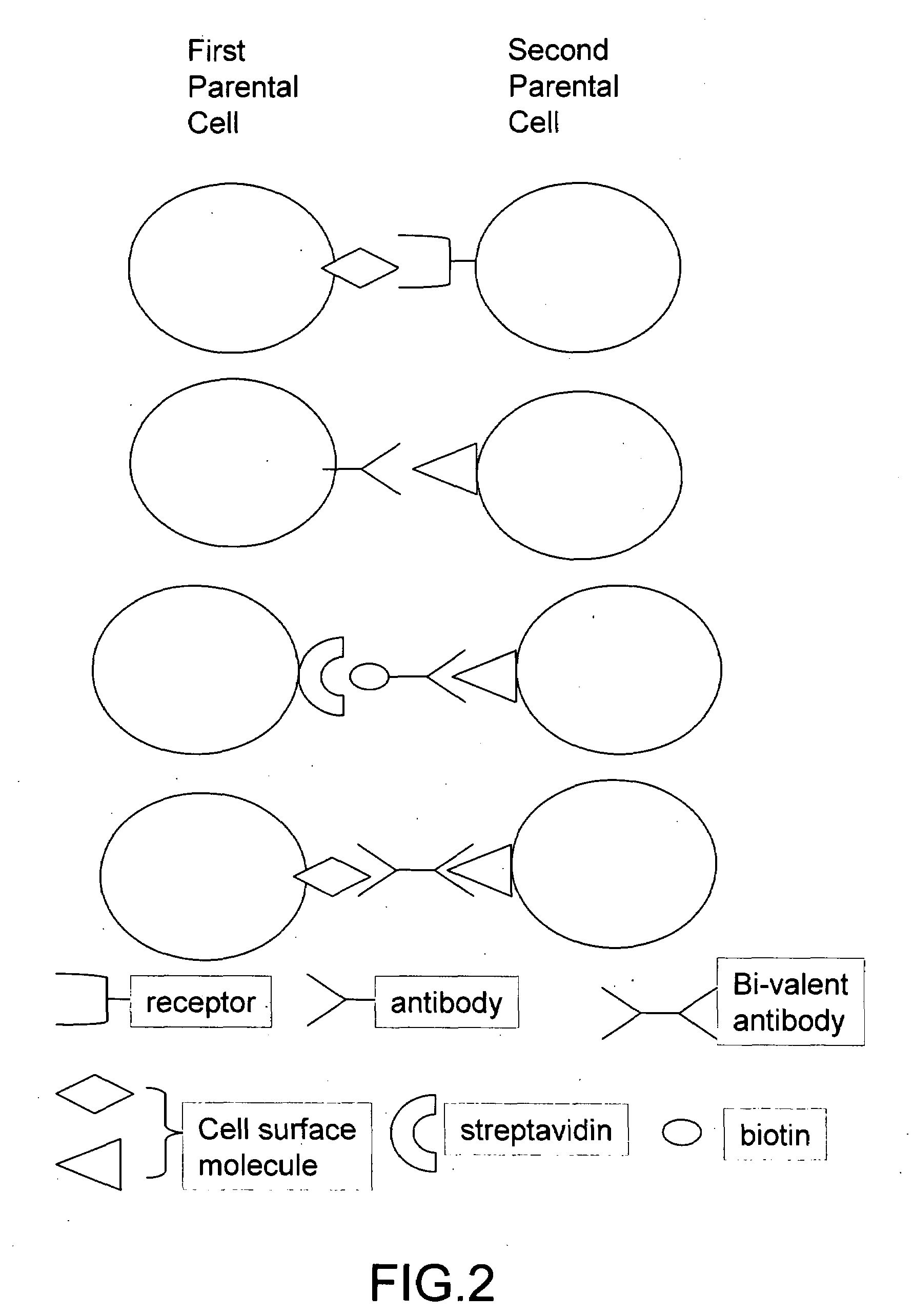
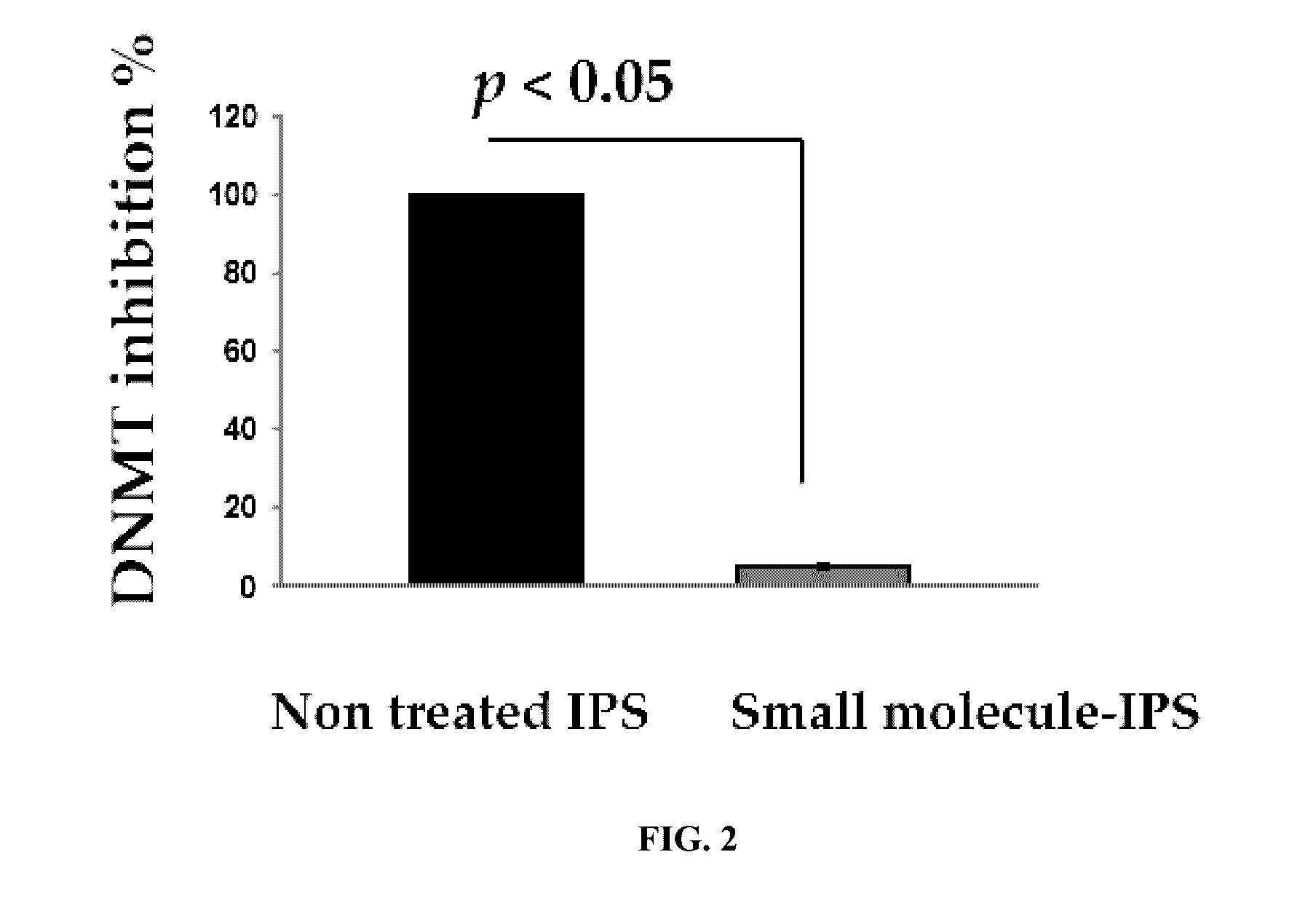
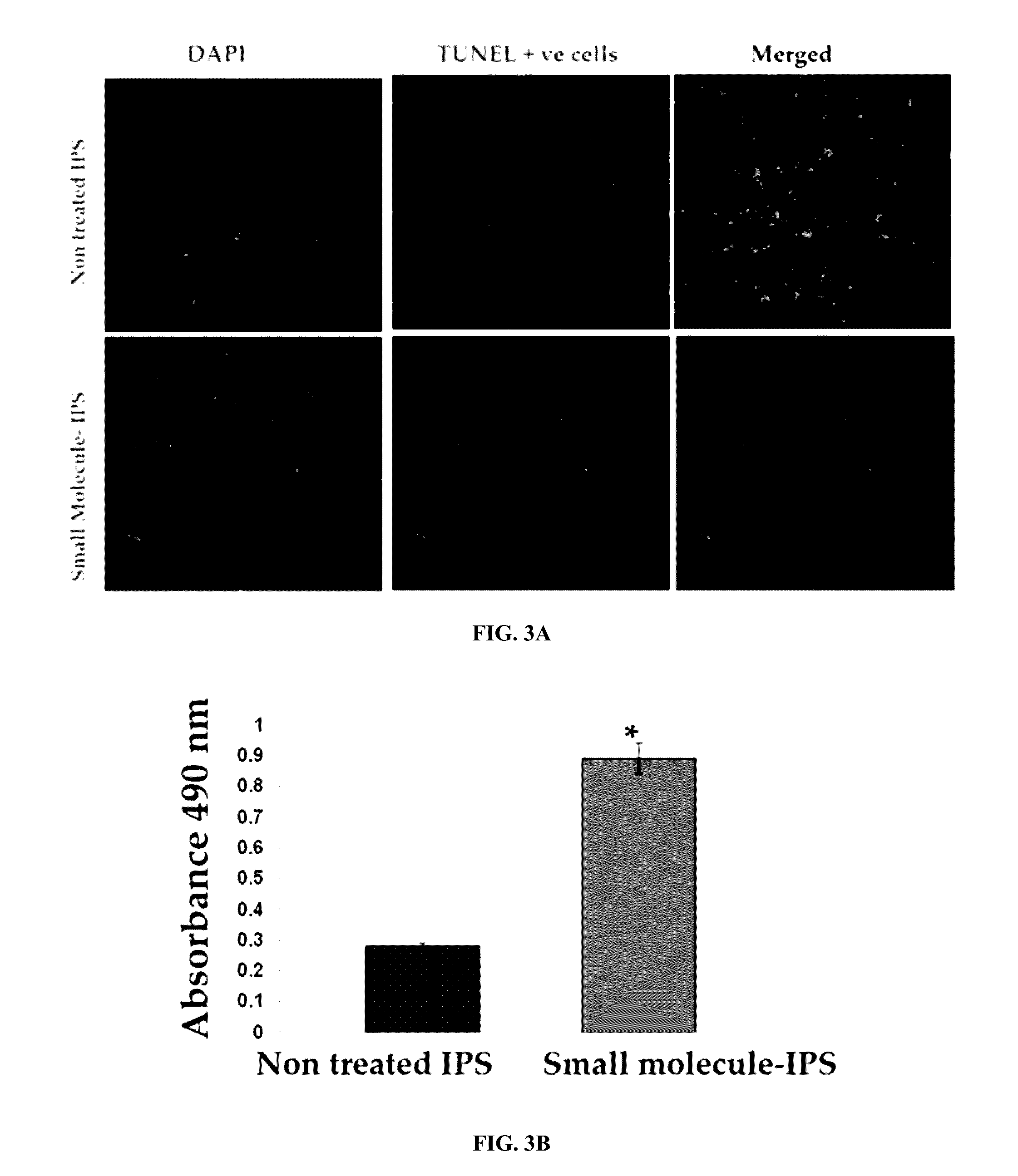
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Parental cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parent cell. (n.d.). In YourDictionary. A cell that is the source of other cells, as a cell that divides to produce two or more daughter cells, or a stem cell that is a progenitor of other cells or is the first in a line of developing cells. "Parent cell.".
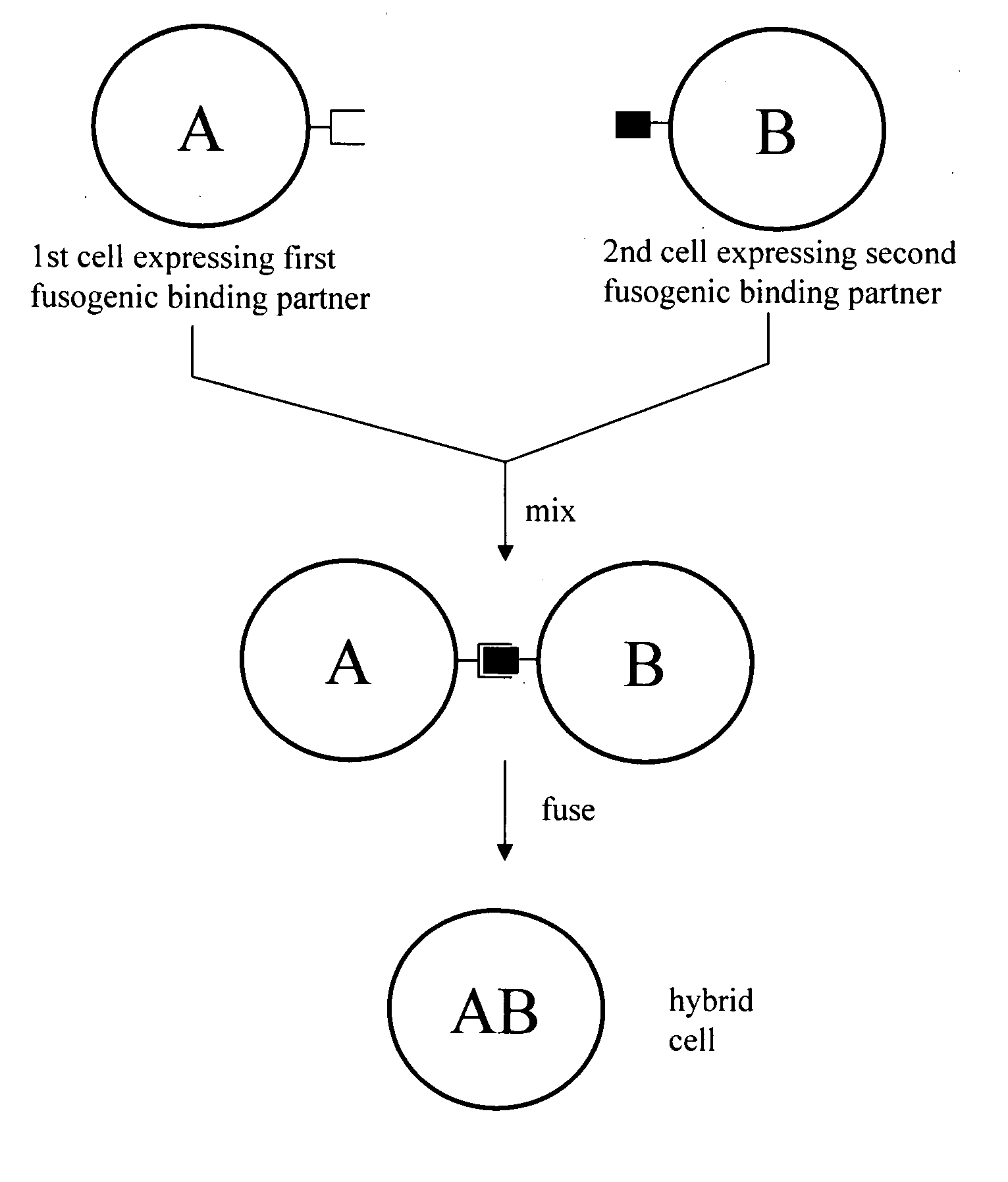
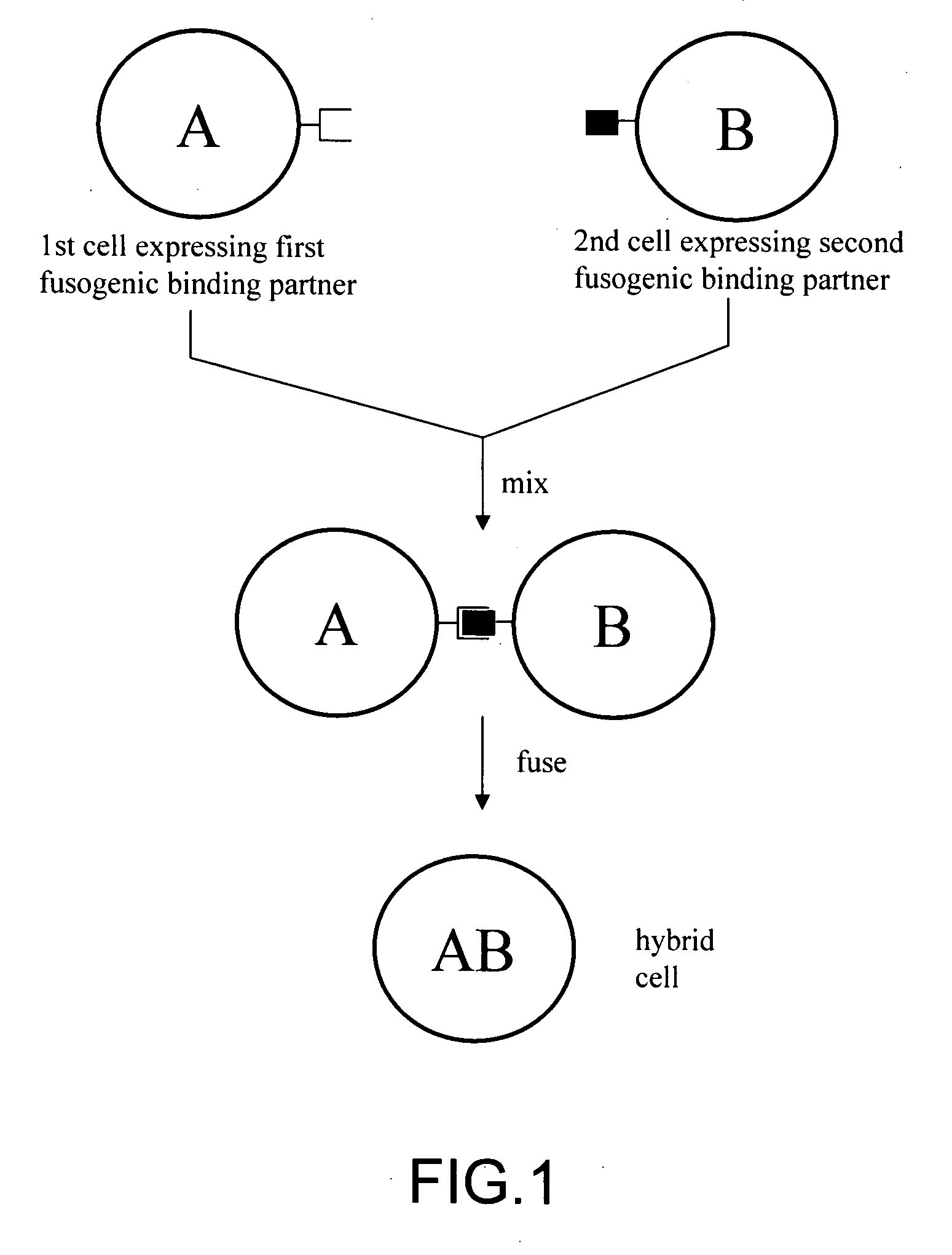
Cell fusion method
ActiveUS7402409B2Increase ratingsAnimal cellsSugar derivativesPolyethylene glycolAntibody-Producing Cells
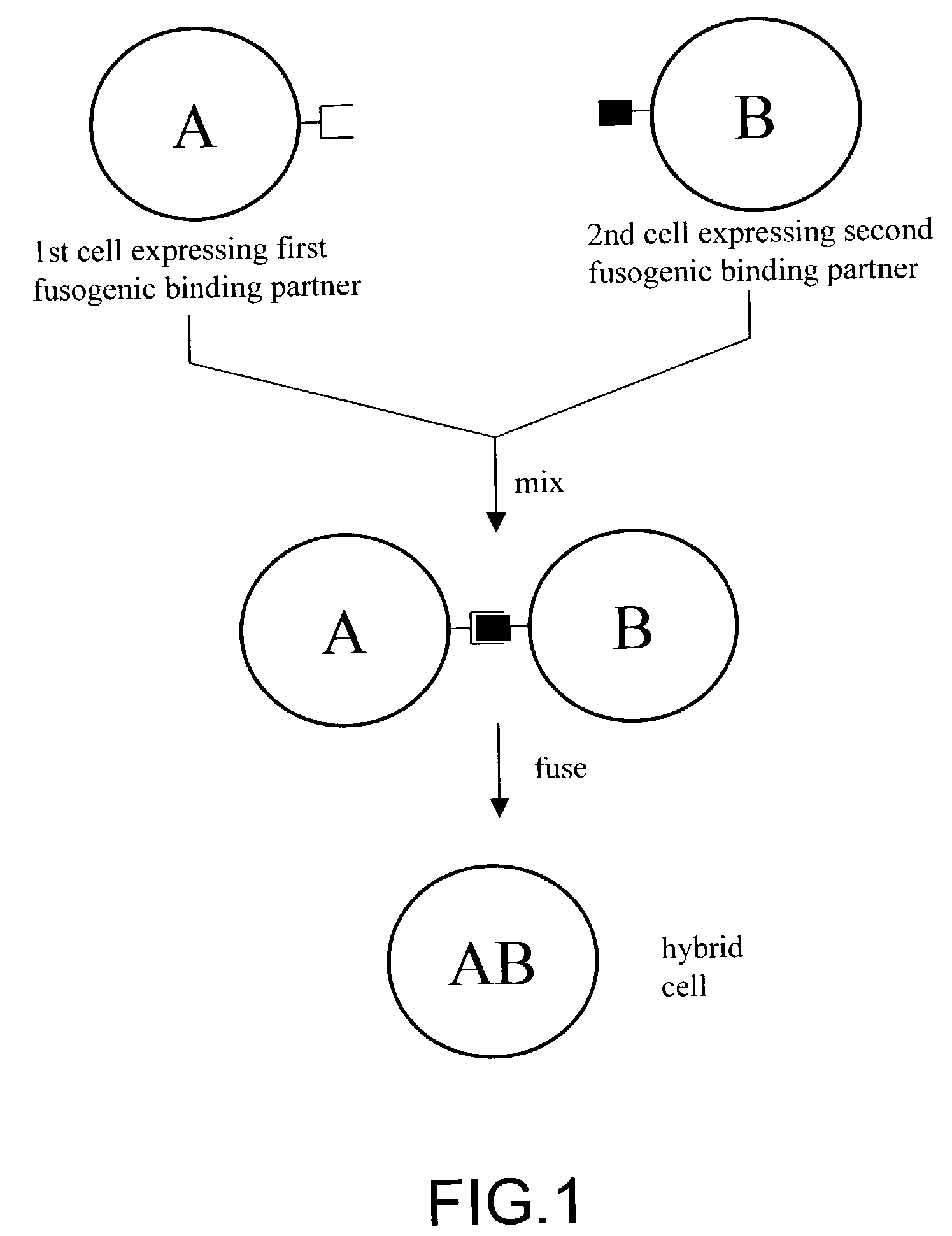
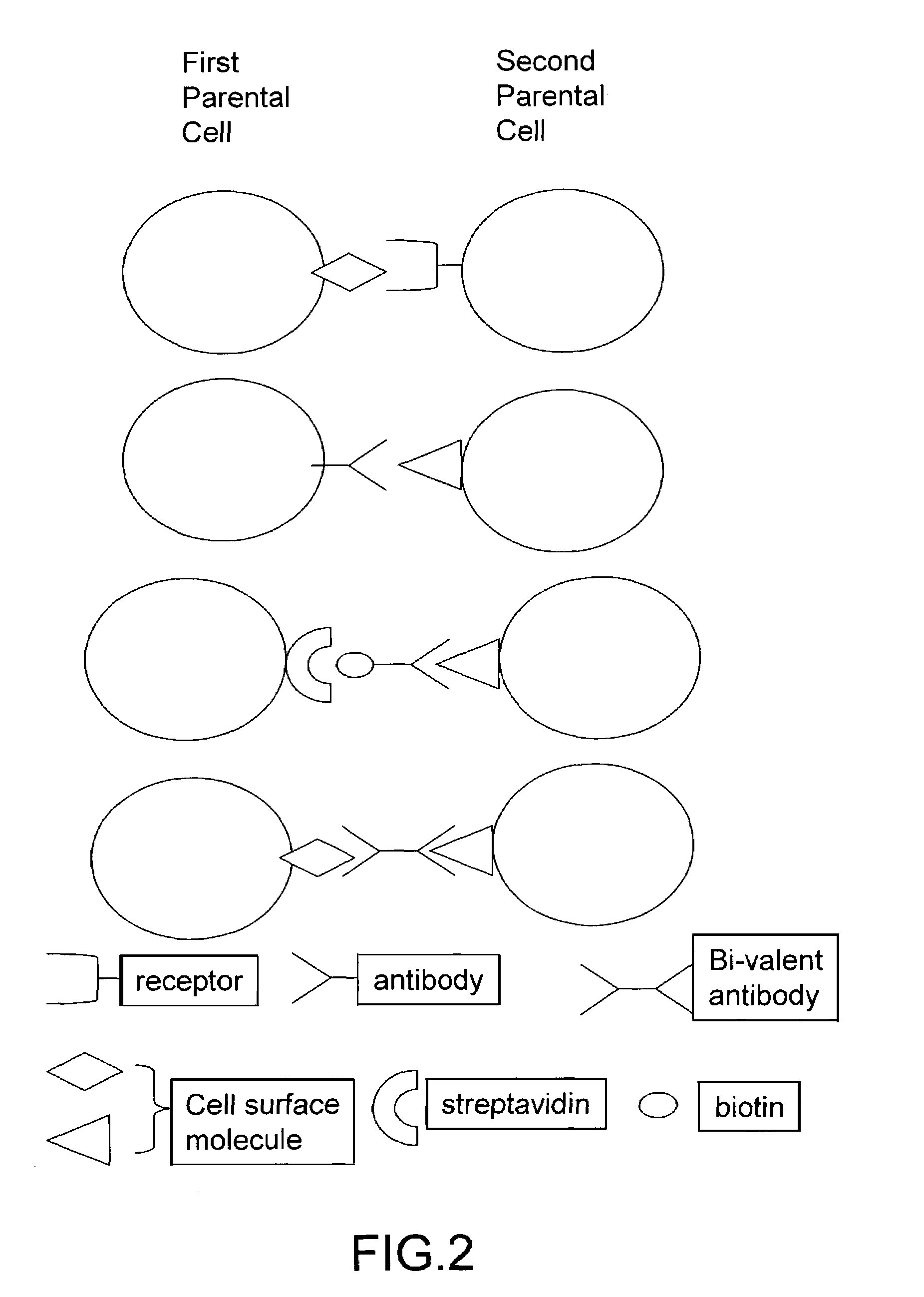
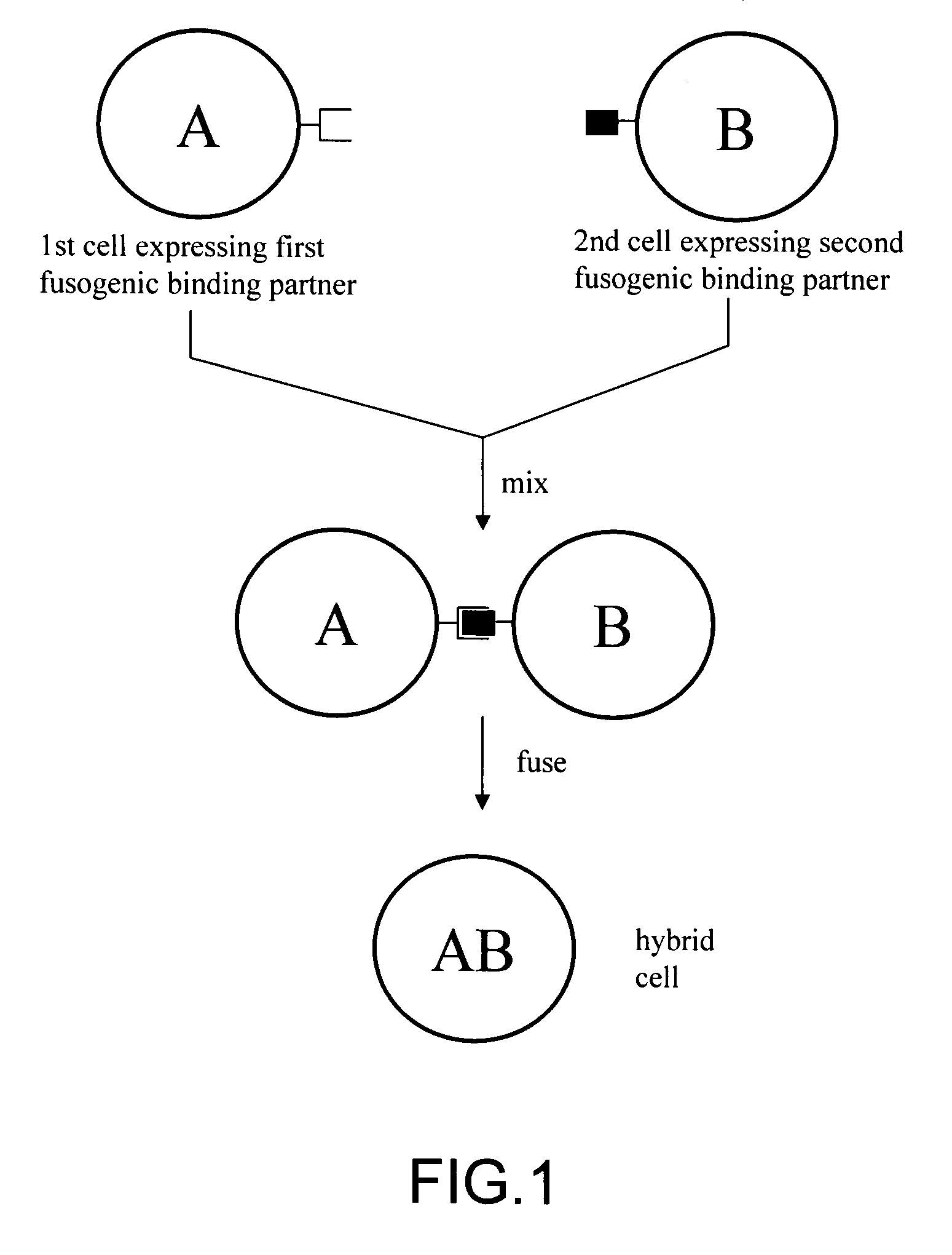
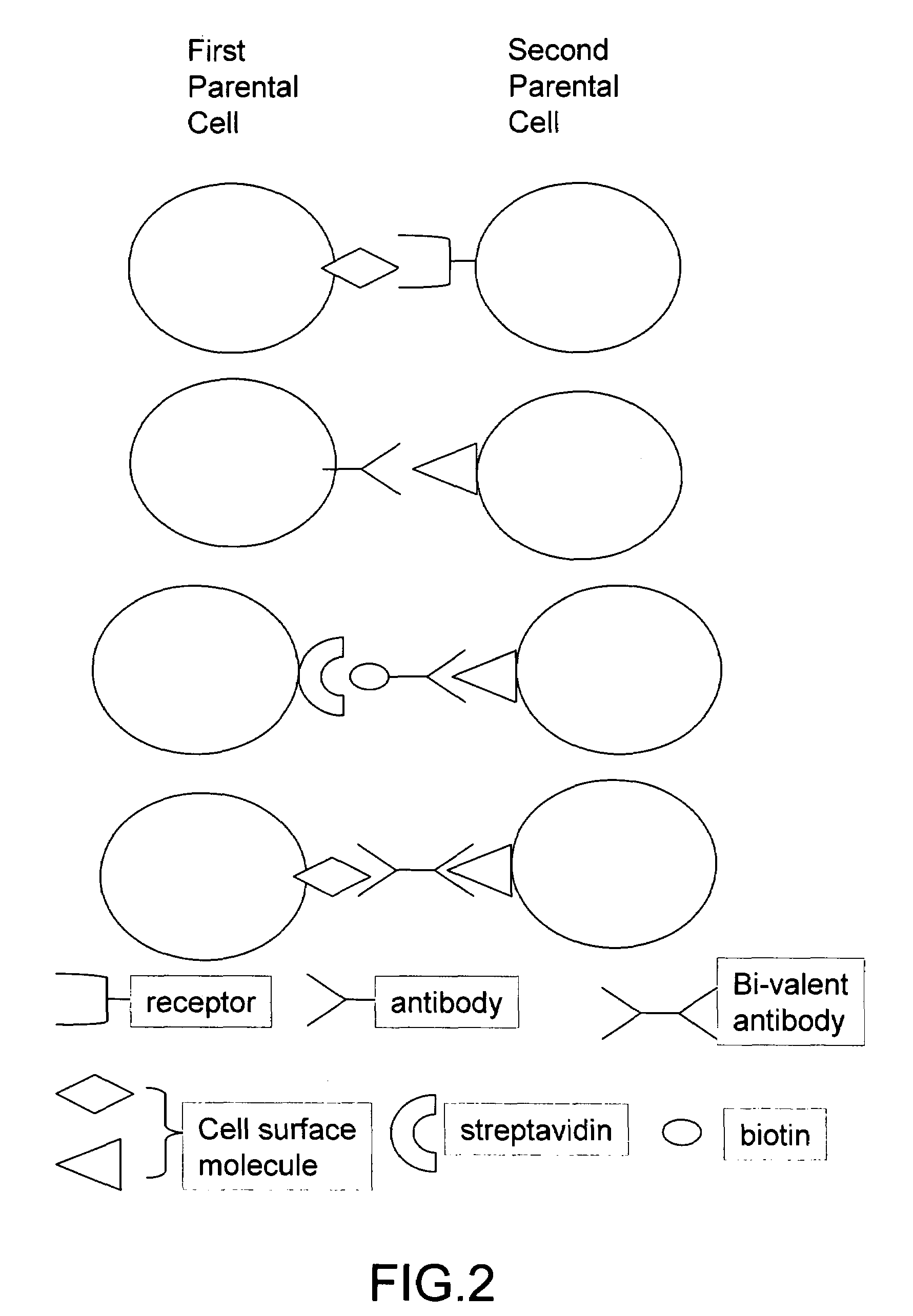
The invention provides methods for fusing a first cell with a second cell to form a hybrid cell. The methods involve incubating a first parental cell producing a first partner of a fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface with a second parental cell producing a second partner of the fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface. In certain embodiments, the parental cells are incubated with a known fusogen such as polyethylene glycol and the fusogenic binding partner pair increases the rate of cell fusion. In many embodiments, the first cell is an antibody producing cell, the second cell is an immortal cell, and the hybrid cell is a hybridoma cell that produces a monoclonal antibody. Also provided by the invention are methods for producing hybridoma cells, and methods for screening those cells for production of a monoclonal antibody of interest. The invention further provides systems and kits for carrying out the subject methods. The subject methods, systems, and kits find use in a variety of different industrial, medical and research applications.
Owner:EPITOMICS INC
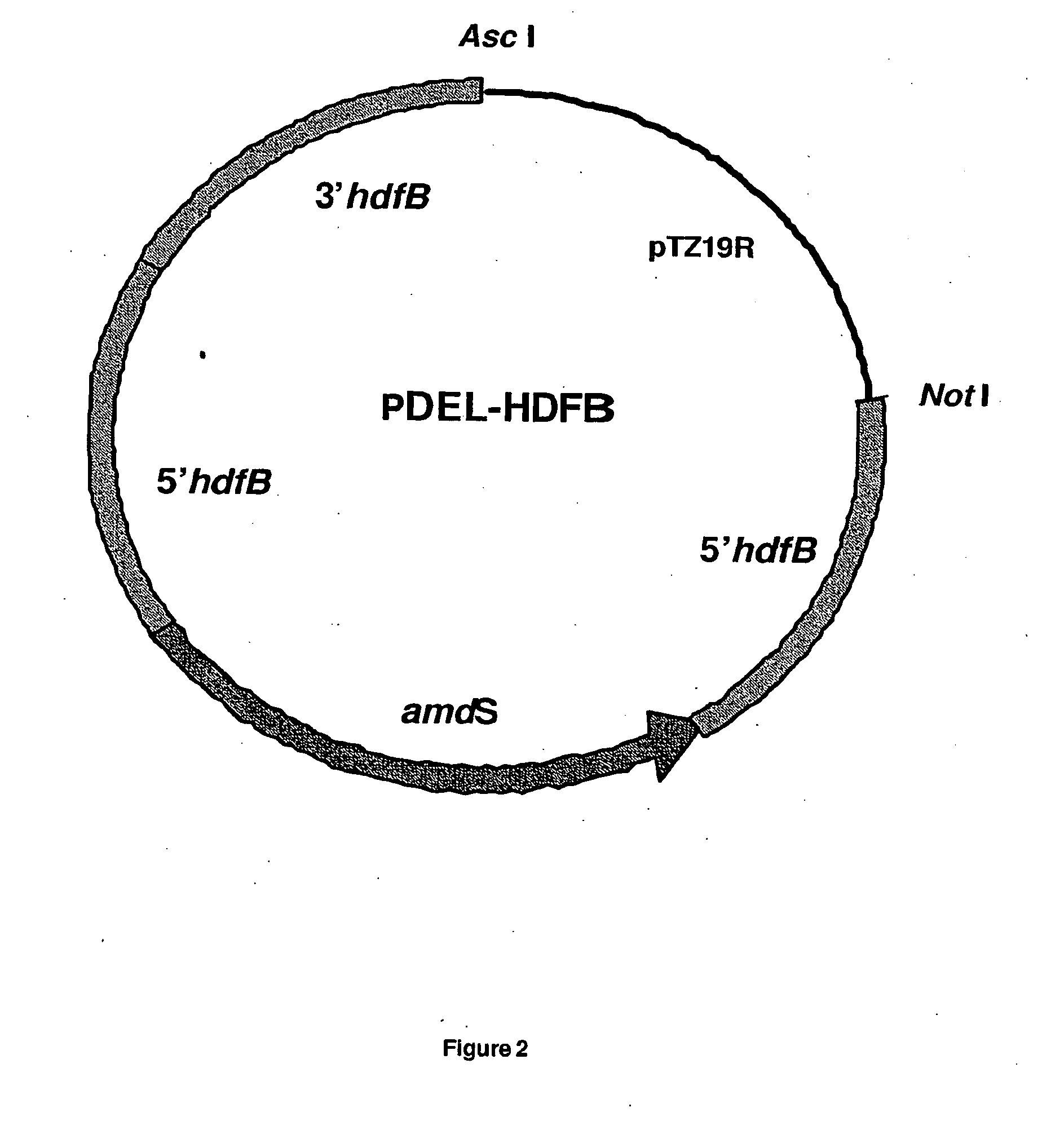
Method of producing a polypeptide using oxaloacetate hydrolase deficient fungal host cells
InactiveUS6936438B2Less of oxaloacetate hydrolaseSugar derivativesBacteriaNucleic acid sequencingMutant
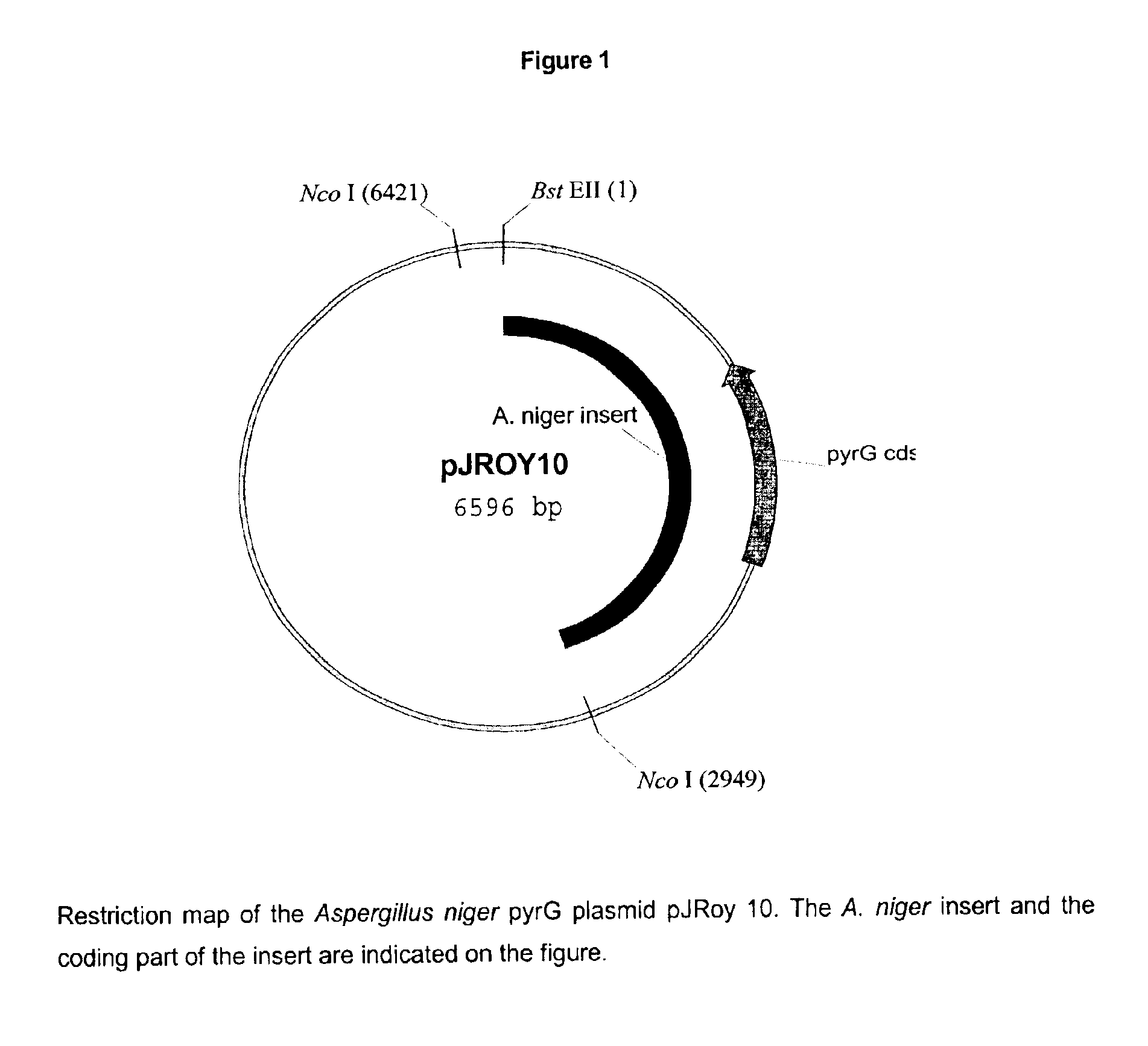
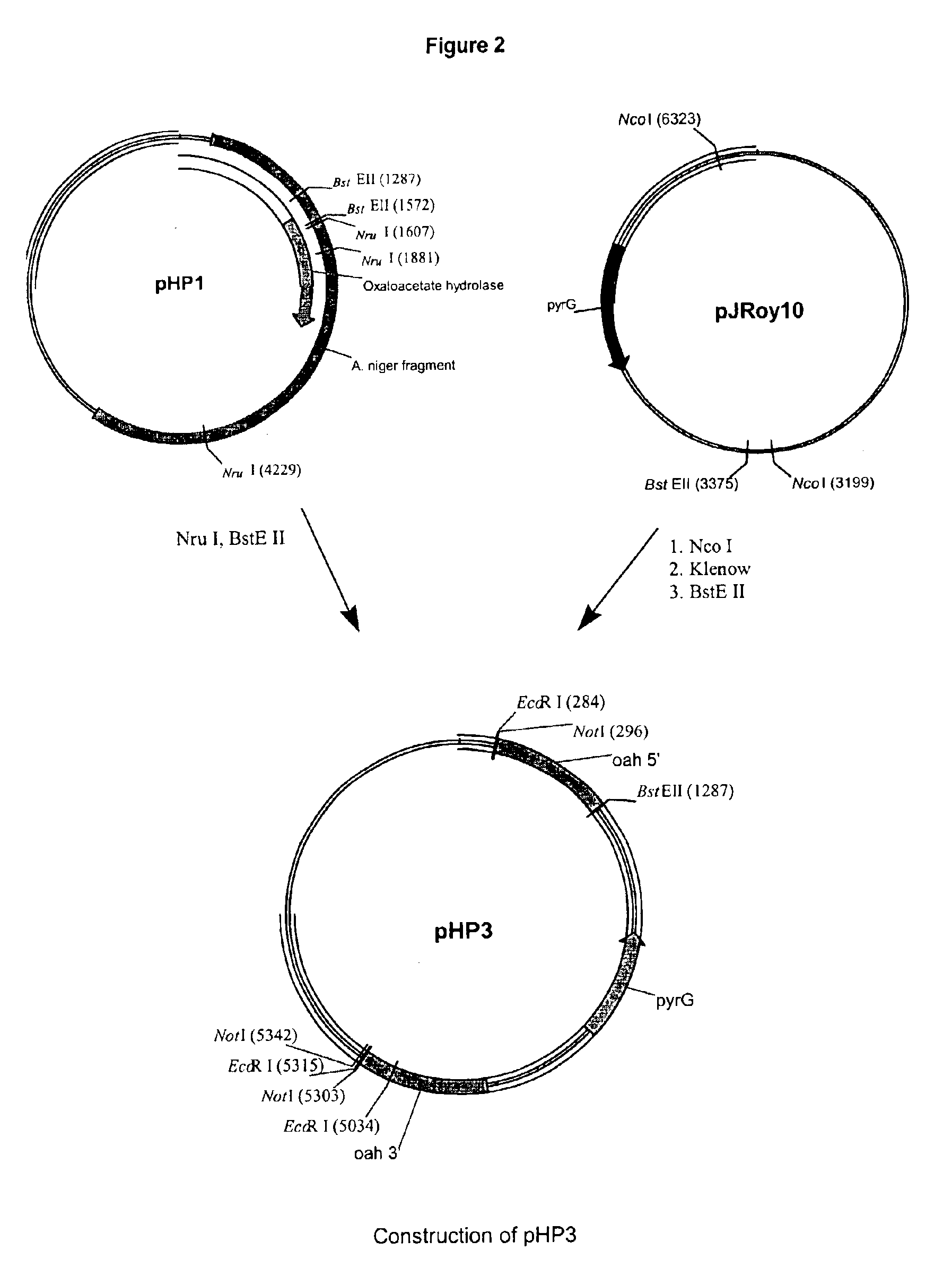
The present invention relates to methods of producing a polypeptide comprising culturing a mutant of a parent cell, wherein the mutant produces less oxaloacetate hydrolase than the parent cell, wherein the oxaloacetate hydrolase (i) has an amino acid sequence that has at least 90% identity with amino acids 1-341 of SEQ ID NO: 2: (ii) is encoded by a nucleic acid sequence having at least 90% homology with a nucleotide sequence comprising nuclotides 1157-1411, 1504-1651 and 1764-2383 of SEQ ID NO: 1: (iii) is encoded by a nucleic acid sequence which hybridizes under high stringency conditions with the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, the cDNA sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, the complementary strand of SEQ ID NO: 1, and / or the complementary strand of the cDNA sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1: and / or (iv) a subsequence of one or both of (i) and (ii), wherein the subsequence encodes a fragment that has oxaloacetate hydrolase activity.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Hybridoma cell line producing monoclonal antibody against foot-and-mouth disease virus, the monoclonal antibody therefrom, immunoassay reagent and kit, and immunoassay method
ActiveUS20110014639A1Useful for developmentImprove efficacyAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementMonoclonal antibody 14G2AStructural protein
Provided herein are a hybridoma cell line producing monoclonal antibody against foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), the monoclonal antibody therefrom, reagent and kit for ELISA, and immunoassay method. The hybridoma cell line is produced by cell fusion of a parental cell and a myeloma cell line and has the same characteristics as the cell line whose strain designation is CmA40 and deposition number is ATCC (To be Provided). The parental cell is a splenocyte isolated from the spleen of a mouse immunized by an antigen derived from a 3ABC non-structural protein (NSP) of FMDV. The antigen used here is expressed by a prokaryotic cell. The monoclonal antibody produced by the hybridoma cell line can specifically recognize a 3ABC polypeptide and does not cross-react with an antiserum of swine vesicular disease virus.
Owner:NAT INST FOR ANIMAL HEALTH COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Oophoroma multidrug resistance cell strain established by etoposide induction
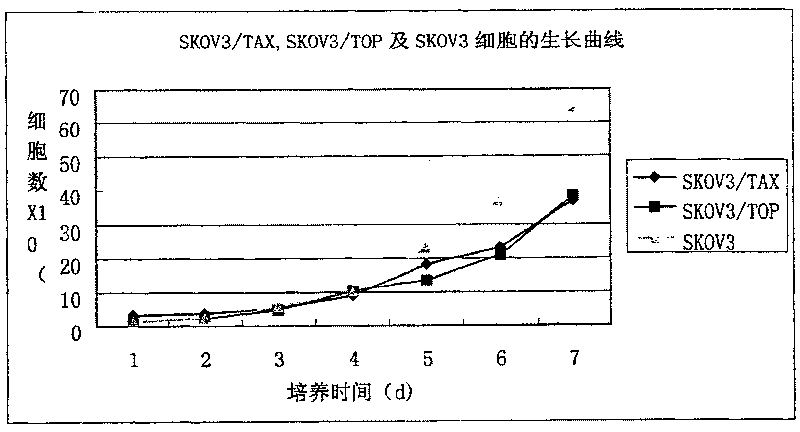
The invention relates to a multidrug resistant cell strain for oophoroma, which is characterized in that a human oophoroma SKOV3 cell strain is selected as a parental cell; the action concentration of chemotherapeutics of etoposide (VP16) is gradually increased from 0.1 mu g / ml to 3 mu g / ml; and drug resistant SKOV3 / VP16 cell strain is established. The SKOV3 / VP16 cell can stably grow, transfer and reanimate in 3 mu g / ml VP16, makes the VP16 generate drug resistant index (RI) of 21.548, and performs intersect drug on MTX, DOX, DDP, VCR, 5-Fu and MMC except the VP16. The invention aims to provide a drug resistant tumor cell model for relative study on the tumor.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN
Cell fusion method
InactiveUS7575896B2Increase ratingsAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyethylene glycolAntibody-Producing Cells
The invention provides methods for fusing a first cell with a second cell to form a hybrid cell. The methods involve incubating a first parental cell producing a first partner of a fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface with a second parental cell producing a second partner of the fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface. In certain embodiments, the parental cells are incubated with a known fusogen such as polyethylene glycol and the fusogenic binding partner pair increases the rate of cell fusion. In many embodiments, the first cell is an antibody producing cell, the second cell is an immortal cell, and the hybrid cell is a hybridoma cell that produces a monoclonal antibody. Also provided by the invention are methods for producing hybridoma cells, and methods for screening those cells for production of a monoclonal antibody of interest. The invention further provides systems and kits for carrying out the subject methods. The subject methods, systems, and kits find use in a variety of different industrial, medical and research applications.
Owner:EPITOMICS INC
Morphological mutants of filamentous fungi
InactiveUS7198938B2Restricted colonial phenotypeExtensive hyphal branchingFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The present invention relates to methods of obtaining a mutant cell from a filamentous fungal parent cell, comprising: (a) obtaining mutant cells of the parent cell; (b) identifying the mutant cell which exhibits a more restricted colonial phenotype and / or a more extensive hyphal branching than the parent cell; and (c) identifying the mutant cell which has an improved property for production of a heterologous polypeptide than the parent cell, when the mutant and parent cells are cultured under the same conditions.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Foot-and-mouth disease hybridoma cell line, monoclonal antibody, detection reagent and kit
ActiveCN102533663AHas the ability to identify specificityNo cross reactionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansVirus peptidesSwine vesicular diseaseStructural protein
The invention provides a hybridoma cell line and a monoclonal antibody thereof, an immune detection reagent containing the monoclonal antibody and a kit thereof, and an immune detection method. The hybridoma cell line is prepared by fusing parental cells and myeloma cells, and has the characteristics represented by the cell line with the preservation number of PTA-11304. The parental cell line is prepared by the following steps that: prokaryotic cells are adopted to express non-structural protein coded by a 3ABC gene fragment of foot-and-mouth disease virus, the non-structural protein is adopted as antigen to immunize mice, and spleen cells of the immunized mice are taken out to prepare the parental cell line. The monoclonal antibody produced from the hybridoma cell line can provide specific recognition for the 3ABC peptide of the foot-and-mouth disease virus, and do not generate the non-specific reaction with the swine vesicular disease antiserum.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method for detecting multi-drug resistance
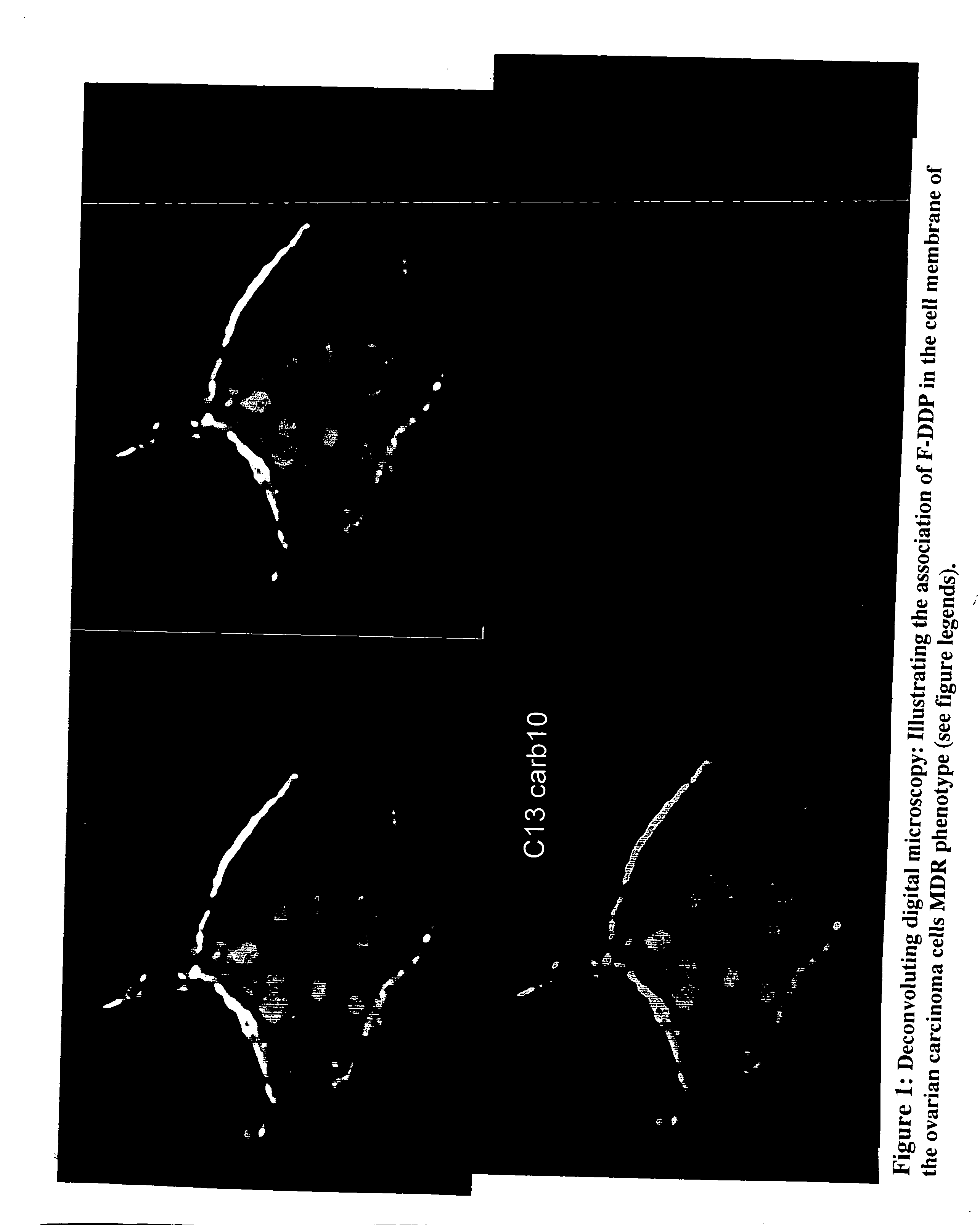
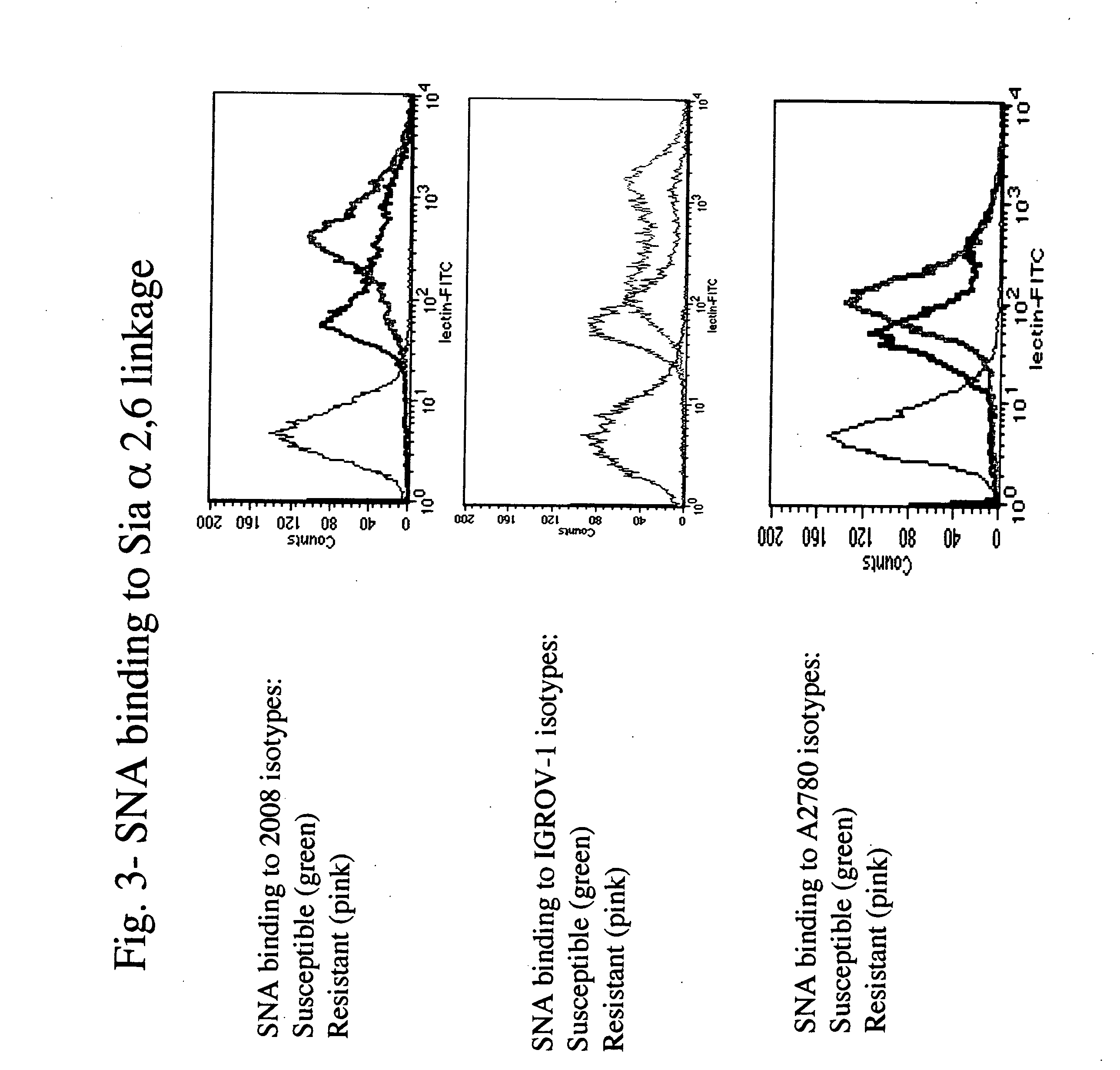
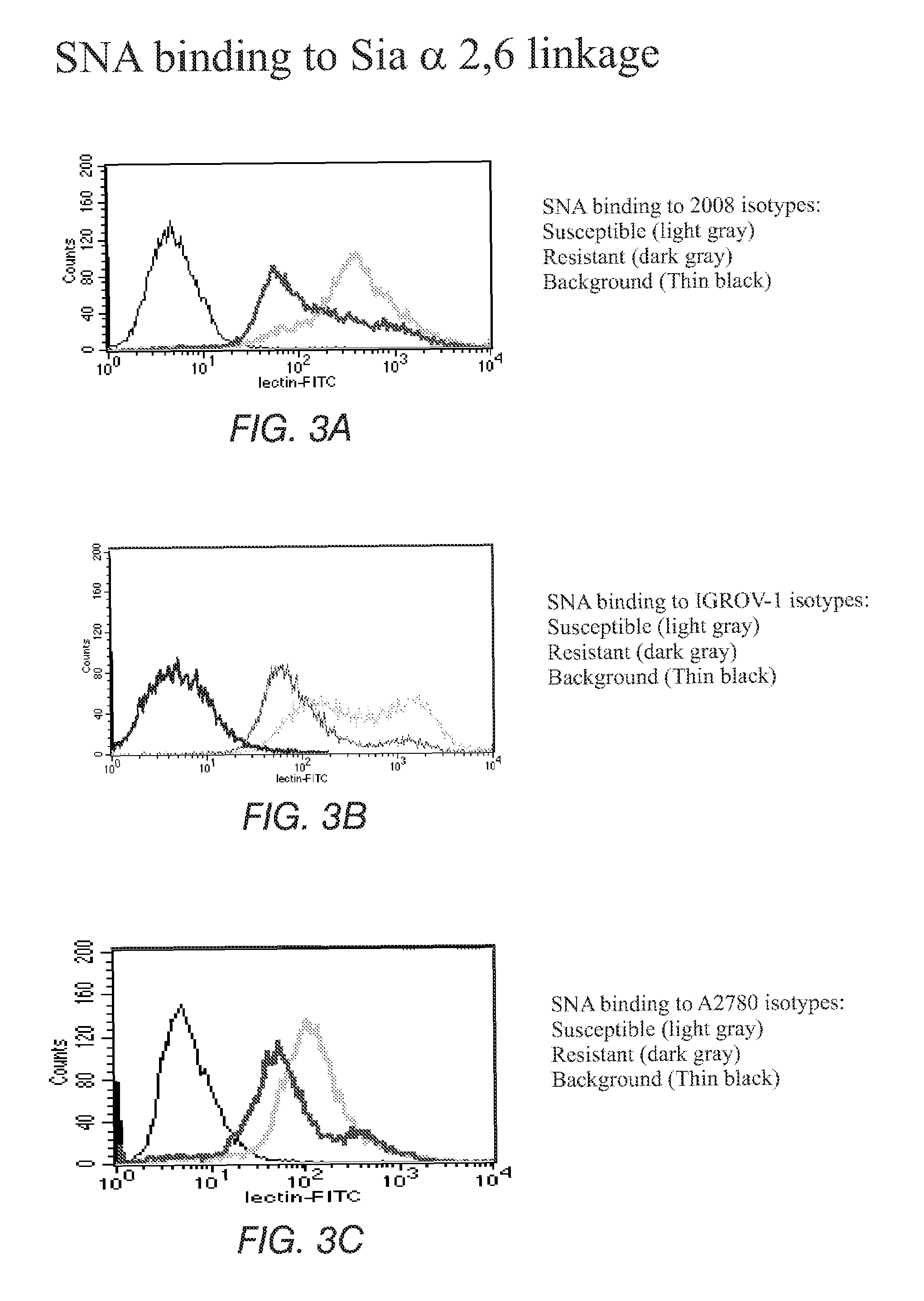
The present invention stems from the realization that the cell surface content of sialic acids is associated with drug susceptibility and resistance in neoplastic and damaged cells. A general decrease in the amounts of the α2-6 linked sialic acid has been confirmed in resistant phenotype compare to its corresponding sensitive parental cells. Treating the resistant phenotype with neuraminidase, an enzyme that removes the sialic acid from the sugar chain, facilitates the drug internalization and reinstalls the cell susceptibility to the drug. Based on these observations, methods for predicting the resistance to a number of drugs and detecting multi-drug resistanc in neoplastic and damaged cells have been invented.
Owner:RAZI NAHID
Somatic haploid human cell line
ActiveUS20170002380A1Speed up the conversion processEven mixtureMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAGenomic mutationChromosomal region
The invention provides for a somatic fully haploid, karyotypically stable human cell line, e.g. obtainable by targeted deletion of one or more disomic chromosomal regions of a somatic near-haploid human parental cell, a method of producing the same, as well as the use of the cell line for producing isogenic cell variants, comprising genomic mutations at different genomic target sites, and a library of such cell variants.
Owner:HORIZON DISCOVERY
Regulated genetic suicide mechanism compositions and methods
ActiveUS20130210121A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPurification methodsCell staining
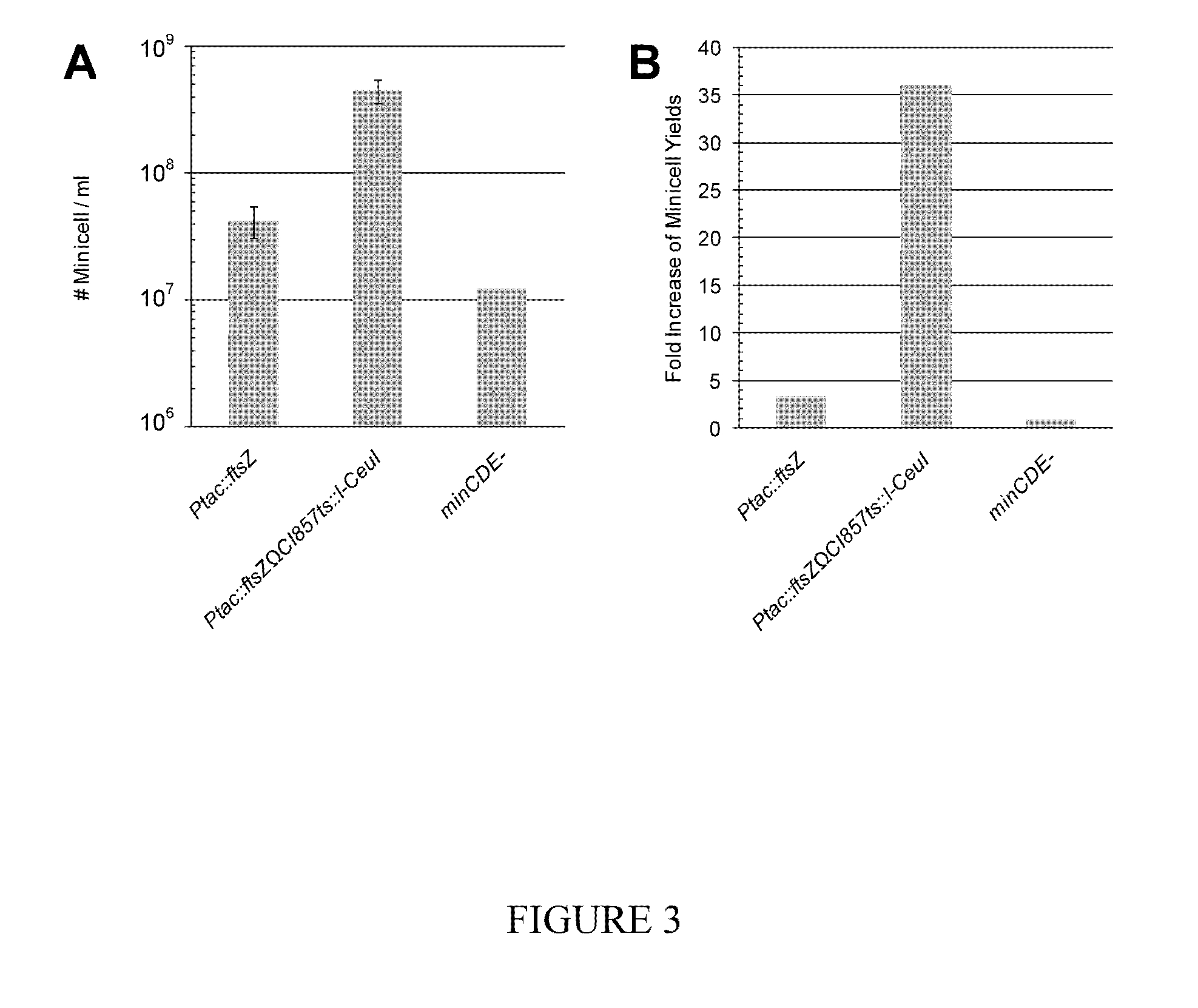
Embodiments of the present invention relates to the incorporation and use of a regulated genetic suicide mechanism for use in the improved purification of biologics, including adjunct use in various eubacterial minicell production and purification methodologies. Described herein are high-yield eubacterial minicell-producing strains with genetic modifications that comprise a regulated genetic suicide mechanism that irreparably destroys the parent cell chromosome such that live parental cells in a culture can be functionally eliminated at any time during the course of a minicell production and purification run. Embodiments of the present invention also describe methods useful in the elimination of live parental cells during the production of other cell-based biologics.
Owner:VAXIION THERAPEUTICS
Trastuzumab drug-resistant human breast cancer cell line and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104762264AStrong drug resistanceIncrease production capacityMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsIn vivoHuman breast
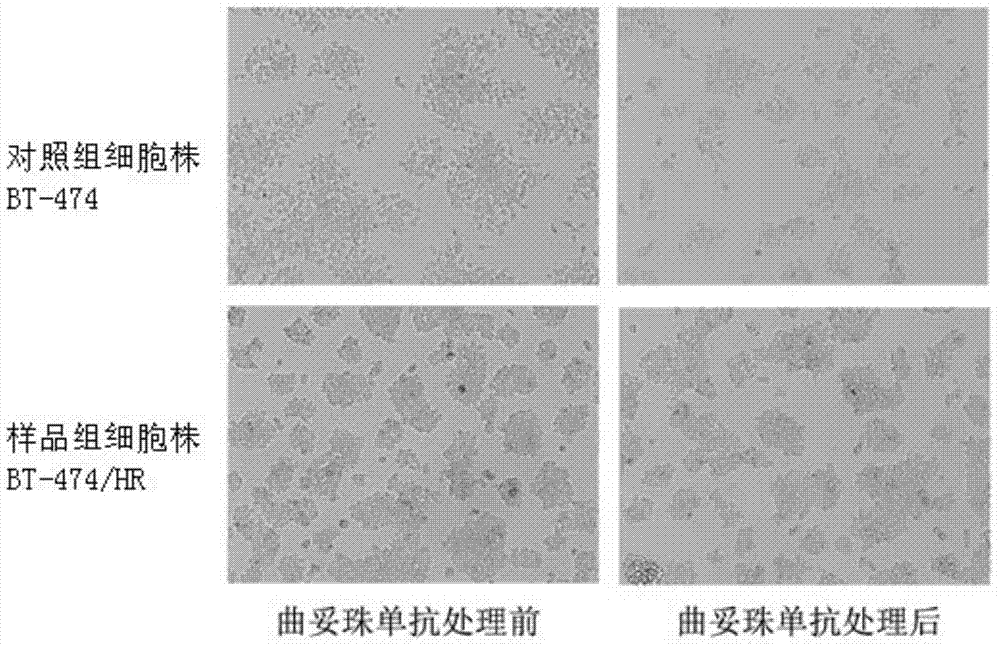
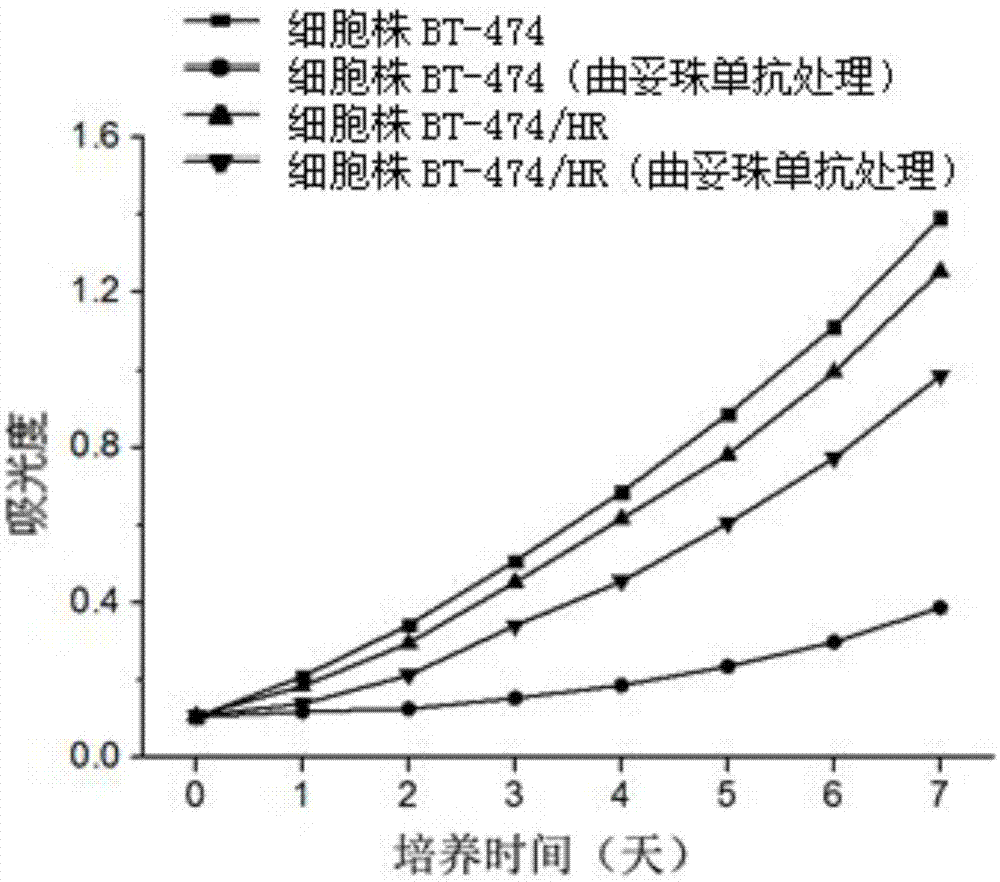
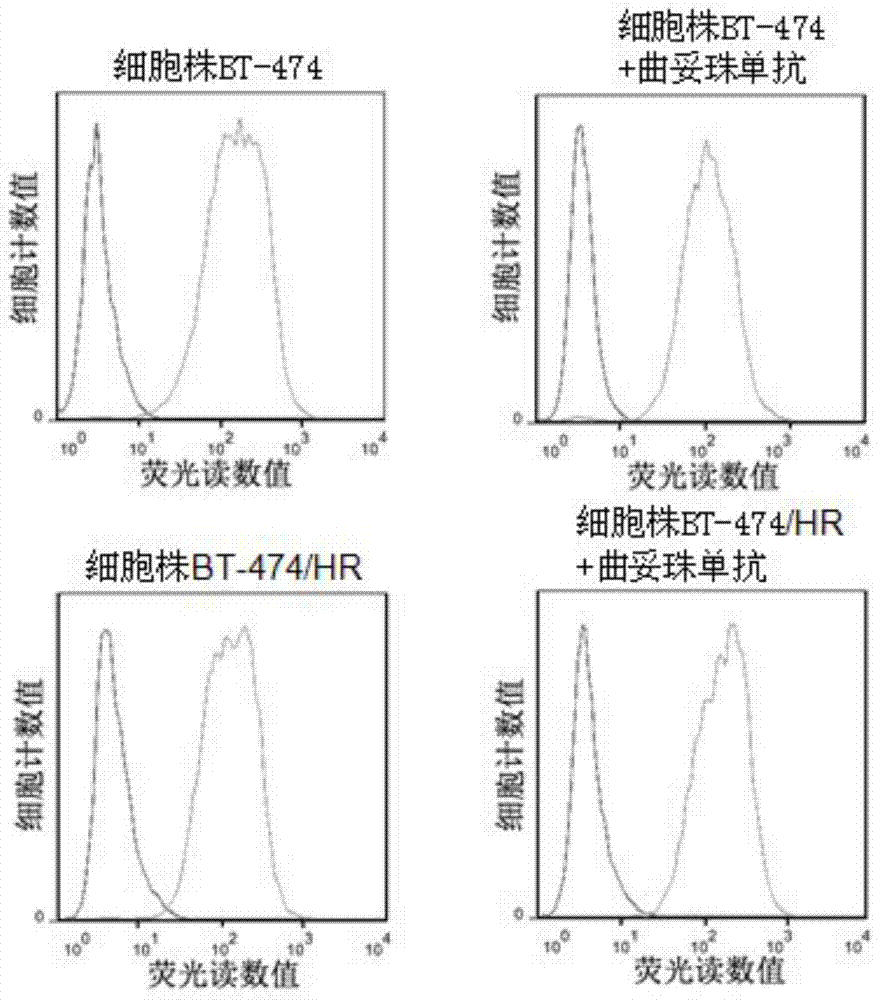
The invention discloses a trastuzumab drug-resistant human breast cancer cell line BT-474 / HR. The human breast cancer cell line has the collection number of CCTCC NO:C2014245 in China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the collection date of the human breast cancer cell line is 14, January in 2015. The invention also discloses a method for constructing the trastuzumab drug-resistant human breast cancer cell line BT-474 / HR. The method comprises the following step of preparing a human breast cancer cell line BT-474 / HR with excellent in-vitro and in-vivo trastuzumab drug resistance by utilizing a human breast cancer cell line BT-474 and combining two means of in-vitro induction and in-vivo induction of trastuzumab. According to the cell line, the HER2 overexpression characteristics of a parental cell line are remained, and the cell line has excellent in-vitro and in-vivo drug resistance on an HER2 targeted antibody drug. Therefore, the human breast cancer cell line can be directly applied to development and research of novel anti-tumor treatment drugs.
Owner:ANHUI ANKE BIOTECHNOLOGY (GRP) CO LTD +1
Hepatic cell lines and stem-like cells, methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20160168536A1Characteristic morphologyImprove plasticityCell differentiationHepatocytesHEPACell biology
New cell lines designated as Hepa-SC and Hepa-RP, originating from human hepatoma line HEPARG® are disclosed. Methods of inducing stemness in parental cells lines using mechano-transduction techniques, and redirecting stem-like cells to reprogrammed cells of a target differentiated population are also described.
Owner:BIOPREDIC INT
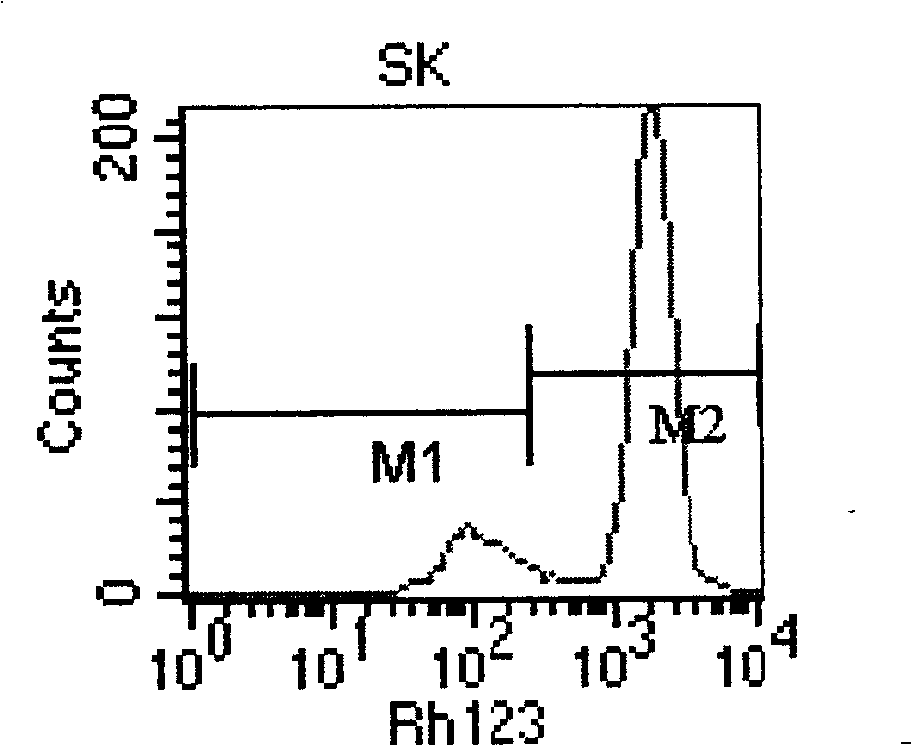
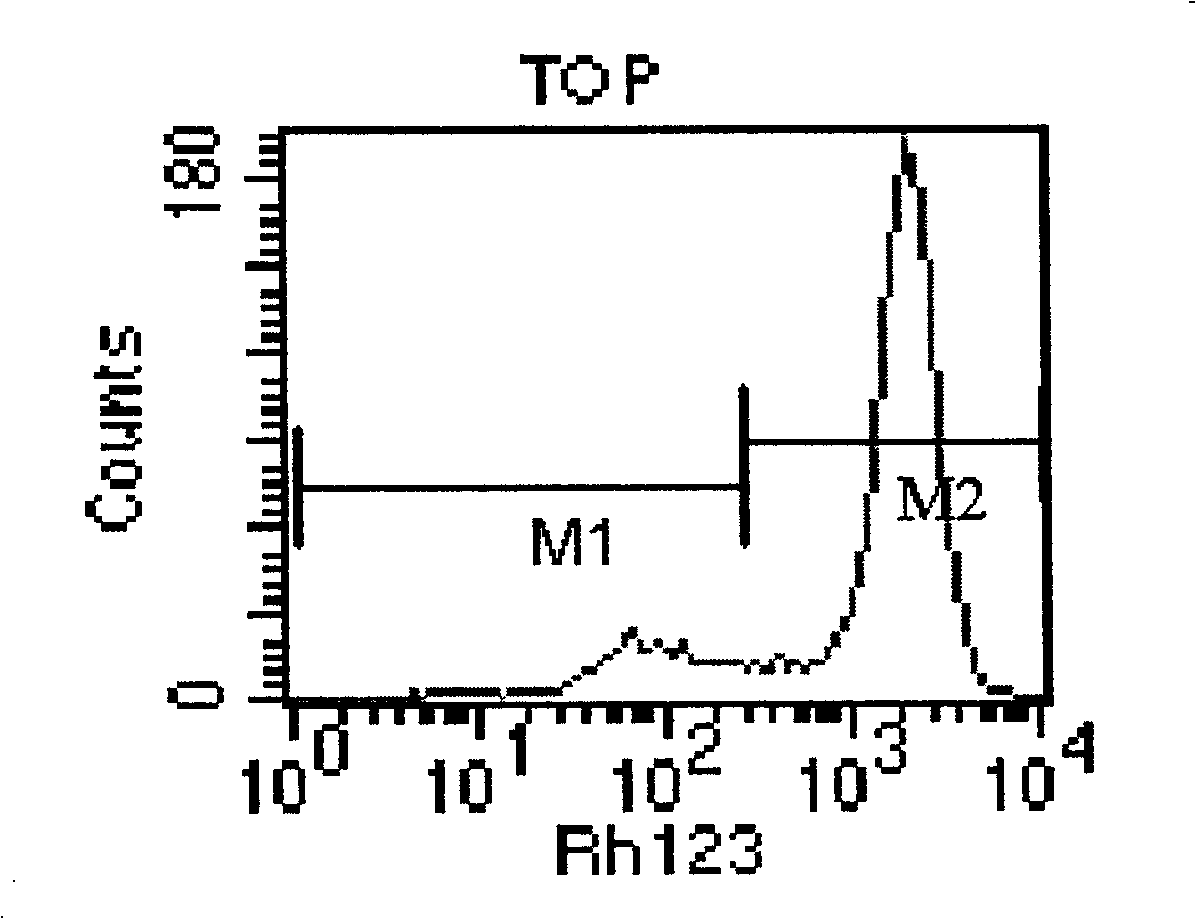
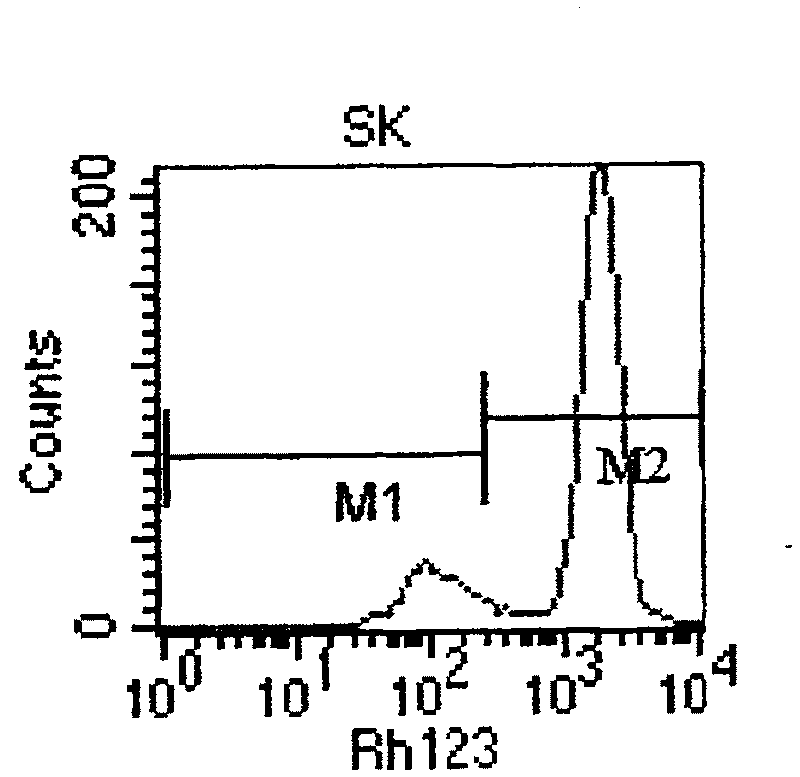
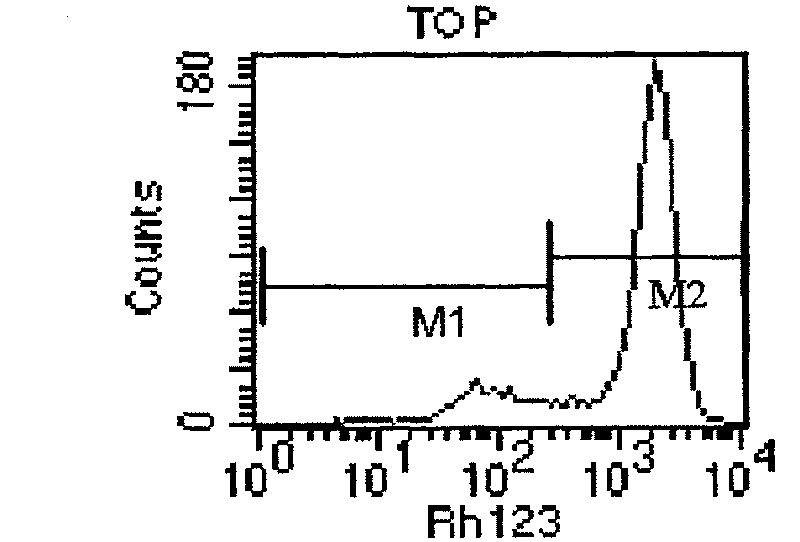
Human ovarian cancer drug-resistant cell strain and culture method thereof
The invention relates to a TOP medicament resistant cell line human ovarian cancer, with a accession number of CGMCC No 1217, which is selecting human ovarian cancer cell line as parental cell, putting the cell into RPMI1640 culture medium containing 15% calf serum, putting into incubator with 5% CO2 and 37 DEG C to culture; acquiring cells in logarithmic growth phase, counting after digesting with 0.25% pancreatin, inoculating 5*105 / ml into culture bottle according to amount of 5ml in each bottle, when cells adheres to wall after 24 hours, reacting for 2 hours with a TOP final content of 2160ng / ml, discarding culture medium, washing by phosphate buffer for 3 times, replacing fresh culture medium, second impulsing after growing is resumed, and repeatedly operating, until it is impulsed with medicament for 13 times. The cell line is constructed for 10 months, medicament resistance of cell is 10.67 per cell, P<0.01 comparing with sensitive cell, has cross resistance to mitoxantrone, camptothecin, vincristine besides resistance to TOP.
Owner:李红霞
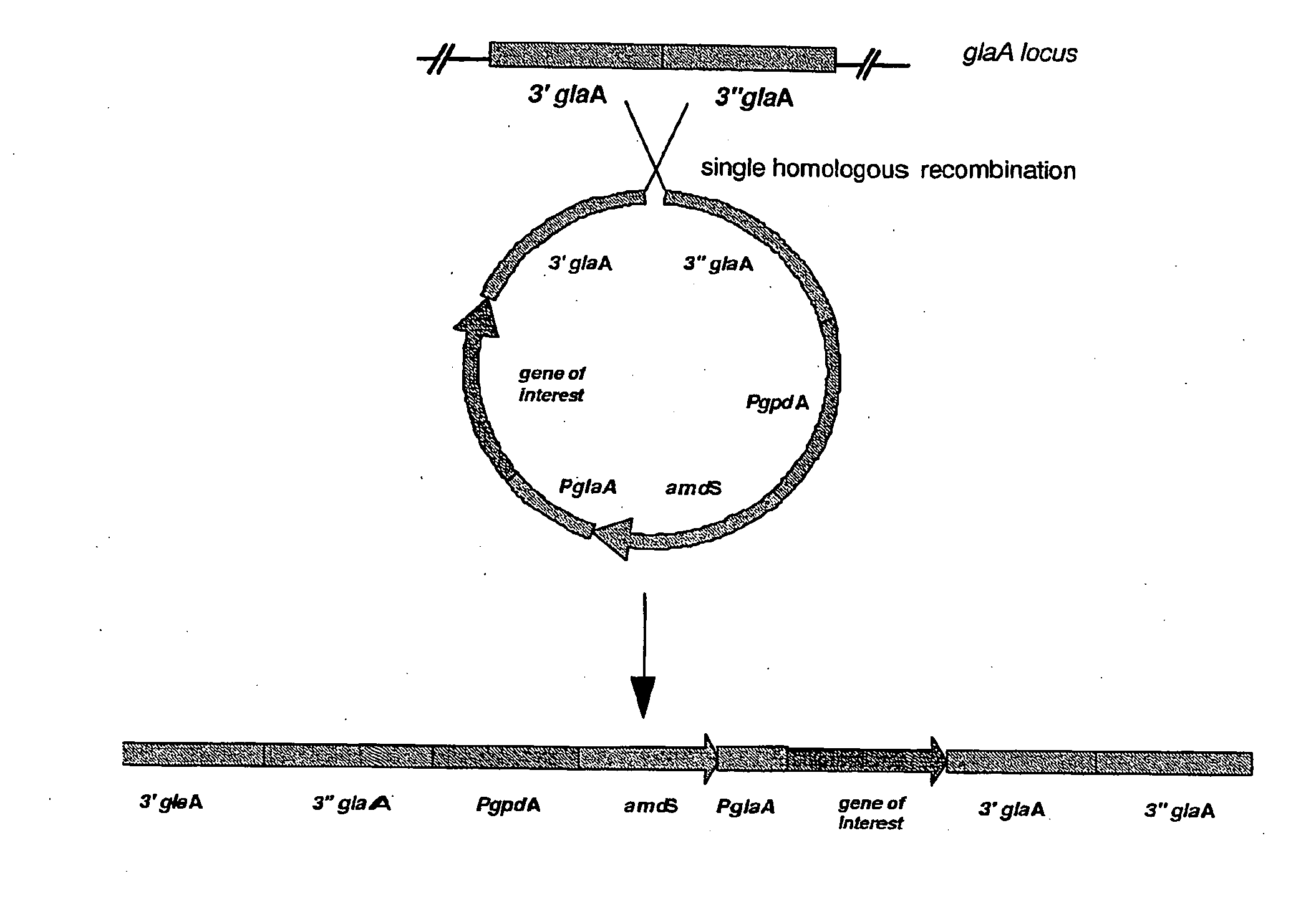
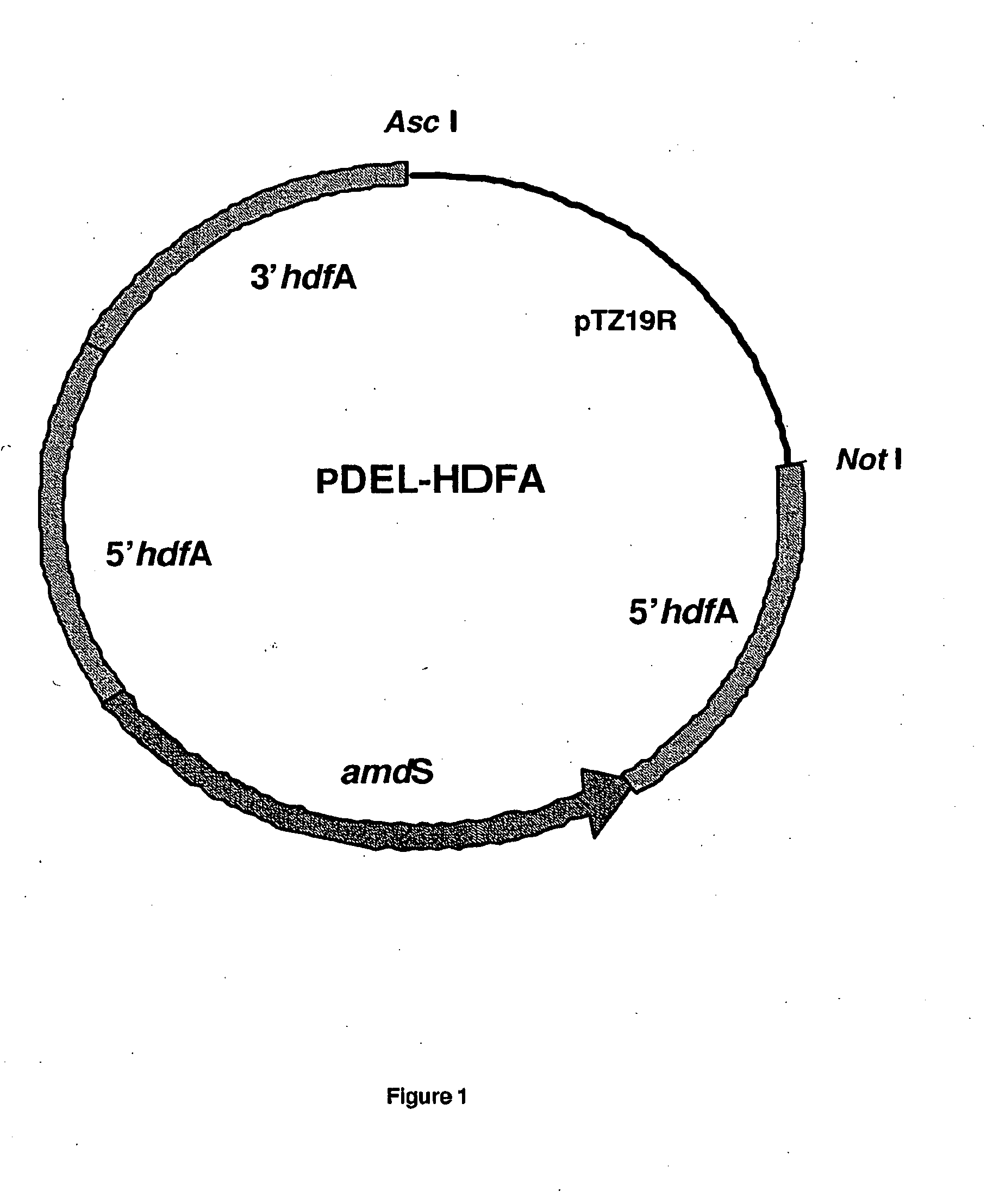
Filamentous Fungal Mutants With Improved Homologous Recombination Efficiency
The present invention relates to a method for increasing the efficiency of targeted integration of a polynucleotide to a pre-determined site into the genome of a filamentous fungal cell with a preference for NHR, wherein said polynucleotide has a region of homology with said pre-determined site, comprising steering an integration pathway towards HR. The present invention also relates to a mutant filamentous fungus originating from a parent cell, said mutant having an HR pathway with elevated efficiency and / or an NHR pathway with a lowered efficiency and / or a NHR / HR ratio with decreased efficiency as compared to said HR and / or NHR efficiency and / or NHR / HR ratio of said parent cell under the same conditions.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
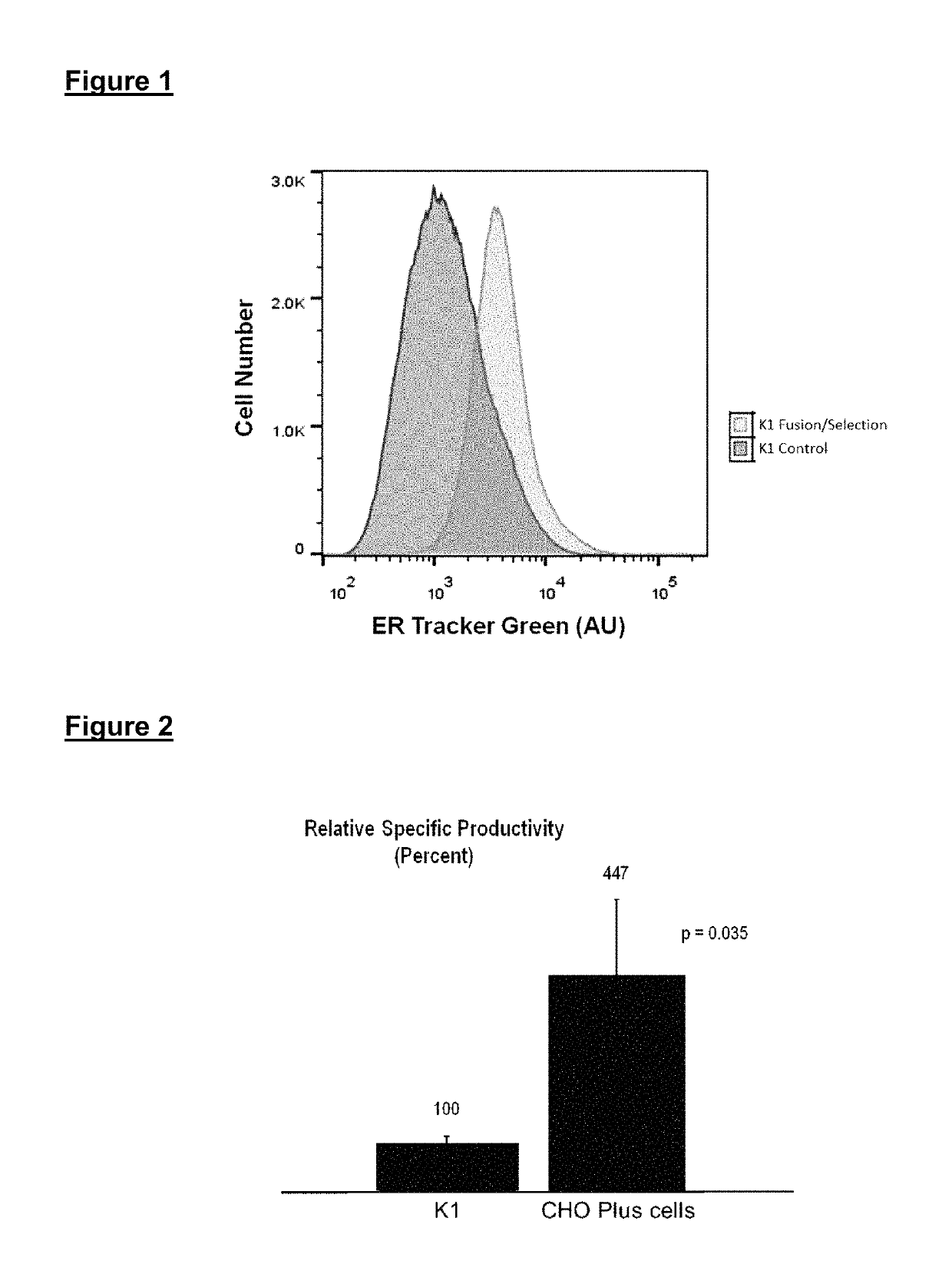
Cell lines for high level production of protein-based pharmaceuticals
ActiveUS10329594B1High densityStably inheritableHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsCulture fluidReticulum cell
This invention provides improved cell lines for manufacture of protein-based pharmaceutical agents, considerably reducing the cost of commercial production. The cell lines are obtained by fusing cells from one or more parental cell populations. The hybrid cells are then selected for one or more characteristics that support protein production on a non-specific basis, such as the level of endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and / or other desired phenotypic features, compared with other hybrids or parental cells in the starting mixture. A gene encoding a therapeutic protein is transfected into the cells before or after one or more cycles of fusion and selection. Depending on the protein product being expressed, cell lines may be obtained that produce as much as eight grams or more of protein per liter of culture fluid.
Owner:CHO PLUS INC
Cell fusion method
InactiveUS20080220431A1Increase ratingsAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyethylene glycolAntibody-Producing Cells
The invention provides methods for fusing a first cell with a second cell to form a hybrid cell. The methods involve incubating a first parental cell producing a first partner of a fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface with a second parental cell producing a second partner of the fusogenic binding partner pair on its surface. In certain embodiments, the parental cells are incubated with a known fusogen such as polyethylene glycol and the fusogenic binding partner pair increases the rate of cell fusion. In many embodiments, the first cell is an antibody producing cell, the second cell is an immortal cell, and the hybrid cell is a hybridoma cell that produces a monoclonal antibody. Also provided by the invention are methods for producing hybridoma cells, and methods for screening those cells for production of a monoclonal antibody of interest. The invention further provides systems and kits for carrying out the subject methods. The subject methods, systems, and kits find use in a variety of different industrial, medical and research applications.
Owner:EPITOMICS INC
Method for detecting multi-drug resistance
The present invention stems from the realization that the cell surface content of sialic acids is associated with drug susceptibility and resistance in neoplastic and damaged cells. A general decrease in the amounts of the α2-6 linked sialic acid has been confirmed in resistant phenotype compare to its corresponding sensitive parental cells. Treating the resistant phenotype with neuraminidase, an enzyme that removes the sialic acid from the sugar chain, facilitates the drug internalization and reinstalls the cell susceptibility to the drug. Based on these observations, methods for predicting the resistance to a number of drugs and detecting multi-drug resistanc in neoplastic and damaged cells have been invented.
Owner:RAZI NAHID
Cervical cancer multidrug resistance cell strain established by cisplatin induction
The invention relates to a multidrug resistant cell strain for cervical carcinoma, which is characterized in that a human cervical carcinoma SiHa cell strain is selected as a parental cell; the action concentration of chemotherapeutics of cis-platinum (cDDP) is gradually increased from 0.1 mu g / ml to 0.2 mu g / ml; and drug resistant SiHa / cDDP cell strain is established. The SiHa / cDDP cell can stably grow, transfer and reanimate in 2 mu g / ml cDDP, makes the cDDP generate drug resistant index (RI) of 16.131, and performs intersect drug on etoposide, taxol, vincristine, methotrexate, doxorubicin and mitomycin C except the cDDP. The invention aims to provide a drug resistant tumor cell model for relative study on the tumor.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN
Human choriocarcinoma multidrug resistant cell lines
ActiveCN109943530AStable growthIncreased drug resistanceTumor/cancer cellsDrug withdrawalCell strain
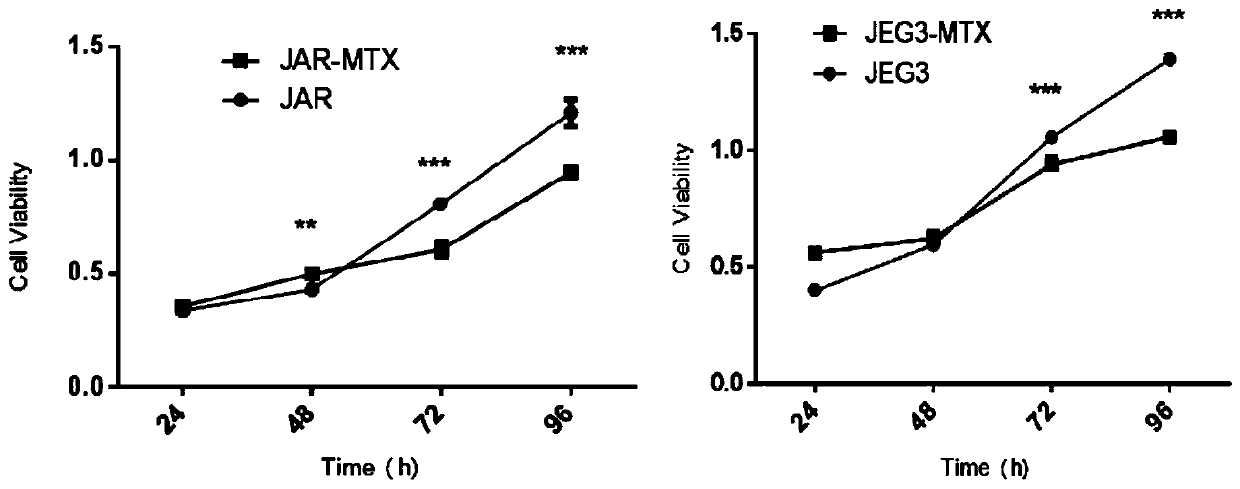
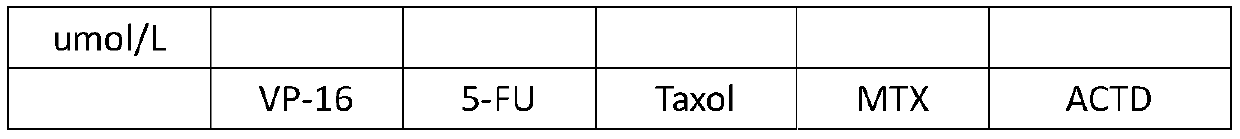
The invention relates to two human choriocarcinoma multidrug resistant cell lines. The preservation numbers of the human choriocarcinoma multidrug resistant cell lines are CCTCC NO: C2018245 or CCTCCNO: C2018246. Human choriocarcinoma JAR and JEG3 cell lines are selected as parental cells, the action concentration of a chemotherapy drug methotrexate (MTX) is gradually increased from 11 micro moleper liter to 88 micro mole per liter to establish JAR / MTX (CCTCC NO: C2018245) and JEG3 / MTX (CCTCC NO: C2018246) drug-resistant cell lines. The JAR / MTX and JEG3 / MTX can stably grow, passage and recover in the MTX of 88 micro mole per liter, and have the drug resistance indexes of 791.50 and 1040.04 to the MTX, and not only have drug resistance to the MTX, but also have cross drug resistance to VP-16, 5-FU, Taxol and ACTD. After the drug resistant cell lines are established, drug withdrawal culture is performed for 3 months, liquid nitrogen freeze saving is performed for half a year, the cellsrecover, and the drug resistance of the cells is redetected, the drug resistance of the two drug resistant cell lines separately accounts for 90% or above of the original drug resistance, and the stability of the drug resistance of the drug resistant cell lines is very good.
Owner:ATTACHED OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY OSPITAL MEDICALCOLLEGE ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hybrid tumor, antihuman bladder cancer monoantibody and guide medicament, and bladder cancer diagnosis agent
InactiveCN101343623AStable secretionEasy to operatePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAbnormal tissue growthAntigen
The invention relates to a hybridoma which can generate a monoclonal antibody against human bladder cancer, and parental cells of which are B lymphocytes of a mouse and myeloma cells of the mouse immunized by E-J cells of a human bladder cancer cell line. The invention also relates to purposes and a preparation method of the hybridoma, the monoclonal antibody generated by the hybridoma, a directional drug against bladder cancer and a bladder cancer immunological diagnostic reagent and a preparation method of the directional drug. The antibody part of the directional drug serves as the monoclonal antibody against human bladder cancer. The diagnostic reagent is composed of an E-J cell lysis liquid of the human bladder cancer cell line and the monoclonal antibody DTB against human bladder cancer coated on an enzyme label plate, and the bladder cancer antigen in urine exfoliated cells is examined through adopting the competitive ELISA method. The specificity of the antibody of the hybridoma is strong; the tumor killing function of the directional drug of the hybridoma is strong without drug tolerance but good specificity; and the diagnostic reagent of the hybridoma has the advantages of damage resistance, high sensibility and specificity as well as convenience and quickness.
Owner:李翀
Human mantle cell lymphoma malignant clone cell strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110438081AStrong in vitro cloning abilityReliable model for the study of malignant clonesMicroorganism based processesTumor/cancer cellsPurification methodsMantle lymphoma
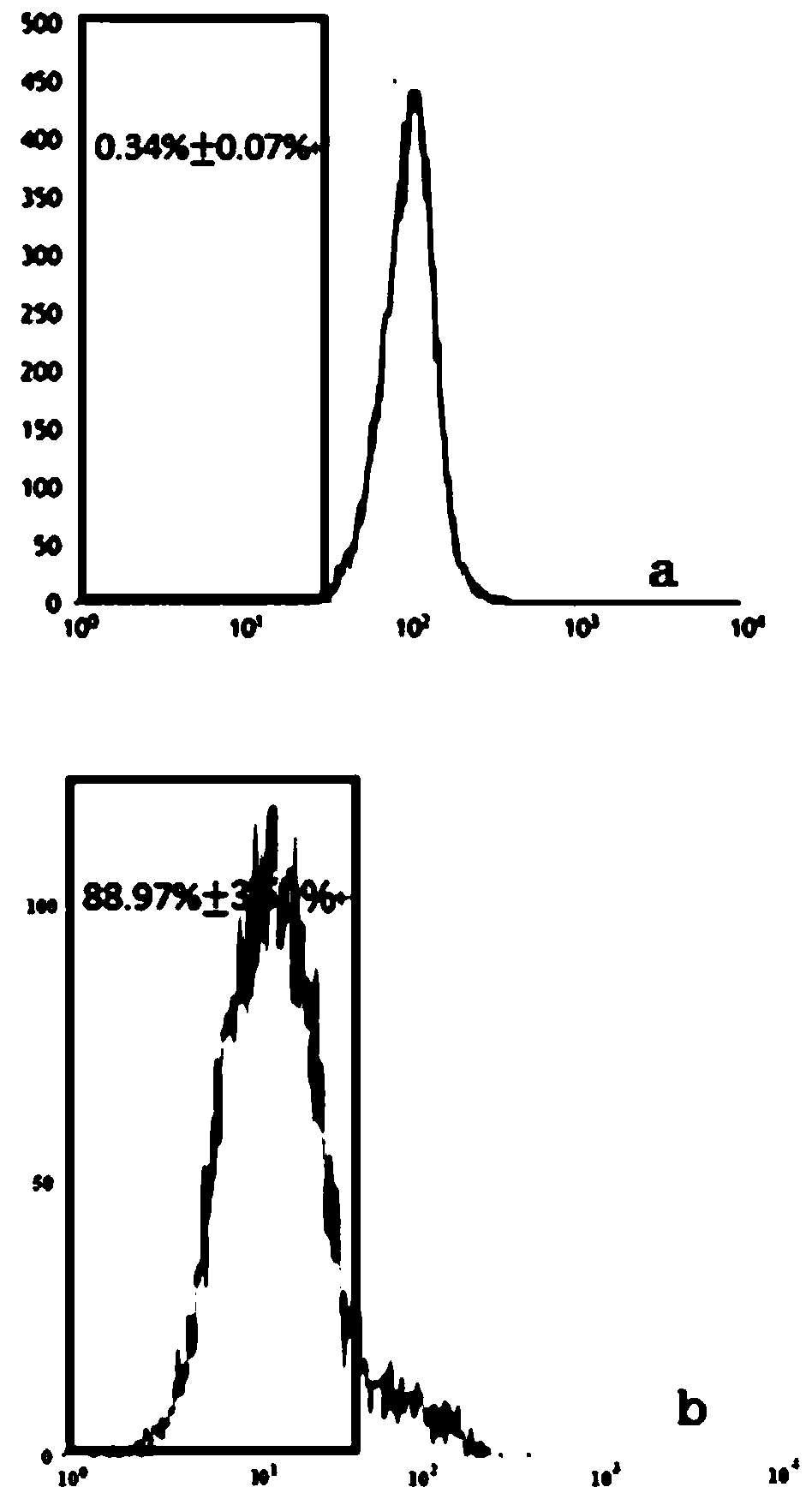
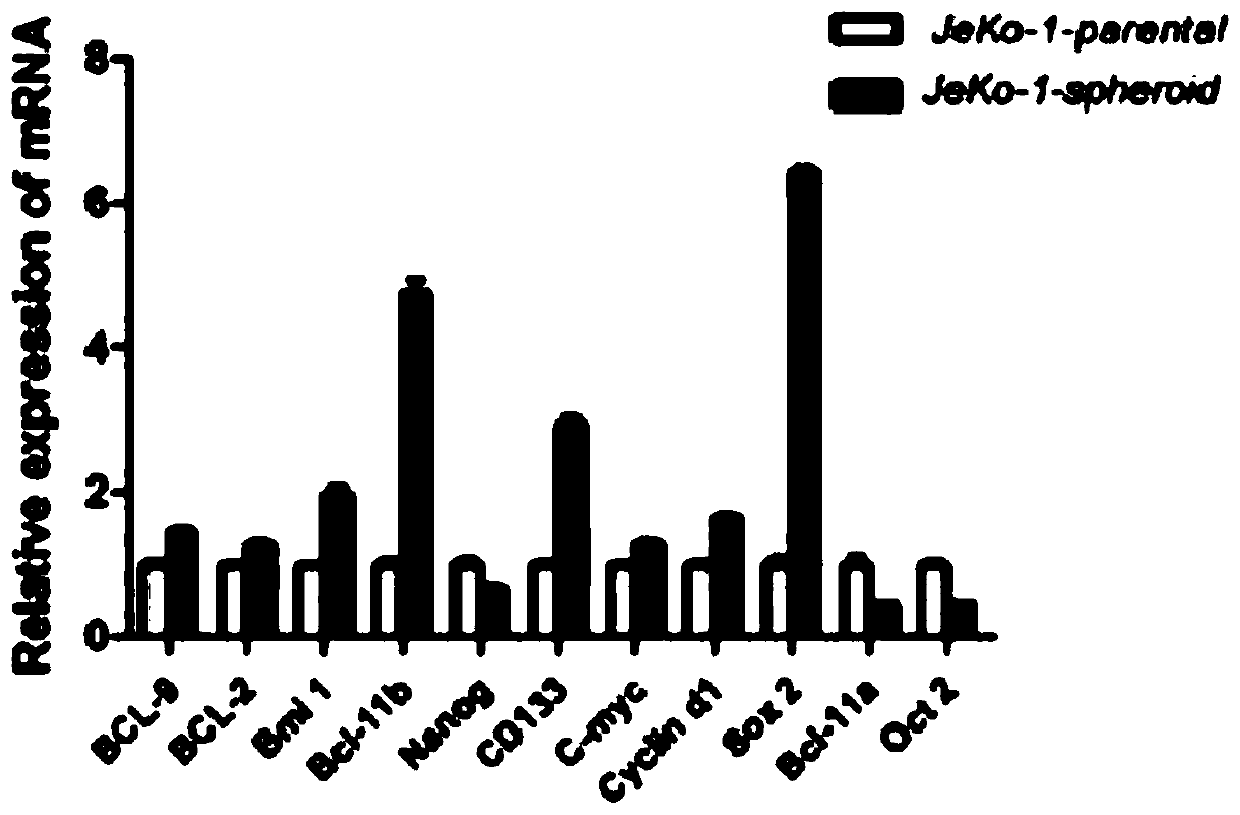
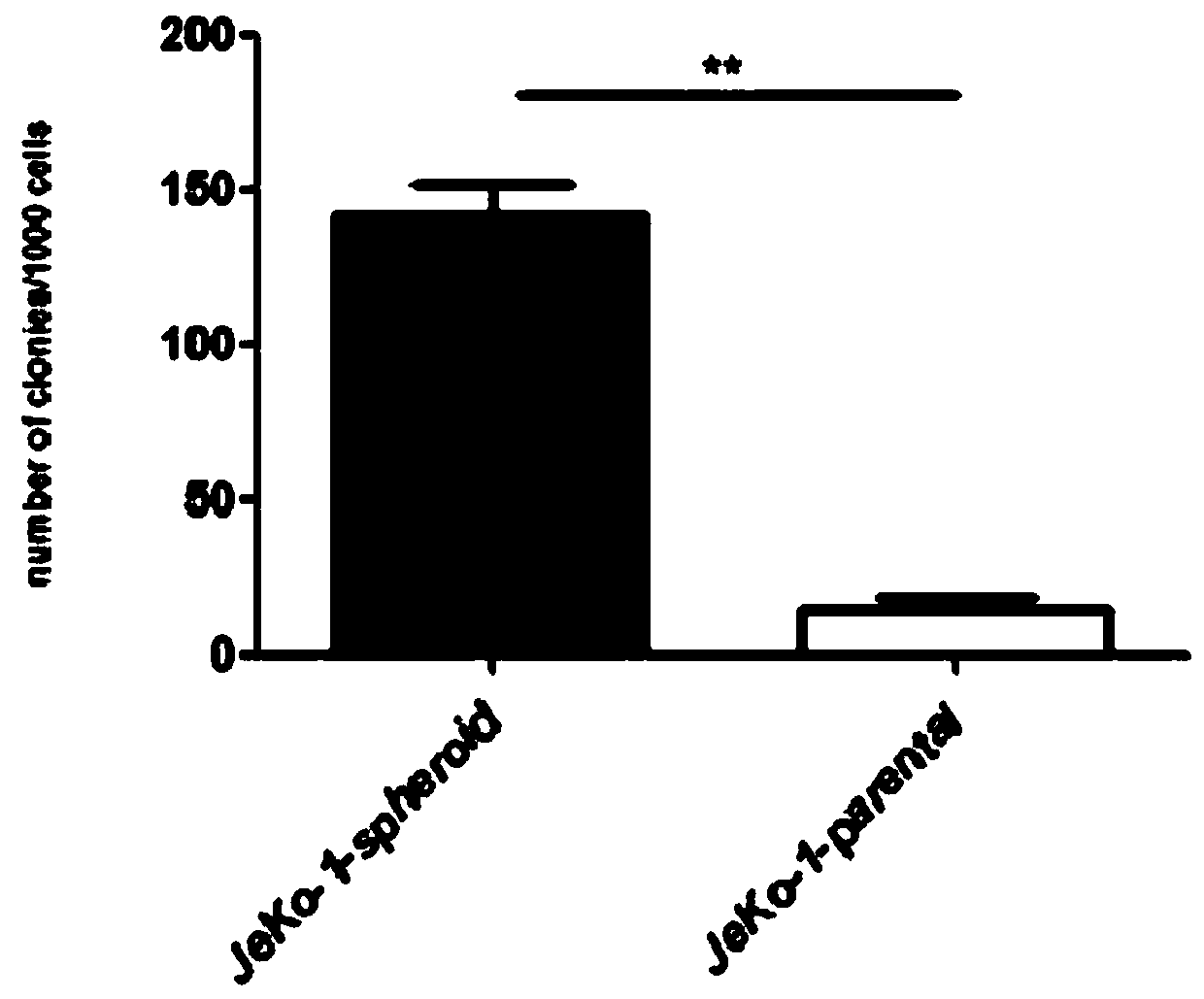
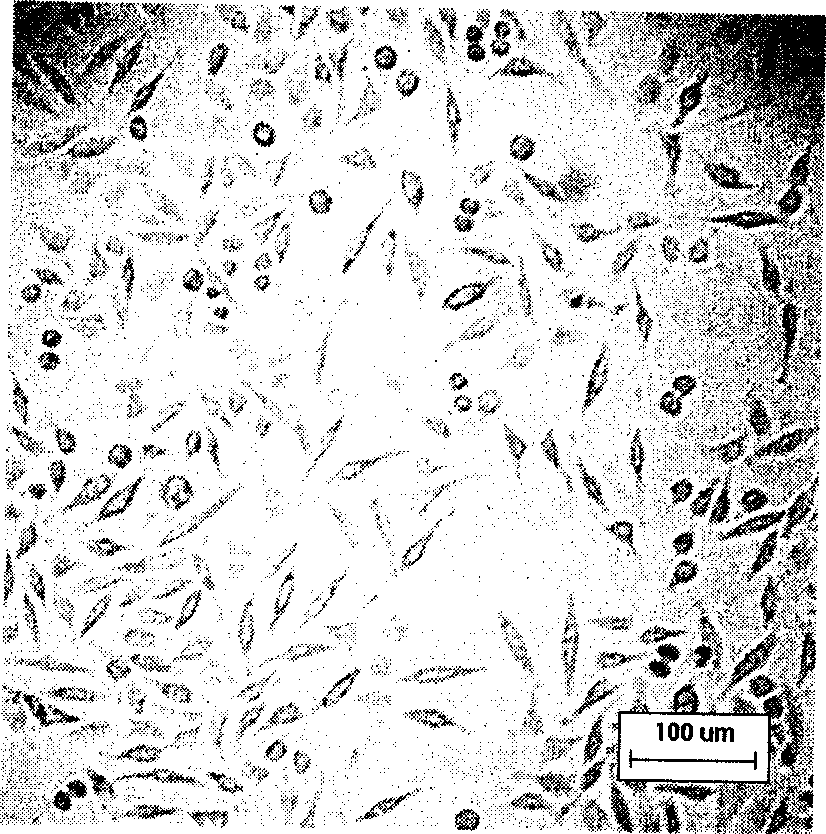
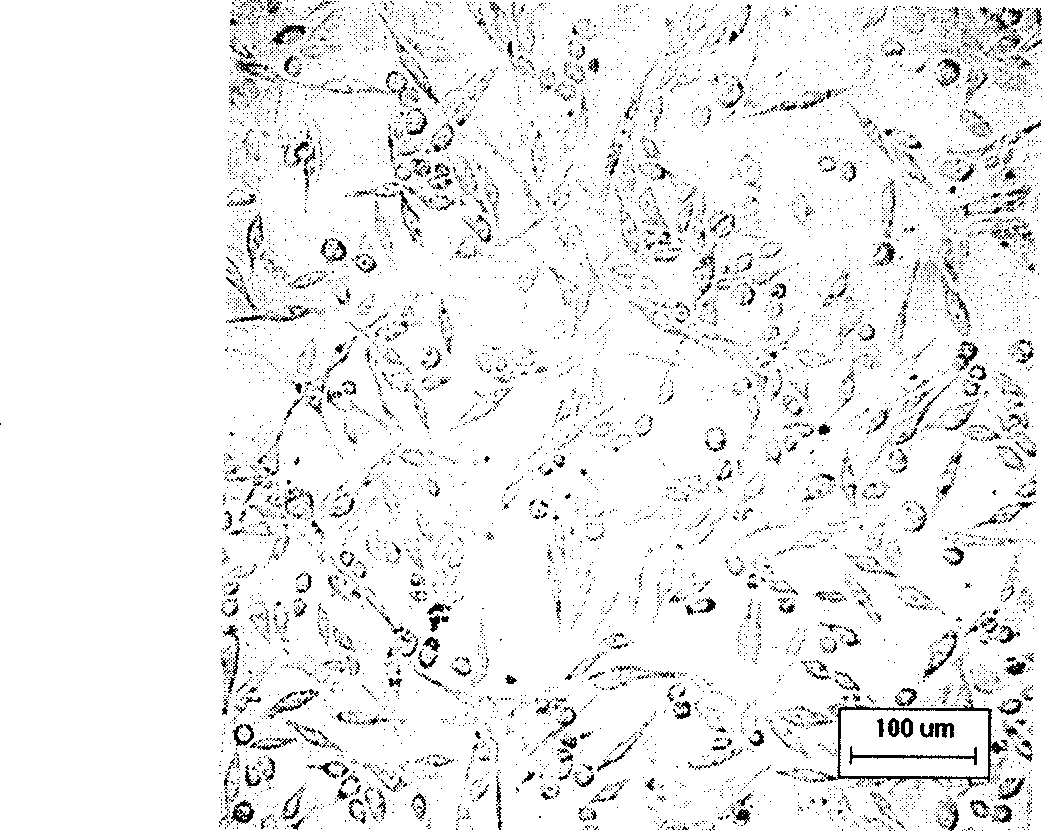
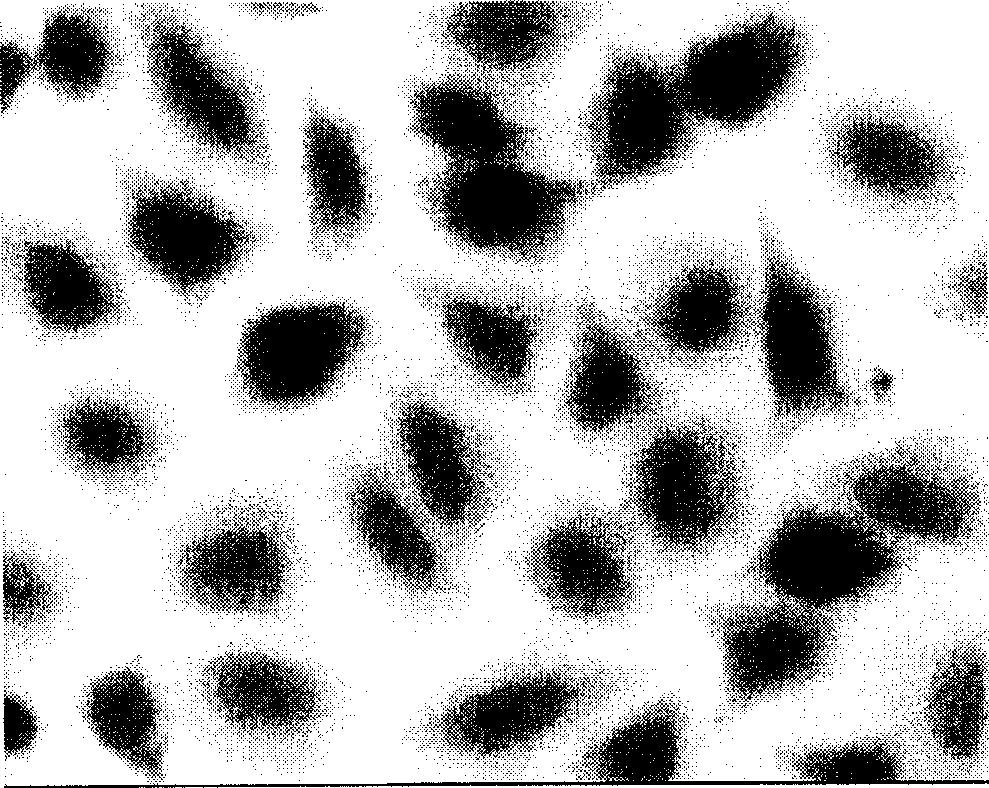
The invention belongs to the technical field of construction of tumor cell lines, and particularly relates to a tumor malignant clone cell line having important abnormal development disintegrating stage of mantle cell lymphoma, and a construction method and application of the tumor malignant clone cell line. The invention provides a human mantle cell lymphoma malignant clone cell strain containingearly malignant clone cells, is named as a human mantle cell lymphoma malignant clone cell strain JeKo-1-spheroid, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), and the preservation number is C2018264. A mature JeKo-1-parental cell strain is used as an induction object, a continuous culture and natural purification methods are used, a malignant clone cell strain containinga mantle cell lymphoma main malignant disintegrating stage is obtained, and the obtained cell strain highly cooperates with primary cells of a patient.
Owner:重庆医药高等专科学校附属第一医院
Cervical cancer multidrug resistance cell strain established by etoposide induction
The invention relates to a multidrug resistant cell strain for cervical carcinoma, which is characterized in that a human cervical carcinoma SiHa cell strain is selected as a parental cell; the action concentration of chemotherapeutics of etoposide (VP16) is gradually increased from 0.1 mu g / ml to 4 mu g / ml; and drug resistant SiHa / VP16 cell strain is established. The SiHa / VP16 cell can stably grow, transfer and reanimate in 4 mu g / ml VP16, makes the VP16 generate drug resistant index (RI) of 24. 019, and performs intersect drug on MTX, cDDP, VCR, 5-Fu and DOX except VP16. The invention aims to provide a drug resistant tumor cell model for relative study on the tumor.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN
Preparation method of miR-126 transfected ovarian cancer cell line
The invention discloses a preparation method of an miR-126 transfected ovarian cancer cell line. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, culture of parental cells: conducting subculturing on a human ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinoma cell line SKOV3; 2, transfection preparation of miR-126: using a lentiviral technology, inoculating the SKOV3 cells in logarithmic phase obtained in the step 1 into a 6 cm petri dish, adding 2 ml of a whole culture medium, and washing medium cells again with 2 ml of a serum-free medium when cells grow to 80%-90% fusion 24 hours later, and getting ready for transfection; and 3, arrangement of an miR-126 transfection overexpression group. The miR-126 transfection overexpression group has the following purposes: observation on biological behavior changes of ovarian cancer cells after miR-126 transfection; and research on effect of miR-126 in occurrence and development of ovarian cancer and searching for new targets for clinical treatment of ovarian cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
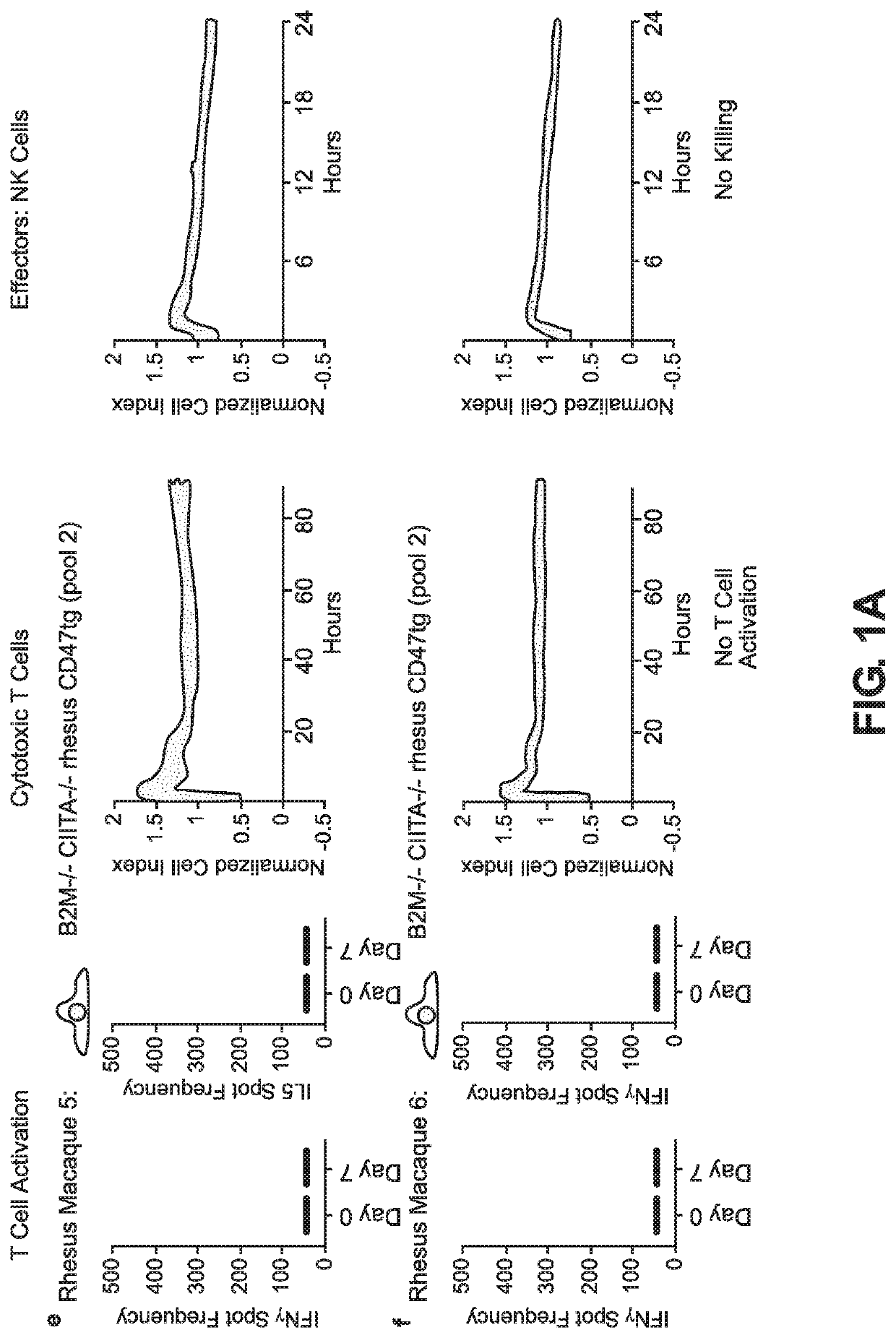
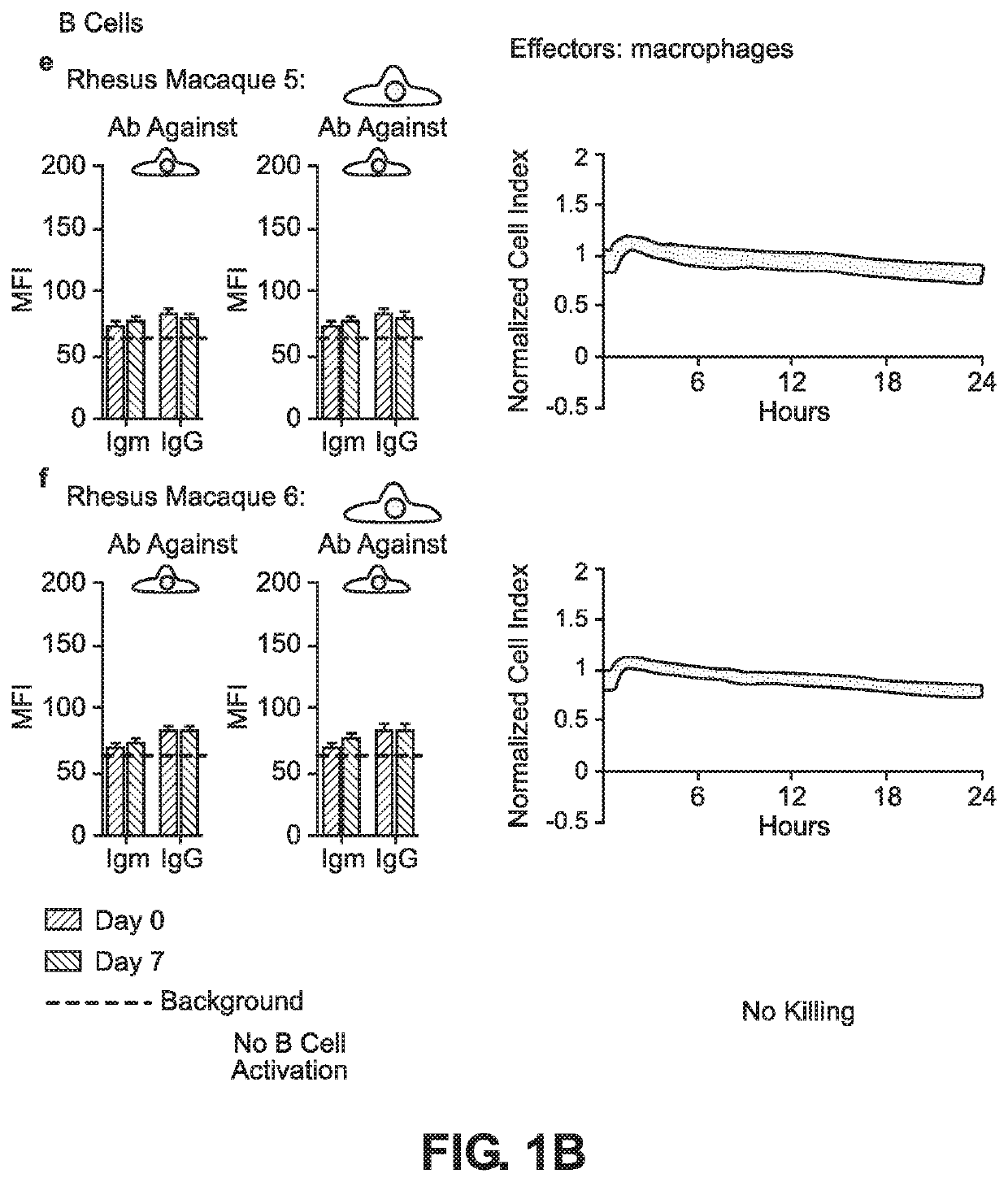
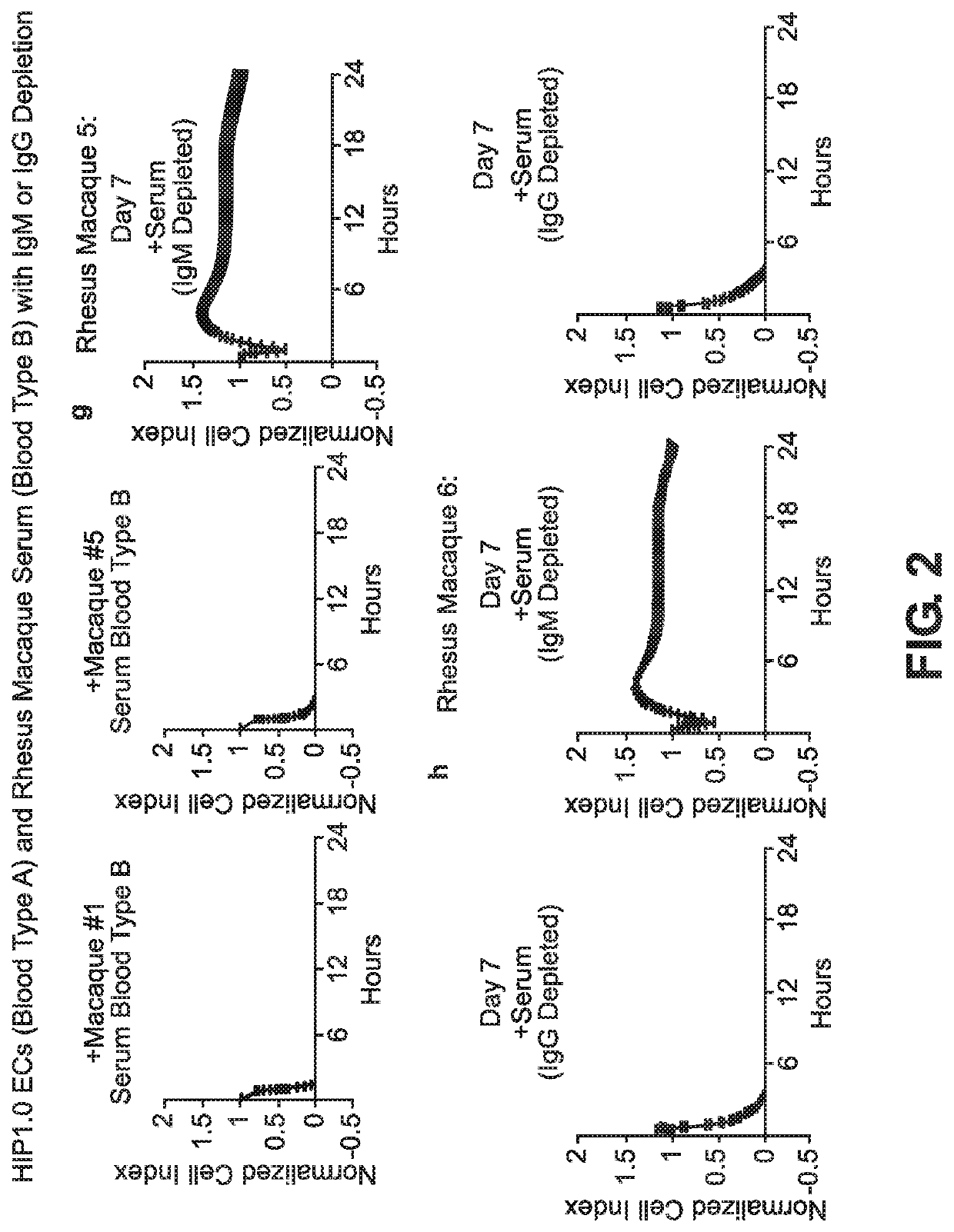
BLOOD TYPE O Rh- HYPO-IMMUNOGENIC PLURIPOTENT CELLS
ActiveUS20200354684A1Reduce functionReduce expressionHydrolasesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellImmune clearance
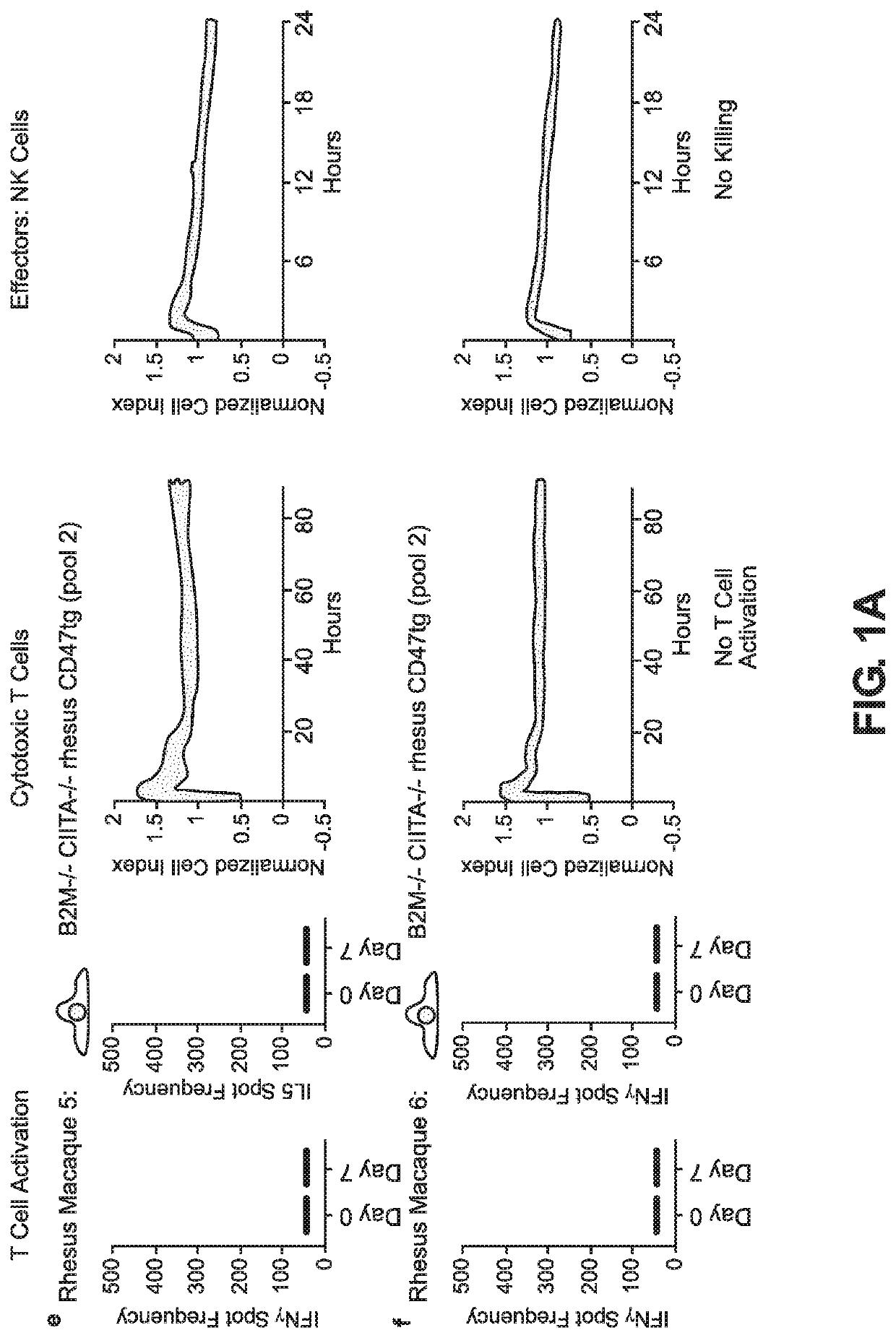
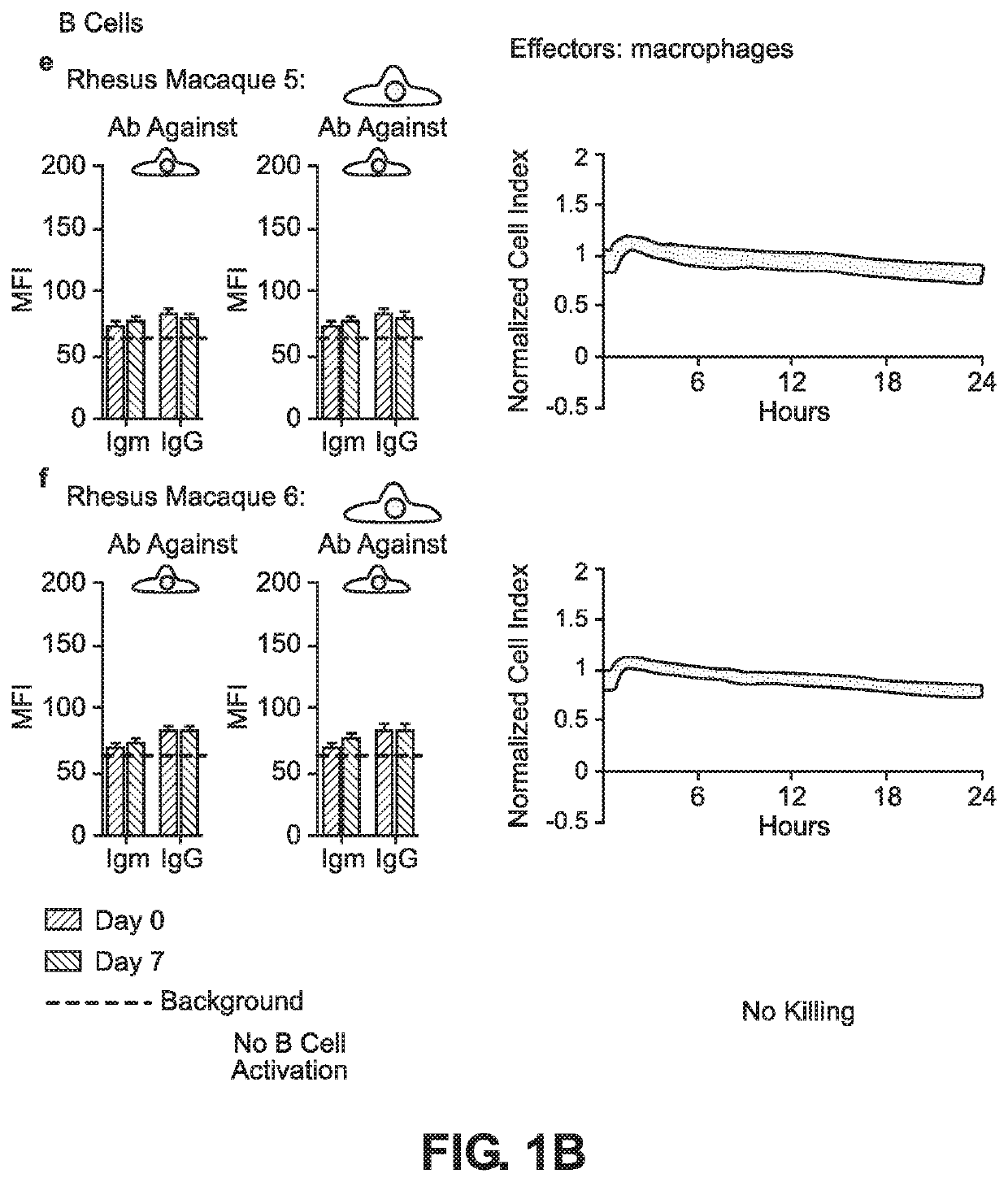
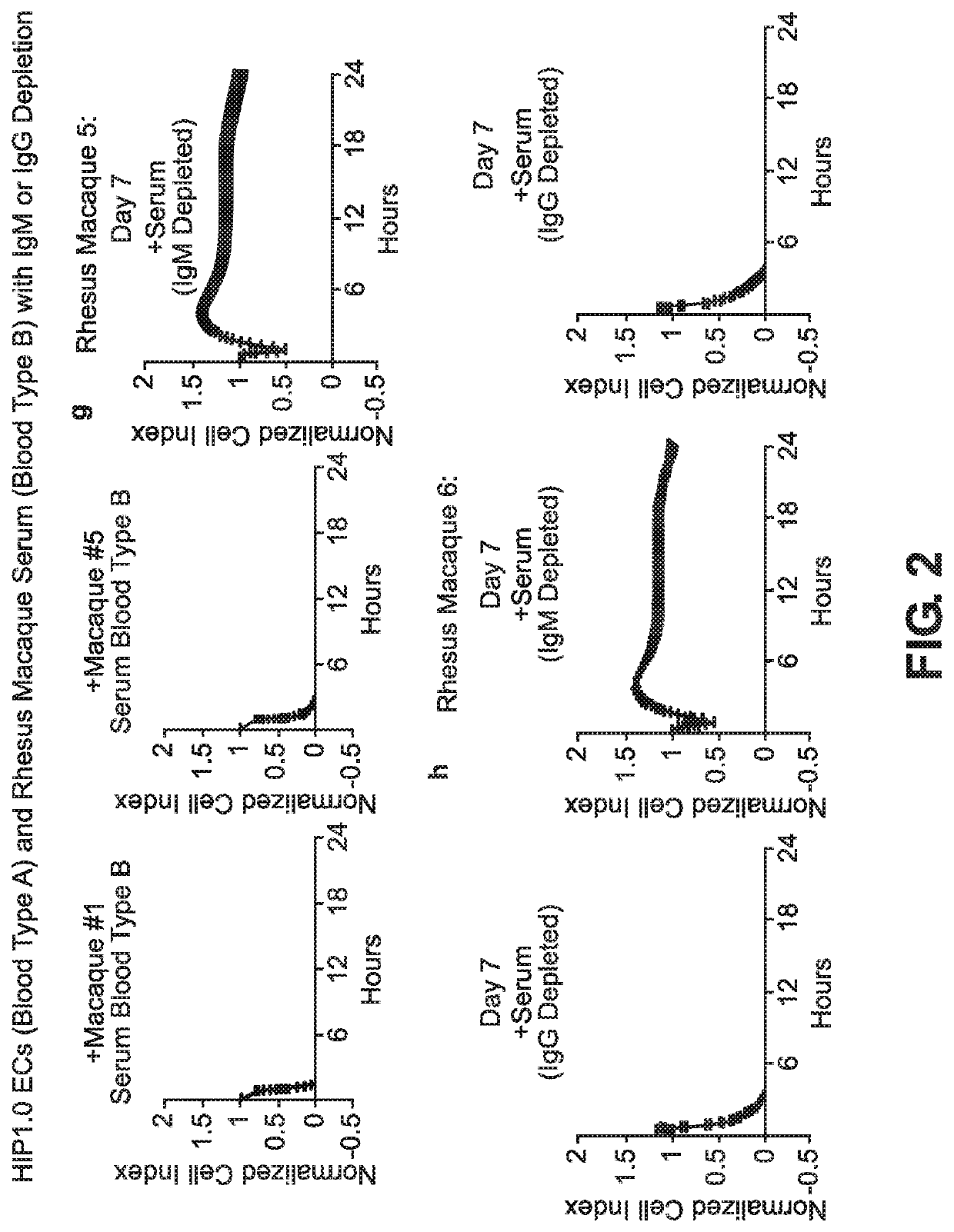
The invention discloses for the first time pluripotent cells, including hypoimmune pluripotent ABO blood type O Rhesus Factor negative (HIPO−) cells, that evade rejection by the host allogeneic immune system and avoid blood antigen type rejection. The HIPO− cells comprise reduced HLA-I and HLA-II expression, increased CD47 expression, and a universal blood group O Rh−(“O−”) blood type. The universal blood type is achieved by eliminating ABO blood group A and B antigents as well as eliminating Rh factor expression, or by starting with an O− parent cell line. These new, novel HIPO− cells evade host immune rejection because they have an impaired antigen presentation capacity, protection from innate immune clearance, and lack blood group rejection. The cells of the invention also include O− pluripotent stem cells (iPSCO−) and O− embryonic stem cells (ESCO−). The invention further provides universally acceptable “off”-the-shelf pluripotent cells and derivatives thereof for generating or regenerating specific tissues and organs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hybridoma cell line producing monoclonal antibody against foot-and-mouth disease virus, the monoclonal antibody therefrom, immunoassay reagent and kit, and immunoassay method
ActiveUS8232048B2Improve efficacyImprove securityAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementMonoclonal antibody 14G2AStructural protein
Provided herein are a hybridoma cell line producing monoclonal antibody against foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), the monoclonal antibody therefrom, reagent and kit for ELISA, and immunoassay method. The hybridoma cell line CmA40 as deposited under American Type Culture Collection patent deposit number PTA-11304 is produced by cell fusion of a parental cell and a myeloma cell line. The parental cell is a splenocyte isolated from the spleen of a mouse immunized by an antigen derived from a 3ABC non-structural protein (NSP) of FMDV. The antigen used here is expressed by a prokaryotic cell. The monoclonal antibody produced by the hybridoma cell line CmA40 as deposited under American Type Culture Collection patent deposit number PTA-11304 can specifically recognize a 3ABC polypeptide and does not cross-react with an antiserum of swine vesicular disease virus.
Owner:VETERINARY RES INST MINISTRY OF AGRI
Generating cardiac progenitor cells from pluripotent stem cells using isoxazole or isoxazole like compounds
ActiveUS20170002329A1Easy to replaceReduce cell deathArtificial cell constructsUnknown materialsPluripotential stem cellDisease
This disclosure provides a chemically modified induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell derived from parental cells and methods for generating the chemically induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, as well as cardiac progenitor cells capable of producing cells of multiple sub-lineages. The iPS cells are useful in method for or regenerating cardiac muscle tissue or to promote the replacement of cardiac scar tissue or to rejuvenating cardiac muscles in a patient in need thereof and to treat cardiac disease.
Owner:IPS HEART
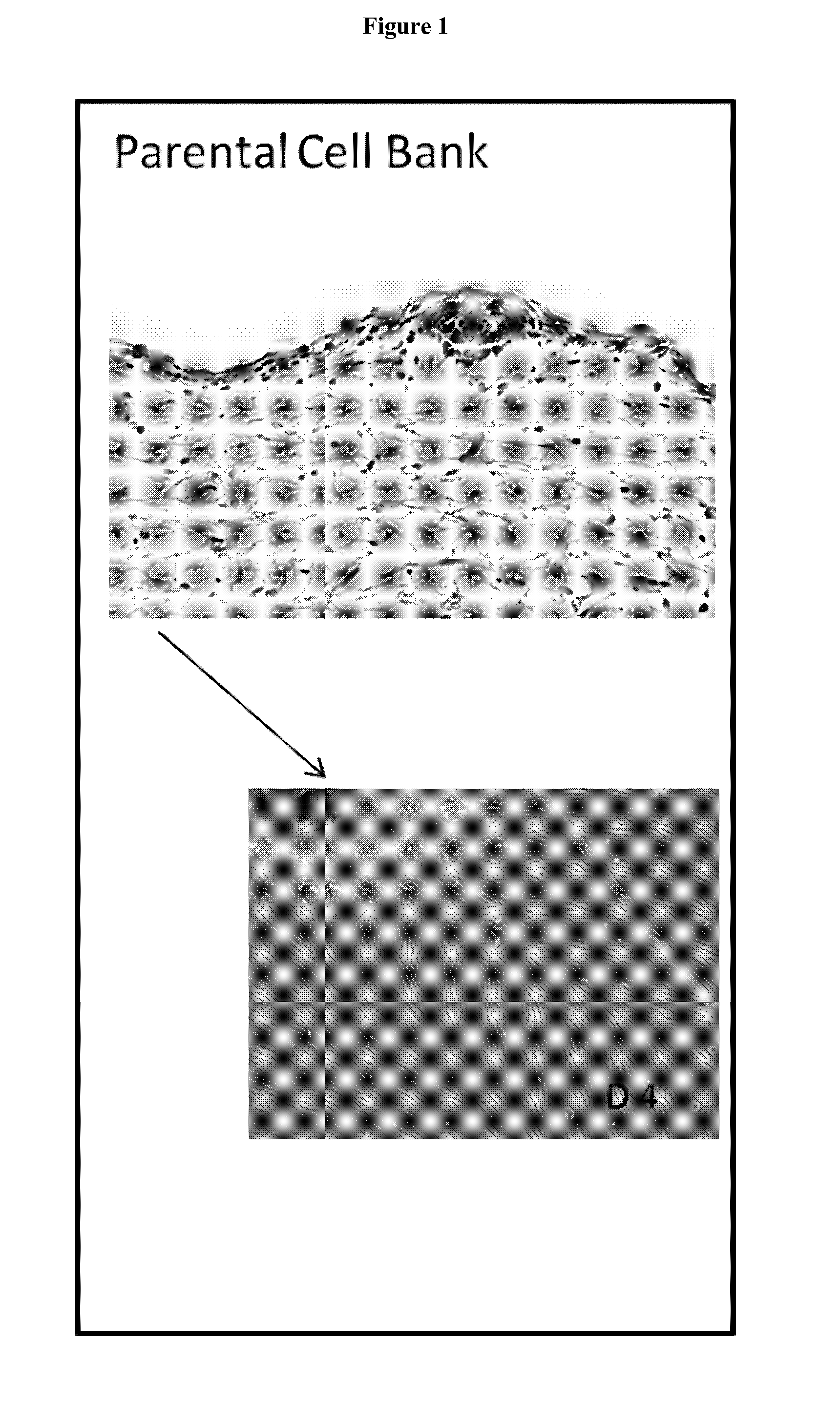
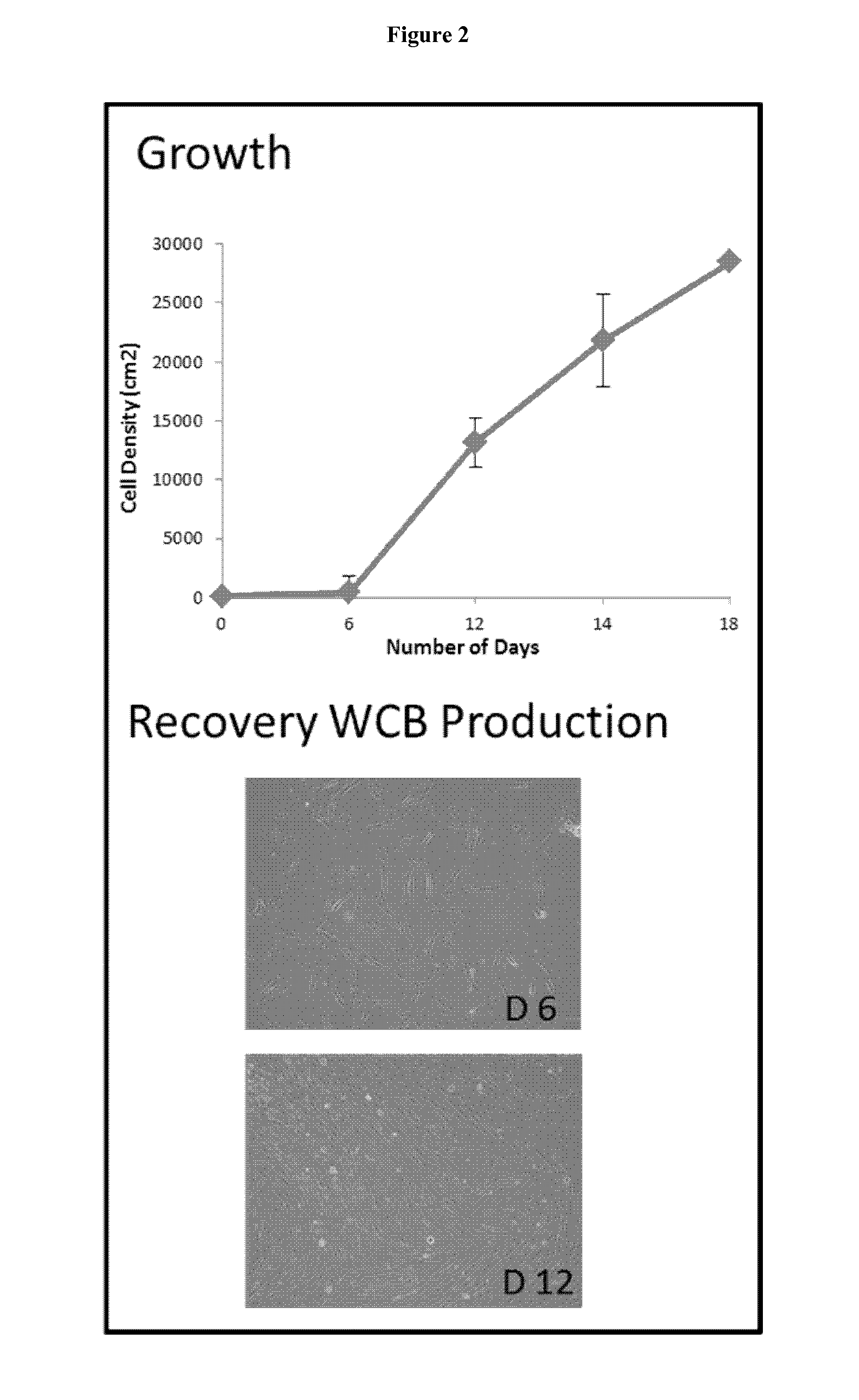
Preparation of parental cell bank from foetal tissue
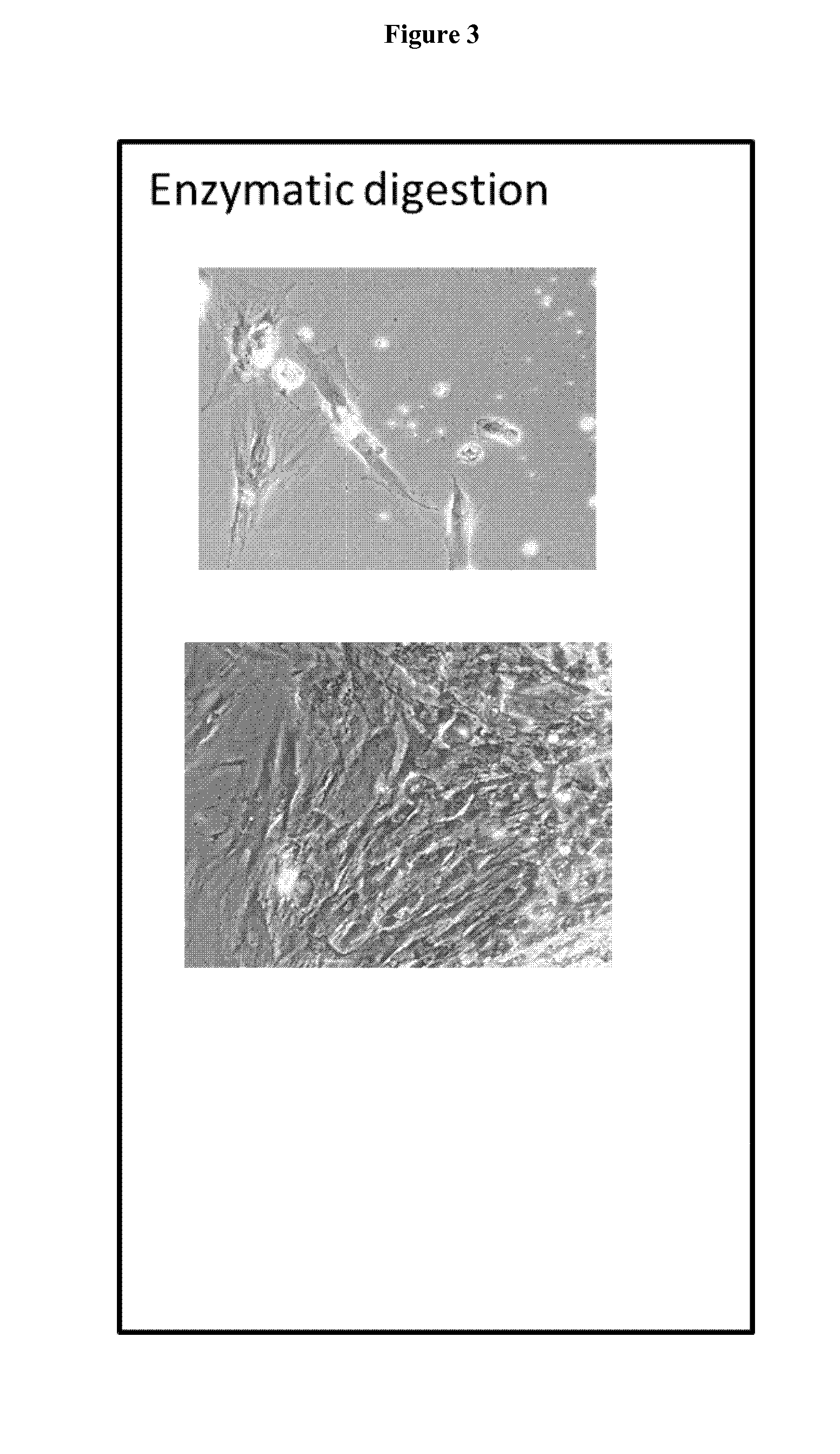
The present invention relates to methods of in vitro preparation of a parental cell bank (PCB) from foetal tissue consisting of foetal epiphyseal tissue, foetal Achilles tendon tissue and foetal skin tissue, using a rapid mechanical primary cell culture selection of cell type to be used in methods for wound and tissue repair.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV VAUDOIS C H U V
Blood type O Rh-hypo-immunogenic pluripotent cells
ActiveUS11162079B2Reduce sensitivityFunction increaseHydrolasesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellImmune clearance
The invention discloses for the first time pluripotent cells, including hypoimmune pluripotent ABO blood type O Rhesus Factor negative (HIPO−) cells, that evade rejection by the host allogeneic immune system and avoid blood antigen type rejection. The HIPO− cells comprise reduced HLA-I and HLA-II expression, increased CD47 expression, and a universal blood group O Rh− (“O−”) blood type. The universal blood type is achieved by eliminating ABO blood group A and B antigents as well as eliminating Rh factor expression, or by starting with an O− parent cell line. These new, novel HIPO− cells evade host immune rejection because they have an impaired antigen presentation capacity, protection from innate immune clearance, and lack blood group rejection. The cells of the invention also include O− pluripotent stem cells (iPSCO−) and O− embryonic stem cells (ESCO−). The invention further provides universally acceptable “off”-the-shelf pluripotent cells and derivatives thereof for generating or regenerating specific tissues and organs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Application of breast cancer multidrug resistant protein molecule IBP
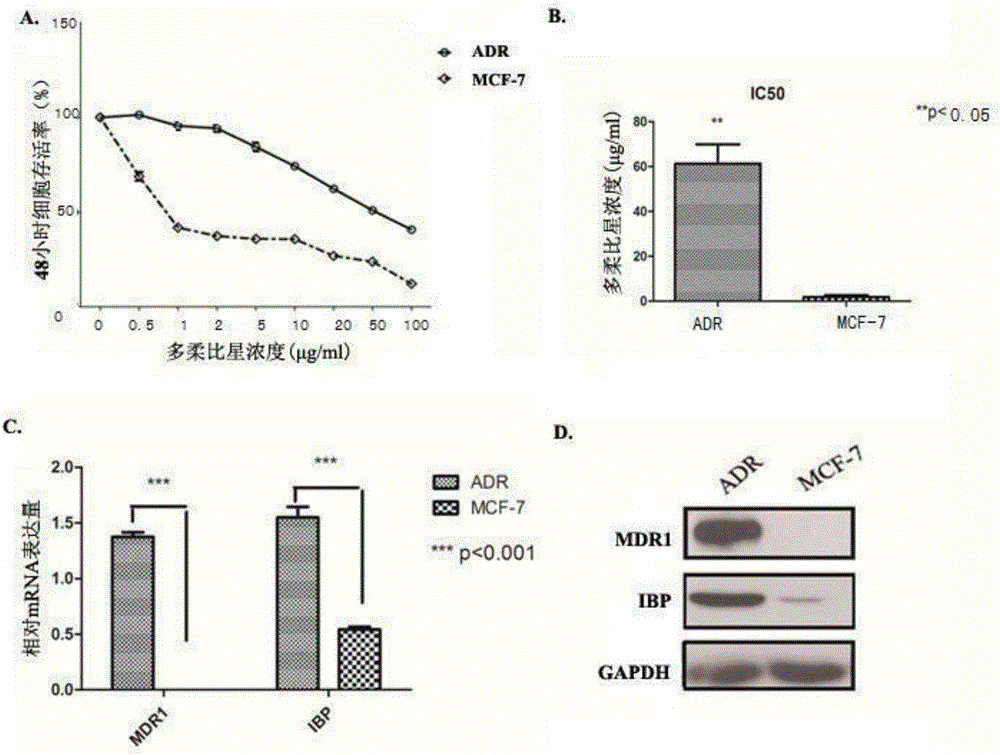
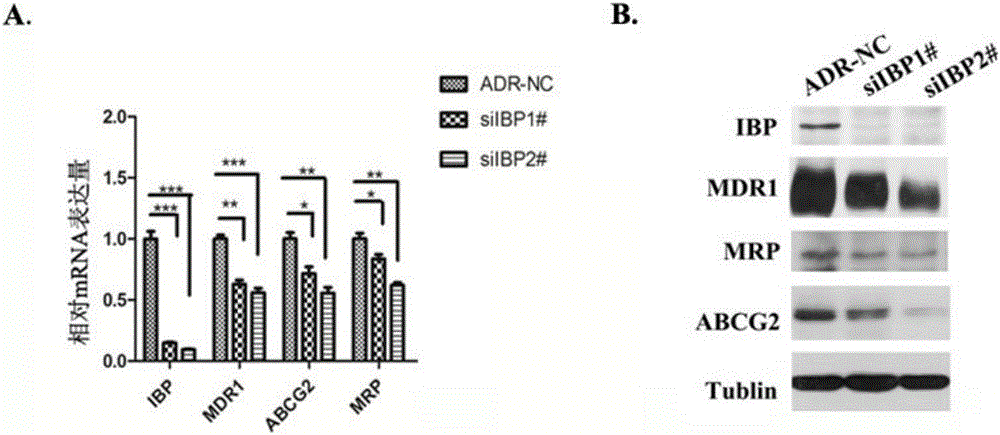
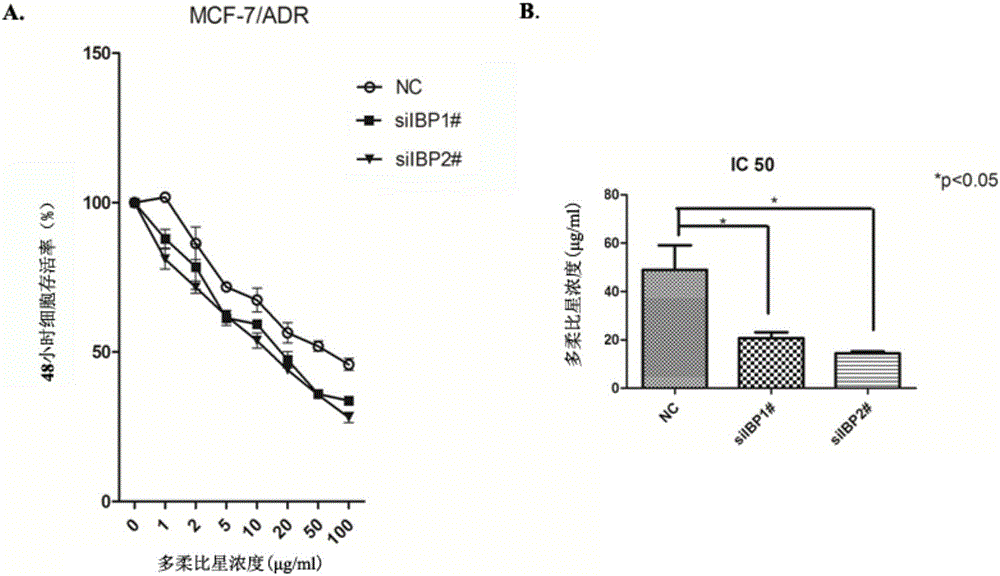
InactiveCN106383235AReduce drug efflux capacityIncreased drug resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisProtein moleculesDrugs sensitivity
The invention discloses an application of a breast cancer multidrug resistant protein molecule IBP, wherein the IBP has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.11; studies find out that expression of the IBP in breast cancer multidrug resistant cells MCF-7 / ADR is significantly higher than expression in MCF-7 parental cells, and moreover, after the expression of the IBP in the breast cancer cells is decreased, the sensibility on a variety of chemotherapy drugs is significantly enhanced; after the expression of the IBP in the MCF-7 / ADR is interfered, the breast cancer drug-resistant cells can be inhibited, besides, expression and drug transport functions of MDR1 and other multidrug resistant related genes in the MCF-7 / ADR are inhibited, and the drug sensitivity is increased; therefore, the IBP can be used as a multidrug resistant target gene for detection of breast cancer, and also can be used for preparing breast cancer multidrug resistant preparations or drugs.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com