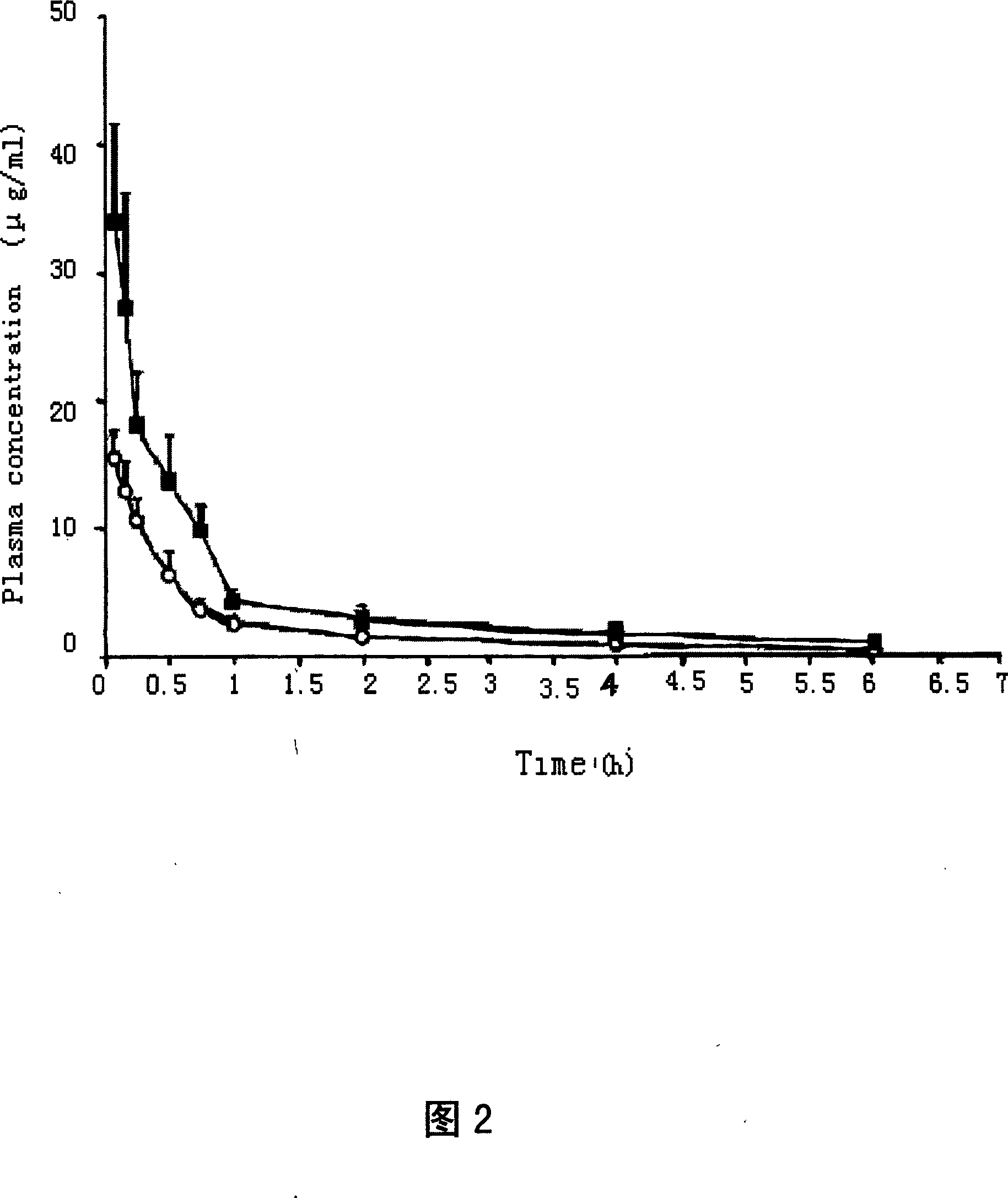
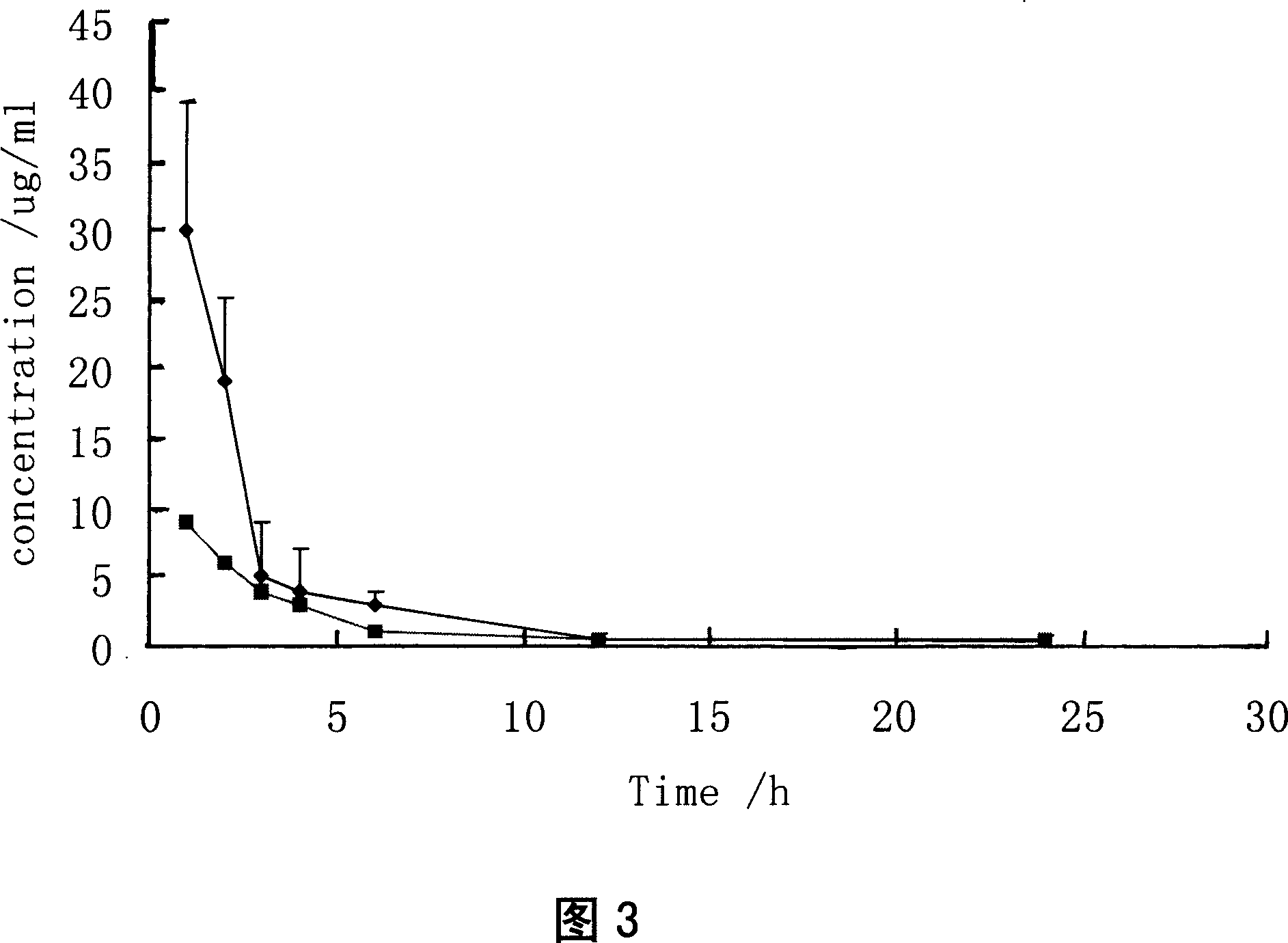
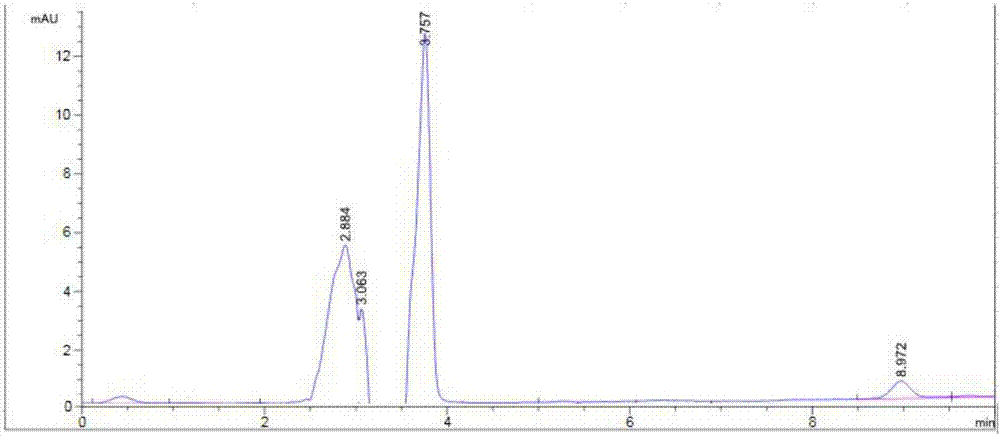
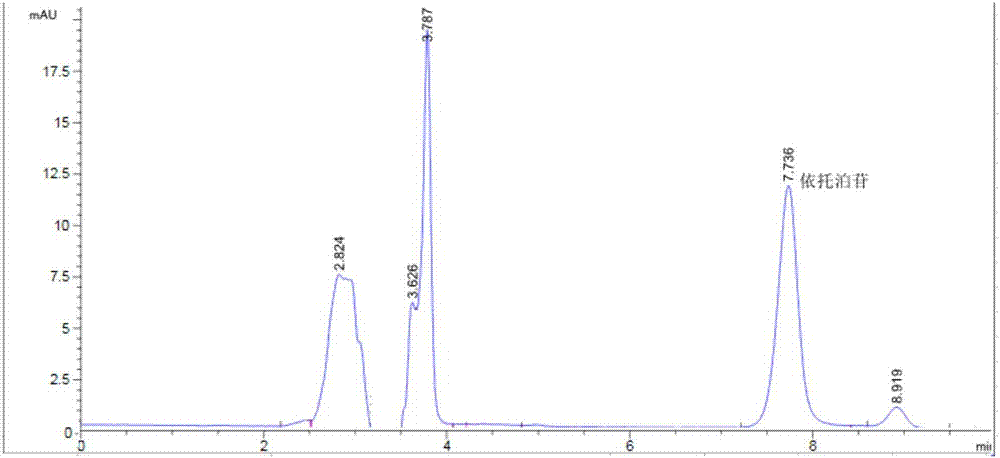
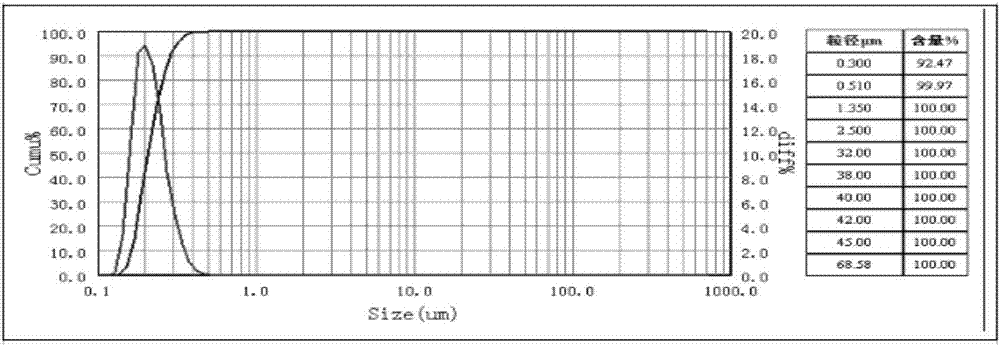
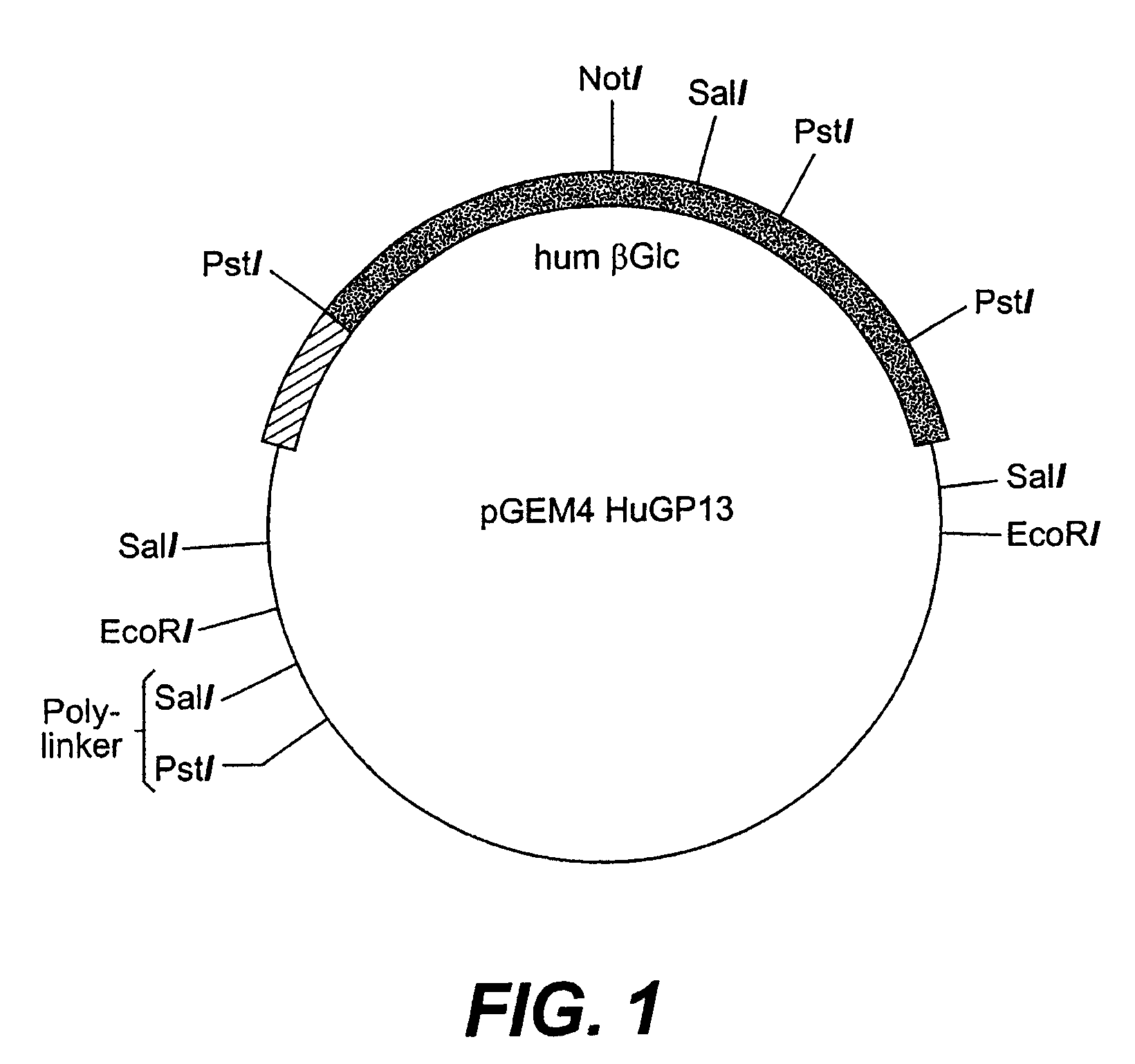
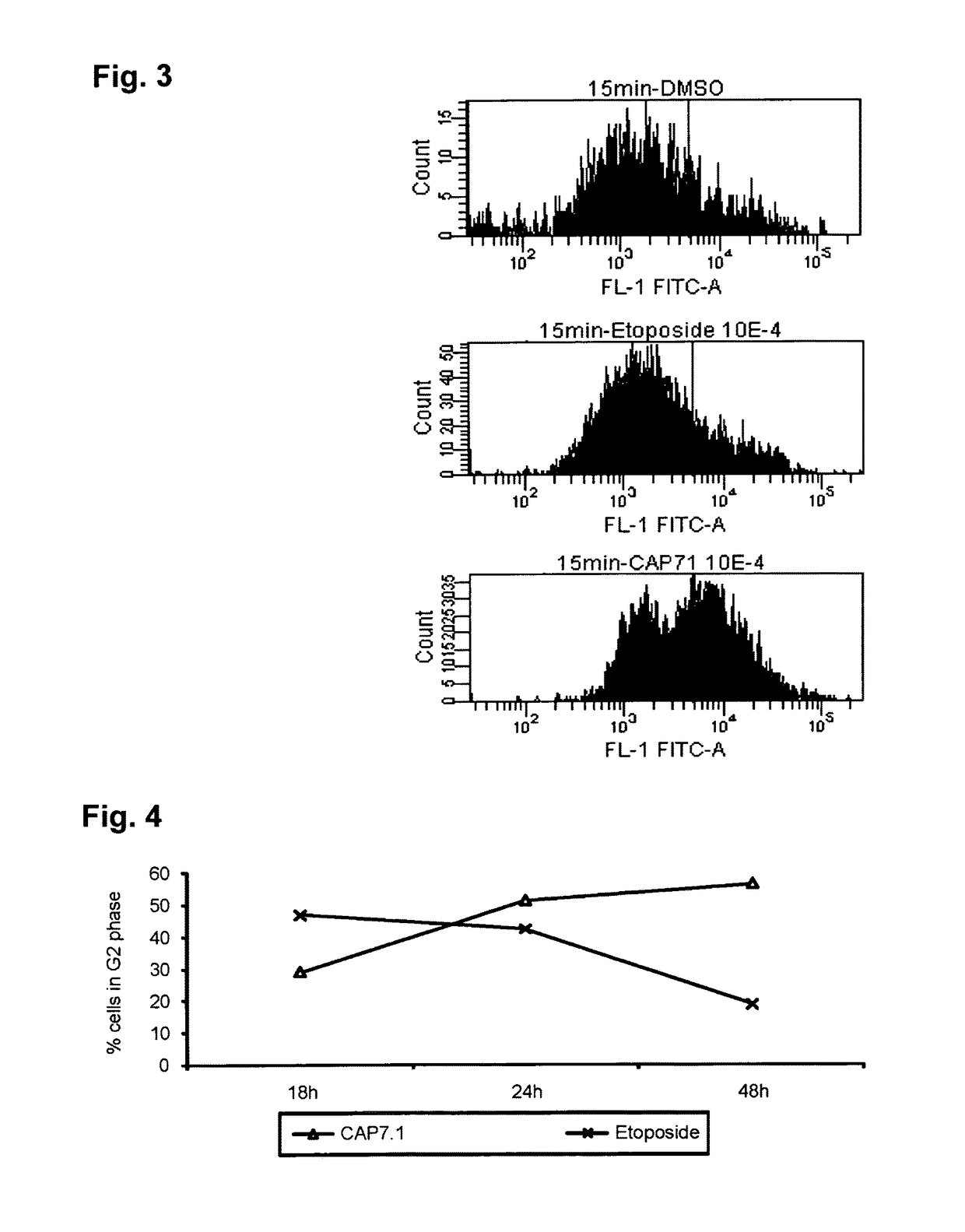
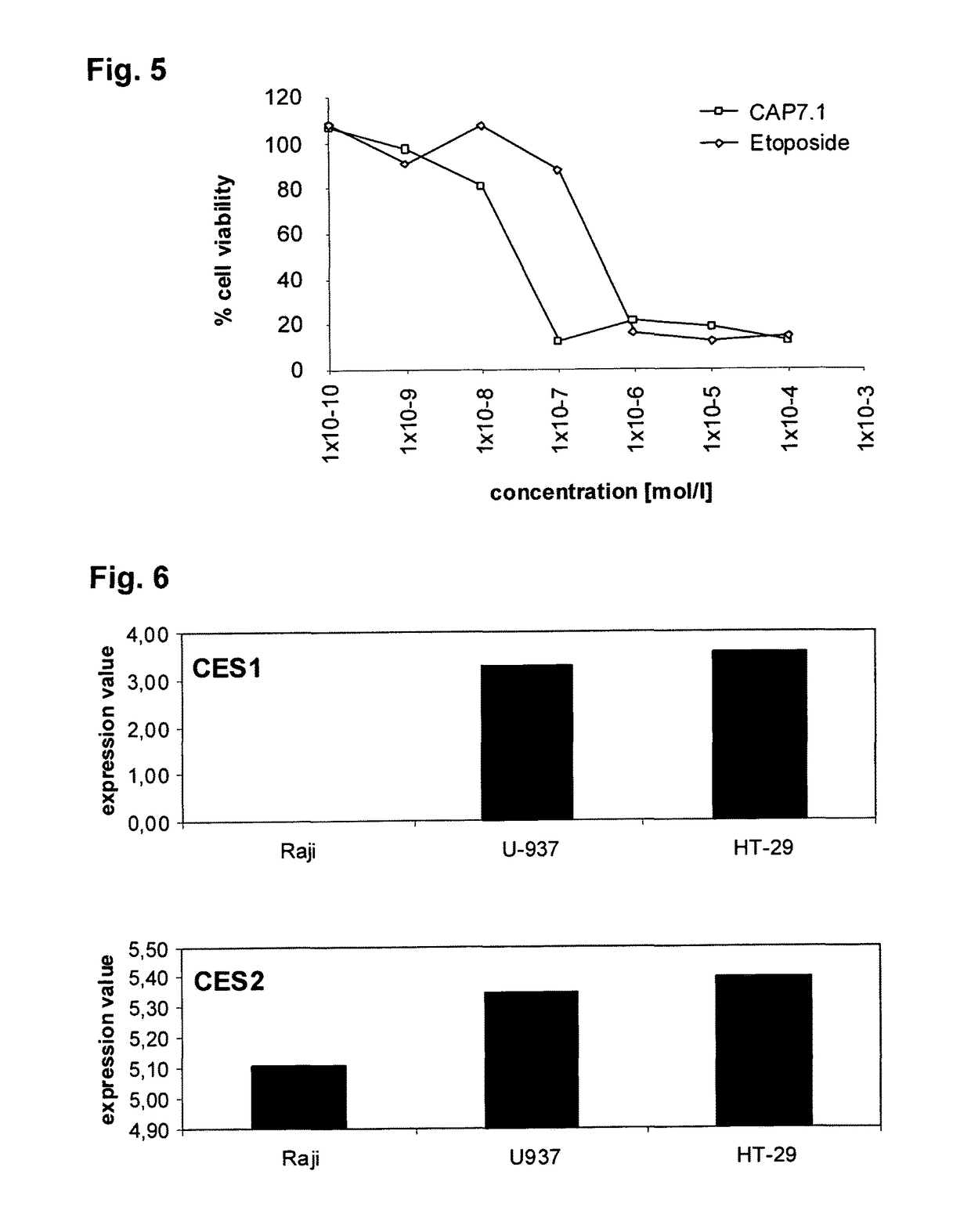
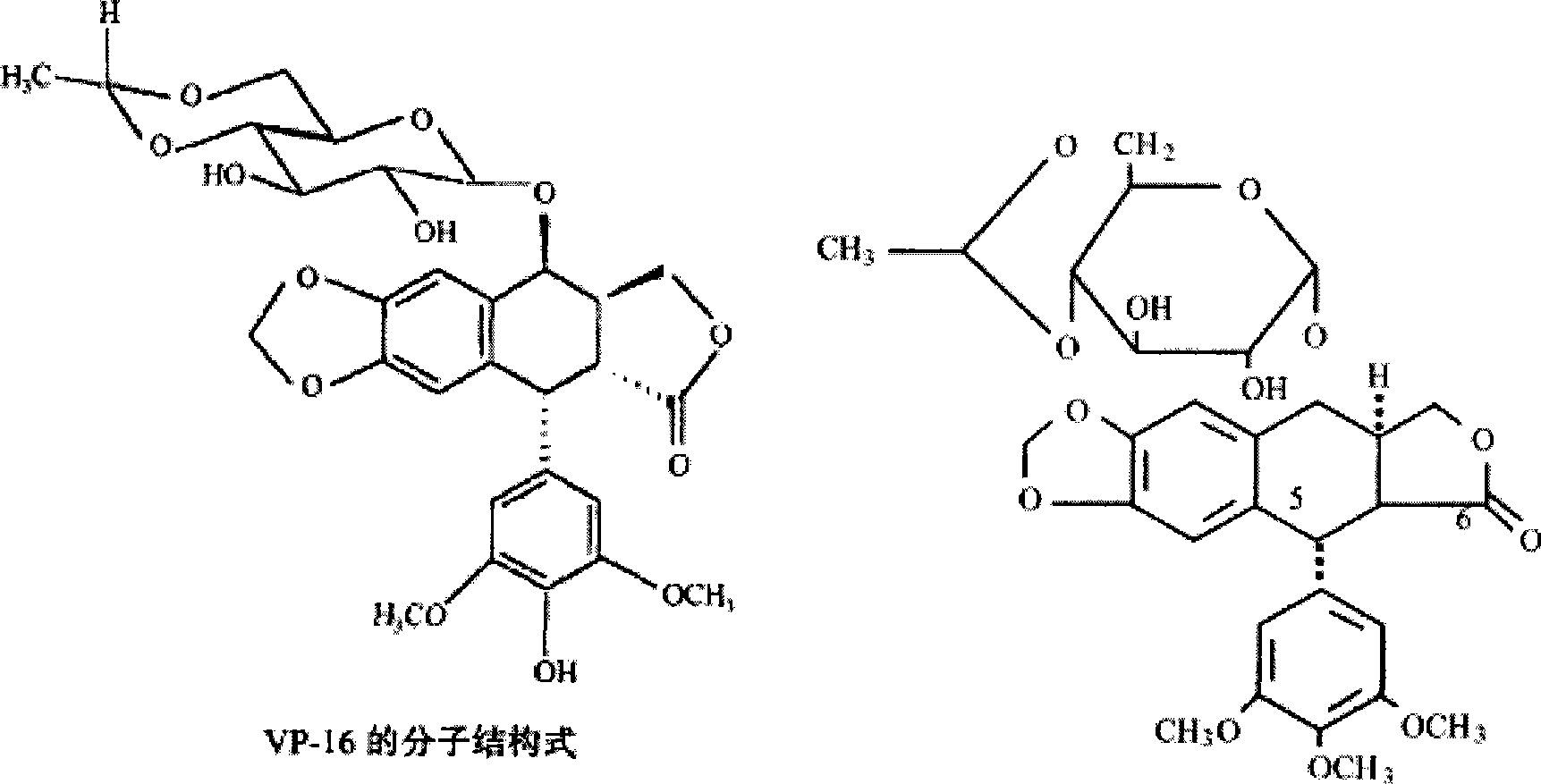
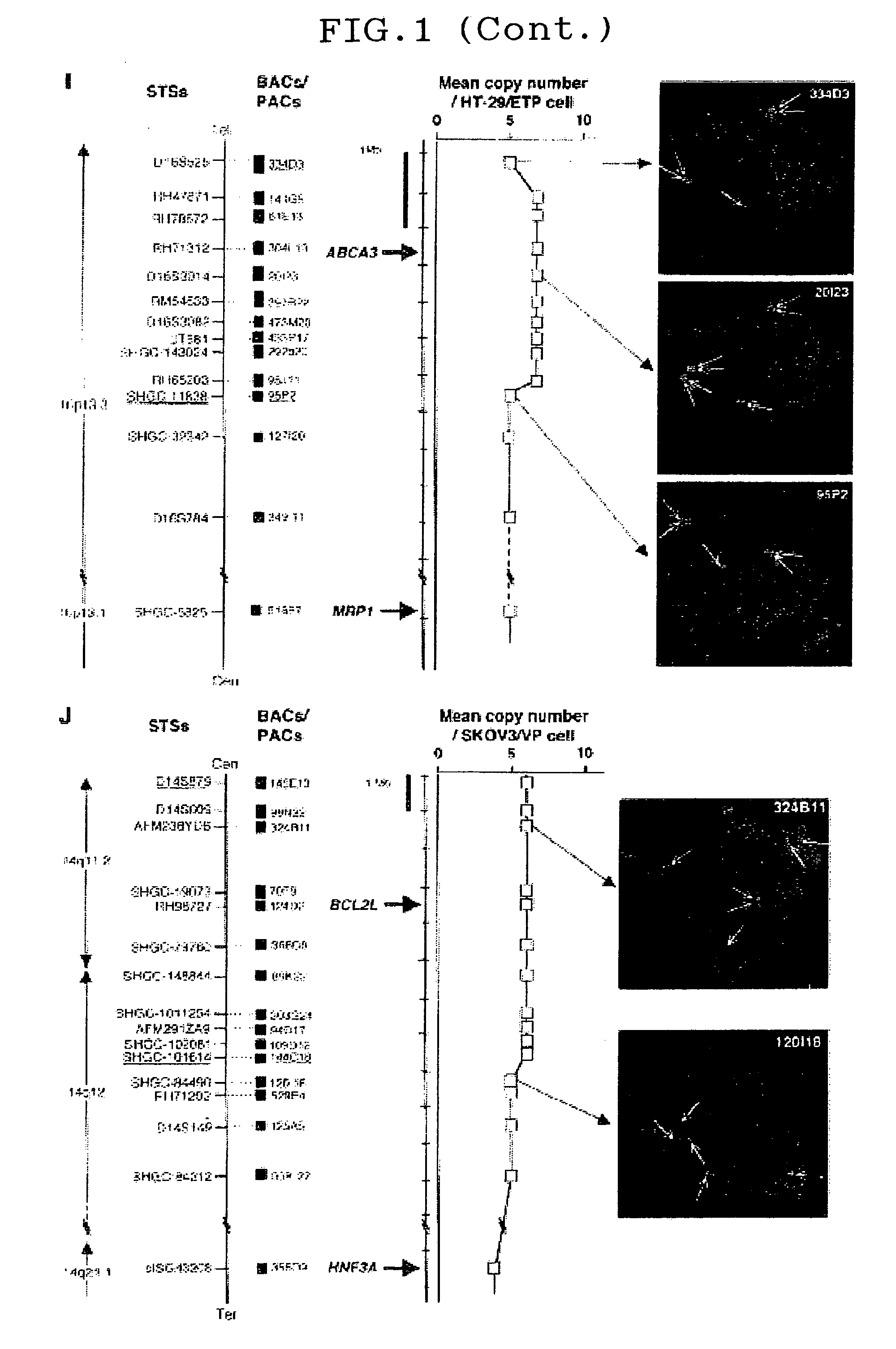
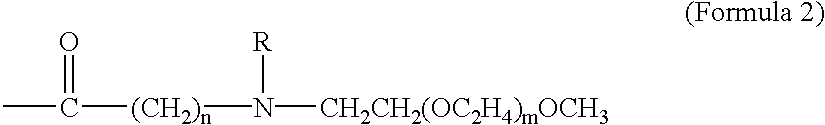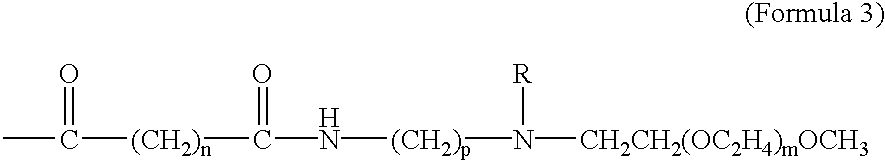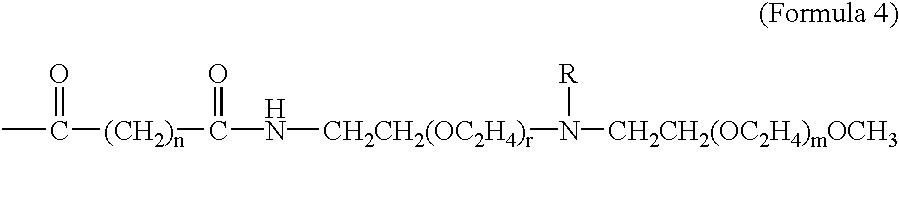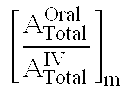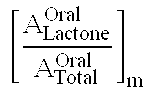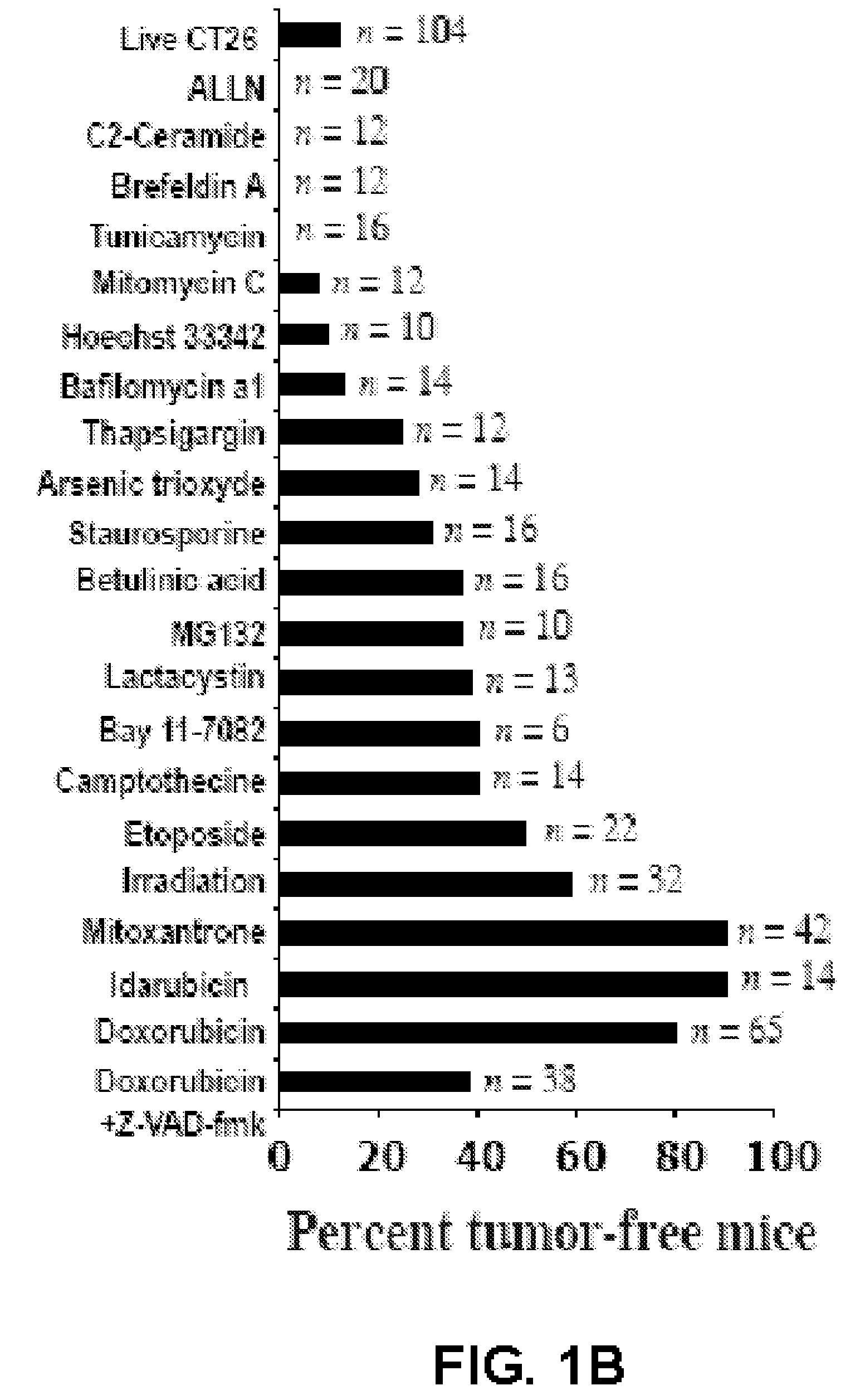Patents
Literature
158 results about "Etoposide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Etoposide is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat certain forms of lung cancer (such as small cell lung cancer).
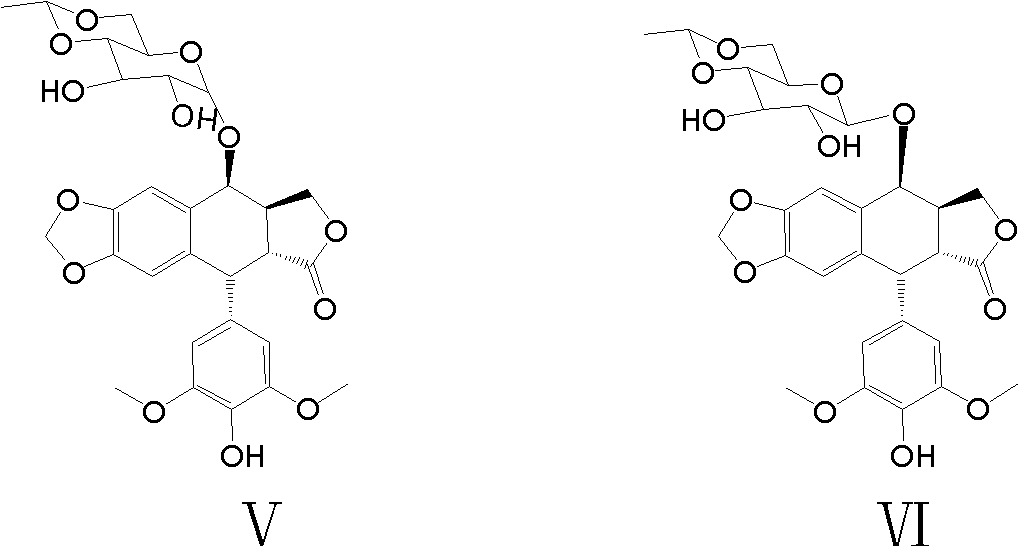
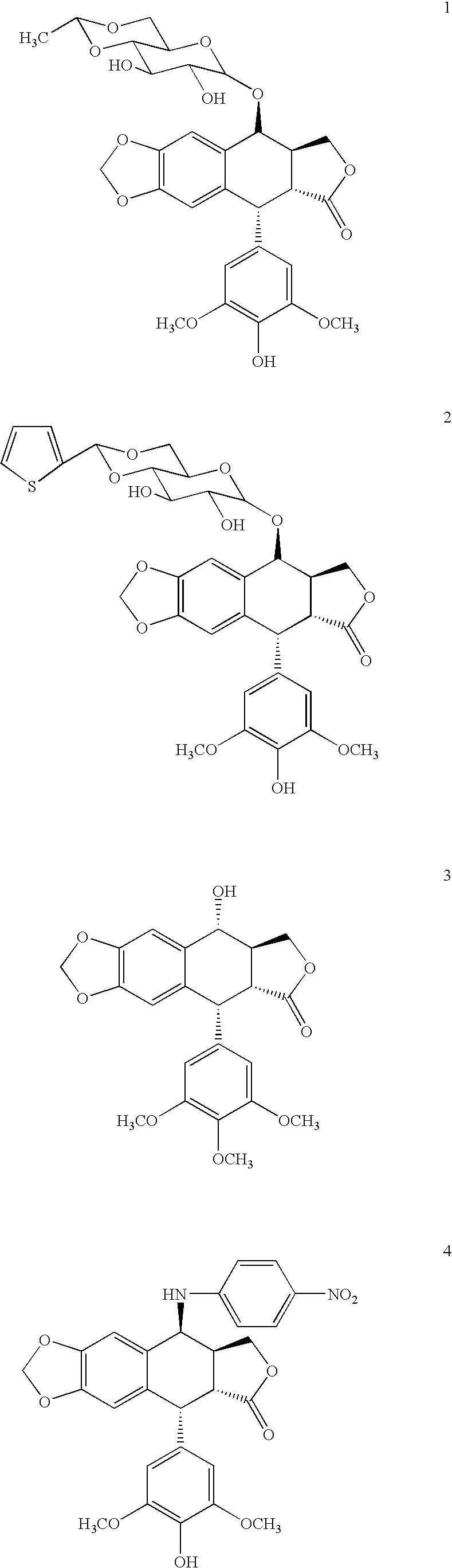
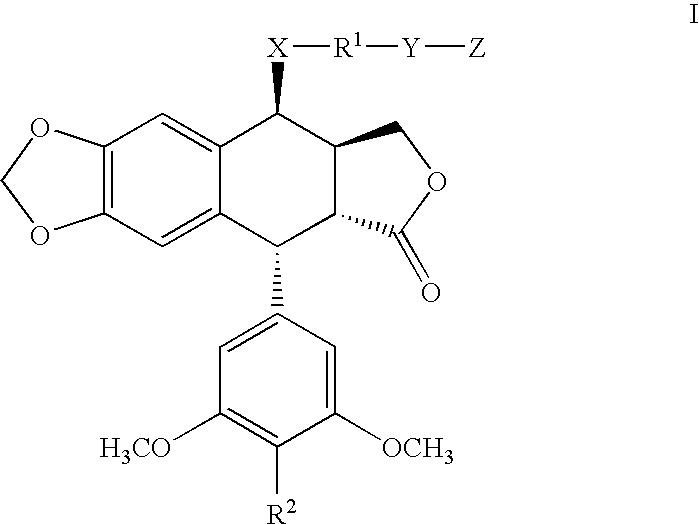
Prodrugs of etoposide and etoposide analogs
The present invention provides amphiphilic prodrugs comprising a therapeutic compound conjugated to an PEG-oligomer / polymer and methods for using said prodrugs to enable oral drug delivery and / or delivery of drugs across the blood brain barrier into the central nervous system.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Compositions and dosage forms for gastric delivery of irinotecan and methods of treatment that use it to inhibit cancer cell proliferation
InactiveUS6881420B2Improve oral bioavailabilityReduced bioavailabilityBiocideCapsule deliveryWhole bodyCancer cell proliferation
The present invention provides oral dosage forms and compositions for administering antineoplastic agents, such as irinotecan, etoposide, paclitaxel, doxorubicin and vincristine, whose oral effectiveness is limited by pre-systemic and systemic deactivation in the GI tract. Gelling of the gastric retention vehicle composition, and in the case of solid forms concomitant expansion of the composition, retains the antineoplastic drug in the patient's stomach, minimizing pre-systemic and / or systemic deactivation of the drug.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Integrin interaction inhibitors for the treatment of cancer
ActiveUS8853149B2Prevent and delay onsetPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesAntiproliferative AgentsIntegrin
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC +1
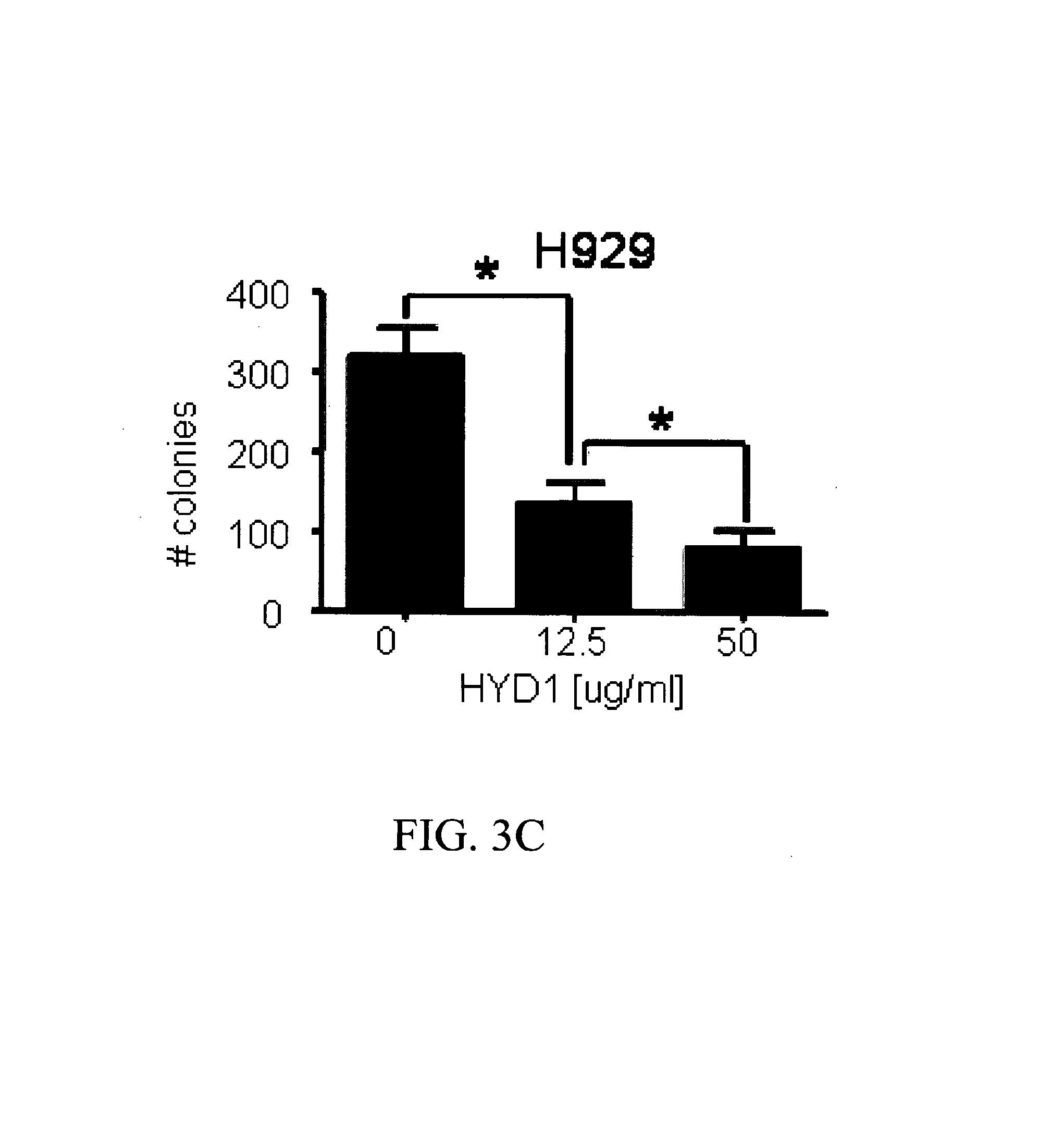
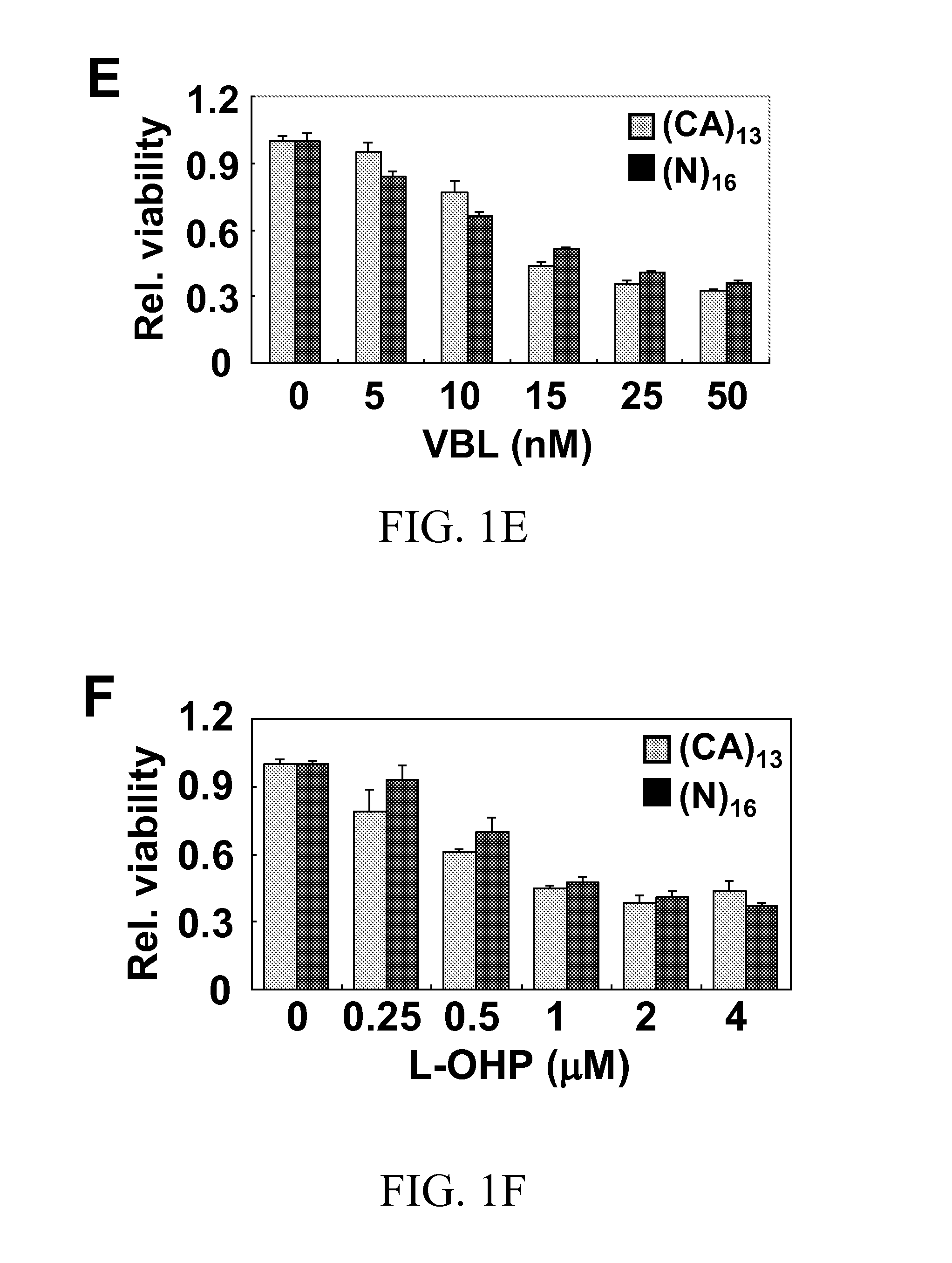
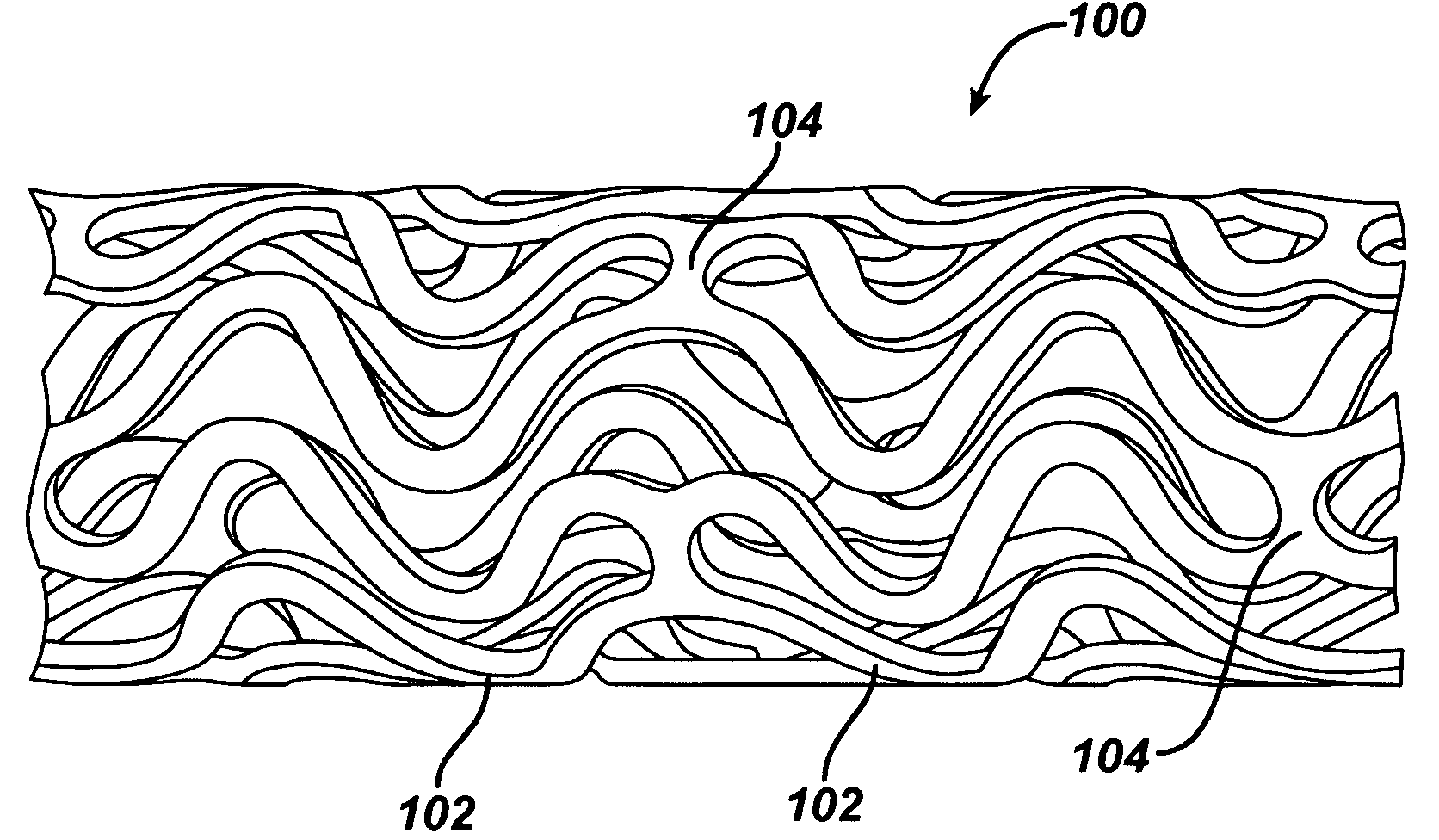
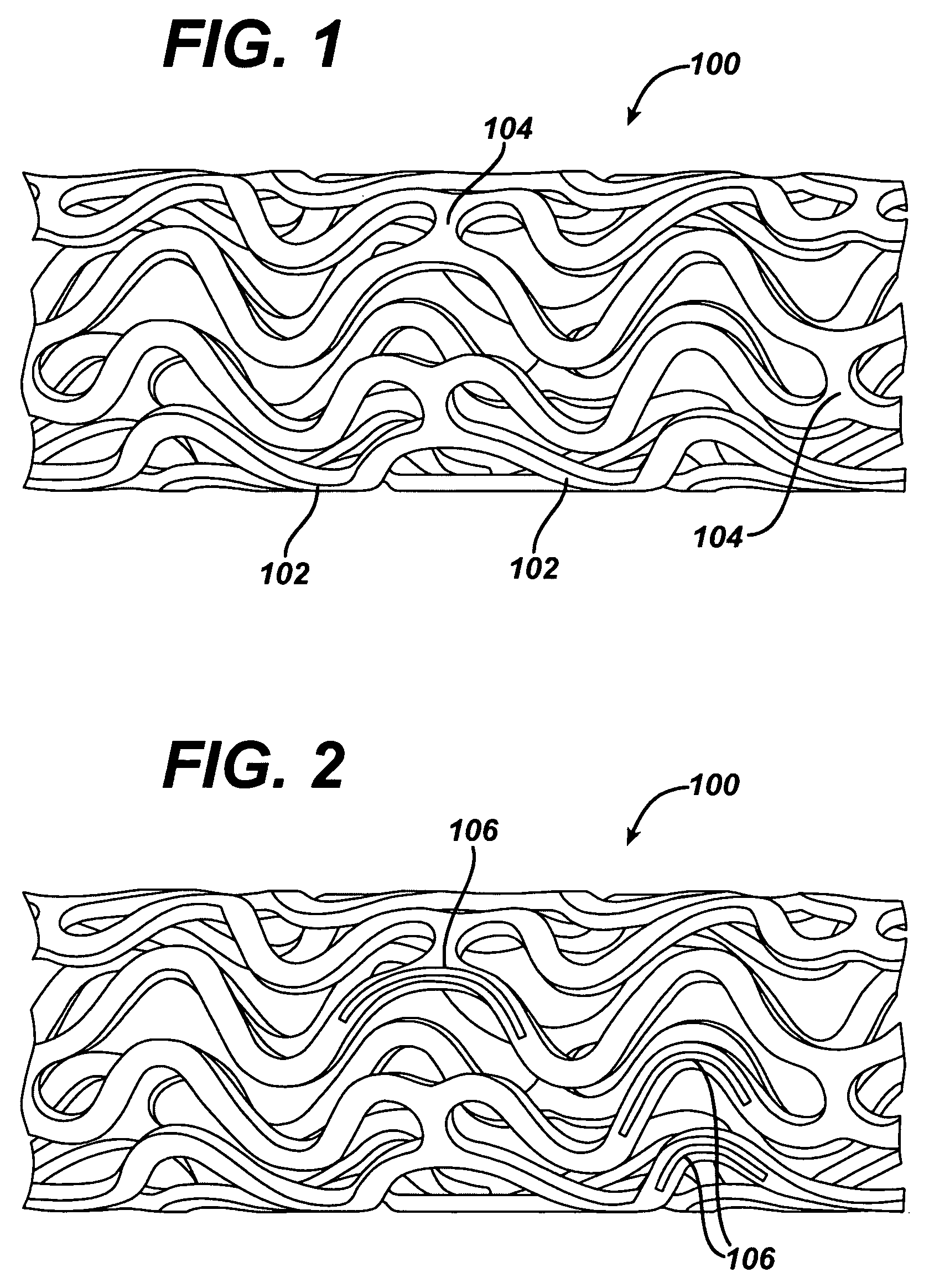
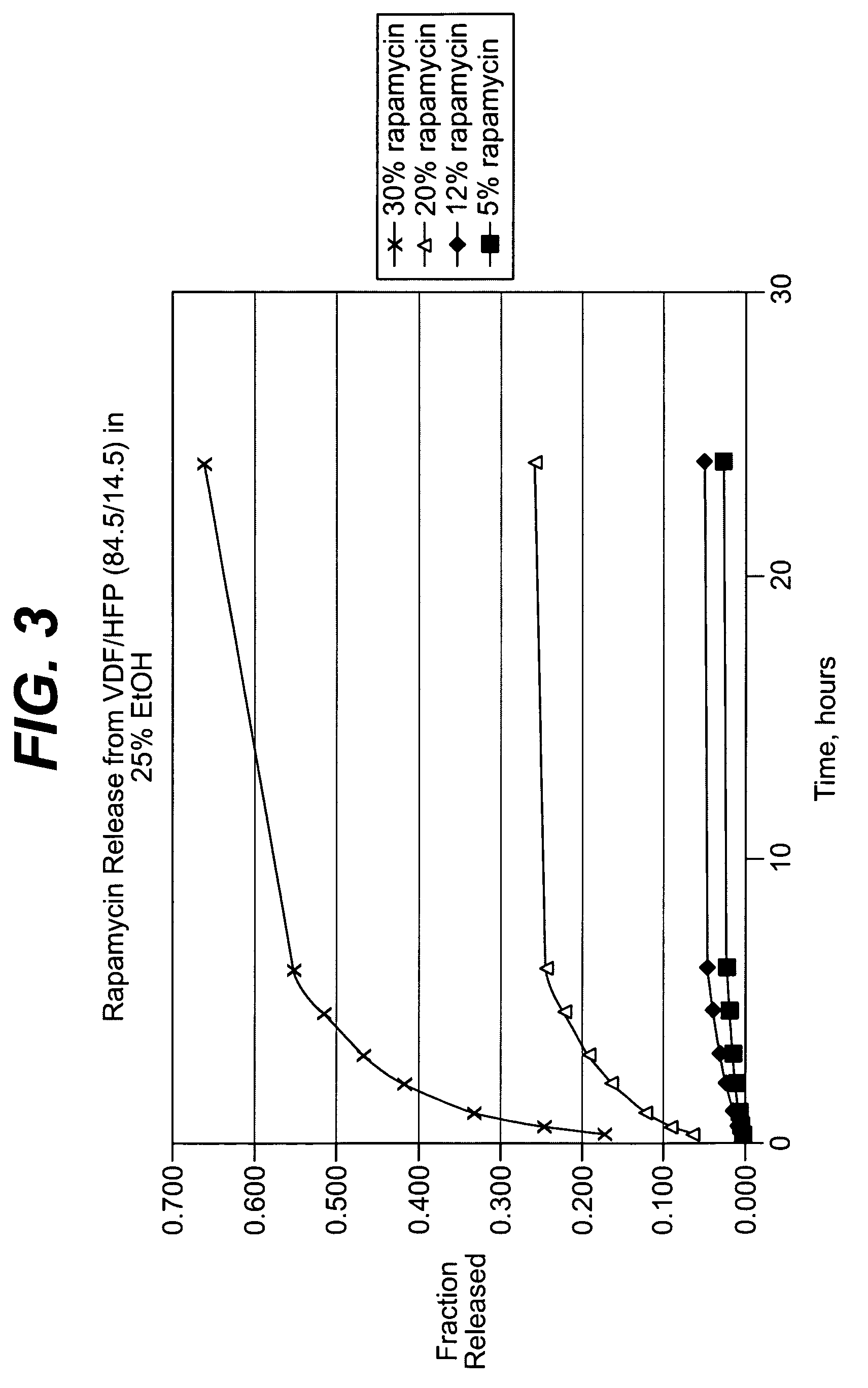
Local vascular delivery of etoposide in combination with rapamycin to prevent restenosis following vascular injury
ActiveUS20050208092A1Reduce frictionLittle strengthBiocideSurgeryPercent Diameter StenosisBlood vessel
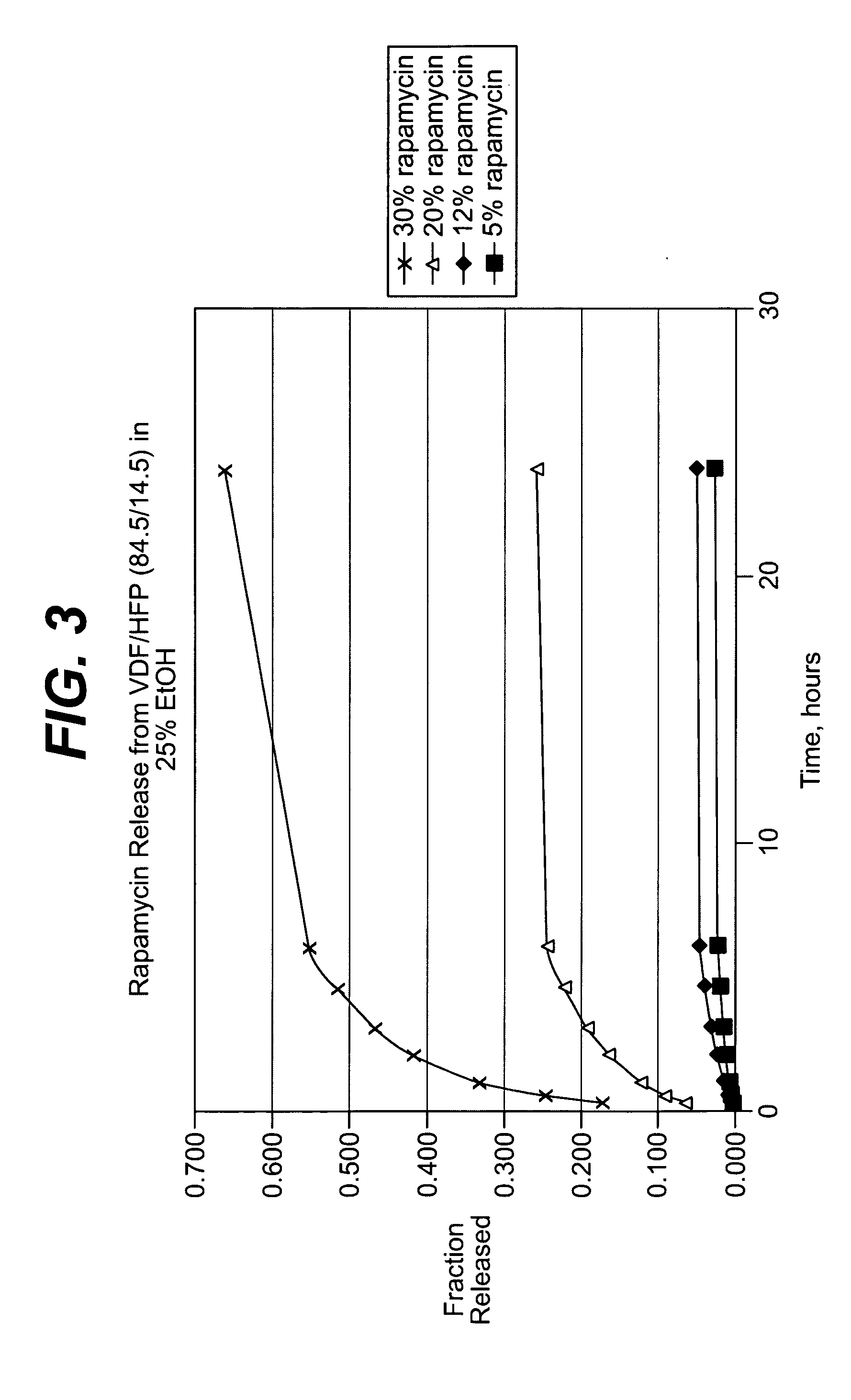
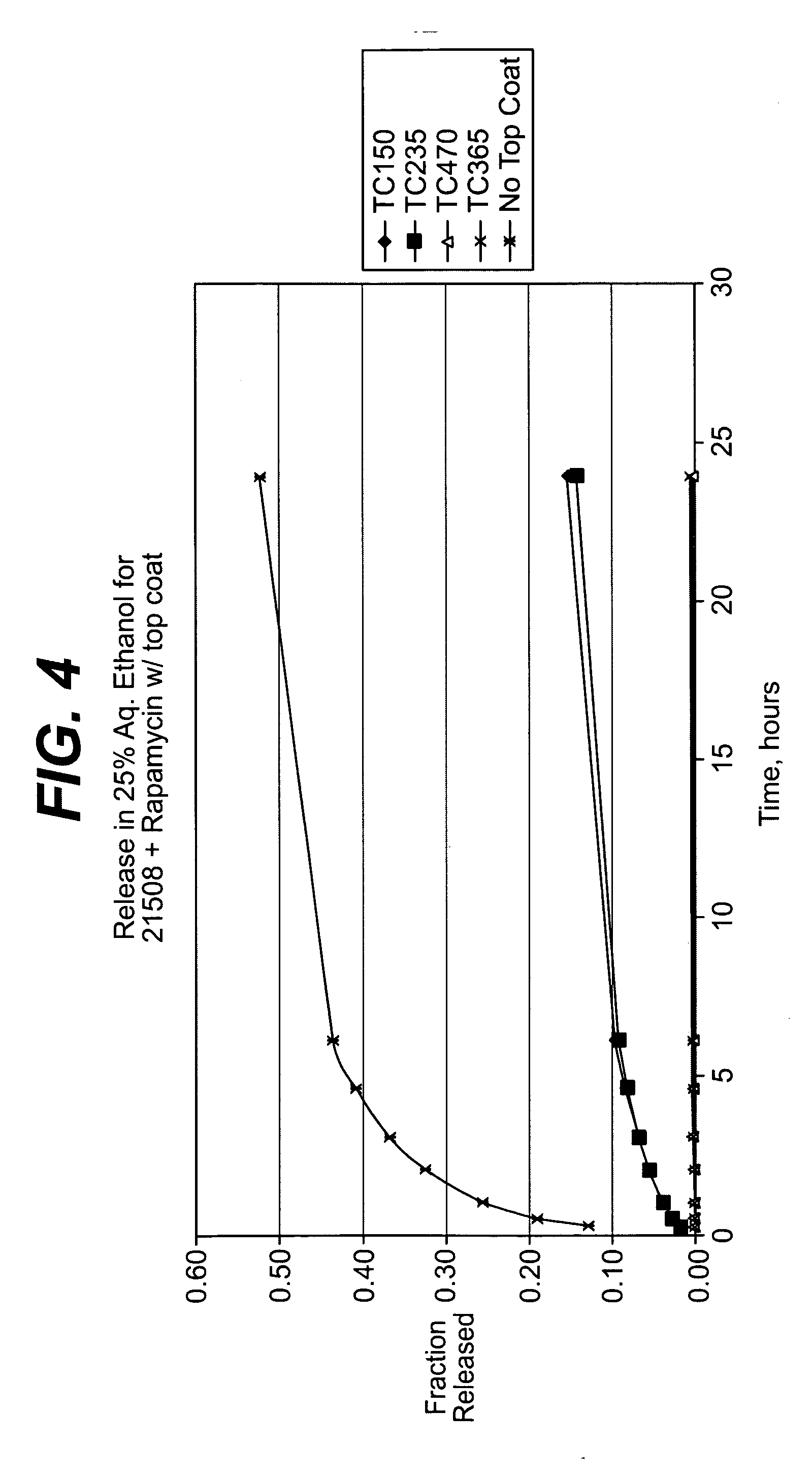
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. In addition, these therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to promote healing, including the formation of blood clots. Also, the devices may be modified to promote endothelialization. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned. In addition, the devices utilized to deliver the implantable medical devices may be modified to reduce the potential for damaging the implantable medical device during deployment. Medical devices include stents, grafts, anastomotic devices, perivascular wraps, sutures and staples. In addition, various polymer combinations may be utilized to control the elution rates of the therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds from the implantable medical devices.
Owner:WYETH
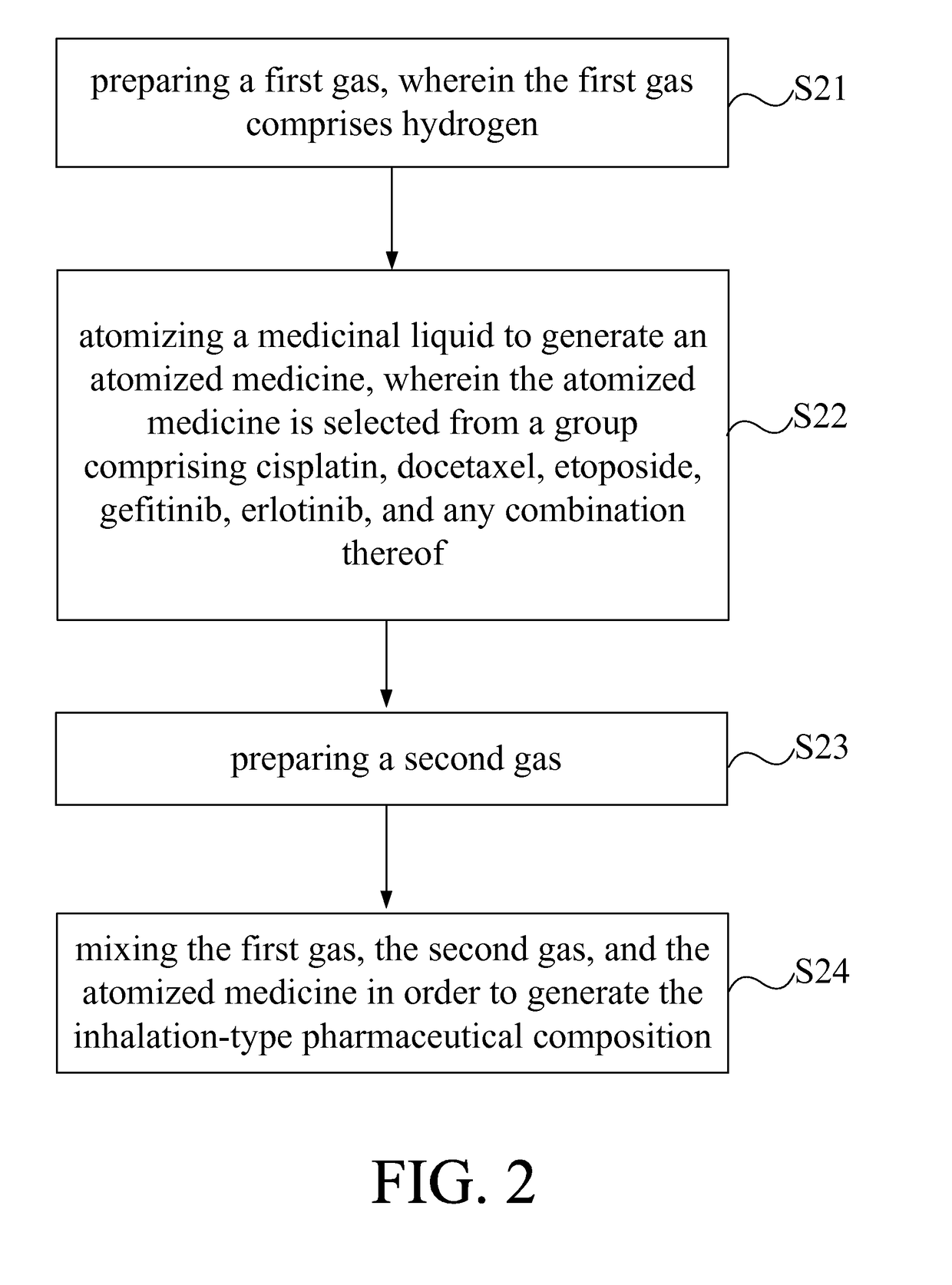
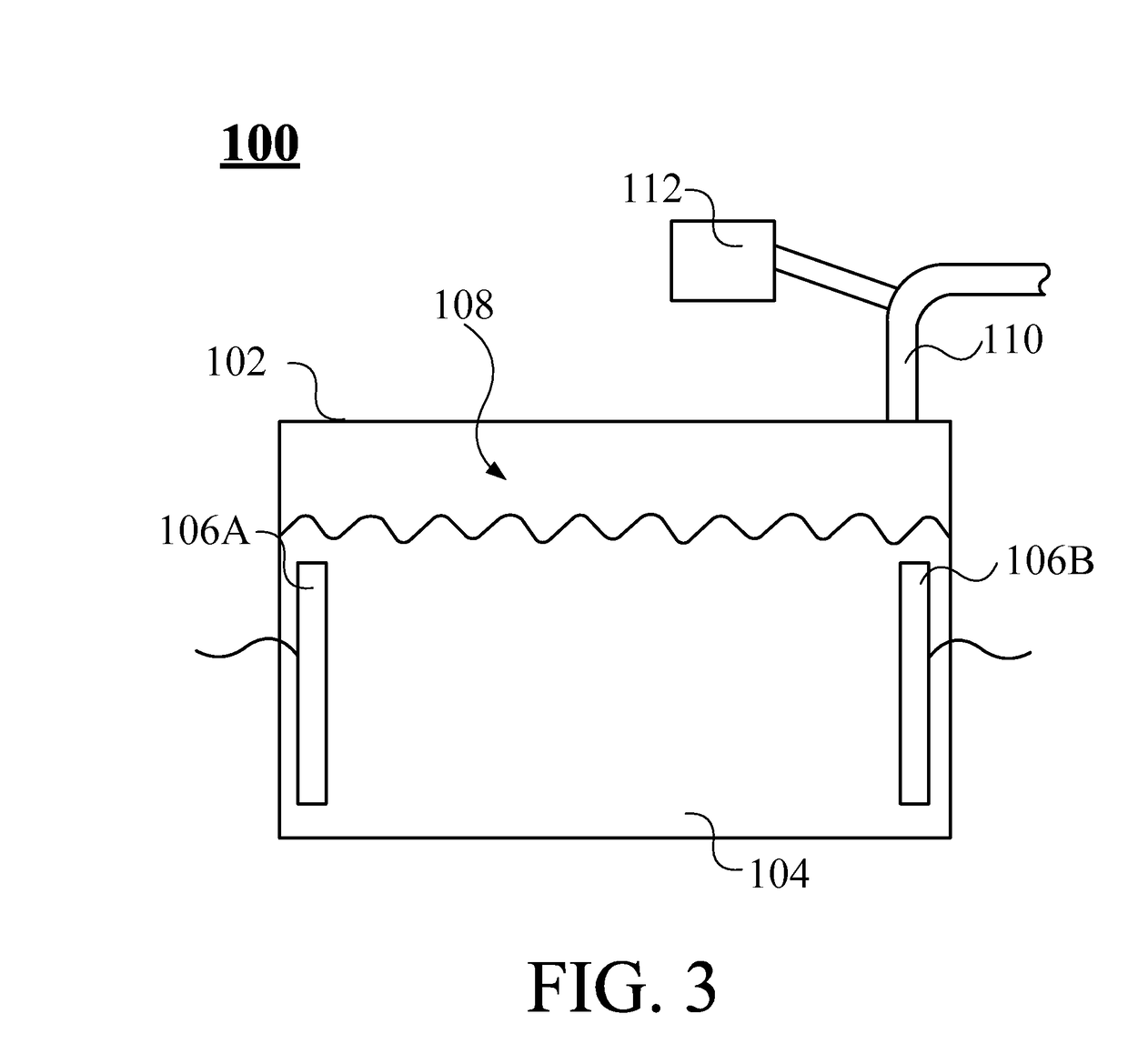
Inhalation-type pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of lung cancer and preparation method thereof
ActiveUS9763946B2Promote absorptionGood curative effectPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSide effectErlotinib
The present invention provides an inhalation-type pharmaceutical composition for lung cancer and preparation method thereof, comprising a first gas and an atomized medicine. The first gas comprises hydrogen. The gas volume concentration of hydrogen in the inhalation-type pharmaceutical composition is between 2 to 96%. The atomized medicine is selected from a group comprising cisplatin, docetaxel, etoposide, gefitinib, erlotinib, and any combination thereof. The inhalation-type pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can remove harmful radicals in the body of the patient through the use of hydrogen while also increases the absorption effect of the medicine for the patient by using an atomized medicine. At the same time, because the use of the small amount of the vaporized pharmaceutical liquid can indirectly reduce the side effects on the user.
Owner:LIN HSIN YUNG
Monoterpene compositions and uses thereof
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the mucosal and oral administration of monoterpenes and derivatives thereof. The compositions of this invention further comprise one or more surfactants and cosolvents and are in the form of self-emulsifying compositions. The compositions of the invention may further comprise water-insoluble therapeutic agents, vaccines and diagnostics. Such agents include but are not limited to taxanes, steroids, topoisomerase inhibitors such as etoposide and other water-insoluble or lipophilic drugs.
Owner:CONSTANTINIDES PANAYIOTISP +3
Predicting responsiveness to cancer therapeutics
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
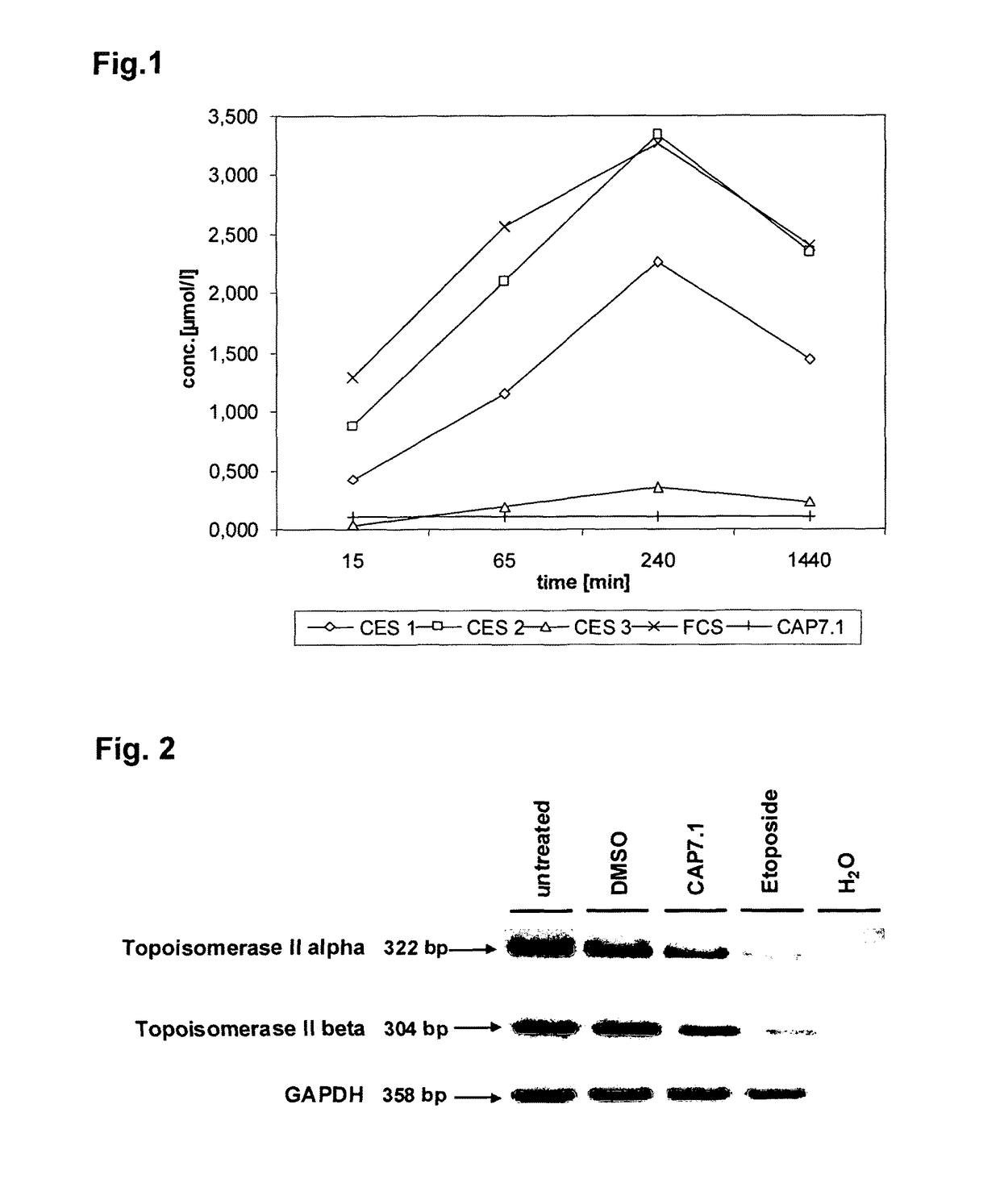
Etoposide preparations and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101259100AImprove solubilityReduce dosageOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhospholipid complexSelf emulsifying
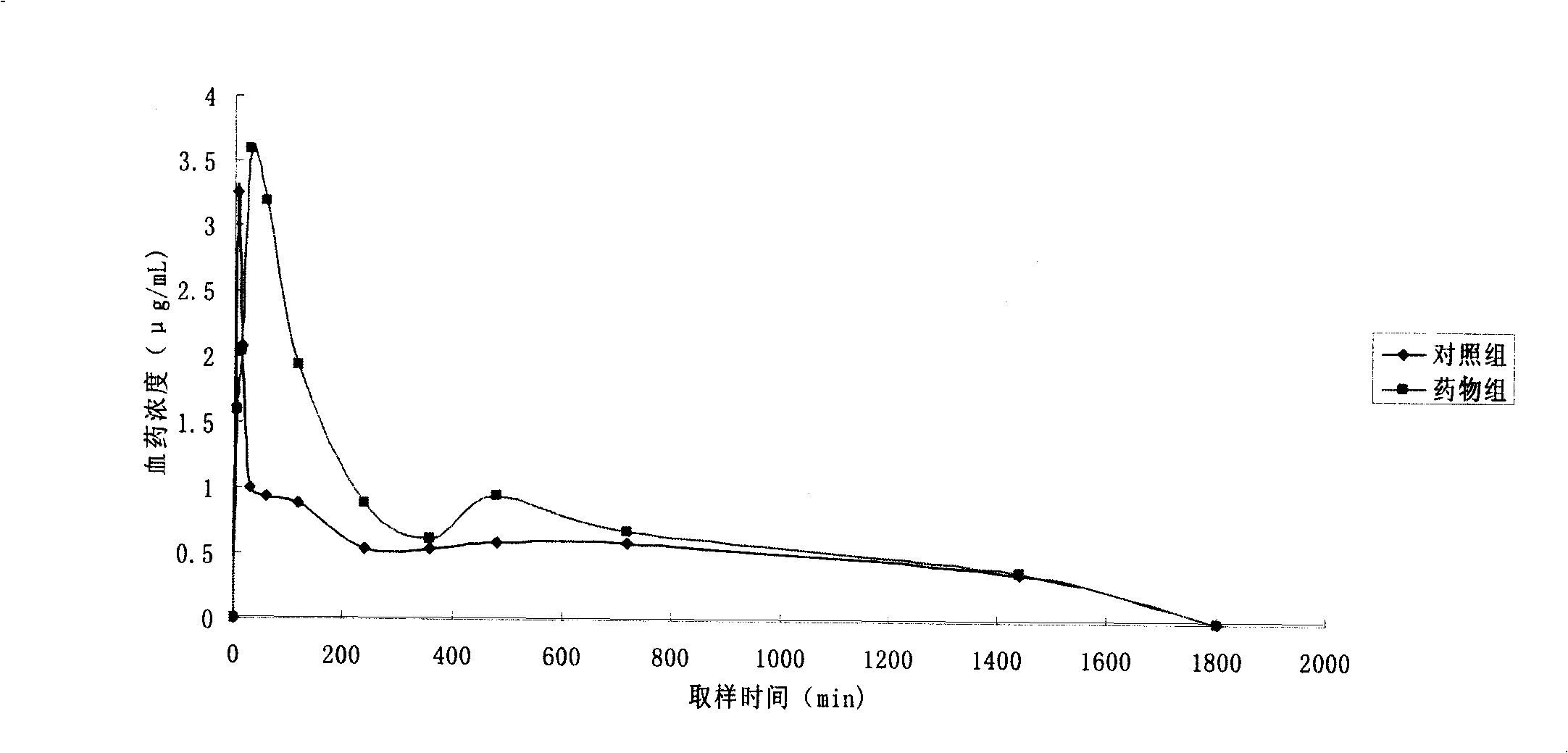
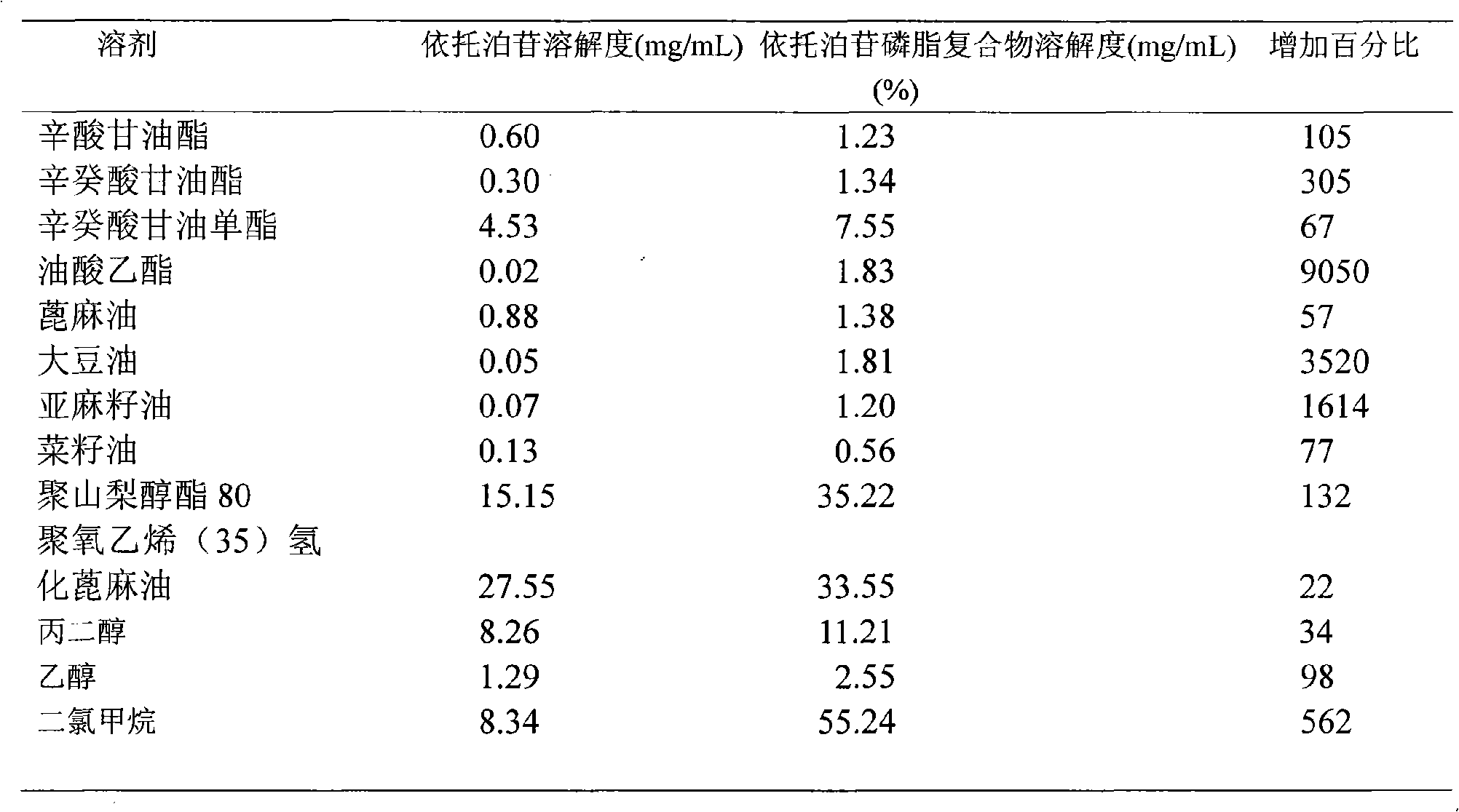
The invention relates to a medicine technical field. Etoposide has broad-spectrum anticancer activity and rather high therapeutic index, however, the etoposide hardly can be dissolved in water and the fat-soluble property is rather poor, the shortcoming of low bioavailability exists to different extent in oral preparations for present clinical use, tablet and soft capsule, for example. The invention aims at improving the hydrophilic property and the lipotropy of the etoposide, promoting the bioavailability of the etoposide and providing an etoposide preparation which has a simple preparation technique and is easily taken. Main medicine of the preparation of the invention is phospholipid compound of etoposide. The invention also provides a self-emulsifying agent and a preparation method thereof. The zooperies is a primary indication that the ACU of the self-emulsifying agent of the phospholipid compound of etoposide is 1.3 to 1.7 times of that of the soft capsules on sale.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Epidithiodioxopiprazines and uses thereof in treating cancer
InactiveUS20120219568A1Good effectGood curative effectHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic chemistryNatural resourceCancer cell
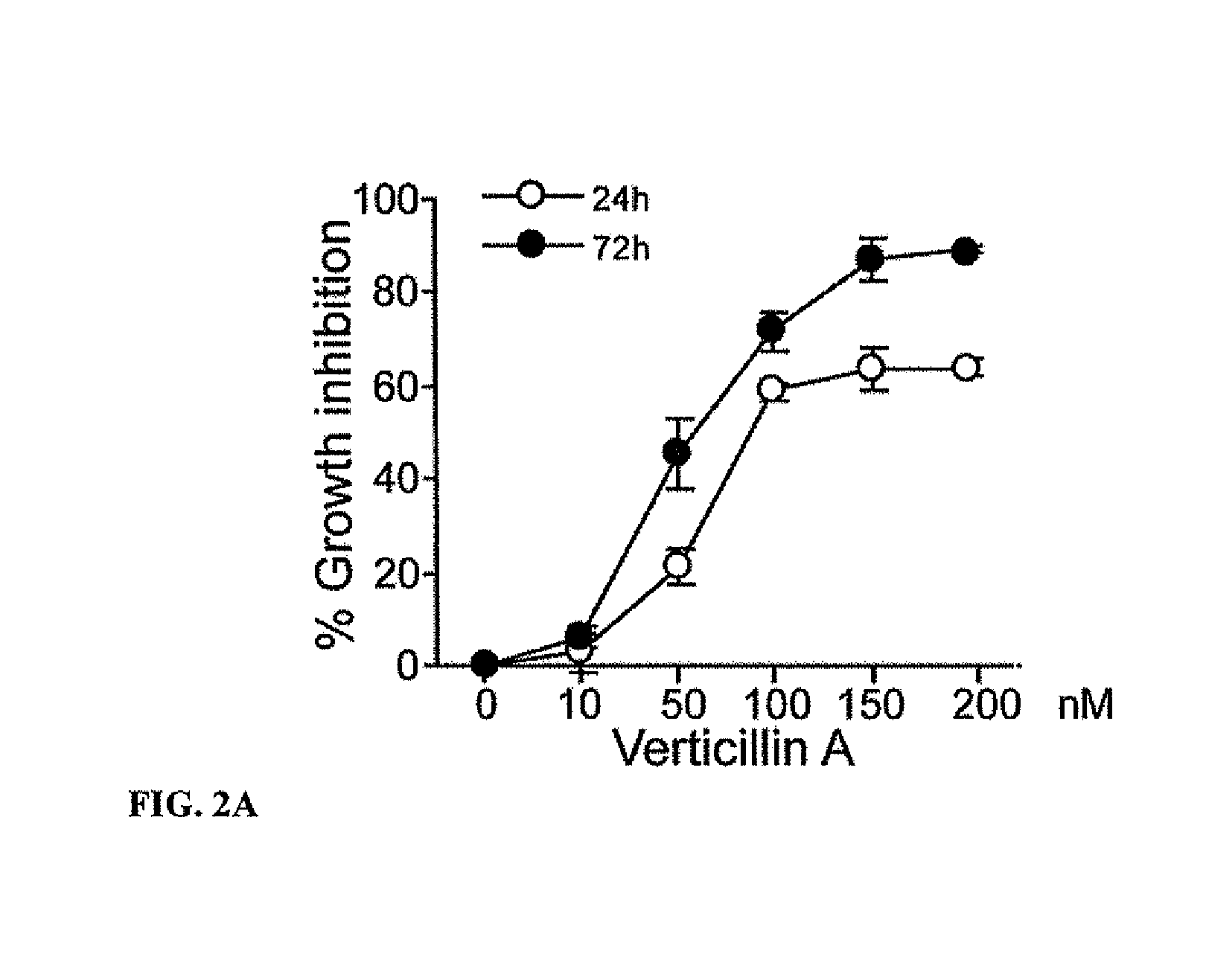
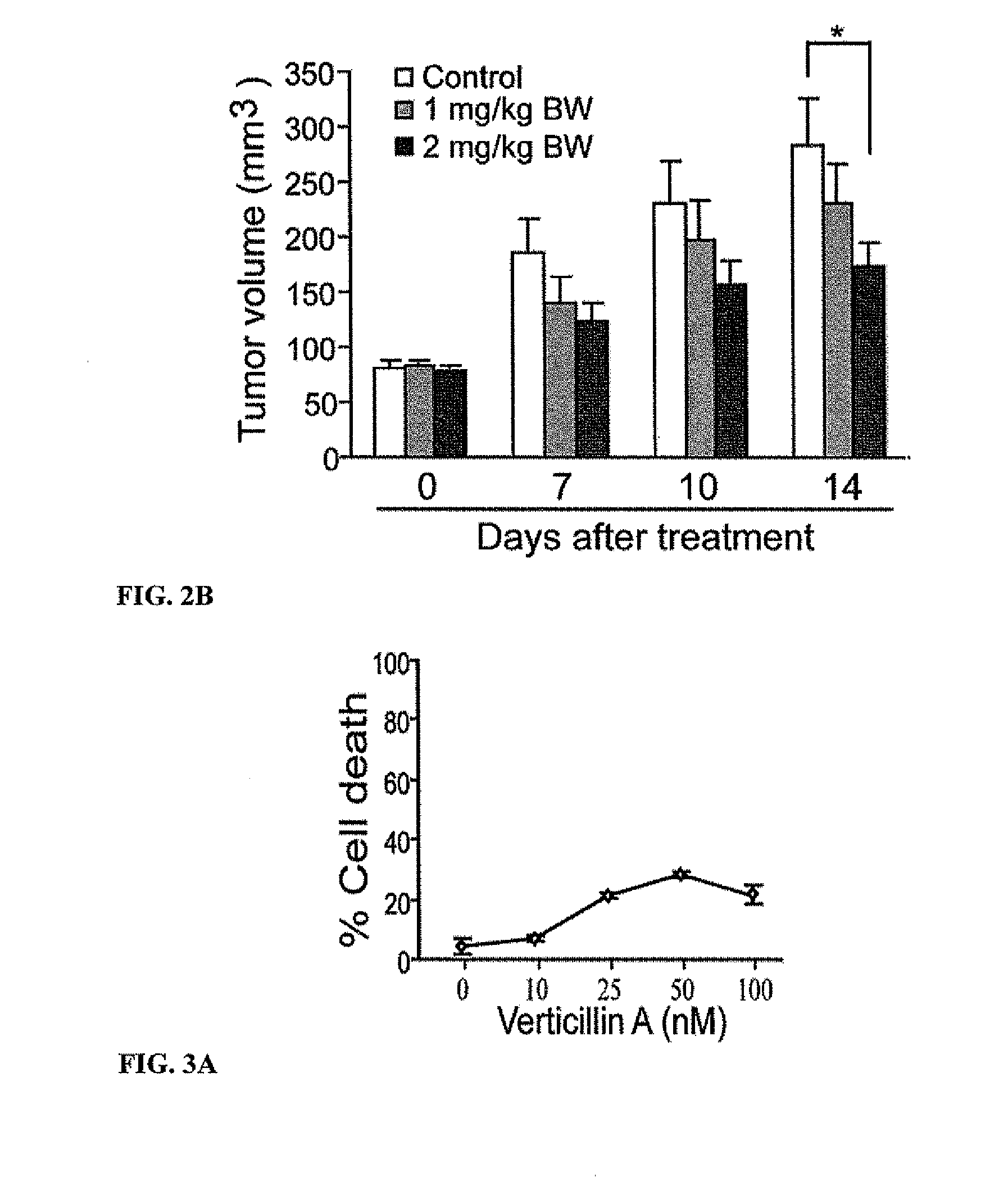
Compositions containing epidithiodioxopiprazines and methods of their use are provided. Epidithiodioxopiprazines can be isolated from natural resources or synthesized de novo. Moreover, epidithiodioxopiprazines, including Verticillin A, are shown to effectively sensitize multiple types of tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In addition, epidithiodioxopiprazines, including Verticillin A, are shown to effectively overcome cancer cell resistance to existing drugs (i.e. Etoposide, Cisplatin, 5-FU and Doxorubicin). Therefore, compositions and methods are provided for use in sensitizing target cancer cells to death receptor- and other anticancer drugs-induced apoptosis. Methods of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof are also provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
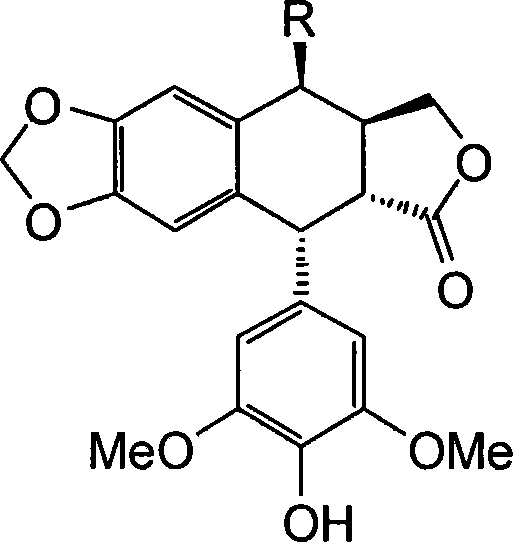
4'-demethylpodoph-yllotoxin derivative, its production and use
InactiveCN101074233AOvercoming Drug Resistance DeficienciesHigh yieldOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsIsomerizationSodium iodide
A 4'-demethylepipodophyllotoxin derivative IIIa-n is prepared by taking etoposide as raw material, reacting with sodium iodide to generate 4-bit iodine substitute and obtain intermediate II, agitating while adding into barium carbonate, regulating reactive system pH 7-8, adding into amino-compound, and reacting to room temperature for 8-10 hrs to obtain final product. It's simple and efficient, it can avoid 4-bit surface isomerization and 4-bit demethylation, it has strong inhibiting function of multiple tumor cell strain and non-toxic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
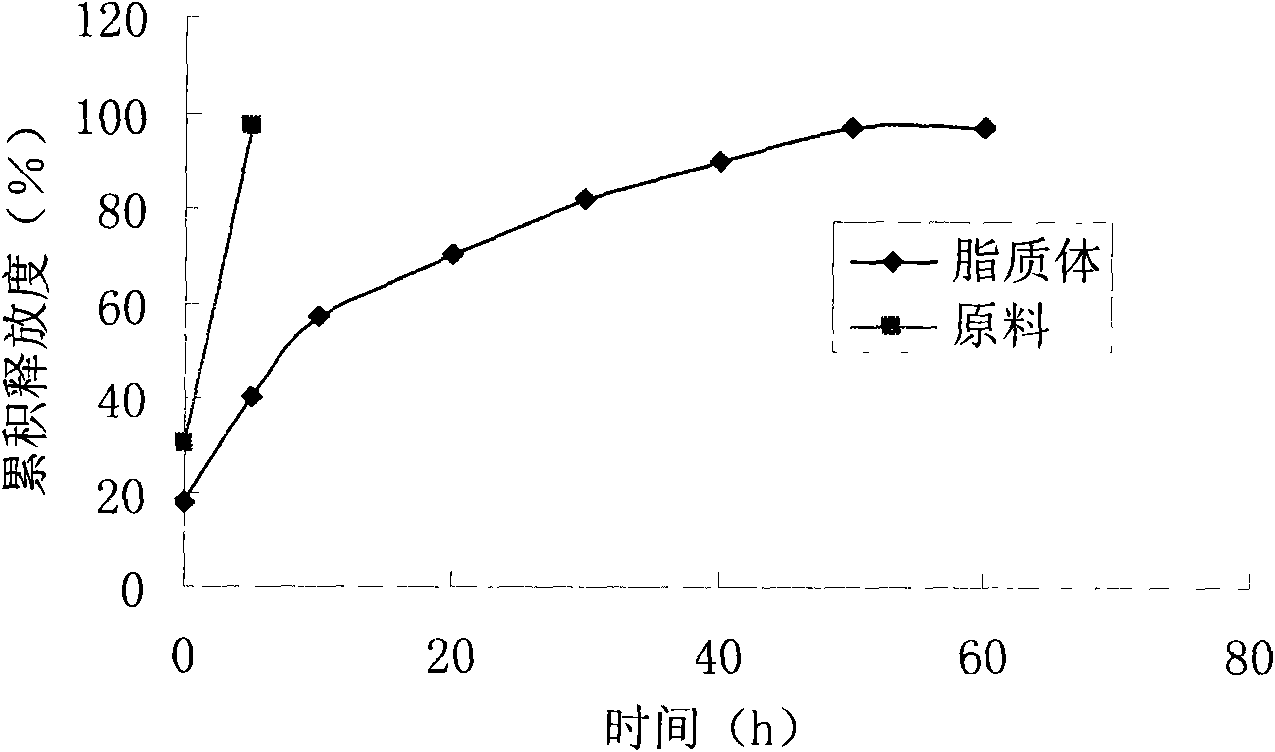
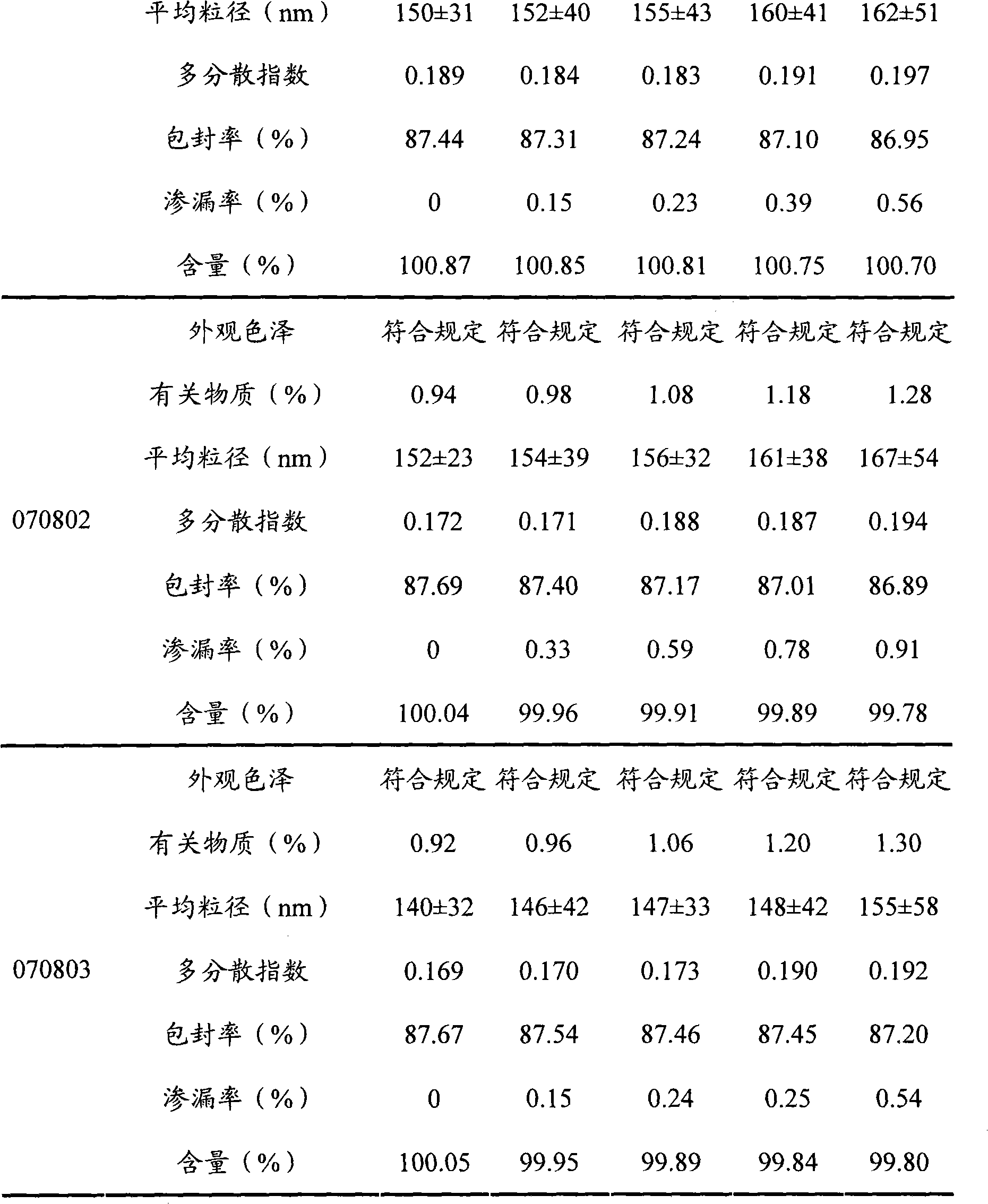
Etoposide lipidosome and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101584662ATargetedGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSolubilitySide effect
The invention provides an etoposide lipidosome used for injection or oral administration. The etoposide lipidosome is characterized in that etoposide is enveloped with phospholipid type substance, and the etoposide lipidosome with small grain size, high entrapment efficiency, good stability and low toxic side effect is prepared. The prepared etoposide lipidosome enhances the solubility and the stability of the etoposide, reduces the toxicity of the etoposide and prolongs the cycling time of the medicine in the blood, thereby improving the therapeutic effect of the medicine; and the preparation prepared by the etoposide lipidosome has the characteristics of low toxicity, low sensitivity and high efficiency on the clinical application. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the etoposide lipidosome, which has simple preparation process and low cost and is suitable for the industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
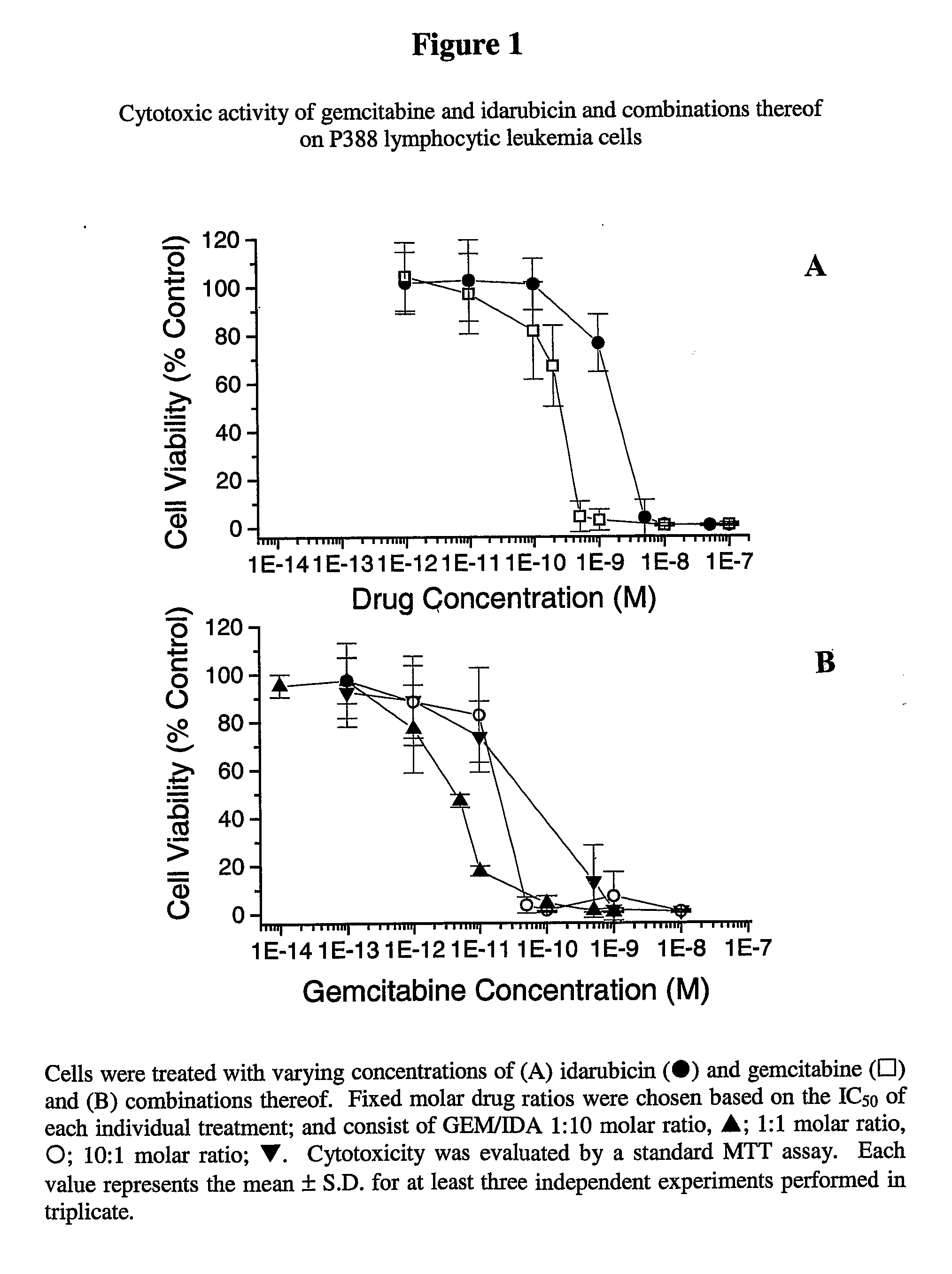
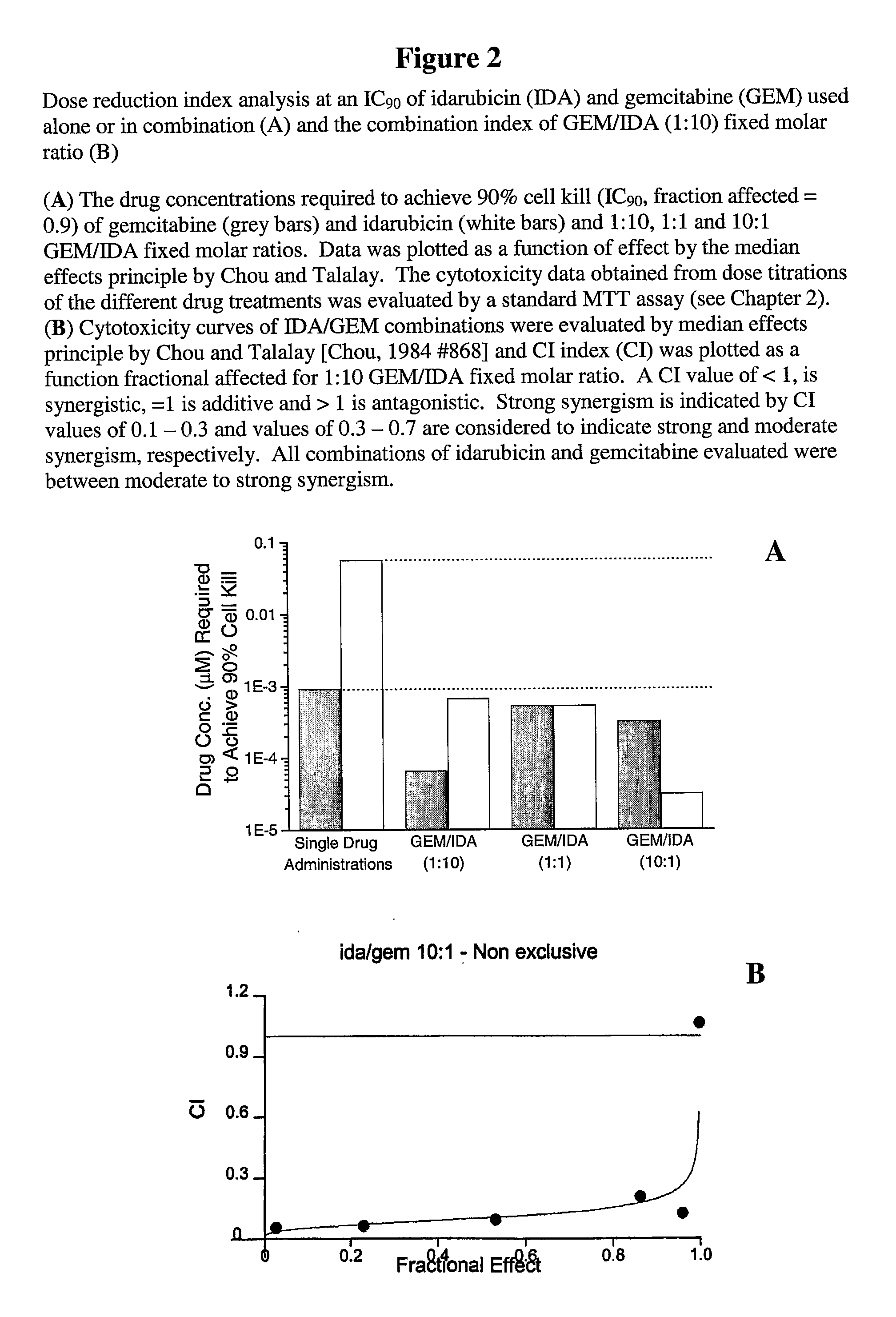
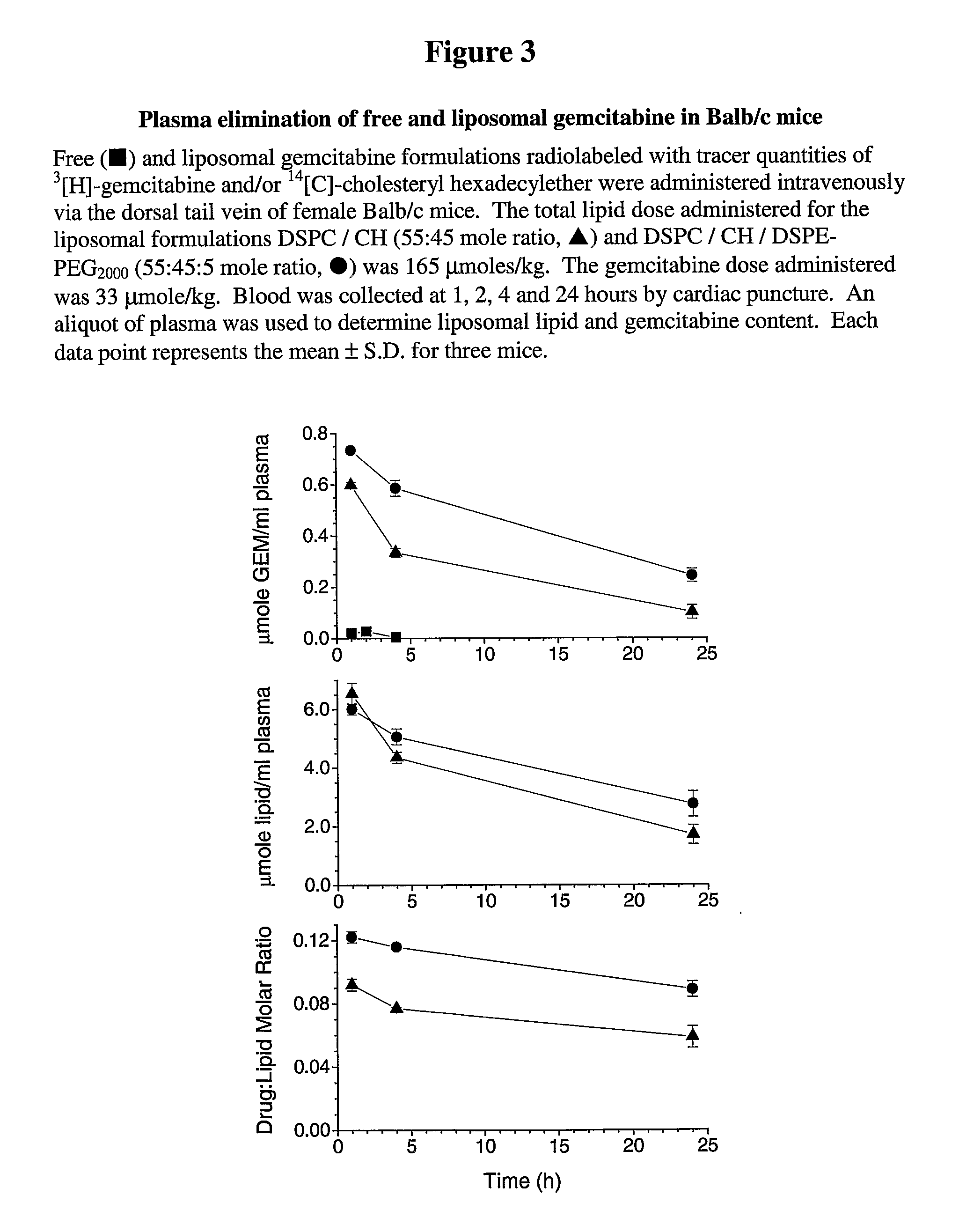
Free or Liposomal Gemcitabine Alone or in Combination with Free or Liposomal Idarubicin
InactiveUS20080213183A1Organic active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsCisplatinMaximum tolerated dose
The use of the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of individual drugs to determine appropriate administration ratios of drugs for combination therapy, wherein the ratios of drugs are fixed based on the same percentage of the MTD for each drug. Furthermore, antineoplastic compositions comprising liposomal encapsulated gemcitabine alone or in combination with free or liposomal encapsulated antineoplastic agents, such as idarubicin, irinotecan, etopside, cisplatin, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, or vincristine are diclosed.
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY
Antineoplastic activities of ellipticine and its derivatives
InactiveUS20070027175A1Remarkable effectImmediate inhibitionBiocideAnimal repellantsCytotoxicityBiology
The present invention describes selective cell growth inhibition of myeloma cells by ellipticine derivatives, 9-methoxy ellipticine and 9-dimethyl amino-ethoxy ellipticine. The cell growth inhibition efficacy was highest for 9-dimethyl amino-ethoxy ellipticine among the ellipcitine derivatives tested. The cell toxicity of 9-dimethyl amino-ethoxy ellipticine was selective for myeloma cells and did not kill normal cells in the effective antineoplastic dose range. 9-dimethyl amino-ethoxy ellipticine was superior to existing antimyeloma drugs, Adriamycin® and Etoposide in eliciting early and better cell growth inhibition response.
Owner:SHAUGHNESSY JOHN JR +1
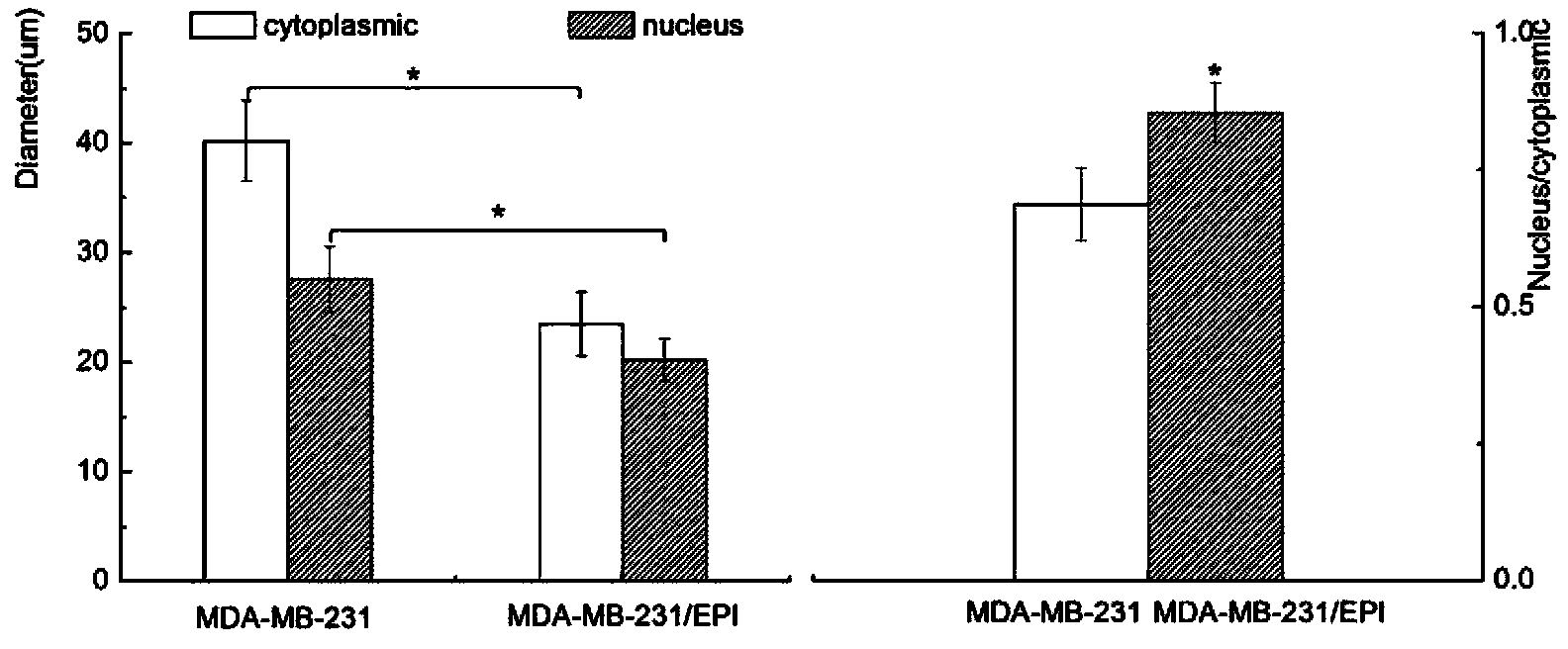
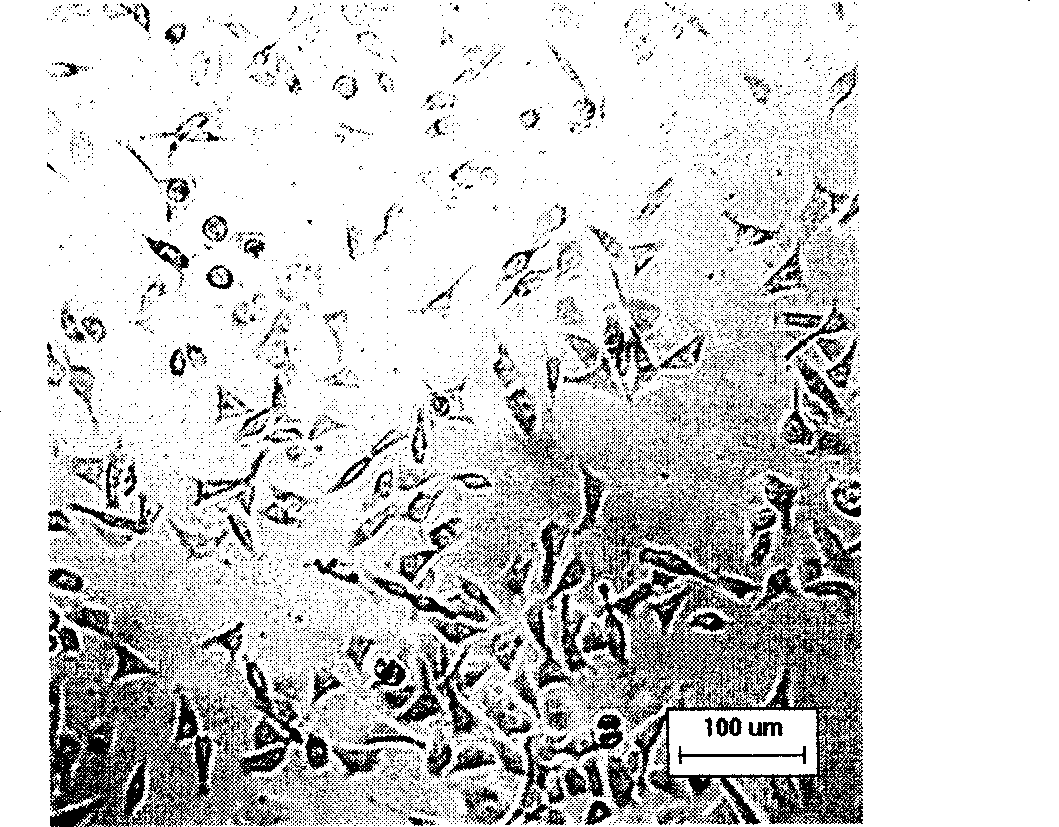
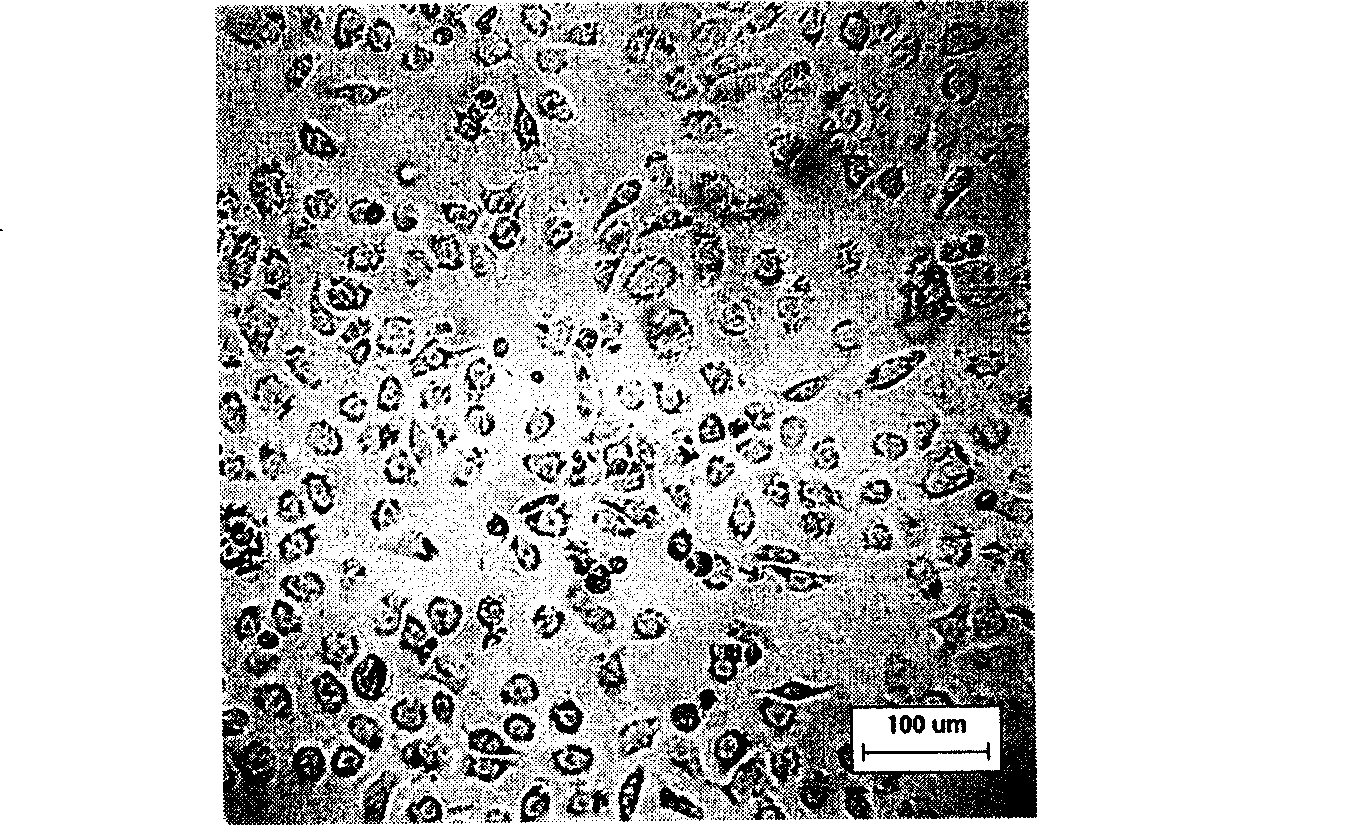
Breast cancer multidrug-resistant cell strain constructed by virtue of epirubicin induction as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN104140953AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTumor therapyCross-resistance
The invention provides a breast cancer multidrug-resistant cell strain constructed by virtue of epirubicin induction, wherein the breast cancer multidrug-resistant cell strain has a collection number of CCTCC C201439. The invention further provides a method for constructing the breast cancer multidrug-resistant cell strain. According to the invention, an MDA-MB-231 / EPI drug-resistant strain is successfully established, wherein a drug-resistant index is 26.27 times, and obvious cross resistance is produced for taxol, etoposide and cis-platinum. A drug-resistant tumor cell model is provided for the following related researches so as to research drug-resistant tumor cell morphology and biological characteristics, research a tumor multidrug resistance mechanism, analyze sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs as well as screen chemotherapeutic drugs, develop tumor drug resistant reverse drugs and research and develop a more effective tumor therapeutic method, and the like.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
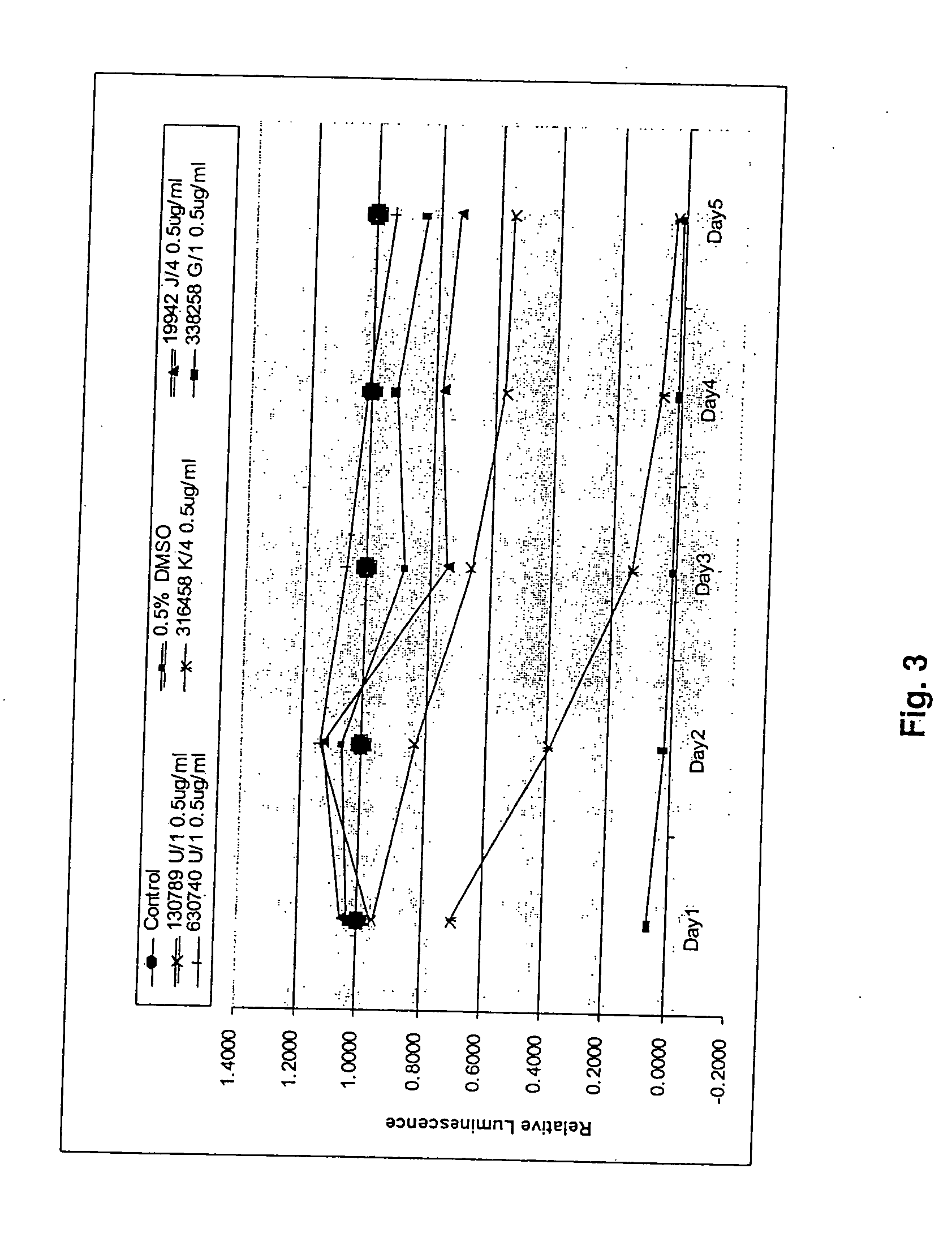
Oophoroma multidrug resistance cell strain established by etoposide induction
The invention relates to a multidrug resistant cell strain for oophoroma, which is characterized in that a human oophoroma SKOV3 cell strain is selected as a parental cell; the action concentration of chemotherapeutics of etoposide (VP16) is gradually increased from 0.1 mu g / ml to 3 mu g / ml; and drug resistant SKOV3 / VP16 cell strain is established. The SKOV3 / VP16 cell can stably grow, transfer and reanimate in 3 mu g / ml VP16, makes the VP16 generate drug resistant index (RI) of 21.548, and performs intersect drug on MTX, DOX, DDP, VCR, 5-Fu and MMC except the VP16. The invention aims to provide a drug resistant tumor cell model for relative study on the tumor.
Owner:THE WEST CHINA SECOND UNIV HOSPITAL OF SICHUAN
Etoposide lyophilized powder for injection
The invention relates to an etoposide lyophilized powder for injection. The powder can overcome the defects of etoposide, improve the bioavailability of etoposide, is convenient to use, can be absorbed fast, and can come into play rapidly. By screening the prescription of the etoposide lyophilized powder for injection, the invention finds that the combined use of a specific excipient with an antioxidant and a chelating agent at the same time can generate a finished product of etoposide lyophilized powder for injection with the advantages of high stability, fewer impurities, little side effect, high safety, convenient storage and use, low production cost, and the like.
Owner:CP PHARMA QINGDAO CO LTD
Preparation method of etoposide
InactiveCN102180920AIncrease contentHigh yieldSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationGlycosideRoom temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method of etoposide, which includes the following steps: preparation of beta-glucoside, coupling reaction and preparation of etoposide. In the step of the preparation of the beta-glucoside, methoxybenzylidene is protected to increase the content of the beta-glucoside; in the step of the coupling reaction, TiCl4 is used as a Lewis acid catalyst to enable the reaction to have better selectivity, so as to improve the conversion rate of a target product, reduce the generation of impurities accordingly, reduce the difficulty of purification for the etoposide, improve the yield and reduce the cost; and in the step of the preparation of the etoposide, diluted hydrochloric acid is used for being stirred at room temperature to obtain a target compound with higher purity, and the purity of obtained etoposide coarse product can reach about 90%, so as to avoid column purification, and also reduce the number of times of recrystallization. The preparation method is simple in operation, also very easy in post-treatment, and high in yield.
Owner:SHANGHAI HENGHE MEDICAL TECH
Water-soluble etoposide analogs and methods of use thereof
Etoposide analogs with improved water-solubility such as 4′-O-Demethyl-4′-(N′,N′-dimethyl-glycyl)-4β-(4″-nitroanilino)-4-desoxy-podophyllotoxin (8) and 4′-O-Demethyl-4′-(N′,N′-dimethyl-glycyl)-4β-(4″-fluoroanilino)-4-desoxy-podophyllotoxin (9) are described, along with pharmaceutical formulations containing the same, methods of use thereof, and intermediates and methods of making the same.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
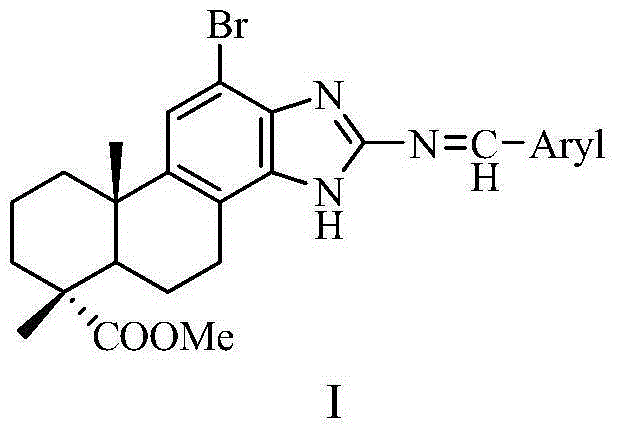
Dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole Schiff base heterocyclic derivatives with anti-tumor activity and preparation method therefor and application thereof
ActiveCN105218621AEnhanced inhibitory effectNovel structureSteroids preparationAntineoplastic agentsPositive controlInhibitory effect
The invention discloses dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole Schiff base heterocyclic derivatives with anti-tumor activity and a preparation method therefor and an application thereof. The invention discloses a dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole Schiff base heterocyclic derivative which has a structure shown in a formula I and pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof (the formula is shown in the description), wherein the formula is shown in the description. The dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole Schiff base heterocyclic derivative and the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof have remarkable anti-tumor activity. Pharmacological experiments show that the dehydroabietic acid benzimidazole Schiff base heterocyclic derivatives have remarkable inhibitory effect on human liver cancer cells HepG2 and SMMC-7721 and the effect of the derivatives is equivalent to positive control etoposide. The derivatives and salt thereof have the potential of developing anti-tumor drugs.
Owner:EFFEPHARM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Injection containing lipoid microsphere of etoposide and its prepn process
InactiveCN1973826ALess irritating to blood vesselsGood chemical stabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMicrosphereIrritation
The present invention belongs to the field of medicine technology, and is especially lipoid microsphere injection containing etoposide and its preparation process. The injection contains etoposide, fat soluble medium, water and surfactant; and consists of oil phase 5-30 wt%, etoposide 0.001-0.5 wt%, surfactant 0.5-5 wt%, osmotic regulator 0.5-5 wt%, and water for injection the rest. Etoposide is high pressure homogenized under the action of high speed airflow to form ultrasonic stirring, so as to be dissolved fast and permeated in molecular form into oil / water interface film. By means of medicine carrying interface film principle, the present invention raises the medicine carrying amount of insoluble etoposide and the stability while lowering the toxicity and blood vessel irritation. The preparation of the present invention has low toxicity, low irritation and high curative effect in clinical application.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
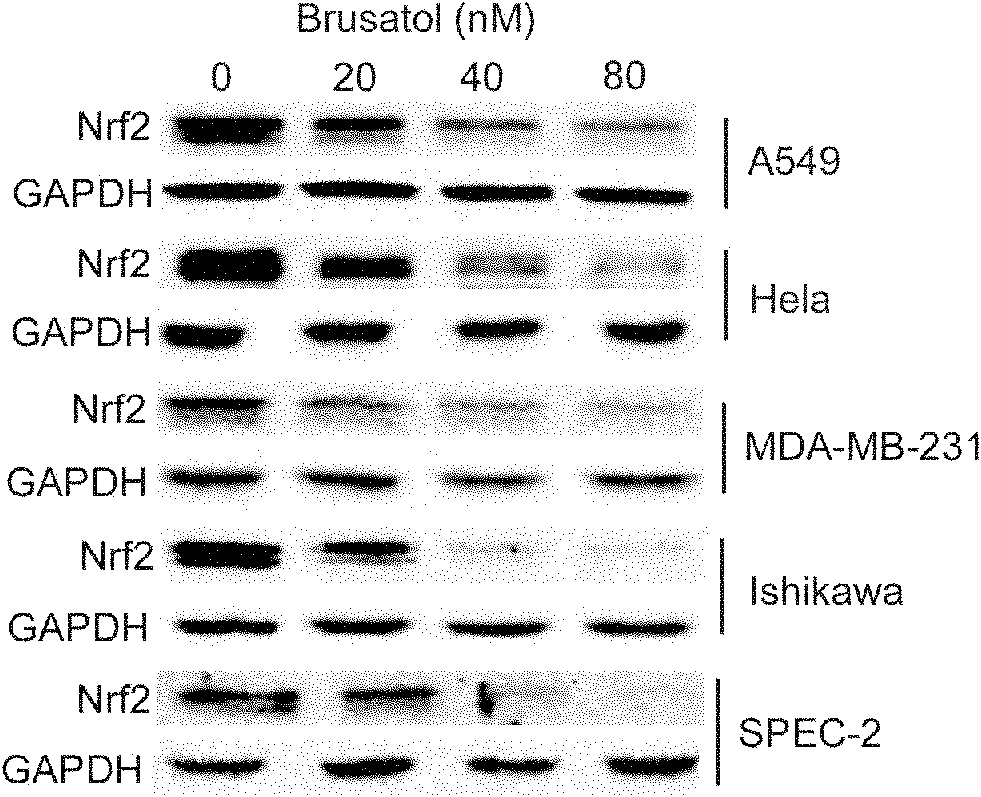
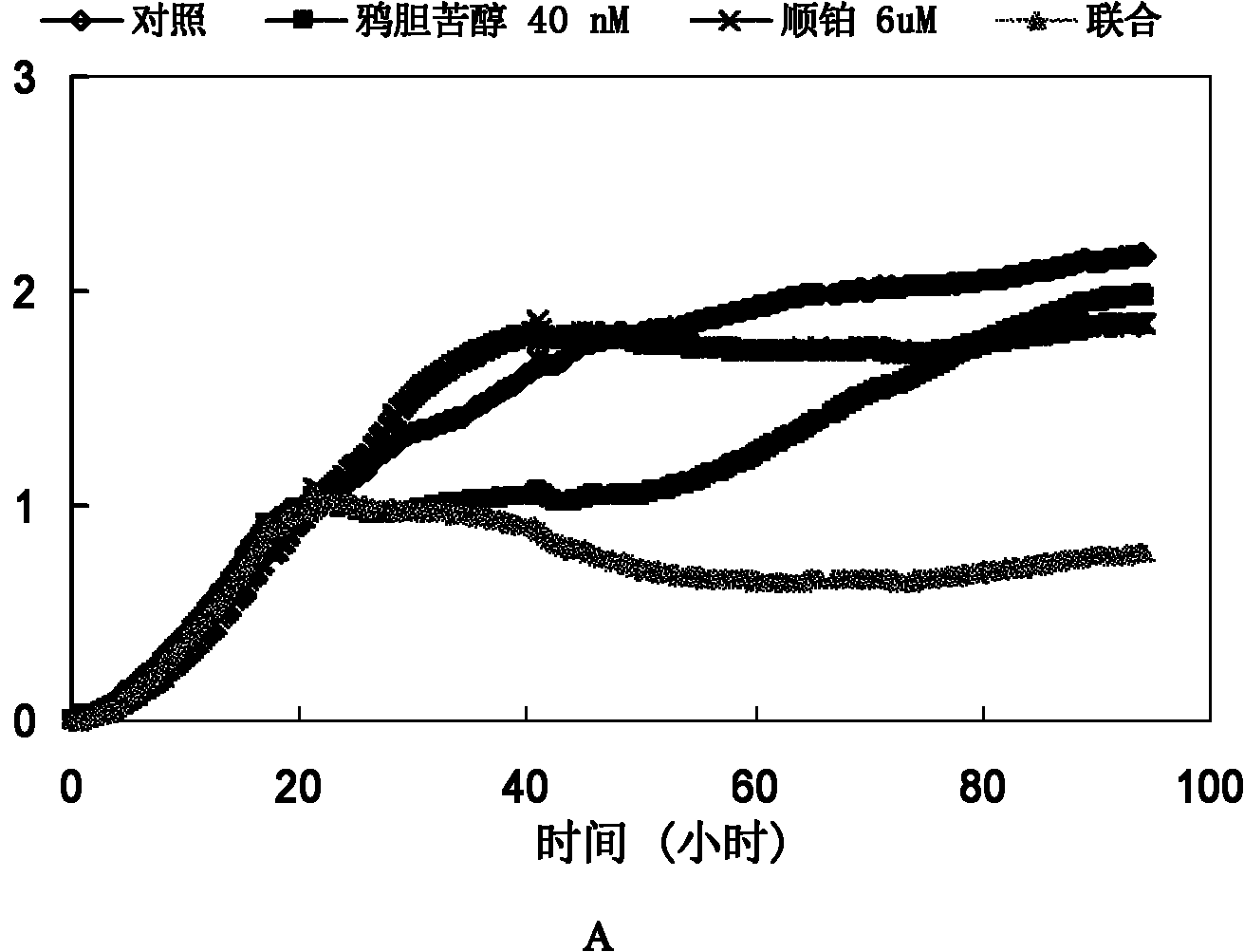
Application of brusatol as chemotherapeutic drug synergist
InactiveCN102106851AIncreased growth inhibitionIncrease lethalityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCarboplatinCancer cell
The invention discloses a new application of brusatol serving as a chemotherapeutic drug synergist, which is combined with a chemotherapeutic drug when in use. The chemotherapeutic drug comprises cis-platinum, carboplatin, oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel, adriamycin or adriamycin. The brusatol provided by the invention can be prepared into an oral preparation or a non-oral preparation accepted pharmaceutically. The beneficial effects of the brusatol applied in preparing the chemotherapeutic drug synergist are as follows: (1) the brusatol can be used in an Nrf2 path, and the killing effect of various chemotherapeutic drugs on the cancer cells can be enhanced; (2) the growth inhibition of low-dose cis-platinum on transplantable tumor of a naked mouse can be increased by the brusatol, thus having clinical application prospects; (3) the cis-platinum content in non-small cell lung cancer cell strains can be increased by the combined use of the brusatol and the cis-platinum; and (4)the toxicity is not discovered when the brusatol and the cis-platinum are together used in the cellular level and in the mouse test work concentration.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
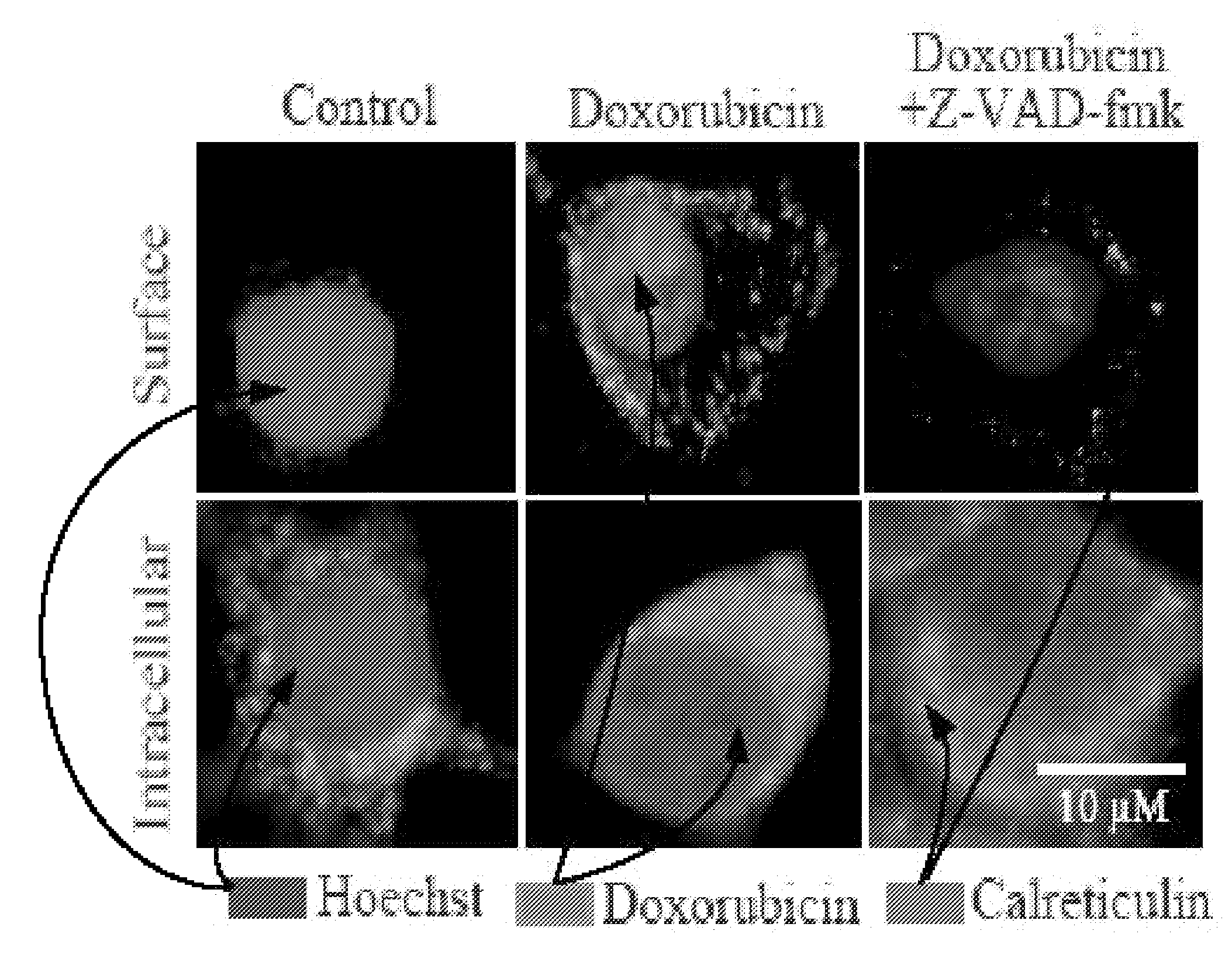
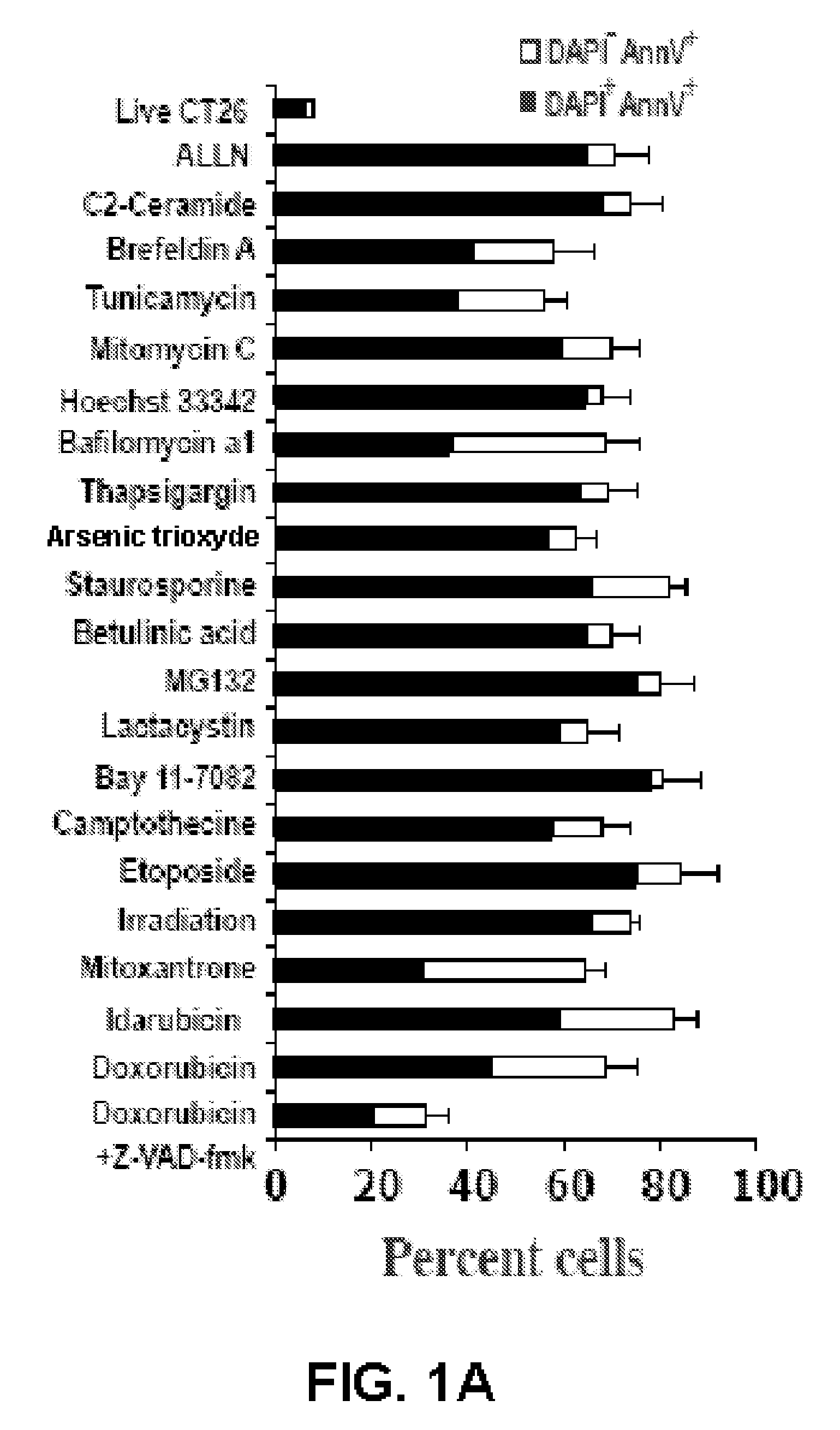
Method for effecting localized, non-systemic and systemic, immunogenic treatment of cancer using CRT translocation
InactiveUS20080214452A1Improve efficiencyImprove responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDendritic cellMitomycin C
Anthracyclines-treated tumor cells are particularly effective in eliciting an anti-cancer immune response, where the rDNA-damaging agents, such as etoposide and mitomycin C do not induce immunogenic cell death. Anthracyclines induce the rapid, pre-apoptotic translocation of calreticulin (CRT) to the cell surface. Blockade or knock down of CRT suppressed the phagocytosis of anthracyclines-treated tumor cells by dendritic cells and abolished their immunogenicity in mammals, such as mice. The anthracyclines-induced CRT translocation was mimicked by inhibition of the protein phosphatase1 / GADD34 complex. Administration of recombinant CRT or inhibitors of protein phosphatase1 / GADD34 restored the immunogenicity of cell death elicited by etoposide and mitomycin C, and enhanced their antitumor effects in vivo. These data identify CRT as a key feature determining anti-cancer immune responses and delineate a possible strategy for immunogenic chemotherapy.
Owner:OBEID MICHEL SARKIS
Etoposide cubic liquid crystal as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107233312AImprove bioavailabilityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsSuppositories deliveryCrystallographySide effect
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicines and in particular relates to an etoposide cubic liquid crystal as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly selecting a lipid material / water system and a stabilizer for preparing the etoposide cubic liquid crystal, wherein the average particle size of the prepared etoposide cubic liquid crystal is 208nm, and the encapsulation efficiency is 60-65%; and secondly preparing the etoposide cubic liquid crystal into a hollow suppository by adopting a special pharmaceutical adjuvant combination, so that drug bioavailability and drug stability are improved, toxic and side effects are reduced, and targeted drug delivery is realized; and a preparation process is simple, instruments are available, and the preparation time is short.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Glycosyl-etoposide prodrugs, a process for preparation thereof and the use thereof in combination with functionalized tumor-specific enzyme conjugates
InactiveUS7241595B2Inhibit tumor growthHigh yieldSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTumor specificEnzyme
The present invention relates to glycosyl-etoposide prodrugs, a process for the preparation thereof and the use thereof in combination with functionalized tumor-specific enzyme conjugates for treating cancers.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA DEUTLAND
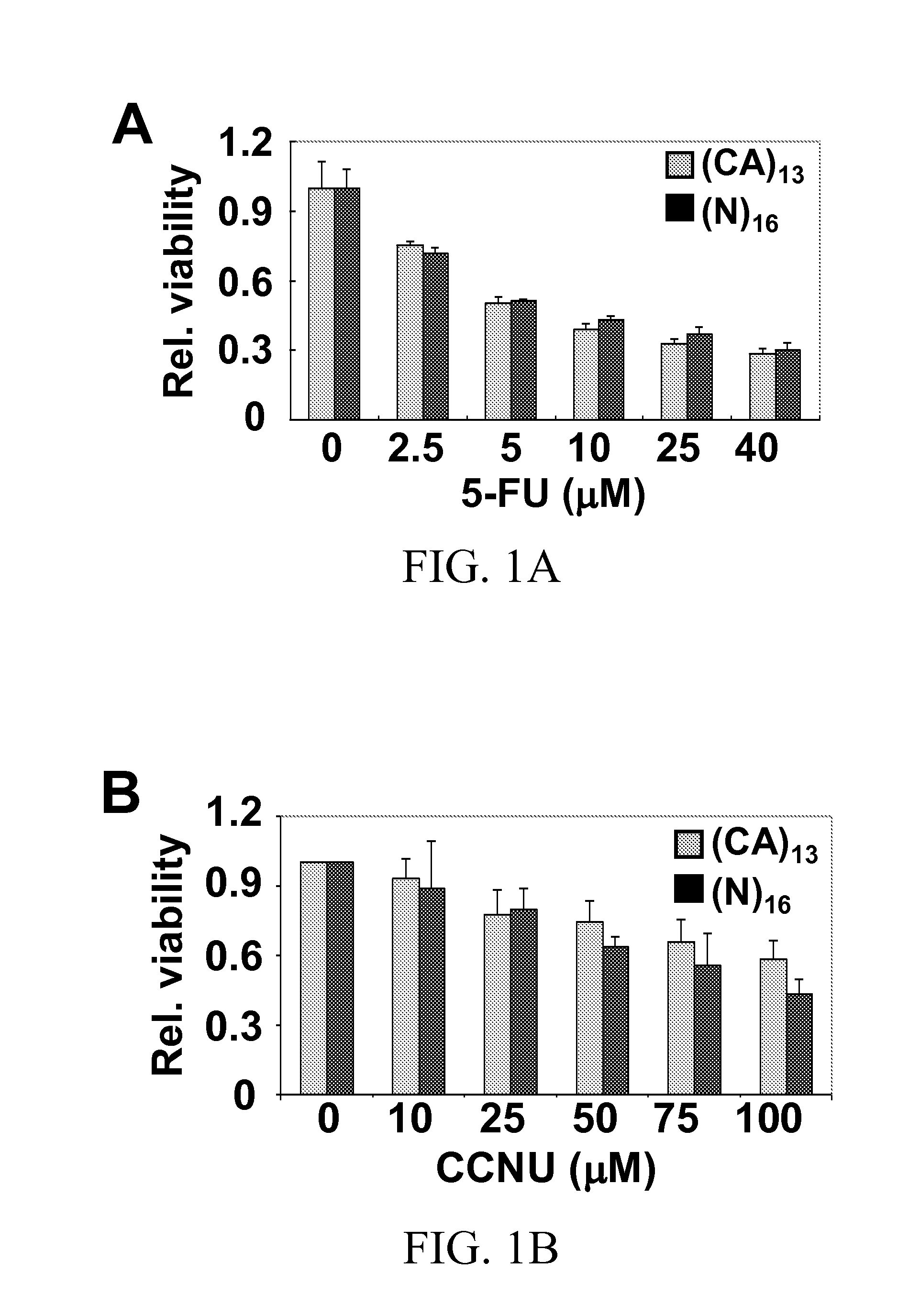
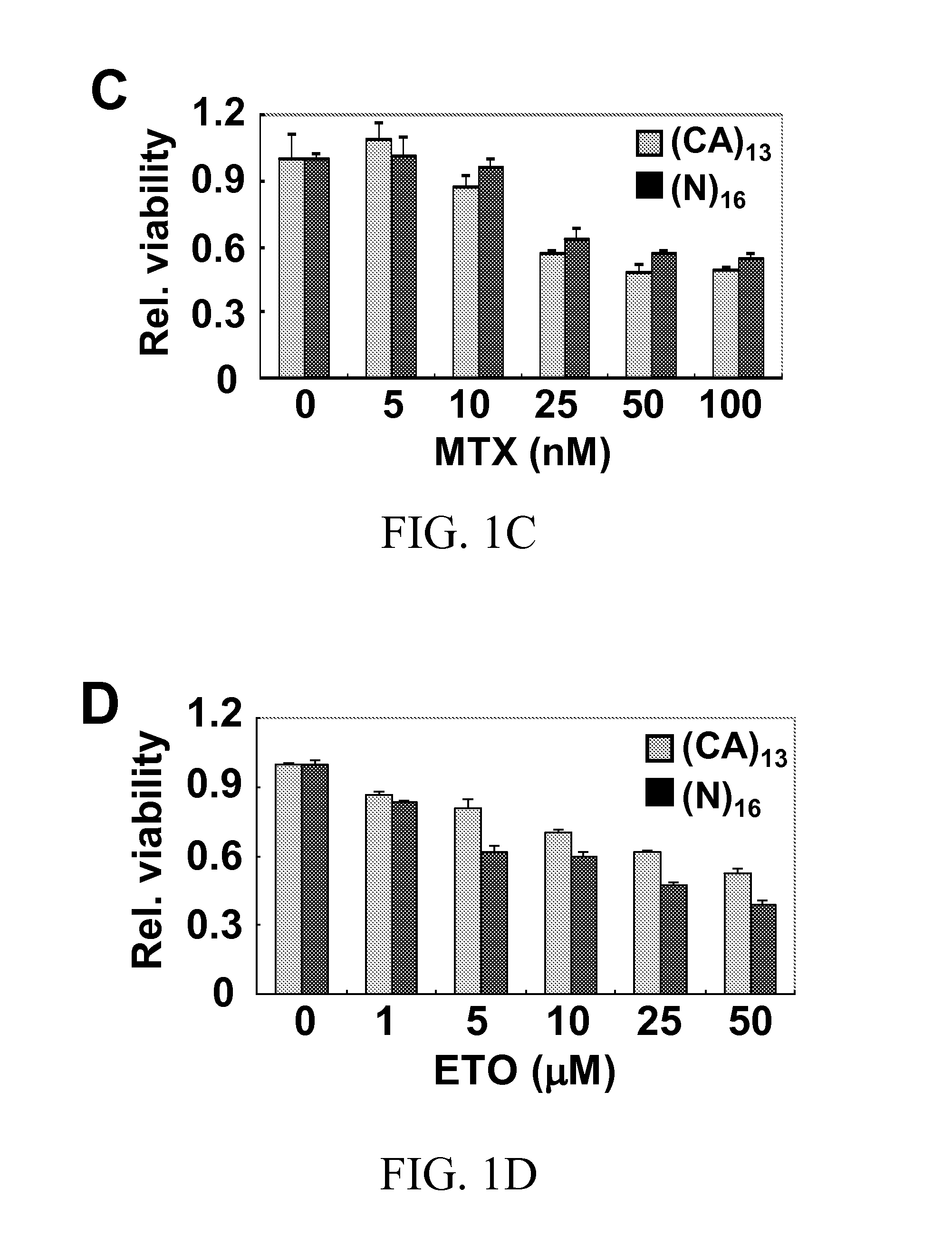
Methods for reducing microsatellite instability induced by chemotherapy and methods for screening antioxidants that suppress drug-induced microsatellite instability while enhancing the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents
InactiveUS20160022605A1Reducing microsatellite instabilityStrong cytotoxicityBiocideCompound screeningAntioxidantCiclopirox
A therapeutic approach to prevent drug resistance and chemotherapy-related secondary cancer associated with DNA mismatch repair (MMR) deficiency is disclosed based on screening antioxidants for reducing microsatellite instability (MSI) while enhancing the cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic agents. The work is based on experiments using antioxidants to target reactive oxygen species generated by oxaliplatin, a commonly used chemotherapeutic agent, and is applicable to other chemotherapeutic agent, and in particular 5-fluorouracil, methotrexate, CCNU, etoposide and vinblastine. In particular oxaliplatin is co-treated with an antioxidant, including CDC, CAPE, ciclopirox ethanolamine, hinokitiol, gossypol, n-Octyl caffeate, baicalein, or curcumin.
Owner:CHANG CHRISTINA LING
Local vascular delivery of etoposide in combination with rapamycin to prevent restenosis following vascular injury
ActiveUS7695731B2Provide controlOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryPercent Diameter StenosisBlood vessel
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. In addition, these therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds may be utilized to promote healing, including the formation of blood clots. Also, the devices may be modified to promote endothelialization. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned. In addition, the devices utilized to deliver the implantable medical devices may be modified to reduce the potential for damaging the implantable medical device during deployment. Medical devices include stents, grafts, anastomotic devices, perivascular wraps, sutures and staples. In addition, various polymer combinations may be utilized to control the elution rates of the therapeutic drugs, agents and / or compounds from the implantable medical devices.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Method, apparatus, and compound for effecting localized, non-systemic, immunogenic treatment of cancer
Anthracyclin-treated turn or cells are particularly effective in eliciting an anti-cancer immune response, where the rDNA-damaging agents, such as etoposide and mitomycin C do not induce immunogenic cell death. Anthracyclins induce the rapid, pre-apoptotic translocation of calreticulin (CRT) to the cell surface. Blockade or knock down of CRT suppressed the phagocytosis of anthracyclin-treated tumor cells by dendritic cells and abolished their immunogenicity in mammals, such as mice. The anthracyclin-induced CRT translocation was mimicked by inhibition of the protein phosphatase1 / GADD34 complex. Administration of recombinant CRT or inhibitors of protein phosphatase1 / GADD34 restored the immunogenicity of cell death elicited by etoposide and mitomycin C, and enhanced their antitumor effects in vivo. These data identify CRT as a key feature determining anti-cancer immune responses and delineate a possible strategy for immunogenic chemotherapy.
Owner:OBEID MICHEL SARKIS
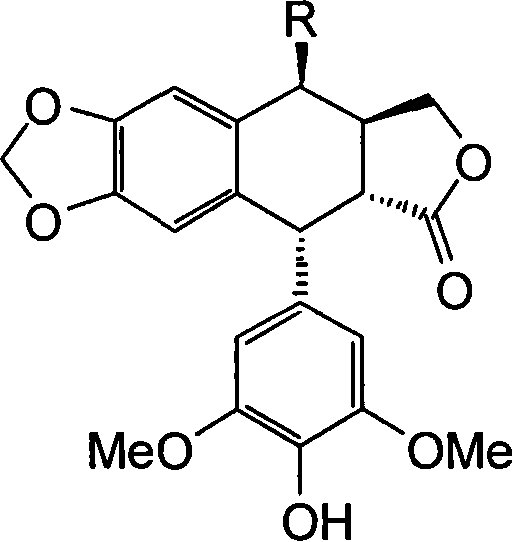
Analogues of etoposide for the treatment of tumours
Compounds for treatment of a patient having a tumor that is metastatic and / or that reduces an organ function, wherein the compounds are of the general formula:wherein X is O, NH and S, wherein n is 0, 1 or 2, wherein R1 and R2 are H, methyl or ethyl, or together form a group CR3R4, and wherein R3 and R4 are H, methyl or ethyl.
Owner:CELLACT PHARMA
Sodium alginate microspheres blood vessel suppository containing etoposide and preparation method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101385696ASolve the problem of water solubilityAddress reactivityOrganic active ingredientsSurgerySmall-cell carcinomaAtherion elymus
The invention belongs to the field of medical embolization devices, relates to a sodium alginate microsphere targeted vascular embolization agent containing an antineoplastic drug and a preparation method thereof. Alginic acid is taken as a pharmaceutical carrier, the antineoplastic drug etoposide is a pharmaceutical active ingredient, divalent metal cation or calcium ion solution is taken as a solidifying agent, and the sodium alginate encapsulates the etoposide to prepare ideal particle size-controllable sodium alginate microspheres comprising the etoposide, thus avoiding toxic side effect of traditional etoposide administration such as anaphylaxis and inconvenience. The vascular embolization agent changes the dosage form and route of administration way of the antineoplastic drug etoposide, has high efficacy and low toxicity, and is safely and effectively applied to clinical application. The vascular embolization agent has the advantages of mild preparation condition and simple and convenient operation, and is fit for large-scale production. The vascular embolization agent can be used for vascular embolization, local targeted tumor treatment, and treating small-cell carcinoma of the lung, oophoroma, carcinoma of testis, gastric cancer and liver cancer by administering the vascular embolization agent during operations.
Owner:BEIJING SHENGYIYAO SCI & TECH DEV
Method of detecting cancer cell acquiring drug-resistance
InactiveUS20090143236A1Detect the resistance to anticancer drugsAccurate collectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementSide effectABCB6
It is an object of the present invention to find out a novel gene marker by which a drug-resistant cancer cell can be detected and provide a means of efficiently and comprehensively detecting a drug-resistant cancer cell using this marker. In the present invention, gene amplifications or deletions have been analyzed in cancer cell strains resistant to drugs, which are anticancer drugs having particularly serious side effects and being administered to cancer patients at a high frequency (namely, camptothecins, cisplatins, etoposides, adriamycins (ADM), and cytosine arabinosides), and parent cancer cell strains. As a result, it was found out that the acquisition of drug-resistance to an anticancer drug in a test cancer cell can be detected by detecting amplification of one or more genes selected from ABC transporter genes and BCL2 family genes consisting of ABCA3 gene, ABCB6 gene, ABCB8 gene, ABCB10 gene, ABCC4 gene, ABCC9 gene, ABCD3 gene, ABCD4 gene, ABCE1 gene, ABCF2 gene, BCL2L2, BCL2L10, BCL2L1, and BCL2A1 which are novel gene markers relating to the acquisition of drug resistance of cancer cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com