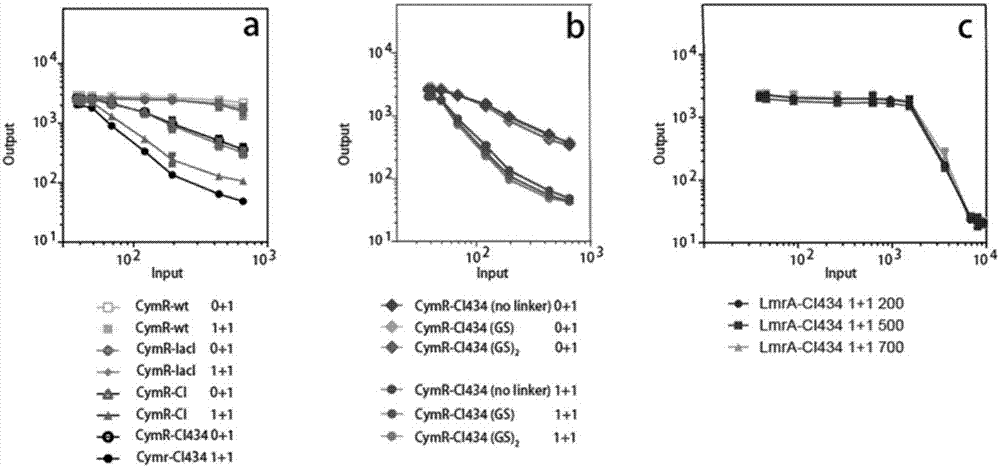
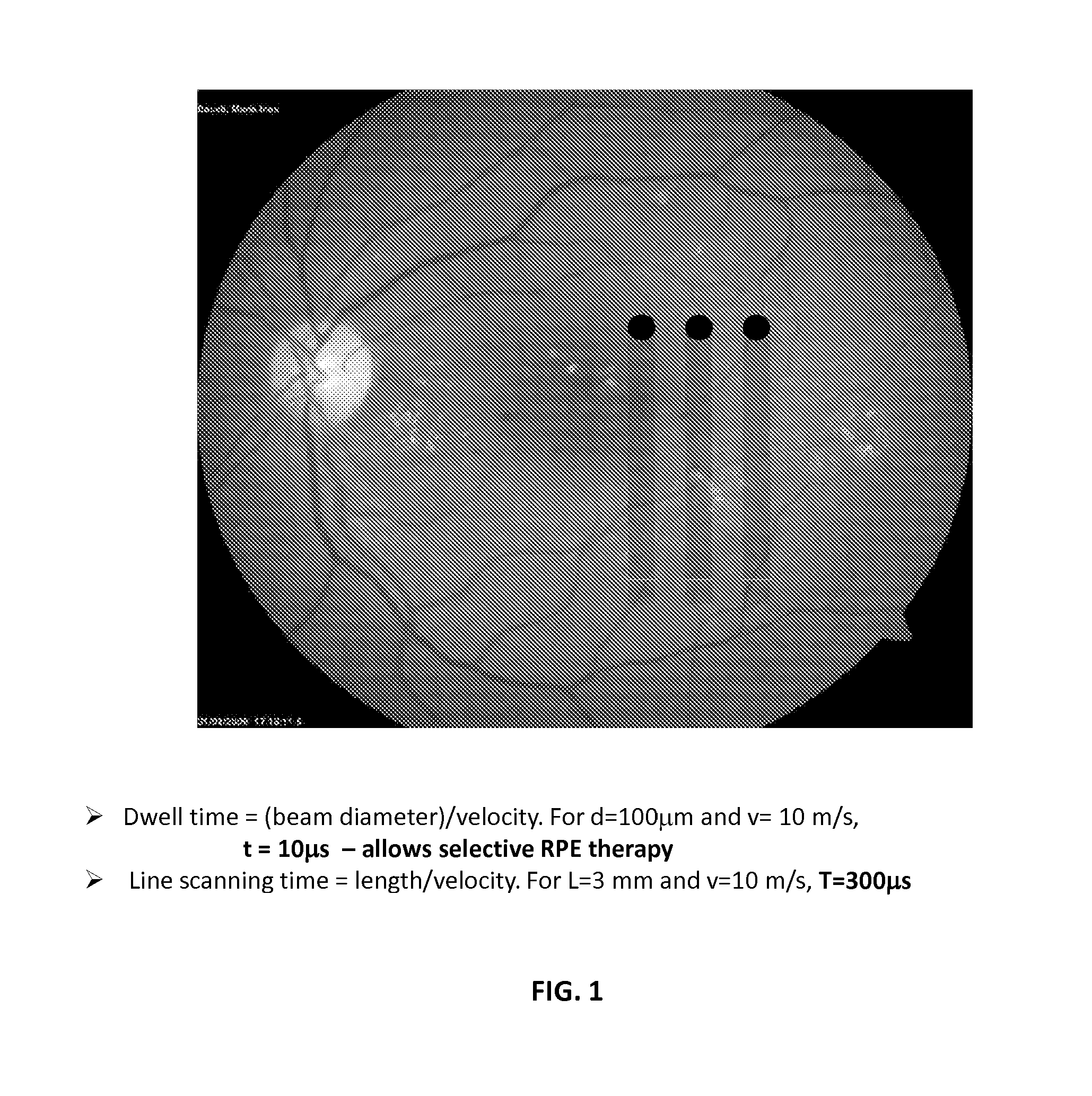
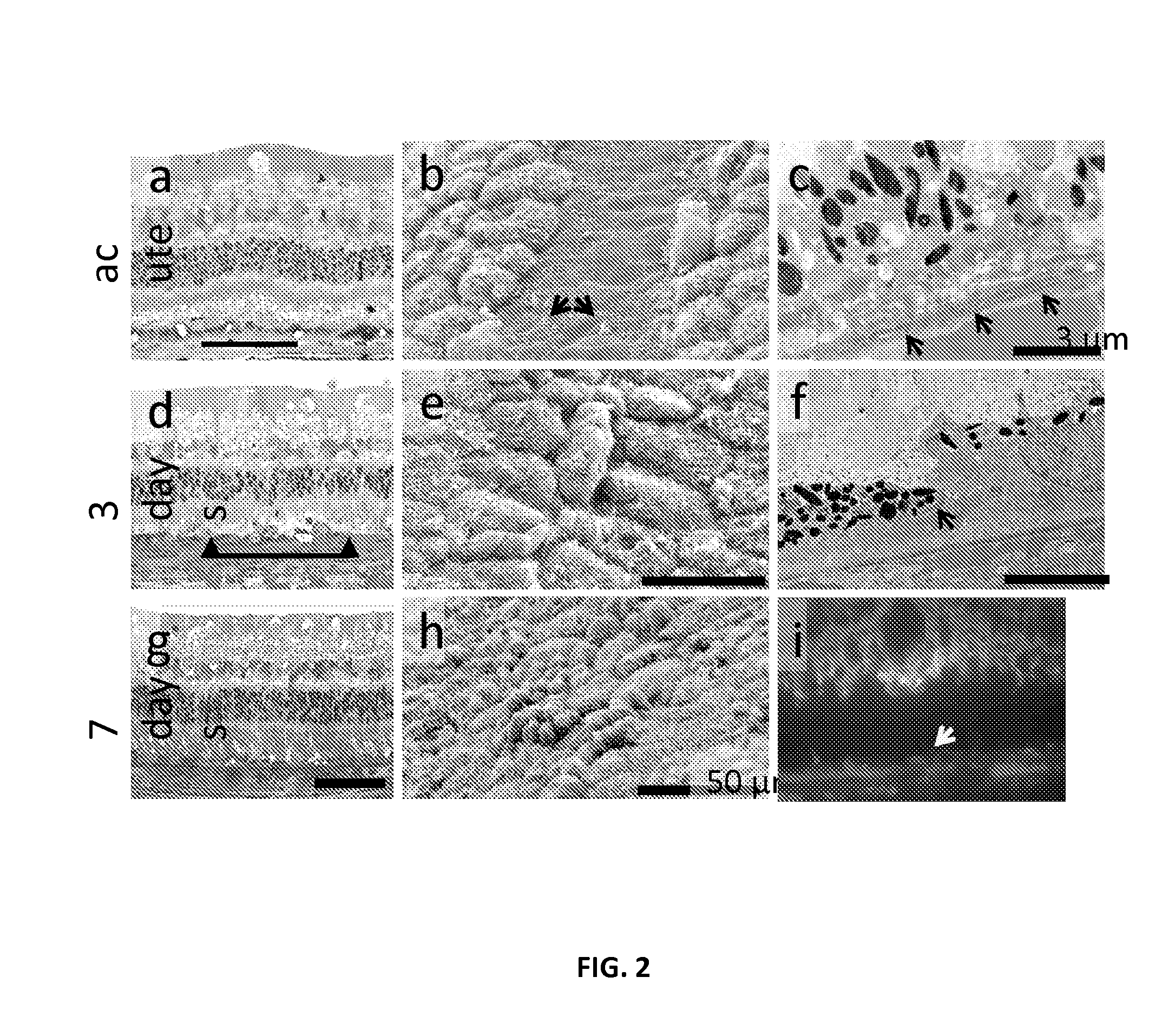
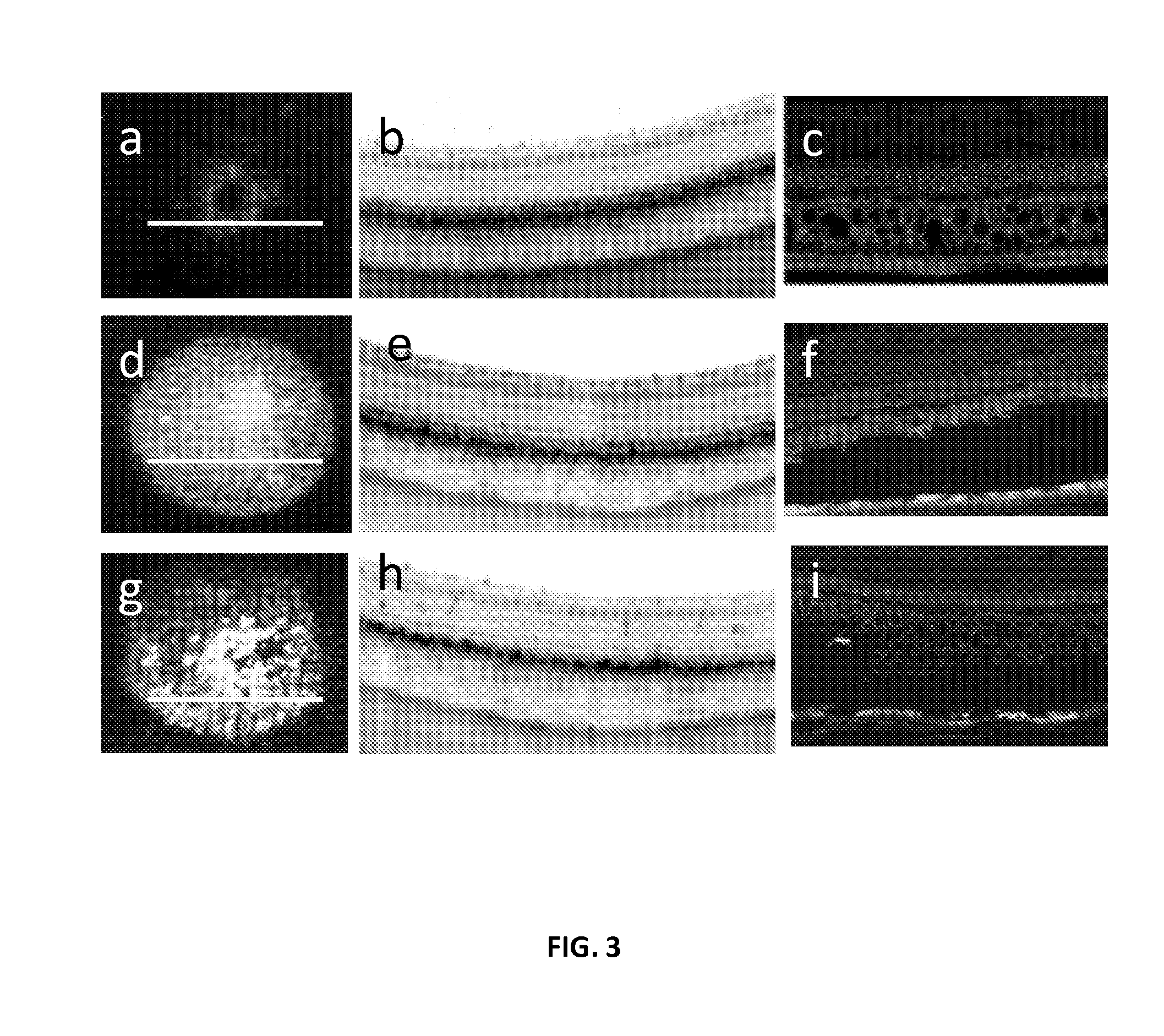
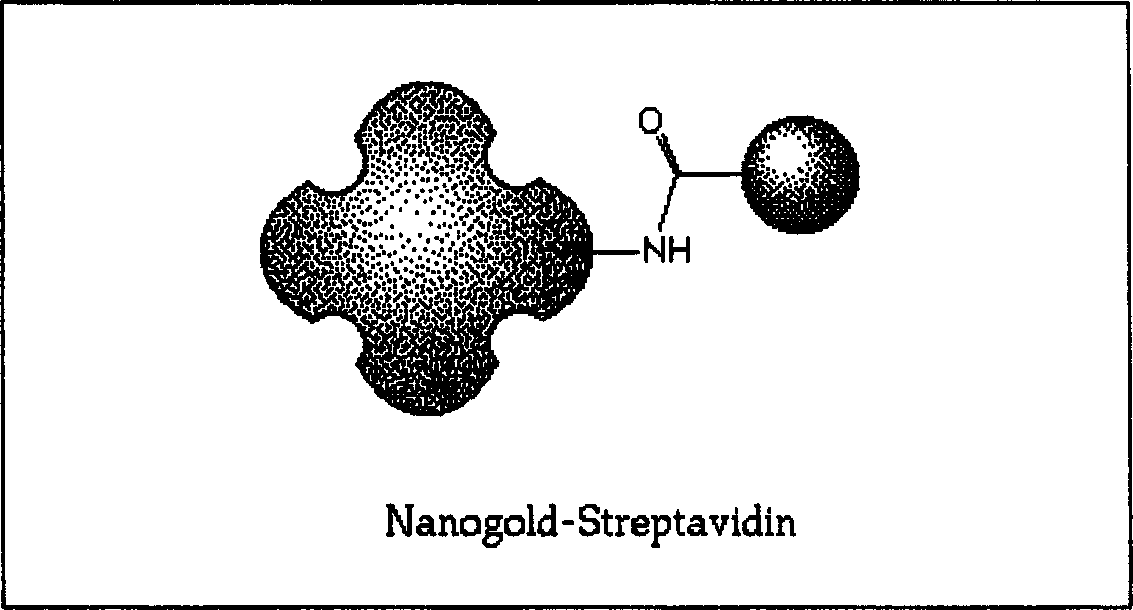Patents
Literature
224 results about "Regulation of gene expression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products (protein or RNA). Sophisticated programs of gene expression are widely observed in biology, for example to trigger developmental pathways, respond to environmental stimuli, or adapt to new food sources. Virtually any step of gene expression can be modulated, from transcriptional initiation, to RNA processing, and to the post-translational modification of a protein. Often, one gene regulator controls another, and so on, in a gene regulatory network.
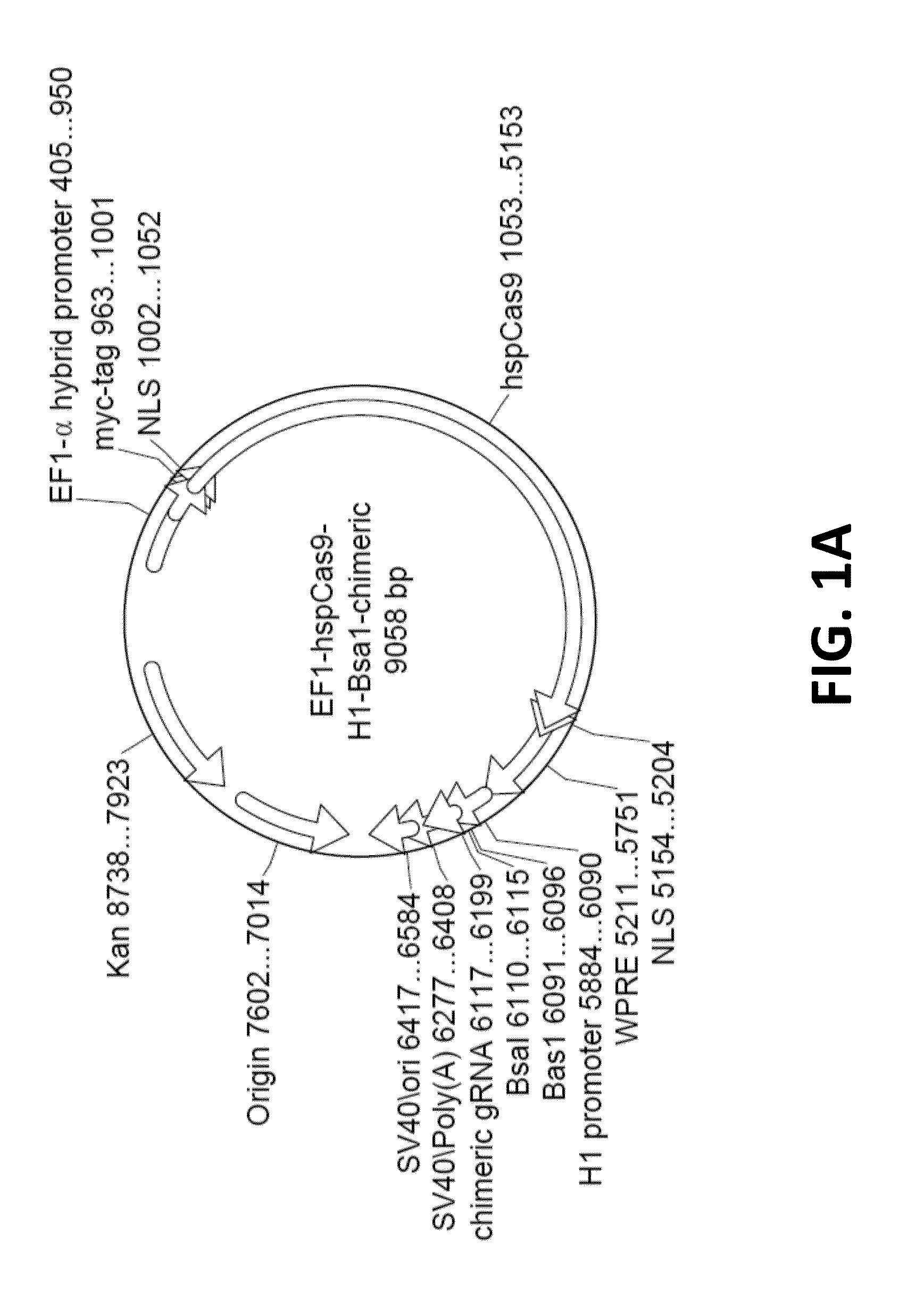
Crispr/cas systems for genomic modification and gene modulation
The invention relates to engineered CRISPR / Cas9 systems for genomic modification and regulation of gene expression in mammalian cells. The specification describes the design and validation of polynucleotides encoding the Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes) Cas9 gene and protein and variants of that protein, where the nucleotide sequence has been optimized for expression in mammalian cells, and also modified by fused sequences that enhance various aspects of the CRISPR / Cas system. The specification also describes systems for RNA-guided genome engineering and gene regulation in mammalian cells, including human cells.
Owner:SYST BIOSCI
Regulation of gene expression
InactiveUS6022863APrevention of fetal rejectionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsMHC class IDisease
The present invention relates to utrons, RNA molecules which contain promoter regulatory motif(s) and DNA analogs thereof and DNA molecules that can be transcribed to produce the foregoing. In particular, the invention provides gene promoter suppressing nucleic acids which suppress transcription from a promoter of interest. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides the TSU gene, nucleotide sequences of the TSU gene and RNA, as well as fragments, homologs and derivatives thereof. Methods of isolating TSU genes are also provided. Therapeutic and diagnostic methods and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. In particular, the invention relates to methods for cell replacement therapy, gene therapy or organ transplantation wherein TSU nucleic acids suppress MHC class I and II gene expression, thus preventing immuno-rejection of non-autologous cells or organs. The invention also provides methods for treatment of diseases or disorders by suppression of MHC class I, MHC class II, ICAM-1, B7-1, B7-2, and / or Fc gamma R expression by provision of TSU function.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Functional arrays for high throughput characterization of gene expression regulatory elements
InactiveUS20070161031A1Good curative effectEliminate side effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGenomicsHuman DNA sequencing
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment, the nucleic acid segment varying in the library and having a diversity of at least 50. The nucleic acid segments can be a large library of gene expression regulatory elements such as transcriptional promoters. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Transcriptional regulatory elements of biological pathways tools, and methods
InactiveUS20090018031A1Determine effectNucleotide librariesLibrary screeningHuman DNA sequencingRegulation of gene expression
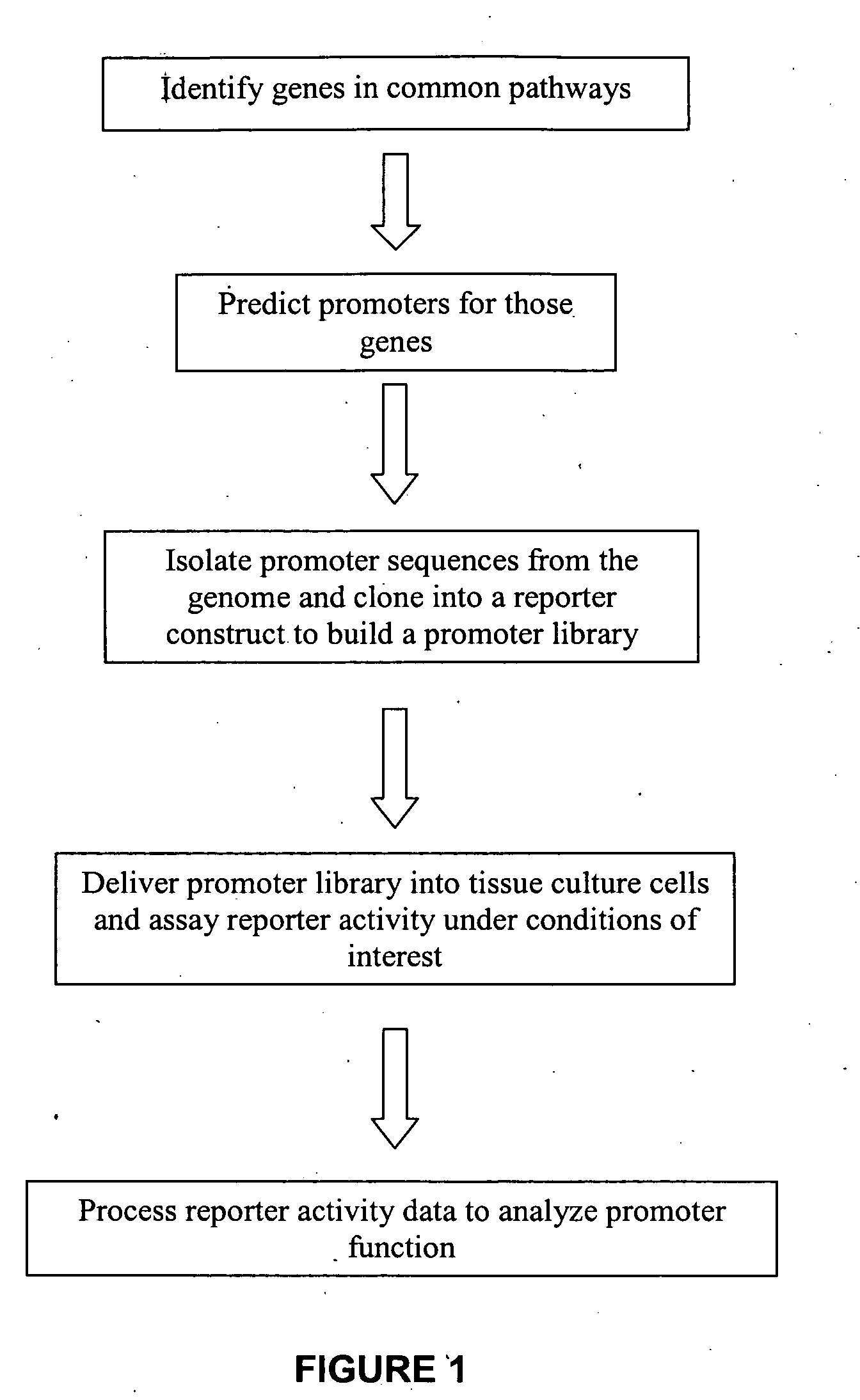
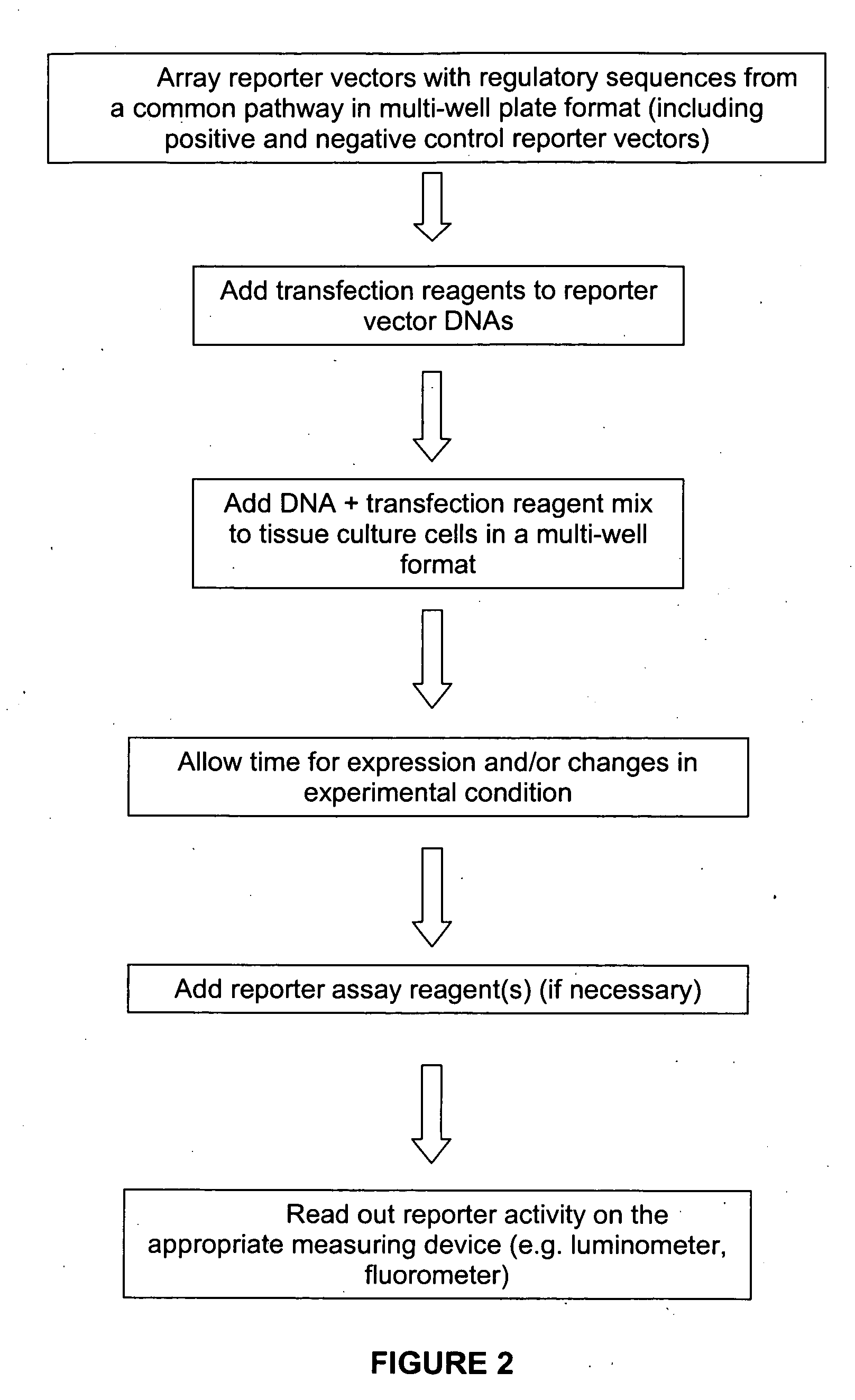
The present invention provides compositions, kits, assemblies, libraries, arrays, and high throughput methods for large scale structural and functional characterization of gene expression regulatory elements in a genome of an organism, especially in a human genome, that are part of a common pathway. In one aspect of the invention, an array of expression constructs is provided, each of the expression constructs comprising: a nucleic acid segment operably linked with a reporter sequence in an expression vector such that expression of the reporter sequence is under the transcriptional control of the nucleic acid segment. The present invention can have a wide variety of applications such as in personalized medicine, pharmacogenomics, and correlation of polymorphisms with phenotypic traits.
Owner:SWITCHGEAR GENOMICS
Regulation of gene expression in plants
InactiveUS20060010517A1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesStarch-branching enzyme IIStarch synthase
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid sequence encoding an enzyme of the starch biosynthetic pathway in a cereal plant, wherein the enzyme is selected from the group consisting of starch branching enzyme I, starch branching enzyme II, starch soluble synthase I, and debranching enzyme, with the proviso that the enzyme is not soluble starch synthase I of rice, or starch branching enzyme I of rice or maize.
Owner:BIOGEMMA SAS +1
Methods and compositions for introduction of exogenous dsrna into plant cells
This invention provides a method to silence an endogenous target gene expression in plants by applying a specific dsRNA onto the exterior surface of a plant. Application, such as by spraying or brushing a plant with dsRNA is done without wounding the plant tissue and cells such as by mechanical-type wounding, particle bombardment or mechanical infection with viral vectors. The present invention enables the regulation of gene expression in plants. In some embodiments of the invention, the dsRNA is directed to an essential gene of a plant pathogen or pest, whereby the pathogen and / or pest damage is controlled, resulting in desired agronomic performance.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Biologic device for regulation of gene expression and method therefor
InactiveUS20070036771A1Desirable effectAltered expressionBiocideInternal electrodesOpen reading frameRegulation of gene expression
A system and device are provided which include a gene regulatory system controlling expression of one or more expression cassettes present in or released by the device, by emitting one or more stimulations. An expression cassette includes a regulatable transcription control element that is responsive to the emitted stimulations linked to an open reading frame of interest. The system optionally includes a sensor to sense a parameter indicative of a need, a telemetry module to receive an external command, or a programmable device, for regulating gene expression of the open reading frame.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
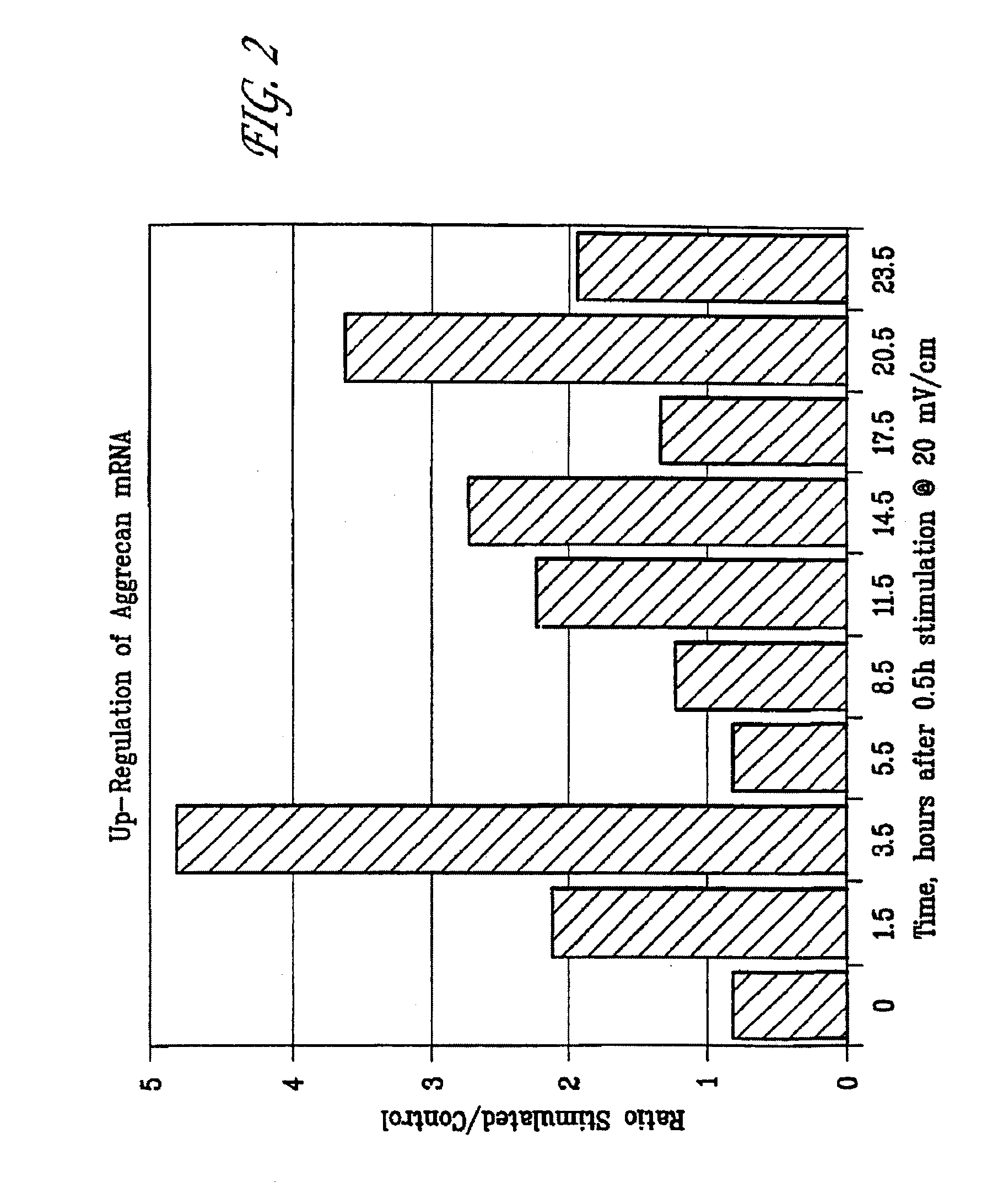
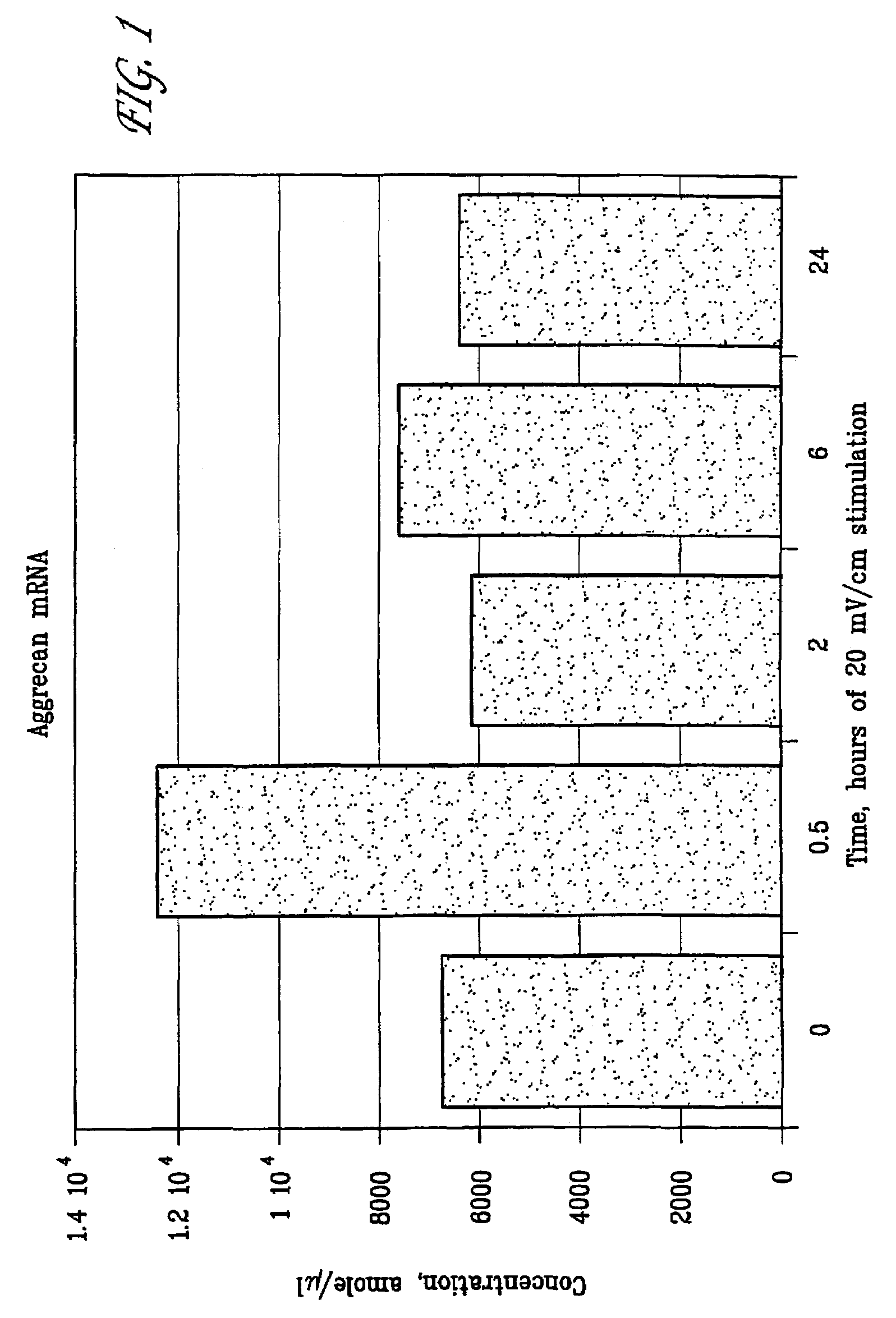
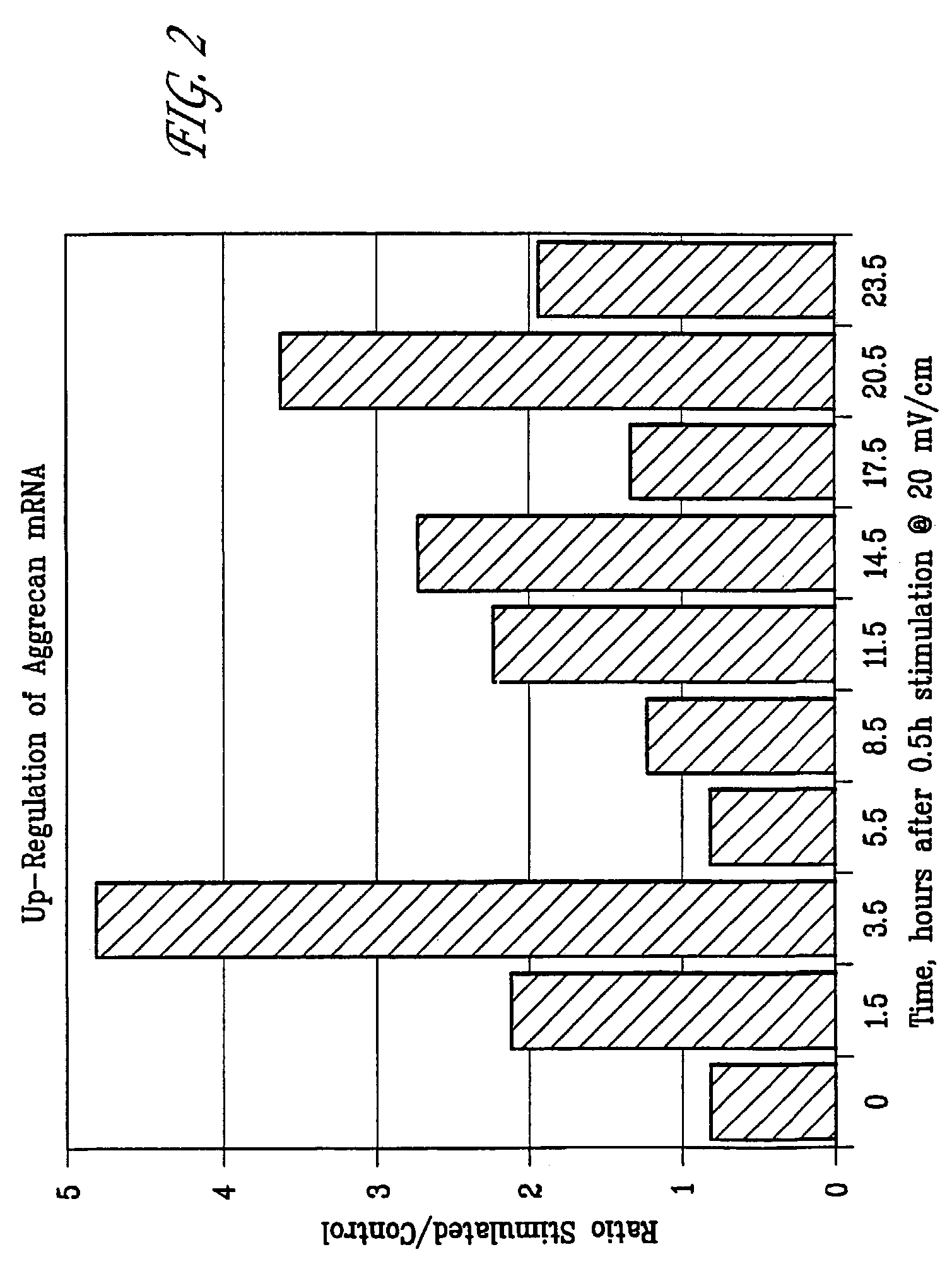
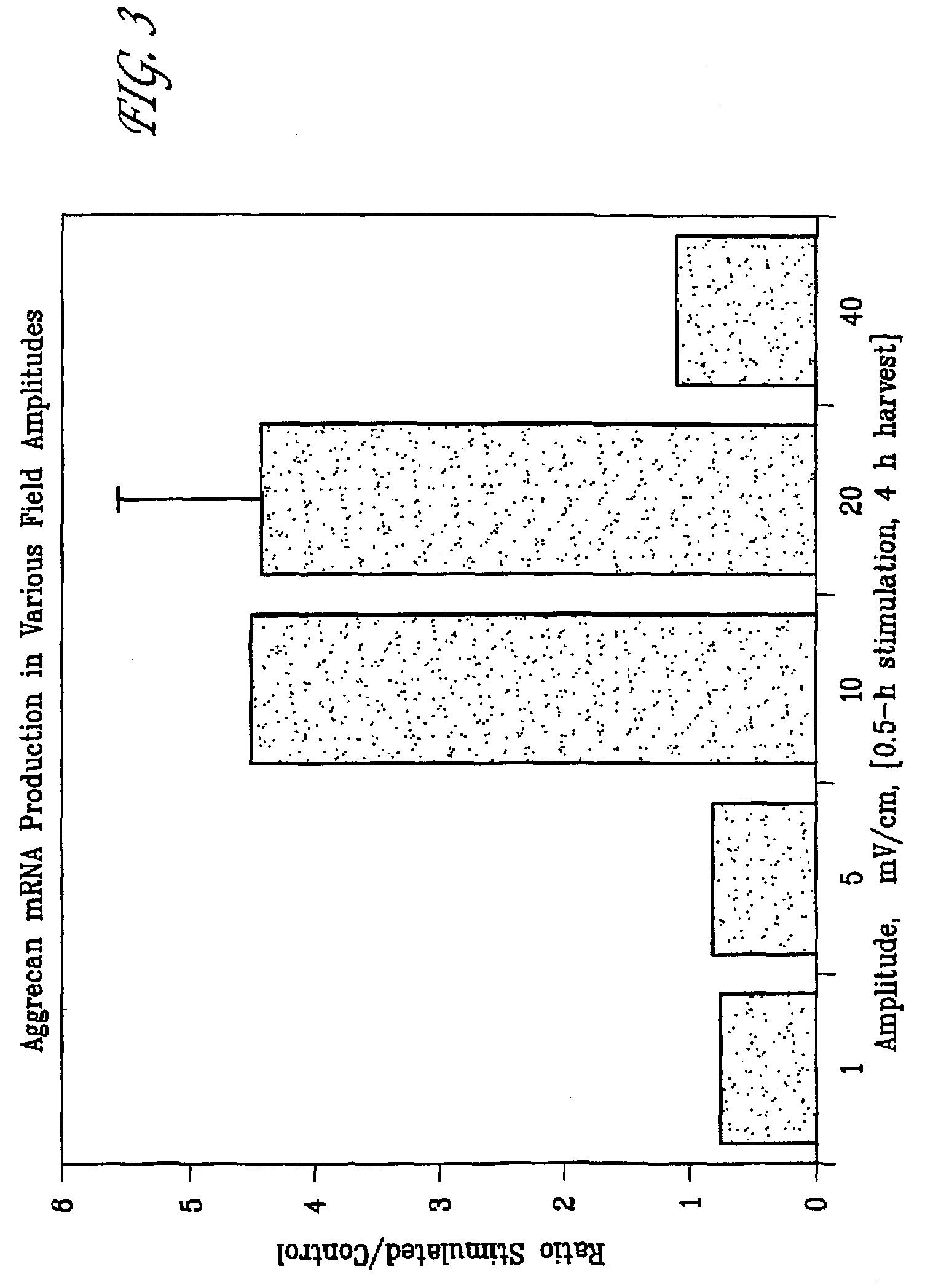
Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene expression in tissue via the application of electric and/or electromagnetic fields
InactiveUS20090018613A1Promote angiogenesisInhibit tumor growthInternal electrodesExternal electrodesLigament healingHuman DNA sequencing
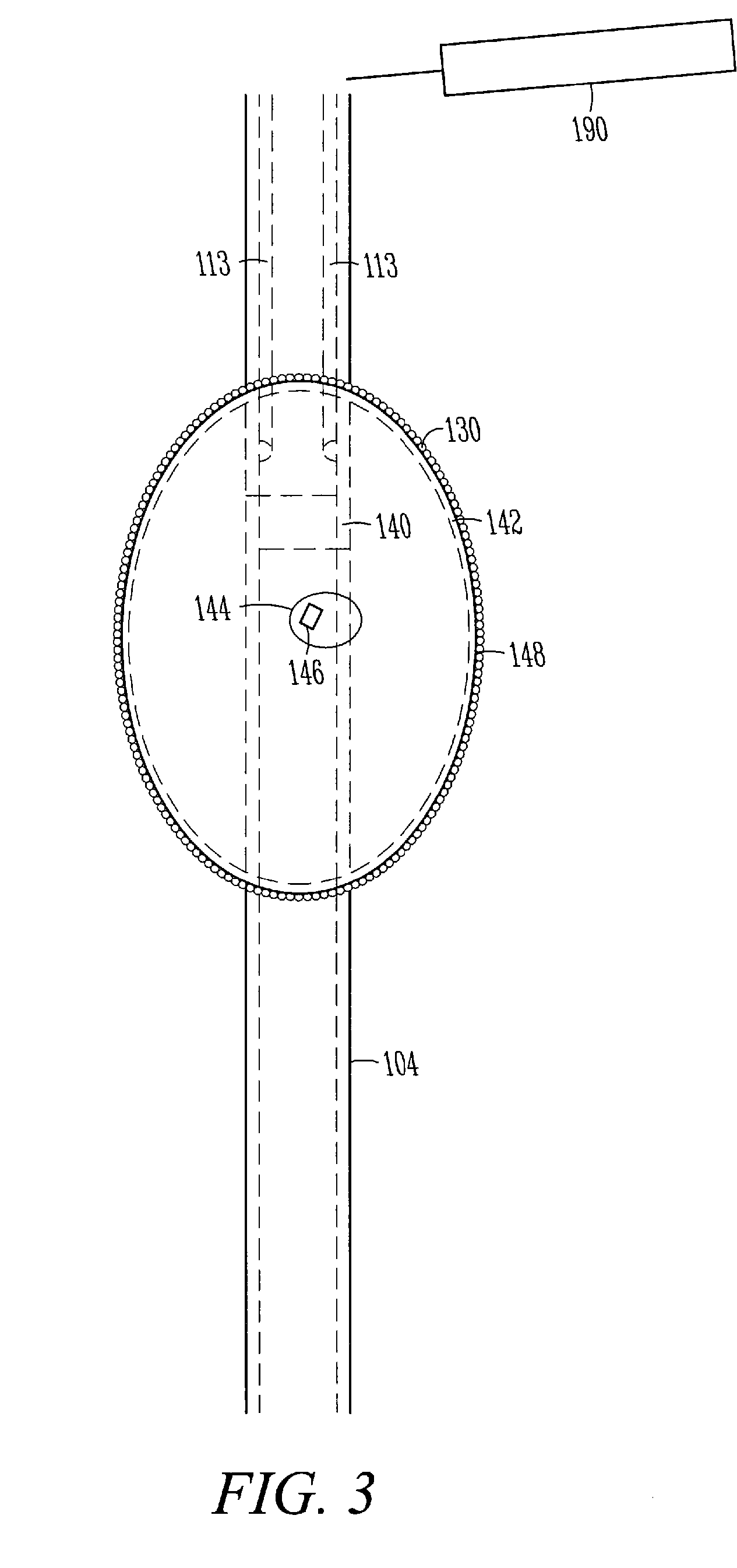
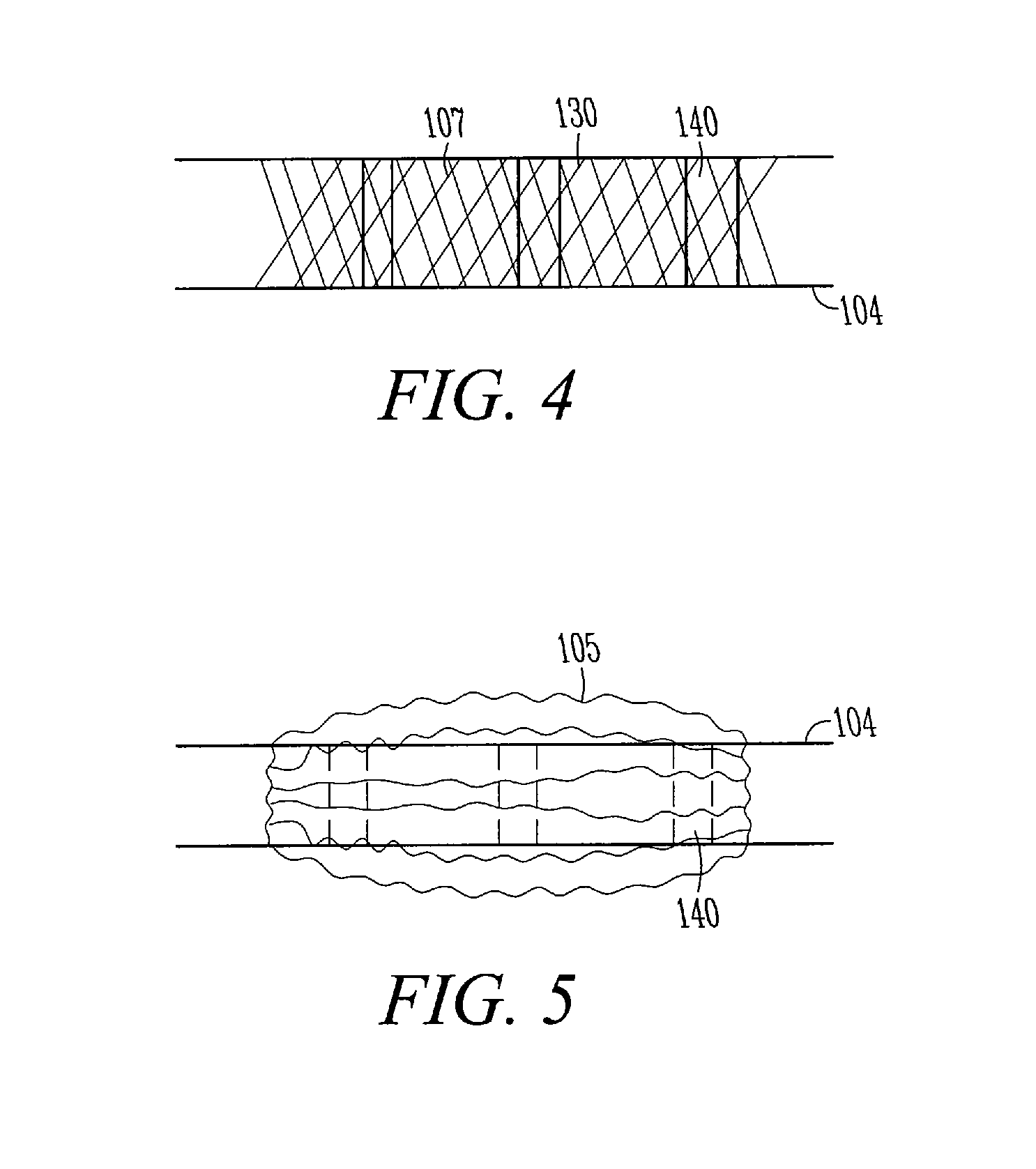
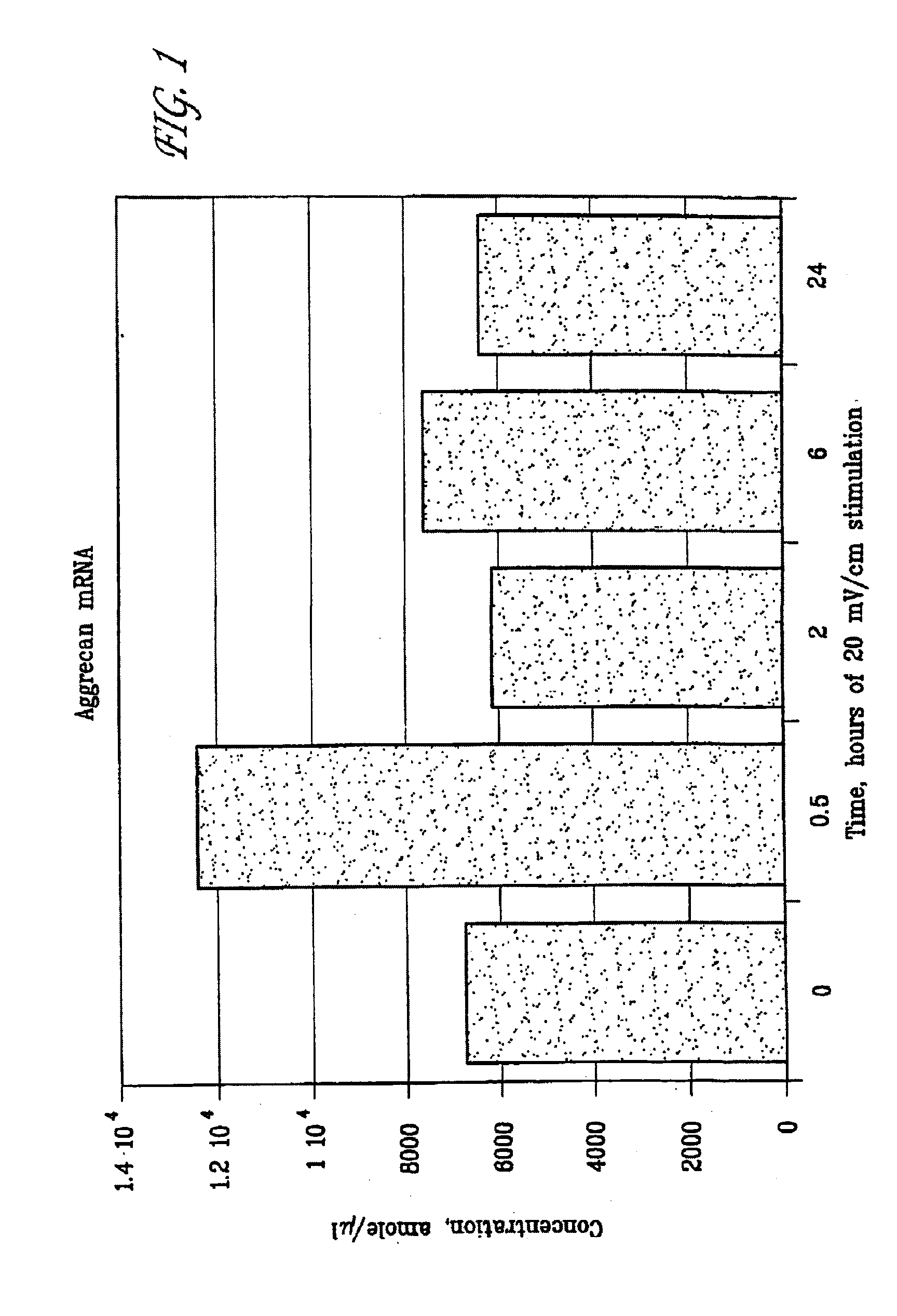
Methods and devices for the regulation of gene expression in tissue by applying an electric and / or electromagnetic field generated by specific and selective signals so as to treat diseases, conditions, and / or tissue. Gene expression is the up-regulation or down-regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are described for the regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) protein gene expression in endothelial cells of various targeted tissues via the capacitive coupling or inductive coupling (e.g., by electrodes or one or more coils or other field generating devices disposed with respect to the targeted cells) of specific and selective signals to the cells of these tissues, where the resultant electric and / or electromagnetic fields treat diseased or injured tissues. The resulting methods and devices are useful for the targeted treatment of peripheral vascular disease, cardiovascular disease, macular degeneration, wound healing, tendon and ligament healing, in preventing tumor growth or spread, and other conditions in which VEGF protein may be implicated.
Owner:GENESTIM
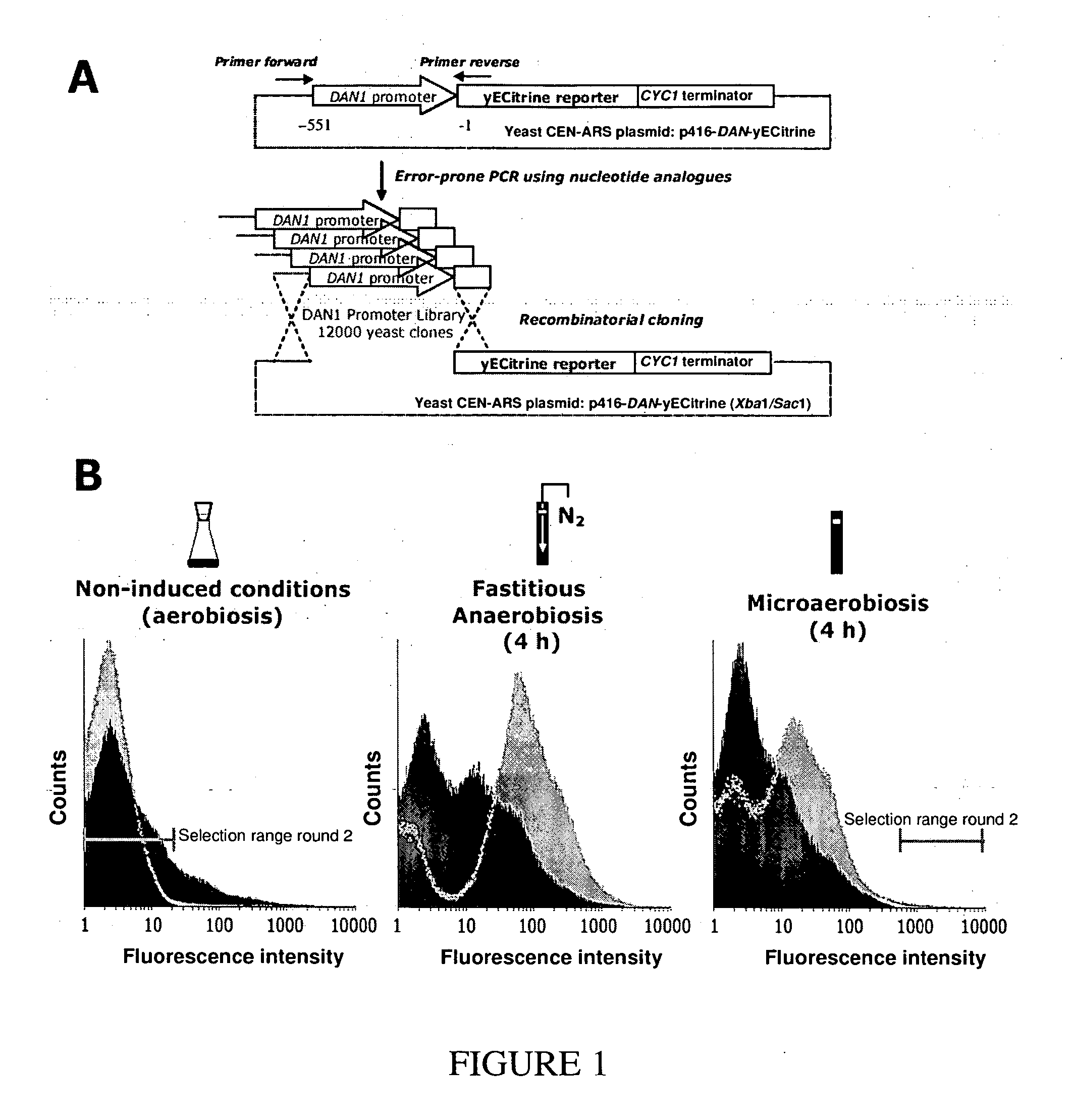
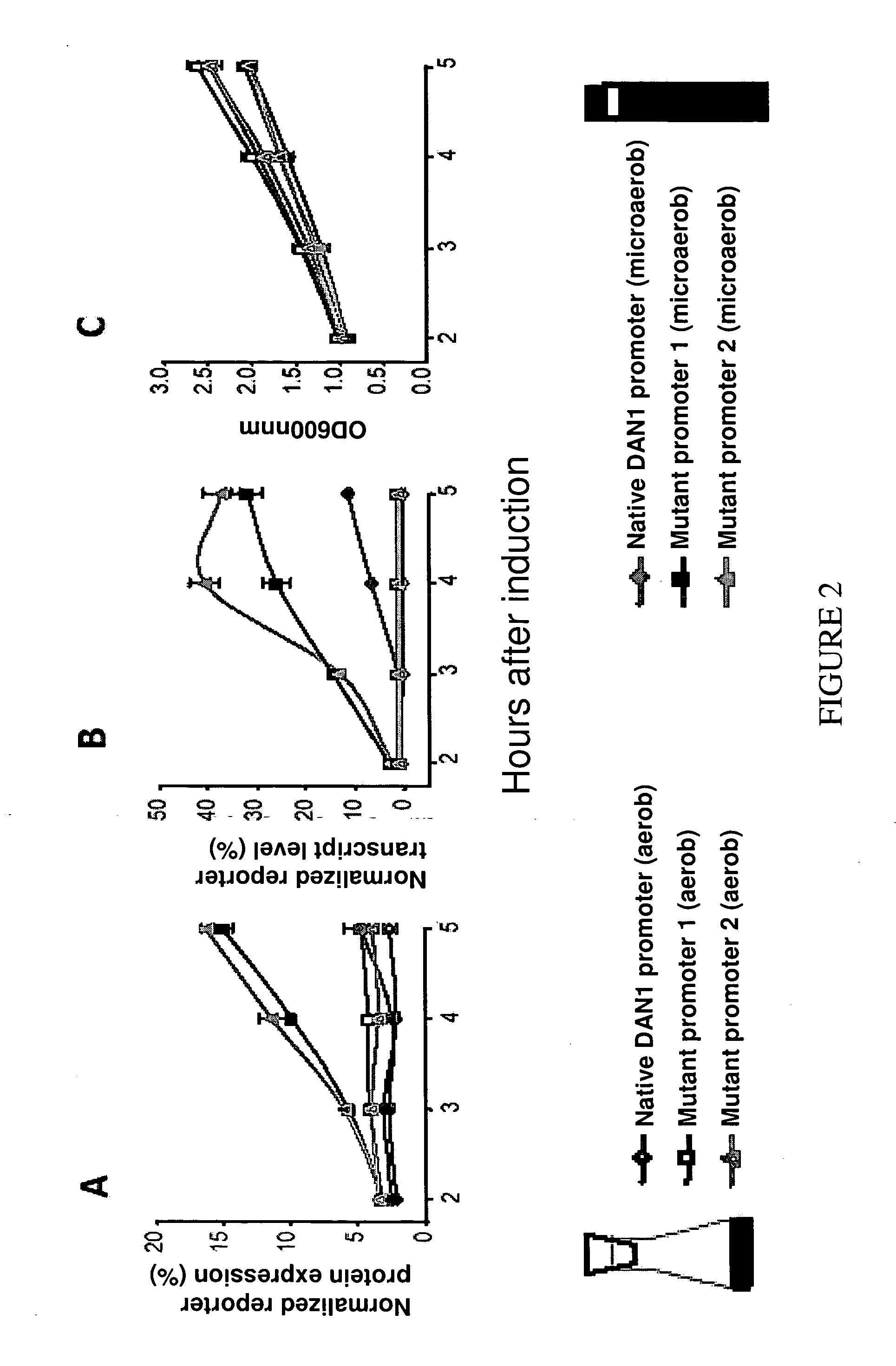
Promoter engineering and genetic control
InactiveUS20070178505A1Easy to producePeptide librariesBacteriaRegulation of gene expressionWild type
The present invention relates to expression vectors, wherein each vector comprises at least one gene of interest and a promoter operatively linked thereto wherein each promoter comprises a nucleic acid, whose sequence is randomly mutated with respect to that of the wild-type promoter and cells comprising the same. Methods utilizing either the vectors or cells of this invention, in optimizing regulation of gene expression, protein expression, or optimized gene or protein delivery are described.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
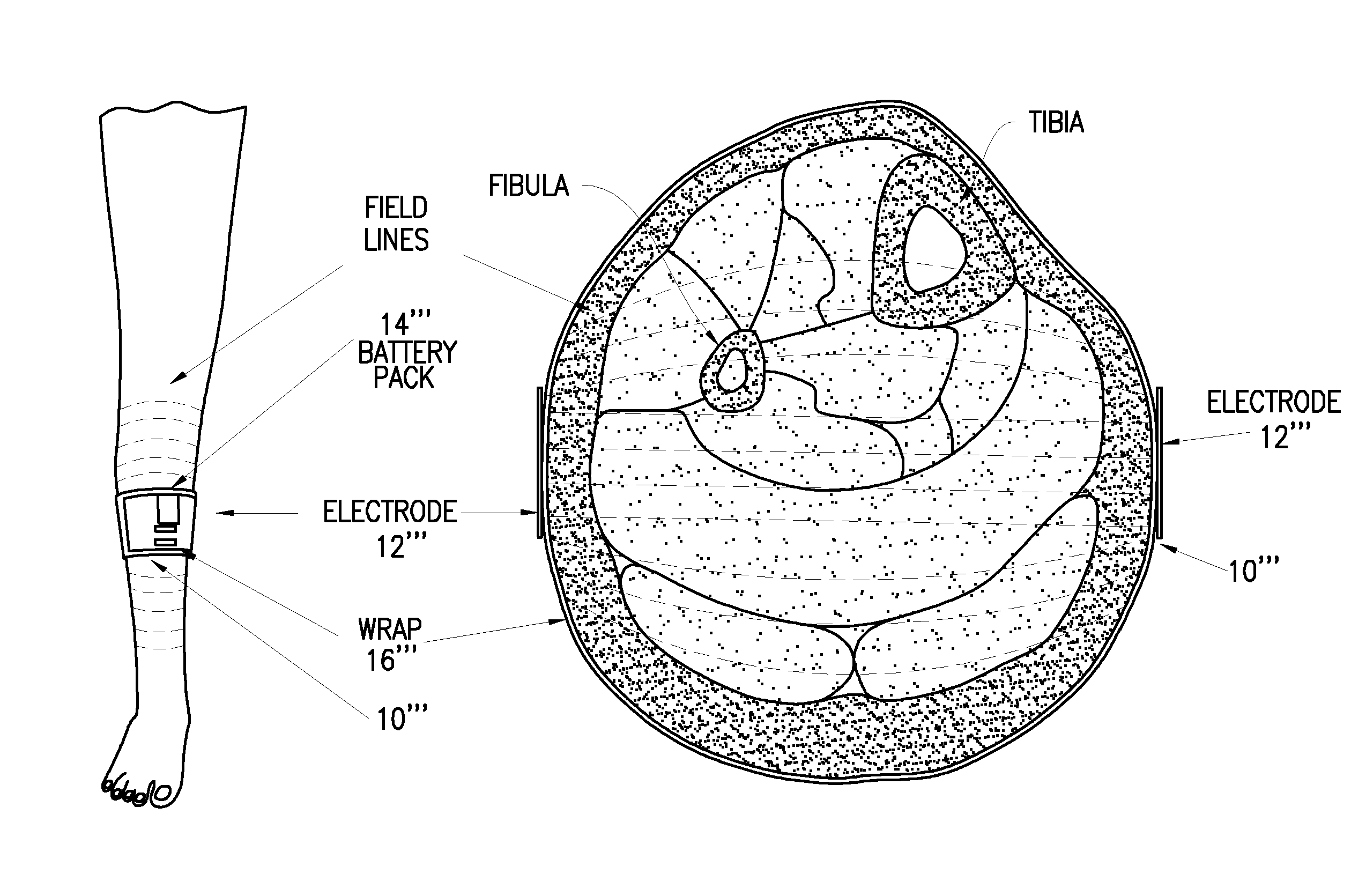
Regulation of genes via application of specific and selective electrical and electromagnetic signals
Methods and devices for the regulation of gene expression by cells via the application of fields generated by specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals so as to target diseased or injured tissue for treatment. By gene expression is meant the up regulation or down regulation of the process whereby specific portions (genes) of the human genome (DNA) are transcribed into mRNA and subsequently translated into protein. Methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of injured or diseased tissue that include providing specific and selective electric and electromagnetic signals and exposing tissue to the fields generated by the signals so as to regulate gene expression. In particular, methods and devices are provided for the targeted treatment of bone defects, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, cancer, and other disease states.
Owner:PENNSYLVANIA THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF
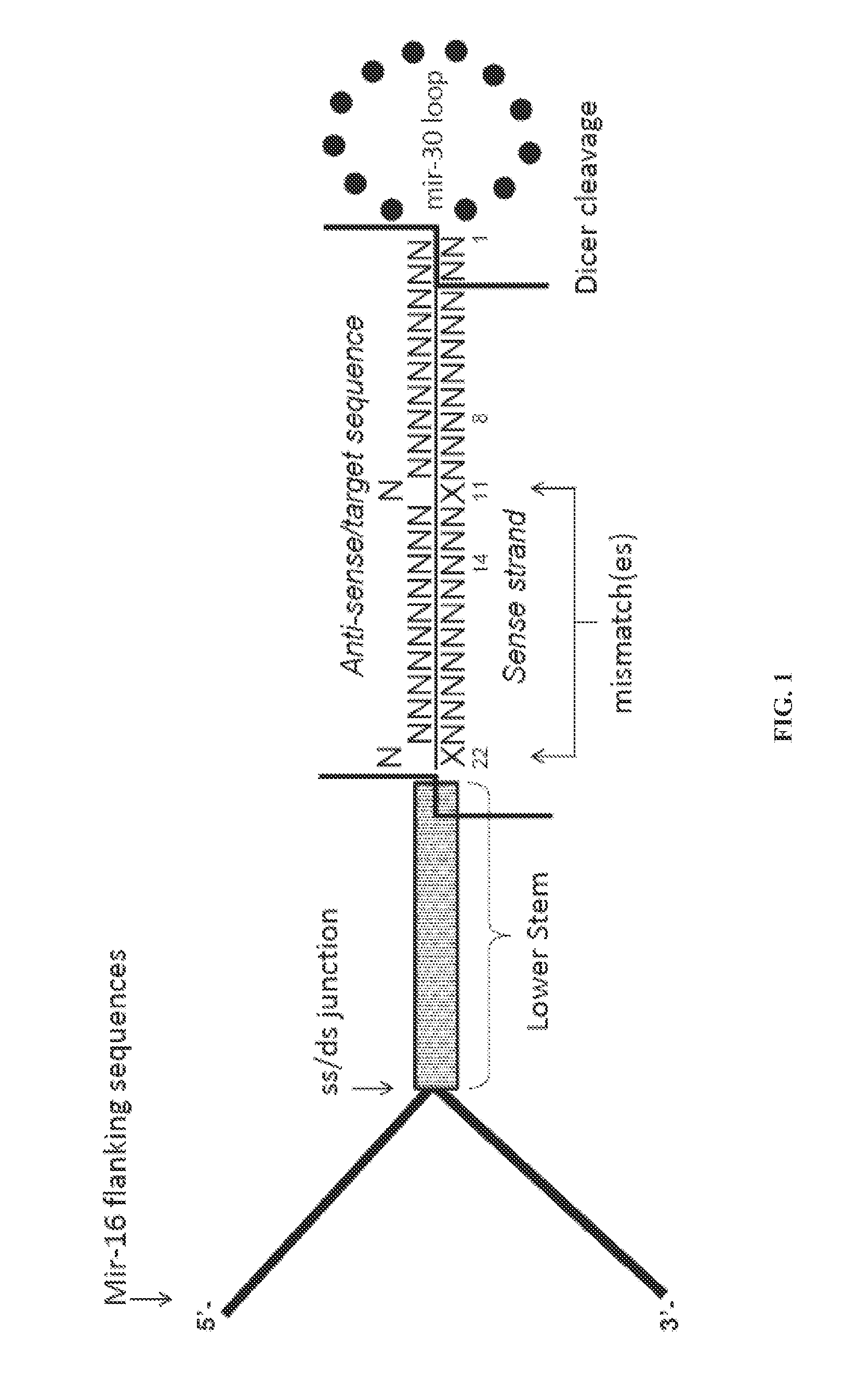
Nucleic acids for down-regulation of gene expression
Recombinant nucleic acid molecules are provided that form hair pin structures and can be used to down-regulate gene expression. For example, a nucleic acid molecule can comprise a flanking and lower stem loop sequence from a mir-16 gene; an antisense target sequence; a mir-30 loop sequence; a complement of the anti-sense target sequence; and a lower stem loop complementary to the mir-16 sequence. Methods for down regulating gene expression in a cell using such recombinant nucleic acid molecules are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA +1
Morpholino-based antisense agent
ActiveUS20120296087A1High activityHigh selectivitySilicon organic compoundsActivity regulationOligomerRegulation of gene expression
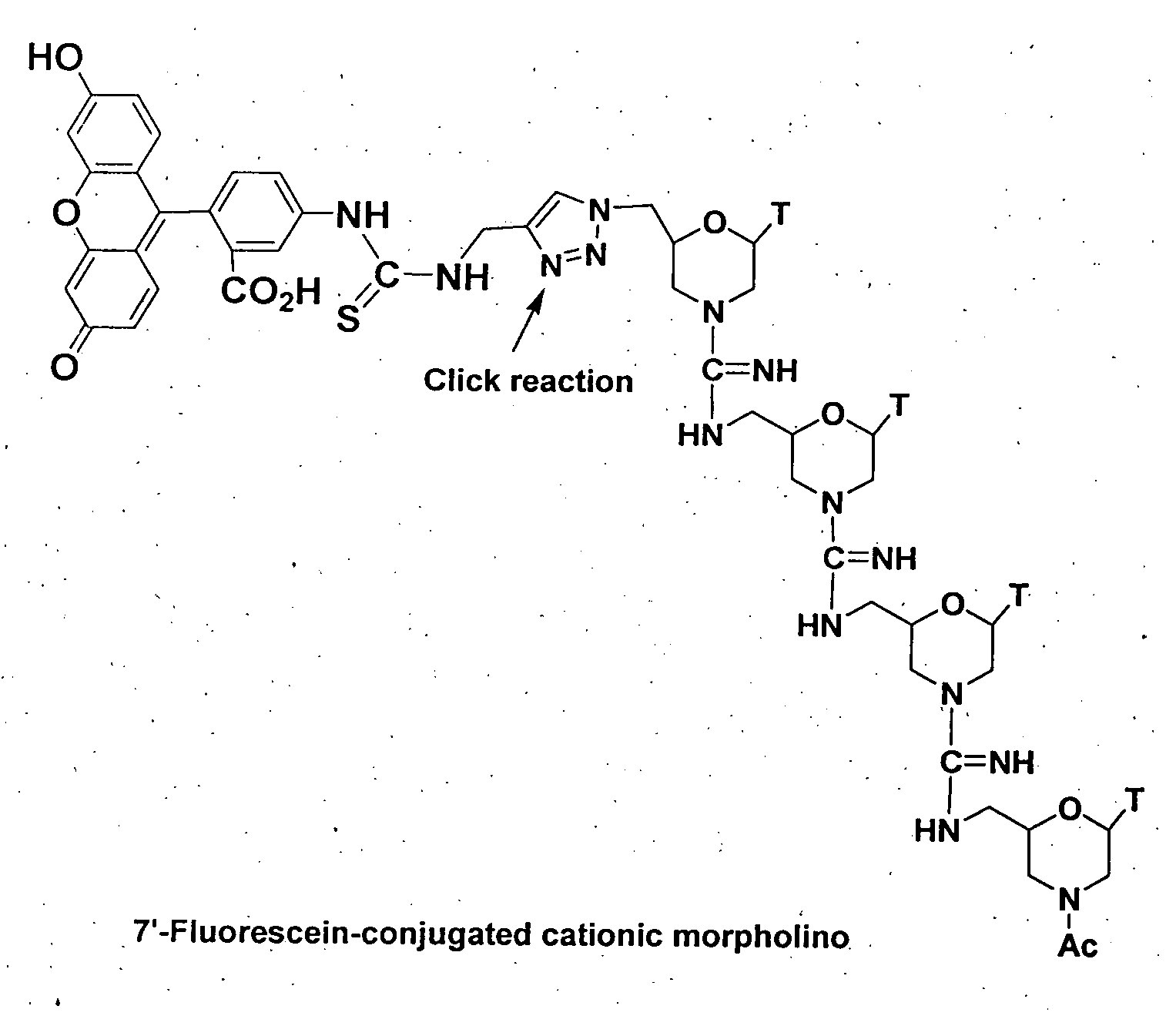
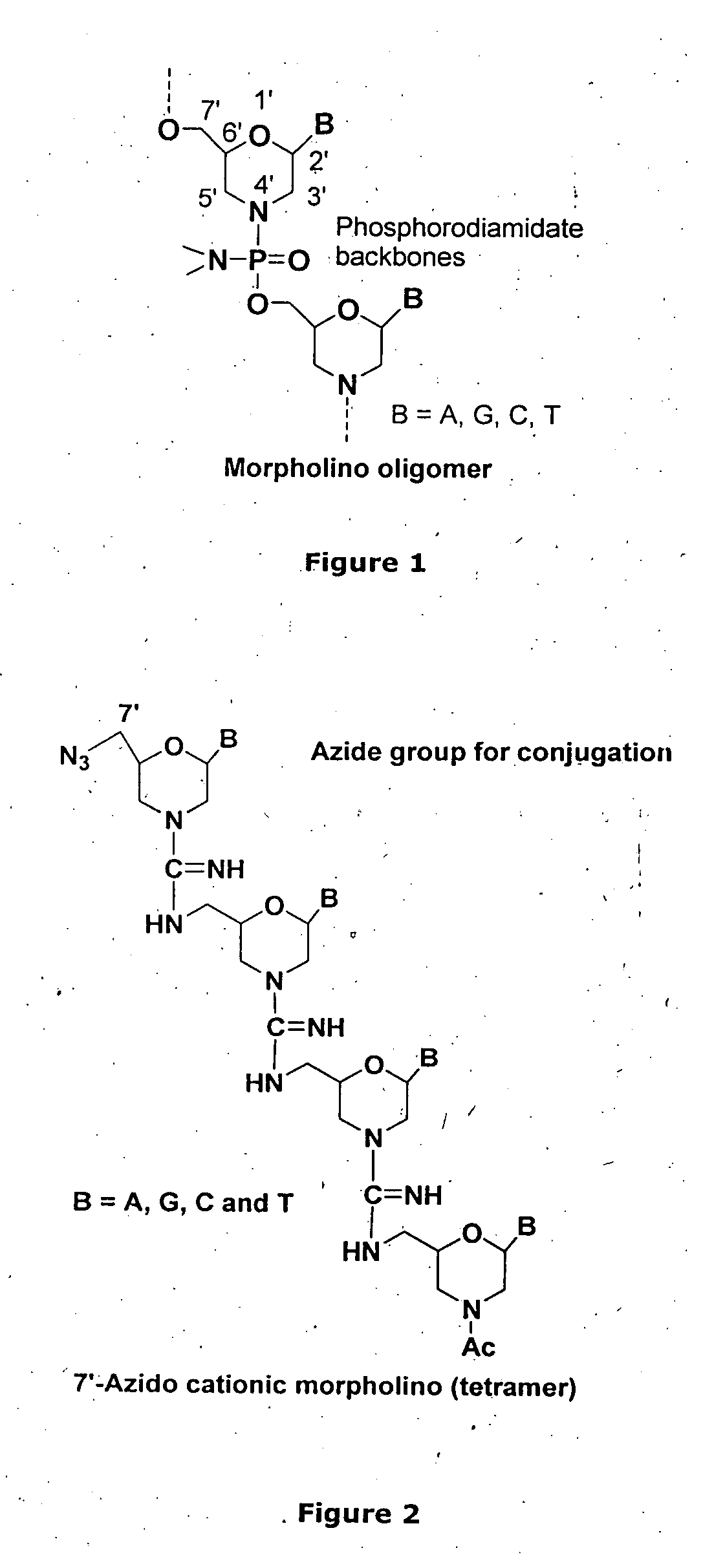
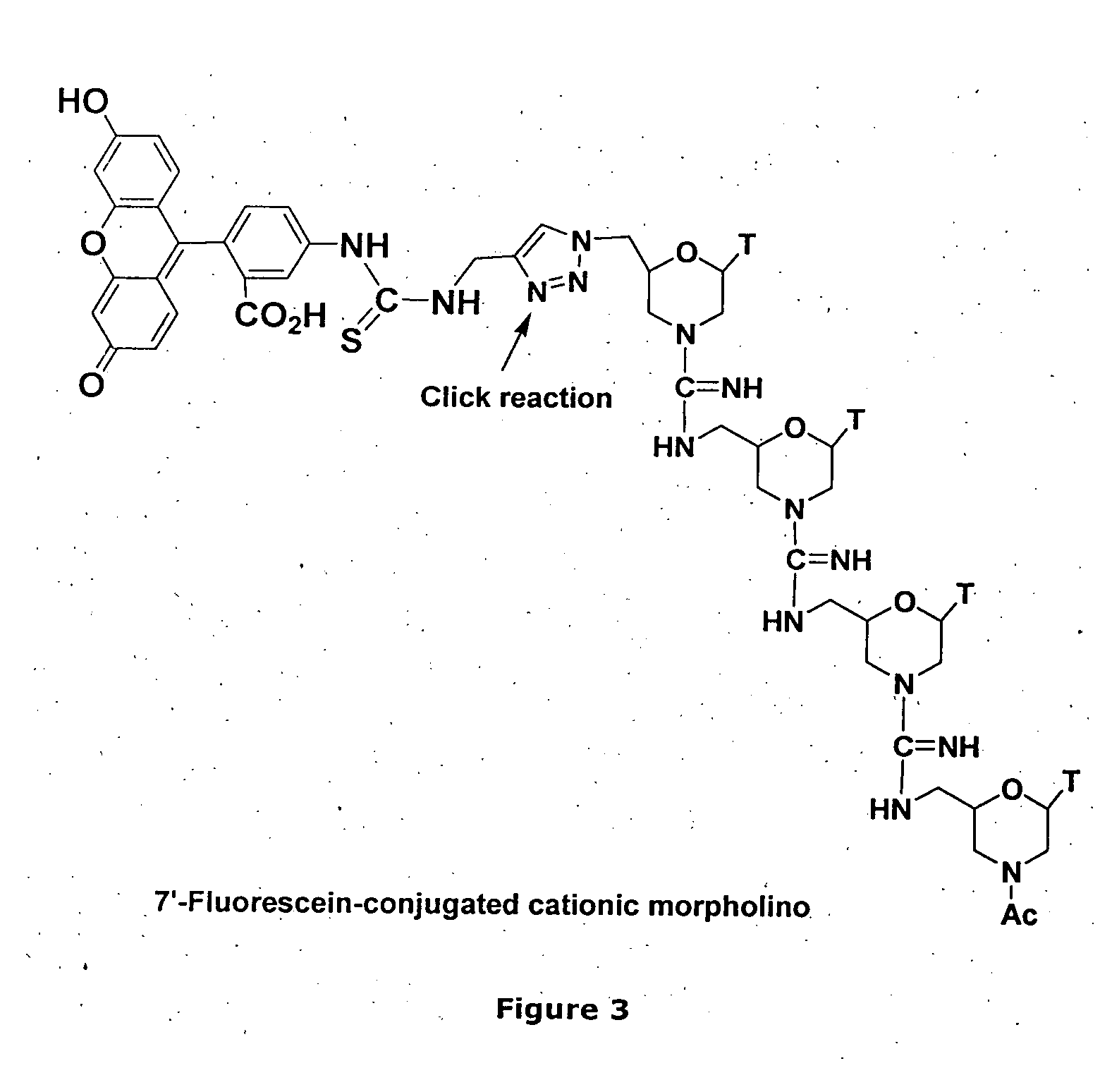
Morpholino-based oligomers suitable as antisense agent comprising modifications of phosphorodiamidate backbone or modification with 5-substituted pyrimidines of morpholino compound that is soluble in culture medium and sufficient for cell penetration thereby eliminating the need for injecting into the cells. Monomers comprising the said oligomers and its method of manufacture, method of manufacture of the said oligomers and its dye, flurophore, drug, biomolecule conjugate wherein the said oligomers find different end use but not limited to regulation of gene expression, tissue culture with improved transfection efficiency and related studies on cellular transfection.
Owner:INDIAN ASSOC FOR THE CULTIVATION OF SCI
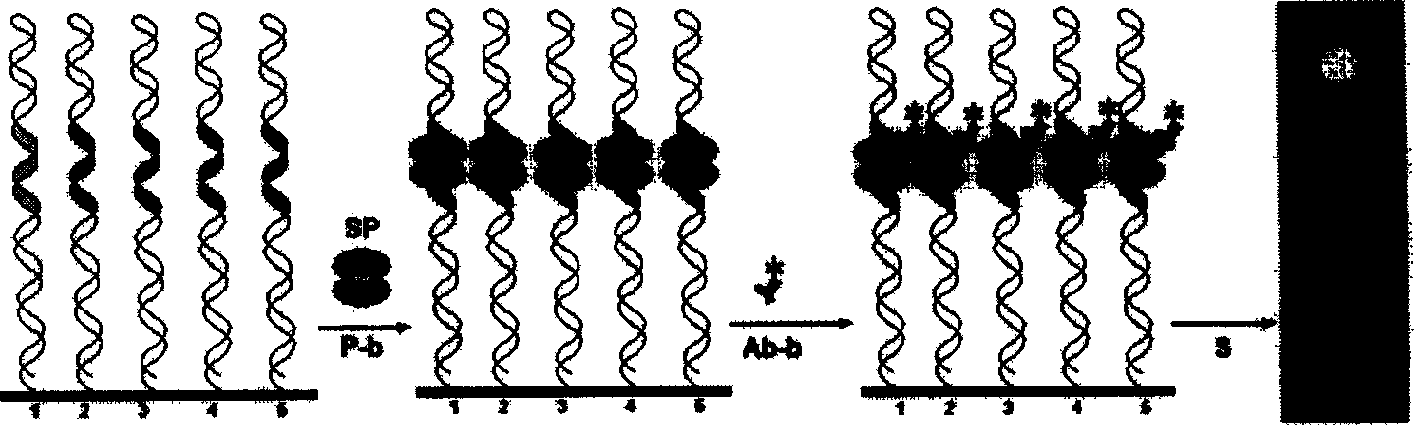
NF-KB detection double-stranded DNA micro array chip and preparation
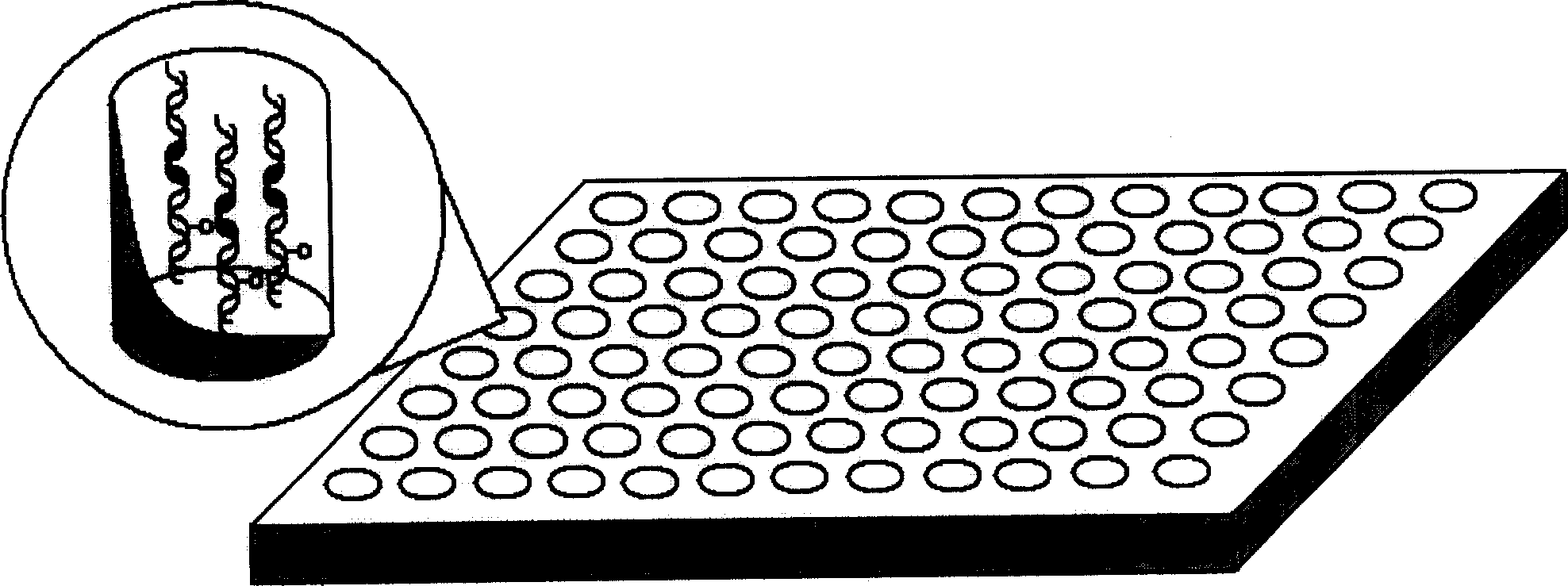
InactiveCN1580278AHigh affinityInhibit bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological studiesRegulation of gene expression
The invention can prepare the microarray of double -stranded DNA(ds DNA) on the surface of solid substrates. By this method, the probes of ds DNA can engomphosised in the nuclear factor kappa B(NF-kappa B) to high-throughpput detect NF-kappa B inside of caryon and screen ds DNA / NF-kappa B molecules interfering dsDNA / NF-kappa B interaction. First, depending on patent technic and others methods of this invention, the invention prepare the microarray of double -stranded DNA(ds DNA) on the surface of solid substrates to allow mounts of dsDNA explorer on the dsDNA micro embattle to link with locus. Second, allow dsDNA micro embattle to across and link with specifically cell nuckoproteides or NF-kappa pure albumen. Third, do qualitative determination or quantiative determination to NF-kappa albumen in special caryon by reaction of NF-kappa B with dsDNA as micro embattle butt.
Owner:王进科 +3
Biomolecular network analysis method based on function module
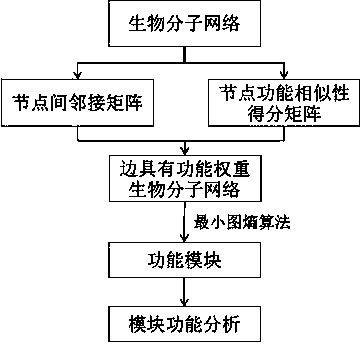
ActiveCN103778349AHigh functional relevanceEfficient integrationSpecial data processing applicationsRegulation of gene expressionComputer science
The invention belongs to the field of a biotechnology, and provides a comparison method based on a function module and used for biomolecular networks such as a genetic expression regulatory network or protein-protein interaction and the like. The method mainly comprises steps as follows: an adjacency matrix Madj of a biological network is built, a function similarity matrix Msim between network nodes is calculated, a function weight matrix ME of a network side is calculated according to the formula as follows: ME=Madj.*Msim, a network module is mined with a minimum graph entropy algorithm, and finally, function enrichment analysis is performed on the network module, wherein the symbols are defined in the instruction.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
Method for regulating gene expression intensity on microbial chromosome by using artificial regulatory element and its library
The invention discloses a method for regulating the expression intensity of genes on microorganism chromosomes by using artificial regulatory elements and libraries thereof. The method for regulating the gene expression intensity on the microbial chromosome by using the artificial regulatory element and its library provided by the present invention includes the following steps: amplify a DNA fragment by PCR, which includes the upstream sequence of the original regulatory region of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome A homologous fragment containing 40-3000 bases, resistance marker gene, artificial regulatory element library or an artificial regulatory element with specific expression strength, homologous to the sequence downstream of the start codon of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome A fragment containing 40-3000 bases; the DNA fragment is electrotransformed into the microorganism, and the original regulatory region of the gene to be regulated on the microbial chromosome is replaced by an artificial regulatory element library or an artificial regulatory element with a specific expression intensity .
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Marking probe of nano microparticle and affinity element and its preparation method as well as application
InactiveCN1415759AResolve connectionSolve the key problems of detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotin-streptavidin complexRegulation of gene expression
A nanopartide and its avidin probe are disclosed. Said gene probe for detecting the mutation or non-mutation of DNA is prepared from nanoparticles or colloidal particles and avidin, streptavidin, or antibiotin through preparing colloidal gold and preparing the compound. Its advantges are high sensitivity, specificity and speed.
Owner:上海华冠生物芯片有限公司
Self-regulation expression system of bacillus subtilis and building method and application of self-regulation expression system
ActiveCN104212830AHigh fluorescence intensityBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionRegulation of gene expressionGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a self-regulation expression system of bacillus subtilis, and a building method and an application of the self-regulation expression system, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The expression system disclosed by the system comprises bacillus subtilis for xylose-induced expression of an endonuclease gene and a plasmid expression vector for constitutive expression of an anti-endonuclease gene. In a culture medium containing an inducer xylose, only the bacillus subtilis containing stably existing expression vector can normally grow. A fluorescent protein gene (gfp), a hyaluronic acid synthase gene (hasA) and a keratinase gene (ker) are respectively expressed by using the expression system disclosed by the invention; and by fermented cultivation, the fluorescence intensity, the hyaluronic acid content and the keratinase activity are respectively improved by 21.8%, 45% and 30.2% in comparison with those of the plasmid maintained by using antibiotic.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
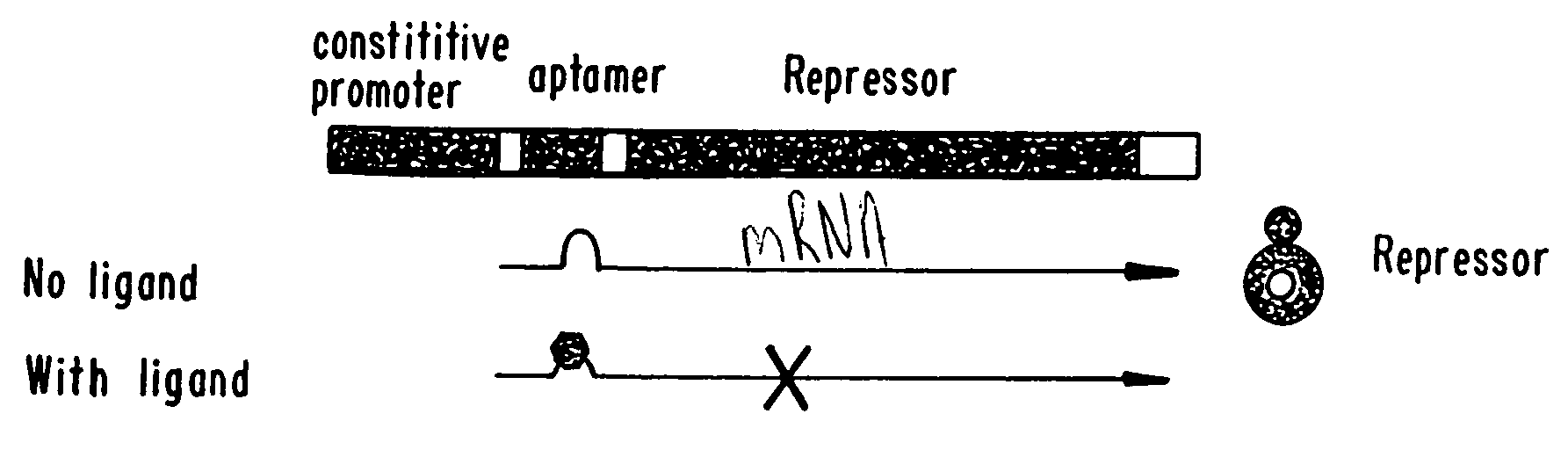
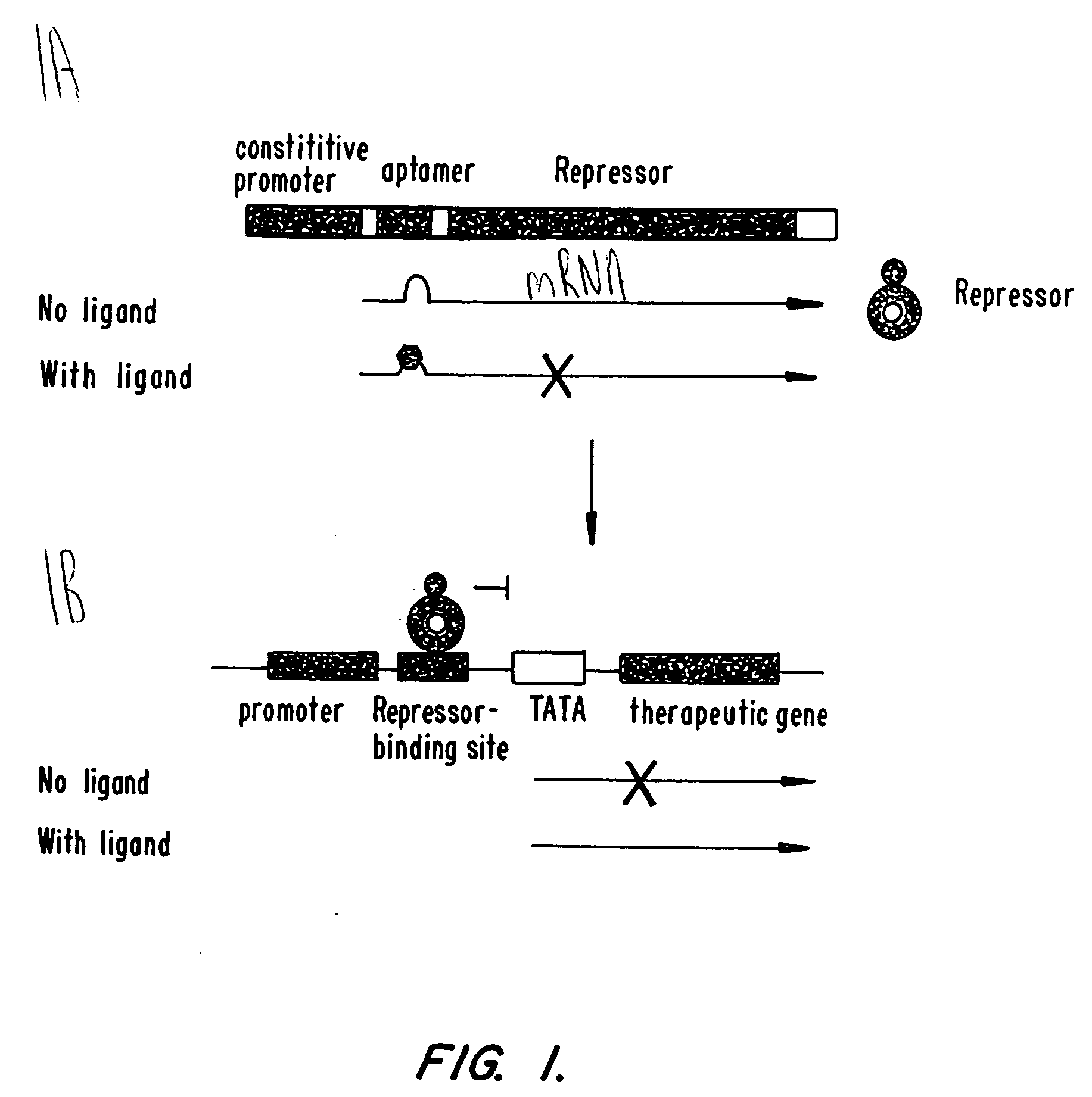
Aptamer-mediated regulation of gene expression
InactiveUS20060128649A1Slow proliferationUndesirable cell proliferationSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsRegulation of gene expressionGene expression level
This invention provides methods of regulating gene expression. An aptamer is positioned in a nucleic acid molecule along with a sequence encoding a transcriptional regulatory polypeptide. The aptamer disrupts translation of the transcriptional regulatory polypeptide when contacted with an aptamer-binding ligand. Gene expression levels can be either increased or decreased by the disclosed methods, depending on whether the transcriptional regulatory polypeptide is a repressor or activator, and the degree of the effect is dependent upon the dose of the ligand. Nucleic acid molecules, expression cassettes, expression vectors and cells useful in the gene regulation methods are also provided.
Owner:CANJI
Assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos
InactiveCN105463089AHigh degree of enrichmentSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationWater bathsFluorescence
The invention relates to an assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing zebrafish embryo sample pretreatment; adding lysis buffer into the embryos; cracking the embryos in a water bath by using a wild-neck spearhead; performing a transposition reaction immediately and purifying DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); determining a cycle number for library establishment by using a real-time fluorescence quantification method; directly performing library establishment and sequencing by using a further PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. A regulatory sequence on genome chromatin can be located and decoded by the ATAC-seq method and a DNase-seq (DNase I hypersensitive sites sequencing) method, but the steps in ATAC-seq are simpler, a required cell quantity is smaller, the ATAC-seq is more helpful under the situation that a large quantity of cells cannot be obtained, and the data enriching degree of the ATAC-seq is higher according to an assay result. The ATAC-seq method is further applied to zebrafish embryo cells. Thus, an effective and simple method is provided for the researches of changes of chromatin structures in early developing processes of living organisms and corresponding gene expression regulation and control researches.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
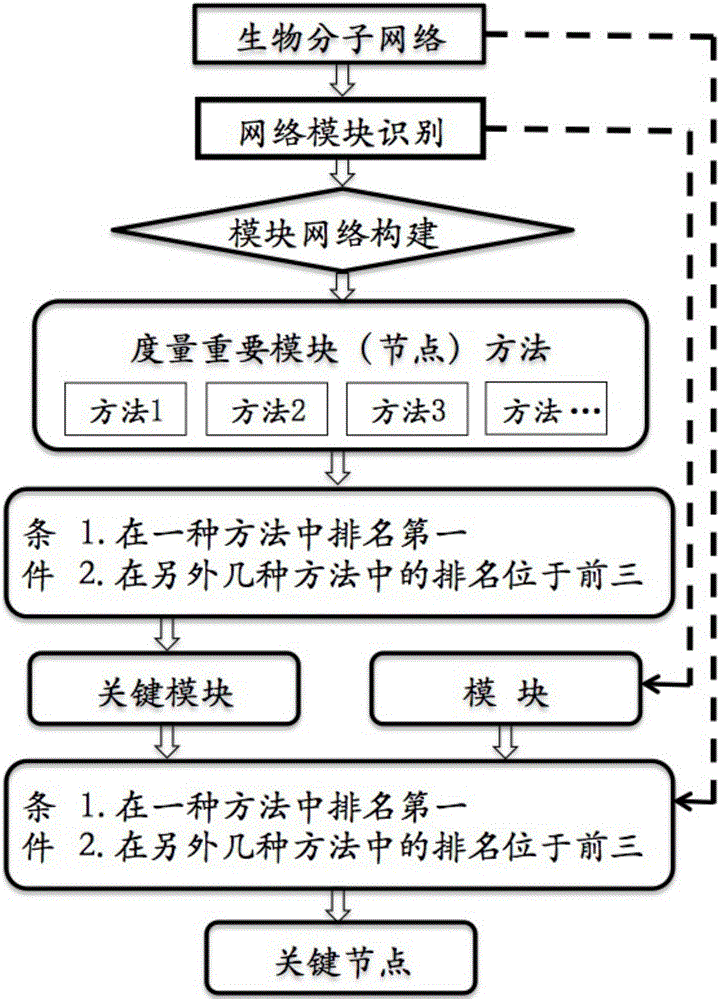
Method for identifying key module or key node in biomolecular network
The invention provides a method for identifying a key module and a key node by fusing multiple methods based on a topological structure of a biomolecular complex network such as a protein interaction network, a gene expression regulation network, a biological metabolism network, an epigenetic network, a phenotype network or a signal conduction network. The method comprises the following main steps of performing module division on the network based on the biomolecular network, and comprehensively and quantitatively identifying the key module and the key node from multiple angles by adopting multiple measurement methods based on the topological structure of the network for the network or each module.
Owner:王忠 +1
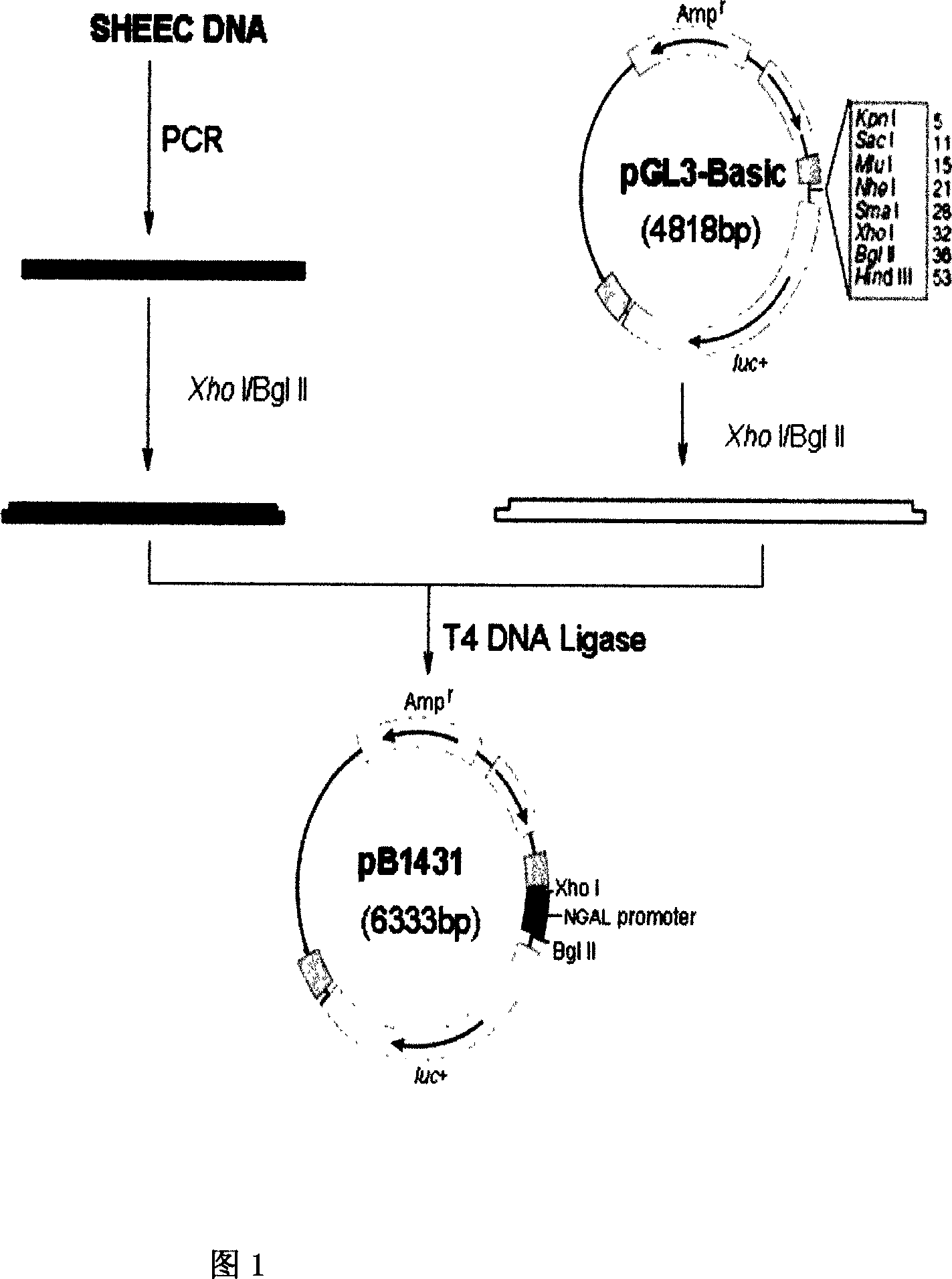
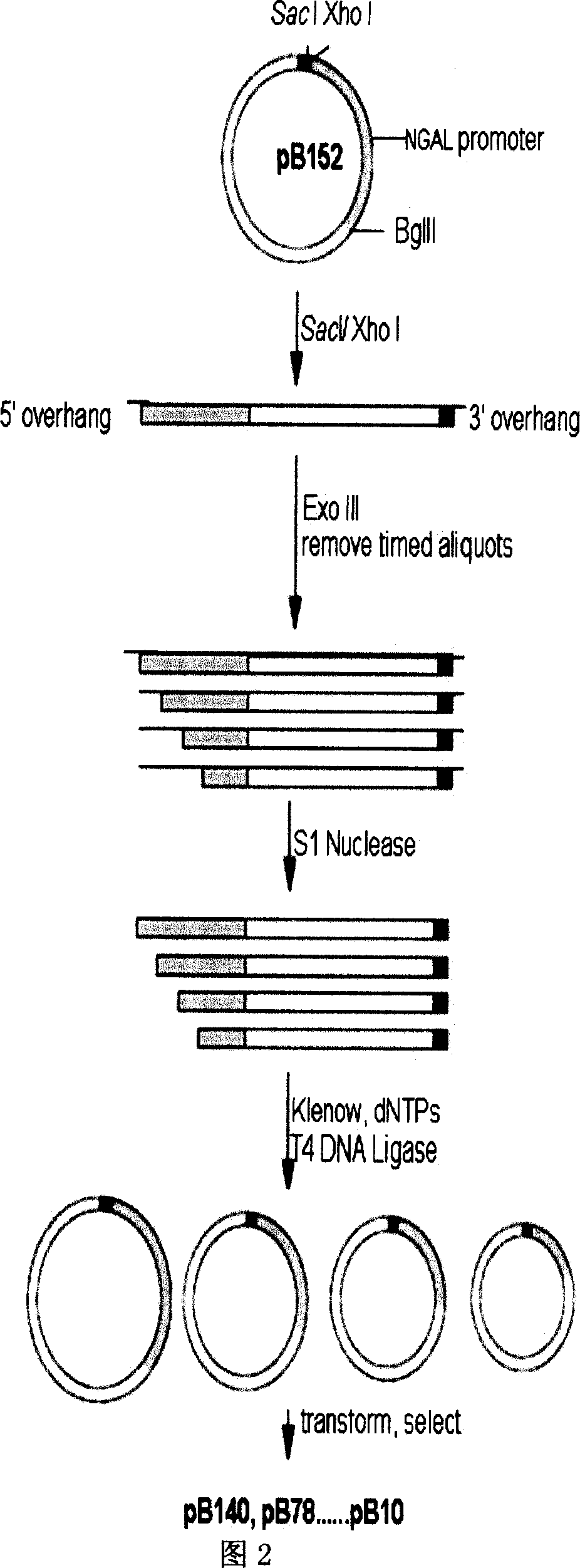
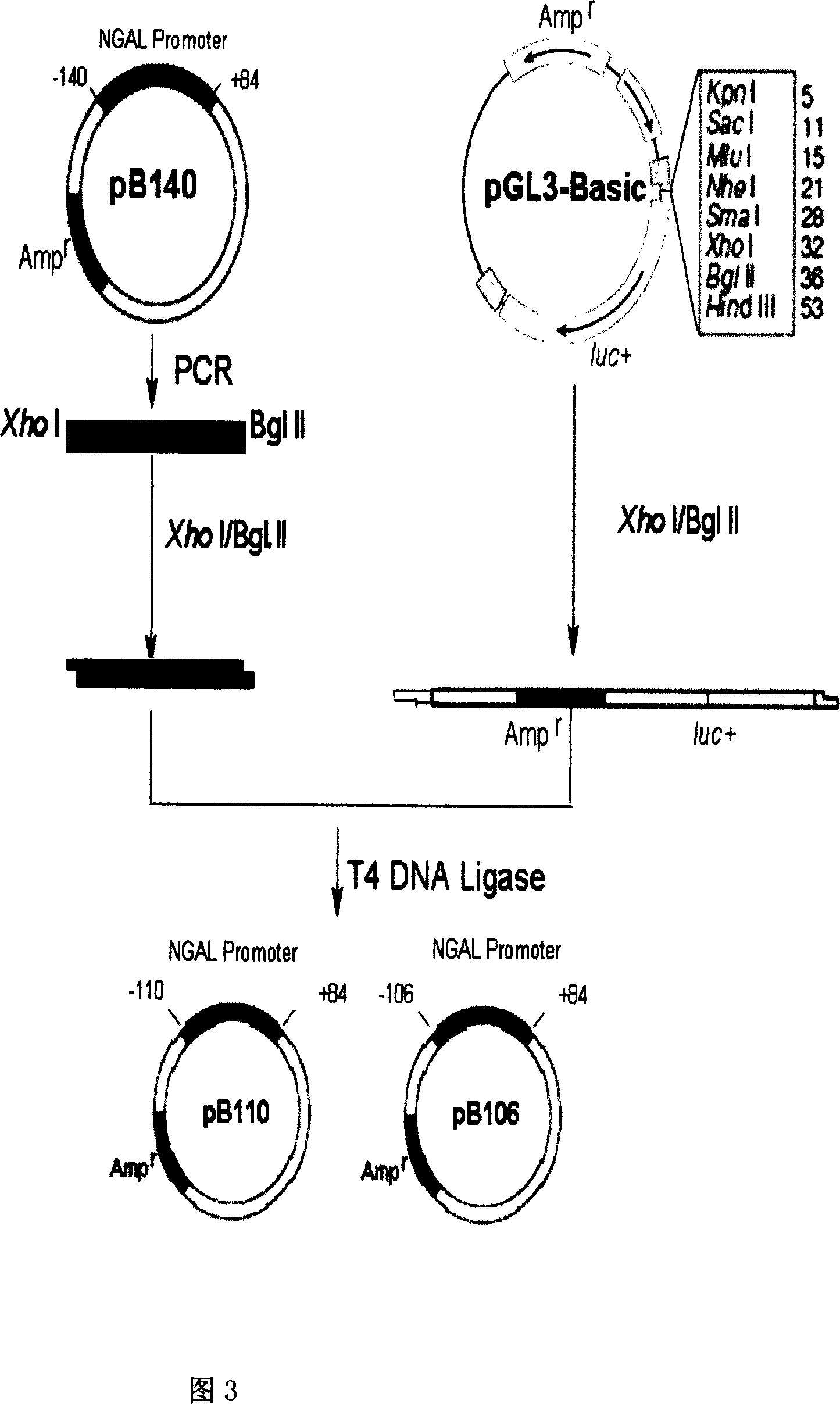
Transcriptional control element of human lung carcinoma cell NGAL gene promoter region
InactiveCN1974768AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionRegulation of gene expressionTranscriptional Regulatory Elements
The present invention relates to gene expression controlling technology, and discloses one kind of transcriptional control element of human lung carcinoma cell NGAL gene promoter region. The present invention identifies human lung carcinoma cell NGAL gene promoter region for the first time, inserts the promoter sequence with gradually deleting 5' end sequence and partial modified controlling element to the upstream of the report gene to constitute serial eukaryotic expression plasmids, transfects mammal cell for instantaneous expression, and determines the key control element of human NGAL gene promoter in lung carcinoma cell transcription activity. The present invention is significant in the research of NGAL in the tumor cell expression control mechanism and NGAL targeting clinical treatment.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
Promoter for regulation of gene expression in plant roots
InactiveUS20130025000A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHeterologousRoot cap
The invention is directed to a promoter isolated from maize. The promoter of the invention have particular utility in driving root preferred expression, specifically root-cap expression, of heterologous genes that impart increased agronomic, horticultural and / or pesticidal characteristics to a given transgenic plant. The invention is also drawn to DNA molecules comprising the promoter of the invention and transformed plant tissues containing DNA molecules comprising a promoter of the invention operably linked to a heterologous gene or genes, and seeds thereof.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Method of high flux screening, capturing and separating target molecule from complex composition matter such as traditional Chinese medicine and chemical mixture
InactiveCN1590560AImprove bindingIncrease transcriptionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipDisease
A process for high-flux screening, capturing and separation of target moleculae from complex substance (Chinese medicine or chemical mixer) includes preparing a ds DNA microarray chip to make its probe have a binding sites of dsDNA bindin, measuring the affinity of the sites, creating the standard affinity parameter system, mixing the microarray chip with said complex substance, reacting, detecting the affinity variation, screening the varied targets, linking them to the surface of chromatographic column, filling the complex substance in it, capturing the effective moleculae by probes, eluting and collecting the effective moleculae.
Owner:王进科 +2
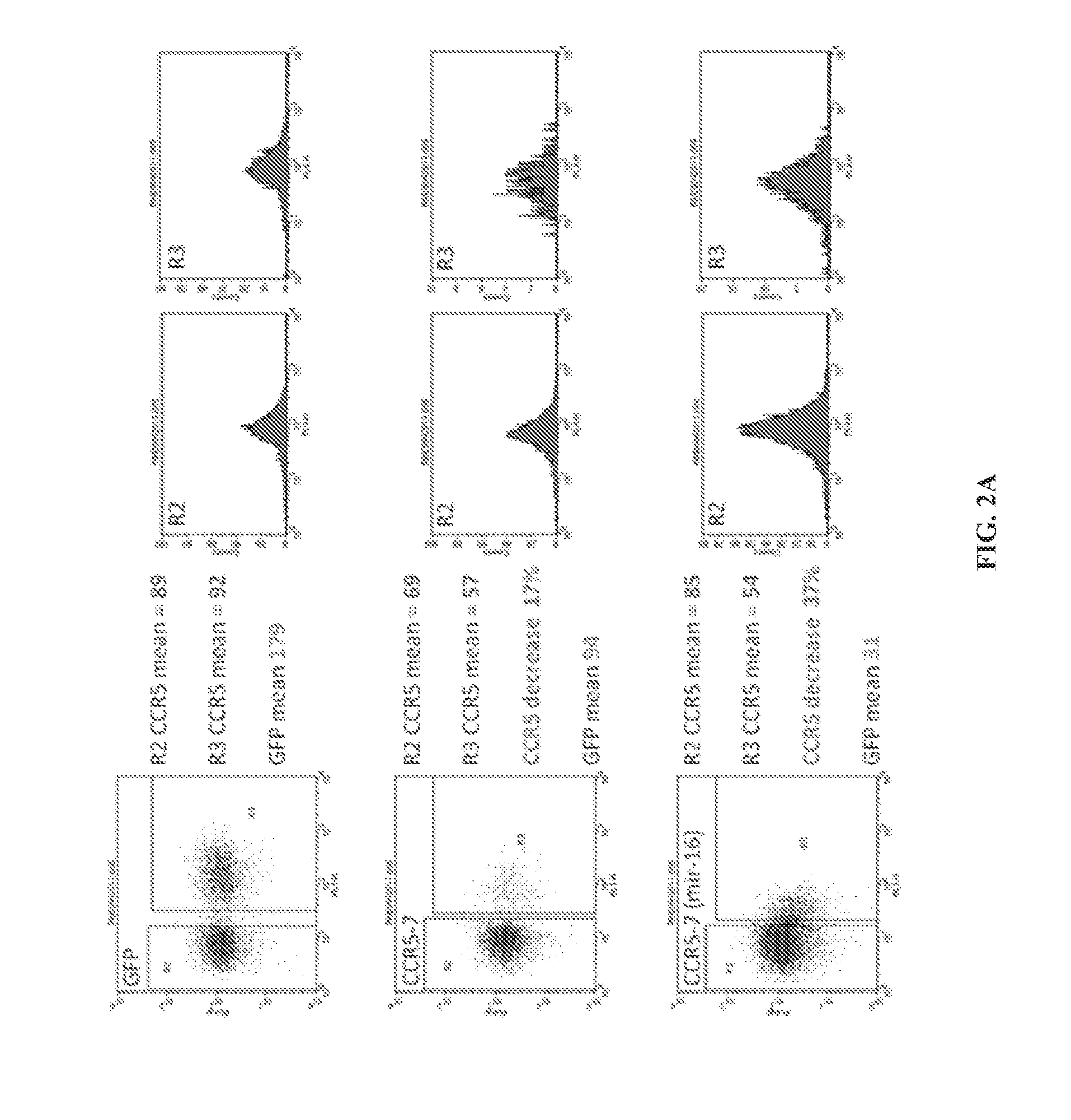
Combination Anti-hiv vectors, targeting vectors, and methods of use
ActiveUS20120076763A1Increase costIncreased toxicityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCell specificRegulation of gene expression
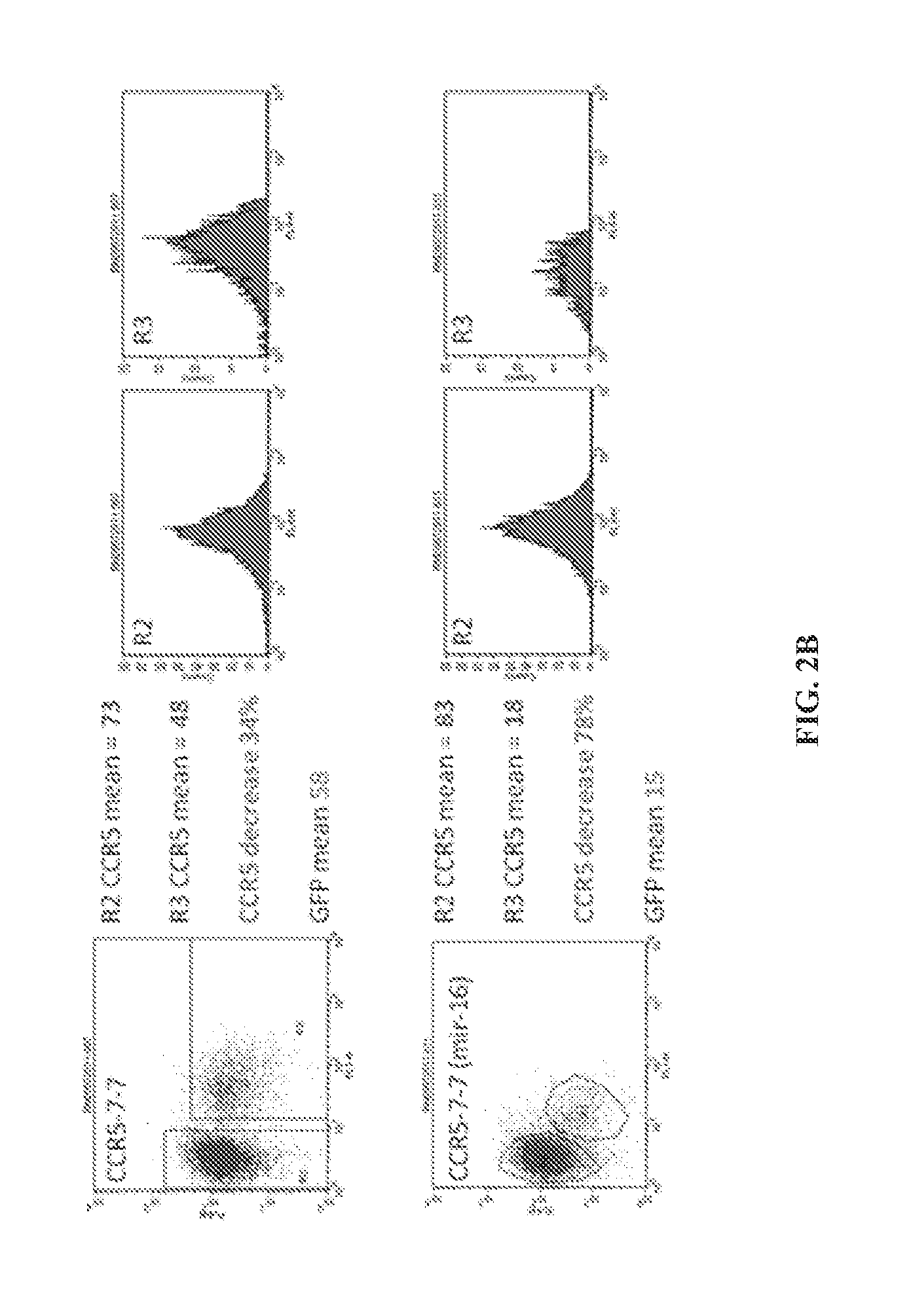
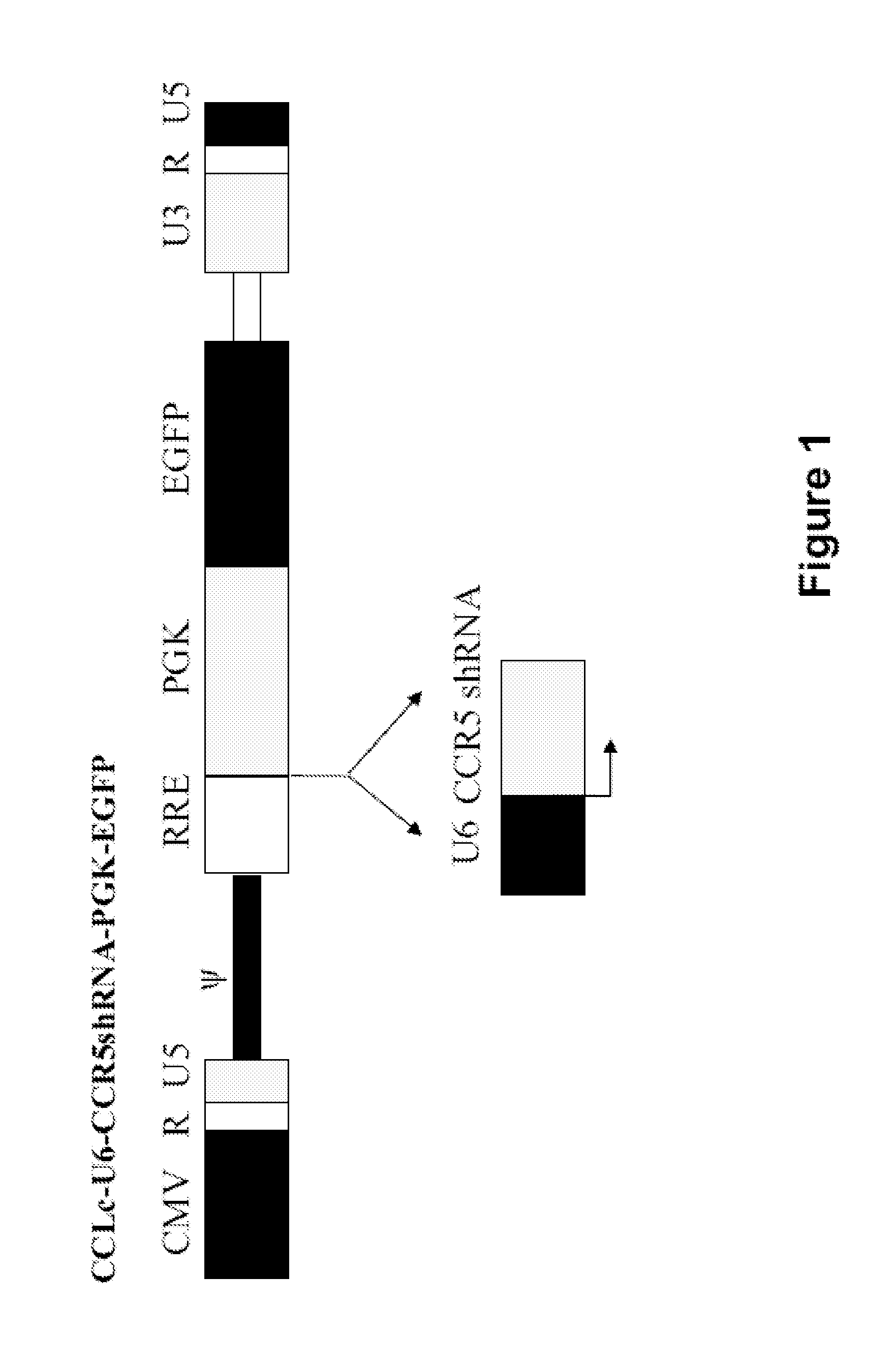
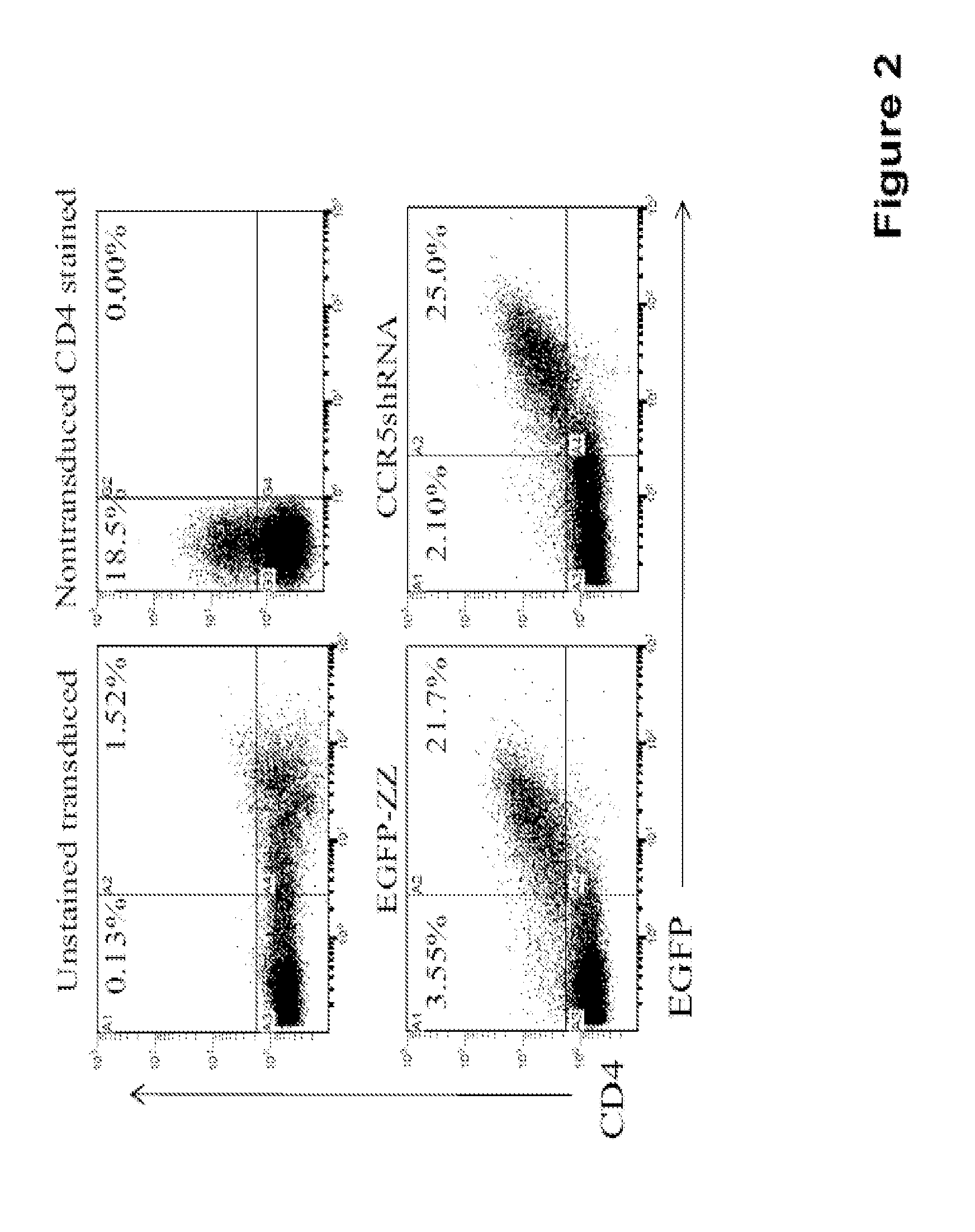
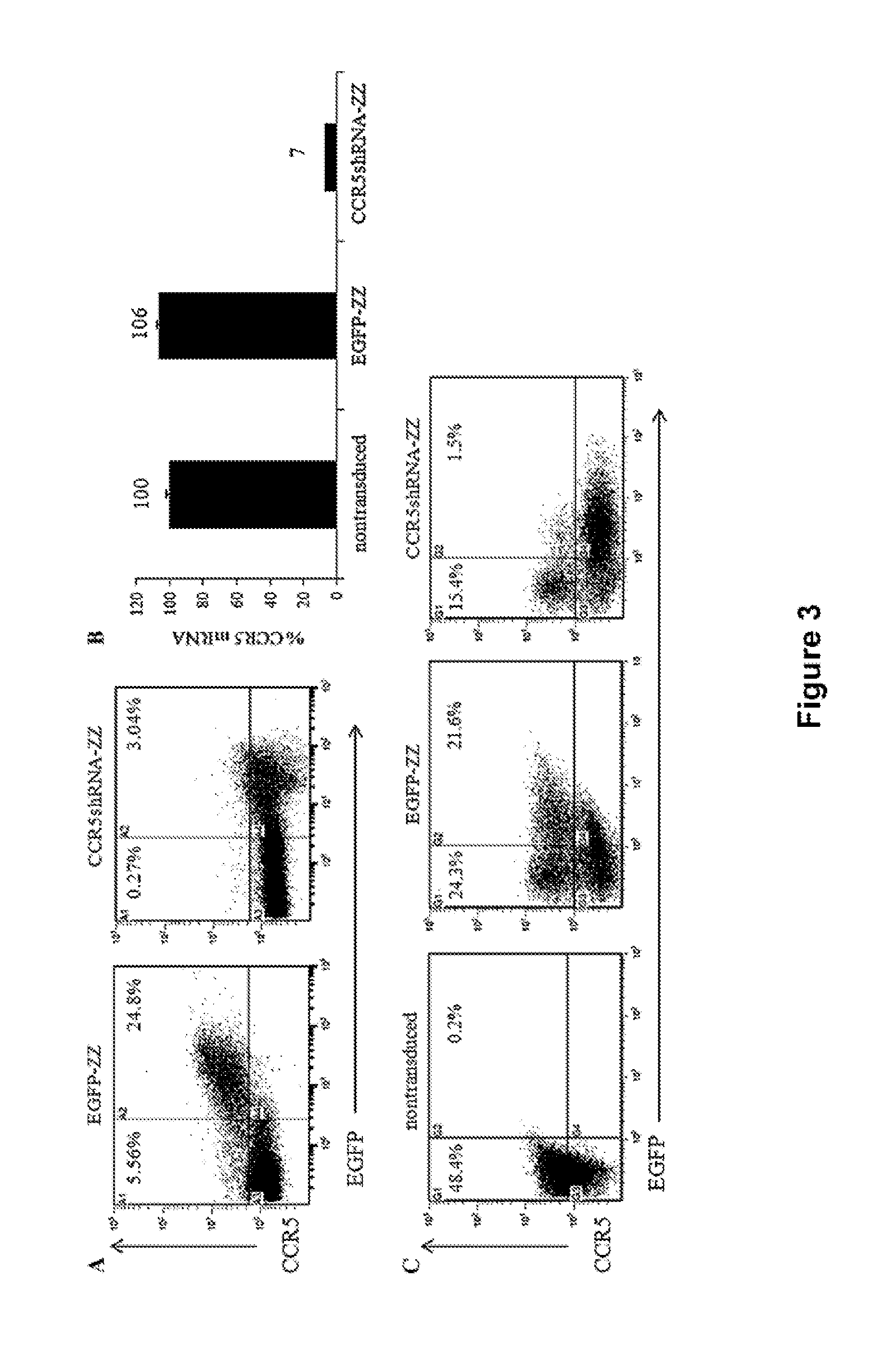
Recombinant lentiviral vectors containing at least: a lentiviral backbone comprising essential lentiviral sequences for integration into a target cell genome; a nucleic acid encoding a CCR5 RNAi; and an expression control element that regulates expression of the nucleic acid encoding the CCR5 RNAi element, are provided by this invention. In an alternative aspect, the vector also contains polynucleotides encoding TRIMS alpha and HIV TAR decoy sequences along with gene expression regulation elements such as promoters operatively linked to the polynucleotides. The vectors are combined with packaging plasmid and envelope plasmids and optionally conjugated to cell-specific targeting antibodies. Diagnostic and therapeutic methods for using the compositions are further provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Gene delivery system having enhanced tumor-specific expression, and recombinant gene expression regulating sequence
ActiveUS20130323206A1Improve anti-tumor effectImprove shortcomingsBiocideVectorsGene deliveryRegulation of gene expression
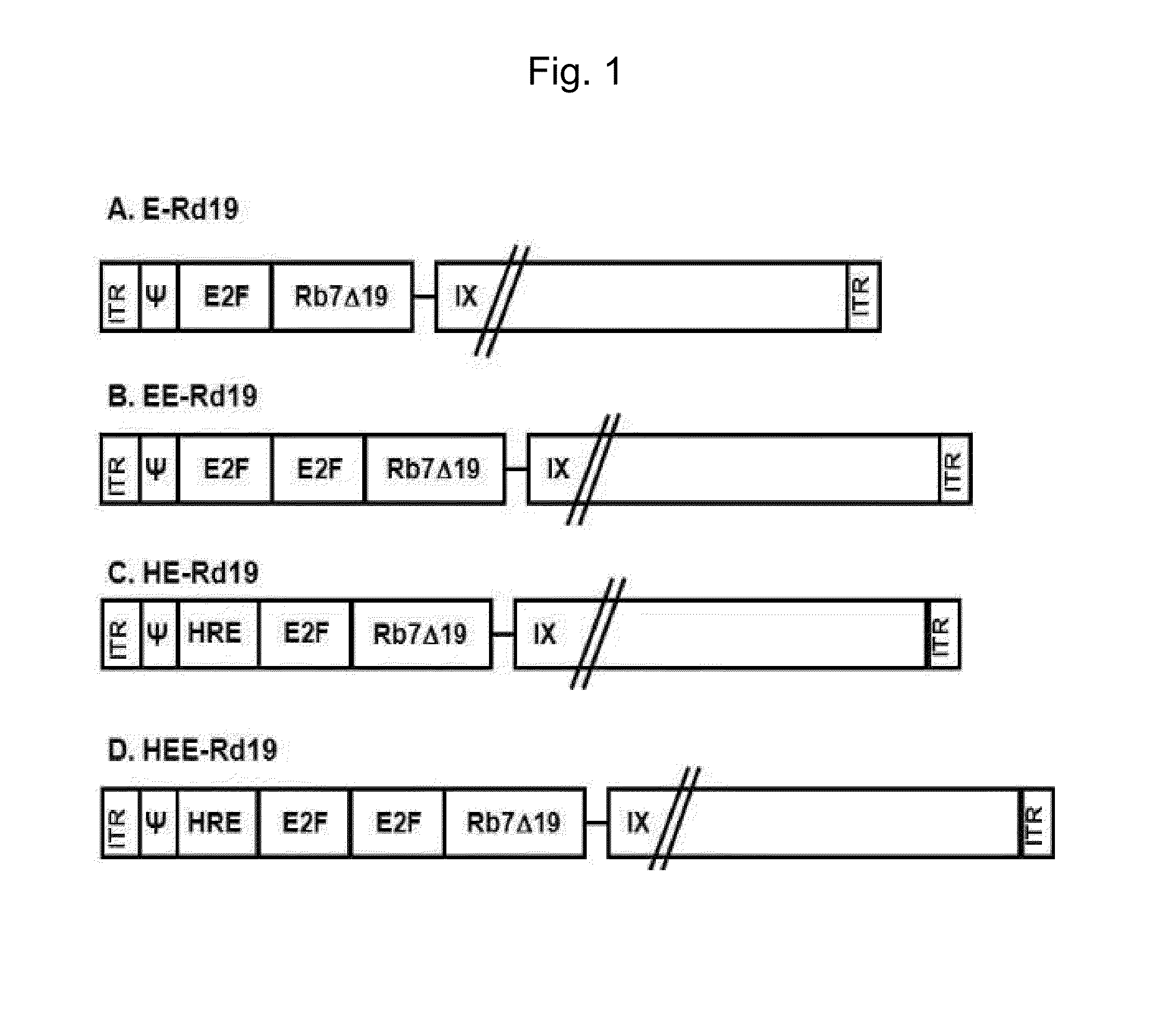
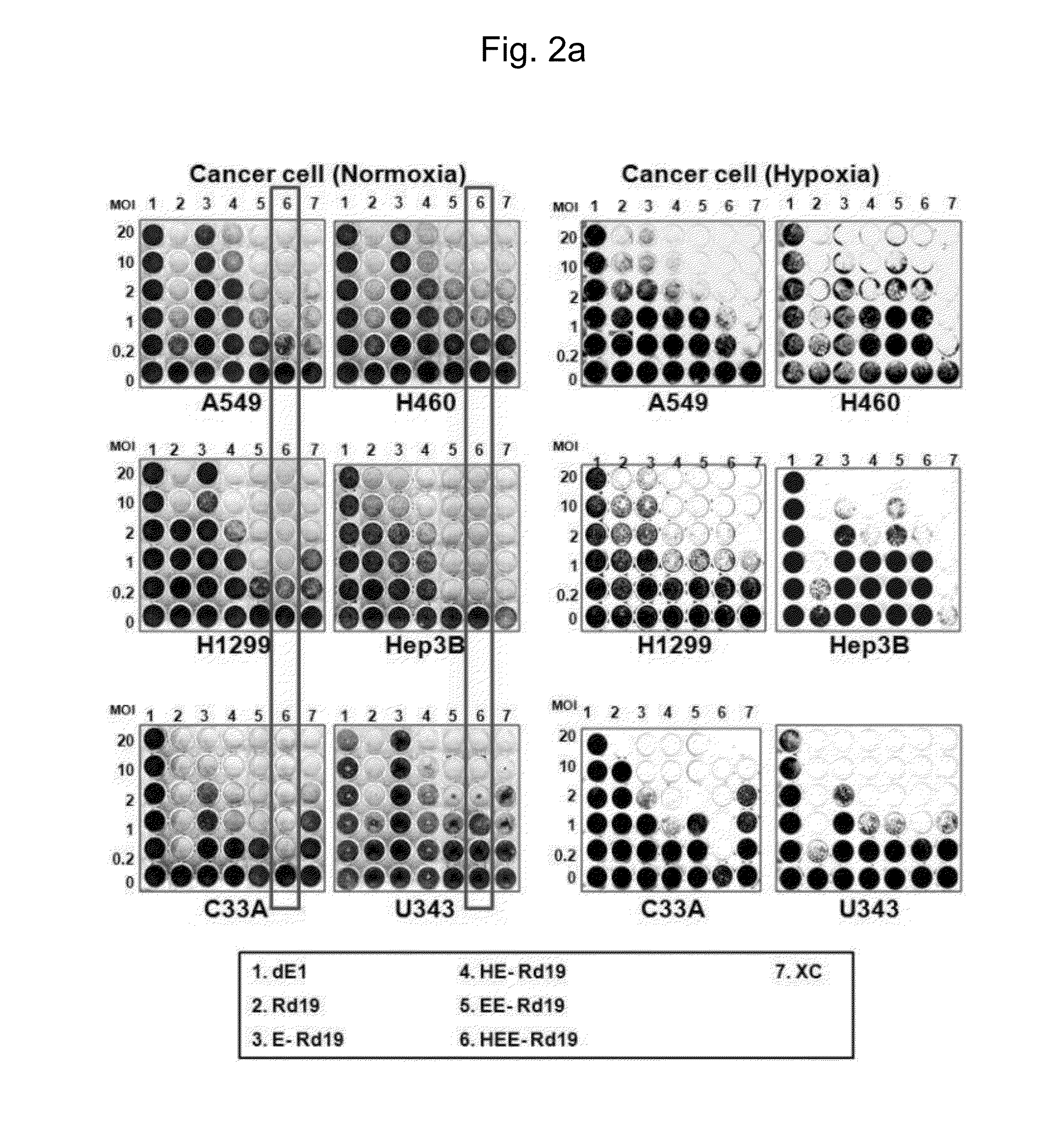
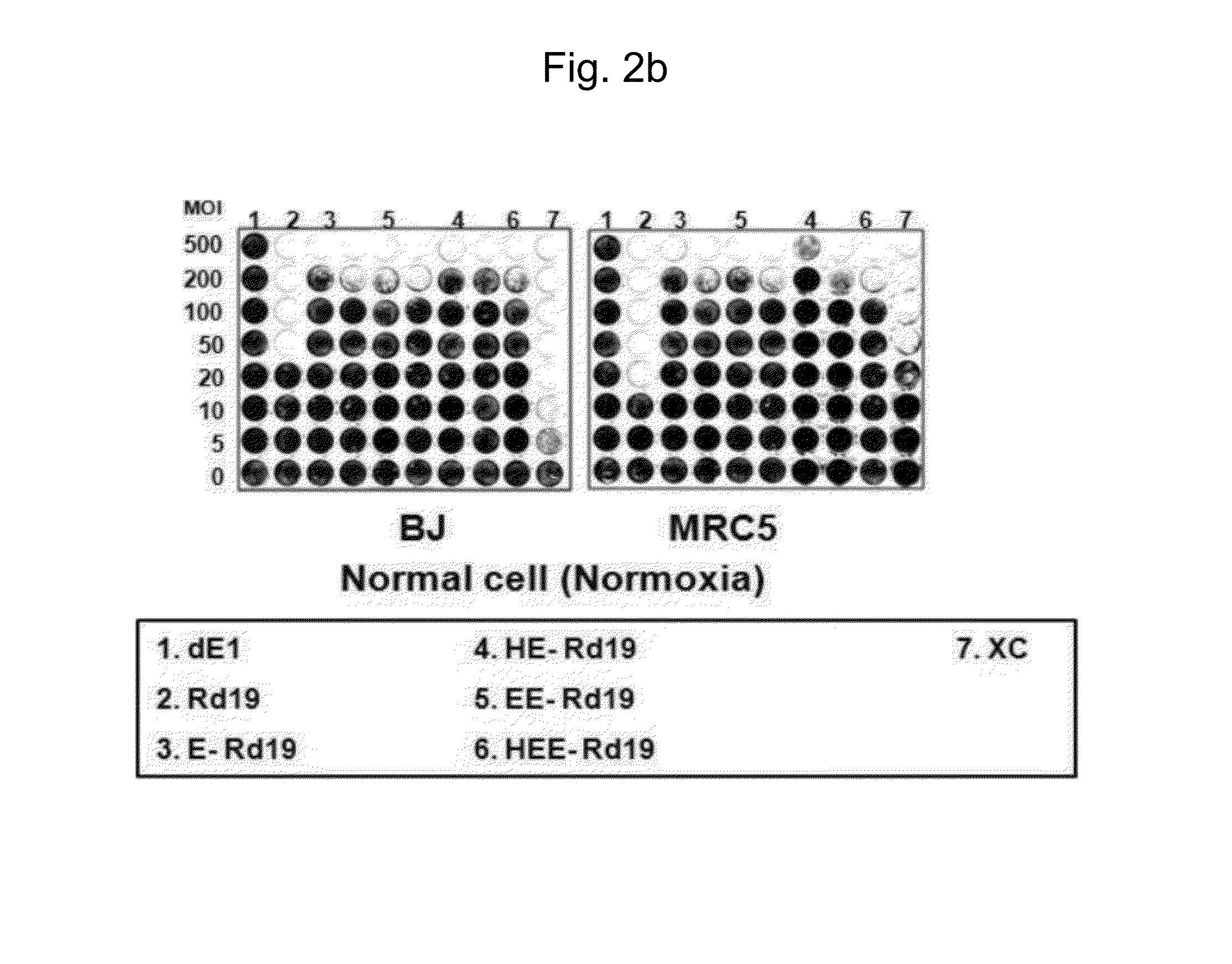
The present invention relates to a gene expression regulating sequence consisting of a combination of HRE, E2F and TERT, and to a gene delivery system having significantly improved selective tumor cell cytotoxicity using same, and more particularly, to a recombinant adenovirus. In addition, the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical antitumor composition comprising the recombinant adenovirus. The replication of the recombinant adenovirus of the present invention is tumor-specifically regulated by the novel gene expression regulating sequence of the present invention, thus enabling the recombinant adenovirus of the present invention to exhibit improved selective tumor cell cytotoxicity or apoptotic potential, and exhibit remarkably improved antitumor effects particularly in hypoxic conditions. In addition, the specific expression of the recombinant adenovirus in tumor cells may increase in vivo stability, and thus may induce greatly improved antitumor effects.
Owner:GENEMEDICINE CO LTD
Repressor protein, regulatory element group, gene expression regulation system and construction method thereof
ActiveCN107344962AAchieve dimerizationTetramerizationVectorsAnimals/human peptidesRegulation of gene expressionBioinformatics
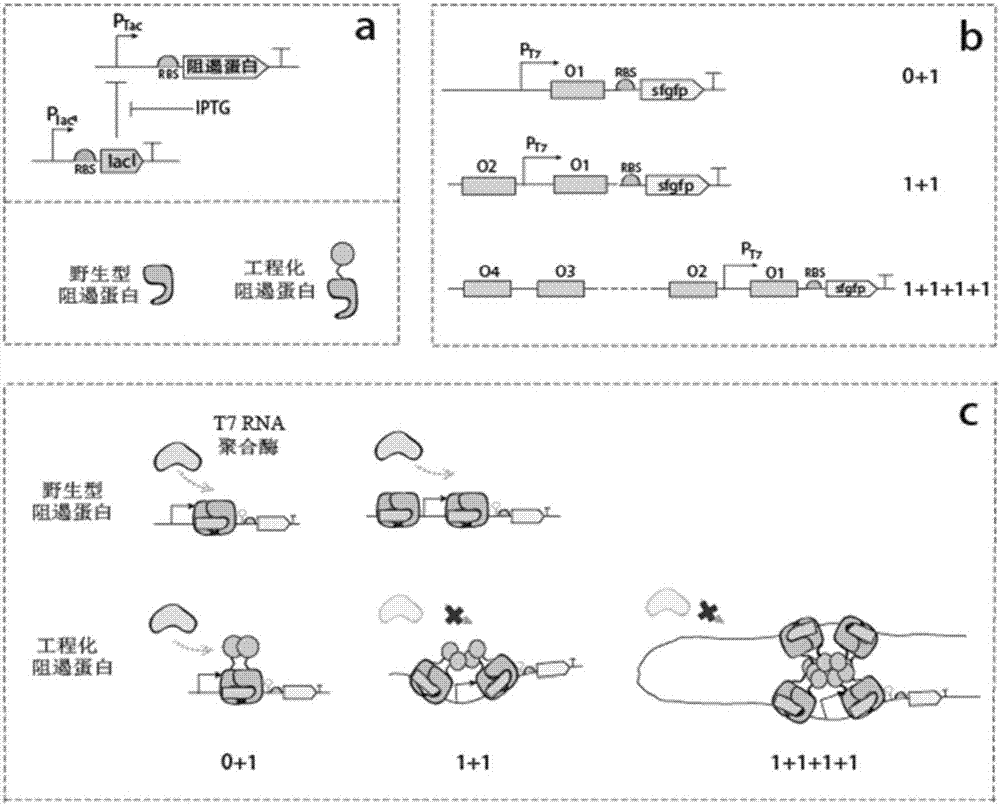
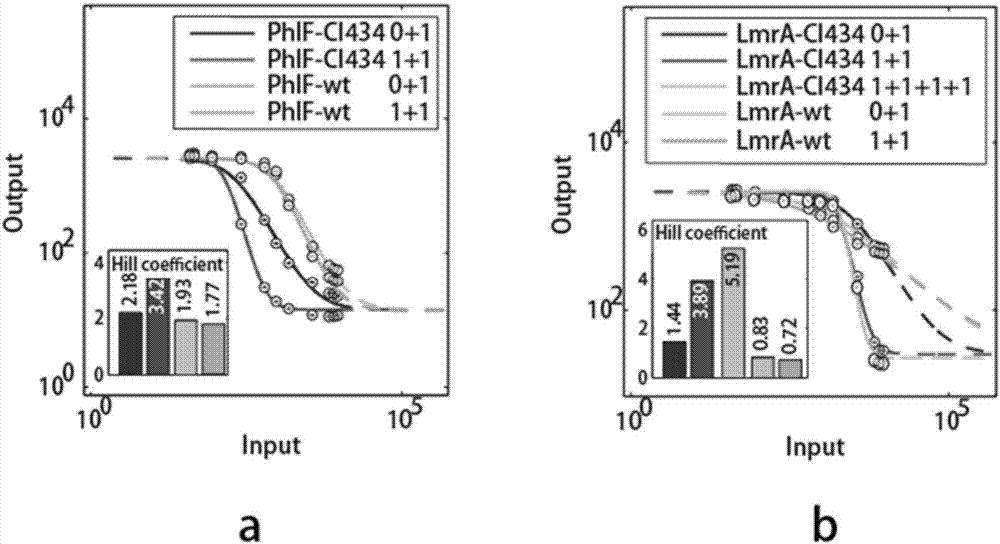
By introducing a multimerized structural domain into a repressor protein and optimizing the number of operator loci interacting with the repressor protein in the preferred embodiment, the invention obtains the repressor protein, a regulatory element group and a gene expression regulation system which have ultrasensitive regulation performance.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical regulation of gene expression in the retina
InactiveUS20150111275A1Reduce the required powerLaser surgeryVectorsRegulation of gene expressionElectromagnetic radiation
The present invention provides methods and compositions for regulating transgene expression in a subject using heat generated by electro-magnetic radiation in a target cell. The heat is generated by a thermo generator resided in the target cell upon application the electromagnetic radiation. The amount of the heat is controlled by the energy delivered by the electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Detecting protein of transcriptional factor through probe of digestion FRET marke nucleic acid of nuclease
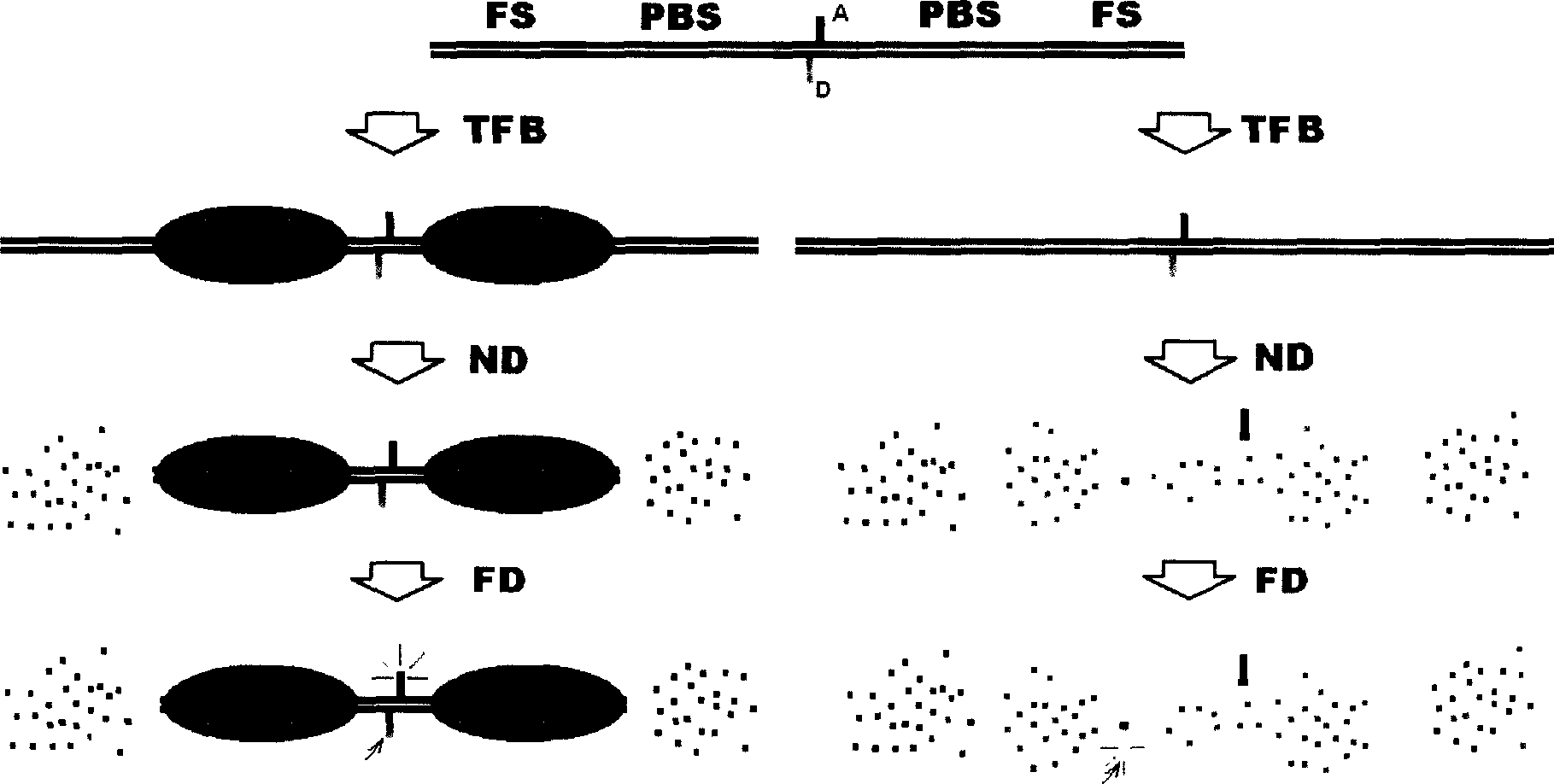
InactiveCN1727895AEfficient analysisEfficient comprehensive analysis and detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceRegulation of gene expressionNucleic Acid Probes
A method for detecting transcription factor protein by nucleic acid probe with nuclease protection PRET label includes preparing fluorescence labeled nucleic acid probe, carrying out combination reaction of nucleic acid probe with transcription factor protein, adding nuclease in combination reaction system to carry out enzyme nick reaction and detecting reaction system by fluorescence to reflect expression and activation level of transcription factor protein.
Owner:王进科 +1
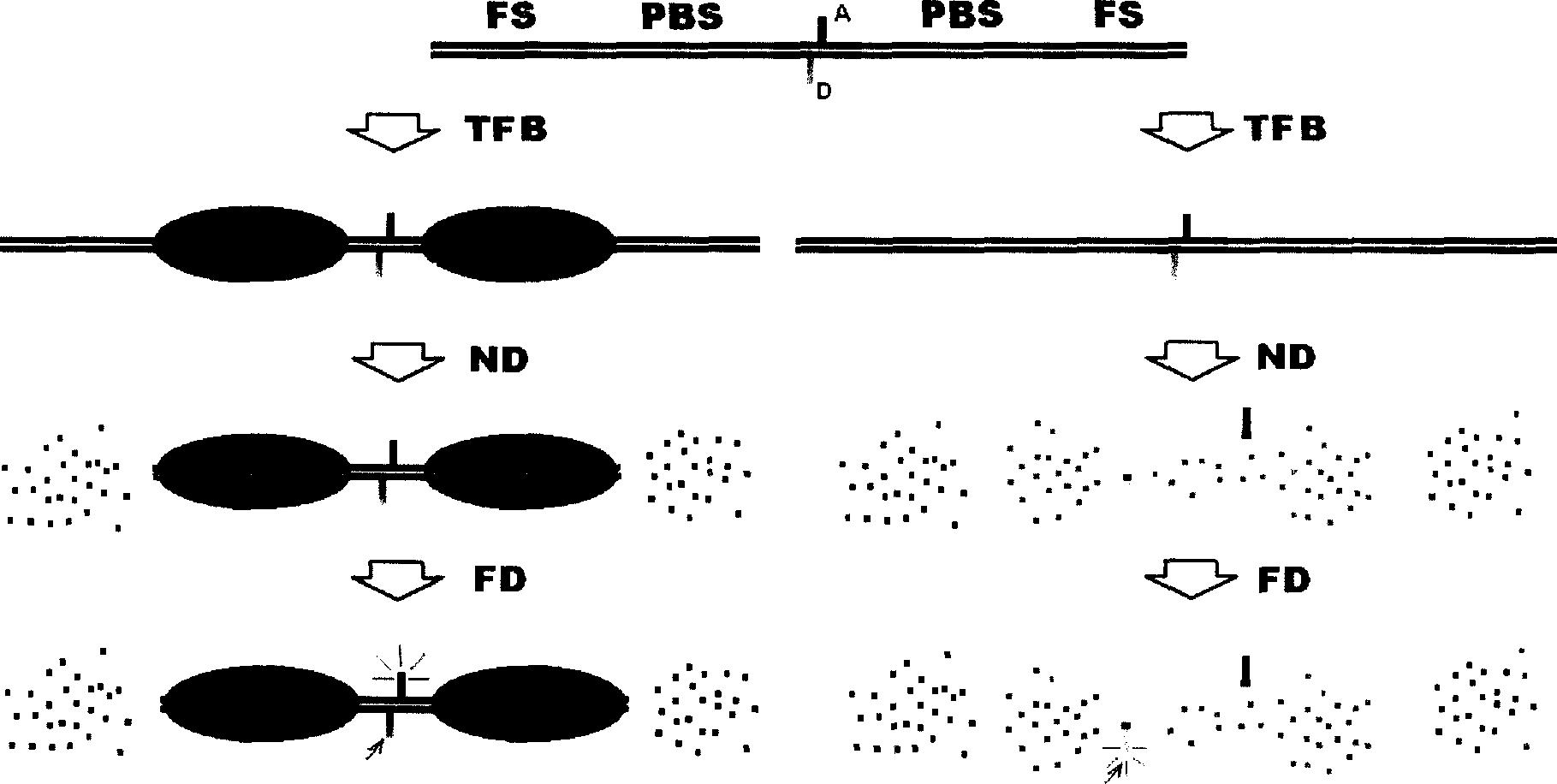
Detection of transcription factor protein by double chain RNA molecule with special labeling fixed to micro-plate coated by exonuclease III
InactiveCN1721547ALimit commercializationHigh Throughput Analysis CapabilitiesMicrobiological testing/measurementRegulation of gene expressionTissue extracts
Transcription factor is one important protein for gene regulation, is center of gene expression regulating passage and network, is important target of functional genome and protein block research and important target site of transcription treatment and medicine research. The present invention proposes exonuclease III digesting double stranded nucleic acid molecule coated in microporous plate and containing special marker to detect transcription factor protein. The process of analyzing transcription factor expression and activation level includes the following steps: preparing nucleic acid; fixing the nucleic acid molecules to the pores of the microporous plate; incubation of cell or tissue extract containing transcription factor in the plate; incubation of exonuclease III reaction liquid in the plate; incubation of specific conjugate with special marker on nucleic acid on the plate; detecting and analyzing the specific conjugate to obtain the expression and activation level.
Owner:王进科 +1
Quinazolinone compositions for regulation of gene expression related to pathological processes
InactiveUS20060258692A1Increase volumeAlteration can be preventedOrganic active ingredientsBiocideQuinazolinoneRegulation of gene expression
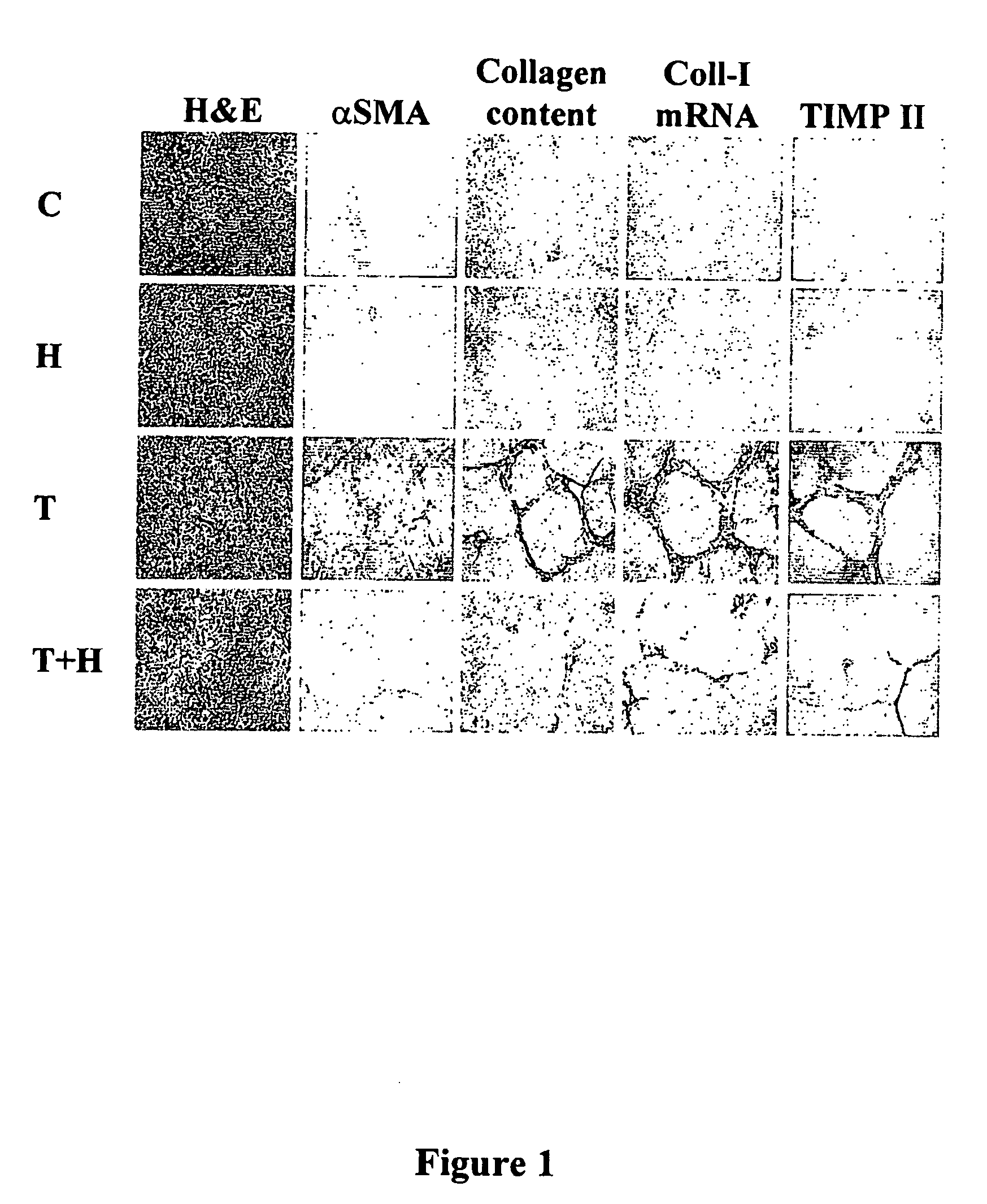
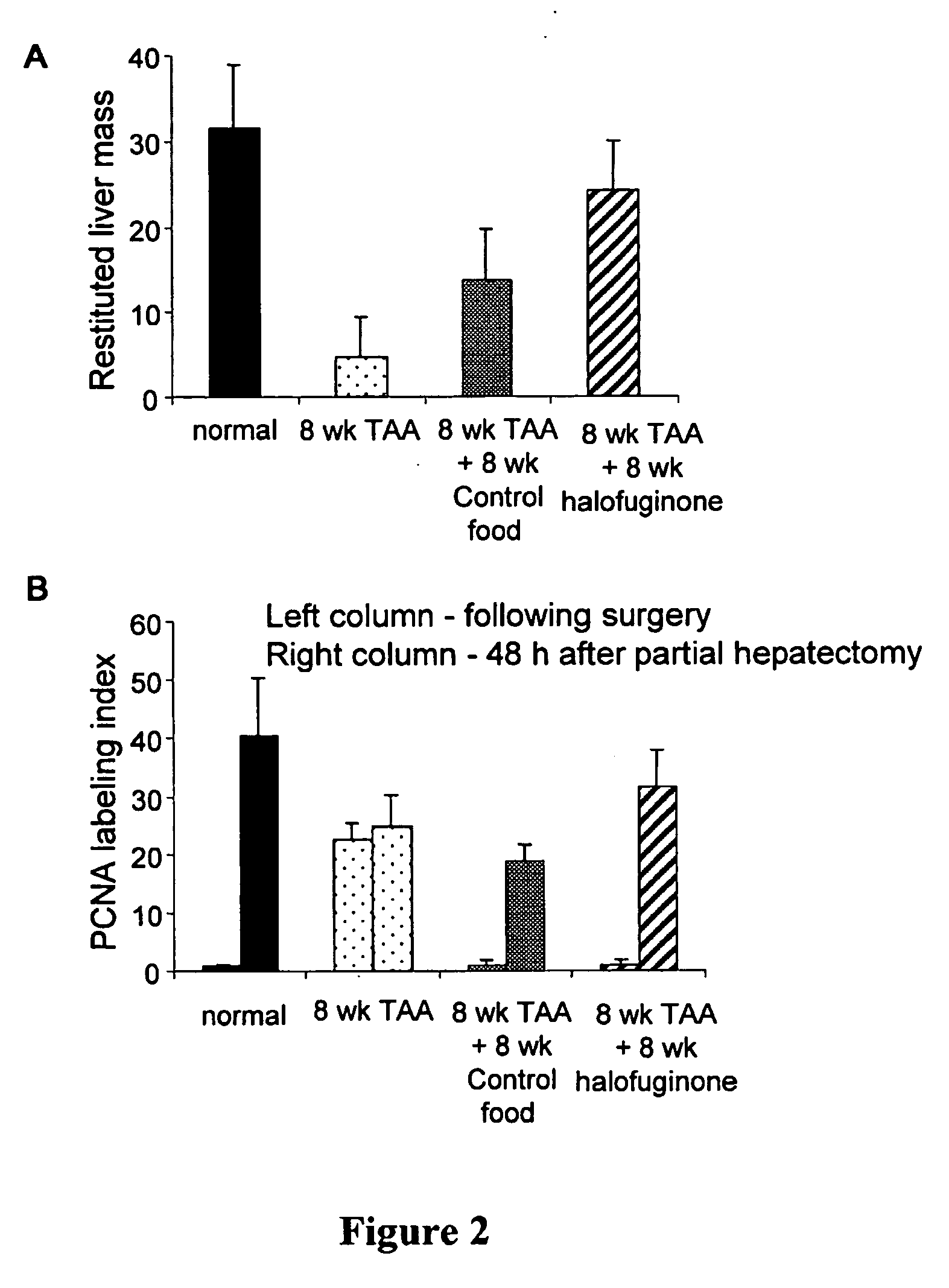
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions for modifying gene expression in a pathological process, thereby preventing or ameliorating said process. More particularly the compositions comprise quinazolinones, especially halofuginone, for inhibiting or preventing alterations in gene expression during fibrosis. The present invention particularly relates to pharmaceutical compositions for improving the regeneration of cirrhotic liver.
Owner:PINES MARK +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com