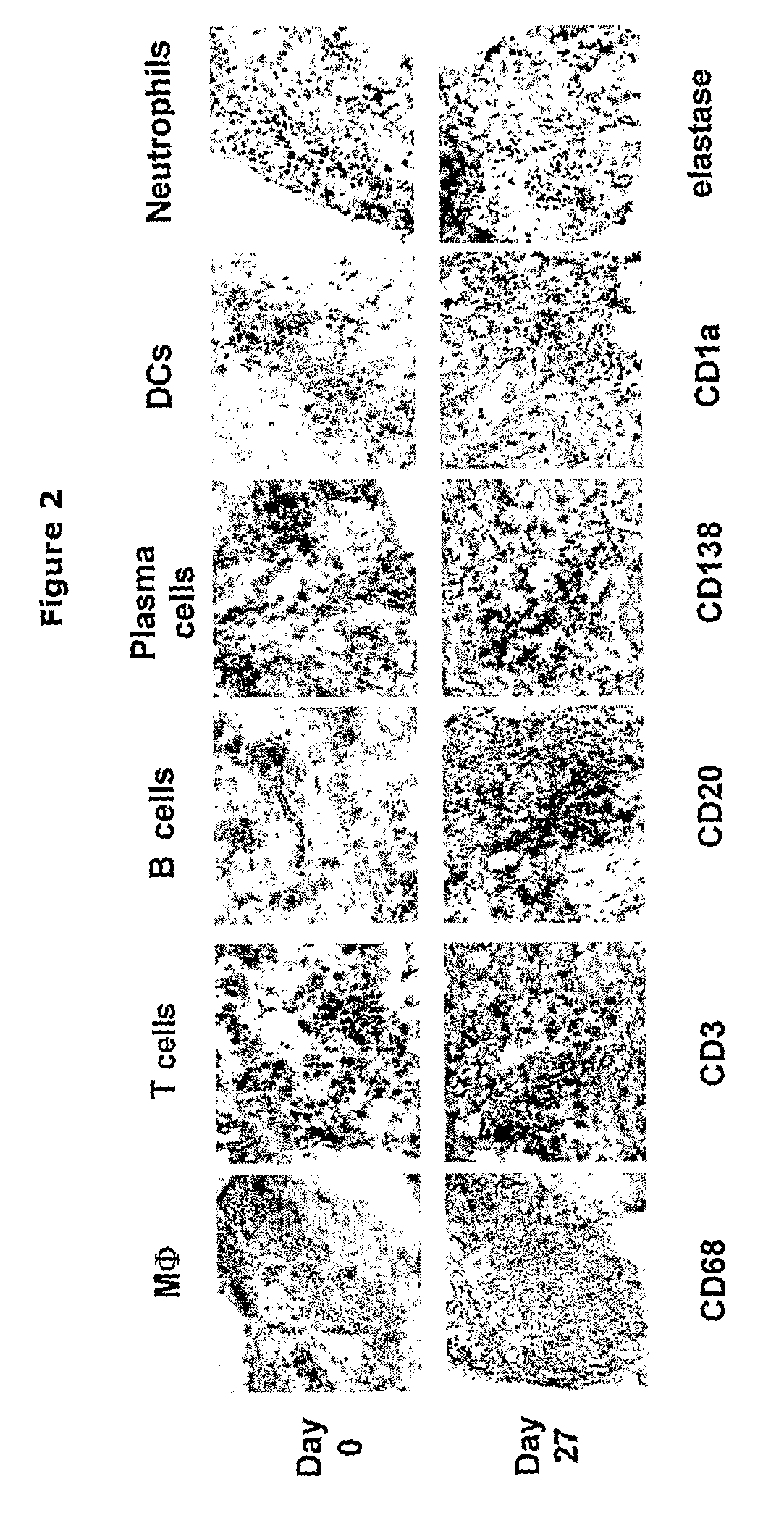
Antibody production methods relating to disruption of peripheral tolerance in B lympho-cytes
InactiveUS6921846B1Increase productionFermentationImmunoglobulins against enzymesMonoclonal antibodyPolyclonal antibodies
The subject invention relates a method for the production of monoclonal antibodies. The method utilizes an immunized animal having antibody-producing cells with disrupted peripheral tolerance. The invention also provides a method for the use of such monoclonal antibodies, and polyclonal antibodies derived from an immunized animal having antibody-producing cells with disrupted peripheral tolerance, for in vitro and in vivo clinical diagnostics and therapeutics.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Preparation of full-length human antibody
InactiveCN1626669AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunoglobulins against virusesAntigenHuman lymphocyte
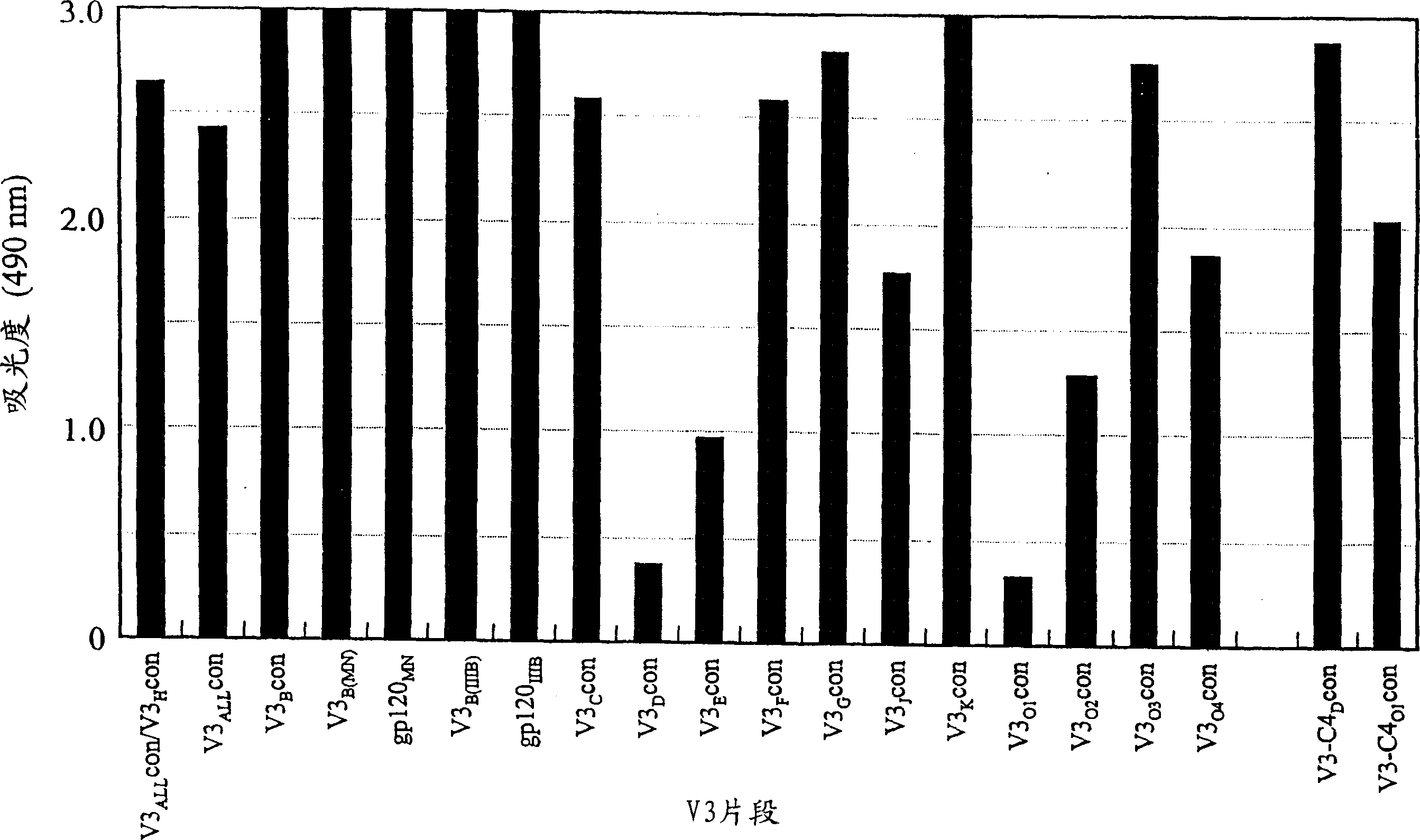
The present invention provides a method for producing a fully humanized antibody that recognizes a predetermined antigen and does not rely on a human donor who has been exposed to the antigen. To achieve this, lymphocytes from natural human donors are immunized in vitro with an antigen of interest, and antibody-producing cells directed against said antigen are then identified. Because lymphocytes immunize in vitro rather than in vivo, it is possible to modulate the antigen or antigen fragment recognized by the antibody. A preferred antigen is an HIV gp120 peptide, especially the co-receptor binding region of gp120.
Owner:CCL HLDG
Method of obtaining antibodies of interest and nucleotides encoding same
ActiveUS9328172B2Limited effectivenessImprove efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePlasma cell
The invention is a methodology which makes it possible to select from a very large number of cells, a single cell or cells of interest and obtain specific information from those cells in a rapid and efficient manner. As an example of the methodology, a large number of antibody producing cells such as plasma cells are separated so that these individual antibody producing plasma cells are placed in individual wells. The cells are allowed to produce antibodies and the antibodies in the wells are then contacted with a protein bound to a solid surface such as a well top. The protein universally and specifically binds antibodies in the wells. The surface or well tray top includes addresses configured such that each address is specifically related to one of the individual wells containing a cell producing antibodies.
Owner:SINGLE CELL TECH INC
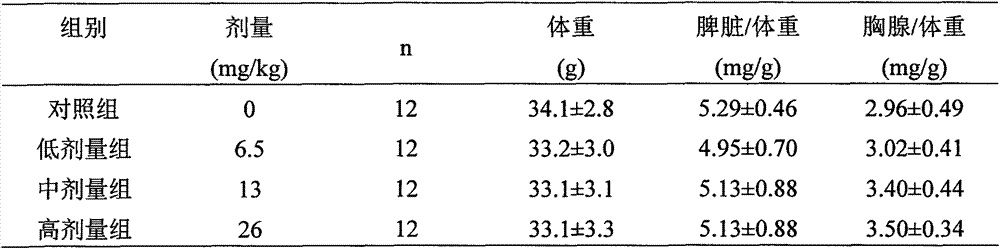
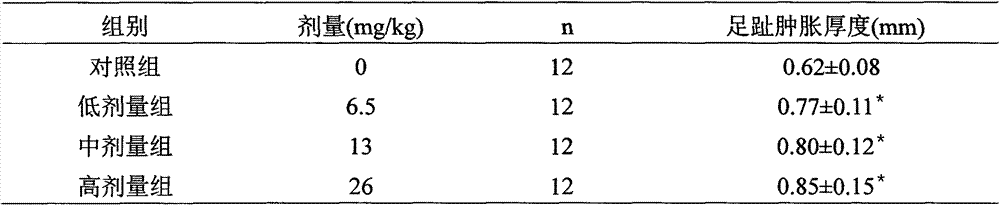
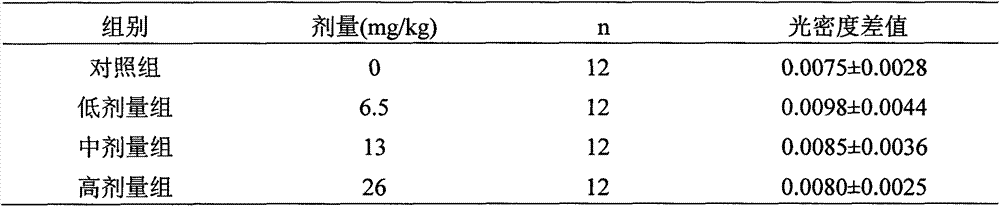
Medicinal and edible composition capable of improving immunity and preparation method of medicinal and edible composition
InactiveCN107441368APromote proliferationImprove lipid metabolismOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersMedicinal herbsRed blood cell
The invention discloses a medicinal and edible composition capable of improving the immunity and a preparation method of the medicinal and edible composition. The composition is composed of the medicinal and edible medicinal materials including wheat seedlings, radix ginseng, arillus longan, mulberries, semen sesami nigrum, rhizoma polygonati and the like, as well as fructooligosaccharide and galactooligosaccharide, the integral regulation advantages of the compound traditional Chinese medicine are exerted, the effect of improving the immune functions is obvious, and the experiment proves that the medicinal and edible composition can reduce the toe swelling thickness of normal mice, and improve the activity of the NK cells, the level of the serum hemolysin, the number of antibody-producing cells, the carbon clearance phagocytosis index and the phagocytosis capacity for chicken erythrocytes of macrophagocytes.
Owner:广州市高纤宝健康食品有限公司
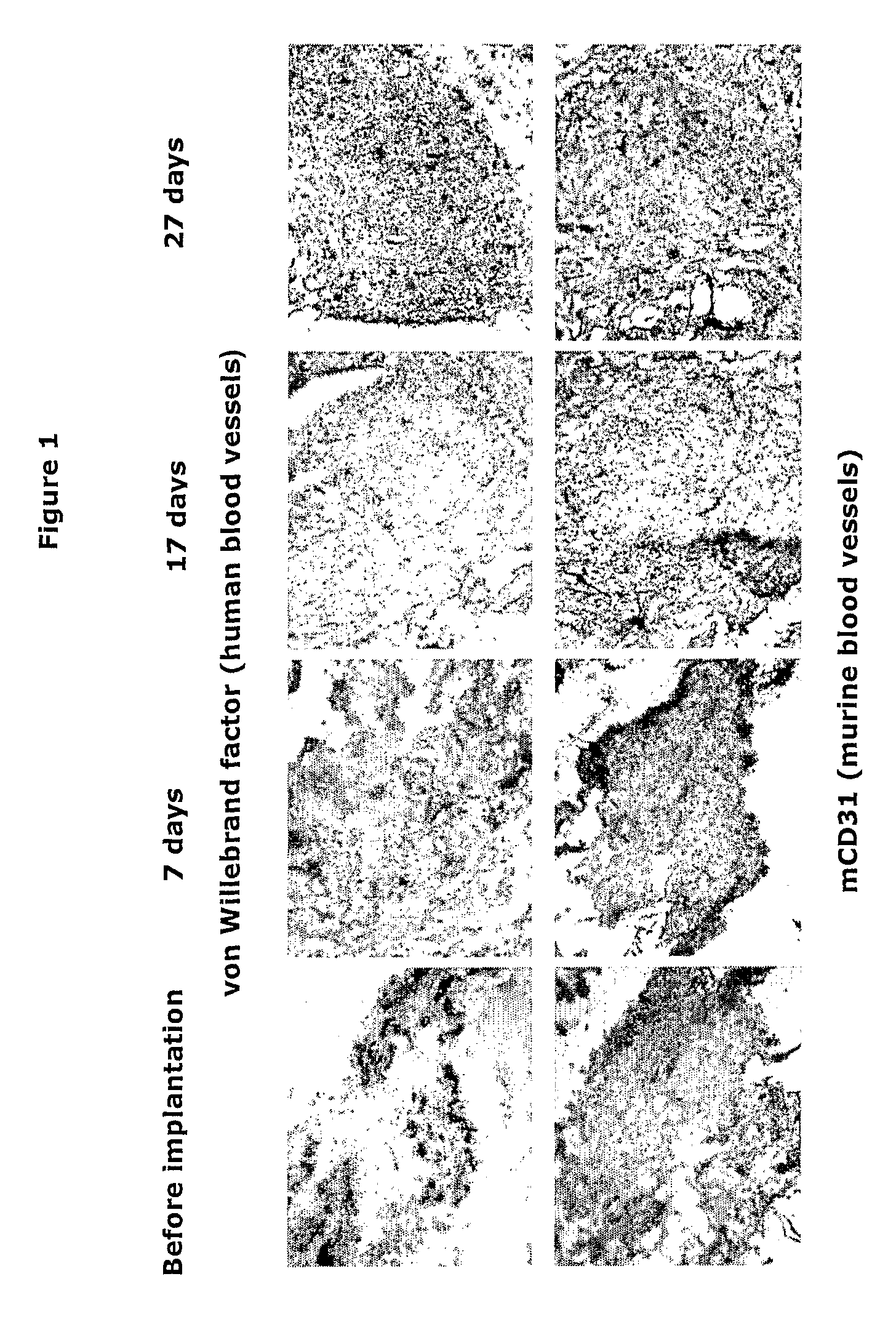
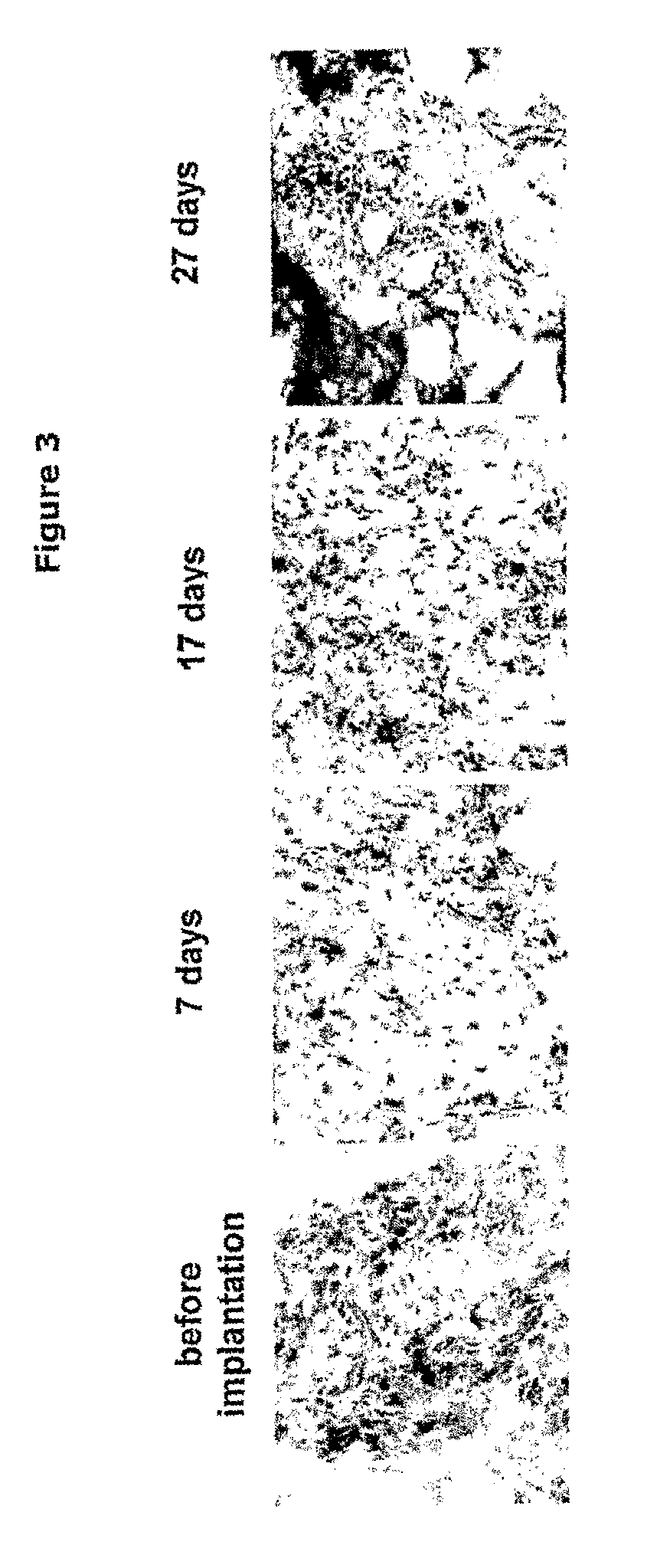
Non-Human mammalian Arthritis Model Featuring Human Antibodies Against Citrul-Linated Proteins
Use of a non-human mammalian disease model, wherein the non-human mammal has been implanted with human synovial tissue or other human inflamed tissue containing anti-CCP (cyclic citrullinated peptide) antibody producing cells for (i) analyzing cellular processes in a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies in such human synovial tissue or other human inflamed tissue, (ii) studying the role of anti-CCP antibodies in the induction and progression of a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies, (iii) testing the efficacy of a therapeutic agent for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies, and (iv) identifying a therapeutic agent useful for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies. In one embodiment the non-human mammalian disease model is a mouse, such as a SCID mouse, and the disease associated with anti-CCP antibodies is arthritis, such as RA (rheumatoid arthritis).
Owner:GENMAB AS
Methods for screening b cell lymphocytes
Methods are described herein for screening an antibody producing cell within a microfluidic environment. The antibody producing cell may be a B cell lymphocyte, which may be a memory B cell or a plasma cell. An antigen of interest may be brought into proximity with the antibody producing cell and binding of the antigen by an antibody produced by the antibody producing cell may be monitored. Methods of obtaining a sequencing library from an antibody producing cell are also described.
Owner:PHENOMEX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com