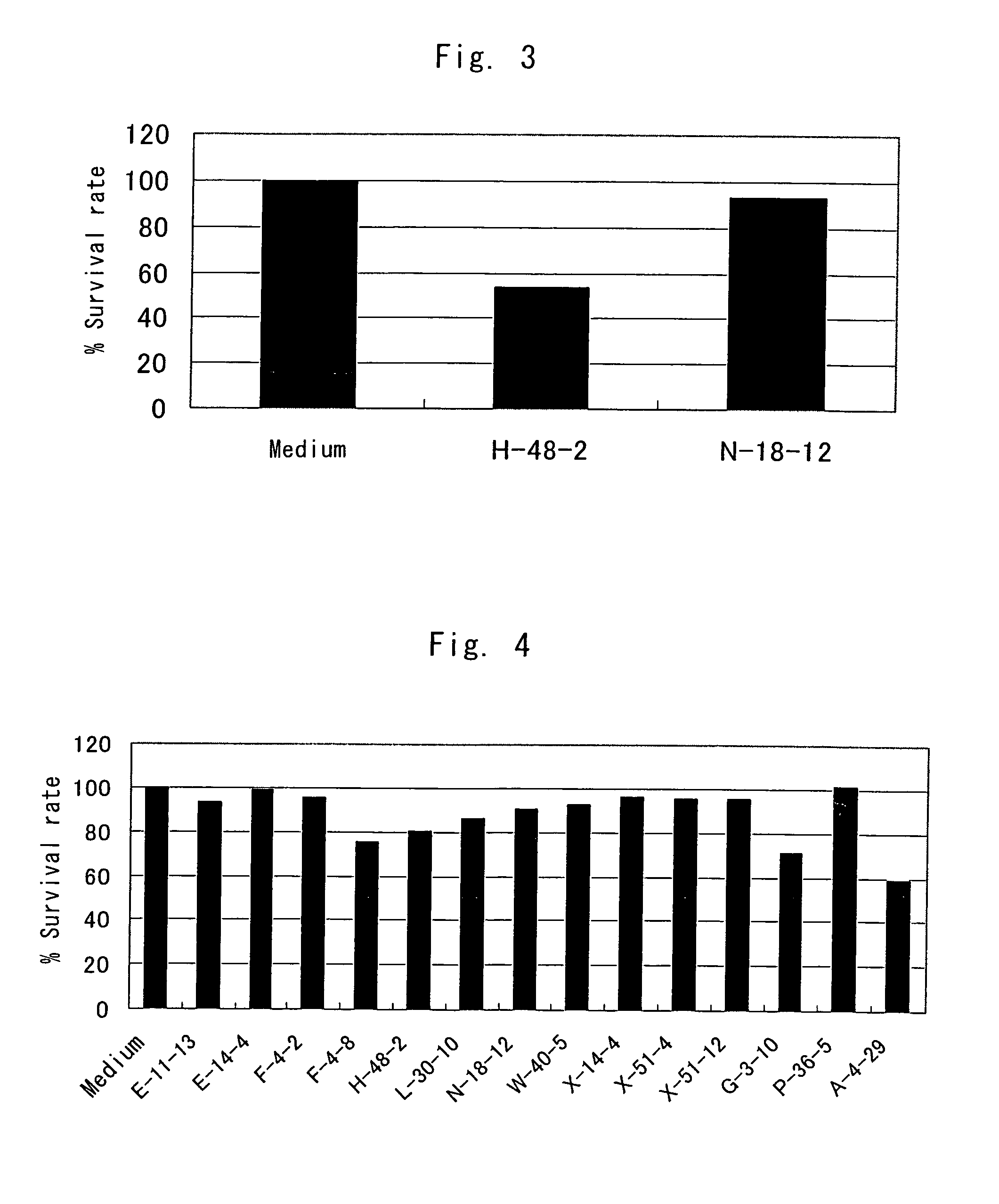
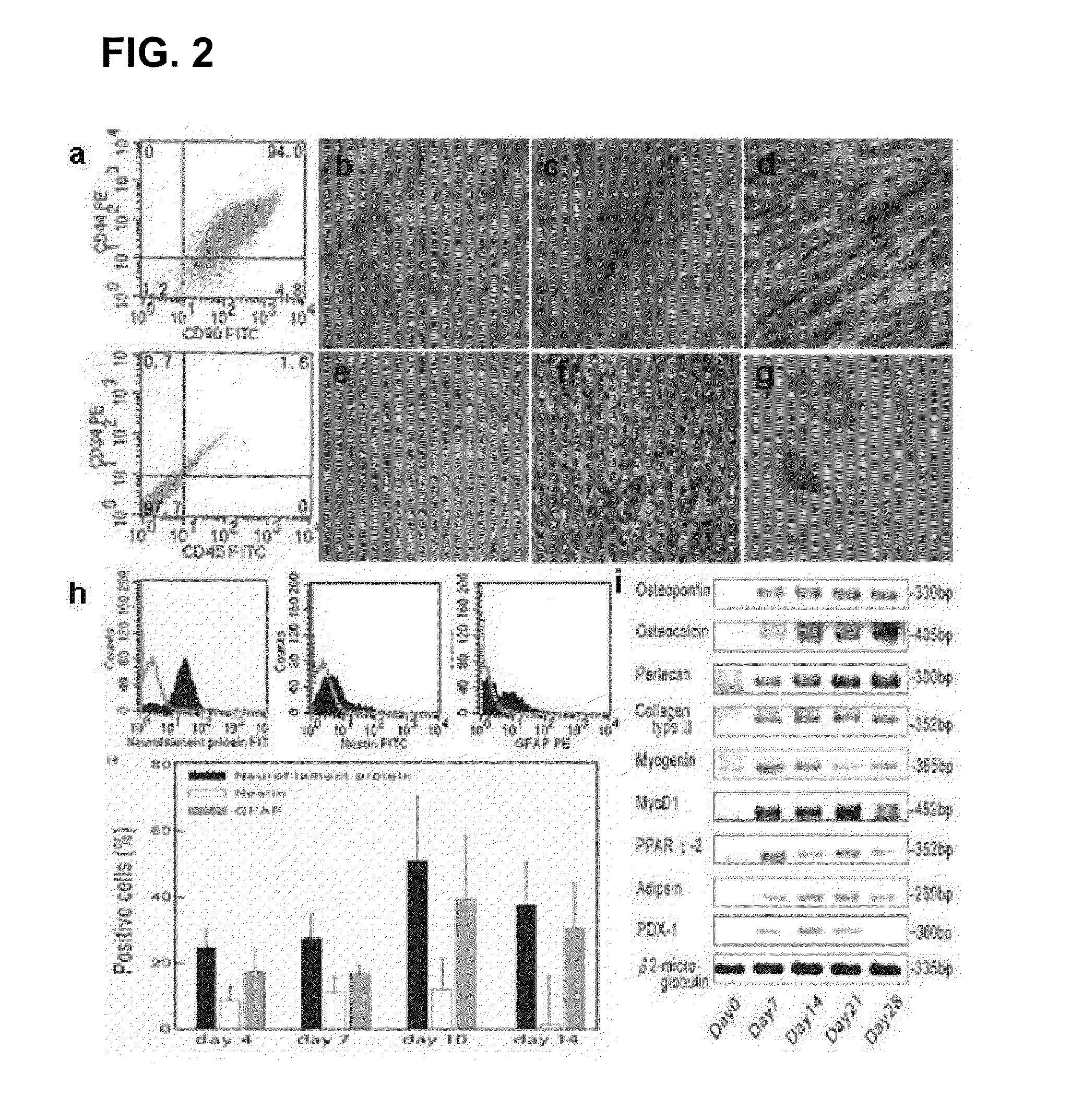
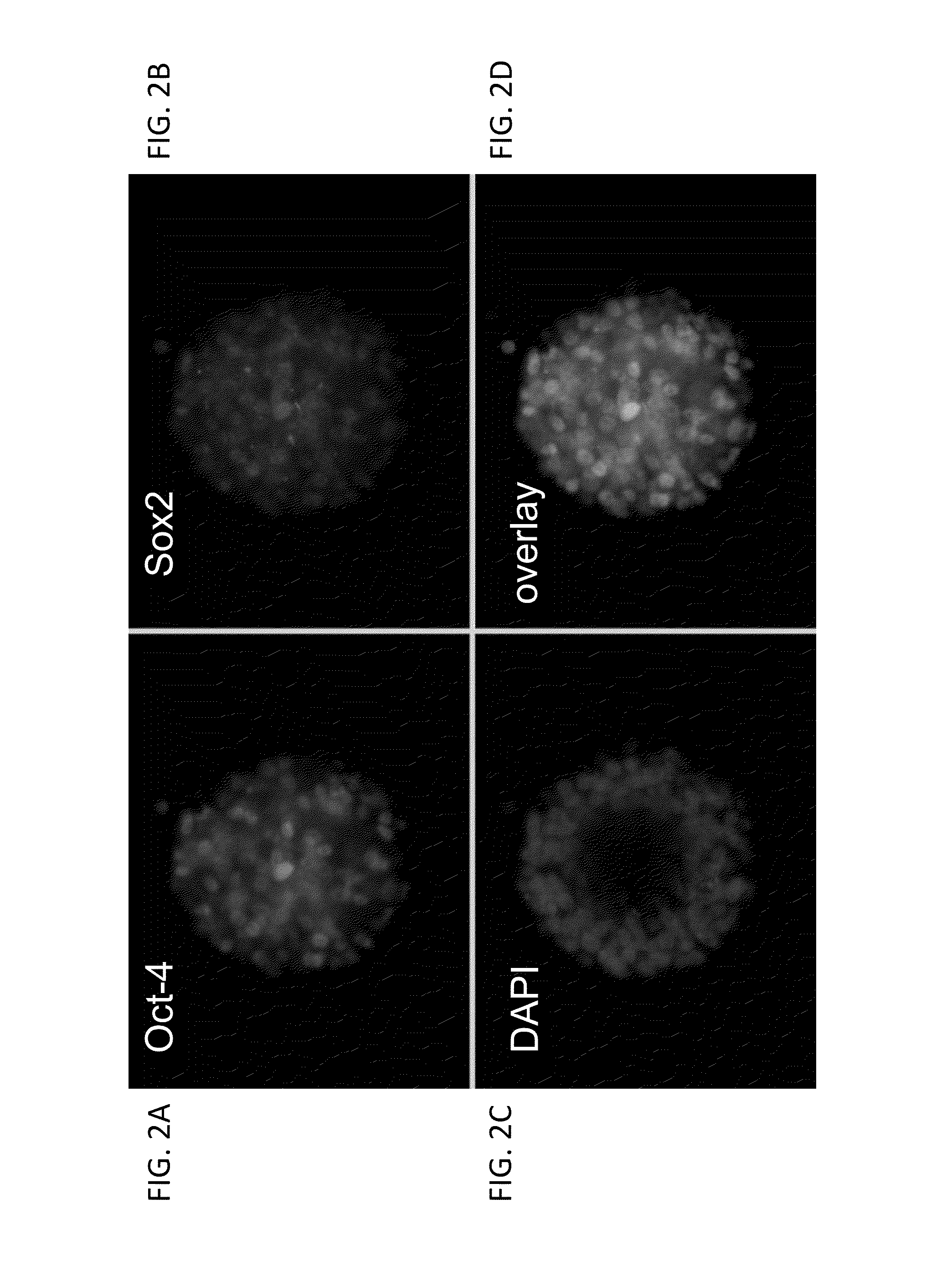
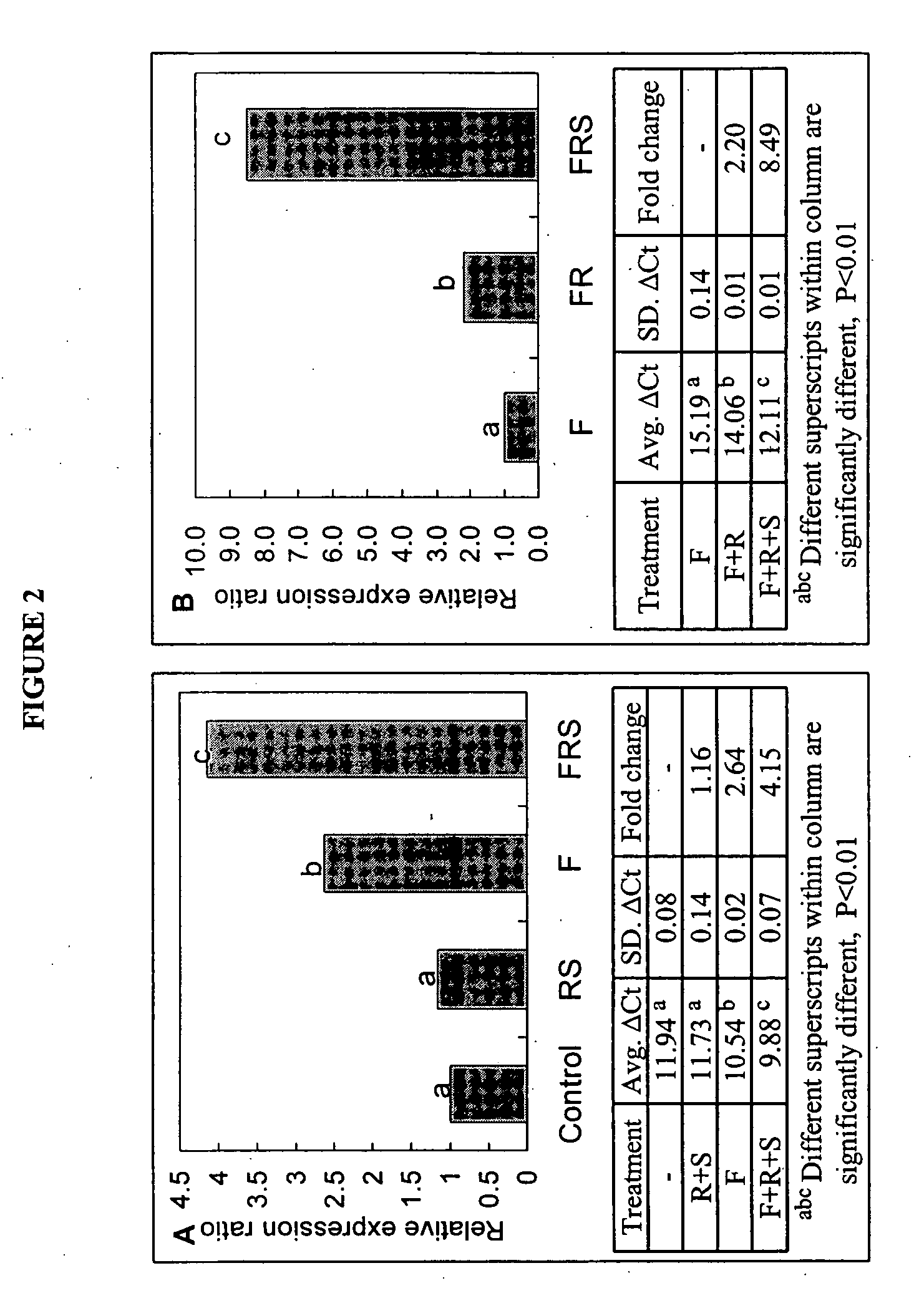
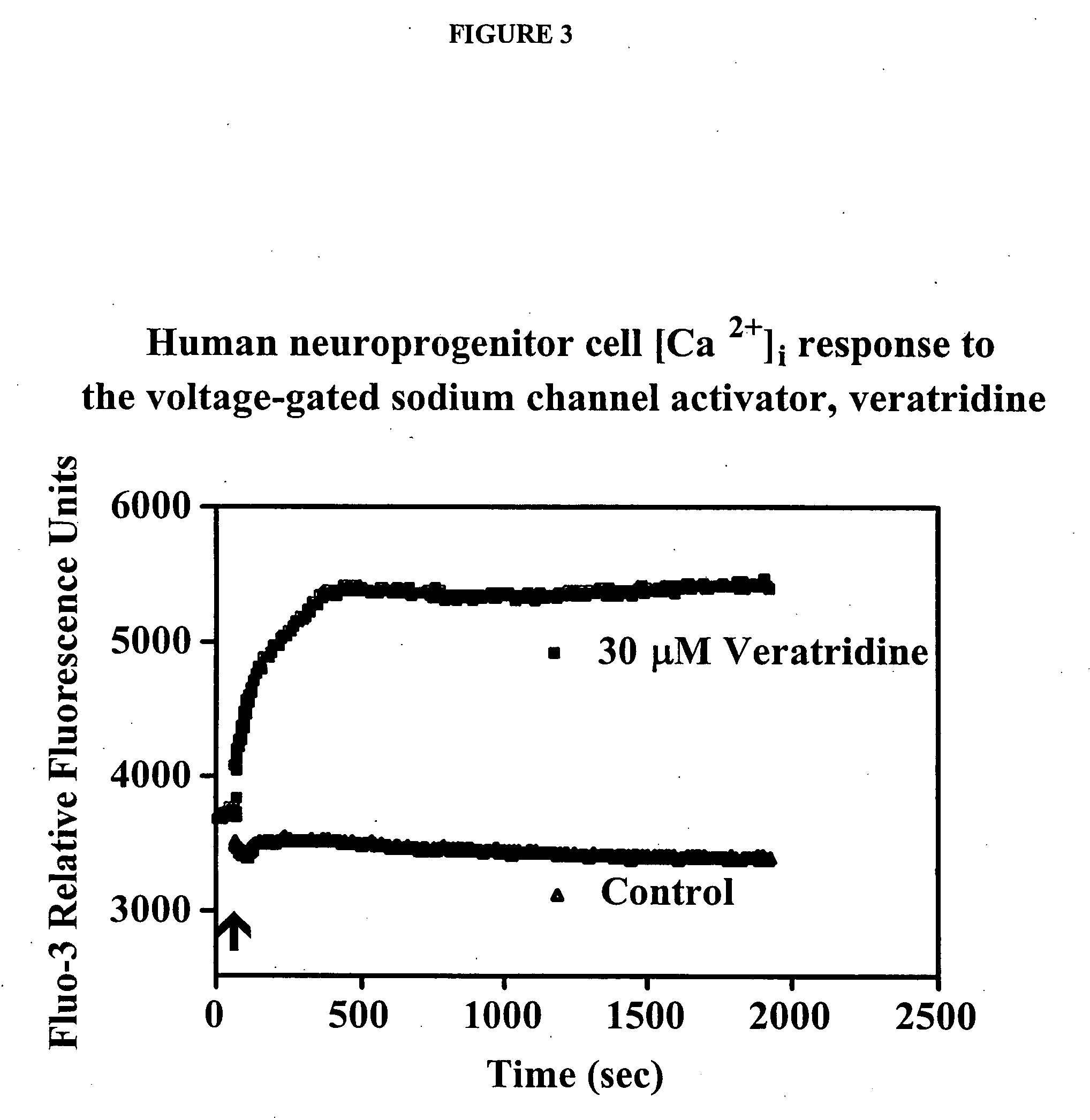
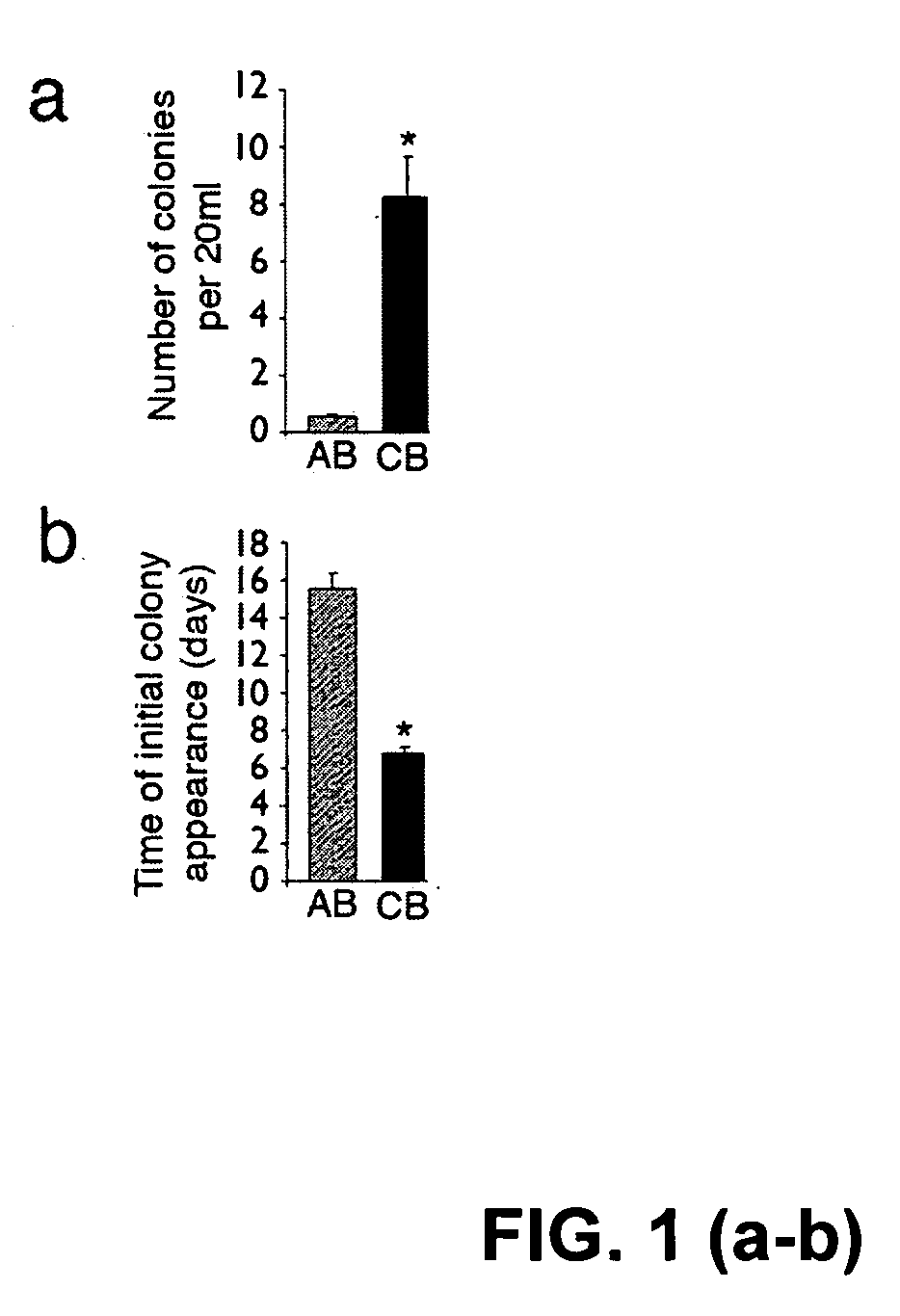
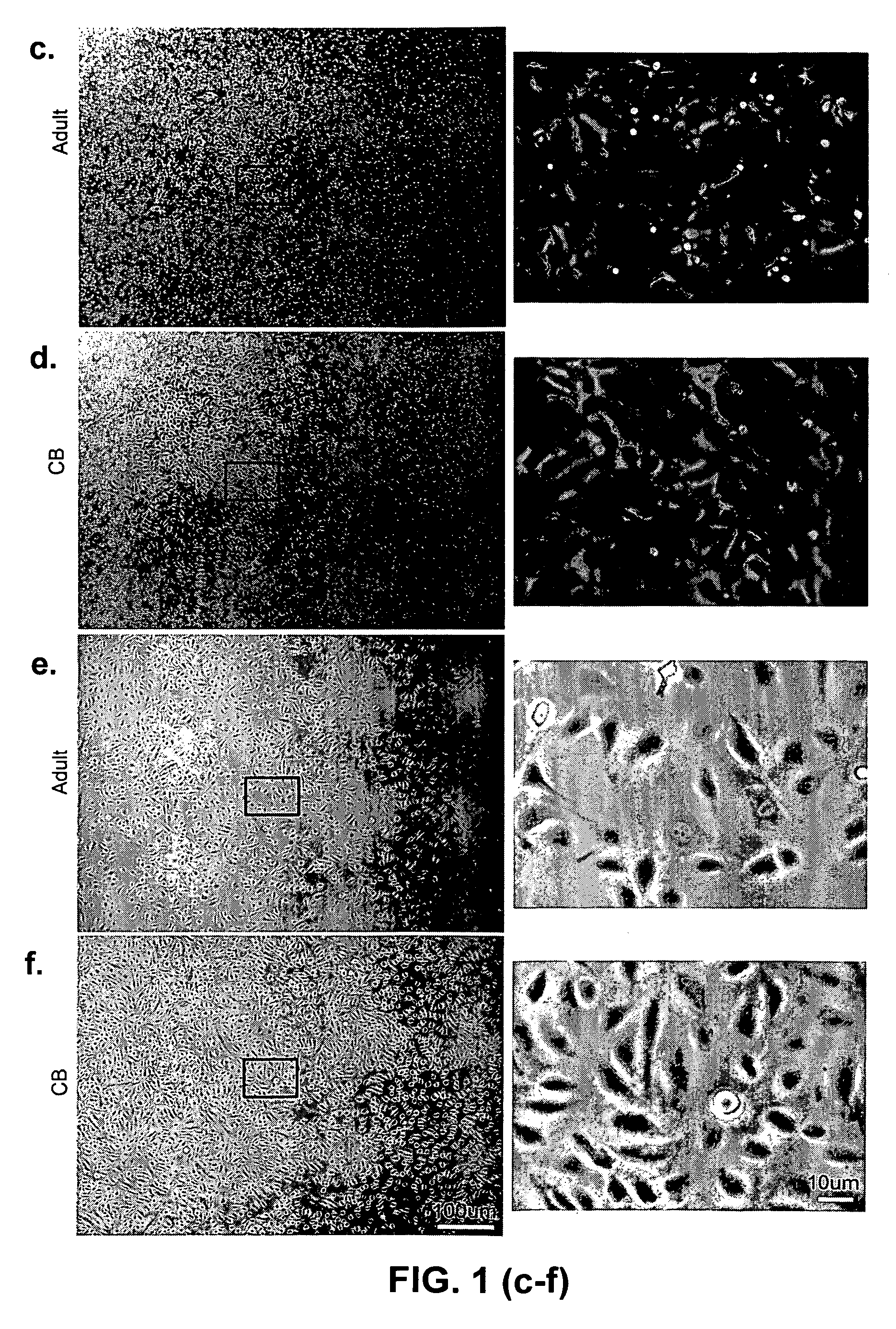
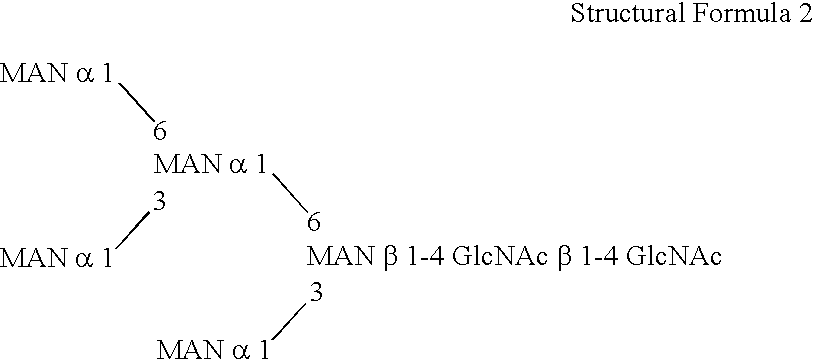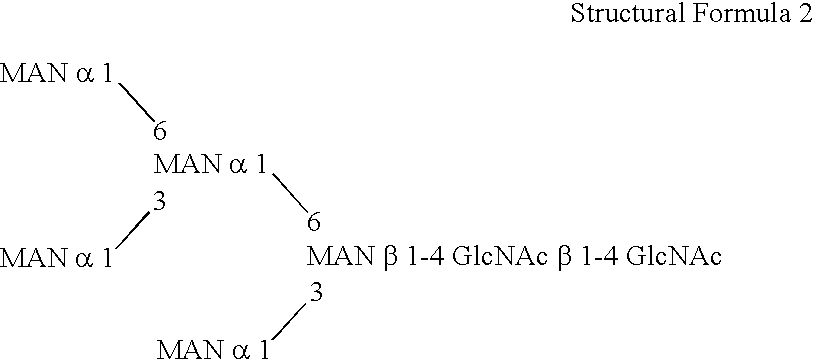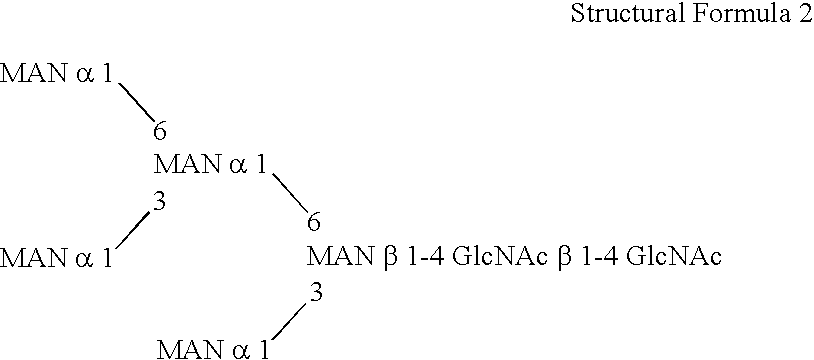Patents
Literature
1339 results about "Human cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
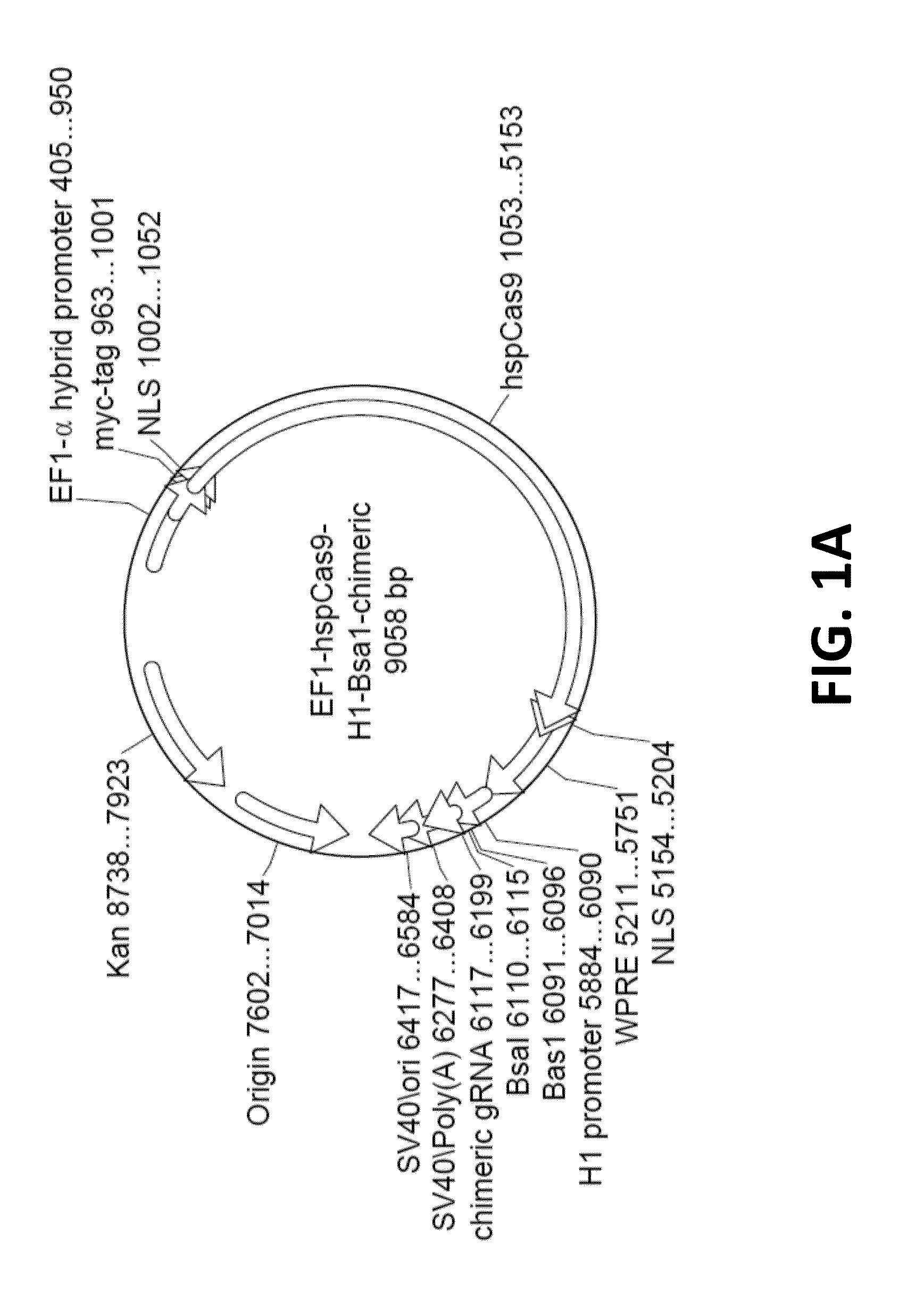
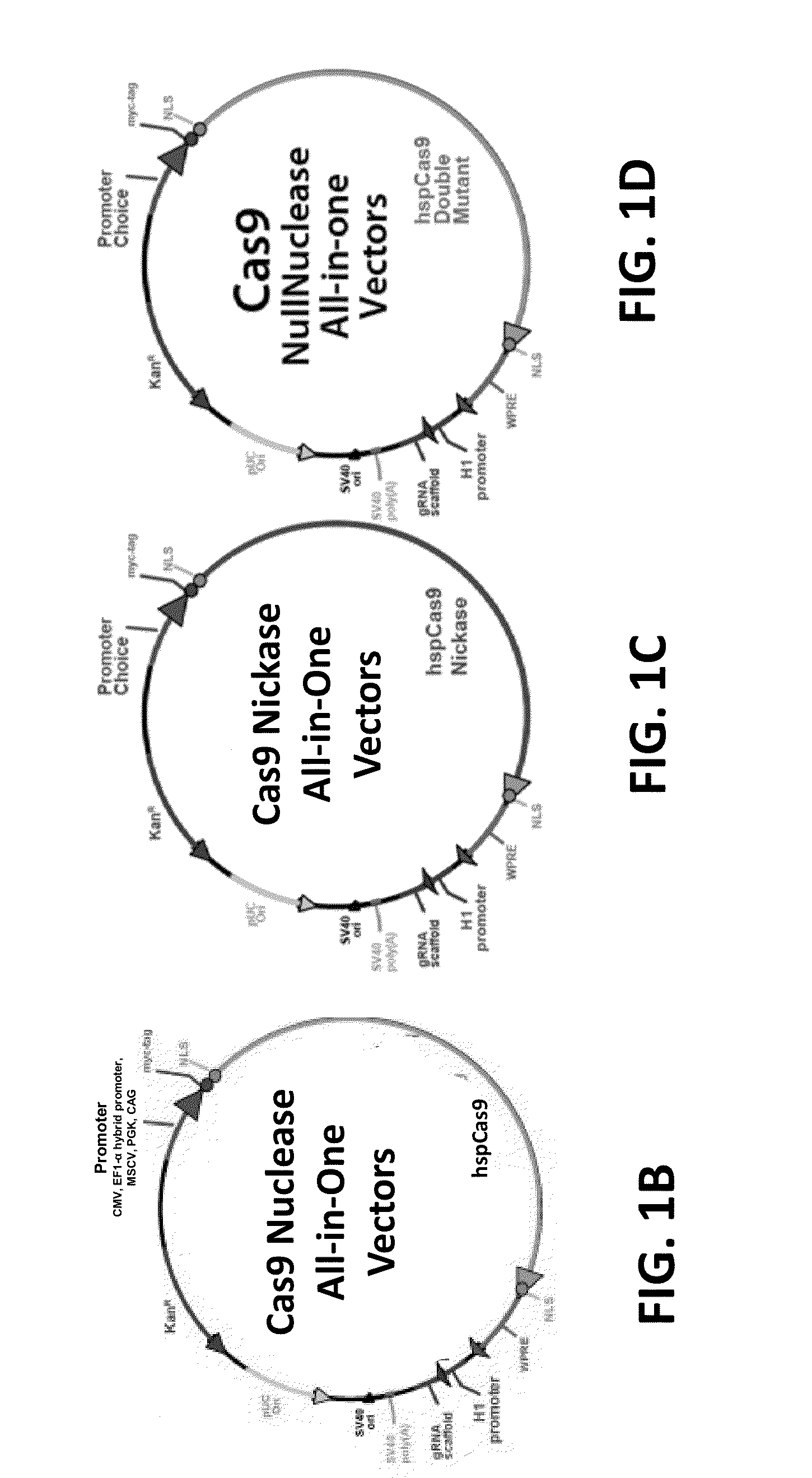
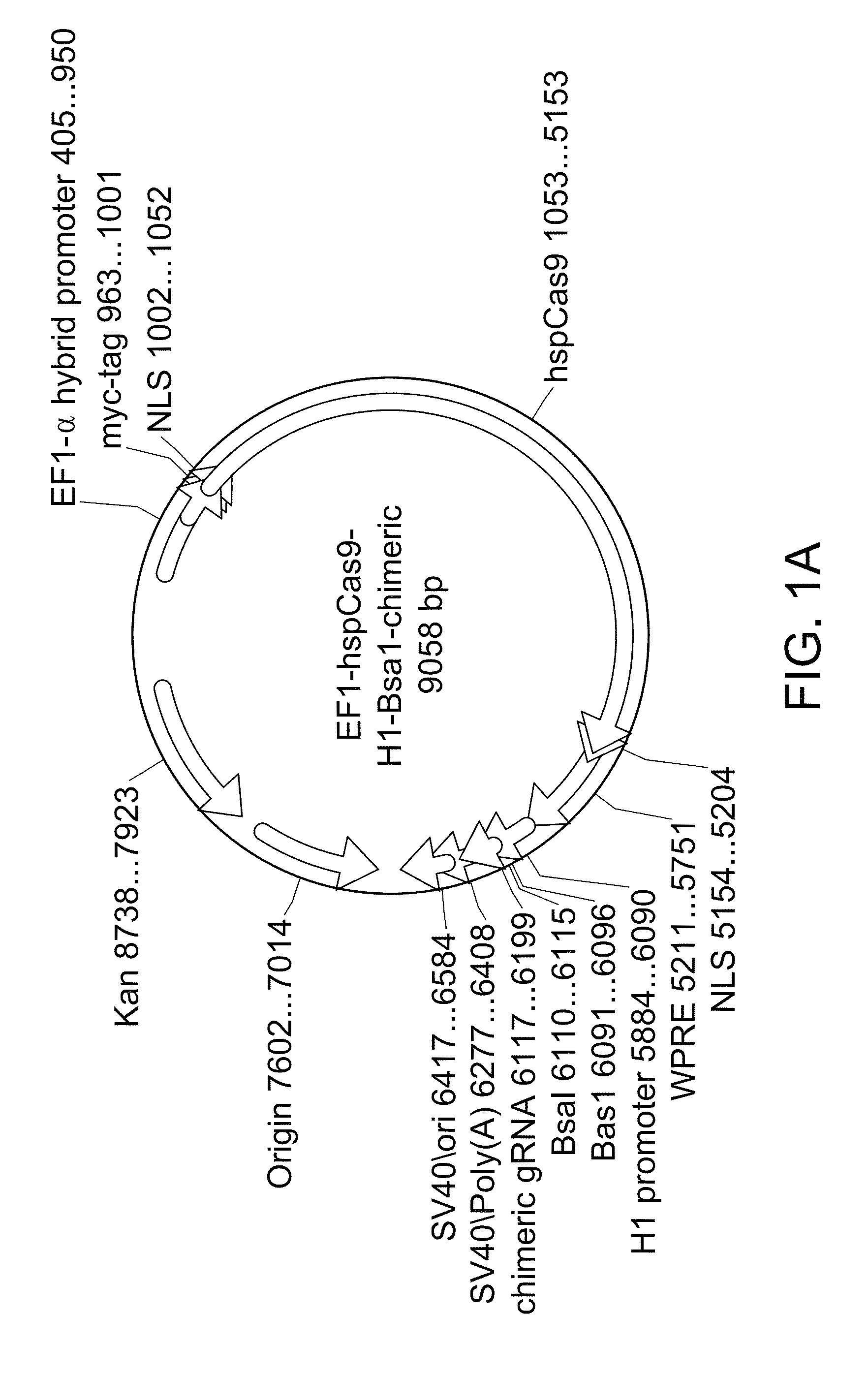
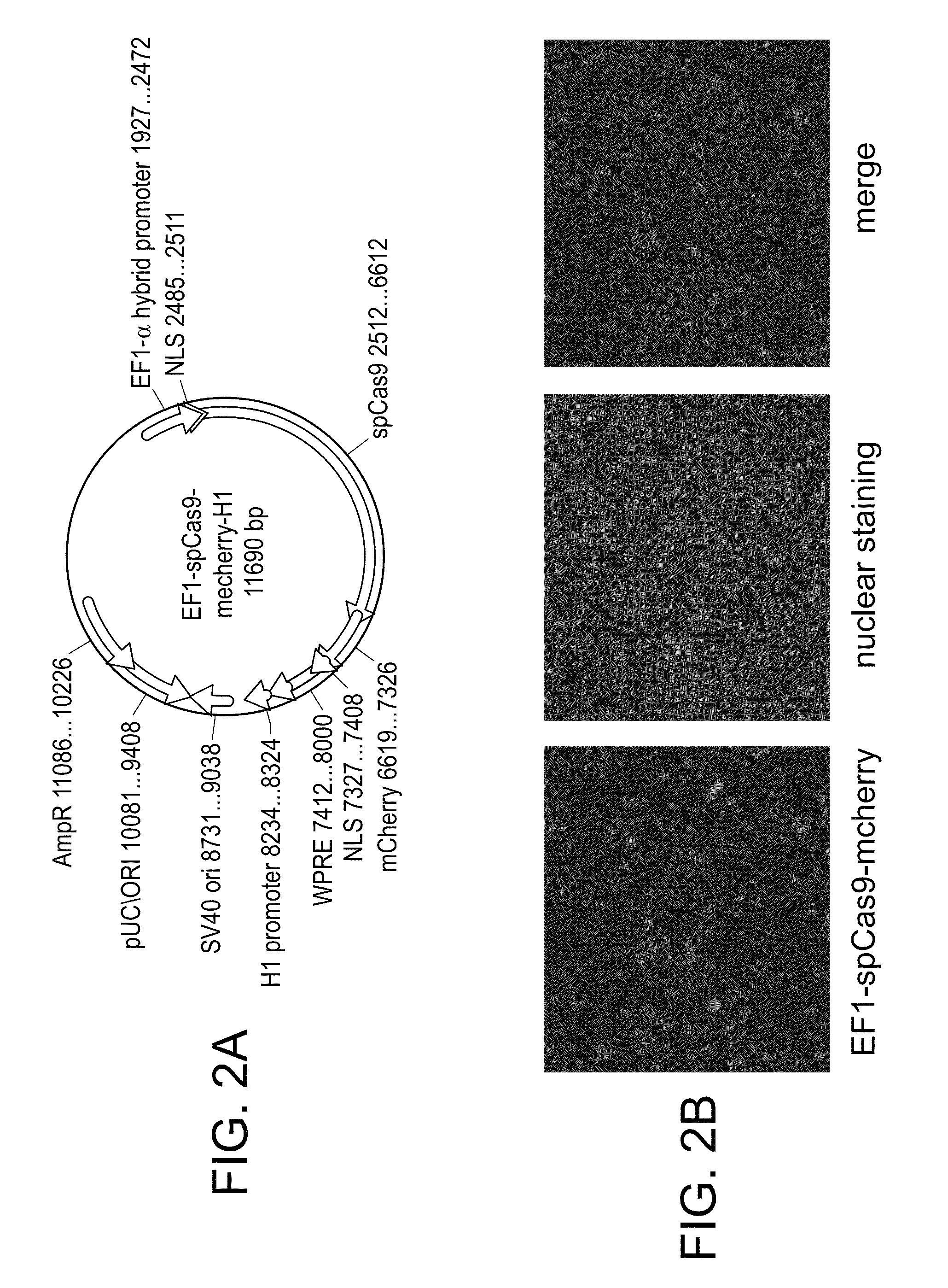
Crispr/cas systems for genomic modification and gene modulation
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification and regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells. The specification describes the design and validation of polynucleotides encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 gene and protein and variants of that protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells, and also modified by fused sequences that enhance various aspects of the CRISPR / Cas system. The specification also describes systems for RNA-guided genome engineering and gene regulation in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
Methods and Compositions for the Targeted Modification of a Genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Adeno-associated virus vectors for expression of factor VIII by target cells
InactiveUS6200560B1Easily transfectedConvenient platformBiocideFactor VIIHigh level expressionHuman cell
The present invention provides improved viral vectors useful for the expression of genes at high levels in human cells. In particular, the present invention provides recombinant adeno-associated vectors (AAV) suitable for gene therapy. These vectors are capable of delivering nucleic acid containing constructs which result in the production of full-length therapeutic levels of biologically active Factor VIII in the recipient individual in vivo. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising such AAV vectors, as well as methods for making and using these constructs.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
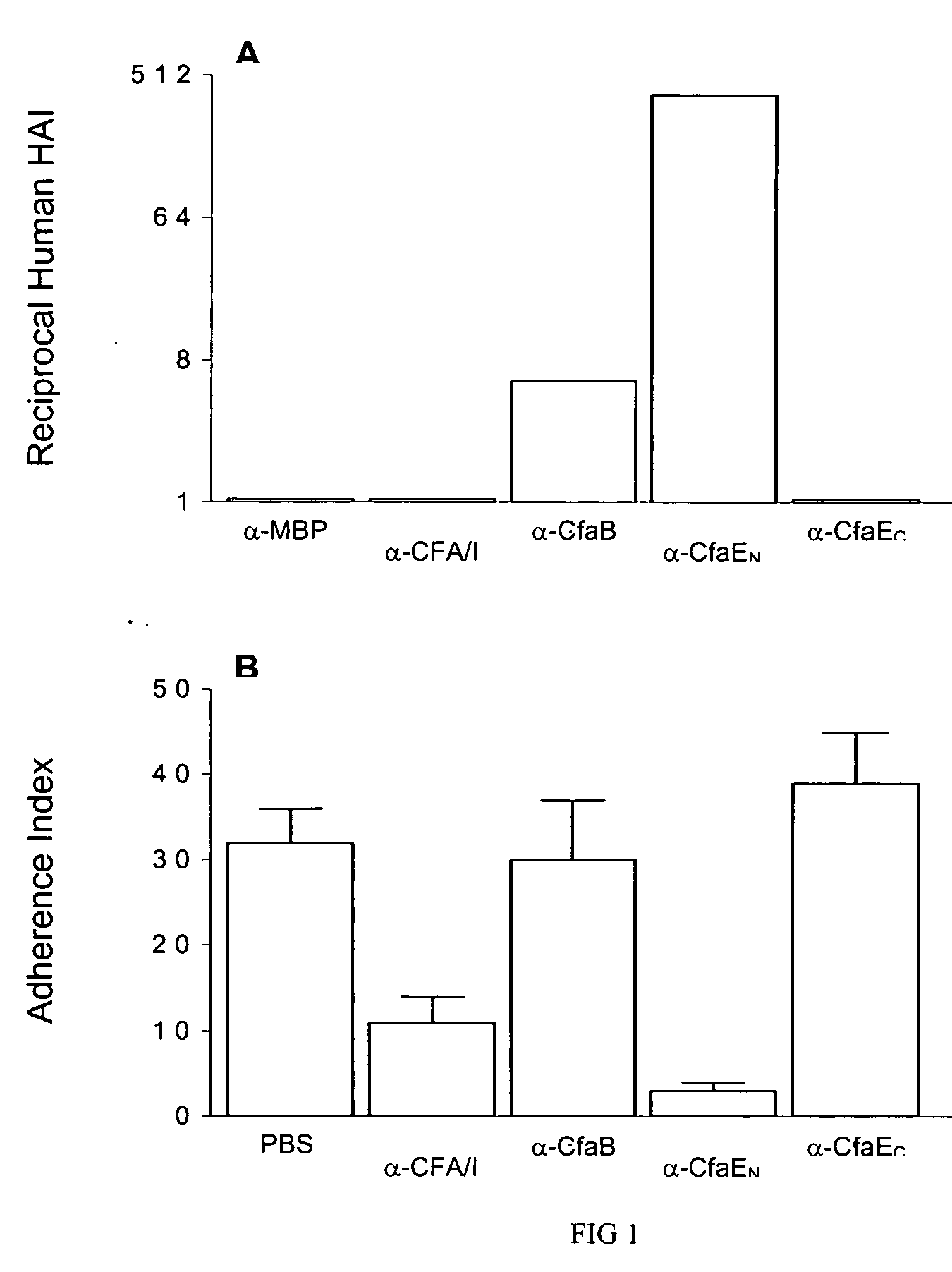
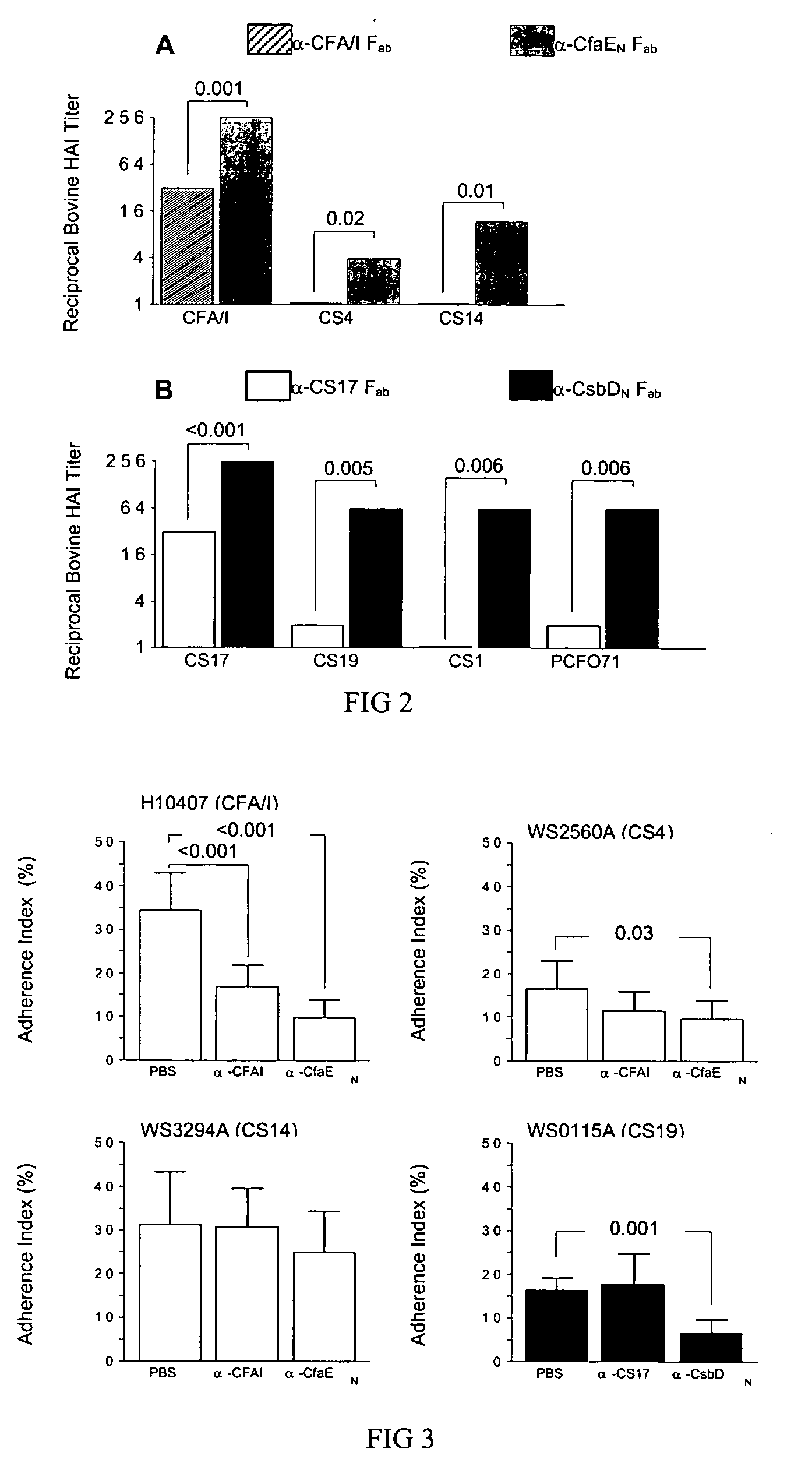
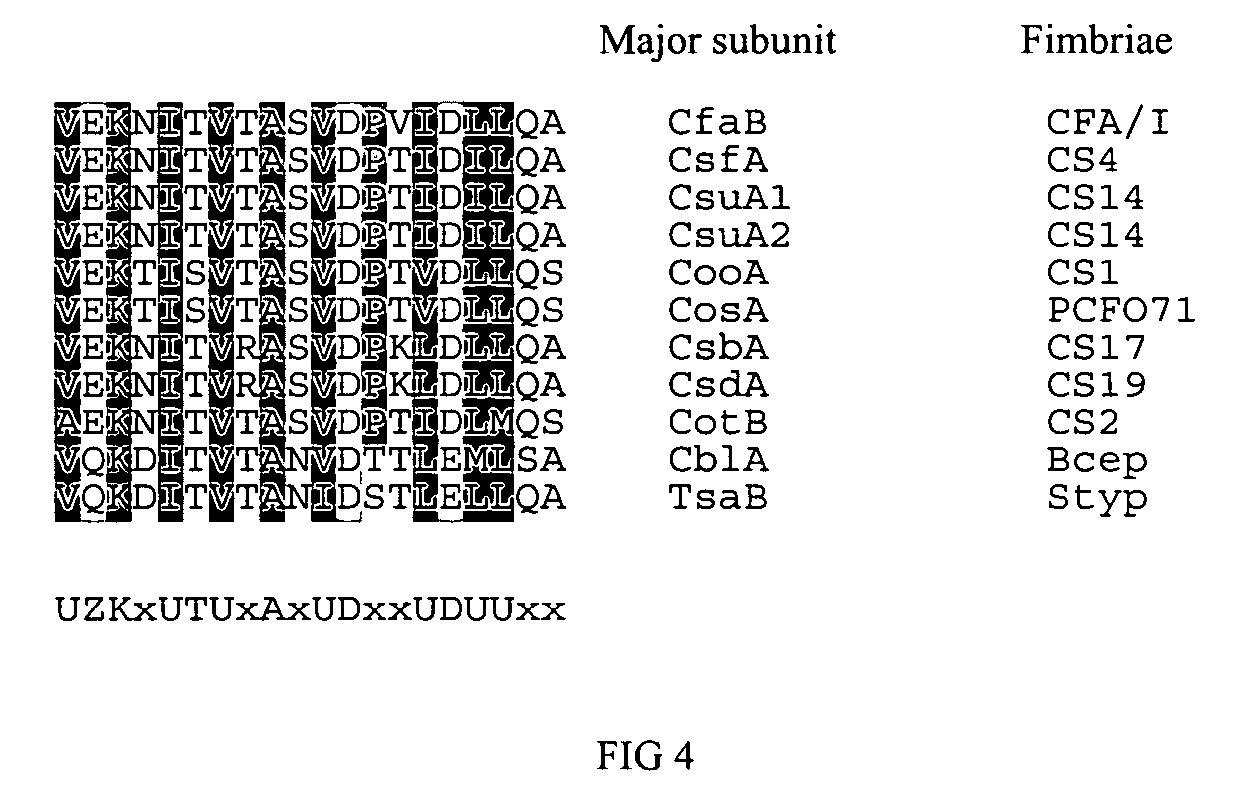
Adhesin as immunogen against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
ActiveUS20060153878A1Inhibition of colonizationAvoid stickingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliDiarrhea
The inventive subject matter relates to the methods for the induction of immunity and prevention of diarrhea resulting from Escherichia coli. The inventive subject matter also relates to the use Escherichia coli adhesins as immunogens and to the construction of conformationally stability and protease resistant Escherichia coli adhesin constructs useful for inducing immunity to Escherichia coli pathogenic bacteria. The methods provide for the induction of B-cell mediated immunity and for the induction of antibody capable of inhibiting the adherence and colonization of Escherichia coli including enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, to human cells.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Adeno-associated vectors for expression of factor VIII by target cells
InactiveUS6221349B1Easily transfectedConvenient platformBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHigh level expressionHuman cell
The present invention provides improved viral vectors useful for the expression of genes at high levels in human cells. In particular, the present invention provides adeno-associated vectors (AAV) suitable for gene therapy. These vectors are capable of delivering nucleic acid containing constructs which result in the production of full-length therapeutic levels of biologically active Factor VIII in the recipient individual in vivo. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising such AAV vectors, as well as methods for making and using these constructs.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Methods and compositions for the targeted modification of a genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods and compositions for the production of guide RNA
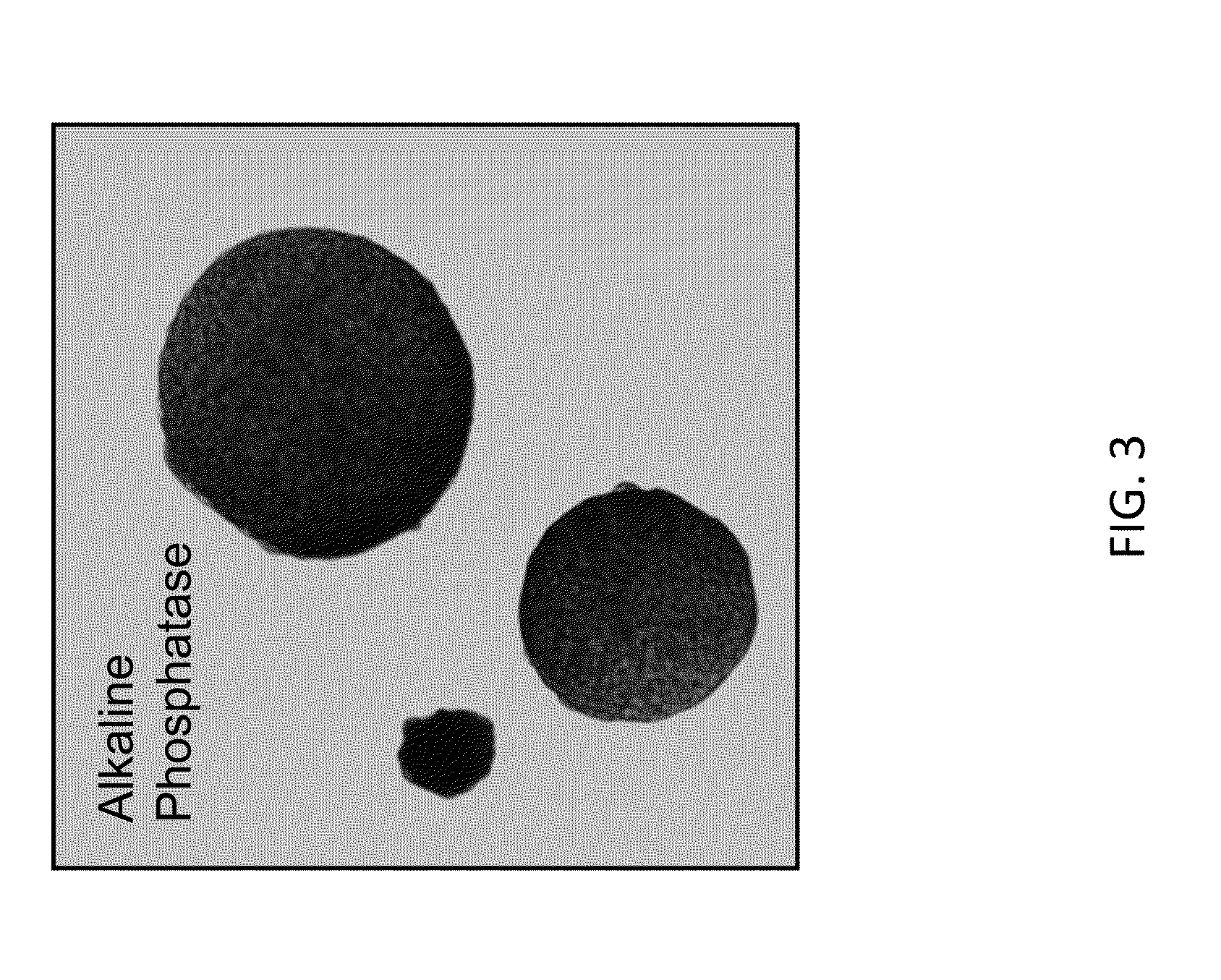
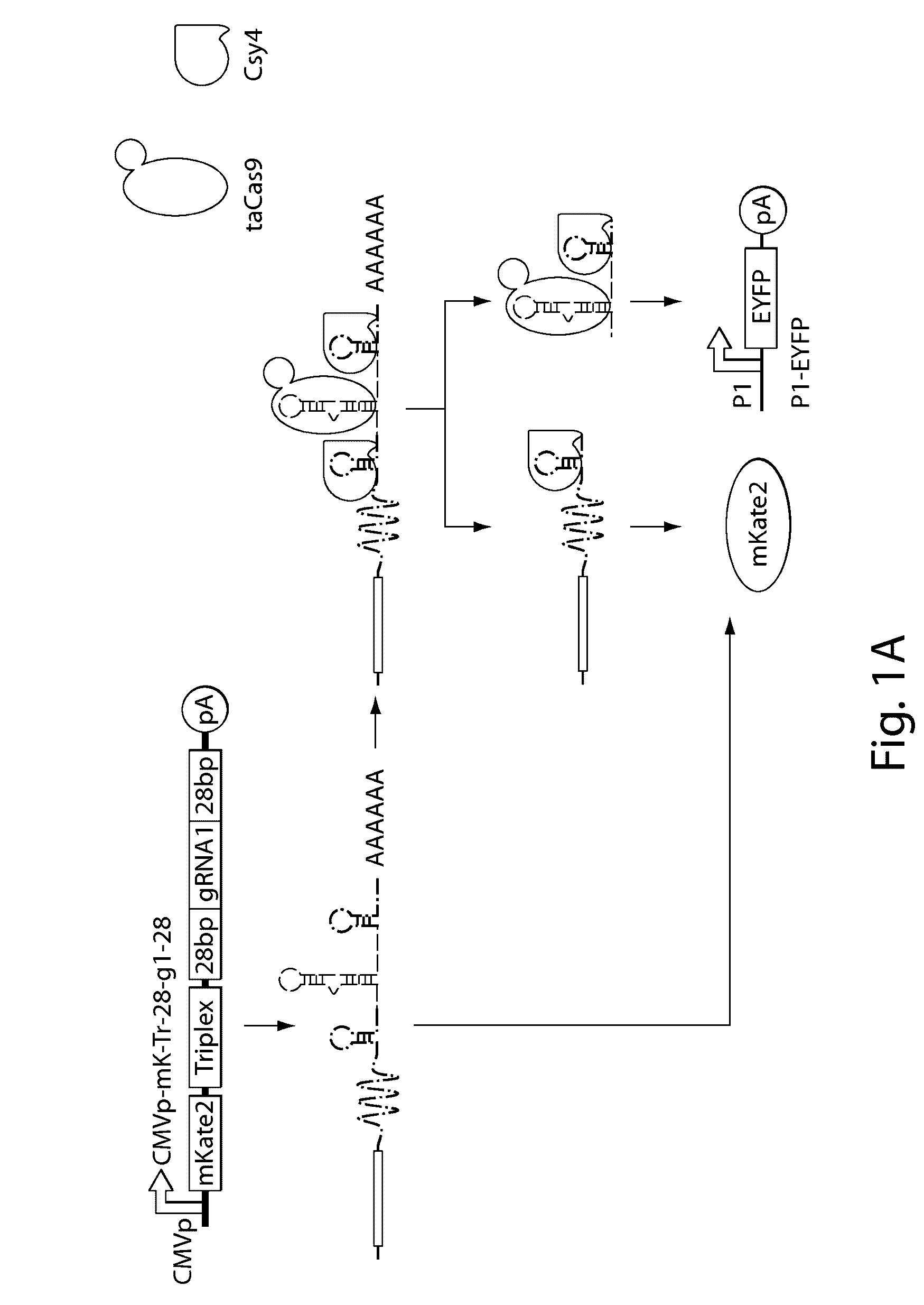
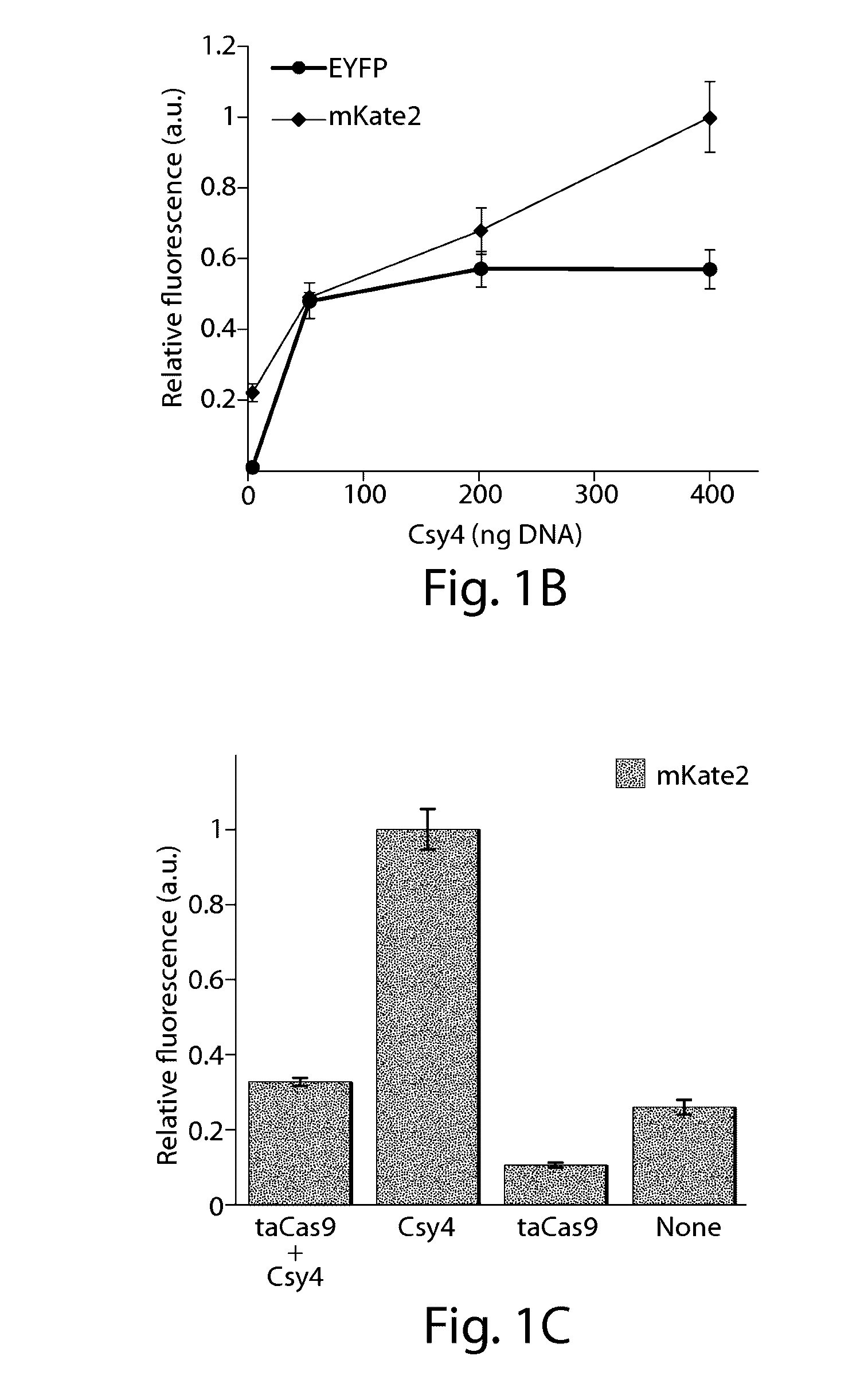
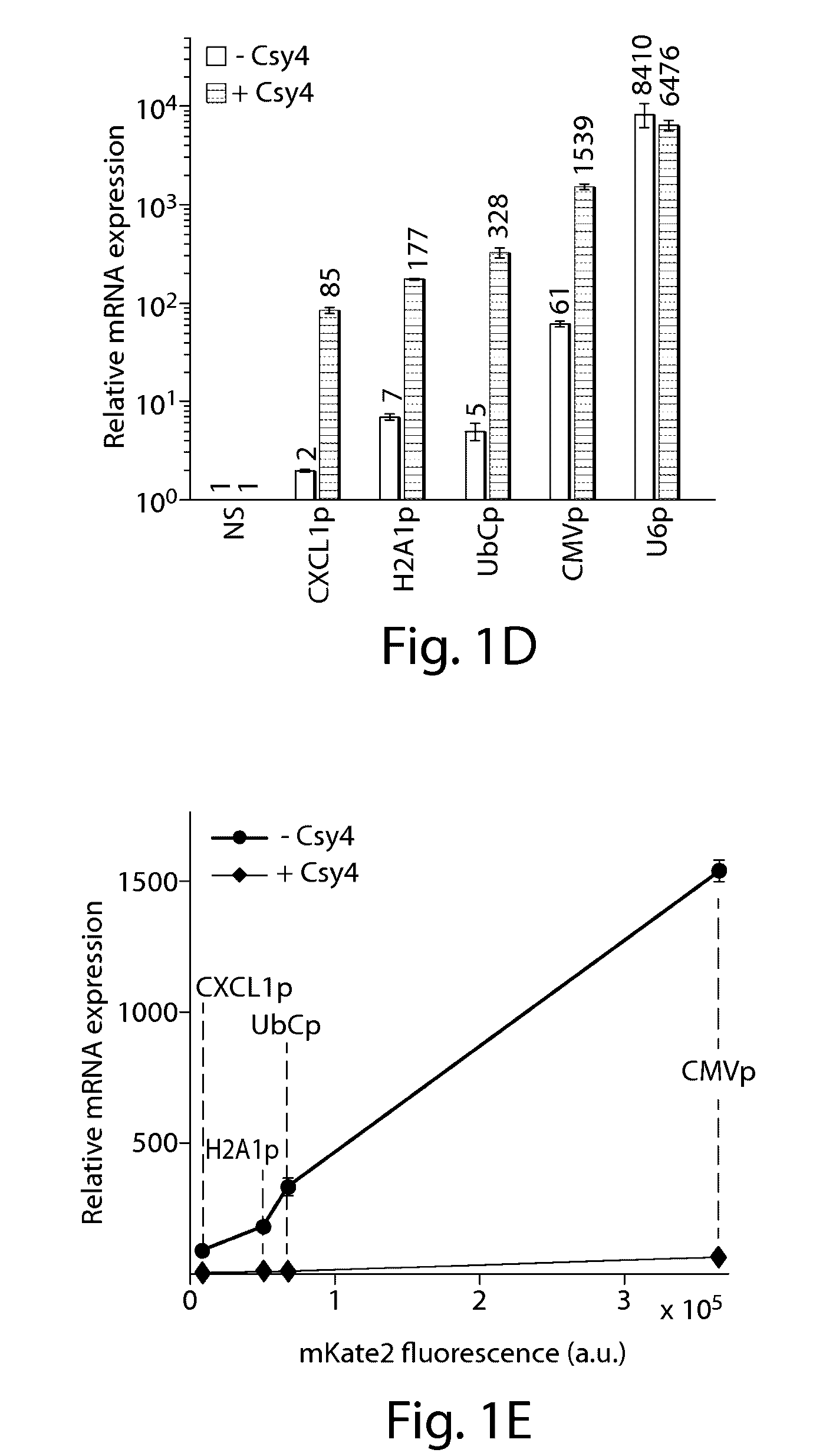
Various aspects and embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods and compositions that combine multiple mammalian RNA regulatory strategies, including RNA triple helix structures, introns, microRNAs, and ribozymes with Cas-based CRISPR transcription factors and ribonuclease-based RNA processing in human cells. The methods and compositions of the present disclosure, in some embodiments, enable multiplexed production of proteins and multiple guide RNAs from a single compact RNA-polymerase-II-expressed transcript for efficient modulation of synthetic constructs and endogenous human promoters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Recombinant protein production in a human cell
InactiveUS6855544B1Easy to handleLarge-scale (continuous) productionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesHamsterHuman cell
Methods and compositions for the production of recombinant proteins in a human cell line. The methods and positions are particularly useful for generating stable expression of human recombinant proteins of interest that are modified post-translationally, for example, by glycosylation. Such proteins may have advantageous properties in comparison with their counterparts produced in non-human systems such as Chinese Hamster Ovary cells.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
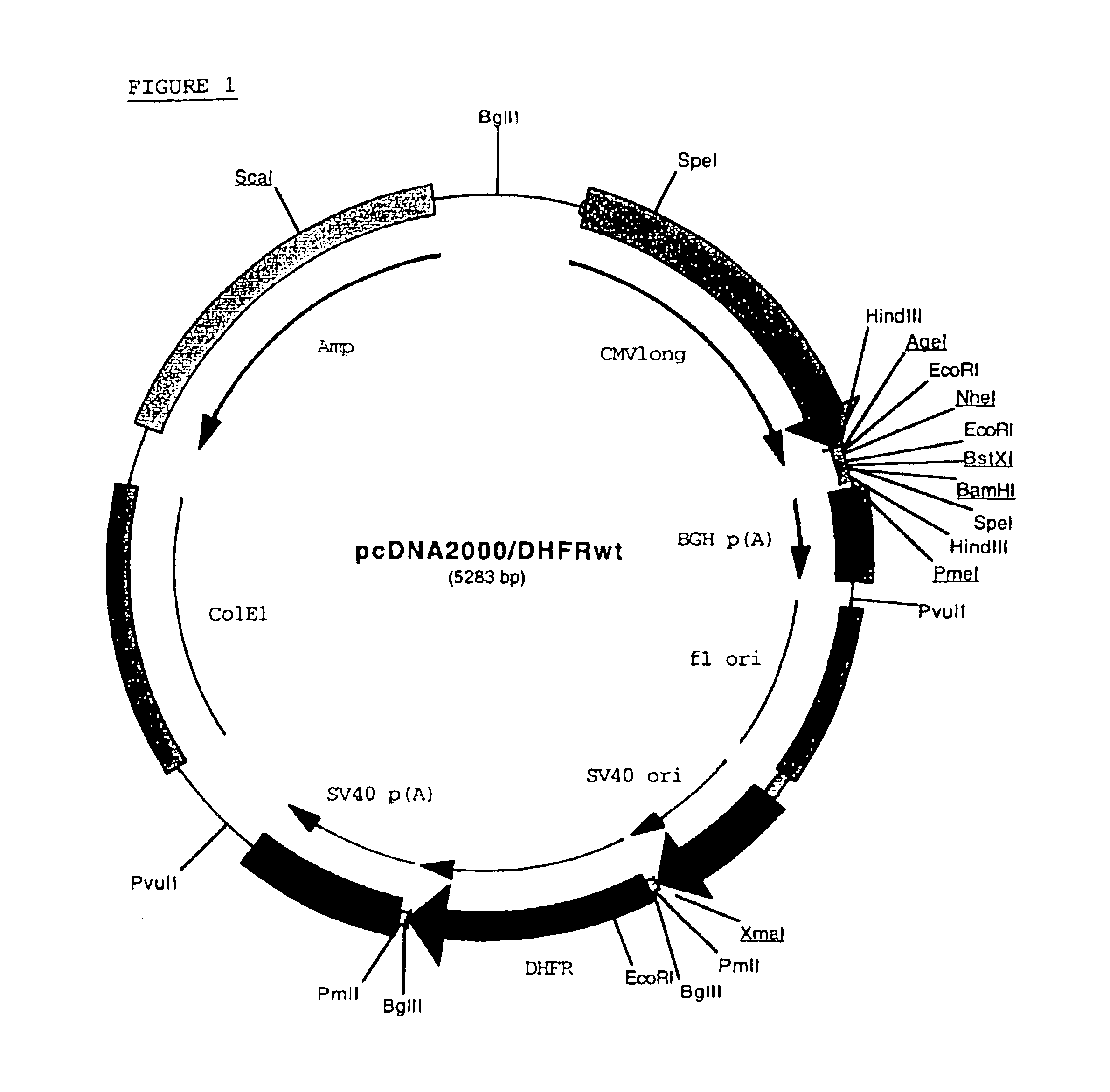
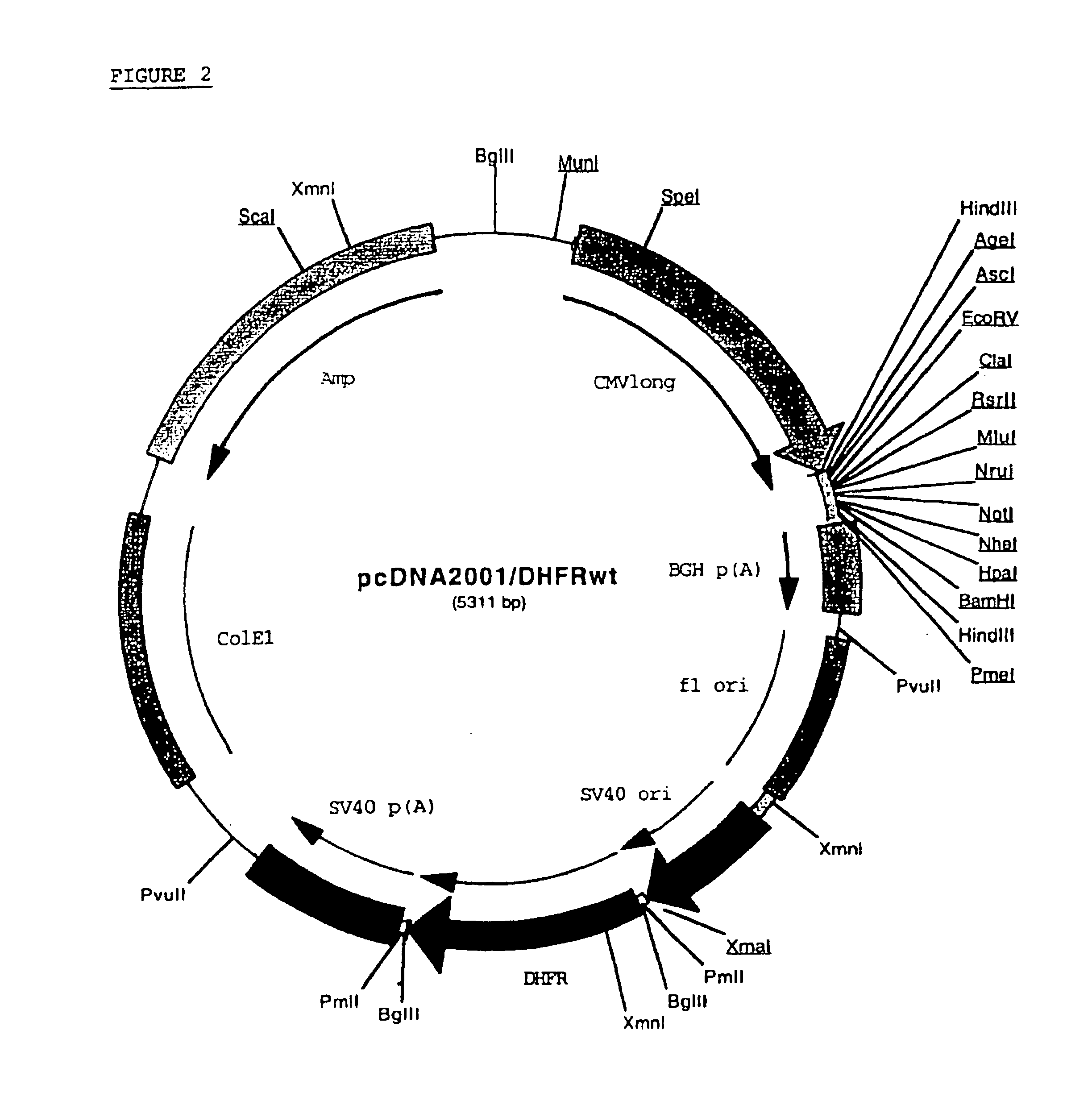
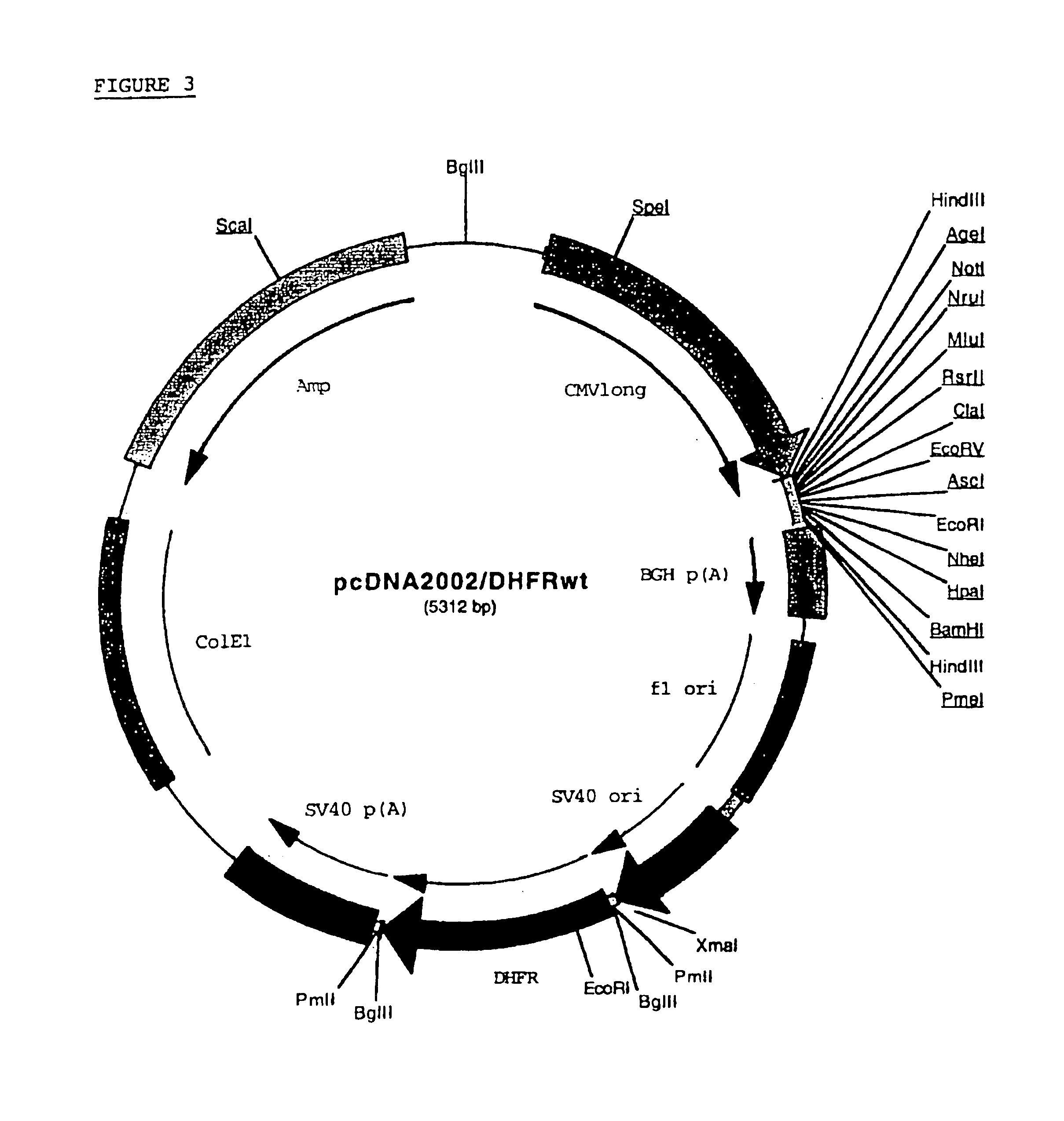
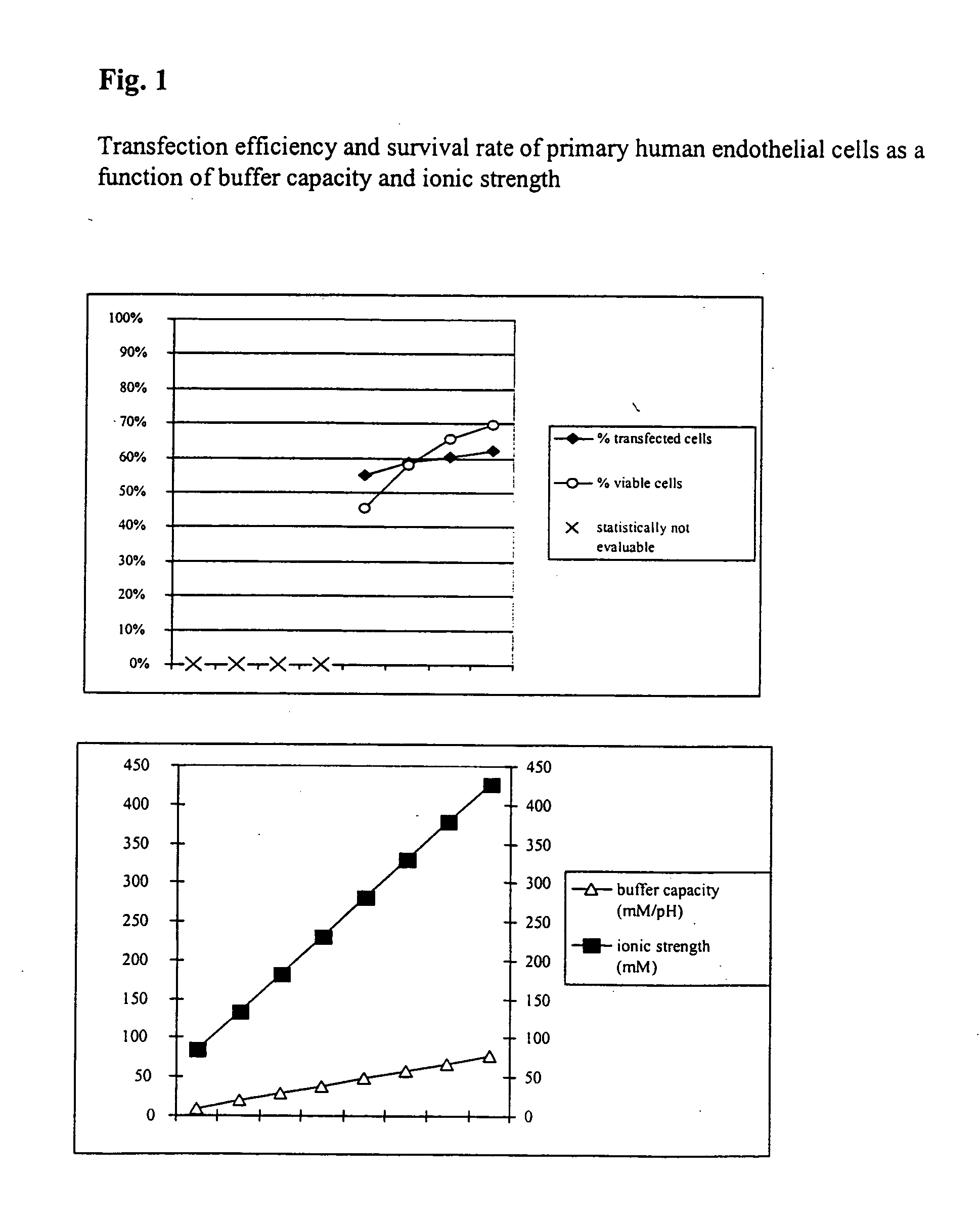
Buffer solution for electroporation and a method comprising the use of the same
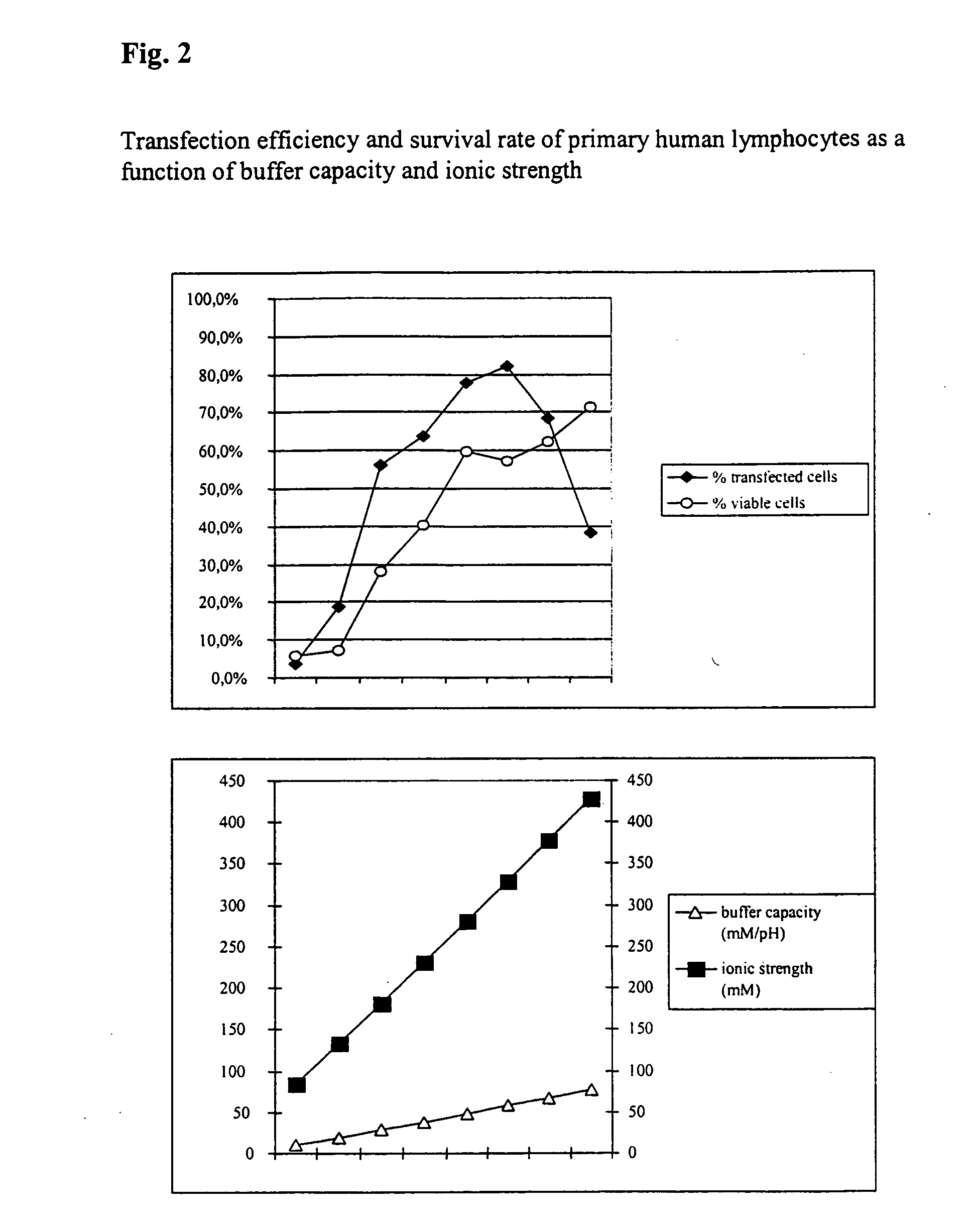
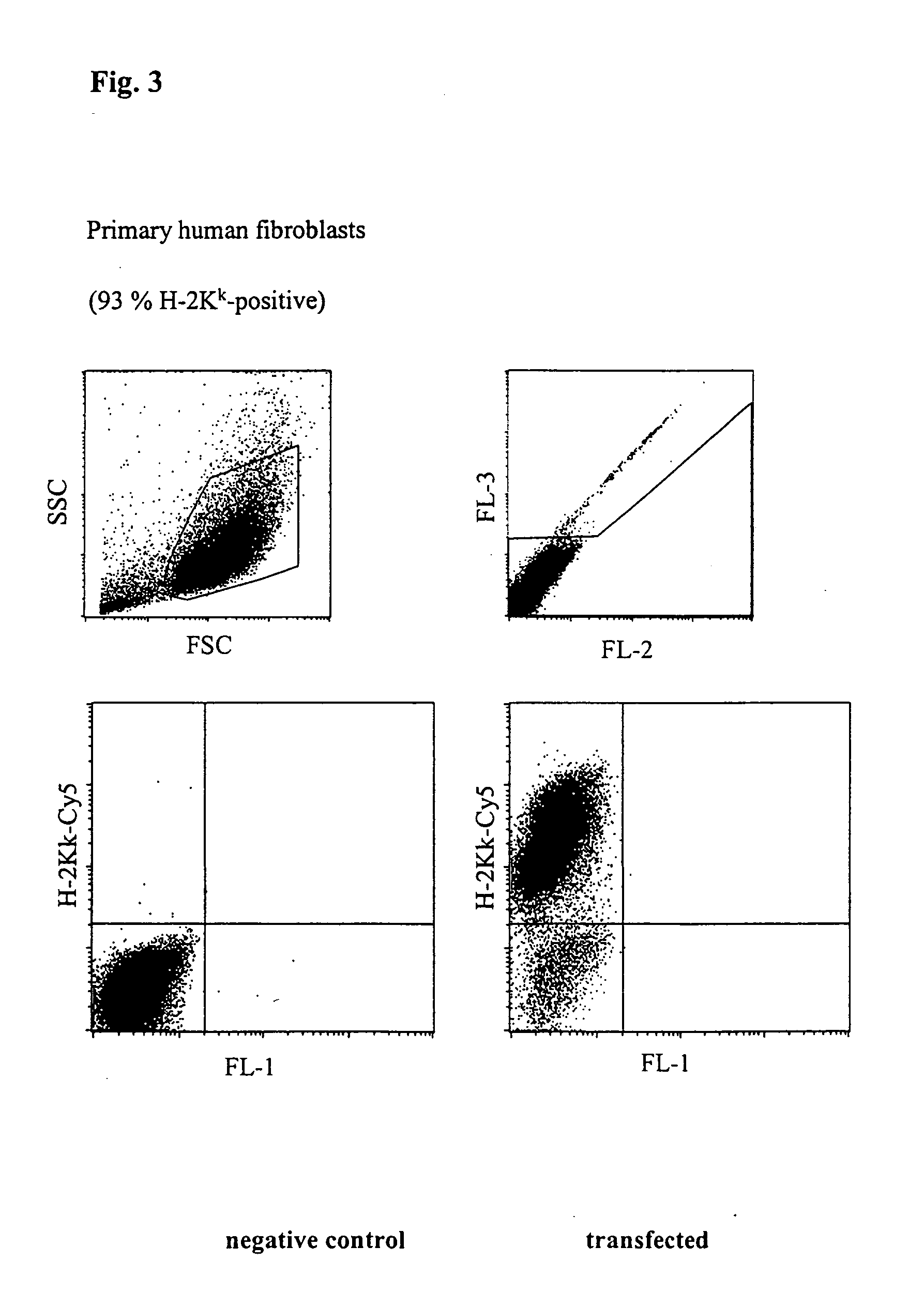
InactiveUS20050064596A1High transfection efficiencyReduce cell deathPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsElectroporationIon
The invention relates to a buffer solution for suspending animal or human cells and for dissolving biologically active molecules in order to introduce said biologically active molecules into the cells using an electric current and to a method for introducing biologically active molecules into animal or human cells using an electric current and a buffer solution. The inventive buffer solution has a buffering capacity of at least 20 mmol*I−1*pH−1 and an ionic strength of at least 200 mmol*I−1 during a change to the pH value from pH 7 to pH 8 and at a temperature of 25° C. The use of a buffer solution of this type in the corresponding method allows biologically active molecules to be introduced into animal and human cells with a high degree of transfection efficiency and at the same time a low cell mortality. Different cell types, in particular dormant and actively dividing cells of low activity, can be successfully transfected in said buffer solution.
Owner:LONZA COLOGNE
Methods, devices, arrays and kits for detecting and analyzing biomolecules
InactiveUS6969615B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue microarrayHuman cell
The present disclosure is directed to devices, arrays, kits and methods for detecting biomolecules in a tissue section (such as a fresh or archival sample, tissue microarray, or cells harvested by an LCM procedure) or other substantially two-dimensional sample (such as an electrophoretic gel or cDNA microarray) by creating “carbon copies” of the biomolecules eluted from the sample and visualizing the biomolecules on the copies using one or more detector molecules (e.g., antibodies or DNA probes) having specific affinity for the biomolecules of interest. Specific methods are provided for identifying the pattern of biomolecules (e.g., proteins and nucleic acids) in the samples. Other specific methods are provided for the identification and analysis of proteins and other biological molecules produced by cells and / or tissue, especially human cells and / or tissue. The disclosure also provides a plurality of differentially prepared and / or processed membranes that can be used in described methods, and which permit the identification and analysis of biomolecules.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE US SEC +1
Methods and compositions for the targeted modification of a genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
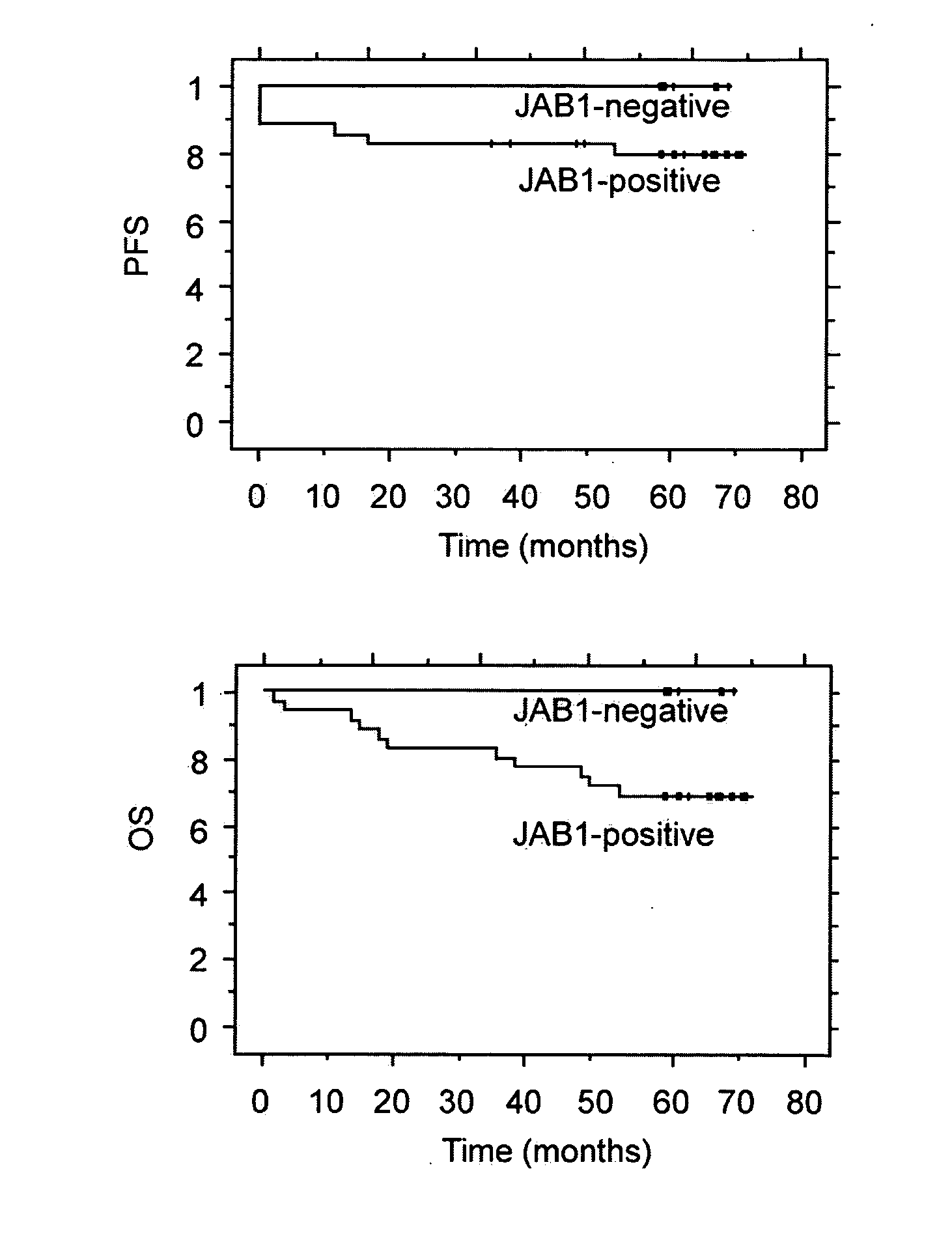
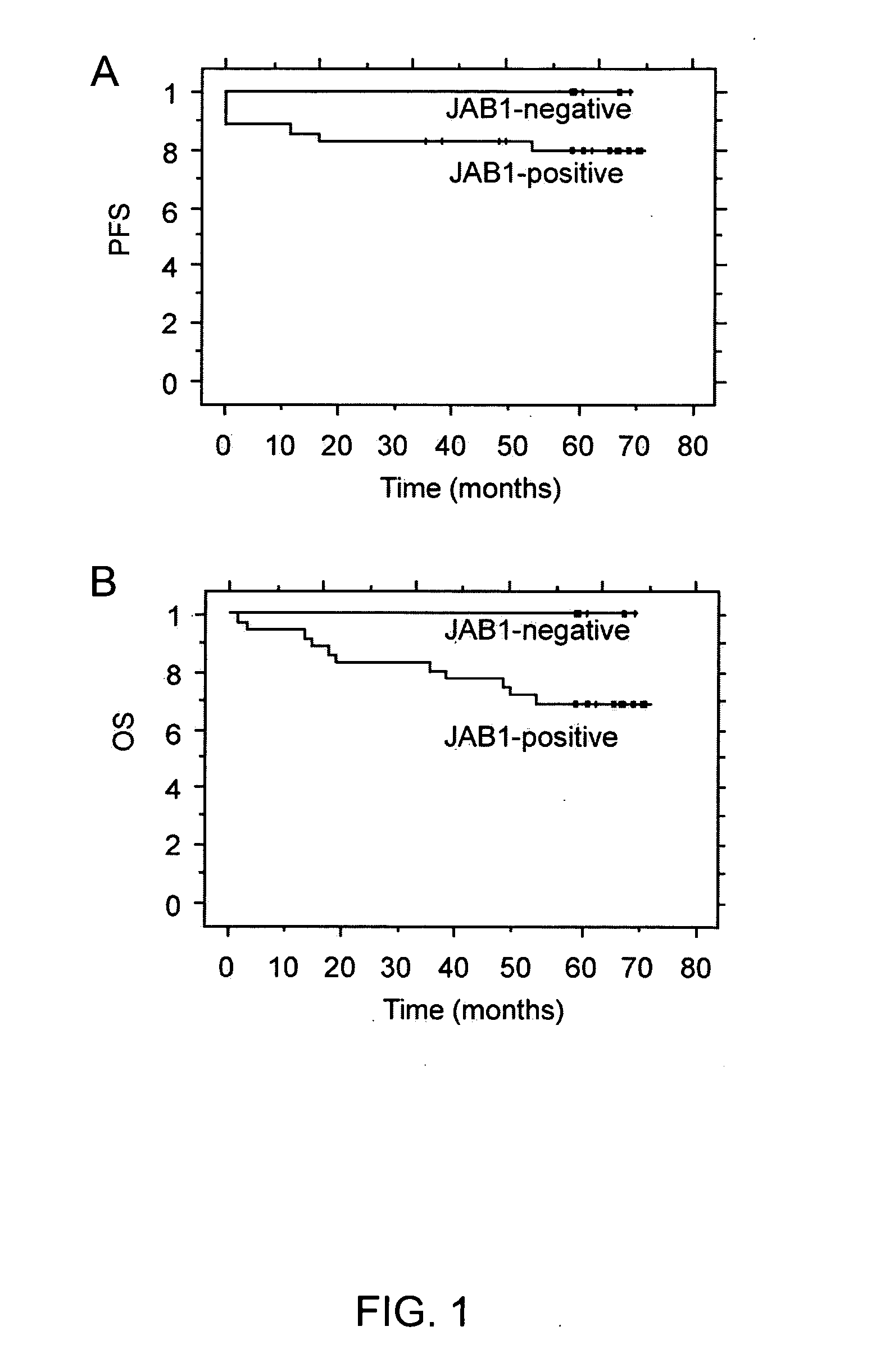
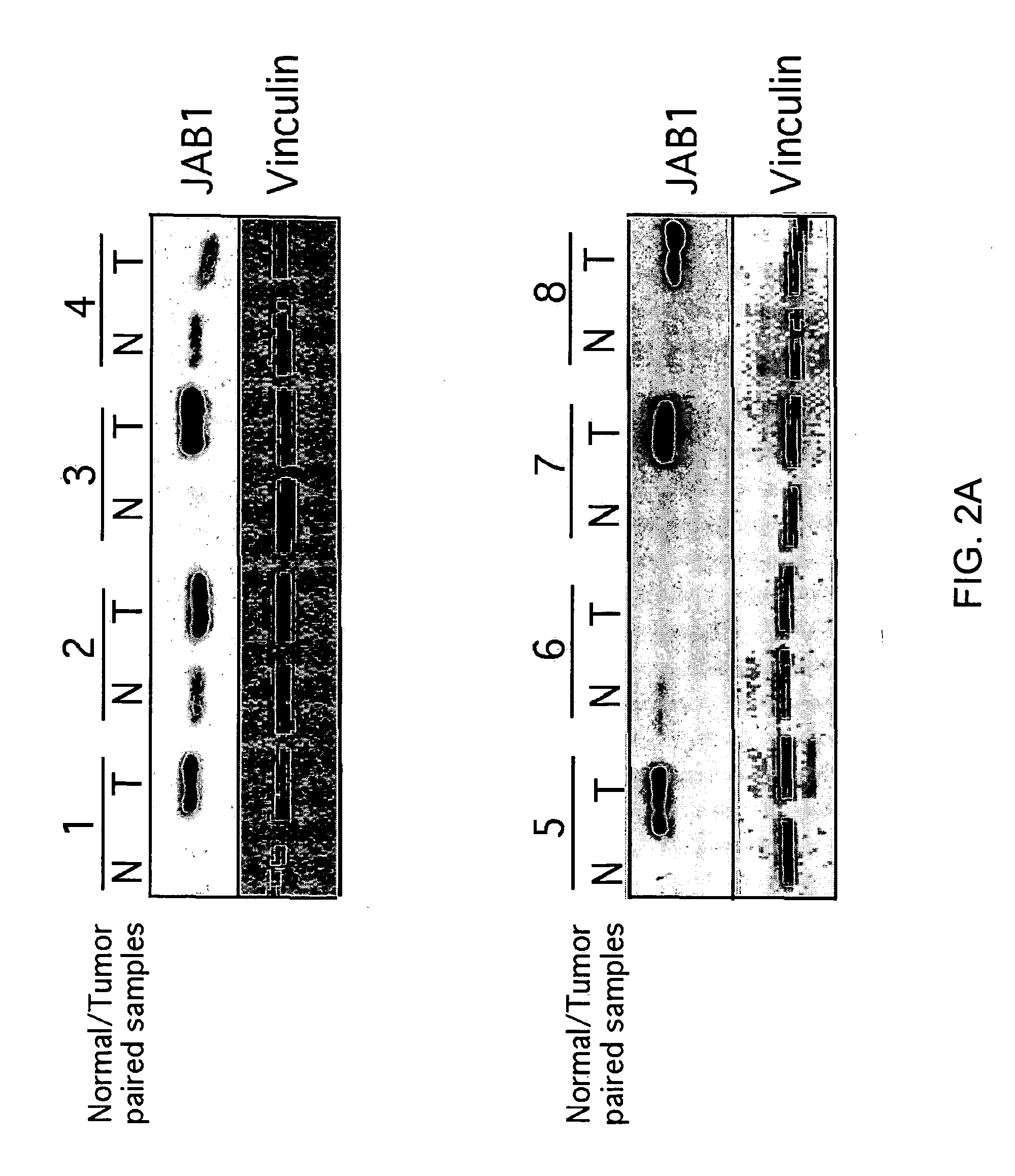
JAB1 as a prognostic marker and a therapeutic target for human cancer
InactiveUS20050069918A1High JAB expressionLower Level RequirementsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHuman cancerHuman cell
Methods of diagnosing and prognosticating the development of human cancers, such as breast cancer, colon cancer, and pancreatic cancer, are provided. The diagnostic and prognostic methods include the detection and / or quantifying of the amount of expression of JAB1 in human cells, particularly in relation to the amount of p27 or c-Jun. In addition, methods for reducing the expression of JAB1 protein in cells and inhibiting its interaction with p27 or c-Jun, for example, are provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compositions and methods directed to CRISPR/Cas genomic engineering systems
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification in mammalian cells. The present specification describes the design and testing of a polynucleotide encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells. The specification also describes all-in-one systems for RNA-guided genome engineering in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
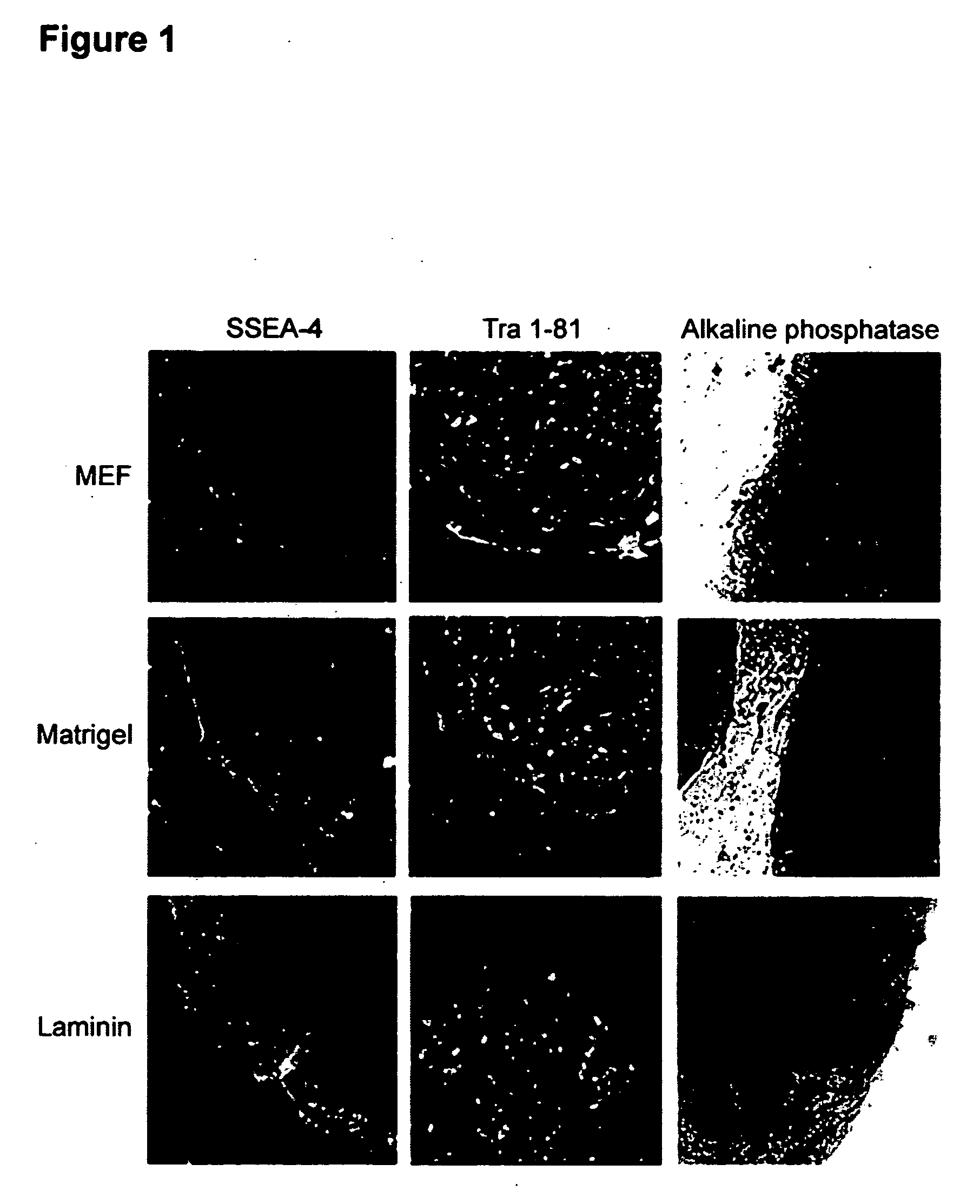
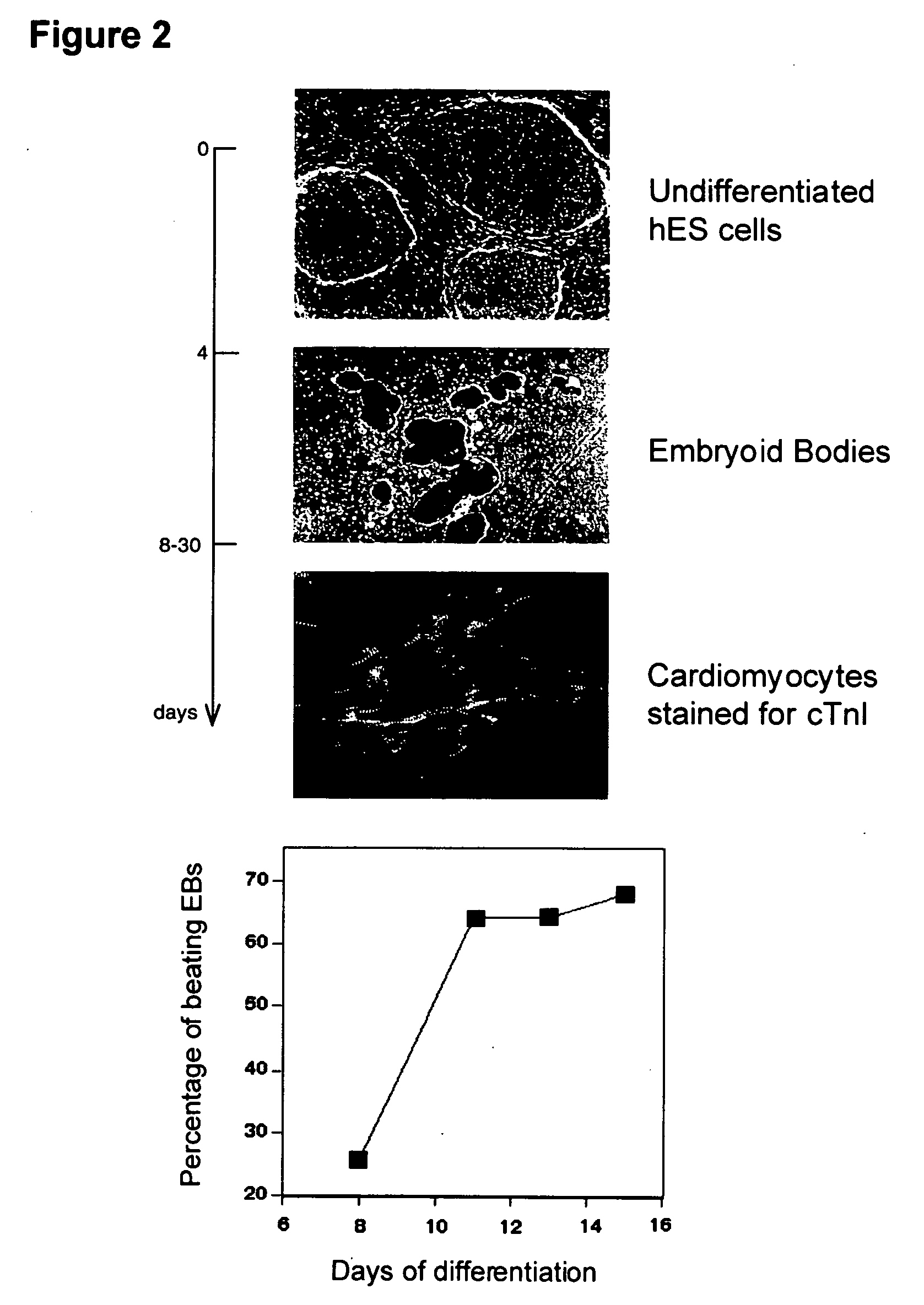
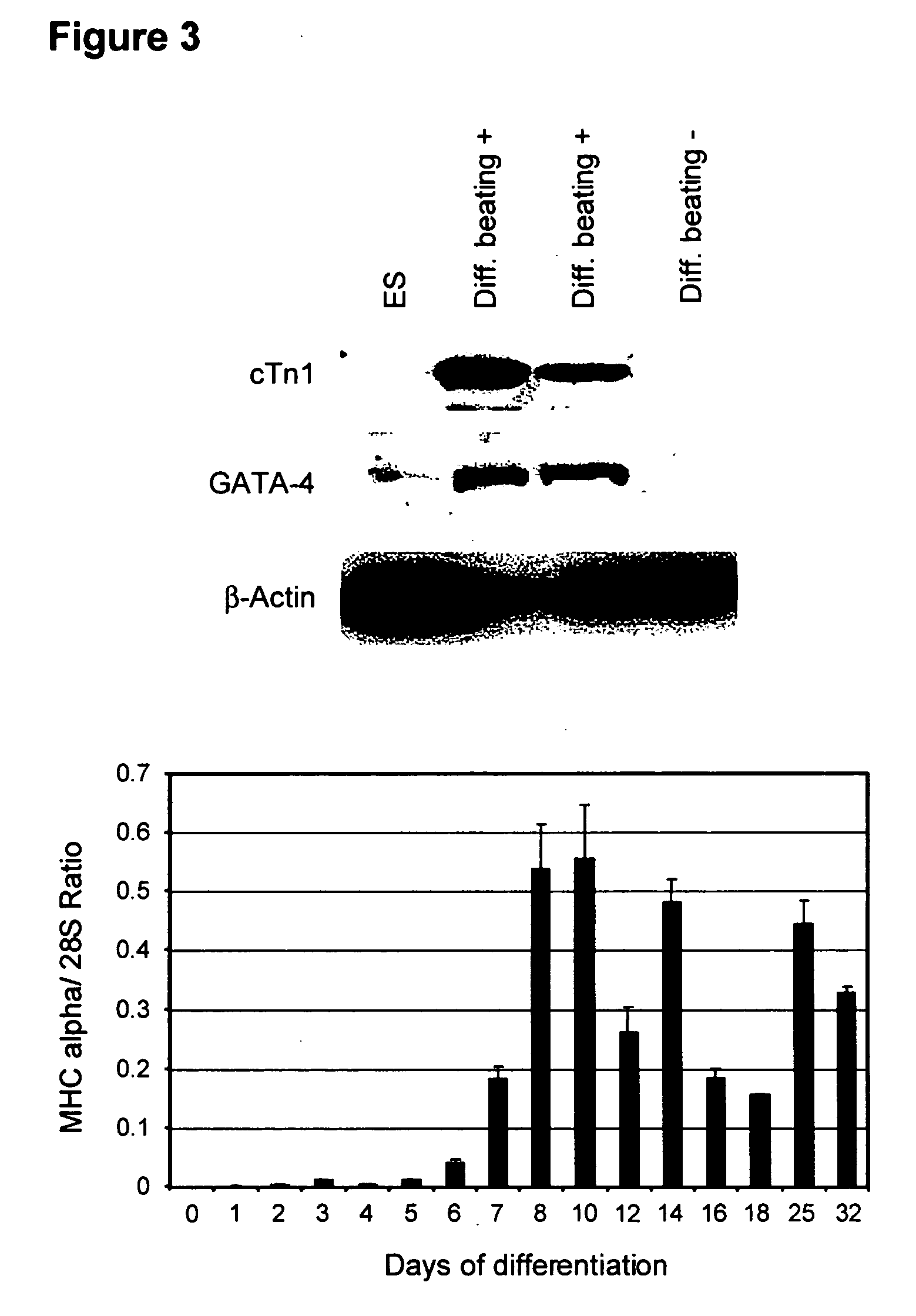
Process for making transplantable cardiomyocytes from human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050054092A1Efficient productionGenetically modified cellsDrug screeningDiseaseHuman cell
This invention provides populations human cells of the cardiomyocyte lineage. The cells are obtained by causing cultures of pluripotent stem cells to differentiate in vitro, and then harvesting cells with certain phenotypic features. Differentiated cells bear cell surface and morphologic markers characteristic of cardiomyocytes, and a proportion of them undergo spontaneous periodic contraction. Highly enriched populations of cardiomyocytes and their replicating precursors can be obtained, suitable for use in a variety of applications, such as drug screening and therapy for cardiac disease.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Modified Vaccinia Ankara virus variant and cultivation method
InactiveUS7445924B2Reduce riskGenetic material ingredientsVirus peptidesSerum free mediaModified vaccinia Ankara
The present invention provides an attenuated virus, which is derived from Modified Vaccinia Ankara virus and characterized by the loss of its capability to reproductively replicate in human cell lines. It further describes recombinant viruses derived from this virus and the use of the virus, or its recombinants, as a medicament or vaccine. A method is provided for inducing an immune response in individuals who may be immune-compromised, receiving antiviral therapy, or have a pre-existing immunity to the vaccine virus. In addition, a method is provided for the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of the virus, or its recombinants, in a vaccinia virus prime / vaccinia virus boost innoculation regimen. The present invention relates to a method of virus amplification in primary cells which are cultivated in a serum free medium. Viruses produced by this method are advantageously free of any infectious agents comprised in animal sera.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Adenovirus vector vaccine for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection
ActiveCN110974950AImprove securityAvoid infectionSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsVector vaccineHuman cell
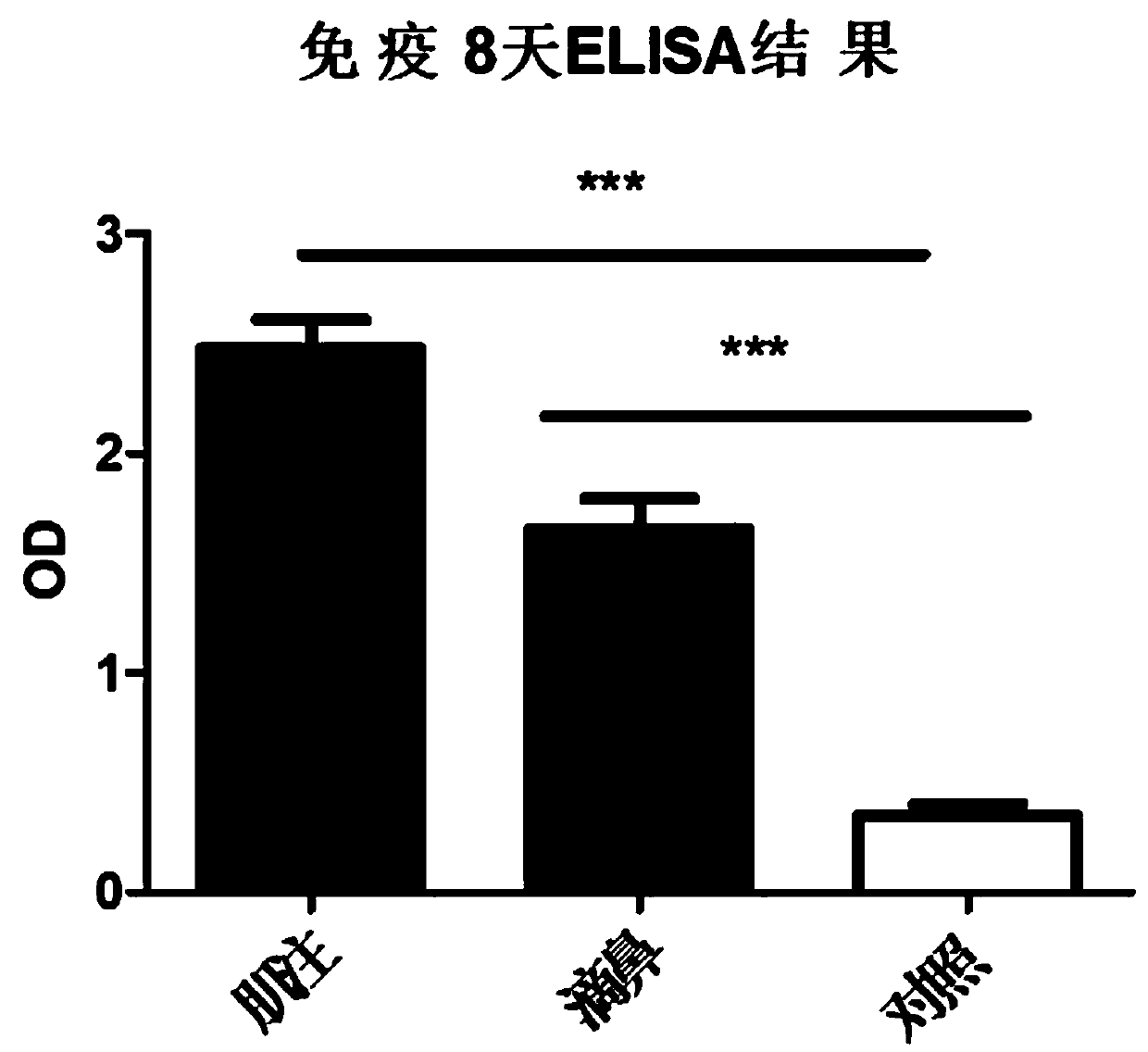
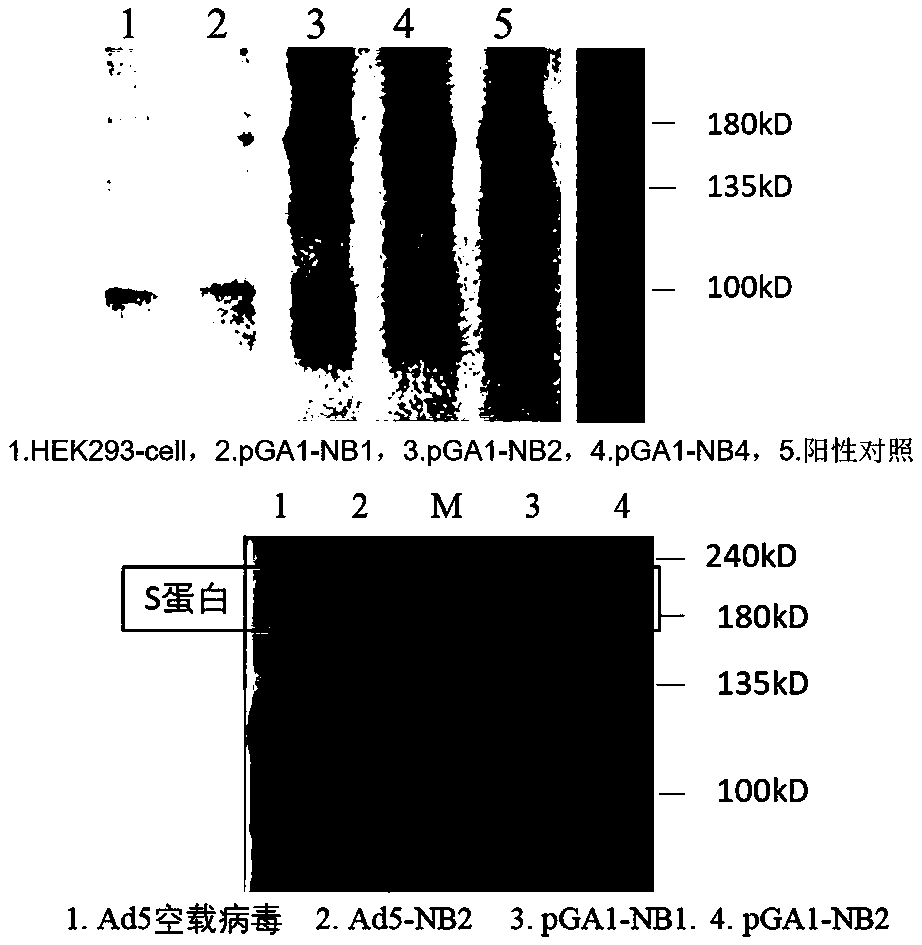
The invention discloses an adenovirus vector vaccine for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. The vaccine comprises a nucleic acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. According to a plurality of embodiments of the invention, the S protein nucleic acid sequence contained in the vaccine is easy to express in human cells, and generation of more S proteins can be induced, so the vaccine is expected to be used as a recombinant virus vaccine for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection. According to a plurality of embodiments of the invention, the vaccine has good security.
Owner:GUANGZHOU N BIOMED LTD
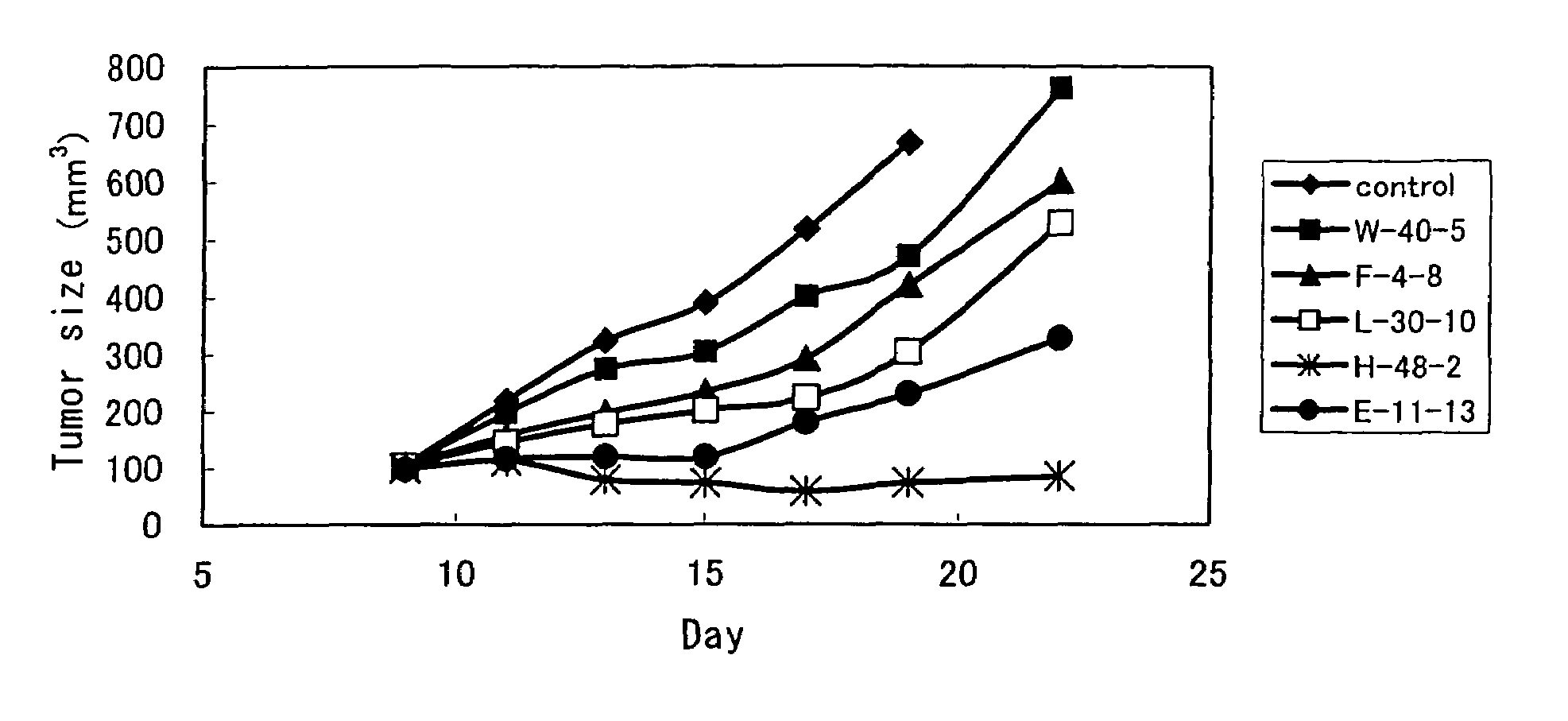
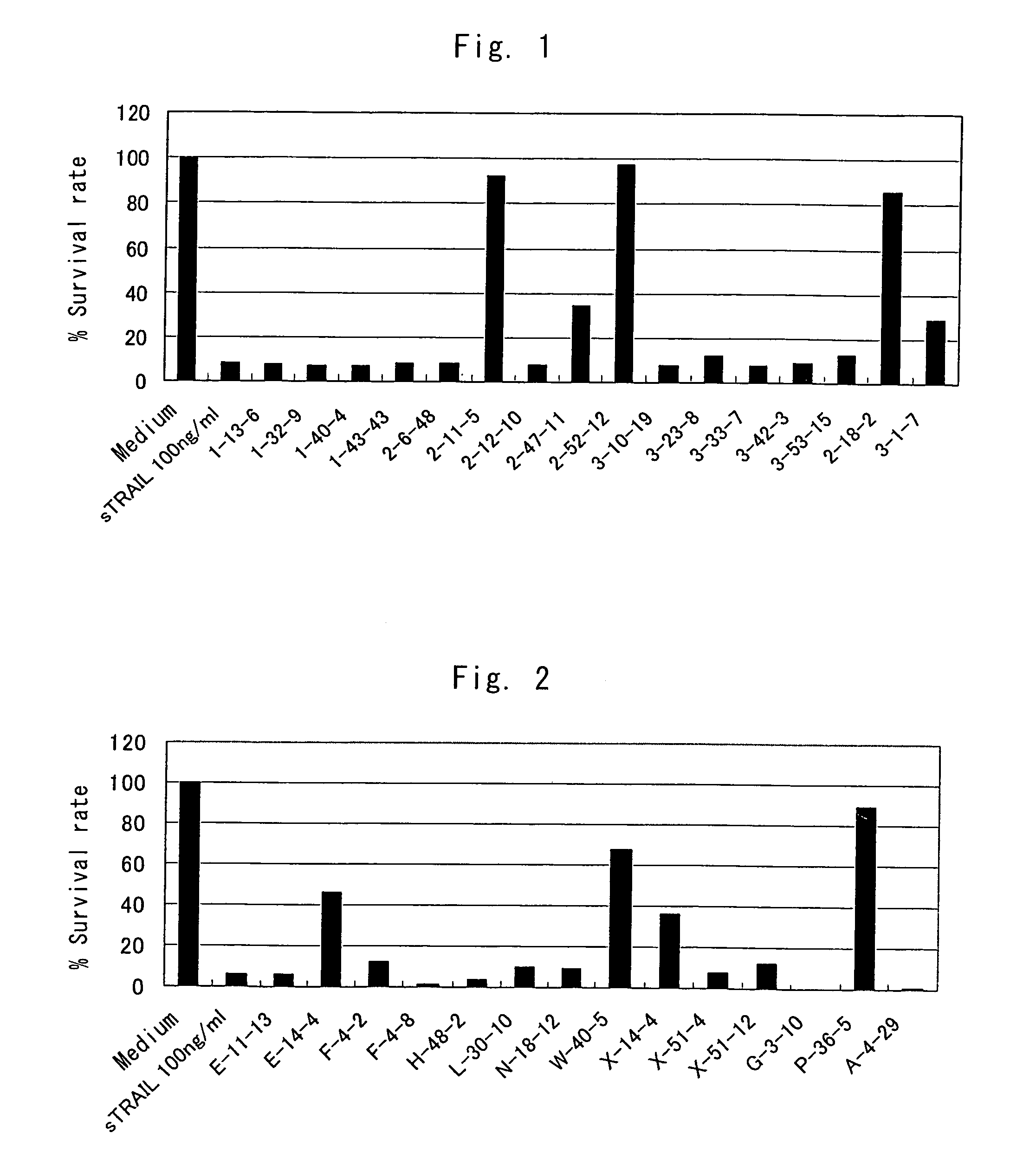
Anti-TRAIL-R antibodies
Anti-TRAIL-R1 and R2 antibodies or functional fragments thereof, having at least one property selected from the following (a) to (c) of:(a) having activity to induce apoptosis in carcinoma cells expressing TRAIL-R1 and / or TRAIL-R2;(b) not having effect on normal human cells expressing TRAIL-R1 and / or TRAIL-R2; and(c) not inducing human hepatocyte toxicity.
Owner:KIRIN BEER KABUSHIKI KAISHI KAISHA
Universal method and composition for the rapid lysis of cells for the release of nucleic acids and their detection
InactiveUS7494771B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid testSolid particle
This invention describes a rapid (10 to 15 minutes), simple, flexible and efficient method of nucleic acids extraction for nucleic acid testing assays. This method has the following basic steps: i) mechanical cell lysis using solid particles in the presence of a chelating agent, followed by ii) controlling the presence and / or activity of NAT assays inhibitors. This method is applicable to various biological samples and universal for microorganisms, as one can use it to extract nucleic acids from test samples containing target viruses, bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, parasites or other eukaryotic cells, including animal and human cells.
Owner:ART RECH & TECH AVANCEES INC ART ADVANCED RES TECH INC +1
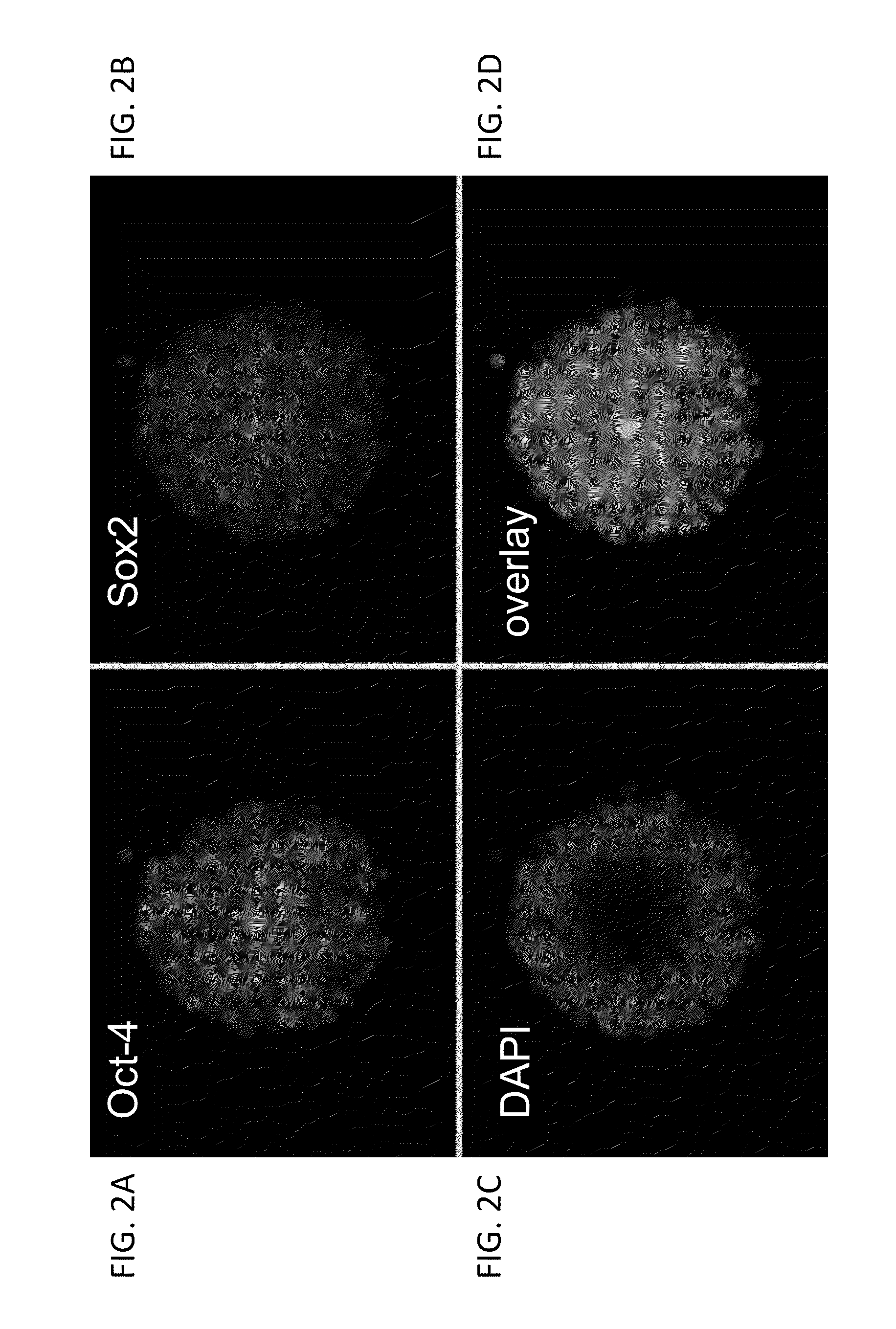
Human trophoblast stem cells and use thereof
Existence of human trophoblast stem (hTS) cells has been suspected but unproved. The isolation of hTS cells is reported in the early stage of chorionic villi by expressions of FGF4, FGFR-2, Oct4, Thy-1, and stage-specific embryonic antigens distributed in different compartments of the cell. hTS cells are able to derive into specific cell phenotypes of the three primitive embryonic layers, produce chimeric reactions in mice, and retain a normal karyotype and telomere length. In hTS cells, Oct4 and fgfr-2 expressions can be knockdown by bFGF. These facts suggest that differentiation of the hTS cells play an important role in implantation and placentation. hTS cells could be apply to human cell differentiation and for gene and cell-based therapies.
Owner:ACCELERATED BIOSCI
Cell freezing medium
The invention provides a cell freezing medium which can be clinically safely used and is used for freezing human cells. The cell freezing medium comprises: 2-8wt% of human albumin, 5-10 volume% of dimethyl sulfoxide, 3.5-5.1wt% of dextranum-40 and 2.75-4.25wt% of glucose.
Owner:BEIJING YONGTAI IMMUNITY APPL TECH
Methods and compositions for the targeted modification of a genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Peptide-based vaccine for influenza
A human synthetic peptide-based influenza vaccine for intranasal administration comprises a mixture of flagella containing at least four epitopes of influenza virus reactive with human cells, each expressed individually in Salmonella flagellin, said influenza virus epitopes being selected from the group consisting of: (i) one B-cell hemagglutinin (HA) epitope; (ii) one T-helper hemagglutinin (HA) or nucleo-protein (NP) epitope that can bind to many HLA molecules; and (iii) at least two cytotoxic lymphocyte (CTL) nucleoprotein (NP) or matrix protein (M) epitopes that are restricted to the most prevalent HLA molecules in different human populations.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Interleukin 15 as Selectable Marker for Gene Transfer in Lymphocytes
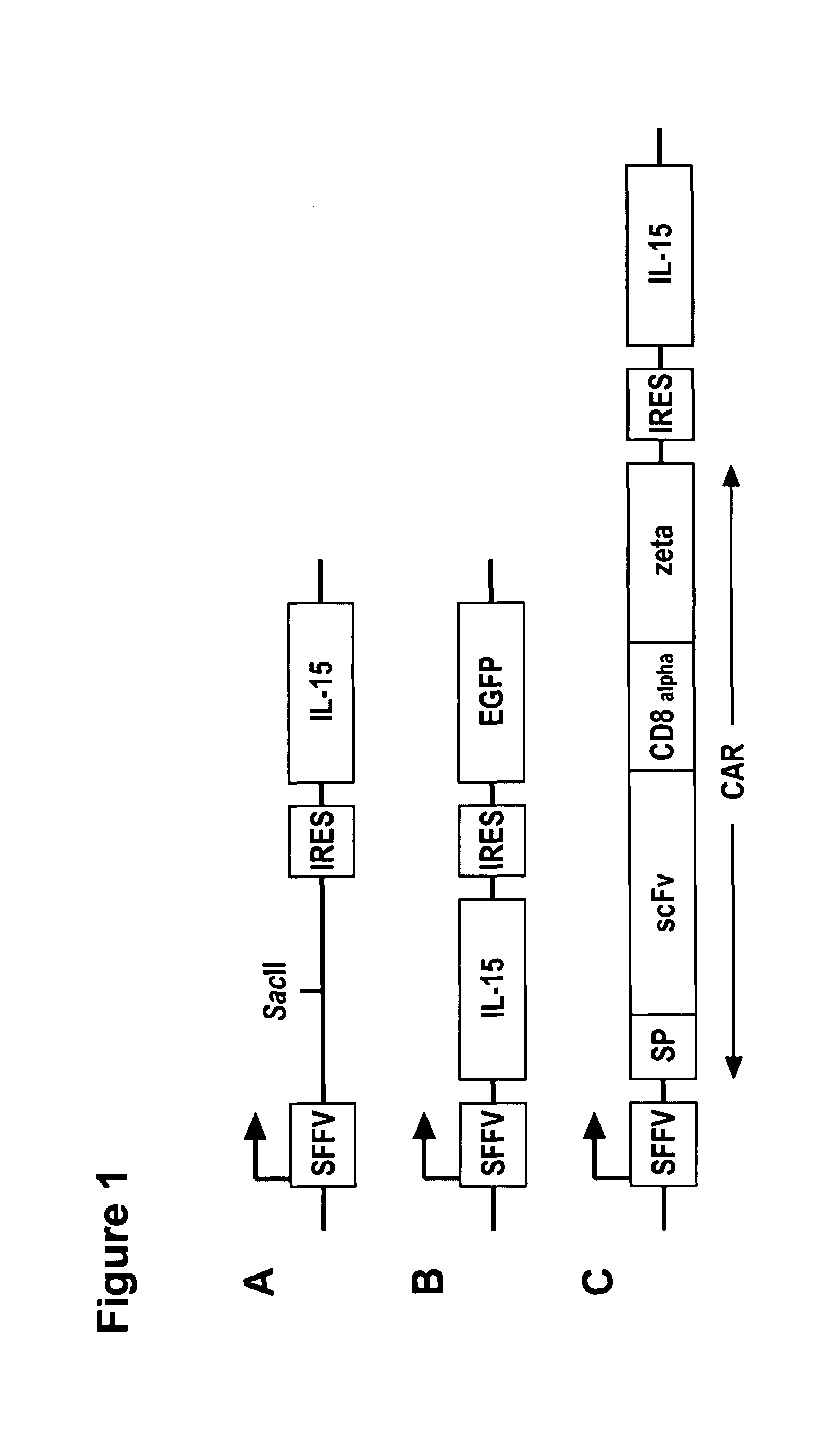
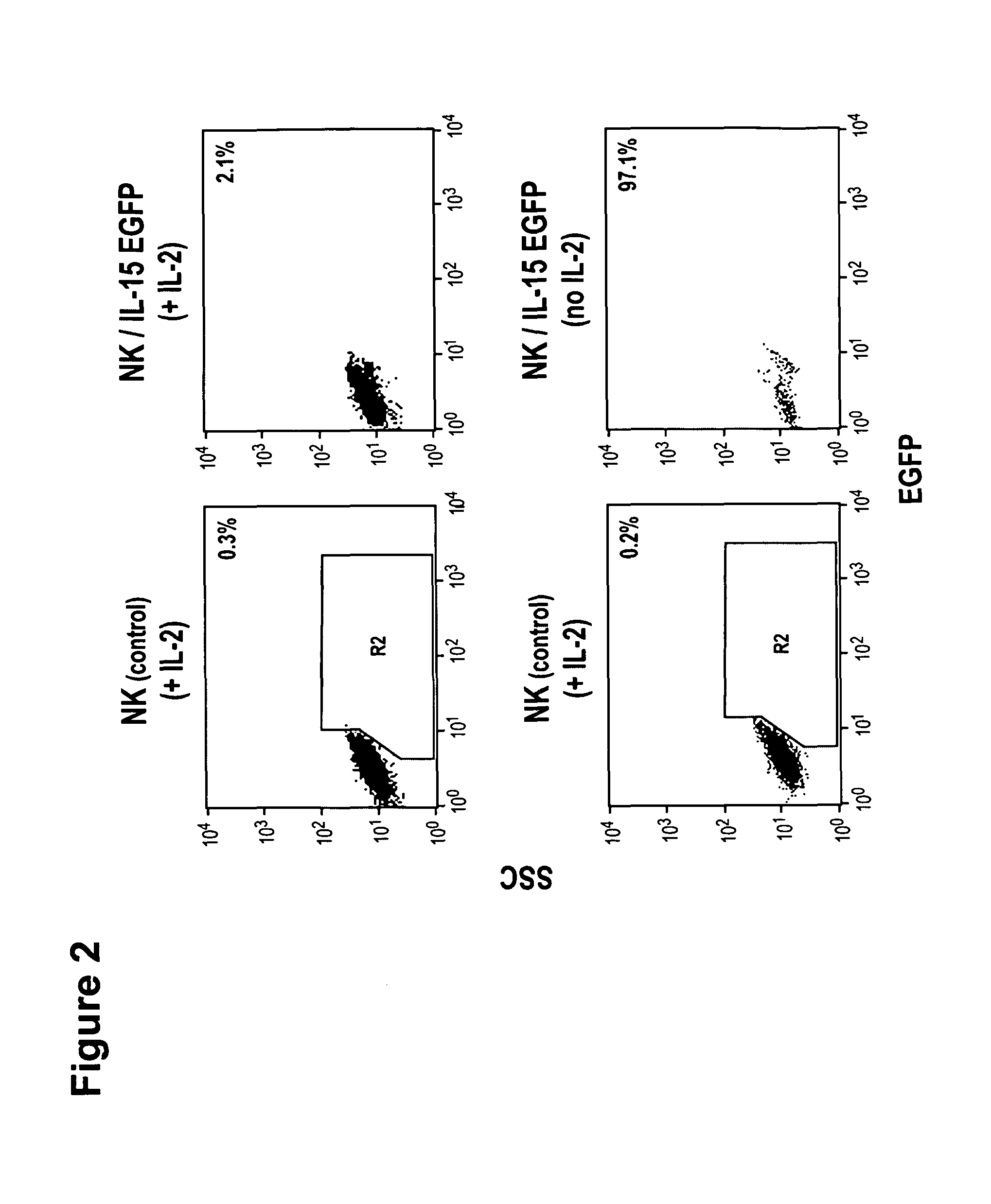
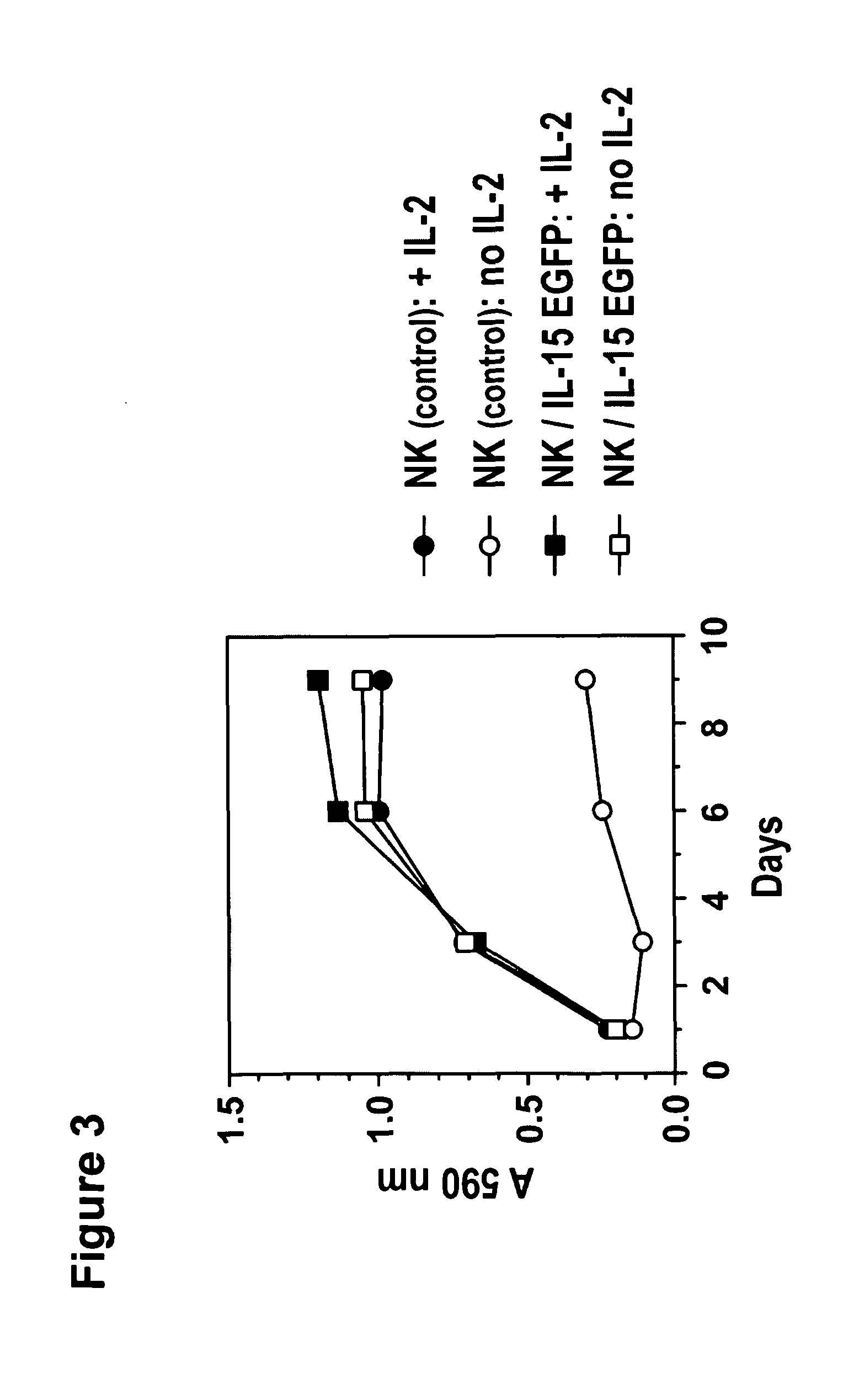
ActiveUS20130280221A1Opening possibilityBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsADAMTS ProteinsAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to the use of interleukin-15 (IL-15) as selectable marker for gene transfer, preferably of at least one gene of therapeutic interest, into a mammalian cell or cell line, in particular a human cell or cell line. The present invention furthermore relates to transgenic mammalian cells or cell lines expressing IL-15 as selectable marker and co-expressing at least one protein of interest encoded by at least one gene of interest, which is preferably a protein of therapeutic interest. The present invention is in particular suitable for chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) as the gene or protein of interest and their expression in lymphocytes. The transgenic mammalian cells and cell lines are furthermore suitable for use as a medicament, in particular in the treatment of cancer and in immunotherapy, such as adoptive, target-cell specific immunotherapy.
Owner:CHEMOTHERAPEUTISCHES FORSCHUNGINSTITUT GEORG SPEYER HAUS
Neuronal progenitors from feeder-free human embryonic stem cell culture
The present invention relates to methods for producing feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells (preferably adherent) from embryonic stems cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells, the feeder cell-free neuroprogenitor cells, preferably human cells themselves, as well as methods for producing feeder cell-free samples of neuronal cells, preferably adherent human neuronal cells and the feeder cell-free neuronal cells themselves. Pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating neurodegenerative diseases as well as the use of the described cells in assay systems is also described.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Isolation, expansion and use of clonogenic endothelial progenitor cells
InactiveUS20050266556A1Increase in HSCHigh activityBiological material analysisMammal material medical ingredientsCord blood stem cellFeeder Layer
A hierarchy of endothelial colony forming cells (EPCs) was identified from mammalian cord blood, umbilical vein and aorta. A newly isolated cell named high proliferative potential—endothelial colony forming cell (HPP-ECFC) was isolated and characterized. Single cell assays were developed that test the proliferative and clonogenic potential of endothelial cells derived from cord blood, or from HUVECs and HAECs. EPCs were found to reside in vessel walls. Use of a feeder layer of cells derived from high proliferative potential-endothelial colony forming cells (HPP-ECPCS) from human umbilical cord blood, stimulates growth and survival of repopulating hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Stimulation of growth and survival was determined by increased numbers of progenitor cells in in vitro cultures and increased levels of human cell engraftment in the NOD / SCID immunodeficient mouse transplant system.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Method and kit for proteomic identification
InactiveUS20020012920A1Cost-effectiveMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHuman cellProteomics
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES US SEC THE DEPT OF +1
Immunocytokine sequences and uses thereof
ActiveUS7169904B2Low immunogenicityGood effectGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHuman cellGlycosphingolipid
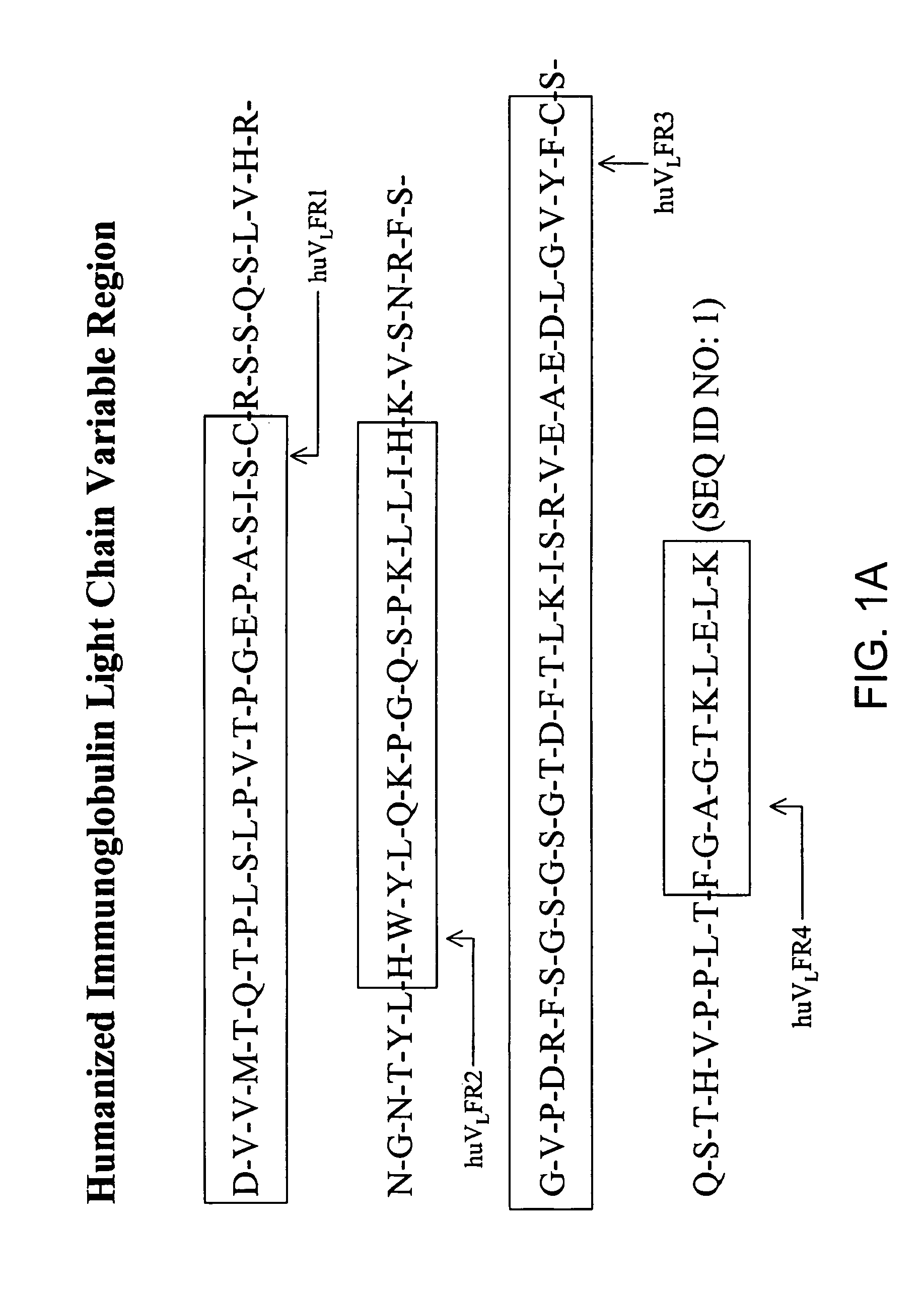
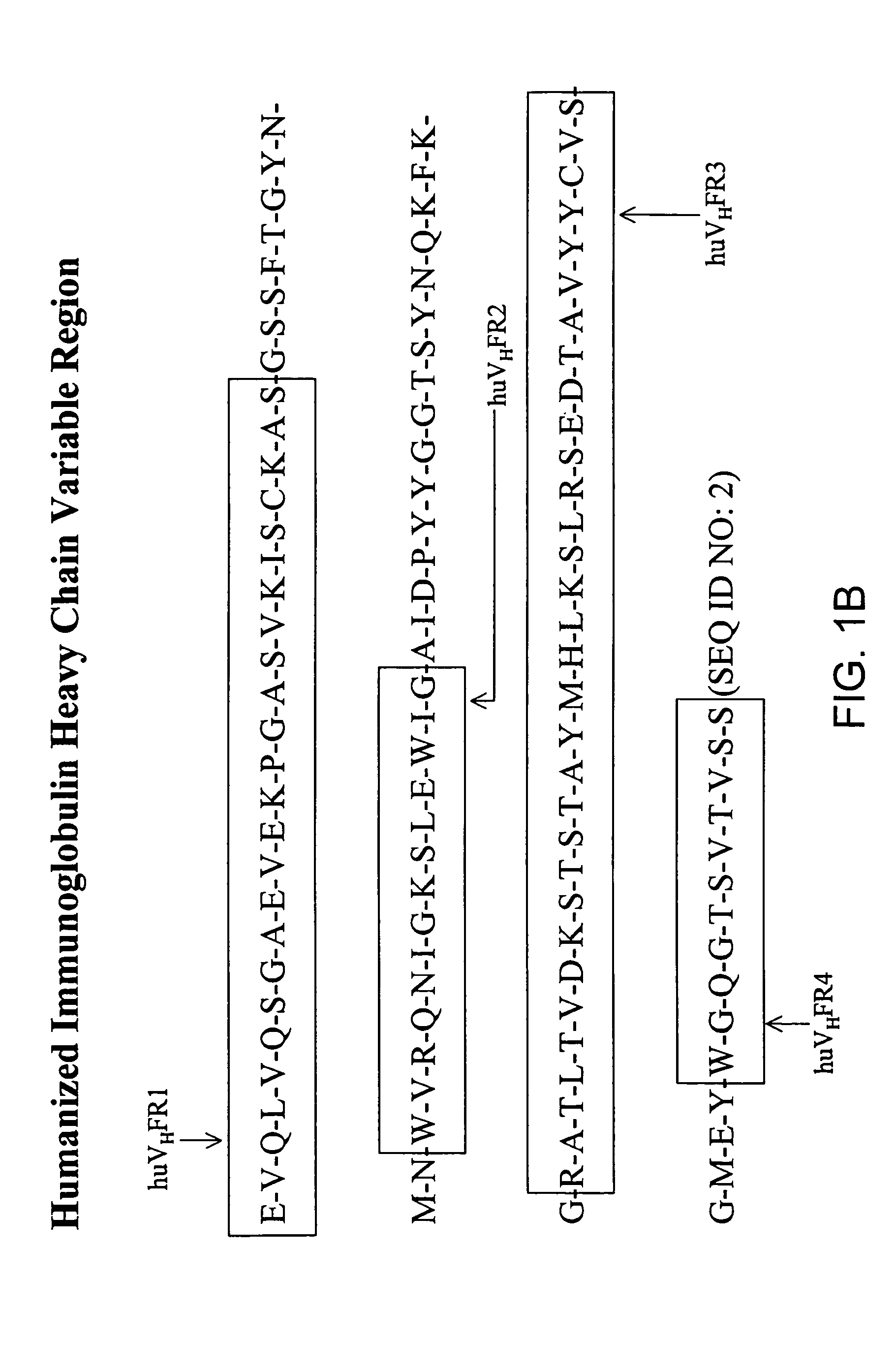
The invention provides a family of antibodies that specifically bind the human cell surface glycosphingolipid GD2. The antibodies comprise modified variable regions, more specially, modified framework regions, which reduce their immunogenicity when administered to a human. The antibodies may be coupled to a therapeutic agent and used in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Modified vaccinia ankara virus variant and cultivation method
InactiveUS20050214323A1Reduce riskViral antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSerum free mediaModified vaccinia Ankara
The present invention provides an attenuated virus, which is derived from Modified Vaccinia Ankara virus and characterized by the loss of its capability to reproductively replicate in human cell lines. It further describes recombinant viruses derived from this virus and the use of the virus, or its recombinants, as a medicament or vaccine. A method is provided for inducing an immune response in individuals who may be immune-compromised, receiving antiviral therapy, or have a pre-existing immunity to the vaccine virus. In addition, a method is provided for the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of the virus, or its recombinants, in a vaccinia virus prime / vaccinia virus boost innoculation regimen. The present invention relates to a method of virus amplification in primary cells which are cultivated in a serum free medium. Viruses produced by this method are advantageously free of any infectious agents comprised in animal sera.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Methylotroph producing mammalian type sugar chain
ActiveUS20060148039A1FungiImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
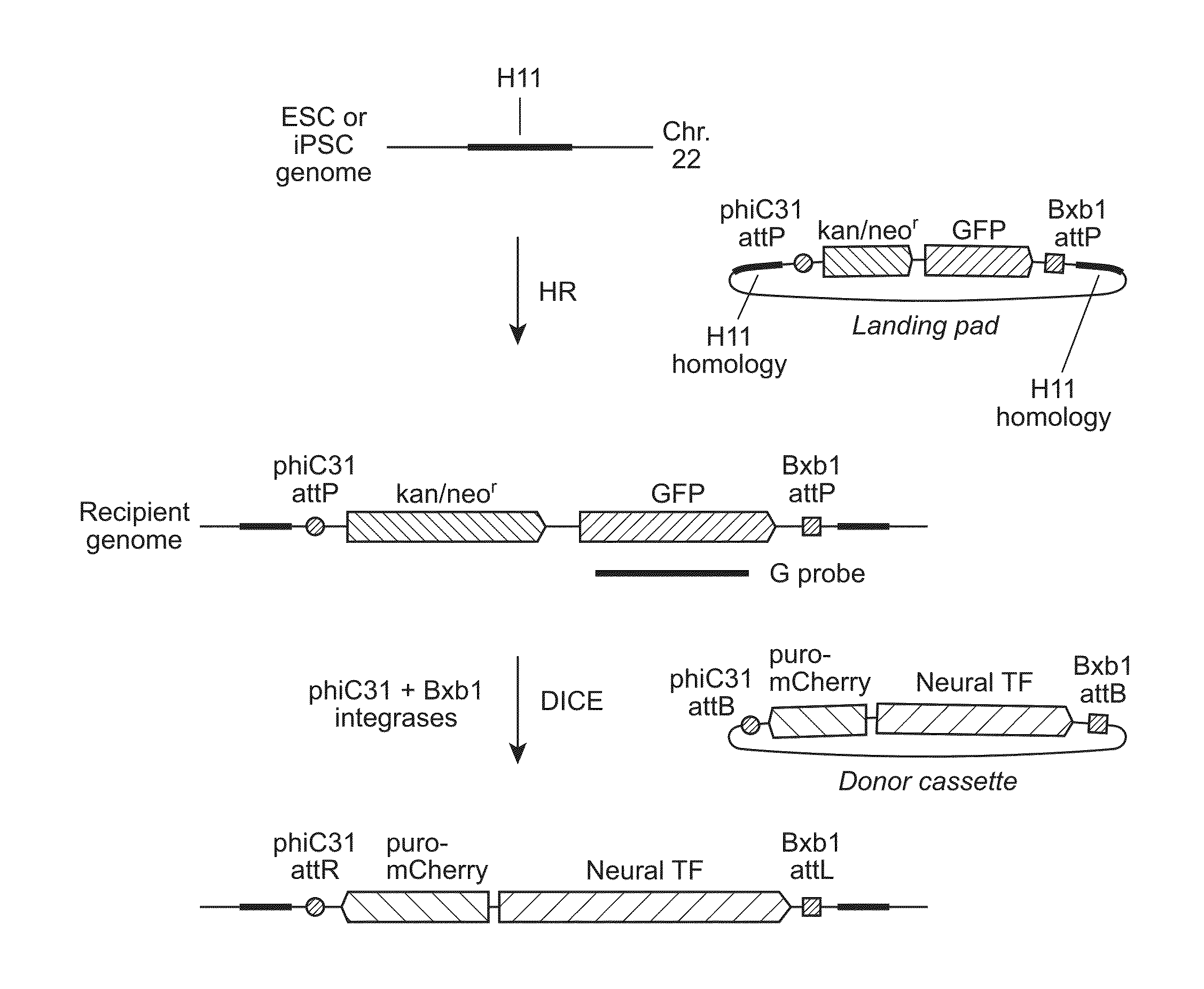
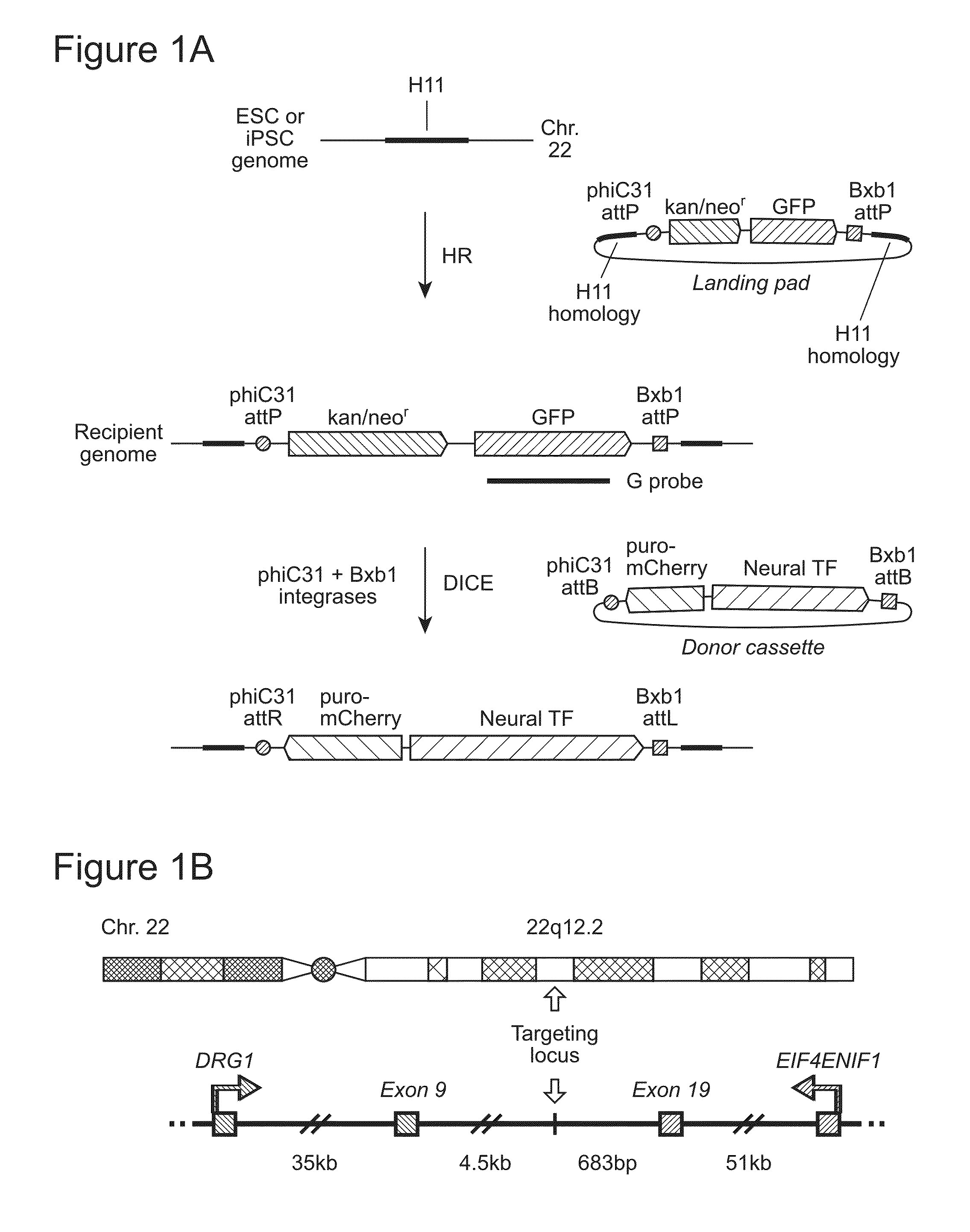
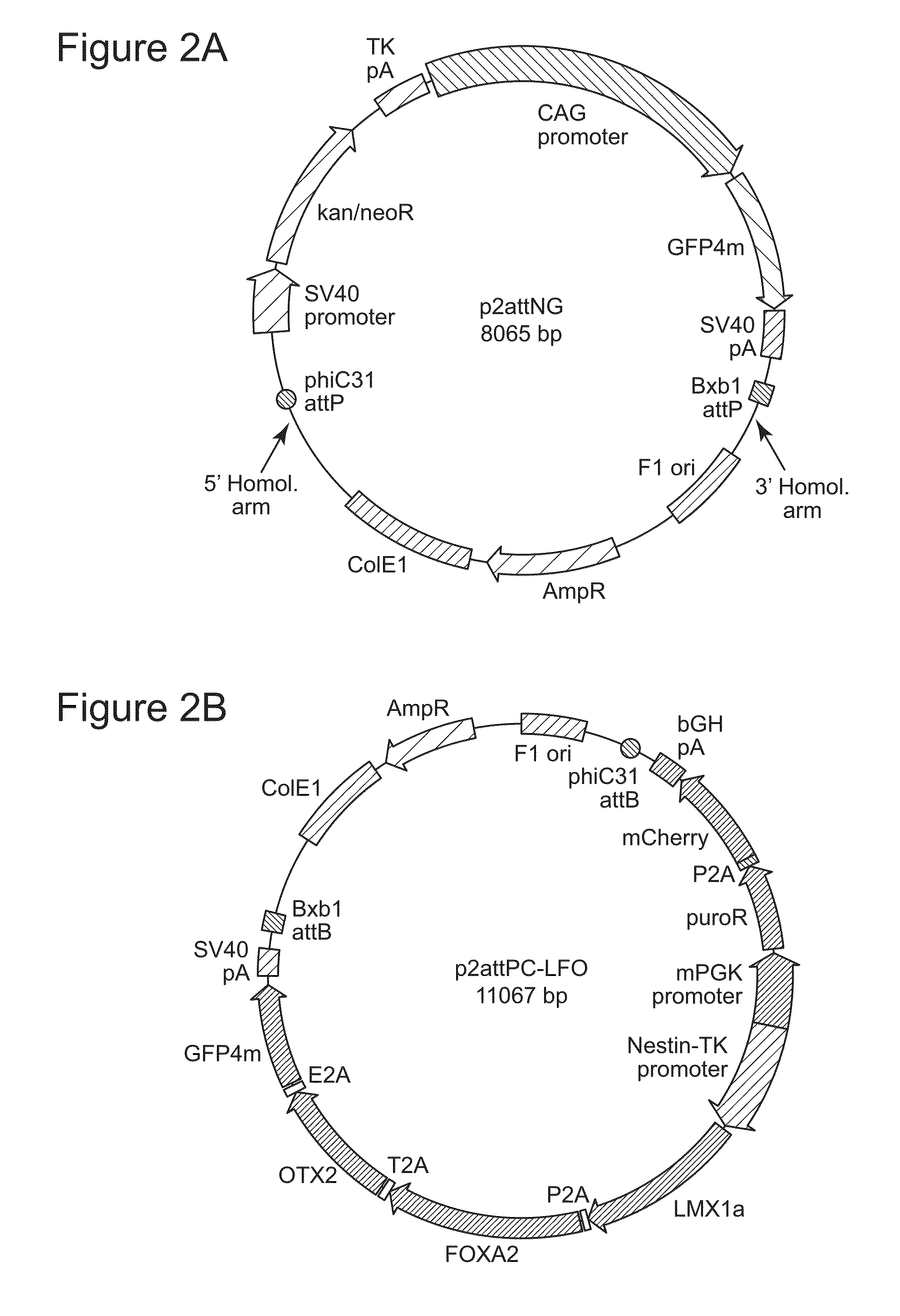
Site-Specific Integration of Transgenes into Human Cells
ActiveUS20150140665A1Easy to optimizeEasy to reorganizeStable introduction of DNAFermentationPresent methodNucleotide
Methods for inserting a polynucleotide sequence into the genome of a human cell are provided. The present methods result in insertion of a polynucleotide sequence of interest into the H11 locus in the genome of a human cell. Also provided are nucleic acids that include sequences for integrating a polynucleotide sequence of interest into the H11 locus in the genome of a human cell. A transgenic human cell including site specific recombination sites at the H11 locus is also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com